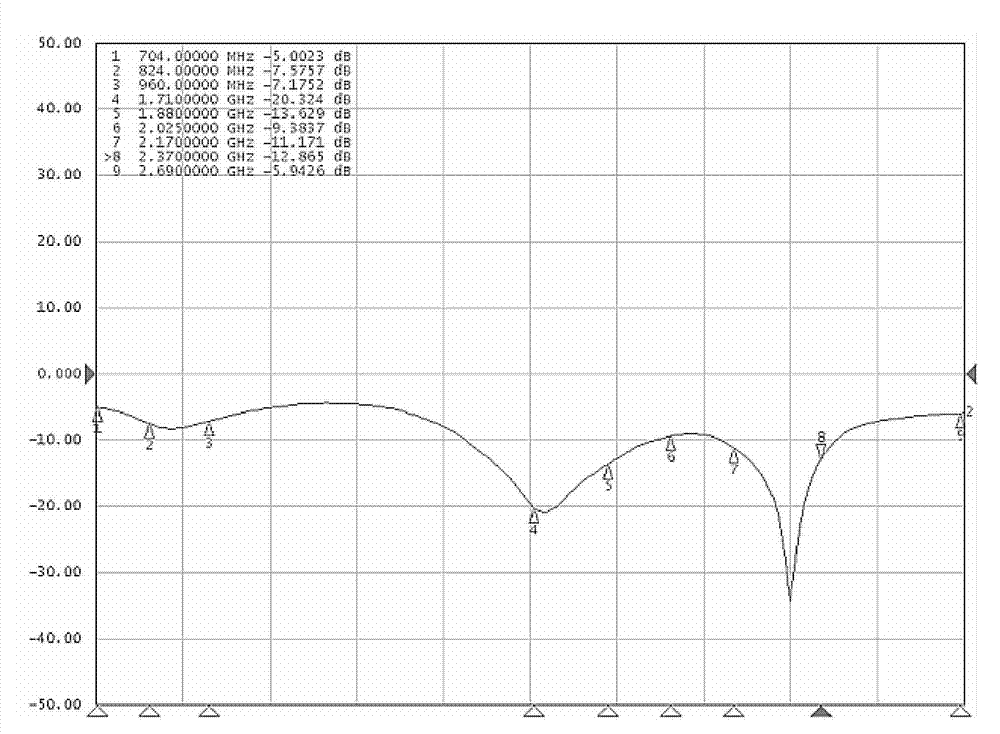
Patents
Literature
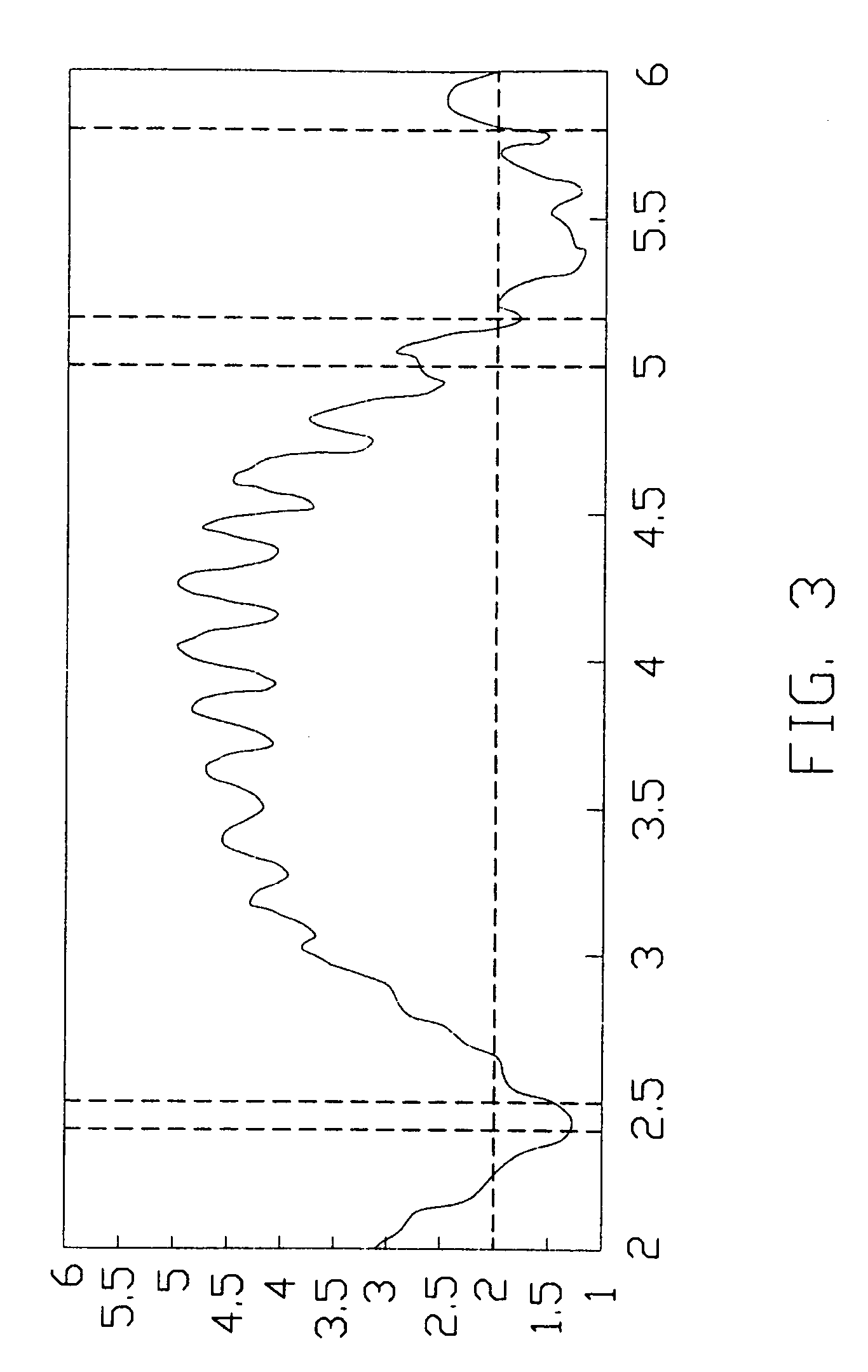
2375 results about "Low frequency band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
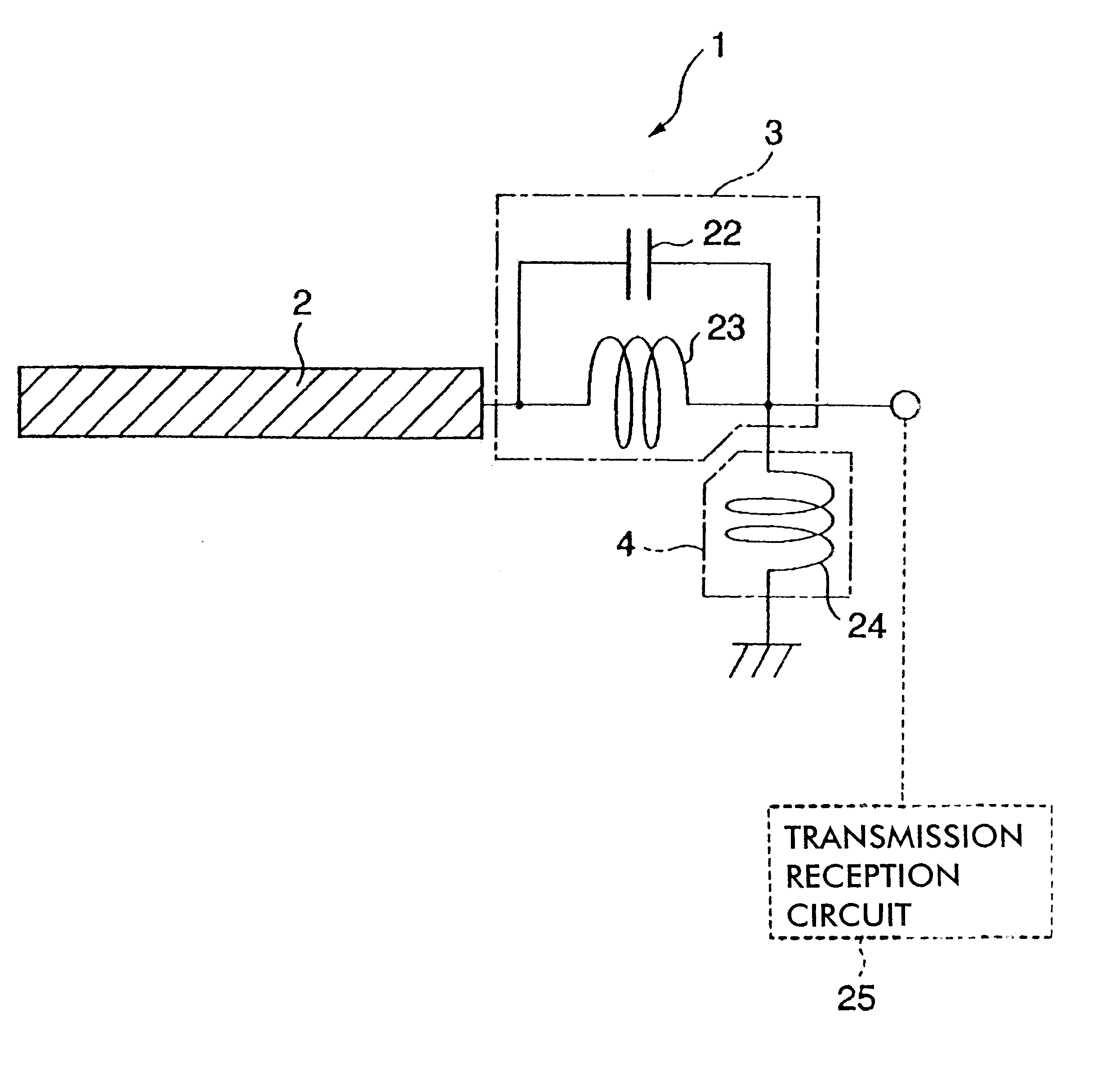
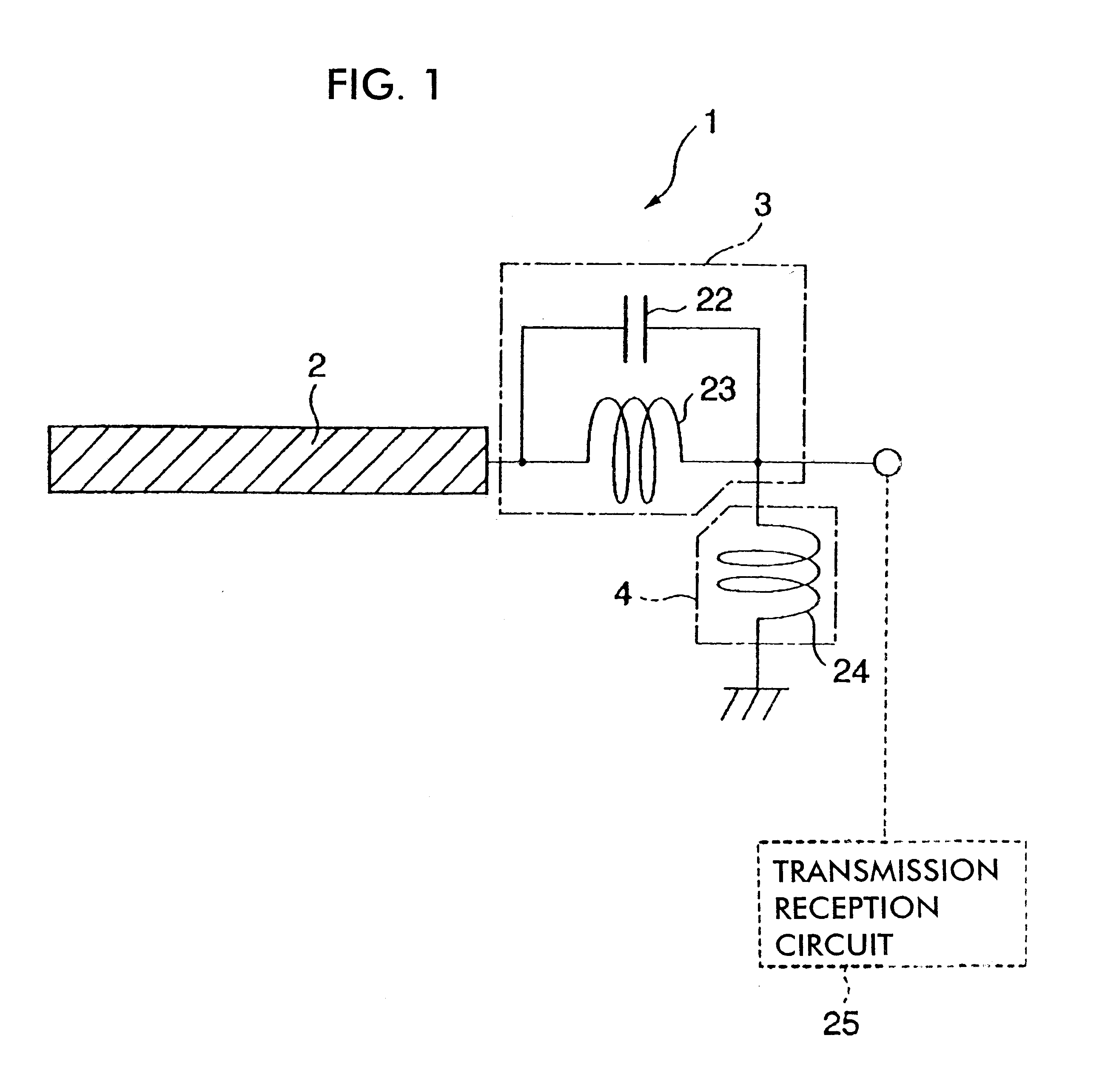
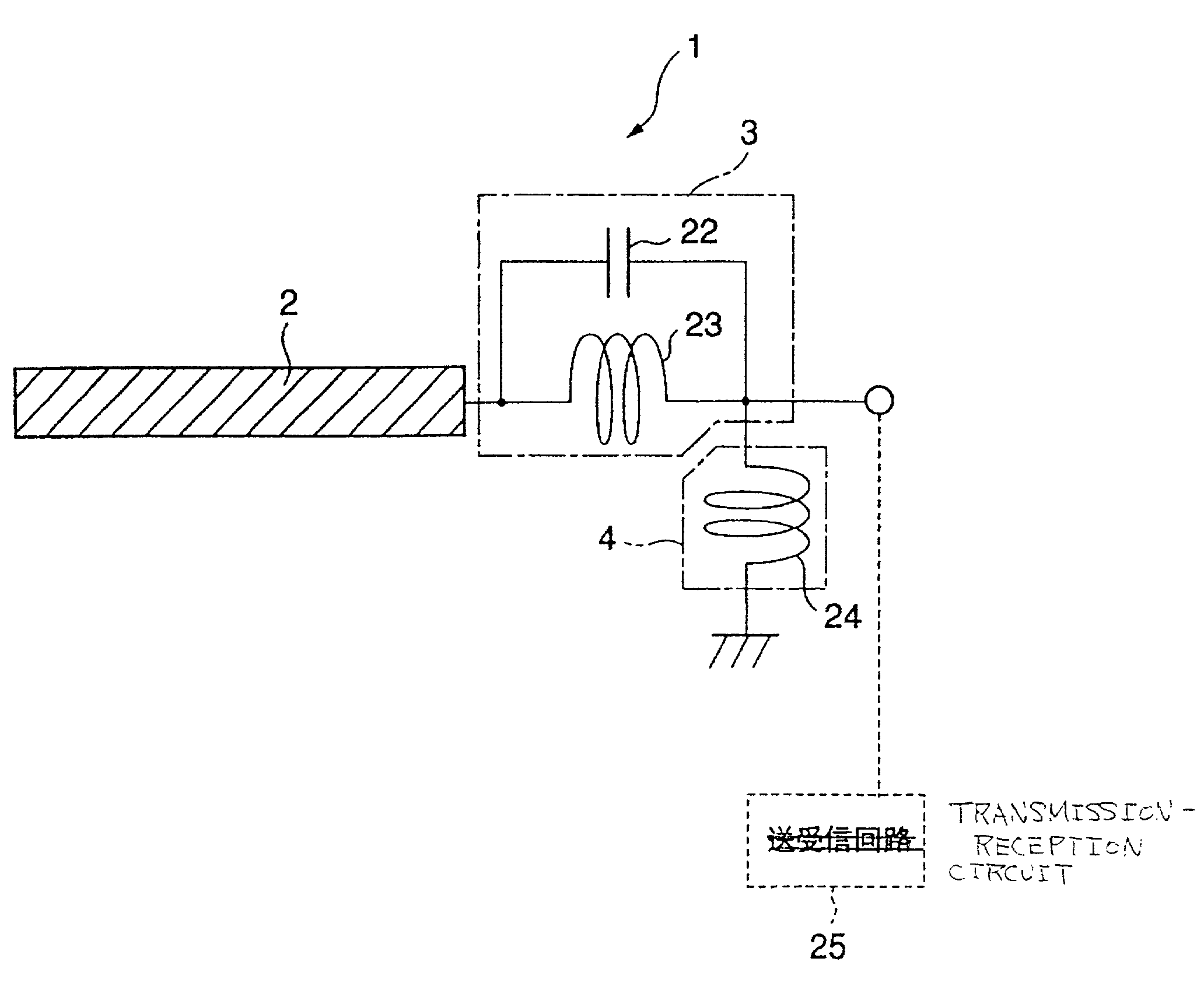
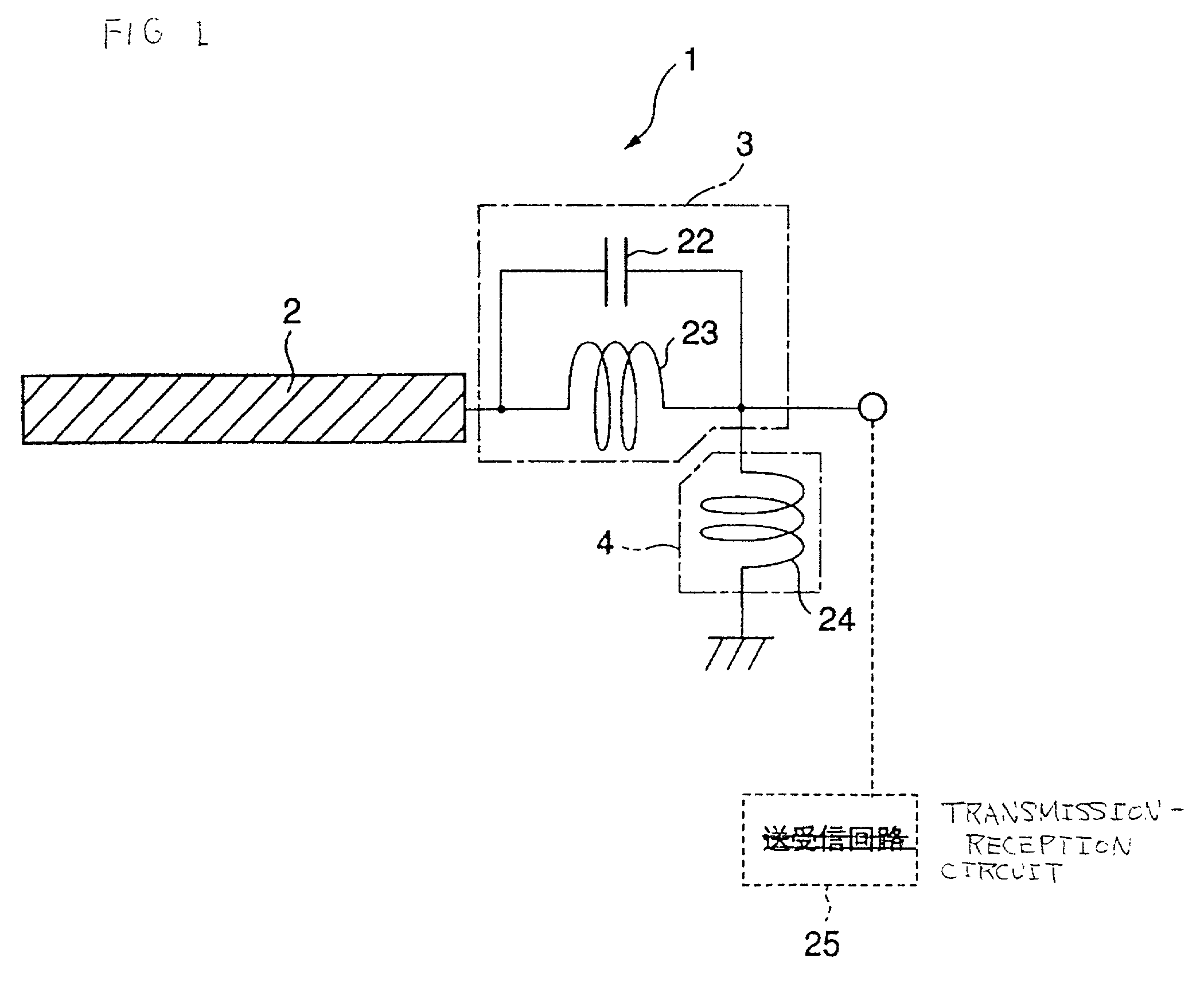
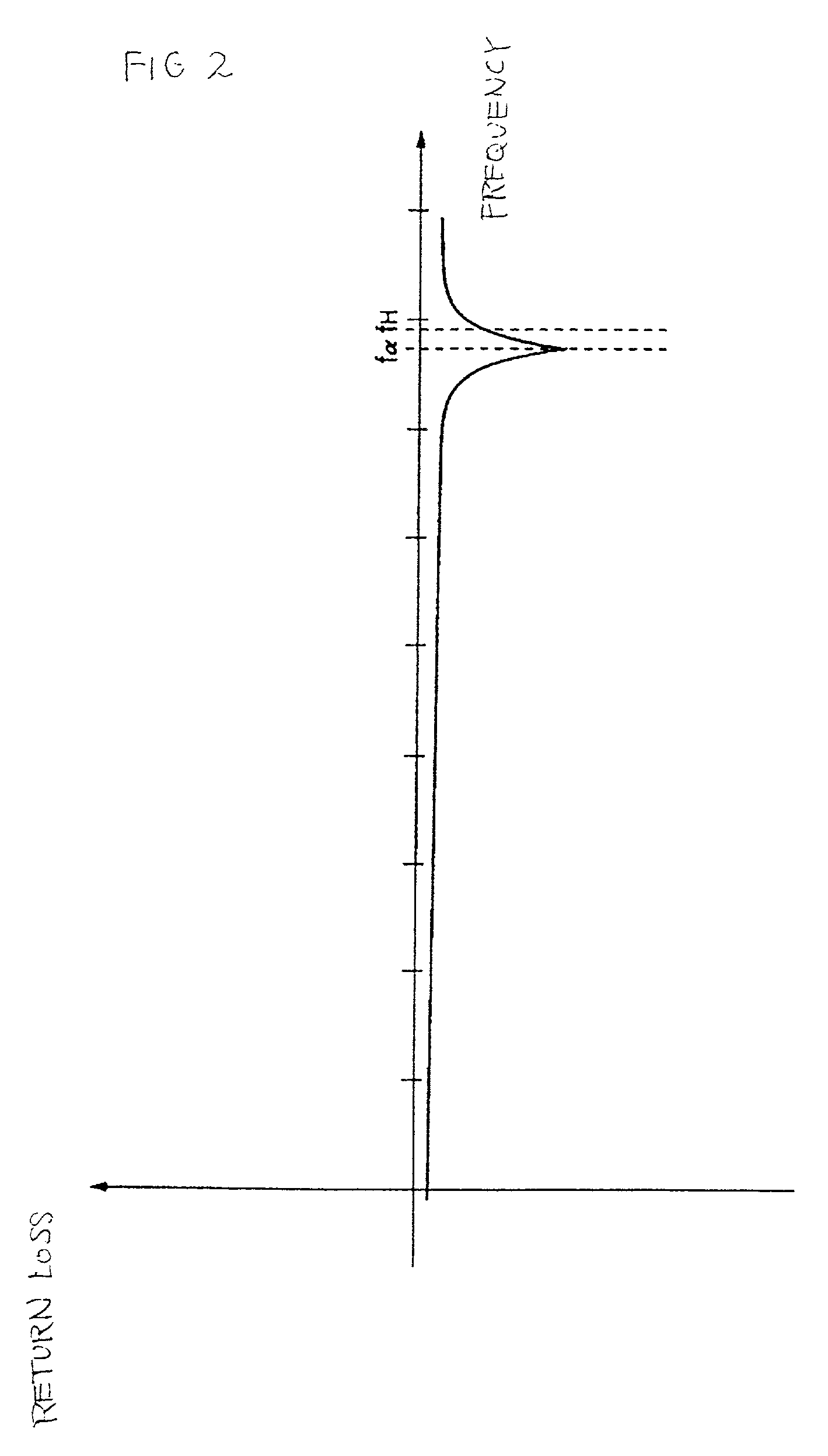
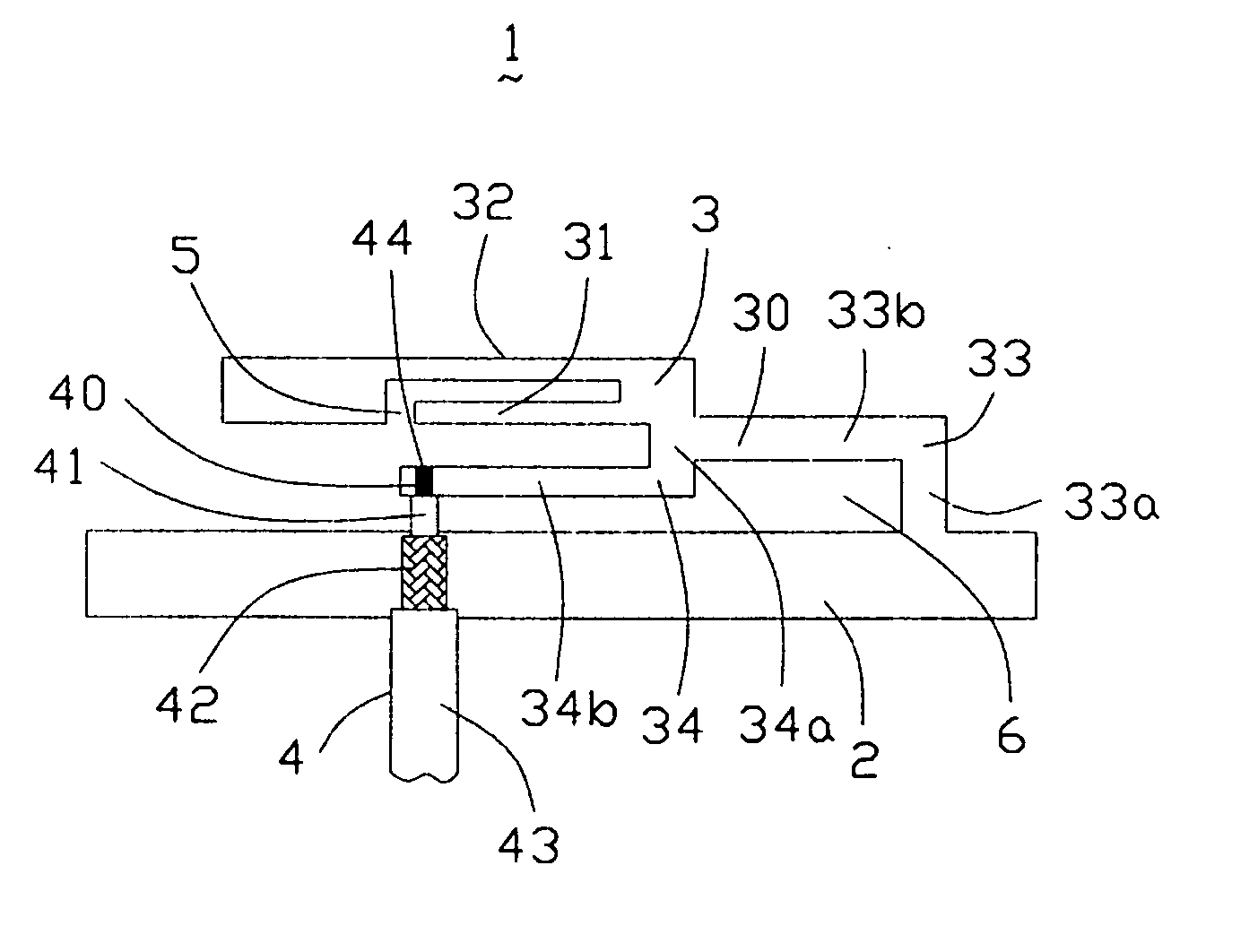
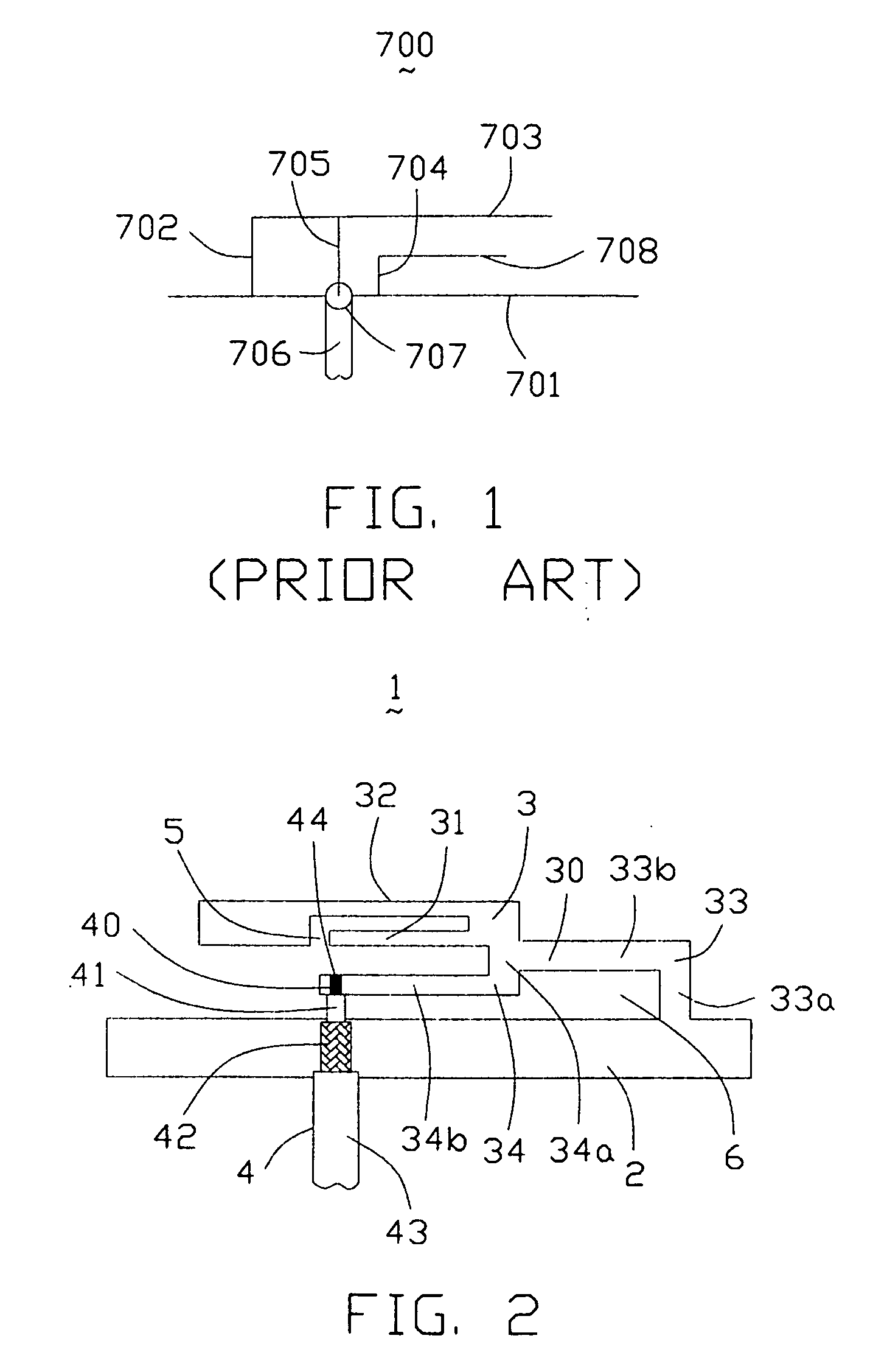
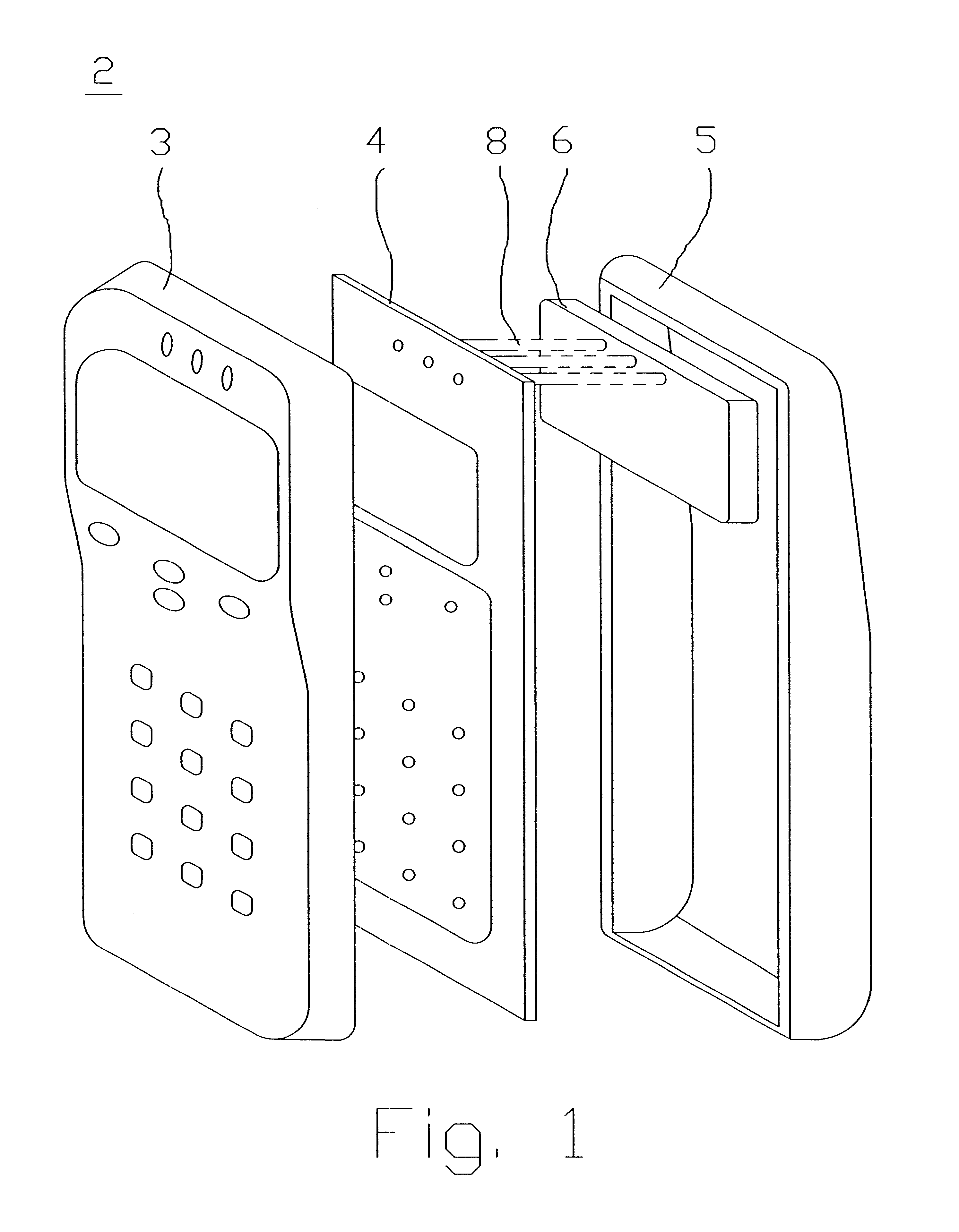
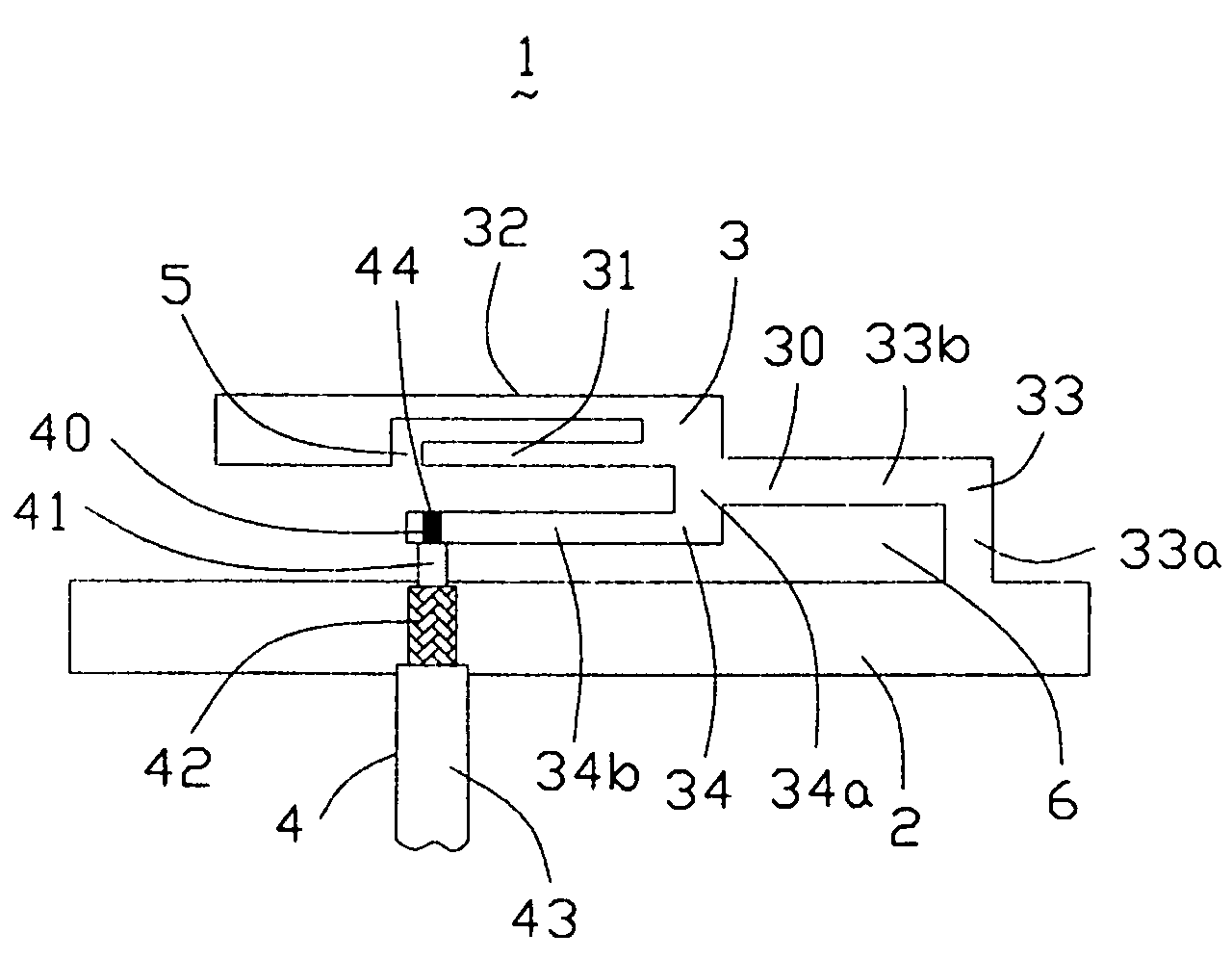
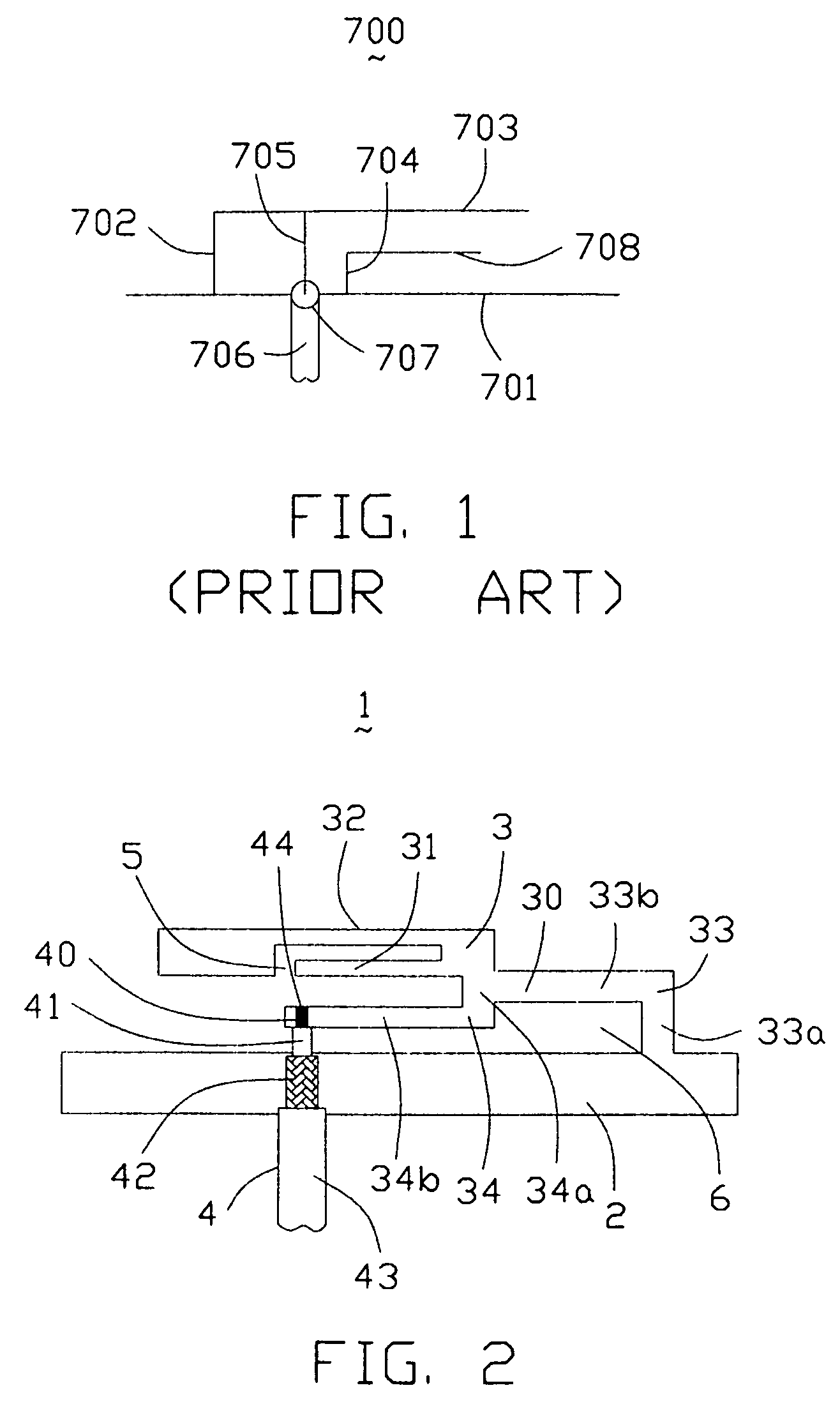
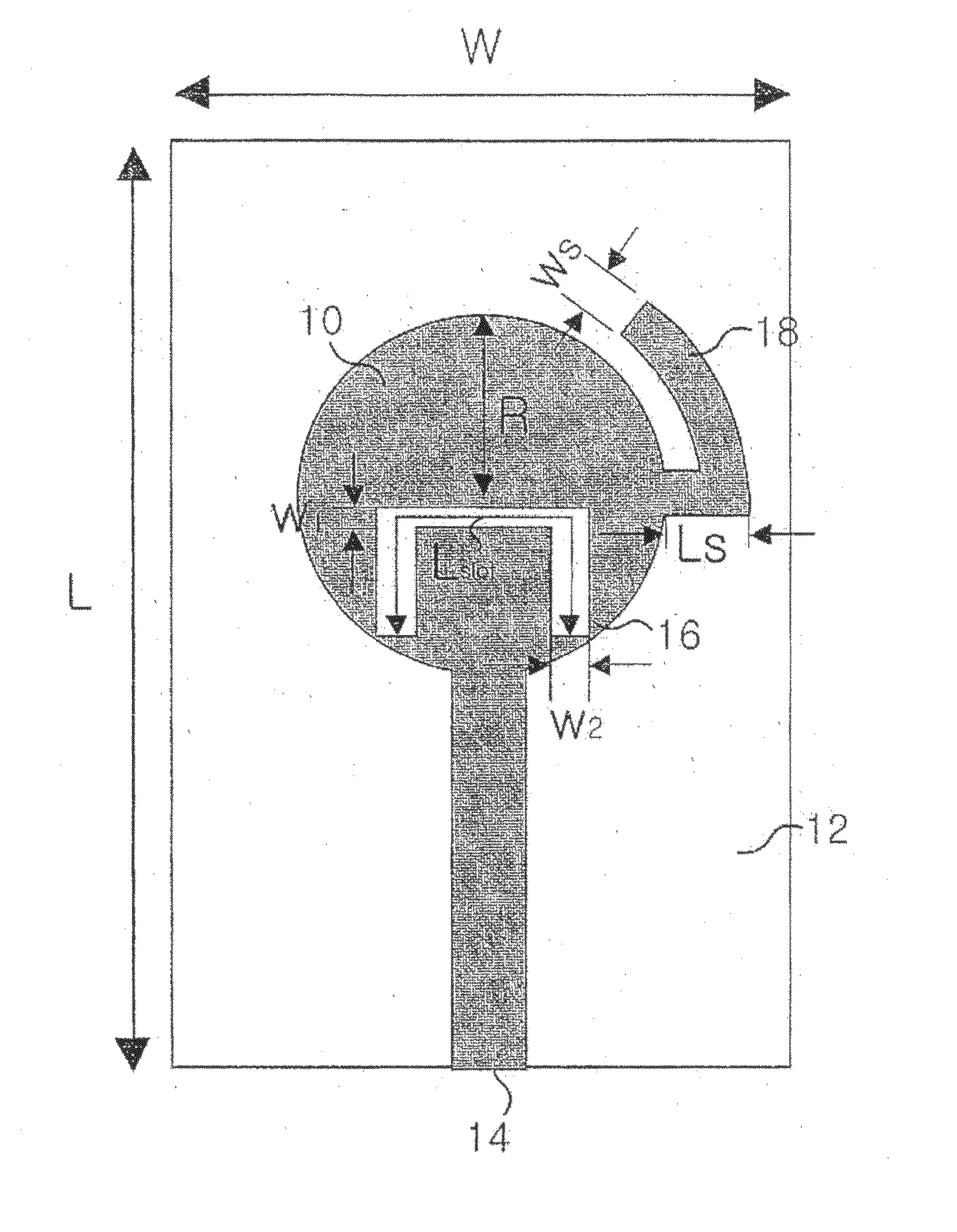
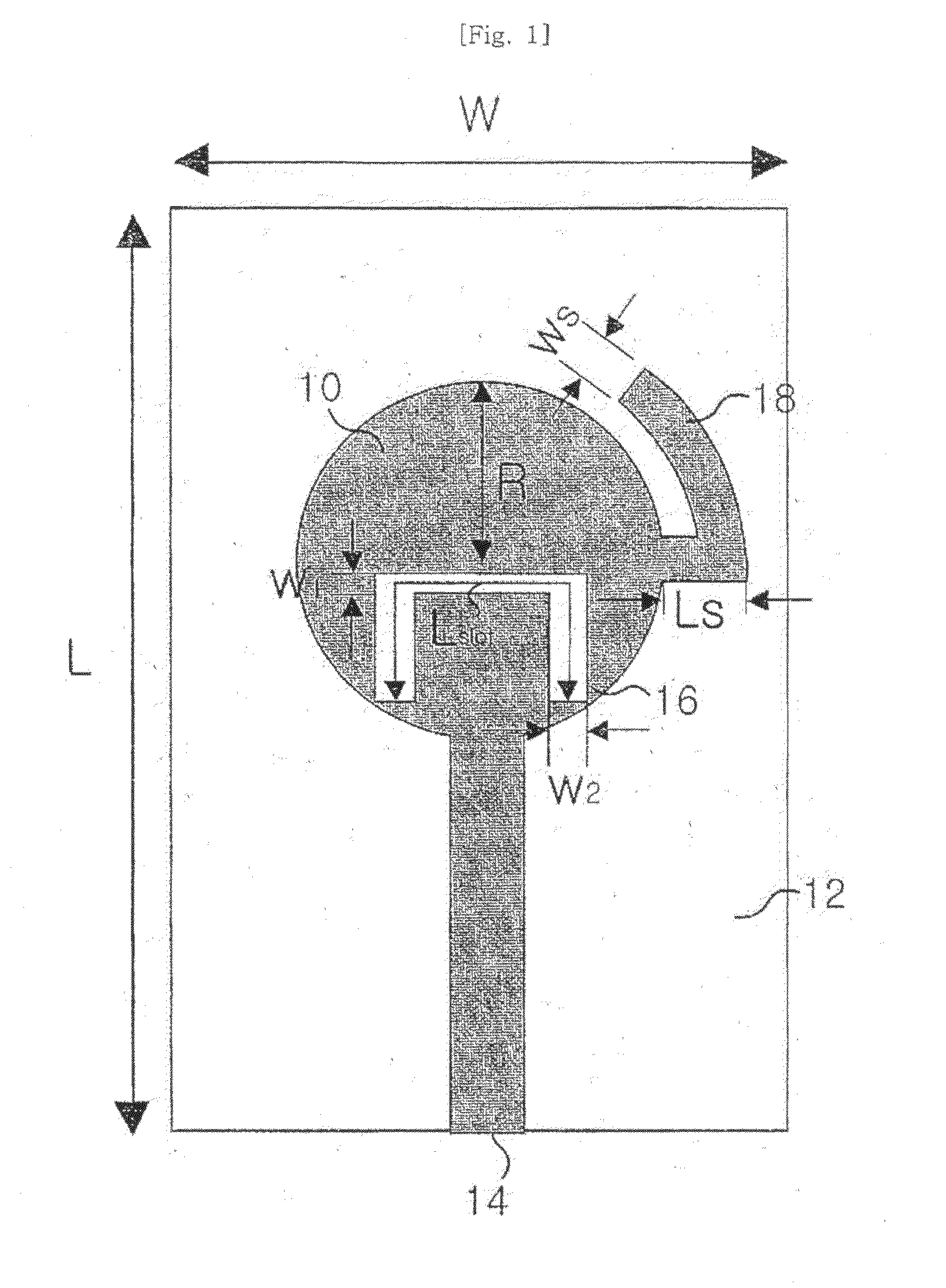
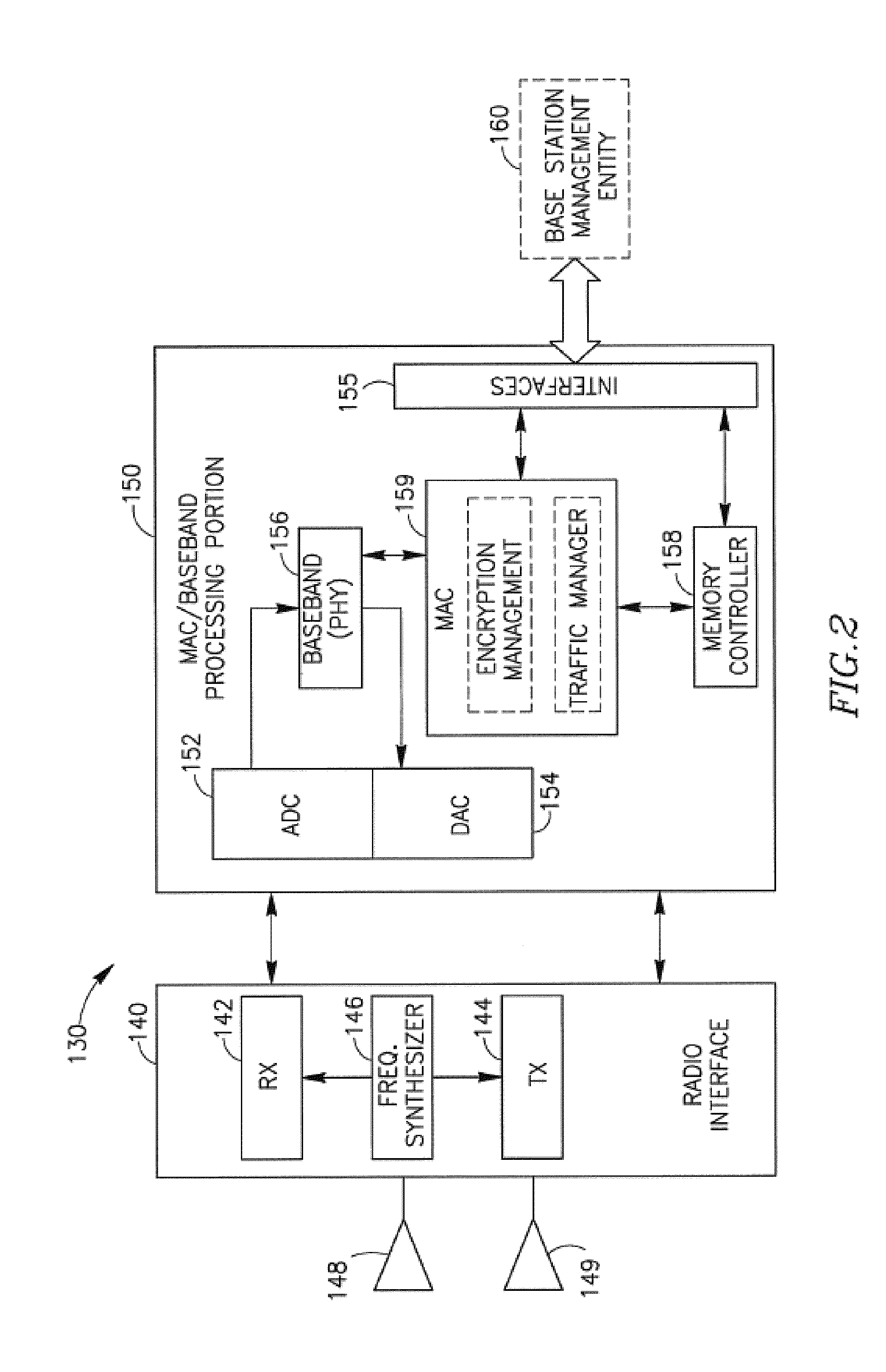
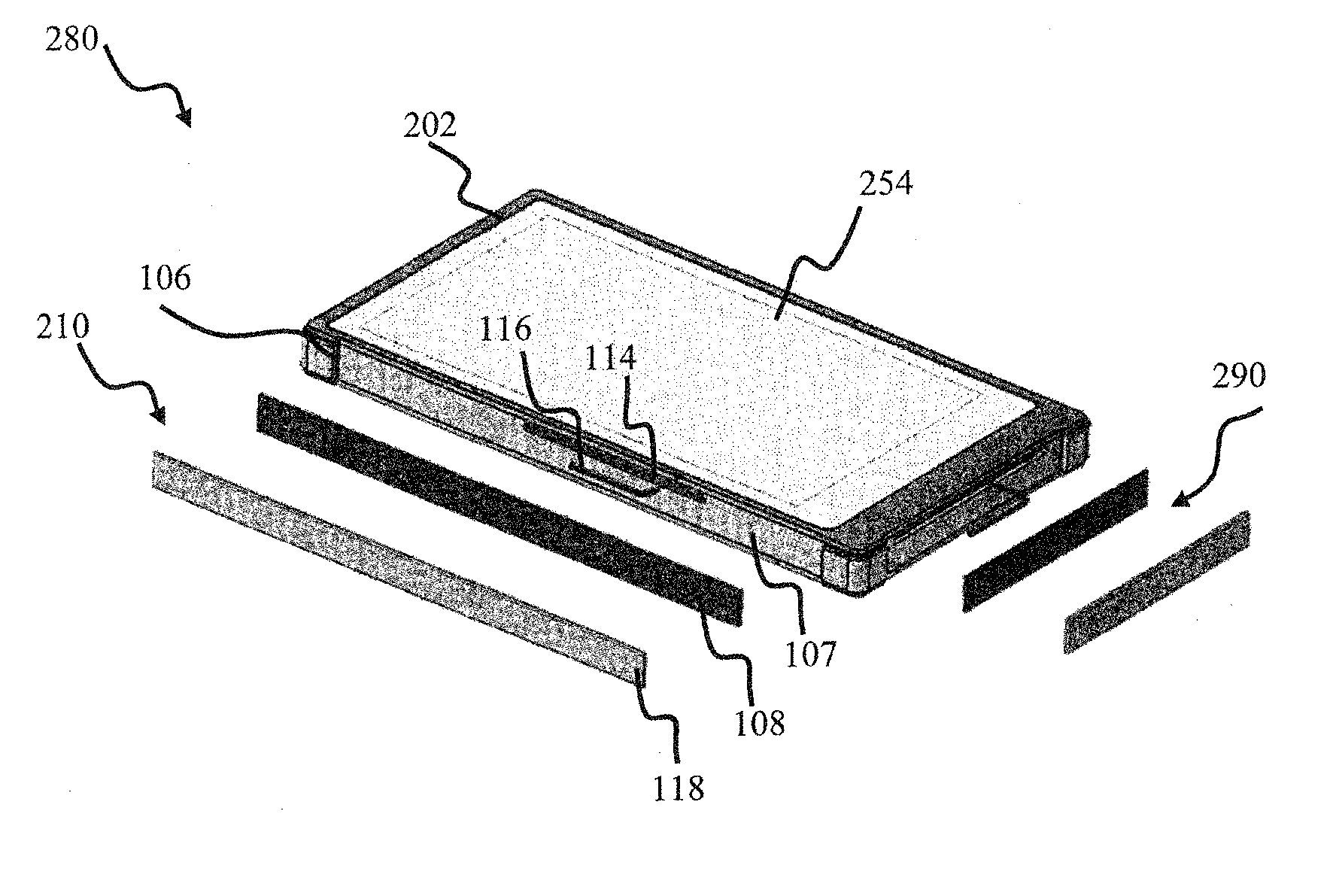
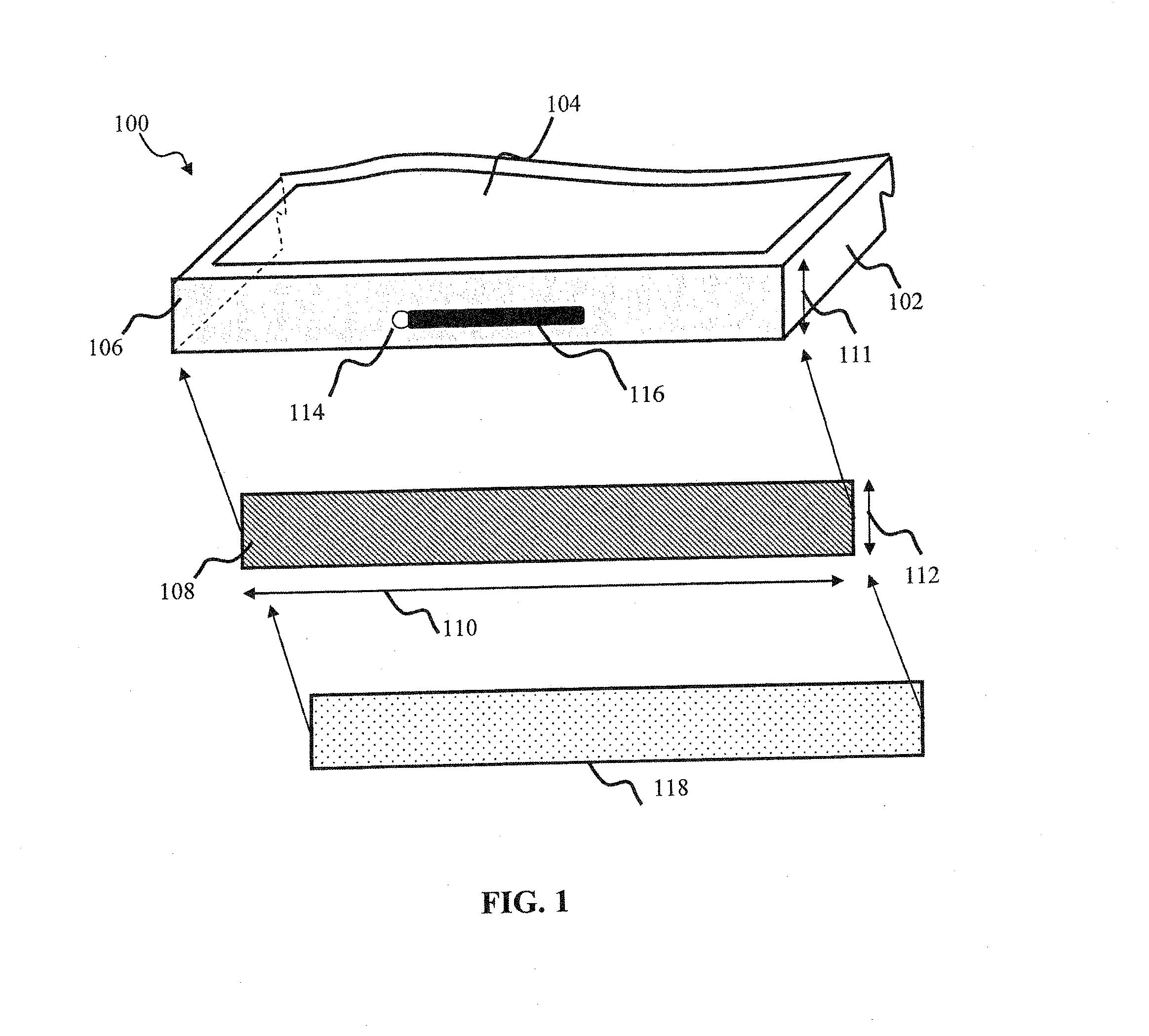
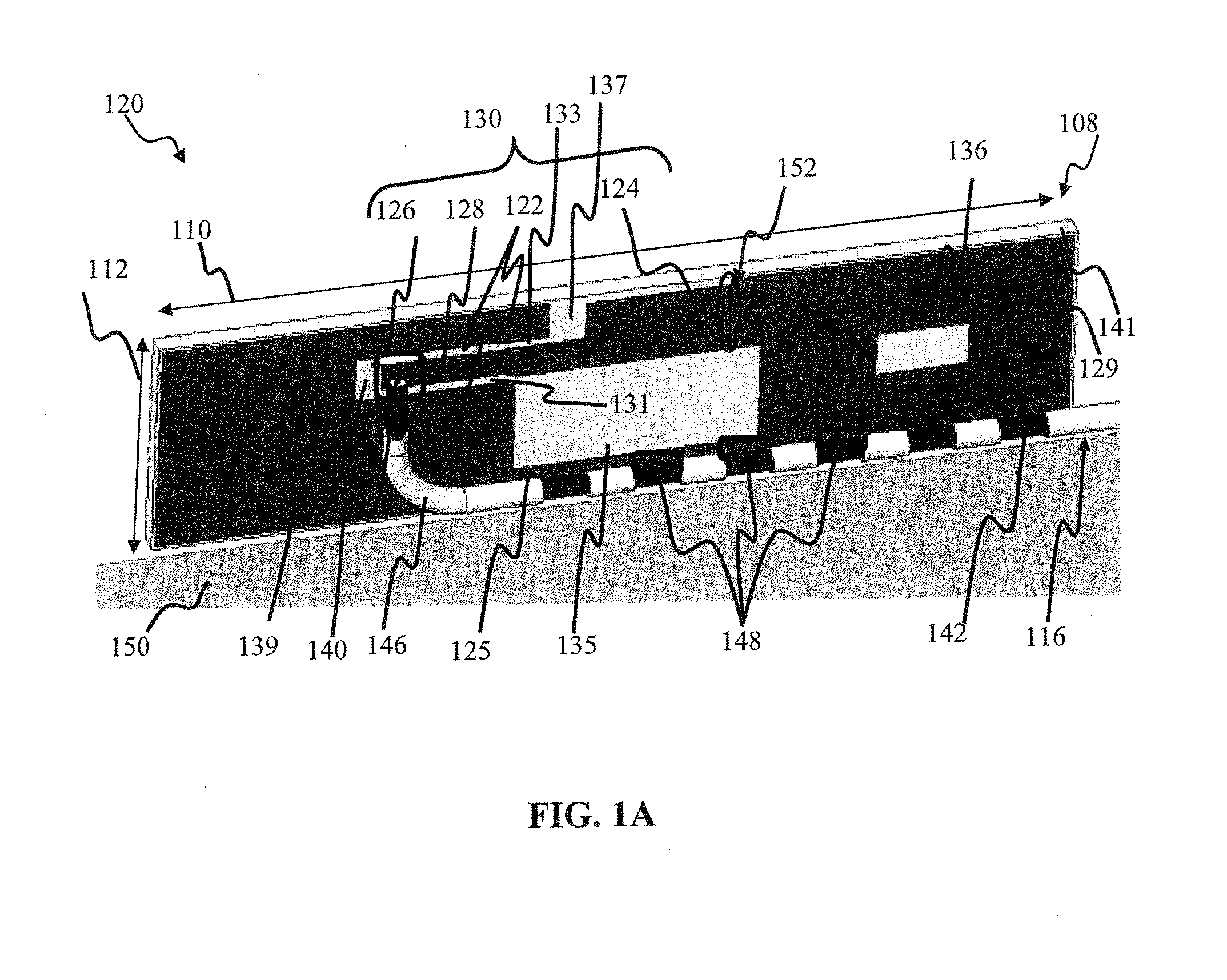
Antenna device and radio equipment having the same
InactiveUS6462716B1Simple circuit configurationReduce conduction lossMultiple-port networksSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
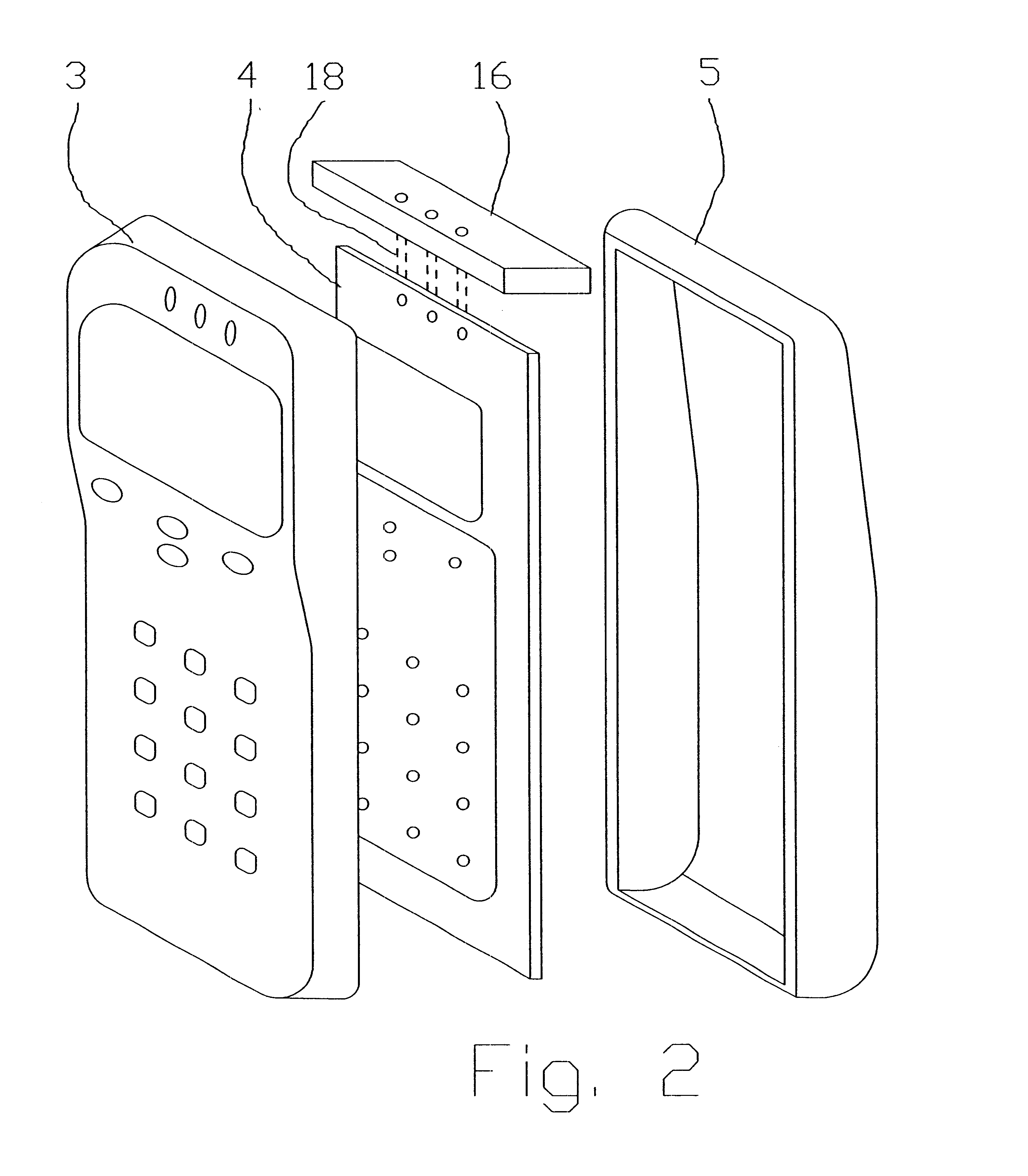
Antenna device and radio equipment having the same
InactiveUS20020044092A1Simple circuit configurationReduce conduction lossMultiple-port networksSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
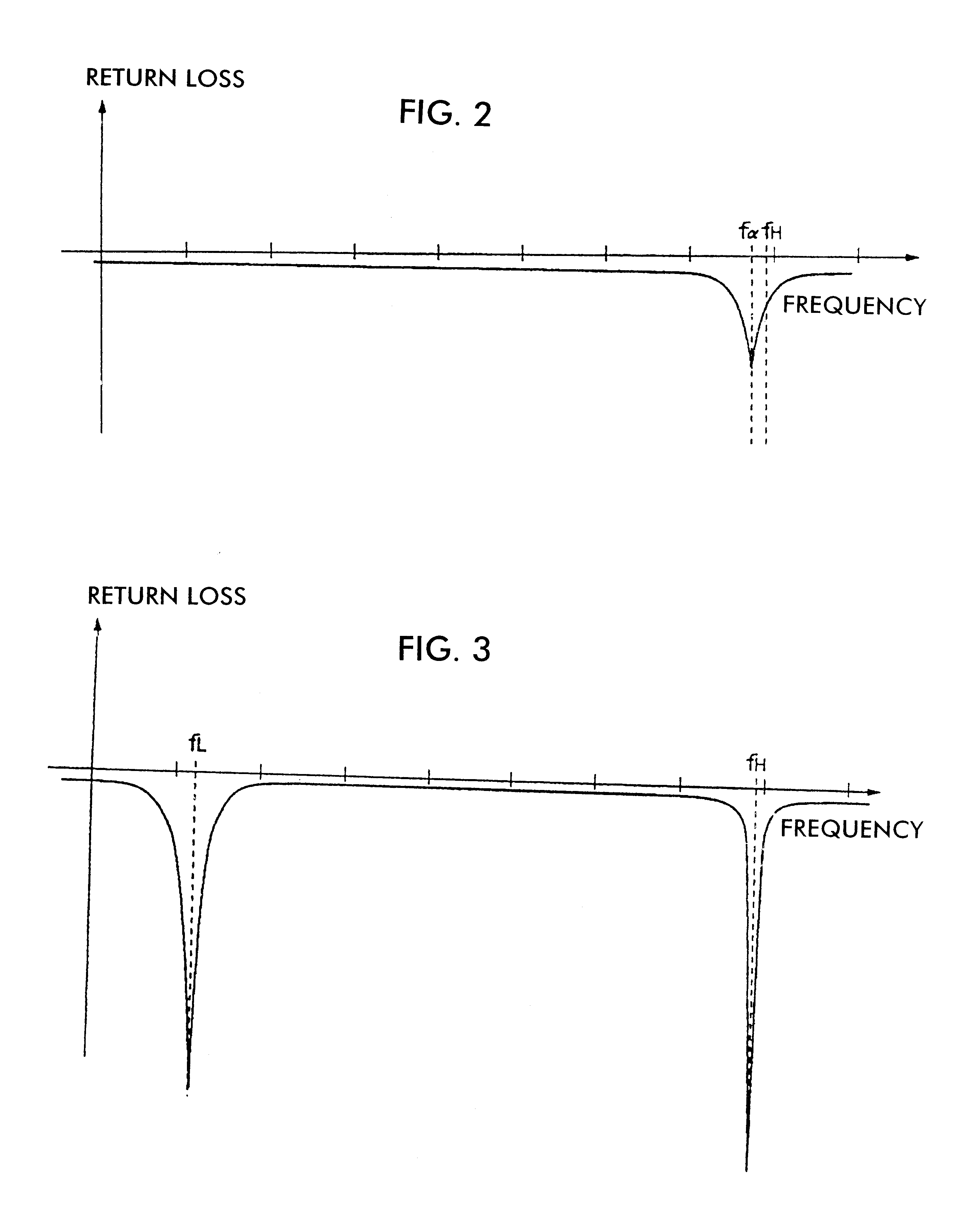
An LC parallel resonance circuit is connected in series with the power supply side of the antenna conductor portion. The antenna conductor portion is configured so as to resonate at a frequency slightly lower than the center frequency in the higher frequency band of two frequency bands for transmitting and receiving radio waves. The LC parallel resonance circuit is configured so as to resonate substantially at the center frequency in the lower frequency band for transmitting and receiving a radio wave and be capable of providing to the antenna conductor portion a capacitance for causing the antenna conductor portion to resonate at the center frequency in the higher frequency band. Thus, a circuit for changing the upper and lower frequency bands is not needed. Such a change-over circuit, which is complicated, causes problems in that the conduction loss increases, and the antenna sensitivity deteriorates. Without need of the change-over circuit, the conduction loss can be reduced, the antenna sensitivity can be enhanced and costs can be reduced.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
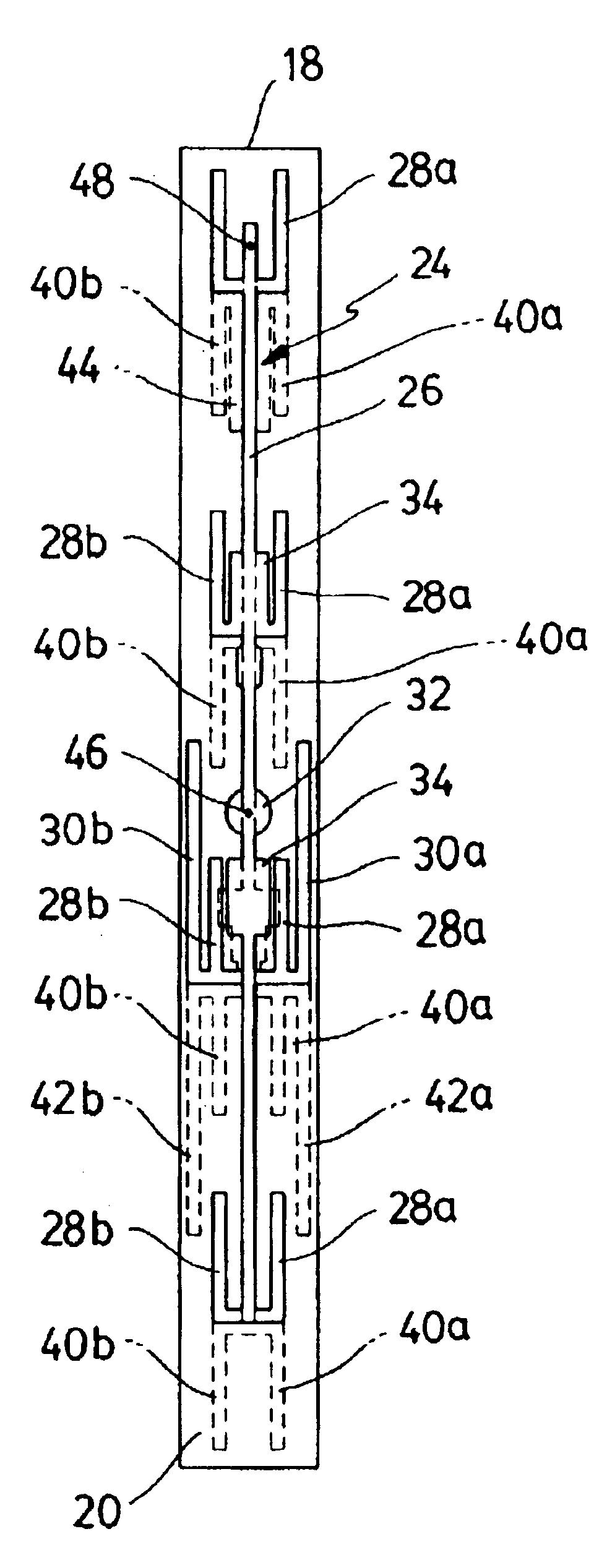
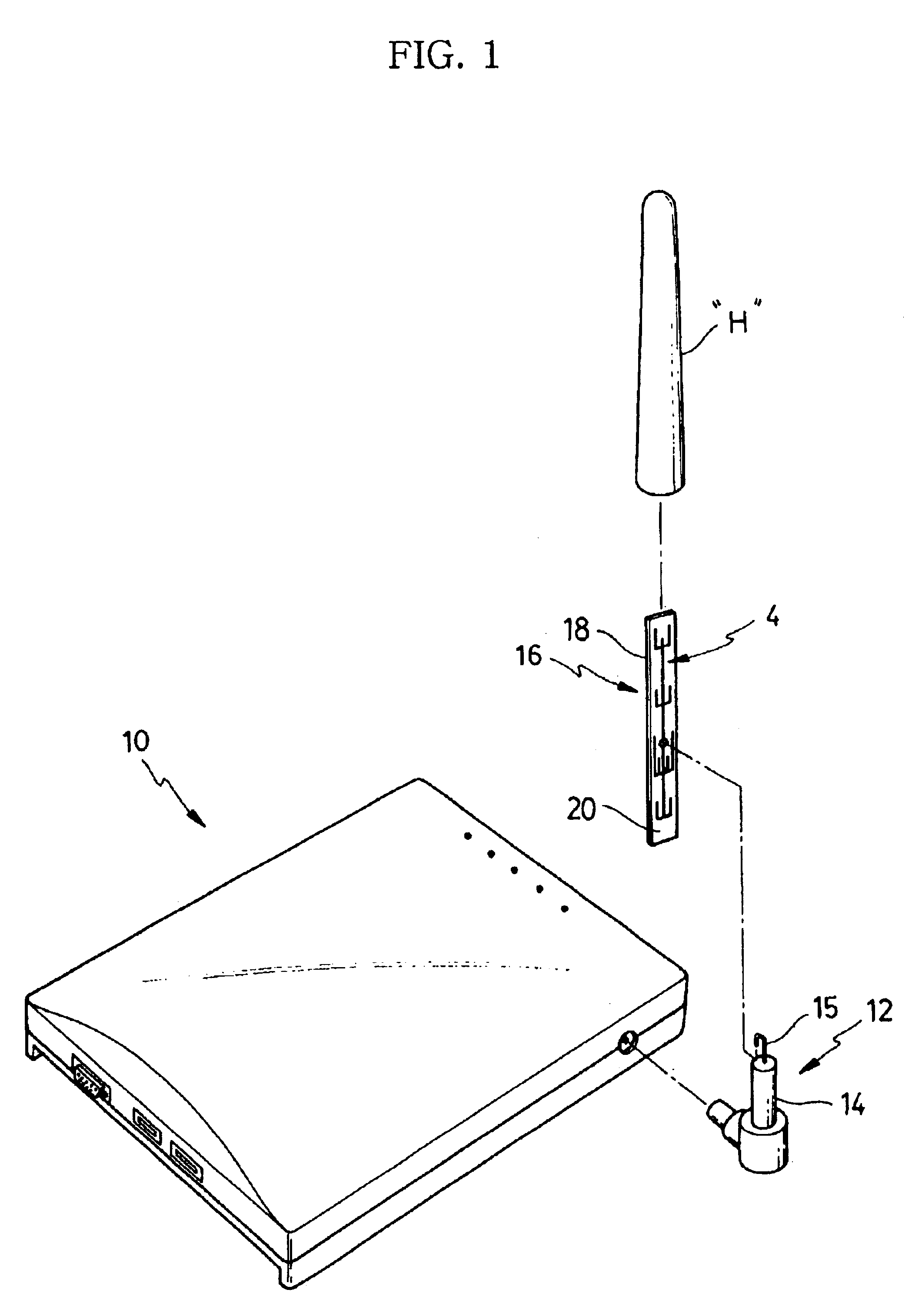
Multi-band antenna
InactiveUS20050190108A1Wide bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandLow frequency band
A multi-band antenna (1) used in an electronic device and formed of a metallic sheet by defining holes therein, including a first radiating portion (30), a second radiating portion (31), a third radiating portion (32), a ground portion (2), and a coaxial transmission line (4). The first radiating portion, the ground portion and the coaxial transmission line cooperatively form a loop antenna operated at a higher frequency band of about 5.15-5.875 GHz. The second radiating portion, the ground portion and the coaxial transmission line cooperatively form a first inverted-F antenna operated at another higher frequency band of about 5.725-5.875 GHz. The third radiating portion, the ground portion and the coaxial transmission line cooperatively form a second inverted-F antenna operated at a lower frequency band of about 2.4-2.5 GHz.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
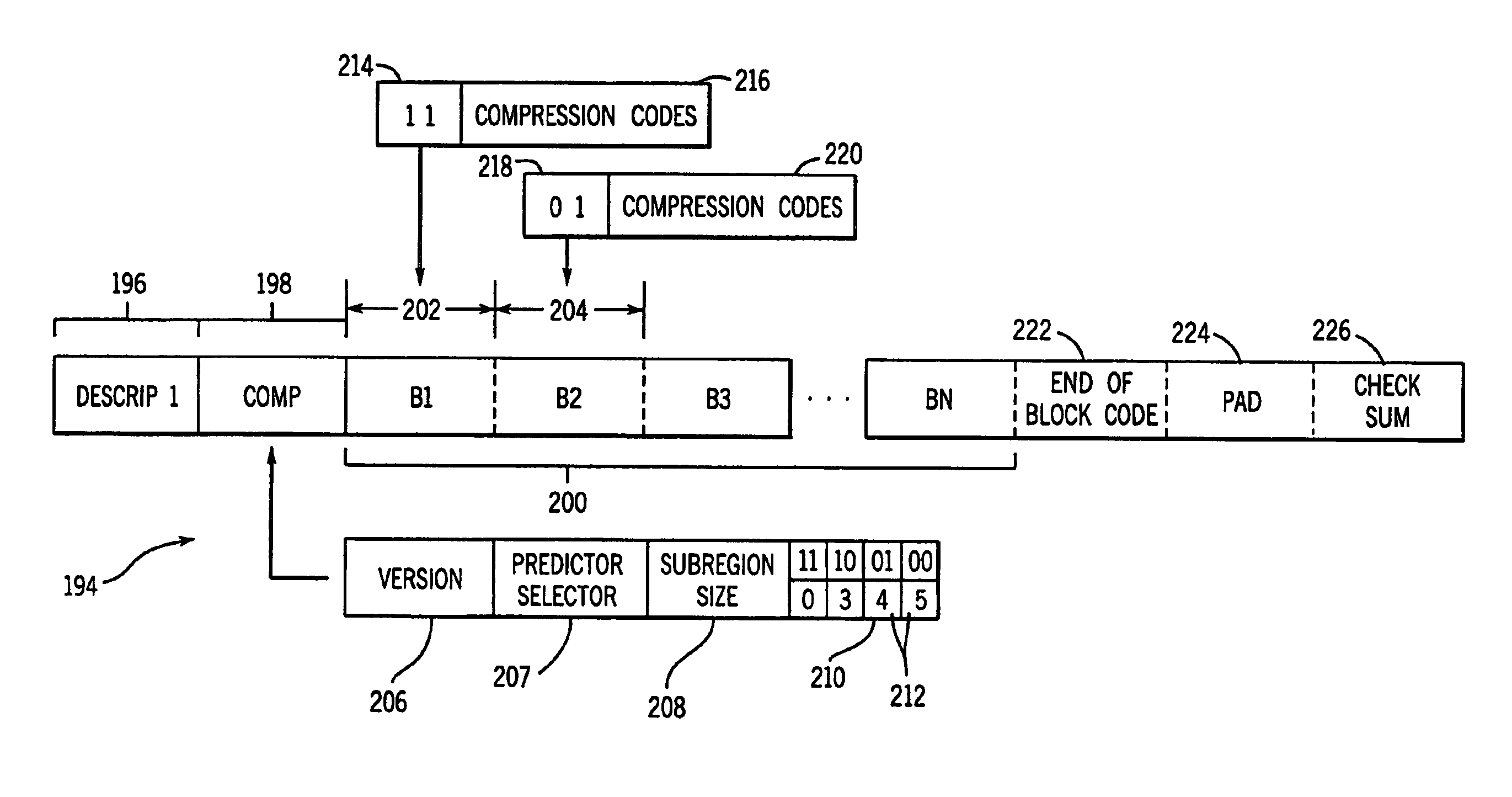
Method and system for lossless wavelet decomposition, compression and decompression of data
InactiveUS6912319B1Big lossRapid and efficient lossless compressionPulse modulation television signal transmissionGeometric image transformationData setImage resolution
Image data is compressed by decomposing the image data into a plurality of resolutions or sized by wavelet decomposition, followed by compression of the resulting data sets. Adaptive Huffman code compression is optimized for compressing the data sets, predictive errors for a low frequency band and the wavelet transformed values for high frequency bands. The image data is thus compressed losslessly and in multiple resolutions such that desired resolution images can be reconstructed and transmitted in accordance with available-bandwidth and viewing capabilities.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Dual-band feed horn with common beam widths
ActiveUS8957821B1Reduces pointing requirementLow efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsDual frequencyLow frequency band
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Chassis-excited antenna apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20120206302A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsLow frequency bandResonator
A chassis-excited antenna apparatus, and methods of tuning and utilizing the same. In one embodiment, a distributed loop antenna configuration is used within a handheld mobile device (e.g., cellular telephone). The antenna comprises two radiating elements: one configured to operate in a high-frequency band, and the other in a low-frequency band. The two antenna elements are disposed on different side surfaces of the metal chassis of the portable device; e.g., on the opposing sides of the device enclosure. Each antenna component comprises a radiator and an insulating cover. The radiator is coupled to a device feed via a feed conductor and a ground point. A portion of the feed conductor is disposed with the radiator to facilitate forming of the coupled loop resonator structure.
Owner:CANTOR FITZGERALD SECURITIES
Enhancing the performance of coding systems that use high frequency reconstruction methods
ActiveUS7050972B2Improve audio qualityBetter trade-offCode conversionSpeech recognitionReconstruction methodComputer module
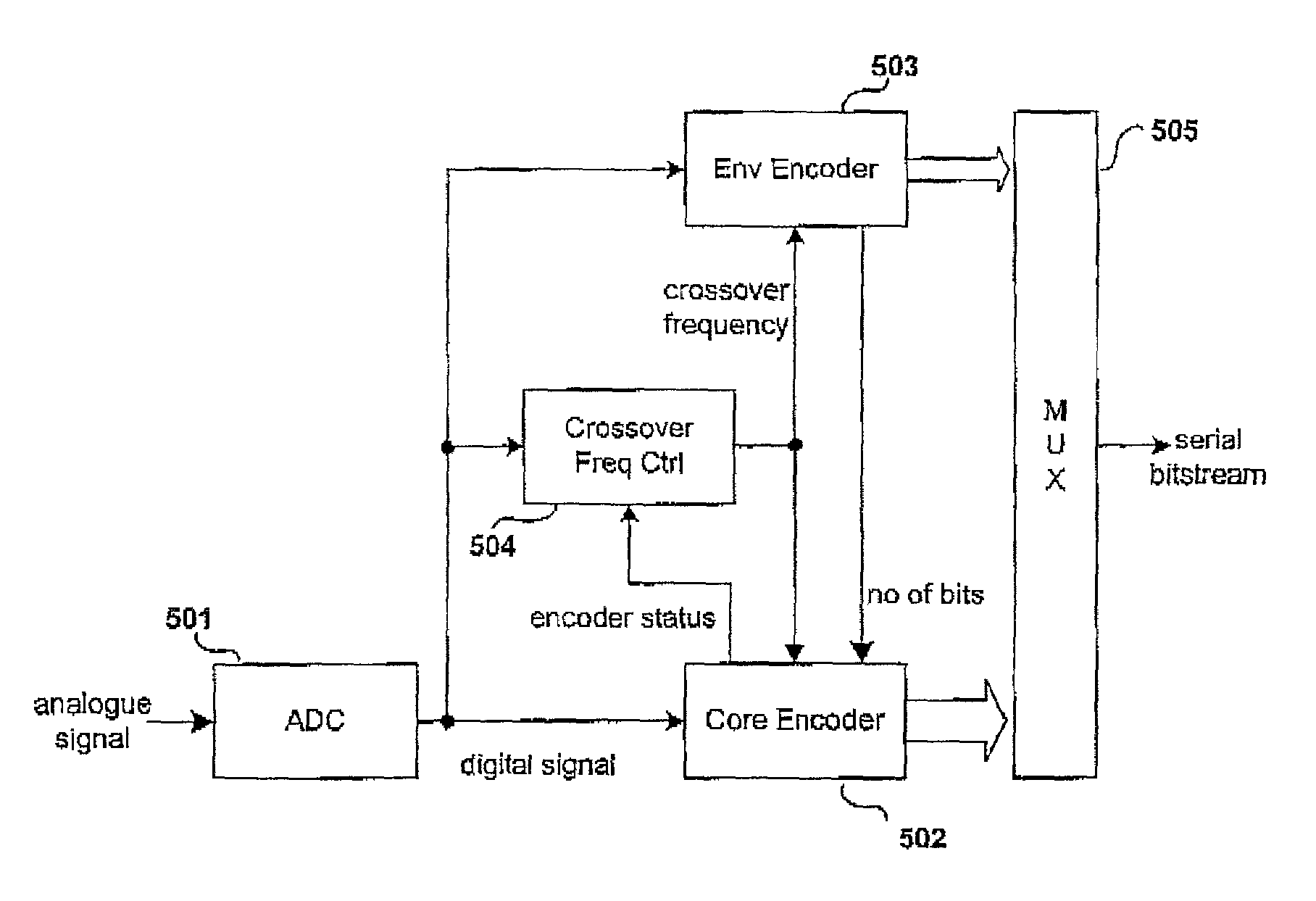
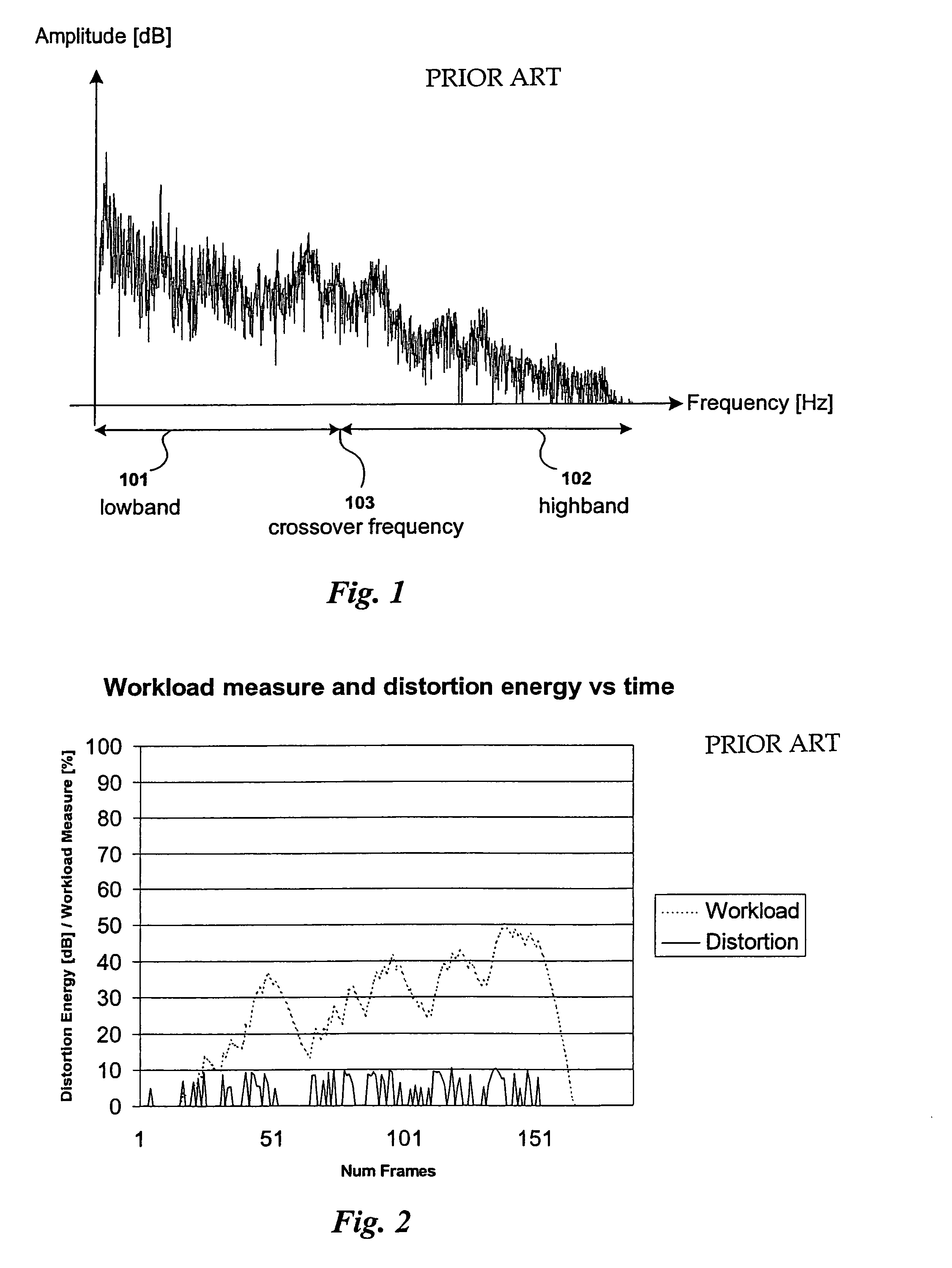
An apparatus for encoding an audio signal to obtain an encoded audio signal to be used by a decoder having a high frequency reconstruction module for performing a high frequency reconstruction for a frequency range above a crossover frequency includes, a core encoder for encoding a lower frequency band of the audio signal up to the crossover frequency, the crossover frequency being variable, and the core encoder being operable on a block-wise frame by frame basis, and a crossover frequency control module for estimating, dependent on a measure of the degree of difficulty for encoding the audio signal by the core encoder and / or a boarder between a tonal and a noise-like frequency range of the audio signal, the crossover frequency to be selected by the core encoder for a frame of a series of subsequent frames, so that the crossover frequency is variable adaptively over time for the series of subsequent frames.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
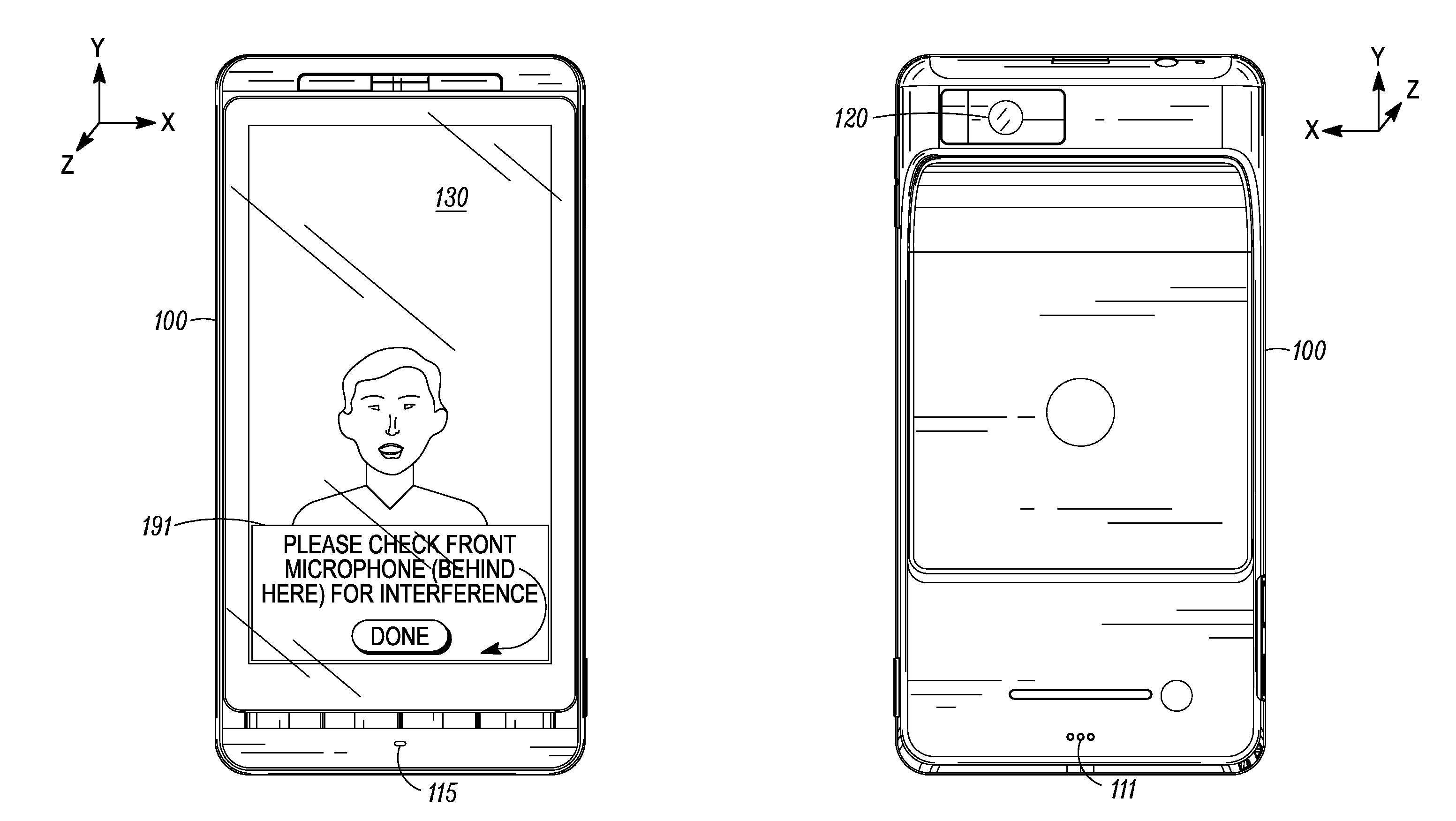
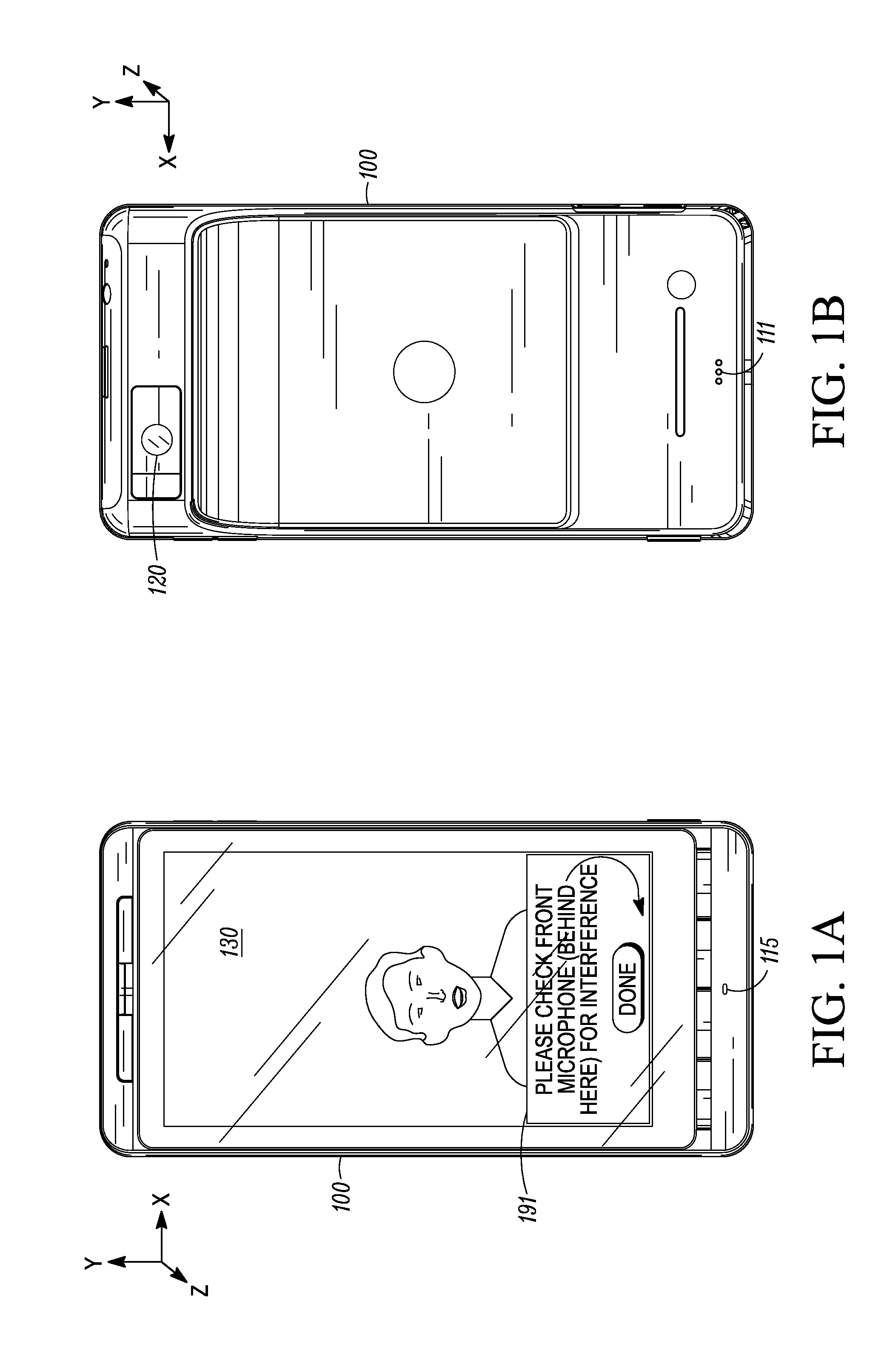
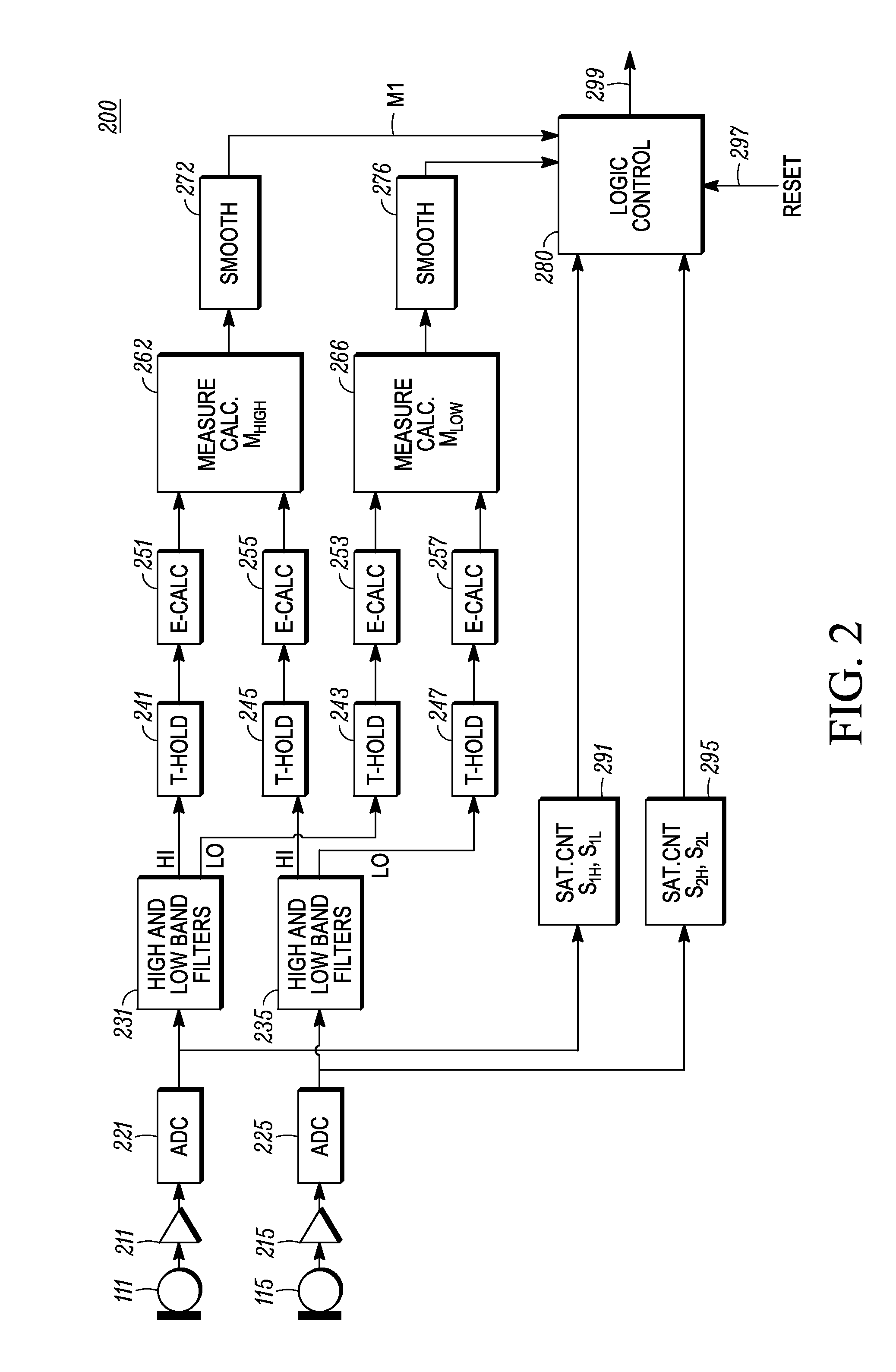
Microphone Interference Detection Method and Apparatus
A method and apparatus for detecting microphone interference includes first and second built-in microphones producing first and second microphone signals. A first filter bank creates first high-frequency-band and first low-frequency-band signals from the first microphone signal. A second filter bank creates second high-frequency-band and second low-frequency-band signals from the second microphone signal. A first measurement calculator determines a high-frequency-band energy value from the first high-frequency-band signal and the second high-frequency-band signal when the first and second high-frequency-band signals' magnitudes exceeds predetermined thresholds. A second measurement calculator calculates a low-frequency-band energy value from the first low-frequency-band signal and the second low-frequency-band signal when the first and second low-frequency-band signals' magnitudes exceed predetermined thresholds. A logic control block, coupled to the first measurement calculator and the second measurement calculator, detects microphone interference and produces an output signal indicating microphone occlusion or wind noise.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method of controlling diaphragm excursion of electrodynamic loudspeakers
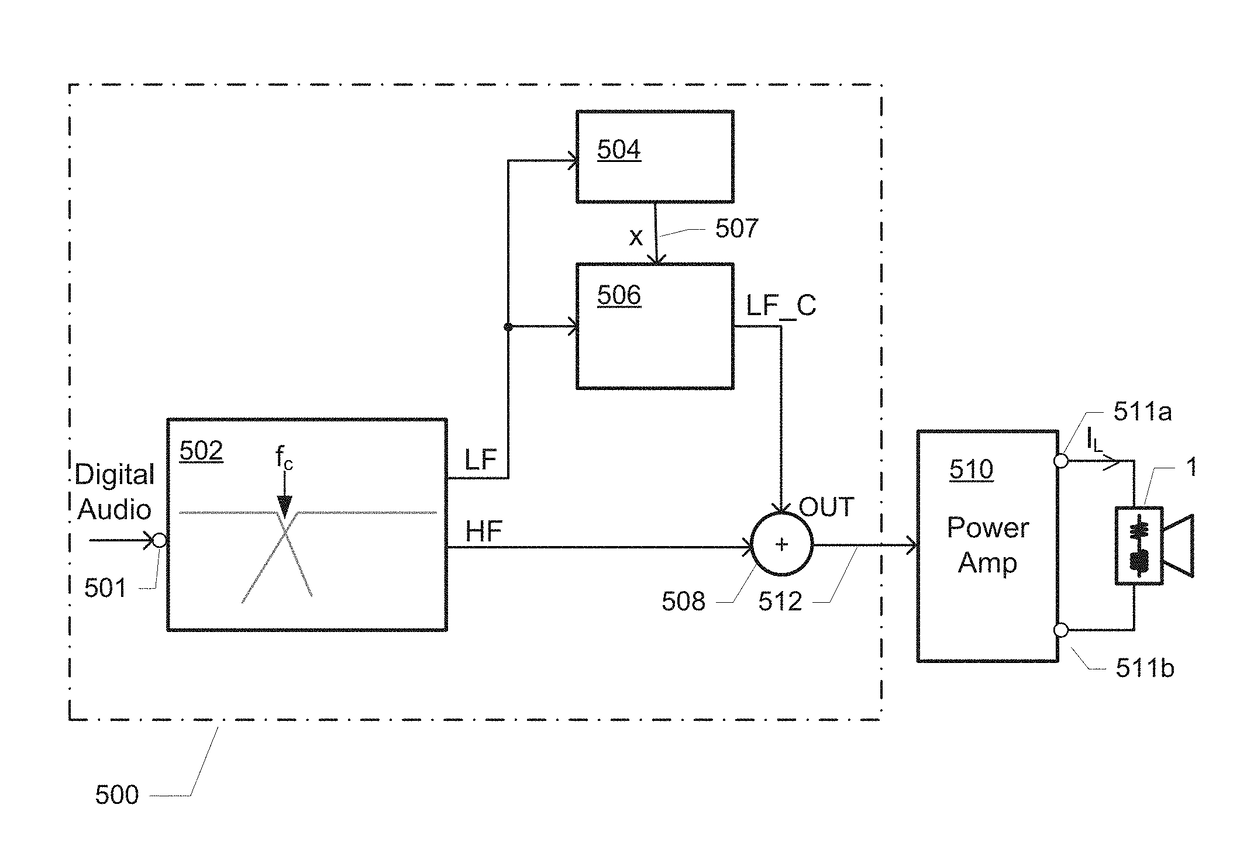
ActiveUS9813812B2Reliable and convenient protectionSignal processingCombination control in untuned amplifierBand splittingLow frequency band
The present application relates in one aspect to a method of controlling diaphragm excursion of an electrodynamic loudspeaker. The method comprises dividing the audio input signal into at least a low-frequency band signal and a high-frequency band signal by a band-splitting network and applying the low-frequency band signal to a diaphragm excursion estimator. The instantaneous diaphragm excursion is determined based on the low-frequency band signal. The determined instantaneous diaphragm excursion is compared with an excursion limit criterion. The low-frequency band signal is limited based on a result of the comparison between the instantaneous diaphragm excursion and the excursion limit criterion to produce a limited low-frequency band signal which is combined with the high-frequency band signal to produce an excursion limited audio signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Internal antennas for mobile communication devices
InactiveUS6466176B1Promote resultsImprove efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandElectrical conductor
A multi-band microwave antenna which is resonant and radiant at a high frequency band and at one or more lower frequency bands includes an electrically-conductive ground plane on one face of a dielectric substrate; an electrically conductive strip line on the opposite face of the dielectric substrate; a curved slot formed in the ground plane having a feed side electromagnetically coupled to the feed end of the strip line, and a load side electromagnetically coupled to the load end of the strip line, such that the slot is resonant and radiant at the high frequency band; and a further electrical conductor electrically connected to the ground plane to serve as a continuation thereof at the load side of the slot and electromagnetically coupled to the slot at the lower frequency bands such as to cause the slot to be resonant and radiant also at the lower frequency band or bands.
Owner:IN4TEL
Dual-band omnidirectional antenna for wireless local area network
InactiveUS6859176B2Easy to operateReduce manufacturing costSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual frequencyOmnidirectional antenna
The present invention relates to a dual-band omnidirectional antenna for wireless LANs. The antenna has a planar dielectric substrate, and first and second conductive patterns. The planar dielectric substrate has two parallel surfaces. The first conductive pattern is arranged on one surface of the substrate, and is provided with a first feeder line arranged on a longitudinal central line of the substrate and a plurality of radiating elements connected to the first feeder line and designed such that some of them operate in a high frequency band (4.9 to 5.85 GHz frequency band), and others thereof operate in a low frequency band (2.4 to 2.5 GHz frequency band). The second conductive pattern is arranged on the other surface of the substrate, and provided with a second feeder line arranged on a longitudinal central line of the substrate and a plurality of radiating elements connected to the second feeder line arid up-down symmetrically arranged with respect to the radiating elements on the first conductive pattern.
Owner:SUNWOO COMM +1
Point-to-multipoint wireless access system
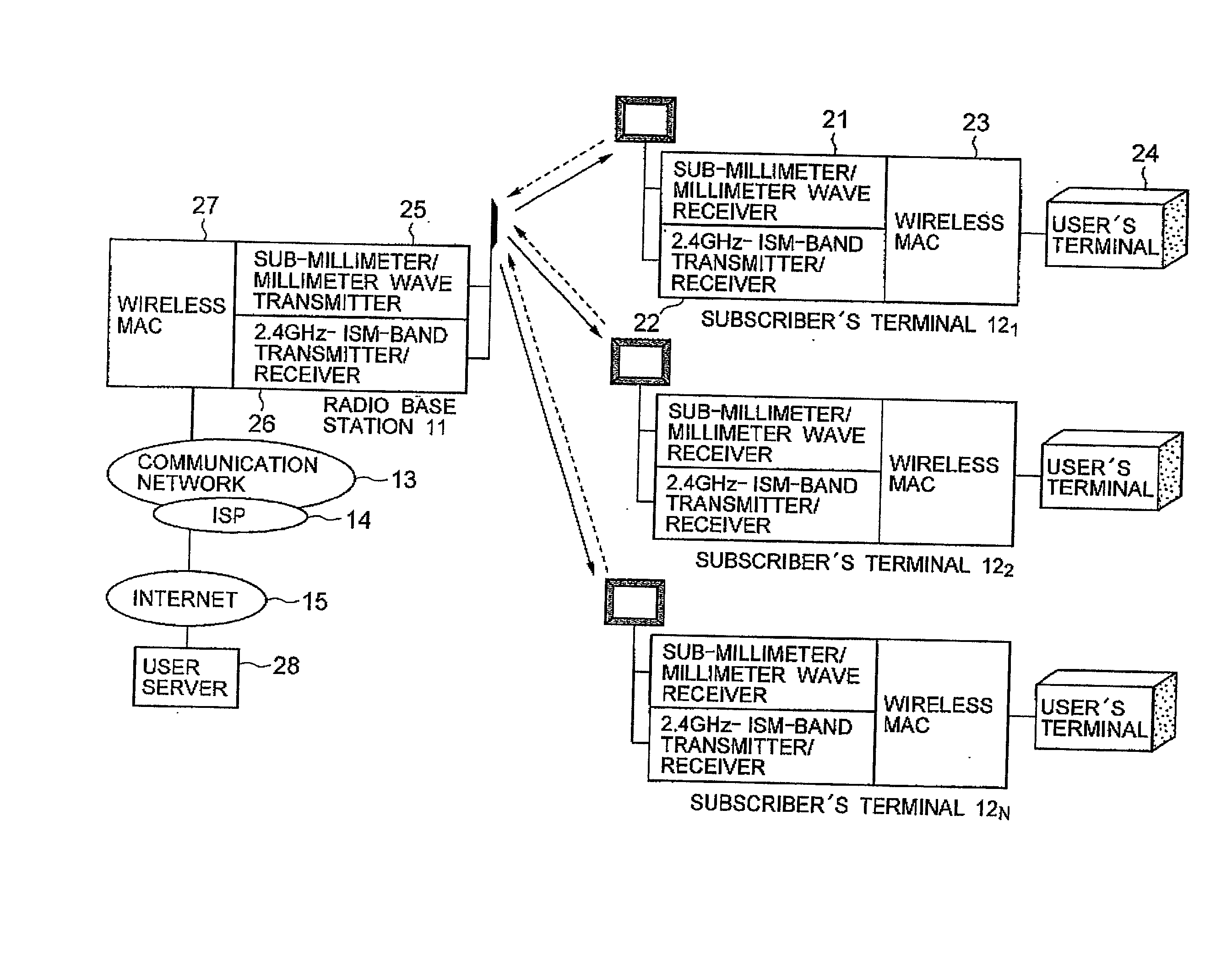
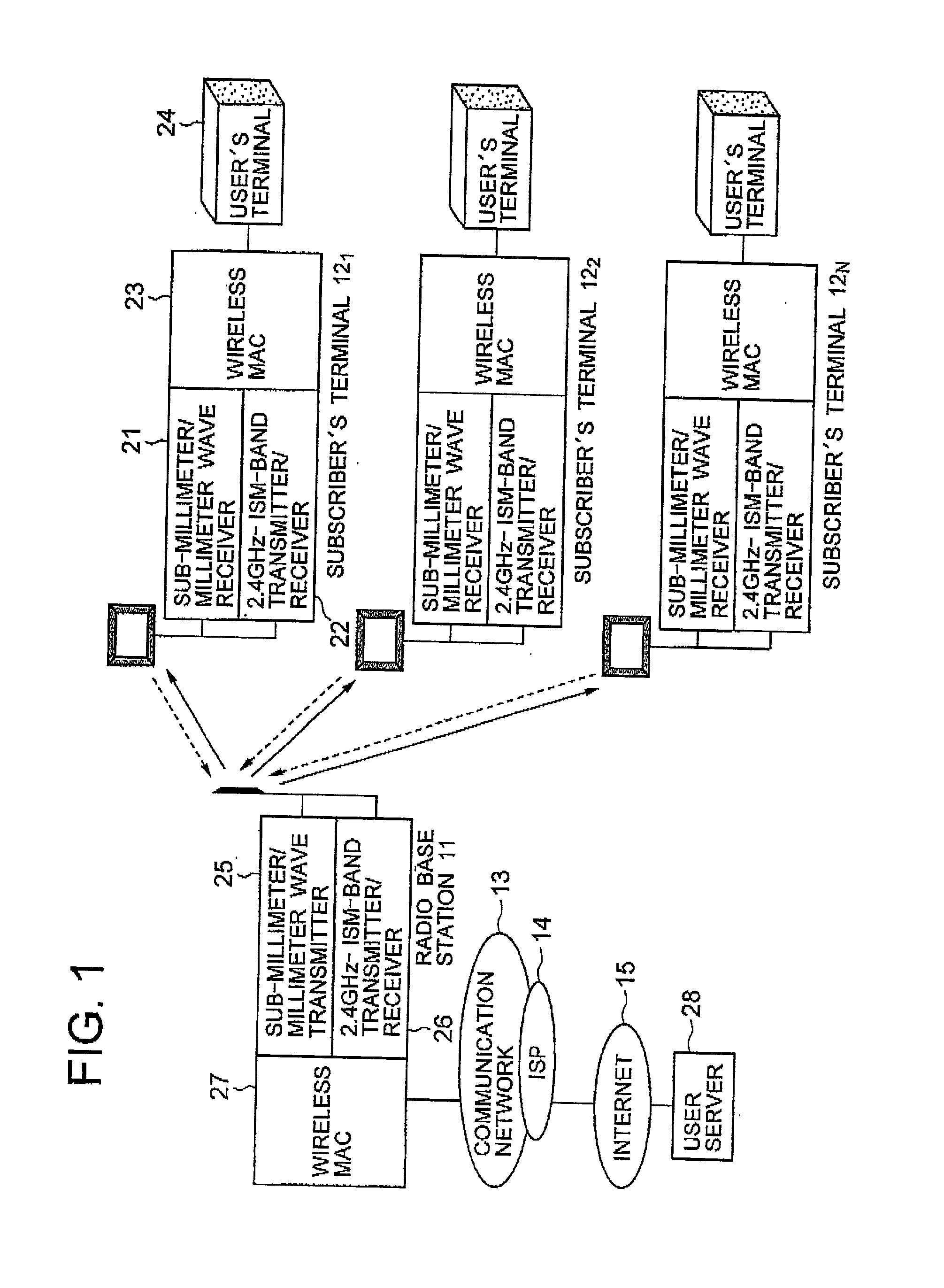
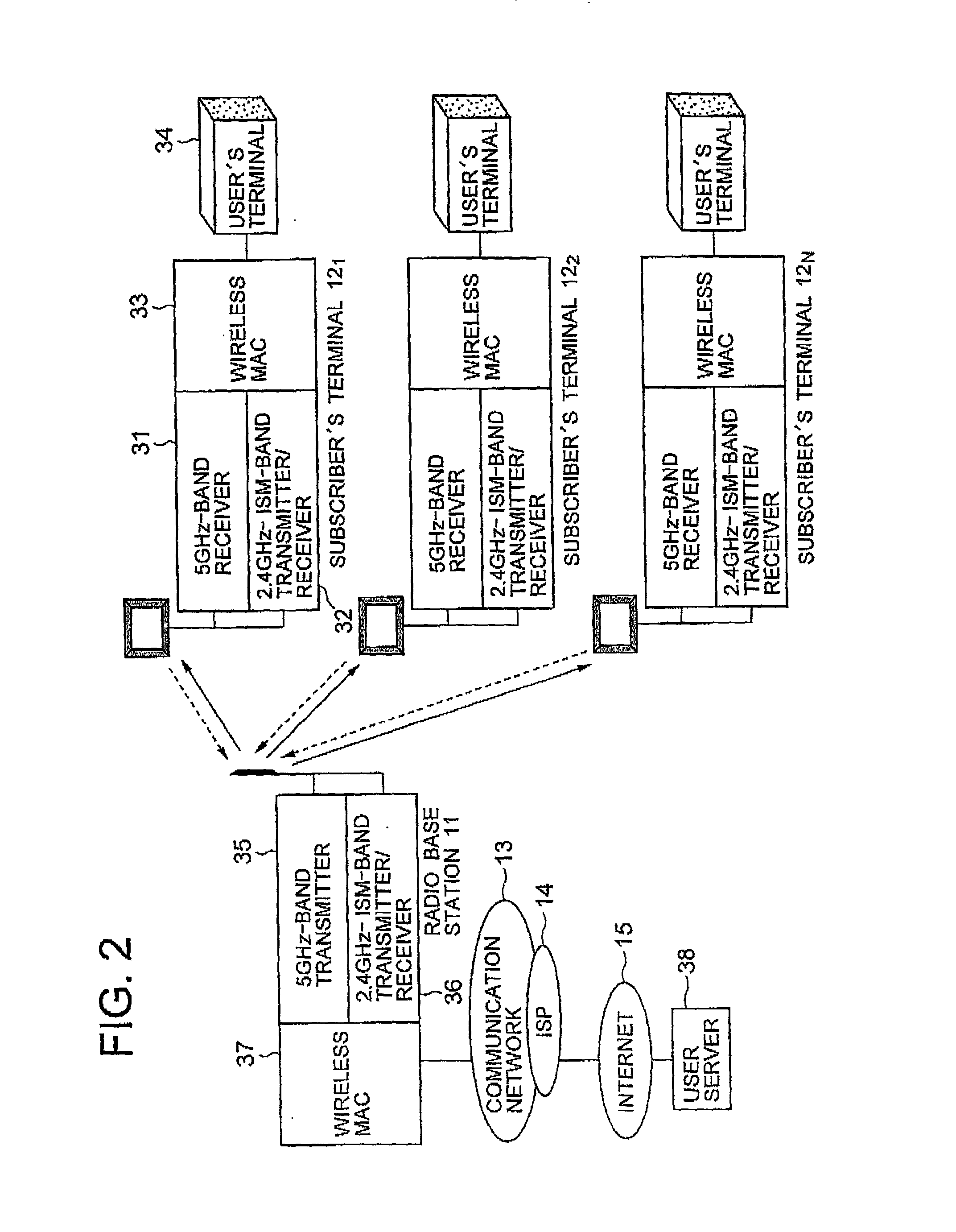
InactiveUS20020045459A1Increase speedData is very largeNetwork topologiesActive radio relay systemsLow frequency bandLicense
A point-to-multipoint wireless access system includes a wireless base station and a plurality of wireless subscriber's terminals, wherein the down-link channels from the base station to the respective subscriber's terminals use a higher frequency band, and the up-link channels from the respective subscriber's terminals to the base station use a lower frequency band which is exempt of license.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multi-band antenna
InactiveUS7119747B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandLow frequency band
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Dual frequency band inverted-F antenna
ActiveUS6930640B2Lower resonance frequencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual frequencyResonance
A dual frequency band inverted-F antenna used for communicating a low frequency signal and a high frequency signal includes a substrate, a ground metal, a vortical metal structure, a short circuit leg, a feeding leg, and a terminal micro strip. The ground metal and the terminal micro strip are formed on the lower surface of the substrate. The vortical metal structure, formed on the upper surface of the substrate, further has a short circuit end and an open circuit end. The short circuit leg connects electrically the short circuit end of the vortical metal structure with the ground metal. The feeding leg extends along a predetermined direction of the vortical metal structure to couple with a feeding circuit on the substrate. The terminal micro strip connects electrically to the open circuit end through a first conductive aperture. By increasing the encircling number of the vortical metal structure, the coupling effect is generated so that the equivalent wavelength of the high frequency signal can be longer, thus the resonance frequency thereof can be reduced, and so a first frequency can be still kept communicating at a lower frequency band and a second frequency can also be added for communicating at a higher frequency band.
Owner:GEMTEK TECH CO LTD
Methods and system for multi-path mitigation in tracking objects using reduced attenuation RF technology
ActiveUS7872583B1Small incremental costImprove accuracyPosition fixationDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingUltrasound attenuation
A method and system for a long range Radio Frequency (RF)-based identification, tracking and locating of objects. The method and system use a narrow bandwidth ranging signal(s), including VHF of lower frequency bands, which minimizes propagation loss and loss of accuracy of the RF locating signals. The method and system includes narrow bandwidth ranging signal multi-path mitigations processor, which further improves the track-locate accuracy. The signal is sent from a Master Unit(s) to a Tag. The signal traveling time is recorded and the distance between the Master(s) and the Tag is calculated. The method and system allow achieving a longer distance of the RF narrow bandwidth ranging signal penetration and an increased accuracy by using VHF bands in conjunction with the narrow bandwidth ranging signal multi-path mitigations processor. The techniques of Digital Signal Processing and Software-Defined Radio are used. The actual waveforms transmitted and received by the radios are defined by the software. The roles of the Master Unit(s) and the Tag can be reversed.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
Antenna device for full metal shell
ActiveCN103401059AImprove frequency band coverageSolving Design ChallengesAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsMetallic enclosureRadio frequency signal
The invention discloses an antenna device for a full metal shell. The antenna device comprises a metal shell arranged at the back of communication equipment, antenna branches and feeding points, wherein a metal frame extending from the back of the communication equipment to the side face is arranged around the periphery of the metal shell; the metal shell is segmented and separated into a first metal shell, a second metal shell and a third metal shell; the feeding points are respectively positioned between the first metal shell and the second metal shell and between the second metal shell and the third metal shell; an antenna branch I arranged at the first metal shell and an antenna II arranged at the third metal shell are respectively connected with a radio-frequency signal source of a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) mainboard arranged on the second metal shell, and signals are correspondingly fed in the first metal shell and the third metal shell through the feeding points. With a three-section type full metal shell structure, the metal frame becomes a part of the antenna, the first metal shell and the third metal shell can be used as antennas at the same time, and the antenna device has the advantages of ultra-wide low-frequency band width and high-frequency band width.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
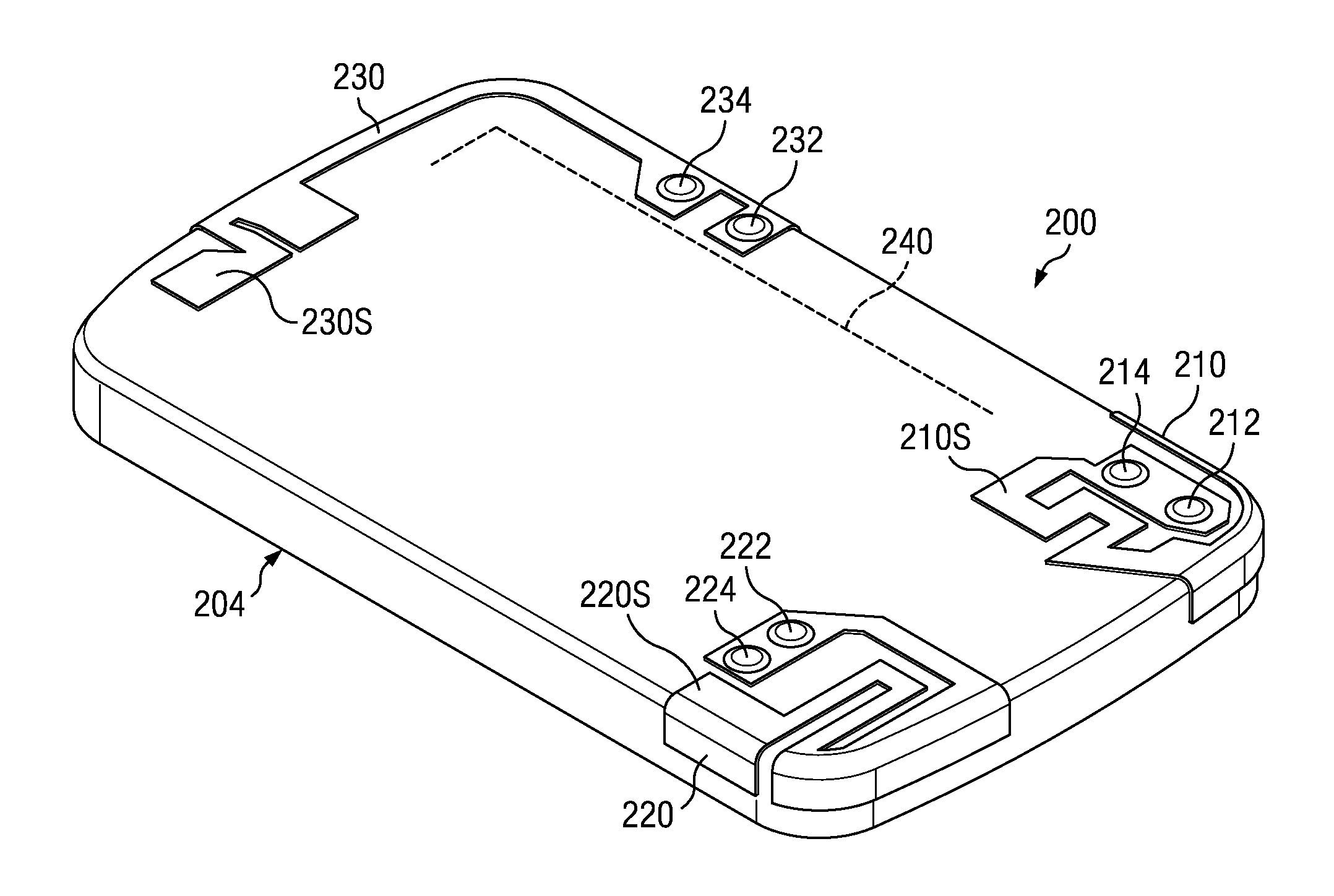
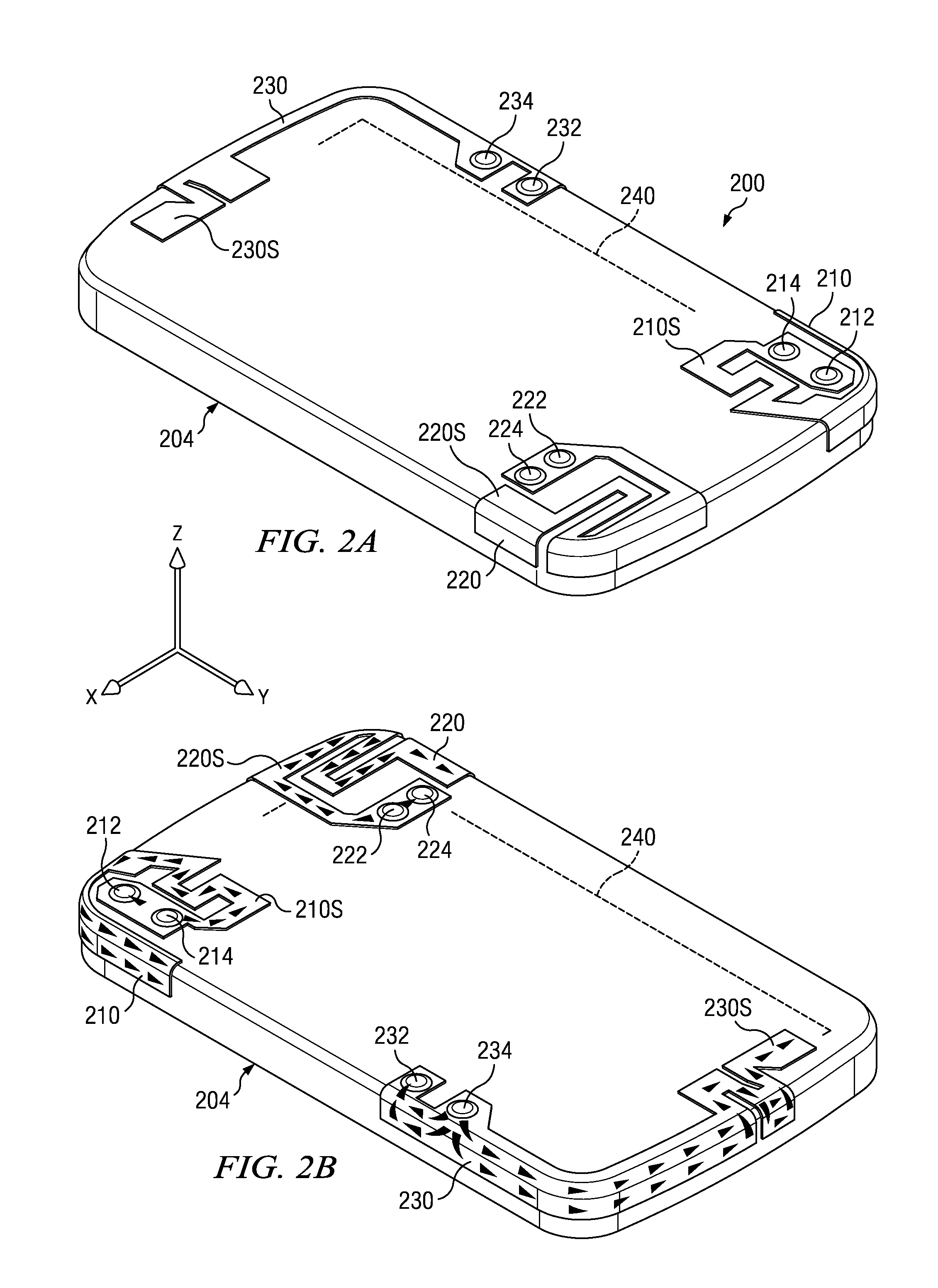
Low frequency dual-antenna diversity system
ActiveUS20110298669A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectricityDielectric substrate
A dual-antenna diversity antenna system that operates within a low frequency band range is disclosed. Two antennas are folded separately onto a single three dimensional dielectric substrate in a meander pattern configuration. Each antenna has an independent feed port and ground pin. The two antennas are configured within a compact mobile terminal to produce high isolation and low correlation at resonating frequencies within the 700 Megahertz frequency band.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
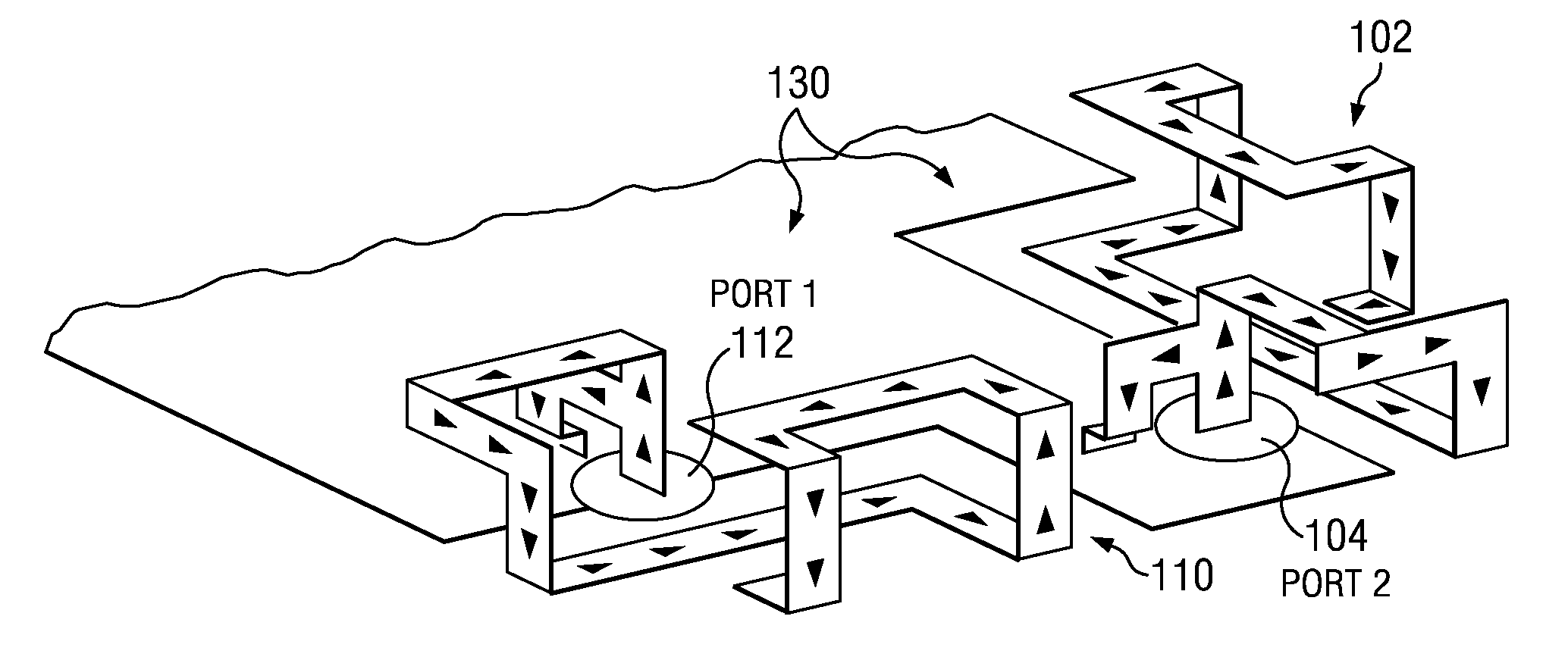
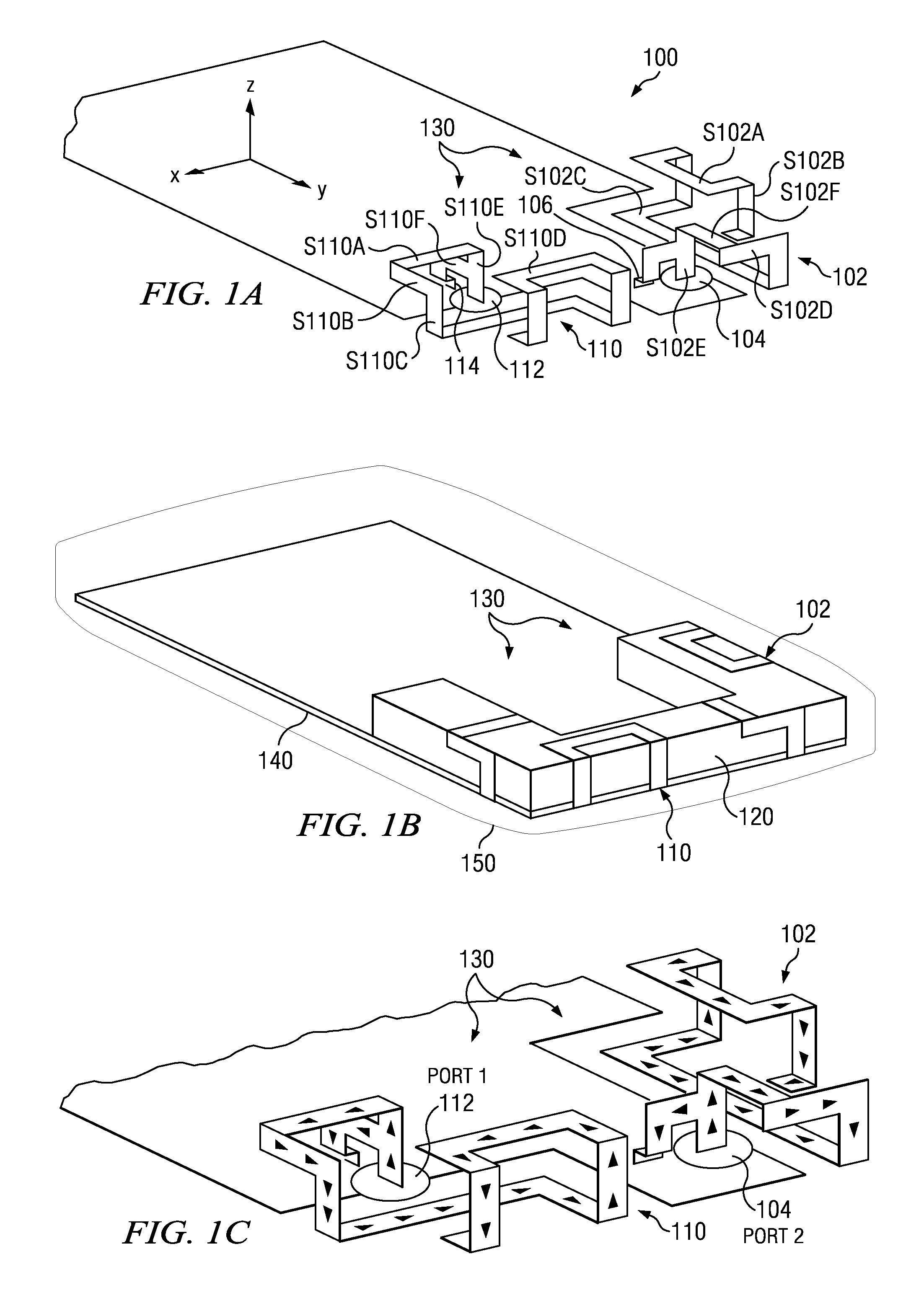
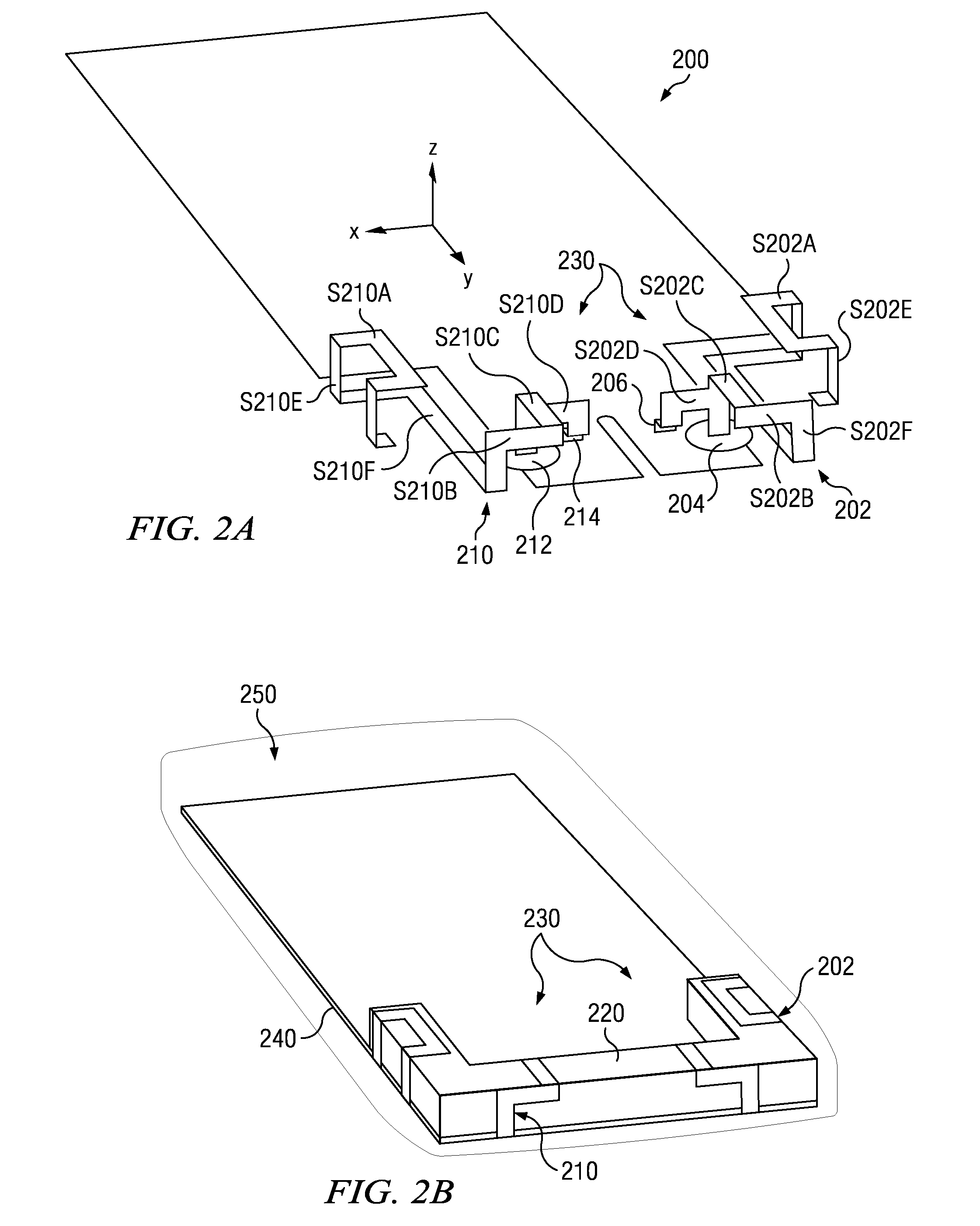
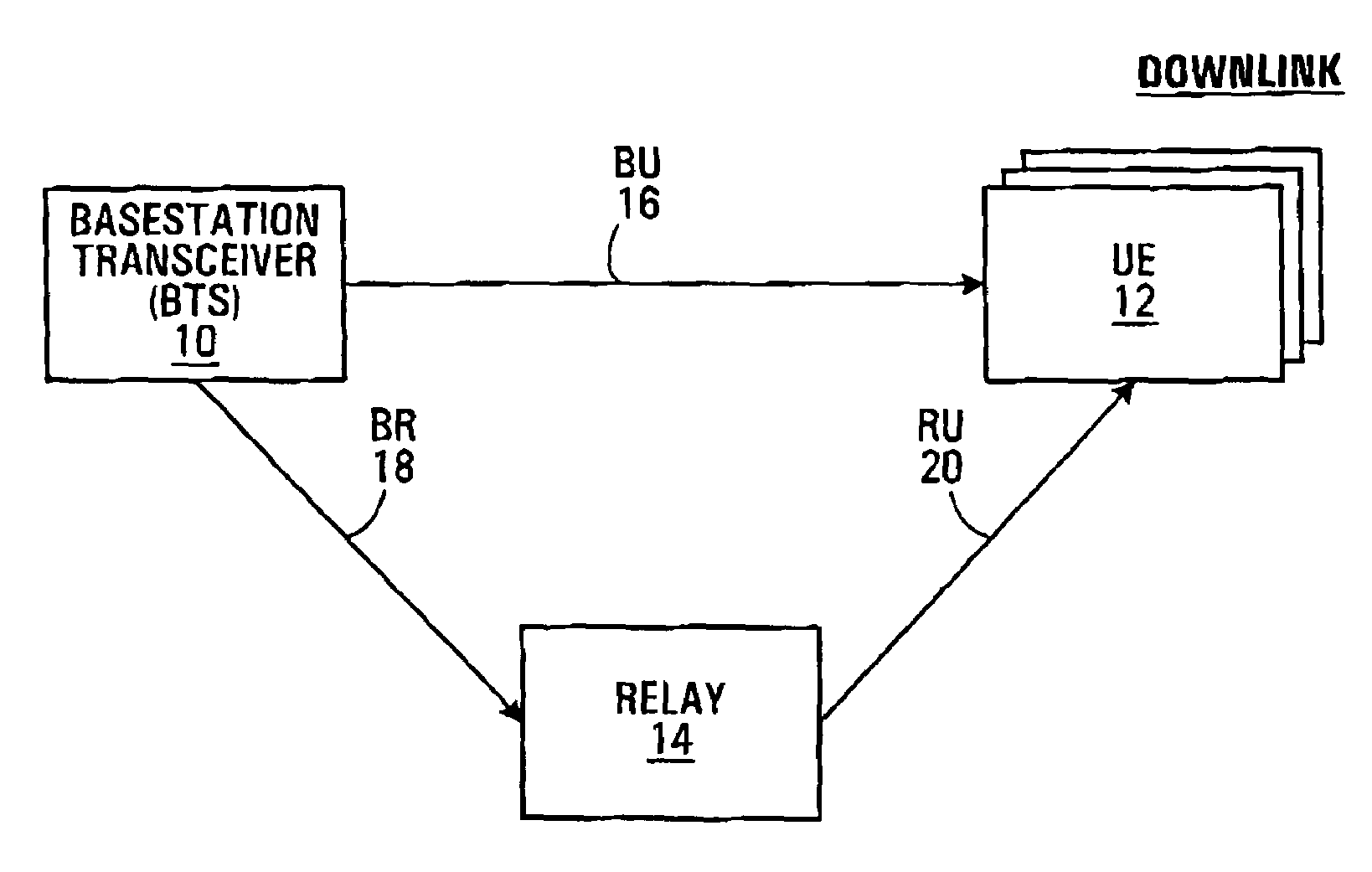
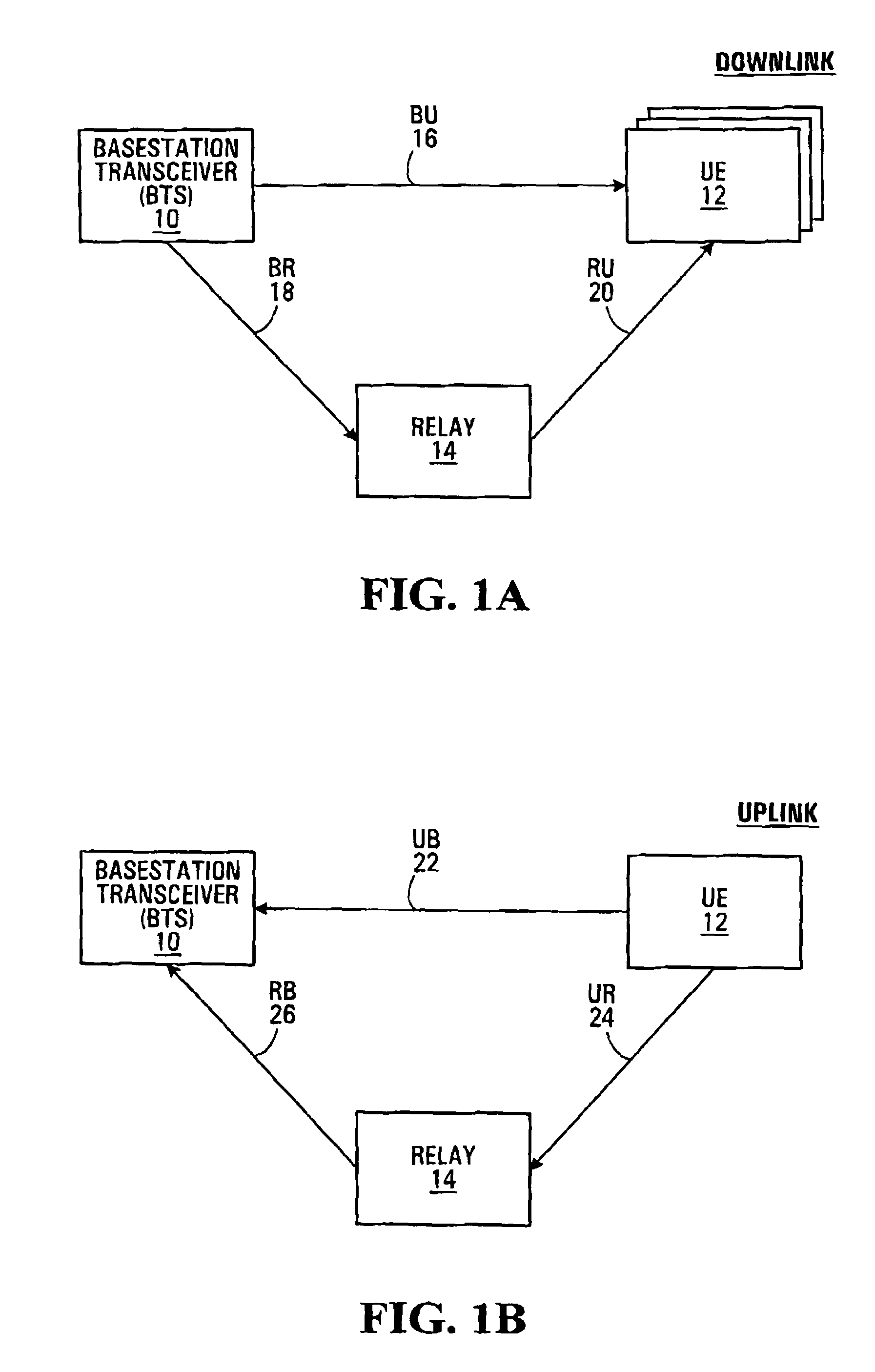
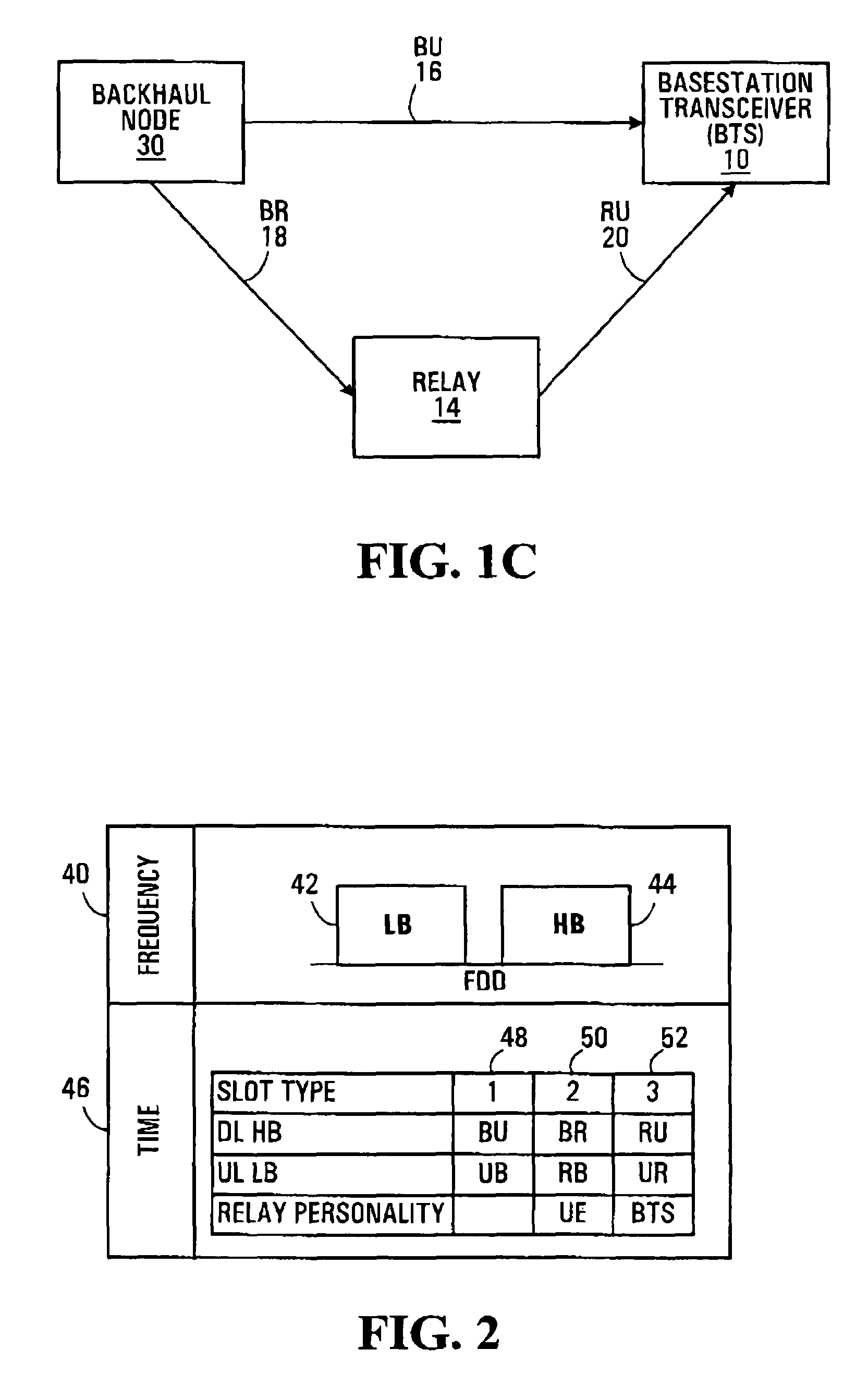
Method and apparatus for relaying a wireless signal
Systems and Methods are provided for relaying wireless signals bi-directionally between user equipment (UE) and base station transceivers (BTS). Various slot types are defined during which a relay node takes on the personality of either the UE or the BTS. In order to implement the relay node with a single transceiver chain, a first switching matrix is used to switch high band and low band RF bandpass filters between receive and transmit paths, and a second switching matrix is used to switch two frequency sources between the receive and transmit path. In this way, a single receive path can function both in the UE and BTS personality, as can the single transmit path.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
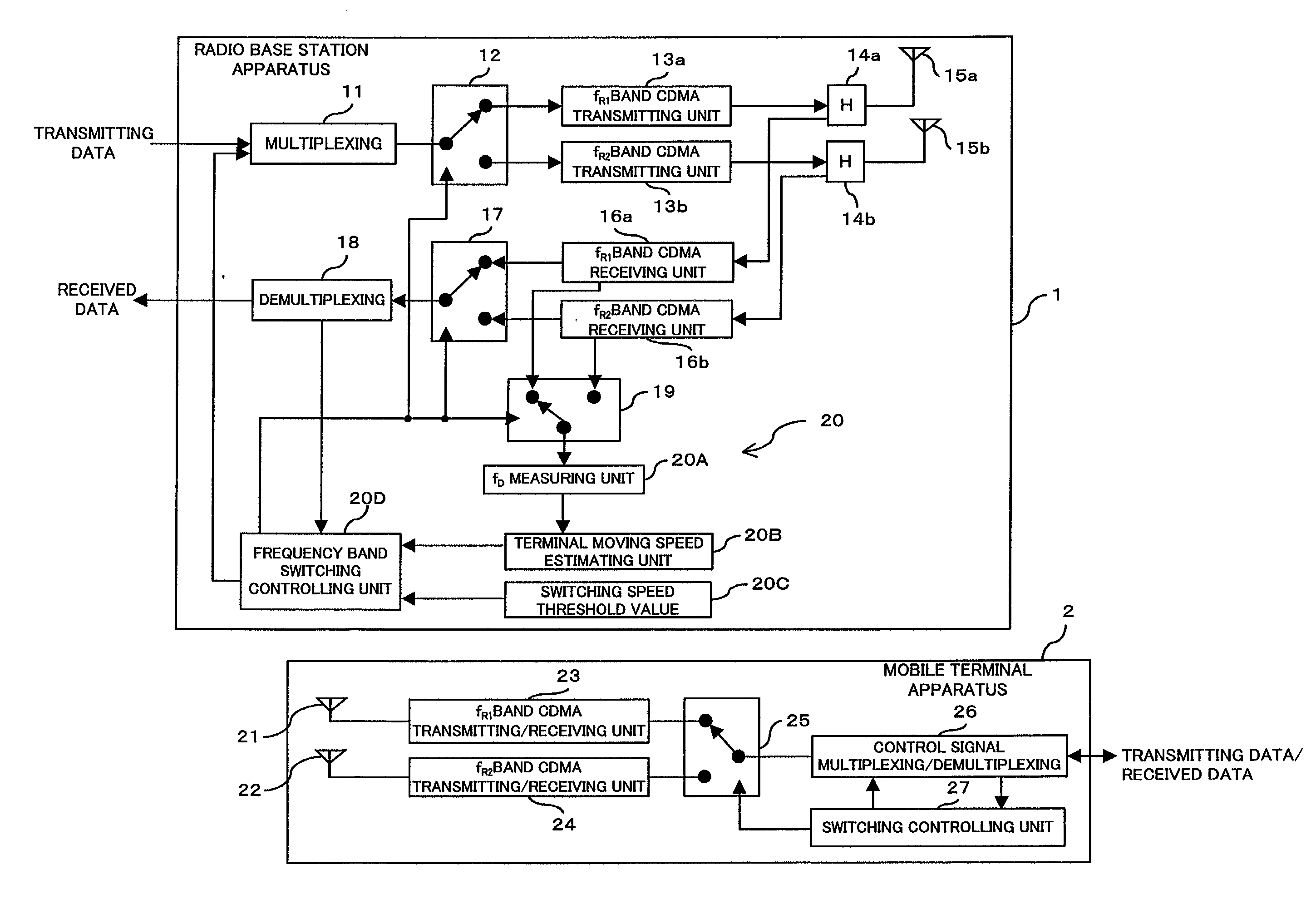
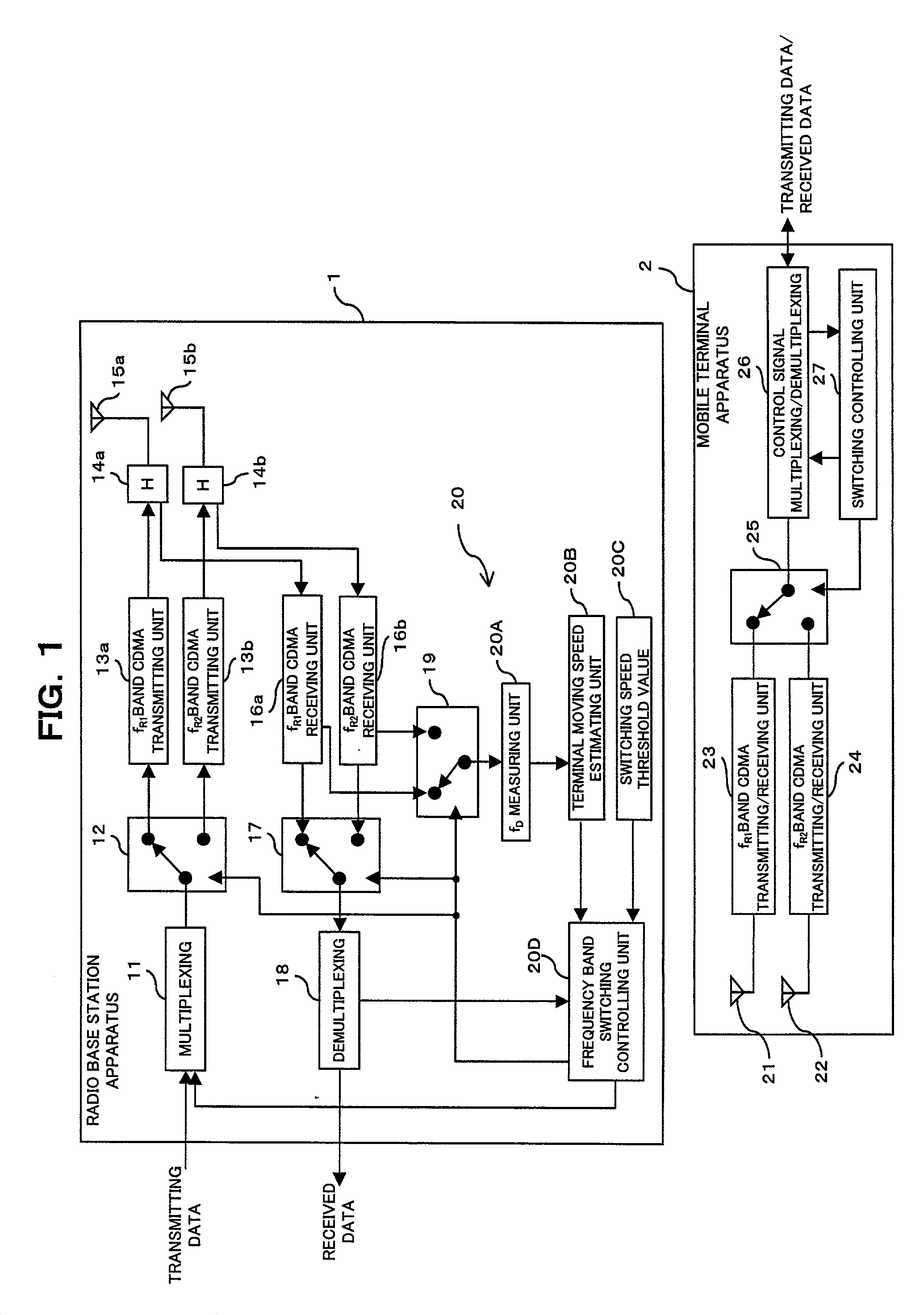
Mobile communication system, and a radio base station, a radio apparatus and a mobile terminal
InactiveUS20030064729A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionLow speedLow frequency band
A mobile communication system comprises a detecting unit to detect information concerning a moving speed of a mobile terminal, and a selection controlling unit to select a use frequency in a higher frequency band when the speed information detected by the detecting unit is a higher speed, while selecting the use frequency in a lower frequency band when the detected information is a lower speed, and assigning it to the mobile terminal. In a mobile communication system in which a relationship between a terminal moving speed (Doppler frequency) and transmission quality degradation is non-monotonous, the communication quality can be improved and the channel capacity can be increased.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Efficient wave propagation for terahertz imaging and sensing
A method of wave propagation from 100–10000 GHz. The currently disclosed method and apparatus adapts micro-opto-electro-mechanical systems (MOEMS) technologies and processes to construct Kinoform optical components from microwave to terahertz range. The method uses induced coupled plasma (ICP) and gray scale processes for upper terahertz band; LIGA-based high aspect ratio (HAR) and gray scale processes are for the mid band; and computer numerical control (CNC) for lower band. In all cases, the thickness of any processed components is about the respective wavelength and system efficiency is about 95%. A Kinoform lens element is designed at 5000 GHz. However, the method is applicable for the entire terahertz band.
Owner:MOTAMEDI MANOUCHEHR E +1
Ultra-wideband antenna having a band notch characteristic
InactiveUS20100182210A1High bandwidthImprove featuresSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsUltra-widebandIntermediate frequency
The present invention discloses an antenna for ultra-wideband (UWB) communication having a band-stop characteristic. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the UWB antenna is a patch antenna employing microstrip feeding. In order to expand a bandwidth at a low frequency band, a stub is formed in a radiating element. Furthermore, since steps are formed in a ground plane, an antenna characteristic at an intermediate frequency band can be improved and a UWB characteristic can be obtained. According to another embodiment of the present invention, the UWB antenna is a patch antenna employing microstrip feeding and has a recess formed in the ground plane, thereby implementing the UWB characteristic. The antenna of the present invention has an inverse U-shaped slot formed in the radiating element, thus implementing the band-stop characteristic at the UNII band. In addition, the antenna of the present invention has includes a ground plane having a small area and has omnidirectional radiating patterns accordingly.
Owner:EMW CO LTD
Planar dual-frequency array antenna
InactiveUS6121931ASimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDual frequencyLow frequency band
PCT No. PCT / IL96 / 00037 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 11, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 11, 1999 PCT Filed Jul. 4, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 01921 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 15, 1998A dual-frequency array antenna having an essentially planar structure with electronic beam steering capability in both a low and high frequency band independently of each other, constructed, in a layered formation, from a top planar array antenna unit operating in the low frequency band and a bottom planar array antenna unit operating in the high frequency band. The top planar array antenna is transparent to frequencies in the high frequency band.
Owner:SKYGATE INT TECH
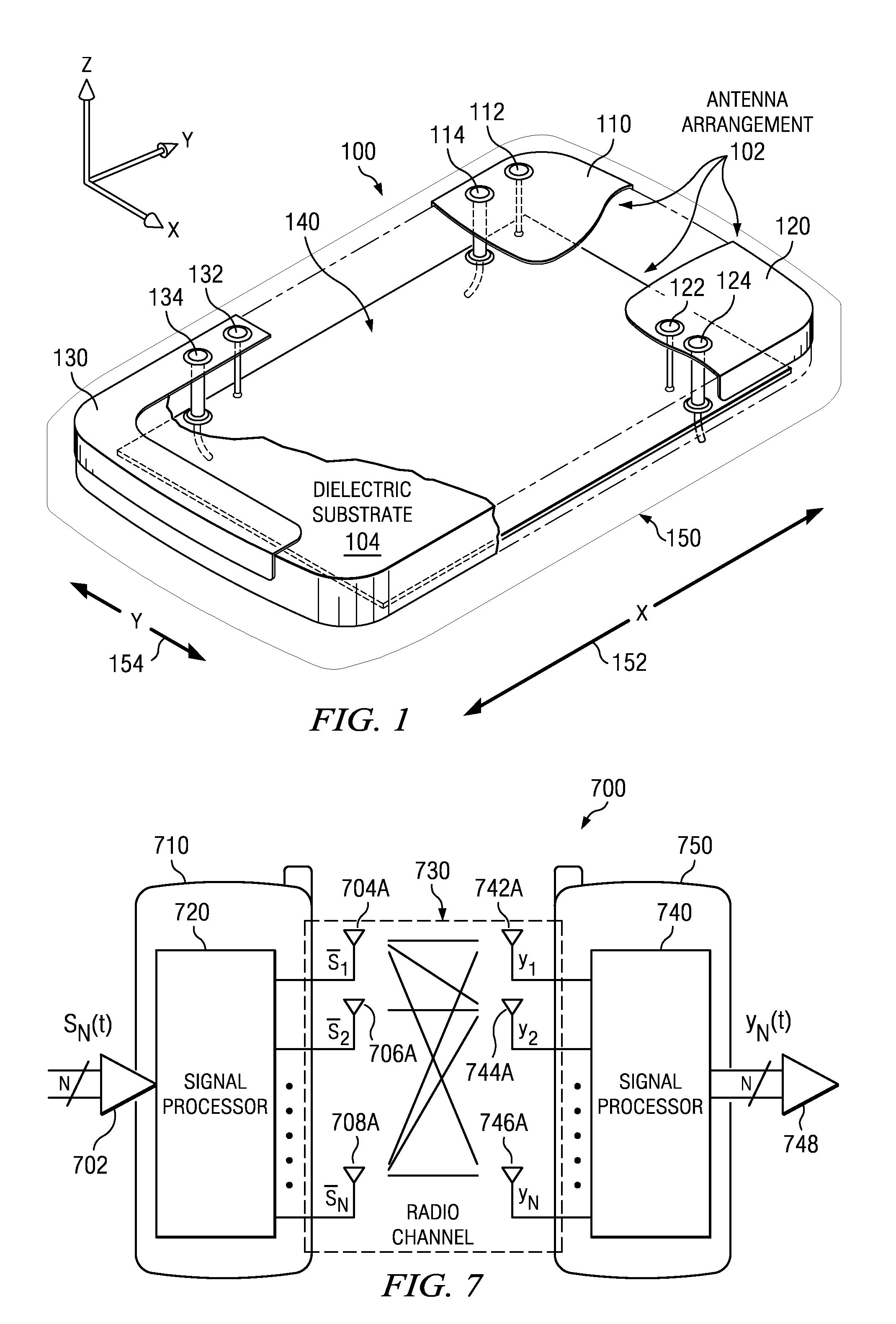
Distributed multiband antenna and methods
ActiveUS20110260939A1Reduced case sizeSimultaneous aerial operationsElongated active element feedPlanar inverted f antennaRadio equipment
A distributed multiband antenna intended for radio devices, and methods for designing manufacturing the same. In one embodiment, a planar inverted-F antenna (PIFA) configured to operate in a high-frequency band, and a matched monopole configured to operate in a low-frequency band, are used within a handheld mobile device (e.g., cellular telephone). The two antennas are placed on substantially opposing regions of the portable device. The use of a separate low-frequency antenna element facilitates frequency-specific antenna matching, and therefore improves the overall performance of the multiband antenna. The use of high-band PIFA reduces antenna volume, and enables a smaller device housing structure while also reducing signal losses in the high frequency band. These attributes also advantageously facilitate compliance with specific absorption rate (SAR) tests; e.g., in the immediate proximity of hand and head “phantoms” as mandated under CTIA regulations. Matching of the low-frequency band monopole antenna is further described.
Owner:CANTOR FITZGERALD SECURITIES
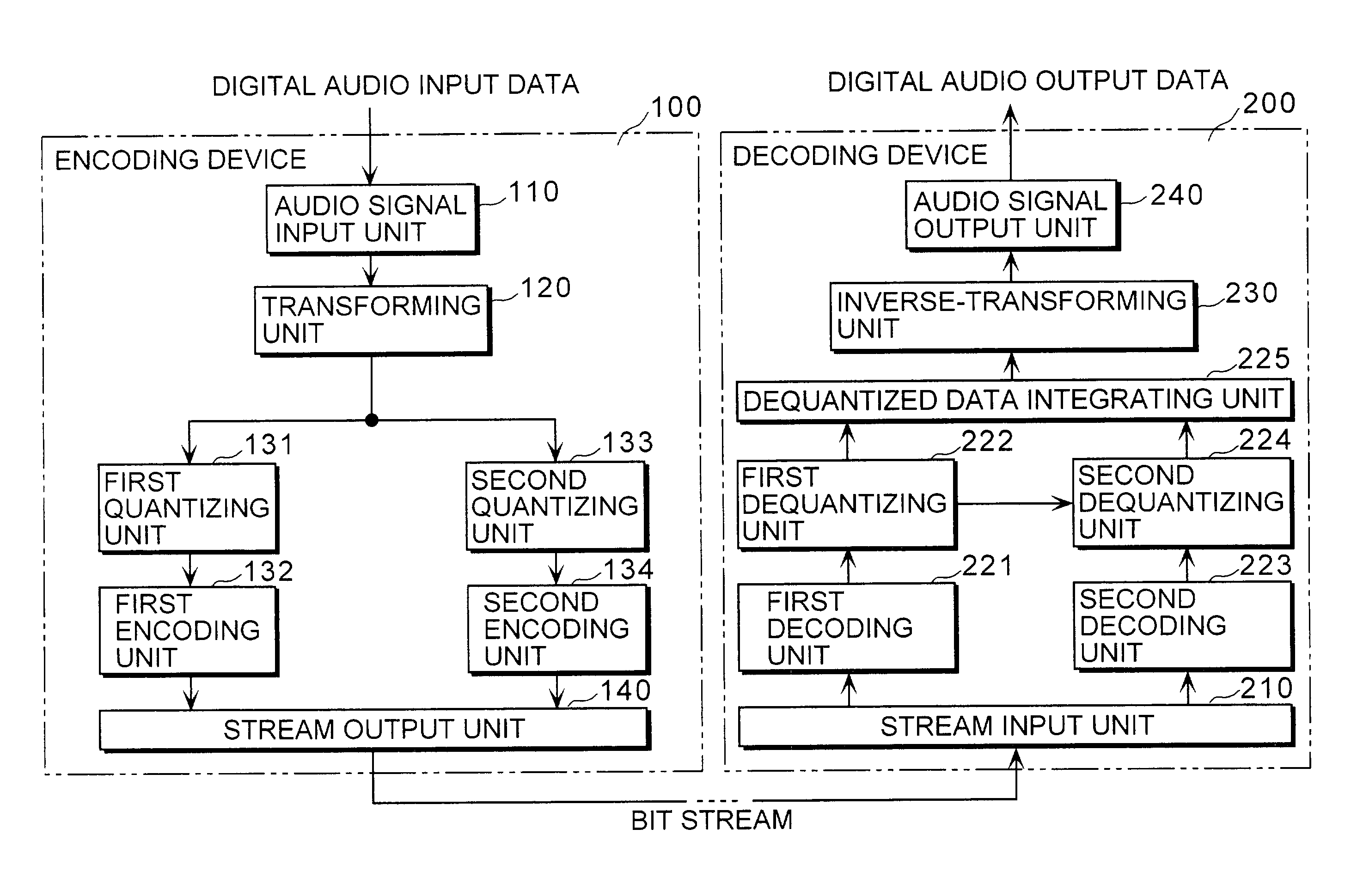
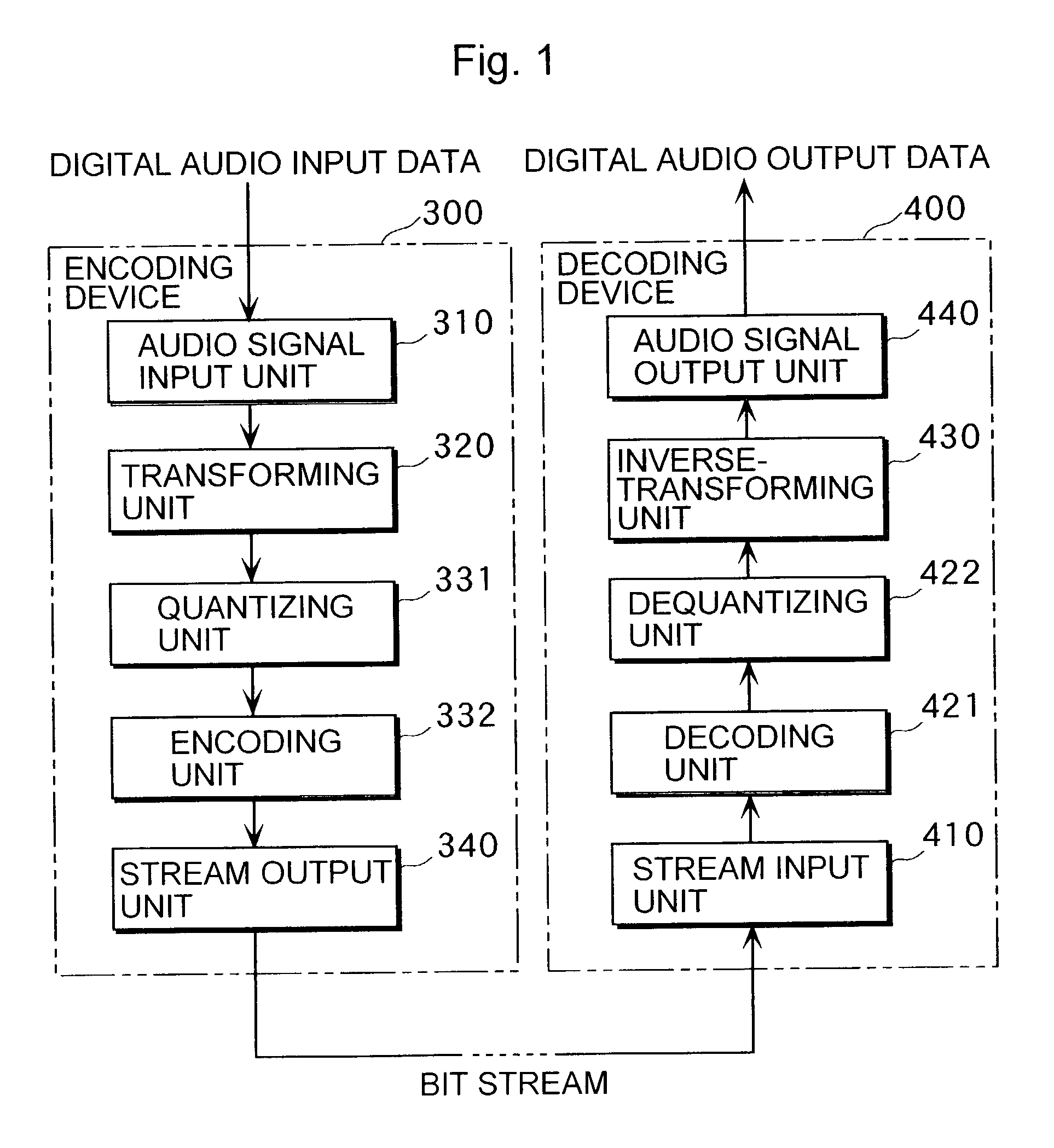
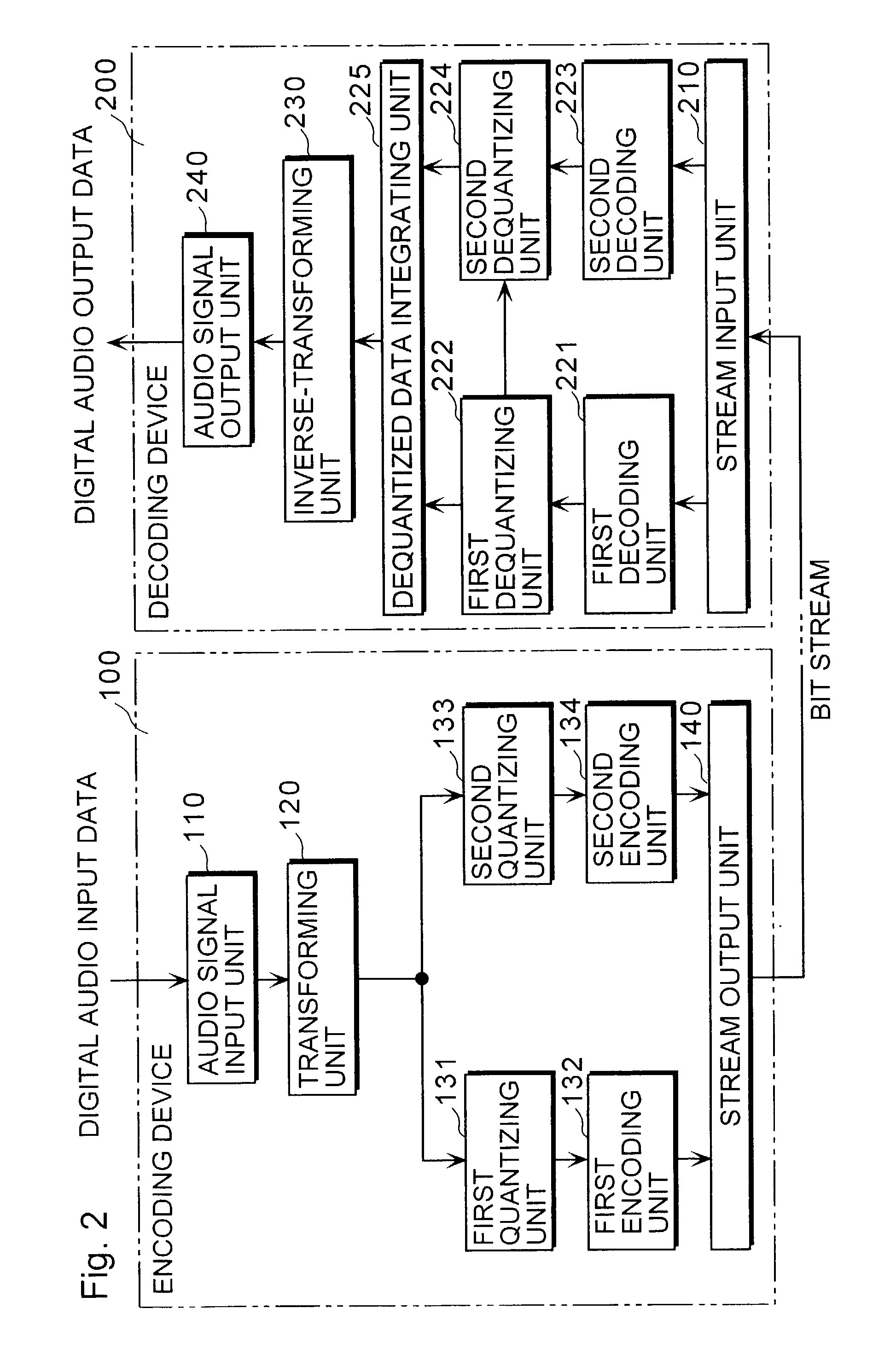
Encoding device decoding device
ActiveUS7283967B2More fidelityReduce transfer rateSpeech analysisVolume compression/expansionFrequency spectrumAlgorithm
An encoding device (100) includes (i) a first encoding unit (132) that encodes spectral data in the lower frequency band represented by a plularity of parameters, out of the spectral data obtained by transforming an audio signal inputted for a fixed time length, (ii) a second quantizing unit (133) that generates sub information representing characteristics of the spectral data in the higher frequency by fewer parameters than those for the lower frequency band, out of the spectral data obtained by the transformation, (iii) a second encoding unit (134) that encodes the generated sub information, and (iv) a stream output unit (140) that outputs the data encoded by the first encoding unit (132) and the data encoded by the second encoding unit (134).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
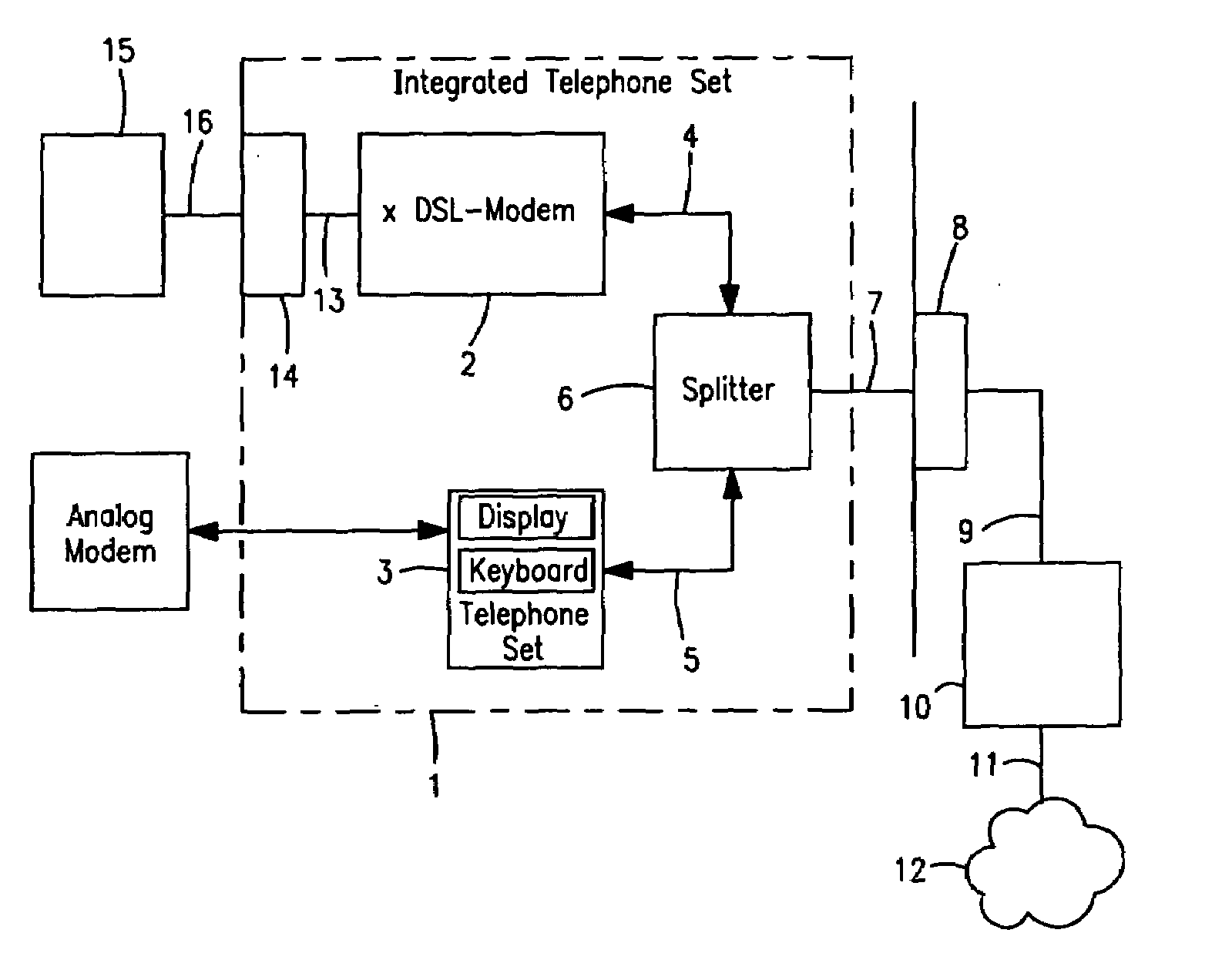
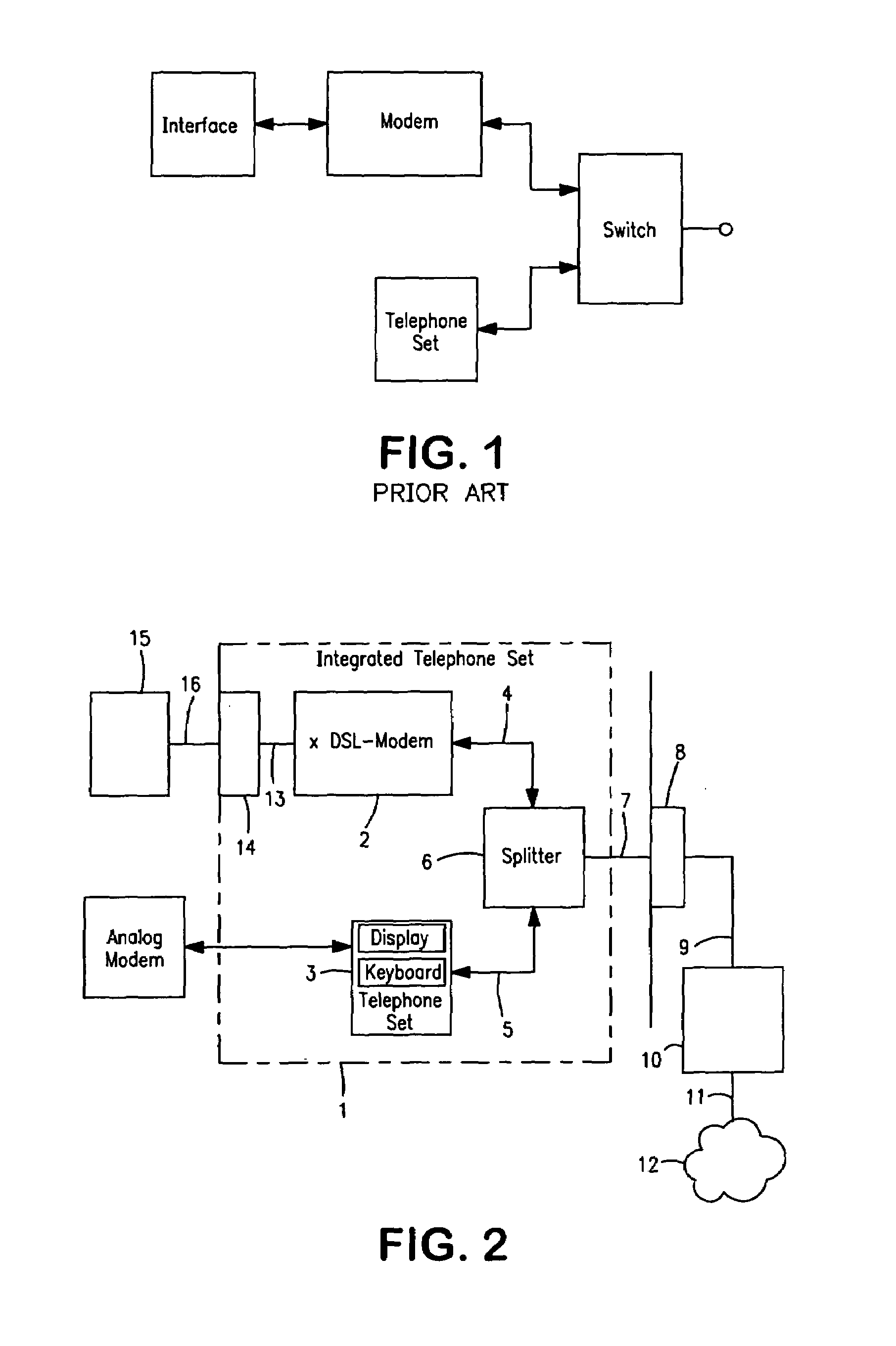
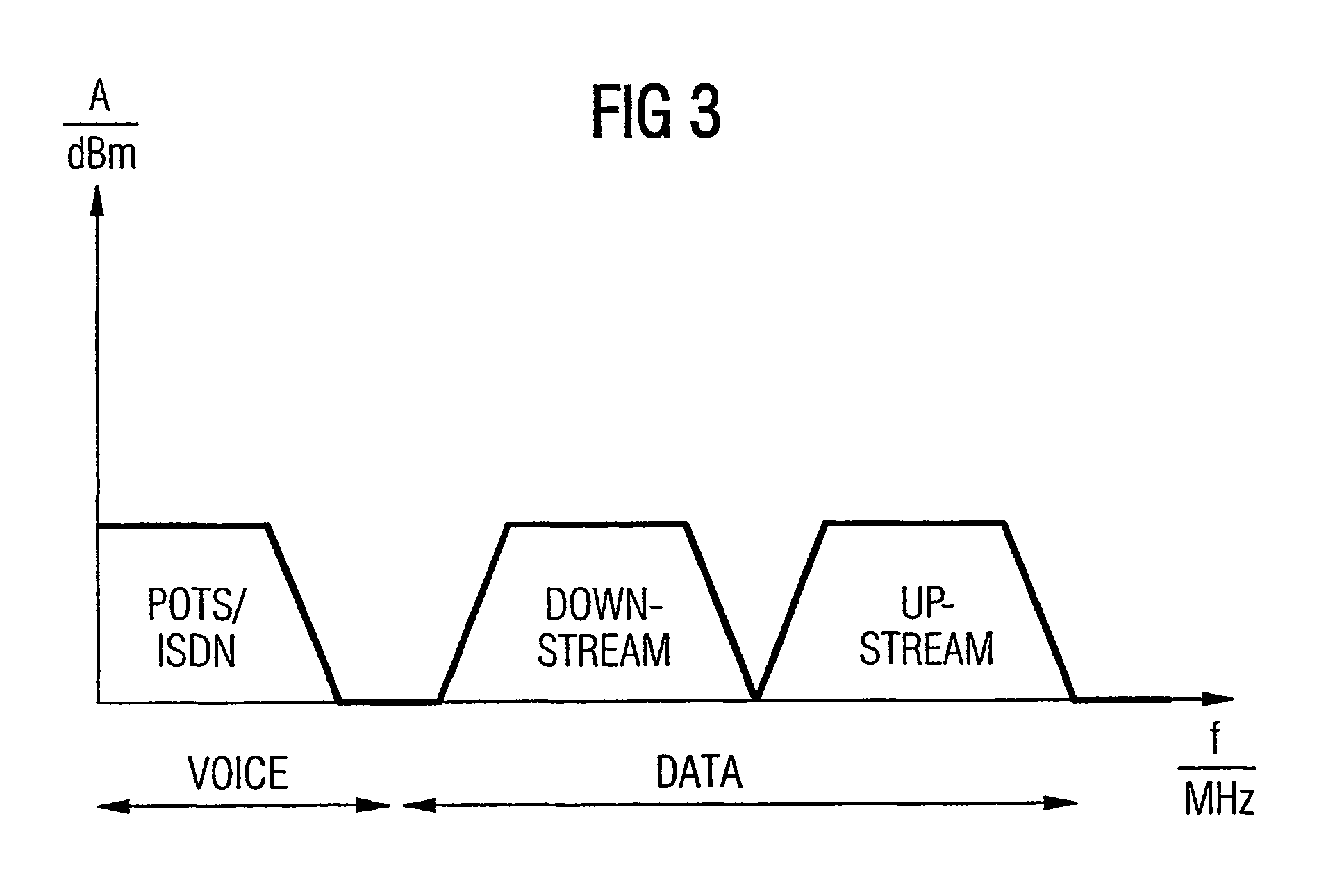
Integrated telephone set with an xDSL-modem
InactiveUS7113574B1Average power consumptionSubstations coupling interface circuitsData switching by path configurationModem deviceData signal
Integrated telephone with an xDSL-modem (2), comprising a splitter unit (6) for separating telephone signals received via a telephone line (9) in a low-frequency band from data signals received in a high-frequency band via the telephone line (9), a telephone set (3) connected to the splitter unit (6) for the transmission of telephone signals in the low-frequency band; and a high-speed xDSL-modem (2) connected to the splitter unit (6) for the transmission of data signals in the high-frequency band.
Owner:INTEL CORP
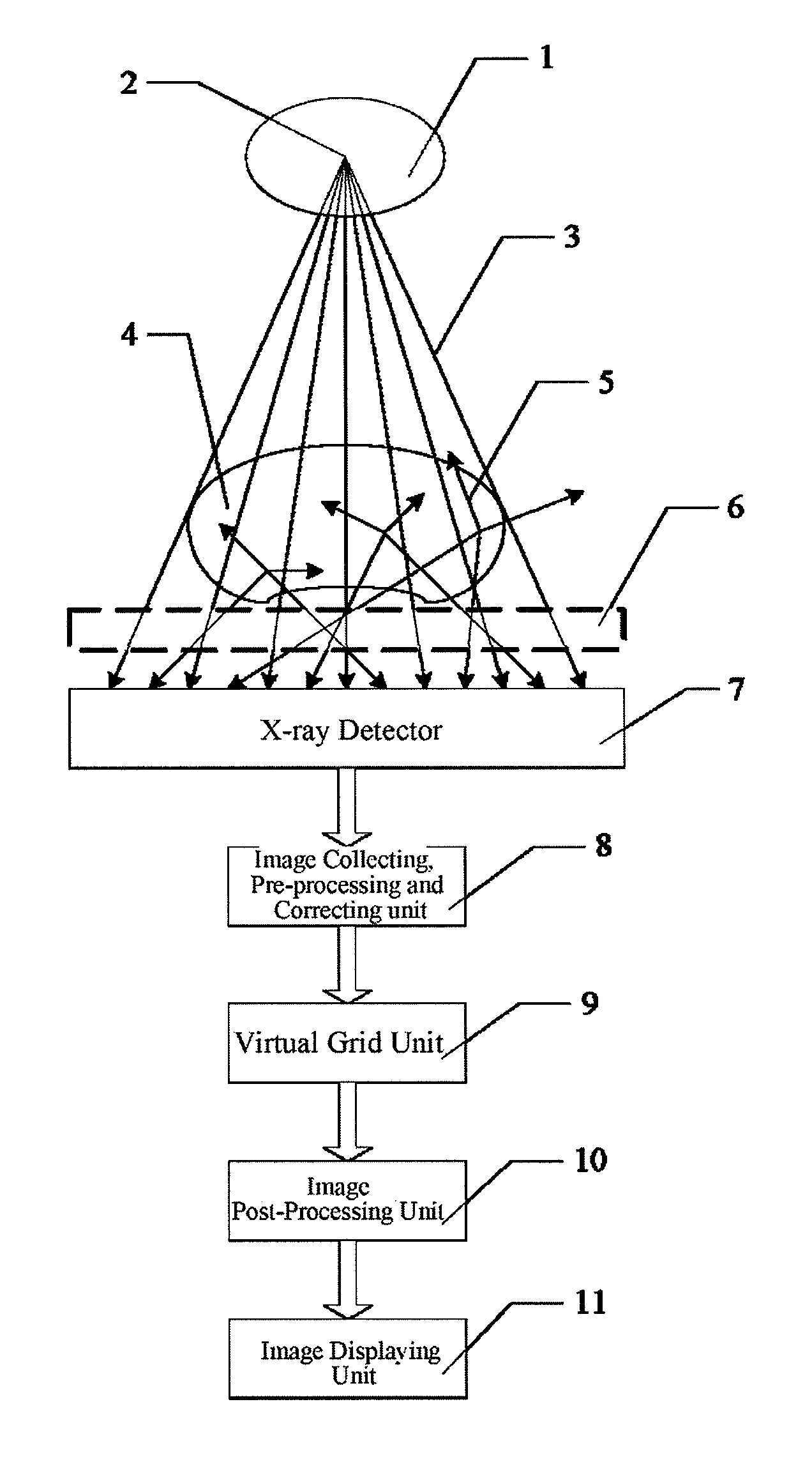
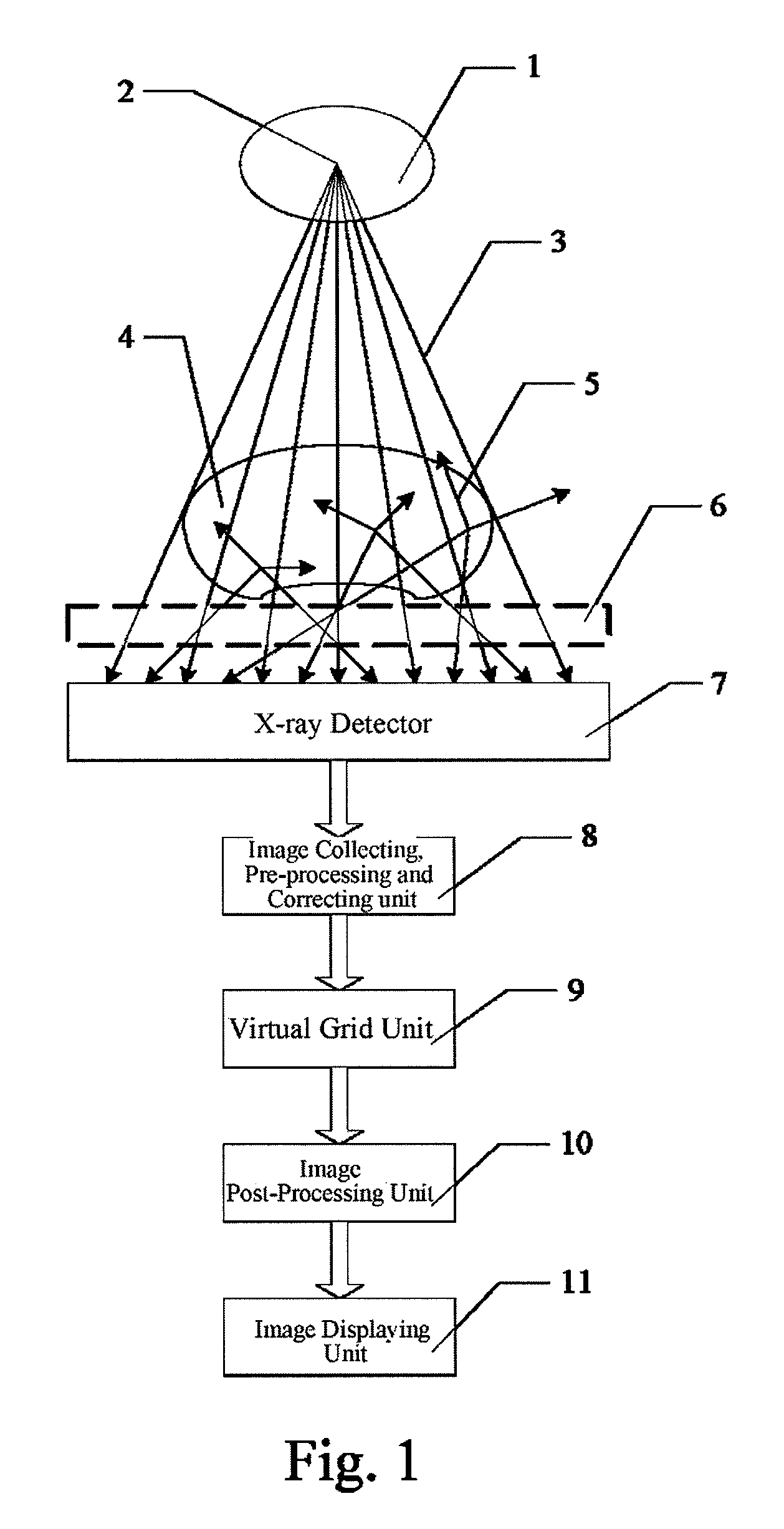
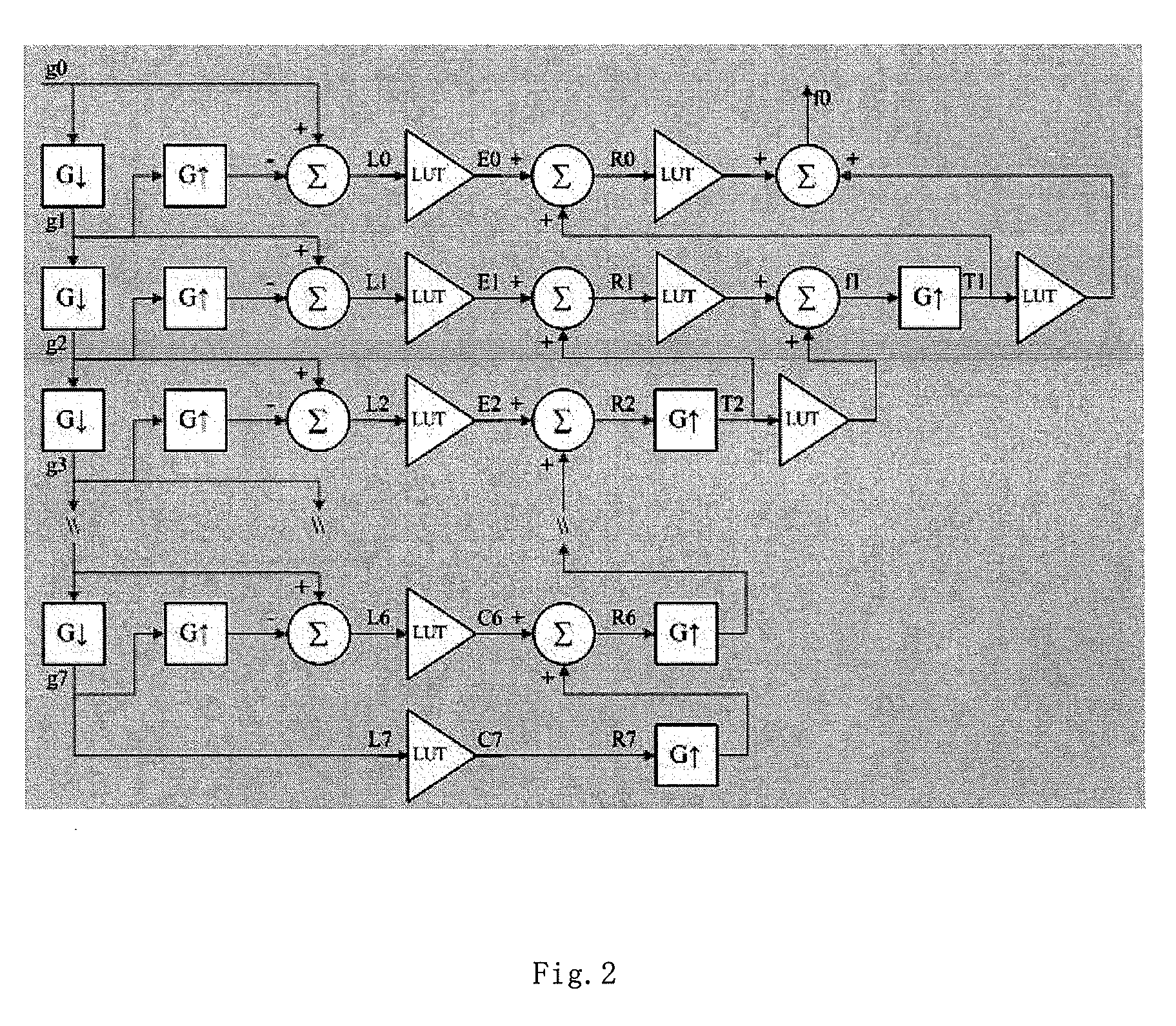
Virtual grid imaging method and system for eliminating scattered radiation effect
InactiveUS8064676B2Eliminate the effects ofComponent can be removedImage enhancementImage analysisMulti bandHigh energy
Owner:BEIJING SINOPHARM HUNDRIC MEDLINE INFO TECH
Frame structure for support of large delay spread deployment scenarios
ActiveUS20110103494A1Network traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionDelay spreadLow frequency band
A frame structure for support of large delay spread deployment scenarios (e.g., cellular system operation in large cell sizes or low frequency bands) is generally presented. In this regard a method is introduced comprising partitioning a radio frame into a plurality of equal-sized (or non-equal-sized) sub-frames to simplify system implementation. Other embodiments are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:APPLE INC
Low frequency diversity antenna system
ActiveUS20110215971A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsLow frequency bandHigh isolation
A diversity antenna system that operates within a low frequency band ranging from 700 Megahertz is disclosed. A plurality of antennas are folded onto a single printed circuit in a meander pattern configuration. Each antenna has an independent feed port and ground pin. The plurality of antennas are configured within a compact mobile phone space to produce a high isolation and low correlation at resonating frequencies within the 700 Megahertz frequency band.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Chassis-excited antenna apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140300518A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorLow frequency band
A chassis-excited antenna apparatus, and methods of tuning and utilizing the same. In one embodiment, a distributed loop antenna configuration is used within a handheld mobile device (e.g., cellular telephone). The antenna comprises two radiating elements: one configured to operate in a high-frequency band, and the other in a low-frequency band. The two antenna elements are disposed on different side surfaces of the metal chassis of the portable device; e.g., on the opposing sides of the device enclosure. Each antenna component comprises a radiator and an insulating cover. The radiator is coupled to a device feed via a feed conductor and a ground point. A portion of the feed conductor is disposed with the radiator to facilitate forming of the coupled loop resonator structure.
Owner:PULSE FINLAND
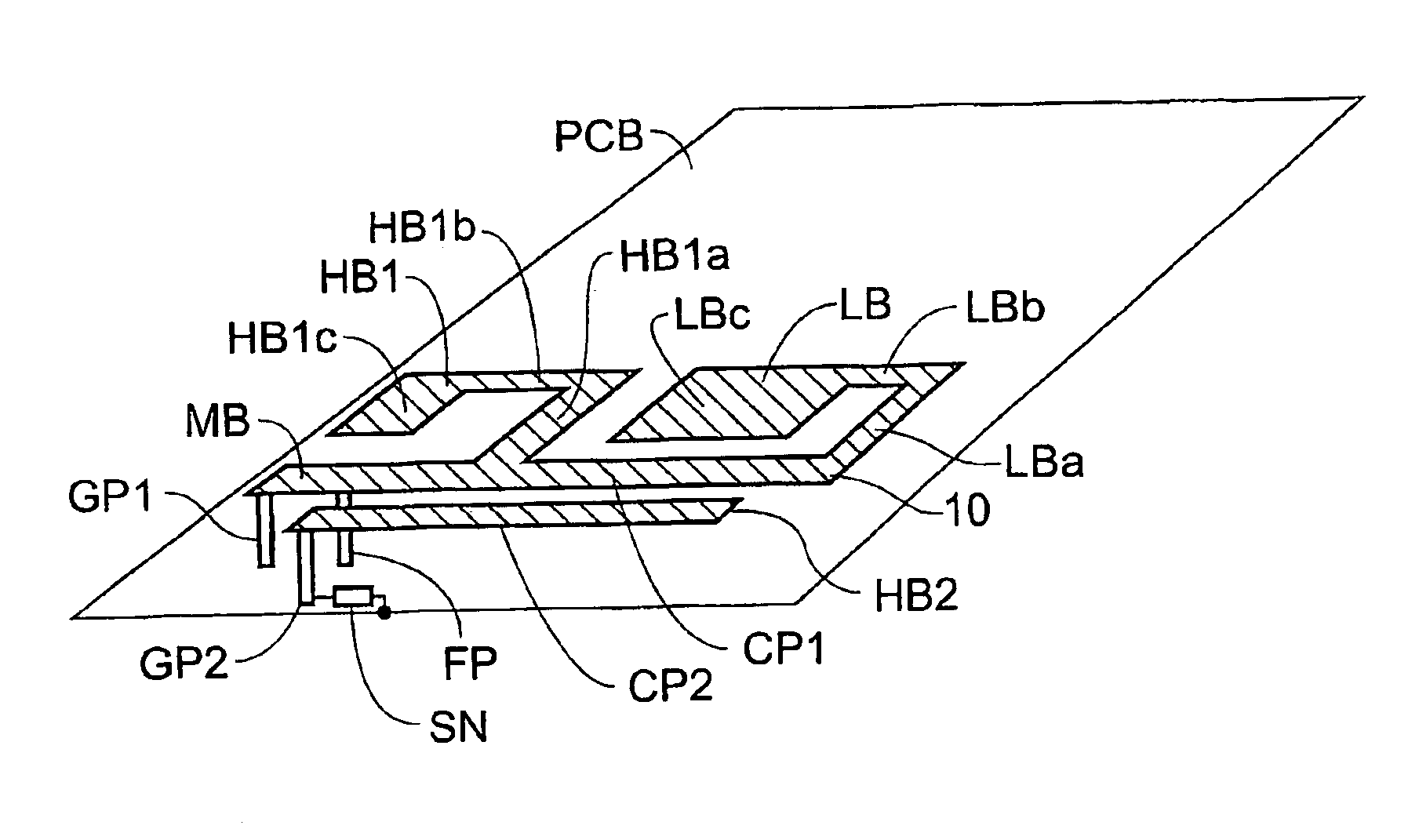
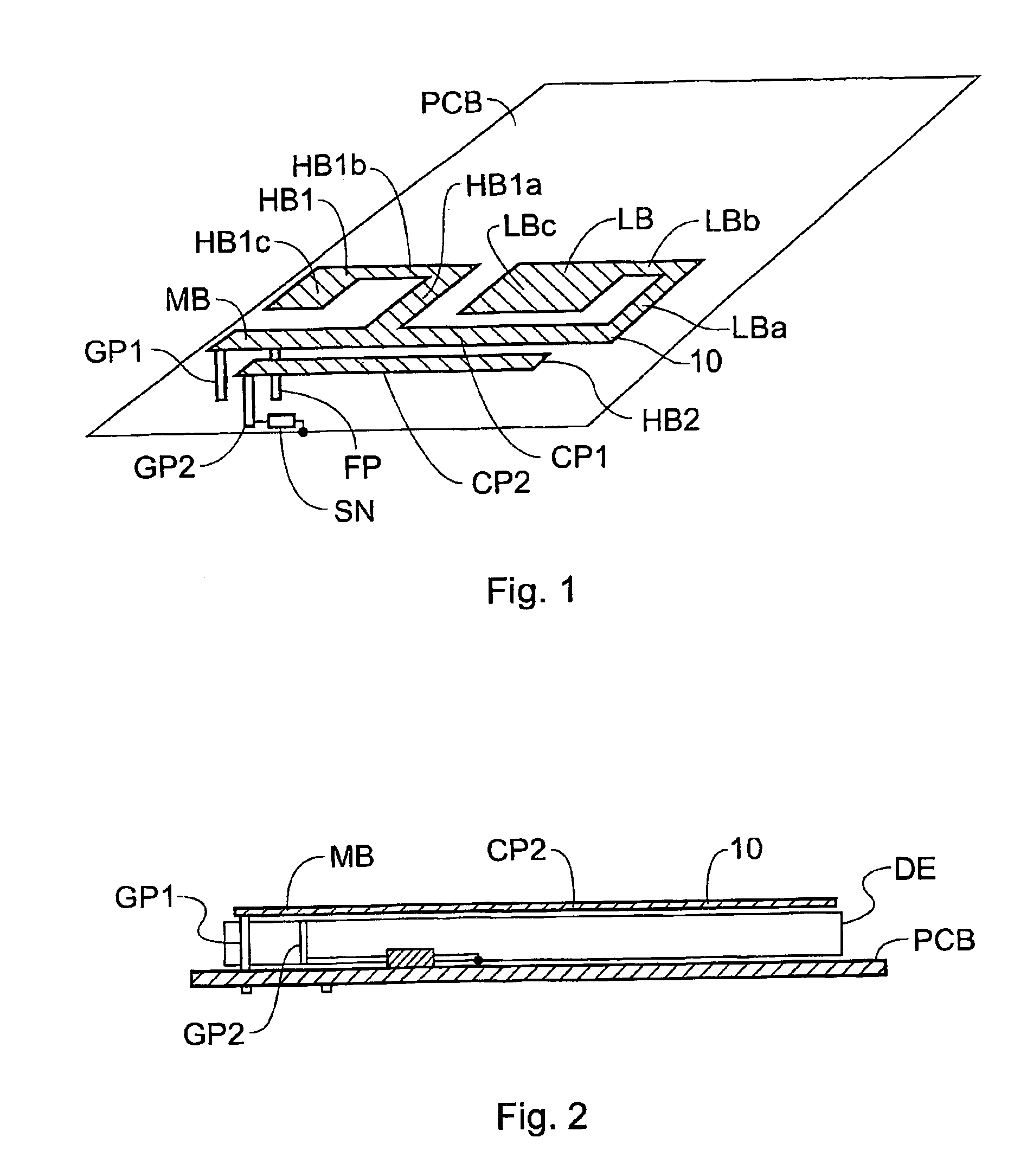
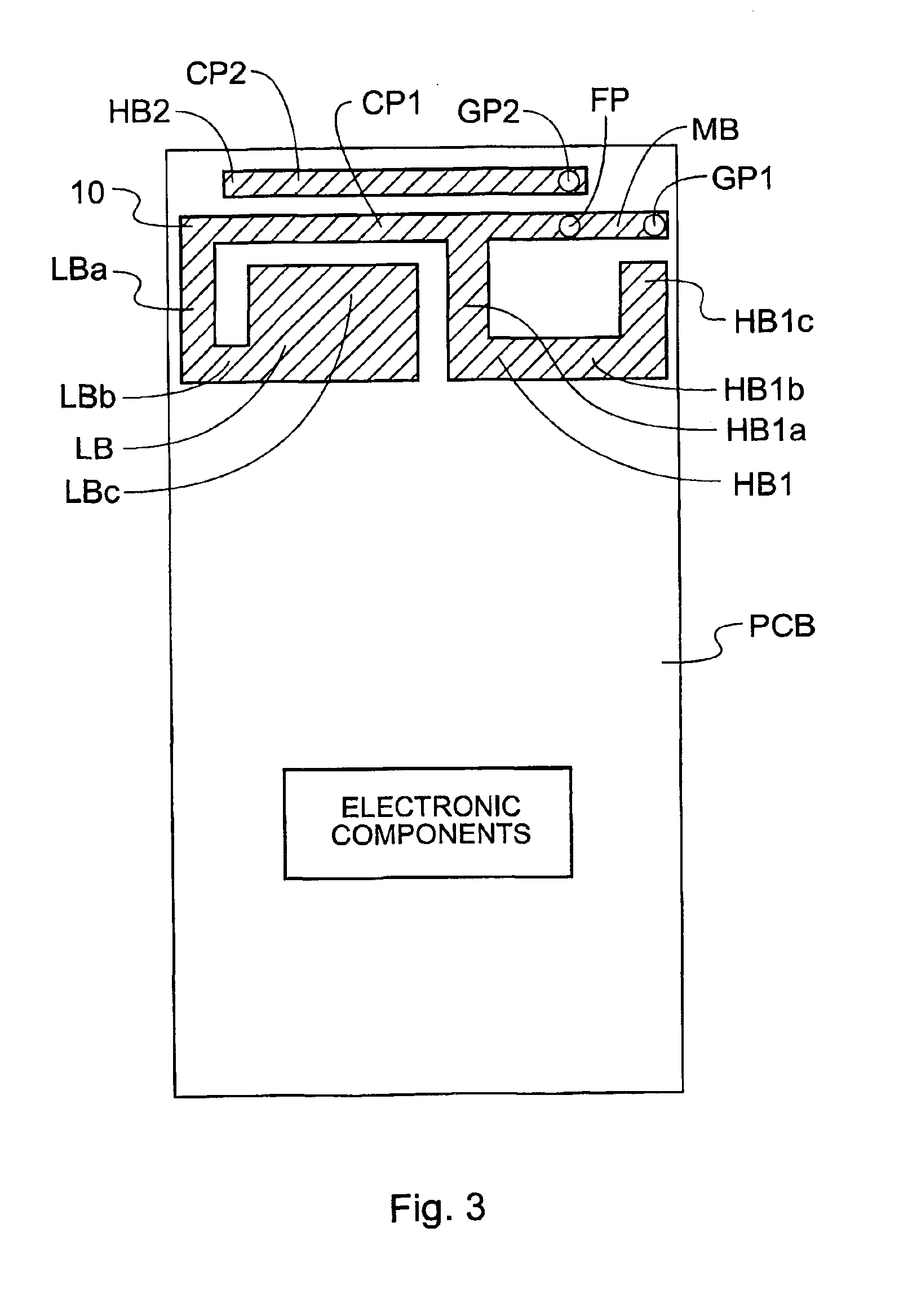
Mobile communication device
InactiveUS6950065B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorNetwork connection
A mobile communications device has a multifrequency band antenna with a low band portion (LB) tuned to a low frequency band, and a first high band portion (HB1) tuned to a first high frequency band at higher frequencies than the low frequency band. The low band portion (LB) and the first high band portion (HB1) have a common first grounding point (GP1), a common feeding point (FP) for feeding input signals to the antenna and for receiving signals from the antenna, and a first conductor portion (CP1), which forms part of the low band portion (LB) and of the first high band portion (HB1). The first conductor portion (CP1) is electrically connected to the first grounding point (GP1) and to the common feeding point (FP). A second high band portion (HB2) is coupled to the first conductor portion (CP1) and tuned to a second high frequency band at a higher frequency than the low frequency band and different from the first high frequency band. A switching network is connected between the second high band portion and ground, allowing the resonant frequency of the second high band portion to be varied, on the basis of a signal which depends on the operating mode of the device, thereby allowing four band operation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com