Patents
Literature
146results about "Combination control in untuned amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
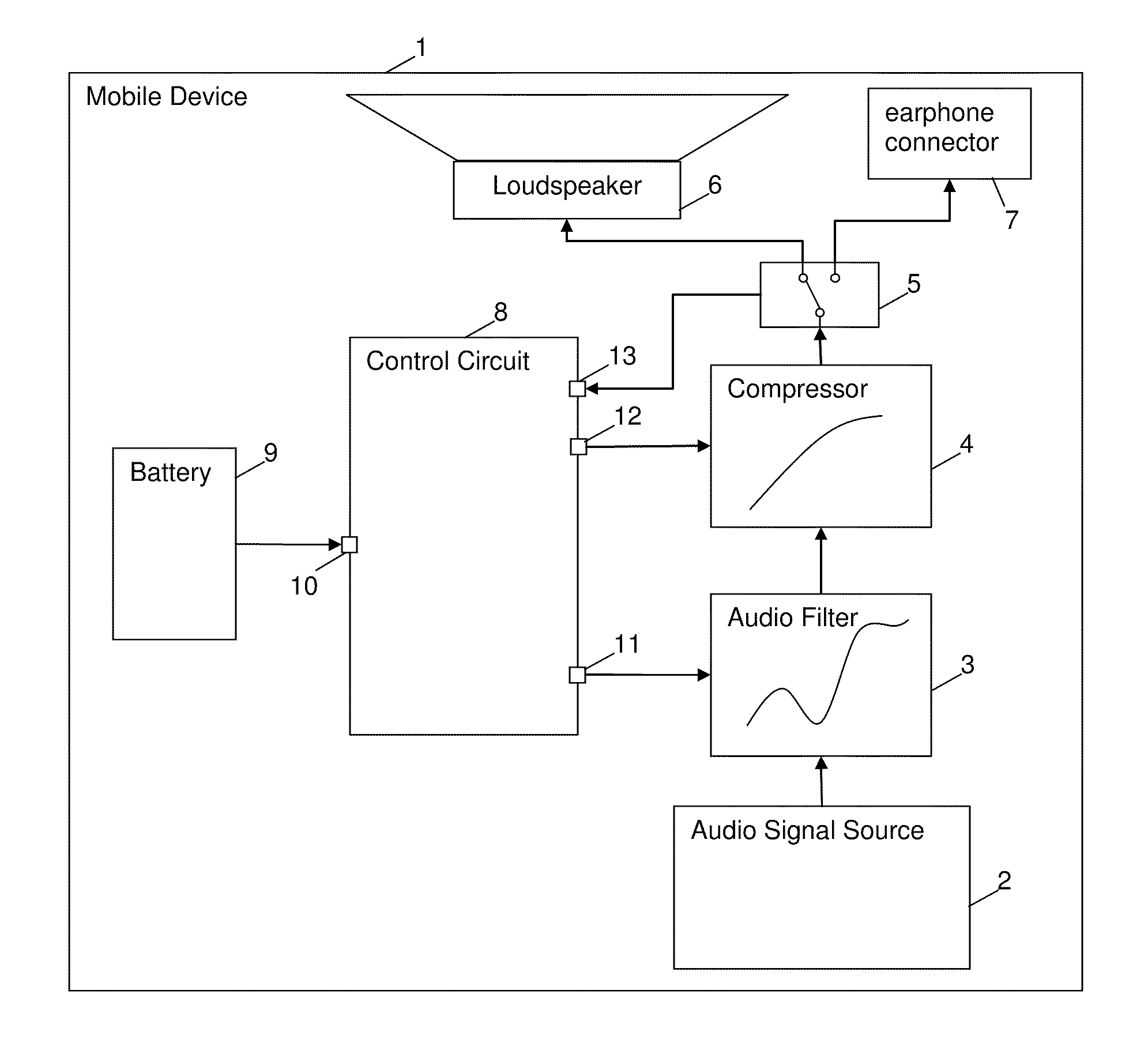
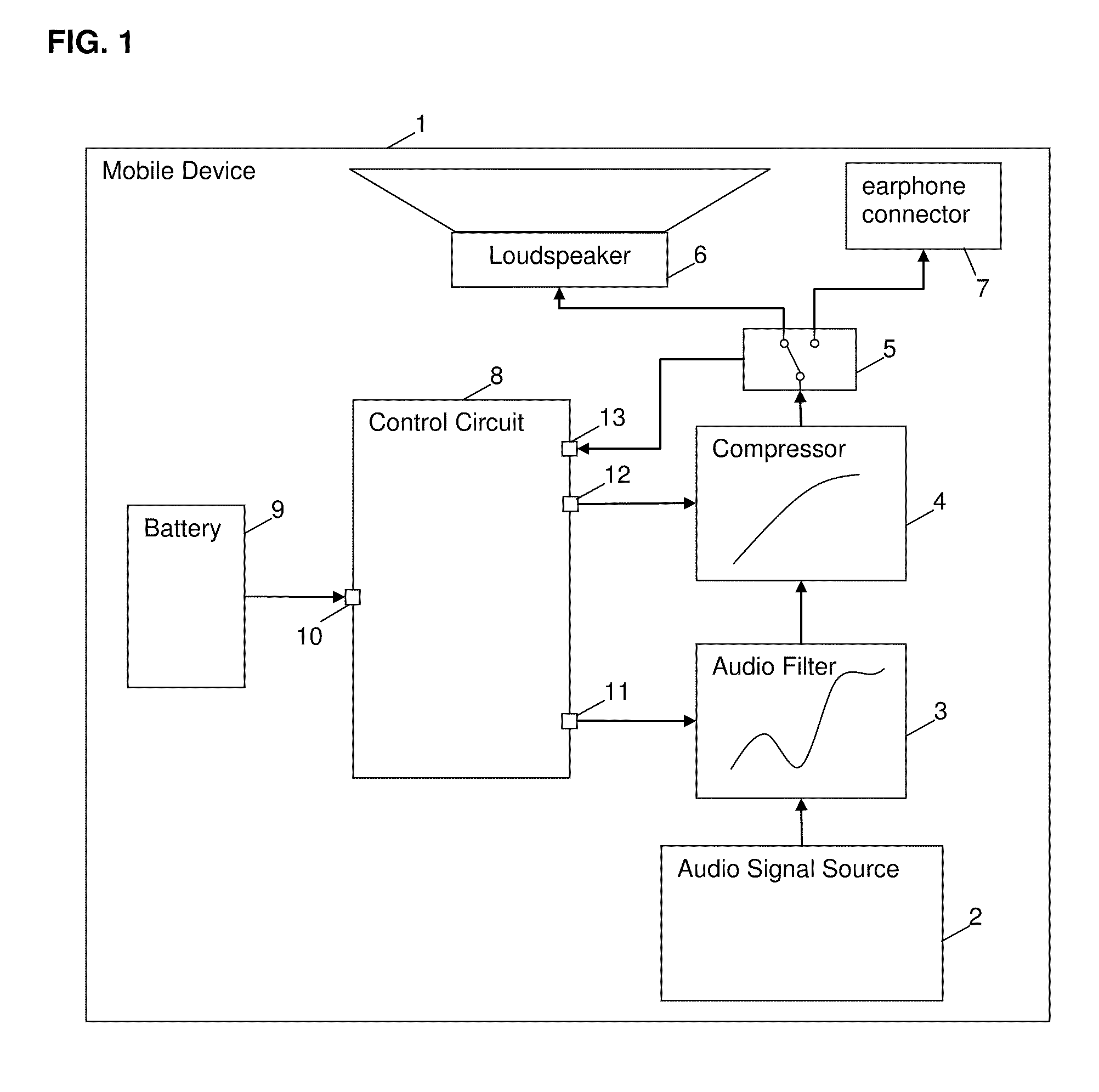
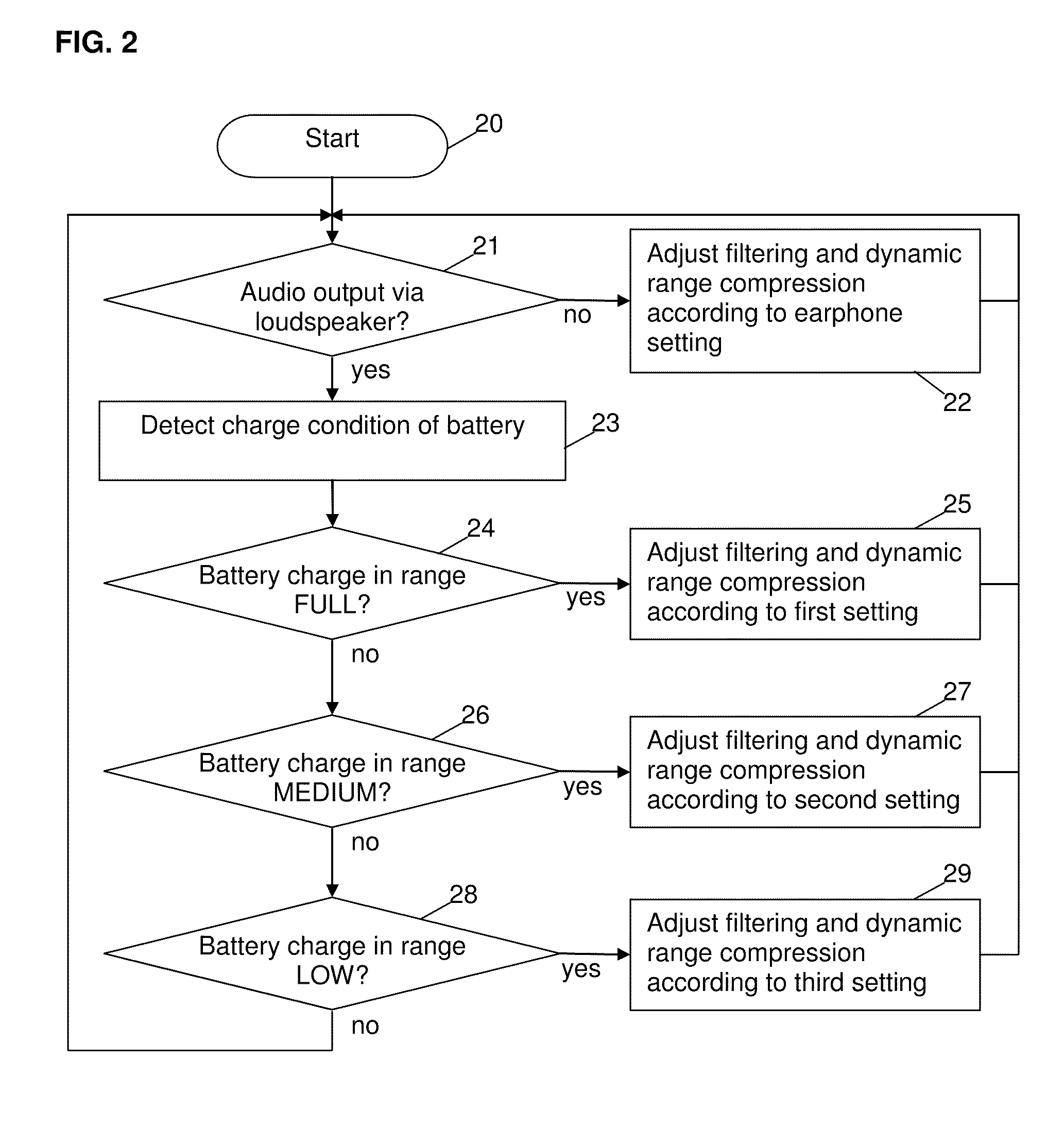
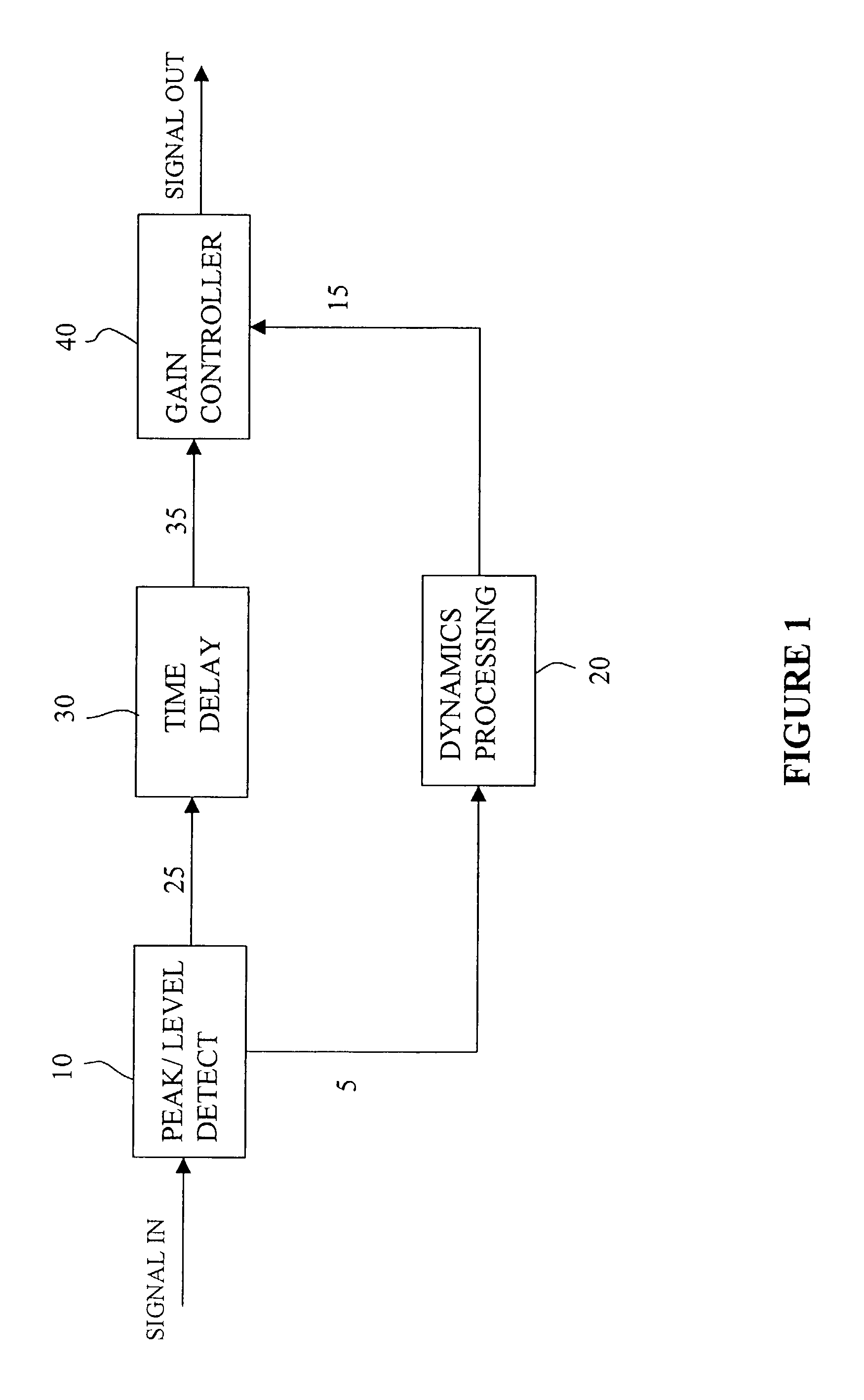
Method and circuit for controlling an output of an audio signal of a battery-powered device
ActiveUS20100322438A1Shorten the timeHigh power consumptionSupply voltage controlEarpiece/earphone attachmentsEngineeringControl circuit
A method and a control circuit for controlling an output of an audio signal of a battery-powered device are described.
Owner:SONY CORP
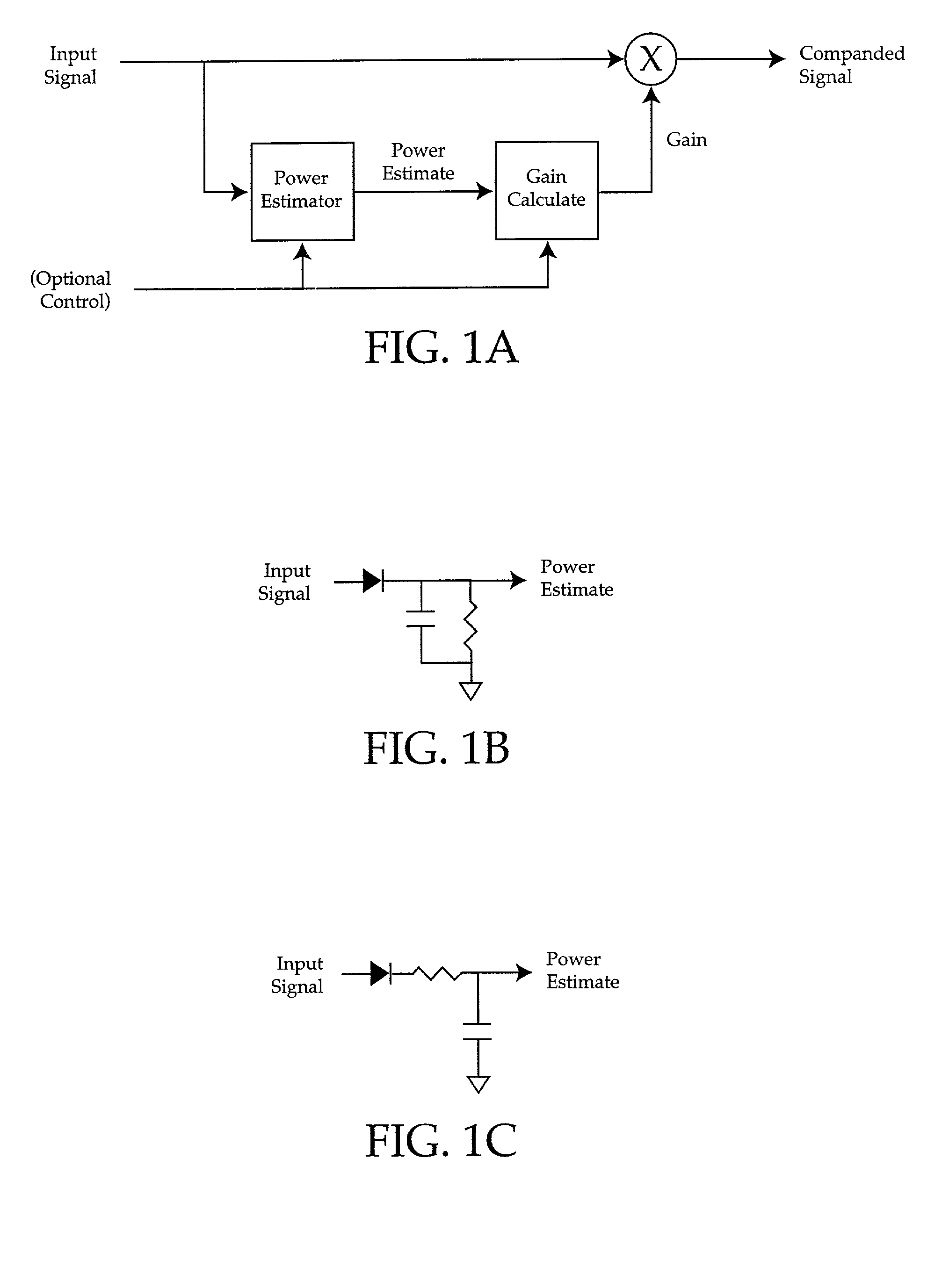
System output control method and apparatus
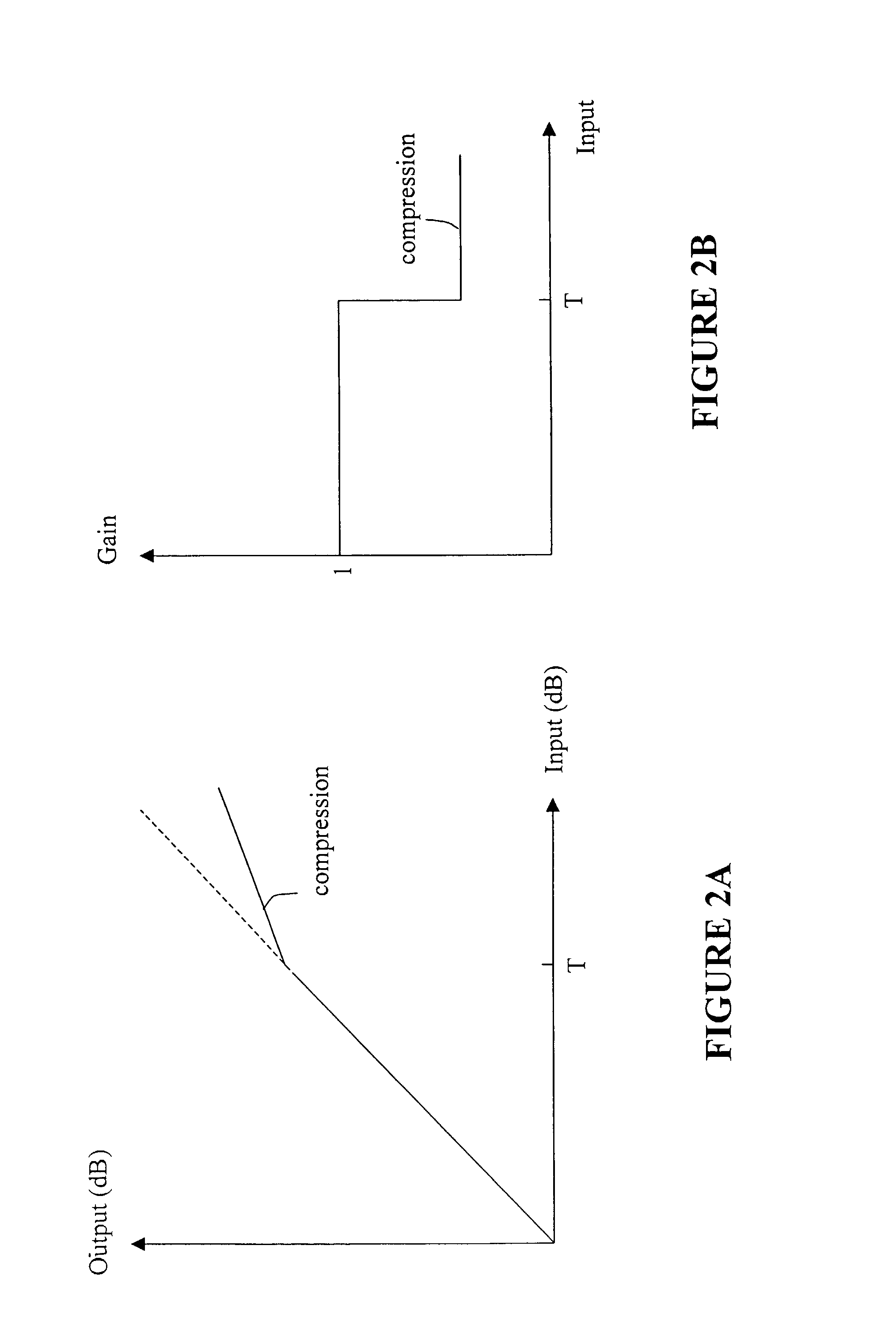
ActiveUS7027981B2Maximum flexibilityImplemented cost-effectivelyVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesGain controlControl systemCompression ratio
Output control system and method includes calculating gain for an input signal, detecting a predetermined condition, and modifying the gain calculation in accordance with one or more kneepoints to provide a varying output signal. A companding ratio is then established in accordance with the kneepoints. System gain is then adjusted, and the companding ratio may be further adjusted by adjusting one of the kneepoints relative to another.
Owner:BIZJAK KARL M
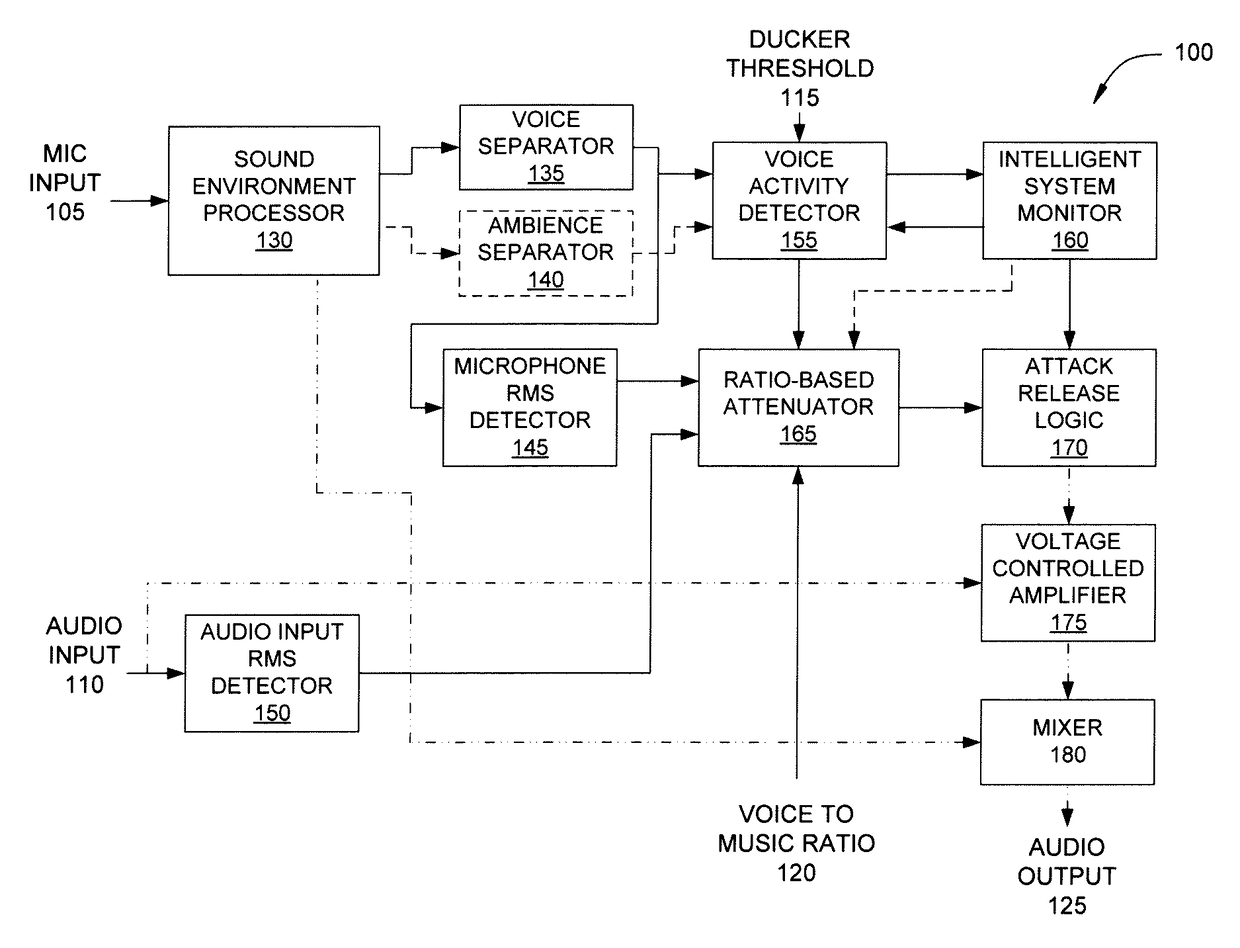
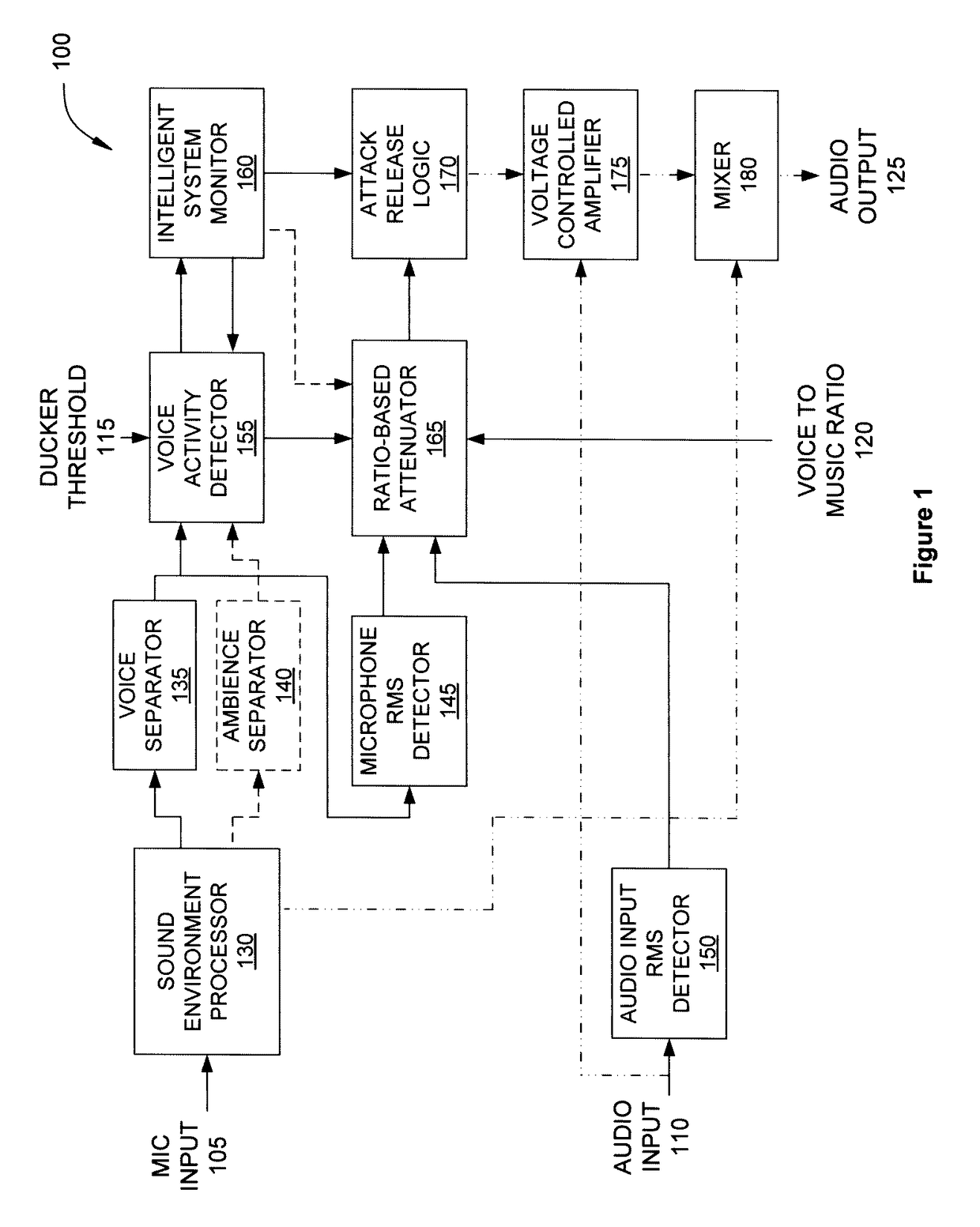
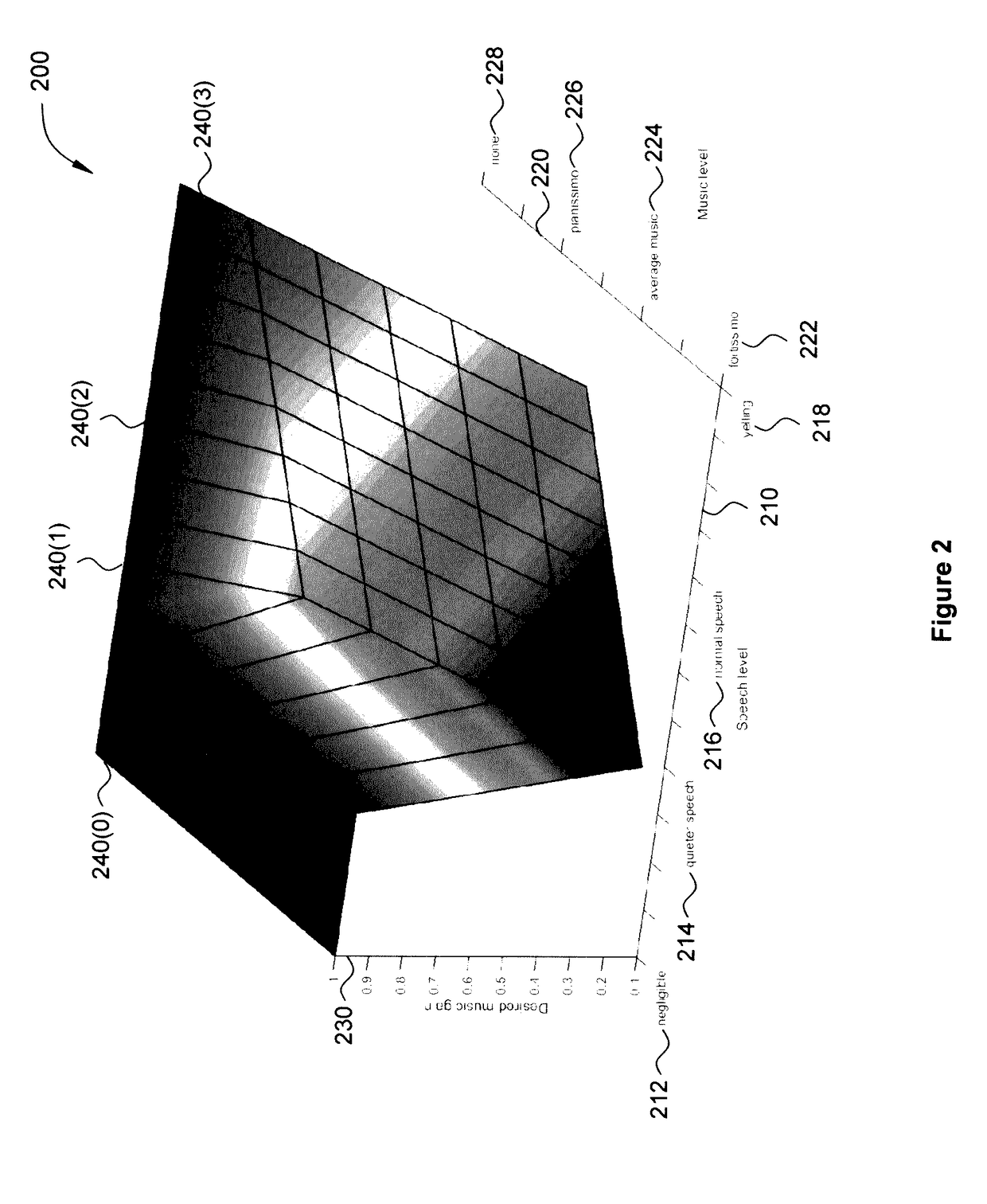
Approach for partially preserving music in the presence of intelligible speech
An audio processing system for a listening device includes an input device, a voice activity detector and a ratio-based attenuator. The input device is configured to receive a first audio signal emanating from an environment and including a signal of interest. The voice activity detector is configured to generate a control signal in response to the first audio signal. The ratio-based attenuator is configured to receive the control signal and determine whether the signal level of the first audio signal exceeds the signal level of an audio signal received from an audio playback device by at least a target difference. If so, then the audio level of the playback audio signal is maintained. Otherwise, the audio level of the playback audio signal is adjusted, where, at the adjusted value, the first signal level exceeds the playback signal level by at least the target difference.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Hearing compensation system incorporating signal processing techniques
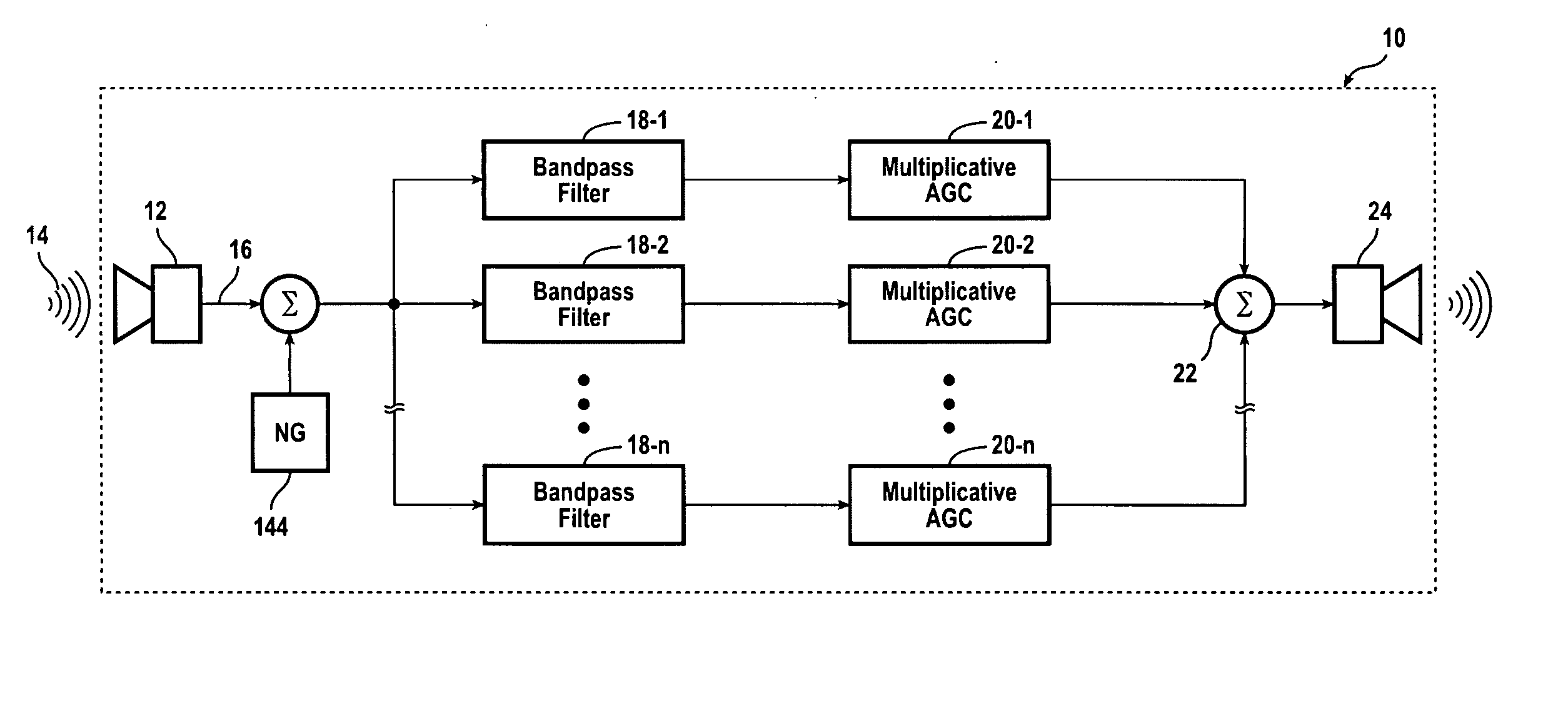
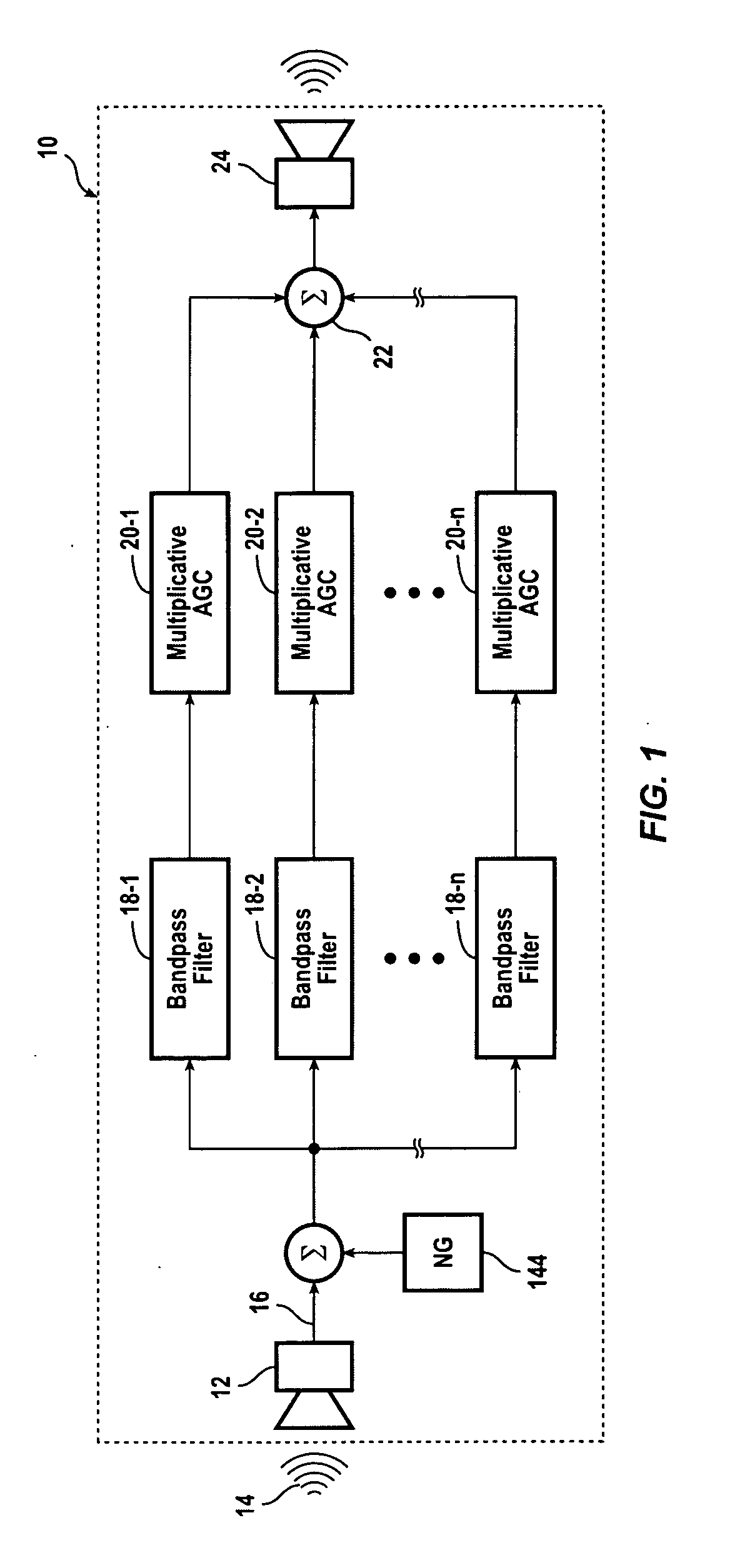
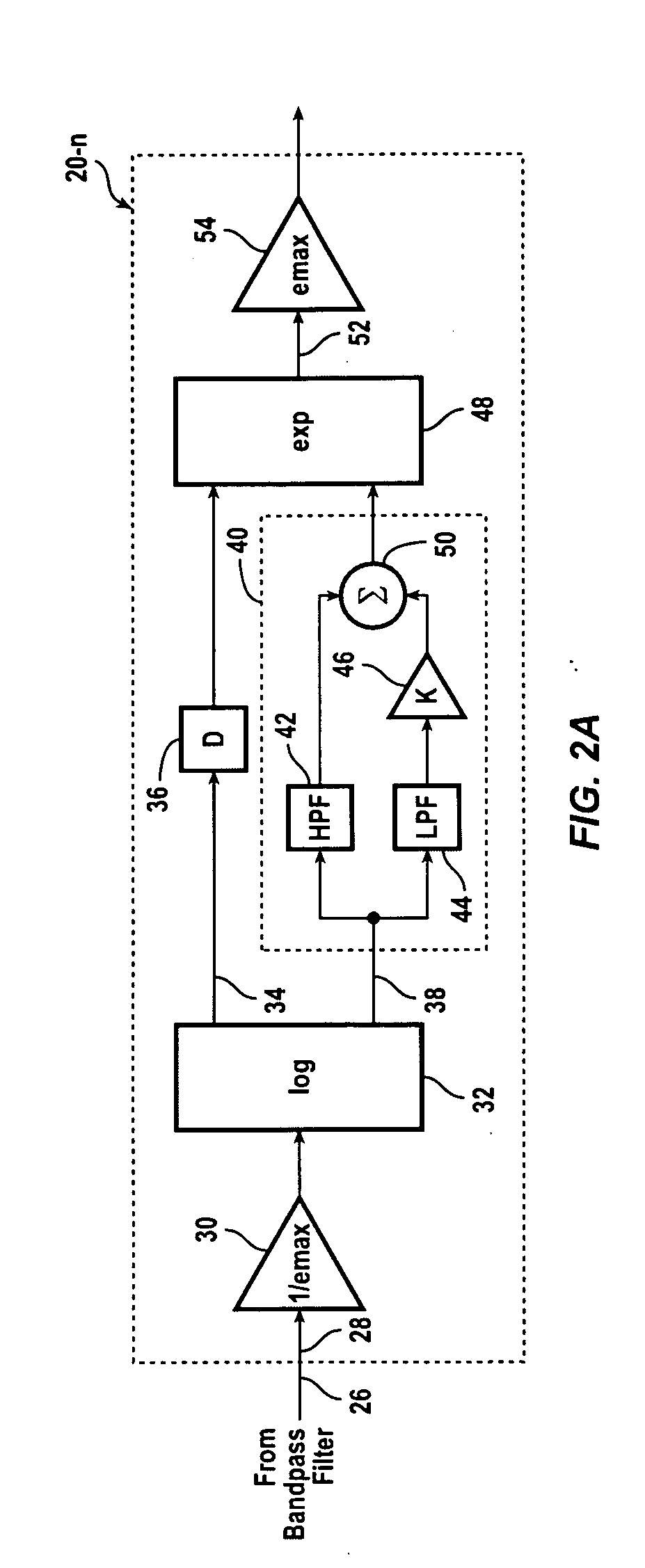
InactiveUS20050111683A1Signal processingCombination control in untuned amplifierBandpass filteringEngineering
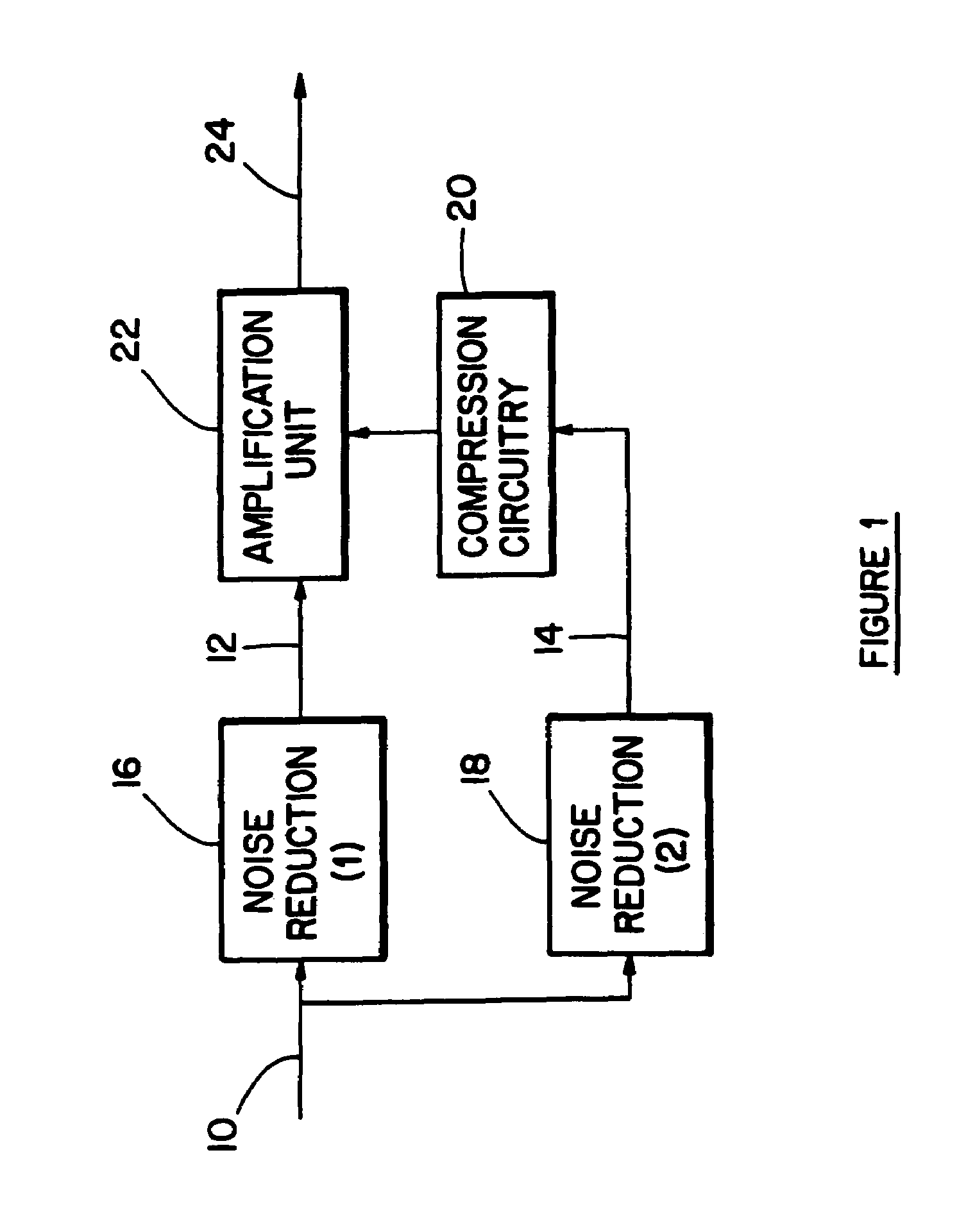
A hearing compensation system comprises a plurality of bandpass filters having an input connected to an input transducer and each bandpass filter having an output connected to the input of one of a plurality of multiplicative automatic gain control (MAGC) circuits whose outputs are summed together and connected to the input of an output transducer. The MAGC circuits attenuate acoustic signals having a constant background level without the loss of speech intelligibility. The identification of the background noise portion of the acoustic signal is made by the constancy of the envelope of the input signal in each of the several frequency bands. The background noise that will be suppressed includes multi-talker speech babble, fan noise, feedback whistle, florescent light hum, and white noise. For use in the consumer electronics field background acoustic noise may be sensed and used to adjust gain in the various MAGC circuits so as to improve a user's listening experience, whether the user is hearing impaired or not.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
Method of controlling diaphragm excursion of electrodynamic loudspeakers
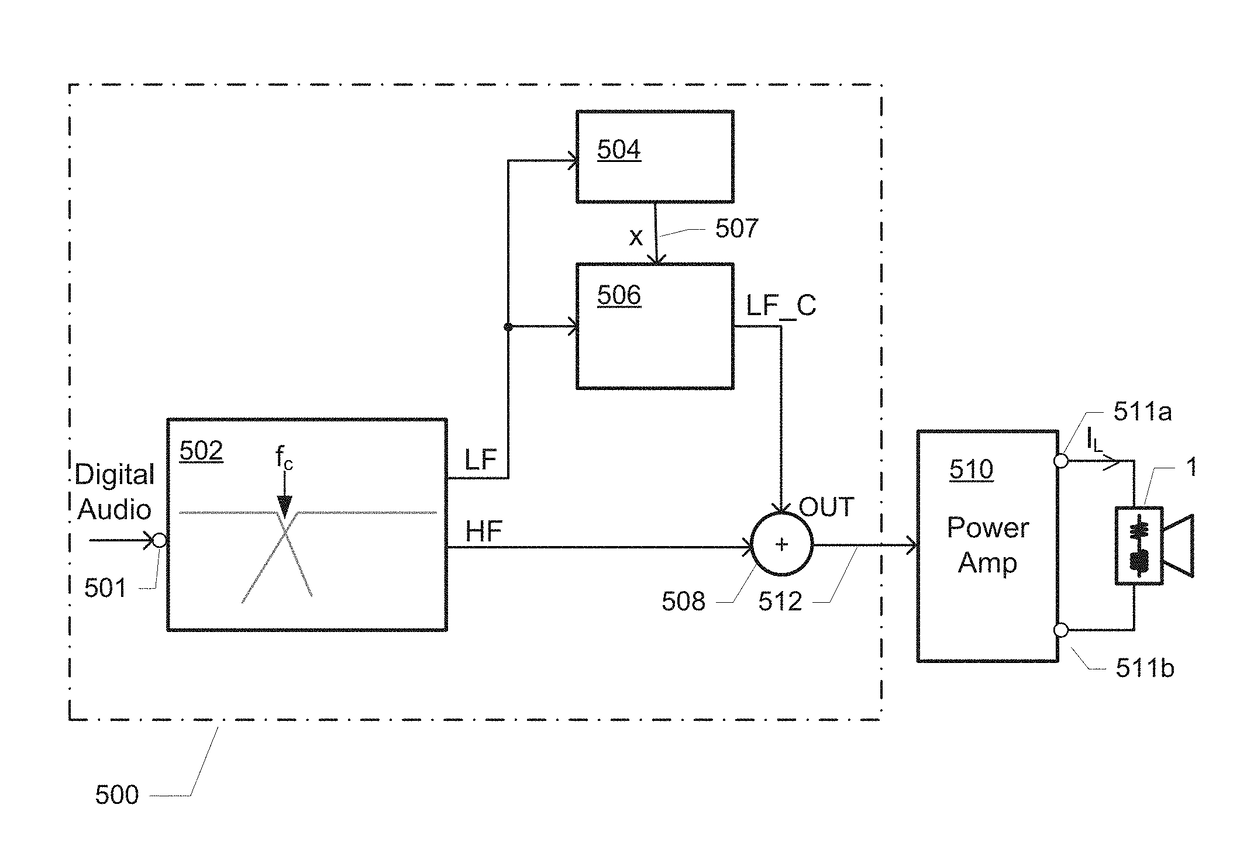
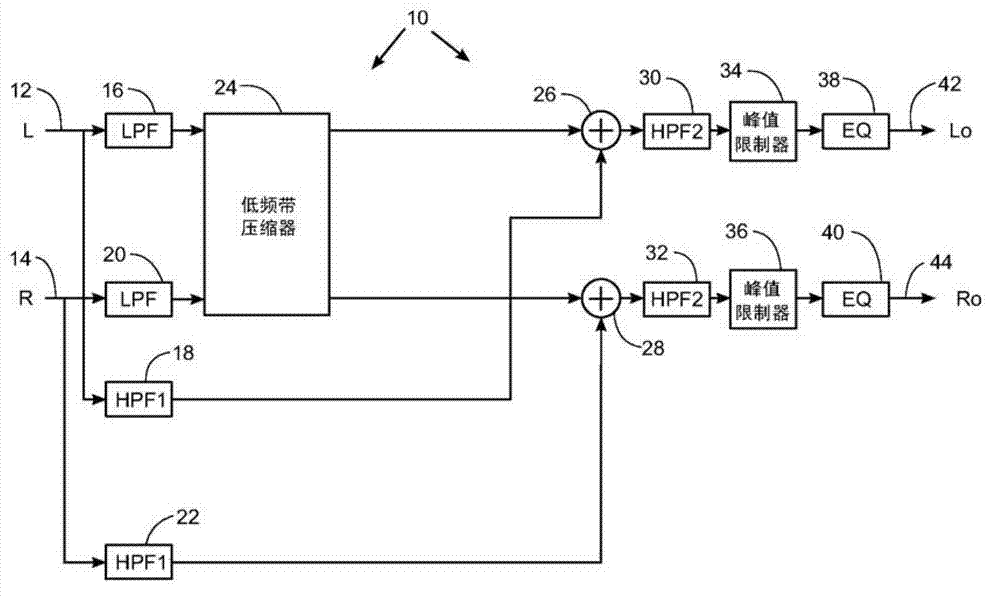
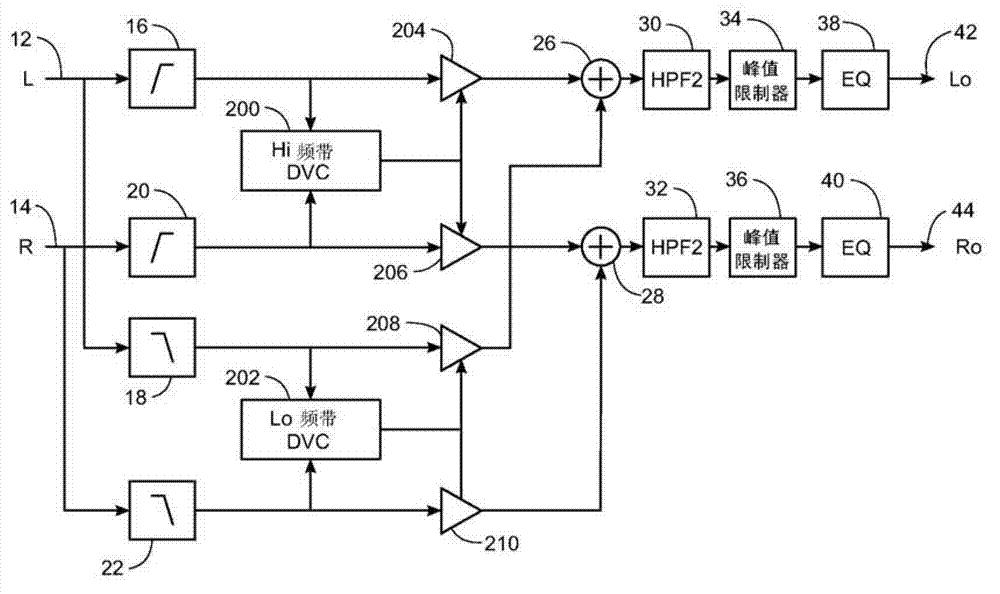
ActiveUS9813812B2Reliable and convenient protectionSignal processingCombination control in untuned amplifierBand splittingLow frequency band
The present application relates in one aspect to a method of controlling diaphragm excursion of an electrodynamic loudspeaker. The method comprises dividing the audio input signal into at least a low-frequency band signal and a high-frequency band signal by a band-splitting network and applying the low-frequency band signal to a diaphragm excursion estimator. The instantaneous diaphragm excursion is determined based on the low-frequency band signal. The determined instantaneous diaphragm excursion is compared with an excursion limit criterion. The low-frequency band signal is limited based on a result of the comparison between the instantaneous diaphragm excursion and the excursion limit criterion to produce a limited low-frequency band signal which is combined with the high-frequency band signal to produce an excursion limited audio signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
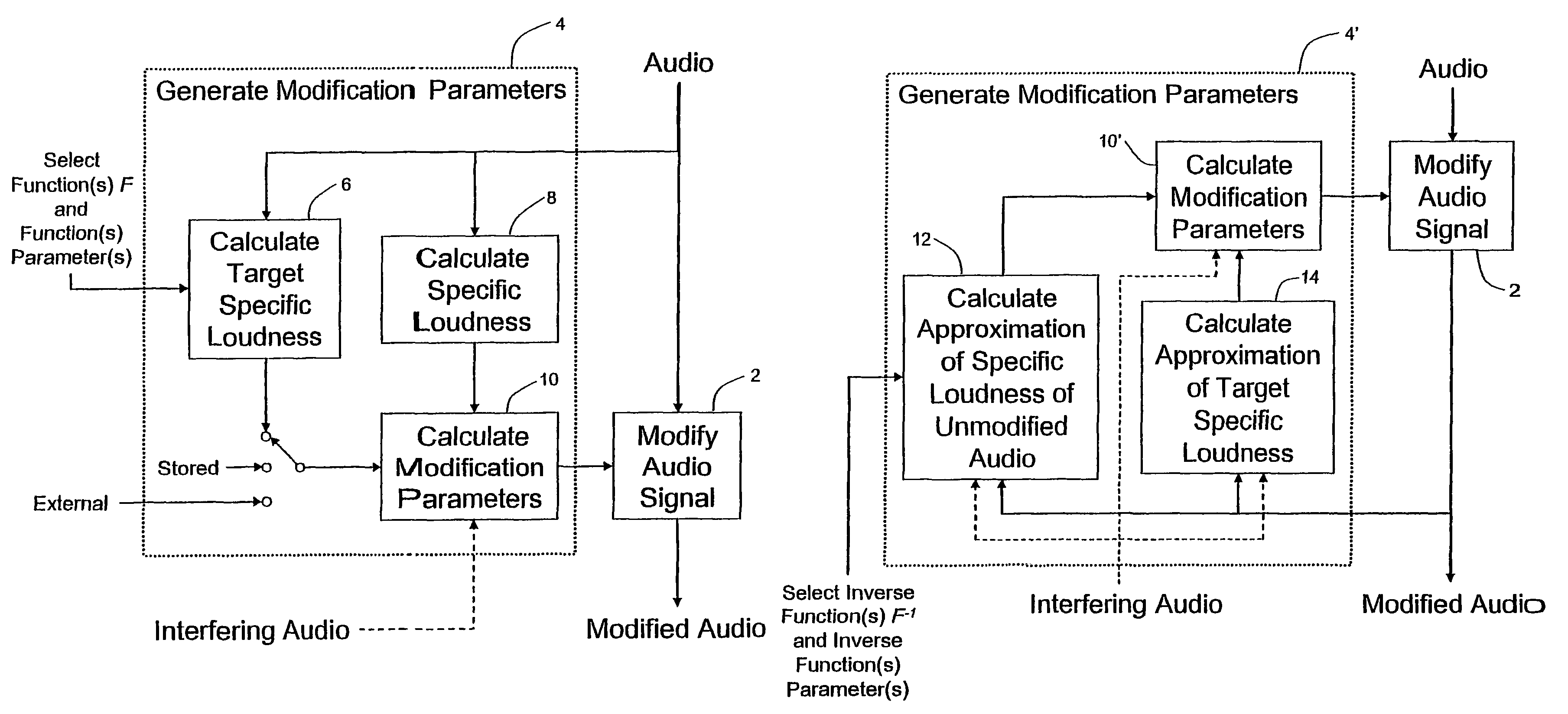
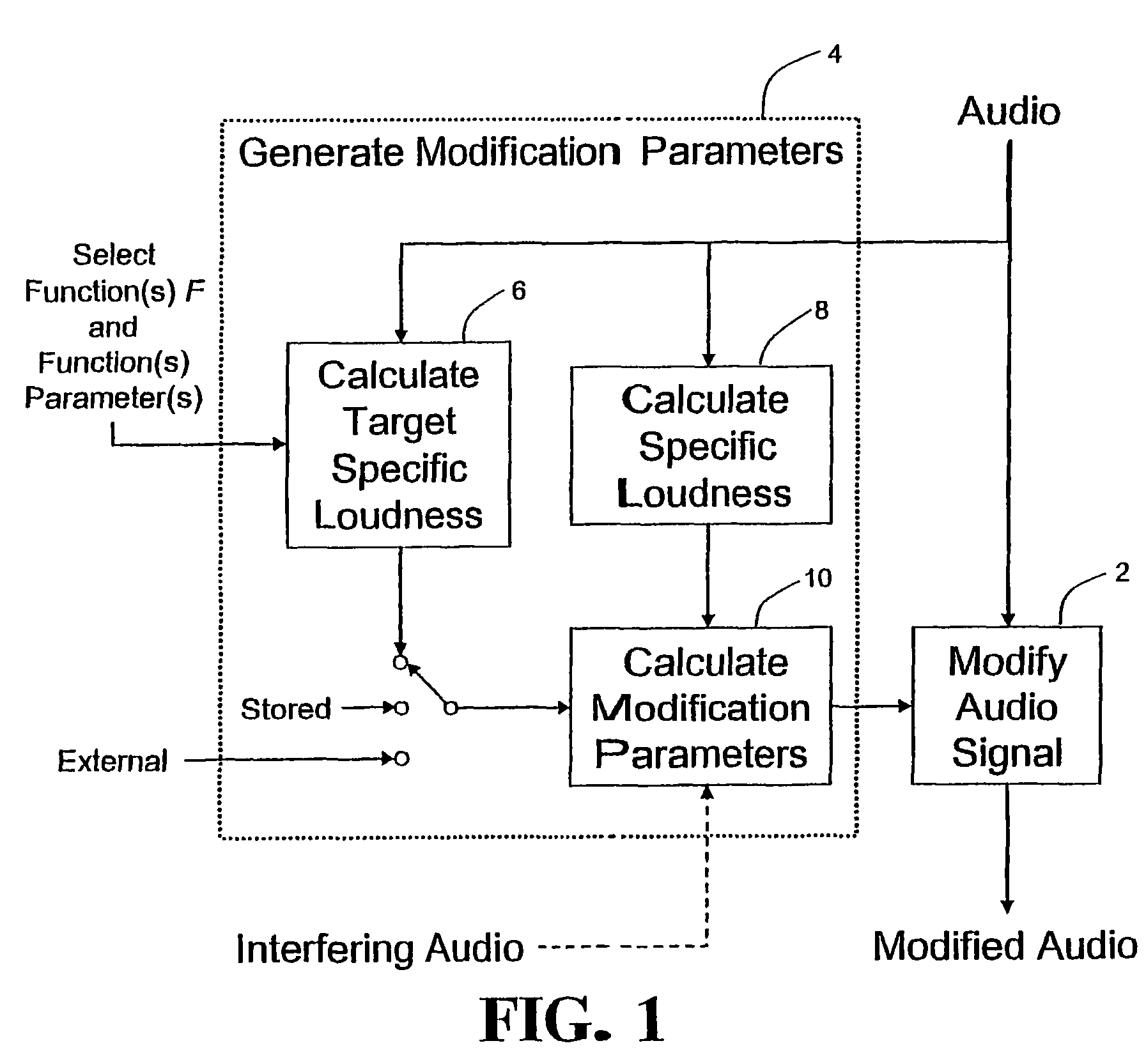
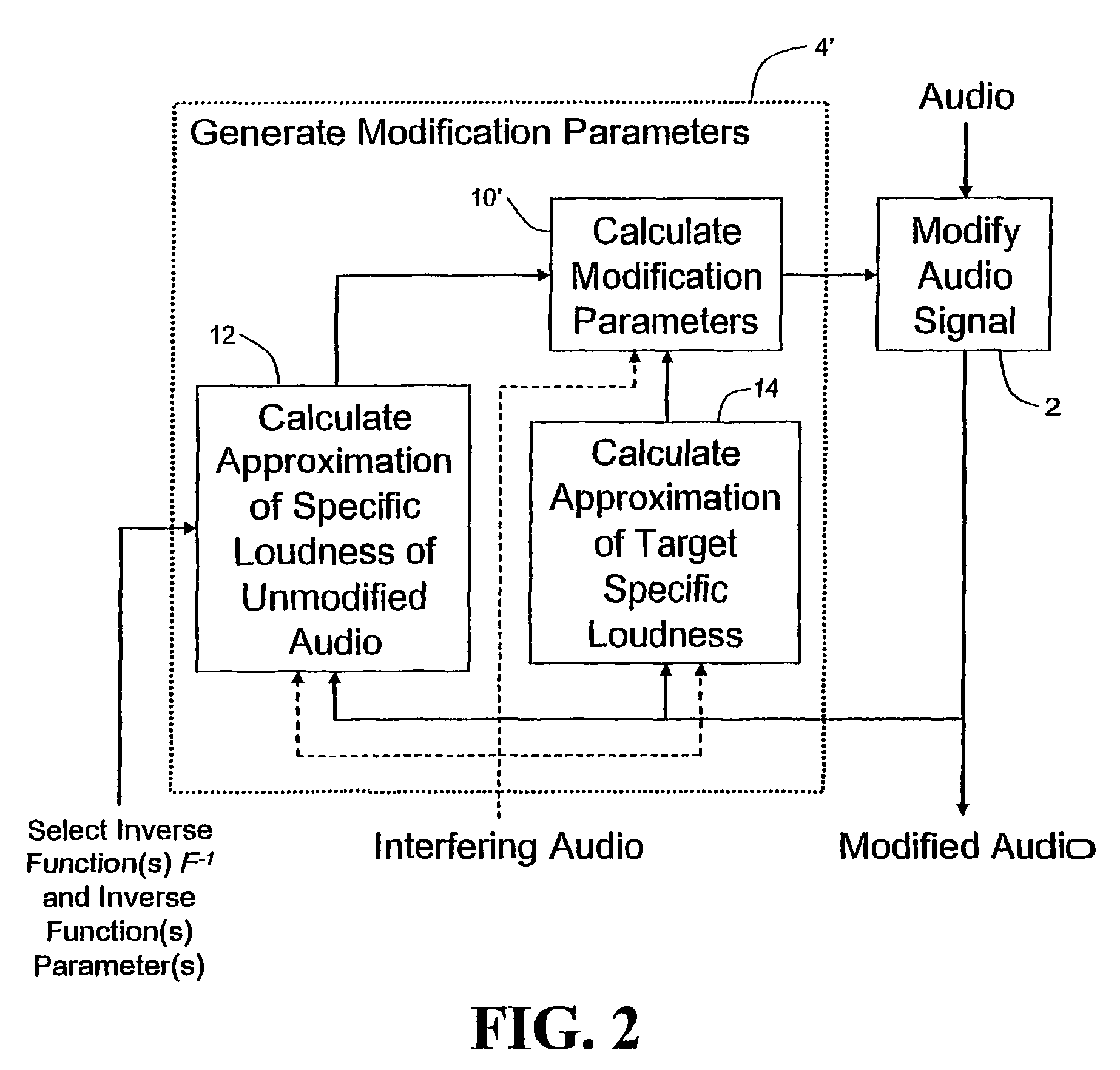
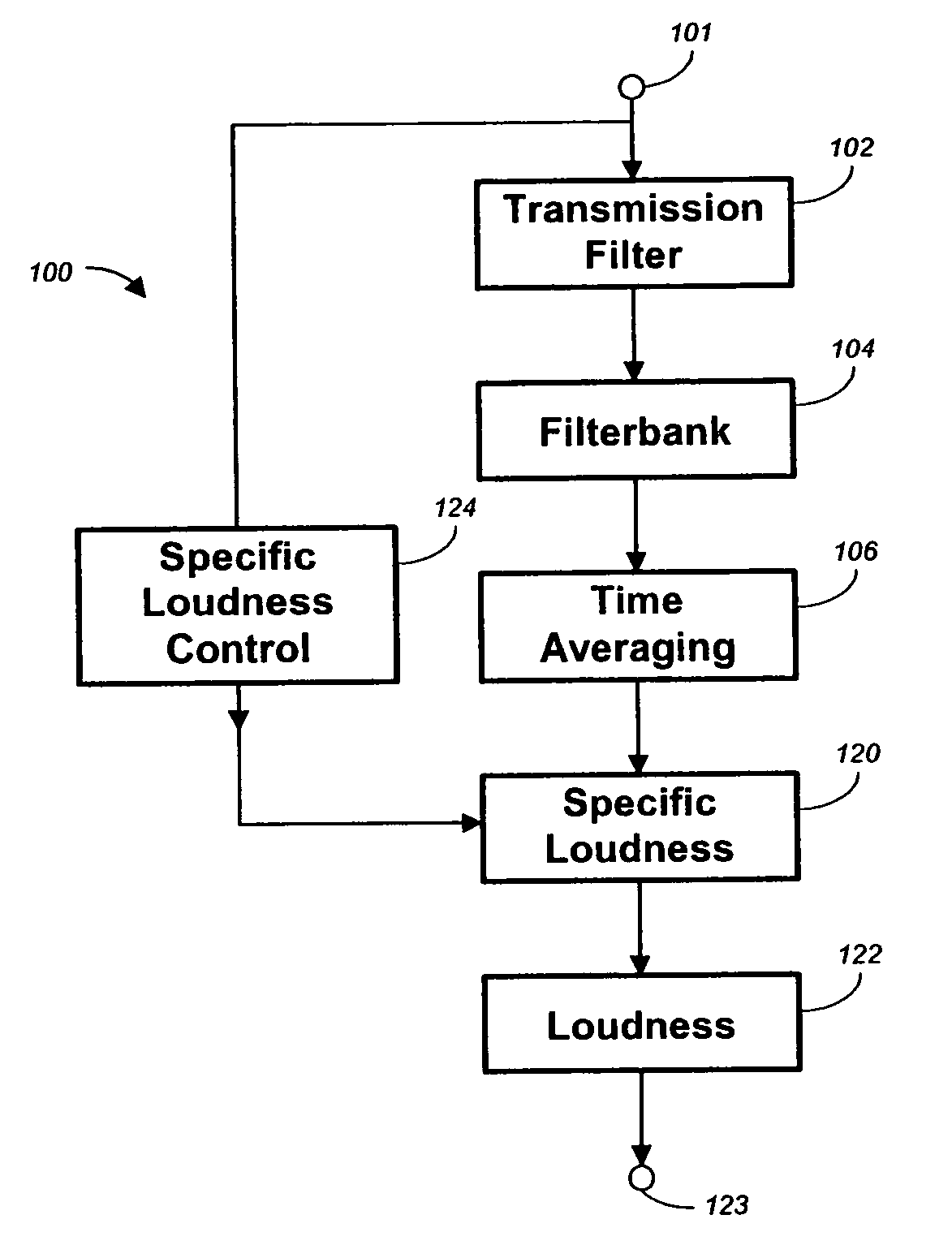
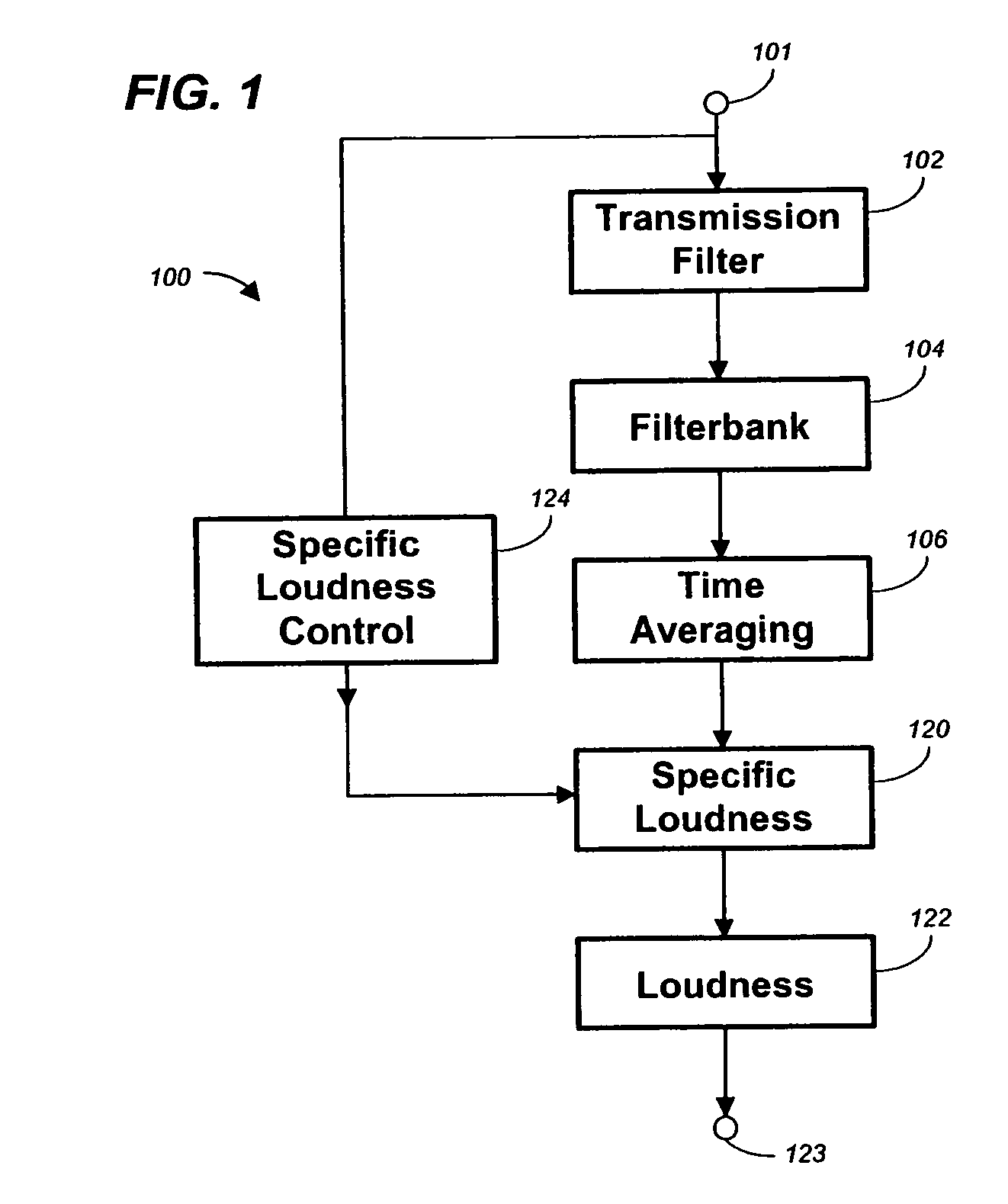
Calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness and/or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal
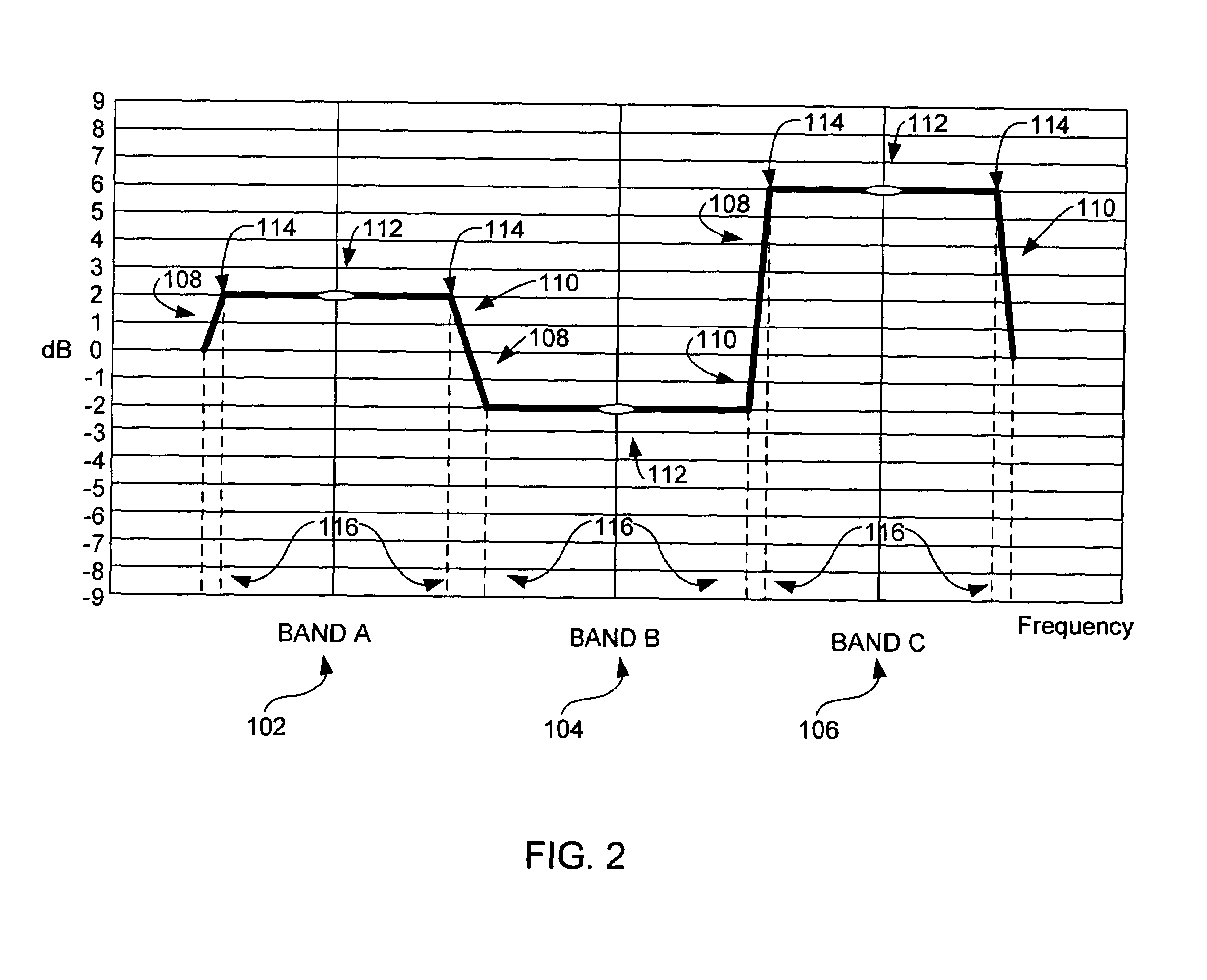
ActiveUS8090120B2Reduce the differenceReduce impactGain controlSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumEqualization
The invention relates to the measurement and control of the perceived sound loudness and / or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal. An audio signal is modified in response to calculations performed at least in part in the perceptual (psychoacoustic) loudness domain. The invention is useful, for example, in one or more of: loudness-compensating volume control, automatic gain control, dynamic range control (including, for example, limiters, compressors, expanders, etc.), dynamic equalization, and compensating for background noise interference in an audio playback environment. The invention includes not only methods but also corresponding computer programs and apparatus.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
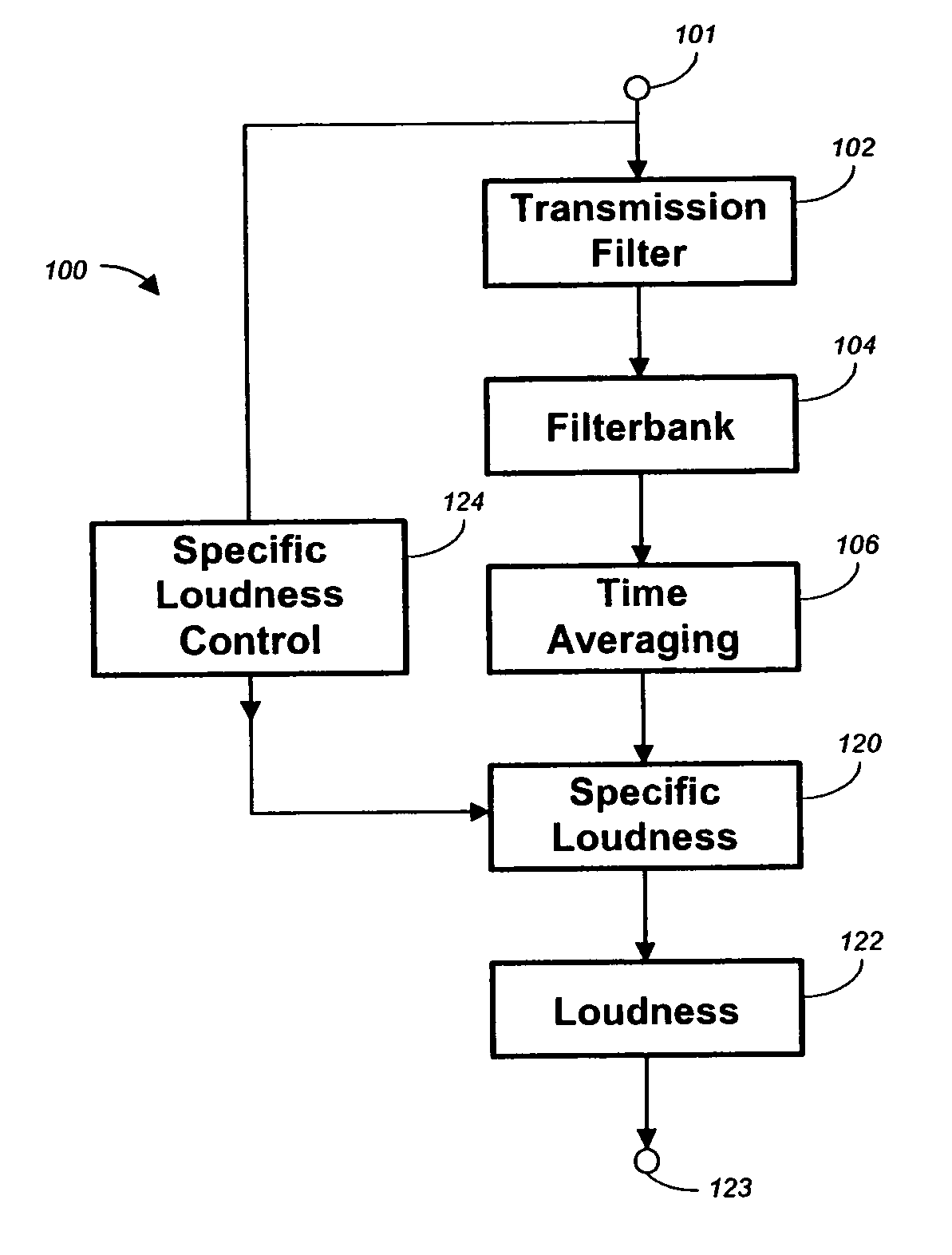
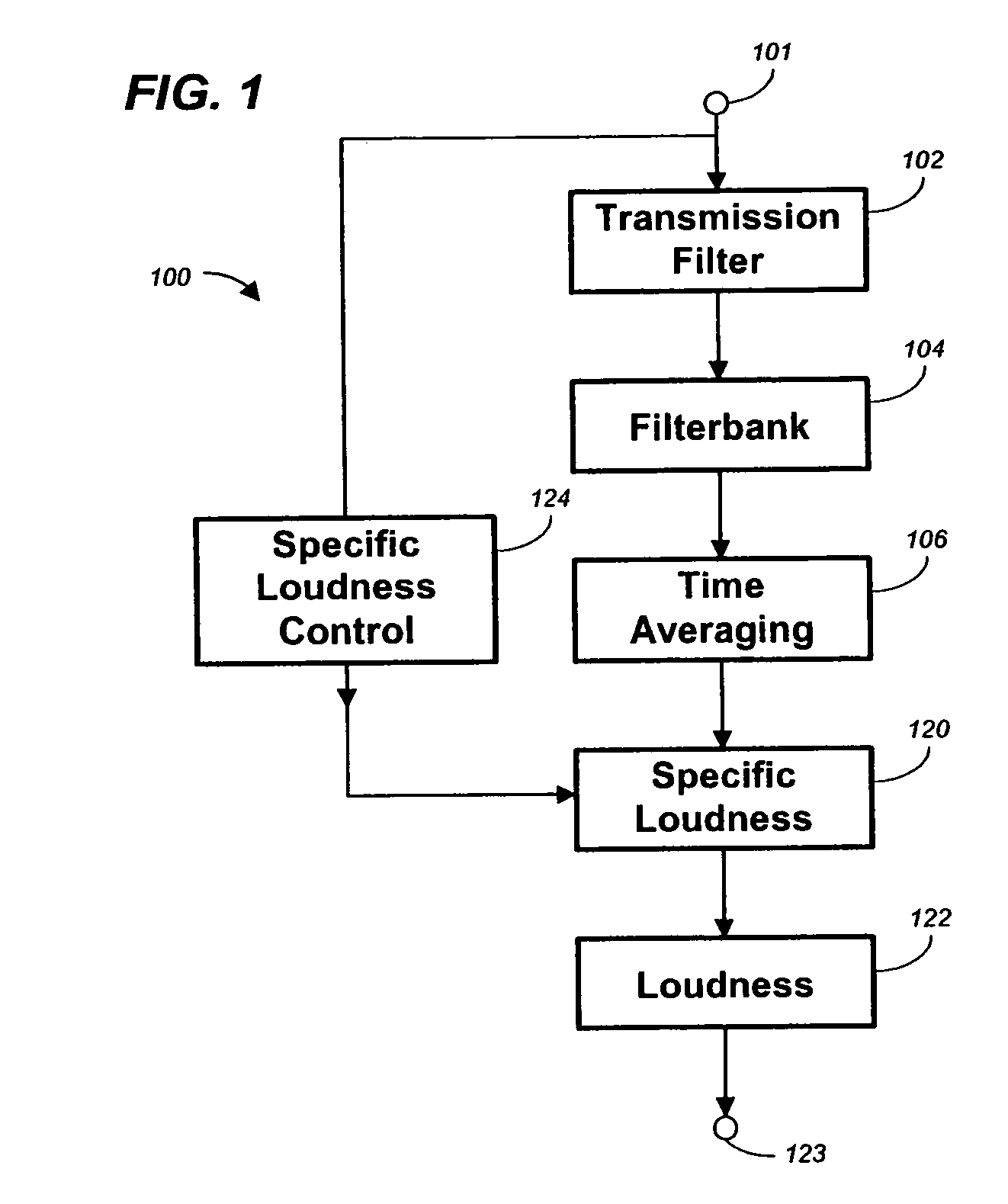
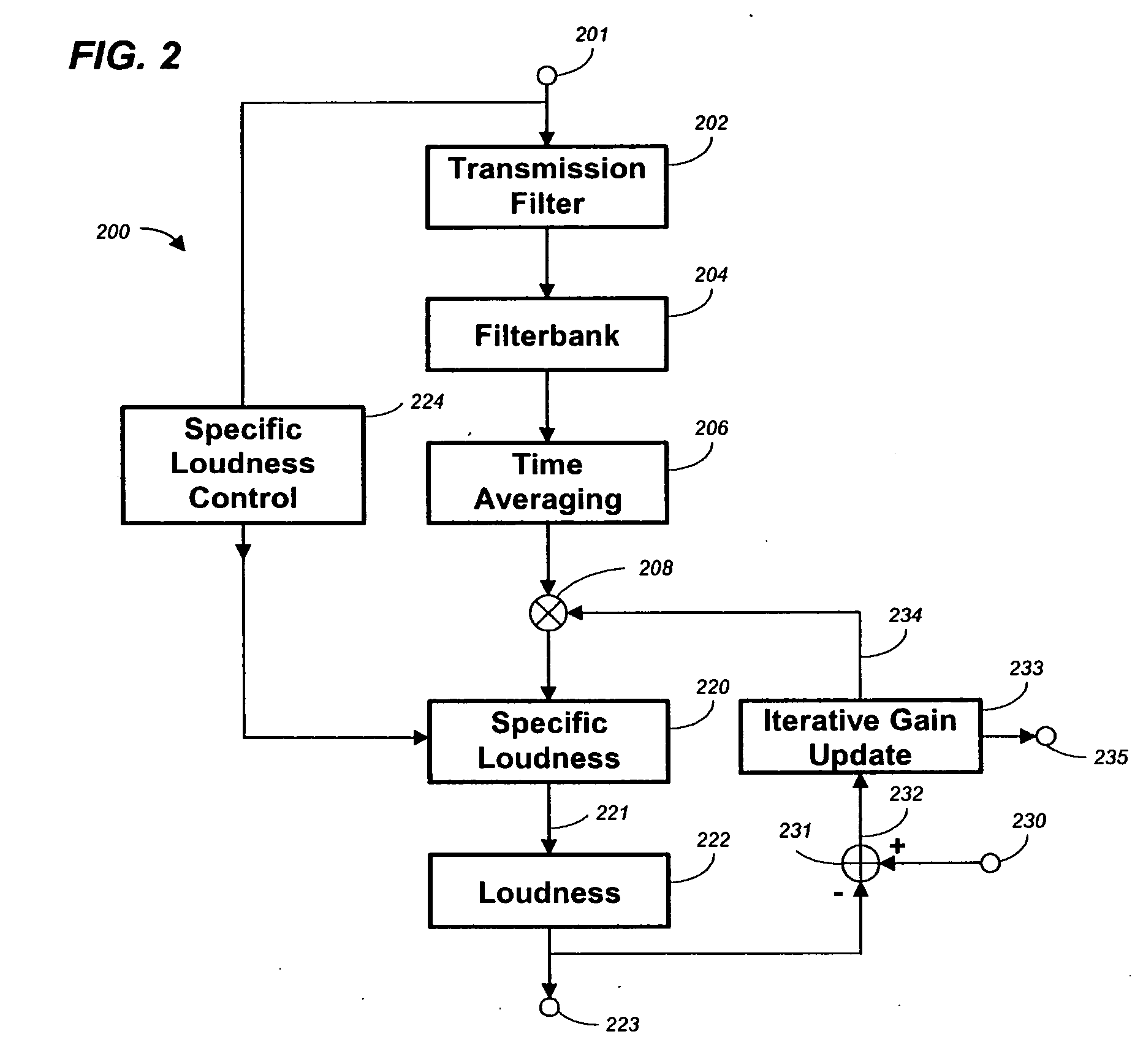
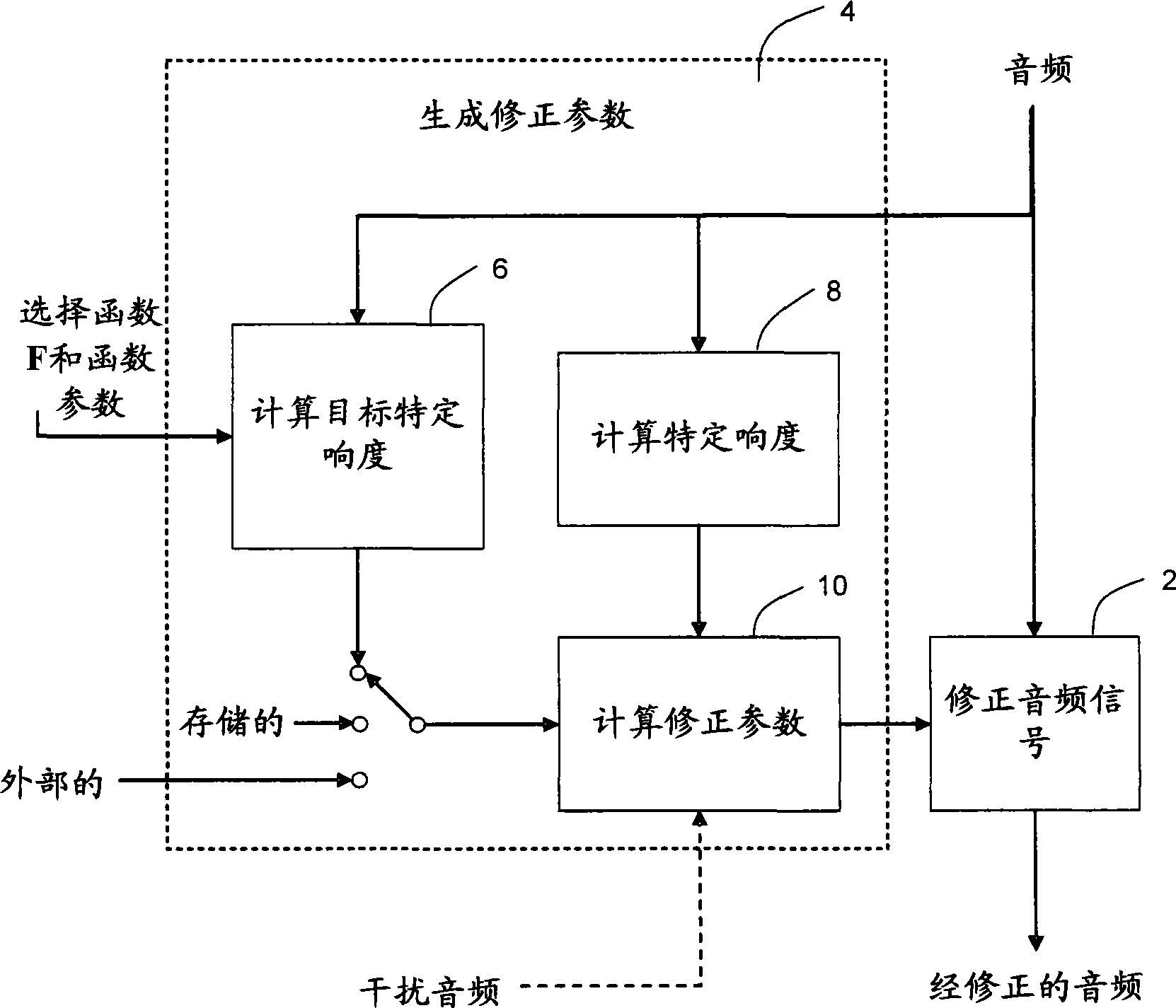
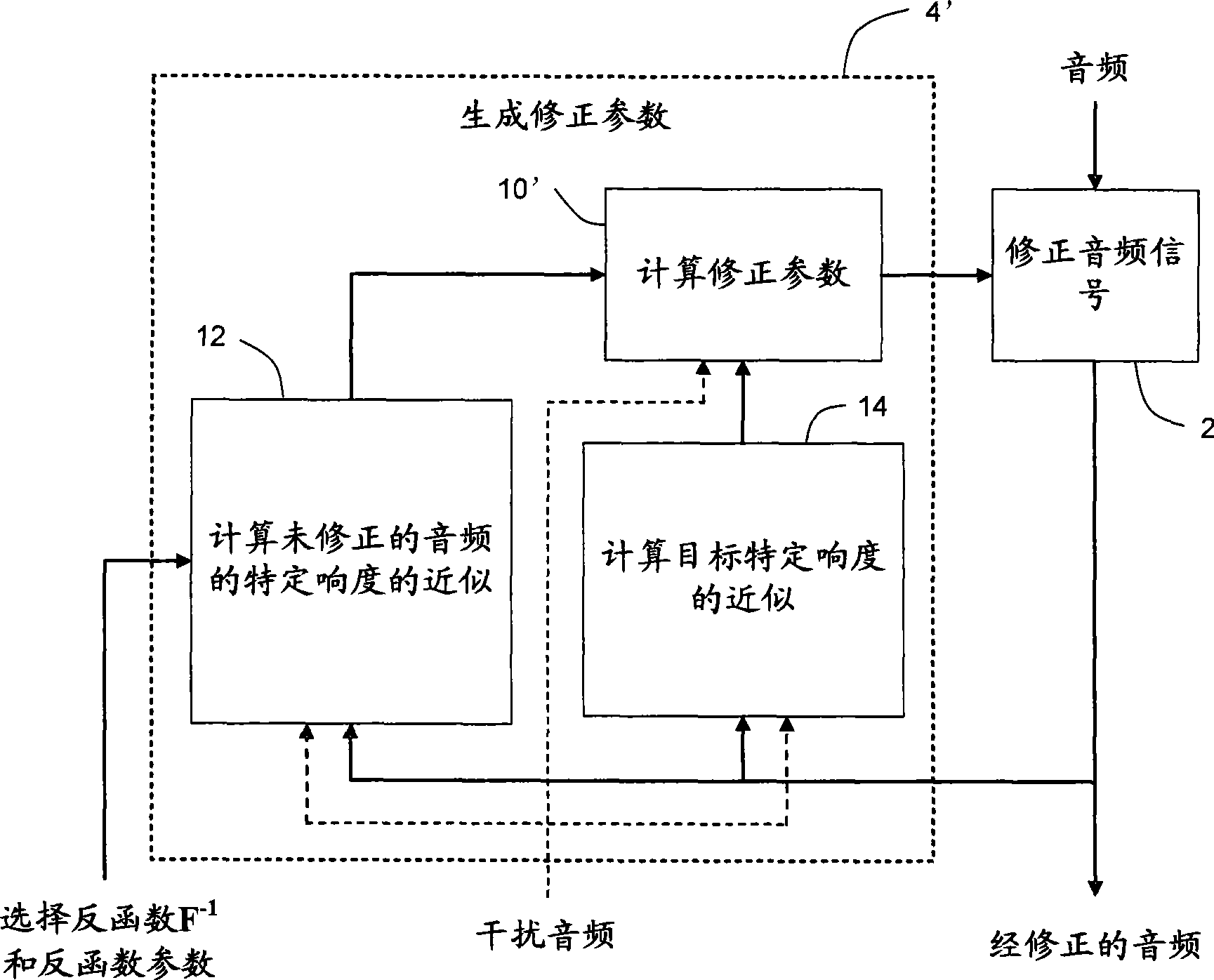
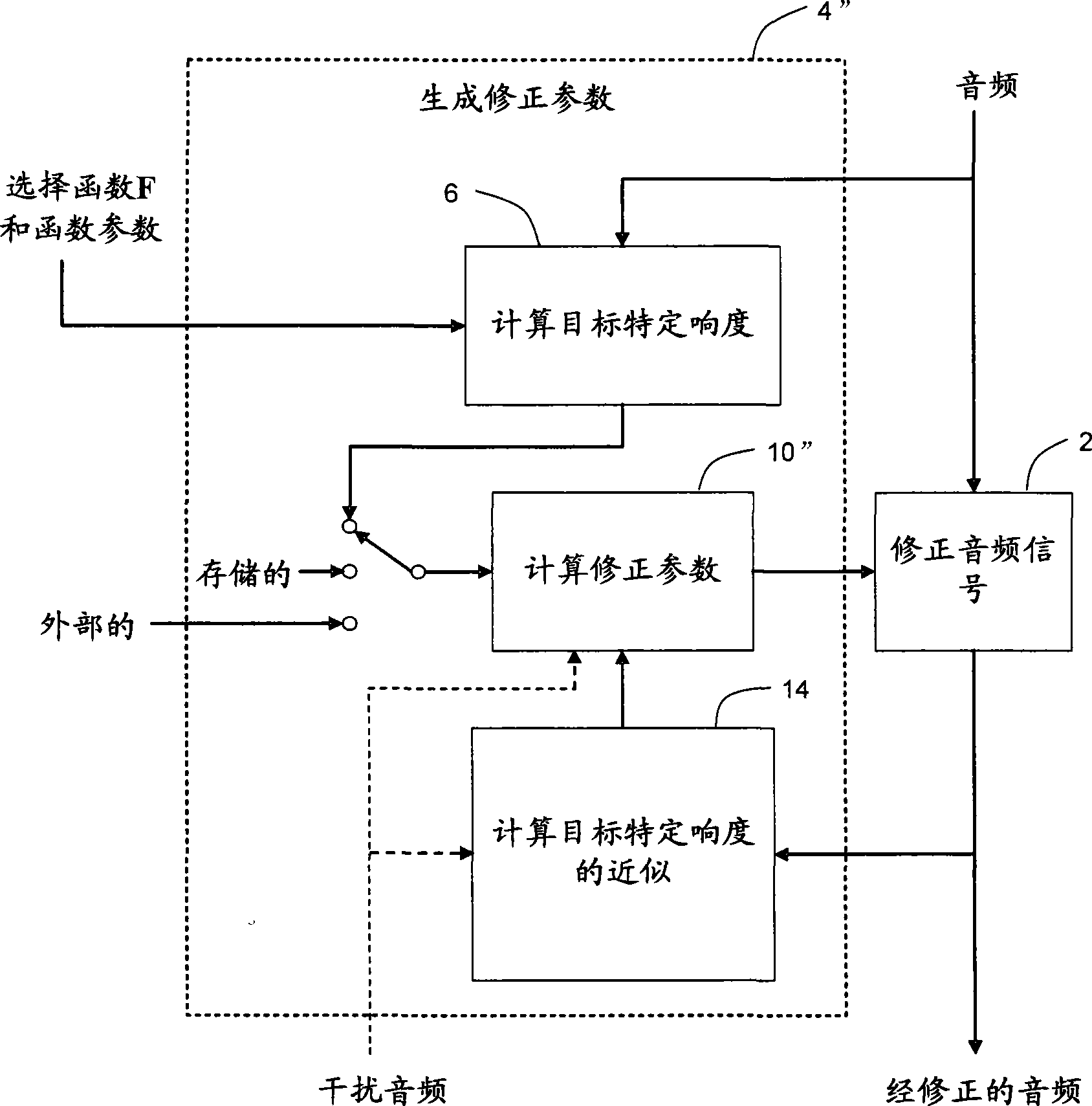
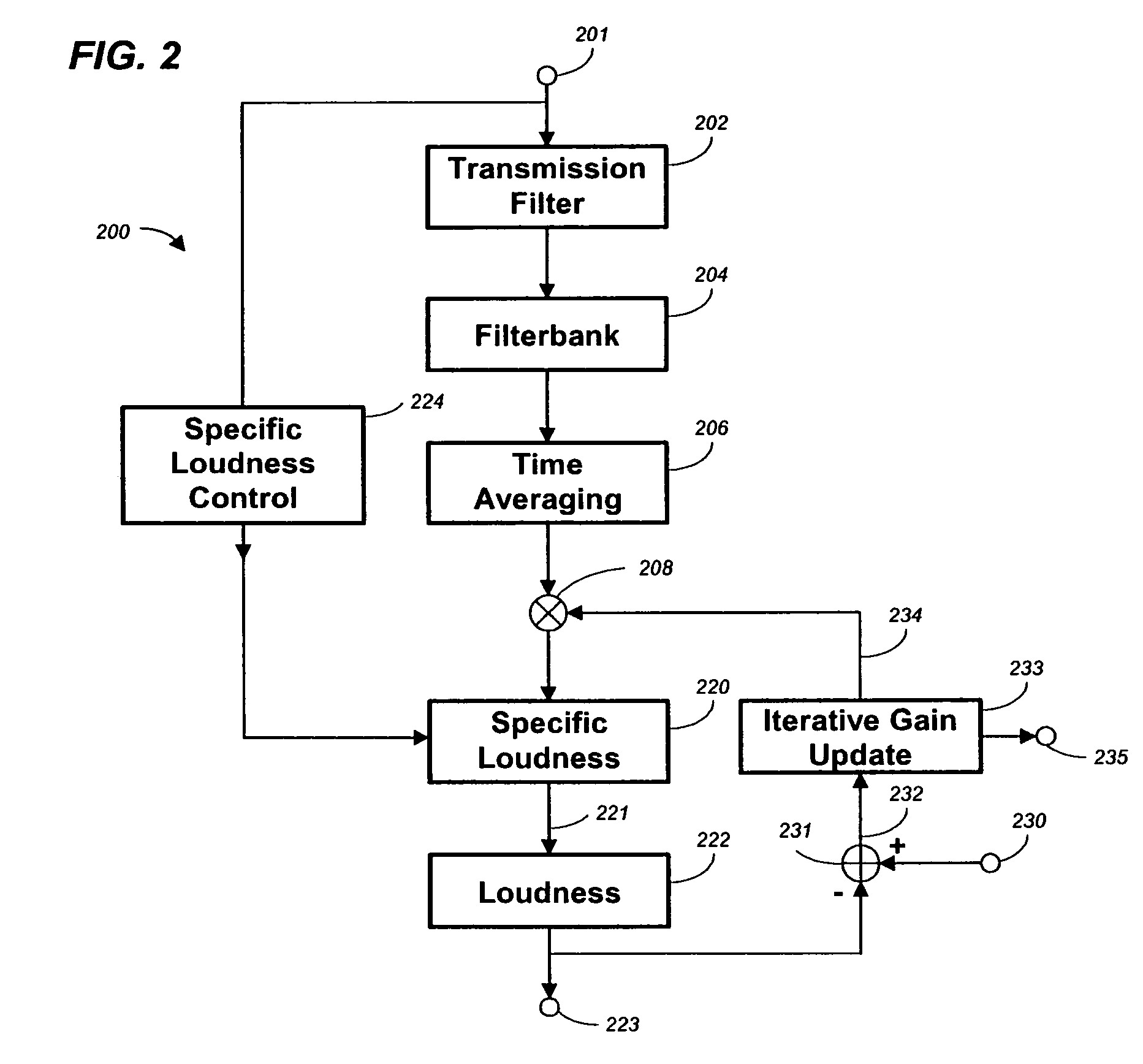
Method, apparatus and computer program for calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness of an audio signal
One or a combination of two or more specific loudness model functions selected from a group of two or more of such functions are employed in calculating the perceptual loudness of an audio signal. The function or functions may be selected, for example, by a measure of the degree to which the audio signal is narrowband or wideband. Alternatively or with such a selection from a group of functions, a gain value G[t] is calculated, which gain, when applied to the audio signal, results in a perceived loudness substantially the same as a reference loudness. The gain calculating employs an iterative processing loop that includes the perceptual loudness calculation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
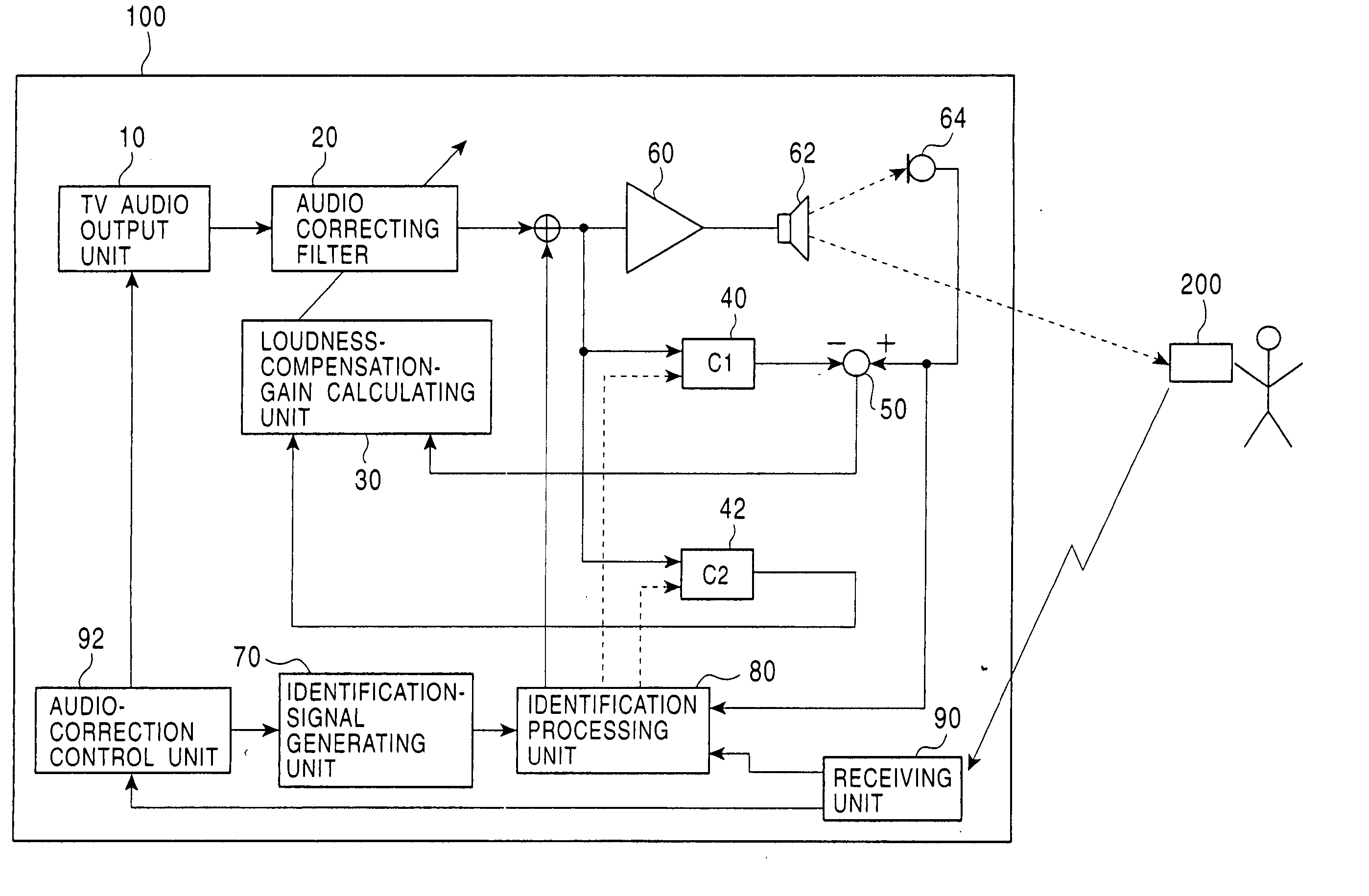
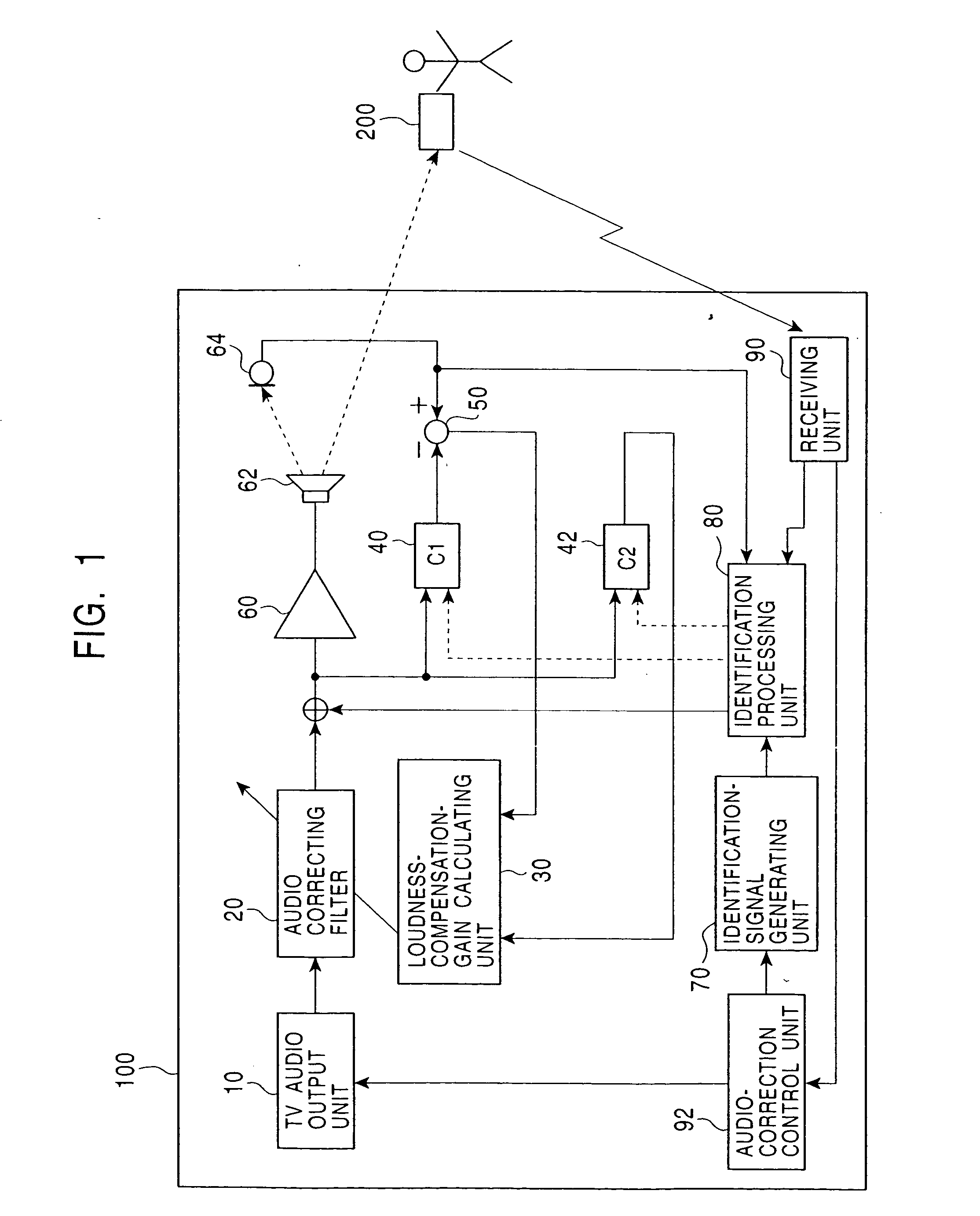
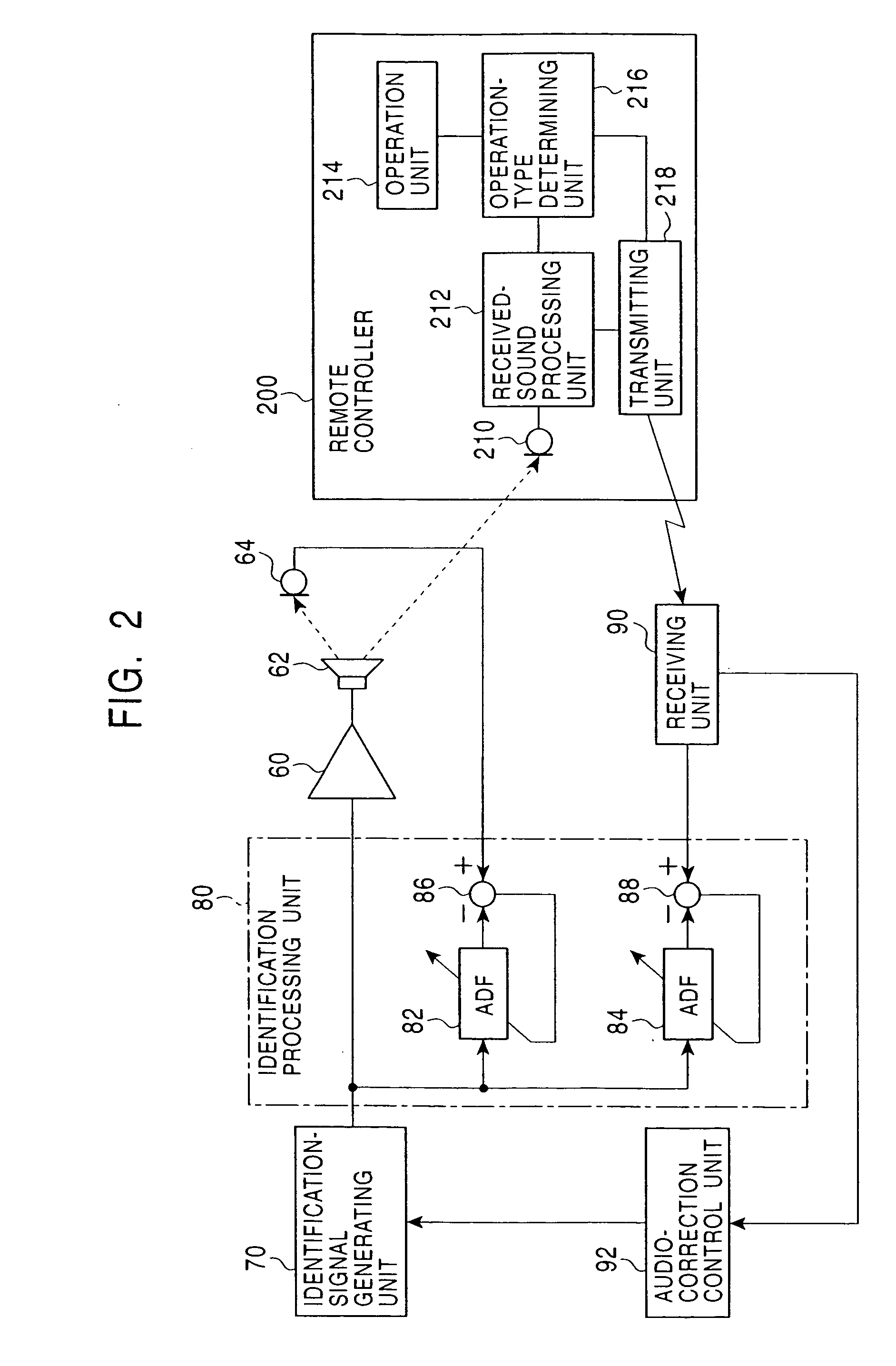
Audio correcting apparatus
InactiveUS20050013443A1Accurate sound pressure levelListen clearlyTelevision system detailsAdaptive networkEnvironmental noiseLoudspeaker
An audio correcting apparatus includes a speaker provided on a television apparatus, a microphone provided on a remote controller, an identifying unit which identifies an acoustic characteristic from the speaker to the microphone, and an acoustic characteristic setting unit having the acoustic characteristic. A signal obtained by allowing an audio signal input to the speaker to pass through the acoustic characteristic setting unit, and a signal representing ambient noise are input to an audio-correcting filter and a loudness-compensation-gain calculating unit. Based on both signals, the sound pressure level of sound output from the speaker is corrected so that the sound output from the speaker is clearly heard when reaching the user without being affected by the ambient noise.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
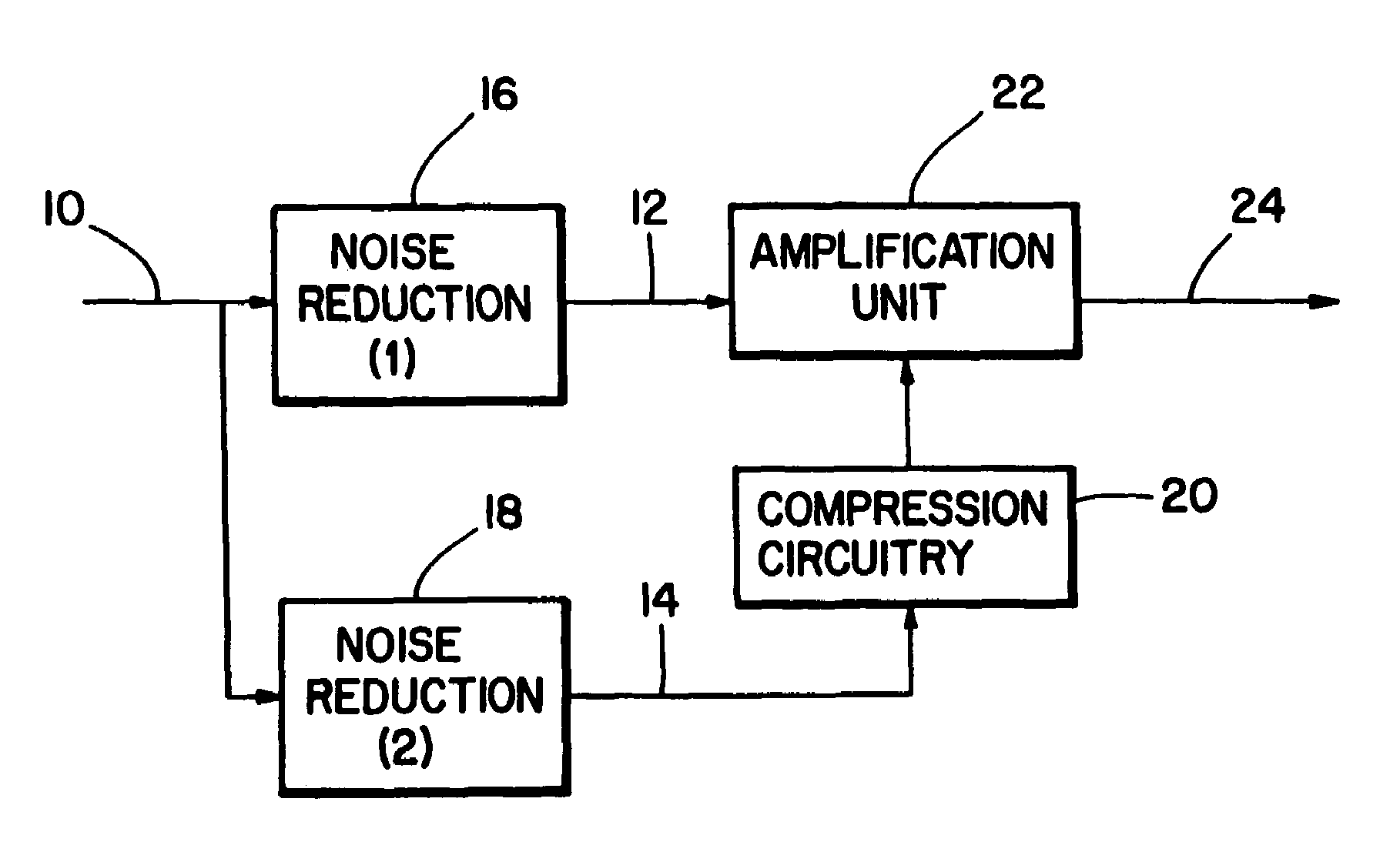
Method and apparatus for noise reduction particularly in hearing aids
InactiveUS7016507B1Boosted speechReduce noiseEar treatmentVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesCompression actionNoise reduction algorithm
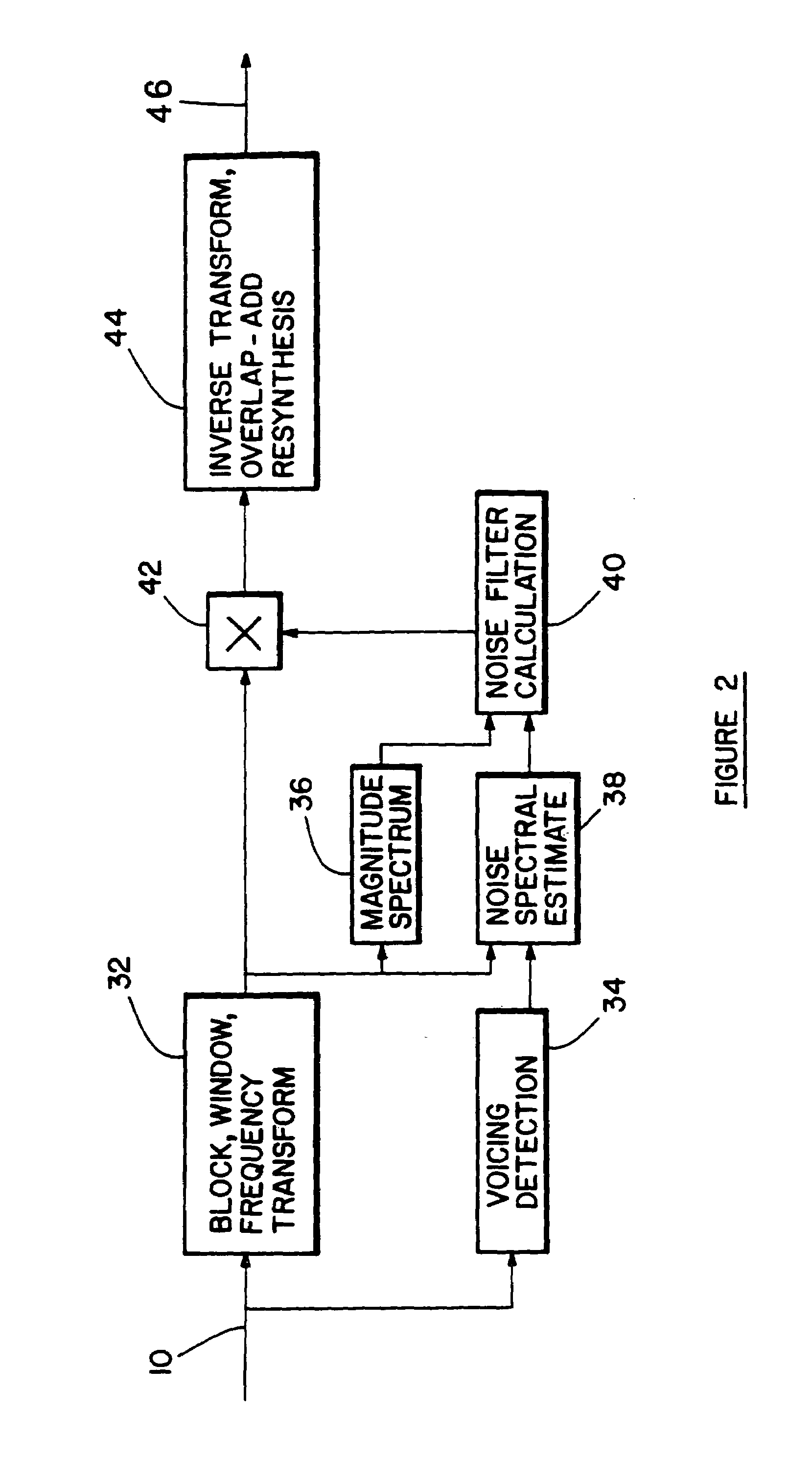
This invention describes a practical application of noise reduction in hearing aids. Although listening in noisy conditions is difficult for persons with normal hearing, hearing impaired individuals are at a considerable further disadvantage. Under light noise conditions, conventional hearing aids amplifying the input signal sufficiently to overcome the hearing loss. For a typical sloping hearing loss where there is a loss in high frequency hearing sensitivity, the amount of boost (or gain) rises with frequency. Most frequently, the loss in sensitivity is only for low-level signals; high level signals are affective minimally or not at all. A compression hearing aid is able to compensate by automatically lowering the gain as the input signal level rises. This compression action is usually compromised under noisy conditions. In general, hearing aids are of lesser benefit under noisy conditions since both noise and speech are boosted together when what is really required is a reduction of the noise relative to the speech. A noise reduction algorithm with the dual purpose of enhancing speech relative to noise and also providing a relatively clean signal for the compression circuitry is described.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Linearized filter band equipment and processes
ActiveUS7266205B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsGraphicsSystems design
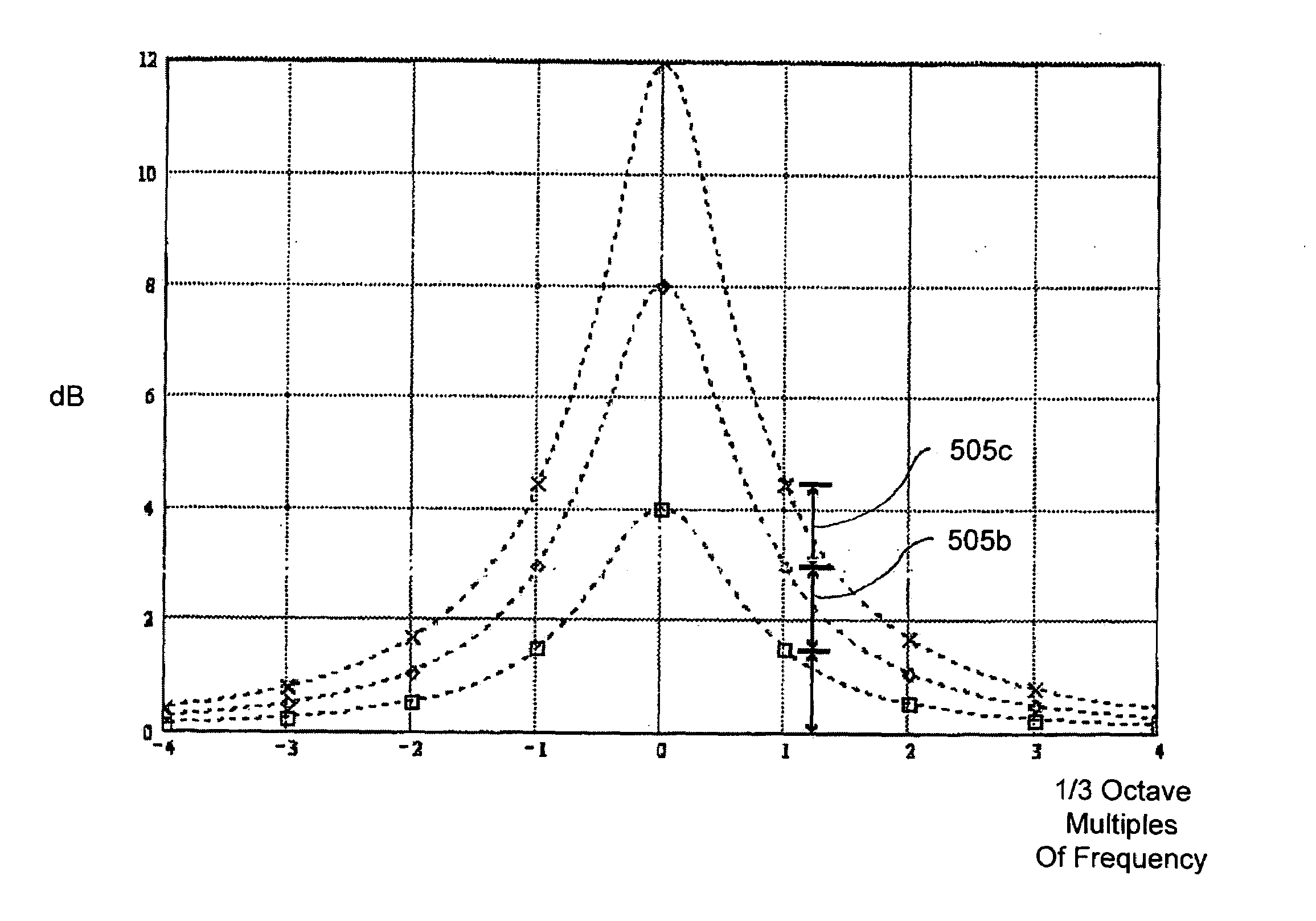
A method for use with equipment having filters, the method characterized by multiplying a matrix having a specified cut-boost setting of a filter of a graphic equalizer by a correction matrix to create a matrix having a corrected cut-boost setting of the filter of the graphic equalizer; adjusting an actual cut-boost setting of the filter of the graphic equalizer to be substantially equal to the corrected cut-boost setting of the filter of the graphic equalizer; and configuring the filter to have a Q value substantially equal to a linearizing Q value. In addition to the foregoing, other method embodiments are described in the claims, drawings, and text forming a part of the present application. In one or more various embodiments, related systems include but are not limited to circuitry and / or programming for effecting the foregoing-referenced method embodiments; the circuitry and / or programming can be virtually any combination of hardware, software, and / or firmware configured to effect the foregoing-referenced method embodiments depending upon the design choices of the system designer.
Owner:INMUSIC BRANDS
Calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness and/or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal
InactiveCN101421781AReduced characteristicsSpecific loudness controlGain controlSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumEqualization
Audio signal processing relating to the measurement and control of the perceived sound loudness and / or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal is useful, for example, in one or more of: loudness-compensating volume control, automatic gain control, dynamic range control (including, for example, limiters, compressors, expanders, etc.), dynamic equalization, and compensating for background noise interference in an audio playback environment. In various embodiments, modification parameters are derived for modifying the audio signal in order to reduce the difference between its specific loudness and a target specific loudness.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
System and method for varying low audio frequencies inversely with audio signal level
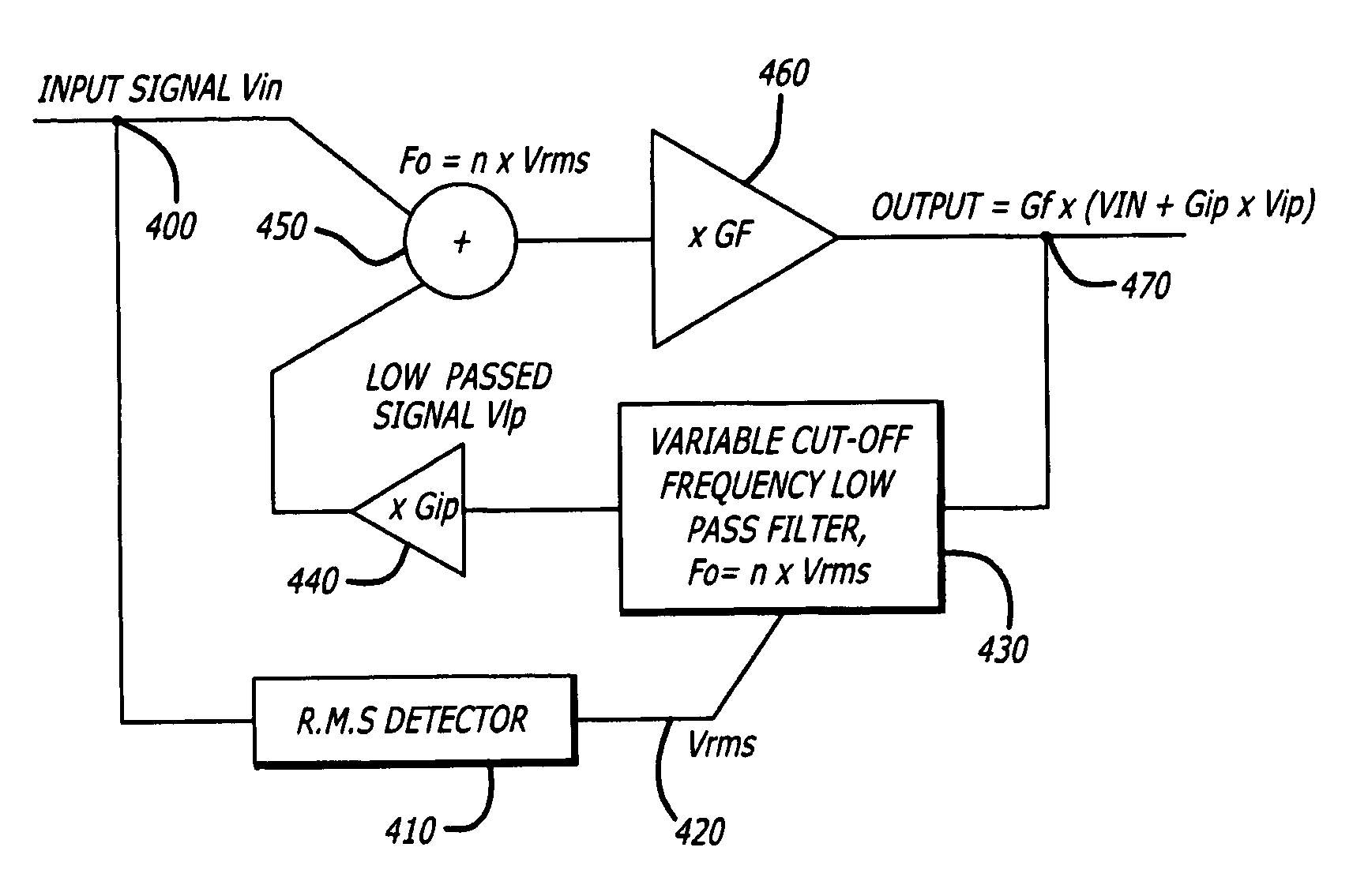
InactiveUS7016509B1Increase contentEasy to removeCombination control in untuned amplifierAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlCapacitanceResistance capacitance
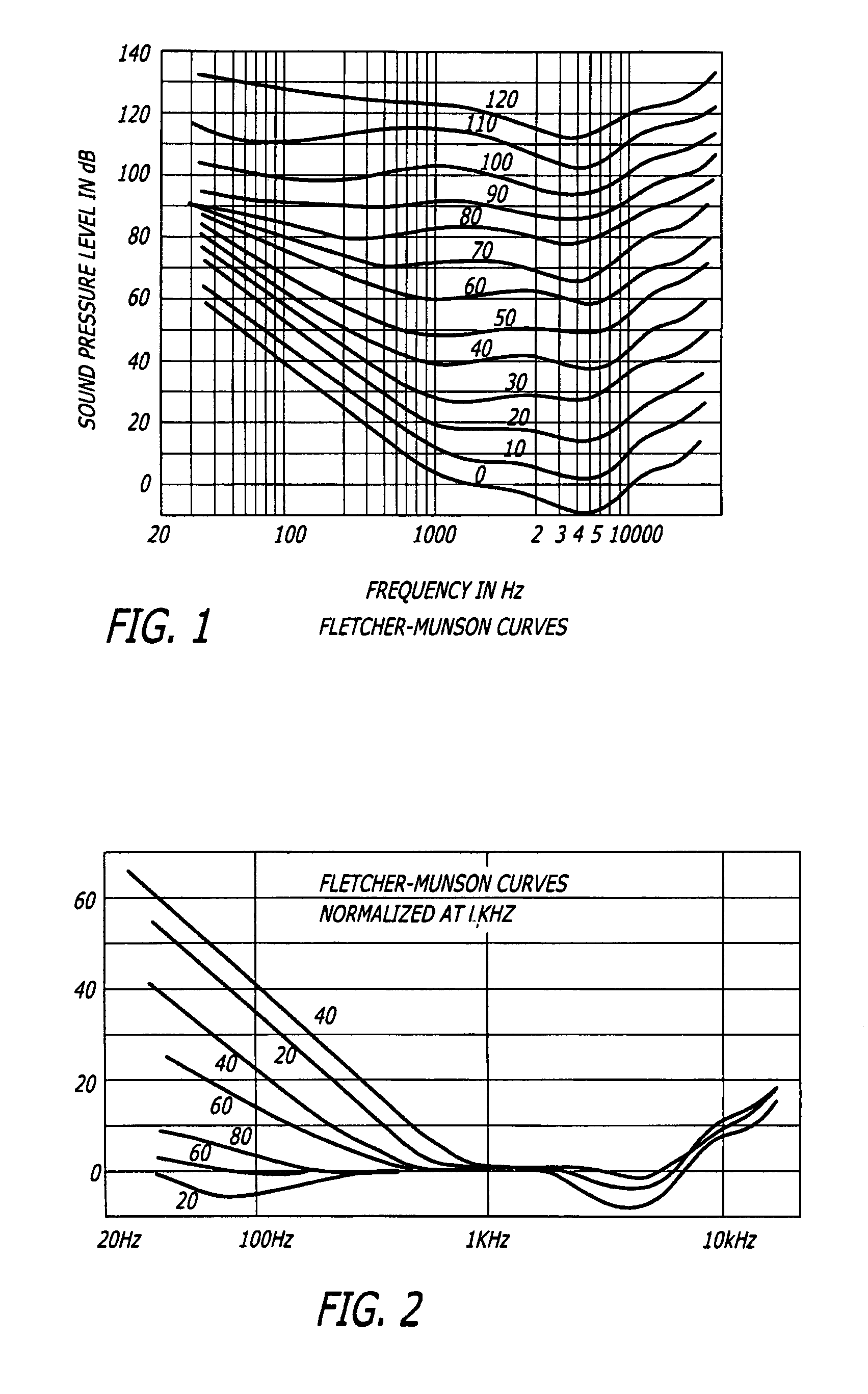
The present invention relates to an auto loudness circuit for performing loudness compensation automatically depending on the signal level. When the signal level decreases, loudness compensation is slowly introduced and as the signal level increases, loudness compensation is quickly removed. To do so, the auto loudness circuit utilizes a filter circuit with the characteristic of a first order bass boost. The filter circuit maintains a corner frequency which is proportional to the inverse of audio level in order to mimic the Fletcher-Munson curves. Because the circuit employs a capacitance-multiplier with a first order resistance capacitance filter, the bass boost is inversely proportional to the signal level. Thus, bass boost is achieved automatically as the program content changes so that the listener is unaware of significant changes in program material as signal levels change either through increase or decrease in volume, crescendo or new material.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Digital audio signal processing
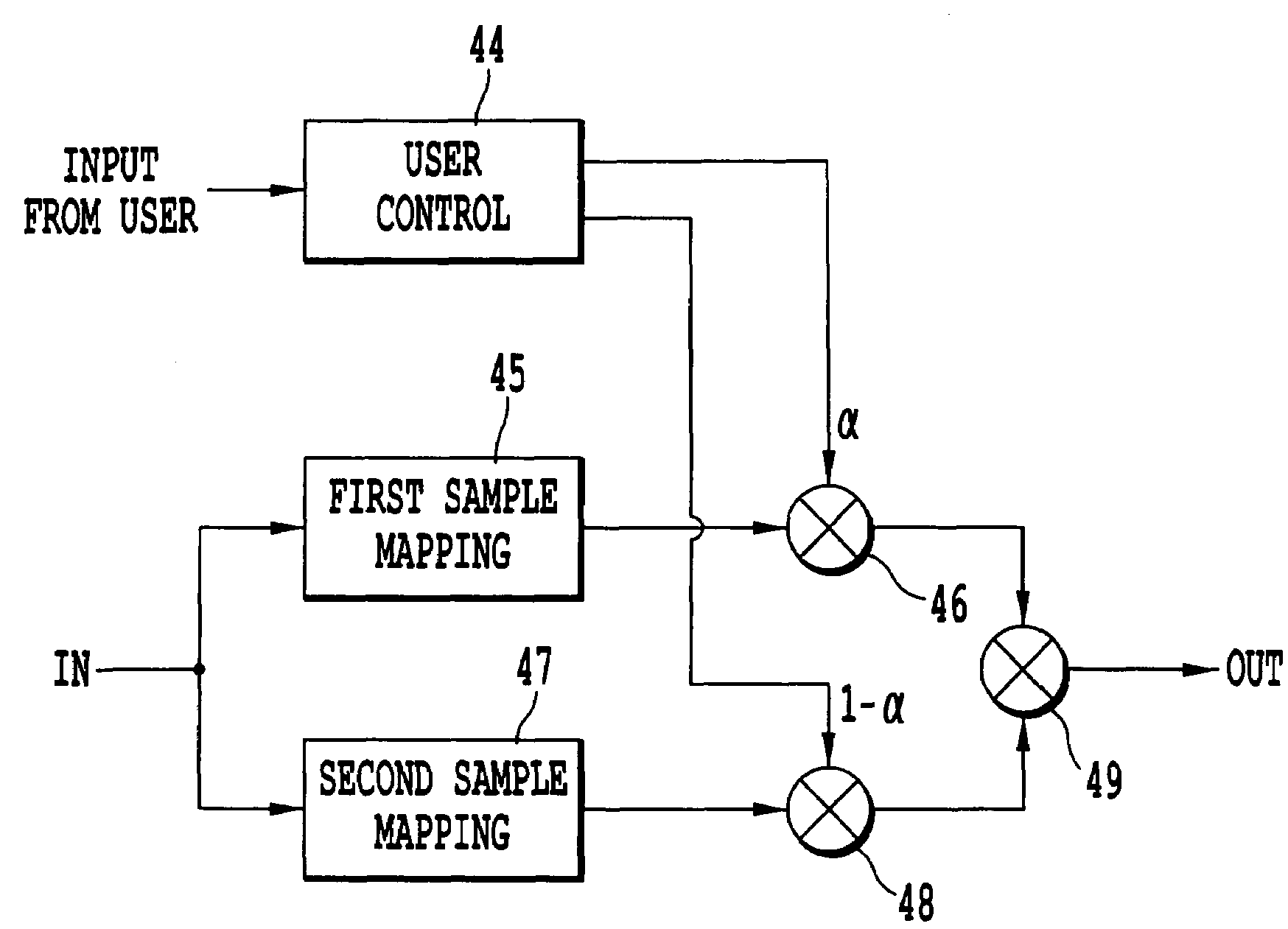
ActiveUS7369906B2Increase the loudnessReduce the possibilityGain controlSpeech analysisDigital signal processingSignal transfer function
A digital audio processor comprises at least one digital audio sample mapping module and produces a sequence of output digital audio sample values by applying a quasi time-invariant transfer function to each input digital audio sample value, the transfer function being arranged so that a ratio of root mean square signal level to peak signal magnitude is lower for the input digital audio signal than for a corresponding portion of the output digital audio signal.
Owner:SONNOX
In-line signal processor
ActiveUS9195433B2Increase or decrease overshoots or undershoots in the signalVolume compression/expansion in digital/coded amplifiersCombination control in untuned amplifierComputer moduleEngineering
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
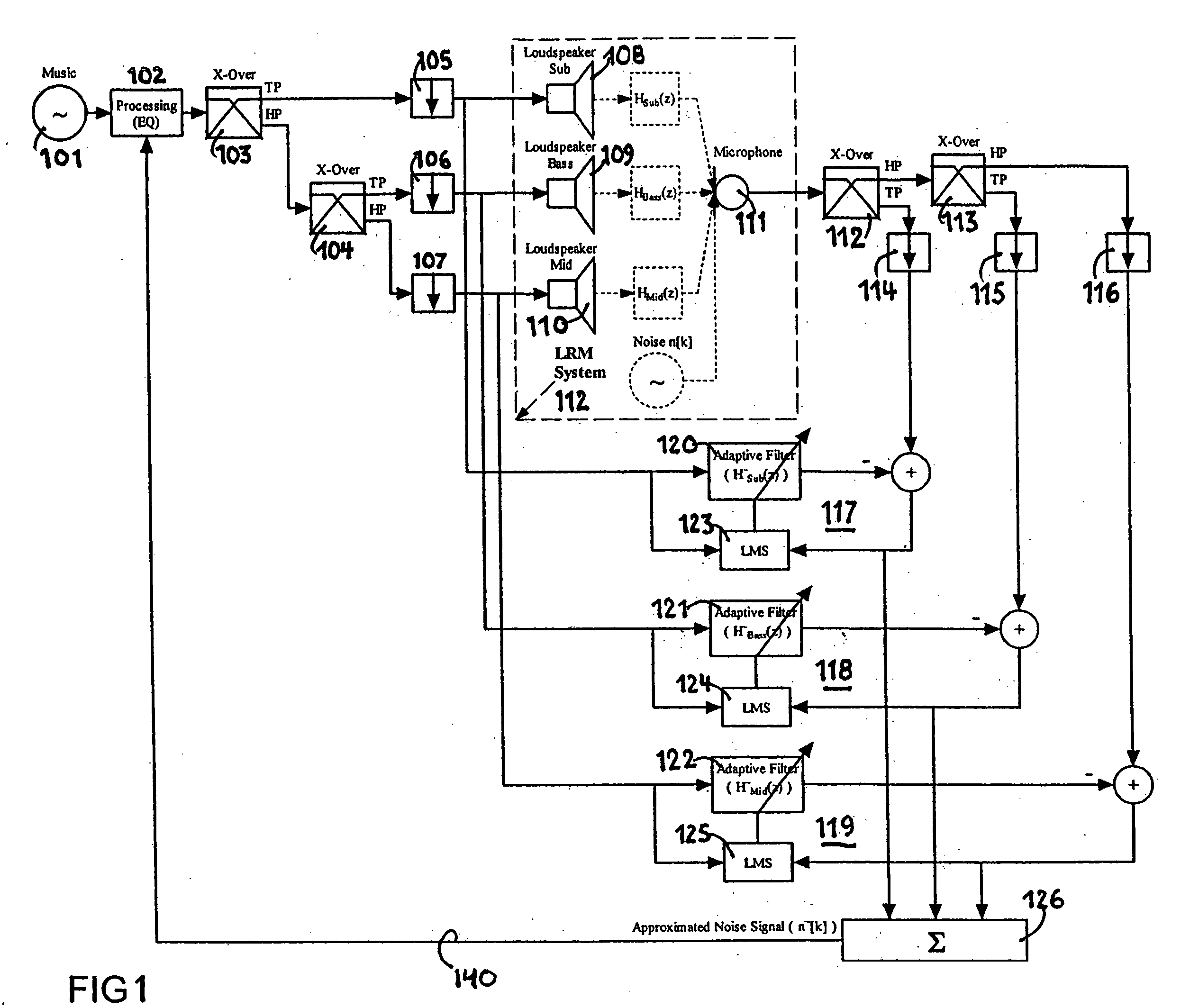
Audio enhancement system
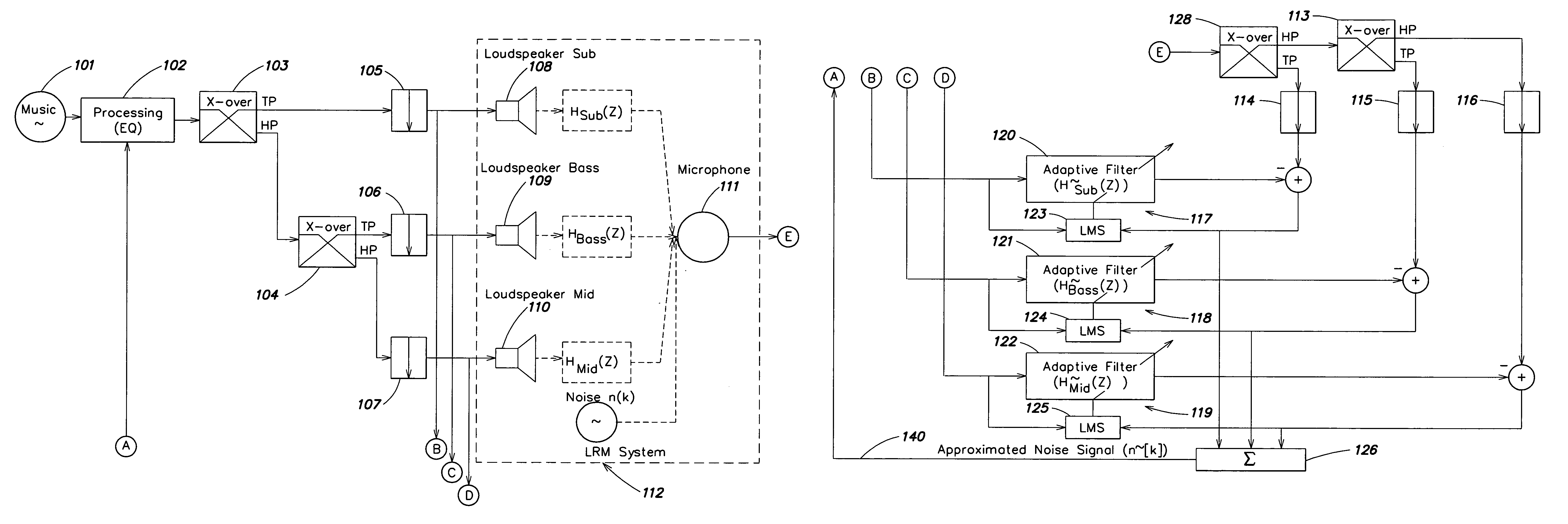
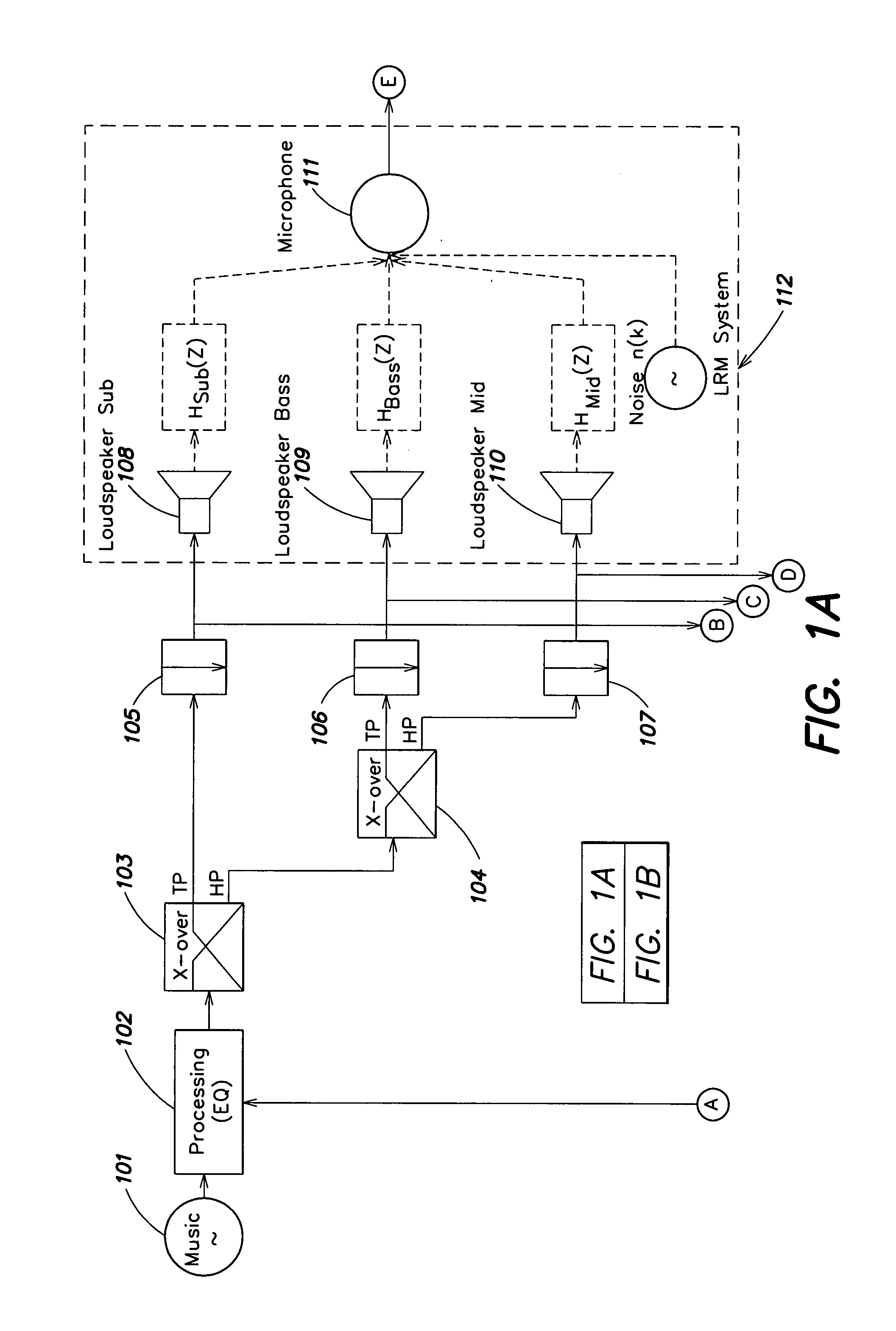
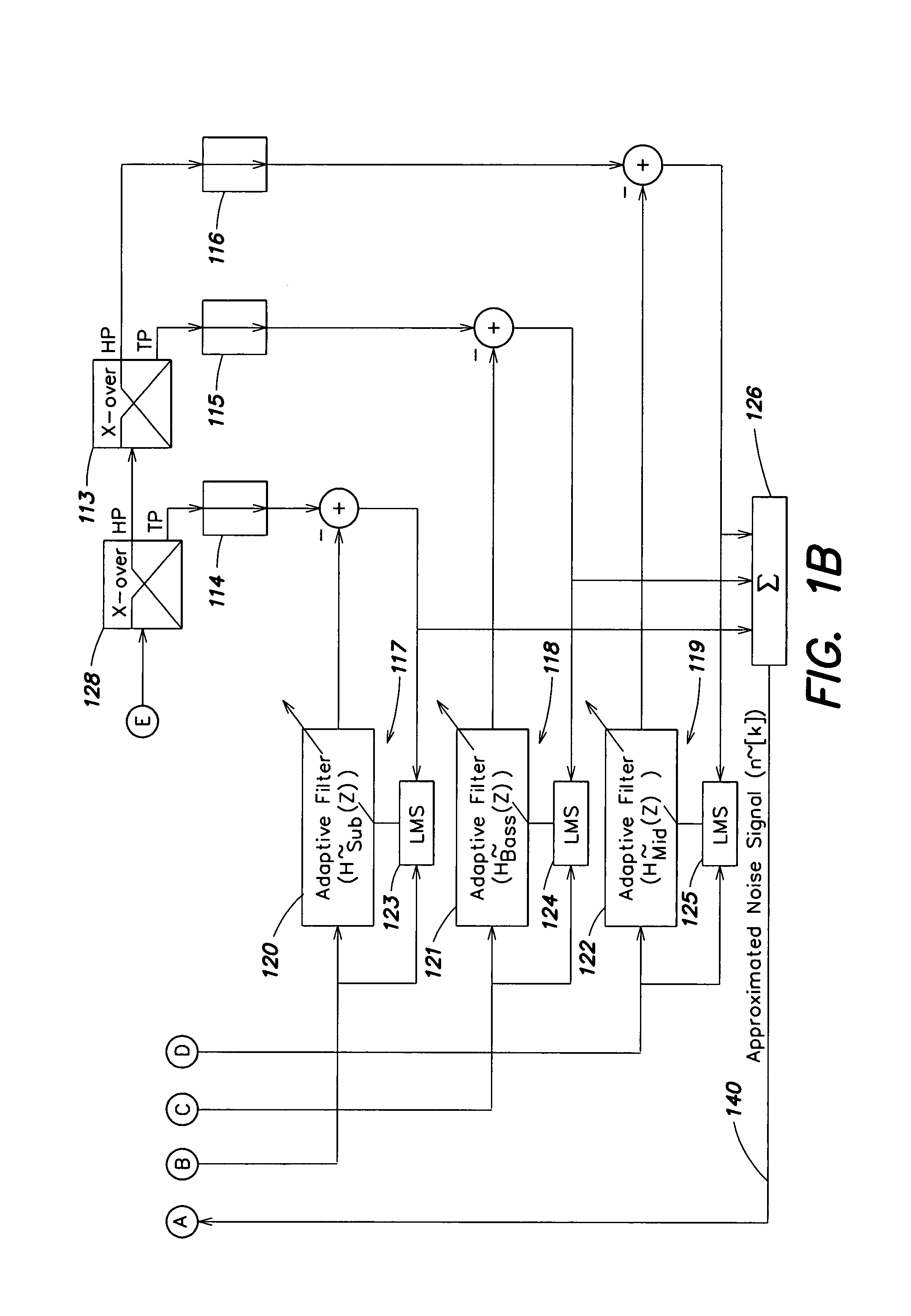
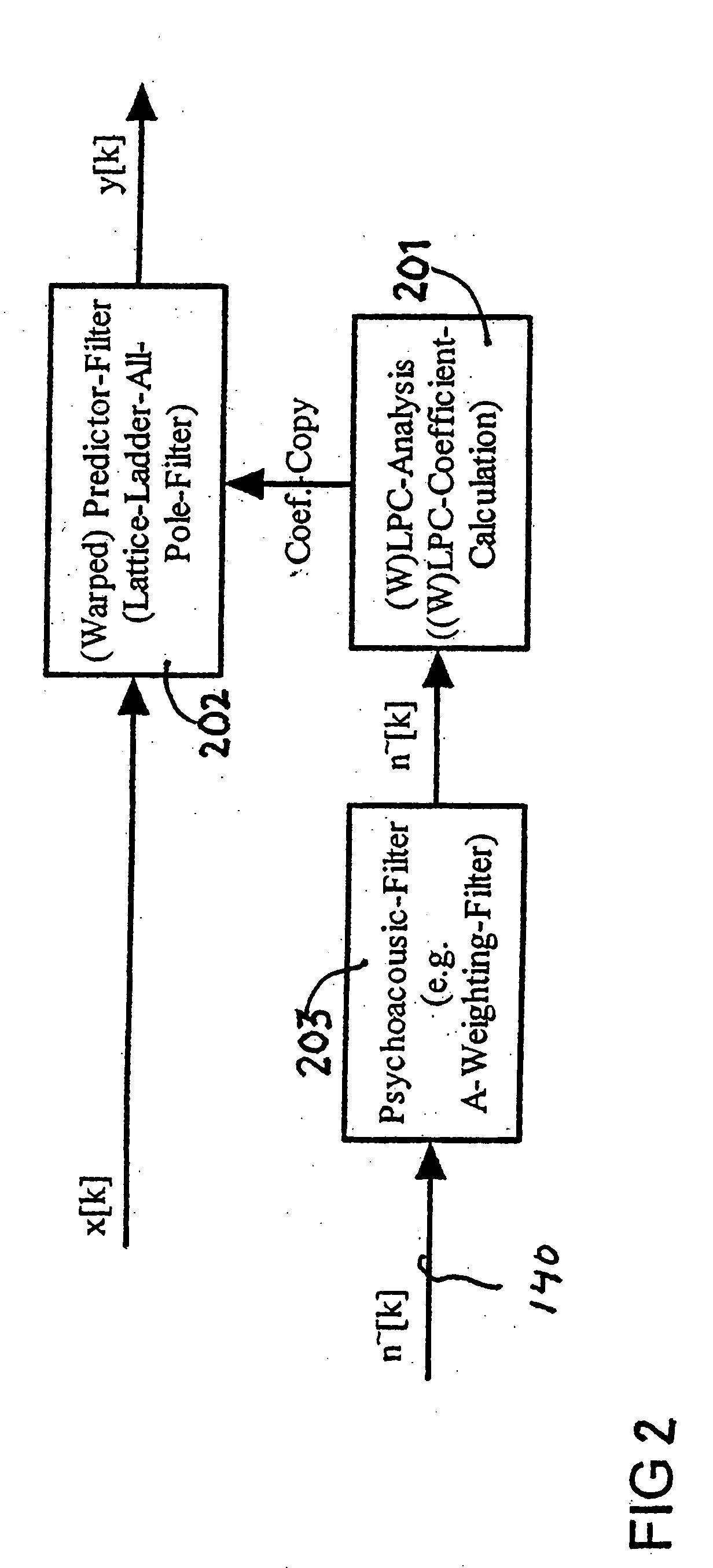
An audio enhancement system for compensating for ambient noise in a listening environment, comprises an audio system that produces an electrical sound signal and generates a sound output from the electrical sound signal. A sensor (e.g., a microphone) senses a total sound signal representative of the total sound level in the listening environment, including the sound output from the audio system and the ambient noise within the listening environment. A processing unit responsive to the total sound signal and the electrical sound signal extracts from the total sound signal an ambient noise signal representative of the ambient noise in the listening environment. A controller responsive to the ambient noise signal performs a linear predictive coding (LPC) analysis and generates a control signal, which is input to an equalizer to adjust the sound output of the audio system in order to compensate for the ambient noise level.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
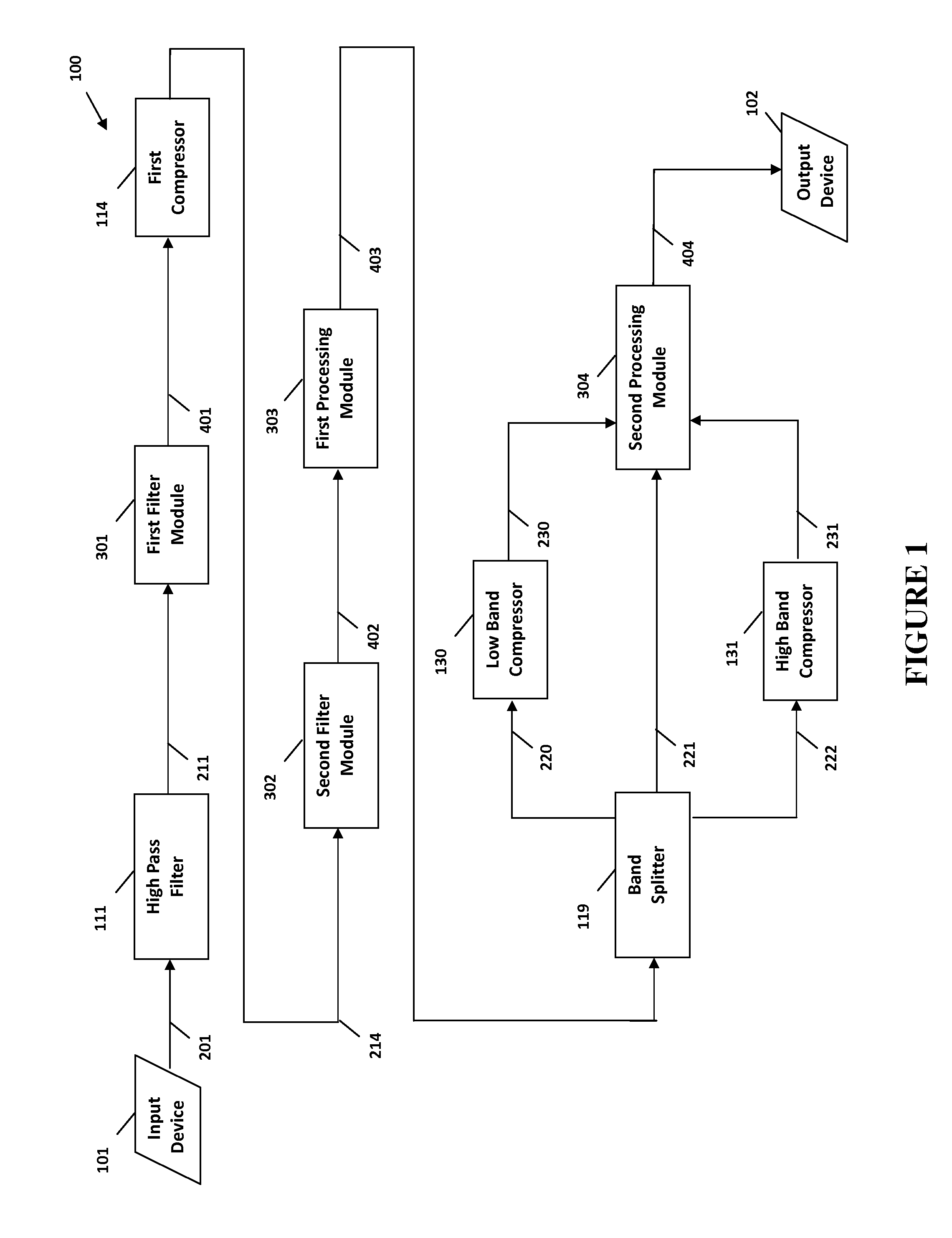
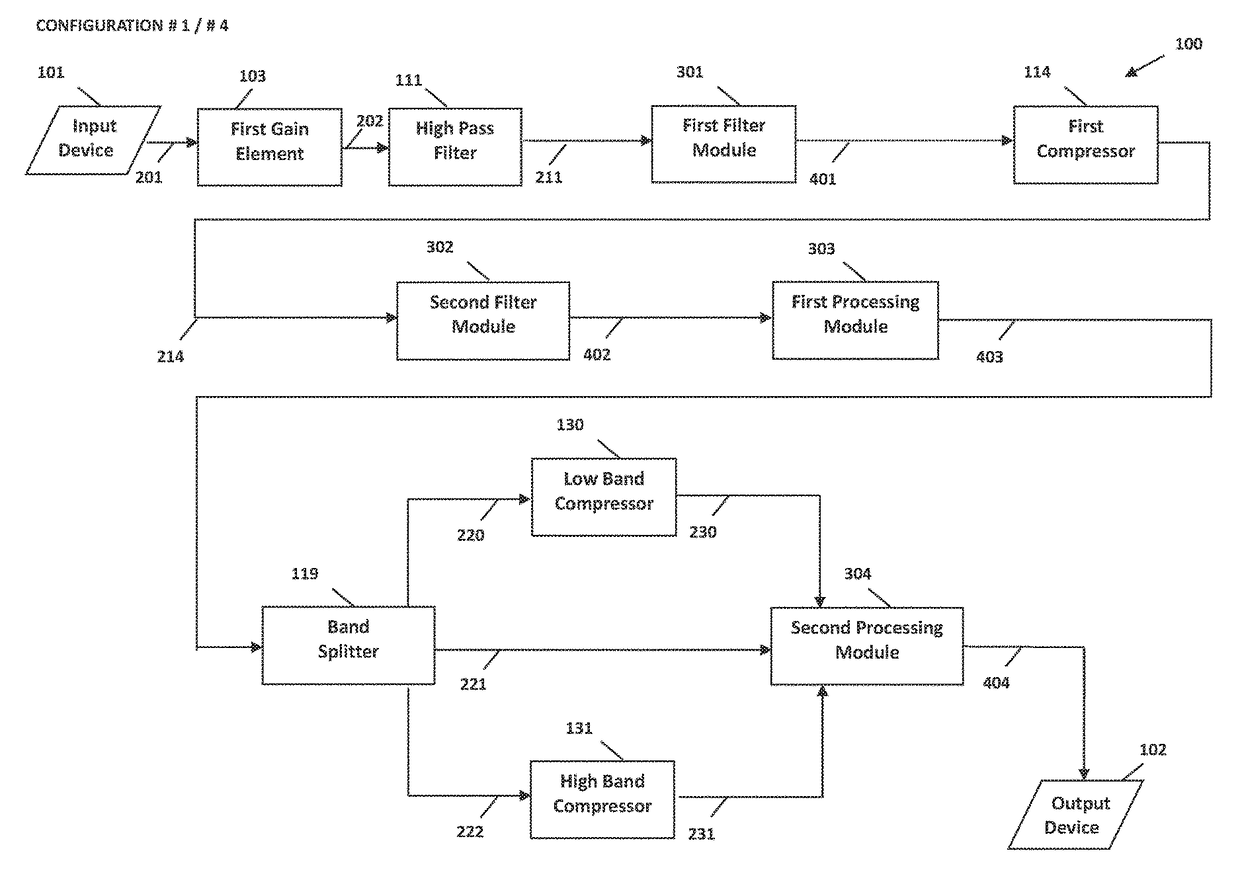
System and method for digital signal processing
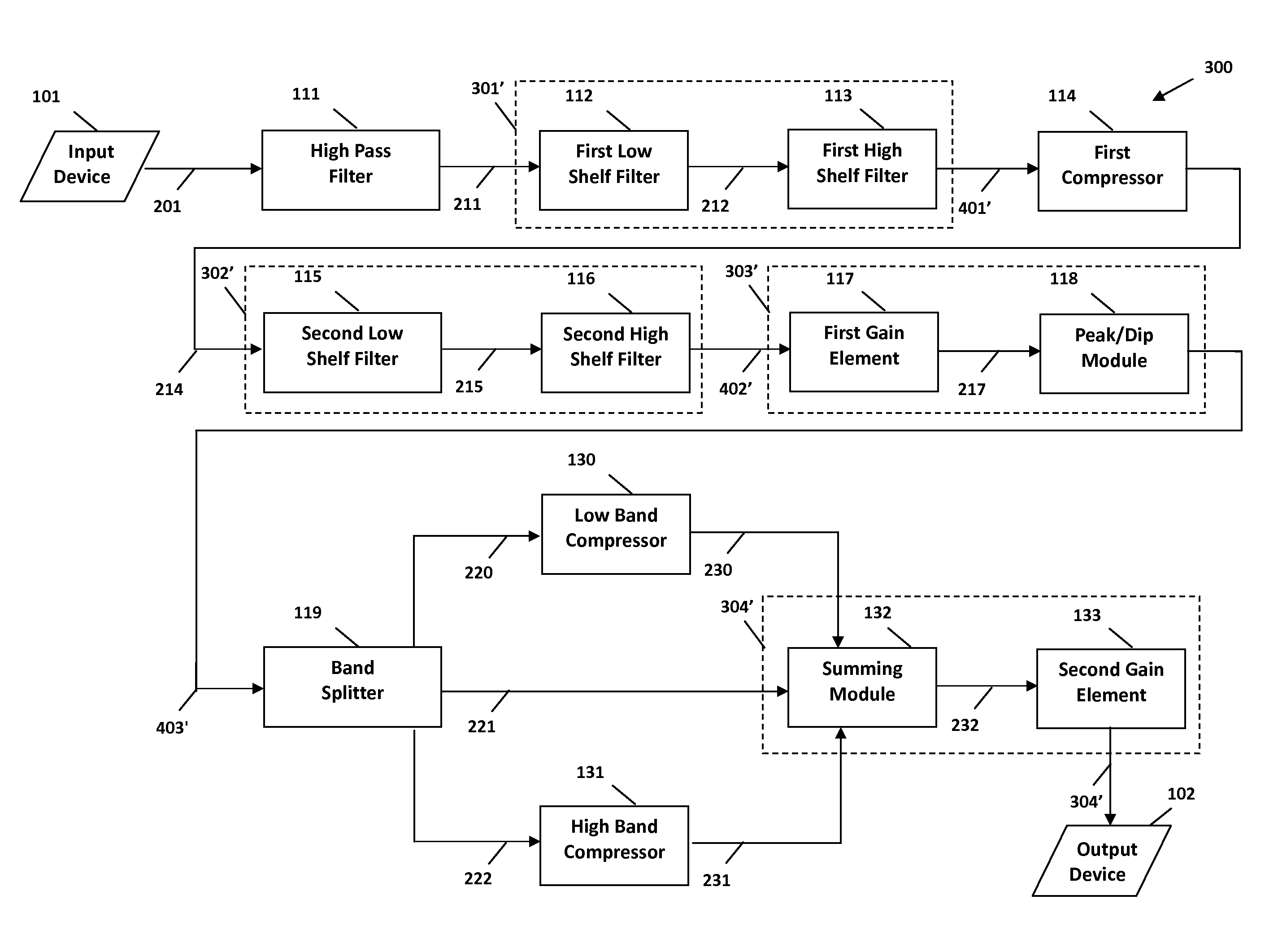
ActiveUS9397629B2Increase or decrease overshoots or undershoots in the signalDigital/coded signal controlSpeech analysisDigital signal processingIntermediate frequency
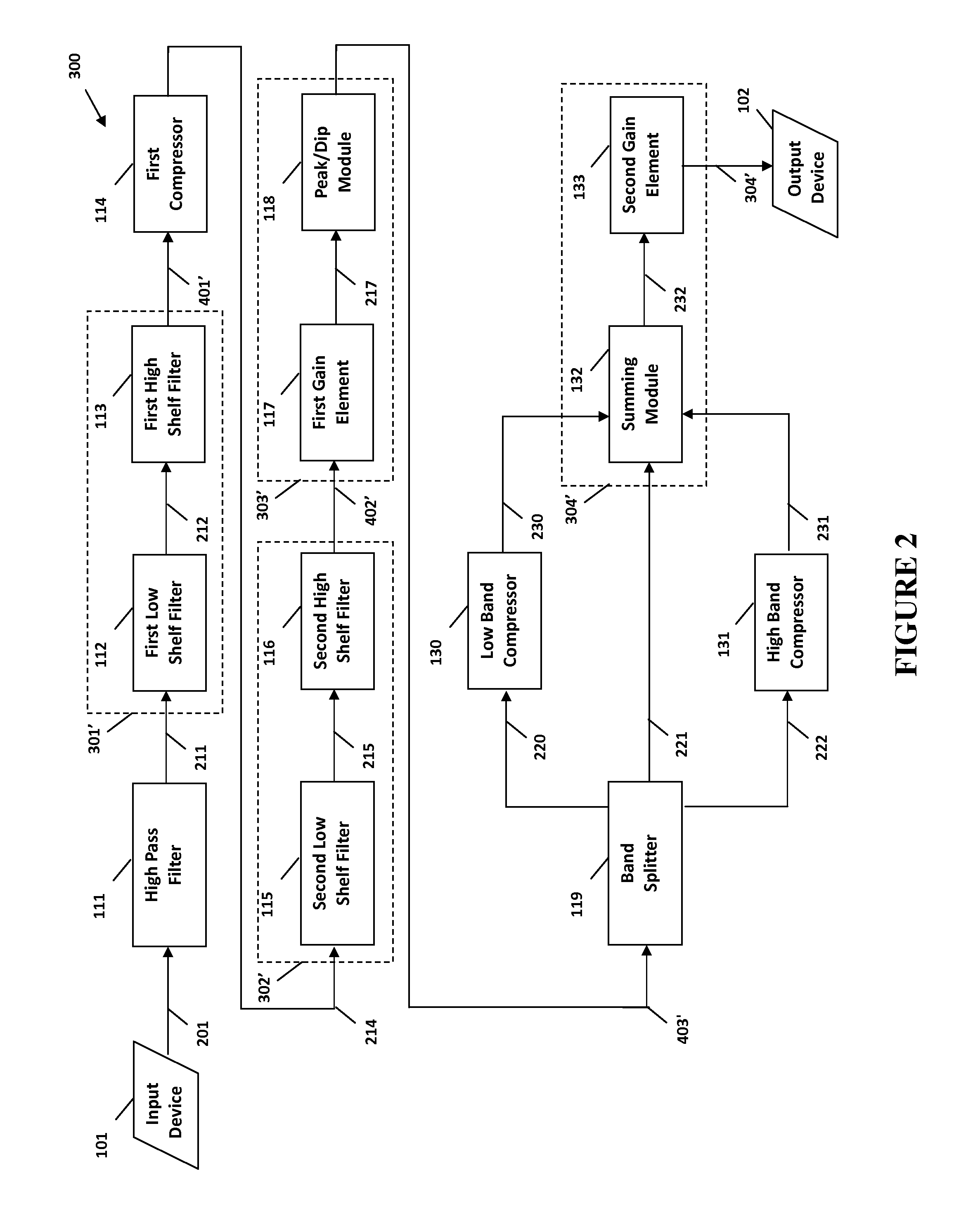
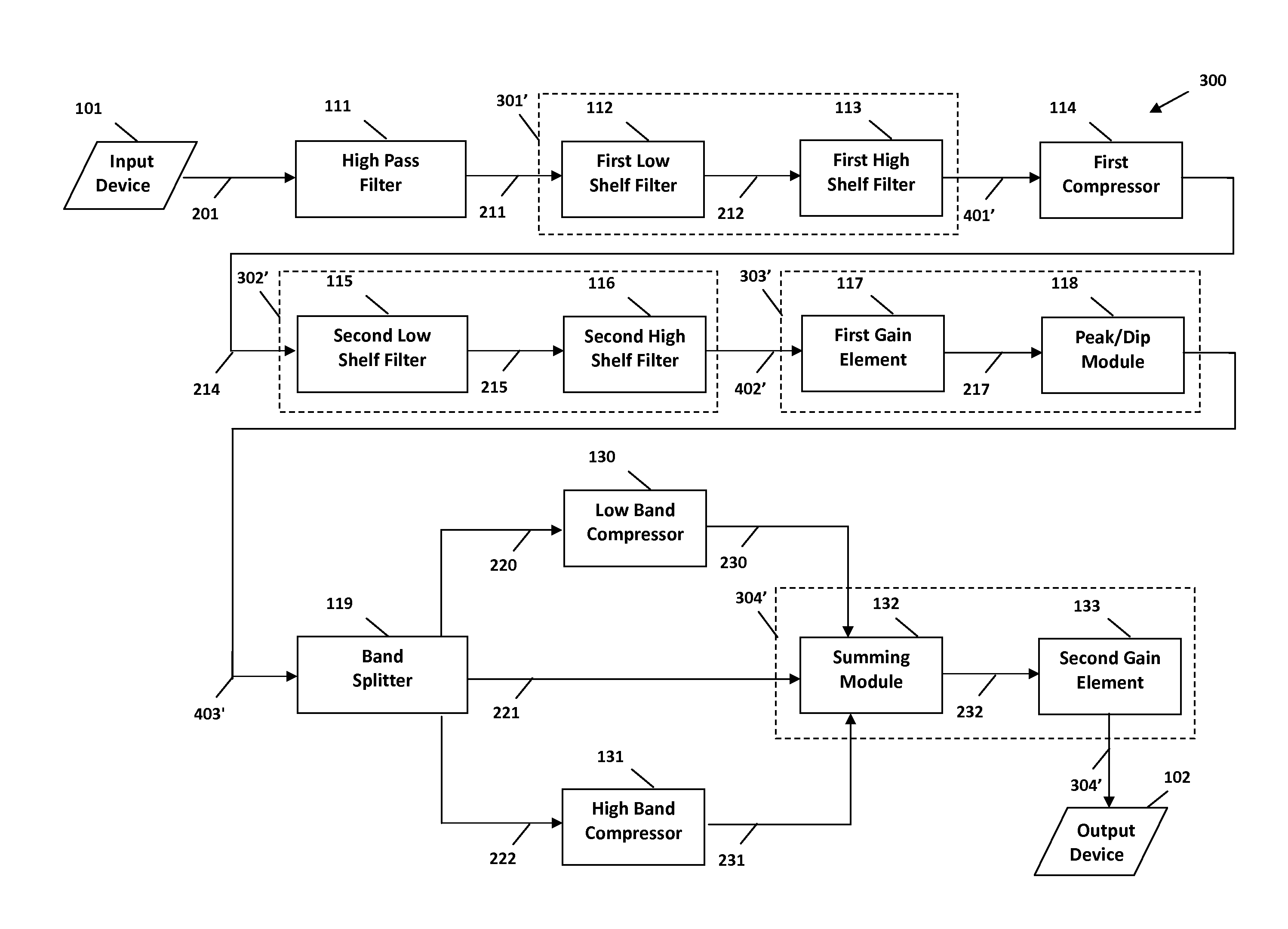
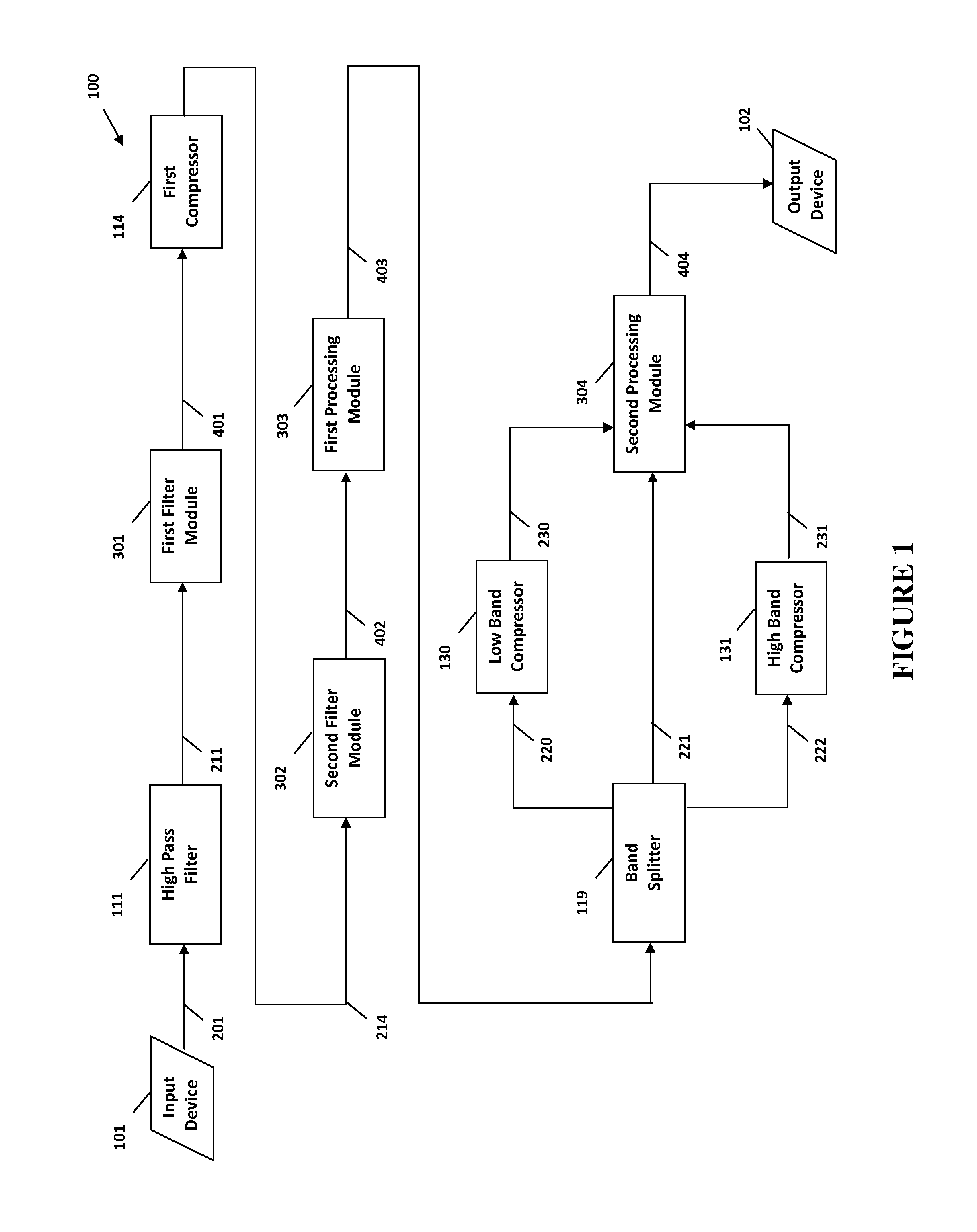
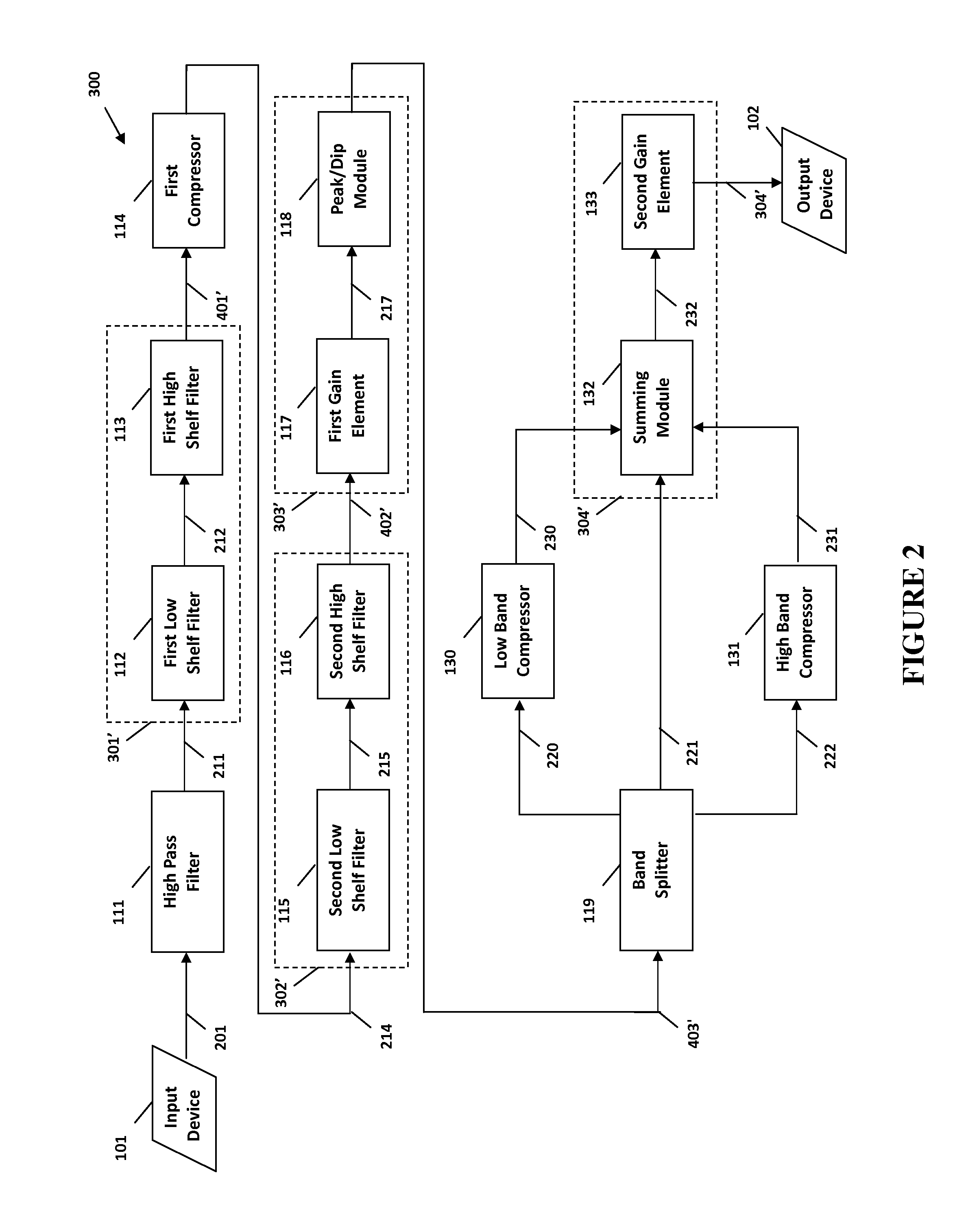
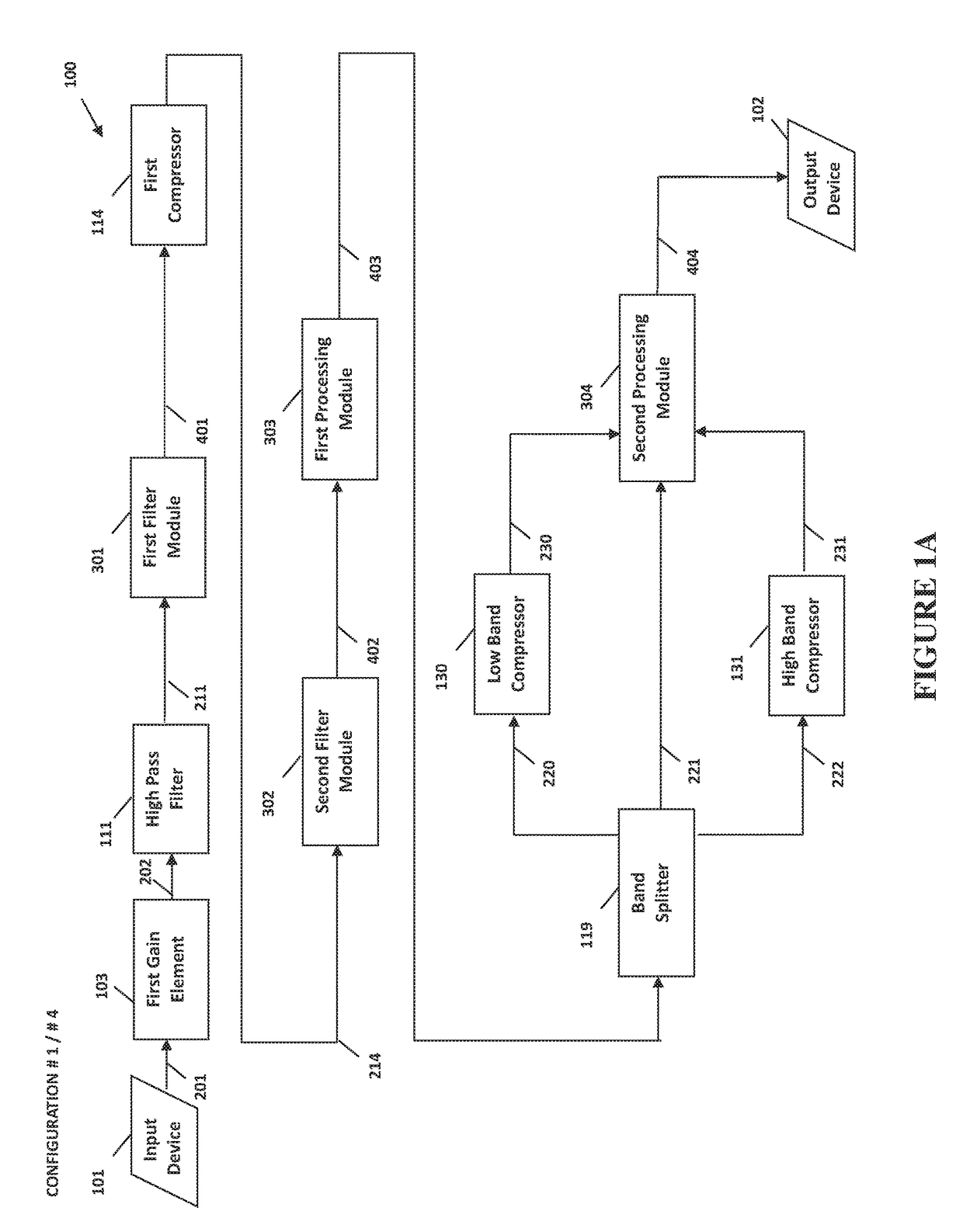
The present invention provides methods and systems for digital processing of an input audio signal. Specifically, the present invention includes a high pass filter configured to filter the input audio signal to create a high pass signal. A first filter module then filters the high pass signal to create a first filtered signal. A first compressor modulates the first filtered signal to create a modulated signal. A second filter module then filters the modulated signal to create a second filtered signal. The second filtered signal is processed by a first processing module. A band splitter splits the processed signal into low band, mid band, and high band signals. The low band and high band signals are modulated by respective compressors. A second processing module further processes the modulated low band, mid band, and modulated high band signals to create an output signal.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
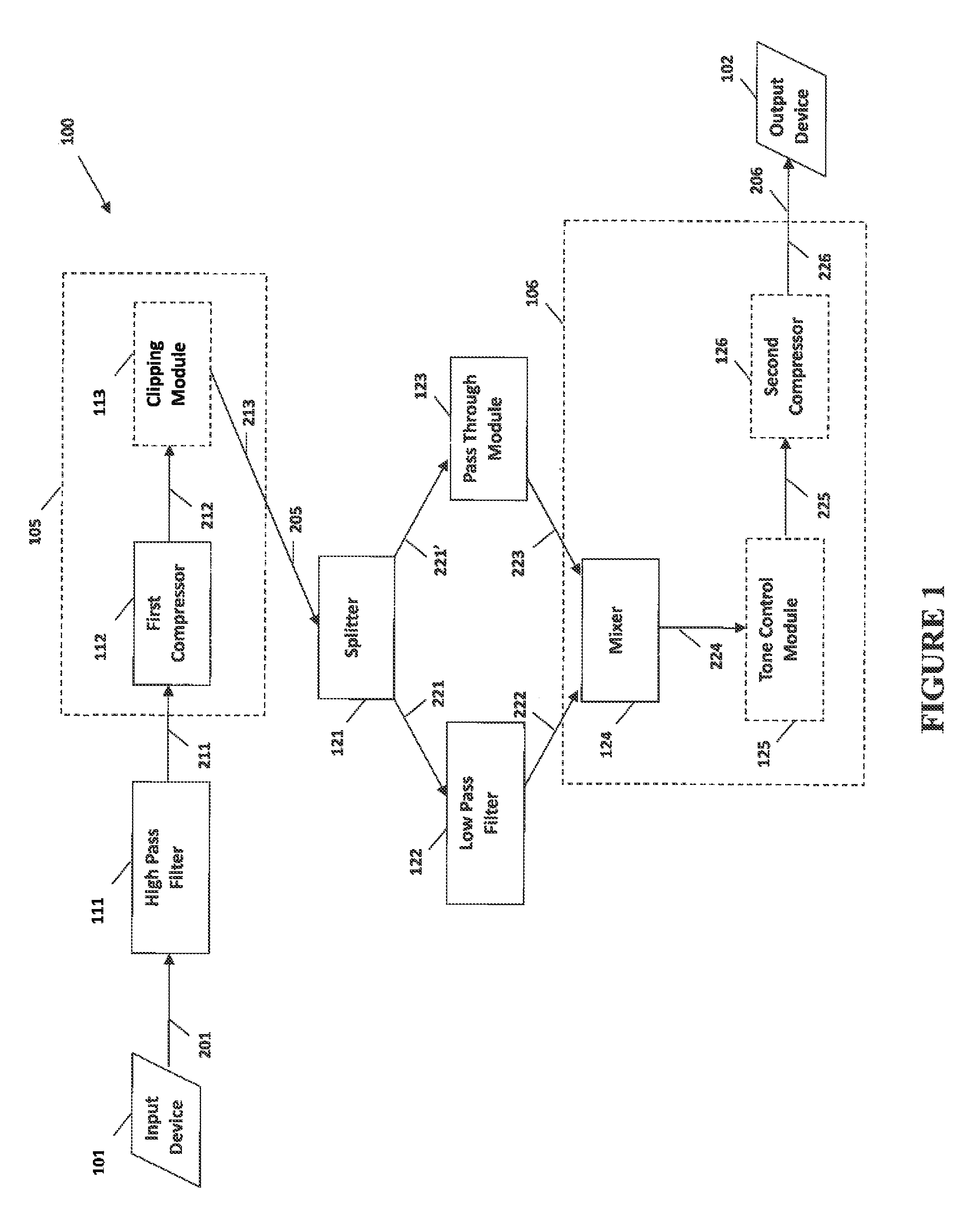
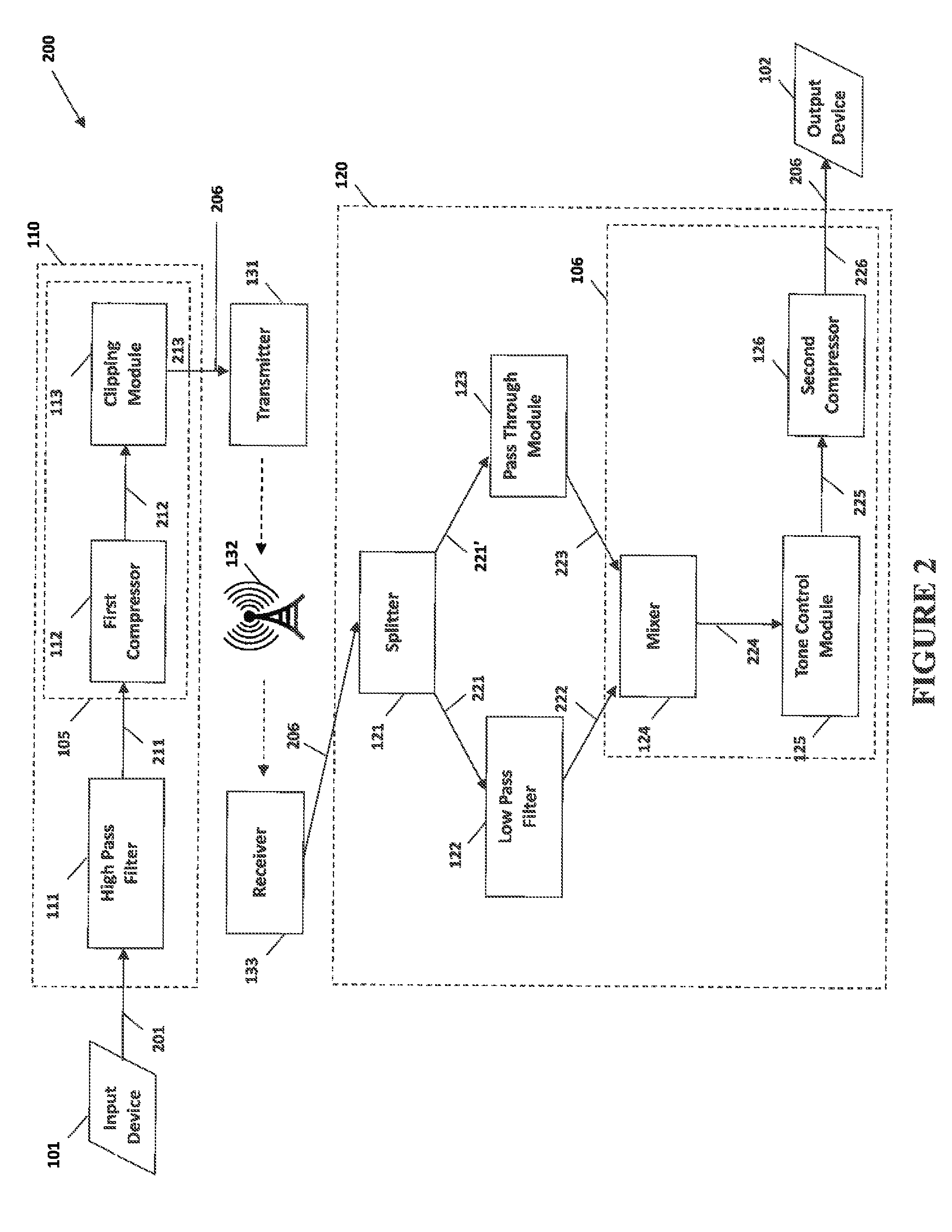
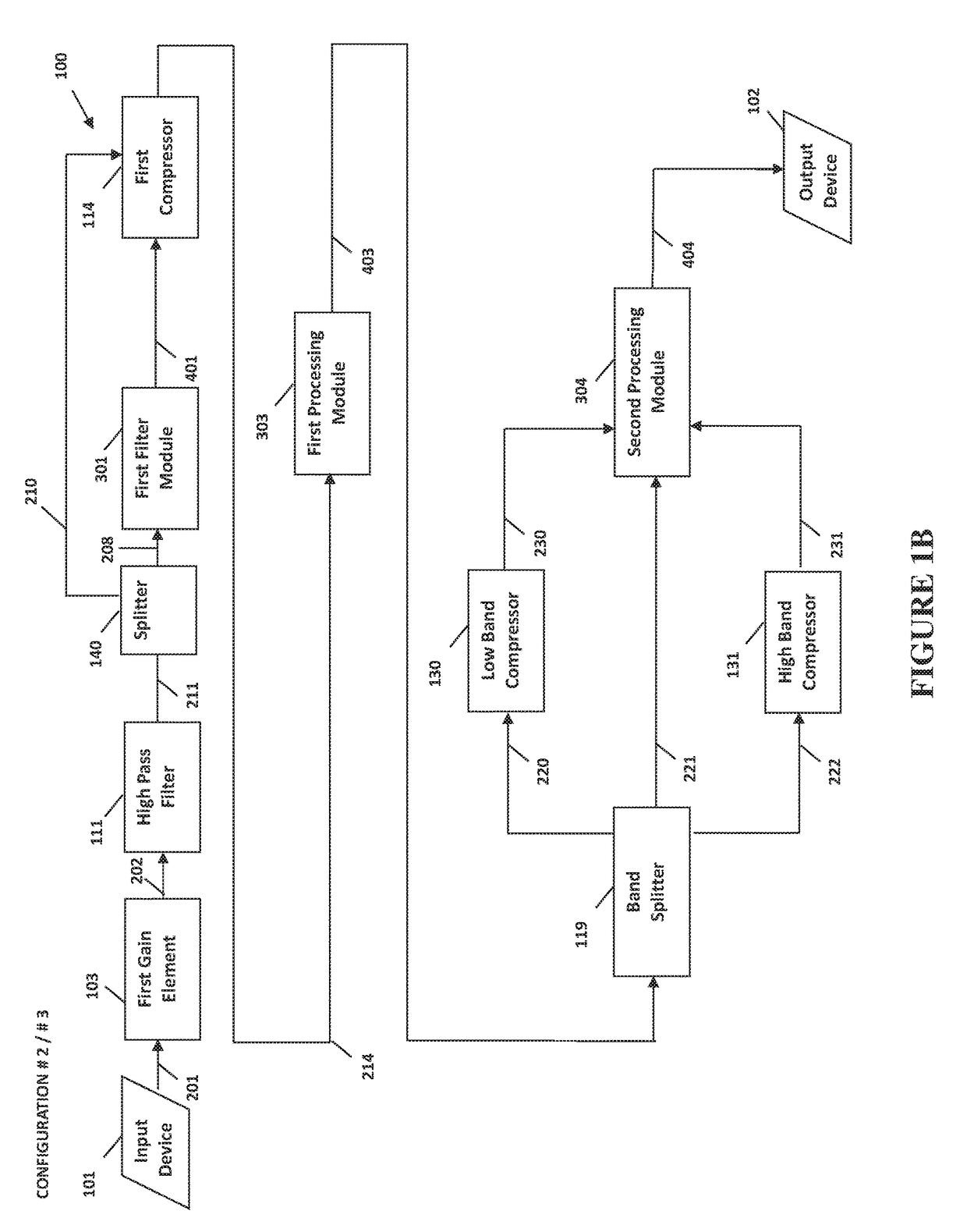
System and method for narrow bandwidth digital signal processing
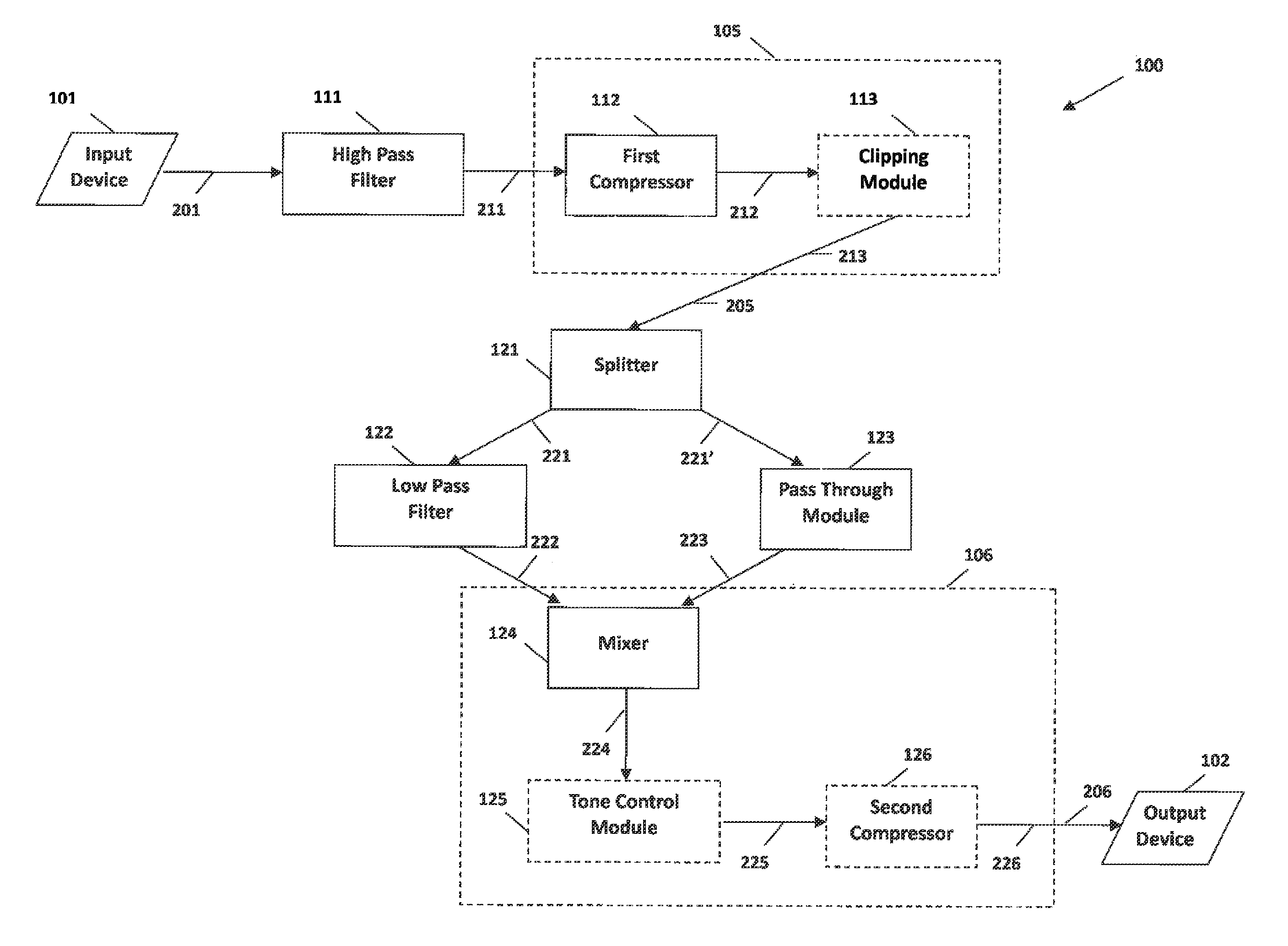
The present invention provides methods and systems for narrow bandwidth digital processing of an input audio signal. Particularly, the present invention includes a high pass filter configured to filter the input audio signal. A first compressor then modulates the filtered signal in order to create a partially processed signal. In some embodiments, a clipping module further limits the gain of the partially processed signal. A splitter is configured to split the partially processed signal into a first signal and a second signal. A low pass filter is configured to filter the first signal. A pass through module is configured to adjust the gain of the second signal. A mixer then combines the filtered first signal and the gain-adjusted second signal in order to output a combined signal. In some embodiments, a tone control module further processes the combined signal, and a second compressor further modulates the processed signal.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
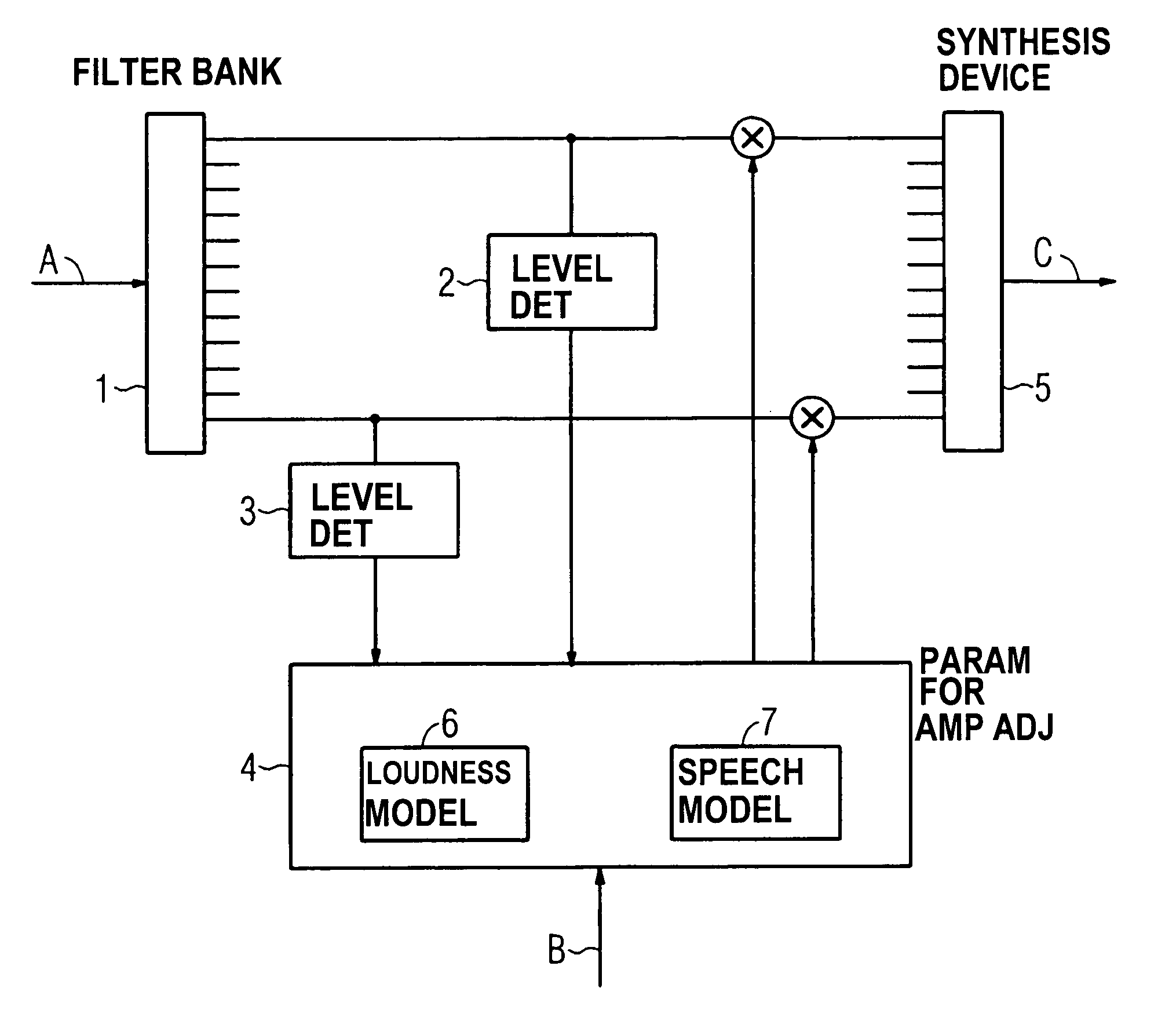
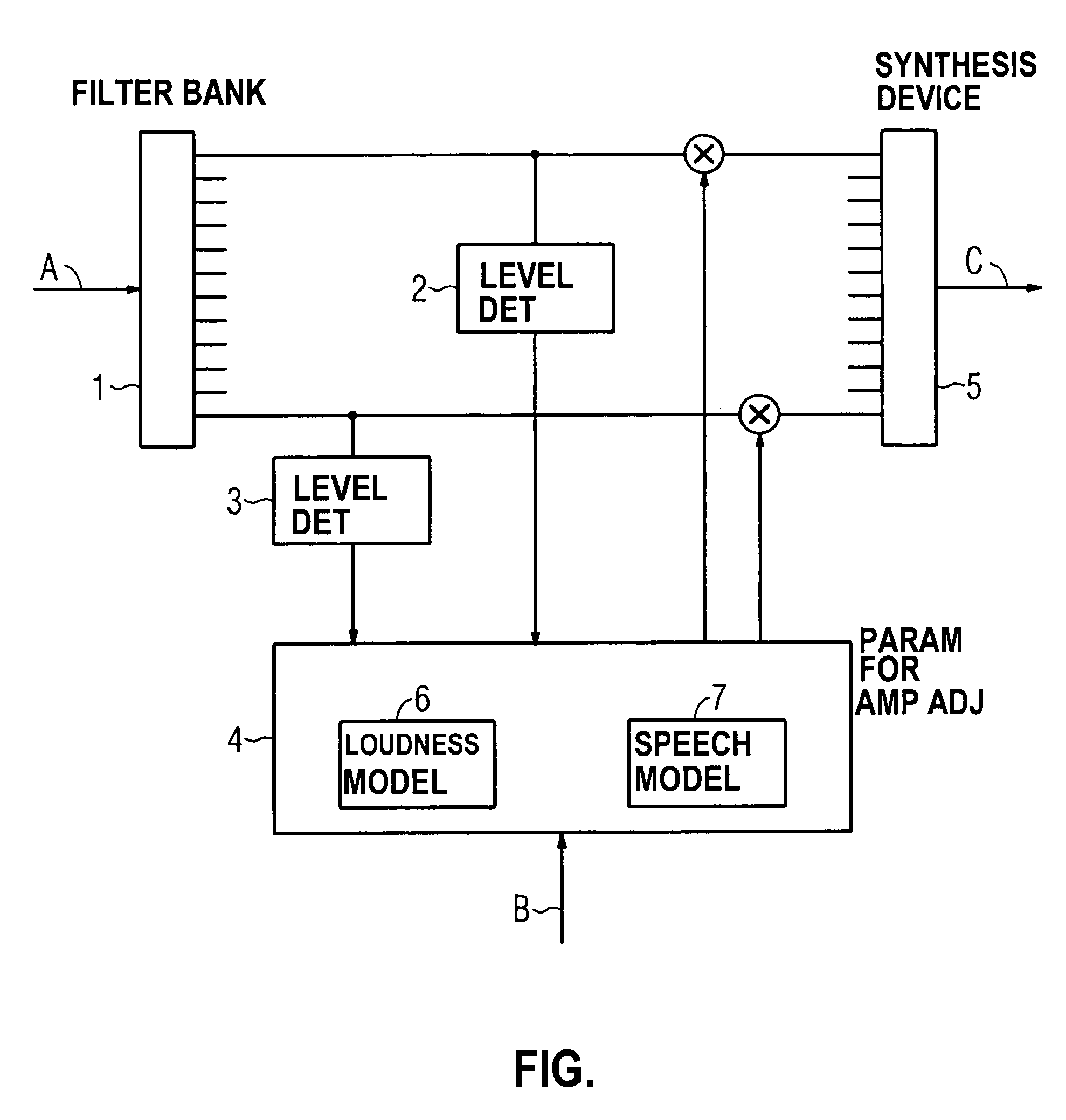
Method for automatic amplification adjustment in a hearing aid device, as well as a hearing aid device
InactiveUS7010133B2Improve understandingHearing aids signal processingCombination control in untuned amplifierHearing aidEngineering
To improve the speech comprehensibility given treatment with a hearing aid device, during the operation of the hearing aid device speech signal levels and noise signal levels are determined in a plurality of frequency bands of an input signal. An automatic adjustment of the amplification follows, dependent on the determined signal level and the signal frequency. The determination of amplification parameters thereby ensues under inclusion of a loudness model and a speech comprehensibility model.
Owner:SIEMENS AUDIOLOGISCHE TECHN
Method, apparatus and computer program for calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness of an audio signal
One or a combination of two or more specific loudness model functions selected from a group of two or more of such functions are employed in calculating the perceptual loudness of an audio signal. The function or functions may be selected, for example, by a measure of the degree to which the audio signal is narrowband or wideband. Alternatively or with such a selection from a group of functions, a gain value G[t] is calculated, which gain, when applied to the audio signal, results in a perceived loudness substantially the same as a reference loudness. The gain calculating employs an iterative processing loop that includes the perceptual loudness calculation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Audio enhancement system and method
ActiveUS20050207583A1Enhance audio listening experienceEar treatmentGain controlEnvironmental noiseControl signal
An audio enhancement system for compensating for ambient noise in a listening environment, comprises an audio system that produces an electrical sound signal and generates a sound output from the electrical sound signal. A sensor (e.g., a microphone) senses a total sound signal representative of the total sound level in the listening environment, including the sound output from the audio system and the ambient noise within the listening environment. A processing unit responsive to the total sound signal and the electrical sound signal extracts from the total sound signal an ambient noise signal representative of the ambient noise in the listening environment. A controller responsive to the ambient noise signal performs a linear predictive coding (LPC) analysis and generates a control signal, which is input to an equalizer to adjust the sound output of the audio system in order to compensate for the ambient noise level.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Audio quality adjustment device
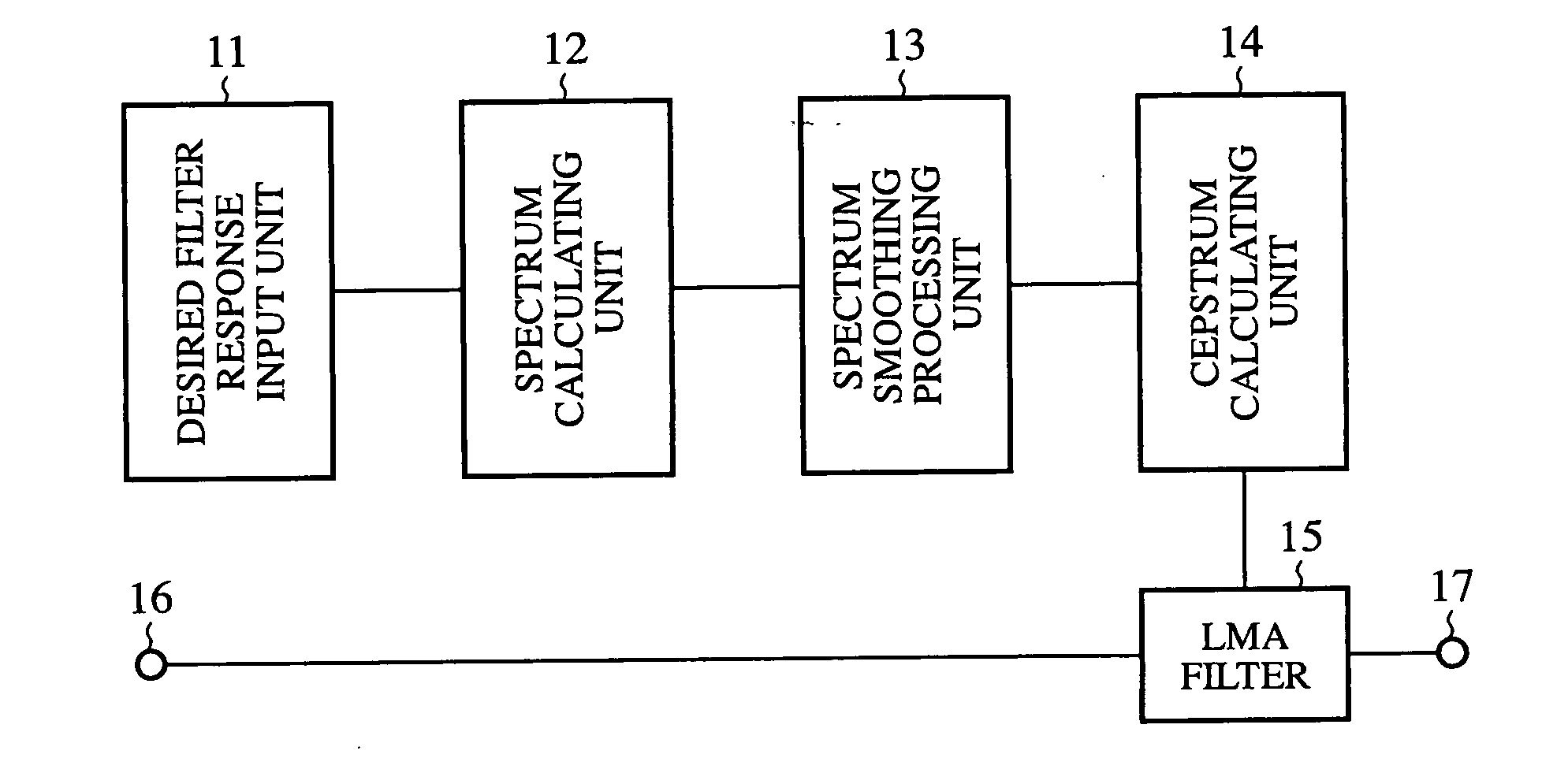
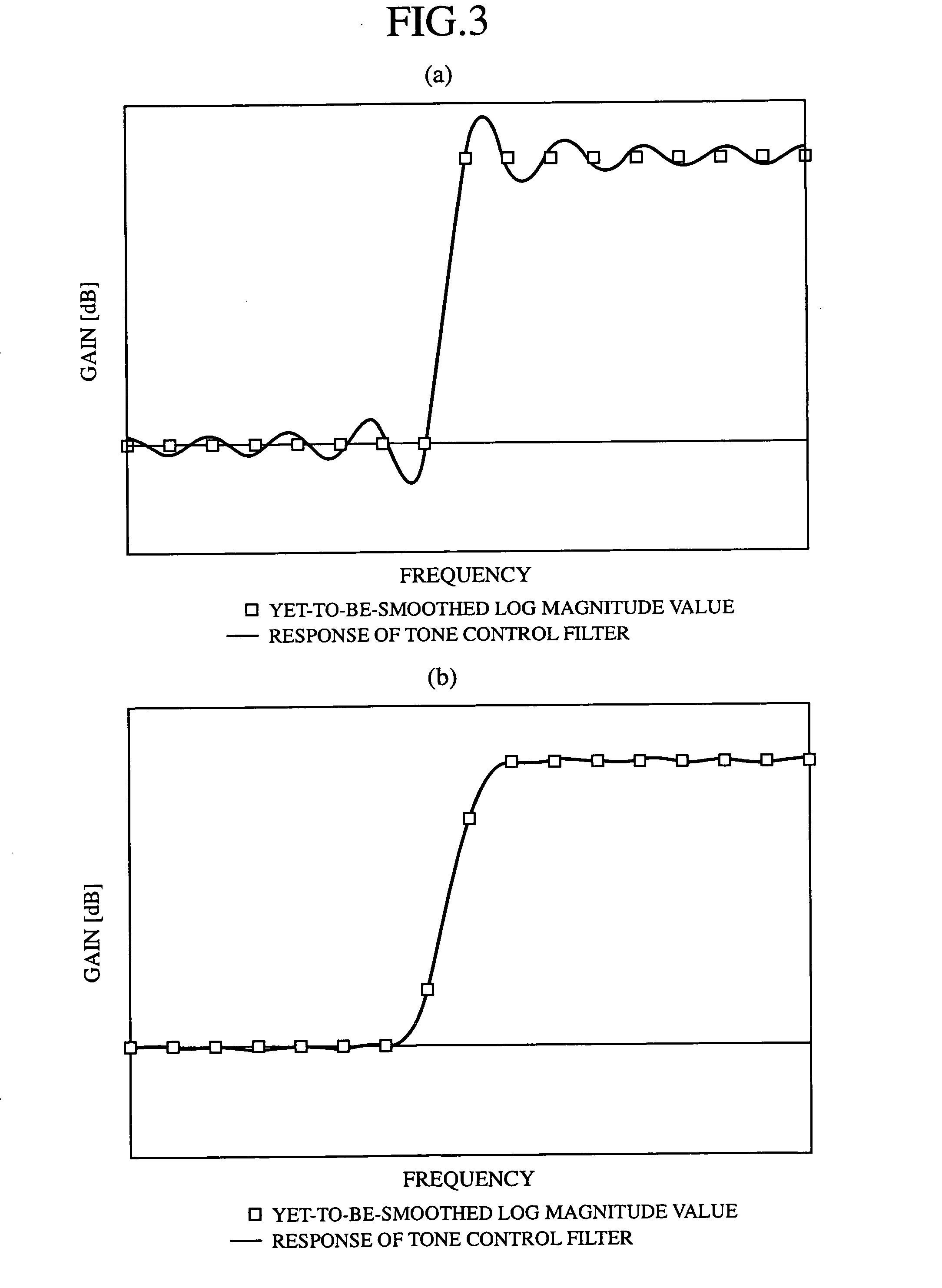
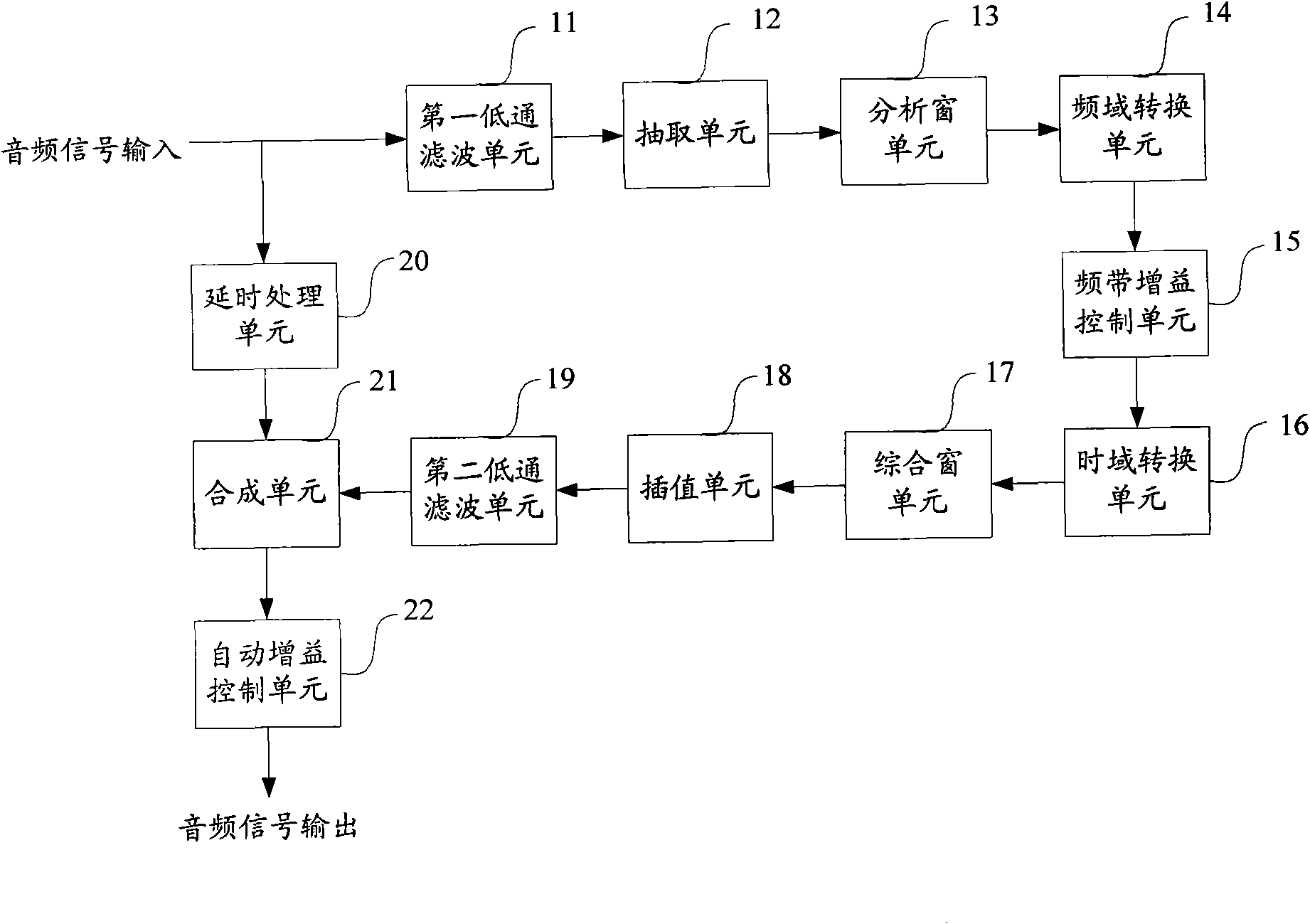
InactiveUS20060182290A1InhibitionImprove precision controlDigital technique networkCombination control in untuned amplifierFrequency spectrumProcessing element
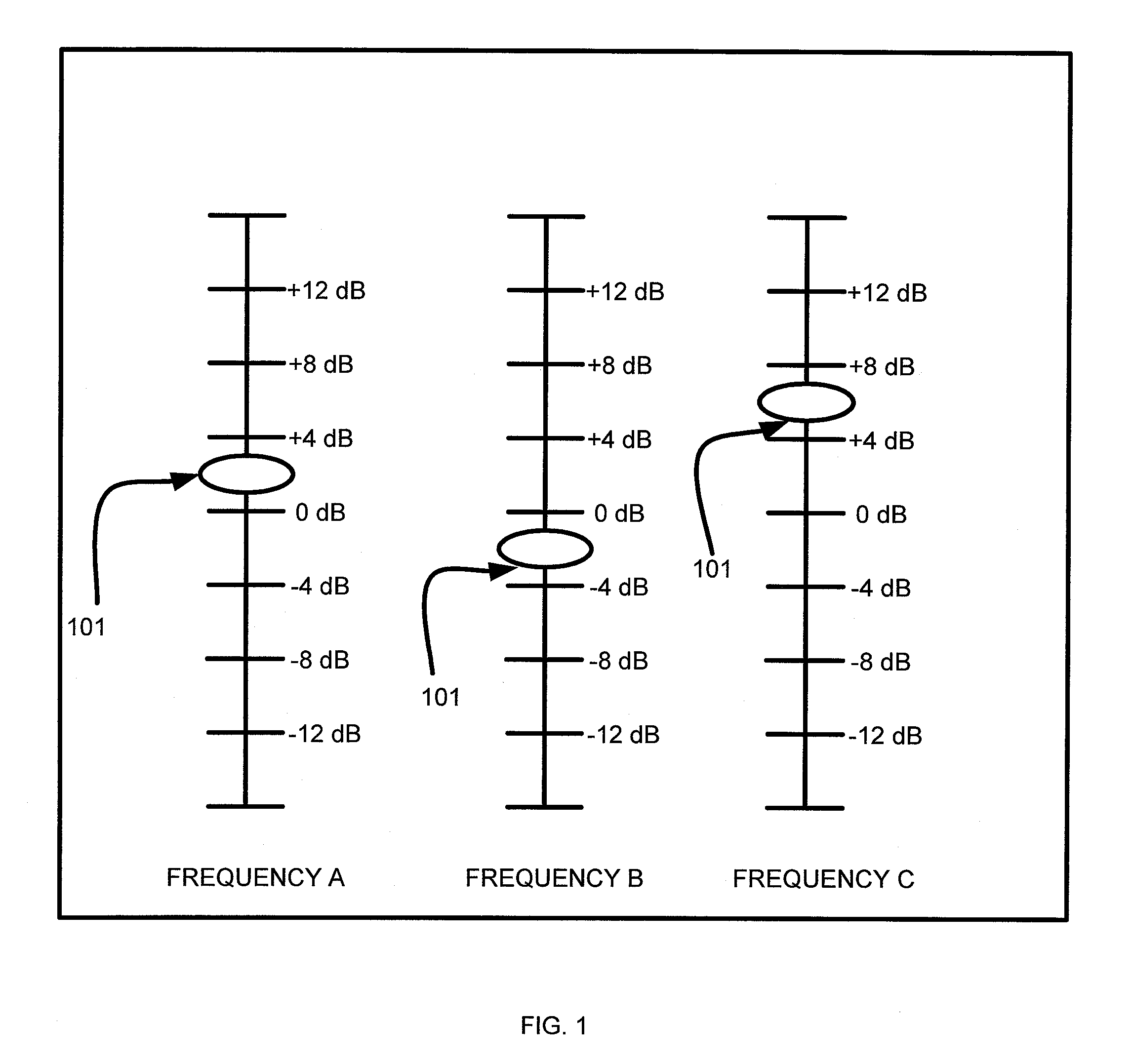
A tone control apparatus is provided with a desired filter response input unit 11 for inputting a desired filter response into the tone control apparatus, a spectrum calculating unit 12 for calculating a Fourier spectrum for the set filter response which is inputted by the desired filter response input unit 11, a spectrum smoothing processing unit 13 for performing smoothing processing on the Fourier spectrum calculated by the spectrum calculating unit 12, a cepstrum calculating unit 14 for converting the Fourier spectrum smoothed by spectrum smoothing processing unit 13 into a cepstrum, and an LMA filter 15 to which the cepstrum calculated by the cepstrum calculating unit 14 is set as the filter factor of the LMA filter. The tone control apparatus also has an input terminal 16 for inputting a sound signal into the LMA filter 15, and an output terminal 17 for outputting a sound signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
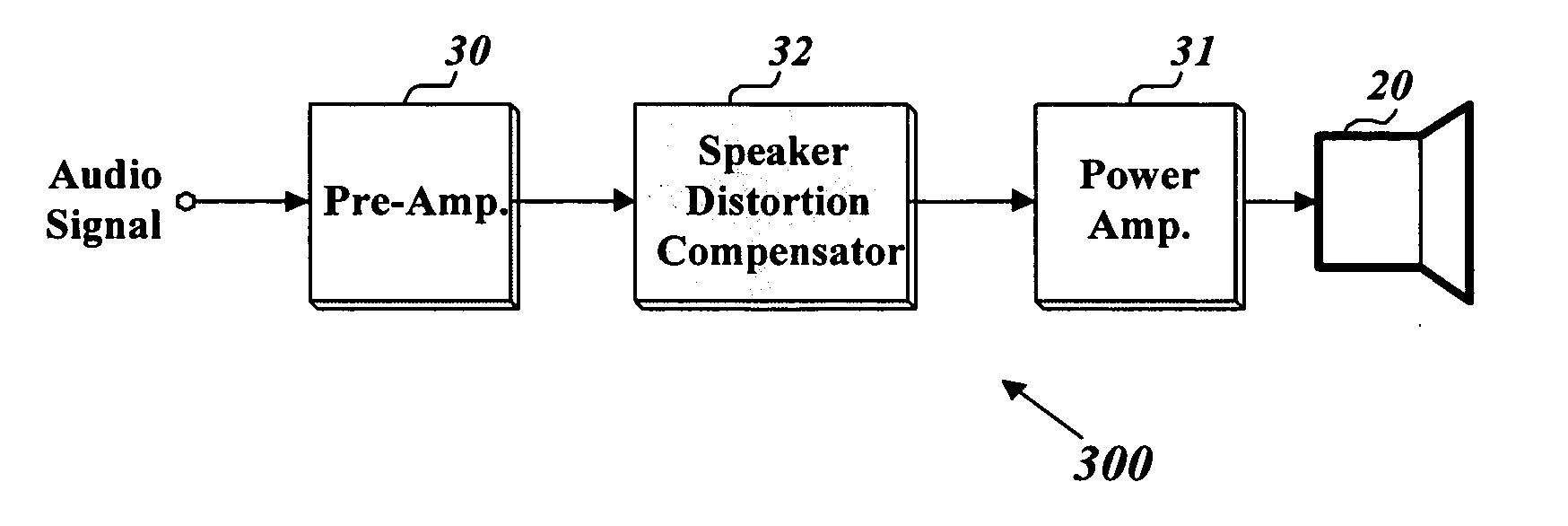
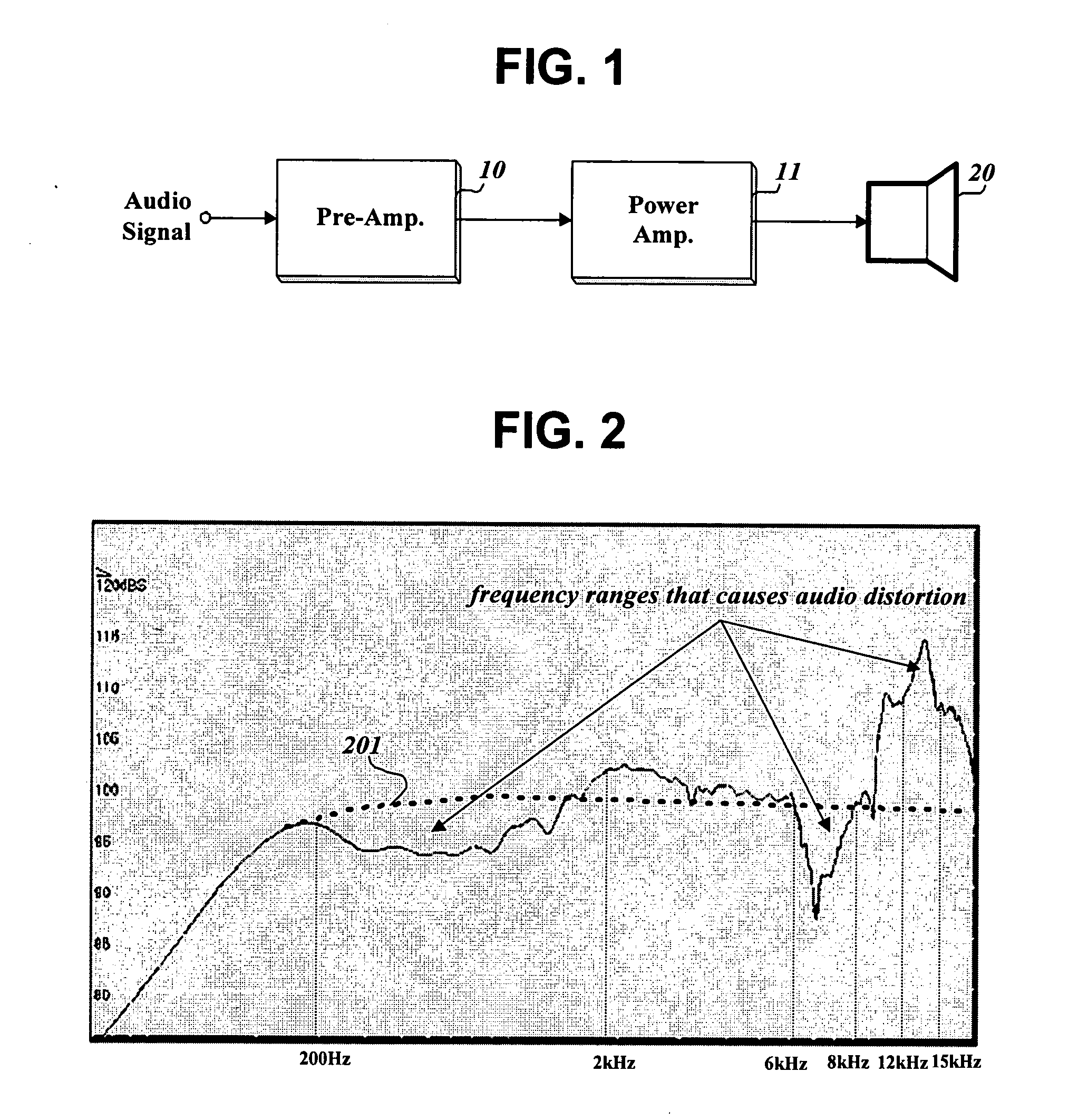
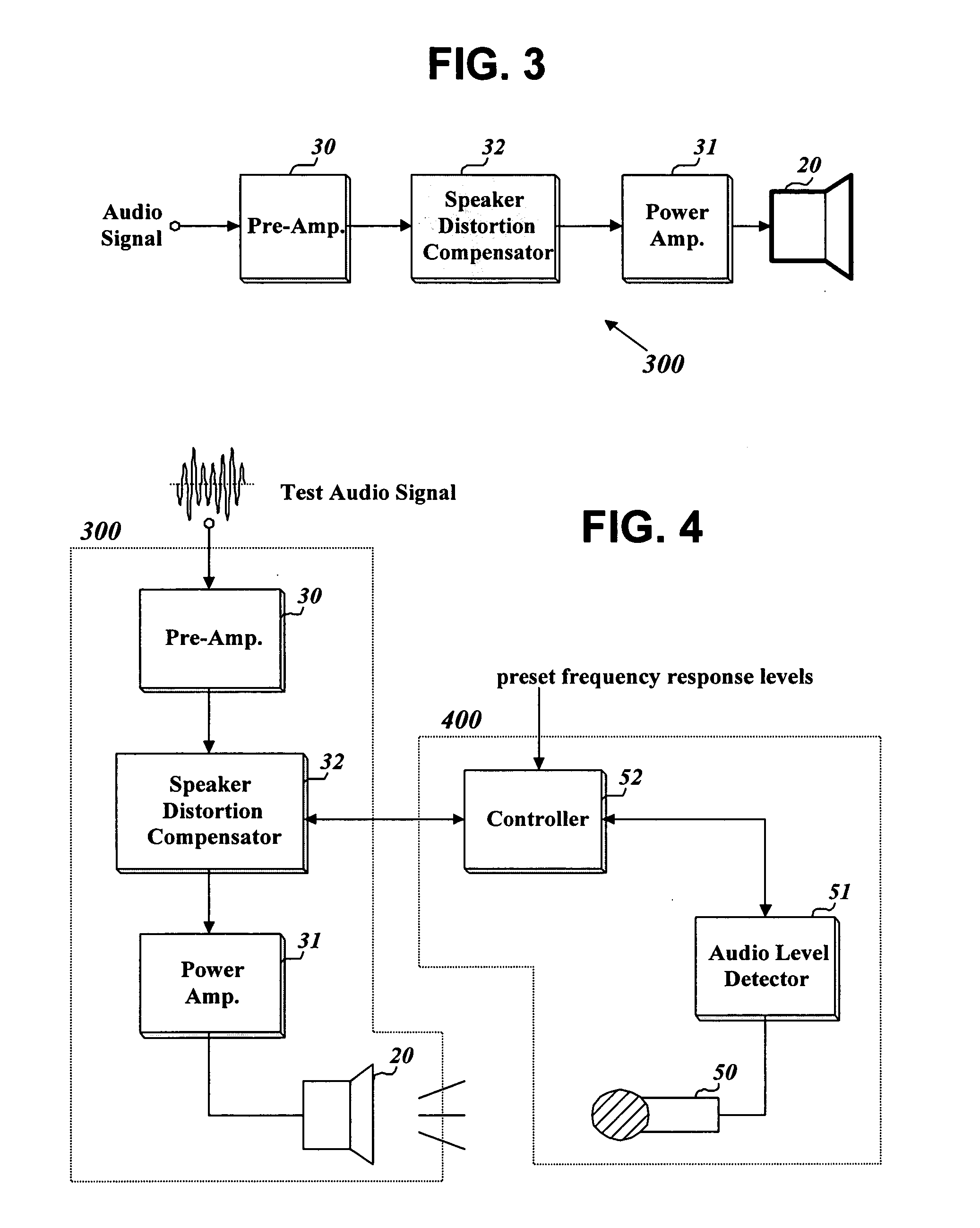
Method and apparatus of compensating for speaker distortion in an audio apparatus
InactiveUS20050195993A1Increase powerCompensation DistortionCombination control in untuned amplifierAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlLoudspeakerComputer science
Embodiments of methods and apparatus of compensating for speaker distortion in an audio apparatus can compensate for frequency components of an input audio signal that will be distorted by a nonflat frequency response of a speaker. The compensation can occur before the input audio signal is applied to the speaker. Thus, the frequency response of the cascaded system including a compensator and the speaker can be flatter than that of the speaker. Embodiments of the present invention can reduce or prevent distortion of an input audio signal distorted by the speaker.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
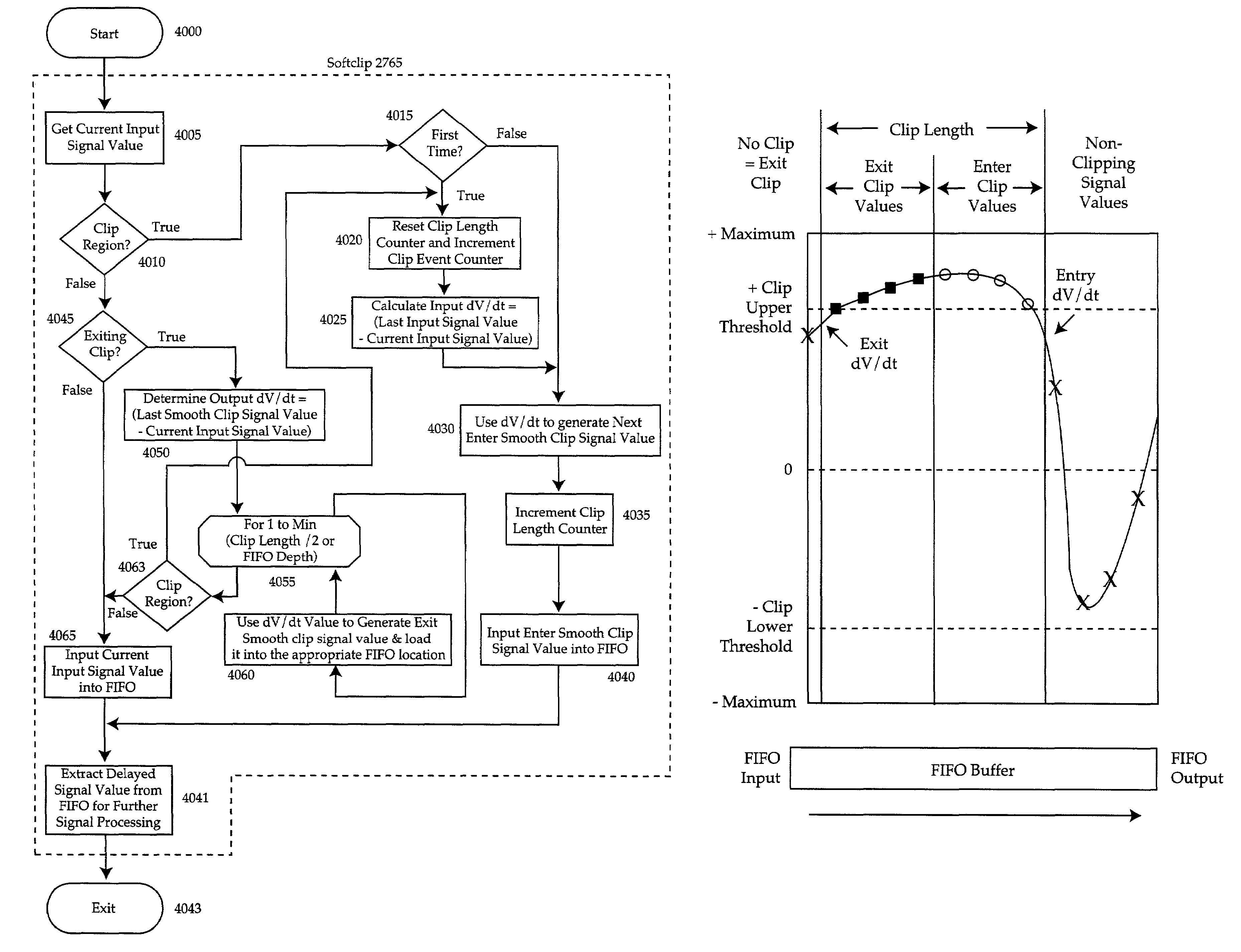
Softclip method and apparatus
InactiveUS7206420B2Cost effectiveMaximum flexibilityVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesGain controlComputer scienceGain cell
A method of matching input amplitudes in a system wherein one or more of a plurality of inputs may be selected, with each input capable of having different characteristics, involving selecting an input signal and mapping the input signal to a predetermined signal amplitude through the use of level matching logic. The level matching logic may include a gain cell for increasing or decreasing the amplitude of the input signal.
Owner:SYFX
System and method for digital signal processing
ActiveUS9906858B2Increase or decrease overshoots or undershoots in the signalVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersVolume compression/expansion in digital/coded amplifiersDigital signal processingComputer module
A system and method for digital processing including a gain element to process an input audio signal, a high pass filter to then filter the signal and create a high pass signal, a first filter module to filter the high pass signal and create a first filtered signal and a splitter to split the high pass signal into two high pass signals. The first filter module filters one high pass signals before a first compressor modulates the signal or a high pass signal to create a modulated signal. A second filter module filters the modulated signal to create a second filtered signal that is processed by a first processing module including a band splitter that splits the signal into low and high band signals that are then modulated by compressors. A second processing module processes the modulated low and high band signals to create an output signal.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
Supper bass boosting method and system
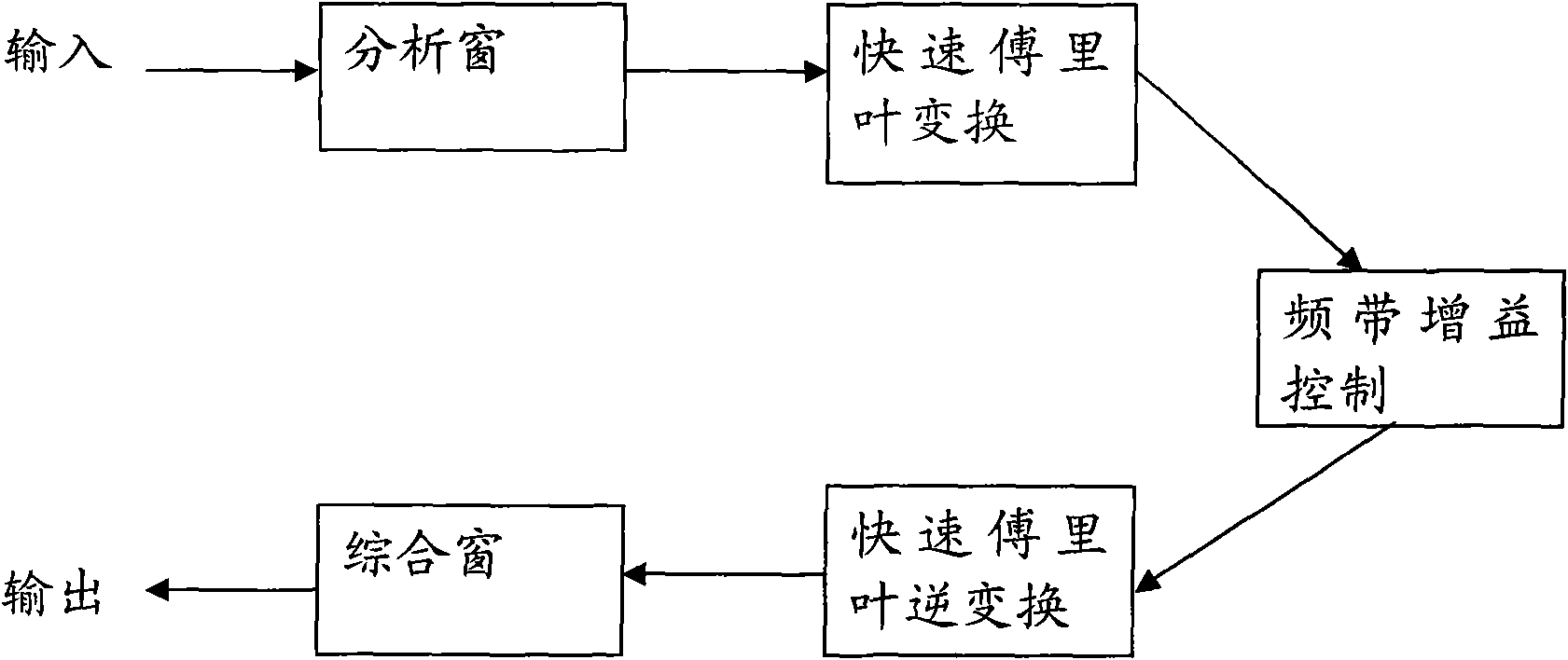
ActiveCN101577848AIncreased Bass BoostAvoid conversionCombination control in untuned amplifierFrequency response correctionTime domainEngineering
The invention discloses a supper bass boosting method and a system, which are used for improving the supper bass boosting effect of an audio-frequency signal and improving processing speed. The supper bass boosting method comprises the following steps of: carrying out low-pass filtering processing to the audio-frequency signal according to preset cut-off frequency, obtaining a time domain low-frequency signal from the audio-frequency signal, and converting the low-frequency signal into a frequency domain low-frequency signal; carrying out frequency band gain control to the frequency domain low-frequency signal which is then reduced into the time domain low-frequency signal and obtaining the low-frequency signal after the signal intensity is strengthened; and synthesizing the low-frequency signal after the signal intensity is strengthened and the audio-frequency signal and carrying out automatic gain control to the synthesized audio-frequency signal.
Owner:WUXI ZGMICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
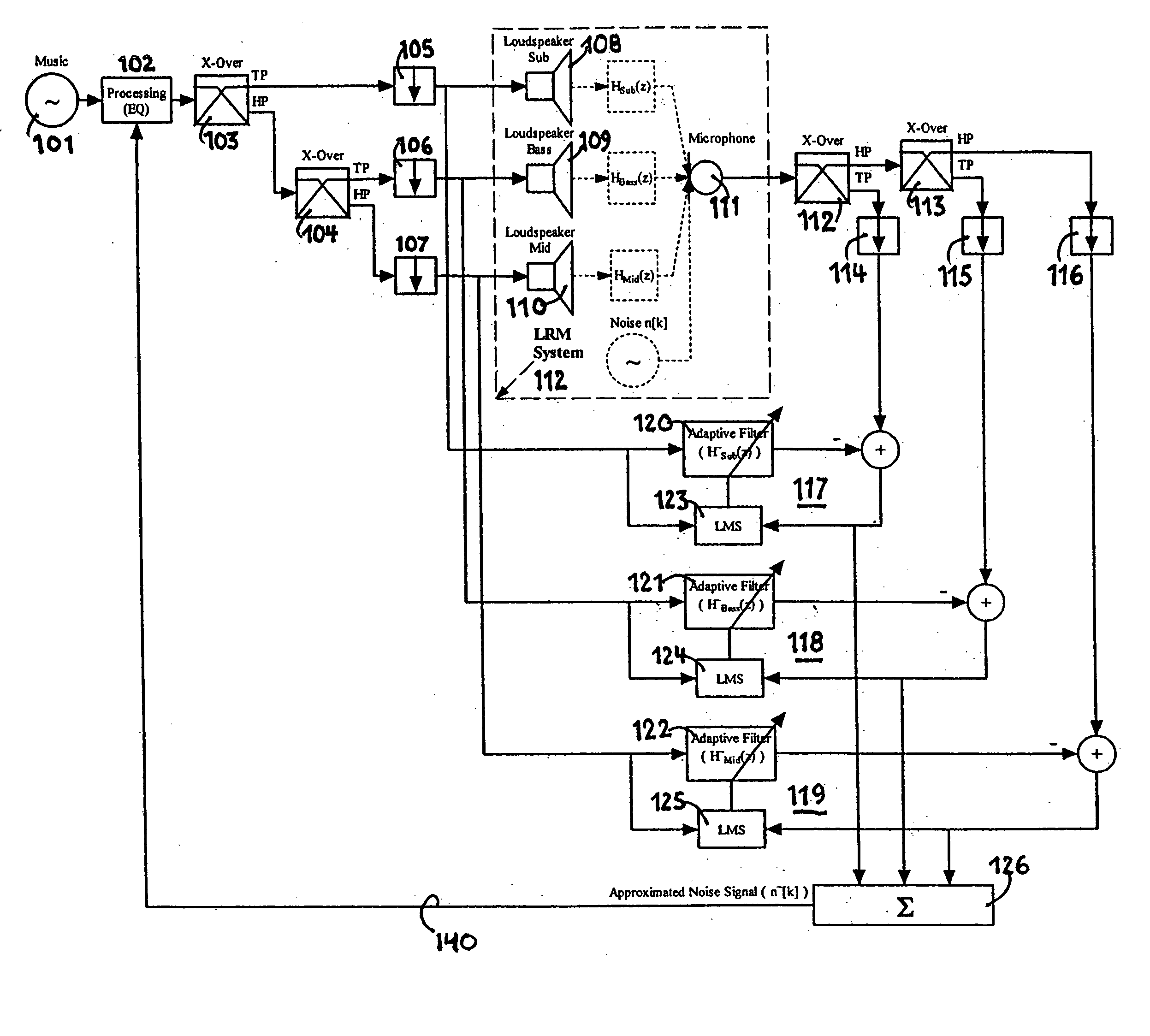
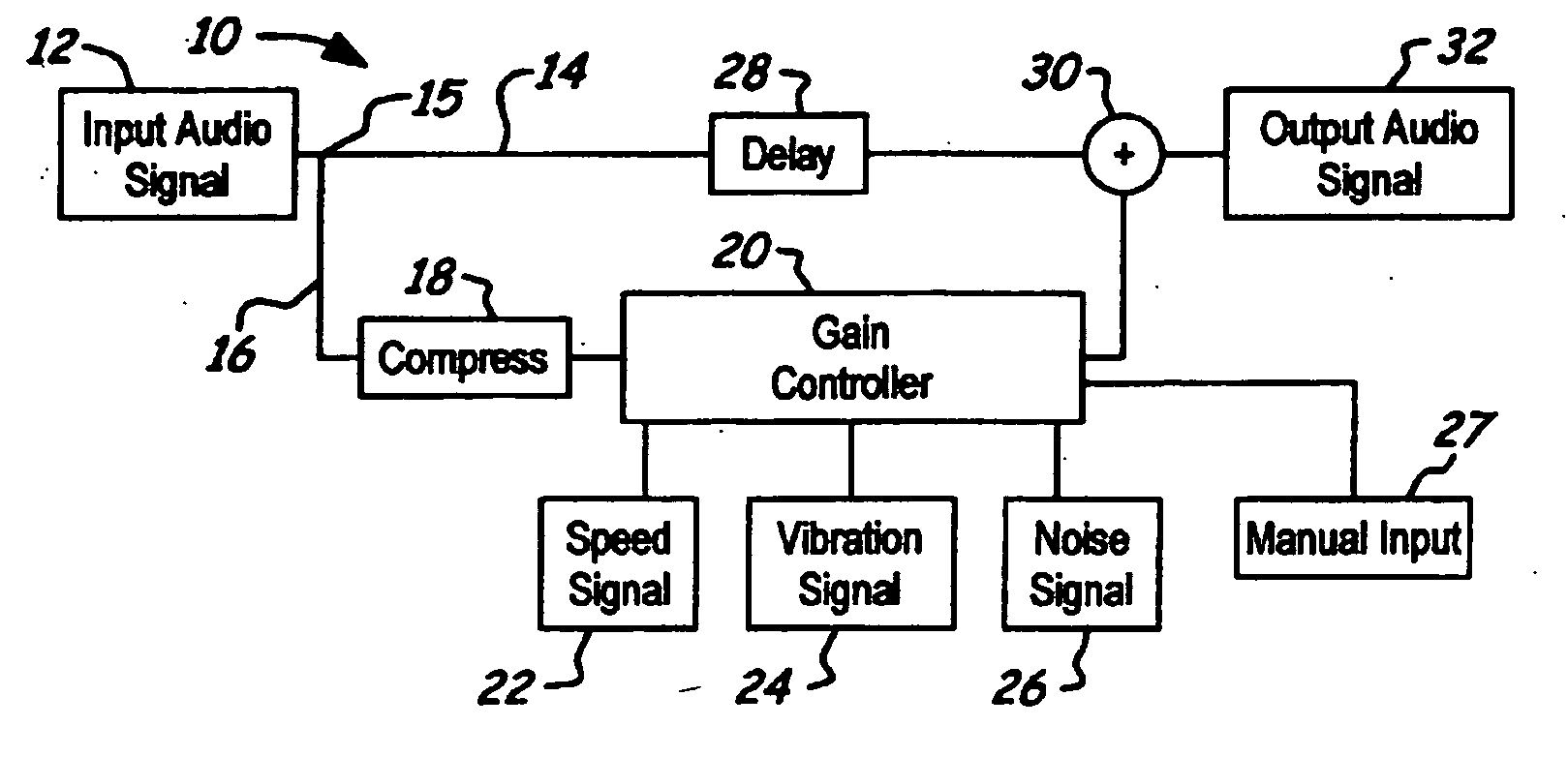
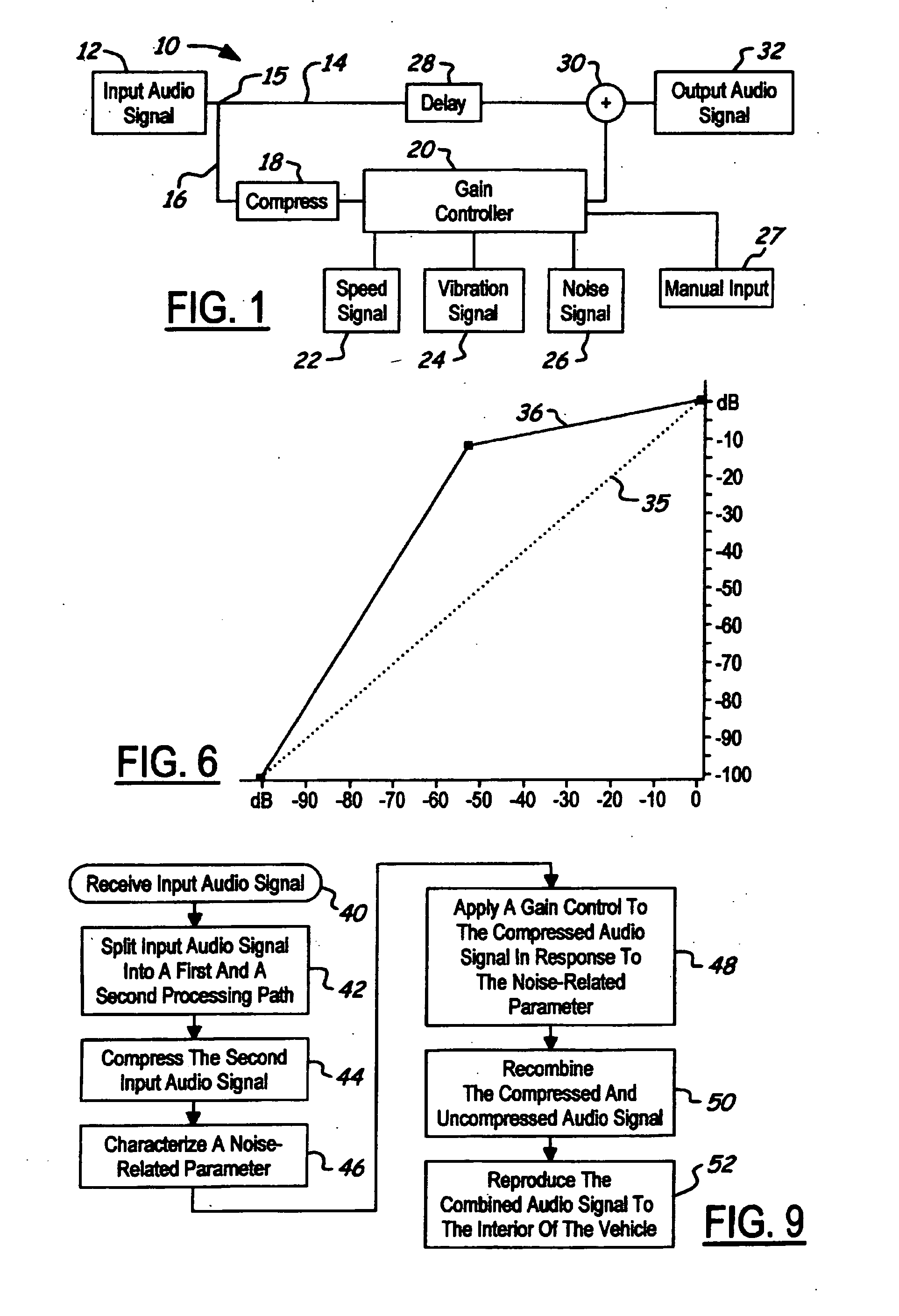
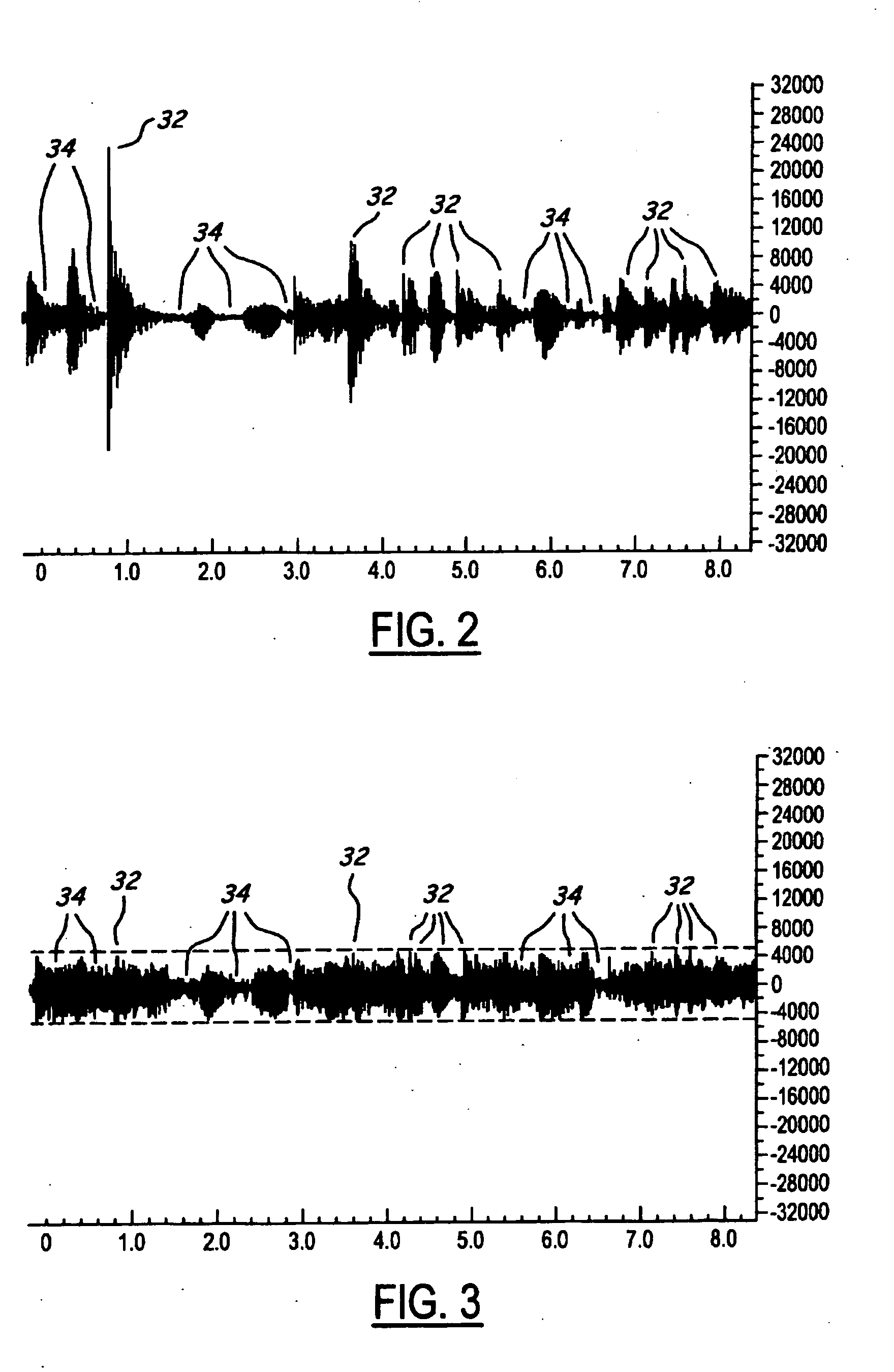
NVH dependent parallel compression processing for automotive audio systems
InactiveUS20050135635A1Combination control in untuned amplifierVolume compression/expansionParallel compressionCar audio system
A method is provided for controlling a dynamic range of audio reproduction in an interior of a vehicle. An input audio signal is received by an audio processor. The input audio signal is split into a first and a second processing path. The input audio signal of the second processing path is compressed. A noise-related parameter of the vehicle is characterized. A gain control is applied to the compressed audio signal of the second processing path in response to the noise-related parameter. The compressed and uncompressed audio signals are synchronously recombined. The combined audio signal is reproduced to the interior of the vehicle.
Owner:LEAR CORP
Compressor based dynamic bass enhancement with EQ
Owner:THAT PTY LTD
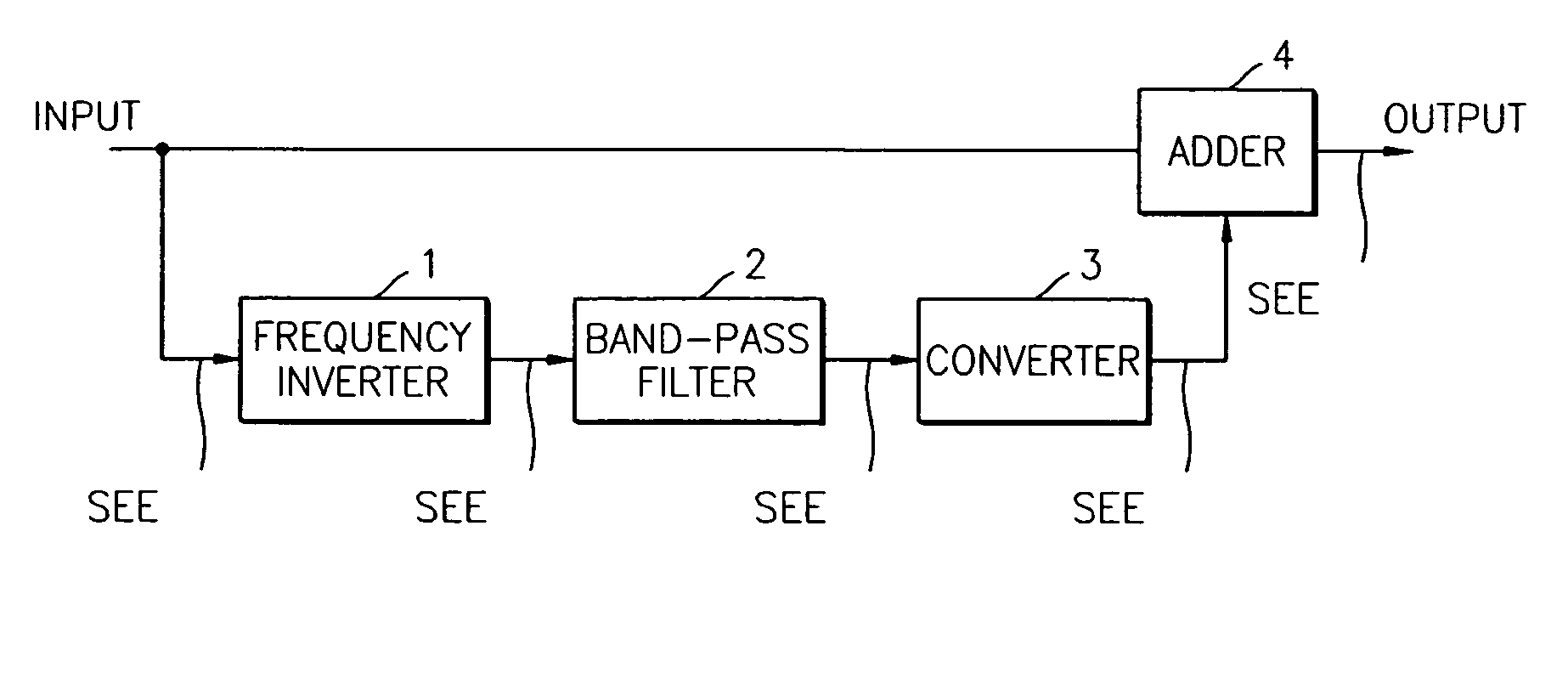
Apparatus and method for reconstructing high frequency part of signal
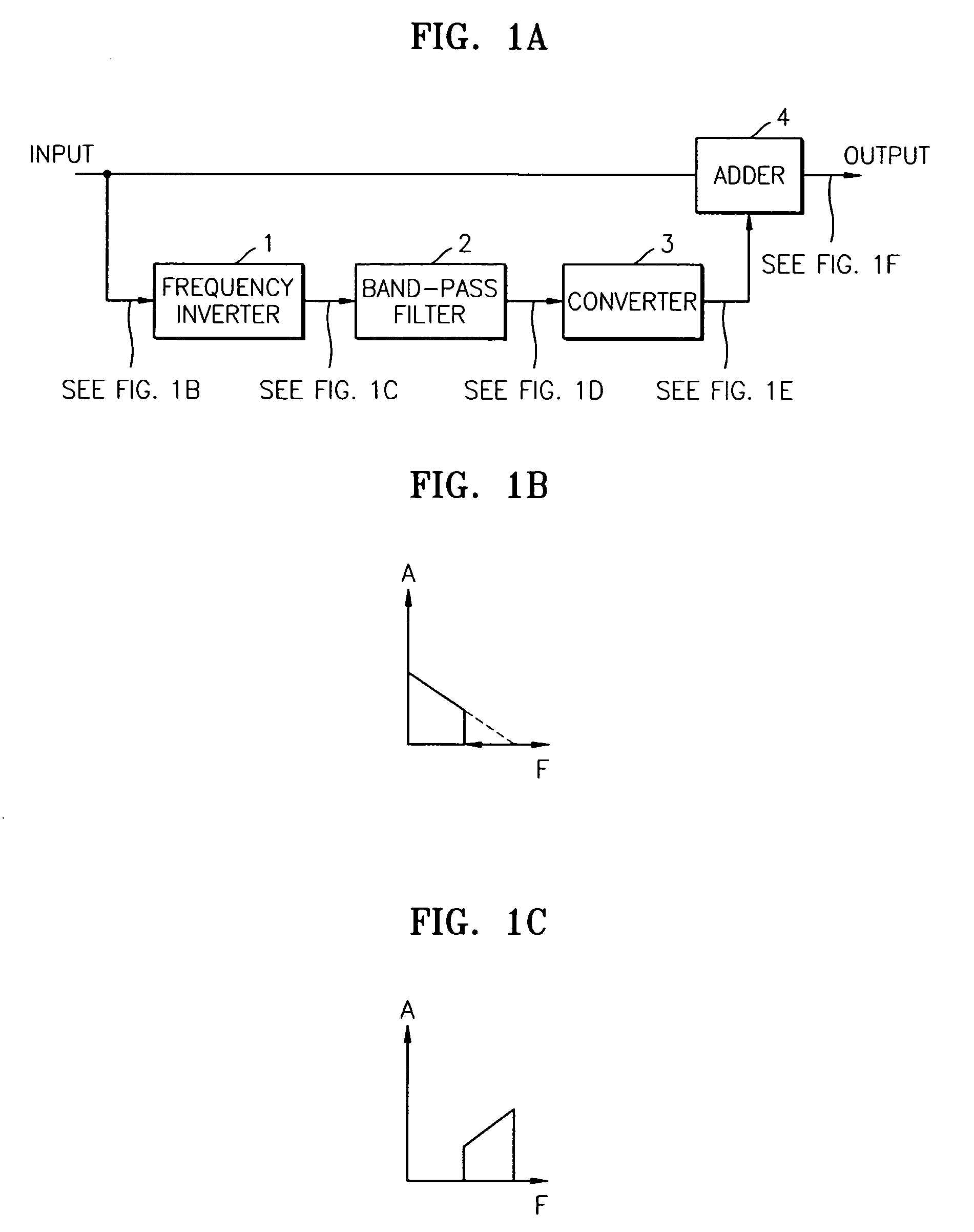
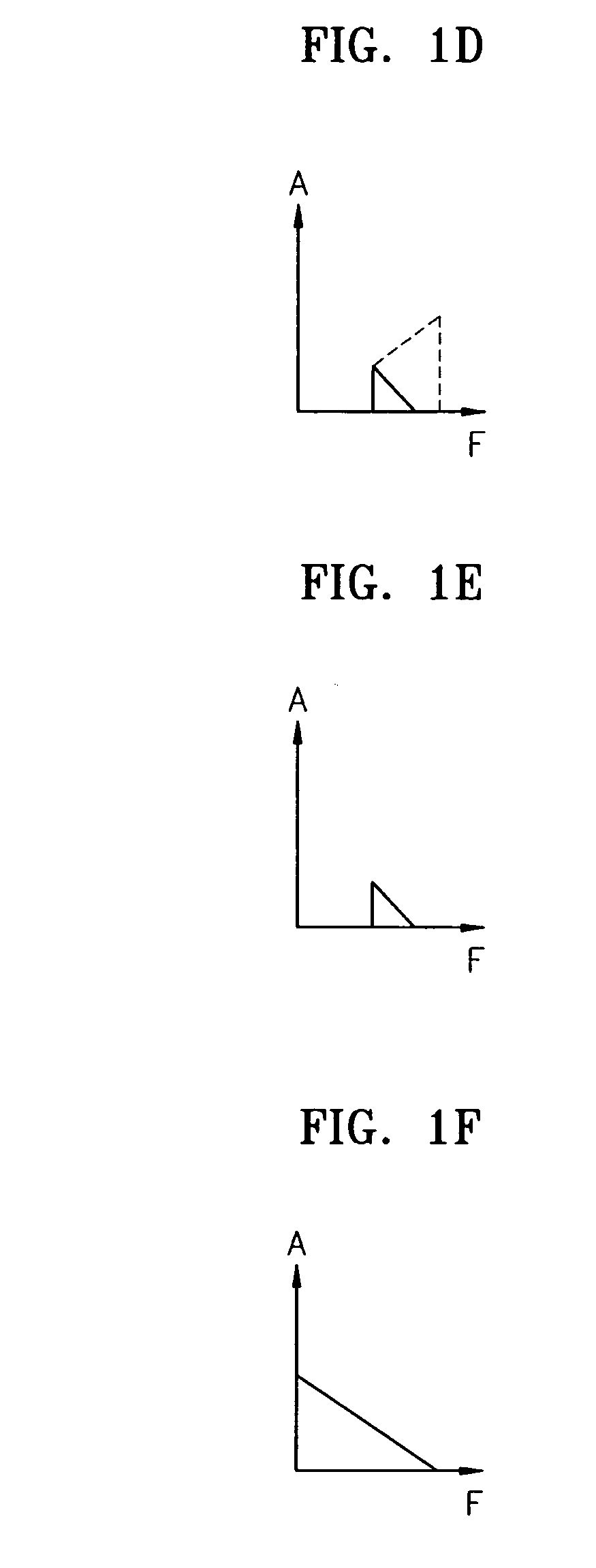
Provided is an apparatus and method for reconstructing the high frequency part of audio signal to improve the quality of the audio signal. The apparatus includes a frequency inverter which inverts the frequency of an input signal; a band-pass filter which filters the high frequency part of the inverted signal; a converter which shifts the frequency of the filtered signal so as not to generate aliasing of the input signal and the filtered signal; and an adder which adds the shifted signal to the input signal. Therefore, hearing perception close to the original signal can be achieved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Voice enhancement system
InactiveCN1620751AGain controlCombination control in untuned amplifierAudio signal flowBackground noise
A method of processing an audio signal in order to overcome background noise extraneous to the audio signal. The method includes comparing a measure of the audio signal in a frequency component of the audio signal to a measure of the noise in a frequency component of the background noise, determining a gain responsive to the comparison and amplifying at least a portion of the audio signal, including at least one frequency segment not included in the frequency component of the audio signal, by the determined gain.
Owner:CLEAR AUDIO
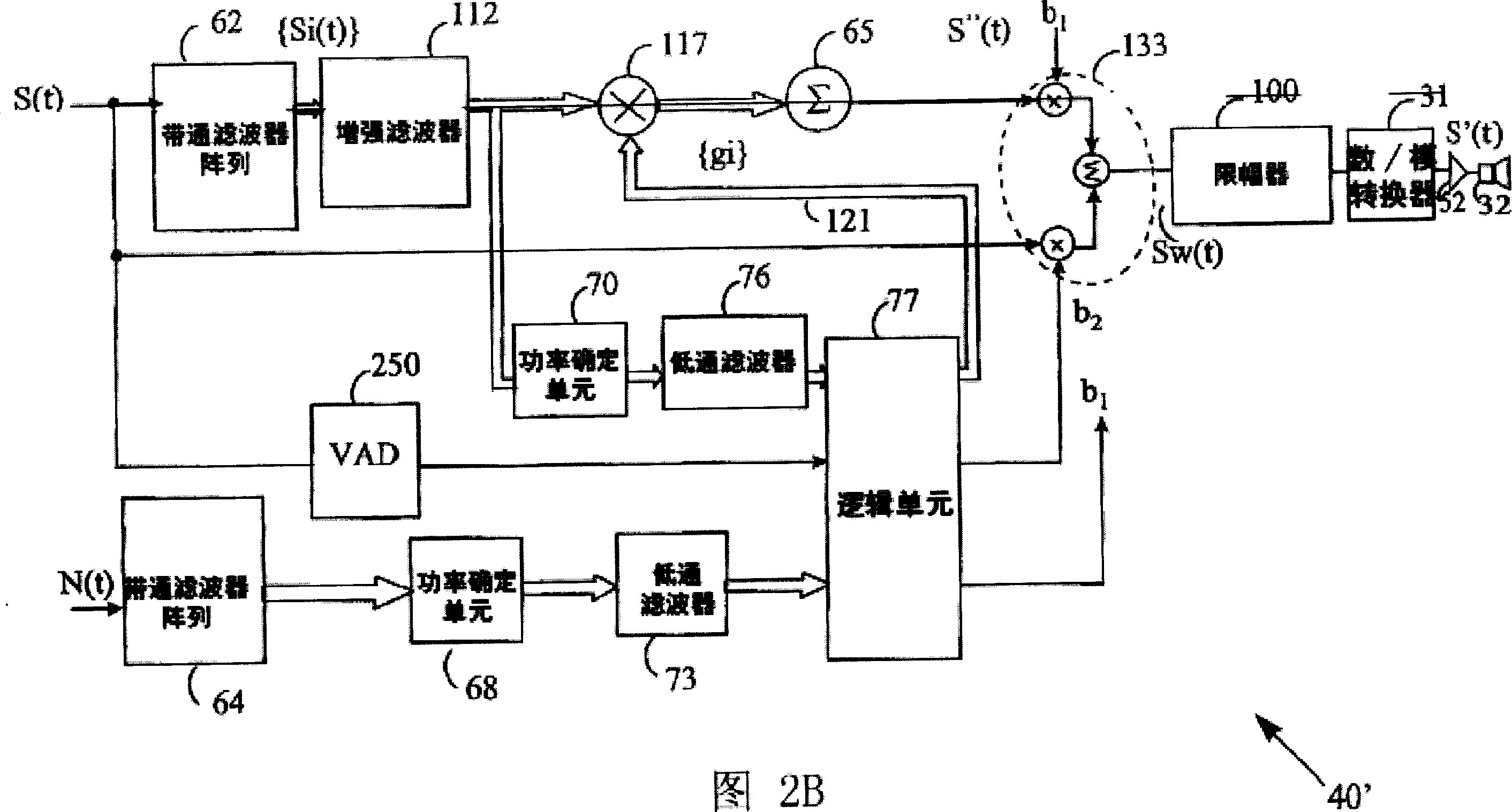
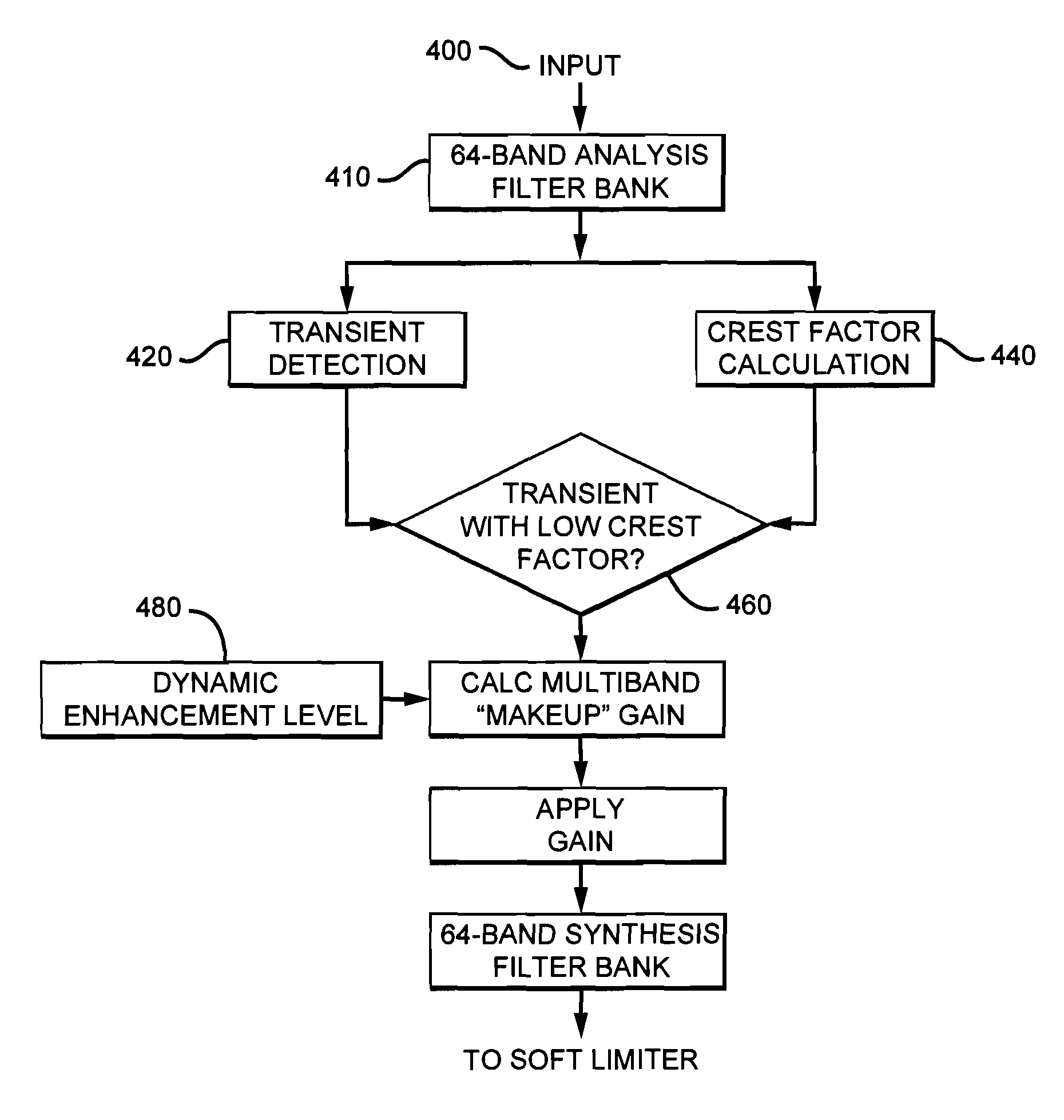
Adaptive dynamic range enhancement of audio recordings
ActiveUS8879750B2Combination control in untuned amplifierVolume compression/expansionTime segmentAudio signal flow
There are provided methods and an apparatus for conditioning an audio signal. According to one aspect of the present invention there is included a method for conditioning an audio signal having the steps of: receiving at least one audio signal, each audio signal having at least one channel, each channel being segmented into a plurality of frames over a series of time; calculating at least one measure of dynamic excursion of the audio signal for a plurality of successive segments of time; filtering the audio signal into a plurality of subbands, each frame being represented by at least one subband; deriving a dynamic gain factor from the successive segments of time; analyzing at least one subband of the frame to determine if a transient exists in the frame; and applying the dynamic gain factor to each frame having a transient.
Owner:DTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com