Patents
Literature
80 results about "Gain cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
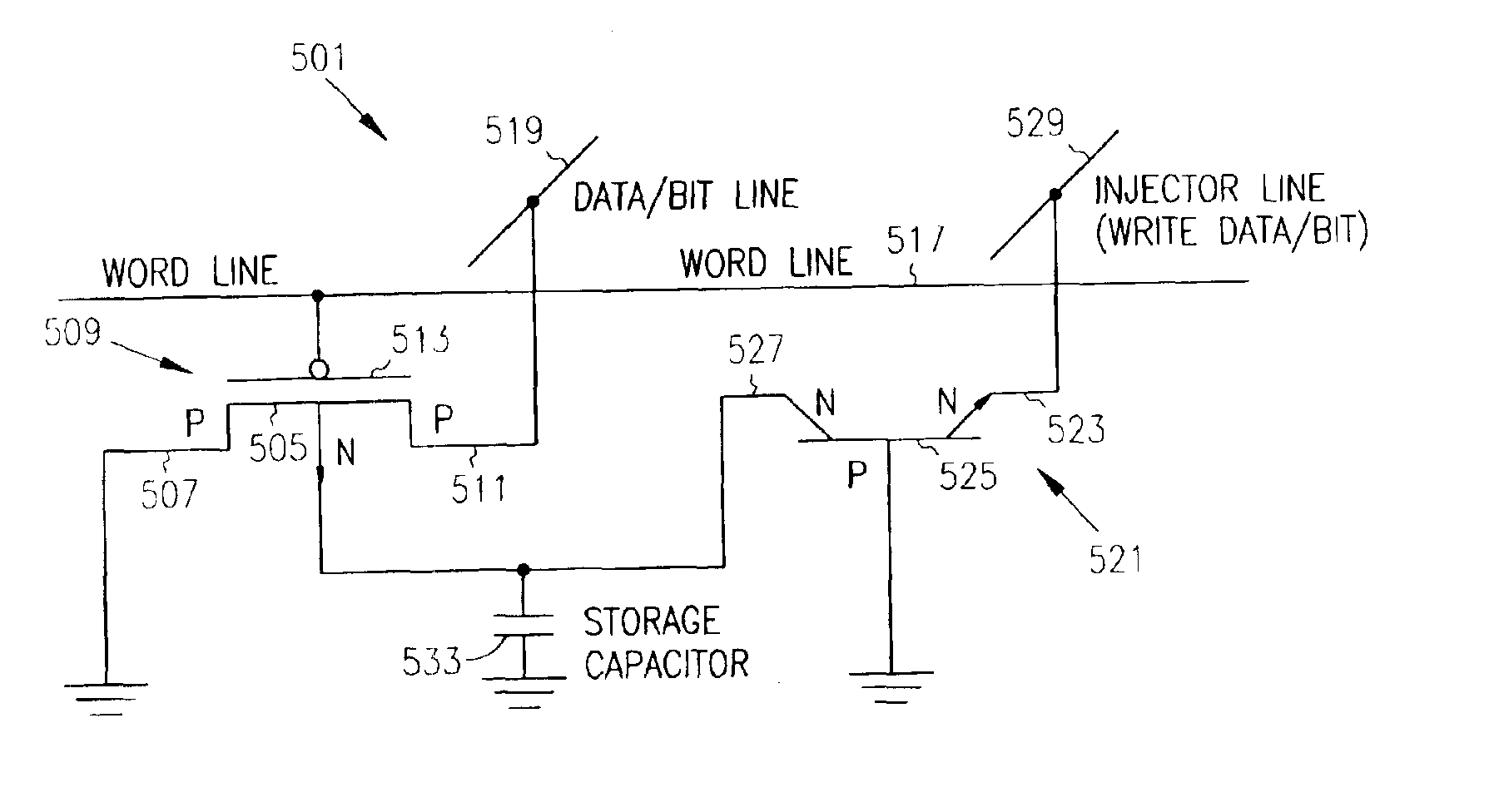
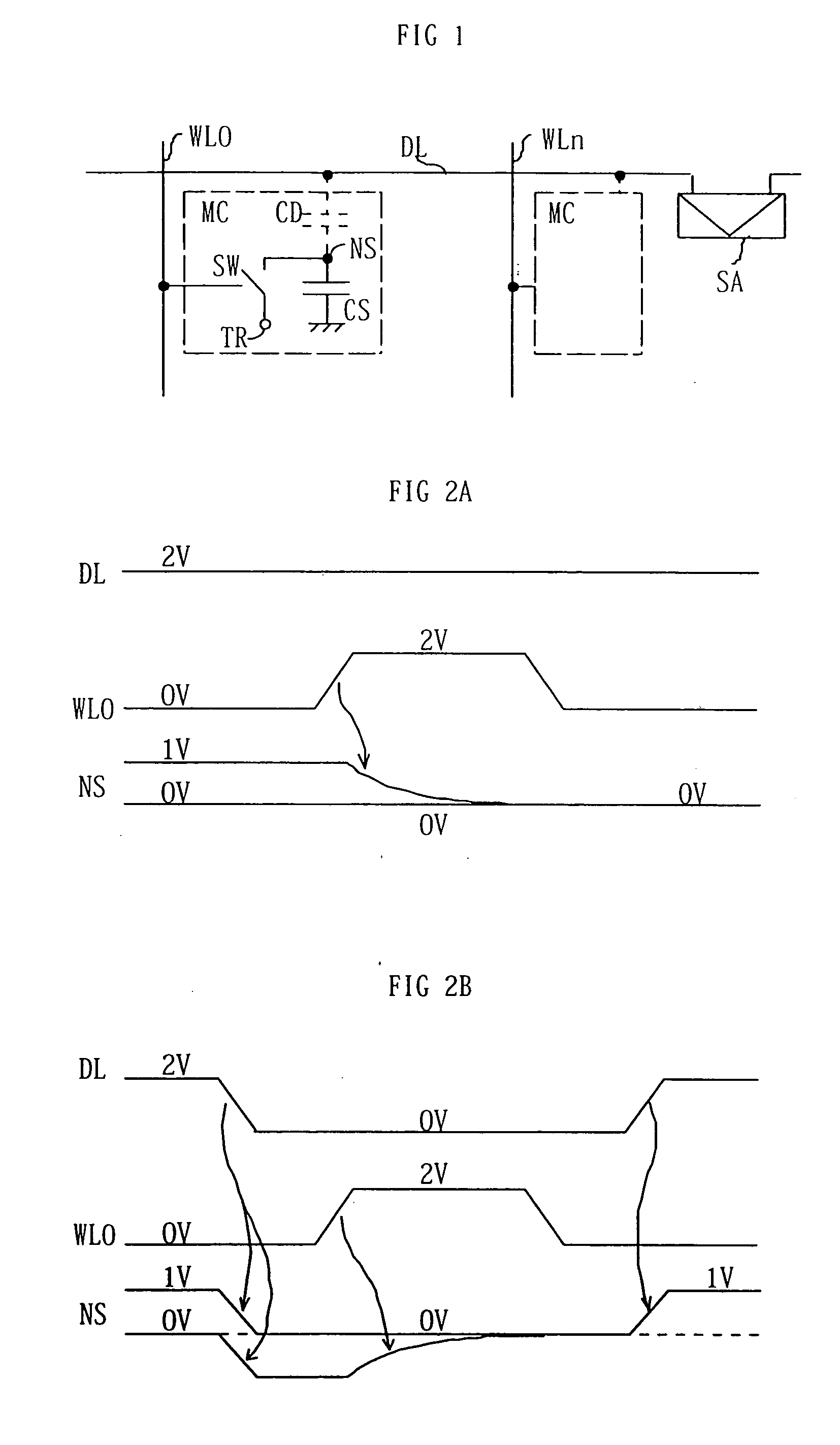
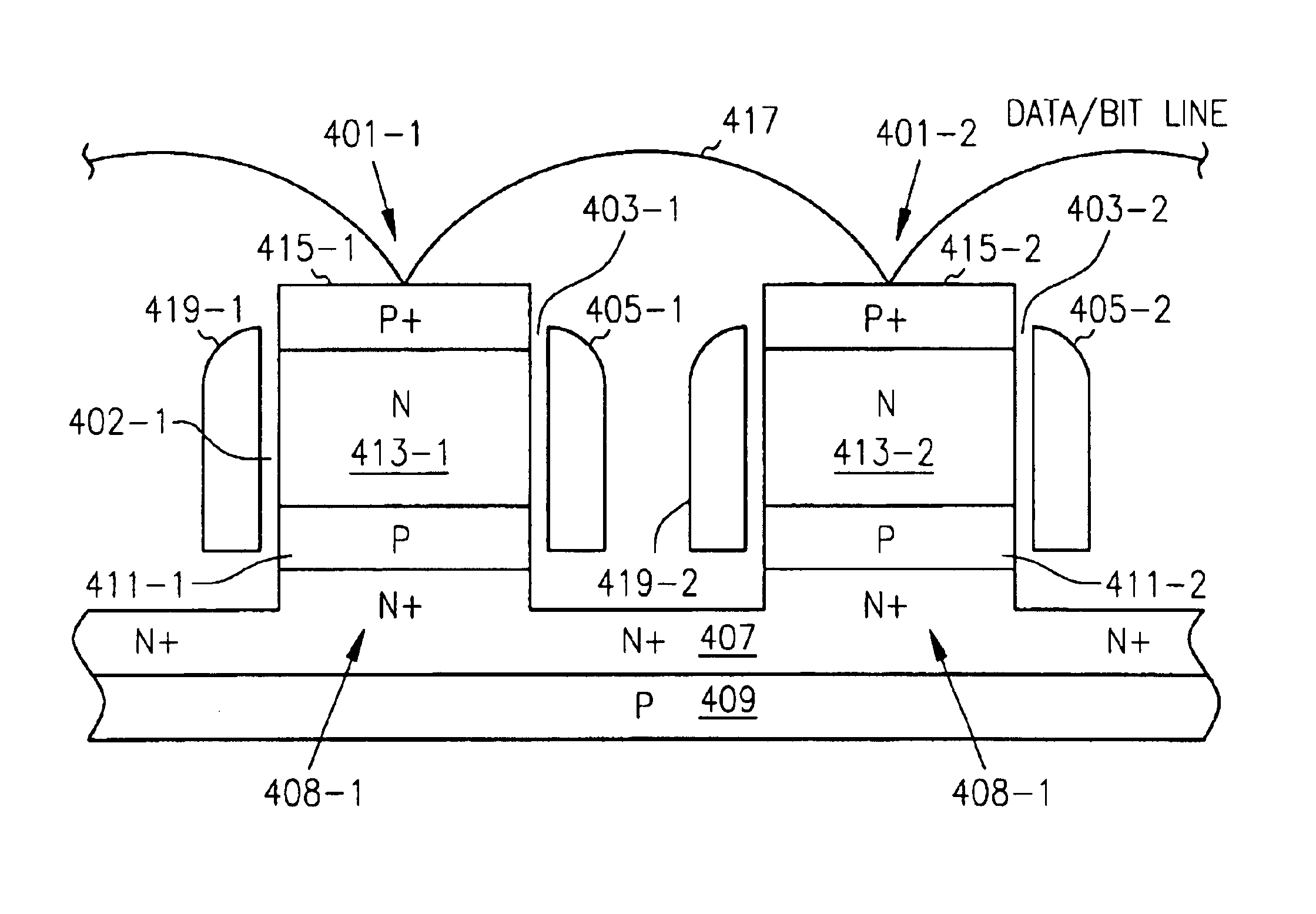
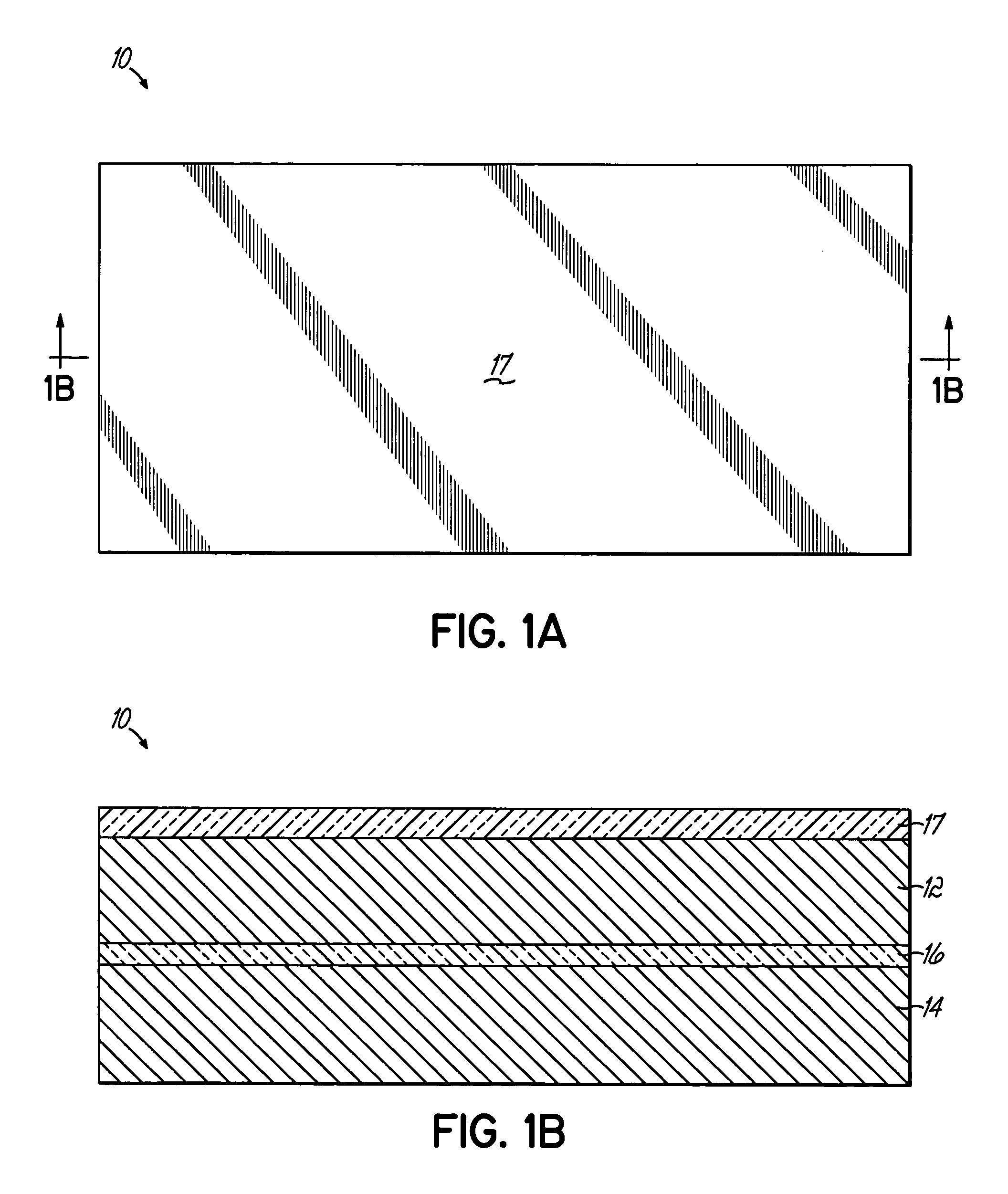
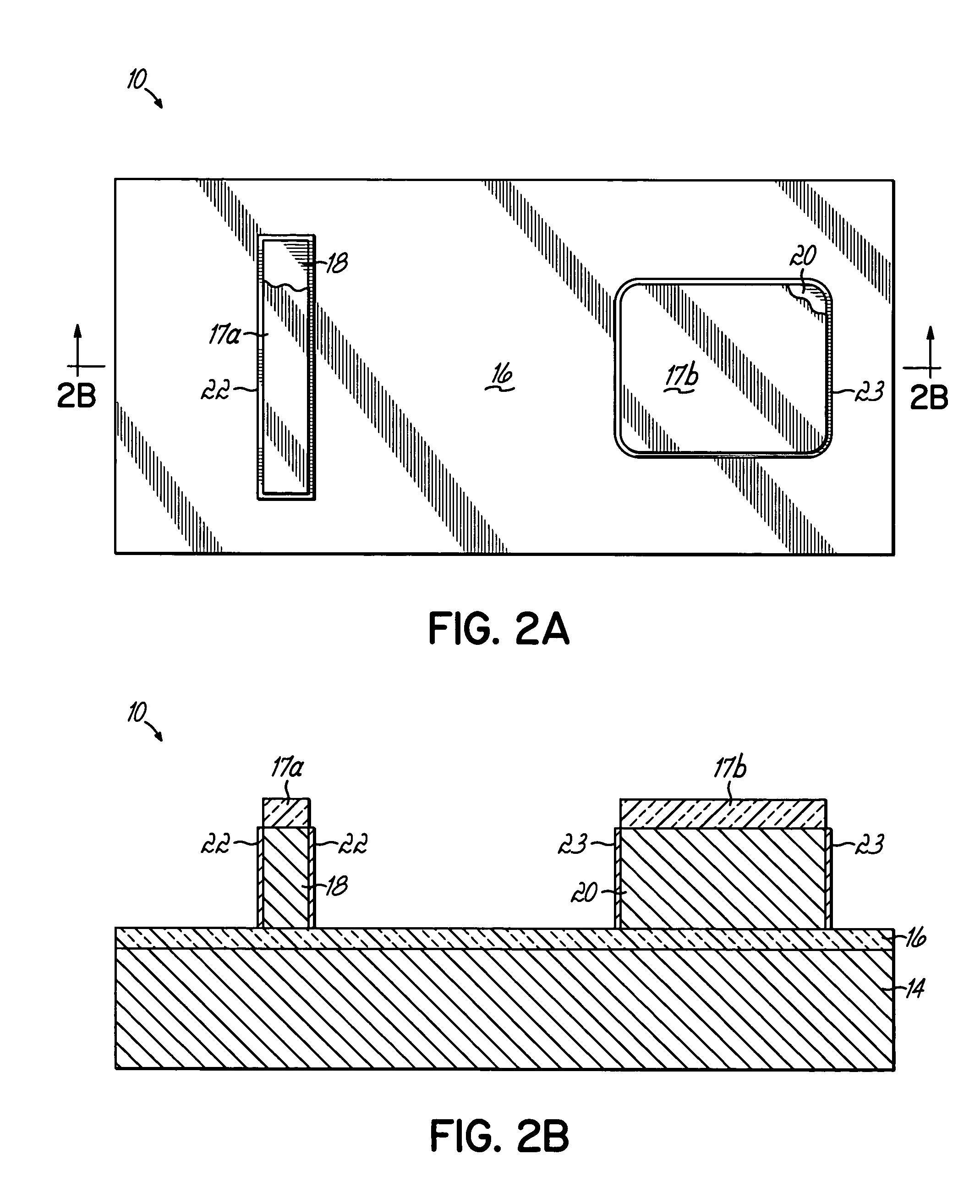
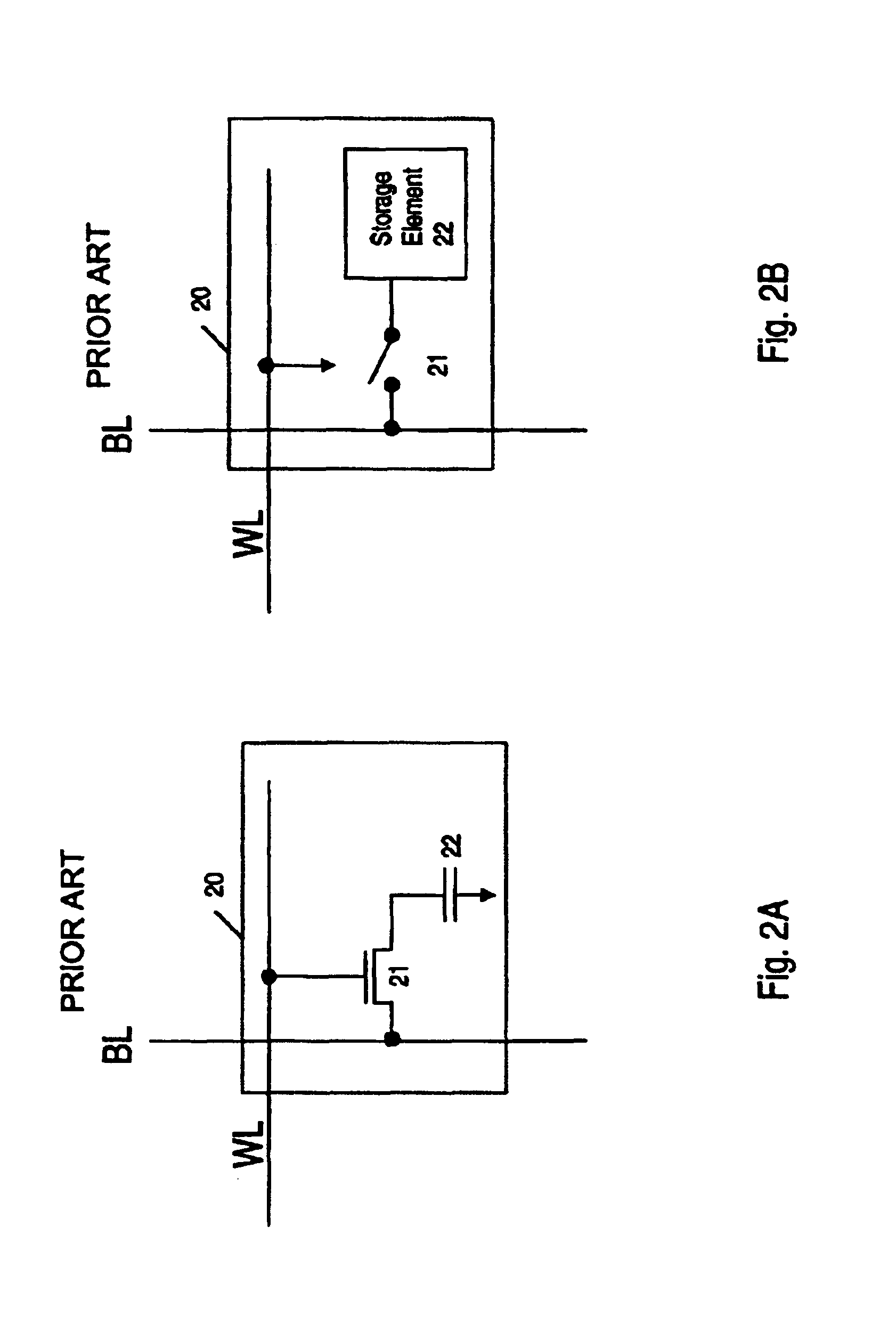
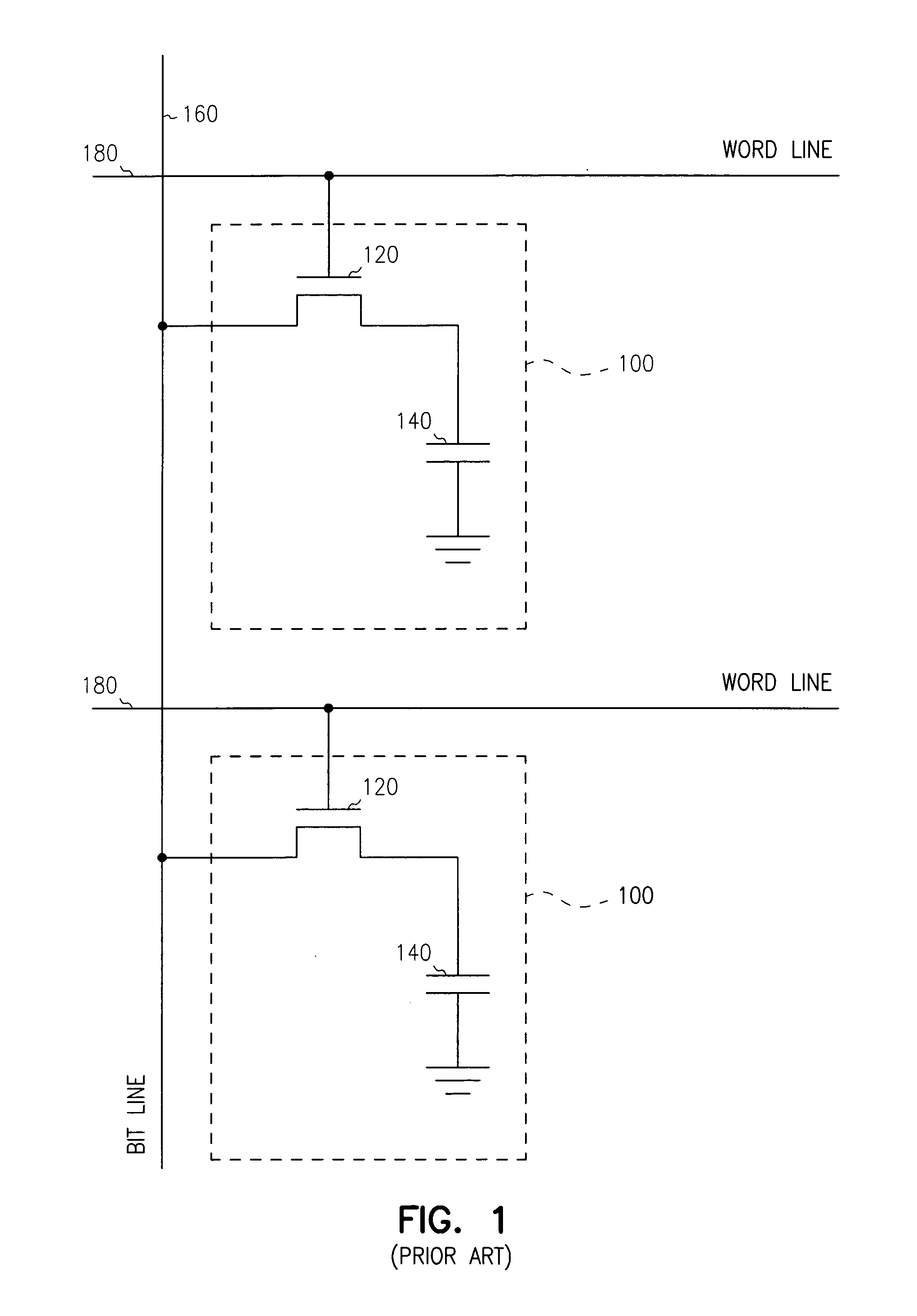
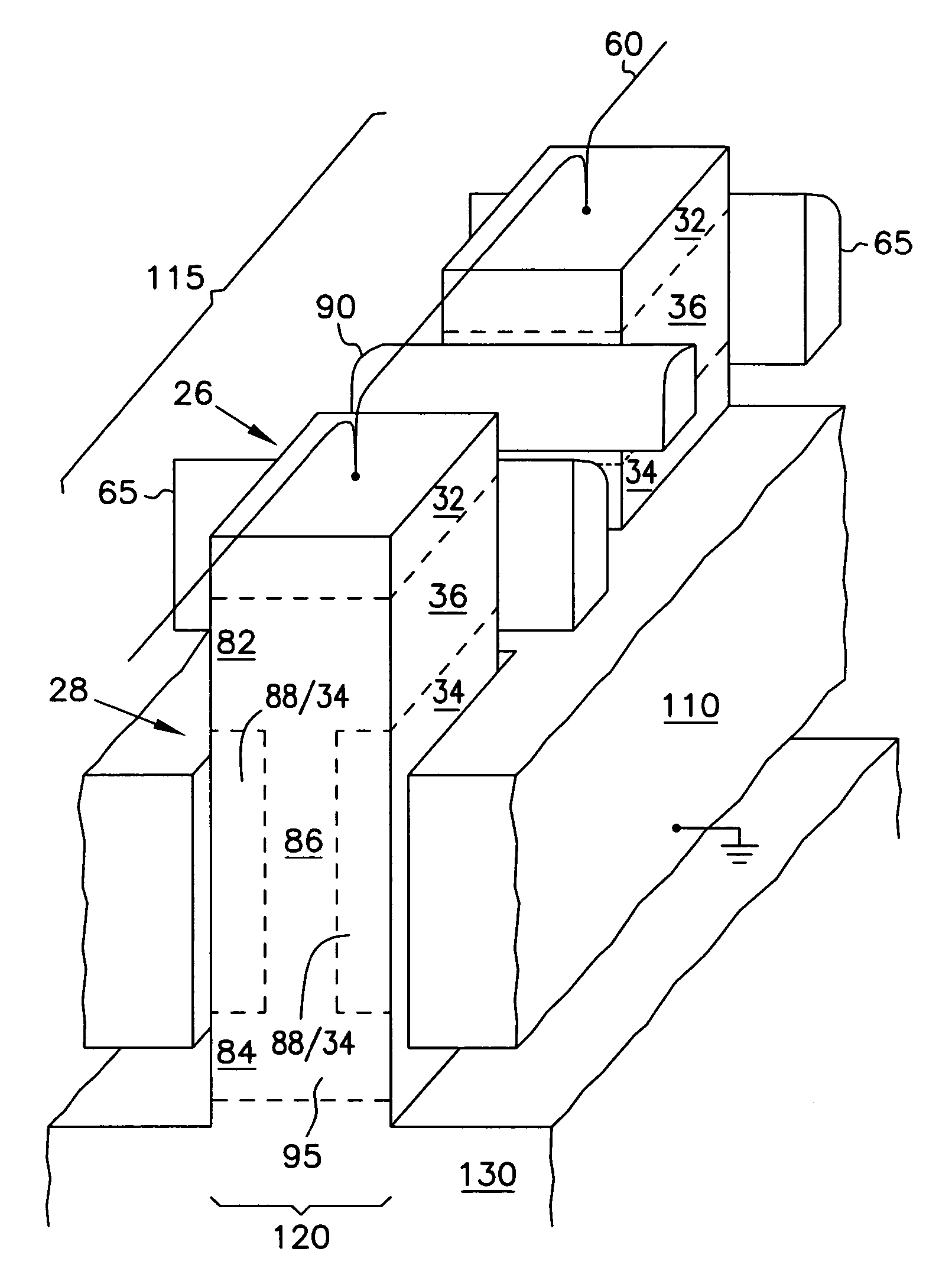
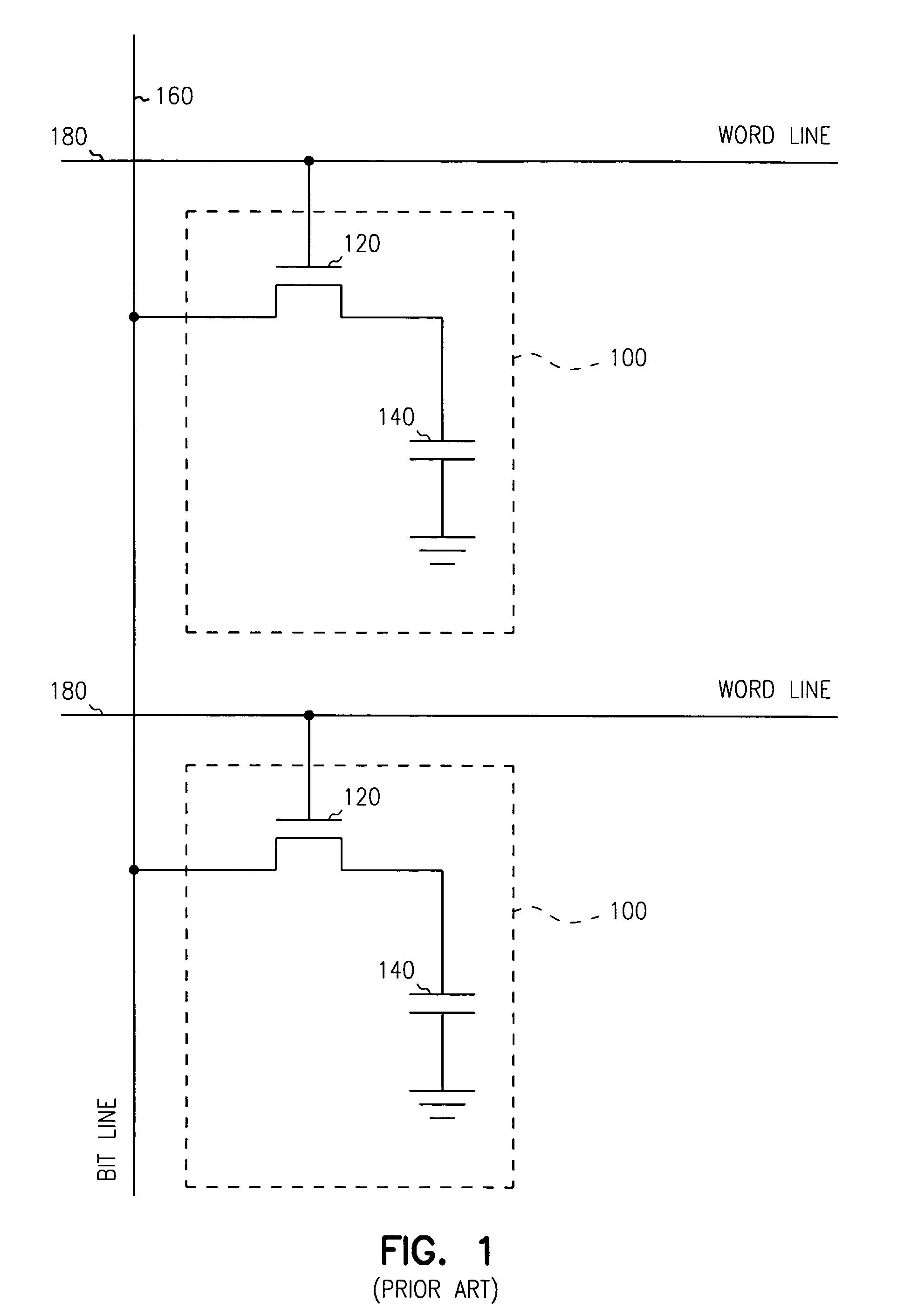
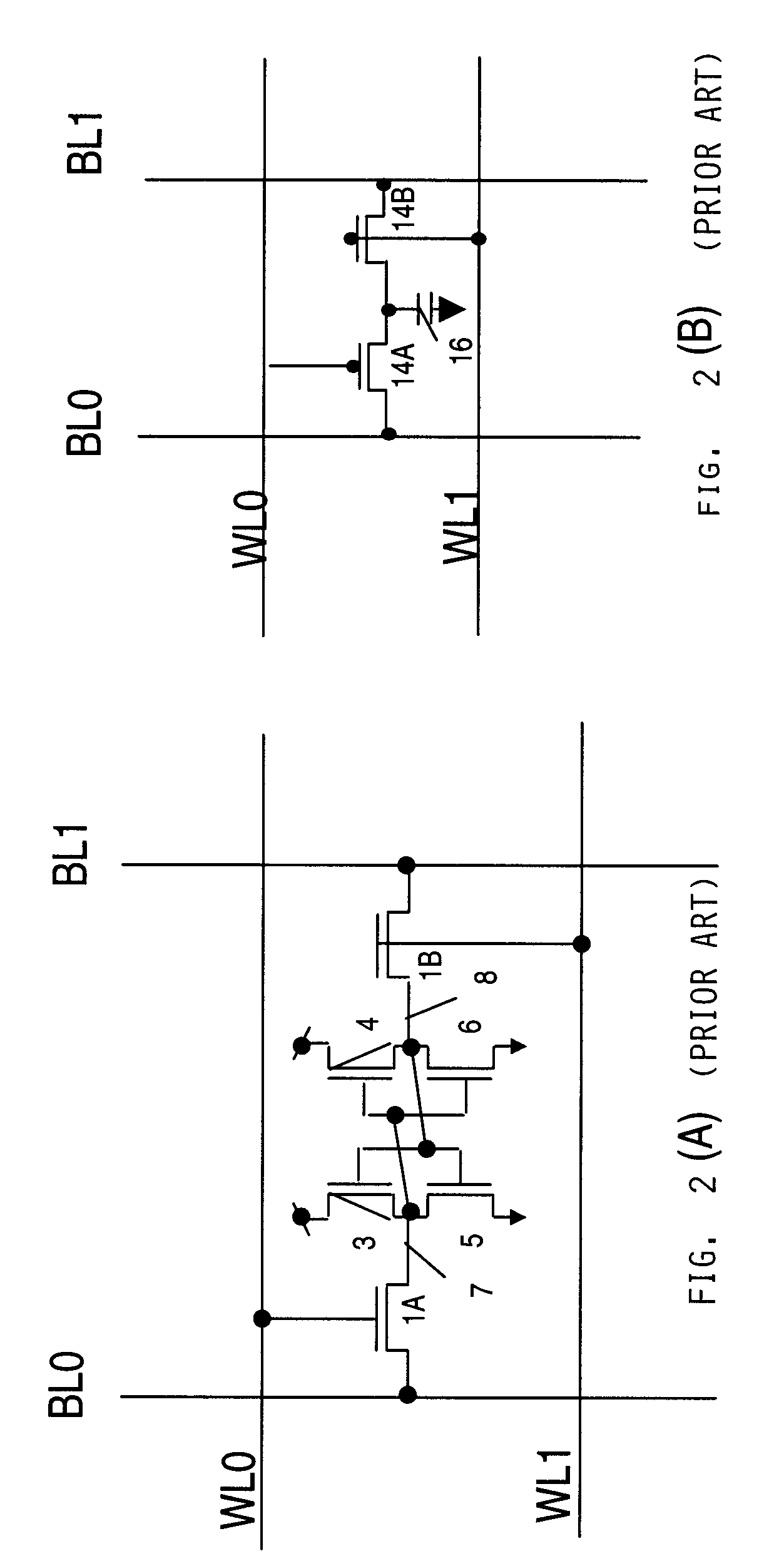
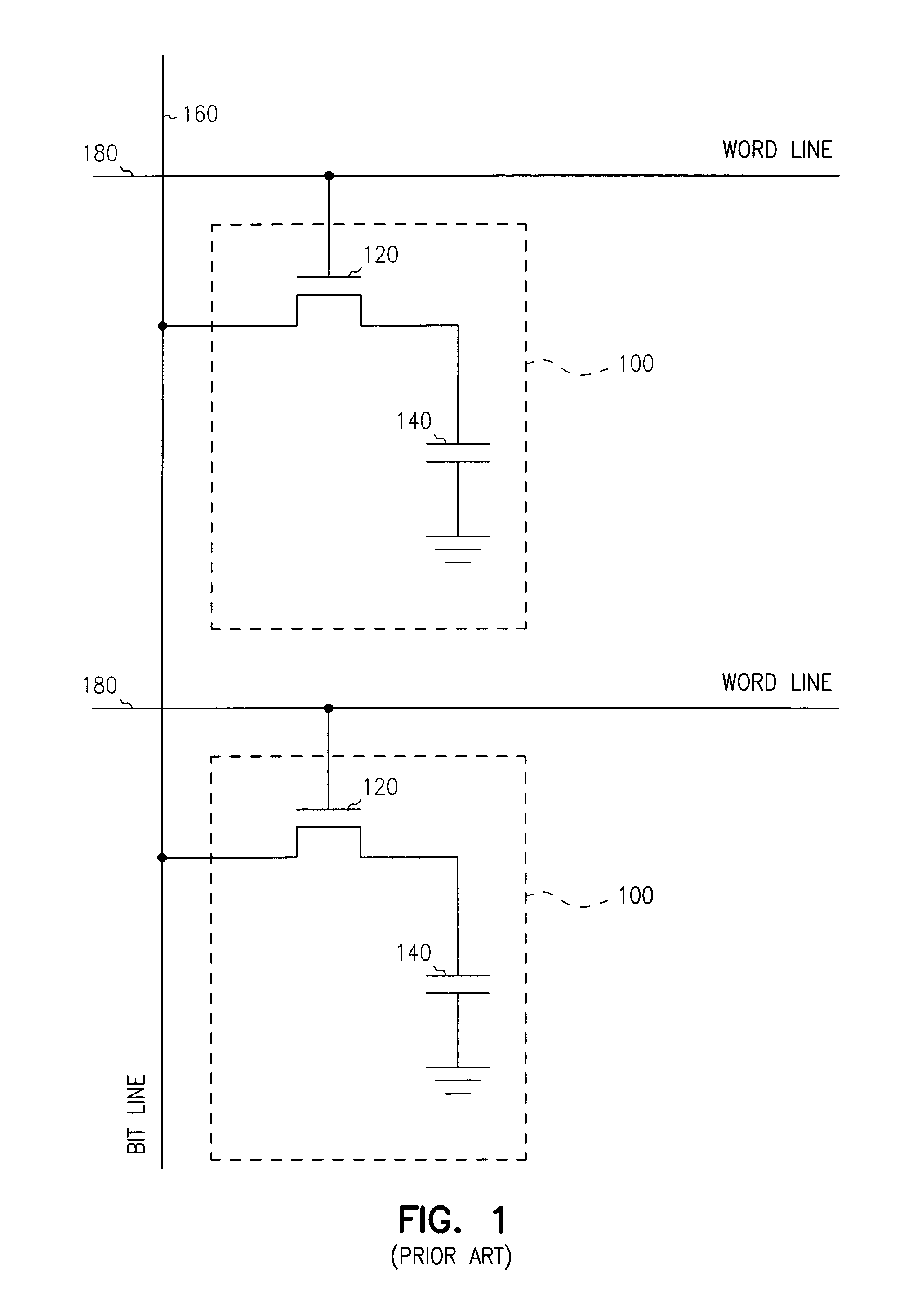
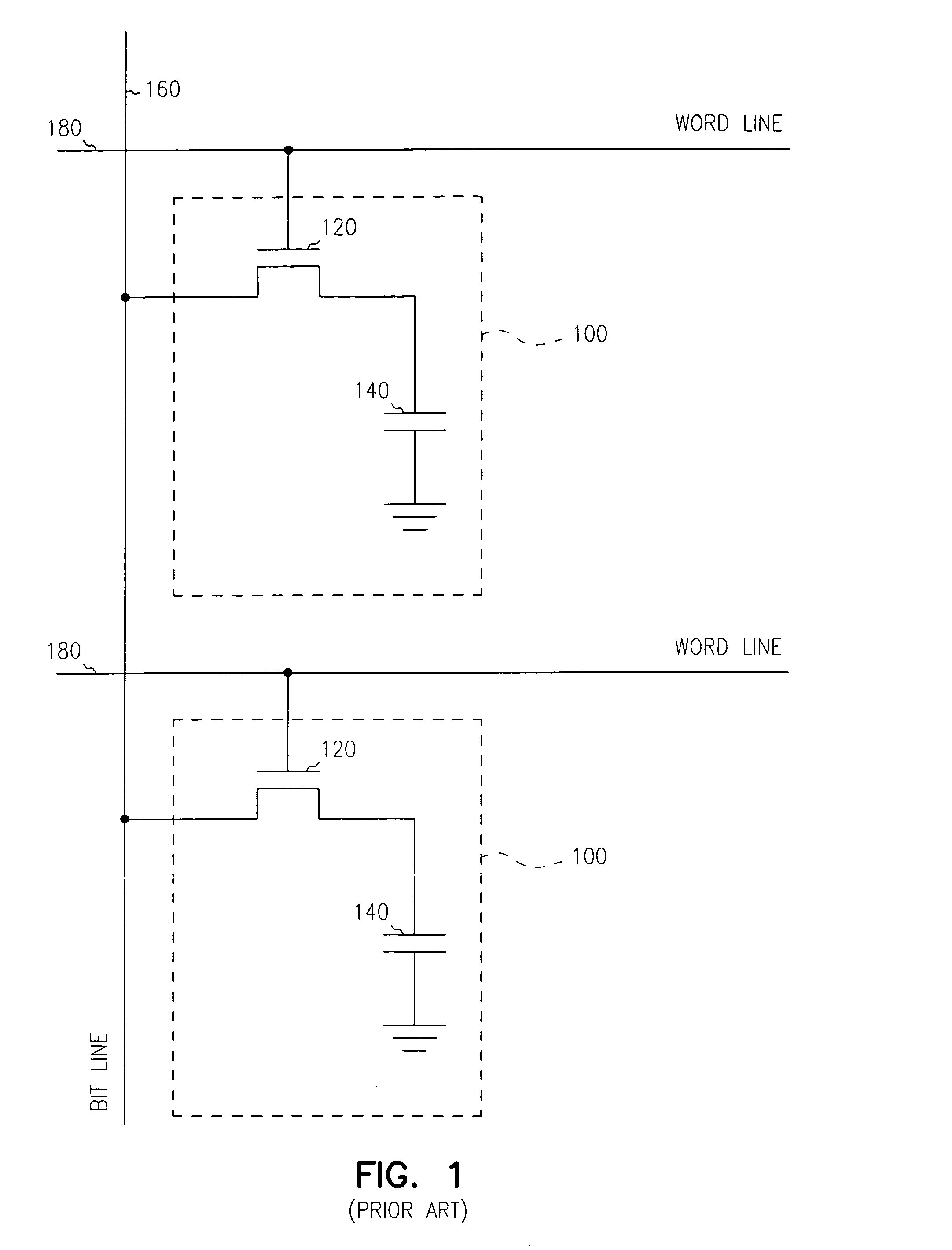
Embedded DRAM gain memory cell having MOS transistor body provided with a bi-polar transistor charge injecting means
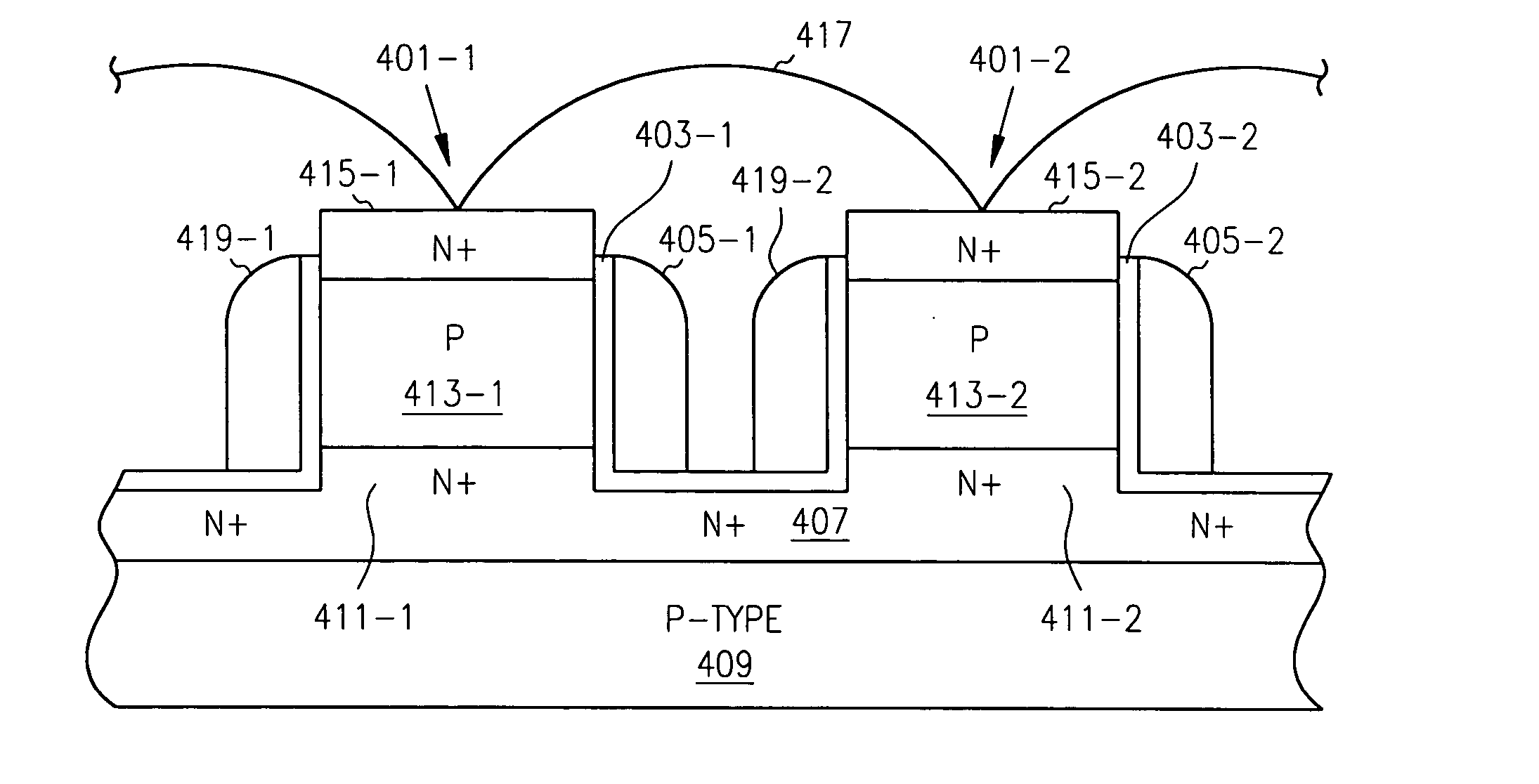
A high density horizontal merged MOS-bipolar gain memory cell is realized for DRAM operation. The gain cell includes a horizontal MOS transistor having a source region, a drain region, and a floating body region therebetween. The gain cell includes a horizontal bi-polar transistor having an emitter region, a base region and a collector region. The collector region for the horizontal bi-polar transistor serves as the floating body region for the horizontal MOS transistor. A gate opposes the floating body region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide. The emitter region for the horizontal bi-polar transistor is coupled to a write data line.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor memories
InactiveUS20050237786A1Reduce areaReduce area requirementsTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh densityComputer science
A high integration dynamic random access memory is provided by this invention. Furthermore, a write method is provided such that cell size of two-and three-transistor gain cell memories is reduced. A dynamic memory incorporating a thin-channel transistor as the write element such that long data storage retention is achieved in the memory devices of this invention. A dynamic memory cell having low operating power and high density is also realized by this invention.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Gain cell type non-volatile memory having charge accumulating region charges or discharged by channel current from a thin film channel path
InactiveUS20050205921A1Write performanceImprove data retentionTransistorSolid-state devicesDrain currentSemiconductor
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Long retention time single transistor vertical memory gain cell
ActiveUS7271052B1High band gap energyAvoid excessive leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh cellRetention time
A single transistor vertical memory gain cell with long data retention times. The memory cell is formed from a silicon carbide substrate to take advantage of the higher band gap energy of silicon carbide as compared to silicon. The silicon carbide provides much lower thermally dependent leakage currents which enables significantly longer refresh intervals. In certain applications, the cell is effectively non-volatile provided appropriate gate bias is maintained. N-type source and drain regions are provided along with a pillar vertically extending from a substrate, which are both p-type doped. A floating body region is defined in the pillar which serves as the body of an access transistor as well as a body storage capacitor. The cell provides high volumetric efficiency with corresponding high cell density as well as relatively fast read times.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Gain cell type non-volatile memory having charge accumulating region charged or discharged by channel current from a thin film channel path
InactiveUS6876023B2Reduce leakage currentWrite performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringLow power dissipation
A semiconductor memory element subject to a threshold voltage controlling method other than those based on low leak currents or on the implantation of impurities. Such semiconductor elements are used to form semiconductor memory elements that are employed in scaled-down structures and are conducive to high-speed write operations thanks to a sufficiently prolonged refresh cycle. These semiconductor memory elements are in turn used to constitute a semiconductor memory device. A very thin semiconductor film is used as channels so that leak currents are reduced by the quantum-mechanical containment effect in the direction of film thickness. An amount of electrical charges in each charge accumulating region is used to change conductance between a source and a drain region of each read transistor structure, the conductance change being utilized for data storage. A channel of a transistor for electrically charging or discharging each charge accumulating region is made of a semiconductor film 5 nm thick at most. The arrangement affords both high-speed data write performance and an extended data retention time. The invention provides a high-speed, power-saving semiconductor device of high integration particularly advantageous for producing a small-scale system of low-power dissipation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
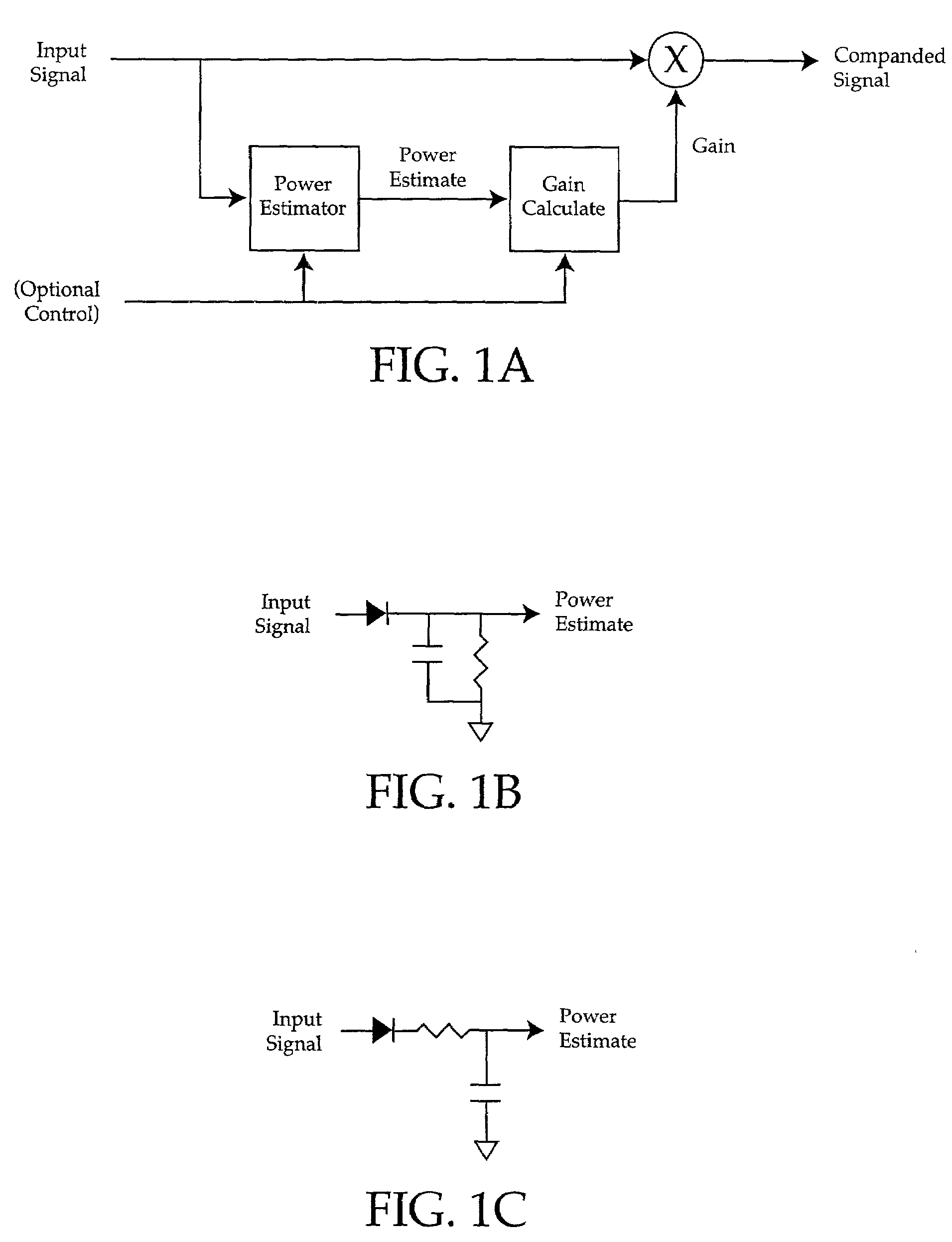
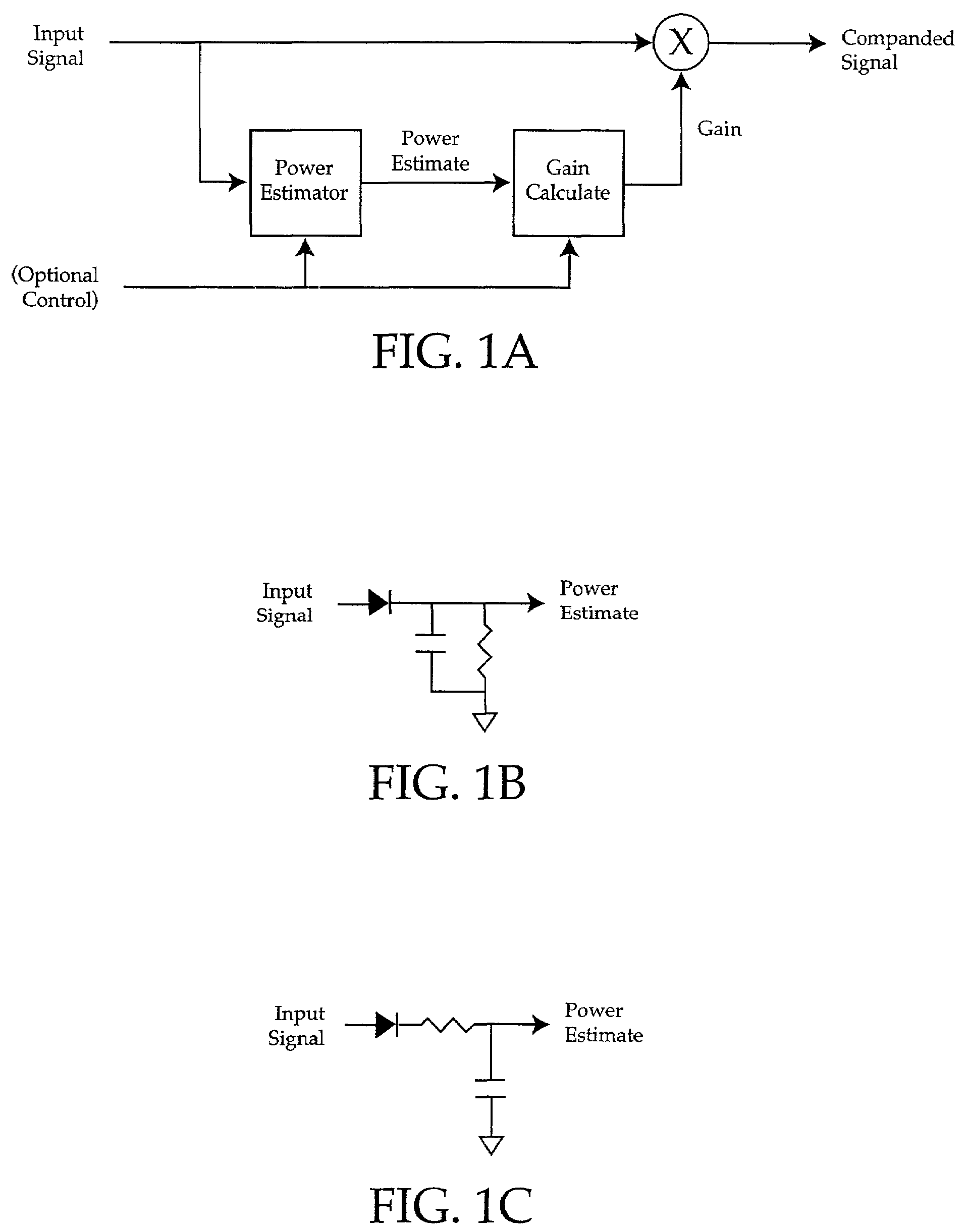
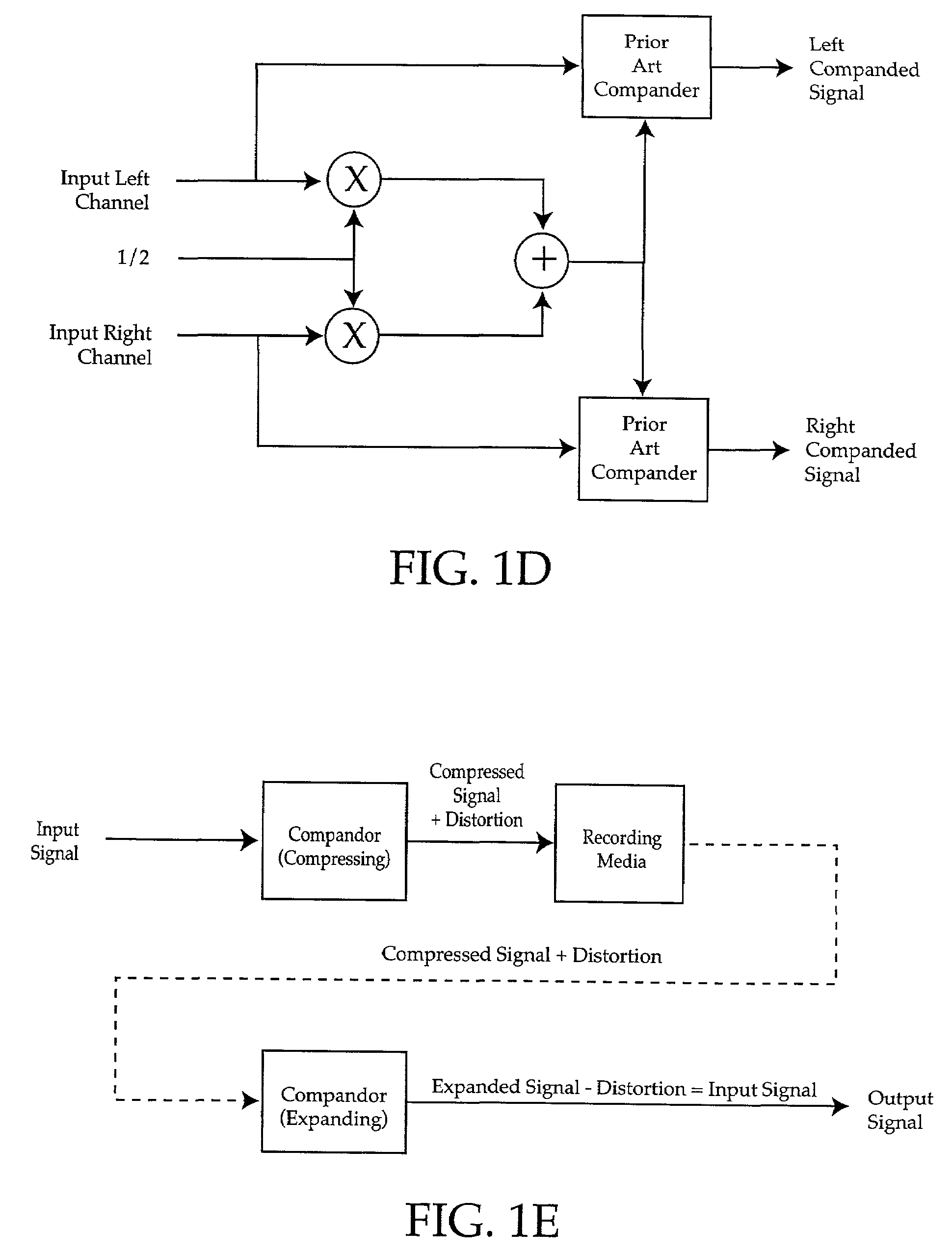
Input level adjust system and method
InactiveUS7190292B2Cost effectiveMaximum flexibilityElectric signal transmission systemsGain controlComputer scienceGain cell
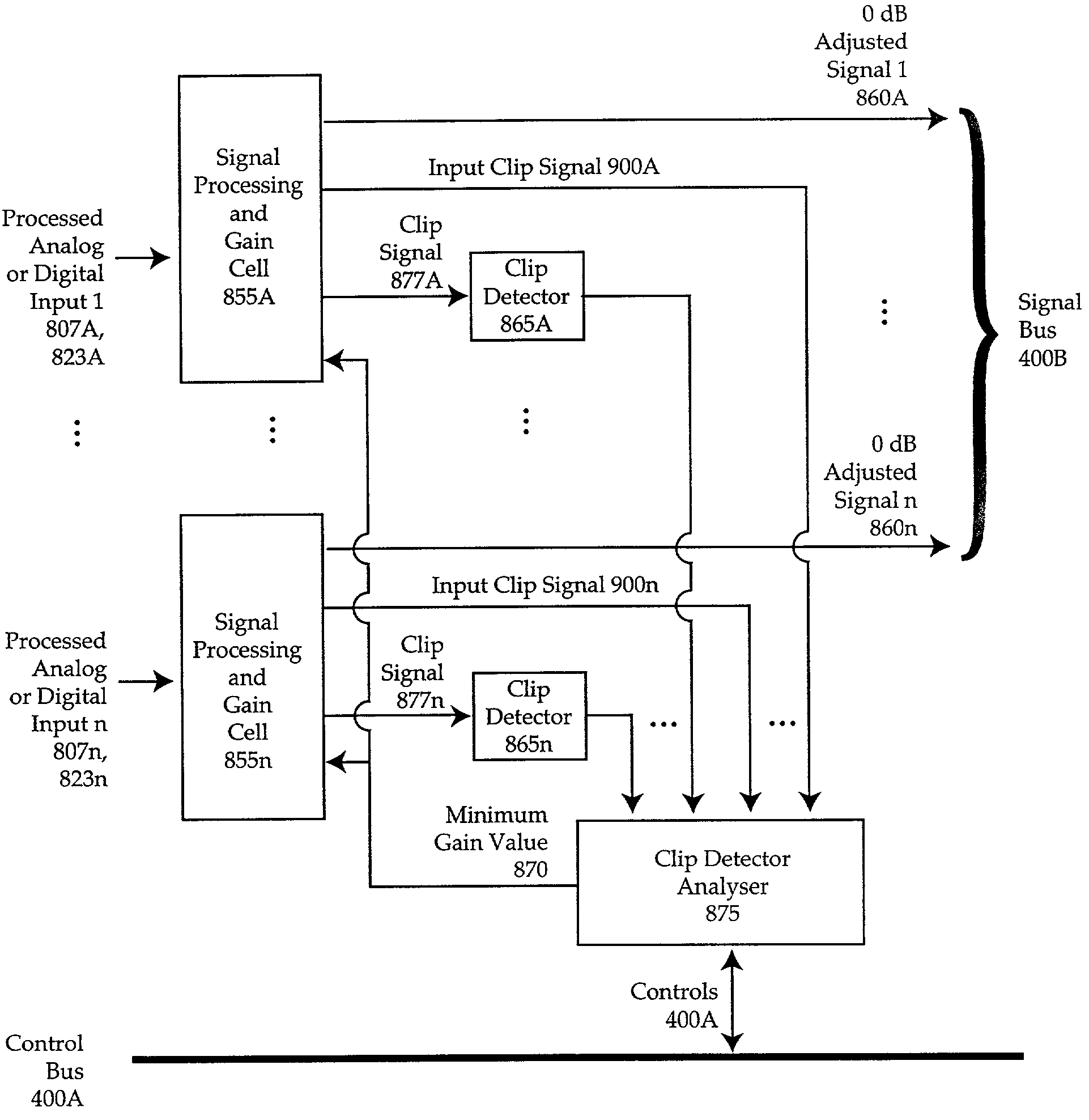
A method of matching input amplitudes in a system wherein one or more of a plurality of inputs may be selected, with each input capable of having different characteristics, involving selecting an input signal and mapping the input signal to a predetermined signal amplitude through the use of level matching logic. The level matching logic may include a gain cell for increasing or decreasing the amplitude of the input signal.
Owner:BIZJAK KARL M
Merged MOS-bipolar capacitor memory cell
A high density vertical merged MOS bipolar capacitor gain cell is realized for DRAM operation. The gain cell includes a vertical MOS transistor having a source region, a drain region, and a floating body region therebetween. The gain cell includes a vertical bi-polar transistor having an emitter region, a base region and a collector region. The base region for the vertical bi-polar transistor serves as the source region for the vertical MOS transistor. A gate opposes the floating body region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide on a first side of the vertical MOS transistor. A floating body back gate opposes the floating body region on a second side of the vertical transistor. The base region for the vertical bi-polar transistor is coupled to a write data word line.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20060227648A1Increase the number ofArea of memory cell is increasedTransistorSolid-state devicesWrite bitComputer science
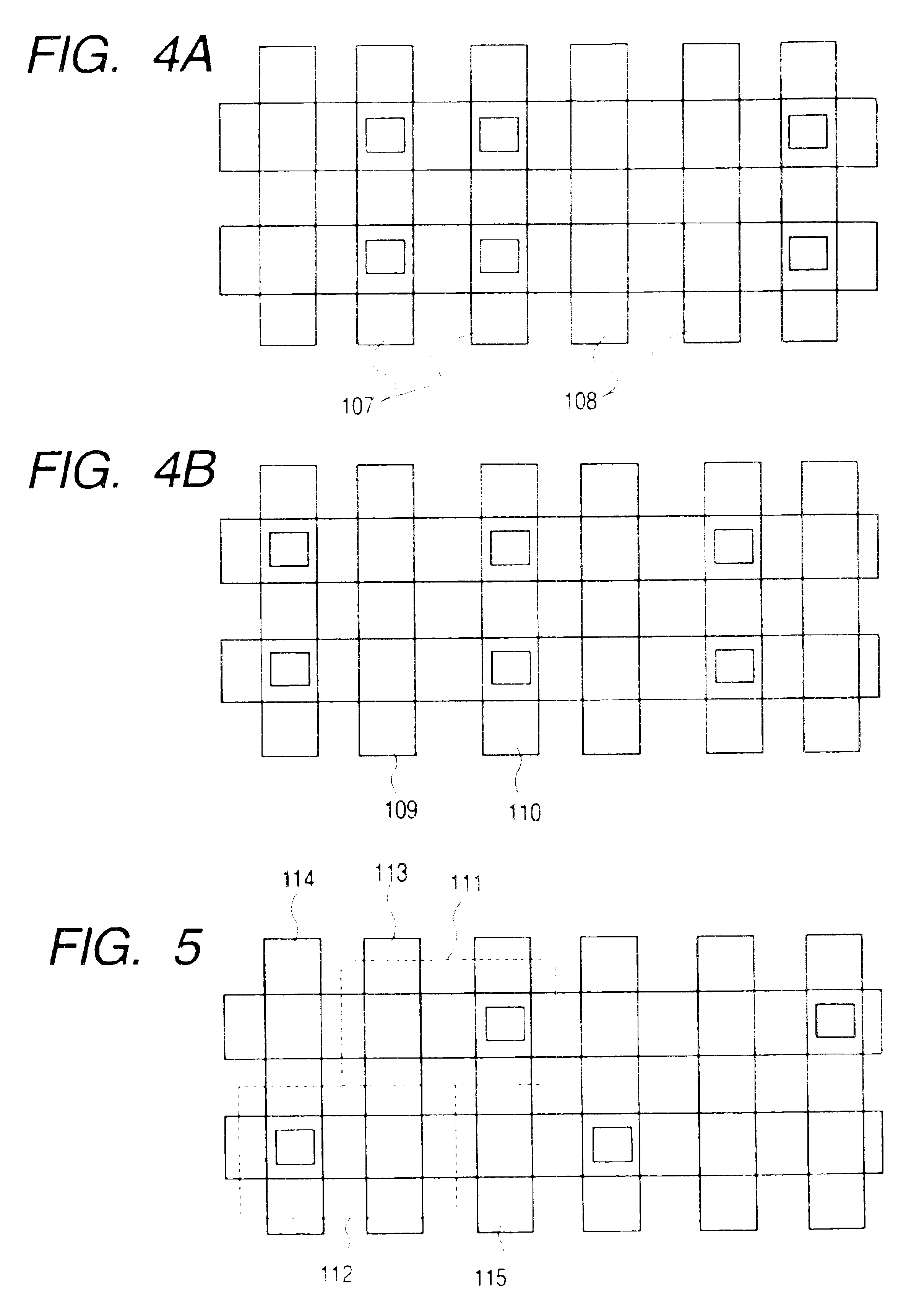
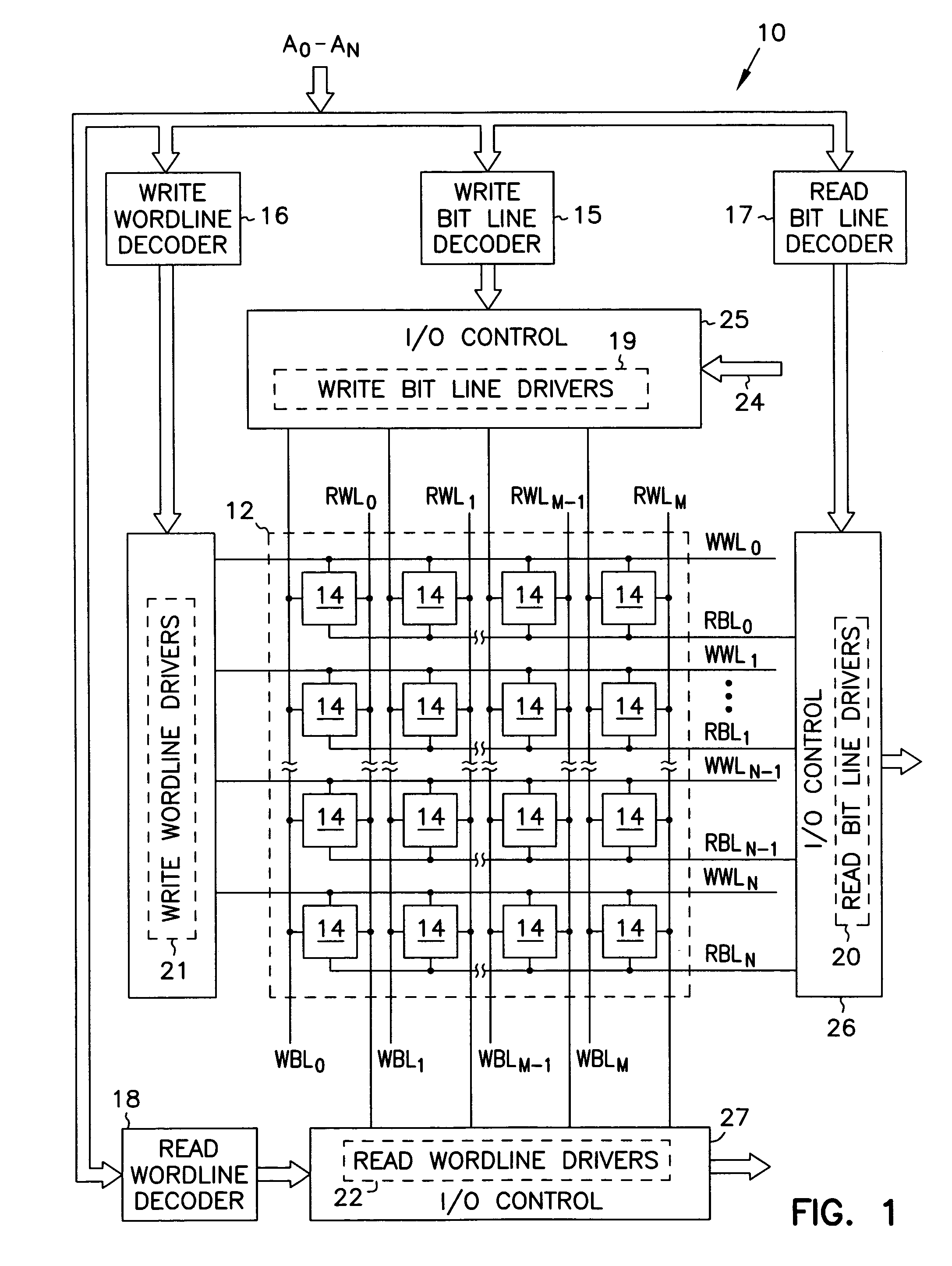
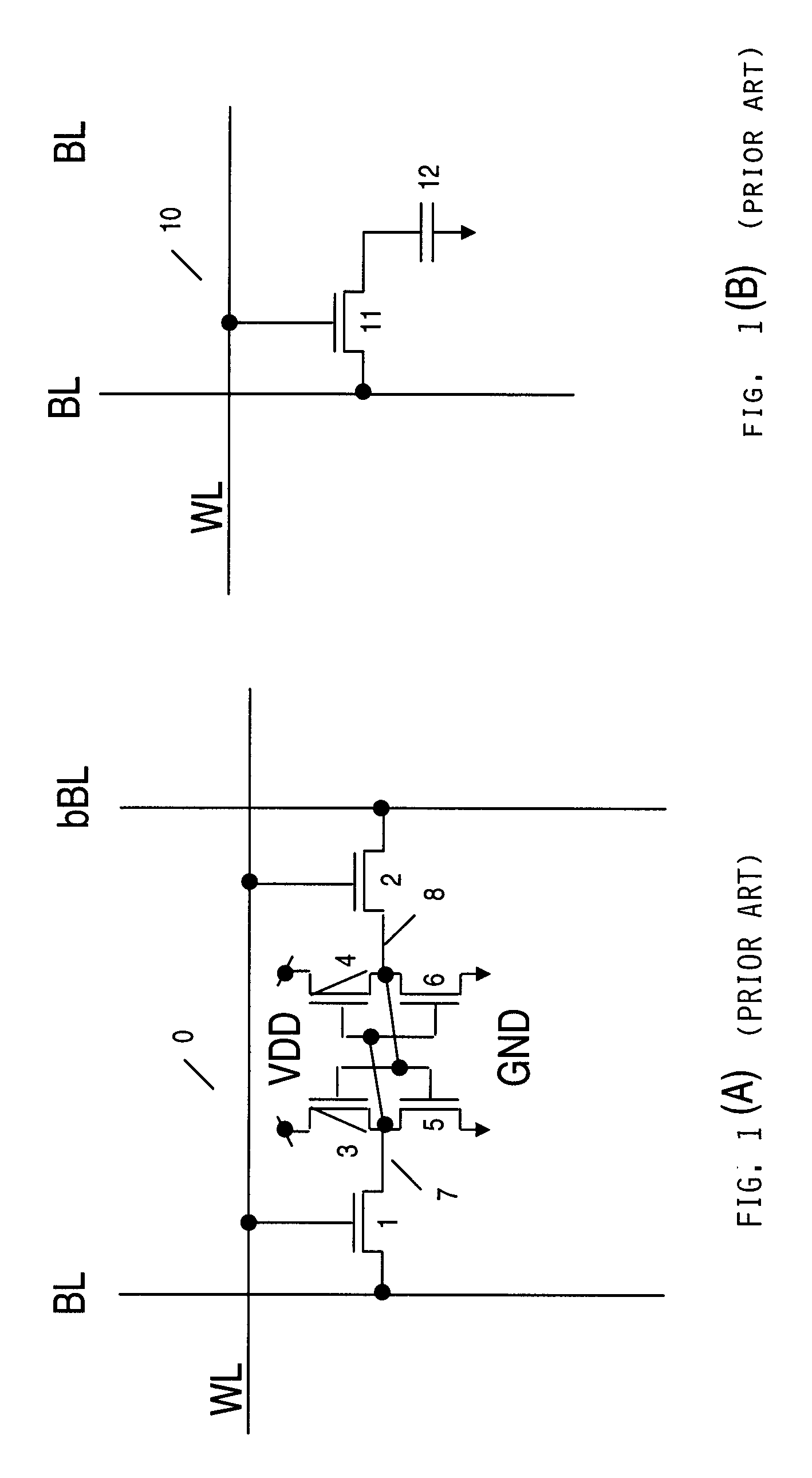
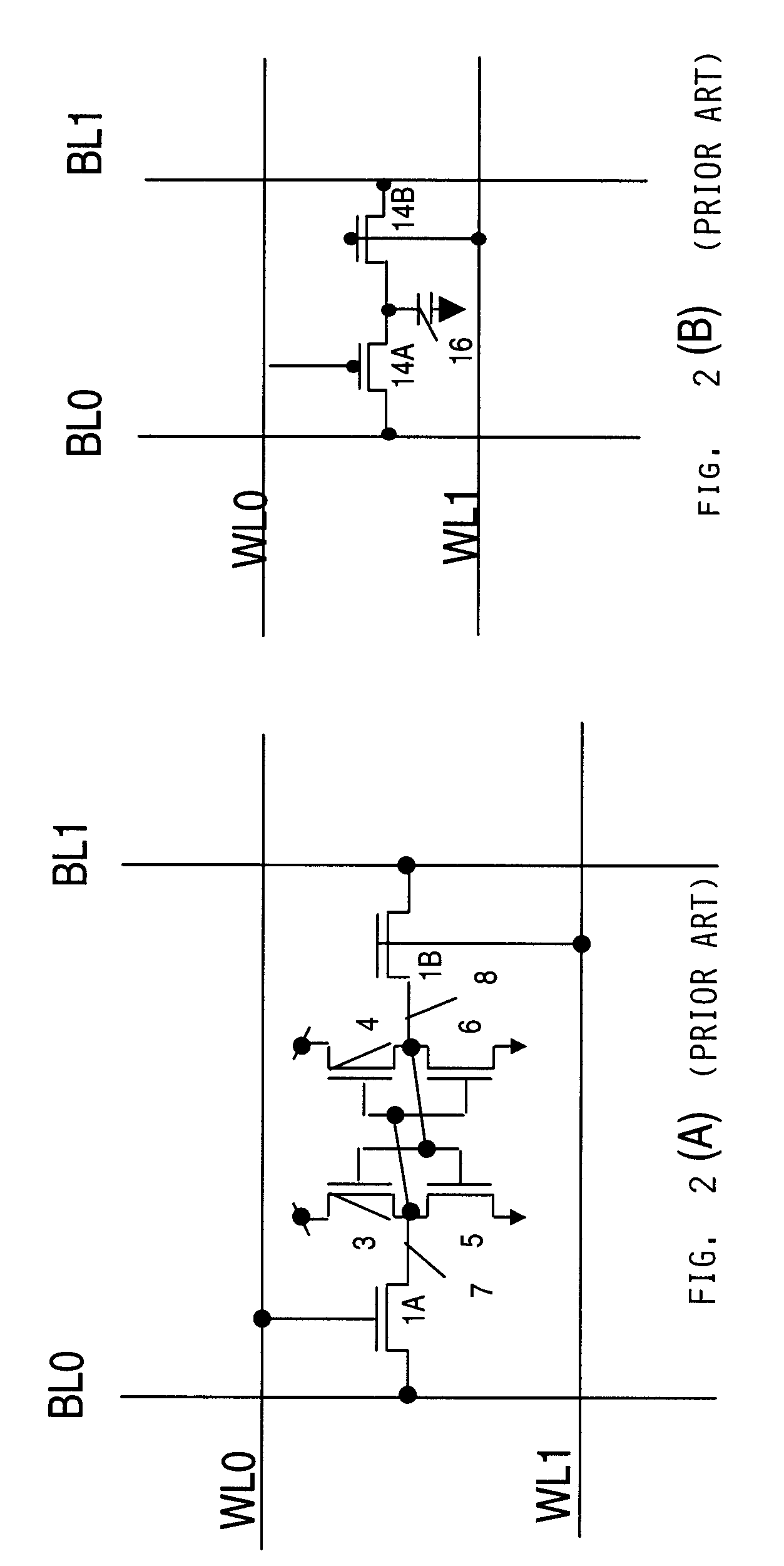
In a two-transistor gain cell structure, a semiconductor memory device capable of stable reading without malfunction and having small-area memory cells is provided. In a two-transistor gain cell memory having a write transistor and a read transistor, a write word line, a read word line, a write bit line, and a read bit line are separately provided, and voltages to be applied are independently set. Furthermore, a memory cell is connected to the same read word line and write bit line as those of an adjacent memory cell.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor memories
InactiveUS6949782B2Reduce areaReduce area requirementsTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh densityComputer science
A high integration dynamic random access memory is provided by this invention. Furthermore, a write method is provided such that the cell size of two-and three-transistor gain cell memories is reduced. A dynamic memory incorporating a thin-channel transistor as the write element such that long data storage retention is achieved in the memory devices of this invention. A dynamic memory cell having low operating power and high density is also realized by this invention.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dual gated finfet gain cell
A memory gain cell for a memory circuit, a memory circuit formed from multiple memory gain cells, and methods of fabricating such memory gain cells and memory circuits. The memory gain cell includes a storage device capable of holding a stored electrical charge, a write device, and a read device. The read device includes a fin of semiconducting material, electrically-isolated first and second gate electrodes flanking the fin, and a source and drain formed in the fin adjacent to the first and the second gate electrodes. The first gate electrode is electrically coupled with the storage device. The first and second gate electrodes are operative for gating a region of the fin defined between the source and the drain to thereby regulate a current flowing from the source to the drain. When gated, the magnitude of the current is dependent upon the electrical charge stored by the storage device.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
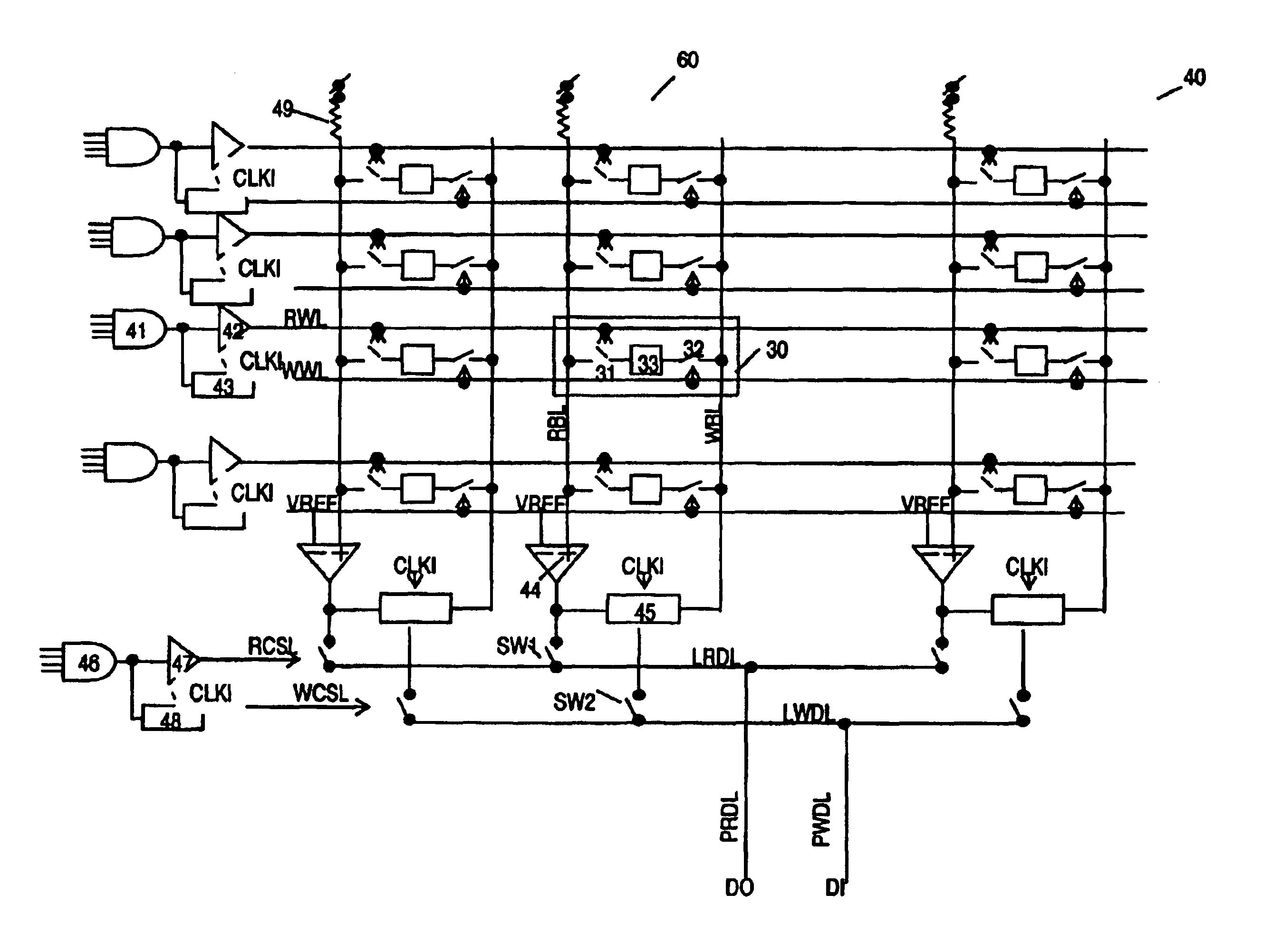
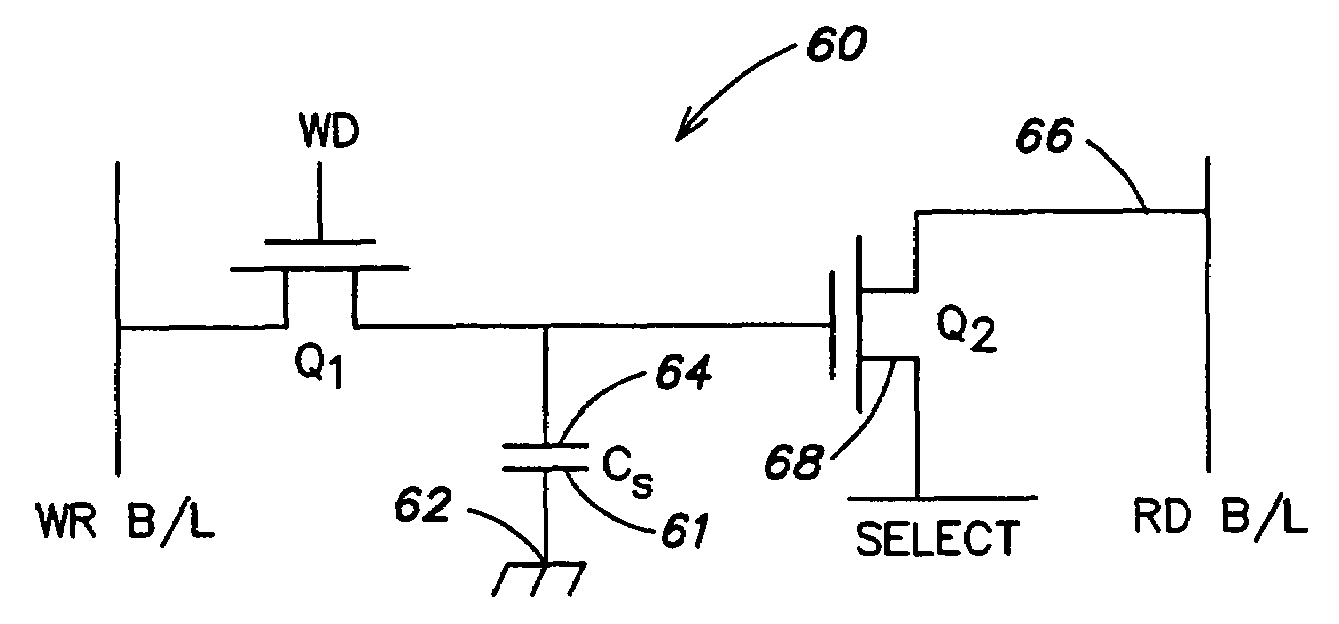
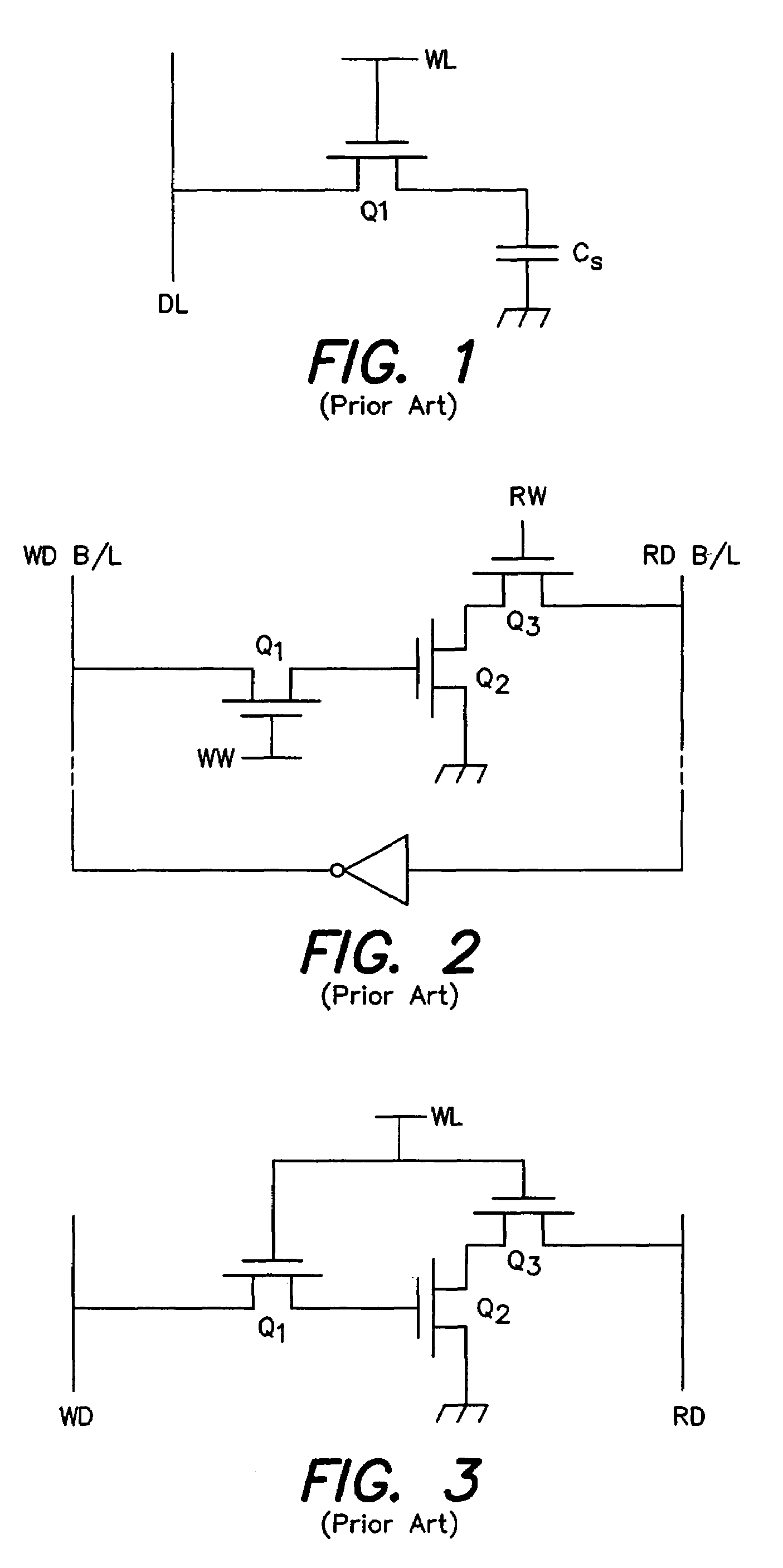
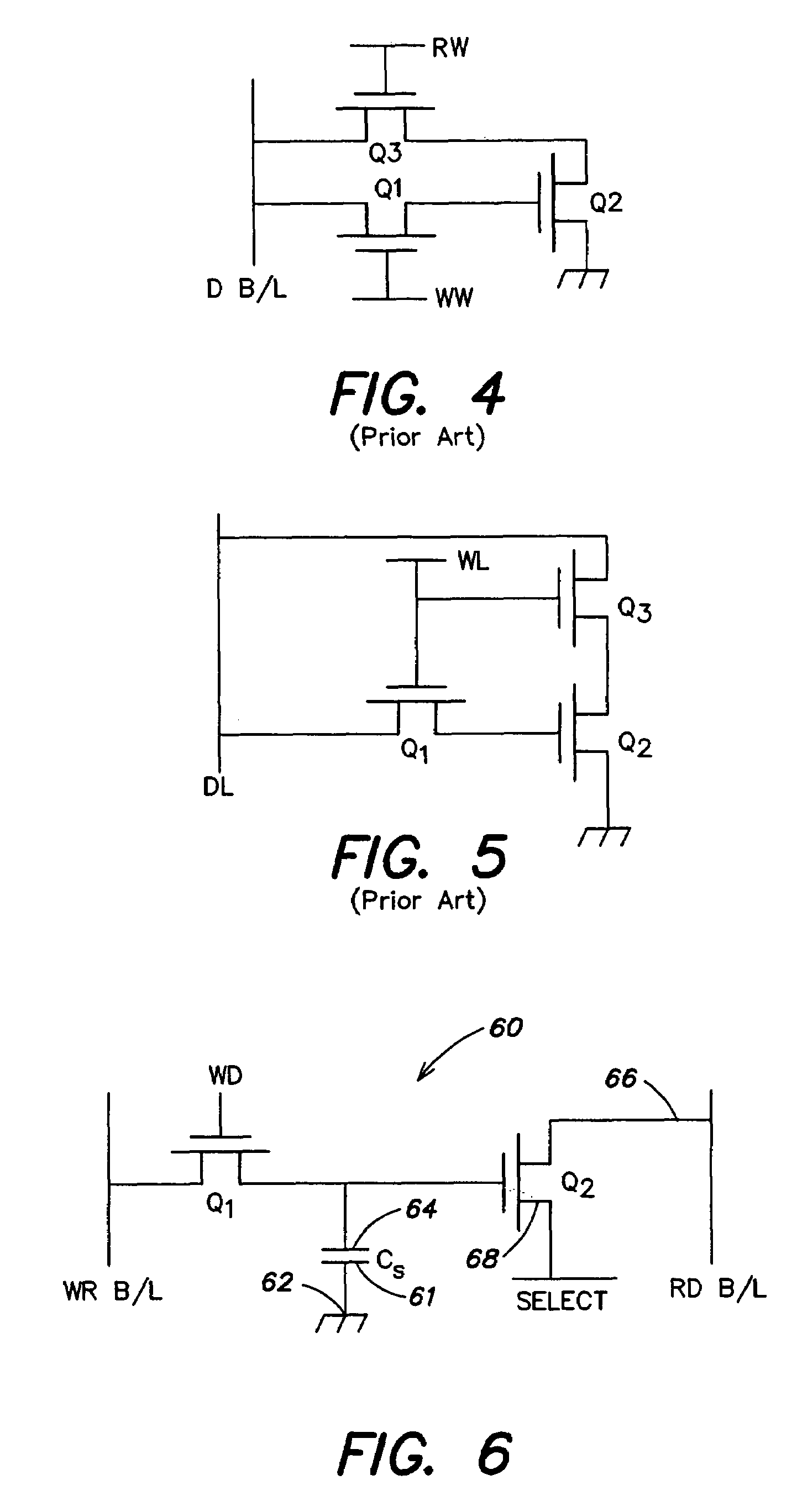
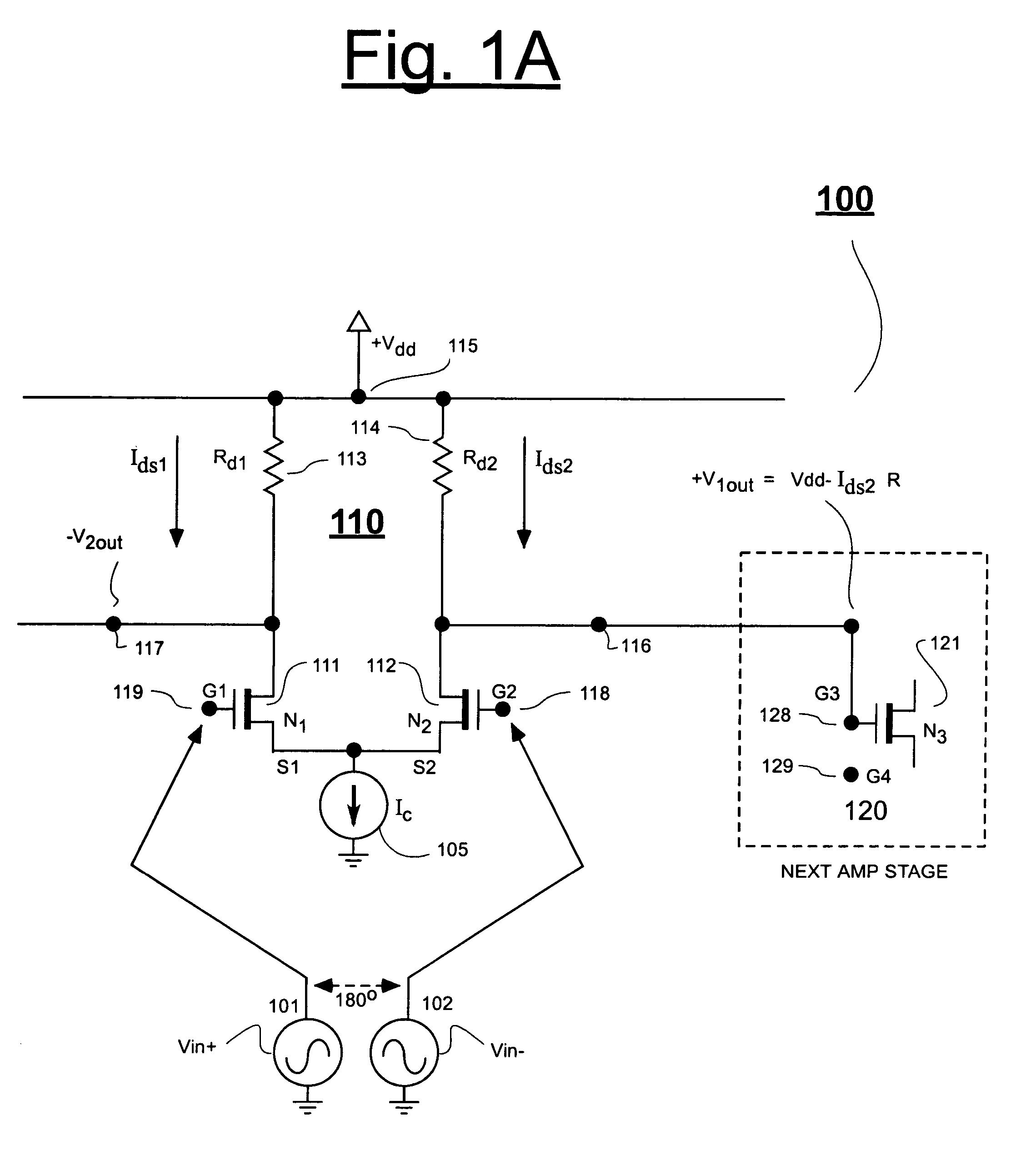
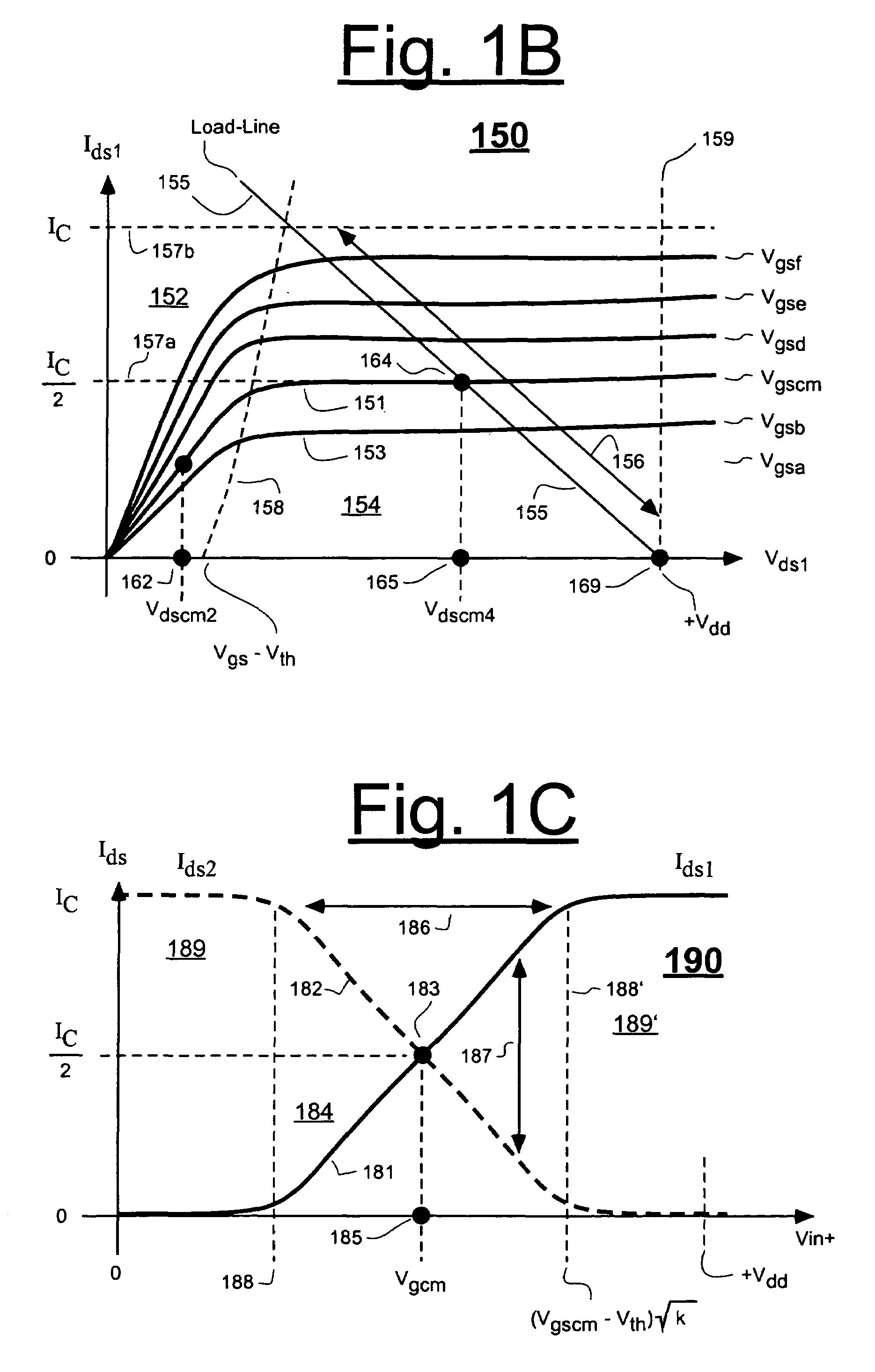
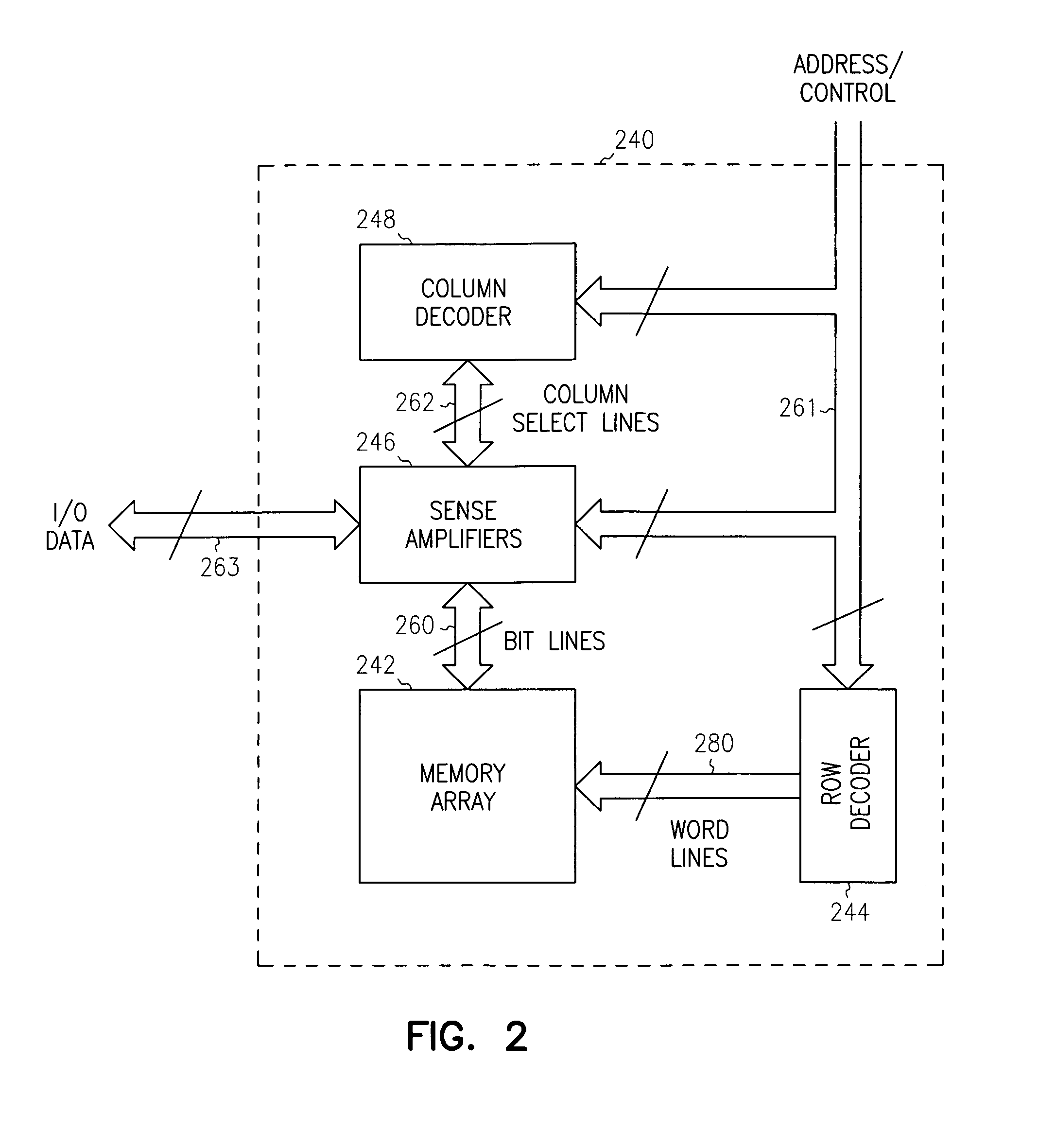
High performance gain cell architecture
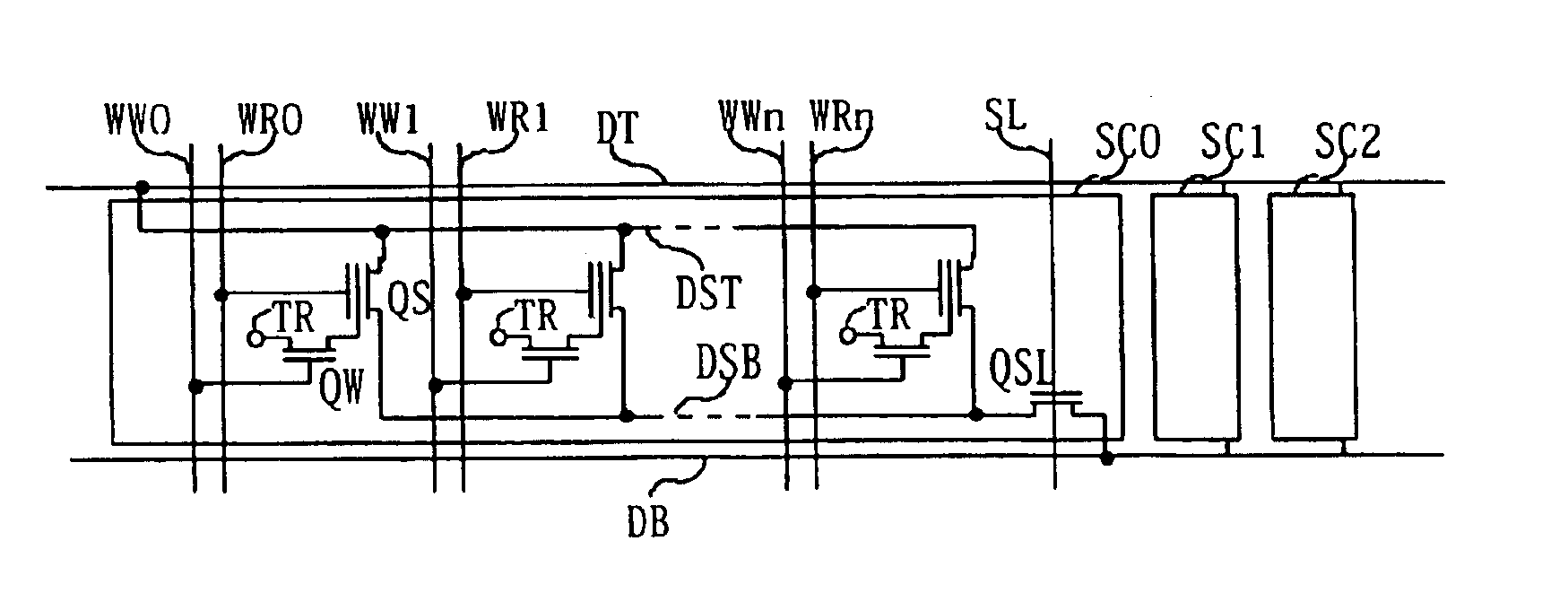
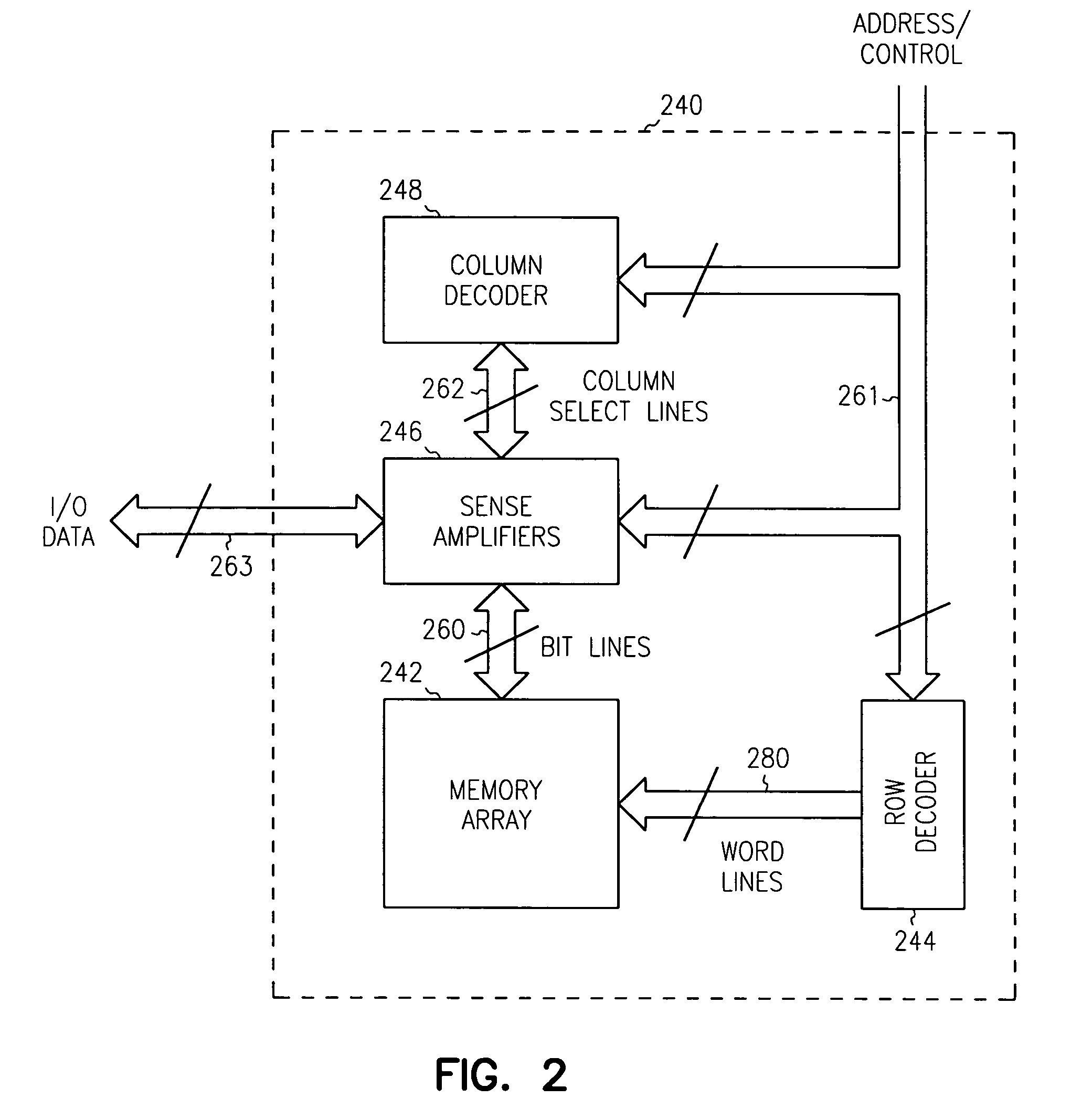
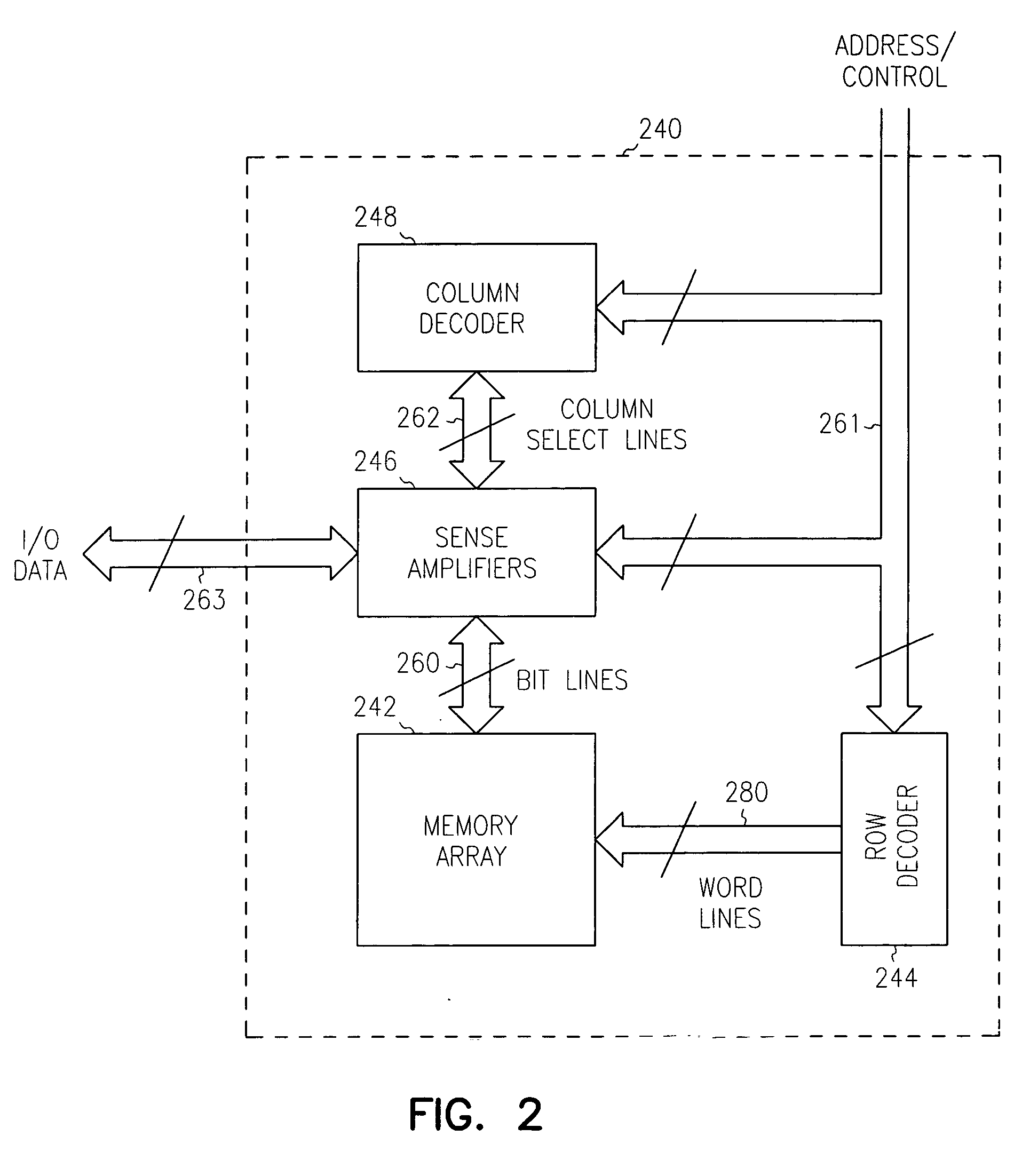
A memory architecture that utilizes single-ended dual-port destructive write memory cells and a local write-back buffer is described. Each cell has separate read and write ports that make it possible to read-out data from cells on one wordline in the array, and subsequently write-back to those cells while simultaneously reading-out the cell on another wordline in the array. By implementing an array of sense amplifiers such that one amplifier is coupled to each read bitline, and a latch receiving the result of the sensed data and delivering this data to the write data lines, it is possible to ‘pipeline’ the read-out and write-back phases of the read cycle. This allows for a write-back phase from one cycle to occur simultaneously with the read-out phase of another cycle. By extending the operation of the latch to accept data either from the sense amplifier, or from the memory data inputs, modified by the column address and masking bits, it is also possible to pipeline the read-out and the modify-write-back phases of a write cycle, allowing them to occur simultaneously. The architecture preferably employs a nondestructive read memory cell such as 2T or 3T gain cells, achieving an SRAM-like cycle and access times with a smaller and more SER immune memory cell.
Owner:IBM CORP
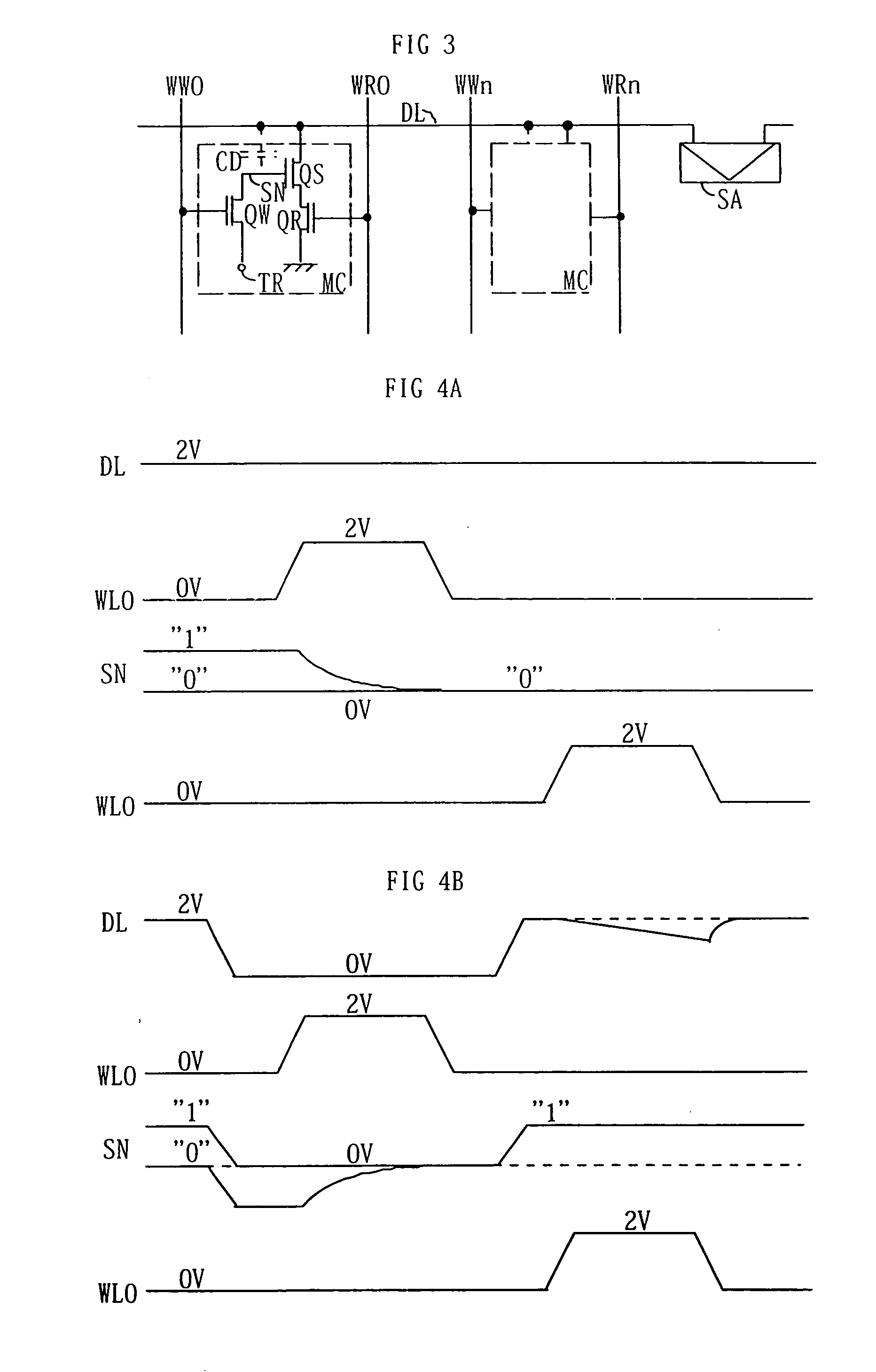
6F2 3-Transistor DRAM gain cell
A high density vertical three transistor memory cell is provided. The high density vertical three transistor memory cell is formed in a vertical pillar. The vertical pillar includes a first vertical transfer device having a source region, a drain region, and a body region therebetween on a first side of the vertical pillar. The vertical pillar also includes a second vertical transfer device having a source region, a drain region, and a body region therebetween on a second side of the vertical pillar. A write data wordline opposes the first vertical transfer device. A read data wordline opposes the second vertical transfer device. A storage capacitor is coupled to the drain region of the first vertical transfer device. The storage capacitor further serves as a gate for a third transistor.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Vertical gain cell and array for a dynamic random access memory and method for forming the same
InactiveUS7049196B2Increase cell densityGreat data retention timeTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETSemiconductor materials
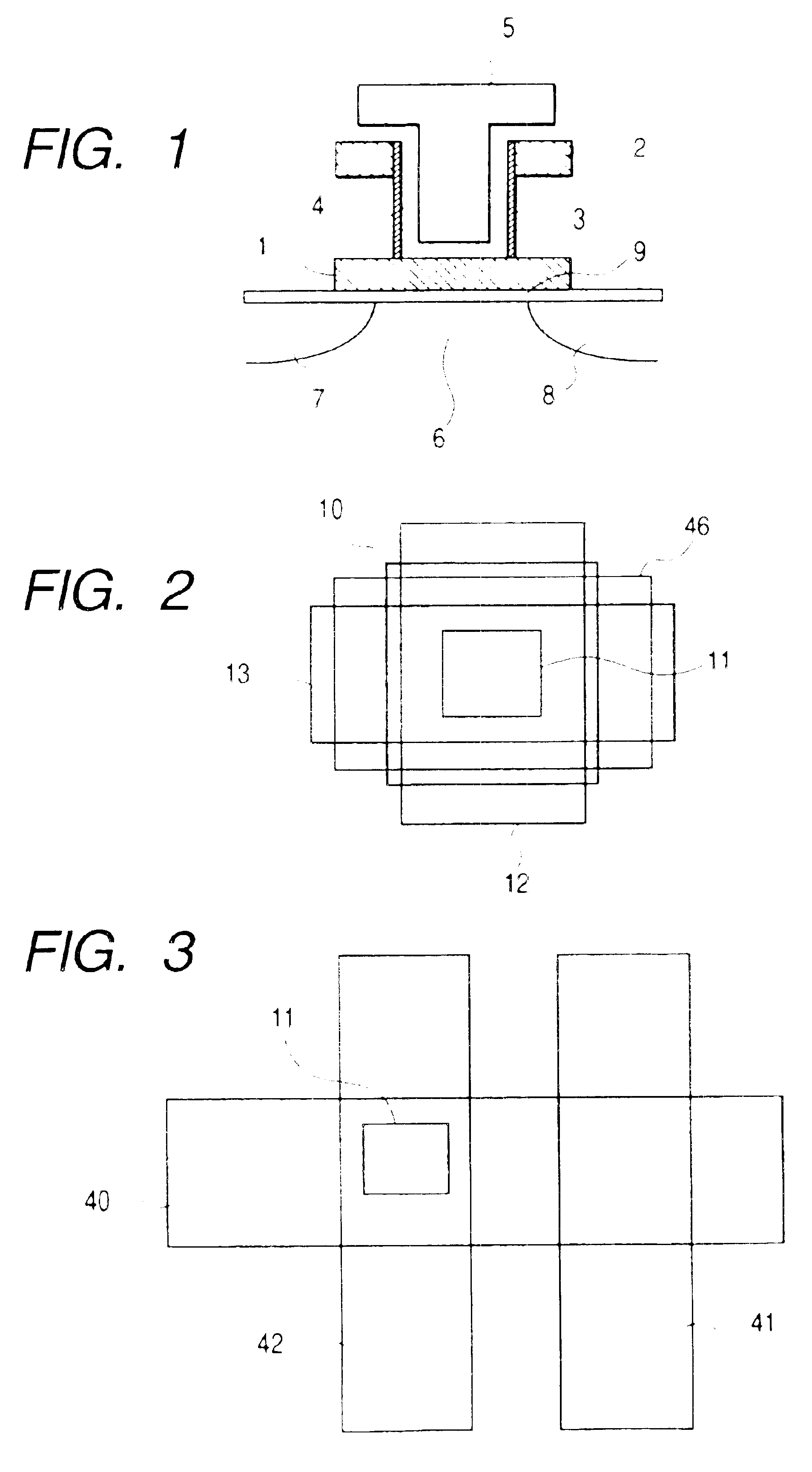
A vertical gain memory cell including an n-channel metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) and p-channel junction field-effect transistor (JFET) transistors formed in a vertical pillar of semiconductor material is provided. The body portion of the p-channel transistor is coupled to a second source / drain region of the MOSFET which serves as the gate for the JFET. The second source / drain region of the MOSFET is additionally coupled to a charge storage node. Together the second source / drain region and charge storage node provide a bias to the body of the JFET that varies as a function of the data stored by the memory cell. A non destructive read operation is achieved. The stored charge is sensed indirectly in that the stored charge modulates the conductivity of the JFET so that the JFET has a first turn-on threshold for a stored logic “1” condition and a second turn-on threshold for a stored logic “0” condition. The charge storage node is a plate capacitor which surrounds the second source / drain region of the MOSFET. The vertical gain cell is fabricated so that the write word line, read bit line, read word line and capacitor are buried beneath the silicon surface. As a result the cell can be fabricated in an area as small as four (4) lithographic feature squares.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Single transistor vertical memory gain cell
A high density vertical single transistor gain cell is realized for DRAM operation. The gain cell includes a vertical transistor having a source region, a drain region, and a floating body region therebetween. A gate opposes the floating body region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide on a first side of the vertical transistor. A floating body back gate opposes the floating body region on a second side of the vertical transistor and is separated therefrom by a dielectric to form a body capacitor.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
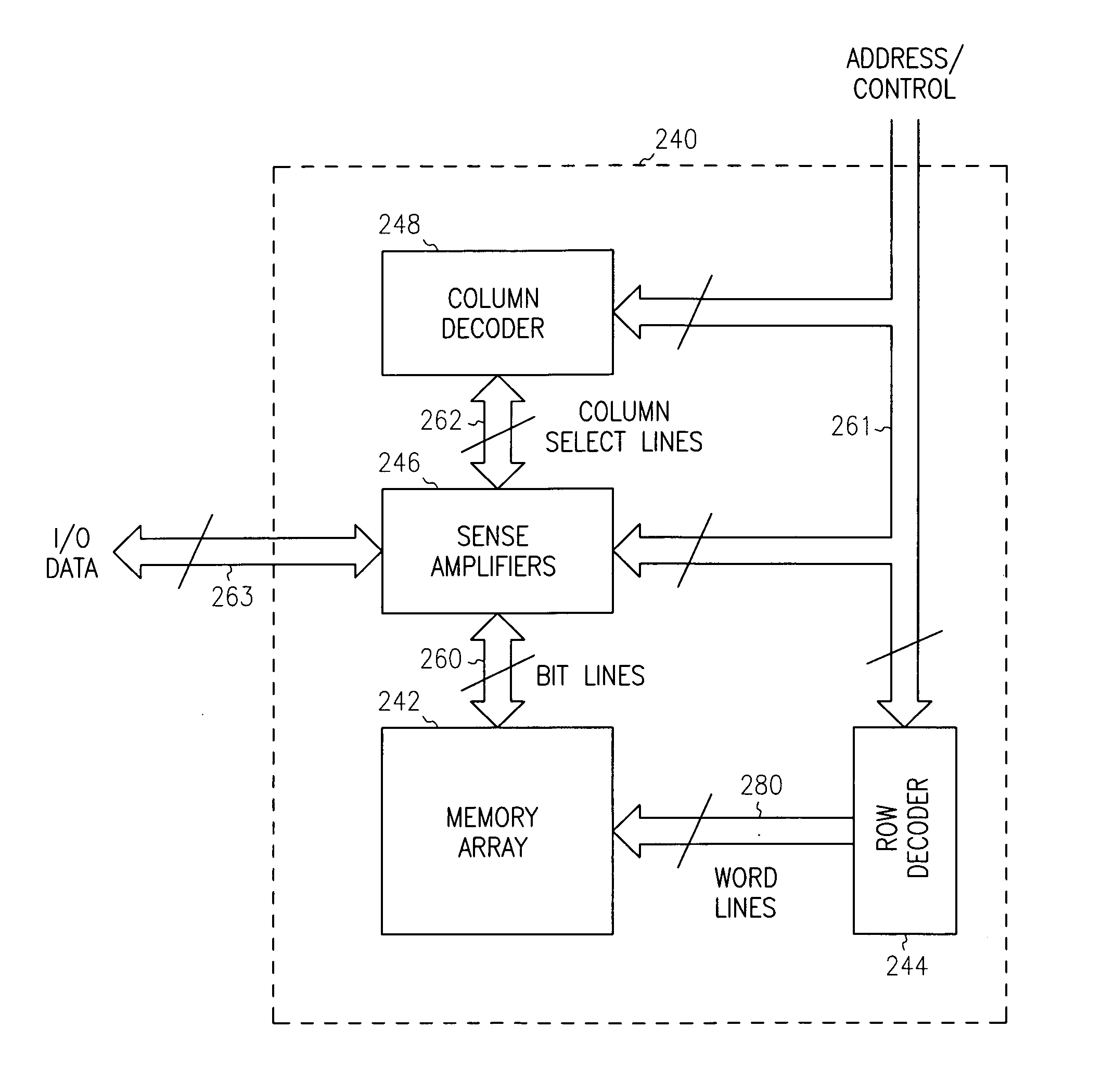
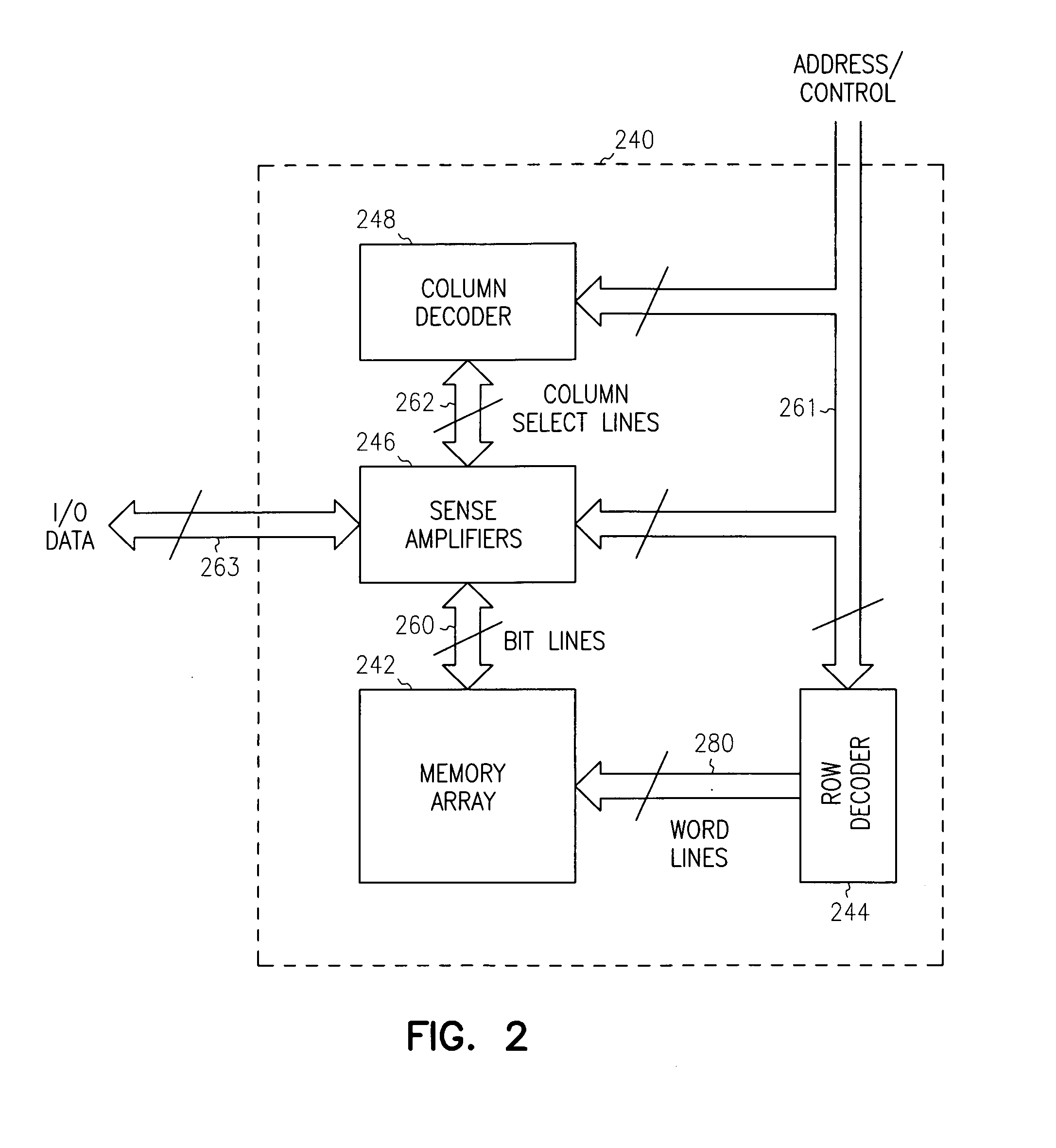
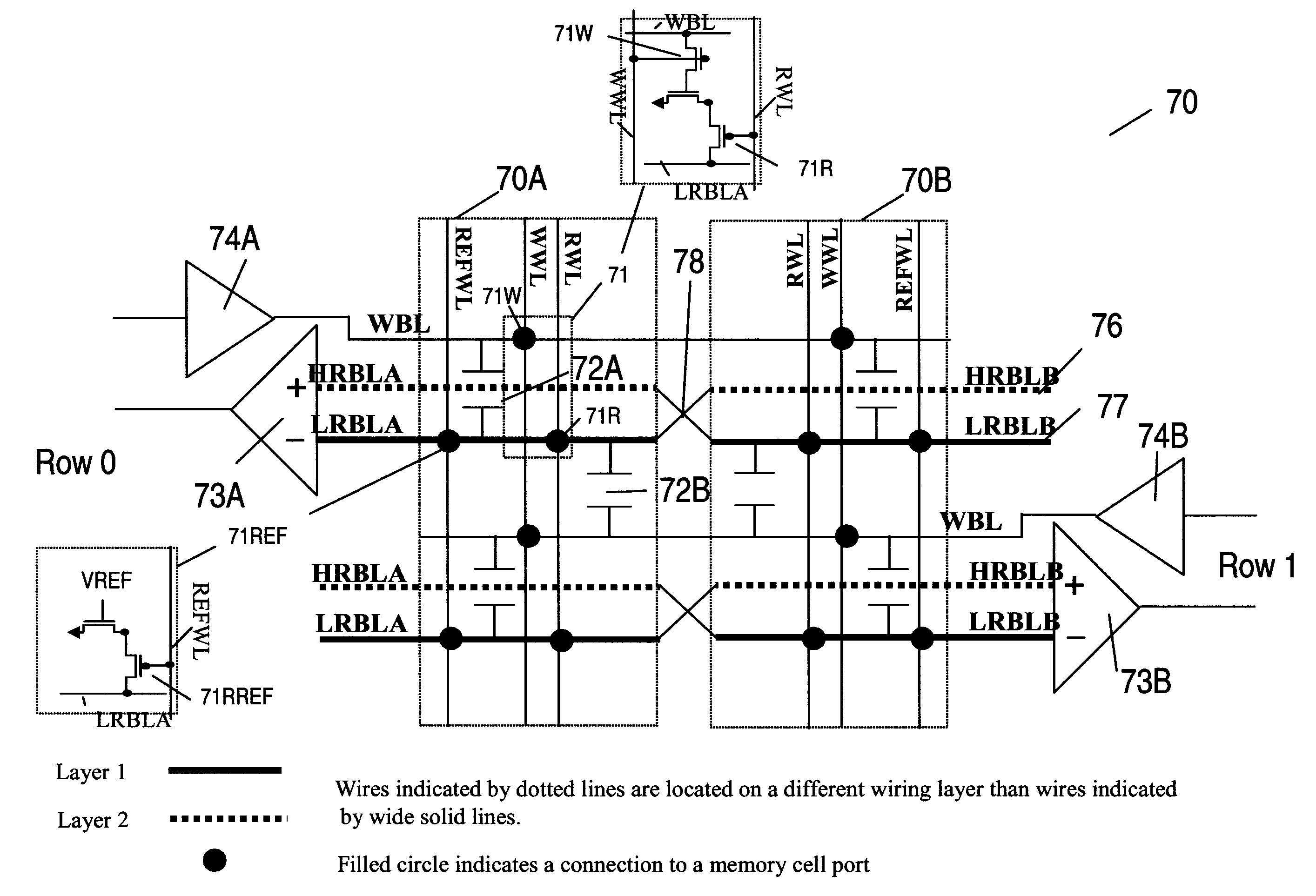
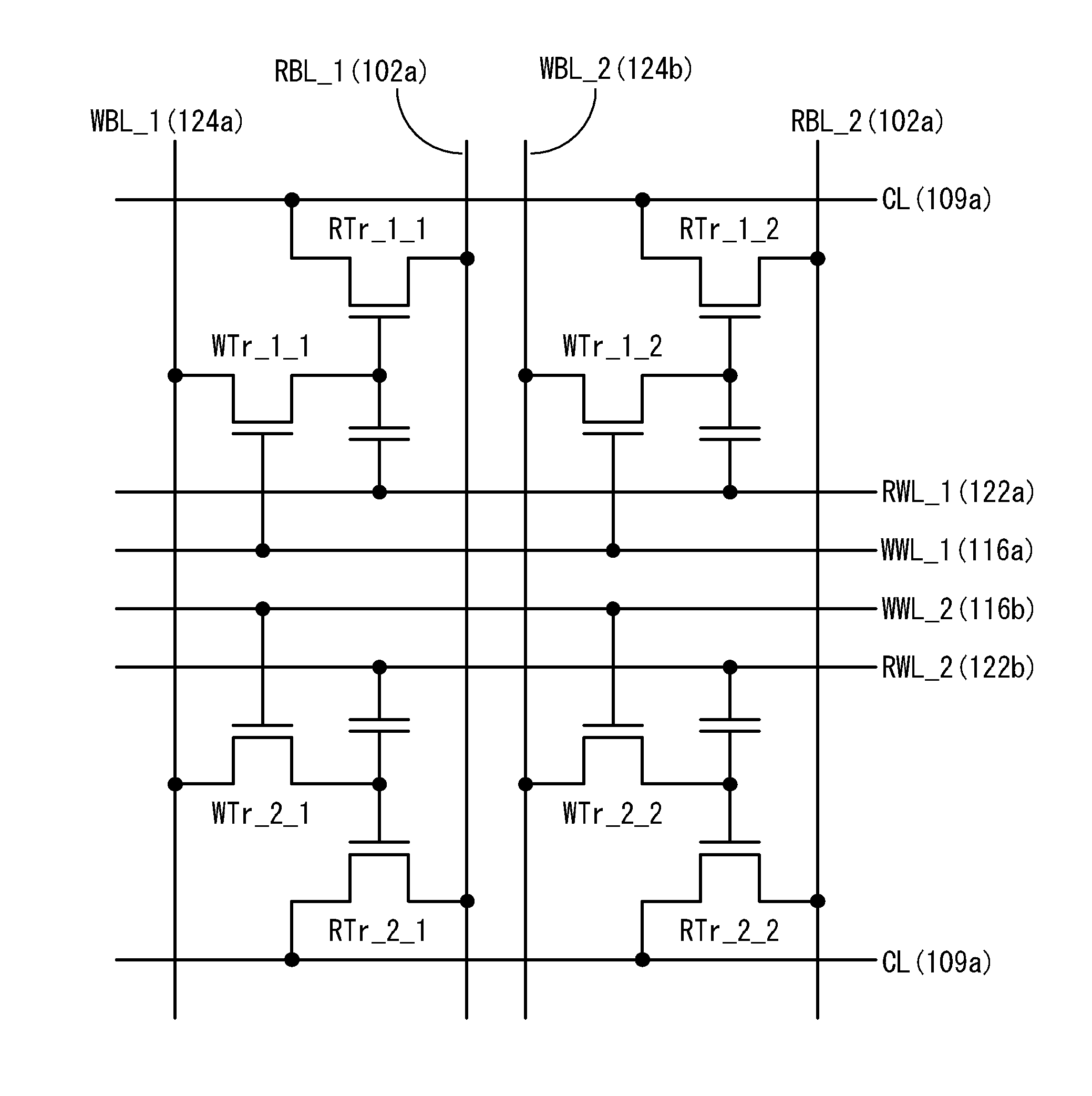
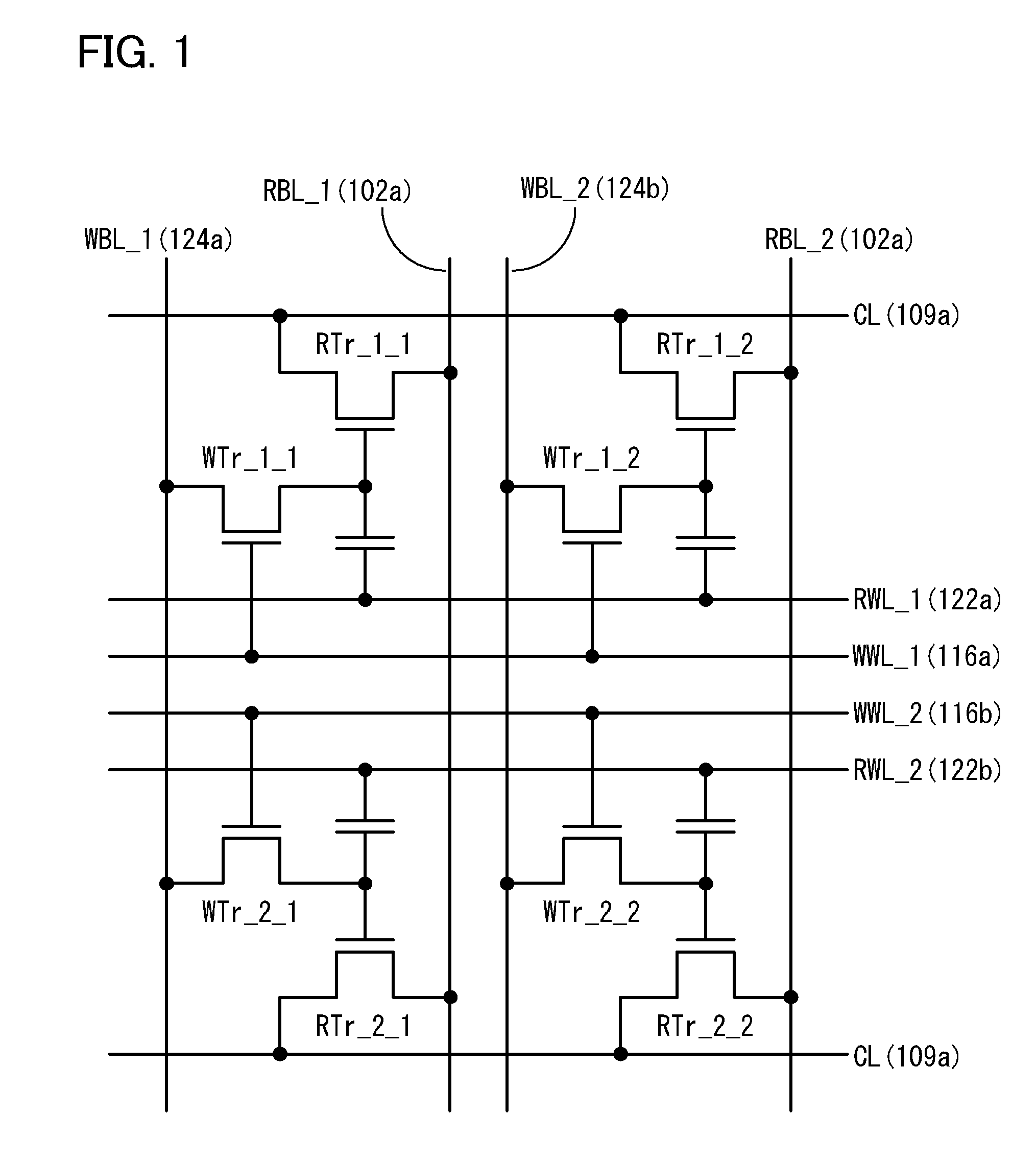
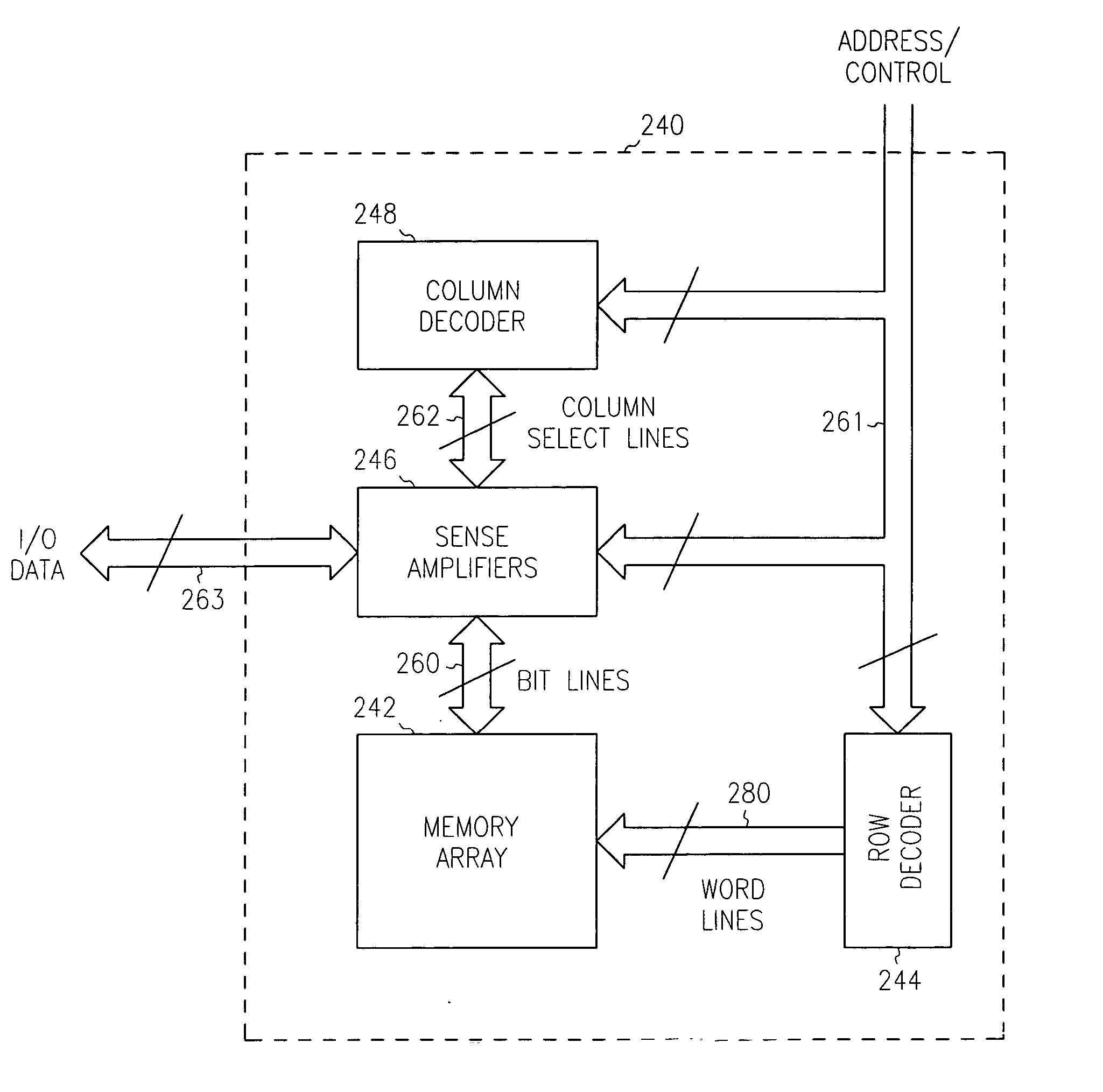
Multi-port memory architecture
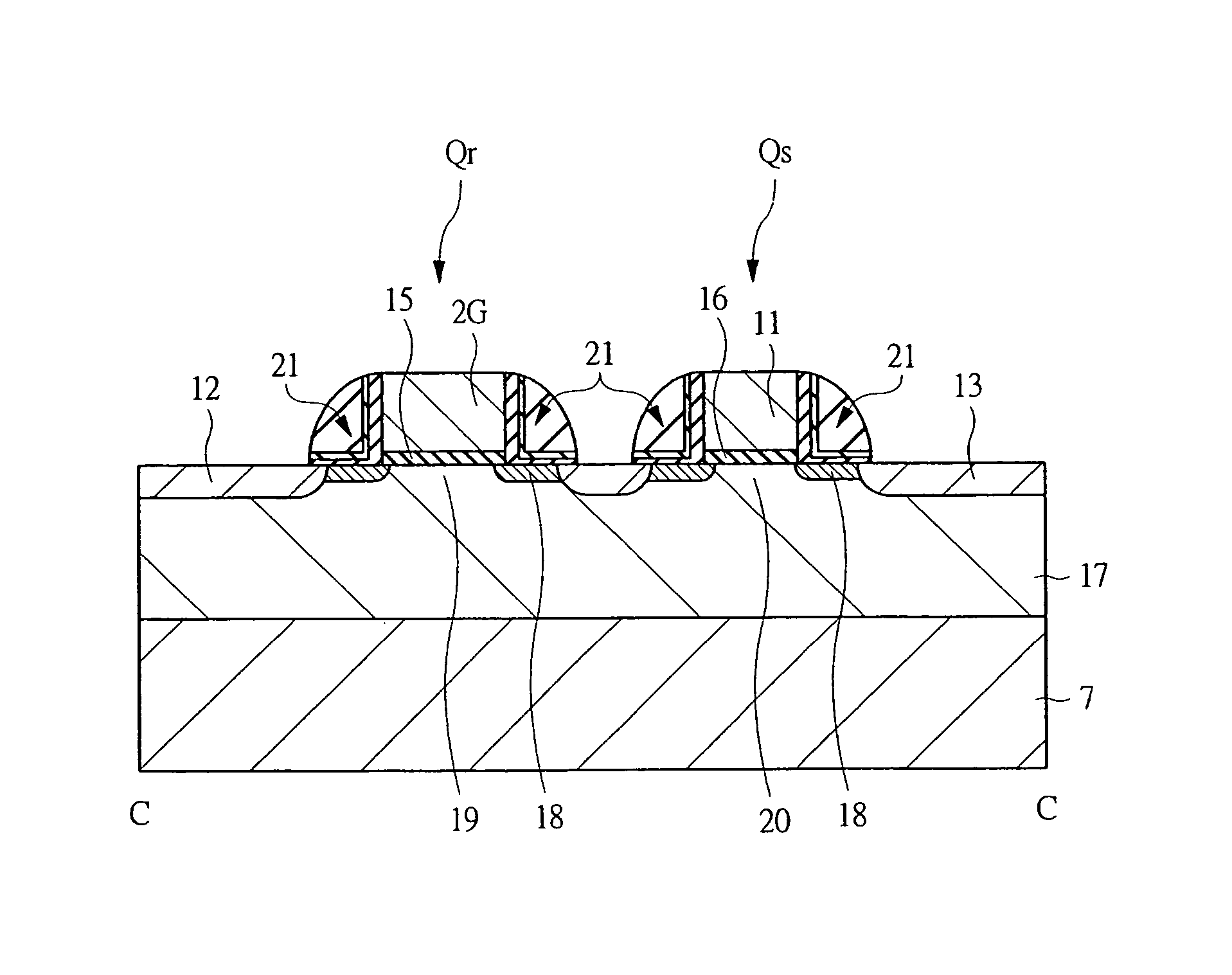
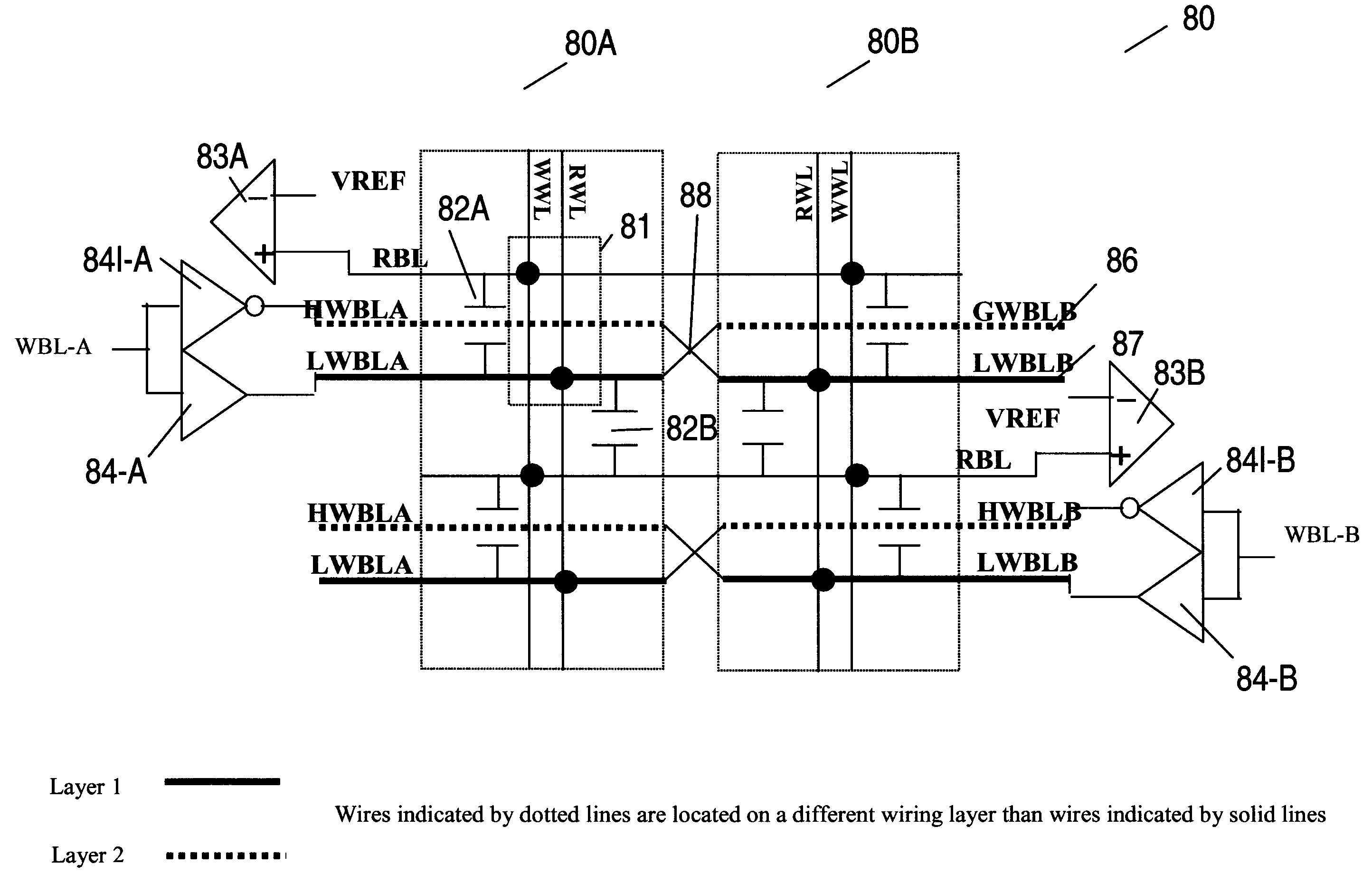
A multi-port memory architecture utilizing an open bitline configuration for the read bitline is described. The memory is sub-divided into two arrays (A and B) consisting of memory gain cells arranged in a matrix formation, the cells having two general ports or separate read and write ports to enable simultaneous a read and write operation. Each memory array includes a reference wordline coupled to reference cells. When the reference cell is accessed, the read bitline (RBL) discharges to a level at half the value taken by a cell storing a 0 or 1. Each pair of RBLB in the same column of the two arrays is coupled to a differential sense amplifier, and each write bitline (WBL) in the two arrays is linked to write drivers WBLs in the two arrays are driven to the same voltage and at the same slew rate. The WBL swing in each array creates coupling noise by the bitline-to-bitline capacitors. For a given sense amplifier and its associated RBLs, the coupling creates an identical coupling noise on RBLA and RBLB that are positioned in the two arrays A and B. This common mode noise is rejected by the differential sense amplifier. Thus, a read sense amplifier can accurately discriminate between the signal by activating the cell by way of RWL, and the reference cell by way of REFWL.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Long retention time single transistor vertical memory gain cell
ActiveUS7151024B1High band gap energyAvoid excessive leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh cellRetention time
A single transistor vertical memory gain cell with long data retention times. The memory cell is formed from a silicon carbide substrate to take advantage of the higher band gap energy of silicon carbide as compared to silicon. The silicon carbide provides much lower thermally dependent leakage currents which enables significantly longer refresh intervals. In certain applications, the cell is effectively non-volatile provided appropriate gate bias is maintained. N-type source and drain regions are provided along with a pillar vertically extending from a substrate, which are both p-type doped. A floating body region is defined in the pillar which serves as the body of an access transistor as well as a body storage capacitor. The cell provides high volumetric efficiency with corresponding high cell density as well as relatively fast read times.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
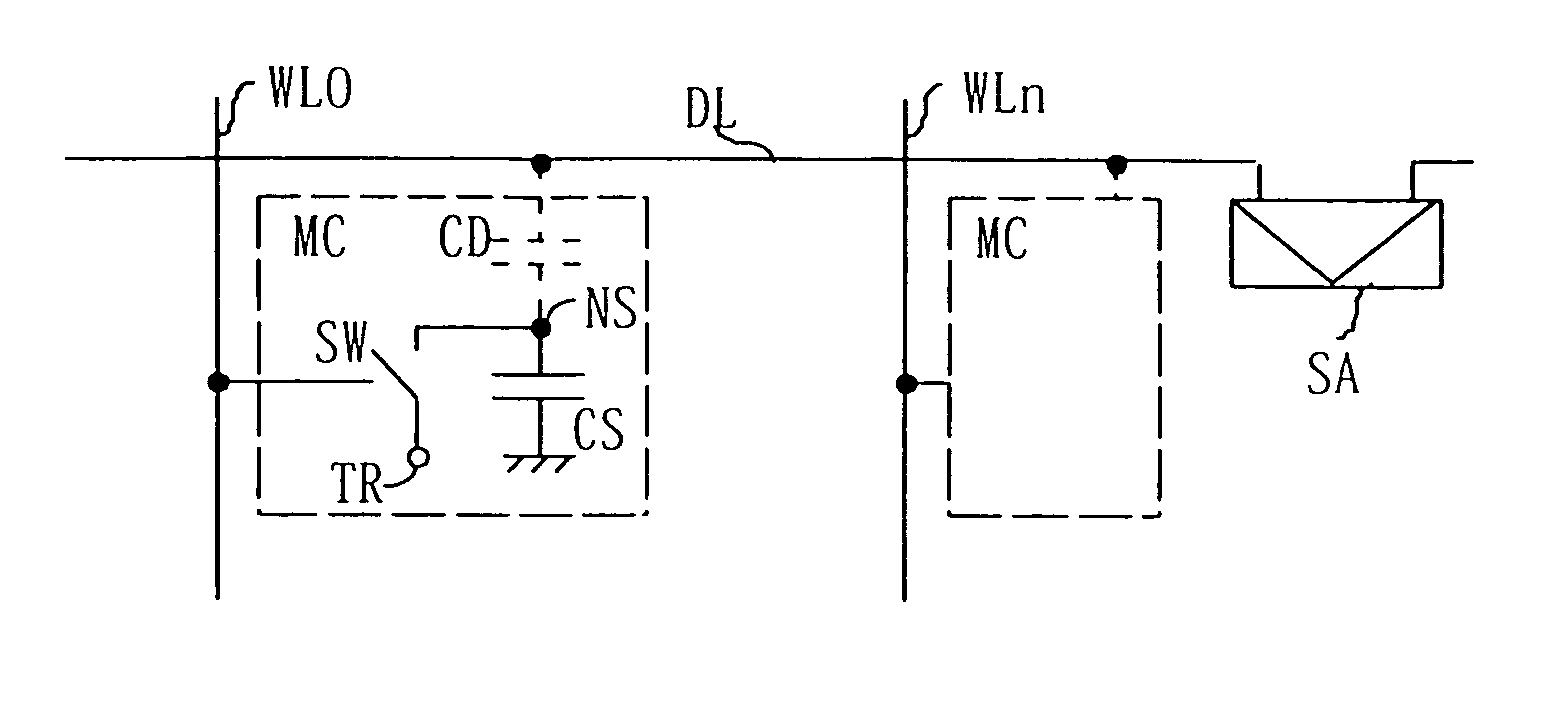
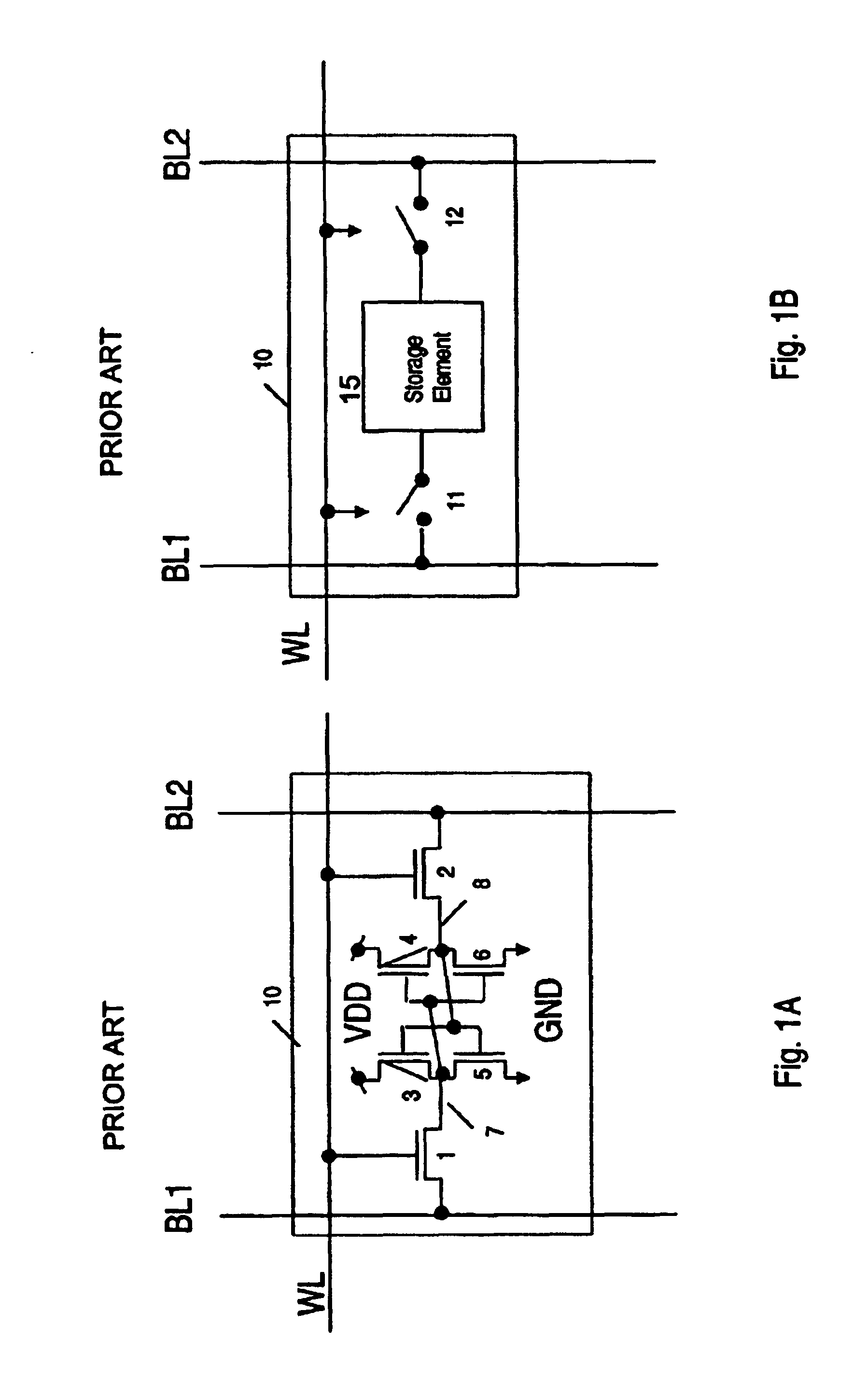
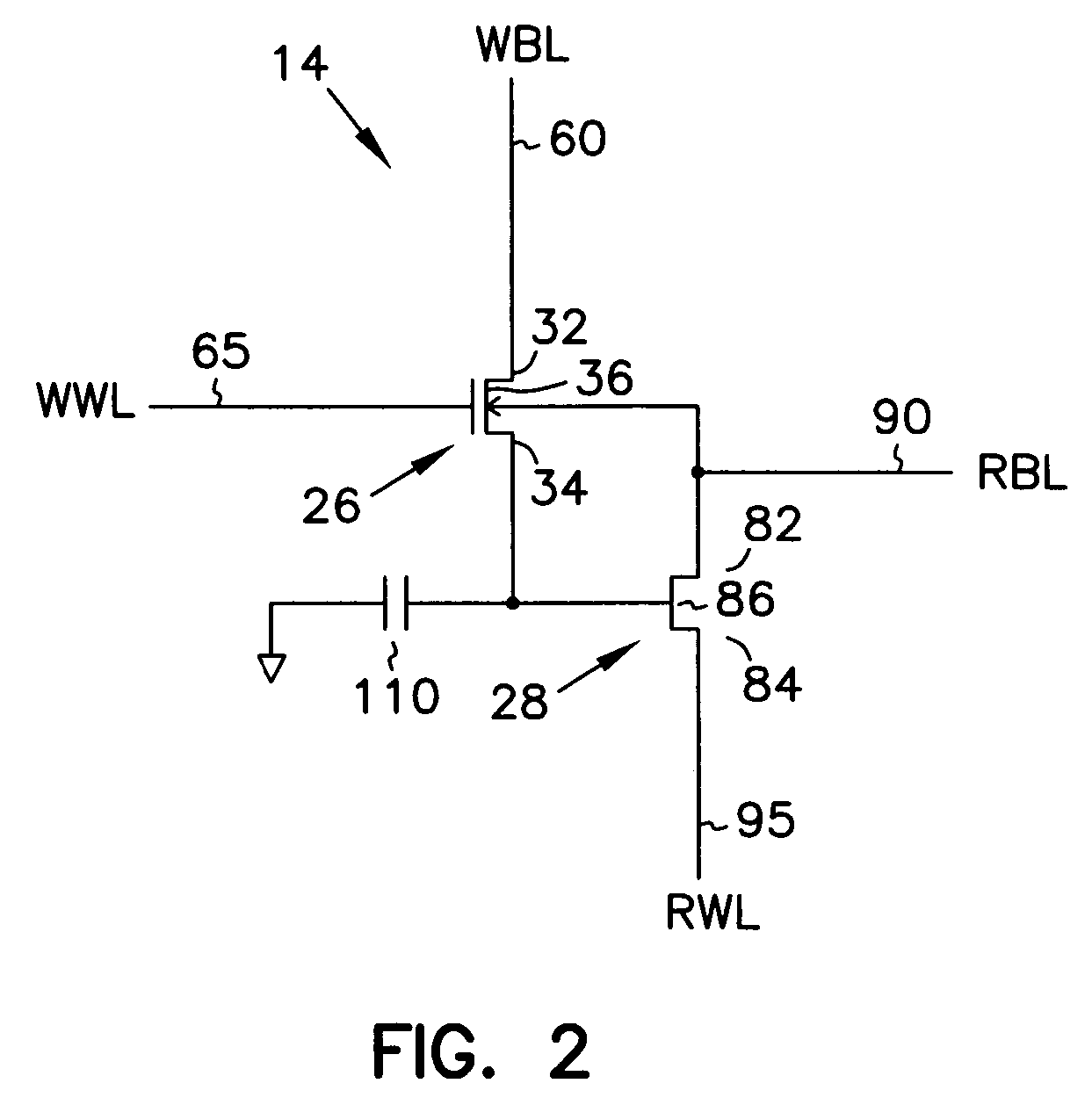
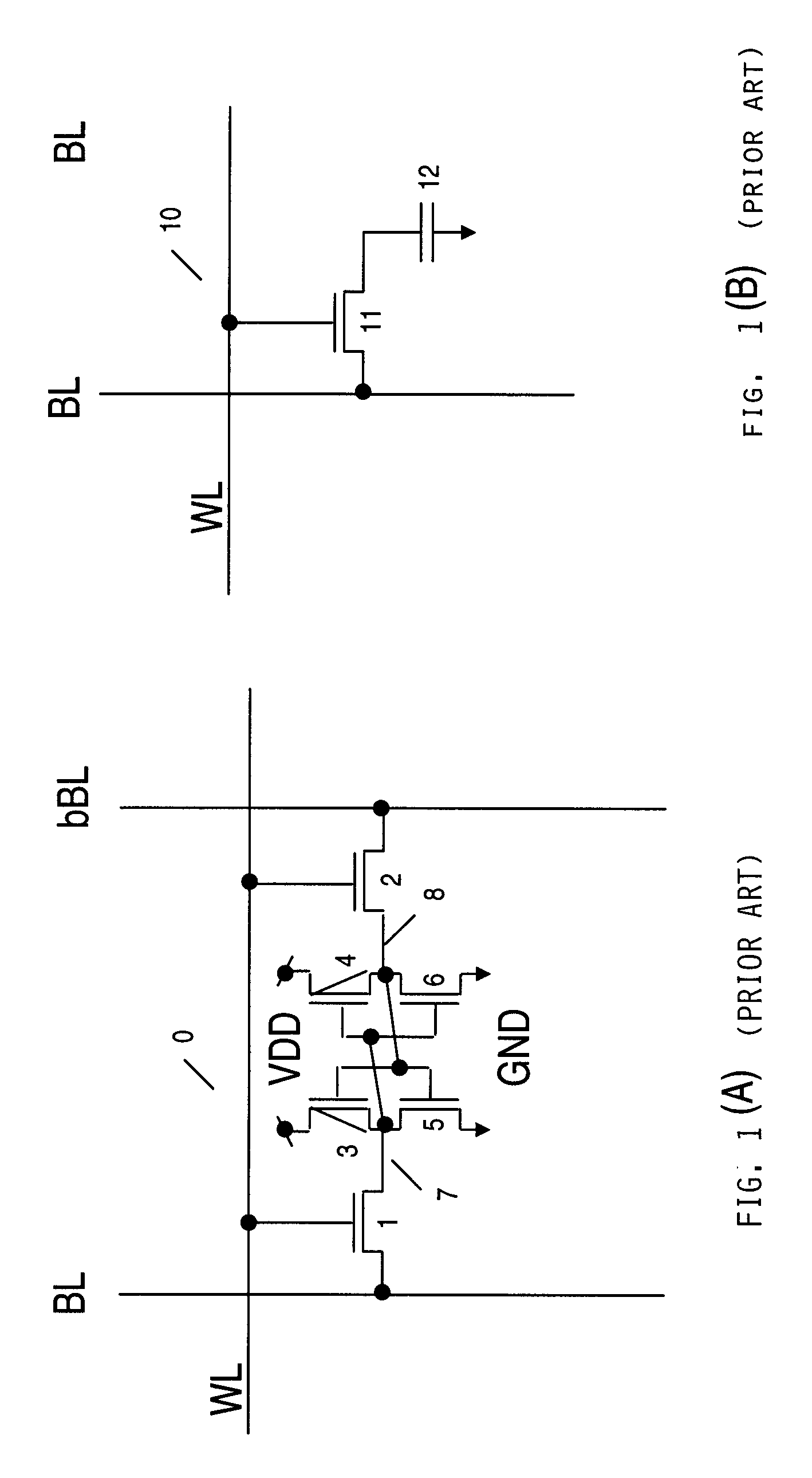
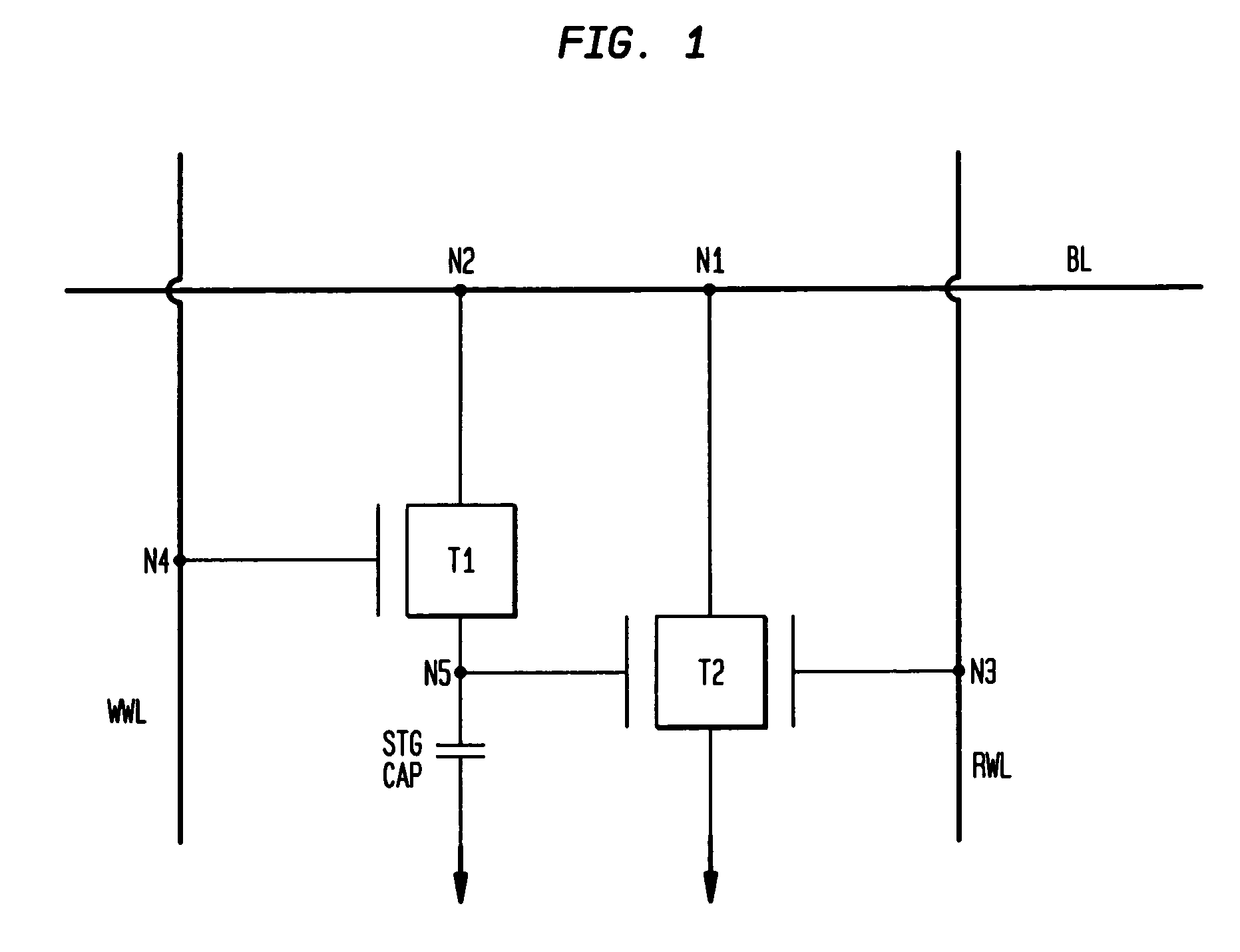
Memory gain cell
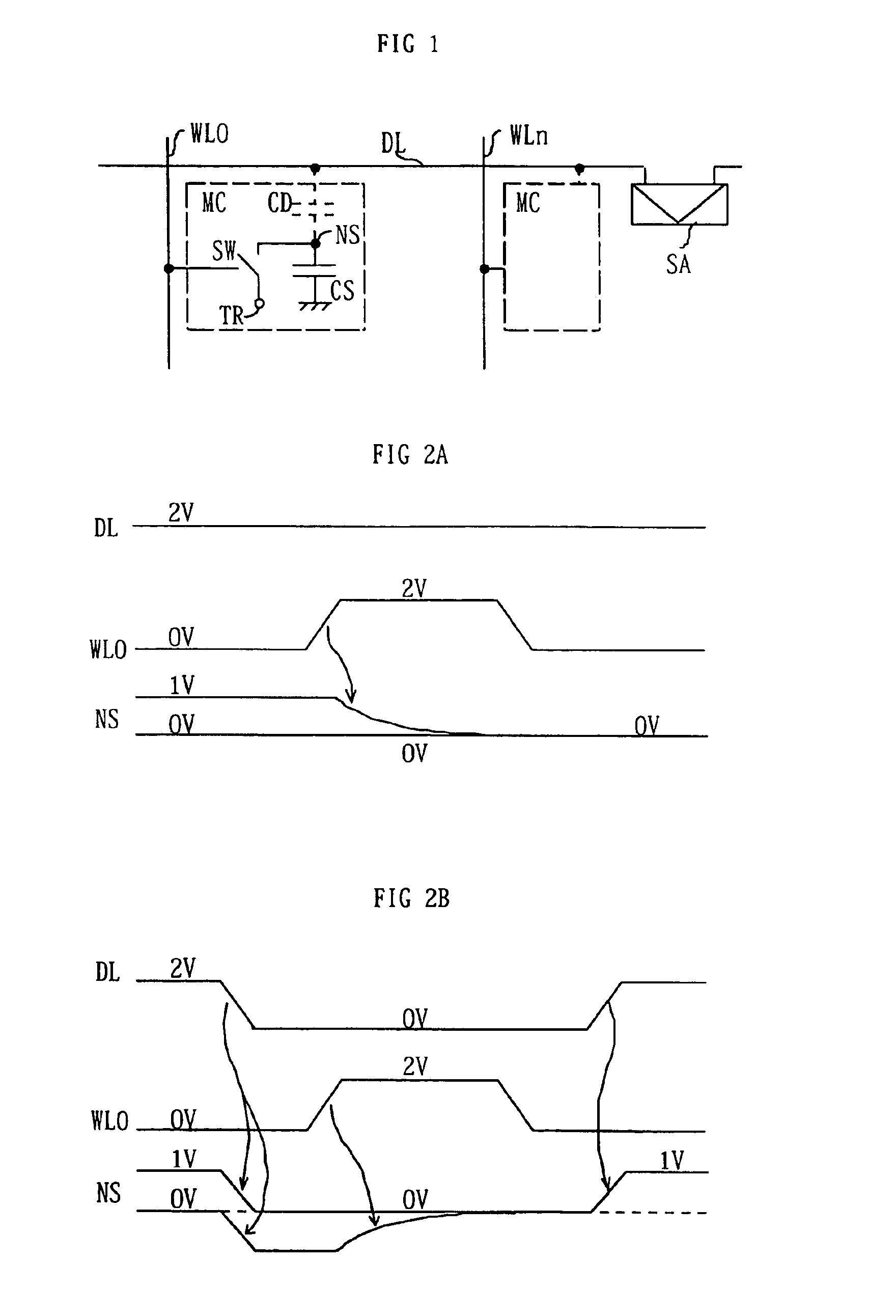
A memory cell includes: a charge storage element (e.g., capacitor); a switch constructed and arranged to selectively connect the charge storage element to a first data line, responsive to a first select signal; and a gain element having an input connected to receive a signal from the capacitor and constructed and arranged to selectively provide a corresponding output signal to a second data line, responsive to a second select signal. The switch can be a FET having a drain connected to the first data line, a source connected to the capacitor and a gate connected to the first select signal. The gain element can be a FET having a gate connected to the capacitor, a source connected to the second data line and a drain selectively connected to one of an upper power supply and a lower power supply. The switch can transfer a signal from the first data line onto the capacitor and can transfer a signal from the capacitor onto the first data line when selected by the first select signal. A two-dimensional array of such memory cells can be formed, wherein the first select signal and the second select signal orthogonally select cells, to facilitate matrix pivot operations and bit interleave / de-interleave operations. Also, a method of addressing an array of such memory cells can comprise: writing groups of bits linearly arrayed with respect to each other; and reading groups of bits linearly arrayed with respect to each other and orthogonally disposed to the groups of bits written.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
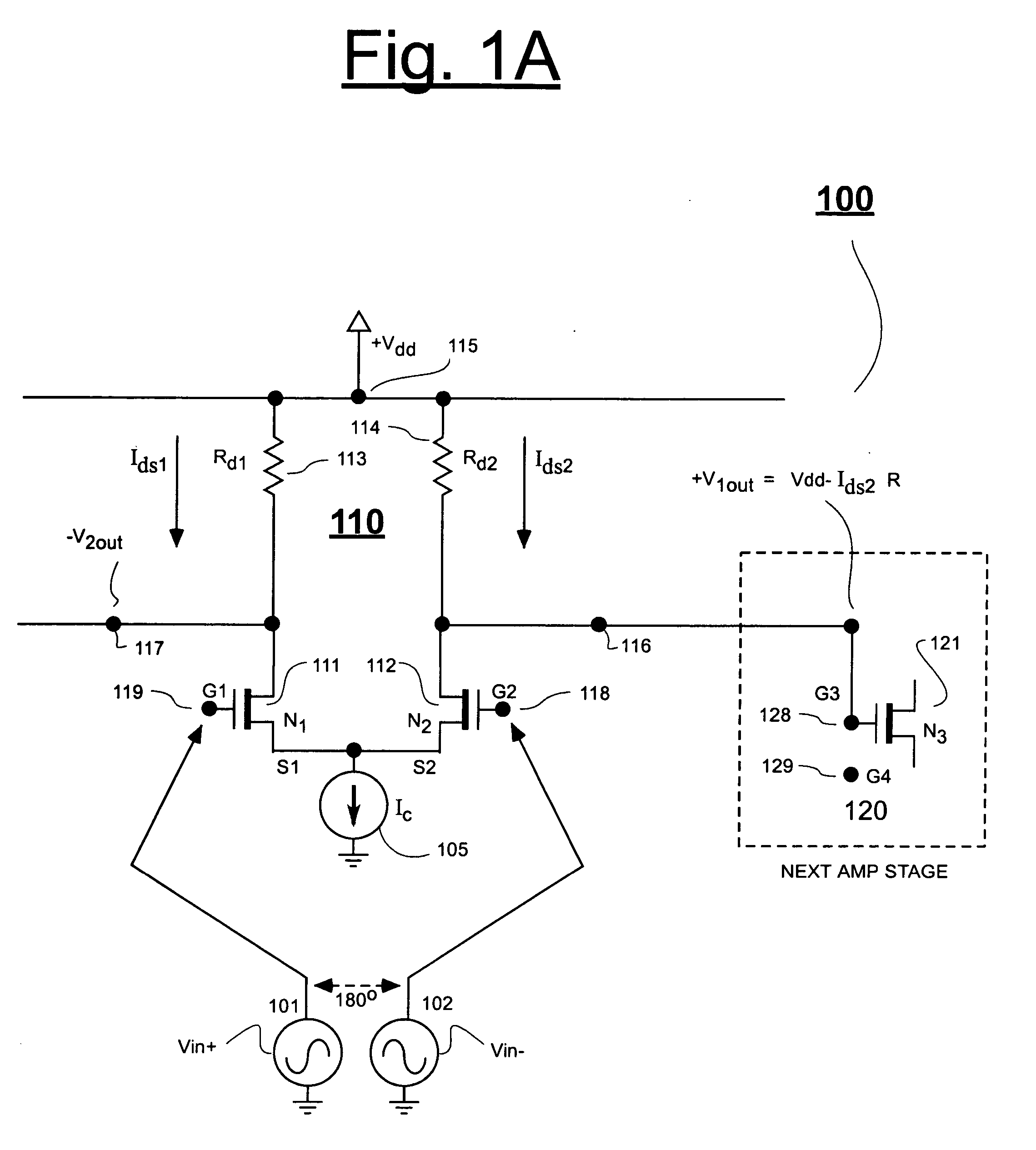
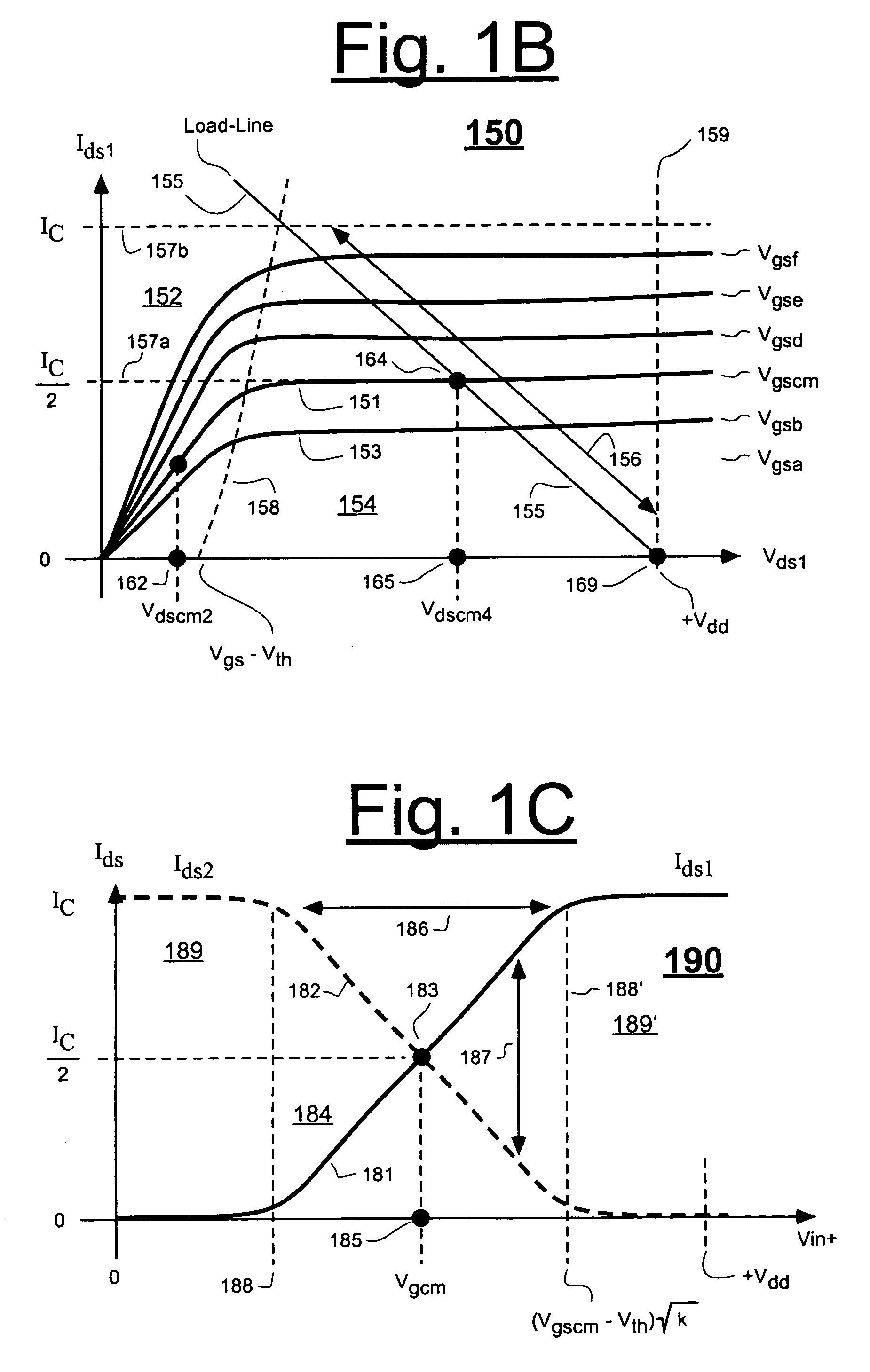
Low voltage broadband gain cell
InactiveUS7170349B2Wide bandwidthReduce capacitive lumping effectAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersLow voltageEngineering
T-coil structures are used in one embodiment to inject programmably-variable amounts of transistor biasing currents into the respective drains of current sinking transistor means of a broadband differential amplifier such that, when the differential amplifier is in common mode, total transistor drain current will exceed total voltage-dropping current passing through corresponding voltage-dropping resistances of the amplifier's transistor means. The T-coil structures keep the parasitic capacitances of the programmable current sources that provide the bias currents de-lumped from capacitances of the amplifier's output nodes and / or capacitances of the amplifier's voltage-dropping resistances (variable resistances) to thereby maintain a wide bandwidth.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS
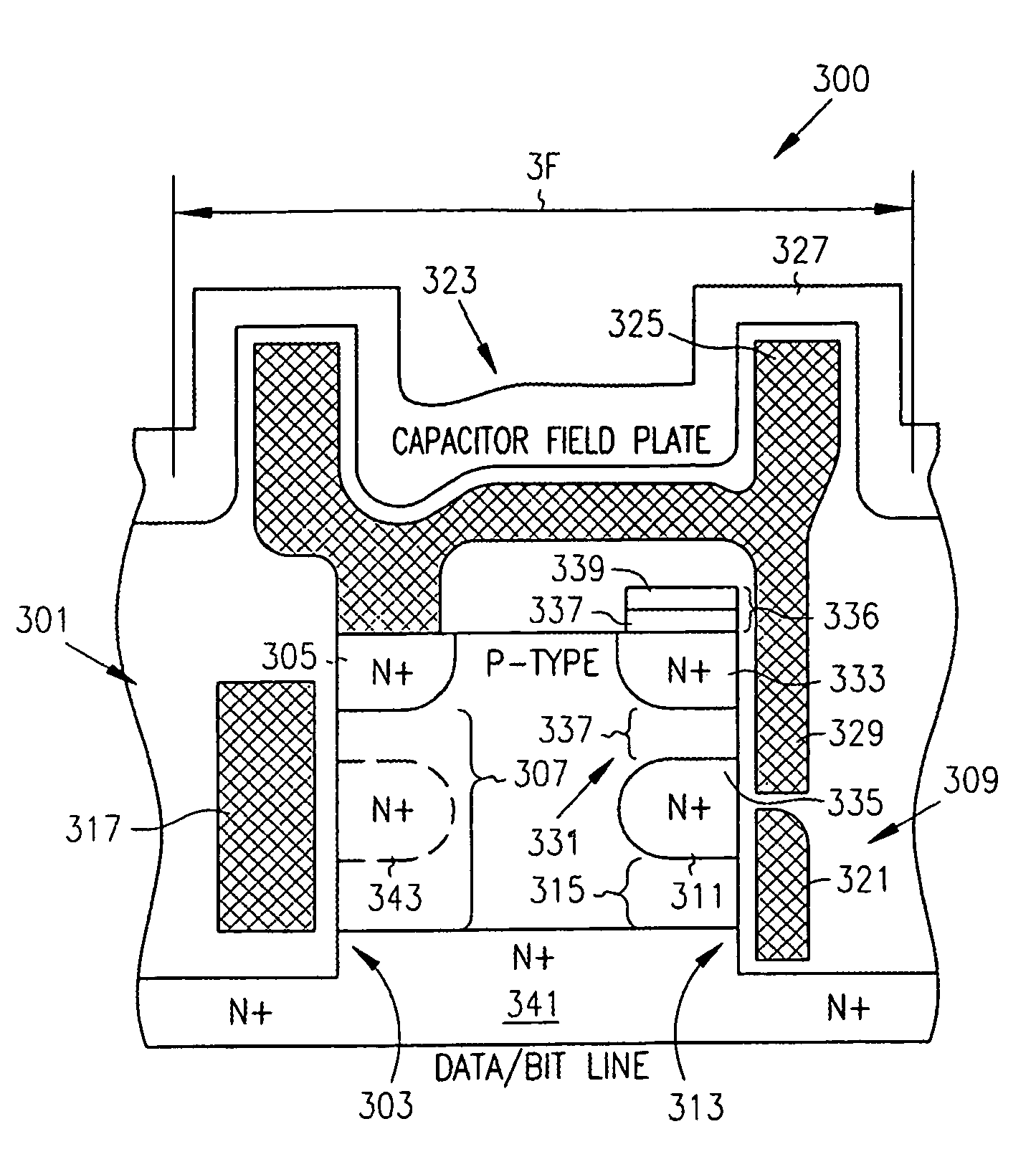
Semiconductor memory device and method of manufacturing semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20120213000A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceParasitic capacitance is generatedTransistorSolid-state devicesWrite bitMemory cell
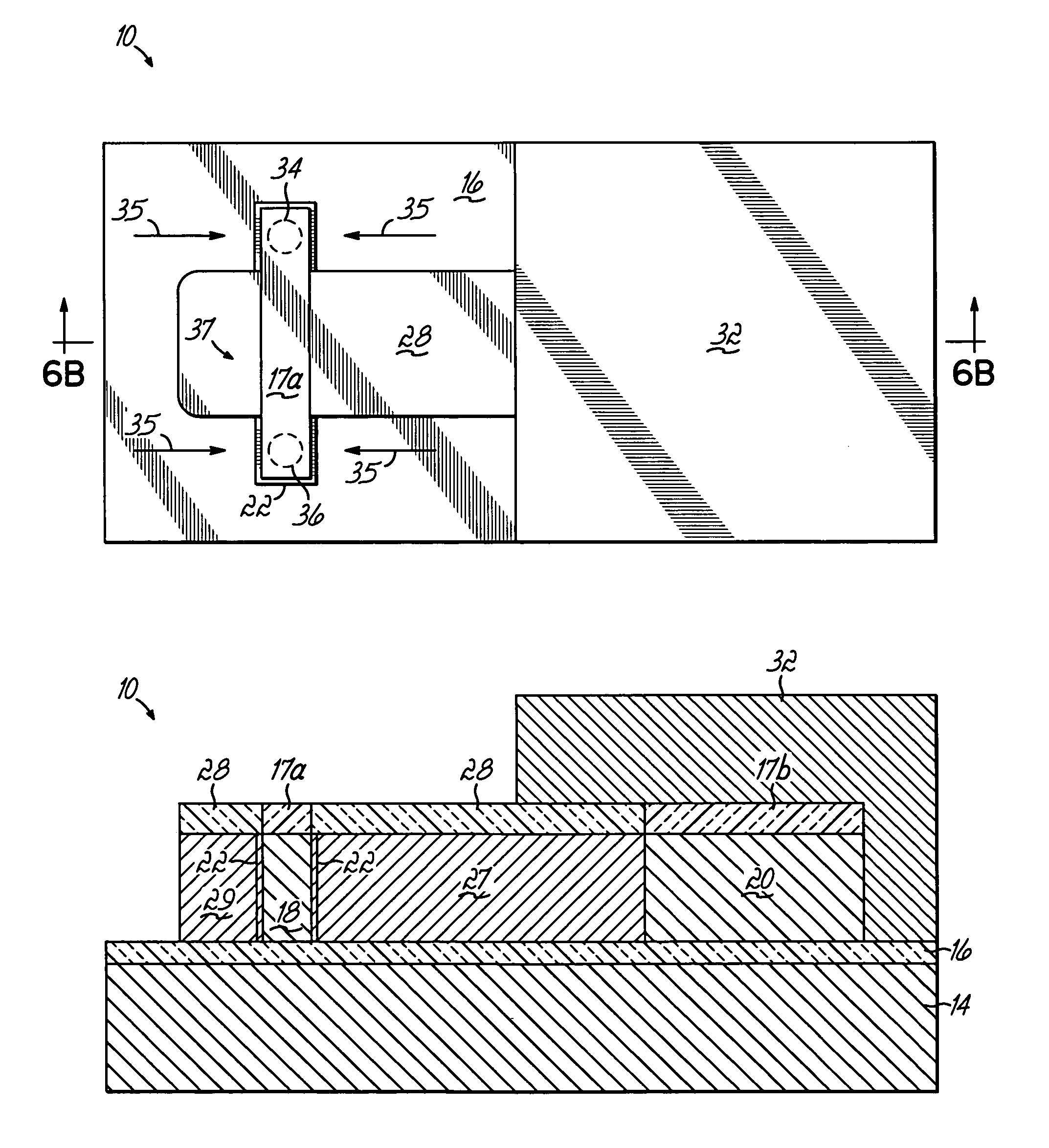
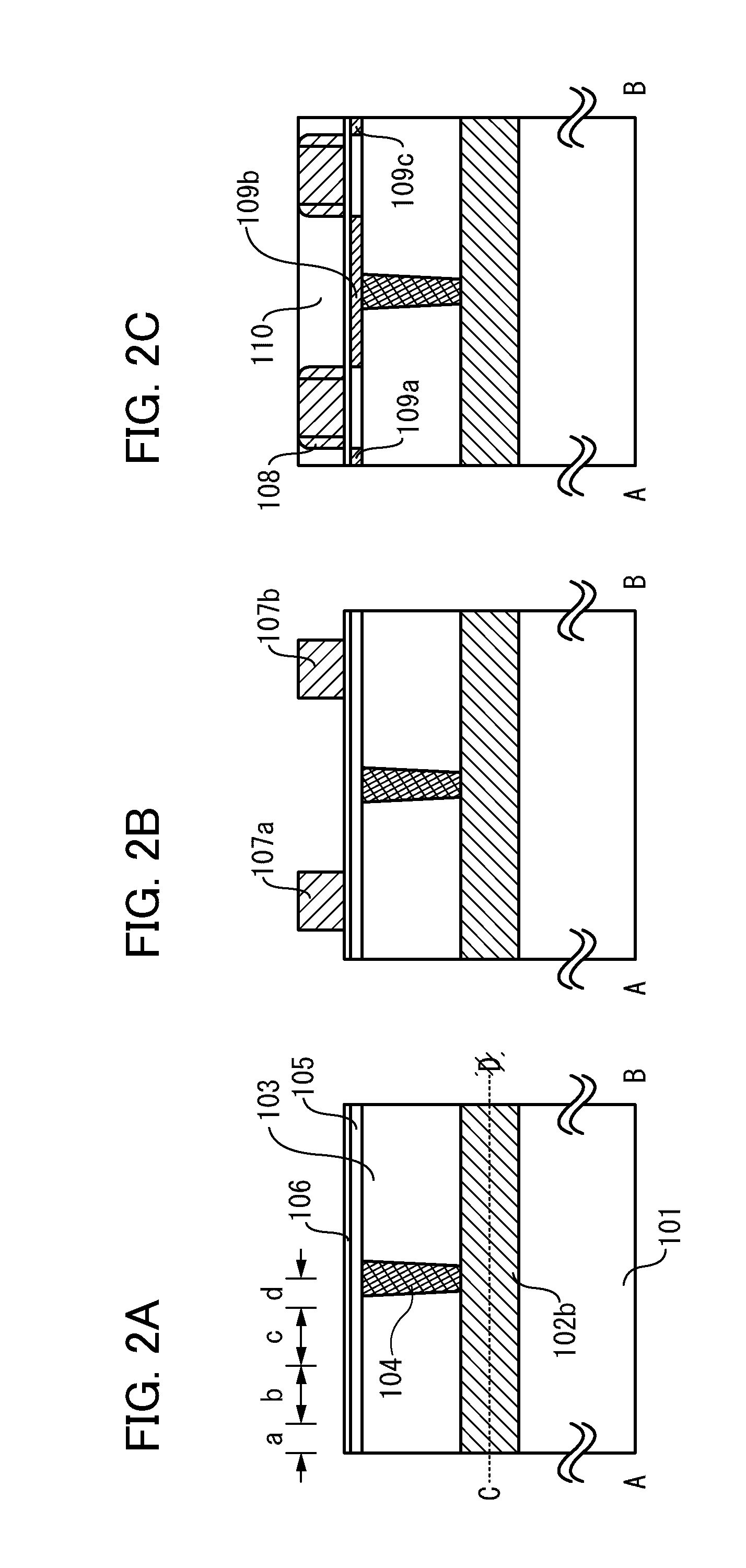
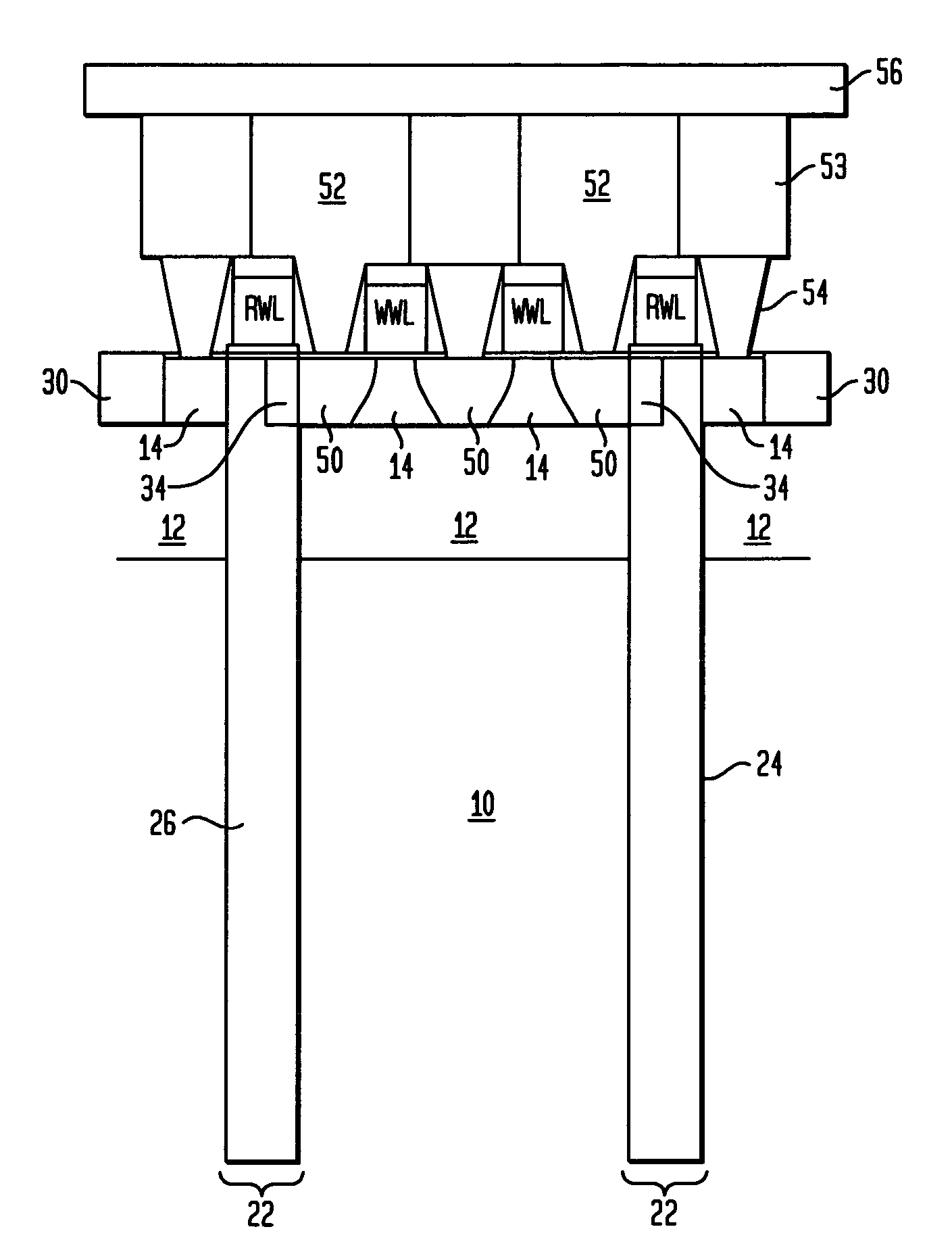
A highly integrated gain cell-type semiconductor memory is provided. A first insulator, a read bit line, a second insulator, a third insulator, a first semiconductor film, first conductive layers, and the like are formed. A projecting insulator is formed thereover. Then, second semiconductor films and a second gate insulating film are formed to cover the projecting insulator. After that, a conductive film is formed and subjected to anisotropic etching, so that write word lines are formed on side surfaces of the projecting insulator. A third contact plug for connection to a write bit line is formed over a top of the projecting insulator. With such a structure, the area of the memory cell can be 4 F2 at a minimum.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Single transistor vertical memory gain cell
A high density vertical single transistor gain cell is realized for DRAM operation. The gain cell includes a vertical transistor having a source region, a drain region, and a floating body region therebetween. A gate opposes the floating body region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide on a first side of the vertical transistor. A floating body back gate opposes the floating body region on a second side of the vertical transistor and is separated therefrom by a dielectric to form a body capacitor.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Gain cell semiconductor memory device and driving method thereof
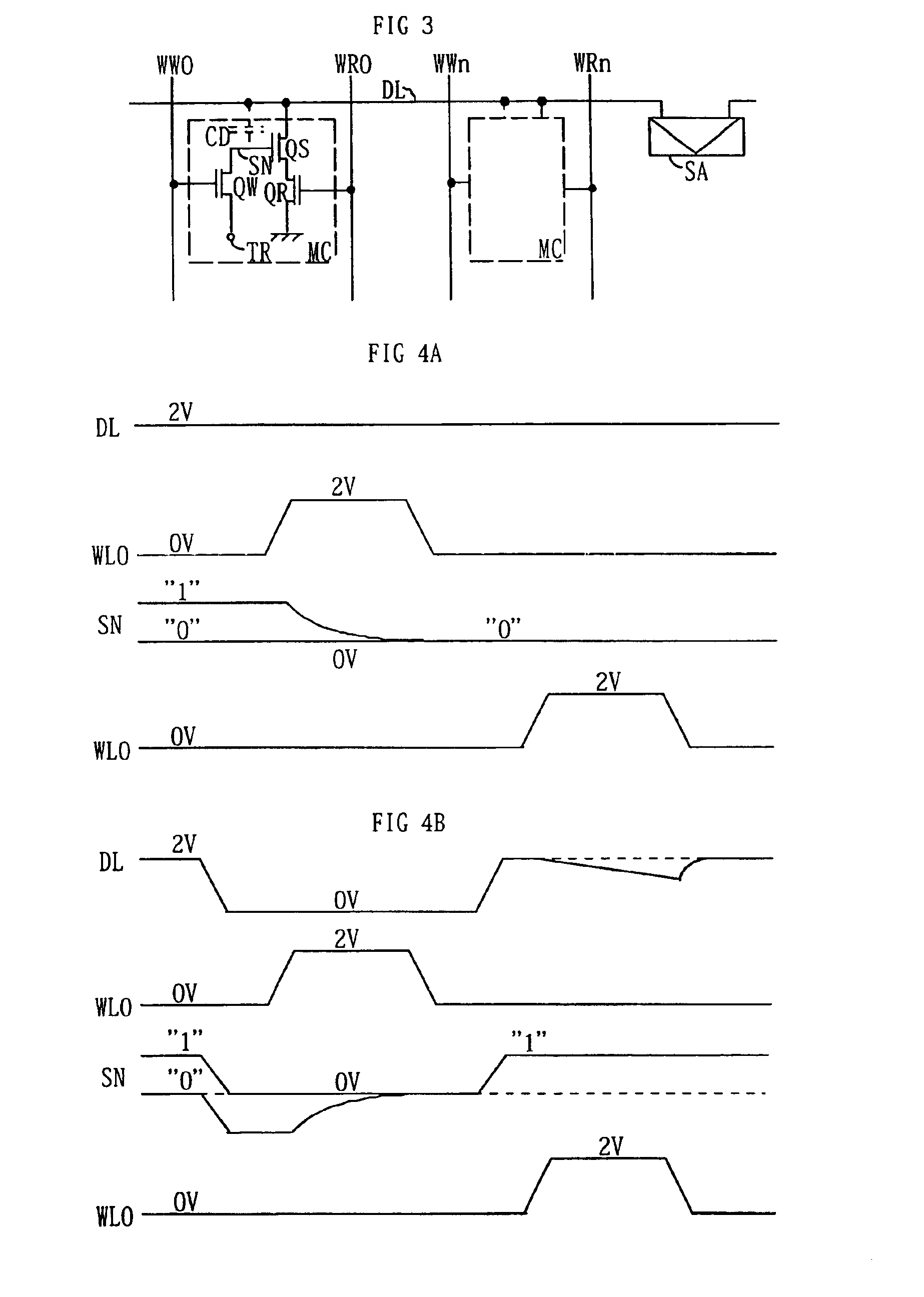
A memory cell including two transistors and one capacitor, which is known as a gain cell, is improved. One electrode of the capacitor is connected to a bit line, and the other electrode thereof is connected to a drain of a write transistor. A source of the write transistor is connected to a source line. As a result, for example, in the case where a stacked capacitor is used, the one electrode of the capacitor can be part of the bit line. Only one specific write transistor is turned on when a potential of the source line and a potential of the write bit line are set; thus, only one memory cell can be rewritten.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Low voltage broadband gain cell
InactiveUS20060061415A1Wide bandwidthReduce capacitive lumping effectAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersLow voltageEngineering
T-coil structures are used in one embodiment to inject programmably-variable amounts of transistor biasing currents into the respective drains of current sinking transistor means of a broadband differential amplifier such that, when the differential amplifier is in common mode, total transistor drain current will exceed total voltage-dropping current passing through corresponding voltage-dropping resistances of the amplifier's transistor means. The T-coil structures keep the parasitic capacitances of the programmable current sources that provide the bias currents de-lumped from capacitances of the amplifier's output nodes and / or capacitances of the amplifier's voltage-dropping resistances (variable resistances) to thereby maintain a wide bandwidth.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS
6F2 3-transistor DRAM gain cell
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
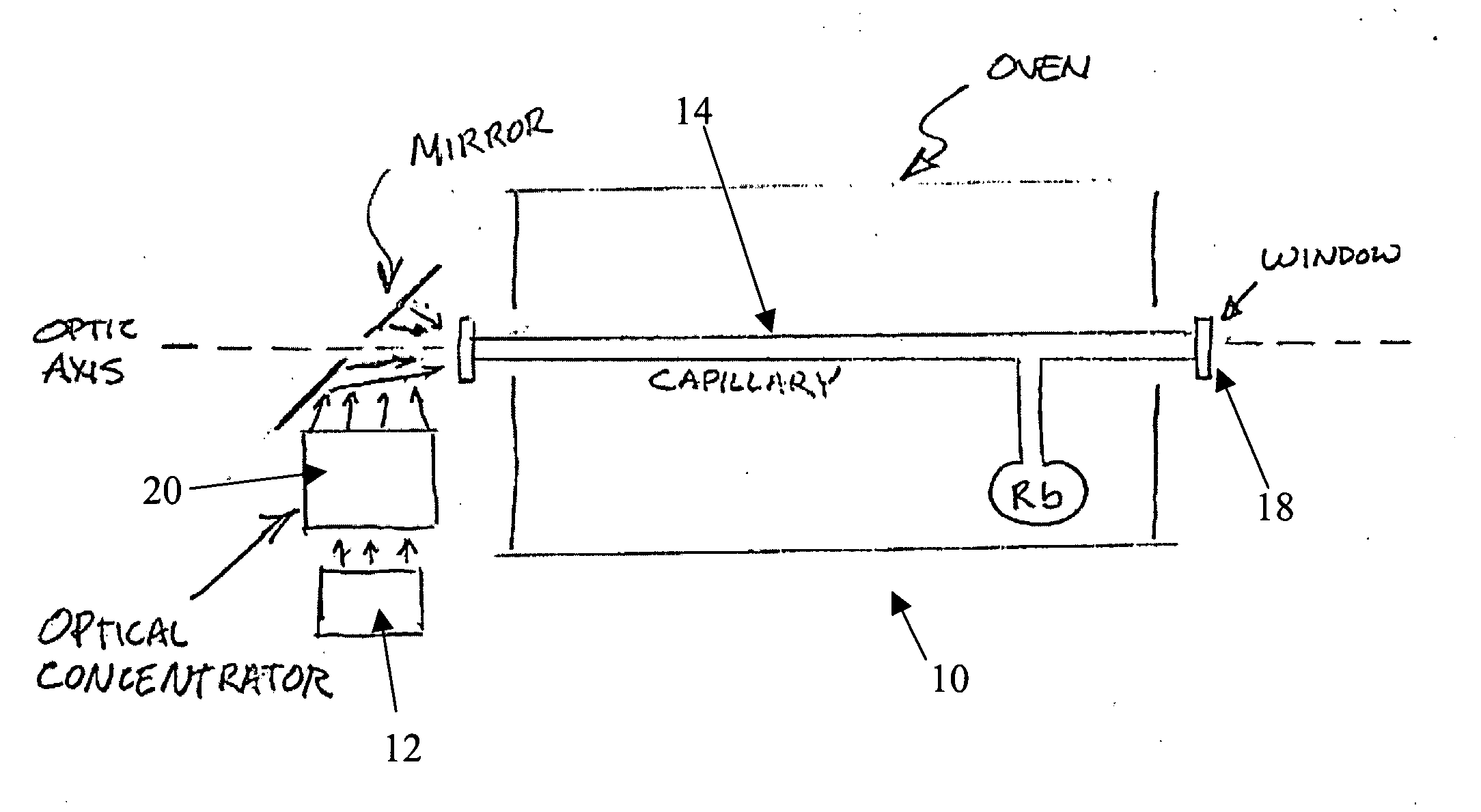
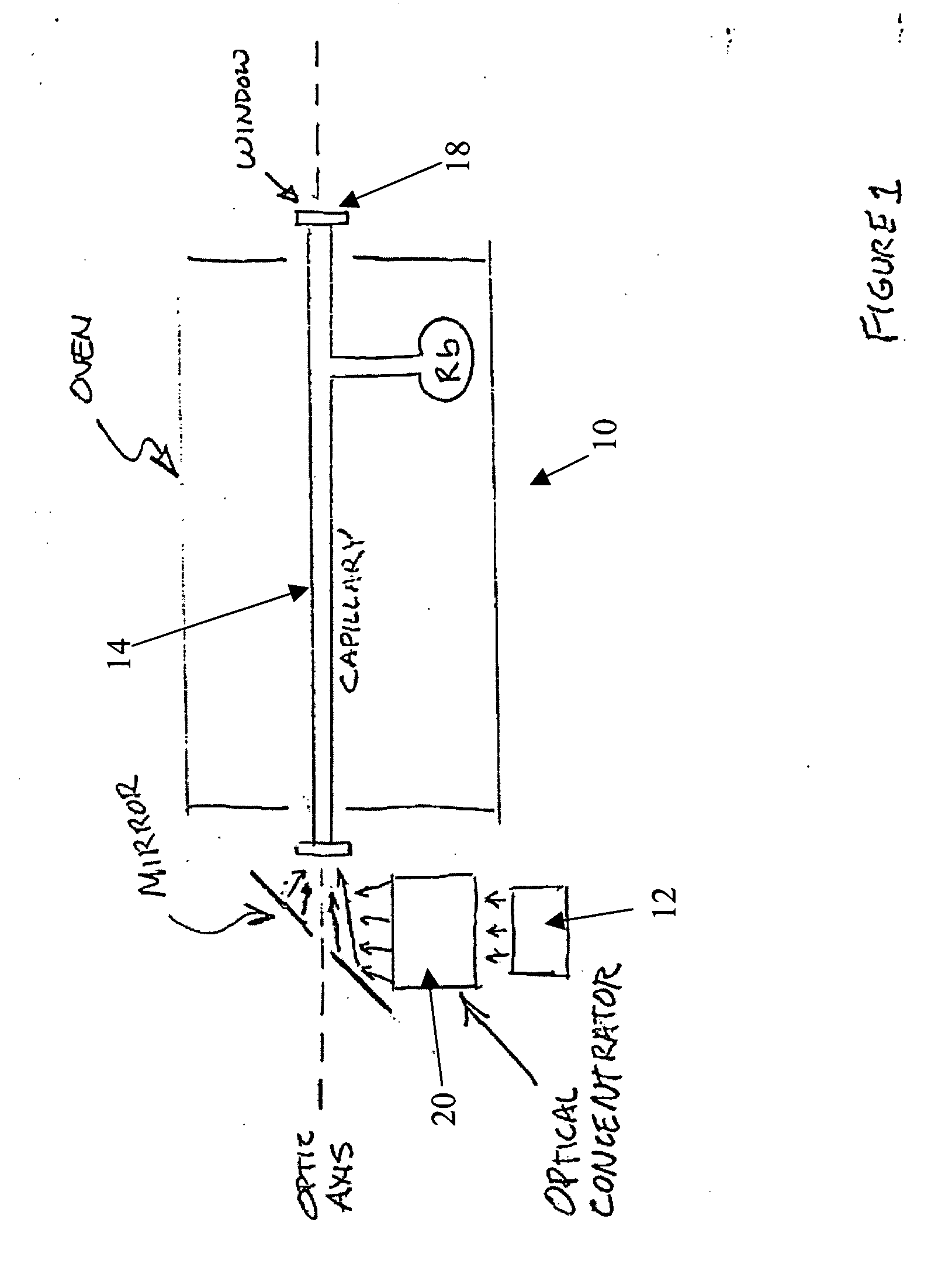
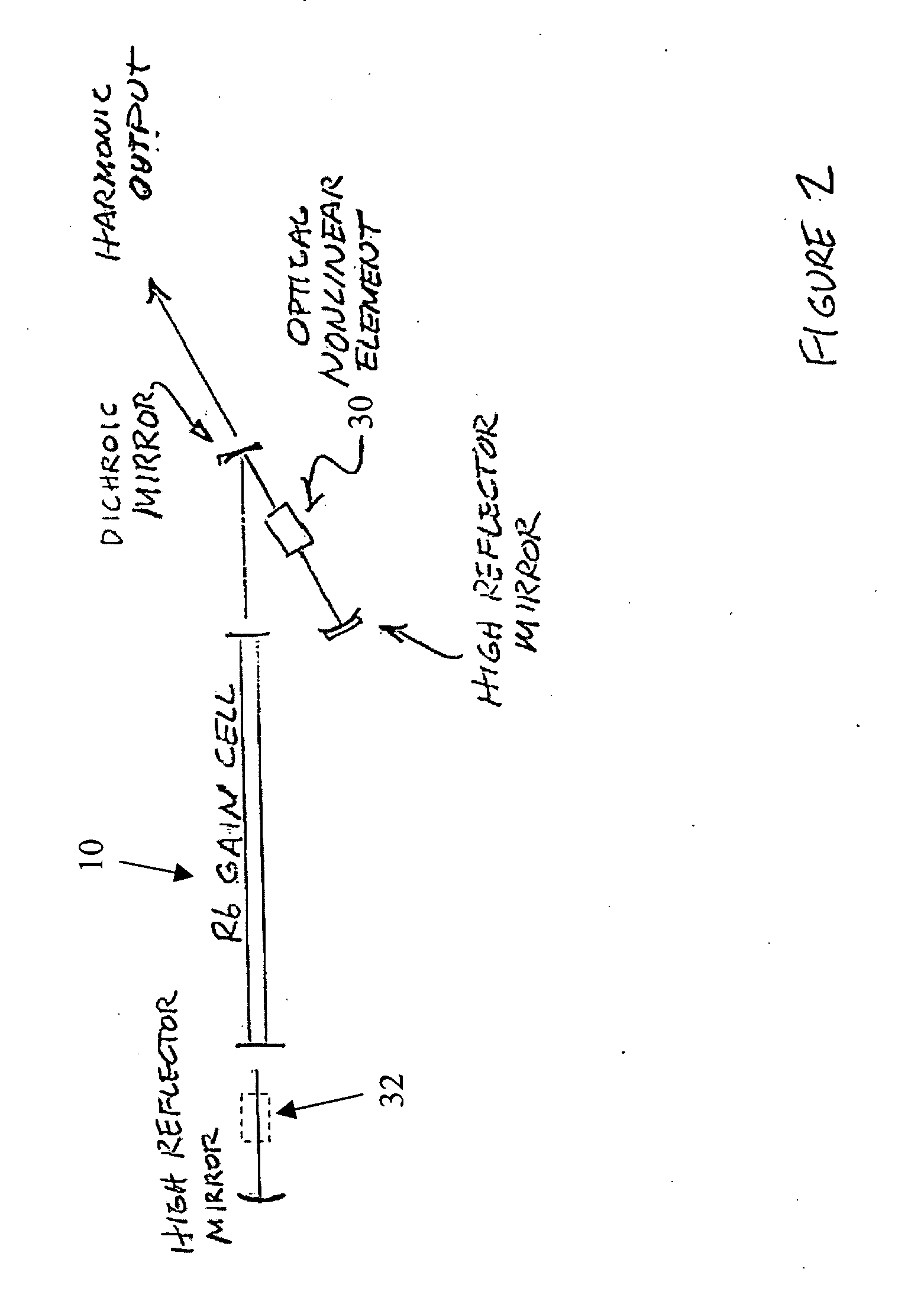
Ultraviolet, narrow linewidth laser system
InactiveUS20050190809A1Improved ultraviolet laser outputSimplified and robust configurationLaser arrangementsActive medium materialNear infrared laserLine width
A laser device is provided for generating an ultraviolet output. The device comprises a laser having at least one diode-pumped alkali metal vapor gain cell for generating a near infrared laser output, and at least two optically-nonlinear crystals. In one particular embodiment, the laser uses a Rb gas cell and generates radiation at a wavelength of about 199 nm and at least 200 mW of power with a linewidth of less than 10 GHz. In another embodiment, narrow linewidth UV light is generated at 265 nm.
Owner:SPECTRA PHYSICS
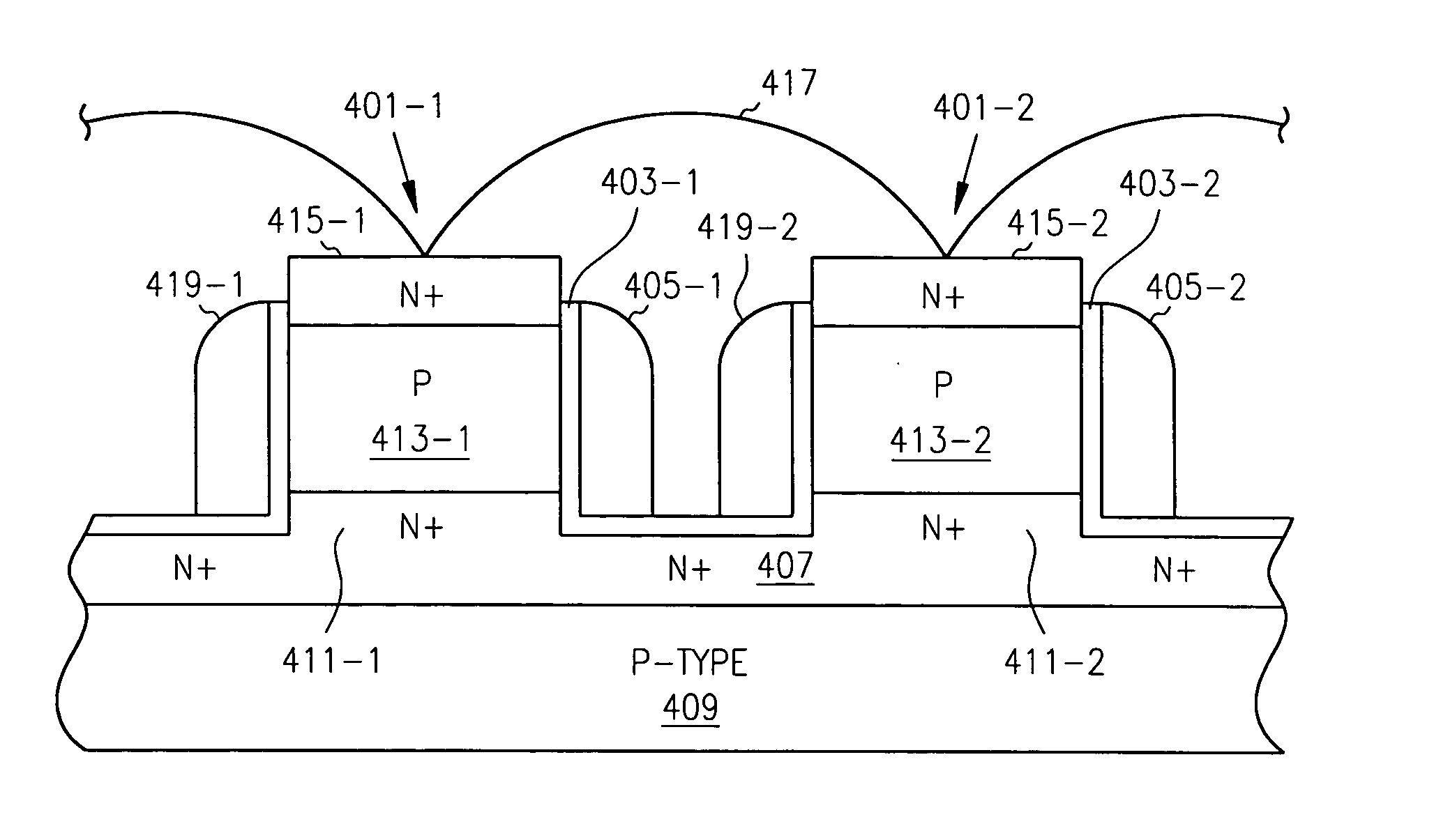
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070063287A1Stable reading operationAvoid insufficient lengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
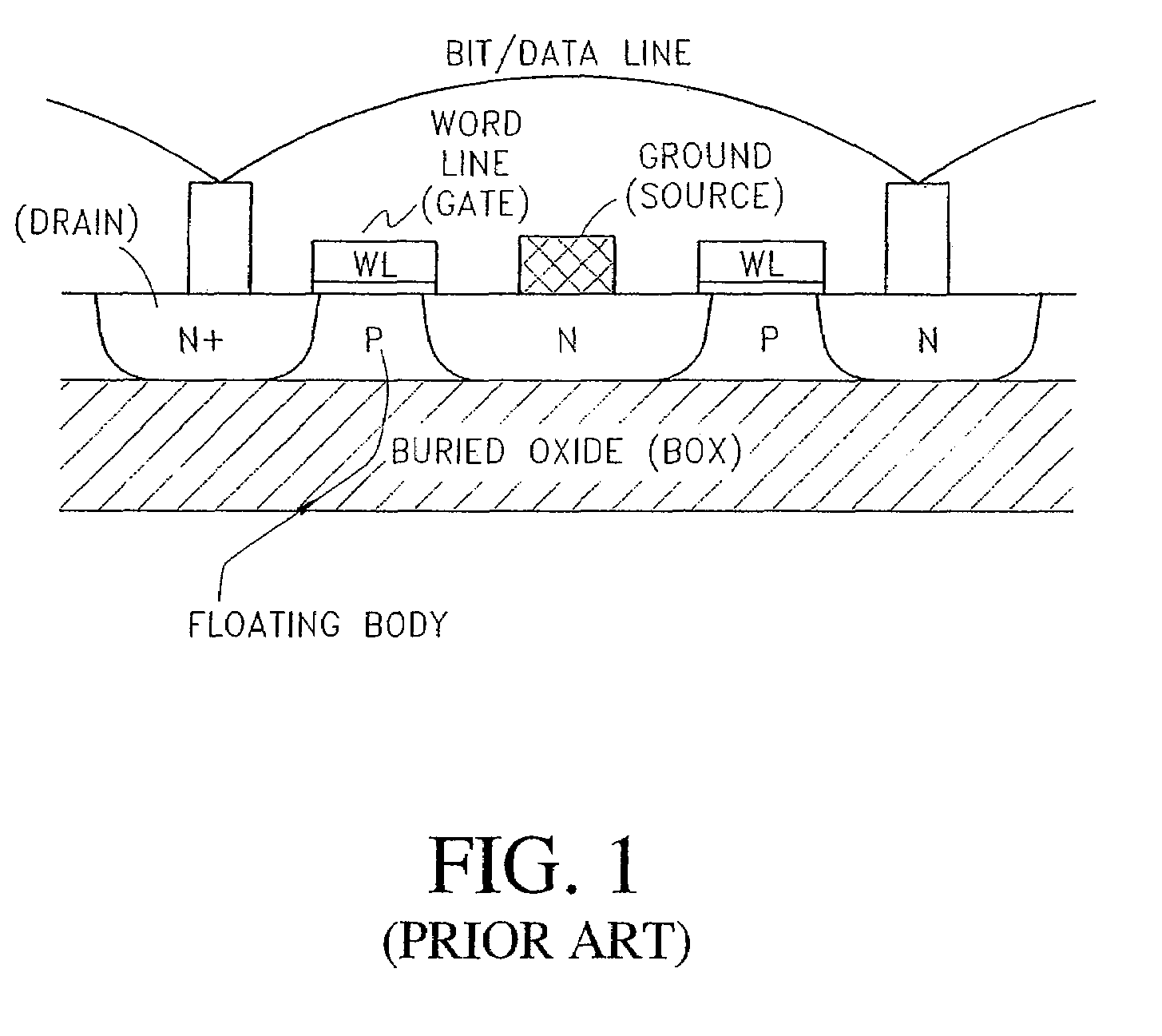
To achieve a stable reading operation in a memory cell having a gain-cell structure, a write transistor is configured, which has a source and a drain that are formed on the insulating layer, a channel formed on the insulating layer and between the source and the drain and made of a semiconductor, and a gate formed on an upper portion of the insulating layer and between the source and the drain and electrically insulated from the channel by a gate insulating film and controlling the potential of the channel. The channel electrically connects the source and the drain on the side surfaces of the source and the drain.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Multi-port memory architecture
A multi-port memory architecture utilizing an open bitline configuration for the read bitline is described. The memory is sub-divided into two arrays (A and B) consisting of memory gain cells arranged in a matrix formation, the cells having two general ports or separate read and write ports to enable simultaneous a read and write operation. Each memory array includes a reference wordline coupled to reference cells. When the reference cell is accessed, the read bitline (RBL) discharges to a level at half the value taken by a cell storing a 0 or 1. Each pair of RBLB in the same column of the two arrays is coupled to a differential sense amplifier, and each write bitline (WBL) in the two arrays is linked to write drivers WBLs in the two arrays are driven to the same voltage and at the same slew rate. The WBL swing in each array creates coupling noise by the bitline-to-bitline capacitors. For a given sense amplifier and its associated RBLs, the coupling creates an identical coupling noise on RBLA and RBLB that are positioned in the two arrays A and B. This common mode noise is rejected by the differential sense amplifier. Thus, a read sense amplifier can accurately discriminate between the signal by activating the cell by way of RWL, and the reference cell by way of REFWL.
Owner:TWITTER INC
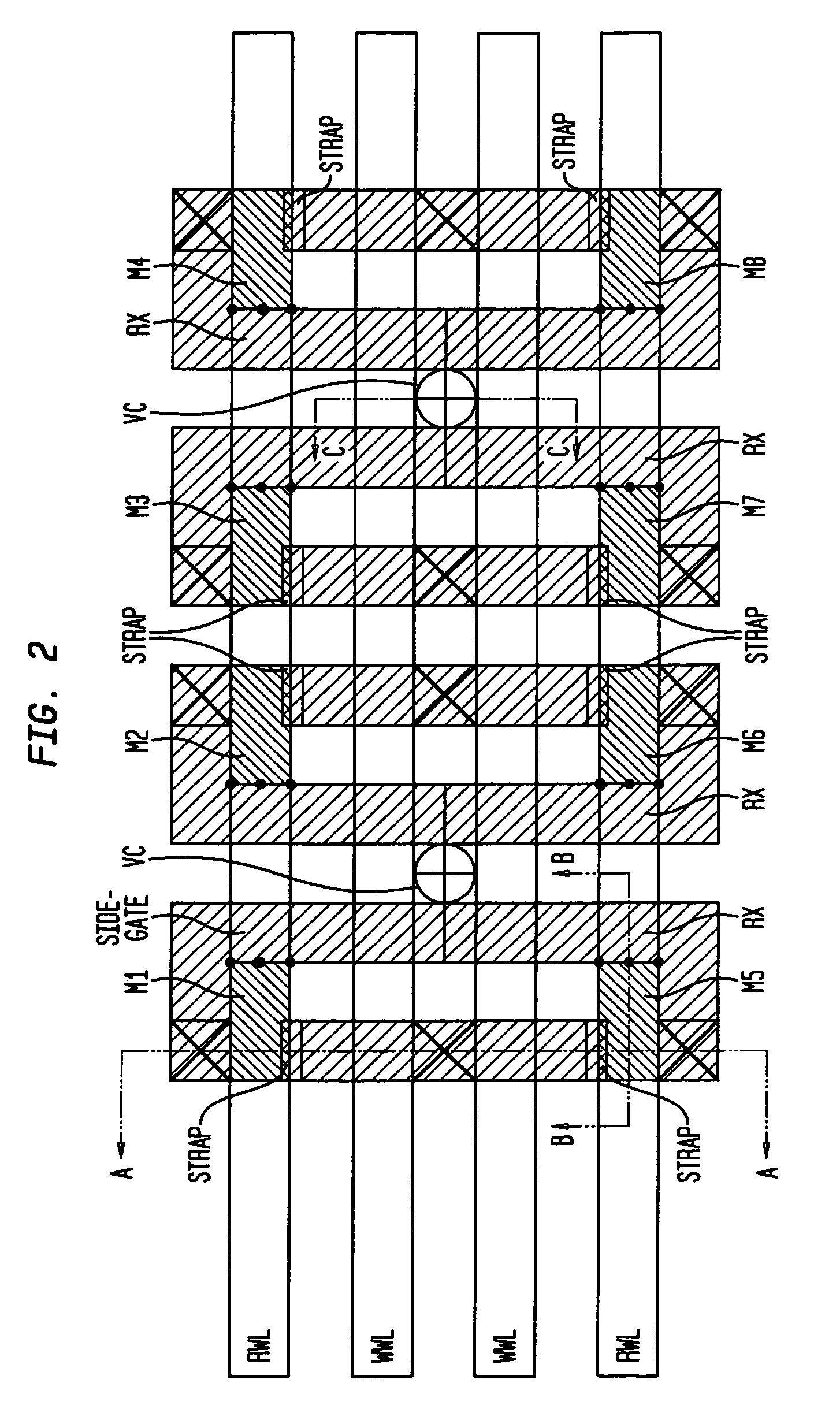
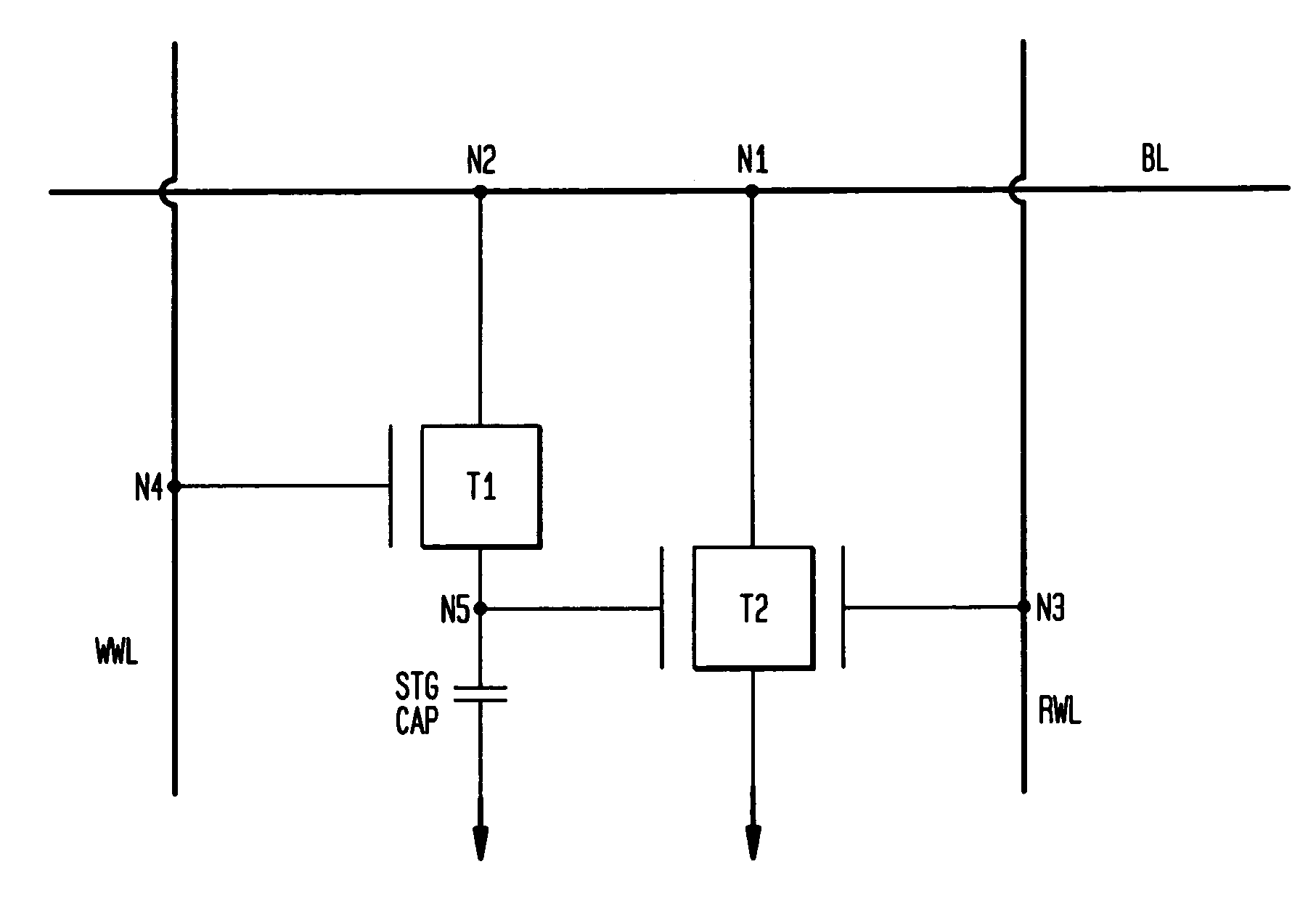
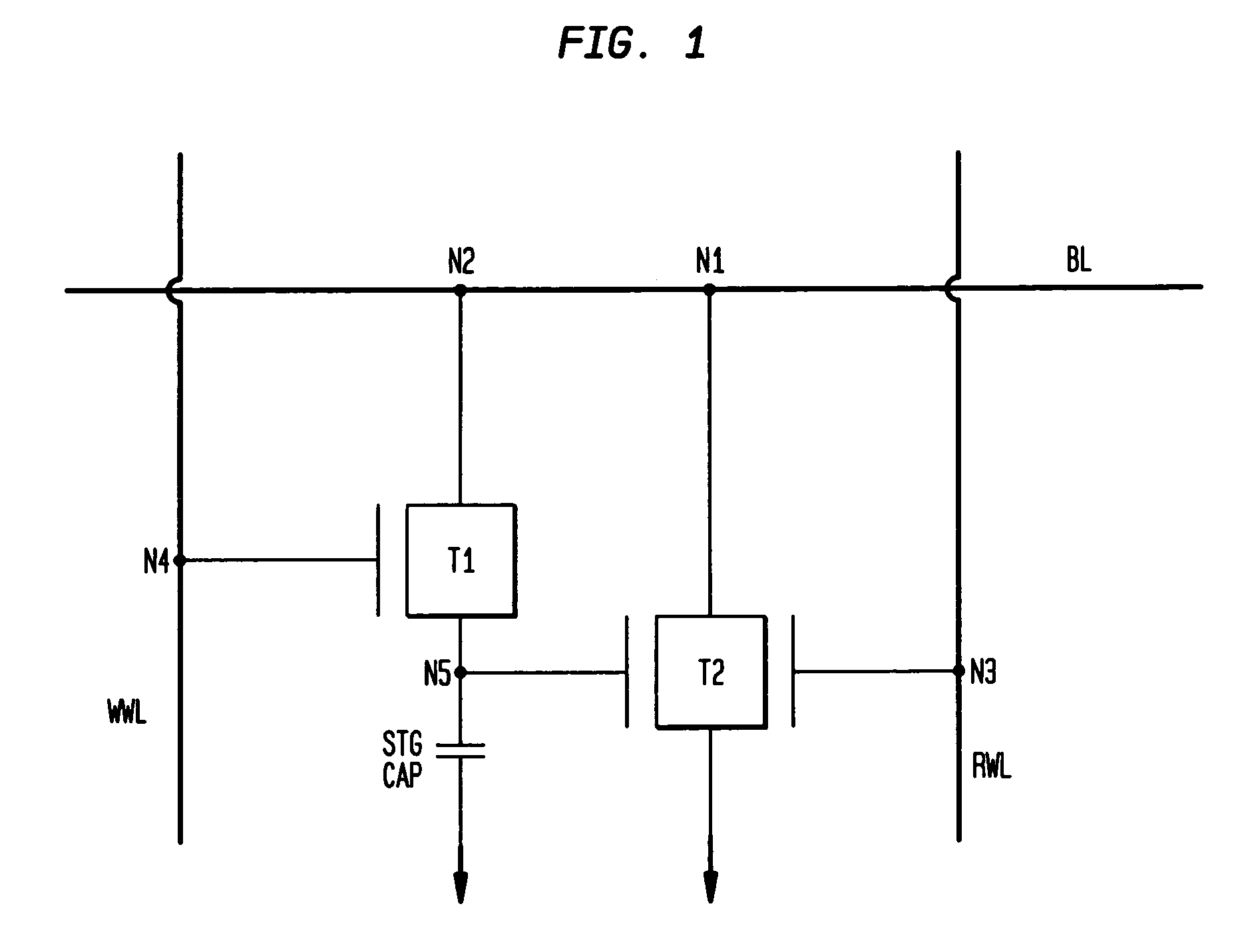
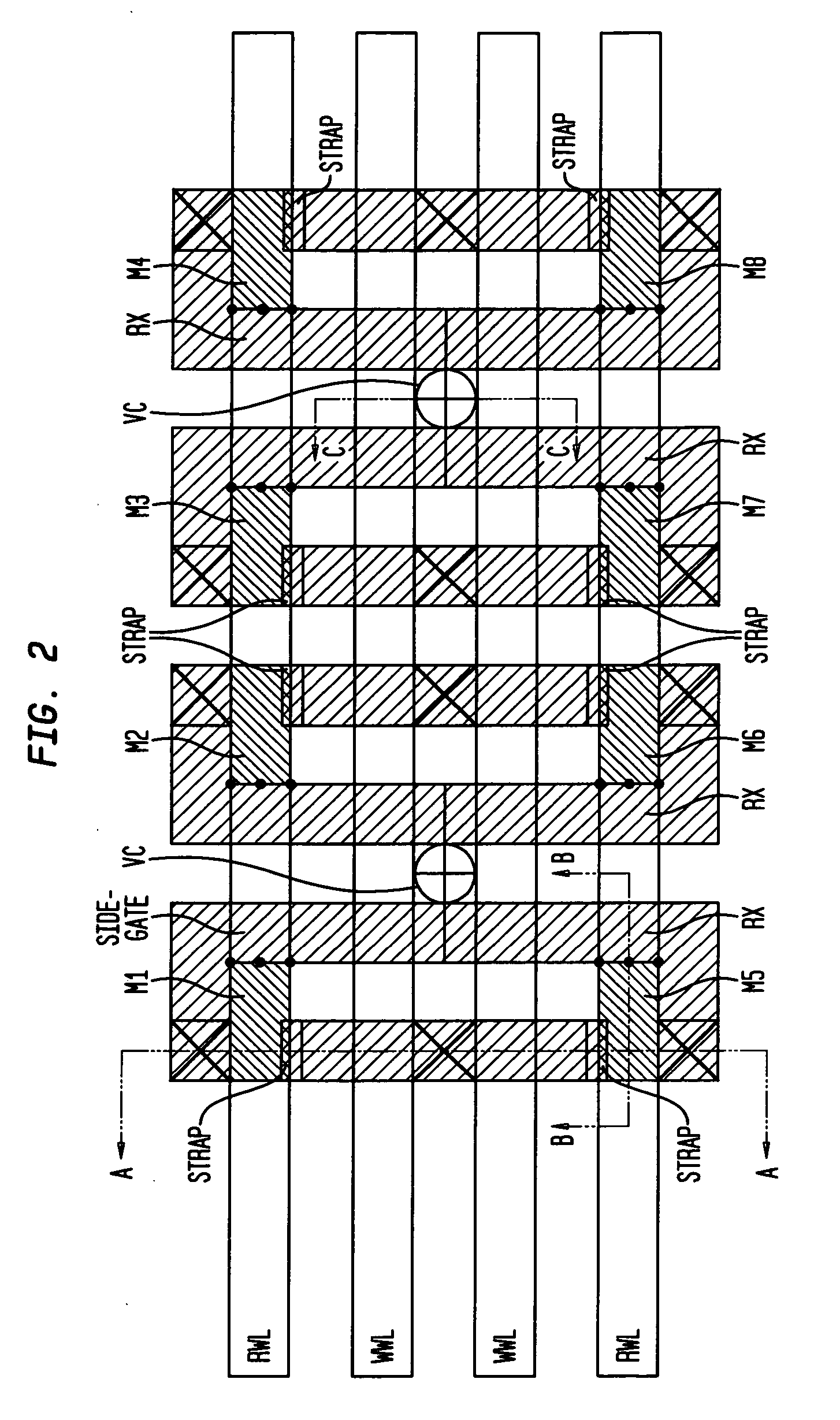
Dual port gain cell with side and top gated read transistor
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
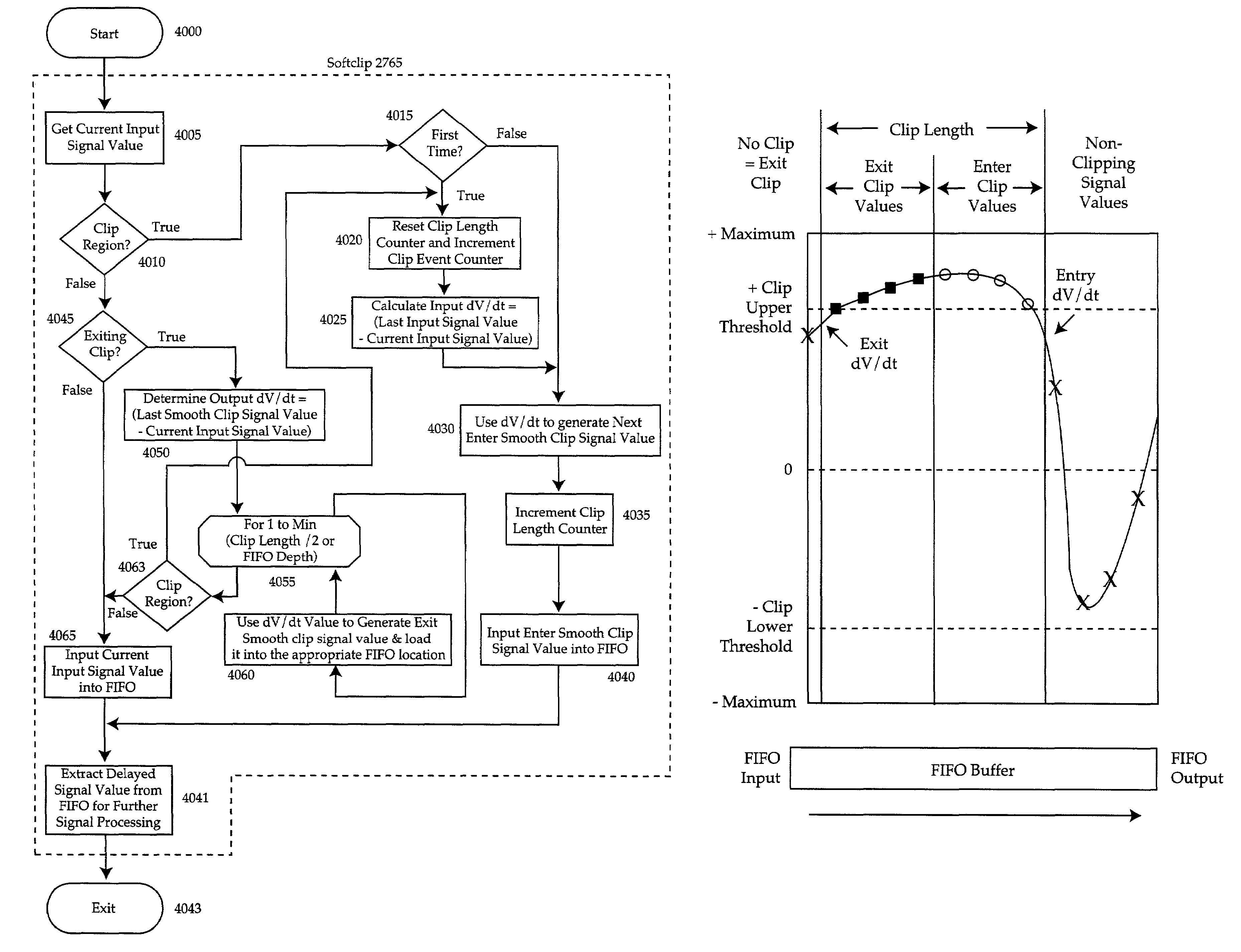
Softclip method and apparatus
InactiveUS7206420B2Cost effectiveMaximum flexibilityVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesGain controlComputer scienceGain cell
A method of matching input amplitudes in a system wherein one or more of a plurality of inputs may be selected, with each input capable of having different characteristics, involving selecting an input signal and mapping the input signal to a predetermined signal amplitude through the use of level matching logic. The level matching logic may include a gain cell for increasing or decreasing the amplitude of the input signal.
Owner:SYFX
Dual port gain cell with side and top gated read transistor
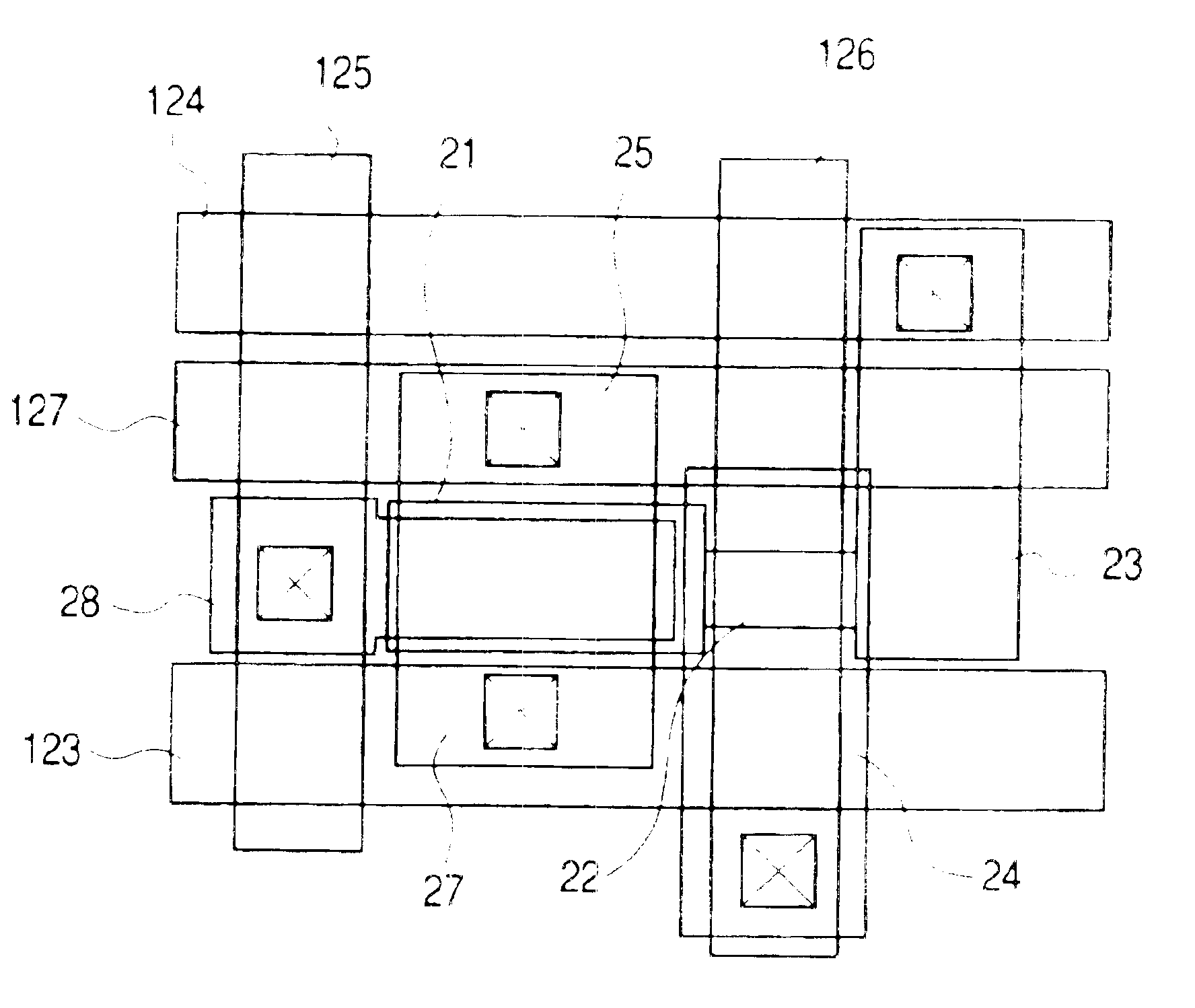
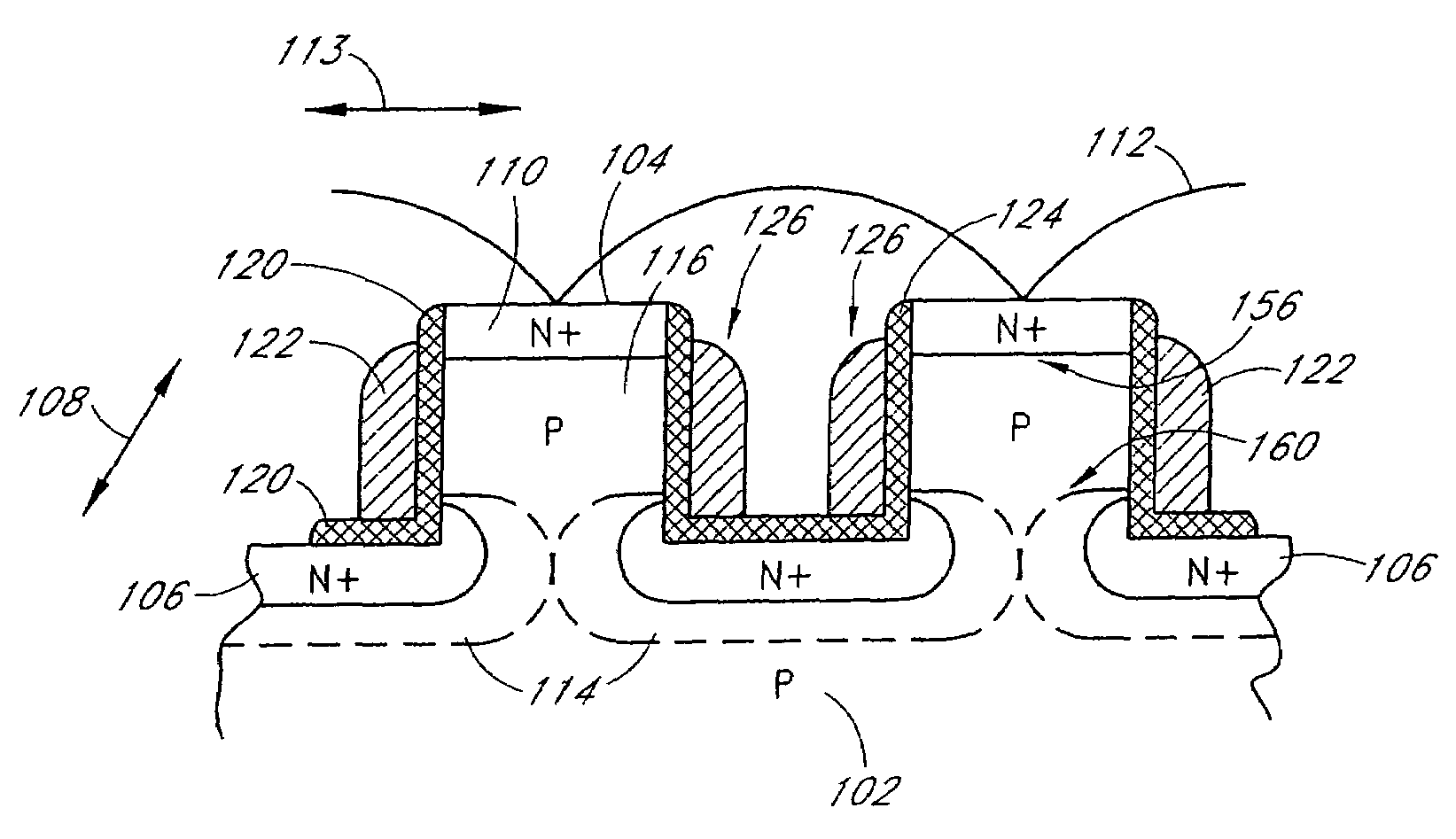
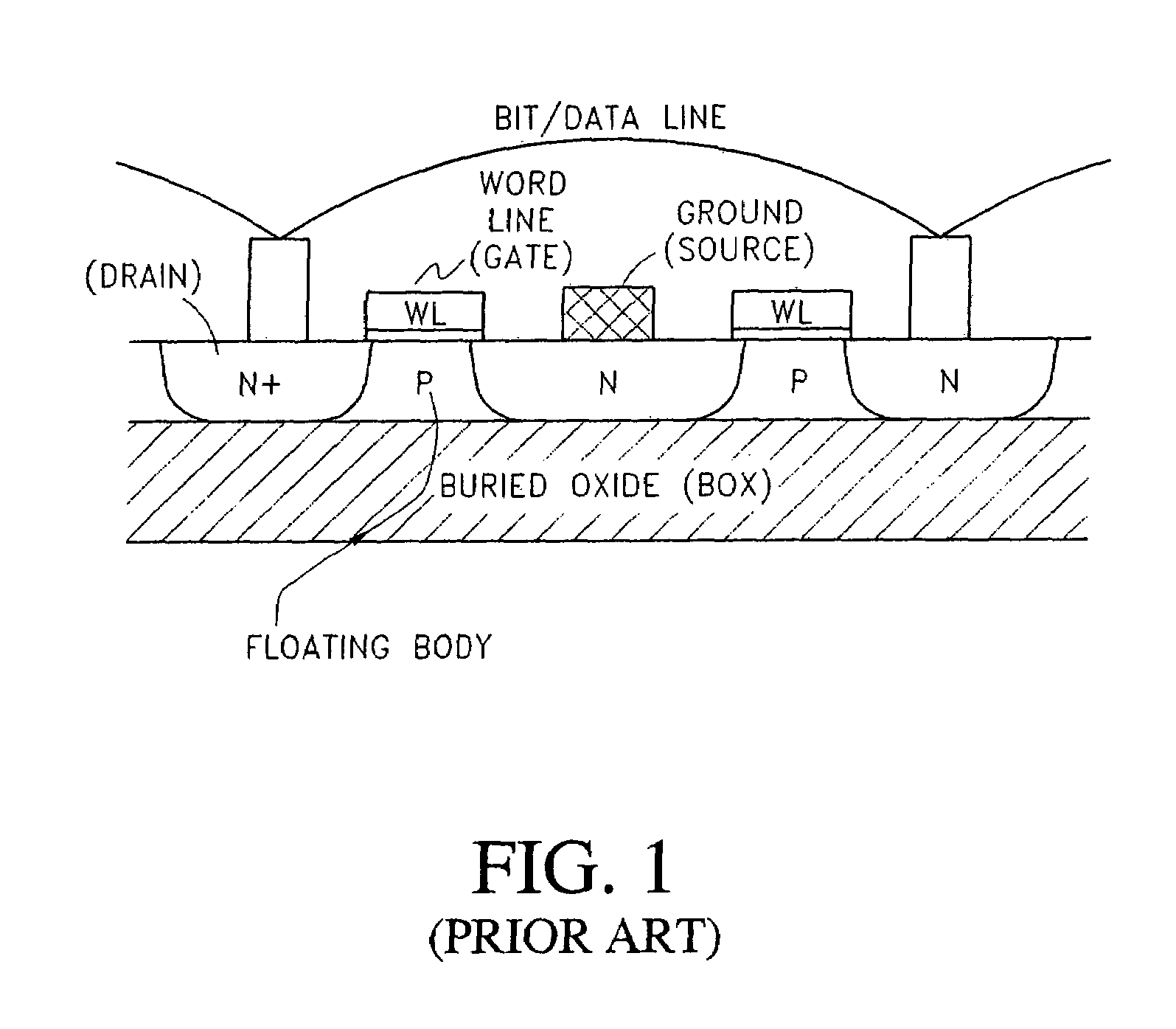
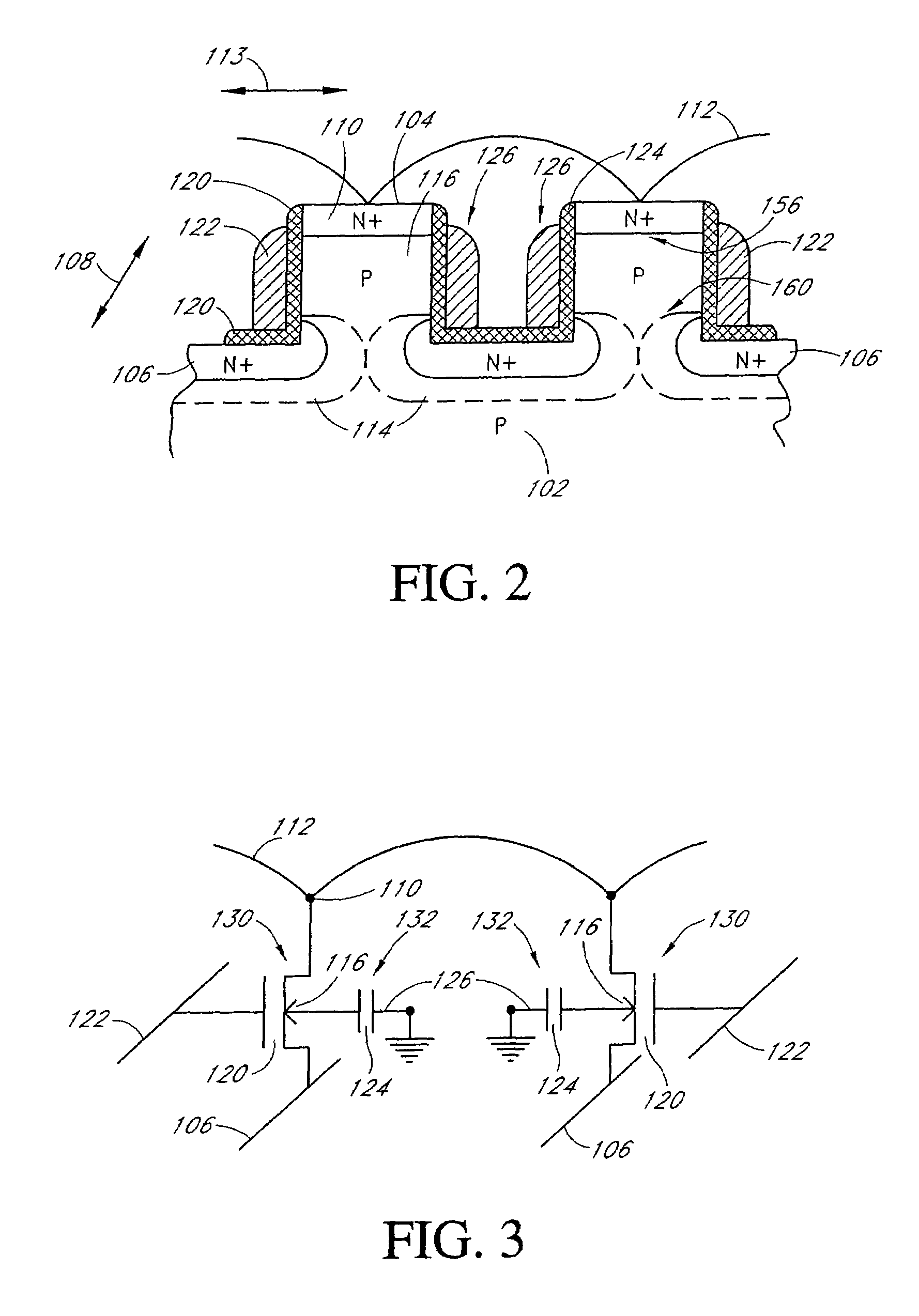
ActiveUS20070047293A1Good conditionVt of the read transistor is highTransistorSolid-state devicesSoi cmosCMOS
A DRAM memory cell and process sequence for fabricating a dense (20 or 18 square) layout is fabricated with silicon-on-insulator (SOI) CMOS technology. Specifically, the present invention provides a dense, high-performance SRAM cell replacement that is compatible with existing SOI CMOS technologies. Various gain cell layouts are known in the art. The present invention improves on the state of the art by providing a dense layout that is fabricated with SOI CMOS. In general terms, the memory cell includes a first transistor provided with a gate, a source, and a drain respectively; a second transistor having a first gate, a second gate, a source, and a drain respectively; and a capacitor having a first terminal, wherein the first terminal of said capacitor and the second gate of said second transistor comprise a single entity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Merged MOS-bipolar capacitor memory cell
A high density vertical merged MOS-bipolar-capacitor gain cell is realized for DRAM operation. The gain cell includes a vertical MOS transistor having a source region, a drain region, and a floating body region therebetween. The gain cell includes a vertical bi-polar transistor having an emitter region, a base region and a collector region. The base region for the vertical bi-polar transistor serves as the source region for the vertical MOS transistor. A gate opposes the floating body region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide on a first side of the vertical MOS transistor. A floating body back gate opposes the floating body region on a second side of the vertical transistor. The base region for the vertical bi-polar transistor is coupled to a write data word line.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com