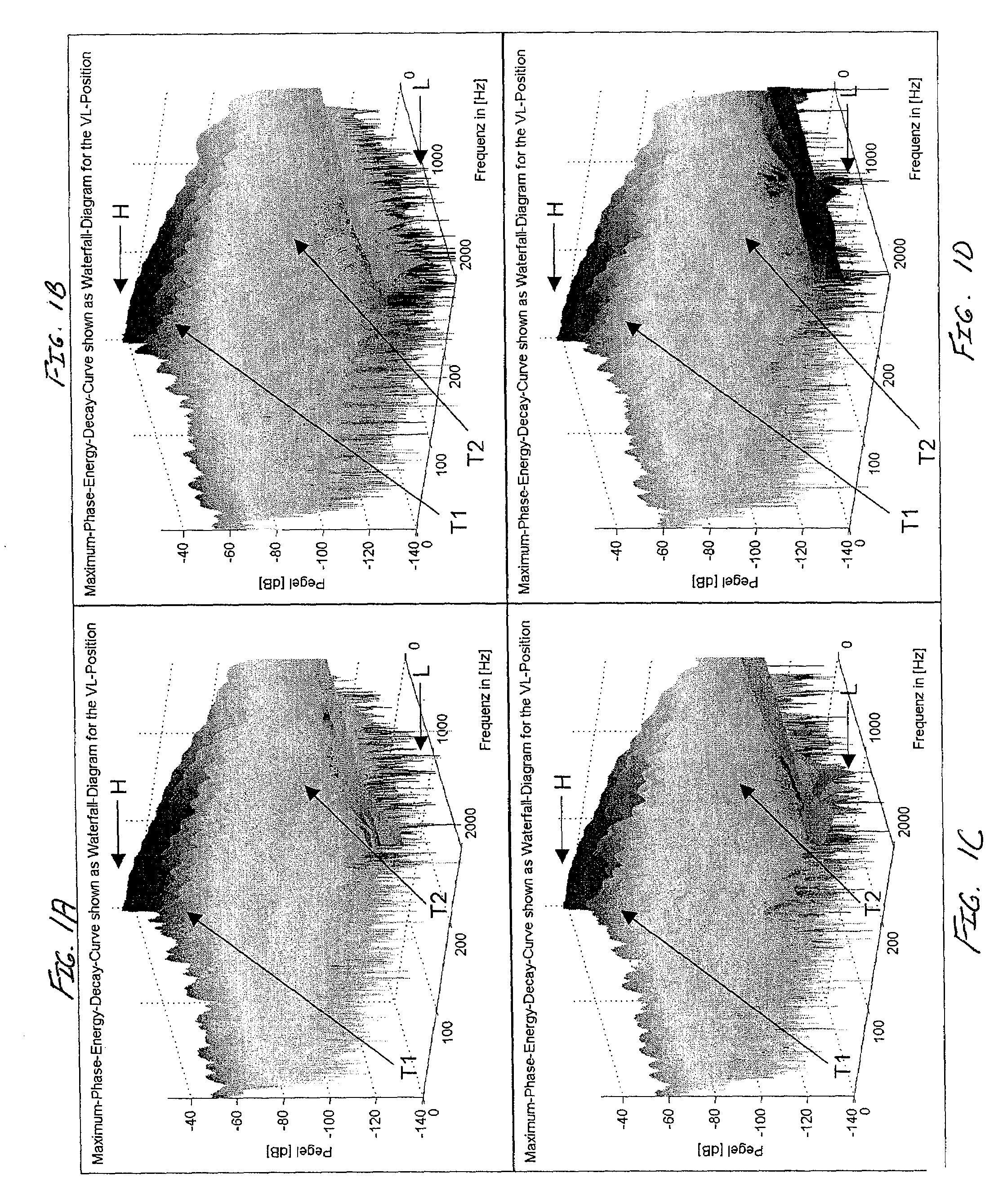
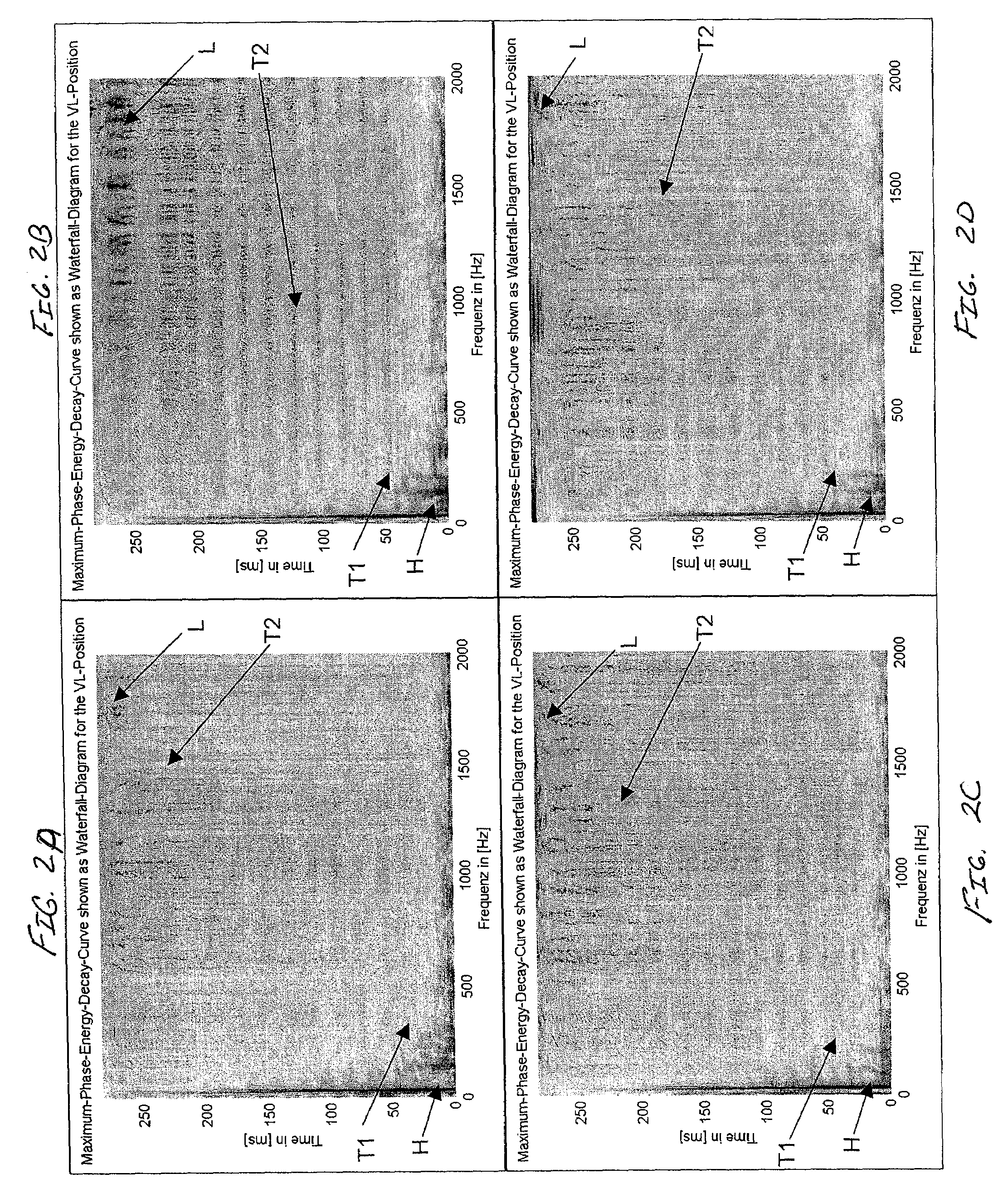
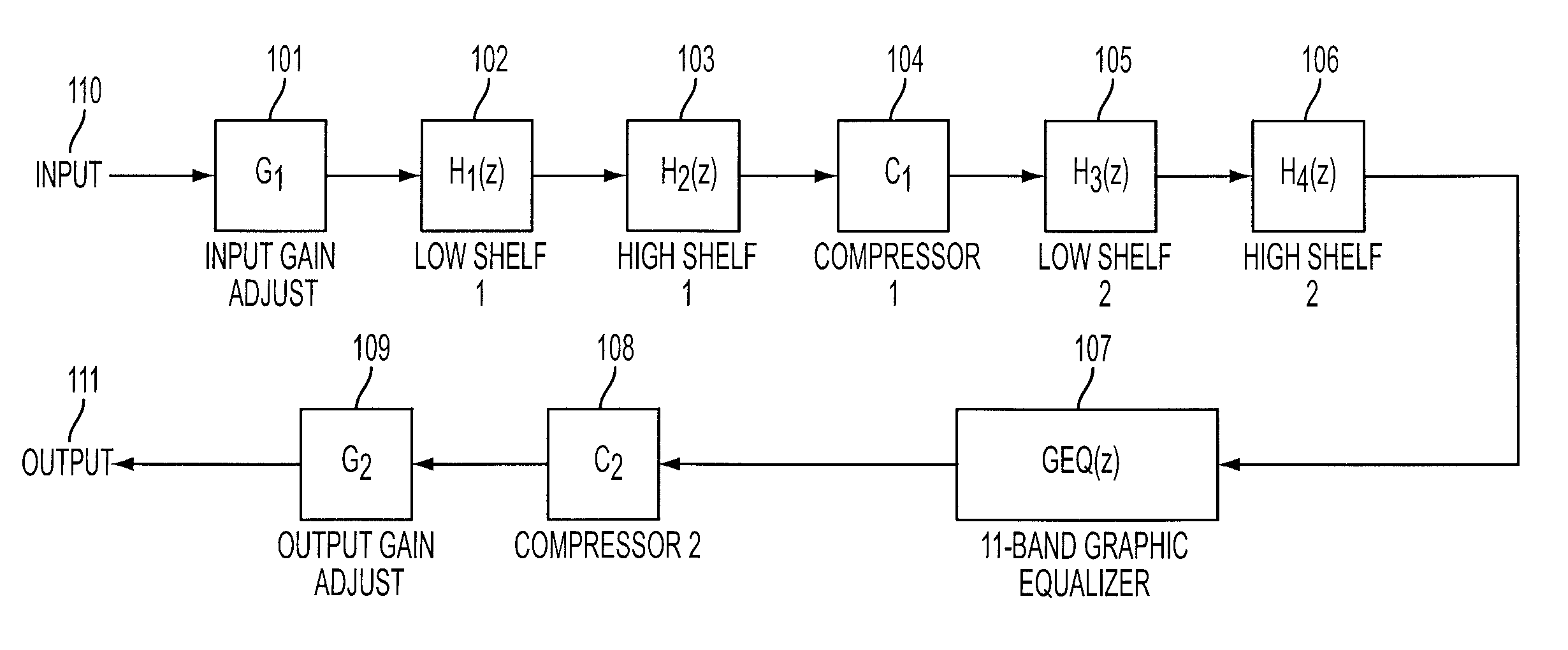
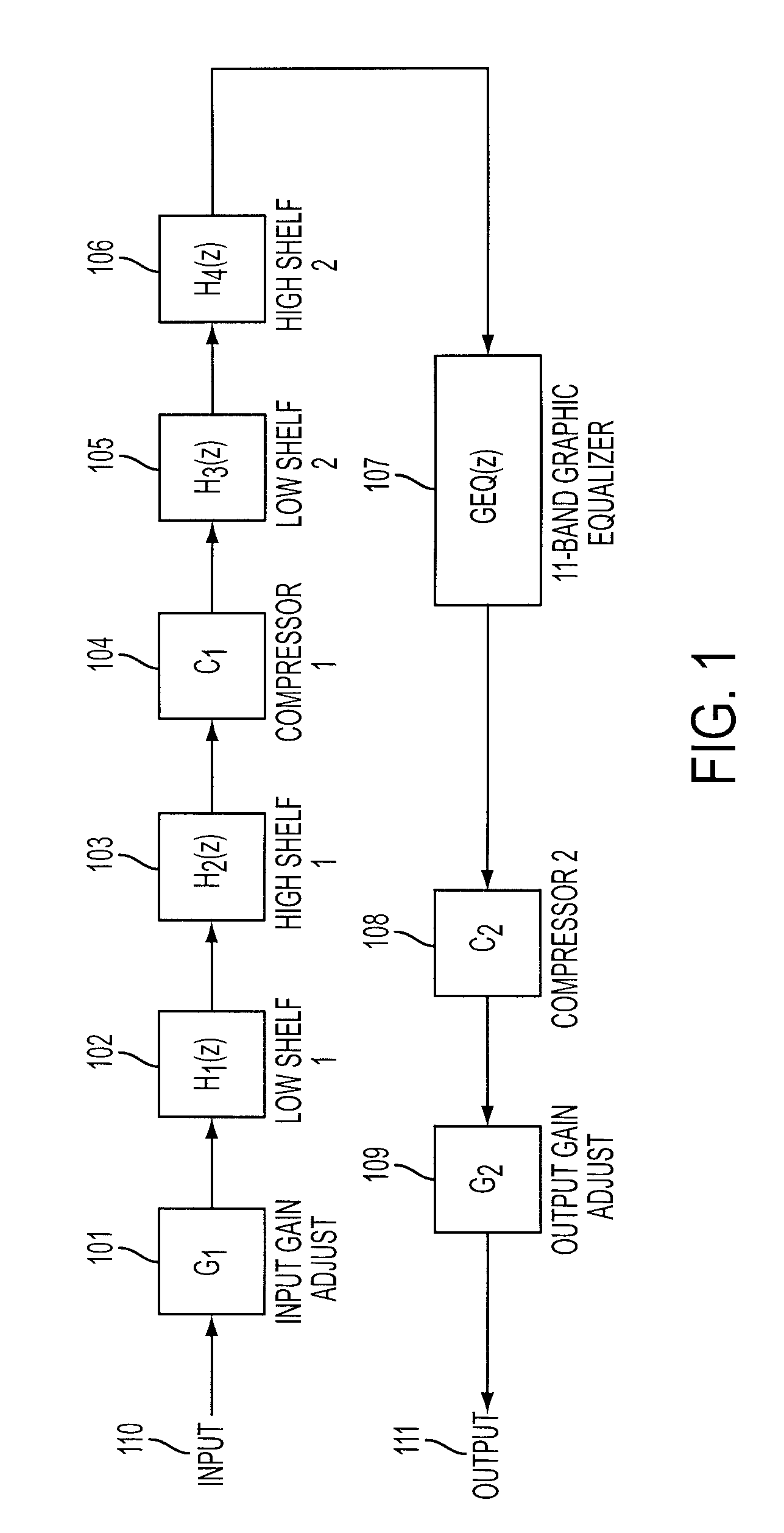
Patents
Literature
344results about "Digital/coded signal combination control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
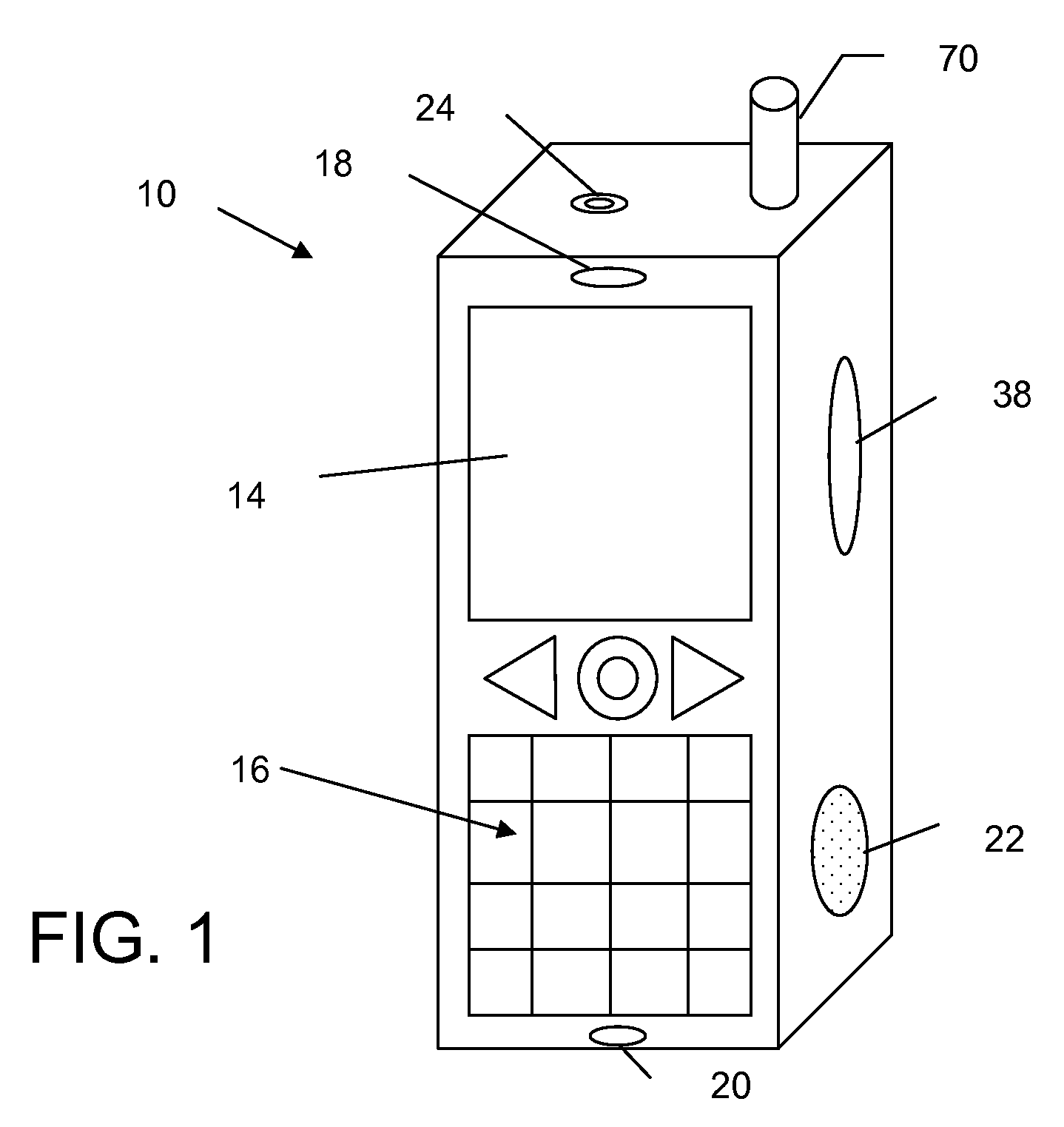
Personalized sound system hearing profile selection process
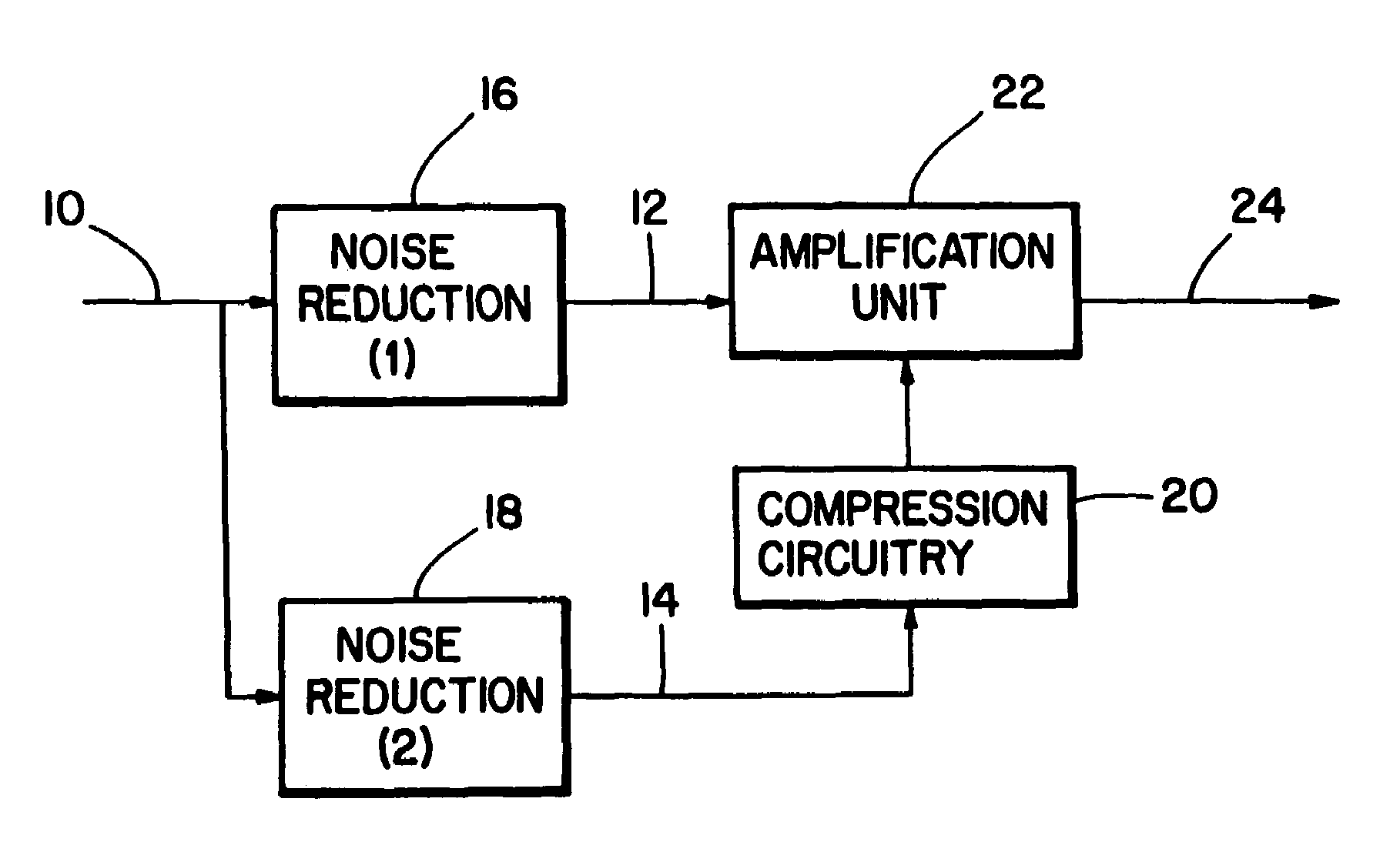
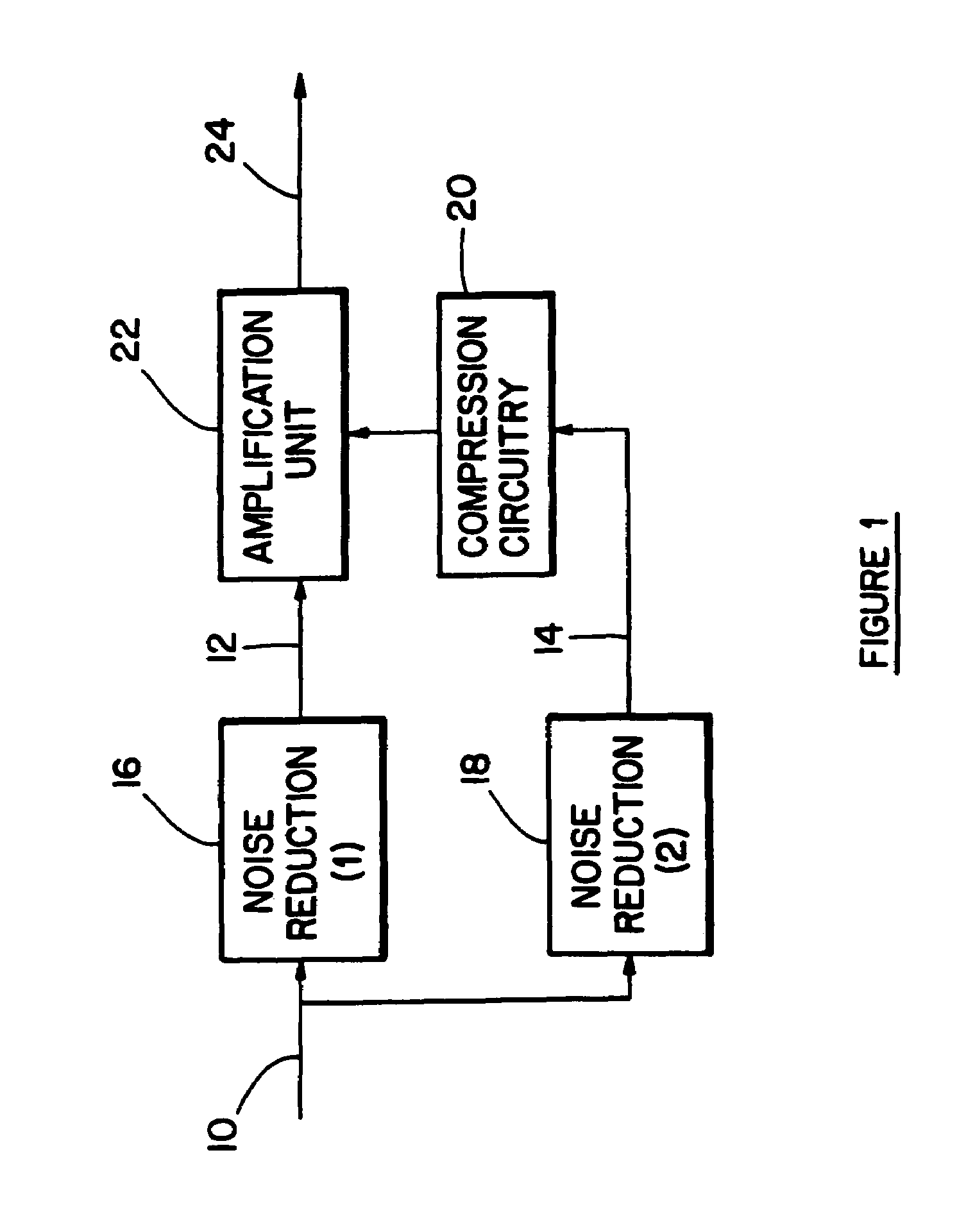
ActiveUS20080165980A1High sensitivityReduce sensitivityStereophonic circuit arrangementsDigital/coded signal combination controlPersonalizationUser input
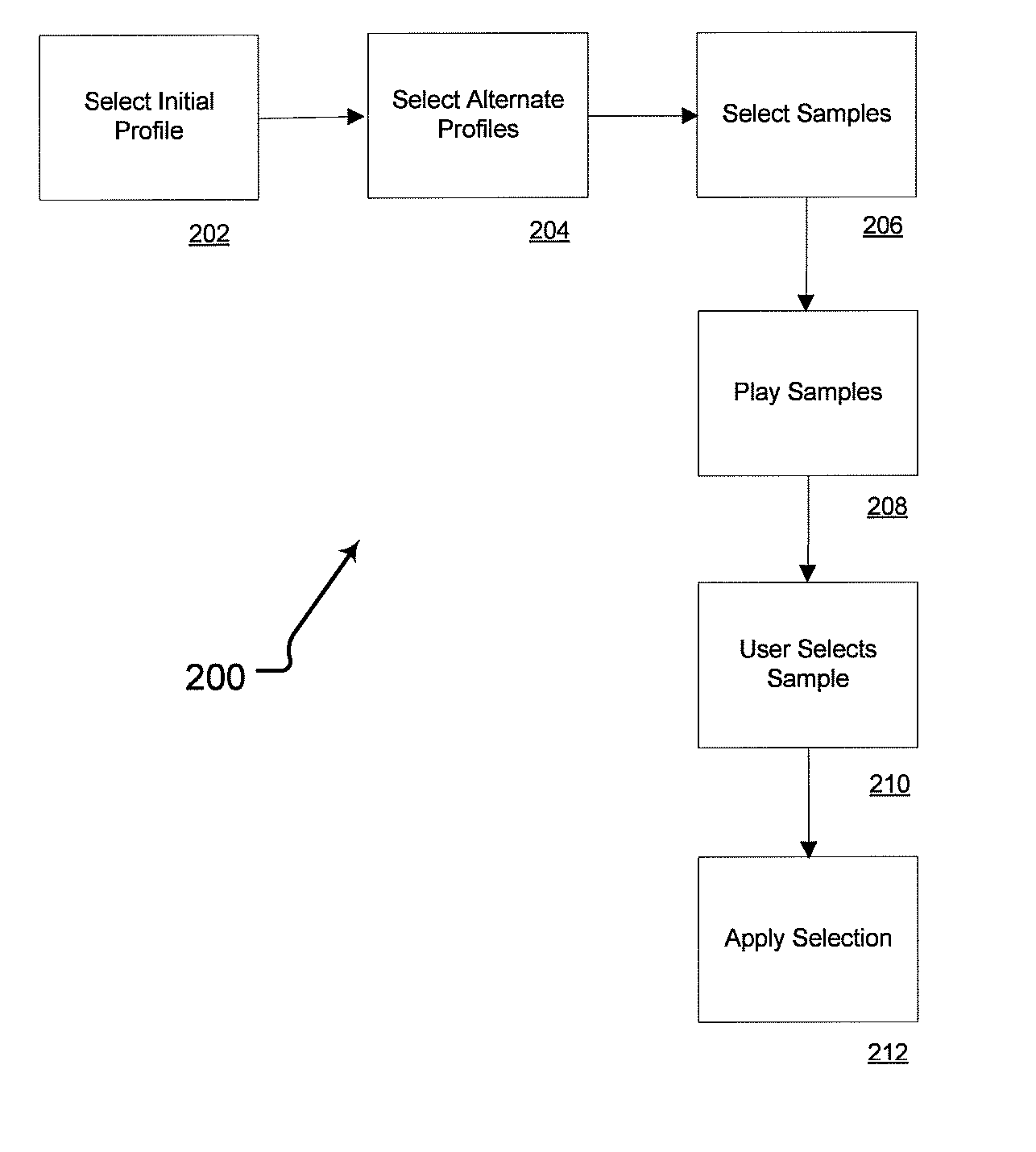
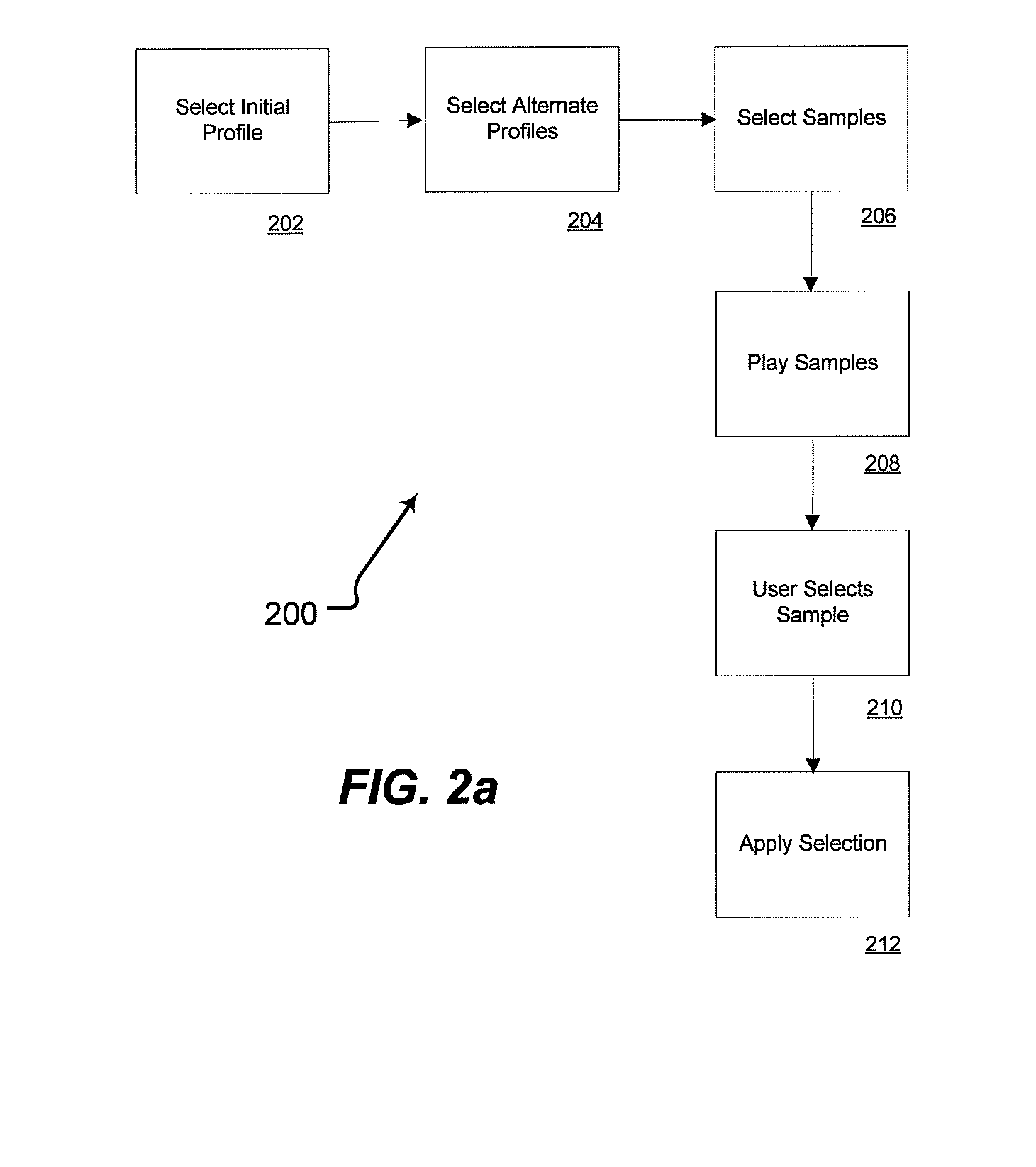
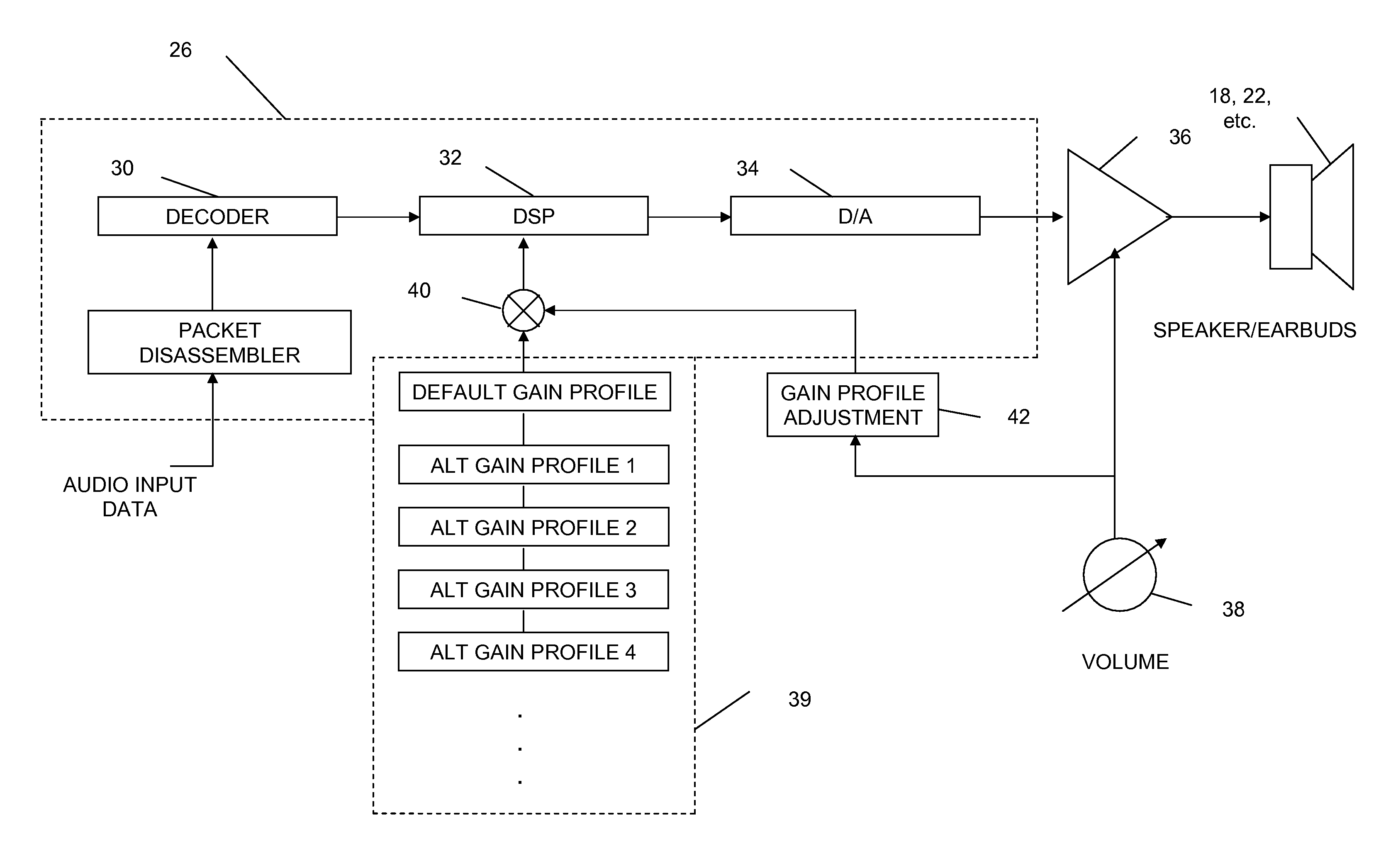
A method of generating a personalized sound system hearing profile for a user. The method begins by selecting an initial profile, based on selected factors of user input. In an embodiment, the initial profile is selected based on demographic factors. Then the system identifies one or more alternate profiles, each having a selected relationship with the initial profile. The relationship between alternate profiles and the initial profile can be based on gain as a function of frequency, one alternate profile having a higher sensitivity at given frequencies and the other a lower sensitivity. The next step links at least one audio sample with the initial and alternate profiles and then plays the selected samples for the user. The system then receives identification of the preferred sample from the user; and selects a final profile based on the user's preference. An embodiment offers multiple sound samples in different modes, resulting in the selection of multiple final profiles for the different modes. Finally, the system may apply the final profile to the sound system.
Owner:HIMPP
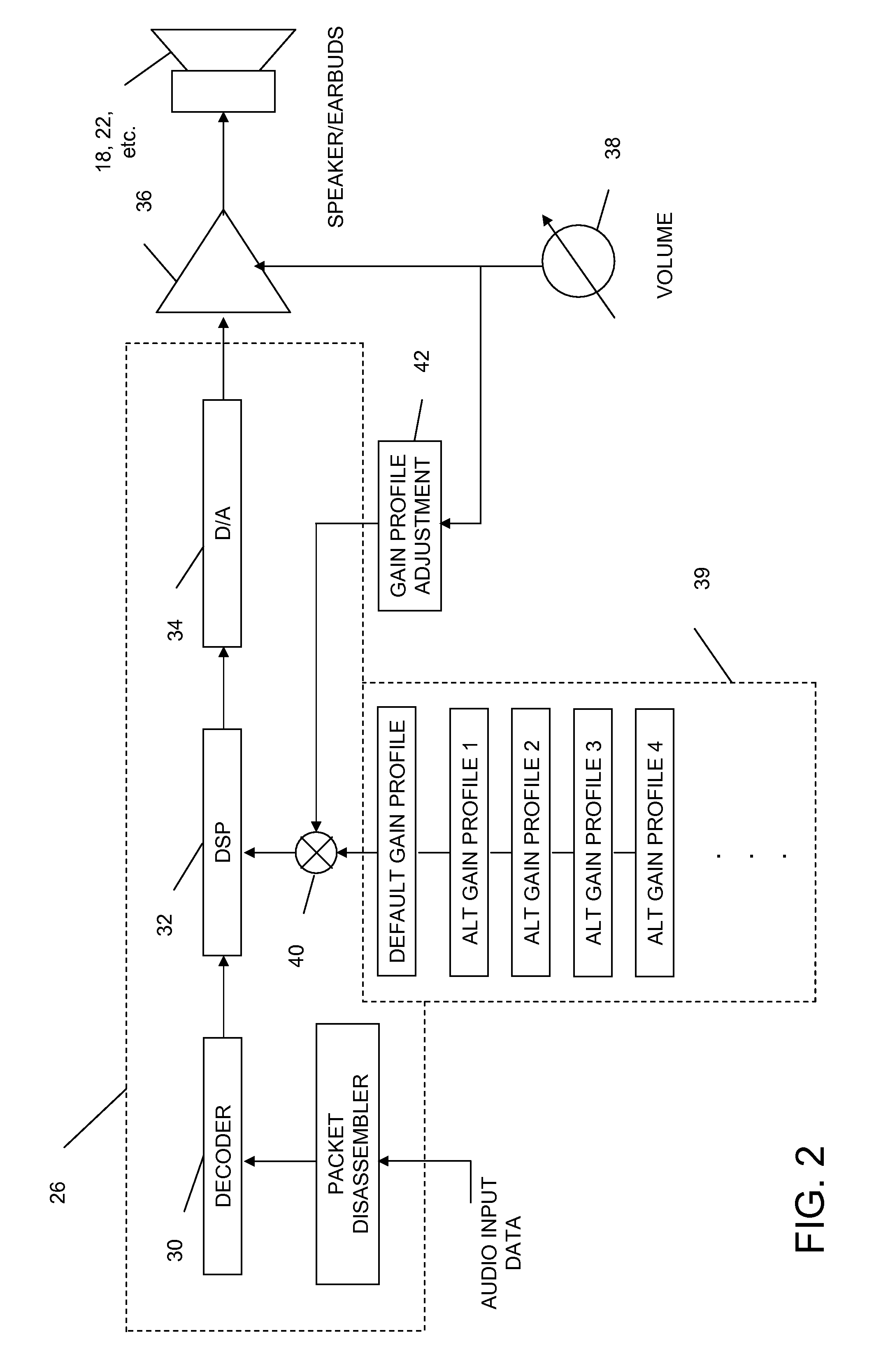
Volume dependent audio frequency gain profile
InactiveUS20080013751A1Adjusts the audio frequency gain profileReduce gainDigital/coded signal combination controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsControl circuitAudio signal flow
An electronic equipment is provided that includes an audio reproduction circuit for receiving an audio signal and reproducing the audio signal in accordance with a preselected audio frequency gain profile. In addition, the electronic equipment includes a volume gain control circuit for providing user adjustable volume gain to the audio signal reproduced by the audio reproduction circuit. The electronic equipment also includes an audio output for outputting the reproduced audio signal. The audio reproduction circuit alters the preselected audio frequency gain profile as a function of the user adjusted volume gain.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
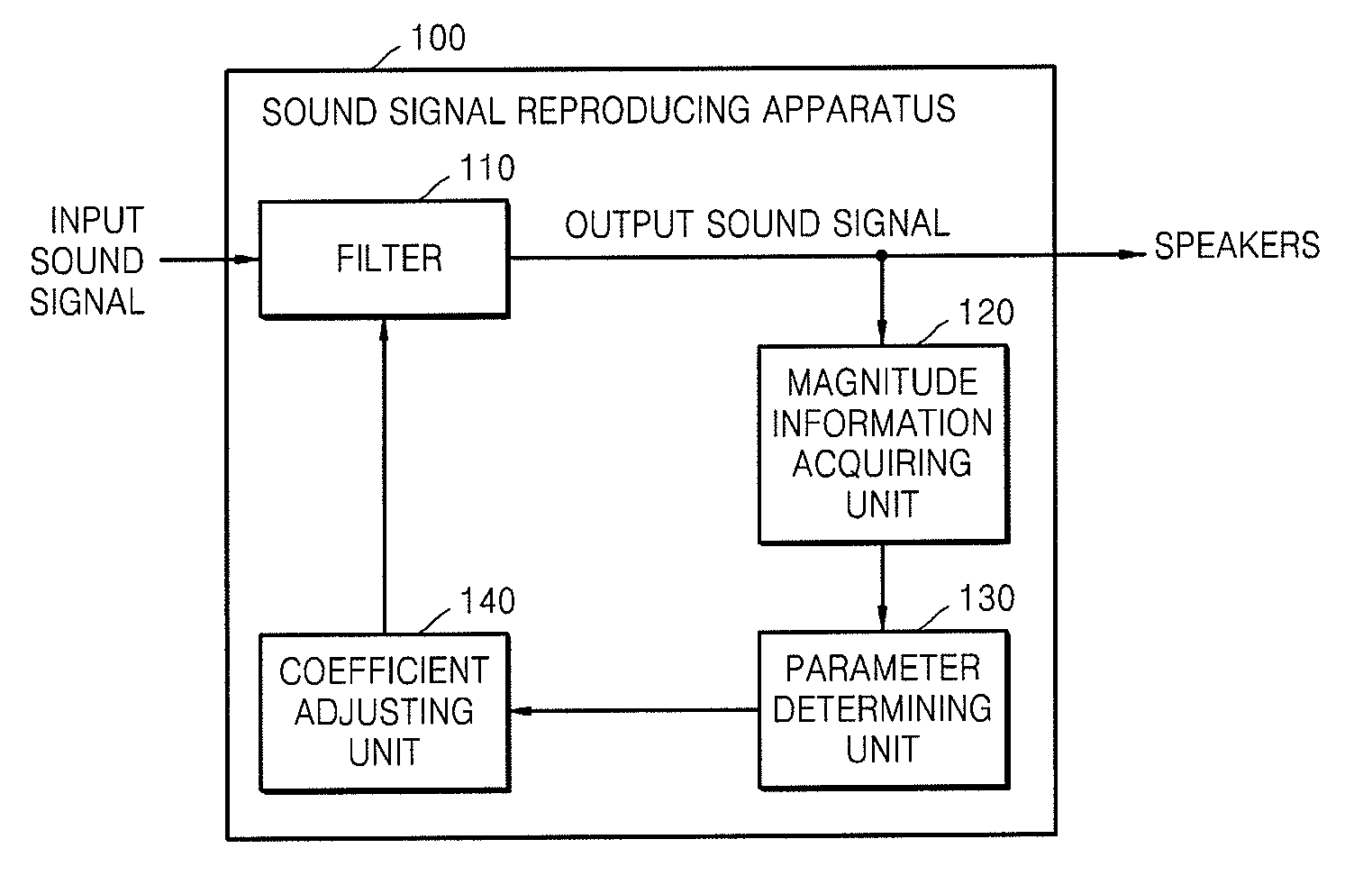
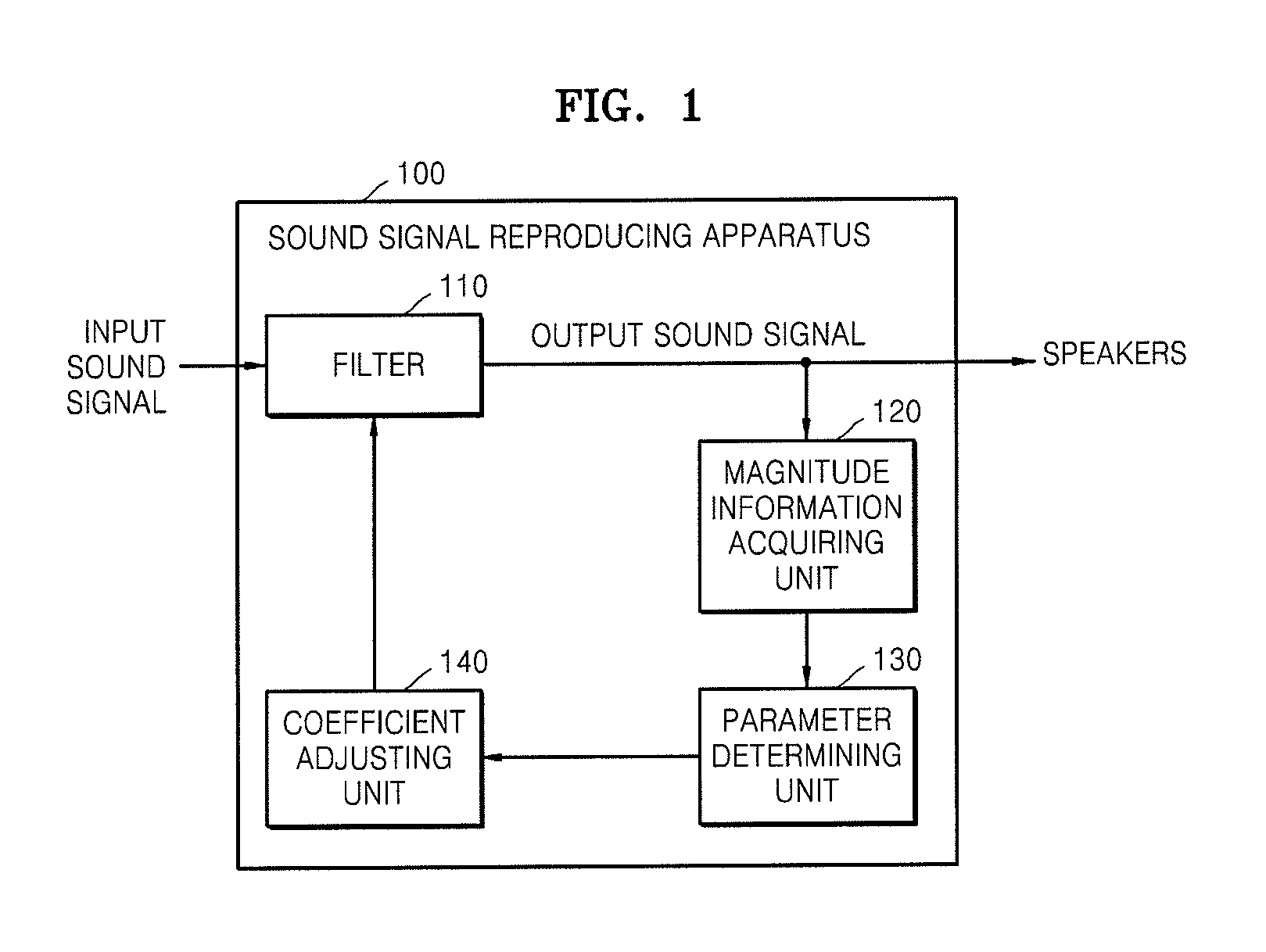
Method and apparatus for reproducing audio signal by adaptively controlling filter coefficient
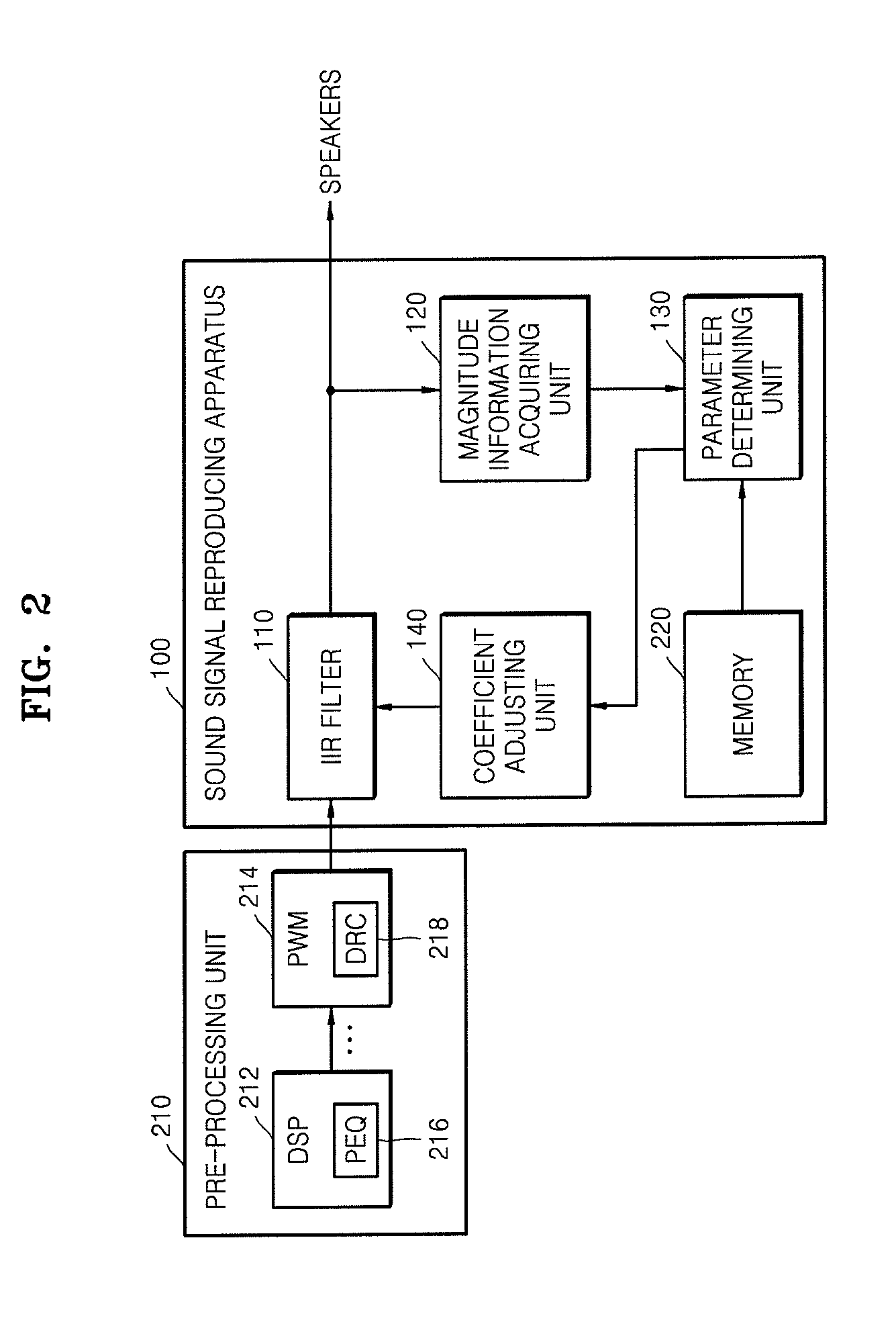
InactiveUS20120051558A1Increase gain valueDigital/coded signal combination controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsAudio signal flowLoudspeaker
A method and an apparatus for reproducing a sound signal are provided. The method includes generating an output sound signal to be transmitted to speakers by transmitting a first input sound signal through a filter; acquiring magnitude information of the output sound signal; determining frequency response parameters related to frequency responses of the filter based on the magnitude information; and adaptively adjusting coefficients of the filter based on the determined frequency response parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
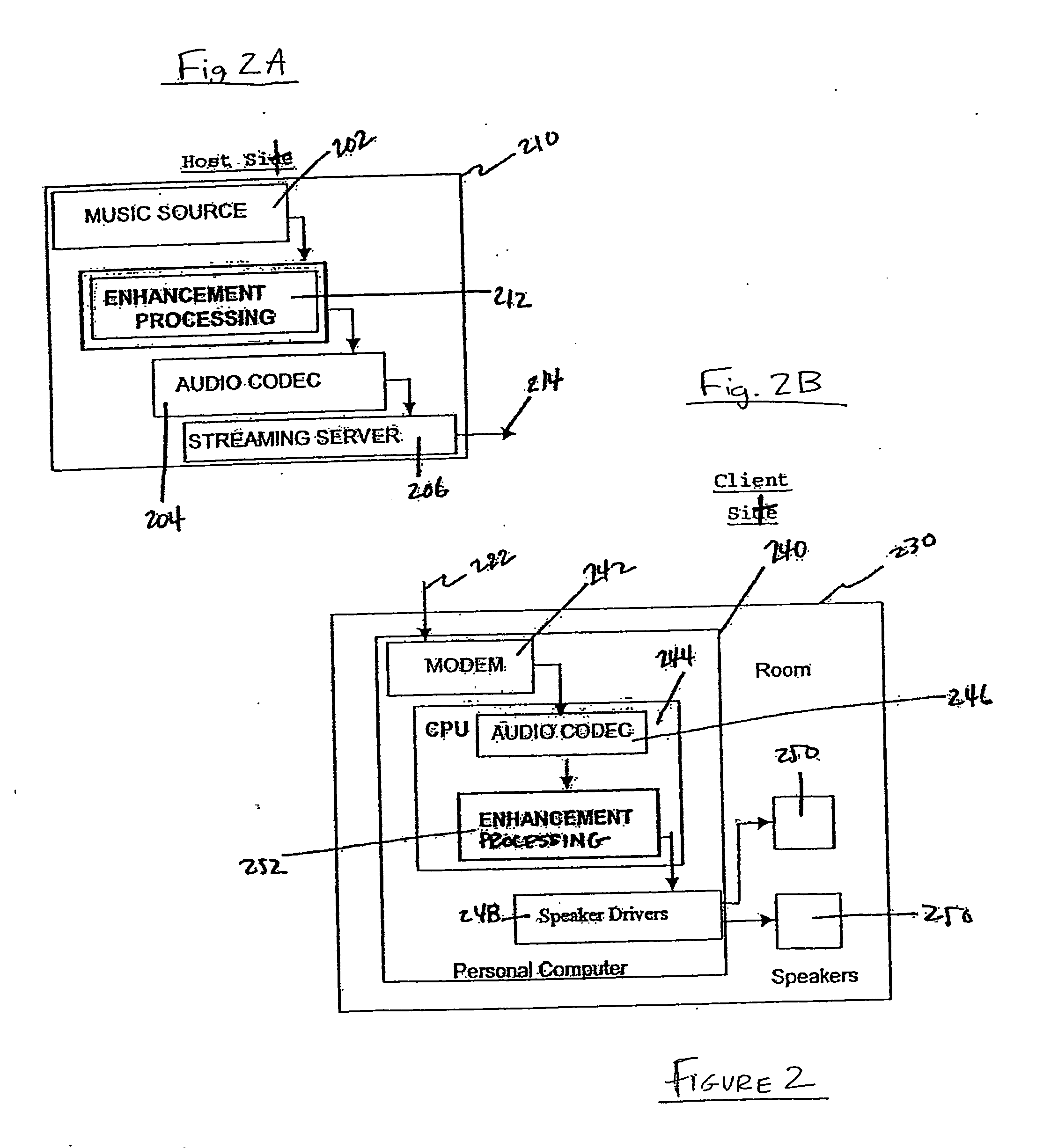
Acoustical virtual reality engine and advanced techniques for enhancing delivered sound
ActiveUS20060098827A1Optimize timingEnhanced audio signalGain controlStereophonic circuit arrangementsClient-sideComputer science
Techniques and systems for enhancing delivered audio signals are disclosed which may be employed in a delivery system at a server side, a client side, or both. The techniques include forming a processed audio signal by processing audio signals through multiple pathways which operate on different frequency bands using dynamic processing and other elements, and thereafter providing recording or listening environment enhancements and other sound enhancements to the processed audio signal. Also disclosed are techniques and systems for implementing the multi-pathway processing and environmental and sound enhancements.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
System output control method and apparatus
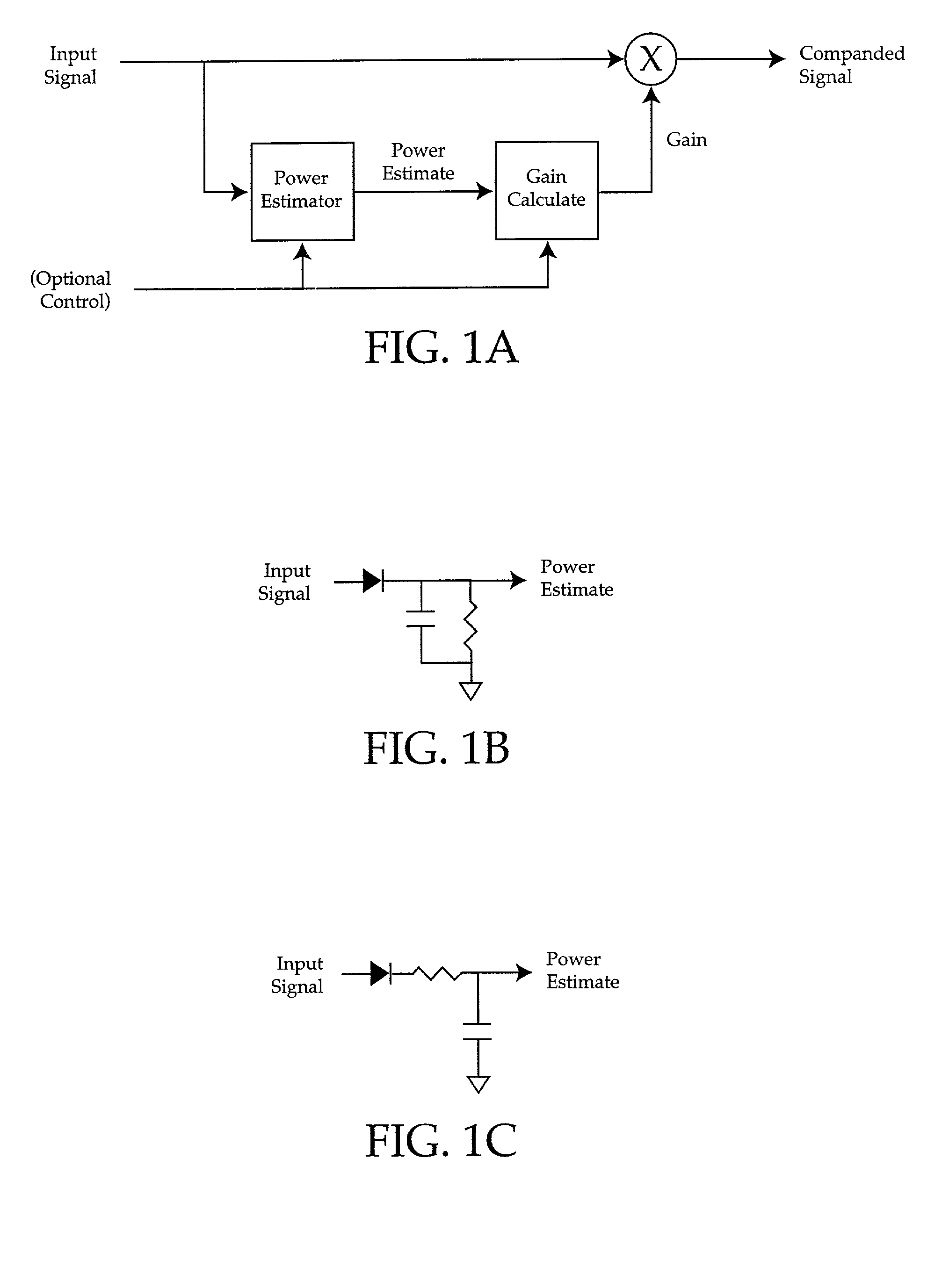
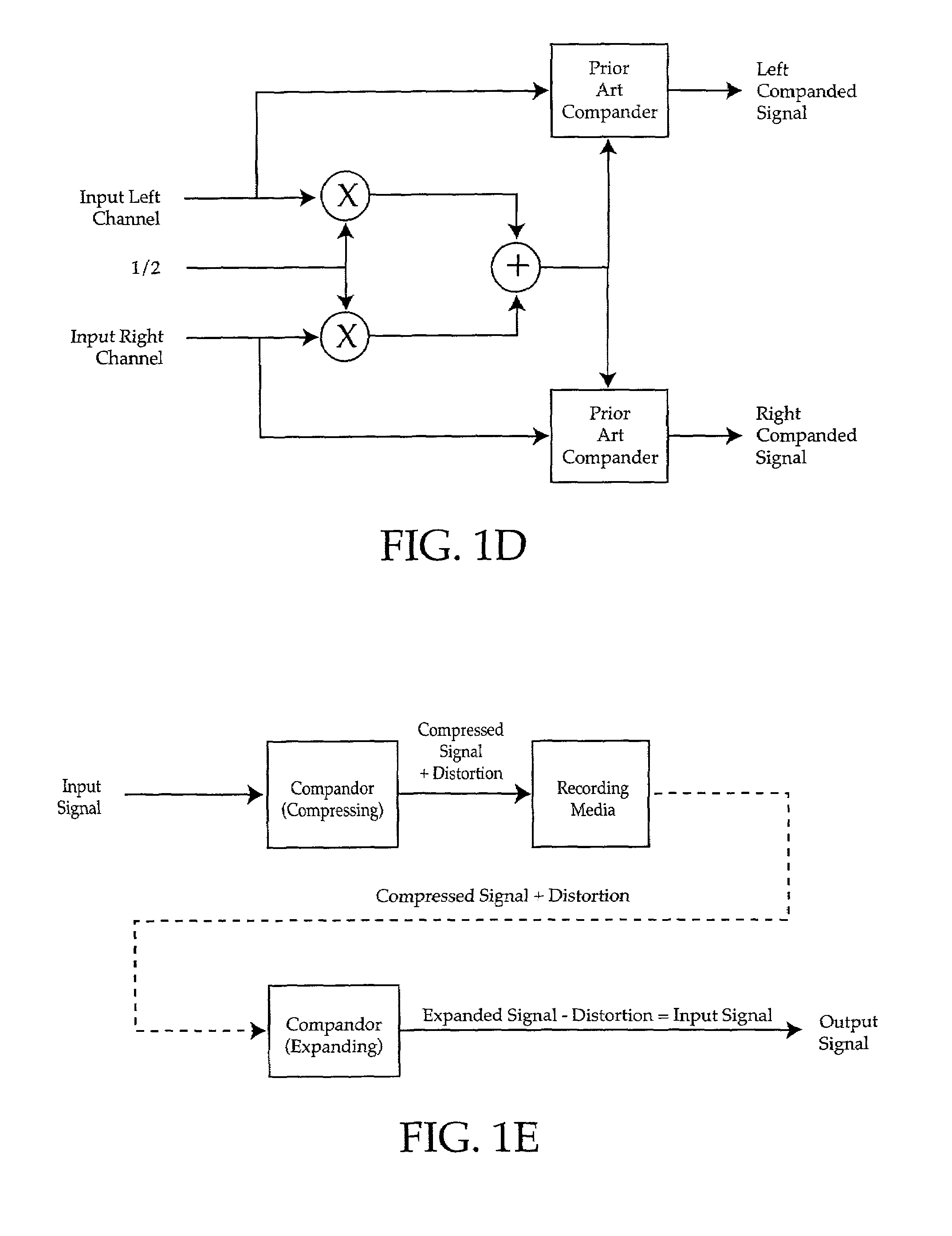
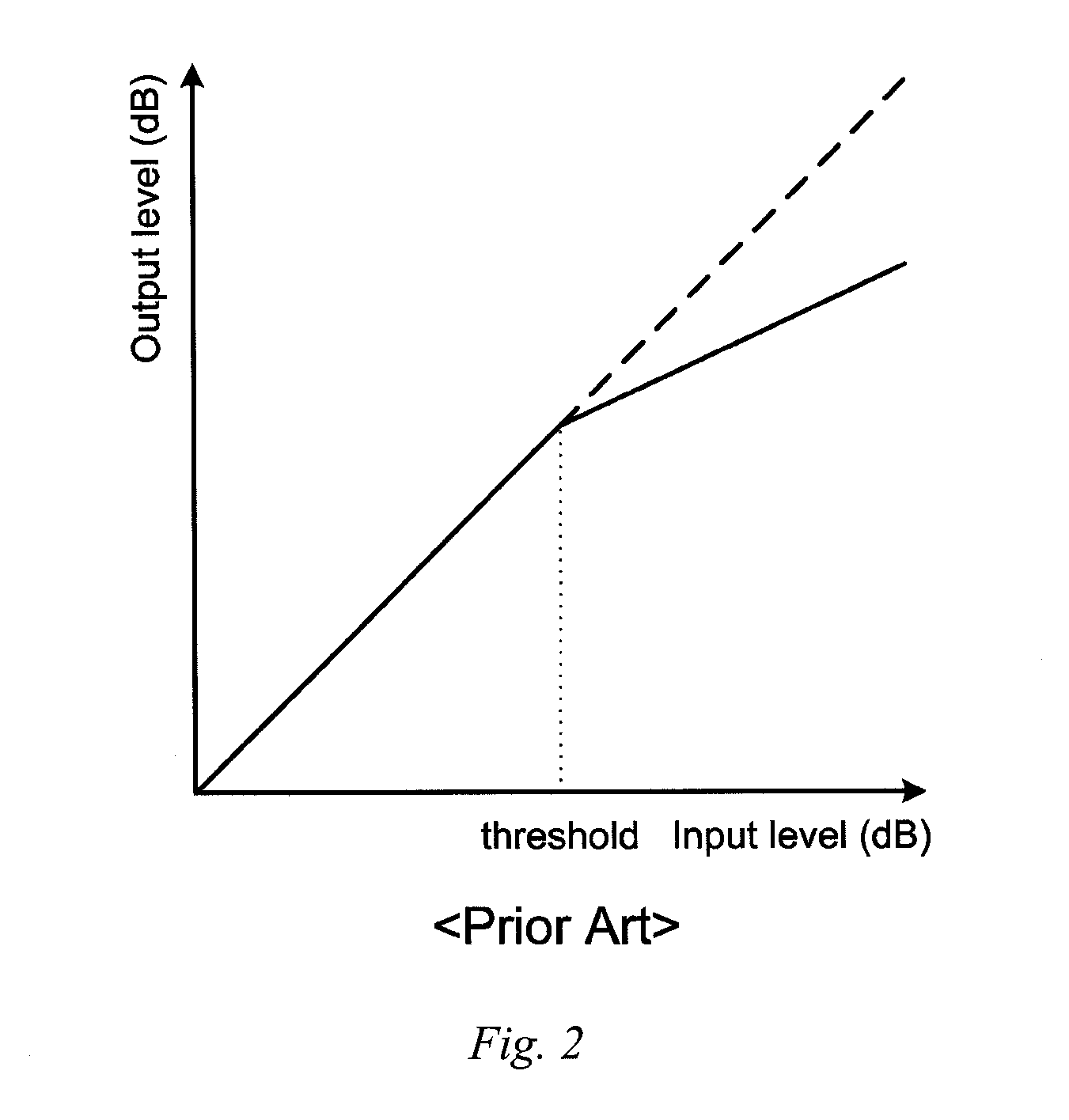
ActiveUS7027981B2Maximum flexibilityImplemented cost-effectivelyVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesGain controlControl systemCompression ratio
Output control system and method includes calculating gain for an input signal, detecting a predetermined condition, and modifying the gain calculation in accordance with one or more kneepoints to provide a varying output signal. A companding ratio is then established in accordance with the kneepoints. System gain is then adjusted, and the companding ratio may be further adjusted by adjusting one of the kneepoints relative to another.
Owner:BIZJAK KARL M
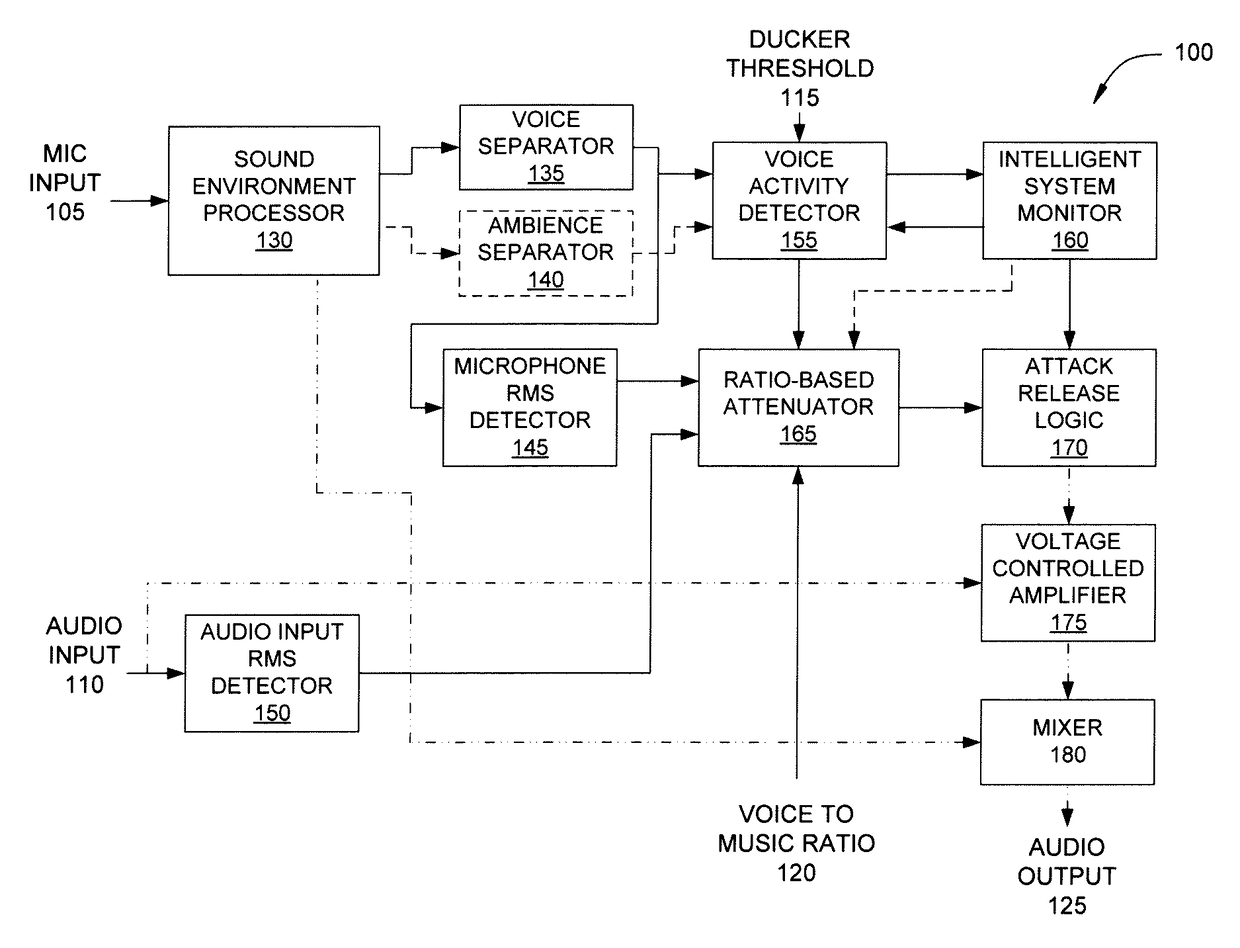
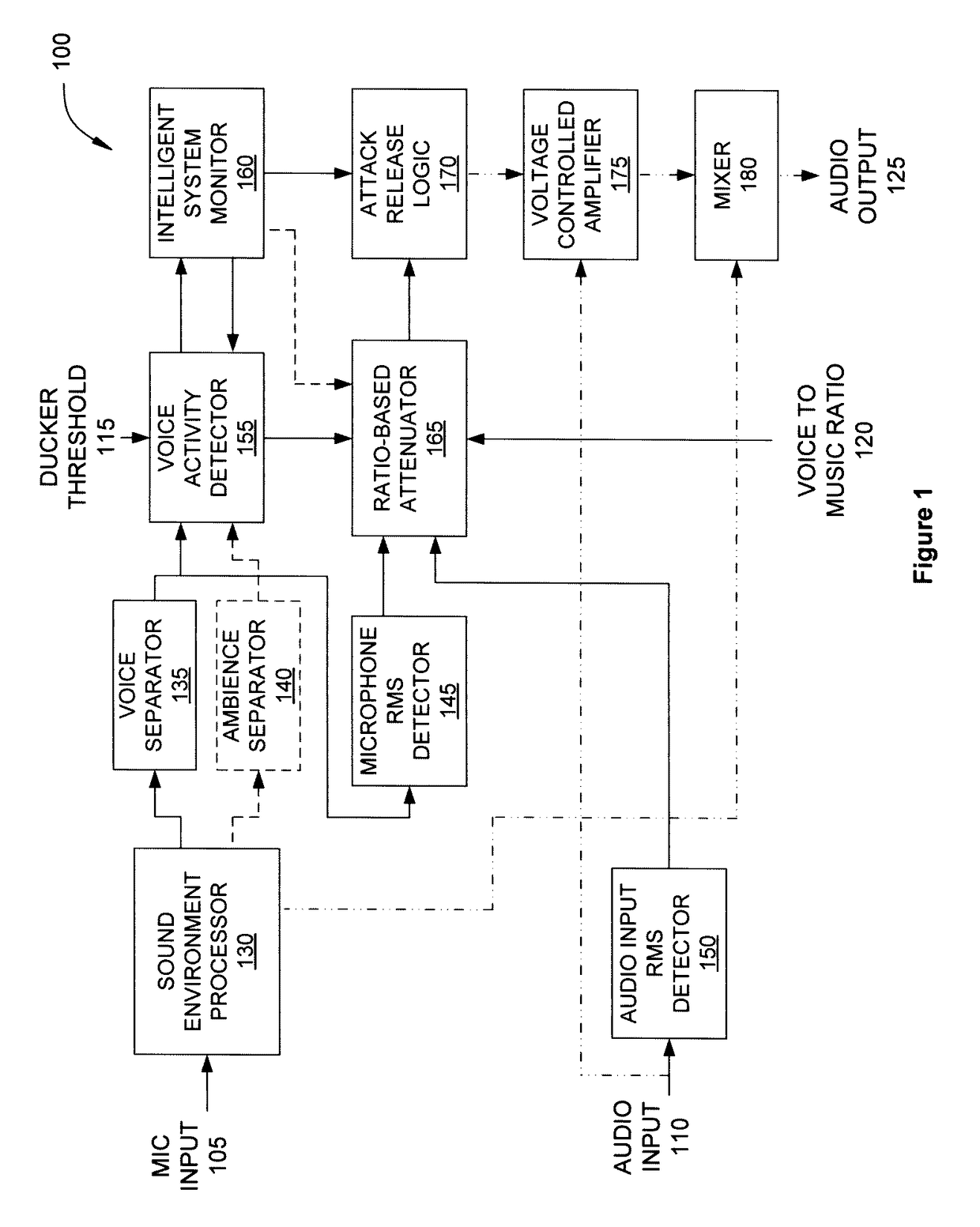
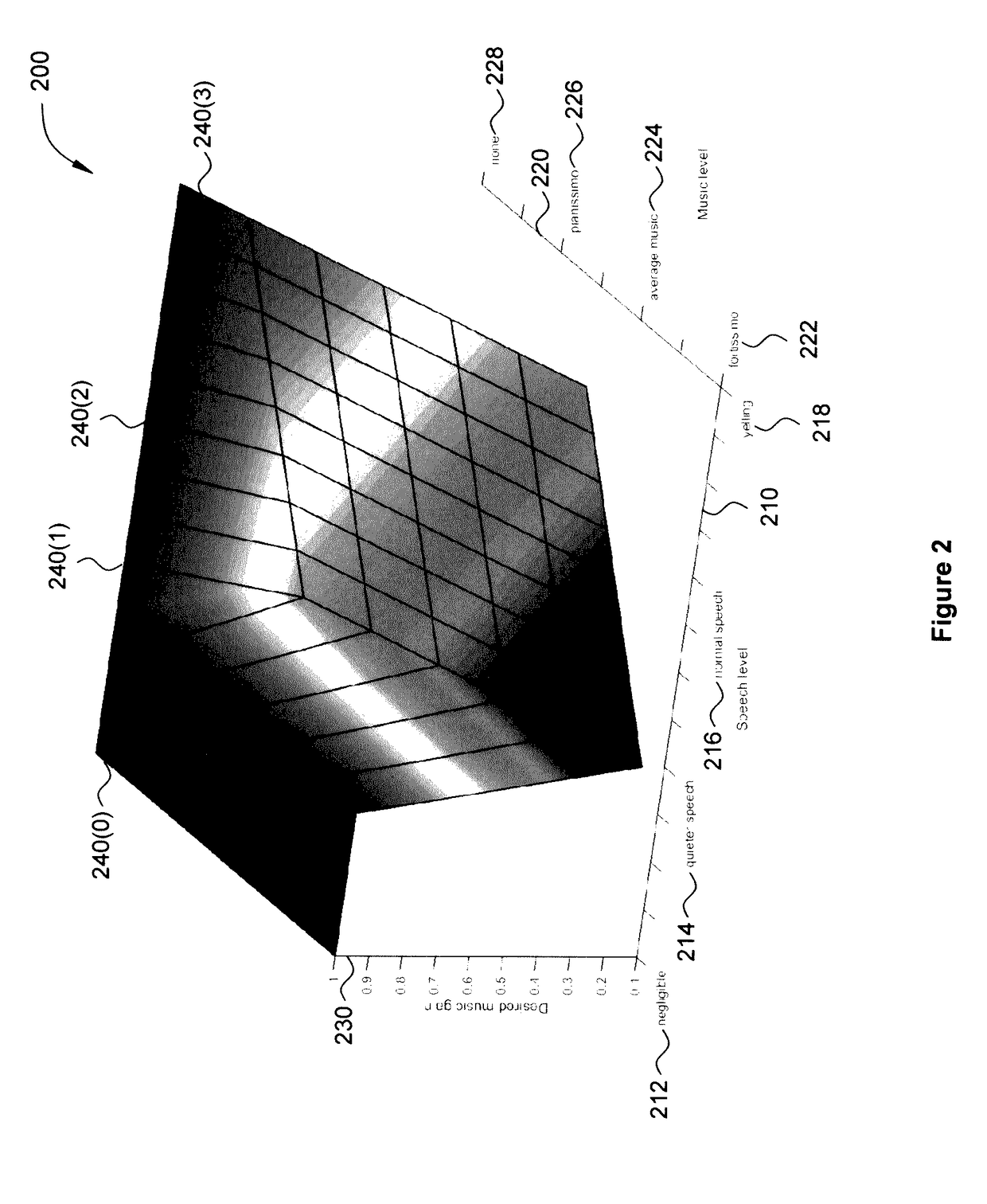
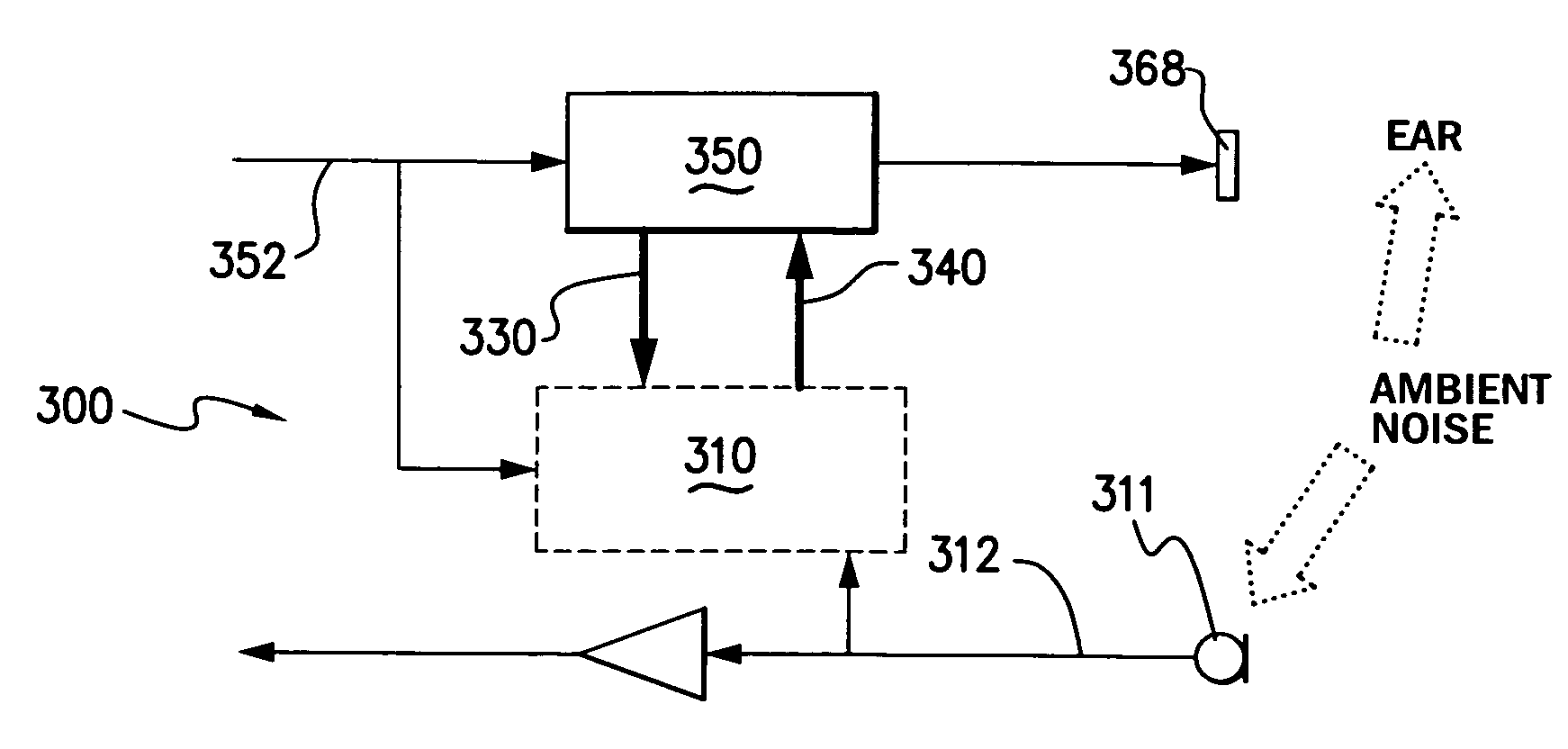
Approach for partially preserving music in the presence of intelligible speech
An audio processing system for a listening device includes an input device, a voice activity detector and a ratio-based attenuator. The input device is configured to receive a first audio signal emanating from an environment and including a signal of interest. The voice activity detector is configured to generate a control signal in response to the first audio signal. The ratio-based attenuator is configured to receive the control signal and determine whether the signal level of the first audio signal exceeds the signal level of an audio signal received from an audio playback device by at least a target difference. If so, then the audio level of the playback audio signal is maintained. Otherwise, the audio level of the playback audio signal is adjusted, where, at the adjusted value, the first signal level exceeds the playback signal level by at least the target difference.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Method and apparatus for adaptive sound processing parameters
InactiveUS20060126865A1Improve matchGain may be prevented from increasingVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesGain controlEngineeringDynamic range
An input sound signal (210) is processed in order to meet a target dynamic range (910, 920). At least one gain, specific to the input sound signal (210), is applied to the input sound signal (210) to produce a processed sound signal (214). A dynamic range of the processed sound signal is measured, and a match of the measured dynamic range with the target dynamic range (910, 920) is determined. The gain is adjusted in accordance with at least one input sound signal-specific parameter, to improve the match of dynamic range of the processed sound signal (214) to the target dynamic range (910, 920). The input sound signal-specific parameter is adaptive in response to at least one monitored signal condition.
Owner:WOLFSON DYNAMIC HEARING
Hearing compensation system incorporating signal processing techniques
InactiveUS20050111683A1Signal processingCombination control in untuned amplifierBandpass filteringEngineering
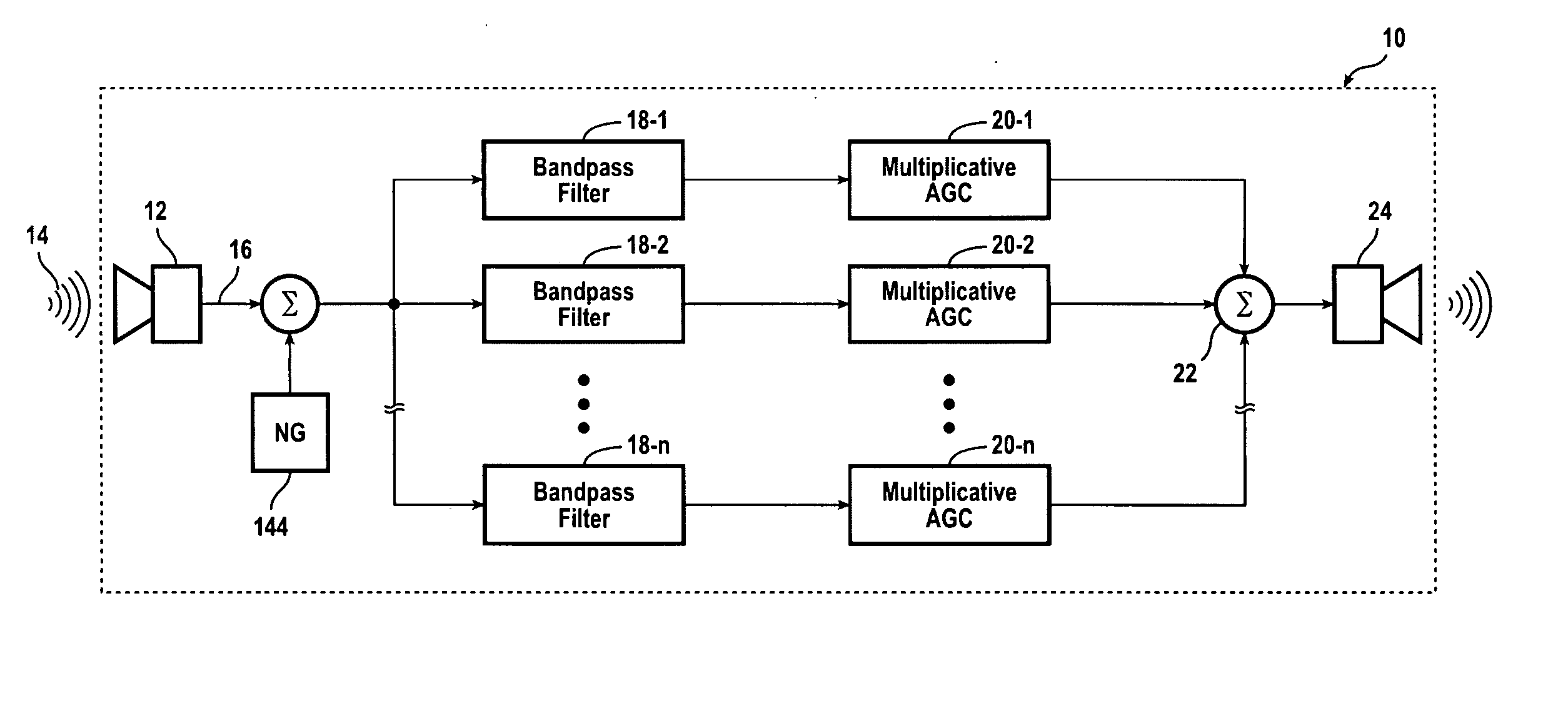
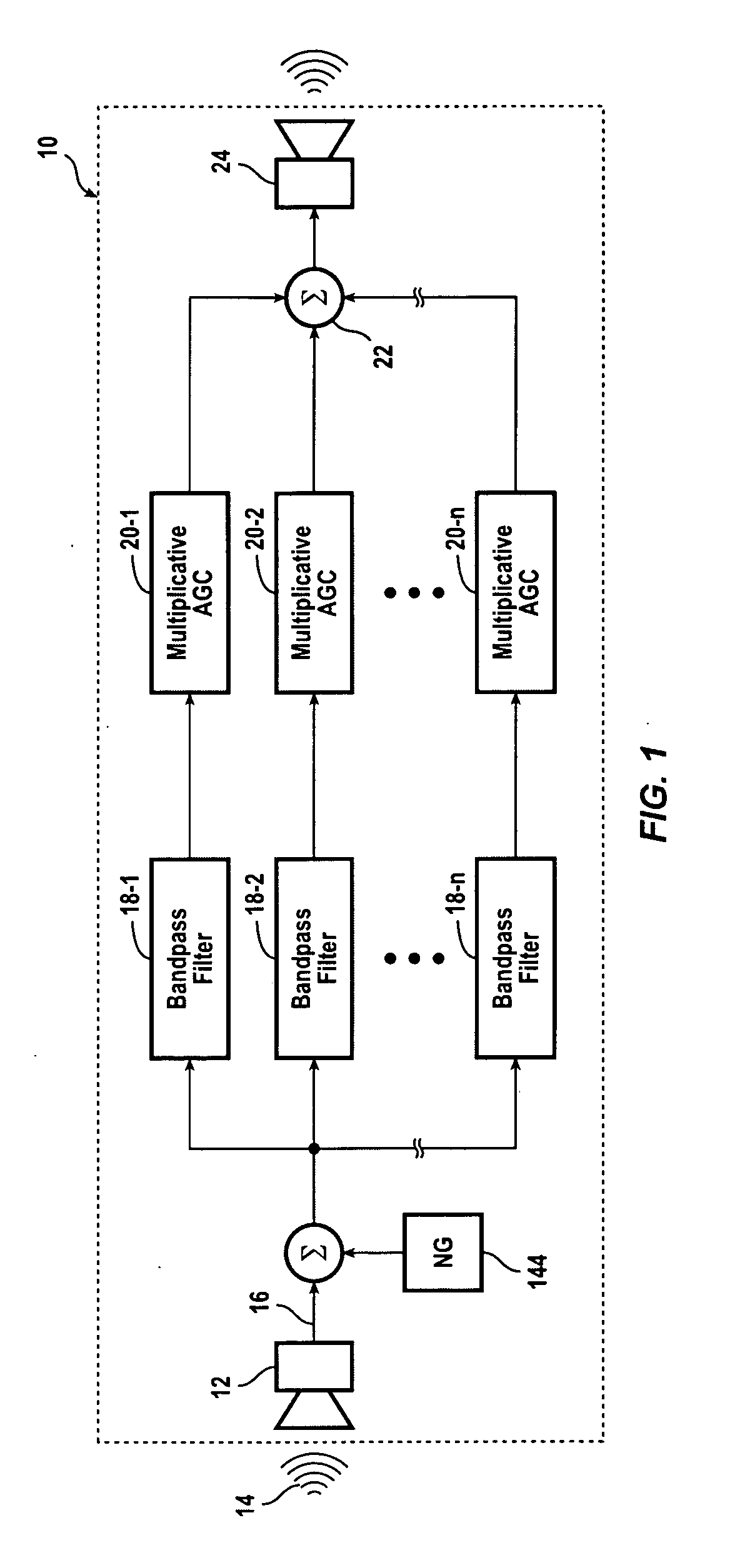
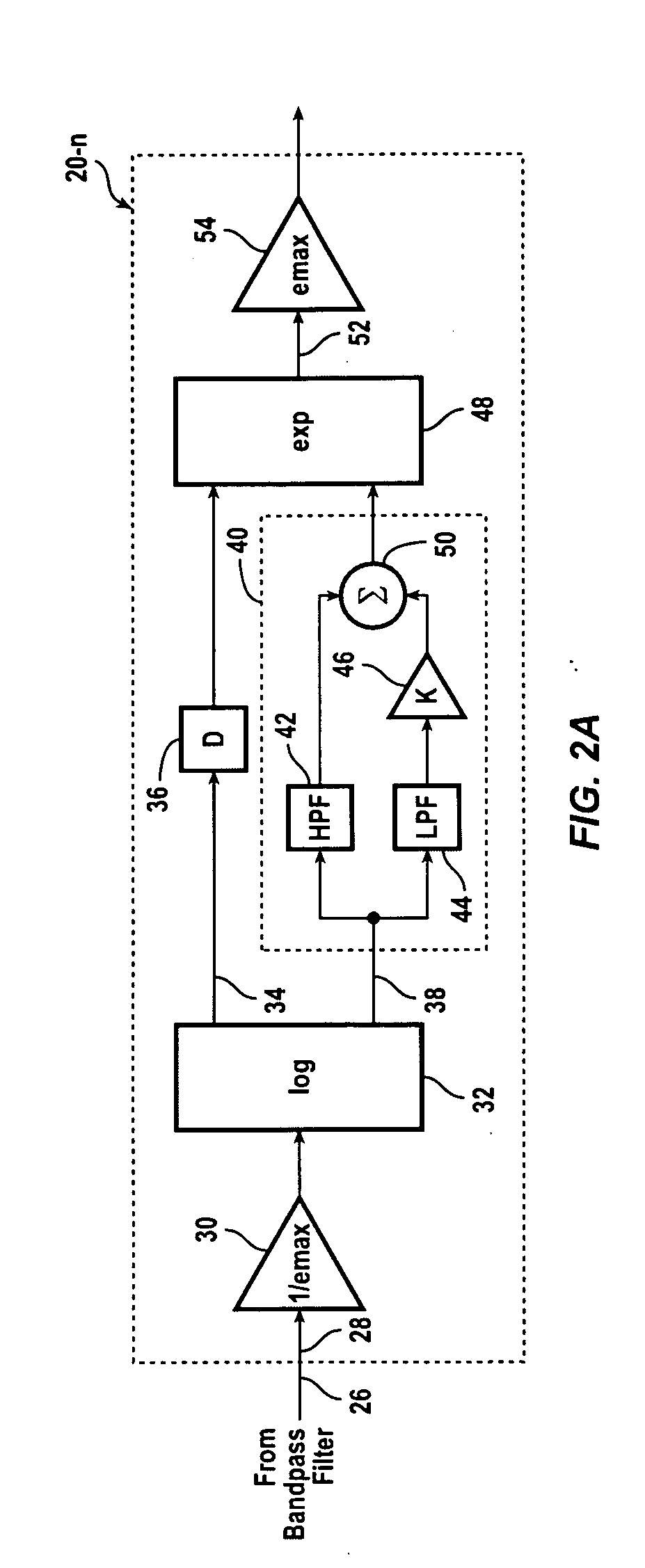
A hearing compensation system comprises a plurality of bandpass filters having an input connected to an input transducer and each bandpass filter having an output connected to the input of one of a plurality of multiplicative automatic gain control (MAGC) circuits whose outputs are summed together and connected to the input of an output transducer. The MAGC circuits attenuate acoustic signals having a constant background level without the loss of speech intelligibility. The identification of the background noise portion of the acoustic signal is made by the constancy of the envelope of the input signal in each of the several frequency bands. The background noise that will be suppressed includes multi-talker speech babble, fan noise, feedback whistle, florescent light hum, and white noise. For use in the consumer electronics field background acoustic noise may be sensed and used to adjust gain in the various MAGC circuits so as to improve a user's listening experience, whether the user is hearing impaired or not.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
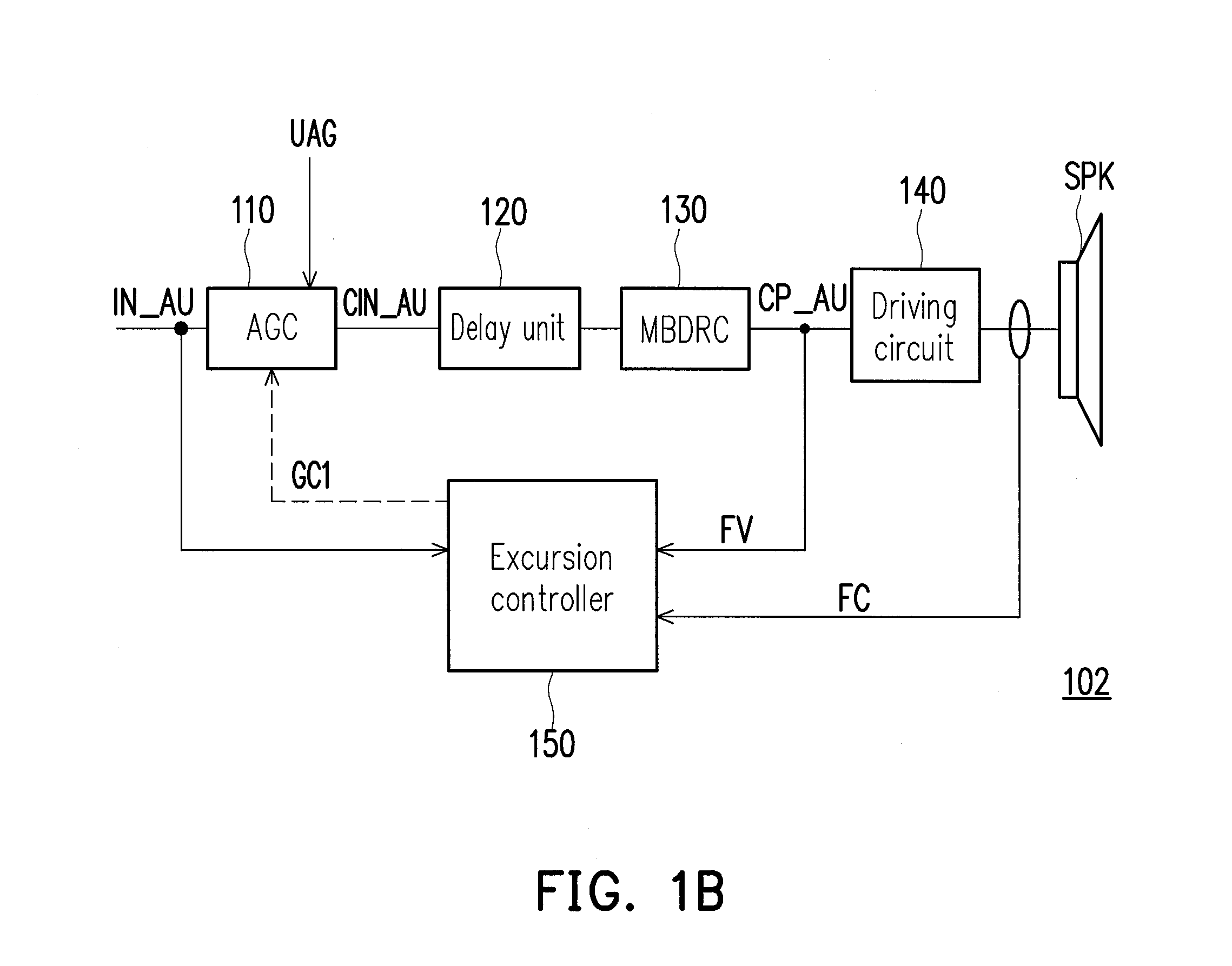
Method of controlling diaphragm excursion of electrodynamic loudspeakers
ActiveUS9813812B2Reliable and convenient protectionSignal processingCombination control in untuned amplifierBand splittingLow frequency band
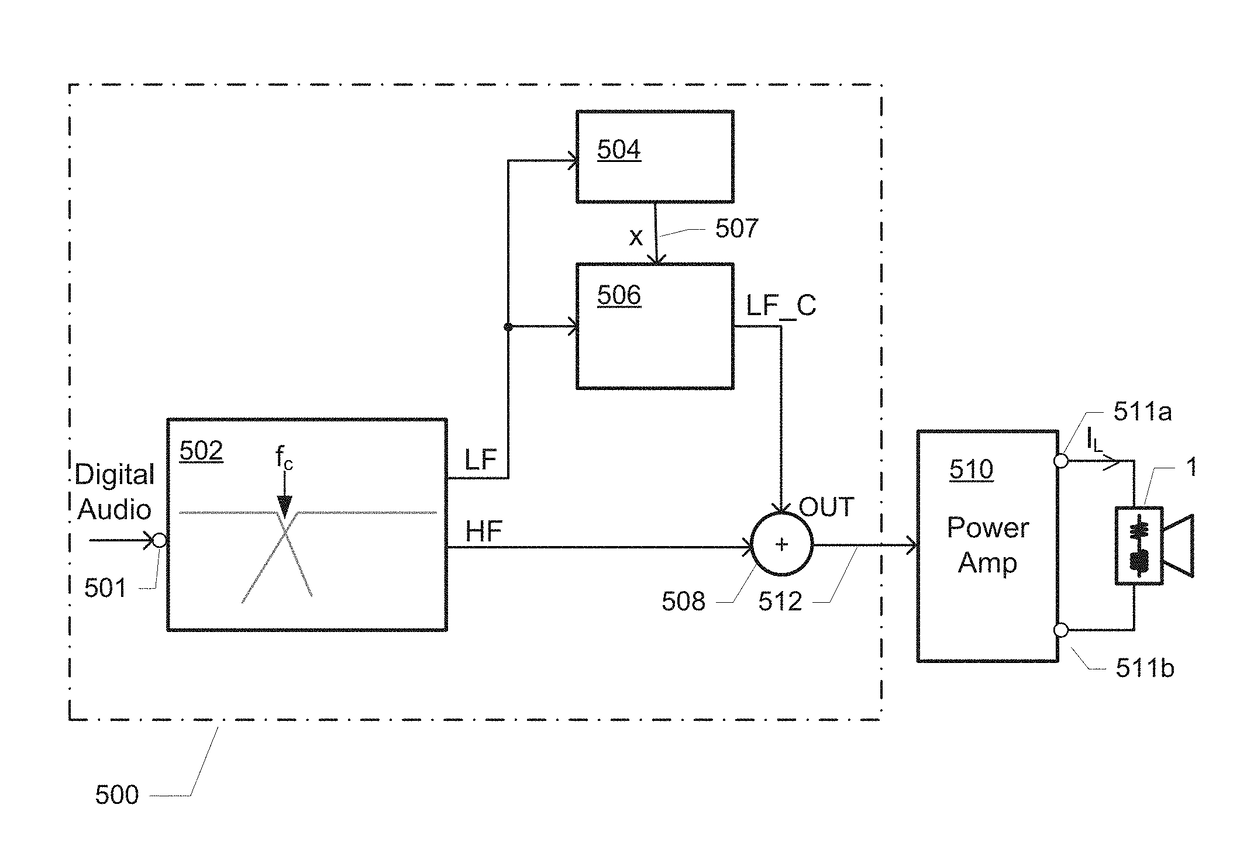
The present application relates in one aspect to a method of controlling diaphragm excursion of an electrodynamic loudspeaker. The method comprises dividing the audio input signal into at least a low-frequency band signal and a high-frequency band signal by a band-splitting network and applying the low-frequency band signal to a diaphragm excursion estimator. The instantaneous diaphragm excursion is determined based on the low-frequency band signal. The determined instantaneous diaphragm excursion is compared with an excursion limit criterion. The low-frequency band signal is limited based on a result of the comparison between the instantaneous diaphragm excursion and the excursion limit criterion to produce a limited low-frequency band signal which is combined with the high-frequency band signal to produce an excursion limited audio signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
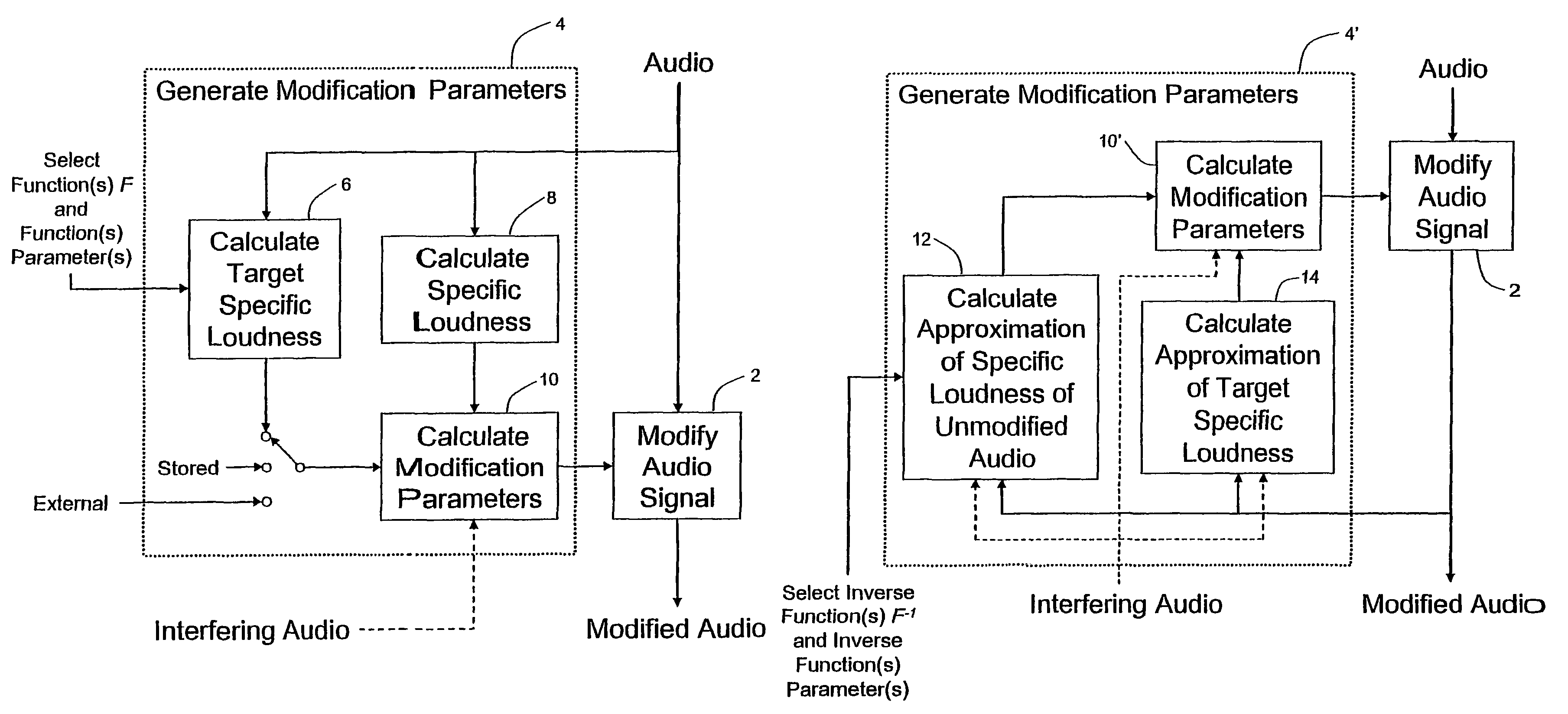
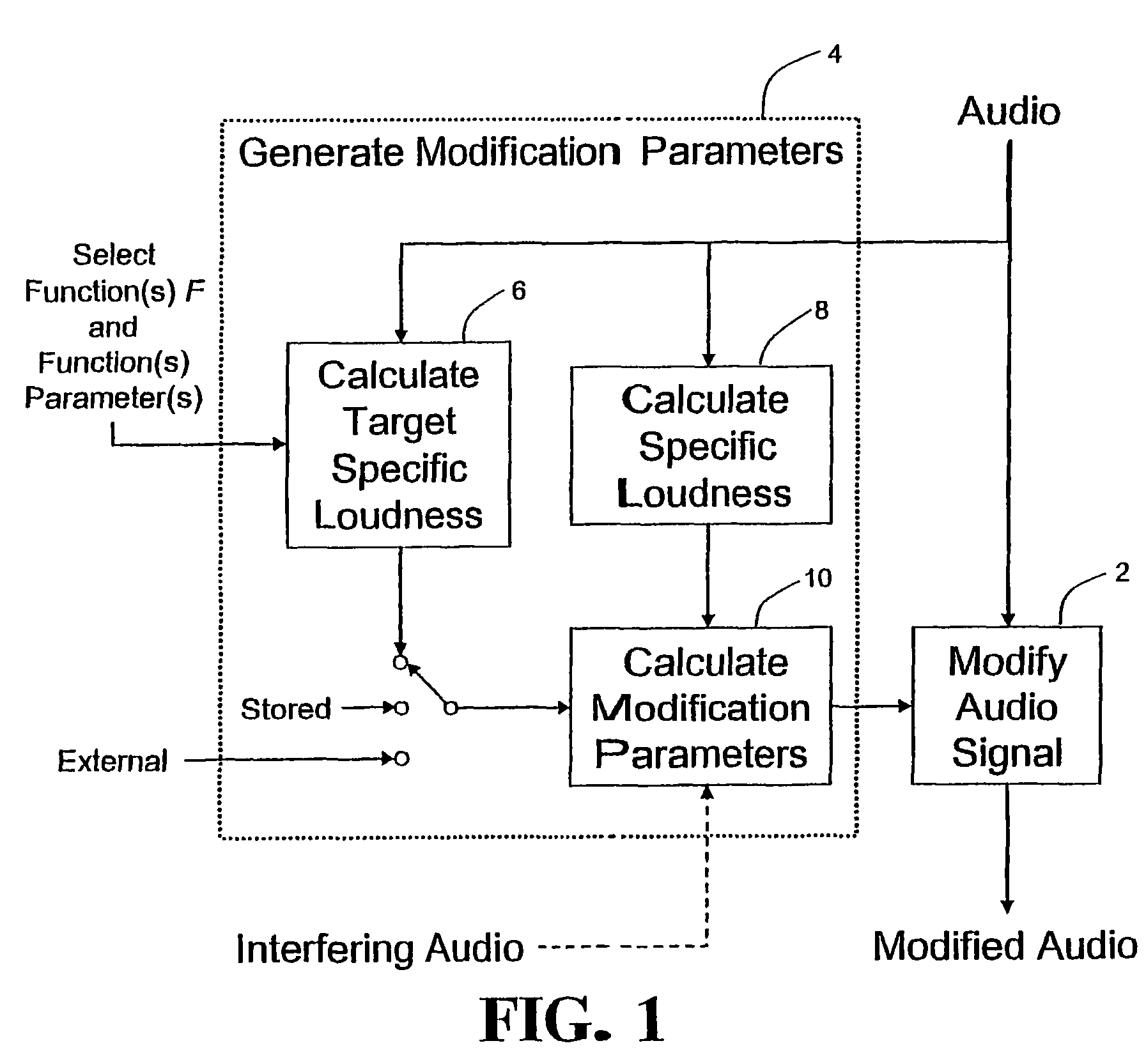
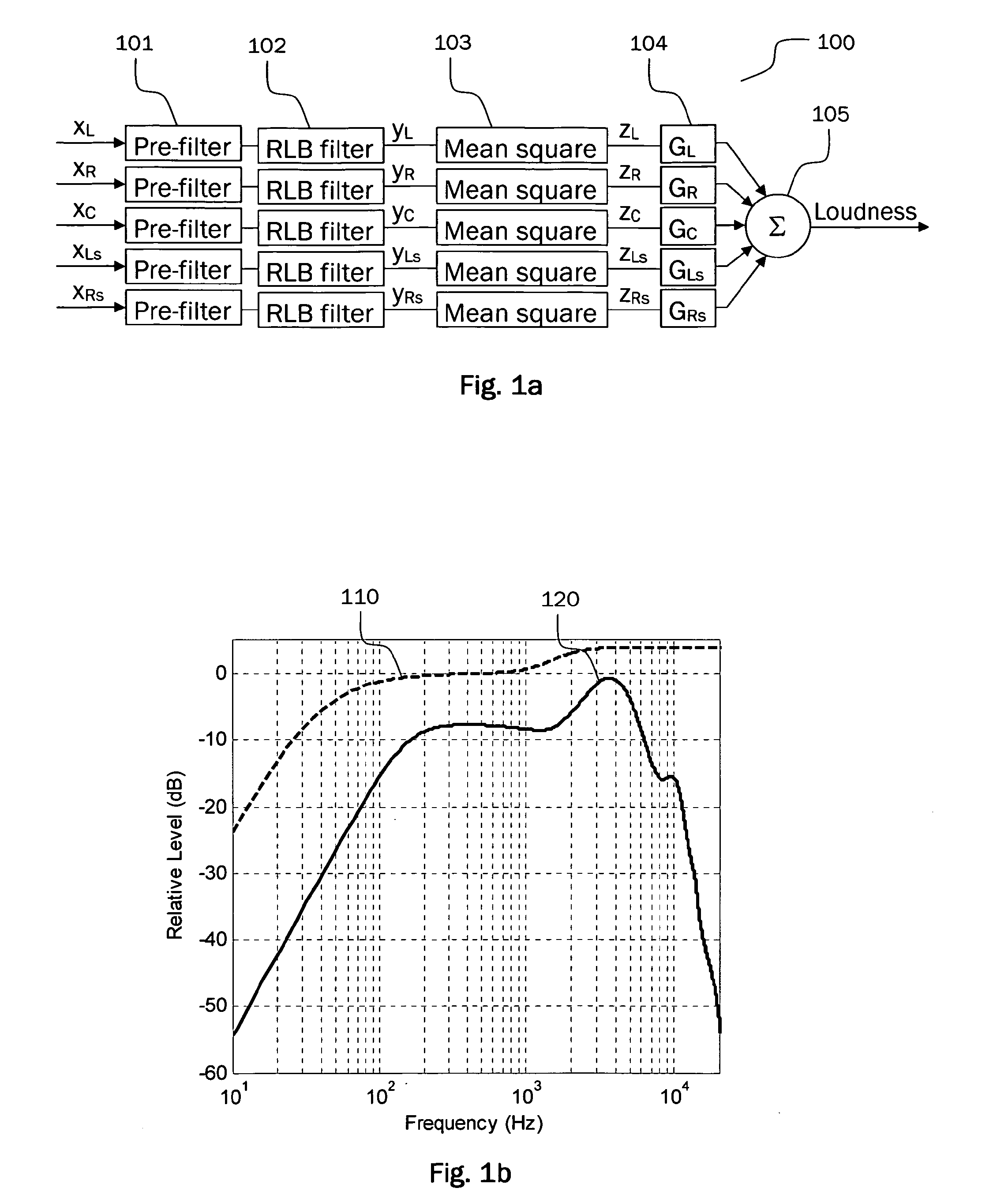
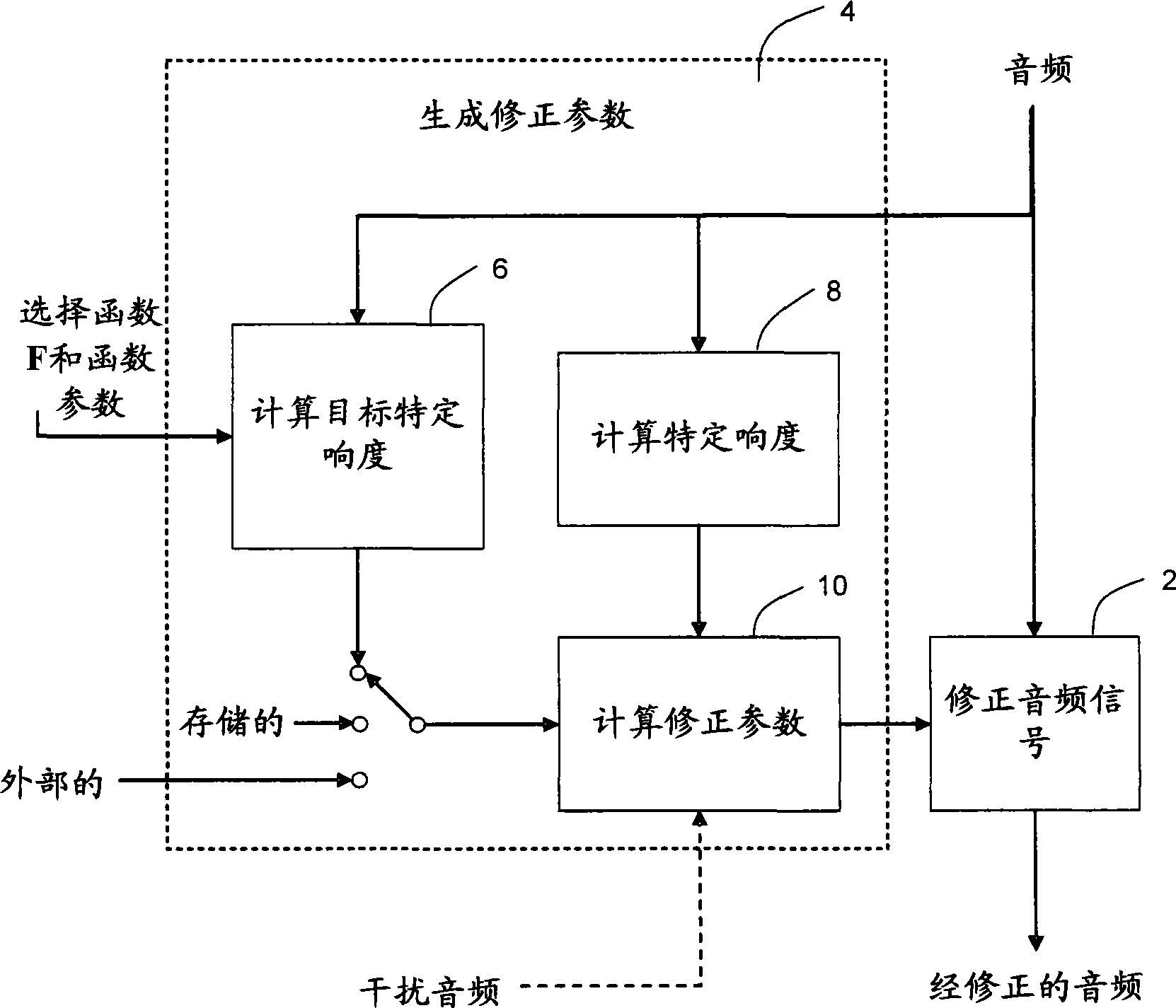
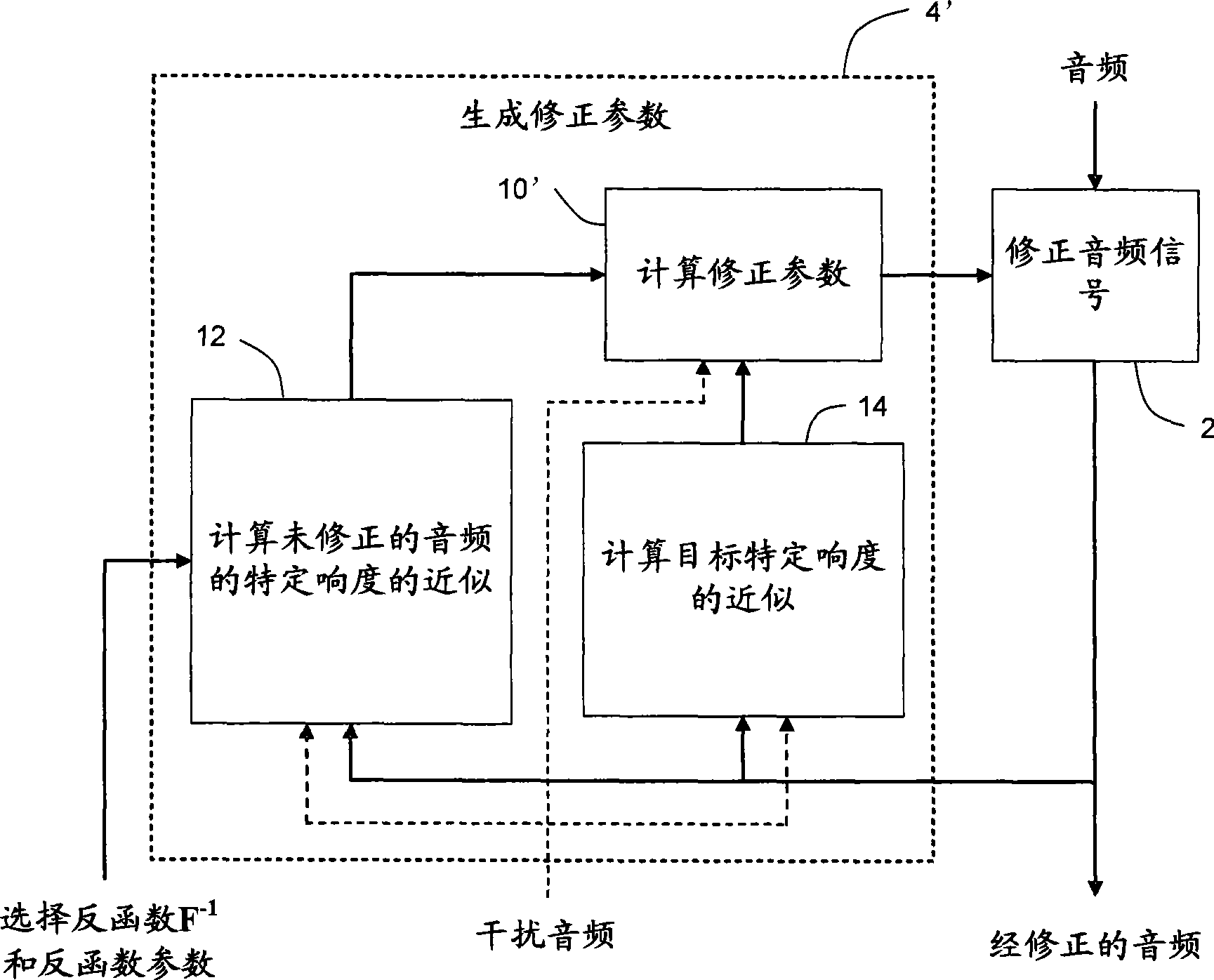
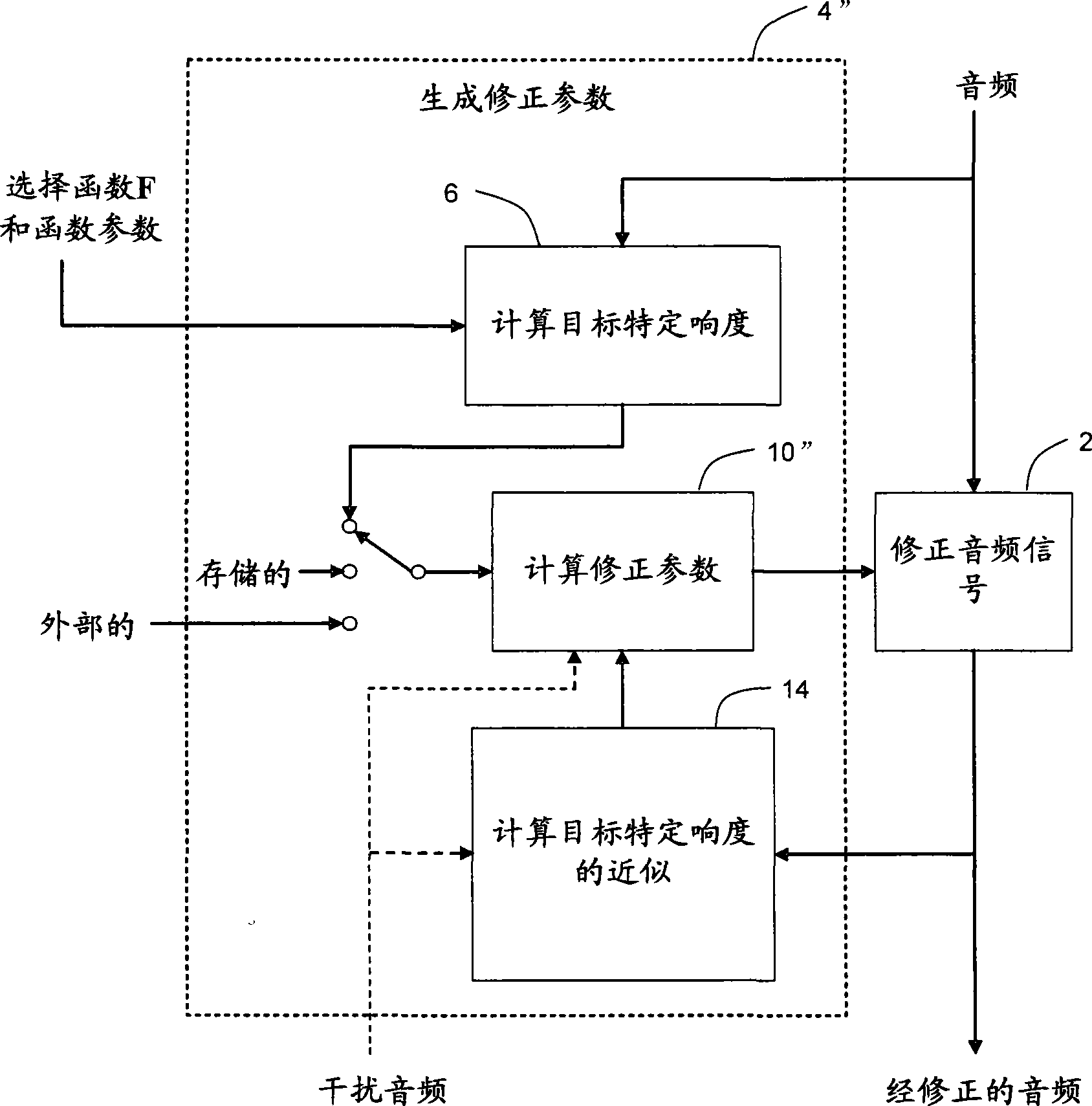
Calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness and/or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal
ActiveUS8090120B2Reduce the differenceReduce impactGain controlSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumEqualization
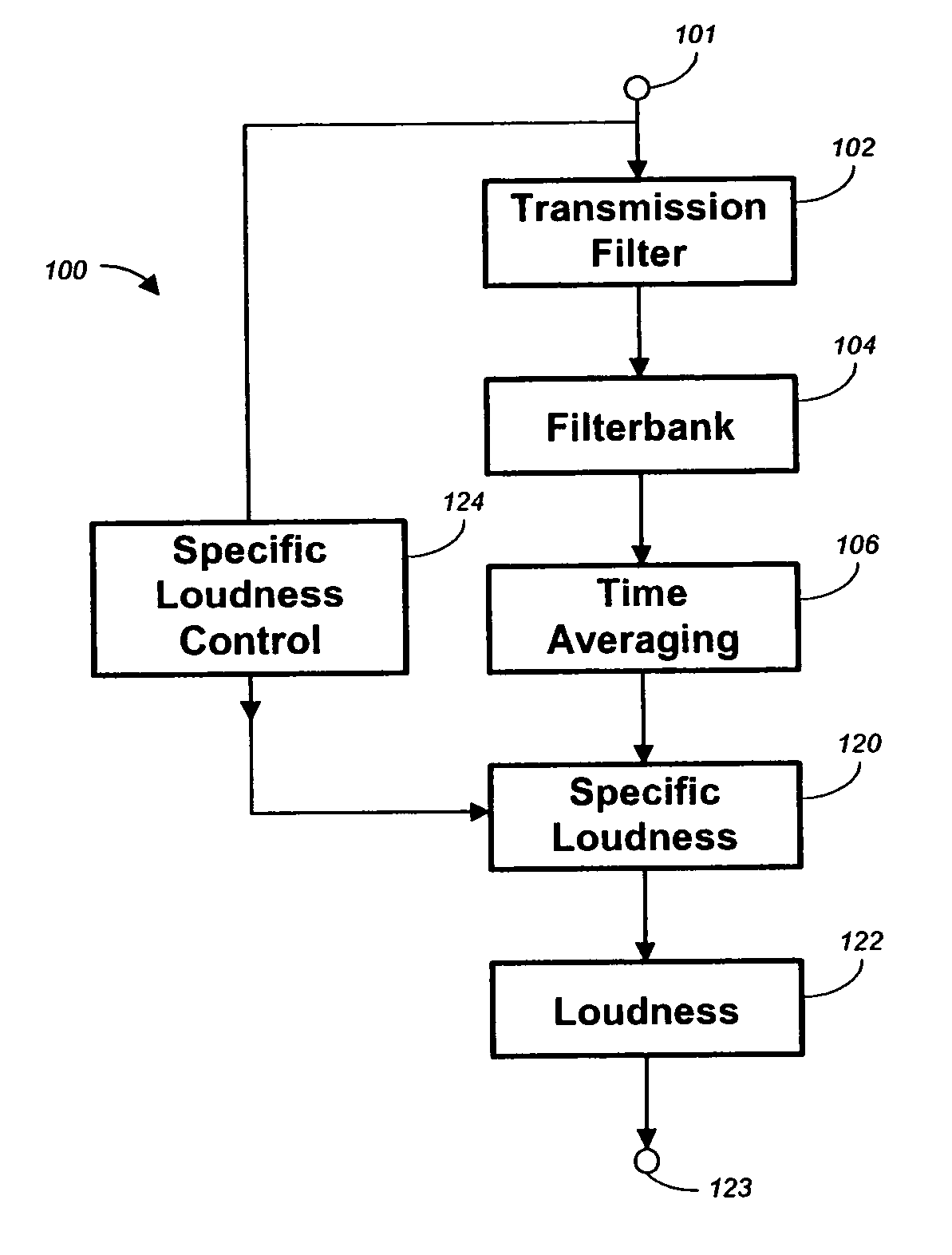
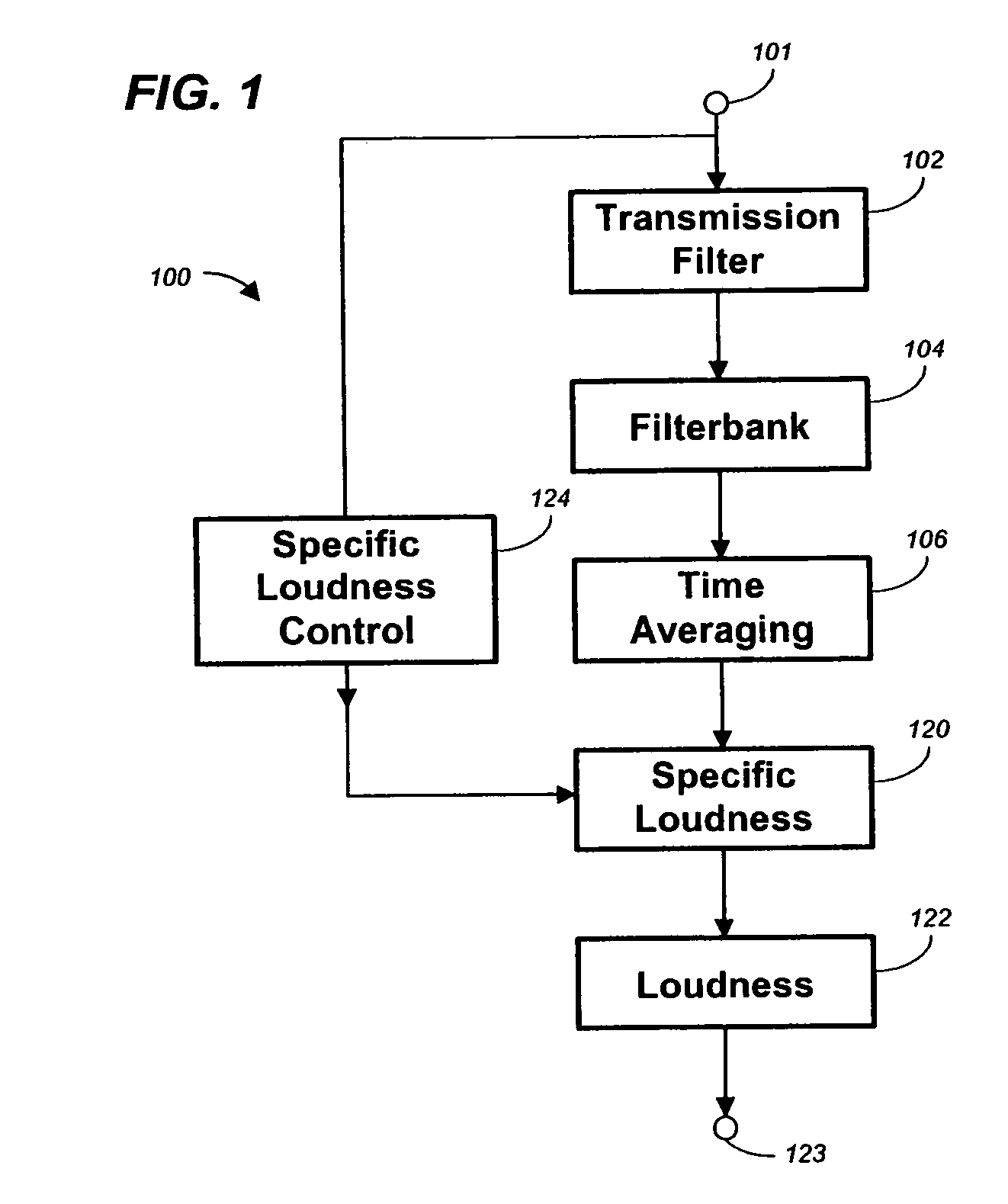
The invention relates to the measurement and control of the perceived sound loudness and / or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal. An audio signal is modified in response to calculations performed at least in part in the perceptual (psychoacoustic) loudness domain. The invention is useful, for example, in one or more of: loudness-compensating volume control, automatic gain control, dynamic range control (including, for example, limiters, compressors, expanders, etc.), dynamic equalization, and compensating for background noise interference in an audio playback environment. The invention includes not only methods but also corresponding computer programs and apparatus.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method, apparatus and computer program for calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness of an audio signal
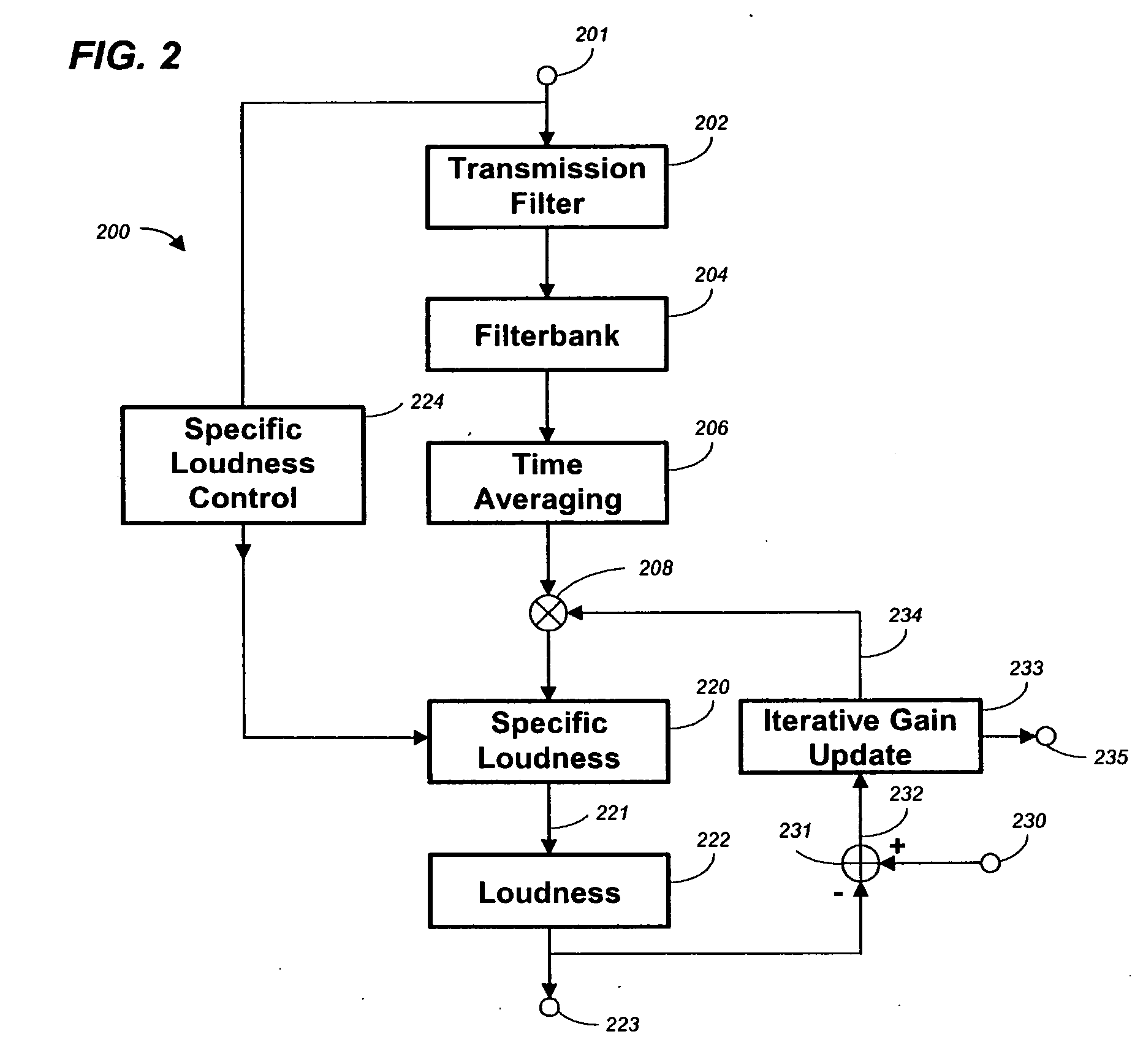
One or a combination of two or more specific loudness model functions selected from a group of two or more of such functions are employed in calculating the perceptual loudness of an audio signal. The function or functions may be selected, for example, by a measure of the degree to which the audio signal is narrowband or wideband. Alternatively or with such a selection from a group of functions, a gain value G[t] is calculated, which gain, when applied to the audio signal, results in a perceived loudness substantially the same as a reference loudness. The gain calculating employs an iterative processing loop that includes the perceptual loudness calculation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Personal audio playback device having gain control responsive to environmental sounds
ActiveUS7903825B1Lower Level RequirementsReduce rateGain controlEarpiece/earphone attachmentsMaterial typeEnvironmental sounds
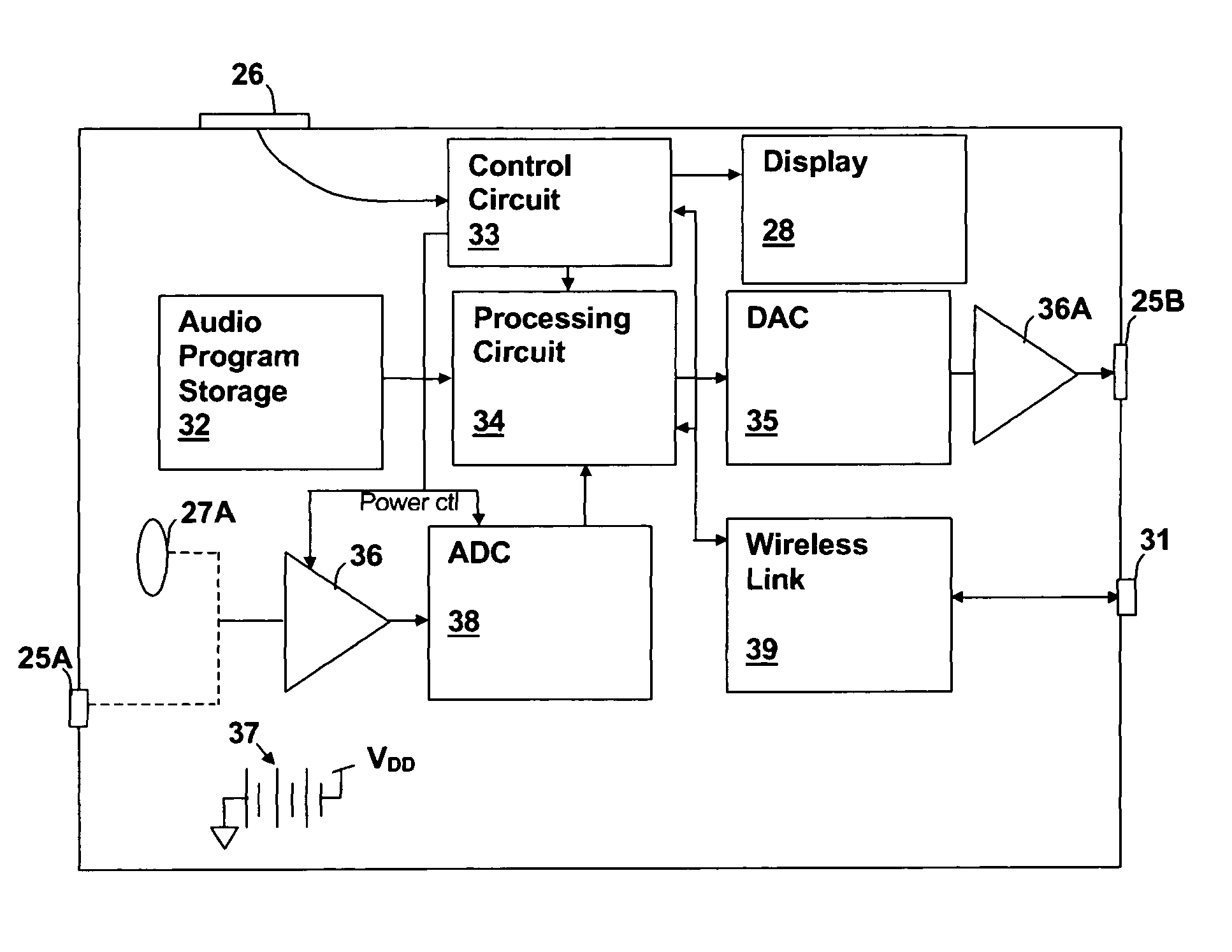
A personal audio playback device having gain control responsive to environmental sounds provides for improved enjoyment of program material played back through headphones, while further providing features for personal safety and communications with others. A microphone is incorporated on the surface of the playback device, which includes an audio output connection for headphones and internal storage for audio program material. The entire device may be incorporated within the headphones, or the headphones may connect through a connector on the housing of the device. The gain, type or position of the program material is controlled in conformity with a detected characteristic of ambient sounds received by the microphone, which may be the amplitude of the signals in one or more frequency bands, or a particular type of sound, such as speech or vehicular sounds. Multiple modes are selectable for processing the audio, selecting program material type and / or re-positioning the program material.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Audio correcting apparatus
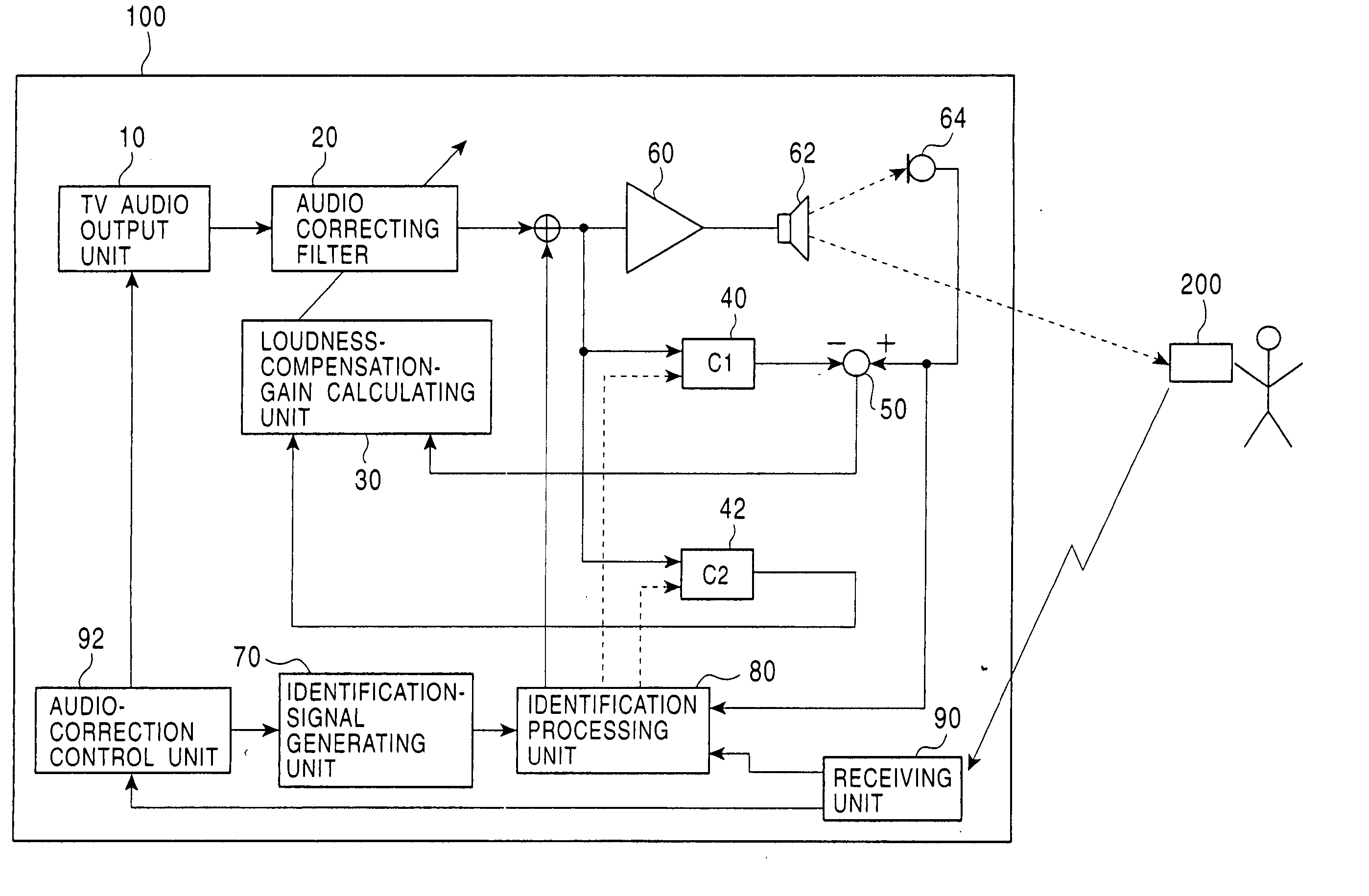
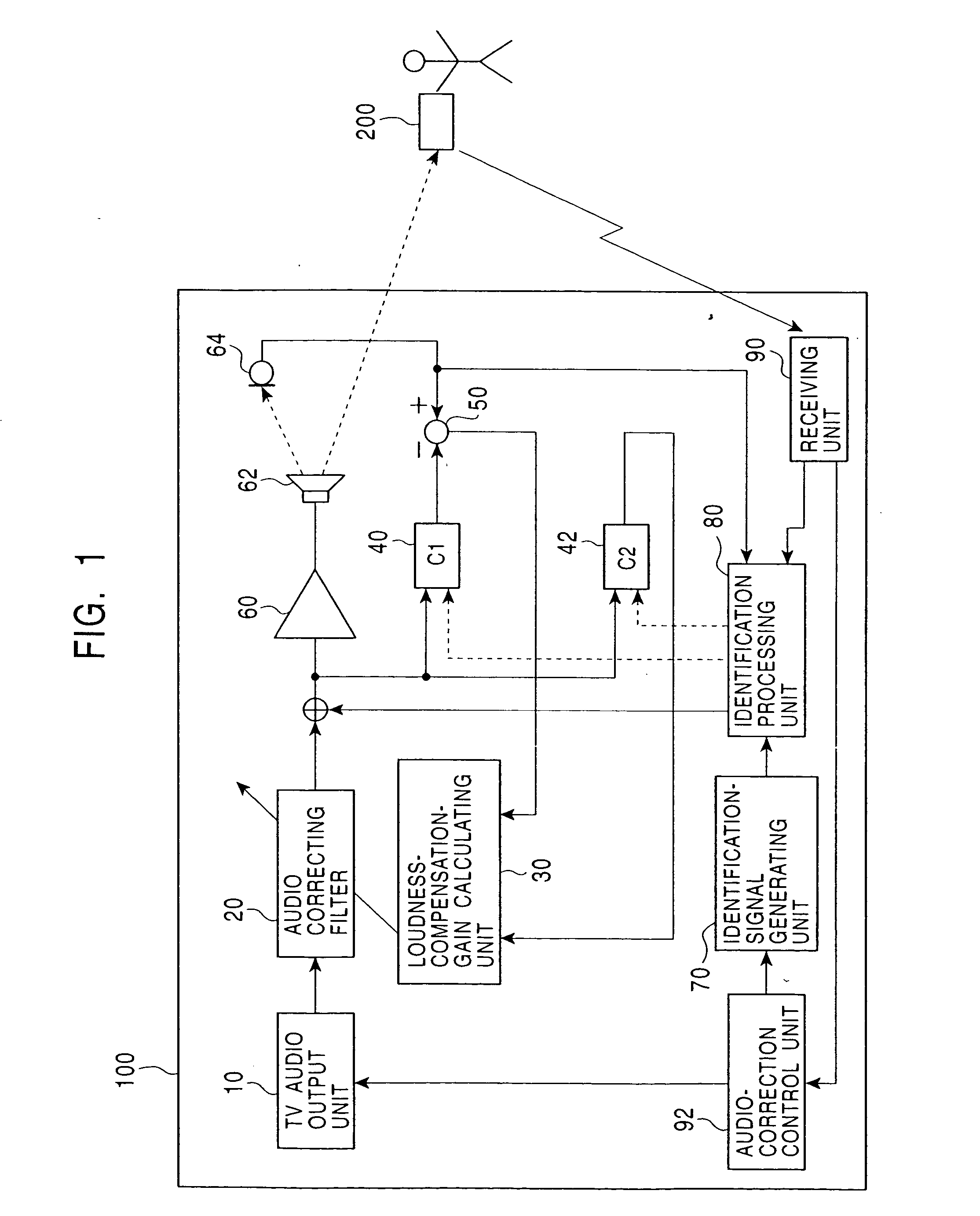
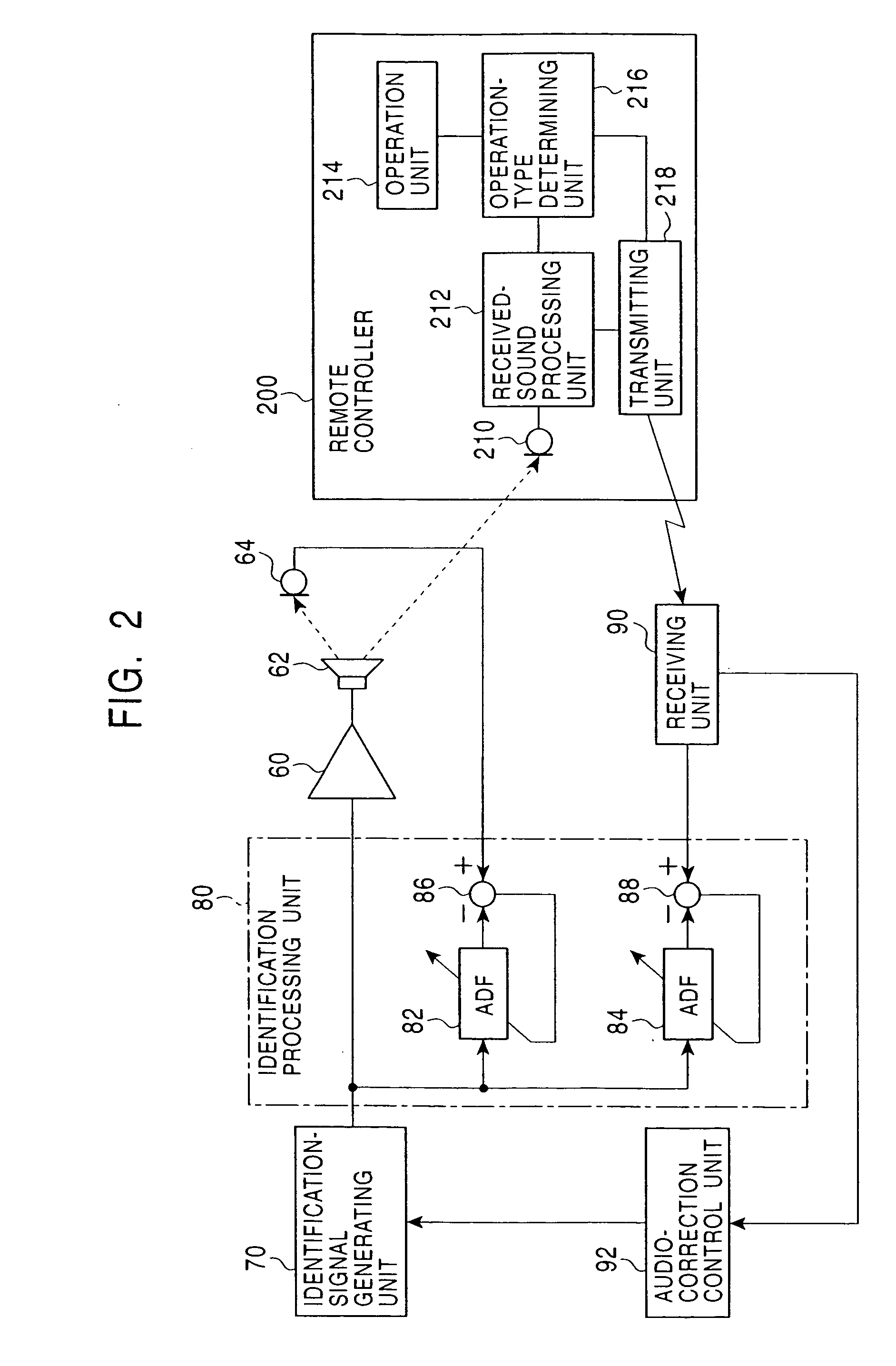
InactiveUS20050013443A1Accurate sound pressure levelListen clearlyTelevision system detailsAdaptive networkEnvironmental noiseLoudspeaker
An audio correcting apparatus includes a speaker provided on a television apparatus, a microphone provided on a remote controller, an identifying unit which identifies an acoustic characteristic from the speaker to the microphone, and an acoustic characteristic setting unit having the acoustic characteristic. A signal obtained by allowing an audio signal input to the speaker to pass through the acoustic characteristic setting unit, and a signal representing ambient noise are input to an audio-correcting filter and a loudness-compensation-gain calculating unit. Based on both signals, the sound pressure level of sound output from the speaker is corrected so that the sound output from the speaker is clearly heard when reaching the user without being affected by the ambient noise.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Dynamic bass boost apparatus and method
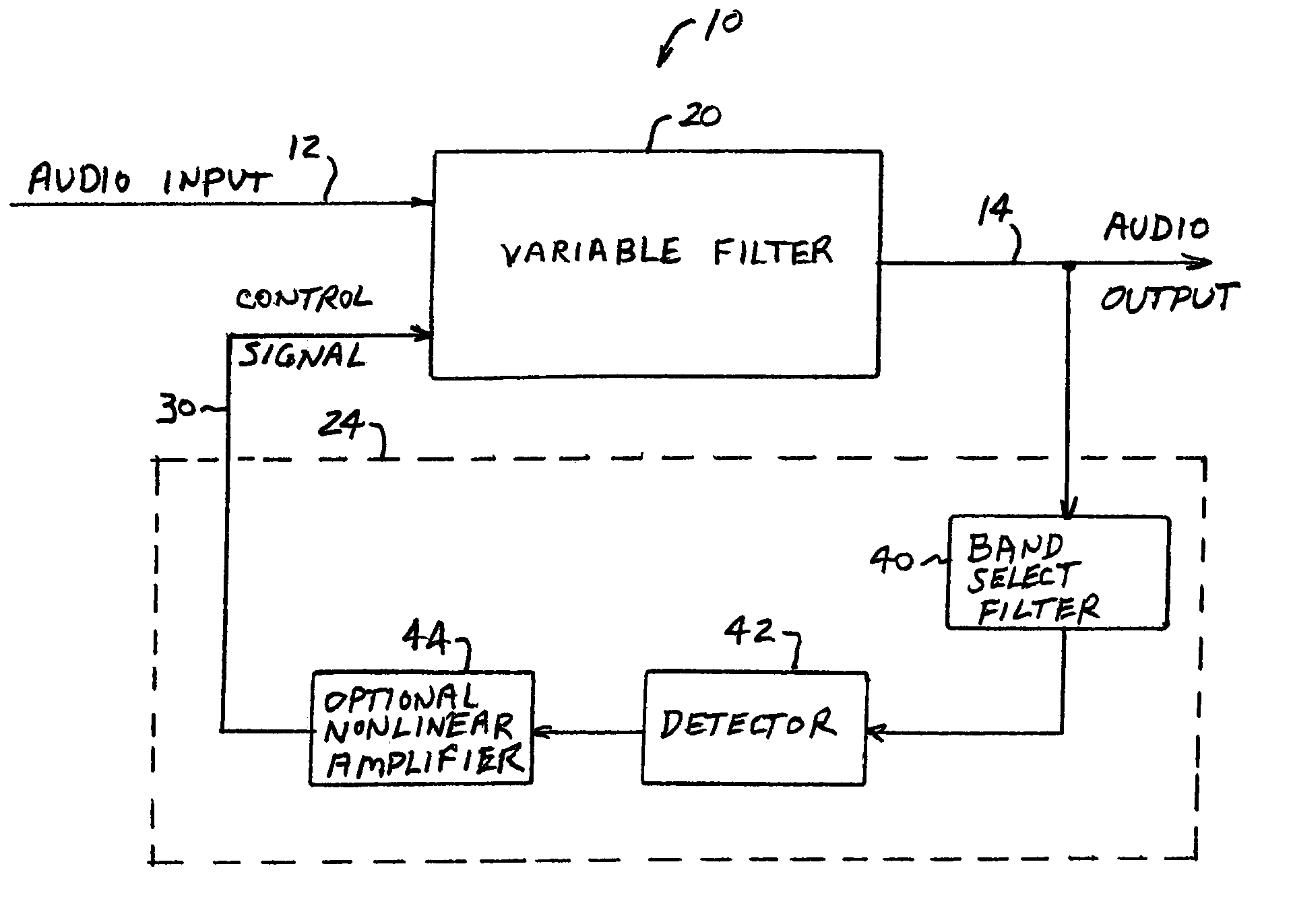
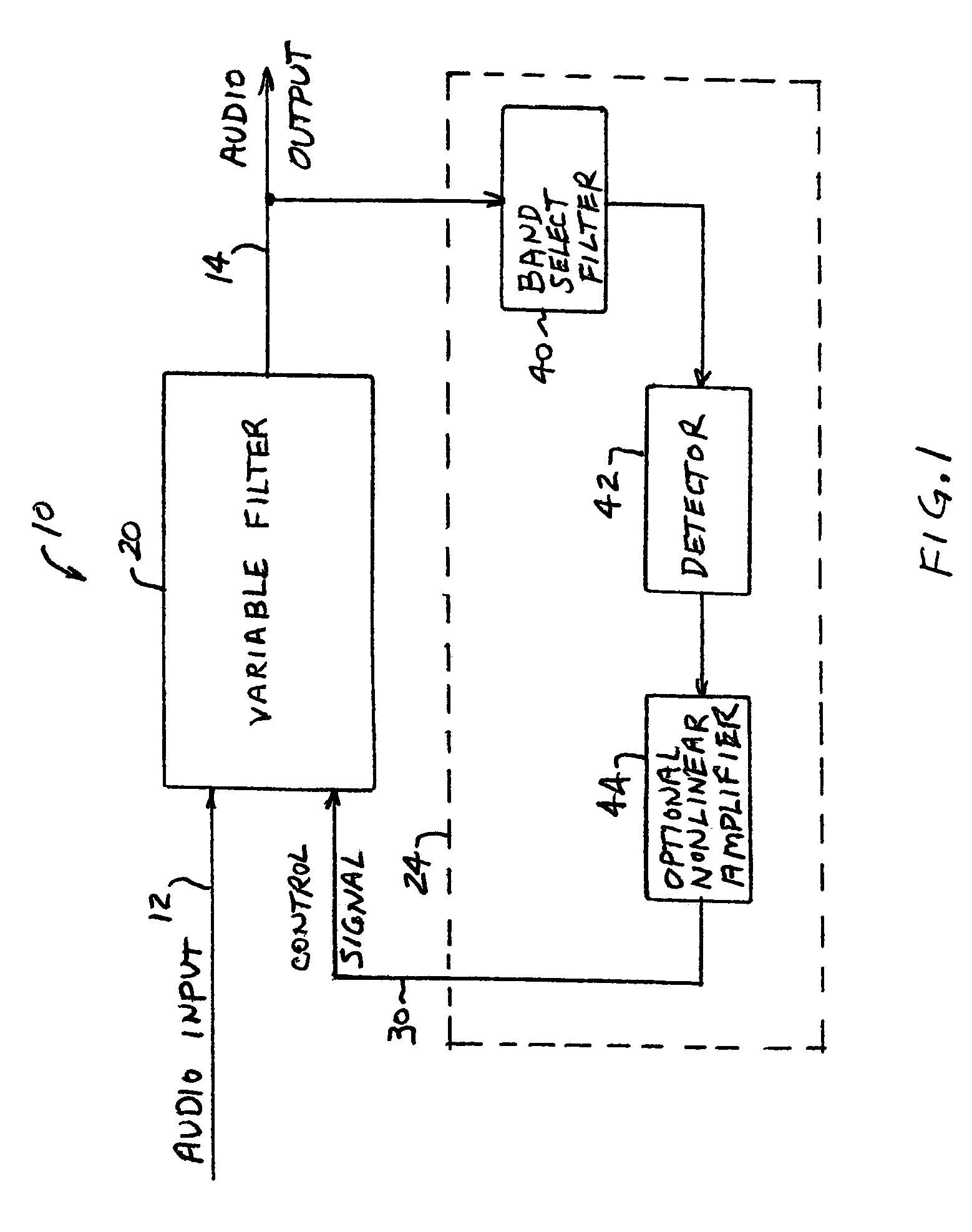
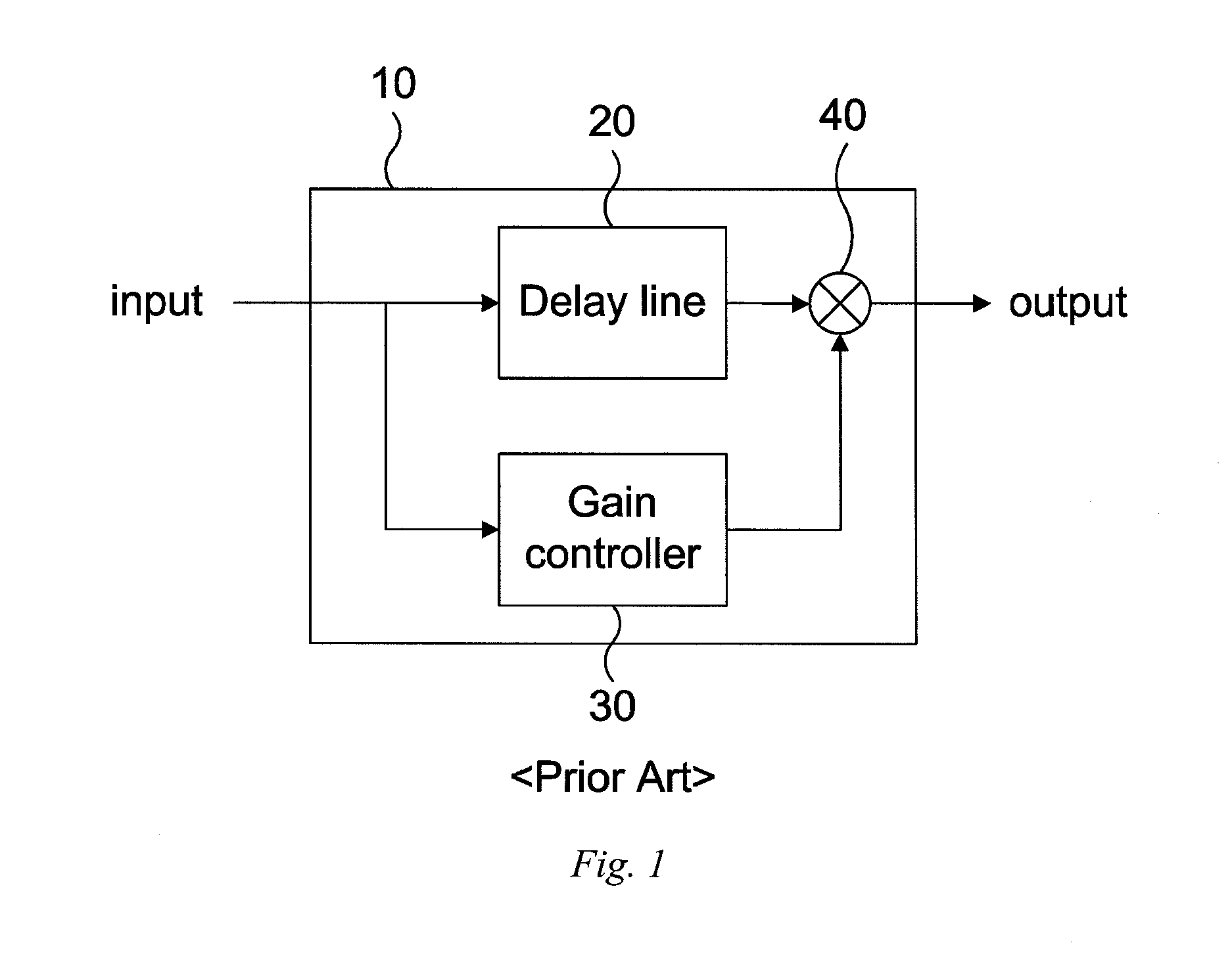
ActiveUS7171010B2Digital/coded signal combination controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsLow-pass filterControl signal
Audio processing methods and apparatus are provided for at least partially compensating for the Fletcher-Munson effect. An audio processor includes a variable filter receiving an input signal and providing a filtered output signal, the variable filter having a fixed cutoff frequency and a quality factor that is controllable in response to a control signal, and a control circuit configured to detect a signal level representative of input signal level in a selected band and to generate the control signal in response to the detected signal level. The control circuit may include a low-pass band select filter and a detector for detecting a signal level in the band selected by the low-pass filter and for generating the control signal.
Owner:BOSTON ACOUSTICS INC
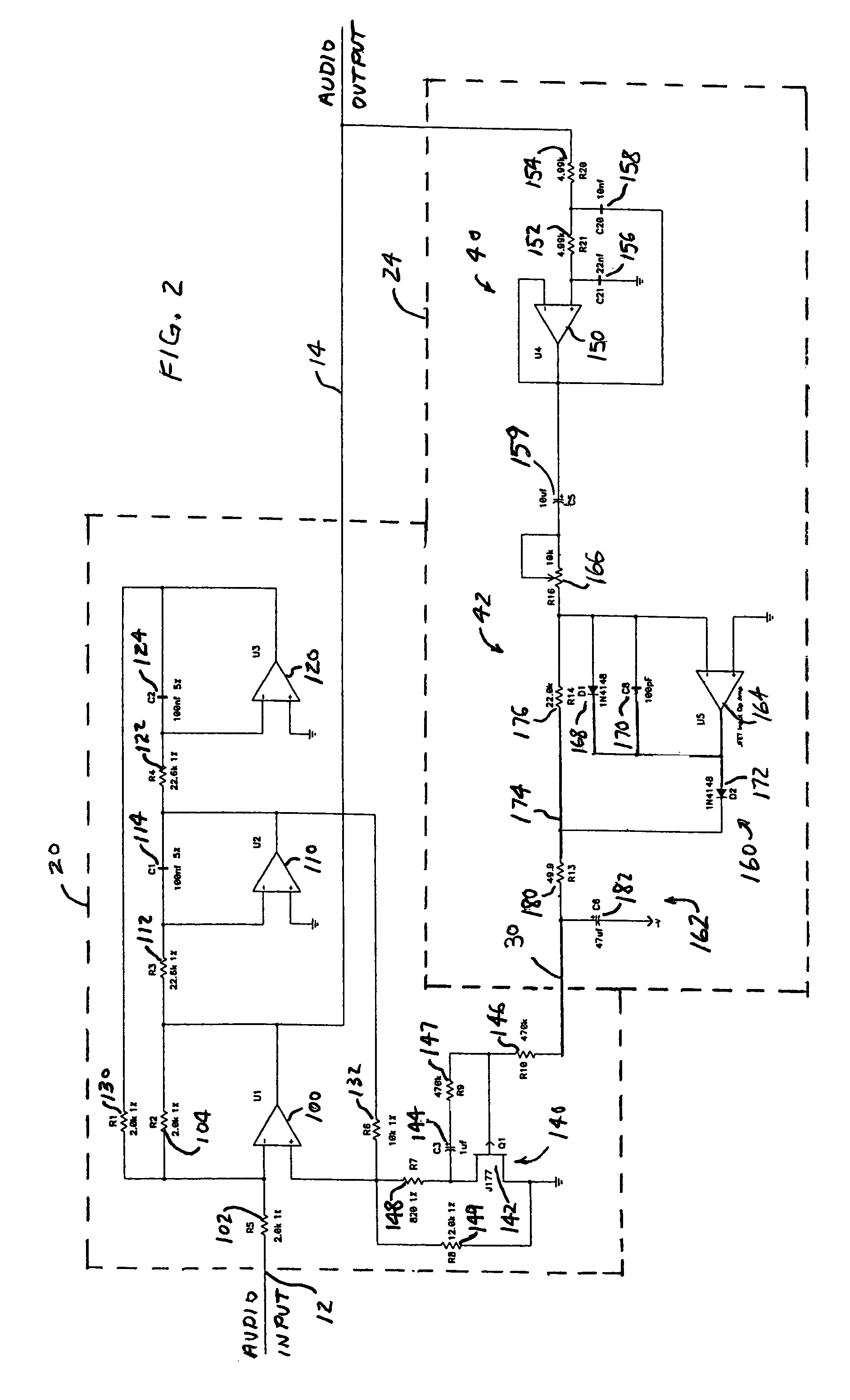
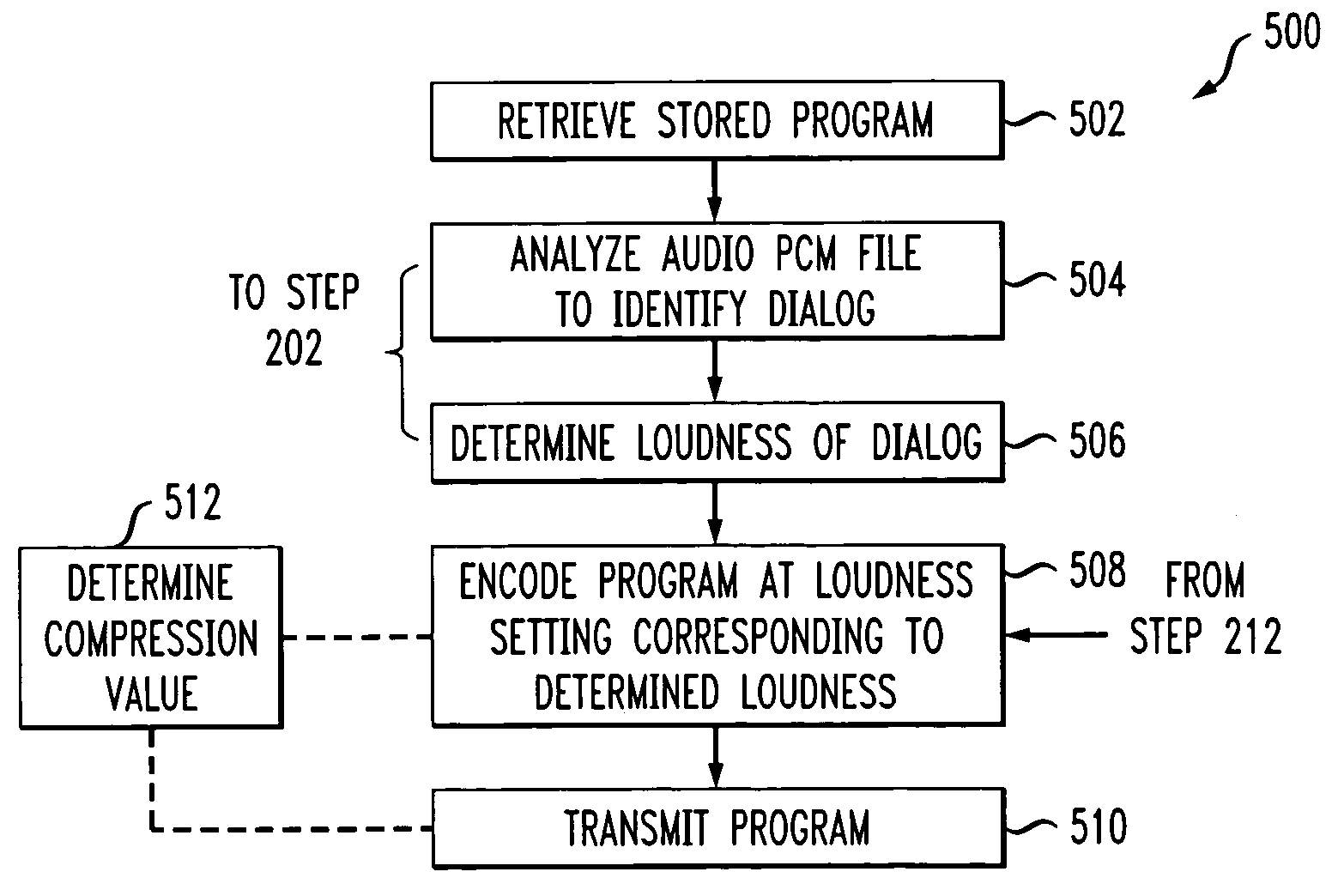
Methods and systems for determining audio loudness levels in programming
An example of a method of correcting an audio level of a stored program asset comprises retrieving a stored program asset having audio encoded at a first loudness setting. Dialog of the audio of the asset is identified, a loudness of the dialog is determined and the determined loudness is compared to the first loudness setting. The asset is re-encoded at a second loudness setting corresponding to the determined loudness, if the first loudness setting and the second loudness are different by more than a predetermined amount. The determined loudness is preferably a DIALNORM of the dialog. The asset may be stored with the re-encoded loudness setting. The method may be applied to programs as they are being received from a source, as well. Aspects of the method may also be applied to programs to be provided by a source. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
Audio gain control using specific-loudness-based auditory event detection
ActiveUS8144881B2Change damageSlow down the rate of change of gainSignal processingGain controlLoudnessComputer science
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Audio Gain Control Using Specific-Loudness-Based Auditory Event Detection
ActiveUS20090220109A1Reduction of audible artifactChange damageSignal processingGain controlLoudnessComputer science
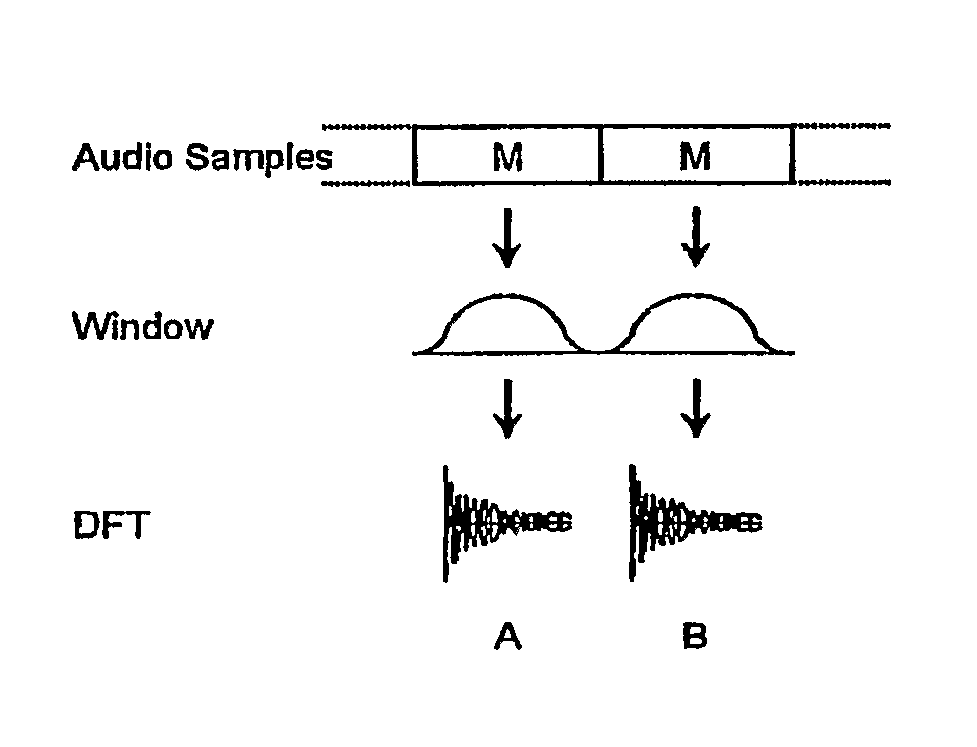
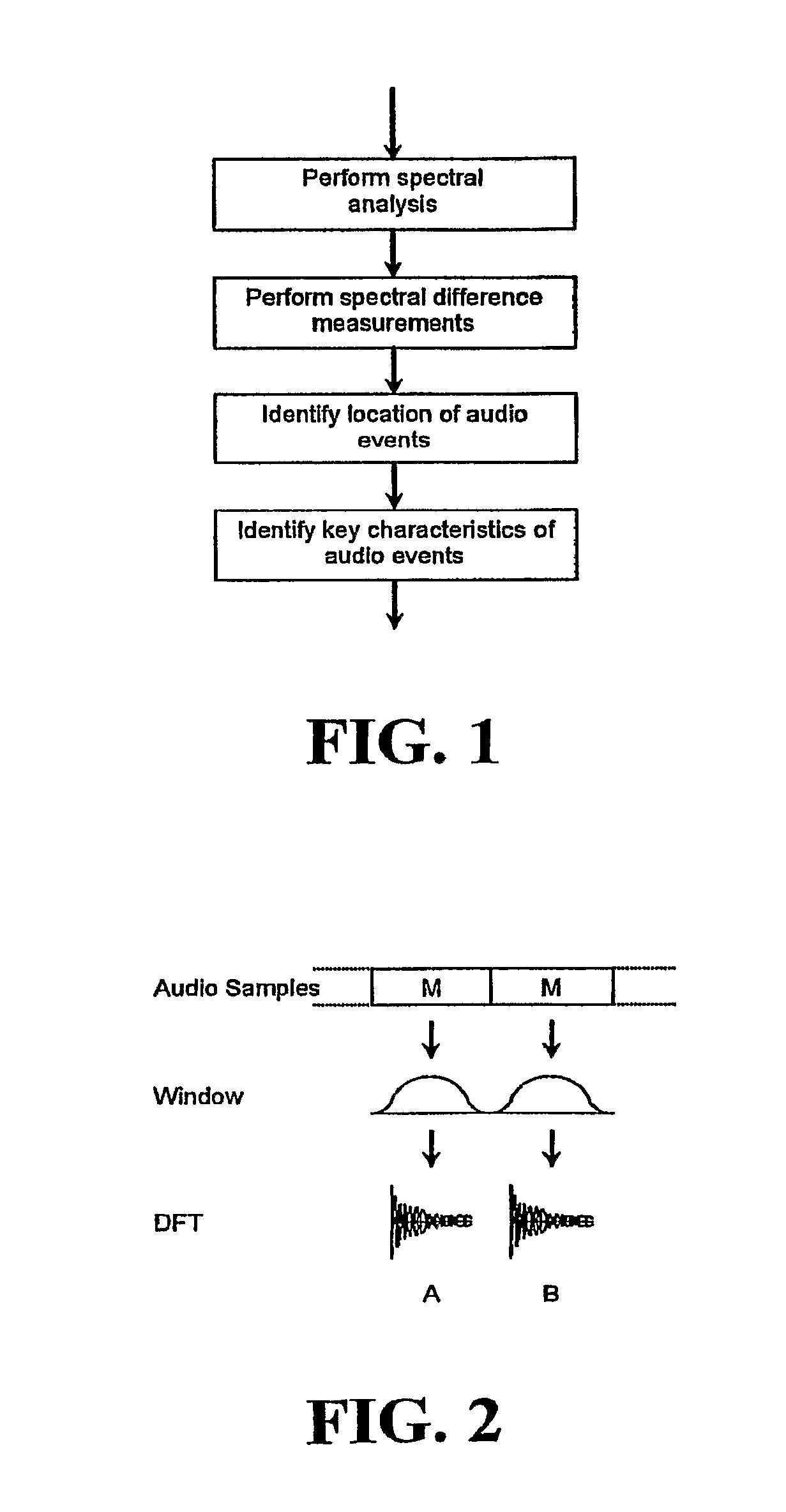
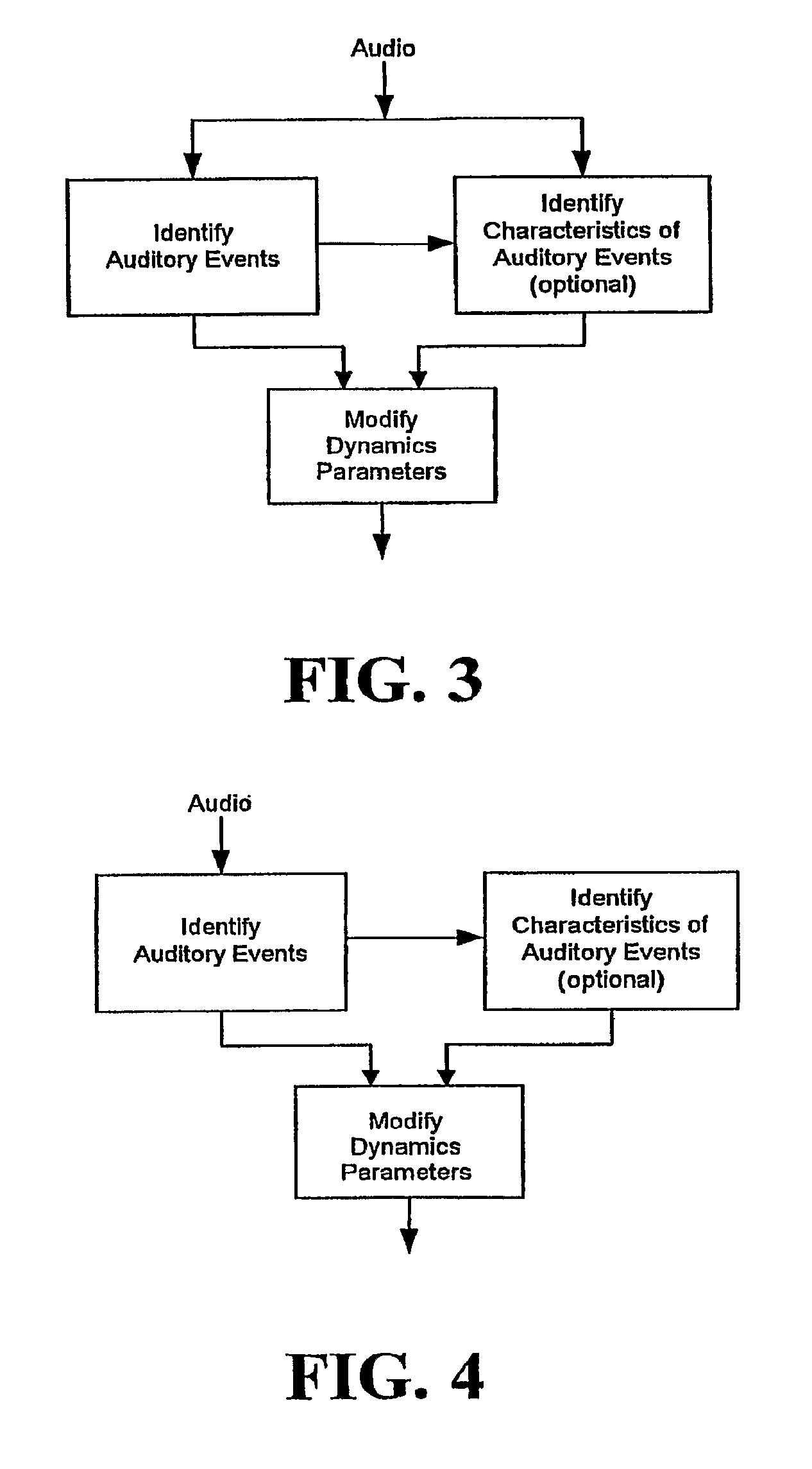
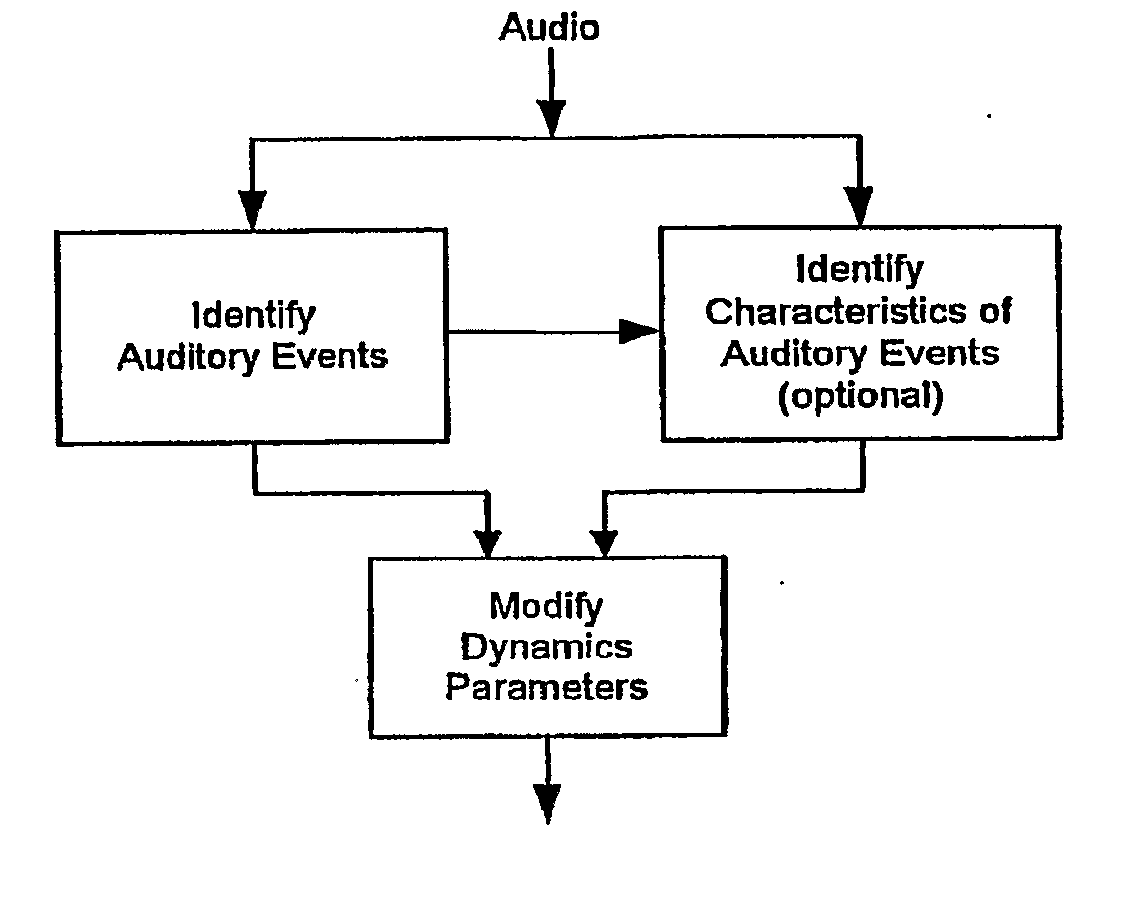
In one disclosed aspect, dynamic gain modifications are applied to an audio signal at least partly in response to auditory events and / or the degree of change in signal characteristics associated with said auditory event boundaries. In another aspect, an audio signal is divided into auditory events by comparing the difference in specific loudness between successive time blocks of the audio signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Transducer displacement protection
ActiveUS20090268918A1Transducer protection circuitsDigital/coded signal combination controlTransducerEngineering
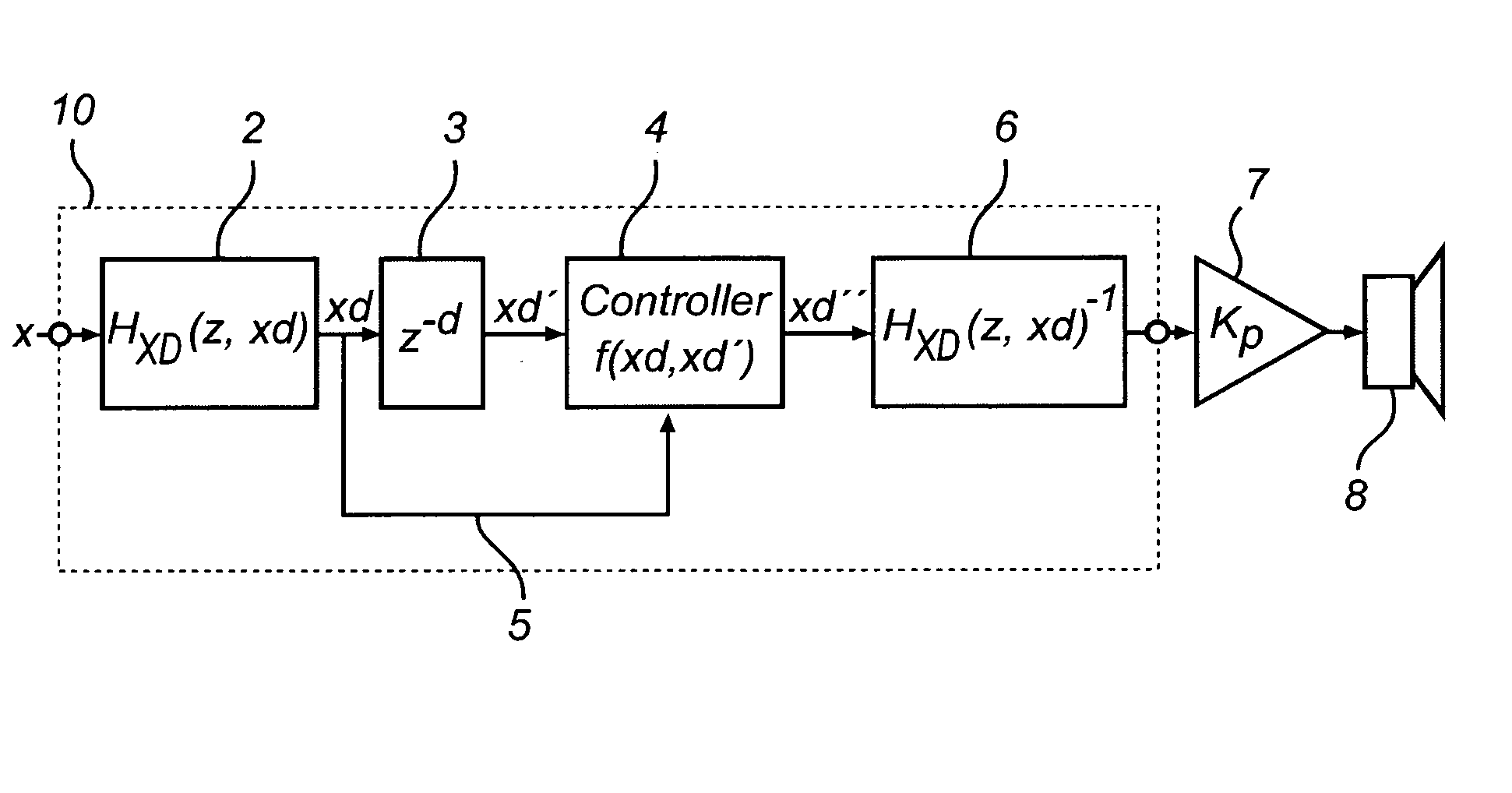
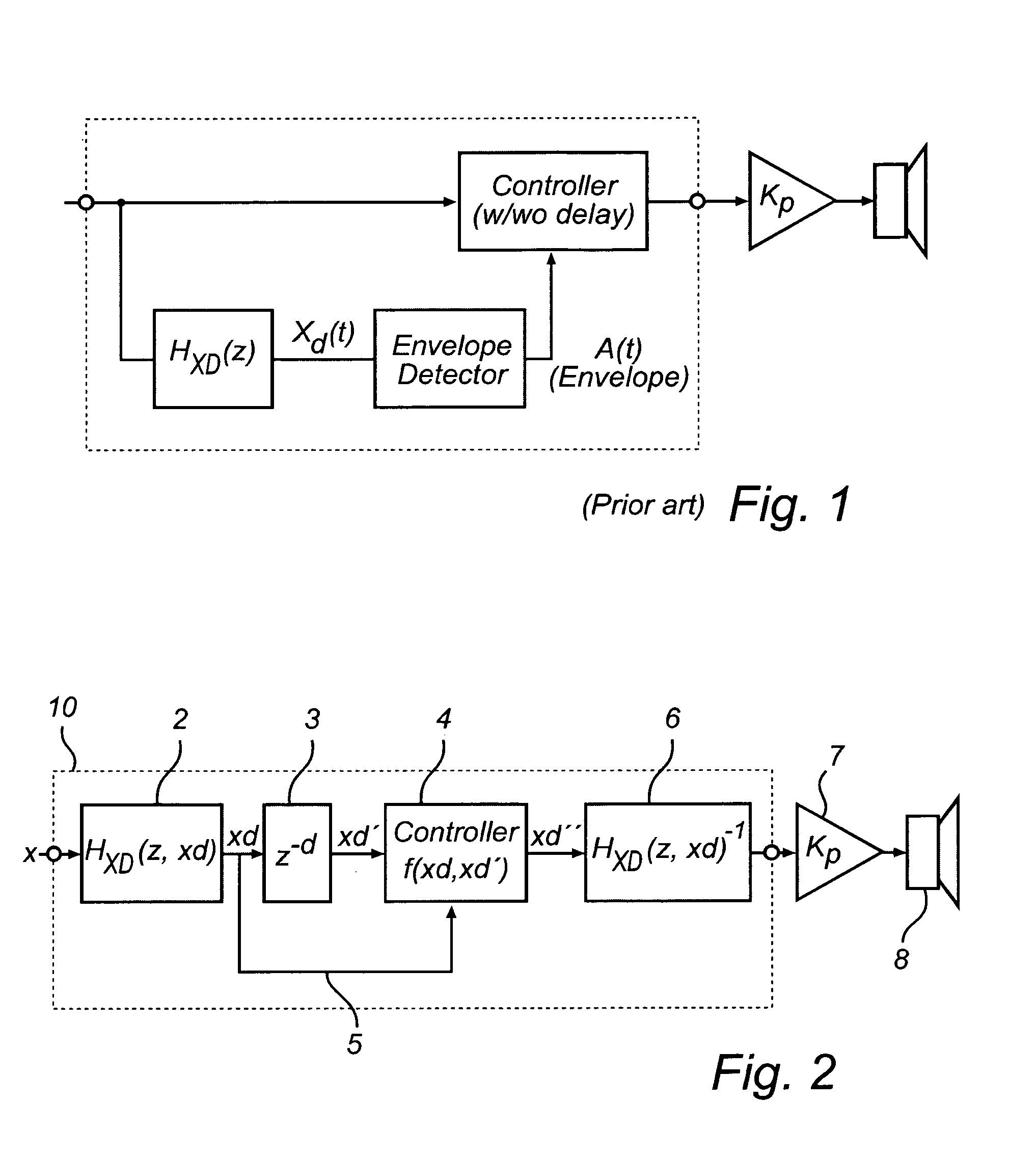
This invention relates to the mechanical protection using digital processing and a predictive estimation of instantaneous displacement of the voice coil in a loudspeaker transducer.The invention solves the problem of limiting the coil displacement of the transducer by applying a look-a-head based linear or non-linear predictor and a controller operating directly on the displacement signal in order to finally convert back into the incoming signal domain.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN ICEPOWER
Ambient audio event detection in a personal audio device headset
ActiveUS8804974B1Lower Level RequirementsReduce rateGain controlEarpiece/earphone attachmentsEarconHeadphones
Ambient audio event detection in a personal audio device headset provides for directive response to external audible events. Depending on the type of event, an alert may be issued, speech may be communicated to another device, program material may be interrupted and / or resumed with or without repositioning, and program material may be modified or selected for compatibility with, or to overcome, the ambient environment indicated by the detected event.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Volume and compression control in movie theaters
InactiveUS7551745B2Reduce gainLess levelingGain controlVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersComputer scienceReproduction
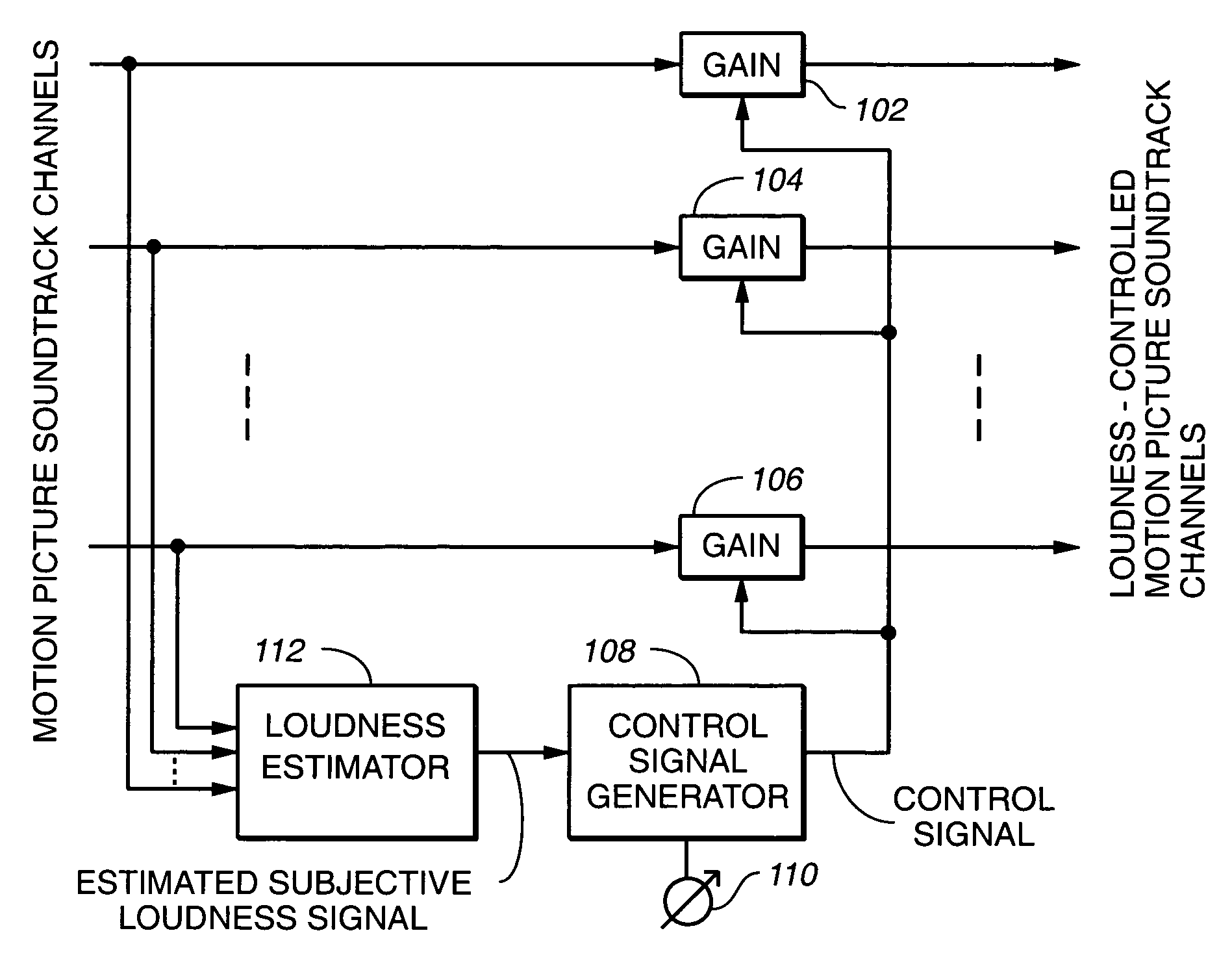
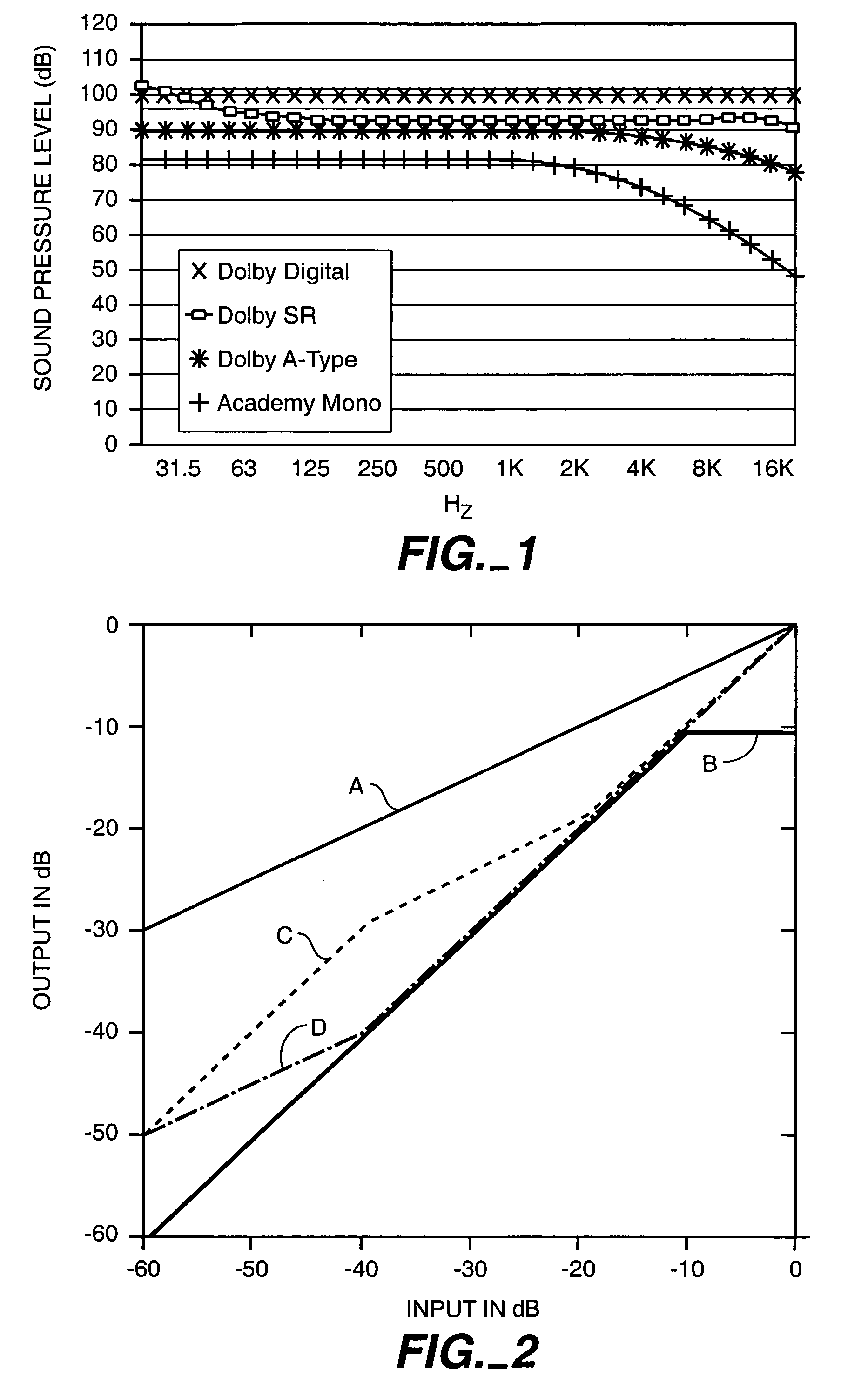
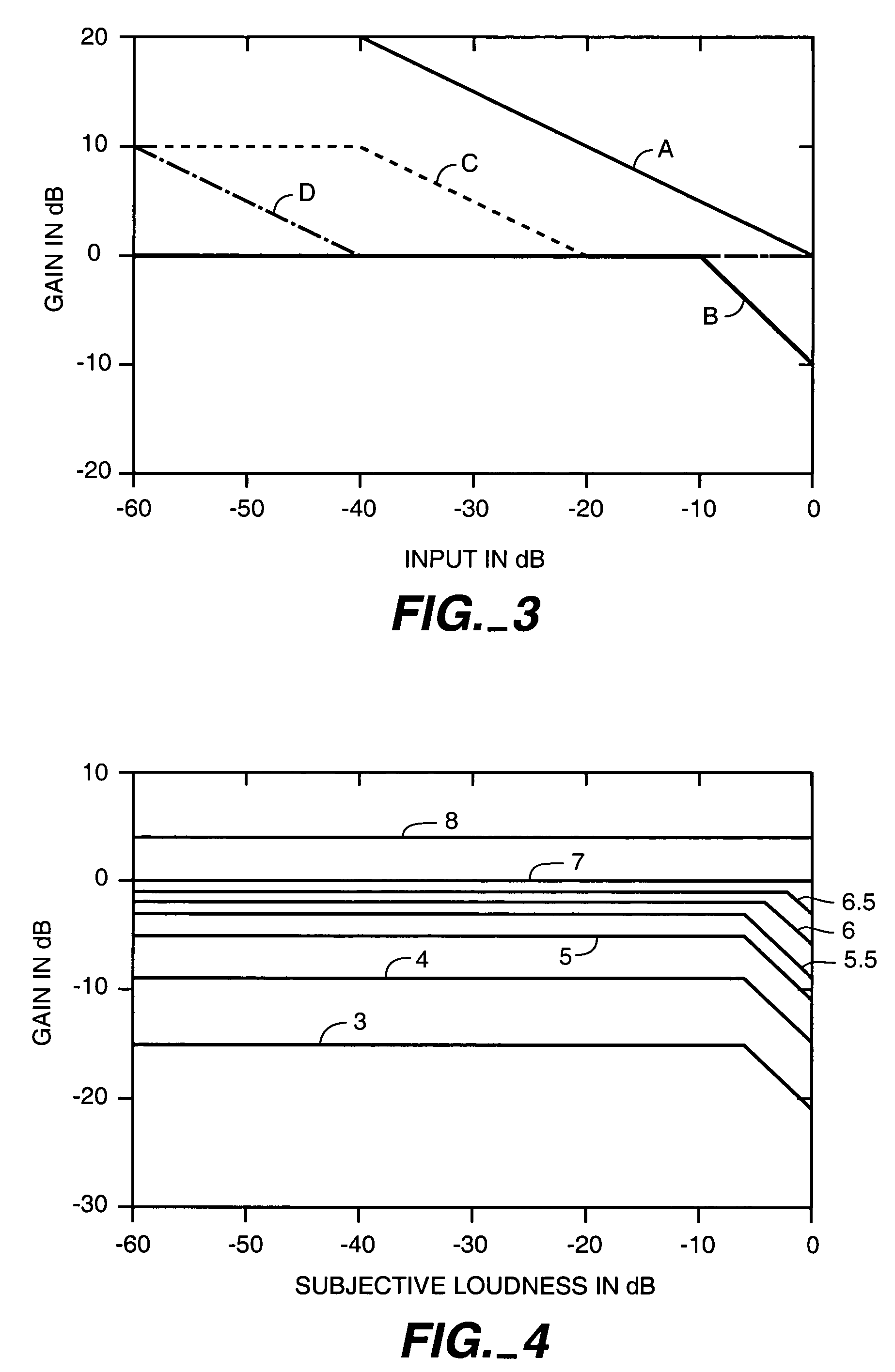
A single control determines both volume and the degree of compression in the reproduction of motion picture soundtracks. For some settings of the control, compression or limiting reduces the highest levels on a movie soundtrack, leaving the dialogue level substantially unchanged, thus removing the reason for complaints from the audience without the danger of making the dialogue too quiet for intelligibility.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
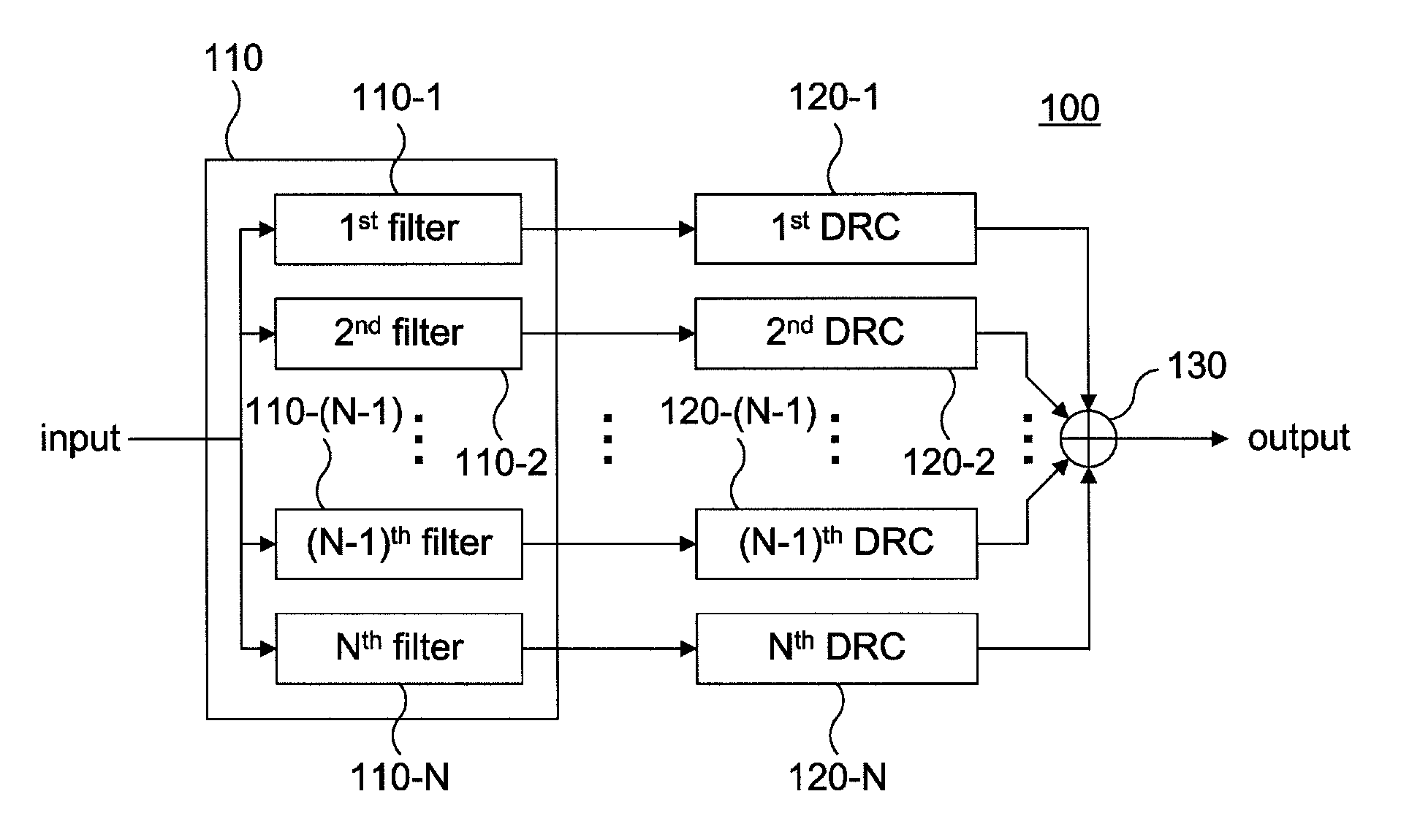
Multiband DRC system and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20110110533A1Increase the loudnessDigital/coded signal combination controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringLoudness
A multiband DRC system and a method for controlling the same are disclosed. In accordance with the present invention, the system and the method are capable of increasing an overall loudness of an output signal by controlling thresholds and gains of plurality of DRCs included in the multiband DRC system according to frequency bands.
Owner:NEOFIDELITY
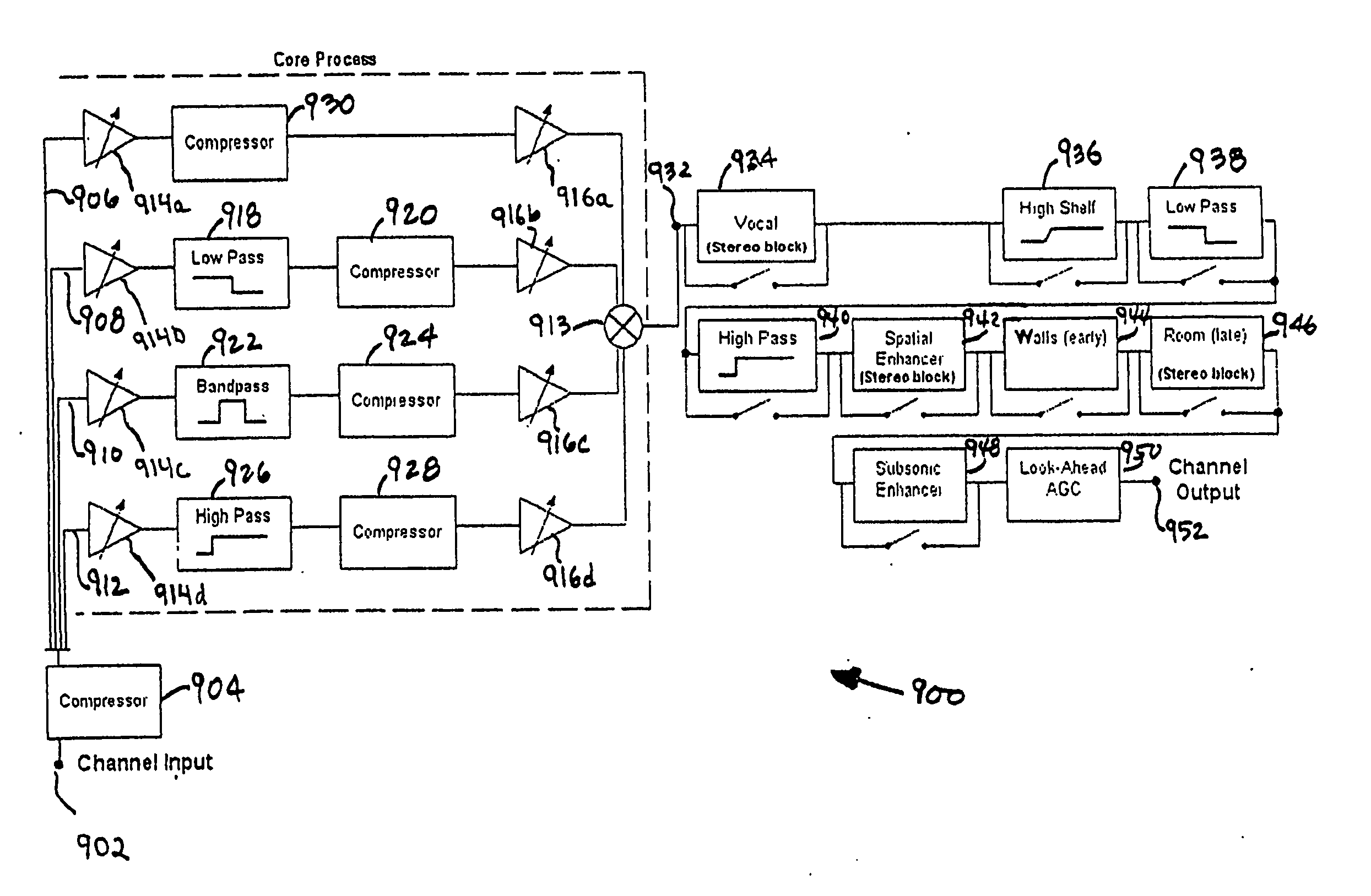
Processing of an audio signal for presentation in a high noise environment
ActiveUS7254243B2Weakening rangeIncreases magnitudeGain controlVolume compression/expansionEngineeringEqualization
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
System and method for processing audio signal
InactiveUS20090086996A1Improve dynamic rangeVolume compression/expansion in digital/coded amplifiersDigital/coded signal combination controlAudio signal flowLoudspeaker
The present invention provides for methods and systems for digitally processing an audio signal. Specifically, the present invention provides for a speaker system that is configured to digitally process an audio signal in a manner such that studio-quality sound that can be reproduced.
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
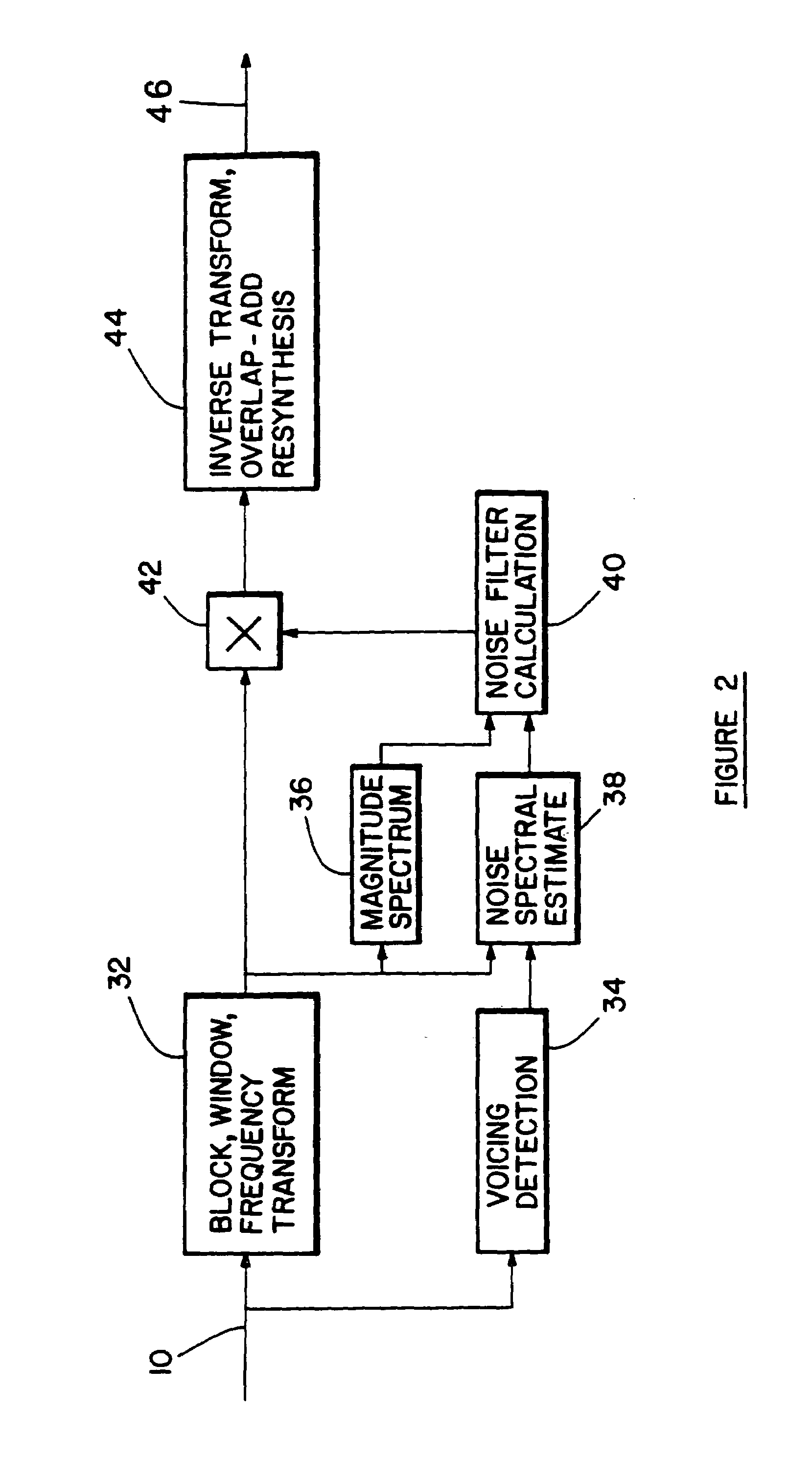
Method and apparatus for noise reduction particularly in hearing aids
InactiveUS7016507B1Boosted speechReduce noiseEar treatmentVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesCompression actionNoise reduction algorithm
This invention describes a practical application of noise reduction in hearing aids. Although listening in noisy conditions is difficult for persons with normal hearing, hearing impaired individuals are at a considerable further disadvantage. Under light noise conditions, conventional hearing aids amplifying the input signal sufficiently to overcome the hearing loss. For a typical sloping hearing loss where there is a loss in high frequency hearing sensitivity, the amount of boost (or gain) rises with frequency. Most frequently, the loss in sensitivity is only for low-level signals; high level signals are affective minimally or not at all. A compression hearing aid is able to compensate by automatically lowering the gain as the input signal level rises. This compression action is usually compromised under noisy conditions. In general, hearing aids are of lesser benefit under noisy conditions since both noise and speech are boosted together when what is really required is a reduction of the noise relative to the speech. A noise reduction algorithm with the dual purpose of enhancing speech relative to noise and also providing a relatively clean signal for the compression circuitry is described.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
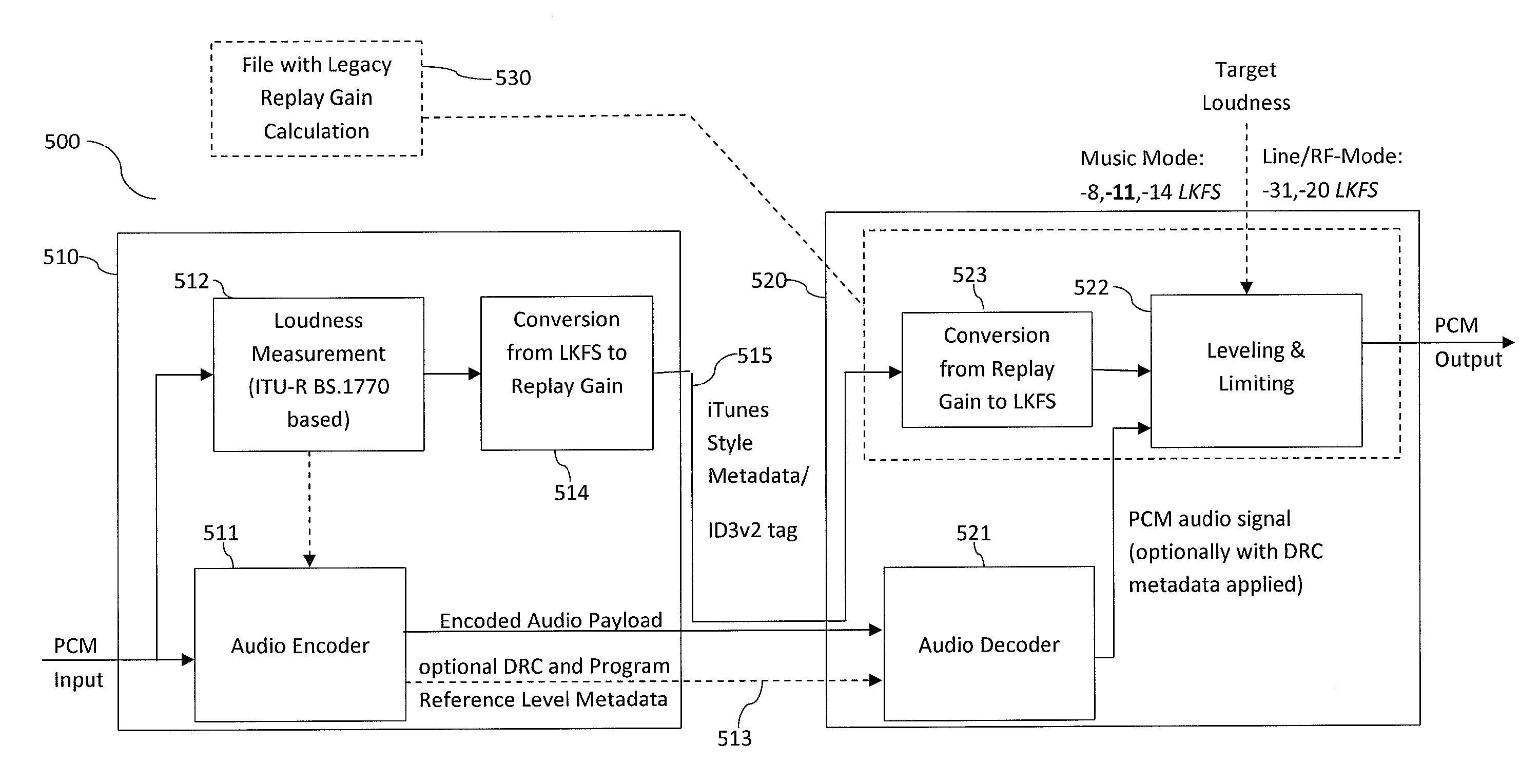
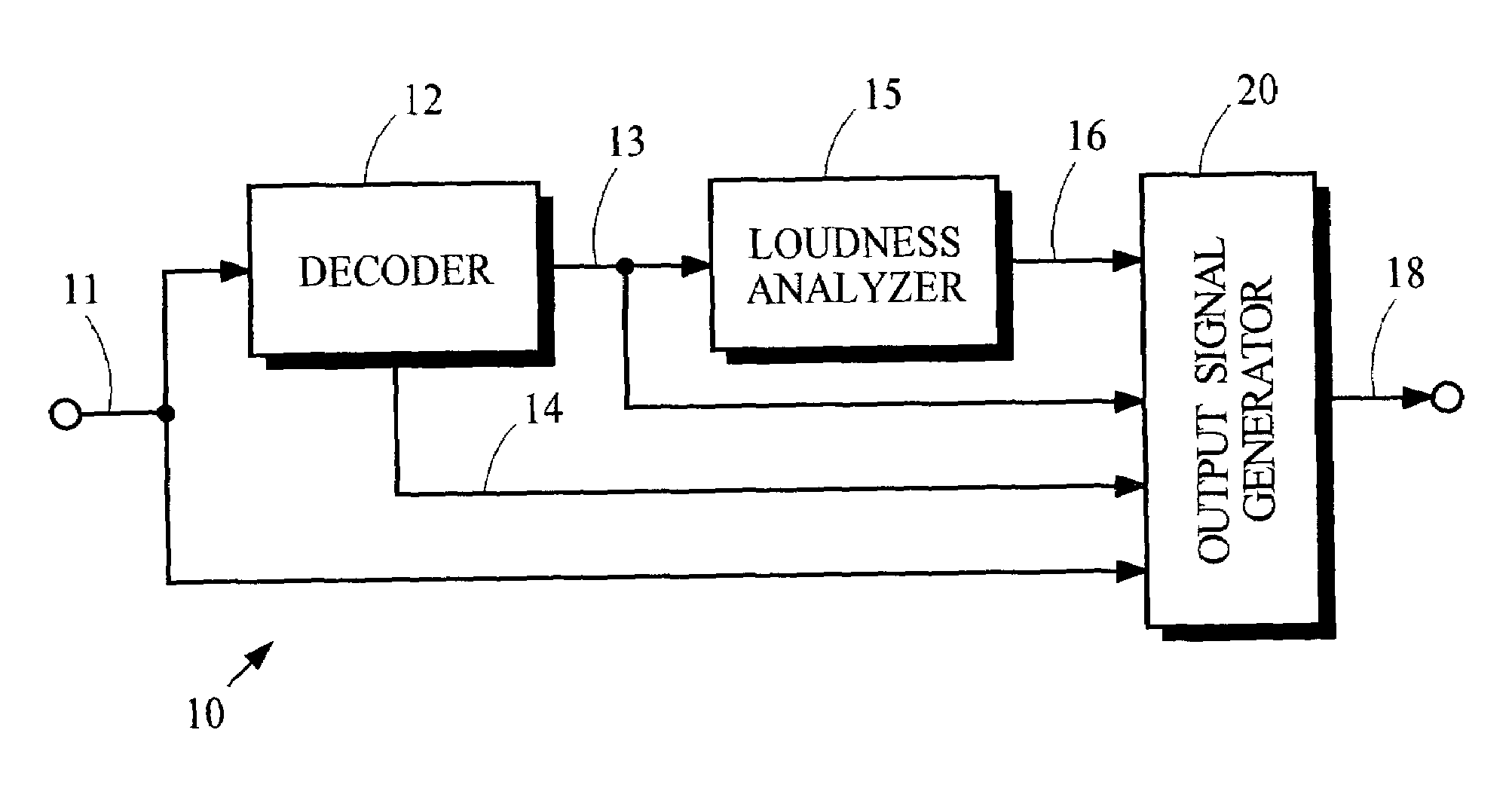
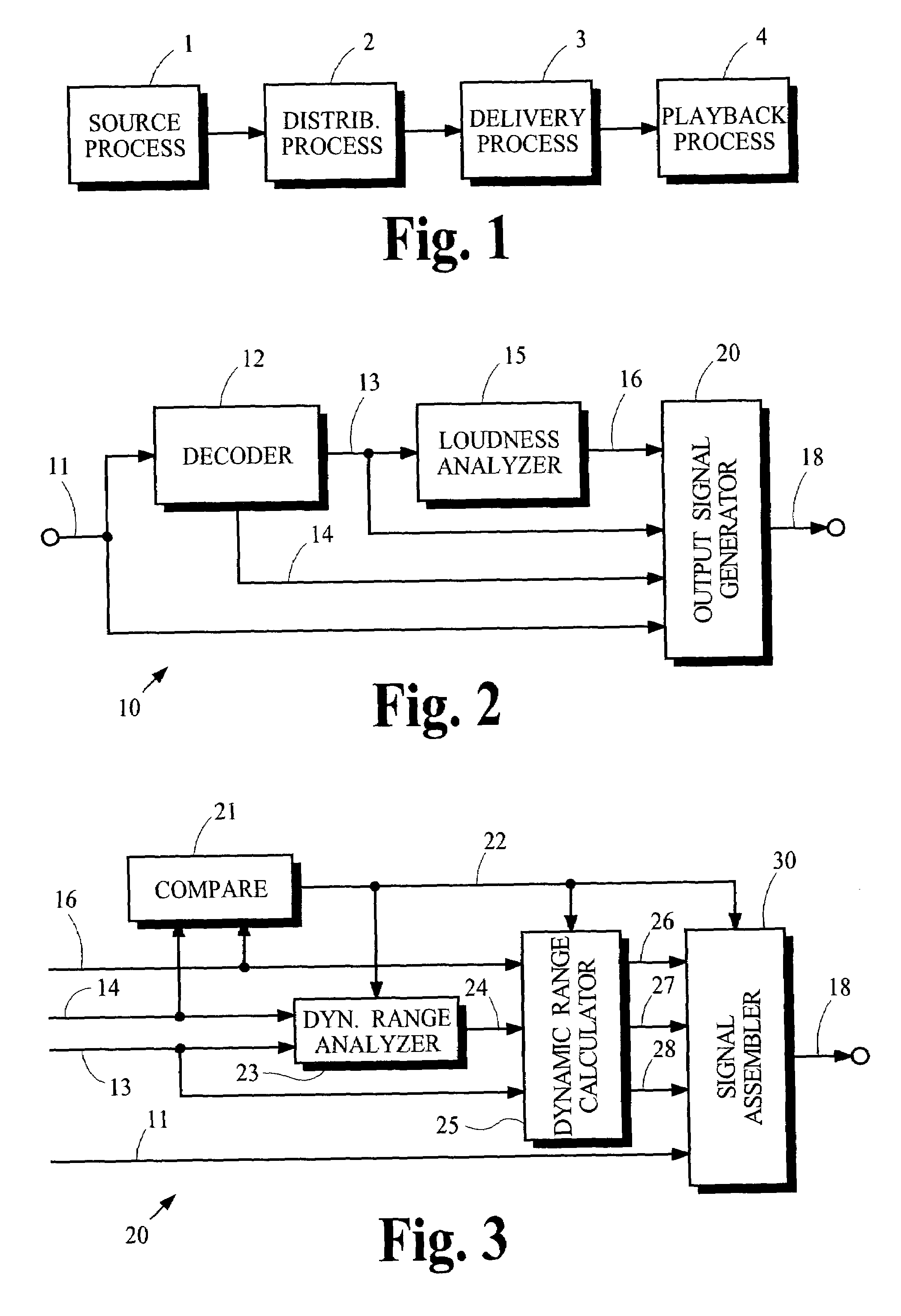
System for combining loudness measurements in a single playback mode
The present document relates to processing of multimedia data, notably the encoding, the transmission, the decoding and the rendering of multimedia data, e.g. audio files or bitstreams. In particular, the present document relates to the implementation of loudness control in multimedia players. A method for providing loudness related data to a media player is described. The method comprises the steps of providing a first loudness related value associated with an audio signal; wherein the first loudness related value has been determined according to a first procedure; of converting the first loudness related value into a second loudness related value using a reversible relation; wherein the second loudness related value is associated with a second procedure for determining loudness related values; of storing the second loudness related value in metadata associated with the audio signal; and of providing the metadata to the media player.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP +1
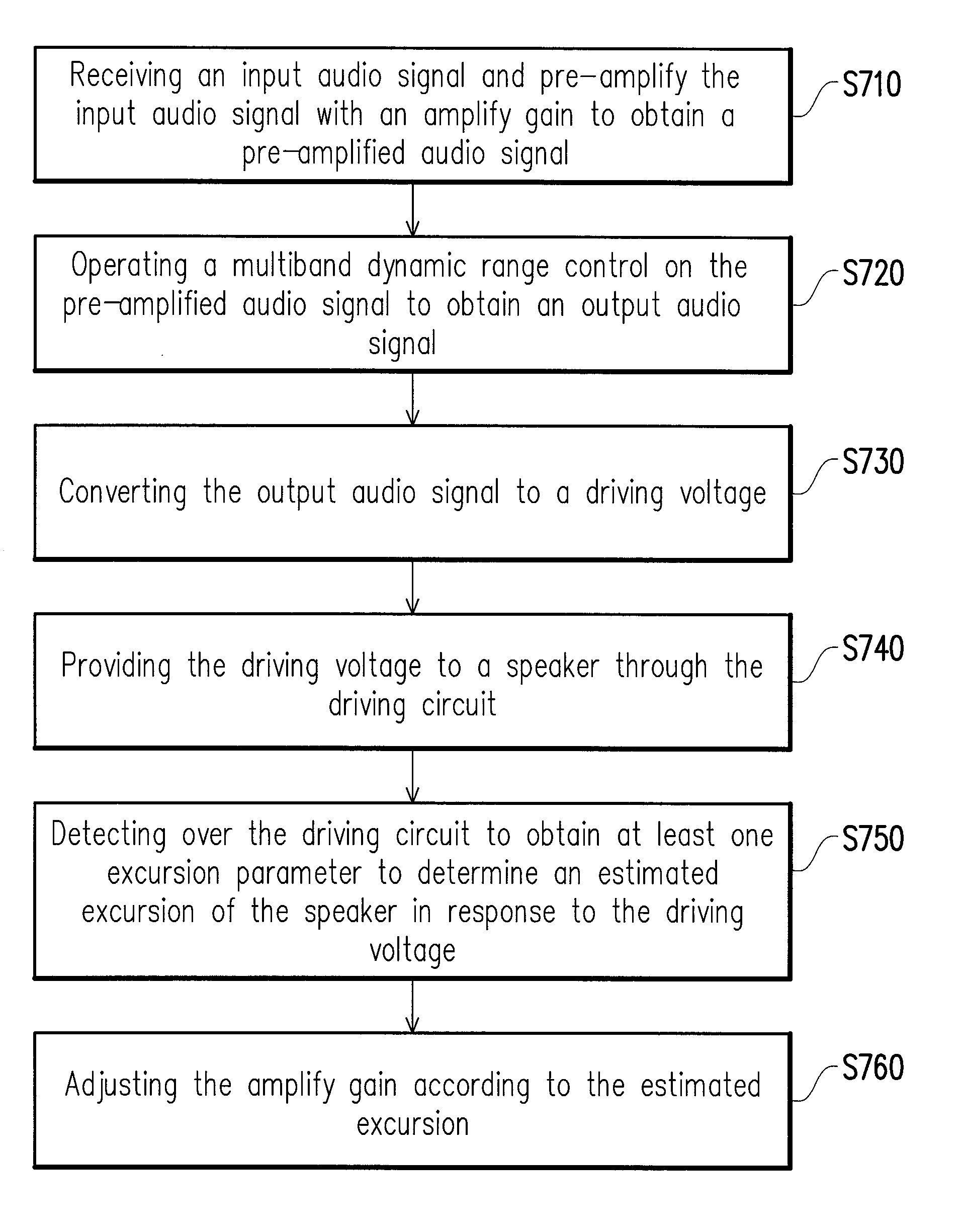
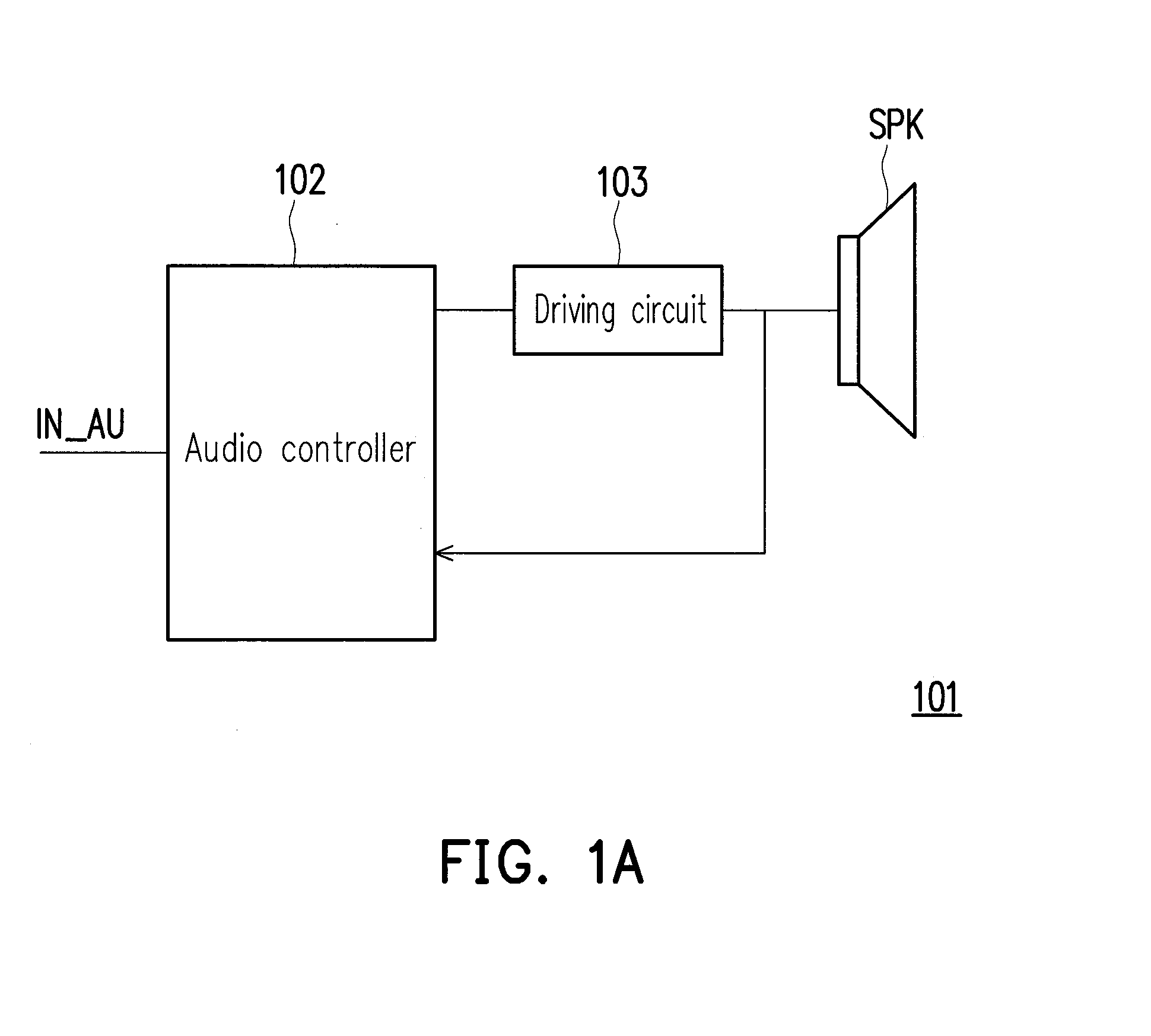
Sound producing system and audio amplifying method thereof
ActiveUS20150010168A1Increase the loudnessImprove sound qualityGain controlTransducer circuit dampingEngineeringLoudspeaker
The invention provides one sound producing system including a speaker, a driving circuit and an audio controller. The speaker is used for producing an audible sound. The driving circuit is connected to the speaker. The audio controller is configured to receive an input audio signal and pre-amplify the input audio signal with an amplify gain to obtain a pre-amplified audio signal; operate a multiband dynamic range control on the pre-amplified audio signal to obtain an output audio signal; convert the output audio signal to a driving voltage; provide the driving voltage to the speaker through the driving circuit; detect over the driving circuit to obtain at least one excursion parameter to determine an estimated excursion of the speaker in response to the driving voltage; and adjust the amplify gain according to the estimated excursion.
Owner:HTC CORP
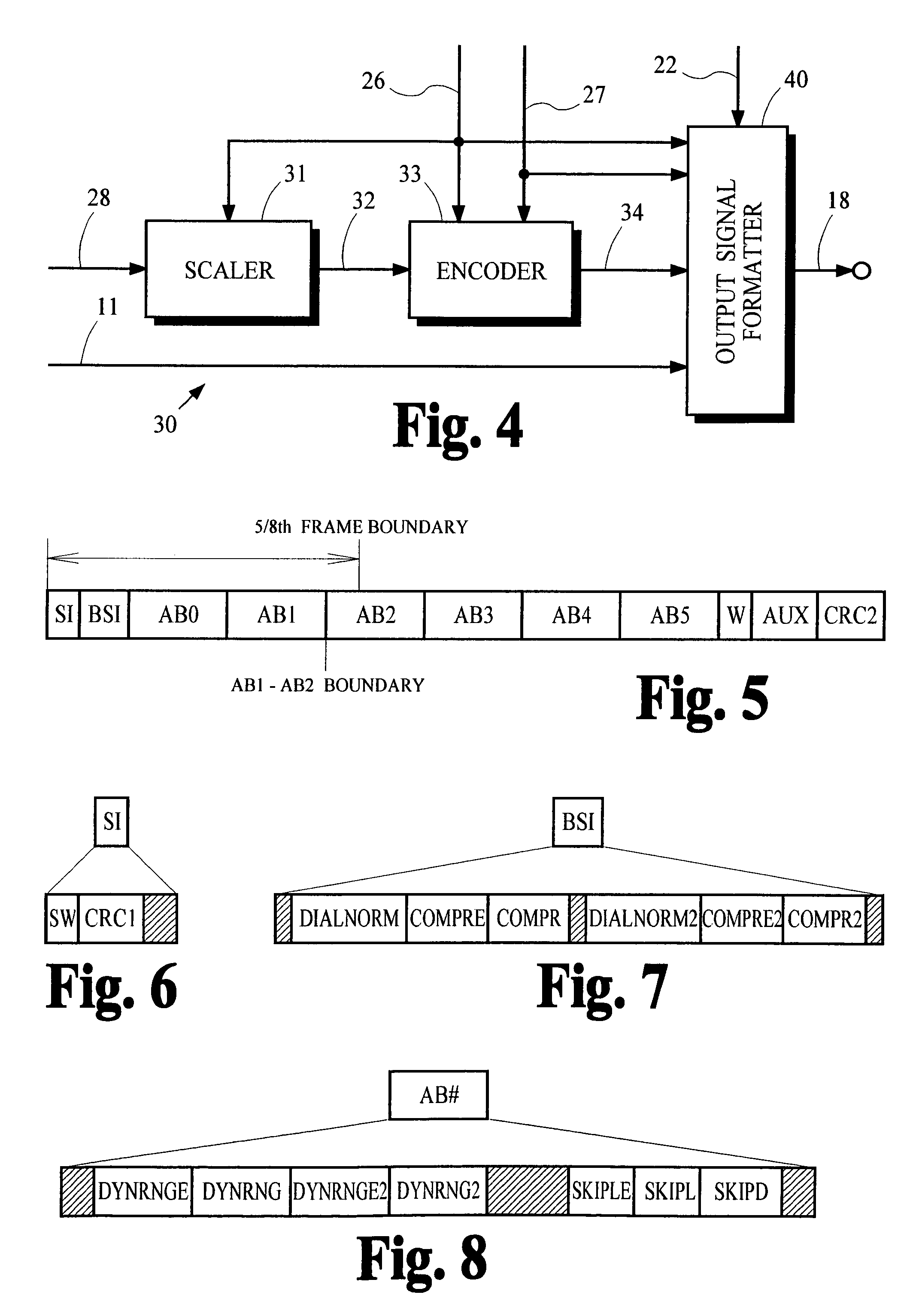
Method for correcting metadata affecting the playback loudness and dynamic range of audio information
A coded signal conveys encoded audio information and metadata that may be used to control the loudness and dynamic range of the audio information during its playback. If the values for these metadata parameters are set incorrectly, annoying fluctuations in loudness during playback can result. The present invention overcomes this problem by detecting incorrect metadata parameter values in the signal and replacing the incorrect values with corrected values.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness and/or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal
InactiveCN101421781AReduced characteristicsSpecific loudness controlGain controlSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumEqualization
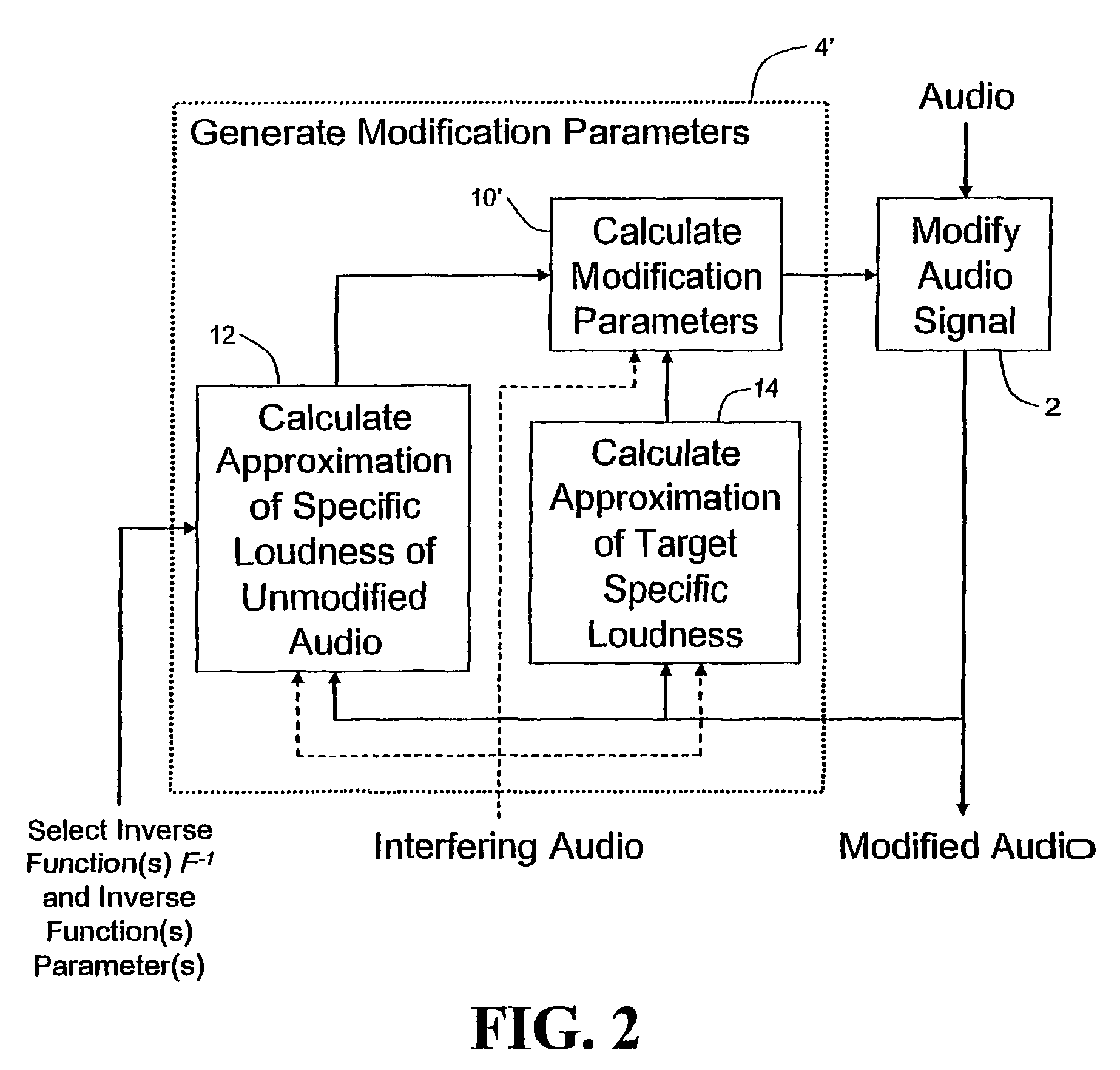
Audio signal processing relating to the measurement and control of the perceived sound loudness and / or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal is useful, for example, in one or more of: loudness-compensating volume control, automatic gain control, dynamic range control (including, for example, limiters, compressors, expanders, etc.), dynamic equalization, and compensating for background noise interference in an audio playback environment. In various embodiments, modification parameters are derived for modifying the audio signal in order to reduce the difference between its specific loudness and a target specific loudness.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
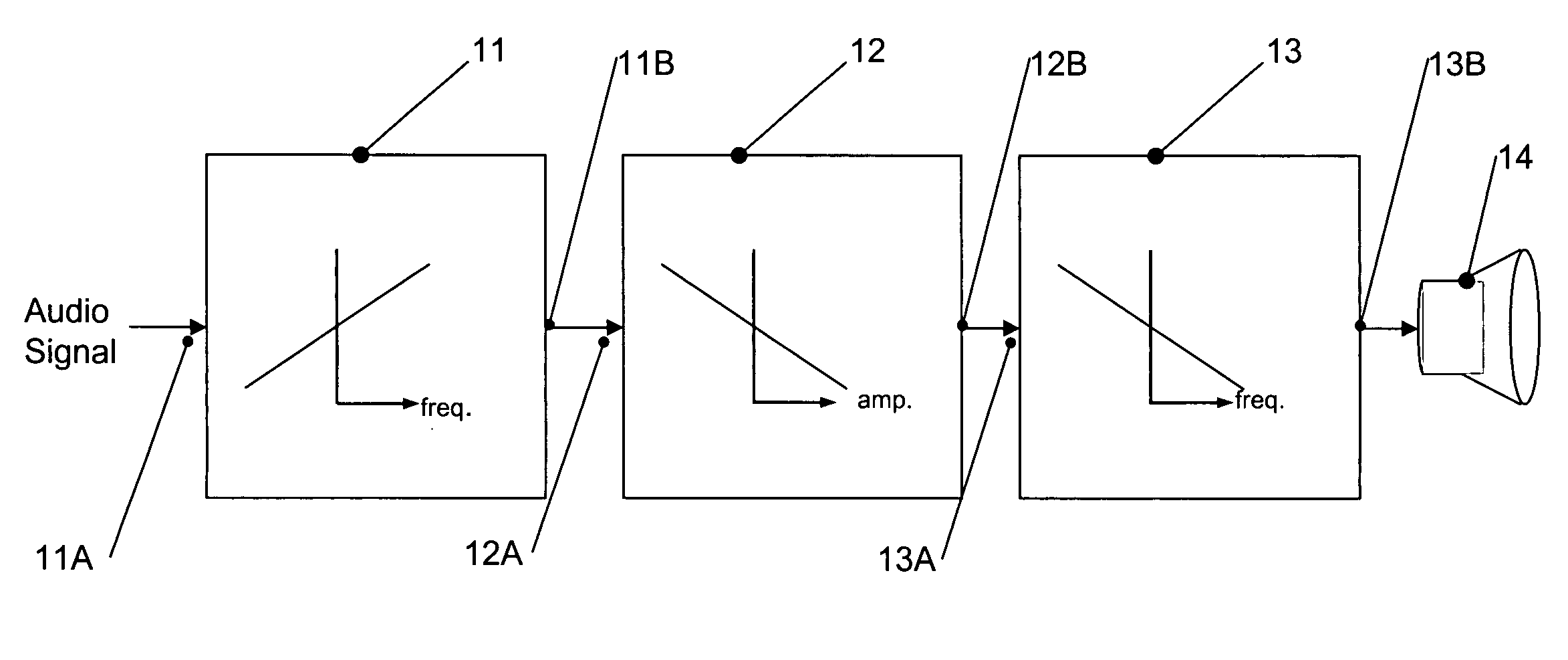
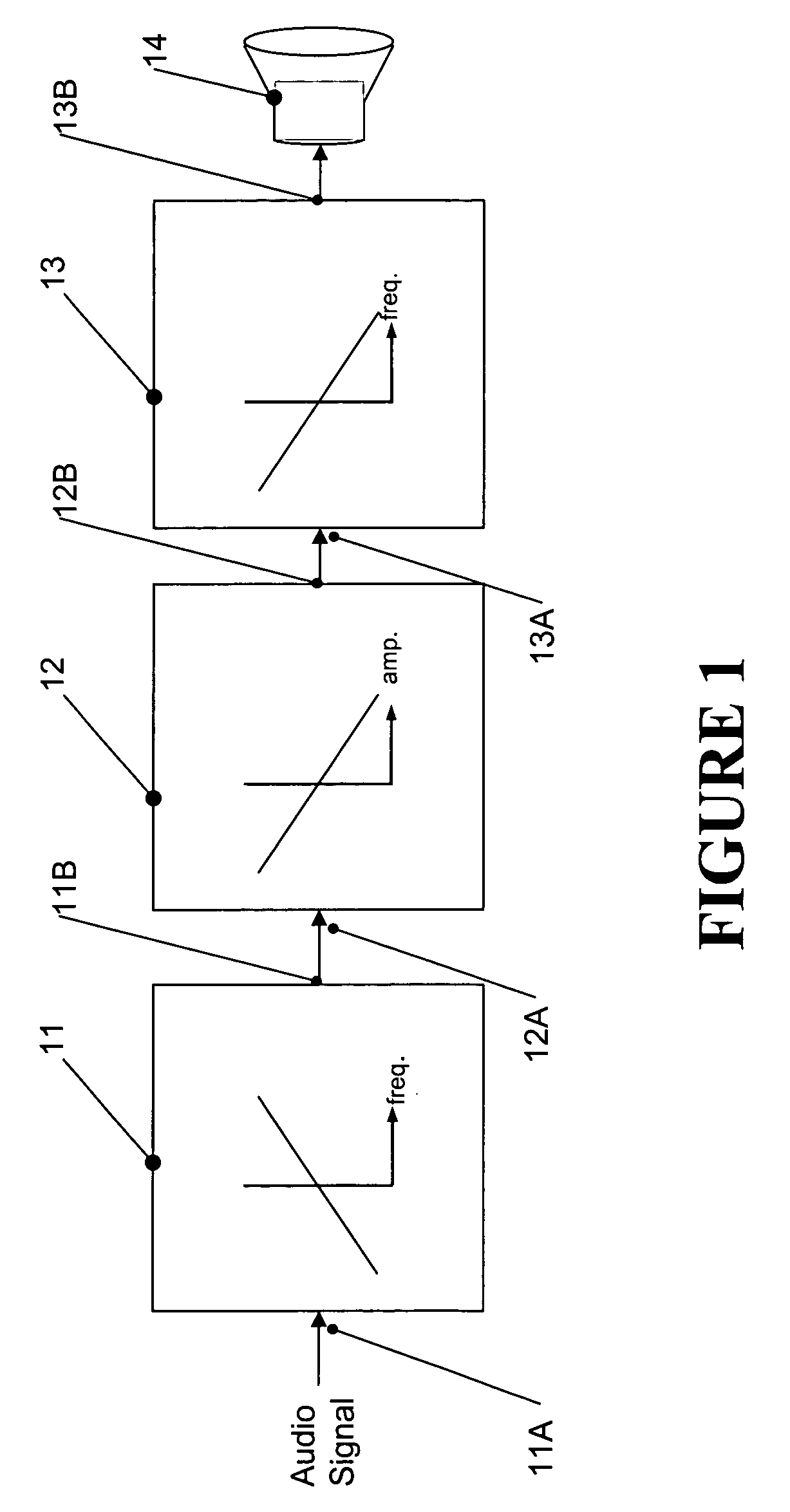
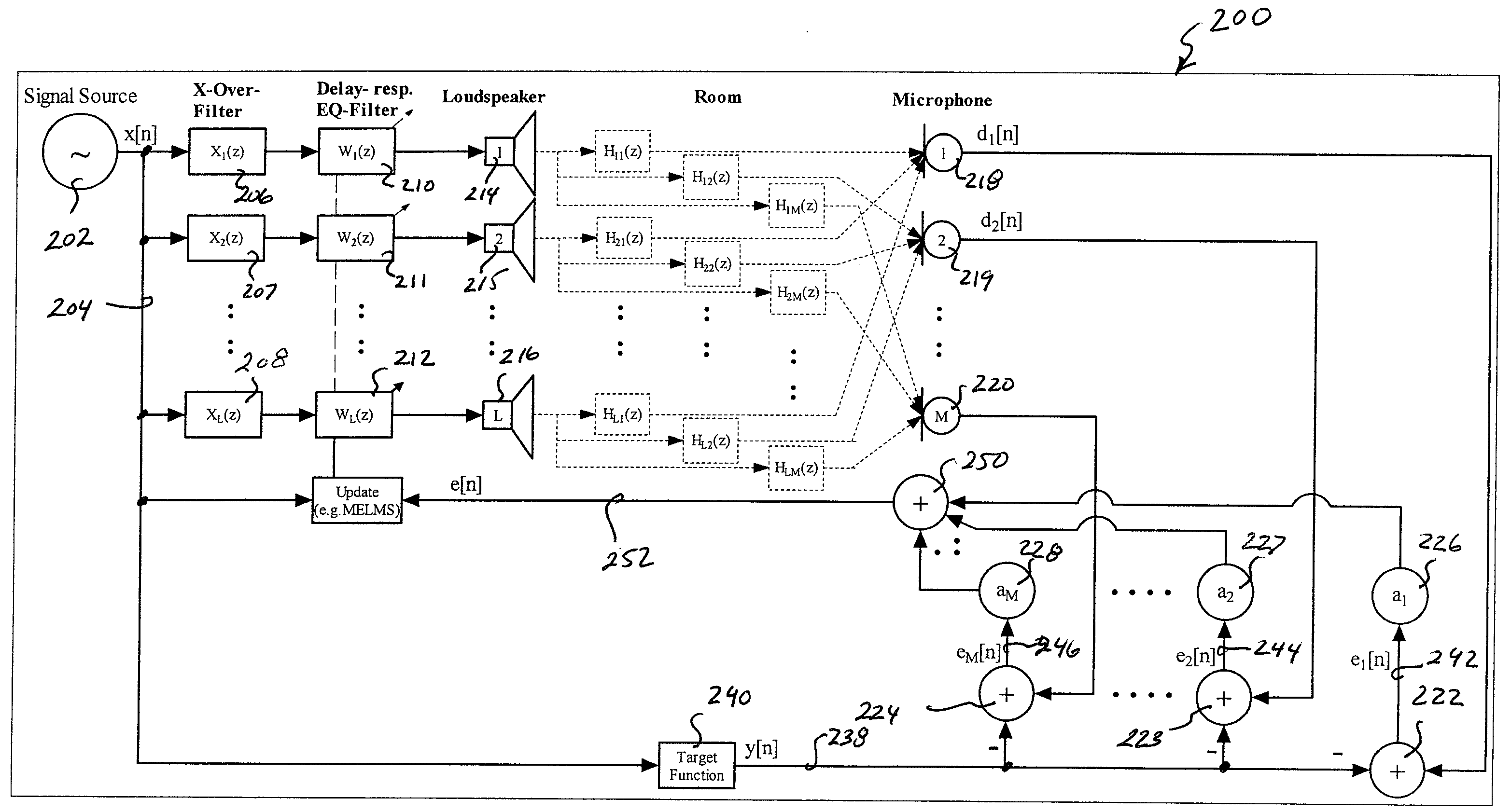
Sound tuning method
The invention relates to a method for automated tuning of a sound system, the sound system comprising delay lines, equalizing filters, and at least two loudspeakers, the method comprising the steps of reproducing a useful sound signal through the loudspeakers, measuring sound pressure values at least one location, providing a target transfer function for tuning the delay lines and the equalizing filters of the sound system, the target transfer function representing a desired transfer characteristics of the sound system, adjusting the delay of the delay lines, and adjusting amplitude responses of the equalizing filters such, that the actual transfer characteristics of the sound system approximates the target function.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
System and method for digital signal processing
ActiveUS8229136B2Constant output levelSimple designPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesGain controlDigital signal processingEngineering
Owner:BONGIOVI ACOUSTICS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com