Patents
Literature
637results about "Automatic tone/bandwidth control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
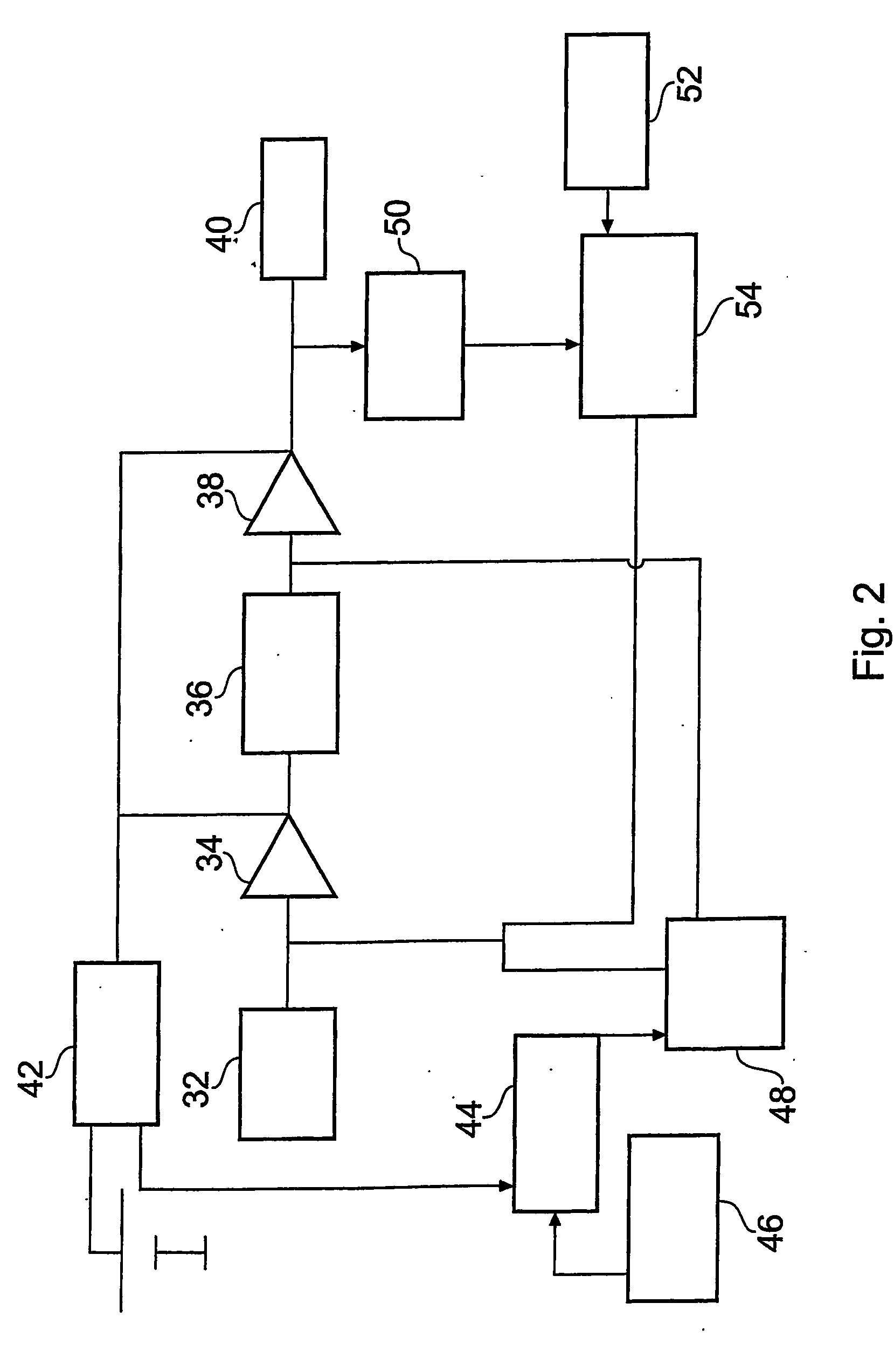
Compensating filters
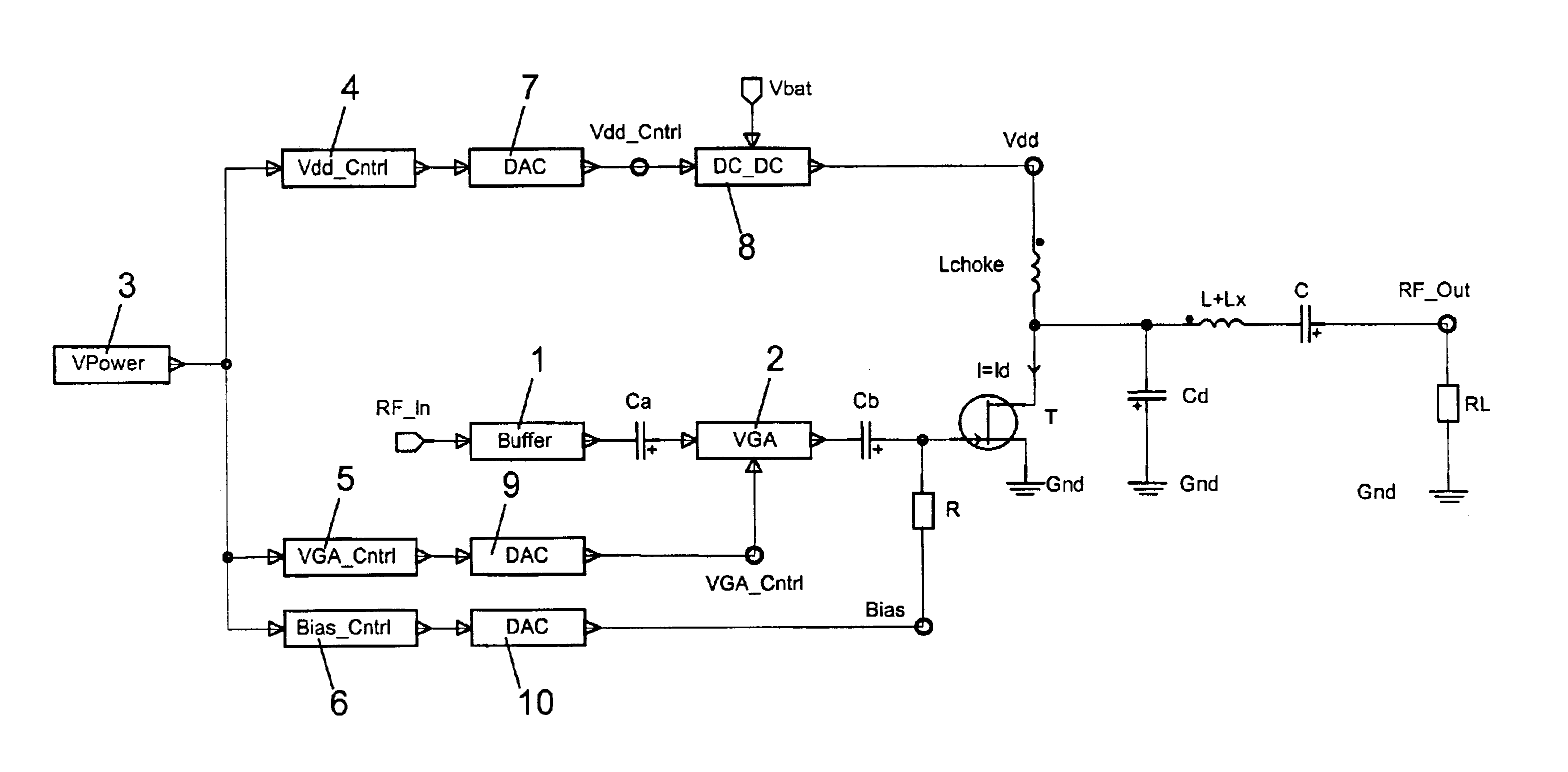
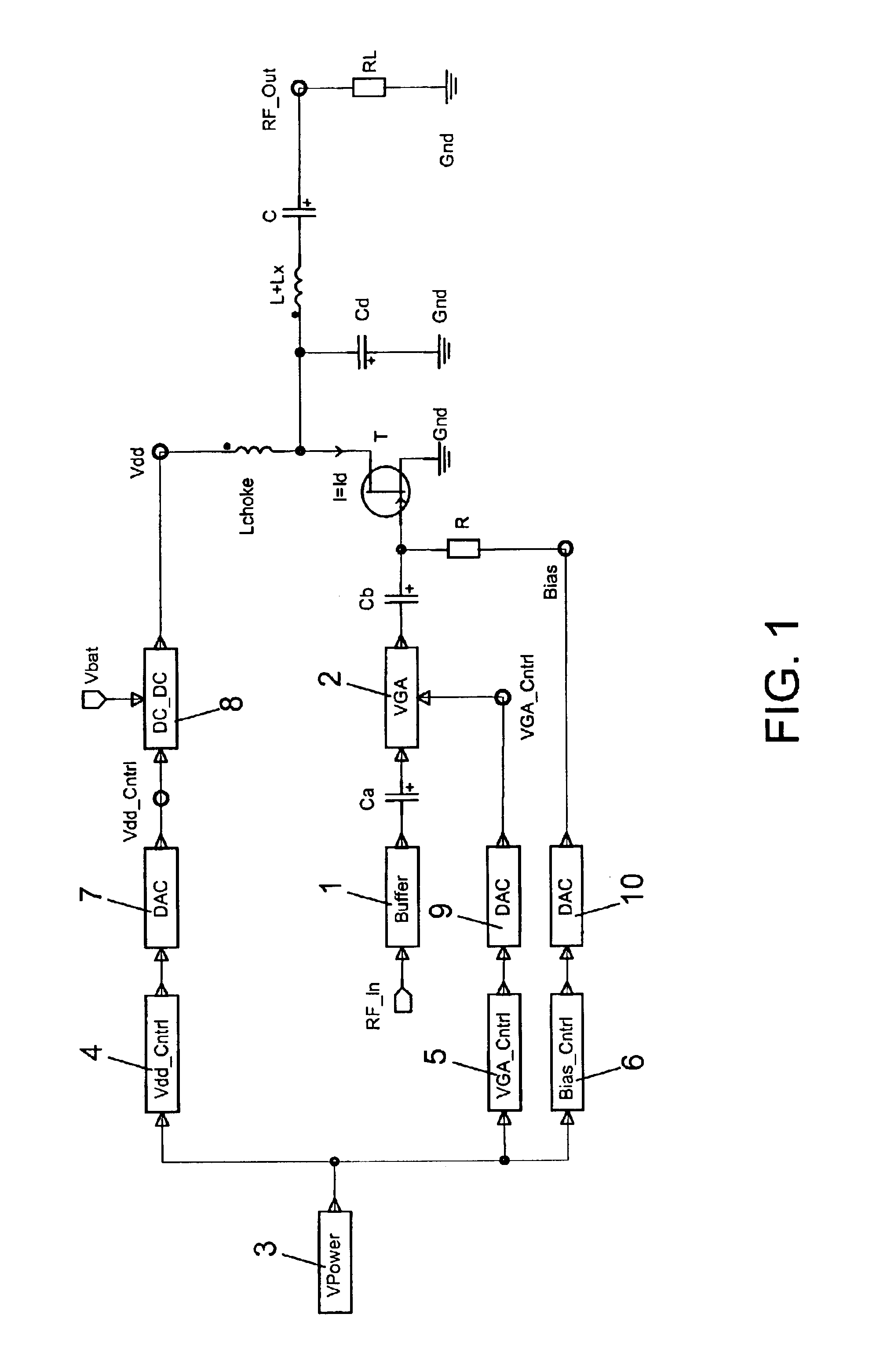
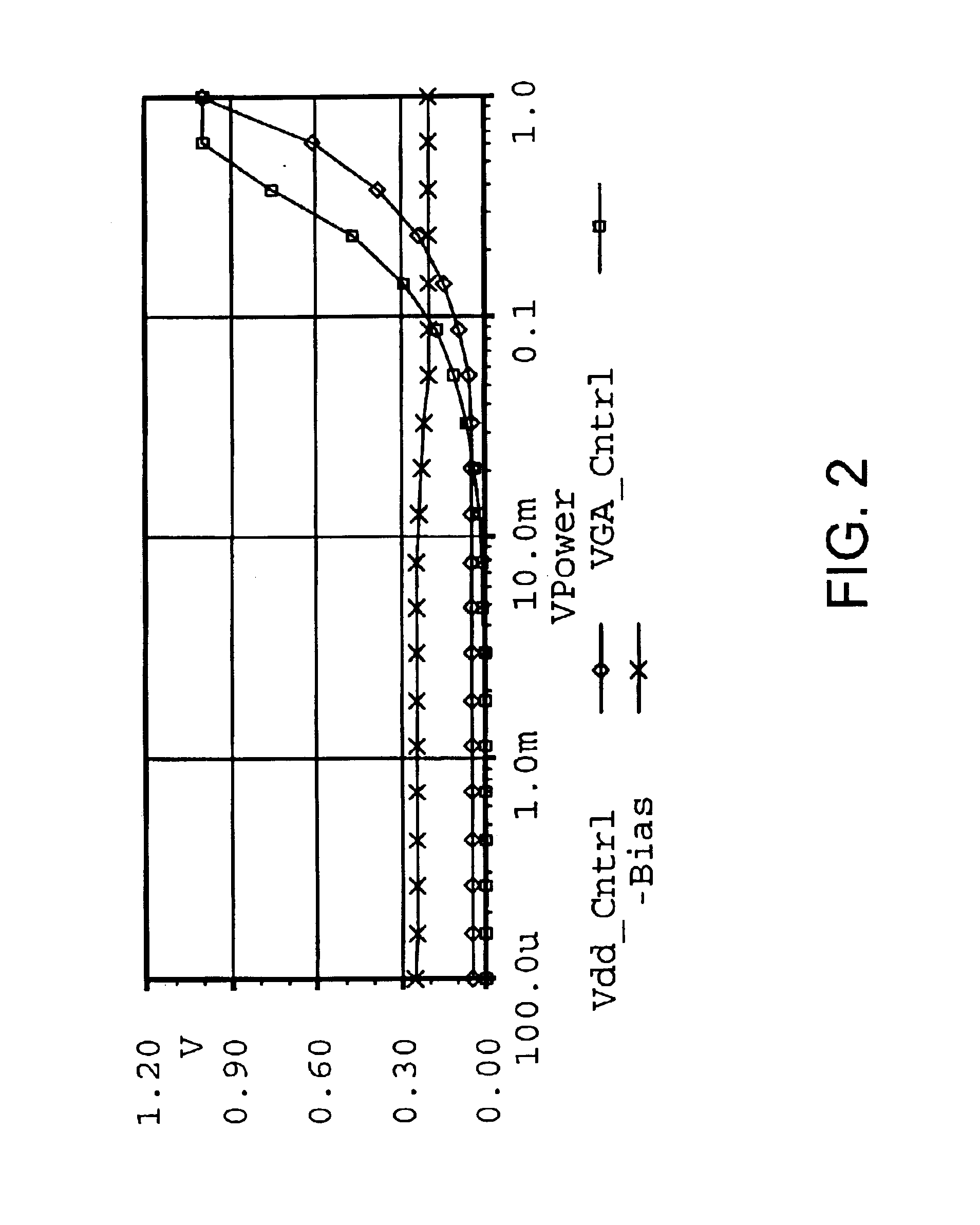
InactiveUS6760451B1Eliminate phase distortionAdaptive networkAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlDigital signal processingAmplitude response
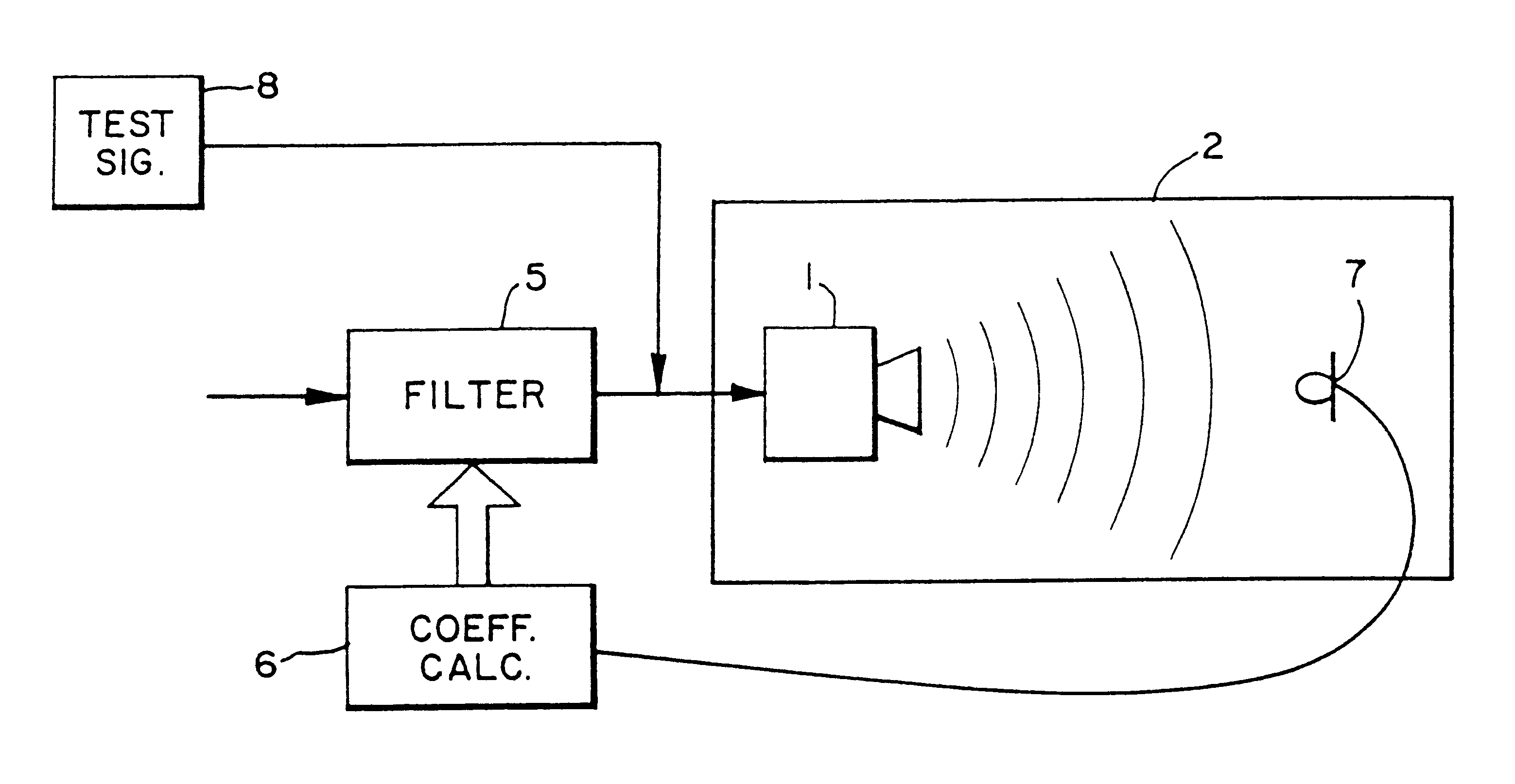
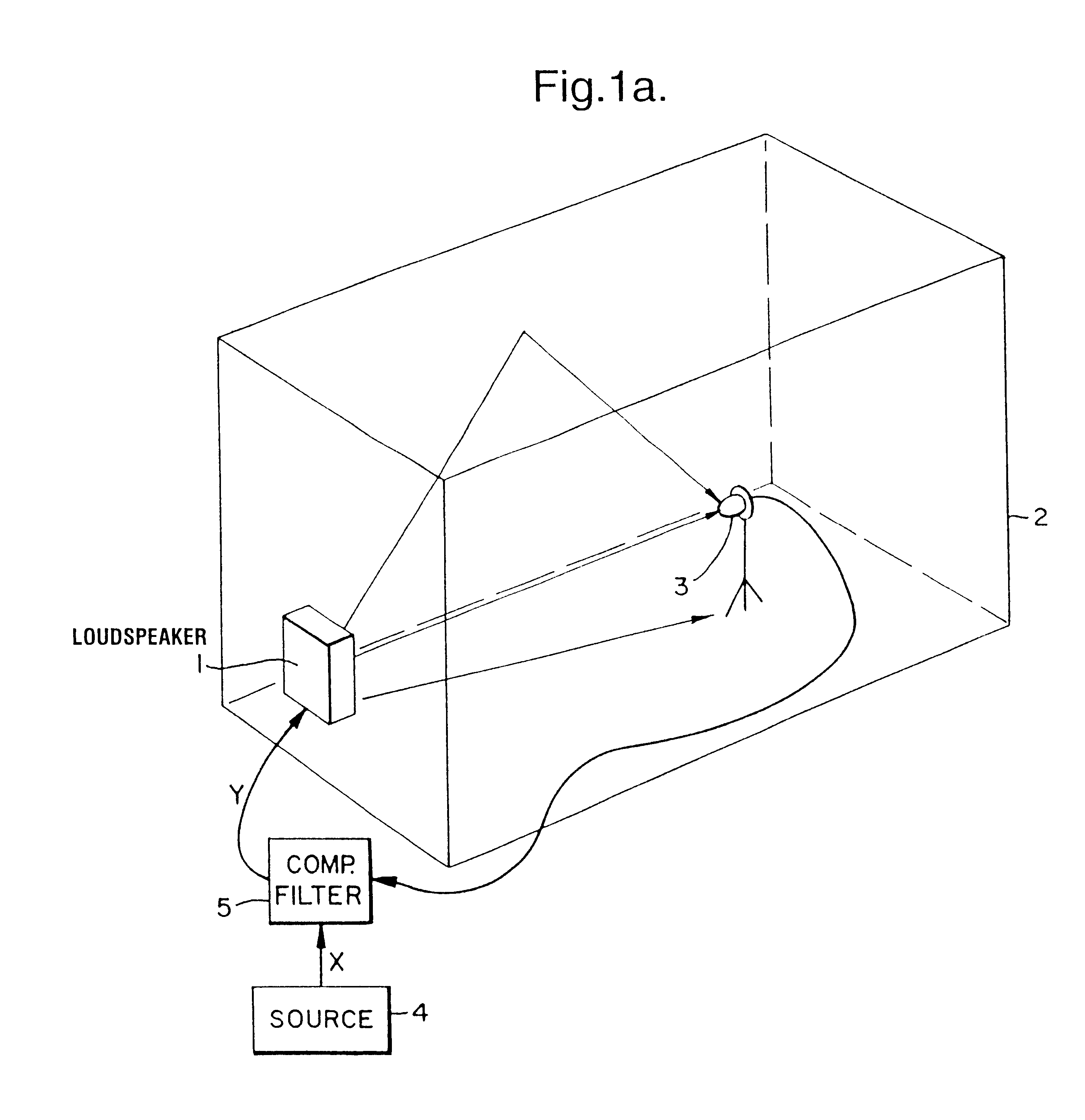
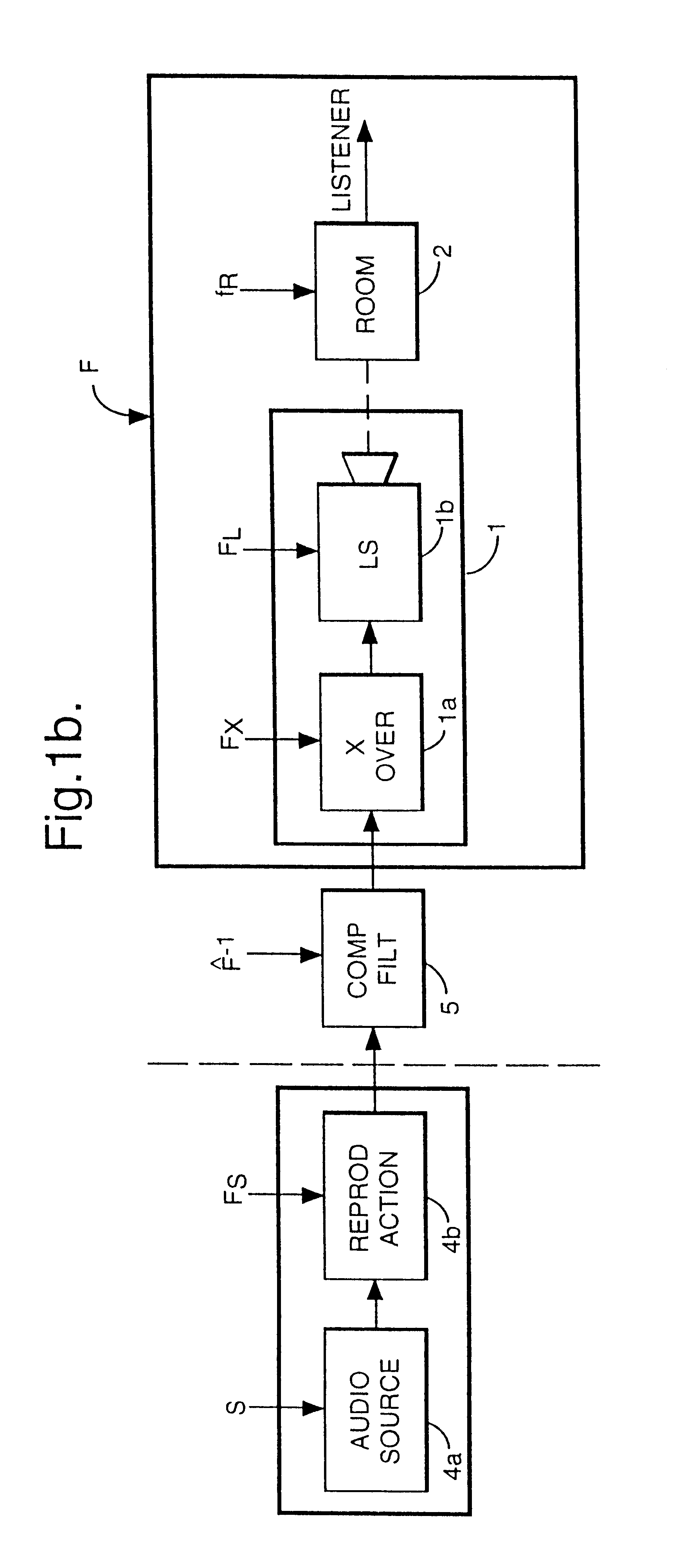
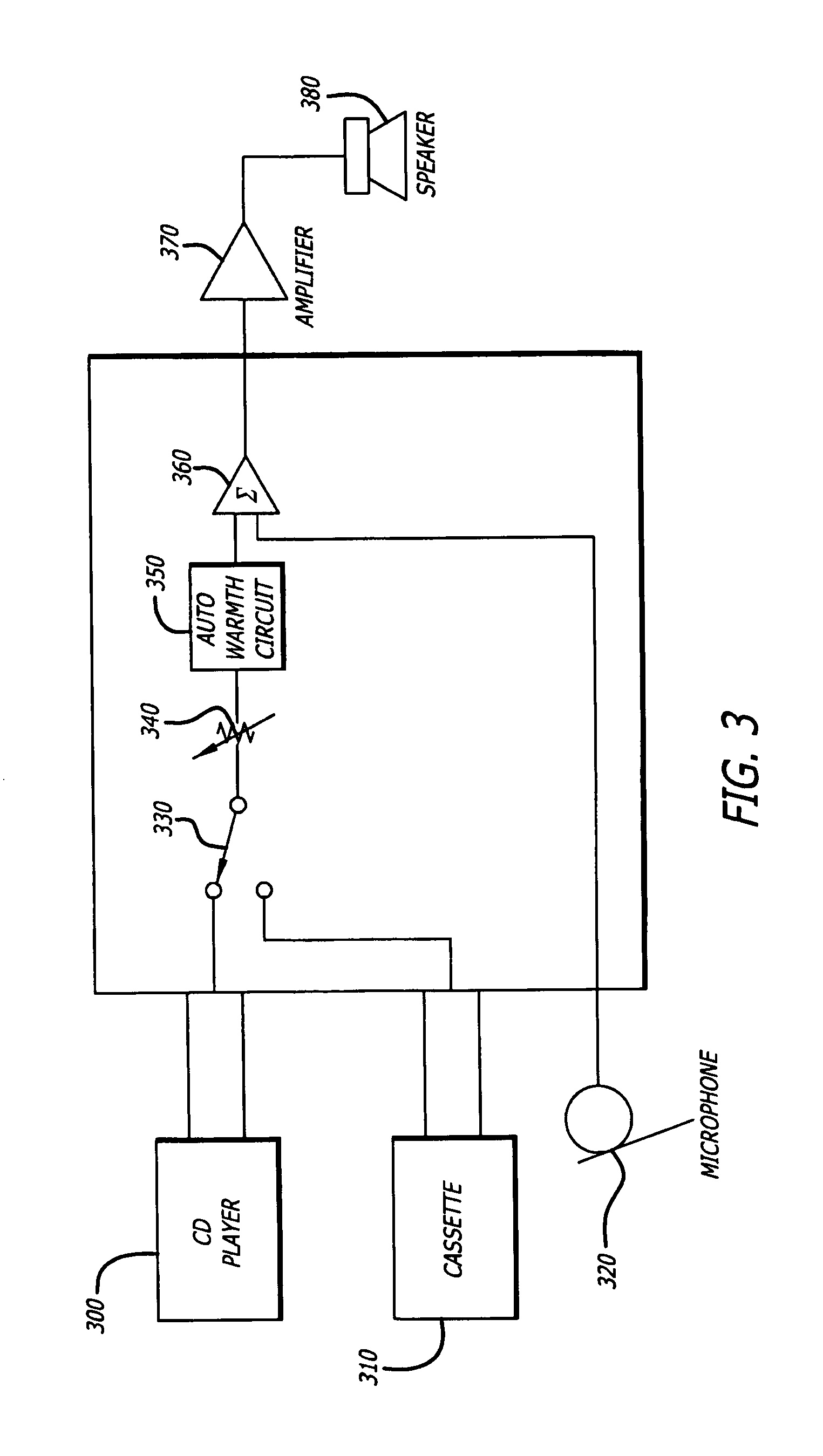
A prefilter (5) for an audio system comprising a loudspeaker (1) in a room (2), which corrects both amplitude and phase errors due to the loudspeaker (1) by a linear phase correction filter response and corrects the amplitude response of the room (2) whilst introducing the minimum possible amount of extra phase distortion by employing a minimum phase correction filter stage. A test signal generator (8) generates a signal comprising a periodic frequency sweep with a greater phase repetition period than the frequency repetition period. A microphone (7) positioned at various points in the room (2) measures the audio signal processed by the room (2) and loudspeaker (1), and a coefficient calculator (6) (e.g. a digital signal processor device) derives the signal response of the room and thereby a requisite minimum phase correction to be cascaded with the linear phase correction already calculated for the loudspeaker (1). Filter (5) may comprise the same digital signal processor as the coefficient calculator (6). Applications in high fidelity audio reproduction, and in car stereo reproduction.
Owner:CRAVEN PETER GRAHAM +1
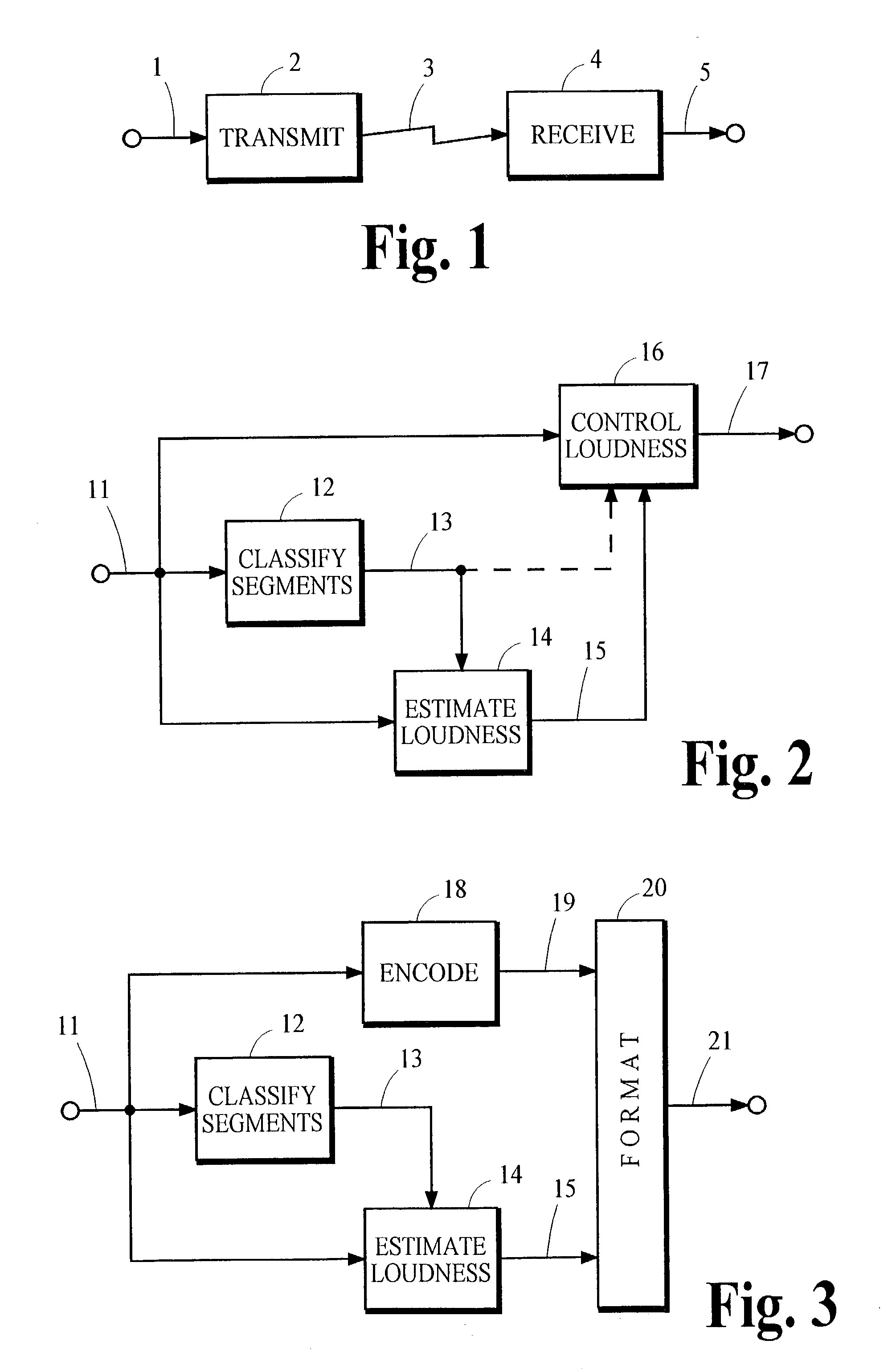
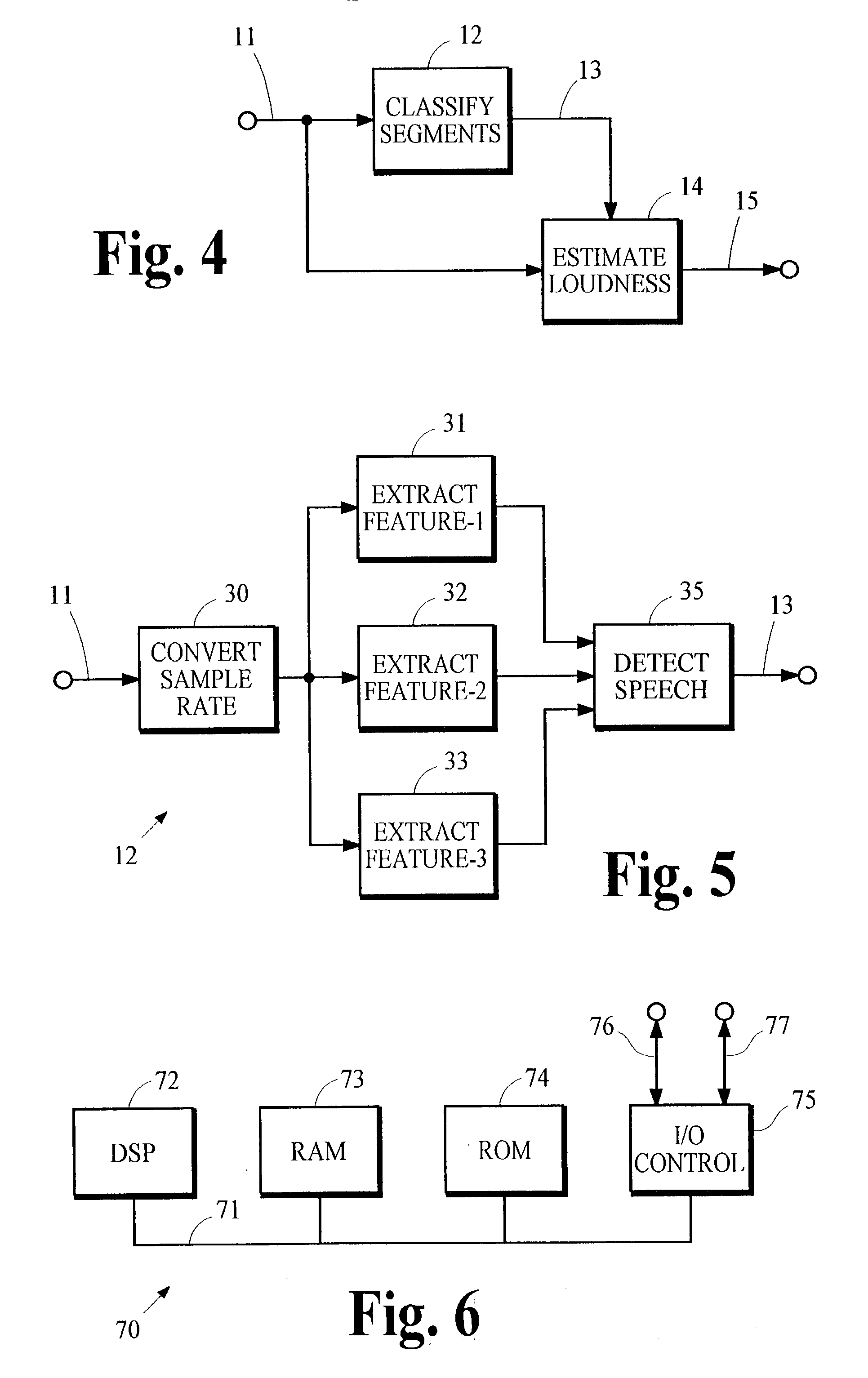
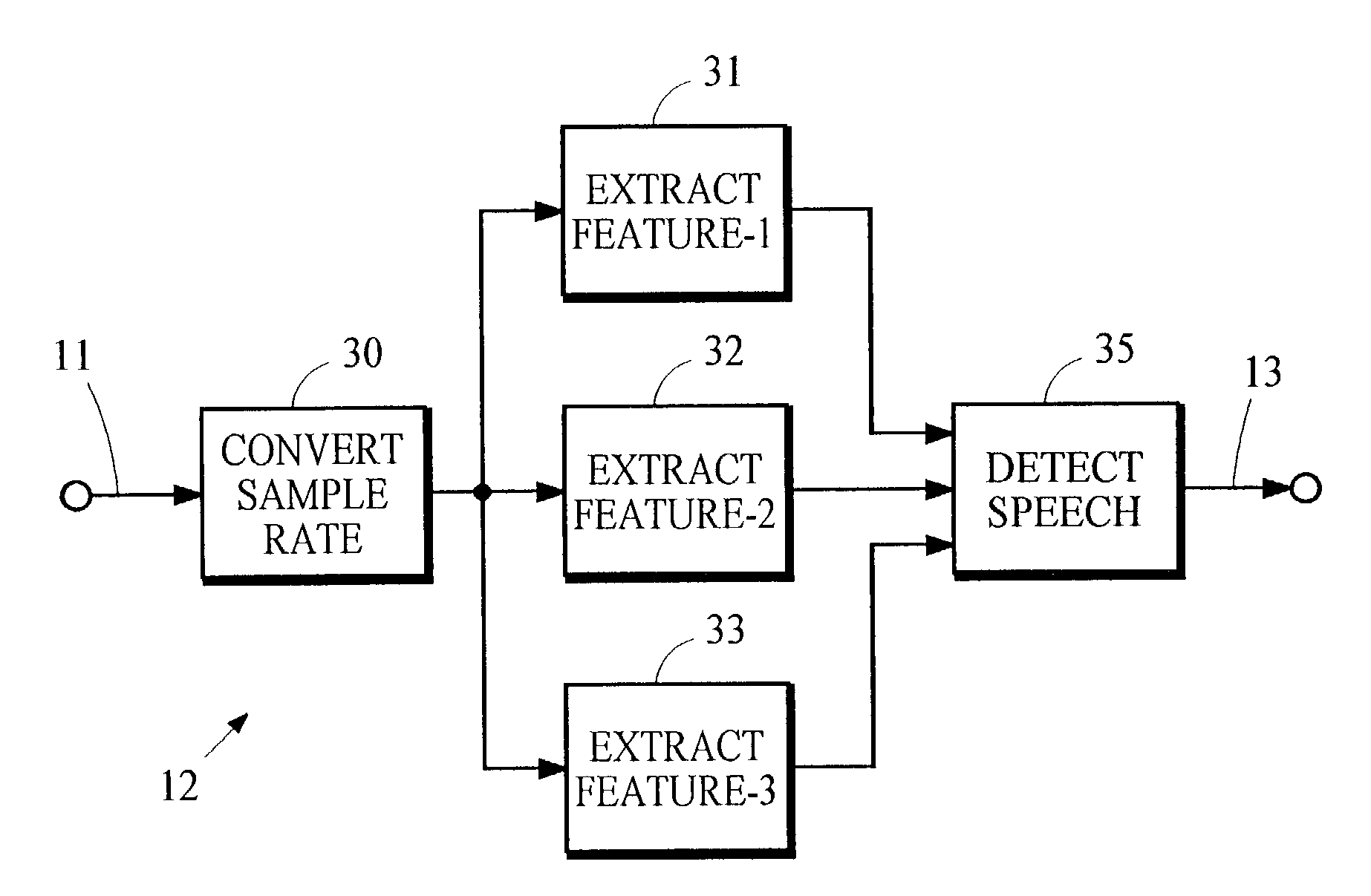
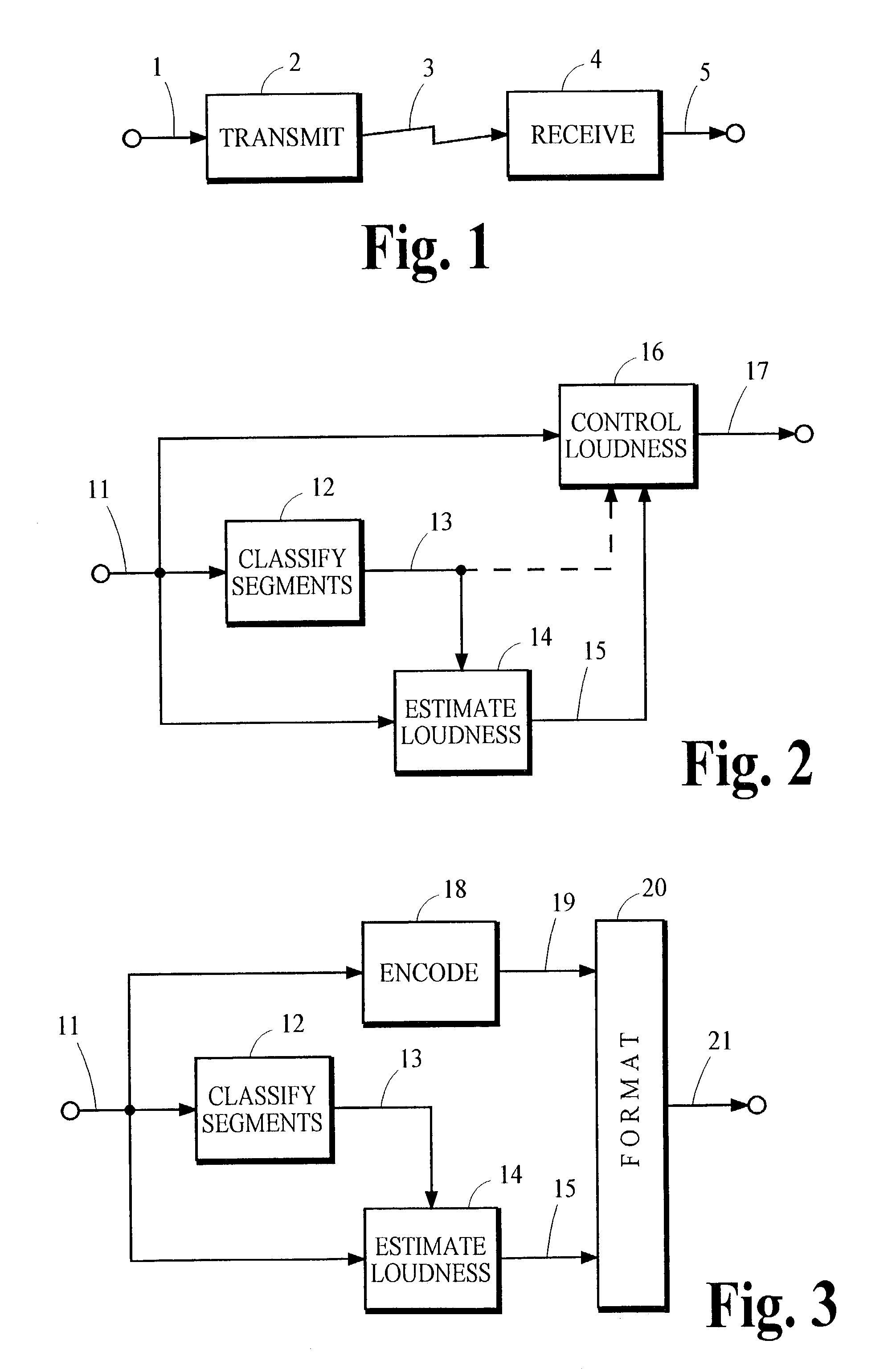
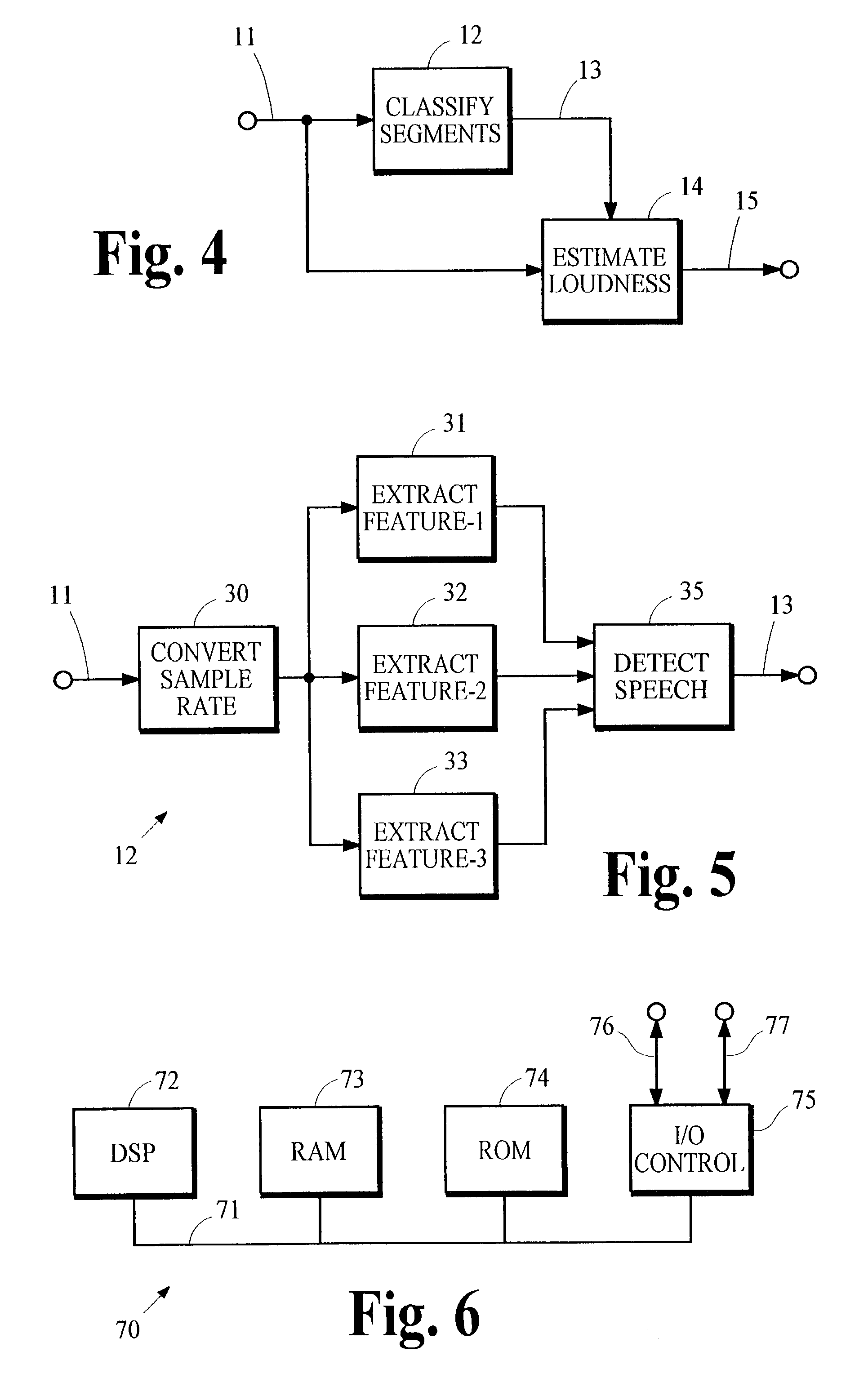
Controlling loudness of speech in signals that contain speech and other types of audio material
InactiveUS20040044525A1Reduce variationControl the loudness of the audio signalSpeech analysisAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlLoudnessSpeech sound
An indication of the loudness of an audio signal containing speech and other types of audio material is obtained by classifying segments of audio information as either speech or non-speech. The loudness of the speech segments is estimated and this estimate is used to derive the indication of loudness. The indication of loudness may be used to control audio signal levels so that variations in loudness of speech between different programs is reduced. A preferred method for classifying speech segments is described.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP +1
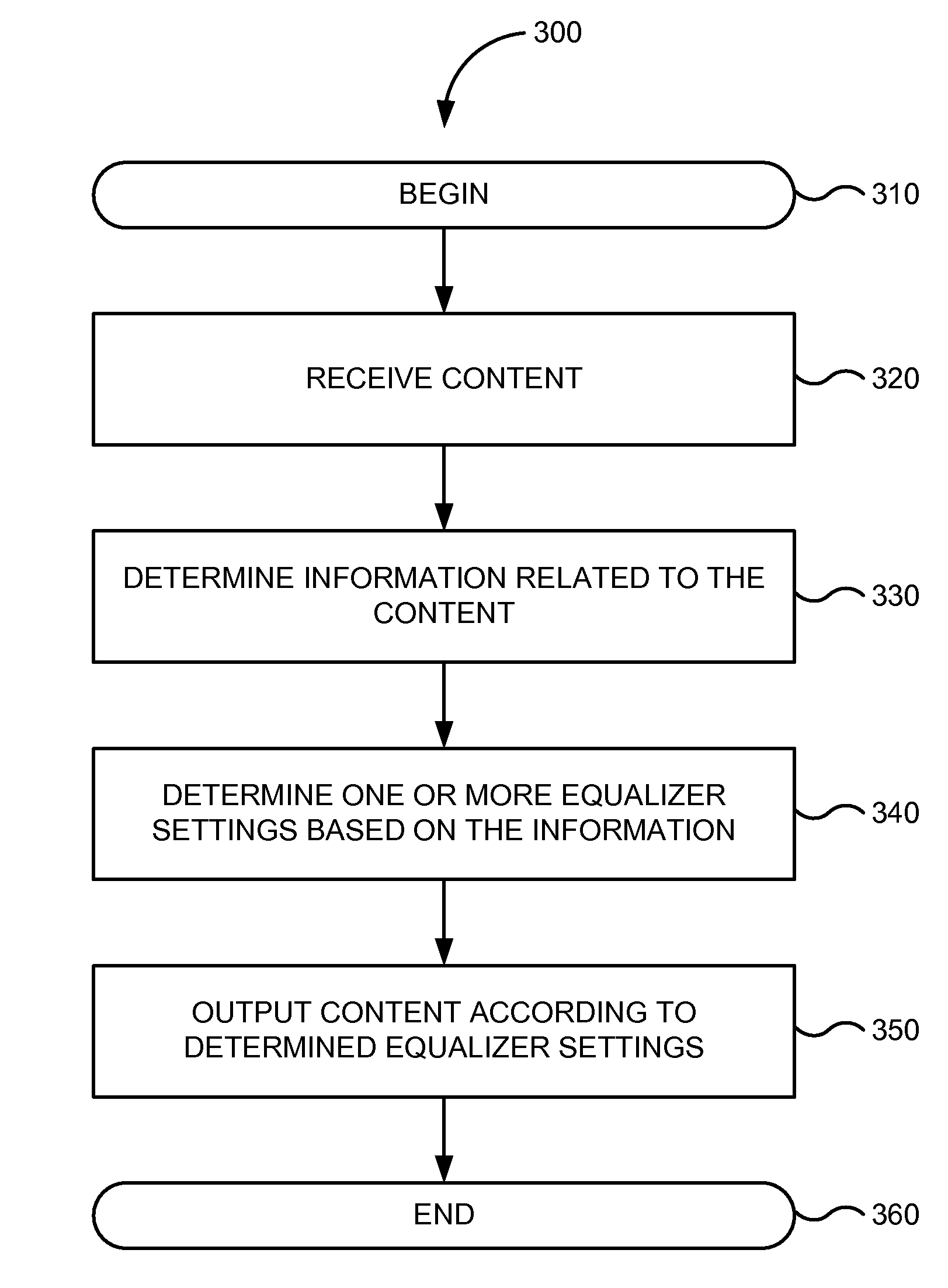
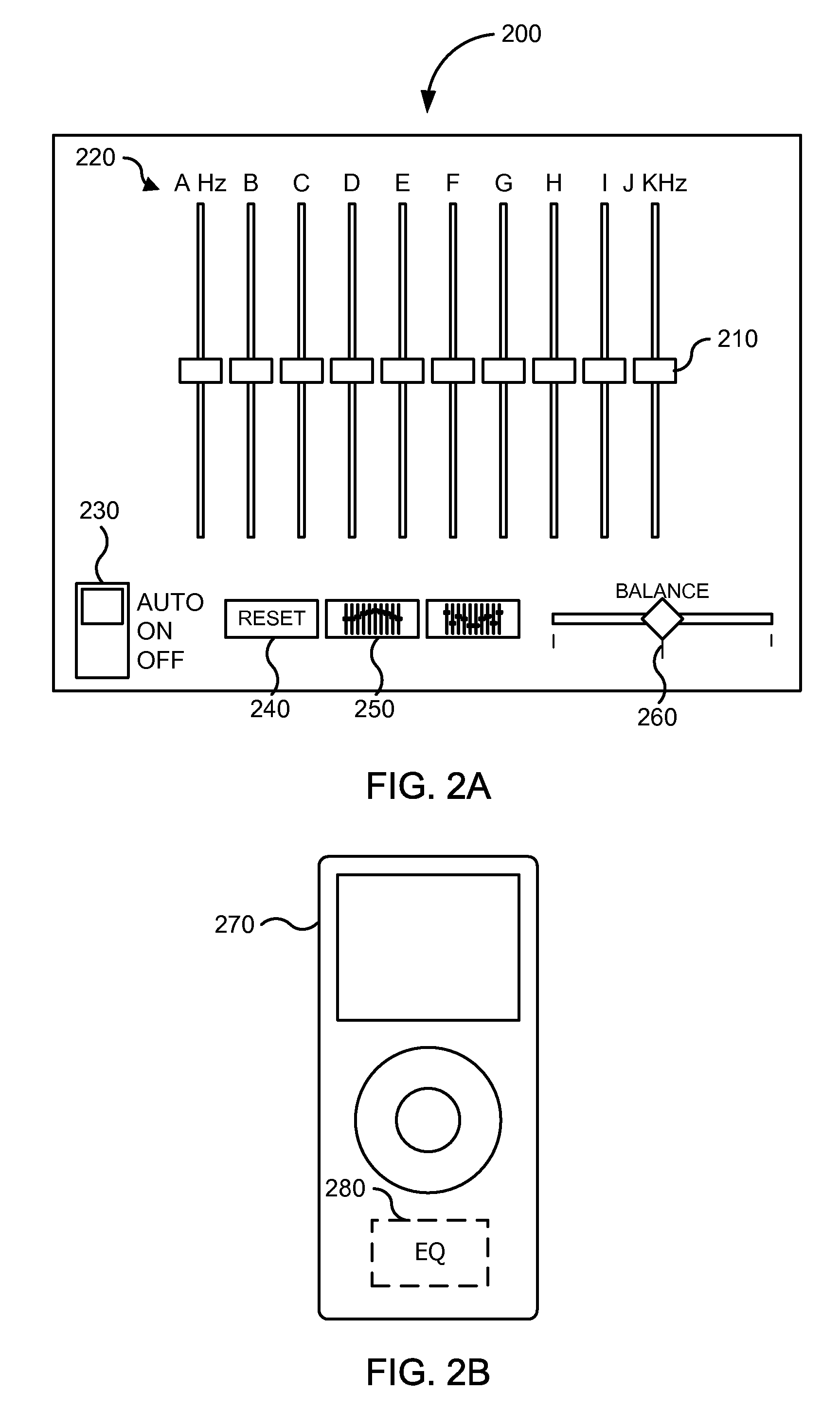
Automatic equalizer adjustment setting for playback of media assets
InactiveUS20090290725A1Automatic tone/bandwidth controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsMetadataStandardization
Systems and methods are disclosed in which correspondences with content or other media assets can be established such that a media player or portable media device can automatically modify or adjust an equalizer setting based on information associated with the content or other media assets. The media player may automatically adjust one or more equalizer settings based on genre, artist, album, or the like. In some embodiments, metadata associated with content or other media assets can be analyzed to determine normalized data thereby potentially grouping content into supersets. Based on the normalized data, the media player may automatically adjust equalizer settings for each superset or grouping of content. Correspondences with one or more accessories may be established such that the media player can automatically modify or adjust an equalizer setting based on the one or more accessories.
Owner:APPLE INC
Controlling loudness of speech in signals that contain speech and other types of audio material
InactiveUS7454331B2Reduce variation in loudnessIncrease the loudnessSpeech analysisAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlLoudnessAudio frequency
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP +1
Enhancing audio using a mobile device
ActiveUS20160035337A1Gain controlVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersNoise levelSound quality
Embodiments disclosed herein enable detection and improvement of the quality of the audio signal using a mobile device by determining the loss in the audio signal and enhancing audio by streaming the remainder portion of audio. Embodiments disclosed herein enable an improvement in the sound quality rendered by rendering devices by emitting an test audio signal from the source device, measuring the test audio signal using microphones, detecting variation in the frequency response, loudness and timing characteristics using impulse responses and correcting for them. Embodiments disclosed herein also compensate for the noise in the acoustic space by determining the reverberation and ambient noise levels and their frequency characteristics and changing the digital filters and volumes of the source signal to compensate for the varying noise levels.
Owner:CAAVO INC
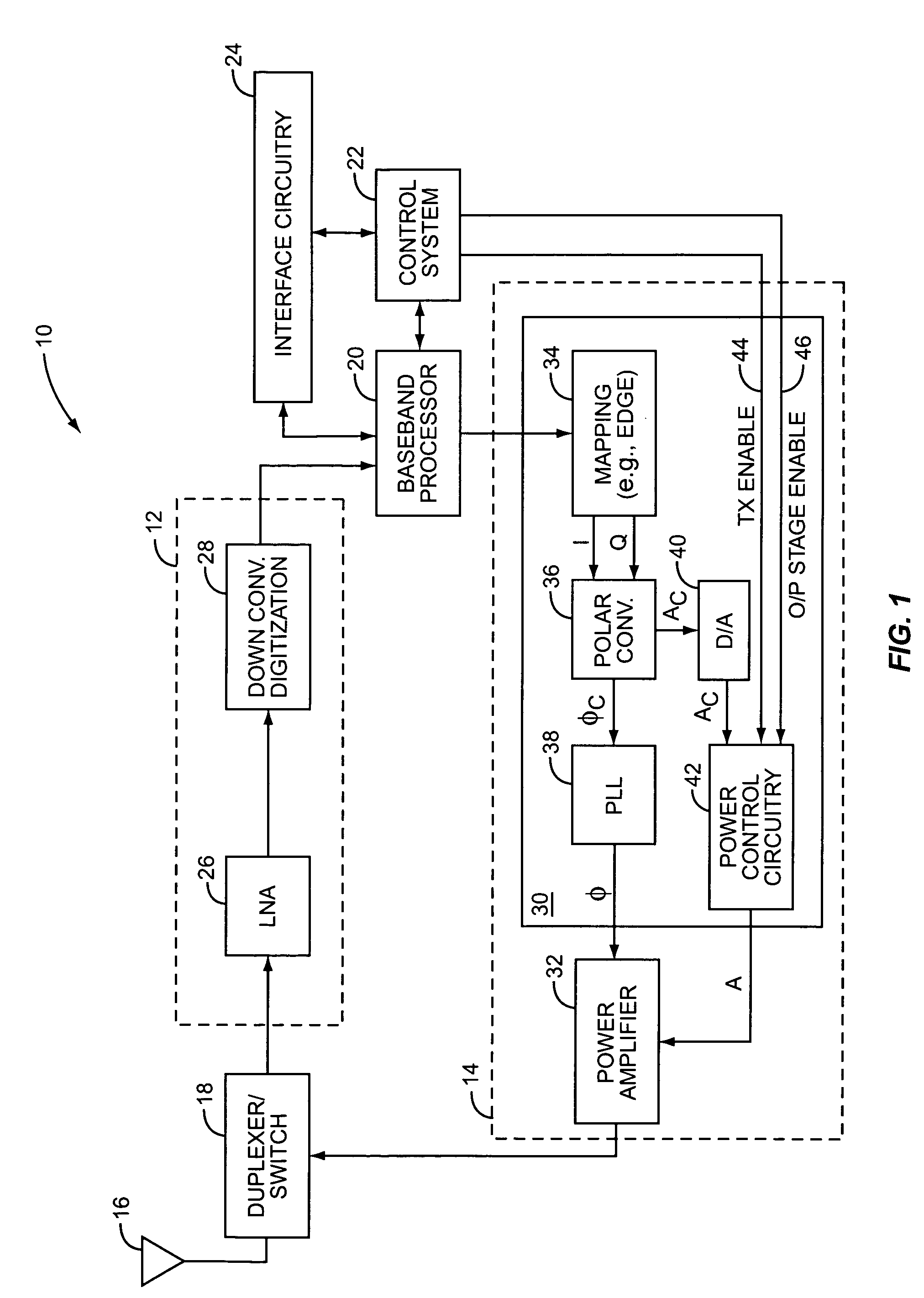
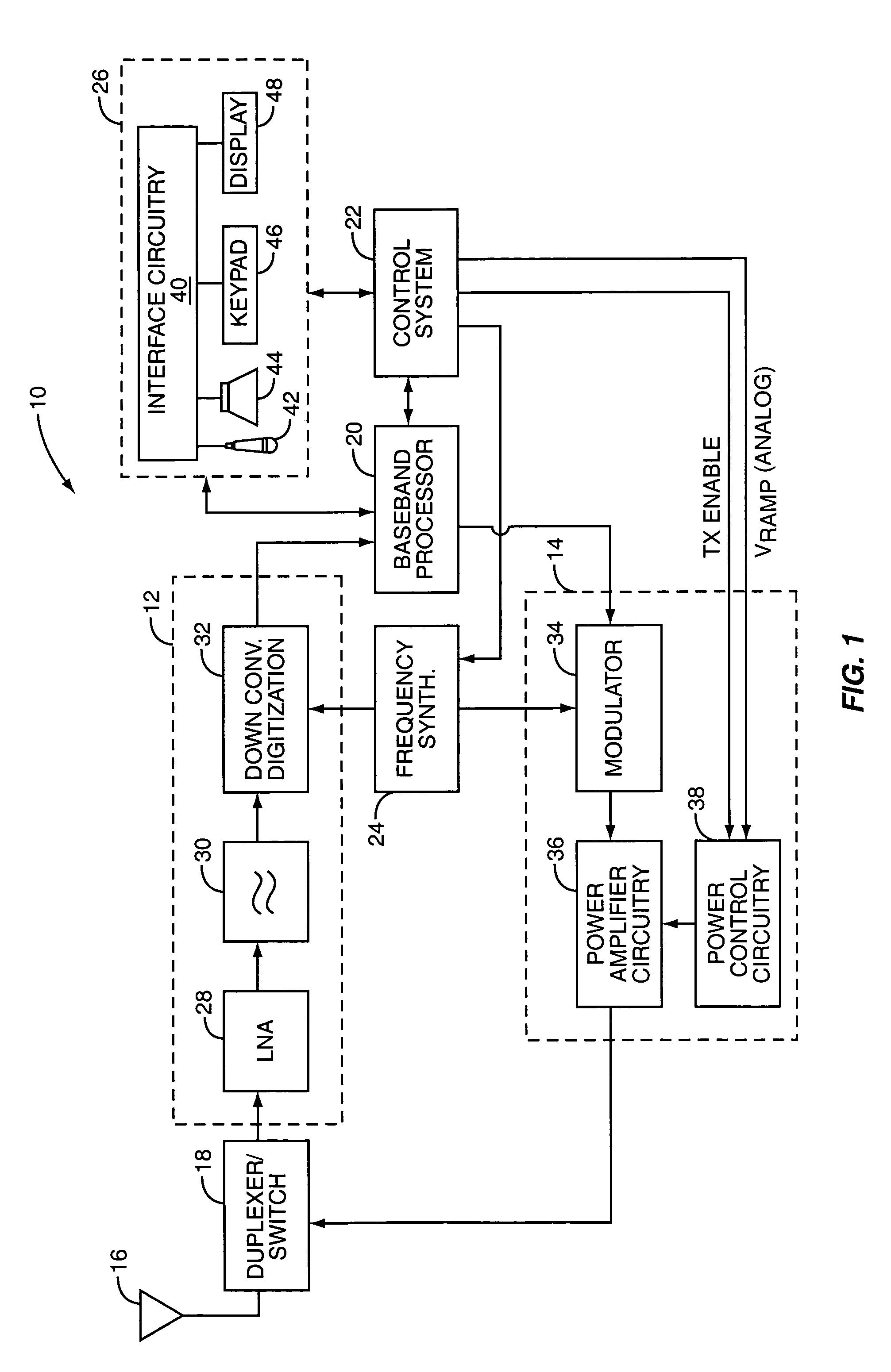
High frequency power amplifier and wireless communication module
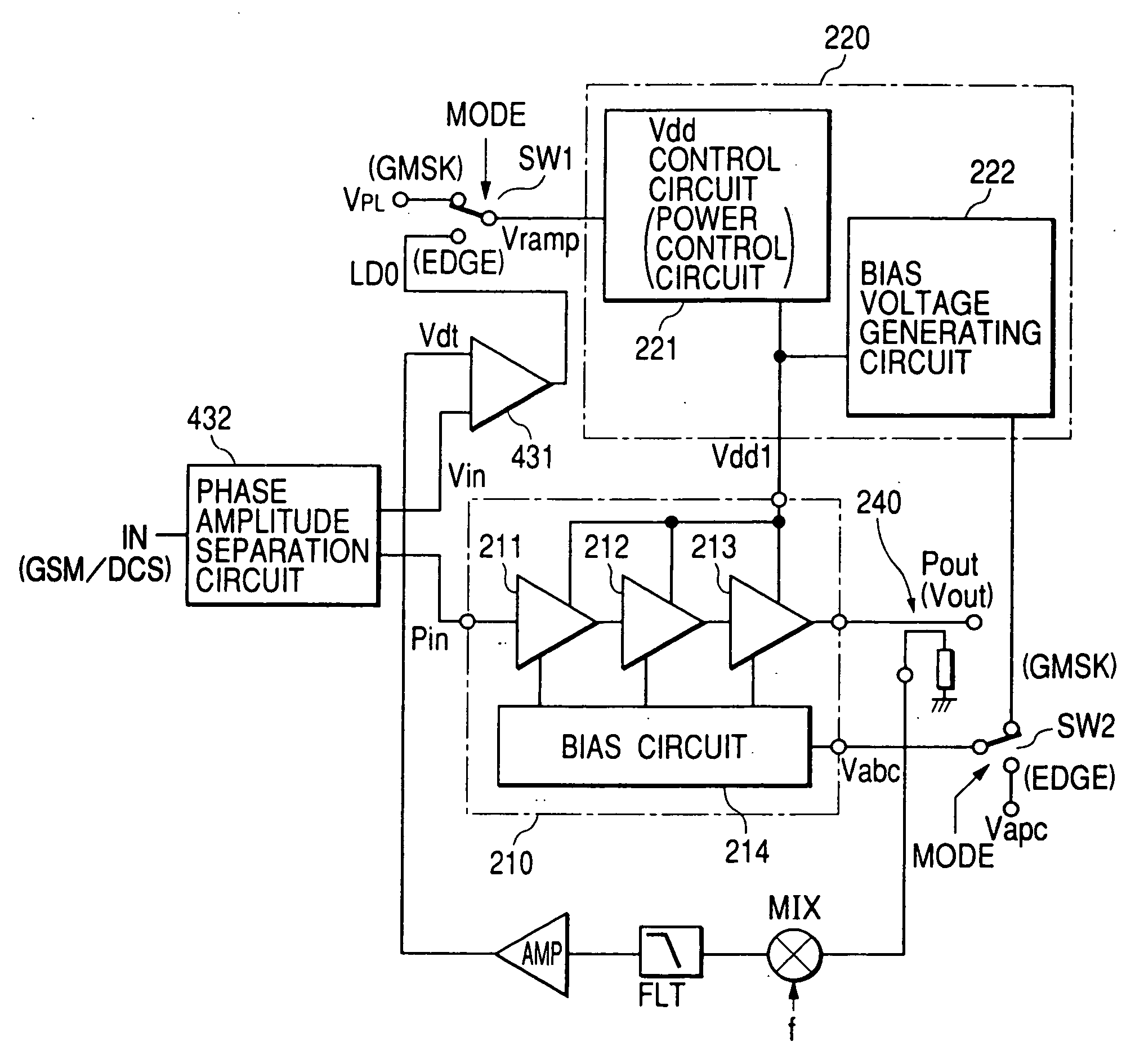
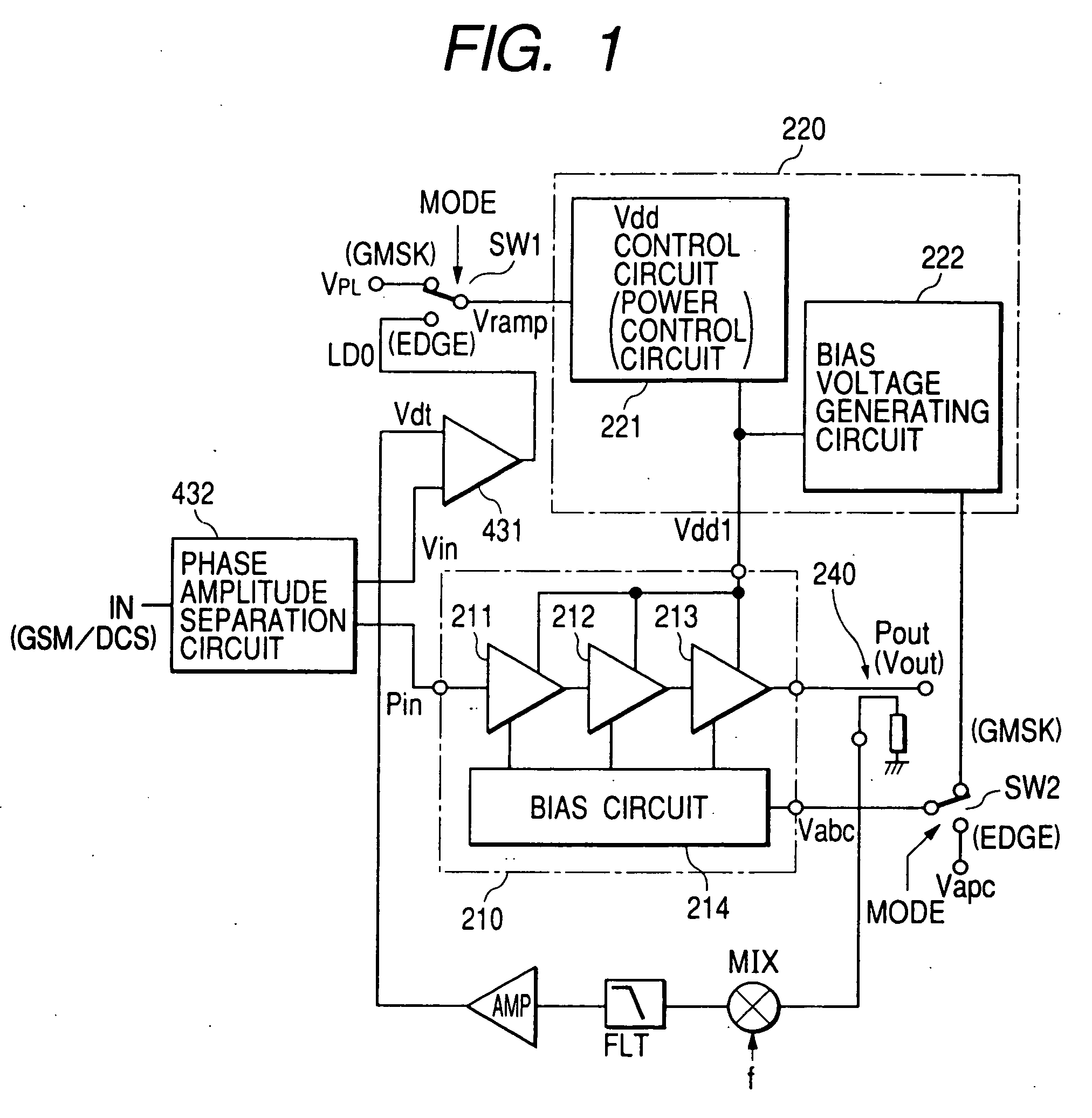
InactiveUS20050200407A1Reduce circuit sizeReduce the packing densityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierHigh frequency power
The present invention provides a high frequency power amplifier of an open-loop type, which outputs a signal having a level corresponding to an output level required under control of a power supply voltage for each output power FET, based on a control signal for the output level. The high frequency power amplifier is provided with a bias voltage generating circuit which generates a gate bias voltage of each output power FET according to an output voltage of a power control circuit for controlling the power supply voltage for the output power FET, based on the control signal for the output level.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
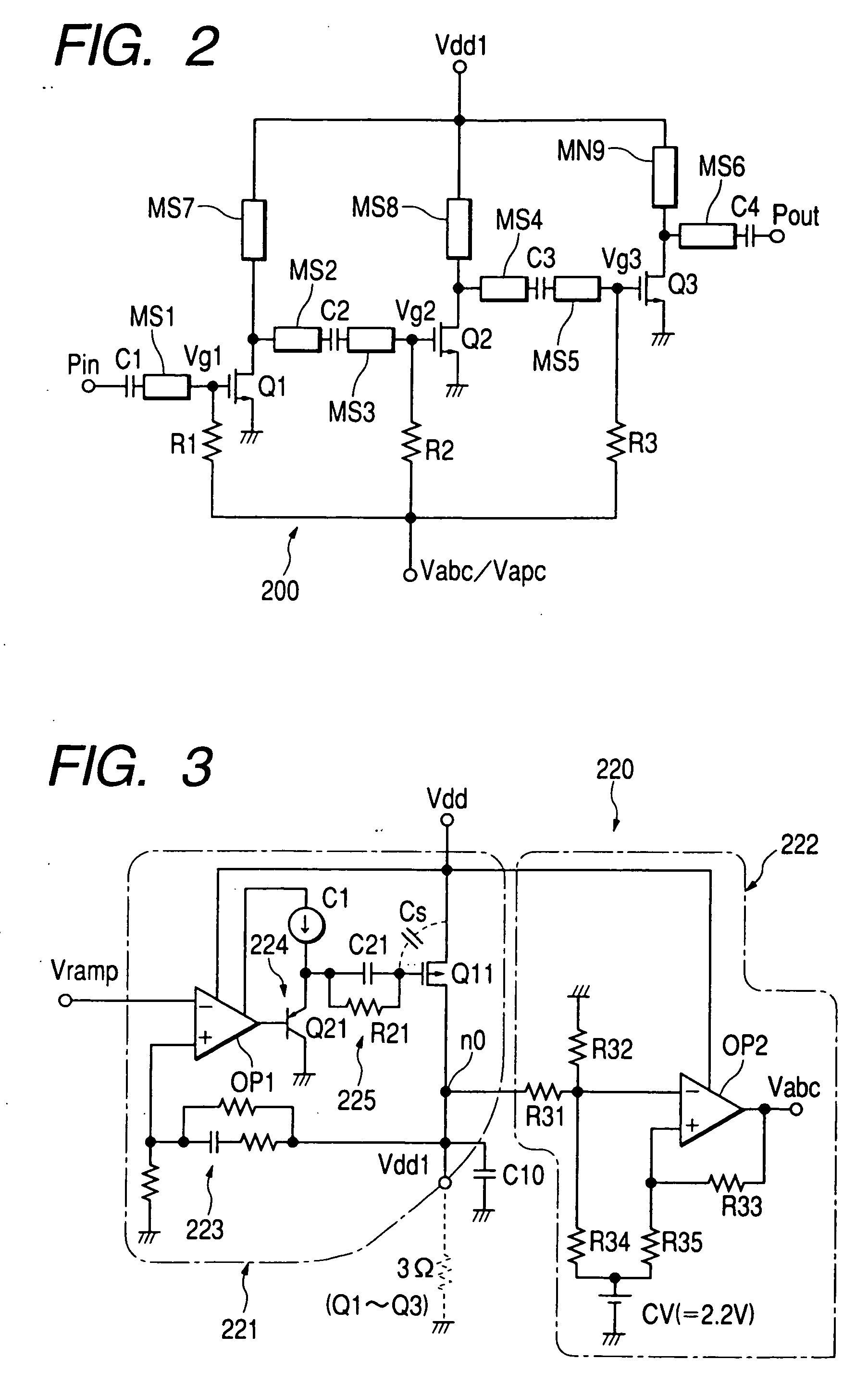
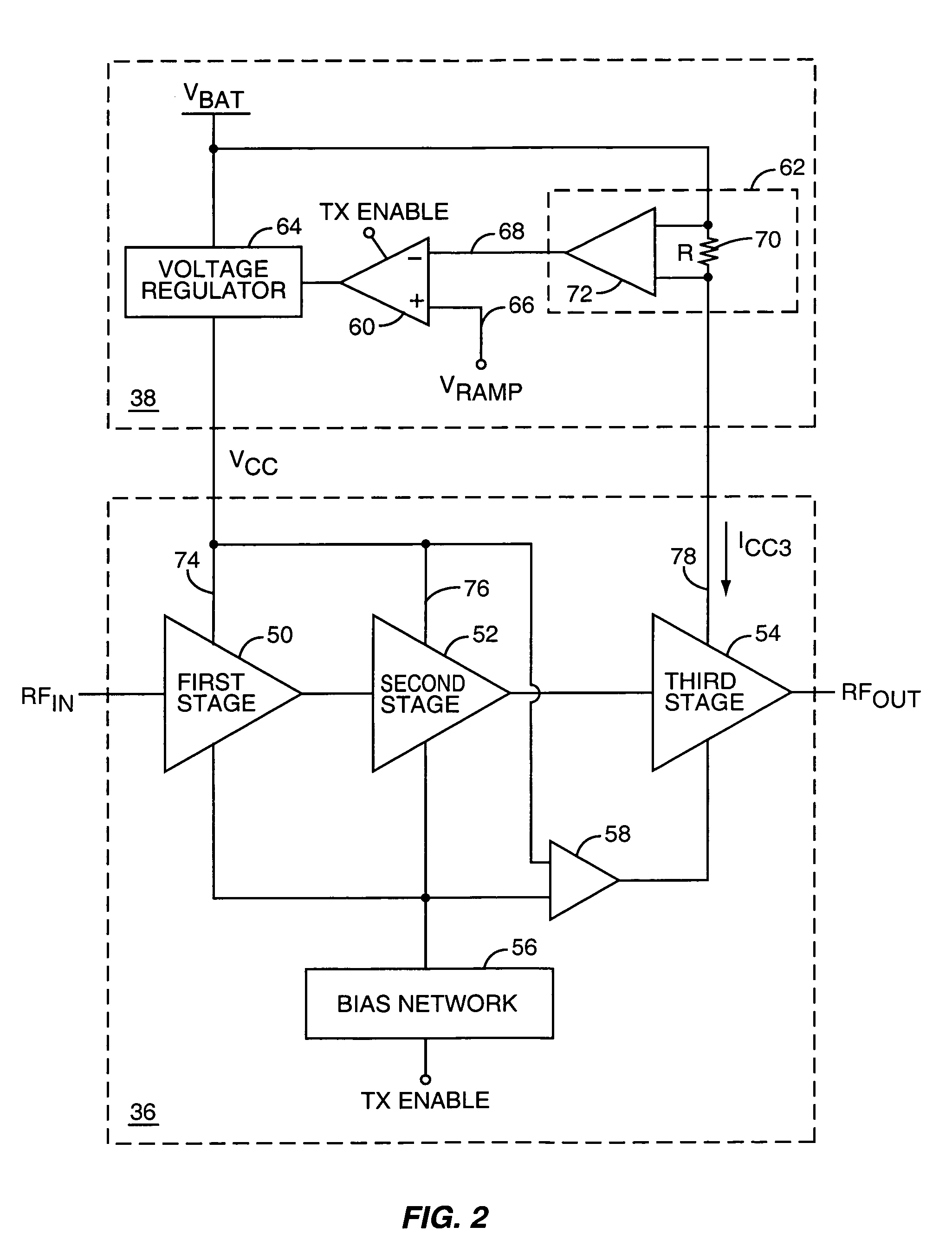
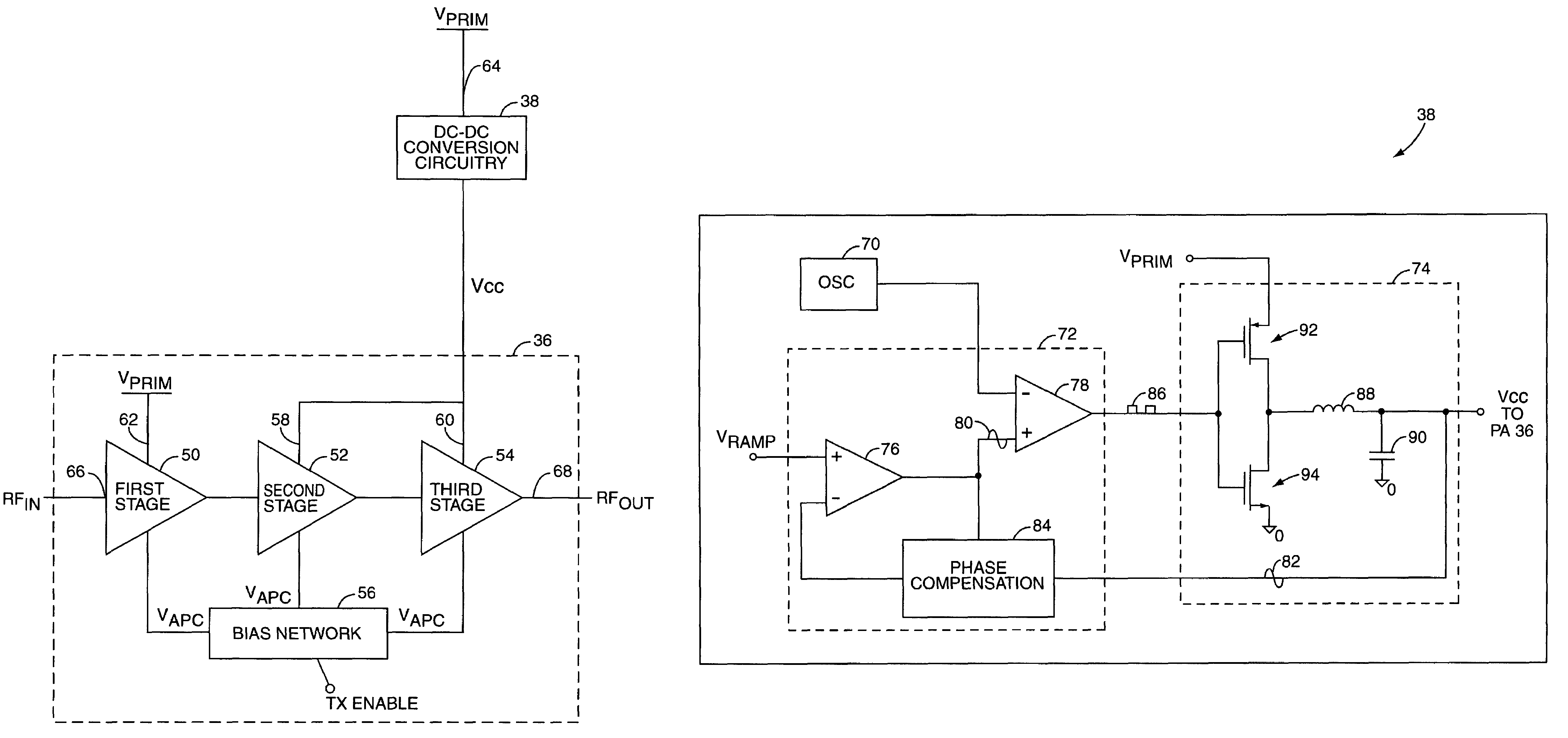
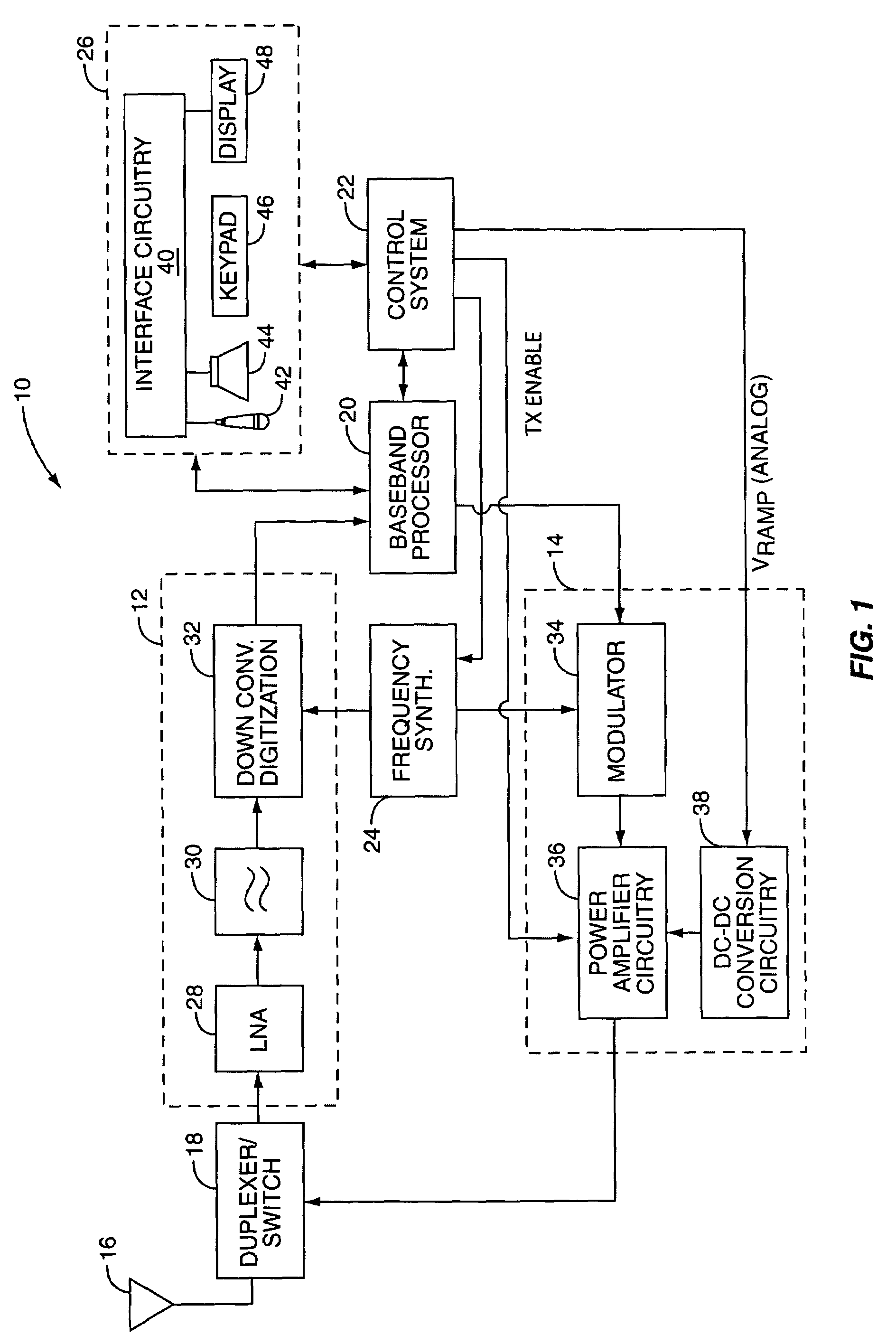
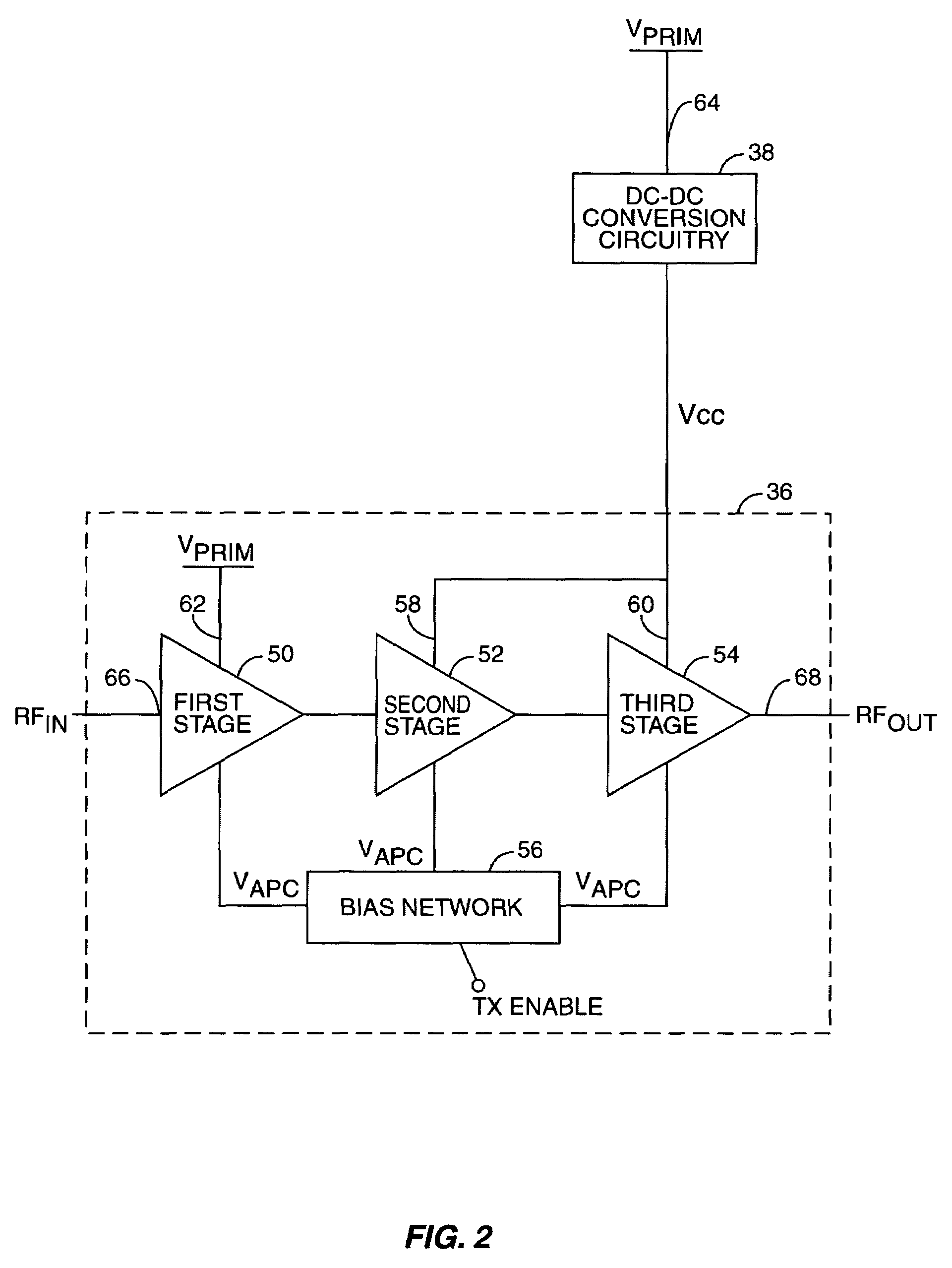
Tailored collector voltage to minimize variation in AM to PM distortion in a power amplifier
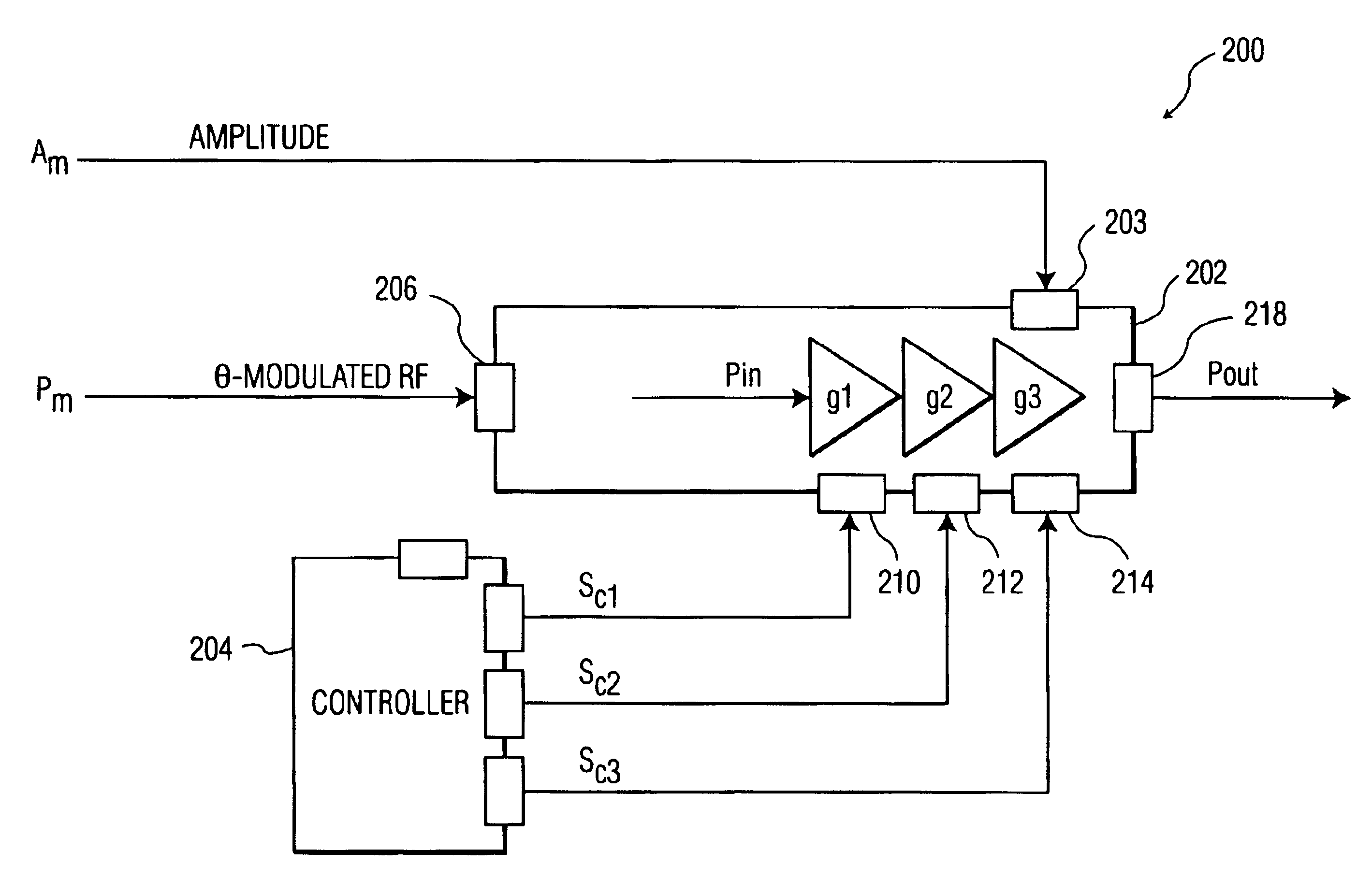
ActiveUS7109791B1Reduce variationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPulse automatic controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
A system is provided for substantially reducing variation in AM to PM distortion of a power amplifier caused by variations in RF drive power and temperature. The system includes power control circuitry and power amplifier circuitry. The power amplifier circuitry includes an input amplifier stage and at least one additional amplifier stage coupled in series with the input amplifier stage. The power control circuitry provides a first supply voltage to the input amplifier stage based on a control signal such that the first supply voltage has a predetermined DC offset with respect to the control signal. The first supply voltage is provided such that the predetermined DC offset substantially reduces variations in the AM to PM distortion of the power amplifier due to variations in radio frequency (RF) drive power.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Power control for a switching mode power amplifier
InactiveUS6917244B2Maintain efficiencyIncrease power levelGain controlPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention relates to a power control structure comprising a switching mode power amplifier for receiving an input signal, for amplifying the received input signal and for providing the amplified signal as output signal. In order to enable a power control over a large range while preserving the efficiency of the power amplifier, the structure further comprises a first control arrangement for controlling the power level of the output signal at least at higher desired power levels by adjusting a power supply provided to the switching mode power amplifier, and in addition a second control arrangement for controlling the power level of the output signal at least at lower desired power levels by adjusting the power of the input signal before it is provided to the switching mode power amplifier. The invention relates equally to a corresponding method.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
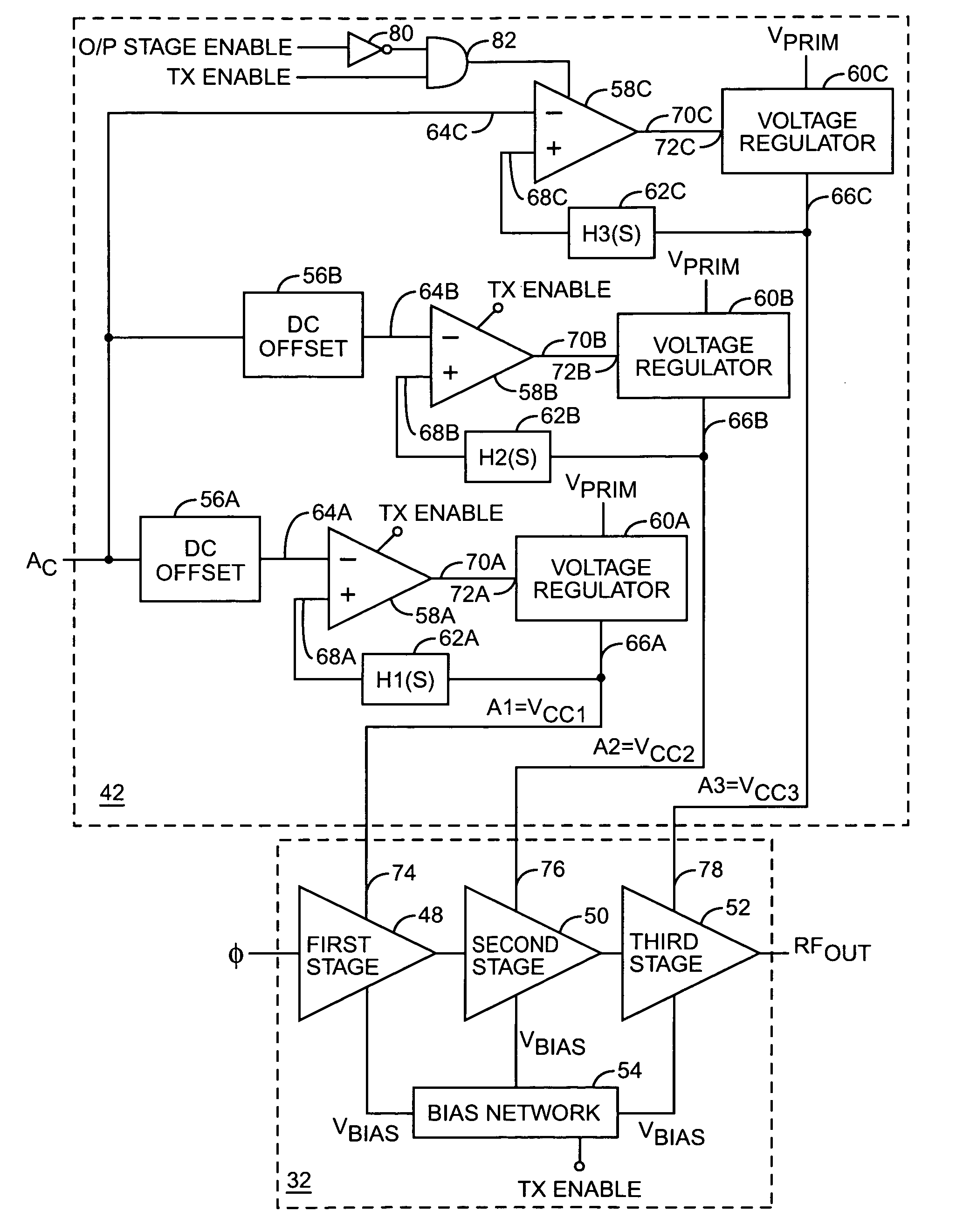
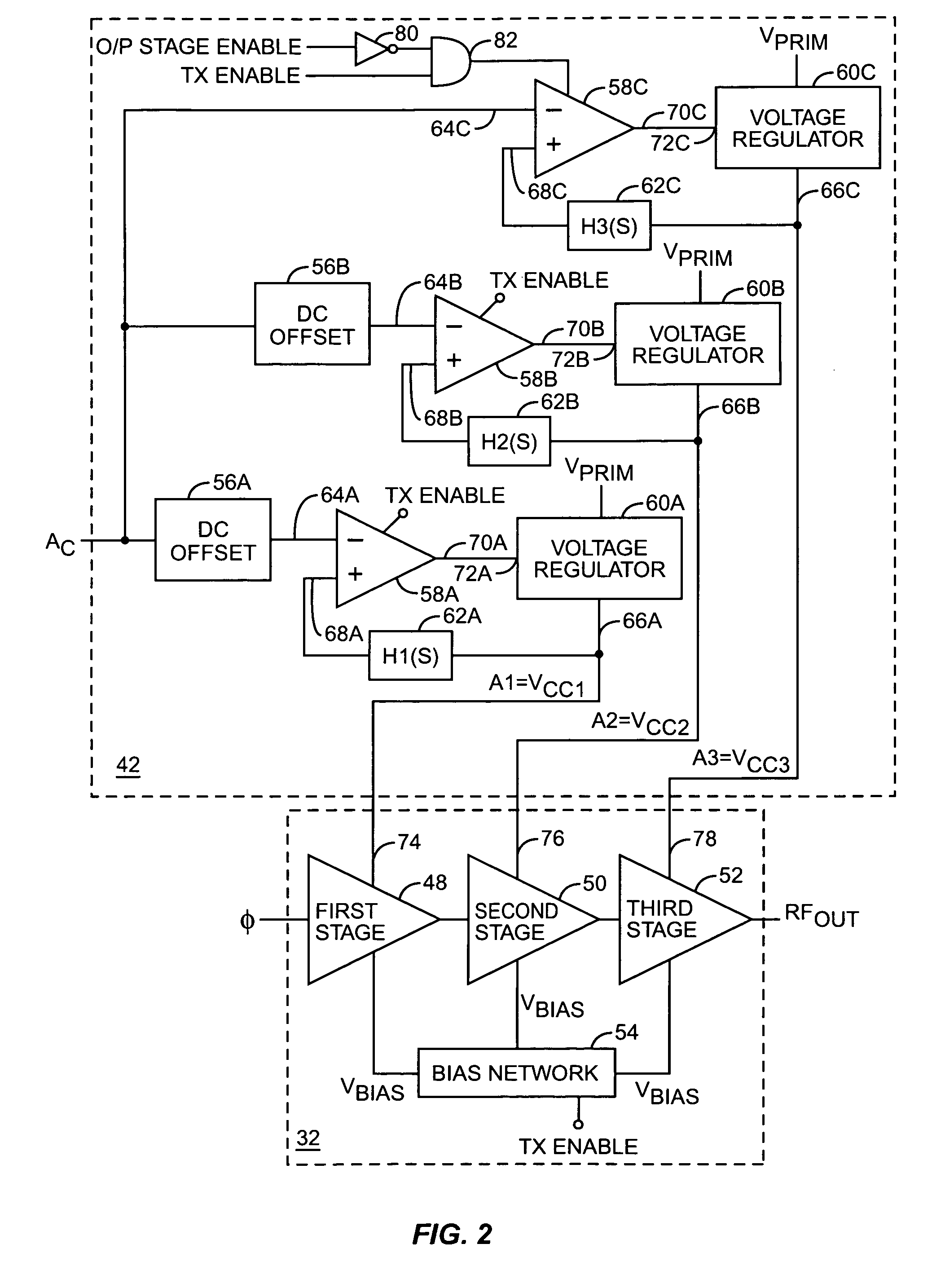
Apparatus, methods and articles of manufacture for control in an electromagnetic processor
InactiveUS6859098B2Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain controlEngineeringControl theory
An apparatus for electromagnetic processing comprises a controller and a processor for receiving an input signal. The processor comprises one or more stages in communication with the controller. The controller is capable of regulating the input signal and the one or more stages to generate an output signal.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Configurable digital loudness compensation system and method
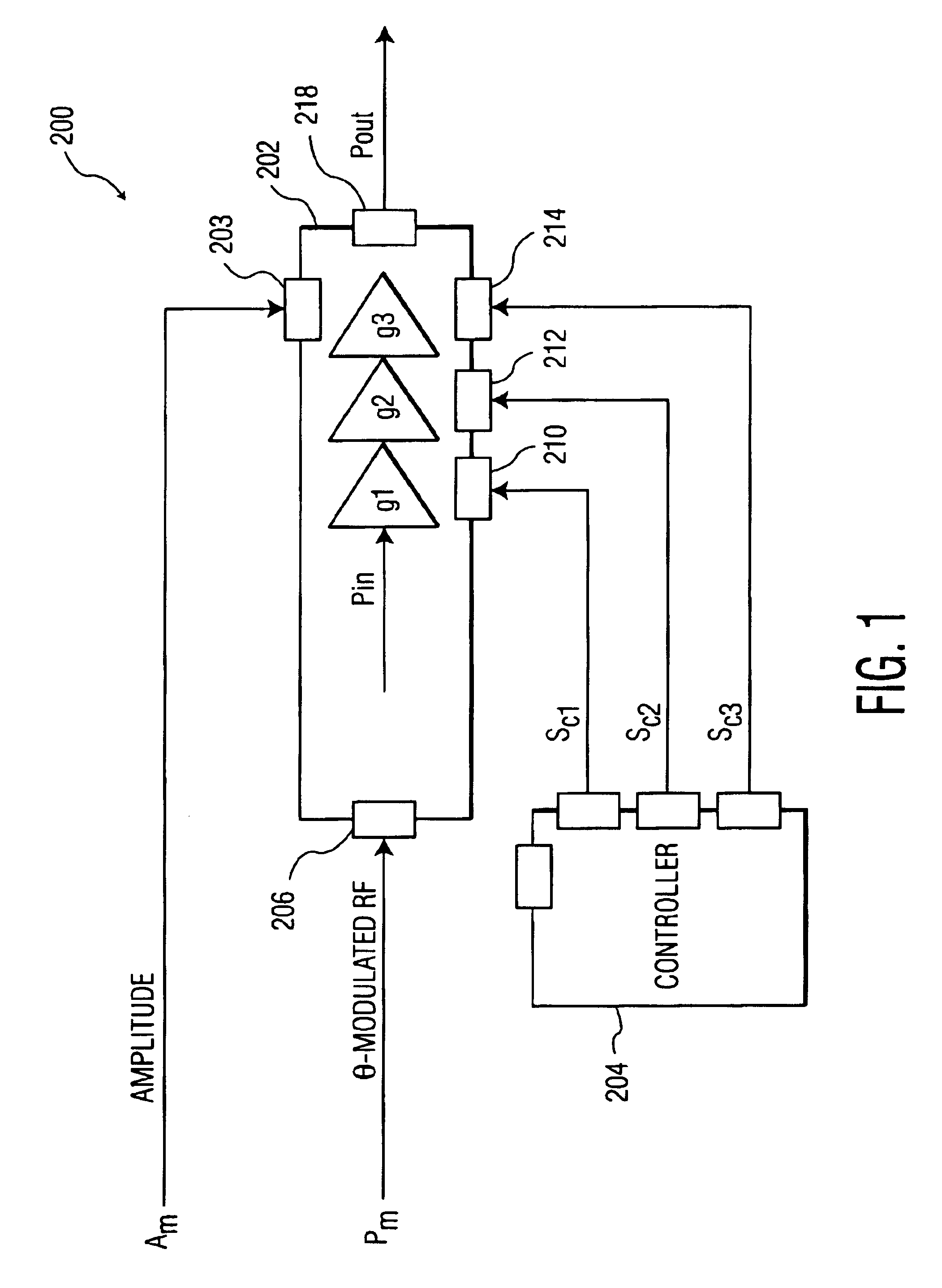
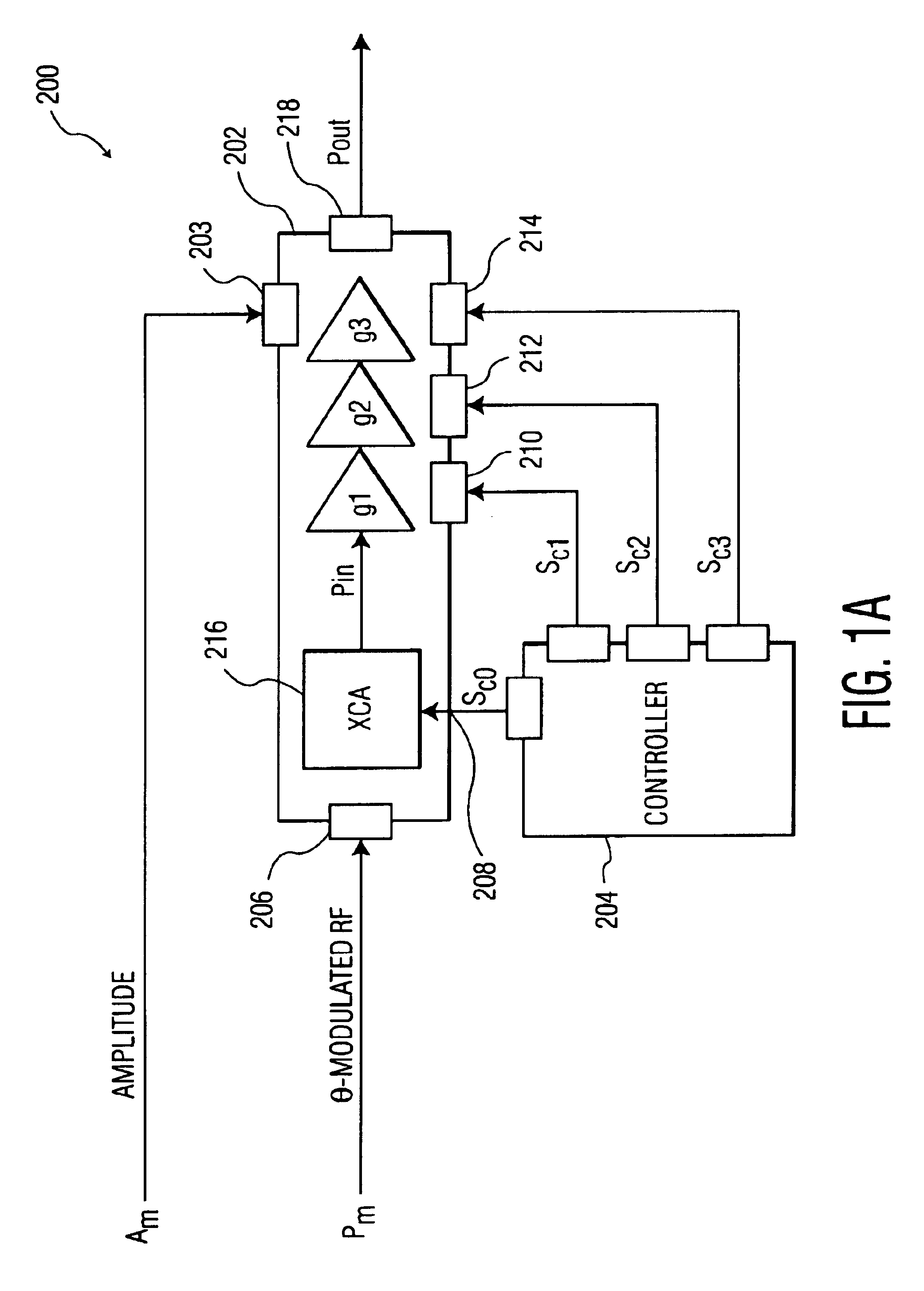
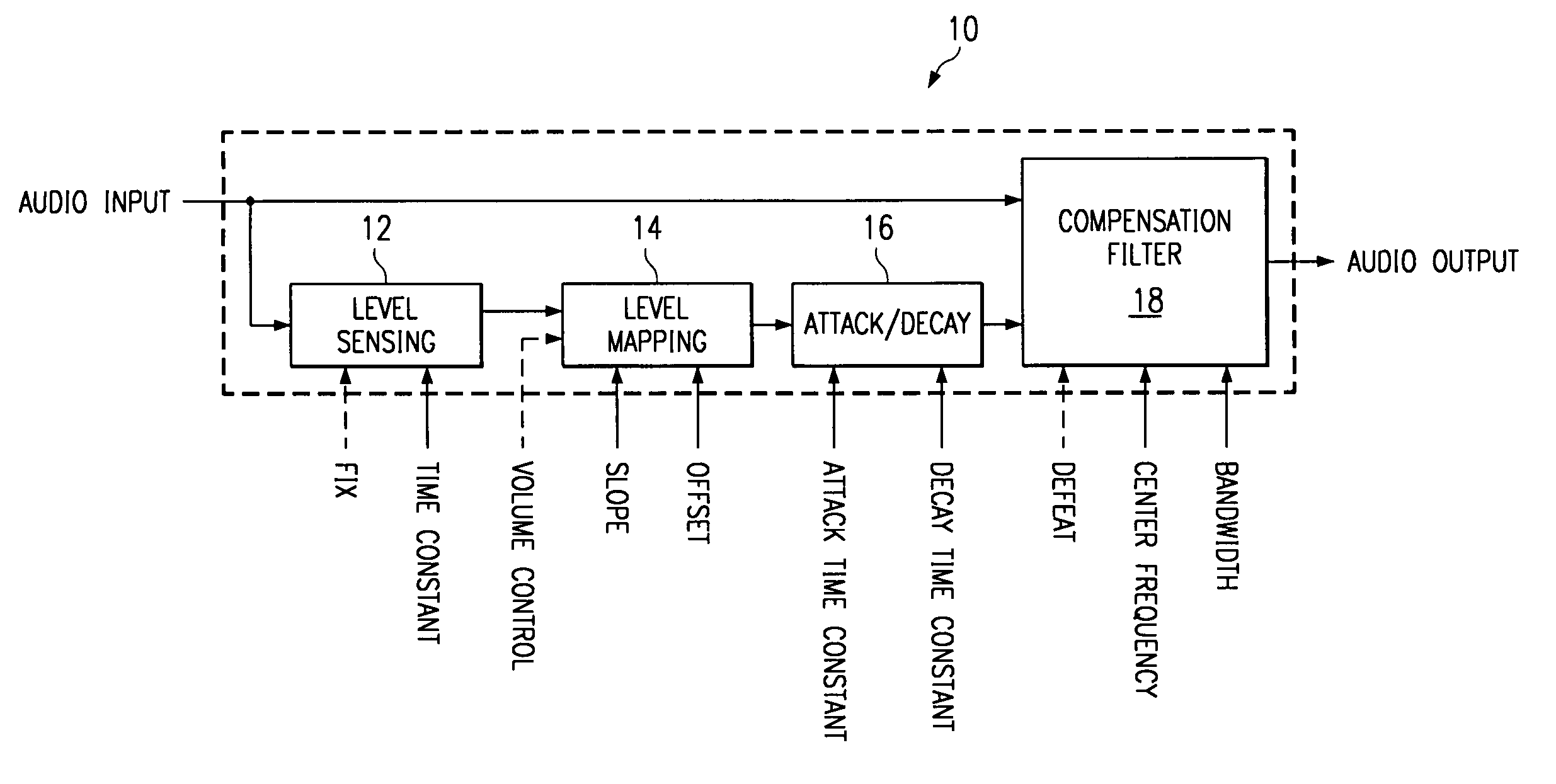
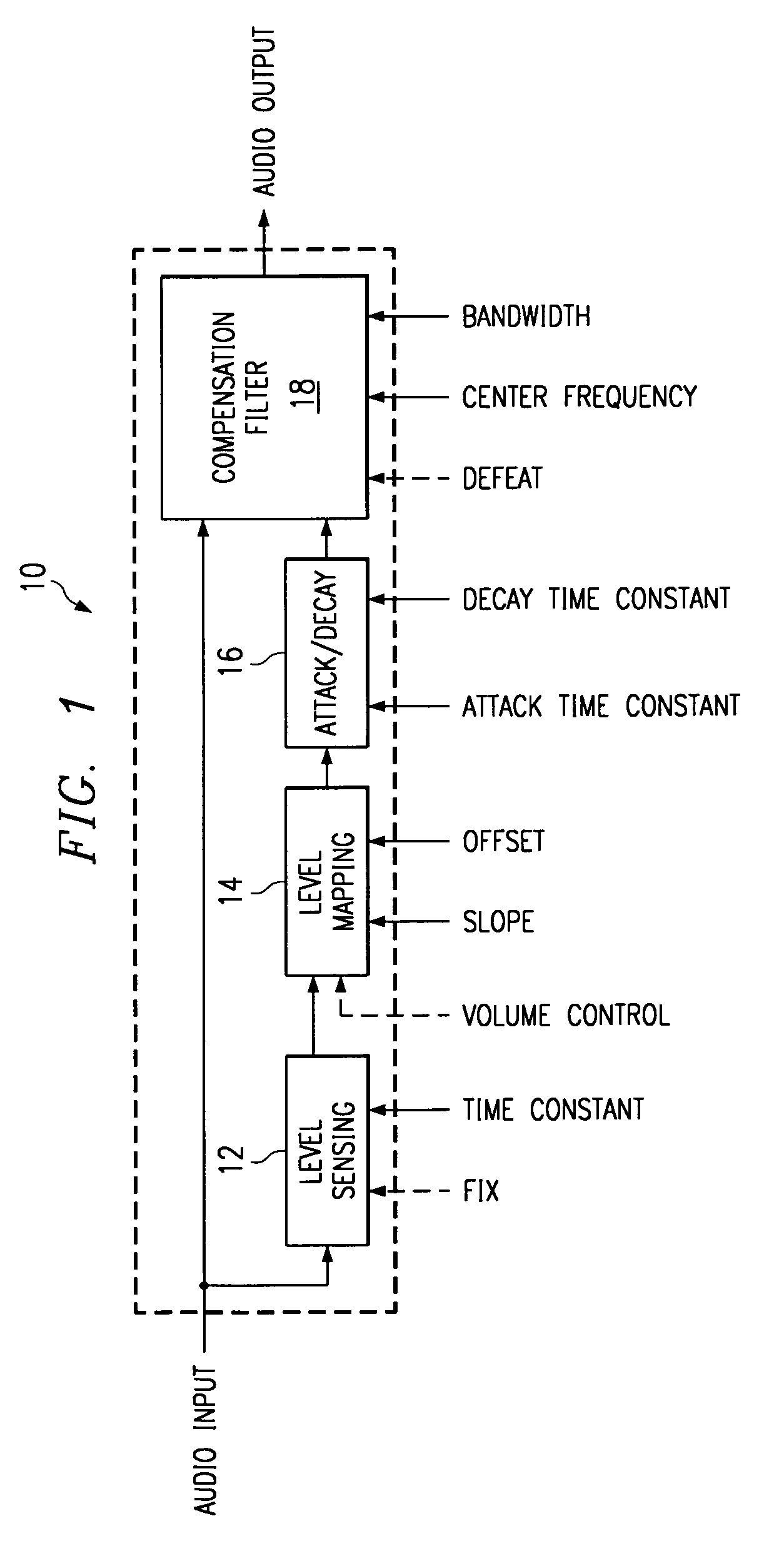
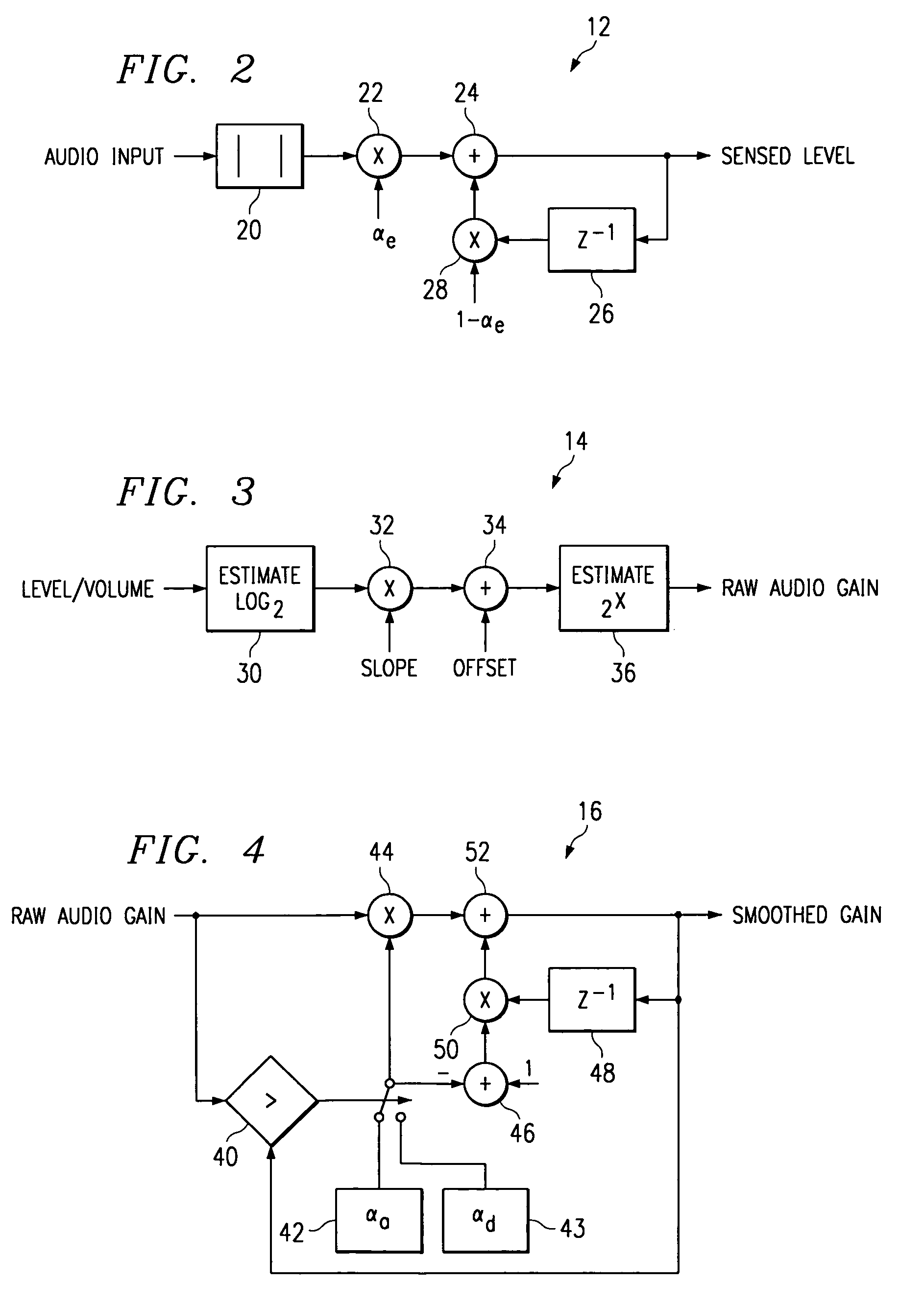
InactiveUS7058188B1Maximum listening pleasureEliminates and reduces disadvantageGain controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlTime segmentLevel sensor
An audio loudness compensation system includes a level sensor receiving an audio input signal and operable to estimate a level of the audio input signal over a first predetermined time period, and a level mapper receiving the estimated level and operable to map the estimated level to a raw audio gain in response to a slope setting and an offset setting. The system further includes an attack and decay filter receiving the raw audio gain and operable to smooth out increasing and decreasing changes in the raw audio gain in response to a second and, possibly a third predetermined time period, and a compensation filter receiving the smoothed raw audio gain and operable to modify the audio input signal in response to the smoothed raw audio gain, a center frequency setting and a bandwidth setting, and generate a loudness compensated audio output signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Audio correcting apparatus
InactiveUS20050013443A1Accurate sound pressure levelListen clearlyTelevision system detailsAdaptive networkEnvironmental noiseLoudspeaker
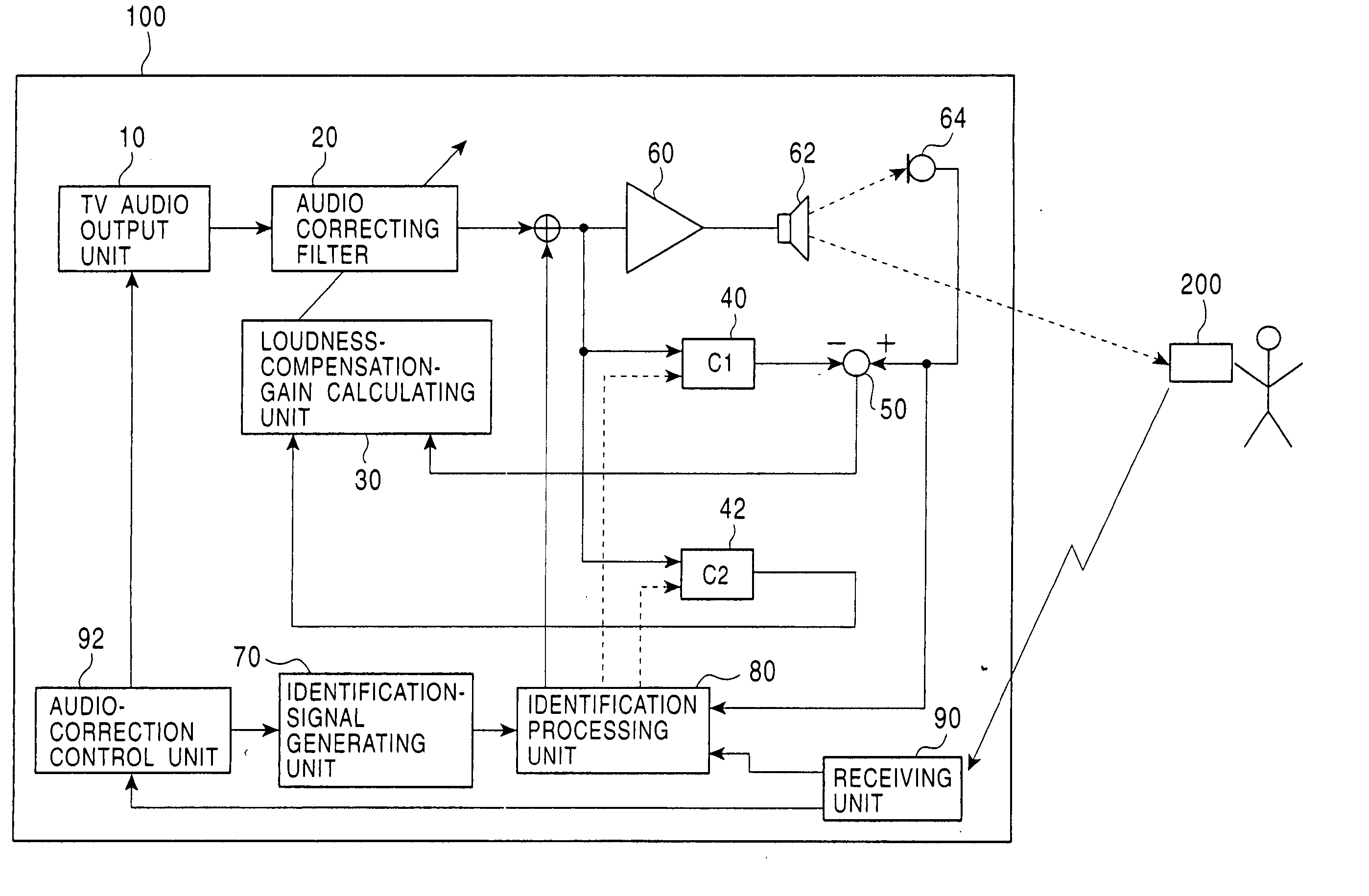
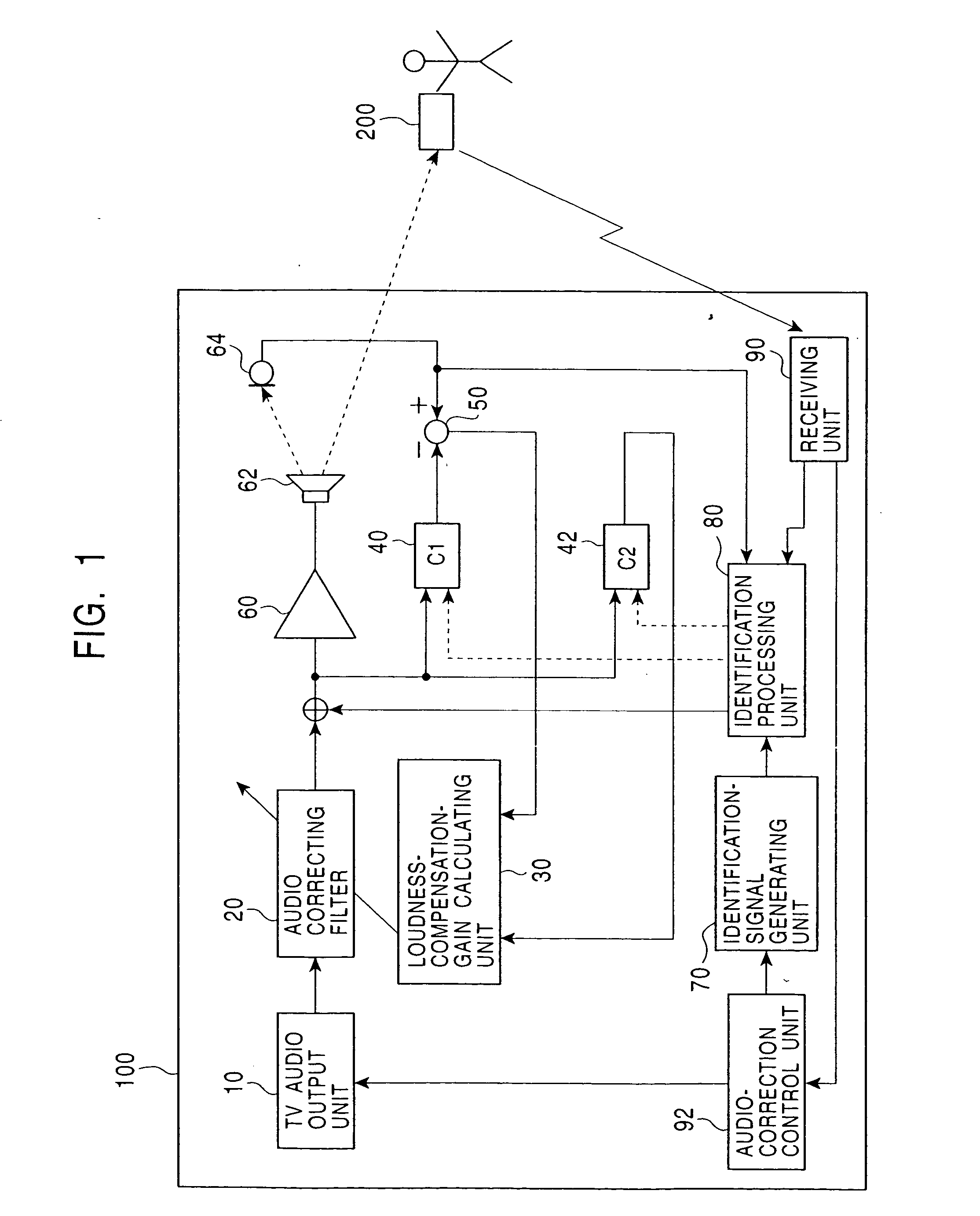
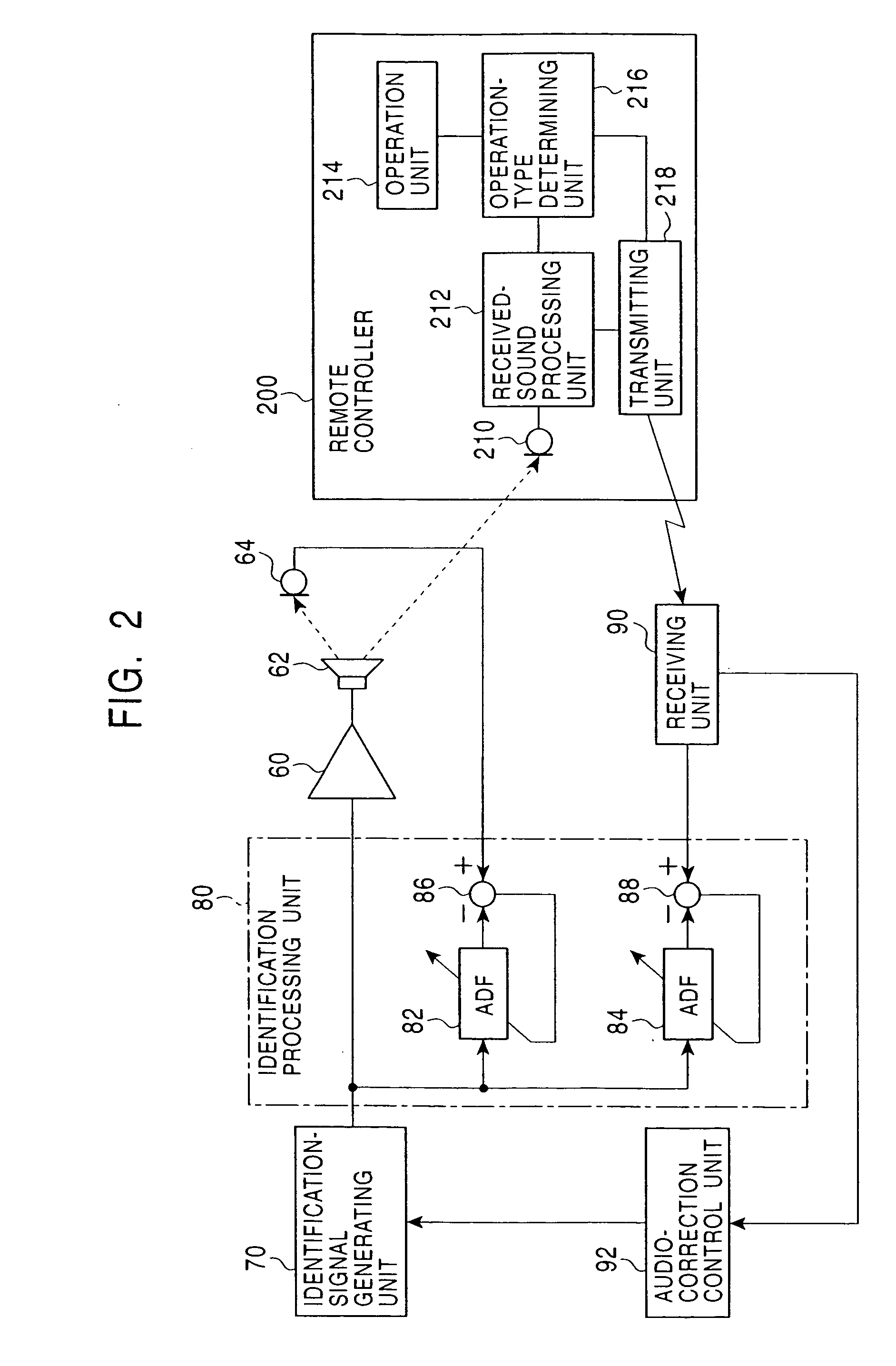
An audio correcting apparatus includes a speaker provided on a television apparatus, a microphone provided on a remote controller, an identifying unit which identifies an acoustic characteristic from the speaker to the microphone, and an acoustic characteristic setting unit having the acoustic characteristic. A signal obtained by allowing an audio signal input to the speaker to pass through the acoustic characteristic setting unit, and a signal representing ambient noise are input to an audio-correcting filter and a loudness-compensation-gain calculating unit. Based on both signals, the sound pressure level of sound output from the speaker is corrected so that the sound output from the speaker is clearly heard when reaching the user without being affected by the ambient noise.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for automatic volume control in an audio system
InactiveUS6868162B1Quick calibrationSet become largeGain controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlAdaptive filterAutomatic control
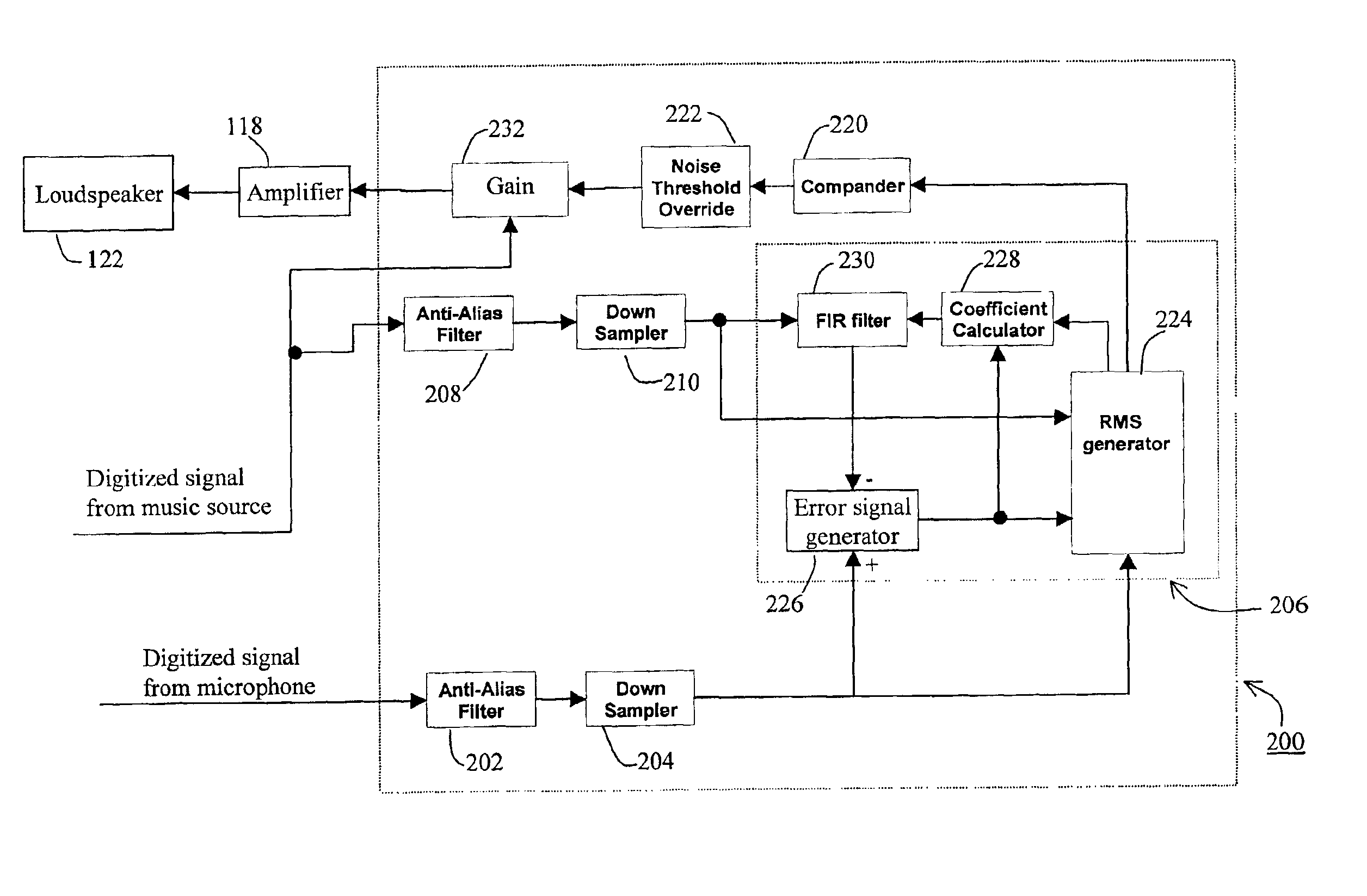
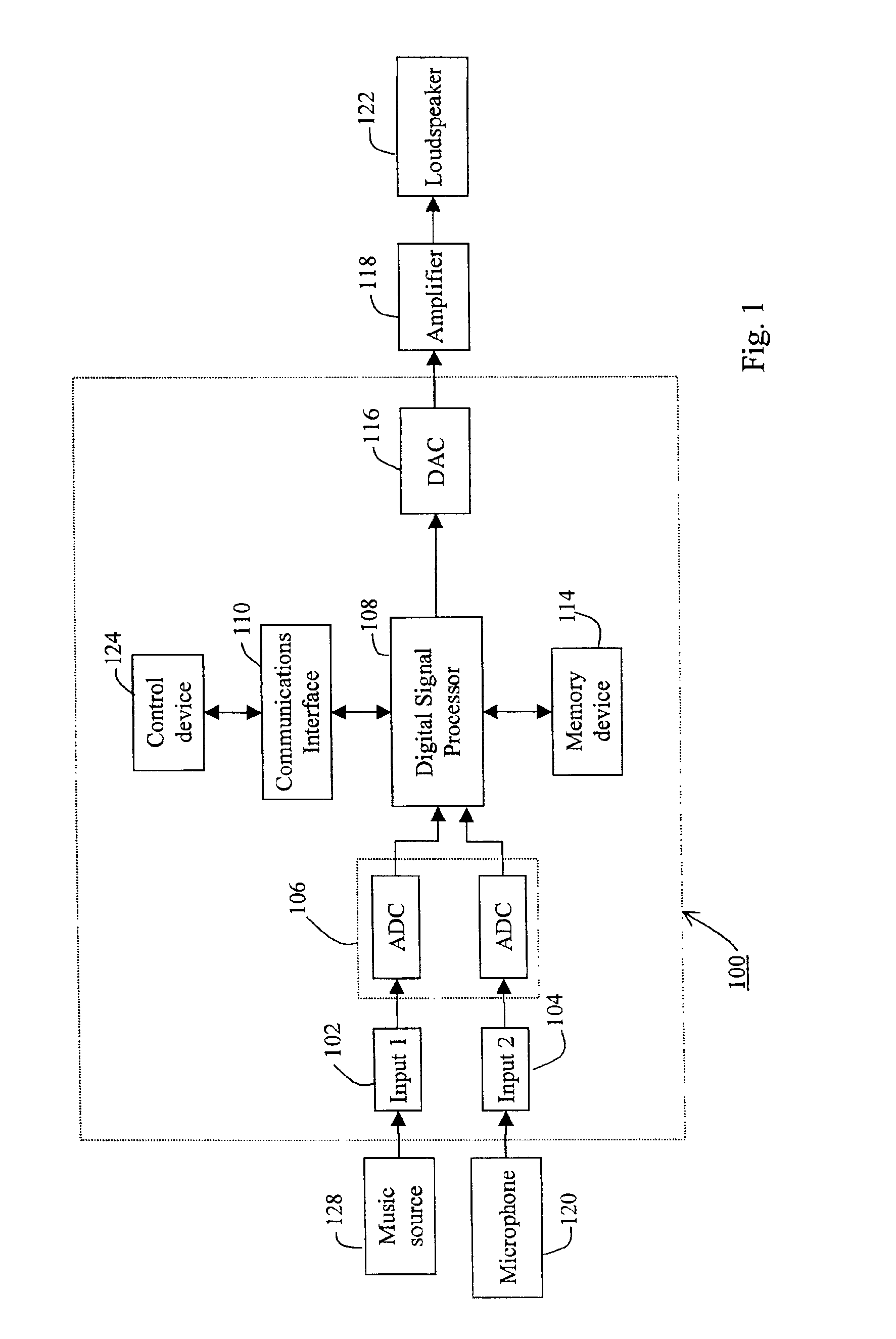
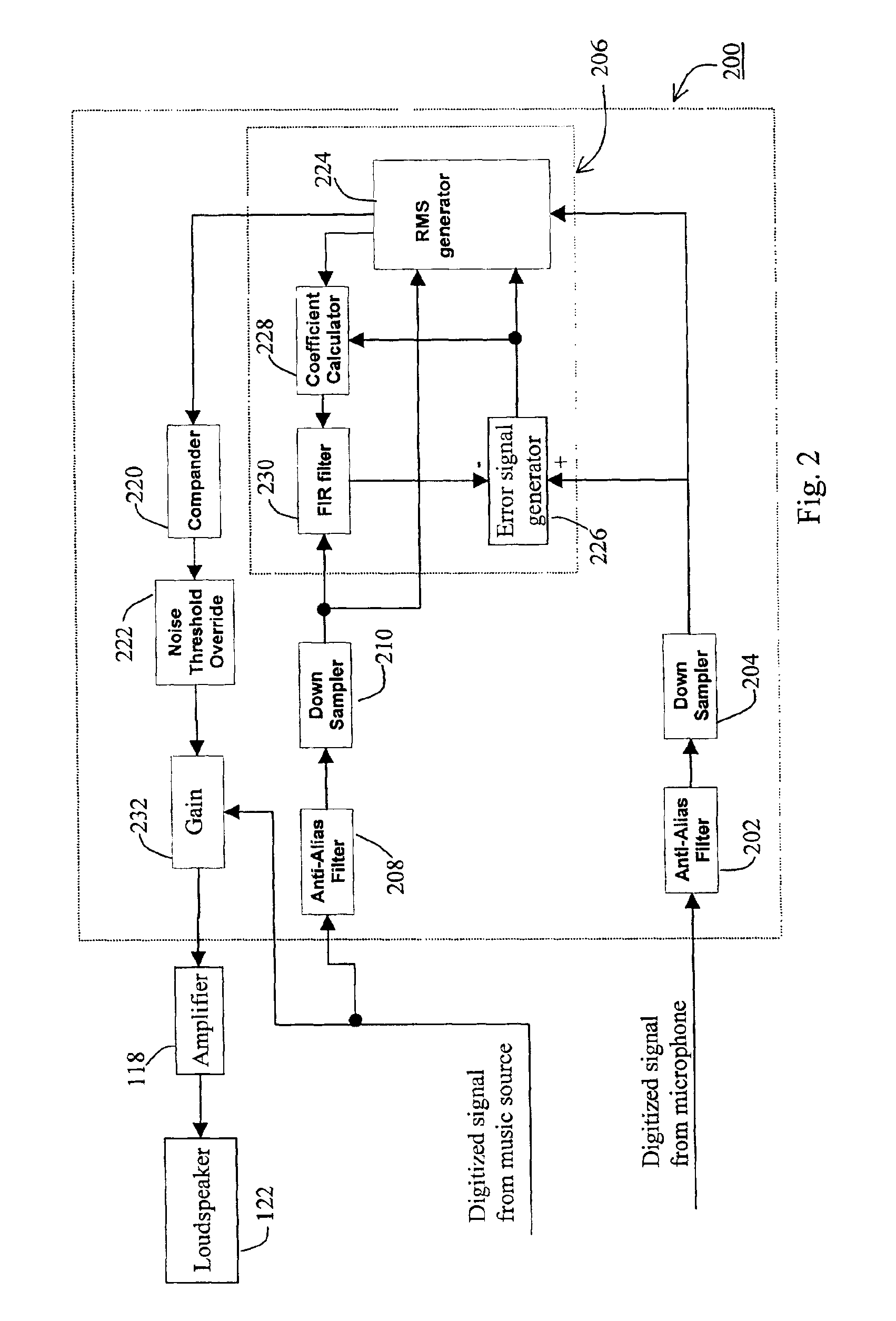
An audio system (100) is provided with improved adaptive filter (206) to automatically adjust signal gain depending on the ambient noise level. The original music signal passes through a normalized adaptive filter (206), and is subtracted from the ambient room signal detected by a microphone (120), resulting in an error signal that is an estimate of the ambient noise. The error signal is used to update a set of adaptation coefficients so that the normalized adaptive filter more accurately simulates the room transfer function, resulting in an better estimate of the ambient noise. The audio system (100) is calibrated automatically upon initial use to determine adaptation coefficients and noise threshold level to prevent runaway gain. System parameters are adjusted using a controller (124) with a user-friendly interface (400).
Owner:MACKIE DESIGNS
Power amplifier control technique for enhanced efficiency
ActiveUS7193459B1High gainImprove PAEPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersPower-added efficiencyAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier configuration including power amplifier circuitry and power control circuitry and having improved Power Added Efficiency (PAE) is provided. The power amplifier circuitry includes one or more input amplifier stages in series with a final amplifier stage. The power control circuitry provides a variable supply voltage to the input amplifier stages based on an adjustable power control signal. The final amplifier stage is powered by a fixed supply voltage. In operation, as output power of the power amplifier is reduced from its highest power level, the variable supply voltage is reduced. Accordingly, RF power of an amplified signal provided to the final amplifier stage from the input amplifier stages decreases, and the final amplifier stage transitions from saturation to linear operation, thereby increasing the gain of the final amplifier stage. Thus, a desired output level can be maintained while operating at lower current levels.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Circuit for power amplification
ActiveUS20060066396A1Reduce decreaseReduce variationHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierReference current
A radio frequency (RF) power amplifier, including an external control loop and a protection circuit, which functions to maintain a constant output power during variations in impedance on the RF load. In the external control loop a collector current from an output transistor is detected and then regulated with respect to a reference current. The regulated signal is utilised to generate a bias control signal which is input to the base electrode of both a driver transistor and the output transistor. The protection circuit detects a voltage envelope at the collector electrode of the output transistor and utilises this signal to form a bias reduction signal which is input to the base electrode of the driver transistor.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
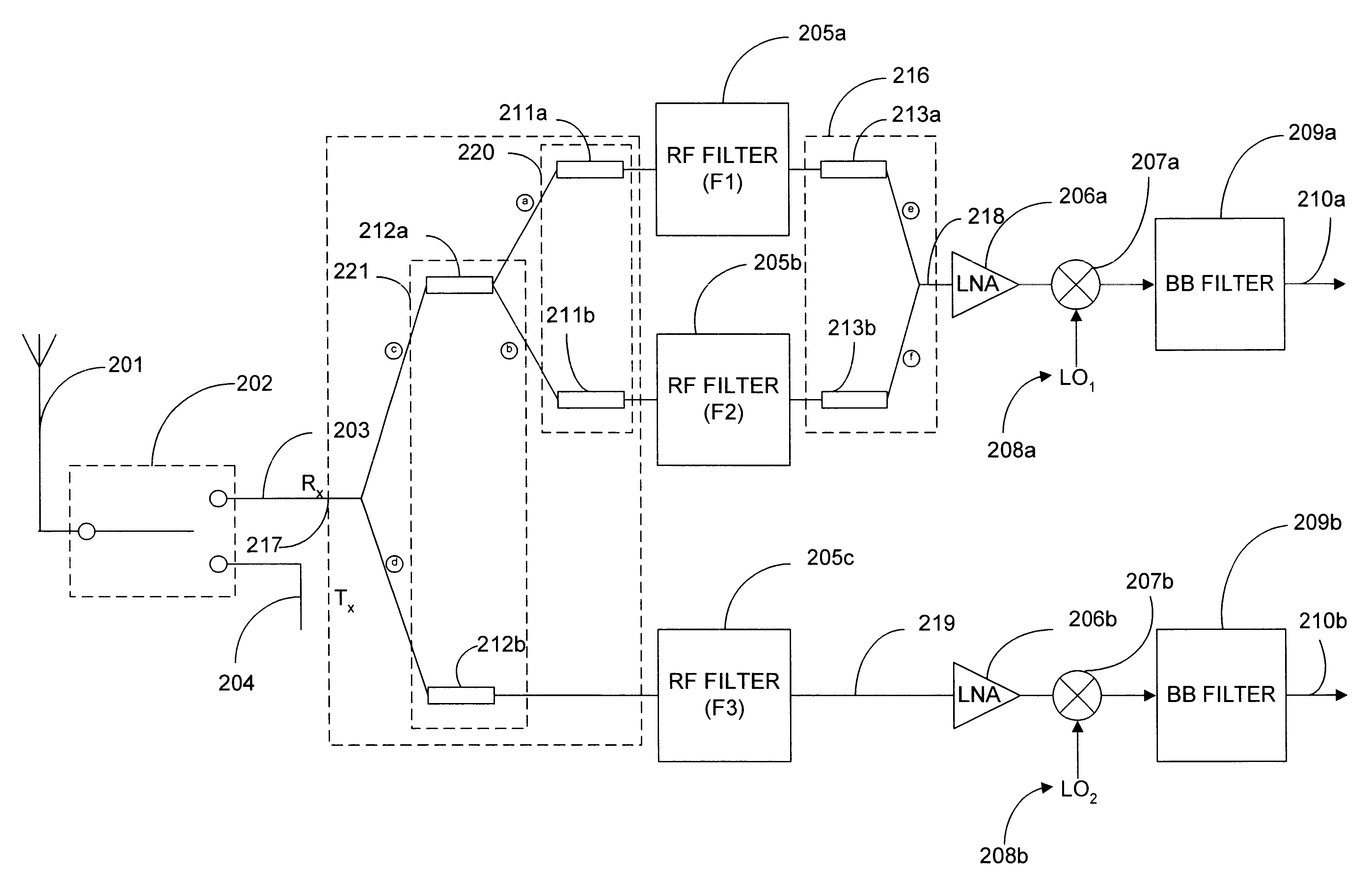
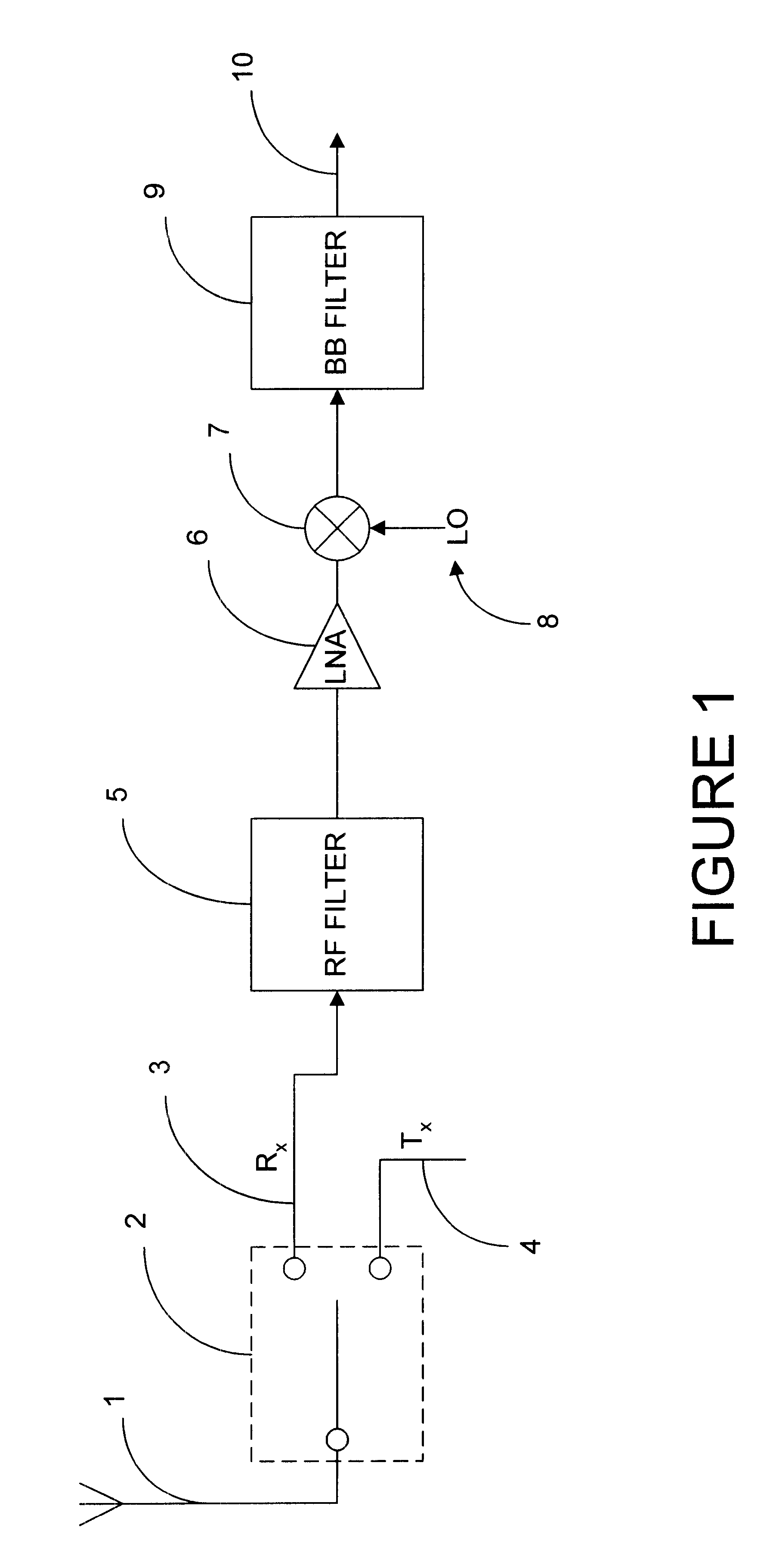
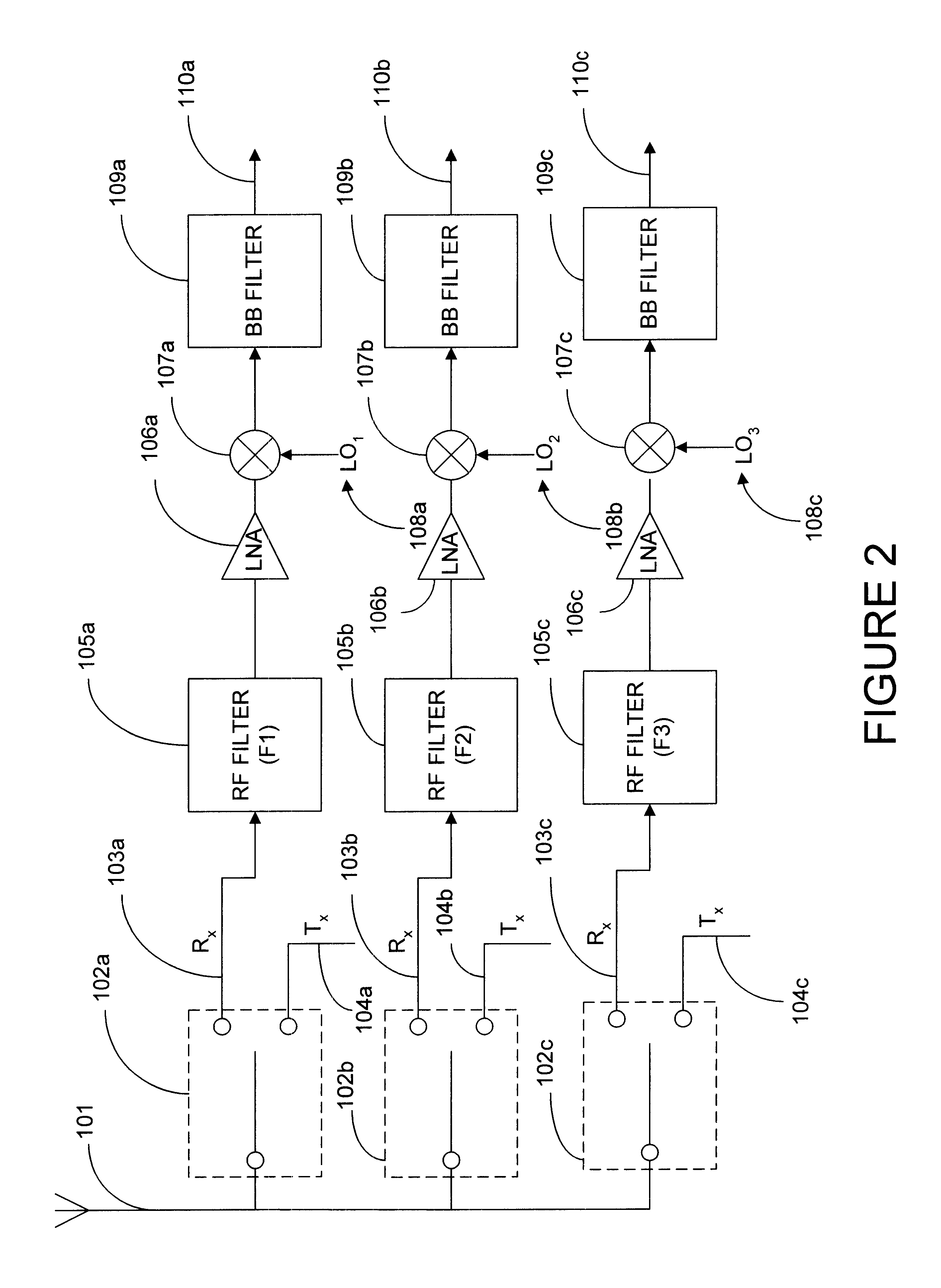
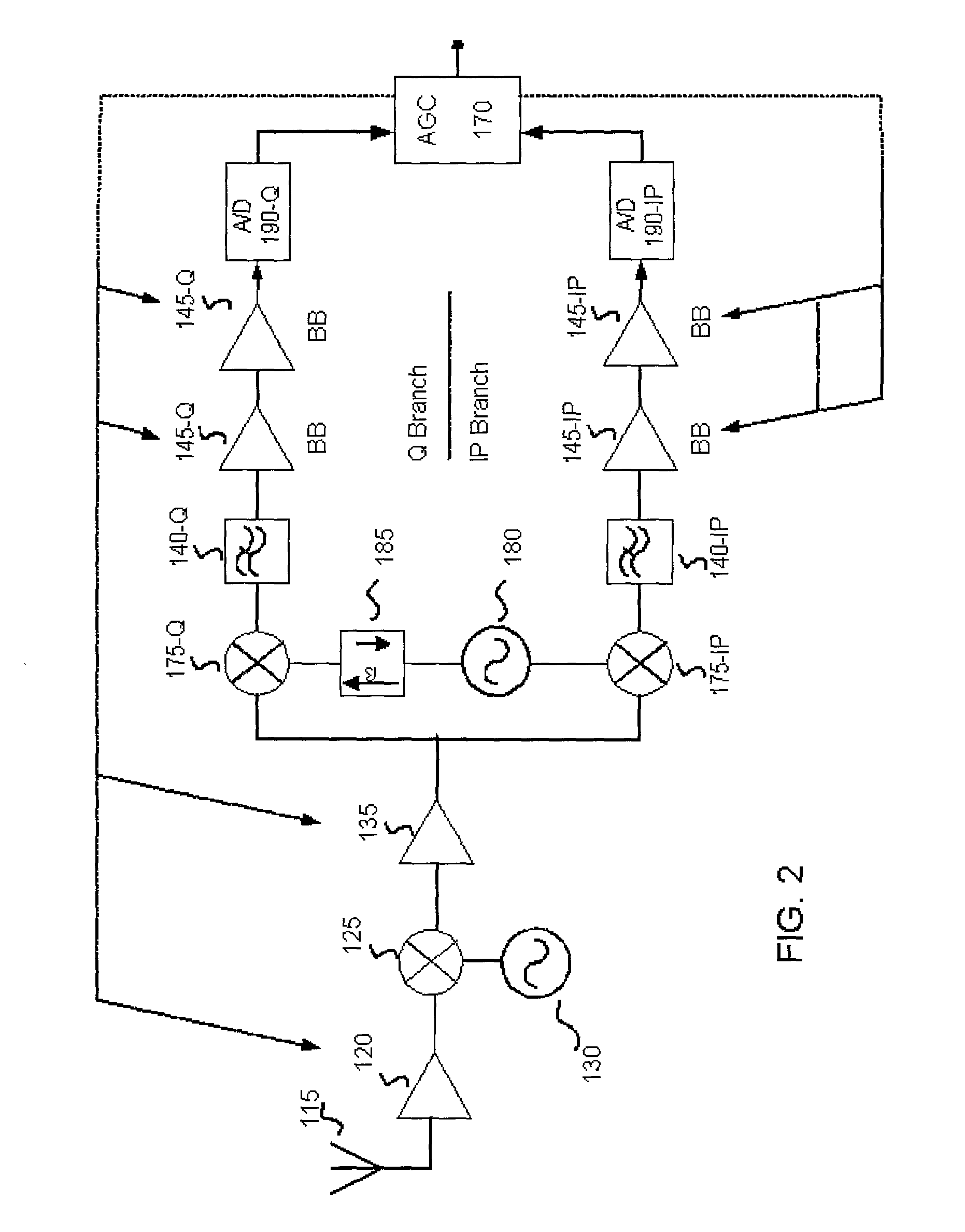
Multi-band filter system for wireless communication receiver
A filter system comprising three or more filters, each having different passbands, and an impedance adjusting network coupled between a filter system ports and each of the ports of at least two of the filters to adjust the port impedances of the filters coupled to the network. The adjusted port impedance of each filter at a frequency representative of at least one of the other filters coupled to the network is at a non-loading level. In one embodiment, the filter system is configured for use in a wireless communication receiver and / or handset.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
High frequency amplifier
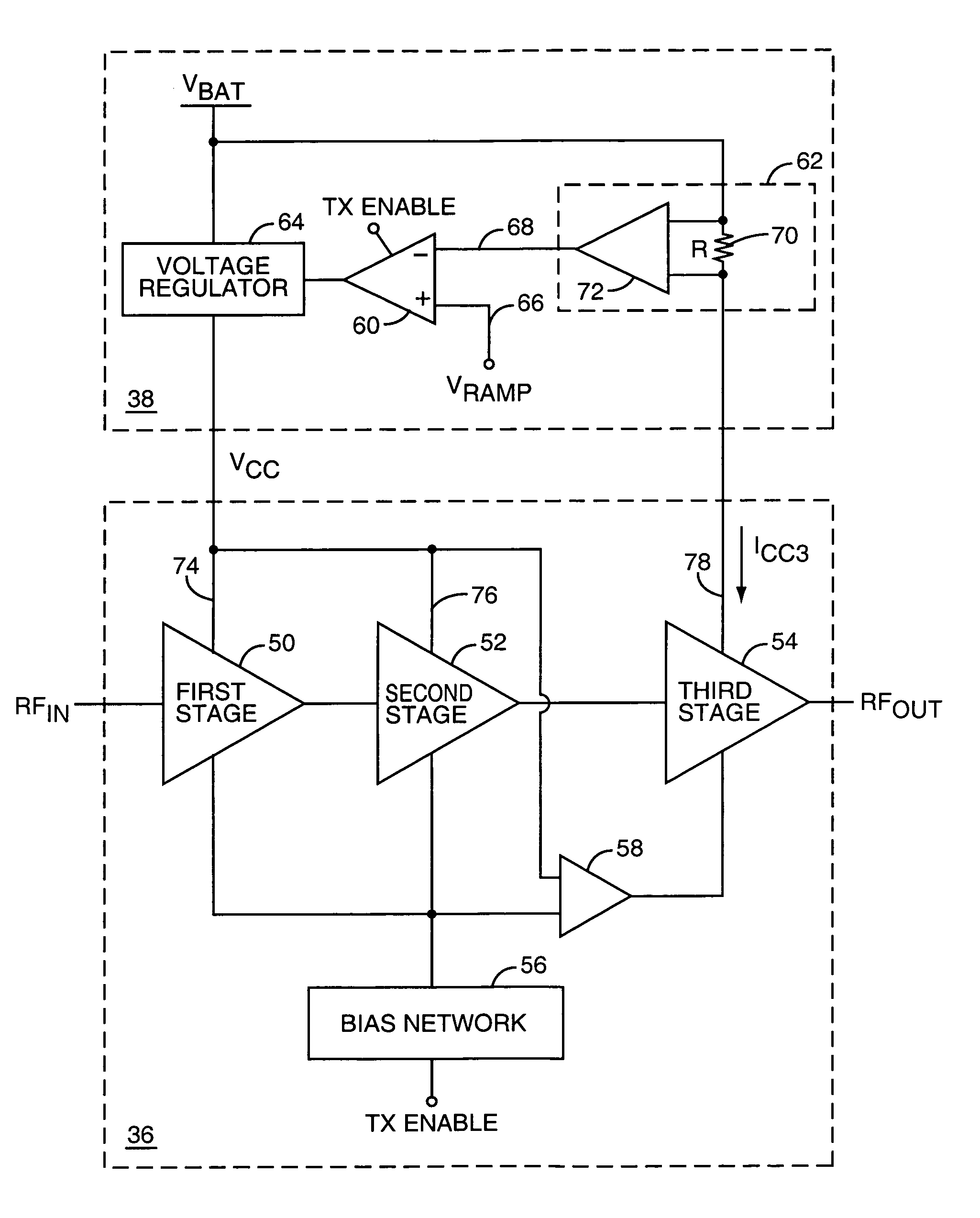
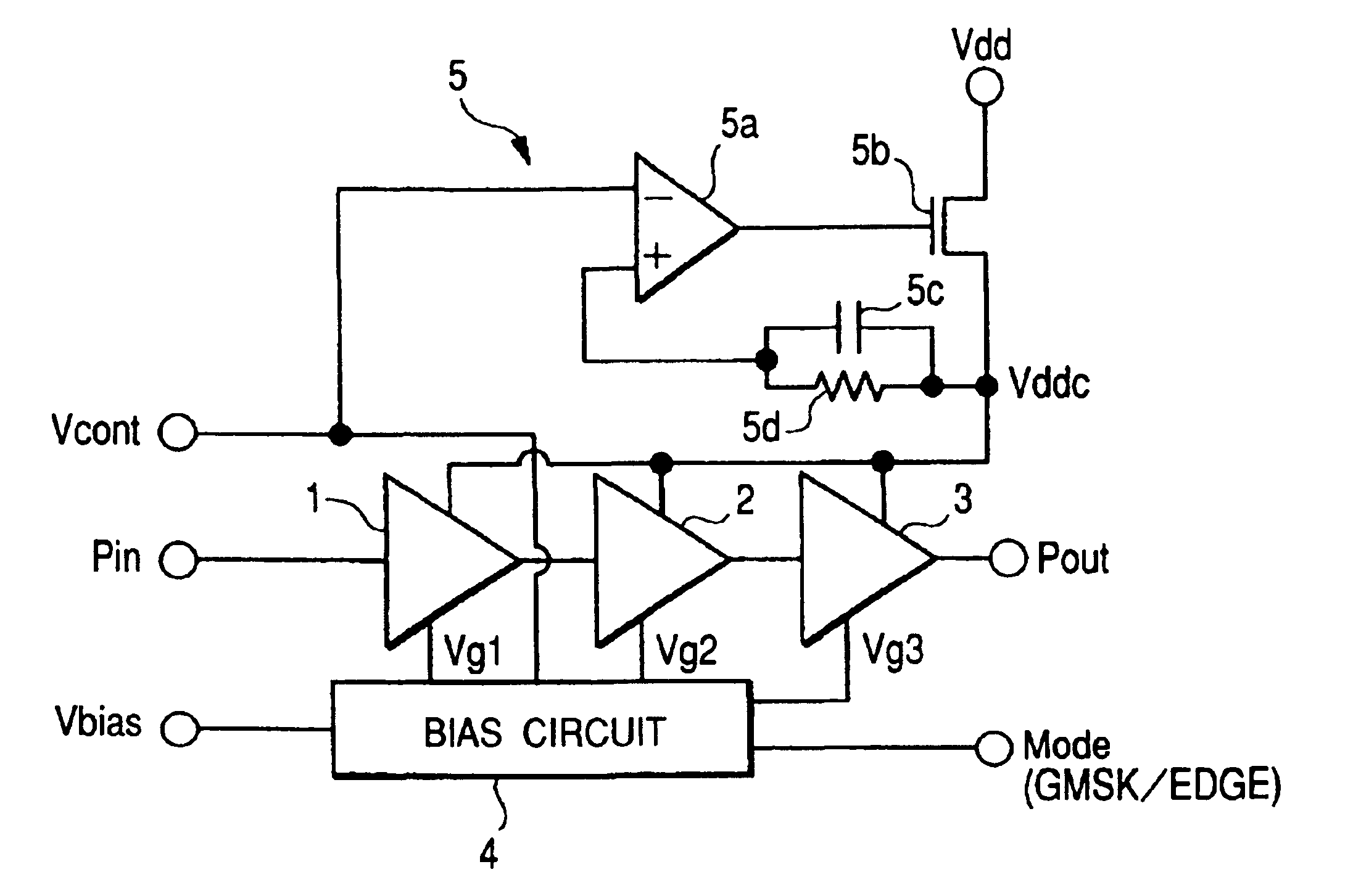
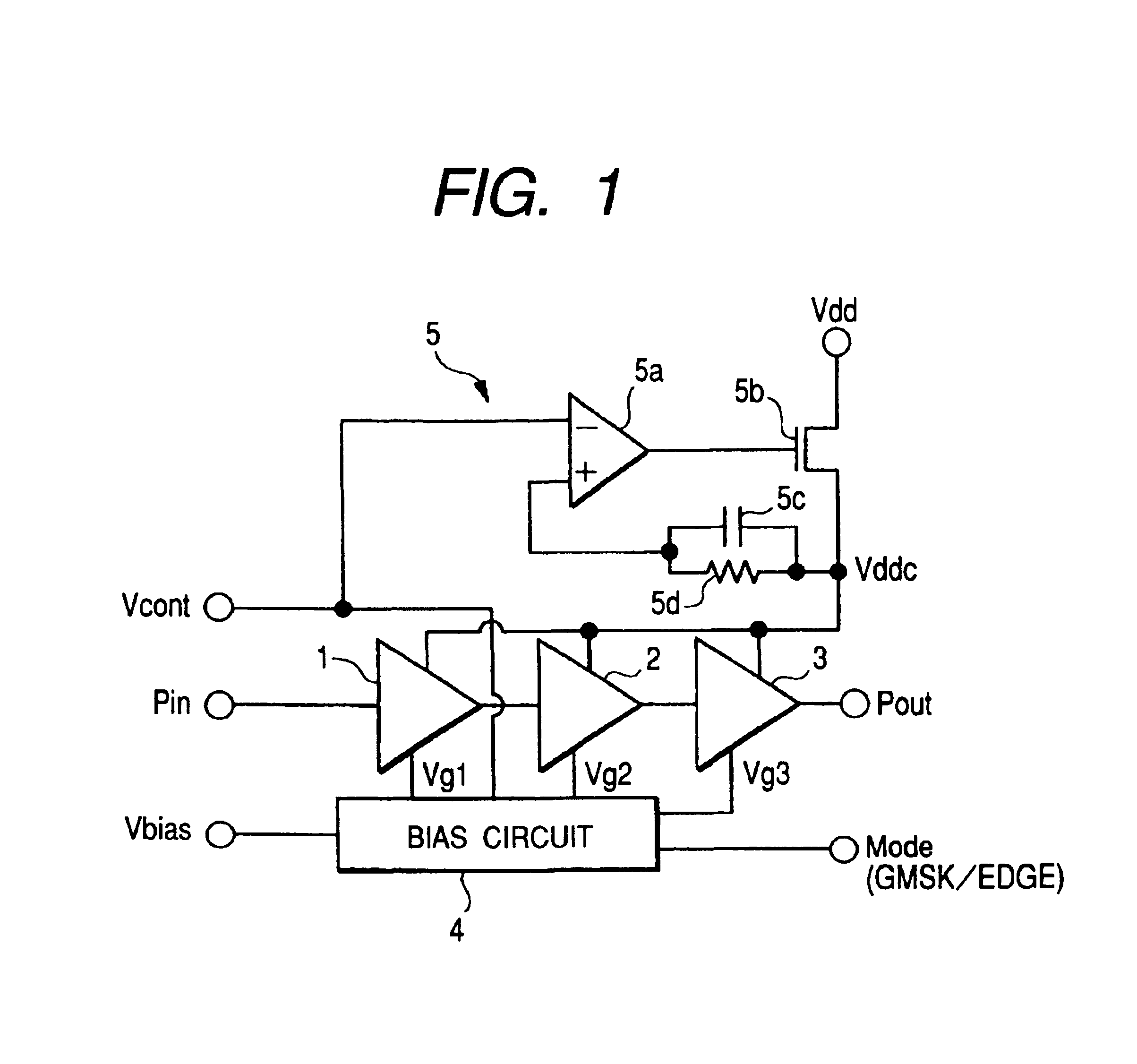
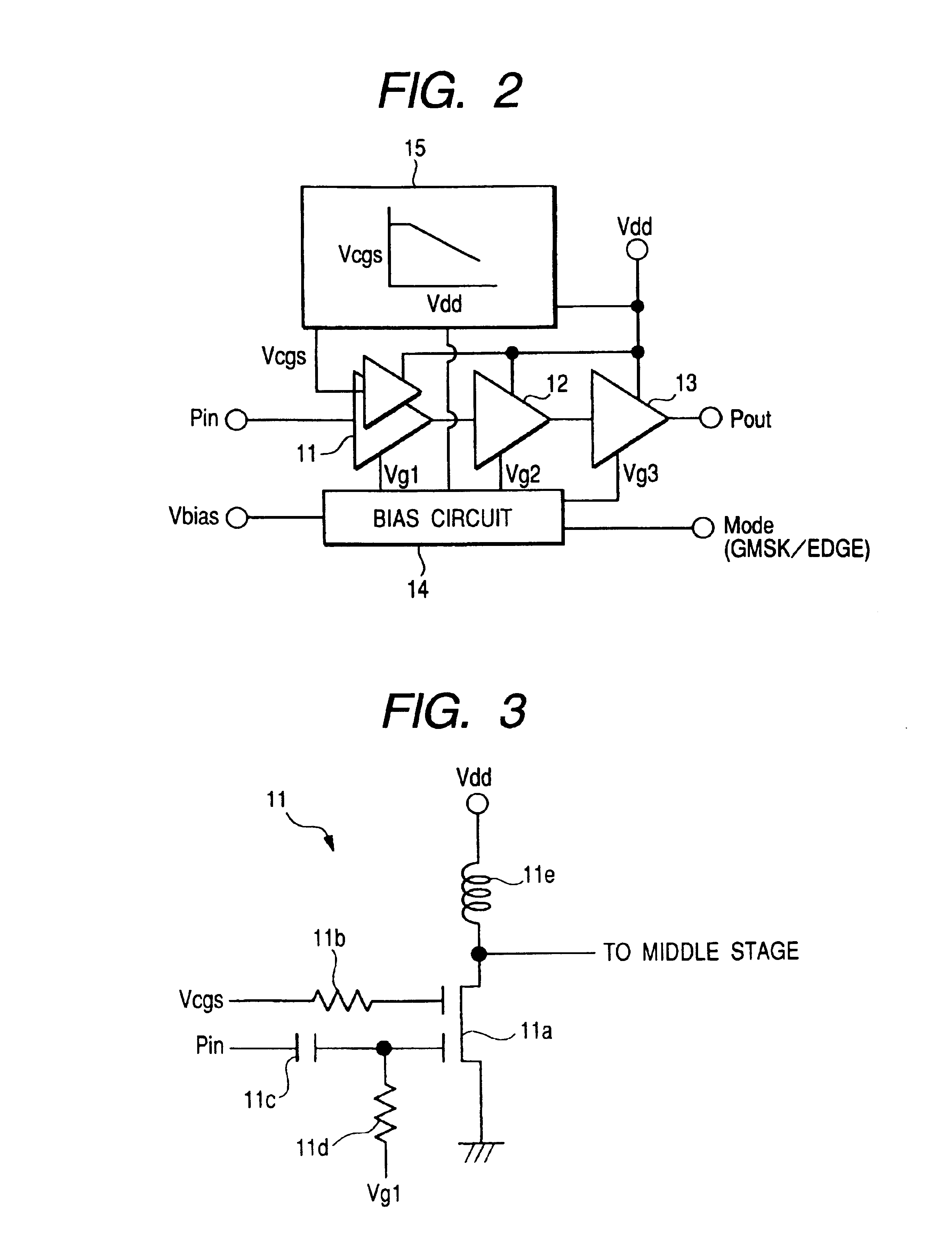
InactiveUS6885246B2Improve variationWithout deteriorationAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationSupply voltage controlAudio power amplifierThree stage
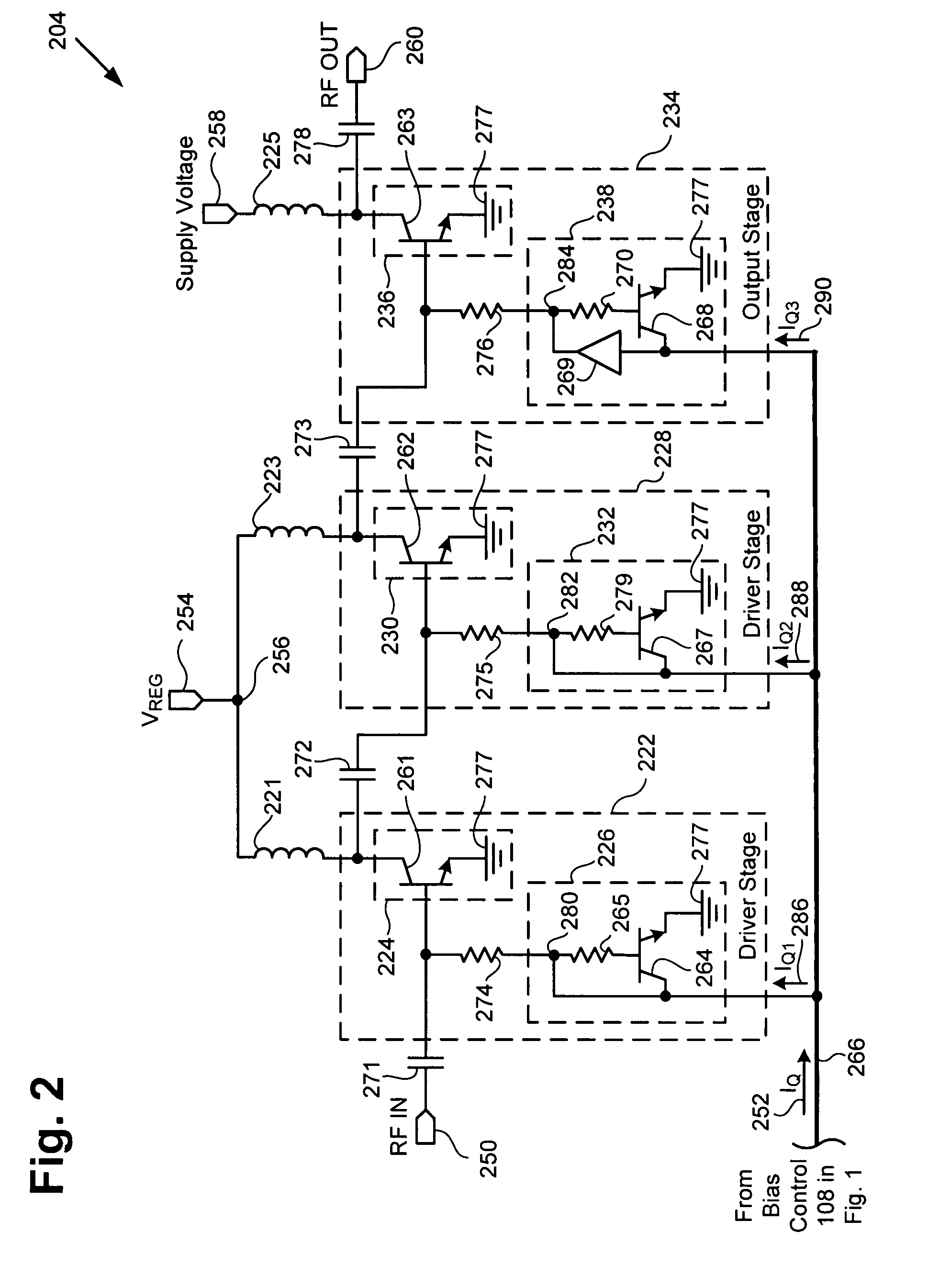
The present invention provides a high frequency amplifier using a power supply voltage regulate circuit for the purpose of compensating for variations in power supply voltage. The high frequency amplifier comprises three-stage power amplifiers which amplify an input signal and output the amplified signal, a bias circuit which supplies bias voltages for controlling these power amplifiers, a regulate circuit which compensates for variations in noise or gain with respect to the variations in the power supply voltage for driving the power amplifiers, etc. The regulate circuit holds constant an output voltage Vddc with respect to variations in power supply voltage Vdd and outputs the constant-held output voltage Vddc as a power supply voltage for the power amplifiers.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
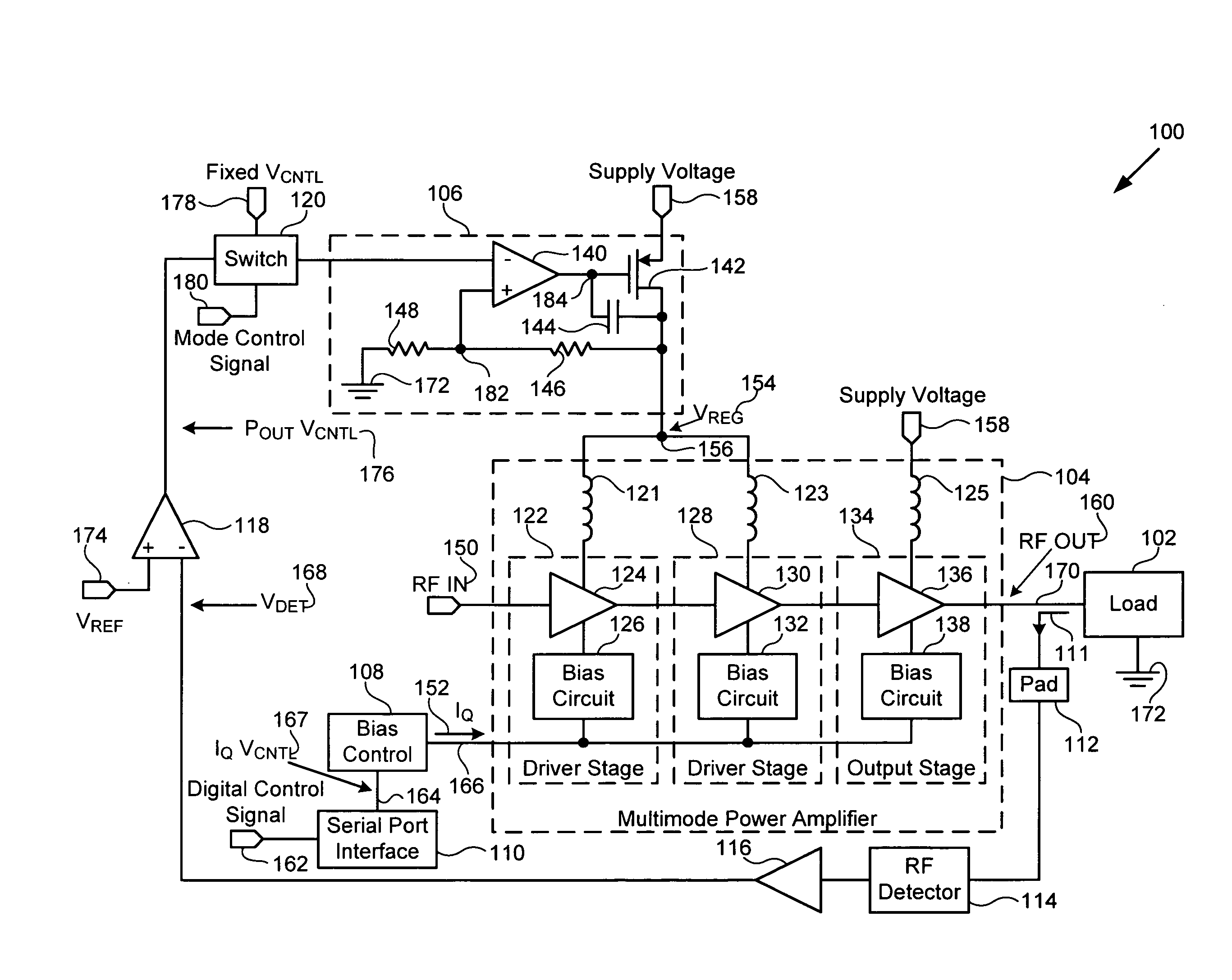
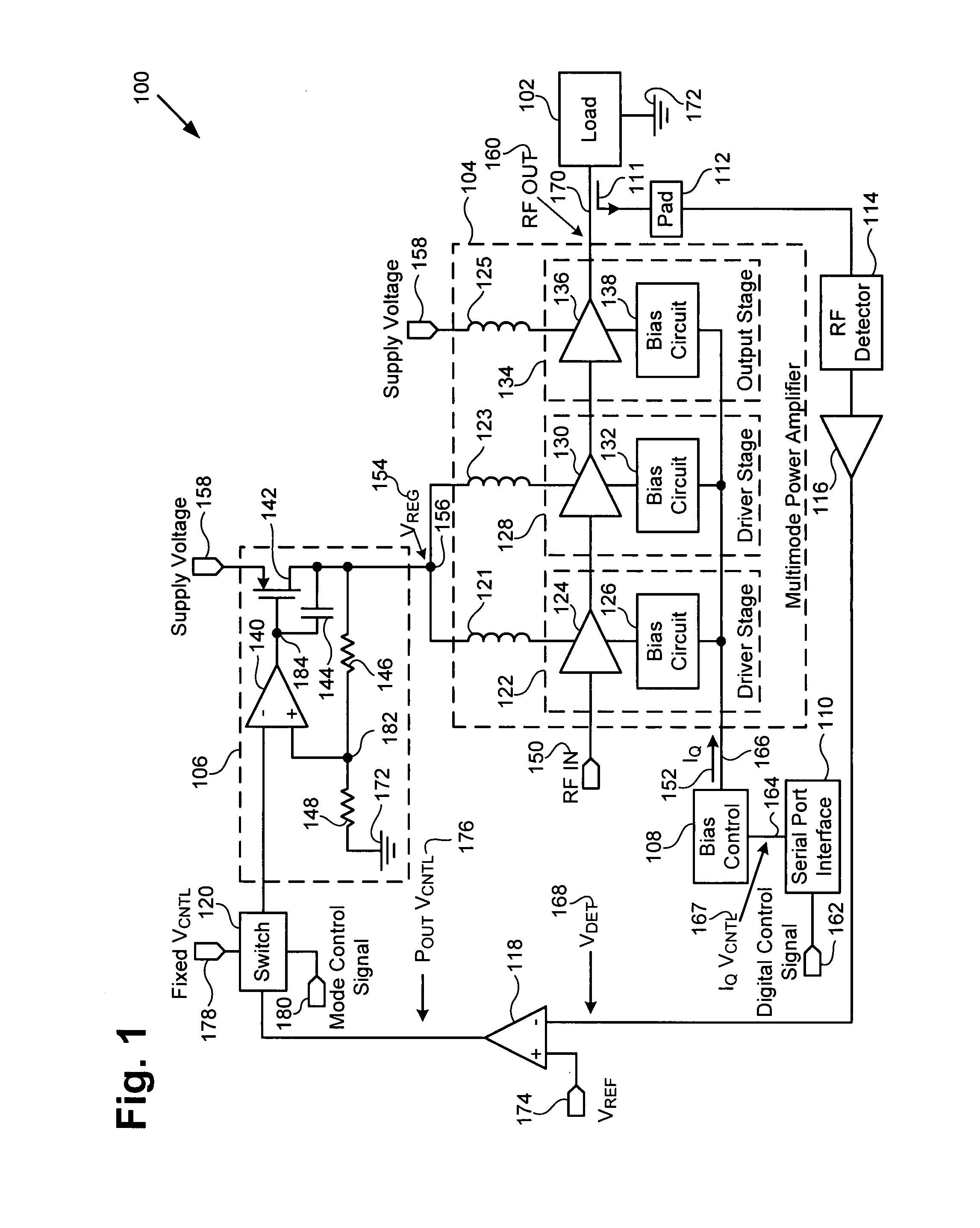
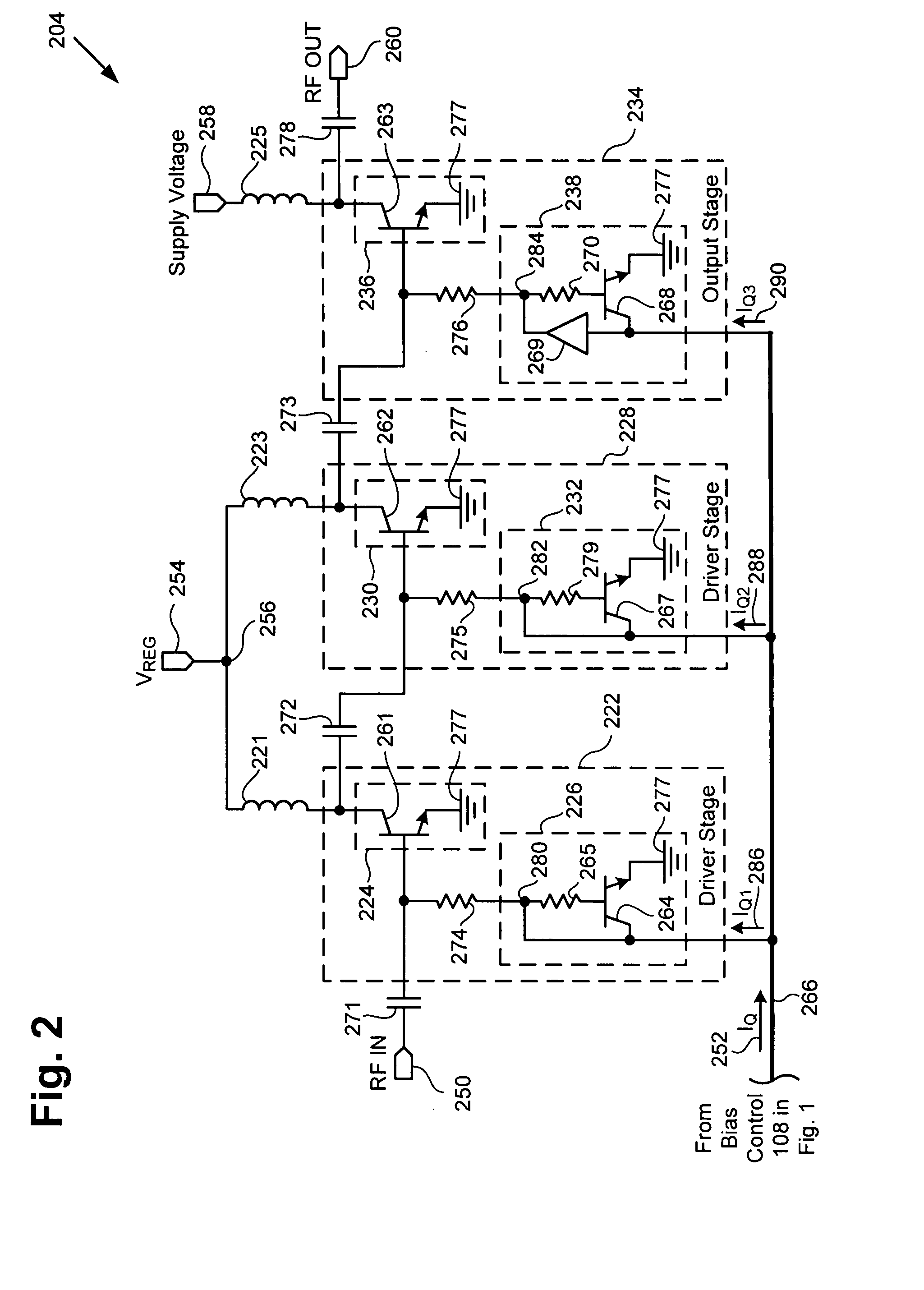
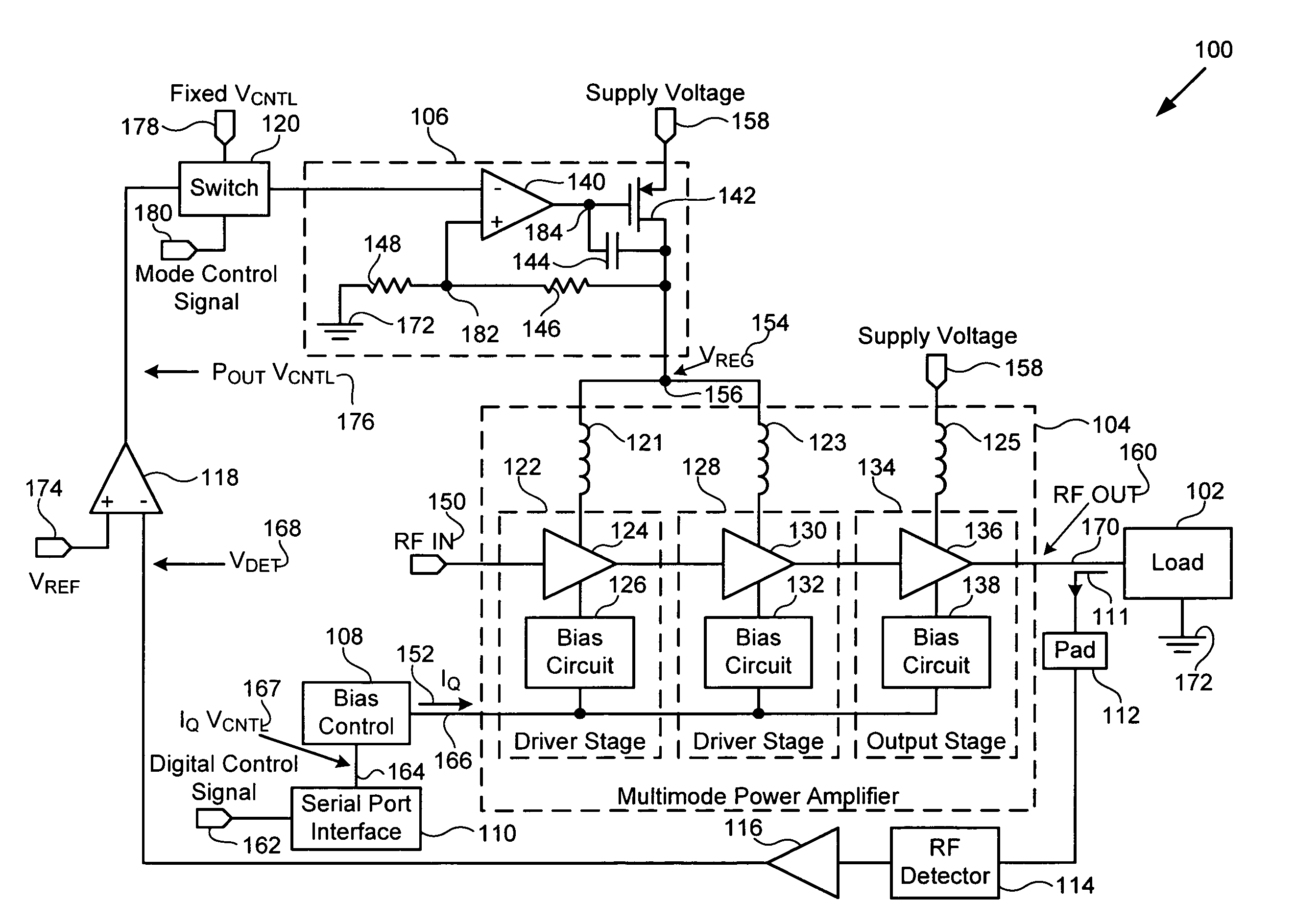
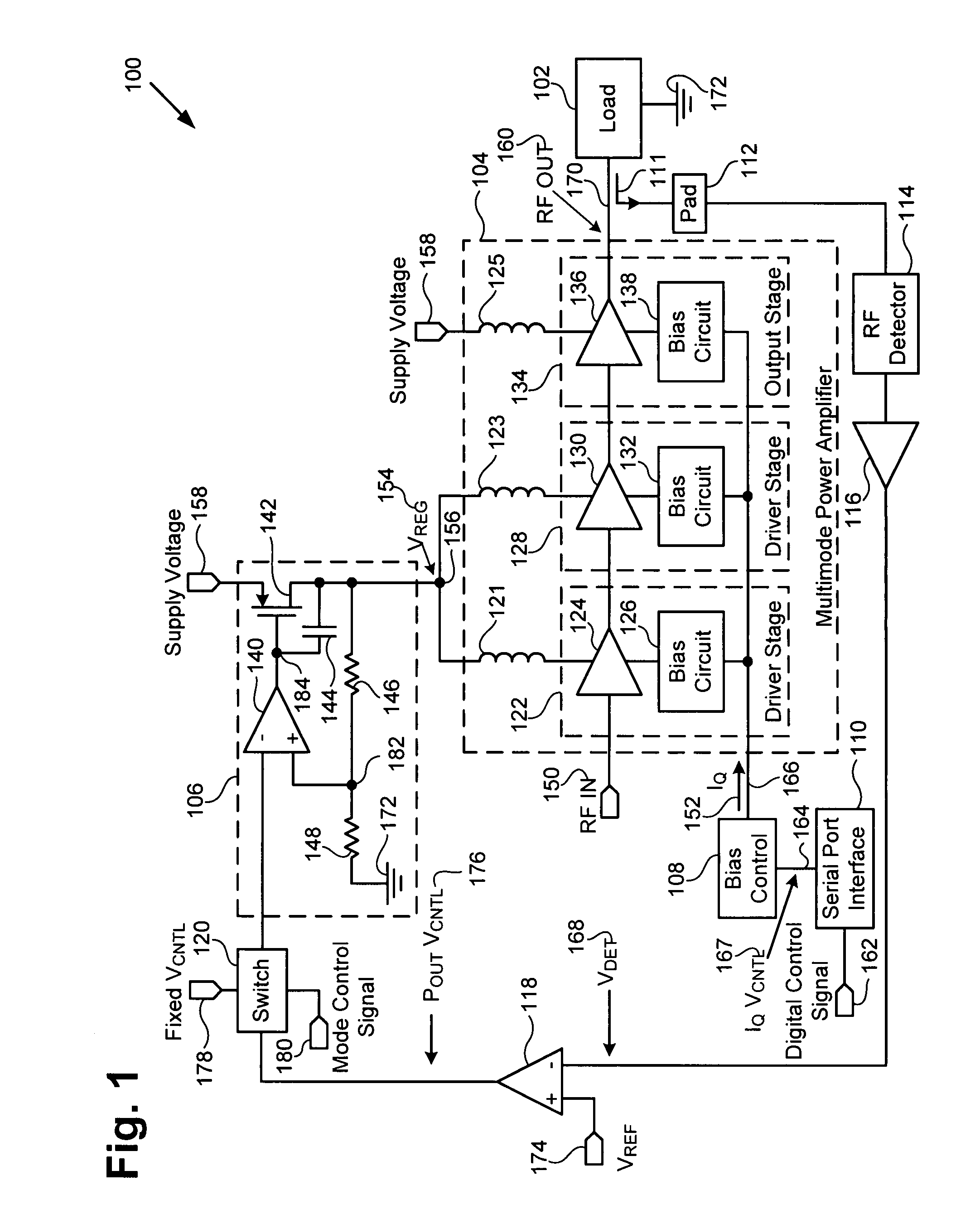
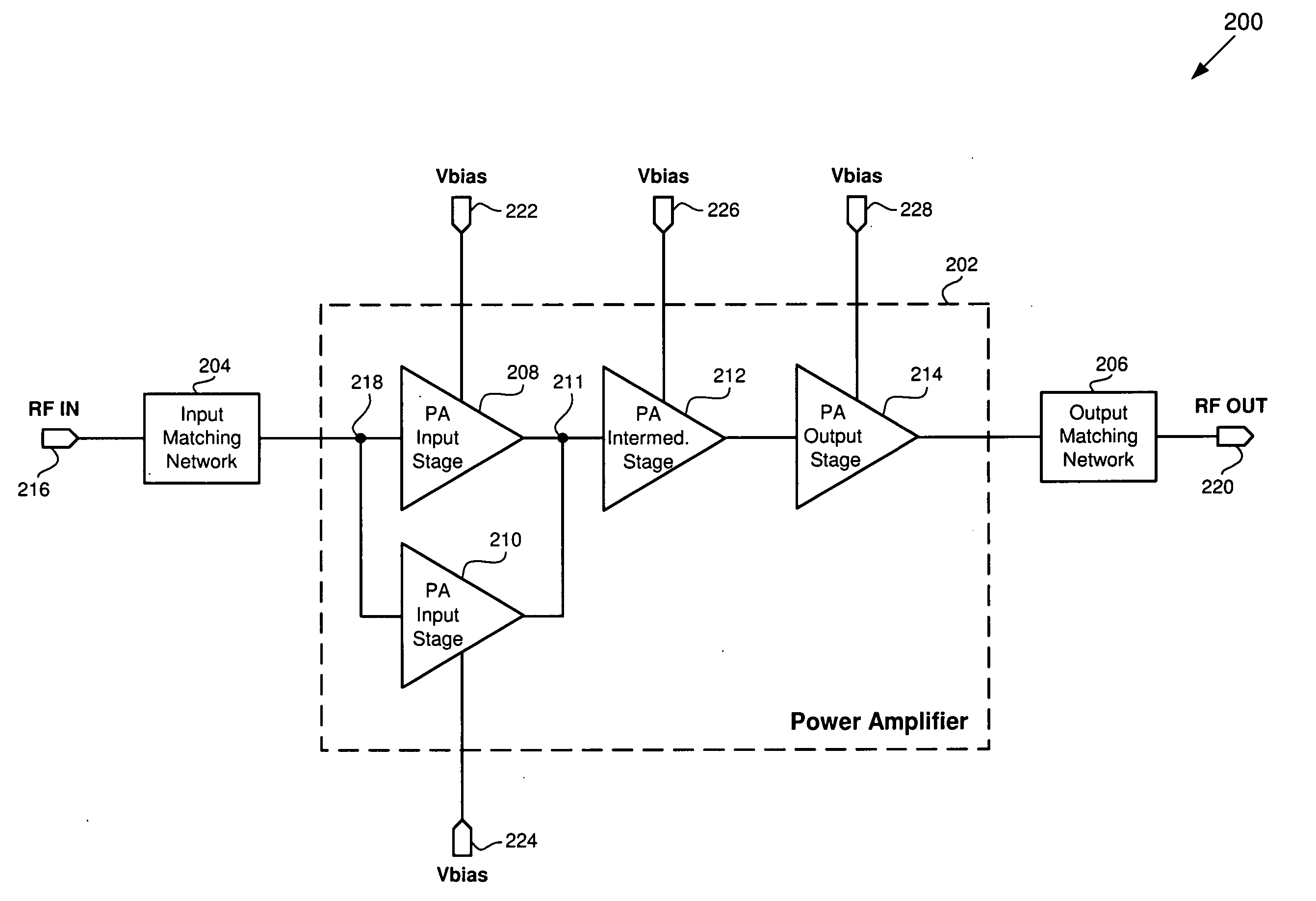
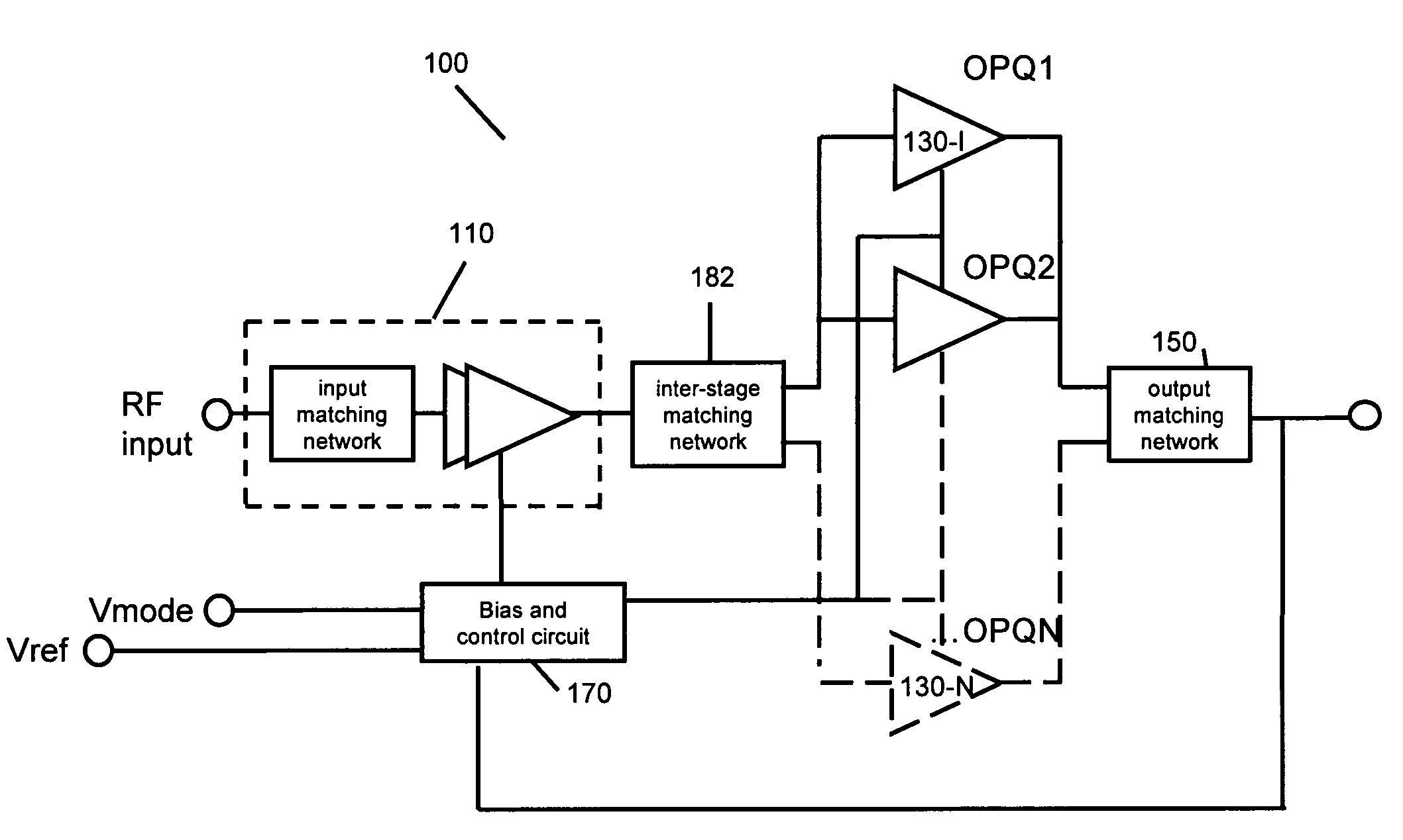
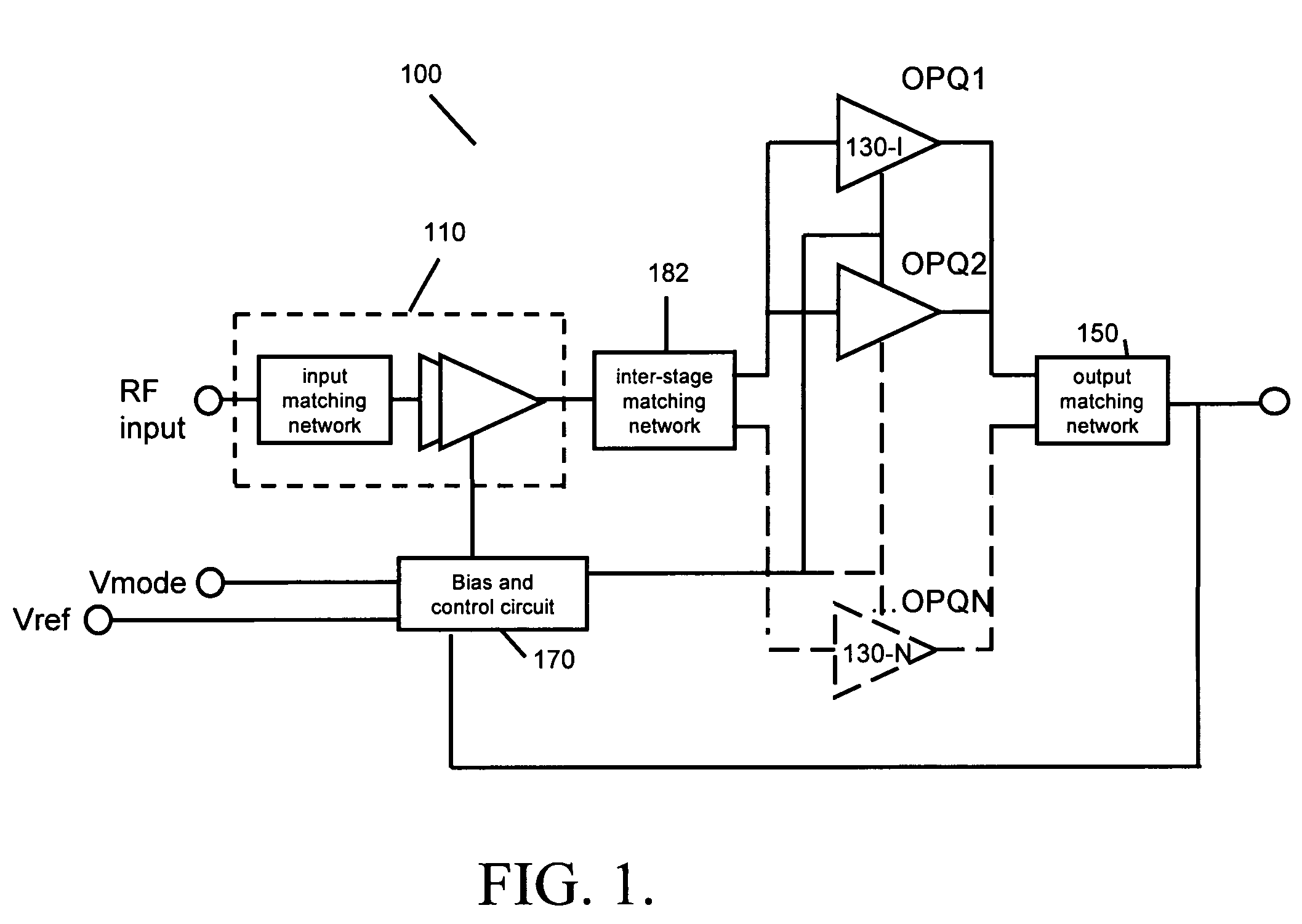
Multimode amplifier for operation in linear and saturated modes
According to an exemplary embodiment, a multimode power amplifier configured to receive an RF input signal and provide an RF output signal in linear and saturated operating modes includes an output stage configured to receive a fixed supply voltage and to provide the RF output signal. The multimode power amplifier further includes at least one driver stage coupled to the output stage, where the at least one driver stage is configured to receive the RF input signal and an adjustable supply voltage. The adjustable supply voltage controls an RF output power of the RF output signal when the multimode power amplifier is in the saturated operating mode. The at least one driver and the output stage are each biased by a low impedance voltage in the linear and saturated operating modes. The adjustable supply voltage can be controlled by a fixed control voltage in the linear operating mode.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Multimode amplifier for operation in linear and saturated modes
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
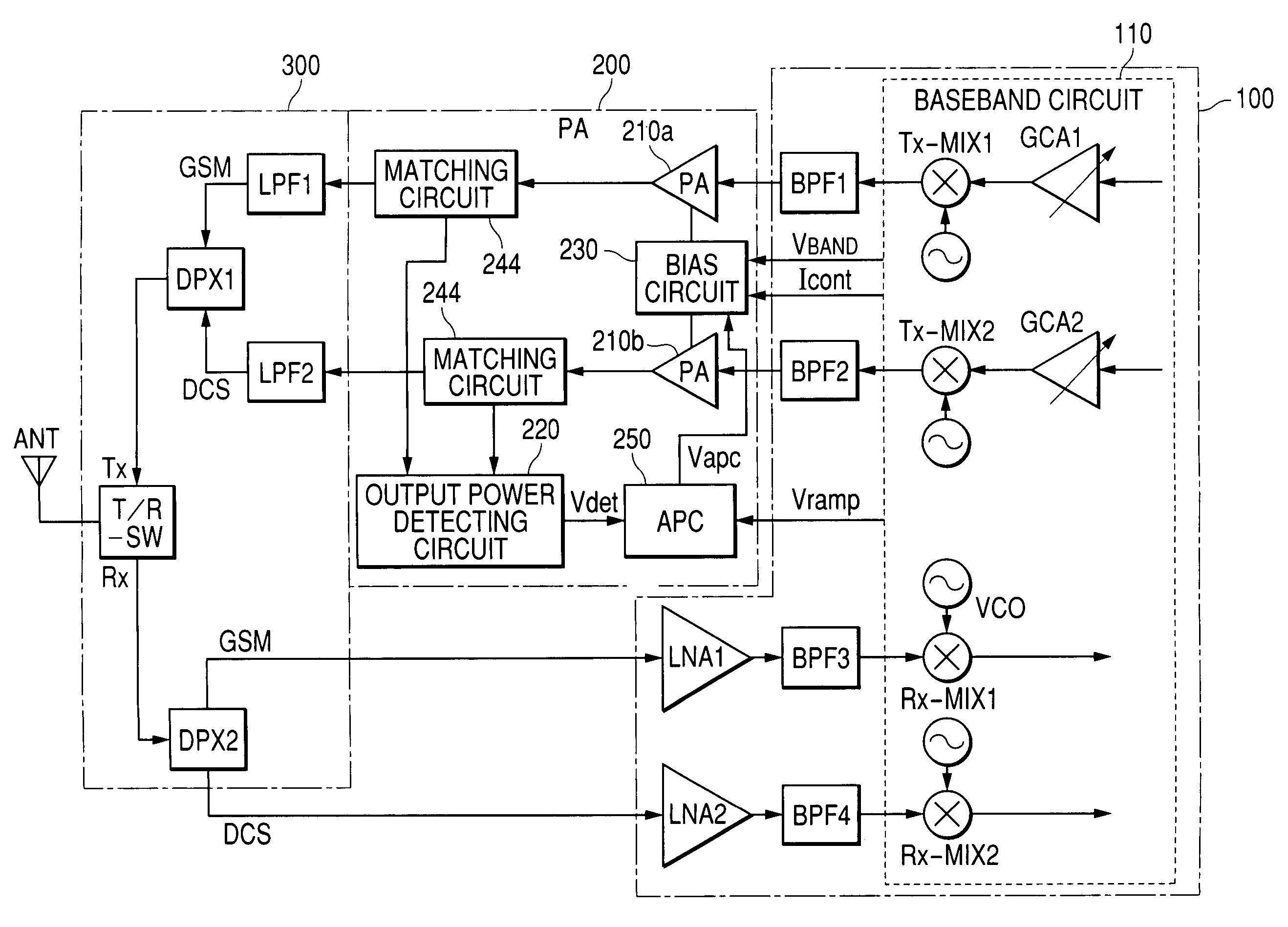
High-frequency power amplification electronic part and wireless communication system
ActiveUS20050168281A1Gain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
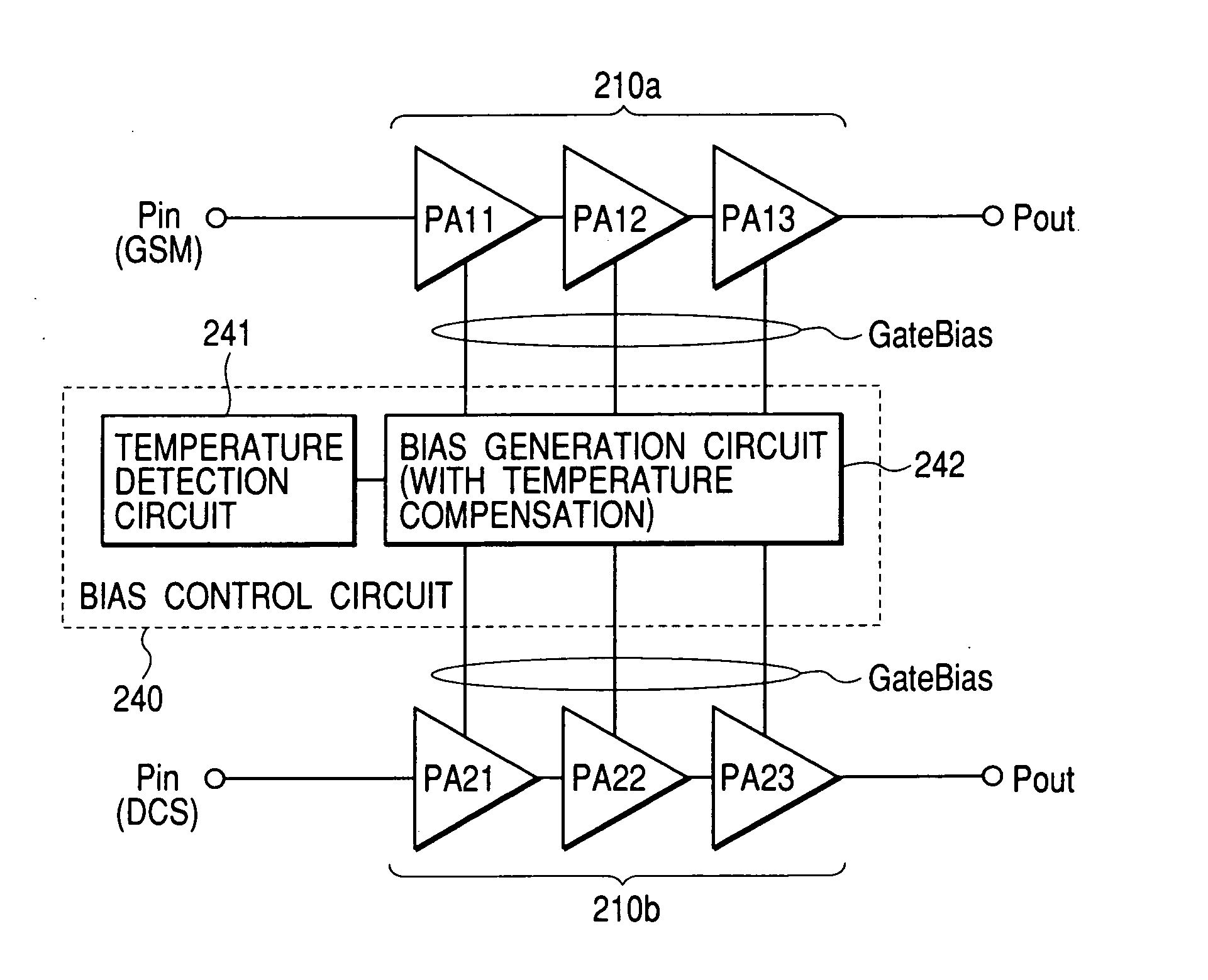
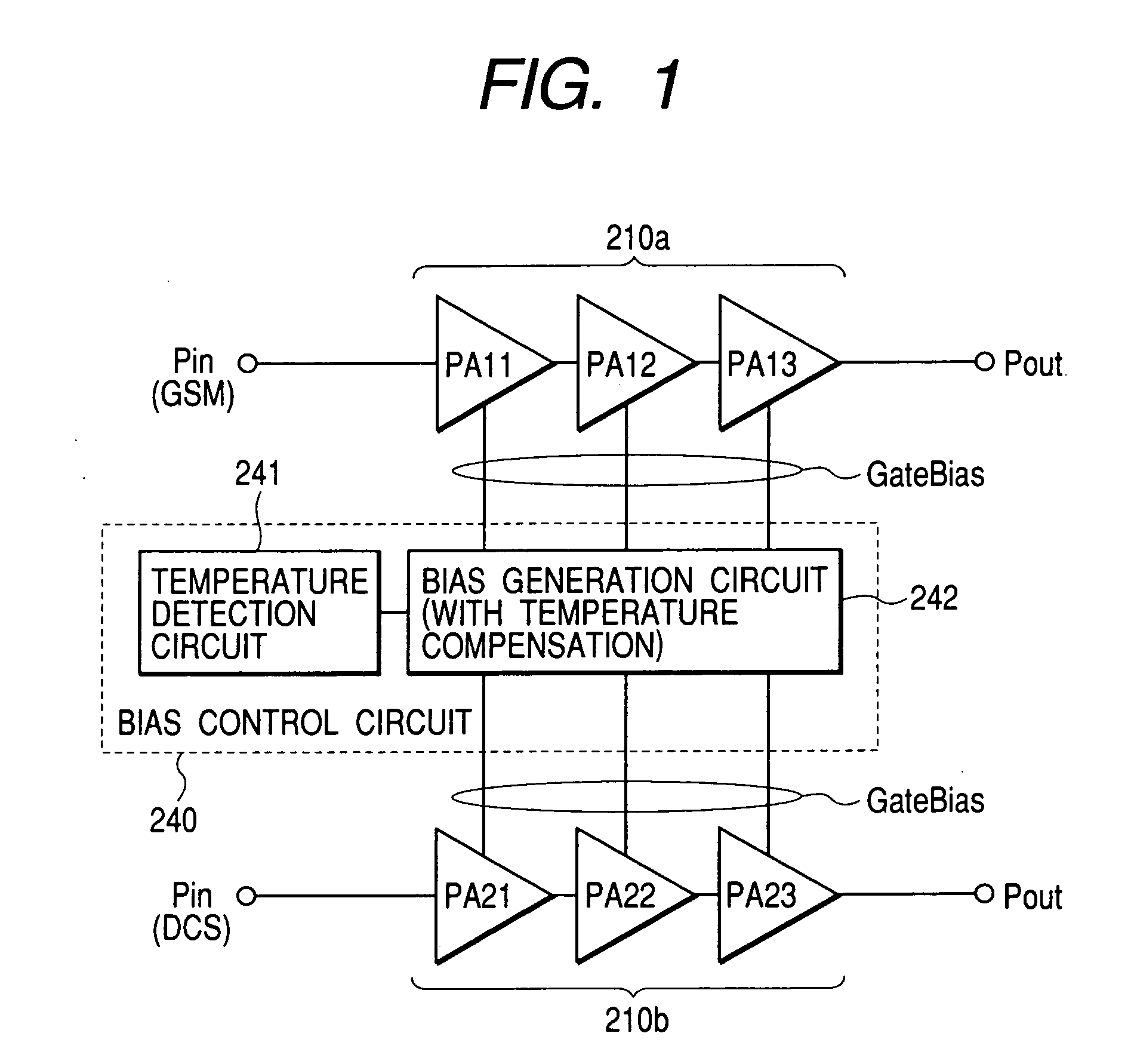
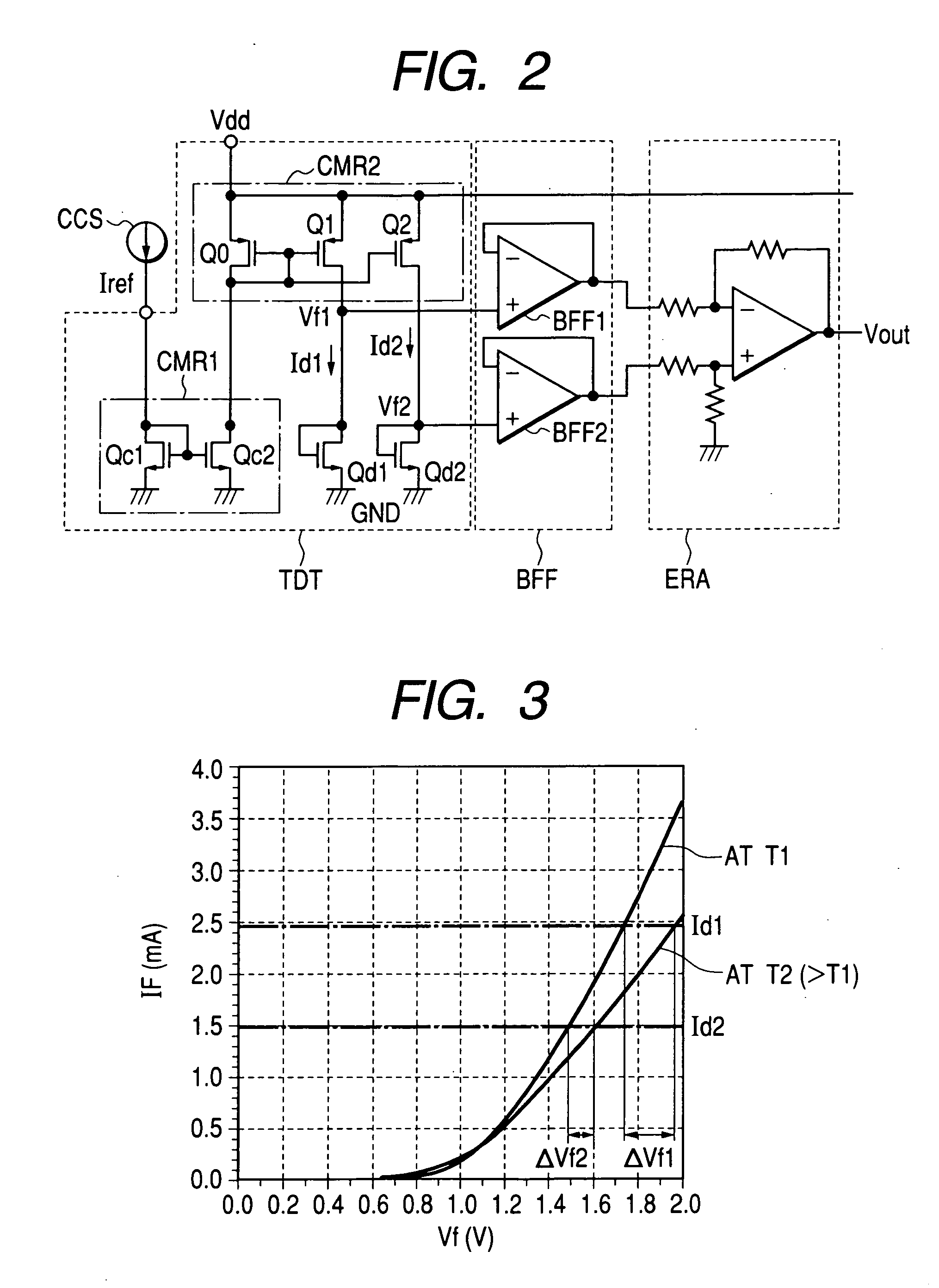
A high-frequency power amplification electronic part is disclosed which comprises a power amplifier circuit and a bias control circuit, the power amplifier circuit having a plurality of amplifier stages for amplifying an input high-frequency signal, the bias control circuit acting to bias the power amplifier circuit. The power amplifier circuit controls output power in accordance with input power that is varied while a gain of the power amplifier circuit is being fixed by either a bias current or a bias voltage supplied from the bias control circuit. The bias control circuit supplies at least two diode characteristic elements with a predetermined current each in order to generate at least two voltages demonstrating different temperature characteristics, the bias control circuit further using the generated voltages as a basis for generating either a plurality of bias currents or a plurality of bias voltages having a desired temperature-dependent rate of change each, the generated bias currents or bias voltages being fed to each of the plural amplifier stages constituting the power amplifier circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
High frequency amplifier circuit
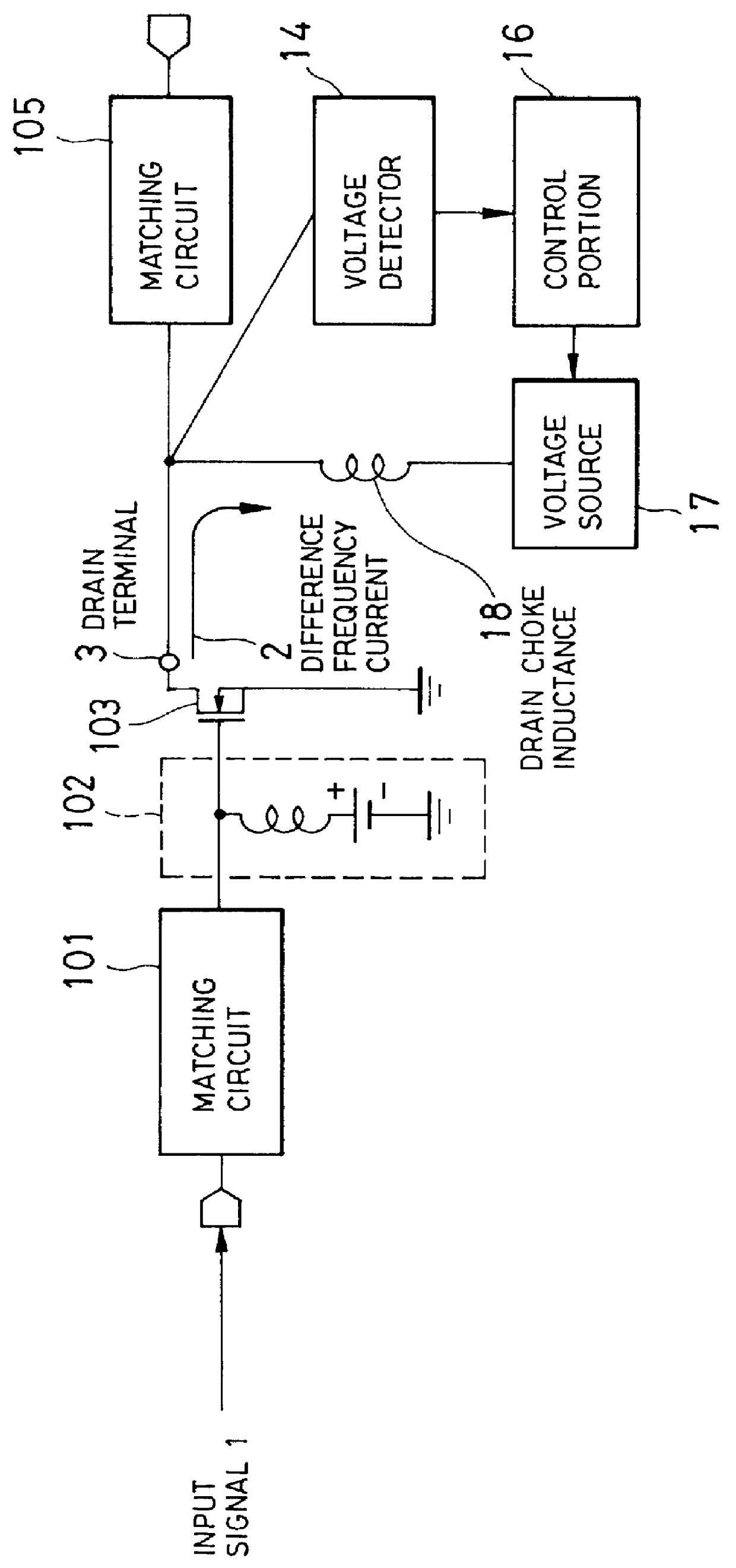
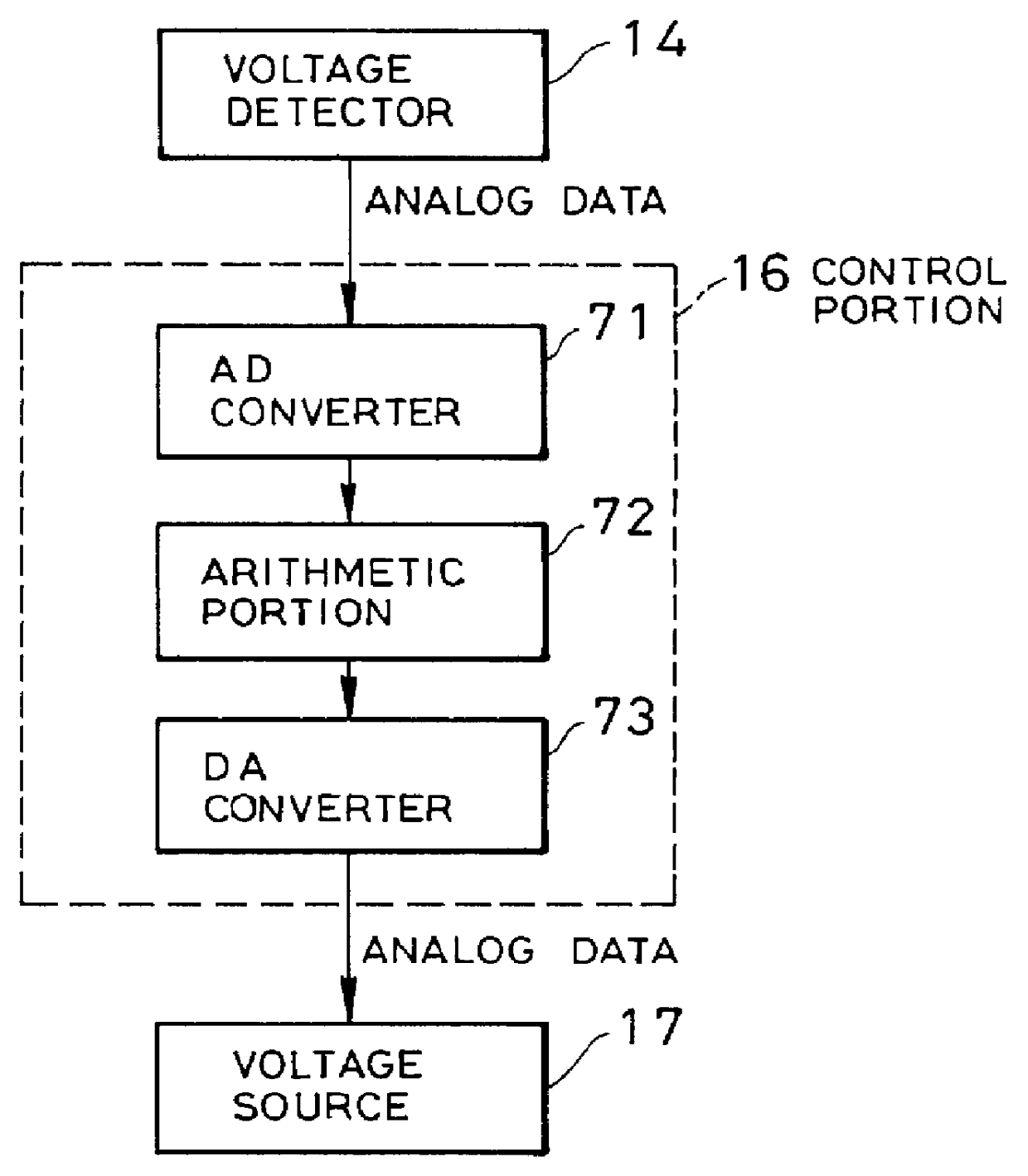
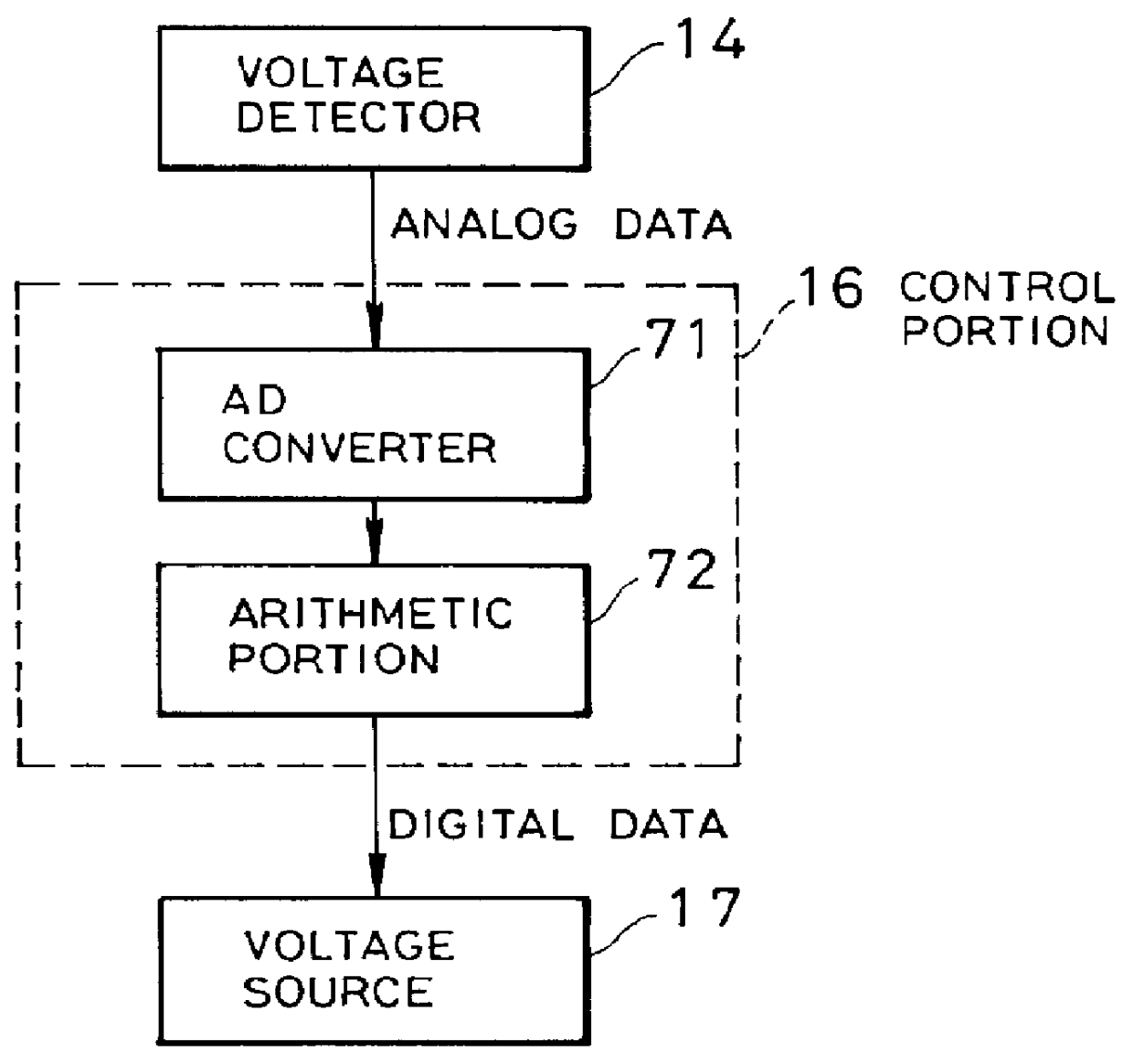
InactiveUS6111461AAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierEngineering
A high frequency amplifier circuit includes the voltage source supplying the power source voltage on the output side of the high frequency amplifying active element. The high frequency amplifier is constructed with a voltage detector detecting a difference frequency voltage of the input signal at a frequency lower than the input signal of the high frequency amplifier circuit and control portion for attenuating the difference frequency voltage from the output signal by controlling the power source voltage on the basis of the difference frequency voltage detected by the voltage detector. Therefore, distortion due to modulating the input signal with the difference frequency component of the input signal can be reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
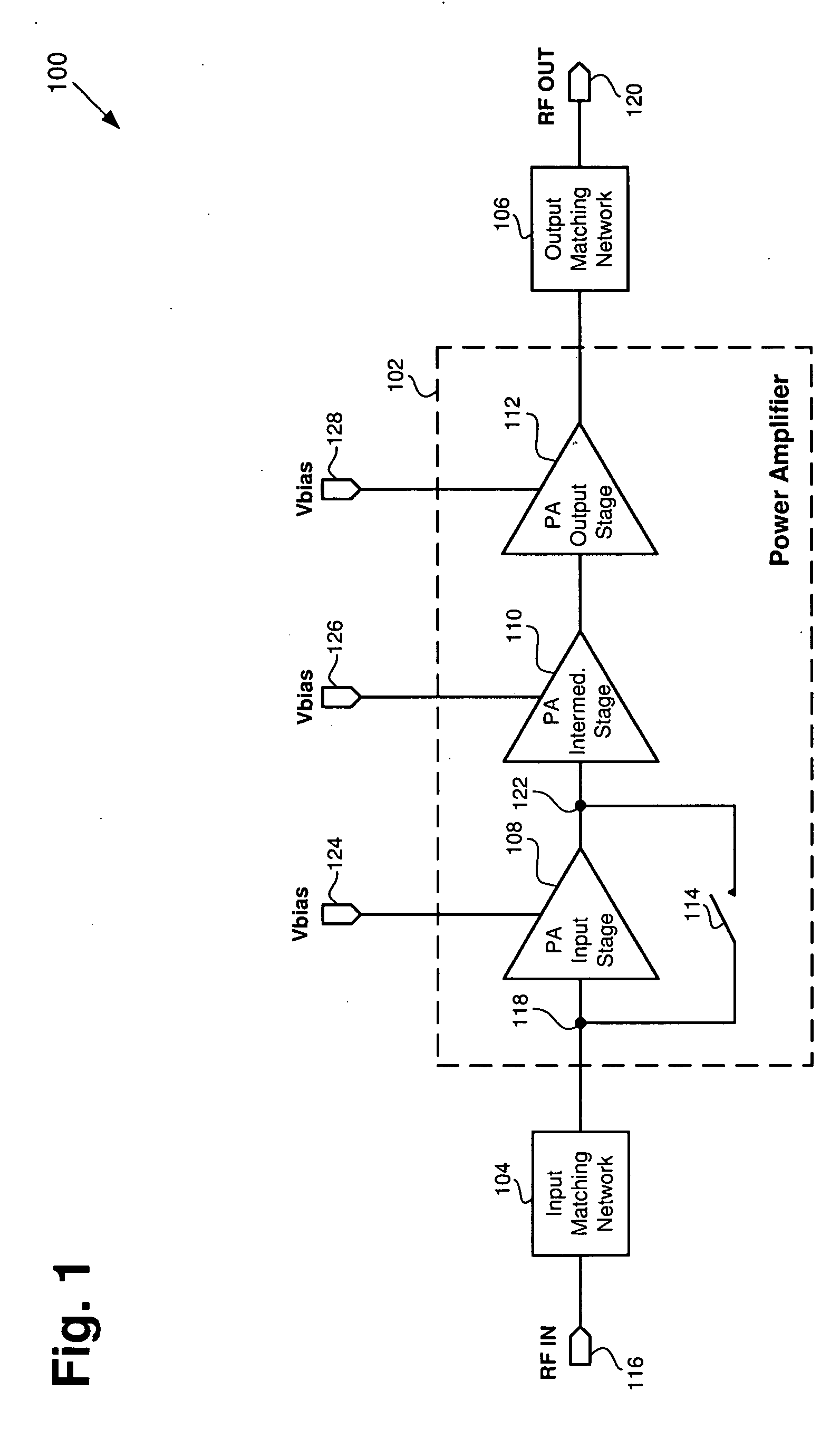
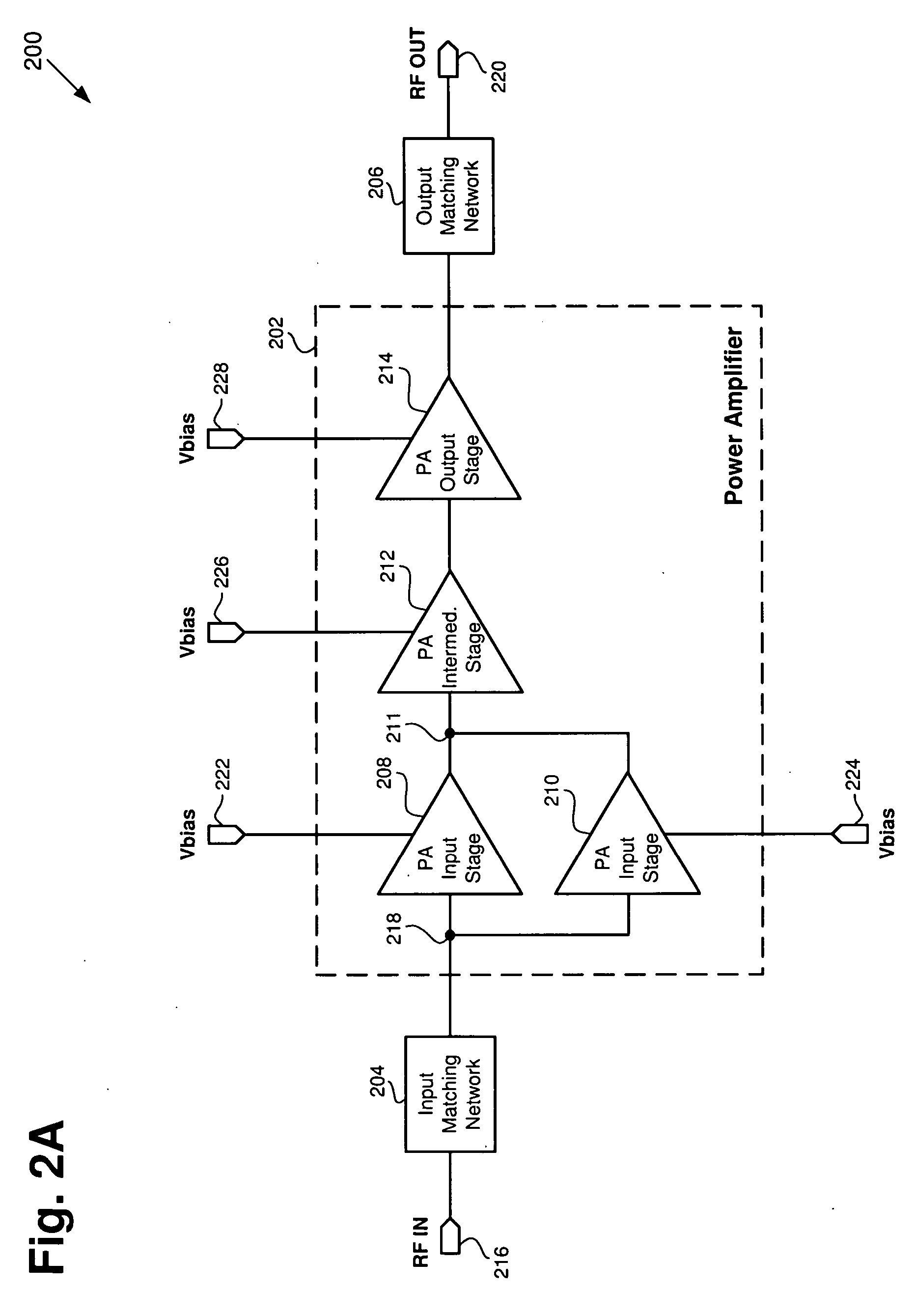
Dual mode power amplifier
A power amplifier is configured to operate in a first gain mode and a second gain mode. A first power amplifier input stage has an input and an output. A second power amplifier input stage has an input and an output, where the output of the second power amplifier input stage is coupled to the output of the first power amplifier input stage. The first input stage is turned on in response to a first bias voltage in the first gain mode and the second input stage is turned on in response to a second bias voltage in the second gain mode. Alternatively, a first input stage and an intermediate stage can be switched off by turning off their respective bias voltages, and a second input stage can be switched on by turning on its respective bias voltage; the intermediate stage and the second input stage sharing a common output.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
In-band and out-of-band signal detection for automatic gain calibration systems
InactiveUS20030012313A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlFinite impulse responseControl system
An embodiment of the present invention provides an automatic gain control system for a wireless receiver that quickly differentiates desired in-band signals from high power out-of-band signals that overlap into the target band. The system measures power before and after passing a received signal through a pair of finite impulse response filters that largely restrict the signal's power to that which is in-band. By comparing the in-band energy of the received signal after filtering to the total signal energy prior to filtering, it is possible to determine whether a new in-band signal has arrived. The presence of this new in-band signal is then verified by a multi-threshold comparison of the normalized self-correlation to verify the presence of a new, desired in-band signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
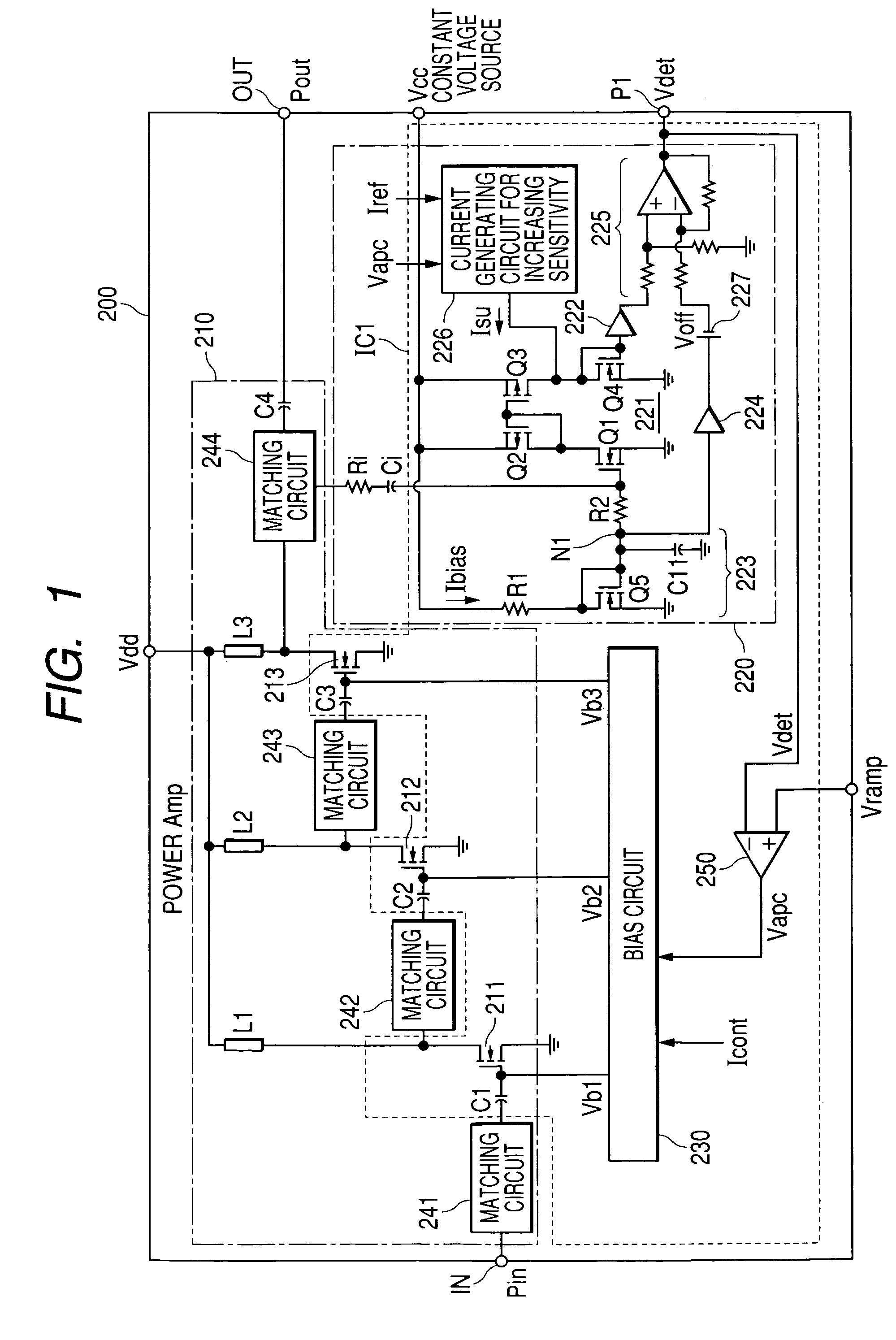
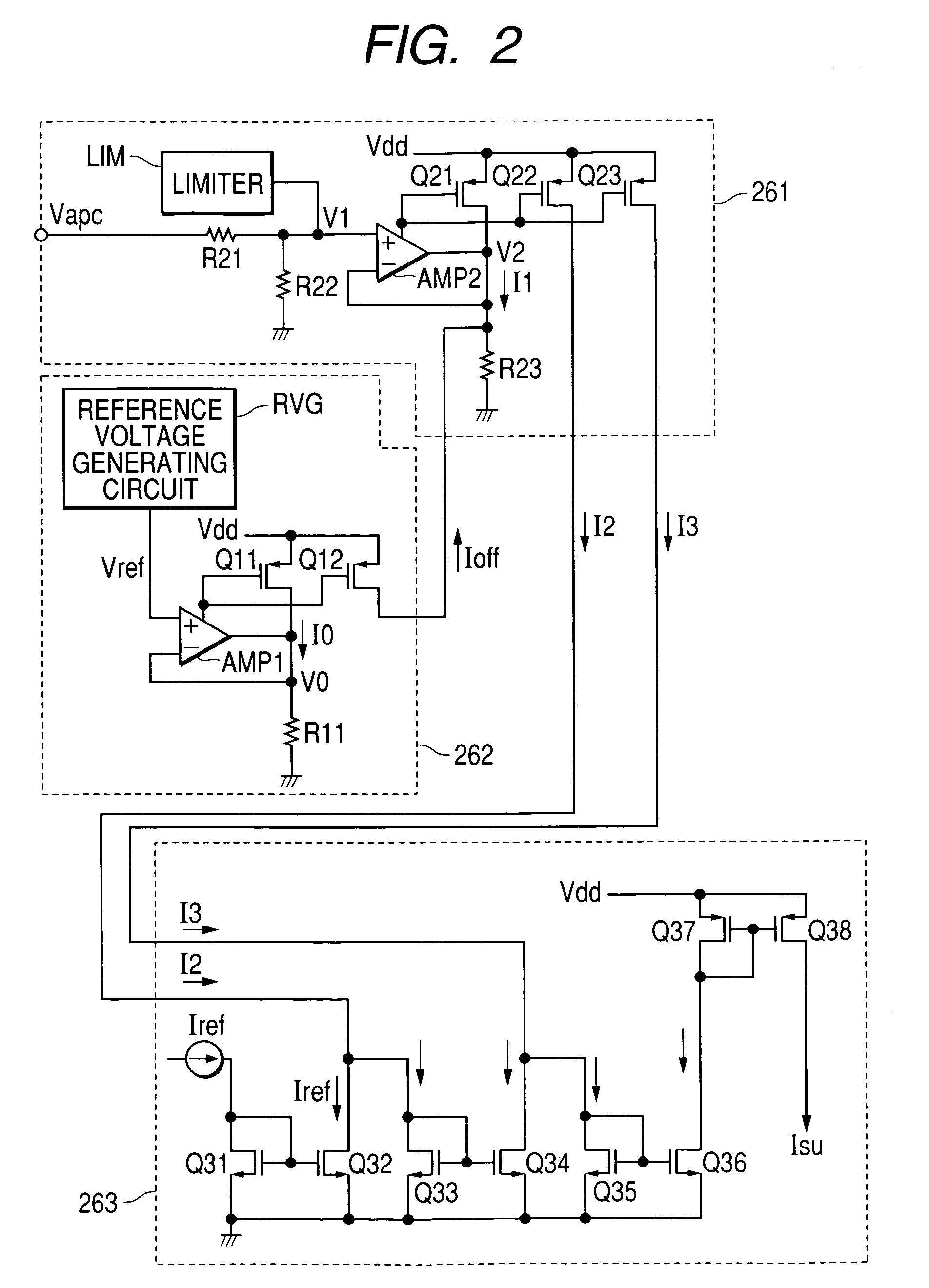
High frequency power amplifier circuit
ActiveUS7333564B2Solve the lack of outputHigh detection sensitivityResonant long antennasGain controlCapacitanceHigh frequency power
The present invention provides a high frequency power amplifier circuit capable of obtaining sufficient detection output even in a range where a request output power level is low and performing a desired output power control by a control loop with the detection output in a radio communication system which detects output power and performs feedback control. An output power detection circuit which detects the level of output power on the basis of an AC signal supplied from a final amplification stage of a high frequency power amplification circuit via a capacitive element has a circuit configuration such that in a state where the output power control voltage is lower than a certain level, current (Isu) according to the output power control voltage is generated and supplied to the output power detection circuit, and detection sensitivity of the output power detection circuit improves according to the current.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
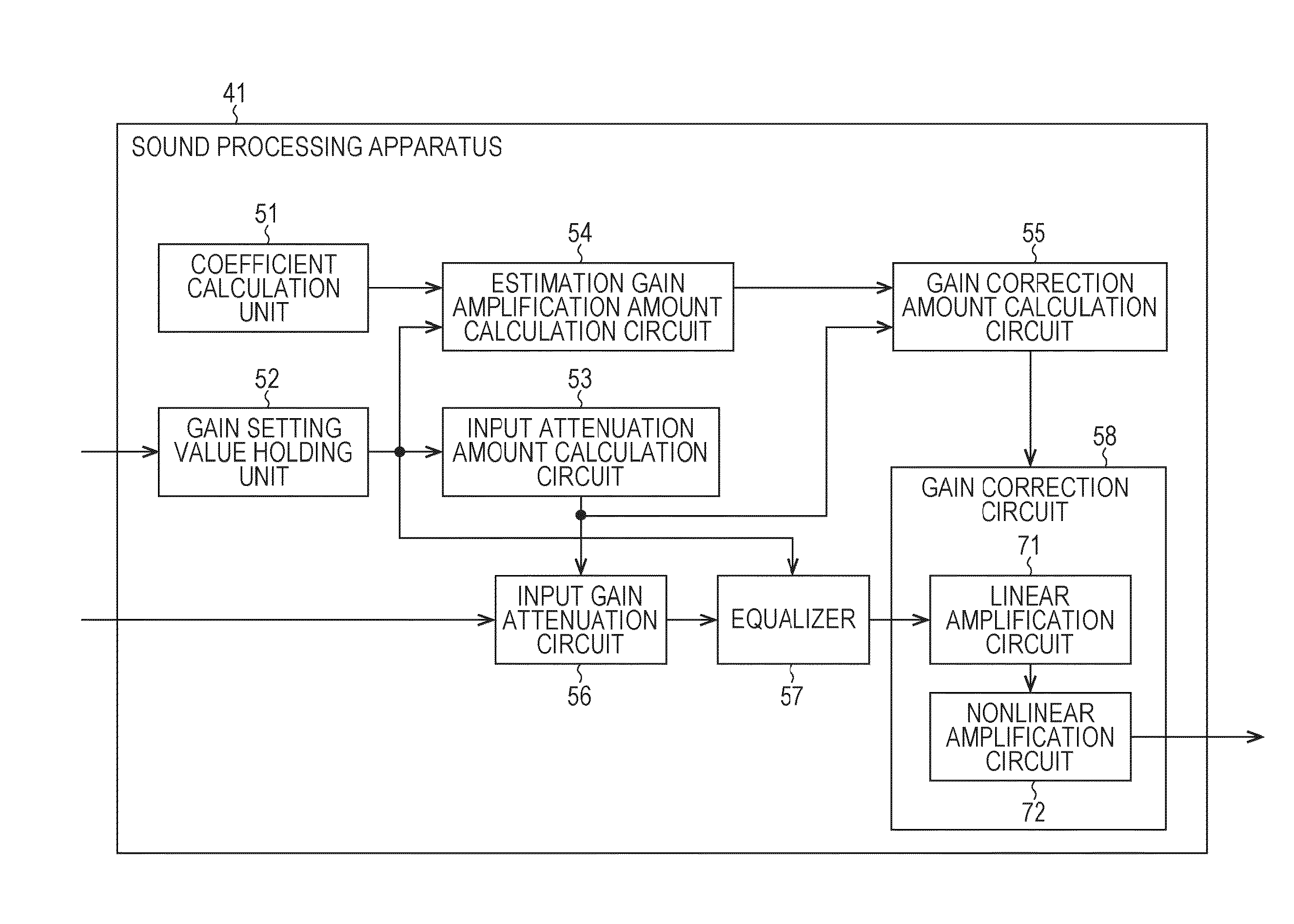
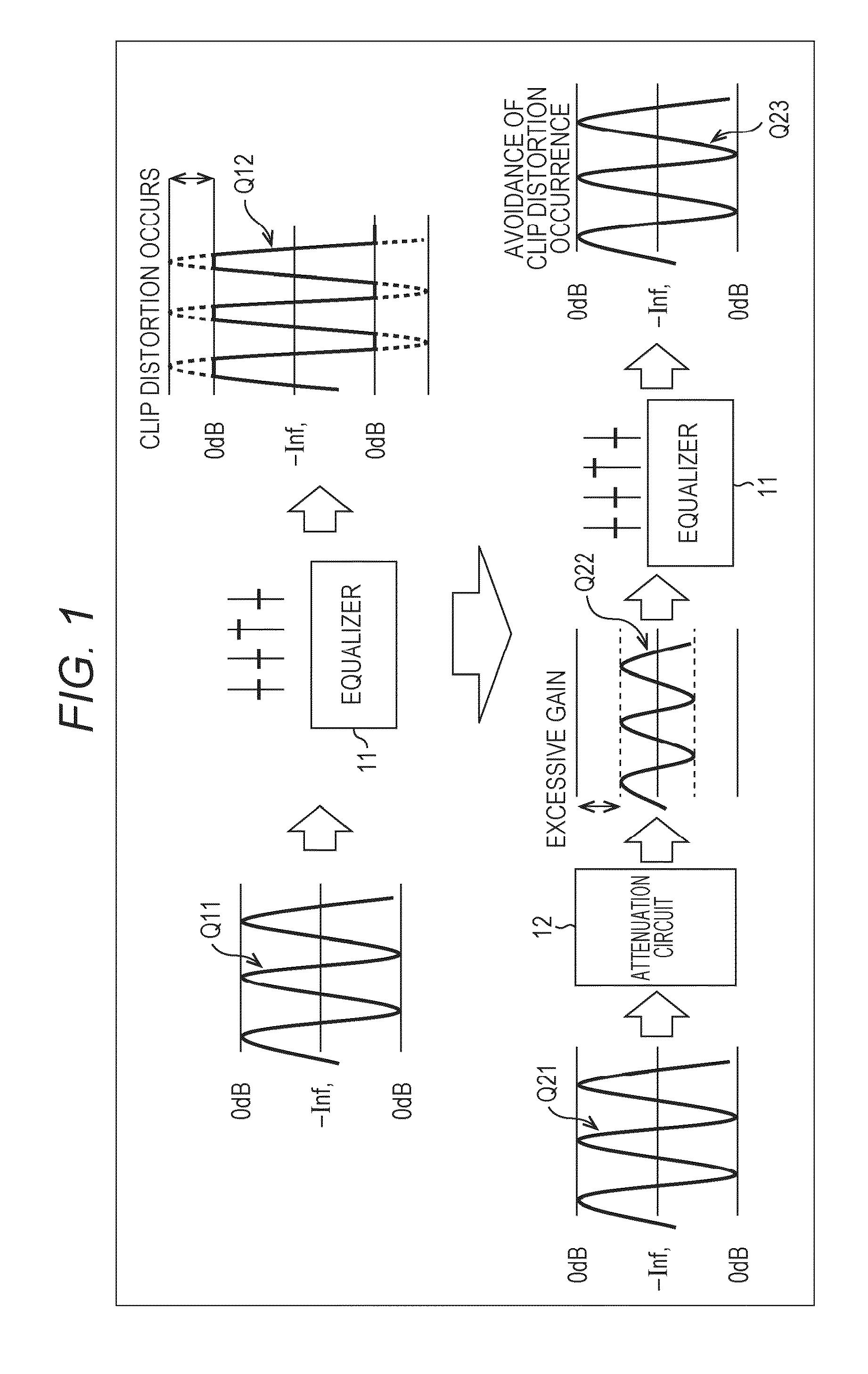
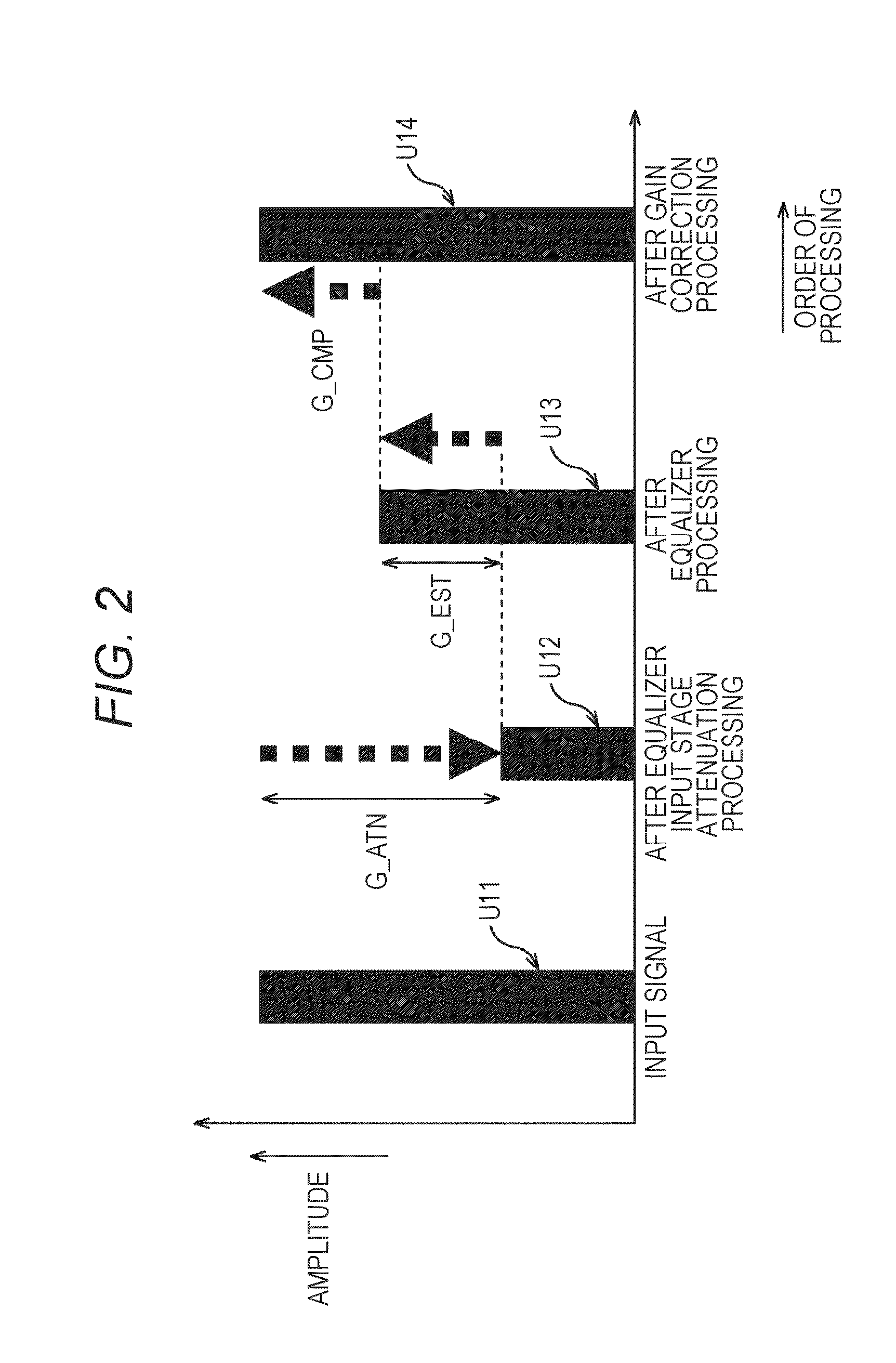
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS9294062B2Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationWeight coefficient
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
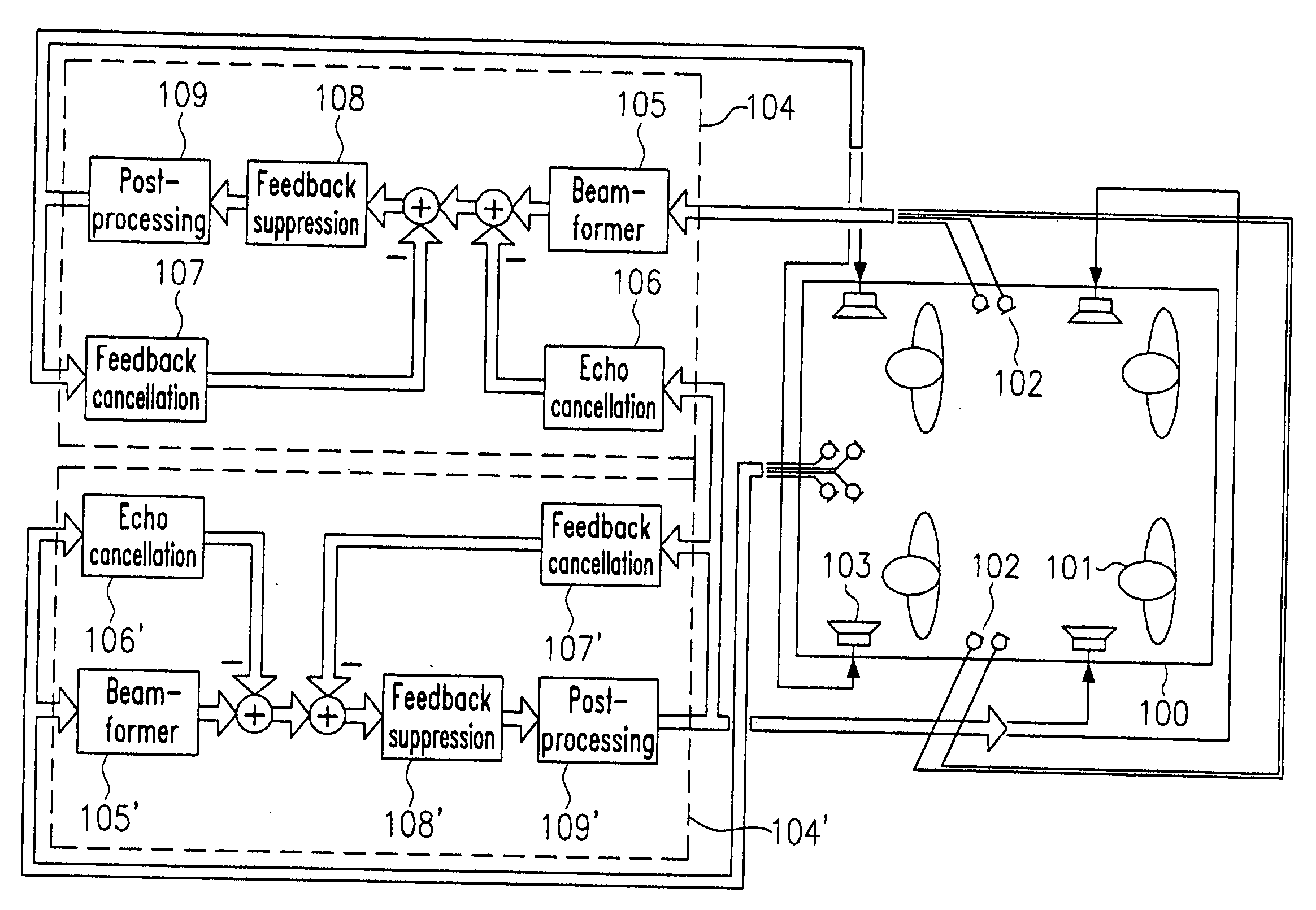
Indoor communication system for a vehicular cabin
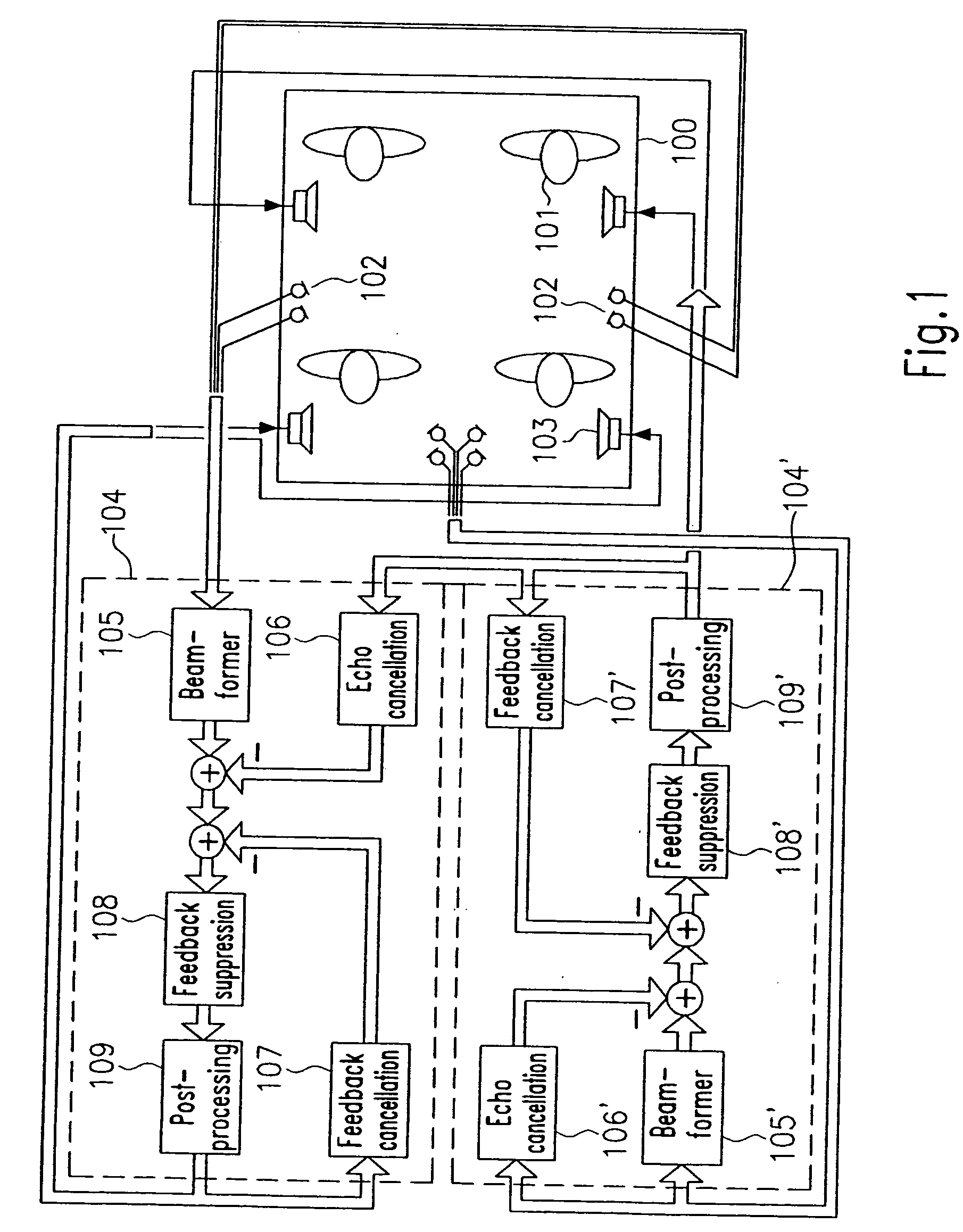
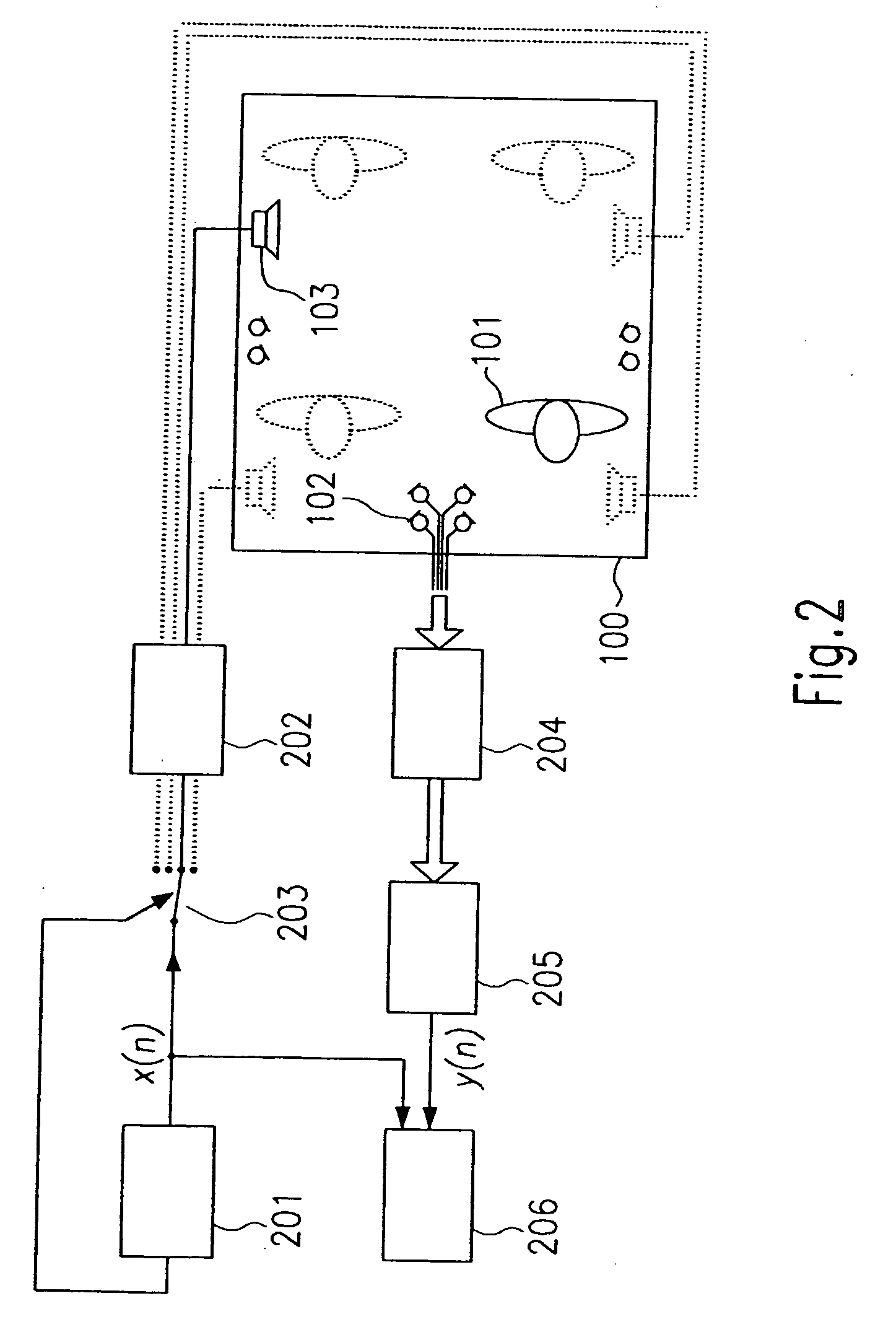
A system automatically determines an equalizing filter characteristic for a communication system within a vehicle. The communication system includes a loudspeaker and a microphone or microphone array. The system transmits a predetermined test signal through the loudspeaker and receive the test signal through the microphone or microphone array. Based on the predetermined test signal and the received test signal, a transfer function is developed. The equalizing filter characteristic is then developed from the transfer function.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
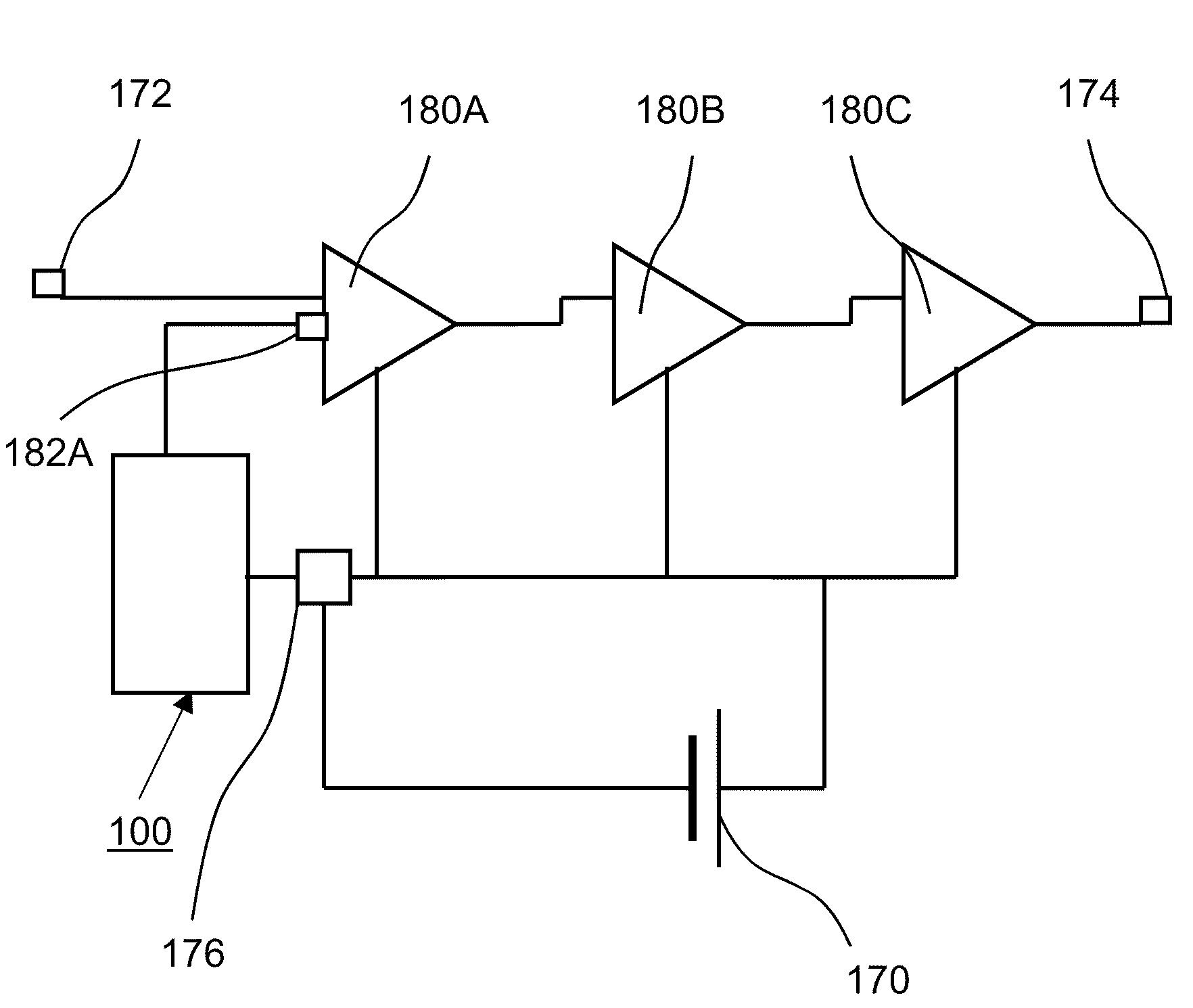
Power amplifier control using a switching power supply
ActiveUS7132891B1Reduce impactReducing spurious energy in outputAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlAmplifier detailsAudio power amplifierSwitching power
A system is provided for adjusting an output power of a multi-stage power amplifier by controlling a supply voltage provided to one or more output amplifier stages of the power amplifier using a switching DC—DC converter. In general, the system includes a power amplifier including an input amplifier stage and one or more output amplifier stages coupled in series with the input amplifier stage. The one or more output amplifier stages receive a variable supply voltage from switching DC—DC conversion circuitry. The switching DC—DC conversion circuitry provides the variable supply voltage based on an adjustable power control signal. By controlling the variable supply voltage provided to the one or more output stages, the switching DC—DC conversion circuitry controls an output power of the power amplifier based on the adjustable power control signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Gain Control for Linear Radio Freqency Power Amplifiers
ActiveUS20100007414A1Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationSupply voltage controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
A bias control circuit is provided comprising an input port for receiving a signal indicative of an amplitude of a supply voltage provided to a multi stage power amplifier circuit. Electronic circuitry, electrically coupled to the input port, generates a bias control signal in dependence upon the signal indicative of a supply voltage for provision to a first stage power amplifier of the multi stage power amplifier circuit. The bias control signal is generated such that a gain change of the multi stage power amplifier circuit due to a supply voltage change is substantially compensated.
Owner:SIGE SEMICON
Multi-mode power amplifier
A power amplifier includes an input network, output stages, coupled in parallel and configured to output power optimally in corresponding power-ranges, the output stages coupled to the input network, an output impedance matching network, coupled to the output stages and not containing a switching element, and a bias-control network, coupled between the output impedance matching network, the input network, and the output stages. In some amplifiers the output impedance matching network does not contain a switching element corresponding to the output stage configured to output power in the highest range. In other amplifiers the bias-control network is configured to isolate output stages by providing a hard shut-off to transistors of the isolated output stages.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
System and method for varying low audio frequencies inversely with audio signal level
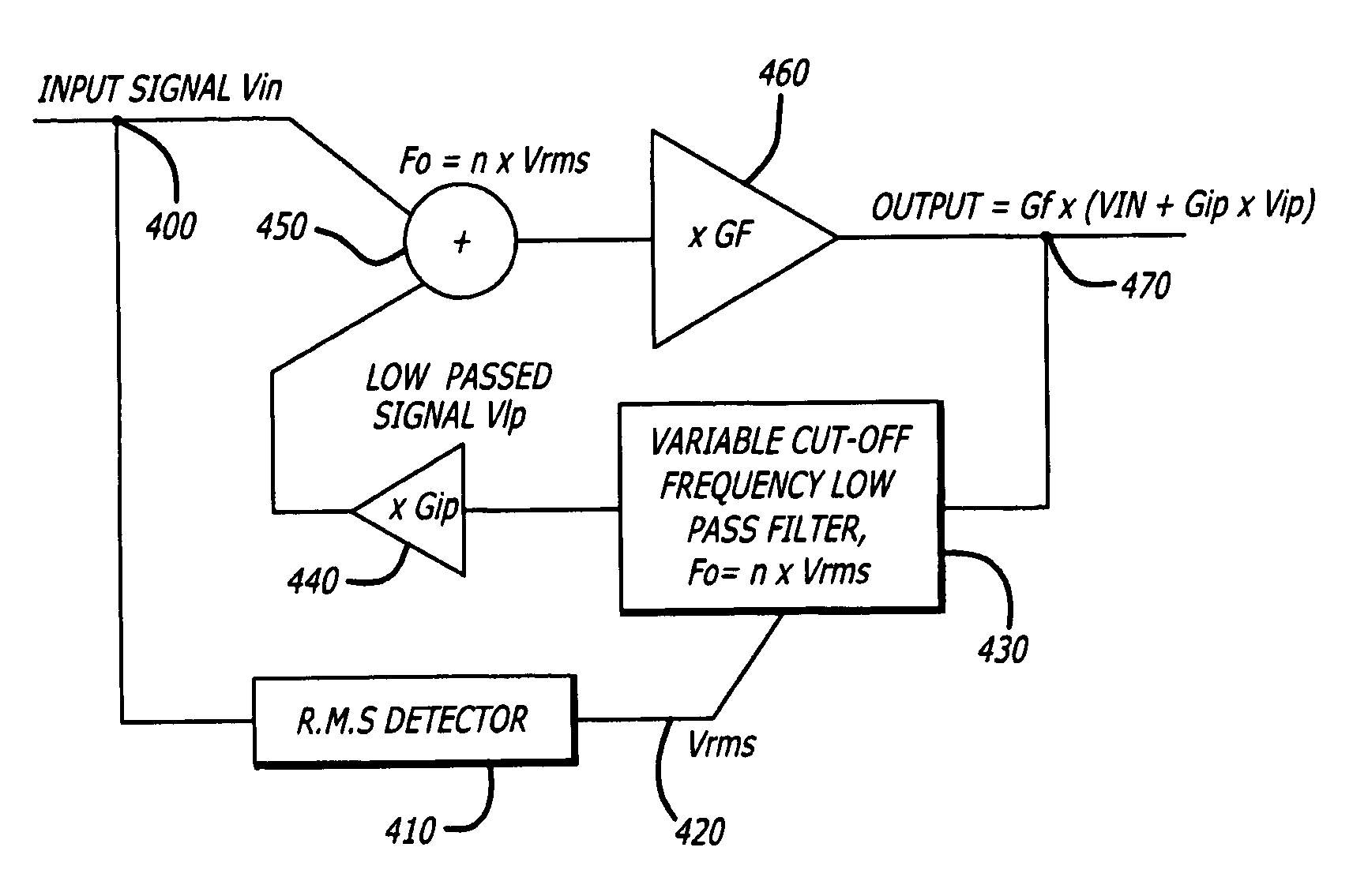
InactiveUS7016509B1Increase contentEasy to removeCombination control in untuned amplifierAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlCapacitanceResistance capacitance
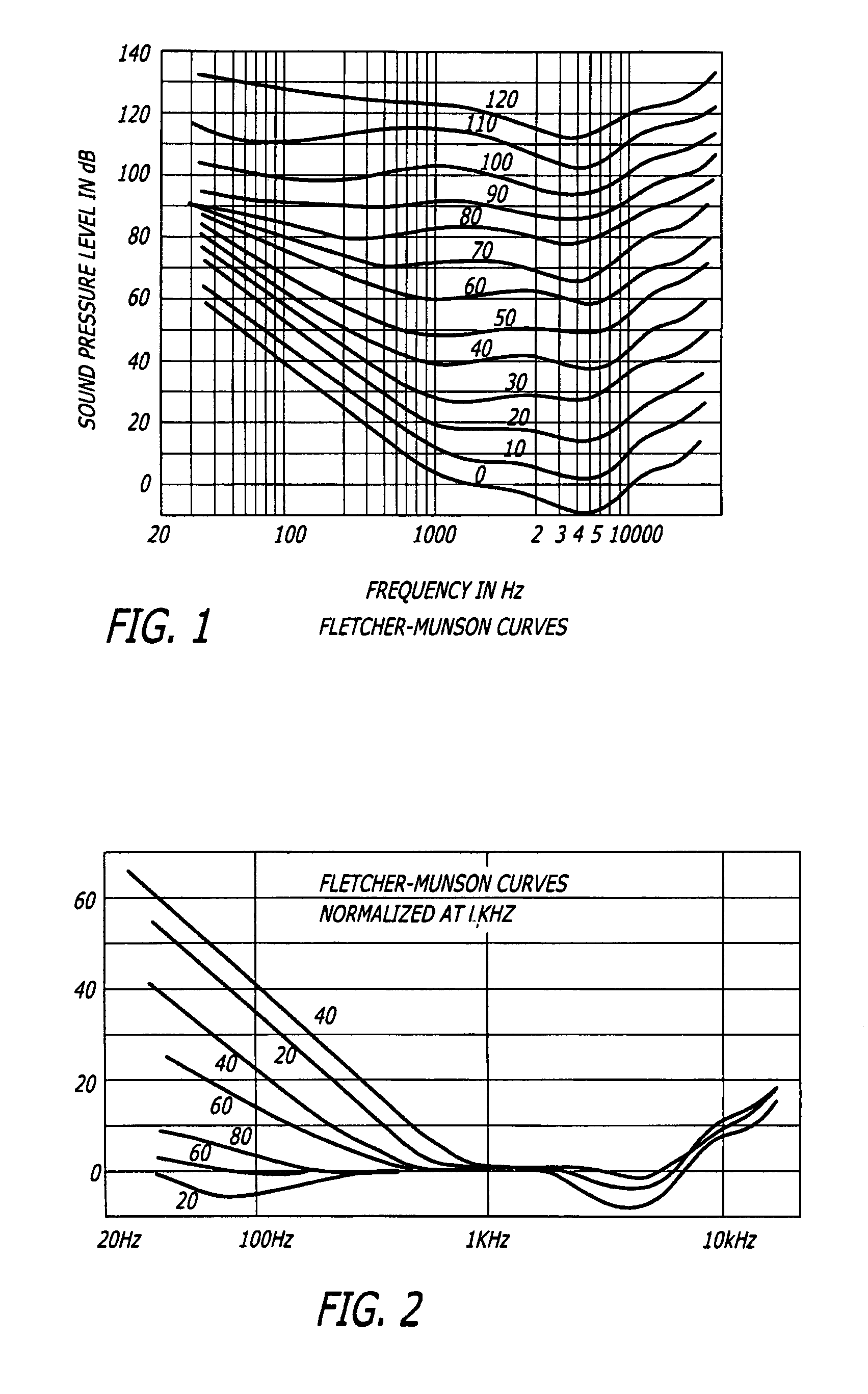
The present invention relates to an auto loudness circuit for performing loudness compensation automatically depending on the signal level. When the signal level decreases, loudness compensation is slowly introduced and as the signal level increases, loudness compensation is quickly removed. To do so, the auto loudness circuit utilizes a filter circuit with the characteristic of a first order bass boost. The filter circuit maintains a corner frequency which is proportional to the inverse of audio level in order to mimic the Fletcher-Munson curves. Because the circuit employs a capacitance-multiplier with a first order resistance capacitance filter, the bass boost is inversely proportional to the signal level. Thus, bass boost is achieved automatically as the program content changes so that the listener is unaware of significant changes in program material as signal levels change either through increase or decrease in volume, crescendo or new material.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Popular searches
Frequency response correction Digital signal tone/bandwidth control Stereophonic systems Record information storage Carrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronising Broadcast services for monitoring/identification/recognition Broadcast information monitoring Broadcast characteristics identification/recognition Transmission Sets with customised acoustic characteristics
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com