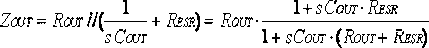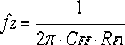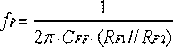Patents
Literature
328 results about "Input amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
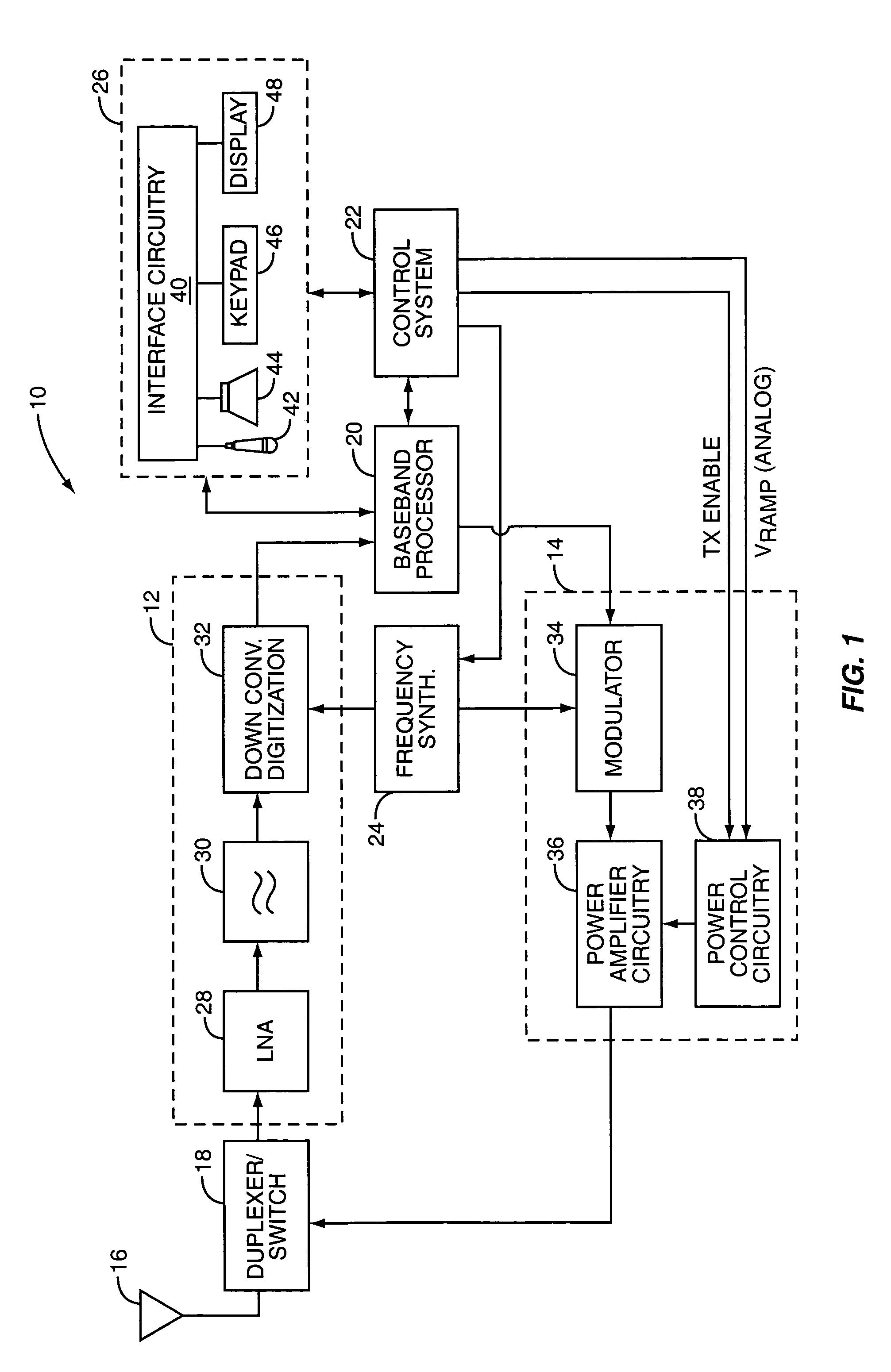
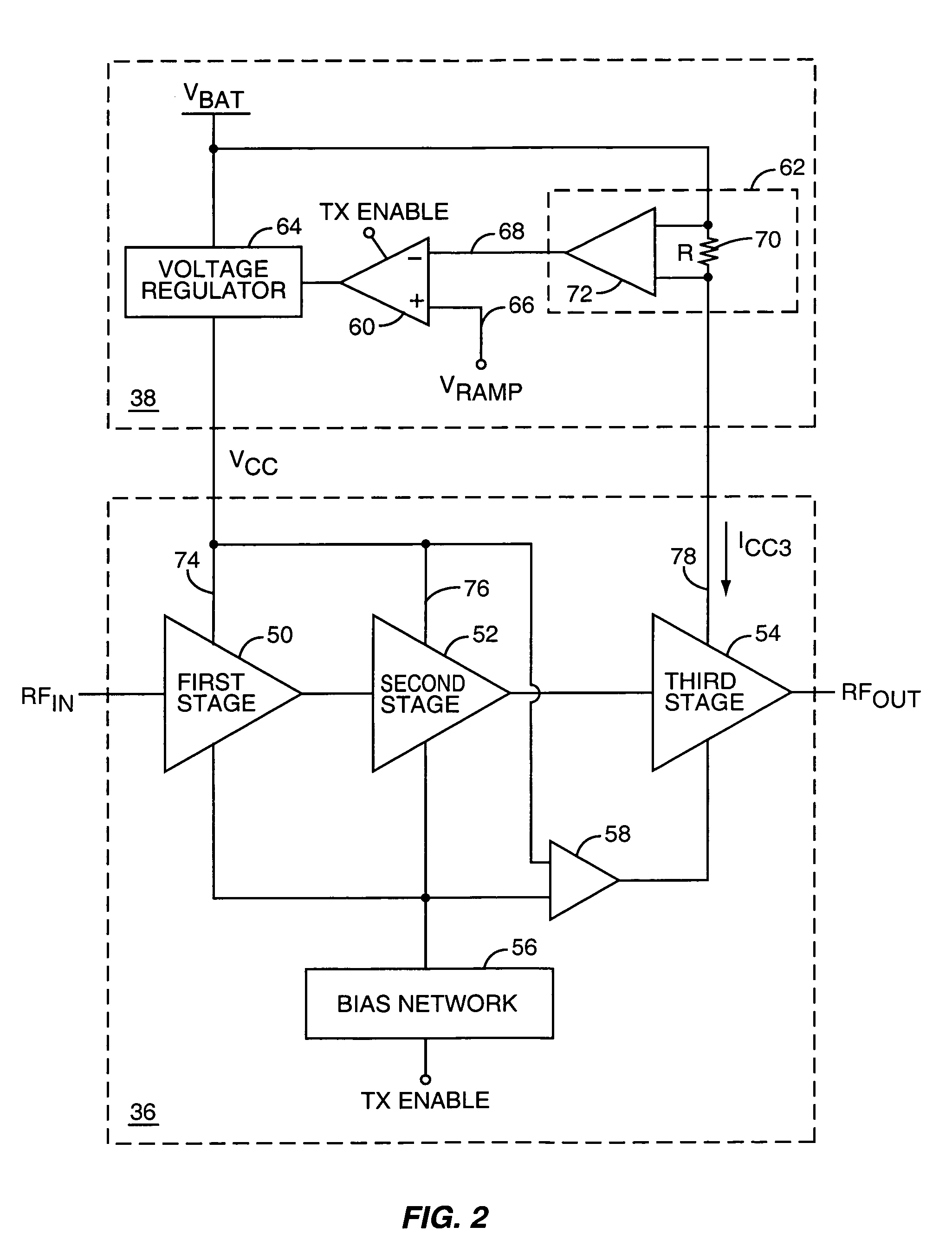
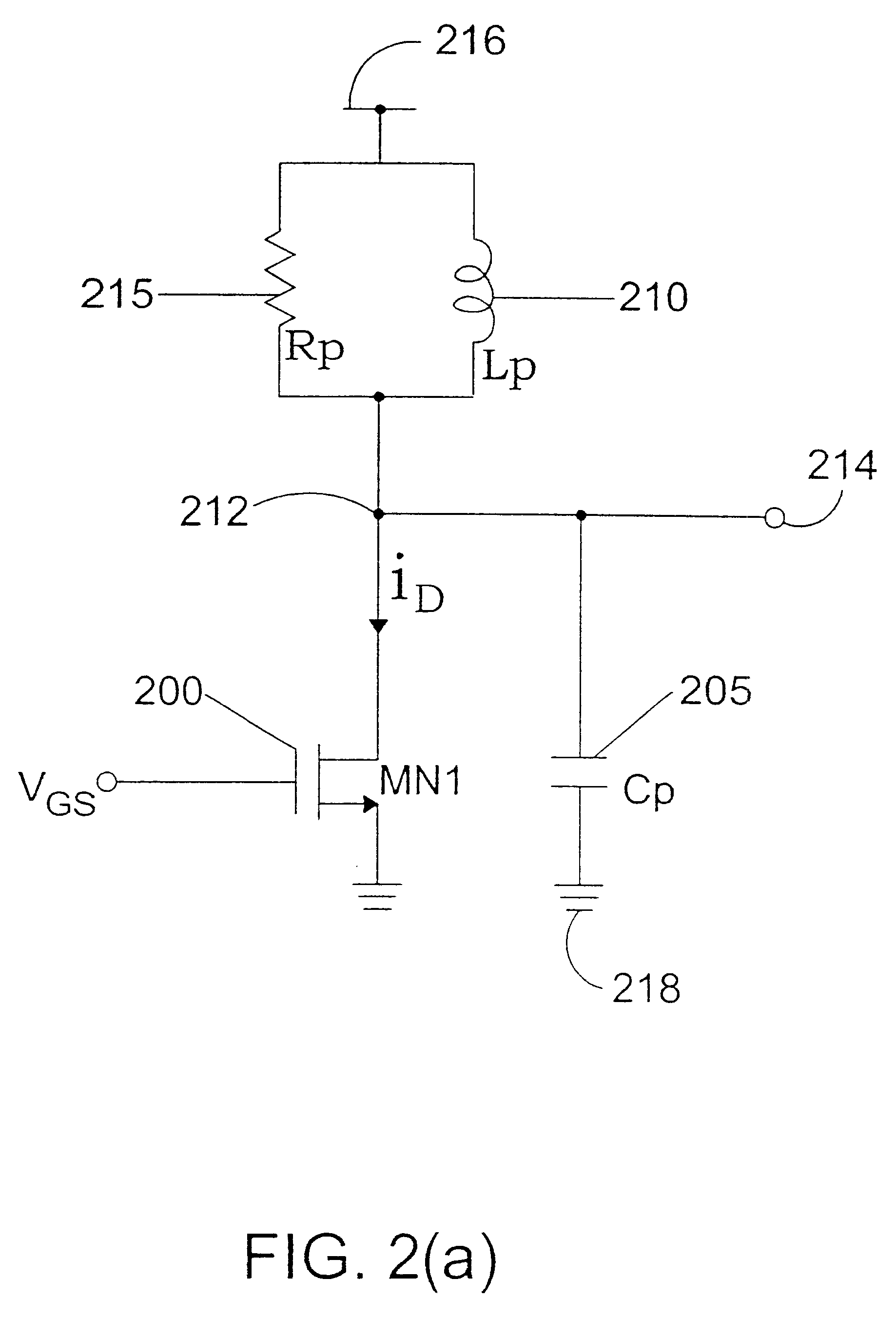
Tailored collector voltage to minimize variation in AM to PM distortion in a power amplifier
ActiveUS7109791B1Reduce variationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPulse automatic controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
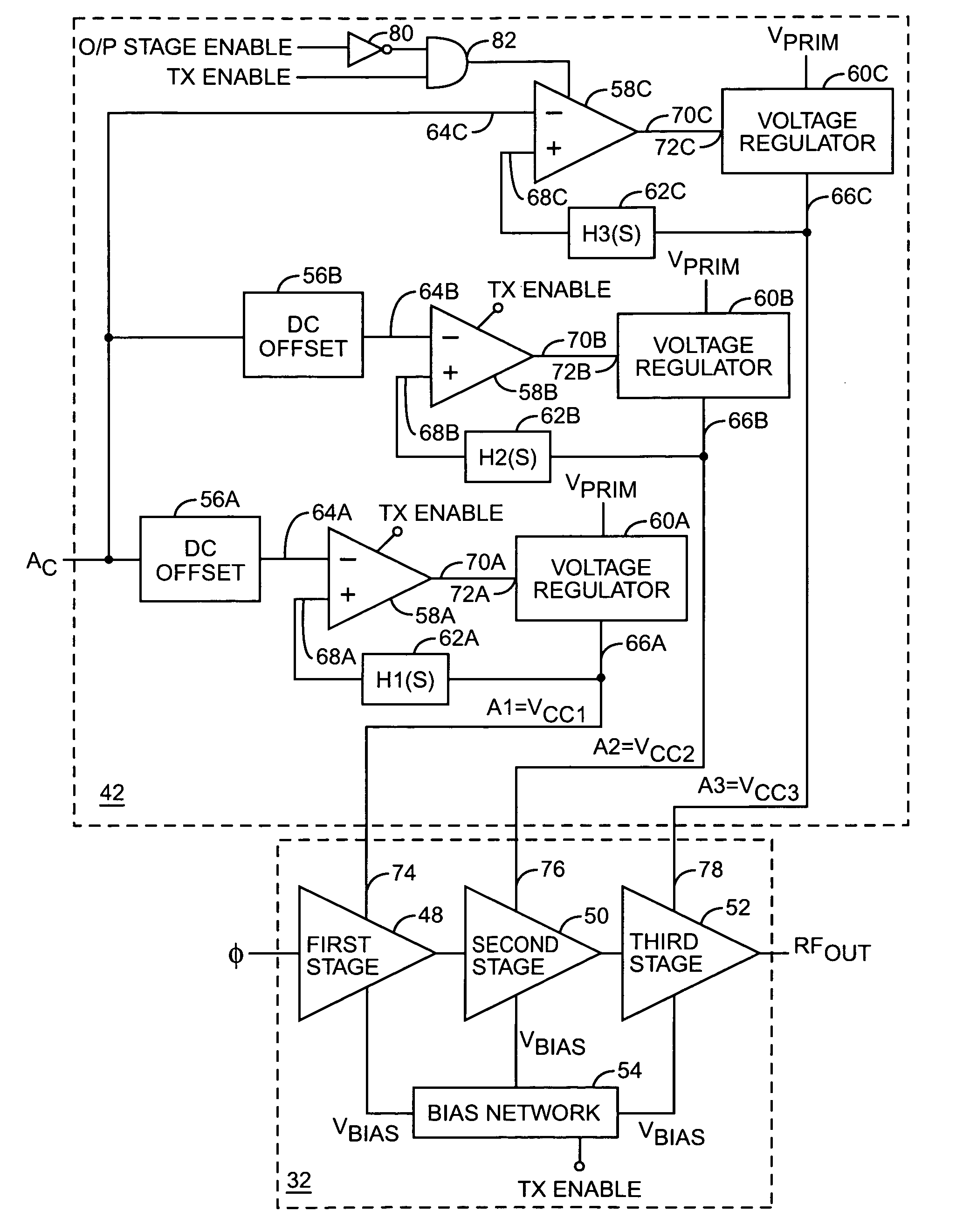
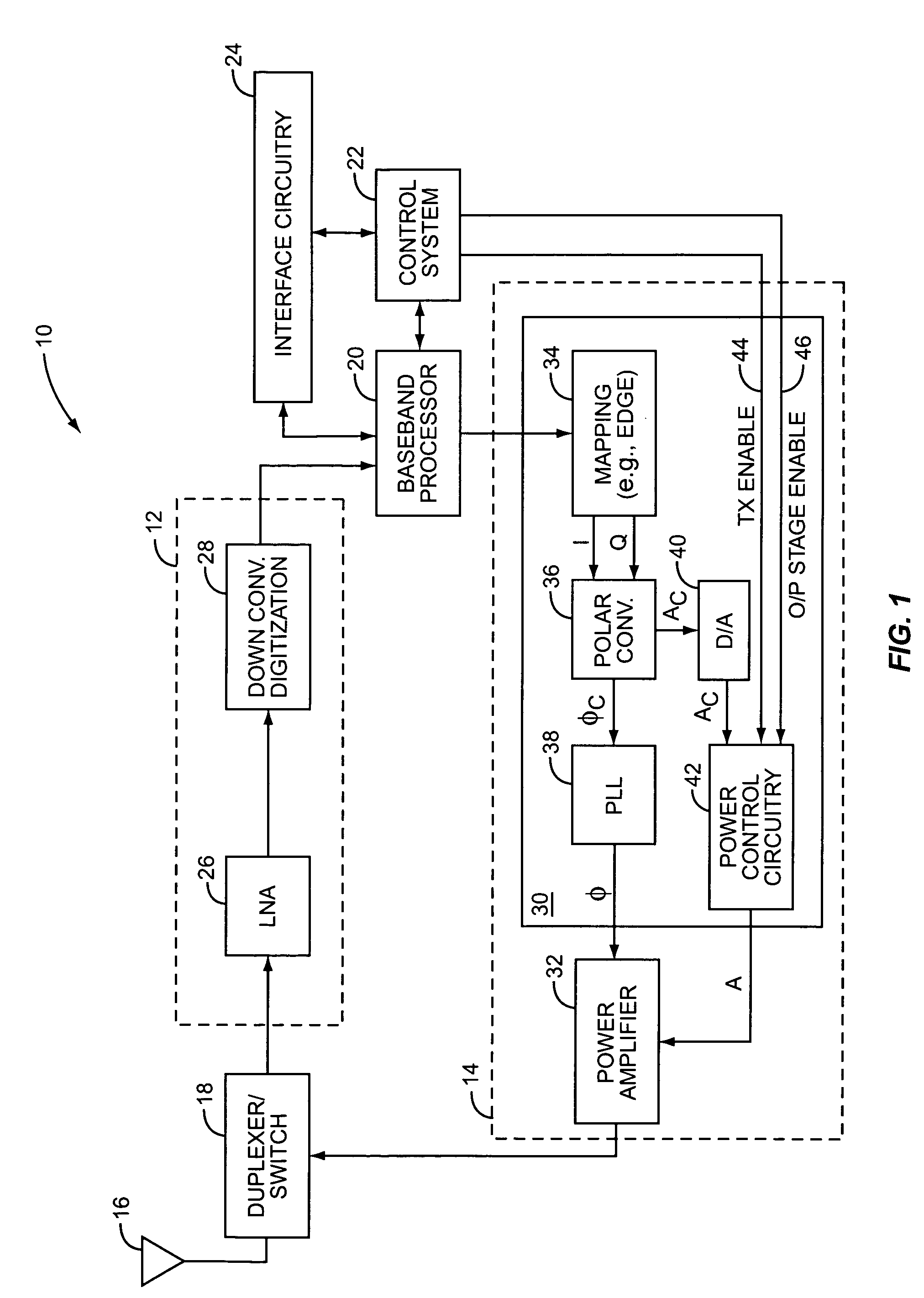
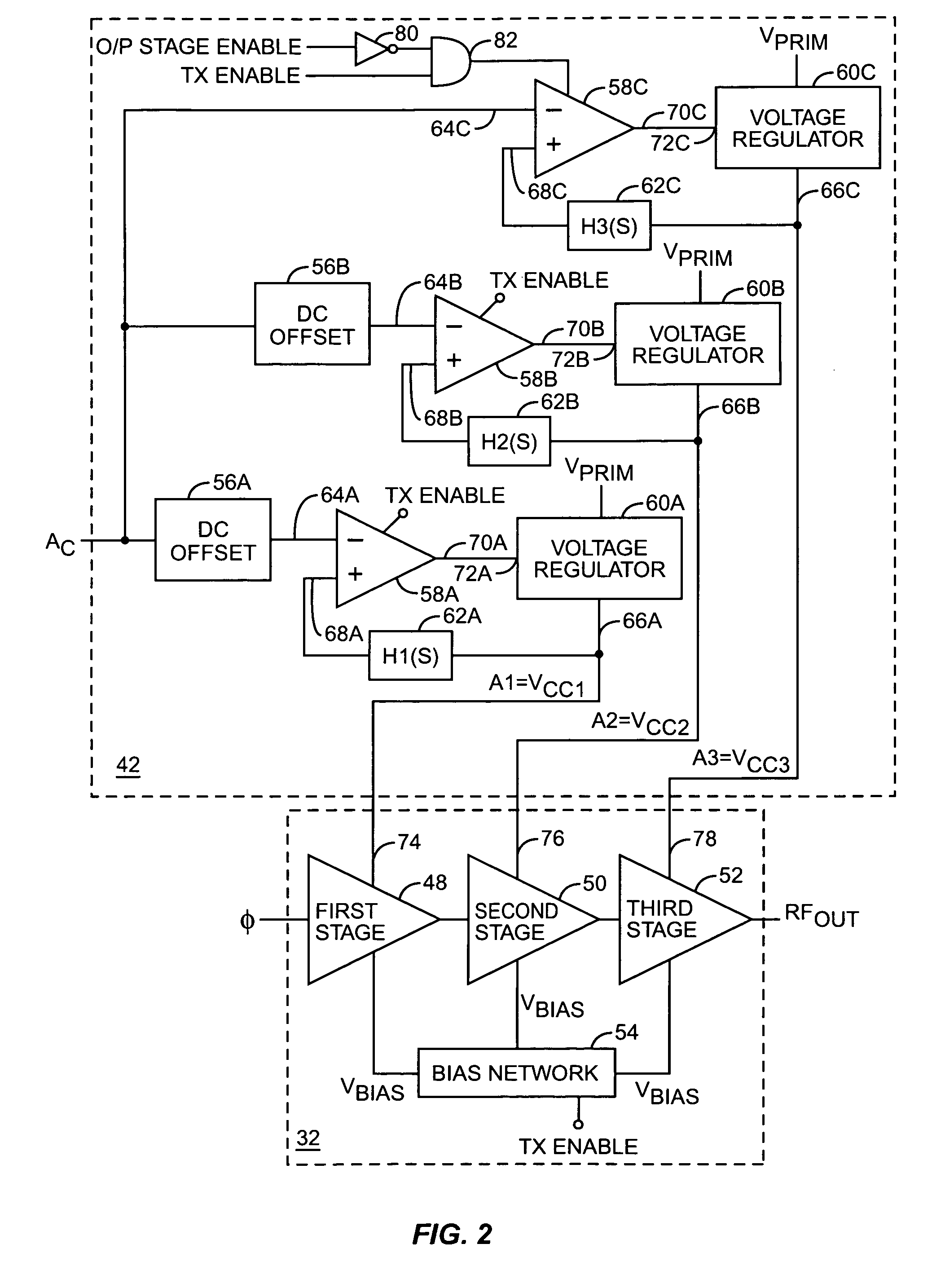
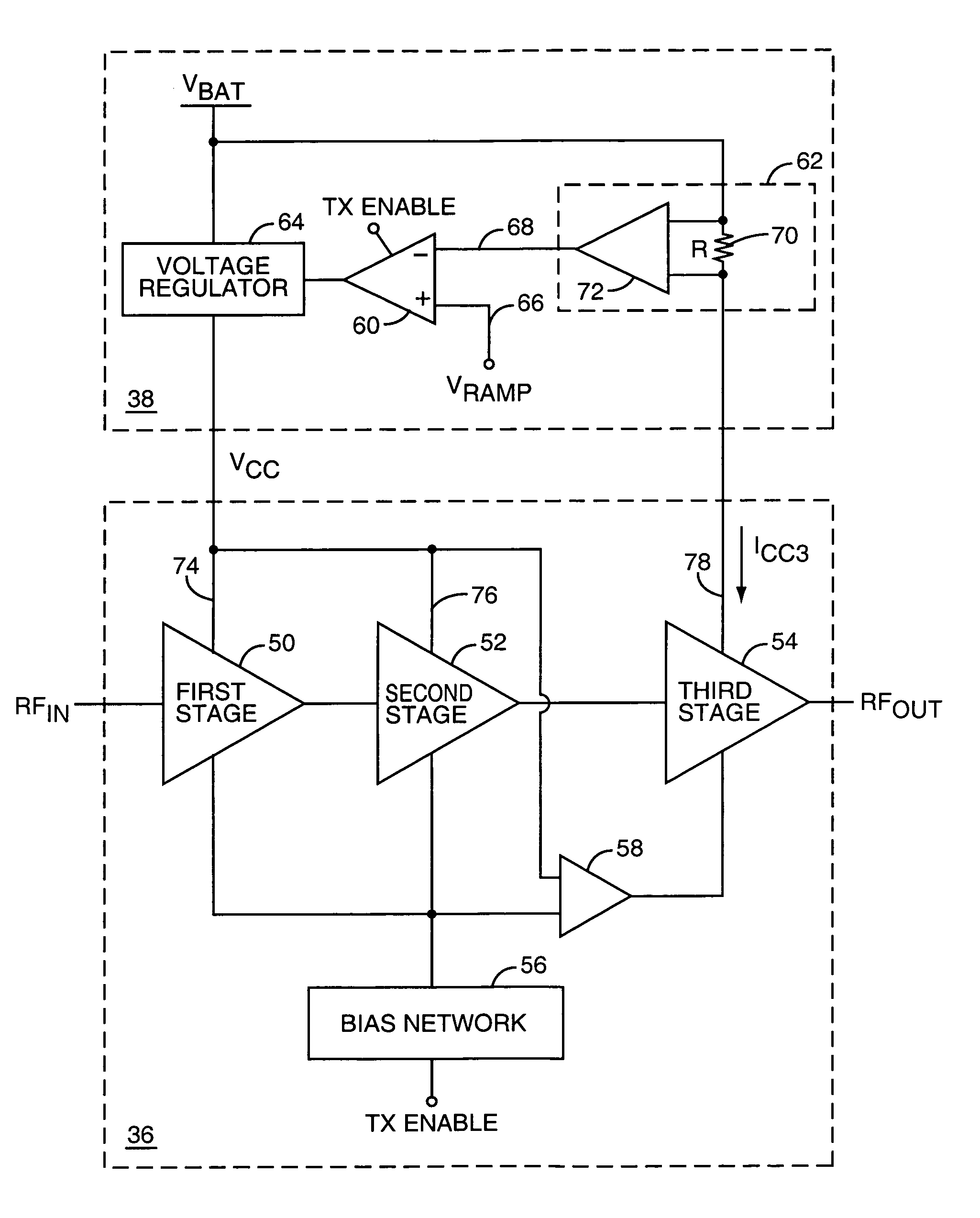
A system is provided for substantially reducing variation in AM to PM distortion of a power amplifier caused by variations in RF drive power and temperature. The system includes power control circuitry and power amplifier circuitry. The power amplifier circuitry includes an input amplifier stage and at least one additional amplifier stage coupled in series with the input amplifier stage. The power control circuitry provides a first supply voltage to the input amplifier stage based on a control signal such that the first supply voltage has a predetermined DC offset with respect to the control signal. The first supply voltage is provided such that the predetermined DC offset substantially reduces variations in the AM to PM distortion of the power amplifier due to variations in radio frequency (RF) drive power.
Owner:QORVO US INC
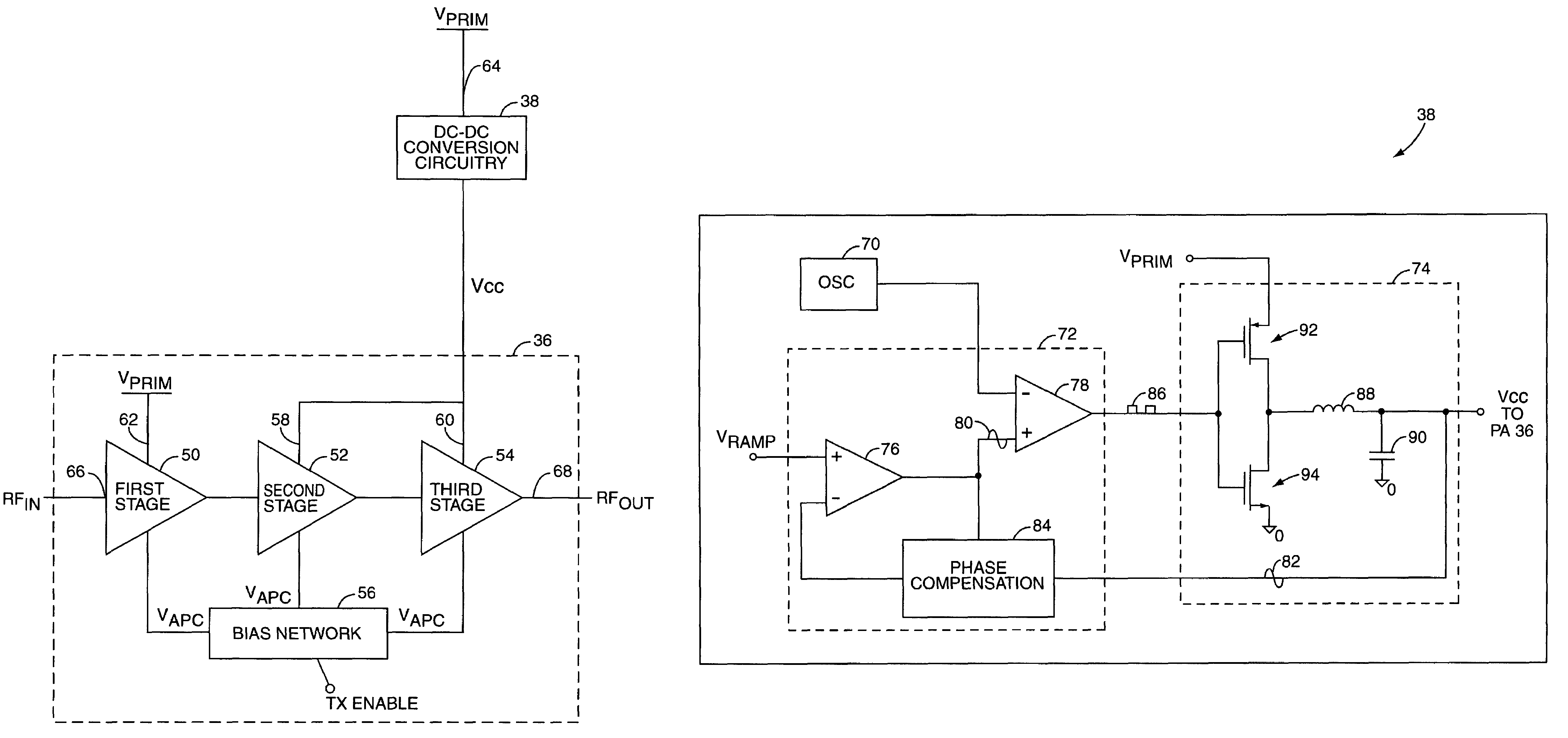
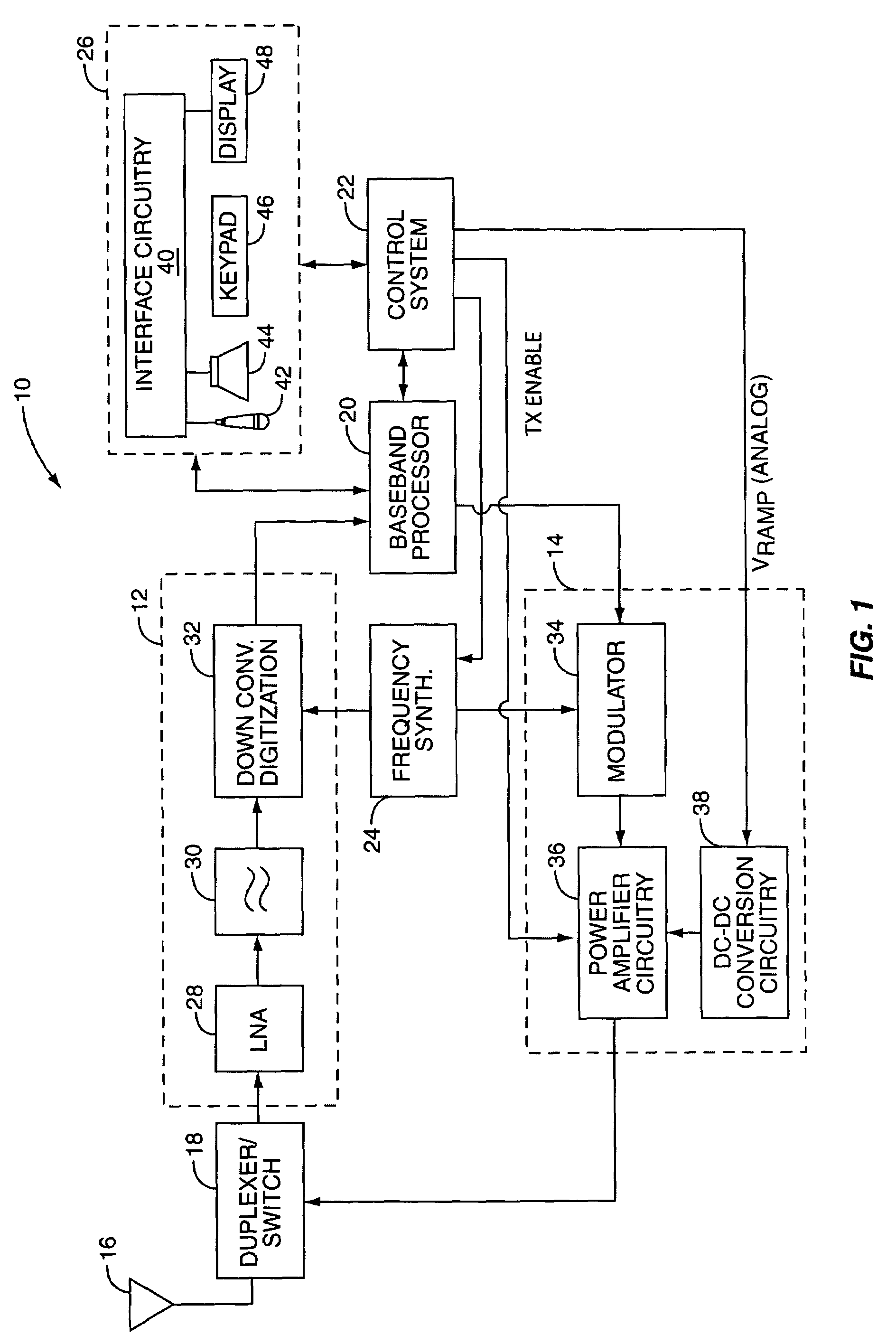
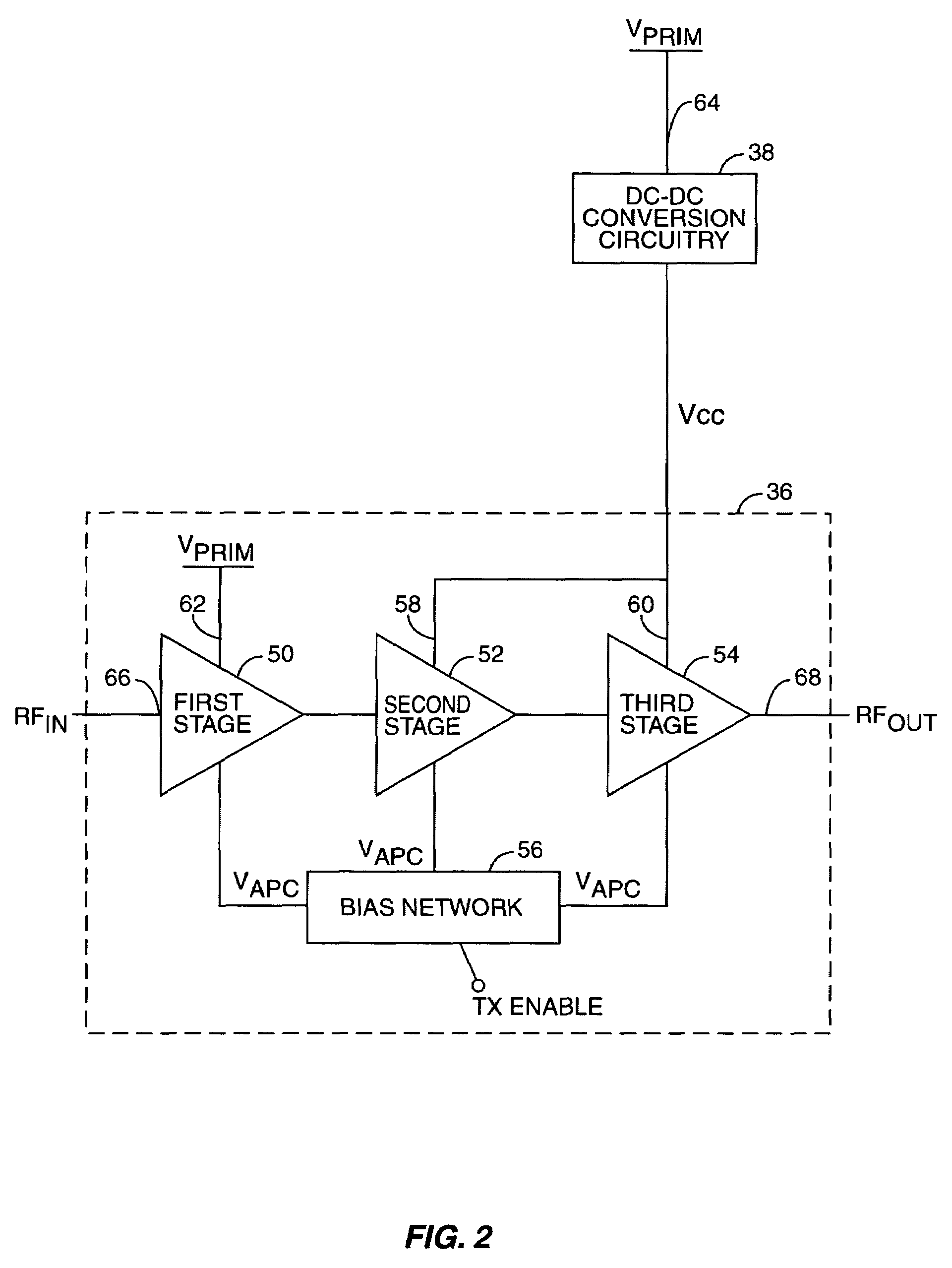
Power amplifier control technique for enhanced efficiency
ActiveUS7193459B1High gainImprove PAEPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersPower-added efficiencyAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier configuration including power amplifier circuitry and power control circuitry and having improved Power Added Efficiency (PAE) is provided. The power amplifier circuitry includes one or more input amplifier stages in series with a final amplifier stage. The power control circuitry provides a variable supply voltage to the input amplifier stages based on an adjustable power control signal. The final amplifier stage is powered by a fixed supply voltage. In operation, as output power of the power amplifier is reduced from its highest power level, the variable supply voltage is reduced. Accordingly, RF power of an amplified signal provided to the final amplifier stage from the input amplifier stages decreases, and the final amplifier stage transitions from saturation to linear operation, thereby increasing the gain of the final amplifier stage. Thus, a desired output level can be maintained while operating at lower current levels.
Owner:QORVO US INC
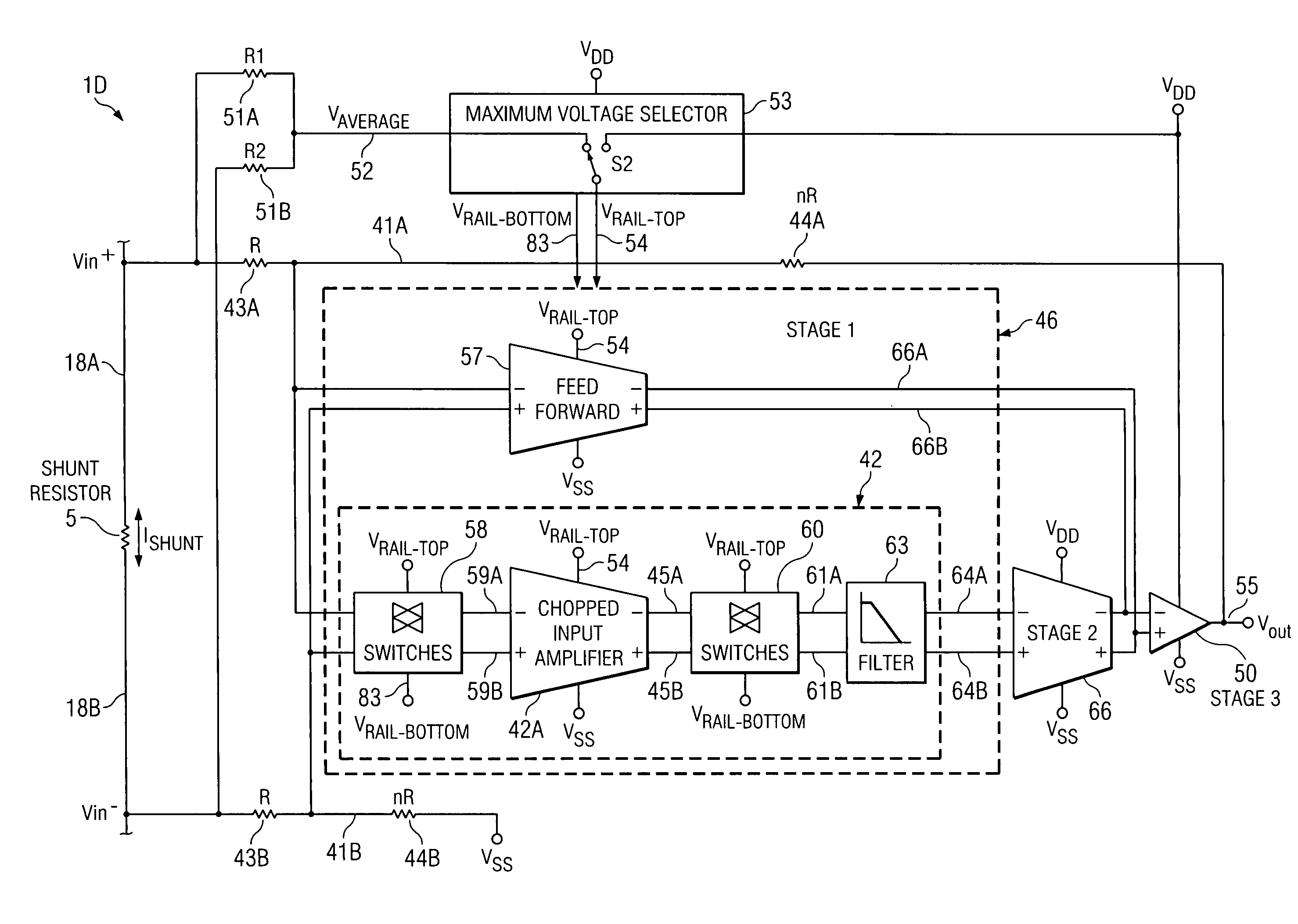
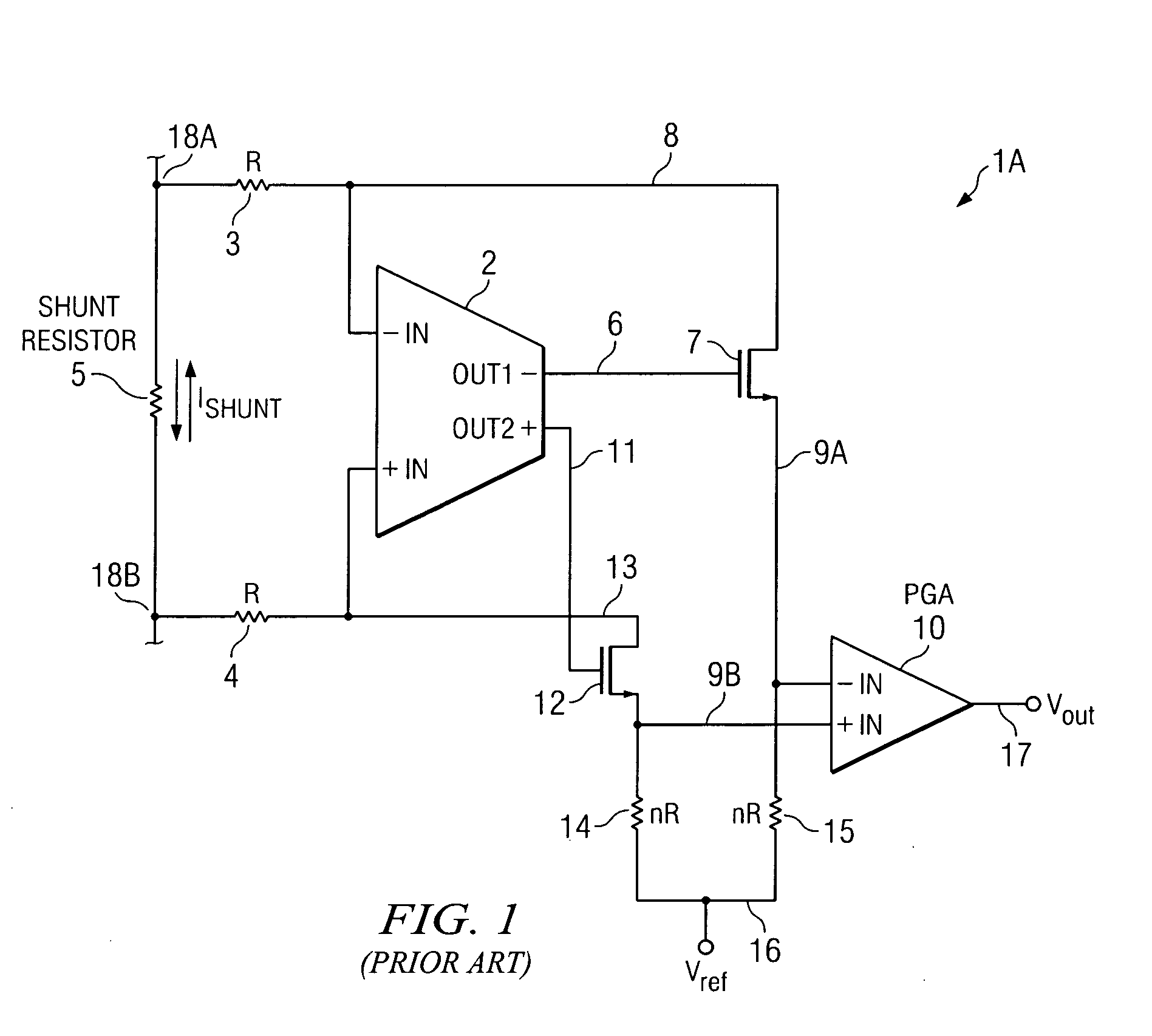
High-voltage differential amplifier and method using low voltage amplifier and dynamic voltage selection
ActiveUS20090174479A1Improve accuracyHigh precision measurementAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierLow voltage
A differential amplifier (1D) includes circuitry (5,R1,R2,52) coupling a common mode component of an input voltage (Vin+−Vin−) to a maximum voltage selector circuit (53) that produces an internal voltage (VRAIL-TOP) equal to the larger of a first supply voltage (VREG) and the common mode component. An input amplifier circuit (46) of the differential amplifier is powered by the internal voltage. The input voltage (Vin+−Vin−) is coupled to inputs (41A,B) of the input amplifier circuit (46). Outputs (64A,B) of the input amplifier circuit (46) are amplified by an output amplifier (50).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High-frequency device
ActiveUS6998710B2Small sizeImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierSemiconductor
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Variable gain current input amplifier and method
ActiveUS20090322429A1High bandwidthHigh currentDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesElectrical conductorVoltage reference
Variable gain circuitry includes a first input transistor (M1) having a source coupled to a first conductor (32), a gate coupled to a first input voltage (Vin+), and a drain coupled to a second conductor (30). An input of a first current mirror (M3,M4) is coupled to the second conductor to receive a current corresponding to the difference between the first input voltage and a second input voltage (Vin−). An output of the first current mirror is coupled to a source of current (M2). A first transistor (M5) has a gate coupled to a third conductor (31), a source coupled to a reference voltage (VSS), and a drain coupled to conduct output current (Iout). A second transistor (M6) and a resistive element (M7) are coupled in series between the third conductor and the first reference voltage (VSS), a gate of the second transistor being coupled to the third conductor to produce a nonlinear relationship between currents of the first transistor and the second transistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
RF Switch with Integrated Tuning
ActiveUS20150249479A1Reduce complexityTransmitters monitoringEcho effect reductionTransceiverRF front end
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Variable gain low-noise amplifier for a wireless terminal
InactiveUS6657498B2Reduces and avoids clippingNot to wasteGain controlGated amplifiersTuned amplifierEngineering
A variable gain, low noise amplifier is described, which is suitable as the input amplifier for a wireless terminal, or as the pre-amplifier stage of a wireless terminal transmitter. The amplifier may achieve variable gain by deploying a network of transistors in a parallel array, each independently selectable by a PMOS switch, and providing the variable resistance for the resonant circuit. Power dissipation can also be mitigated by using a network of driving transistors, each independently selectable by a PMOS switch. The resonant frequency of the amplifier may be made tunable by providing a selection of optional pull-up capacitors.
Owner:GCT SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Power amplifier control using a switching power supply
ActiveUS7132891B1Reduce impactReducing spurious energy in outputAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlAmplifier detailsAudio power amplifierSwitching power
A system is provided for adjusting an output power of a multi-stage power amplifier by controlling a supply voltage provided to one or more output amplifier stages of the power amplifier using a switching DC—DC converter. In general, the system includes a power amplifier including an input amplifier stage and one or more output amplifier stages coupled in series with the input amplifier stage. The one or more output amplifier stages receive a variable supply voltage from switching DC—DC conversion circuitry. The switching DC—DC conversion circuitry provides the variable supply voltage based on an adjustable power control signal. By controlling the variable supply voltage provided to the one or more output stages, the switching DC—DC conversion circuitry controls an output power of the power amplifier based on the adjustable power control signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Chopper chopper-stabilized instrumentation and operational amplifiers
ActiveUS7132883B2Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierInstrumentation amplifier
Chopper chopper-stabilized instrumentation and operational amplifiers having ultra low offset. The instrumentation amplifiers use current-feedback, and include, in addition to a main chopper amplifier chain, a chopper stabilized loop for correcting for the offset of the input amplifiers for the input signal and for receiving the feedback of the output voltage sense signal. Additional loops, which may include offset compensation and autozeroing loops, may be added to compensate for offsets in the chopper stabilized loop for correcting for the offset of the input amplifiers. Similar compensation is disclosed for decreasing the offset in operational amplifiers.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
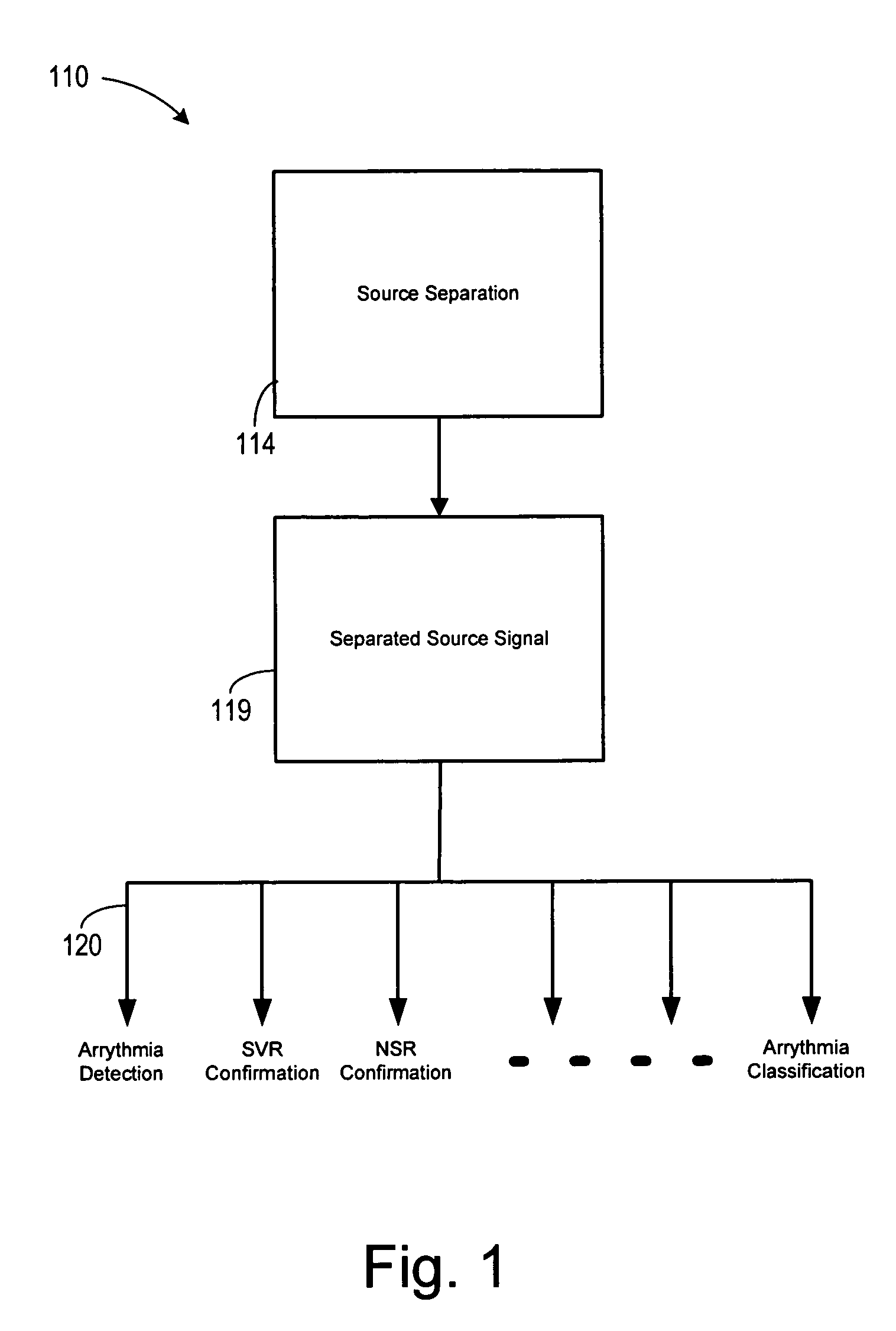
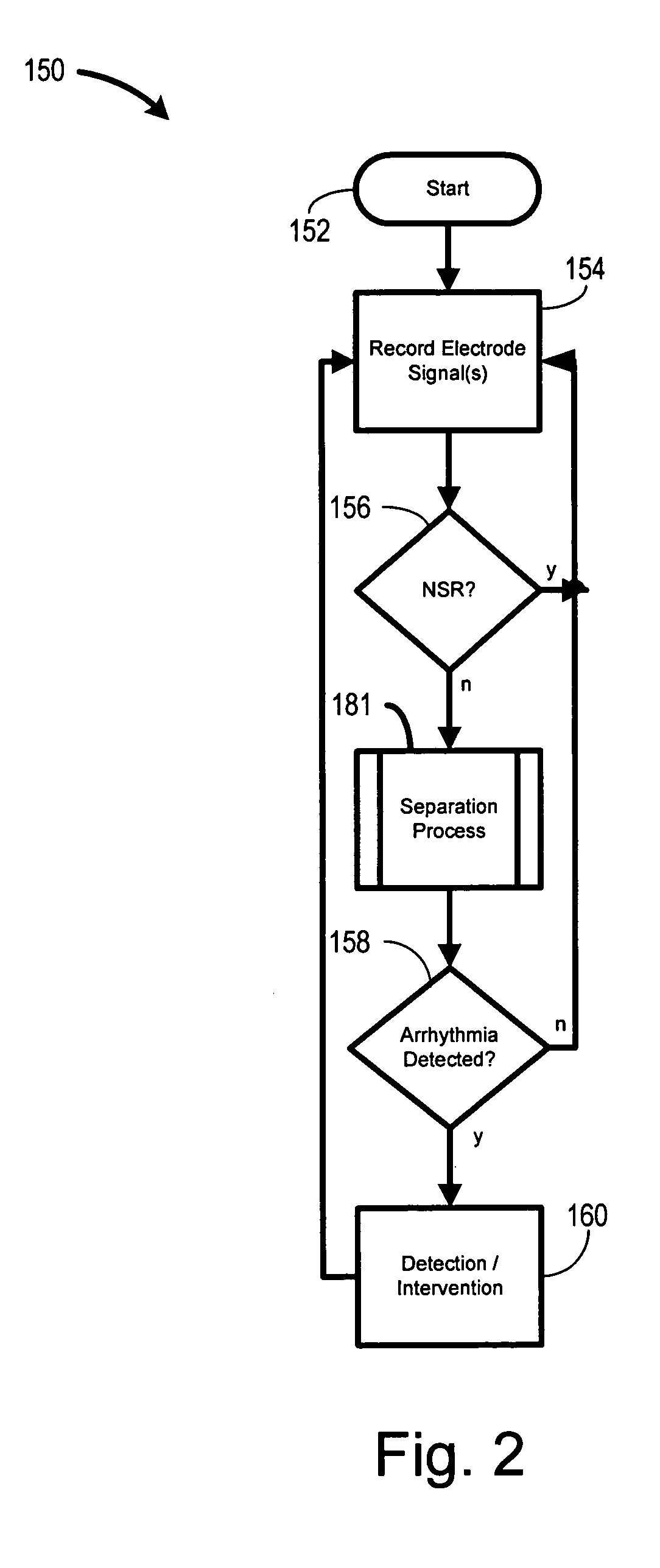
Biopotential signal source separation using source impedances
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
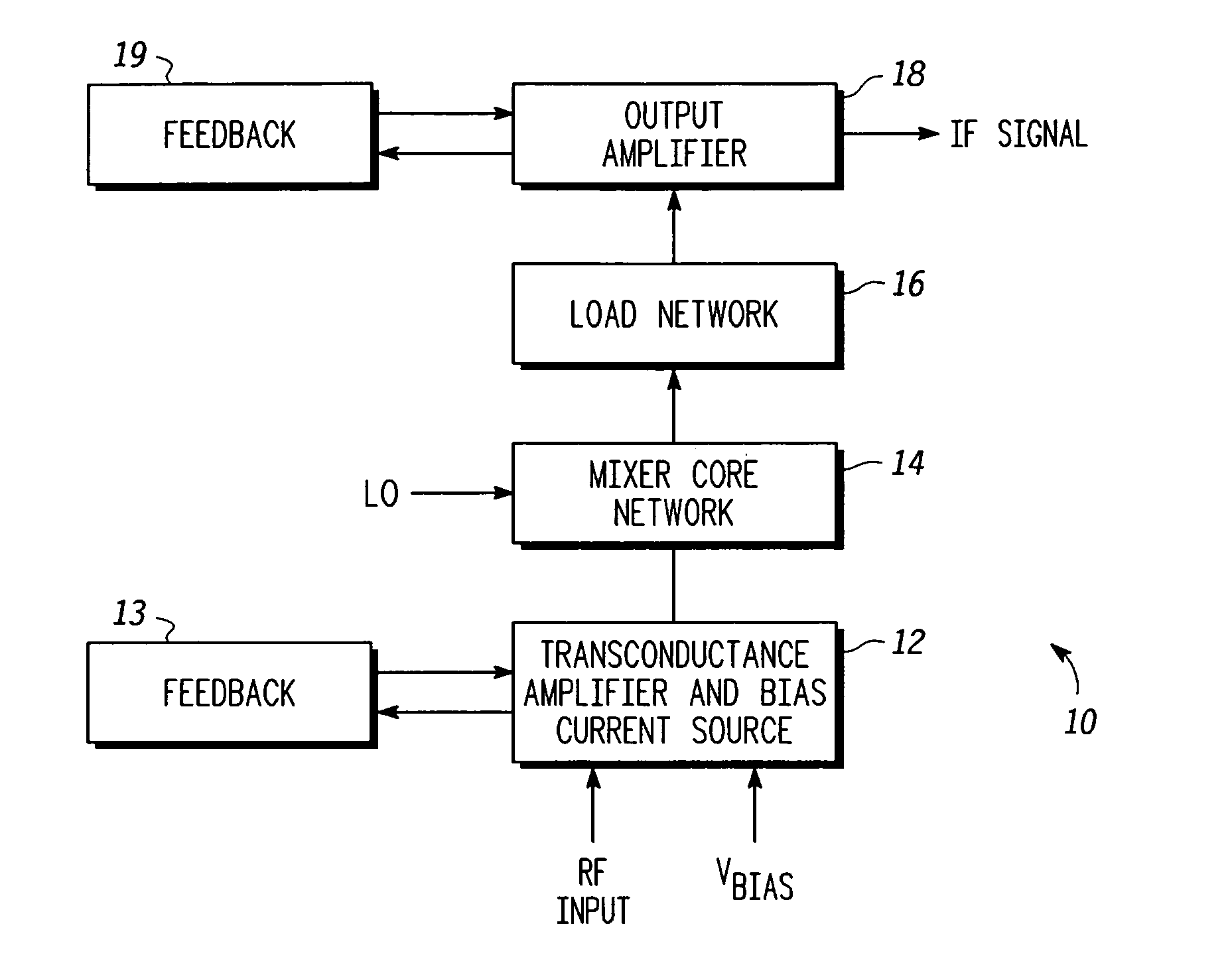
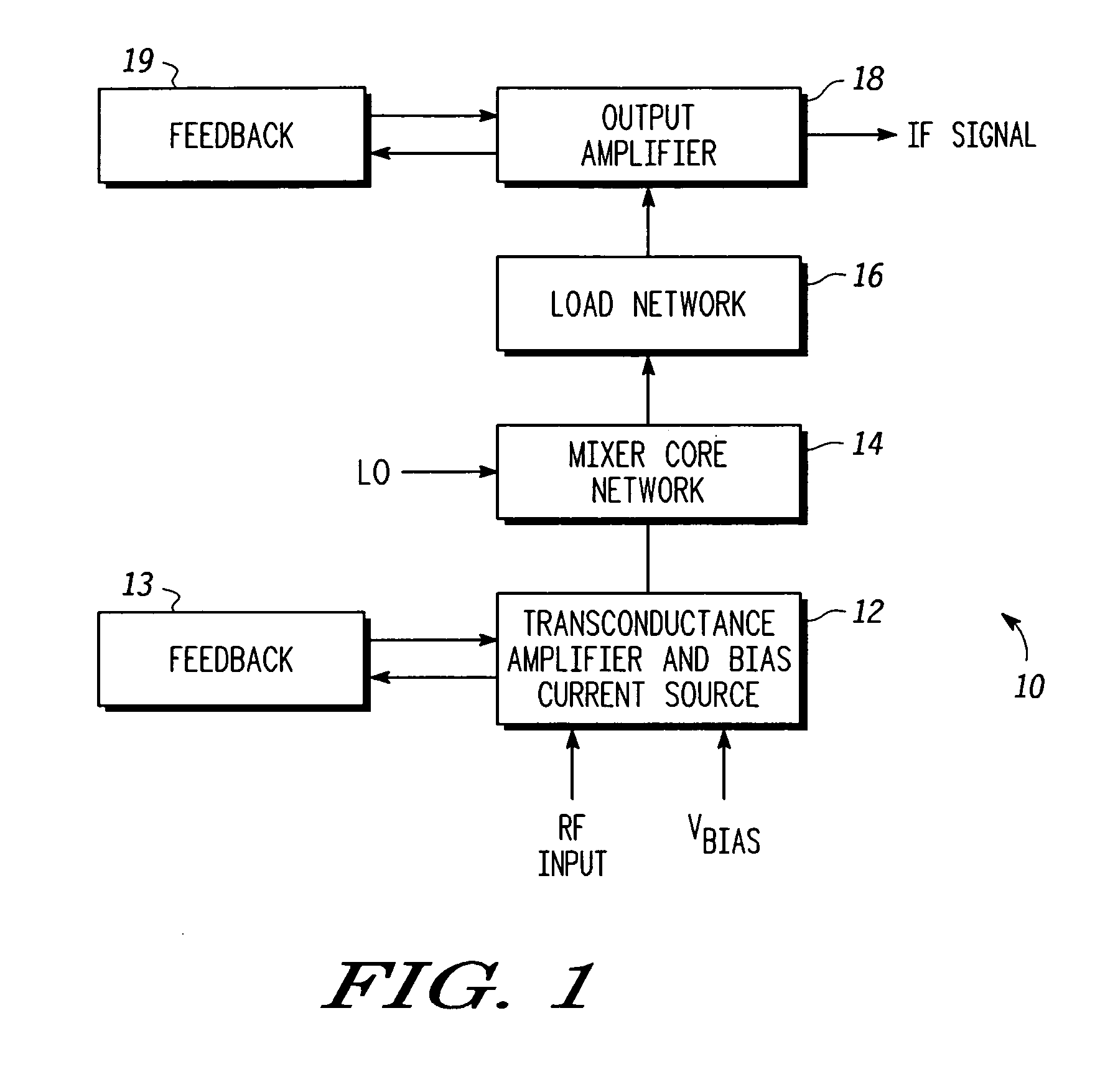
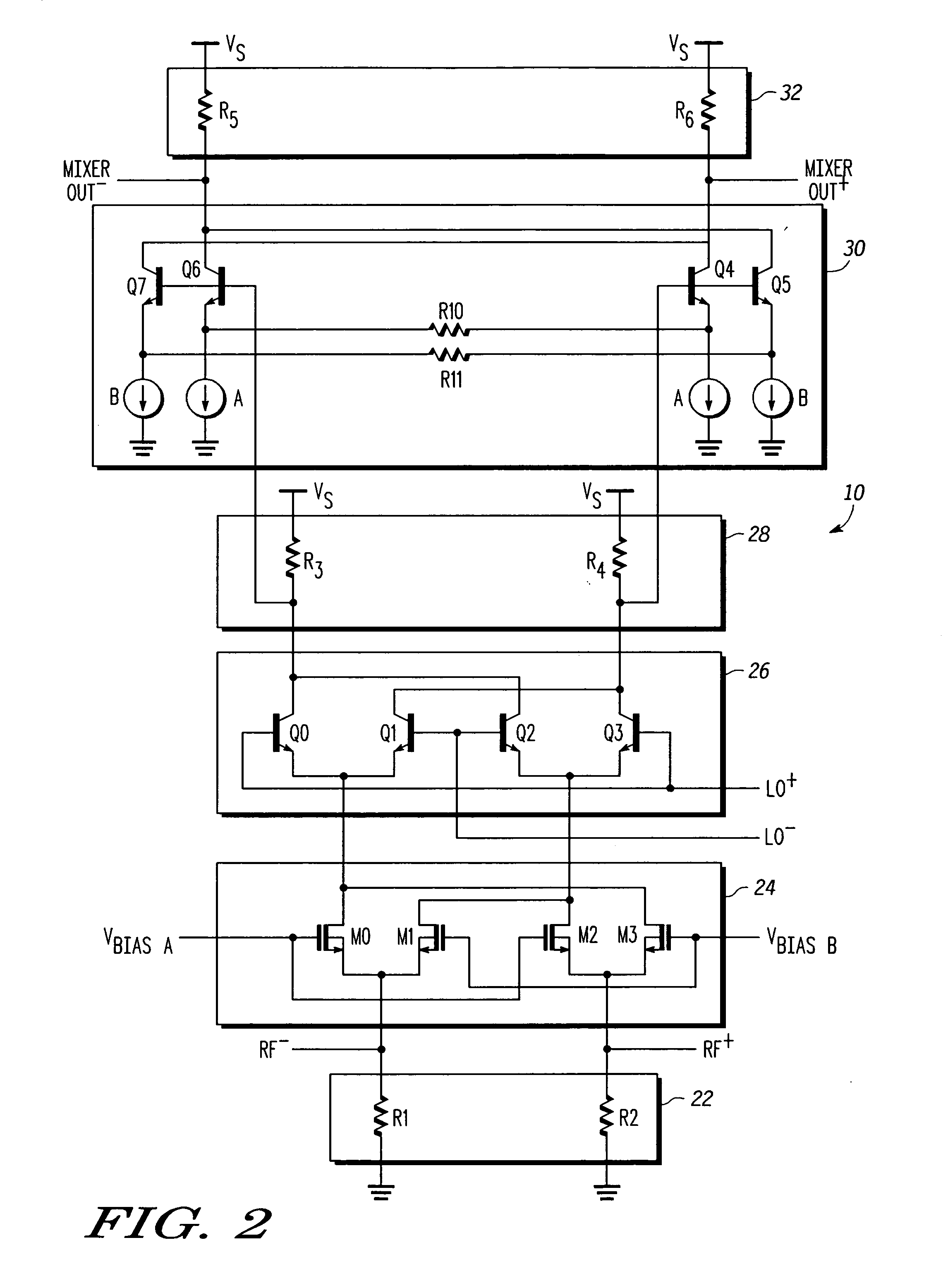
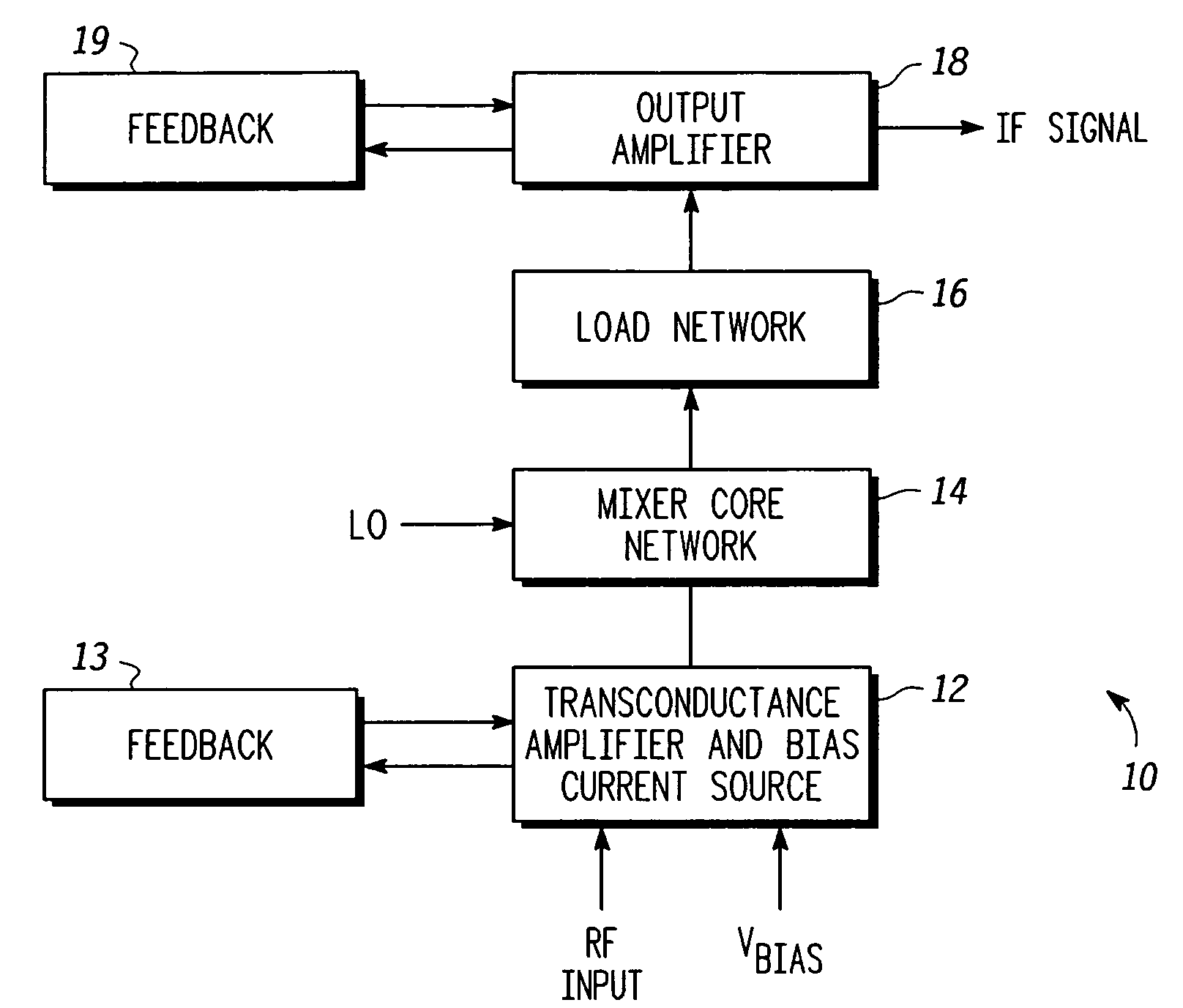
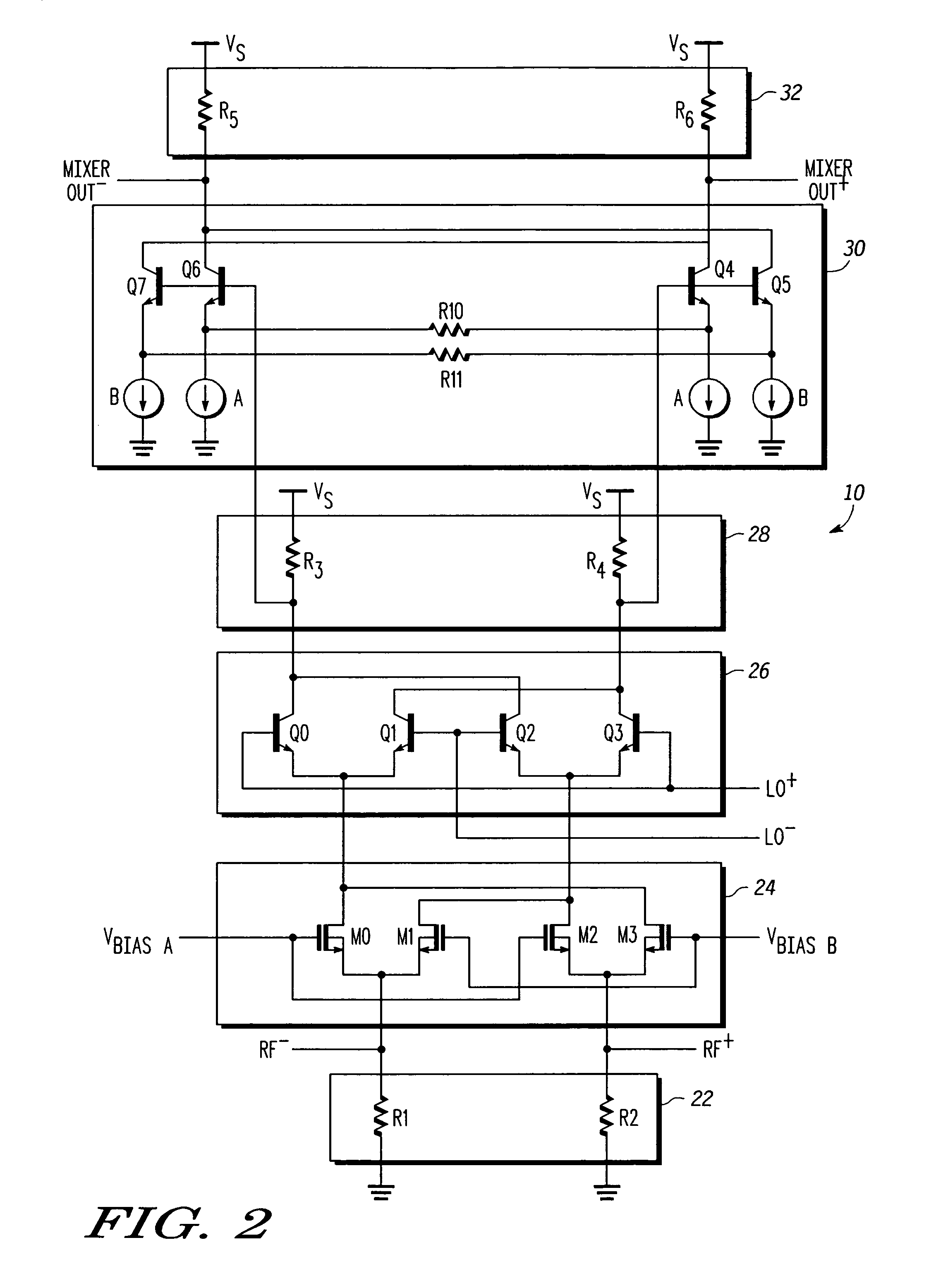
Linearized and balanced mixer apparatus and signal mixing method
Method and apparatus are provided for linearized balanced signal mixing. A signal mixing circuit (10) for translating a radio frequency (RF) signal is provided comprising an input amplifier (12), a mixer network (14), and an output buffer amplifier (18). The input amplifier (12) is configured to produce an amplified RF signal and cancel an input third-order intermodulation (IM3) distortion in the amplified RF signal with a cross-coupled feedback amplifier (13). The mixer network (14) is configured to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal based on the amplified RF signal and a local oscillator signal. The output amplifier (18) is configured to buffer the IF signal and cancel an output IM3 distortion in the IF signal with a cross-coupled feedback amplifier (19). The input amplifier (12) and cross-coupled feedback amplifier (13) also serve as a bias current source for the mixer network (14), thus lowering the supply voltage required for the mixing circuit (10).
Owner:APPLE INC
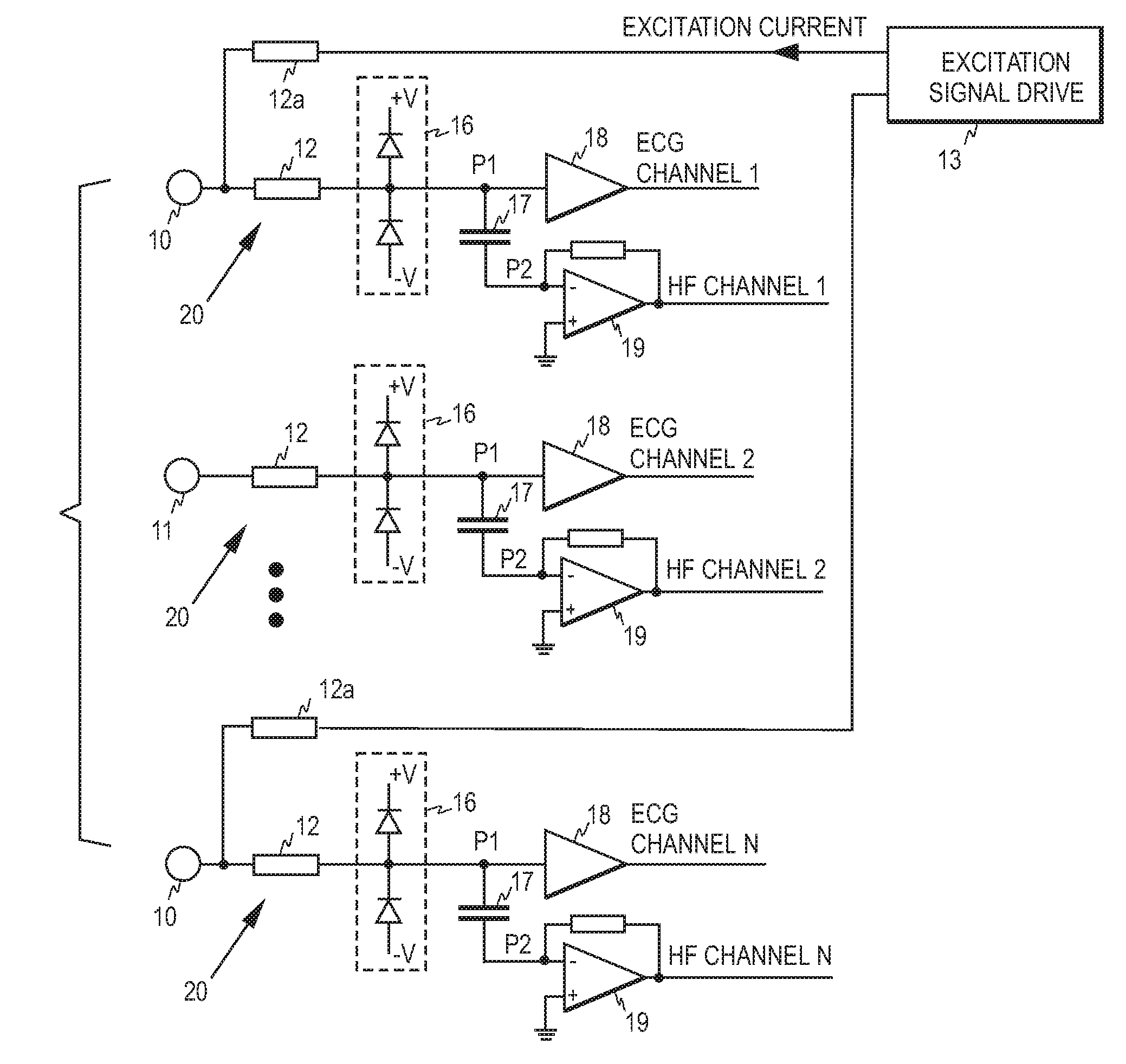
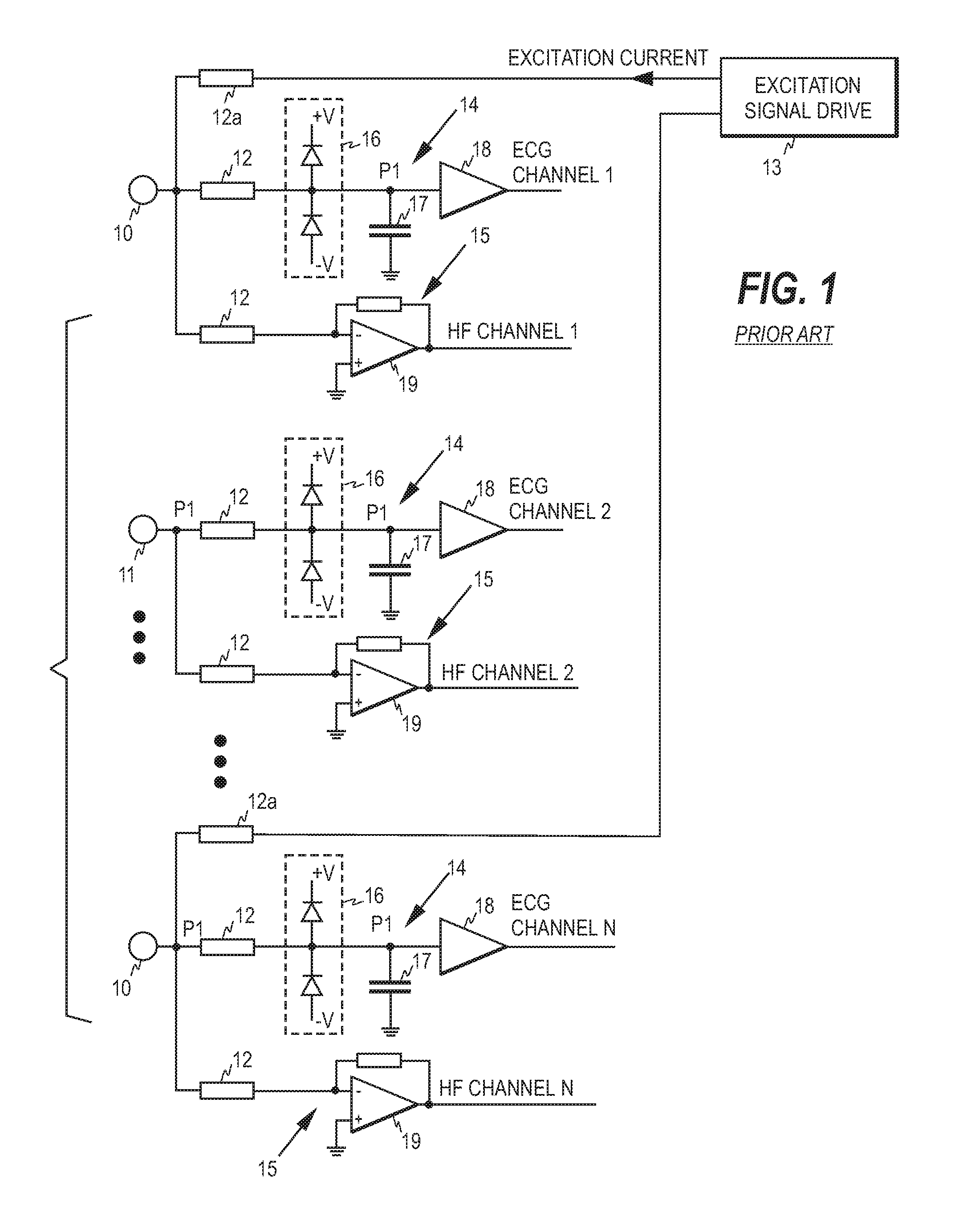
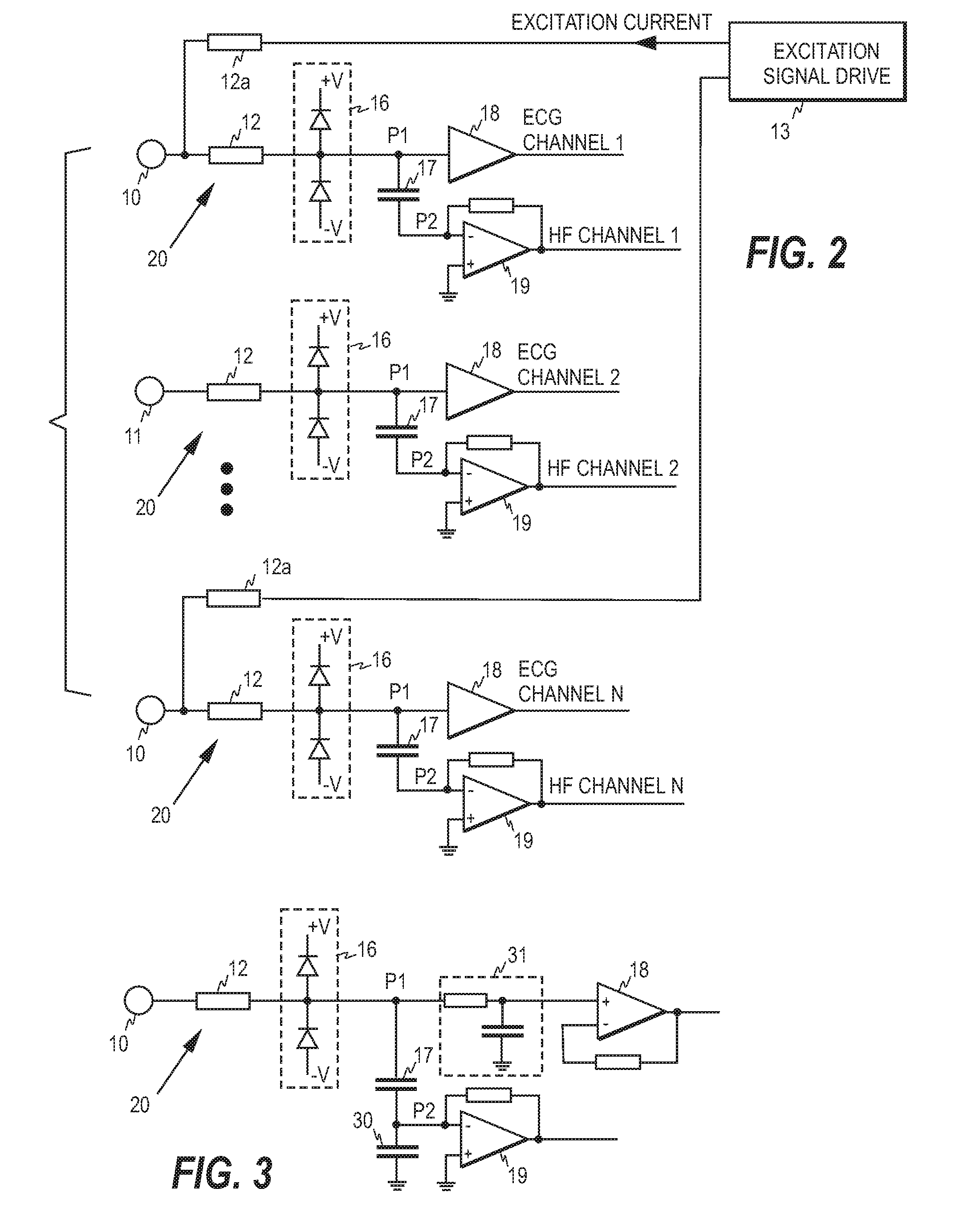
ECG front end and method for acquiring ECG signals
An ECG front end and a method for acquiring ECG signals are disclosed. The front end comprises a plurality of parallel measurement branches, each measurement branch comprising a protection resistor having a first terminal and a second terminal, wherein the first terminal is connectable to a respective ECG electrode. Each measurement branch comprises a first input amplifier operatively connected to the second terminal of the protection resistor and a capacitor having a first and a second terminal, wherein the first terminal of the capacitor is operatively connected to a point between the first input amplifier and the second terminal of the protection resistor and the second terminal of the capacitor is connected to a virtual ground of a second input amplifier. Each first input amplifier serves as a source of an ECG channel signal and each second input amplifier as a source of high frequency signal components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Low-power output controlled circuit
InactiveUS6653878B2High power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierSwitched current
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Apparatus and method for automatic mode selection in a communications receiver
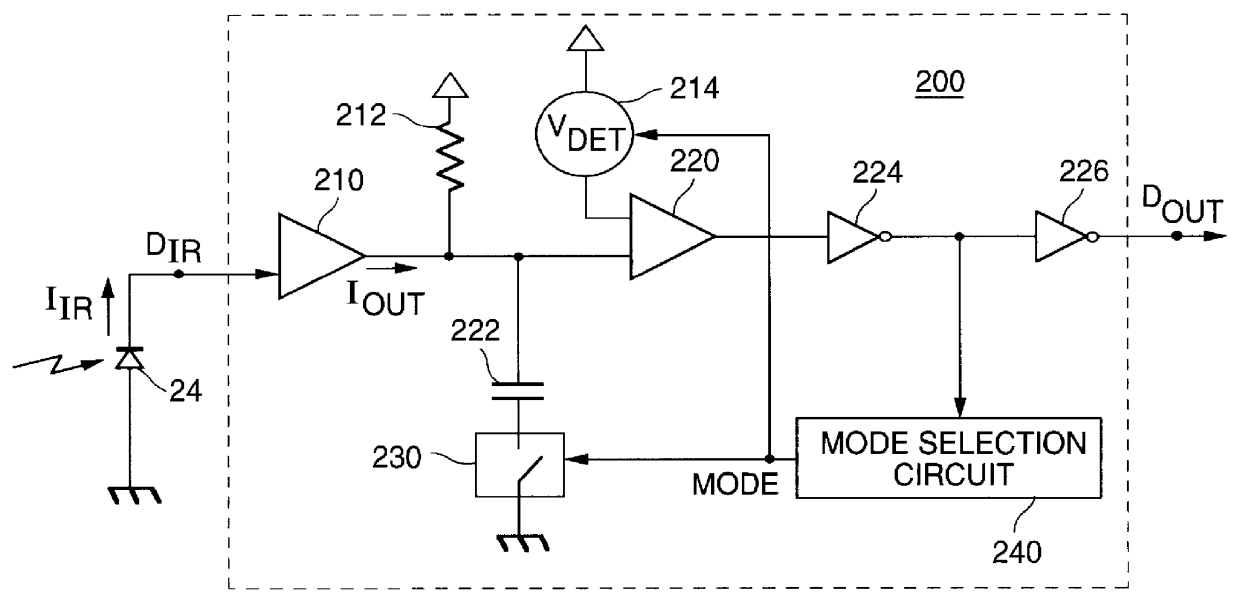
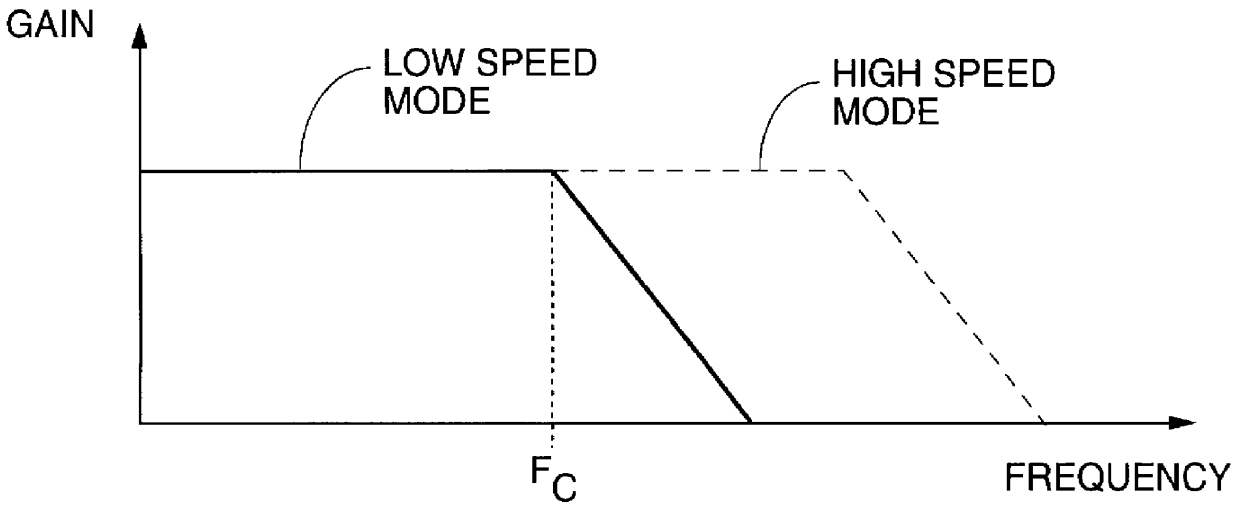
InactiveUS6118829ADc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesInput amplifierMultiple pulse
A method and apparatus are shown for automatically adjusting a response bandwidth and input sensitivity of a communications receiver responsive to a frequency of a received data signal. The response bandwidth is adjusted by switching a low pass filter into a receive path of the receiver when the received data signal is a low speed data signal and switching the low pass filter out of the receive path when the received data signal is a high speed data signal. The input sensitivity is adjusted by either changing a detection threshold of a comparator in the receive path or varying a gain of an input amplifier in the receive path. The high speed data signal is discerned when the low pass filter limits the response bandwidth of the receiver by a mode selection circuit which examines the duration of multiple pulses in a pulse train in the received data signal.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Transconductance filter control system
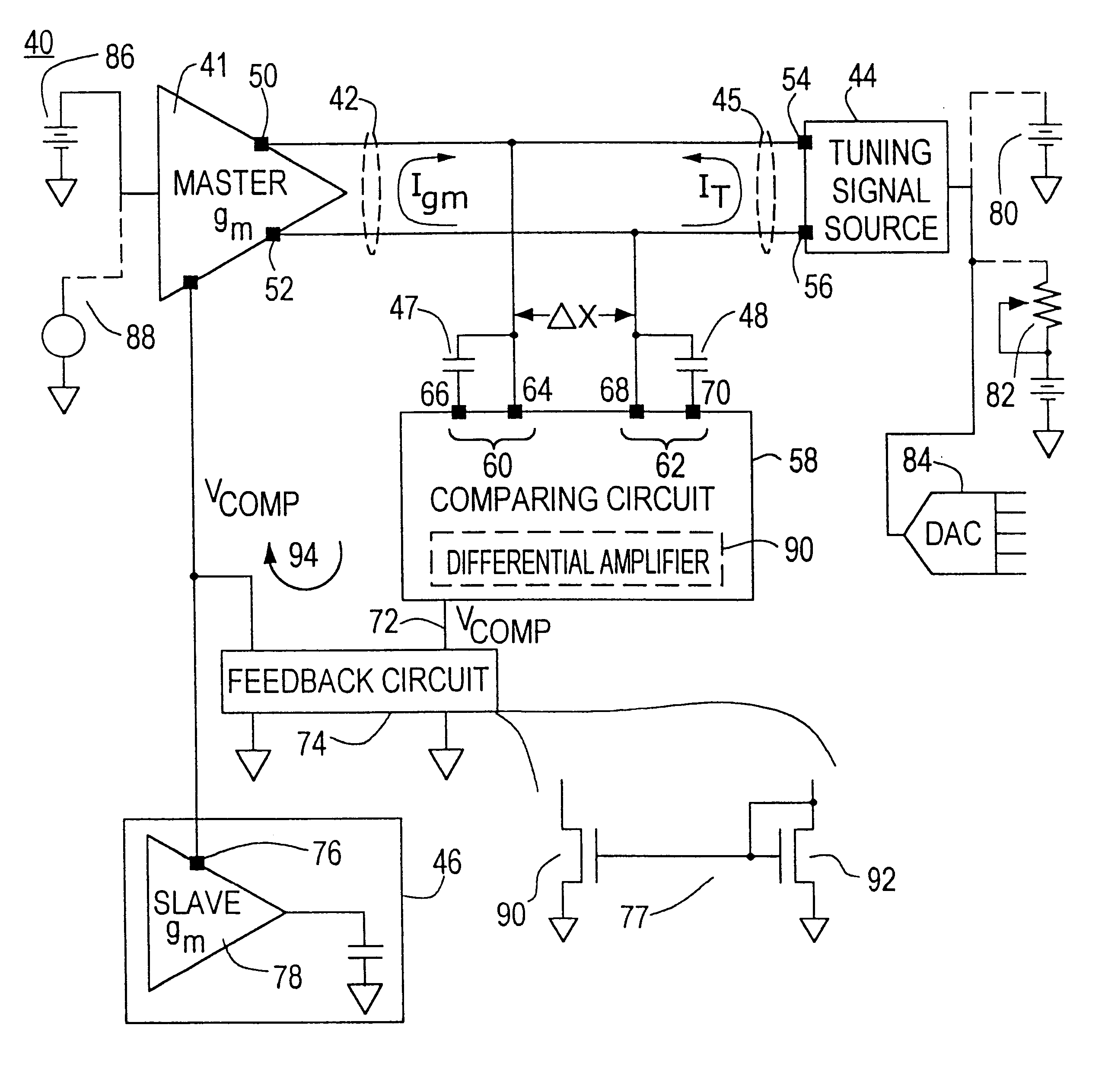
InactiveUS6172569B1Increase power consumptionIncrease in sizeContinuous tuning detailsGain controlAudio power amplifierControl system
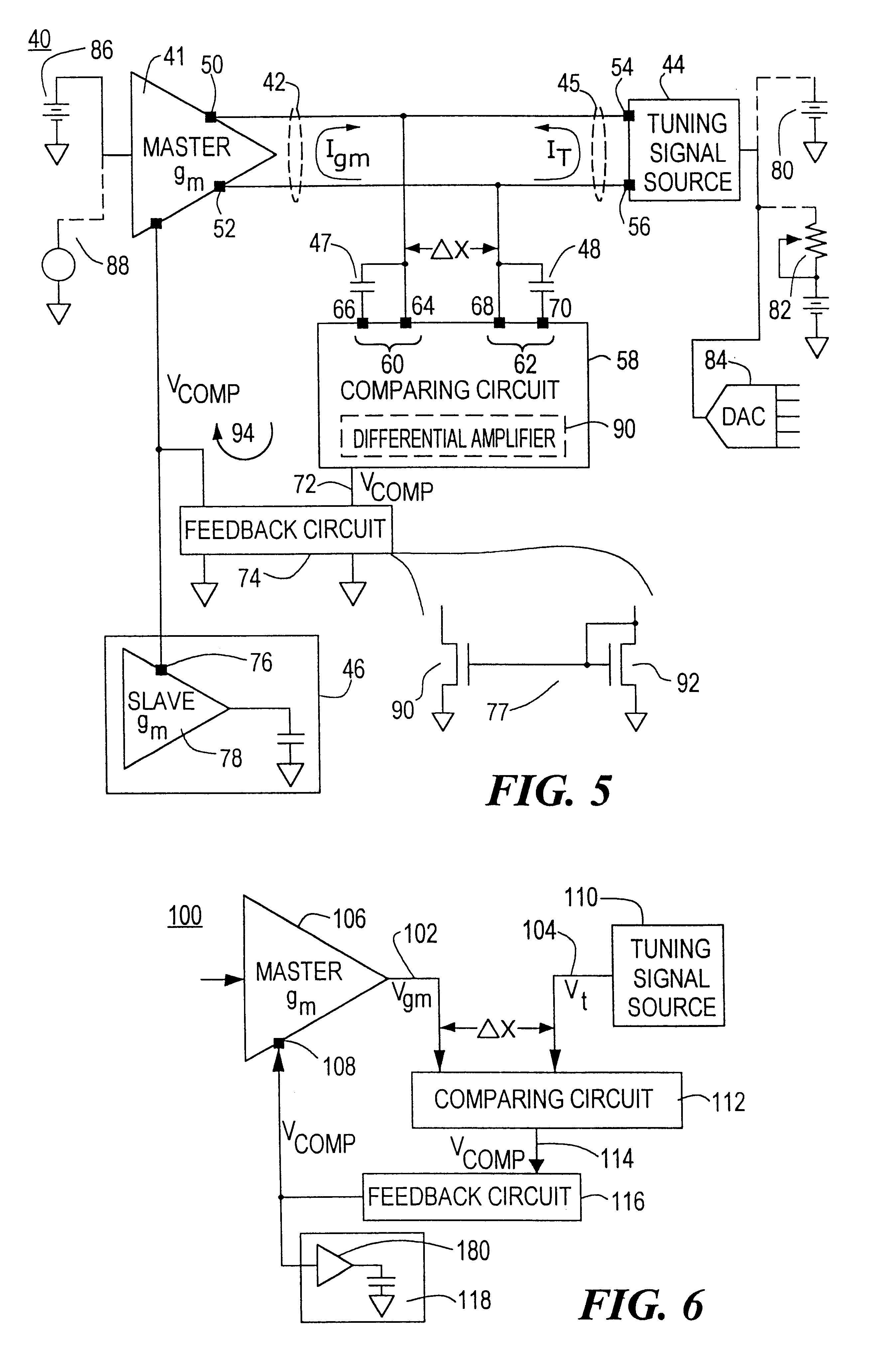
A transconductance filter control system for compensating for drift in transconductance of a slave transconductance amplifier in a continuous time transconductance filter including: a master transconductance amplifier having an output which is a function of its transconductance and a control input for controlling the transconductance of the master transconductance amplifier; a tuning signal source for providing a tuning signal representative of a preselected characteristic of the transconductance filter; a comparing circuit, responsive to any deviation from a predetermined difference between the tuning signal and the output of the master transconductance amplifier, representative of a deviation of the transconductance of the master transconductance amplifier, for providing a compensation signal; and a circuit for applying the compensation signal to the control input of the master transconductance amplifier and to the control input of the slave transconductance amplifier in the transconductance filter to adjust the transconductance of both the master and slave transconductance amplifiers and restore the predetermined difference between the tuning signal and the output of the master transconductance amplifier.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC +1
Distributed optical fibre temperature sensor system
InactiveCN1400453AImprove measurement efficiencyEasy to useRadiation pyrometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiberRayleigh scattering
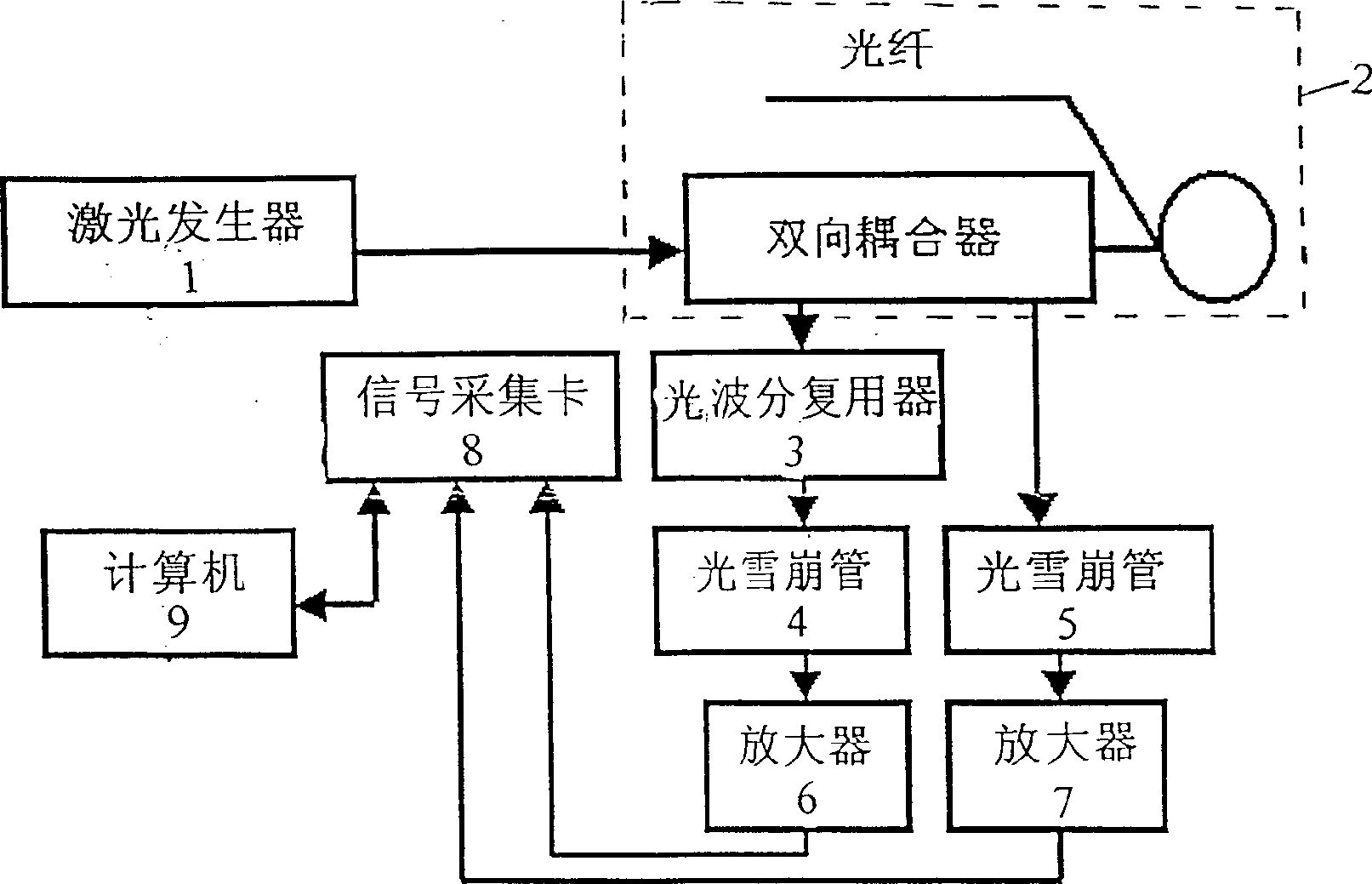
The distributed optical fiber temperature sensor is a kind of temperature-measuring equipment. It includes laser generator, optical fiber with bidirectional coupler, light wave-division multiplexer (WDM), two light avalanche transistor, two amplifiers, signal-sampling cara and computer. The generated laser pulse enters the fiber-optical to output back dispersion light whose echo channel has two paths; one path as Raman back dispersion light separated by the light WDM enters one avalanche transistor and the other path as Rayleigh back dispersion light enters the other end. Two avalanche transistor make the photoelectric conversion, and the output signals apart enter the amplifier whose output end linked with the input end of the signal-sampling card whose output end linked with the computer.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Low duty cycle distortion differential to CMOS translator
ActiveUS7176720B1Easy to implementReduce dependencePulse generation by non-linear magnetic/dielectric devicesDifferential amplifiersCMOSTransmission gate
Disclosed is a circuit comprising a differential input amplifier stage, a capacitor stage, an inverter chain stage, and a biasing circuit. The inverter chain stage may be formed with or without feedback depending on whether a clock signal or data signal is to be translated using the disclosed circuit. The biasing circuit can be formed using either inverters or transmission gates. Moreover, the biasing circuit, the inverter chain stage, and the amplifier stage can be connected to a power down circuit which, when the translator is not being used, will ensure various circuitry of the translator will not consume extensive power. The inverter chain stage, biasing circuit, and capacitor stage are formed on both an upper and lower section to produce true and complementary outputs that have a consistent and equal delay from the transitions of the incoming differential input signal so as to minimize jitter and associated duty cycle of the translated output.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Receiver having full signal path differential offset cancellation capabilities
InactiveUS7180354B2Eliminates differential offsetPulse automatic controlAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential signalingOffset cancellation
There is described an improved receiver which first comprises an analog input amplifier a sample and hold differential circuit and two stages of differential comparators that are connected in series, wherein the first stage consists of two comparators and the second stage of one comparator. By properly activating the switches with signals generated by a dedicated control logic, the input differential signal is sampled in the sample and hold circuit to generate first and second differential signals. The first differential signal holds a first state and the second differential signal propagates the second state. As result, the signal output by the second comparator stage reflects the differential offset minus the offset compensation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low-dropout linear voltage stabilizer
ActiveCN103713682AImprove stabilityImprove PSRRElectric variable regulationCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a low-dropout linear voltage stabilizer. The low-dropout linear voltage stabilizer comprises an error amplifier, a regulation pipe, a sampling circuit and a miller capacitor, and further comprises a cathode-input amplifier. The cathode-input amplifier is arranged between the miller capacitor and the grid electrode of the regulation pipe. The miller capacitor is connected with the cathode-input amplifier and the drain electrode of the regulation pipe. The cathode-input amplifier buffers samples of the miller capacitor and then feeds the samples back to the output end of the error amplifier. The miller capacitor and the grid electrode of the compensating pipe are isolated through a buffer while main poles and auxiliary poles are separated, and therefore the aims of increasing stability of the circuit and improving the PSRR are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
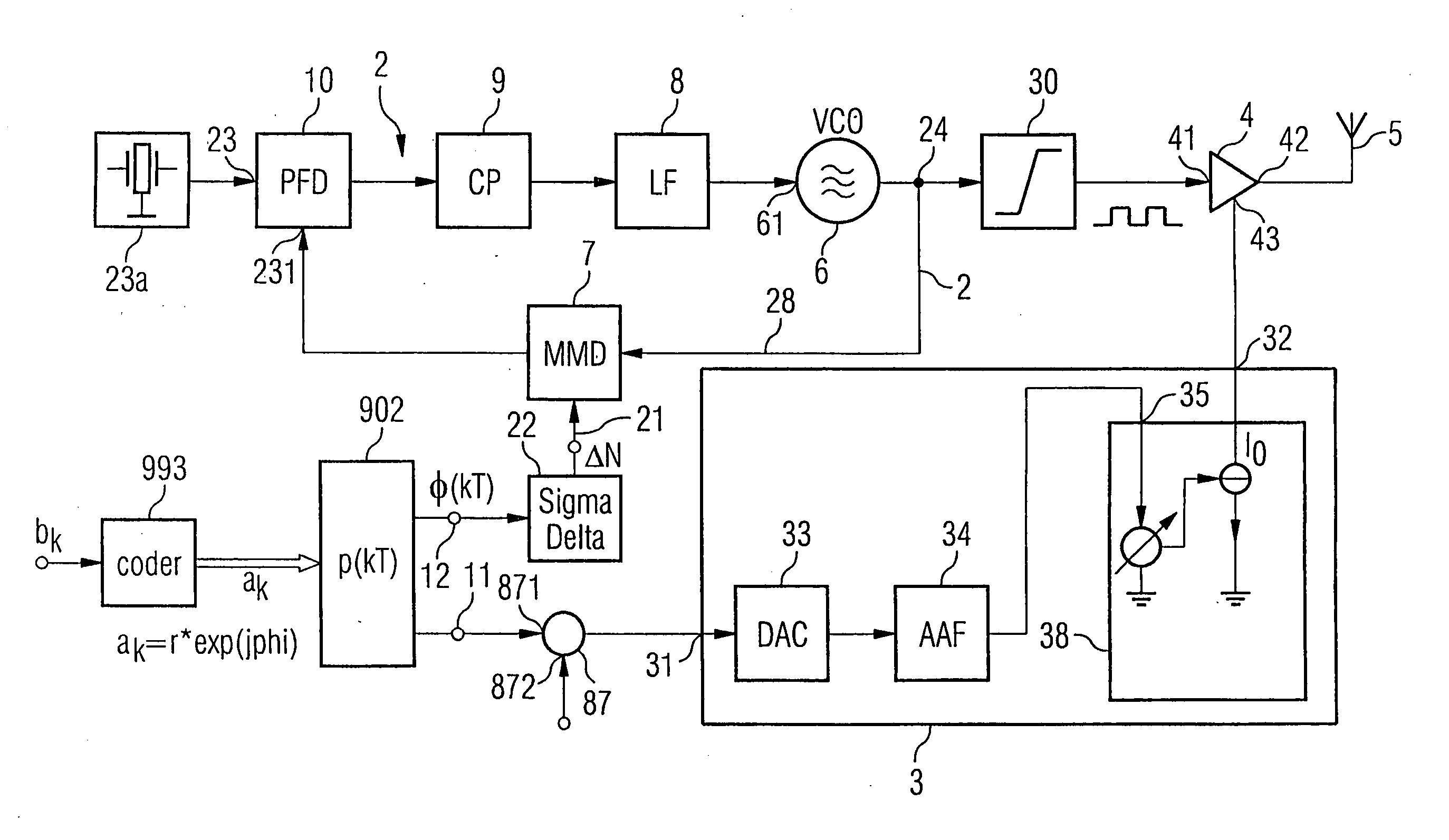
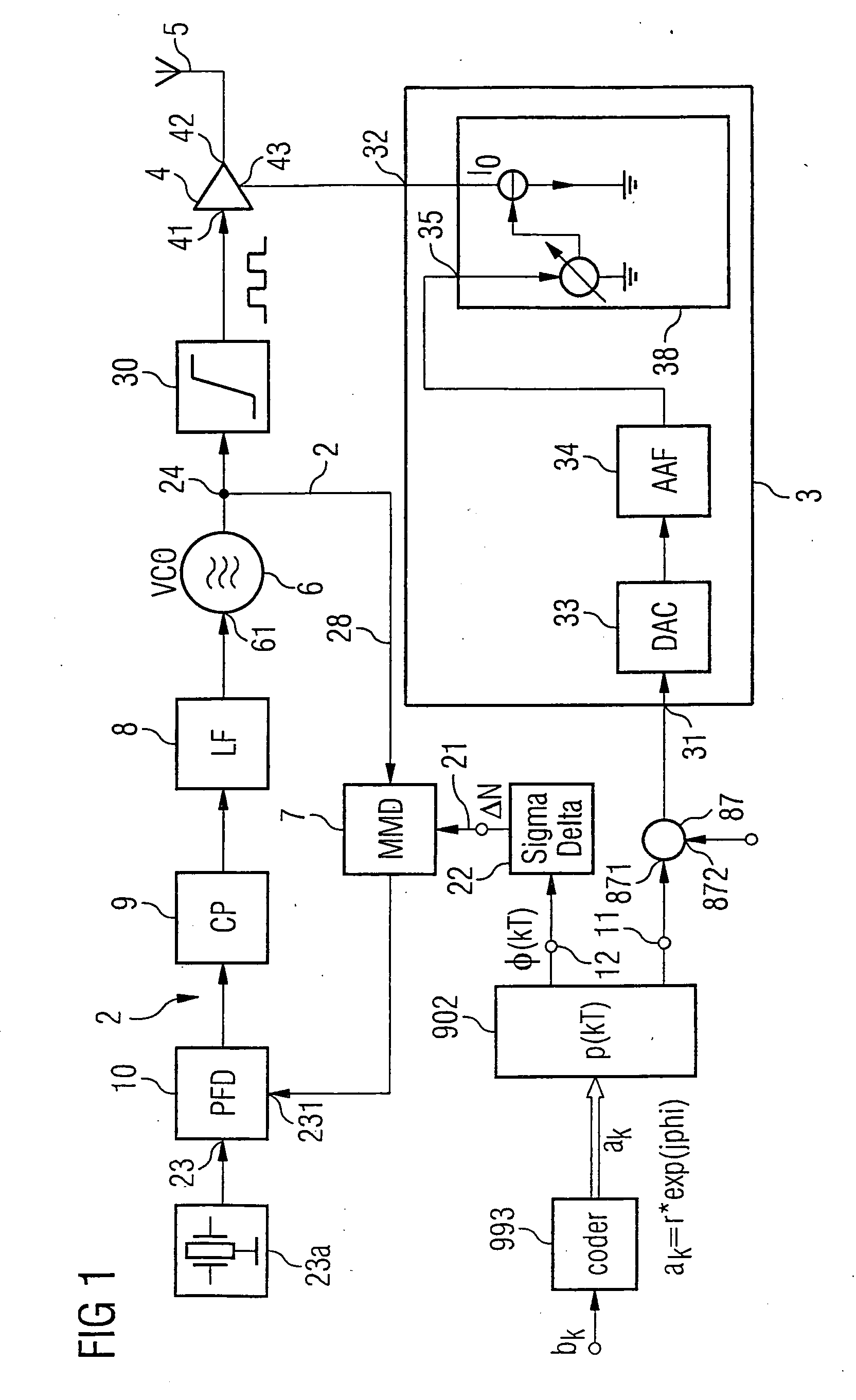
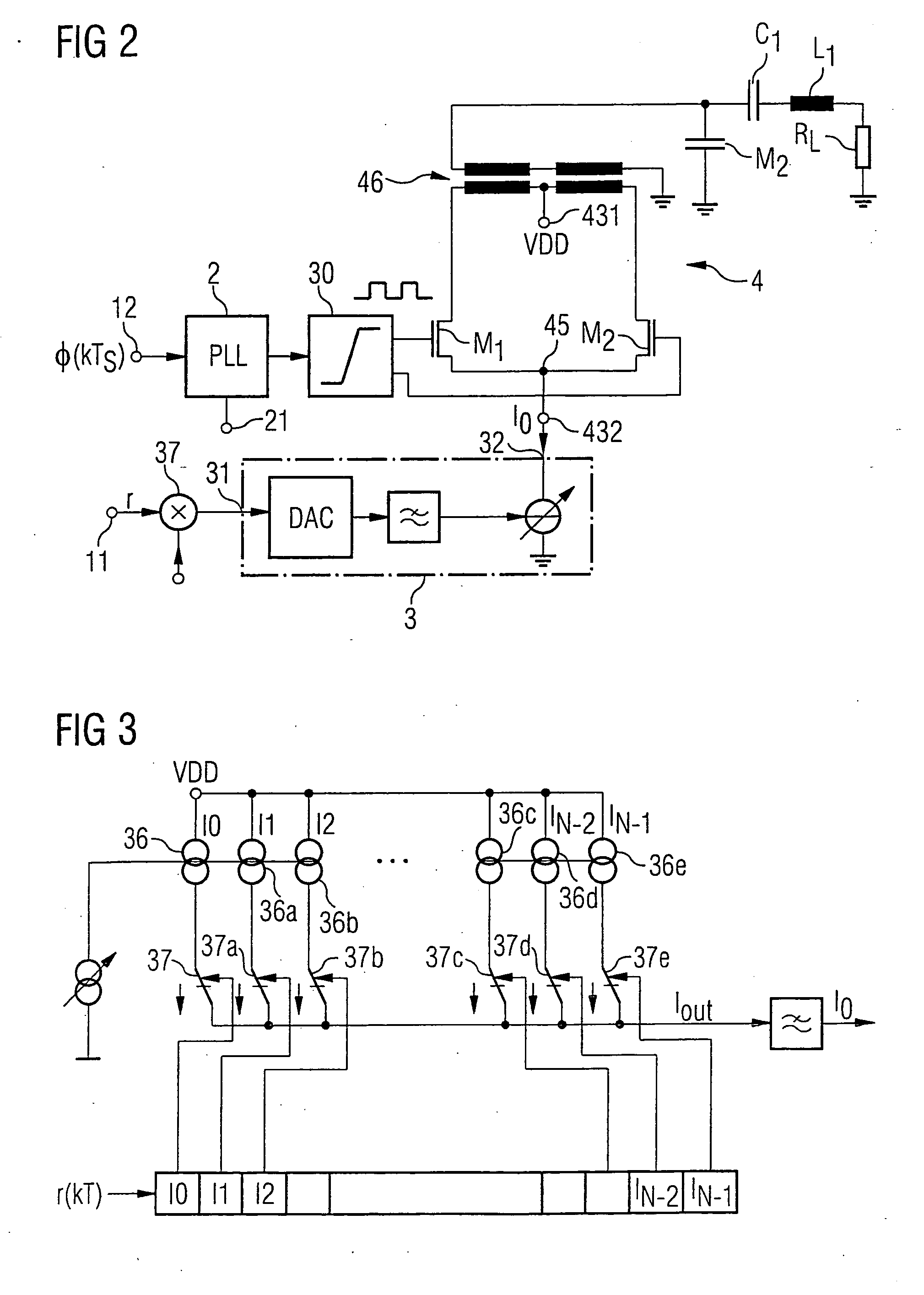
Polar modulator and method for modulation of a signal
InactiveUS20060160499A1Reduce power supply voltageFunction increaseResonant long antennasModulated-carrier systemsCarrier signalEngineering
A modulated carrier signal is produced from a phase modulation signal in a phase locked loop in a polar modulator. This carrier signal is converted via a limiting amplifier to a square-wave signal, which is supplied to an amplifier. At the same time, an amplitude modulation signal at one input is connected to a control input of a controllable current source. The controllable current source is designed to emit a supply current at a current output as a function of the amplitude modulation signal at the control input. The current output of the controllable current source is connected to a supply input of the amplifier. The supply current for the amplifier is thus modulated on the basis of the amplitude information to be transmitted. The processing of the amplitude information within the current domain makes it possible to produce the polar modulator according to the invention as an integrated circuit, using CMOS technology.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Mixed compensating type high-stability LDO (low-dropout regulator) chip circuit
The invention provides a mixed compensating type high-stability LDO (low-dropout regulator) chip circuit. The mixed compensating type high-stability LDO chip circuit comprises a differential input amplifier A1, a push-pull buffer amplifier A2, an integrated PMOS (p-channel metal oxide semiconductor) device P0, a resistor Rc, a resistor RF1, a resistor RF2, a capacitor Cc, a capacitor CFF, a chip output capacitor Cout, an equivalent series resistor Resr of the Cout and a chip output load Rload, and is characterized in that the A1 is in output connection with the A2, the Rc and the Cc are serially connected to be bridged at two ends of the A2, the A2 is in output connection with a grid electrode of the P0, a drain electrode of the P0 is an output end Vout and connected with one ends of the RF1, the Cout and the Rload, the RF1 and the RF2 are grounded in a series connection mode, the CFF is bridged at two ends of the RF1, an intersection of the RF1 and the RF2 is connected to an input negative terminal of the A1, the Cout and the Resr are grounded in a series connection mode, and the other end of the Rload is grounded. The mixed compensating type high-stability LDO chip circuit adopts ESR (equivalent series resistance) compensation, miller compensation and front feed-forward capacitance compensation, and stability of the LDO system is improved.
Owner:厦门立昂电子科技有限公司
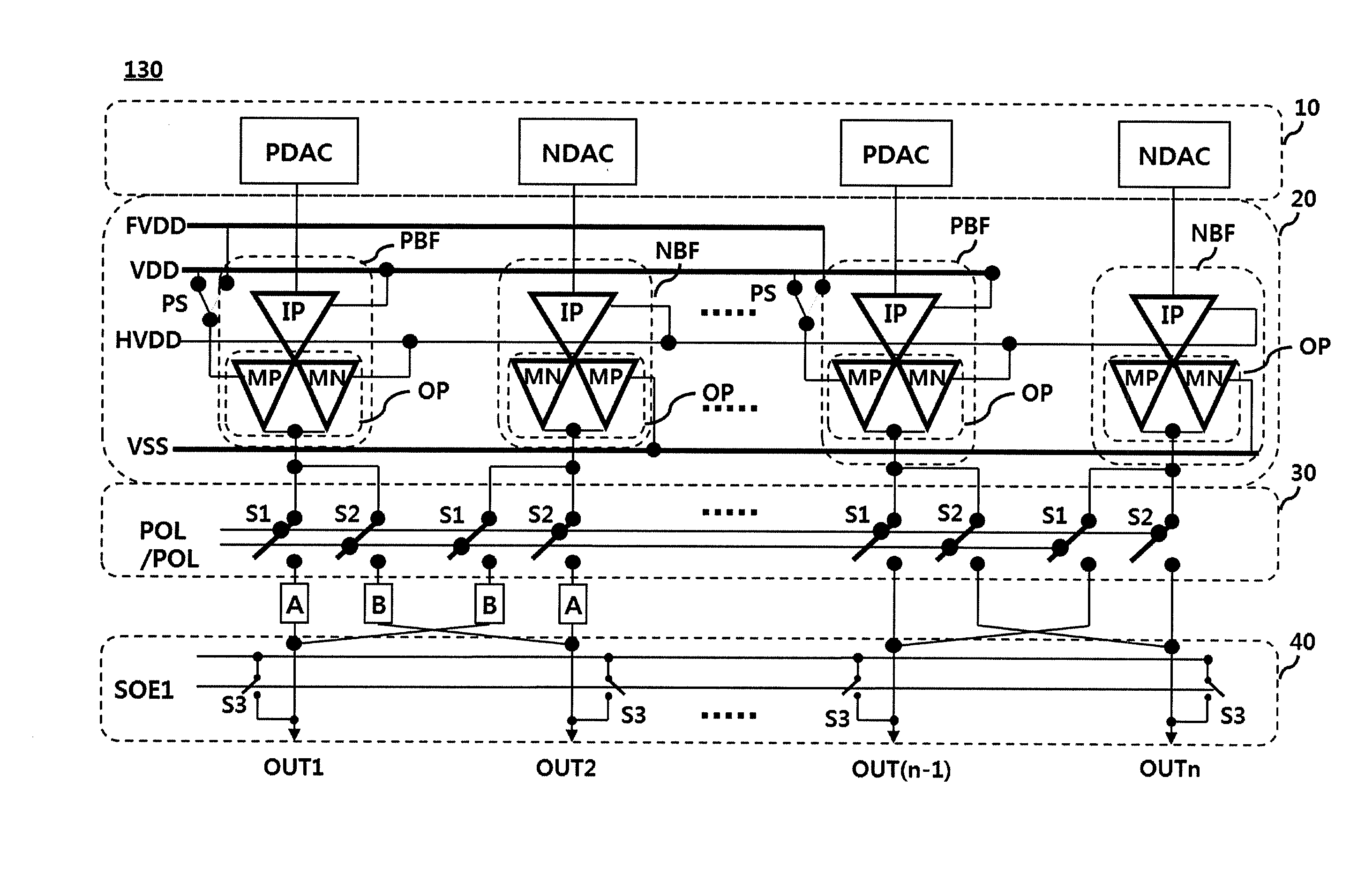
Data driving apparatus for liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20150002503A1Total current dropReduce the temperatureCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayPower flow
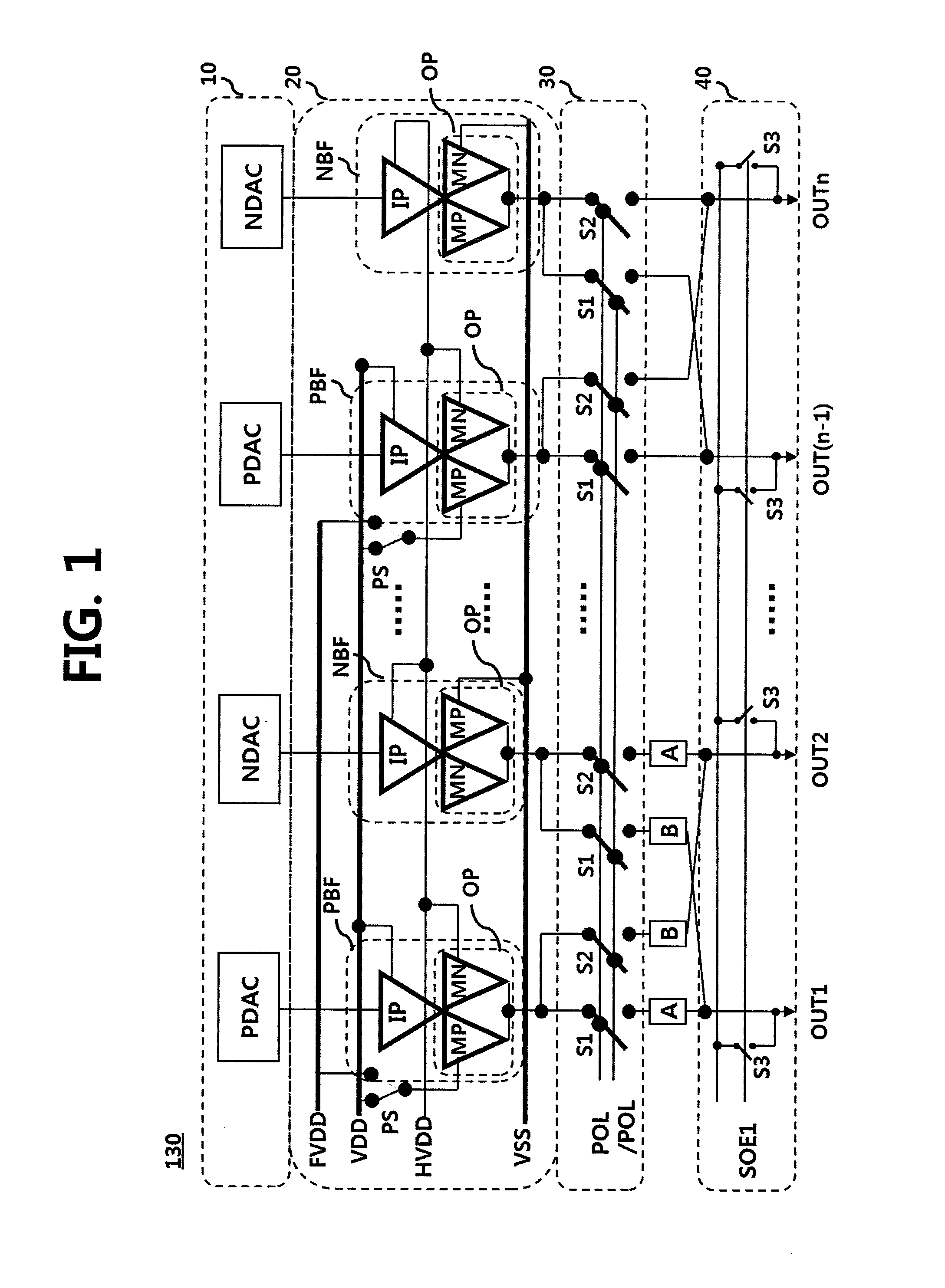
A data driving apparatus for a liquid crystal display device includes an output buffer for buffering and outputting a data voltage input from a digital-analog converter, wherein the output buffer includes an input amplifier for amplifying and outputting current proportional to the data voltage, an outputter for supplying a data voltage corresponding to the input data voltage to an output channel using charging and discharging current proportional to output current from the input amplifier, a control switch unit connected between the input amplifier and the outputter, for driving the outputter in a switching mode to precharge the output channel in a precharge period prior to a data supplying period in which the outputter outputs the data voltage, and a mode controller for controlling the control switch unit in response to an input control signal.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Memory control module and method for operating a memory control module
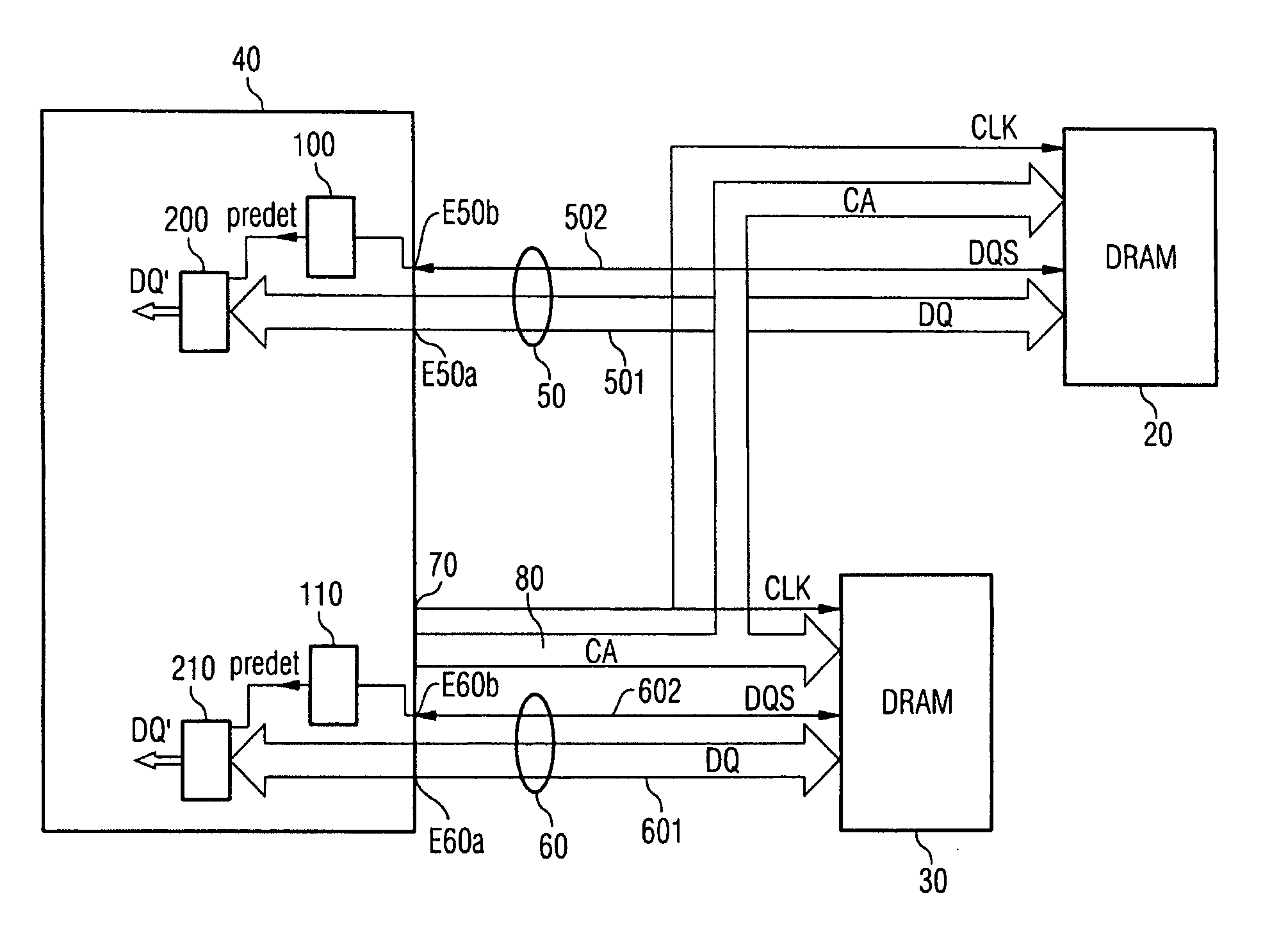
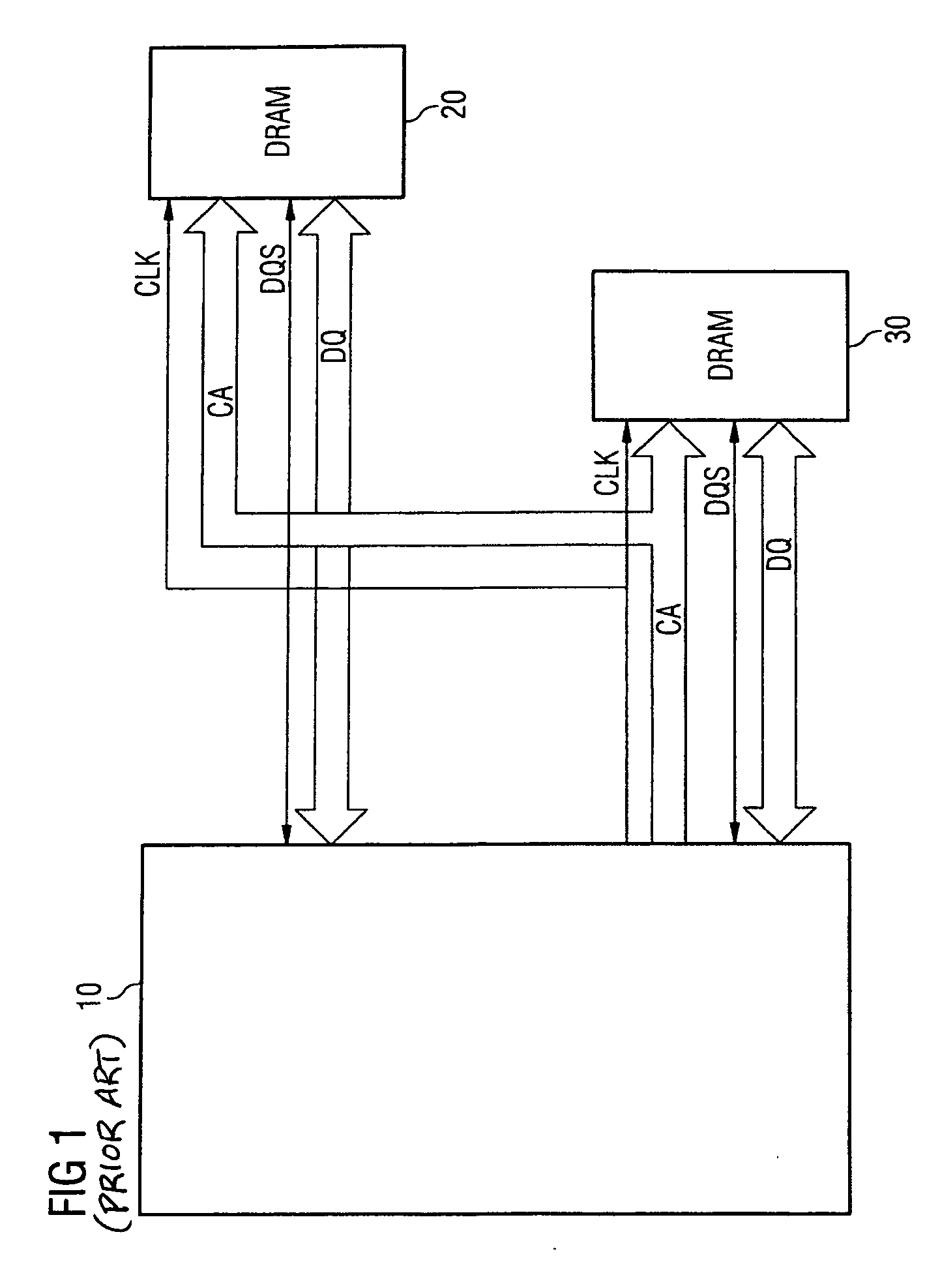
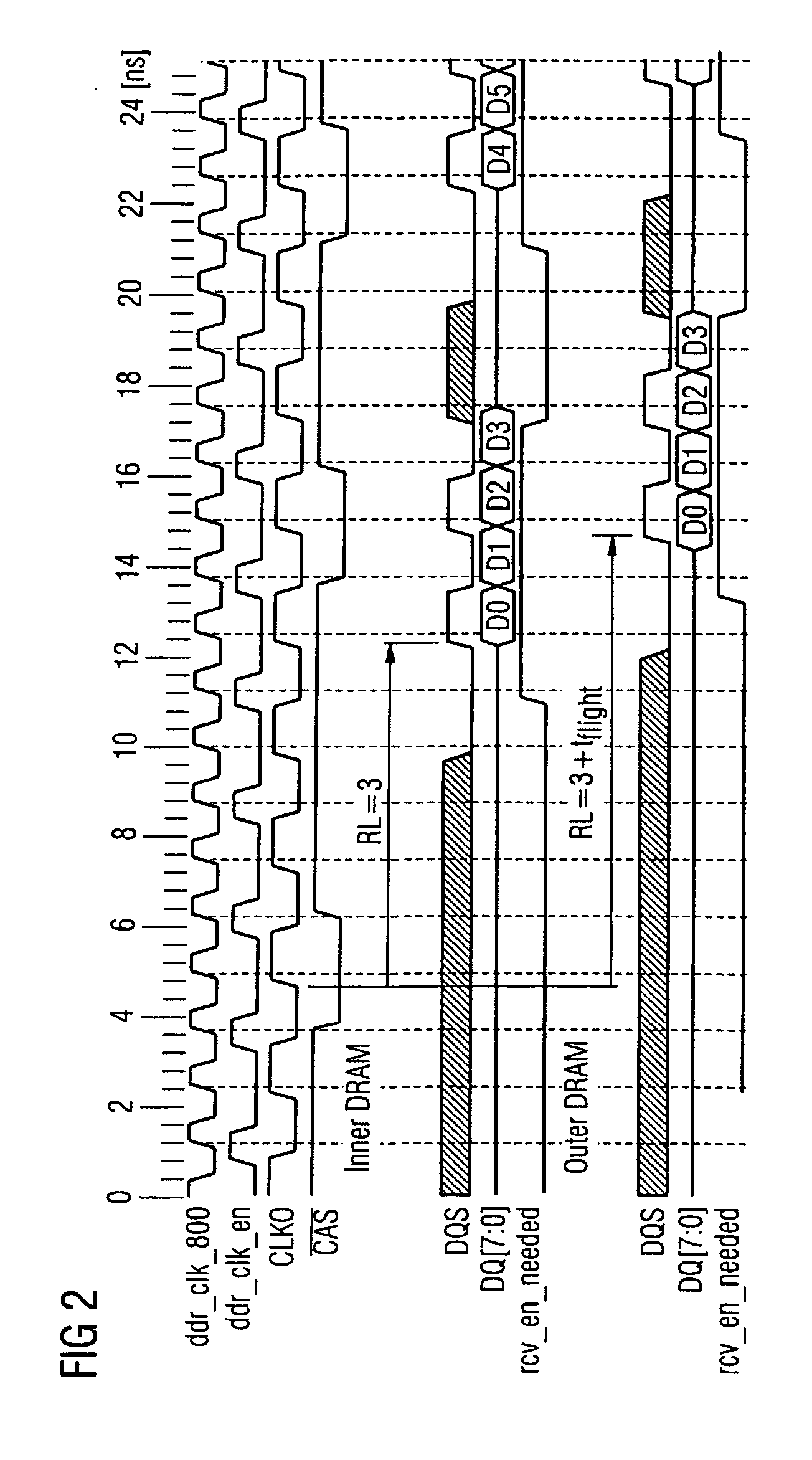
InactiveUS20060077730A1Easy to detectPoint to optimizationDigital storageElectric digital data processingAudio power amplifierControl signal
The invention relates to a method for transmitting memory data from a memory to a memory control module, in which method a read command is transmitted from the memory control module to the memory, and the memory data which correspond to the read command are transmitted from the memory to the memory control module, a sampling control signal which controls the acceptance of the memory data into the memory control module being transmitted from the memory to the memory control module in parallel with the memory data. In order to avoid defective data transmission between the memory and the memory control module as reliably as possible, the sampling control signal is transmitted with a preamble which indicates the imminent beginning of data transmission, for the sampling control signal to be monitored for the presence of the preamble, and for a data input amplifier of the memory control module to be switched on only when the presence of the preamble is detected.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
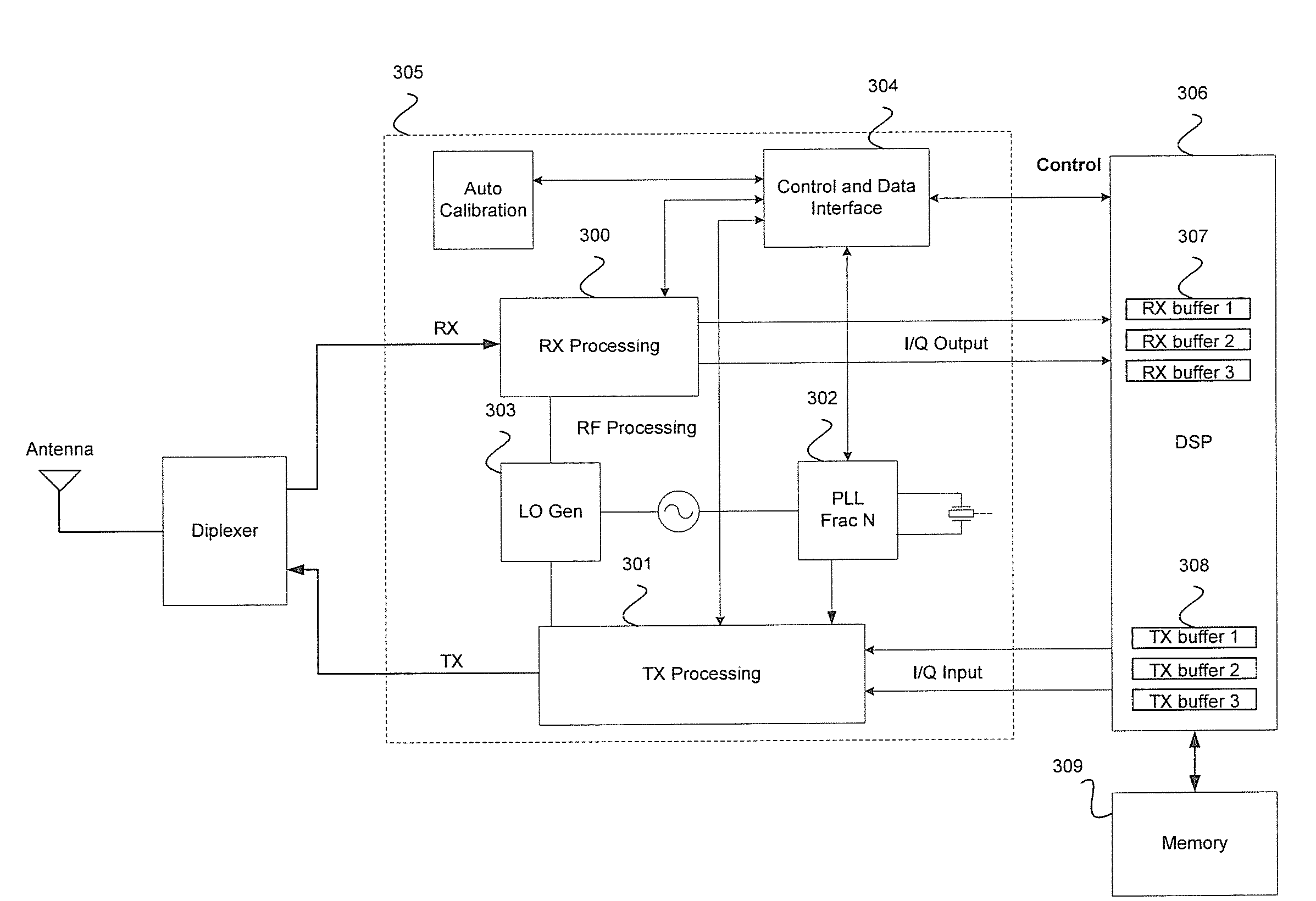
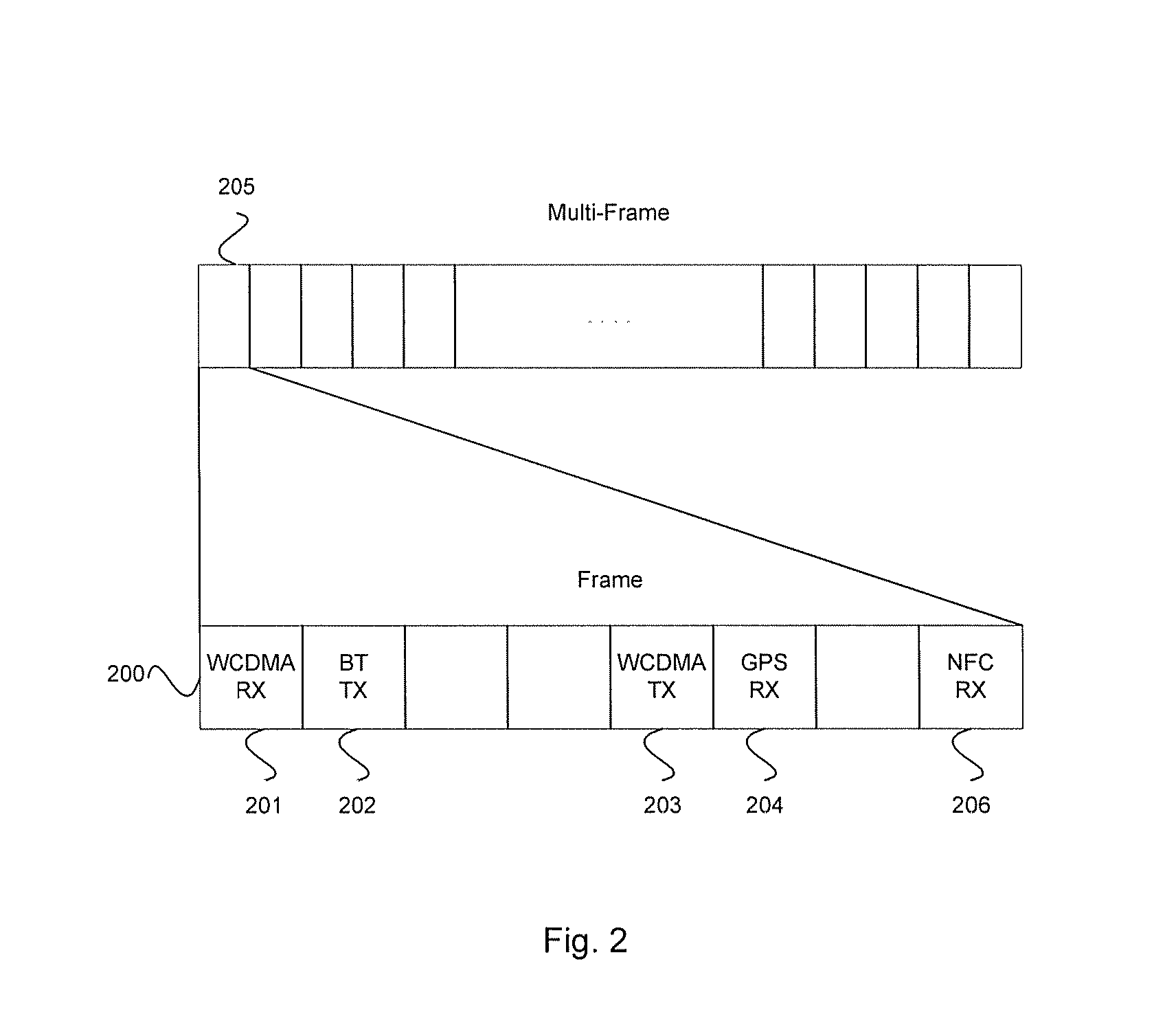
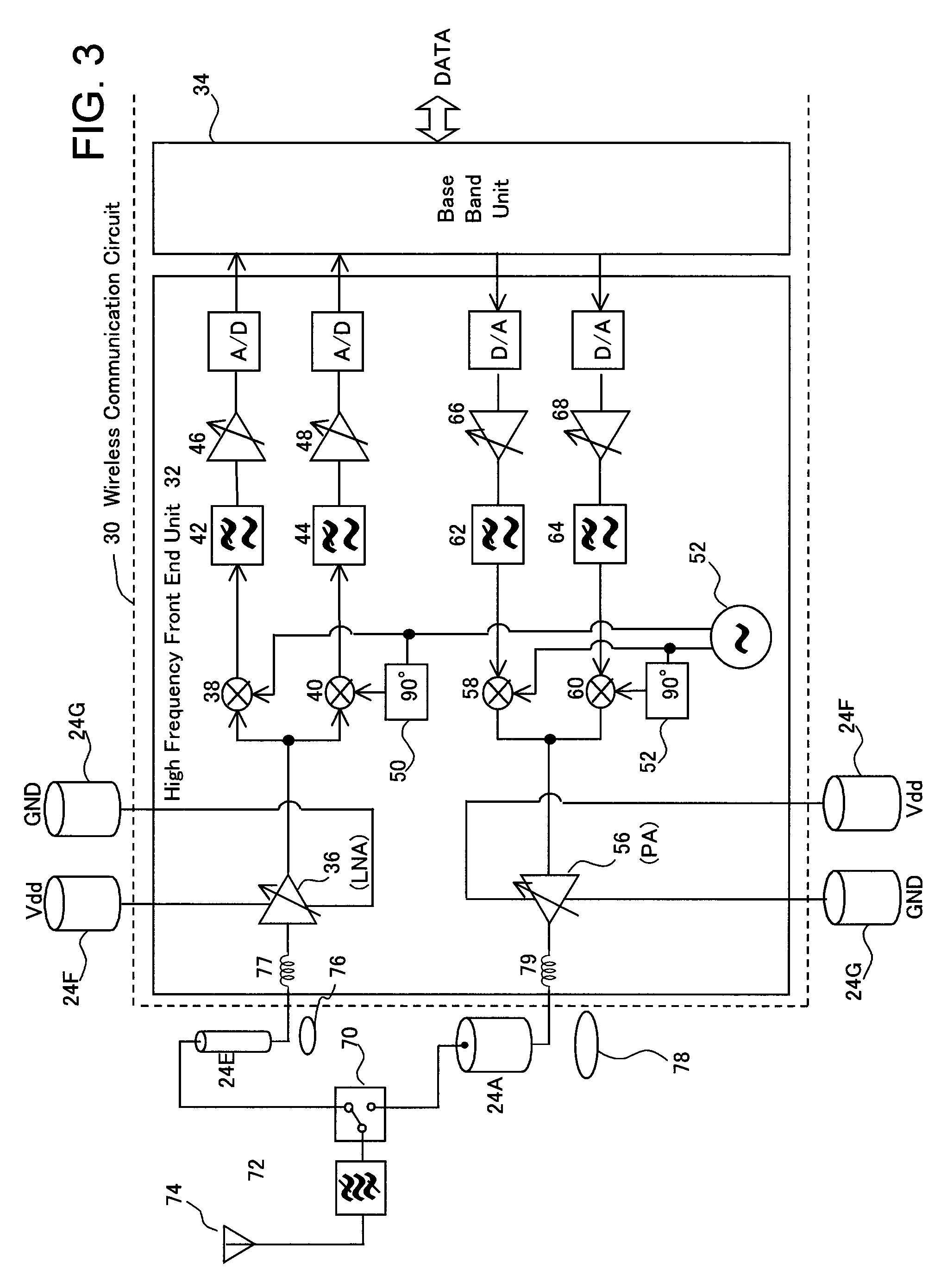
Method and System for Minimizing Power Consumption in a Communication System
ActiveUS20080080549A1Minimize power consumptionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierCommunications system
Certain embodiments of the invention may be found in a method and system for minimizing power consumption in a communication system. Exemplary aspects of the invention may comprise configuring a supply voltage of an amplifier to enable communication of data using a first communication protocol during a first timeslot in a TDM frame, reconfiguring the supply voltage of the amplifier to enable communication of data using a different communication protocol, and adjusting the supply voltage of the amplifier in proportion to the envelope of a baseband signal conforming to one of the communication protocols. The first and second communication protocols may conform to various communication protocols, such as WCDMA, HSDPA, HSUDPA, GSM, GPRS, EDGE, WiMAX, OFDM, UWB, ZigBee, and Bluetooth. The baseband signal may be delayed by a number of samples before being input into the amplifier.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
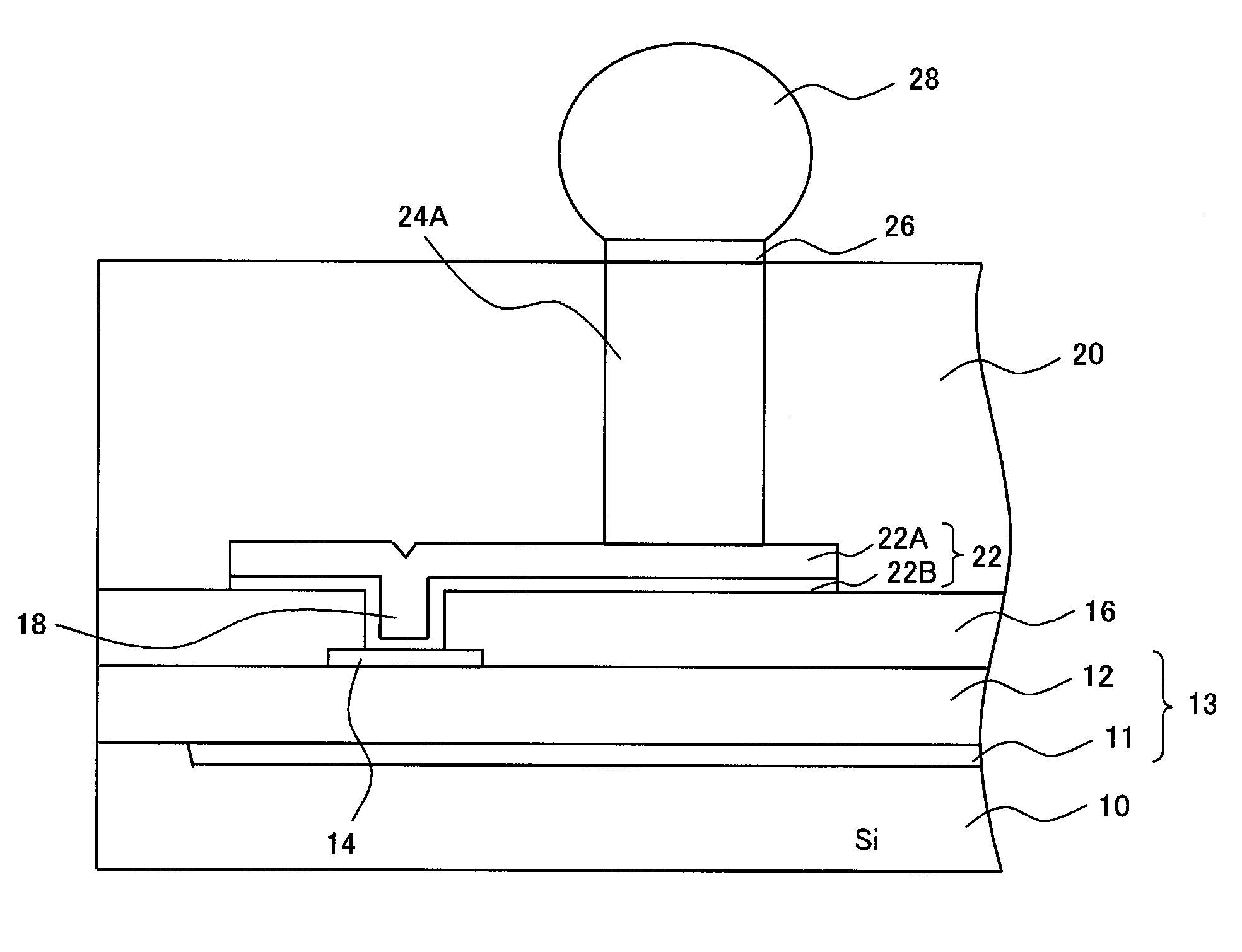
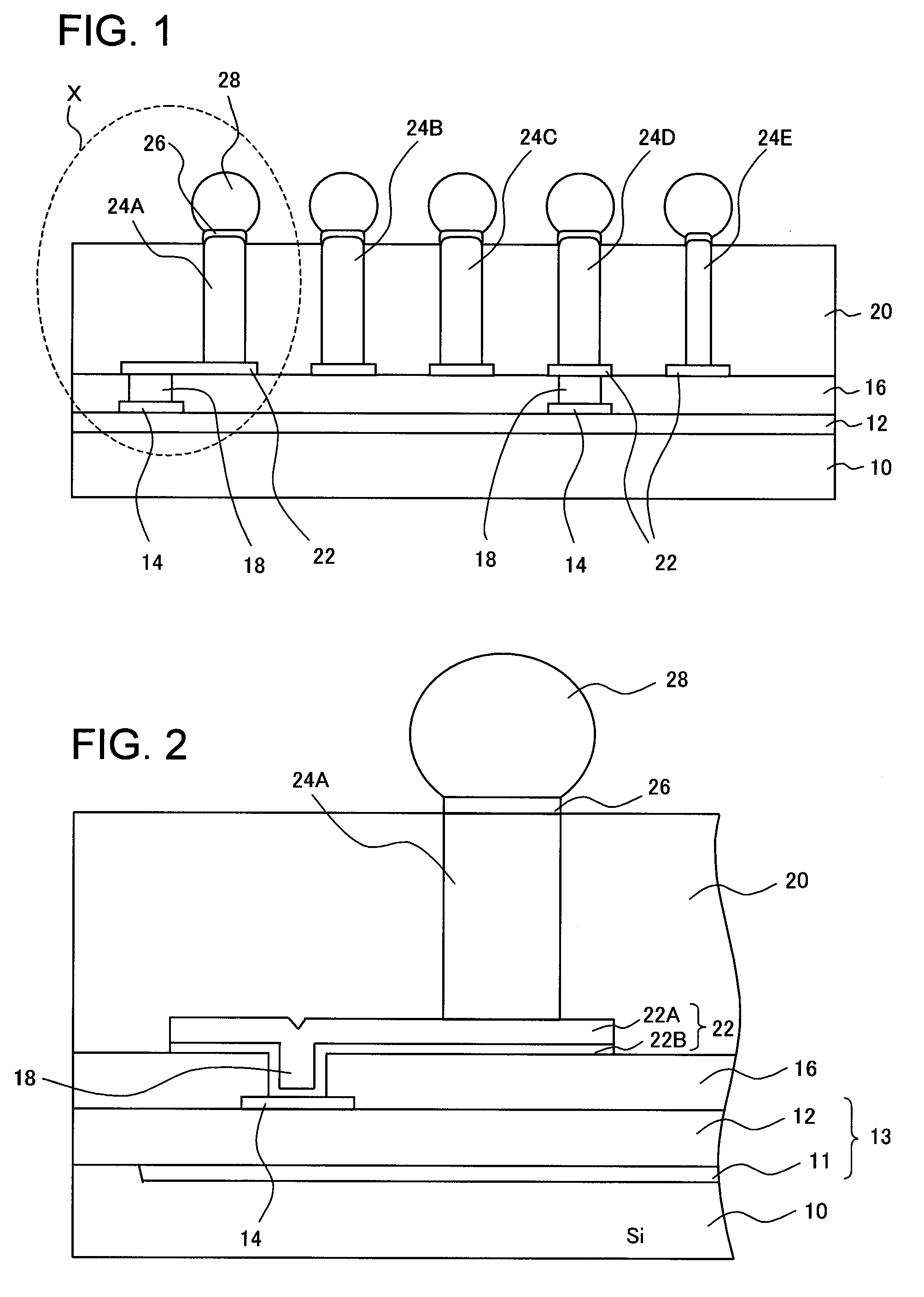
High-frequency device
ActiveUS20050139981A1Small sizeImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierSemiconductor
A high-frequency device has a semiconductor substrate; a high-frequency circuit layer formed on the substrate and including a circuit element and a multilayer wiring layer; electrically conductive pads; rewiring layers connected to the electrically conductive pads; an electrically insulating sealing layer formed on the first electrically insulating layer and the rewiring layer and having a thickness larger than the multilayer wiring layer; electrically conductive posts provided inside the electrically insulating sealing layer and between the rewiring layer and the mounting connection terminals. A first electrically conductive post corresponding to a power source has a first diameter; a second electrically conductive post corresponding to an input of input amplifier has a second diameter less than the first diameter; and a third electrically conductive post corresponding to an output of power output amplifier has a third diameter larger than the second diameter.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
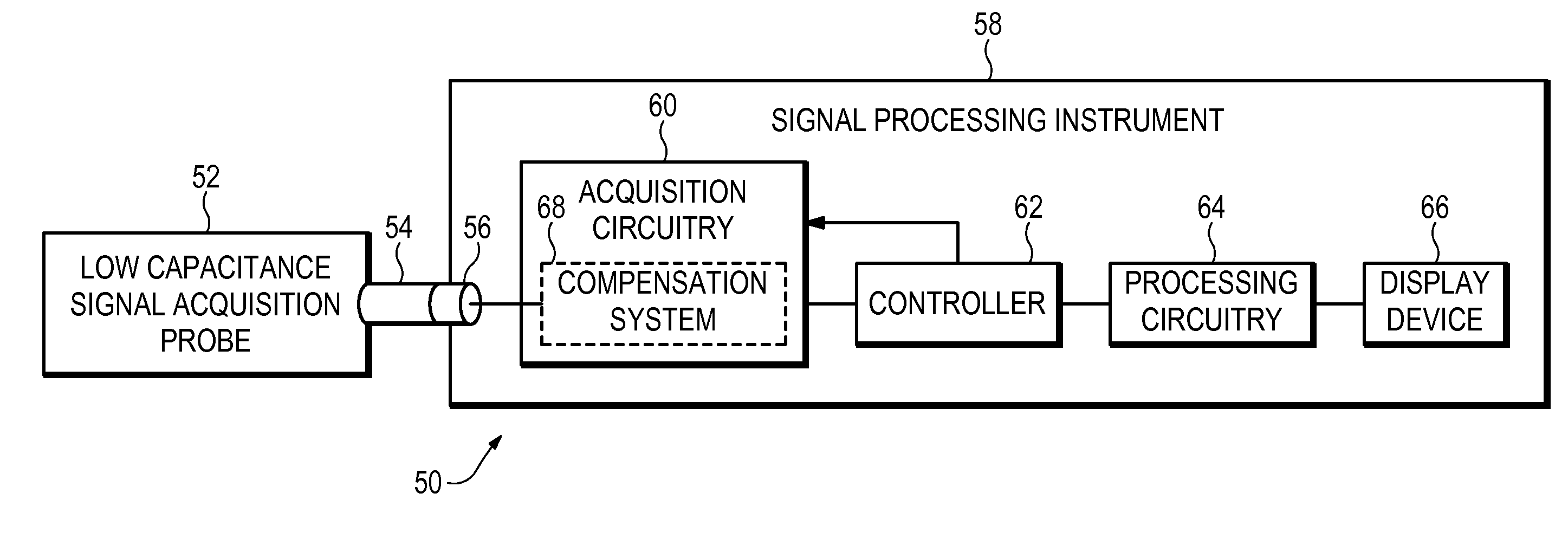
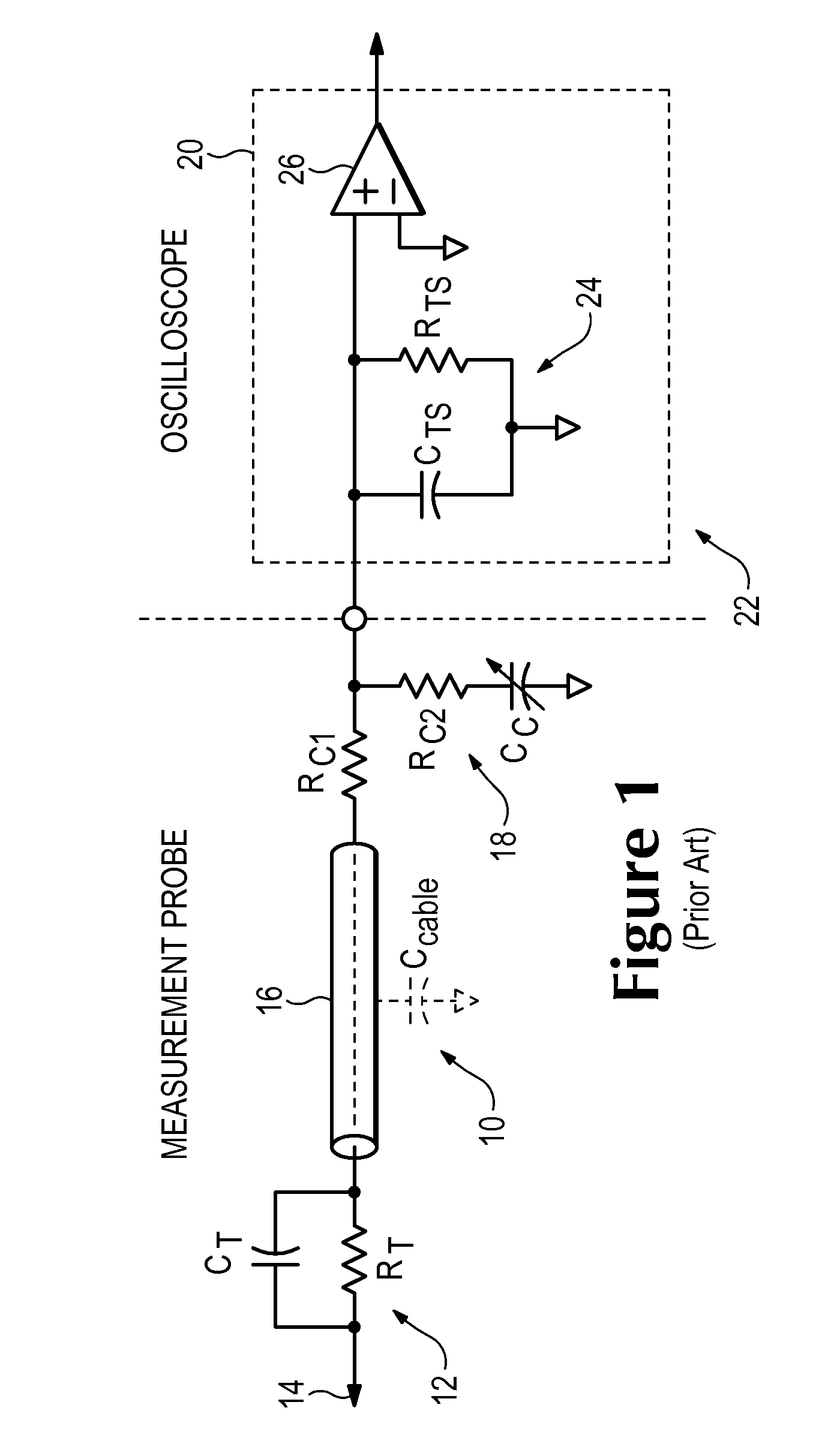
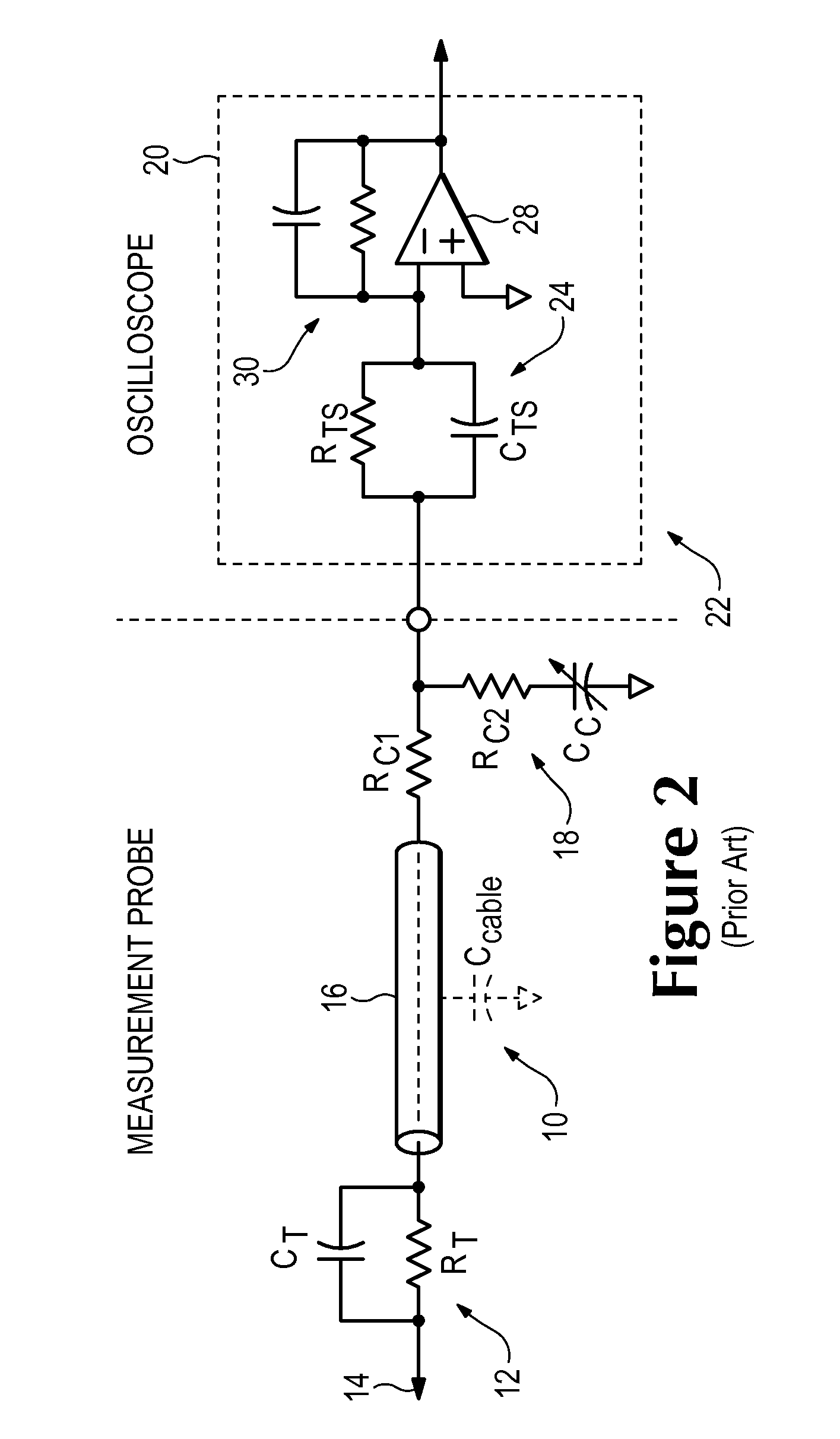
Signal Acquisition System Having Reduced Probe Loading of a Device Under Test
ActiveUS20110074392A1Improve flatnessSpectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceAudio power amplifierElectrical conductor
A signal acquisition system has a signal acquisition probe having probe tip circuitry coupled to a resistive center conductor signal cable. The resistive center conductor signal cable of the signal acquisition probe is coupled to a compensation system in a signal processing instrument via an input node and input circuitry in the signal processing instrument. The signal acquisition probe and the signal processing instrument have mismatched time constants at the input node with the compensation system having an input amplifier with feedback loop circuitry and a shunt pole-zero pair coupled to the input circuitry providing pole-zero pairs for maintaining flatness over the signal acquisition system frequency bandwidth.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Floating input amplifier for capacitively coupled communication
ActiveUS20050285683A1Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifiers controlled by lightCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
One embodiment of the present invention provides a capacitively-coupled receiver amplifier that has an input with no DC coupling. A DC voltage is programmed on the input. During programming, a transmitter is held at a voltage at a midpoint between a voltage that represents a logical “1” and a voltage that represents a logical “0” and the input voltage of the receiver amplifier is programmed to be substantially the switching-threshold voltage for the receiver amplifier. Then, during normal data communication, the transmitter drives high and low electrical signals that are coupled to the receiver amplifier. Since the input of the receiver amplifier has been substantially set to the DC voltage, the receiver amplifier need not control the DC voltage of the input for each transition in the electrical signals.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
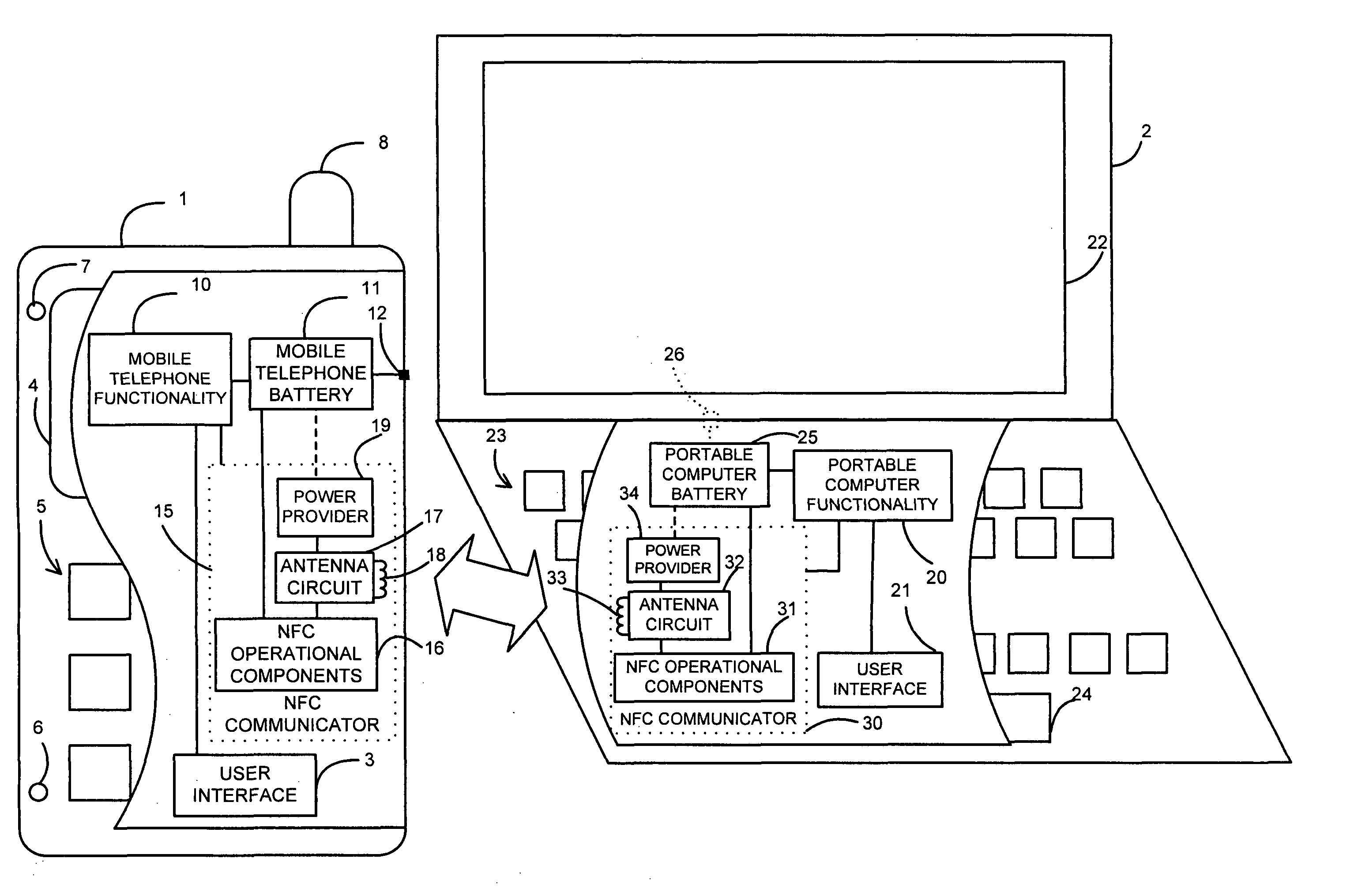
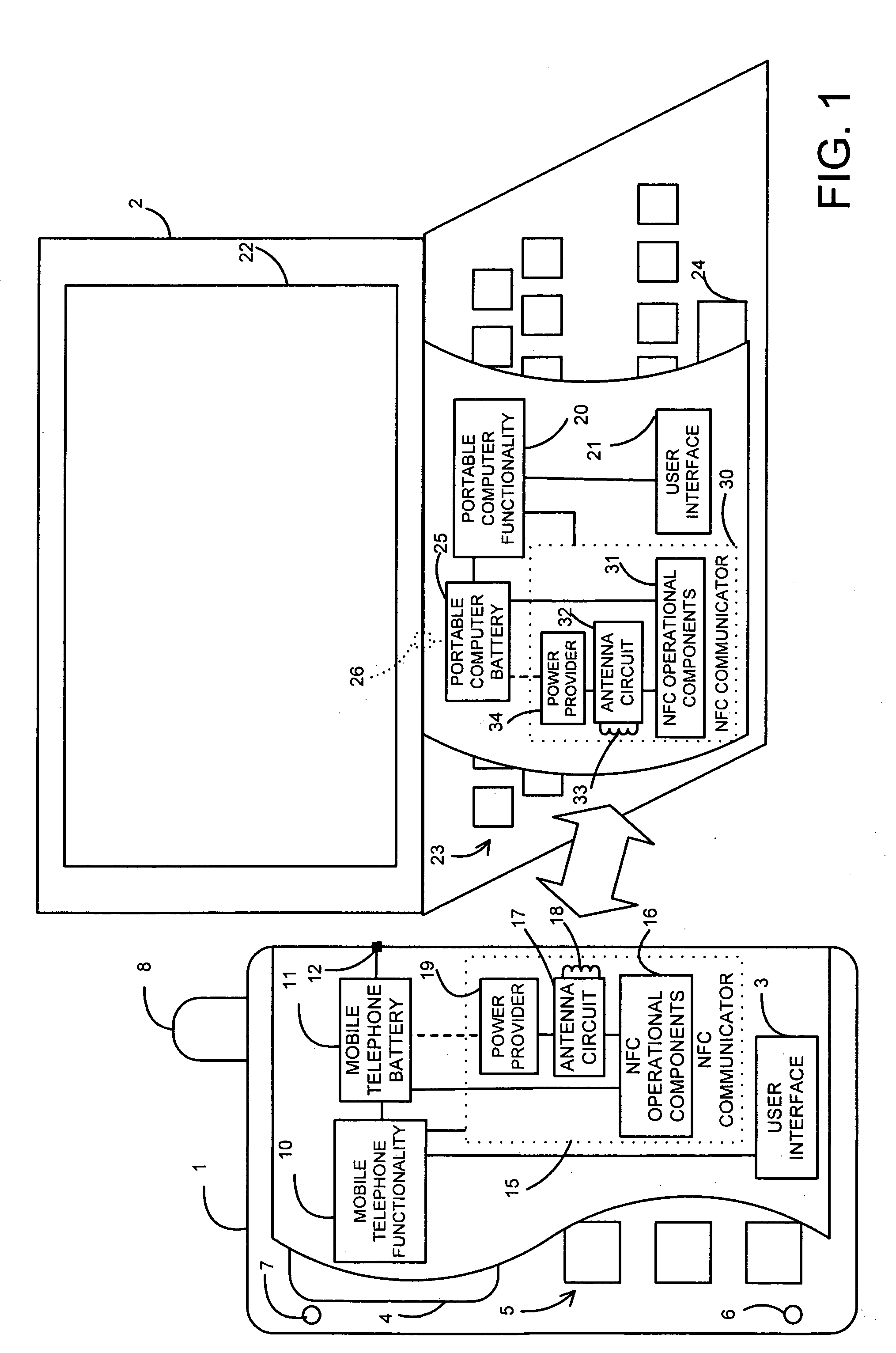
Near field RF communicators and near field RF communications-enabled devices
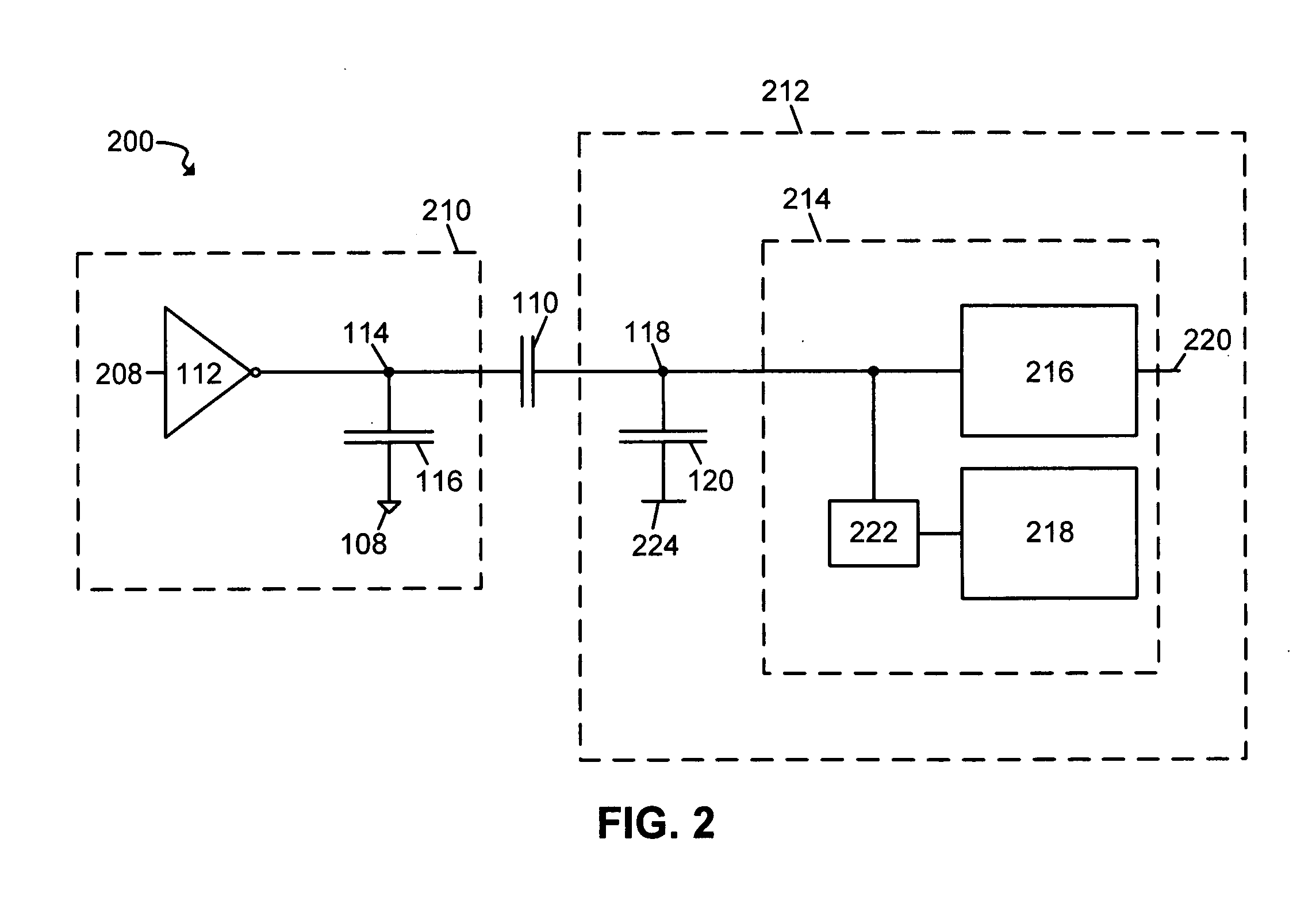
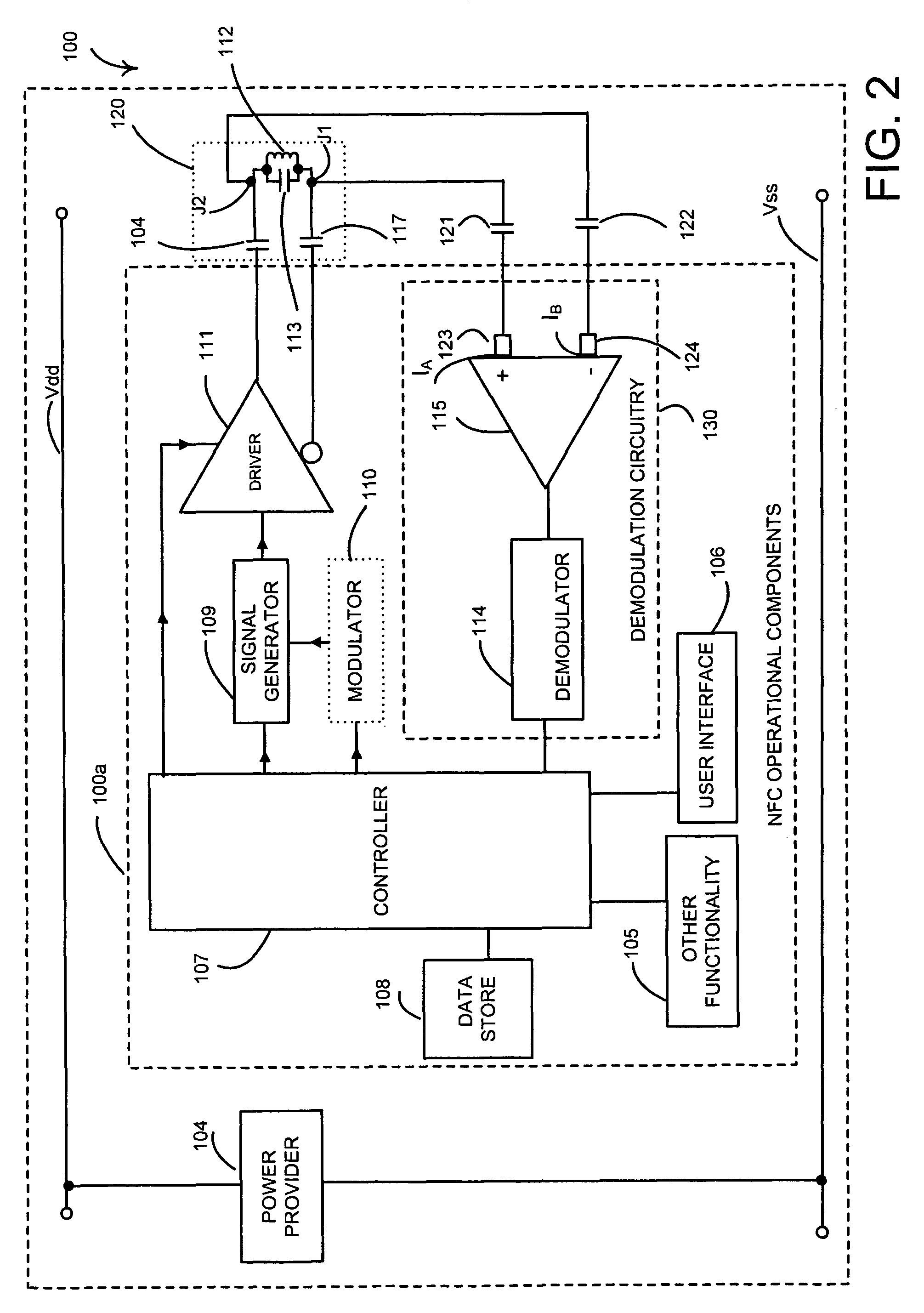
ActiveUS8565675B2Less noise sensitiveMinimisationFrequency demodulator arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsAudio power amplifierRadio frequency signal
A near field RF communicator has an antenna circuit (120) to receive a modulated radio frequency signal by inductive coupling and demodulation circuitry (130 or 131) to extract the modulation from a received modulated radio frequency signal inductively coupled to the antenna circuit. The demodulation circuitry has a virtual earth input comprising a current mirror. The demodulation circuitry may be formed by an amplifier (115 or 116) and a demodulator (114) coupled to an output of the amplifier. The amplifier may be a single input amplifier (116) coupled to an output of the antenna circuit or may be a differential amplifier (115) having first and second inputs to receive the modulated radio frequency signal from first and second outputs of the antenna circuit, with each amplifier input providing a virtual earth input.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Linearized and balanced mixer apparatus and signal mixing method
Method and apparatus are provided for linearized balanced signal mixing. A signal mixing circuit (10) for translating a radio frequency (RF) signal is provided comprising an input amplifier (12), a mixer network (14), and an output buffer amplifier (18). The input amplifier (12) is configured to produce an amplified RF signal and cancel an input third-order intermodulation (IM3) distortion in the amplified RF signal with a cross-coupled feedback amplifier (13). The mixer network (14) is configured to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal based on the amplified RF signal and a local oscillator signal. The output amplifier (18) is configured to buffer the IF signal and cancel an output IM3 distortion in the IF signal with a cross-coupled feedback amplifier (19). The input amplifier (12) and cross-coupled feedback amplifier (13) also serve as a bias current source for the mixer network (14), thus lowering the supply voltage required for the mixing circuit (10).
Owner:APPLE INC
Battery tester
InactiveUS8193771B2High impedance inputElectrophonic musical instrumentsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectricityAudio power amplifier
Owner:NUWAVE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com