Transconductance filter control system
a control system and filter technology, applied in gain control, frequency selective two-port networks, continuous tuning, etc., can solve the problems of large silicon wafer or circuit size, large power consumption, and inability to manually adjus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Other objects, features and advantages will occur to those skilled in the art from the following description of a preferred embodiment and the accompanying drawings, in which:
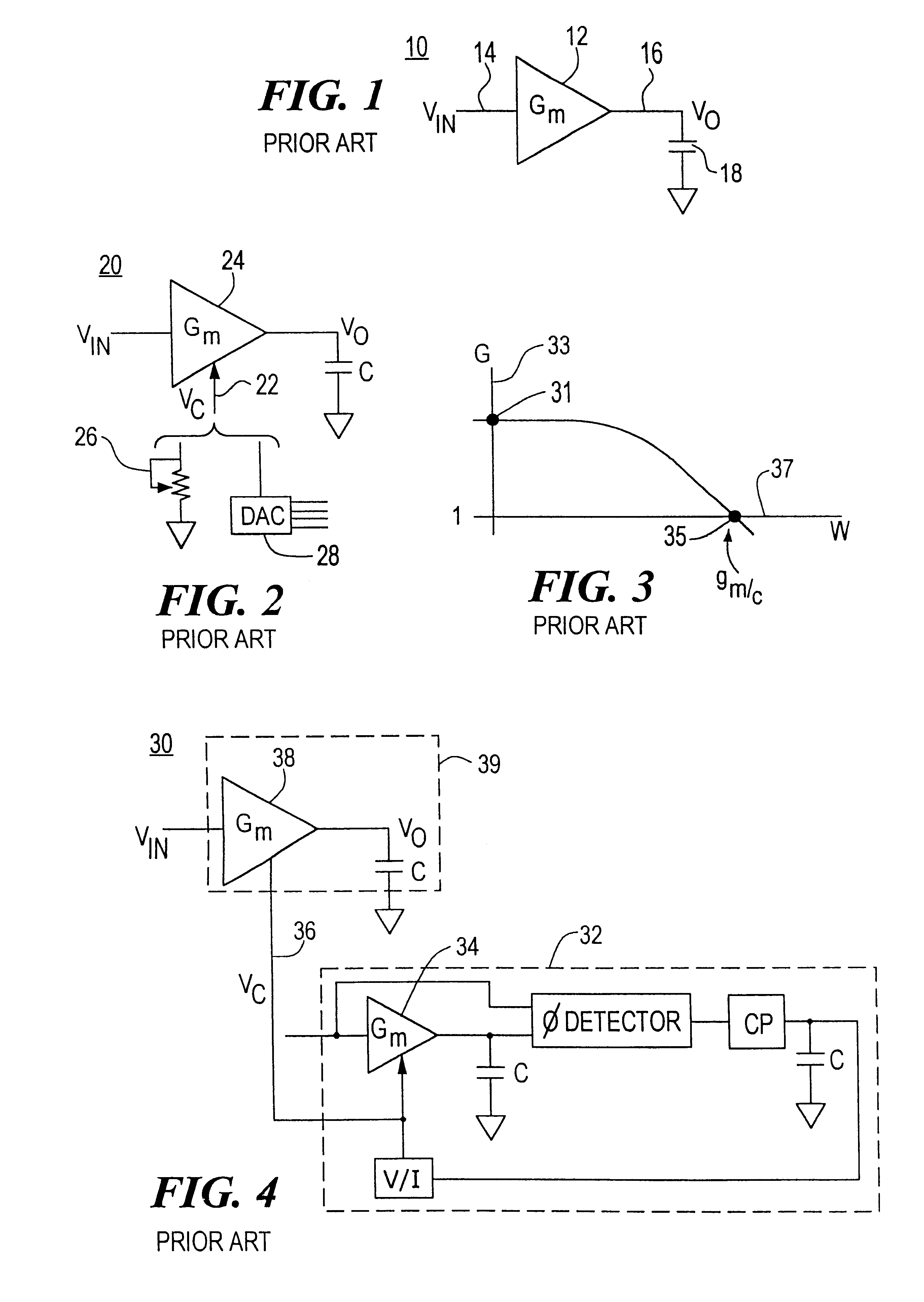
FIG. 1 is a schematic view of a prior art transconductance filter circuit;
FIG. 2 is a schematic view of a prior art transconductance filter circuit incorporating a manual transconductance control circuit;
FIG. 3 is a graph showing the frequency response of a prior art transconductance filter;
FIG. 4 is a schematic view of a prior art transconductance filter circuit incorporating a phase look loop based automatic transconductance control circuit;
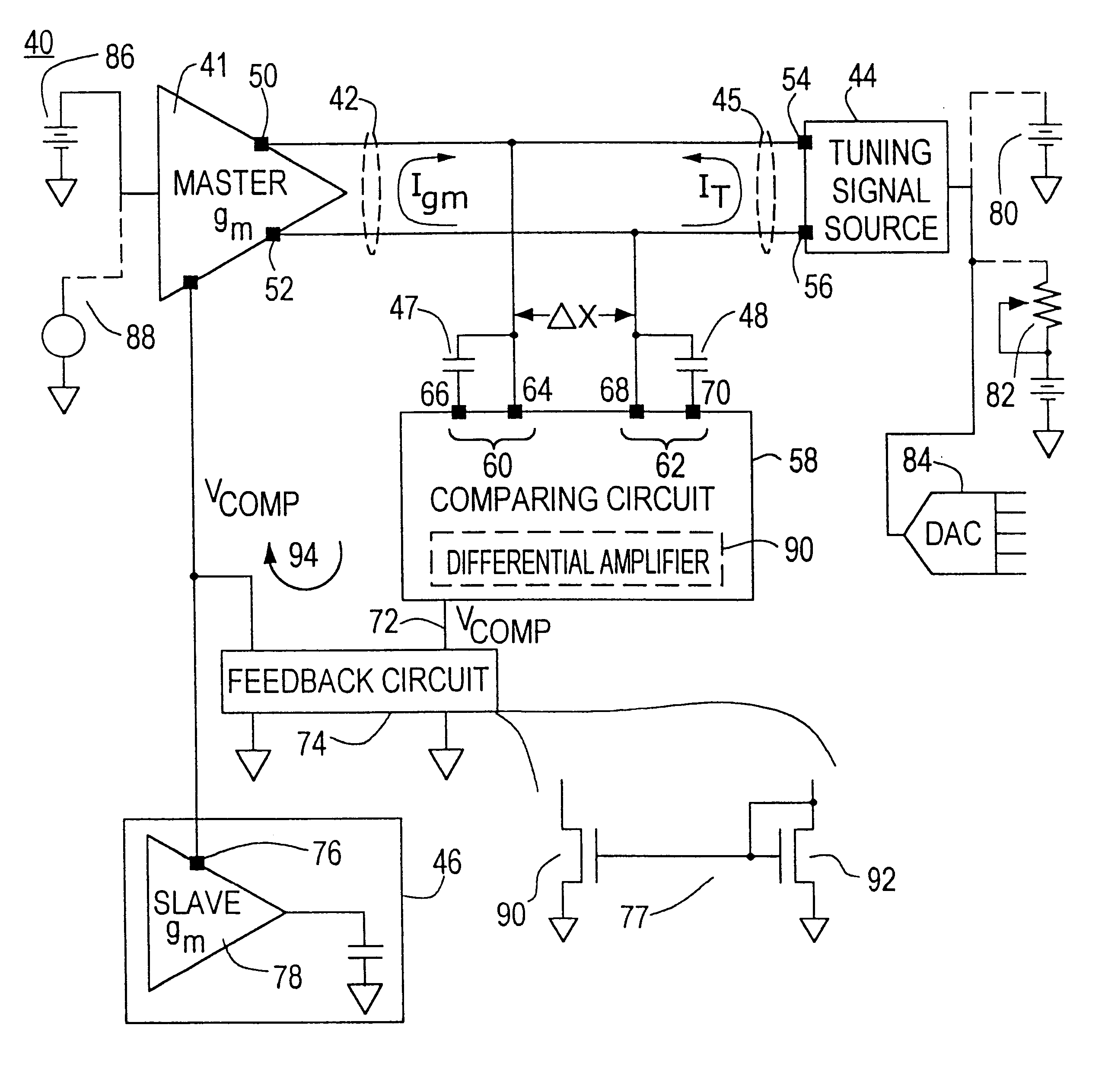
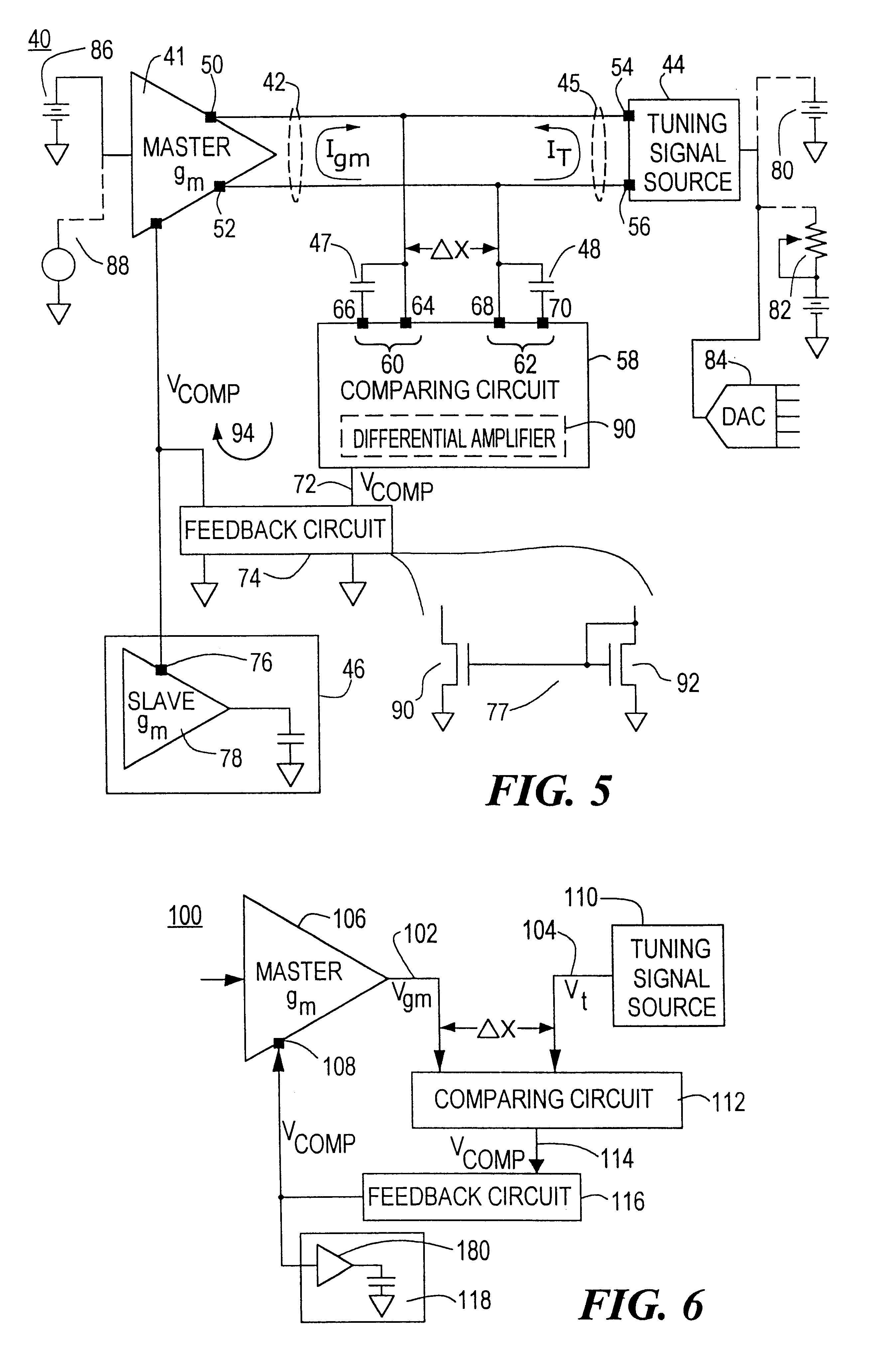
FIG. 5 is a schematic view of the transconductance filter control system of this invention in which the output of the master transconductance amplifier and the tuning signal are currents;
FIG. 6 is a diagrammatic view of another embodiment of the transconductance filter control system of this invention in which the output of the master transconductance amplifier and the tun...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com