Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Point to optimization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
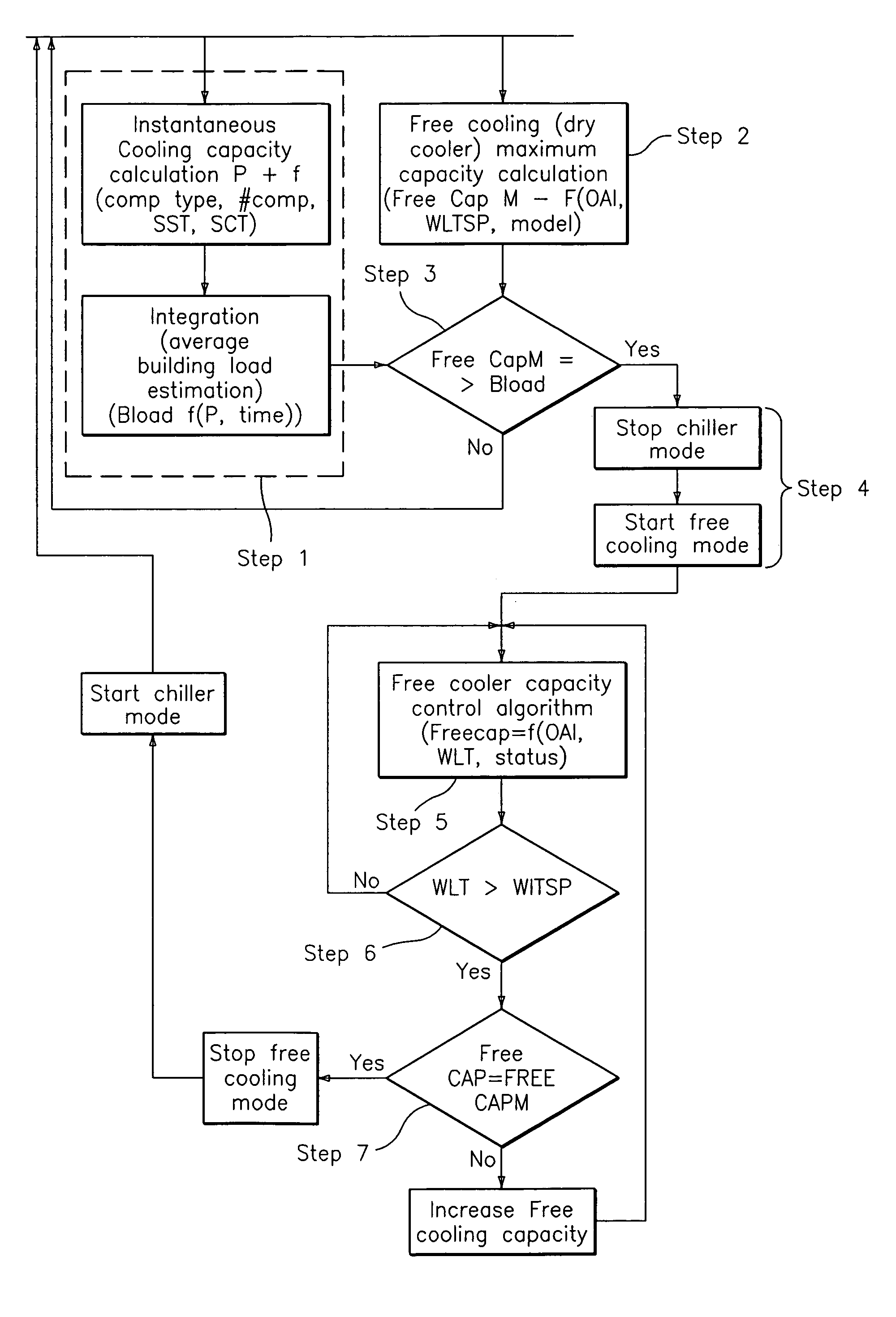
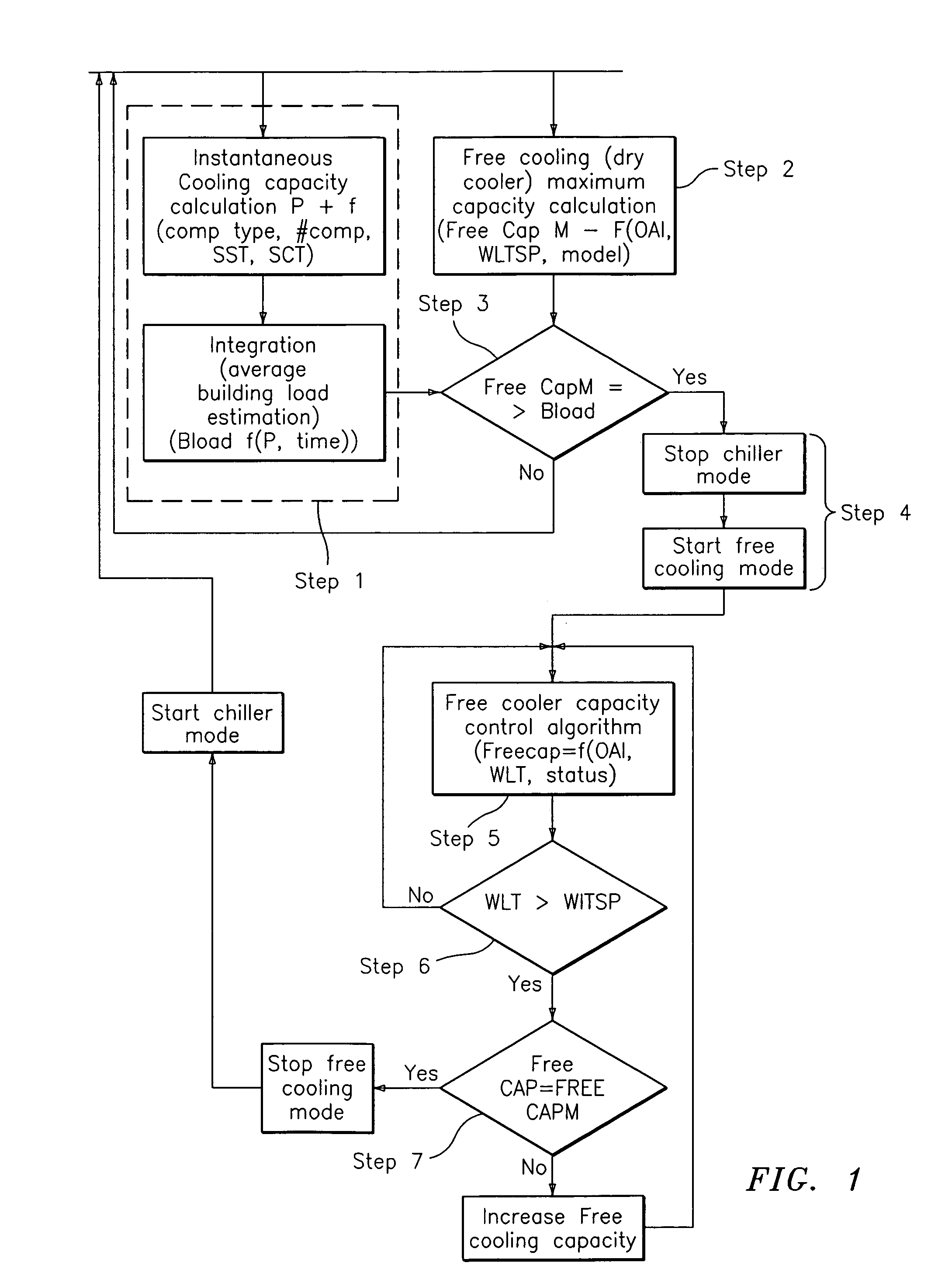
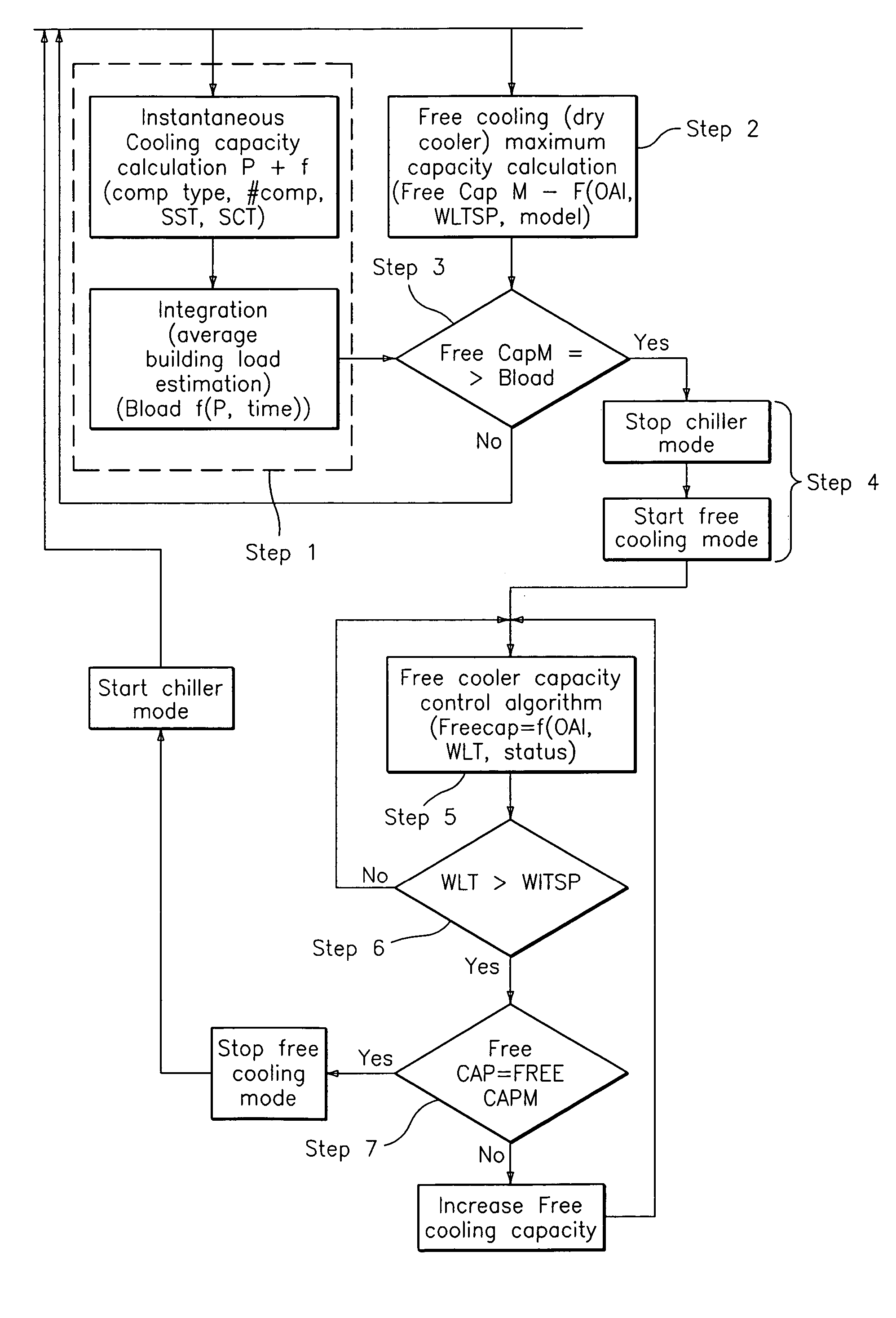
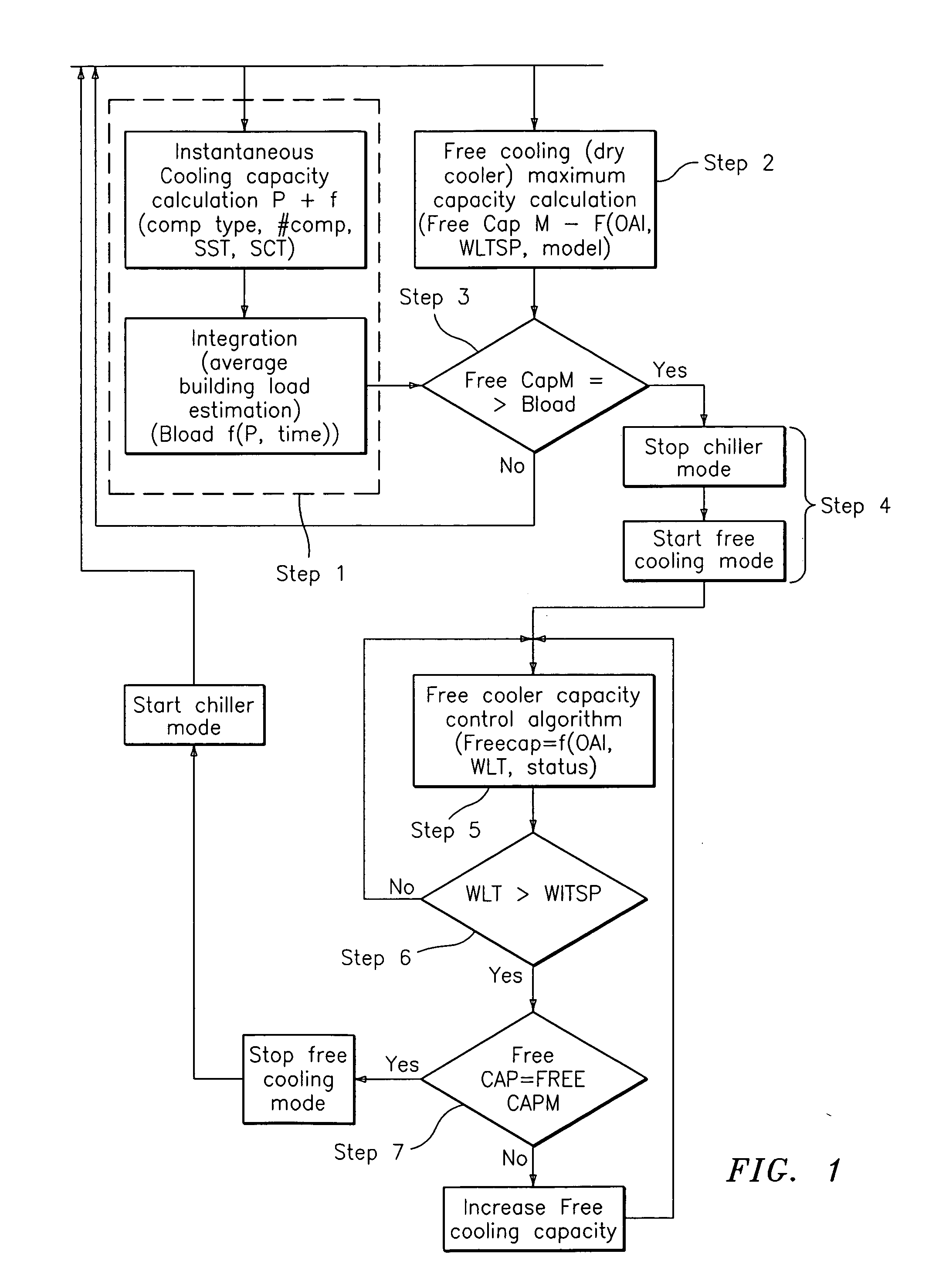
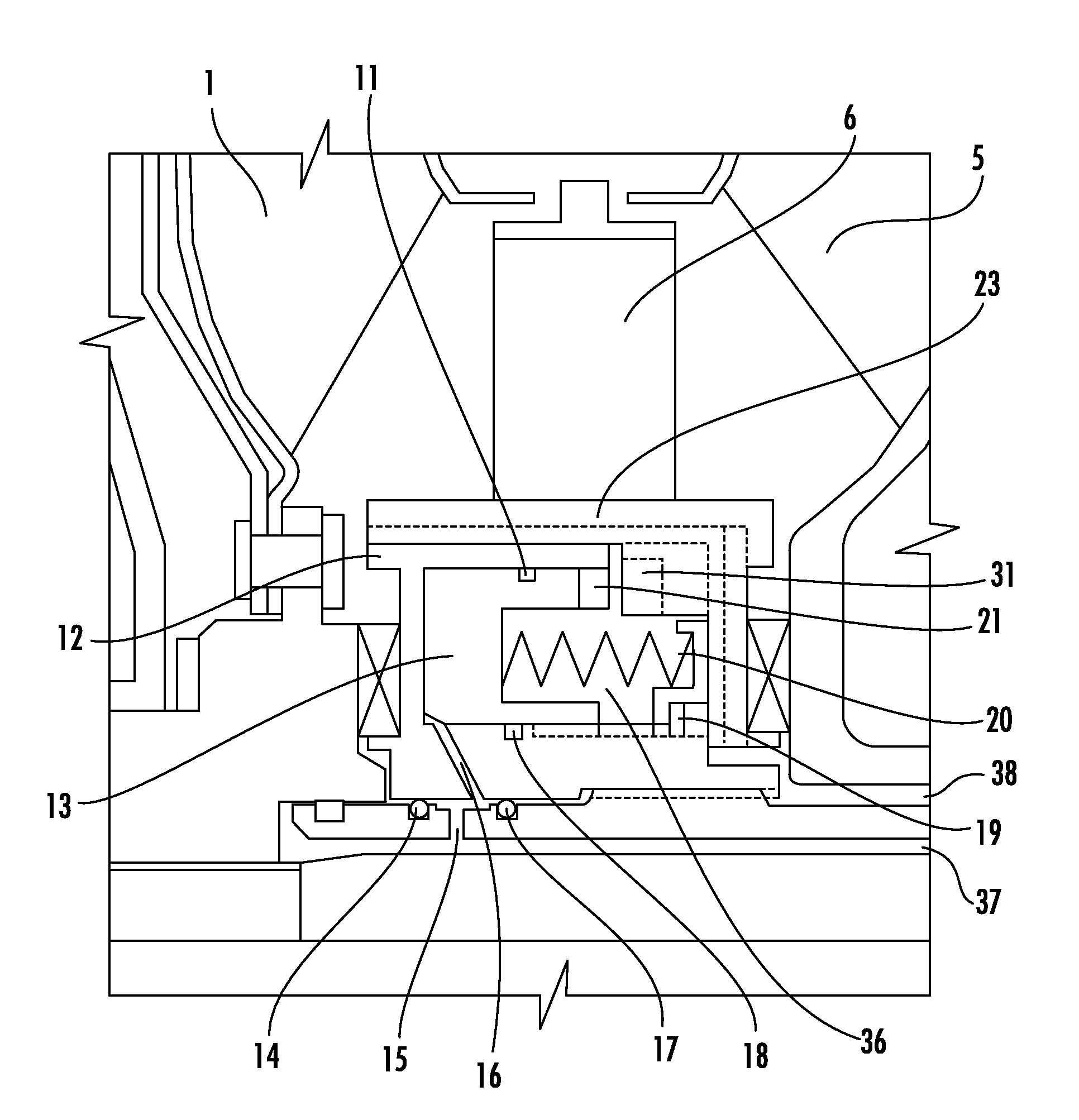
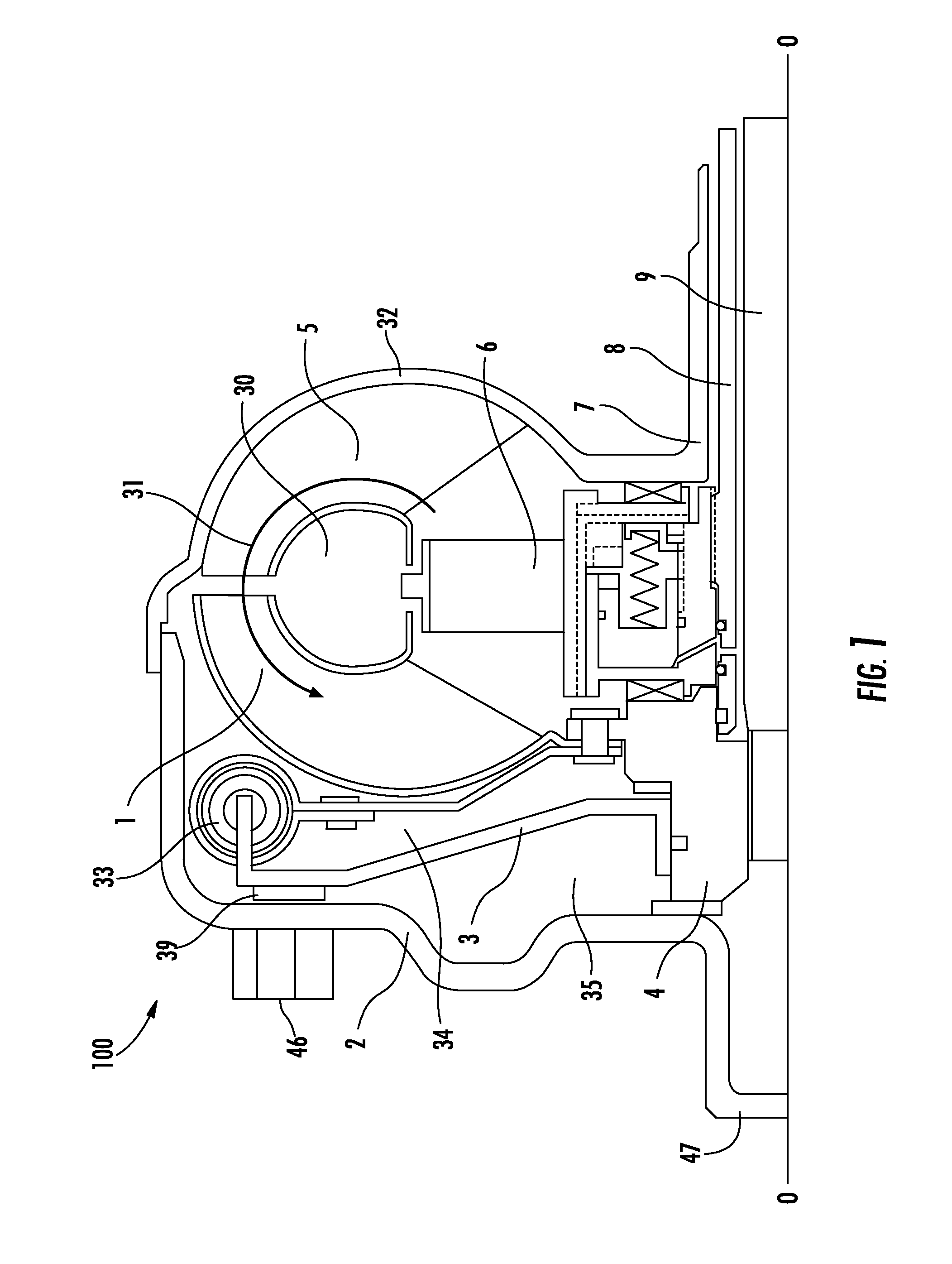
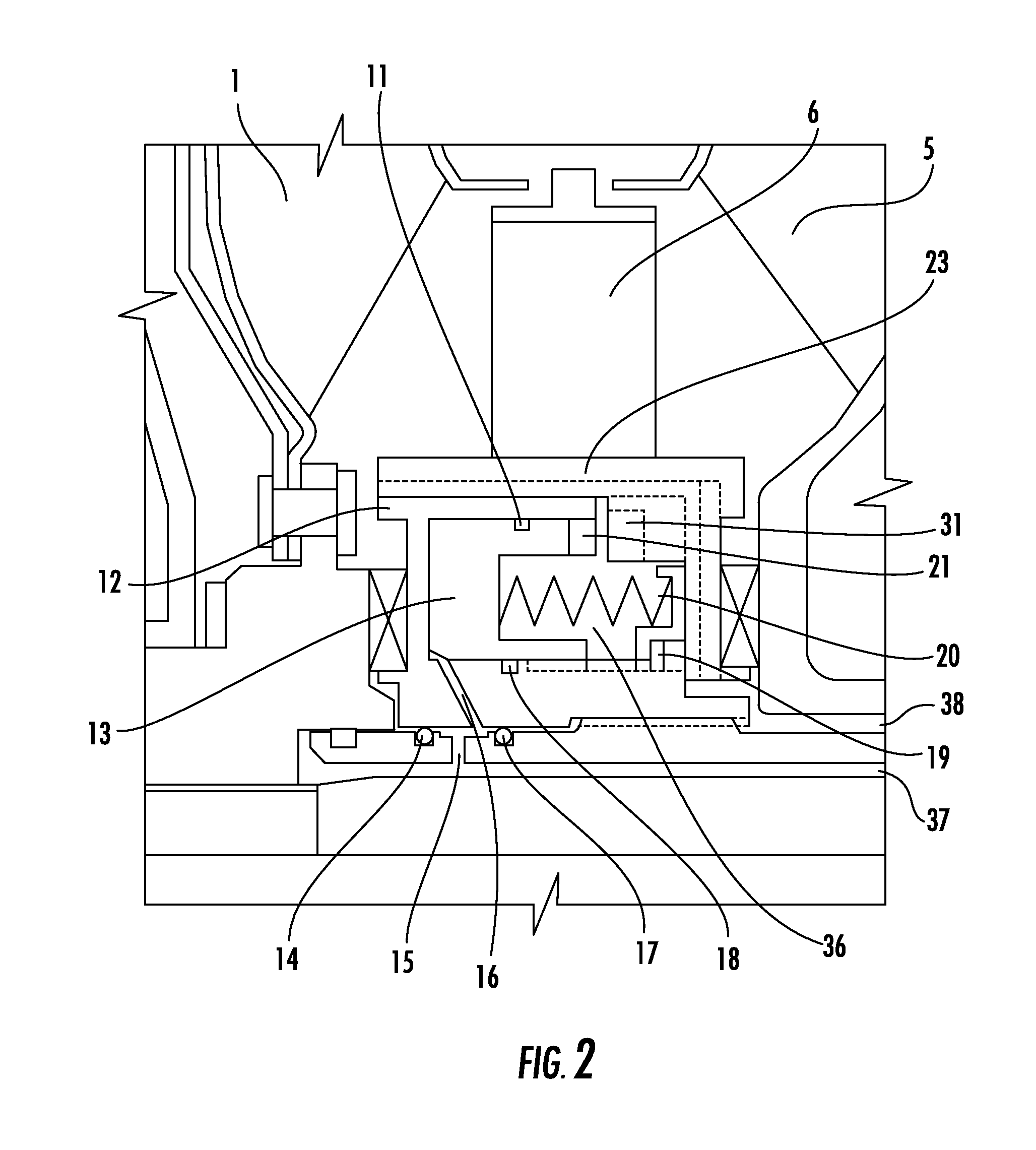
Free cooling activation optimized controls
ActiveUS7036330B2Point to optimizationMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsFree coolingEngineering
A method for optimizing free cooling activation comprising the steps of operating an air conditioning unit in a chiller mode, determining a building load, determining a free cooler maximum available capacity (FreeCapM), and activating a free cooling mode of the air conditioning unit when the free cooler maximum available capacity is greater than or equal to the building load.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
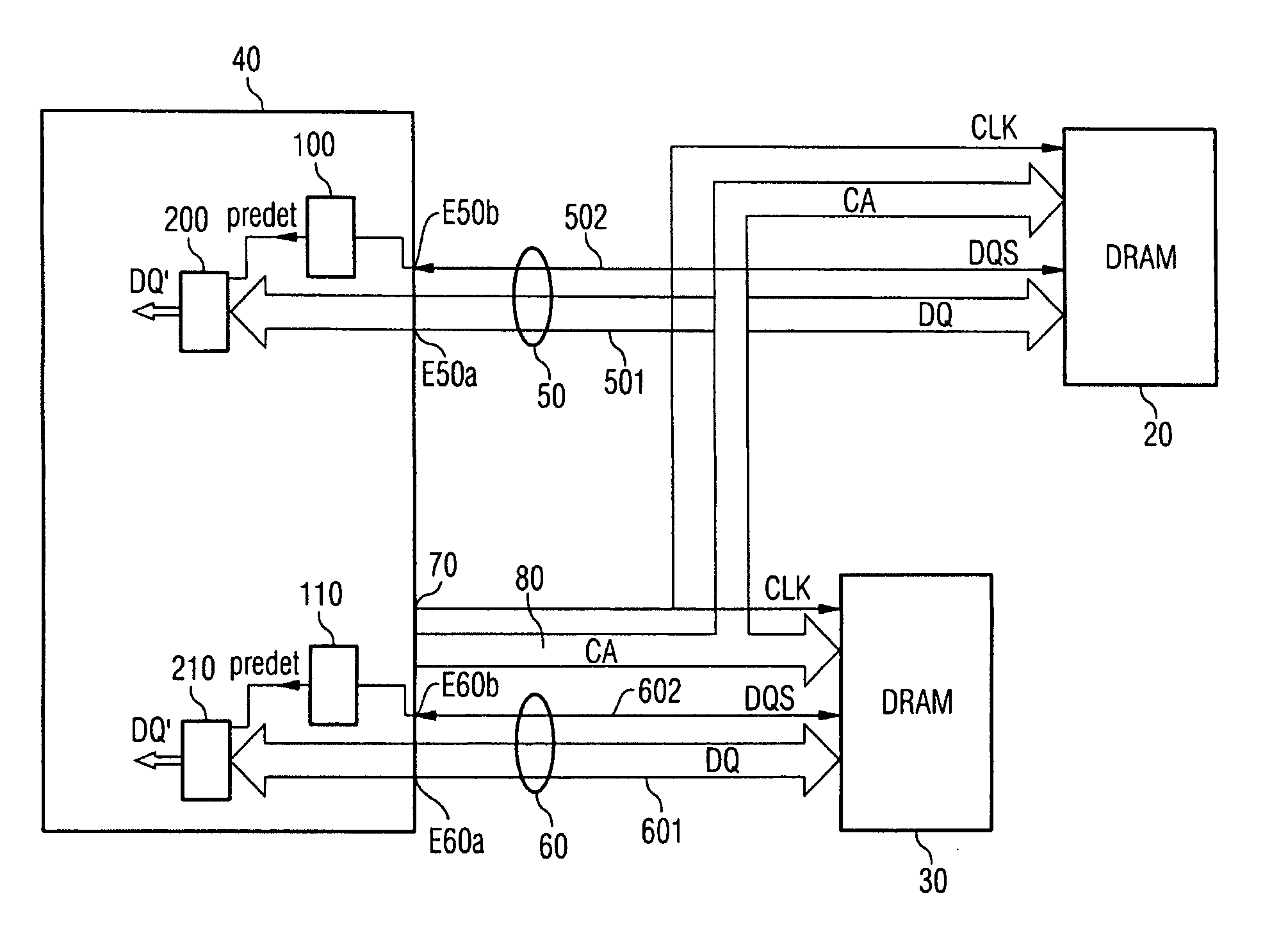
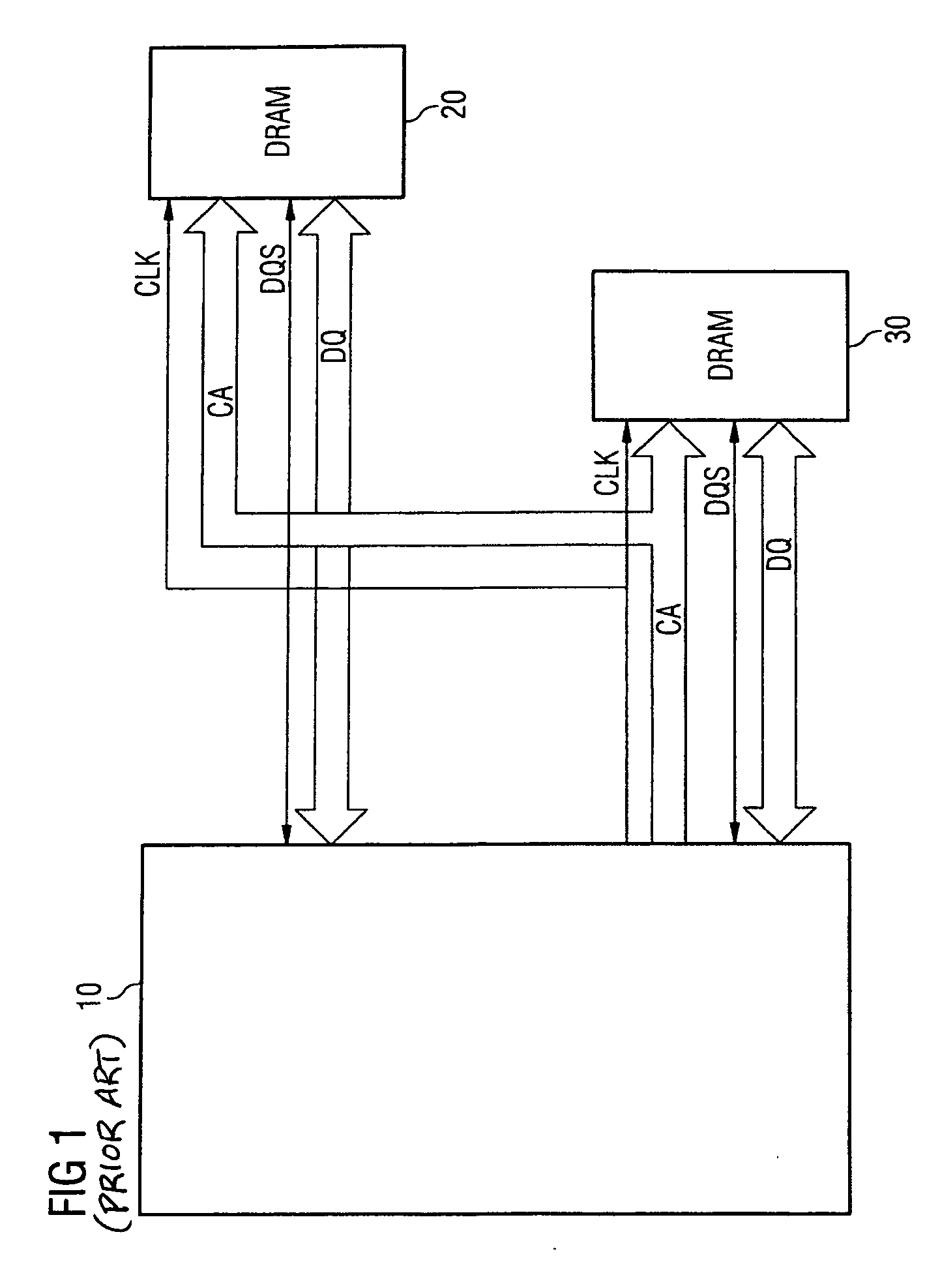
Memory control module and method for operating a memory control module
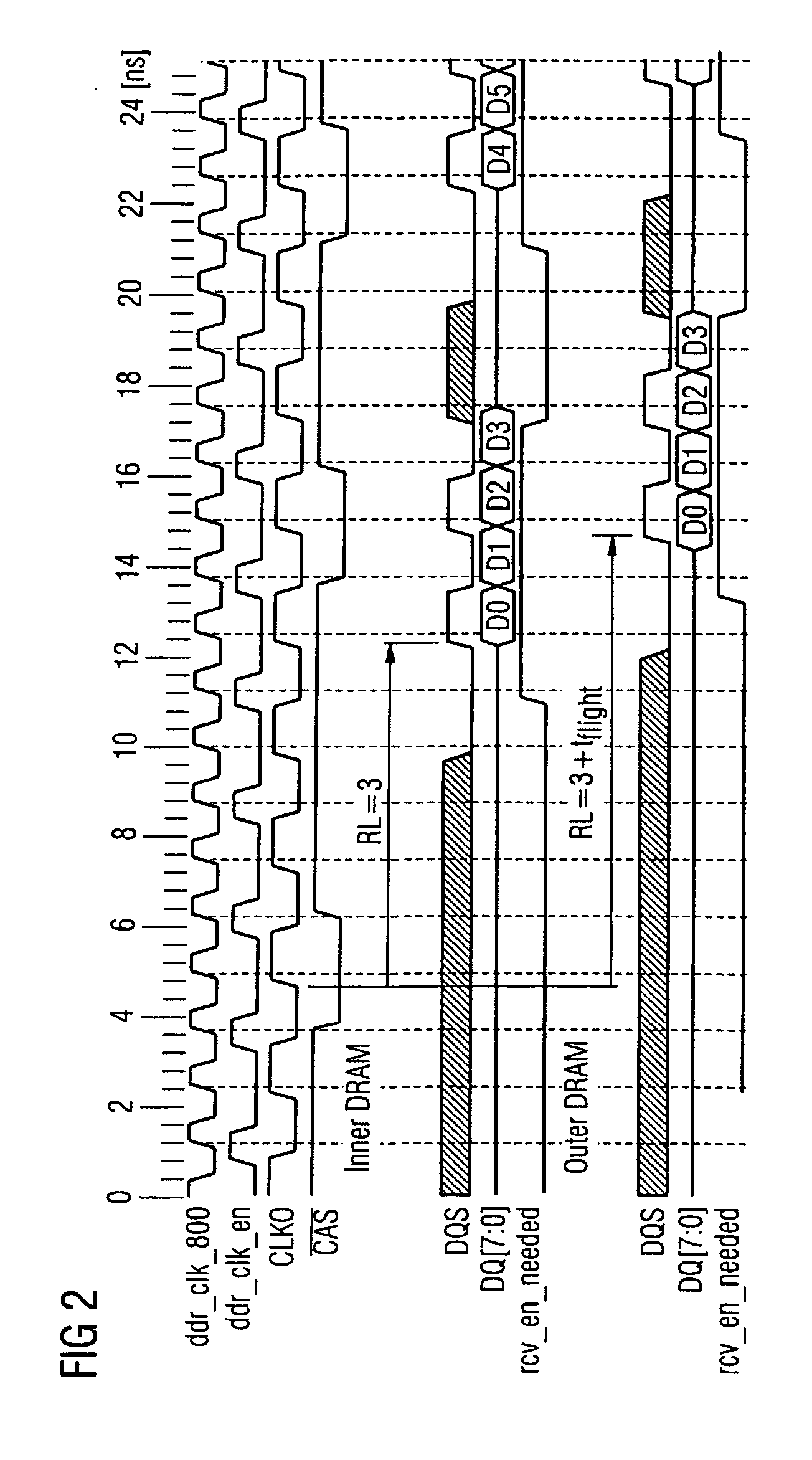
InactiveUS20060077730A1Easy to detectPoint to optimizationDigital storageElectric digital data processingAudio power amplifierControl signal
The invention relates to a method for transmitting memory data from a memory to a memory control module, in which method a read command is transmitted from the memory control module to the memory, and the memory data which correspond to the read command are transmitted from the memory to the memory control module, a sampling control signal which controls the acceptance of the memory data into the memory control module being transmitted from the memory to the memory control module in parallel with the memory data. In order to avoid defective data transmission between the memory and the memory control module as reliably as possible, the sampling control signal is transmitted with a preamble which indicates the imminent beginning of data transmission, for the sampling control signal to be monitored for the presence of the preamble, and for a data input amplifier of the memory control module to be switched on only when the presence of the preamble is detected.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Broadband wireless distribution system for mobile platform interior
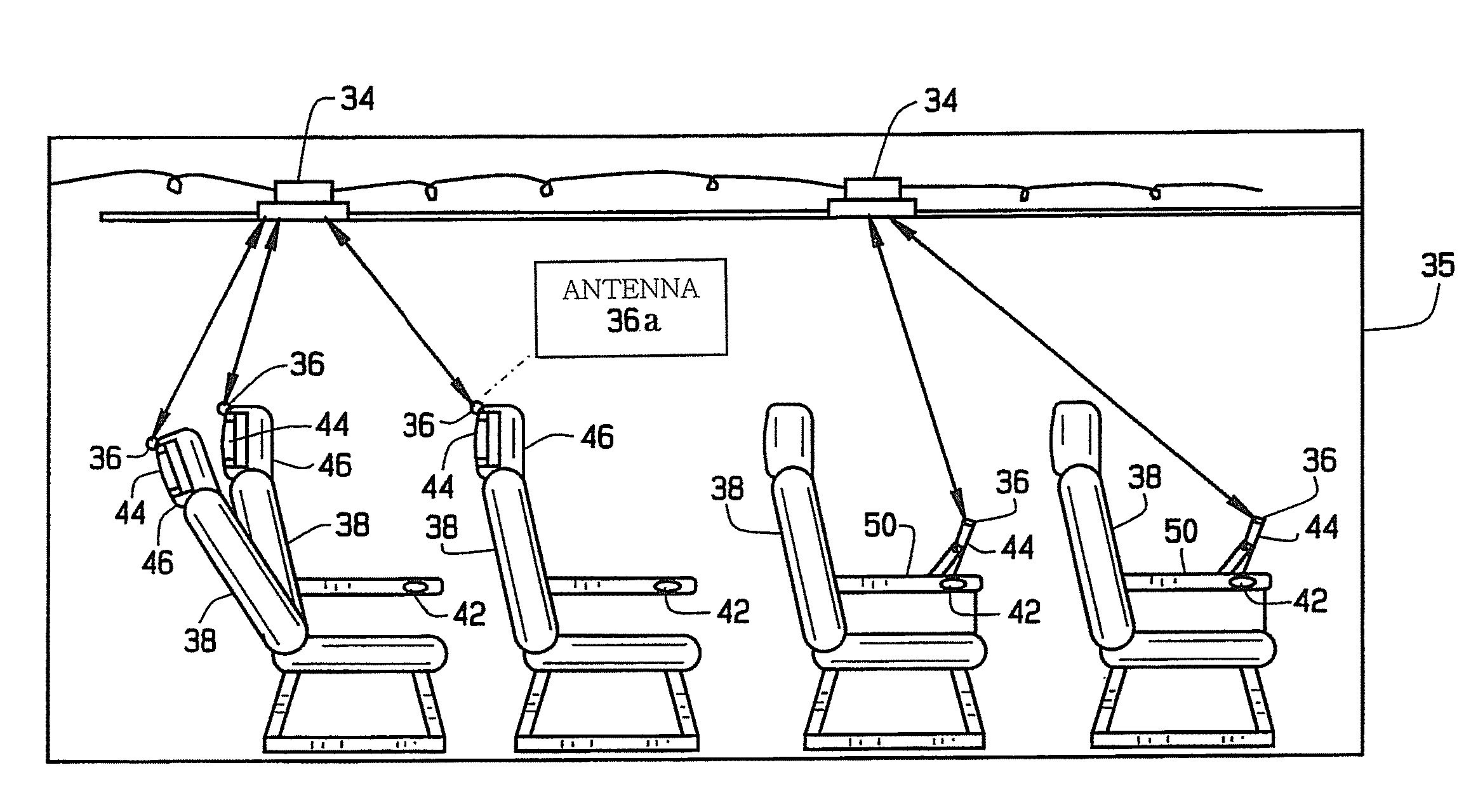
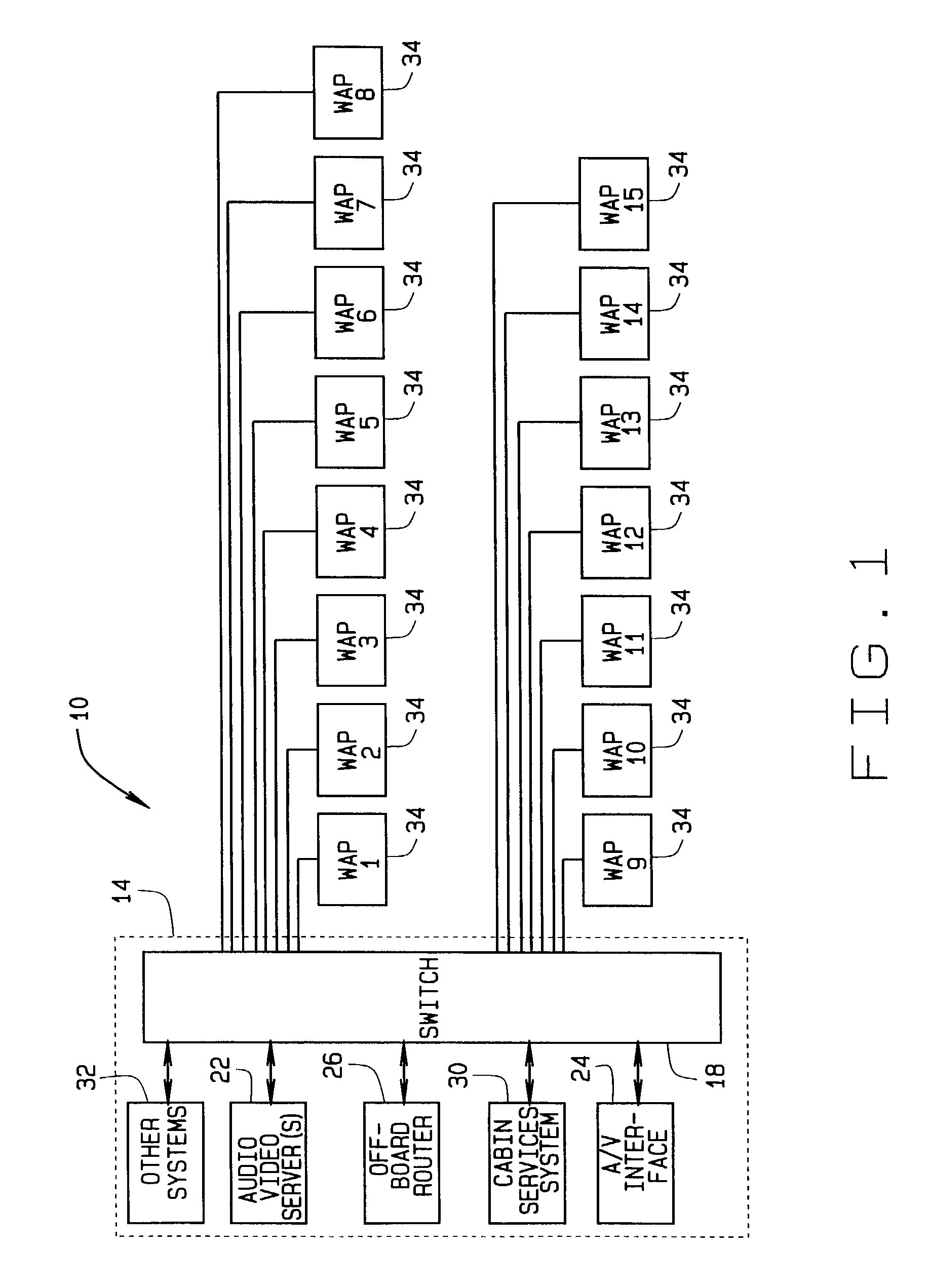
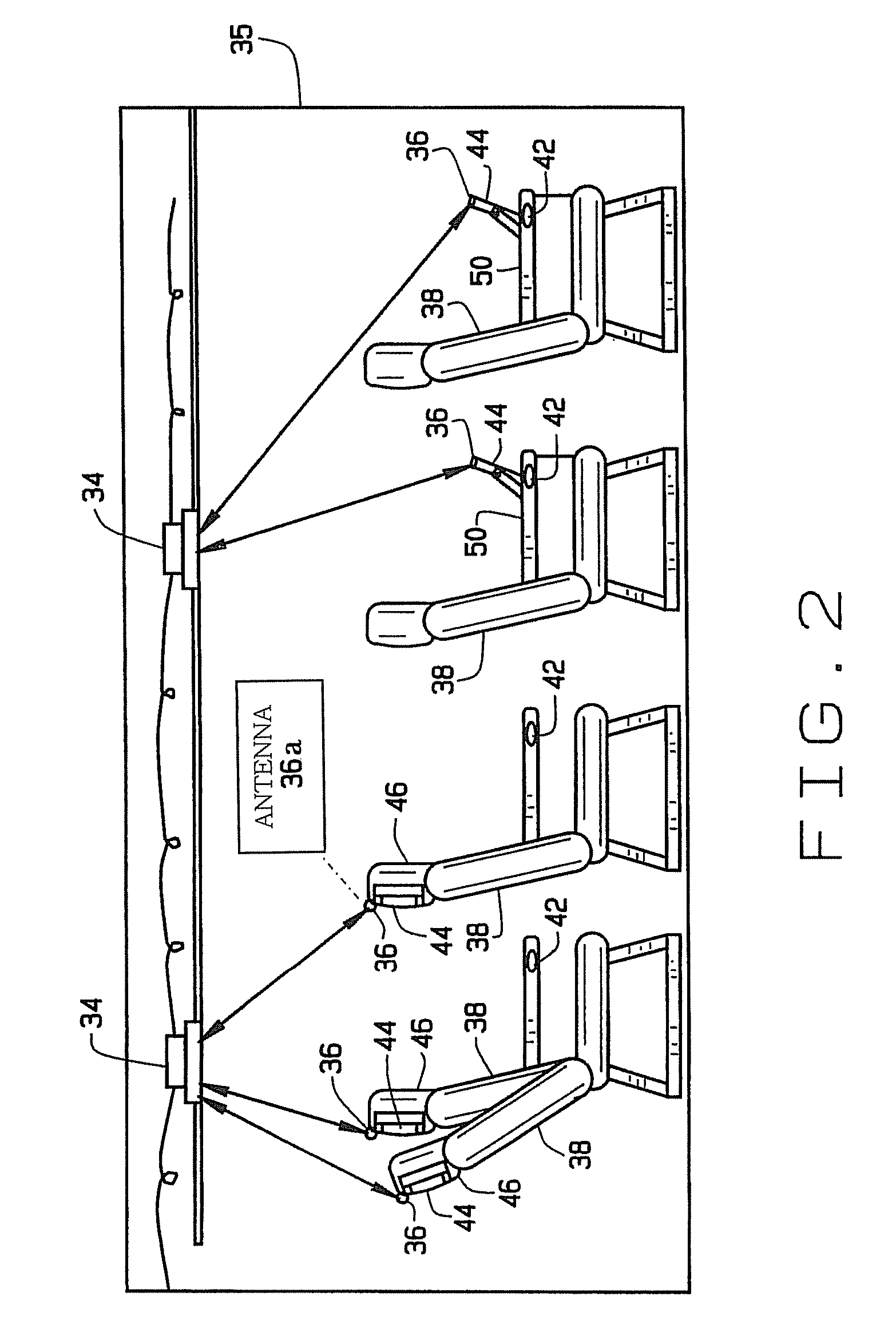
ActiveUS7769398B2Increase heightReduce interferenceBroadcast specific applicationsGHz frequency transmissionBroadbandInterface circuits
A broadband wireless distribution network for a passenger cabin area of a mobile platform. The broadband wireless distribution network includes a plurality of wireless access points (WAPs) connected to a server and switching system and a plurality of wireless network interface circuits (NICs) strategically located about the passenger cabin. Additionally the broadband wireless distribution network includes a plurality of antennas connected to the WAPs such that at least one antenna is connected to each WAP. The antennas are capable of providing RF coverage patterns to specific overlapping areas within the passenger cabin, thereby allowing communication between each WAP and at least one NIC.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Electromechanical coupling-based direction adjustment method of large-scale forming double-reflection surface antenna
ActiveCN105206941AImproved beam pointing offsetPoint to optimizationAntennasElectricityElement model
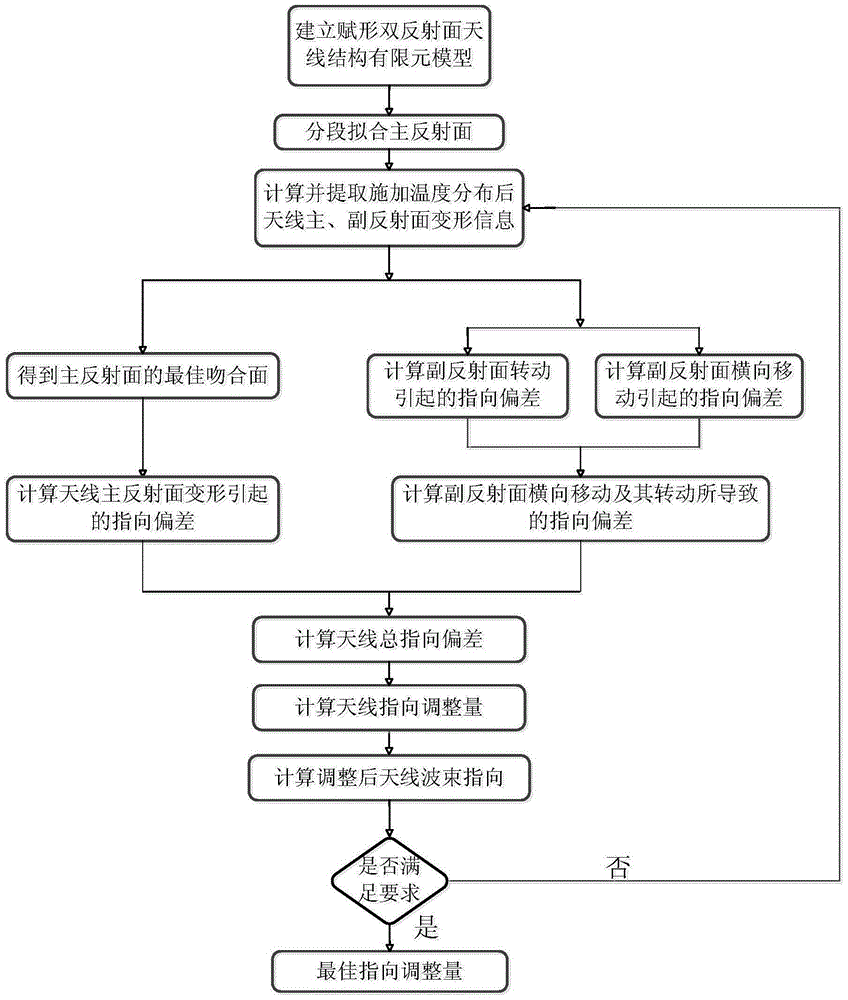
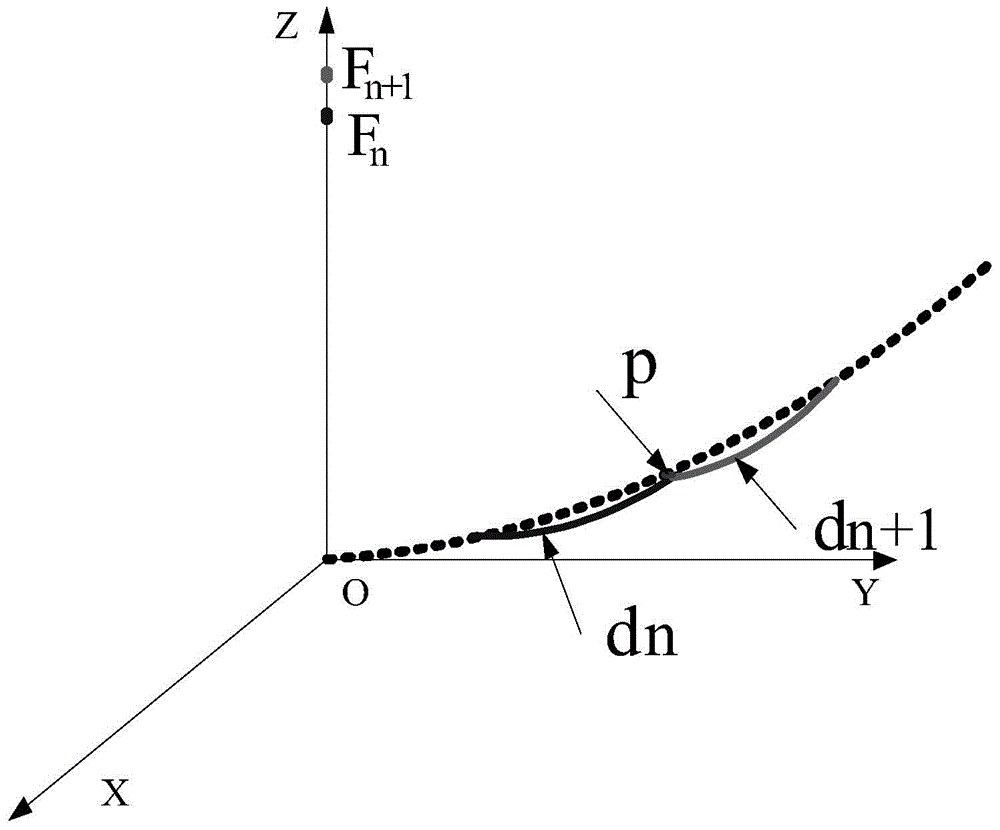
The invention discloses an electromechanical coupling-based direction adjustment method of a large-scale forming double-reflection surface antenna. The method includes the following steps that: (1) the finite element model of an antenna structure is established; (2) the piecewise fitting surface of the forming main reflection surface of the antenna is determined; (3) finite element node coordinates after the thermal deformation of the main reflection surface, as well as the rotation angle and vertex displacement quantity of an auxiliary reflection surface are calculated; (4) the optimal matching surface of the forming main reflection surface of the antenna after deformation is determined; (5) antenna direction deviation caused by temperature distribution of the main reflection surface of the antenna is calculated; (6) direction deviation of the auxiliary reflection surface caused by the thermal deformation of the antenna is calculated; (7) total direction deviation caused by the structural thermal deformation of the antenna is calculated; (8) the total direction deviation of the antenna under a local coordinate system is converted into direction adjustment quantity of the antenna under a geodetic coordinate system; and (9) the direction of the antenna and the direction of beams after adjustment are calculated. According to the method of the invention, the electric performance of the antenna is improved through adjusting the azimuth pitch angle of an antenna servo system. The analysis and calculation processes of the method are more concise and efficient.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Pixel electrode structure and liquid crystal display panel
ActiveCN105137678AImprove electric field distributionPoint to optimizationNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Free cooling activation optimized controls
ActiveUS20050284162A1Point to optimizationMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsFree coolingAir conditioning
A method for optimizing free cooling activation comprising the steps of operating an air conditioning unit in a chiller mode, determining a building load, determining a free cooler maximum available capacity (FreeCapM), and activating a free cooling mode of the air conditioning unit when the free cooler maximum available capacity is greater than or equal to the building load.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
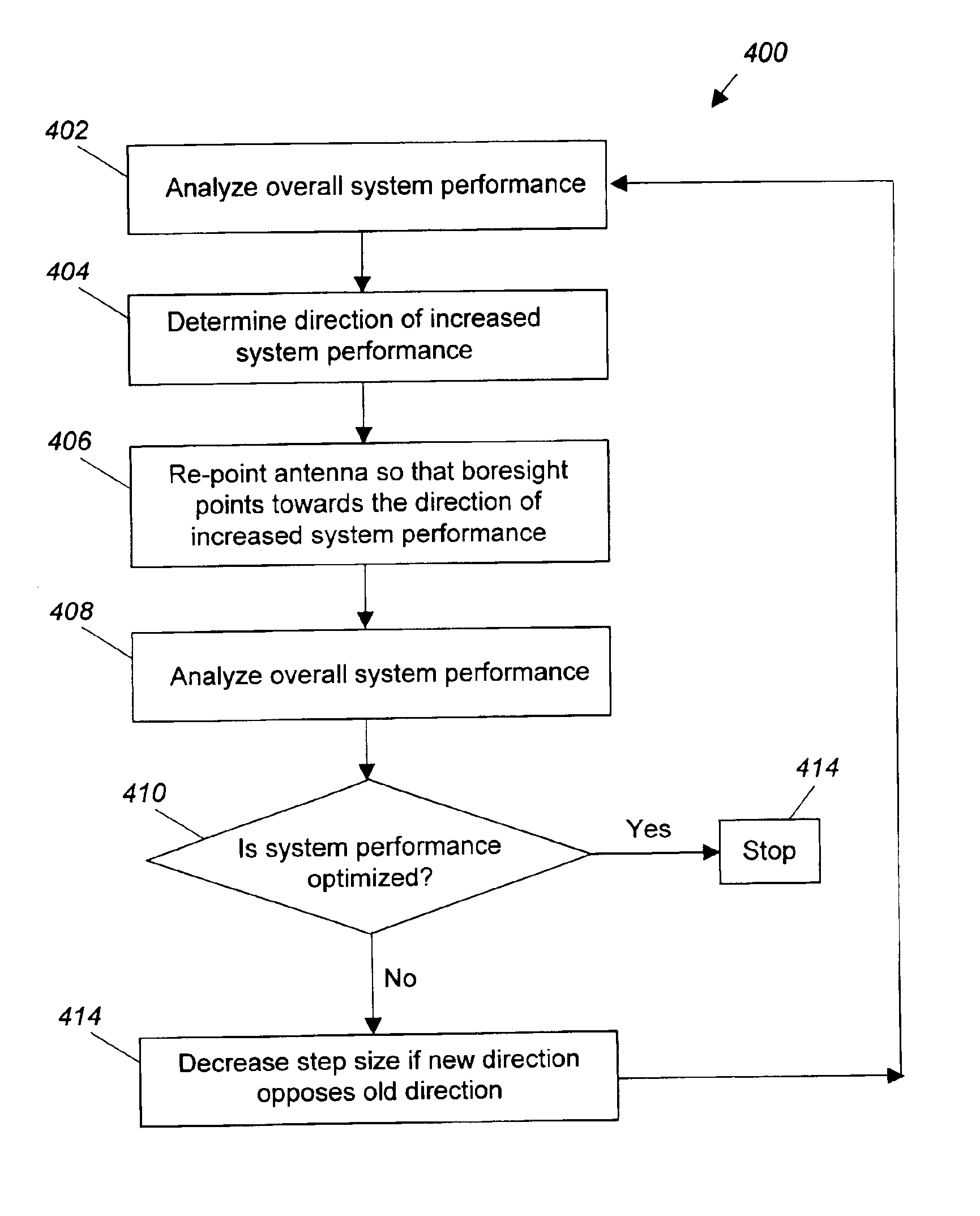
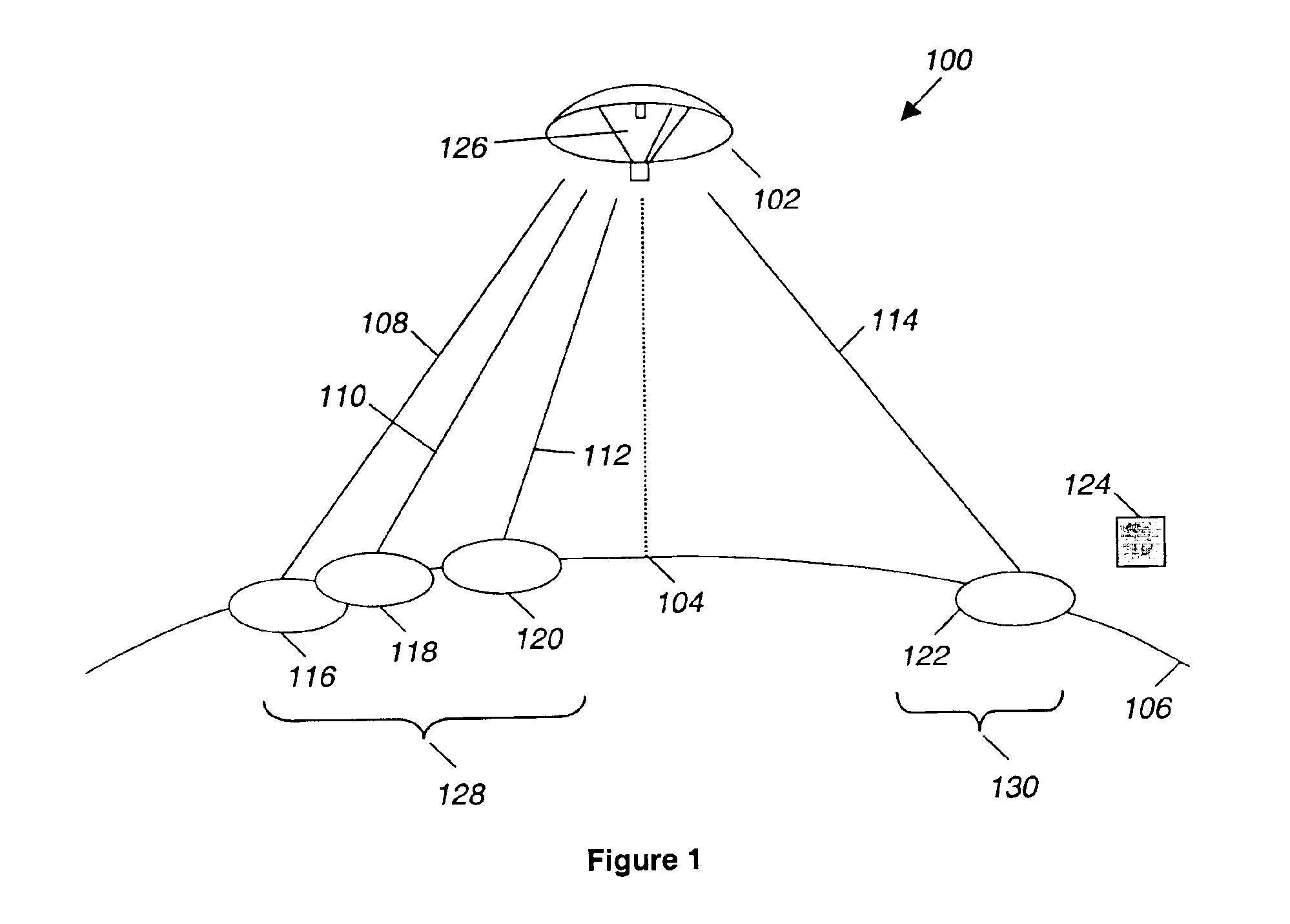
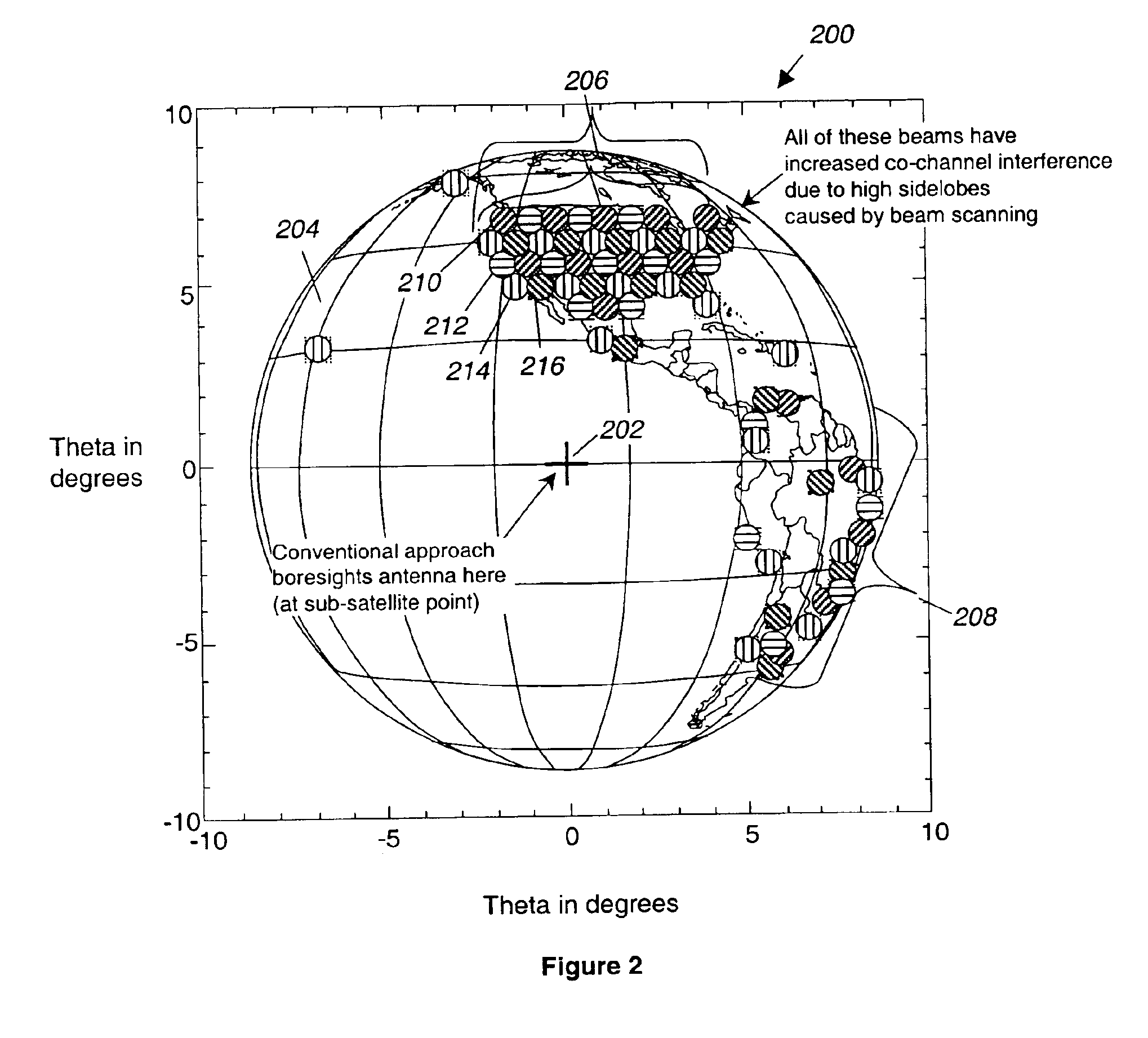
Reducing co-channel interference in satellite communications systems by antenna re-pointing
InactiveUS6940452B2Improve performancePoint to optimizationAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio transmissionCommunications systemHigh density
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
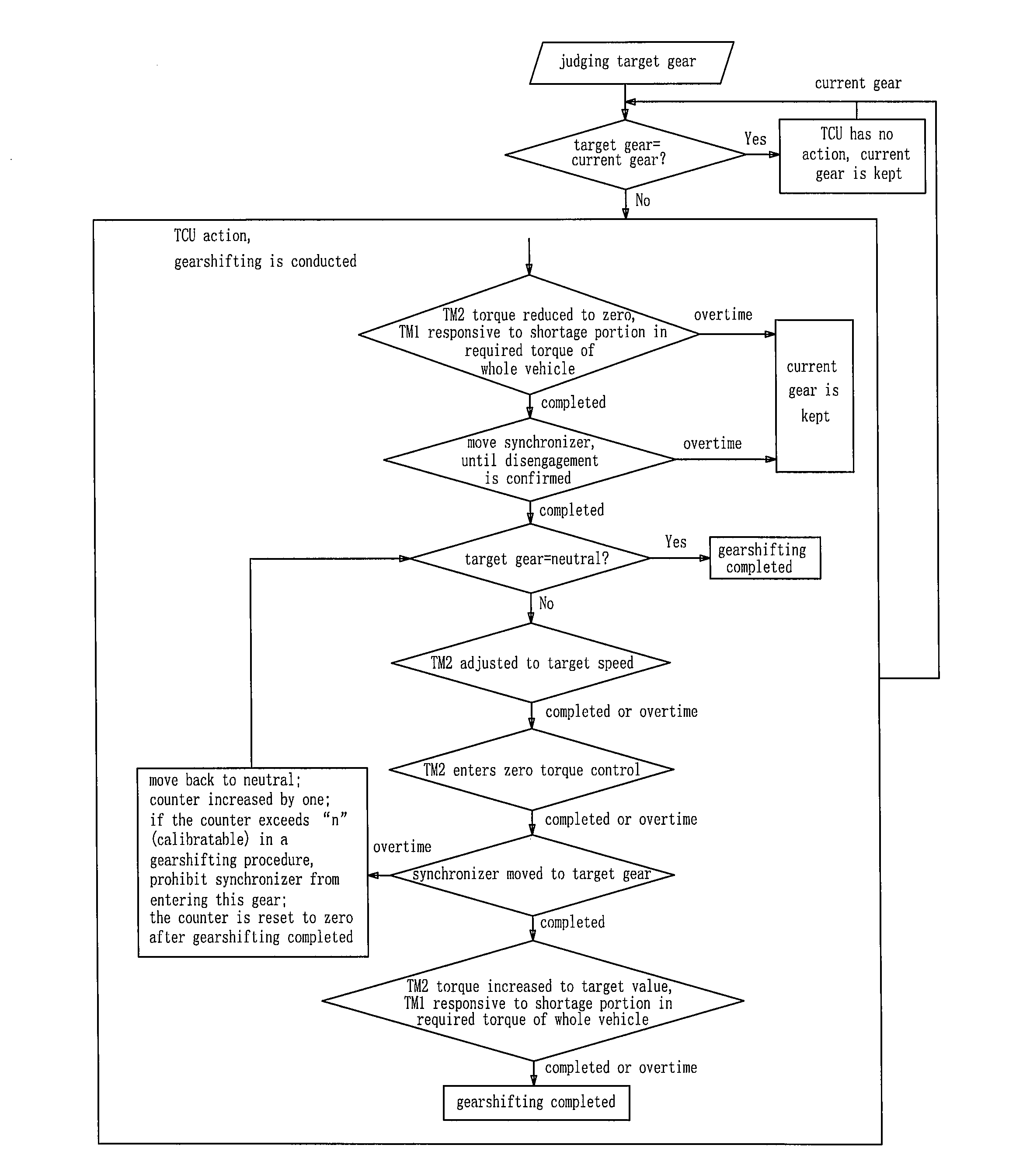
Controlling apparatus and method for electric drive transmission of dual-motor electric vehicle
ActiveUS20160347320A1Optimizing motor working pointWide rangeSpeed controllerElectric devicesElectric power transmissionElectricity
A controlling apparatus and method for an electric drive transmission used in a dual-motor electric vehicle are disclosed, wherein when the second motor is in the zero torque state, the synchronizer is shifted to a neutral position, the second motor the required torque being kept to be zero; after shifted to the neutral position, if the target gear position is the neutral position, gearshifting is completed, an if the target gear position is not the neutral position, speed control to the second motor is conducted to adjust its speed towards a target speed; once the second motor is adjusted to the target speed, the second motor is subjected to zero torque control, the second motor the required torque being zero; once the second motor comes into a zero torque state, the synchronizer is shifted to a target gear position, the required torque of the second motor being kept to be zero; once the synchronizer is located in the target gear position, the required torque of the second motor changes towards a target value at a proper changing rate; once the second motor real torque and is equal to or larger than target torque, gearshifting is judged as completed. Loss in wheel driving torque caused by the second motor in the whole gearshifting procedure is compensated by the first motor, so that gearshifting without power interruption can be achieved.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
Controlling apparatus and method for electric drive transmission of dual-motor electric vehicle
ActiveUS9623872B2Convenience to workStrategy is limitedSpeed controllerElectric devicesElectric machineElectric drive
A controlling apparatus and method for an electric drive transmission used in a dual-motor electric vehicle are disclosed, wherein when the second motor is in the zero torque state, the synchronizer is shifted to a neutral position, the second motor the required torque being kept to be zero; after shifted to the neutral position, if the target gear position is the neutral position, gearshifting is completed, an if the target gear position is not the neutral position, speed control to the second motor is conducted to adjust its speed towards a target speed; once the second motor is adjusted to the target speed, the second motor is subjected to zero torque control, the second motor the required torque being zero; once the second motor comes into a zero torque state, the synchronizer is shifted to a target gear position, the required torque of the second motor being kept to be zero; once the synchronizer is located in the target gear position, the required torque of the second motor changes towards a target value at a proper changing rate; once the second motor real torque and is equal to or larger than target torque, gearshifting is judged as completed. Loss in wheel driving torque caused by the second motor in the whole gearshifting procedure is compensated by the first motor, so that gearshifting without power interruption can be achieved.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
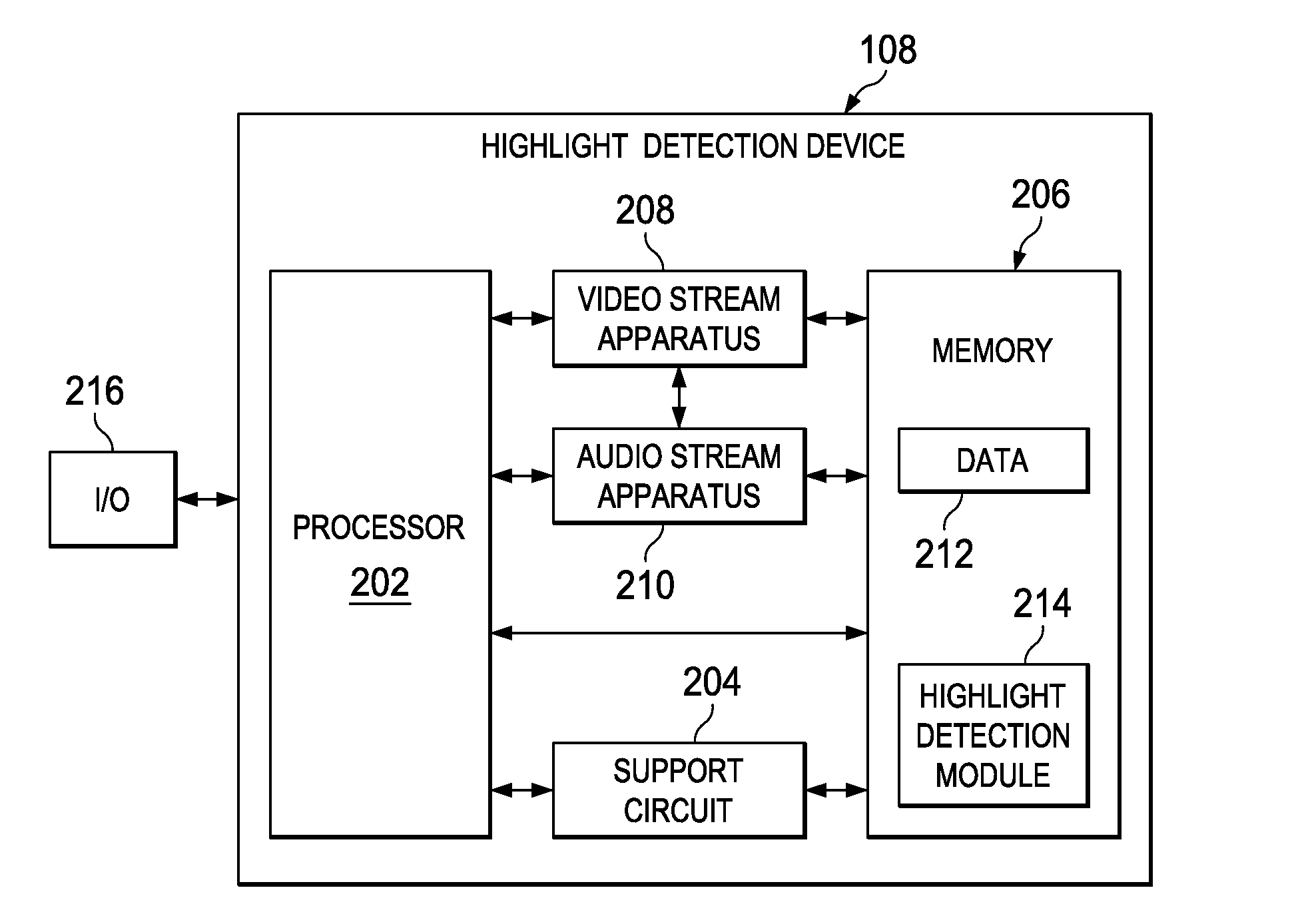
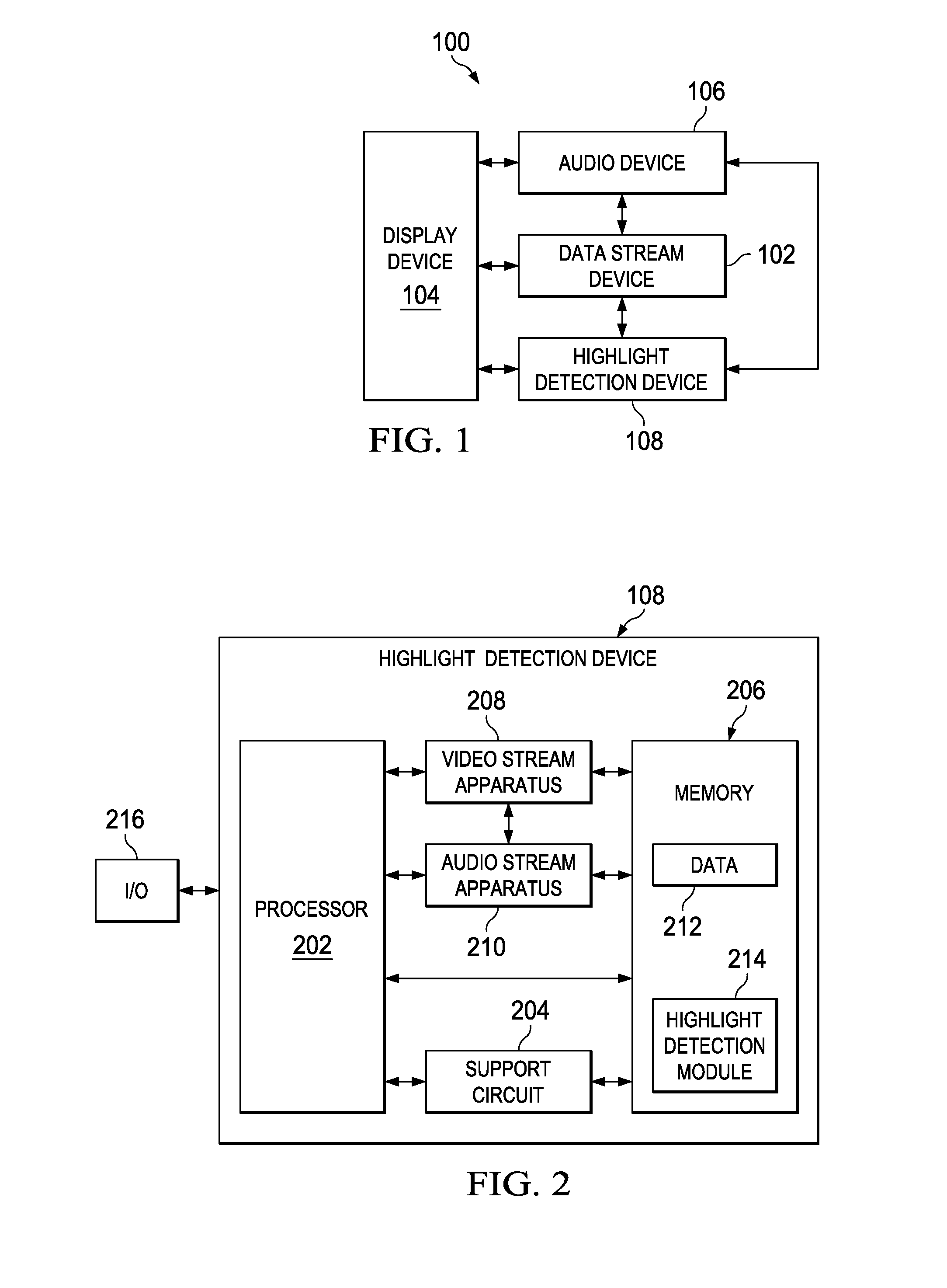
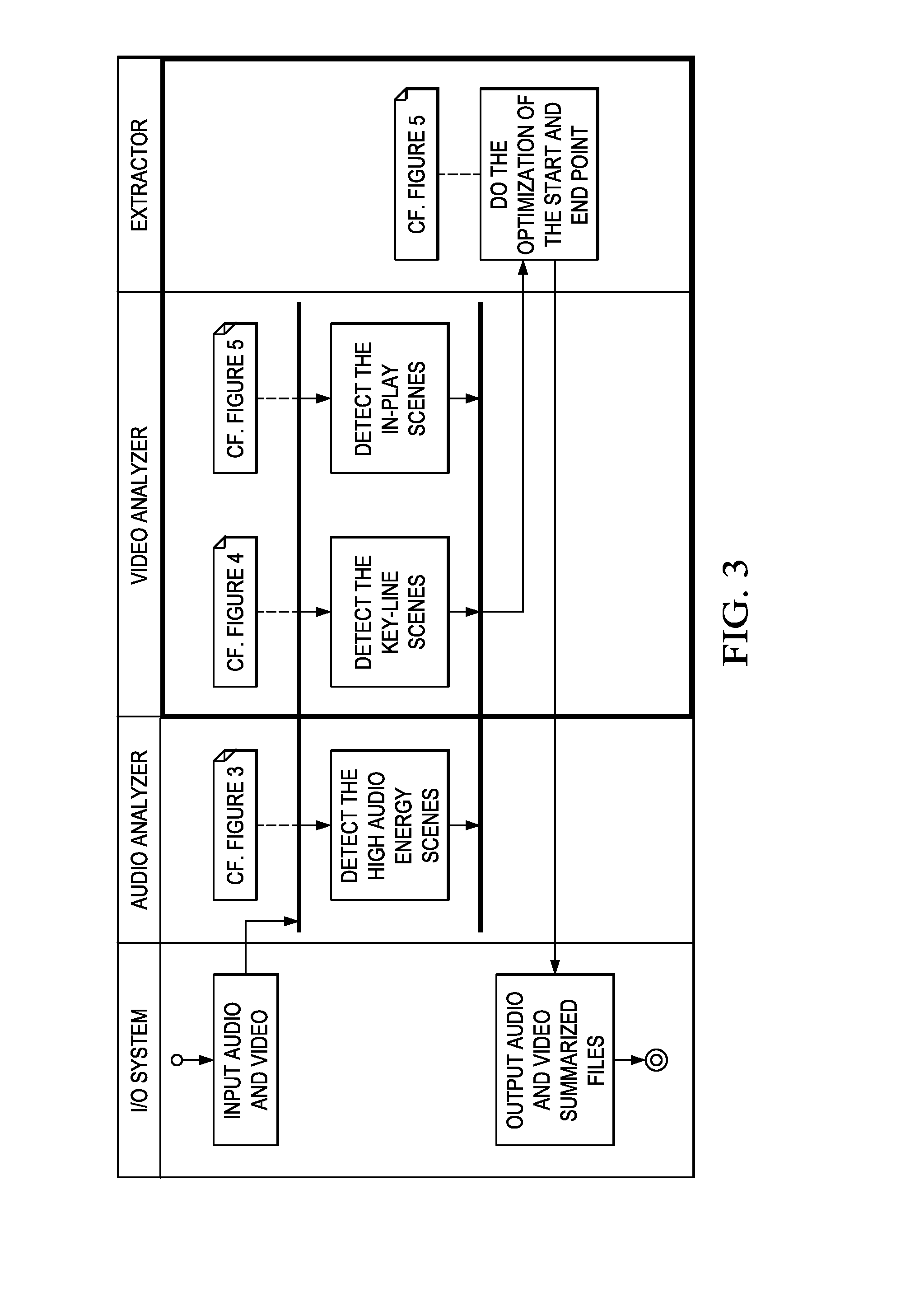
Method and Apparatus for Enhancing Highlight Detection
InactiveUS20100194988A1Point to optimizationColor signal processing circuitsRecord information storageAudio frequencyMultimedia
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Torque converter having a reactor controlled by a jaw clutch
ActiveUS20160238116A1Optimize torque converter coupling point behaviorImprove fuel economyFluid actuated clutchesInterengaging clutchesClutch controlNuclear engineering
A torque converter in which the standard one-way clutch, otherwise known as an overrunning brake, on the reactor, otherwise known as a stator, is replaced with a jaw clutch. When the jaw clutch is engaged, the reactor is non-rotate. When the jaw clutch is disengaged, the reactor spins freely. The jaw clutch can be placed on the same hydraulic fluid circuit as a bypass clutch.
Owner:CHEN ZHONGTAI
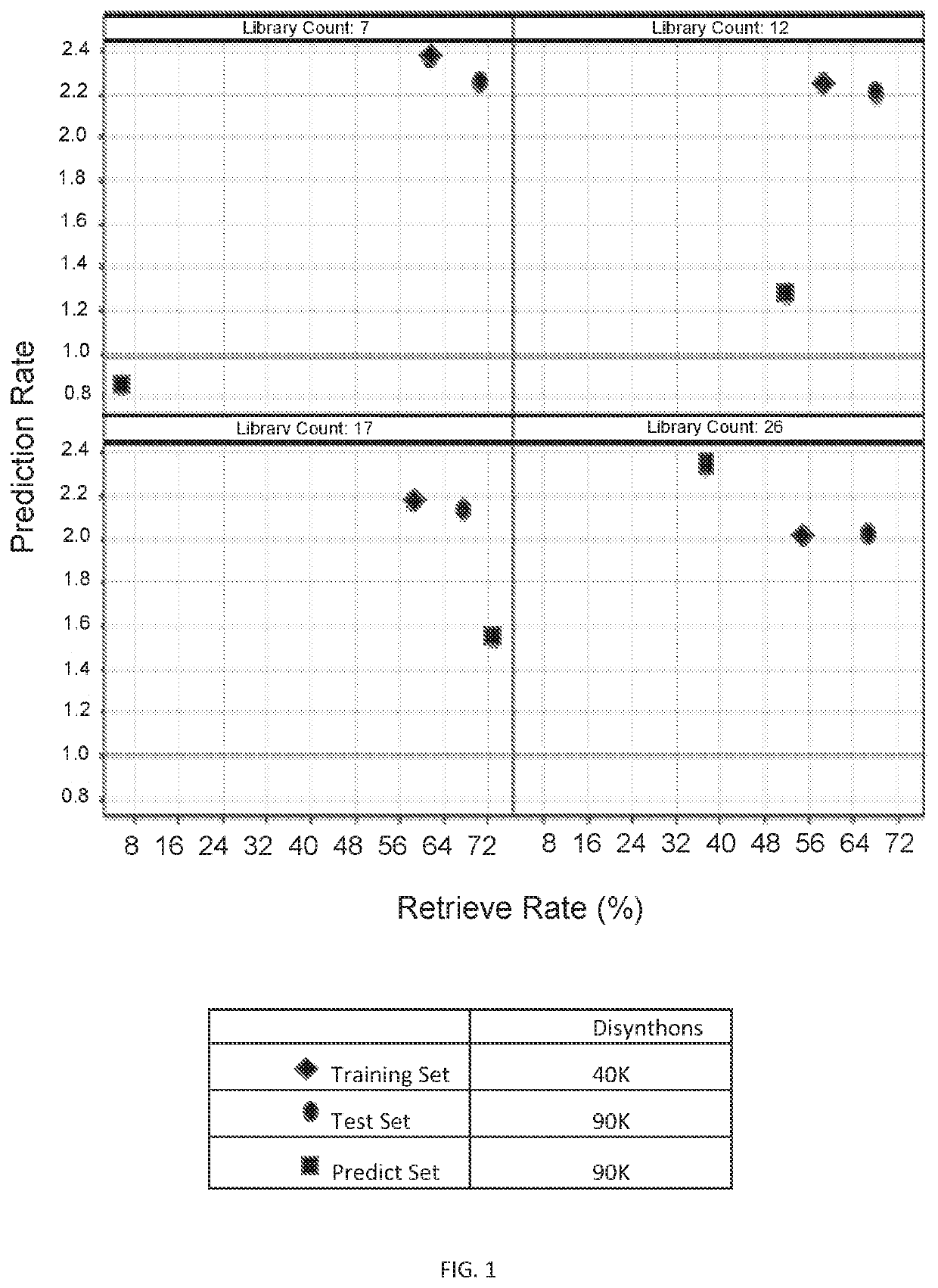
Methods for identifying compounds
PendingUS20200143903A1High confidence predictionPoint to optimizationPeptide librariesMolecular designData setVirtual screening
The present disclosure provides virtual screening methods utilizing data sets from nucleotide-encoded libraries (e.g., DNA-encoded libraries). These methods allow for high confidence predictions of binding interactions between candidate compounds and proteins of interest useful for the development of therapeutics.
Owner:X CHEM
Method and device to compensate for a dip in the output voltage of a motor-vehicle alternator
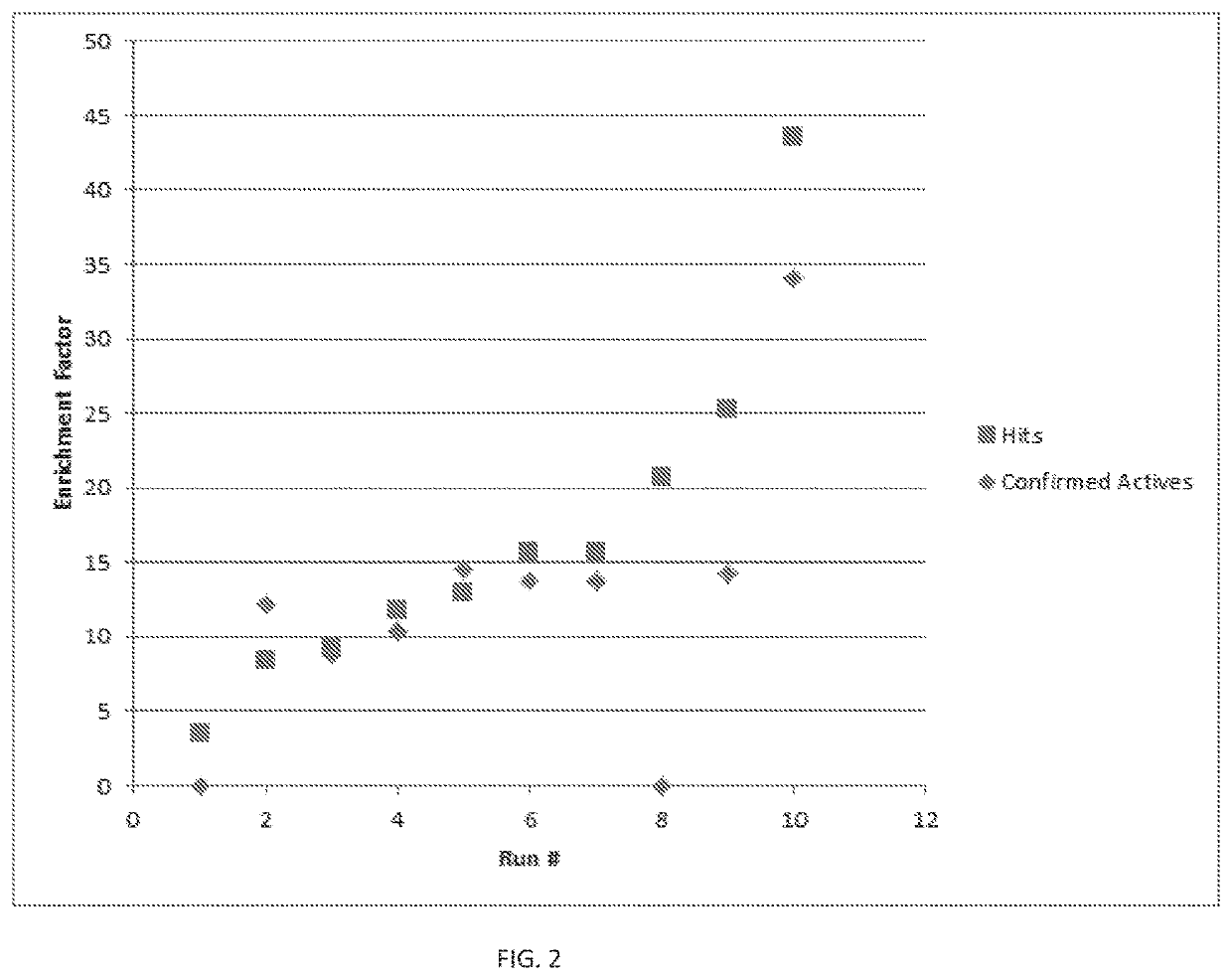
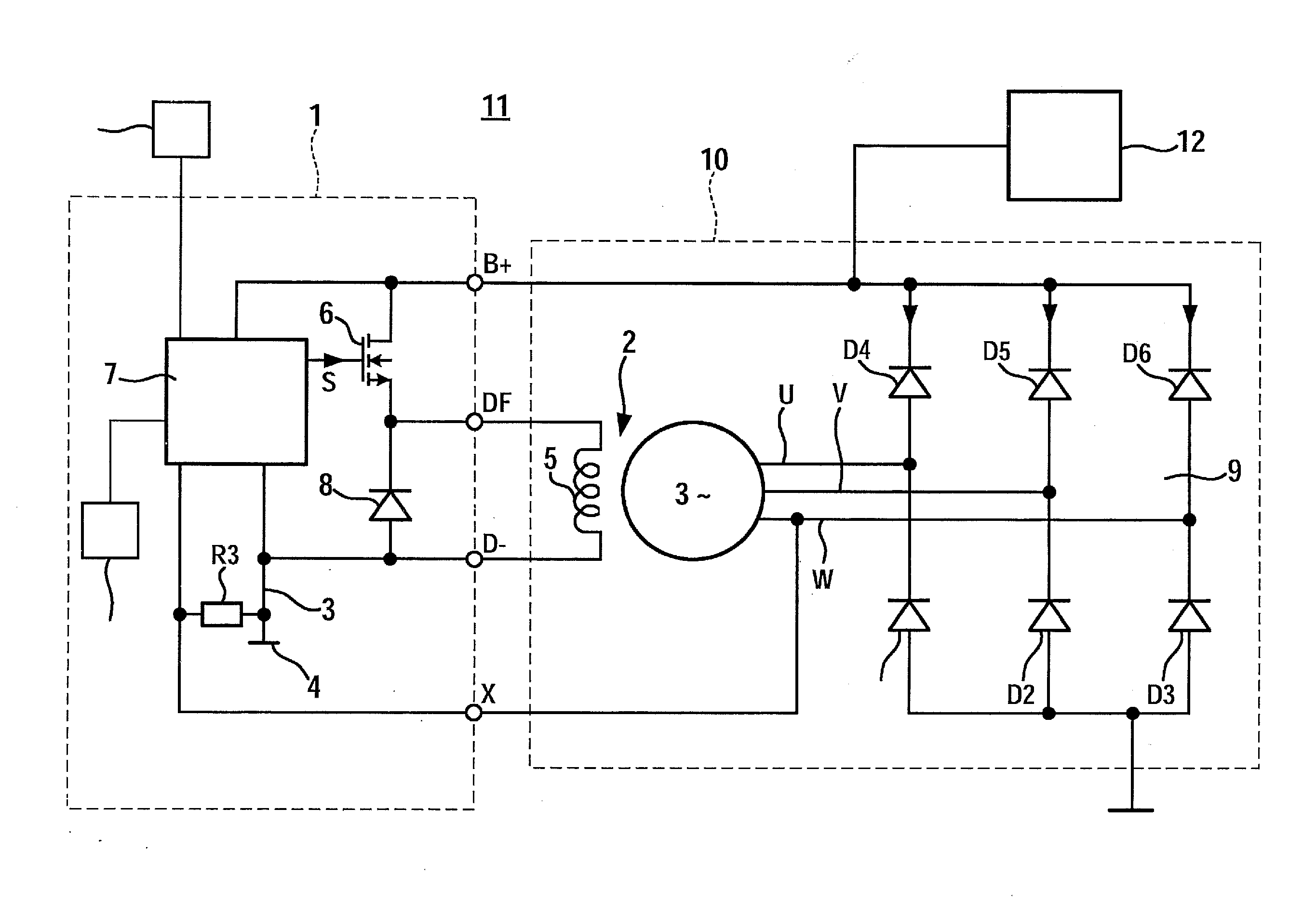
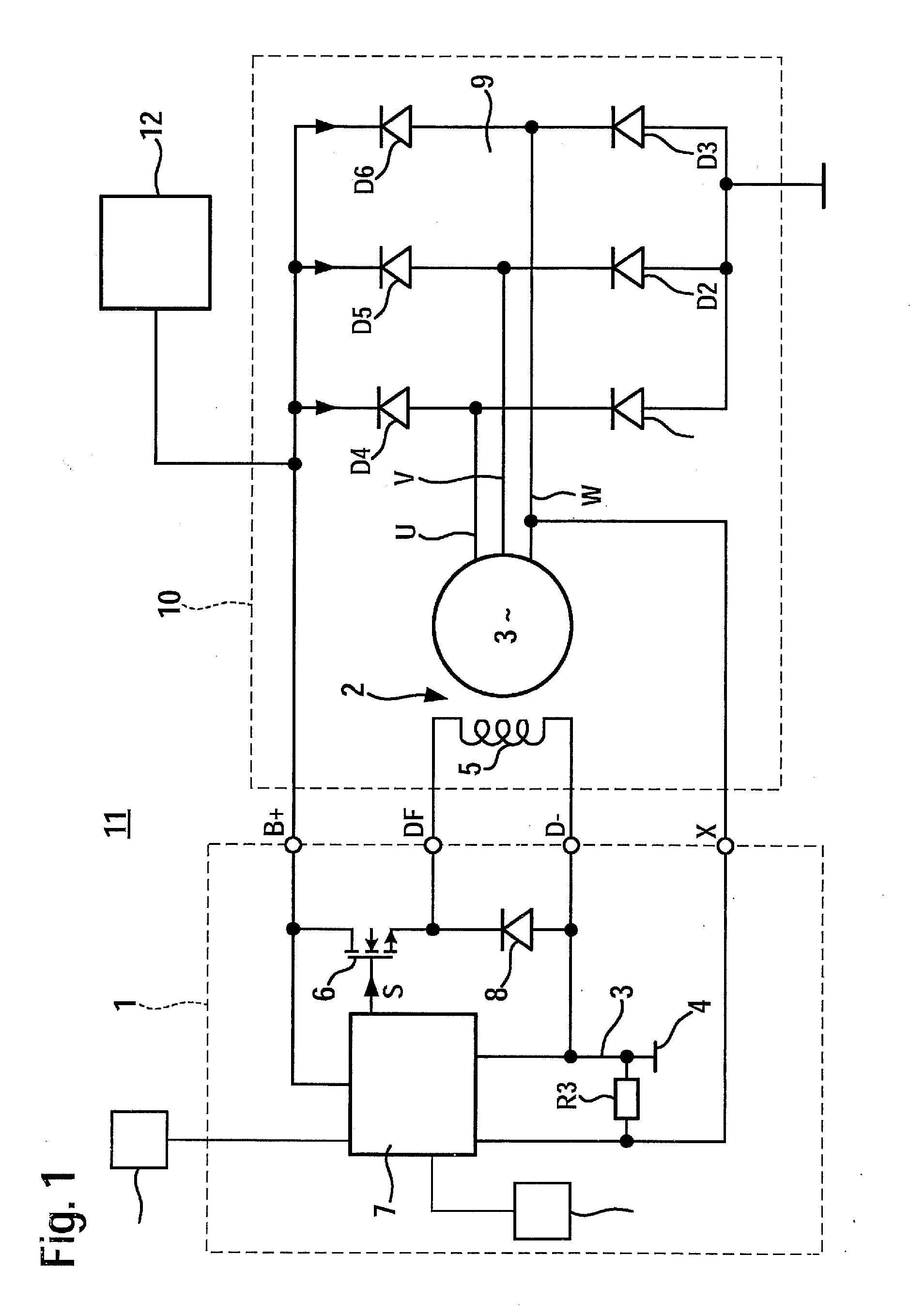
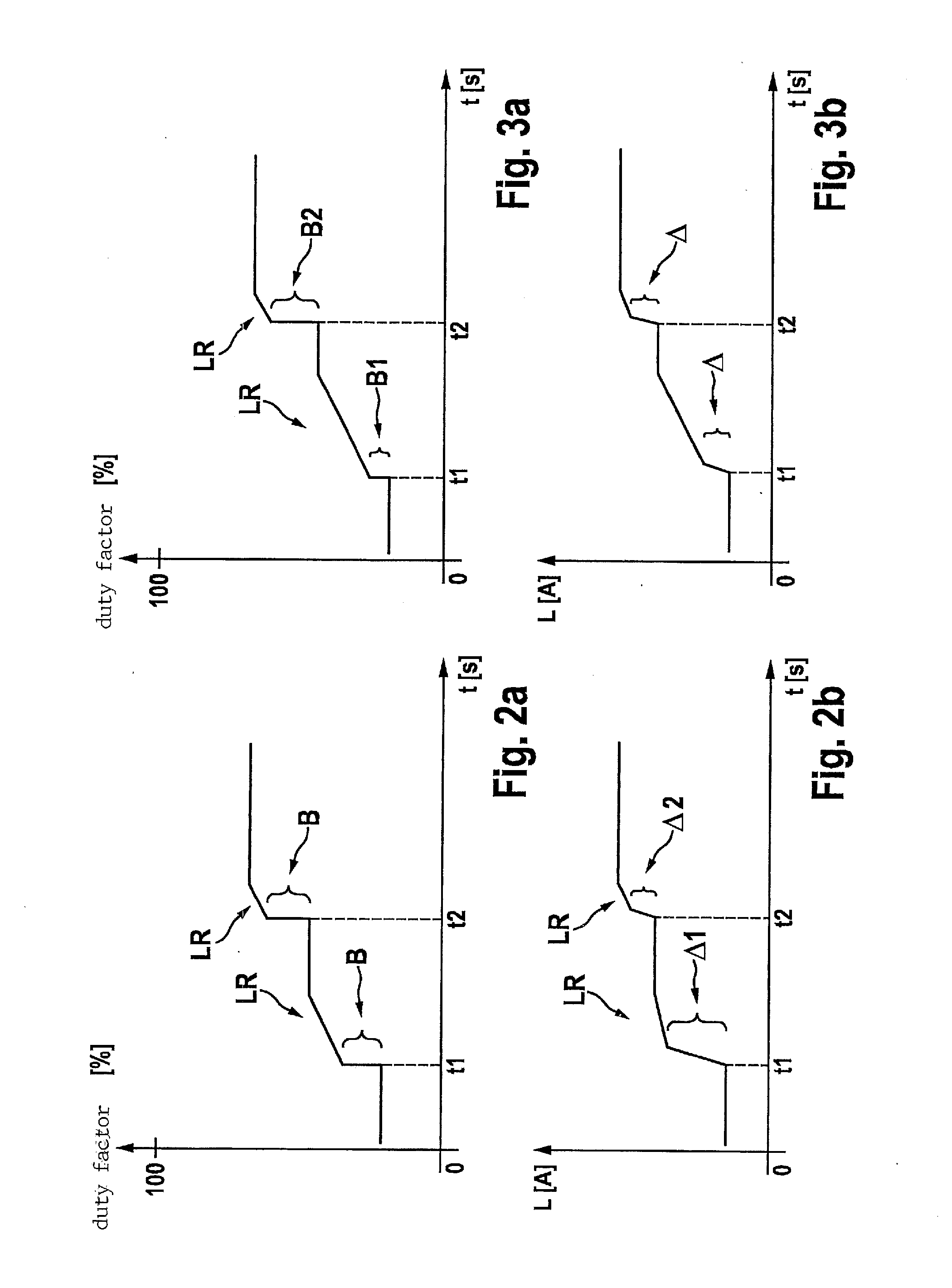
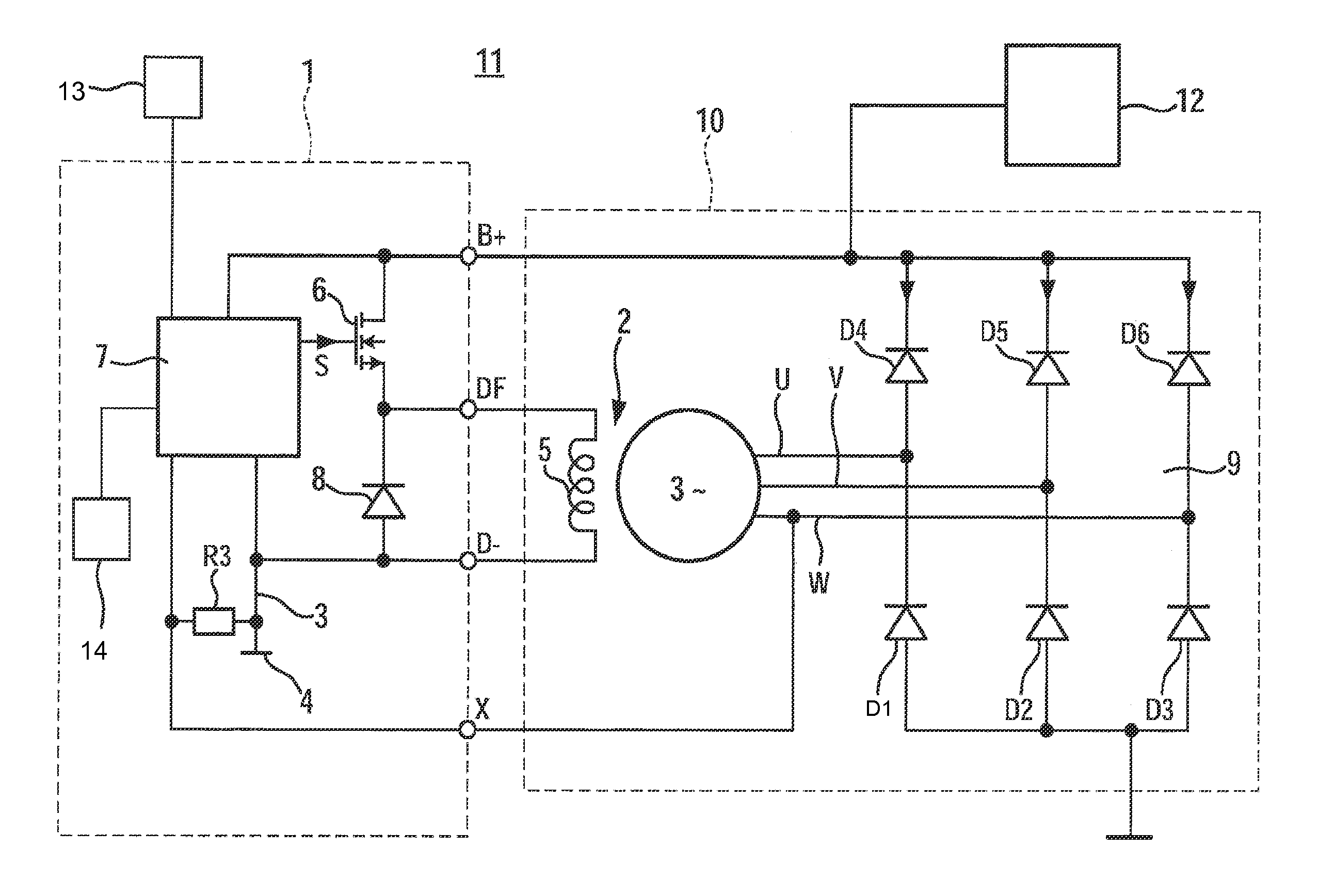
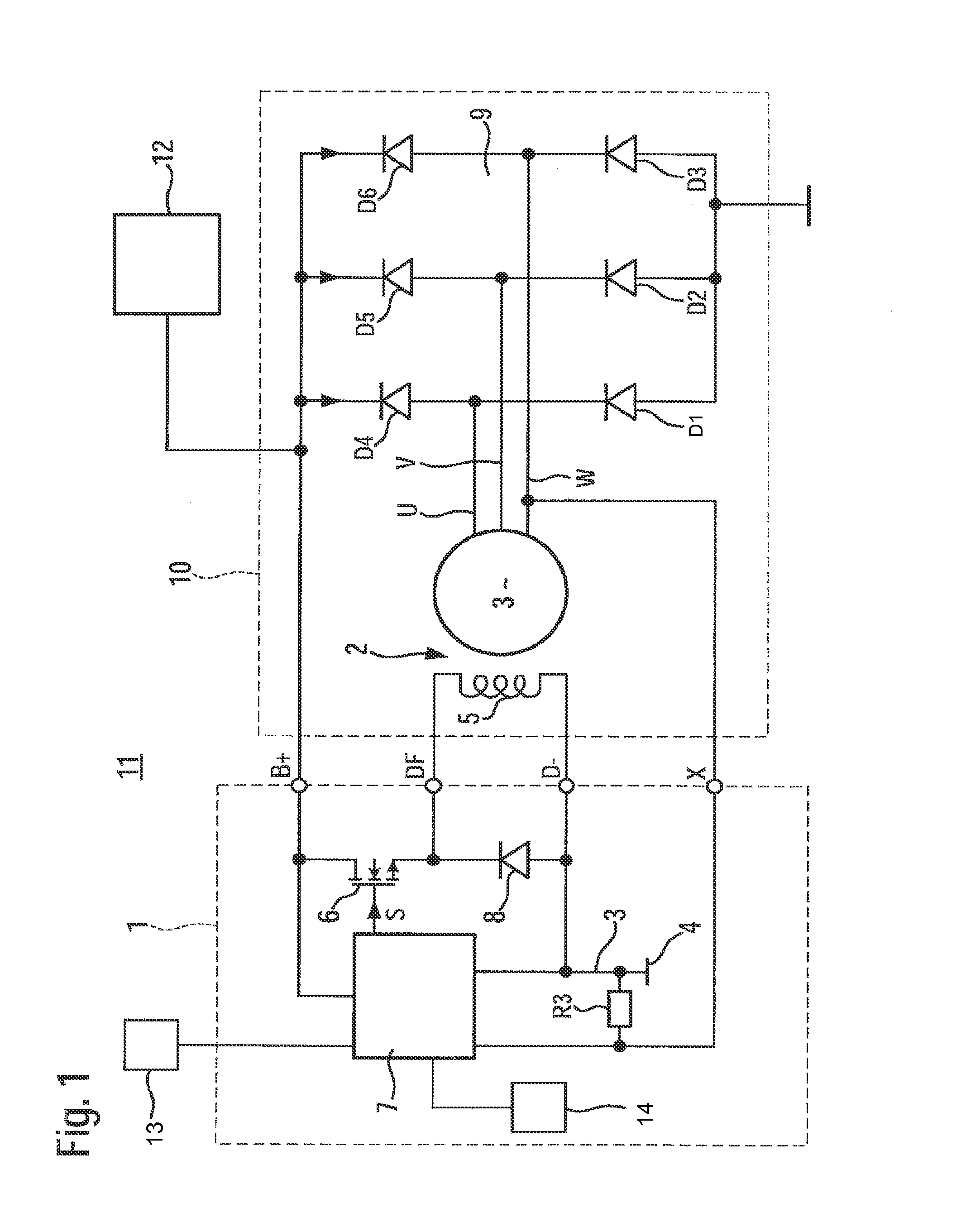
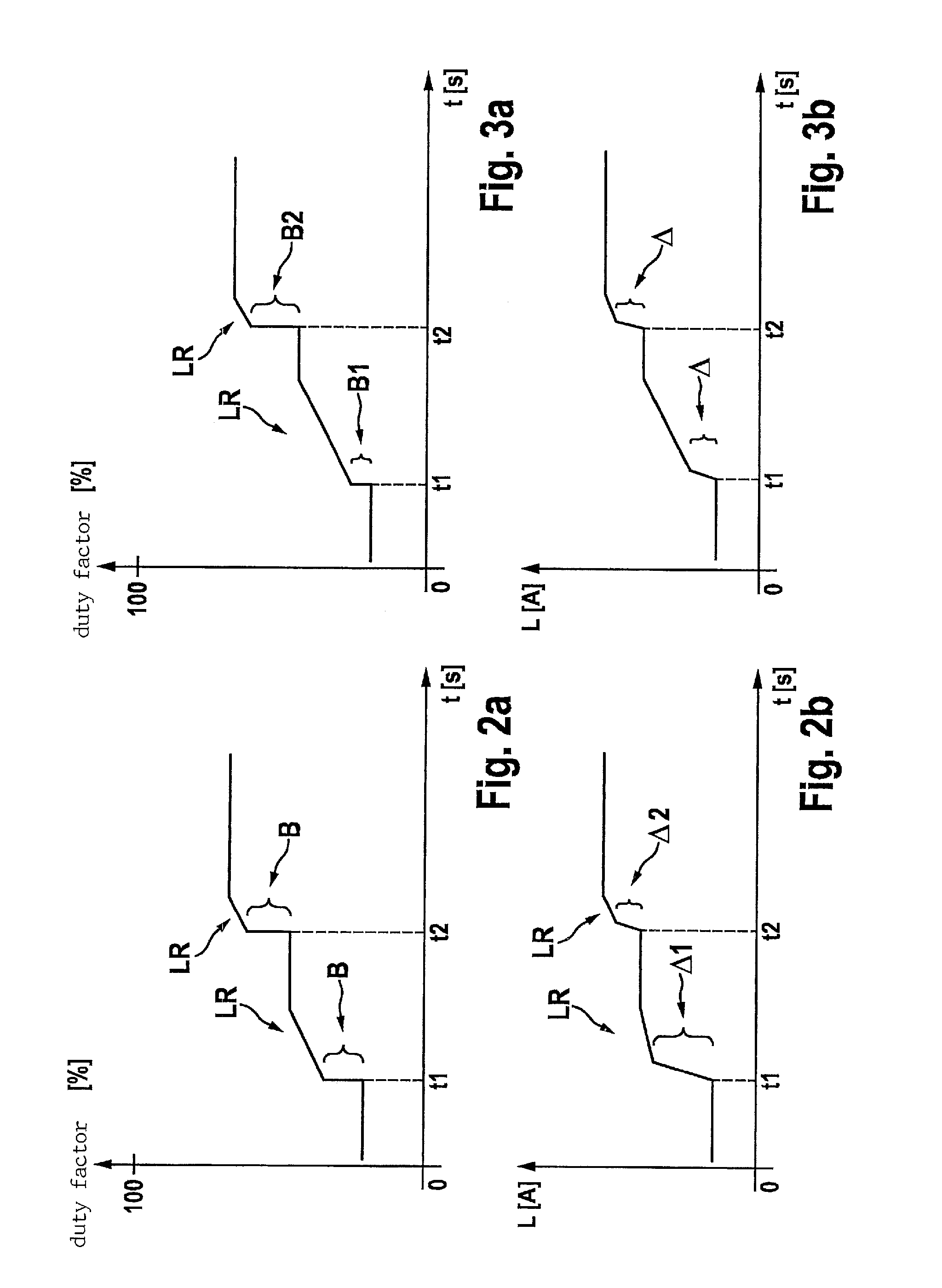
ActiveUS20130141055A1Point to optimizationComplex functionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric generator controlAlternatorControl signal
A dip in the output voltage of a motor-vehicle alternator, owing to a connecting of a load or a change in speed, is compensated with the aid of an alternator regulator which provides a control signal that has a duty factor and increases the excitation current of the motor-vehicle alternator. After the occurrence of the voltage dip, in a first step, the duty factor of the control signal is increased by a differential amount, and in a subsequent second step, the rate of correction is limited. After the occurrence of the voltage dip, parameters describing the instantaneous working point of the motor-vehicle alternator are determined, and in the first step, the differential amount is set as a function of the working point.
Owner:SEG AUTOMOTIVE GERMANY GMBH
Constellation satellite solar cell array sun tracking method
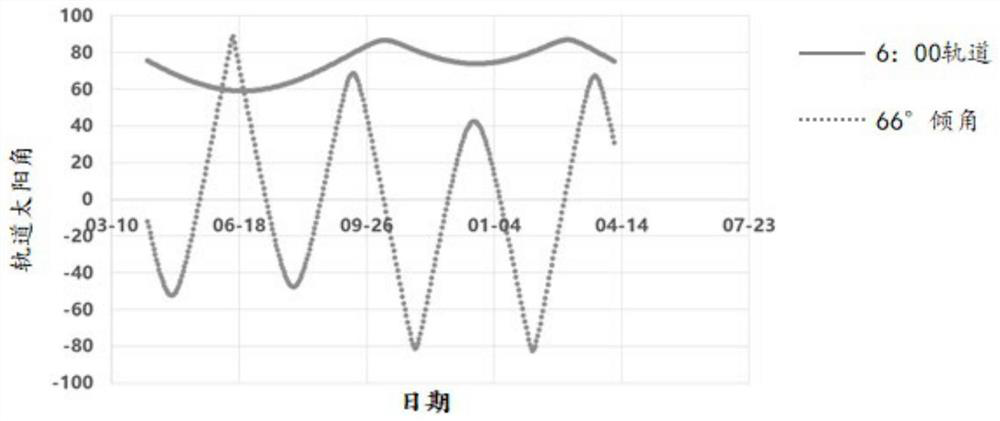
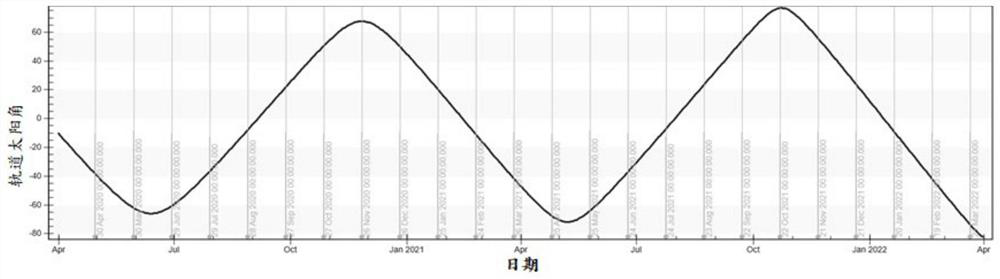
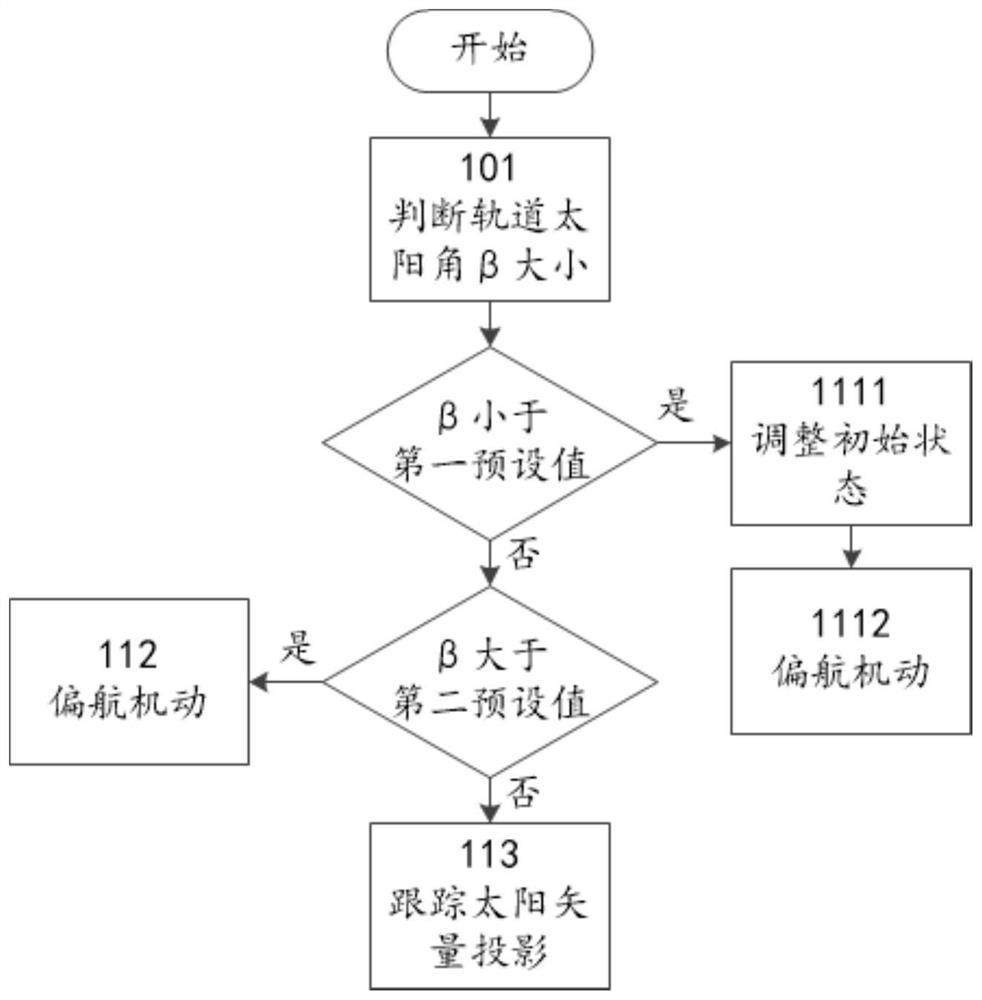
ActiveCN111717415ASolve the problem of large fluctuationsStay orientedCosmonautic power supply systemsArtificial satellitesSolar angleEngineering
The invention discloses a constellation satellite solar cell array sun tracking method. A one-dimensional yaw maneuvering strategy is adopted for sun orientation; the maneuvering of the solar cell array is controlled according to the size of the solar angle of the orbit; when the orbit solar angle is smaller than a first preset value, the normal initial state of the solar cell array is adjusted, the normal direction of the solar cell array is made to be consistent with the flight direction of a constellation satellite, and the solar cell array is controlled within a preset time period T beforeand after the sun passes through the top, so that one-dimensional yawing maneuver is achieved by 180 degrees; when the orbit solar angle is greater than a second preset value, the normal direction ofthe solar cell array is controlled to be fixed on the normal direction of the orbit plane to face the direction of the sun; and when the orbit solar angle is greater than or equal to the first presetvalue and less than or equal to the second preset value, the normal direction of the solar cell array is controlled to enable the solar cell array to track the projection of the sun vector in the horizontal plane.
Owner:上海中科辰新卫星技术有限公司
Air vent for use in a vehicle
InactiveCN108790704AAchieve rotationPoint to optimizationAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
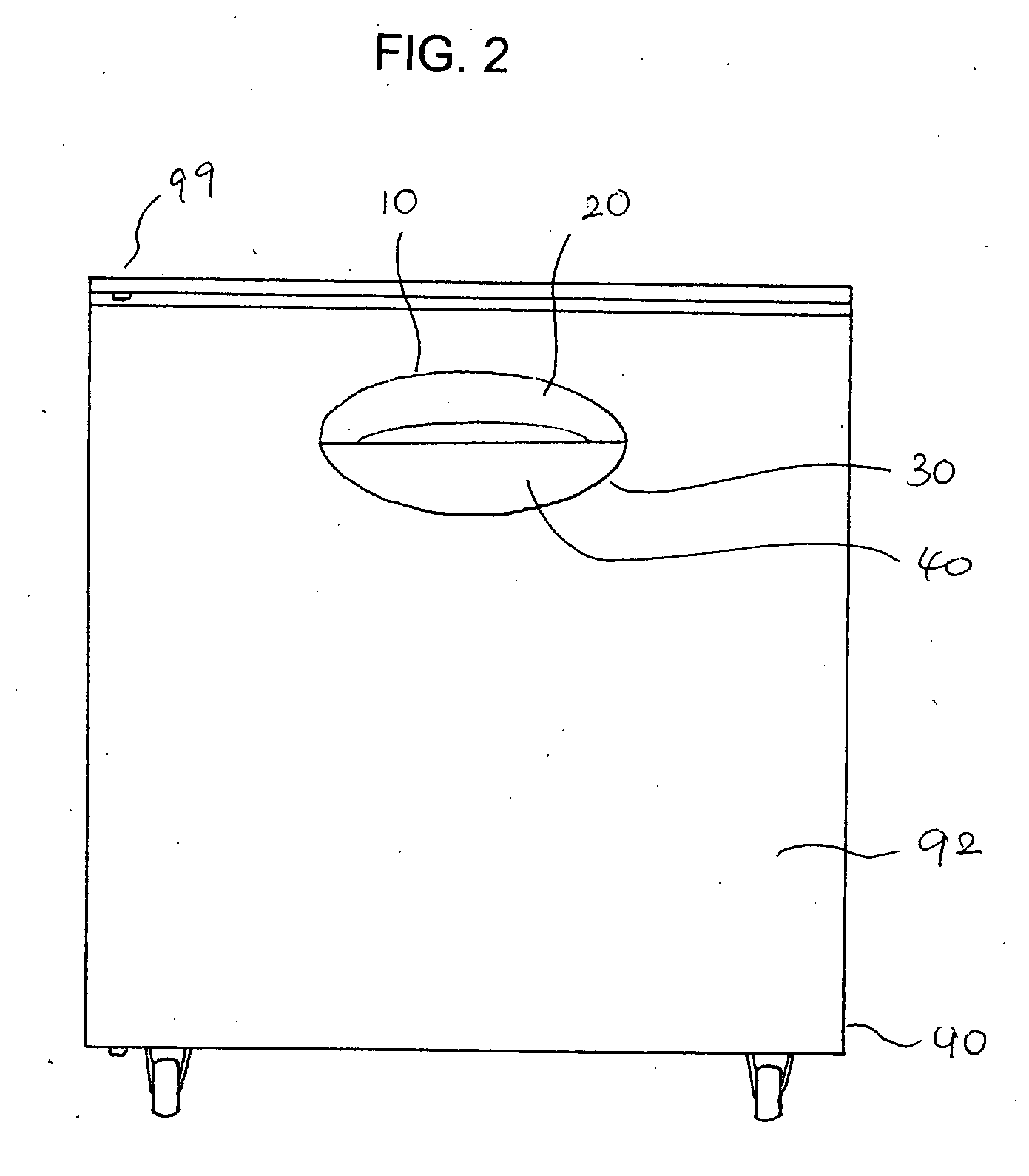
Door handle for refrigerators and kitchen units
InactiveUS20060282986A1Avoid hard activationPoint to optimizationTravelling carriersHoldersRight triangleEngineering
A door handle includes a base plate and a lip plate. The base plate has a front surface, a rear surface, and an edge connecting the front and rear surfaces, and the lip plate has a top surface, a bottom surface, an edge connecting the top and bottom surfaces, and a coated portion fixed on the top surface. A part of the edge of the base plate is adjacent to a part of the edge of the lip plate, and a gap is provided between the front surface of the base plate and the bottom surface of the lip plate. The lip plate partly covers the base plate allowing a hand to access the gap provided between the base plate and the lip plate. The base plate is integrated with the door of the refrigerators or the kitchen units. The door handle is substantially right triangular, rectangular, or circular.
Owner:KIM BRIAN S
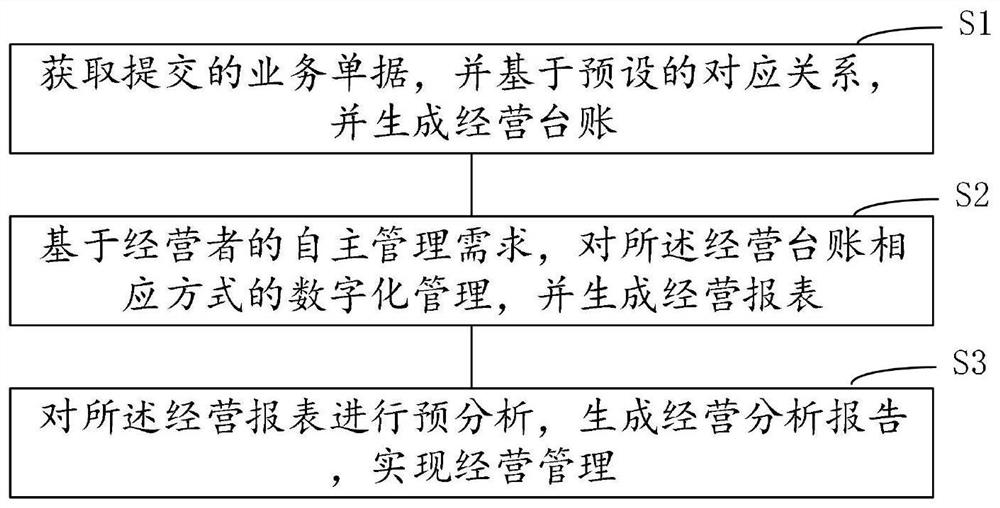
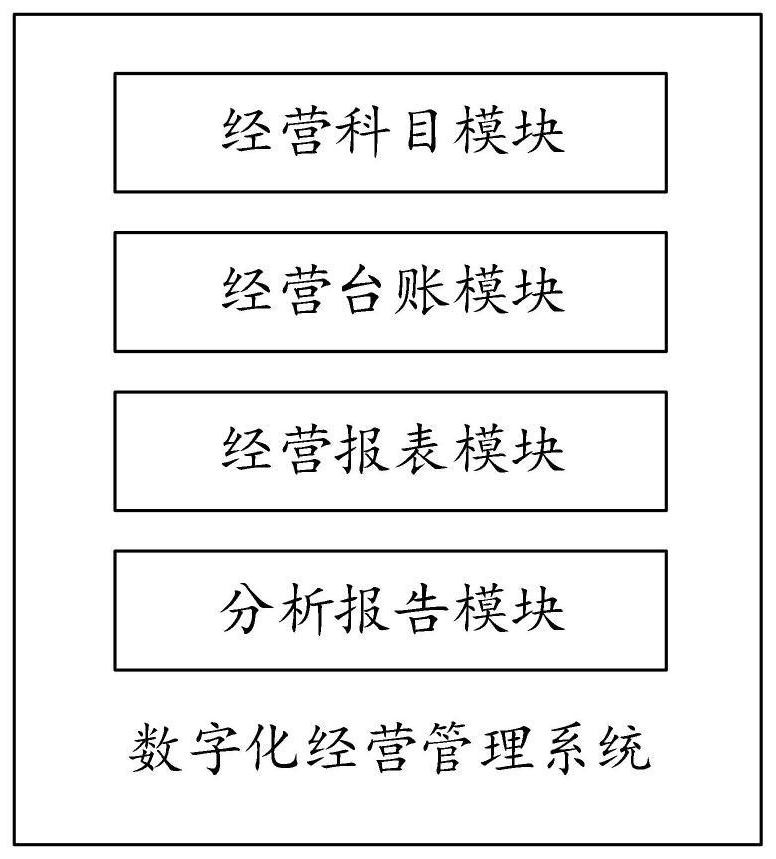
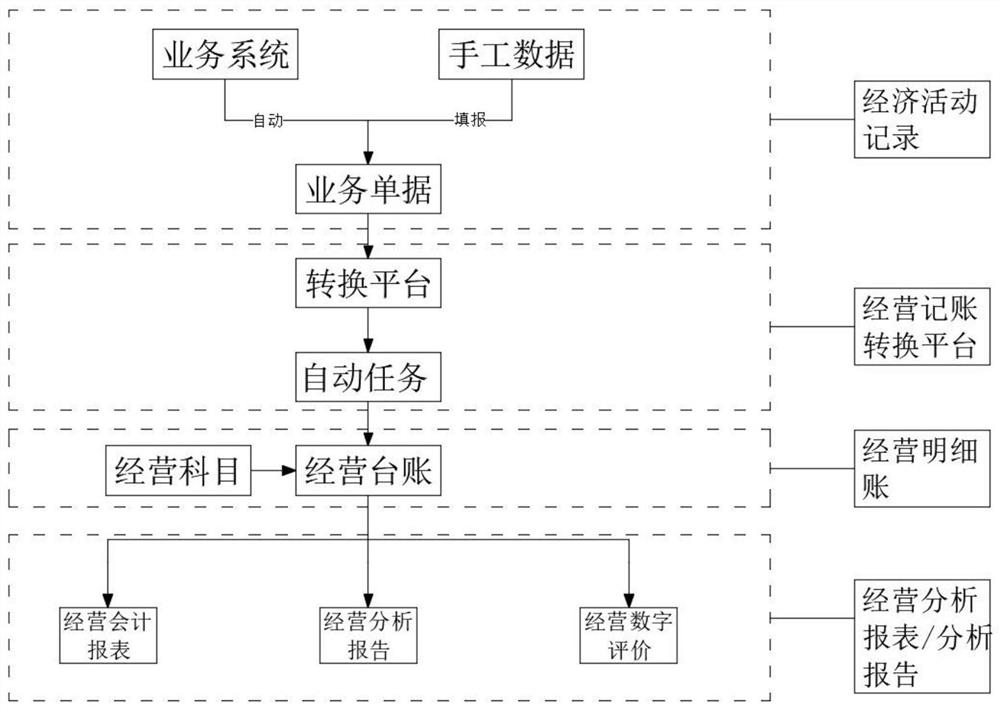
Digital operation management method and system for operator to autonomously analyze and make decisions
ActiveCN113628023AImprove daily work efficiencyEffectively support self-managementFinanceDatabase management systemsBusiness PersonnelService personnel
The invention provides a digital operation management method and system for an operator to autonomously analyze and make decisions, and the method comprises the steps: S1, obtaining a submitted business document, and generating an operation ledger based on a preset corresponding relation; S2, digitally managing the operation ledger in a corresponding mode based on the self-management requirement of an operator, and generating an operation report; and S3, pre-analyzing the operation report, generating an operation analysis report, and realizing operation management. By automatically generating ledgers, reports, analysis reports and the like, service personnel can watch conveniently, meanwhile, the time for bookkeeping and operation analysis is shortened, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:北汽蓝谷信息技术有限公司
Method and device to compensate for a dip in the output voltage of a motor-vehicle alternator
ActiveUS8963509B2Point to optimizationComplex functionBatteries circuit arrangementsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAlternatorControl signal
A dip in the output voltage of a motor-vehicle alternator, owing to a connecting of a load or a change in speed, is compensated with the aid of an alternator regulator which provides a control signal that has a duty factor and increases the excitation current of the motor-vehicle alternator. After the occurrence of the voltage dip, in a first step, the duty factor of the control signal is increased by a differential amount, and in a subsequent second step, the rate of correction is limited. After the occurrence of the voltage dip, parameters describing the instantaneous working point of the motor-vehicle alternator are determined, and in the first step, the differential amount is set as a function of the working point.
Owner:SEG AUTOMOTIVE GERMANY GMBH
Drawer-type row-state thermo-sensitive primter
InactiveCN1340419AHigh positioning accuracyImprove printing qualityOther printing apparatusWebs handlingRolling paperHeat sensitive
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
AR simulation game gun
The invention relates to AR simulation game intelligent equipment, in particular to an AR simulation game gun. A magnet sleeve is fixed at the tail end of a gun body, and a push-pull type electromagnet is fixedly embedded in the magnet sleeve; a sliding groove is formed outside the magnet sleeve; an empty cavity matched with the magnet sleeve is formed in the front end of a gun support, a clamp matched with the sliding groove is arranged on the inner wall of the empty cavity, and a pull spring is arranged between the gun support and the end face of the push-pull type electromagnet; a push rodend of the push-pull type electromagnet points at the side wall of the empty cavity in the gun support; a fixed support is fixed below a gun sleeve, and a battery pack is fixedly embedded in the outerportion, adjacent to the fixed support, of the gun sleeve. The AR simulation game gun of the structure can not only perfectly simulate recoil force generated by gun shooting, but also integrate intelligent equipment, and conveniently matches with a VR game to conduct virtual game score value determination and pointing.
Owner:重庆第五维科技有限公司
Apparatus and method for electron beam evaporation
InactiveUS6495216B2Improve distributionPoint to optimizationElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingEvaporationEngineering
Disclosed is an electron beam evaporator for installation in a vacuum apparatus which provides for variable positioning during or between applications of a coating. The apparatus has a carrier plate which is a flat hollow body, the top cover plate of which supports the evaporator. The hollow body is disposed over the bore in the tank such that it can be turned about the main axis of the bore. The component assemblies of the electron beam evaporator are vacuum-tight on the cover plate and the connecting lines are carried through the interior of the hollow body to the component assemblies.
Owner:LEYBOLD OPTICS
Reduced graph generation method and device
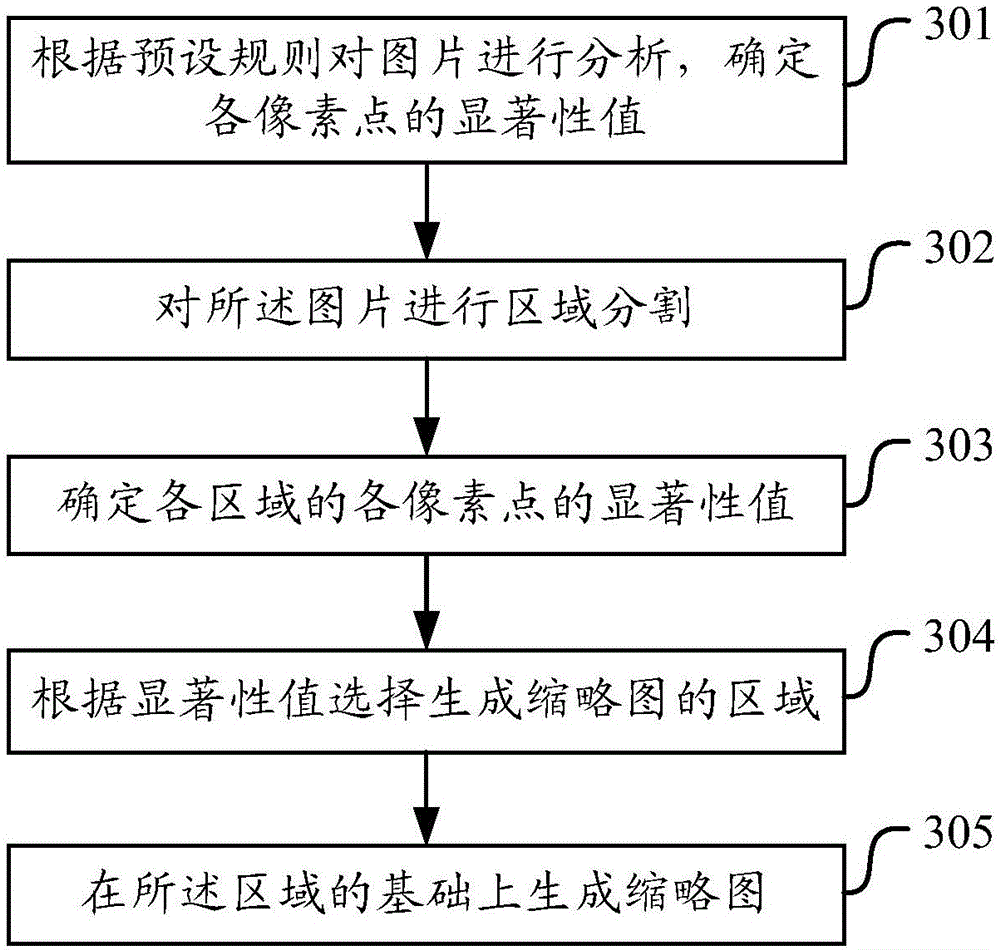
InactiveCN106251283AImprove efficiencyImprove experienceImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmThumbnail
The embodiments of the invention provide a reduced graph generation method and device. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing a picture according to a preset rule, and determining a significance value of each pixel point; performing area segmentation on the picture; determining the significance value of each pixel point of each area; according to the significance value, selecting an area where a reduced graph is generated; and generating the reduced graph on the basis of the area. By use of the scheme provided by the embodiments of the invention, the generated reduced graph can represent an original picture most, can be well directed to and represent the original picture, and improves the efficiency and experience of a user in checking a graph database.
Owner:LETV HLDG BEIJING CO LTD +1
Portable multifunctional rock-soil body structure reconstruction auxiliary tool
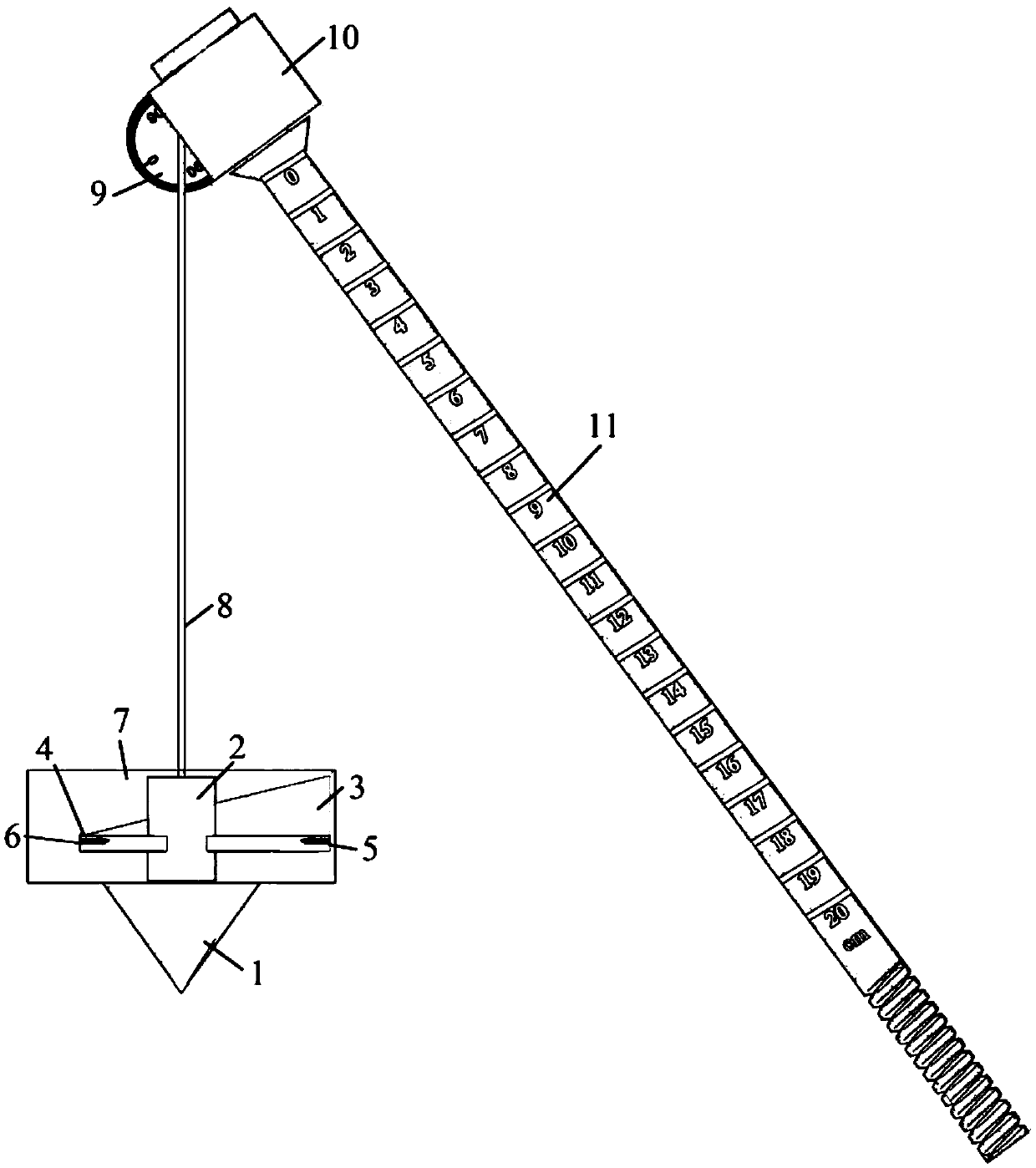
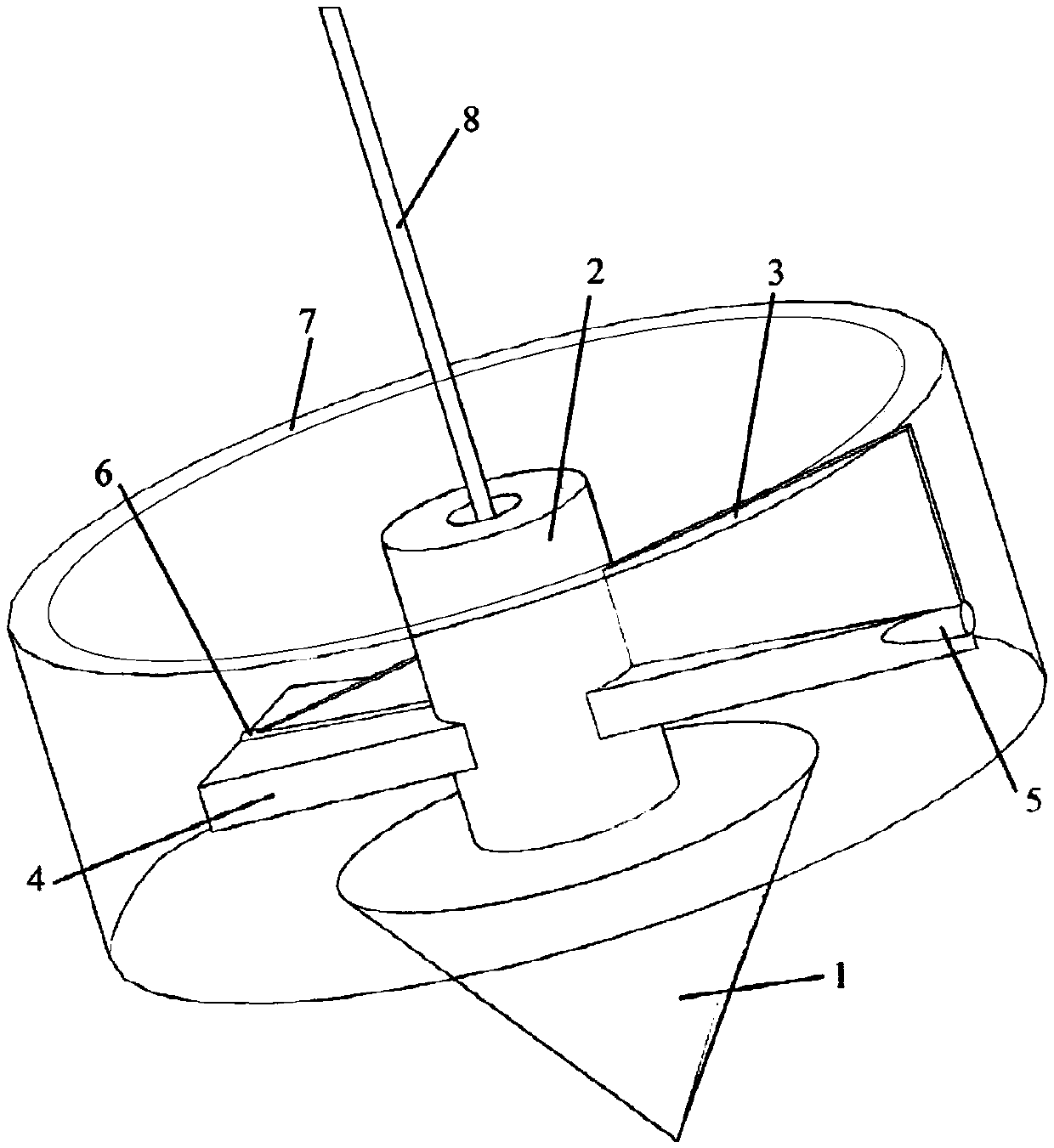
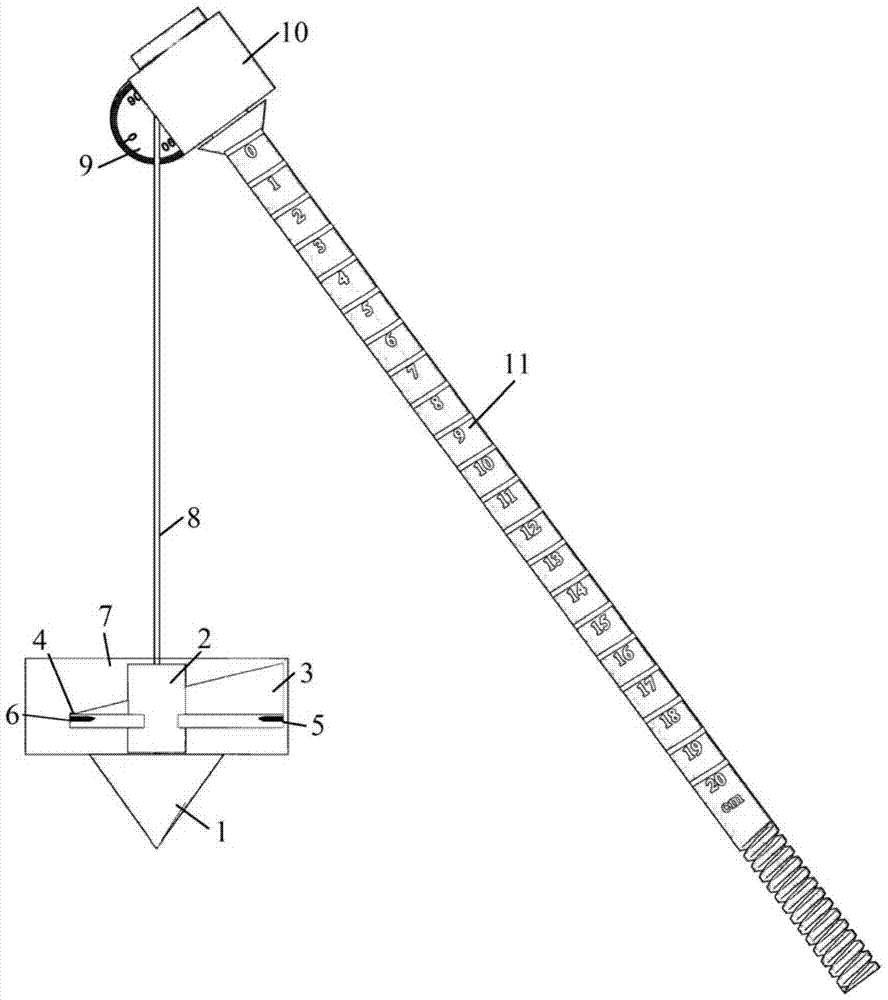
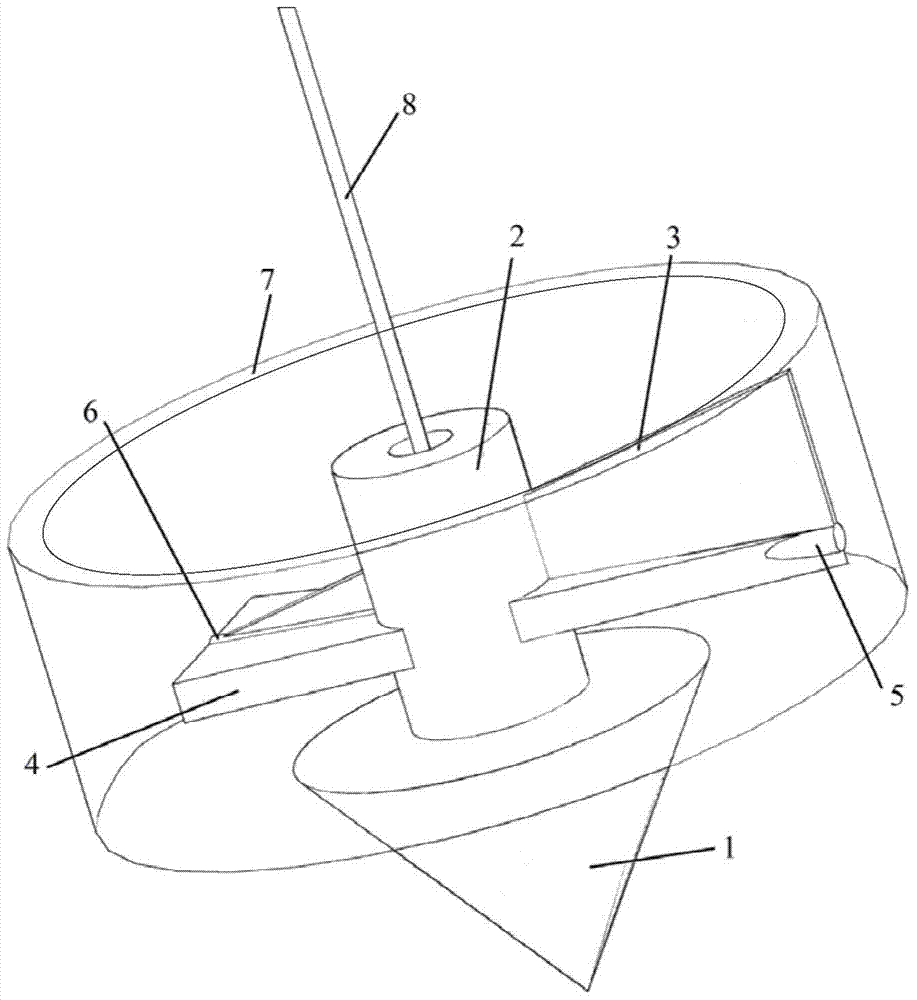
The invention relates to a portable multifunctional rock-soil body structure reconstruction auxiliary tool which comprises a gravity cone, a direction pointing assembly, an angle measurement assembly, a suspension rod and a base, the gravity cone is connected with the angle measurement assembly through a suspension rope, the direction pointing assembly is arranged on the suspension rope in a sleeving mode, the angle measurement assembly is arranged at the top end of the suspension rod in a sleeving mode, and the bottom end of the suspension rod is connected with the base; in the measurement process, the base is fixed to the structural face of a geological body, and the position of the suspension rod is adjusted, so that the suspension rod is perpendicular to the structural face, after the whole tool is in the balanced state, the spatial true dip angle of the structural face is obtained through the angle between the suspension rope on the angle measurement assembly and the suspension rod, and spatial orientation direction pointing is conducted through the direction pointing assembly. Compared with the prior art, the tool has the advantages of being comprehensive in function, wide in applicability, convenient to operate in practice and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Laser pointer for campus teaching based on cloud server
InactiveCN111009171APoint to optimizationEnhanced interactionReadingElectrical appliancesLaser transmitterSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a laser pointer for campus teaching based on a cloud server. The invention belongs to the technical field of teaching appliances. The laser pointer for campus teaching based ona cloud server comprises a pointer body, and a laser emitter is fixedly mounted at the front end of a pointer main body through an electric telescopic rod. The laser emitter with the electric telescopic rod is arranged on the pointer main body, and the electric telescopic rod is used for prolonging the length of the laser pointer, so pointer pointing is convenient, the laser emitter is used for laser pointing to an external projector and highlights key points of a brief report, meanwhile, a retractable handwriting display screen is arranged on the pointer main body, a teacher can mark contenton an electronic display screen and synchronize the handwriting display screen with courseware content of the projector, therefore, teaching content can be enriched easily, the teacher can walk at any place in a classroom to give a lesson, interaction between the teacher and students is effectively improved, and the teacher does not need to give a lesson only by means of the projector.
Owner:郭鸿波
Draw shaft intelligent monitoring device
InactiveCN110855951AAccurate monitoringAchieve regulationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsBall screwElectric machinery
The invention discloses a draw shaft intelligent monitoring device, and belongs to the technical field of draw shaft monitoring devices. The draw shaft intelligent monitoring device comprises a vertical rod, the outer wall at the bottom end of the vertical rod is rotationally connected with a bottom rod distributed circumferentially, and the end, away from the vertical rod, of the bottom rod is rotationally connected with a side supporting rod; a mounting block is fixedly arranged at the top of the vertical rod, and the end, away from the bottom rod, of the side supporting rod is rotationallyconnected with the mounting block; a fixing block is fixedly arranged at the top of the mounting block, a ball screw is rotatably connected to one side of the fixing block, a driving motor is arranged at one end of the ball screw, and a screw nut used in cooperation with the ball screw is arranged at the other end of the ball screw. A camera for monitoring is arranged in a draw shaft from the topof the draw shaft, so that the danger brought to the personnel due to holding a flashlight manually with a hand for monitoring is avoided; and the camera can rotate relative to the inner wall of thedraw shaft, and therefore the inner wall of the draw shaft can be conveniently and accurately monitored.
Owner:南京丰濠网络科技有限公司
Directing sound field of actuator
InactiveCN102007778AIncrease capacitanceReduce in quantityElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsEngineeringElectrostatic actuator
The invention relates to a plate-like electrostatic actuator which comprises at least one plate-like stator (2) with an electrode (4) formed on its surface and at least one moving diaphragm (3), and in which a signal is transmitted to the electrode along a signal line (5). In the solution of the invention, the delay directing the sound field of the actuator is formed at least partly of an RC circuit composed of components of the actuator.
Owner:PANPHONICS OY
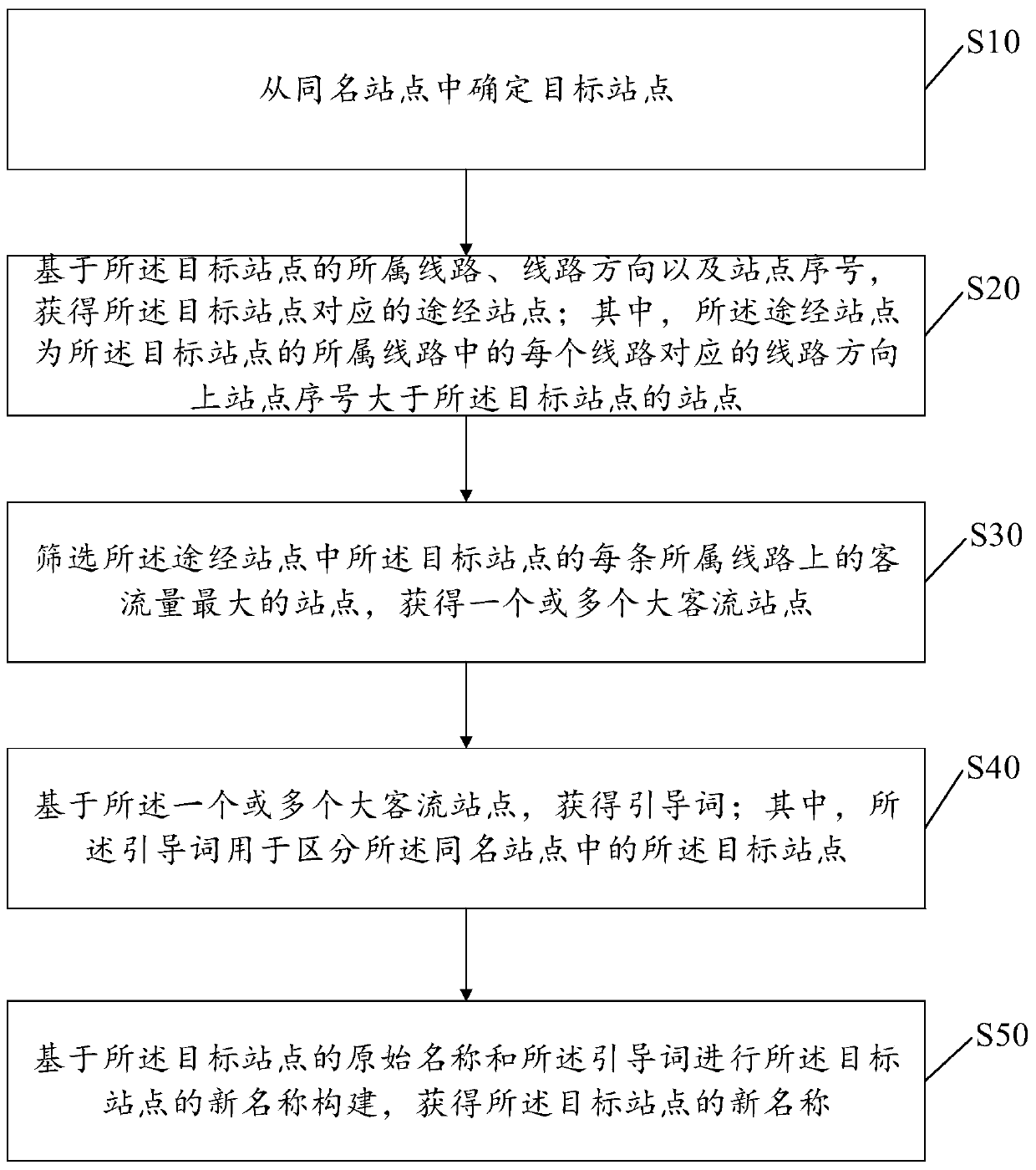
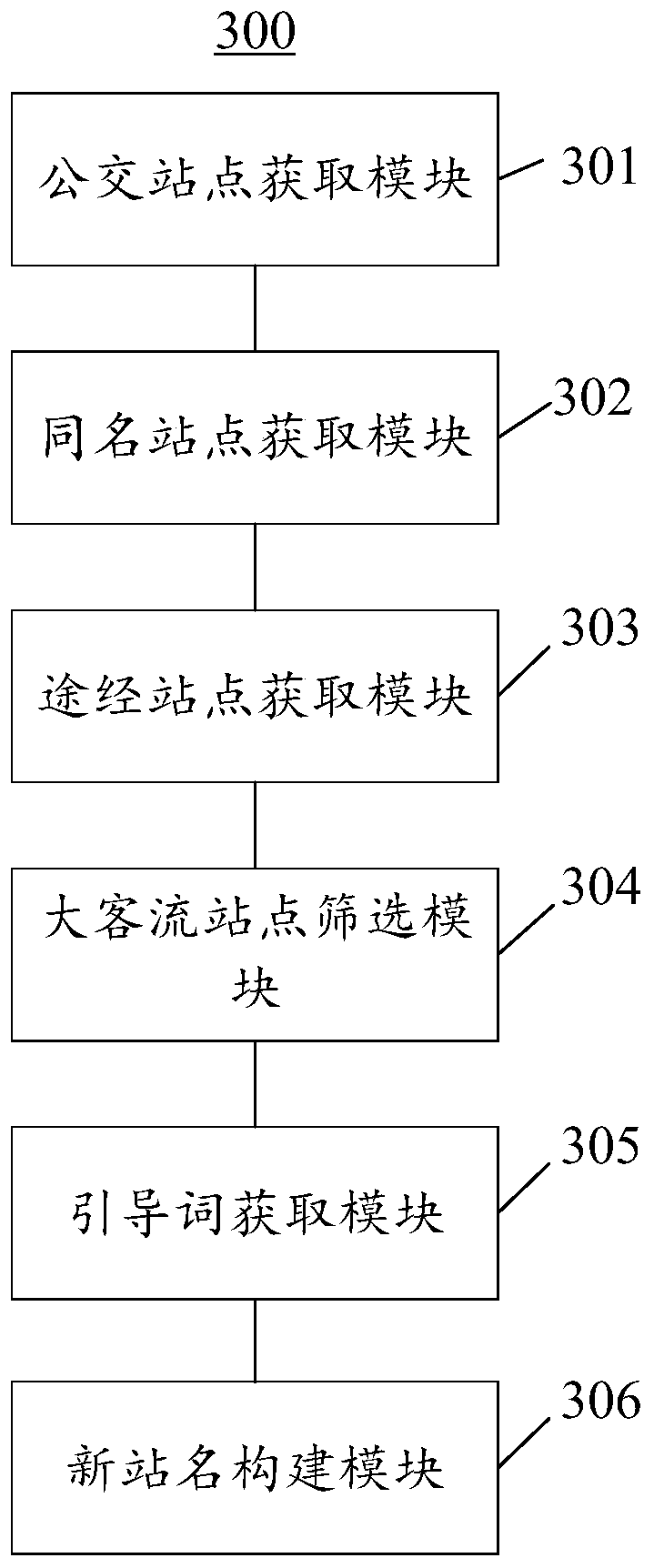
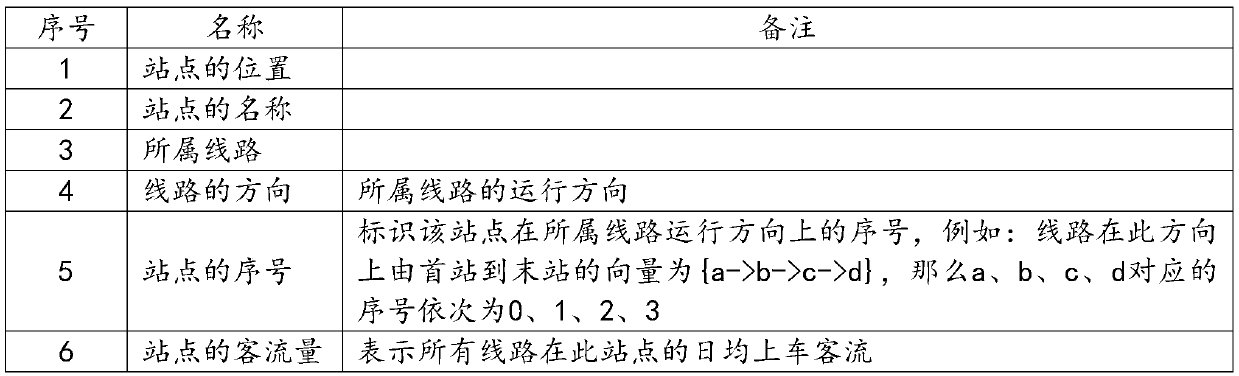
Bus midway station name generation method and device
PendingCN111476032AGuaranteed resolutionResolve ambiguous referencesForecastingNatural language data processingSerial codeComputer engineering
The invention discloses a bus midway station name generation method and device. The method comprises the steps: acquiring a bus station set; grouping bus stations in the bus station set based on namesto obtain a plurality of homonymous station sets, wherein each homonymous site set comprises one or more homonymous sites; based on the route to which the target station belongs, the route directionand the station serial number, obtaining a passing station corresponding to the target station; screening the station with the maximum passenger flow volume on each line of the target station in the passing stations to obtain one or more large passenger flow stations; obtaining a guide word based on the one or more large passenger flow stations; and constructing a new name of the target site basedon the original name of the target site and the guide word to obtain the new name of the target site. The new station name constructed by the invention can effectively solve the problem that the original station name cannot be explained clearly.
Owner:武汉元光科技有限公司
Compass pointing optimization method and system for mobile terminal
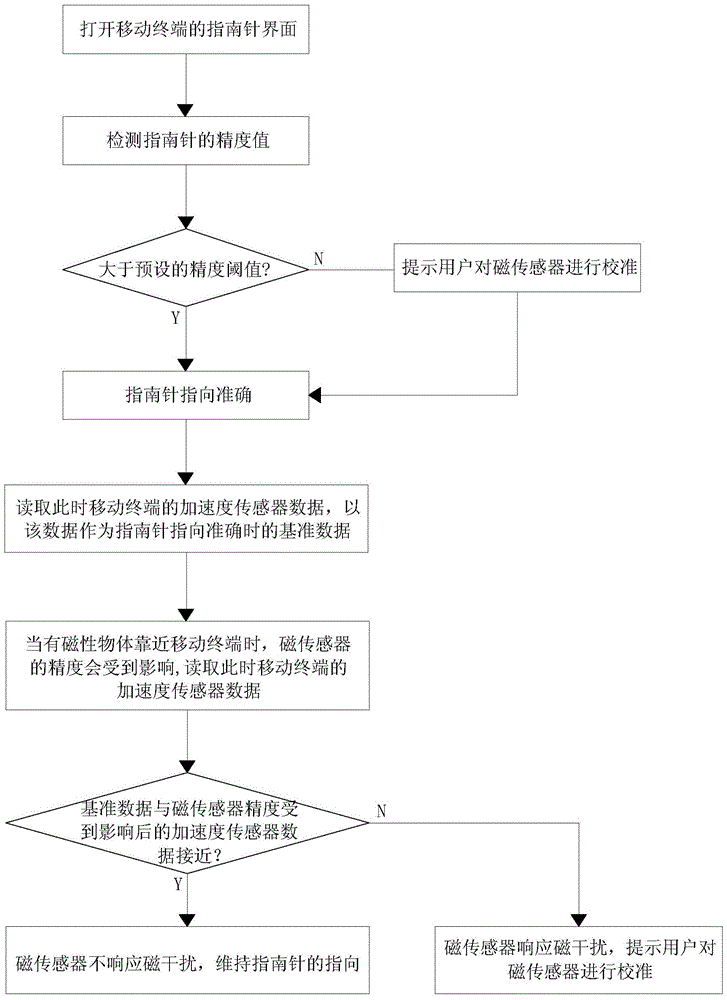
InactiveCN104135576BPointing accuratelyPoint to optimizationTelephone set constructionsCompassesBaseline dataMagnetic disturbance
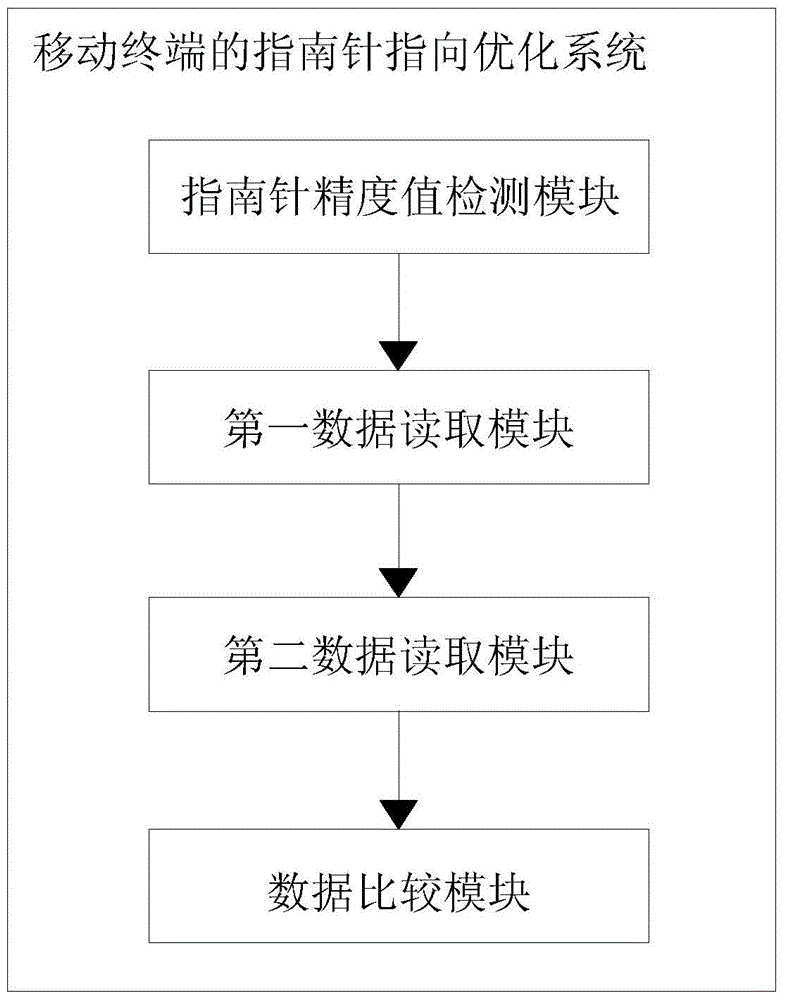
The invention discloses a compass positioning optimization method and system for a mobile terminal. The method comprises the steps that when positioning of a compass of the mobile terminal is accurate, acceleration sensor data are read at the moment, and the data serve as benchmark data for accurate positioning of the compass; when a magnetic object is close to the mobile terminal, the precision of a magnetic sensor is affected, and acceleration sensor data are read at the moment; the benchmark data read when the compass positioning is accurate are compared with acceleration sensor data read when the precision of the magnetic sensor is affected; if the two groups of data are approximated to each other, the magnetic sensor produces no response to magnetic disturbance, and positioning of the compass is kept; if not, the magnetic sensor produces a response to the magnetic disturbance, and a user is prompted to calibrate the magnetic sensor. The system comprises a compass precision value detection module, a first data reading module, a second data reading module and a data comparing module. The compass positioning optimization method and system enable the compass to achieve accurate positioning even when the precision of the magnetic sensor is affected.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
A Portable Multifunctional Reconstruction Auxiliary Tool for Rock and Soil Structures
The invention relates to a portable multifunctional rock-soil body structure reconstruction auxiliary tool which comprises a gravity cone, a direction pointing assembly, an angle measurement assembly, a suspension rod and a base, the gravity cone is connected with the angle measurement assembly through a suspension rope, the direction pointing assembly is arranged on the suspension rope in a sleeving mode, the angle measurement assembly is arranged at the top end of the suspension rod in a sleeving mode, and the bottom end of the suspension rod is connected with the base; in the measurement process, the base is fixed to the structural face of a geological body, and the position of the suspension rod is adjusted, so that the suspension rod is perpendicular to the structural face, after the whole tool is in the balanced state, the spatial true dip angle of the structural face is obtained through the angle between the suspension rope on the angle measurement assembly and the suspension rod, and spatial orientation direction pointing is conducted through the direction pointing assembly. Compared with the prior art, the tool has the advantages of being comprehensive in function, wide in applicability, convenient to operate in practice and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
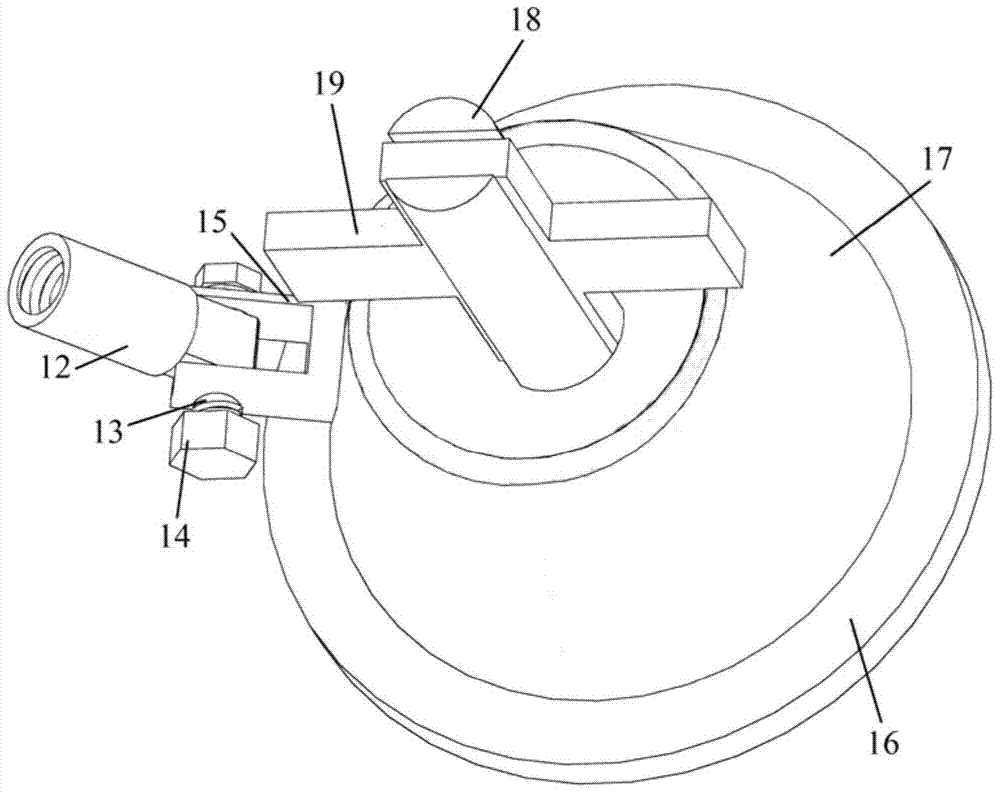
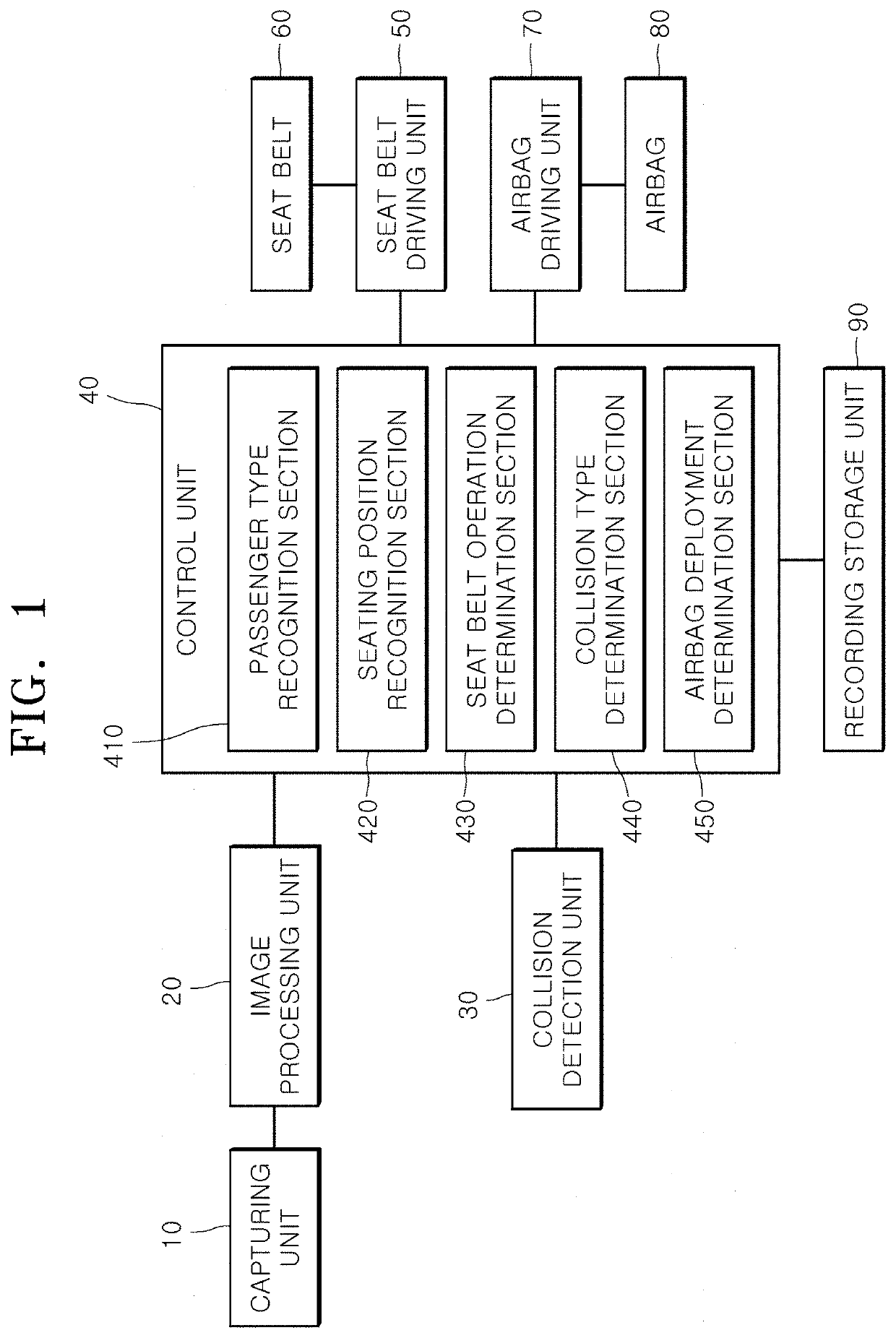
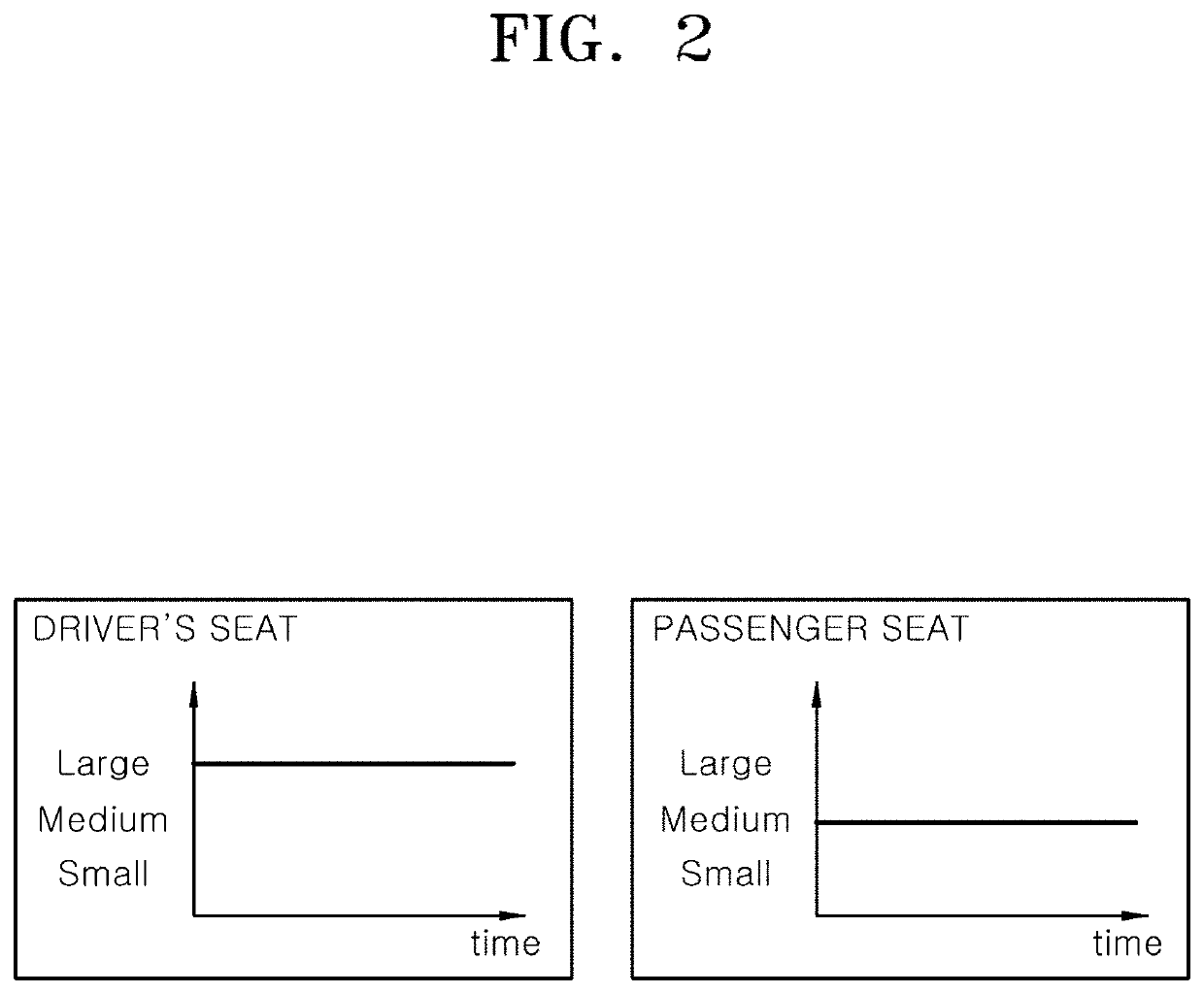
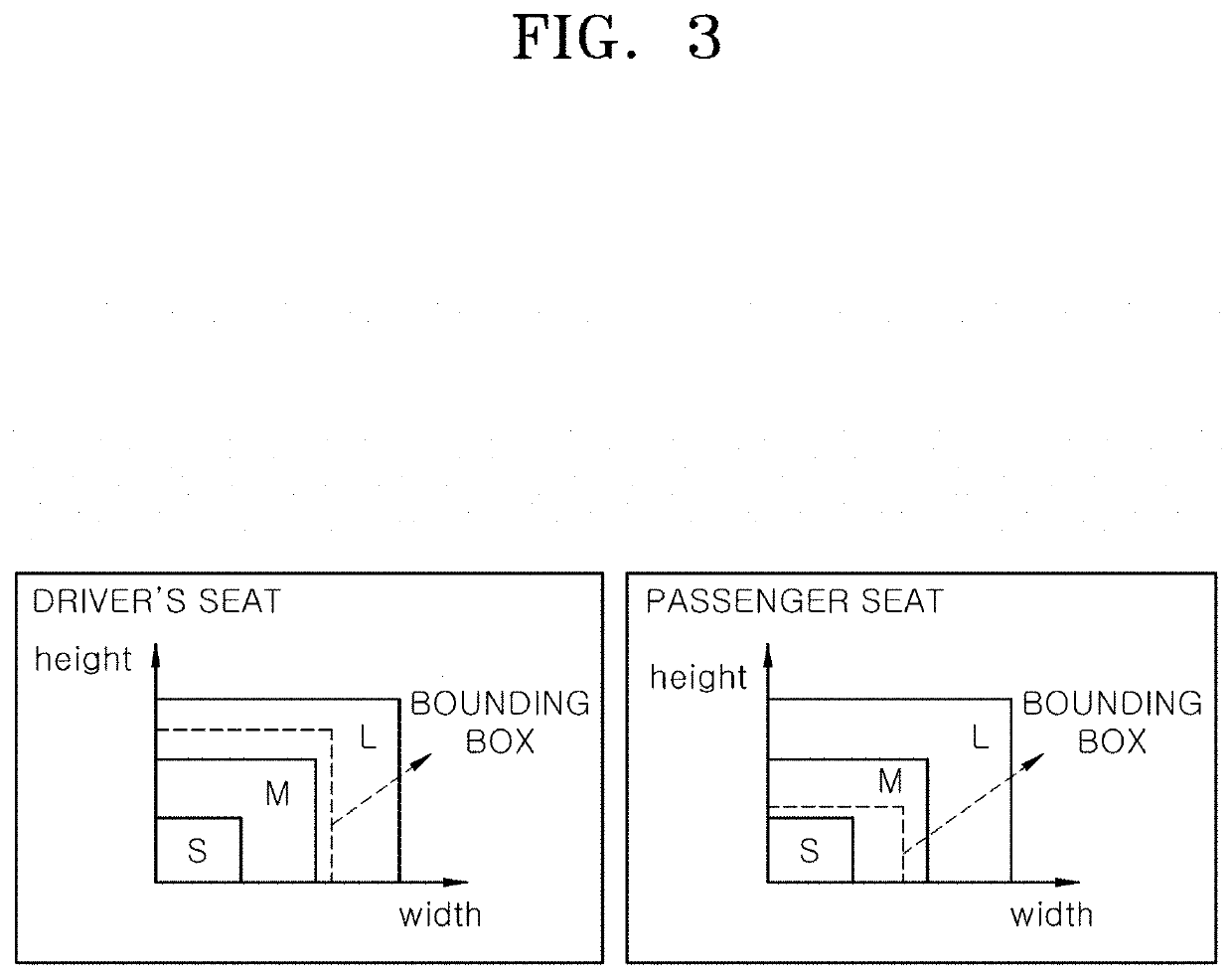
Apparatus for protecting passenger in vehicle and control method thereof
PendingUS20220306027A1Point to optimizationMinimize malfunctionBelt control systemsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementImaging processingSeat belt
An apparatus for protecting a passenger in a vehicle and a control method thereof. The apparatus includes a collision detection unit that detects a predicted collision state and a collision state of a vehicle; a seat belt driving unit that adjusts tension of a seat belt according to an operation mode; an airbag driving unit that deploys each of a plurality of airbags according to a driving signal; a capturing unit that captures images of an interior of the vehicle; an image processing unit that extracts passenger information by processing images inputted from the capturing unit; and a control unit that recognizes a passenger type and a seating position based on the passenger information, operates the seat belt driving unit by setting the operation mode, adjusts deployment time points of the plurality of airbags, and outputs the driving signal to the airbag driving unit.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com