Patents
Literature
482 results about "Virtual ground" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
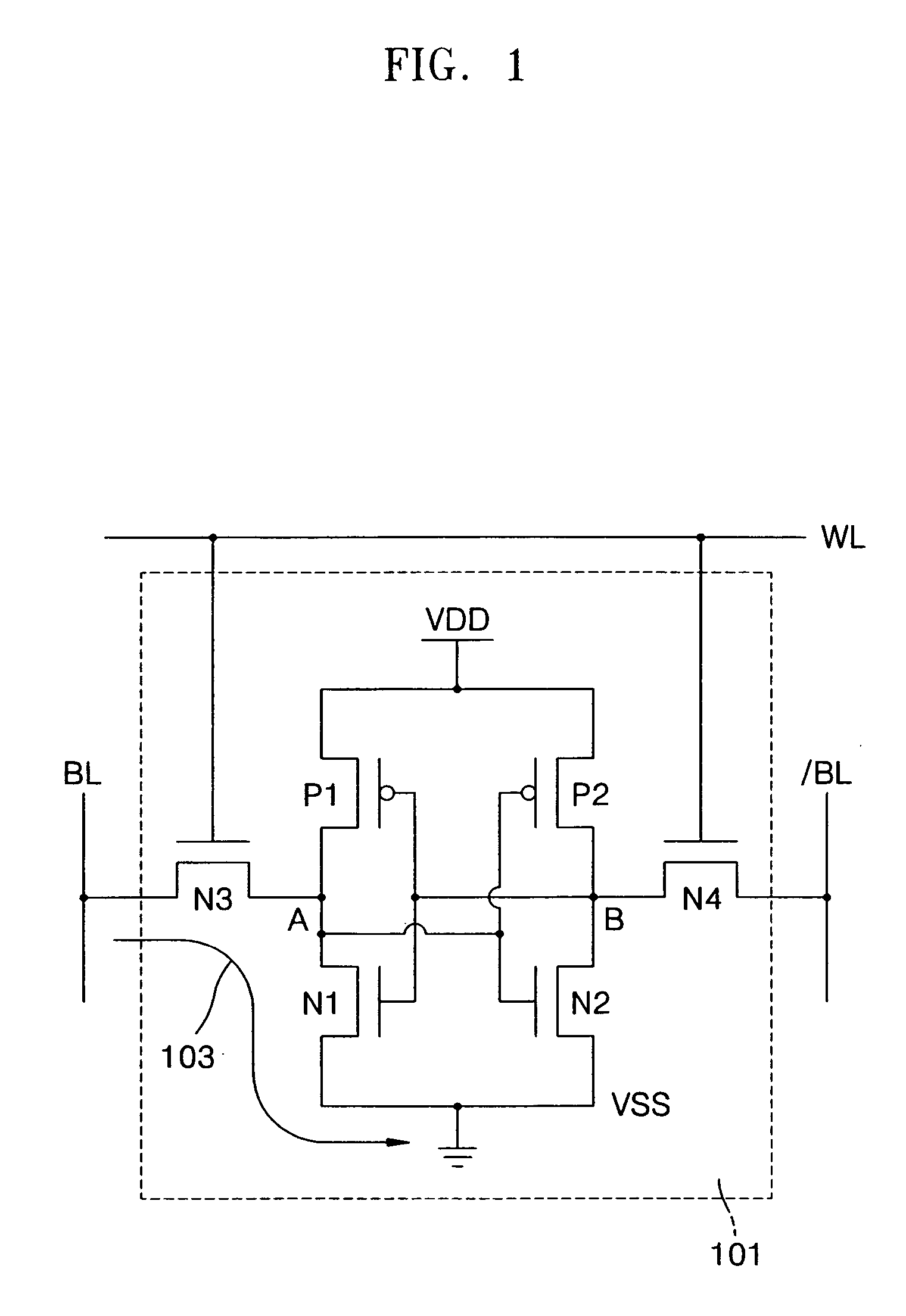
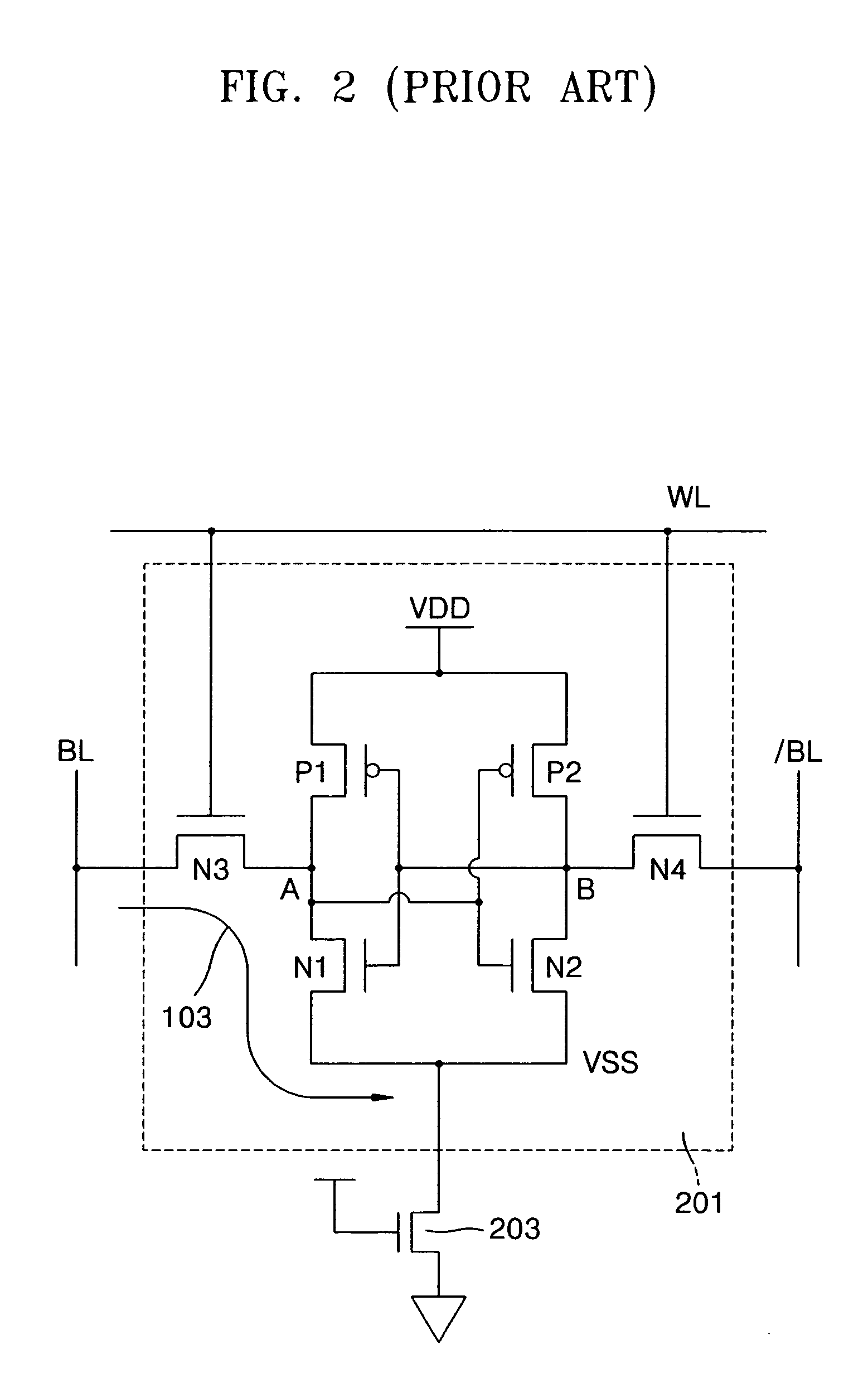
In electronics, a virtual ground (or virtual earth) is a node of a circuit that is maintained at a steady reference potential, without being connected directly to the reference potential. In some cases the reference potential is considered to be that of the surface of the earth, and the reference node is called "ground" or "earth" as a consequence.
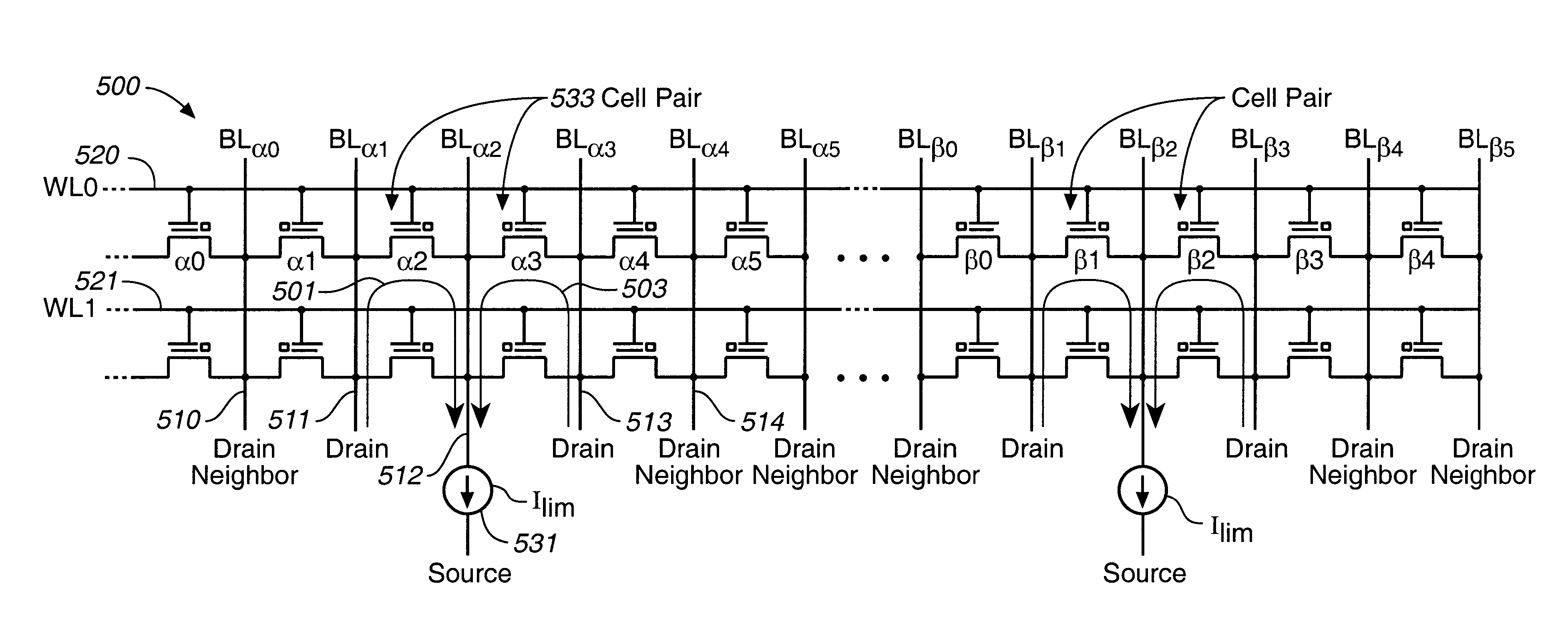
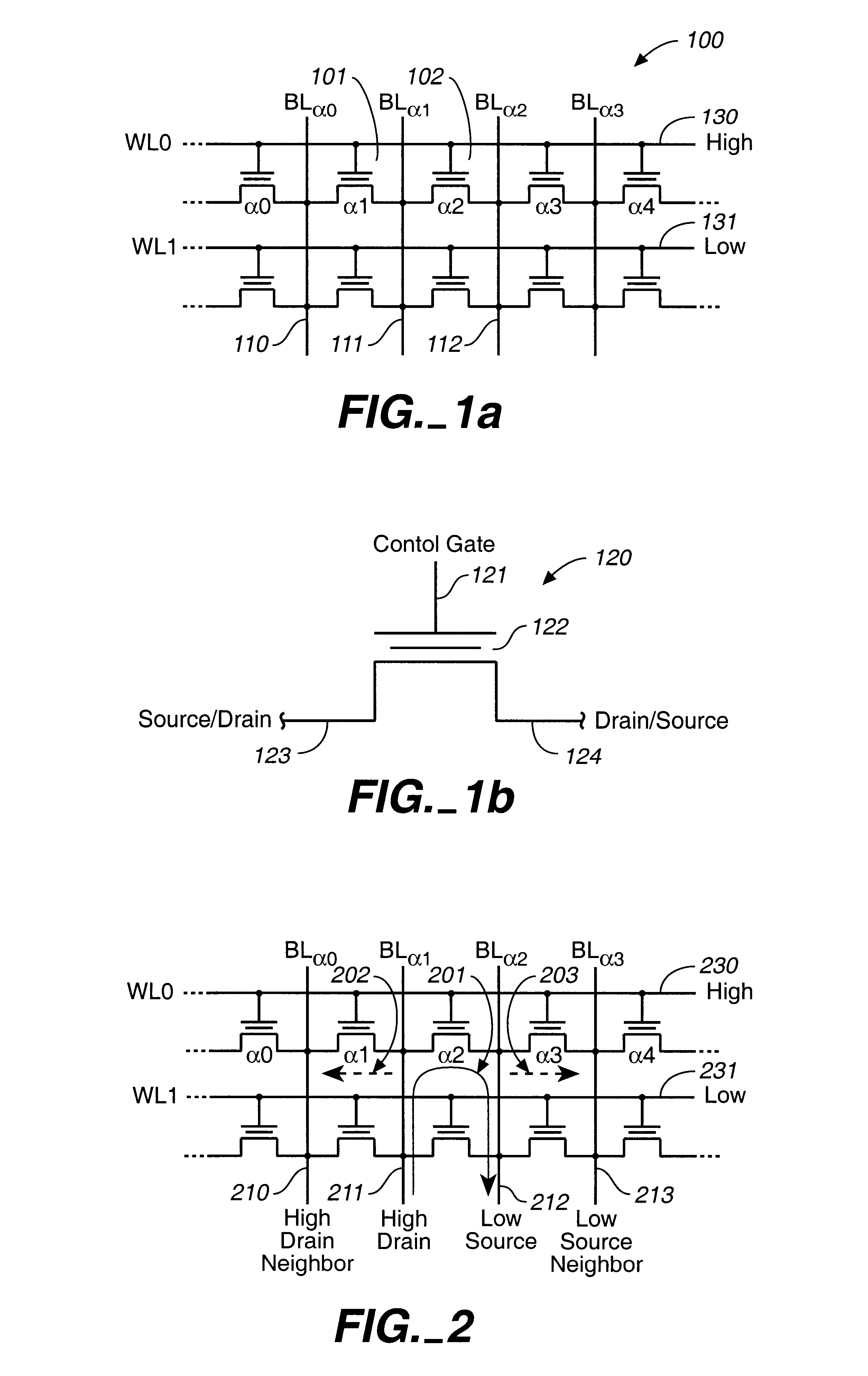
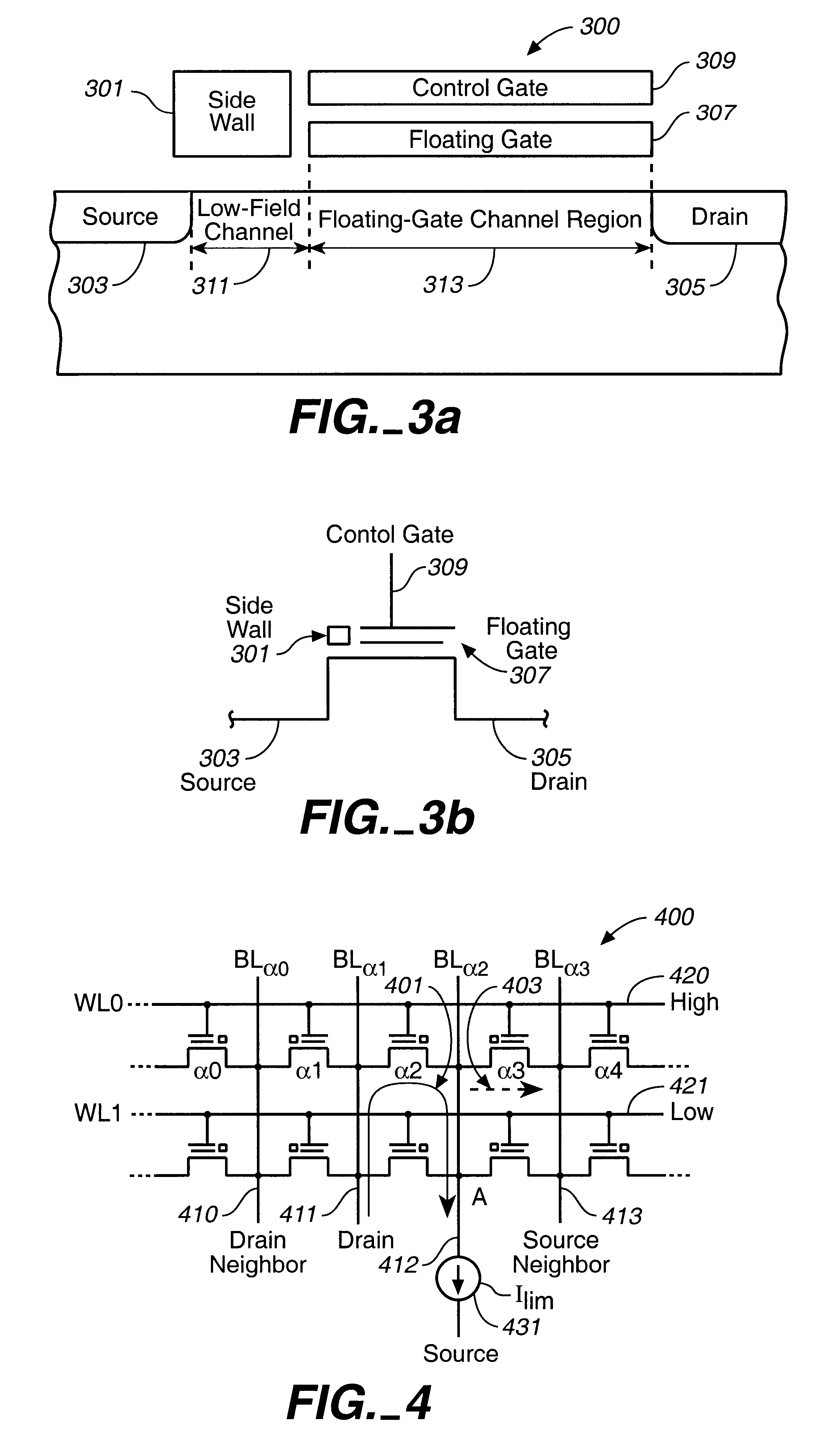
Dual-cell soft programming for virtual-ground memory arrays
A technique for controlling the soft-program current in virtual-ground FLASH memory arrays is described. It is based on biasing the array bit-lines such that all current supplied to the array is used entirely towards the soft-programming of selected cells. The result is control of the soft-programming current and the programming rate of individual cell pairs. The benefit of soft-programming is then realized during the actual cell programming with the improved control of current and program rate. This is described with respect to an embodiment that uses source-side injection as the means for programming memory cells and with respect to a second embodiment based on a cell with dual floating gates.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
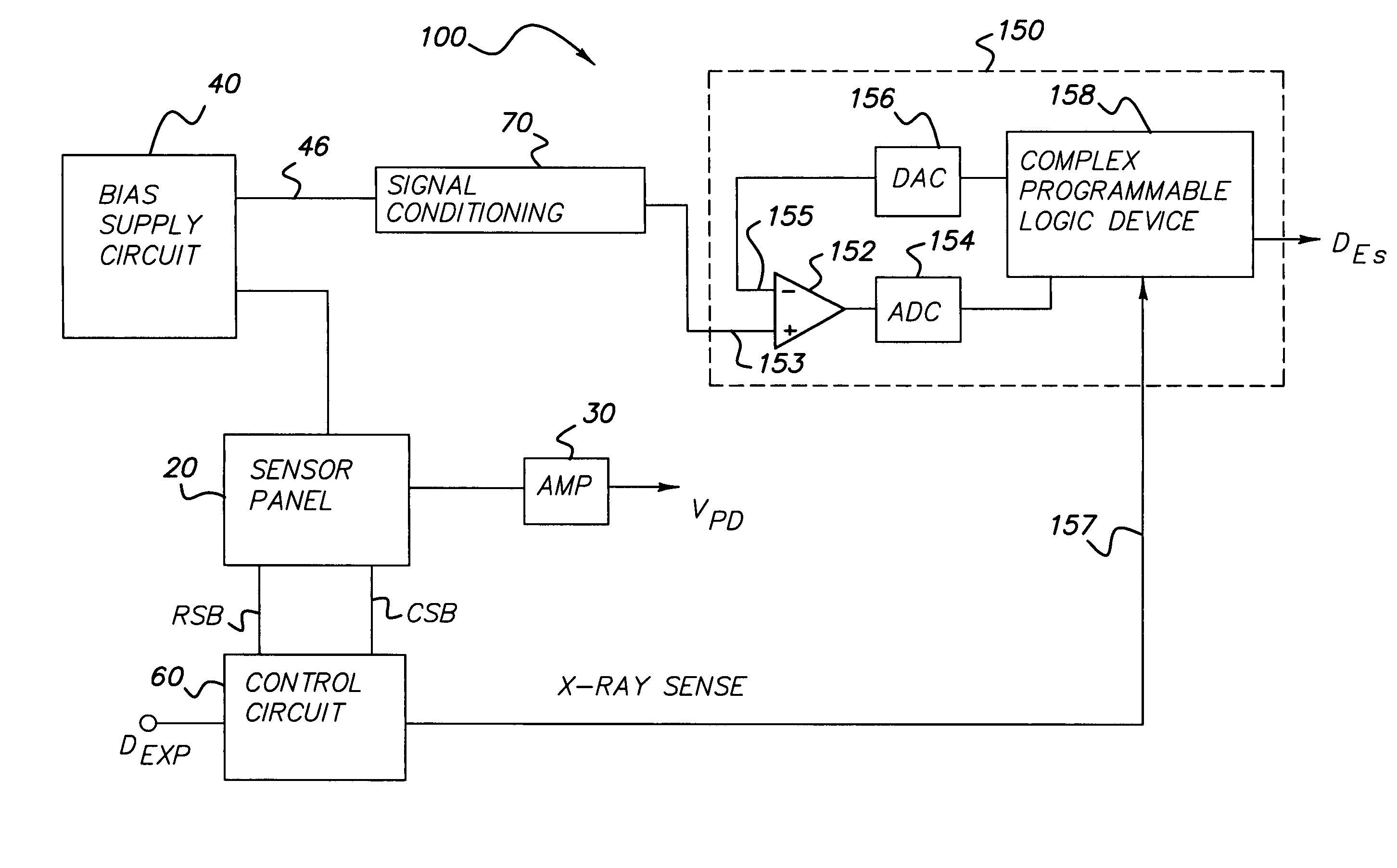
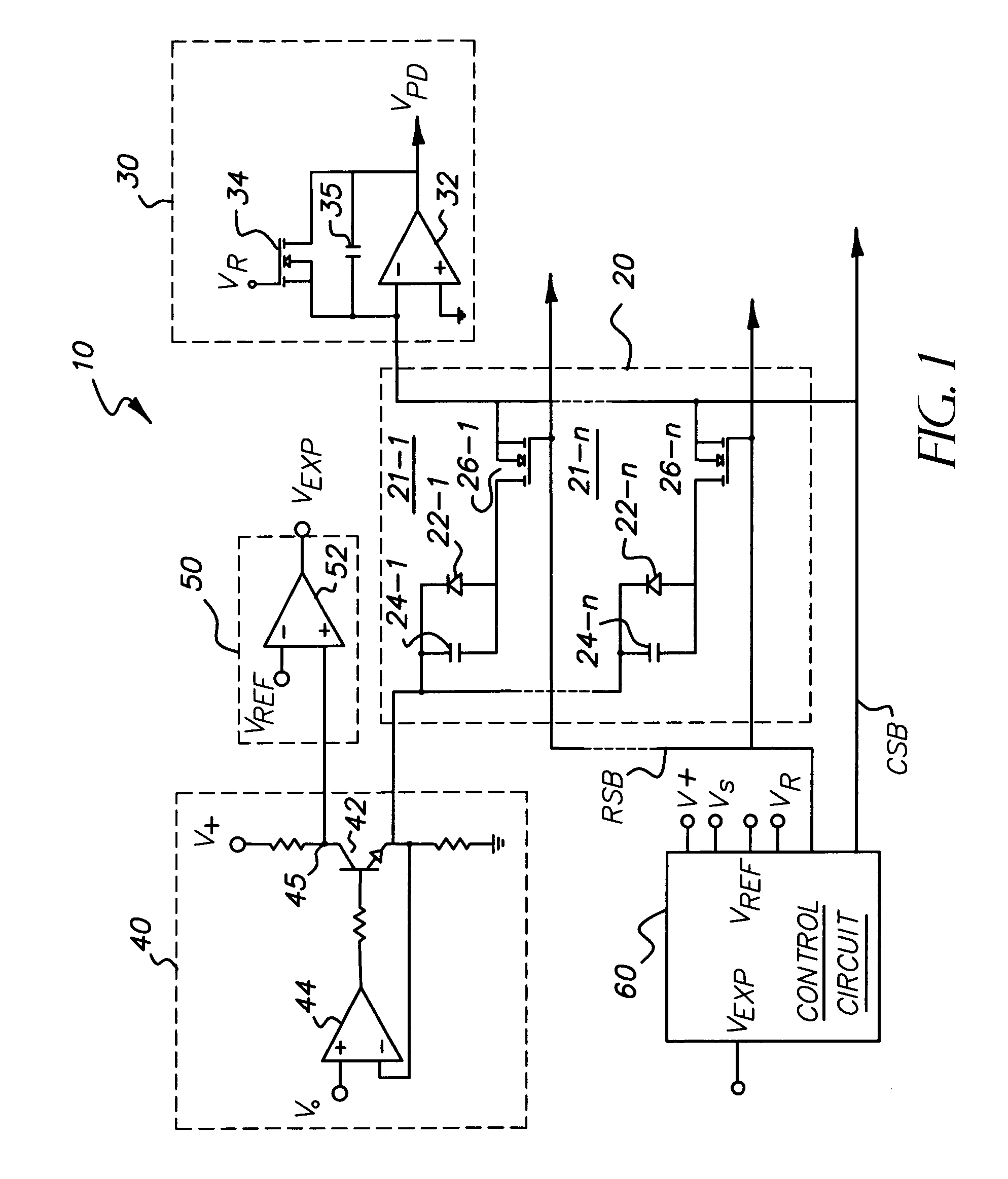
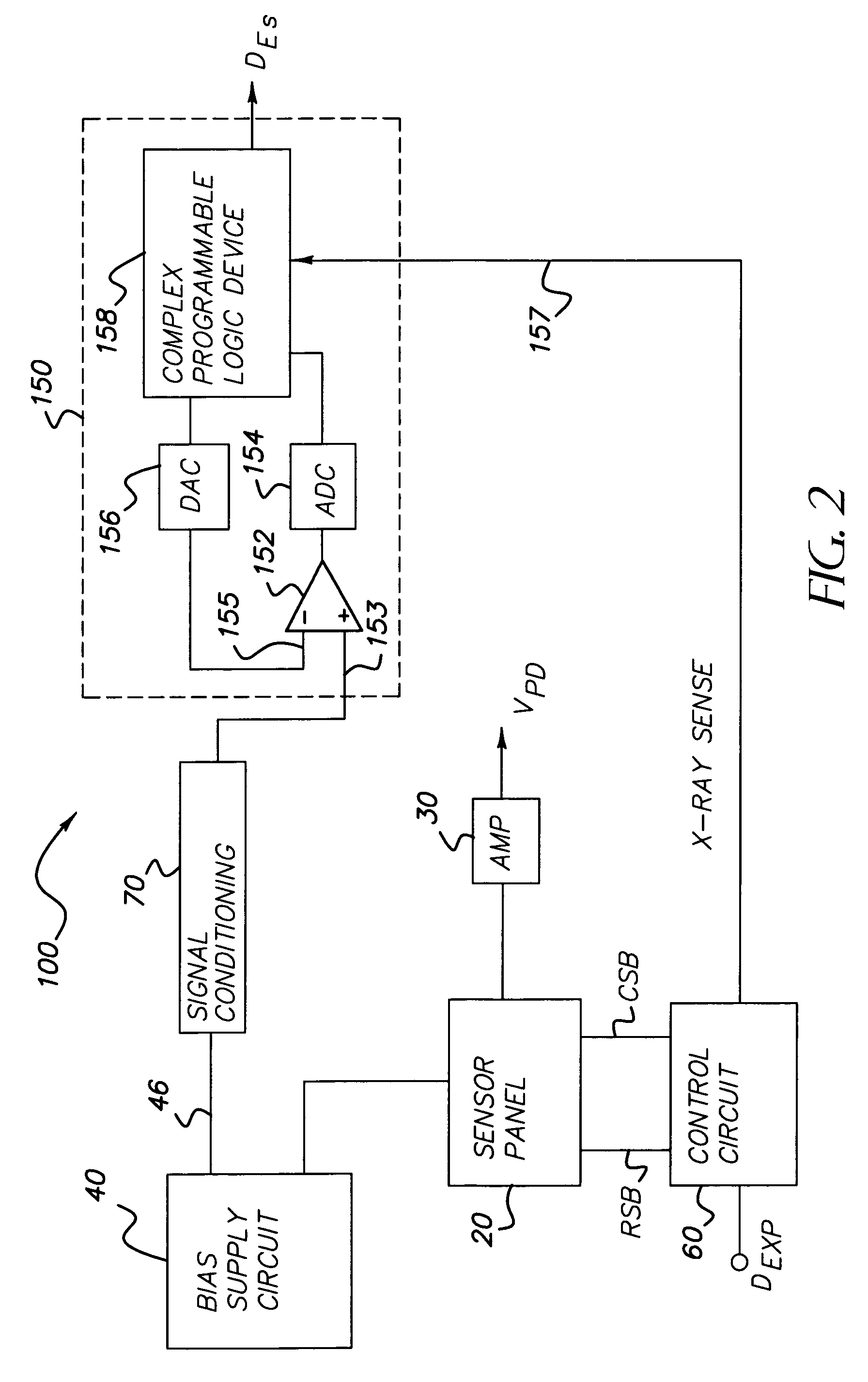
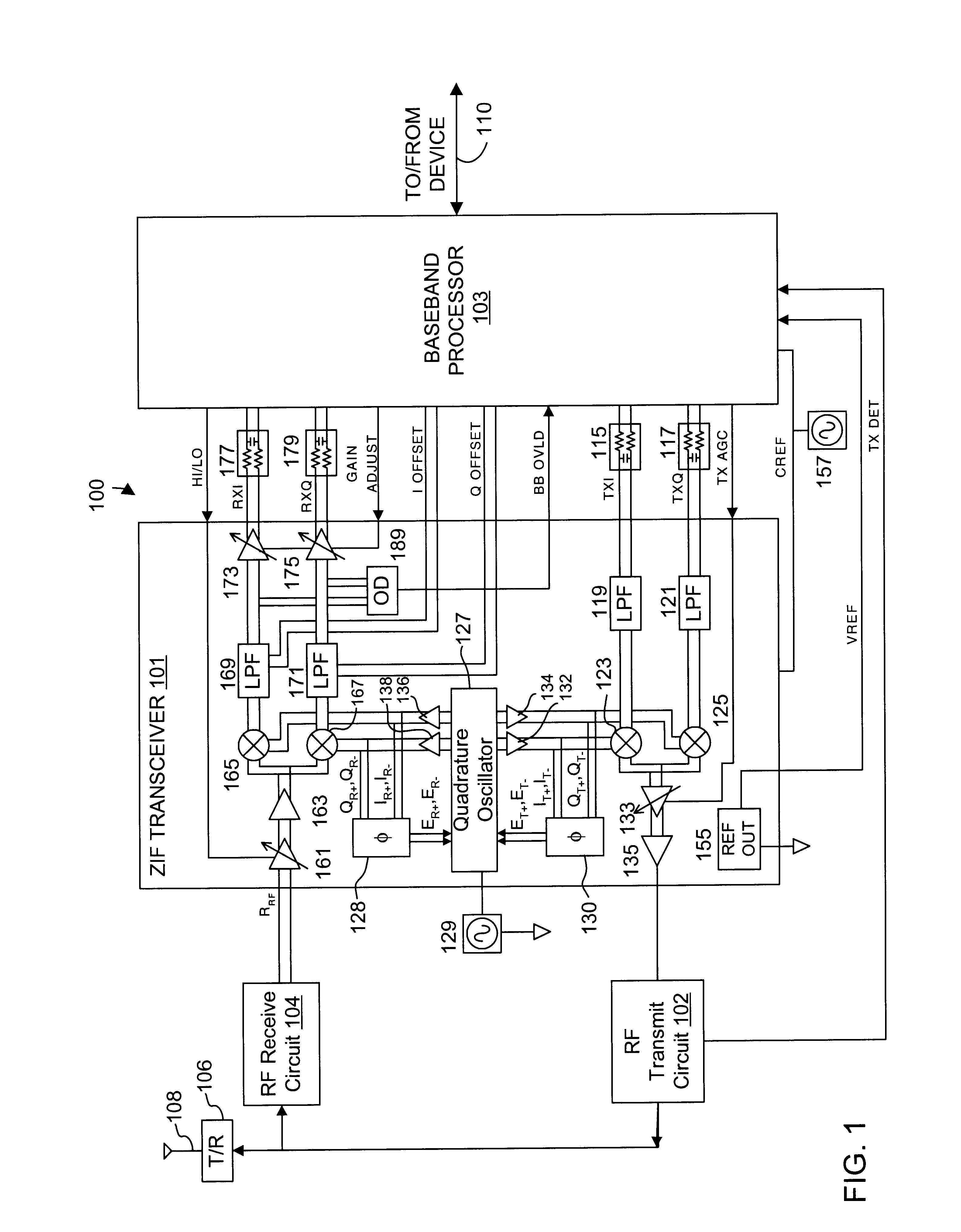
Wireless X-ray detector for a digital radiography system with remote X-ray event detection
ActiveUS7211803B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioQuick checkMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDetector circuitsX-ray
A wireless X-ray detector for a digital radiography system with remote detection of impinging radiation from the system X-ray source onto a sensor panel having amorphous or crystalline silicon photodiodes or metal insulated semiconductor (MIS) sensors. Changes in current in the photodiode bias supply circuit is sensed to generate a signal indicating presence of radiation. Improved detection of X-ray cessation is achieved either by leaving at least one line of sensors connected between the bias supply circuit to a virtual ground during charge accumulation or by using an X-ray presence detector circuit that increases the sensitivity of the detector circuit to bias circuit current changes occurring after onset of the radiation.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
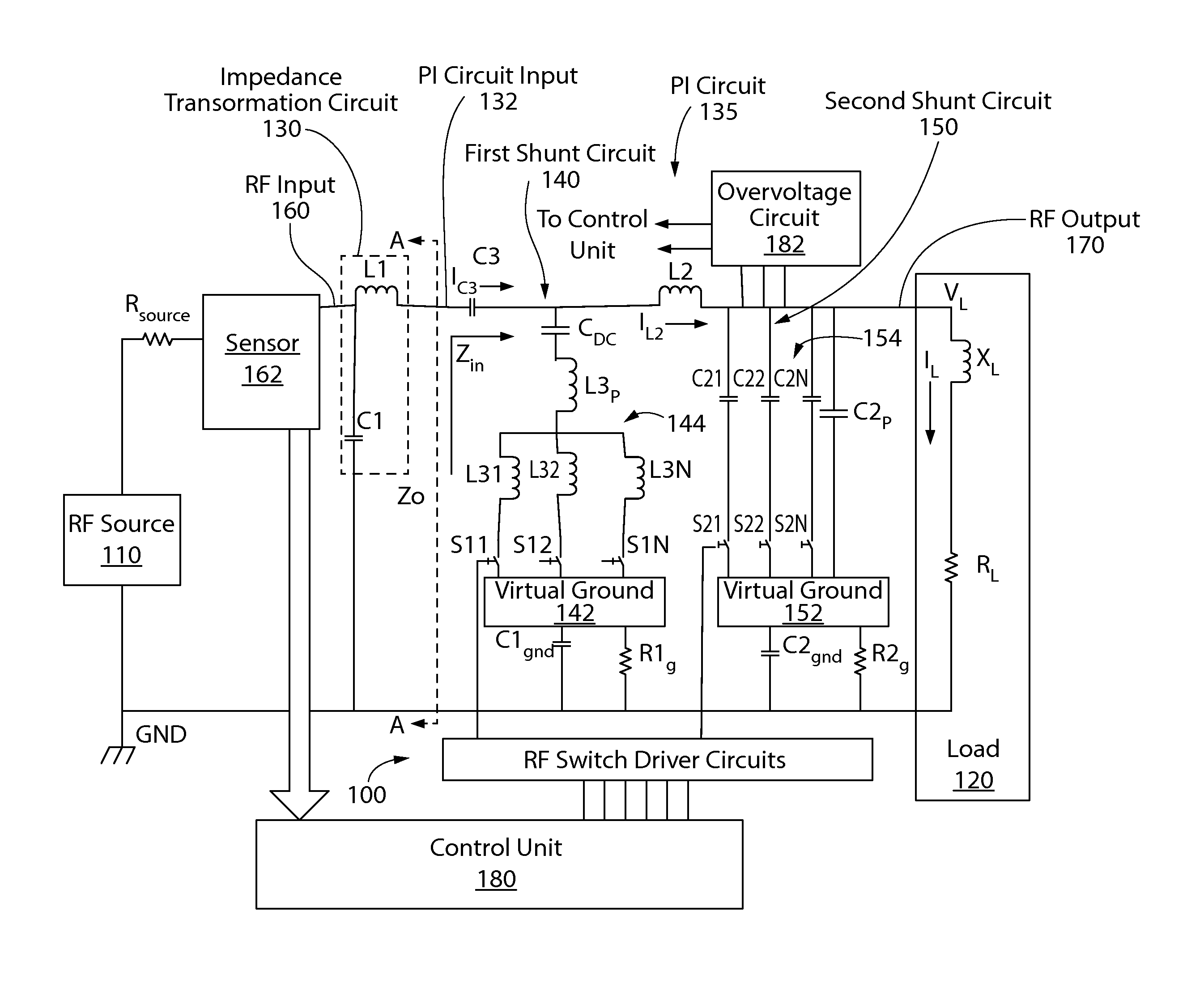
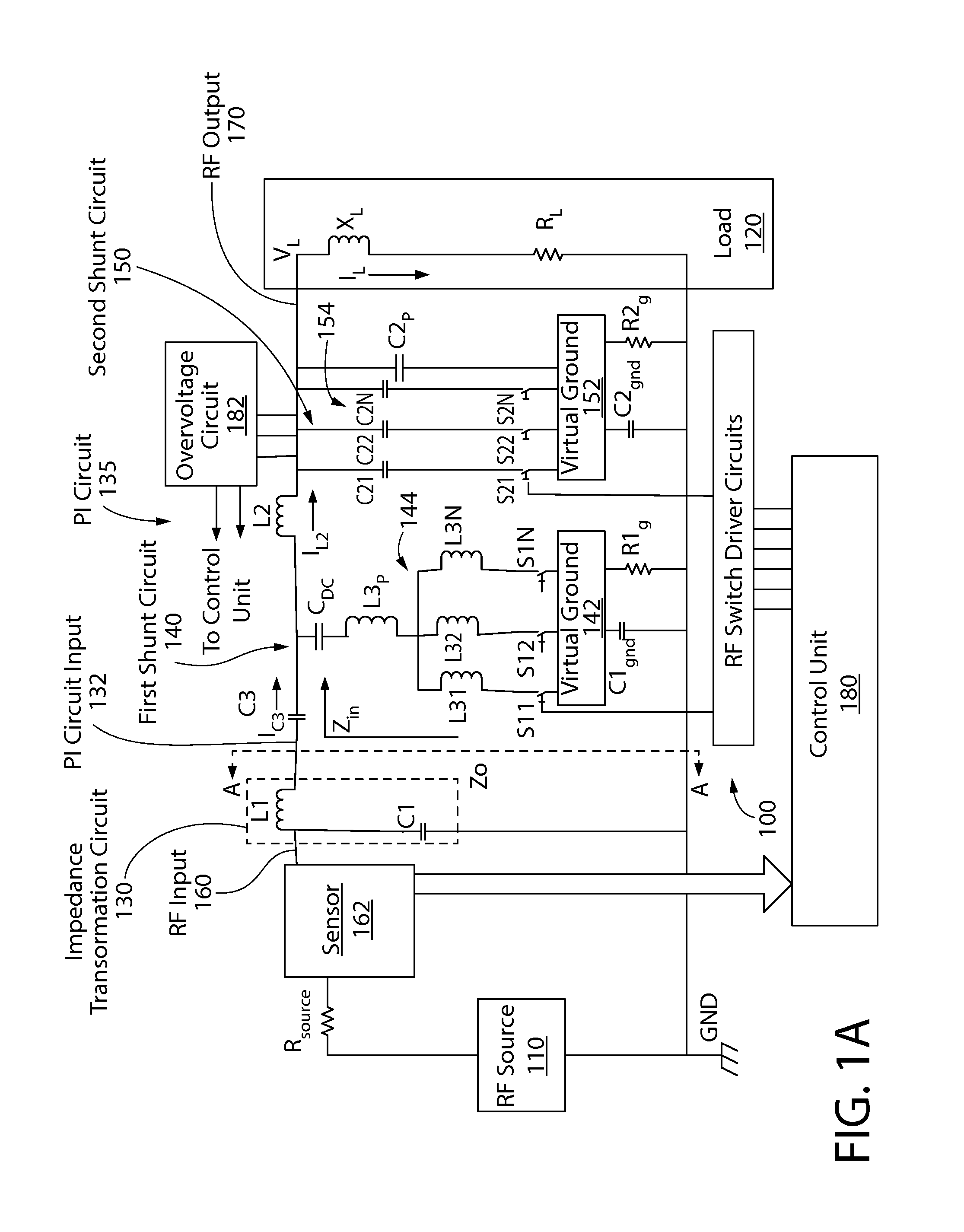
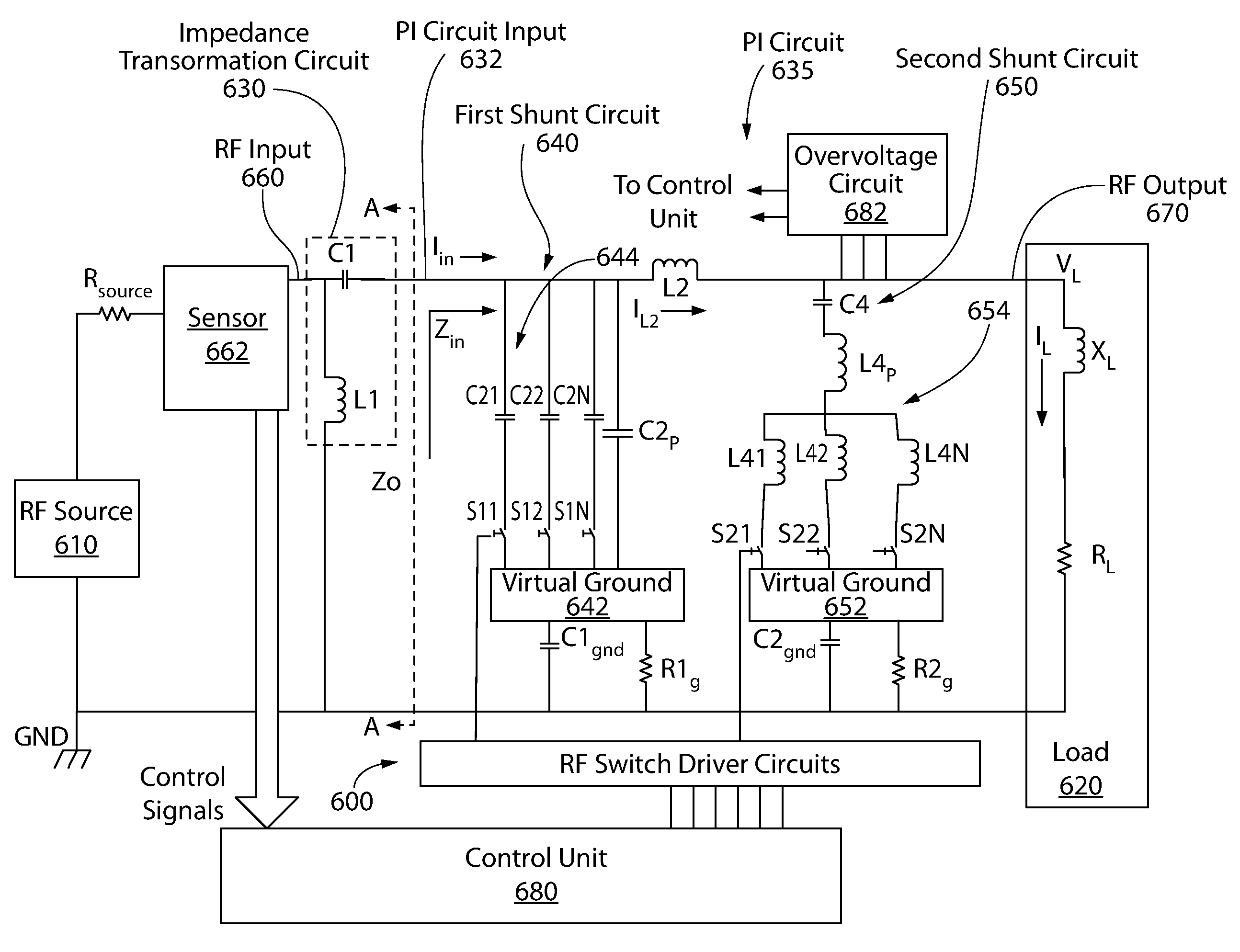
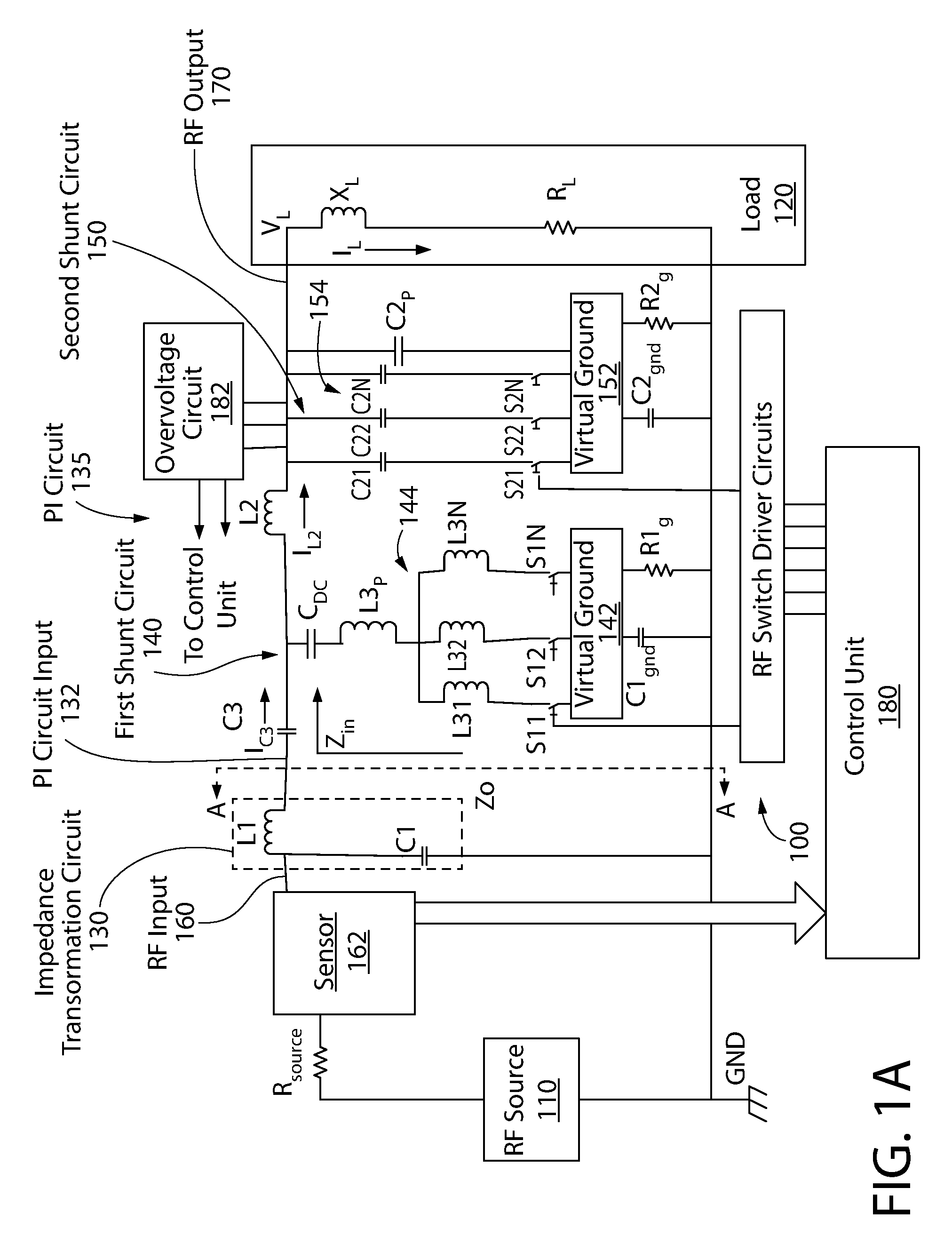
RF impedance matching network
An RF impedance matching network includes a transformation circuit configured to provide a transformed impedance; a first shunt circuit in parallel to the RF input, the first shunt circuit including a first shunt variable capacitance component comprising (a) a plurality of first shunt capacitors coupled in parallel, and (b) a plurality of first shunt switches coupled to the plurality of first shunt capacitors and configured to connect and disconnect each of the plurality of first shunt capacitors to a first virtual ground; and a second shunt variable capacitance component including (a) a plurality of second shunt capacitors coupled in parallel, and (b) a plurality of second shunt switches coupled to the plurality of second shunt capacitors and configured to connect and disconnect each of the plurality of second shunt capacitors to a second virtual ground.
Owner:ASM AMERICA INC
SRAM employing virtual rail scheme stable against various process-voltage-temperature variations
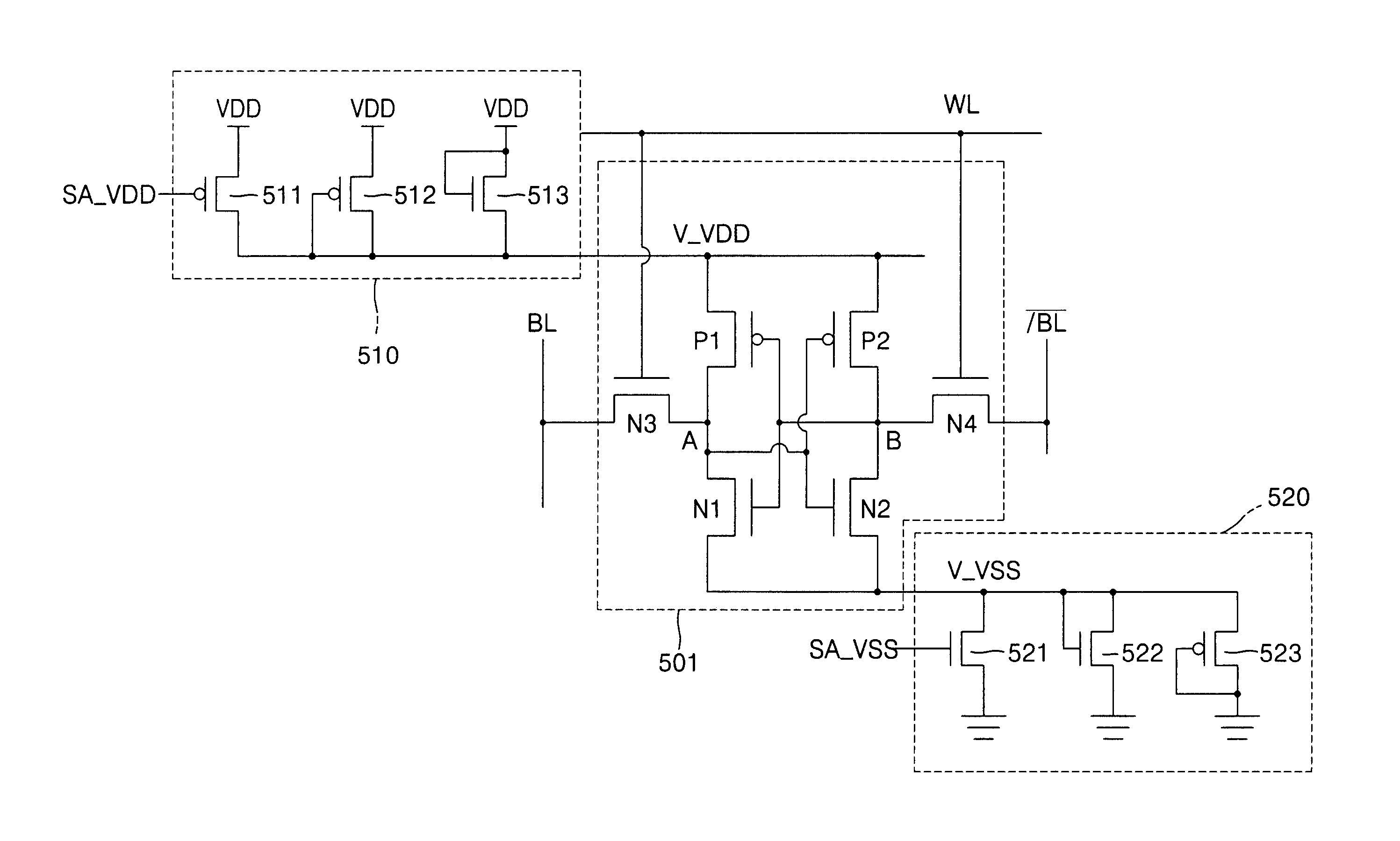
An SRAM employs a virtual rail configuration that is stable against process-voltage-temperature (PVT) variation. The SRAM provides a virtual power supply voltage to an SRAM cell that is obtained by lowering a power supply voltage by a threshold voltage of a transistor and a virtual ground voltage obtained by raising a ground voltage by a threshold voltage of a transistor. Due to the use of PMOS and NMOS transistors of diode types connected between the power supply voltage and the virtual power supply voltage and the use of NMOS and PMOS transistors of diode types connected between the ground voltage and the virtual ground voltage, a virtual power supply voltage level and a virtual ground voltage level that are stable even against various PVT variations are provided, so that low-leakage current characteristics are stable.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mass storage array and methods for operation thereof
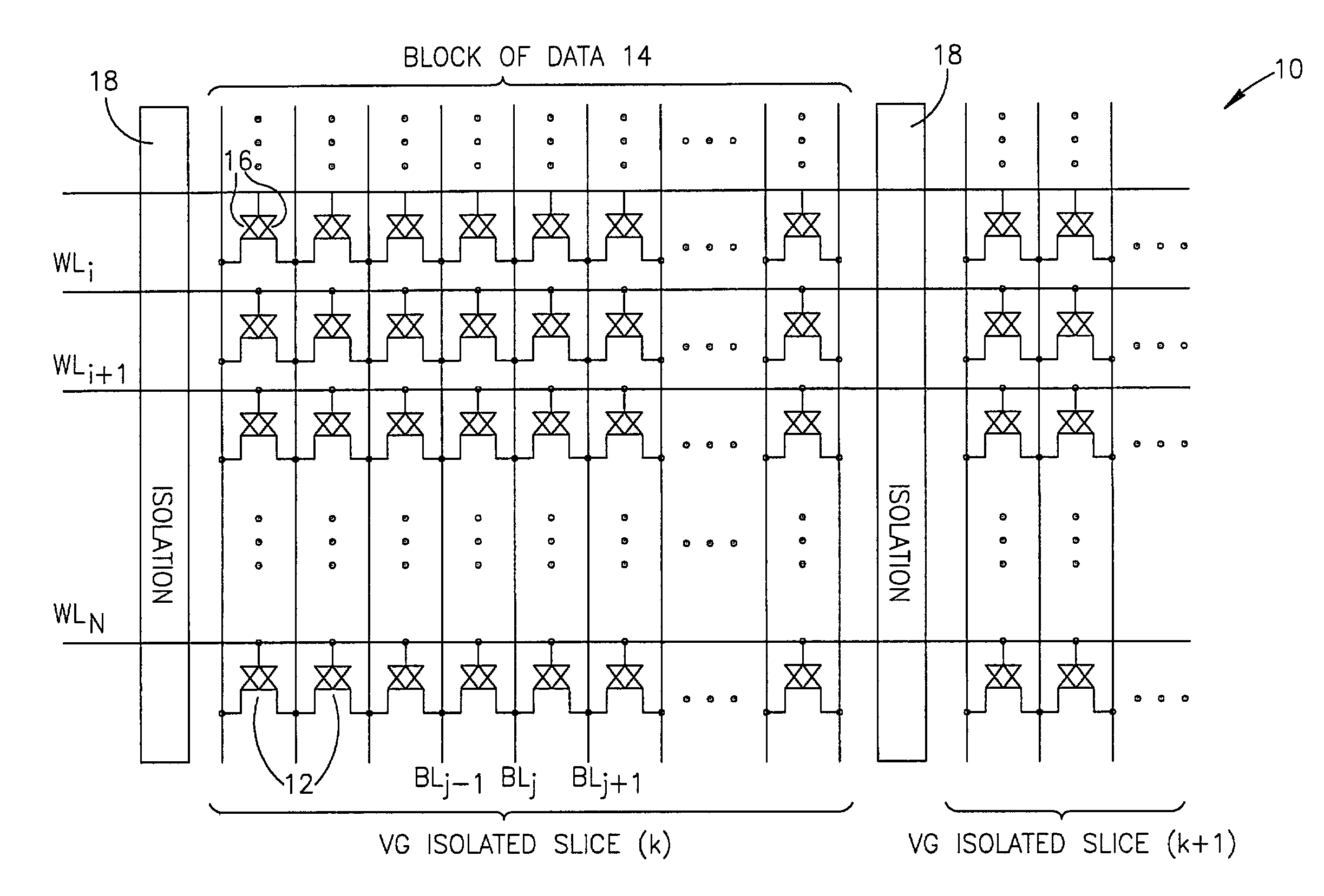
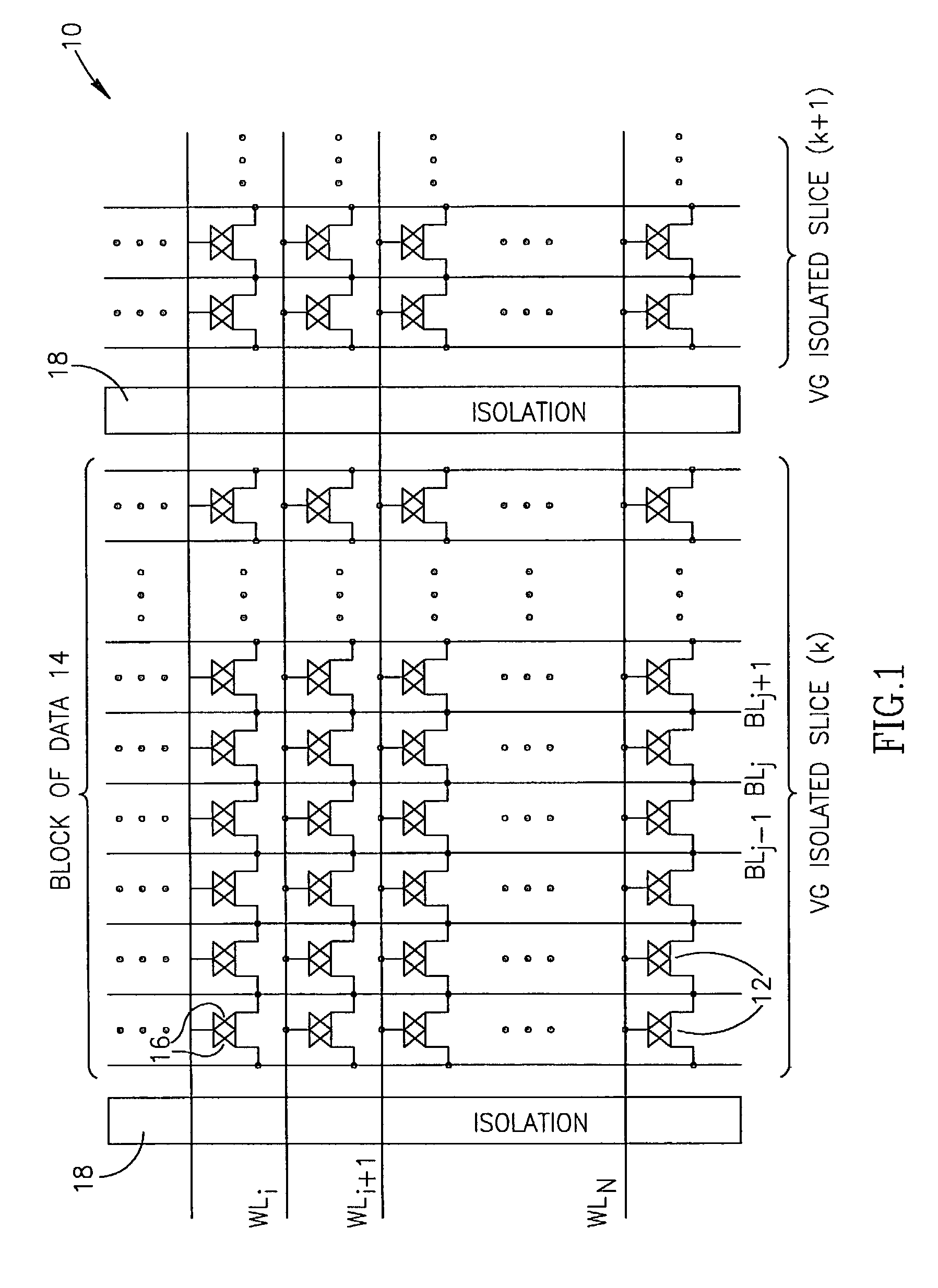
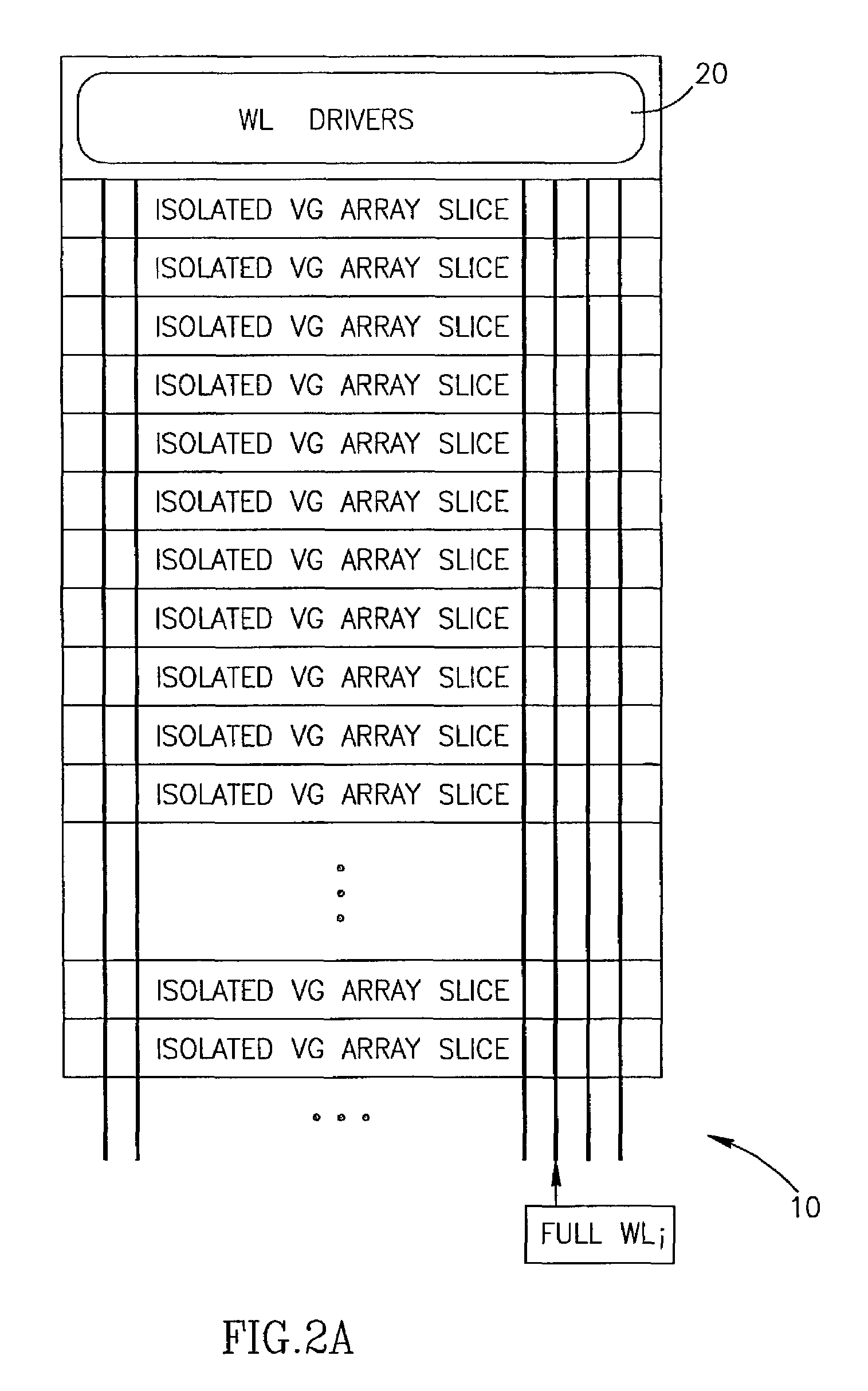
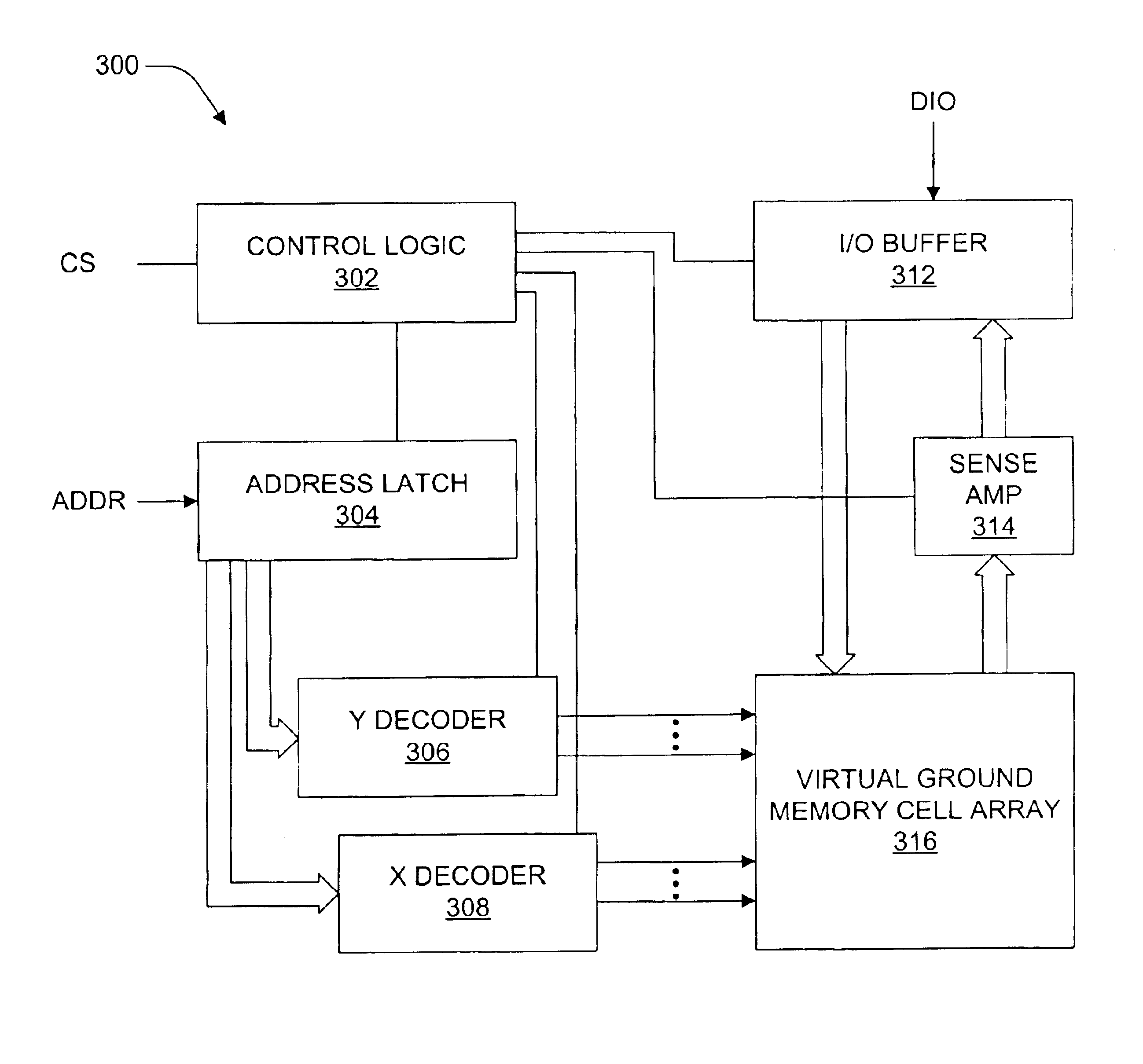
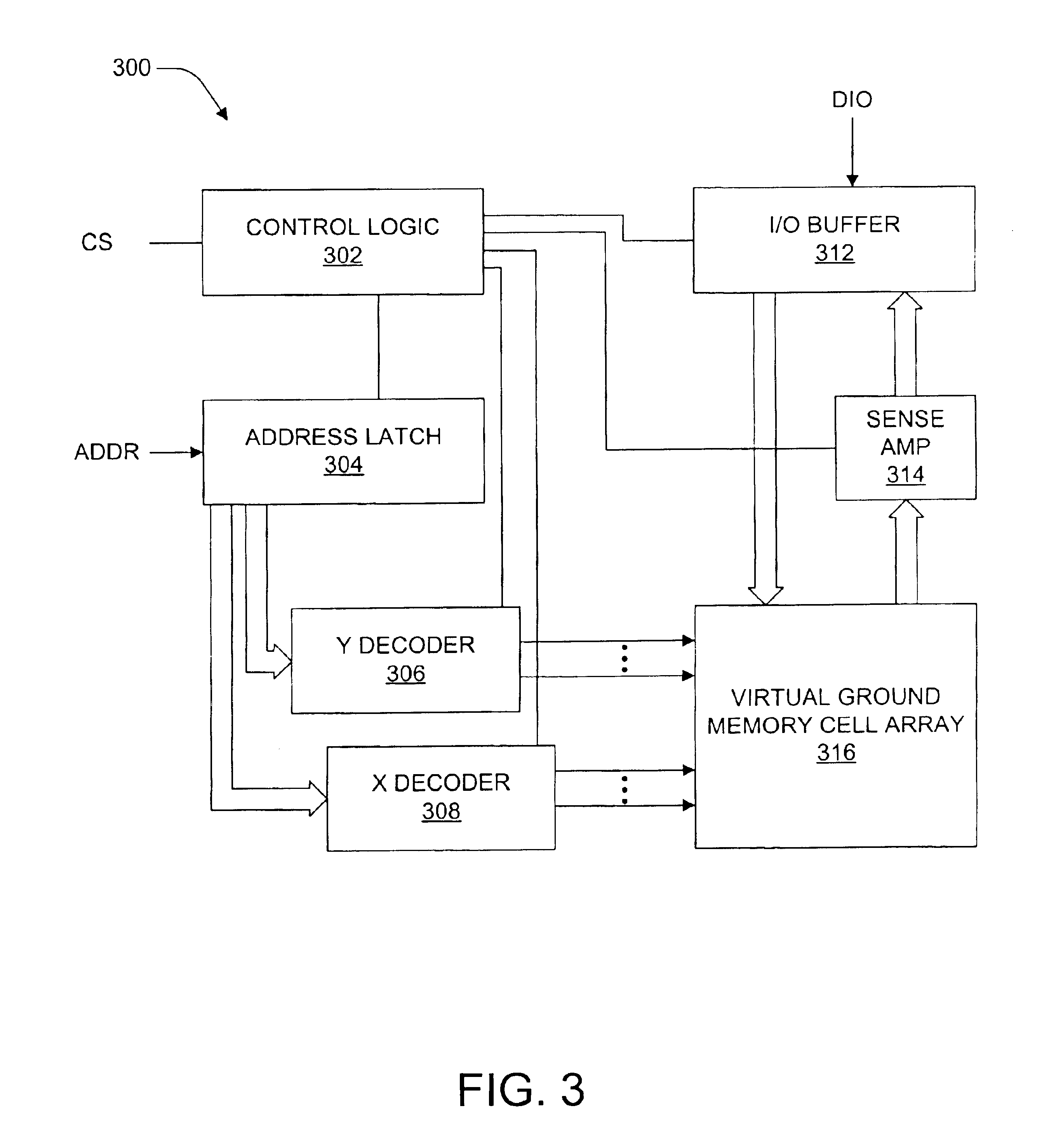
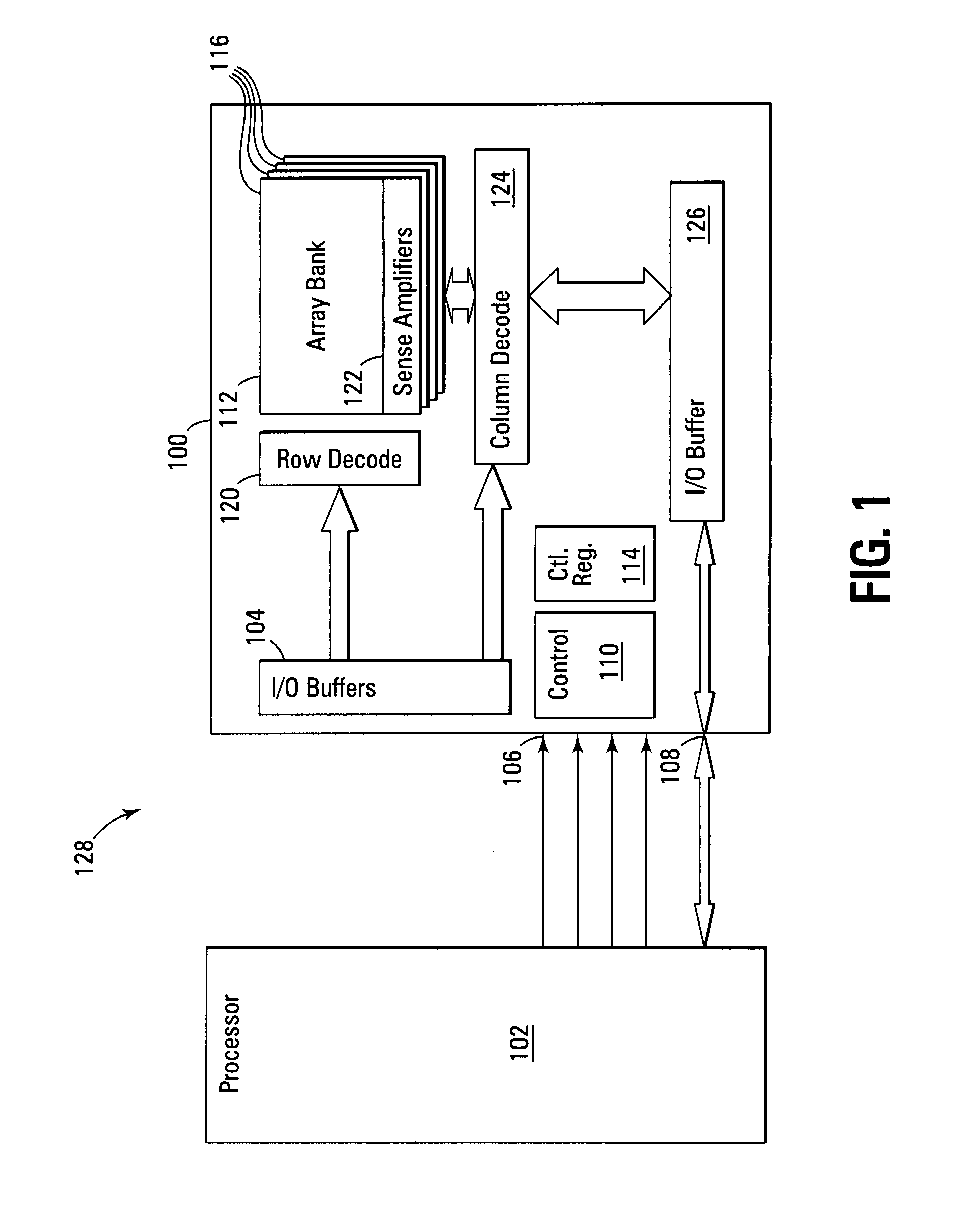
Apparatus including a virtual ground array, which includes memory cells connected in rows and columns to word lines and bit lines, respectively. The virtual ground array includes at least one block of data, and peripheral circuitry adapted to simultaneously access a plurality of subsets of the at least one block of data stored in the memory cells along at least one word line. Methods for operating the virtual ground array in a mass storage device include simultaneously accessing a plurality of subsets of at least one block of data stored in the memory cells along at least one word line.
Owner:SAIFUN SEMICON +1
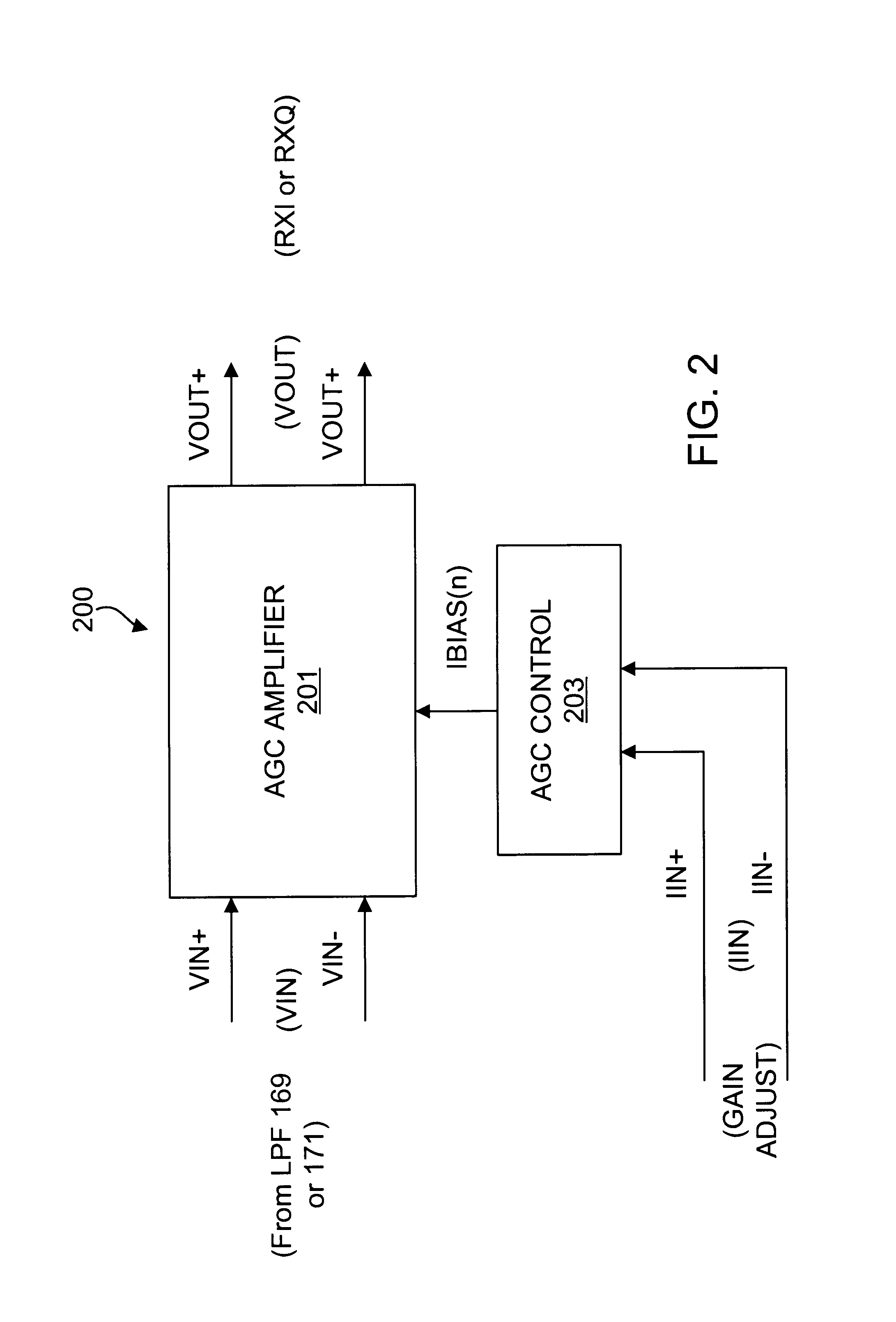
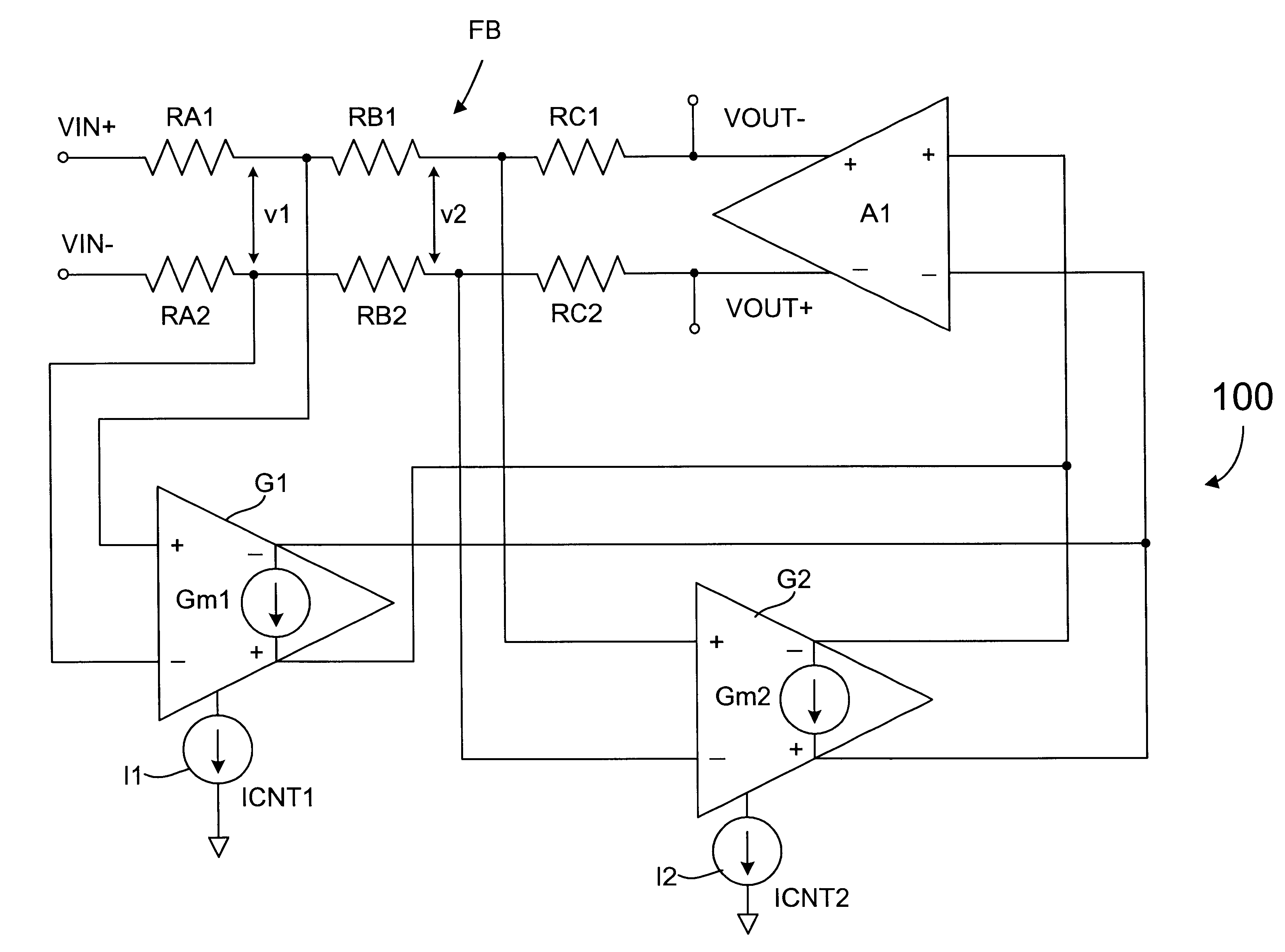
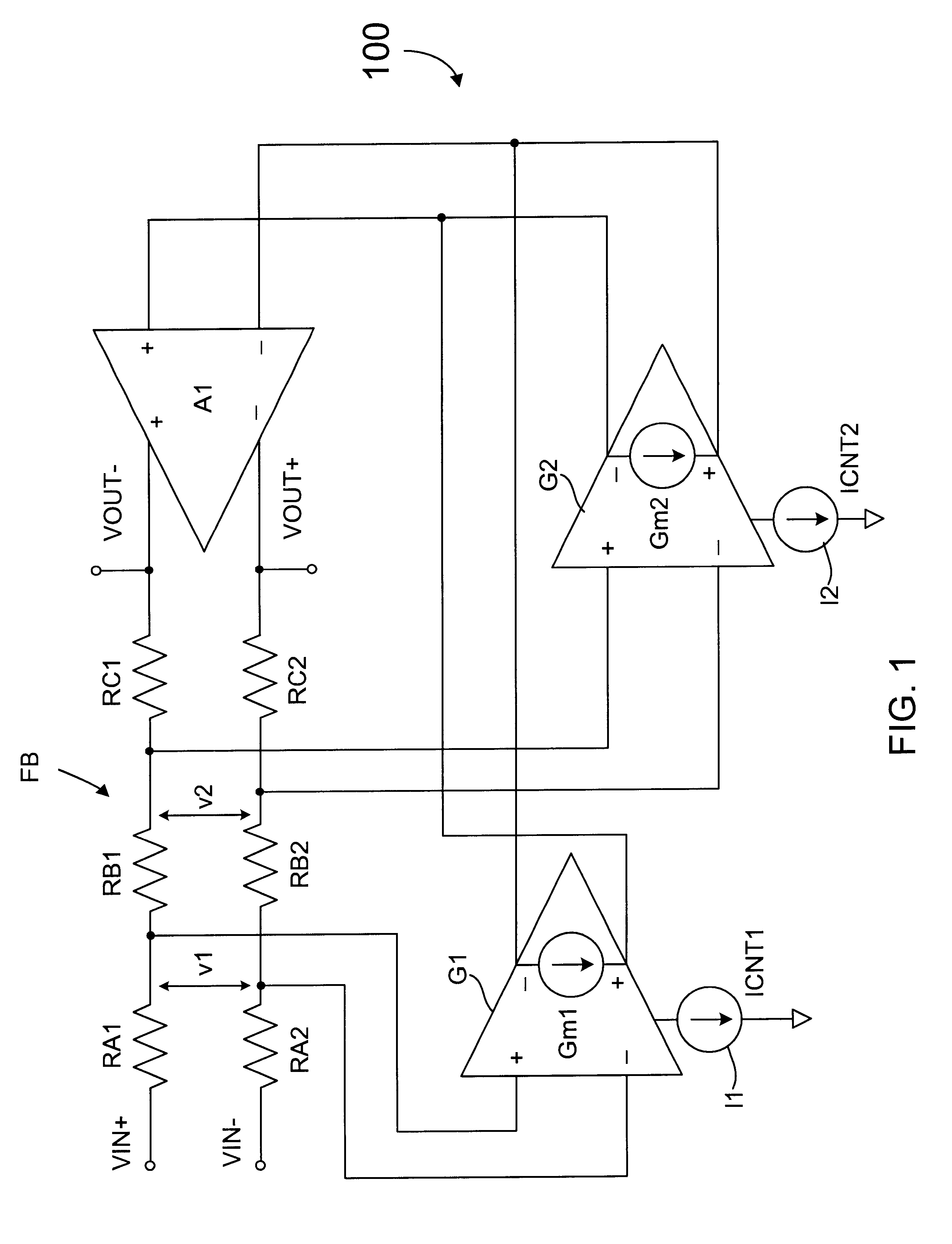
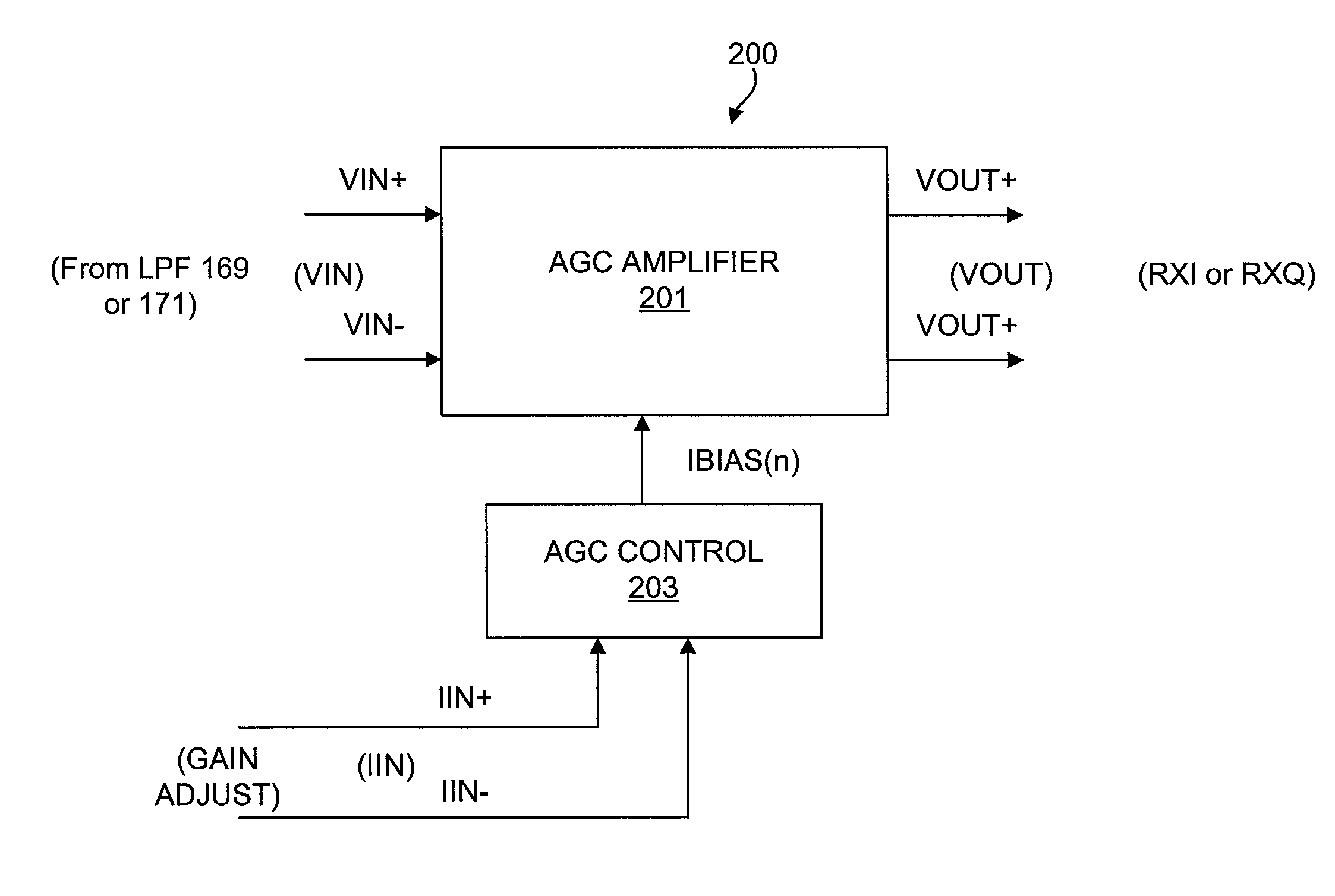
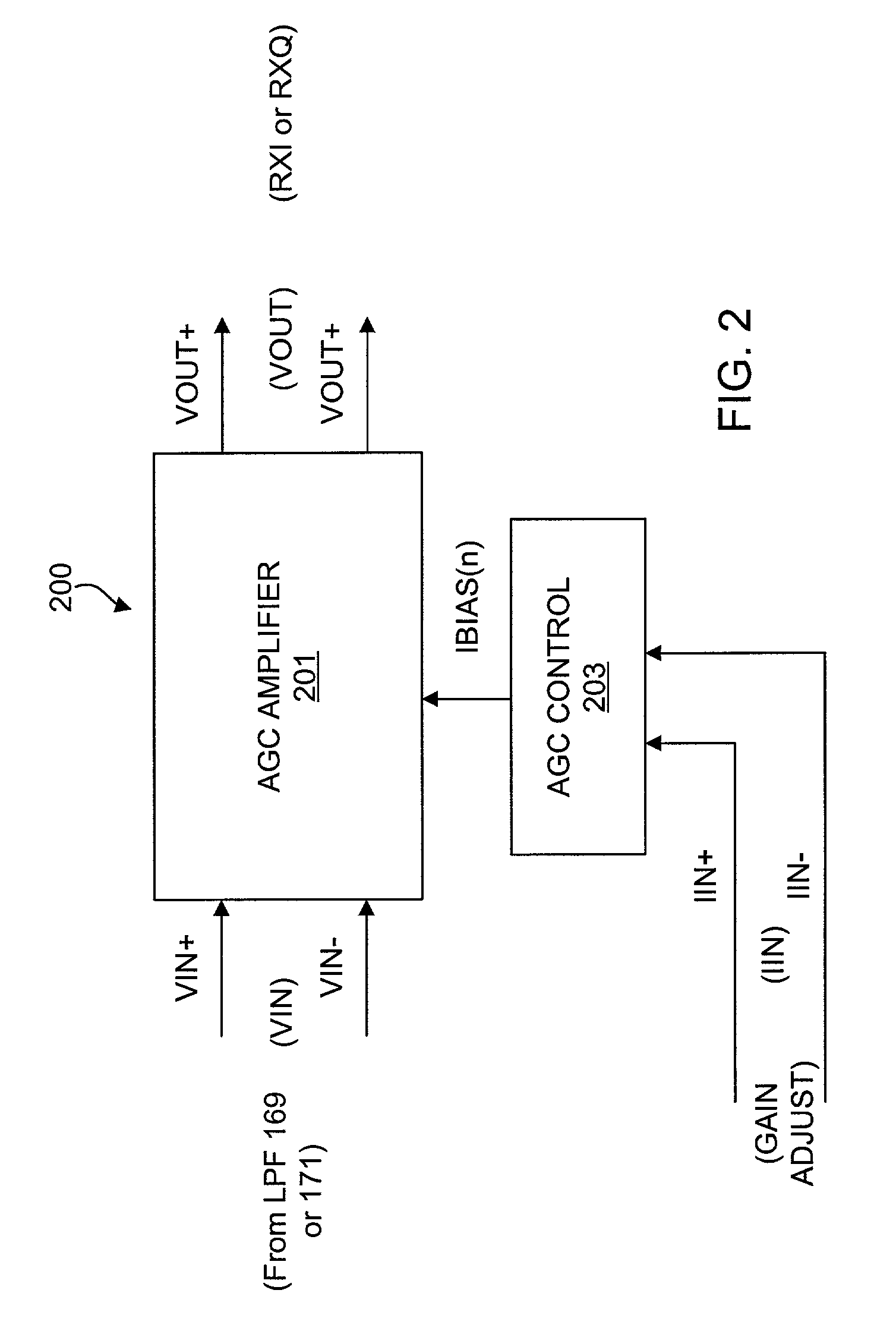
Precision automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS6763228B2Low absolute gain toleranceImprove matchResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierClosed loop
An automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier including a high gain transimpedance amplifier, a resistive feedback network and multiple transconductance stages coupled in the feedback path of the AGC amplifier. The feedback network receives an input signal and is coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and has multiple intermediate nodes. Each transconductance stage has an input coupled to an intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. Each transconductance stage is independently controllable to position a virtual ground within the feedback network to control closed loop gain. Each transconductance stage may have a bias current input coupled to a bias current control circuit. The control circuit controls each bias current to vary the gain of the AGC amplifier. The bias currents may be linearly controlled employing a ramp function to achieve a linear in dB gain response.
Owner:M RED INC
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20050265107A1Avoid delayTotal current dropTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineVirtual ground
In a memory cell array in a hierarchical bit line mode in which sub-arrays in a virtual ground line mode are arranged in a column direction, data is read out at high speed, preventing fluctuation in wiring capacity of a main bit line. In each sub-array, one of a source electrode or a drain electrode in each of the memory cells in the same column is connected to a common first bit line, and the other thereof is connected to a second bit line. The first bit lines of one half of the sub-arrays positioned in the same column are connected to the first main bit line through selection transistors and the second bit lines thereof are connected to the second main bit line through selection transistors, and the first bit lines of the other half of the sub-arrays positioned in the same column are connected to the second main bit line through selection transistors and the second bit lines thereof are connected to the first main bit line through selection transistors.
Owner:SHARP KK
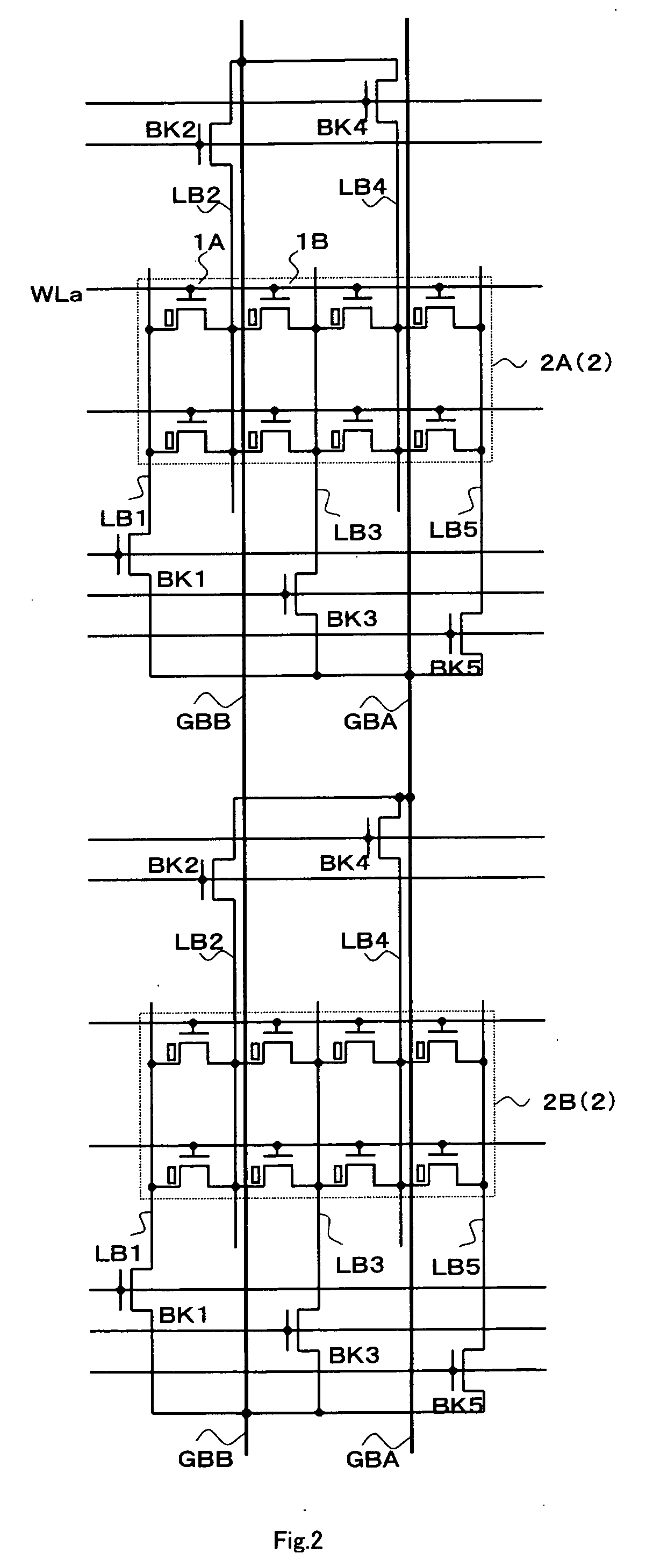
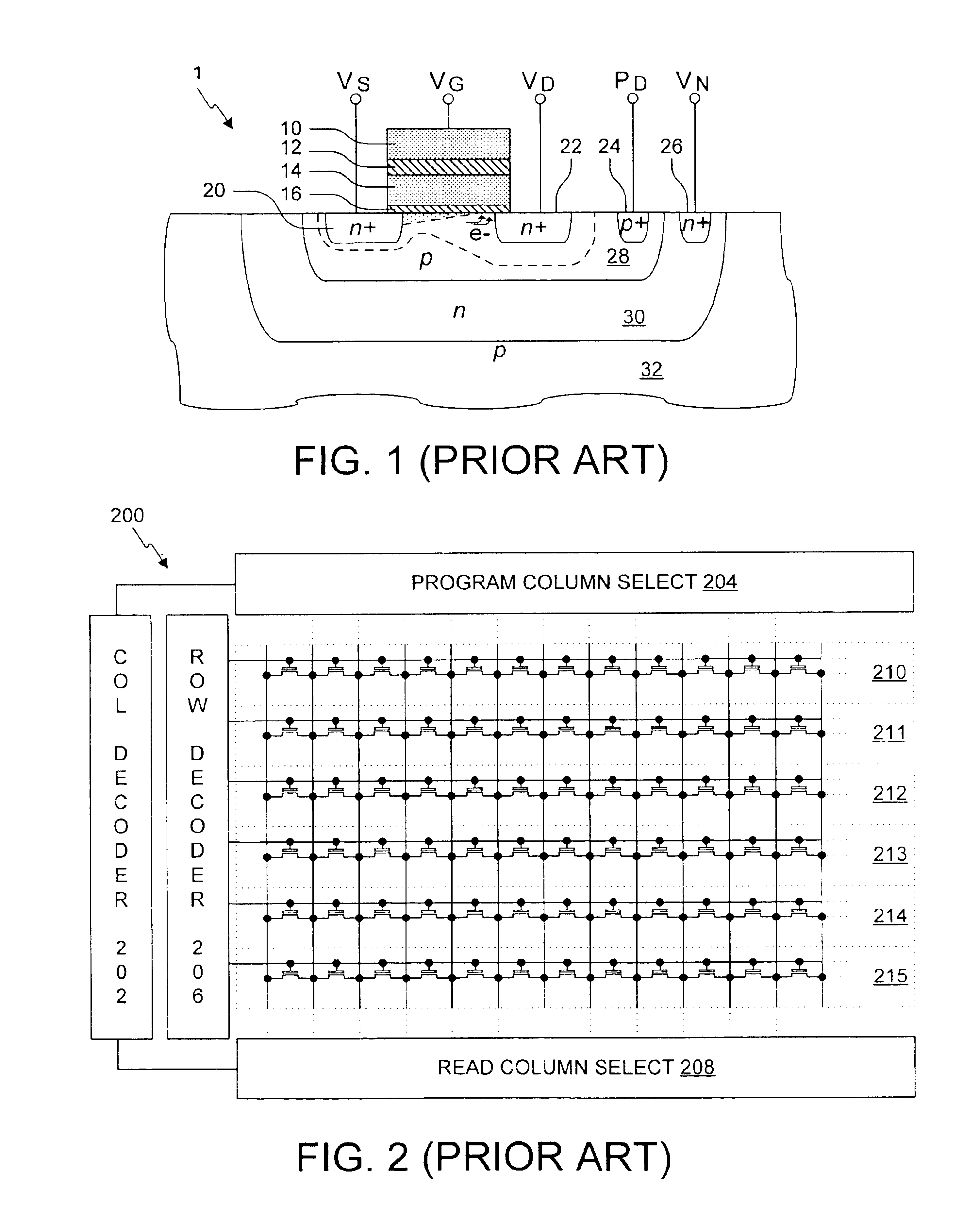
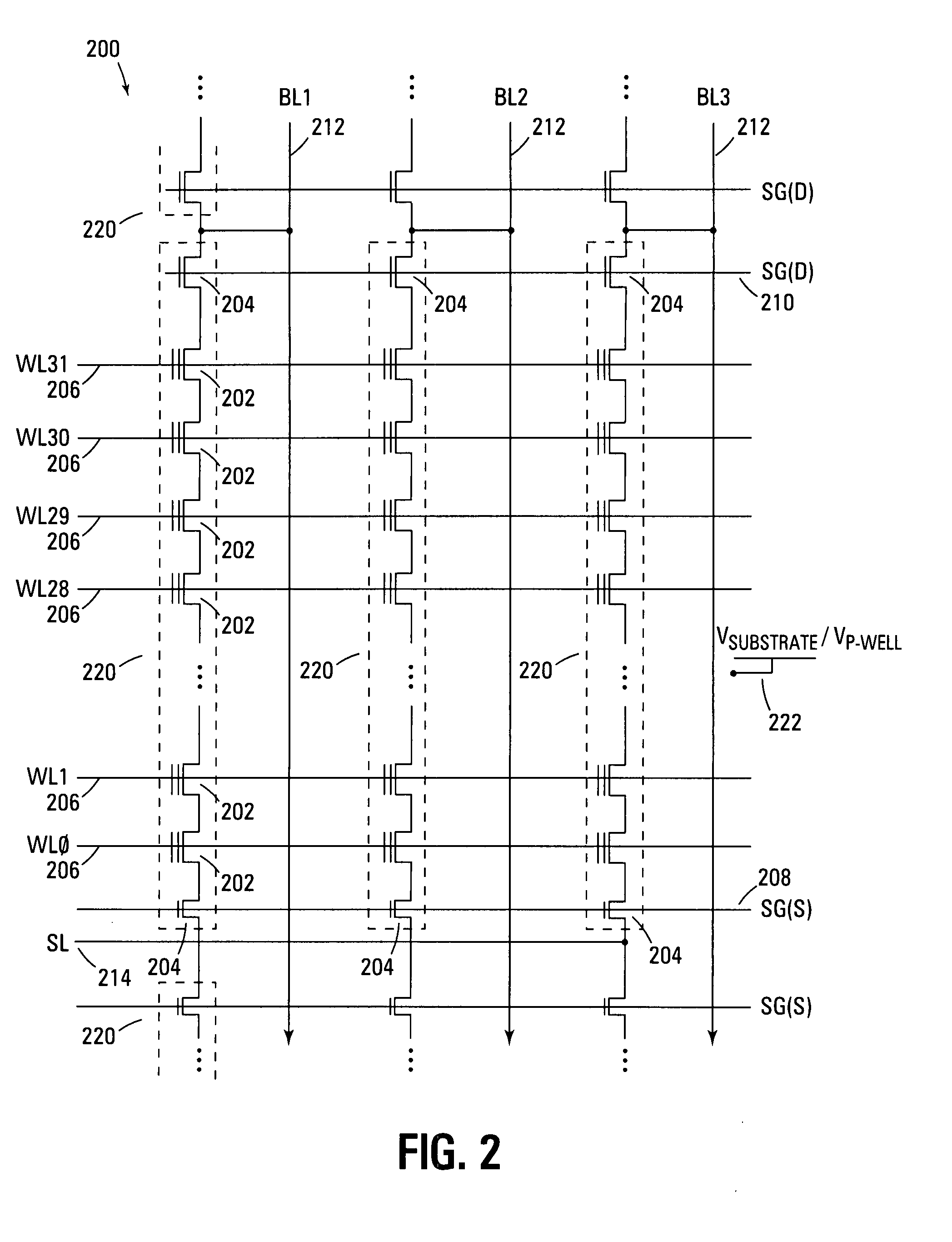
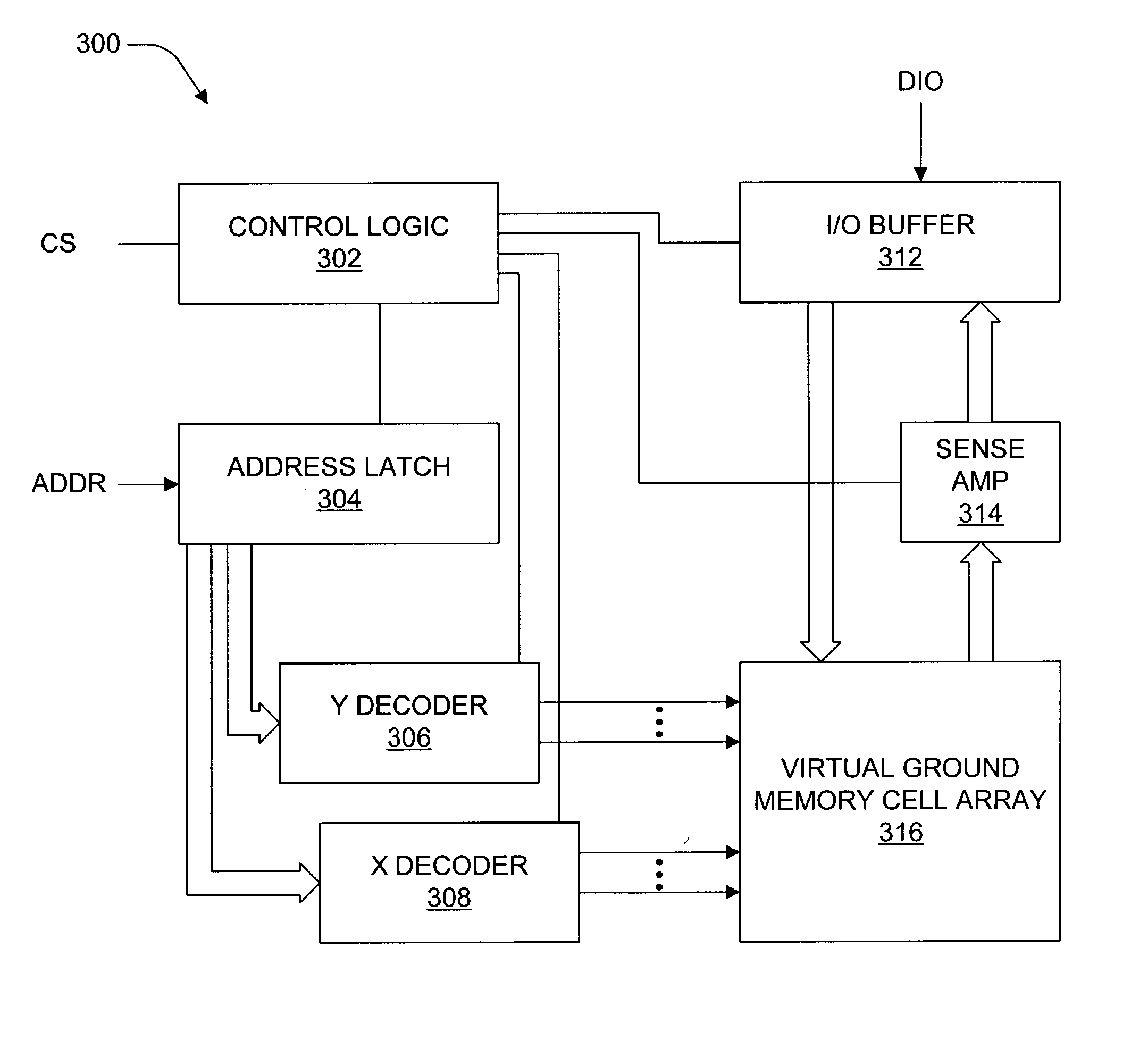
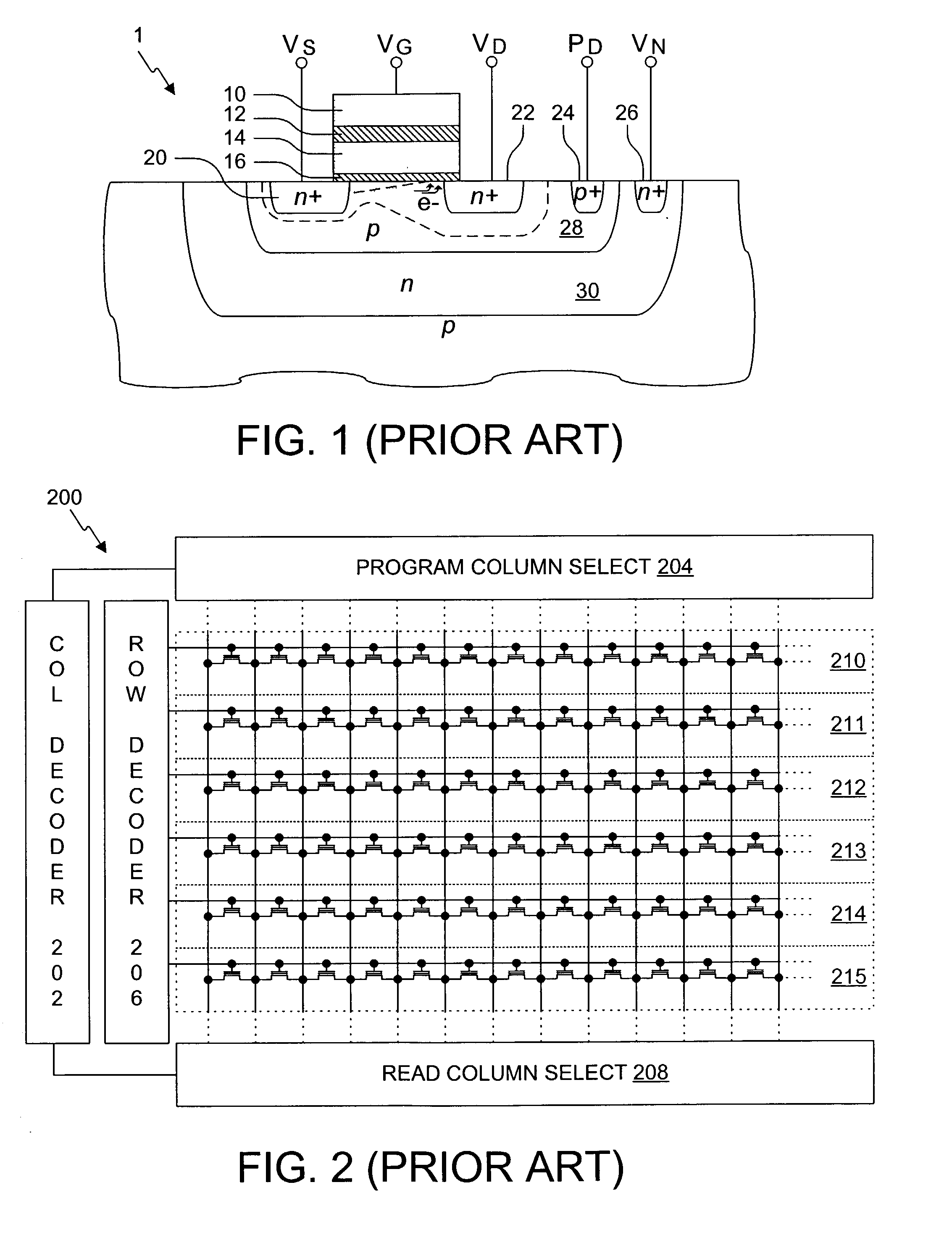
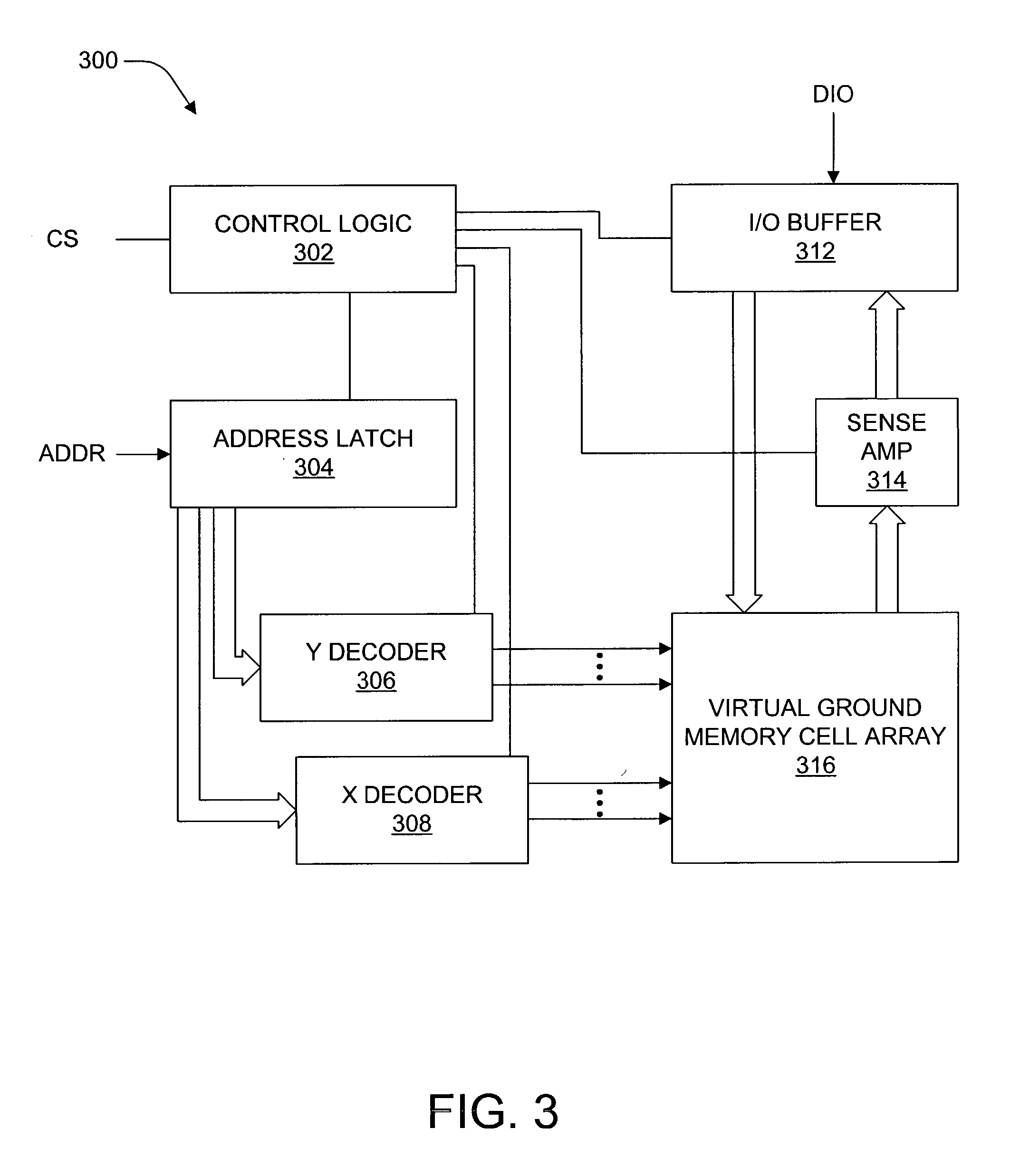
Virtual ground nonvolatile semiconductor memory array architecture and integrated circuit structure therefor
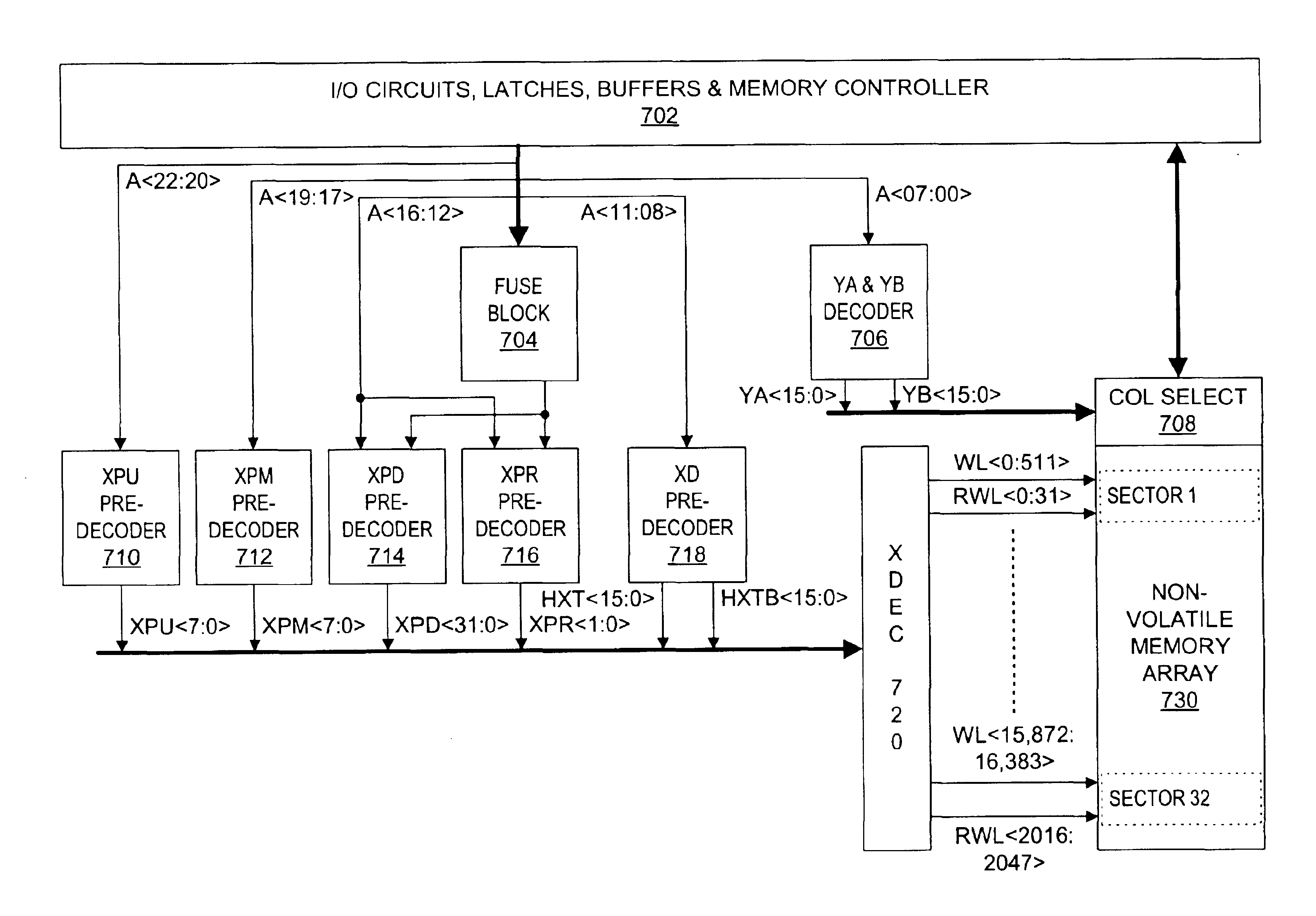
In nonvolatile memory cell array, the memory cells of each sector are organized into groups of successive cells, the groups preferably being of the same size and preferably isolated from one another in both the row and column directions by a suitable isolation structure such as field dielectric or trench dielectric. Because of cell group isolation, each group of column lines may be decoded by its own relatively small program column select, which preferably is replicated in essentially identical form for all groups of column lines. While each program column select preferably is used to decode one group of column lines, larger program column selects may be used if desired to decode two or more groups of column lines. Read column selects may decode one or more groups of column lines as desired. The number of column lines decoded may the same as or different than the number of column lines decoded.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
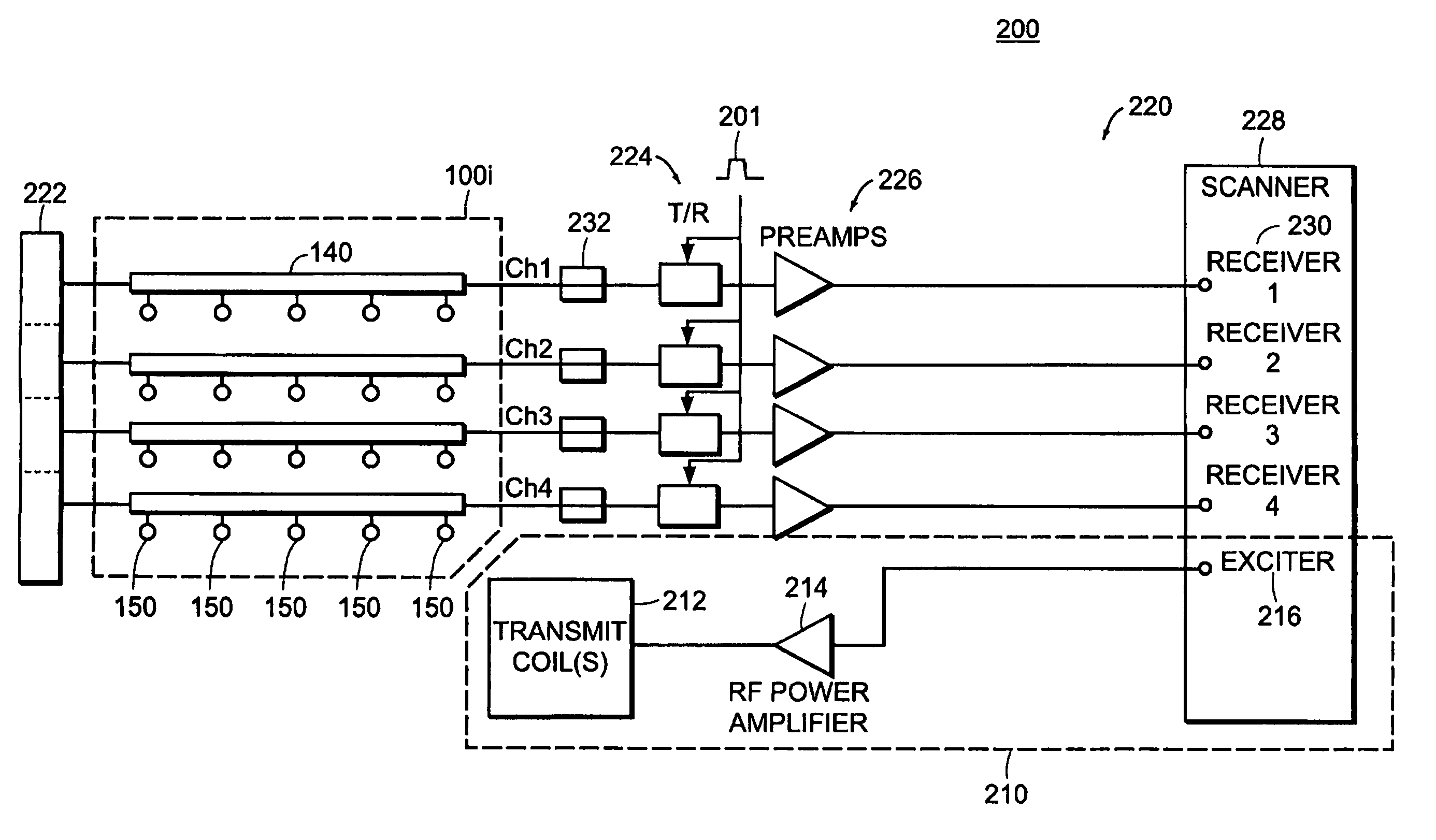
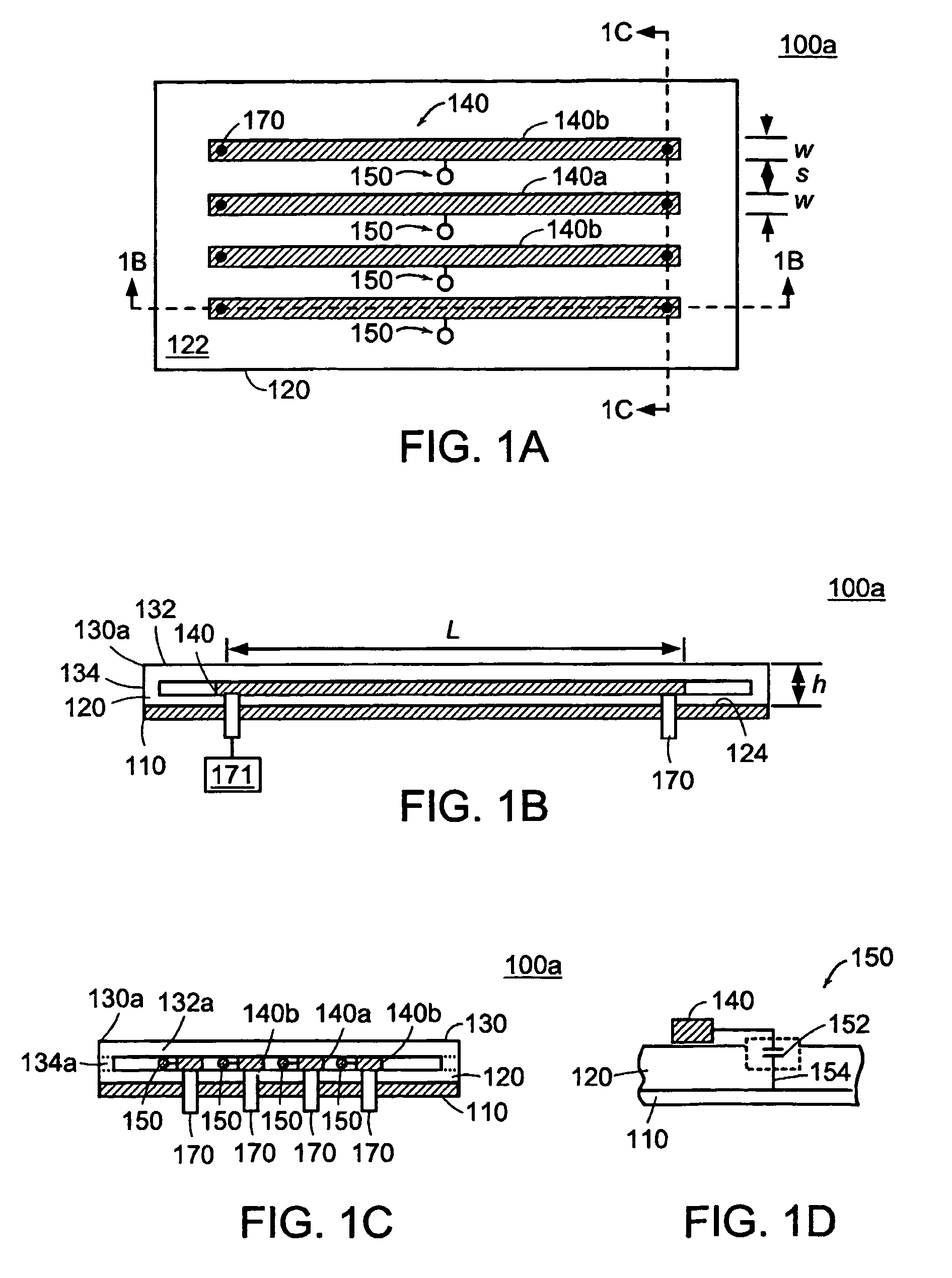
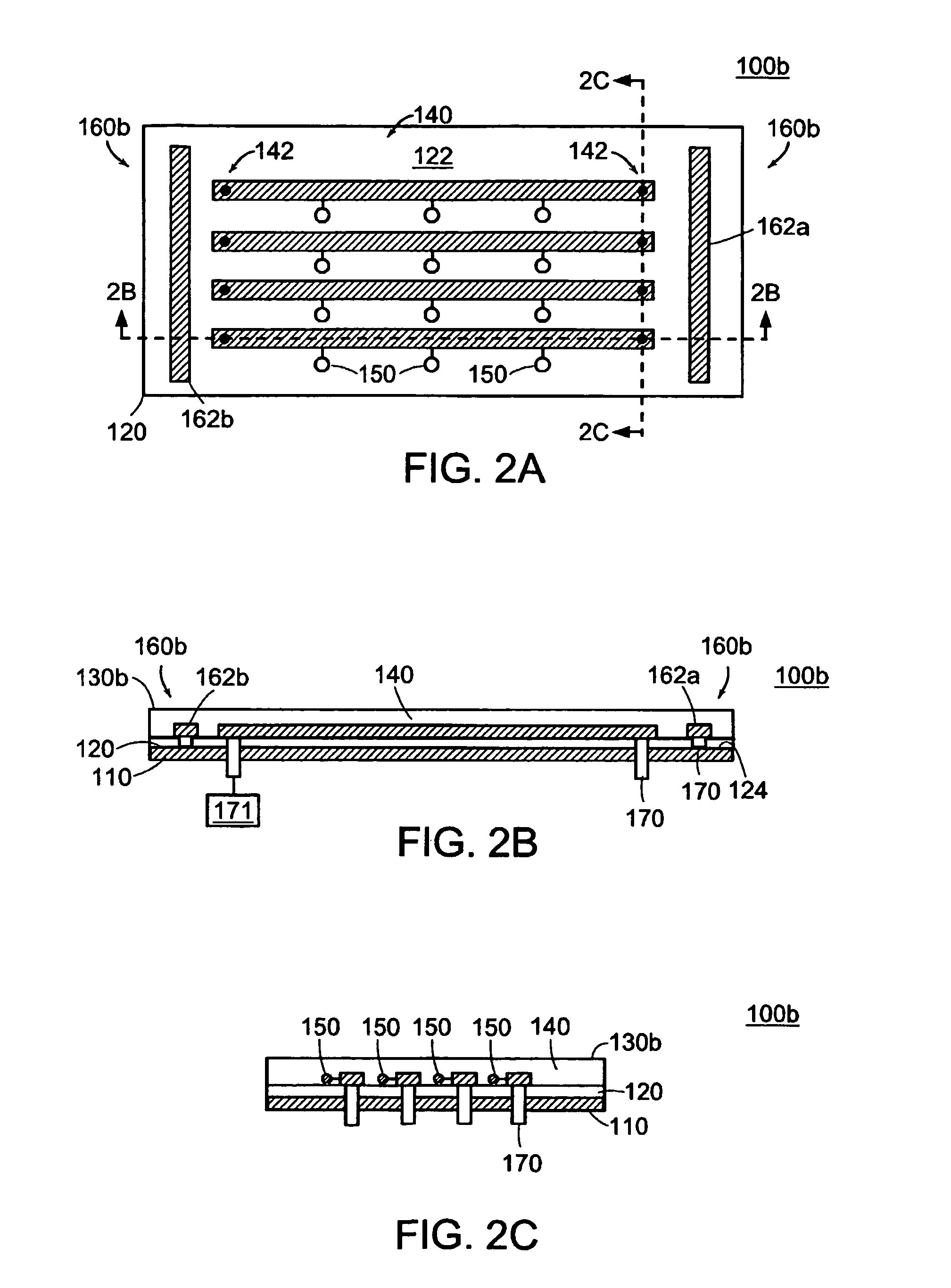
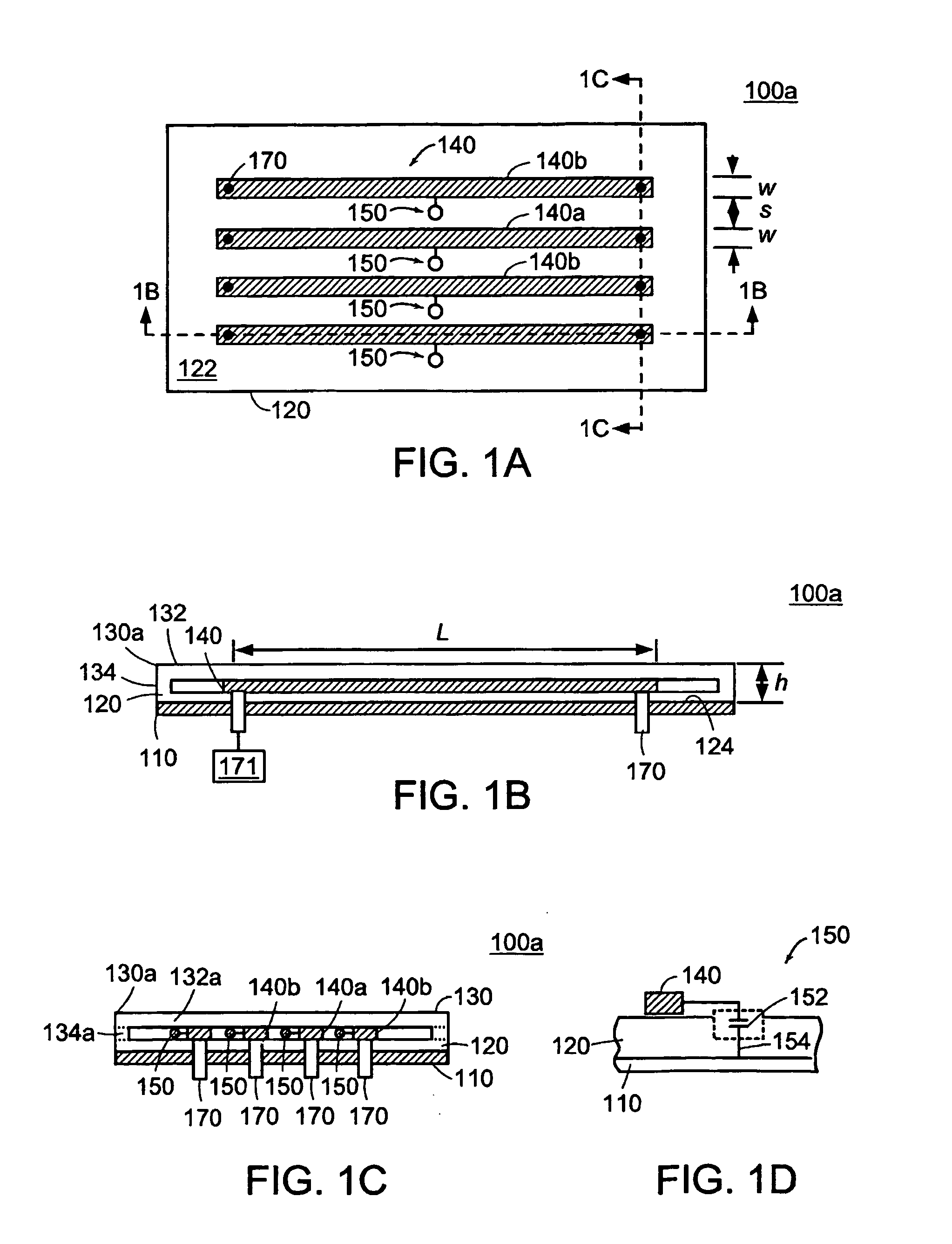
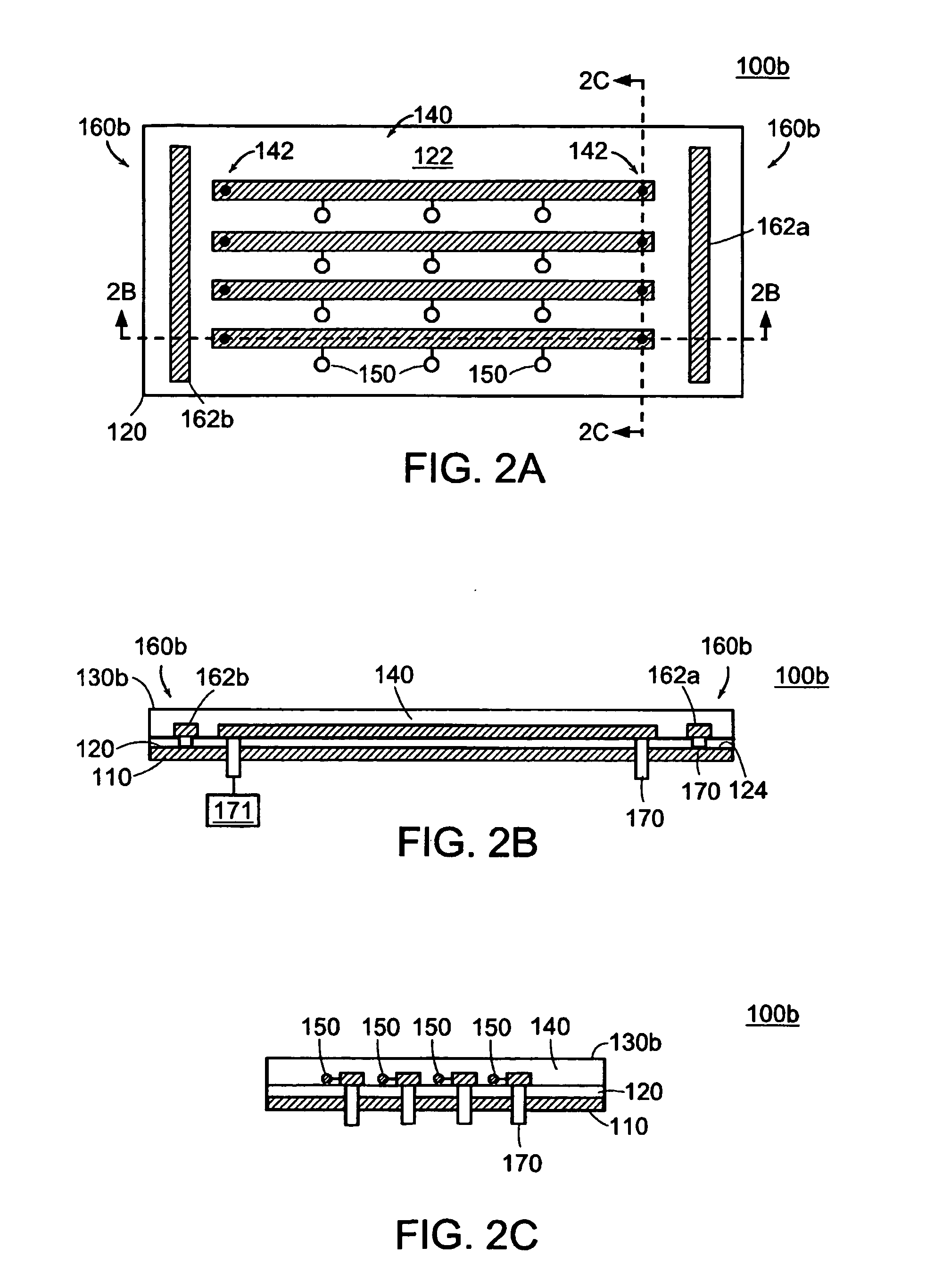
MRI tunable antenna and system
InactiveUS7088104B2Reduce couplingImprove performanceElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceElectrical conductorLength wave
A strip array antenna including a number of conductors (14) that are connected to ground or virtual ground though at least one reactive component (150). The apparent electrical length of conductors (140) is tuned so that it equals an integer multiple of a quarter wavelength at the operating frequency.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
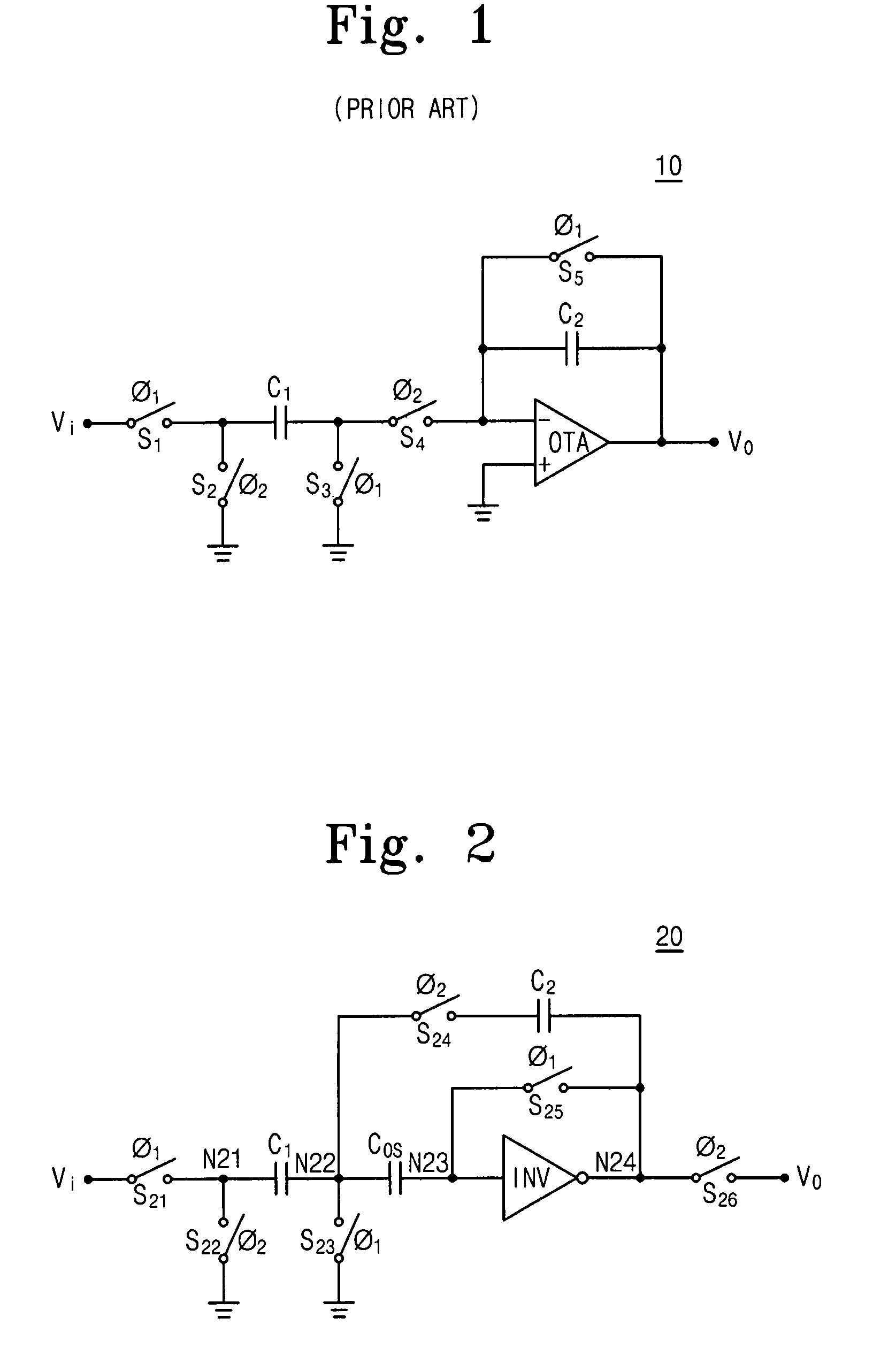
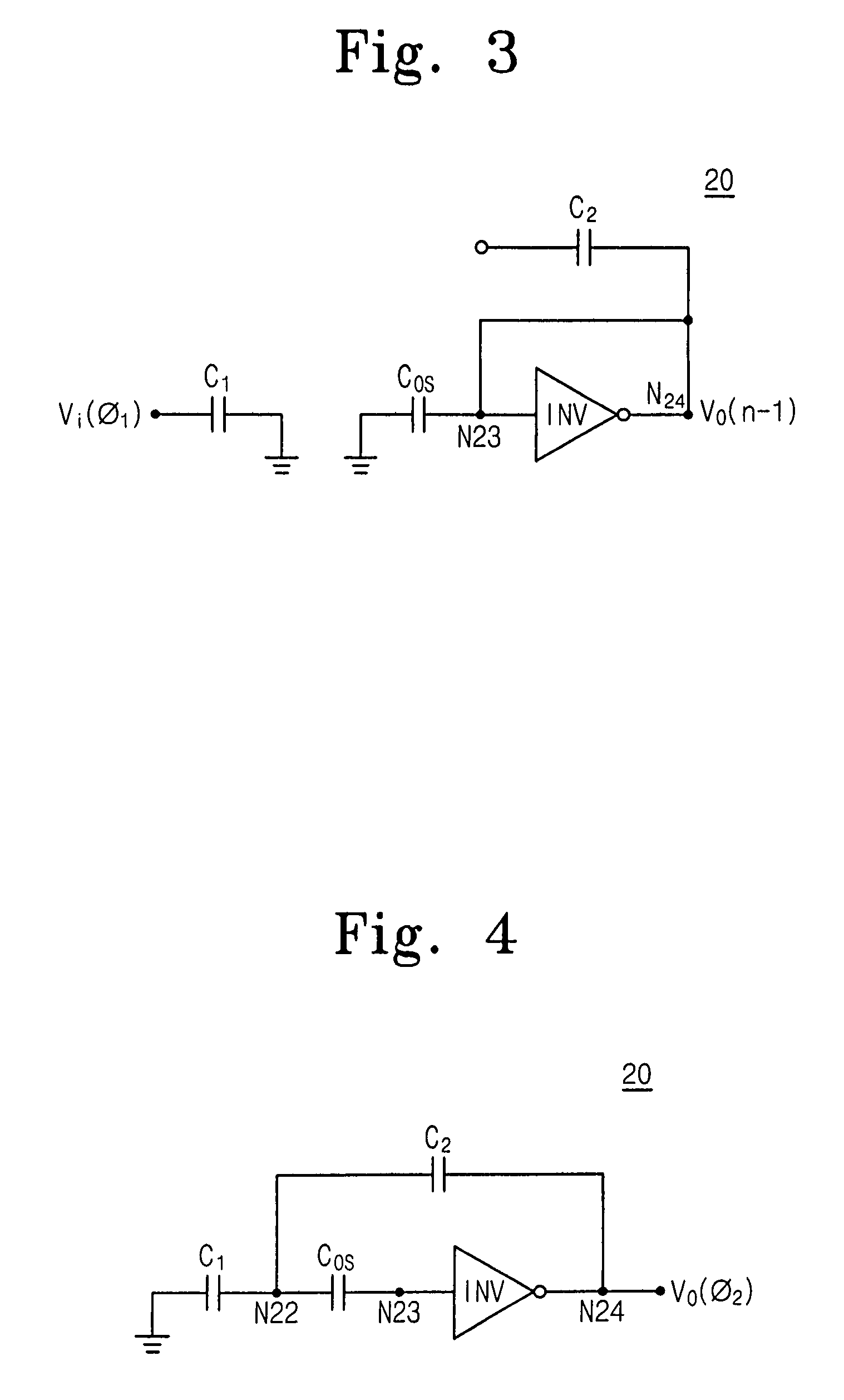
Switched capacitor circuit with inverting amplifier and offset unit
ActiveUS7800427B2Reduce power consumptionReduce circuit areaAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionComputing operations for integral formationCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A switched capacitor circuit includes an amplifier, a charging unit, an offset unit, and an integrating unit. The charging unit is coupled between an input node and a first node, and is for accumulating charge corresponding to an input signal during a sampling mode. The offset unit is coupled between the first node and an input of the amplifier, and is for maintaining the first node to be a virtual ground during an integrating mode. The integrating unit is coupled between the first node and an output of the amplifier, and is for receiving charge from the charging unit during the integrating mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
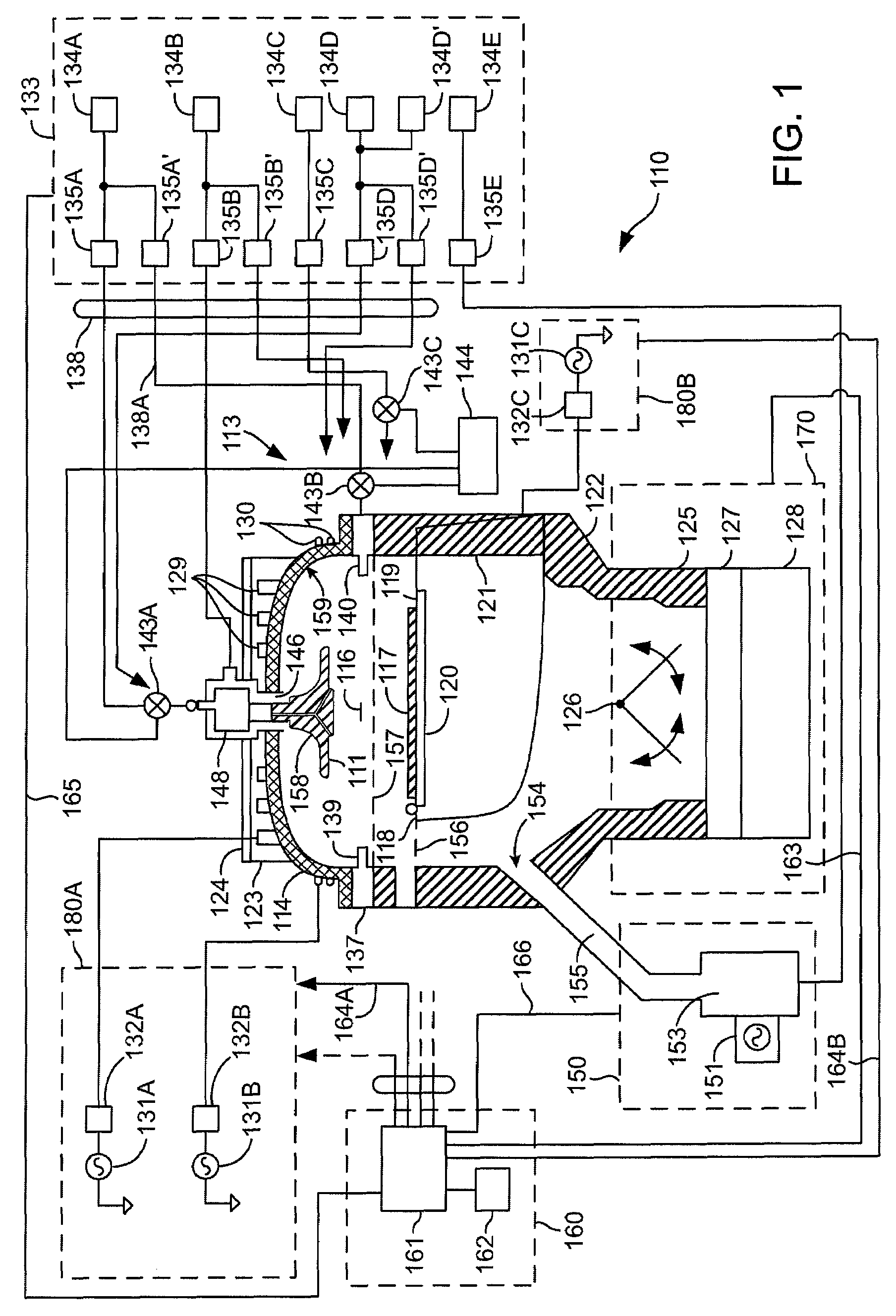
Internal balanced coil for inductively coupled high density plasma processing chamber
A coil is provided for use in a semiconductor processing system to generate a plasma with a magnetic field in a chamber. The coil comprises a first coil segment, a second coil segment and an internal balance capacitor. The first coils segment has a first end and a second end. The first end of the coil segment is adapted to connect to a power source. The second coil segment has a first and second end. The second end of the first coil segment is adapted to connect to an external balance capacitor. The internal balance capacitor is connected in series between the second end of the first coil segment and the first end of the second coil segment. The internal balance capacitor and the coil segments are adapted to provide a voltage peak along the first coil segment substantially aligned with a virtual ground along the second coil segment.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Virtual ground single transistor memory cell, memory array incorporating same, and method of operation thereof
InactiveUS6873004B1Simple planEnhanced CHE generationTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringVirtual ground
An asymmetrical virtual ground single transistor floating gate memory cell has a floating gate that overlies a channel region in a p-well, the channel region lying between a heavily doped n+ drain region and a lightly doped n− source region. A heavily doped p+ region known as a “halo” is disposed in the channel adjacent the heavily doped n+ drain. The floating gate is spaced away from the channel region by a generally thin tunnel oxide. A lightly doped source with a graded source / channel junction reduces source side CHE generation. In one variation, a thicker oxide between the source and the floating gate reduces CHE injection from the source side. A heavily doped drain with a halo implant in the channel adjacent the drain enhances drain side CHE generation.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
SRAM cell with common bit line and source line standby voltage
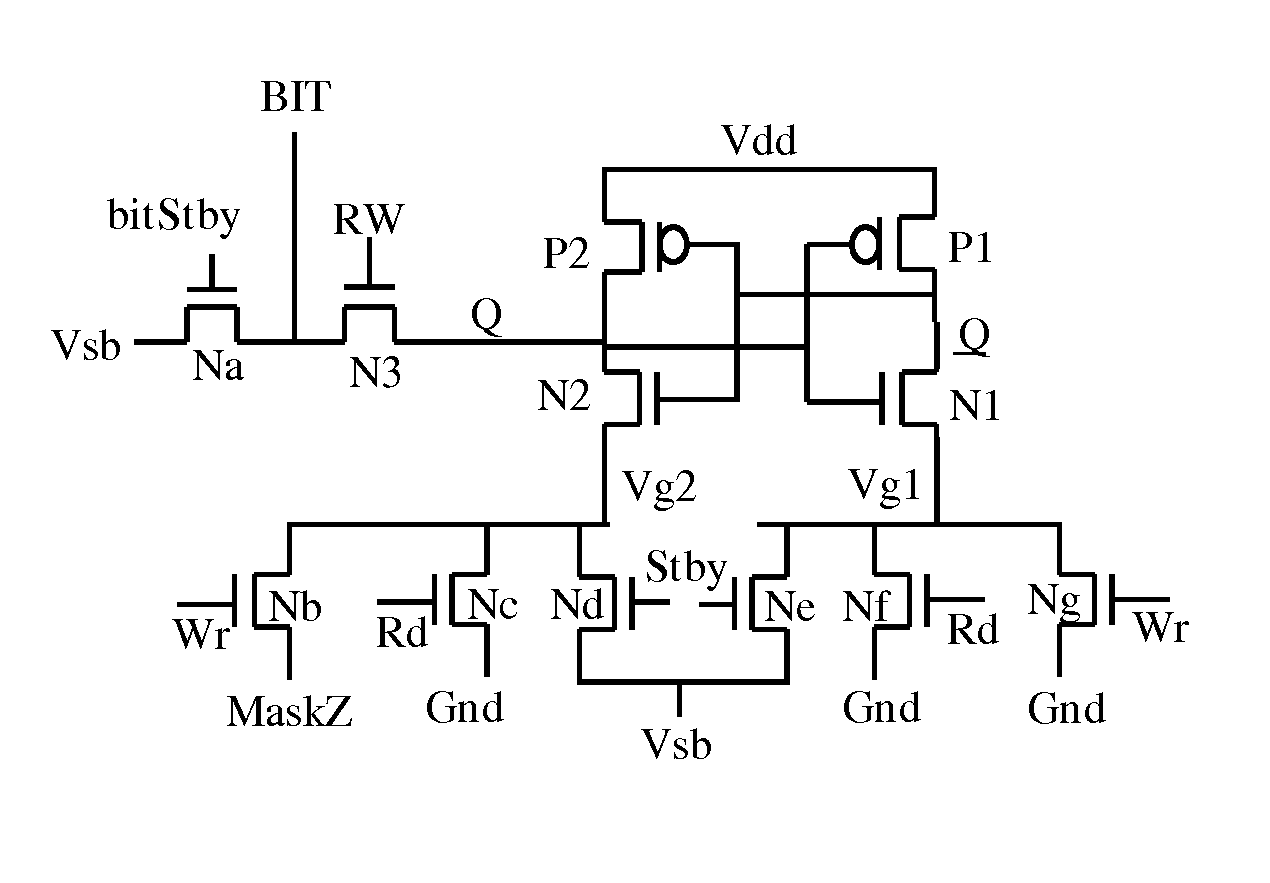
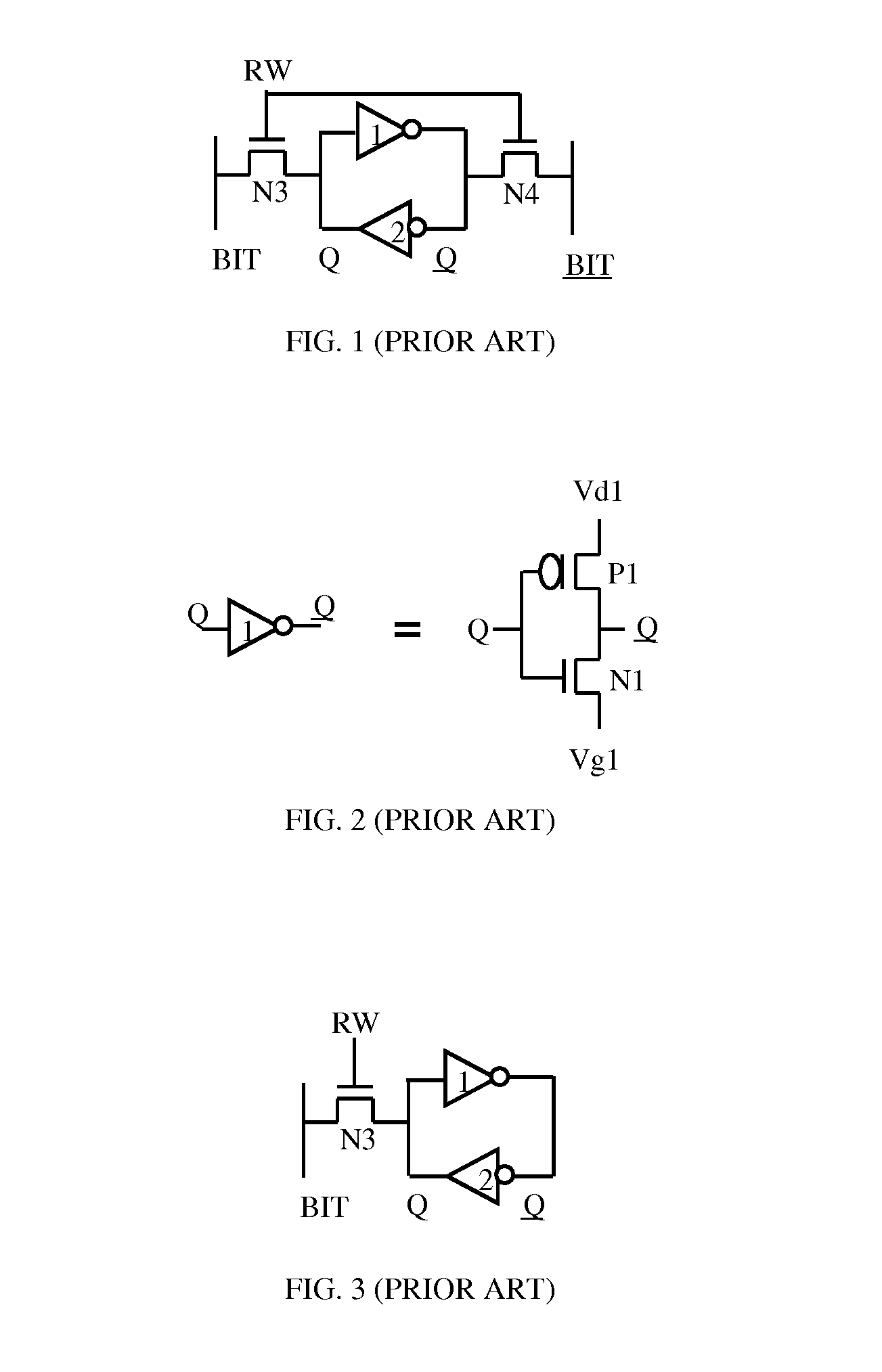
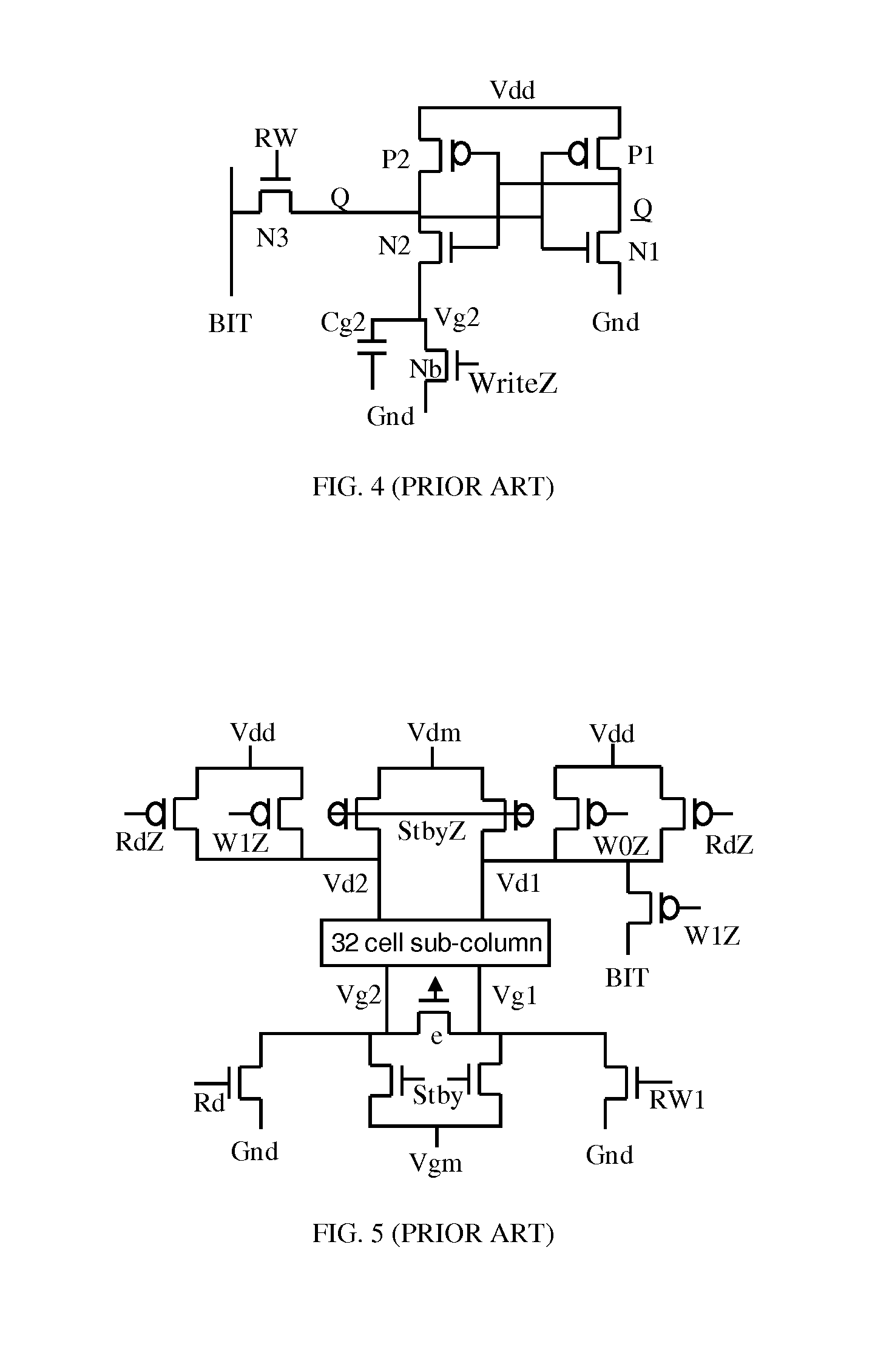
A high threshold five transistor SRAM bit cell with cross-coupled inverters has a single BIT line, a common logic 1 supply voltage, and two logic 0 virtual ground source voltages. The BIT line is coupled to the bit cell by a pass transistor. When BIT line and virtual ground lines are not otherwise being used, they are connected to a common standby voltage that substantially lowers bit cell standby leakage. Writing is performed by driving a data signal through the pass transistor and is facilitated by creating a voltage differential on the virtual ground lines. Reading is also performed through the pass transistor wherein the BIT line is initially at the standby voltage, and is then driven lower or higher depending upon the data value stored in the bit cell.
Owner:HOBSON RICHARD FREDERIC +1
Mri tunable antenna and system
InactiveUS20050062472A1Minimize EMMinimizes interactionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceElectrical conductorLength wave
A strip array antenna including a number of conductors (14) that are connected to ground or virtual ground though at least one reactive component (150). The apparent electrical length of conductors (140) is tuned so that it equals an integer multiple of a quarter wavelength at the operating frequency.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
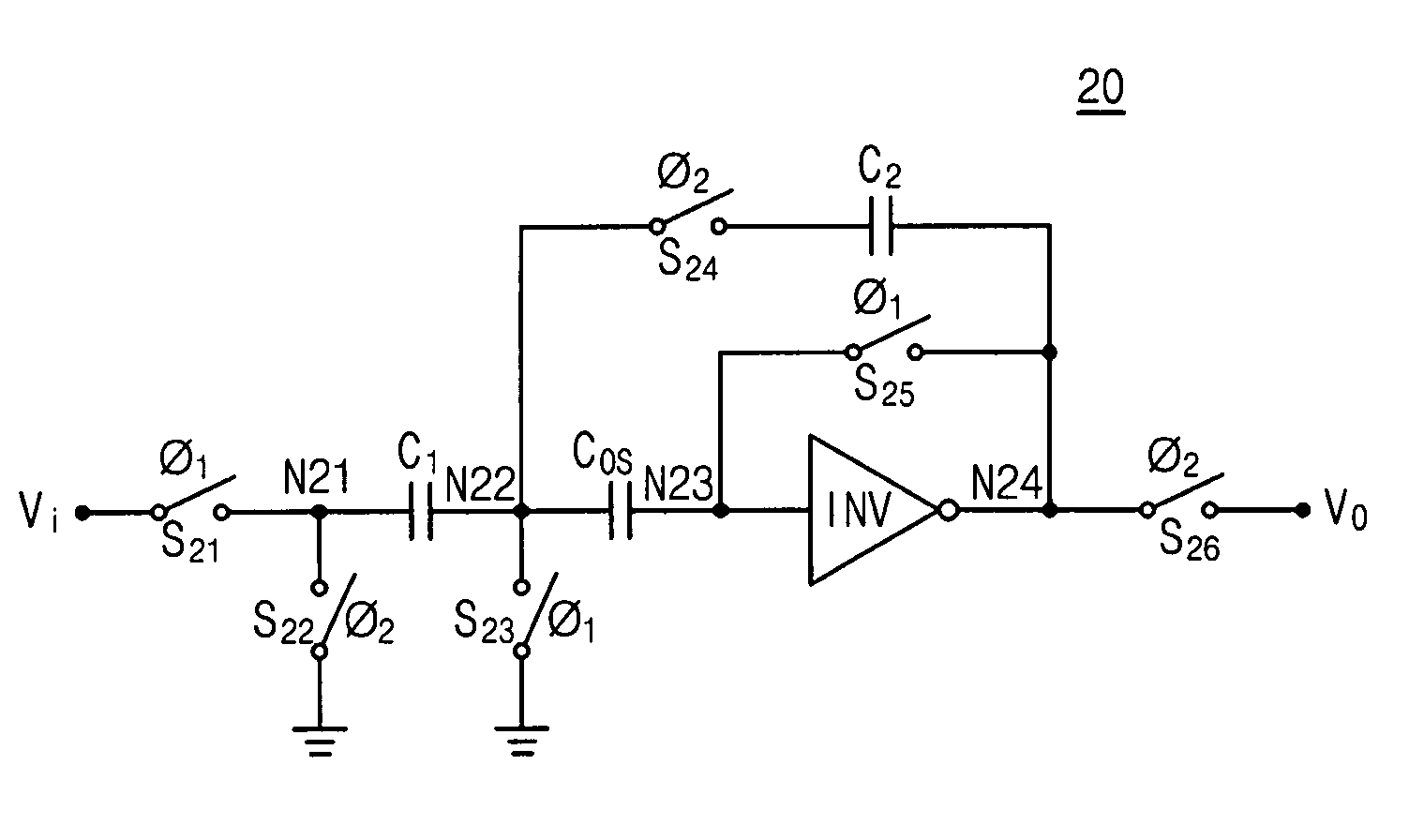
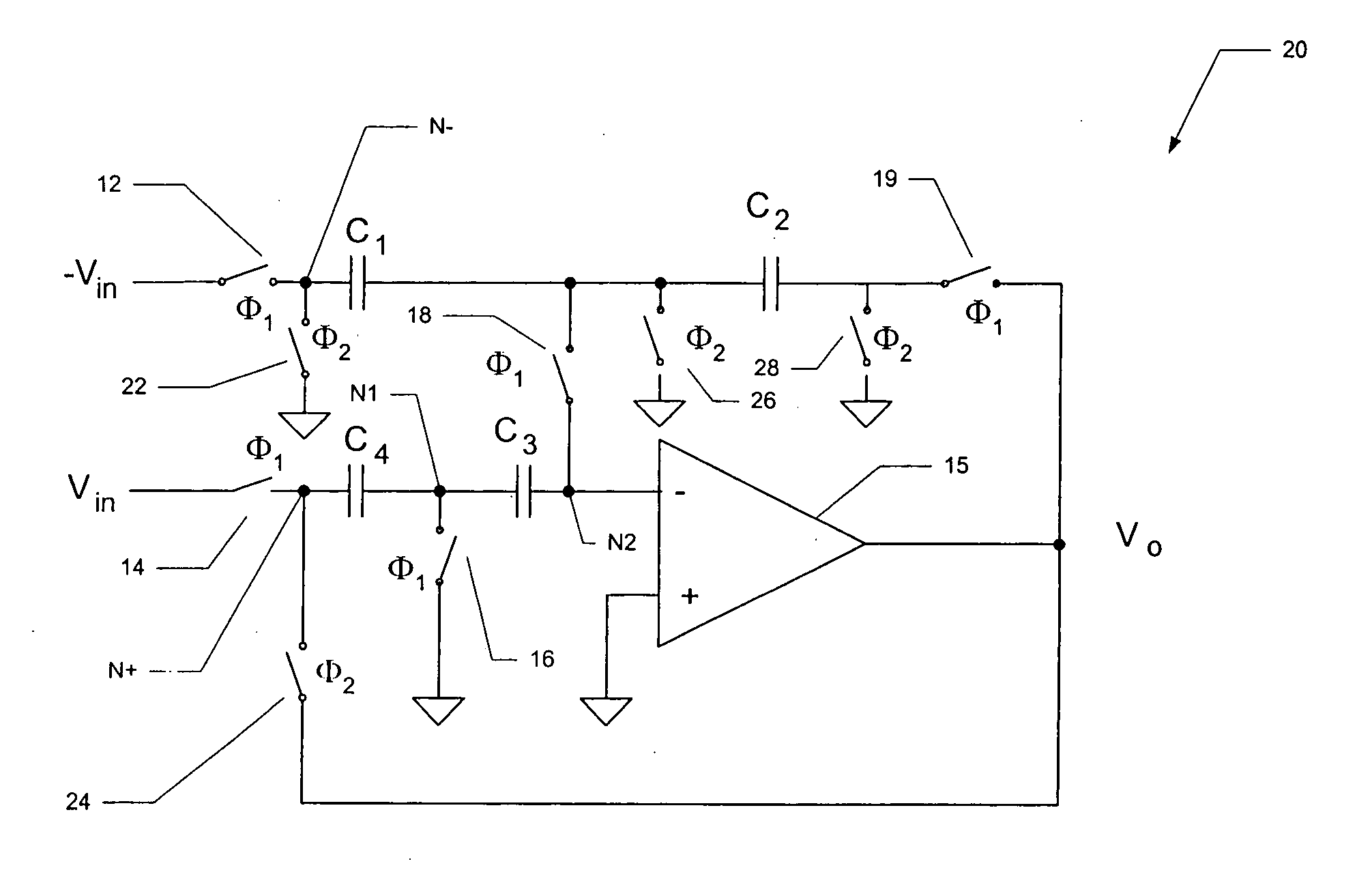
Switched-capacitor circuits with reduced finite-gain effect
ActiveUS20060071709A1Minimize impactGood effectAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
Operational amplifier circuits (20, 30) including error capacitors (C3, C13) for storing finite gain effect error voltages for correction of output voltages of the circuits (20, 30), are disclosed. The circuits (20, 30) are operated in a sample clock phase to produce an approximation of the output voltage, using negative polarity versions of the input voltages to the circuit. The approximate output voltage is used to produce and store an error voltage, corresponding to the differential voltage at the input of the operational amplifier (15, 25), relative to virtual ground. This error voltage is then subtracted from the input voltage applied in the operate clock phase, to correct for the finite gain effect. A pipelined analog-to-digital converter (50) using the disclosed operational amplifier circuits (20, 30) is also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for providing row redundancy in nonvolatile semiconductor memory
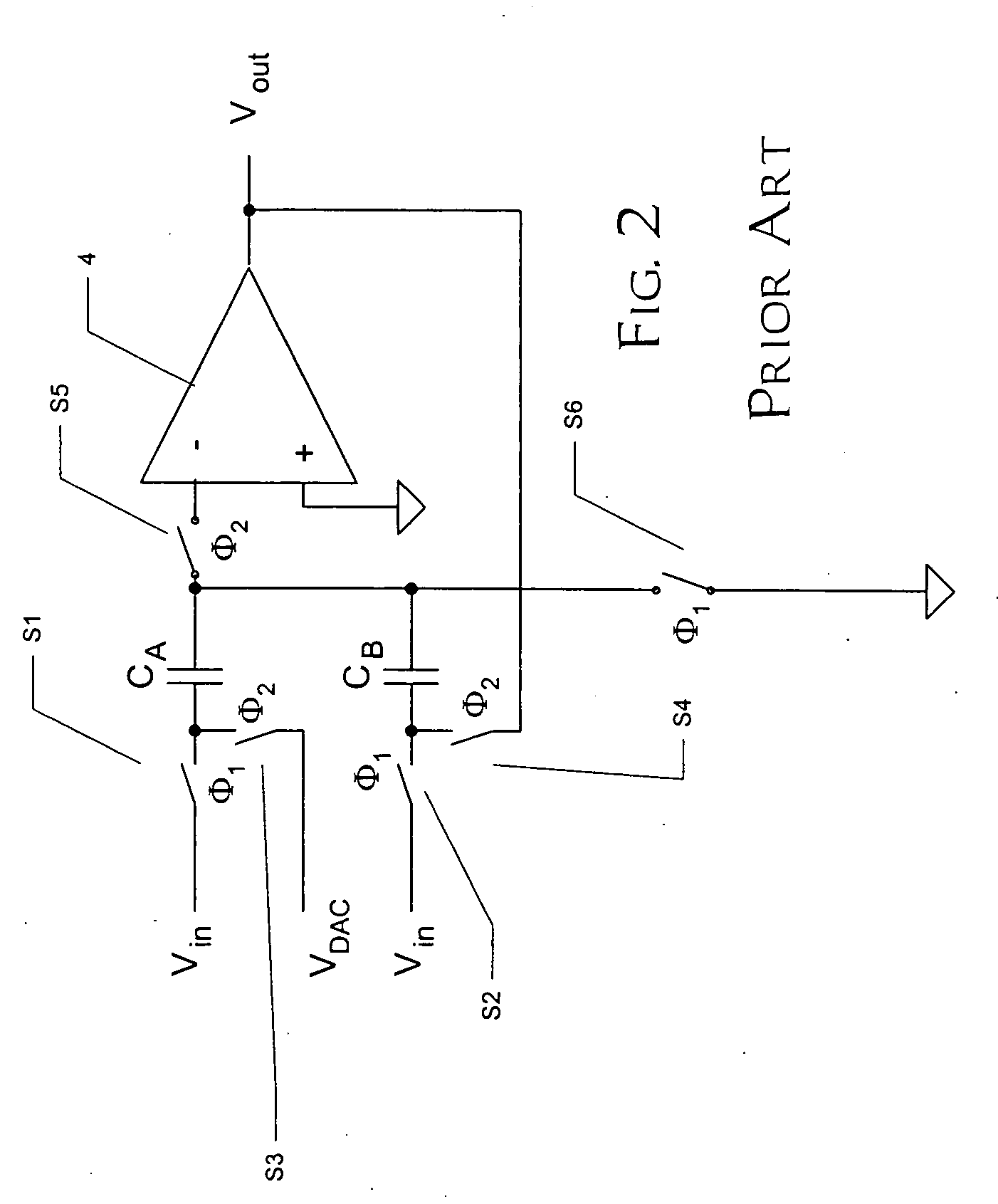
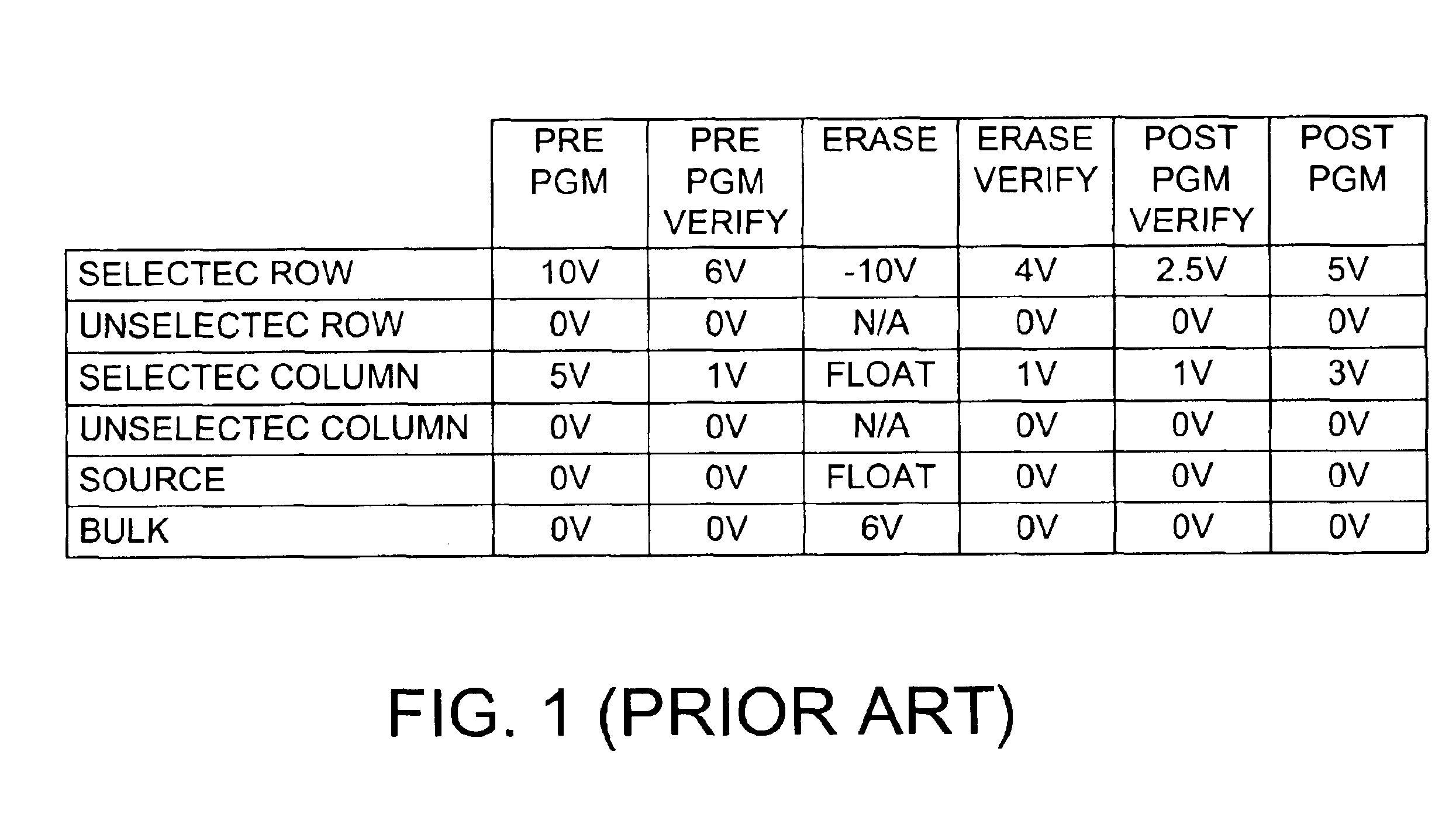
In a NOR-type flash memory of either the ETOX or virtual ground type that is programmed using electron injection and erased using FN tunneling, and that has row redundancy, the typical sequence of operations used for an embedded sector erase, namely the Preprogram, Preprogram Verify, Erase, Erase Verify, Post-Program Verify, and Post-Program operations, need not be performed for the data cells on bad or shorted rows or in unused redundant rows. Instead, the bad or shorted rows or the unused redundant rows are suitably biased so that the threshold voltages of the data cells in these rows tend to converge to a threshold voltage near the UV erased threshold.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for zero-sequence damping and voltage balancing
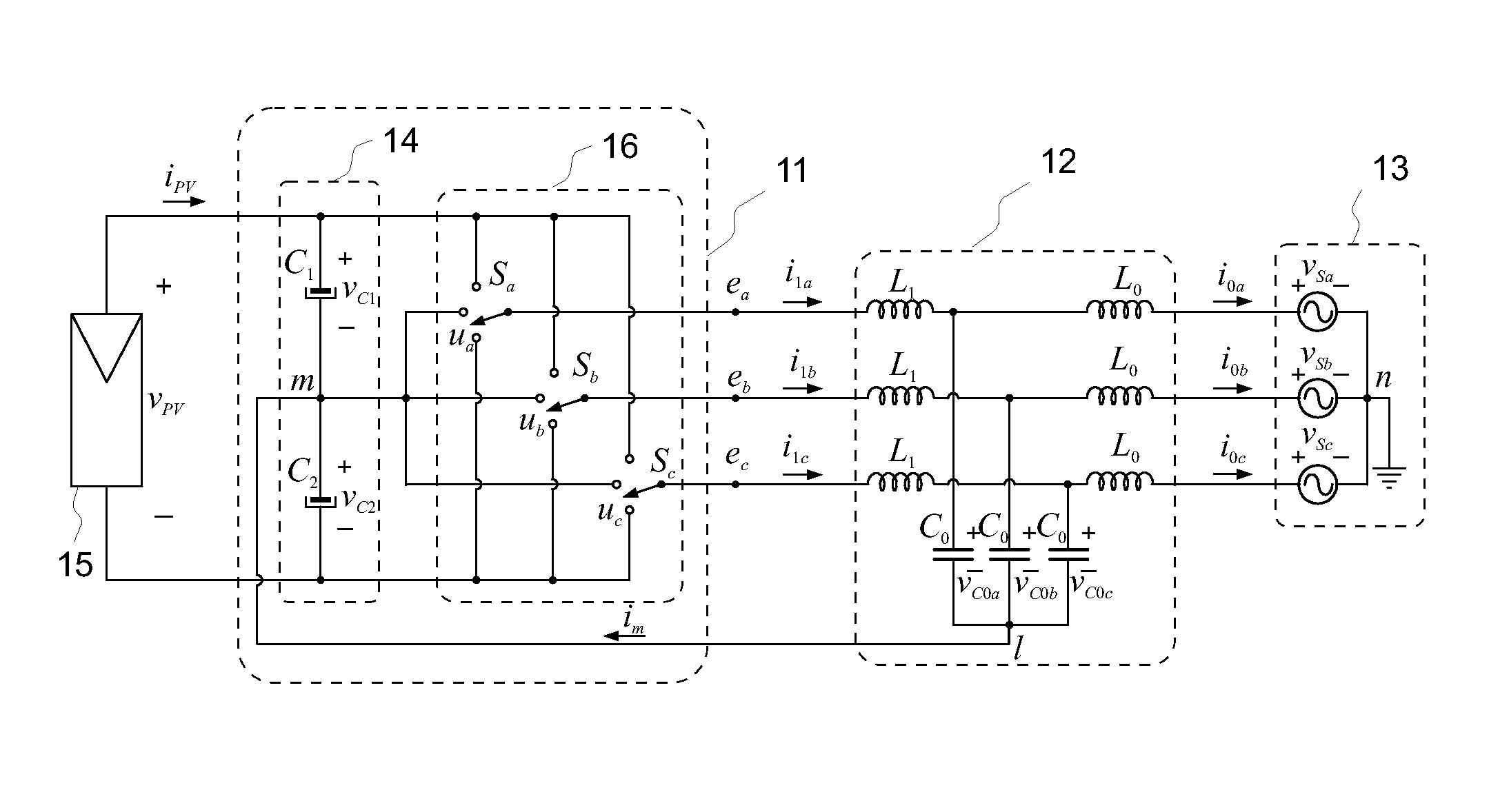
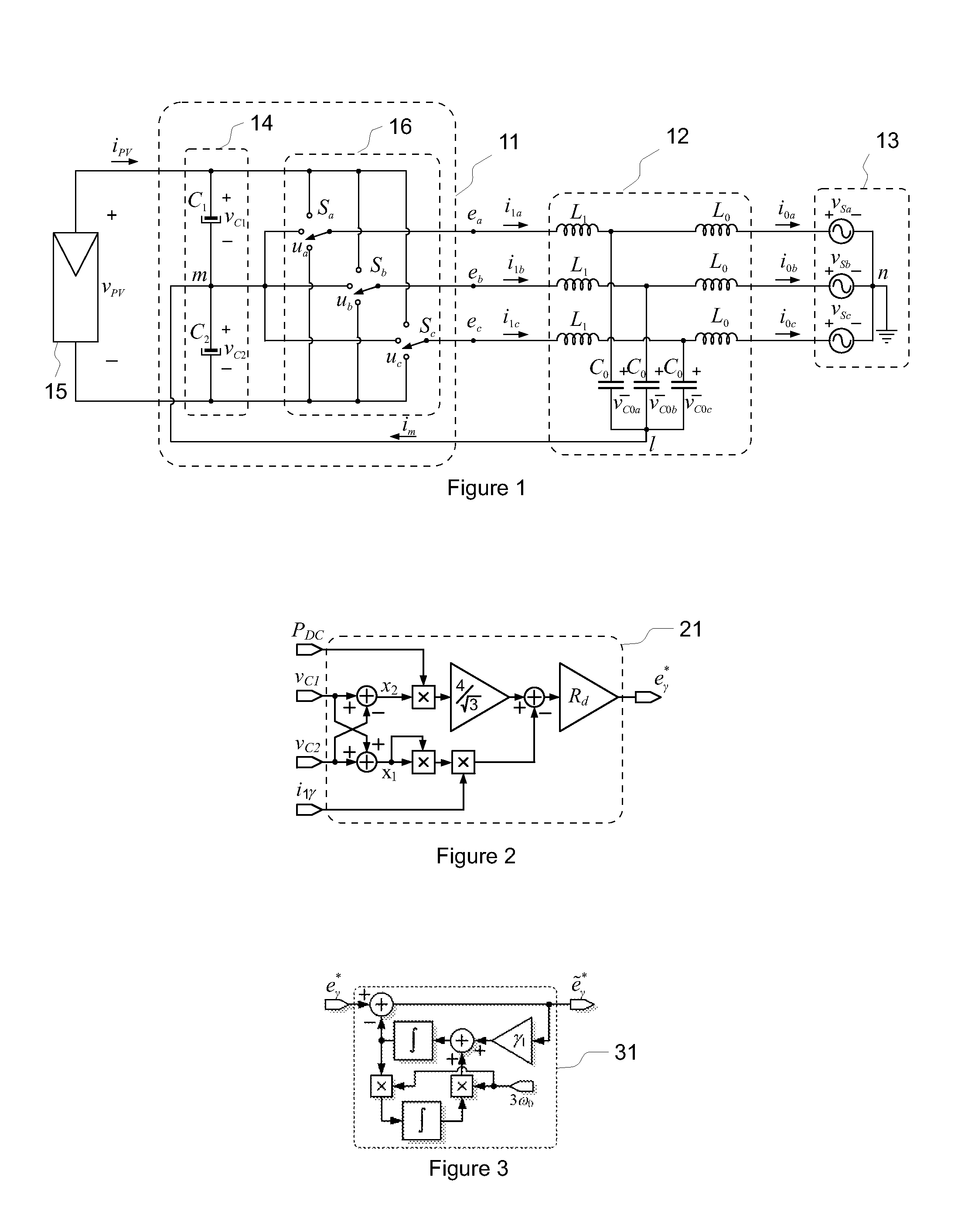
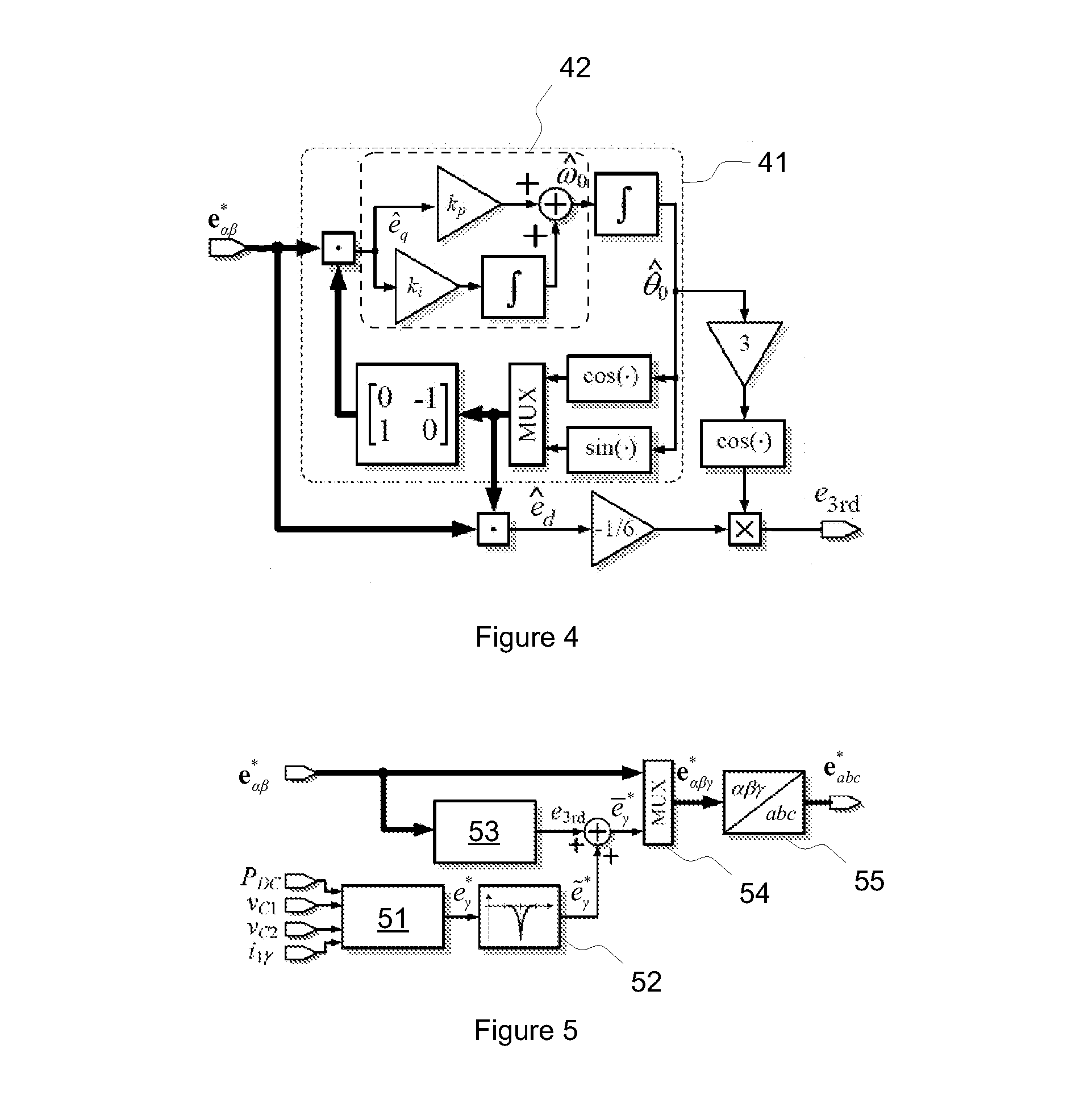
ActiveUS20130329471A1Attenuate the zero-sequence resonanceReduce lossesPhotovoltaic energy generationDc-ac conversion without reversalPower gridVoltage reference
An exemplary method and an apparatus implementing the method for an arrangement having a three-phase, multi-level inverter, an output LCL-filter connecting the inverter to a grid, and a virtual-ground connection between the LCL-filter and the neutral point of the DC-link. The method includes determining a zero-sequence component of an LCL-filter inverter-side current, calculating a zero-sequence damping and balancing voltage term based on the LCL-filter inverter-side current zero-sequence component and voltages over the two halves of the DC-link, and adding the zero-sequence damping and voltage balancing term to the output voltage reference.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Local self-boost inhibit scheme with shielded word line
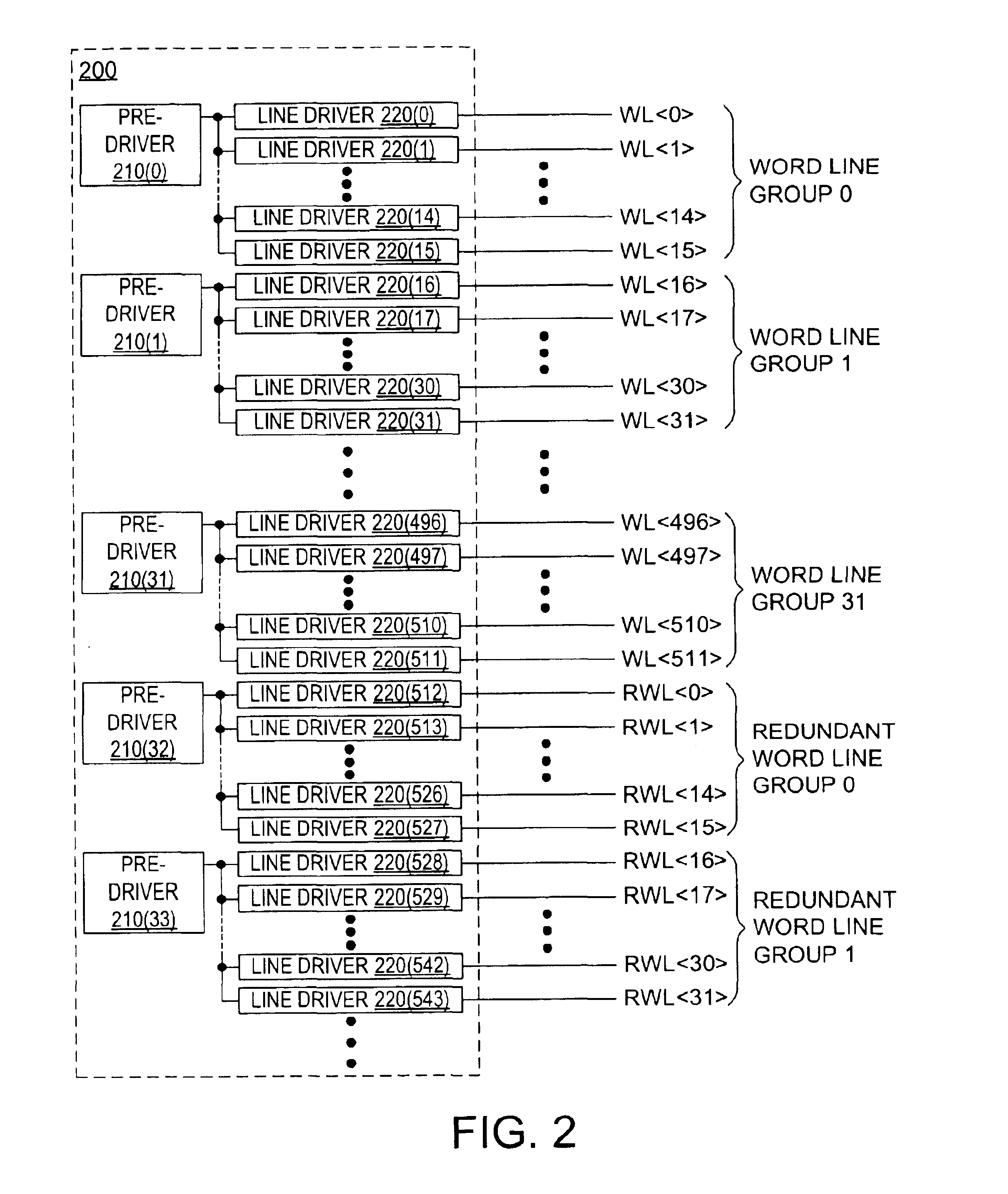
A NAND architecture non-volatile memory device and programming process is described that reduces the effects of word line to word line voltage coupling by utilizing sets of two or more adjacent word lines and applying the same voltage to each in array access operations. This allows each word line of the set or pair to shield the other from word line to word line capacitive voltage coupling. In NAND memory string embodiments the various cells of strings of non-volatile memory cells are programmed utilizing modified or unmodified drain-side self boost, source-side self boost, local self boost, and virtual ground programming processes that utilize two or more “blocking” memory cells on either the source line side and drain line side of a selected memory cell. The paired blocking cells shield each other during programming to reduce coupled noise, to prevent charge leakage from the boosted channel of the selected memory cell.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
RF impedance matching network
Owner:ASM AMERICA INC
Non-Volatile Memory Embedded In A Conventional Logic Process And Methods For Operating Same
InactiveUS20070279987A1Minimizes probabilityHighly optimized SoCSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineFowler nordheim
A non-volatile memory system including an array of cells, each having an access transistor and a capacitor sharing a floating gate. The access transistors in each row are fabricated in separate well regions, which are independently biased. Within each row, the source of each access transistor is coupled to a corresponding virtual ground line, and each capacitor structure is coupled to a corresponding word line. Alternately, the source of each access transistor in a column is coupled to a corresponding virtual ground line. Within each column, the drain of each access transistor is coupled to a corresponding bit line. Select memory cells in each row are programmed by band-to-band tunneling. Bit line biasing prevents programming of non-selected cells of the row. Programming is prevented in non-selected rows by controlling the well region voltages of these rows. Sector erase operations are implemented by Fowler-Nordheim tunneling.
Owner:MOSYS INC
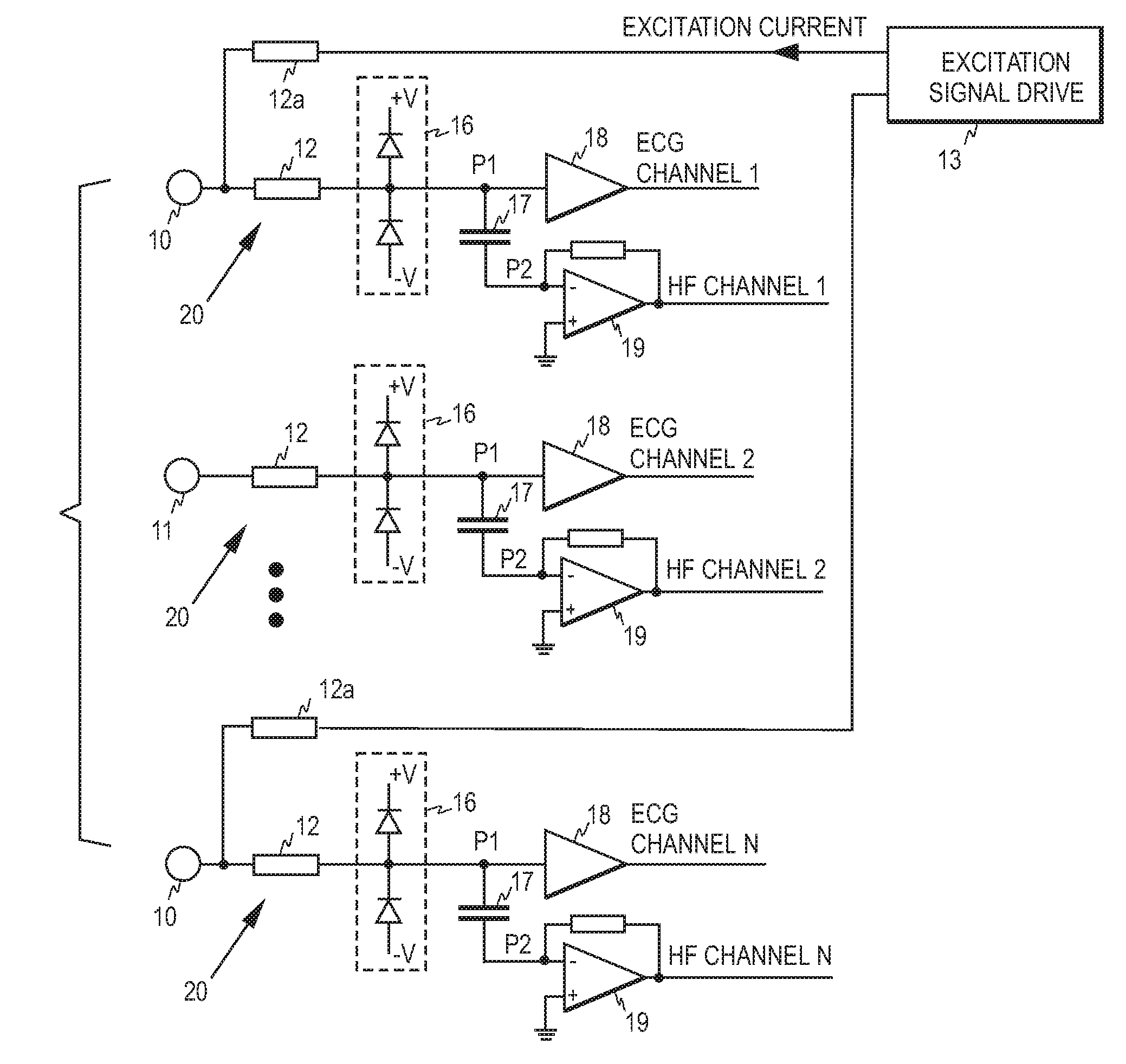
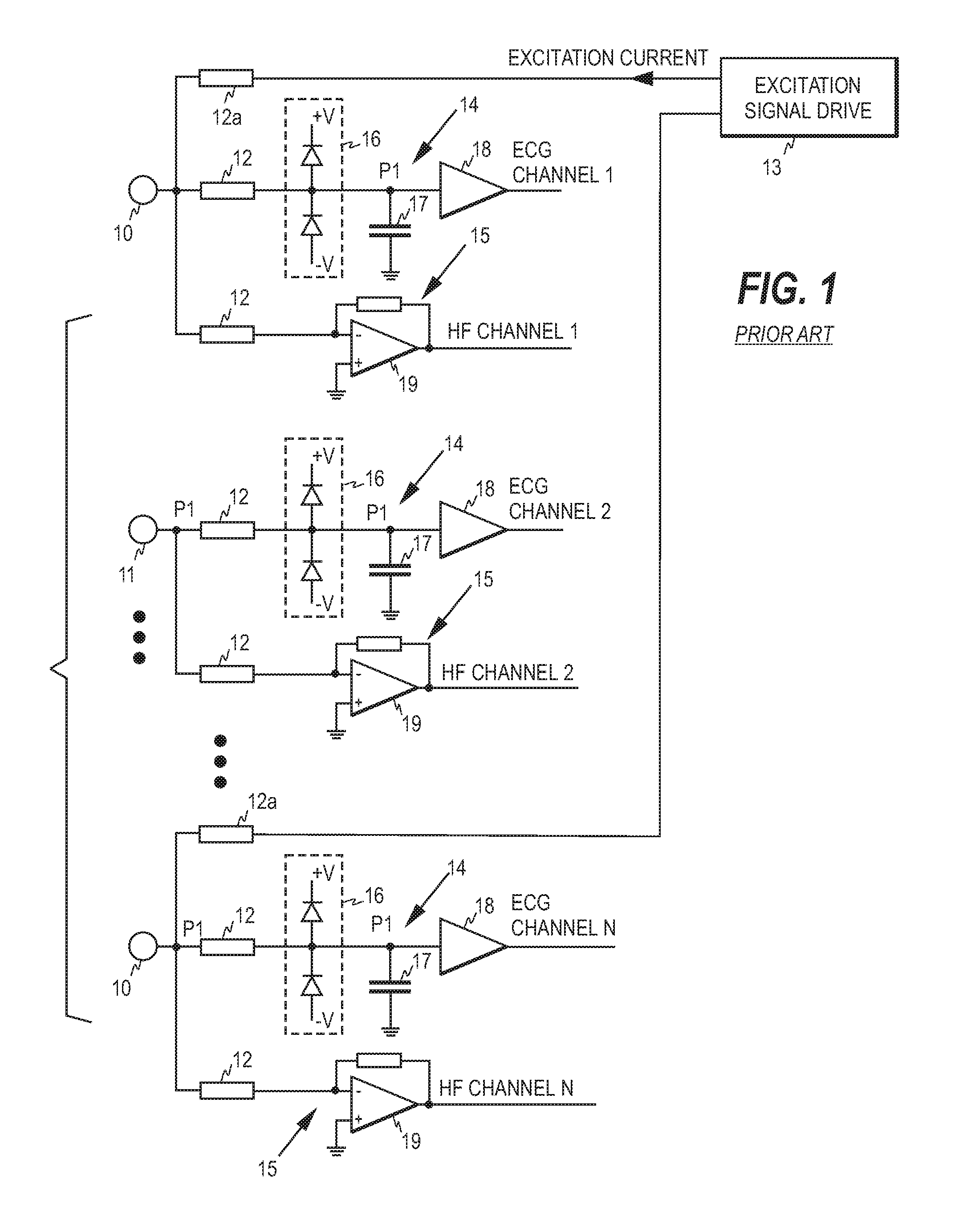
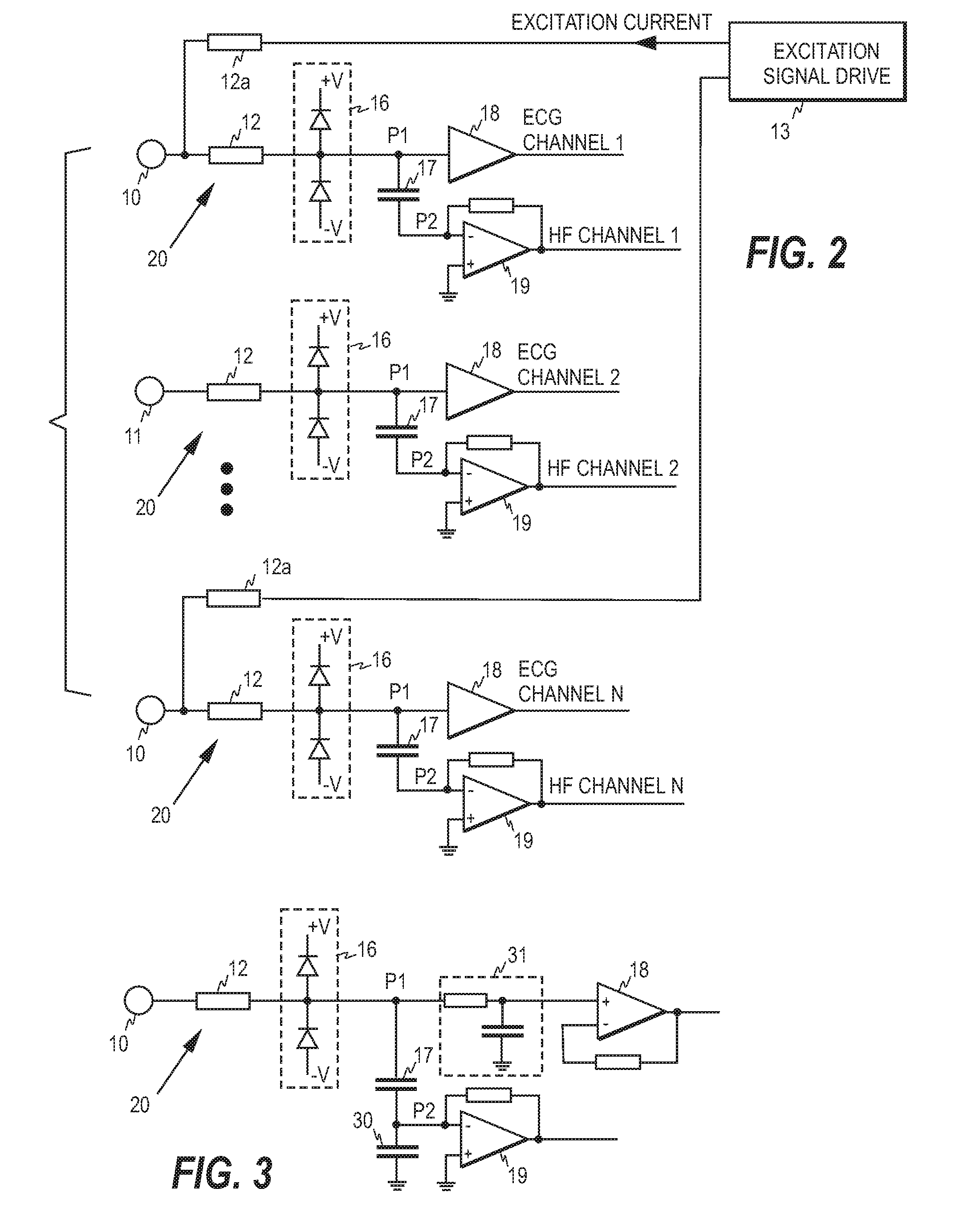
ECG front end and method for acquiring ECG signals
An ECG front end and a method for acquiring ECG signals are disclosed. The front end comprises a plurality of parallel measurement branches, each measurement branch comprising a protection resistor having a first terminal and a second terminal, wherein the first terminal is connectable to a respective ECG electrode. Each measurement branch comprises a first input amplifier operatively connected to the second terminal of the protection resistor and a capacitor having a first and a second terminal, wherein the first terminal of the capacitor is operatively connected to a point between the first input amplifier and the second terminal of the protection resistor and the second terminal of the capacitor is connected to a virtual ground of a second input amplifier. Each first input amplifier serves as a source of an ECG channel signal and each second input amplifier as a source of high frequency signal components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Standby leakage current reduction circuit and semiconductor memory device comprising the standby leakage current reduction circuit
ActiveUS20070147159A1Reduce standby leakage currentReduce excessive power consumptionDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
Embodiments of the invention provide a standby leakage current reduction circuit and a semiconductor memory device comprising the standby leakage current reduction circuit. The invention provides a circuit adapted to reduce standby leakage current in a semiconductor memory device comprising memory cells. The circuit comprises a bias signal generator adapted to generate a bias signal, wherein a voltage level of the bias signal is set in accordance with a result of a standby leakage current test. The circuit further comprises a ground voltage controller adapted to receive the bias signal from the bias signal generator and to control a level of a voltage apparent on a virtual ground terminal in response to the bias signal while the semiconductor memory device is in a standby mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Internal balanced coil for inductively coupled high density plasma processing chamber
A coil is provided for use in a semiconductor processing system to generate a plasma with a magnetic field in a chamber. The coil comprises a first coil segment, a second coil segment and an internal balance capacitor. The first coils segment has a first end and a second end. The first end of the coil segment is adapted to connect to a power source. The second coil segment has a first and second end. The second end of the first coil segment is adapted to connect to an external balance capacitor. The internal balance capacitor is connected in series between the second end of the first coil segment and the first end of the second coil segment. The internal balance capacitor and the coil segments are adapted to provide a voltage peak along the first coil segment substantially aligned with a virtual ground along the second coil segment.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods and apparatuses for a ROM memory array having a virtually grounded line
Methods and apparatuses in which a ROM memory array has virtual-grounded source lines programmed in layer physically higher than the diffusion layer. The ROM memory array may include a diffusion layer, one or more virtual-grounded source lines, and one or more bit lines. At least one of the virtual-grounded source lines is programmed with a layer physically higher than the diffusion layer.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Automatic gain control circuit with high linearity and monotonically correlated offset voltage
InactiveUS6538507B2Easily and reduced and eliminatedLow absolute gain toleranceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAutomatic controlAudio power amplifier
An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit including a high gain amplifier, a feedback network and two transconductance amplifiers. The feedback network has a first end that receives an input signal of the AGC circuit, a second end coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and two intermediate nodes. Each transconductance amplifier has an input coupled to a respective intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. The transconductance amplifiers collectively control a position of a virtual ground within the feedback network to control gain of the AGC circuit. The transconductance amplifiers each include an attenuator and a transconductance stage coupled between the feedback network and the high gain amplifier and are configured to operate linearly across a relatively wide input voltage range. The input offset voltage of the AGC circuit varies monotonically with gain of the AGC circuit.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
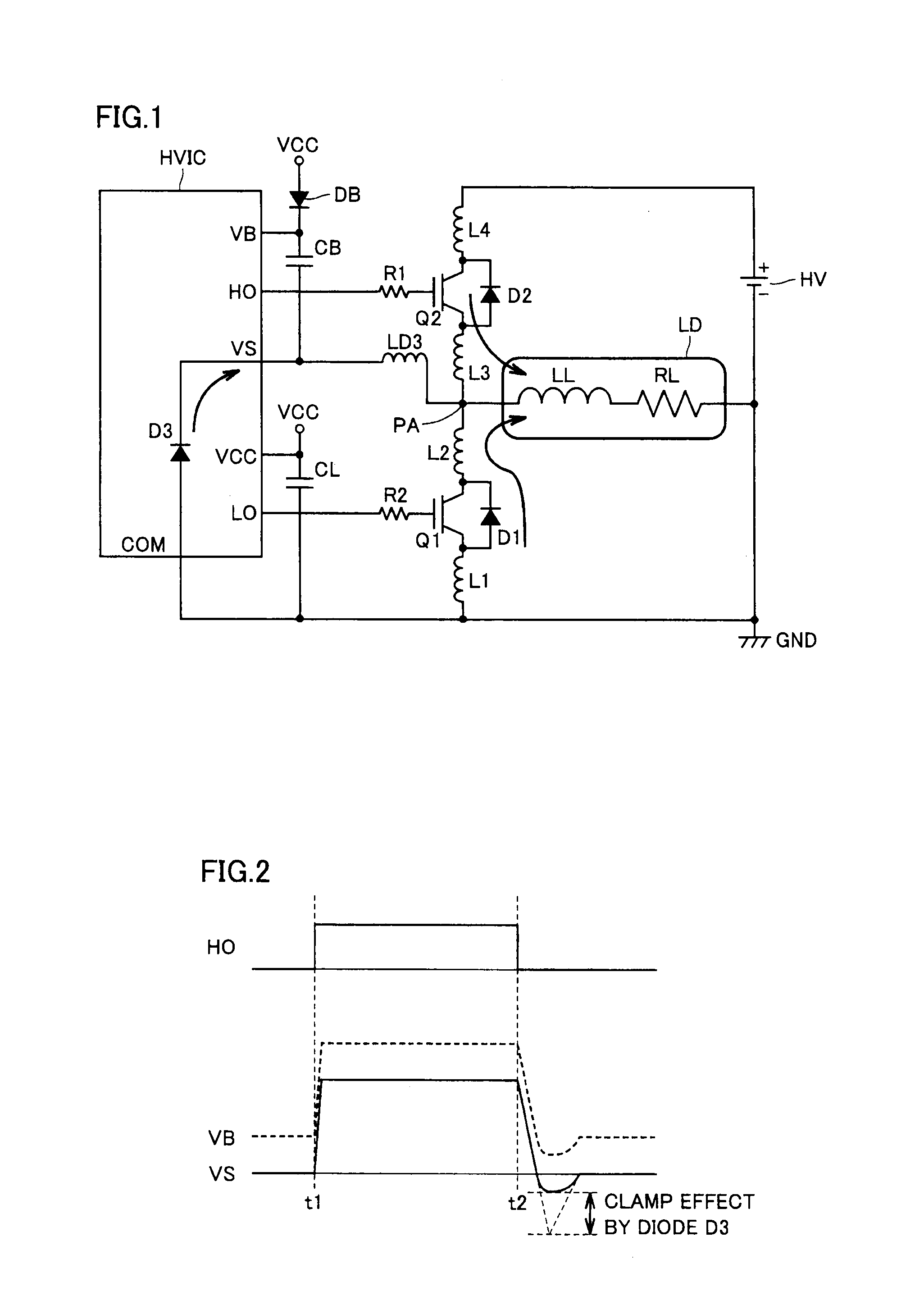
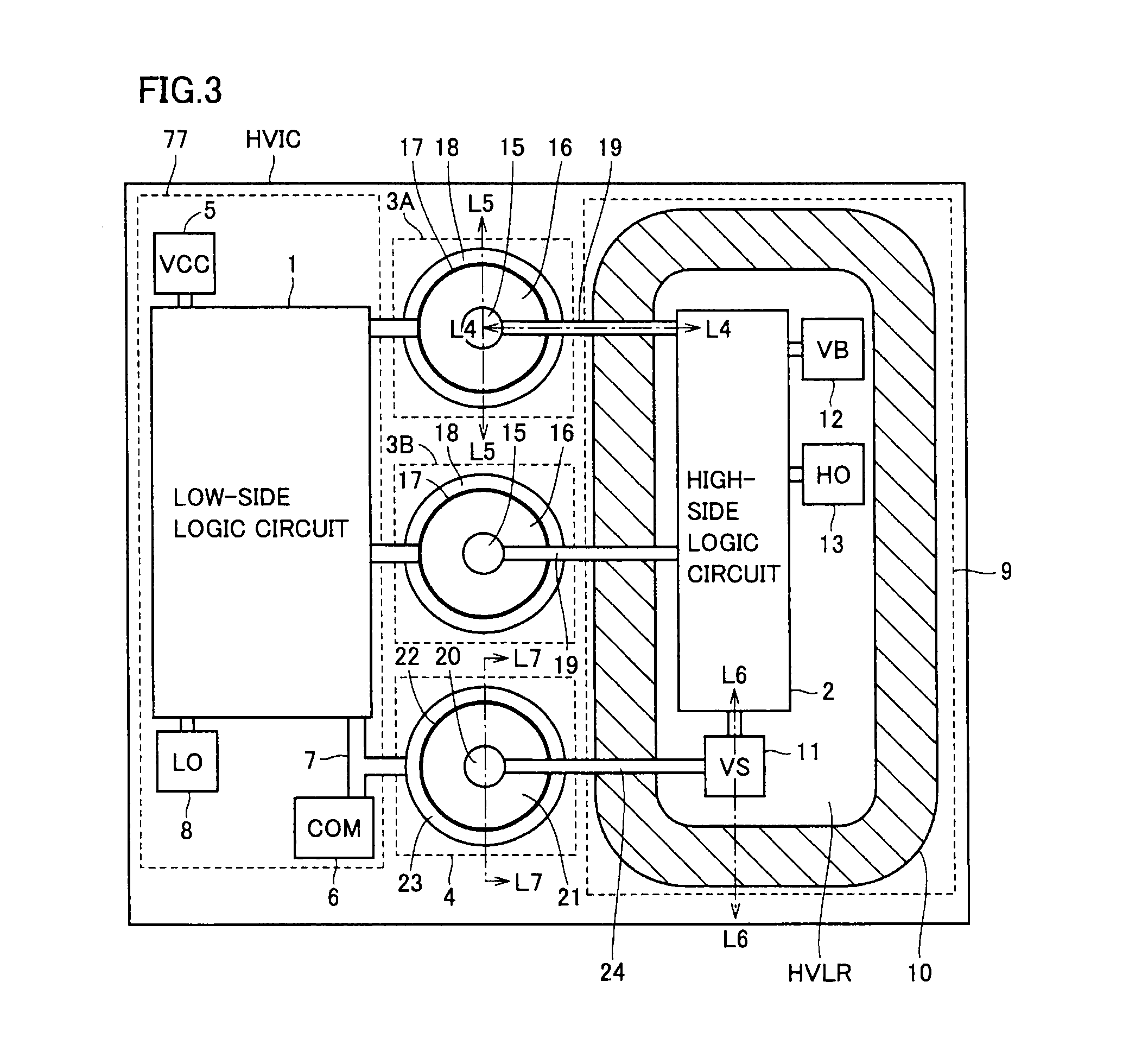
Semiconductor device driving bridge-connected power transistor
ActiveUS20100283116A1Increase can be suppressedAvoid misuseTransistorConversion constructional detailsVirtual groundSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a low-side circuit, high-side circuit, a virtual ground potential pad, a common ground potential pad and a diode, formed on a semiconductor substrate. The low-side circuit drives a low-side power transistor. The high-side circuit is provided at a high potential region, and drives a high-side power transistor. The virtual ground potential pad is arranged at the high potential region, and coupled to a connection node of both power transistors to supply a virtual ground potential to the high-side circuit. The common ground potential pad supplies a common ground potential to the low-side circuit and high-side circuit. The diode has its cathode connected to the virtual ground potential pad and its anode connected to the common ground potential pad.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Precision automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS20020086651A1Low absolute gain toleranceImprove matchResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierClosed loop
An automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier including a high gain transimpedance amplifier, a resistive feedback network and multiple transconductance stages coupled in the feedback path of the AGC amplifier. The feedback network receives an input signal and is coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and has multiple intermediate nodes. Each transconductance stage has an input coupled to an intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. Each transconductance stage is independently controllable to position a virtual ground within the feedback network to control closed loop gain. Each transconductance stage may have a bias current input coupled to a bias current control circuit. The control circuit controls each bias current to vary the gain of the AGC amplifier. The bias currents may be linearly controlled employing a ramp function to achieve a linear in dB gain response.
Owner:M RED INC
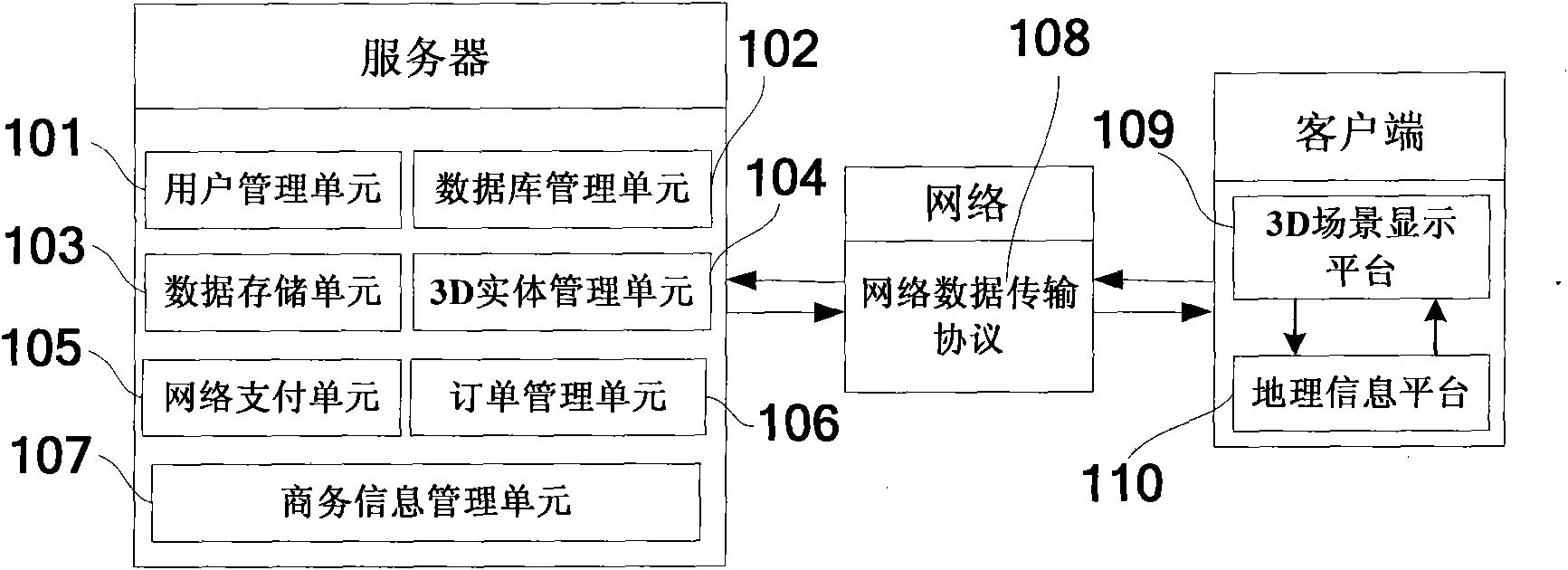
Method for building three-dimensional (3D) panoramic live-action network business platform
The invention relates to a method for building a three-dimensional (3D) panoramic live-action network business platform. In a method, panoramic live-action image technology is organically combined with 3D modeling technology so as to build the 3D panoramic live-action network business platform which is fully constituted by the real environment of an entity merchant. The method comprises the following steps of: building a system framework of the 3D panoramic live-action network business platform; acquiring data needed for building the platform; building an outer panoramic live-action display screen, establishing a virtual ground and setting the roaming mode of a user according to the acquired data and synchronizing the roaming position of the user to the geographic information of the real world; and adding a 3D virtual label, a virtual counter, a virtual goods shelf and a commodity 3D entity model in the context of the 3D panoramic live-action network business platform to realize online transaction so as to obtain the 3D panoramic live-action network business platform. The platform can be taken as the extension for network business of the entity merchant, so that network trust level of the merchant is raised and a new technical route is provided for the building of the network business platform.
Owner:沈阳迅景科技有限公司
Virtual ground nonvolatile semiconductor memory array architecture and integrated circuit structure therefor
In nonvolatile memory cell array, the memory cells of each sector are organized into groups of successive cells, the groups preferably being of the same size and preferably isolated from one another in both the row and column directions by a suitable isolation structure such as field dielectric or trench dielectric. Because of cell group isolation, each group of column lines may be decoded by its own relatively small program column select, which preferably is replicated in essentially identical form for all groups of column lines. While each program column select preferably is used to decode one group of column lines, larger program column selects may be used if desired to decode two or more groups of column lines. Read column selects may decode one or more groups of column lines as desired. The number of column lines decoded may the same as or different than the number of column lines decoded.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
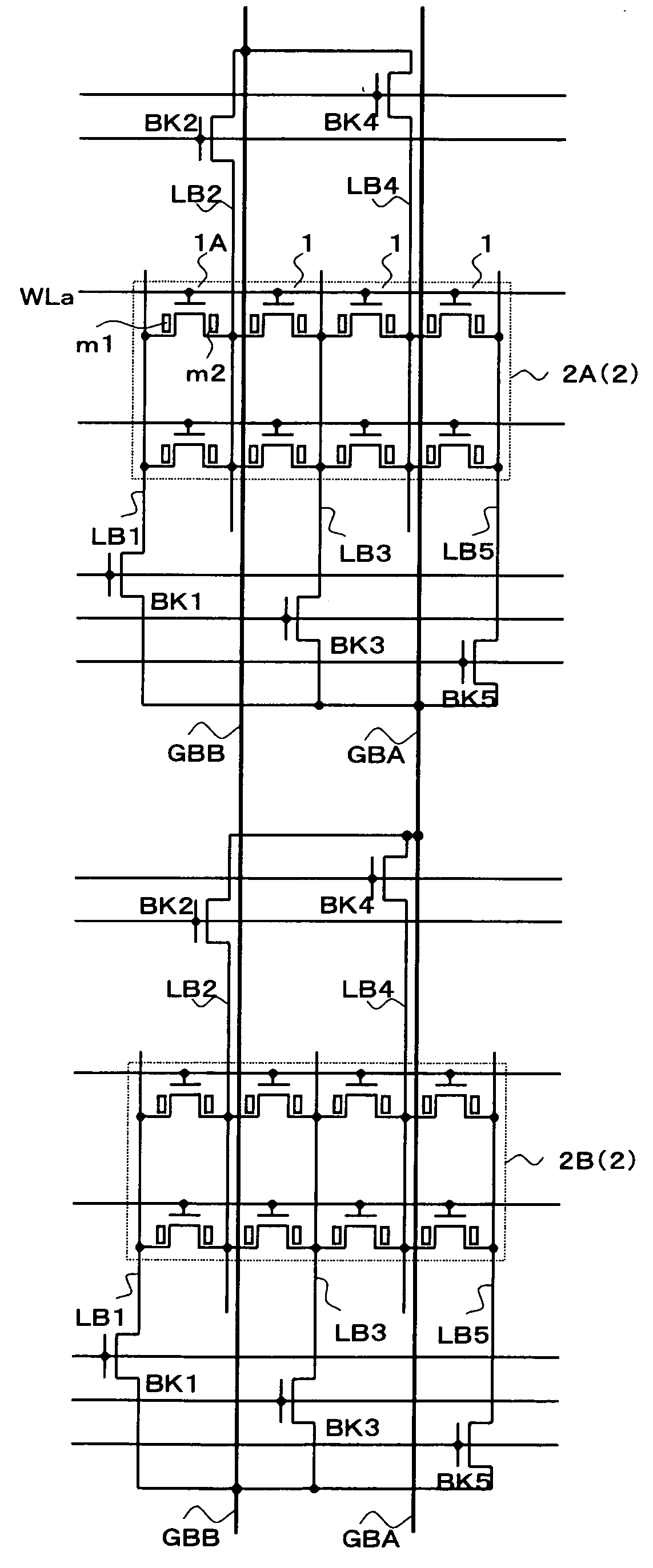
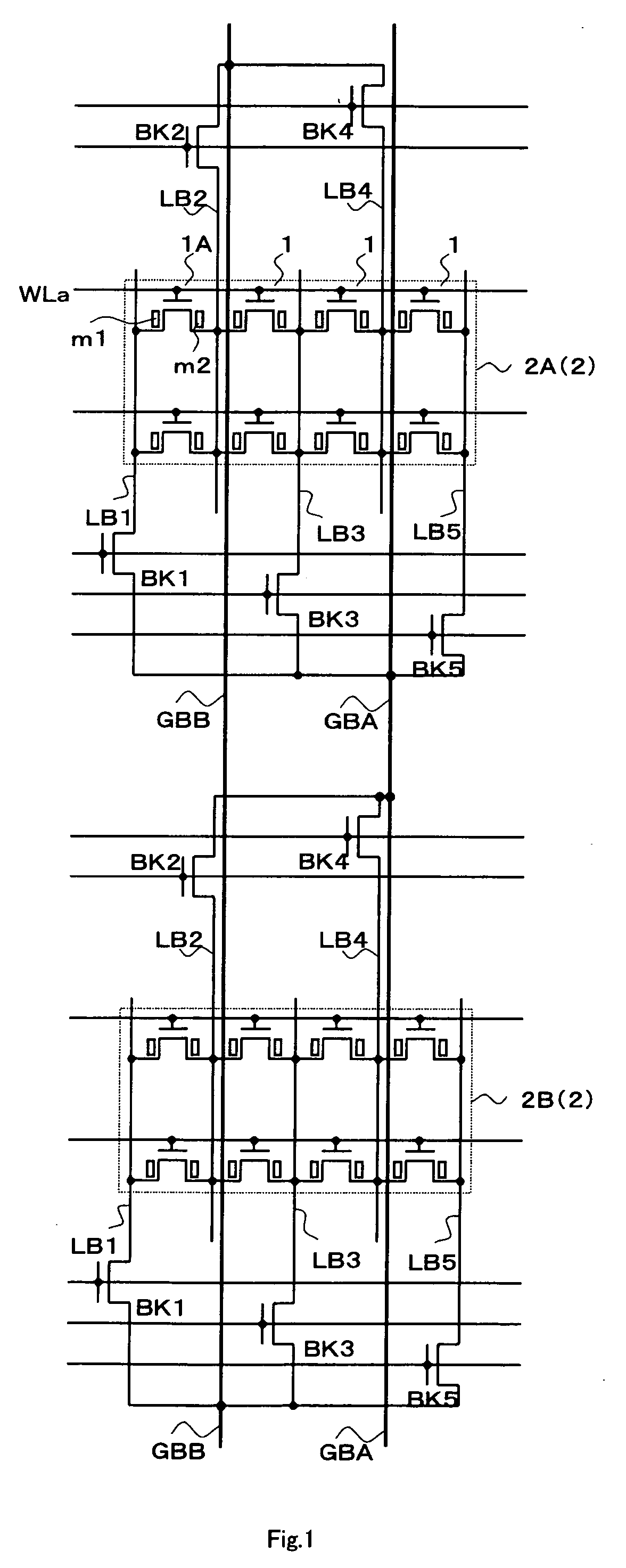
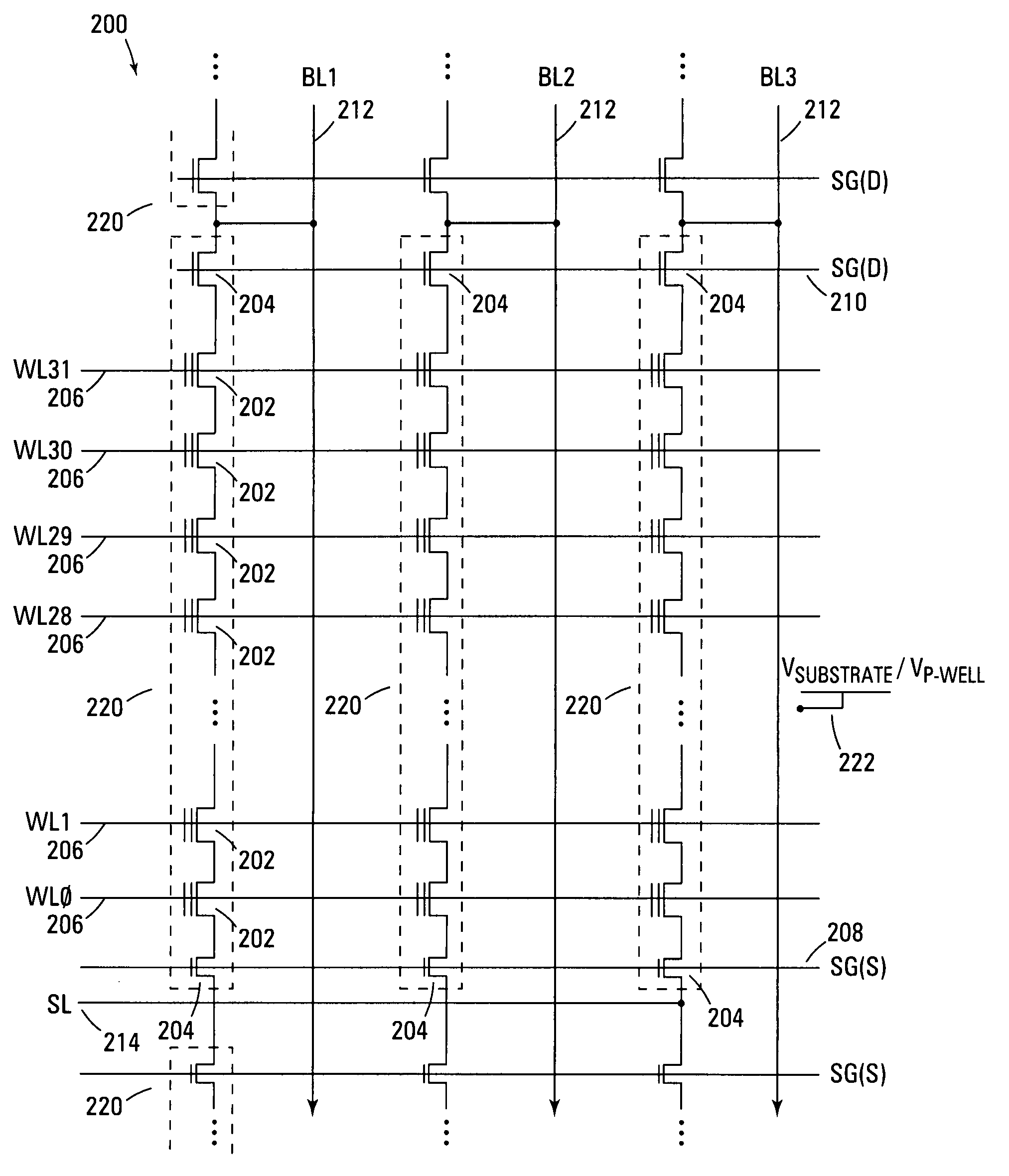
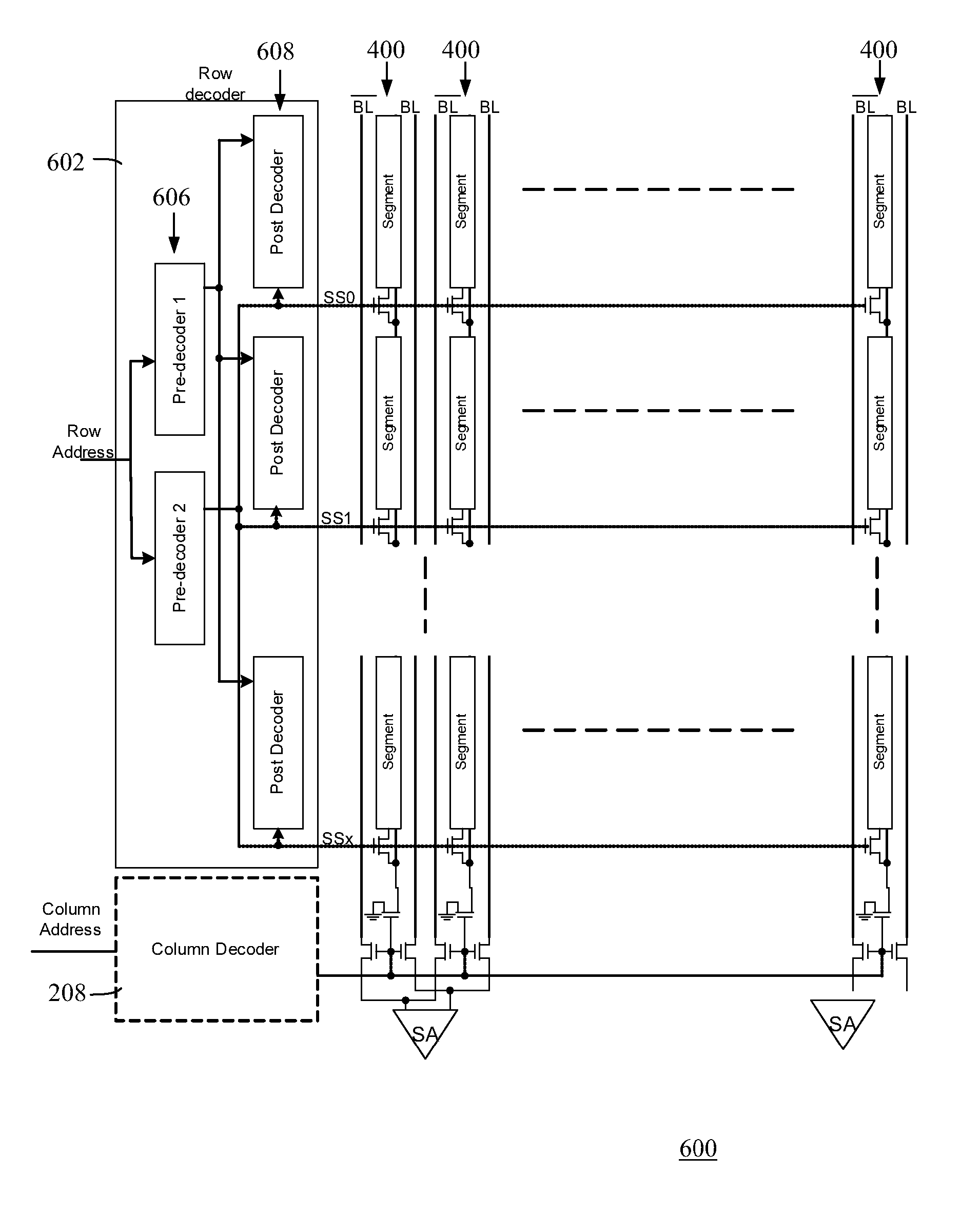
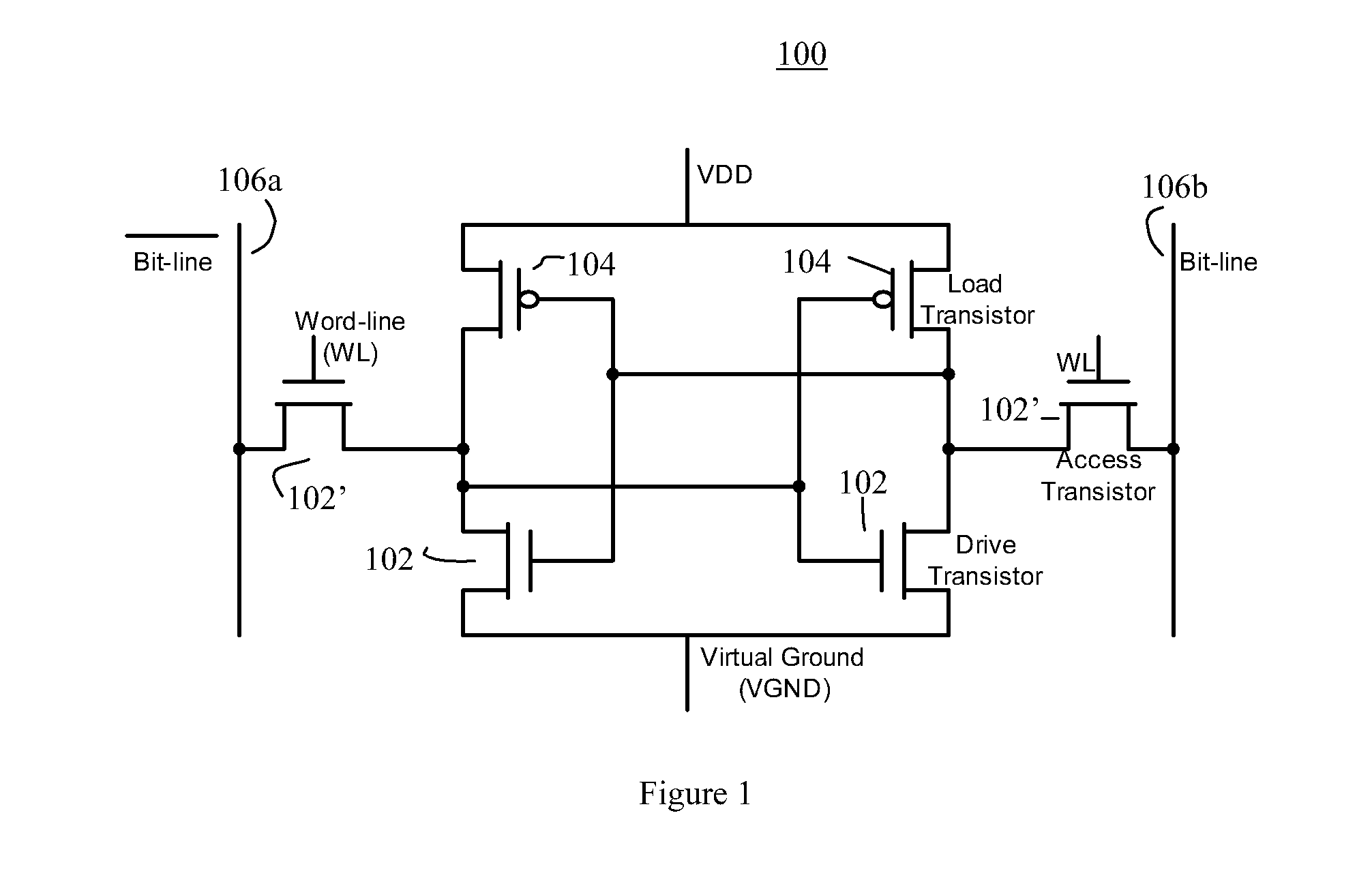
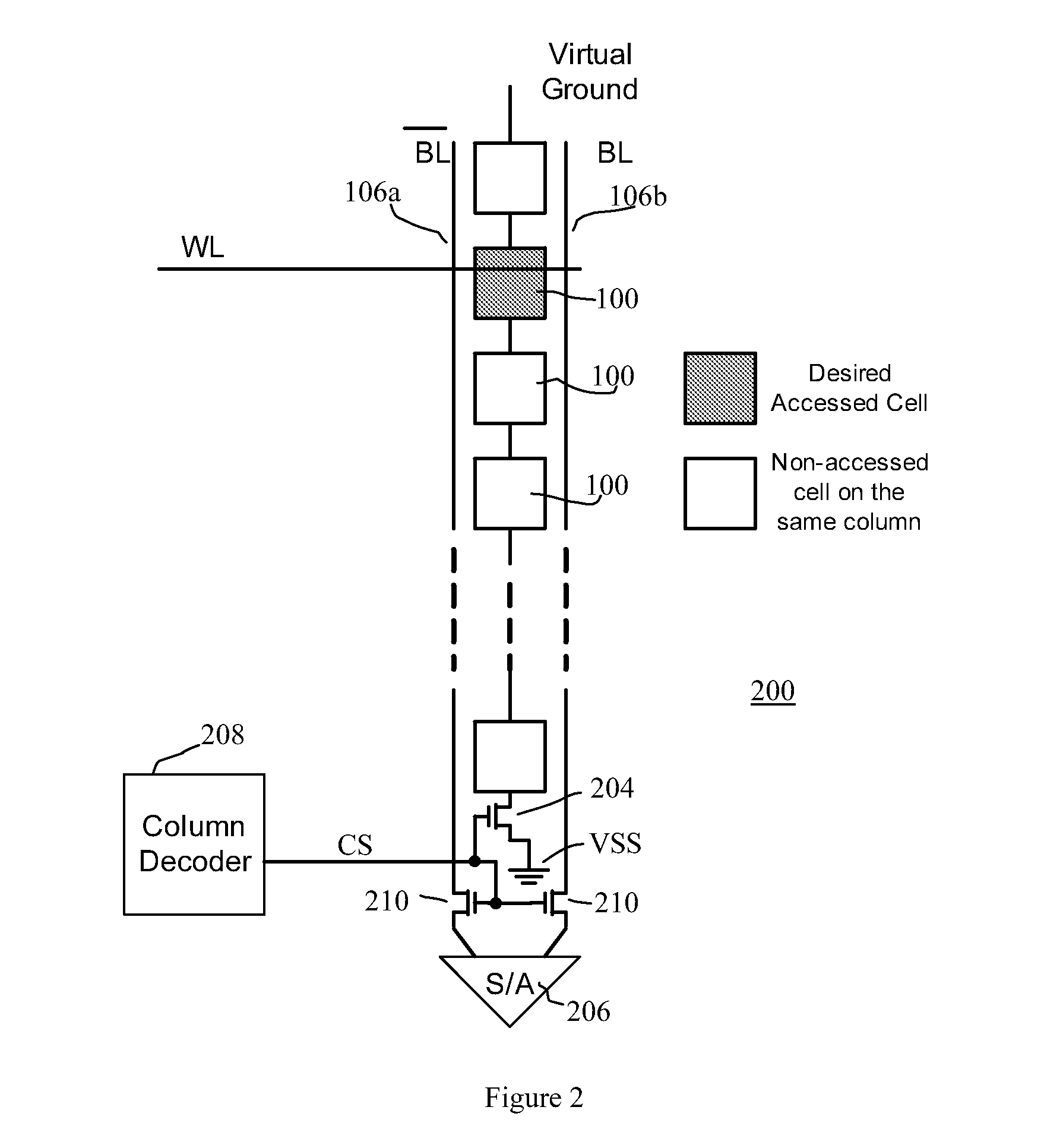
Segmented Column Virtual Ground Scheme In A Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) Circuit
InactiveUS20070217262A1Power write operationTotal current dropRead-only memoriesDigital storageStatic random-access memoryLow voltage
A static random access memory (SRAM) cell array is provided that reduces leakage current. The SRAM cell array is configured in a plurality of columns. Each of the columns comprises: a column virtual ground node; a column switch for selectively coupling the column virtual ground node to one of a ground or a nominal low voltage; and a plurality of segments. Each of the segments comprises: a segment virtual ground node; a plurality of SRAM cells including a virtual ground signal coupled to the segment virtual ground node; and a virtual ground switch for selectively coupling the segment virtual ground node to one of either a nominal low voltage or the column virtual ground node. A method for operating the SRAM cell array is also described.
Owner:SACHDEV MANOJ +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com