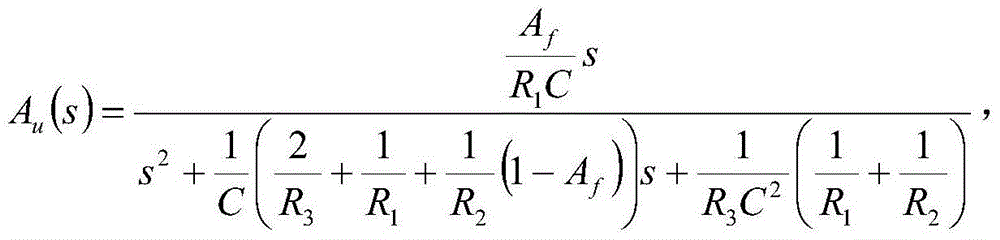Patents
Literature
93 results about "Resistive feedback" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
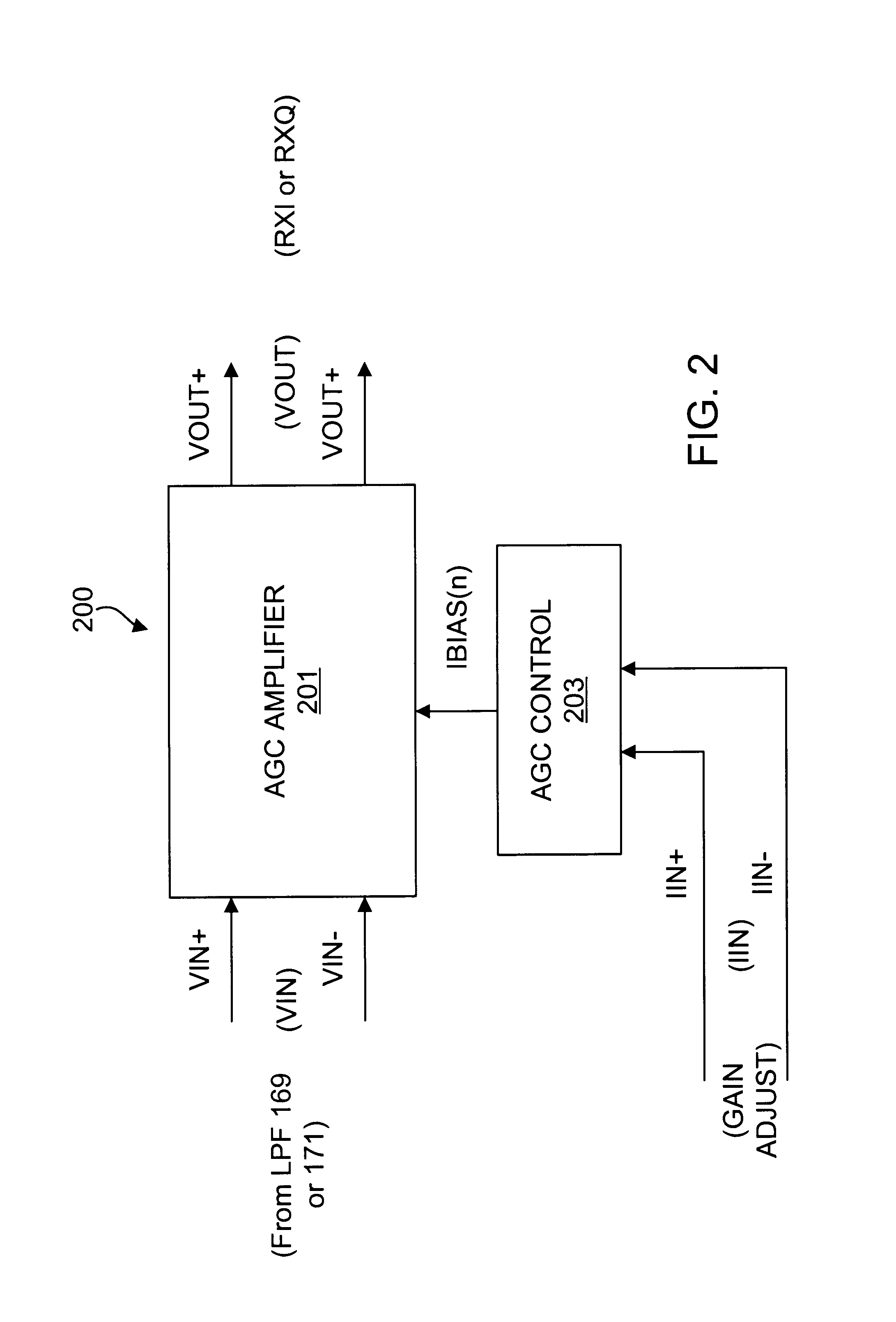
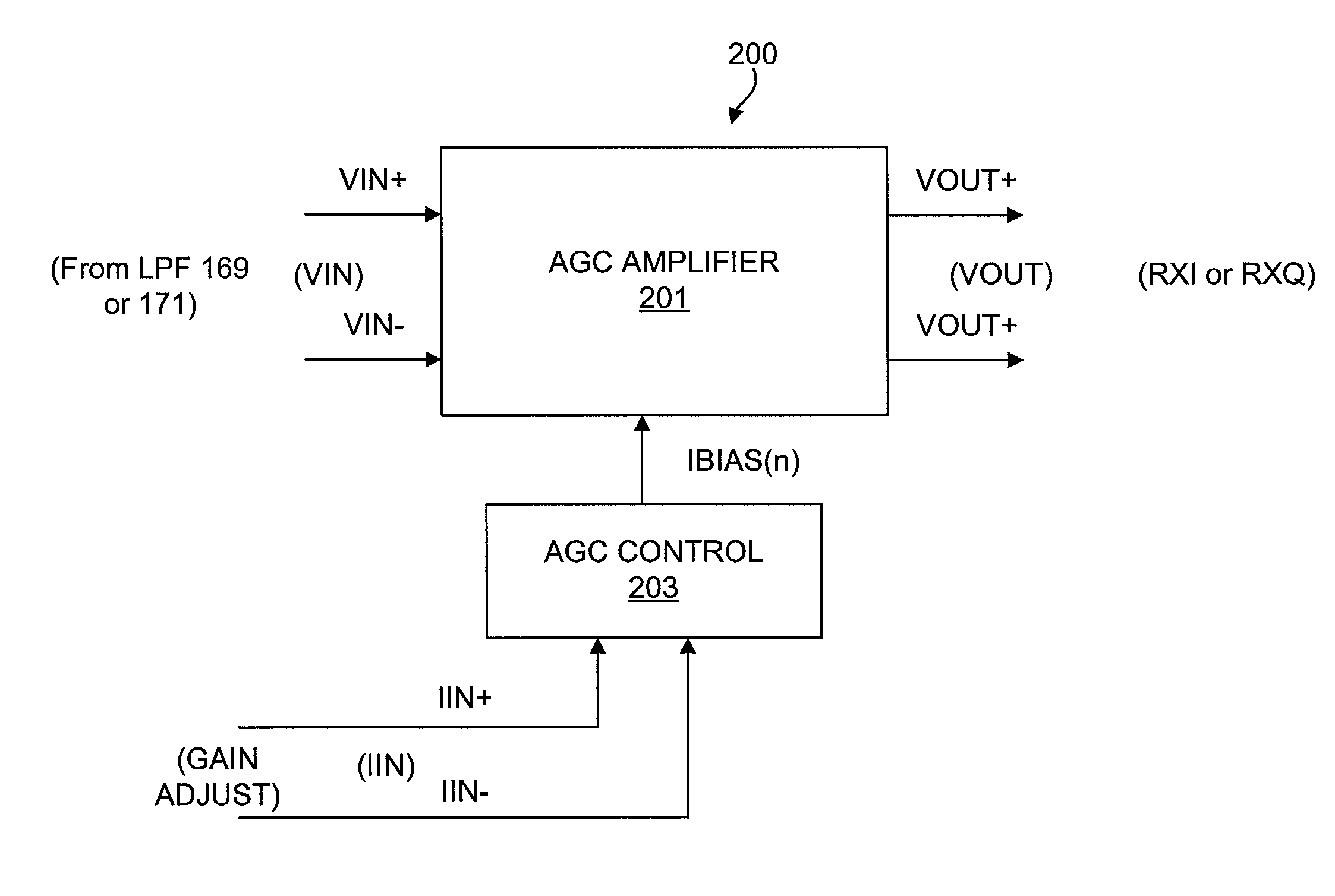
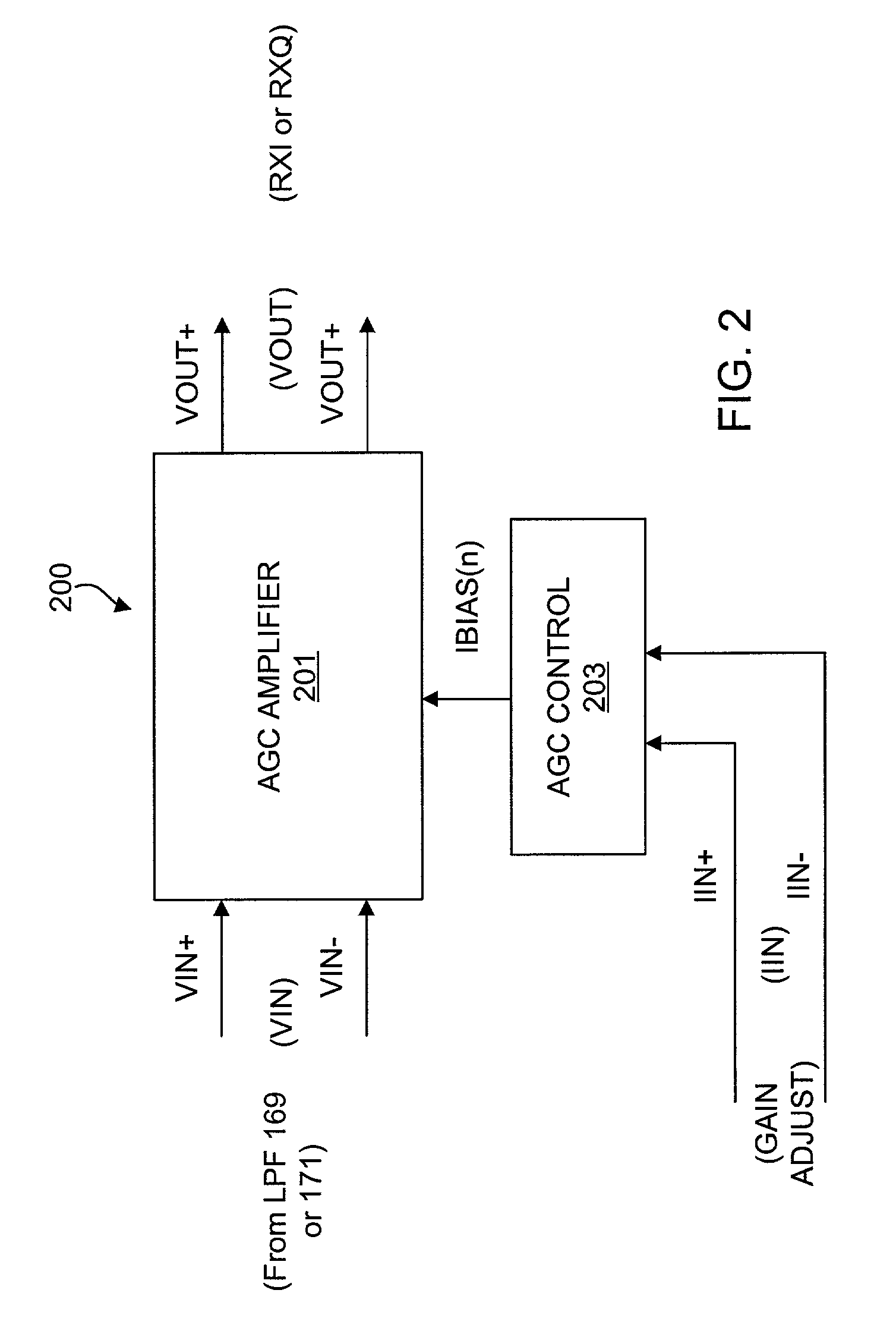
Precision automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS6763228B2Low absolute gain toleranceImprove matchResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierClosed loop
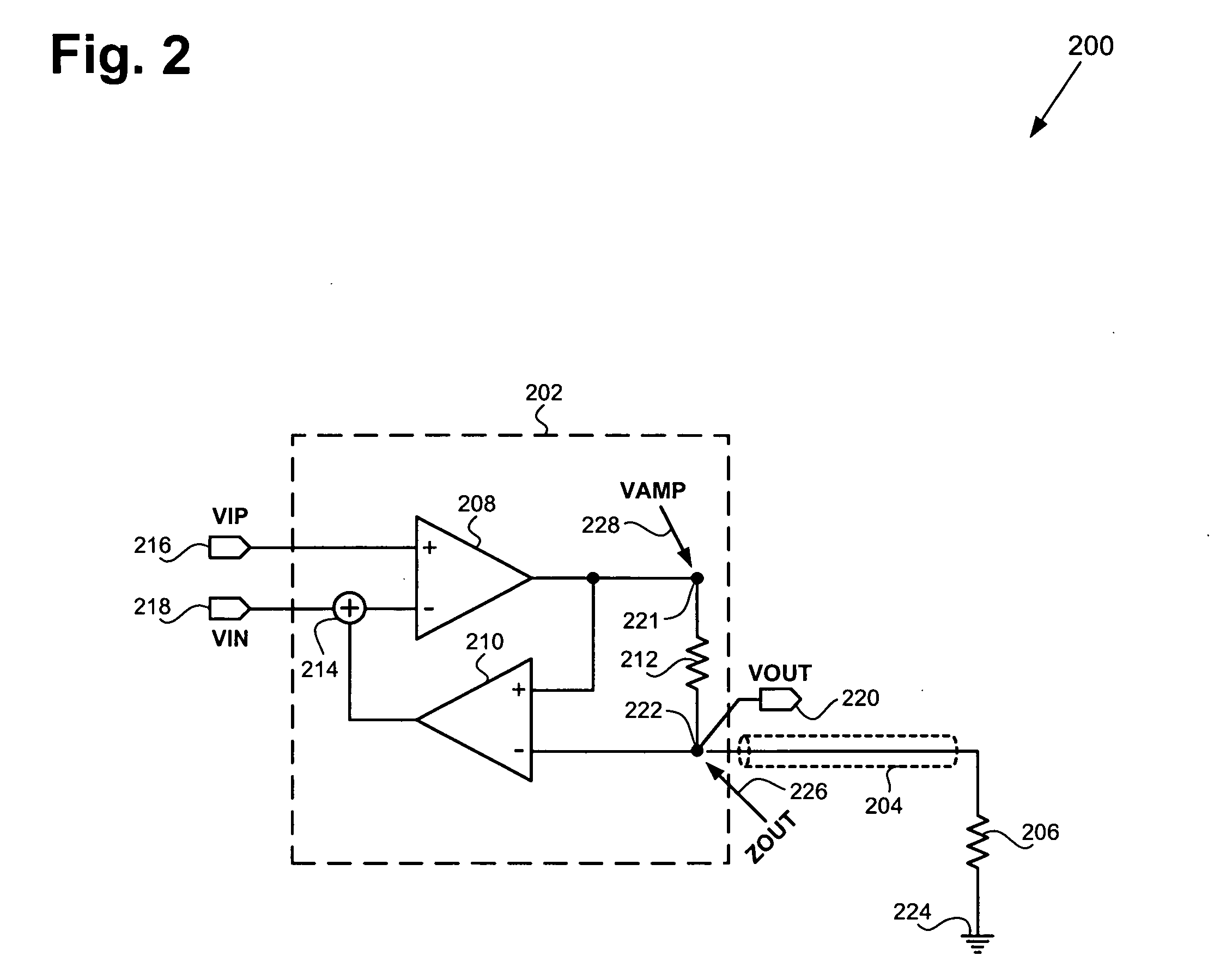
An automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier including a high gain transimpedance amplifier, a resistive feedback network and multiple transconductance stages coupled in the feedback path of the AGC amplifier. The feedback network receives an input signal and is coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and has multiple intermediate nodes. Each transconductance stage has an input coupled to an intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. Each transconductance stage is independently controllable to position a virtual ground within the feedback network to control closed loop gain. Each transconductance stage may have a bias current input coupled to a bias current control circuit. The control circuit controls each bias current to vary the gain of the AGC amplifier. The bias currents may be linearly controlled employing a ramp function to achieve a linear in dB gain response.
Owner:M RED INC
Precision automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS20020086651A1Low absolute gain toleranceImprove matchResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierClosed loop
An automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier including a high gain transimpedance amplifier, a resistive feedback network and multiple transconductance stages coupled in the feedback path of the AGC amplifier. The feedback network receives an input signal and is coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and has multiple intermediate nodes. Each transconductance stage has an input coupled to an intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. Each transconductance stage is independently controllable to position a virtual ground within the feedback network to control closed loop gain. Each transconductance stage may have a bias current input coupled to a bias current control circuit. The control circuit controls each bias current to vary the gain of the AGC amplifier. The bias currents may be linearly controlled employing a ramp function to achieve a linear in dB gain response.
Owner:M RED INC
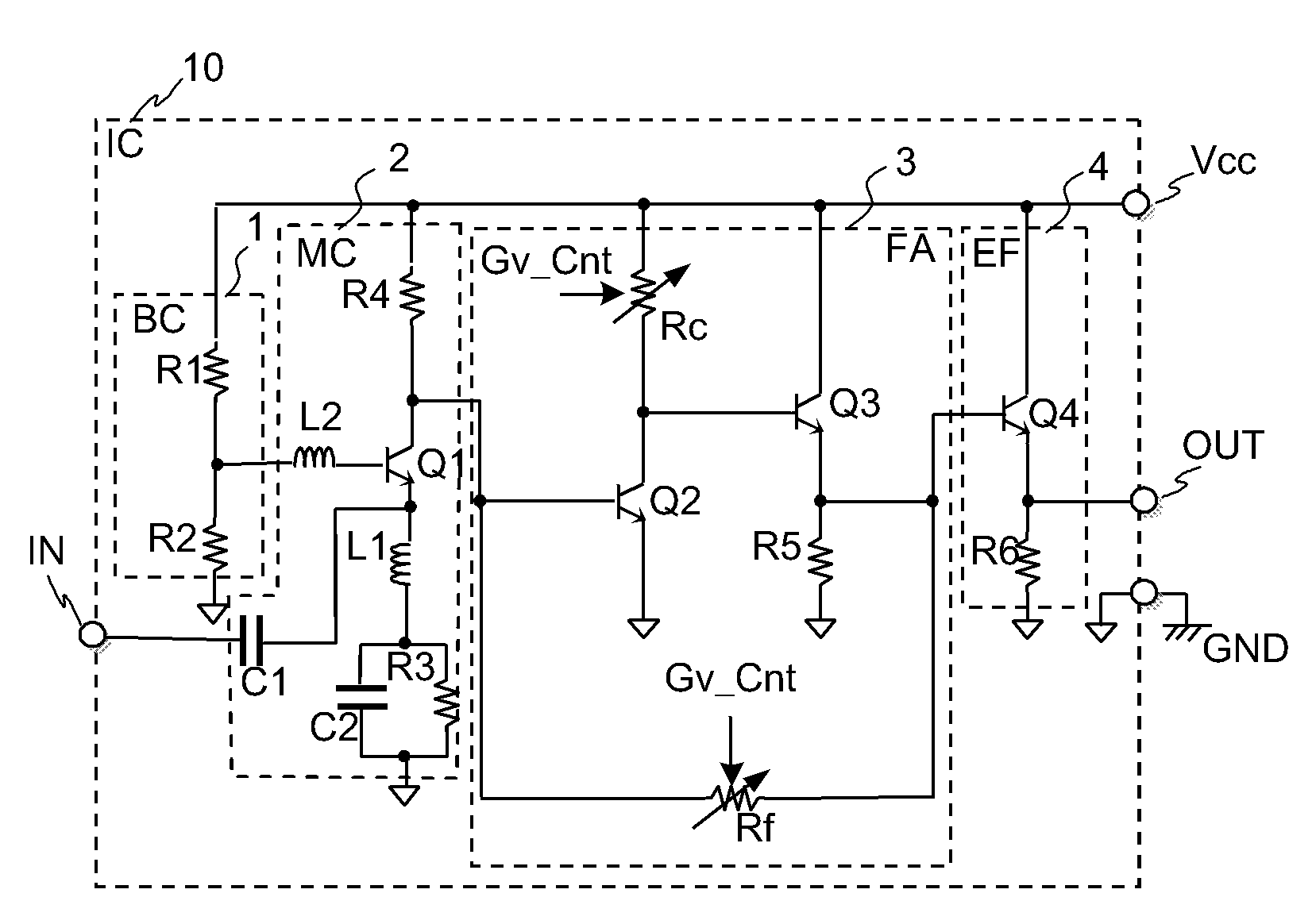
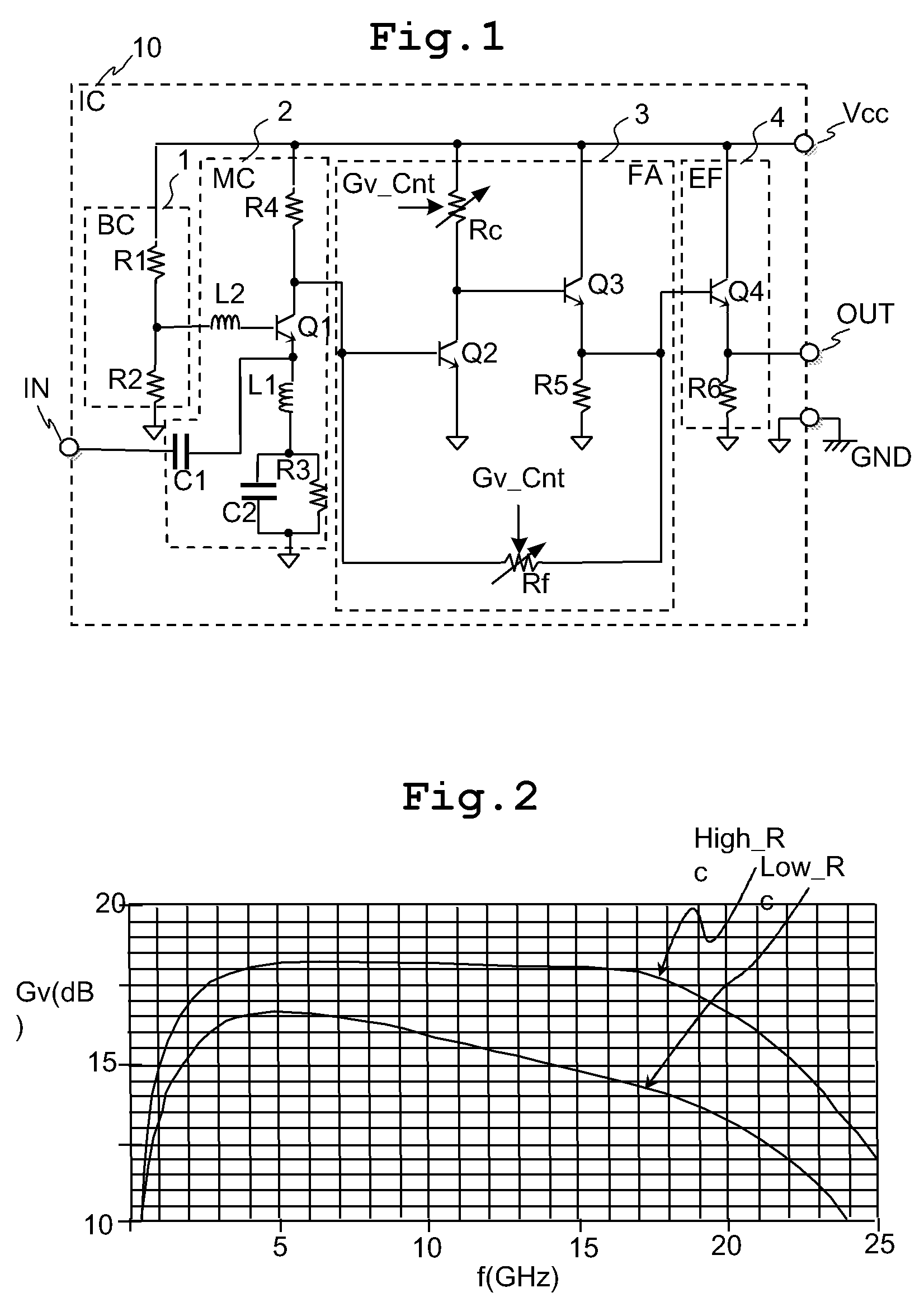
Semiconductor integrated circuit with variable gain amplifier
InactiveUS7821335B2Reduce voltageImprove noise figureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlHigh resistanceClosed loop
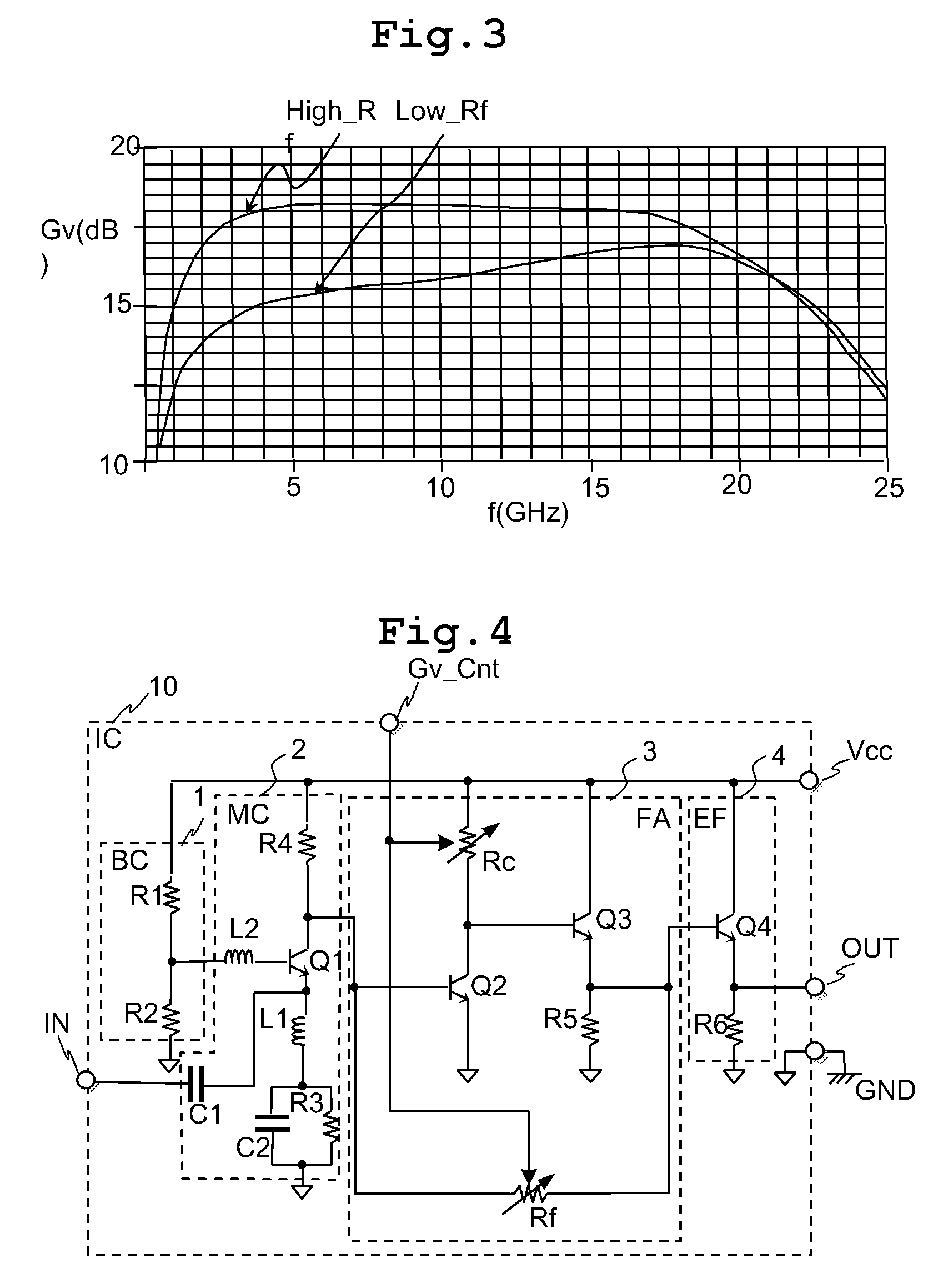
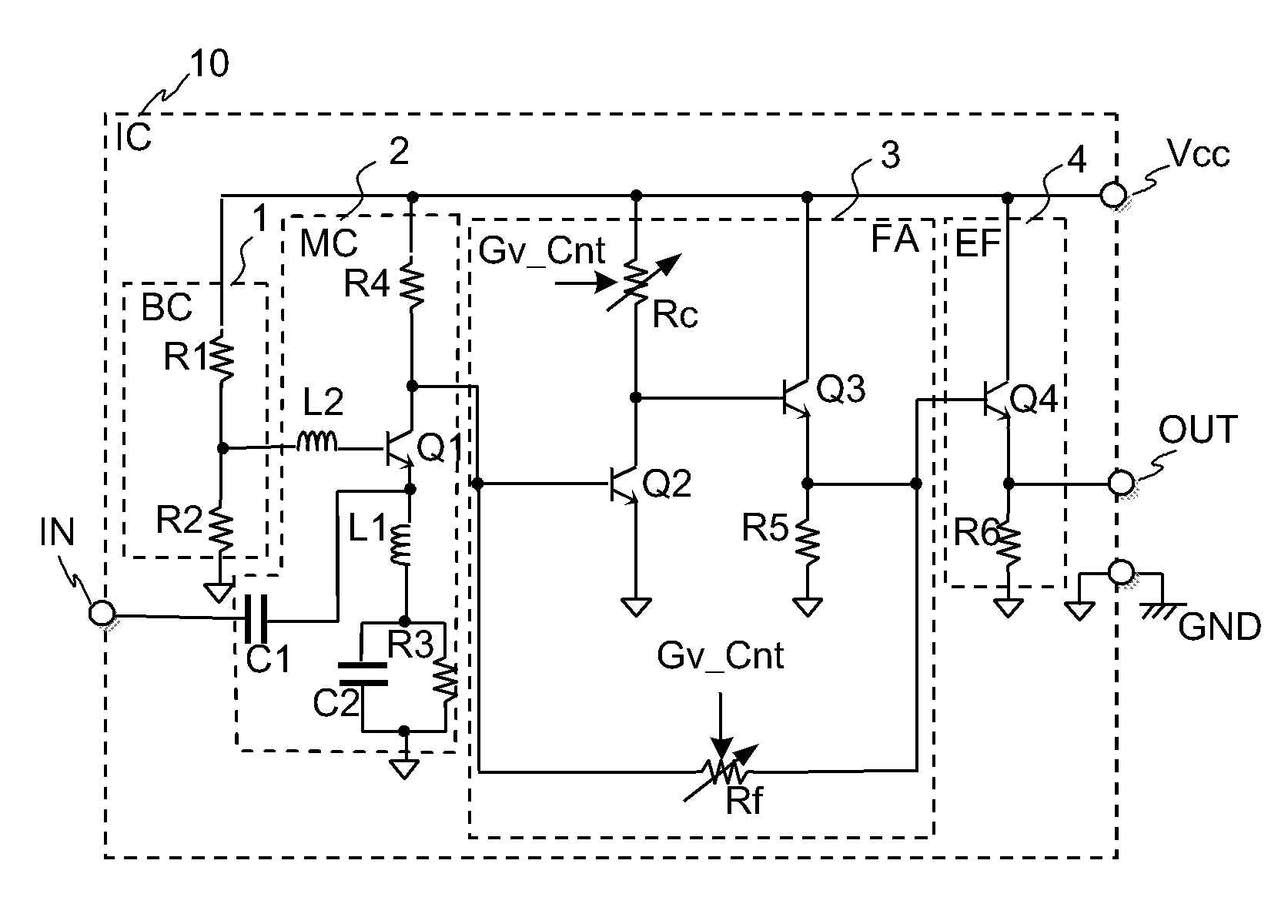
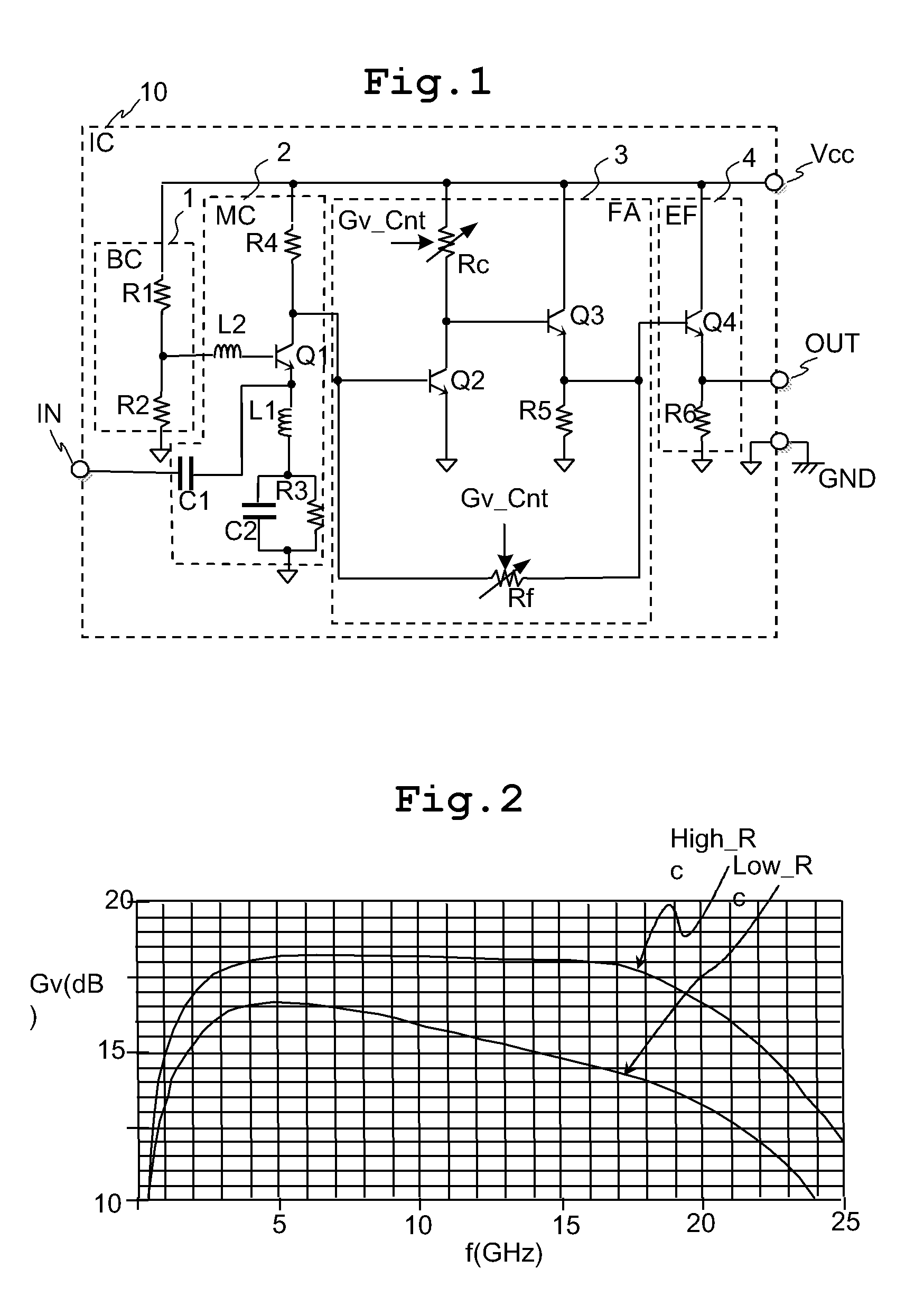
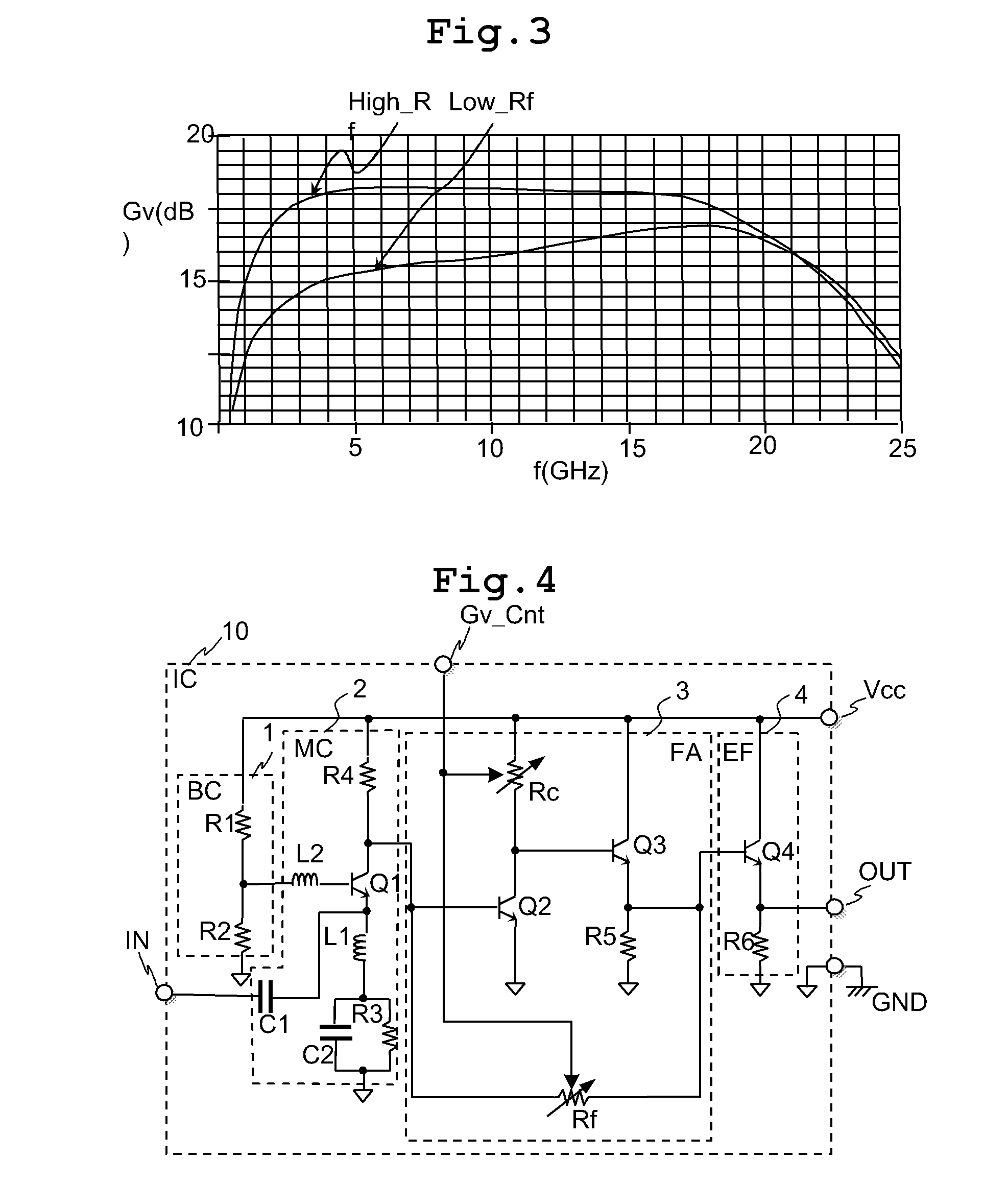
The variable gain amplifier includes a bias circuit (BC) 1, a matching circuit (MC) 2, a variable gain resistive feedback amplifier (FA) 3 and an output follower (EA) 4. The resistance values of the load resistance Rc and feedback resistance Rf are changed in cooperation. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a high resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a high gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a high resistance, the feedback time constant τfb(c1)≈2π·RfCbe / (1+gmRc) of the closed loop of the resistive negative feedback amplifier 3 becomes substantially constant, and then the amplifier has a gain small in frequency dependency over a wide bandwidth. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a low resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a low gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a low resistance. The feedback resistance Rf with the low resistance increases the negative feedback quantity, and thus the amplifier is set to a low gain. Also, the load resistance Rc is made a low resistance, and the feedback time constant τfb(c1) becomes substantially constant. The gain is not lowered further in a high frequency region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Fine step and large gain range programmable gain amplifier
ActiveUS7098738B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioAmplificationGain controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
A programmable gain amplifier with three stages uses fine steps, has a large gain range, and is monotonic. The first stage comprises several amplifiers, each including a resistive feedback loop. The feedback loop comprises a series of resistors, with each resistor acting as a tap. Since the number of resistors in the loop is unchanging, monotonicity and stability is guaranteed when resistance is increased using successive taps. A switch system connects two taps at a time to an interpolation stage. Each of these taps corresponds to a specific resistor level, and thus a gain level. The interpolation stage uses a plurality of current sources inside a feedback amplifier to control the interpolation, in order to provide fine gain steps.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Noise-canceling for differential amplifiers requiring no external matching
ActiveUS20110267144A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersTransformerImpedance matching
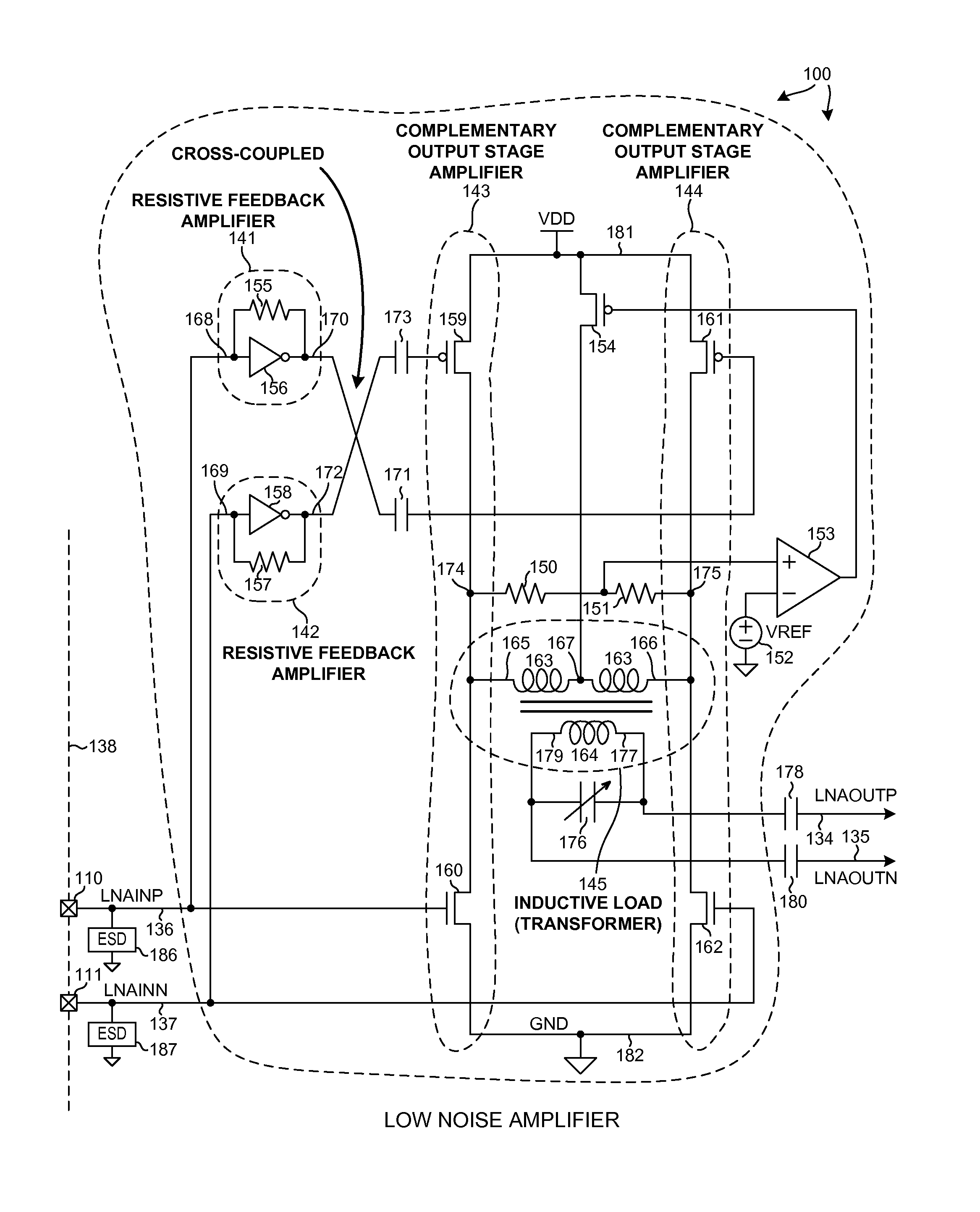
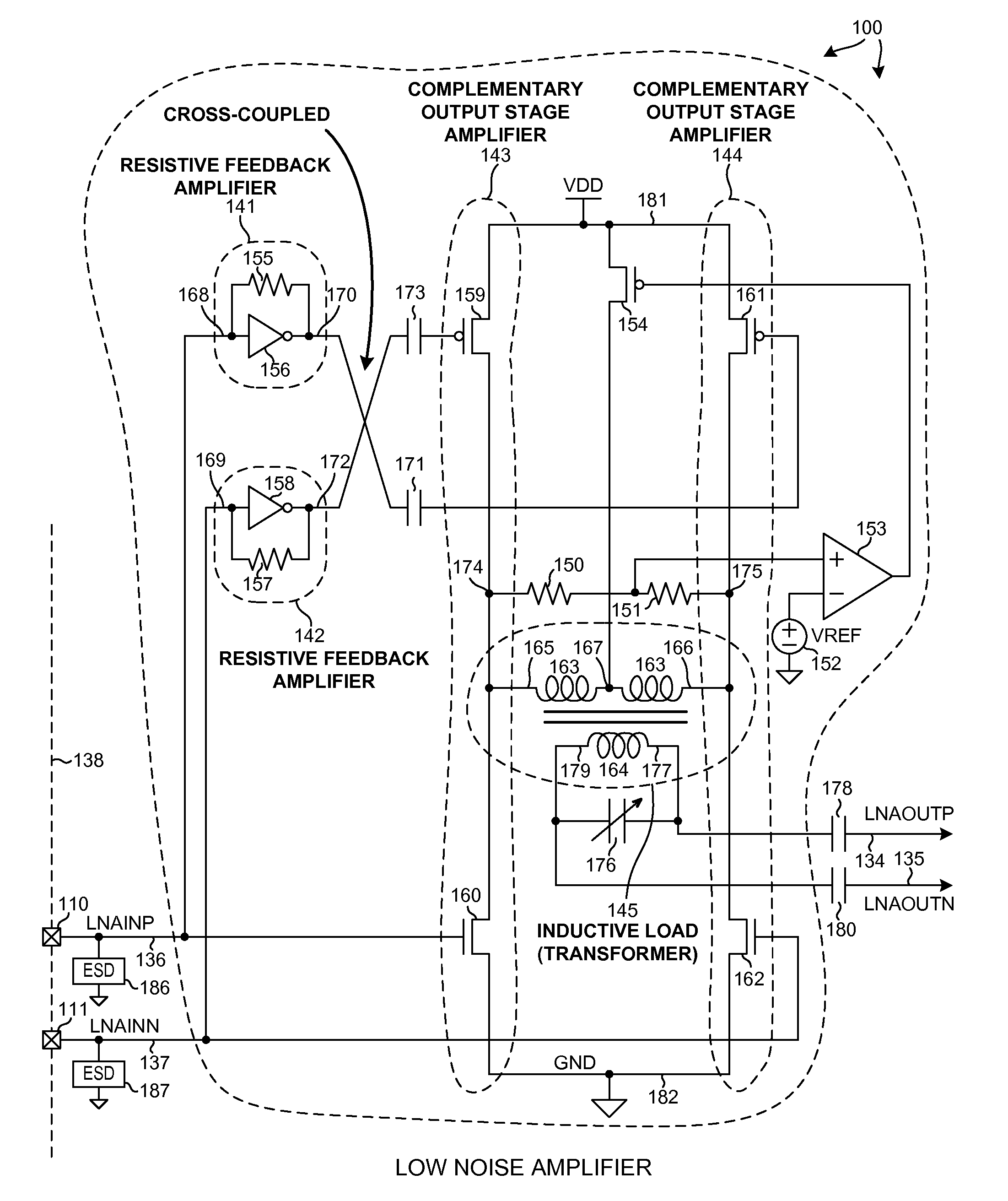
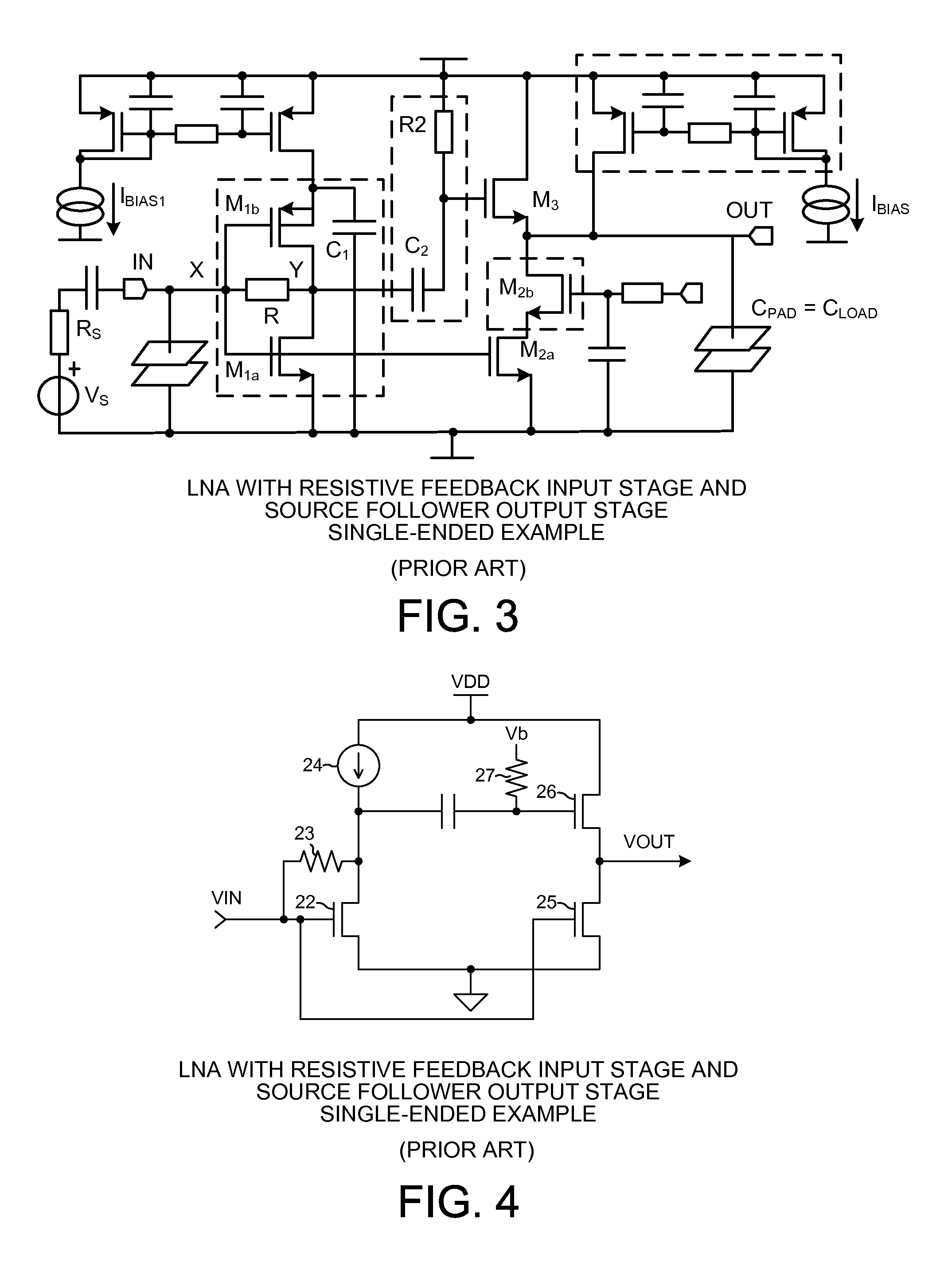
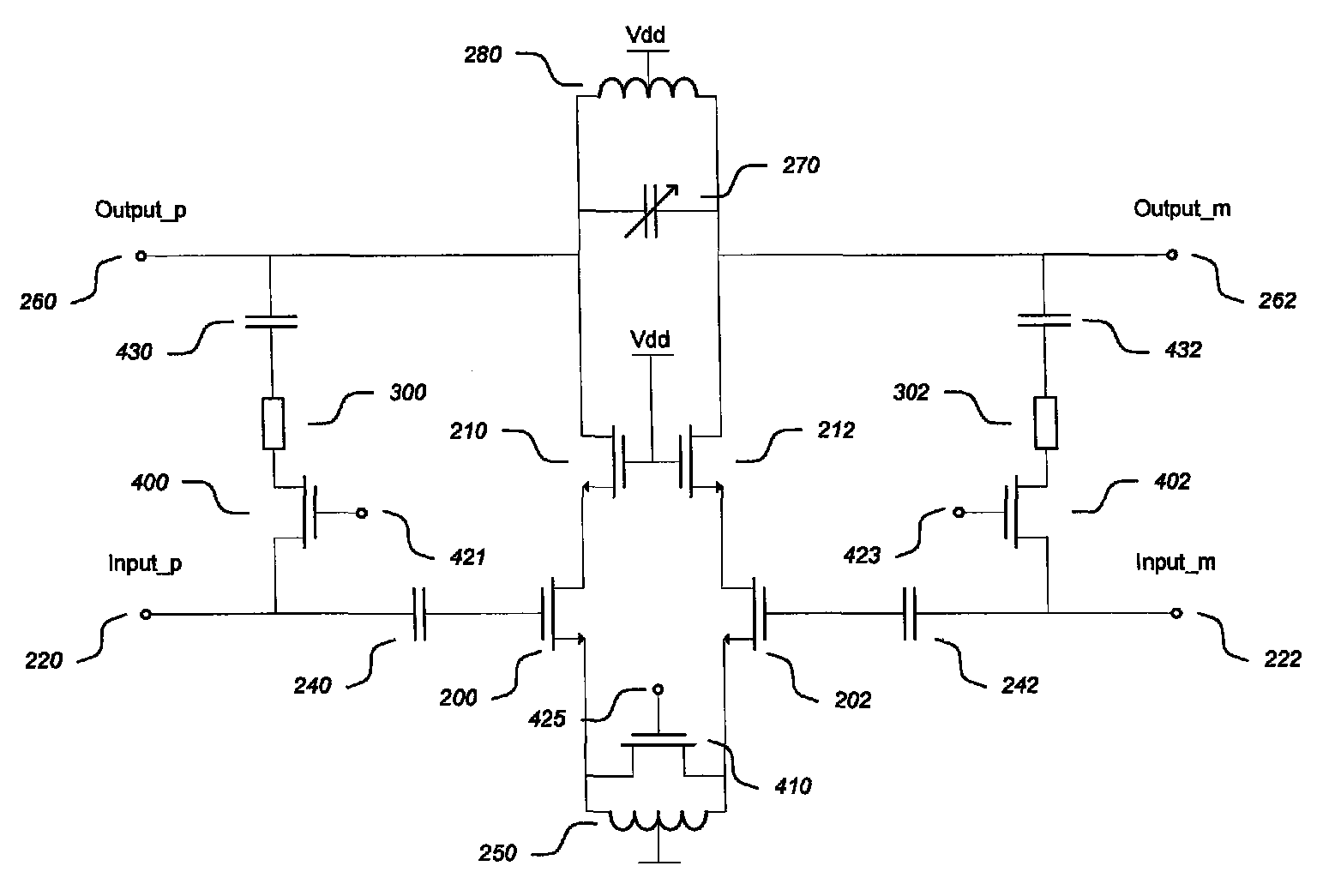
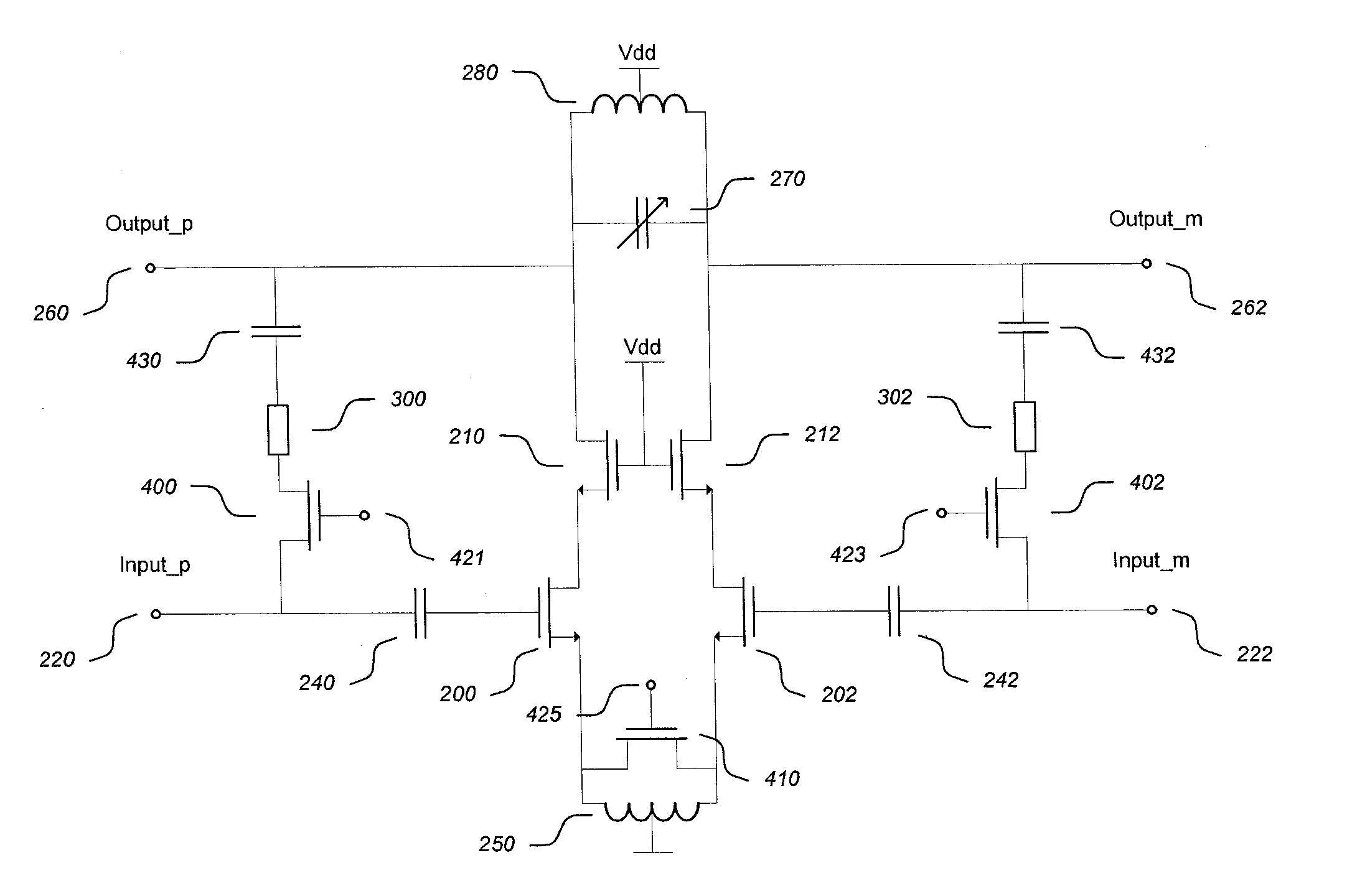
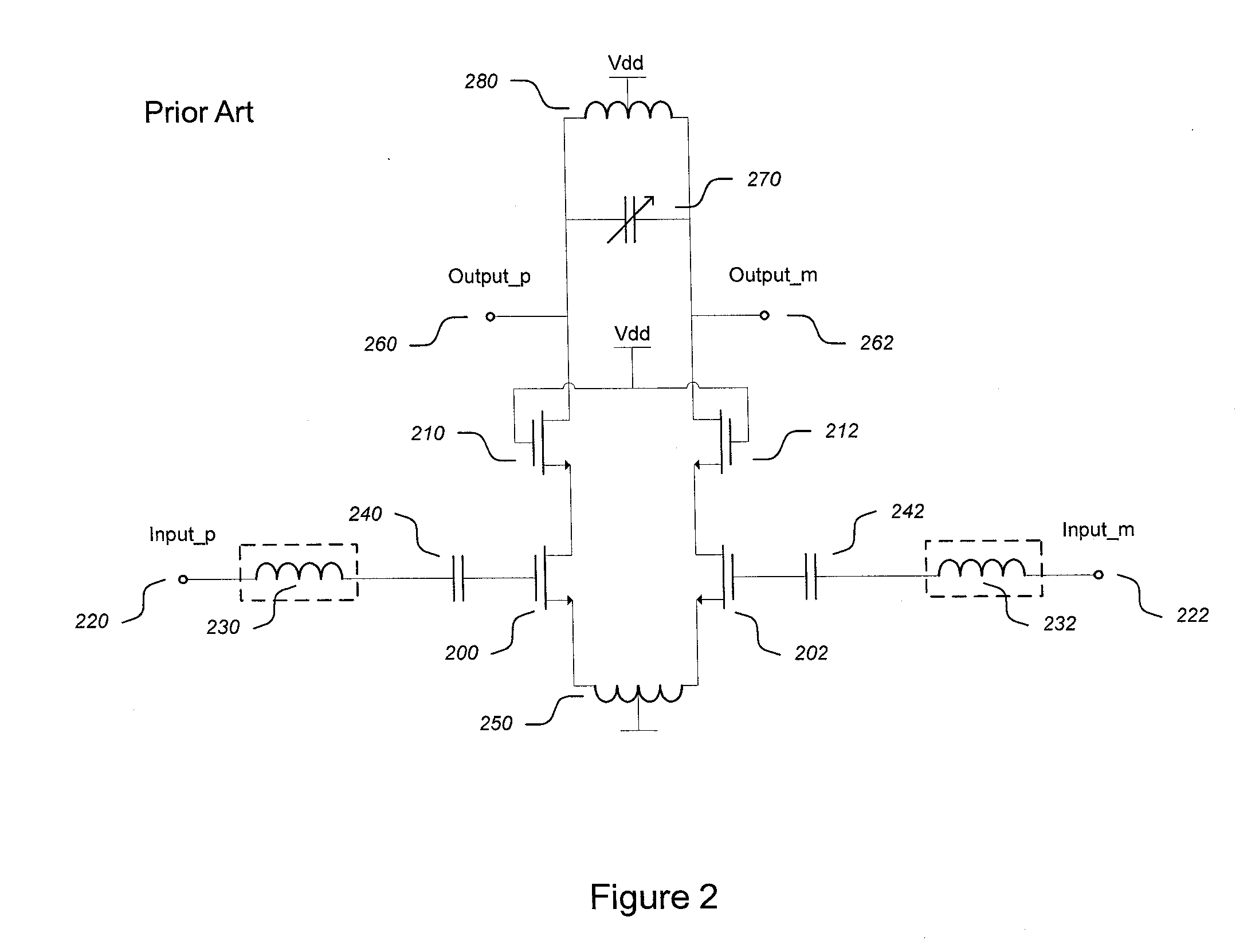
A differential Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) includes a first stage of resistive feedback amplifiers and second stage of complementary amplifiers, where the outputs of the first stage are coupled to the inputs of the second stage in a cross-coupled fashion. An inductive load, such as a transformer, combines signals output from the complementary amplifiers of the second stage. In one example, the LNA has an input impedance of less than 75 ohms, a noise factor of less than 2 dB, and a gain of more than 20 dB. Due to the low input impedance, the LNA is usable to amplify a signal received from a source having a similar low impedance without the use of an impedance matching network between the output of the source and the input of the LNA.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit with variable gain amplifier
InactiveUS20090102552A1Reduce voltageImprove noise figureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlHigh resistanceClosed loop
The variable gain amplifier includes a bias circuit (BC) 1, a matching circuit (MC) 2, a variable gain resistive feedback amplifier (FA) 3 and an output follower (EA) 4. The resistance values of the load resistance Rc and feedback resistance Rf are changed in cooperation. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a high resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a high gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a high resistance, the feedback time constant τfb(c1)≈2π·RfCbe / (1+gmRc) of the closed loop of the resistive negative feedback amplifier 3 becomes substantially constant, and then the amplifier has a gain small in frequency dependency over a wide bandwidth. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a low resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a low gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a low resistance. The feedback resistance Rf with the low resistance increases the negative feedback quantity, and thus the amplifier is set to a low gain. Also, the load resistance Rc is made a low resistance, and the feedback time constant τfb(c1) becomes substantially constant. The gain is not lowered further in a high frequency region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Noise-canceling for differential amplifiers requiring no external matching
A differential Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) includes a first stage of resistive feedback amplifiers and second stage of complementary amplifiers, where the outputs of the first stage are coupled to the inputs of the second stage in a cross-coupled fashion. An inductive load, such as a transformer, combines signals output from the complementary amplifiers of the second stage. In one example, the LNA has an input impedance of less than 75 ohms, a noise factor of less than 2 dB, and a gain of more than 20 dB. Due to the low input impedance, the LNA is usable to amplify a signal received from a source having a similar low impedance without the use of an impedance matching network between the output of the source and the input of the LNA.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
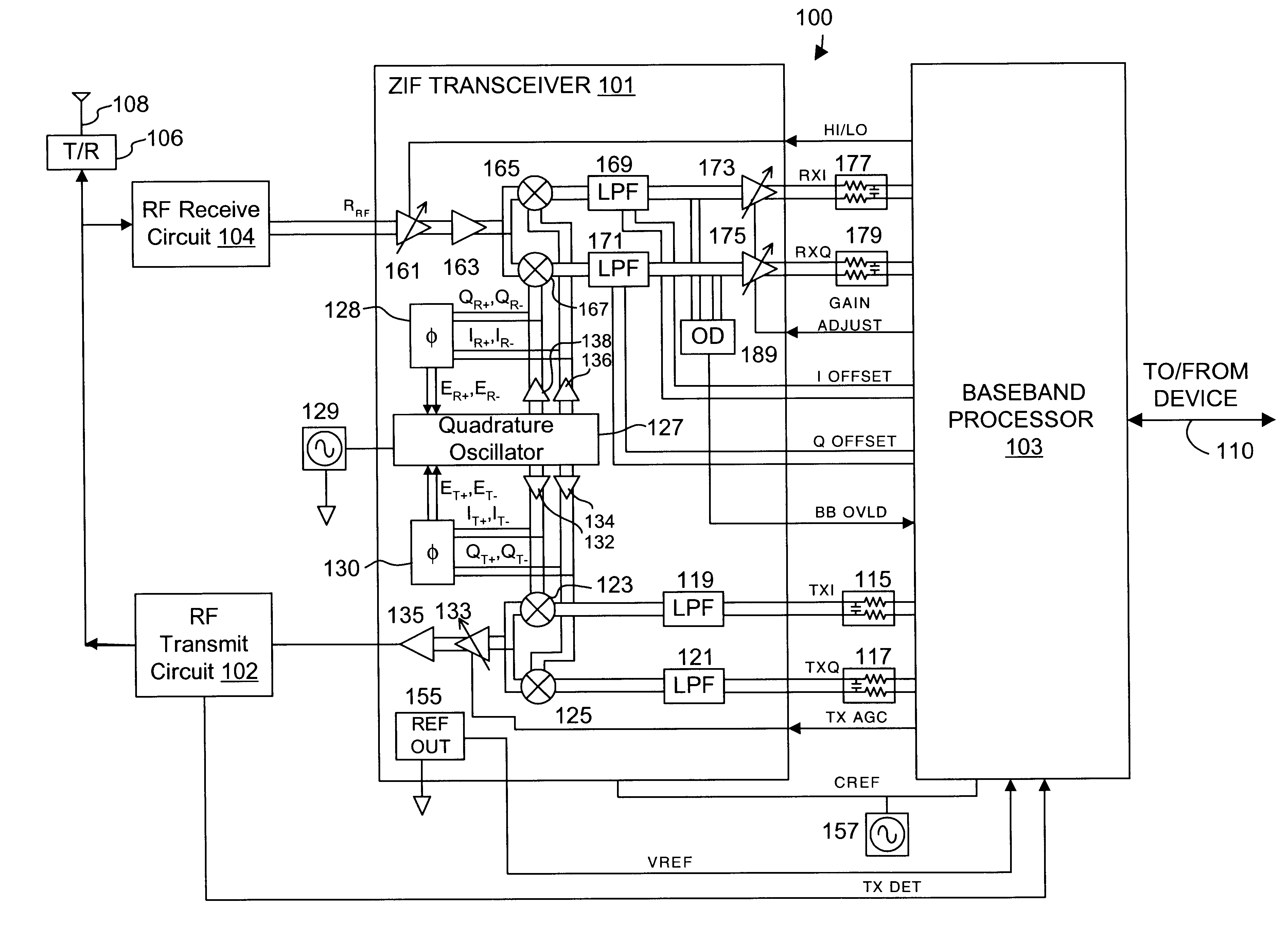
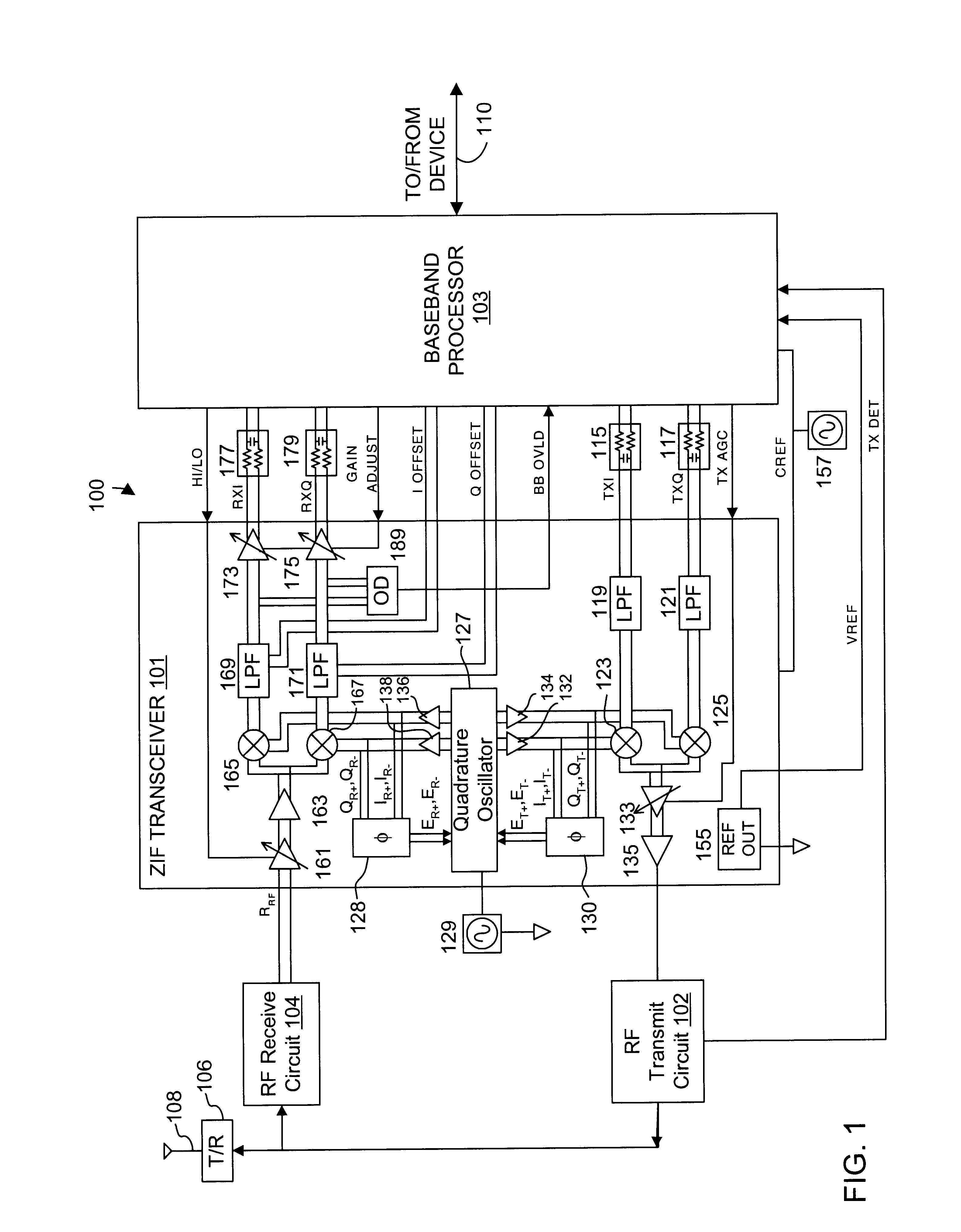
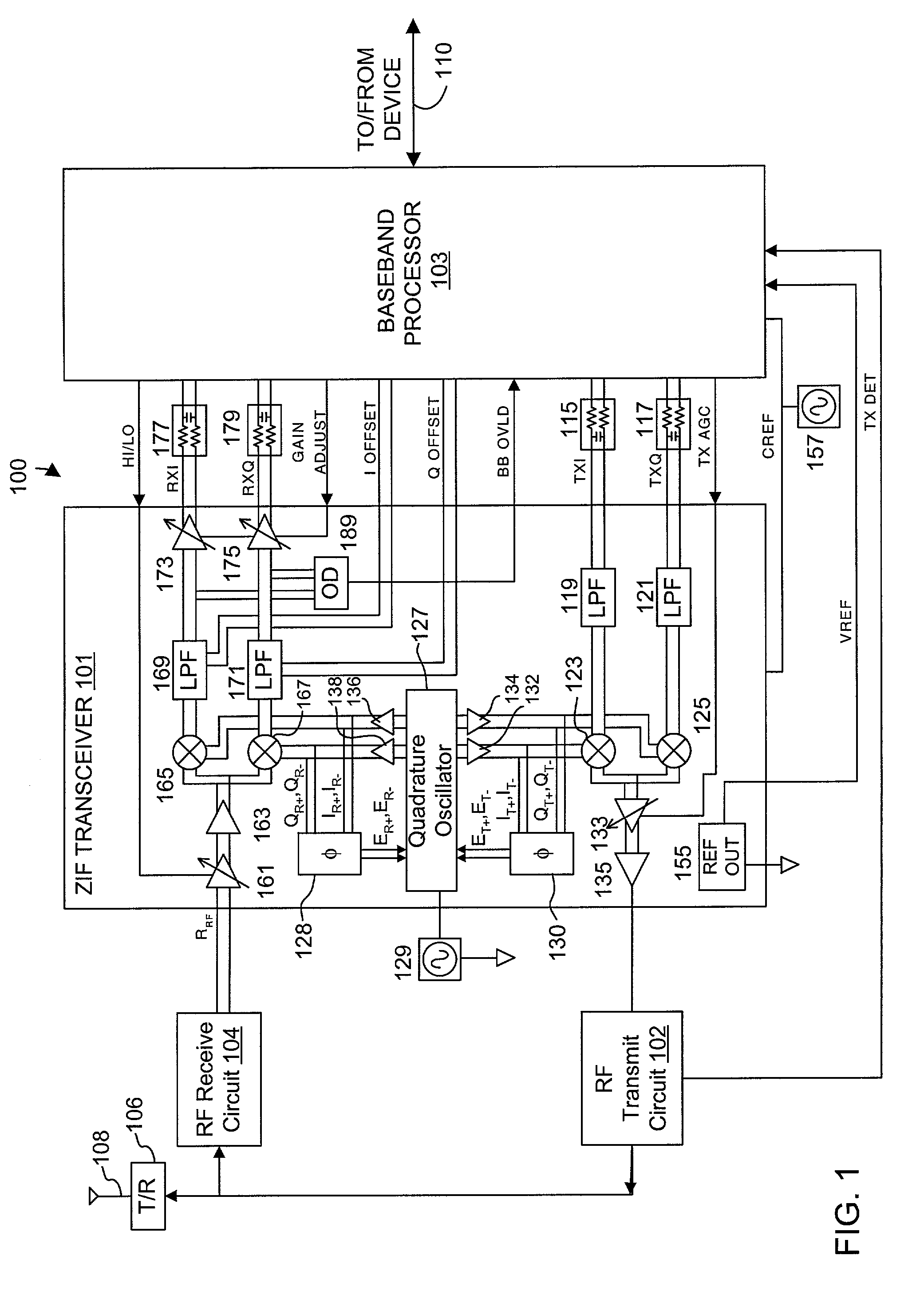
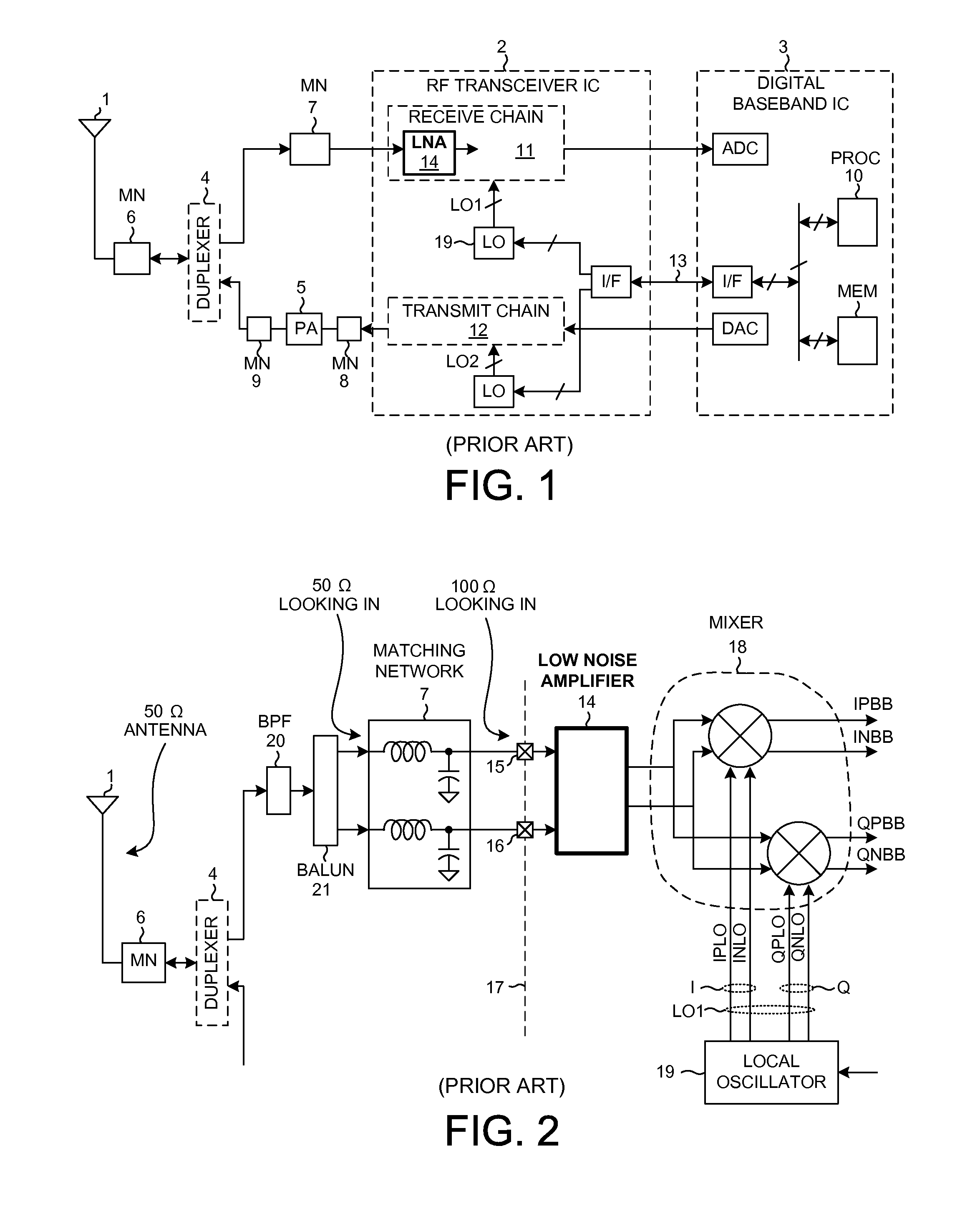
Direct conversion receiver
InactiveUS20110043286A1Modulation transferenceAmplifier combinationsQuadrature samplingDirect-conversion receiver
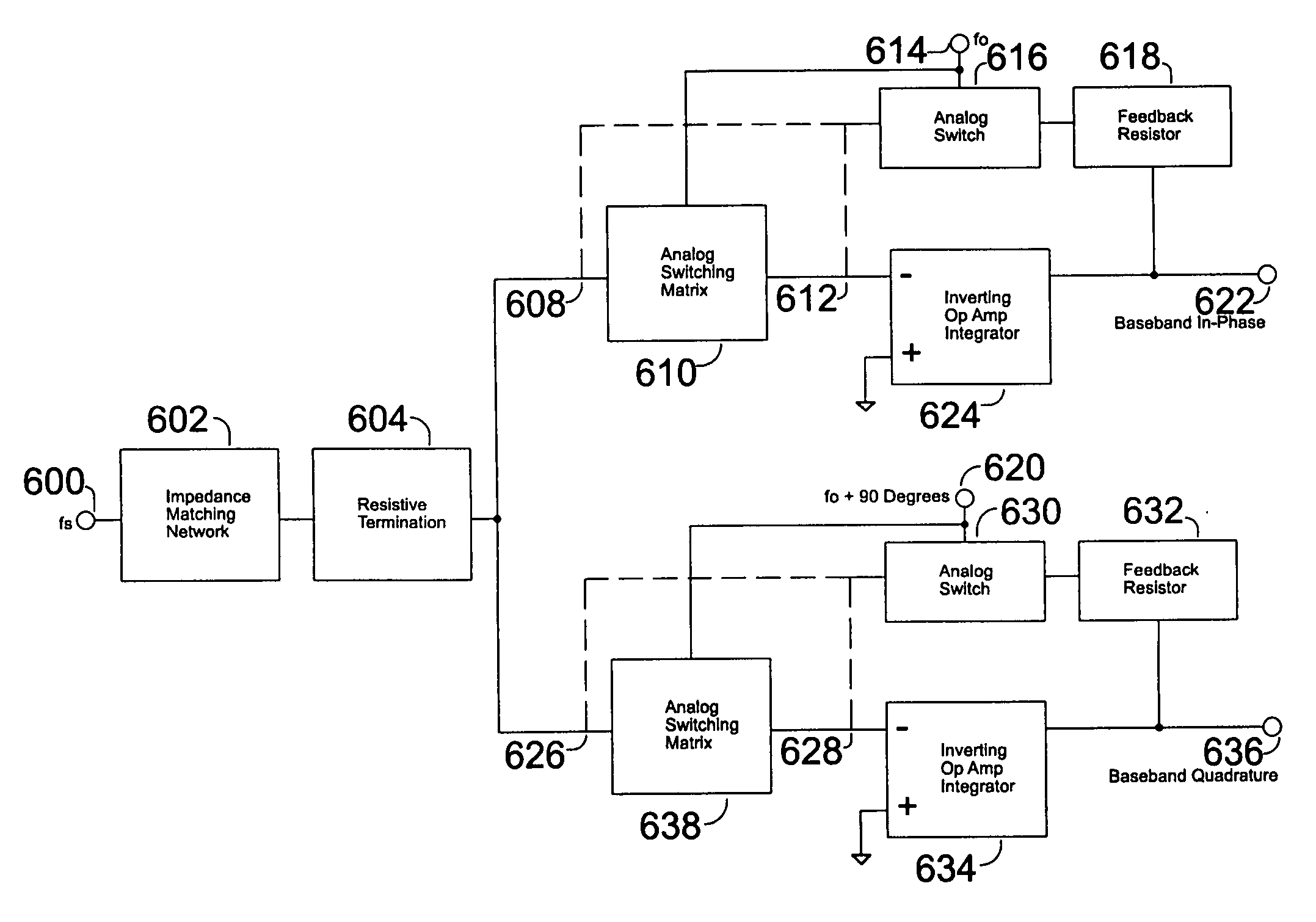
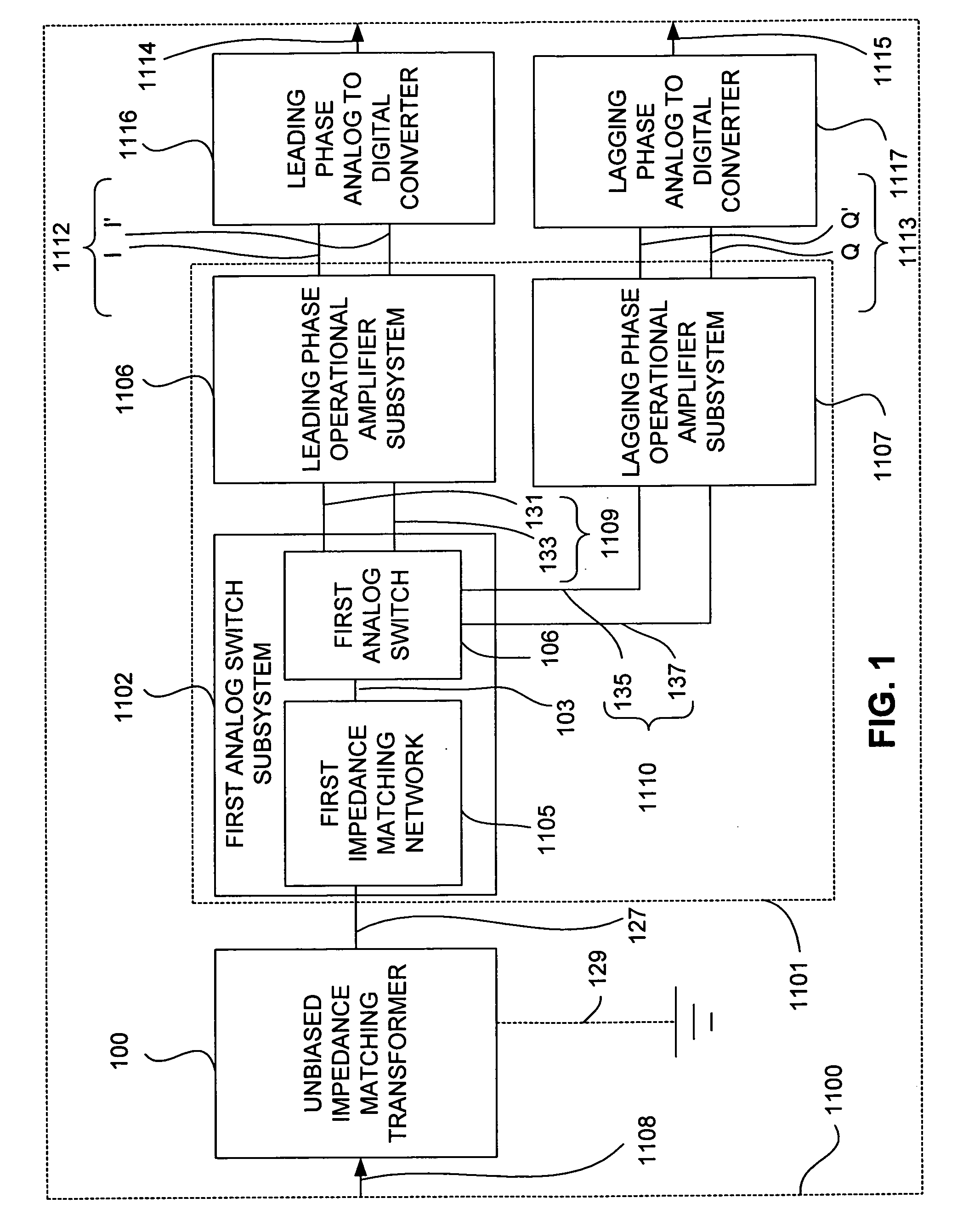
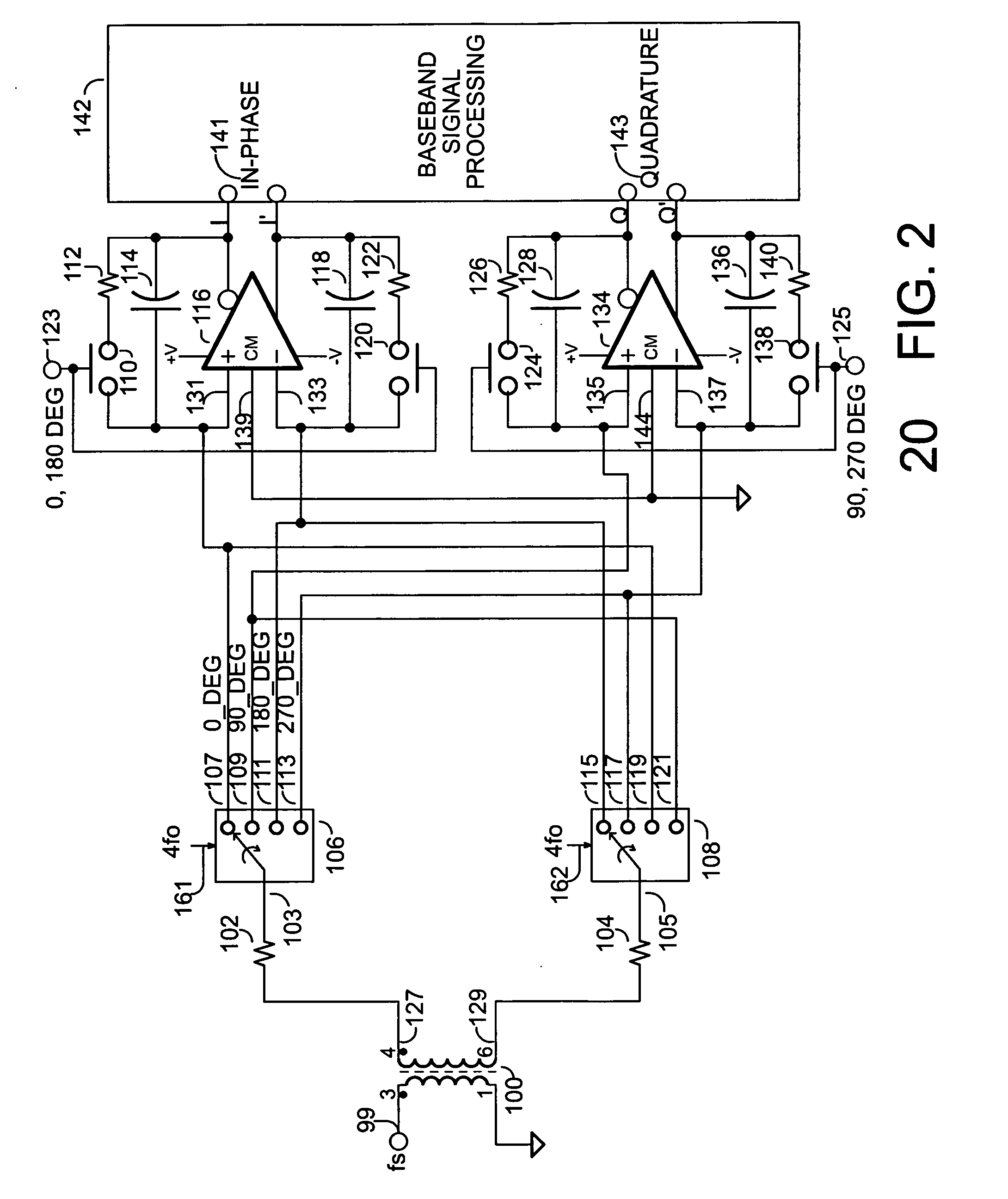
In accordance with at least one embodiment, apparatus providing a direct conversion receiver comprises a phase sampling detector (e.g., a quadrature sampling detector), which comprises a leading phase operational amplifier subsystem and a leading phase analog switch, as well as a lagging phase operational amplifier subsystem and a lagging phase analog switch. In accordance with at least one embodiment, a leading phase analog switch output terminal is coupled to a first leading phase operational amplifier input of the leading phase operational amplifier subsystem, and the leading phase analog switch output terminal is maintained continually at a ground potential. In accordance with at least one embodiment, at least one of element selected from a group consisting of: a resistor feedback switch, a commutating input switch in a resistive feedback loop, a differential capacitor, an unbiased analog switch input terminal, and an unbiased analog switch output terminal is provided.
Owner:YOUNGBLOOD GERALD
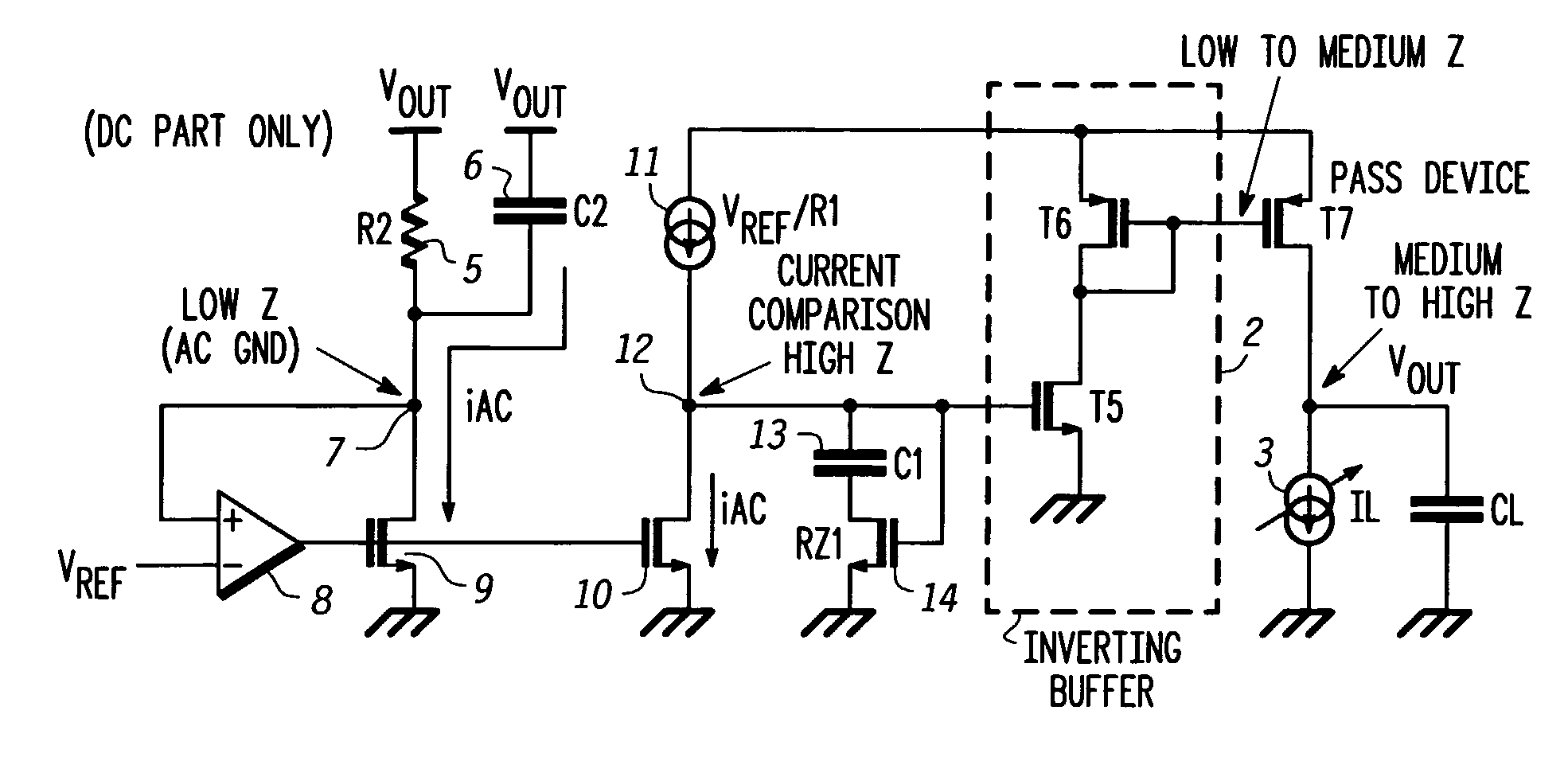
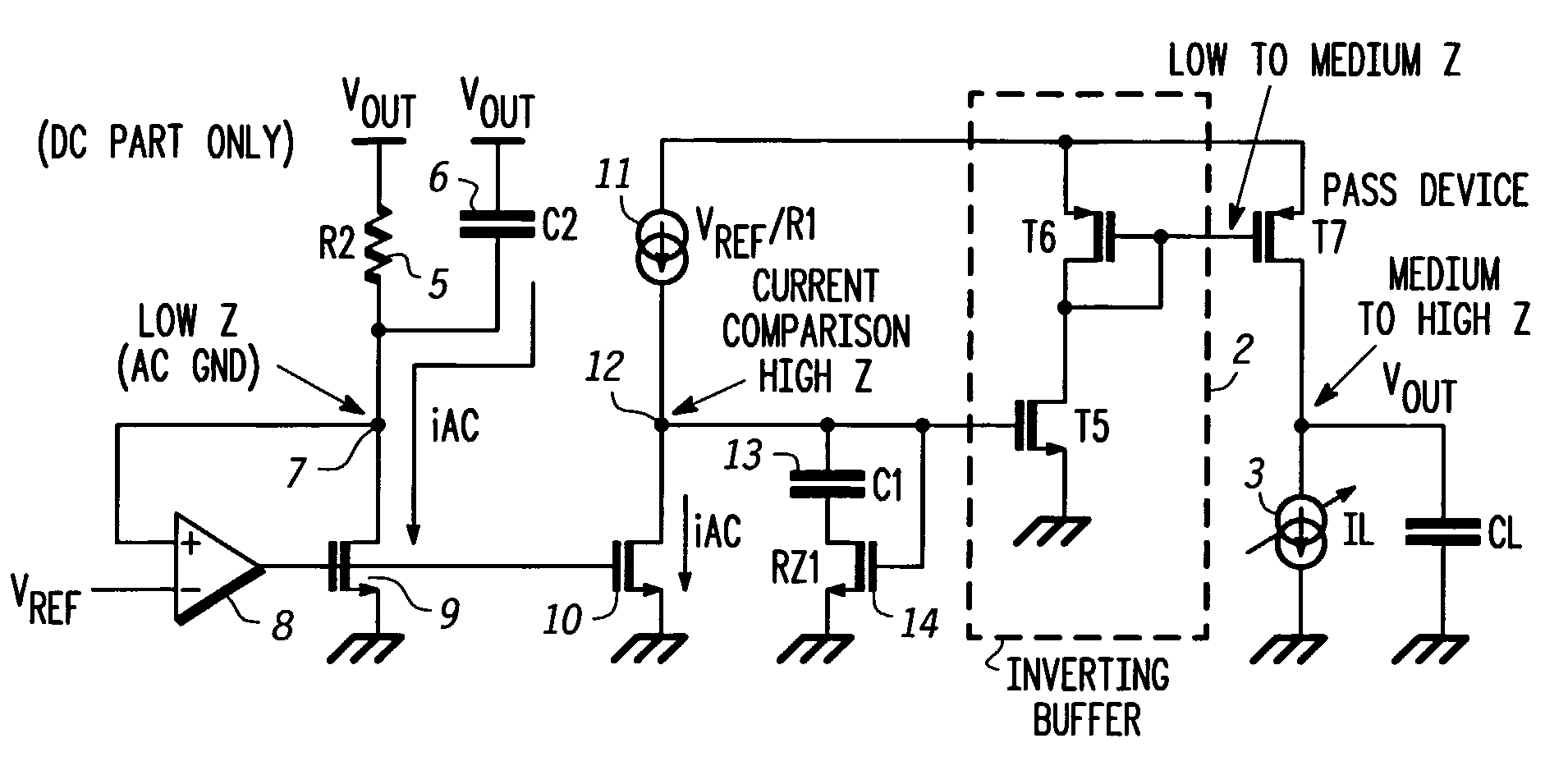
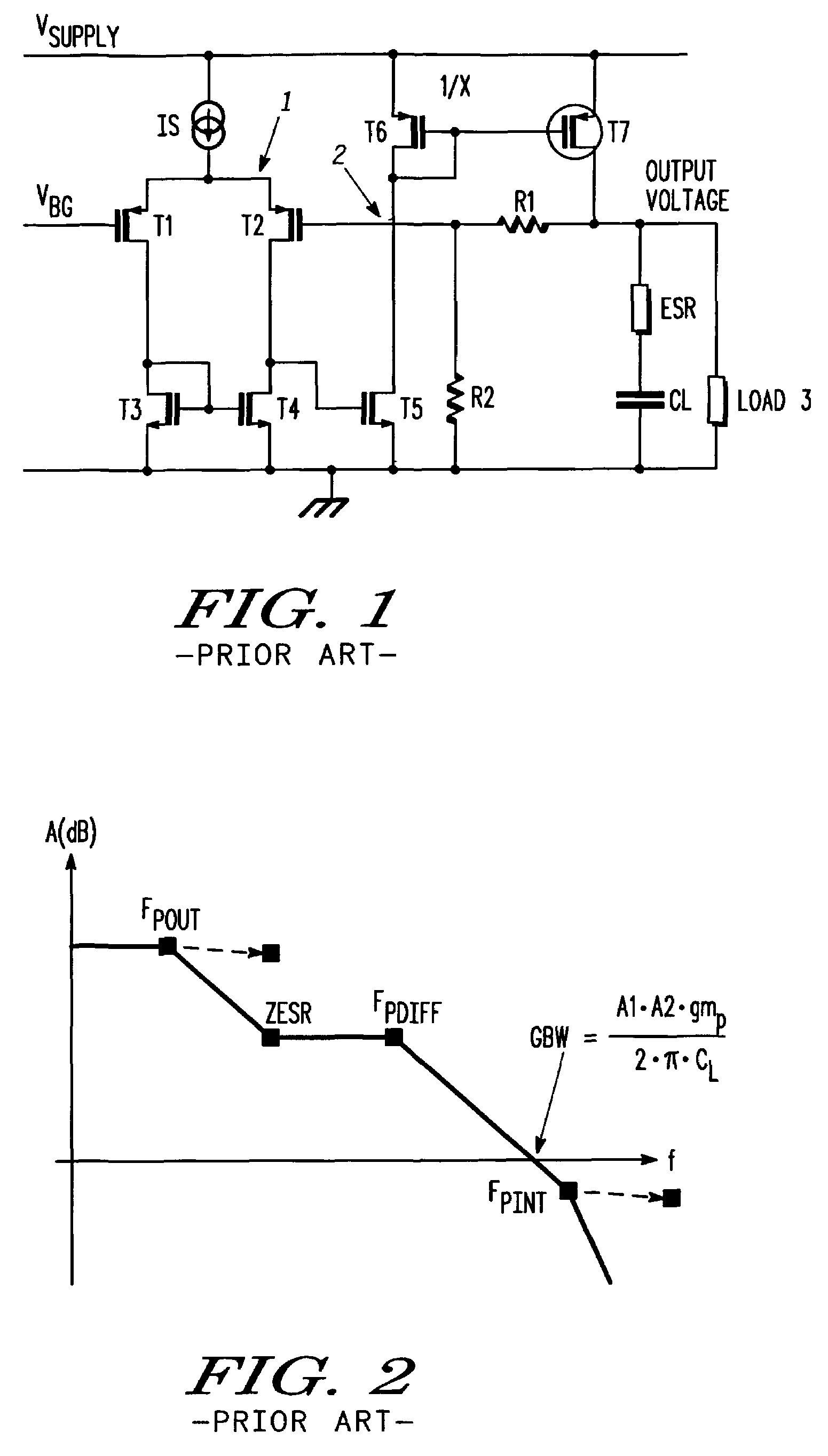
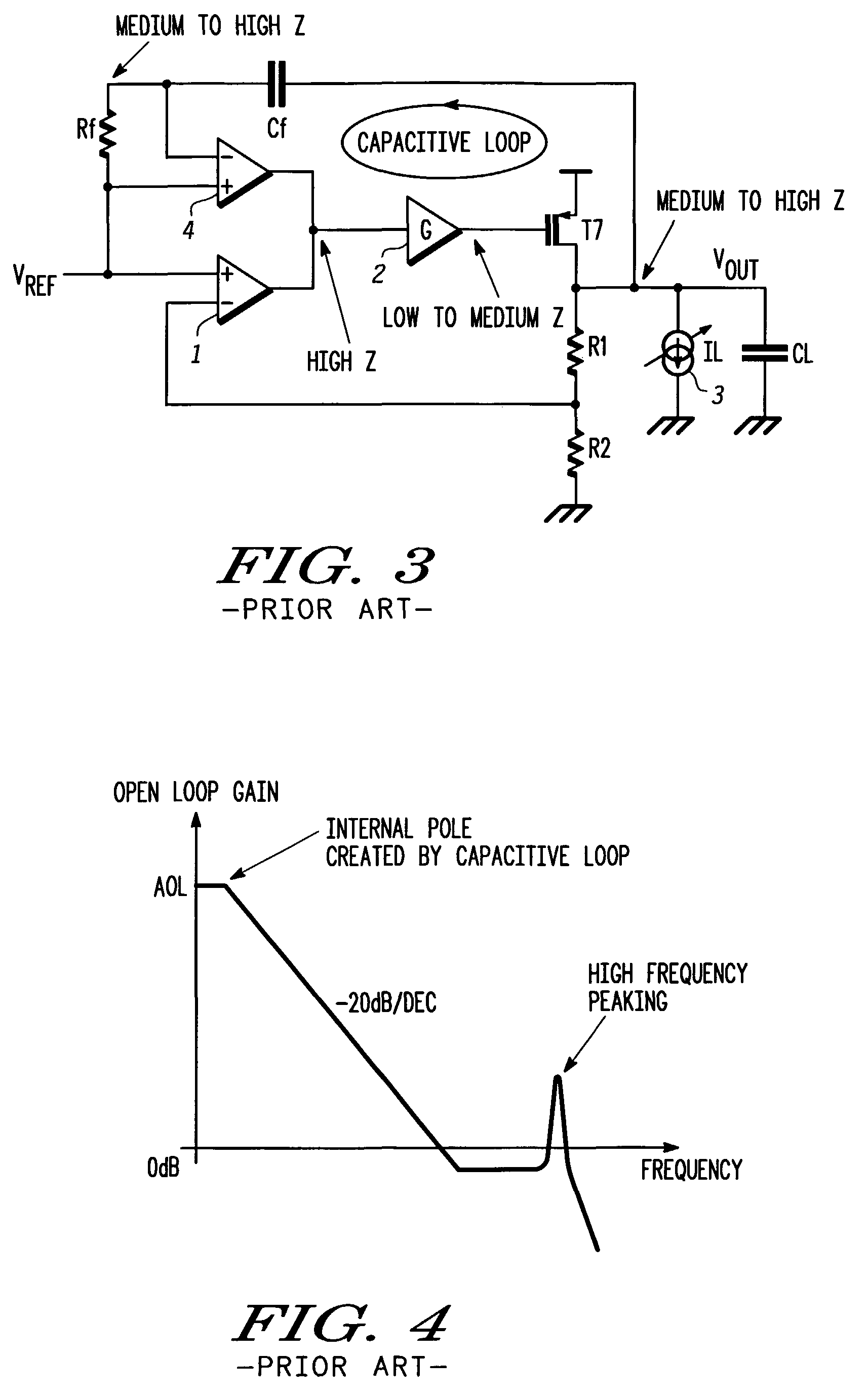
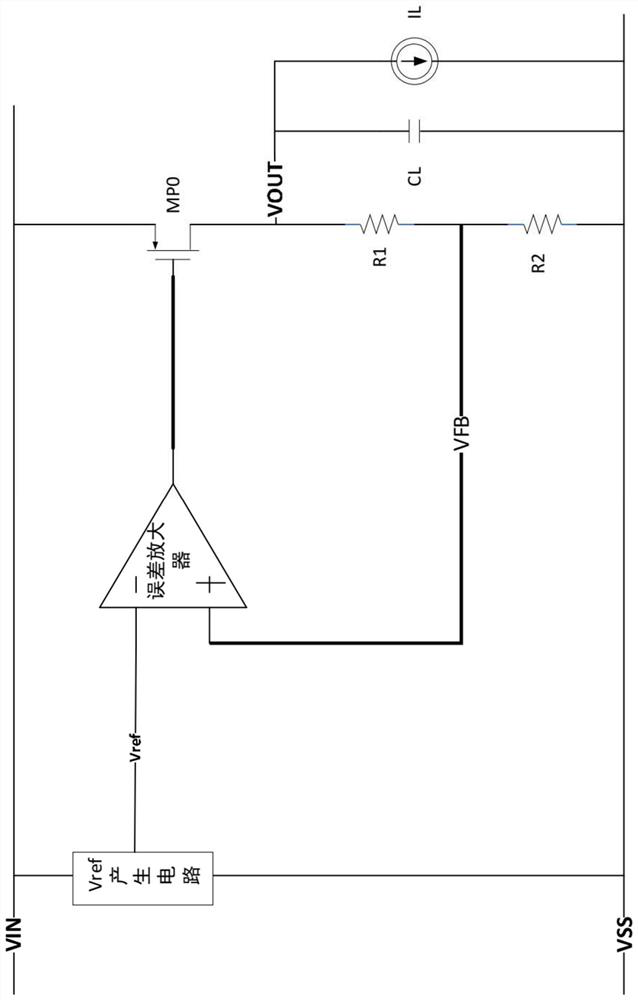
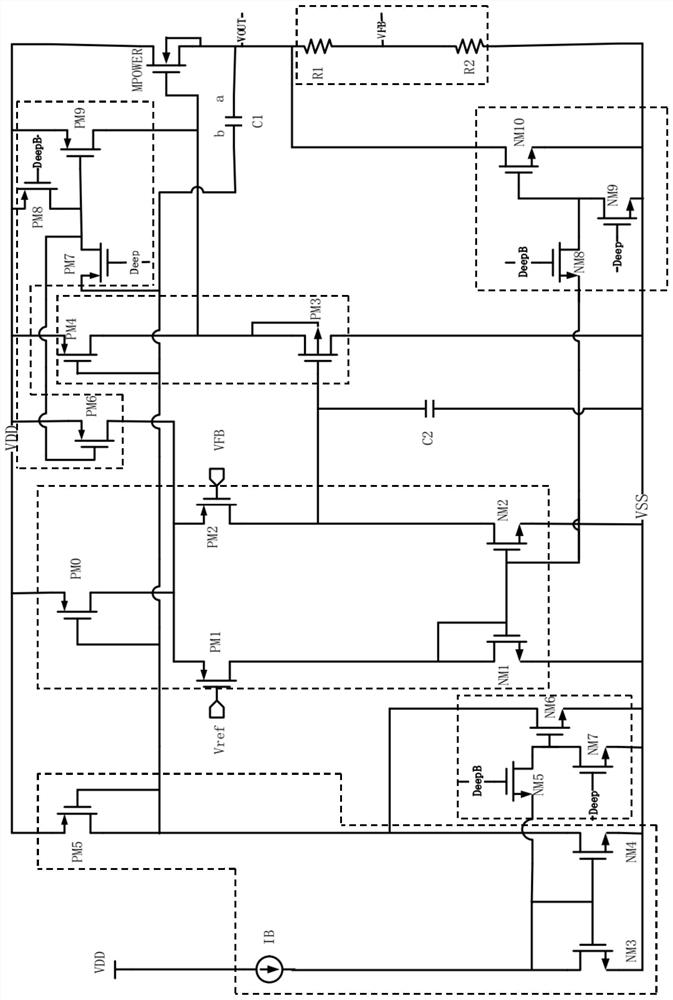
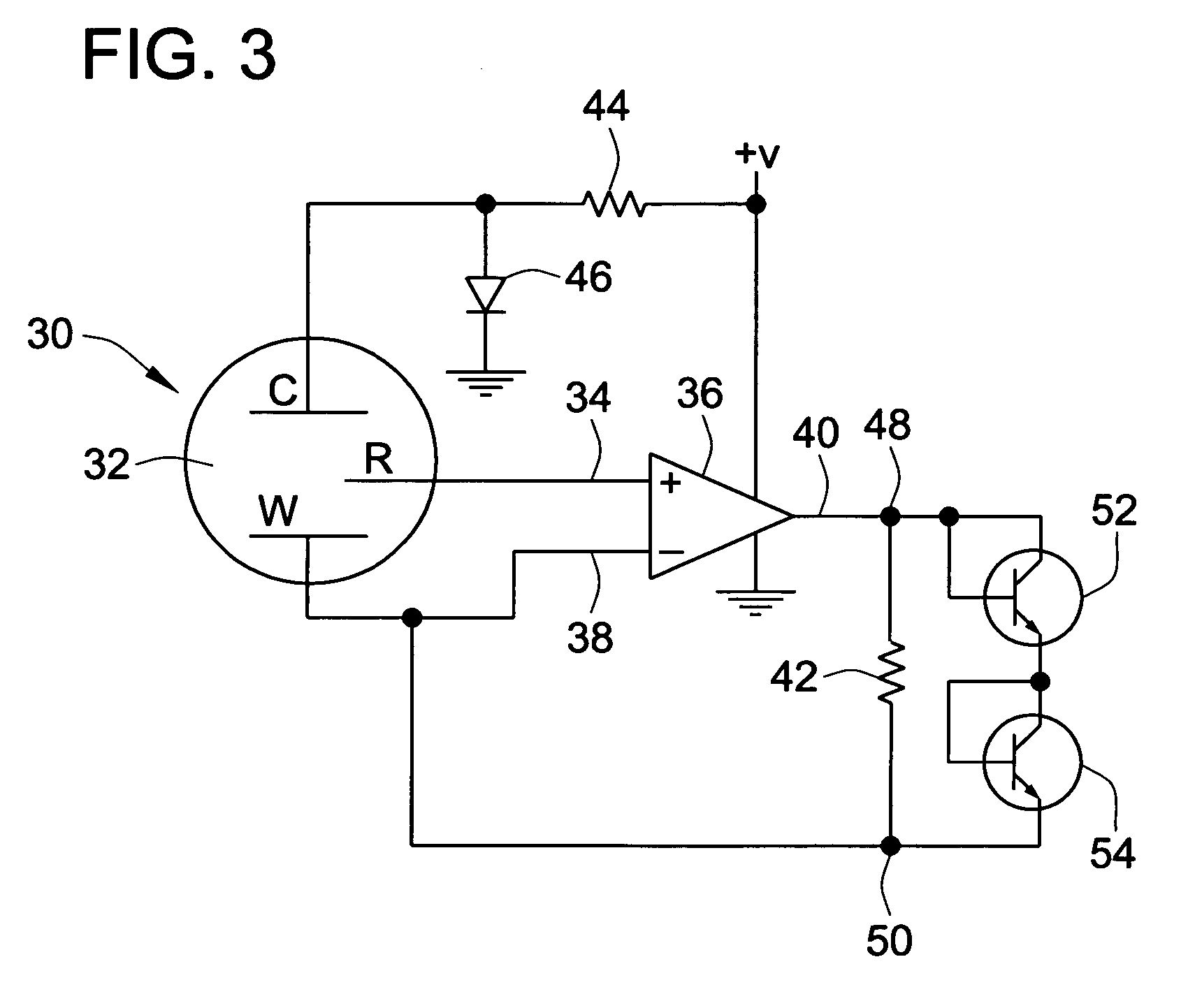
Low drop-out dc voltage regulator
A low drop-out DC voltage regulator for regulating a voltage from a DC power supply applied to a load at an output of the regulator and comprising a pass device for controlling flow of current from the power supply to the load so as to control the output voltage at the regulator output, and a feedback loop for controlling the pass device. The feedback loop comprises a resistive feedback path and a capacitive feedback path that includes a feedback capacitive element in series, and comparator means responsive to signals from the feedback paths for applying to the pass device an error signal that is a function of the value of the output voltage relative to a nominal value so as to control the output voltage. The comparator means comprises feedback current producing means for maintaining a common point of the resistive feedback path and the capacitive feedback path at a reference voltage so as to produce a feedback current flowing in the resistive feedback path and in the capacitive feedback path in parallel between the regulator output and the common point, and current comparison means responsive to relative values of the feedback current and of a reference current for producing the error signal.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Dual gate low noise amplifier
InactiveUS6801088B2Occupying less real estateImprove performanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noiseAudio power amplifier
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Single slice high-gain low-noise amplifier
InactiveCN101136613AHigh gainImprove stabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierHigh volume manufacturing
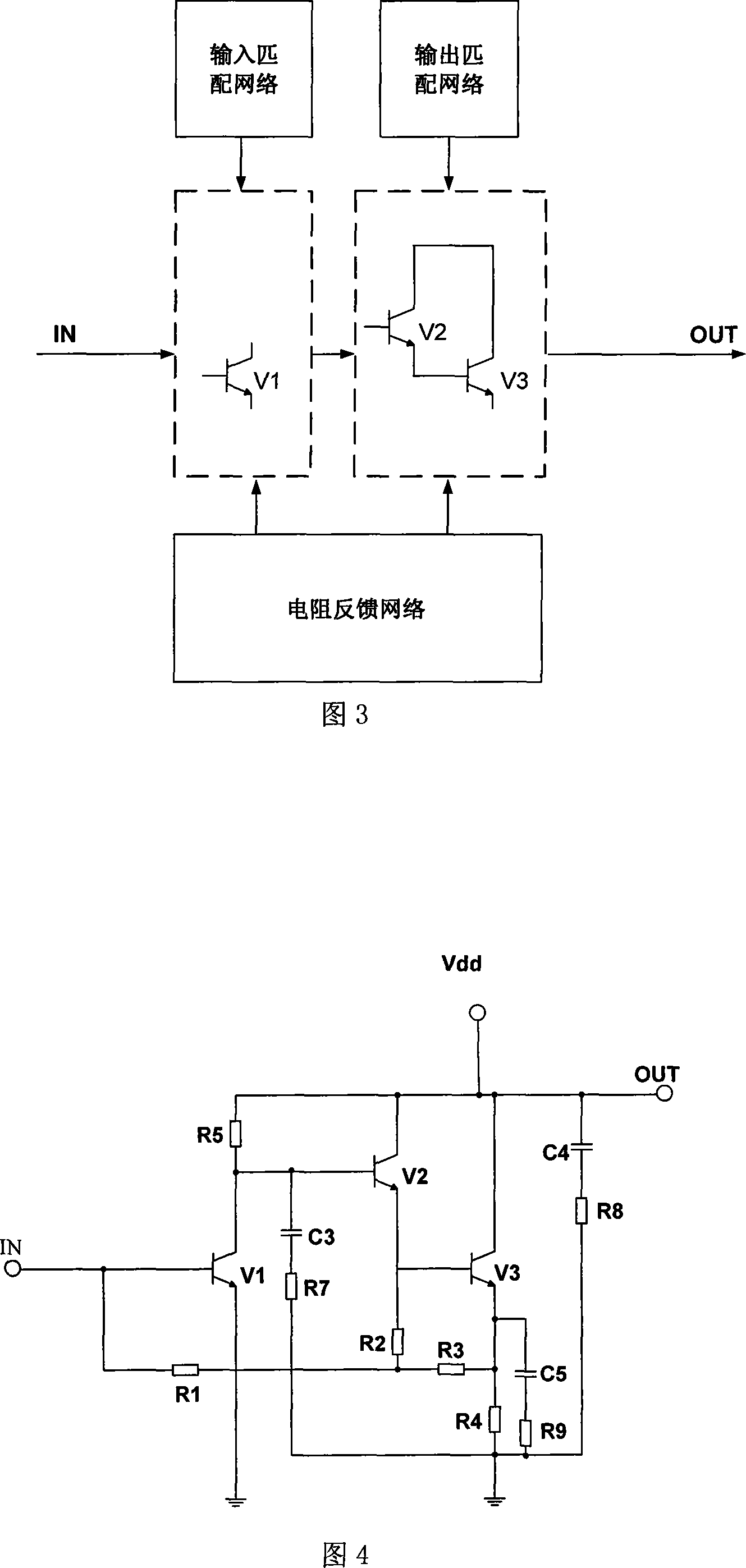
This invention discloses a single-chip high gain and low noise amplifier including: a primary amplifier, a secondary amplifier, a resistance feed-back network, an input match network and an output match network, in which, the amplifier works in the bands of 10MHz-550MHz not needing input and output matches from outside, so the circuit is simple and the volume is small.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Low drop-out DC voltage regulator
A low drop-out DC voltage regulator for regulating a voltage from a DC power supply applied to a load at an output of the regulator and comprising a pass device for controlling flow of current from the power supply to the load so as to control the output voltage at the regulator output, and a feedback loop for controlling the pass device. The feedback loop comprises a resistive feedback path and a capacitive feedback path that includes a feedback capacitive element in series, and comparator means responsive to signals from the feedback paths for applying to the pass device an error signal that is a function of the value of the output voltage relative to a nominal value so as to control the output voltage. The comparator means comprises feedback current producing means for maintaining a common point of the resistive feedback path and the capacitive feedback path at a reference voltage so as to produce a feedback current flowing in the resistive feedback path and in the capacitive feedback path in parallel between the regulator output and the common point, and current comparison means responsive to relative values of the feedback current and of a reference current for producing the error signal.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
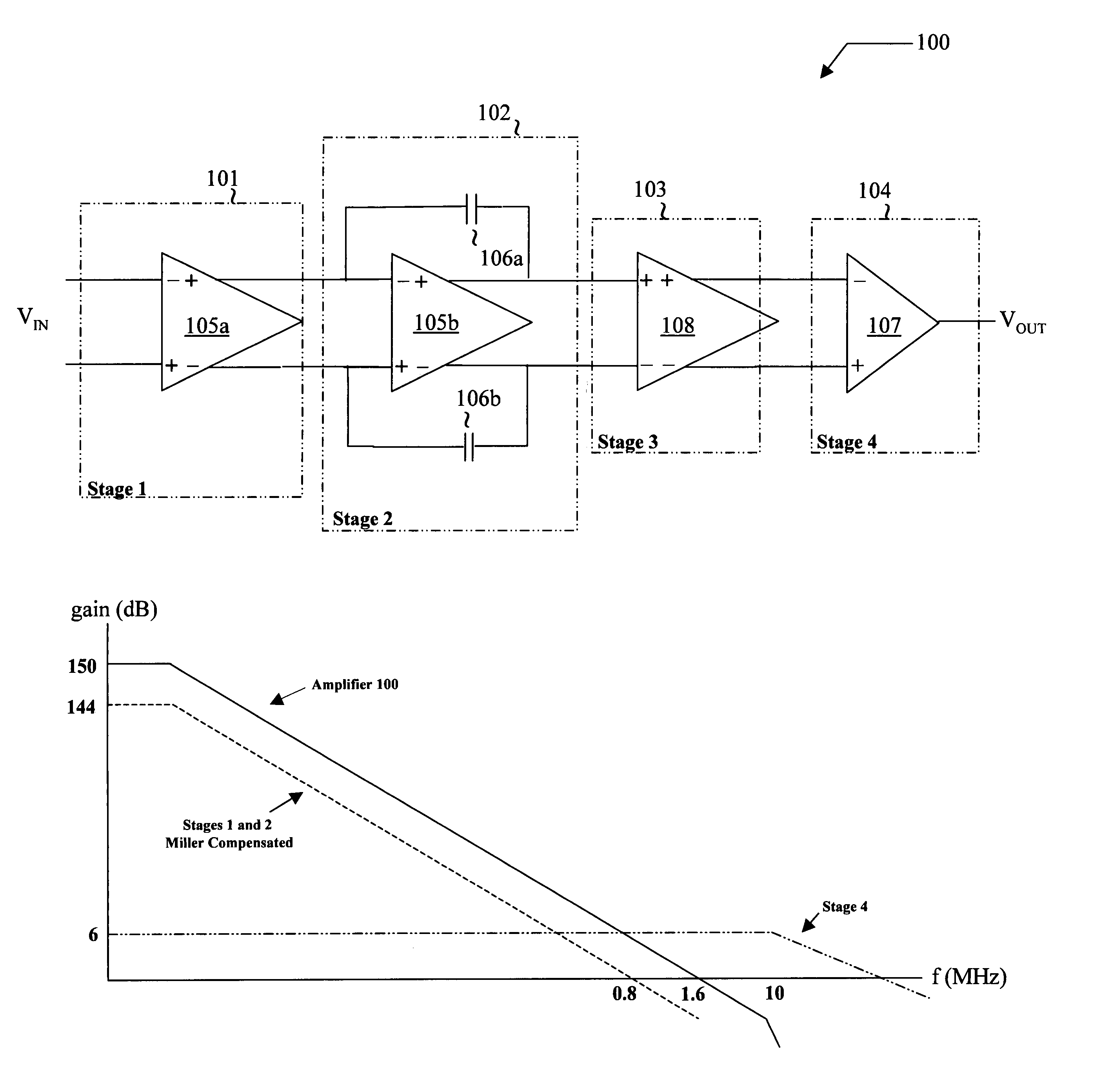
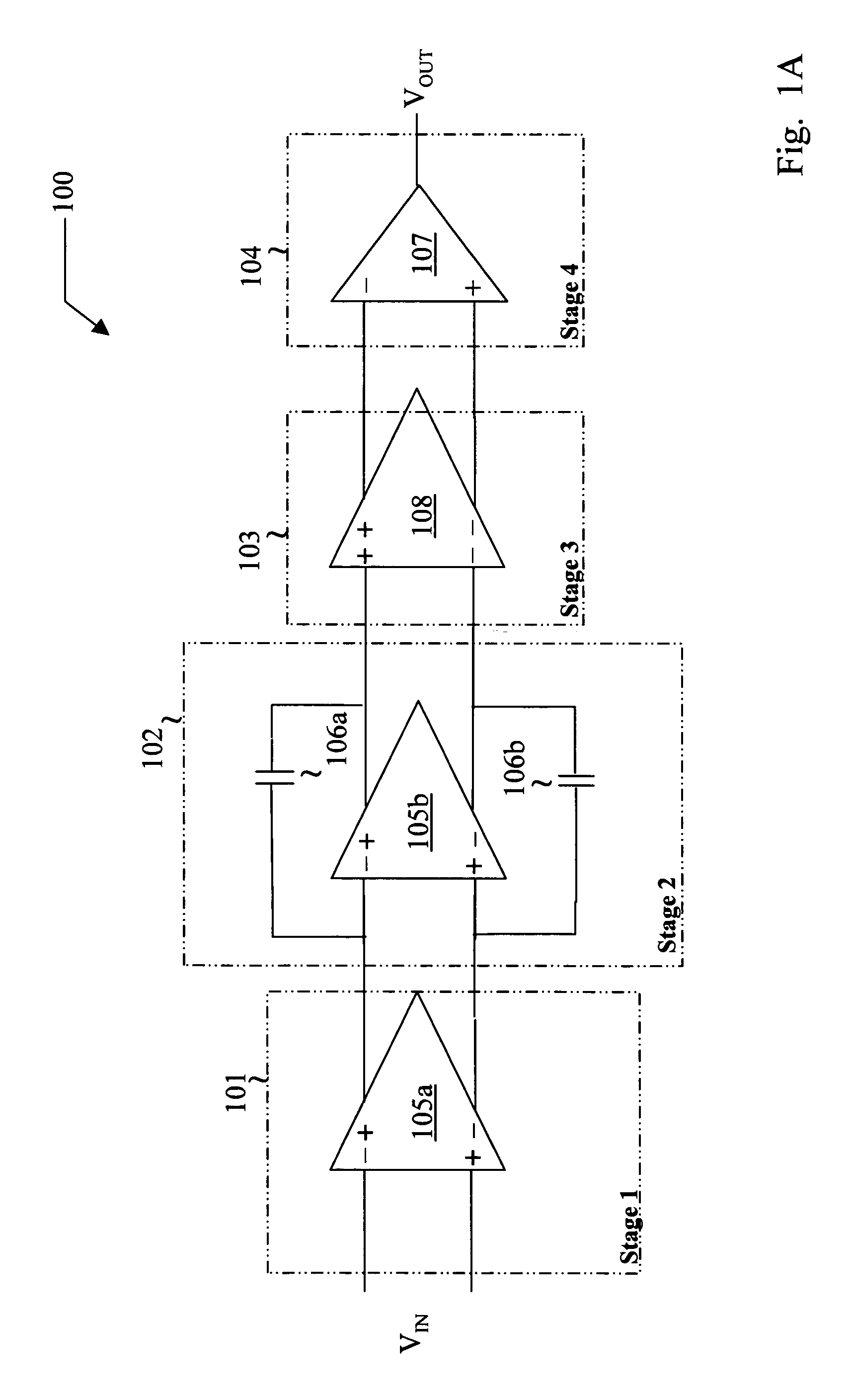
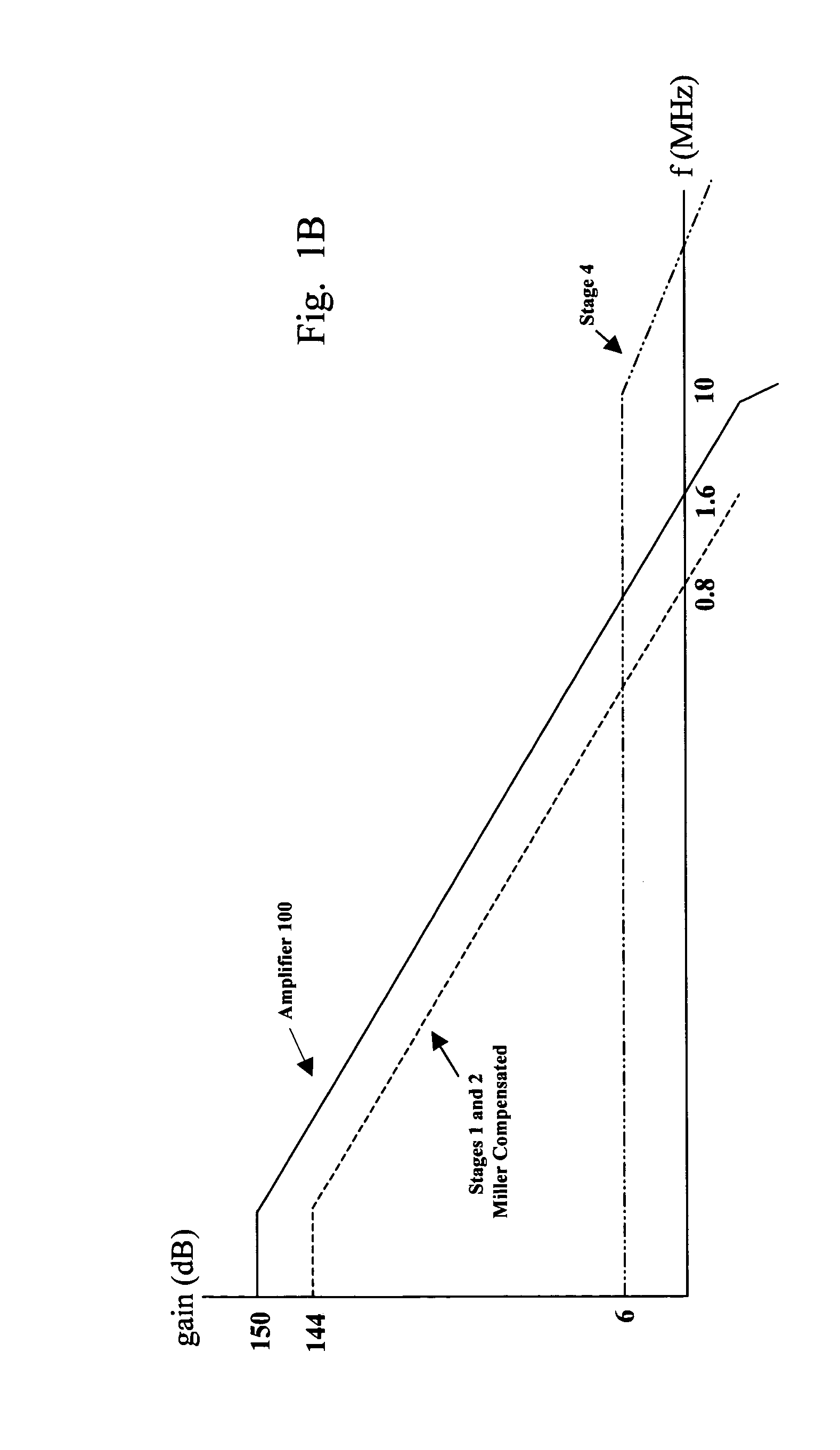
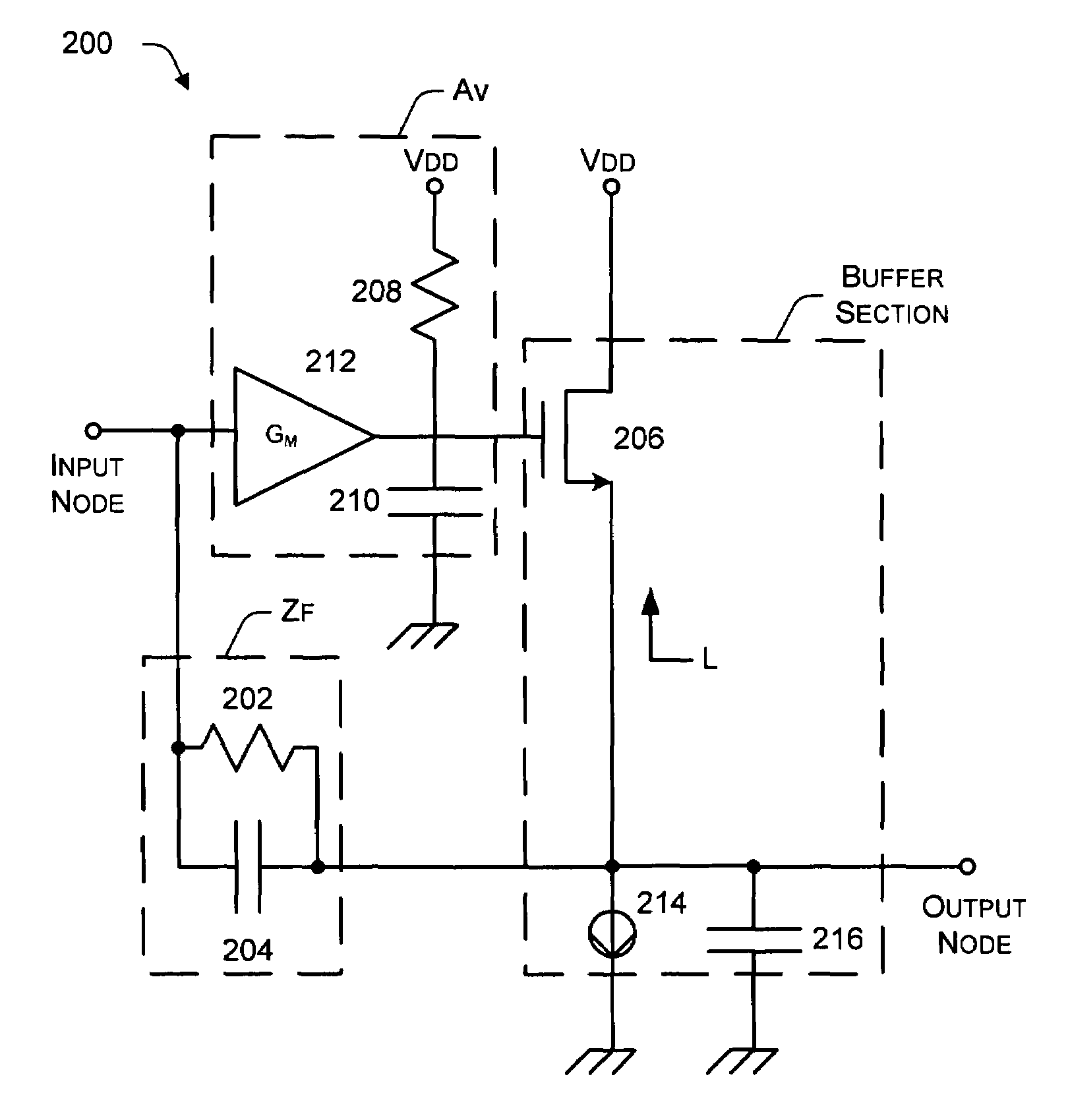
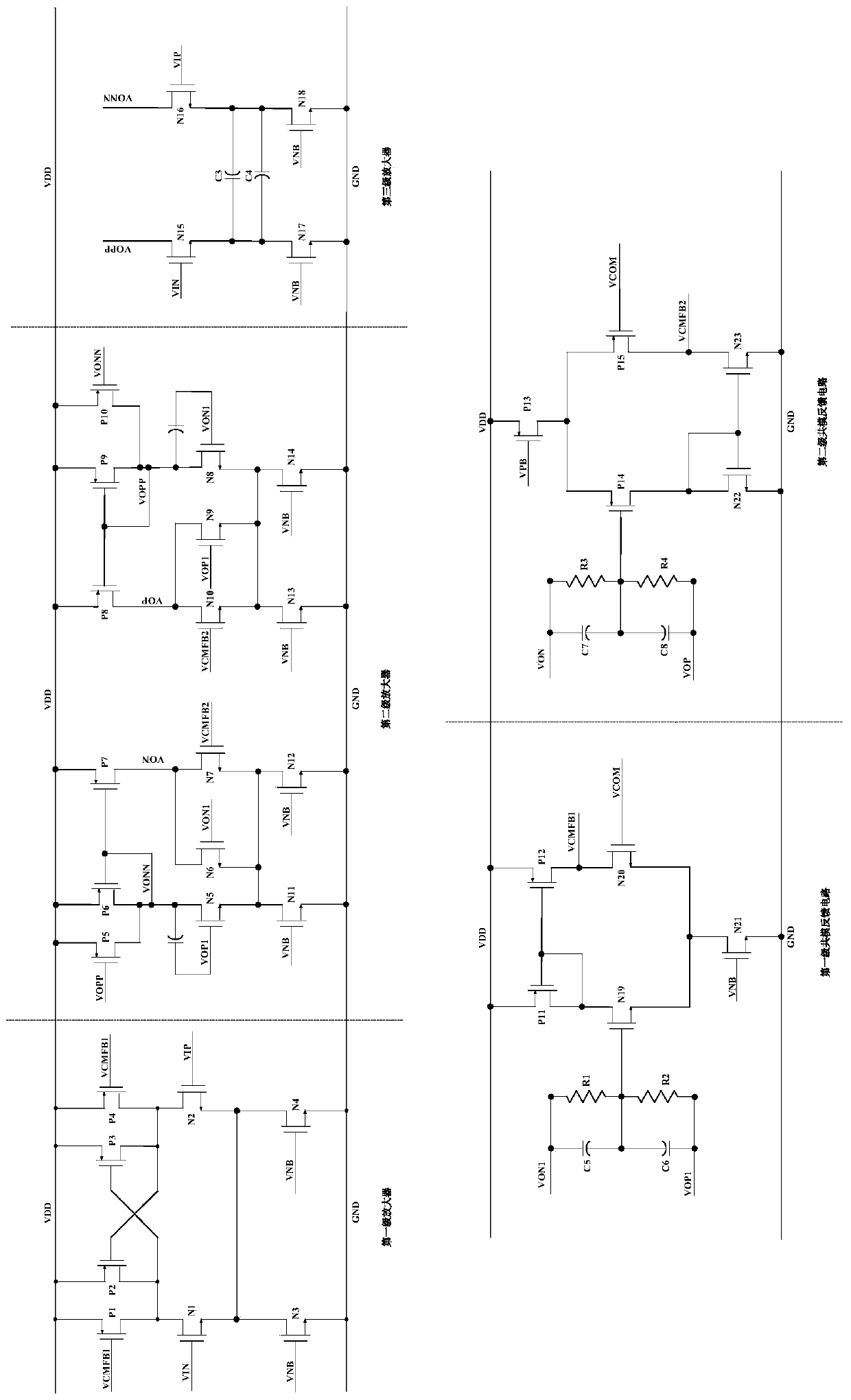
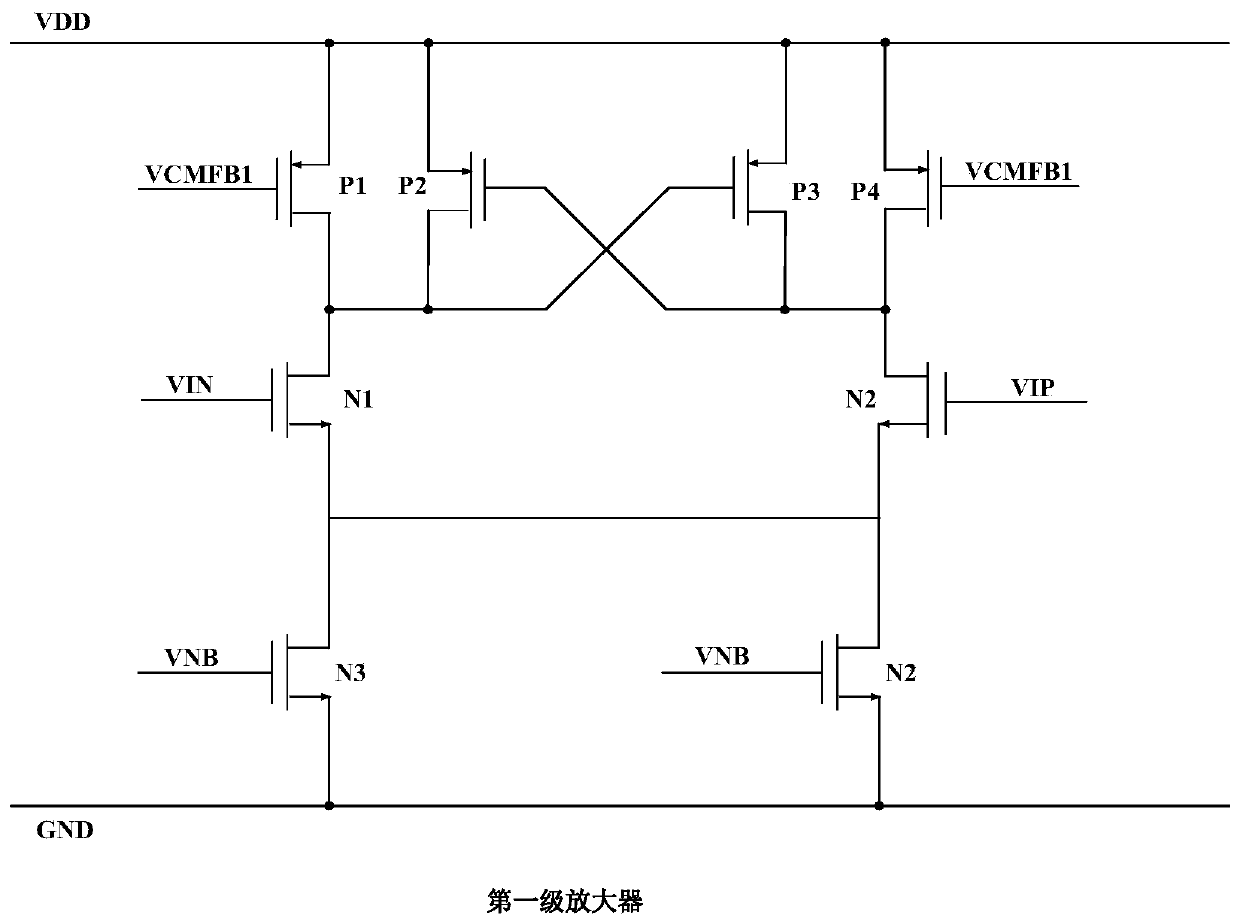
Multiple-stage operational amplifier and methods and systems utilizing the same
ActiveUS7202746B1Reduce device power consumptionReduce loadNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsEngineeringFrequency response
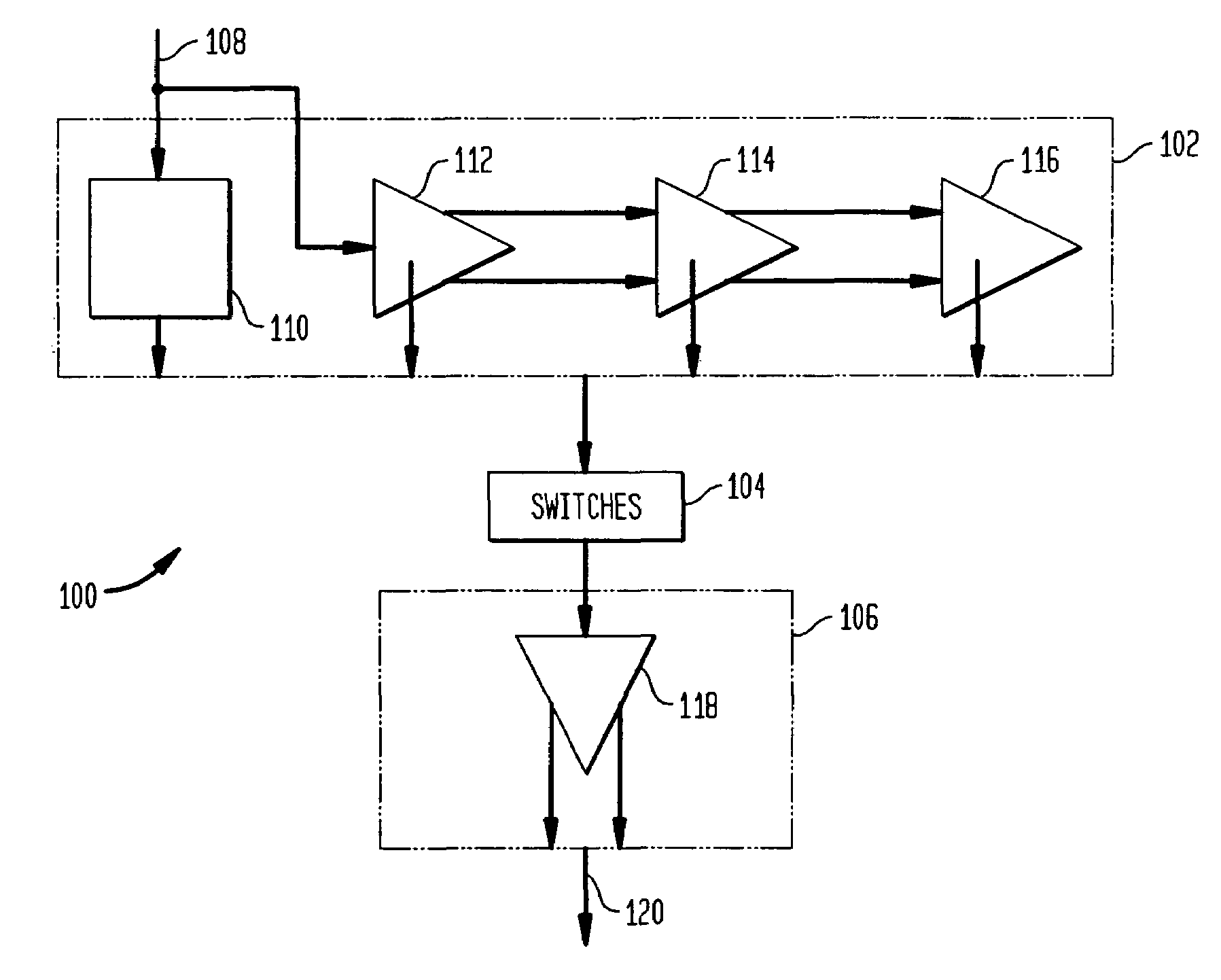
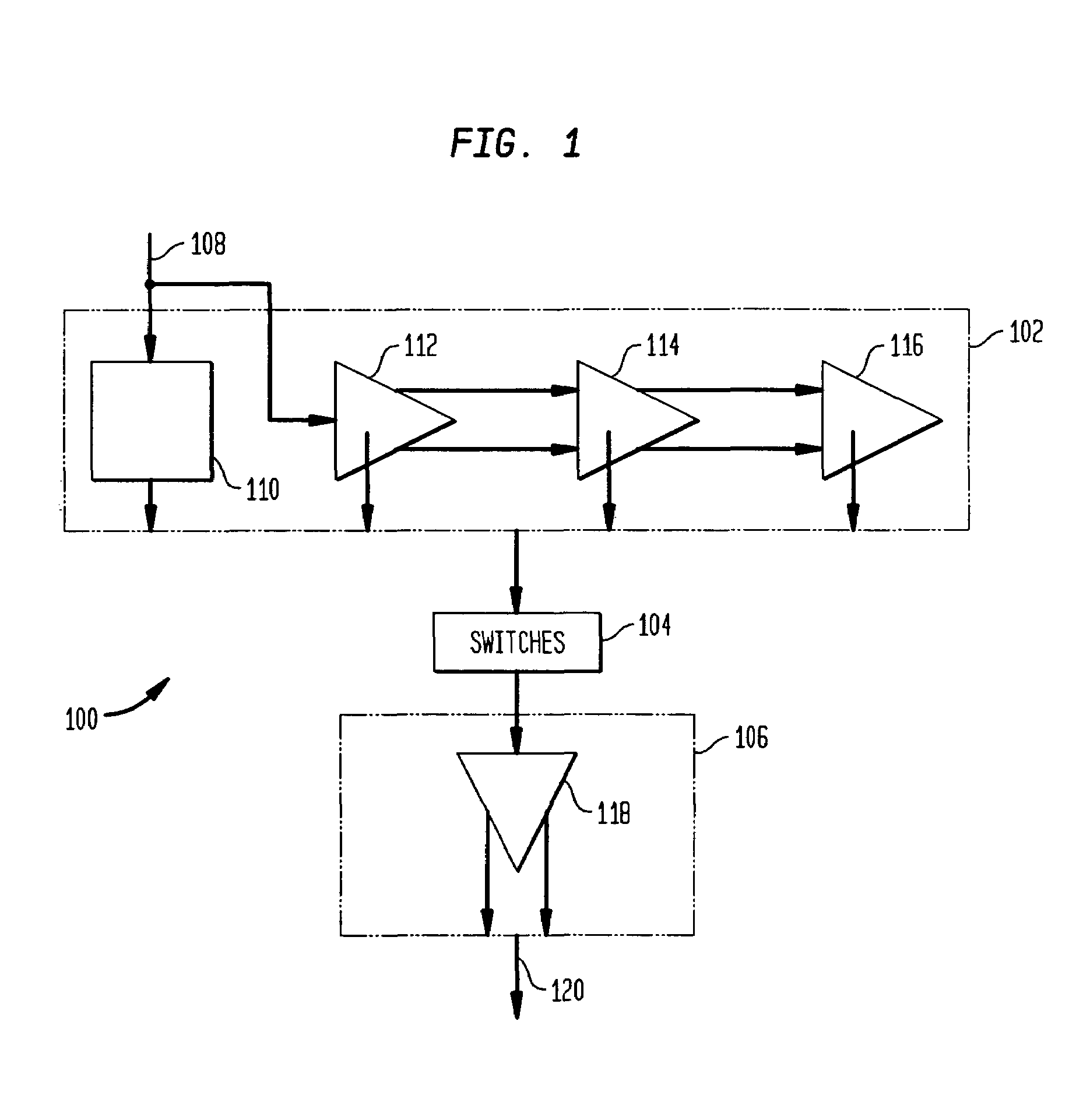
A multiple-stage operational amplifier including a gain stage for amplifying an input signal and implementing a dominant pole producing a frequency response having a gain roll-off with frequency and a unity gain frequency. An intermediate stage is coupled to an output of the gain stage and has a high input impedance and a low output impedance. A high gain amplifier configured as a low gain output stage using resistive feedback and coupled to an output of the intermediate stage drives an output of the operational amplifier and implements a dominant pole at a frequency substantially higher than the unity gain frequency implemented by the dominant pole implemented the gain stage.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
CMOS low-distortion low-noise amplifier circuit
PendingCN111934627AStable DC operating pointBandwidthAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersParasitic capacitorLow noise
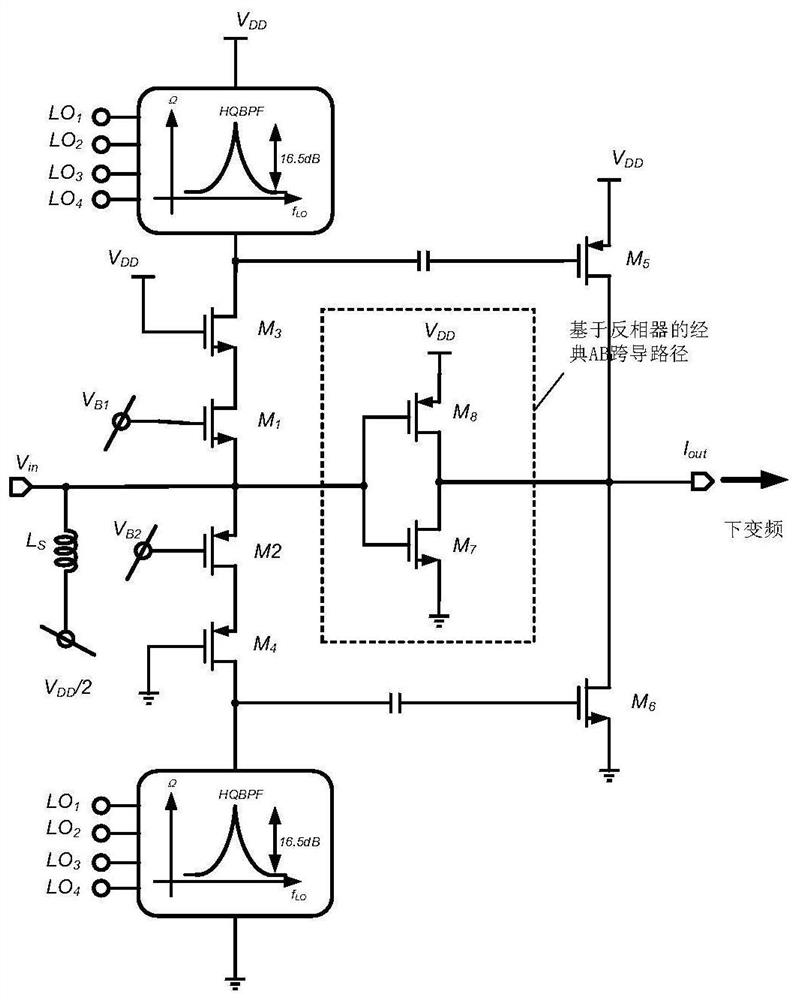
The invention discloses a CMOS low-distortion low-noise amplifier circuit, which is applied to the field of radio frequency integrated circuits, and aims to solve the problems that the third-order intermodulation linearity of an amplifier circuit in the prior art is below 0dBm, and a large signal interference environment is difficult to deal with. The transconductance input stage adopts a complementary common-source stage structure, so that the current efficiency is doubled; the linearity improving stage adopts a complementary common-emitter stage to improve the small signal linearity of the complementary common-source stage; the feedback stage adopts a source follower to solve the second-order interaction problem of nonlinear active feedback; an off-chip element and an input parasitic capacitor form a [pi]-type matching network to enhance the input matching bandwidth, so that an on-chip high-capacity inductor is prevented from being used; and the common-mode feedback circuit detects common-mode voltage of an output port of the low-noise amplifier circuit and compares the common-mode voltage with a reference voltage, and an obtained error signal is in feedback connection with gridsof the Mp1 and the Mp2 through a bias resistor for dynamic adjustment, so that the circuit works at a stable direct-current working point.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Amplifier
ActiveUS8378748B2Reduce areaLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
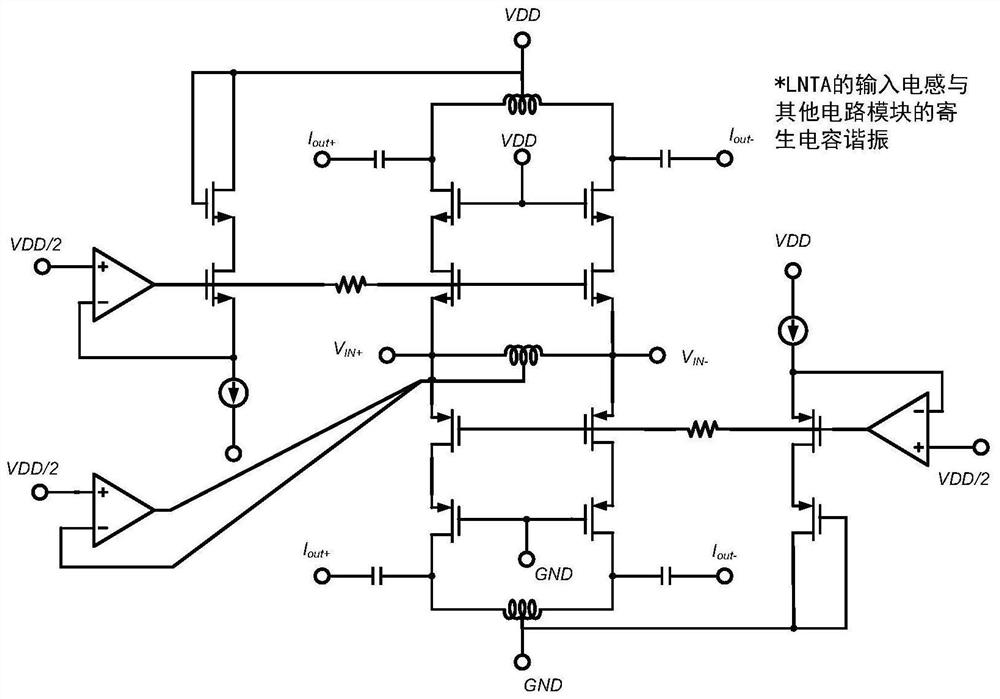
The invention relates to a configurable low noise amplifier circuit which is configurable between a first topology in which the low noise amplifier circuit includes a degeneration inductance whereby the low noise amplifier circuit operates as an inductively degenerated low noise amplifier, and a second topology in which the low noise amplifier circuit includes a feedback resistance whereby the low noise amplifier circuit operates as a resistive feedback low noise amplifier.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High-precision current detection circuit based on CPU (Central Processing Unit)
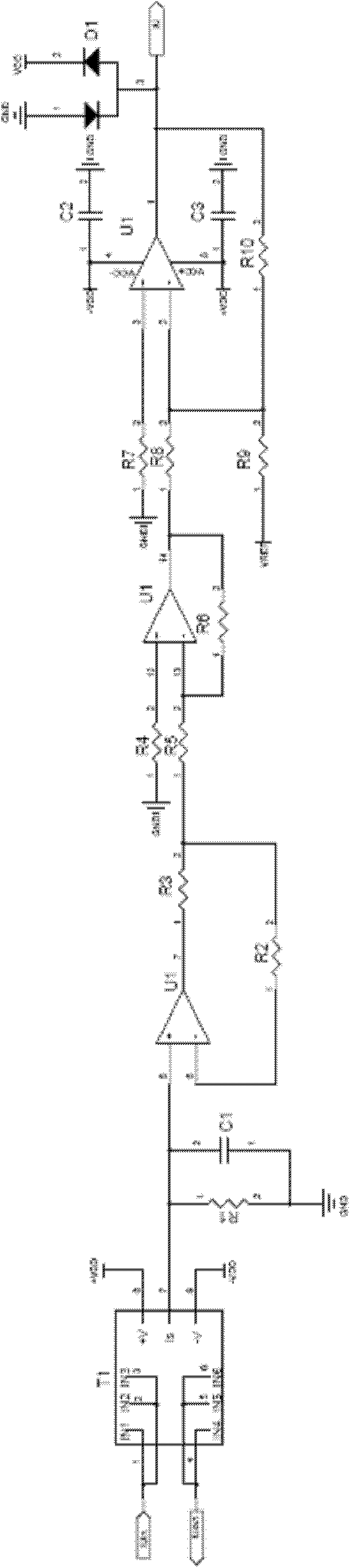
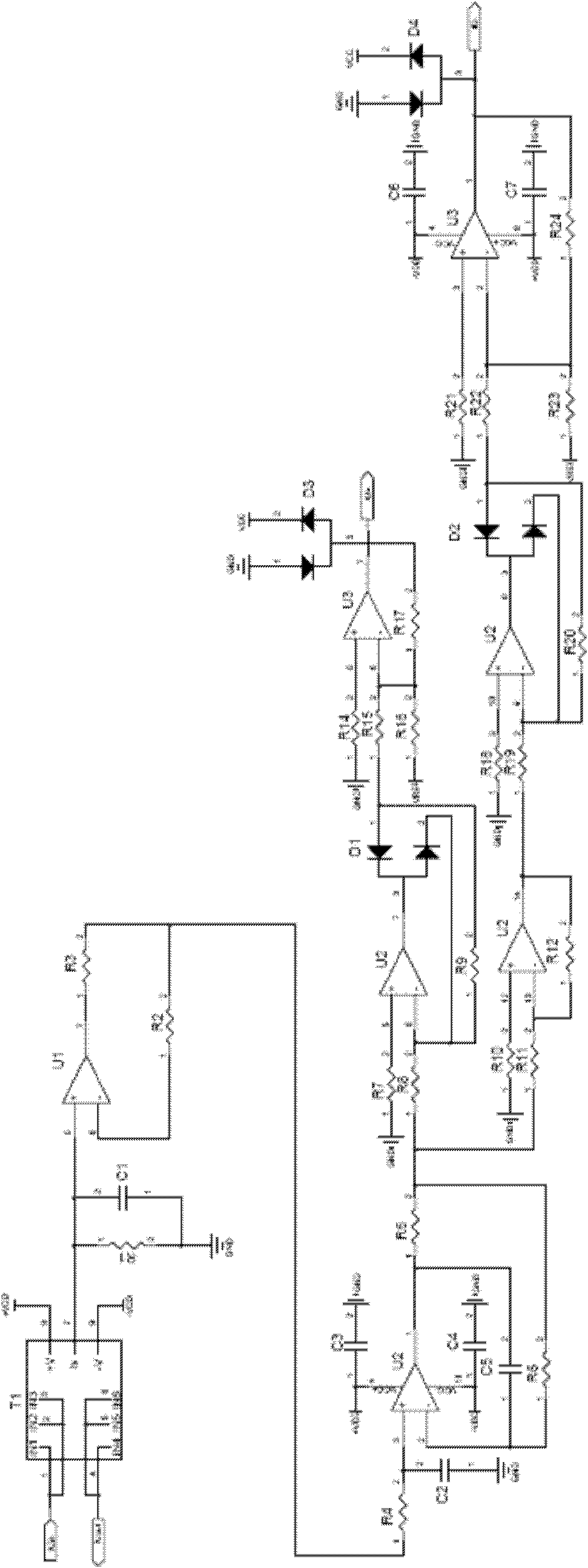
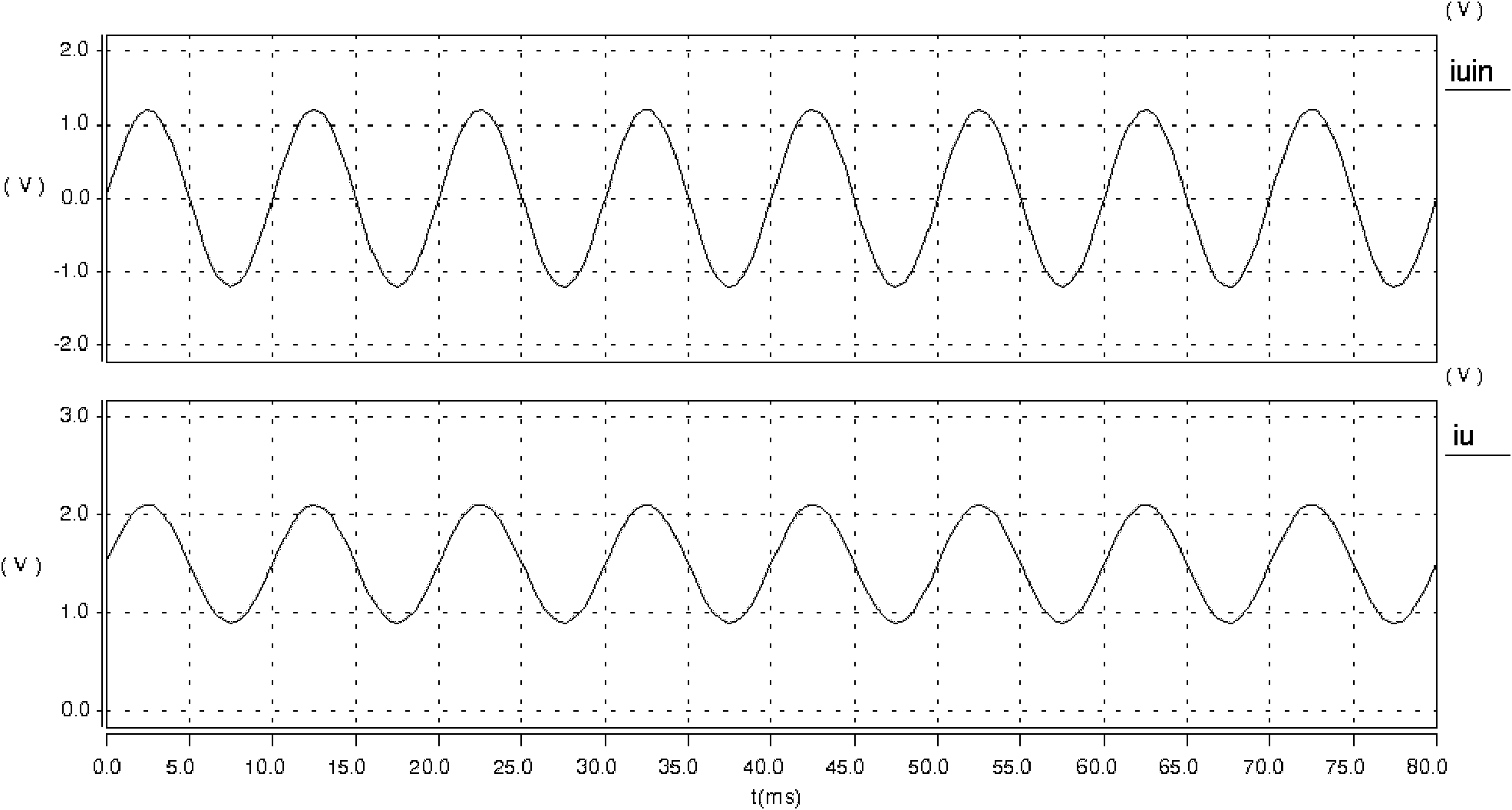
InactiveCN102495275AHigh precisionReduce dependencyMeasurement using digital techniquesCapacitanceCurrent sensor
The invention relates to a high-precision current detection circuit based on a CPU (Central Processing Unit). The detection current is mainly composed of a plurality of filter capacitors, a bypass capacitor, a following resistor, an input resistor, a feedback resistor, an absolute value diode, a protected diode and an operational amplifier, wherein when the circuit works, detected current IUin passes through a current Hall sensor T1 to be converted into weak current IS; a voltage value, which corresponds to the IS, is obtained through a sampling resistor R1 and then the voltage value is carried out by operational amplification and following to obtain a voltage value IU corresponding to a circuit to be detected; the current IU, which passes through a current sensor, passes through a filtering circuit formed by a resistor R4 and the filter capacitor C2, and then is divided into two paths after the following of operational amplification U2; one path of the current passes through an absolute value circuit and a reverse uplifting circuit to obtain a positive half-wave of the current; and the other path of the current is reversed and passes through the absolute value circuit and the reverse uplifting circuit to obtain a negative half-wave of the current. The high-precision current detection circuit based on the CPU has the advantages that: a detected signal is amplified under the condition that an AD (Analog to Digital) linear zone is not changed, so that the precision can be greatly improved.
Owner:WISDRI WUHAN AUTOMATION
Line driver with active termination
ActiveUS7019552B2Reduce the voltage amplitudeReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingSymmetric configurationImpedance matching
The line driver with active termination includes: a differential amplifier having an inverting output terminal, a non-inverting output terminal, an inverting input terminal, and a non-inverting input terminal; a first resistor unit coupled to the inverting input terminal; a impedance matching resistor unit coupled to the non-inverting output terminal; and a resistive feedback network, having a plurality of resistors in symmetric configuration. The resistive feedback network further includes: a second resistor unit coupled to the impedance matching resistor unit and the inverting input terminal; a third resistor unit coupled to the non-inverting output terminal and the inverting input terminal; a fourth resistor unit coupled to the impedance matching resistor unit and the inverting input terminal; and a fifth resistor unit coupled to the inverting output terminal and the inverting input terminal. Each of the resistor units and the impedance matching resistor unit includes a plurality of resistors in symmetric configuration.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
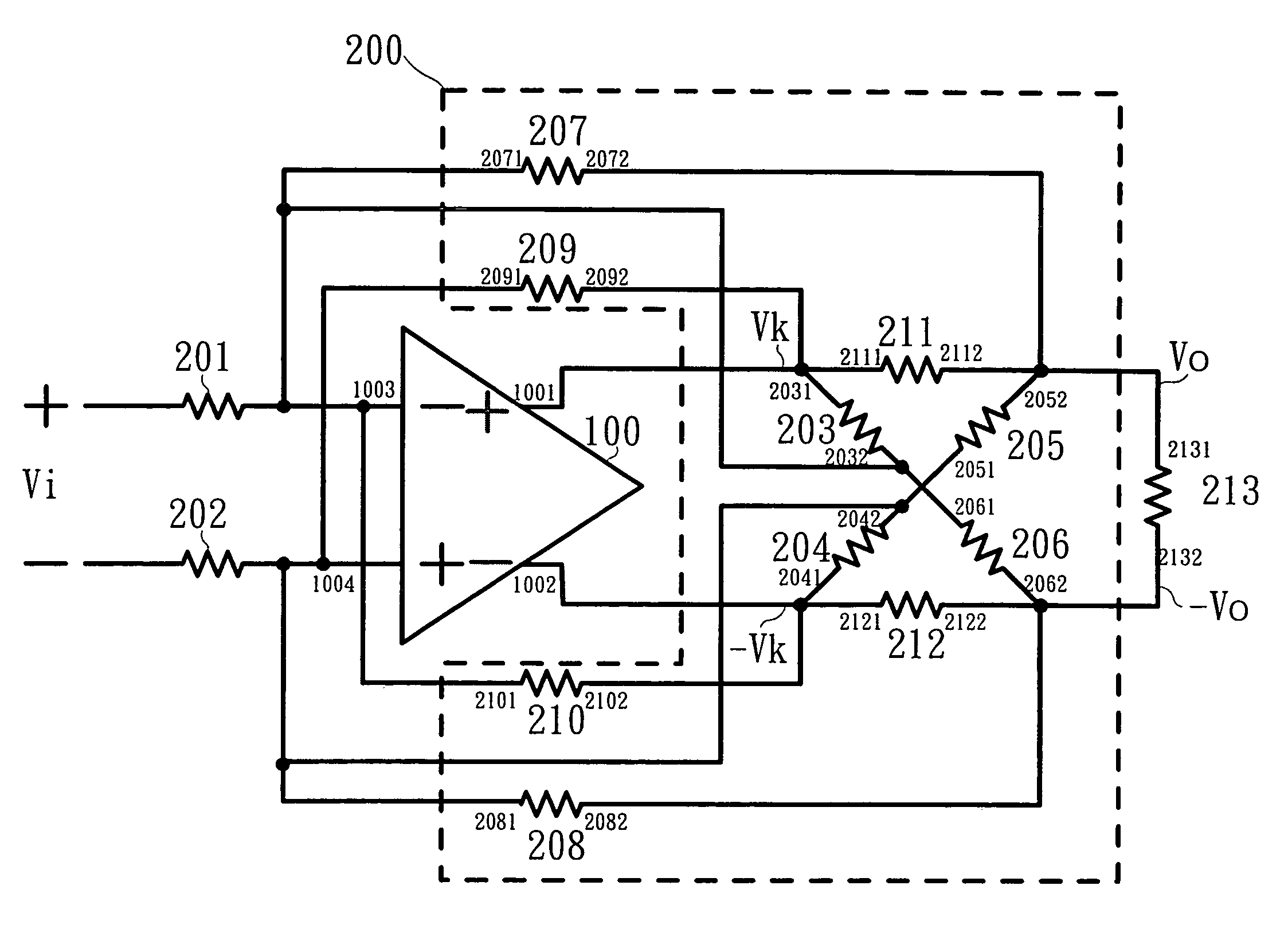
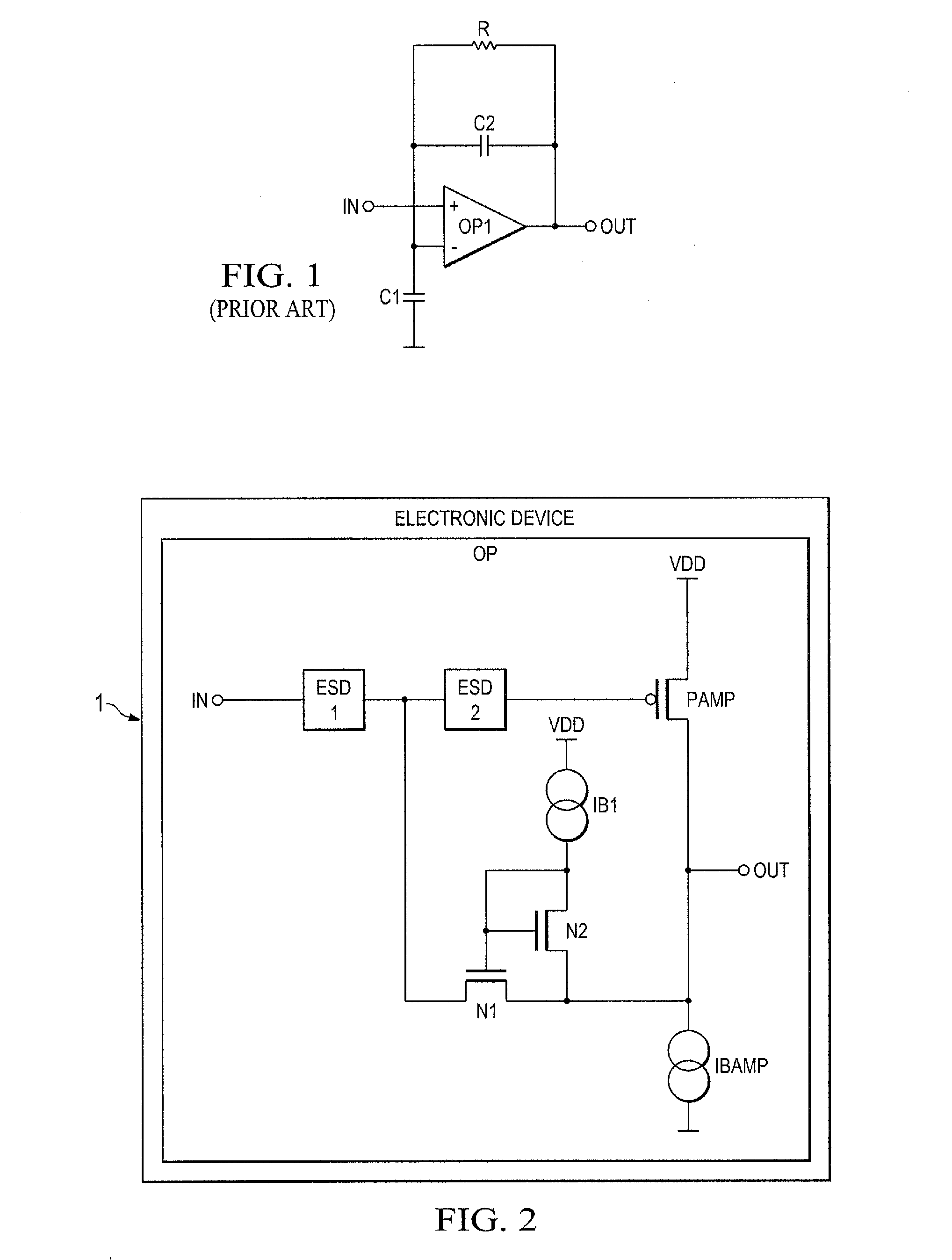
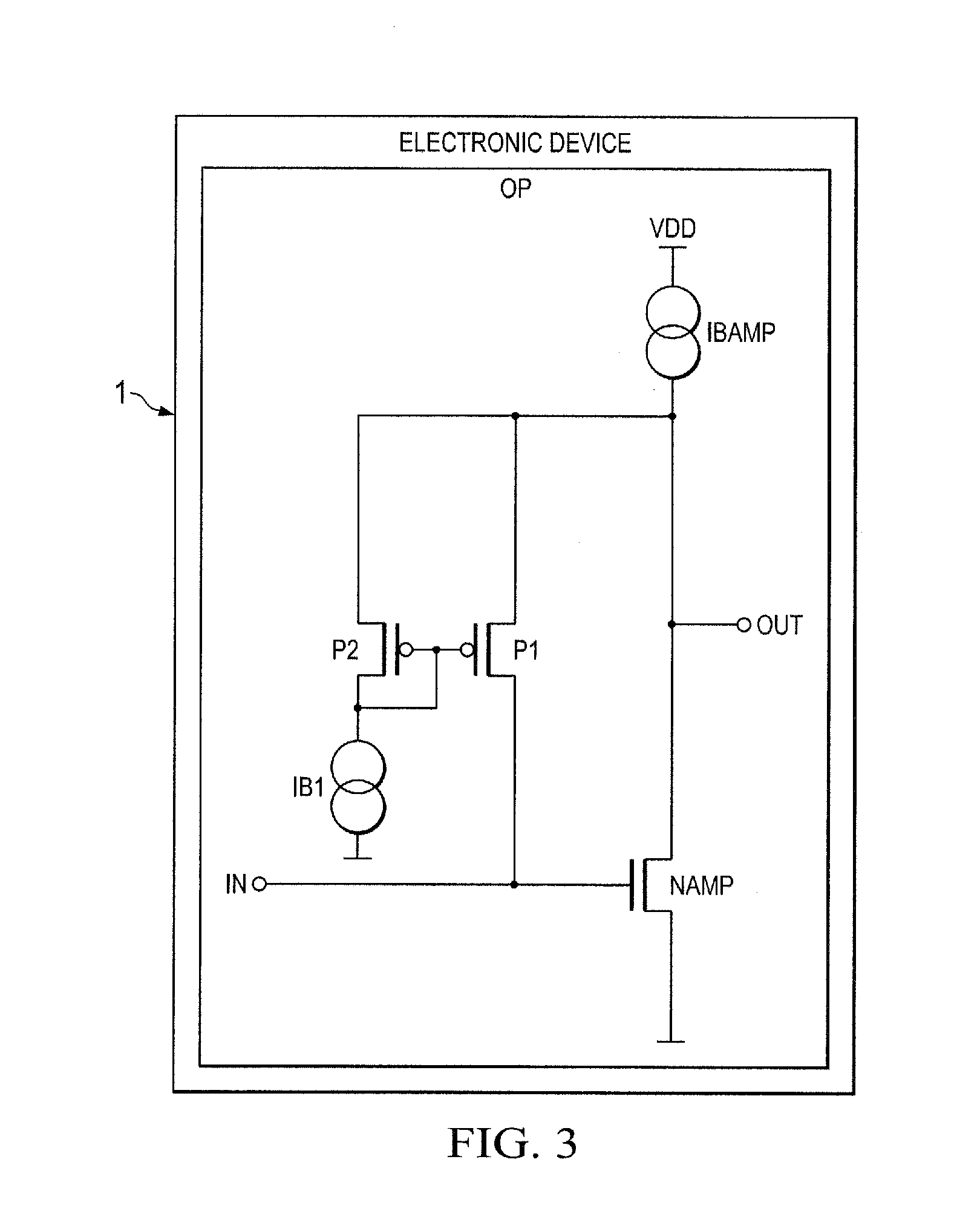
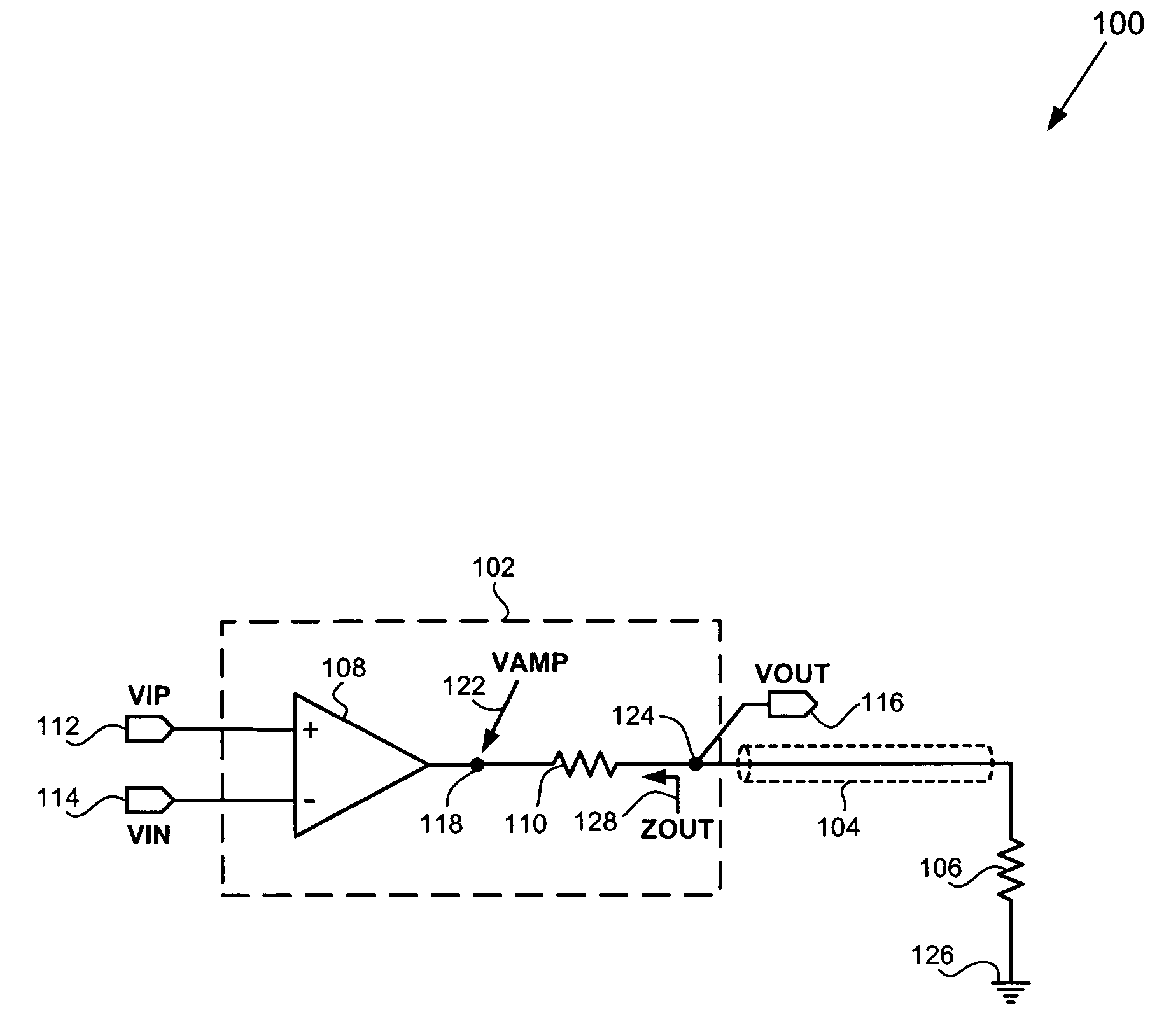
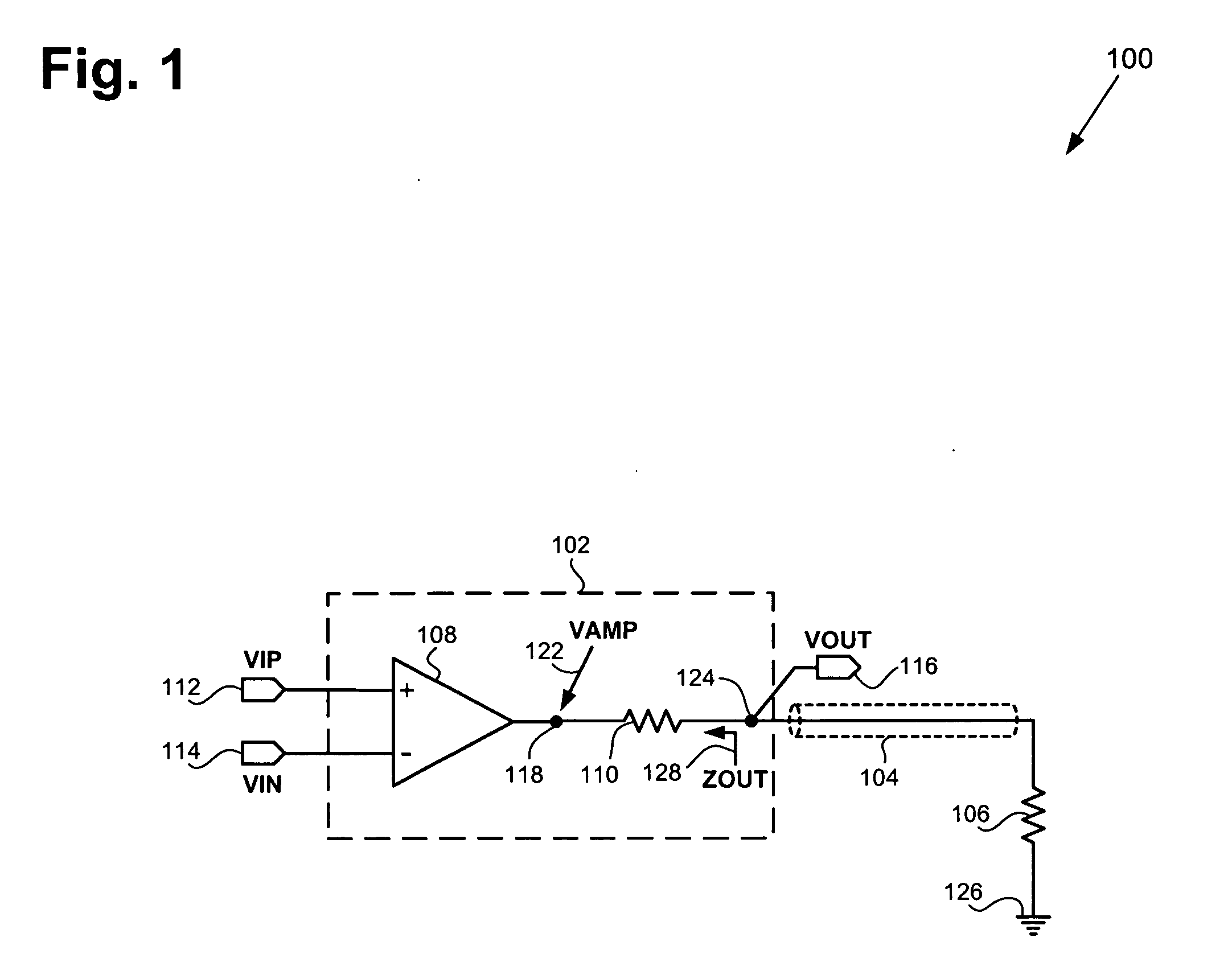
Electronic device and method for an amplifier with resistive feedback
ActiveUS20130009706A1Reduce impactSupply voltage range of the amplifier to be very smallHigh frequency amplifiersLow noise amplifierAudio power amplifierResistive feedback
An electronic device comprising an amplifier having at least a first input transistor of a first doping type. A first transistor is coupled with a channel as a feedback path between an output of the amplifier and a control gate of the first input transistor forming an input of the amplifier. A diode-coupled second transistor is coupled with a channel between a first current source and the output of the amplifier wherein a control gate of the first transistor is coupled between the first current source and the diode-coupled second transistor and the first transistor is of a second doping type which is opposite to the first doping type of the first input transistor of the amplifier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Low return loss resistive feedback amplifier
ActiveUS7423489B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:APPLE INC
Amplifier
ActiveUS20120293262A1Reduce areaLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierInductance
The invention relates to a configurable low noise amplifier circuit which is configurable between a first topology in which the low noise amplifier circuit includes a degeneration inductance whereby the low noise amplifier circuit operates as an inductively degenerated low noise amplifier, and a second topology in which the low noise amplifier circuit includes a feedback resistance whereby the low noise amplifier circuit operates as a resistive feedback low noise amplifier.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
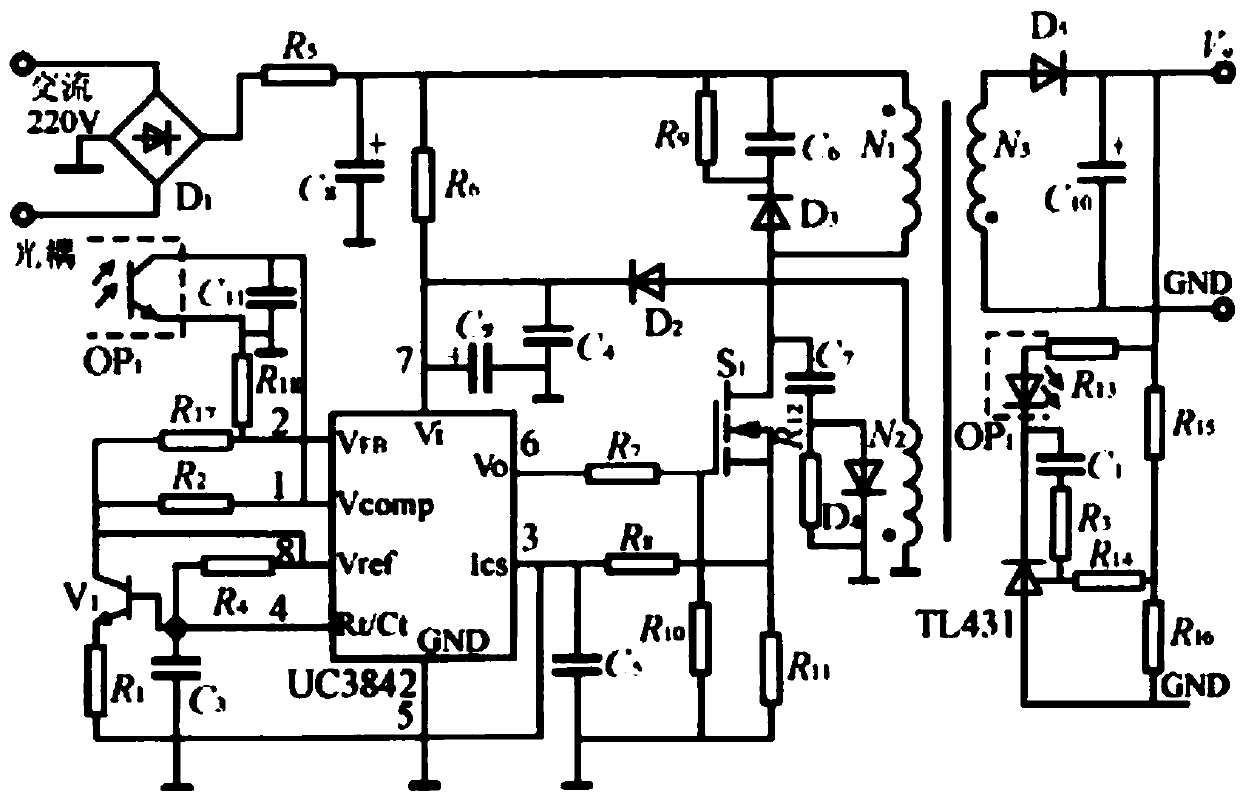
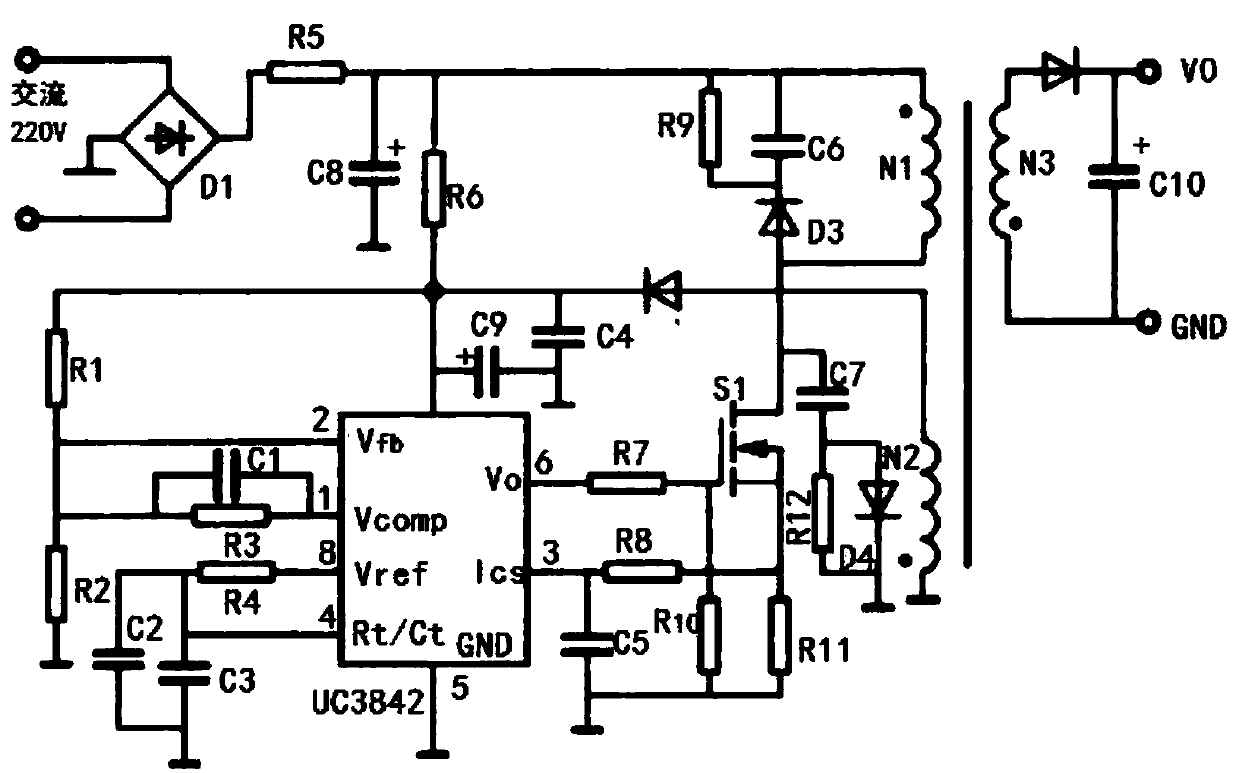
Switching power supply protection circuit based on UC3842
PendingCN107947549ASimplifies Frequency CompensationSimplified output power is smallPower conversion systemsHigh frequencyTransformer
The invention discloses a switching power supply protection circuit based on UC3842, and relates to the field of electronic technology power supplies. The circuit comprises a rectifier circuit, a highfrequency transformer, a MOS power transistor and a current type pulse width modulation chip UC3842. An emitter follower is connected with the sampling voltage site of the chip UC3842. A sampling resistor is a non-inductive resistor. A feedback circuit is controlled by TL431 and an optocoupler. According to the invention, the emitter follower is connected with the sampling voltage site of the UC3842; an artificial slope synchronized with a pulse width modulation clock is added to the control voltage; delta I disturbance can be reduced to zero in the subsequent period; and even if the system works under duty cycle greater than 50% or continuous inductor current conditions, the system is stable.
Owner:MIANYANG HIGHLY TECH JINGWEIDA SCI
Line driver with active termination
InactiveUS20080101592A1Accurate output impedanceReduce power consumptionInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentAudio power amplifierEngineering
A line driver comprises a driving amplifier receiving an input of the line driver, a current sense resistor connected between the driving amplifier output and the line driver output, and a feedback amplifier sensing the voltage across the current sense resistor and providing a corresponding feedback voltage that is proportional to the output current to the driving amplifier, thereby determining an output impedance at the line driver output. Precise output impedance can be realized by using a high precision resistor as the current sense resistor, and using resistive feedback amplifiers with accurate gains as the driving and feedback amplifiers. The resistance of the current sense resistor can be substantially less than the line driver output impedance, and the driving amplifier output voltage swing can be substantially less than twice the line driver output voltage swing.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Narrow-band filter with linearly adjustable center frequency
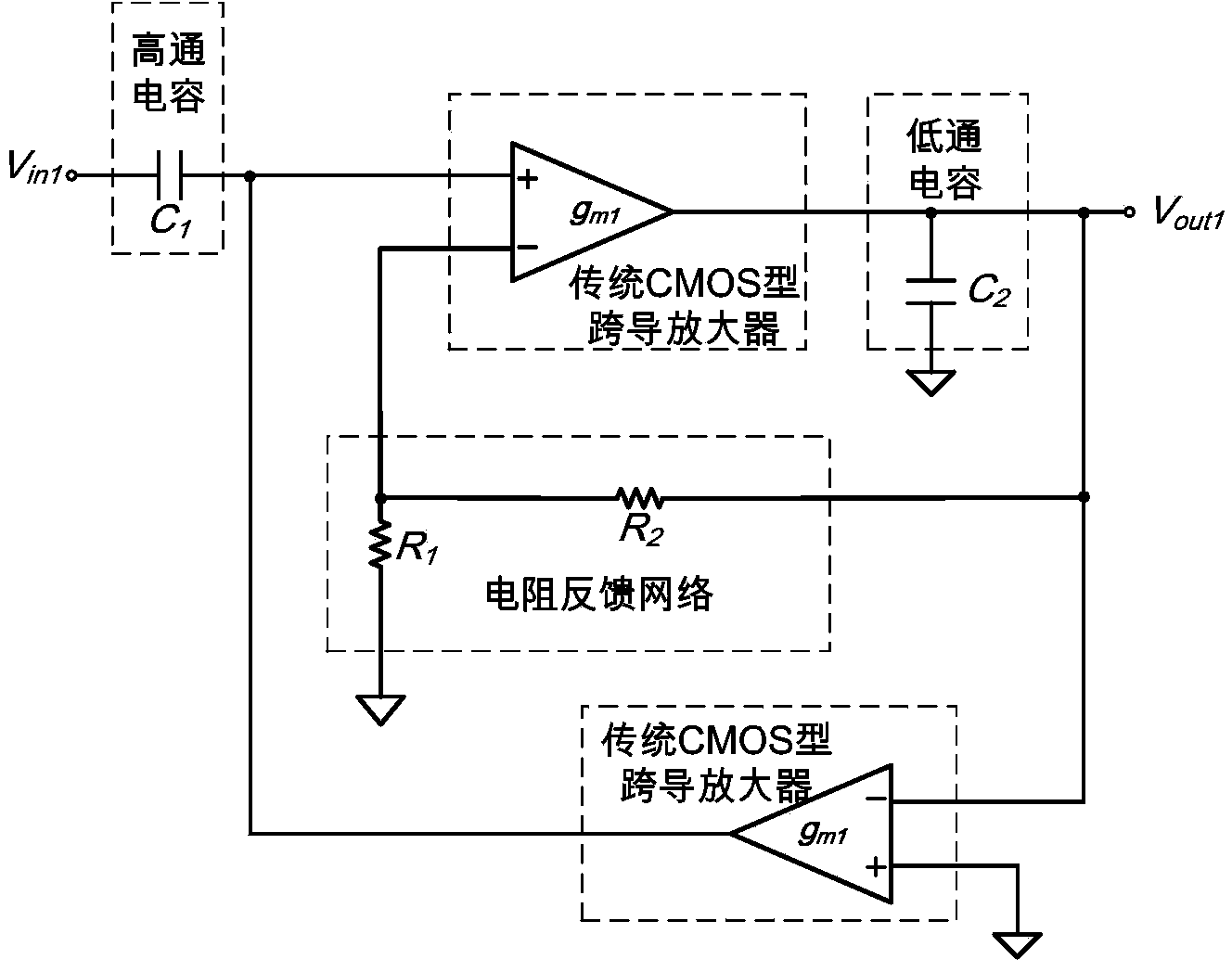
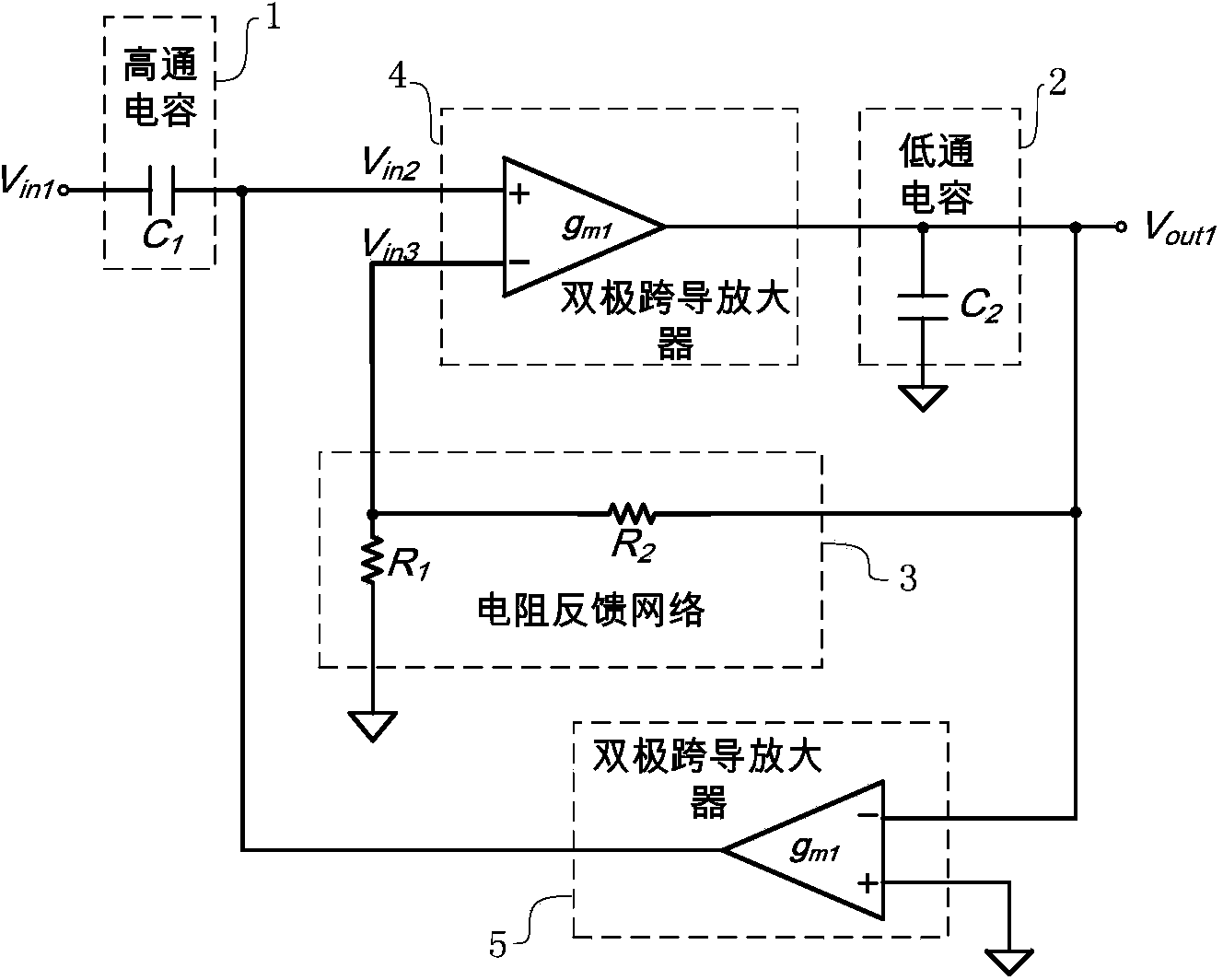
ActiveCN103780223AExpand the input rangeLinear adjustableMultiple-port active networksCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
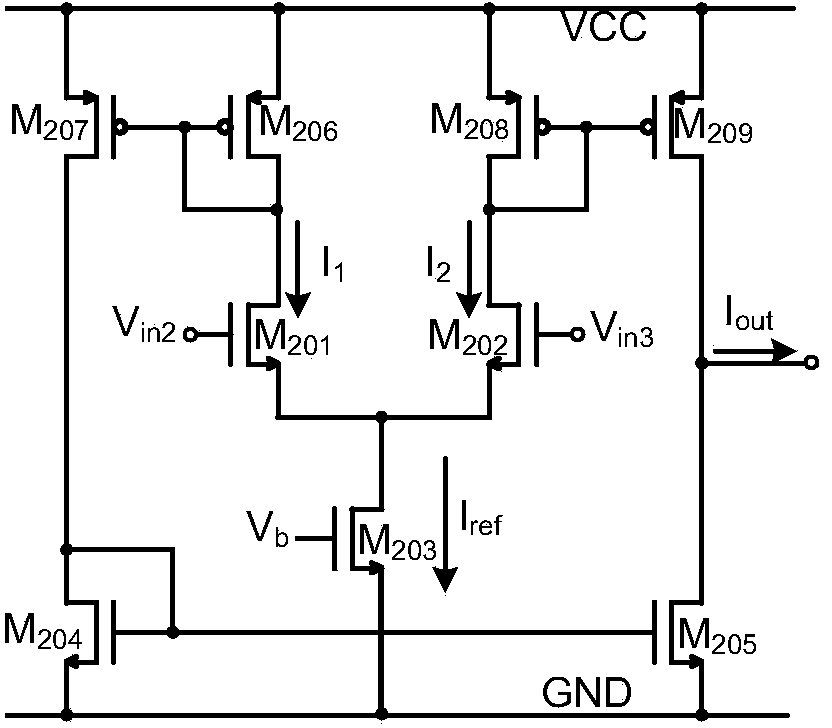
The invention discloses a narrow-band filter with the linearly adjustable center frequency. The narrow-band filter with the linearly adjustable center frequency mainly solves the problems that an existing narrow-band filter is small in dynamic input range, and the center frequency can not be linearly adjusted. The narrow-band filter with the linearly adjustable center frequency comprises a high-pass capacitor (1), a low-pass capacitor (2), a resistive feedback network (3) and two bipolar transconductance amplifiers (4 and 5), wherein the positive phase input end of the first amplifier is connected with the output end of the high-pass capacitor, the output end of the first amplifier is connected with the positive end of the low-pass capacitor, and the first amplifier is fed back to the negative phase input end through the resistive feedback network, so that a negative voltage feedback structure is formed; the negative input end of the second amplifier is connected with the output end of the first amplifier, the positive phase input end of the second amplifier is grounded, and the output end of the second amplifier is connected with the positive phase input end of the first amplifier, so that a negative current feedback structure is formed. According to the narrow-band filter with the linearly adjustable center frequency, the dynamic input range of the filter is enlarged through the two bipolar transconductance amplifiers, a linearly adjustable transconductance value is provided for the filter, the center frequency can be linearly adjusted, and the narrow-band filter can be used for infrared receiver circuits.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
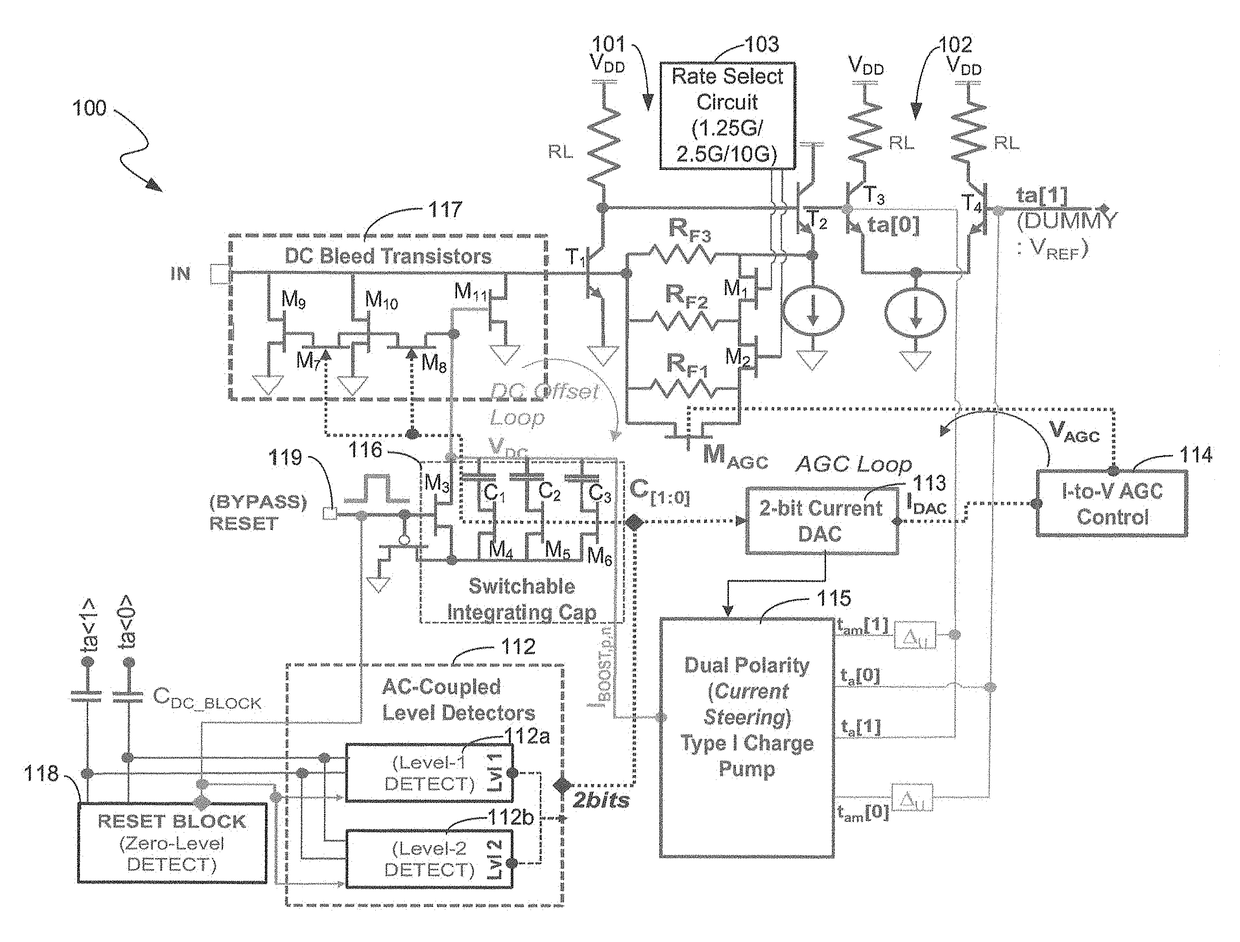
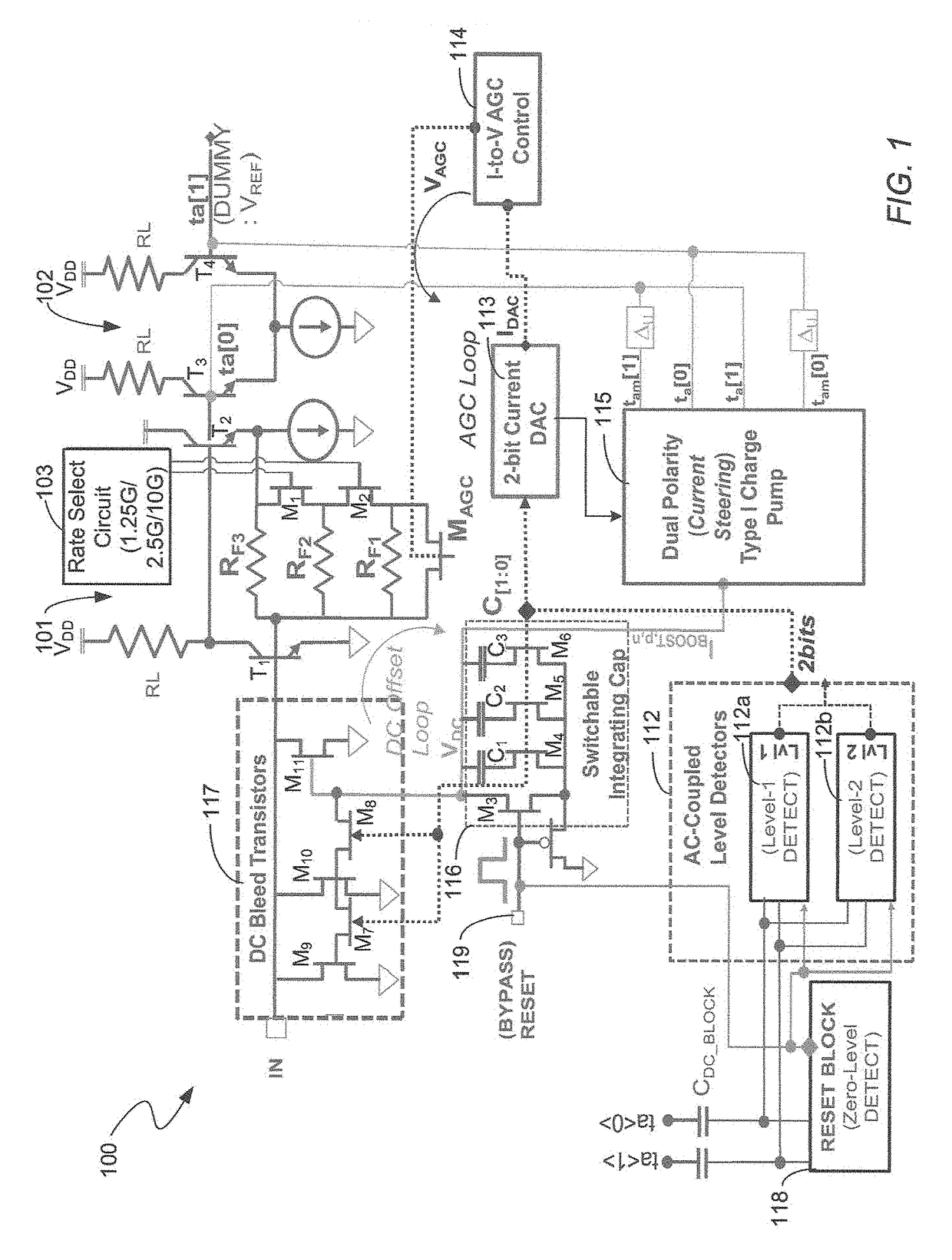
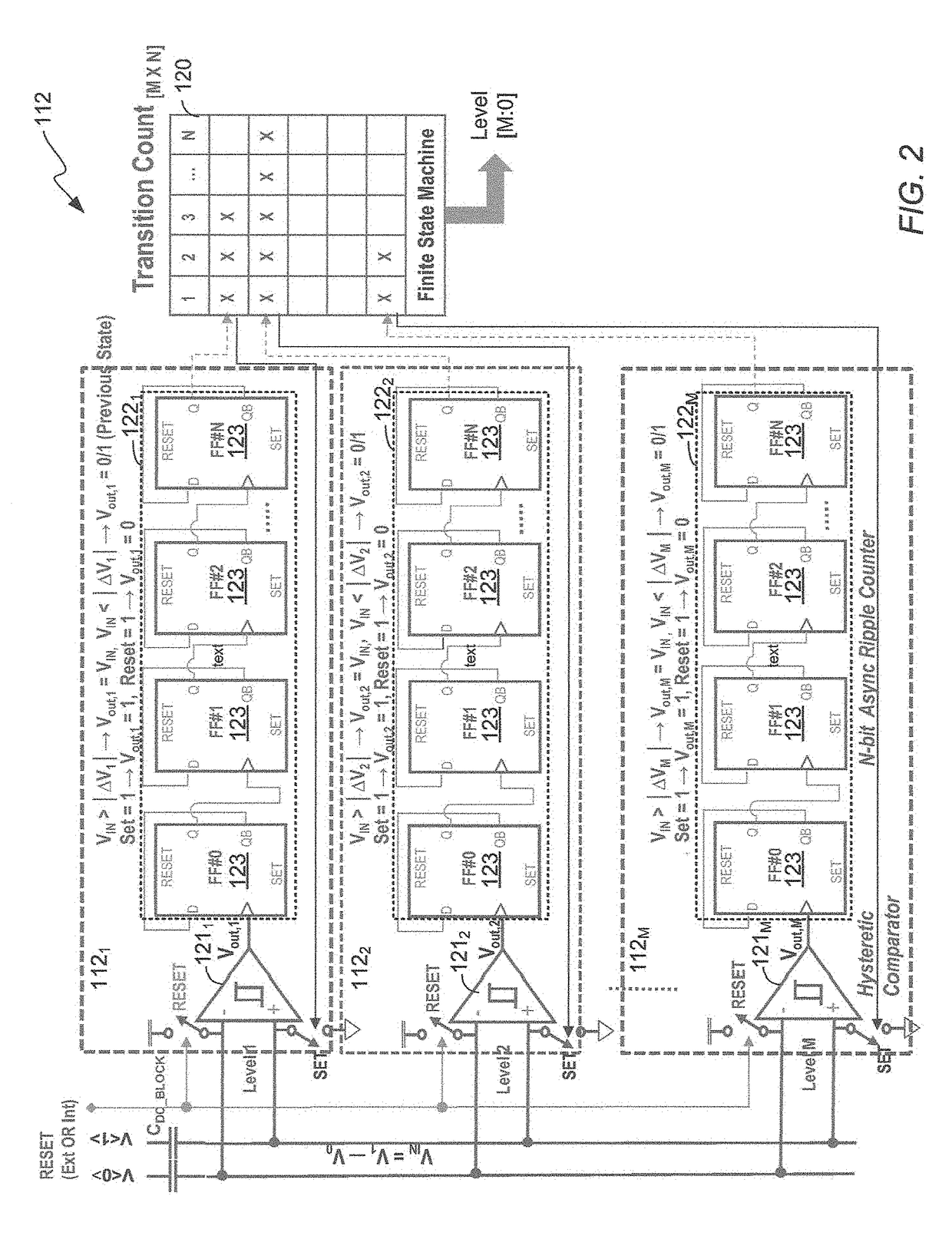
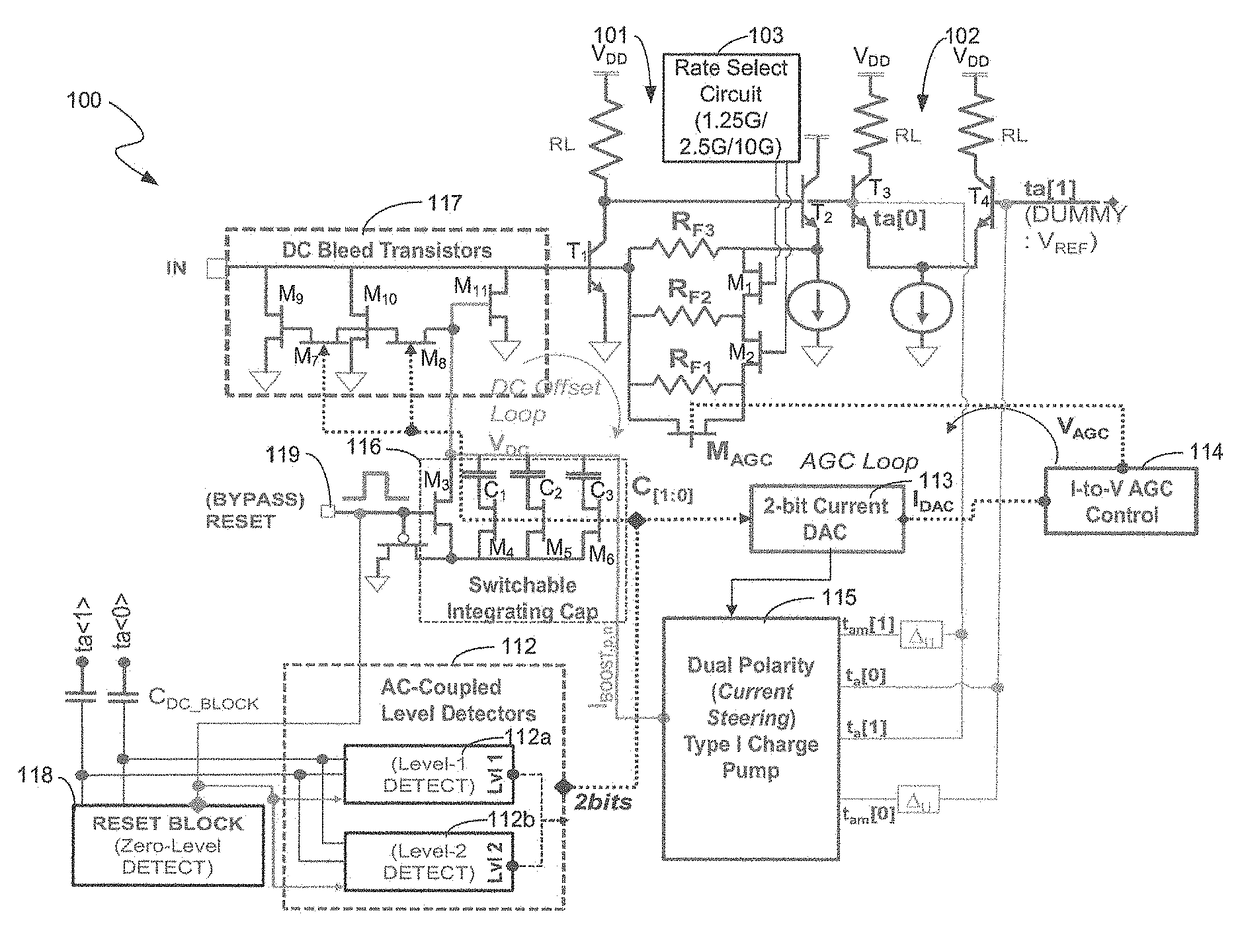
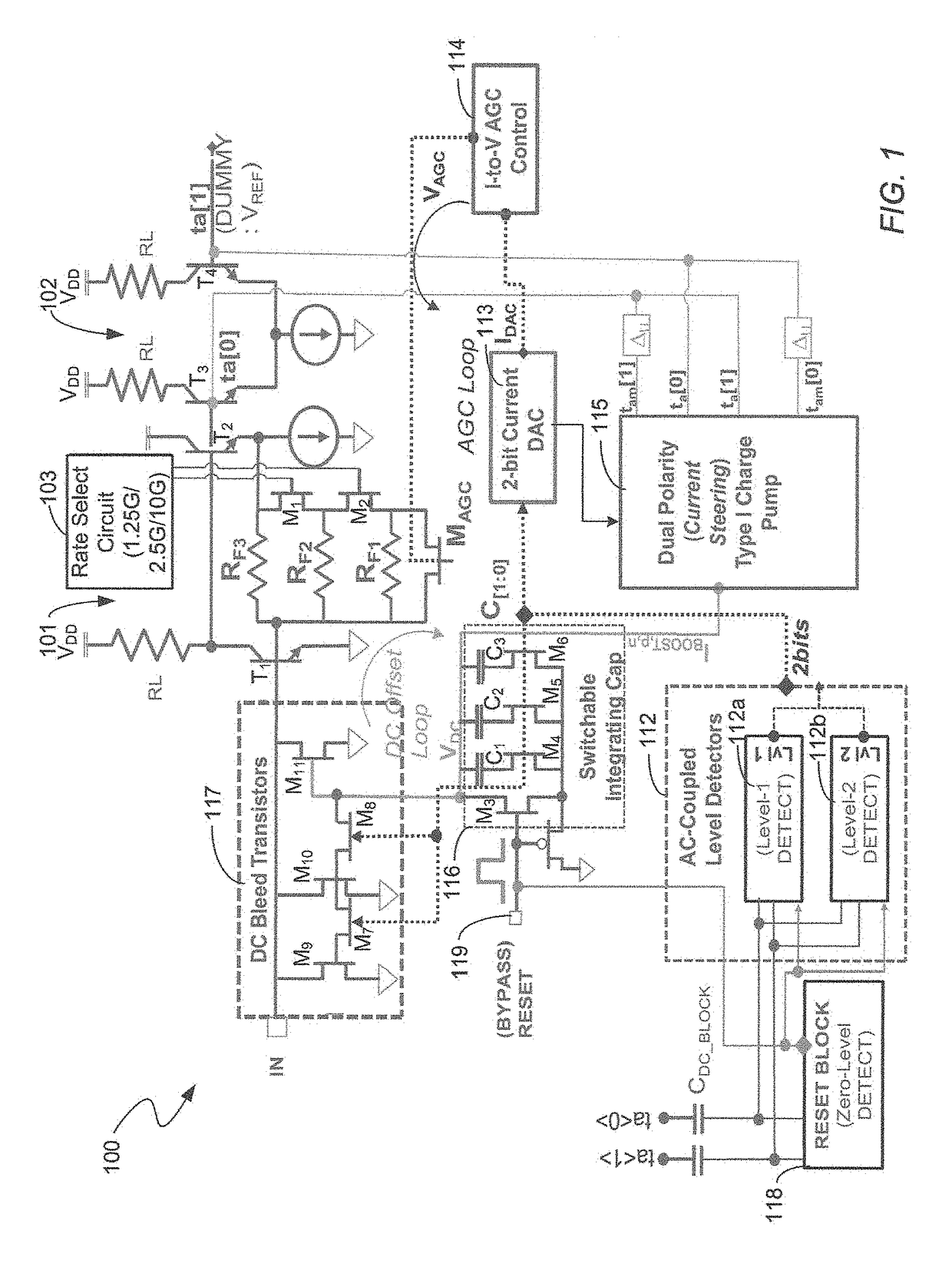
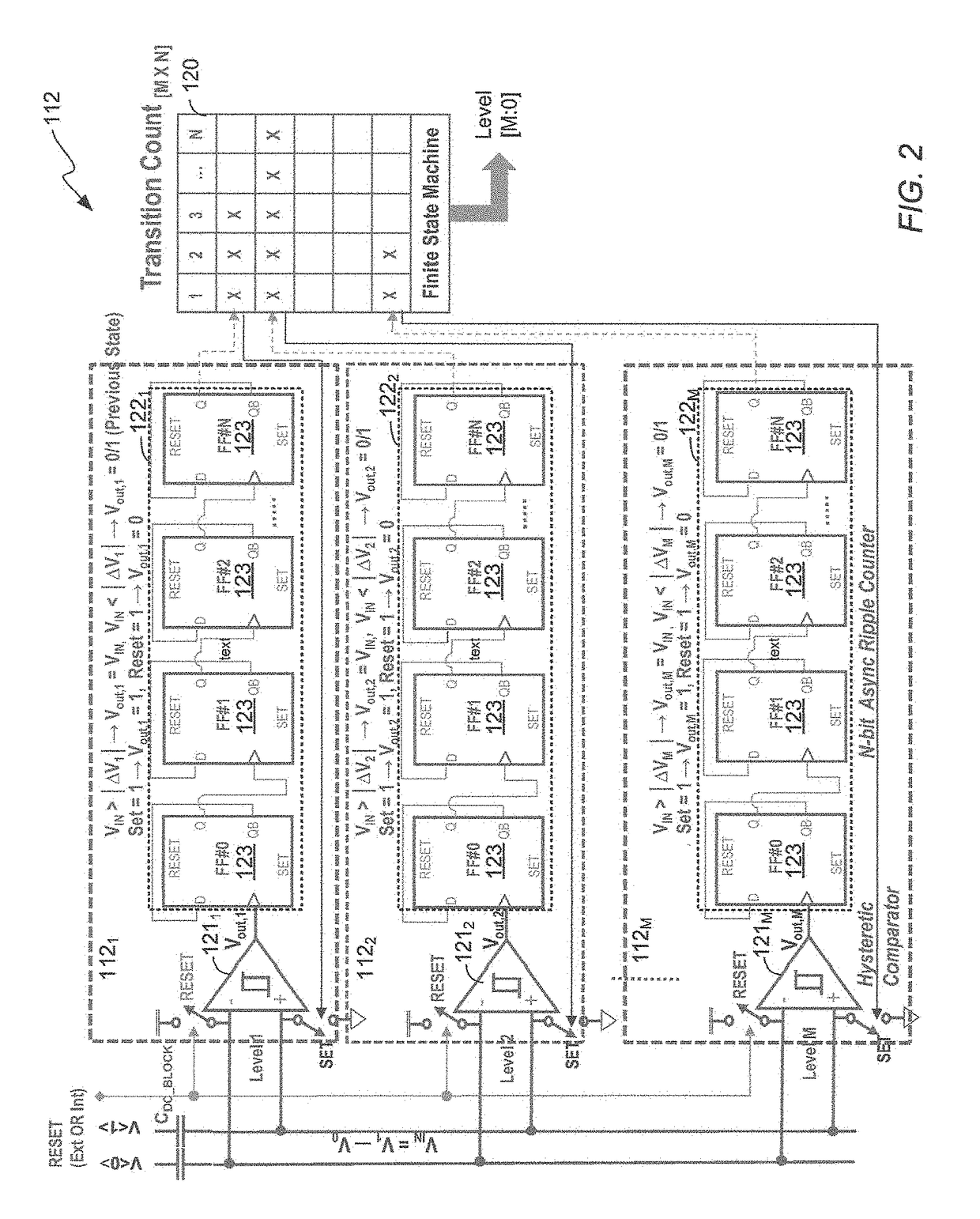
Multi-data rate, burst-mode transimpedance amplifier (TIA) circuit
A burst-mode TIA circuit for use in PON receivers is provided that supports multiple data rates, has high receiver sensitivity, wide dynamic range, and that performs burst-mode synchronization very quickly. The multi-rate burst-mode TIA circuit has a high-speed data path that has low input-referred noise. Based on the chosen data rate at which the multi-rate burst-mode TIA circuit will operate, the rate select switch selects an appropriate feedback resistor of the resistive feedback network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low dropout linear regulator circuit with low power consumption and fast transient response
ActiveCN114167933AImprove load response speedImproved load transient performanceEfficient power electronics conversionElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorHemt circuits
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic circuits and semiconductors, and particularly relates to a low dropout regulator circuit. A low dropout linear regulator circuit with low power consumption and fast transient response comprises an error amplifier; the grid electrode of the series adjustment power tube is connected with the output end of the error amplifier; the resistance feedback network is provided with a first resistor and a second resistor which are connected in series, the common end of the first resistor and the second resistor serves as a feedback end, and the other end of the second resistor is grounded; the non-inverting input end of the error amplifier is connected with reference voltage, and the inverting input end is connected with the feedback end; the drain electrode of the series adjustment power tube is connected with the power input end, and the source electrode is connected with the circuit output end which is further connected with the other end of the first resistor. And the output end of the biasing circuit is respectively connected with the error amplifier and the output end of the circuit. The low dropout linear regulator circuit has a fast load transient response function, and the load response speed of the low dropout linear regulator circuit is improved through a simple circuit.
Owner:上海瓴瑞微电子有限公司
Electrochemical sensing circuit having high dynamic range
InactiveUS7182845B2High sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrochemical gas sensor
An electronic sensing circuit for an electrochemical gas sensor cell providing high dynamic range is described. The electronic circuit utilizes an amplifier with a resistive feedback element to provide high sensitivity linear sensing of low detected gas concentrations. The electronic circuit also provides the ability to source sufficient current to prevent the electrochemical gas sensor cell from becoming biased under very high gas concentration conditions. This operation is enabled by adding a non-linear element in the feedback path of the amplifier, which non-linear element begins to conduct during the high gas concentration conditions.
Owner:MAPLE CHASE
Multi-data rate, burst-mode transimpedance amplifier (TIA) circuit
A burst-mode TIA circuit for use in PON receivers is provided that supports multiple data rates, has high receiver sensitivity, wide dynamic range, and that performs burst-mode synchronization very quickly. The multi-rate burst-mode TIA circuit has a high-speed data path that has low input-referred noise. Based on the chosen data rate at which the multi-rate burst-mode TIA circuit will operate, the rate select switch selects an appropriate feedback resistor of the resistive feedback network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Radio frequency ultra wide band-driven amplifier chip
PendingCN110798162AIncrease phase desireImprove linearityGain controlAmplifiers with multiple amplifying elementsUltra-widebandCapacitance
The invention discloses a radio frequency ultra wide band-driven amplifier chip which comprises two input resistors, two feedback resistors and an operational amplifier. The operational amplifier comprises three amplifiers including a first-stage amplifier, a second-stage amplifier and a third-stage amplifier, the two common-mode feedback circuits comprise a first-stage common-mode feedback circuit and a second-stage common-mode feedback circuit; wherein the first-stage amplifier and the second-stage amplifier are in direct-current coupling, the input end of the third-stage amplifier is connected with the input end of the first-stage amplifier, and the output end of the third-stage amplifier is connected with the output end of the second-stage amplifier to form a feedforward structure; according to the invention, high bandwidth and linearity can be realized, and compared with a traditional two-stage or three-stage amplifier with a compensation capacitor Cc, the amplifier provided by the invention is more suitable for a resistance feedback structure and can realize better performance.
Owner:XIAN BORUI JIXIN ELECTRONICS TECH
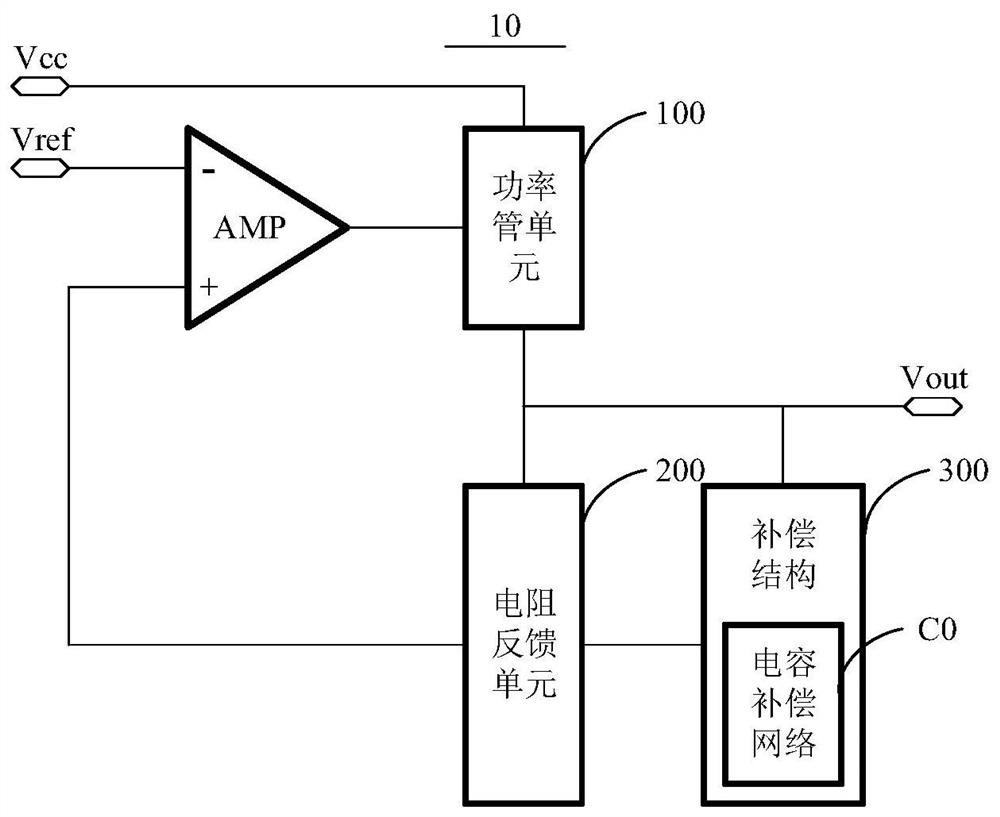
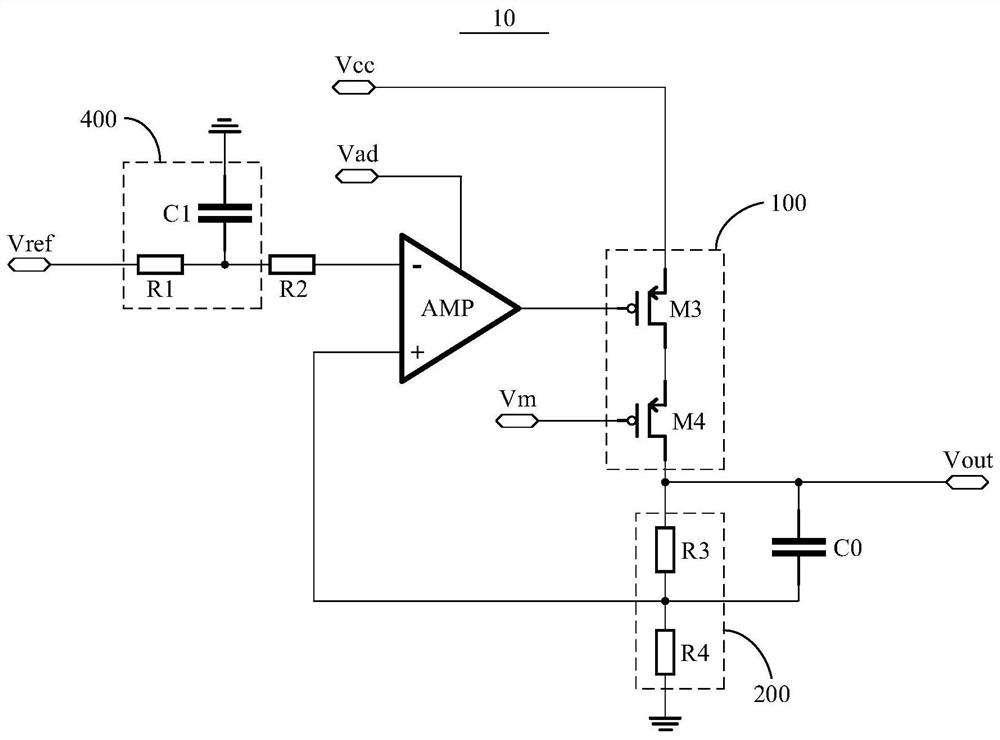
Low dropout regulator, power supply system and electronic equipment
The invention relates to the technical field of power supply management, in particular to a low dropout linear regulator, a power supply system and electronic equipment. The low dropout linear regulator provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises an operational amplifier, a power tube unit, a resistance feedback unit and a compensation structure, a reference voltage is connected to the anti-phase end of the operational amplifier, and the in-phase end of the operational amplifier is connected with the output end of the resistance feedback unit; the output end of the operational amplifier is connected with the control end of the power tube unit, the first end of the power tube unit is connected with a first power supply voltage, the second end of the power tube unit is connected with the input end of the resistance feedback unit and serves as the output end of the low dropout linear regulator, and one end of the compensation structure is connected with the input end of the resistance feedback unit; the other end of the compensation structure is connected with the output end of the resistance feedback unit, and the compensation structure comprises a capacitance compensation network. According to the low dropout linear regulator, a power supply system and the electronic equipment provided by the embodiment of the invention, flicker noise generated by a circuit can be suppressed.
Owner:CHENGDU AMBIT TECH CO LTD
Approximate sine carrier generator with wide-temperature application function and stable and controllable frequency
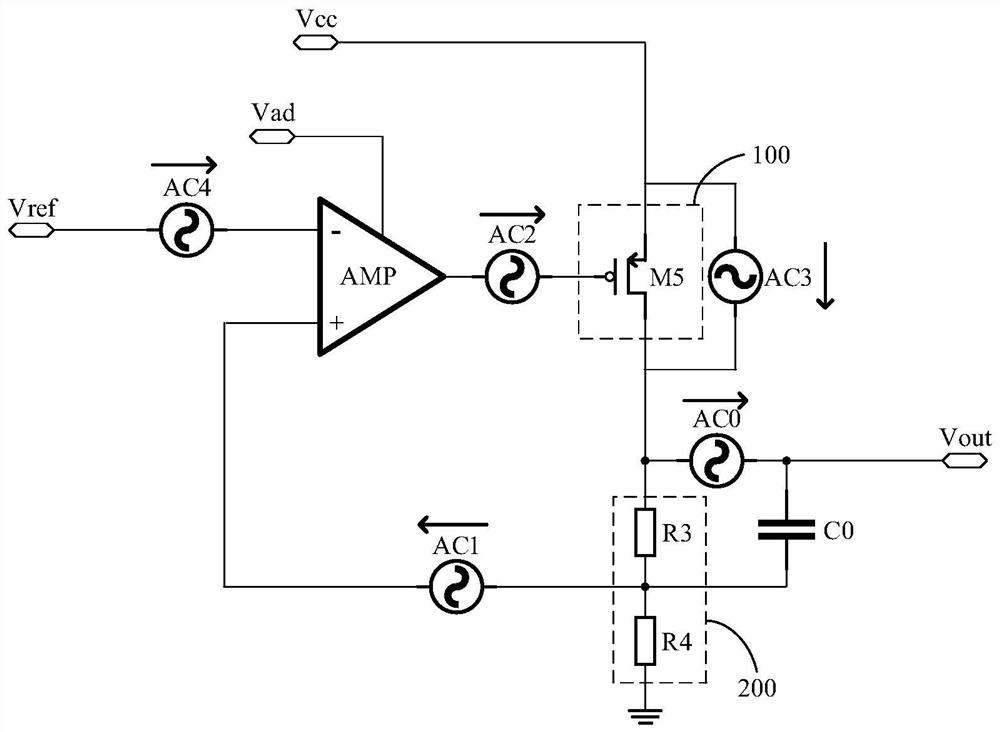
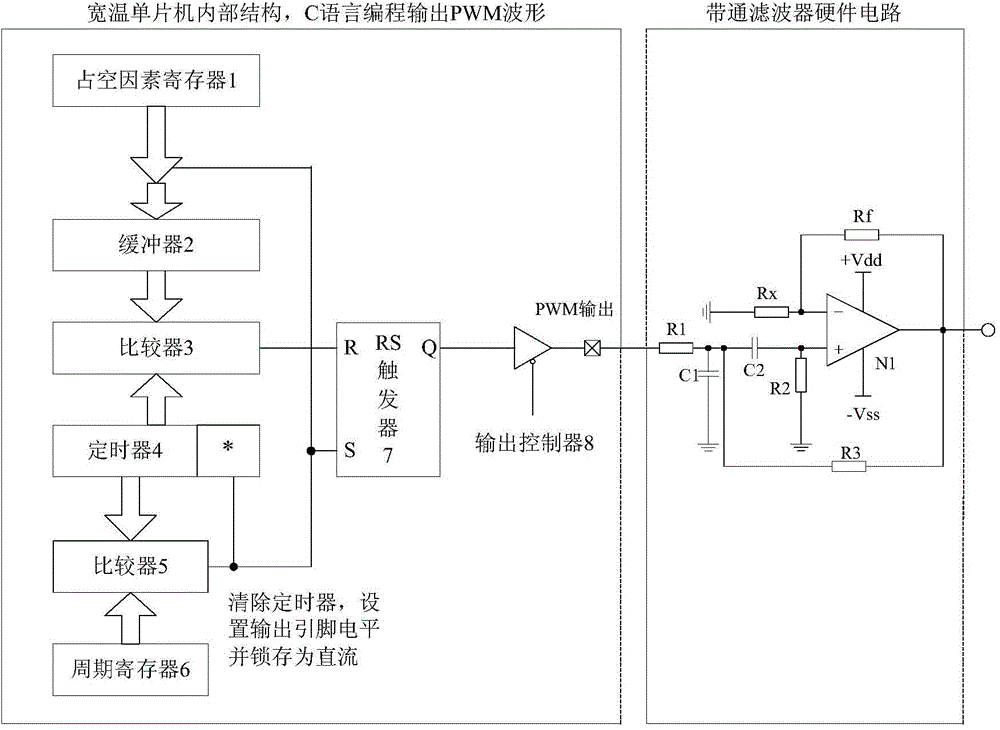
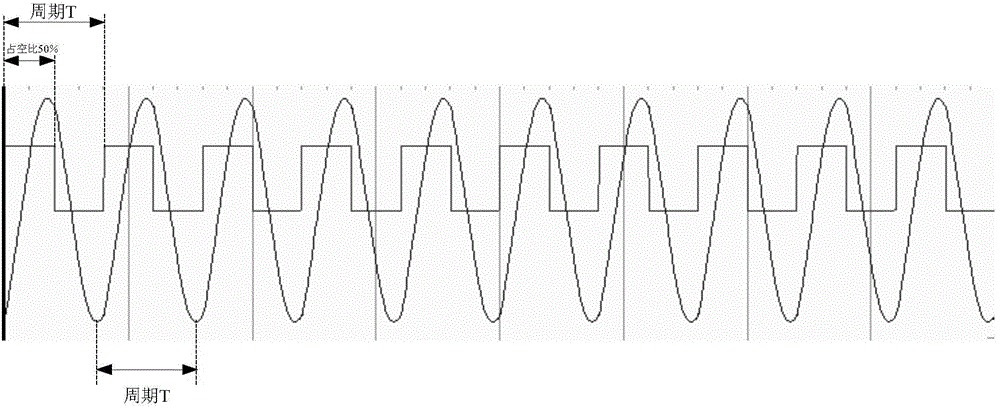
ActiveCN104065360AEasy to implementLow costSinusoidal oscillations train generatorFrequency stabilizationBandpass filtering
The invention relates to an approximate sine carrier generator with the wide-temperature application function and stable and controllable frequency. The approximate sine carrier generator comprises a PWM generation circuit and a band-pass filter connected with the PWM generation circuit. The PWM generation circuit is composed of a wide-temperature single-chip microcomputer combination internal structure in a C language programming or assembly language programming mode. The band-pass filter is a standard voltage controlled voltage source two-stage band-pass filter. The wide-temperature single-chip microcomputer internal structure with the PWM output function comprises a duty factor register 1, a buffer 2, a comparator 3, a timer 4, a comparator 5, a period register 6, an RS trigger 7 and an output controller 8. The band-pass filter comprises a low-pass filter resistor R1, a capacitor C1, a high-pass filter capacitor C2, a resistor R2, a feedback resistor R3, an in-phase proportion operational circuit resistor Rx, a resistor Rf and an operational amplifier N1. The approximate sine carrier generator can achieve the wide-temperature application function, the frequency is stable and controllable, and generated approximate sine waves can be used as adjusted carrier waves in a digital modulation system.
Owner:航天科工惯性技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com