Patents
Literature
130results about How to "Improve noise figure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
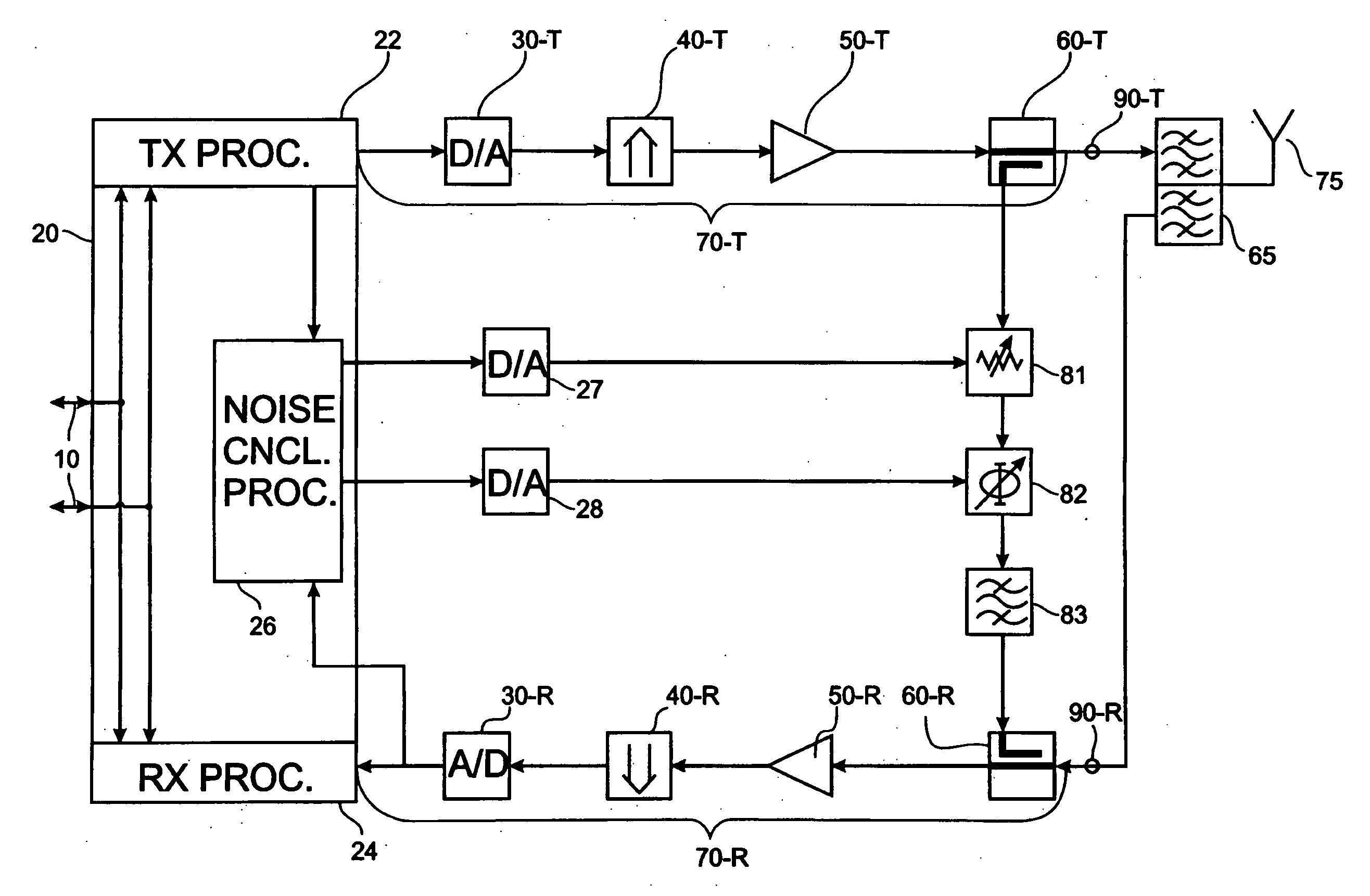
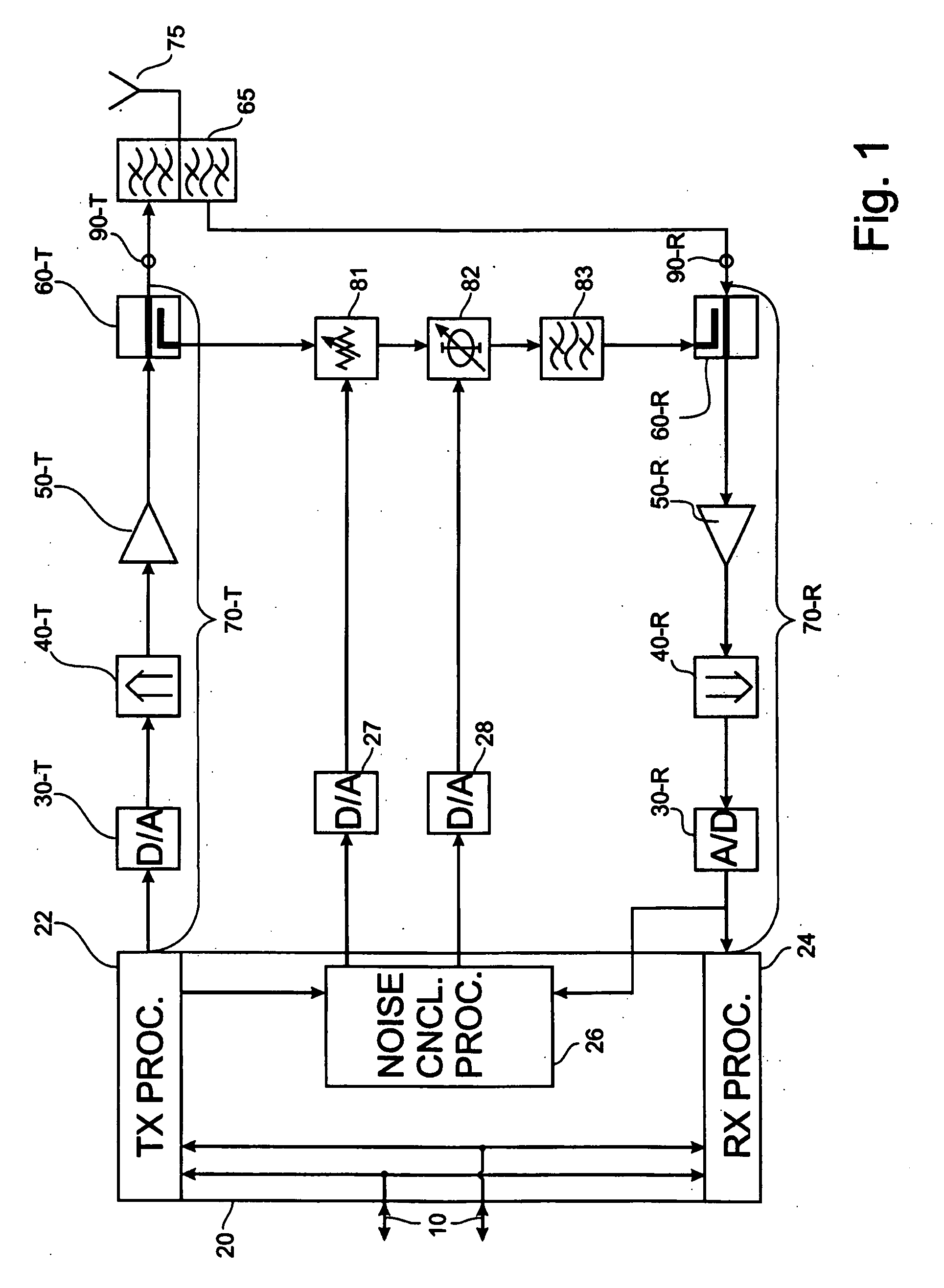
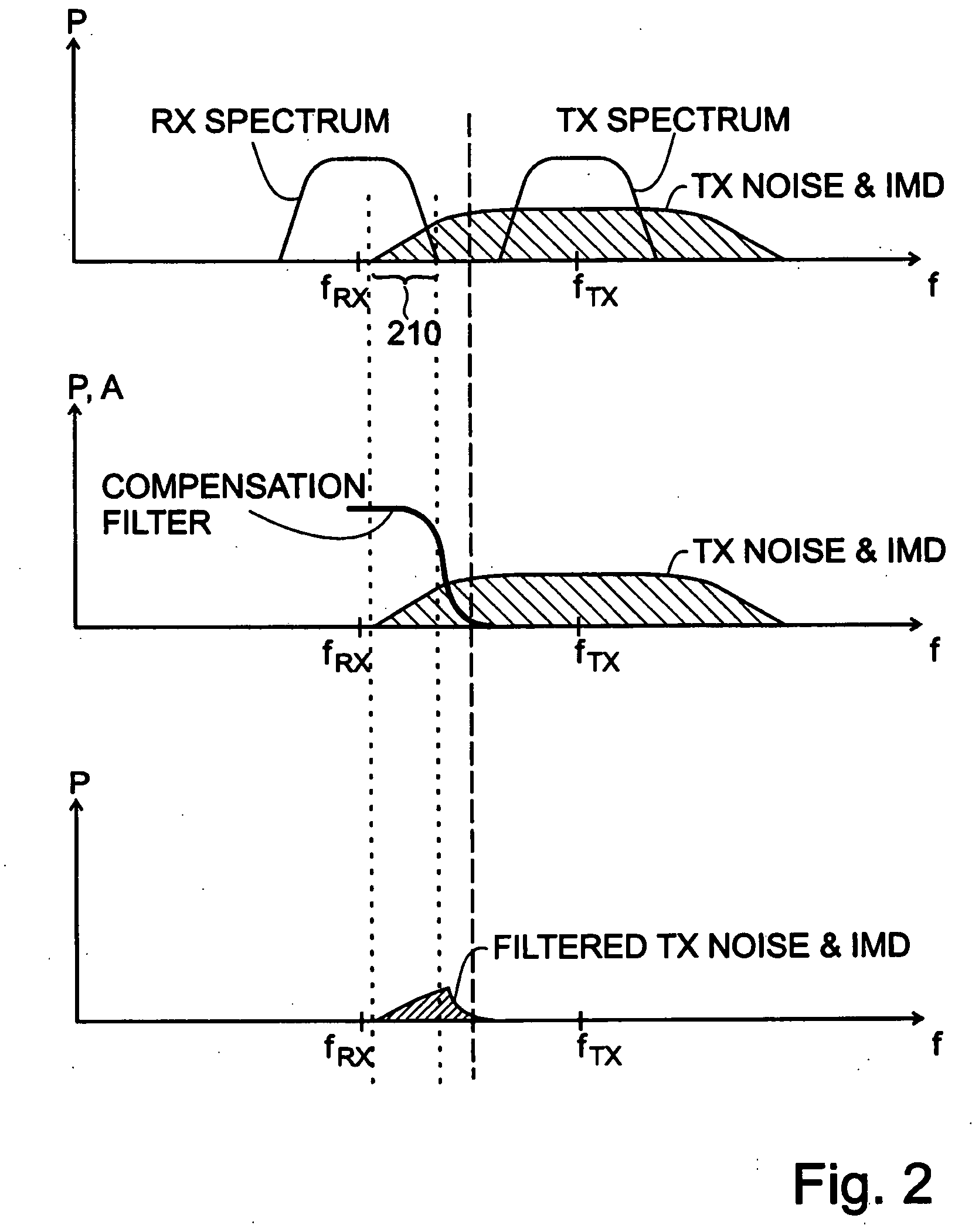
Method and apparatus for interference cancellation
ActiveUS20100197231A1Lower performance requirementsLow costTransmission noise suppressionInterference cancellerTransceiver
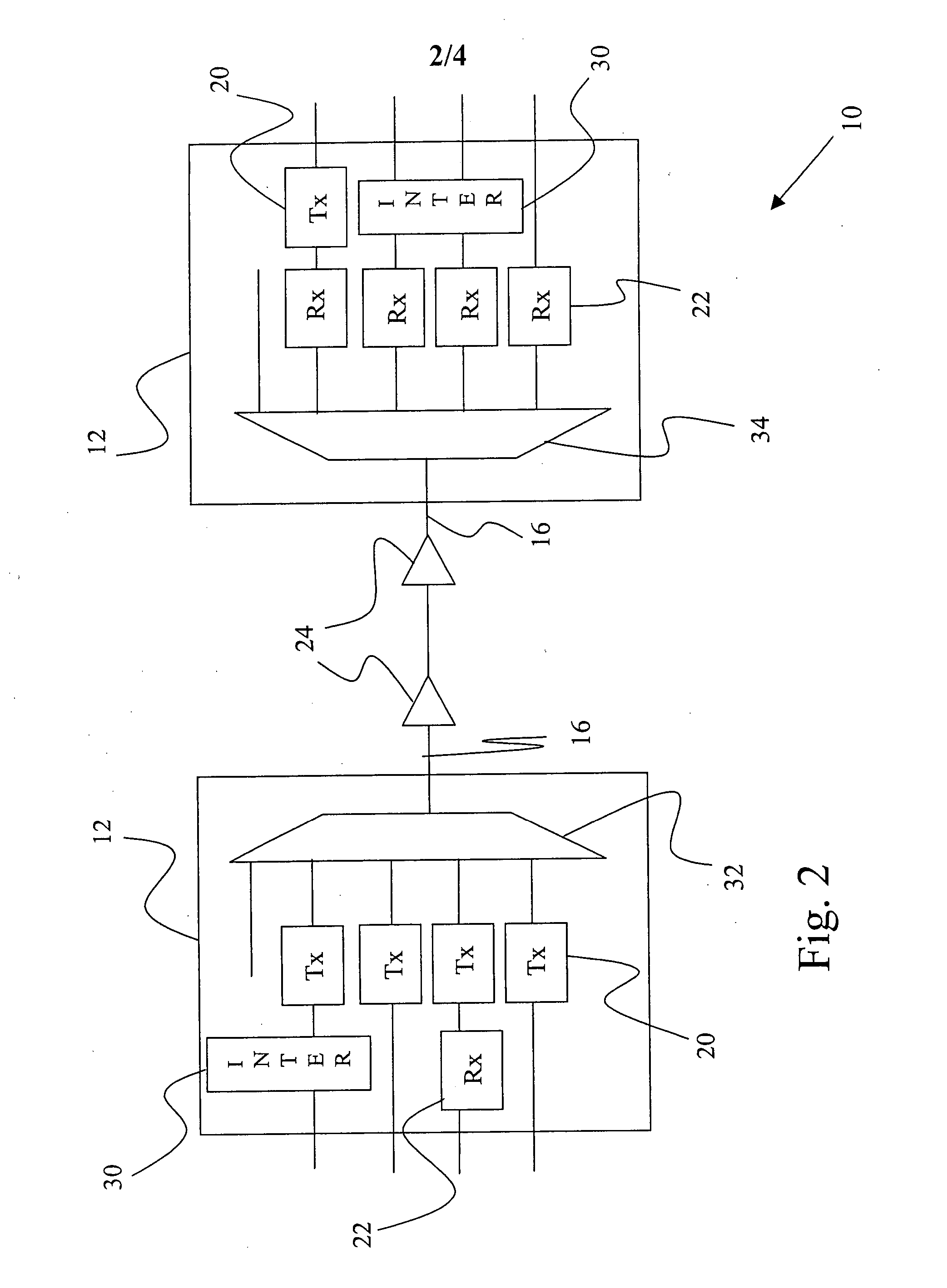
An interference canceller between a transmit chain and a receive chain of a transceiver is proposed to complement the action of a diplexer, or duplex filter, that is part of the transceiver. The interference canceller comprises a transmit chain tap, a receive chain coupler for coupling an interference compensation signal into the receive chain, and an interference signal processing path between the transmit chain tap and the receive chain coupler. The interference signal processing path comprises a filter having filtering characteristics similar or corresponding to the filtering characteristic of a receive portion of said diplexer. A corresponding method for interference cancellation is also proposed. Computer-program products for the manufacture of the interference canceller and the execution of the method are also proposed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
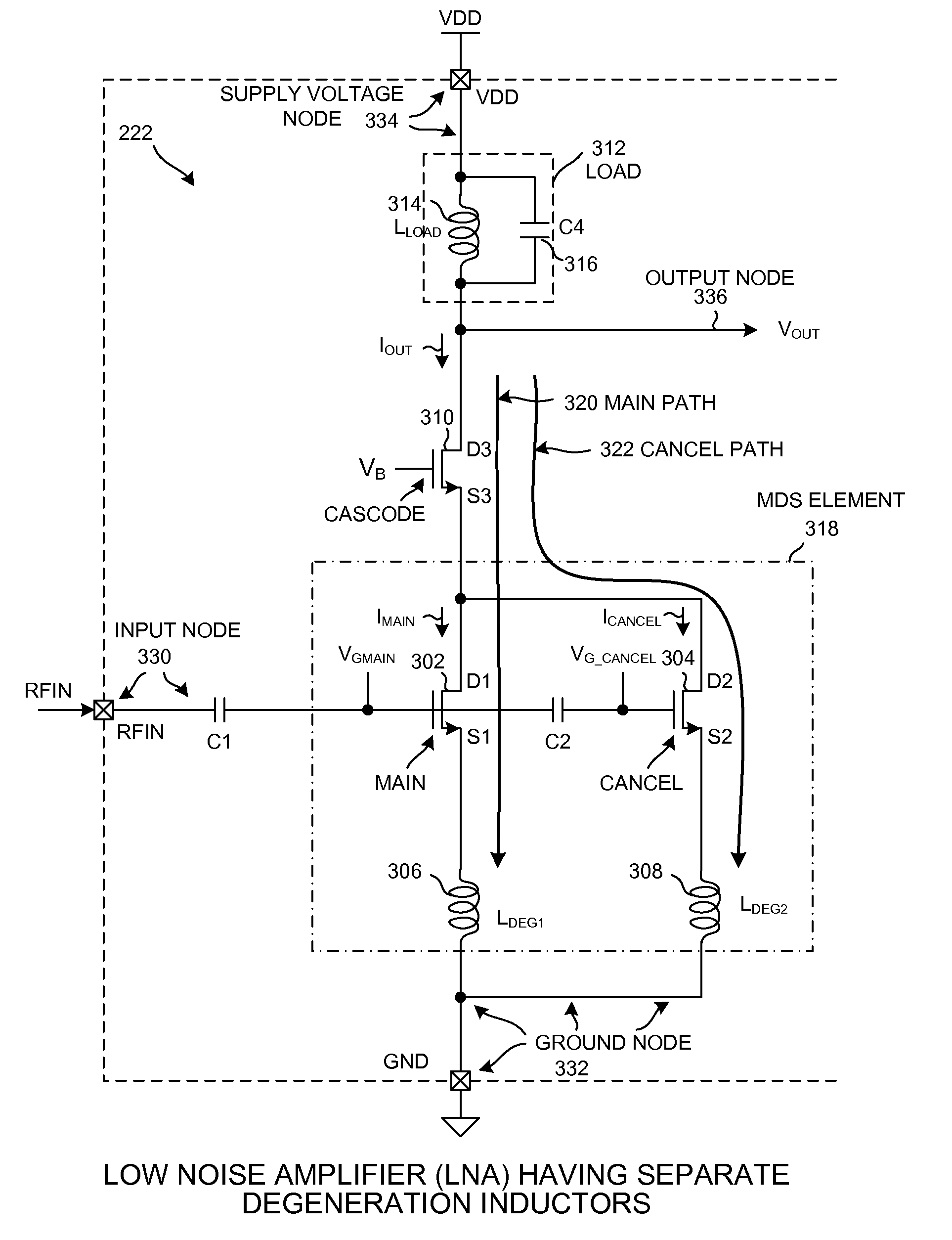
Multi-linearity mode lna having a deboost current path
ActiveUS20090174481A1Easy to adjustLess iterationGain controlGated amplifiersNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
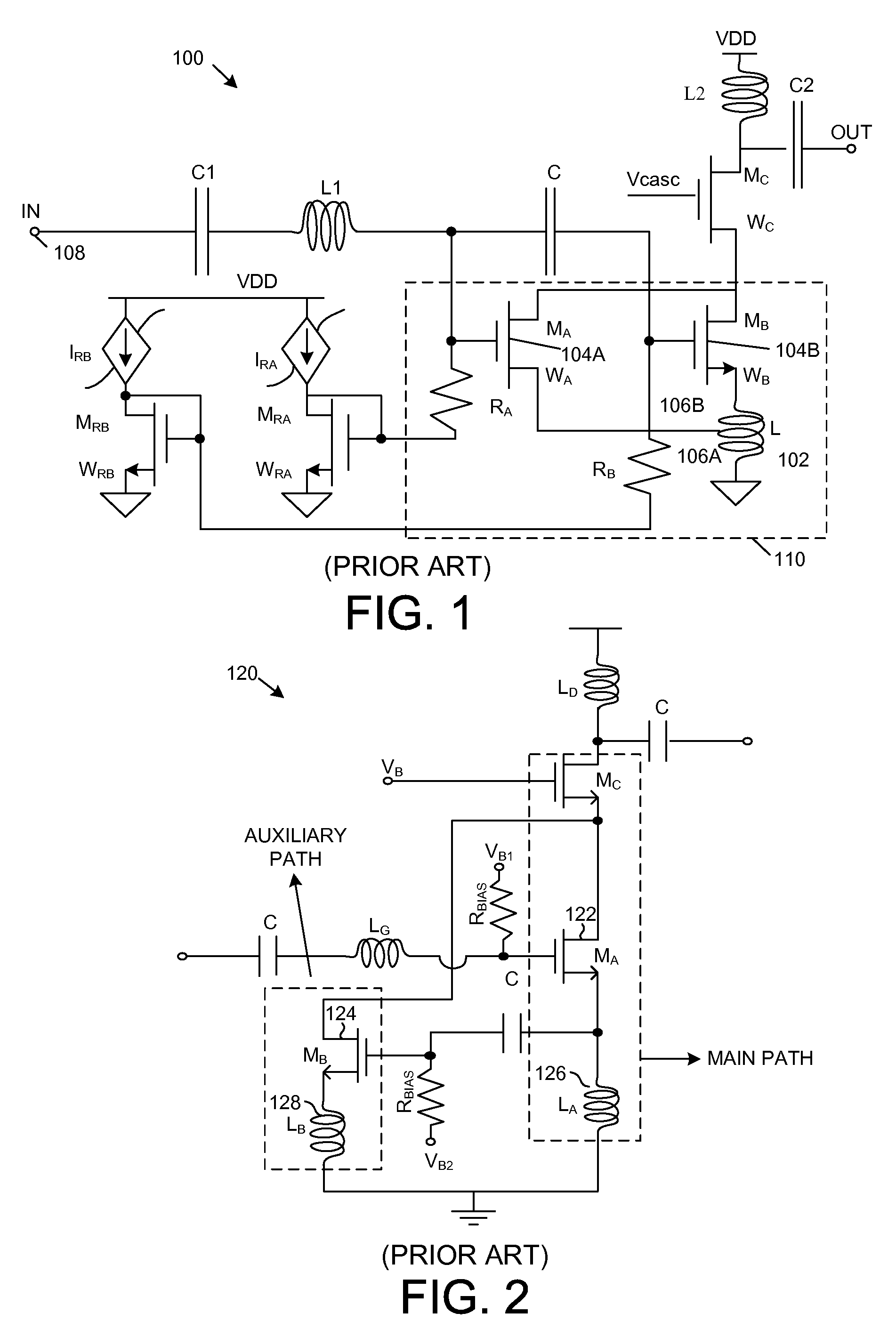
A modified derivative superposition (MDS) low noise amplifier (LNA) includes a main current path and a cancel current path. Third-order distortion in the cancel path is used to cancel third-order distortion in the main path. In one novel aspect, there is a separate source degeneration inductor for each of the two current paths, thereby facilitating tuning of one current path without affecting the other current path. In a second novel aspect, a deboost current path is provided that does not pass through the LNA load. The deboost current allows negative feedback to be increased without generating headroom problems. In a third novel aspect, the cancel current path and / or deboost current path is programmably disabled to reduce power consumption and improve noise figure in operational modes that do not require high linearity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Ultra high-speed si/sige modulation-doped field effect transistors on ultra thin soi/sgoi substrate
InactiveUS20050045905A1Improve RF performanceUltra-high speed performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow noiseUltra high speed
A silicon and silicon germanium based semiconductor MODFET device design and method of manufacture. The MODFET design includes a high-mobility layer structure capable of ultra high-speed, low-noise for a variety of communication applications including RF, microwave, sub-millimeter-wave and millimeter-wave. The epitaxial field effect transistor layer structure includes critical (vertical and lateral) device scaling and layer structure design for a high mobility strained n-channel and p-channel transistor incorporating silicon and silicon germanium layers to form the optimum modulation-doped heterostructure on an ultra thin SOI or SGOI substrate capable of achieving greatly improved RF performance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
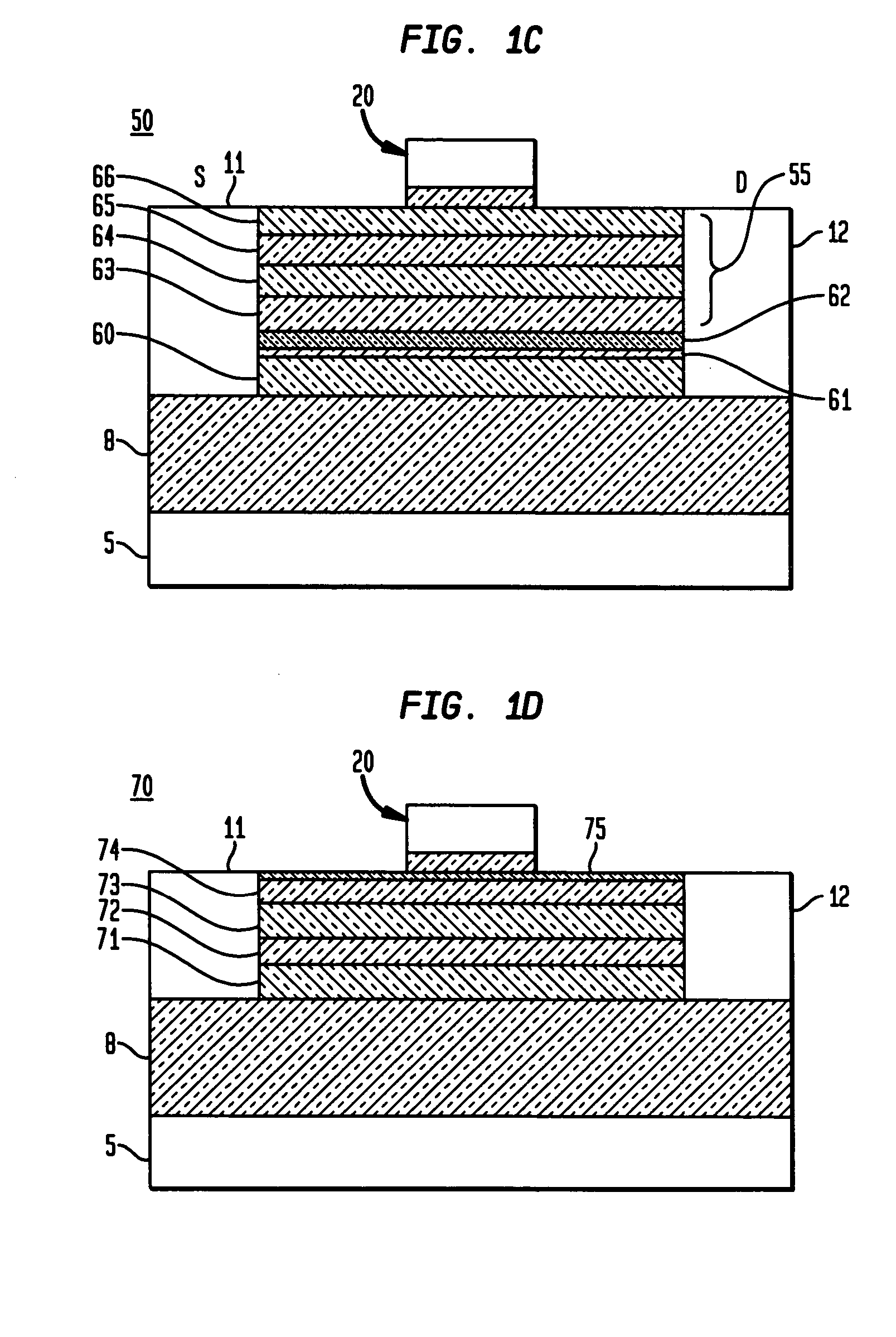
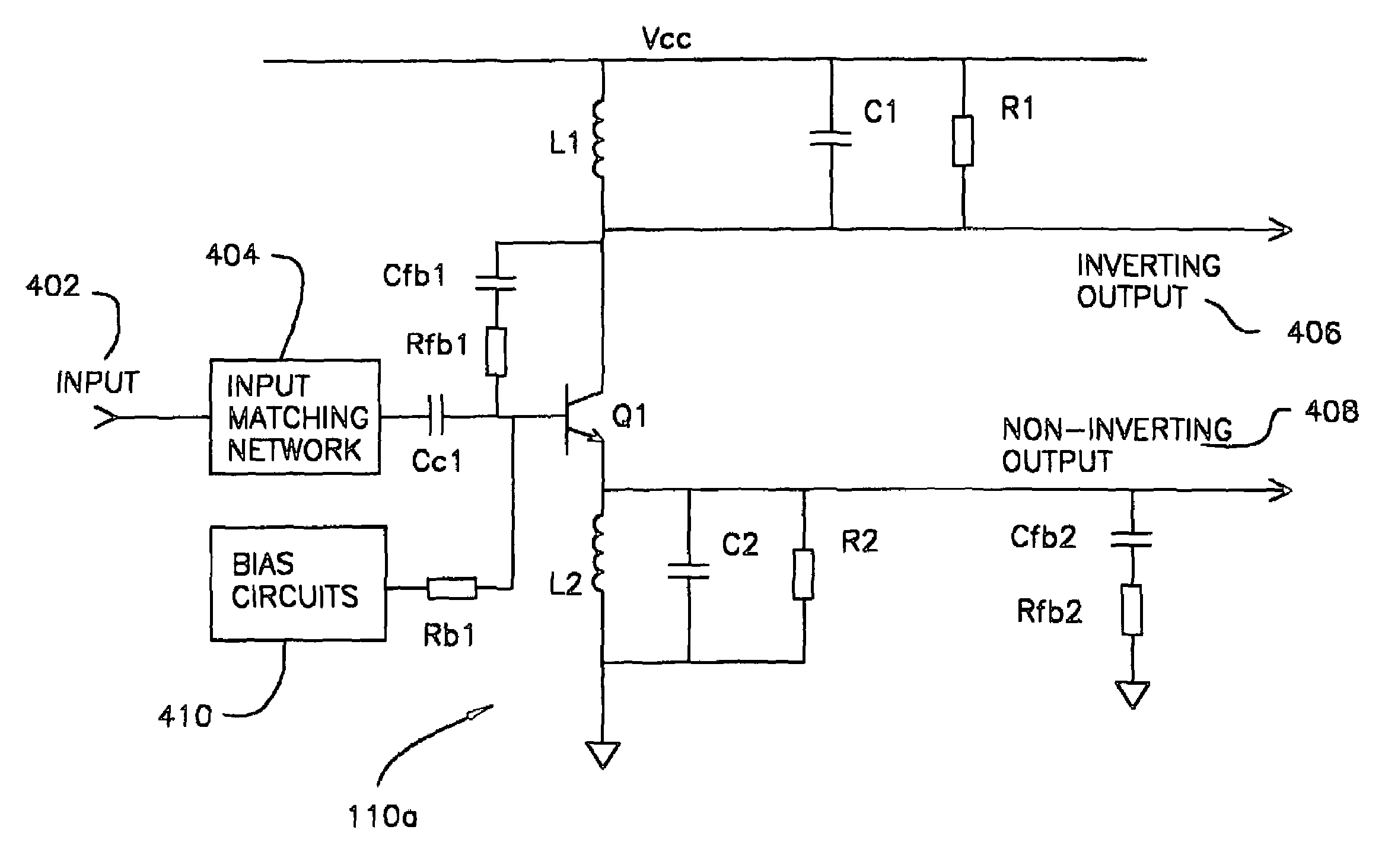
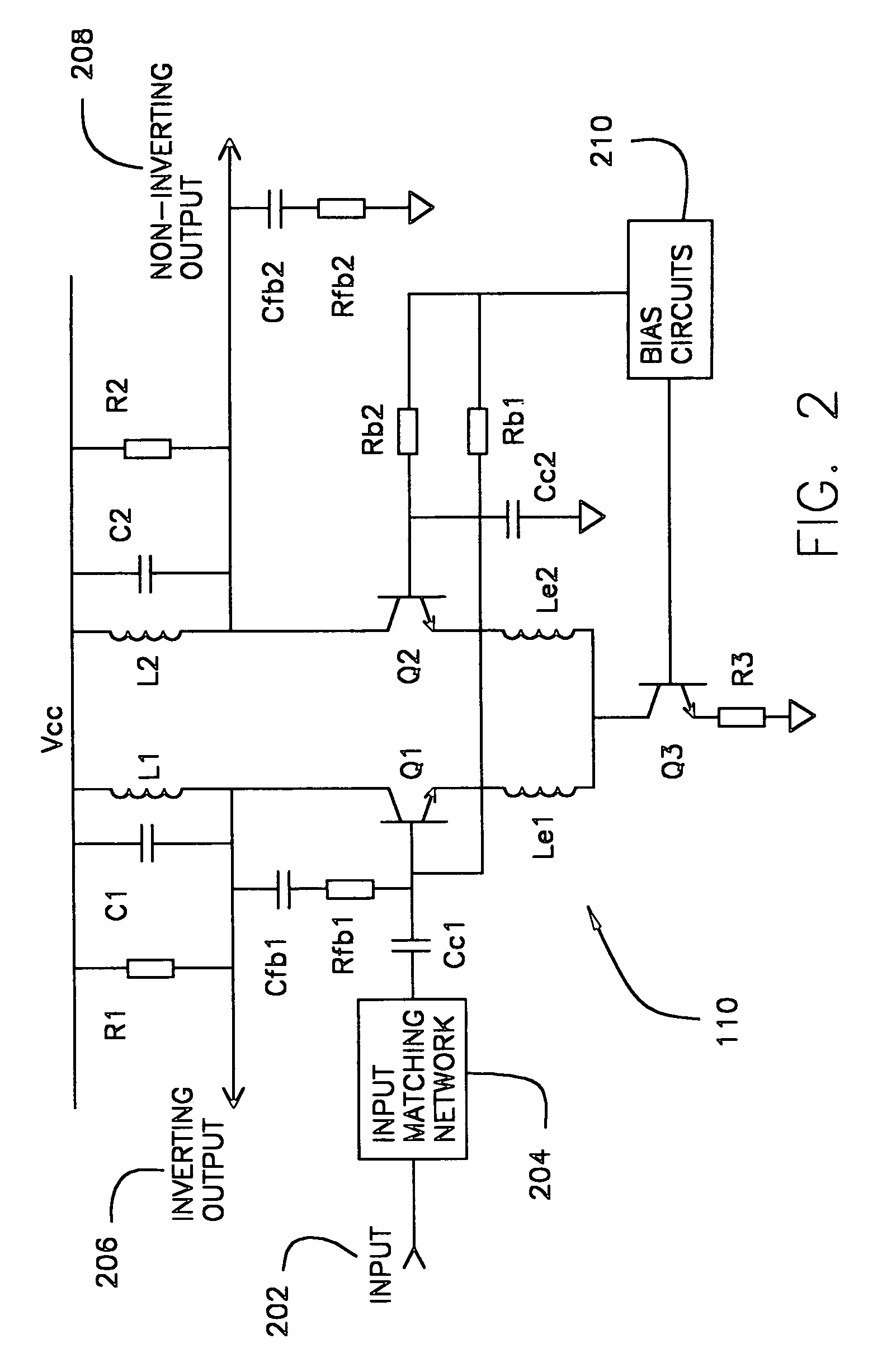
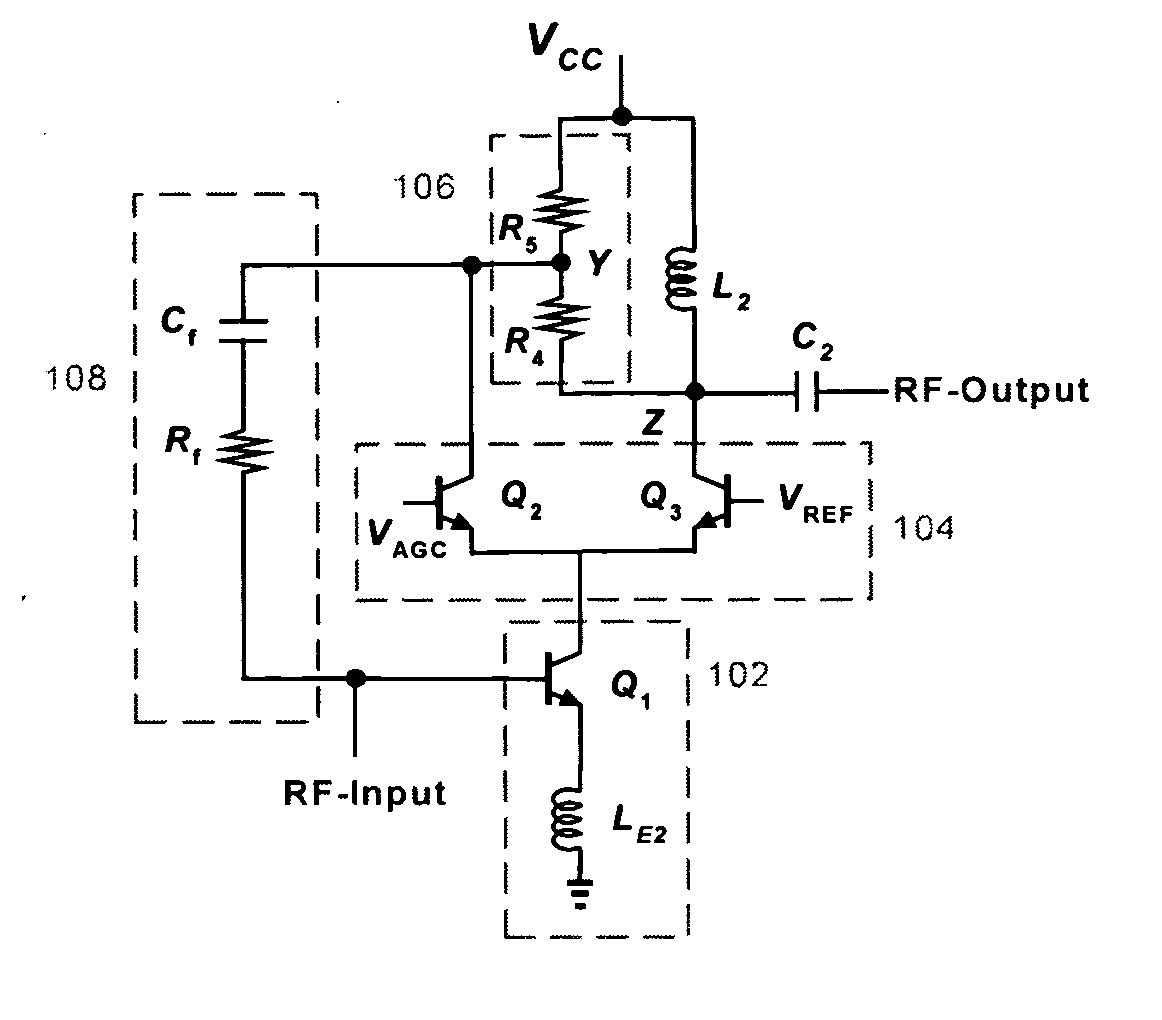
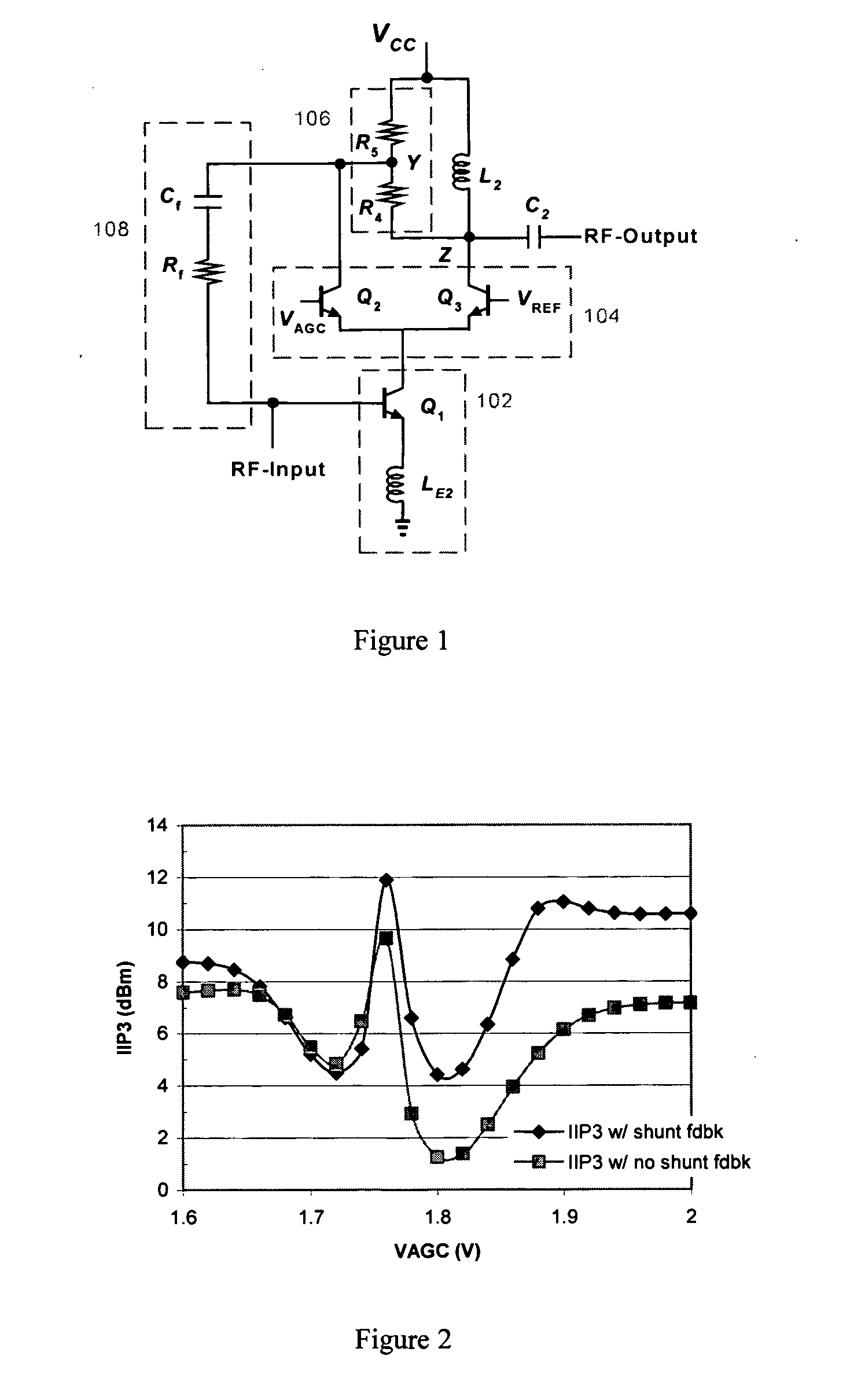
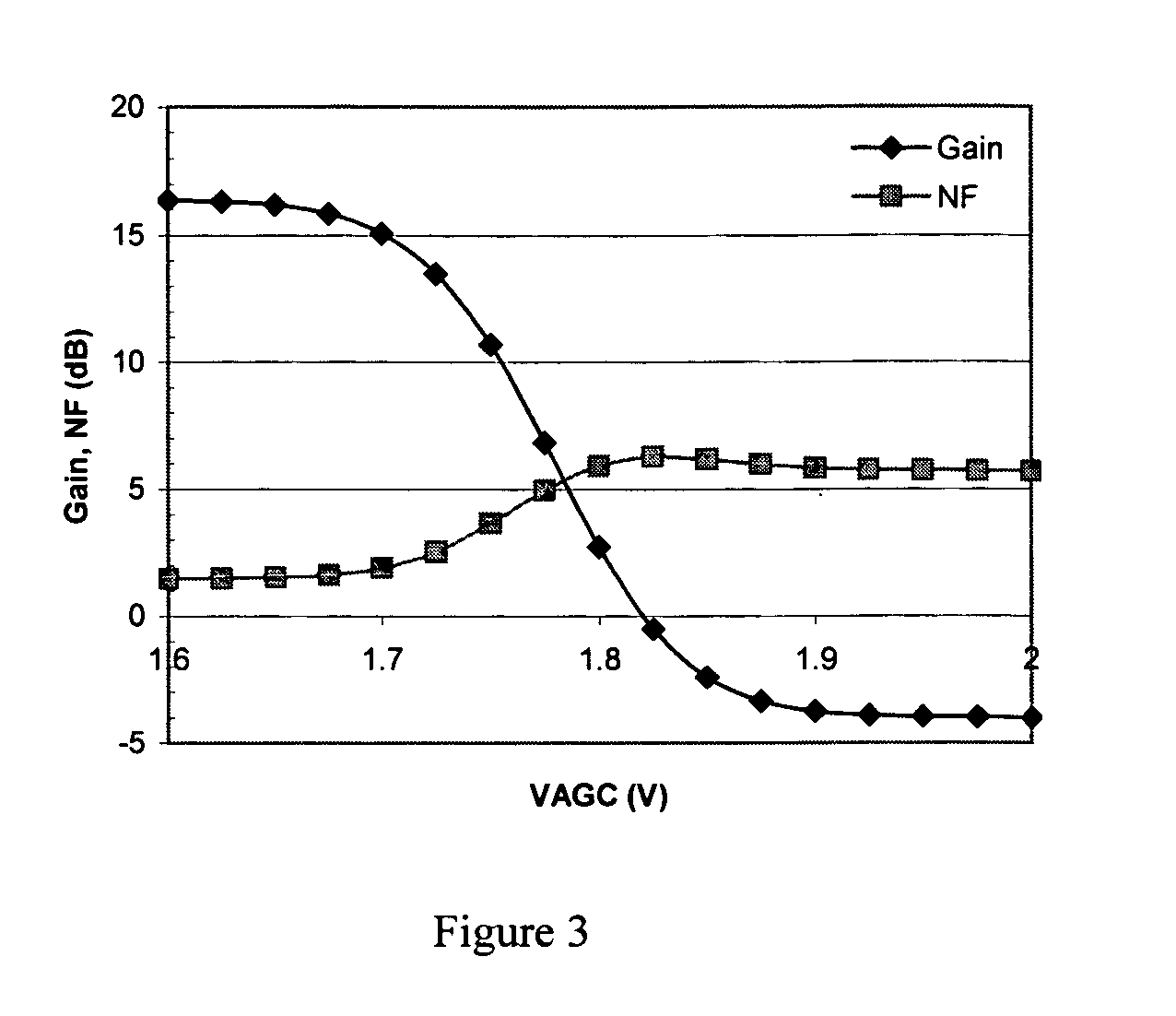
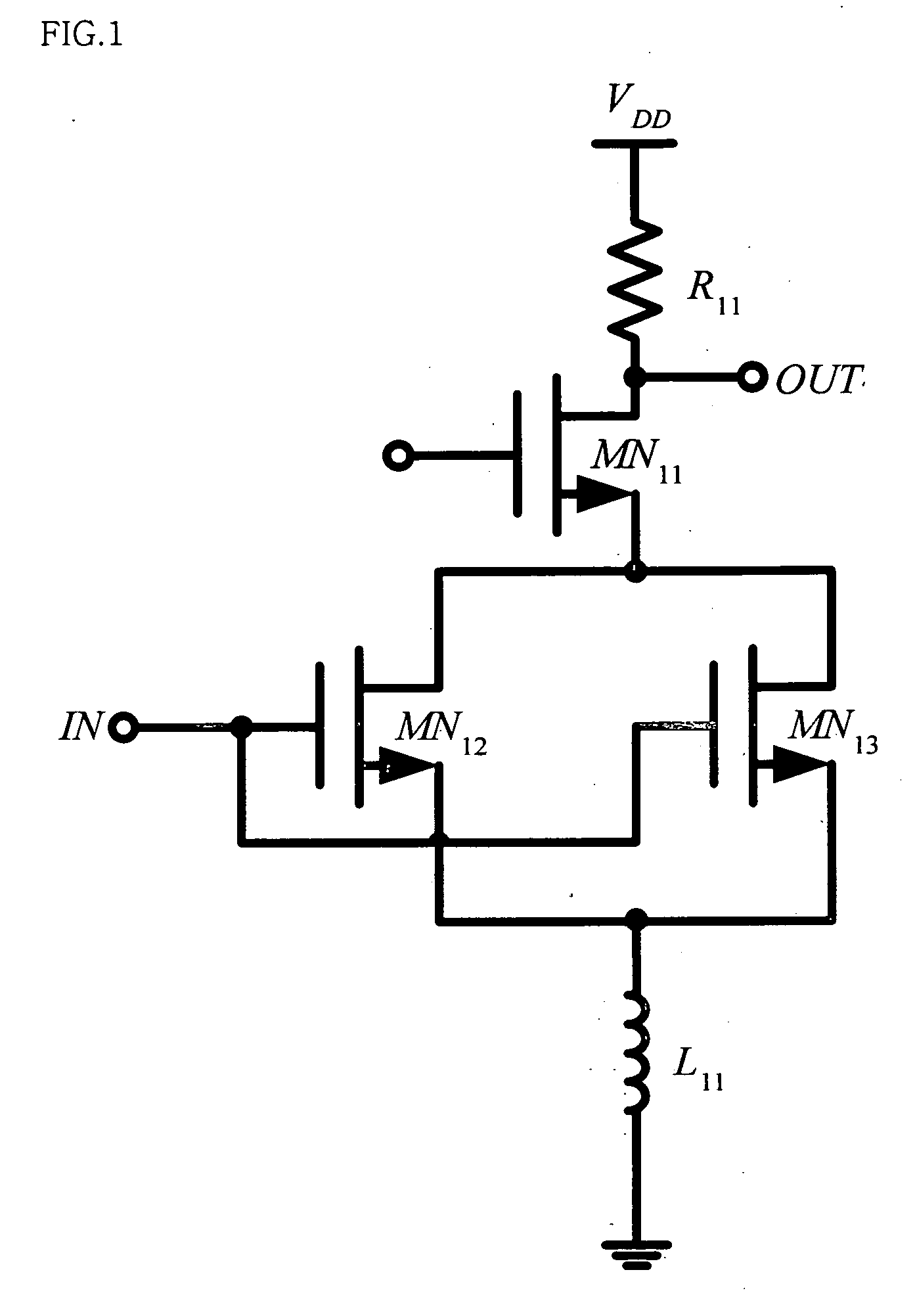
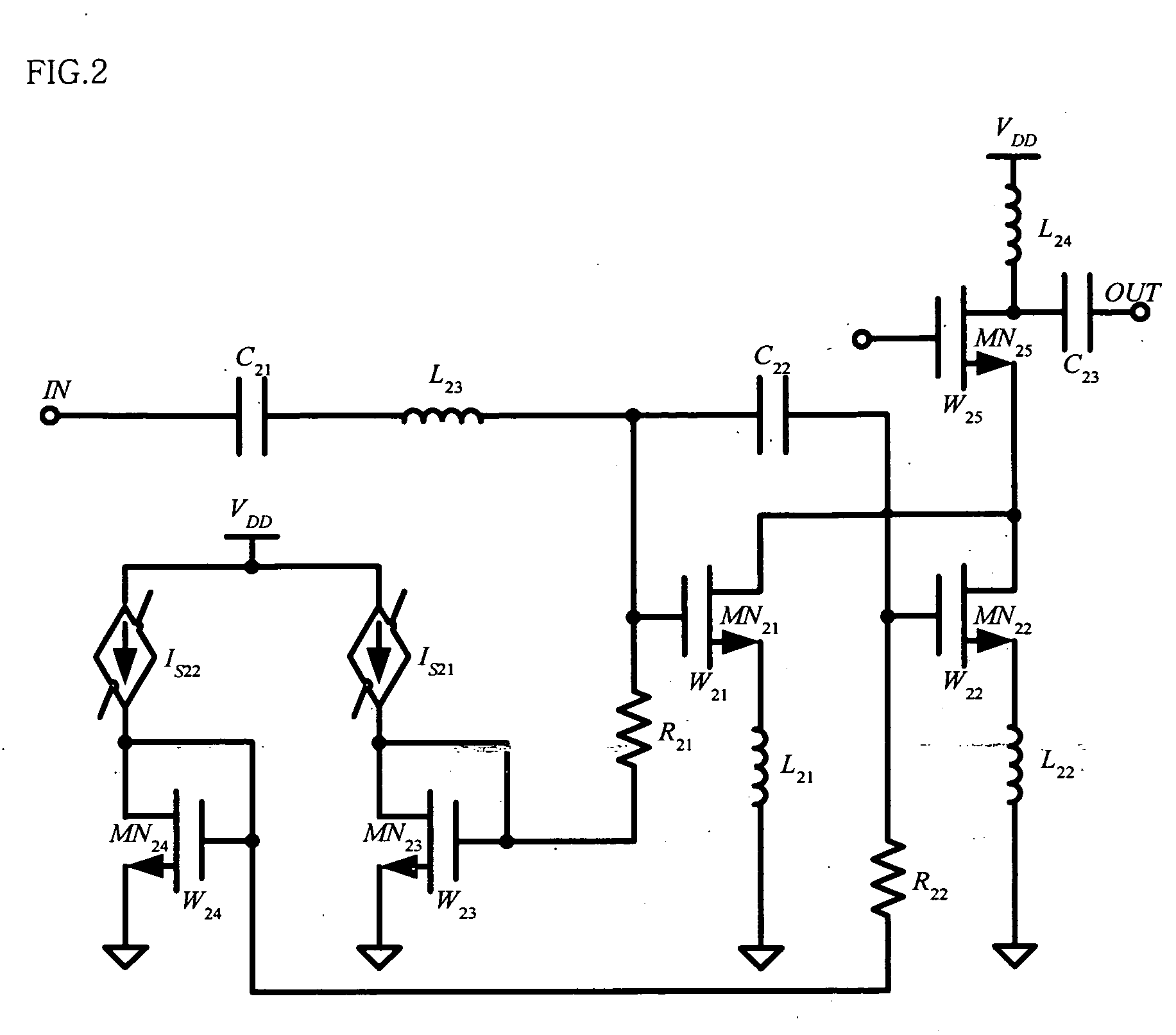
Two-stage variable-gain mixer employing shunt feedback
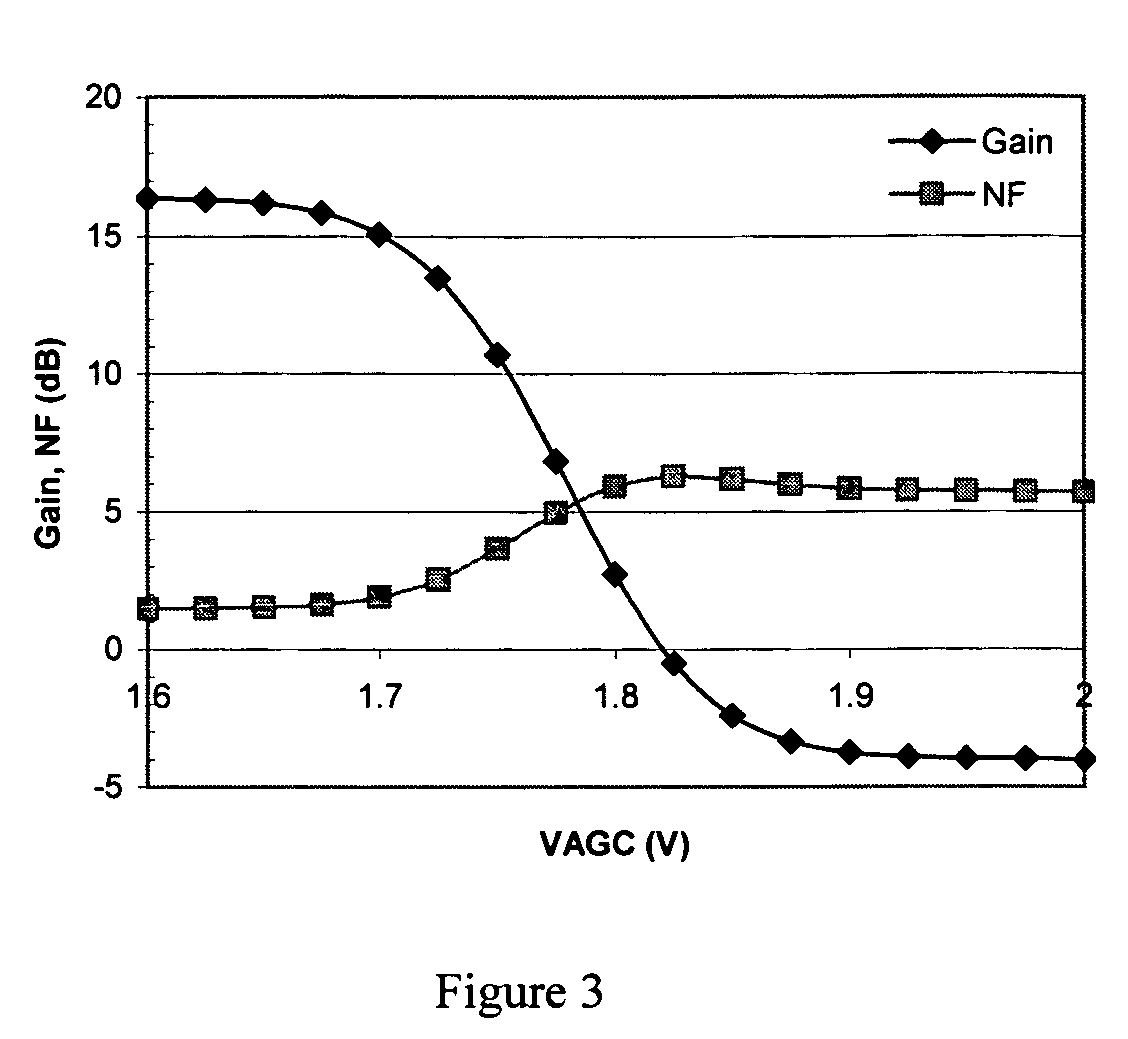
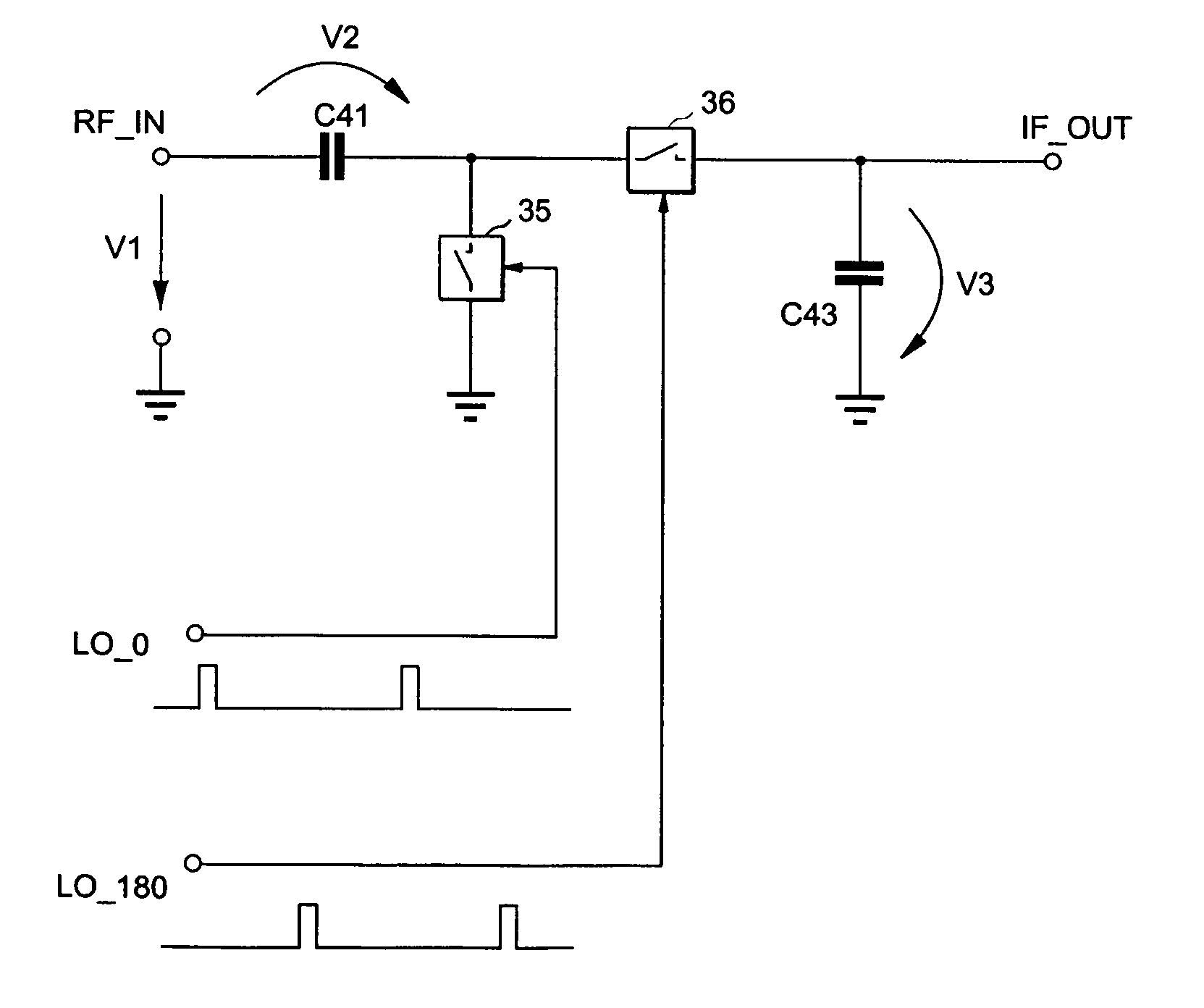
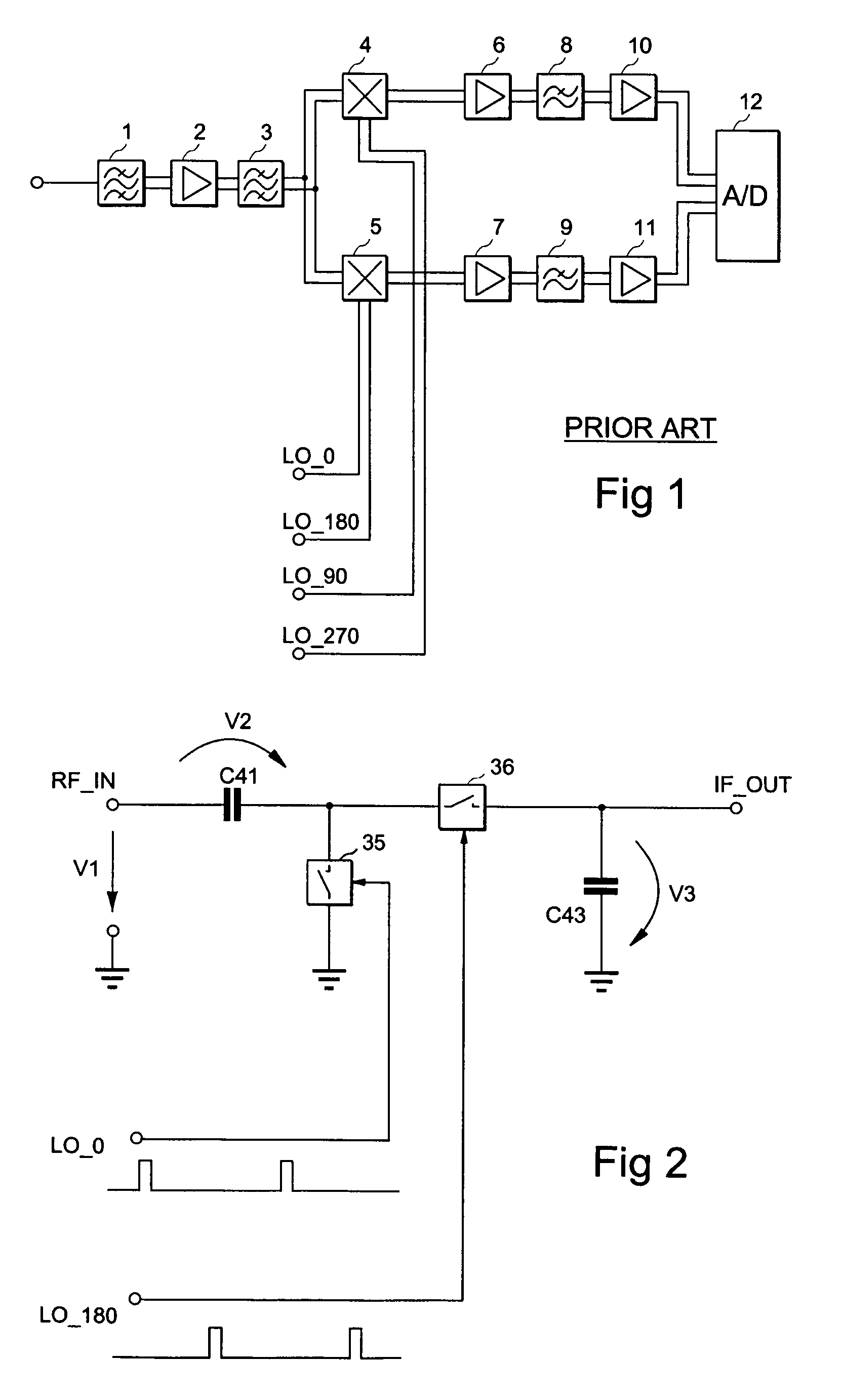
InactiveUS7035616B2Improve noise figureIncreased power consumptionBalance-unbalance networksModulation transference balanced arrangementsFrequency mixerEngineering
Owner:IBM CORP
Continuous variable-gain low-noise amplifier
InactiveUS20050134385A1Little changeImprove reverse isolationNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
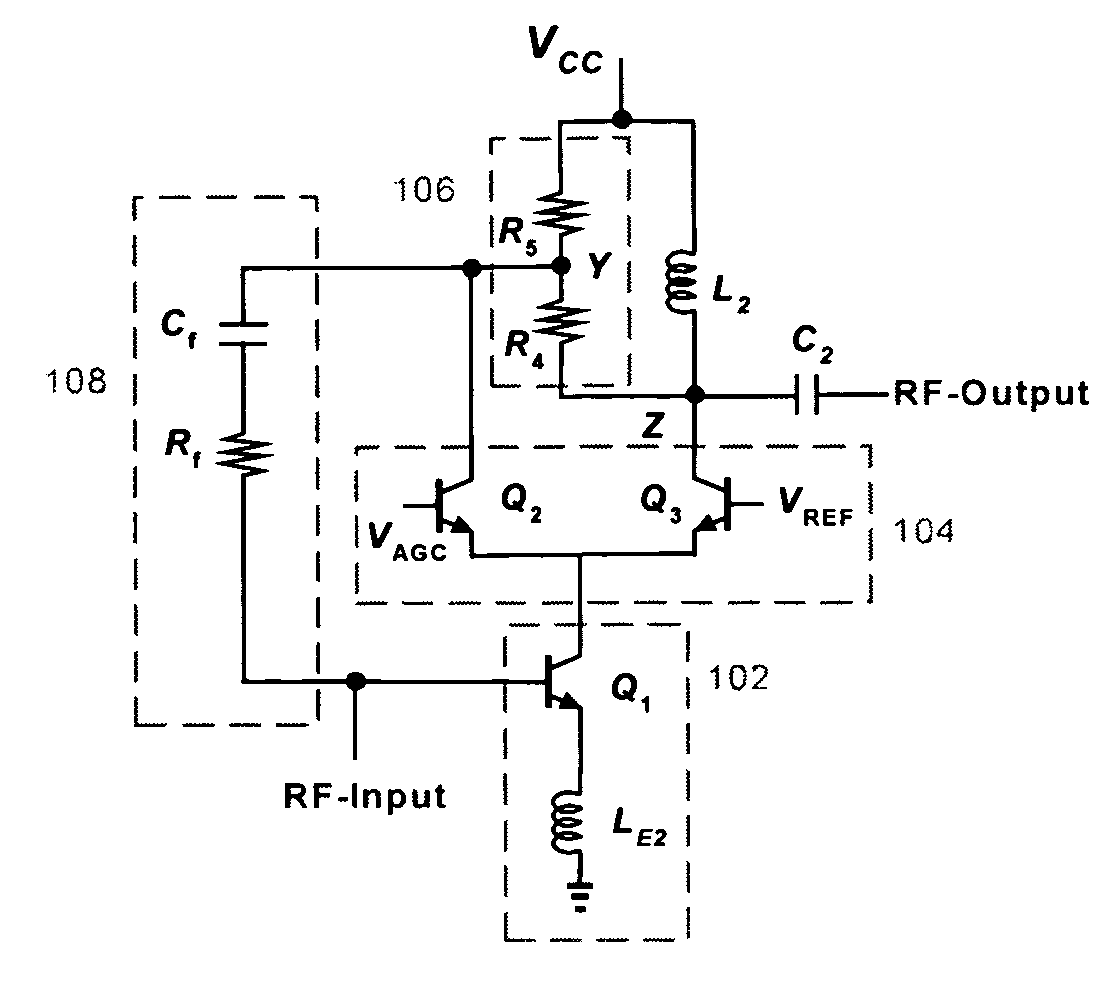
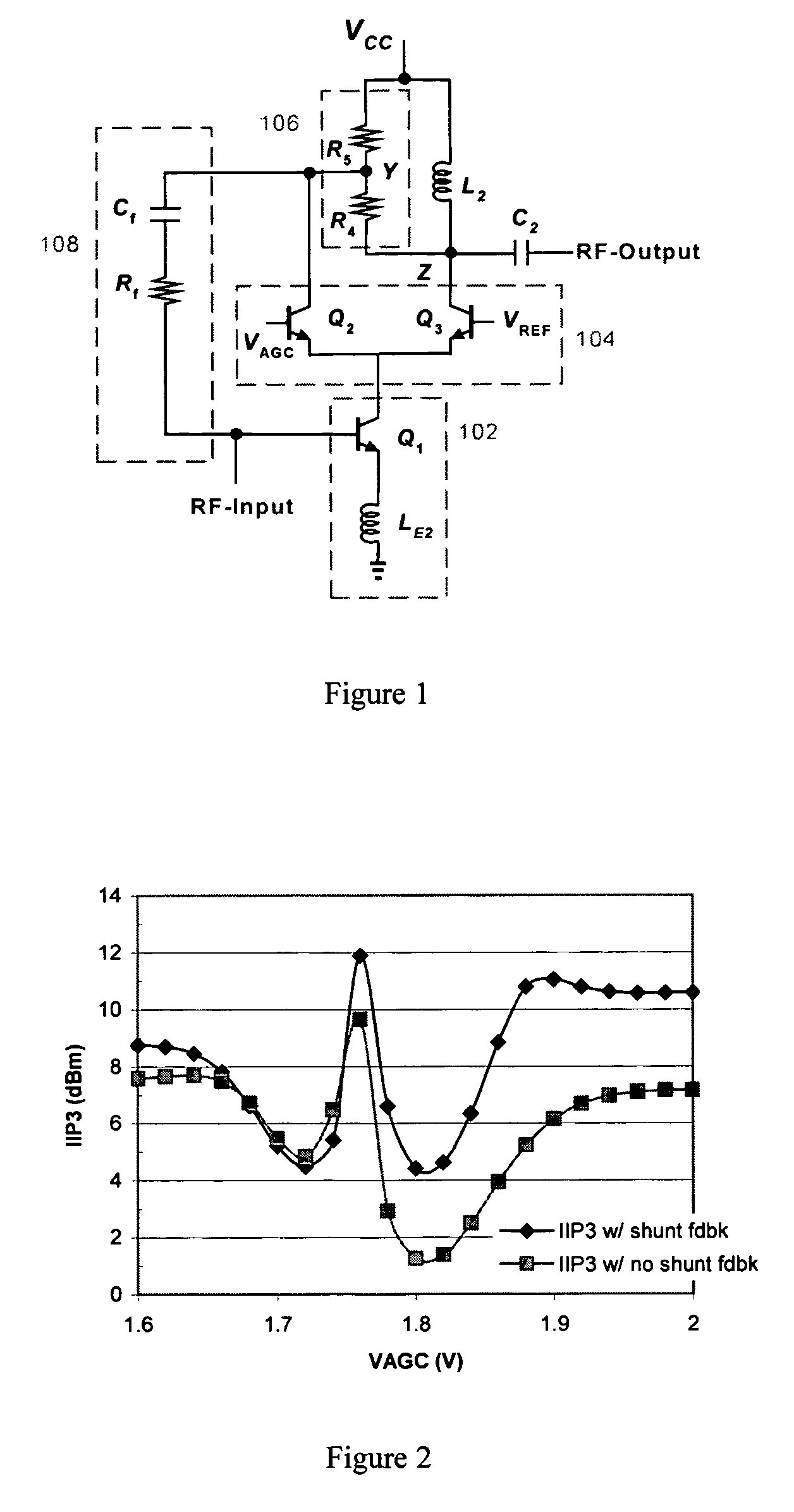
Continuous variable-gain low-noise amplifier. The amplifier continuously adjusts its gain between well-defined high and low values by using a cascode current-steering circuit to partition signal current between two different nodes of an output loading network. A shunt feedback network connected from an intermediate node of the loading network to the input provides negative feedback that linearizes the amplifier as its gain is decreased. The circuit degrades the noise figure at lower gains by varying the gain without directly dumping the signal current to the power supply. The circuit produces only small changes in input and output impedances and preserves an improved reverse-isolation cascode characteristic as the gain is controlled.
Owner:QUINTIC MICROELECTRONICS WUXI
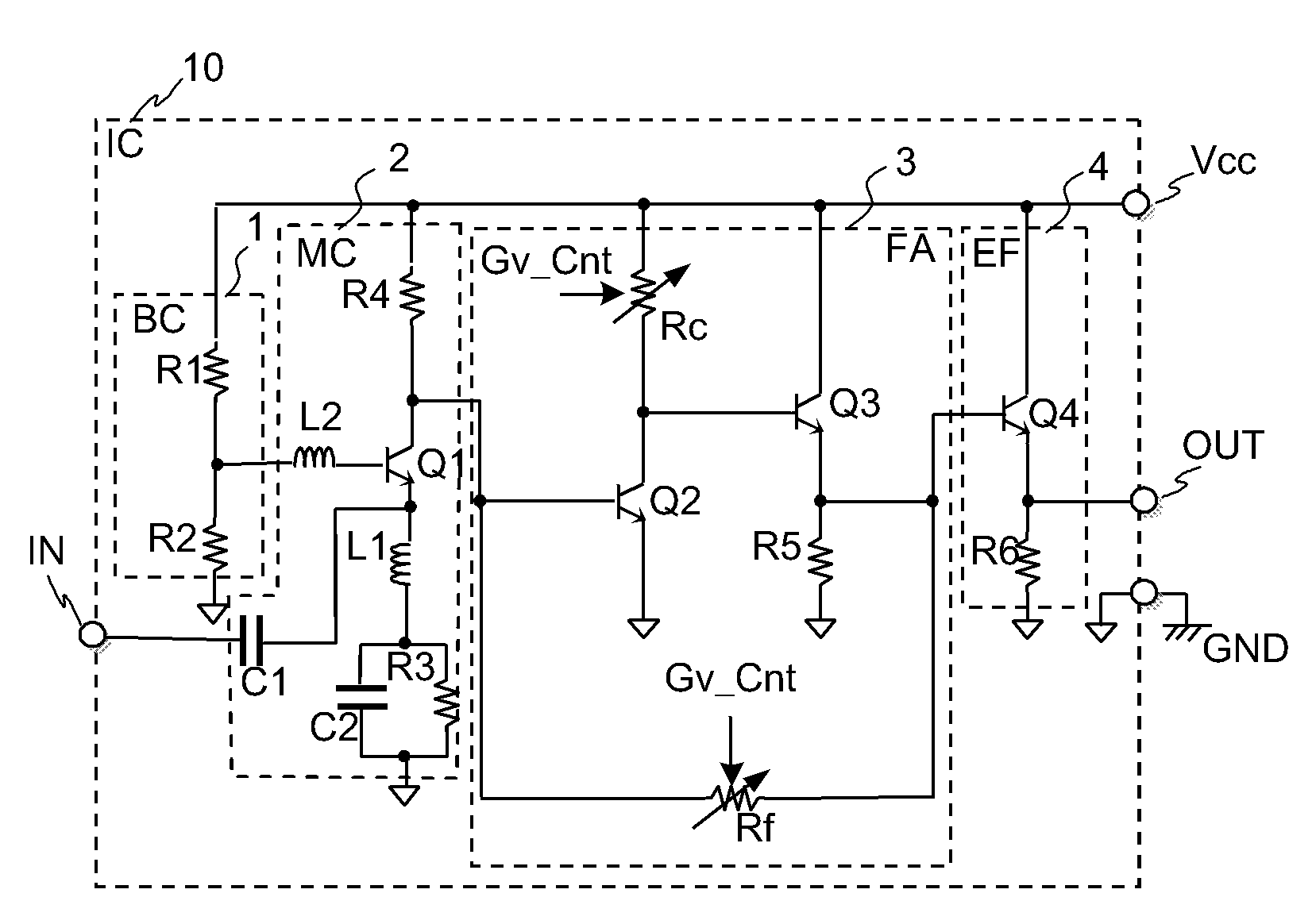
Semiconductor integrated circuit with variable gain amplifier
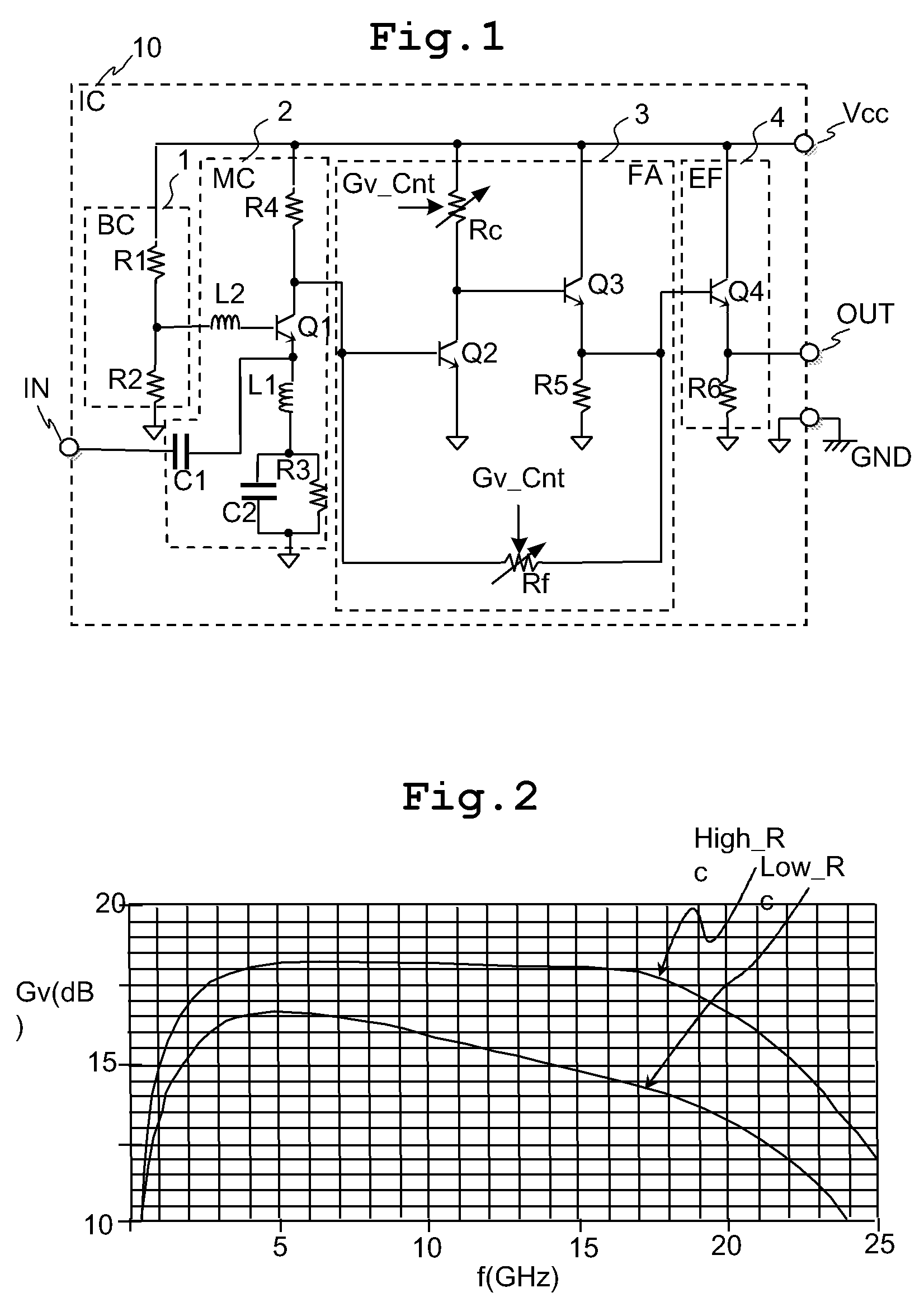
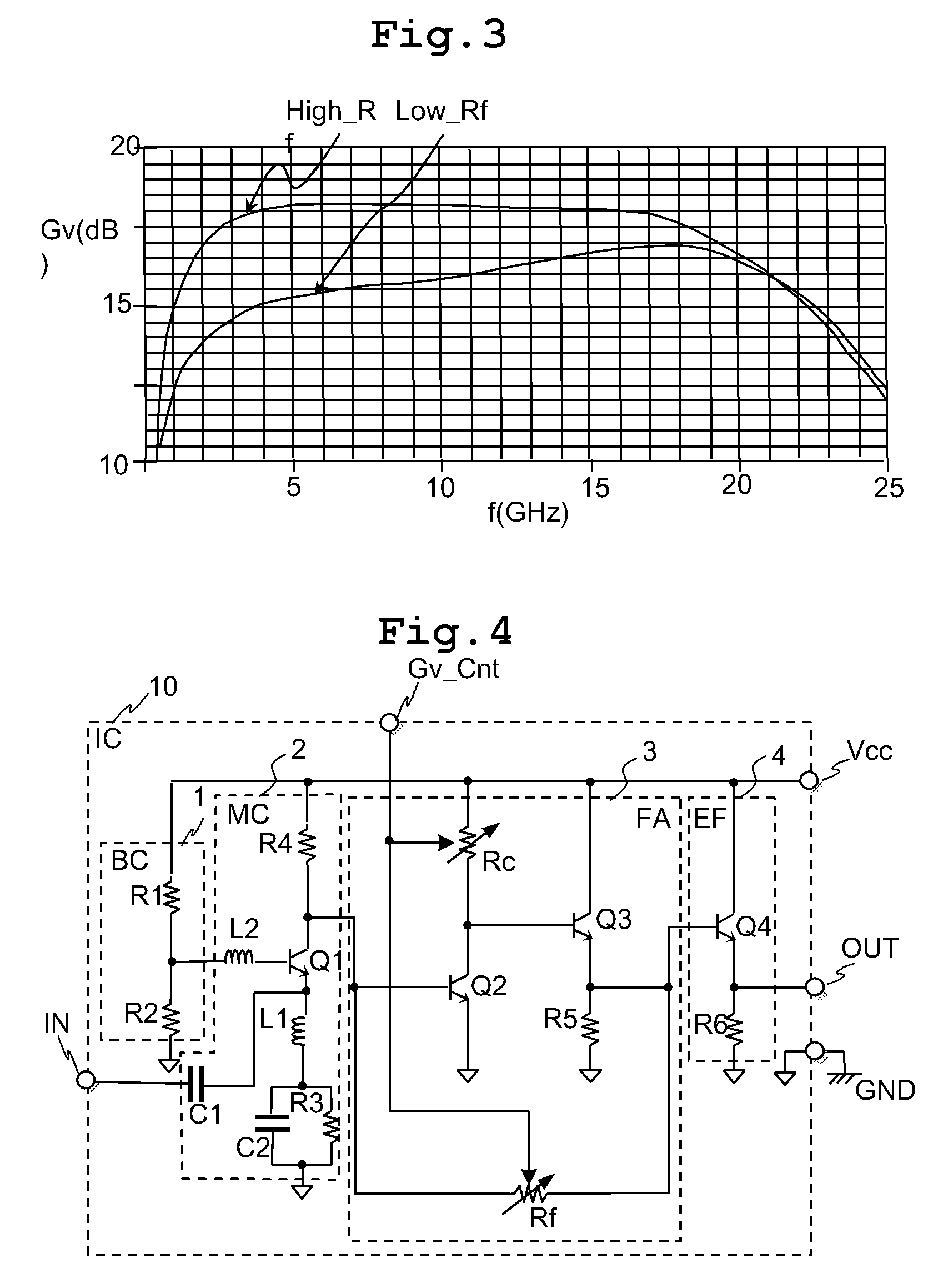
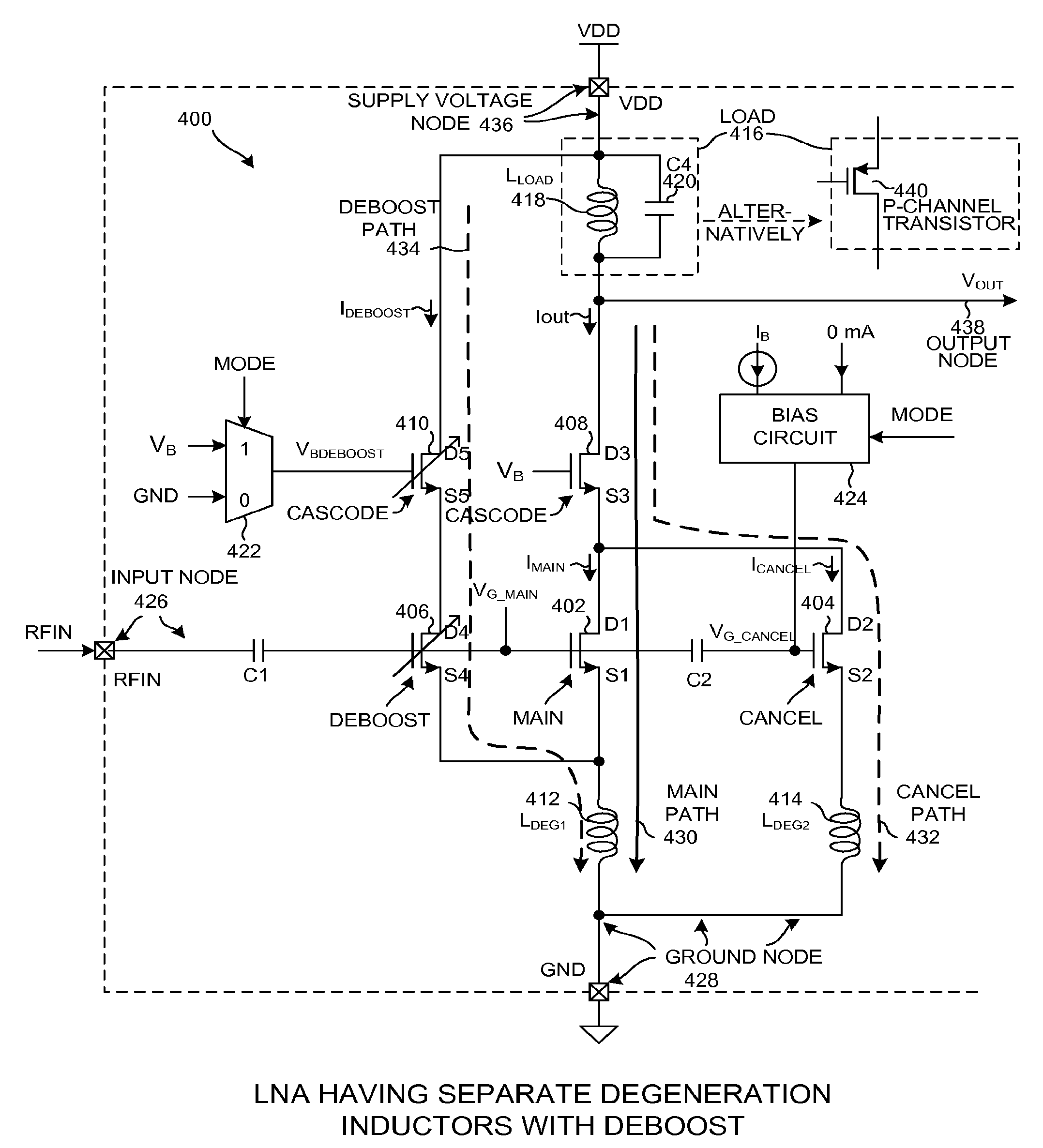
InactiveUS7821335B2Reduce voltageImprove noise figureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlHigh resistanceClosed loop
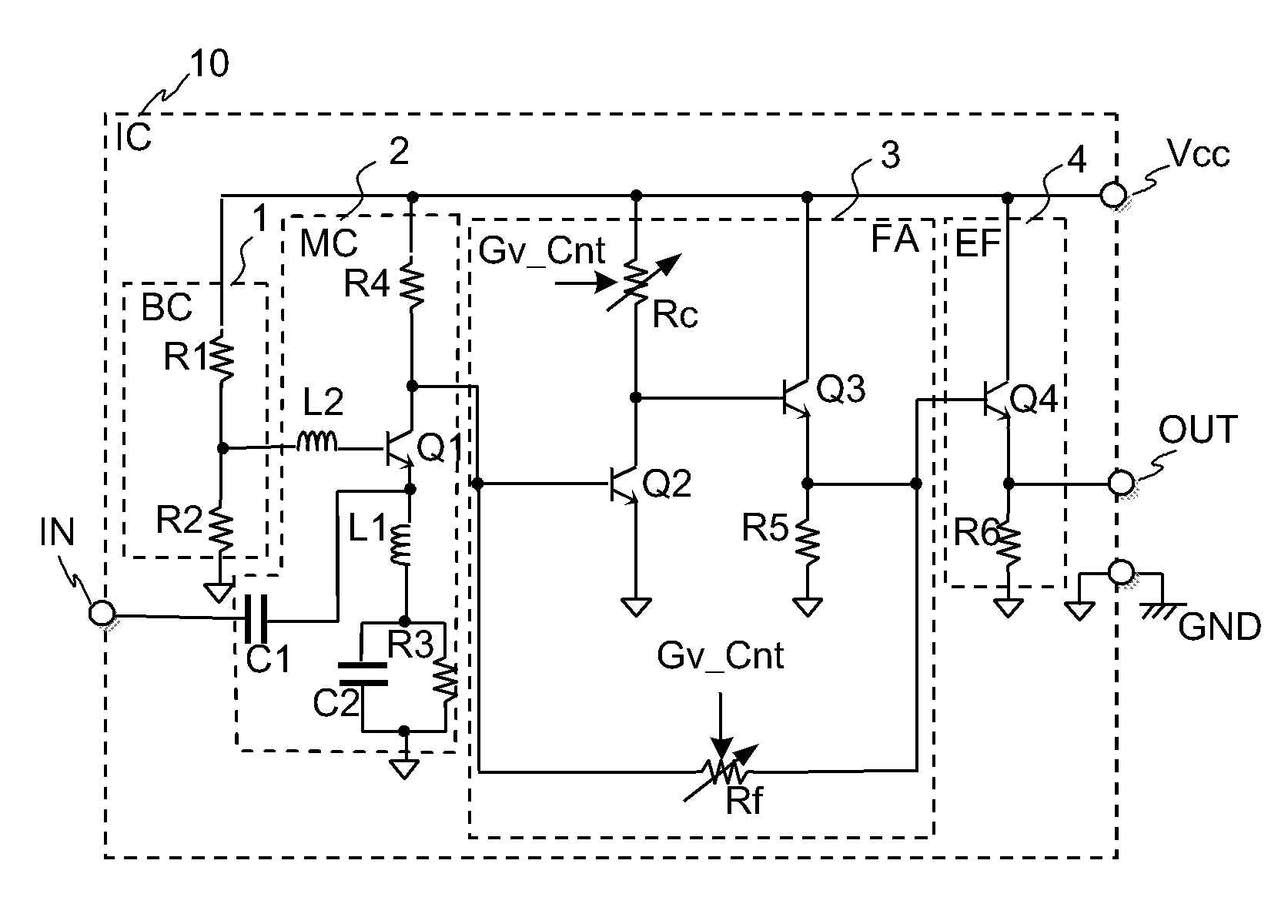
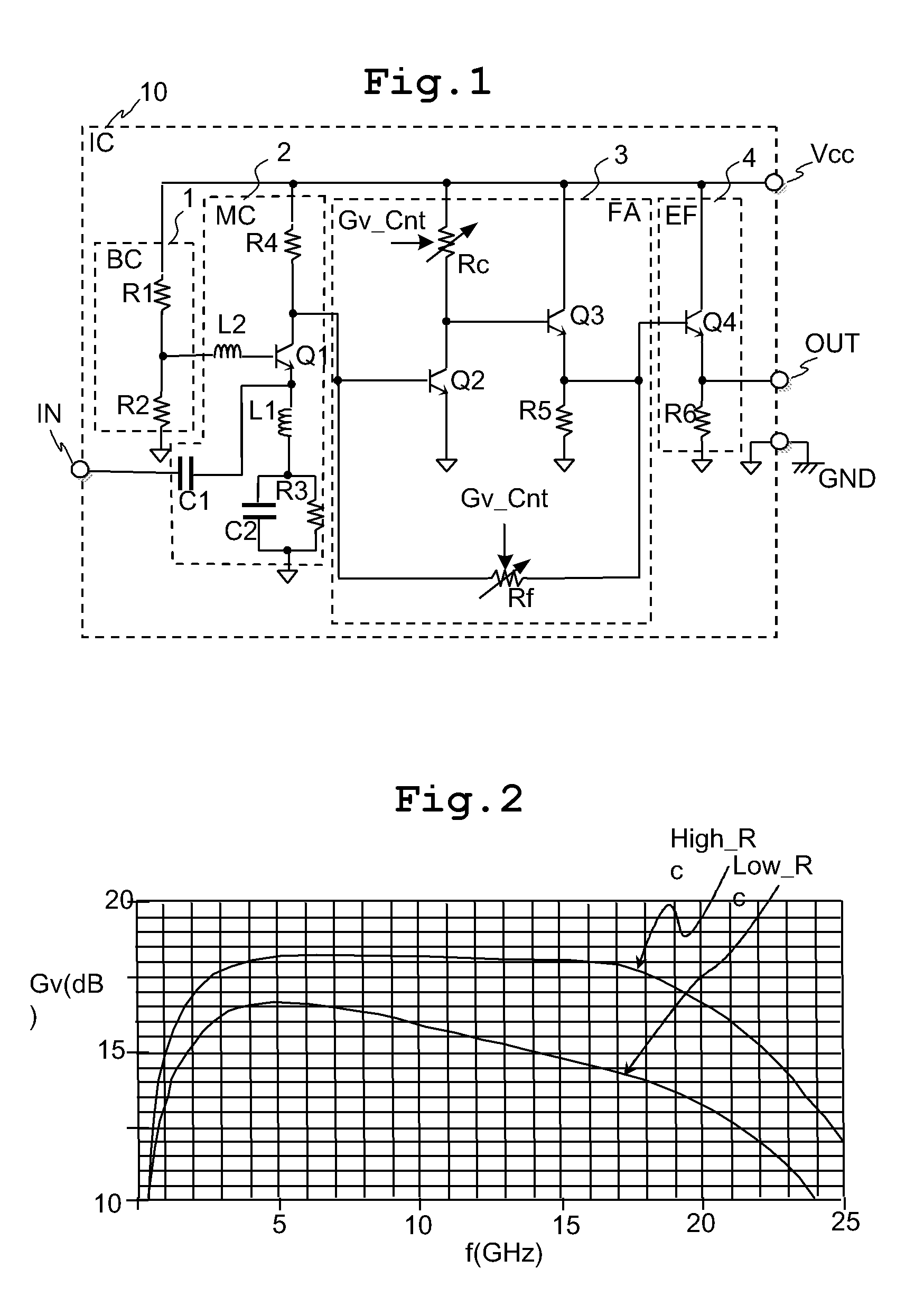
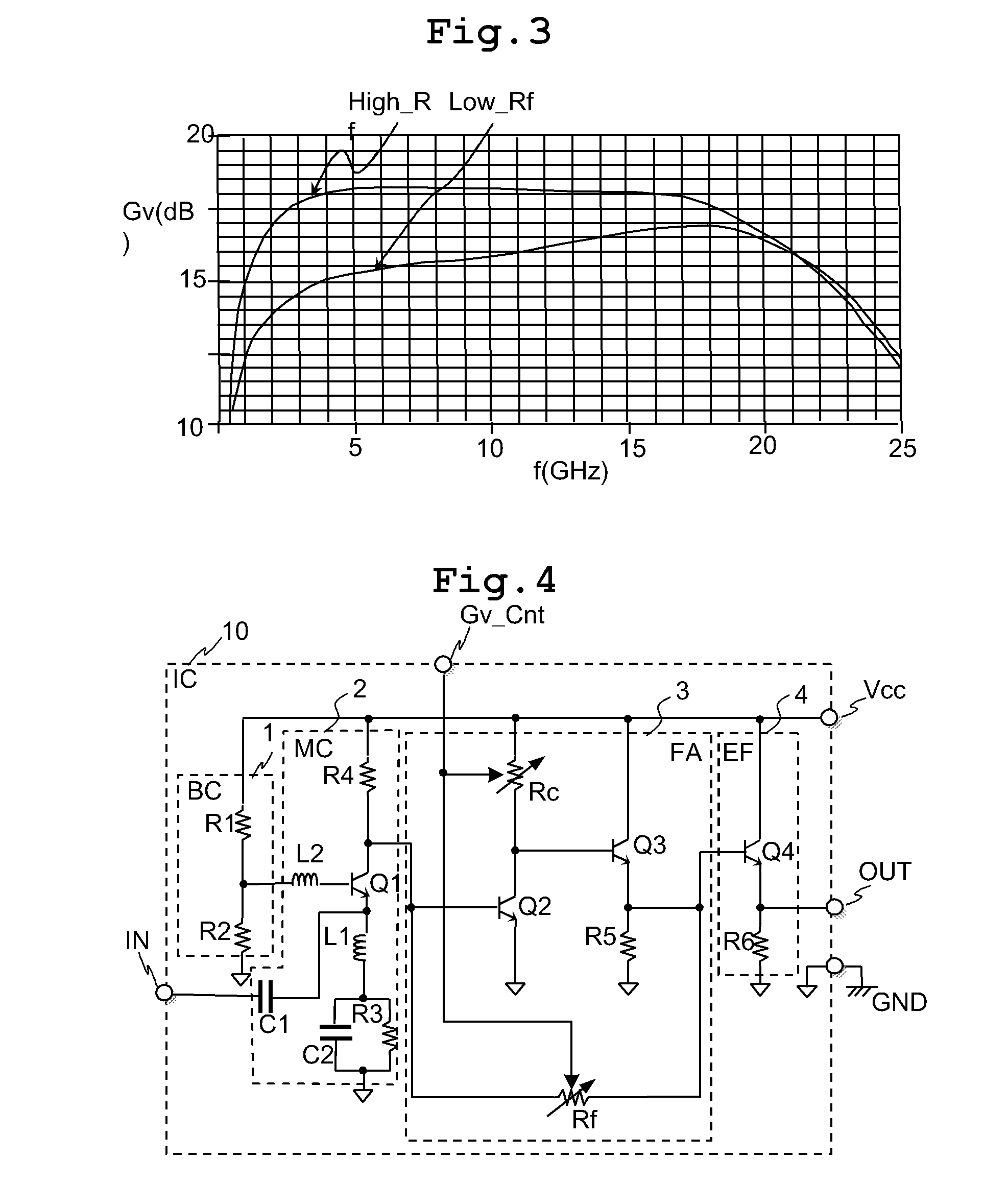
The variable gain amplifier includes a bias circuit (BC) 1, a matching circuit (MC) 2, a variable gain resistive feedback amplifier (FA) 3 and an output follower (EA) 4. The resistance values of the load resistance Rc and feedback resistance Rf are changed in cooperation. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a high resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a high gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a high resistance, the feedback time constant τfb(c1)≈2π·RfCbe / (1+gmRc) of the closed loop of the resistive negative feedback amplifier 3 becomes substantially constant, and then the amplifier has a gain small in frequency dependency over a wide bandwidth. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a low resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a low gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a low resistance. The feedback resistance Rf with the low resistance increases the negative feedback quantity, and thus the amplifier is set to a low gain. Also, the load resistance Rc is made a low resistance, and the feedback time constant τfb(c1) becomes substantially constant. The gain is not lowered further in a high frequency region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Multi-linearity mode LNA having a deboost current path
ActiveUS7696828B2Easy to adjustReduce noiseGated amplifiersGain controlNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
A modified derivative superposition (MDS) low noise amplifier (LNA) includes a main current path and a cancel current path. Third-order distortion in the cancel path is used to cancel third-order distortion in the main path. In one novel aspect, there is a separate source degeneration inductor for each of the two current paths, thereby facilitating tuning of one current path without affecting the other current path. In a second novel aspect, a deboost current path is provided that does not pass through the LNA load. The deboost current allows negative feedback to be increased without generating headroom problems. In a third novel aspect, the cancel current path and / or deboost current path is programmably disabled to reduce power consumption and improve noise figure in operational modes that do not require high linearity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Highly-integrated MEMS-based miniaturized transceiver
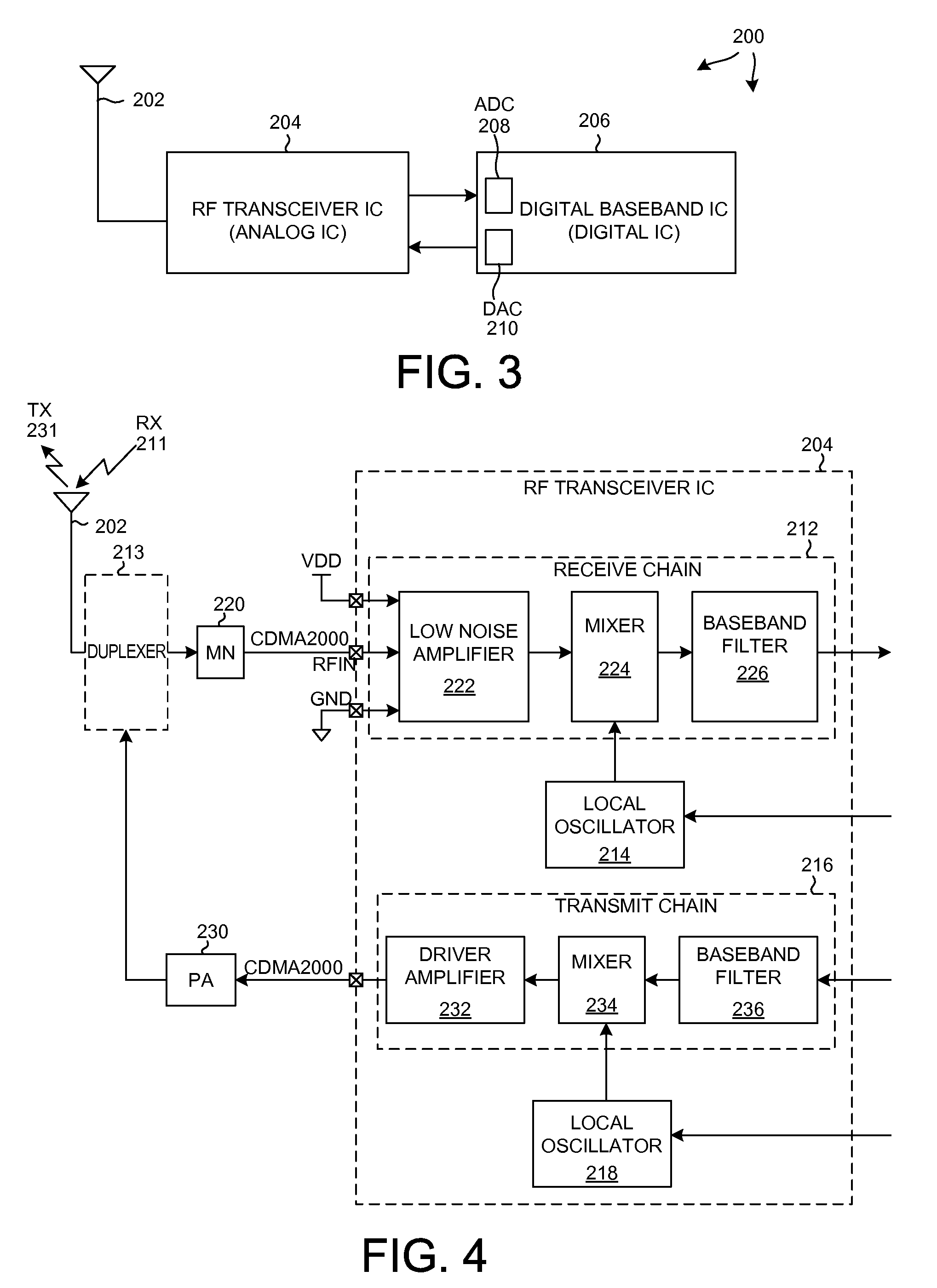
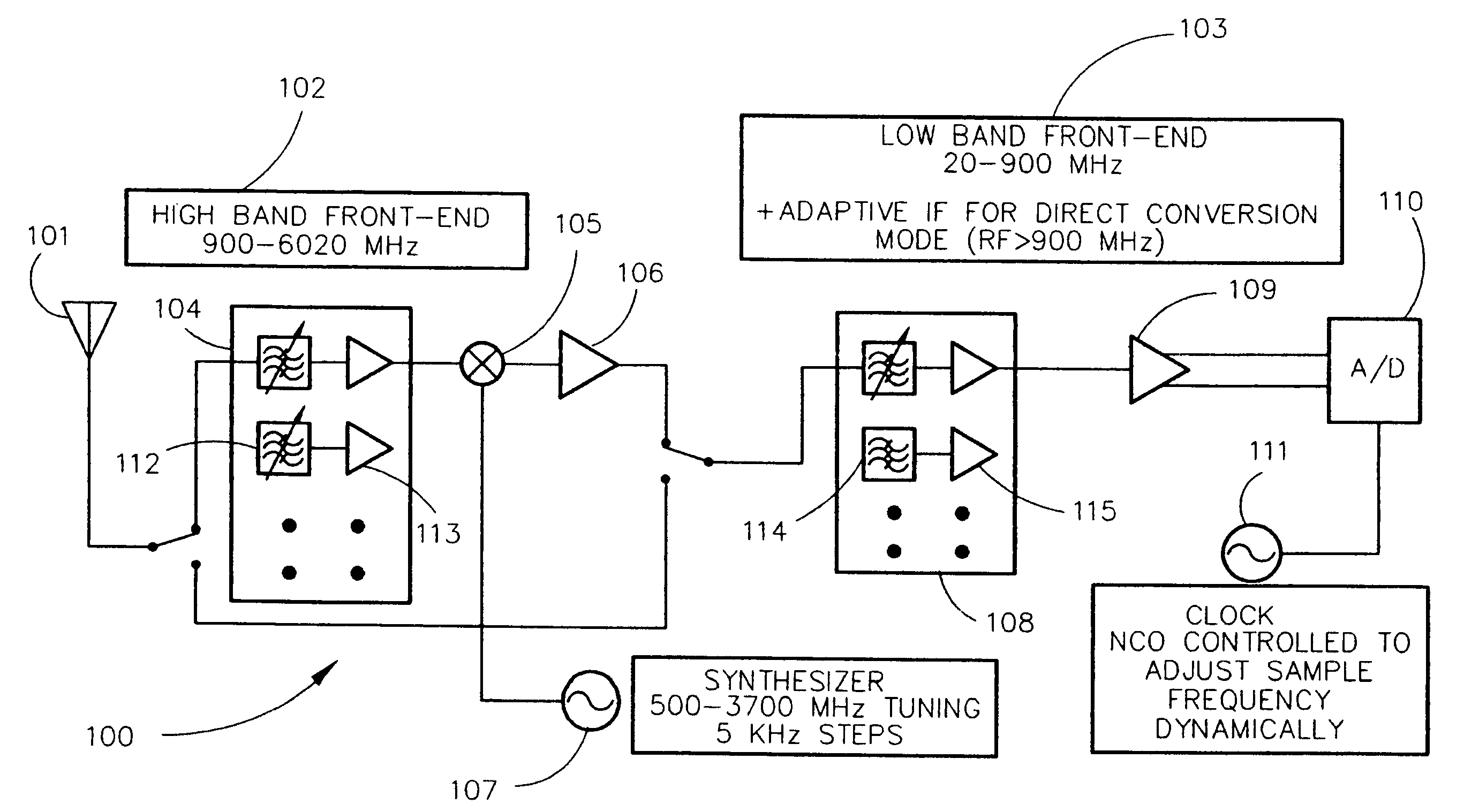
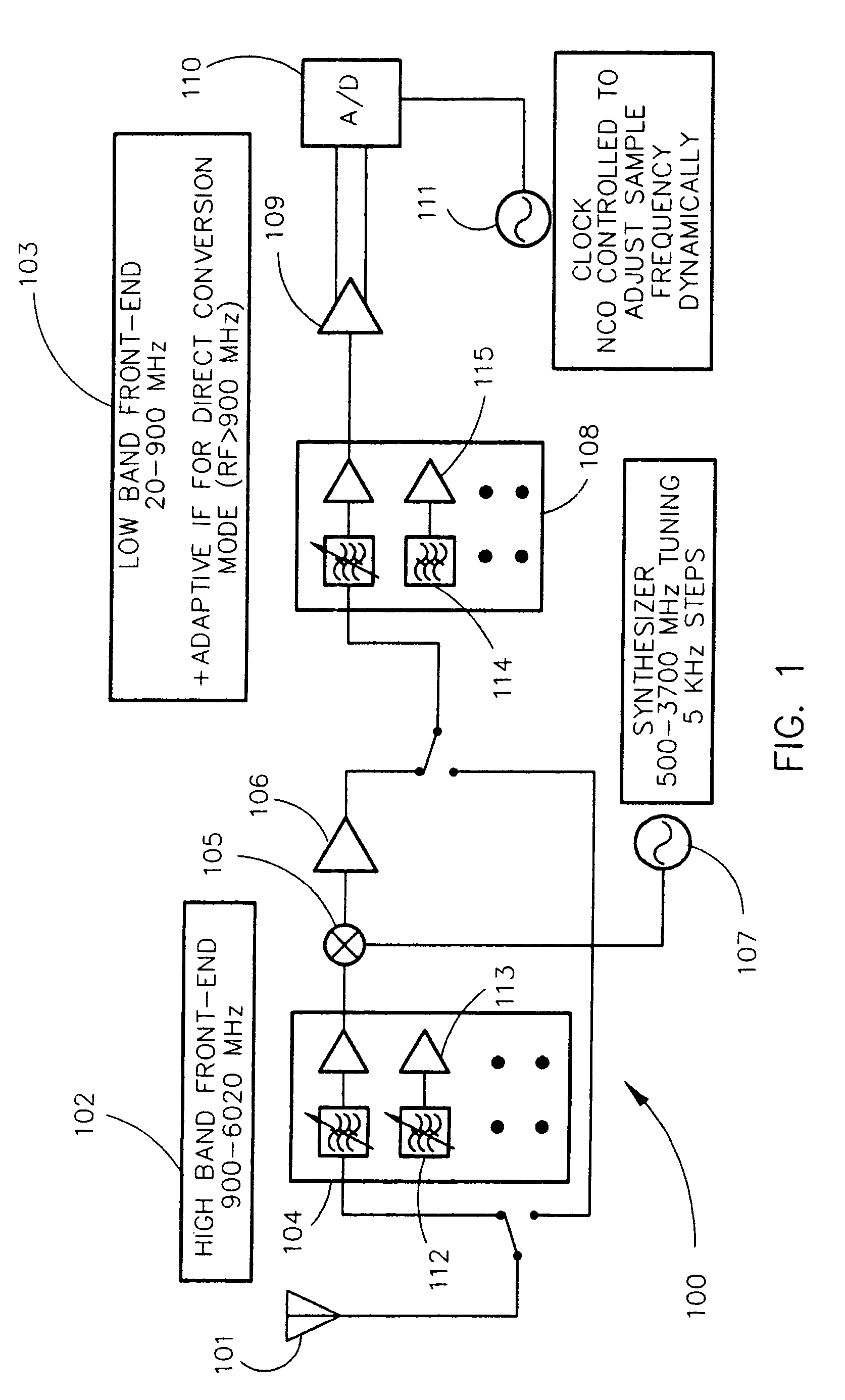
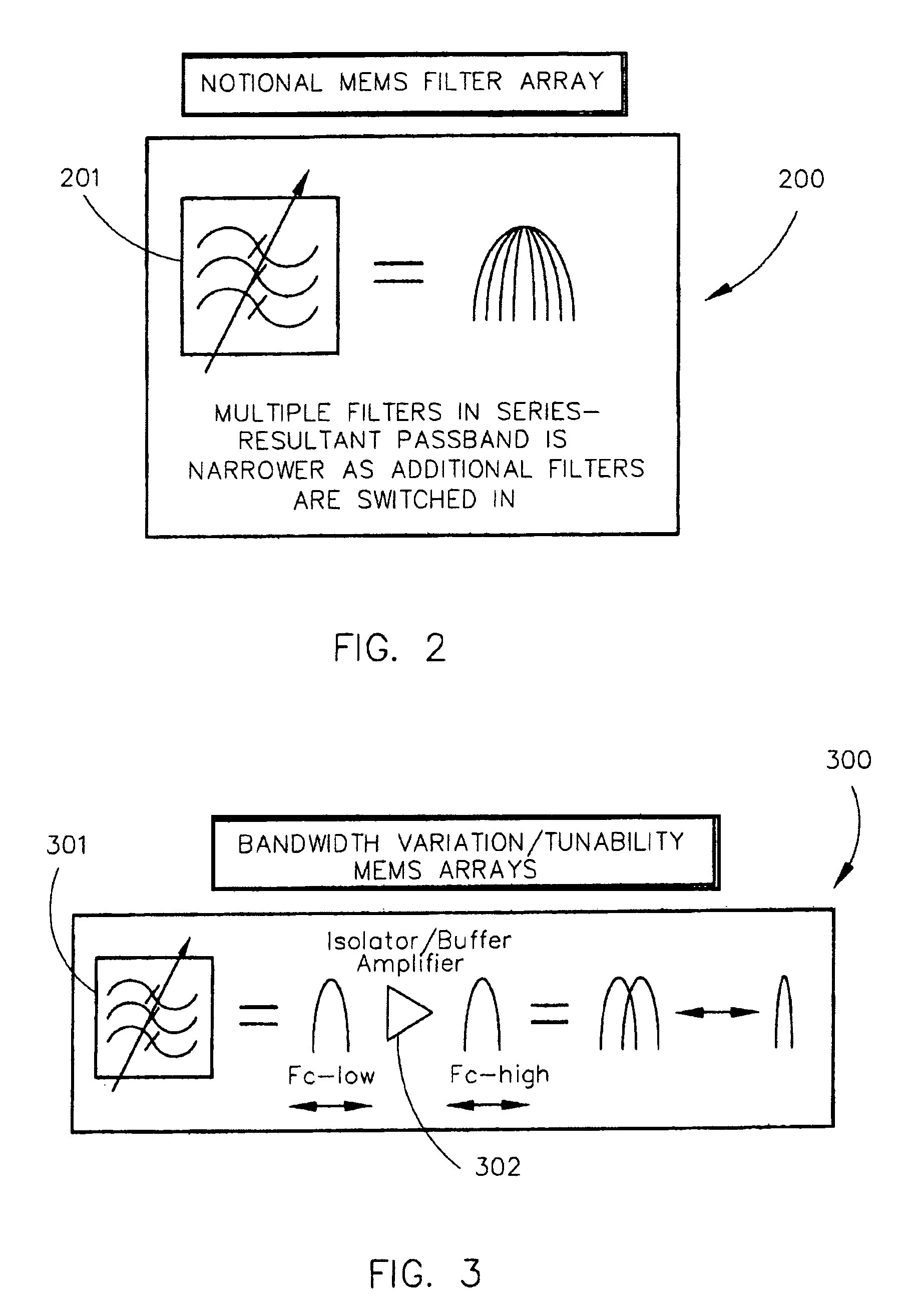
ActiveUS7403756B1Mitigate analog-to-digital conversion overload protectionImprove noise figureTransmissionDigital signal processingTransceiver
The present invention is directed to a highly-integrated MEMS-based miniaturized transceiver. The transceiver utilizes a low band front-end to direct sample low band signals and a high band front-end to translate high band signals that cannot be directly sampled to low band before low band front-end processing. The low band front-end comprises an array of High-Q MEMS (microelectromechanical systems)-based filters / resonators separated by isolation amplifiers in selectable cascade with narrower bandwidth filters. Dynamic tuning ability is provided through the isolation amplifiers and the sample frequency of the analog-to-digital converter. This architecture is amenable to monolithic fabrication. The input frequency range is scalable with analog-to-digital conversion sampling rate improvements. Re-utilization of filters is spatially efficient and cost effective. Tuning time is limited only by the analog-to-digital conversion and digital signal processing, not synthesizer settling times. This architecture eliminates major sources of traditional intermodulation distortion and reduces complex hardware, increasing reliability.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit with variable gain amplifier
InactiveUS20090102552A1Reduce voltageImprove noise figureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlHigh resistanceClosed loop
The variable gain amplifier includes a bias circuit (BC) 1, a matching circuit (MC) 2, a variable gain resistive feedback amplifier (FA) 3 and an output follower (EA) 4. The resistance values of the load resistance Rc and feedback resistance Rf are changed in cooperation. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a high resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a high gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a high resistance, the feedback time constant τfb(c1)≈2π·RfCbe / (1+gmRc) of the closed loop of the resistive negative feedback amplifier 3 becomes substantially constant, and then the amplifier has a gain small in frequency dependency over a wide bandwidth. In a case of making the load resistance Rc a low resistance to set the low noise amplifier to a low gain, the feedback resistance Rf is also made a low resistance. The feedback resistance Rf with the low resistance increases the negative feedback quantity, and thus the amplifier is set to a low gain. Also, the load resistance Rc is made a low resistance, and the feedback time constant τfb(c1) becomes substantially constant. The gain is not lowered further in a high frequency region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Ultra high-speed Si/SiGe modulation-doped field effect transistors on ultra thin SOI/SGOI substrate
ActiveUS6855963B1Improve RF performanceUltra-high speed performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow noiseUltra high speed
A silicon and silicon germanium based semiconductor MODFET device design and method of manufacture. The MODFET design includes a high-mobility layer structure capable of ultra high-speed, low-noise for a variety of communication applications including RF, microwave, sub-millimeter-wave and millimeter-wave. The epitaxial field effect transistor layer structure includes critical (vertical and lateral) device scaling and layer structure design for a high mobility strained n-channel and p-channel transistor incorporating silicon and silicon germanium layers to form the optimum modulation-doped heterostructure on an ultra thin SOI or SGOI substrate capable of achieving greatly improved RF performance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
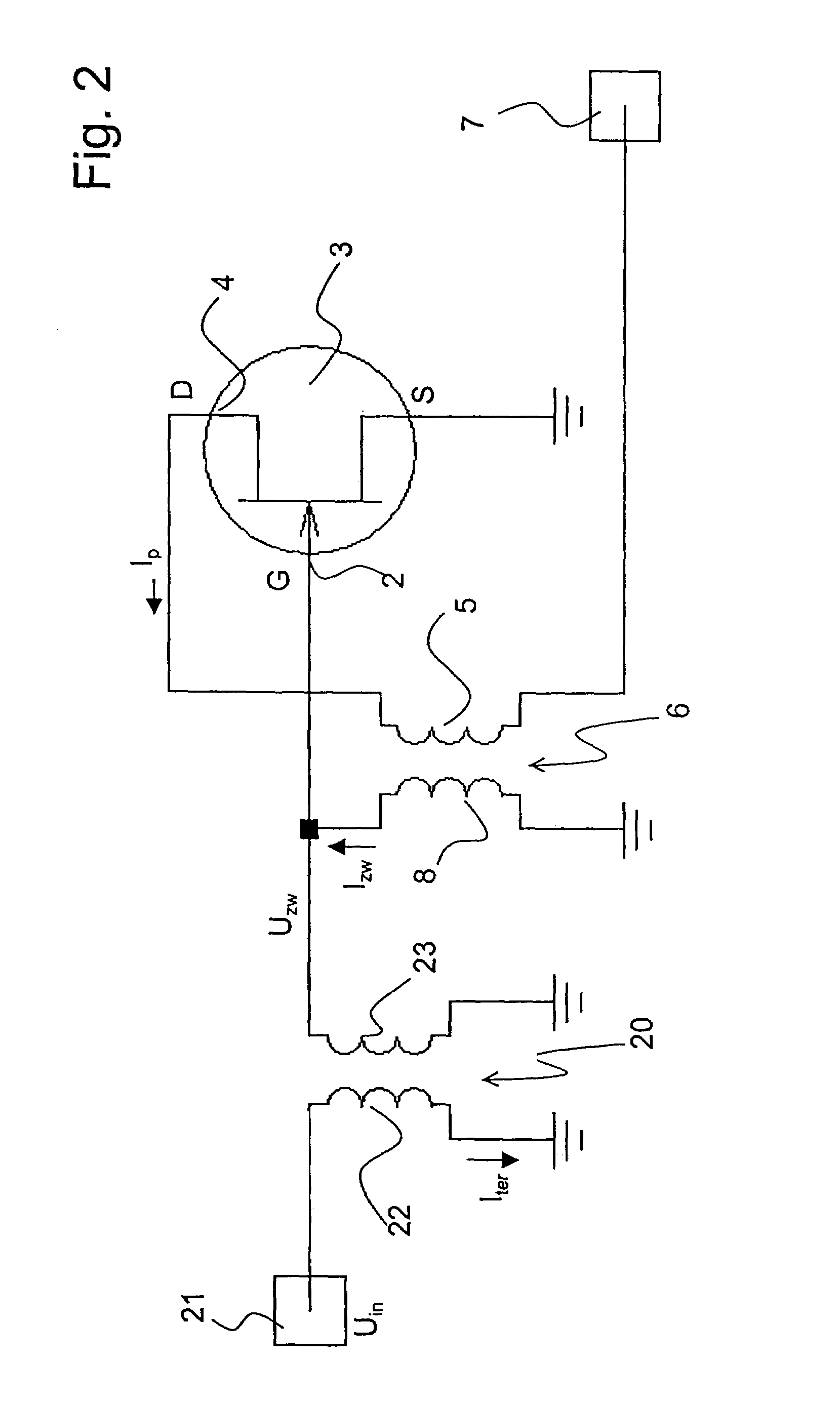
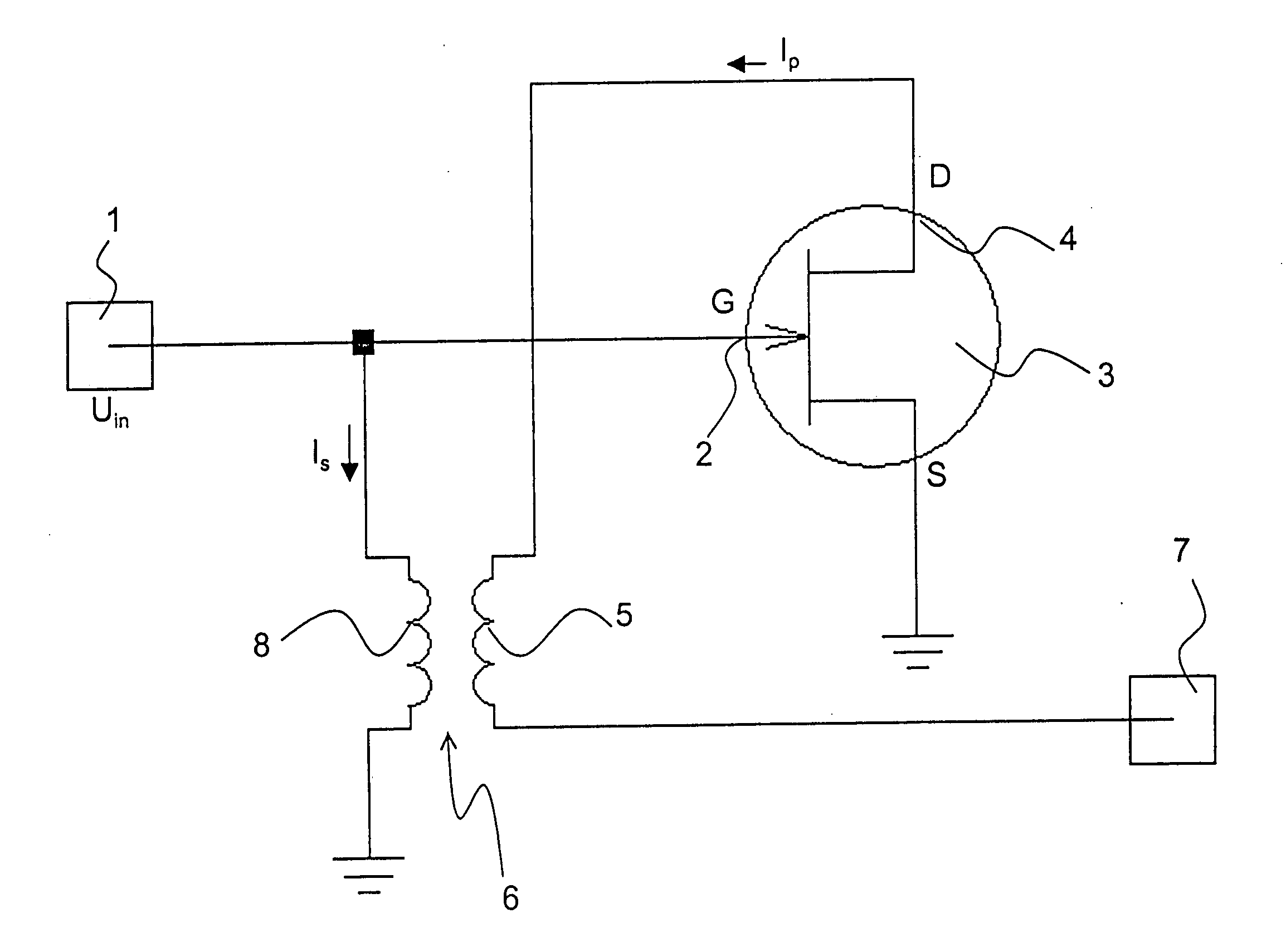
Low-noise preamplifier, in particular, for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
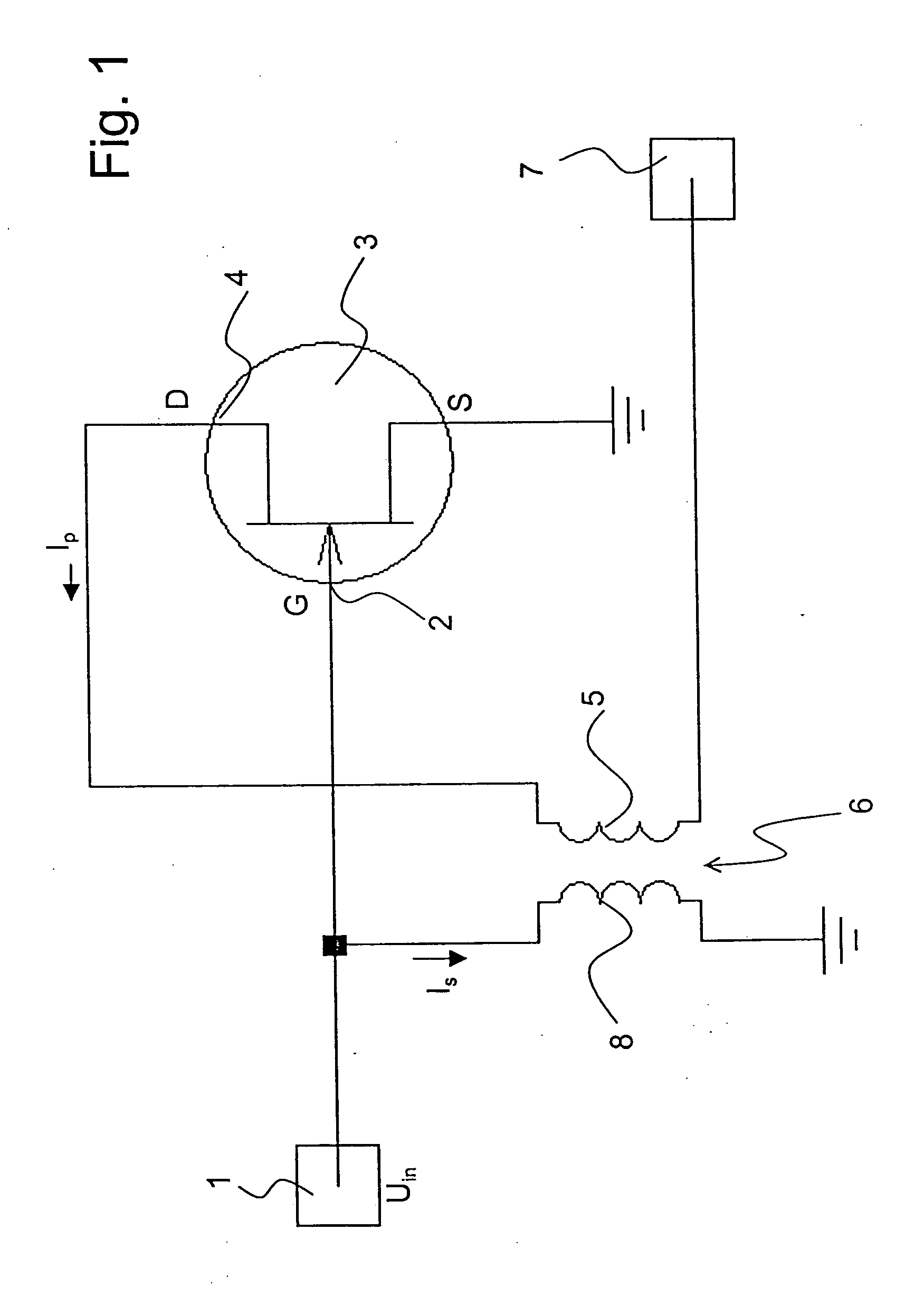
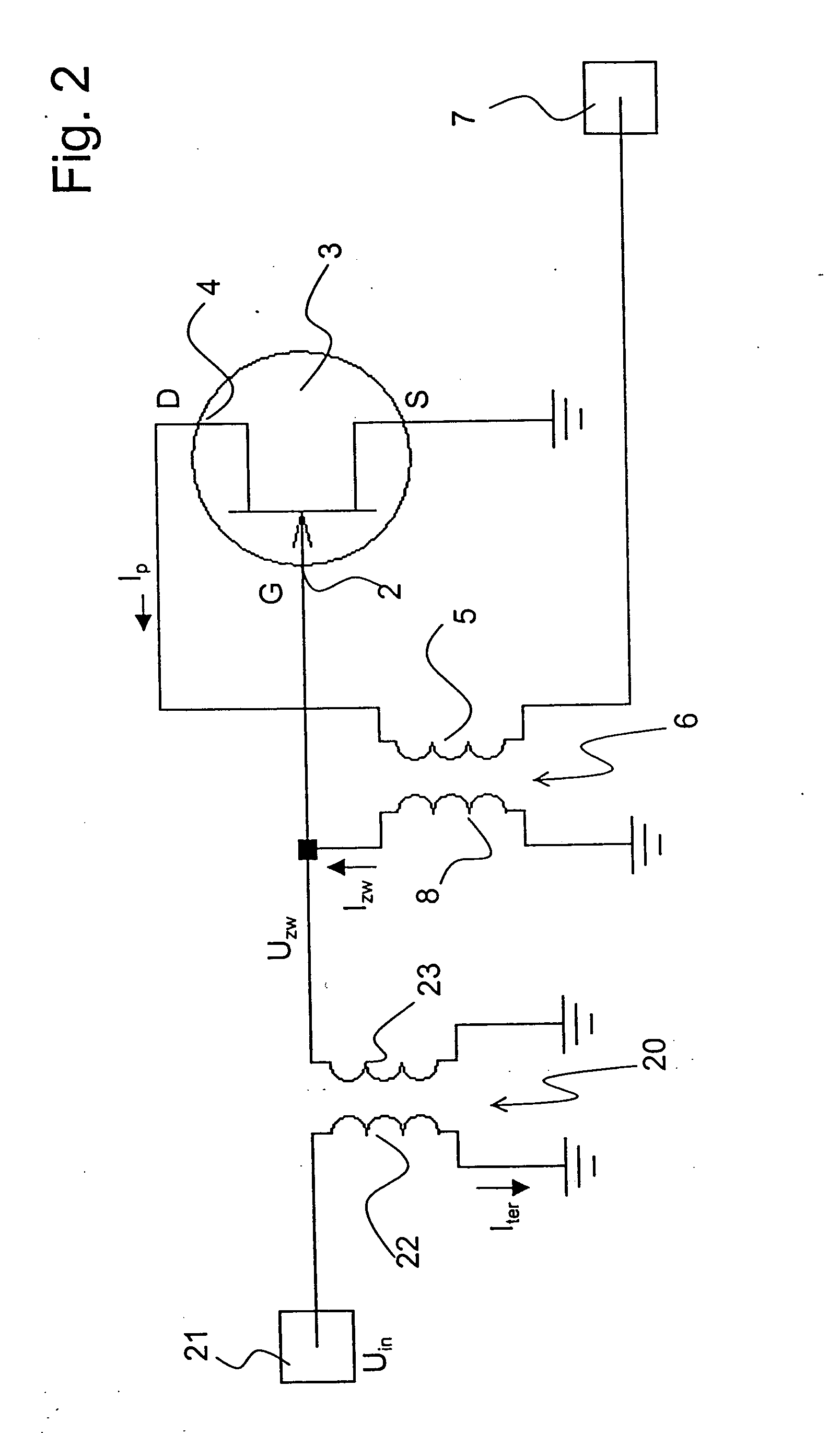
ActiveUS7123090B2Lower input impedanceImprove noise figureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noiseTransformer
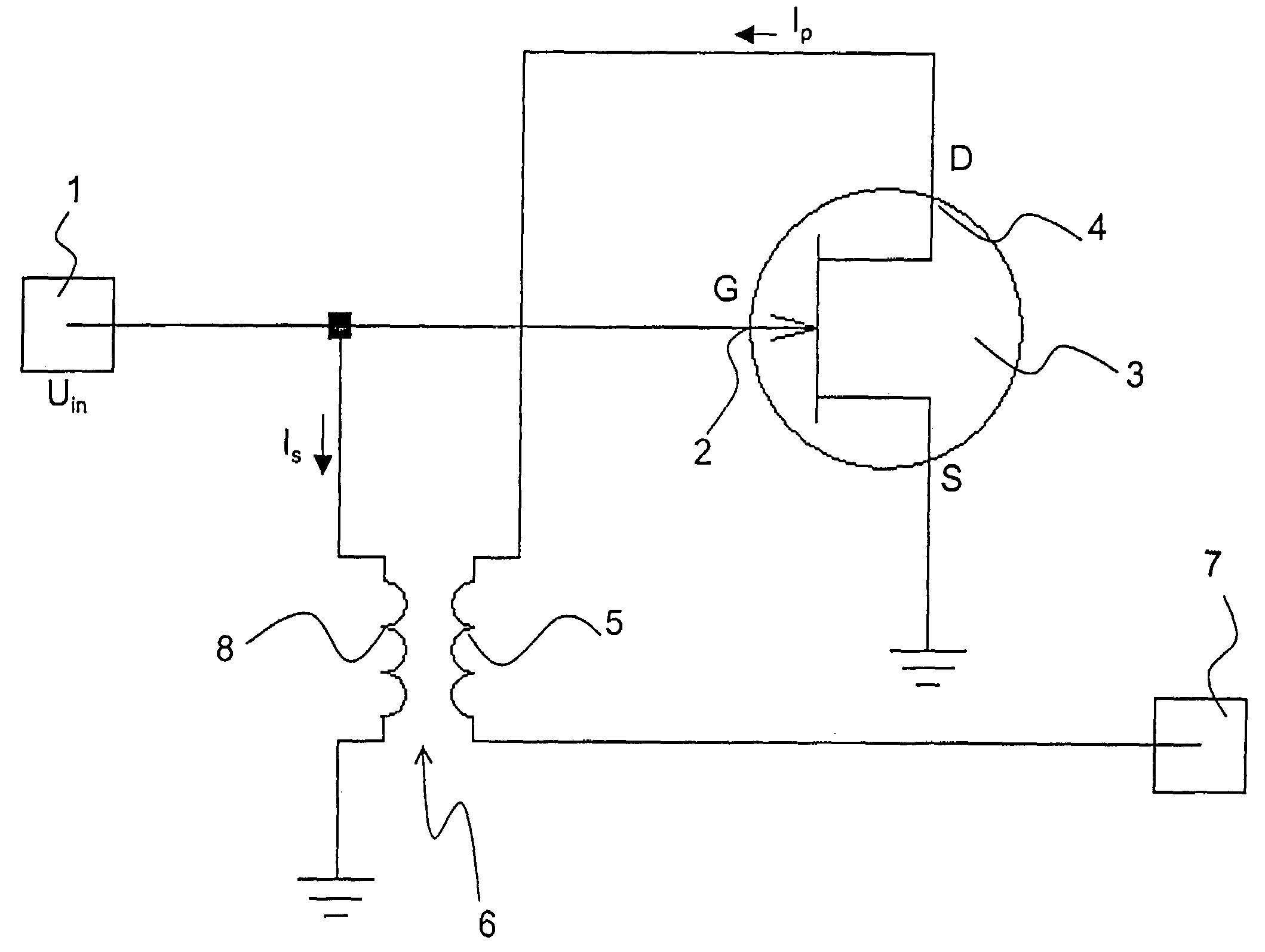
A low-noise preamplifier with an electronic amplifying element having an input (2) and an output (4), and with a first transformer (6) having a primary winding (5) and a secondary winding (8) is characterized in that the input (2) of the electronic amplifying element is the base of a transistor, the gate (G) of a field effect transistor (FET) or the grid of a vacuum tube, and the output (4) of the electronic amplifying element is the collector, the drain (D) or the anode, the output current (Ip) being passed from the electronic amplifying element through the primary winding (5) of the first transformer (6) to the output (7) of the preamplifier, wherein the secondary winding (8) of the first transformer (6) is connected to the input (2) of the electronic amplifying element. This preamplifier can be operated with extremely low noise and at any input impedance, in particular, at 50 ohms or 75 ohms.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Single-ended input and differential output parallel dual-frequency low noise amplifier and design method thereof
ActiveCN102355200AAchieve improvementIncrease system areaAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersDual frequencyAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a single-ended input and differential output parallel dual-frequency low noise amplifier (LNA) and a design method thereof. The LNA can be applied to a digital TV, wireless communication and a navigation receiver and mainly comprises an input matching network, a main amplification circuit, an output network and a single-ended to differential circuit. The main amplification circuit adopts a cascode structure and has favorable reverse isolation degree; the input matching network enables the LNA to realize impedance matching and noise matching simultaneously in input stage and dual frequency ranges, and thus the noise performance of the circuit is improved at the same time of ensuring the maximum power transmission; and the singled-ended to differential circuit ensures that the LNA can be directly cascaded with a front-end antenna and a rear-end mixer circuit and easy to integrate. The LNA disclosed by the invention not only has a simple design, but also ensures that the system power consumption and area are reduced due to parallel dual-frequency receiving.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
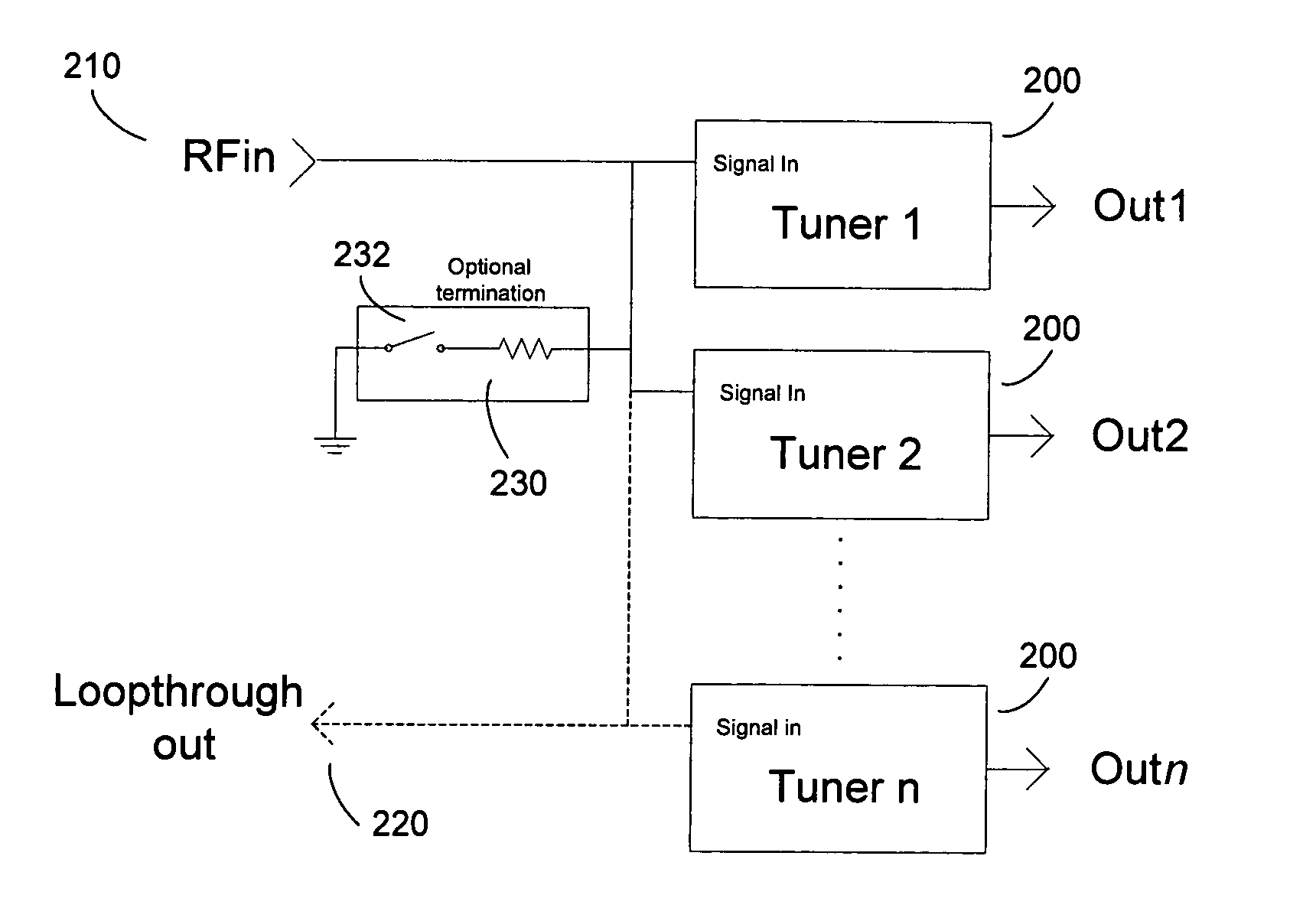
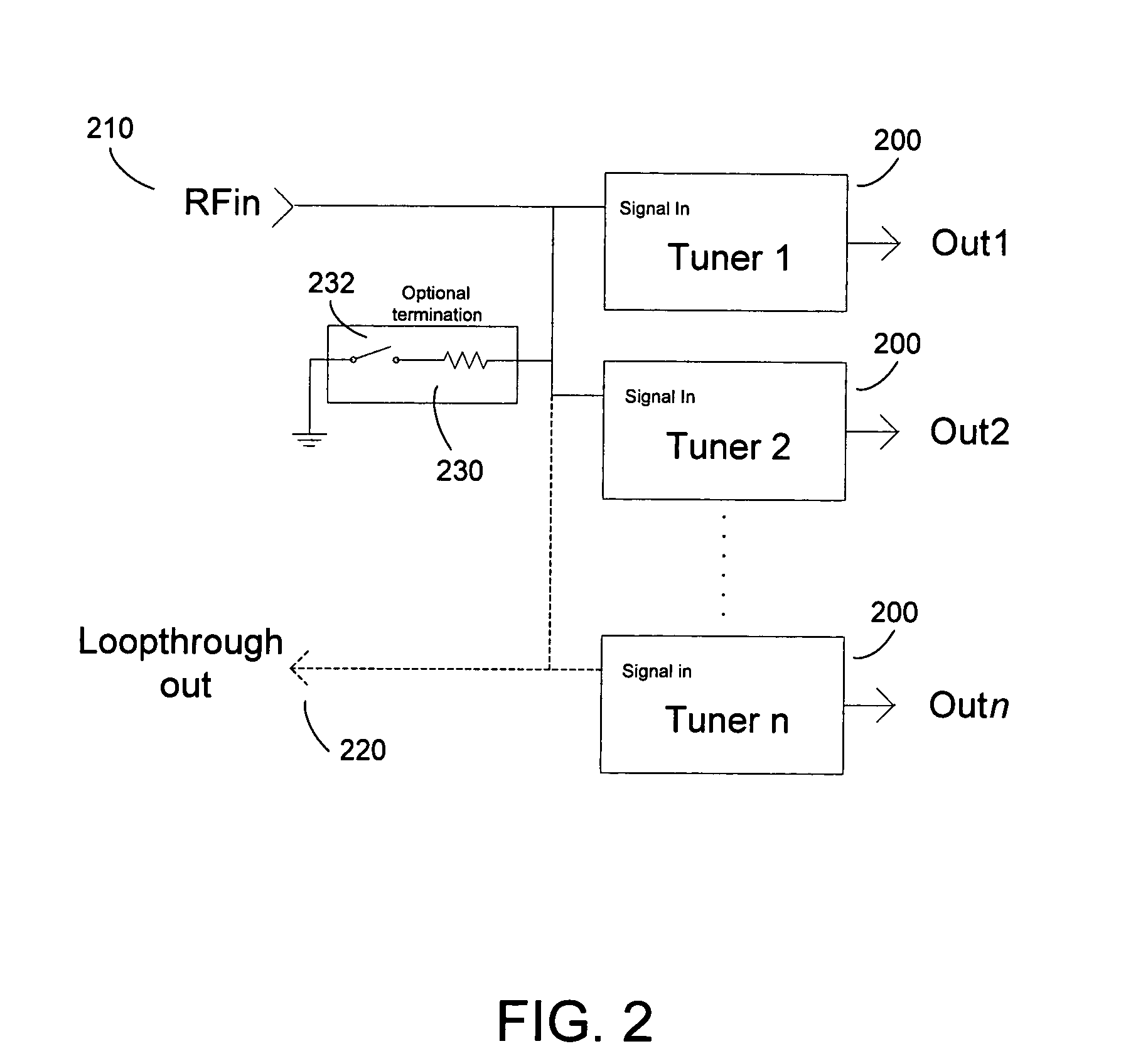
Tuner design and system for lossless interconnect of multiple tuners
InactiveUS20060128328A1Improve noise figureNot cause additional lossMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsDigital videoTelevision receivers
Tuners with high input impedance are connected to a common radio frequency (RF) signal source. A termination load external to the tuners provides matched impedance loading for the transmission line or cable driving the tuners. Alternatively, the termination load can be located inside one tuner with a switch to enable or disable the load. All tuners receive the same signal and no signal degradation is caused when connecting multiple tuners. The multiple tuner connection is useful in television signal receiving devices that receive more than one independent channel, such as digital video recorders or picture-in-picture television receivers.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Ultra high-speed Si/SiGe modulation-doped field effect transistors on ultra thin SOI/SGOI substrate
InactiveUS20050127392A1Improve RF performanceImprove noise figureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow noiseEngineering
A silicon and silicon germanium based semiconductor MODFET device design and method of manufacture. The MODFET design includes a high-mobility layer structure capable of ultra high-speed, low-noise for a variety of communication applications including RF, microwave, sub-millimeter-wave and millimeter-wave. The epitaxial field effect transistor layer structure includes critical (vertical and lateral) device scaling and layer structure design for a high mobility strained n-channel and p-channel transistor incorporating silicon and silicon germanium layers to form the optimum modulation-doped heterostructure on an ultra thin SOI or SGOI substrate capable of achieving greatly improved RF performance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Amplifier circuit having improved linearity and frequency band using multiple gated transistor
InactiveUS7319364B2Increase the frequency bandImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
Disclosed herein is an amplifier circuit having improved linearity and frequency band using a MGTR. The amplifier circuit comprises an amplification unit including a main transistor and an auxiliary transistor, an attenuation unit including inductors respectively connected to the source of the main transistor and the source of the auxiliary transistor, a capacitor connected at one end thereof to the sources of the main transistor and auxiliary transistor and connected at the other end thereof to the gates of the main transistor and auxiliary transistor, and an output unit connected to the drains of the main transistor and auxiliary transistor.
Owner:INTEGRANT TECH
High-sensitivity wireless receiving device and high-frequency unit used therefor
InactiveUS6963758B2Improve noise figureSensitive highSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentBandpass filteringAudio power amplifier
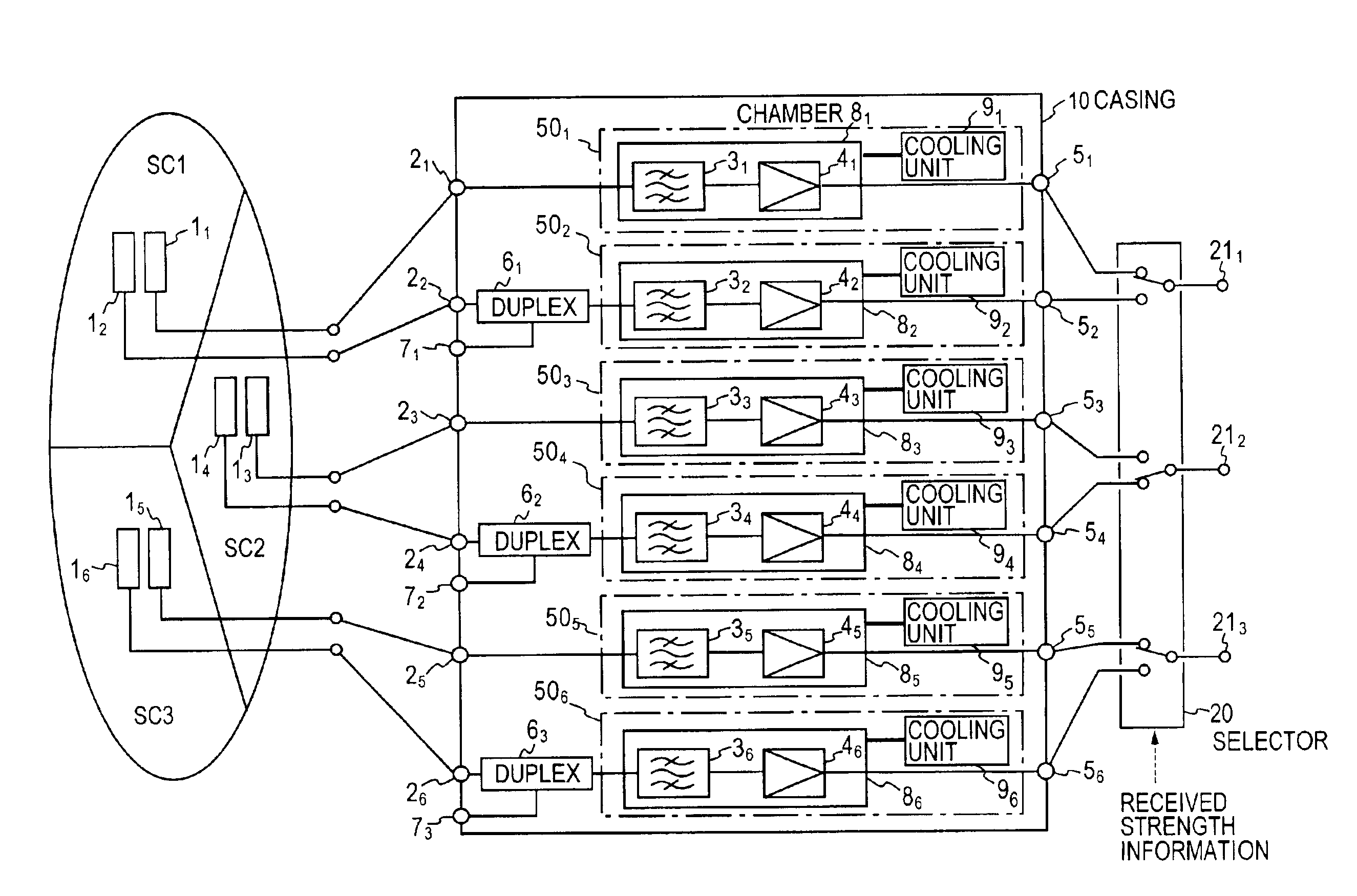
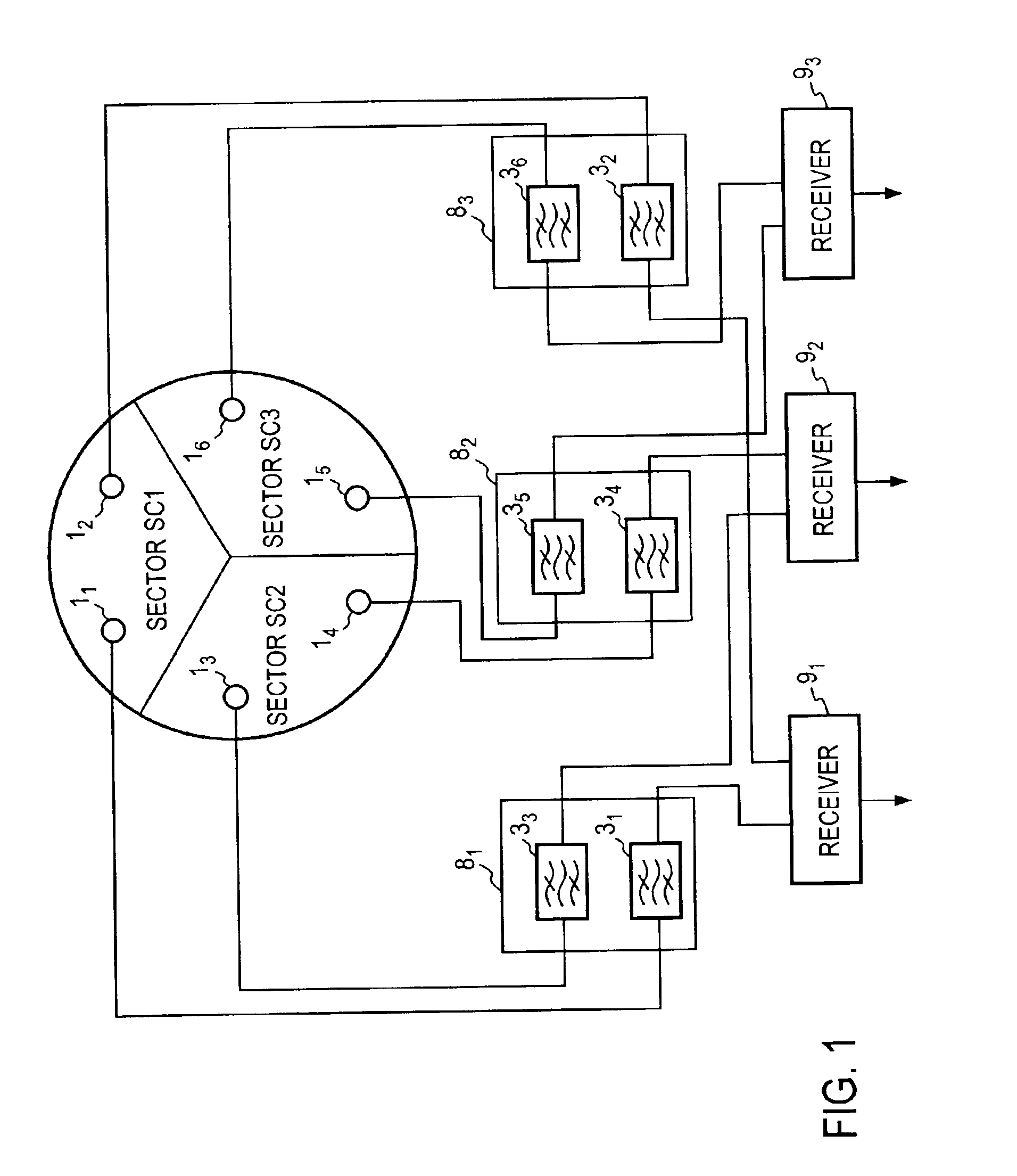
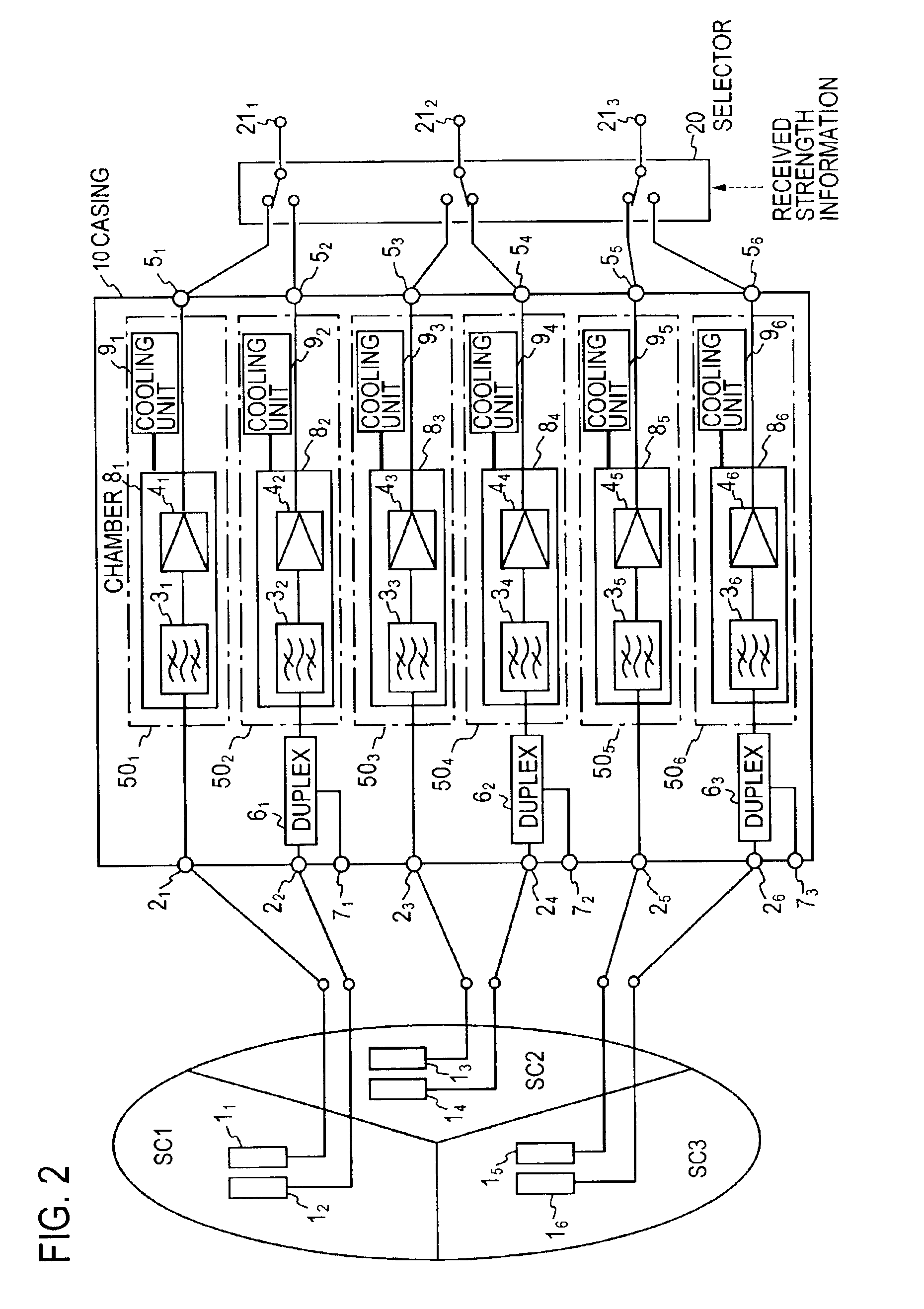
In a high sensitive radio receiver system for a diversity reception from two antennae per each of three sectors (SC1, SC3, SC3), a series connection of a bandpass filter (31 to 36) and a low noise amplifier (41 to 46) is contained in each of a plurality of vacuum chambers (81 to 86), the interior of which is cooled by a distinct, separate cooling unit (91 to 96). The two antennae per sector are connected to bandpass filters contained in different vacuum chambers.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
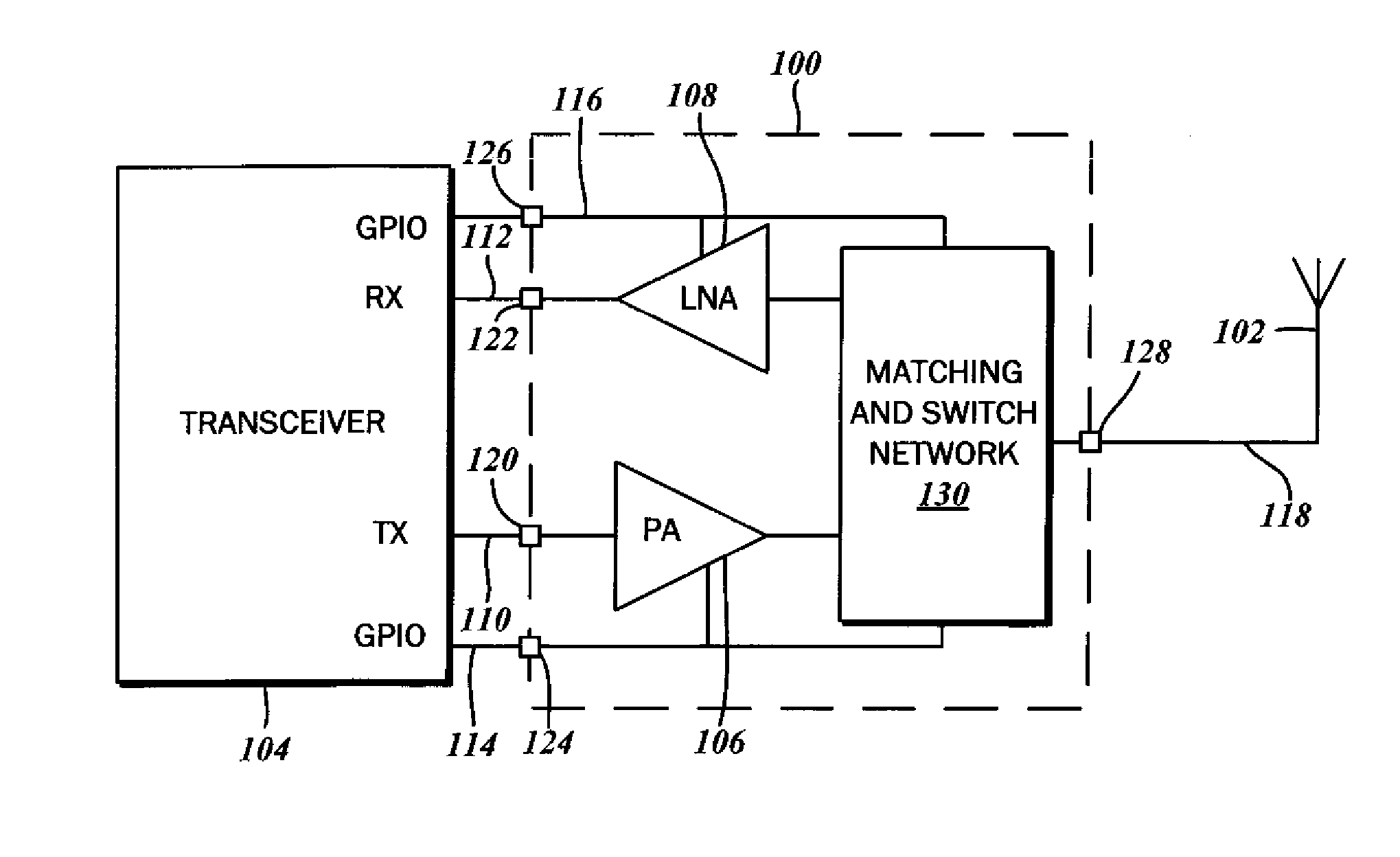
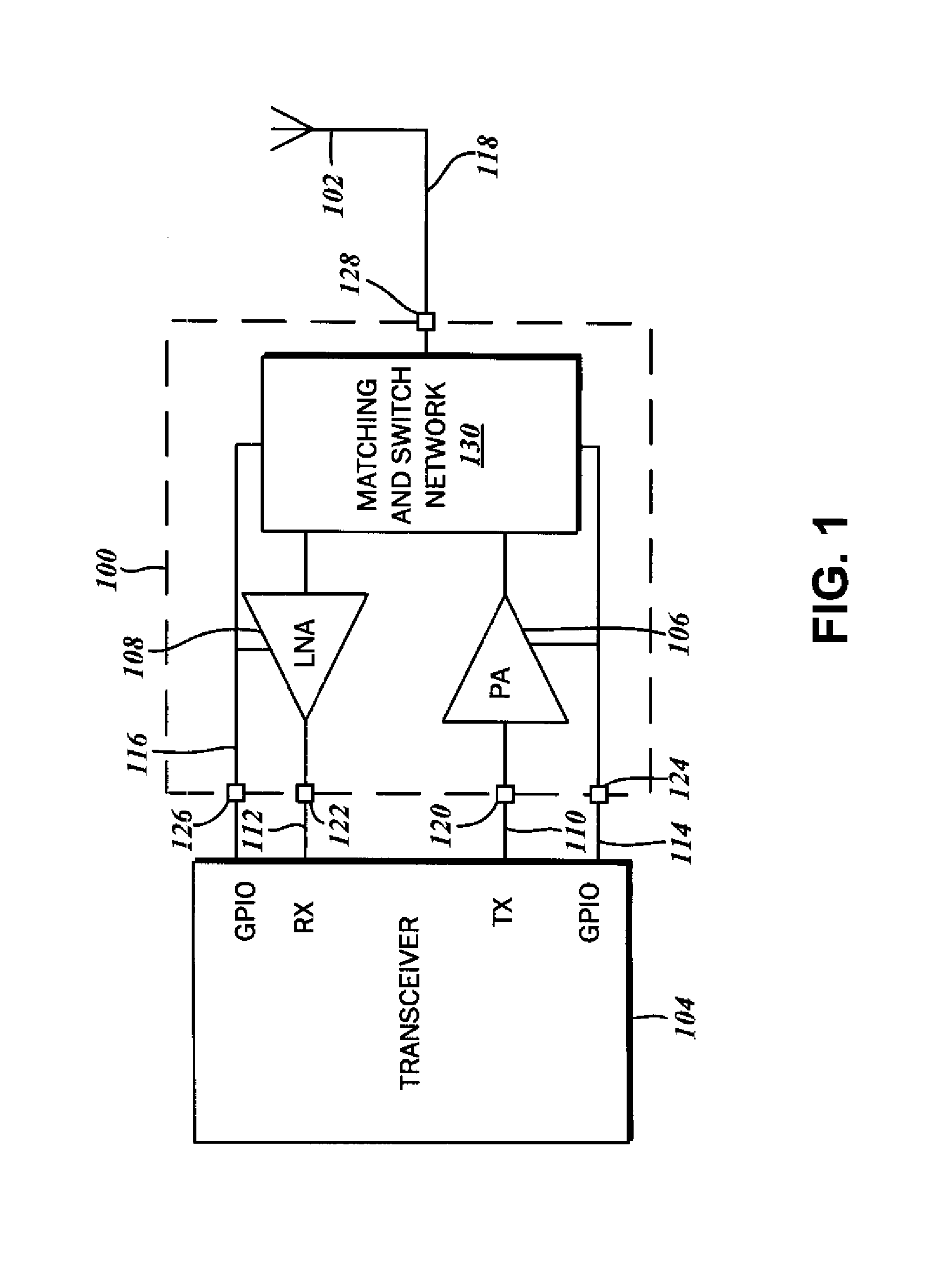
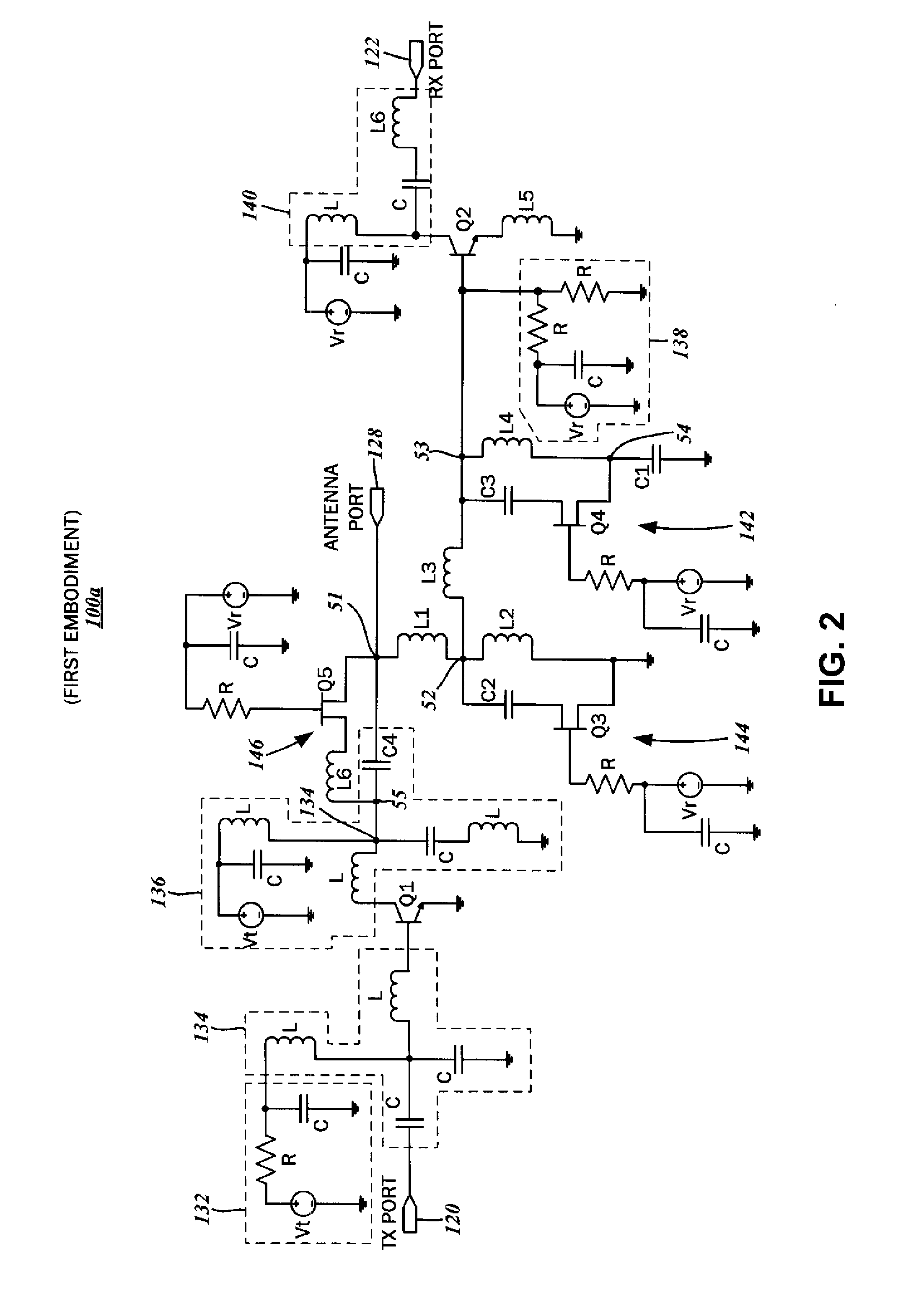
Increased receive sensitivity radio frequency front end integrated circuits
A front end circuit for coupling an antenna to a radio frequency (RF) transceiver is disclosed. An antenna port connectible to the antenna is provided, as well as a power amplifier coupled to a signal output of the RF transceiver and a low noise amplifier coupled to the signal input of the RF transceiver. The front end circuit includes a switching network that is connected to the antenna port, the power amplifier, and the low noise amplifier. Additionally, there is at least one resonant circuit and a control circuit coupled to a receive enable line of the transceiver. This resonant circuit defines a parallel resonance with a first resonant resistance in the operating frequency band upon activation in the receive mode. The resonant circuit also defines a substantially high transistor impedance upon deactivation in the transmit mode.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Amplifier circuit having improved linearity and frequency band using multiple gated transistor
InactiveUS20060091962A1Increase the frequency bandImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFrequency bandInductor
Disclosed herein is an amplifier circuit having improved linearity and frequency band using a MGTR. The amplifier circuit comprises an amplification unit including a main transistor and an auxiliary transistor, an attenuation unit including inductors respectively connected to the source of the main transistor and the source of the auxiliary transistor, a capacitor connected at one end thereof to the sources of the main transistor and auxiliary transistor and connected at the other end thereof to the gates of the main transistor and-auxiliary transistor, and an output unit connected to the drains of the main transistor and auxiliary transistor.
Owner:INTEGRANT TECH
Continuous variable-gain low-noise amplifier
InactiveUS7164318B2Improve linearityLittle changeNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
Continuous variable-gain low-noise amplifier. The amplifier continuously adjusts its gain between well-defined high and low values by using a cascode current-steering circuit to partition signal current between two different nodes of an output loading network. A shunt feedback network connected from an intermediate node of the loading network to the input provides negative feedback that linearizes the amplifier as its gain is decreased. The circuit degrades the noise figure at lower gains by varying the gain without directly dumping the signal current to the power supply. The circuit produces only small changes in input and output impedances and preserves an improved reverse-isolation cascode characteristic as the gain is controlled.
Owner:QUINTIC MICROELECTRONICS WUXI
Multi-function passive frequency mixer
ActiveUS7630700B2Reduce power consumptionReduced space requirementsModulation transferenceElectronic switchingCapacitanceLocal oscillator signal
A frequency-mixing device performing voltage multiplying and low-pass filtering operations in addition to frequency mixing is provided. The three operations may be carried out with the same components by designing the frequency mixer appropriately. The frequency mixer comprises a first capacitance connected in series to the input of the frequency-mixing device, a first switch connected in parallel to the first capacitance, a second switch connected in series to the first capacitance, and a second capacitance connected in parallel to the second switching means. The switches are controlled by a local oscillator signal to close and open alternately according to a change in the voltage level of the first oscillator signal.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Comb spectrum generation system based on cyclic frequency shift pattern and application method thereof
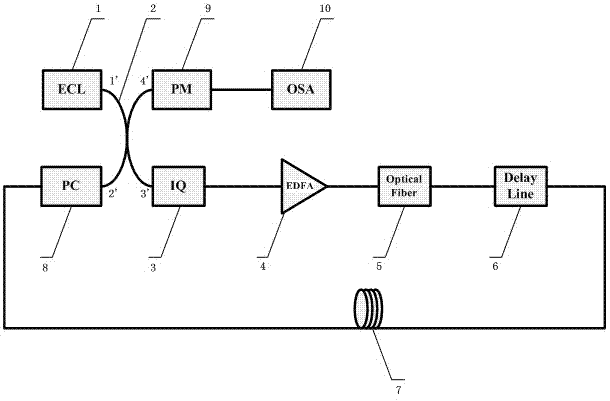
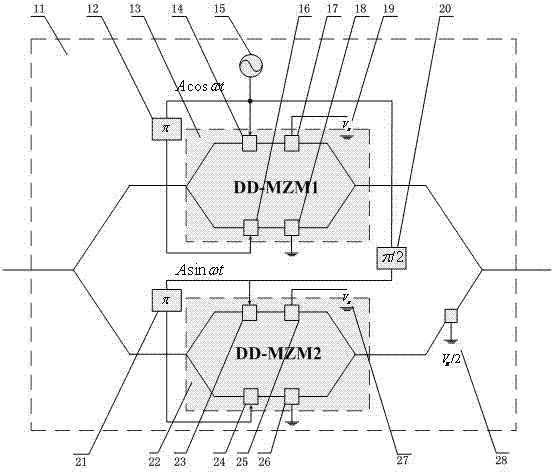
InactiveCN103036621AReduce system complexityImprove flatness and stabilityElectromagnetic transmissionPhysicsVIT signals
The invention relates to a comb spectrum generation system based on a cyclic frequency shift pattern and an application method of the comb spectrum generation system based on a cyclic frequency shift pattern. The comb spectrum generation system based on the cyclic frequency shift pattern comprises an external-cavity semiconductor laser, a 3 dB coupler, a polarization controller, an intelligence quotient (IQ) modulator, a phase modulator, an optical frequency spectrum analyzer, a cosine microwave signal source, a phase shifter, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, an optical filter, an adjustable optical delay line, a direct current bias supply and a section of optical fiber. Cosine radio-frequency signals, reversed cosine radio-frequency signals, sine radio frequency signals with same frequency, and reversed sine radio frequency signals with same frequency are inputted into the IQ modulator. Down-converted signals of optical carrier can be produced through adding appropriate bias voltage to a direct current electrode. The down-converted frequency is four radio frequency (RF) electrode incoming frequency. Elements of coupled seed light and the down-converted light of the optical carrier are modulated by the IQ modulator in a loop circuit. Flat comb spectrum can be obtained through reasonable gain conditions of the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier and choices of the optical carrier bandwidth.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Low noise amplifier for current reuse and noise cancellation
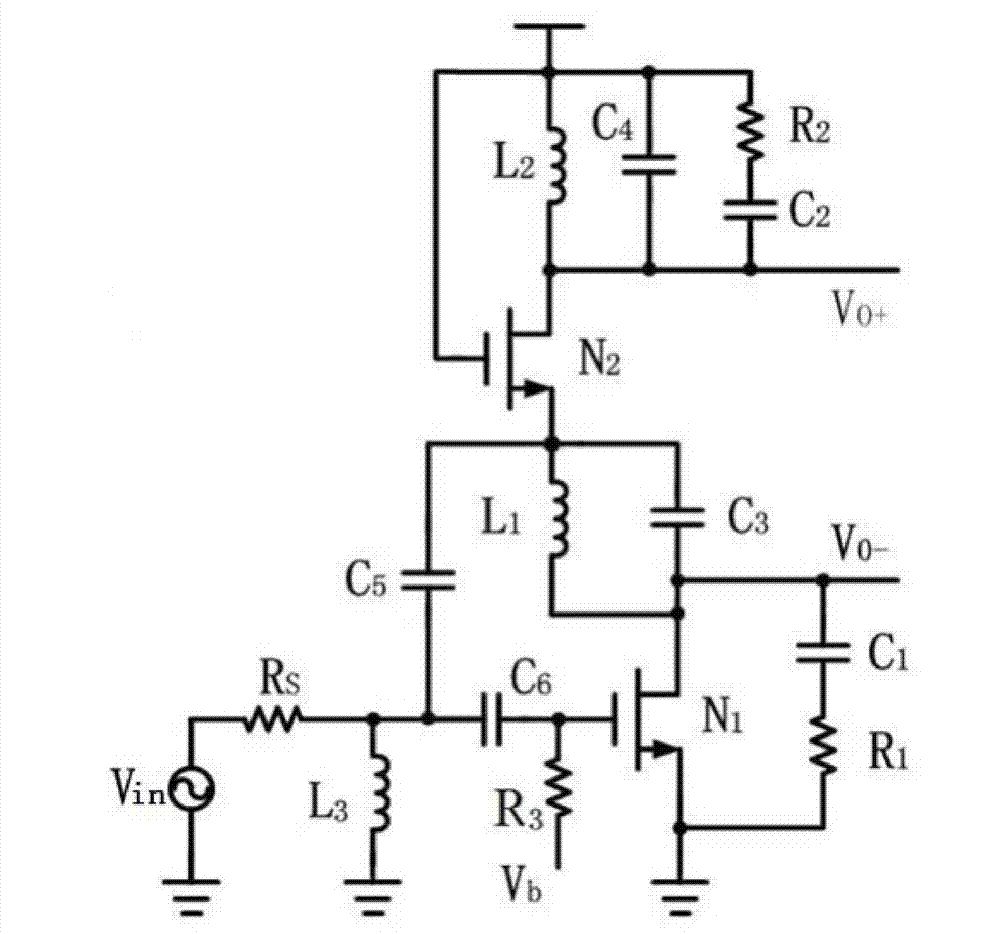
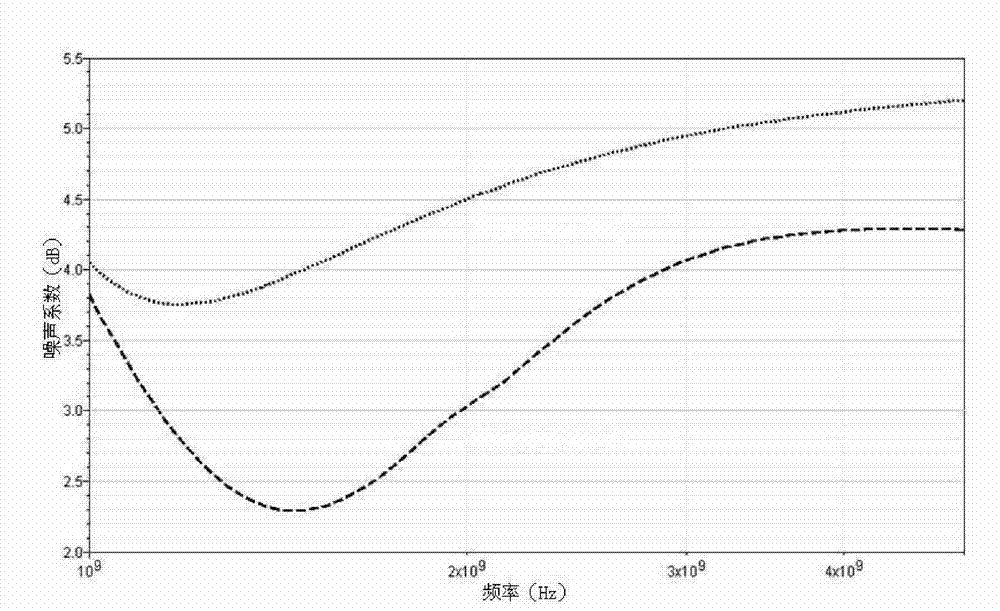
InactiveCN102969984ALower noise figureImprove noise figureAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceCapacitanceCommon source
The invention discloses a low noise amplifier for current reuse and noise cancellation. The amplifier comprises a common-source amplifier, a common-gate amplifier, a signal isolation and current reuse network and an off-chip receiving network, wherein the common-source amplifier comprises a first N-type metal oxide transistor, a first resistor, a third resistor, a first capacitor and a sixth capacitor; the common-gate amplifier comprises a second N-type metal oxide transistor, a second resistor, a second capacitor and a fifth capacitor; the signal isolation and current reuse network comprises a first resonant network and a second resonant network; the first resonant network consists of a first inductor and a third capacitor; the second resonant network consists of a second inductor and a fourth capacitor; and the off-chip receiving network comprises a second inductor, a signal source of an artificial antenna and an antenna internal resistor. The low noise amplifier in such a structure has a noise cancellation function and simultaneously reuses the static bias current of the common-gate amplifier and the common-source amplifier, thereby having a low noise coefficient and a low power consumption function.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
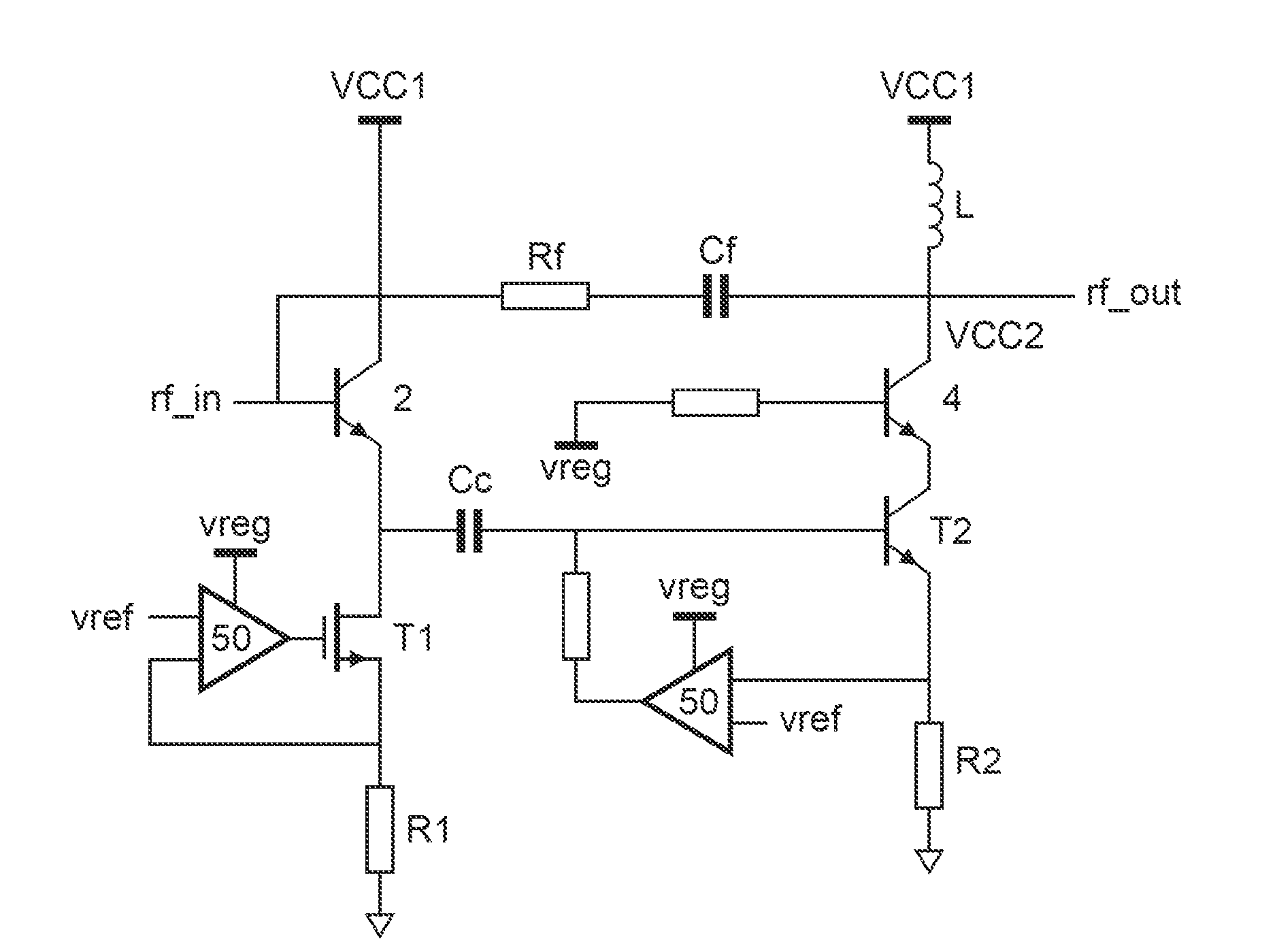
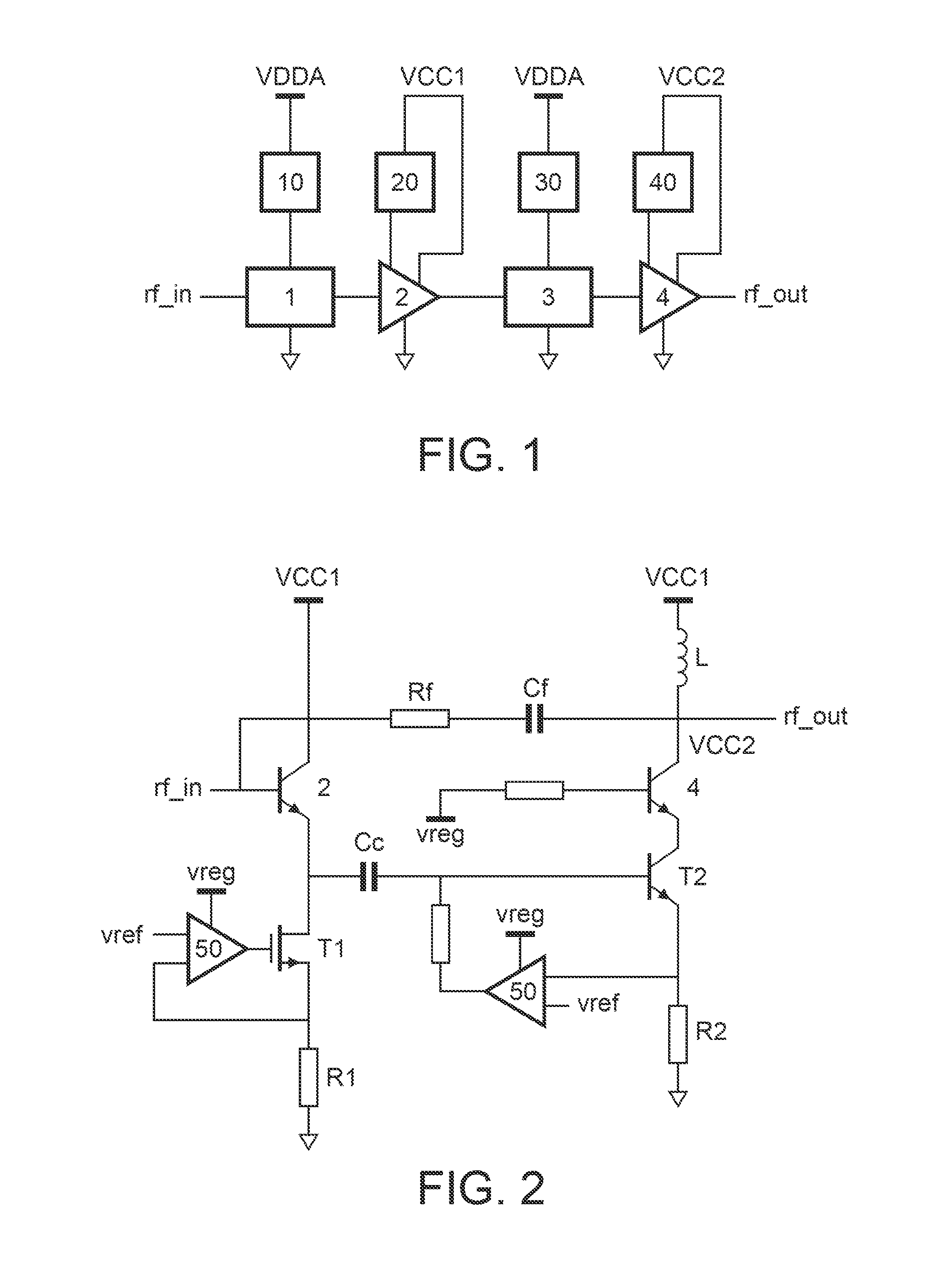
Variable gain amplifier
ActiveUS20120206205A1Improve linearityImprove noise figureHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
The invention relates to a variable gain amplifier comprising a first attenuator (1) for receiving an input signal (rf_in) and for transmitting a first attenuated input signal to a first amplifier (2) for amplifying the first attenuated input signal and for generating a first amplified signal to a second attenuator (3) for attenuating the first amplified signal and for transmitting a second attenuated signal to a second amplifier (4) for amplifying the second attenuated signal and for generating an output signal (rf_out). The first attenuator (1) is supplied from a first supply voltage source (10). The second attenuator (3) is supplied from a second supply voltage source (30). The first amplifier (2) is supplied from a third supply voltage source (20), and the second amplifier (4) is supplied from a fourth supply voltage source (40).
Owner:NXP BV
Low-noise preamplifier, in particular, for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
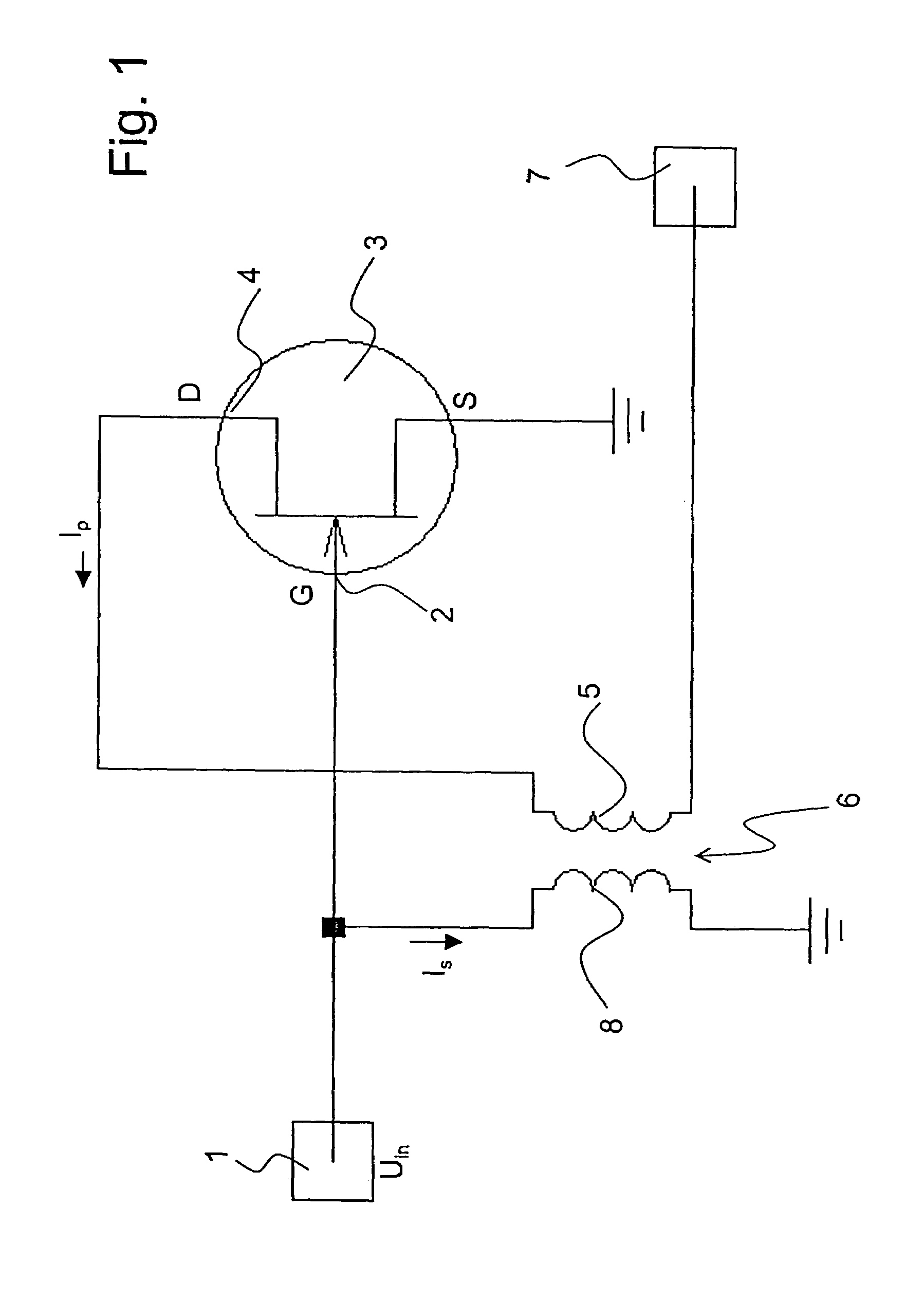
ActiveUS20050001680A1Lower input impedanceImprove noise figureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noiseTransformer
A low-noise preamplifier with an electronic amplifying element having an input (2) and an output (4), and with a first transformer (6) having a primary winding (5) and a secondary winding (8) is characterized in that the input (2) of the electronic amplifying element is the base of a transistor, the gate (G) of a field effect transistor (FET) or the grid of a vacuum tube, and the output (4) of the electronic amplifying element is the collector, the drain (D) or the anode, the output current (Ip) being passed from the electronic amplifying element through the primary winding (5) of the first transformer (6) to the output (7) of the preamplifier, wherein the secondary winding (8) of the first transformer (6) is connected to the input (2) of the electronic amplifying element. This preamplifier can be operated with extremely low noise and at any input impedance, in particular, at 50 ohms or 75 ohms.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Optical communication systems including optical amplifiers an amplification methods
InactiveUS20080074732A1Improve system performanceHigh gainLaser detailsFibre transmissionOptical amplifierOptical communication
Optical systems of the present invention include first and second optical amplifiers that are operated individually to provide gain profiles that do not conform with a desired composite, or overall or total, gain profile, e.g., substantially flat, but to produce a desired composite noise figure profile, e.g., substantially flat or otherwise, for the amplifiers. Generally, the desired composite noise figure profile is produced, while attempting to minimize the deviation of the composite gain profile from the desired composite gain profile.
Owner:OPTIC153 LLC
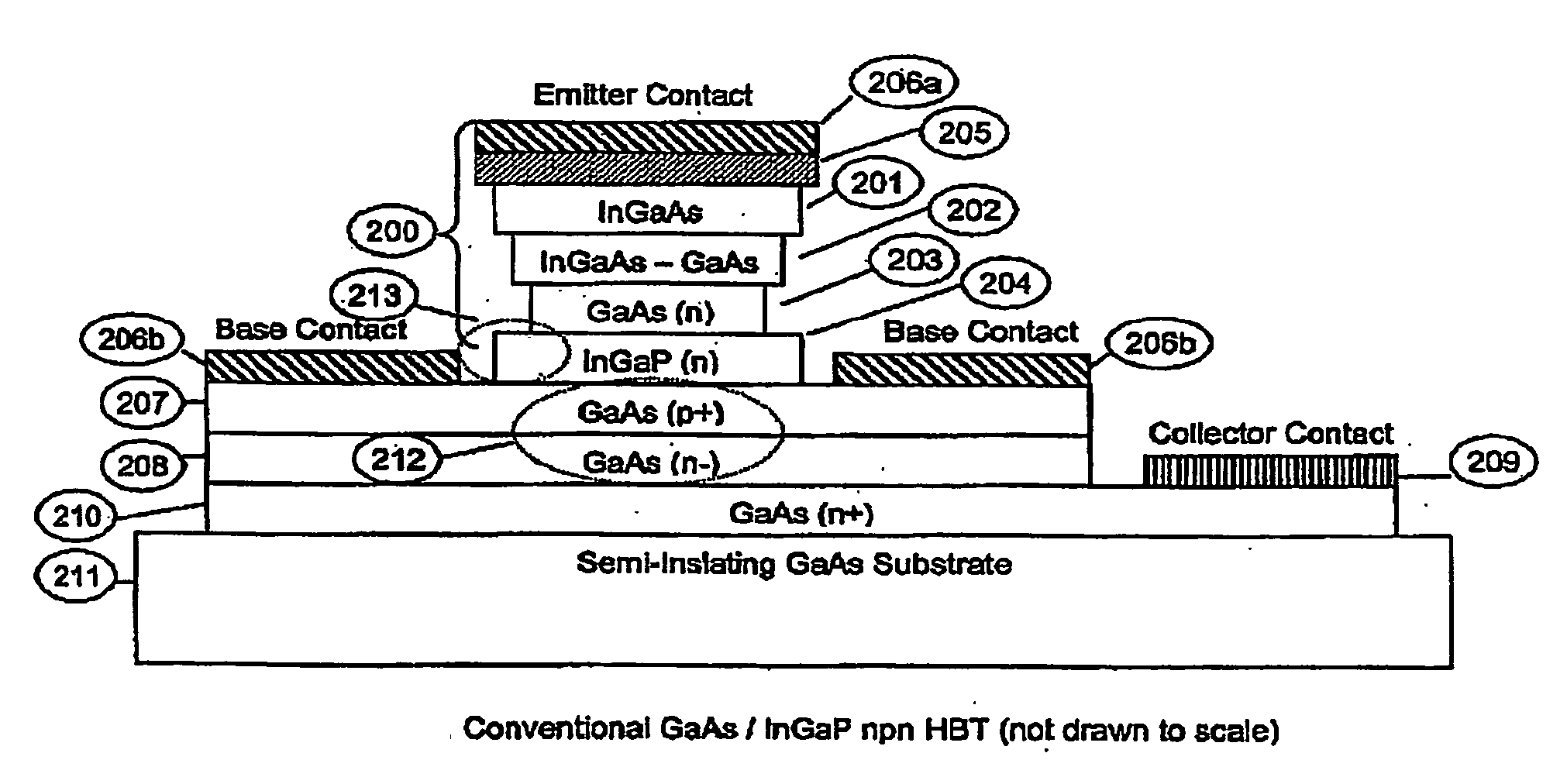
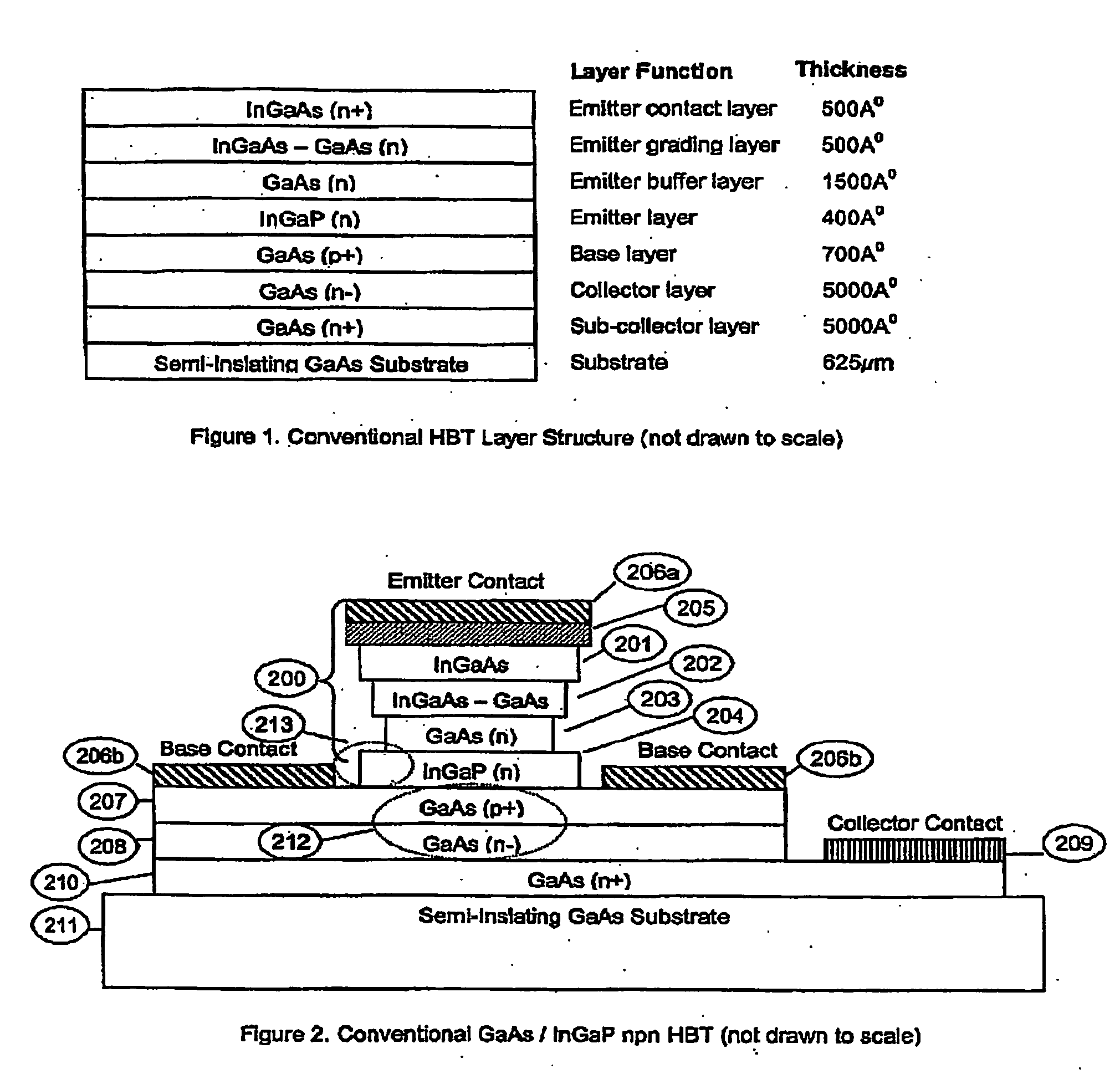
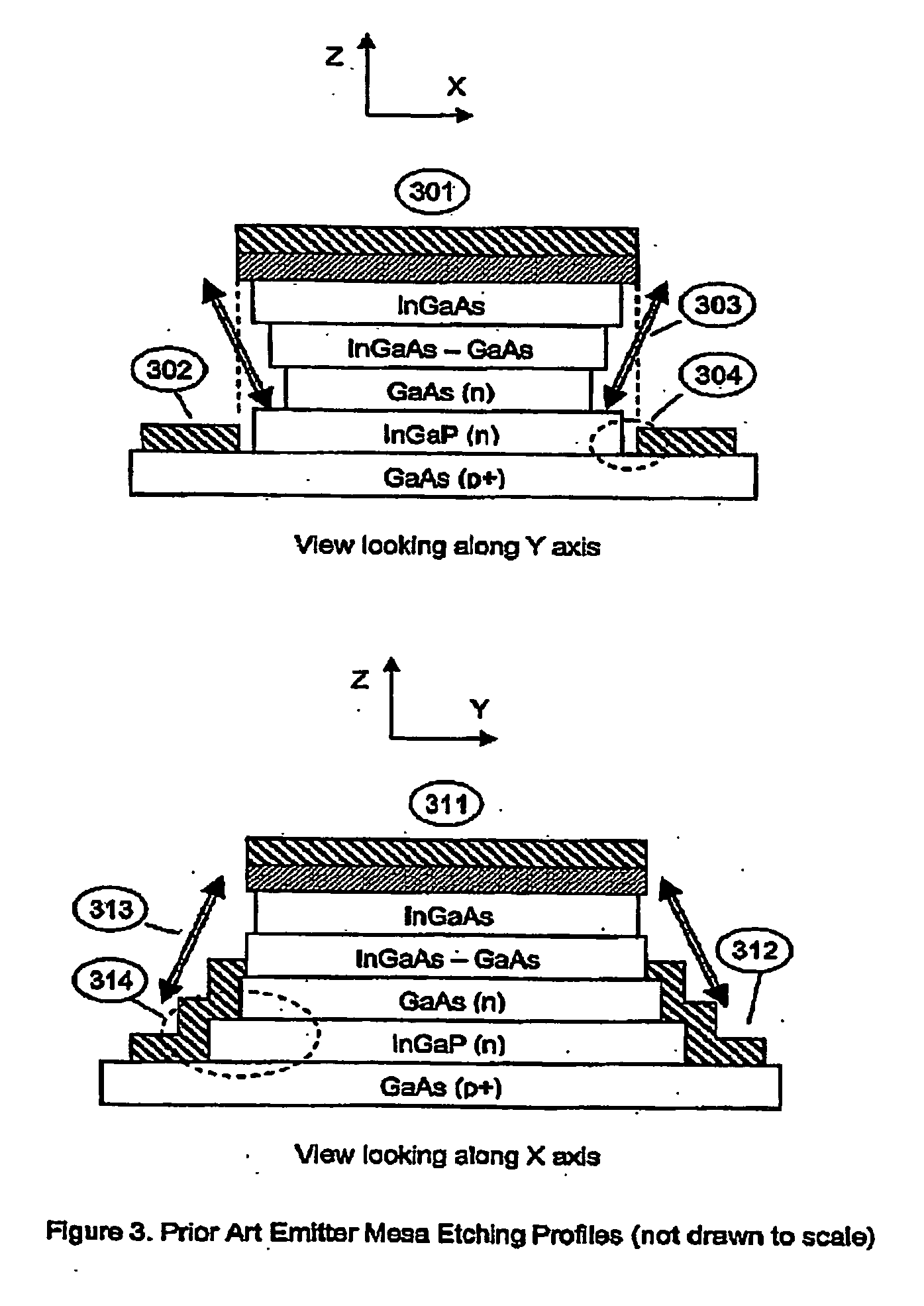
Heterjunction bipolar transistor with tunnelling mis emitter junction
InactiveUS20060284282A1Improve performanceAvoid sizeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare earthEngineering
A manufacturing method and structure for a MIS Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor (HBT) is provided including a GaAs substrate which has a collector region; a base layer coupled to the collector region; the ultra-thin insulating layer including a rare earth oxide coupled to the base layer; and an emitter structure including metal layers coupled to the ultra-thin insulating layer.
Owner:EPITACTIX PTY LTD
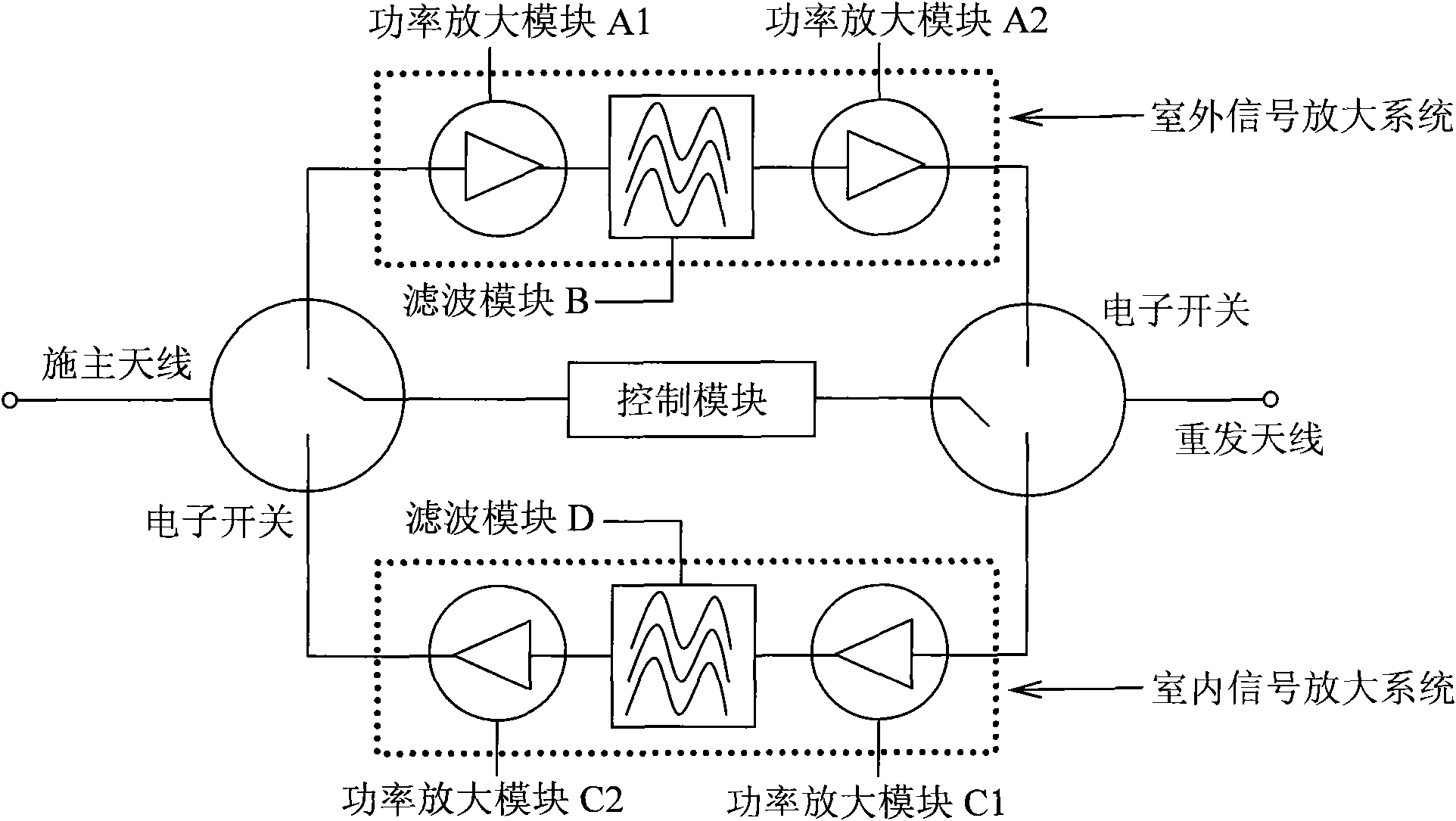
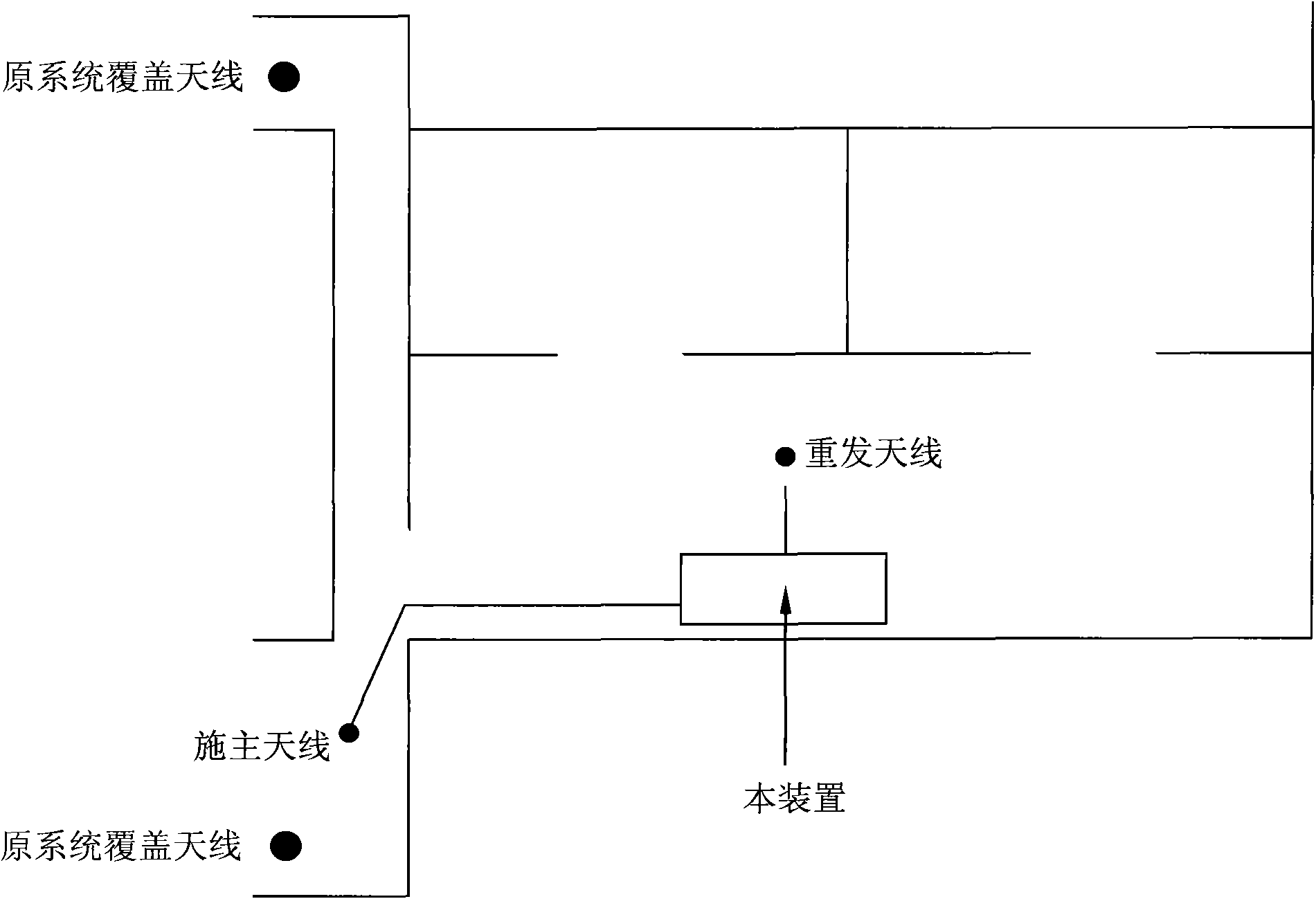
Wireless communication network optimization device
InactiveCN101808340APrecise control of blind filling areaAvoid costly retrofitsNetwork planningSignal amplificationMobile phone
The invention relates to the field of wireless communications, in particular to a wireless communication network optimization device, which comprises a donor antenna, an outdoor signal amplification system, a control module, an indoor signal amplification system and a retransmission antenna. The donor antenna is used for receiving a weak outdoor wireless communication signal and retransmitting an indoor mobile phone user signal after processing of the network optimization device; the outdoor signal amplification system is used for amplifying the power of the received weak outdoor wireless communication signal; the indoor signal amplification system is used for amplifying the power of the received mobile phone user wireless communication signal; the retransmission antenna is used for transmitting an outdoor wireless communication signal after processing of the network optimization device and receiving the mobile phone user wireless communication signal; and the control module is used for controlling operation of the donor antenna, the outdoor signal amplification system, the indoor signal amplification system and the retransmission antenna. The device has the advantages of low manufacturing cost and simple installation.
Owner:北京联动原创科技有限公司
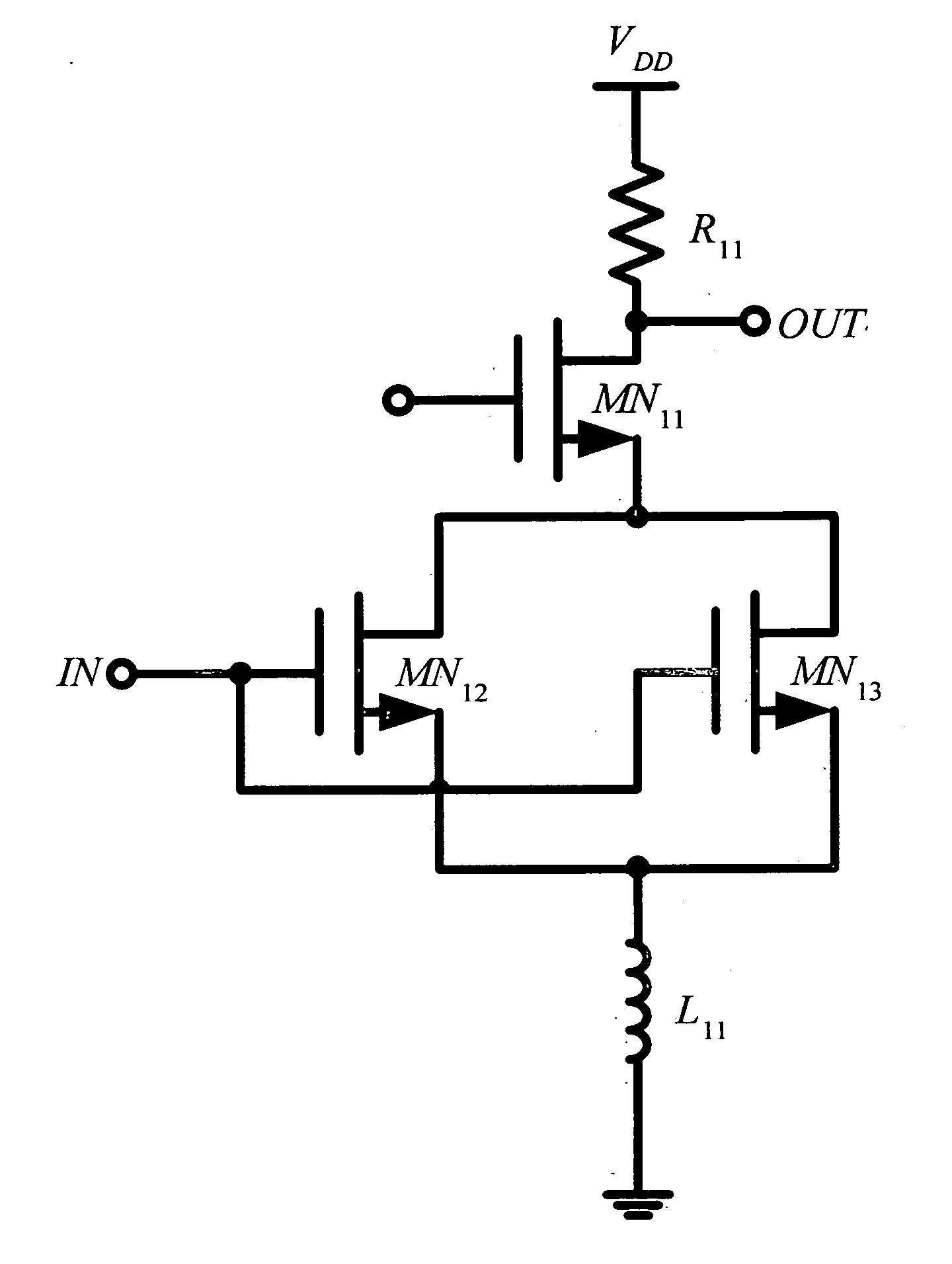
Input impedance matching circuit for low noise amplifier
InactiveUS7298213B2Improve noiseImprove noise figureMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlInput impedanceImpedance matching
An input impedance matching circuit for a low noise amplifier includes a source pad, a gate pad, an input transistor, a source degeneration inductor and a matching capacitor. The gate pad receives an input signal and the input transistor amplifies the input signal transmitted from the gate pad. The source degeneration inductor electrically coupled to an external ground voltage is adapted for input impedance matching of the low noise amplifier. The source pad is coupled to a source electrode of the input transistor and the matching capacitor is formed between the gate pad and the source pad extending the source pad to be disposed under the gate pad. Accordingly, impedance matching of the low noise amplifier may be facilitated and the gain and noise figure of the low noise amplifier may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low noise amplifier for bioelectricity detection
ActiveCN110417360AImprove noise figureImprove Noise PerformanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier combinationsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention relates to a low-noise amplifier for bioelectricity detection. The low-noise amplifier comprises an input chopper circuit (1), an input coupling capacitor module (2), a two-stage operational amplifier module (3), a capacitance negative feedback loop (4), a positive feedback input impedance lifting loop (5) and an electrode direct-current offset elimination loop (6). According to thelow-noise amplifier, the noise coefficient of the low-noise amplifier is improved by adopting the two stages of operational amplifier modules for current multiplexing; the noise performance of the low-noise amplifier is further improved, meanwhile, the direct-current offset voltage between electrodes in the analog front-end circuit is restrained through the electrode direct-current offset eliminating loop, and therefore the quality of signals received by the analog front-end circuit is guaranteed.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
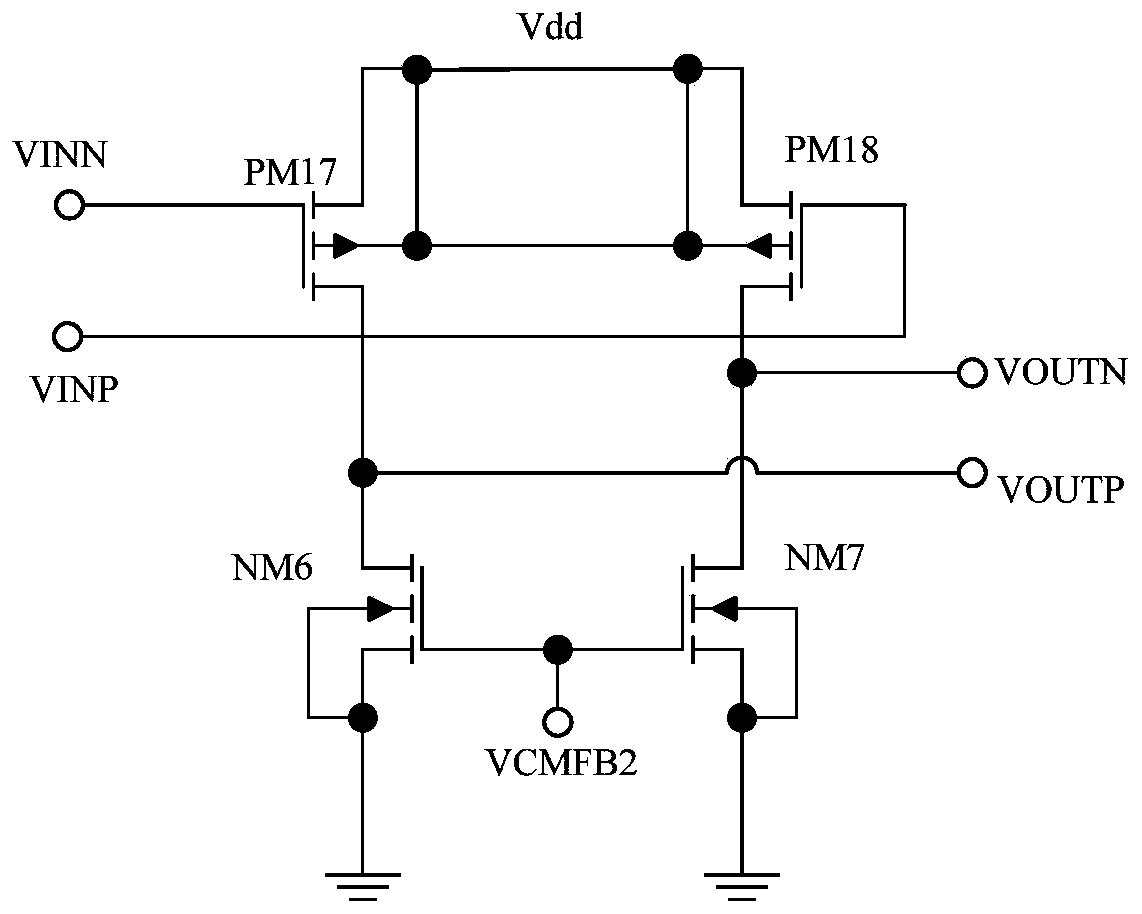
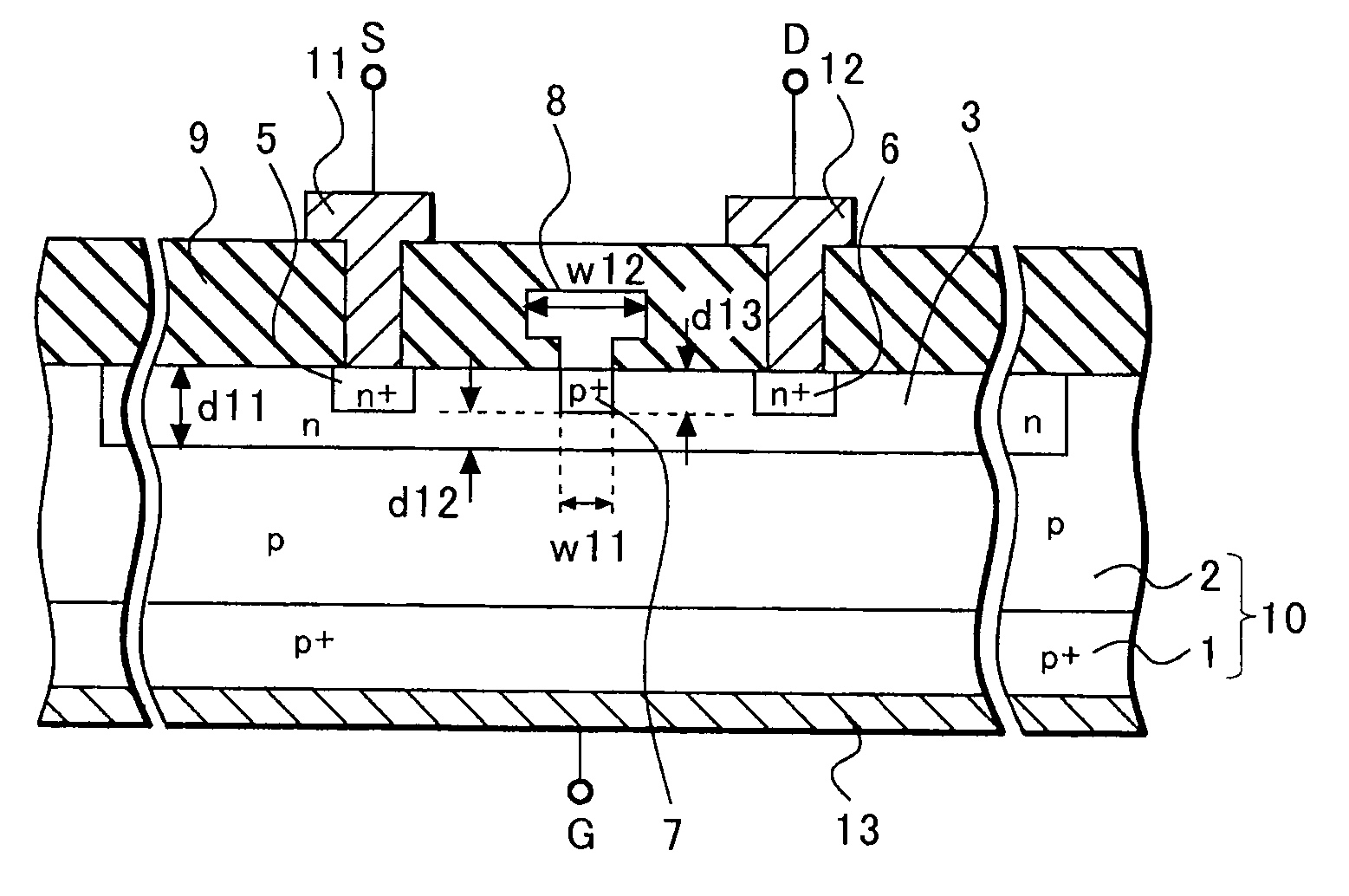
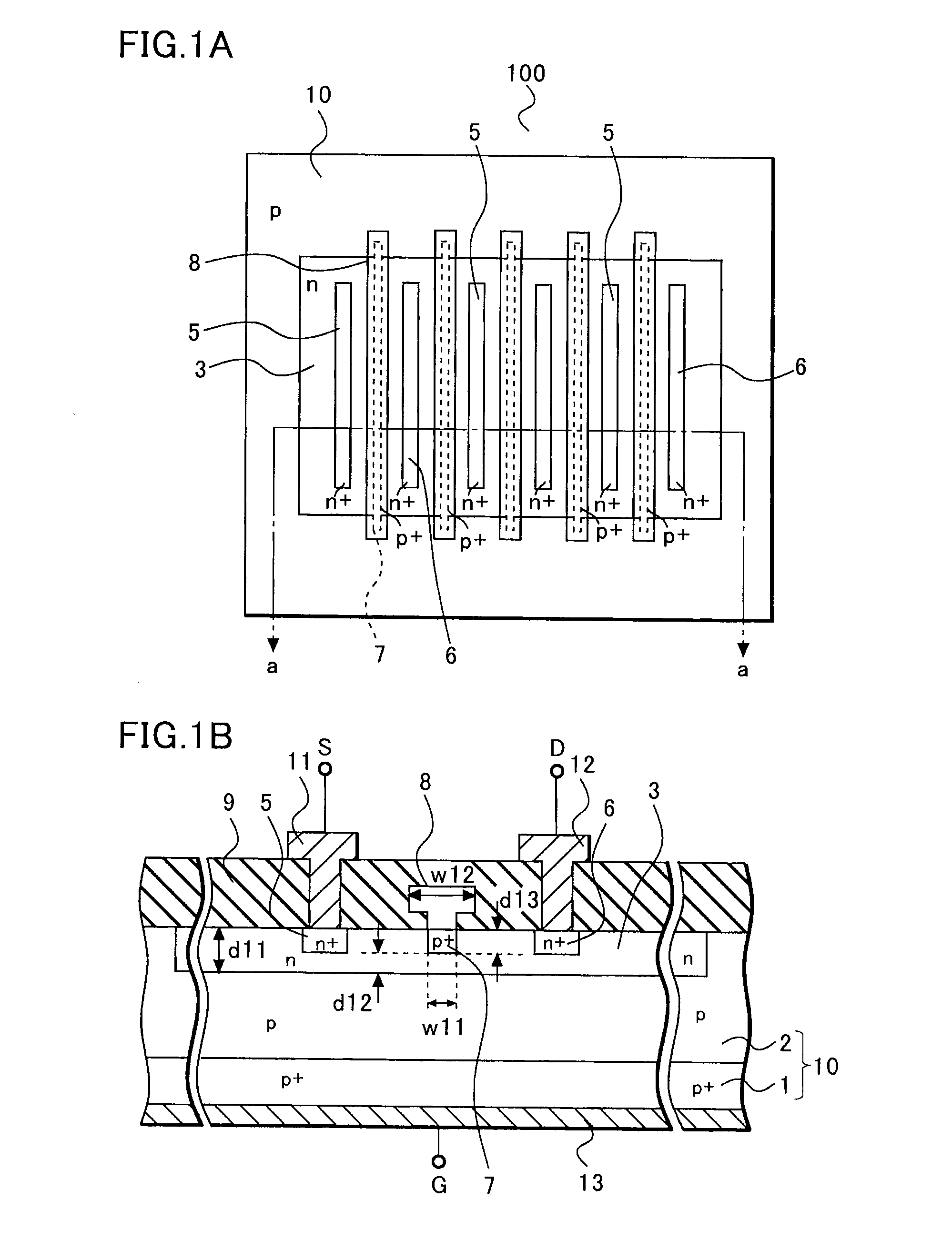
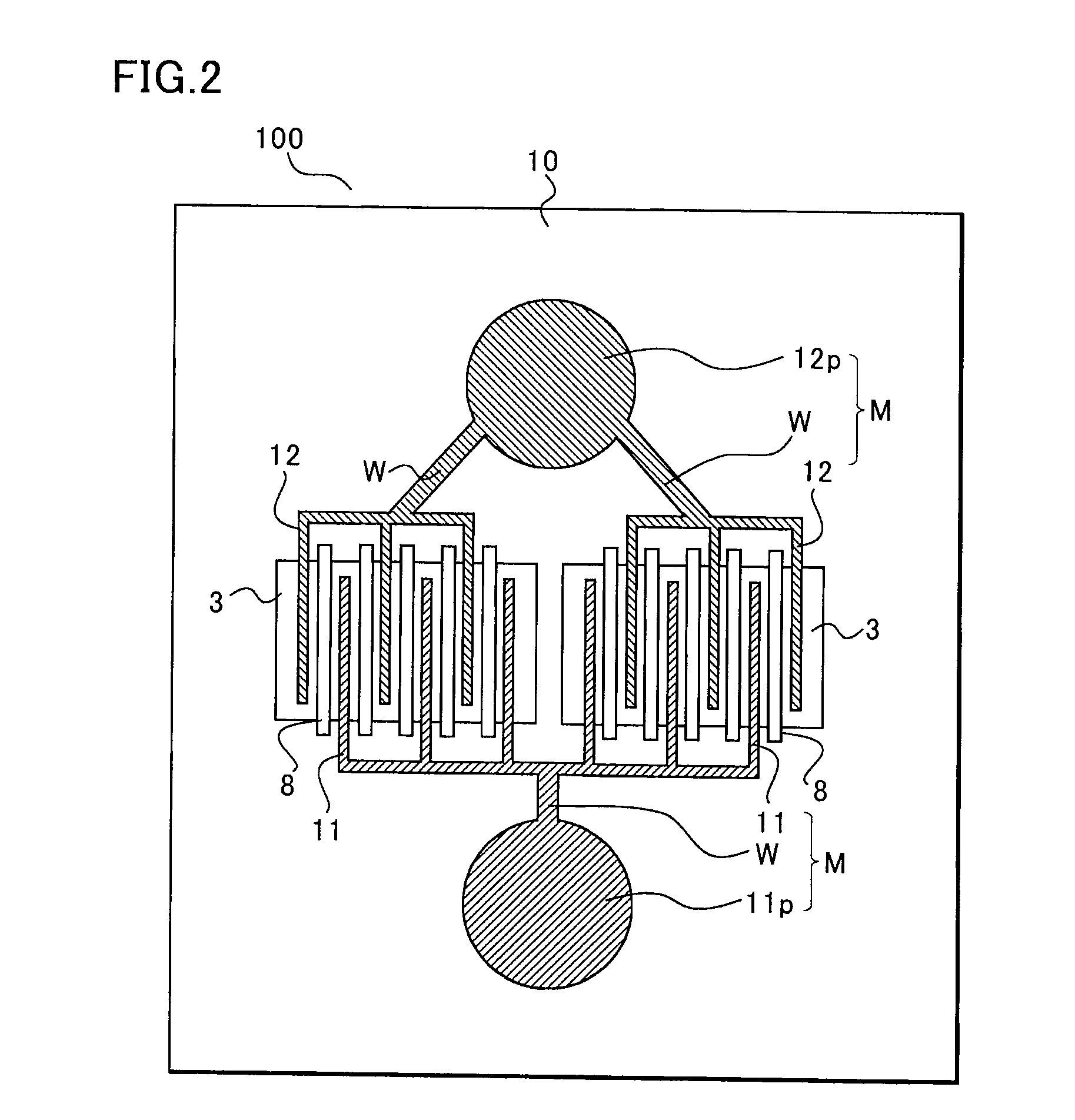
Junction field effect transistor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080048214A1Reduce areaRaise the cutoff frequencyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
According to a junction FET of the present invention, the depth of a channel region is made shallow by selectively performing ion implantation and diffusion. Since the channel region forms a pn junction together with a p type semiconductor layer with relatively low impurity concentration, the improvement in the high frequency characteristic and the reduction in the amount of the leakage current because of the reduction in a junction capacitance can be achieved. Moreover, the depth of a gate region is also made shallow by ion implantation, and thus the reduction in noise because of the reduction in the internal resistance can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com