Patents
Literature
352results about How to "Raise the cutoff frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
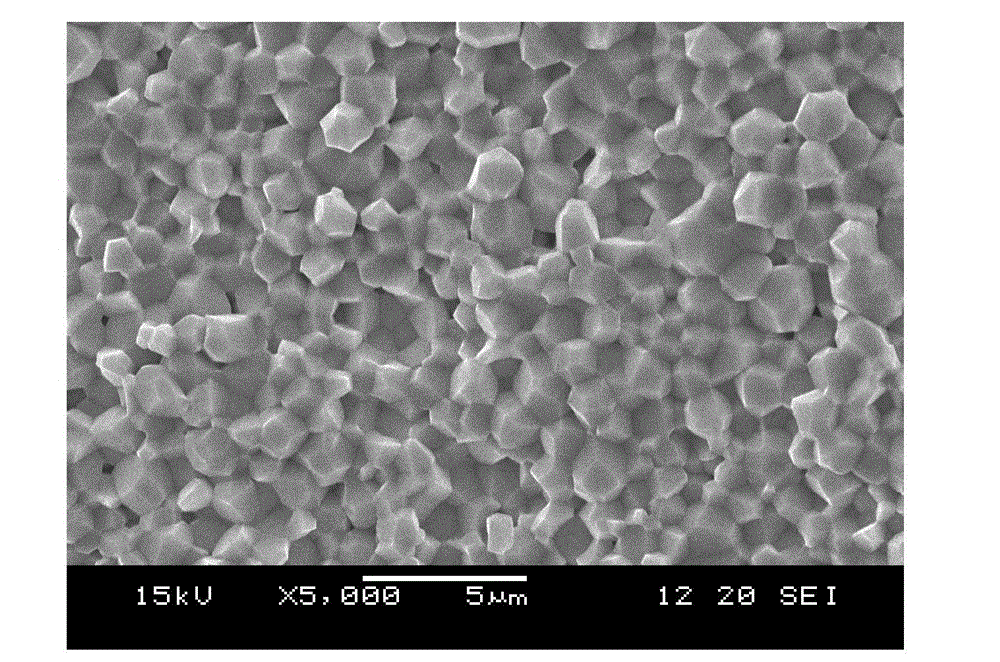
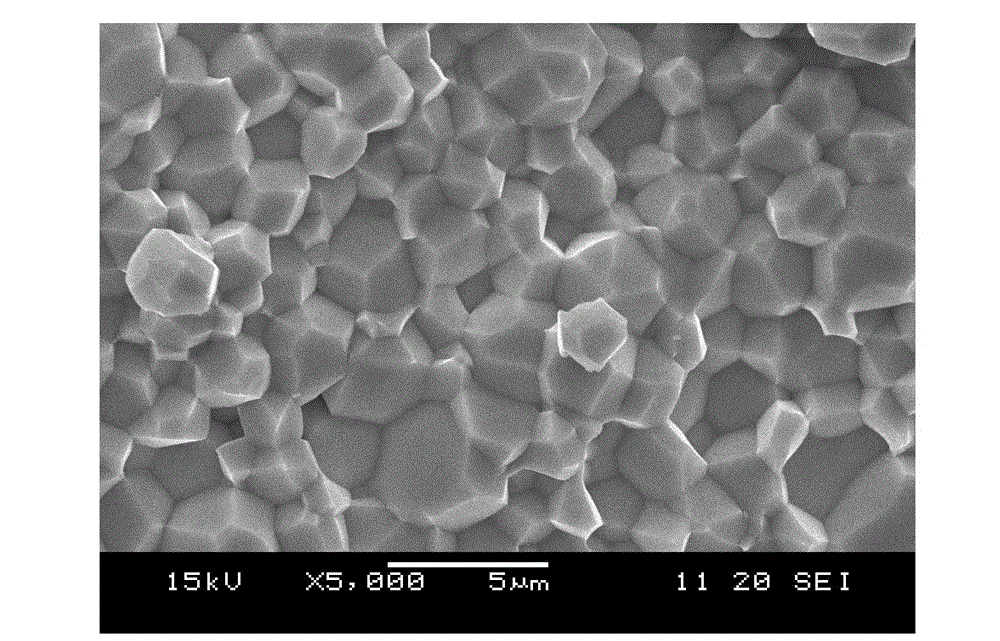
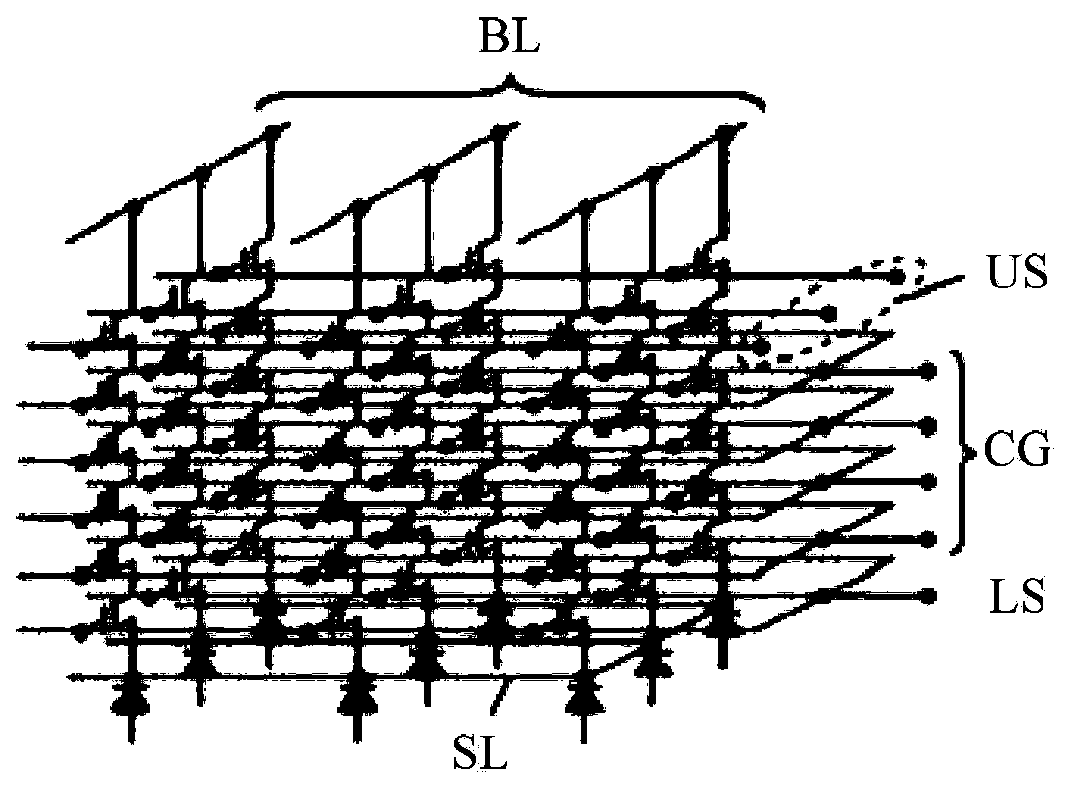
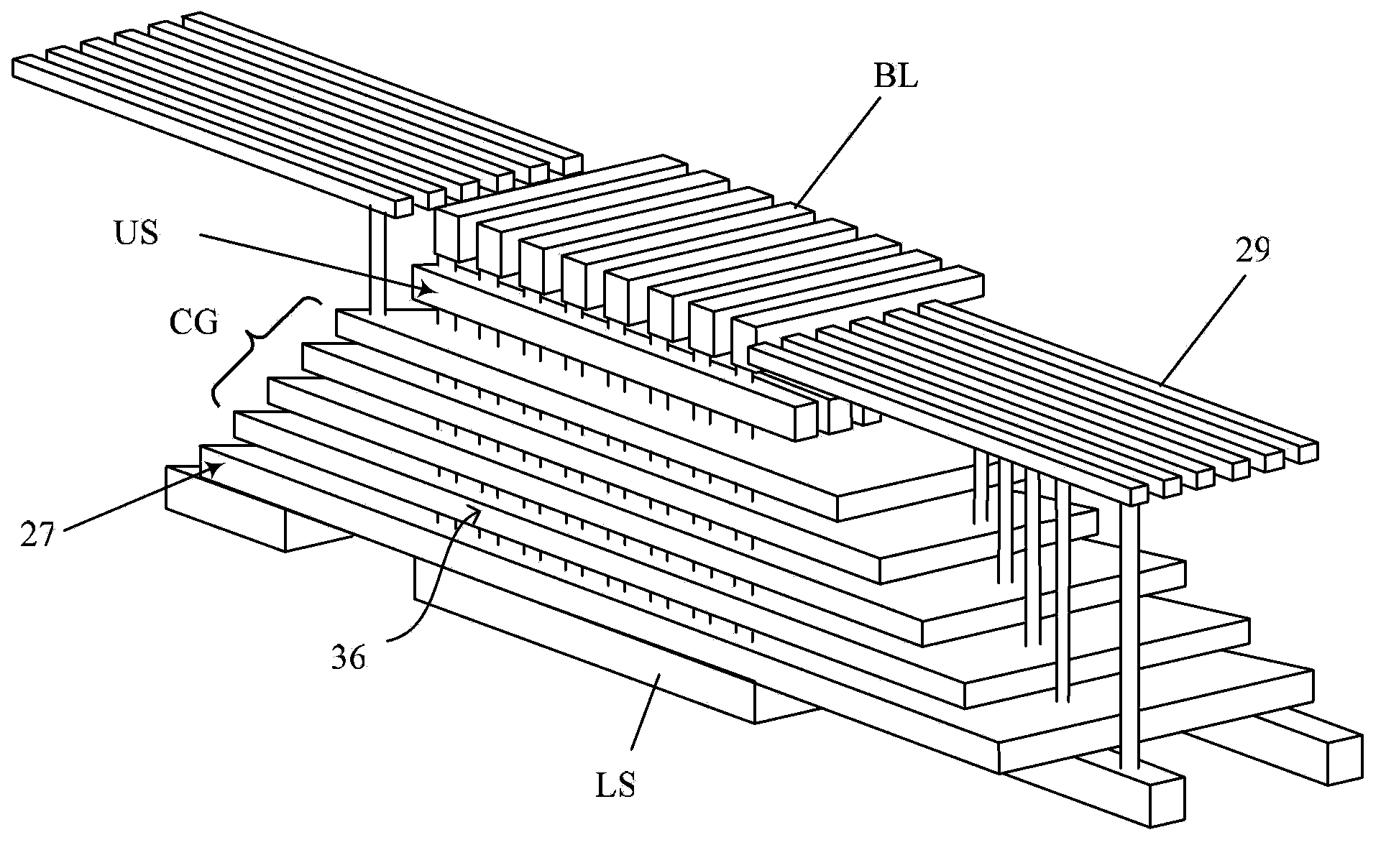
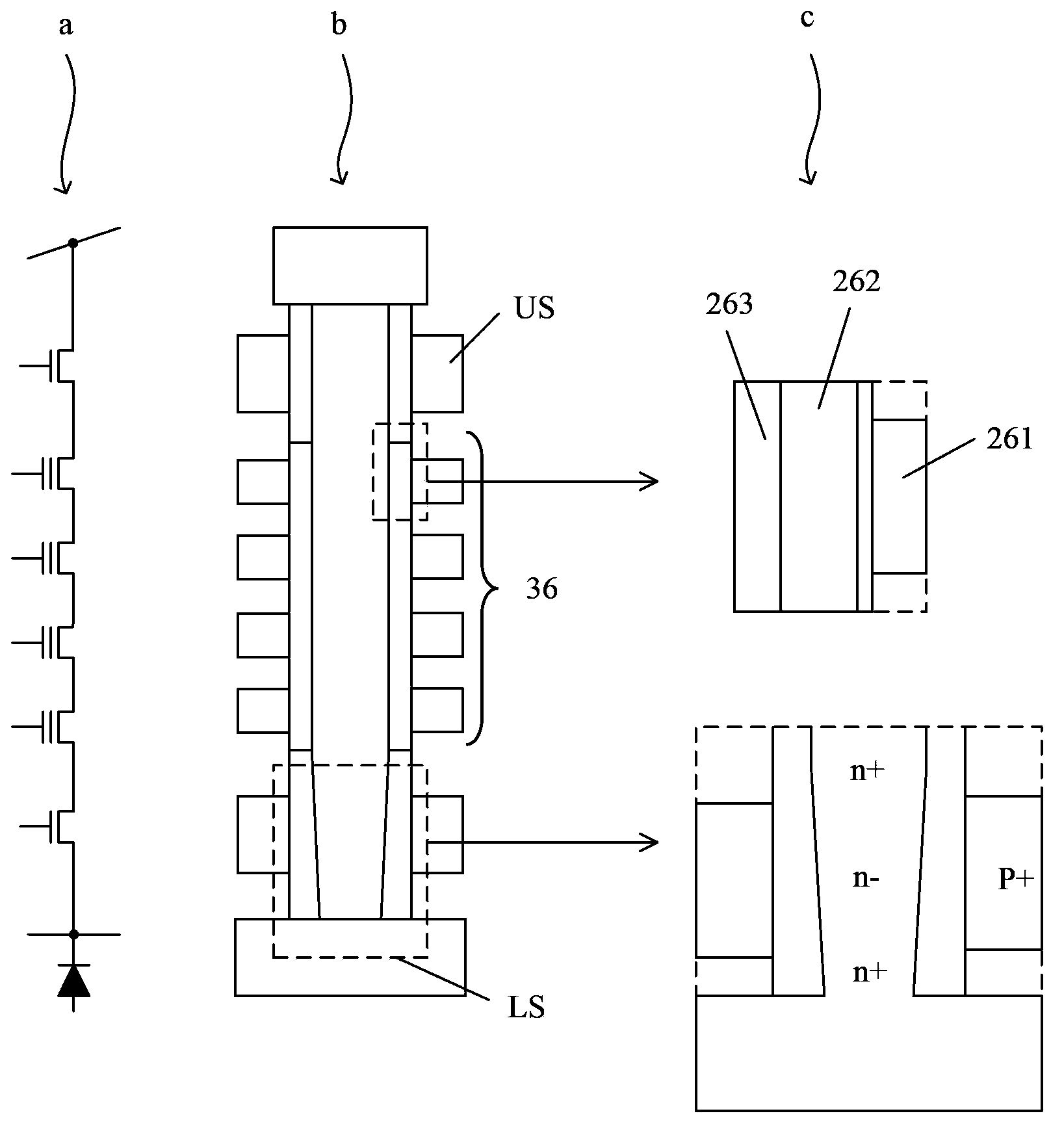
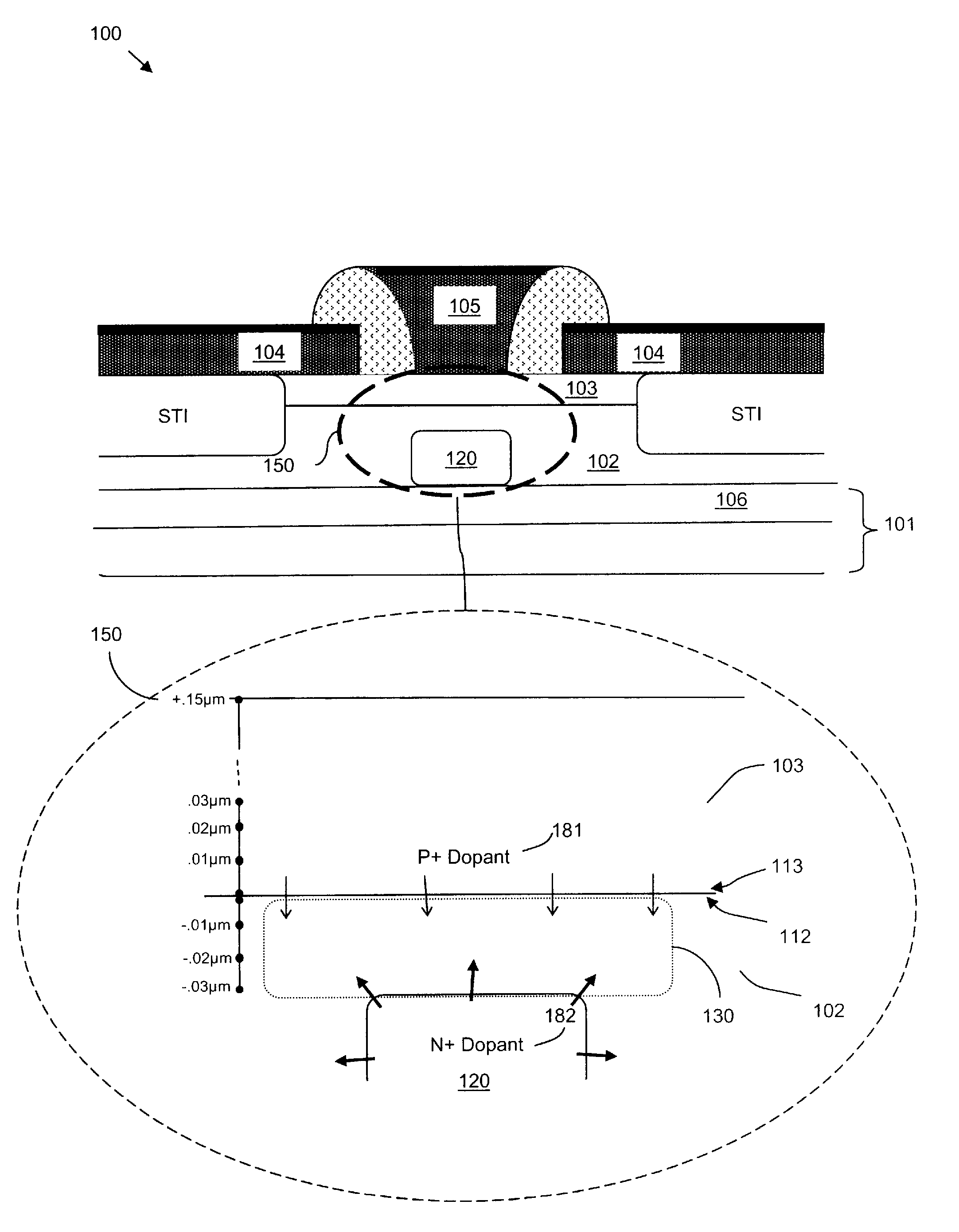
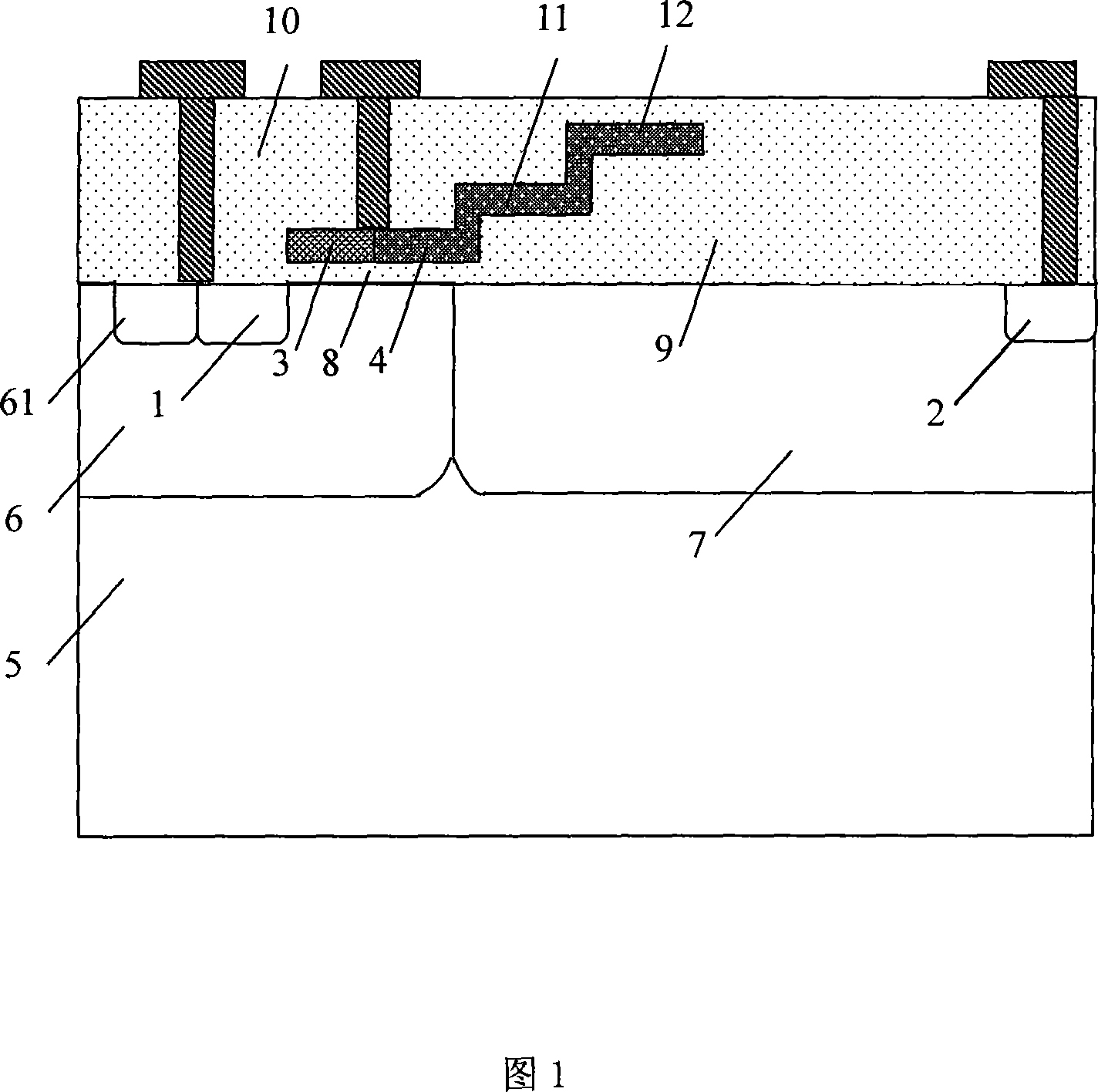
3D (three-dimensional) NAND memory and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103680611AImprove controlReduce parasitic parametersSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesInput controlComputer science
The invention discloses a 3D (three-dimensional) NAND memory and a manufacturing method of the 3D NAND memory. The 3D NAND memory comprises multiple layers of storage arrays and multiple layers of control grid circuits, wherein each layer of the control grid circuit is electrically connected to the same layer of the storage array, so that selection of each layer of the storage array is realized; each layer of the control grid circuit is obtained by cascading a same number of transistors; grids of all the transistors of the control grid circuits are electrically connected to control wires; the number of the control wires is as the same as that of the transistors comprised in each layer of the control grid circuit; the grids of different transistors positioned on the same layer of the control grid circuit are electrically connected to different control wires. According to the 3D NAND memory, a small number of input control wires SSL select a large number of control grid layers through the control grid circuits, so that the area and the volume of the whole memory cannot be enlarged due to the increase of the number of the required layers of control grids when the storage capacity of the memory is improved due to the increase of the number of storage unit layers.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
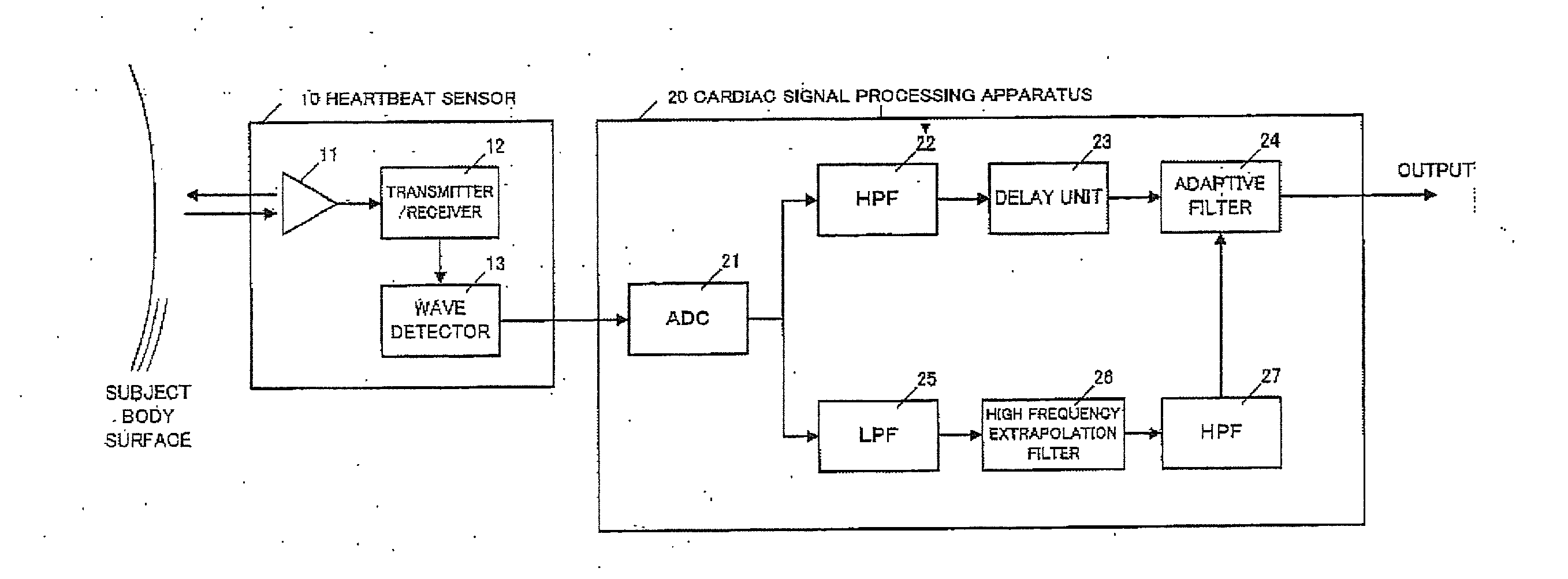
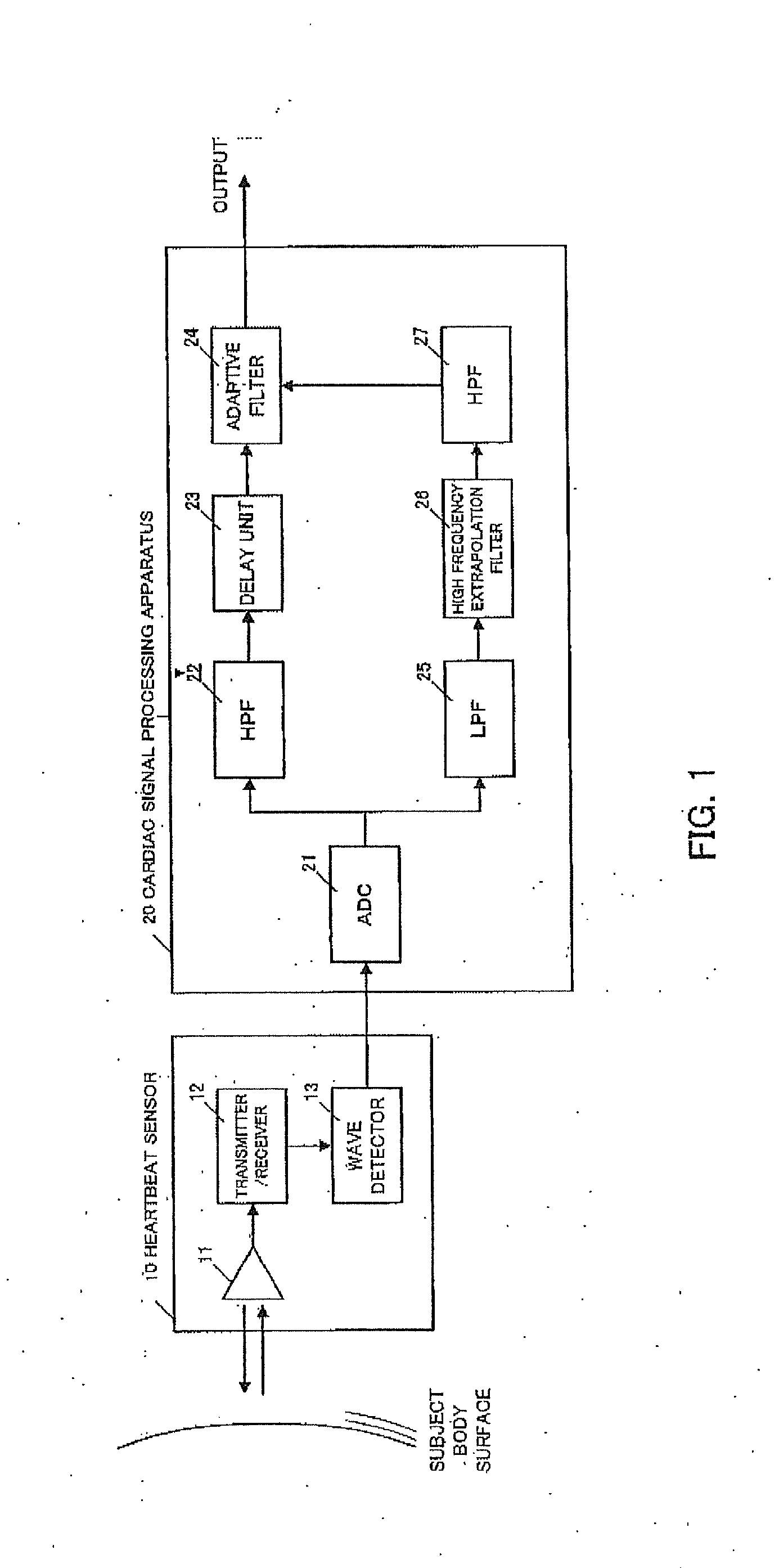
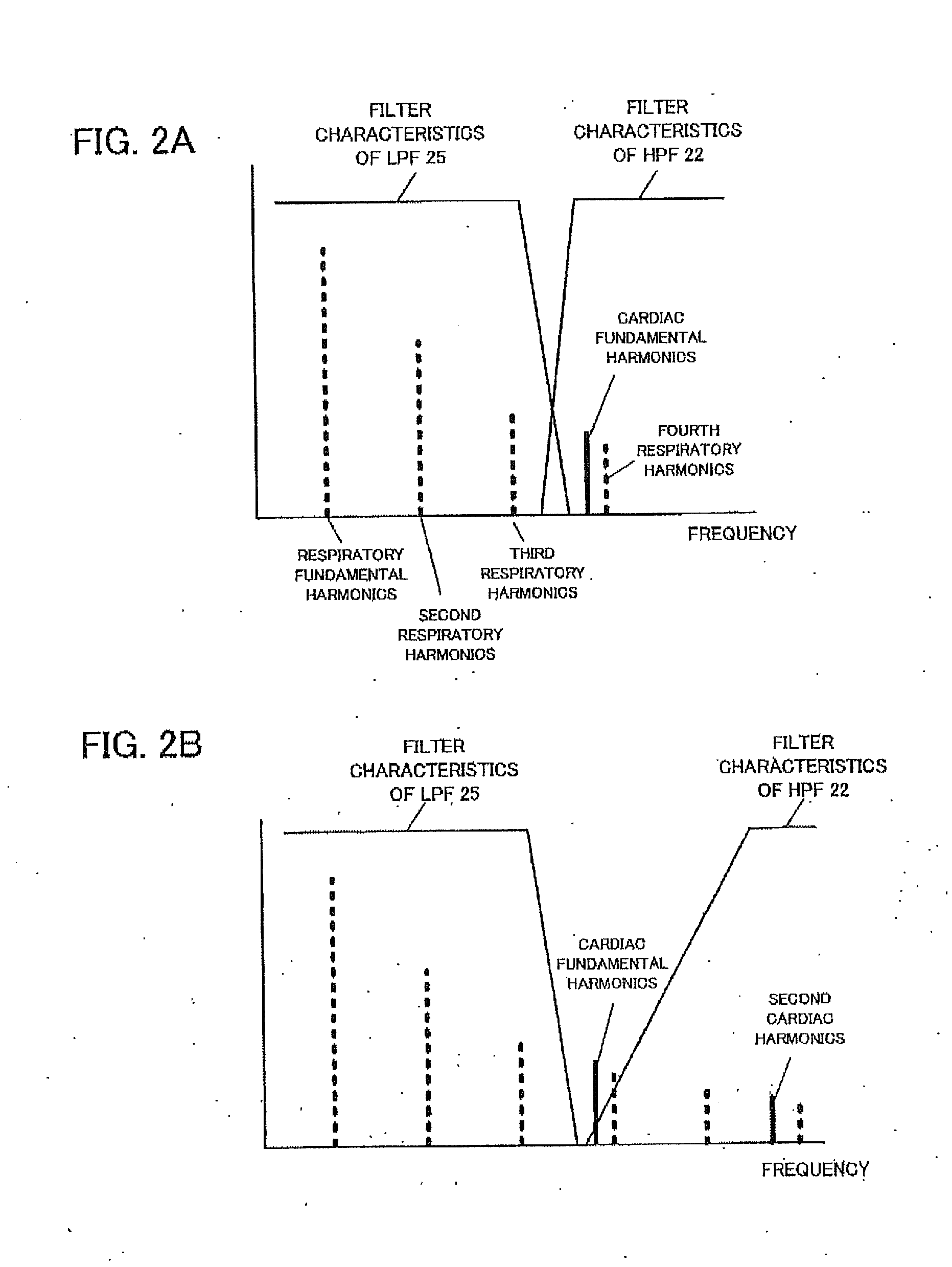
Cardiac signal processing apparatus and cardiac signal processing method
ActiveUS20130197377A1Eliminate distractionsComponent with highCatheterSensorsBand-pass filterEngineering
A cardiac signal processing apparatus includes: a unit for acquiring, from a heartbeat sensor, cardiac signals relating to heartbeats of a subject; a low-pass filter for allowing passage of those cardiac signals having a first predetermined frequency or lower, among the cardiac signals; higher harmonic noise acquisition unit for acquiring harmonic signals of low-frequency noise by performing high frequency extrapolation on the signals output from the low-pass filter; a high-pass filter for allowing passage of those cardiac signals having a second predetermined frequency or higher, among the cardiac signals; and higher harmonic noise removal unit for removing the harmonic signals of low-frequency noise from the signals output from the high-pass filter. It is thus made possible to remove noise from the cardiac signals and to obtain desirable heartbeat detection characteristics.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Air-gap grapheme transistor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102074584ALow dielectric constantSmall overall permittivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIntegrated circuit manufacturingAND gate
The invention belongs to the technical field of carbon integrated circuit manufacturing, in particular relates to an air-gap grapheme transistor and a manufacturing method thereof. In the method, gate electrodes and gate medium grow on a silicon base and then source and drain graphics are formed; grapheme is transformed to the formed source and drain graphics so as to separate the grapheme from the gate medium; and the air-gap is used to separate the grapheme from the gate medium so as to eliminate the growth process of a buffer layer on the grapheme, thus high mobility of carriers in the grapheme is retained maximally, and deterioration for the surface properties of the grapheme is reduced, thereby further improving electrical properties of grapheme devices.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Low-power consumption receiver capable of dynamically detecting barrage jamming signal
ActiveCN101277121ALow design requirementsLow order requirementsTransmissionLow-pass filterSystem configuration
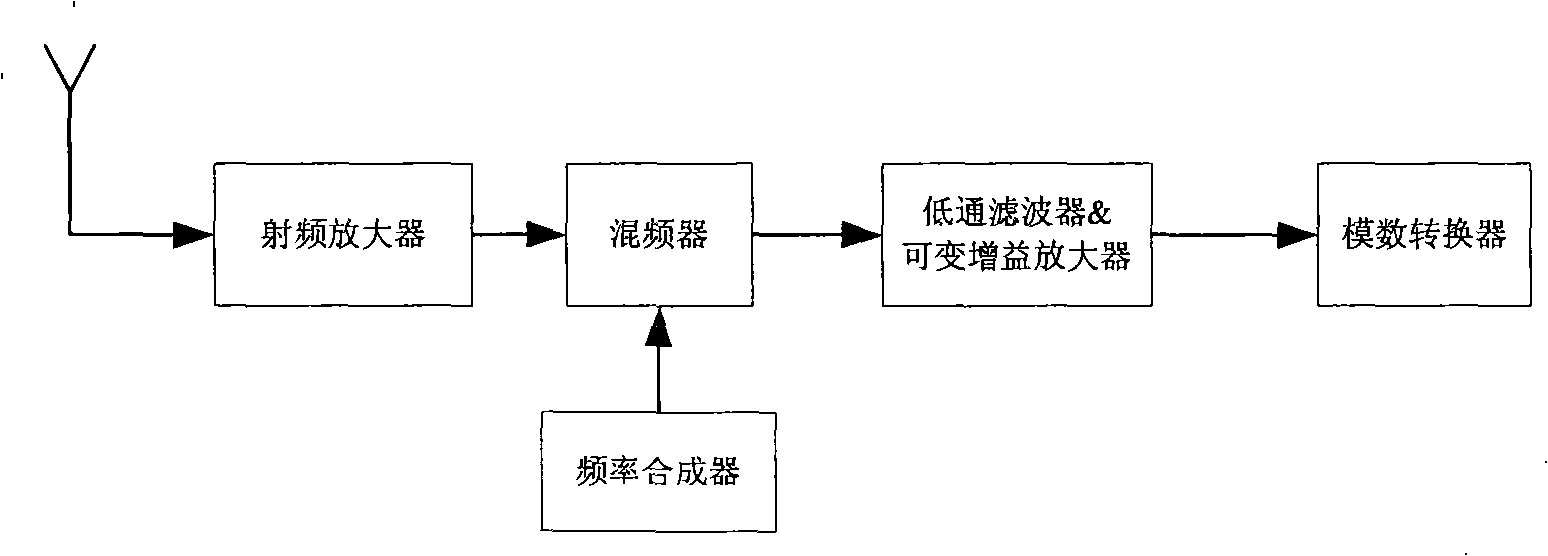
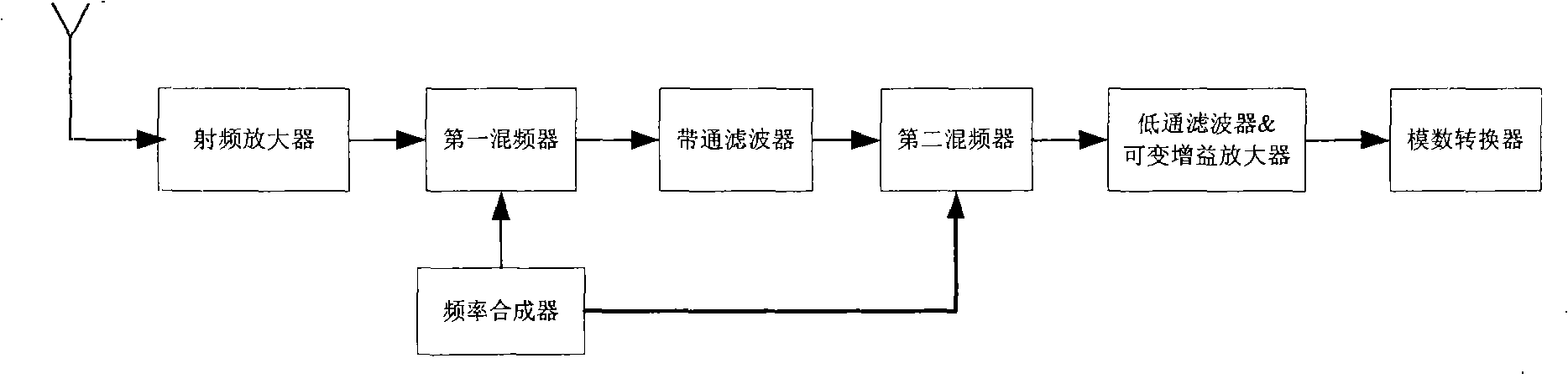
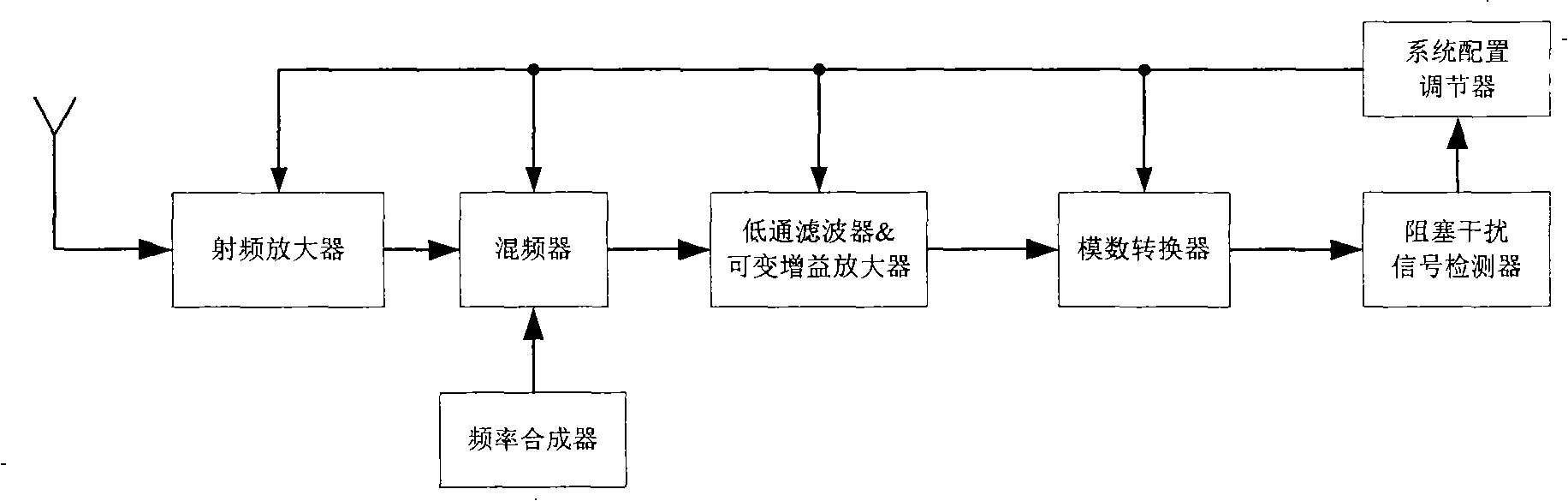
The present invention relates to a low power consumption receiver which can dynamically detect the blocking interference signal and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The receiver comprises the following components: a radio frequency amplifier, a frequency synthesizer, a first frequency mixer, a low-pass filter, a variable gain amplifier and an analog-digital converter which are connected in sequence. The receiver also comprises a blocking interference signal detector and a system configuration regulator connected with the detector. The input end of the blocking interference signal detector can be connected with the output end of the analog-digital converter, and can be connected with the input ends and output ends of the low-pass filter and variable gain amplifier at the same time. The output end of the system configuration regulator is connected with at least one device in all devices respectively, or is connected with a plurality of receiving chains which arecomposed of the devices through an N-route multiplexer. The receiver presented by the invention can automatically detect the strength of the blocking interference signal and regulates the system configuration correspondingly. The receiver is leaded to work in different working modes in order to adapt different working environments.
Owner:ALTO BEAM (CHINA) INC
Silicon germanium heterojunction bipolar transistor structure and method
InactiveUS20080265282A1Minimizes unwanted defect-enhanced diffusionMinimize diffusionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureRapid thermal annealing
Disclosed is an improved semiconductor structure (e.g., a silicon germanium (SiGe) hetero-junction bipolar transistor) having a narrow essentially interstitial-free SIC pedestal with minimal overlap of the extrinsic base. Also, disclosed is a method of forming the transistor which uses laser annealing, as opposed to rapid thermal annealing, of the SIC pedestal to produce both a narrow SIC pedestal and an essentially interstitial-free collector. Thus, the resulting SiGe HBT transistor can be produced with narrower base and collector space-charge regions than can be achieved with conventional technology.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Filtering image data to obtain samples mapped to pixel sub-components of a display device
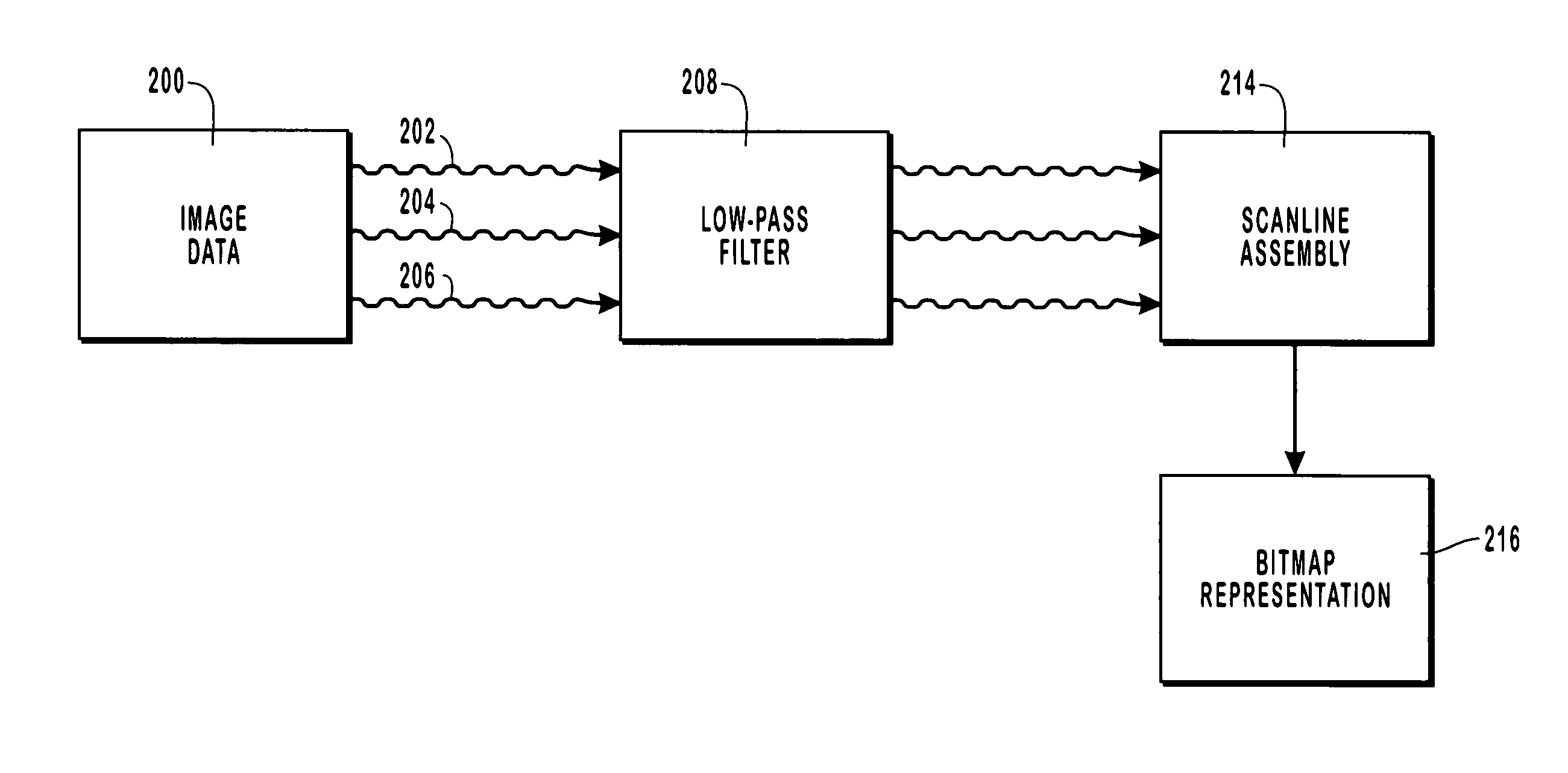
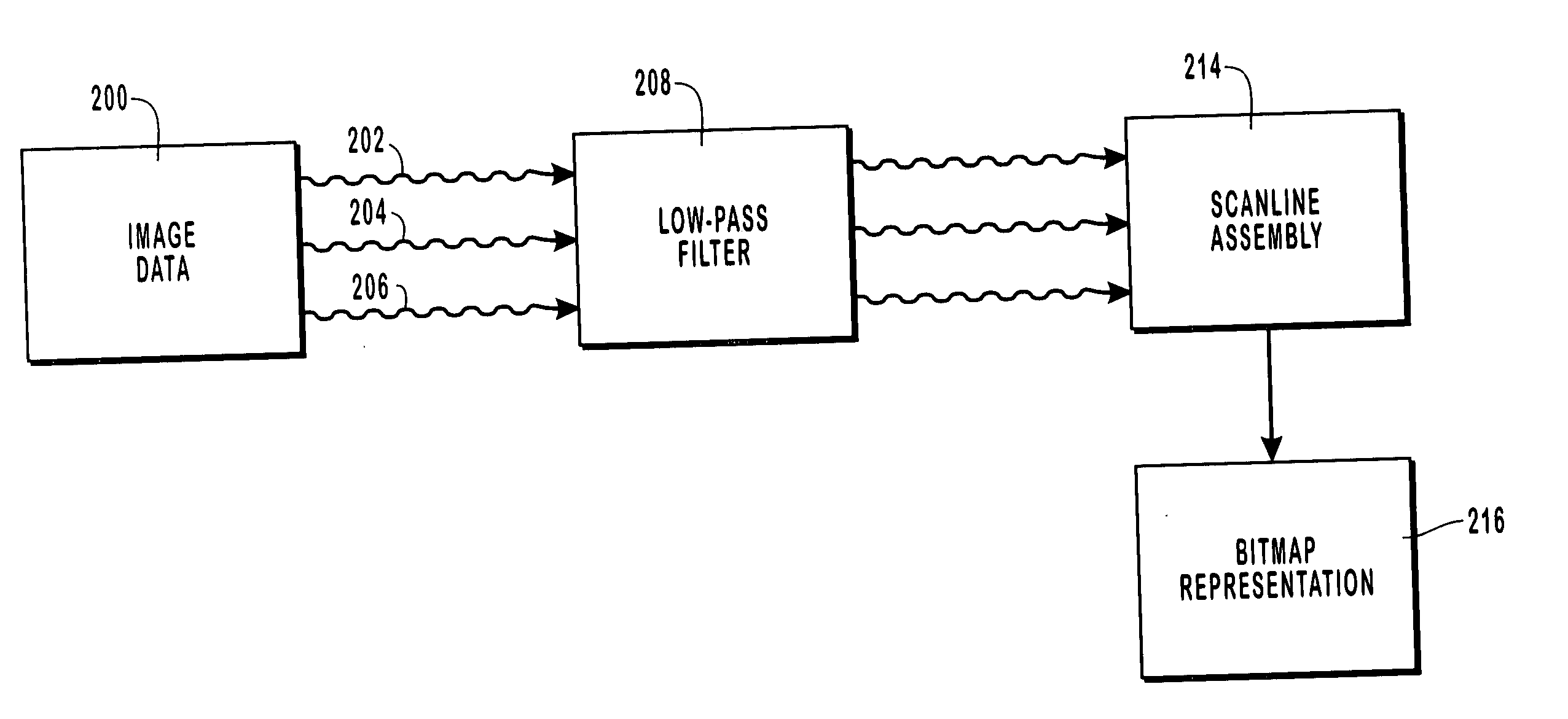
InactiveUS6973210B1Great sharpnessReduce colorStatic indicating devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionNyquist frequency
Image data processing and image rendering methods and systems whereby images are displayed on display devices having pixels with separately controllable pixel sub-components. Image data, such as data encoded in a three-channel signal, is passed through a low-pass filter to remove frequencies higher than a selected cutoff frequency, which obtain samples from the color components of the signal that map spatially different image regions to individual pixel sub-components. It has been found that color aliasing effects can be significantly reduces at a cutoff frequency somewhat higher than the Nyquist frequency, while enhancing the spatial resolution of the image. The image data is then pass through sampling filters, A generalized set of filters includes nine filters, one for each combination of one color and one pixel sub-component. The filtering coefficients of the filters can be selected to optimize of approximate an optimization of an error metric, which represents the color and luminance errors perceived on the display device. In this manner, a desired balance between color accuracy and luminance accuracy can be obtained. The samples mapped to individual pixel sub-components are used to generate luminous intensity values for the displayed image.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Electronic component package
InactiveUS20070241447A1Small signal transmission lossRaise the cutoff frequencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectric substrateElectronic component
An electronic component package includes a dielectric substrate having a first surface where an electronic component is sealed. A first signal line connecting to the electronic component and a first ground conductor are formed on the first surface of the dielectric substrate. A second signal line connected to an outside connection electrode and a second ground conductor are formed on a second surface of the dielectric substrate. The first ground conductor and the second ground conductor are connected by a plurality of ground conductor via-holes. A substrate-buried signal line connected to the first signal line and the second signal line is provided inside of the dielectric substrate so as to be put between the first ground conductor and the second ground conductor above and below and between the ground conductor via-holes on the right and left.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for operating a binaural hearing system and binaural hearing system
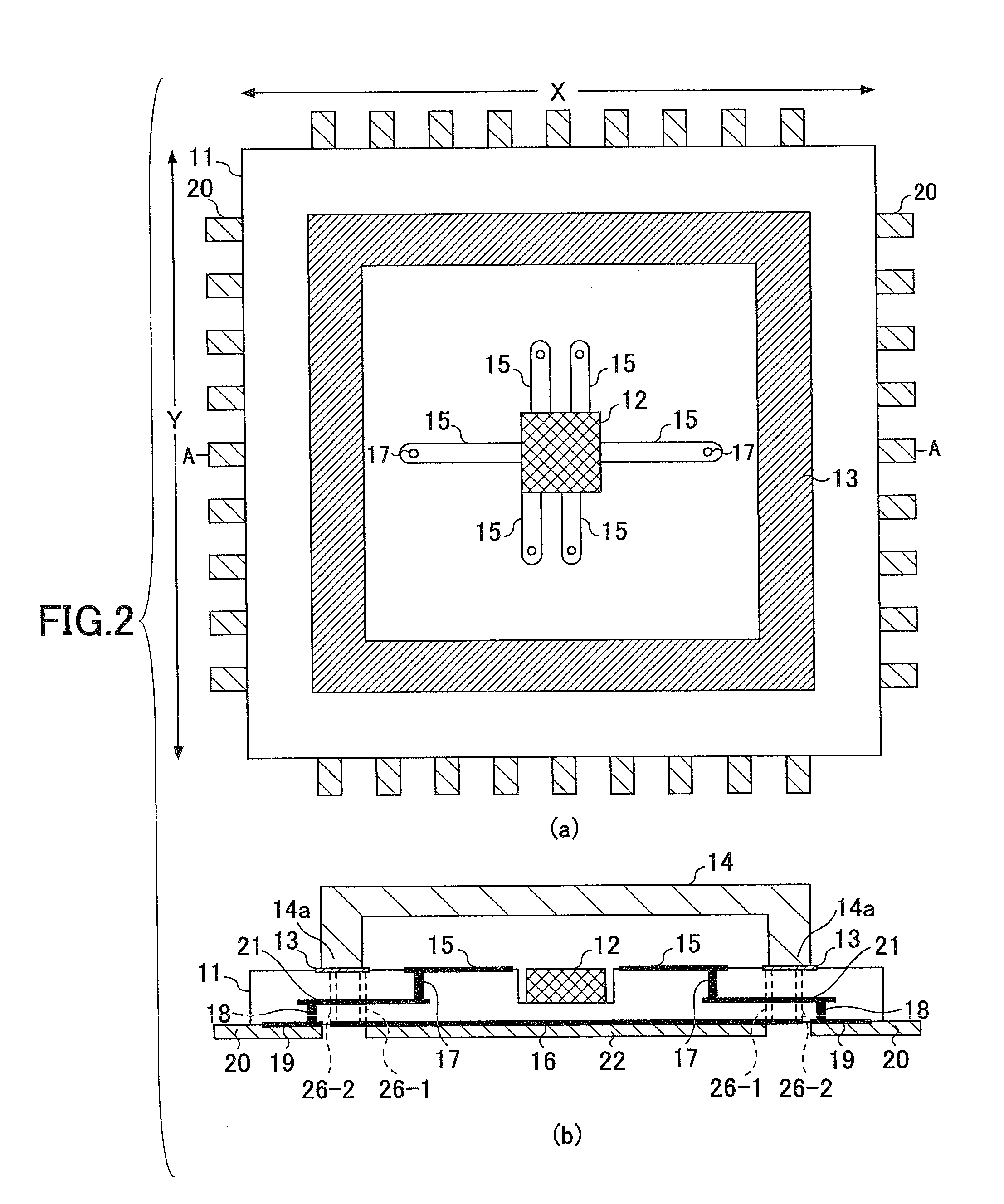
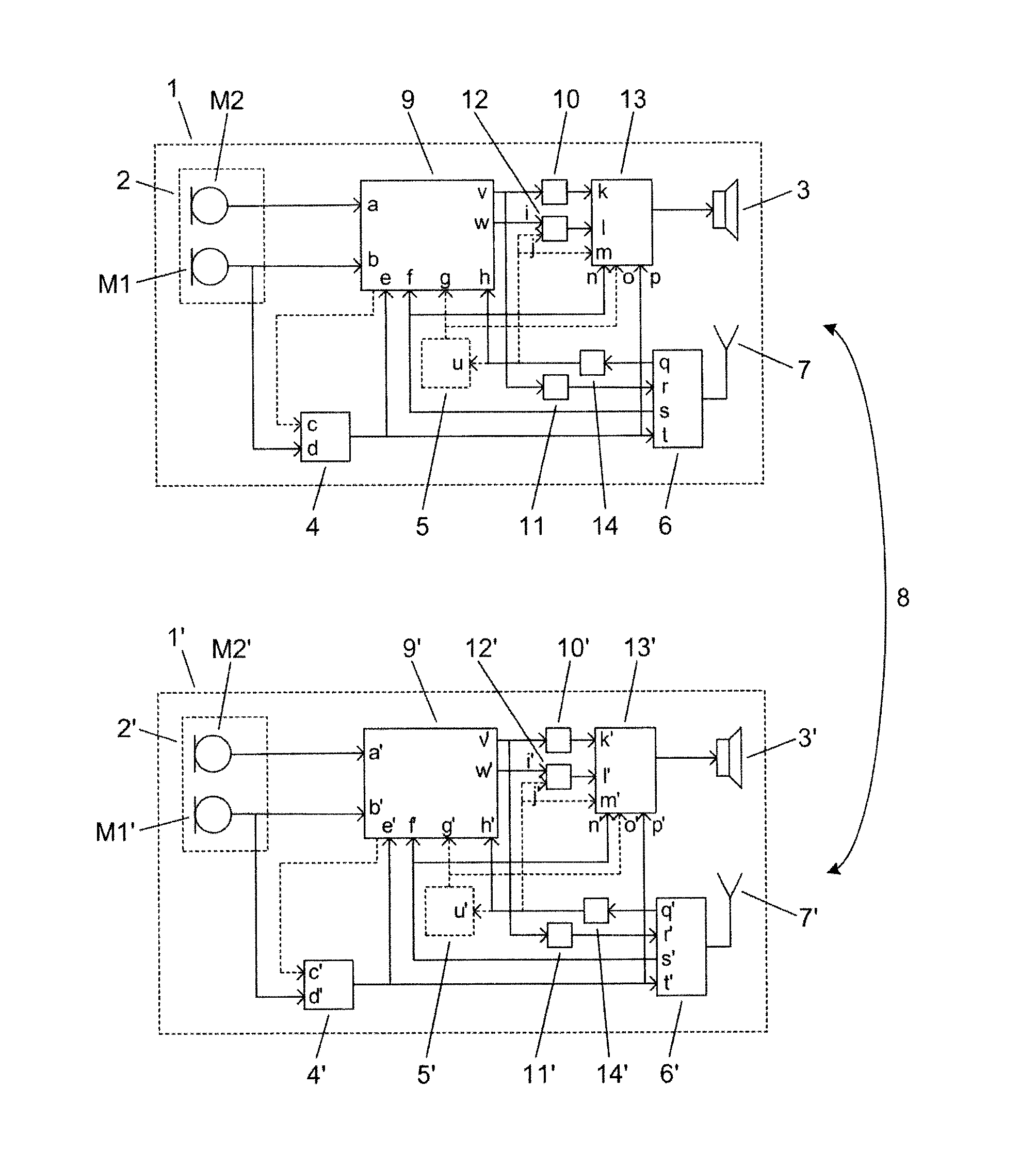
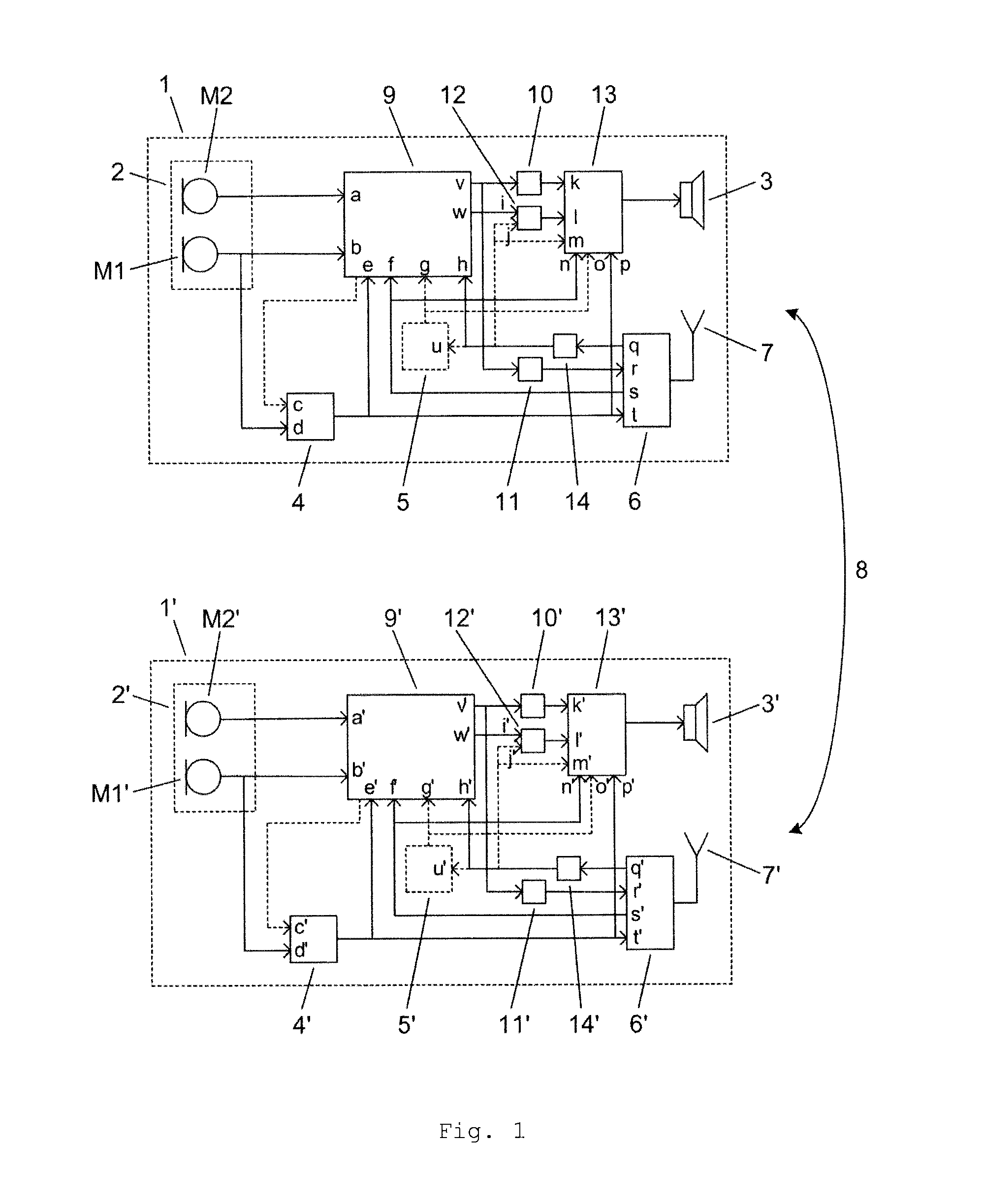
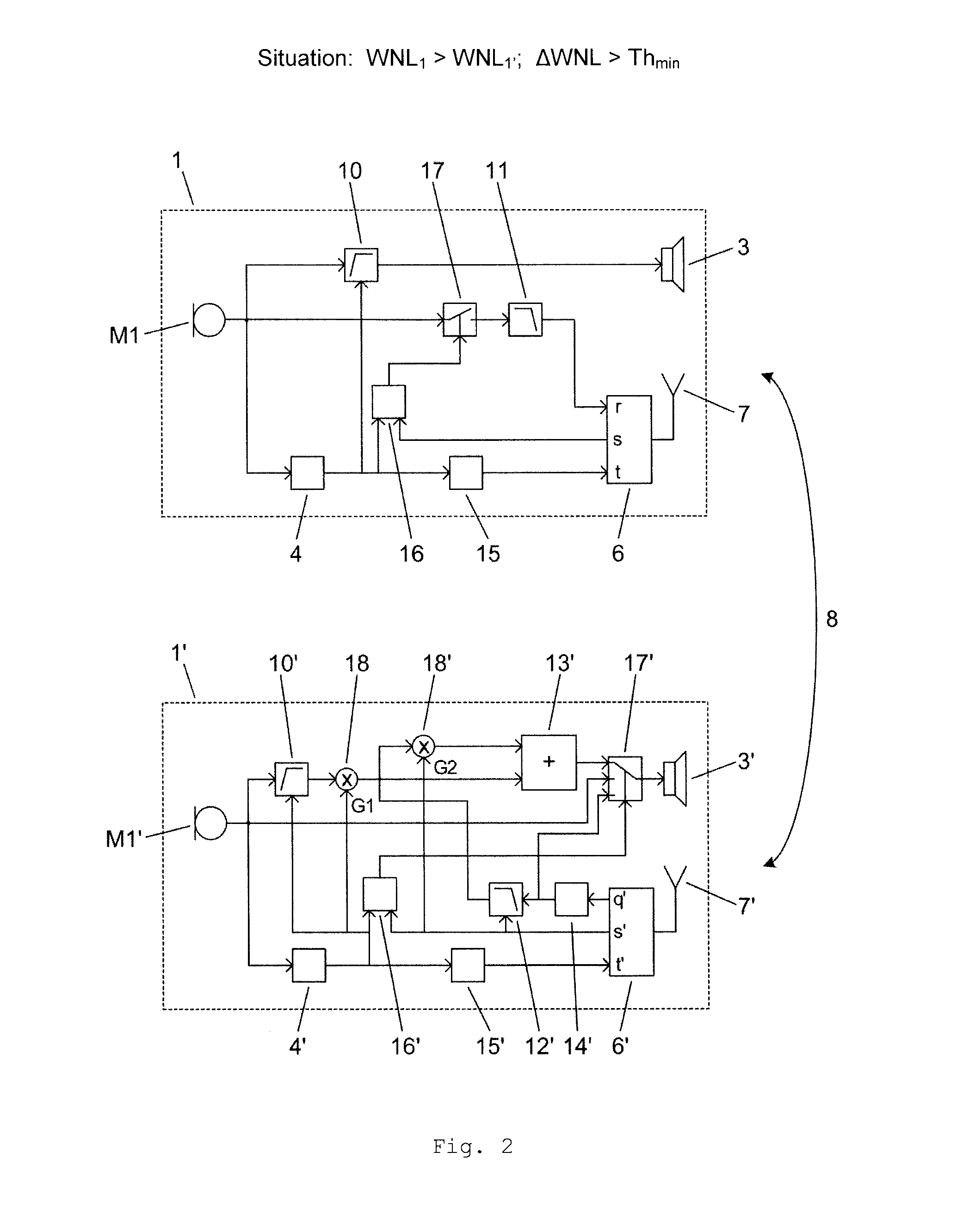
ActiveUS20150249892A1Improves hearing perceptionReduce adverse effectsDeaf-aid setsEngineeringHearing perception
The present invention proposes a method for operating a binaural hearing system with two hearing devices (1, 1′) operationally interconnected by means of a bidirectional link (8) which improves hearing perception in windy listening situations. The method comprises determining the level of wind noise present at each of the two hearing devices (1, 1′) and sending the audio signal picked-up at the first hearing device (1) to the second hearing device (1′) via the link (8) and then providing an output signal derived from the received signal to the electrical-to-mechanical output converter (3′) of the second hearing device (1′) if the level of wind noise at the second hearing device (1′) exceeds the level of wind noise at the first hearing device (1) by a pre-set threshold value. Furthermore, a binaural hearing system capable of performing such a method is given.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Common-mode filter
ActiveUS7078988B2Improve pressure resistanceImprove reliabilityMultiple-port networksApparel holdersEngineeringConductor Coil
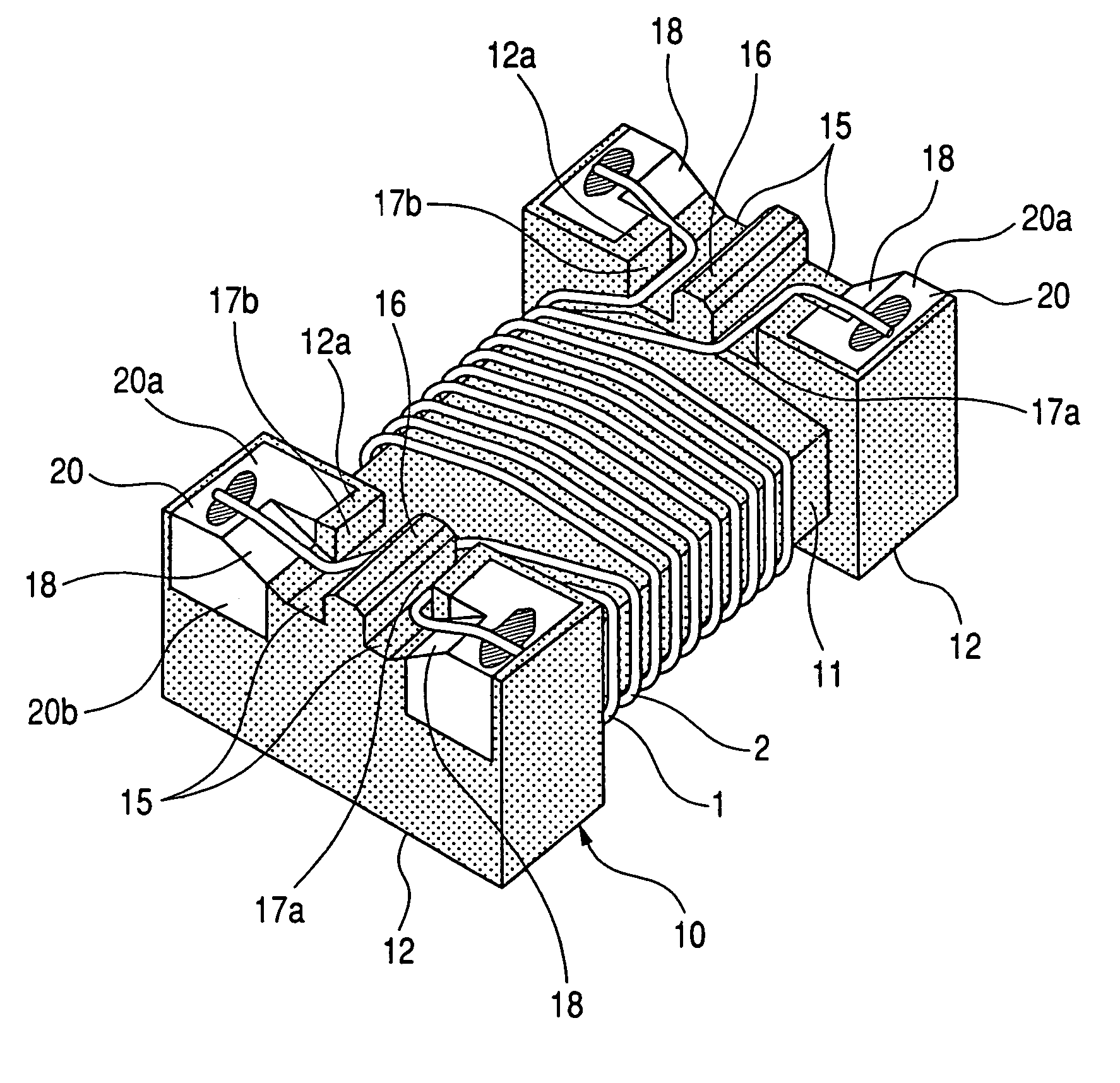
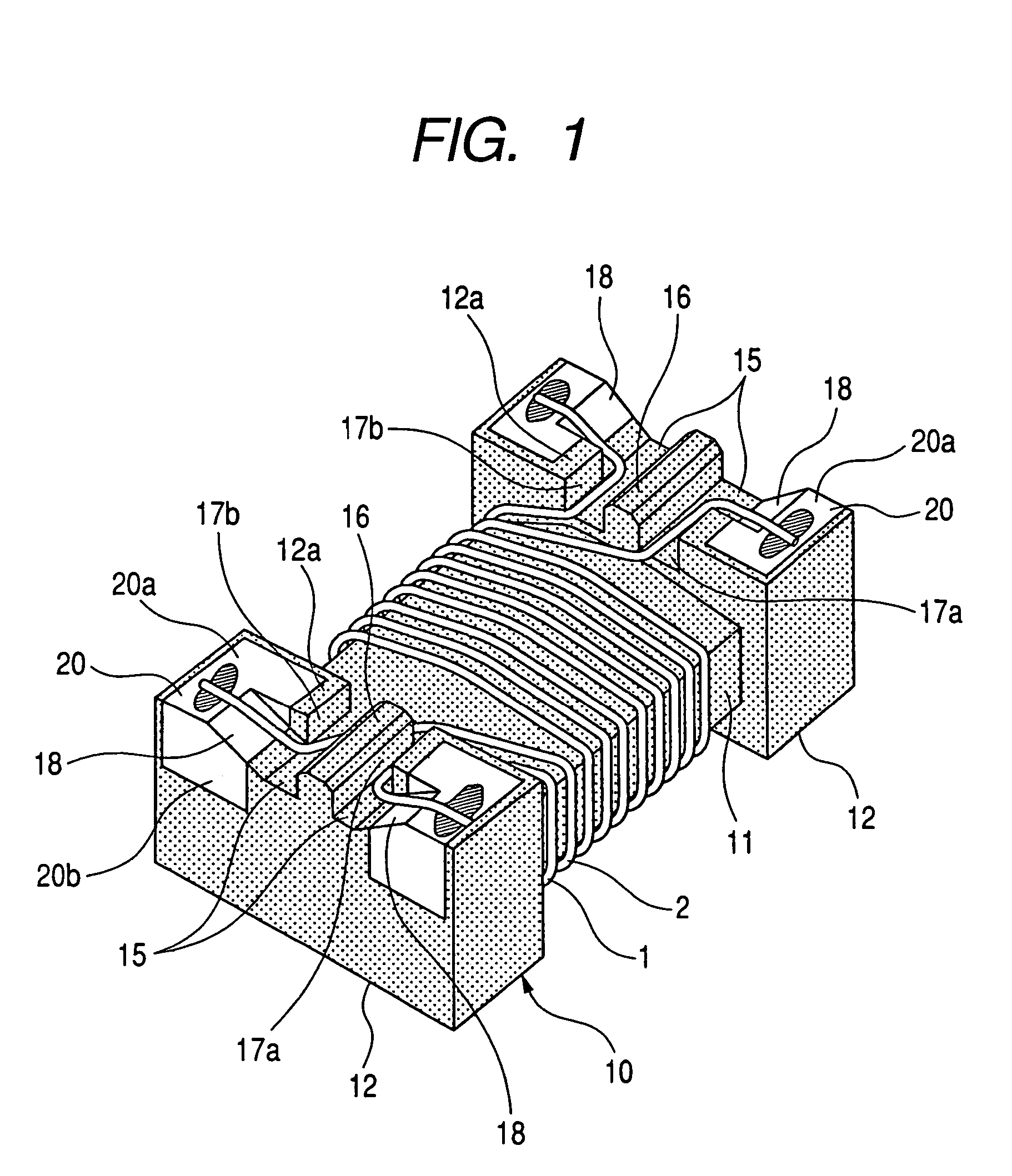
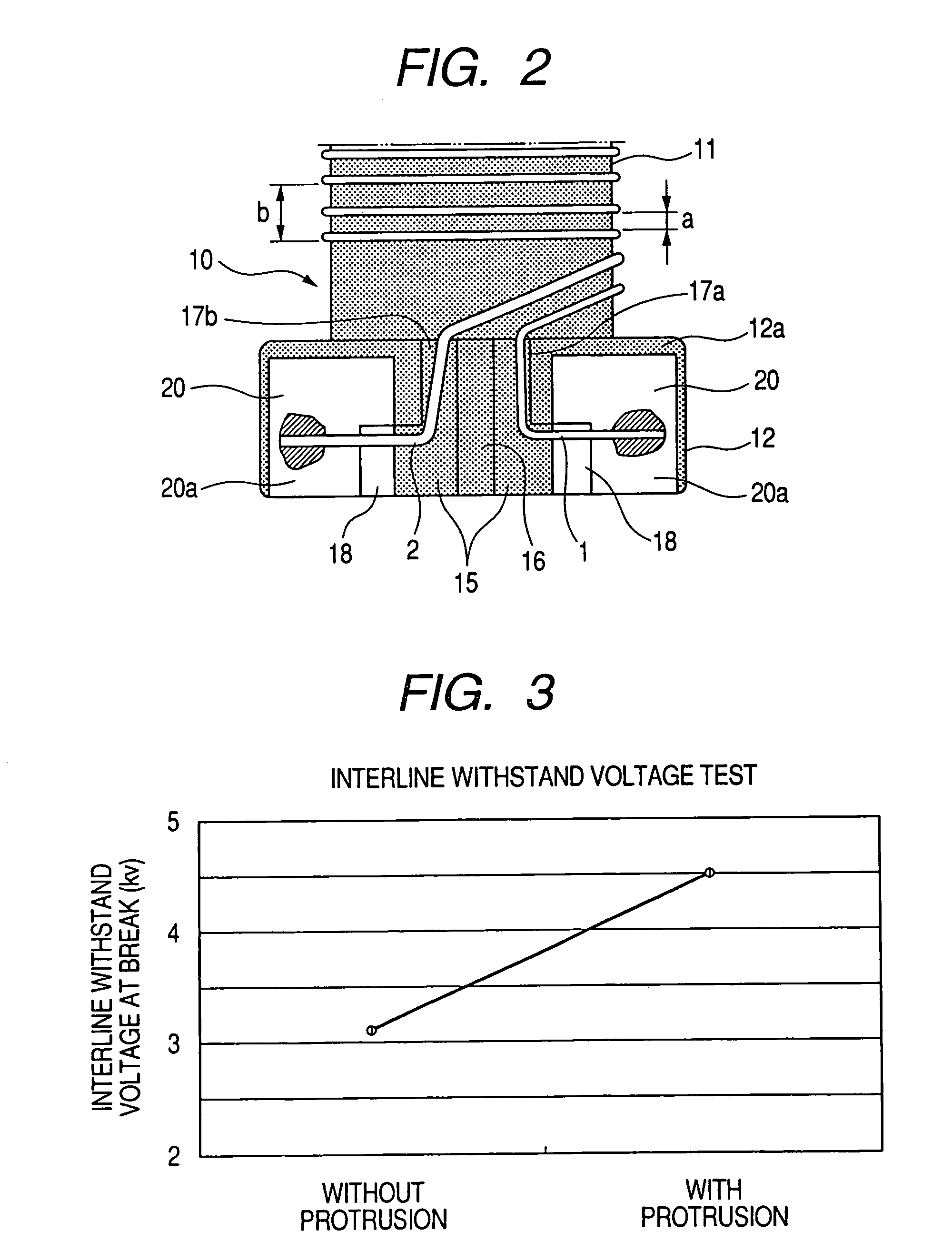
A common-mode filter with a drum type core including a core portion and flange portions. Electrodes are provided on the flange portions and a pair of wires are wound on the core portion. The wound pair of wires have ends connected to respective ones of the electrodes. Each of the flange portions has a groove between corresponding two of the electrodes and a separation protrusion for separating the groove into two lead-out groove portions. The pair of wires are wound on the core portion in such a distributed winding manner that an inter-wire distance between the pair of wires and a winding pitch between adjacent turns in each of the pair of wires are provided. The wires are one-by-one led out through the lead-out groove portions while separated by the separation protrusions so that the ends of the pair of wires are connected to respective electrodes.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
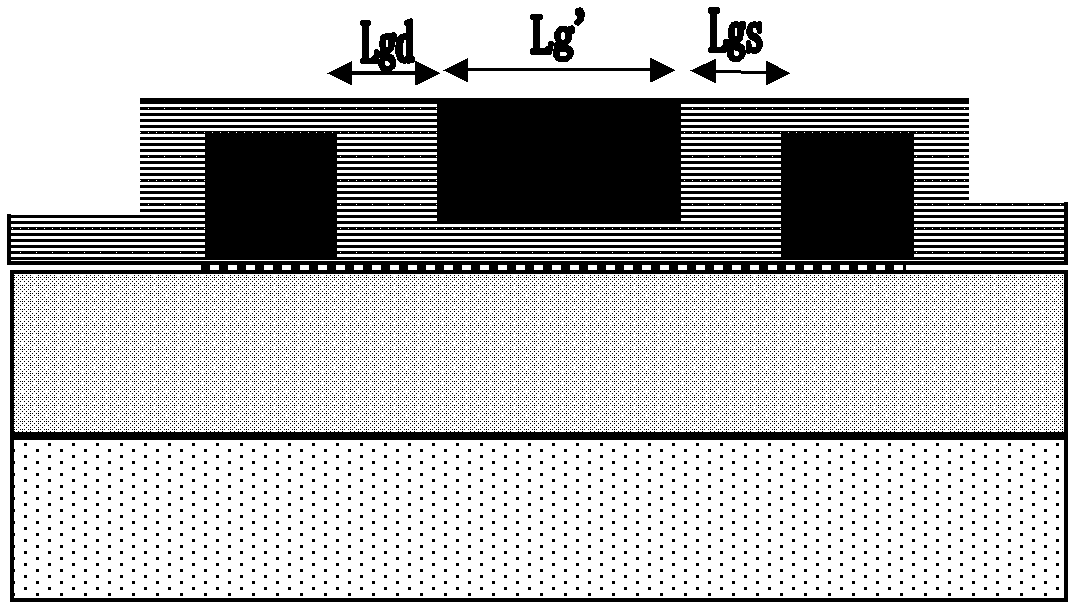
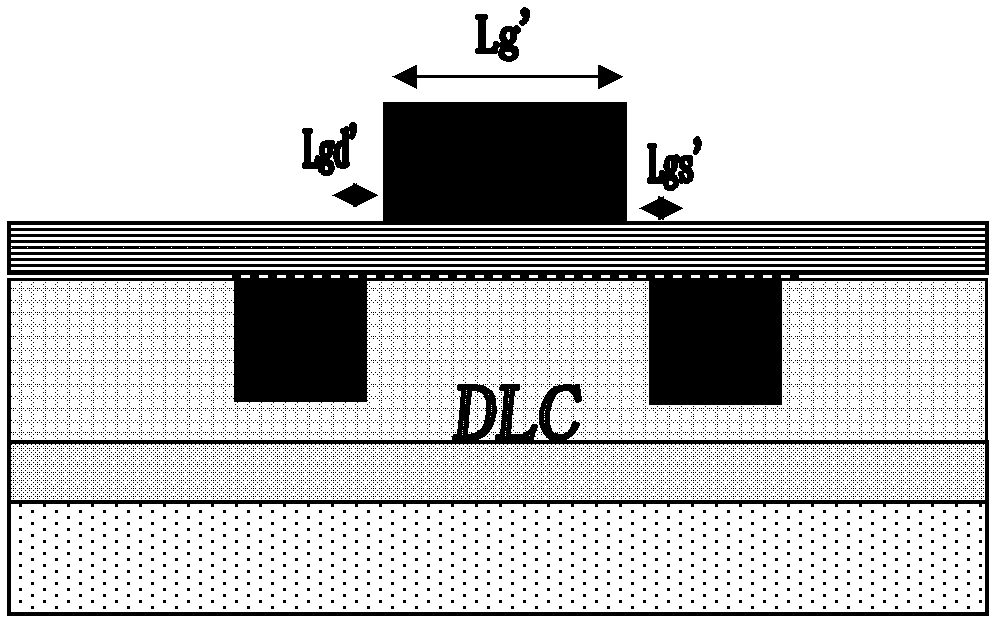
Source-drain buried graphene transistor device on diamond-like carbon substrate and manufacture method
InactiveCN103000669ALower channel resistanceReduce horizontal spacingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricDiamond-like carbon
A source-drain buried graphene transistor device on a diamond-like carbon substrate and a manufacture method are applicable to radio frequency communication. The manufacture method includes: firstly, depositing a layer of diamond-like carbon amorphous carbon smooth in surface and stable in chemical property on the substrate by the aid of a magnetic filtered cathode vacuum arc system; secondly, etching a source trench and a drain trench on the diamond-like carbon amorphous carbon insulating layer and filling electrode metal into the trenches; thirdly, planarizing and cleaning the surface of the substrate prior to transferring graphene grown by a chemical vapor deposition method to the cleaned substrate; fourthly, growing gate insulating dielectric by an atomic layer deposition method and sputtering gate electrode metal; and finally, forming a metal gate by means of reactive ion etching and depositing low-K insulating dielectric to protect the device. Carrier mobility of a graphene transistor is high, and the source-drain buried structure is capable of decreasing the graphene length of a region uncovered by the gate, so that gate-source capacitance, gate-drain capacitance and channel resistance are reduced, and high-frequency performance and efficiency of the graphene transistor are improved. The source-drain buried graphene transistor device can be widely applied to small-sized high-frequency graphene integrated circuits.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
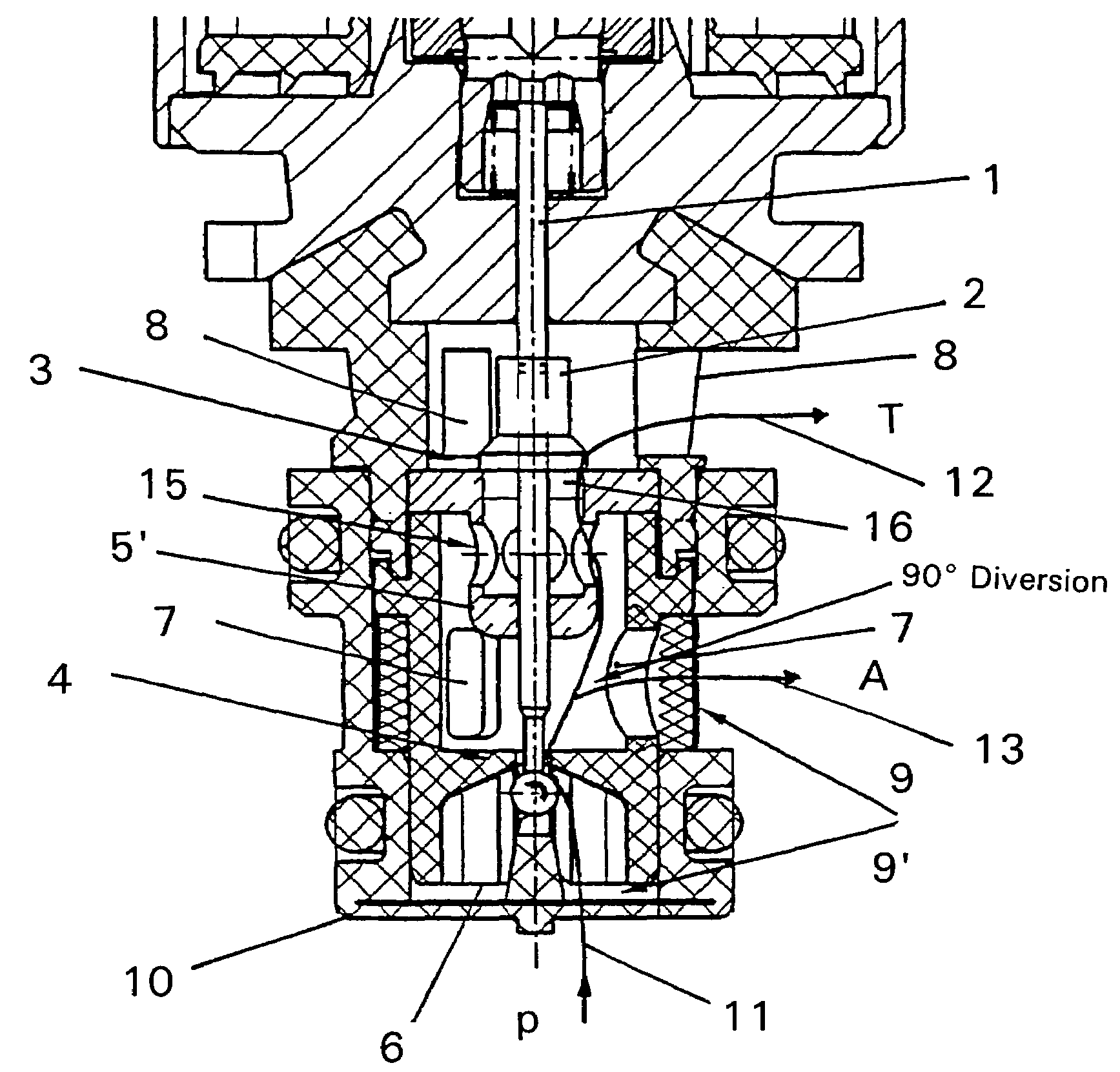
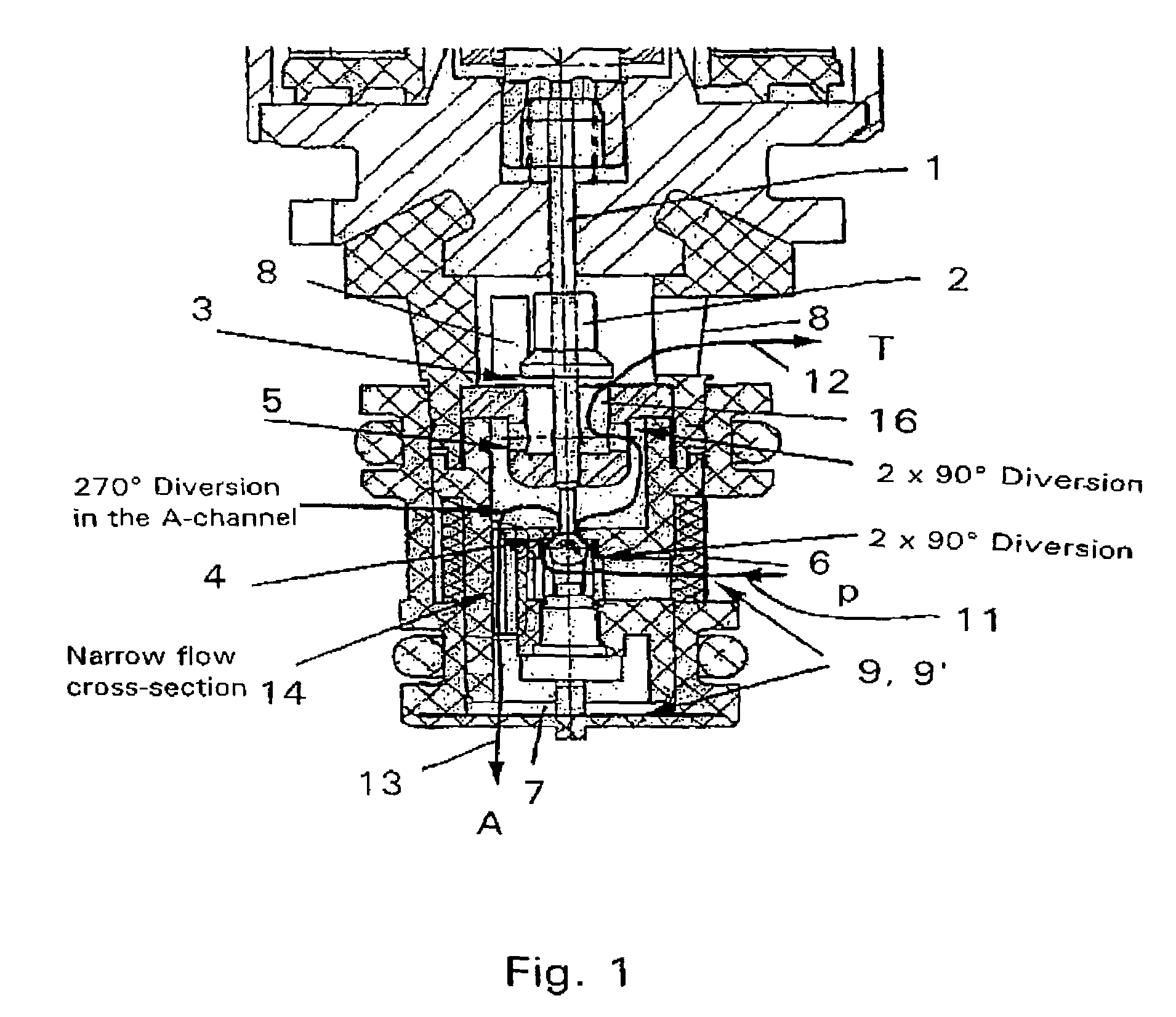
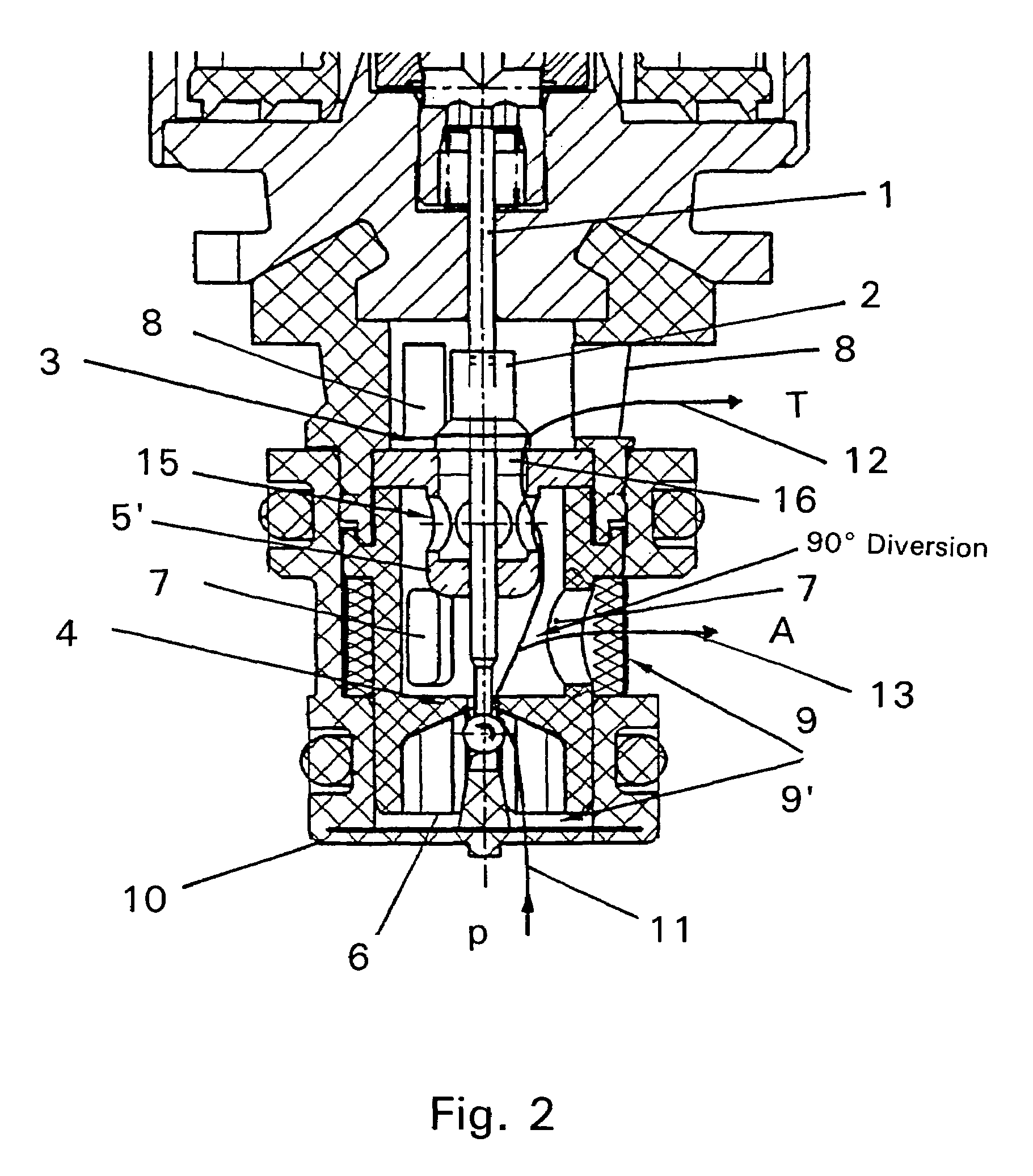
Proportional pressure control valve
ActiveUS7516756B2Low flow resistanceImprove dynamic tuning performanceClutchesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFlow diverterPressure controlled ventilation
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Semiconductor light emitting device having quantum well layer sandwiched between carrier confinement layers
InactiveUS20050145857A1Quality improvementRaise the cutoff frequencyLaser detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsQuantum well
The principal surface of a substrate made of a group III-V compound semiconductor material is about a (100) plane. A light emitting lamination structure is disposed on the principal surface. In the light emitting lamination structure, a quantum well layer is sandwiched by a pair of carrier confinement layers made of a semiconductor material having a band gap wider than a semiconductor material of the quantum well layer. The pair of carrier confinement layers are sandwiched by a pair of clad layers made of a semiconductor material having a band gap wider than the band gap of the semiconductor material of the carrier confinement layers. Thicknesses of the quantum well layer and the carrier confinement layers, as well as compositions of the semiconductor materials thereof, are set such that light emission recombination of electrons and holes occurs in the quantum well layer and not in the carrier confinement layers.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
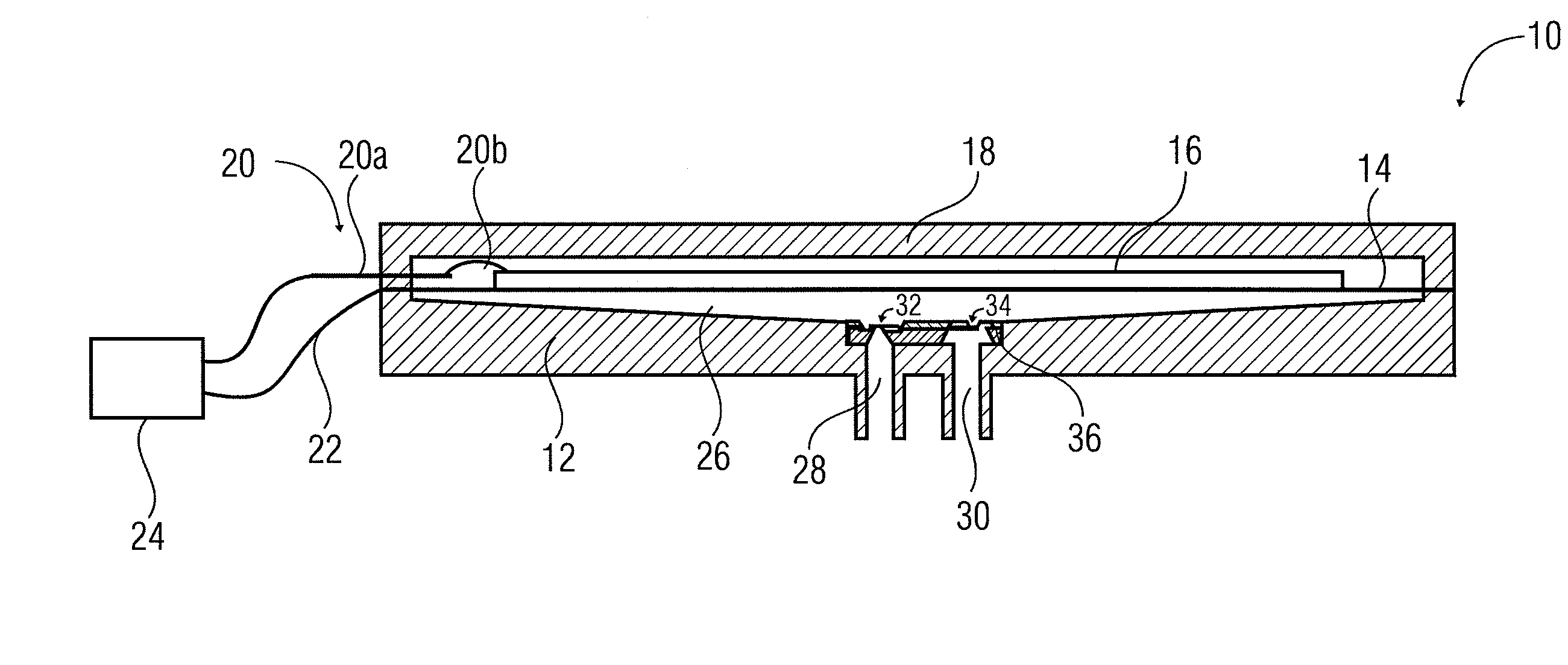
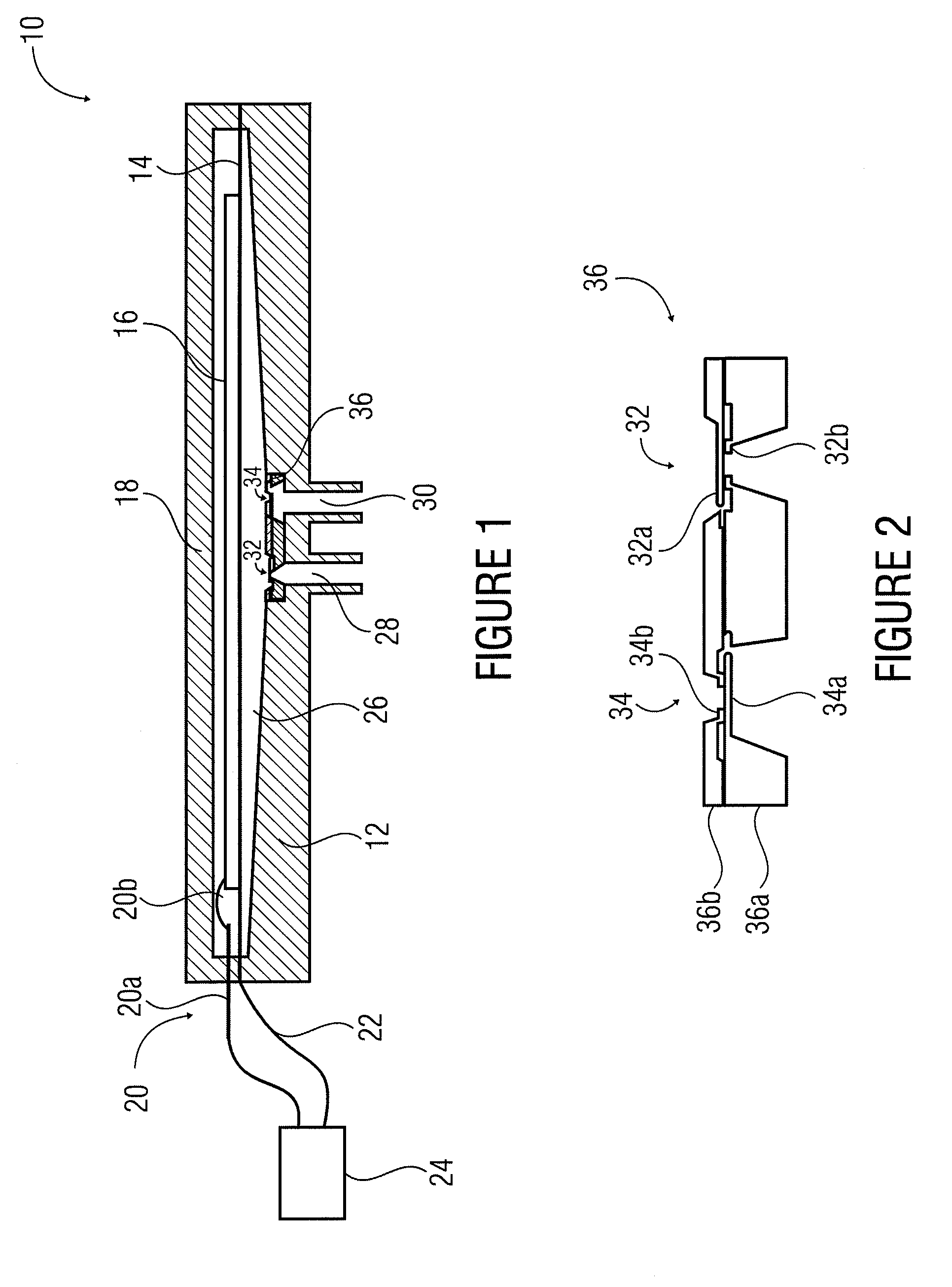
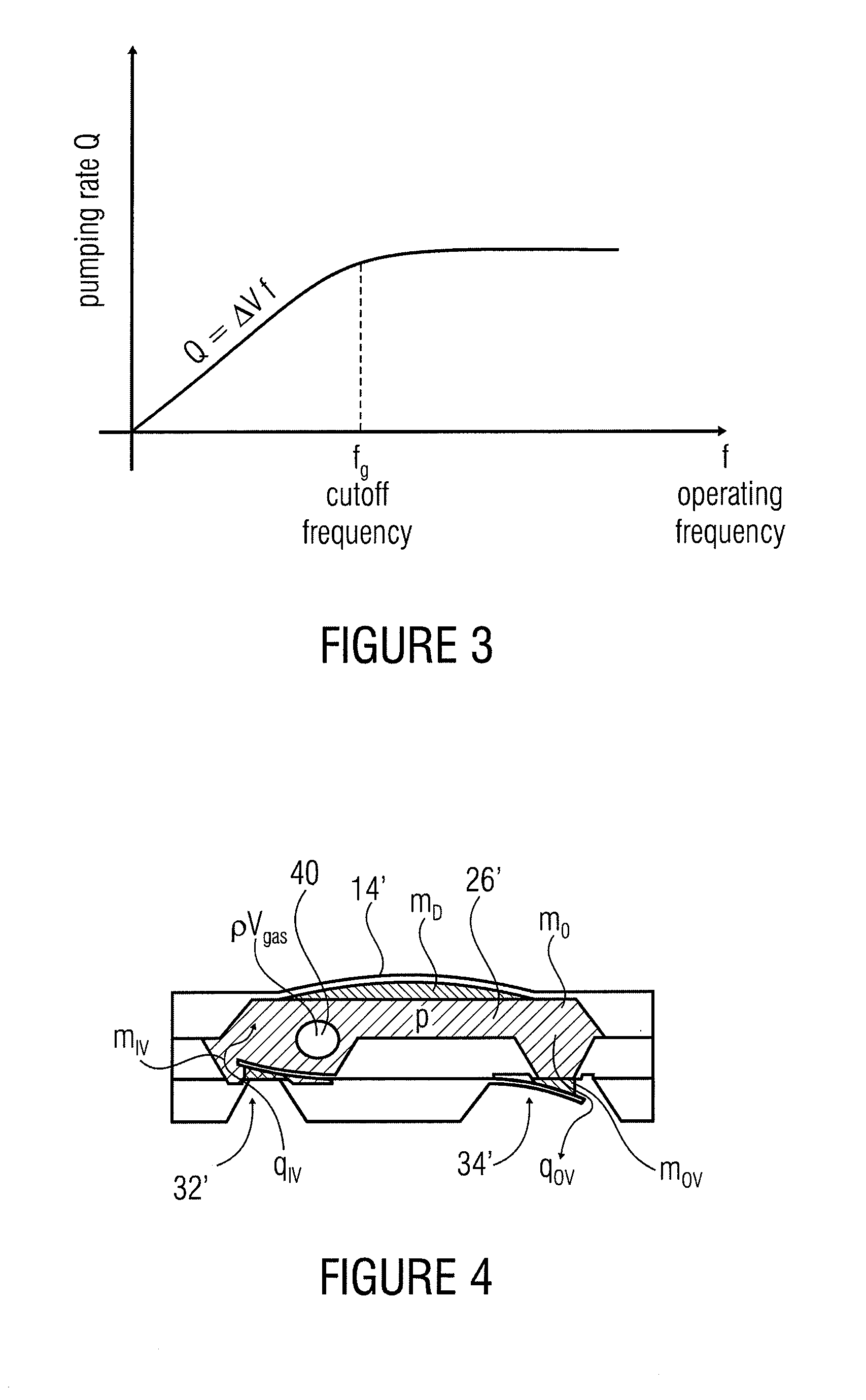
Diaphragm Pump
ActiveUS20110061526A1Small sizeLarge stroke volumeFlexible wall reciprocating enginesFlexible member pumpsDiaphragm pumpPump chamber
A diaphragm pump includes a pump chamber having an inlet opening and an outlet opening. A passive silicon check valve is provided at the inlet opening, and a passive silicon check valve is provided at the outlet opening. The diaphragm pump further includes a metallic pump diaphragm that adjoins the pump chamber.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
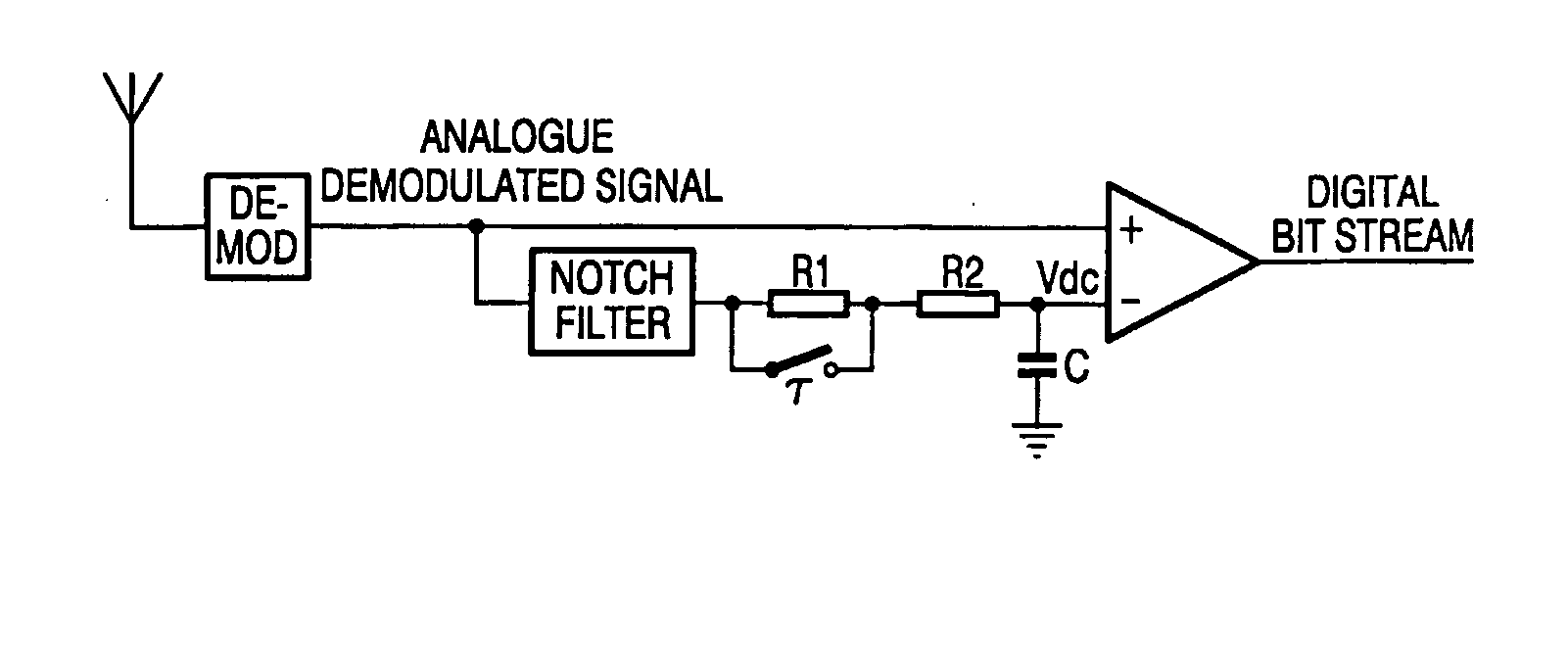
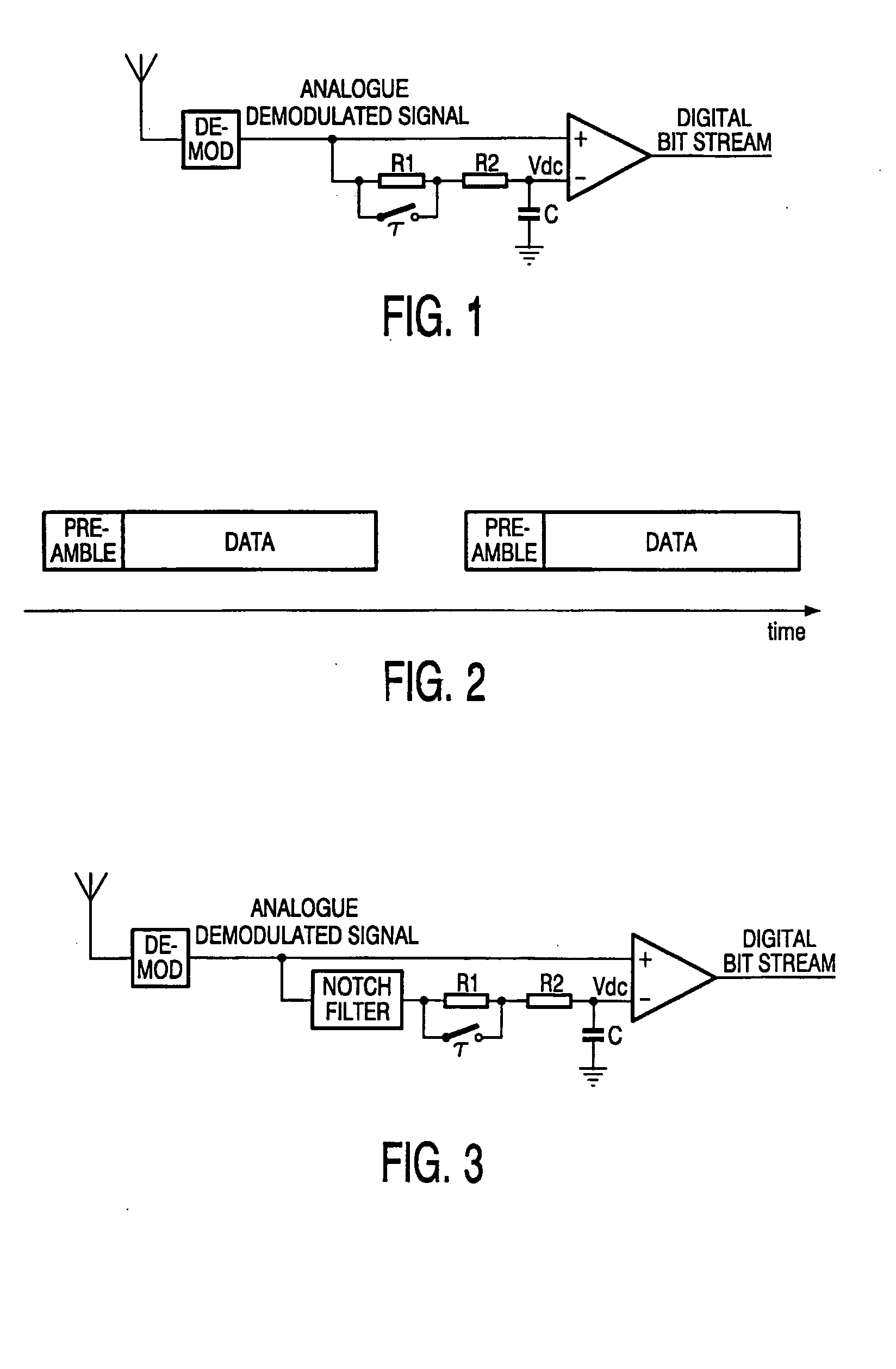
Fast settling data slicer comprising a low-pass filter with switchable cut-off frequency and a notch-filter
InactiveUS20050036568A1Easy to implementImproved noise suppressionDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsLow-pass filterAnalog signal
A data slicer circuit for extracting data from a received analogue signal having a preamble and a data portion with the data. The circuit comprises a low pass filter for obtaining a DC value of the received signal, and a comparator for comparing the received analogue signal to the DC value of the received signal. In dependence on the comparison of the received analogue signal to the DC value of the received signal, the comparator generates a digital bit stream. A filter for rejecting the preamble frequency receives analogue signal and feeds a filtered signal to the low pass filter. By rejecting the preamble frequency, before or after, the low pass filter a shorter settling time can be obtained.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Class D audio amplifier with adjustable loop filter characteristics
ActiveCN104272589ARaise the cutoff frequencyAc-dc conversionLow frequency amplifiersLoop filterAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to a class D audio amplifier comprising a pulse width modulator, an adjustable loop filter and a feedback loop. The pulse width modulator generates a first set of pulse width modulated control signals at an adjustable modulation frequency for respective switch control terminals of a first output driver. A controller of the class D audio amplifier is configured to control frequency response characteristics of the adjustable loop filter based on a frequency setting of the adjustable modulation frequency.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
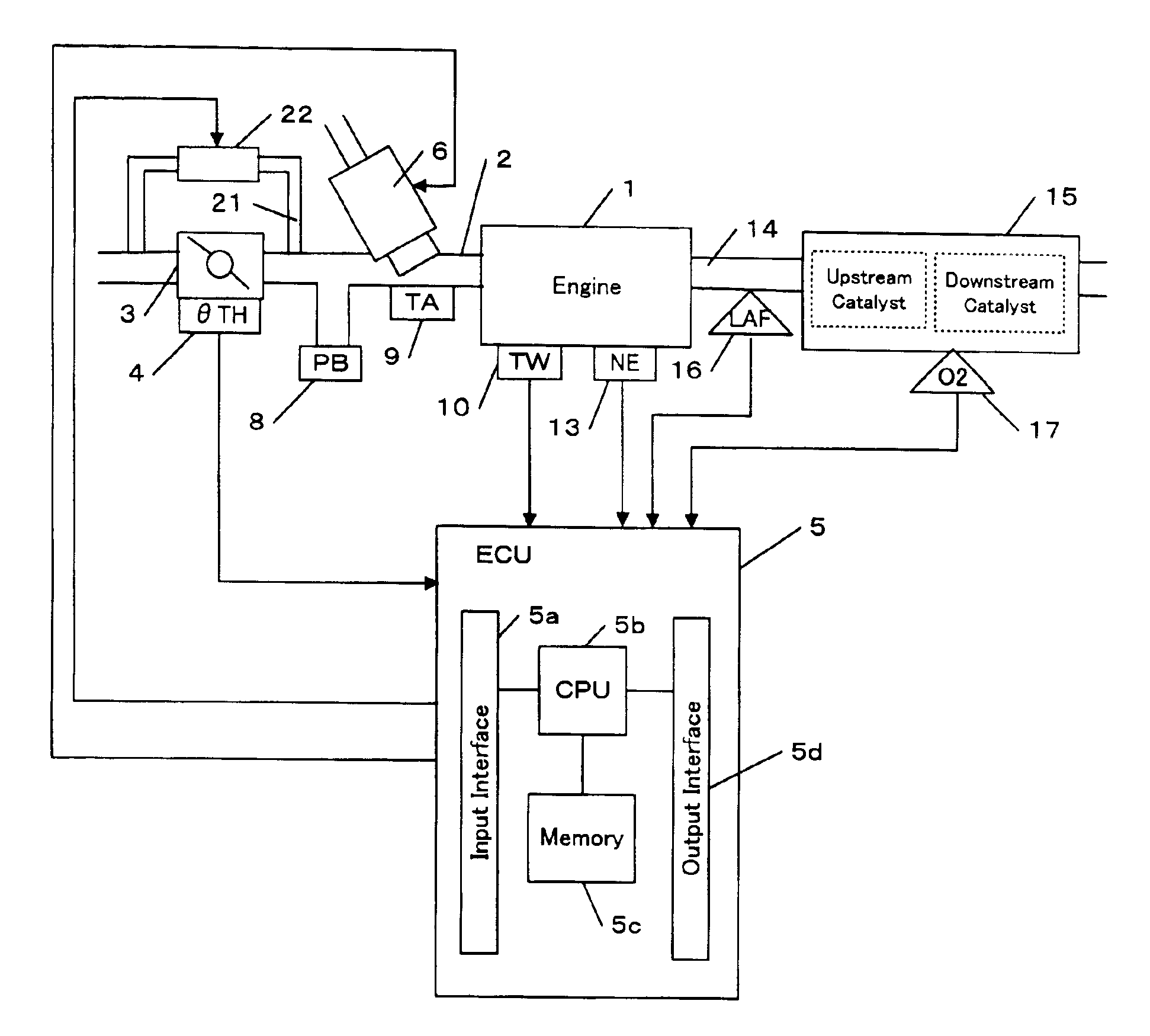
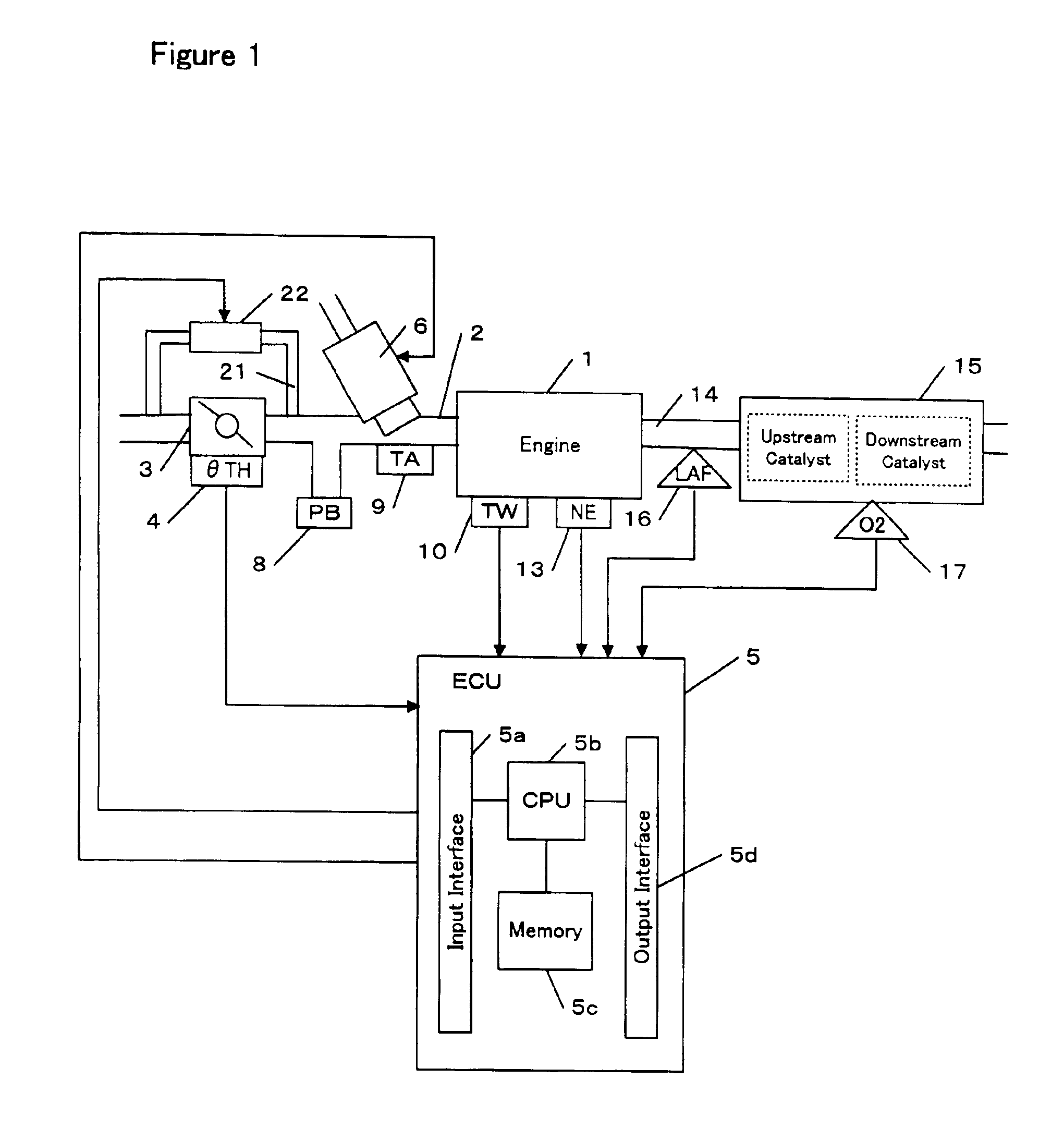
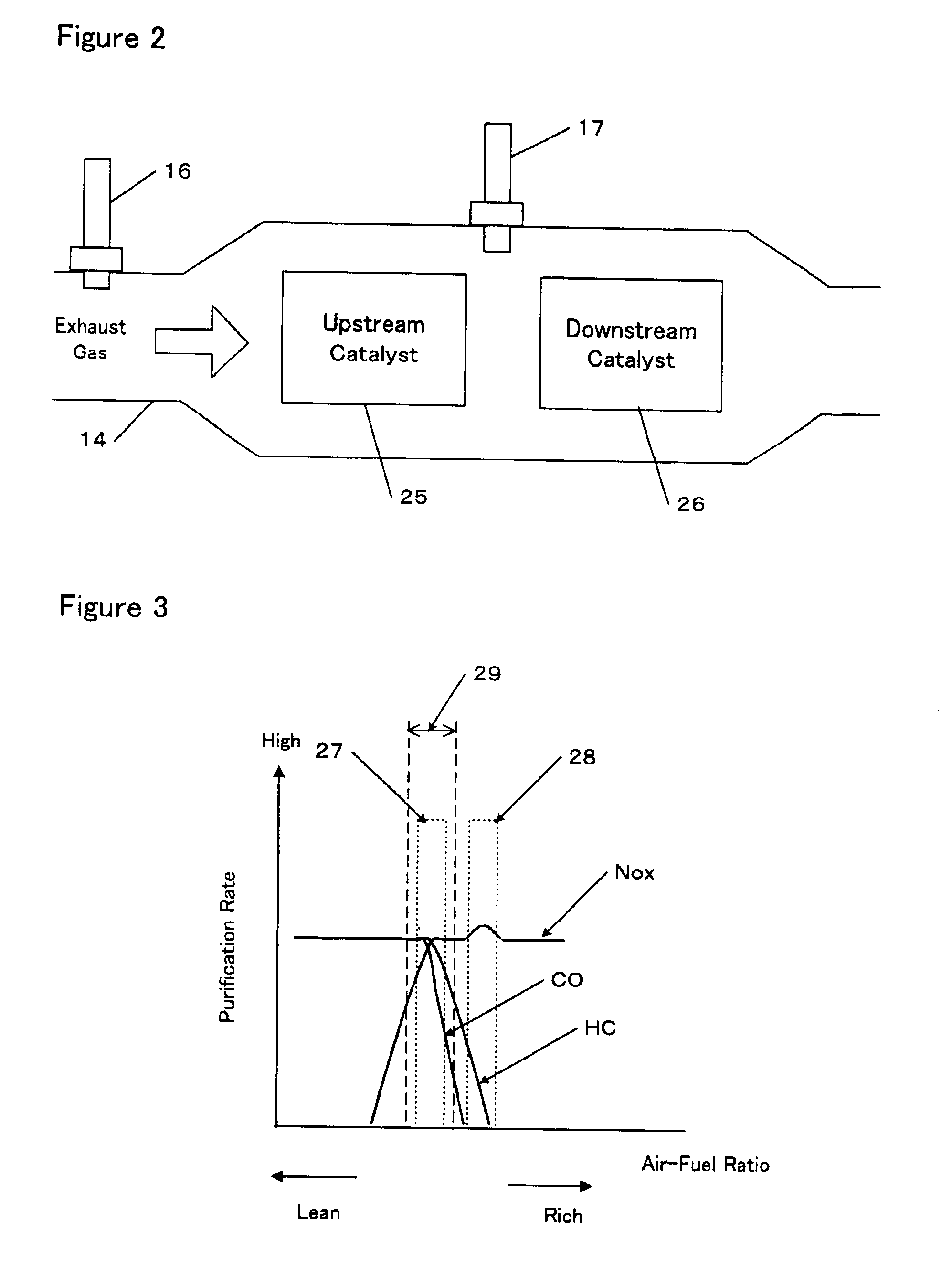
Vehicle controller for controlling an air-fuel ratio
ActiveUS6904355B2Good accuracyWithout reduce accuracyAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlImage resolutionAir–fuel ratio
A vehicle controller for controlling the air-fuel ratio of an engine is provided. In one embodiment, the controller comprises a first exhaust gas sensor provided downstream of the catalyst for detecting oxygen concentration of exhaust gas, a first decimation filter connected to the first exhaust gas sensor, and a control unit connected to the first decimation filter. The control unit determines a manipulated variable for manipulating the air-fuel ratio. The first decimation filter oversamples, low-pass filters and then downsamples the output of the first exhaust gas sensor. The first decimation filter can remove chemical noise from the output of the exhaust gas sensor. In another embodiment, a second decimation filter is connected to a second exhaust gas sensor provided upstream of the catalyst for detecting the air-fuel ratio of the exhaust gas. The second decimation filter oversamples, low-pass filters and then downsamples the output of the second exhaust gas sensor. The second decimation filter can compensate the shortage of resolution of the air-fuel ratio sensor.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
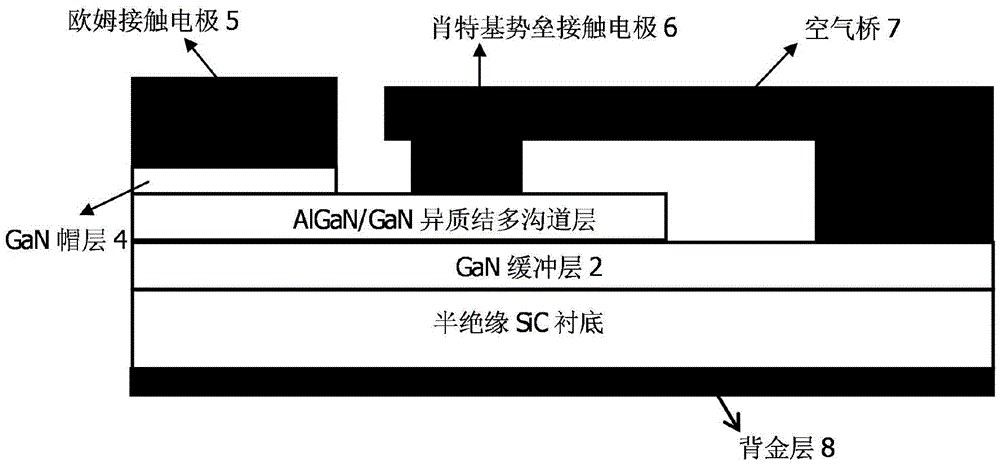
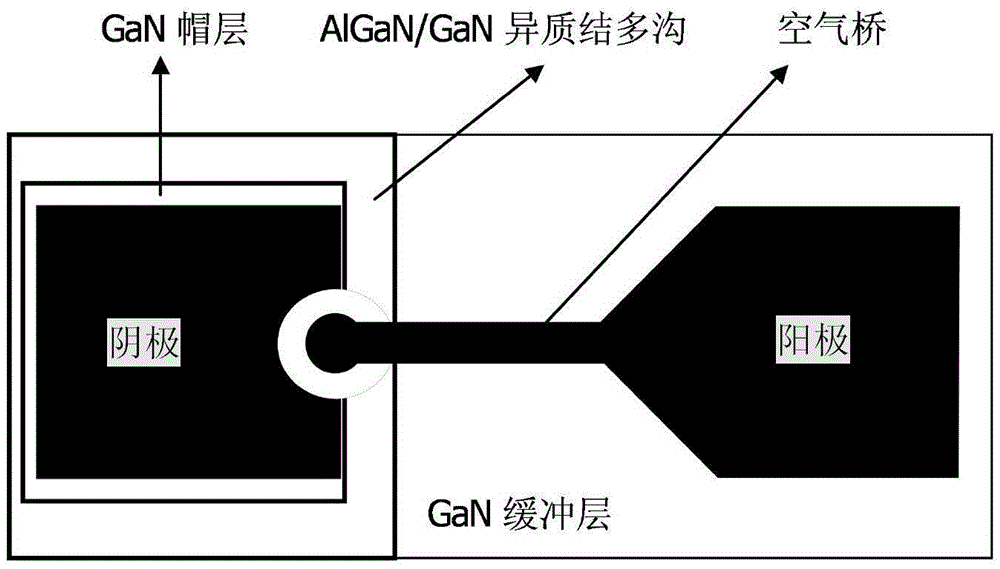
AlGaN/GaN heterojunction multi-channel structure based terahertz schottky diode and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveCN105679838AImprove mobilityRaise the cutoff frequencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeHeterojunctionSchottky barrier
The invention discloses an AlGaN / GaN heterojunction multi-channel structure based terahertz schottky diode and a manufacturing method therefor, and mainly aims to solve the problem of low doping mobility ratio, high series resistance and low cut-off frequency of the existing GaN schottky diode. The AlGaN / GaN heterojunction multi-channel structure based terahertz schottky diode comprises a main body part and an auxiliary body part, wherein the main body part comprises (1) a semi-insulating SiC substrate, (2) a GaN buffer layer, (3) an AlGaN / GaN heterojunction multi-channel layer, and (4) a GaN cap layer from the bottom up; the auxiliary body part comprises (5) an ohmic contact electrode (negative electrode), (6) a schottky barrier contact electrode (positive electrode), (7) an air bridge and (8) a back gold layer, wherein the AlGaN / GaN heterojunction multi-channel layer adopts an AlGaN / GaN type superlattice structure; the superlattice has 2-6 periods; and the thicknesses of the GaN layer and the AlGaN layer are both 10-20nm in each period, and the Al component accounts for 30% of the AlGaN layer. According to the terahertz schottky diode provided by the invention, the conventional n type doping process can be avoided; the multi-layer two-dimensional electron gas channels formed by polarization are adopted, so that the electron mobility is improved, the series resistance is lowered, and the cut-off frequency is improved, so that the AlGaN / GaN heterojunction multi-channel structure based terahertz schottky diode is applicable to operations under terahertz frequency bands.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for inhibiting second harmonic current of preceding-stage inverter of two-stage inverter and control circuit of preceding-stage inverter of two-stage inverter
InactiveCN102843020ASecond Harmonic Current SuppressionRaise the cutoff frequencyPower conversion systemsBand-pass filterVoltage reference
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting second harmonic current of a preceding-stage inverter of a two-stage inverter and a control circuit of the preceding-stage inverter of the two-stage inverter. By the method, the low-frequency pulse current of the preceding-stage direct current inverter can be inhibited obviously, the dynamic performance can be improved and the dynamic response speed is increased. The control circuit of the preceding-stage inverter consists of a band-pass filter, a voltage regulator, a summator, a power-width modulation (PWM) modulator and a driving circuit. The work principle is as follows: a voltage sampling circuit detects intermediate bus voltage, compares the intermediate bus voltage with a voltage reference signal to generate an error signal and transmits the error signal to the voltage regulator; a current sampling circuit detects the inductive current of the preceding-stage direct current inverter; the inductive current of the preceding-stage direct current inverter, an output signal of band-pass filter and an output signal of the voltage regulator are added by the summator to generate a modulation signal; the modulation signal is transmitted to a PWM modulation circuit; and a driving signal of a switch tube is acquired by the driving circuit, so that operation of the preceding-stage direct current inverter is controlled.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
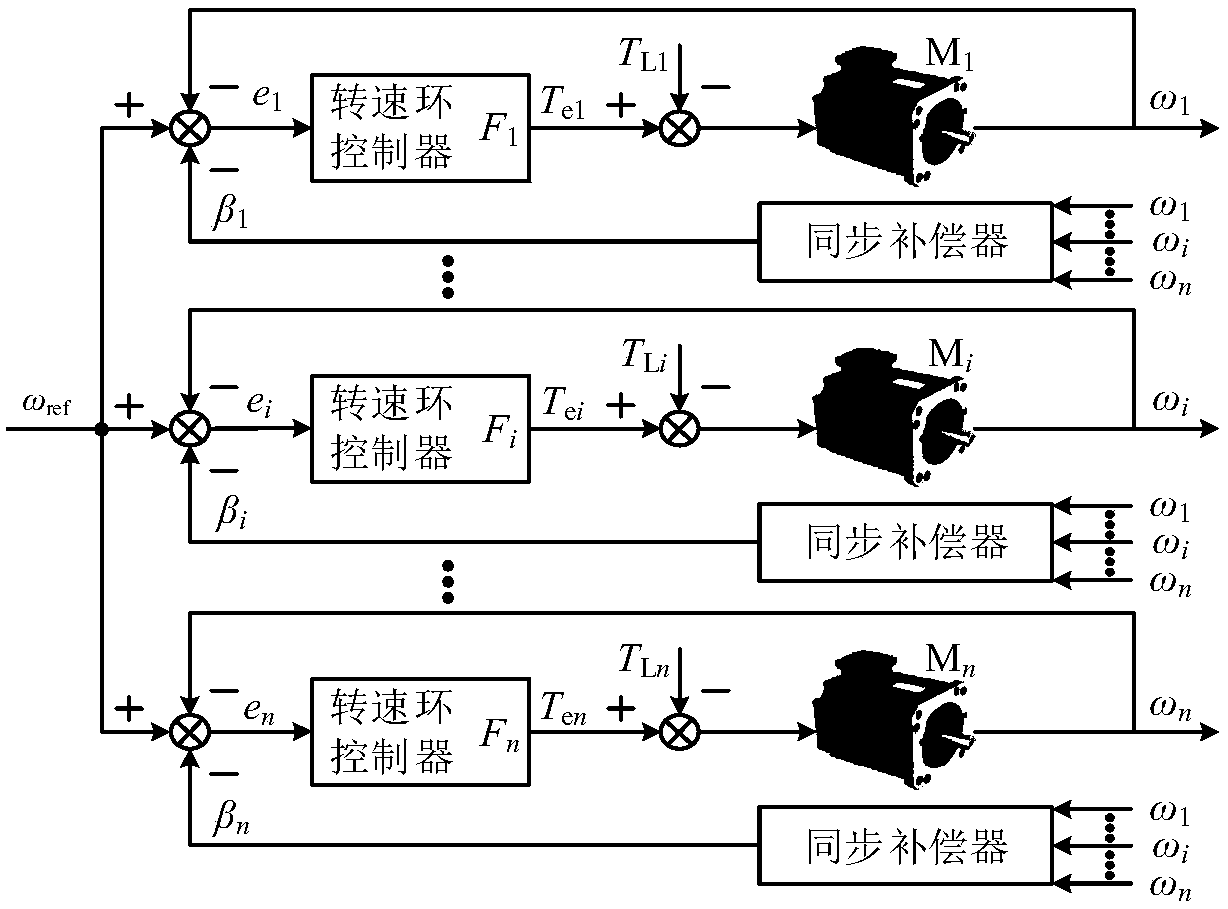
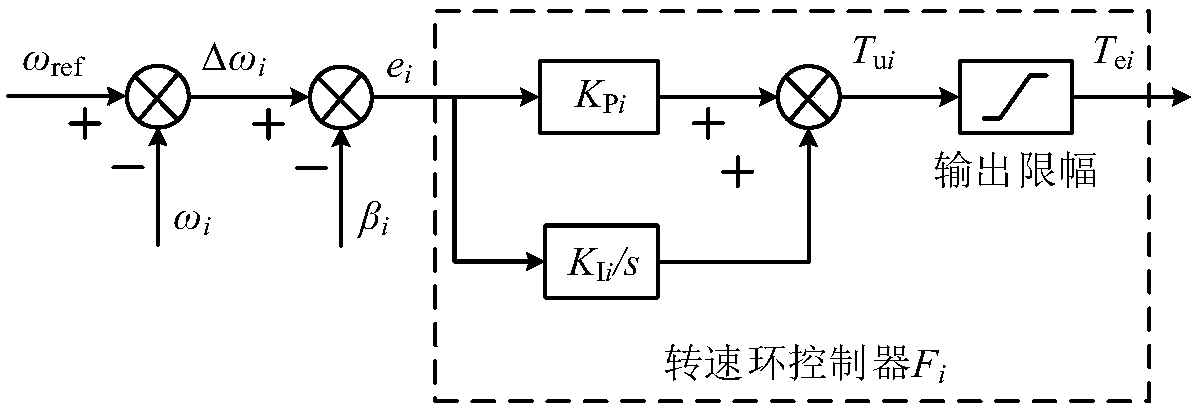
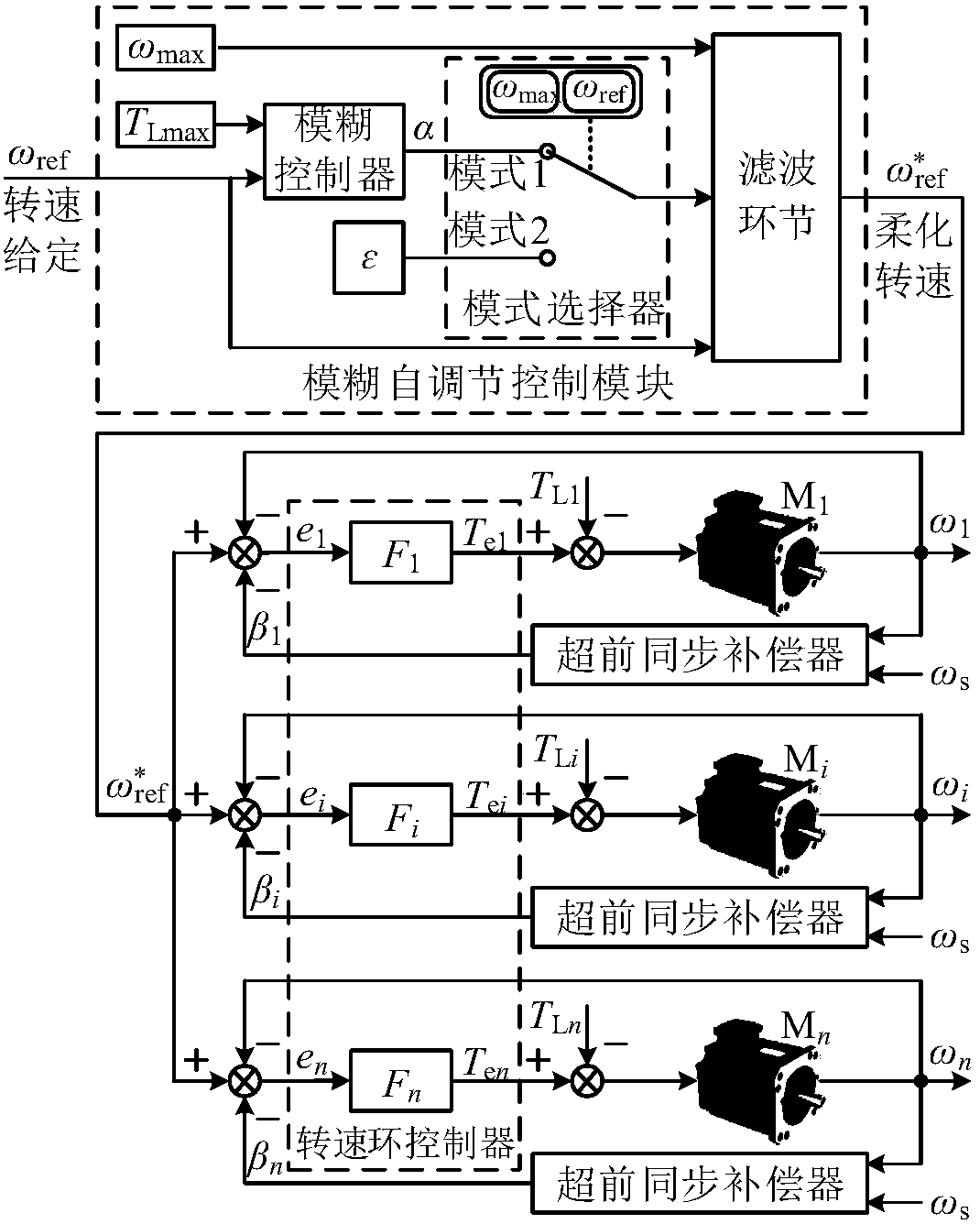
Fuzzy self-adjusting deviation coupling multi-motor synchronous control method
ActiveCN108322101AImprove synchronicityReduce synchronization errorMultiple dynamo-electric motors speed regulationFuzzy control systemControl theory
The invention provides a fuzzy self-adjusting deviation coupling multi-motor synchronous control method. The method comprises the steps that a fuzzy self-adjusting filter controller which is formed bycombining a fuzzy controller and a first-order inertial filter and is used for controlling multiple motors is designed; given rotation speed and torque are used as the input of the fuzzy self-adjusting filter controller; softened rotation speed is used as the output of the fuzzy self-adjusting filter controller, wherein the softened rotation speed refers to the given rotation speed actually received by each motor; a lead correction link is introduced to design a lead synchronization compensator, and the response speed of each motor is accelerated while the start synchronization performance isimproved; in the start process and steady-state running sudden load, a synchronization error is calculated; the dynamic response speed characteristics of the motors are compared; and the effectiveness of the lead synchronization compensator to improve the dynamic response speed of the motors is verified. According to the invention, the synchronization performance of multiple motors at the start and the sudden change of the given rotation speed is improved, and the synchronization performance of multiple motors in steady-state sudden load is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
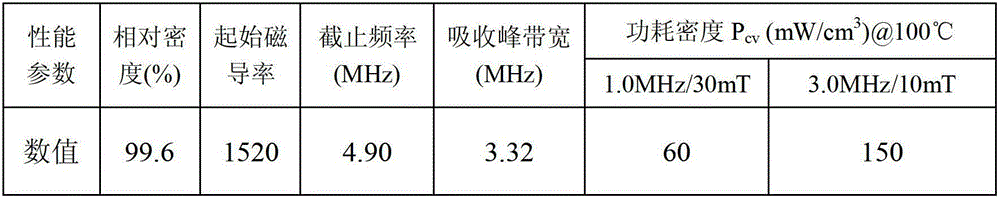
Ultralow-high-frequency-loss-power MnZn ferrite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102976739AExquisite control of sizeFinely tuned dispersionChemical compositionAverage size
The invention relates to an ultralow-high-frequency-loss-power MnZn ferrite and a preparation method thereof. The ultralow-high-frequency-loss-power MnZn ferrite is composed of a spinel-structure main crystal phase and a doping component in the grain boundary and crystal, wherein the chemical composition of the spinel-structure main crystal phase is [MnxZnyFe<2>]Fe2<3>O4. The microstructure is characterized in that the relative density of the sintered body is 99.2-99.6%, the average size of the crystal grains is 2.0 mu m@30mT / 1MHz / 100 DEG C and 145<=P[cv]<=160mW / cm<3>@10mT / 3MHz / 100 DEG C.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050001238A1High cutoff frequencyReduce capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceEngineering
A bipolar transistor is provided in which both the base resistance and the base-collector capacitance are reduced and which is capable of operating at a high cutoff frequency. The semiconductor device is structured so that the emitter and extrinsic base are separated from each other by an insulator sidewall and the bottom faces of the insulator sidewall, and the emitter are approximately on the same plane. The extrinsic base electrode and the collector region are separated from each other by an insulator.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Novel double-loop control method for dual-active bridge DC/DC converter based on double phase-shift control
ActiveCN106849668ARapid designSimple designEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDouble phaseLoop design
The invention discloses a novel double-loop control method for a dual-active bridge DC / DC converter based on double phase-shift control. Under a double phase-shift control mode, a transfer function from the internal and external phase-shift angles to output voltage in different operating modes are obtained by using a small signal modeling technique in order to guide the inner-loop design of the dual-active bridge DC / DC converter. By establishing a relation between a loss model and peak current in different operating modes, the internal and external phase-shift angles in different operating modes during the optimal peak current are obtained so as to guide the outer-loop design of the dual-active bridge DC / DC converter. The use of a double-loop control compensation system can increase the cutoff frequency of the system, can greatly improve the dynamic response of the system, can reduce the static error of the system, and can realize the fast response speed and precision. The control method of replacing the optical loss with the optical peak current can simplify controller design and realize the real-time control of the converter.
Owner:NANJING NARI GROUP CORP +2
Filtering image data to obtain samples mapped to pixel sub-components of a display device
InactiveUS20050238228A1Reduce colorRaise the cutoff frequencyImage enhancementImage analysisLuminous intensityLow-pass filter
Image data processing and image rendering methods and systems whereby images are displayed on display devices having pixels with separately controllable pixel sub-components. Image data, such as data encoded in a three-channel signal, is passed through a low-pass filter to remove frequencies higher than a selected cutoff frequency, which obtain samples from the color components of the signal that map spatially different image regions to individual pixel sub-components. It has been found that color aliasing effects can be significantly reduces at a cutoff frequency somewhat higher than the Nyquist frequency, while enhancing the spatial resolution of the image. The image data is then passed through sampling filters, A generalized set of filters includes nine filters, one for each combination of one color and one pixel sub-component. The filtering coefficients of the filters can be selected to optimize of approximate an optimization of an error metric, which represents the color and luminance errors perceived on the display device. In this manner, a desired balance between color accuracy and luminance accuracy can be obtained. The samples mapped to individual pixel sub-components are used to generate luminous intensity values for the displayed image.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
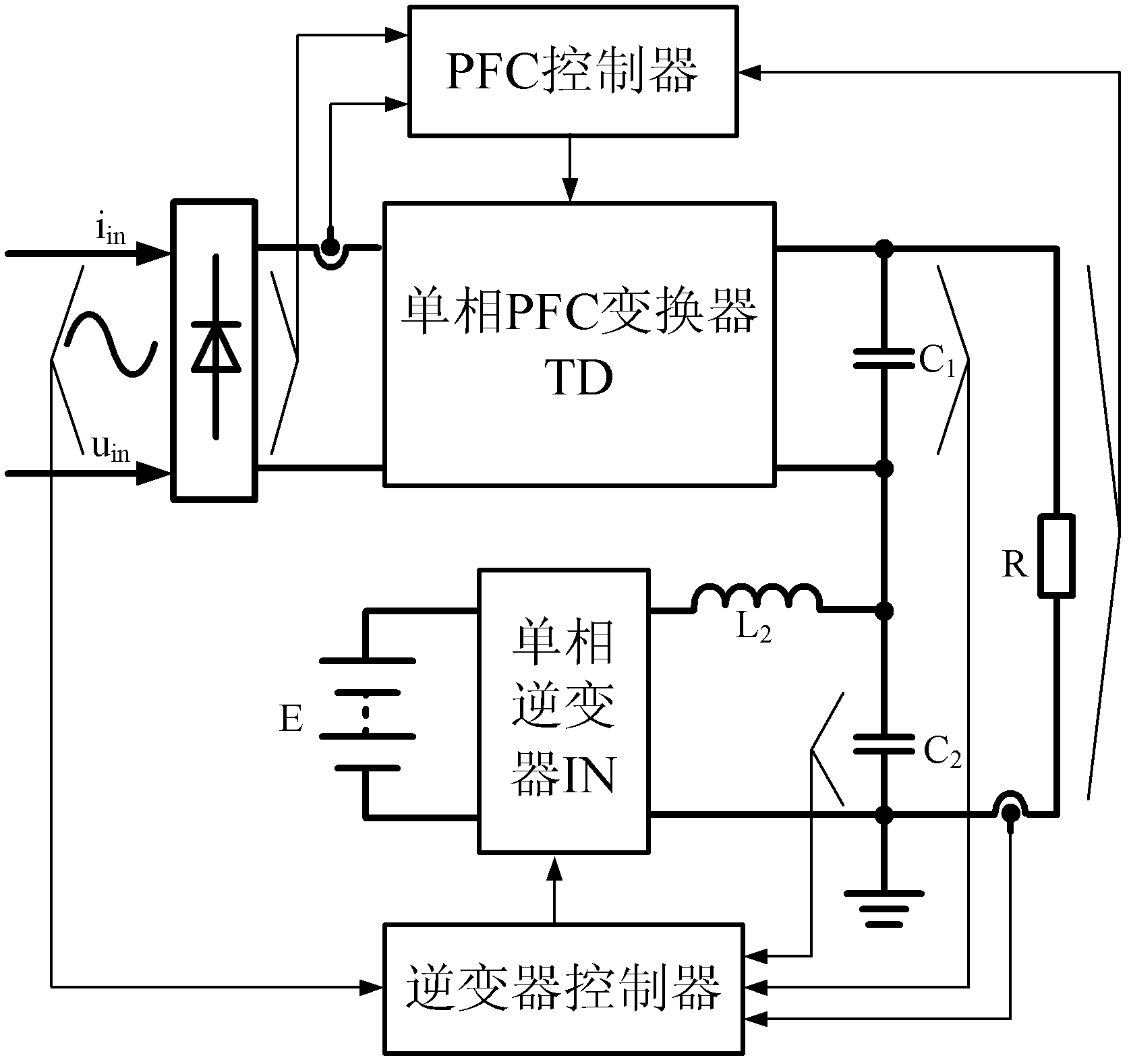
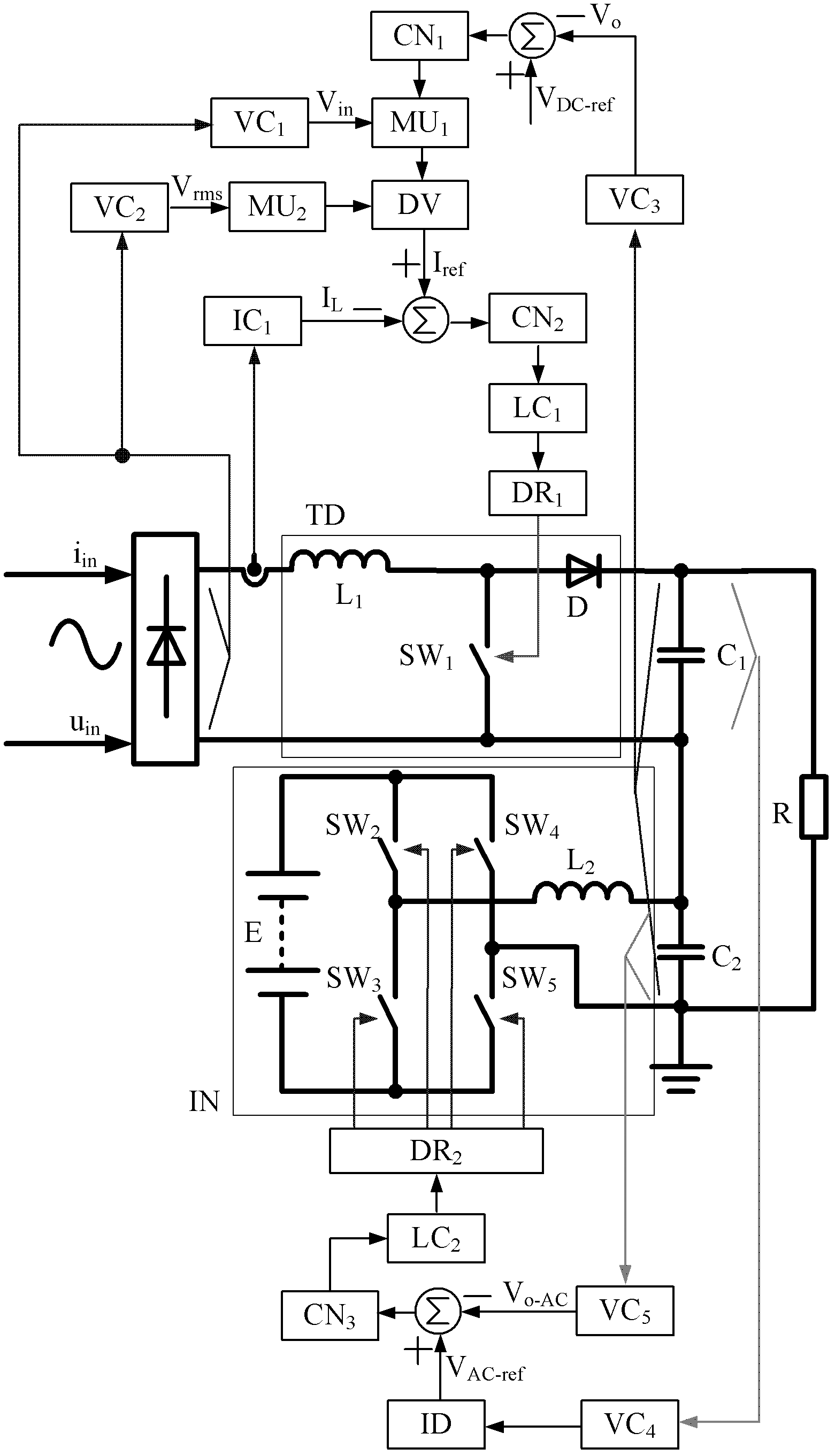
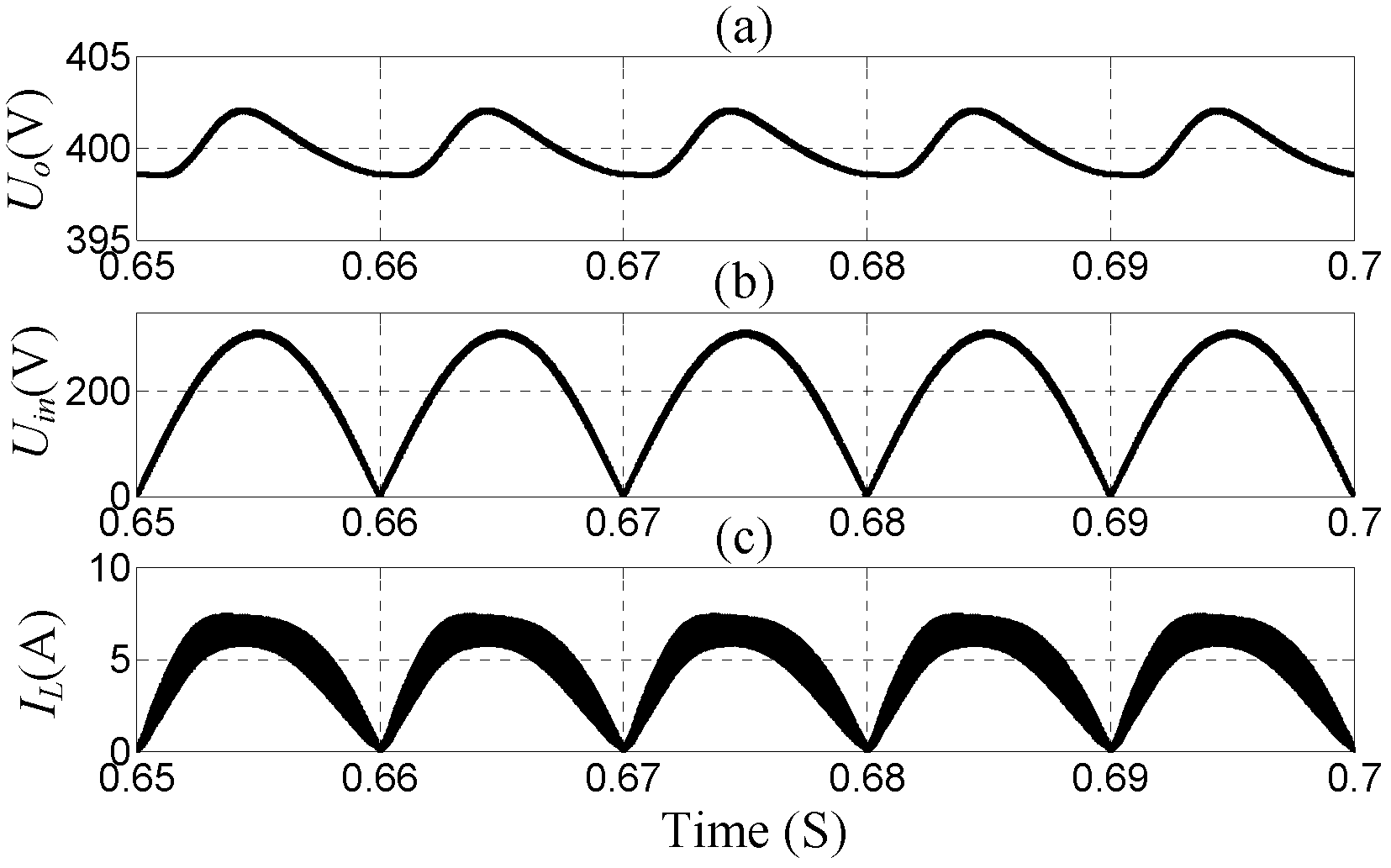
Power factor correction (PFC) conversion control method for low output voltage ripple and device thereof
InactiveCN102545563AImprove efficiencyRaise the cutoff frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsLoop controlTarget signal
The invention discloses a power factor correction (PFC) conversion control method for low output voltage ripple and a device thereof. After a single-phase PFC controller is used for sampling the input voltage, inductive current and output voltage of a single-phase PFC converter, a control signal of the PFC convertor is obtained through a PFC control strategy; and a controller of a single-phase inverter is used for sampling the input voltage and load current of the single-phase PFC converter to obtain a control target signal of the single-phase converter and sampling the alternating-current output voltage of the converter simultaneously, and ripple same-amplitude phase reversion is realized for the alternating-current output voltage of the converter and the direct-current output voltage of the PFC converter by using an inverter double closed-loop control strategy. Due to the adoption of the method and the device, a high power factor is realized, the output power frequency ripple voltage of the single-phase PFC converter is eliminated simultaneously, the dynamic response of a system is improved, and the problems of low efficiency and high cost of the conventional twos-stage PFC converter are solved. The device can be also applied to low-ripple high-PFC AC / DC (Alternating Current / Direct Current) constant current source design.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Horizontal dispersion oxide semiconductor of heterogeneous bar multi-step field electrode board
InactiveCN101079446AIncrease the number ofIncrease the average electric fieldSemiconductor devicesDouble diffusionTransconductance
The invention discloses a lateral double diffusion metal oxide semiconductor of a heterogeneous grip multi step field polar plate, which is characterized by the following: equipping with the heterogeneous double-grip structure of the source grip and the leakage grip; composing the multi step field polar plate of the first step field polar plate and the second step field polar plate, connecting with the source grip, the leakage grip, the first step field polar plate and the second step field polar plate orderly; equipping with the source and the leakage in the channel trap section and the trap drift section; equipping with grip oxide layer among the source grip, the leakage grip and the channel trap section, equipping with the trap contact hole in the channel trap section; equipping the field oxide layer among the first step field polar plate, the second step field polar plate and the trap draft section; covering the oxide layer on the multi step field polar plate; making the channel trap section and the trap draft section on the underlay. The invention improves the driving current and the transconductance, which reduces the conducting resistance and the power consumption.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Film speaker array
ActiveCN102143425ALarge piezoelectric responseLight in massElectrostatic transducer loudspeakersElectricityFerroelectret
The invention relates to a film speaker array, which comprises a piezoelectric electret film and a circuit board assembly, wherein the piezoelectric electret film is a porous polymer film, and electrode arrays are respectively and correspondingly arranged on two sides of the piezoelectric electret film; a speaker circuit, and a circuit board input end and a circuit board output end which are electrically connected with a speaker circuit are arranged on the circuit board assembly, and the circuit board output end is electrically connected with electrode arrays arranged on two sides of the piezoelectric electret film. The film speaker array made of porous polymer film is integrated with the advantage of high directivity of the speaker array and the advantages of lightness, thinness, softness, simple structure, high reliability and low cost of the polymer piezoelectric electret, and greatly expands the application range of the speaker array, thereby being an alternative replacing the traditional speaker array in the theater, the meeting place, the classroom, the museum, the gymnasium and other circumstances.
Owner:SHENZHEN HORN AUDIO
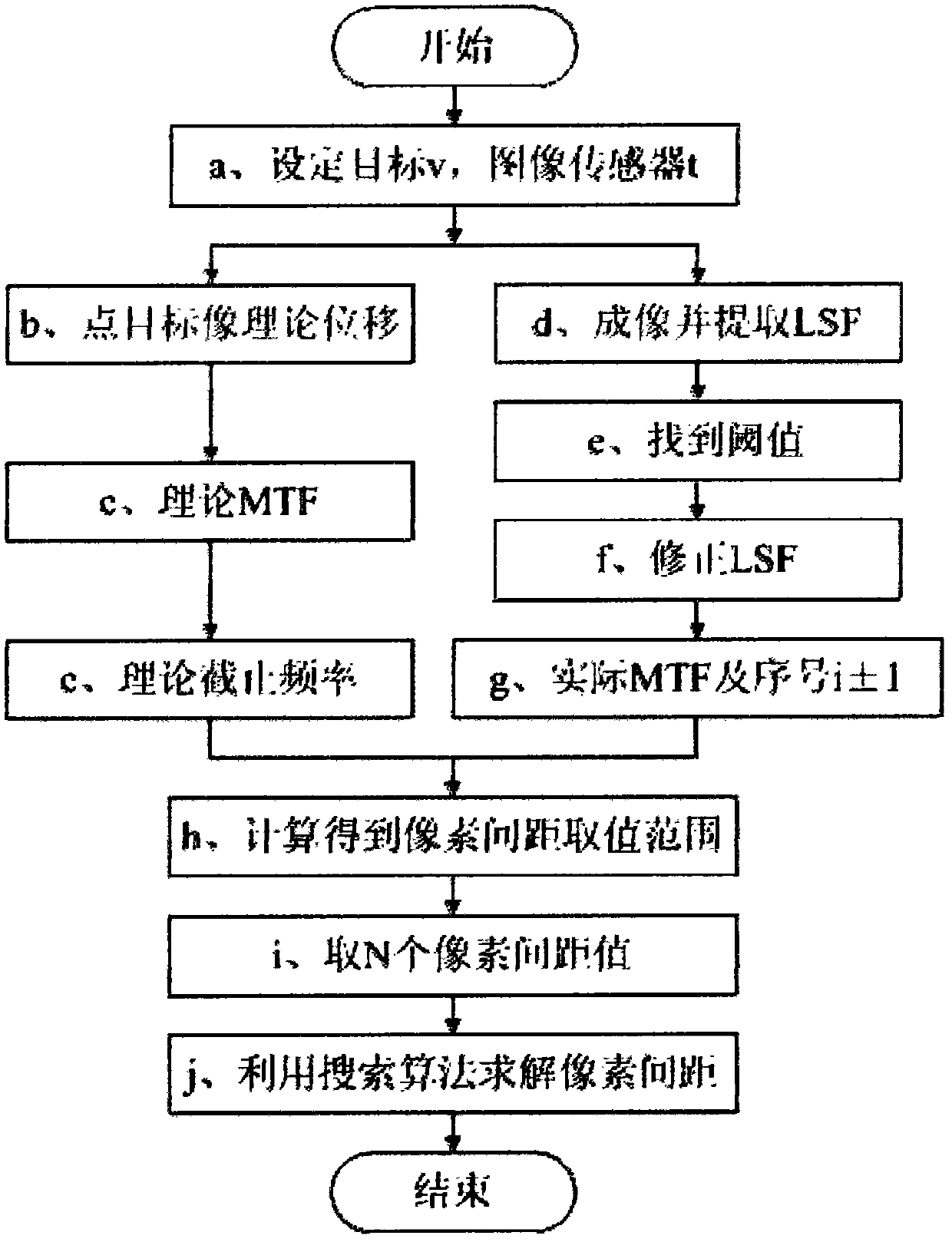
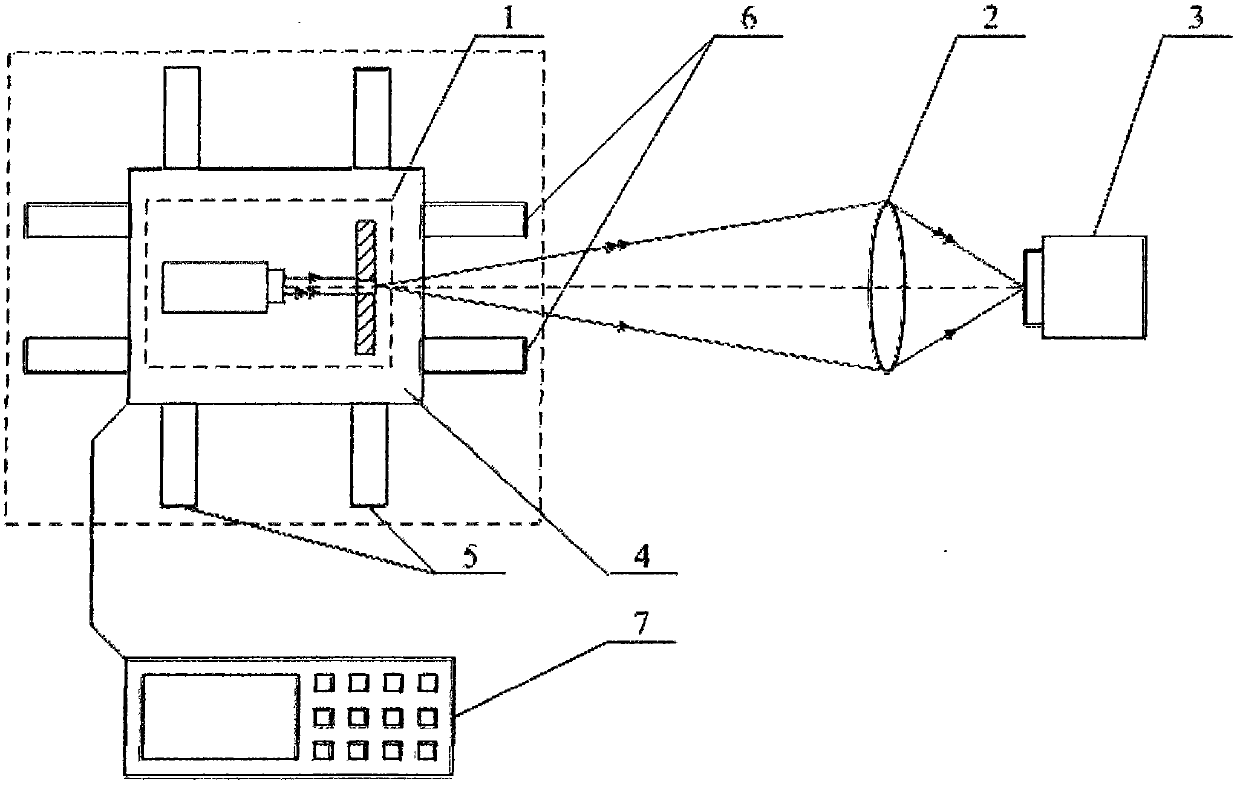
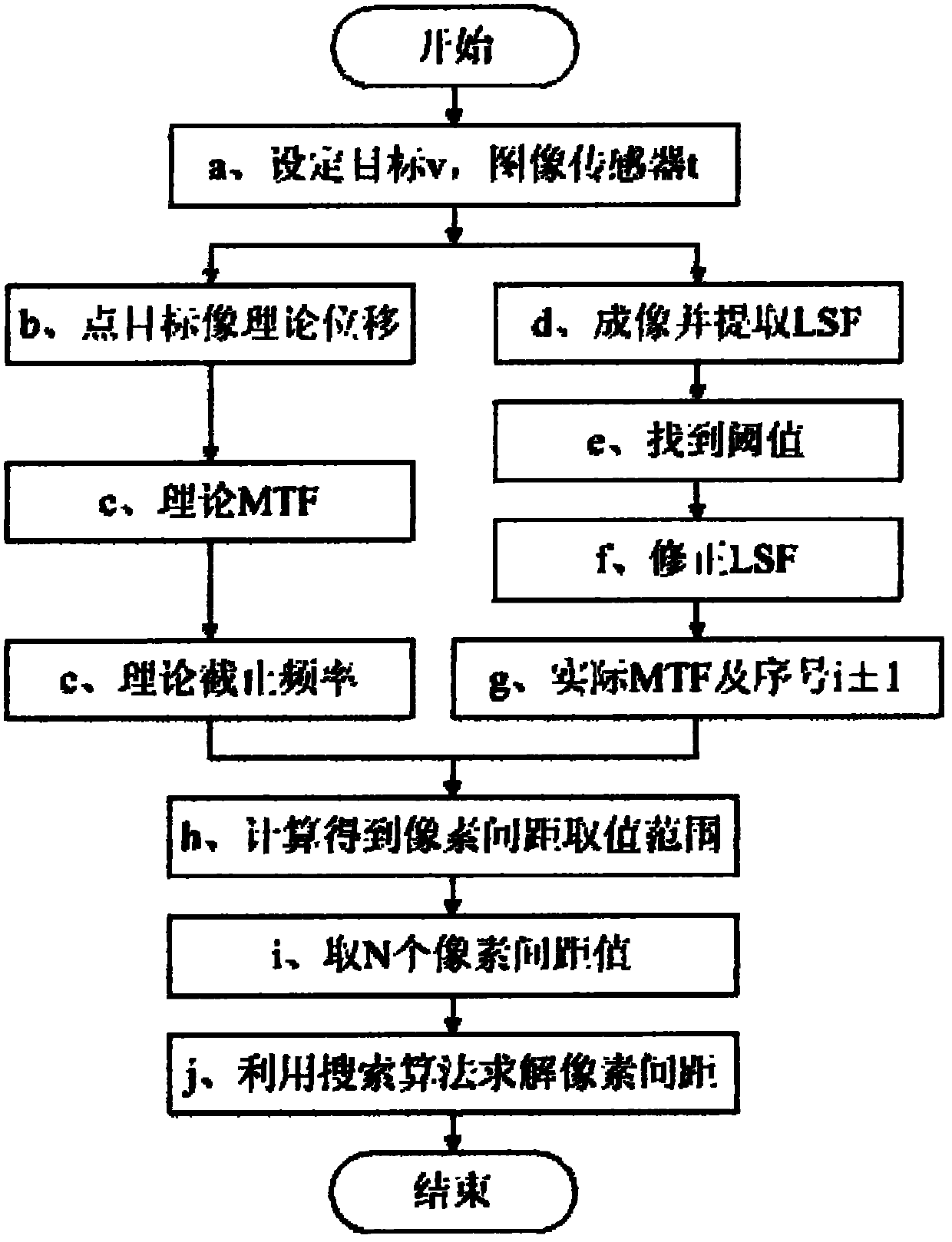
Method and device for measuring space of pixels of image sensor by using constant-speed movable point target
The invention relates to a method and device for measuring the space of pixels of an image sensor by using a constant-speed movable point target, belonging to the field of the measurement of length, width or thickness by adopting the optical method. The method comprises the following steps: imaging the point target in the constant-speed movement state to obtain a linear image, searching the value taking range of the space of the pixels in the frequency domain, and calculating the space of the pixels by using the search algorithm according to the characteristic that the actual modulation transfer function curve and the theoretical modulation transfer function curve which are relevant to the space of the pixels can coincide best under the least square condition. The device is characterized in that a sliding block which bears the point target is arranged on a first guide rail and a second guide rail, when a controller controls the sliding block to move at constant speed on the first guide rail, the controller also controls the sliding block to move on the second guide rail, the movement in two directions matches with each other so that the point target is imaged on the surface of image sensor by calibrating the focus. Due to the adoption of the method and the device for measuring the space of pixels of the image sensor, the errors between the single-time measurement results can be reduced, and the repeatability of the measurement results can be improved accordingly.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
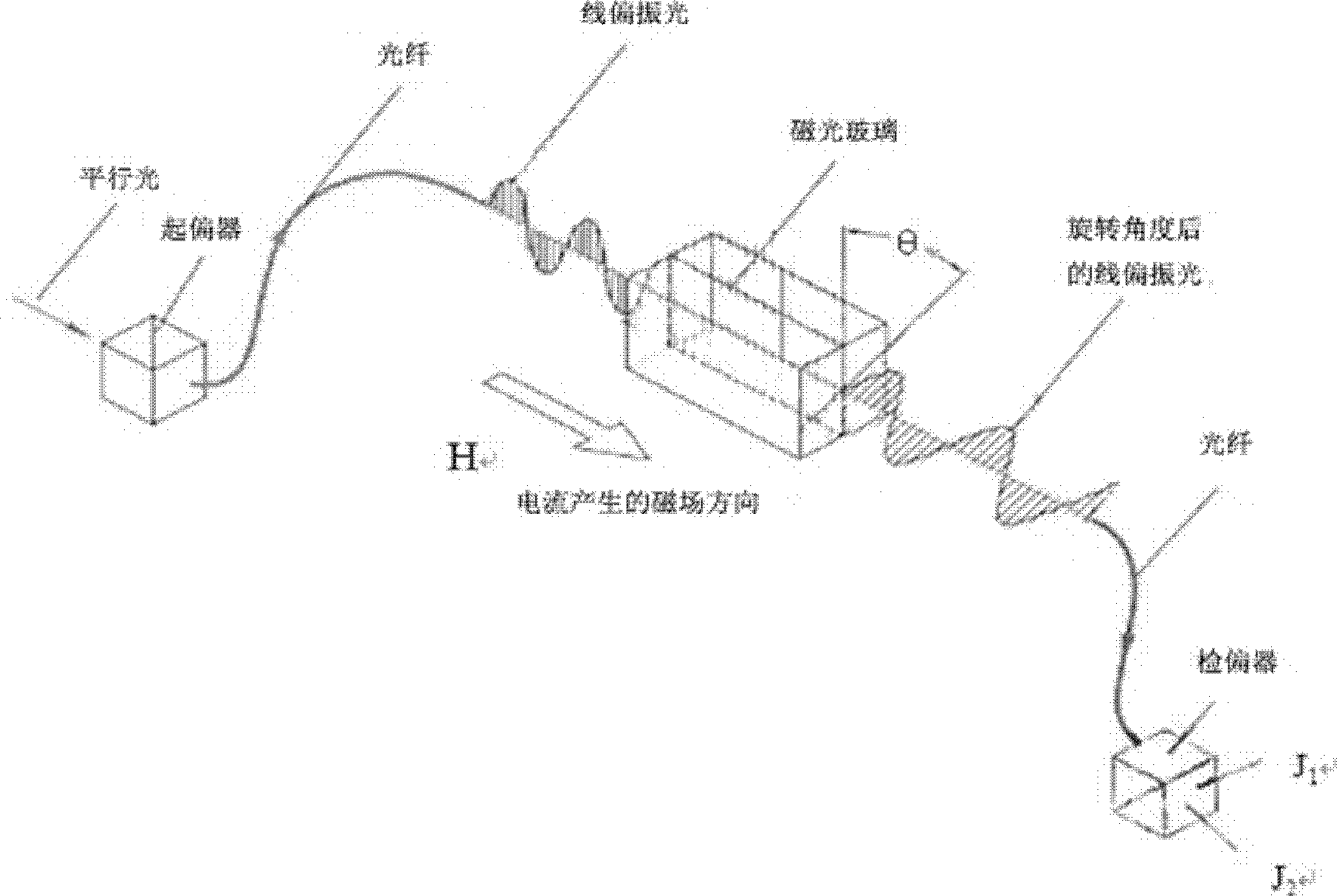
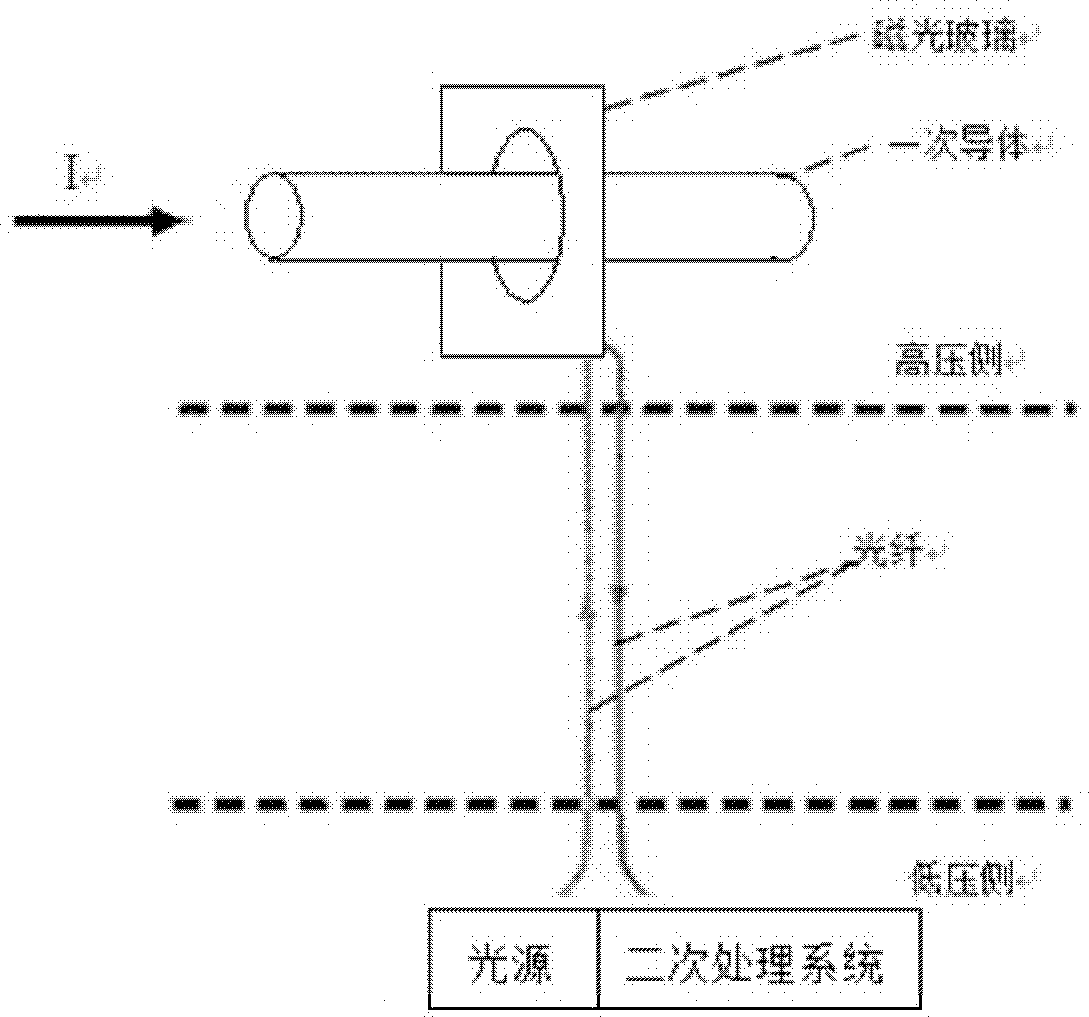
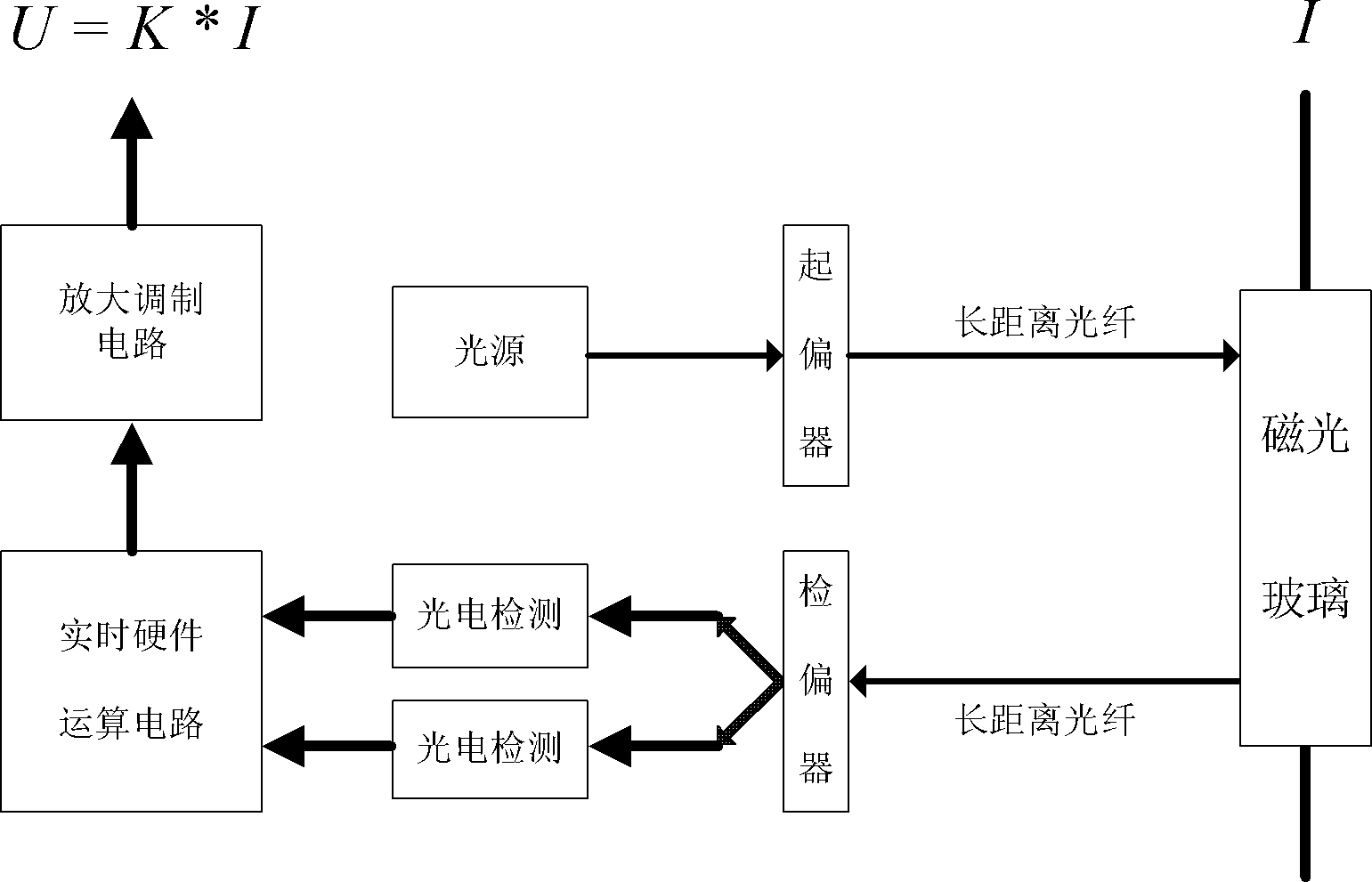
Traveling wave distance measurement device based on passive magnetooptic glass current transformer principle
InactiveCN102323516AImprove reliability and flexibilityNo bit errors will occurFault locationComplex programmable logic deviceCurrent amplitude
The invention relates to a traveling wave distance measurement device based on a passive magnetooptic glass current transformer principle. A small voltage signal reflecting primary side current amplitude of a transmission line is obtained by adopting a passive magnetooptic glass electronic current transformer, and a high-speed acquiring circuit is controlled by a CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device) for recording and sampling 625KHz travelling wave data and starting the sampling of 20KHz criterion data. When the transmission line fails, the travelling wave distance measurement device judges whether the transmission line fails through the sampled 20KHz data, and controls a 625KHz high-speed sampling part to completely record high-speed sampled data comprising travelling signals and sends data to a background computer through communication, and the background computer automatically computes and recognizes a failed travelling wave head through a wavelet algorithm after obtaining dual-end circuit data, and realizes failure location of the transmission line according to different moments of the wave head arriving at a dual-end bus.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Wide temperate zone terahertz wave detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107331729AStrong ionic bondImprove transconductanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Ohmic contact
The present invention belongs to the detector technology field, in particular relates to a wide temperate zone terahertz wave detector and a preparation method thereof. According to the present invention, by taking an aluminum gallium nitrogen / gallium nitrogen high electron mobility field effect transistor (HEMT) as a basic structure, by the substrate and by utilizing an epitaxy method, an aluminum gallium nitrogen / gallium nitrogen layer is prepared; then an active area table-board, a gate medium, an ohmic contact window and an electrode are prepared, so that an obtained two-dimensional electron gas in the field effect transistor has the higher electron concentration and mobility, a spectral detector of realizing the high speed, high sensitivity and high signal to noise ratio detection of a THz wave on an over room temperature condition is obtained, and finally, the wide temperate zone detection of the THz wave is realized.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
W-band even-order sub-harmonic mixer
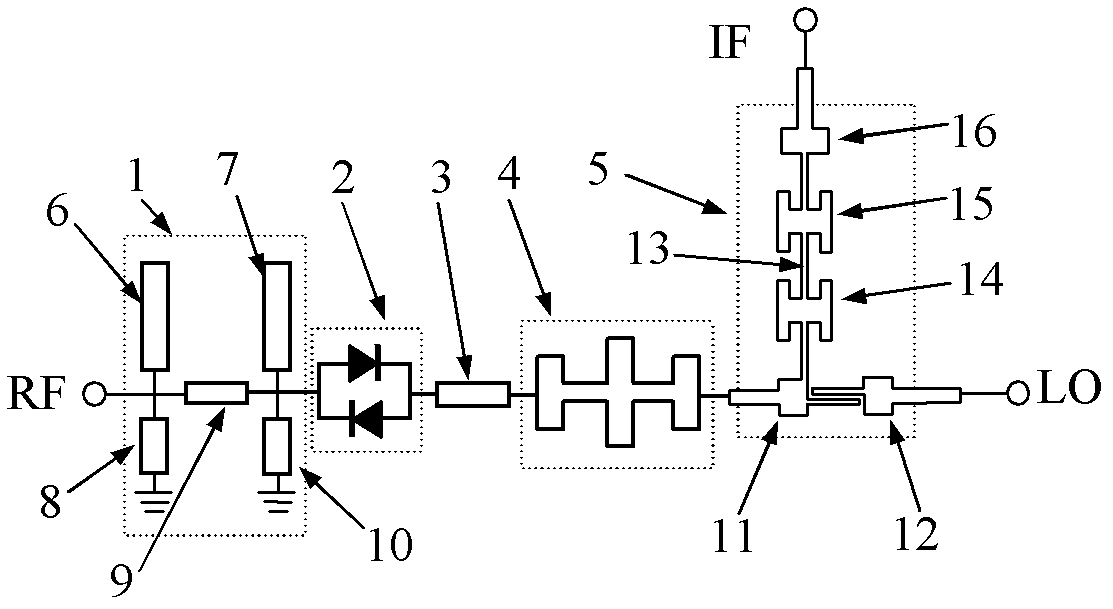
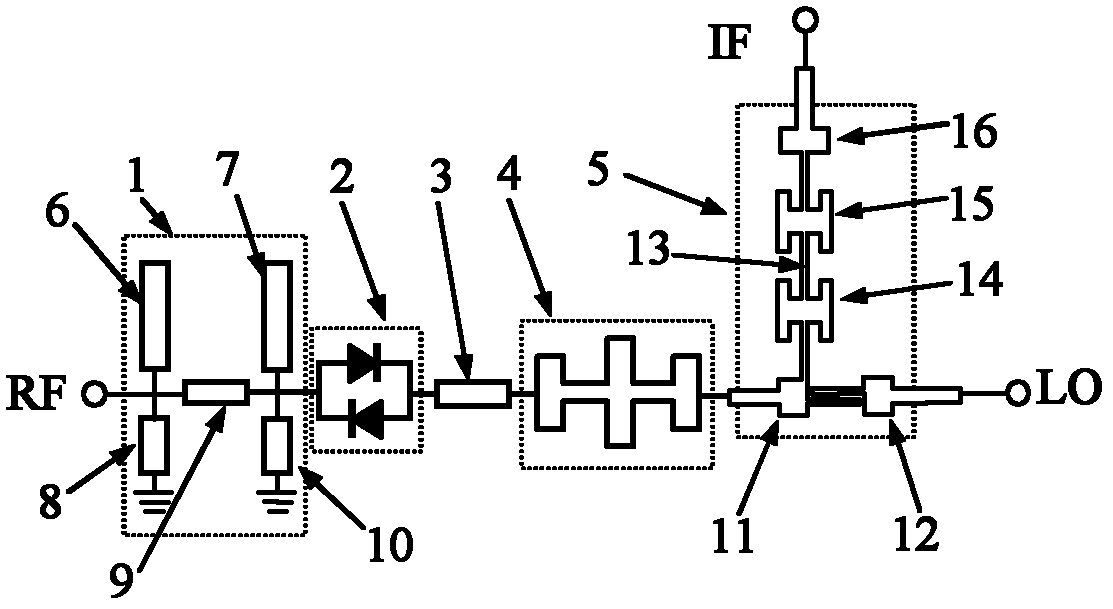
InactiveCN102611390ARaise the cutoff frequencyImprove loss performanceMultiple-port networksModulation transference by diodesLocal oscillator signalIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a W-band even-order sub-harmonic mixer, which comprises a radio-frequency broadband band-pass filter, an anti-parallel diode pair, a phase adjusting transmission line, a local oscillator low-pass filter and a duplexer, wherein one end of the local oscillator low-pass filter is connected with a common port of the duplexer while the other end of the local oscillator low-pass filter is connected with the phase adjusting transmission line, and the anti-parallel diode pair is bridged between the radio-frequency broadband band-pass filter and the phase adjusting transmission line. The W-band even-order sub-harmonic mixer realizes mutual isolation of radio-frequency signals, local oscillator signals and intermediate frequency signals by means of the radio-frequency broadband band-pass filter, the local oscillator low-pass filter and the duplexer, and the mixer can realize wide operation bandwidth as the radio-frequency broadband band-pass filter, the local oscillator low-pass filter and the duplexer have wide bandwidth.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com