Patents
Literature
62results about "Modulation transference by diodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
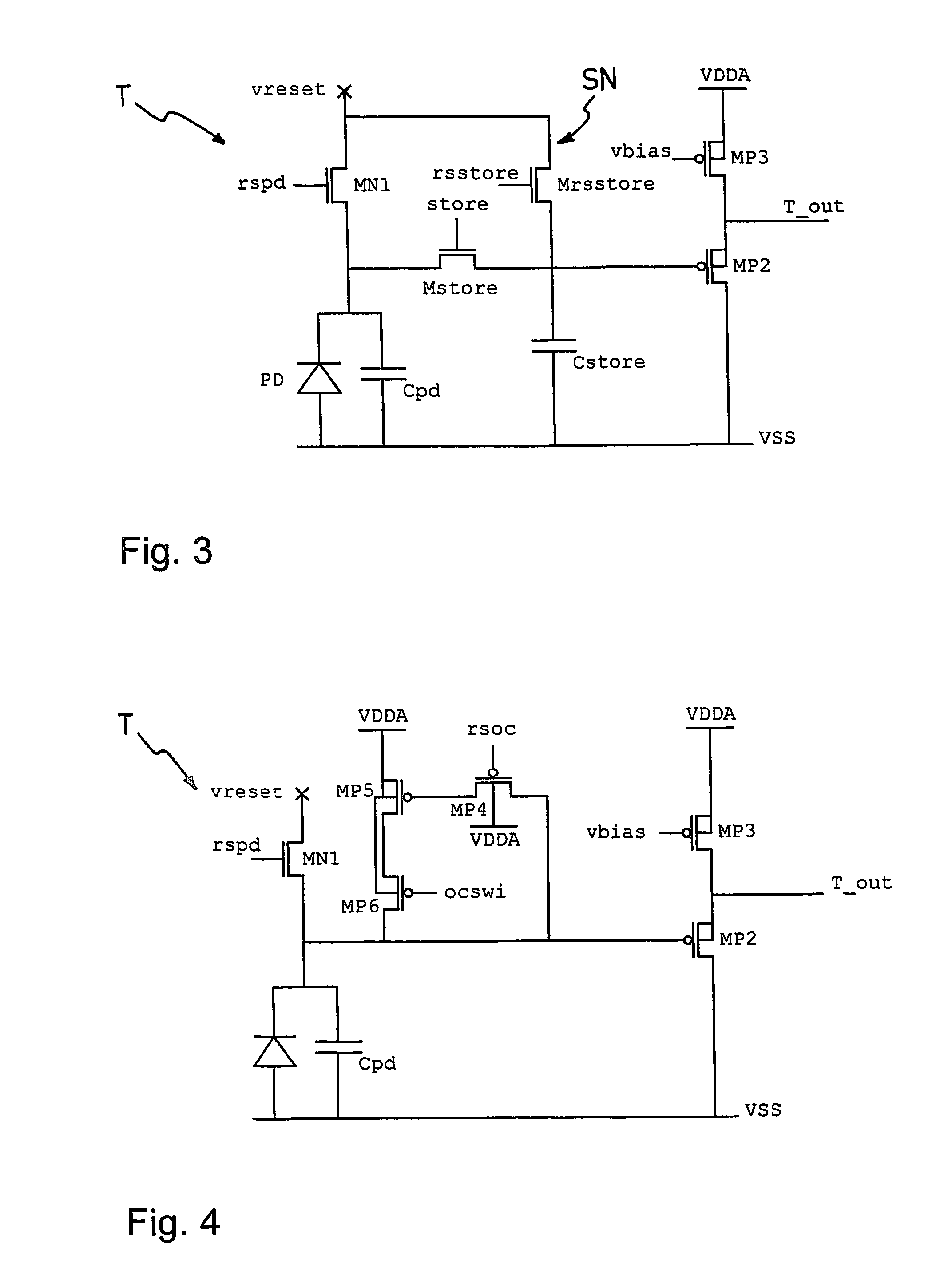
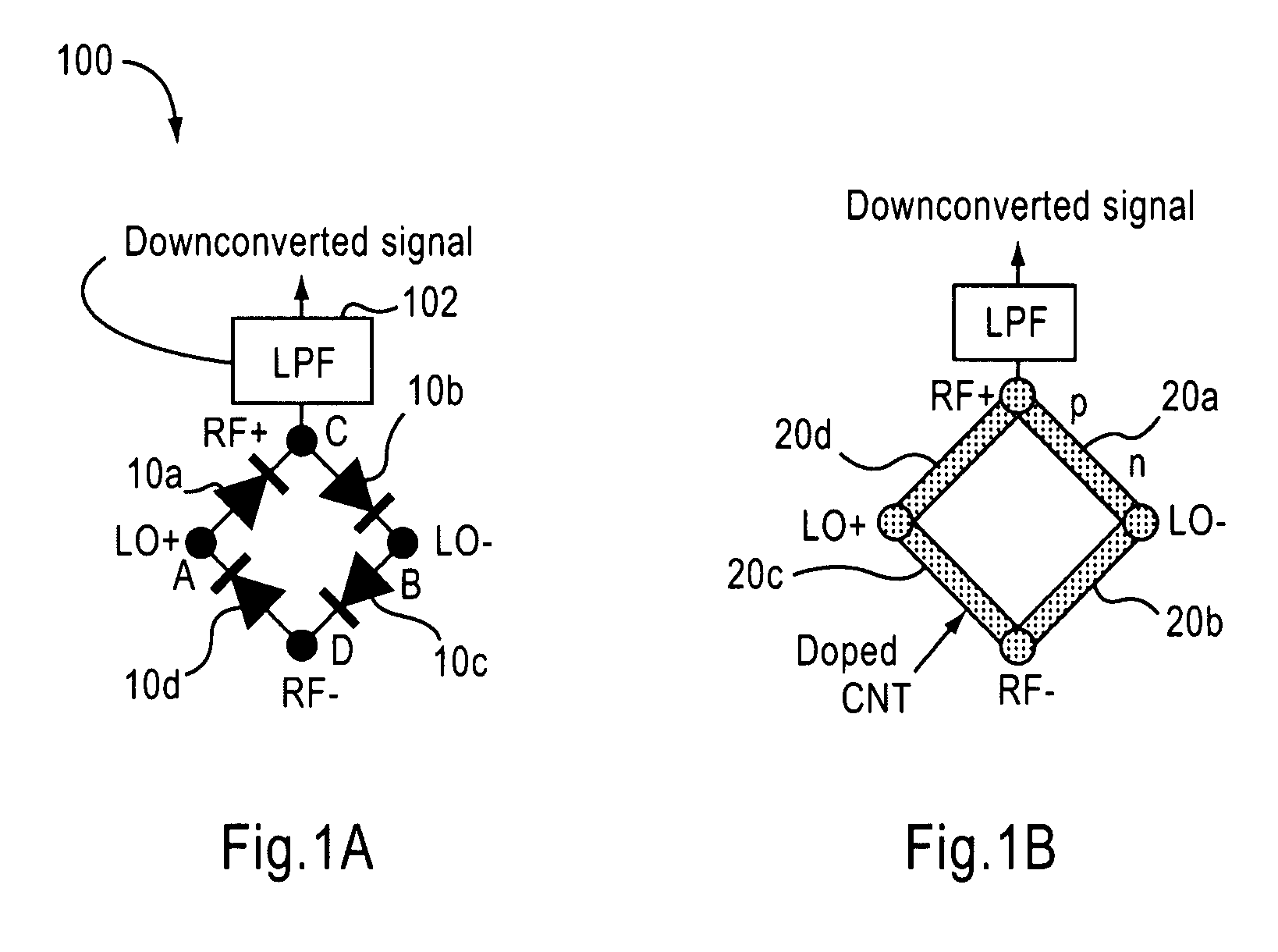
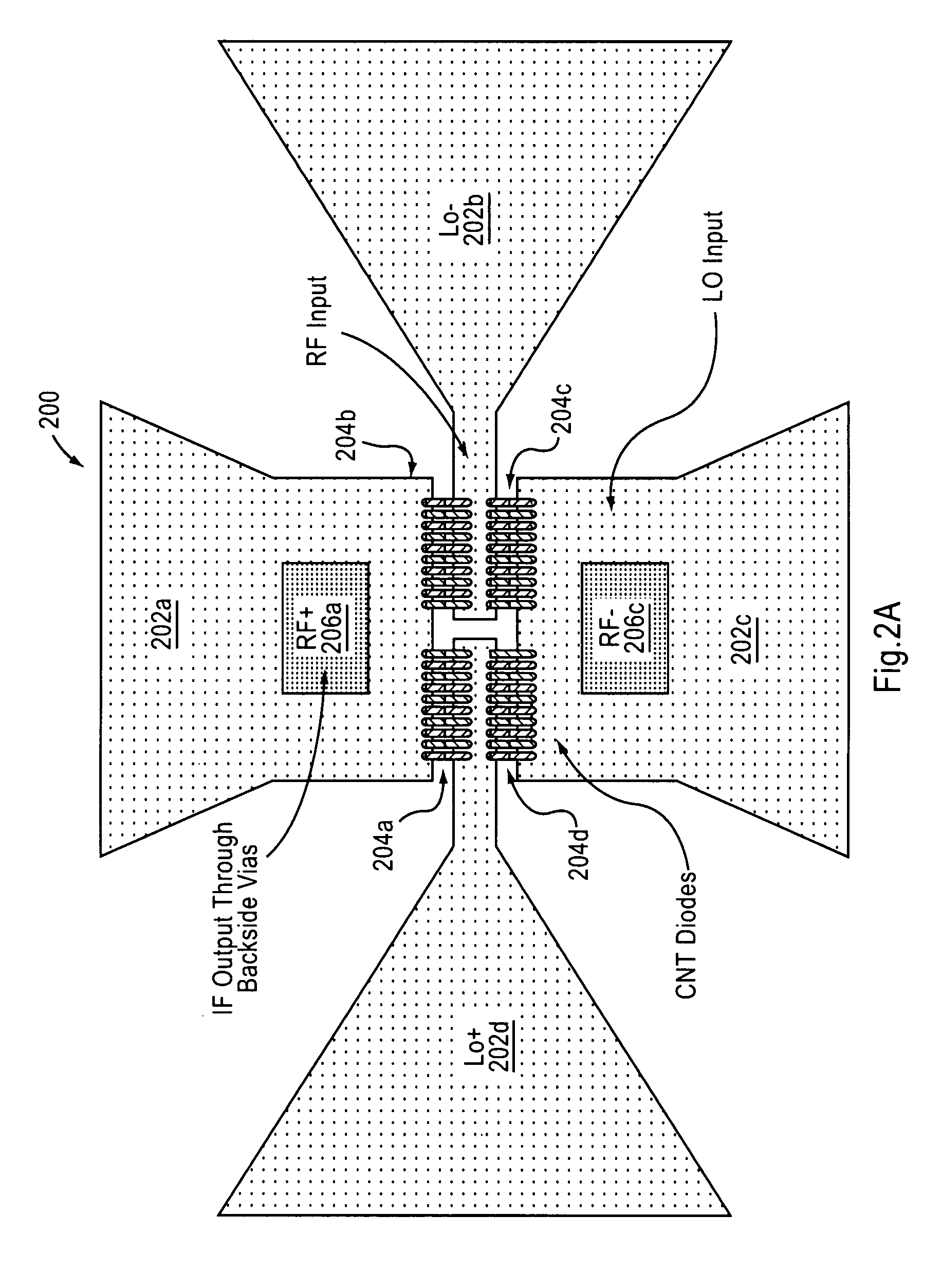
Carbon nanotube devices and method of fabricating the same
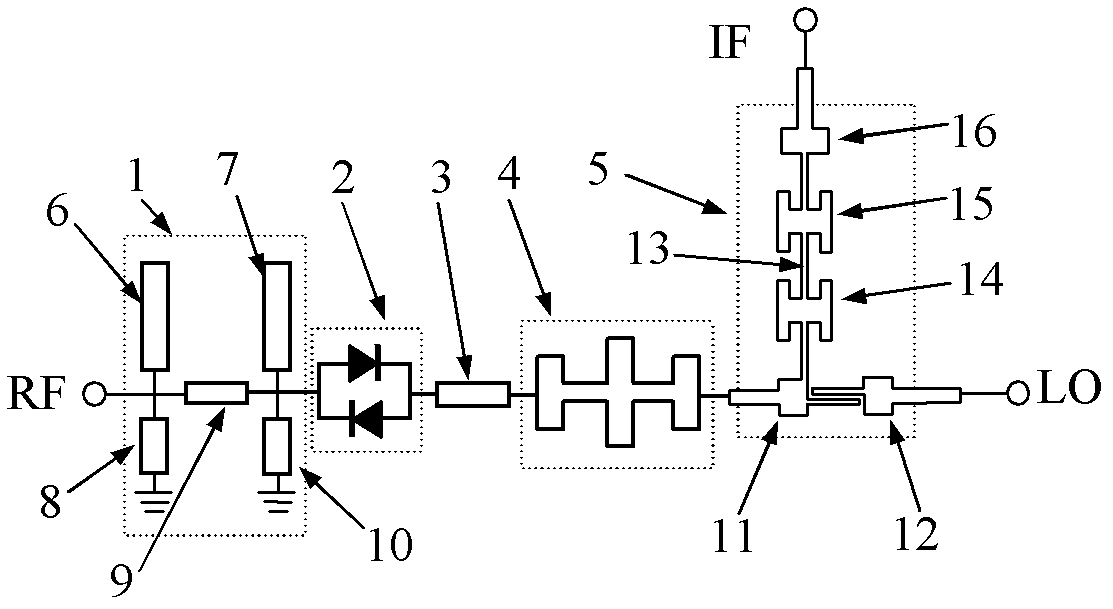
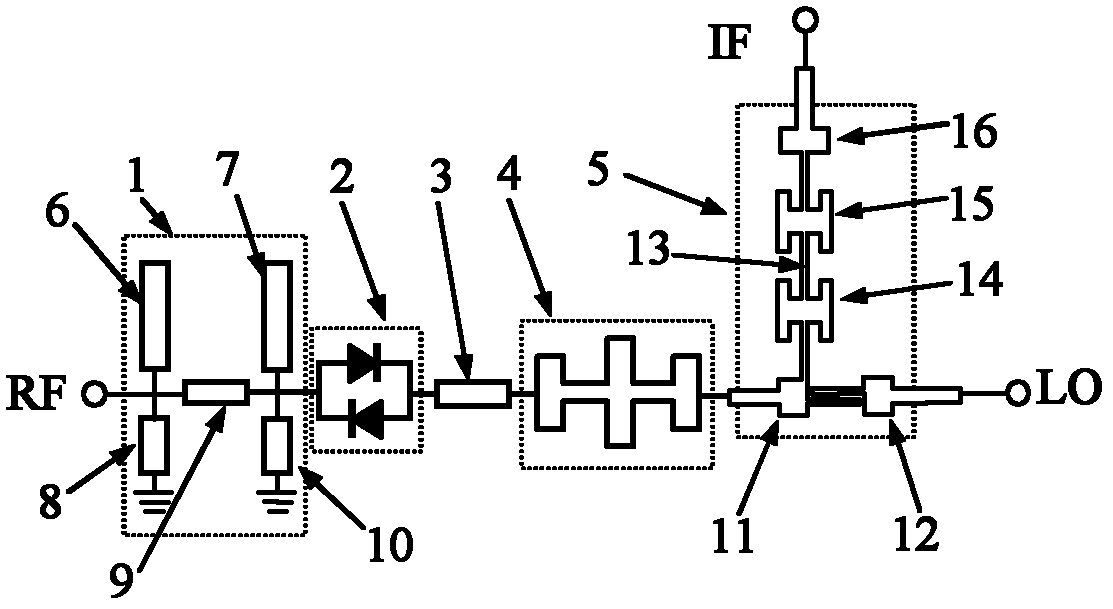
ActiveUS20120182178A1Modulation transference by diodesMaterial analysis by optical meansCarbon nanotubeFocal Plane Arrays
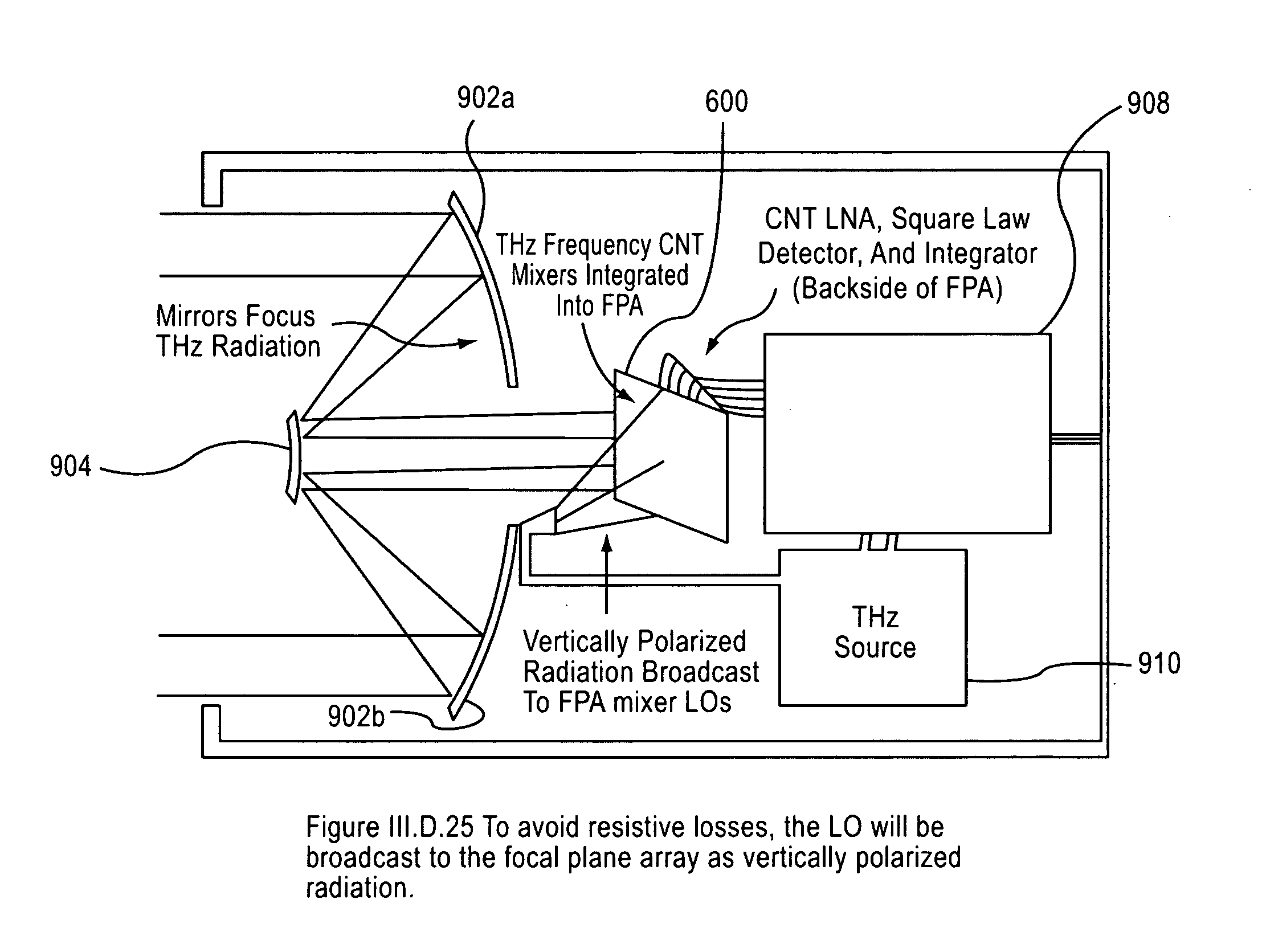
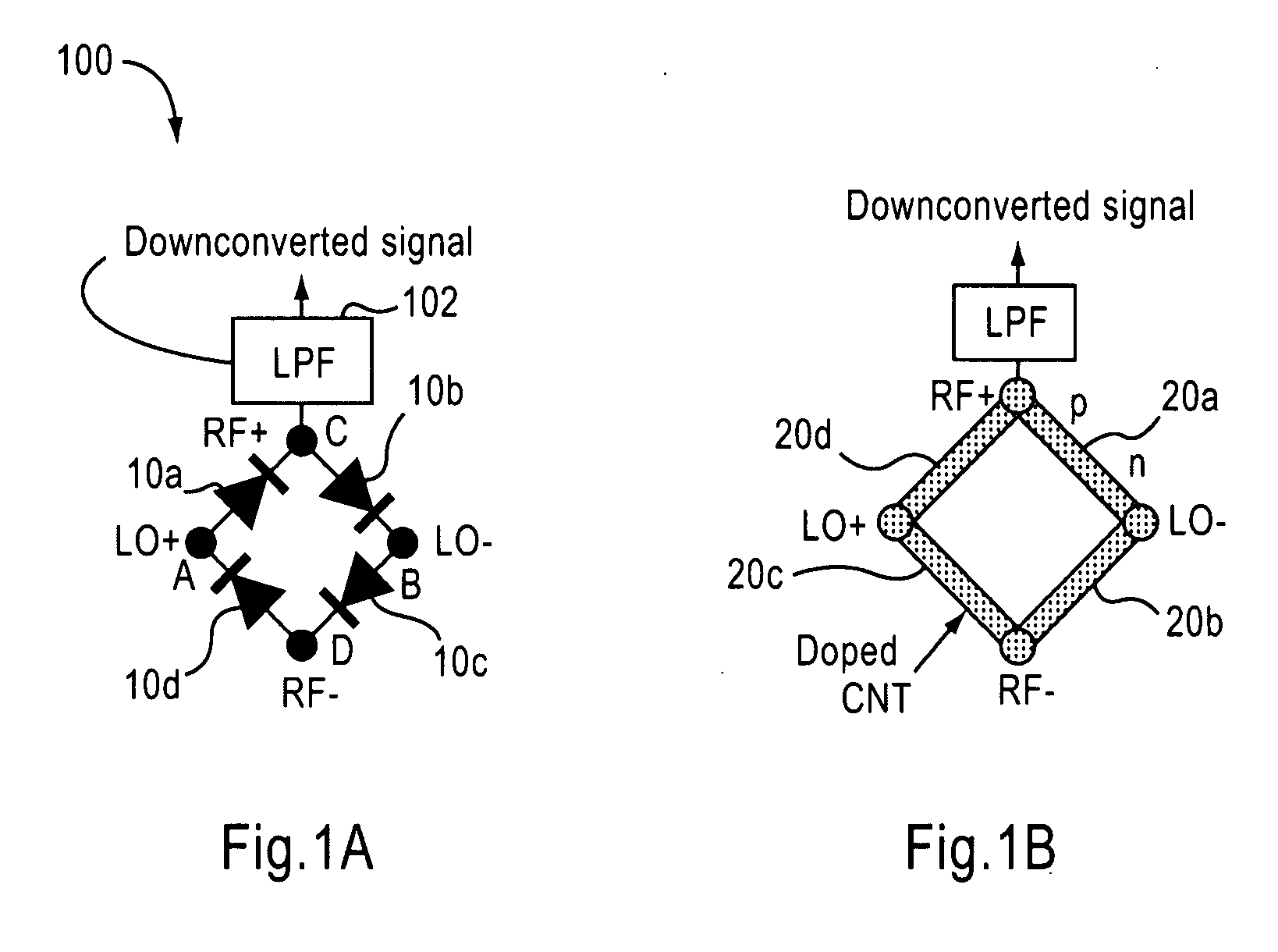
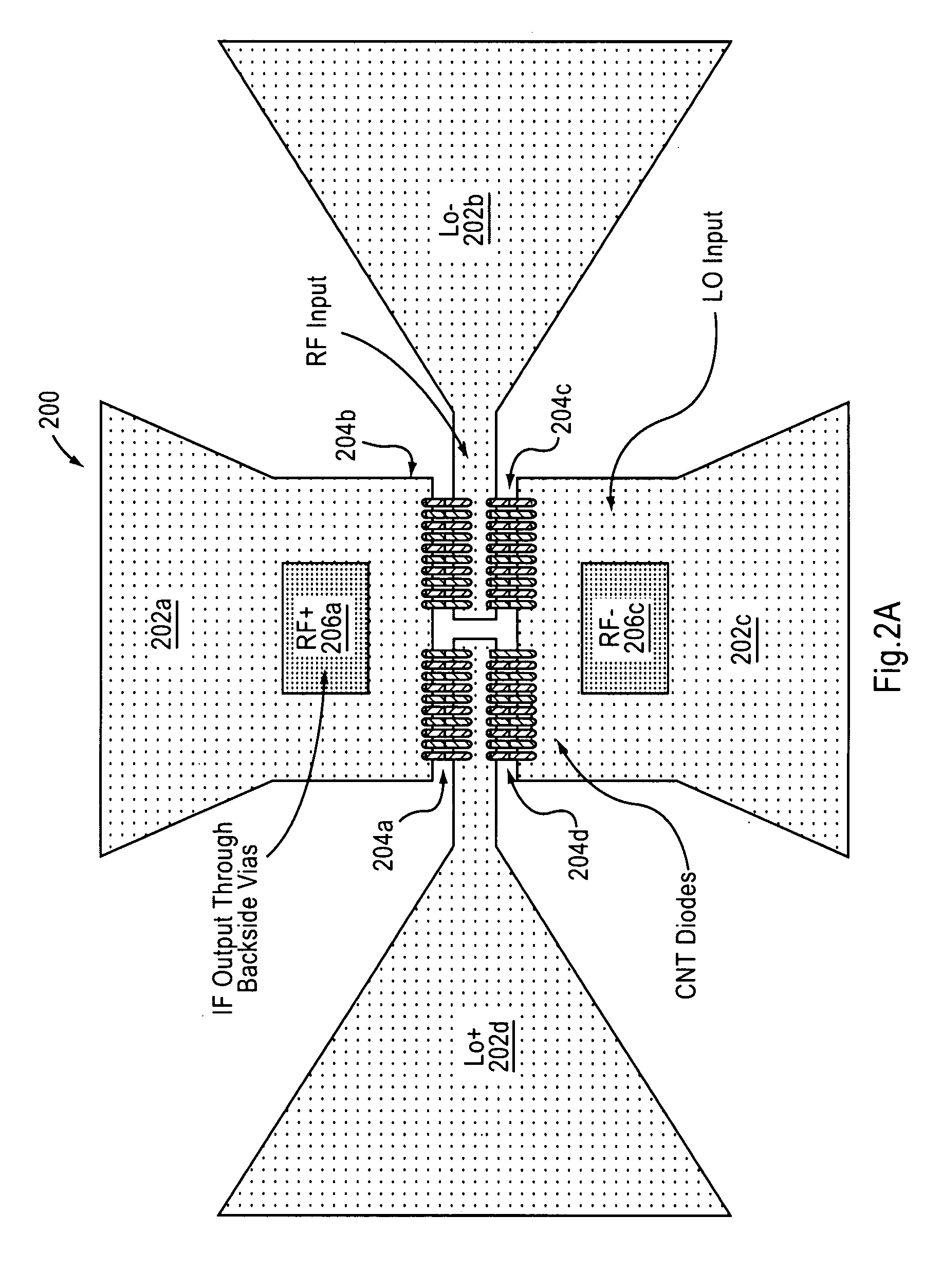
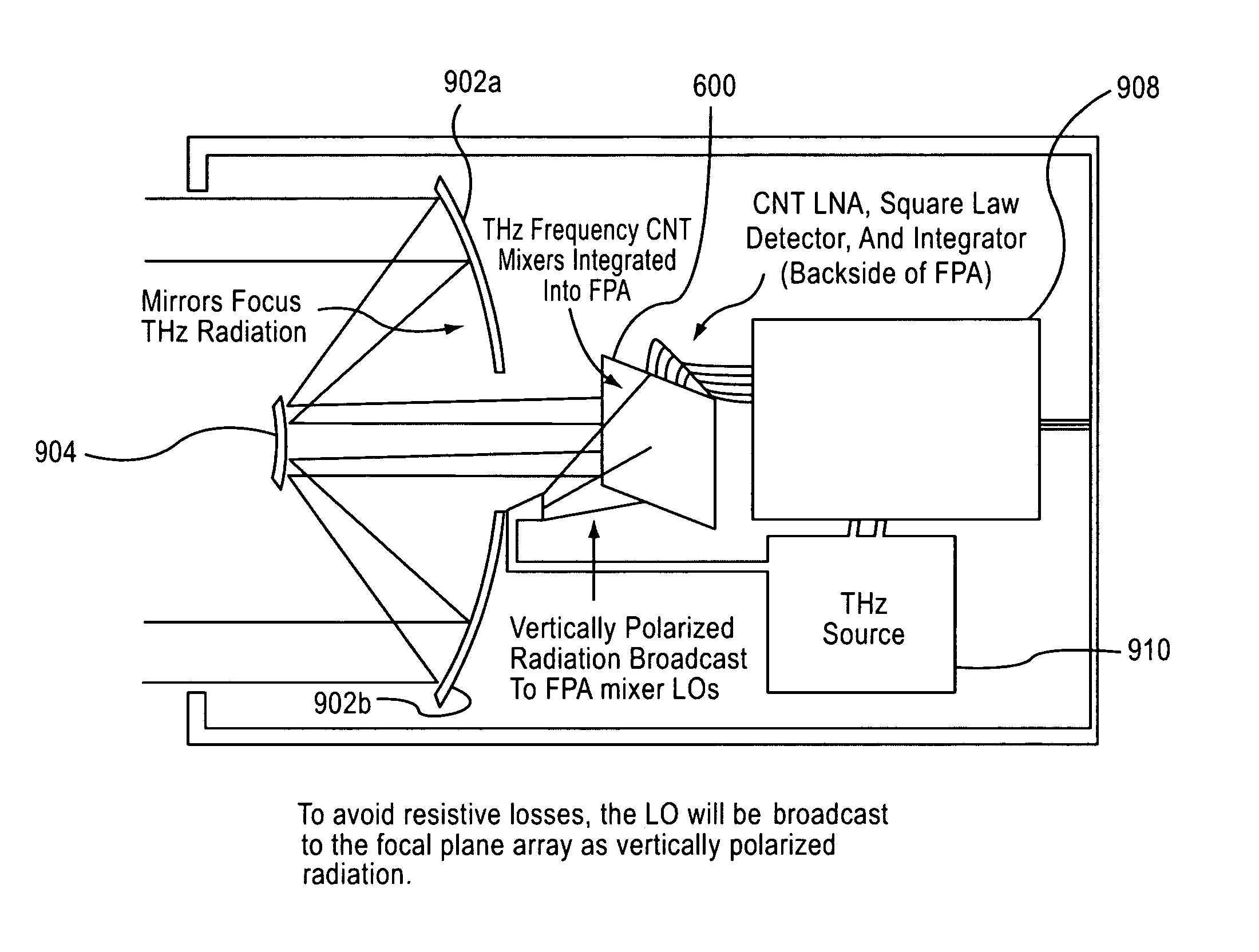
An imaging system includes an RF source, a focal plane array and device for focusing the RF signal from the RF source. The focal plane array includes a plurality of carbon nanotube mixers for capturing RF signals and down-converting the signals to a selected bandwidth and output an output signal. The device focuses the RF signal output from said RF source onto the focal plane array.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Diode mixer
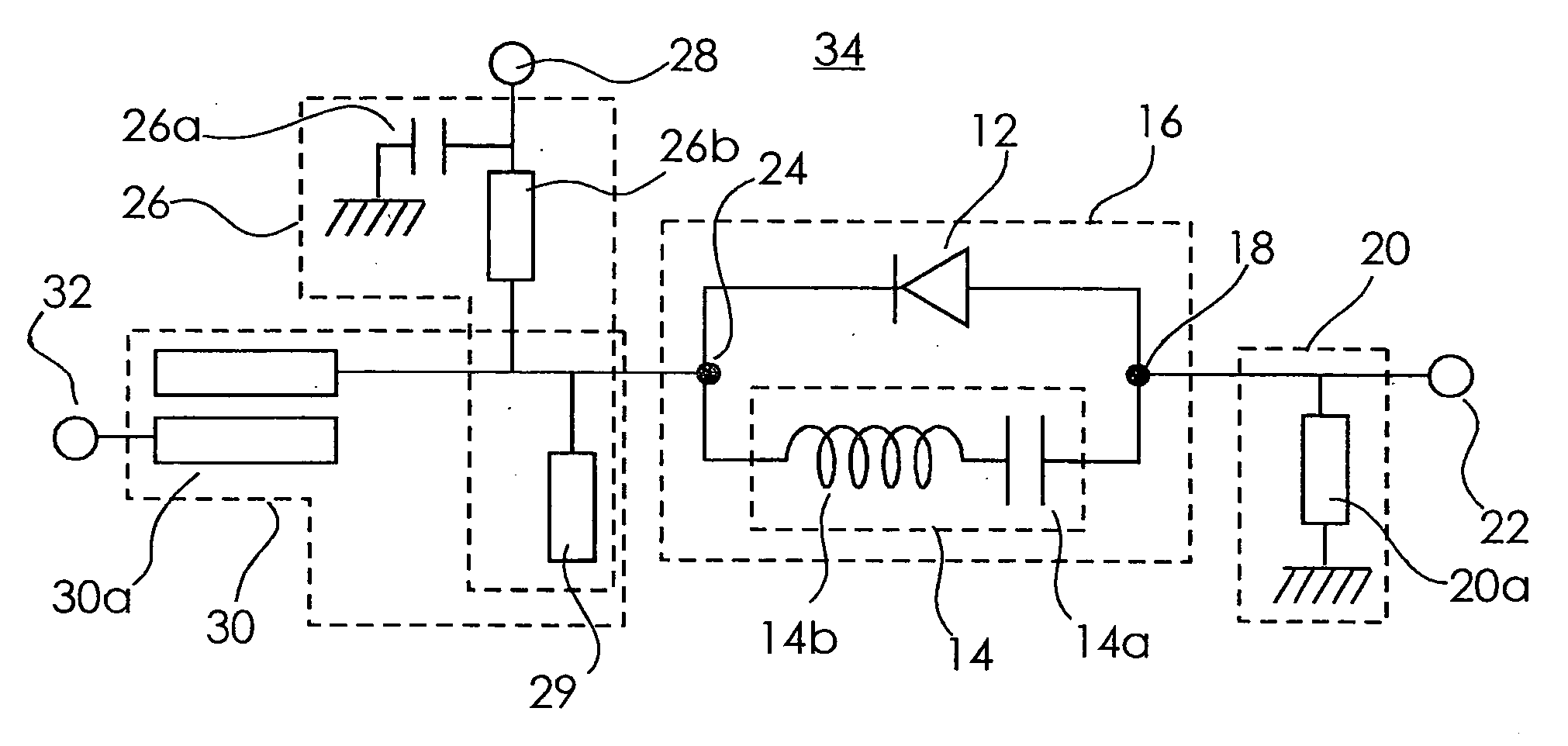
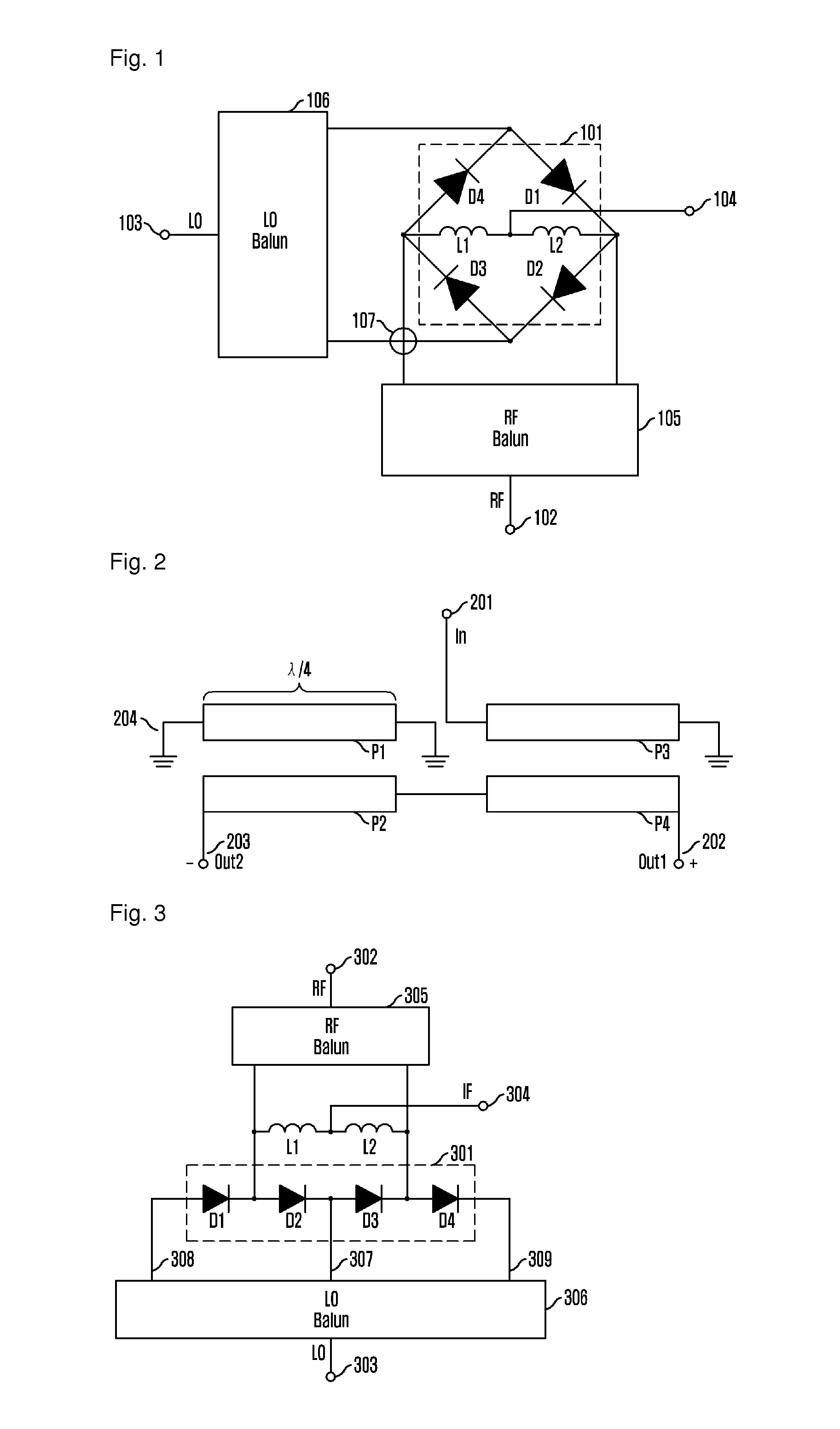
ActiveUS20060040637A1Improve conversion efficiencyImprove noise characteristicsModulation transference by diodesTransmissionEngineeringInductor
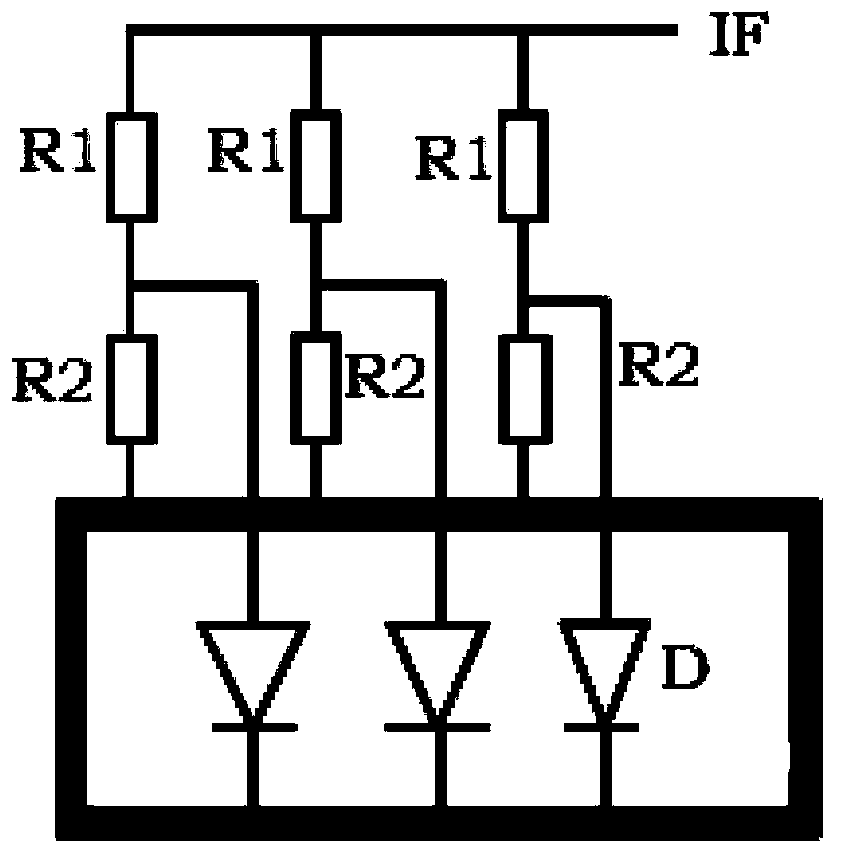
A diode mixer comprises a mixer diode section which has a first circuit including an inductor and a capacitor connected in series and a diode connected in parallel with the first circuit and which includes a first connecting portion to which one end of the first circuit and the anode of the diode are connected, and a second connecting portion to which the other end of the first inductor circuit and the cathode of the diode are connected; an LO signal port connected to the first connecting portion via a first branching circuit and receiving an LO signal; an IF signal port connected to the mixer diode section via a second branching circuit; and an RF signal port connected to the mixer diode section through a third branching circuit. The inductor and the capacitive component of the diode constitute a resonant circuit.
Owner:ARIGNA TECH LTD
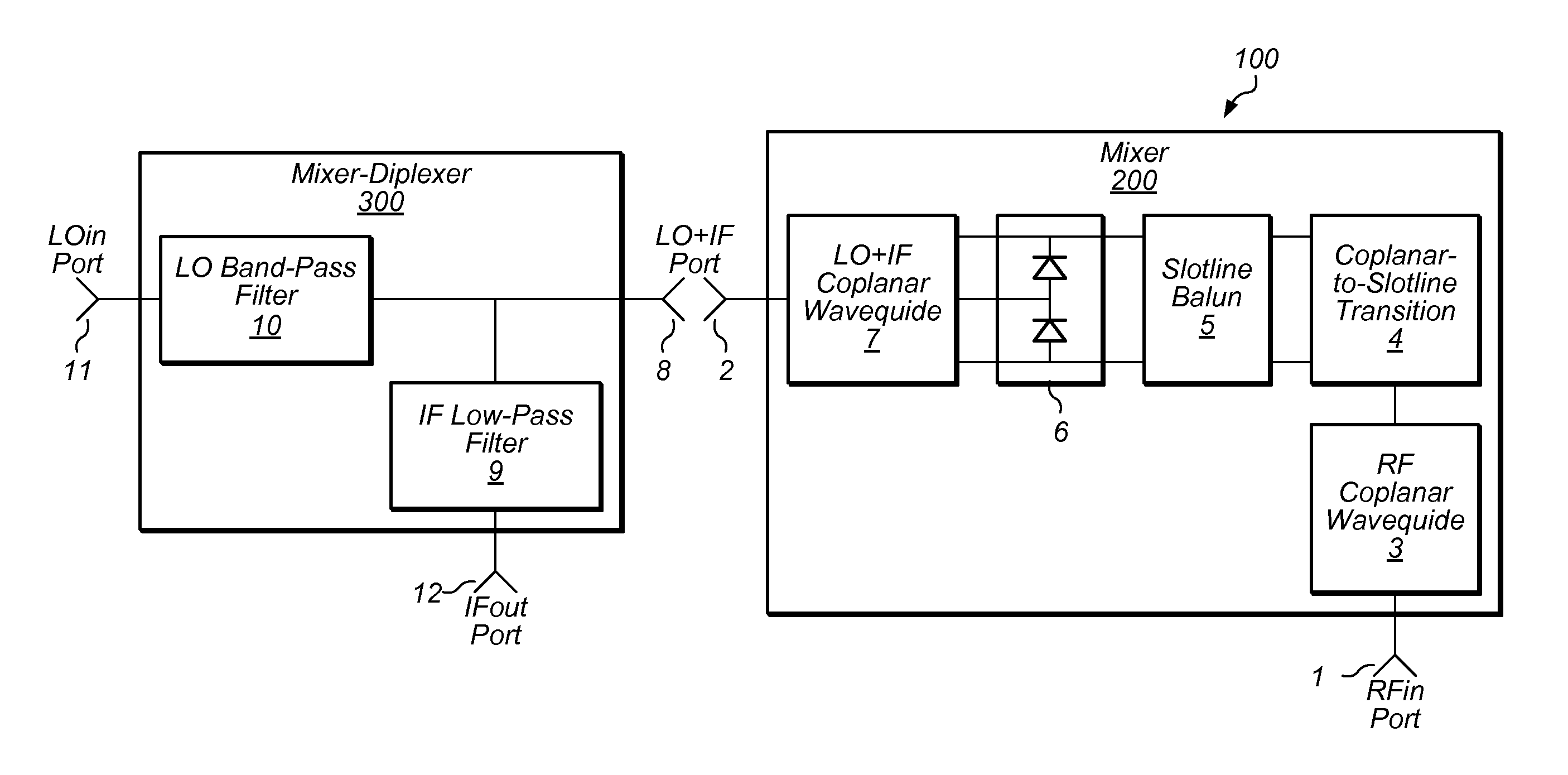
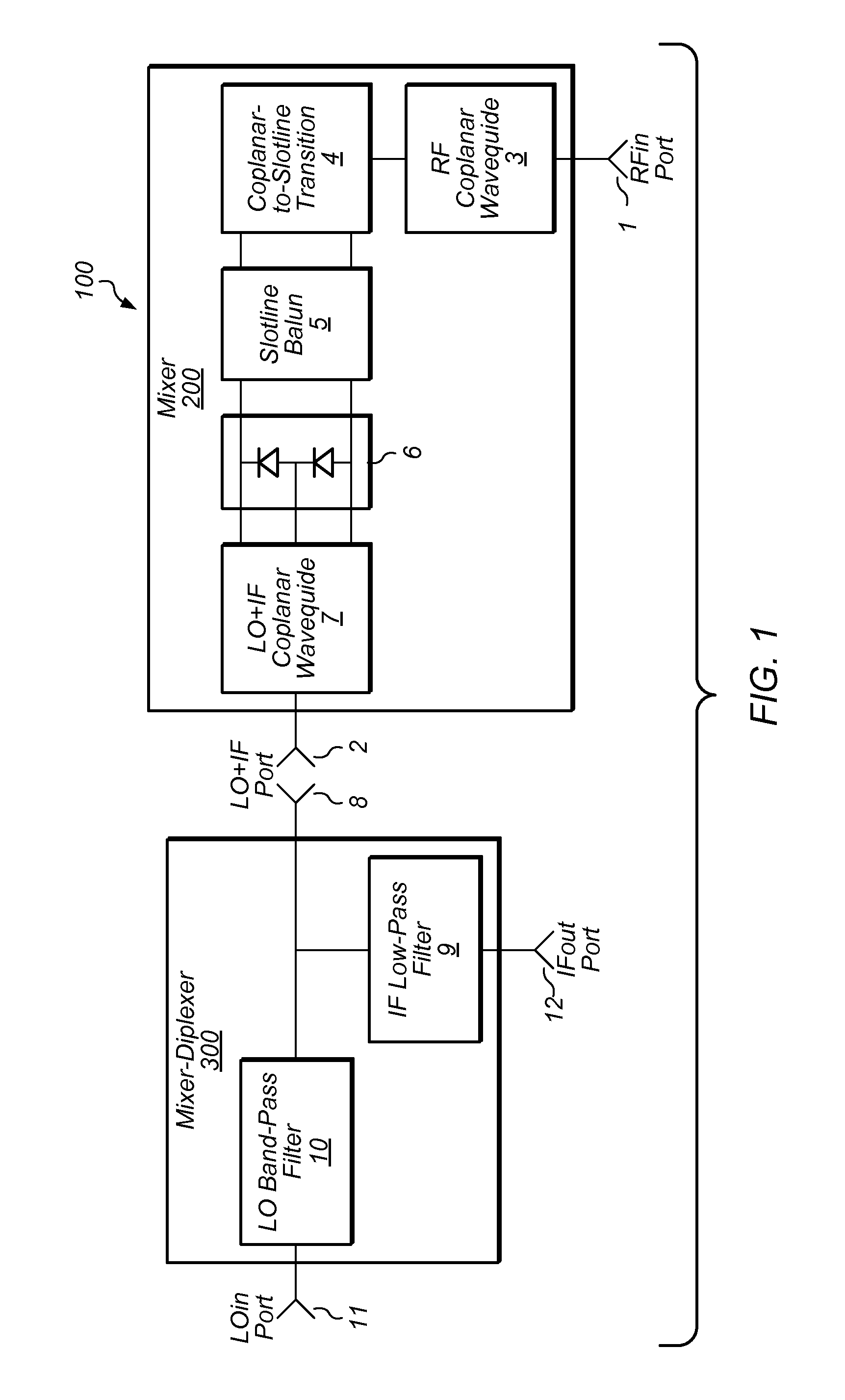
Ultra-Broadband Planar Millimeter-Wave Mixer with Multi-Octave IF Bandwidth
ActiveUS20140300430A1Low conversion lossImprove consistencyModulation transference by diodesTransmissionOctaveBaseband
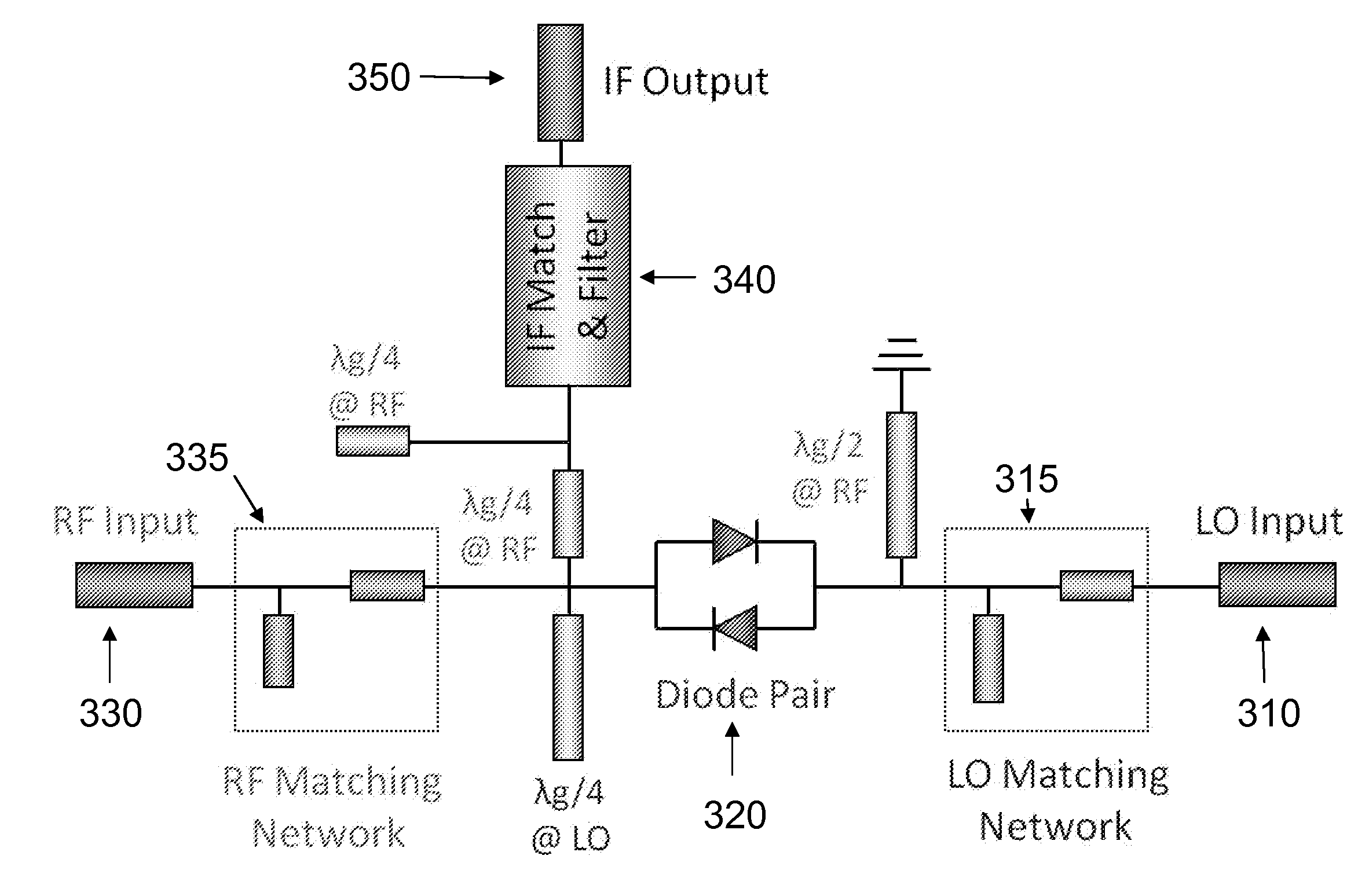
In some embodiments, a system may include a passive uniplanar single-balanced millimeter-wave mixer. In some embodiments, a three-port diode-tee IC forming a mixer core is coupled between an end of a slotline balun and a second coplanar balun. The operational bandwidth of a mixer structure is enhanced by optimizing the distance between the mixer diode-tee core and the back-short circuits. The frequency separation of LO and IF signals may be accomplished by means of stand-alone three-port filter-diplexer device. The system may allow wider than a frequency octave operational bandwidth for a frequency converter device all the way into millimeter wave frequencies at the same time as supporting the operational bandwidth for baseband IF signal over more than six frequency octaves. In some embodiments, the system may accomplish a 500 MHz to 34.5 GHz continuous IF bandwidth with RF signal sweeping from 33 GHz to 67 GHz and local oscillator at 67.5 GHz fixed frequency.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Micrometer wave and milimeter wave guartic harmonic mixer
InactiveCN1444309AImprove performanceLow costModulation transference by diodesAntennasLow-pass filterHarmonic mixer
A microwave and millimetric wave quartic frequency mixer is composed of a stopping direct coupler, two stage microstrip oper wires, a schottky reverse diode pair, two stage compact microphand resonance units, two microband high-low impedance line low pass filter. Since the used local frequency is 1 / 4 of the basic wave frequency mixer, its performance is increased greatly, and the compact microband resonance unit can either transfer the local signal and provide RF signal circuit or flexible adjust the idle terminal reactivity load, so as to suppress the idle frequency to reduce frequency conversion loss.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
W-band even-order sub-harmonic mixer
InactiveCN102611390ARaise the cutoff frequencyImprove loss performanceMultiple-port networksModulation transference by diodesLocal oscillator signalIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a W-band even-order sub-harmonic mixer, which comprises a radio-frequency broadband band-pass filter, an anti-parallel diode pair, a phase adjusting transmission line, a local oscillator low-pass filter and a duplexer, wherein one end of the local oscillator low-pass filter is connected with a common port of the duplexer while the other end of the local oscillator low-pass filter is connected with the phase adjusting transmission line, and the anti-parallel diode pair is bridged between the radio-frequency broadband band-pass filter and the phase adjusting transmission line. The W-band even-order sub-harmonic mixer realizes mutual isolation of radio-frequency signals, local oscillator signals and intermediate frequency signals by means of the radio-frequency broadband band-pass filter, the local oscillator low-pass filter and the duplexer, and the mixer can realize wide operation bandwidth as the radio-frequency broadband band-pass filter, the local oscillator low-pass filter and the duplexer have wide bandwidth.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Electrical circuit, apparatus and method for the demodulation of an intensity-modulated signal
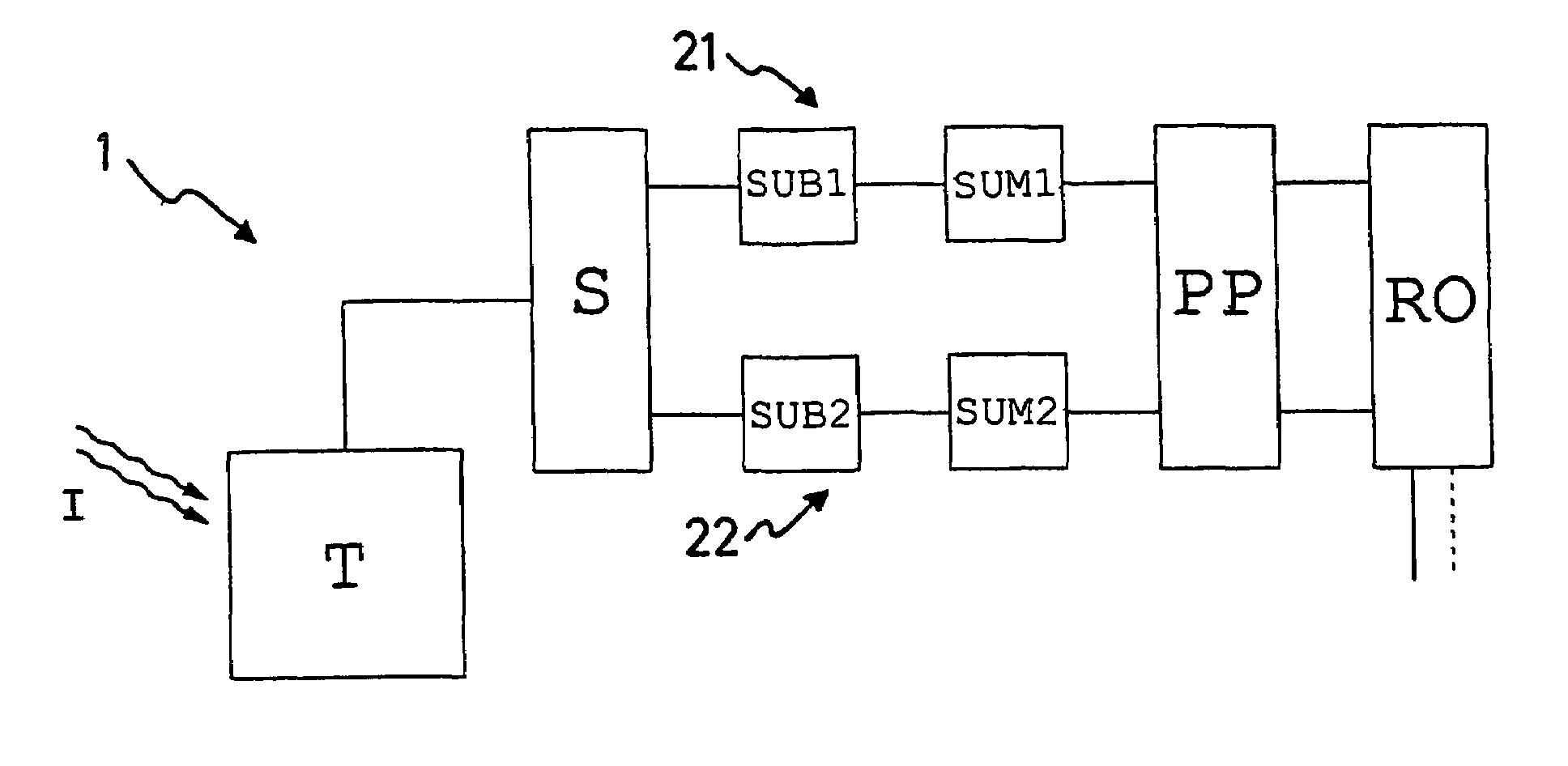
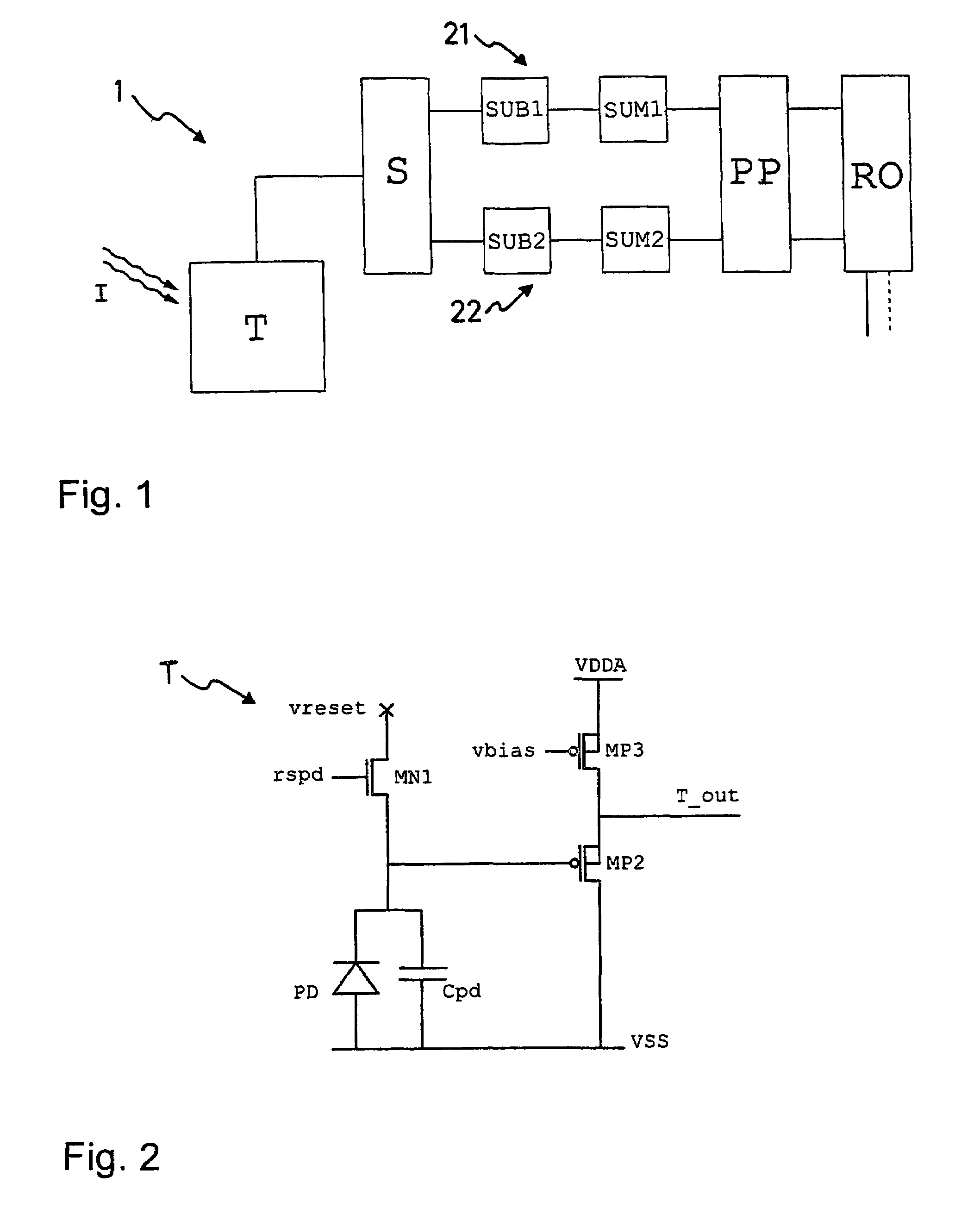
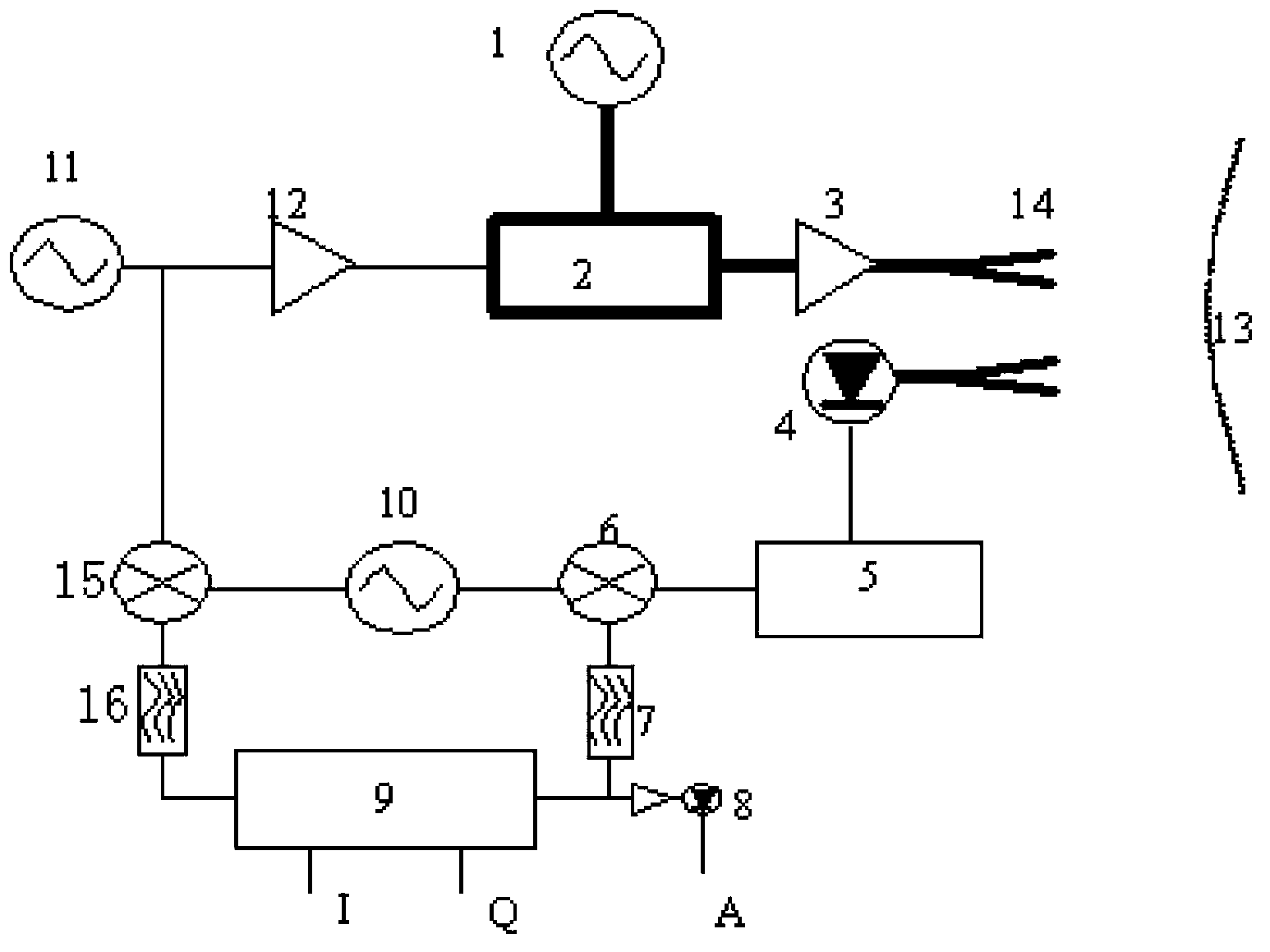
ActiveUS7595476B2Small sizeReduce power consumptionRadiation pyrometryModulation transference by diodesOptical radiationTime shifting
A modulated optical radiation field (I) whose modulation amplitude and temporal phase depend on the local position can be detected with a plurality of pixels 1. Each pixel 1 consists of a transducing stage (T) that converts incoming light (I) into a proportional electric signal, a sampling stage (S), two subtraction / summation stages (SUB1, SUM1; SUB2, SUM2), and an output stage. Each pixel can be addressed individually. The optical radiation field (I) is locally sensed and sampled at a frequency that is four times the wavefield's modulation frequency. The subtraction / summation stages (SUB1, SUM1; SUB2, SUM2) accumulate differences of two samples per modulation period, separated by half the period, during several averaging periods; the two stages are time shifted with respect to each other by a quarter period. The resulting two output signals are employed for the determination of the local envelope amplitude and the temporal phase. These pixels 1 can be realized with circuits that consume very little electric power require small areas, enabling the realization of large numbers of pixels in linear or two-dimensional array sensors.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
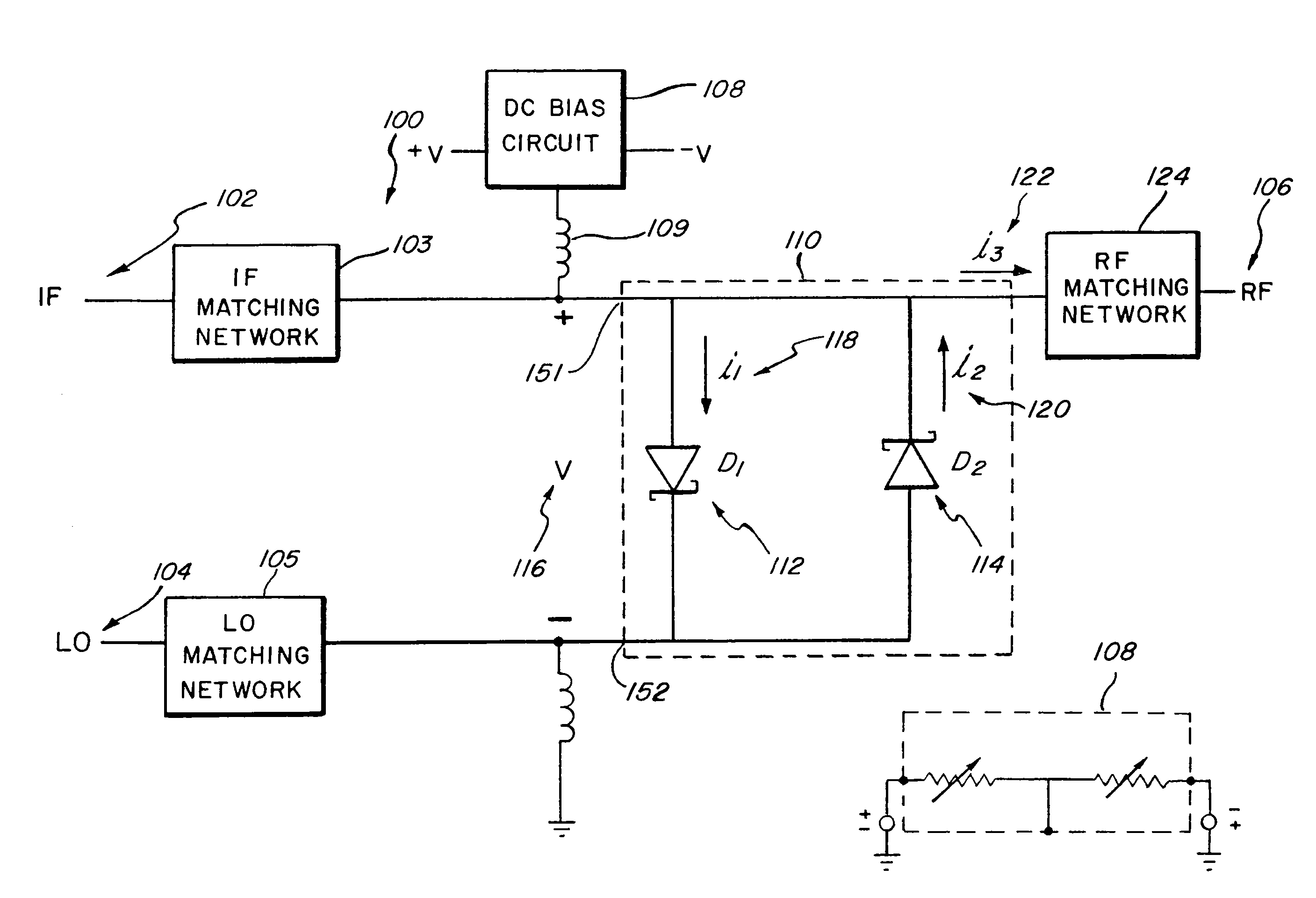
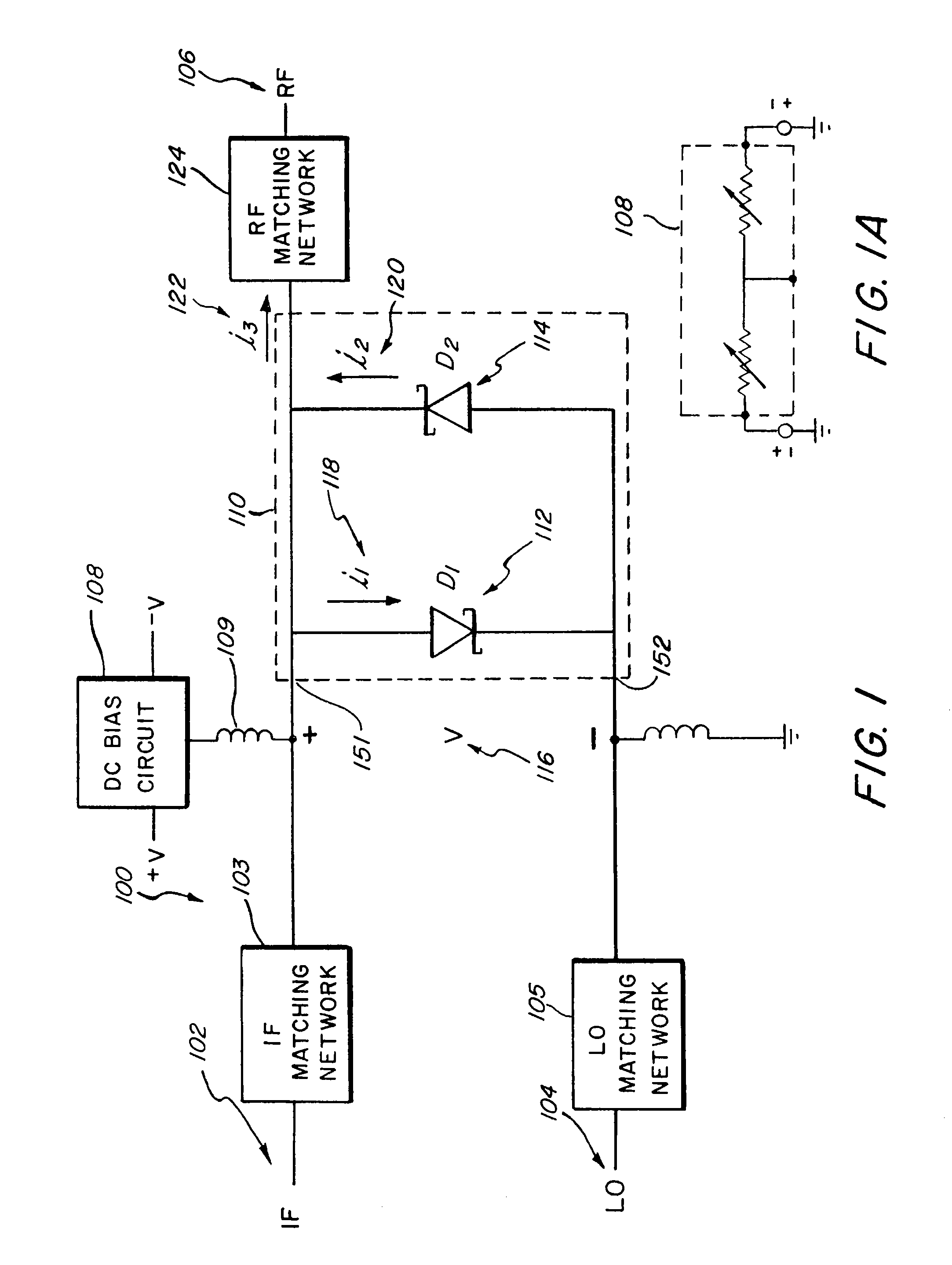
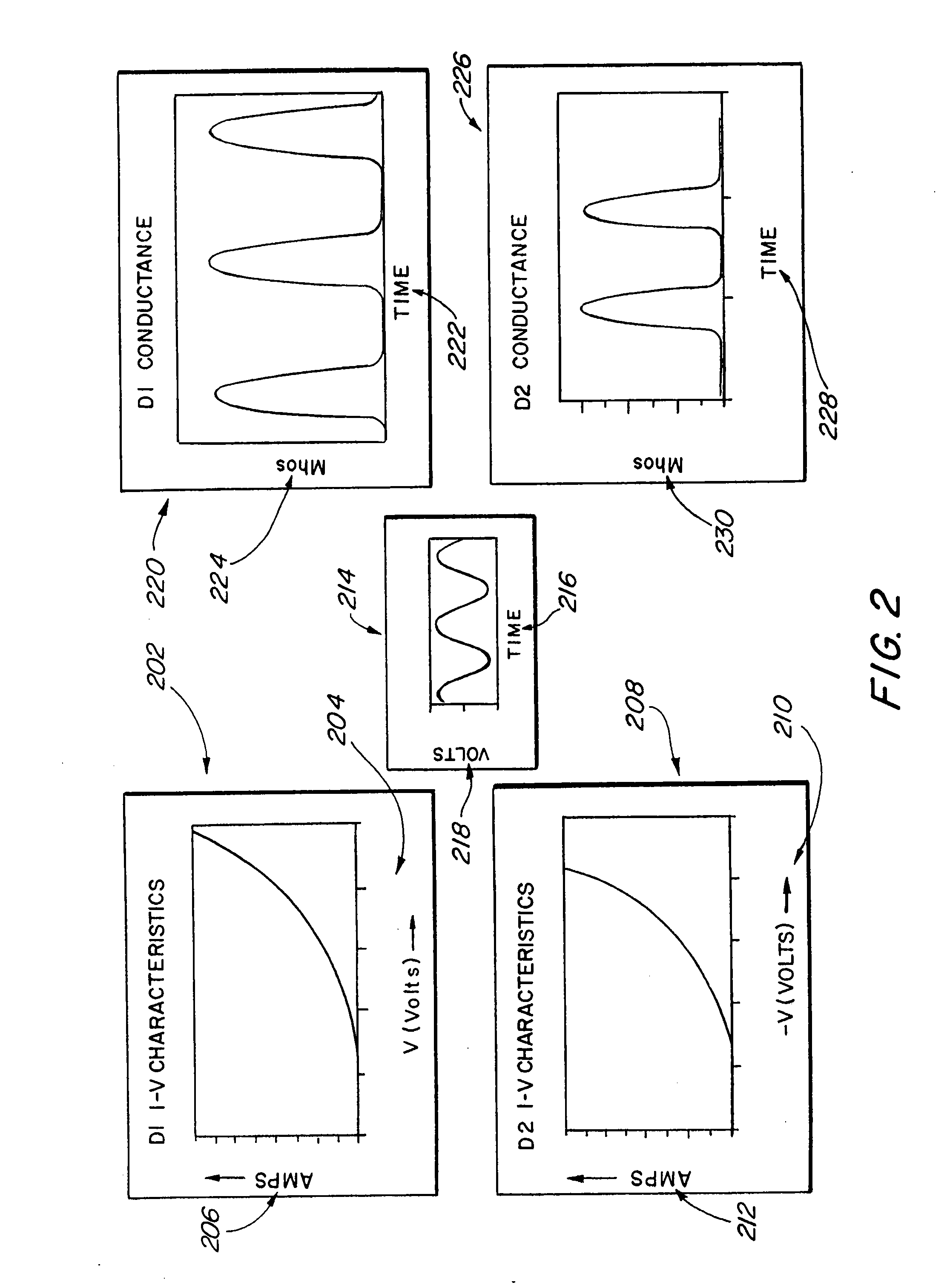
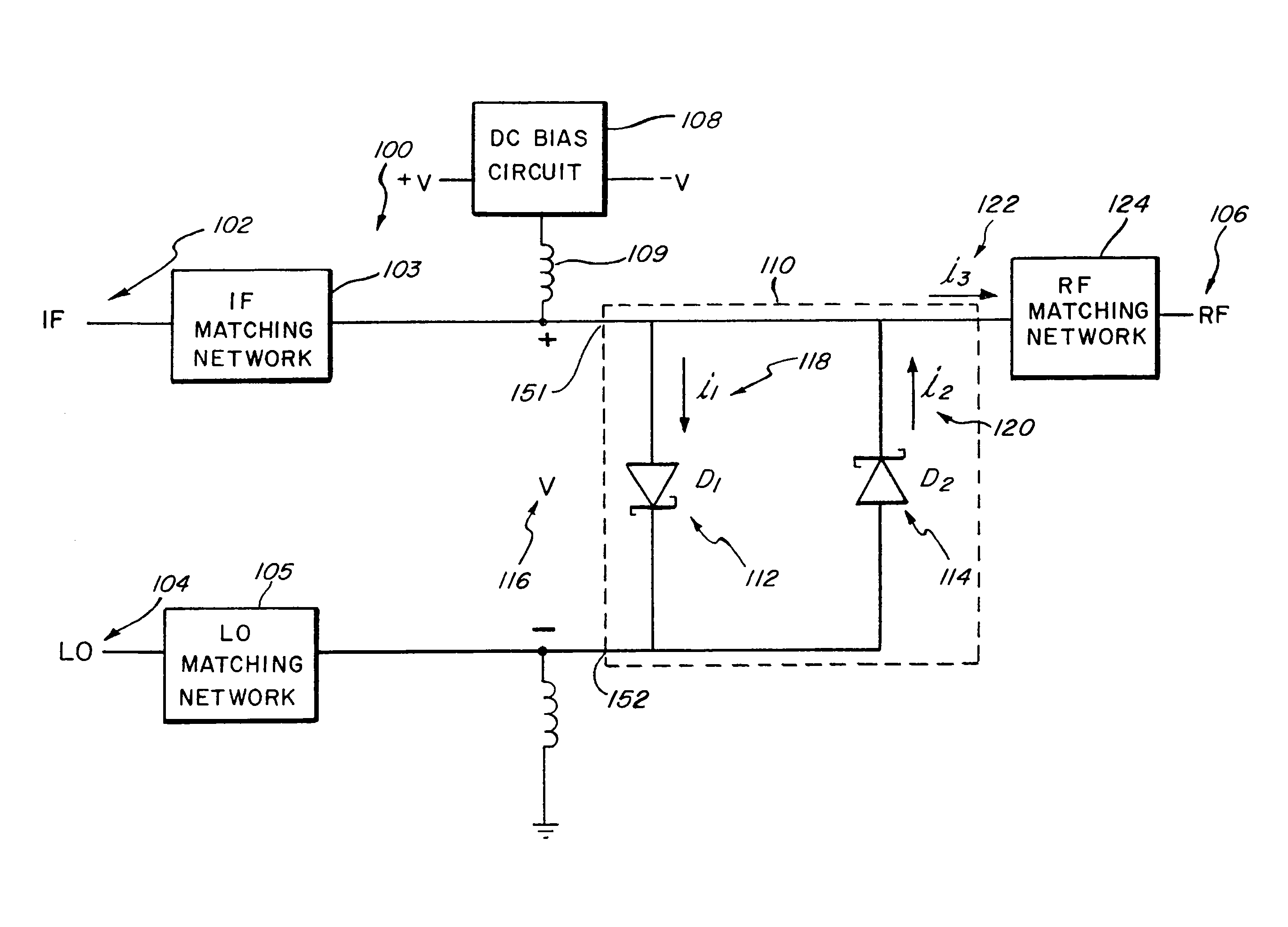
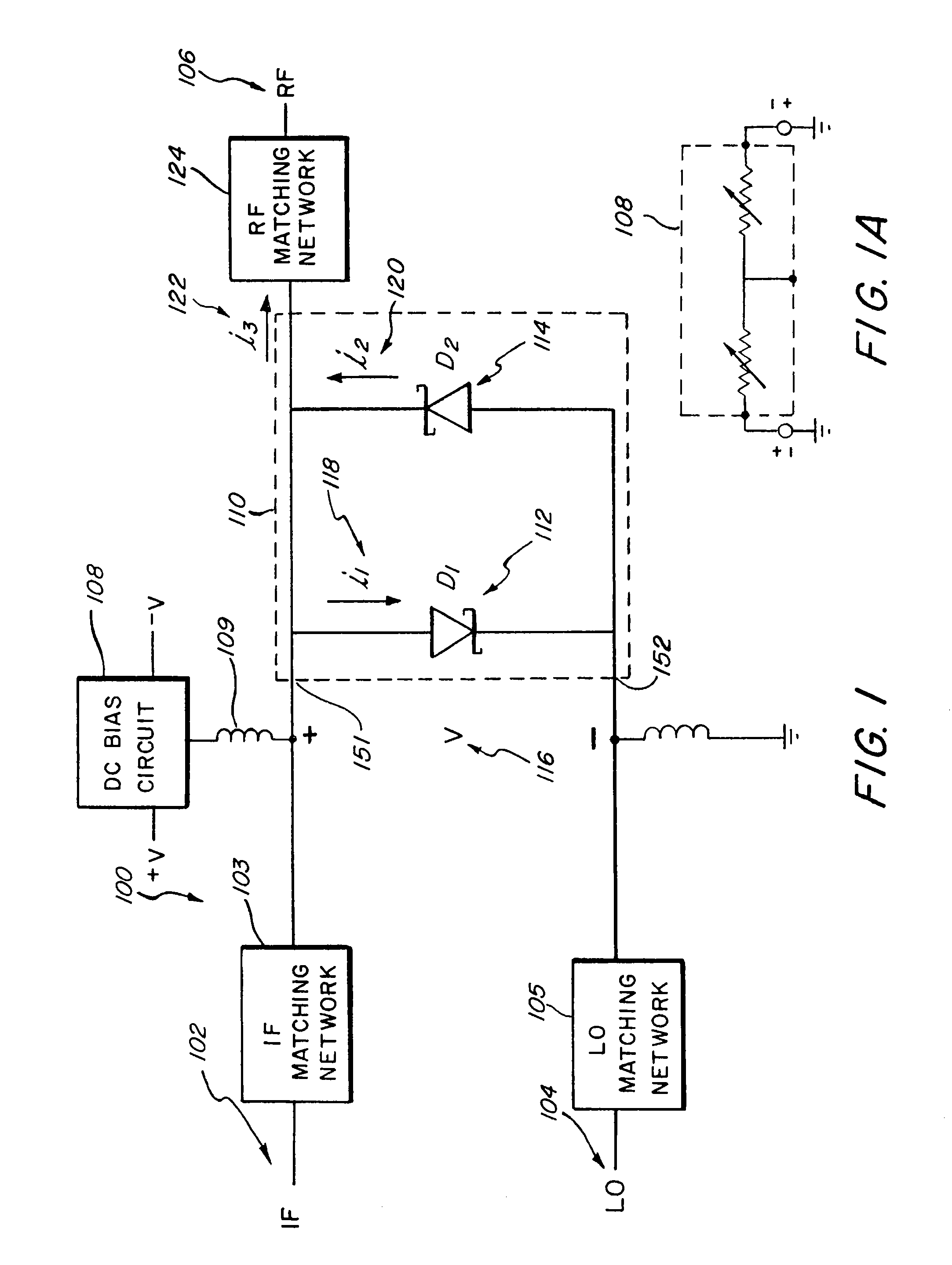
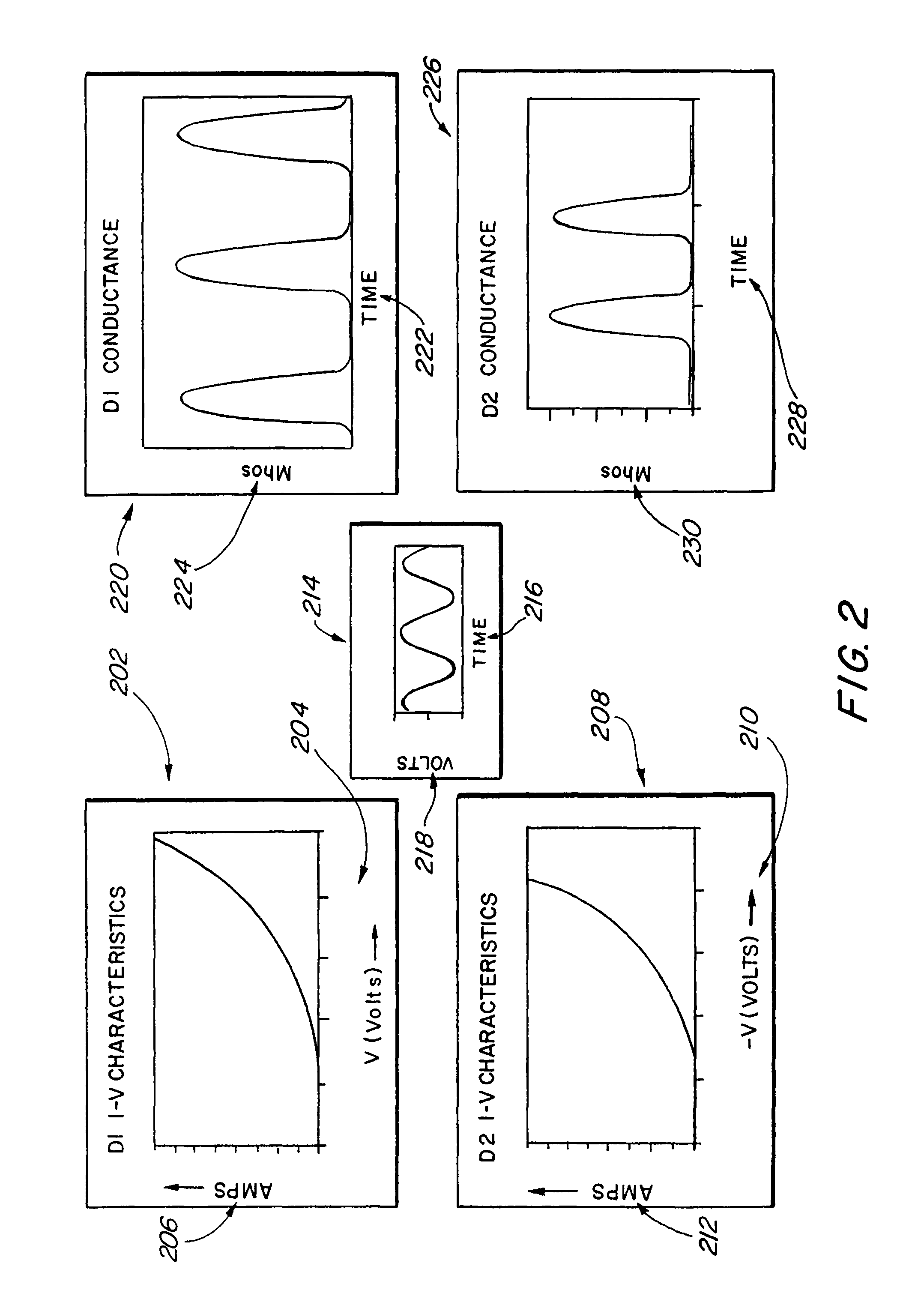
Systems, devices, and methods for suppressing frequency spurs in mixers
ActiveUS20090149150A1Reduce leakageModulation transference by diodesSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionCapacitanceFrequency mixer
Systems, devices and methods are disclosed for suppressing the 2LO frequency spur, output from a mixer. In various exemplary embodiments, a DC bias circuit is electrically connected to provide DC bias to one or more non-linear elements of the mixer. The biasing voltage is used to cause the current-voltage characteristics and / or junction capacitances between non-linear elements to be more symmetric and / or to suppress 2LO leakage currents that form 2LO frequency spurs at the output of the mixer. The non-linear elements may comprise one of: BJT's, diodes, and FET's. The mixer may be one of: a subharmonic mixer; a fundamental resistive mixer; a fundamental subharmonic transconductance mixer; and a fundamental transconductance mixer comprising an anti-parallel diode pair. The system may further be configured to automatically determine an appropriate DC bias voltage level that will improve one of the LO-IF isolation and the LO-RF isolation.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Pulse modulation circuitry
InactiveUS20070072573A1Raise the ratioModulation transference by diodesAngle modulationEngineeringRadio frequency
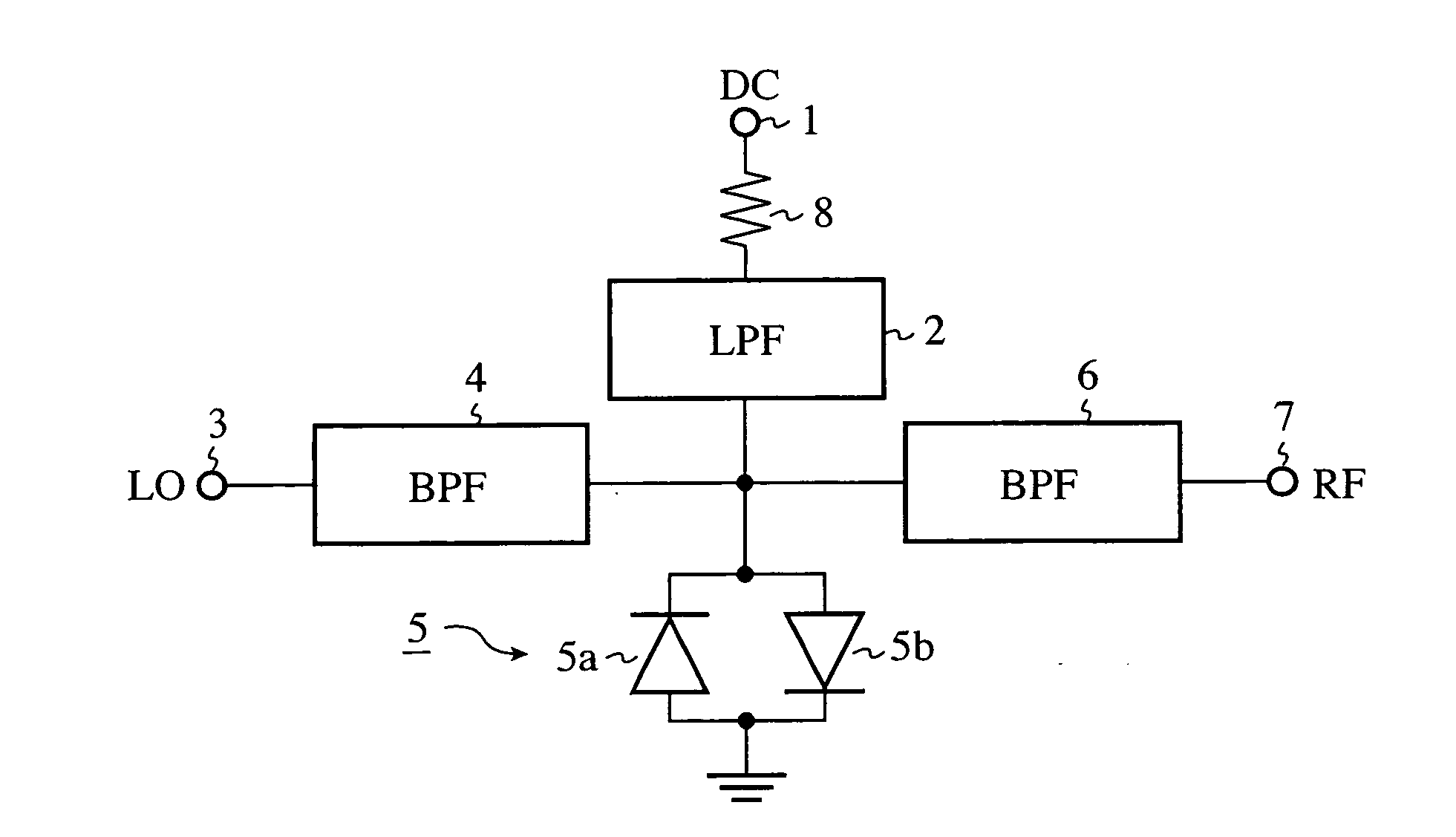
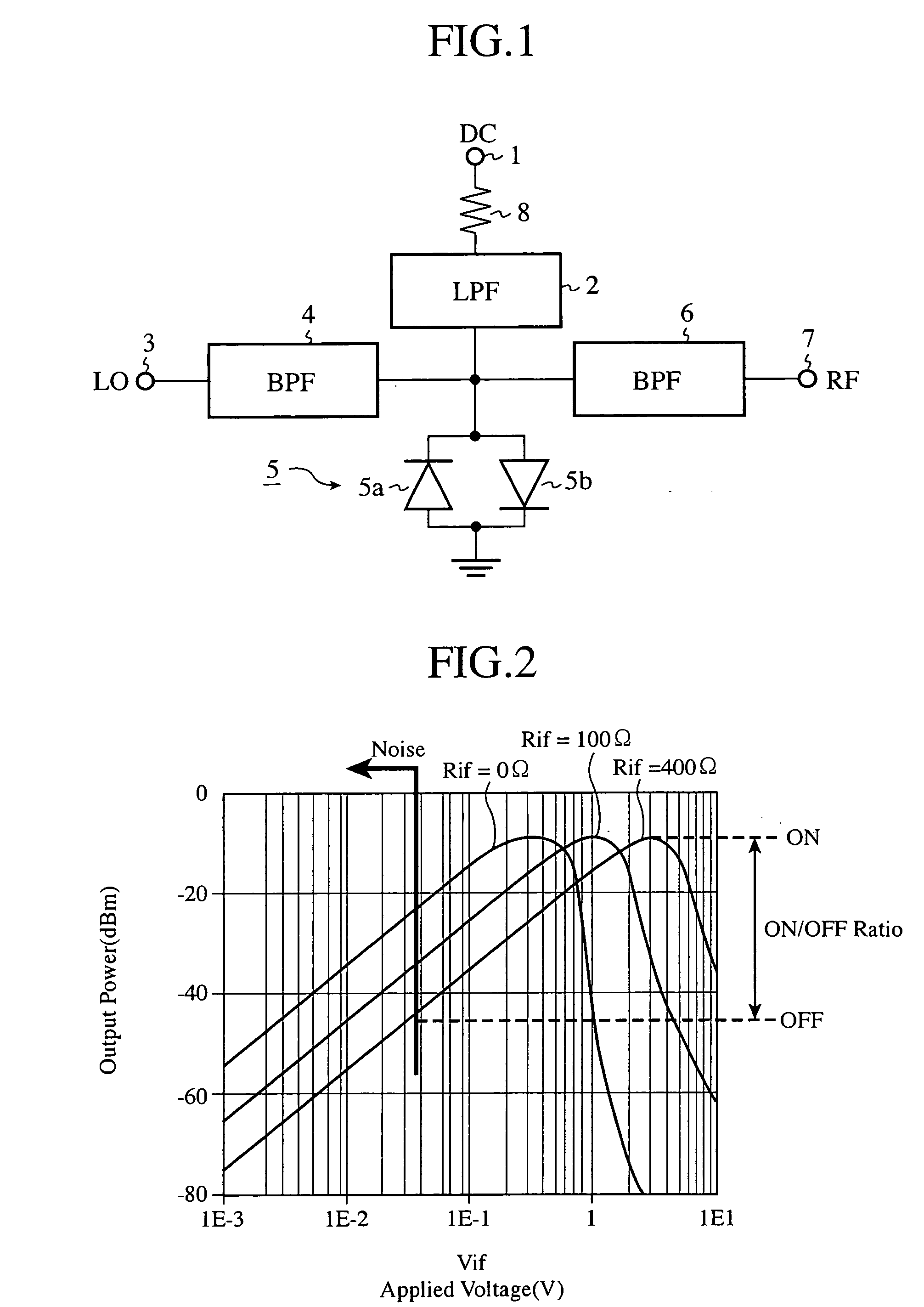
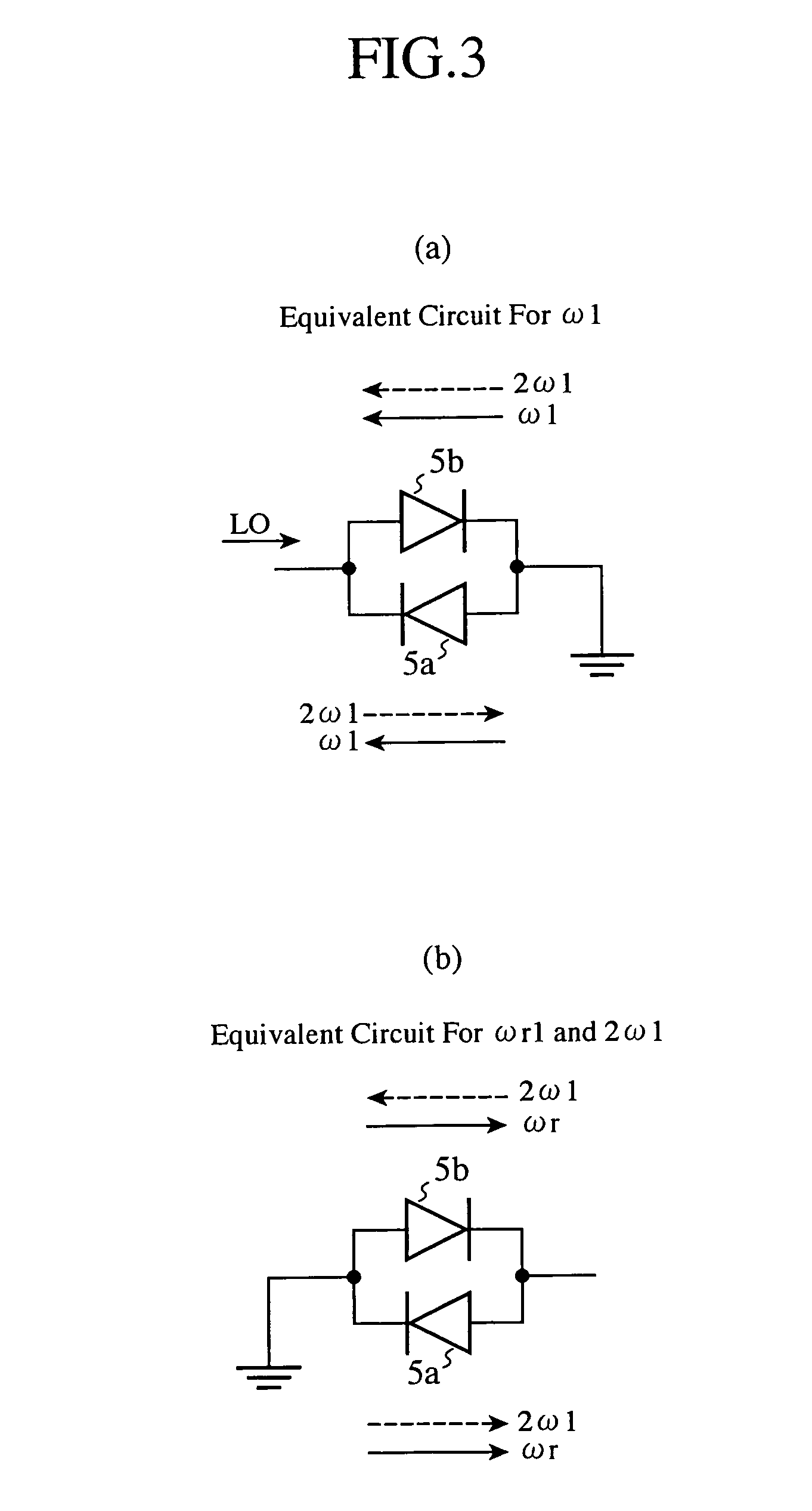
A resistor 8 for dividing a voltage applied to an anti-parallel diode pair 5 for mixing a DC pulsed signal and a local oscillation signal LO is disposed in pulse modulation circuitry. Therefore, the ratio of the output power of an RF pulsed signal outputted to an RF pulse output terminal 7 at the time of the ON state and the output power at the time of the OFF state can be increased.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
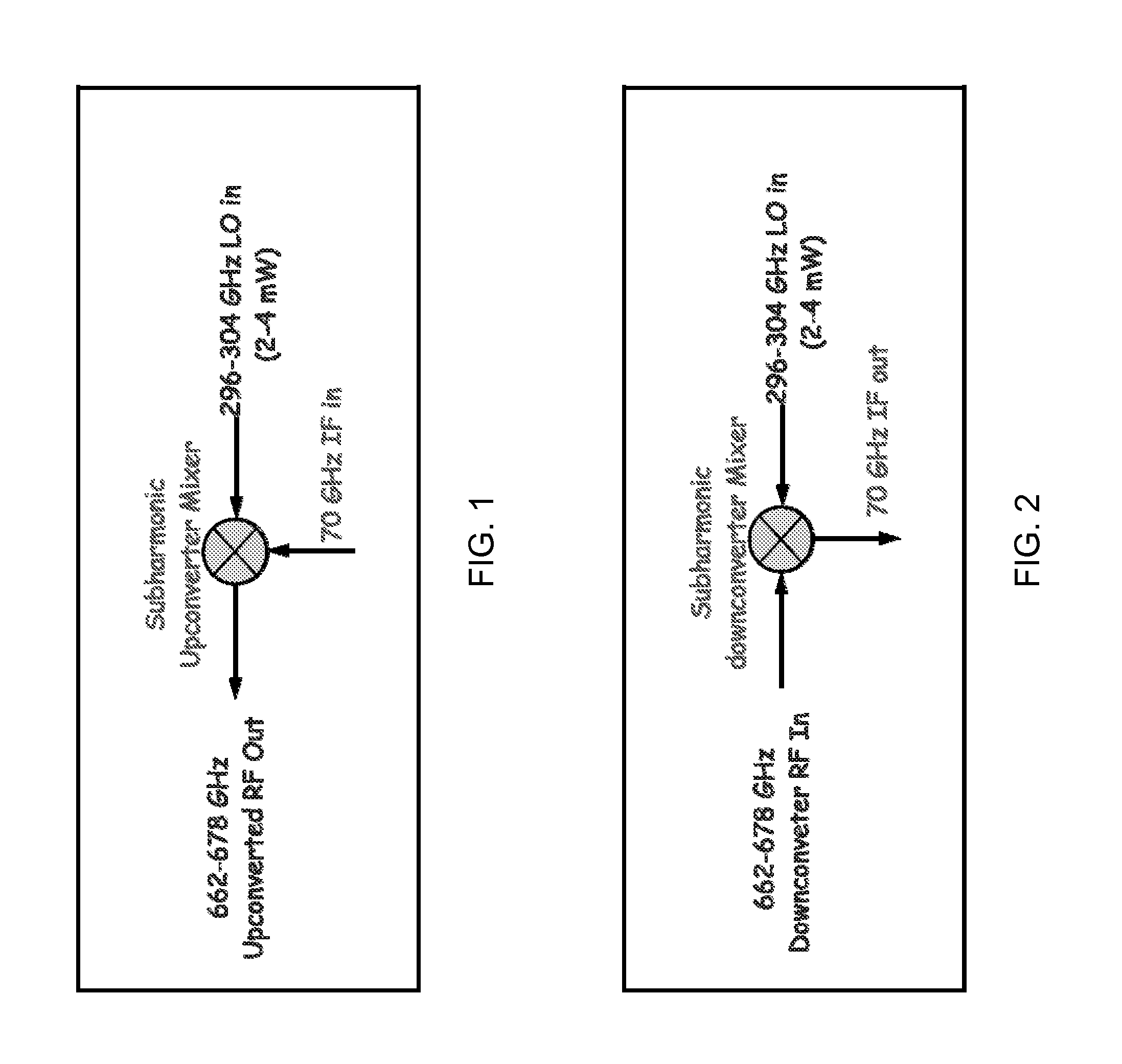
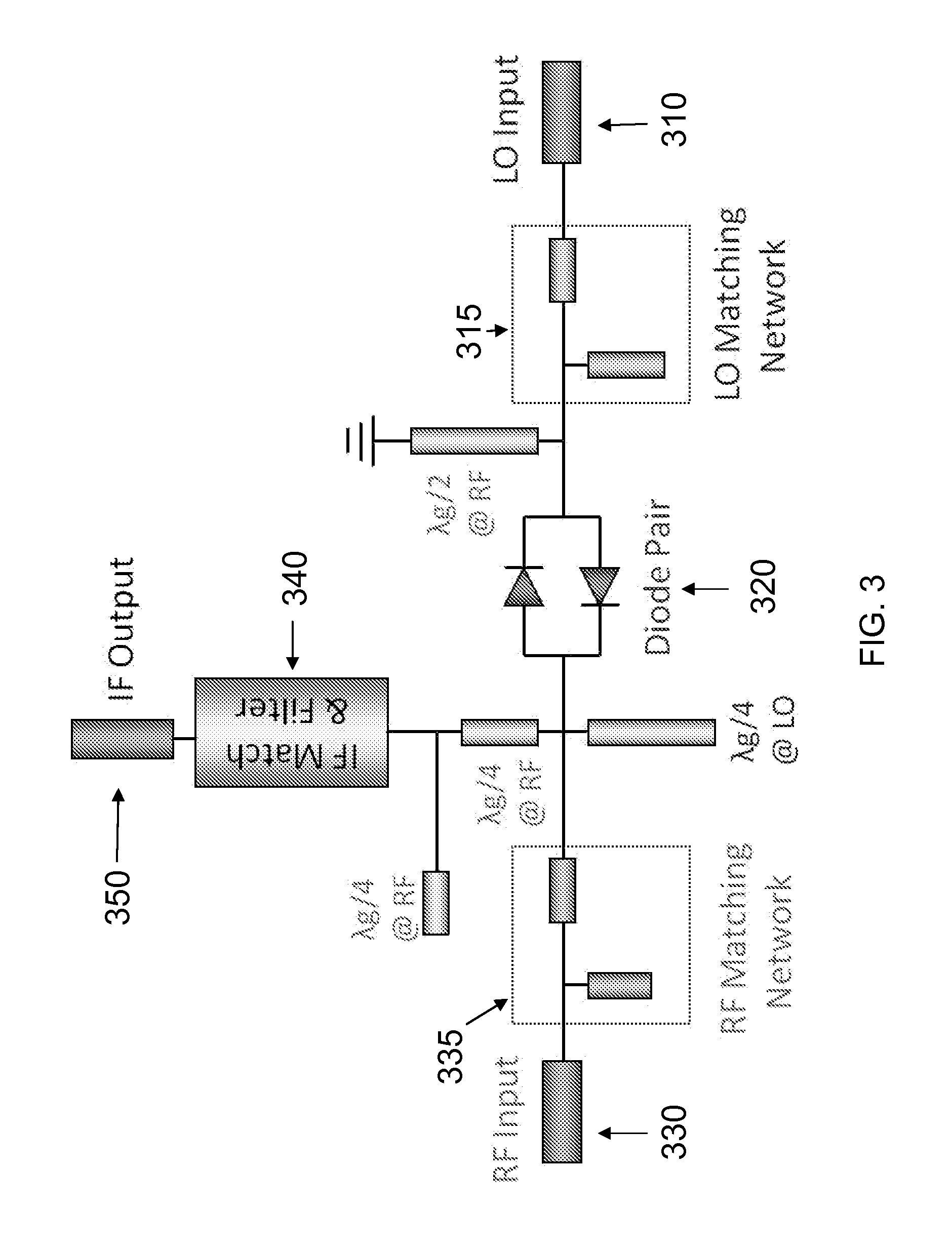
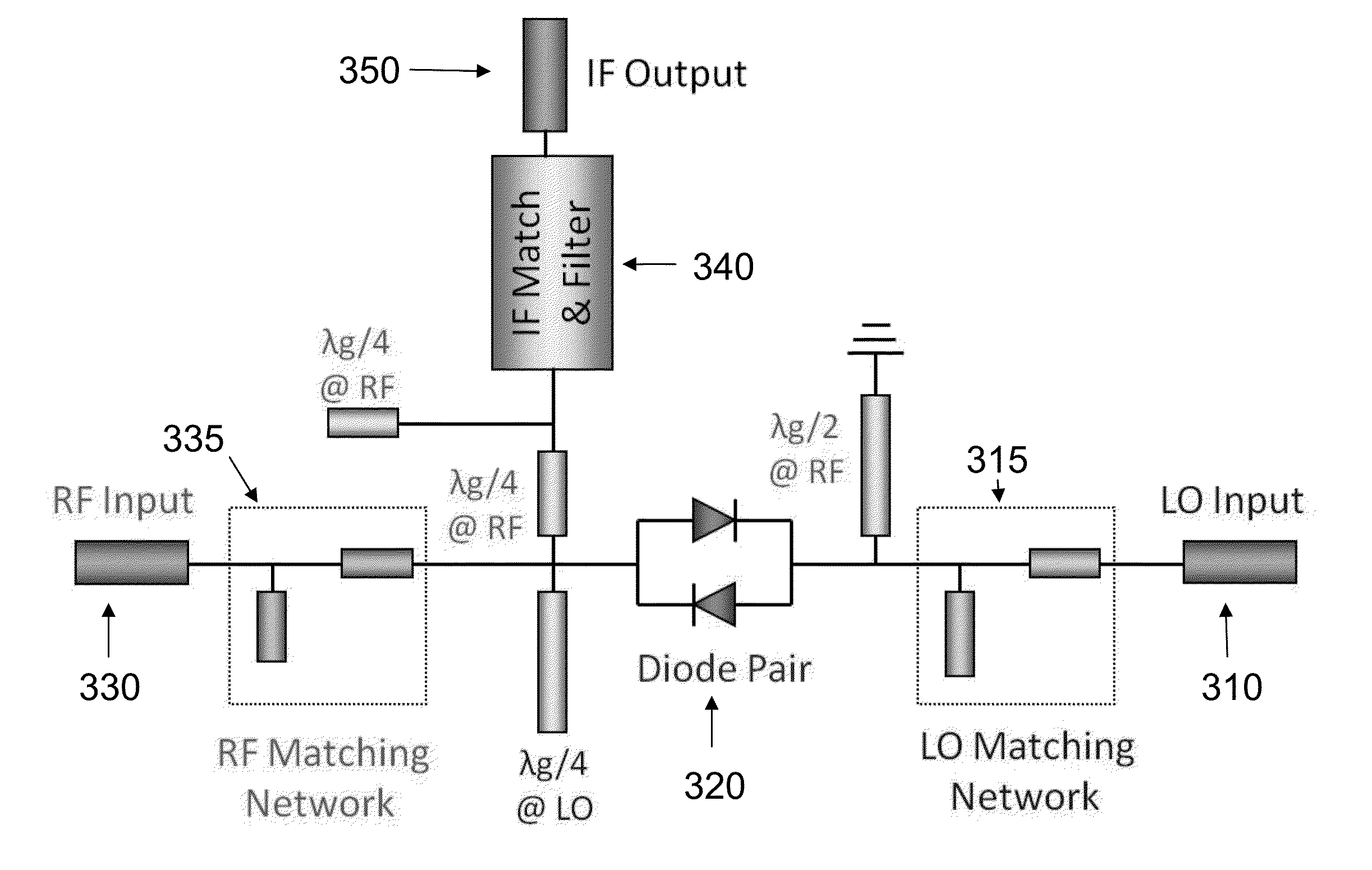
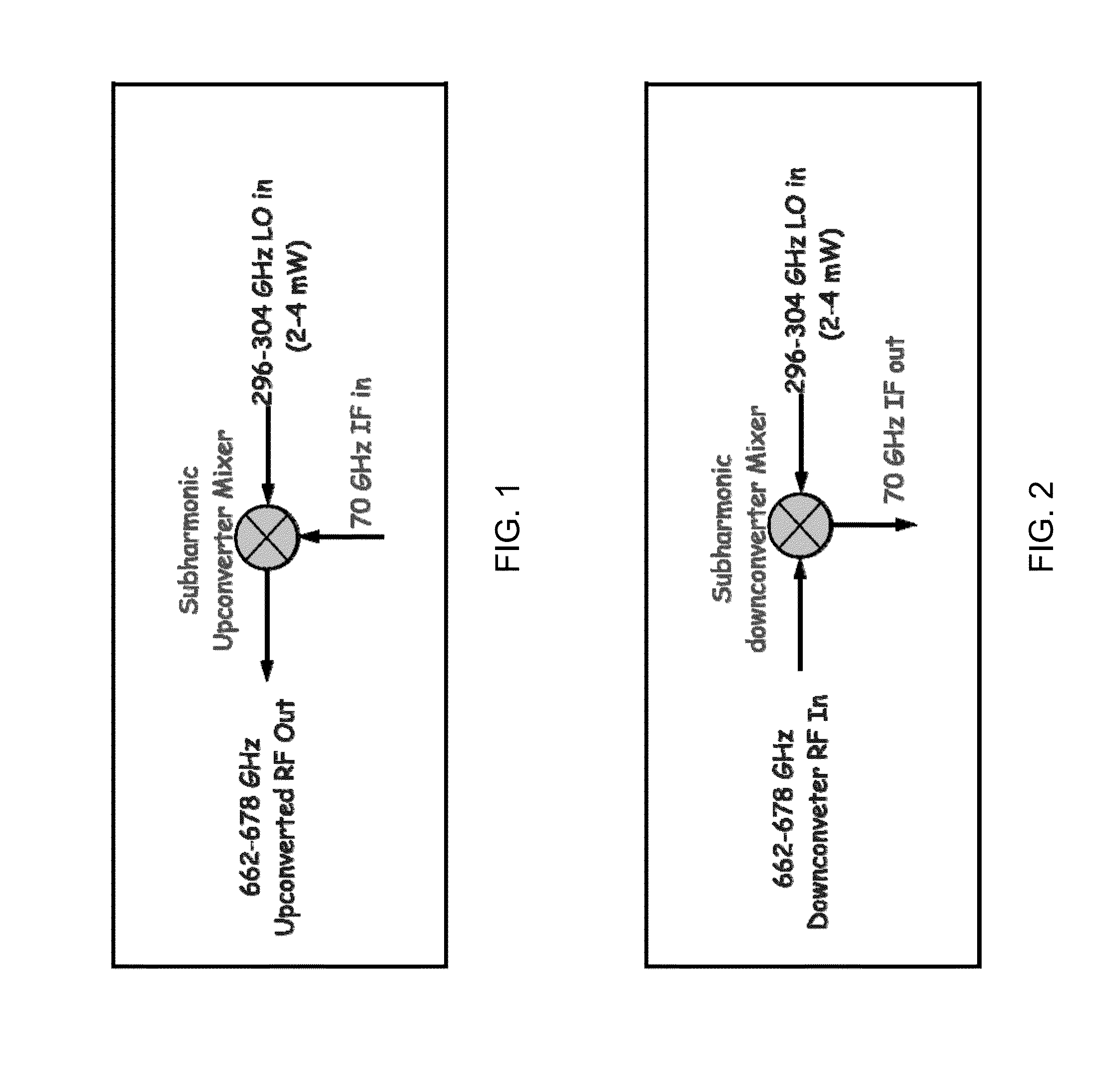
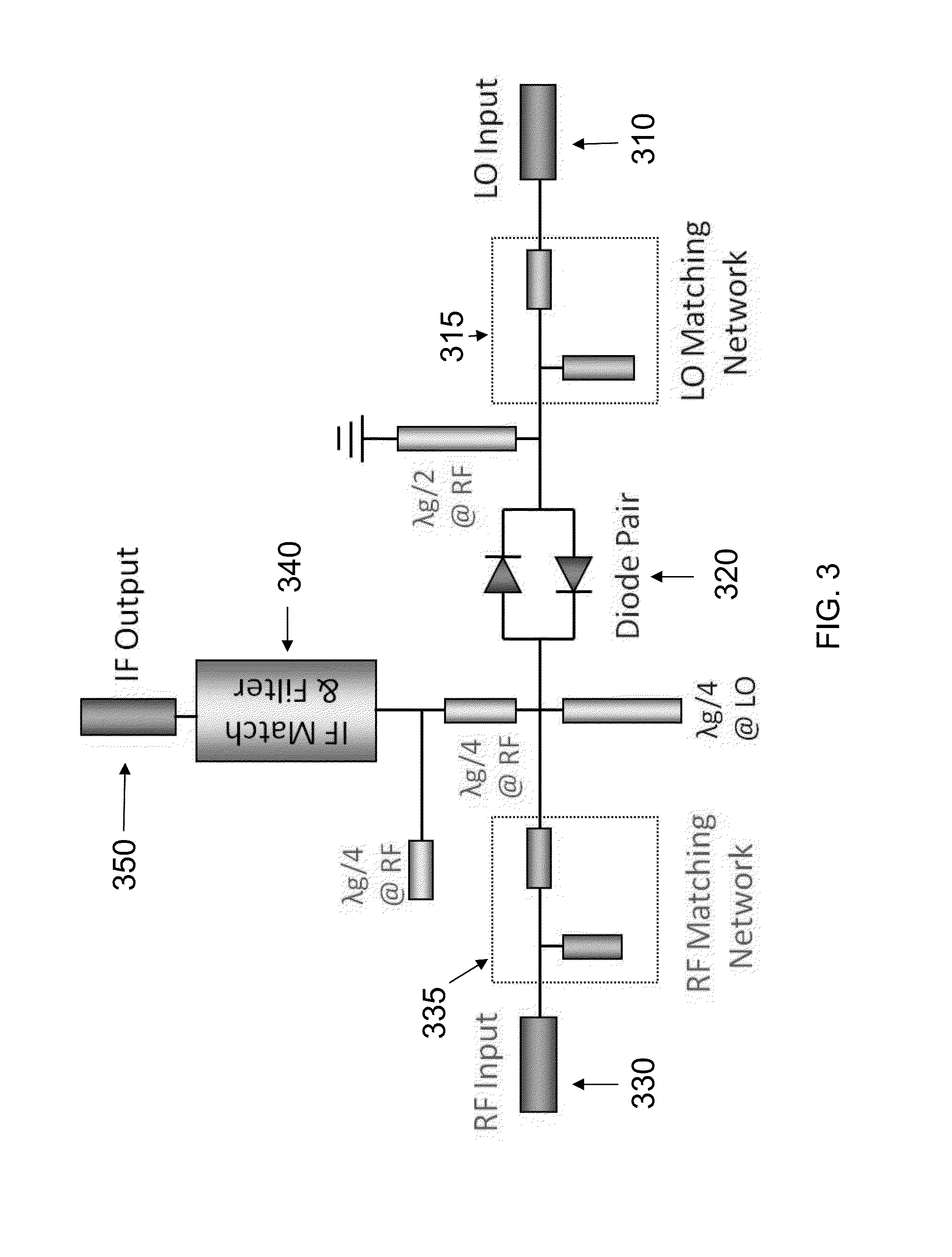
670 ghz schottky diode based subharmonic mixer with cpw circuits and 70 ghz if
ActiveUS20120280742A1Modulation transference by diodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBandpass filteringFrequency mixer
A coplanar waveguide (CPW) based subharmonic mixer working at 670 GHz using GaAs Schottky diodes. One example of the mixer has a LO input, an RF input and an IF output. Another possible mixer has a LO input, and IF input and an RF output. Each input or output is connected to a coplanar waveguide with a matching network. A pair of antiparallel diodes provides a signal at twice the LO frequency, which is then mixed with a second signal to provide signals having sum and difference frequencies. The output signal of interest is received after passing through a bandpass filter tuned to the frequency range of interest.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Double balanced mixer
ActiveUS9780728B1Good conversion gainIncrease valueTransistorMultiple-port networksBalanced mixerSignal on
A FET based double balanced mixer (DBM) that exhibits good conversion gain and IIP3 values and provides improved linearity and wide bandwidth. In one embodiment, a first balun is configured to receive a local oscillator (LO) signal and generate two balanced LO signals that are coupled to two corresponding opposing nodes of a four-node FET ring. A second balun is configured to pass an RF signal on the unbalanced side. The FET ring includes at least four FETs connected as branches of a ring, with the source of each FET connected to the drain of a next FET in the ring. Each FET is preferably fabricated as, or configured as, a low threshold voltage device having its gate connected to its drain, which causes the FET to operate as a diode, but with the unique characteristic of having close to a zero turn-on voltage.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Improved sub-harmonic mixer based on coplanar waveguide transmission line
ActiveCN104660171AHigh precisionReduce the difficulty of assemblyModulation transference by diodesIntermediate frequencyLow-pass filter
The invention discloses an improved sub-harmonic mixer based on a coplanar waveguide transmission line. The improved sub-harmonic mixer is characterized in that a dielectric substrate is arranged on the inner bottom surface of a main air chamber; a coupling probe, the coplanar waveguide transmission line, a local oscillator matching line and a micro-strip line structure are arranged on the dielectric substrate; the coplanar waveguide transmission line comprises a matching line, a first horizontal transmission line and a local oscillator low-pass filter matching line which are connected in sequence from left to right; the micro-strip line structure comprises a second horizontal transmission line, a third horizontal transmission line, a fourth horizontal transmission line and an intermediate-frequency low-pass filter matching line which are connected in sequence from left to right; the coplanar waveguide transmission line further comprises two grounding lines respectively positioned on the two sides of the matching line; the two grounding lines are connected with the inner wall of the main chamber. The improved sub-harmonic mixer further comprises planar Schottky anti-parallel mixer diodes, wherein an ohmic contact layer of one of the mixer diodes is connected with the front surface, far away from the dielectric substrate, of the matching line, and an ohmic contact layer of the other mixer diode is connected with the front surface, far away from the dielectric substrate, of the grounding line.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Broadband amplitude modulation millimeter wave reflection system based on waveguide modulation technology
InactiveCN103532492AReduce lossLow costModulation transference by diodesPulse automatic controlDiscriminatorBandpass filtering
The invention belongs to the technical field of nuclear fusion plasma microwave diagnosis and in particular relates to a broadband low-loss high-frequency microwave modulator based on a rectangular waveguide and a broadband amplitude modulation millimeter wave reflection system based on the waveguide modulator. A quartz crystal oscillator B is connected with a power amplifier; the power amplifier is connected with an intermediate frequency input end of the waveguide modulator; a microwave source is connected with a microwave input end of the waveguide modulator; the waveguide modulator is connected with a microwave amplifier; the microwave amplifier is connected with a horn antenna; a microwave detector is connected with a frequency-selecting amplifier; the frequency-selecting amplifier is connected with a down converter A; the quartz crystal oscillator B is also connected with a down converter B; a quartz crystal oscillator A is respectively connected with the down converter A and the down converter B; the down converter A is connected with a band-pass filter A; the band-pass filter A is connected with a phase discriminator; the down converter B is connected with a band-pass filter B; the band-pass filter B is connected with the phase discriminator. According to the system, low-loss ultrahigh-frequency microwave amplitude modulation can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
Mixer and converter using same
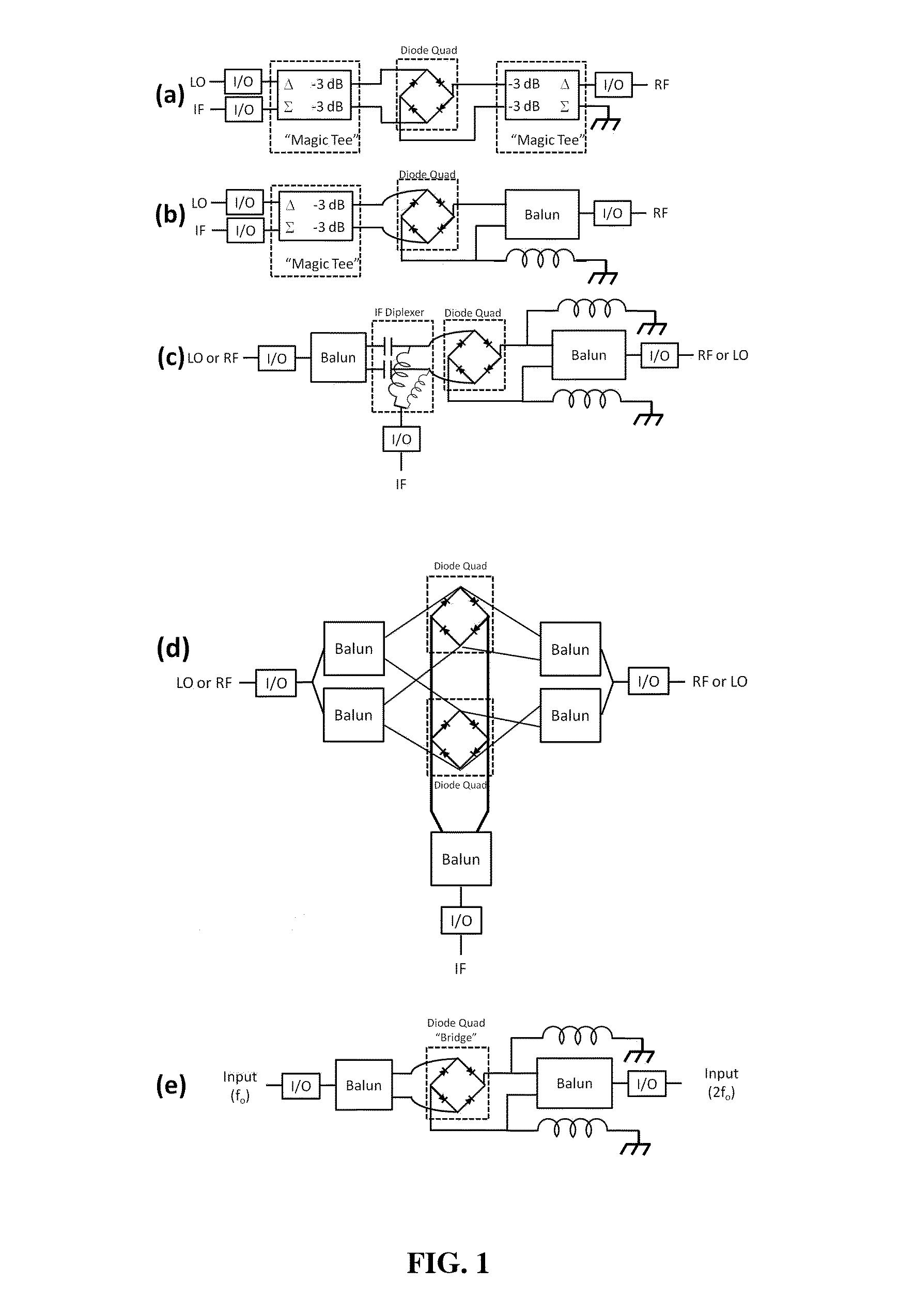
InactiveUS20020126019A1Prevents degradation of its characteristicLoss in the mixer is greatly decreasedModulation transference by diodesModulation transference by distributed inductance and capacitanceBalanced mixerFrequency mixer
A mixer, which is a single balanced mixer, includes an LO port for inputting an LO signal, an RF port for inputting an RF signal, an IF port for outputting an IF signal, a balun for converting an unbalanced signal into a balanced signal, and a pair of mixer diodes connected in series. The mixer further includes a high-pass filter for blocking LO and IF signals and passing an RF signal and a low-pass filter for blocking LO and RF signals and passing an IF signal.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Mixer fabrication technique and system using the same
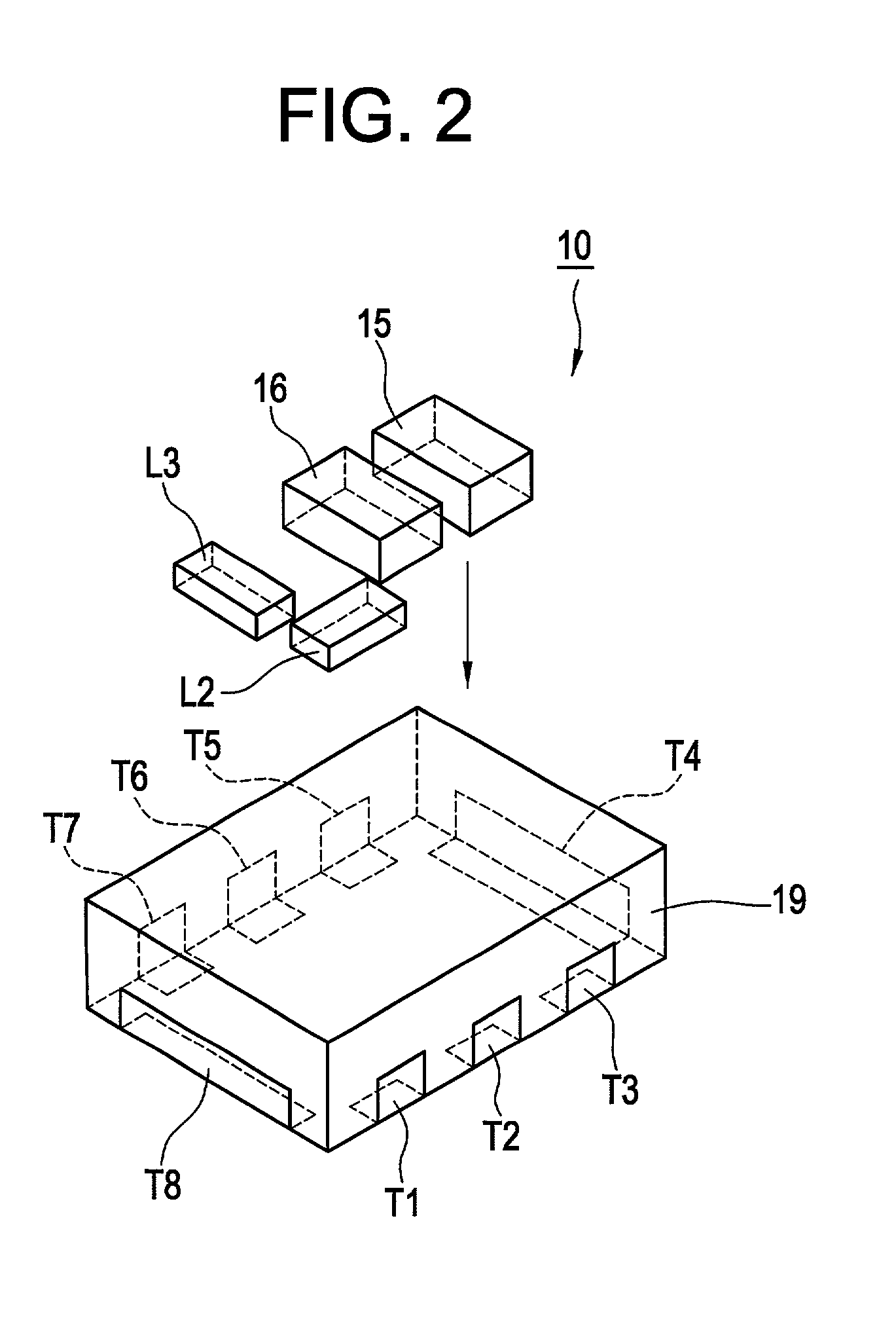
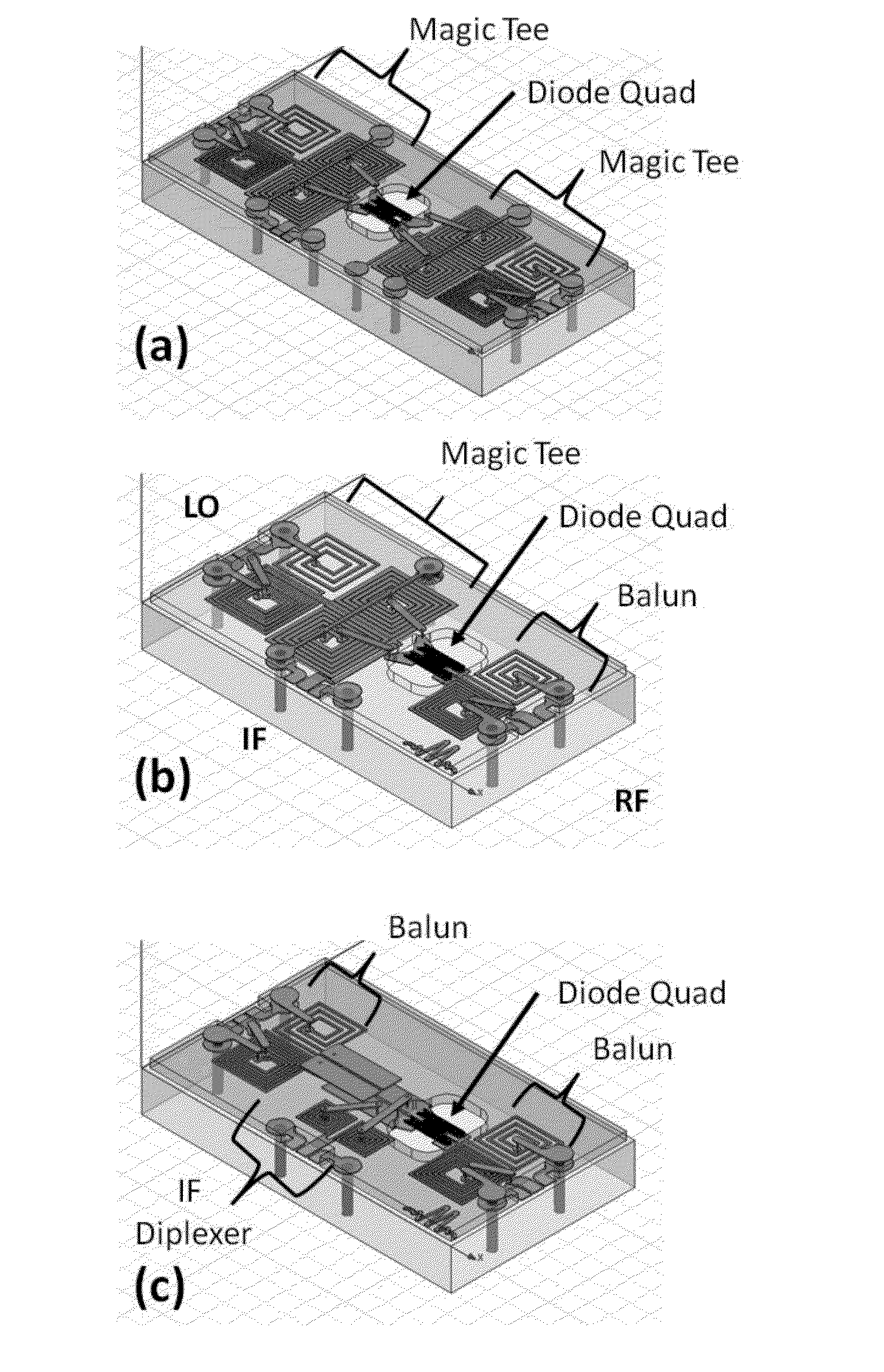
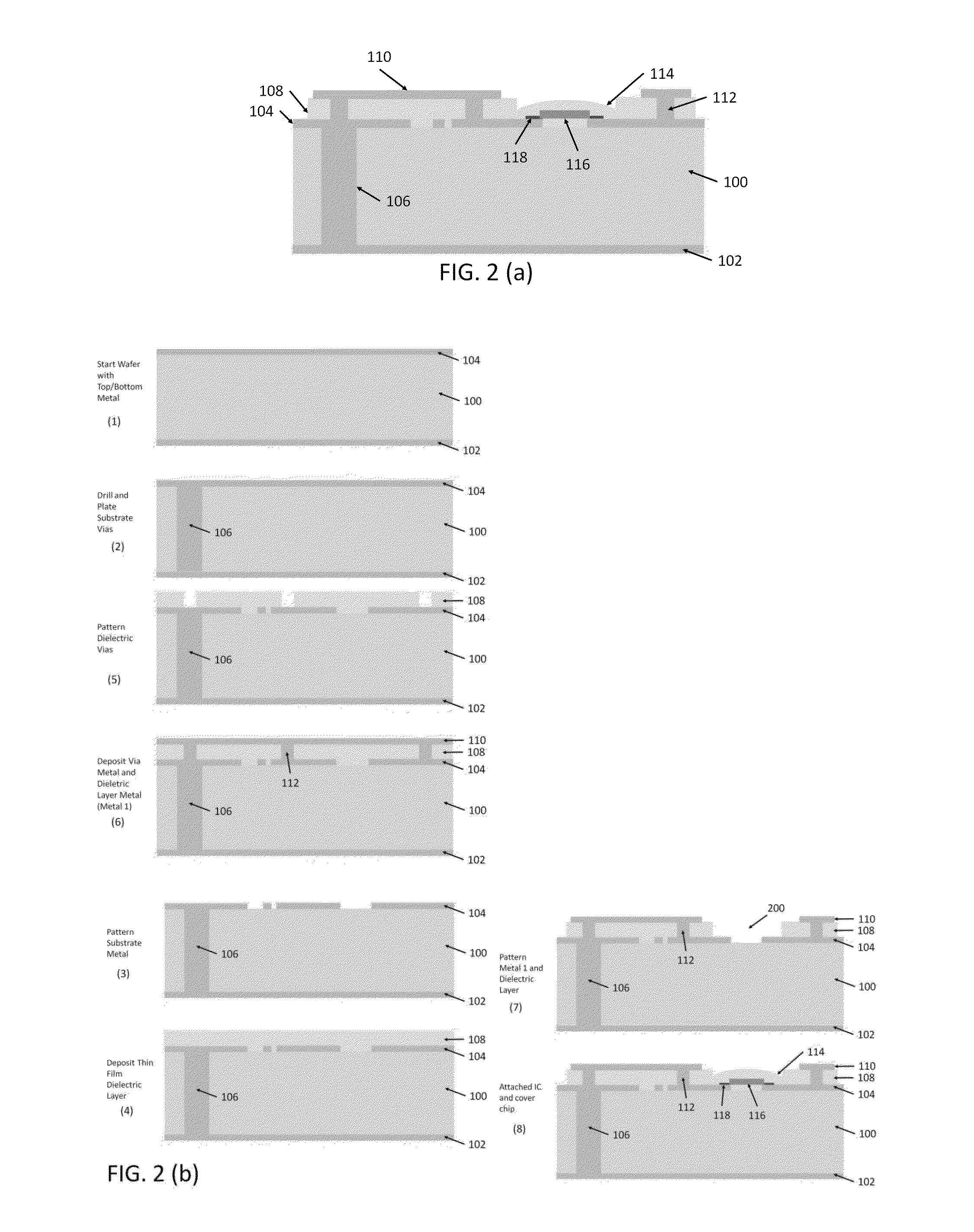
InactiveUS20140097882A1High-frequency limitSuperior to hybrid mixersPrinted circuit assemblingComputations using contact-making devicesMicrowaveManufacturing technology
An improved microwave mixer manufactured using multilayer processing includes an integrated circuit that is electrically connected to a top metal layer of a substrate. The microwave mixer includes: a first metal layer; a dielectric substrate on the first metal layer; a second metal layer directly on the substrate, at least two passive circuits arranged on the second metal layer and a top layer metal; a thin dielectric layer on the second metal layer, wherein the top layer metal is directly on the thin dielectric layer; an integrated circuit (IC) attached to the second metal layer, wherein the IC includes at least one combination of non-linear devices, and wherein the IC is directly connected to the passive circuits on the second metal layer; and a protection layer on the IC.
Owner:MARKI MICROWAVE
Systems, devices, and methods for suppressing frequency spurs in mixers
ActiveUS8559905B2Reduce leakageModulation transference by diodesCommunication jammingCapacitanceNonlinear element
Systems, devices and methods are disclosed for suppressing the 2LO frequency spur, output from a mixer. In various exemplary embodiments, a DC bias circuit is electrically connected to provide DC bias to one or more non-linear elements of the mixer. The biasing voltage is used to cause the current-voltage characteristics and / or junction capacitances between non-linear elements to be more symmetric and / or to suppress 2LO leakage currents that form 2LO frequency spurs at the output of the mixer. The non-linear elements may comprise one of: BJT's, diodes, and FET's. The mixer may be one of: a subharmonic mixer; a fundamental resistive mixer; a fundamental subharmonic transconductance mixer; and a fundamental transconductance mixer comprising an anti-parallel diode pair. The system may further be configured to automatically determine an appropriate DC bias voltage level that will improve one of the LO-IF isolation and the LO-RF isolation.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Diode mixer
ActiveUS7363020B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove noise characteristicsModulation transference by diodesTransmissionCapacitanceEngineering
Owner:ARIGNA TECH LTD
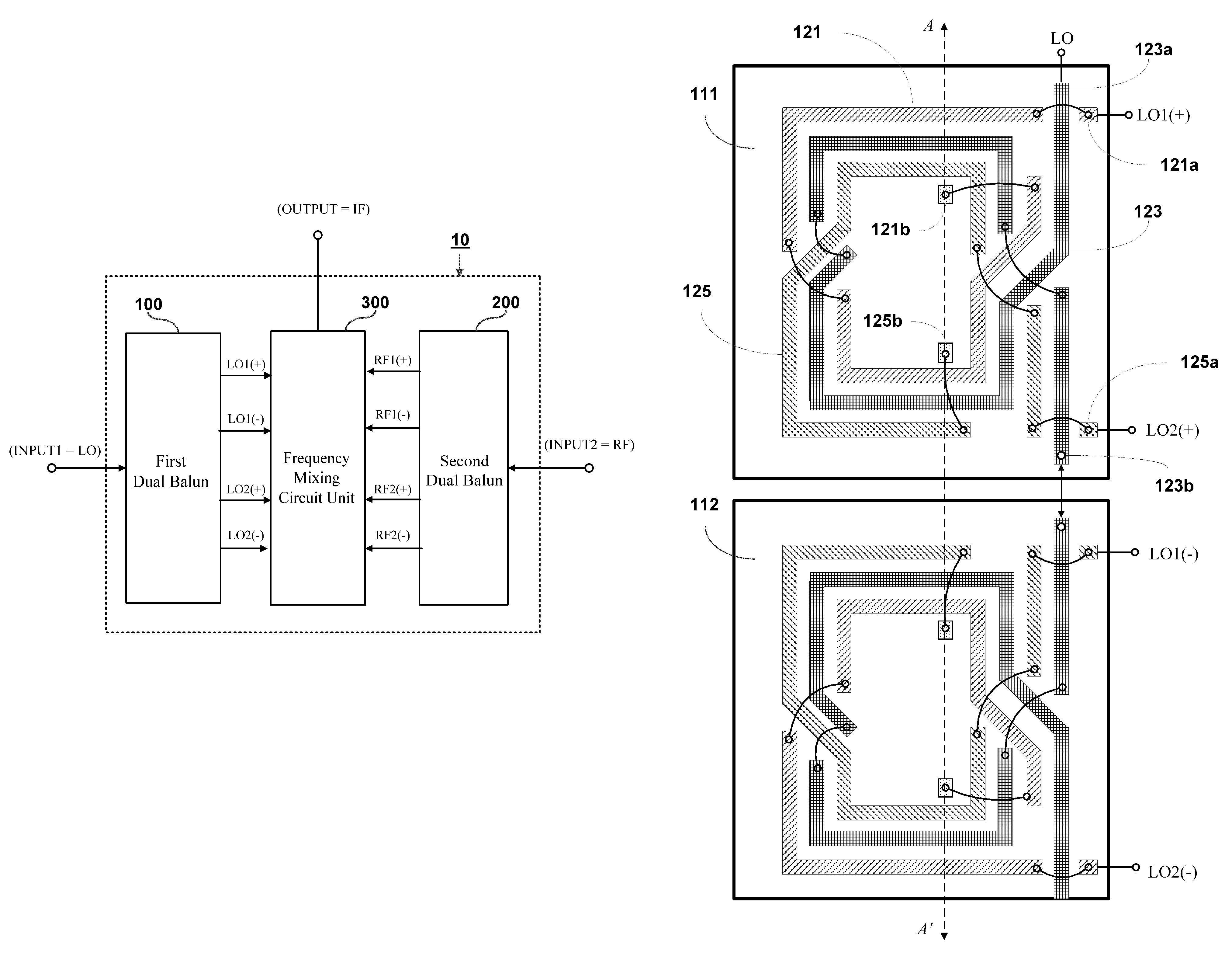
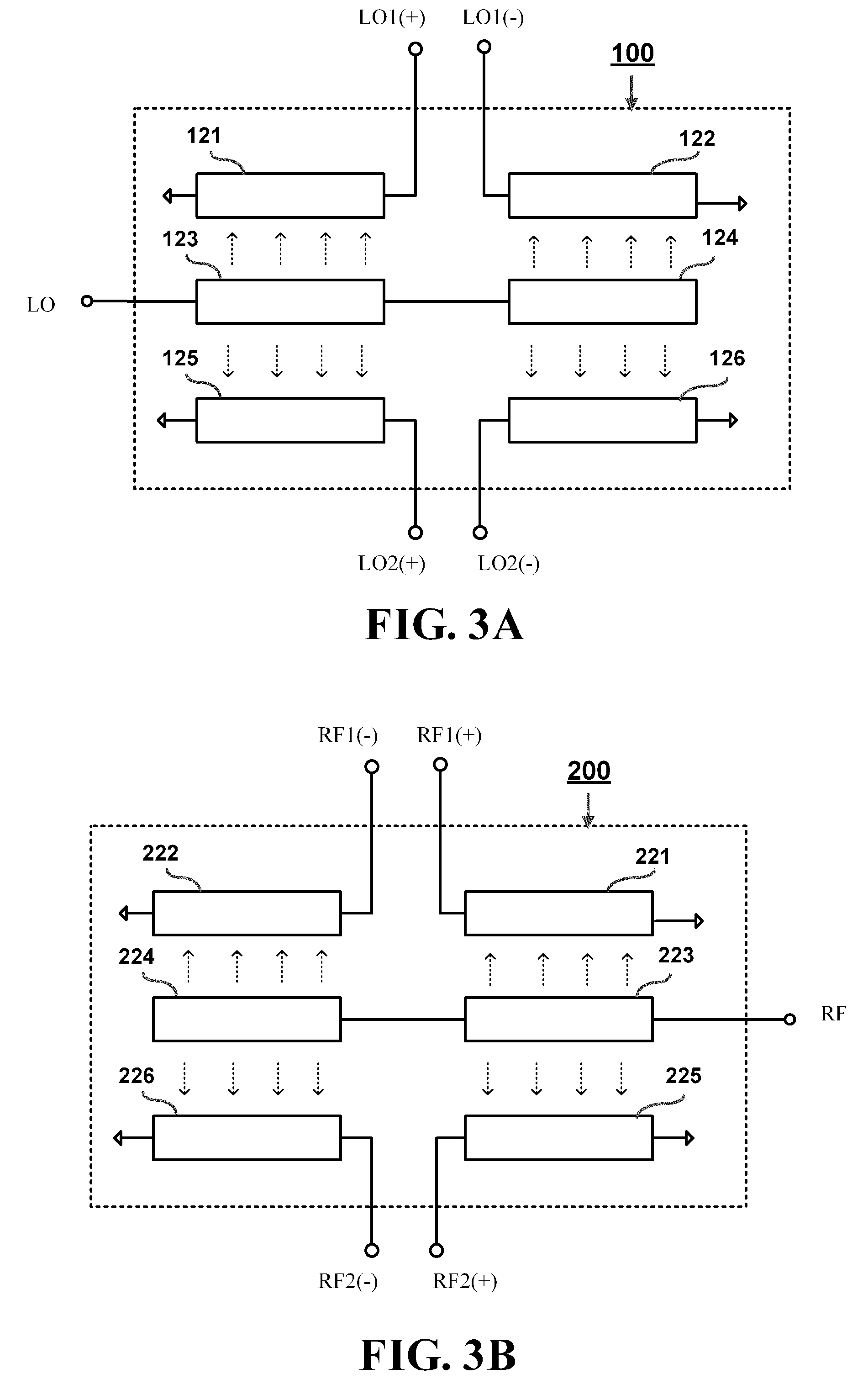
Miniaturized dual-balanced mixer circuit based on a trifilar layout architecture
ActiveUS20100079223A1Reduce layout spacingModulation transference by diodesOne-port networksBalanced mixerEngineering
A miniaturized dual-balanced mixer circuit based on a trifilar layout architecture is proposed, which is designed for use to provide a frequency mixing function for millimeter wave (MMW) signals, and which features a downsized circuit layout architecture that allows IC implementation to be more miniaturized than the conventional star-type dual-balanced mixer (DBM). The proposed miniaturized dual-balanced mixer circuit is distinguished from the conventional star-type DBM particularly in the use of a trifilar layout architecture for the layout of two balun circuit units. This feature allows the required layout area to be only about 20% of that of the conventional star-type DBM.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
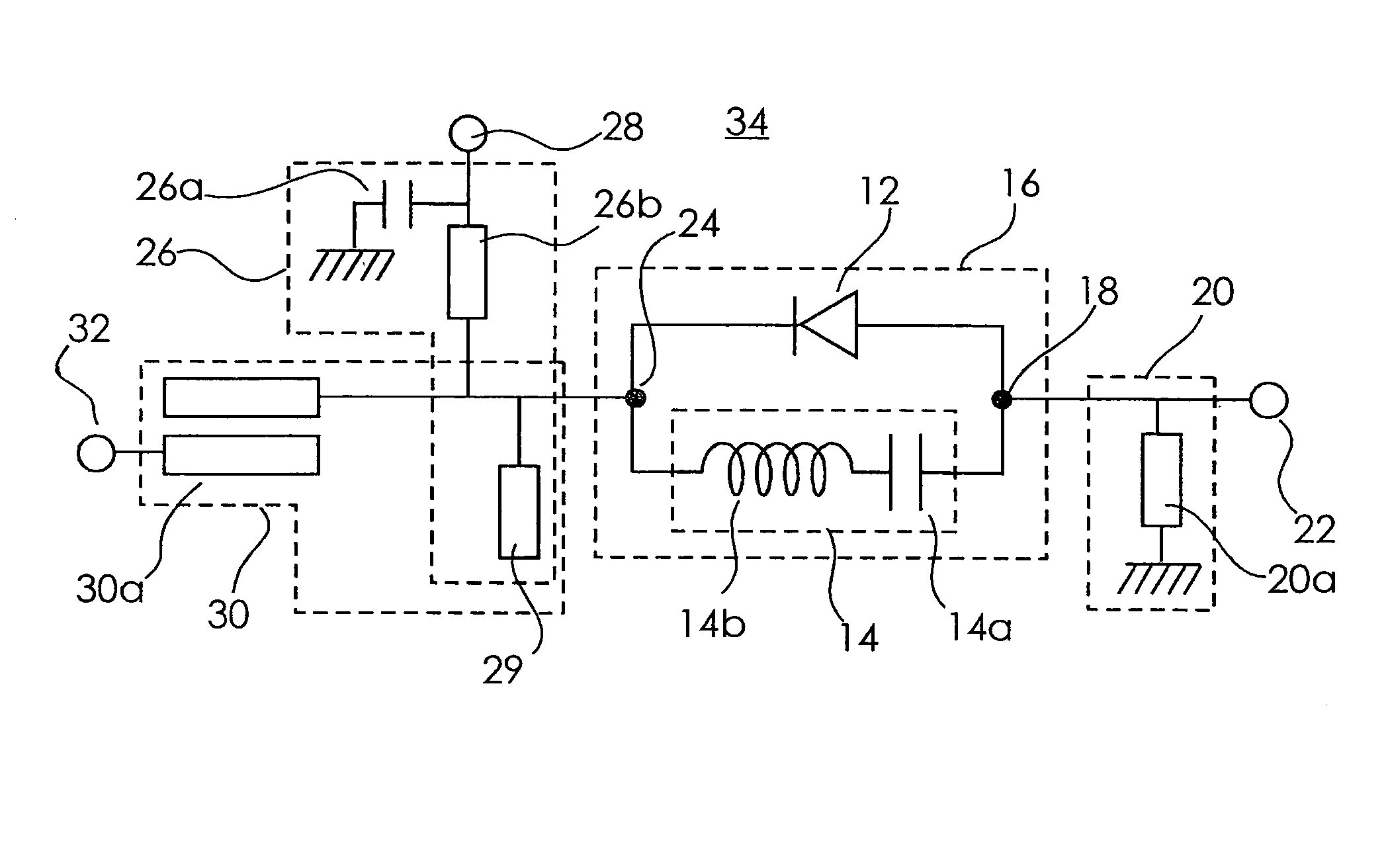
Frequency translating devices and frequency translating measurement systems with DC bias added to a mixer diode
InactiveUS7095989B2Improve reciprocityPeak to peak voltage rangeResonant long antennasModulation transference by diodesCapacitanceIntermediate frequency
A frequency translating device (FTD) includes at least one mixer diode connected to down-convert a radio frequency (RF) to an intermediate frequency (IF) and to up-convert an IF to an RF and a source of direct current (DC) bias that is connected to the mixer diode. The source of DC bias provides DC bias to the mixer diode that moves the voltage applied to the mixer diode closer to the threshold voltage of the mixer diode. The mixer diode is turned on in response to the DC bias and a local oscillator (LO) drive. Because DC bias is applied to the mixer diode, the peak to peak voltage range of the LO drive can be reduced, thereby reducing the voltage-dependent capacitance of the mixer diode, causing the FTD to exhibit improved reciprocity. The FTD can be used in a three-pair measurement system to determine the conversion response of another FTD.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Intelligent water affair data aggregation terminal
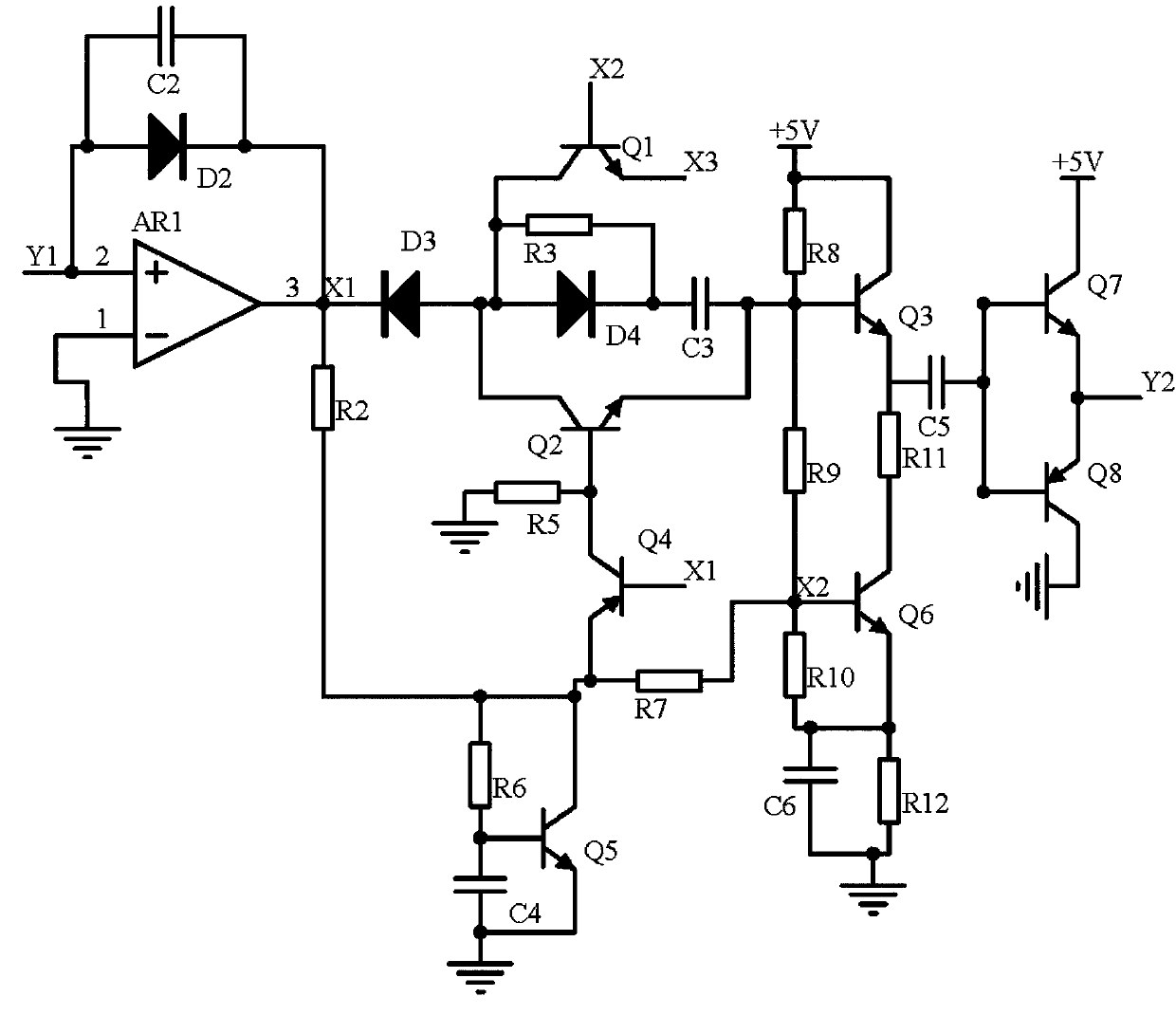
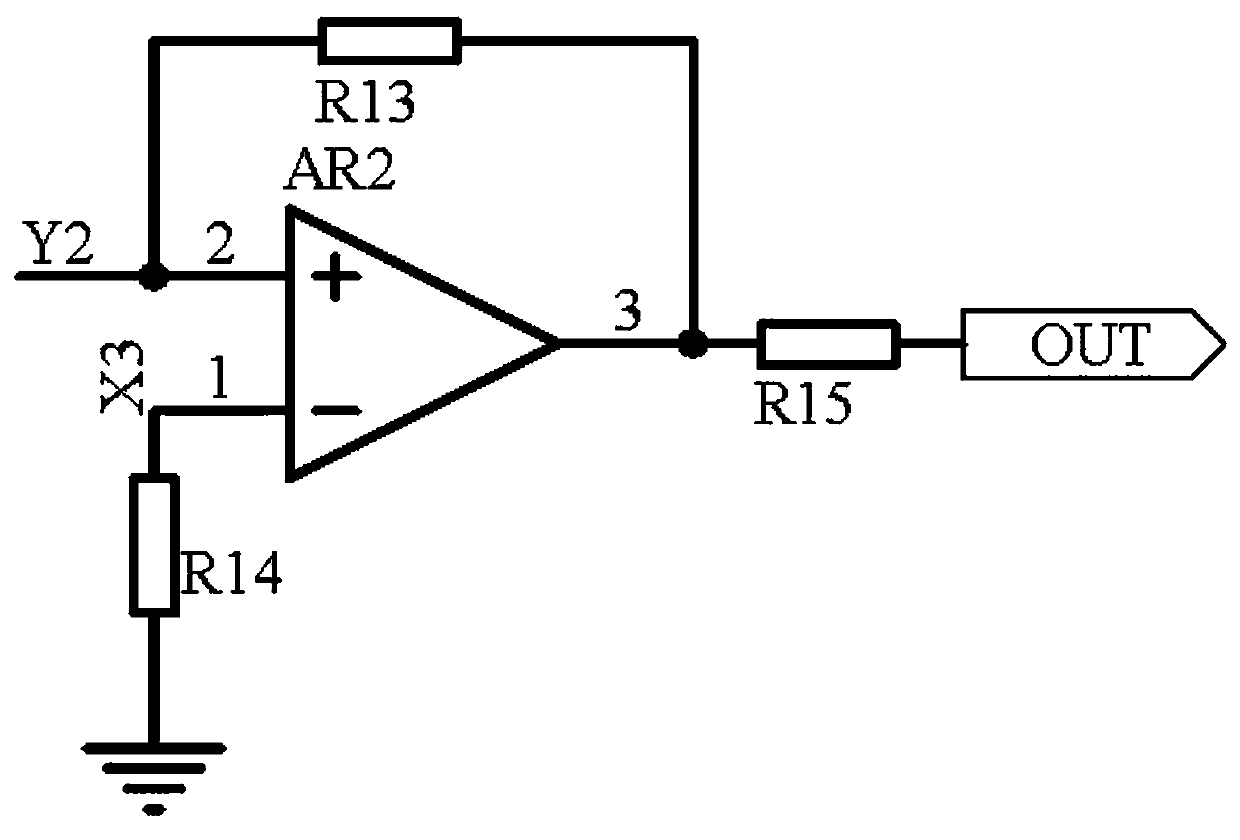
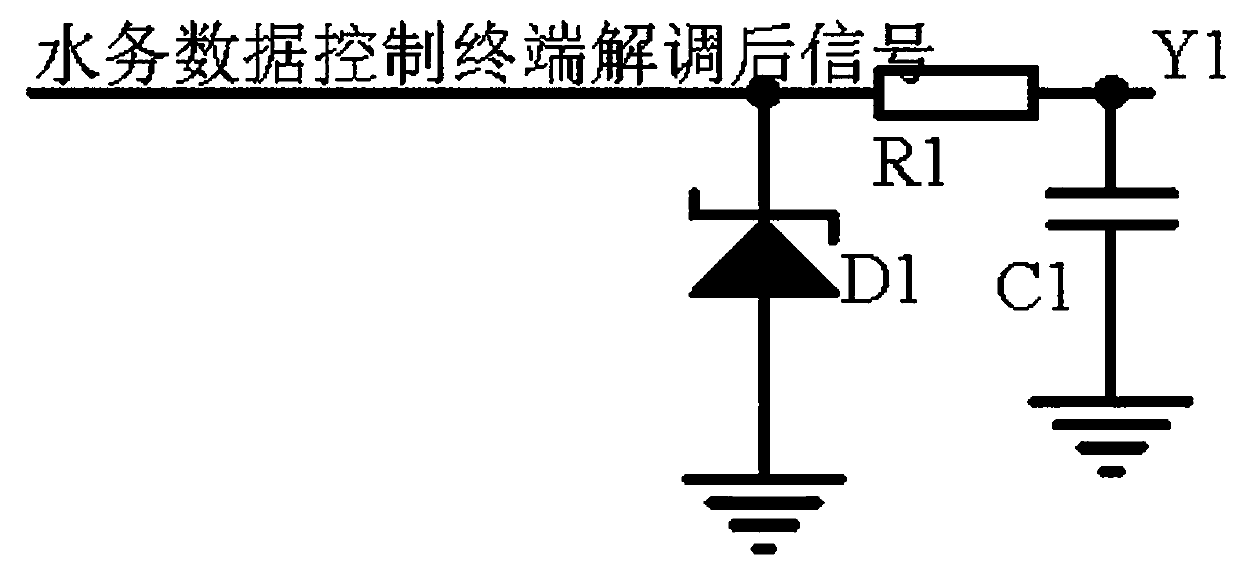
InactiveCN110661492AAvoid distortionImprove stabilityProgramme controlModulation transference by diodesCapacitanceData aggregator
The invention discloses an intelligent water affair data aggregation terminal. The circuit comprises a signal receiving circuit, a delay feedback circuit and an operational amplifier output circuit. The signal receiving circuit receives signals demodulated by the water affair data control terminal to stabilize voltage stabilization by using voltage-regulator tube D1, the delay feedback circuit forms an average circuit by using an operational amplifier AR1, a diode D2, a diode D3 and a capacitor C2; extraction of mean signals, one path of an output signal of the operational amplifier AR1 buffers the signal by using a buffer circuit consisting of a diode D4, a triode Q2 and a capacitor C3; in the second path, a triode Q5 and a capacitor C4 are used to form a time-delay circuit time-delay signal; finally, the two paths of signals are input into a frequency modulation circuit composed of a triode Q3, a triode Q6 and resistors R8-R10 to adjust the signal frequency. A triode Q7 and a triodeQ8 are used to form a push-pull circuit to prevent signal distortion, an operational amplifier output circuit uses an operational amplifier AR2 to amplify signals in the same phase and then outputs the signals, and the problem that the instantaneous transmission throughput of the signals is too large is solved.
Owner:河南沃海水务有限公司
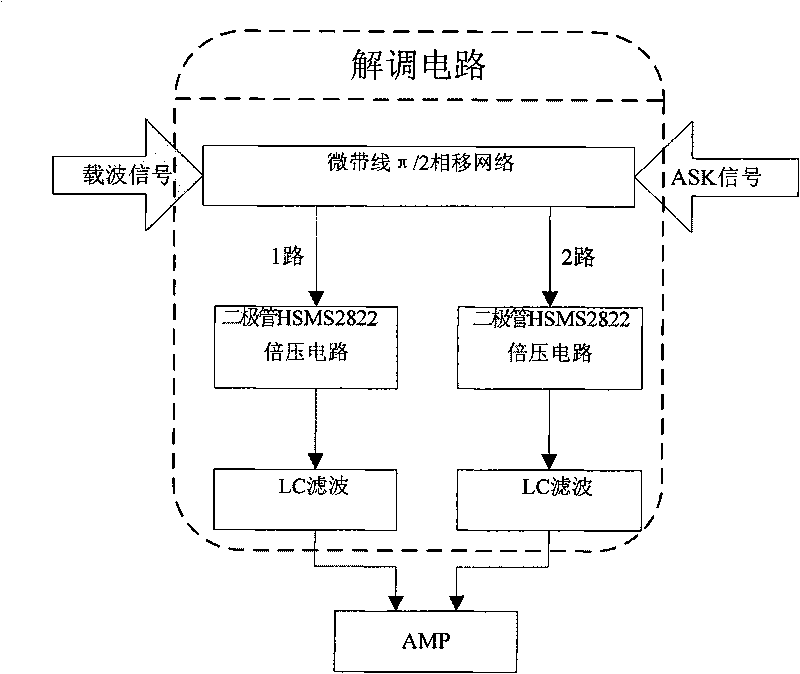
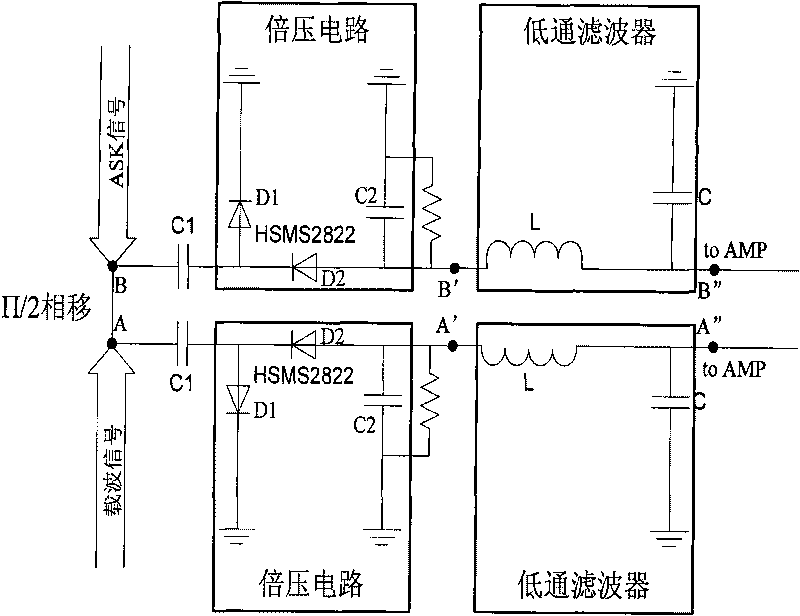
Uhf reader demodulation circuit
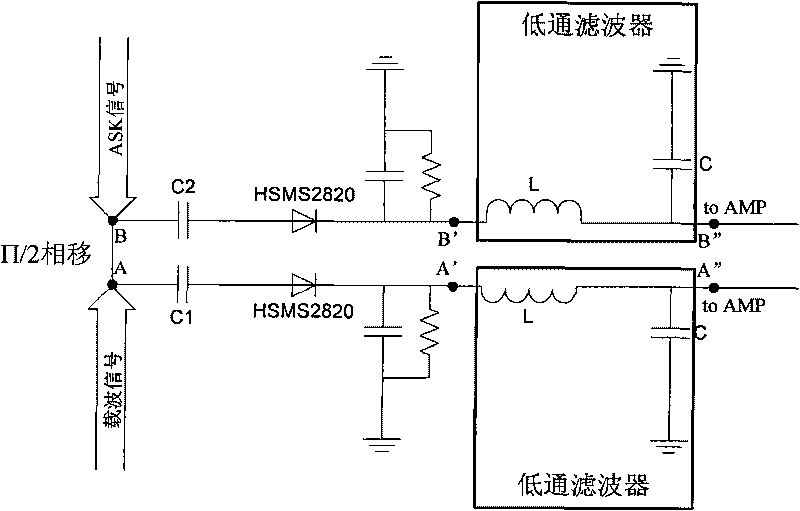
InactiveCN101706879ARealize demodulationLow gainModulation transference by diodesCo-operative working arrangementsPhase shiftedLow-pass filter
The invention relates to a uhf reader, in particular to a uhf reader demodulation circuit, which comprises a 50 ohm microstrip line phase shifting device, a two-way diode mixer circuit and a two-way LC low pass filter; wherein the 50 ohm microstrip line phase shifting device is used for respectively realizing a pi / 2 phase shifting on an input carrier signal and an ASK signal; the two-way diode mixer circuit is a voltage-multiplying circuit which is used for mixing the carrier signal and the ASK signal which are subjected to phase shifting by the 50 ohm microstrip line phase shifting device; and the two-way LC low pass filter is used for filtering the carrier signal from a mixing signal and outputting to a difference amplifier. By adopting a simple Schottky diode as a mixing element and designing a mixing circuit into a voltage-multiplying mode to improve receiving sensitivity, the invention simply realizes ASK demodulation and solves the problem of low gain of passive mixing voltage.
Owner:WUHAN WINNINGCHINA MICROSYST TECH
Ultra-broadband planar millimeter-wave mixer with multi-octave IF bandwidth
ActiveUS8868021B1Eliminate bandingLow conversion lossResonant long antennasModulation transference by diodesOctaveEngineering
In some embodiments, a system may include a passive uniplanar single-balanced millimeter-wave mixer. In some embodiments, a three-port diode-tee IC forming a mixer core is coupled between an end of a slotline balun and a second coplanar balun. The operational bandwidth of a mixer structure is enhanced by optimizing the distance between the mixer diode-tee core and the back-short circuits. The frequency separation of LO and IF signals may be accomplished by means of stand-alone three-port filter-diplexer device. The system may allow wider than a frequency octave operational bandwidth for a frequency converter device all the way into millimeter wave frequencies at the same time as supporting the operational bandwidth for baseband IF signal over more than six frequency octaves. In some embodiments, the system may accomplish a 500 MHz to 34.5 GHz continuous IF bandwidth with RF signal sweeping from 33 GHz to 67 GHz and local oscillator at 67.5 GHz fixed frequency.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Mixer for eliminating second-order inter-modulation distortion and relevant transconductor circuit of mixer
ActiveCN102347730ASolve the problem of removing second-order intermodulation distortionModulation transference by diodesNegative feedbackFrequency mixer
The invention discloses a transconductor circuit which is applicable to a mixer and used for eliminating second-order inter-modulation distortion. The transconductor circuit comprises a first transistor, a second transistor and a negative feedback circuit, wherein bases / gates of the first transistor and the second transistor are respectively coupled with a first input end and a second input end and used for receiving a differential input signal; an input end of the negative feedback circuit is coupled to emitters / sources of the first transistor and the second transistor, and an output end of the negative feedback circuit is coupled to the bases / gates of the first transistor and the second transistor; and the negative feedback circuit is used for adjusting voltages of the bases / gates of the first transistor and the second transistor according to a voltage difference between a detection voltage and a reference voltage of the emitters / sources of the first transistor and the second transistor.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Dual-port planar harmonic mixer for spread spectrum
PendingCN110572130AEasy to assembleSimple structureSpectral/fourier analysisModulation transference by diodesFourth harmonicLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a dual-port planar harmonic mixer for spread spectrum. The dual-port planar harmonic mixer comprises a radio frequency band-pass filter, a radio frequency input matching circuit, Schottky diode pairs which are reversely connected in parallel, a local oscillator intermediate frequency matching circuit and a local oscillator intermediate frequency low-pass filter. The harmonic mixer provided by the invention has the advantages of wide bandwidth and simple circuit structure, can be realized by a pure planar microstrip circuit, and is convenient to integrate with other planar circuits. By adjusting the parameters of each component in the circuit, the structure is suitable for higher harmonic mixing above fourth harmonic mixing, and by combining with a built-in spread spectrum local oscillator of the frequency spectrograph, the microwave frequency band frequency spectrograph can be conveniently expanded to millimeter waves and even terahertz bands.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
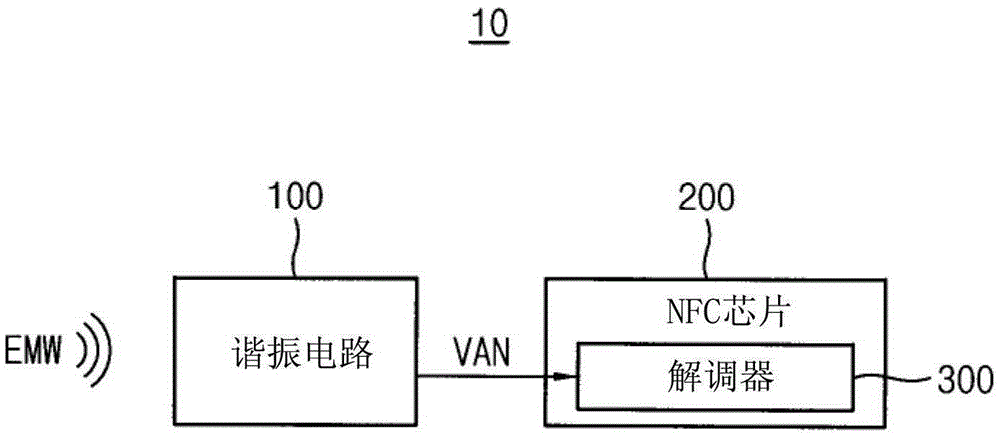
Demodulator for near field communication
ActiveCN105591657AModulation transference by diodesAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsScale downCharge and discharge
A demodulator for near field communication is provided. The demodulator for near field communication may include: a scale down circuit configured to receive first and second modulated signals from first and second power electrodes, and configured to provide a scale down signal to a first node by scaling down magnitudes of the first and second modulated signals; a current source coupled between the first node and a ground voltage, and configured to generate a constant current flowing from the first node to the ground voltage; a charge store circuit coupled between the first node and ground voltage, and configured to perform charge and discharge operations alternately, based on the scale down signal and constant current, to output an envelope signal, which corresponds to an envelope of the scale down signal; and / or an edge detector configured to generate input data, which correspond to the first and second modulated signals, based on a transition of the envelope signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
670 GHz Schottky diode based subharmonic mixer with CPW circuits and 70 GHz IF
ActiveUS8693973B2Modulation transference by diodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBandpass filteringFrequency mixer
A coplanar waveguide (CPW) based subharmonic mixer working at 670 GHz using GaAs Schottky diodes. One example of the mixer has a LO input, an RF input and an IF output. Another possible mixer has a LO input, and IF input and an RF output. Each input or output is connected to a coplanar waveguide with a matching network. A pair of antiparallel diodes provides a signal at twice the LO frequency, which is then mixed with a second signal to provide signals having sum and difference frequencies. The output signal of interest is received after passing through a bandpass filter tuned to the frequency range of interest.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Miniaturized dual-balanced mixer circuit based on a trifilar layout architecture
ActiveUS8064870B2Reduce layout spacingModulation transference by diodesComputing operation arrangementsBalanced mixerEngineering
A miniaturized dual-balanced mixer circuit based on a trifilar layout architecture is proposed, which is designed for use to provide a frequency mixing function for millimeter wave (MMW) signals, and which features a downsized circuit layout architecture that allows IC implementation to be more miniaturized than the conventional star-type dual-balanced mixer (DBM). The proposed miniaturized dual-balanced mixer circuit is distinguished from the conventional star-type DBM particularly in the use of a trifilar layout architecture for the layout of two balun circuit units. This feature allows the required layout area to be only about 20% of that of the conventional star-type DBM.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Carbon nanotube devices and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS8548415B2Modulation transference by diodesMaterial analysis by optical meansCarbon nanotubeFocal Plane Arrays
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Passive broadband mixer
ActiveCN109450381AOptimization of isolation indexModulation transference by diodesModulation with suppressed carrierCommunications systemFrequency mixer
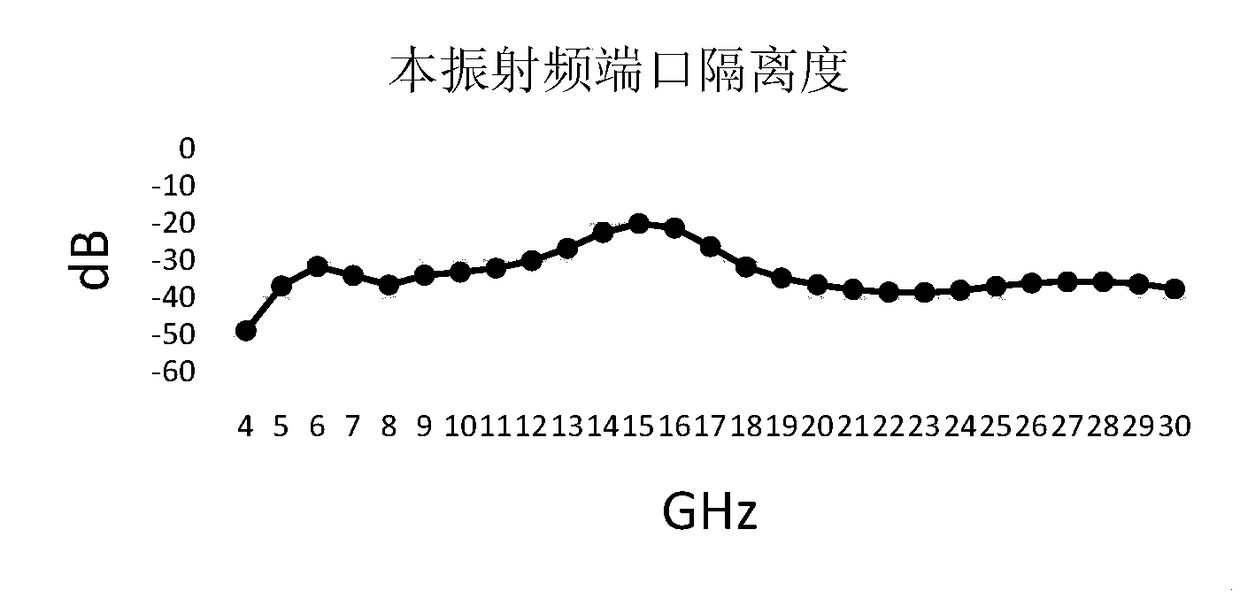
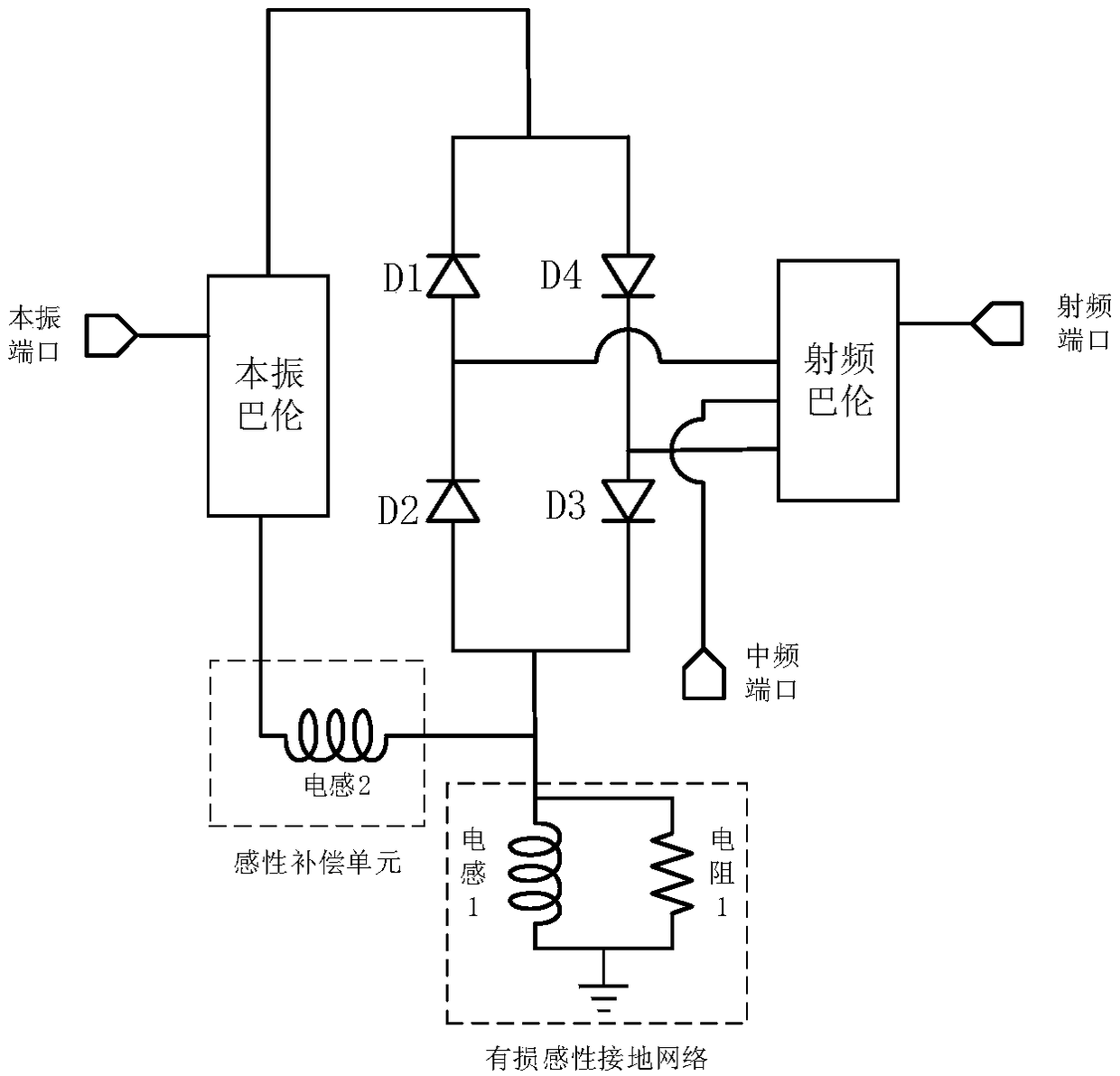
The invention discloses a passive broadband mixer, comprising: a local oscillator balun, a radio frequency balun, a first diode D1, a second diode D2, a third diode D3, a fourth diode. D4, an inductive compensation unit and lossy inductive grounding network. The passive broadband mixer disclosed by the invention can realize a mixer with a bandwidth ratio of less than 1:7, and a point with deteriorative isolation is effectively suppressed without affecting the full-band variable frequency loss; and in the full-band of the design, the full-band index of a local oscillator radio frequency port isoptimized, and the application of the broadband mixer in a communication system can be well met.
Owner:NANJING MILEWEI CORP
3-way balun for planar-type double balanced mixer
InactiveUS8558635B2Reduce parasitic effectsSimple processModulation transference by diodesOne-port networksDouble balanced mixerElectrical and Electronics engineering
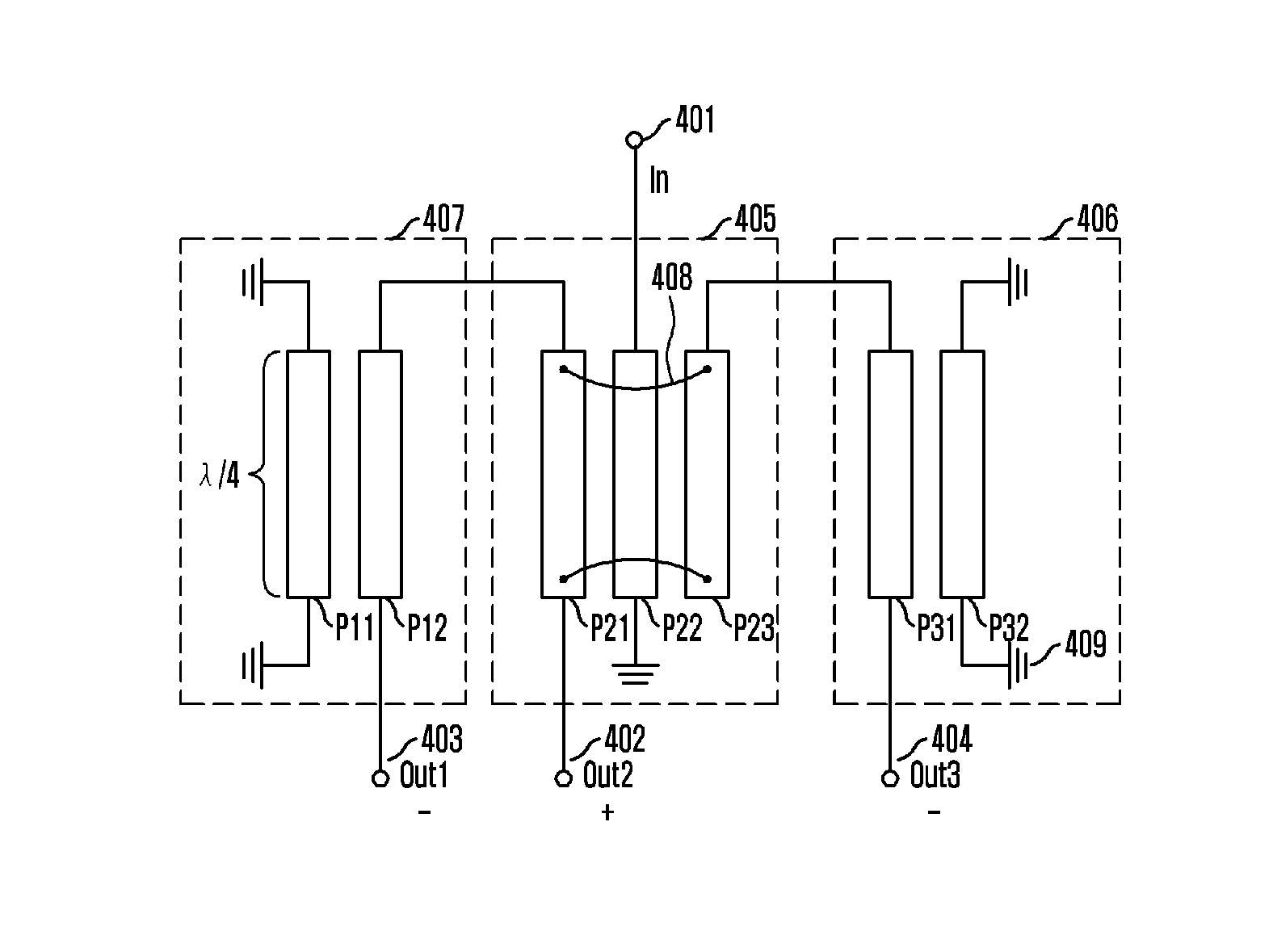
Provided is a 3-way balun for a double balanced mixer. This research provides a 3-way balun available for a planar-type double balanced mixer and a planar-type double balanced mixer employing the same. The 3-way balun includes a first output unit for receiving and outputting an input signal of a predetermined frequency; and second and third output units connected to the first output unit and outputting signals whose phase is different by 180 from a phase of a signal of the first output unit and amplitude is a half of an amplitude of the signal outputted from the first output unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for generating ultralow-phase-noise multi-point agile frequency signals
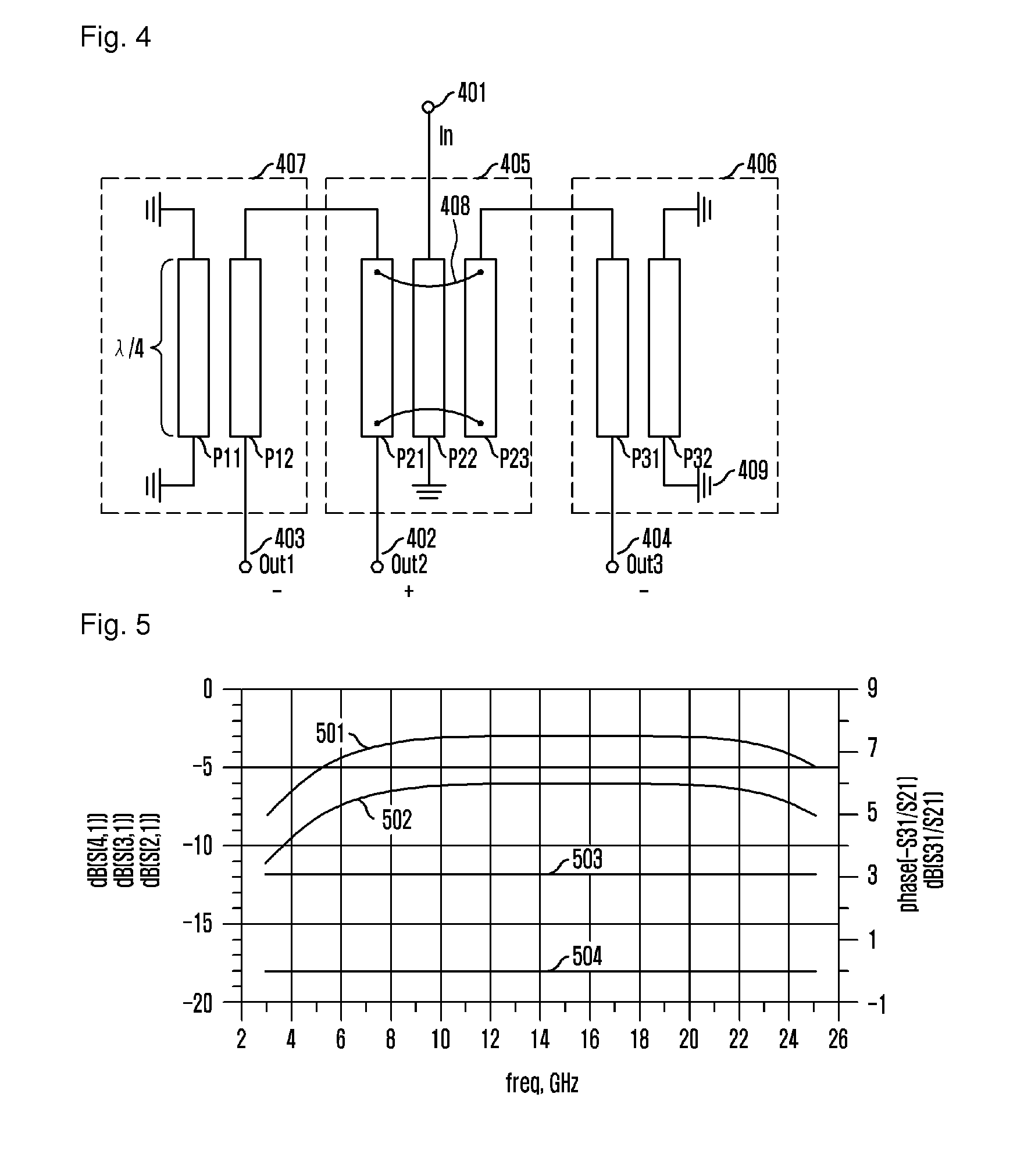
PendingCN110138342AIdeal Phase Noise IndexFast switching speedWave based measurement systemsModulation transference by diodesUltra-widebandPhase noise
The invention relates to a method for generating an ultralow-phase-noise multi-point agile frequency signal, which comprises the following steps of accessing a replaceable comb-shaped spectrum generator, and directly carrying out frequency multiplication on a reference frequency signal through the comb-shaped spectrum generator to obtain a frequency signal; adopting a band-pass filter to completefirst-time frequency selection filtering work; and adopting a switch filter with a plurality of paths of filtering units to filter out required frequency signals according to frequency segments. A comb spectrum generator is introduced to output signals in a direct frequency multiplication mode, phase noise is deteriorated only according to a frequency multiplication coefficient, other phase noisedeterioration factors are not introduced, and an ideal phase noise index can be obtained; meanwhile, by replacing the comb spectrum, changing the reference frequency and replacing the filter frequency, output of frequency signals of different frequency bands can be achieved, and L-KU frequency band ultra-wideband coverage is achieved; the switching speed of the plurality of frequency points is theswitching time of the switch, so that the switching speed is high; the clutter suppression degree is improved, and stray leakage is reduced.
Owner:韩杰峰
Popular searches
Radio wave reradiation/reflection Electromagnetic wave demodulation Coupling devices Photoelectric discharge tubes Amplifiers controlled by light Light polarisation measurement Angle demodulation by phase difference detection Transmission noise suppression Diode Modulation transference balanced arrangements
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com