Patents
Literature
659results about "Sinusoidal oscillation interference reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
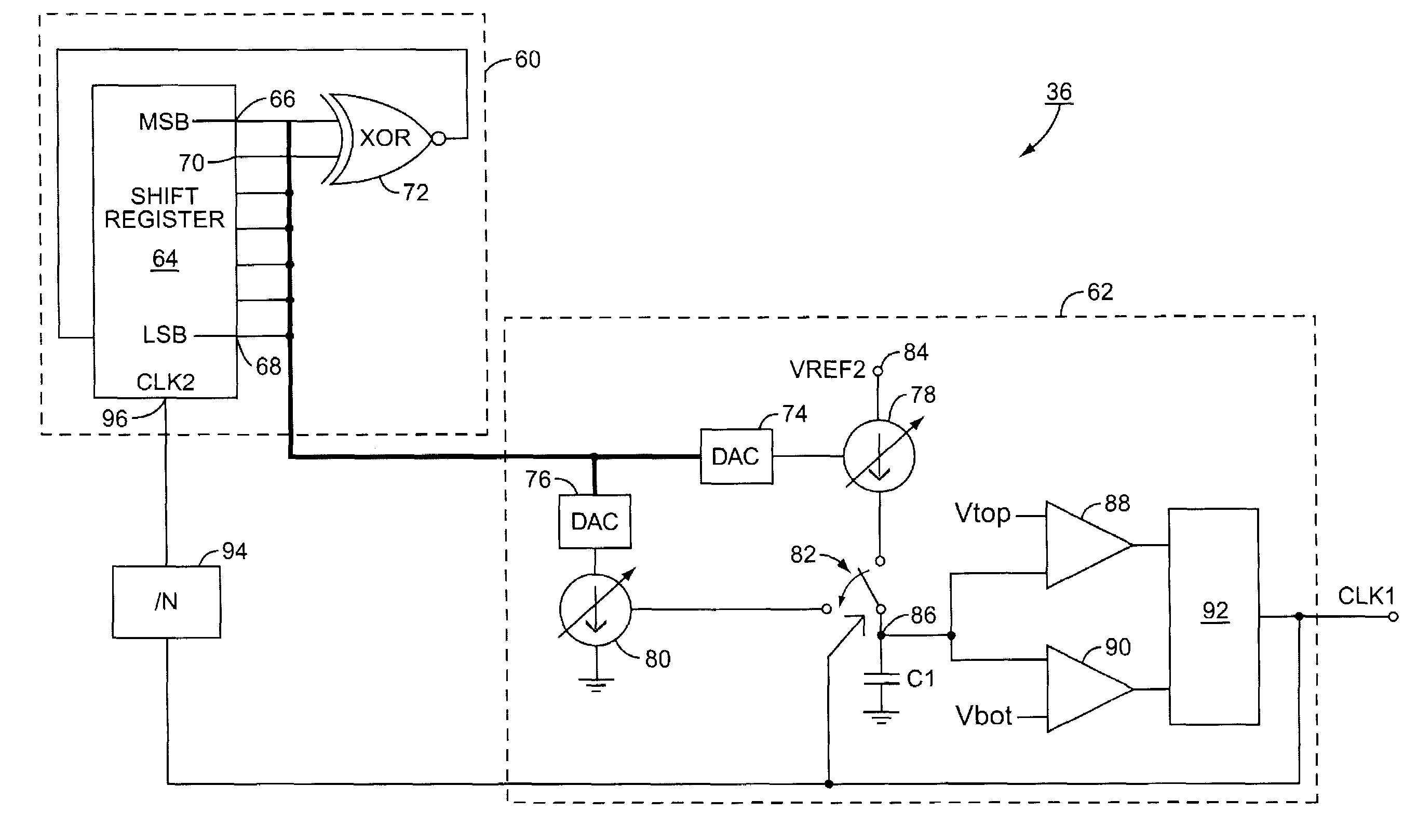
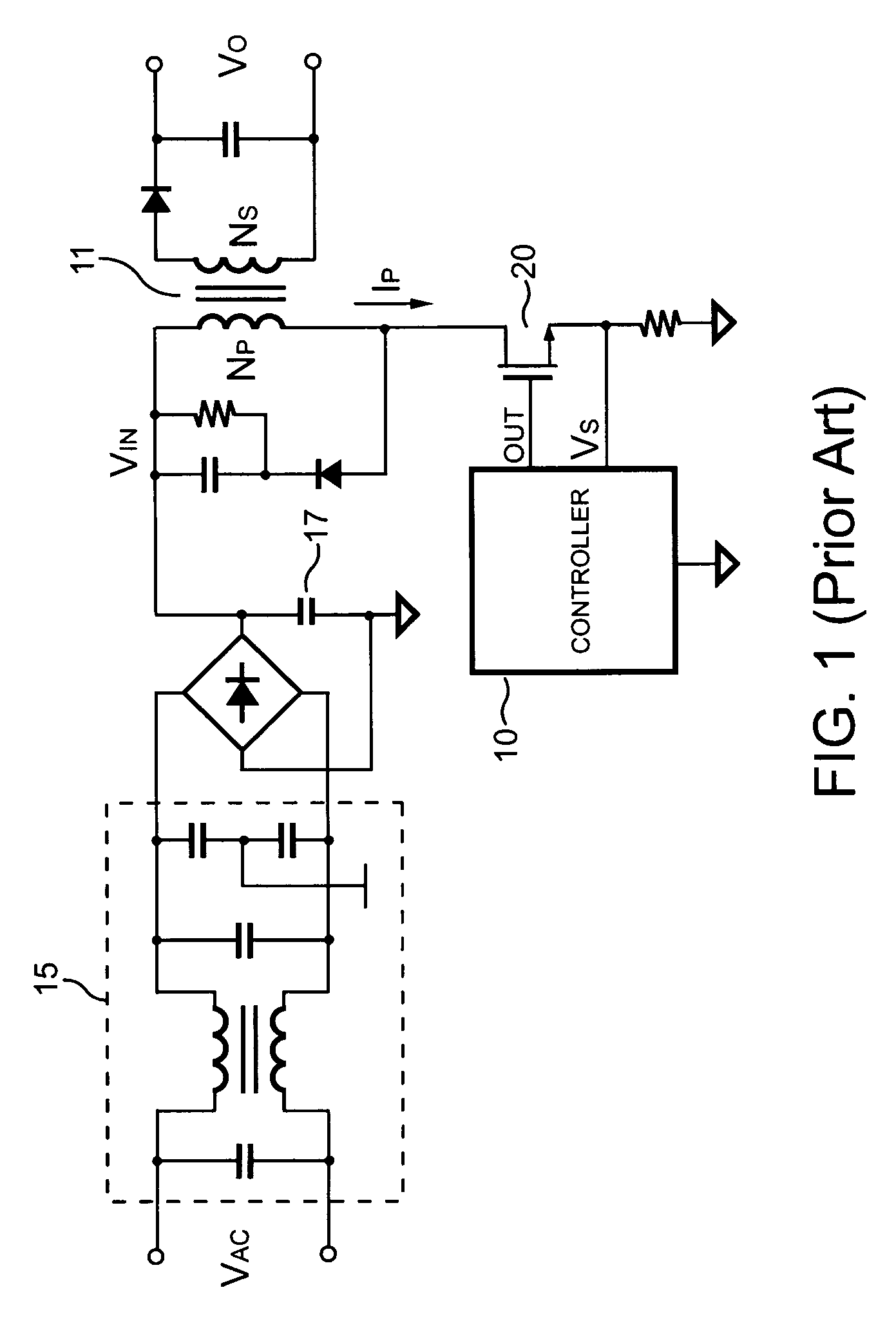
DC-DC converter with reduced electromagnetic interference
InactiveUS6969978B2Emission reductionLess spaceDc-dc conversionPulse duration/width modulationDc dc converterControl system
A DC-DC converter includes a variable frequency oscillator, a control system and a power train. The DC-DC converter is well suited for use in a cell phone. The control system uses the output of the oscillator to control the power train. The oscillator varies its frequency as a function of a pseudo random number generator, thereby reducing electromagnetic interference caused by ripple in the output of the DC-DC converter.
Owner:QORVO US INC
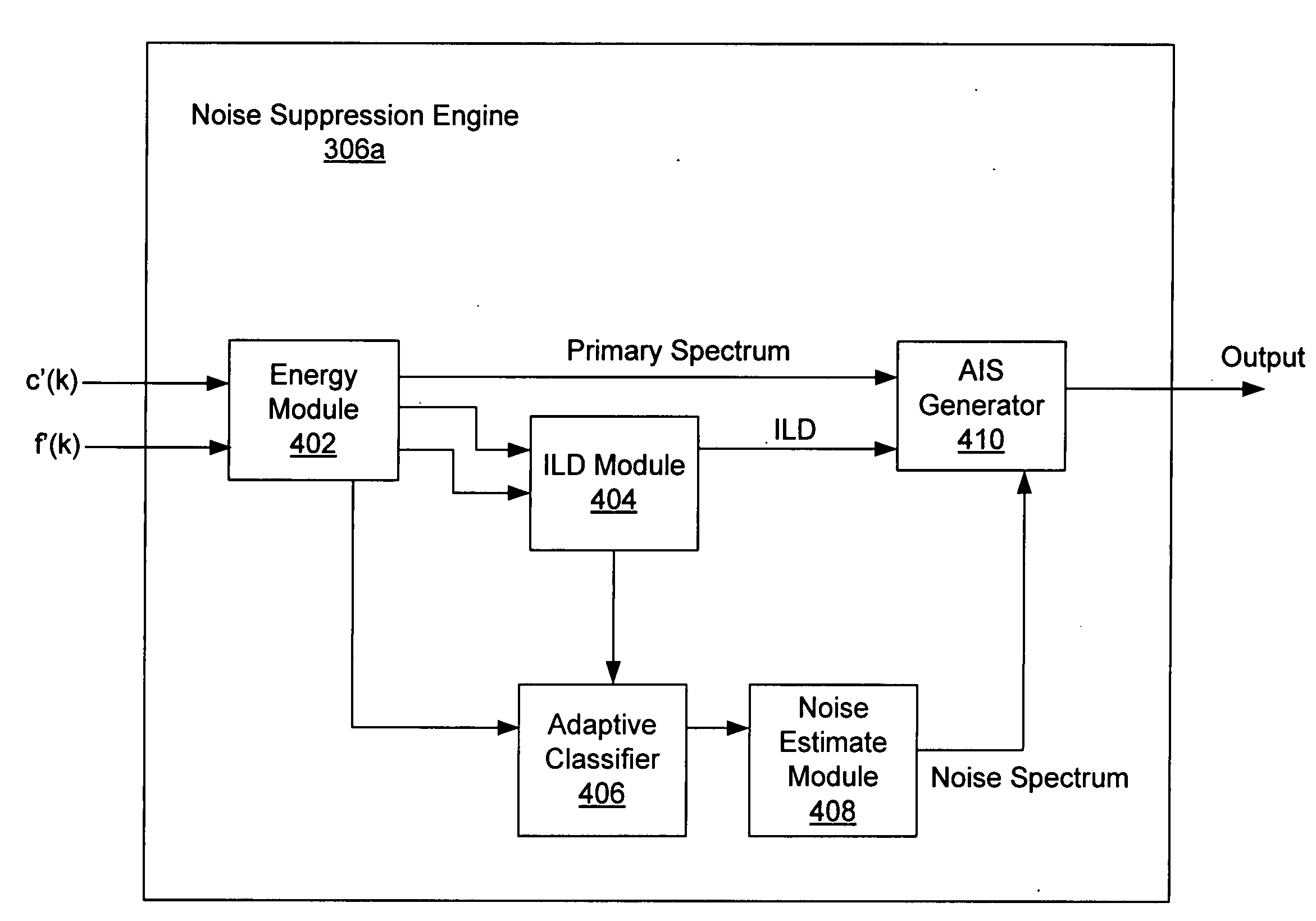
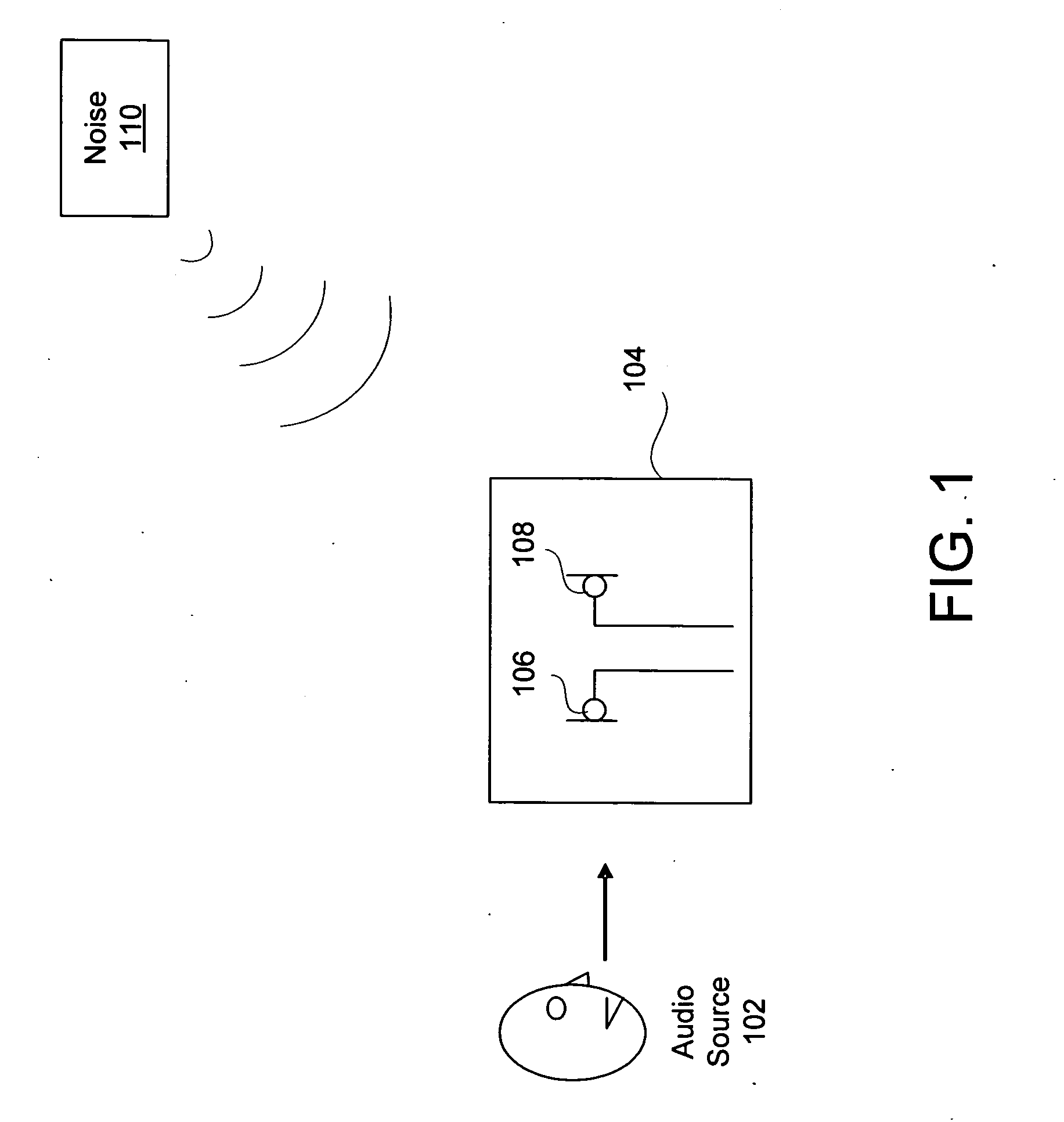
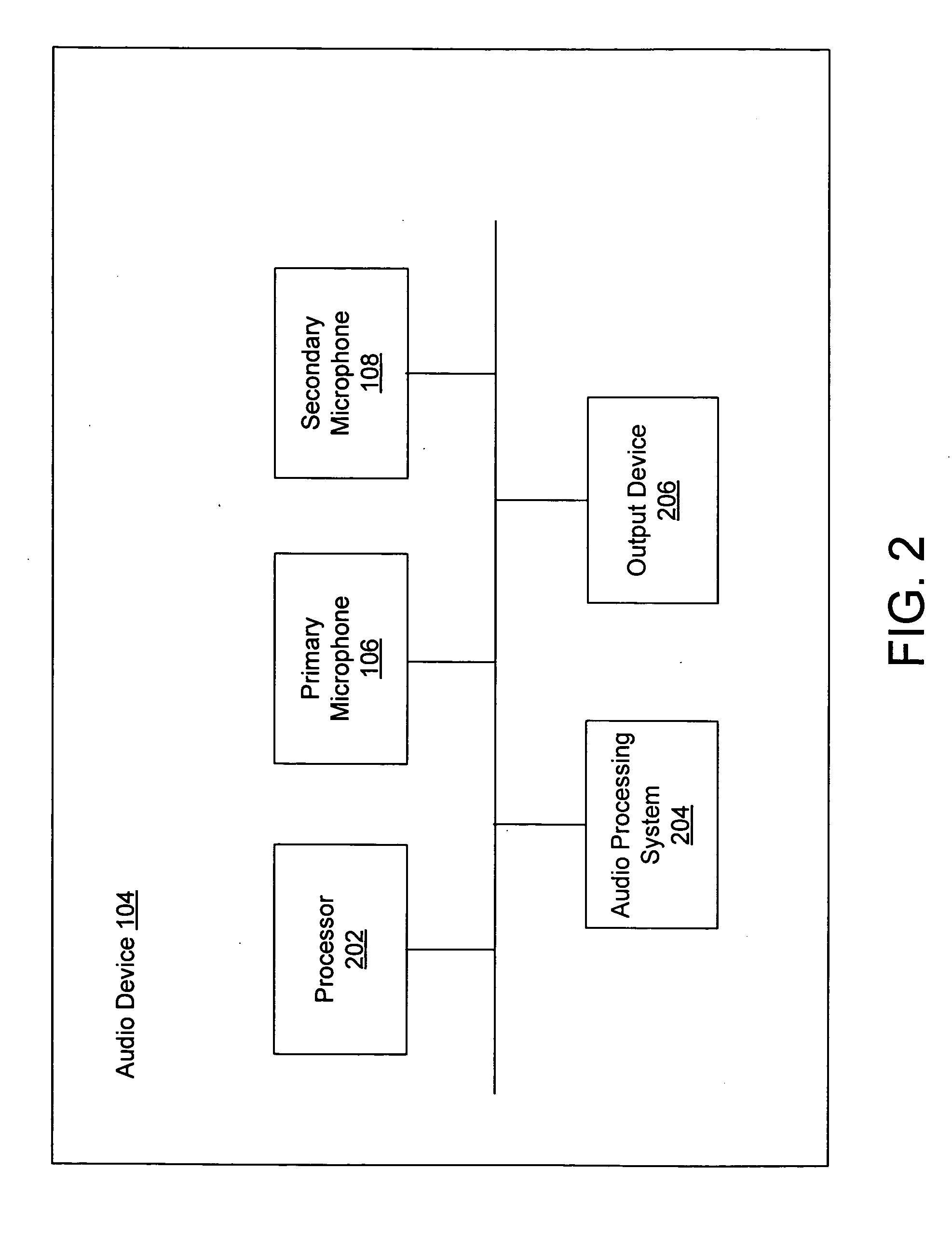
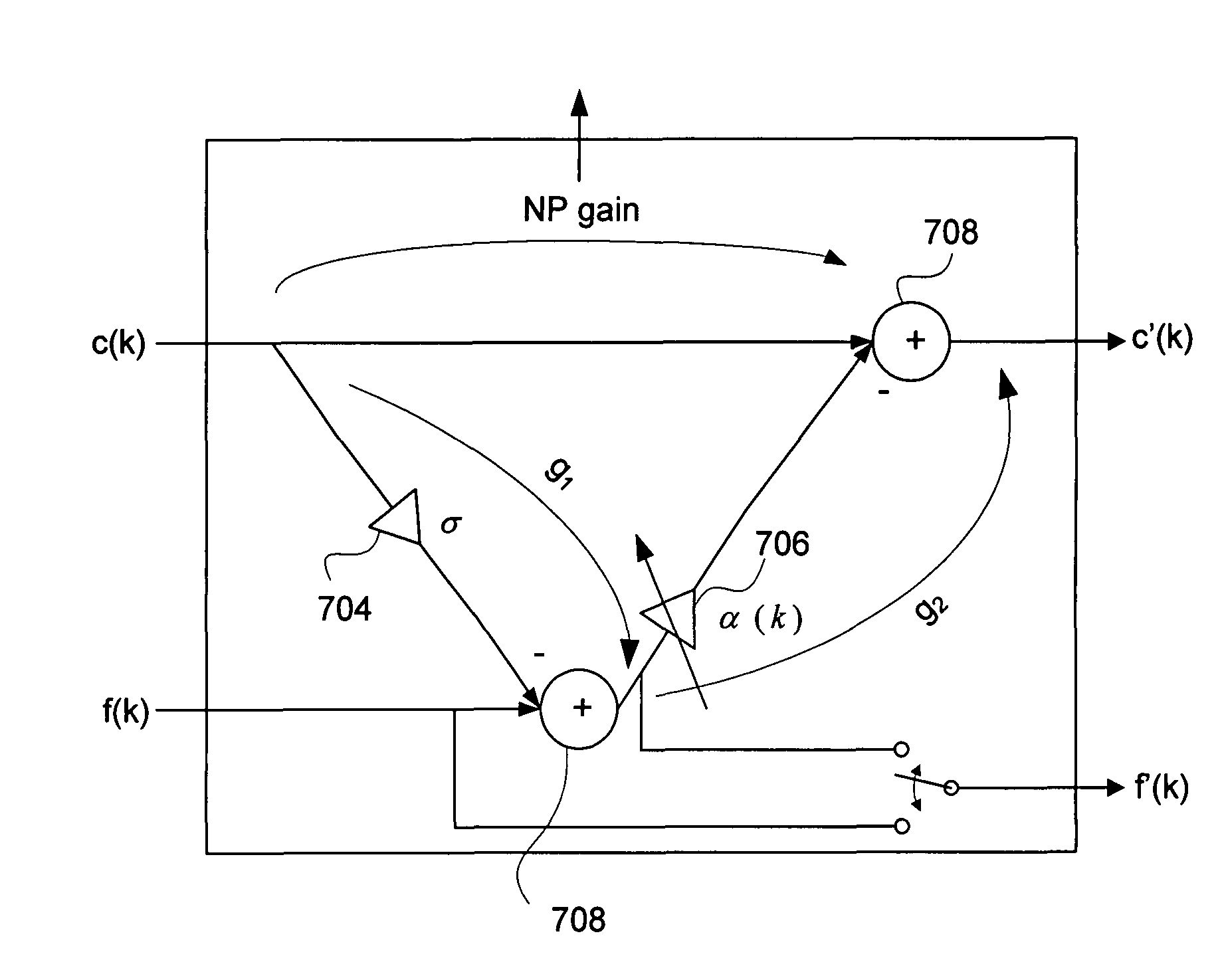
System and method for providing noise suppression utilizing null processing noise subtraction
Systems and methods for noise suppression using noise subtraction processing are provided. The noise subtraction processing comprises receiving at least a primary and a secondary acoustic signal. A desired signal component may be calculated and subtracted from the secondary acoustic signal to obtaining a noise component signal. A determination may be made of a reference energy ratio and a prediction energy ratio. A determination may be made as to whether to adjust the noise component signal based partially on the reference energy ratio and partially on the prediction energy ratio. The noise component signal may be adjusted or frozen based on the determination. The noise component signal may then be removed from the primary acoustic signal to generate a noise subtracted signal which may be outputted.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
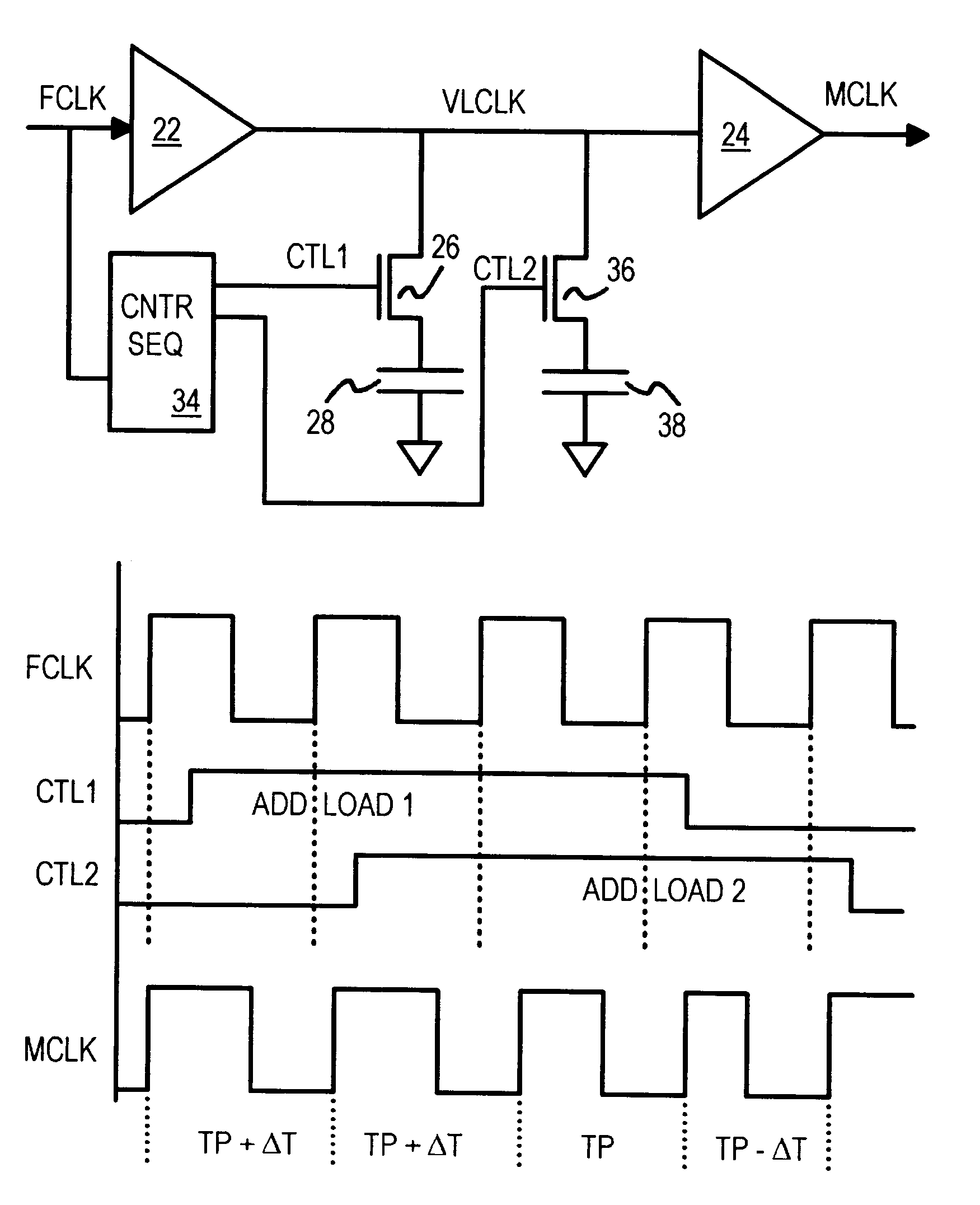
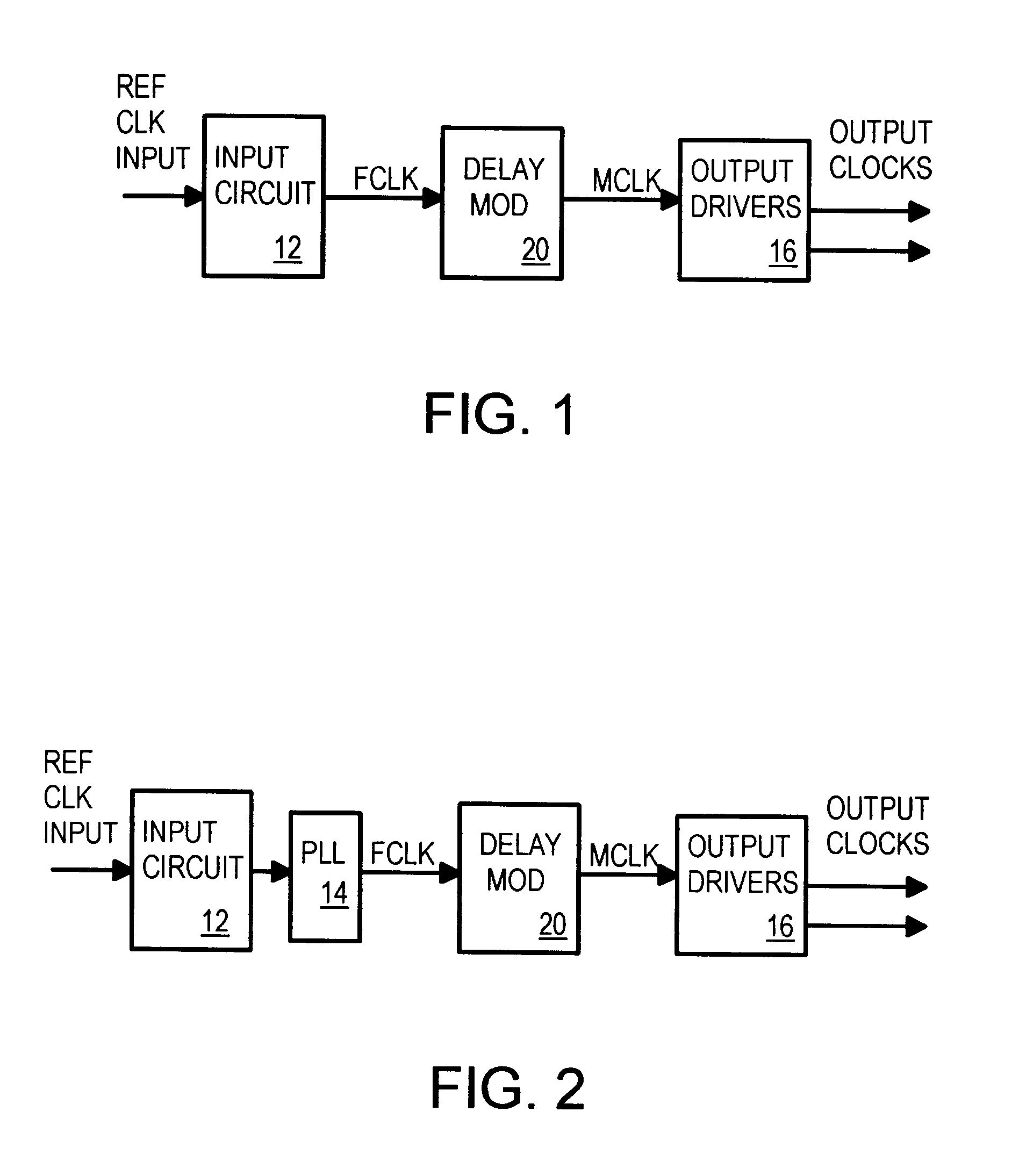
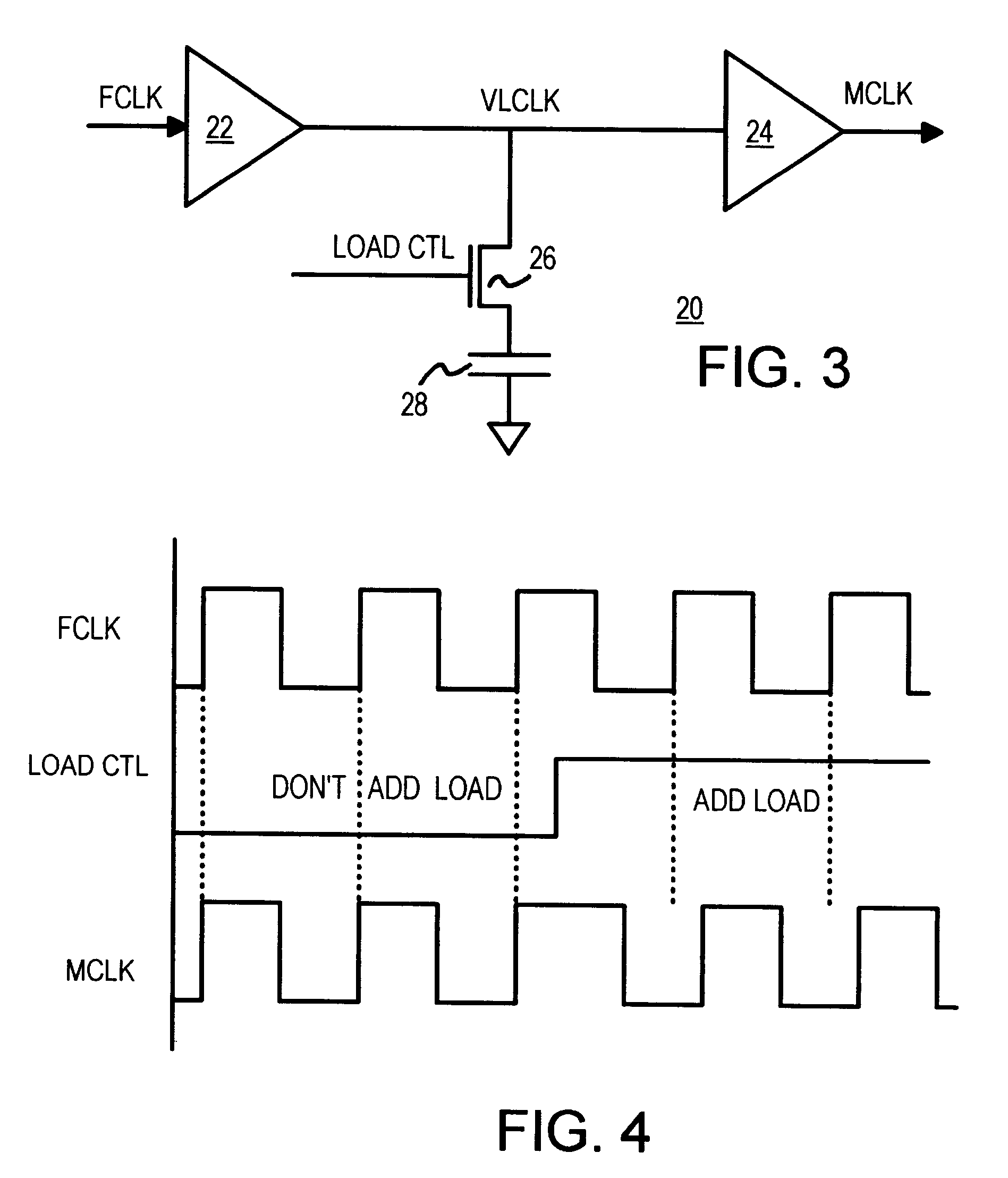
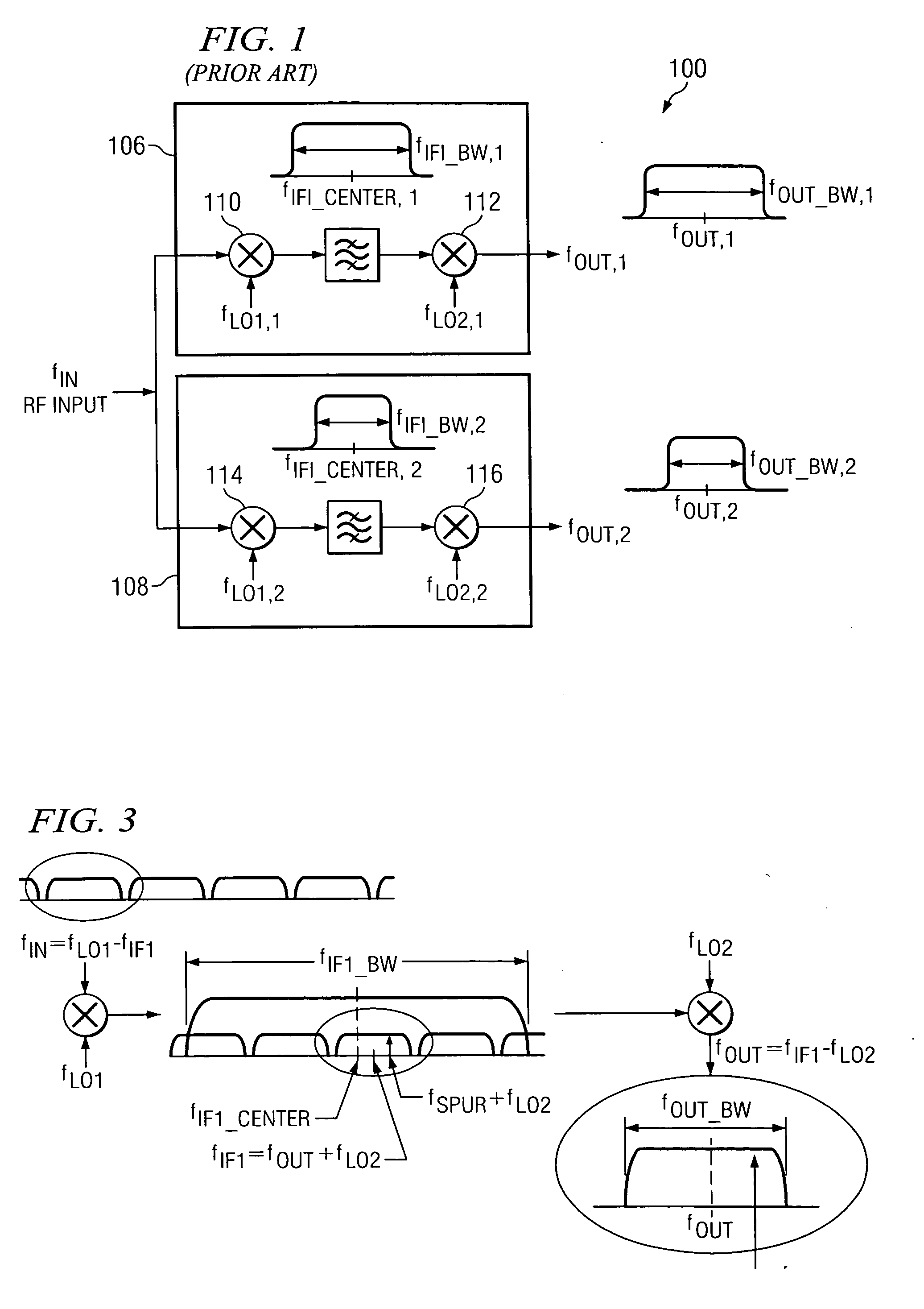
Spread-spectrum clock buffer/driver that modulates clock period by switching loads
A clock modulator spreads the frequency spectrum of an input clock to generate an output clock. A capacitor is connected to an intermediate clock node by a load-switching transistor. When the transistor is turned on, the capacitor increases the loading on the intermediate clock node, increasing delay. When the transistor is turned off, the delay is reduced. Output clock cycle periods are extended when delay is added, and reduced when the transistor turns off. A counter or sequencer is clocked by the input clock and drives the load-switching transistor. The transistor is turned on and off for alternate cycles when the counter is a toggle flip-flop, spreading the frequency over two frequencies every two clock cycles. Two capacitors of different sizes, connected to the intermediate clock node by two transistors, can be switched by a 2-bit sequencer, spreading the output clock over 7 frequencies every 7 clock cycles.
Owner:DIODES INC
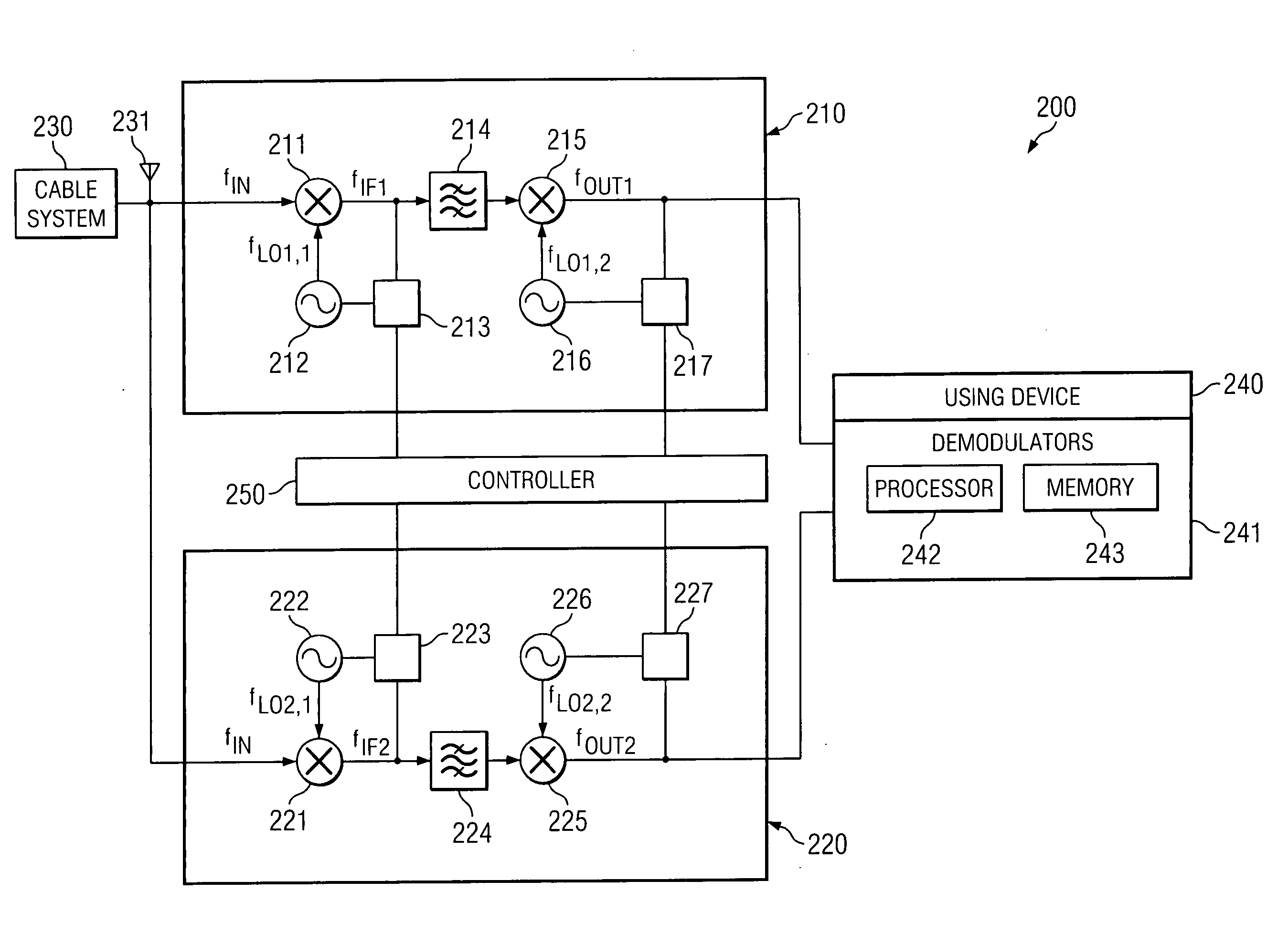
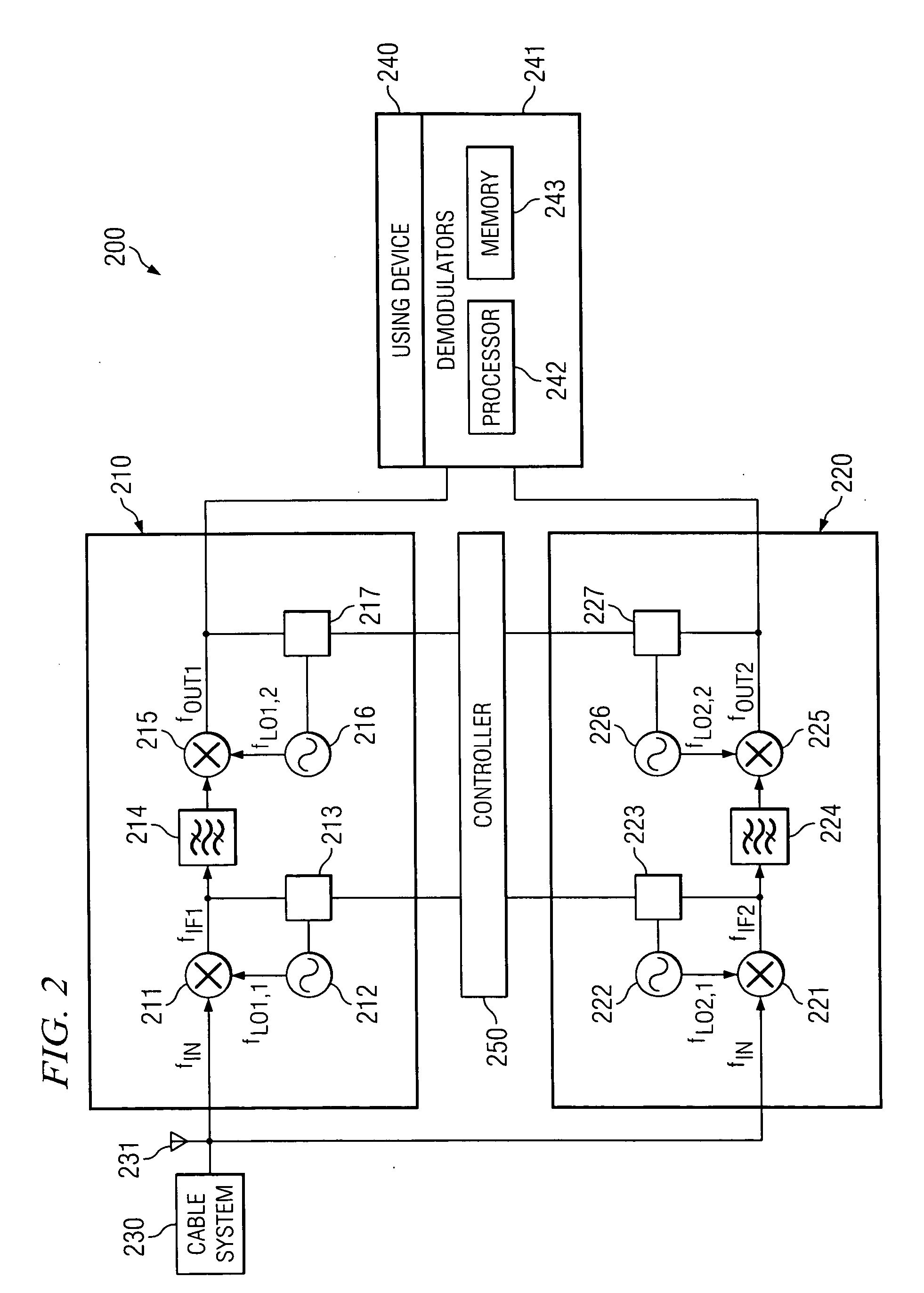
System and method of eliminating or minimizing LO-related interference from tuners
InactiveUS20060068708A1Reduce and eliminate interferenceGood choiceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHarmonicLocal oscillator
Disclosed are systems and methods of eliminating or reducing interference resulting from harmonics of local oscillator frequencies of mixers. In one embodiment, a determination is made as to a zone or zones in which harmonics result in undesired spur generation. Inter-tuner spurs and intra-tuner spurs may be identified such that frequency information of the identified spurs may be utilized to define a plurality of exclusion zones. LO frequencies may subsequently be efficiently selected in view of the exclusion zone information. Embodiments may also determine a score for identified spurs which may be used to optimally select from within a set of spur-generating local oscillator frequencies.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
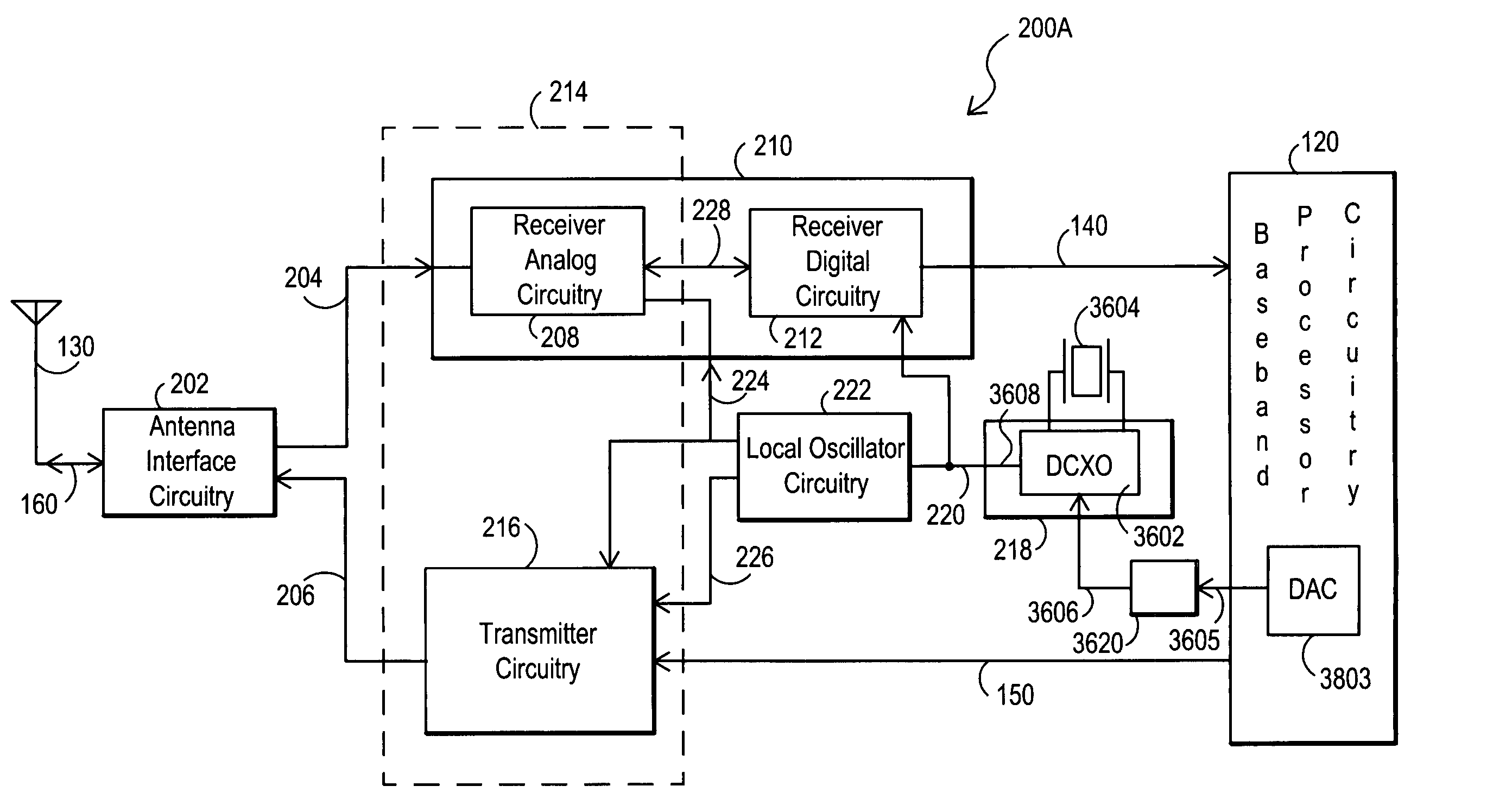
Systems and methods for providing an adjustable reference signal to RF circuitry
InactiveUS7035607B2Guaranteed interference effectReduce the impact of interferenceAutomatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayPulse automatic controlControl signalEngineering
Frequency modification circuitry may be employed as part of a crystal oscillator circuit to generate a reference signal with adjustable frequency. The frequency modification circuitry may be implemented as part of a crystal oscillator circuit that includes digitally controlled crystal oscillator (“DCXO”) circuitry and a crystal. The frequency modification circuitry may adjust the frequency of the reference signal in response to one or more frequency control signals. In one example, the frequency modification circuitry may include variable capacitors such as one or more continuously variable and / or discretely variable capacitors for providing coarse and / or fine adjustment of the reference signal frequency.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
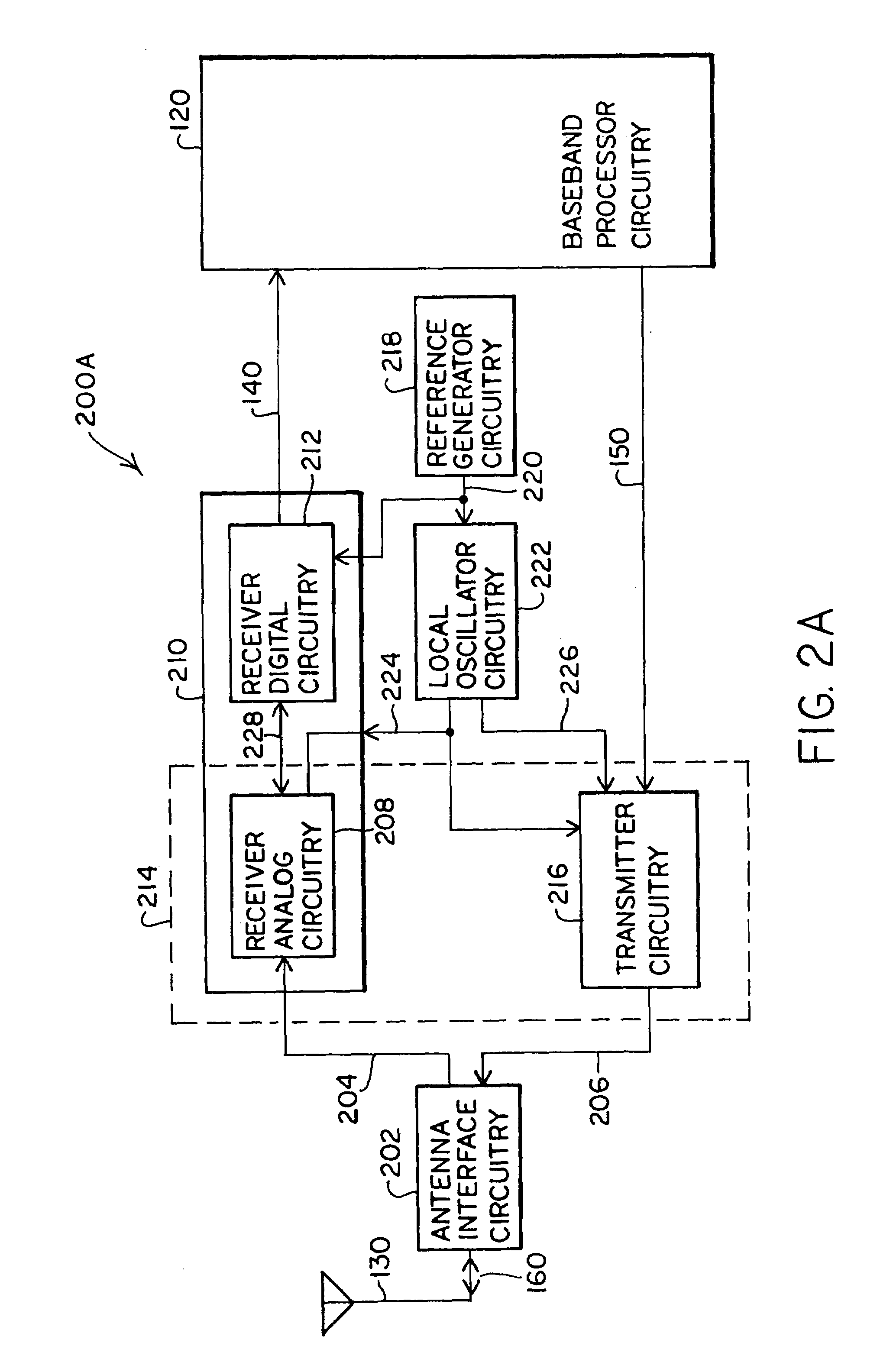
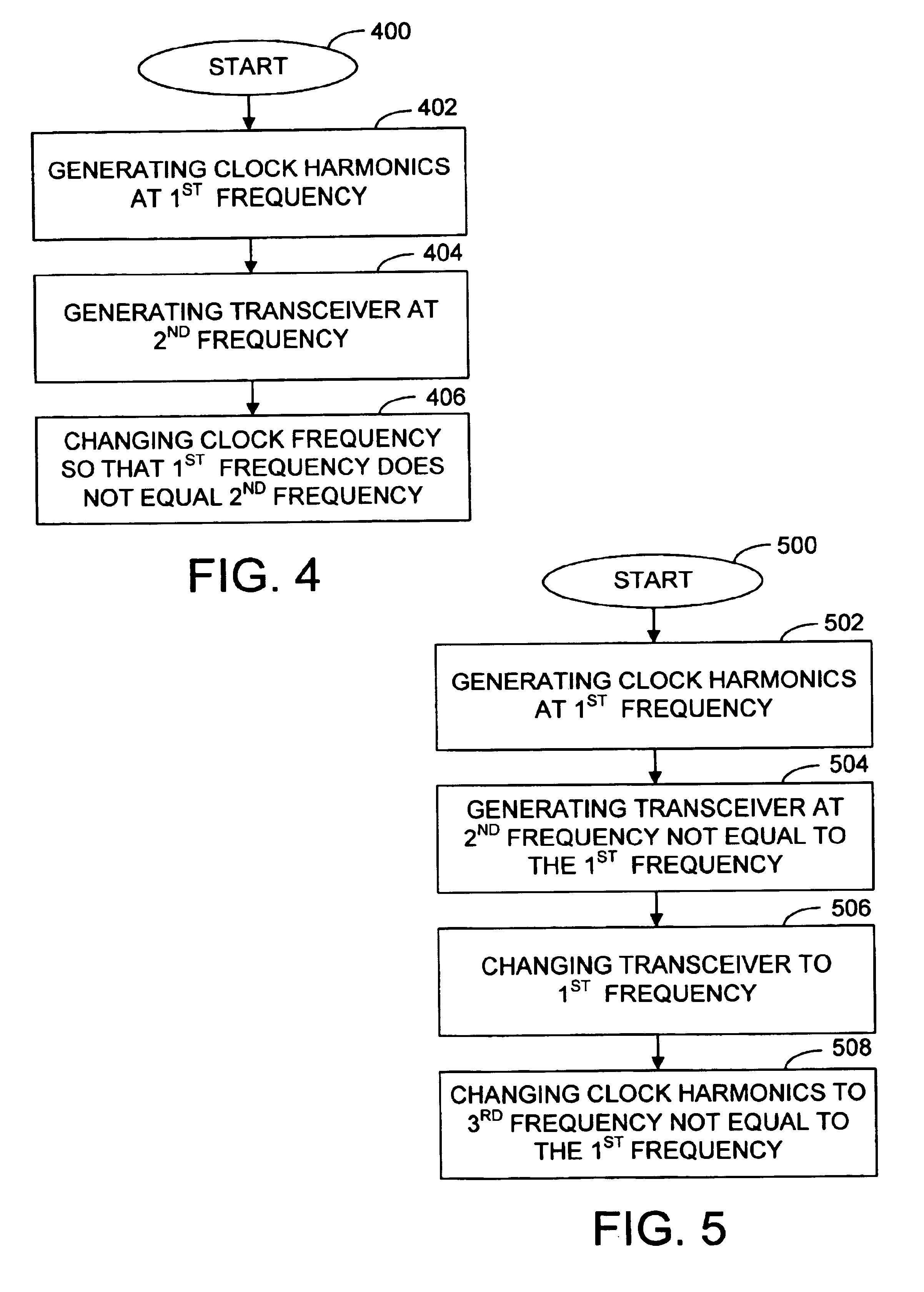
Selecting clock frequencies for baseband devices
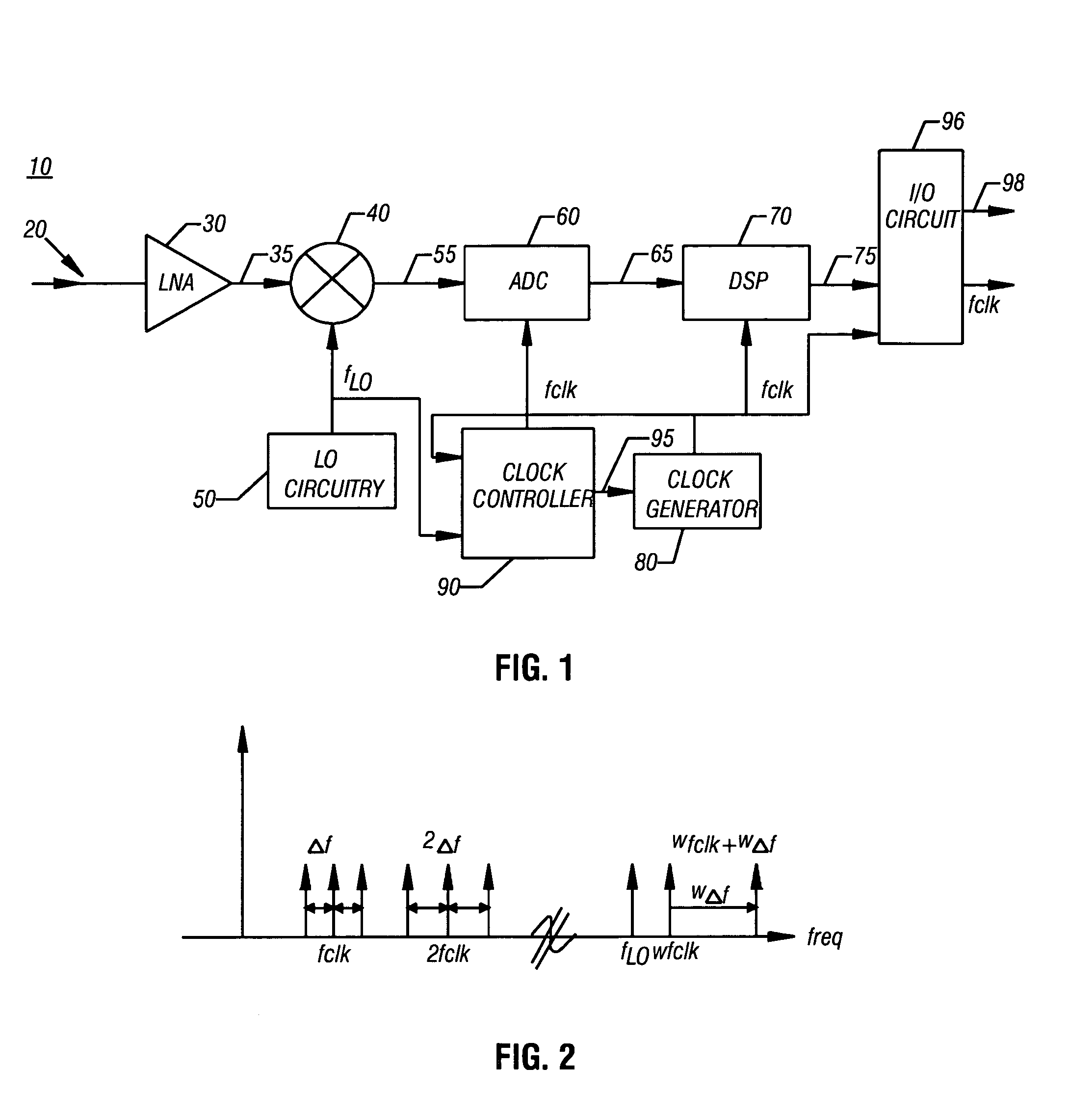
ActiveUS20050265486A1Avoid interferencePhase-modulated carrier systemsSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionFrequency spectrumClock rate
Various embodiments of the present invention include methods and apparatus for receiving a radio frequency (RF) signal spectrum in a receiver; mixing the RF signal spectrum with a first local oscillator (LO) frequency to obtain a first downmixed signal; and converting the first downmixed signal to a first digital signal using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) having an adjustable clock frequency selected to avoid interference with the first LO frequency. The adjustable clock frequency may be adjusted by a predetermined amount, by phase modulation, or in other manners.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
IC receiver to minimize tracking error
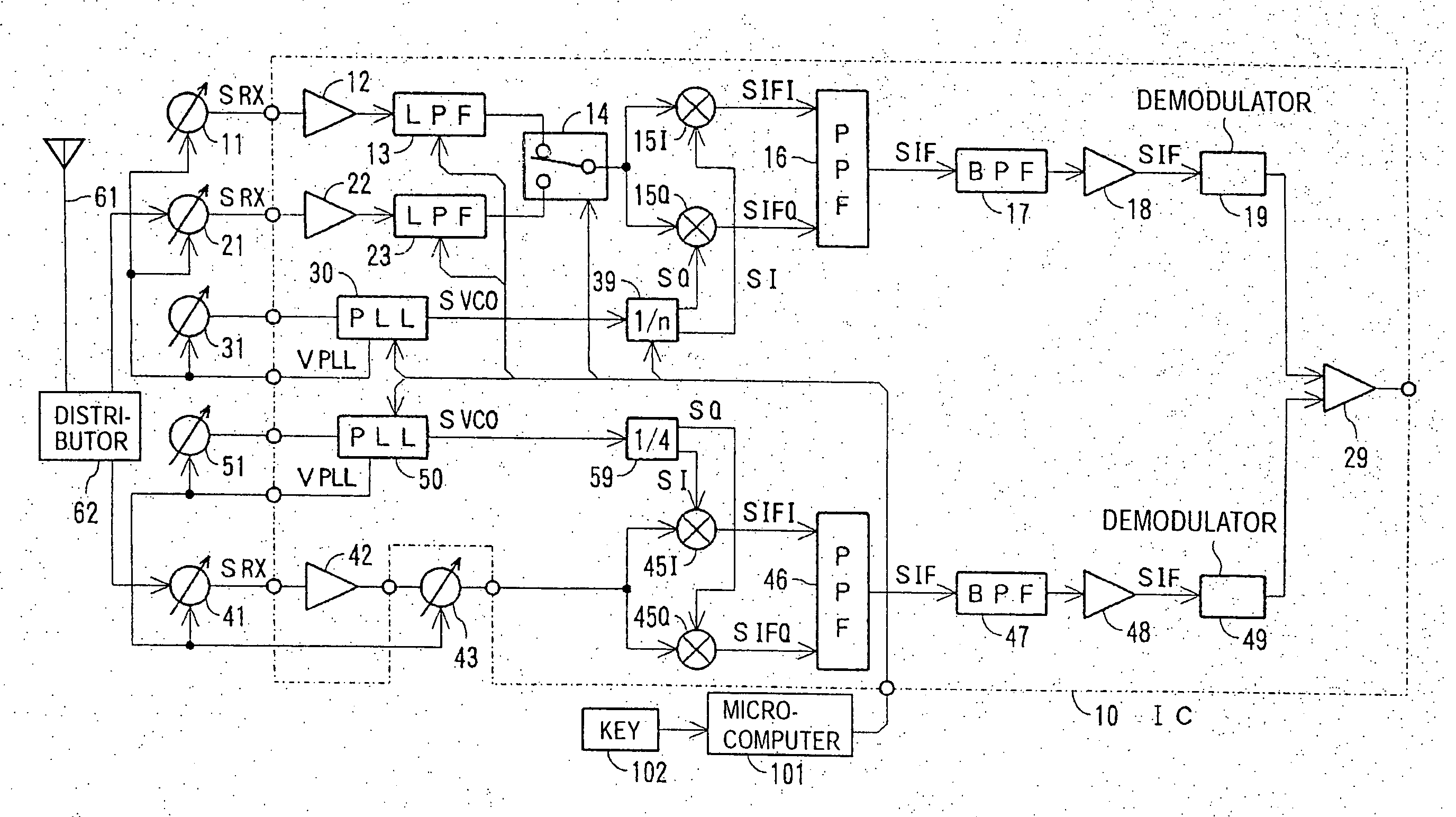
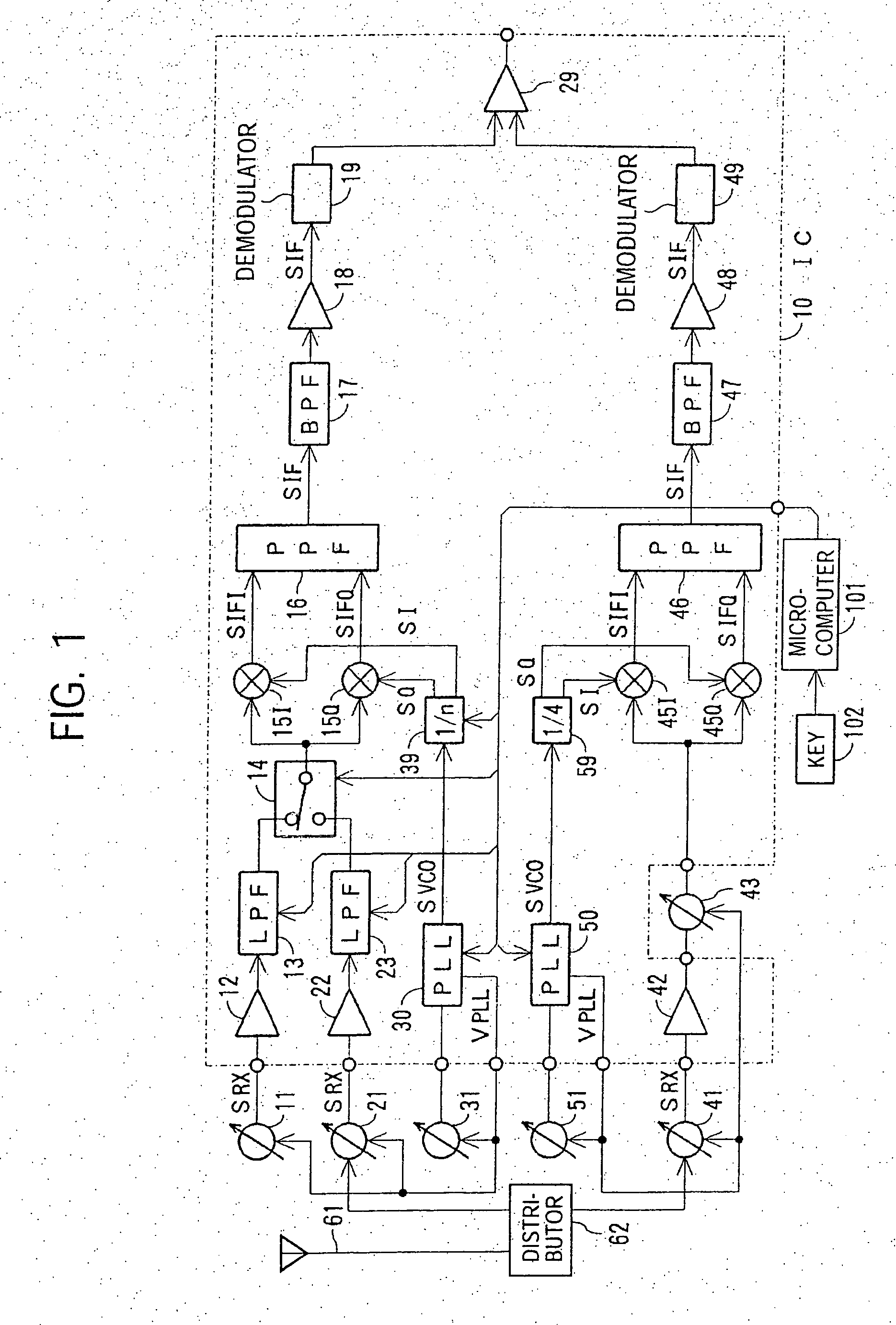
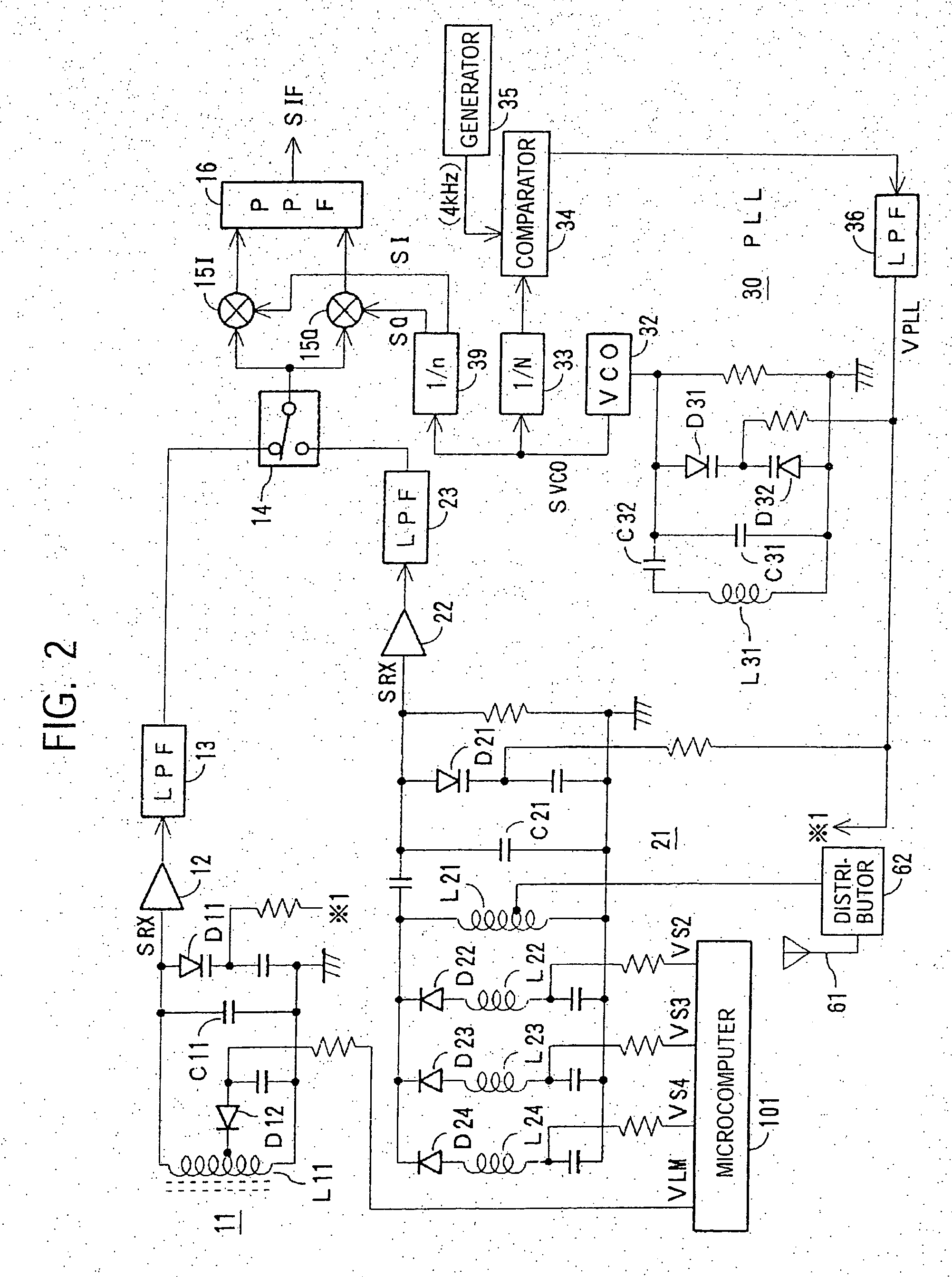
InactiveUS20070004371A1Low costReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionMulti bandFrequency conversion
A multi-band receiver in which characteristics including a tracking error are improved is provided with a variable frequency oscillator circuit, a variable divider circuit (39) for dividing an oscillation signal (SVCO) of the variable frequency oscillator circuit, and mixer circuits (15I) and (15Q) for subjecting a received signal SRX to frequency conversion into an intermediate frequency signal (SIF) by a local oscillation signal (SLO). A divided output of the variable divider circuit (39) is supplied as the local oscillation signal (SLO) to each of the mixer circuits (15I) and (15Q). When a signal in a first frequency band is received, the division ratio n of the variable divider circuit (39) and the oscillation frequency of the variable frequency oscillator are changed to change the reception frequency in the first frequency band. When a signal in a second frequency band is received, at least the oscillation frequency of the variable frequency oscillator circuit is changed to change the reception frequency in the second frequency band.
Owner:SONY CORP
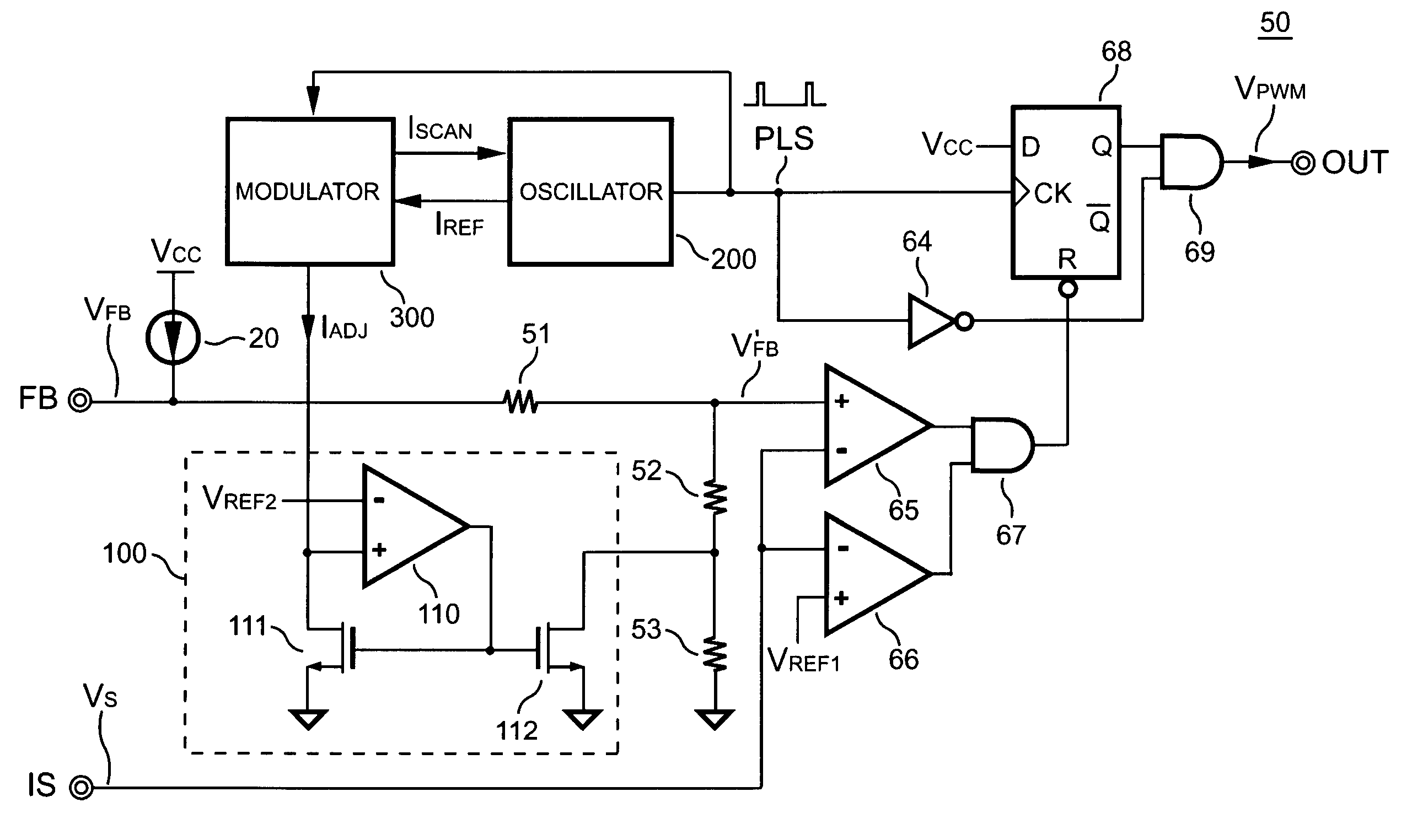
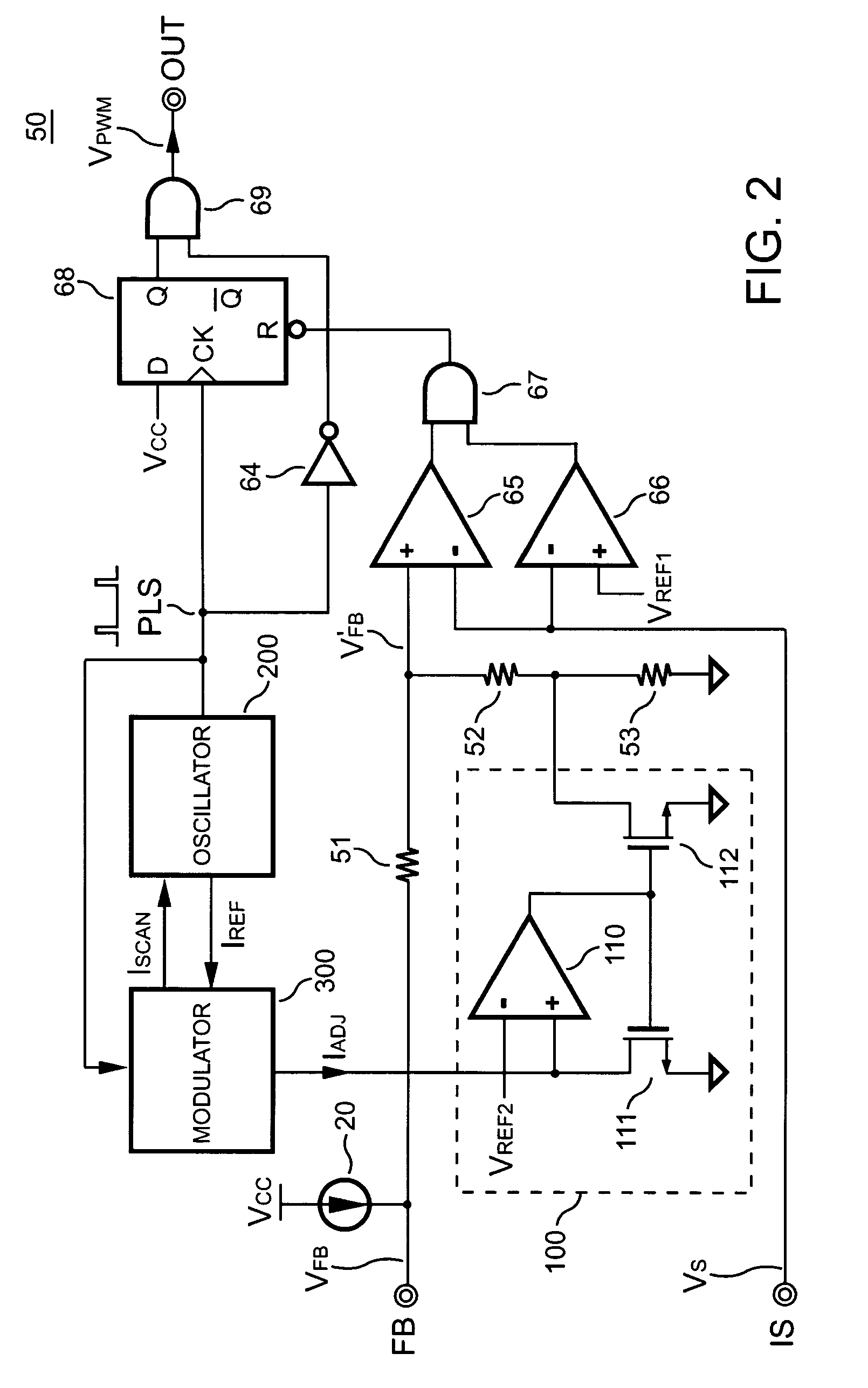
PWM controller having frequency jitter for power supplies
ActiveUS7026851B2Undesired ripple signal can be eliminatedLower impedanceDc-dc conversionElectric pulse generatorUltrasound attenuationAttenuation ratio
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
System and method for enhanced interoperability between a plurality of communication devices
InactiveUS20050191964A1Avoid interferenceInterference minimizationHybrid switching systemsData switching by path configurationTime domainTransceiver
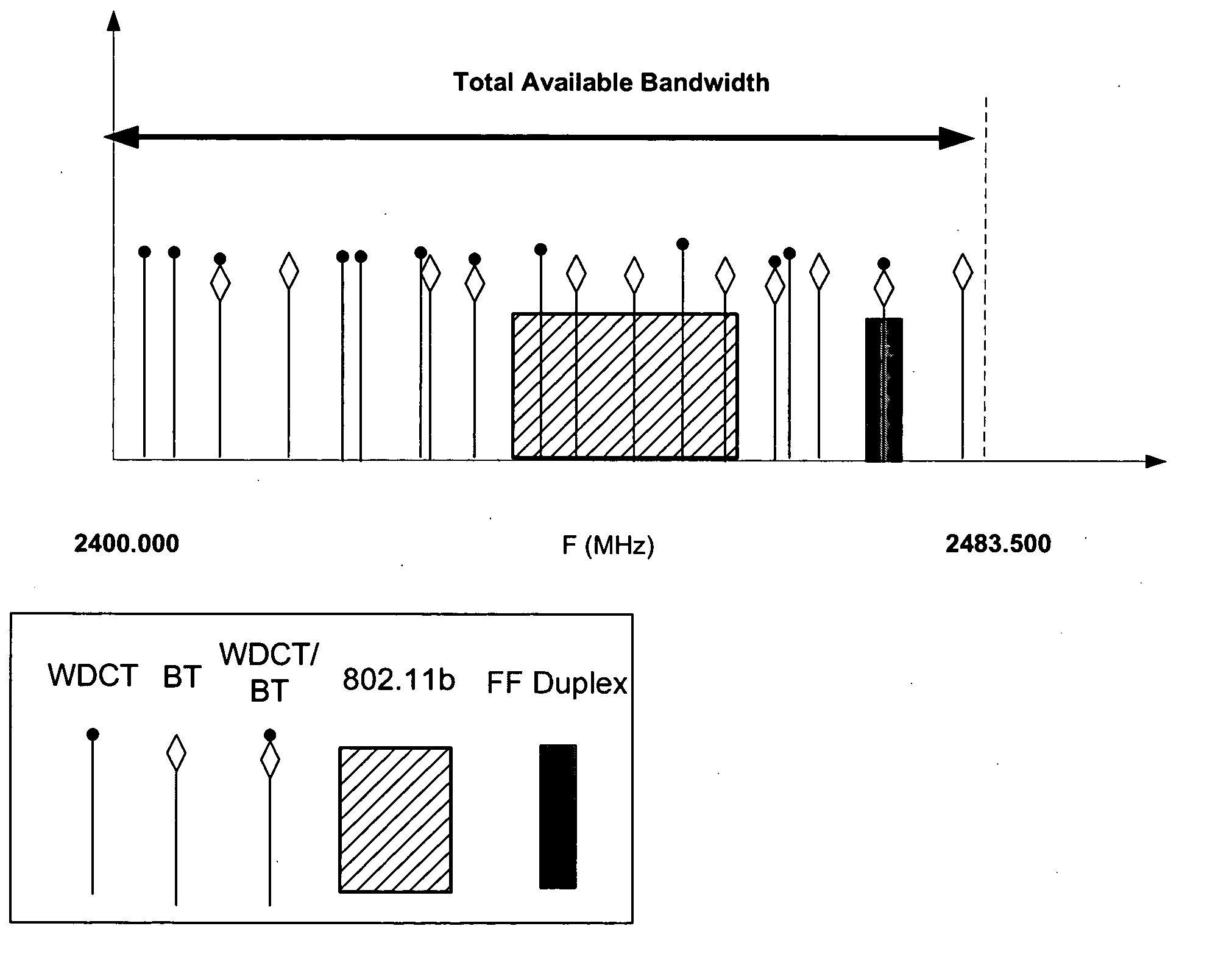
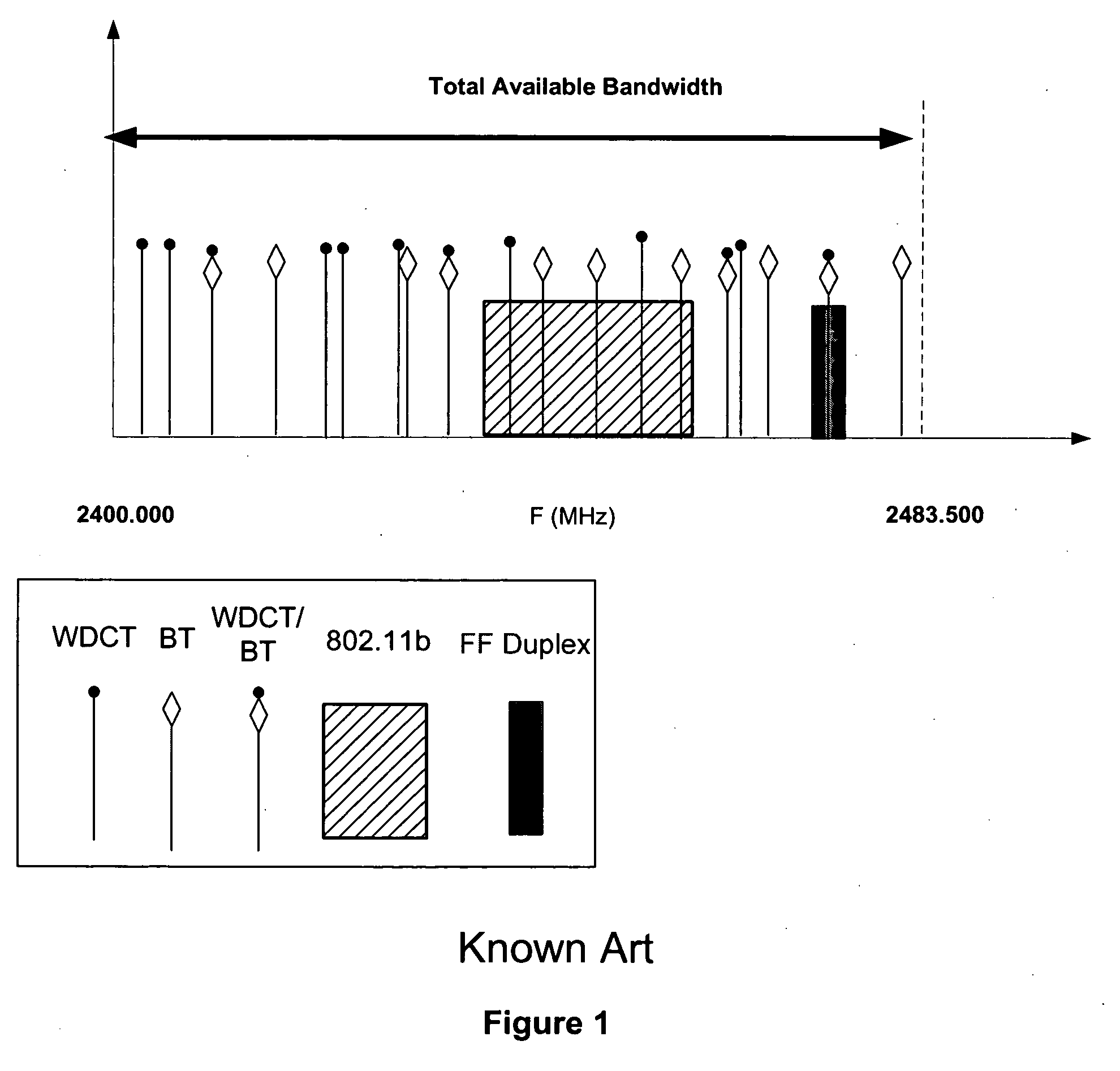
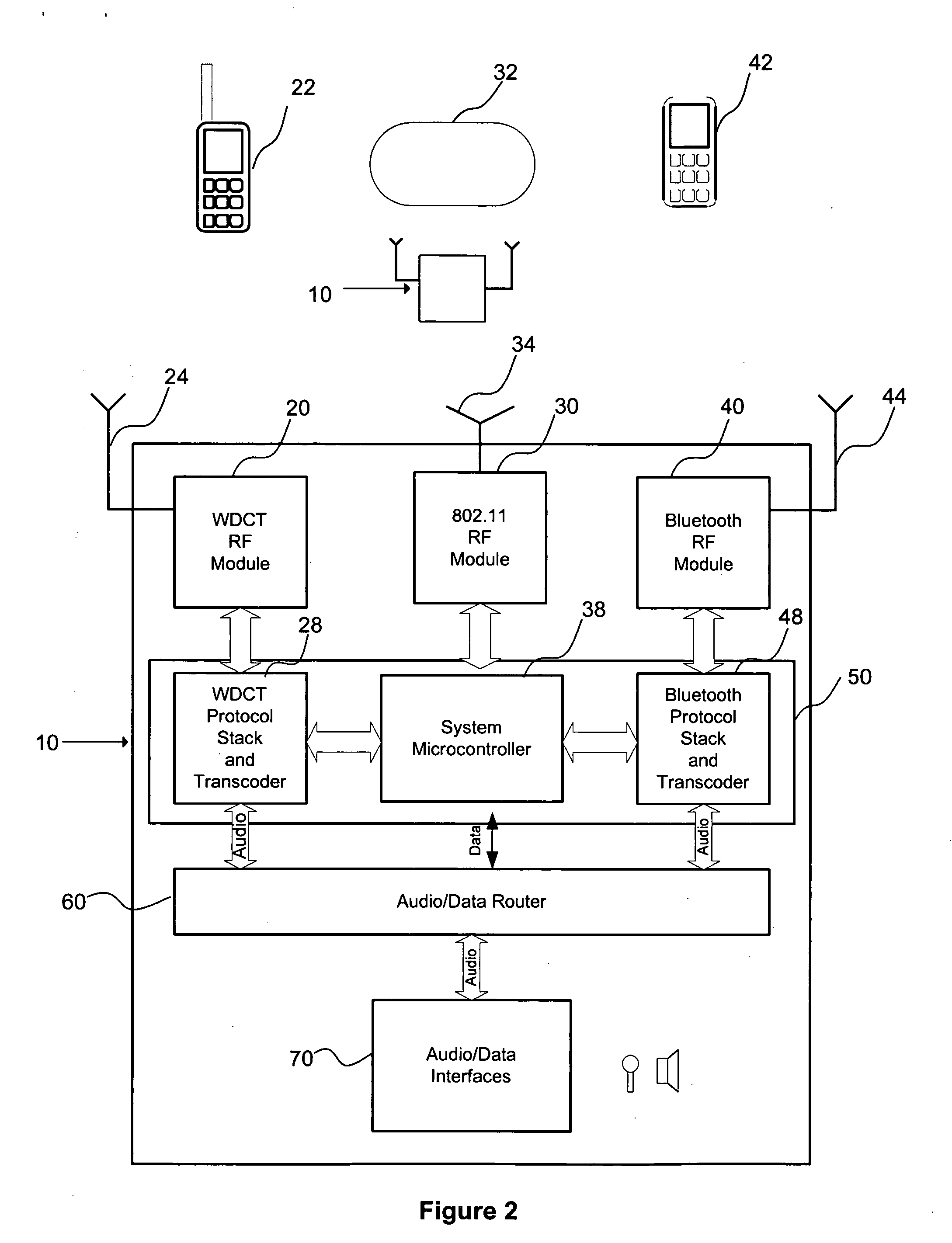
A system for allowing BT, WDCT, and 802.11 transceivers to operate in close proximity with a minimum of interference, is disclosed. In an exemplary embodiment, a method for avoiding interference between a first FHSS device and other RF devices using 802.11 or FHSS protocols is disclosed. The first FHSS device initially detects the presence of an interfering RF device (“interferer”), for example a device employing 802.11 protocol, and adjusts the frequency of channels used for operation of the first device accordingly to avoid overlap with the 802.11 band. In the presence of an additional interferer, for example, a second FHSS device emitting an interfering signal, the first FHSS device may segregate its operation channels to achieve maximum frequency separation from an 802.11 and second FHSS device. In addition, the first and third devices may also multiplex their transmit / receive timing to avoid interference in time domain. By avoiding interference in time domain, first and third device can occupy the same channels in the frequency band achieving further frequency separation from the 802.11 device.
Owner:VTECH TELECOMM
Method and system for a second order input intercept point (IIP2) correction
In RF transceivers, a method and system for a second order input intercept point (IIP2) correction are provided. A DC offset sensor may detect DC offset voltages produced by blocker signals in “I” and “Q” signal component paths in an RF receiver. The DC offset sensor may generate control signals which may be utilized by a first and second injection circuits to generate DC offset currents that compensate for the DC offset voltages in the signal component paths. An injection circuit may utilize current drivers to generate binary weighted currents which may be added together to produce a DC offset current. The polarity of the DC offset current and the selection of which current drivers to use may be determined by the control signals. A calibration voltage may also be utilized to correct or adjust the gain in the injection circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
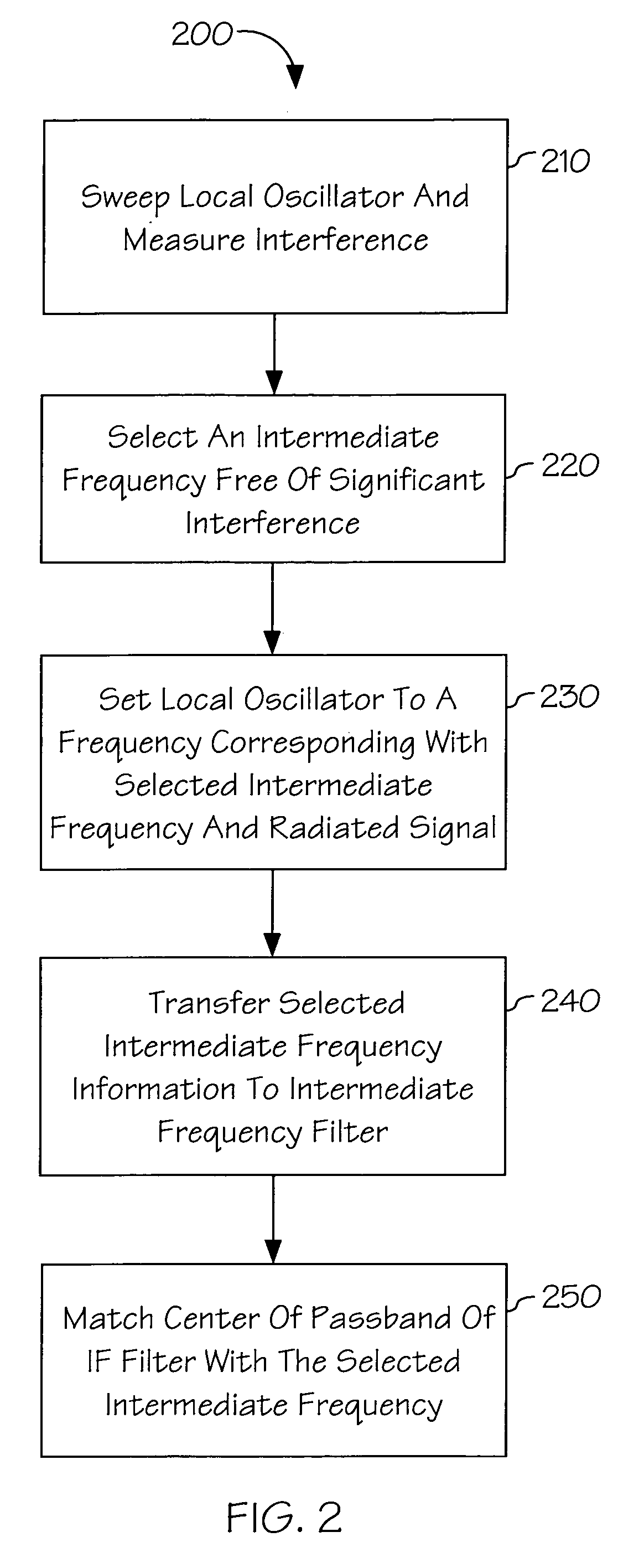
Intermediate frequency tuner
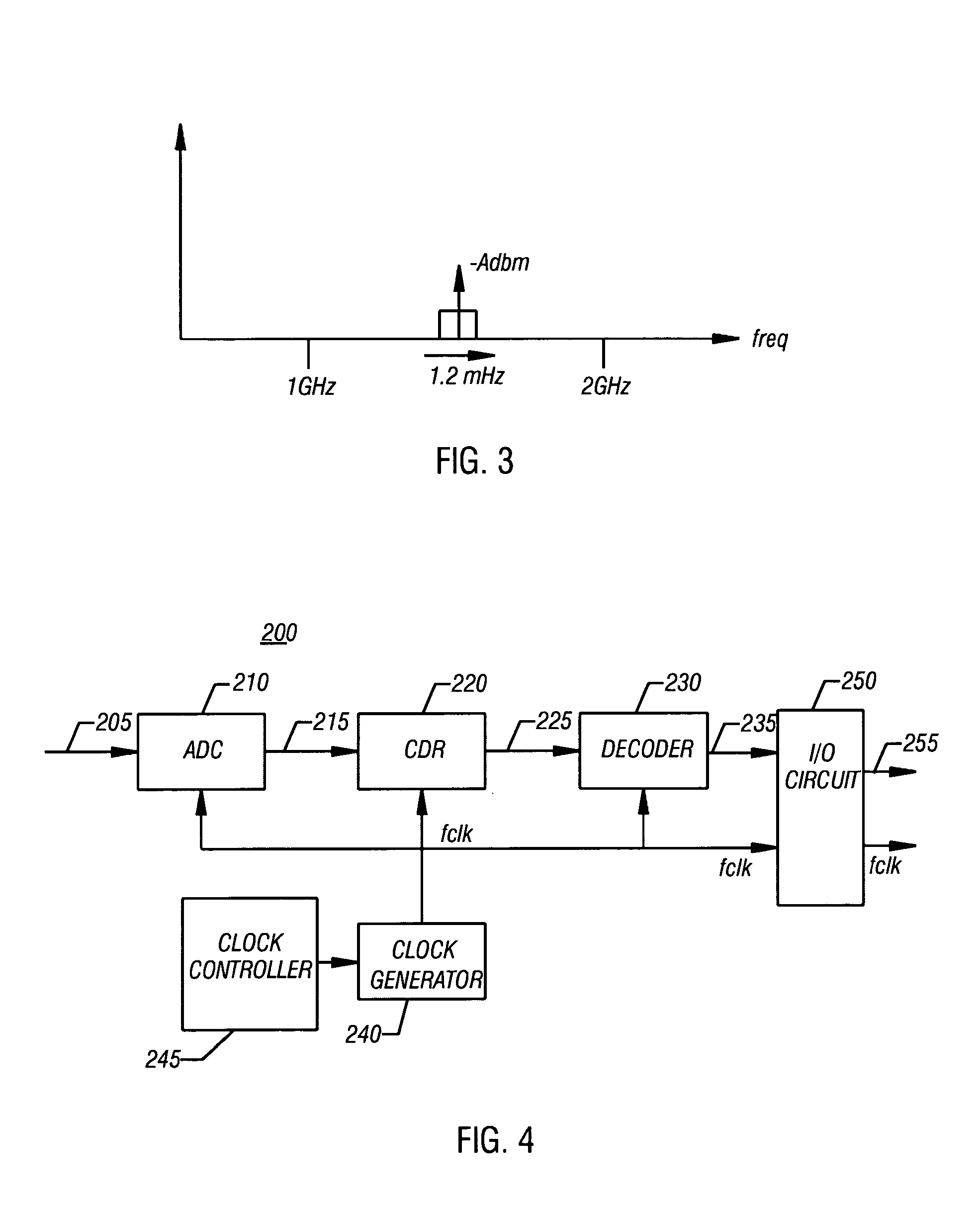
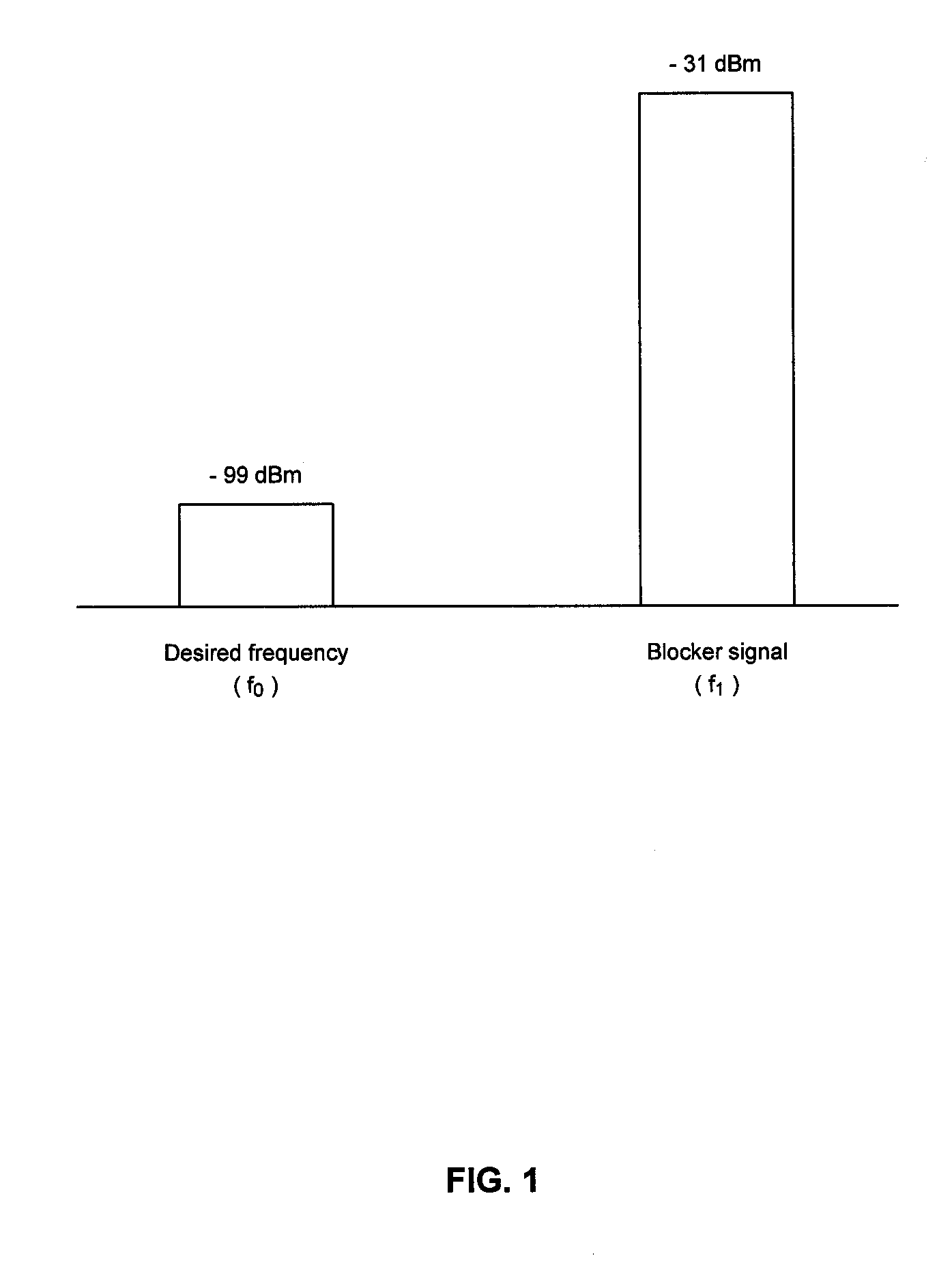
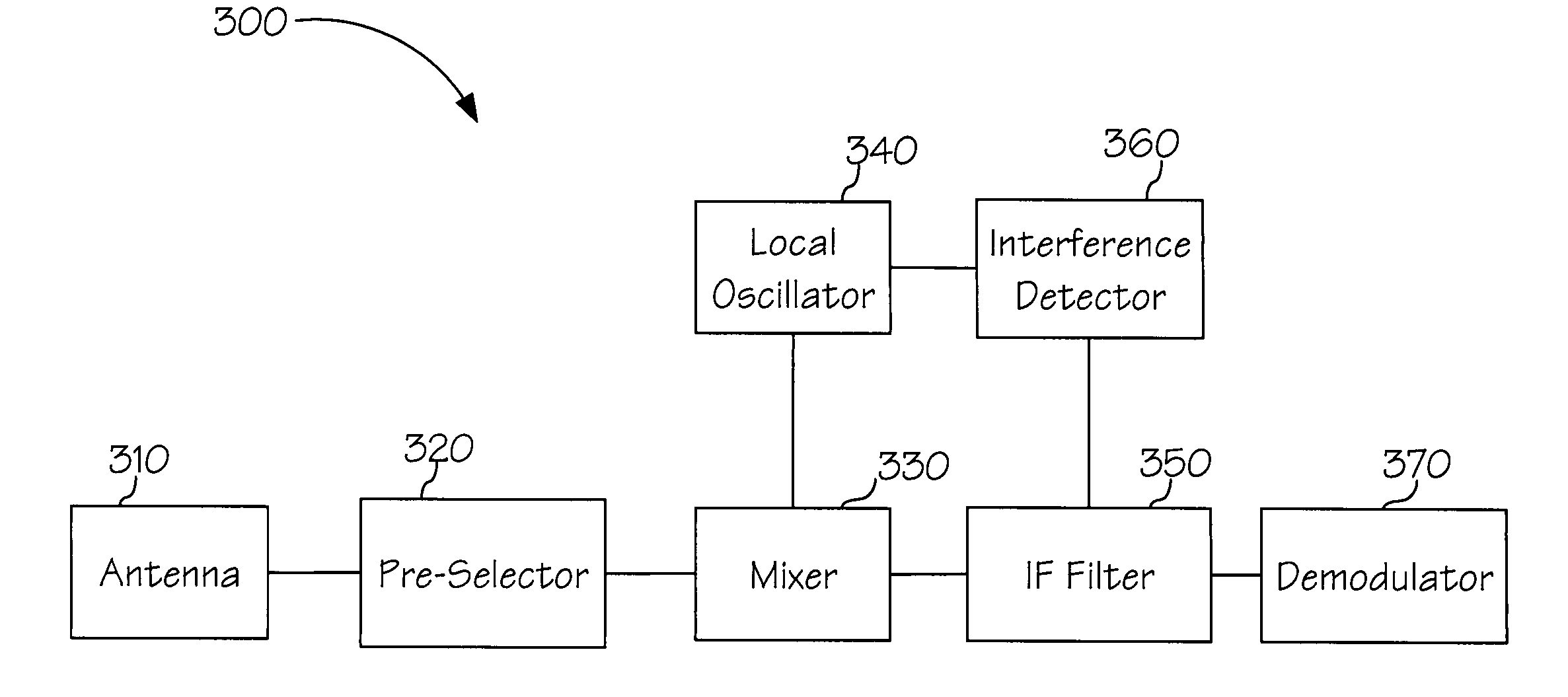
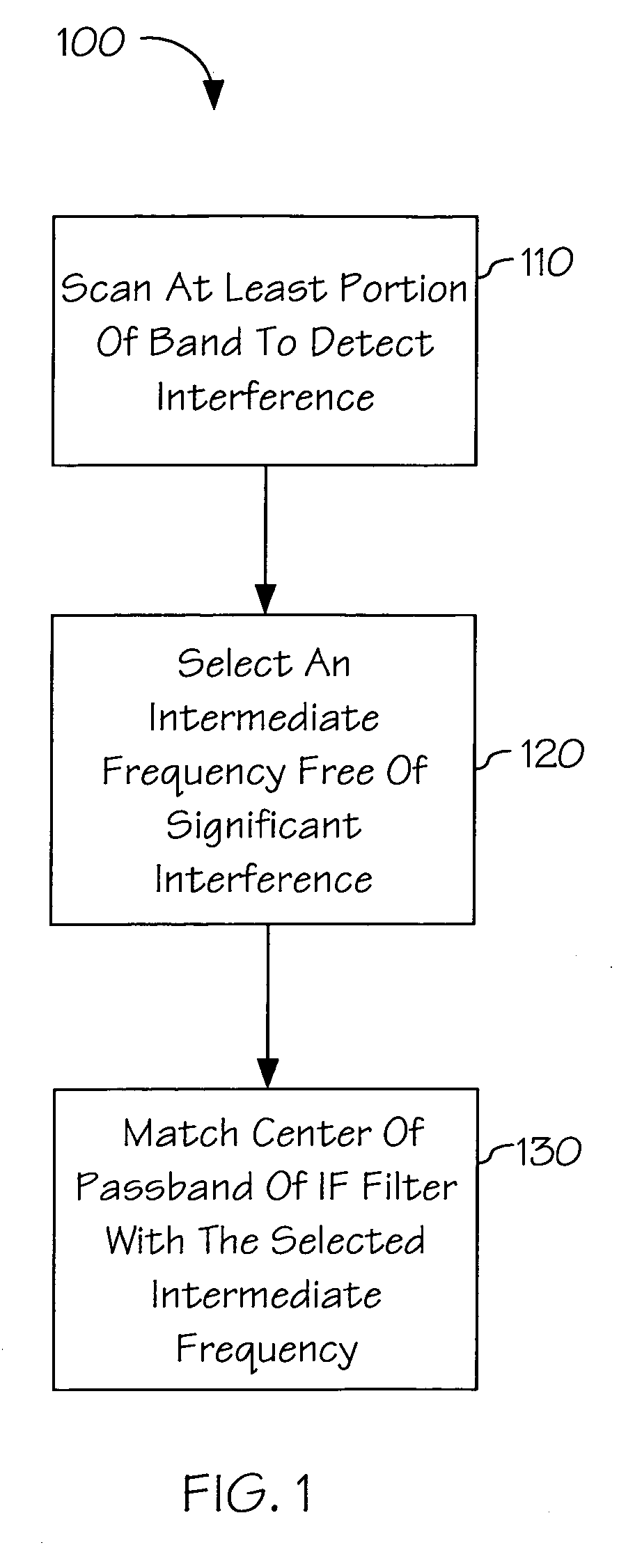
InactiveUS7155196B1Improve transceiver performanceImprove performanceTransmission monitoringSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionTransceiverIntermediate frequency
The present invention is a method and apparatus for optimizing performance of a transceiver selecting and processing an intermediate frequency free of significant interference, such as noise. A frequency band may be scanned to detect interference upon which an intermediate frequency free of significant interference may be selected. This may enhance performance of the receiver by reducing the effects of noise. Additionally, perrformance may be further optimized by adjusting the passband of the filter such that the center of the passband matches the selected intermediate frequency. This may provide stability as centering of the passband may account for process, voltage and temperature variations and errors. Further, performance may be enhanced by ensuring desirable signal attributes are passed through the filter.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Television receiver suitable for multi-standard operation and method therefor
ActiveUS20050266818A1Television system detailsModulation transferenceFrequency spectrumLocal oscillator signal
A receiver (1100) includes a direct digital frequency synthesizer (130), a mixer (105), and a clock source (1110, 1130). The direct digital frequency synthesizer has an input terminal for receiving a first clock signal at a first frequency, and an output terminal for providing a digital local oscillator signal synchronously with the first clock signal. The mixer (105) has a first input terminal for receiving a radio frequency (RF) signal, a second input terminal coupled to the output terminal of the direct digital frequency synthesizer (130), and an output terminal for providing an IF signal having a spectrum centered about a selectable one of a plurality of center frequencies. The clock source (1110, 1130) has an output terminal for providing the first clock signal without using any harmonic frequency that overlaps the spectrum for any of the plurality of center frequencies.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
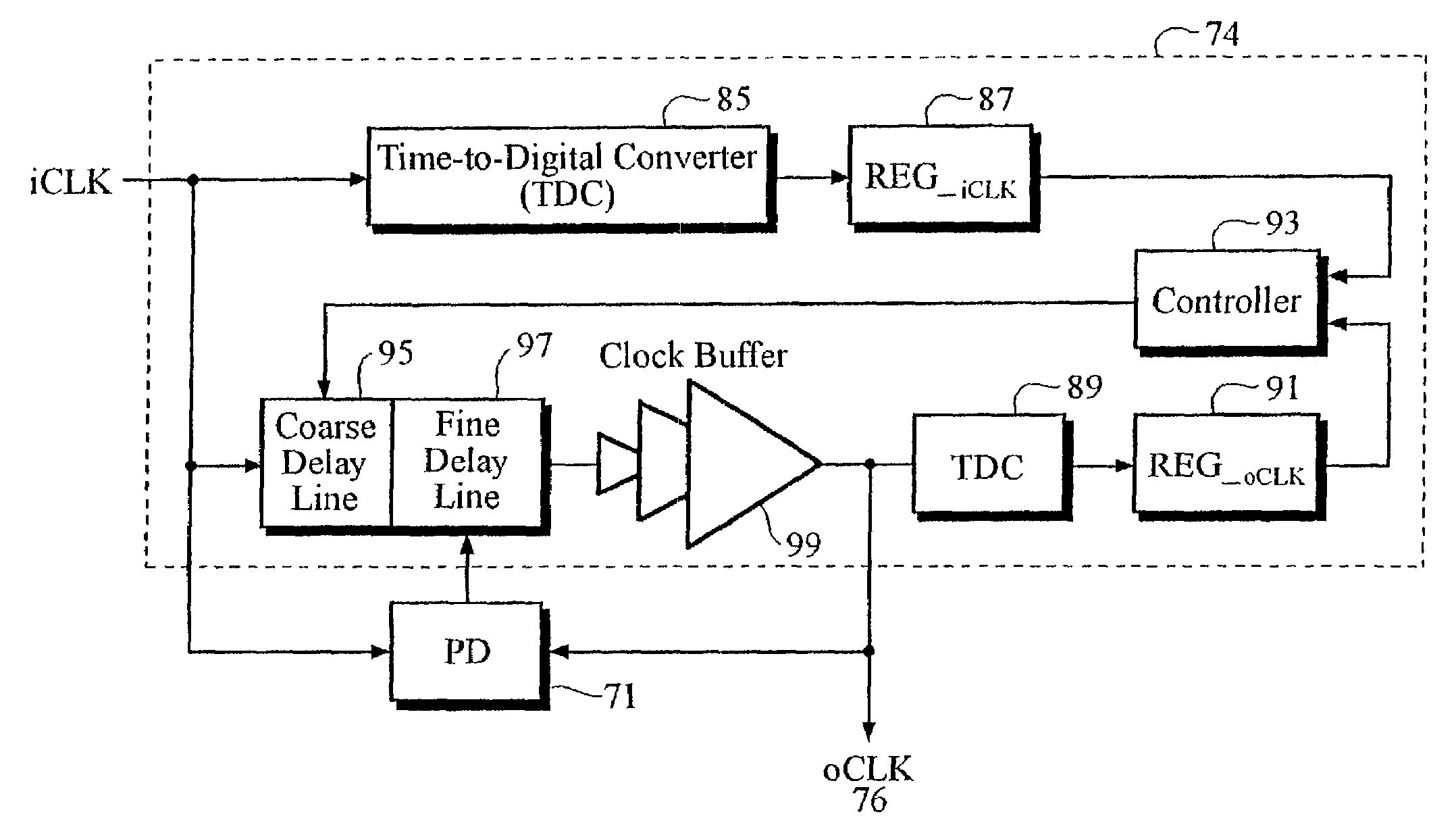
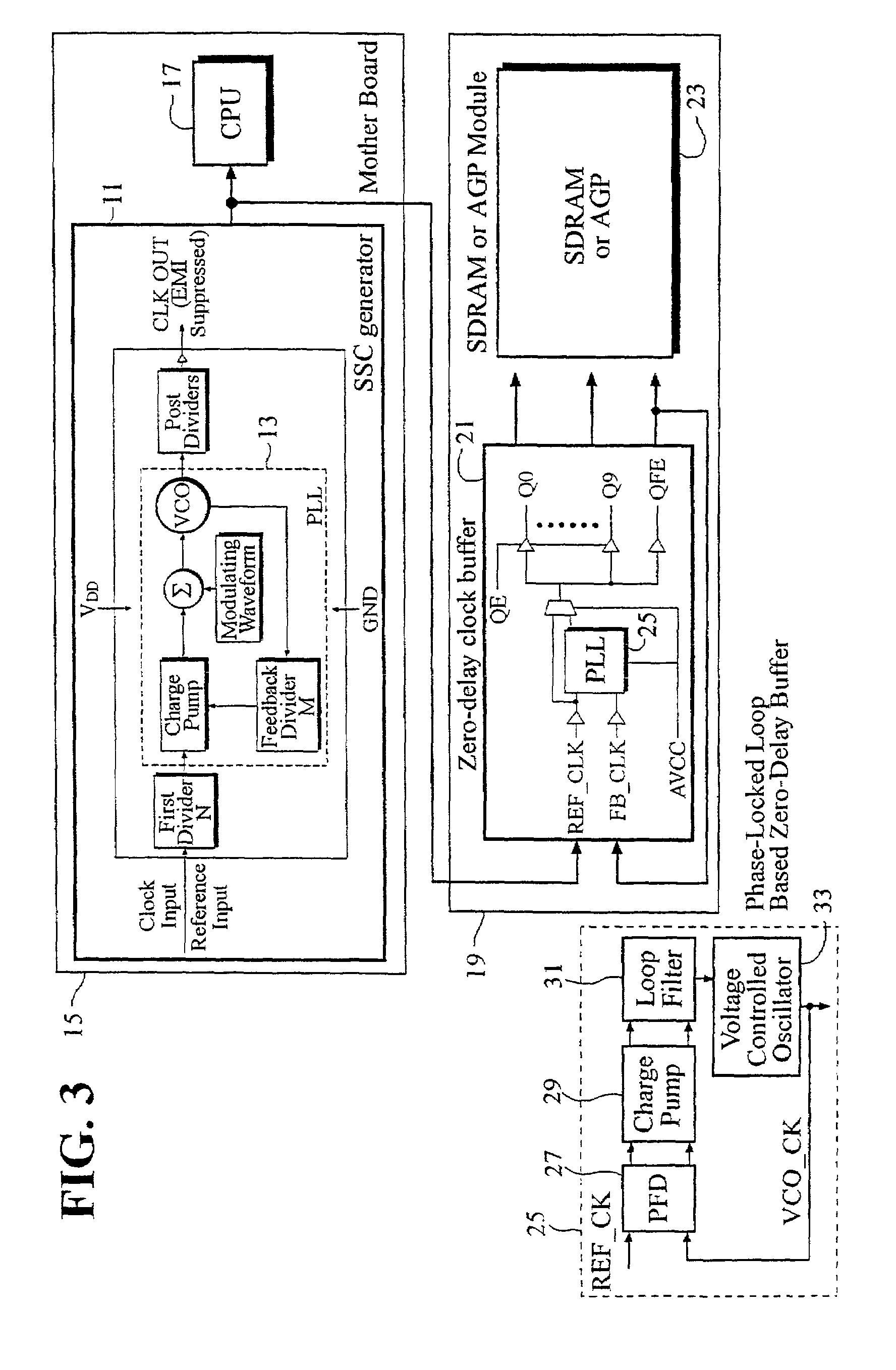
Zero-delay buffer circuit for a spread spectrum clock system and method therefor
InactiveUS6993109B2Improve efficiencyEliminate phase differencePulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsPhase detectorPhase difference
A clock recovery circuit and a method for reducing electromagnetic emission (EMI) and increasing an attainable clock frequency includes a spread spectrum clock (SSC) generator that receives an input clock signal and generates a frequency-modulated clock signal, and a zero-delay buffer circuit that receives and buffers said modulated clock frequency signed to generated an output clock signal. The frequency-modulated clock signal and the output clock signal are phase-aligned such that there is no phase difference between the output clock signal and the modulated frequency clock signal. The clock recovery circuit also includes a delay-locked loop (DLL) circuit that reduces related art jitter and skew characteristics, and a phase detector circuit that eliminates phase ambiguity problems of a related art phase detector.
Owner:ANAPASS
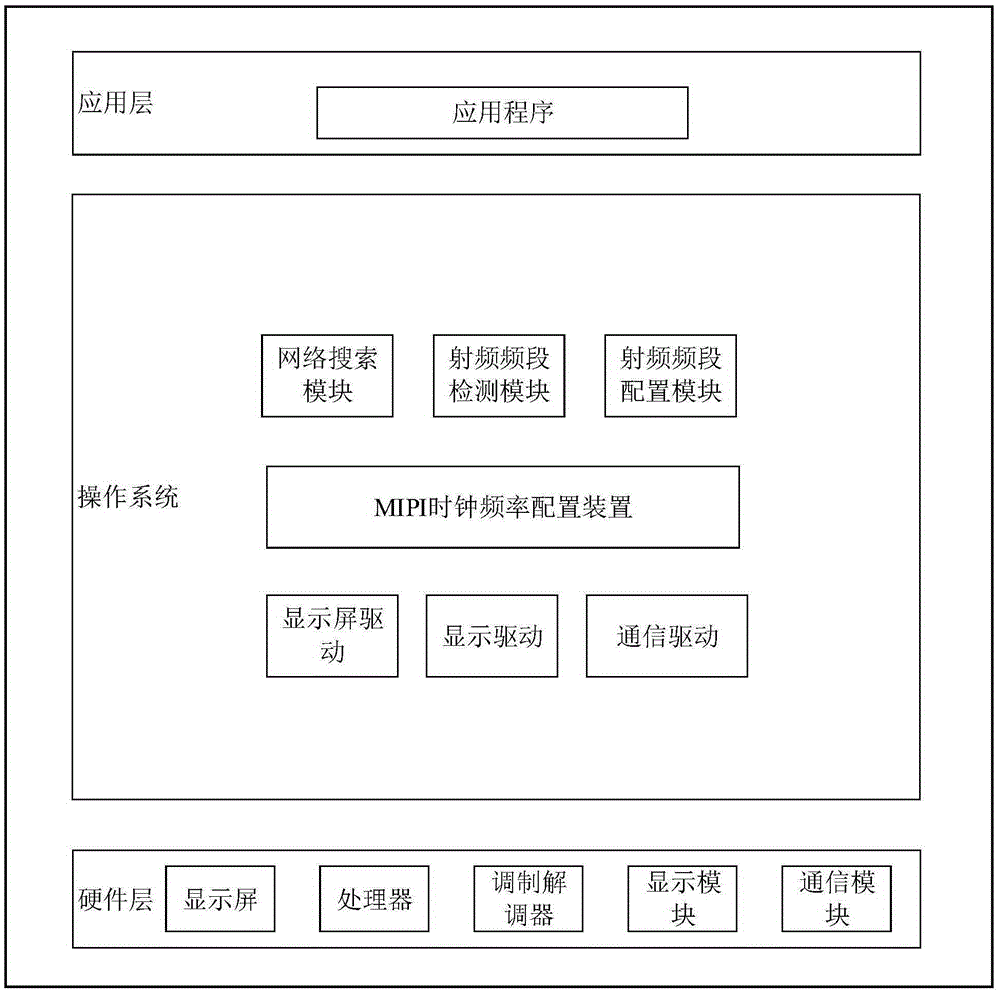
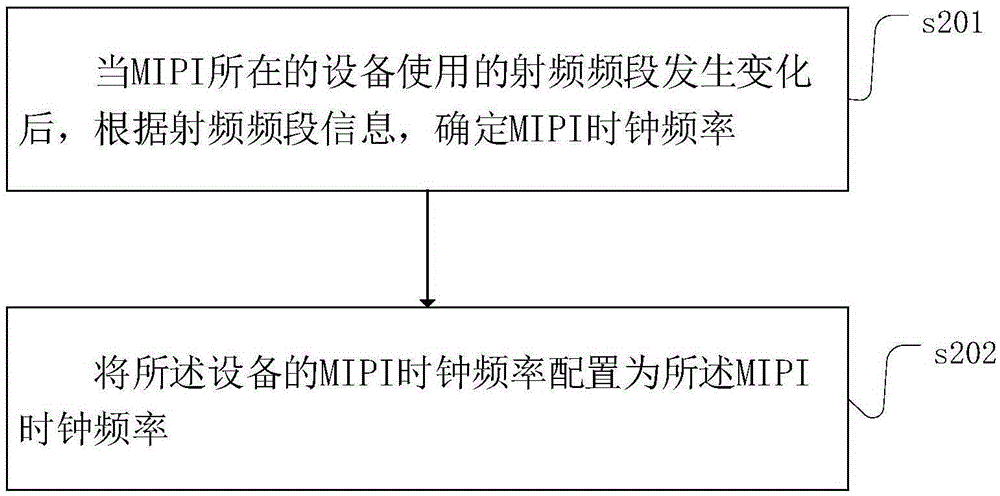
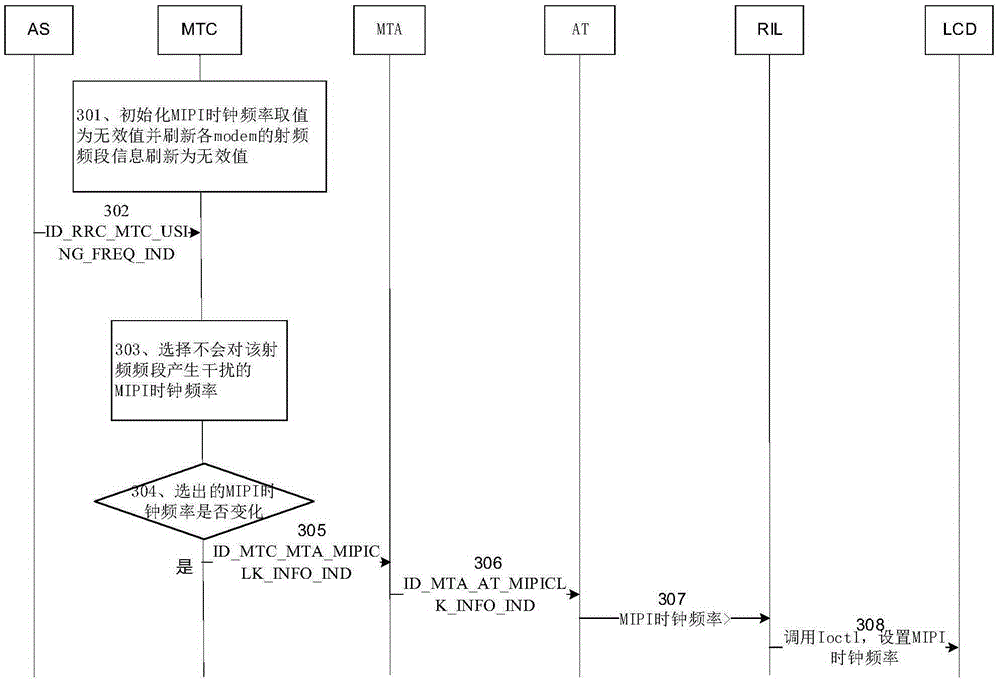
Method and device for reducing interference of mobile industry processor interface to communication quality
ActiveCN105357033AInterference will notImprove communication qualityPower managementCathode-ray tube indicatorsCommunication qualityRadio frequency
The invention provides a method and a device for configuring a clock frequency of a mobile industry processor interface (MIPI). When a radio frequency band used by a device in which the MIPI is changes, an MIPI clock frequency is determined according to radio frequency band information, wherein the radio frequency band information comprises a radio frequency band used by the device at present, and the determined MIPI clock frequency does not interfere with the radio frequency band used by the device at present; and the MIPI clock frequency of the device is configured to be the determined MIPI clock frequency. Through adoption of the method, when the radio frequency band of the device changes, the MIPI clock frequency does not interfere with the communication of the device, so that device communication quality and stability are improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
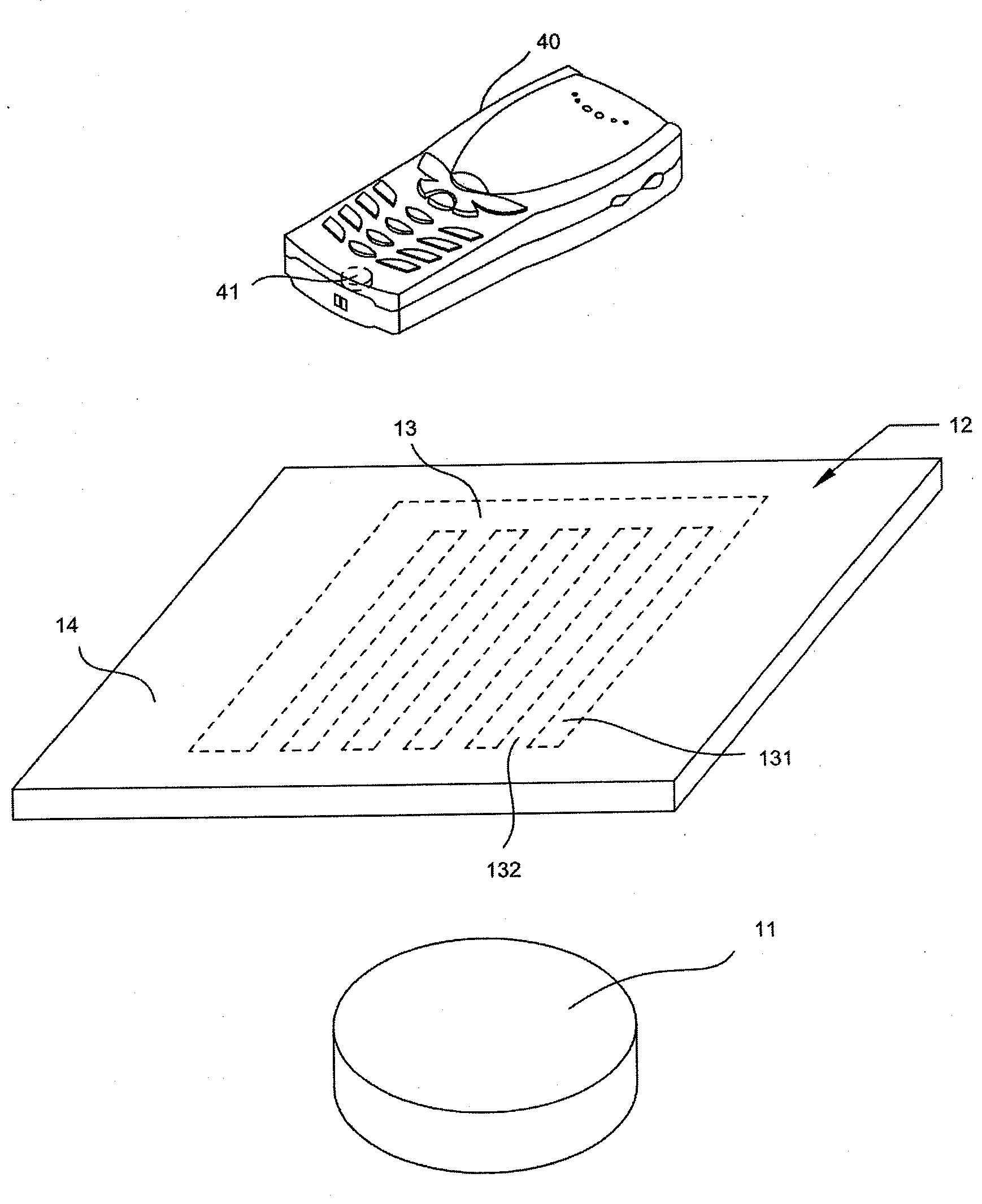
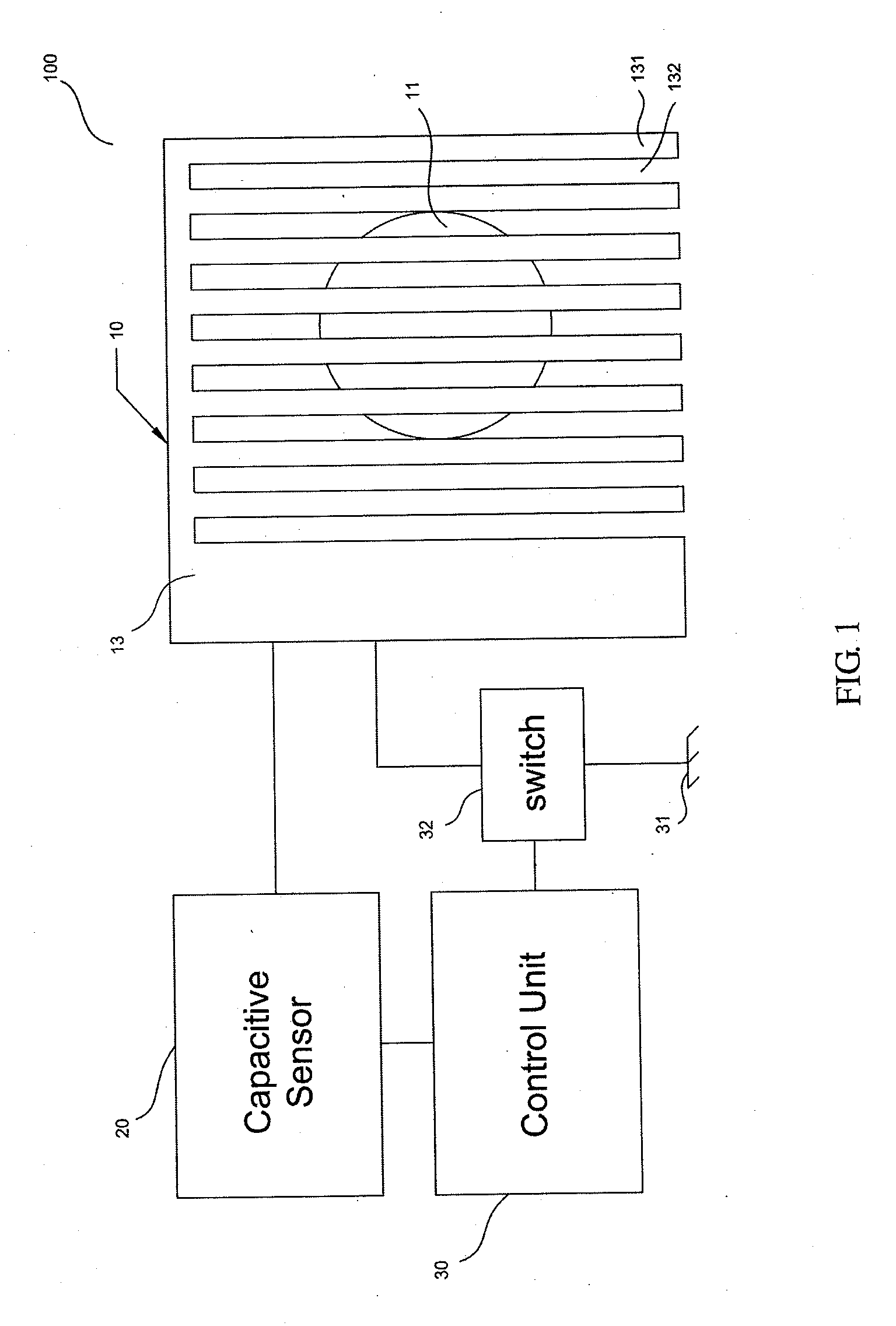
Wireless charger with combined electric radiation shielding and capacitive sensing functions
InactiveUS20140197782A1TransformersPower network operation systems integrationElectricityCapacitive sensing
A wireless charger with combined electric radiation shielding and capacitive sensing functions is provided. The wireless charger comprises a charging module, a capacitive sensor, and a control unit. The charging module comprises a first coil, a placing area, and a comb-shaped shielding located between the placing area and the first coil. The capacitive sensor is connected to the comb-shaped shielding to detect the capacitance varient between the comb-shaped shielding and the environment. When the wireless charger is in a standby mode, the comb-shaped shielding is for sensing capacitance. When the capacitance varient exceeds a predefined threshold and an electronic device for wireless charging is placed on the placing area, the control unit switches the wireless charger to a charging mode and the comb-shaped shielding is for electric radiation shielding.
Owner:LITE ON TECH CORP
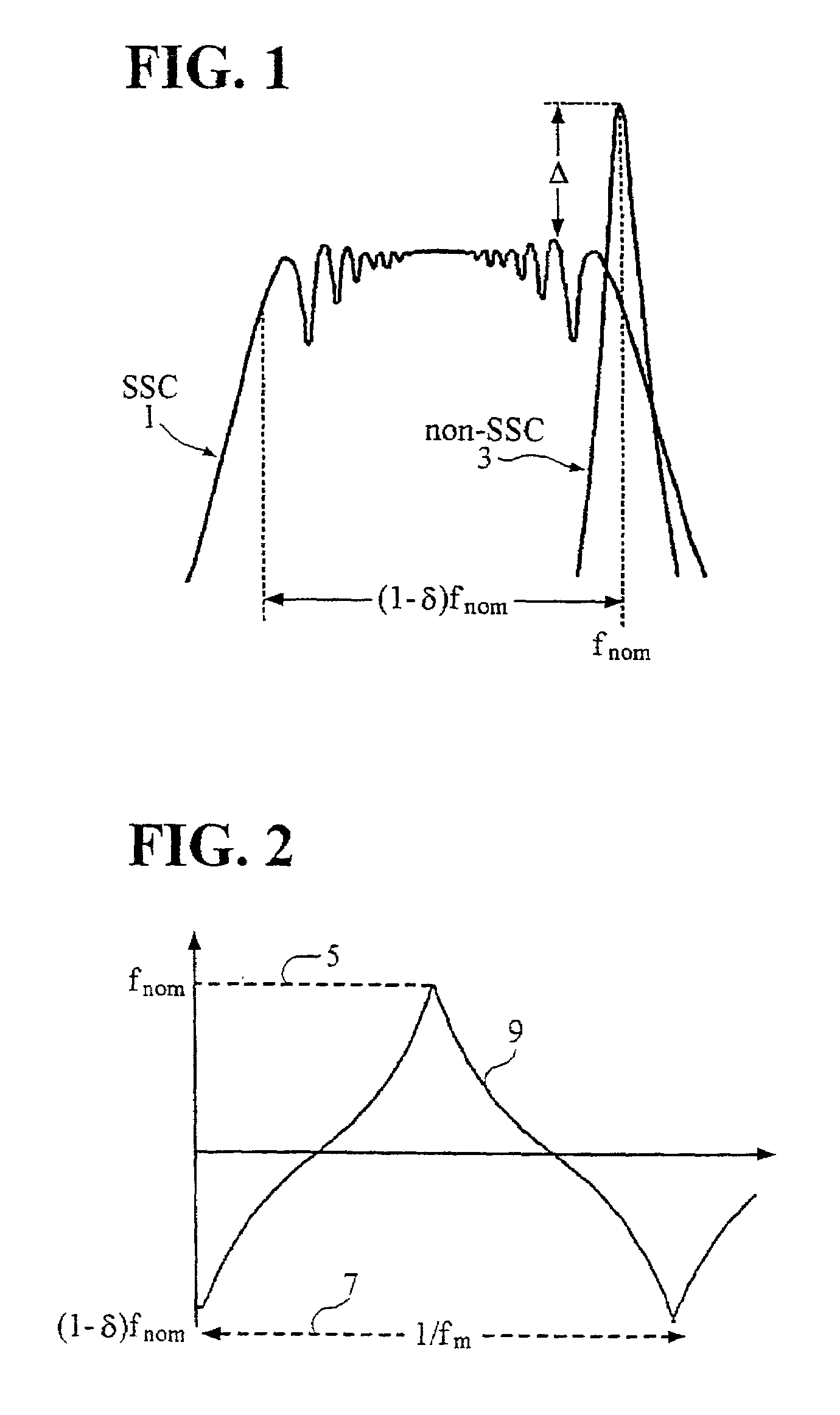
Spread spectrum clock generator and integrated circuit device using the spread spectrum clock generators
ActiveUS20050008113A1Prevents precipitous phase variationInhibitionPulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsPhase variationElectromagnetic interference
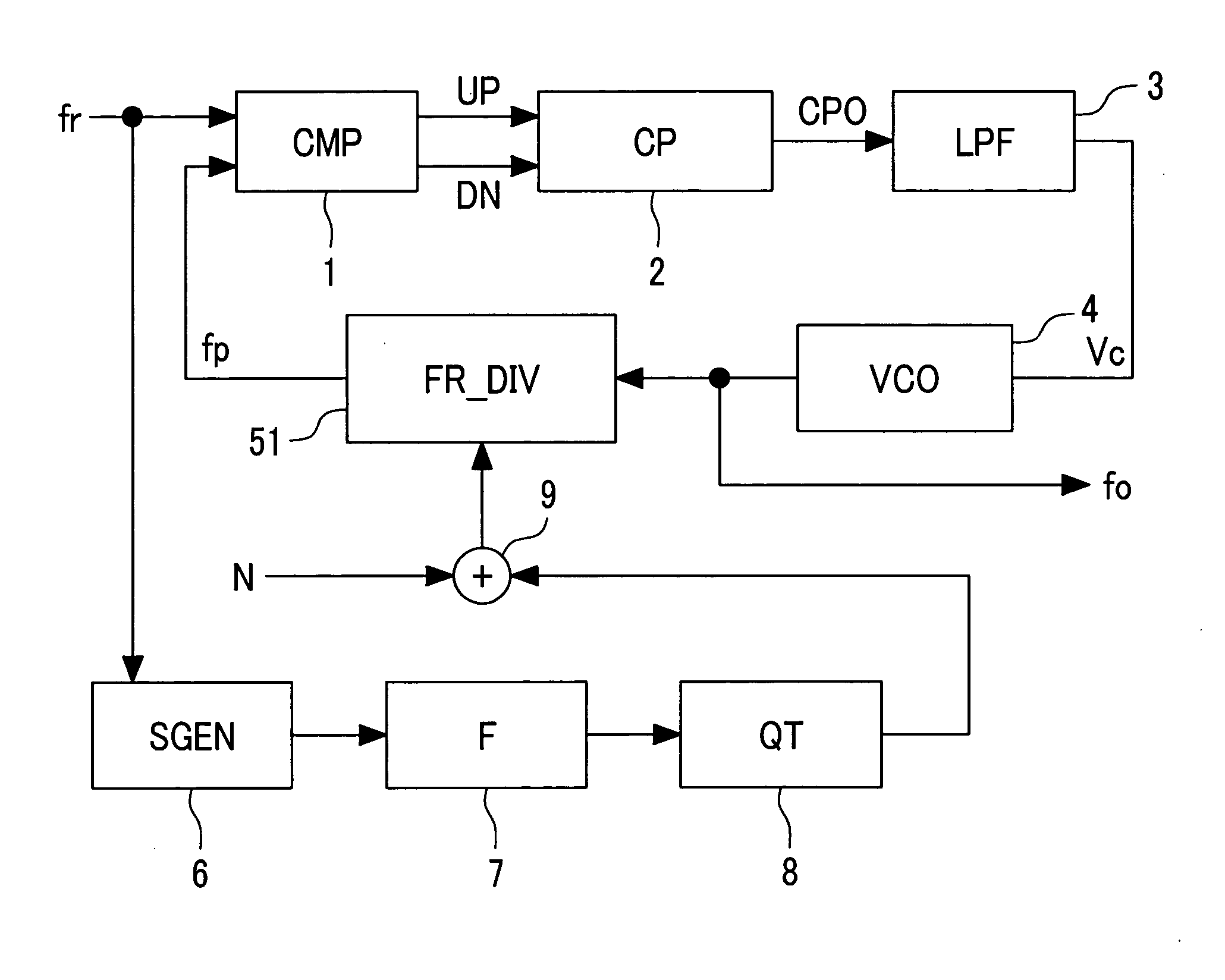
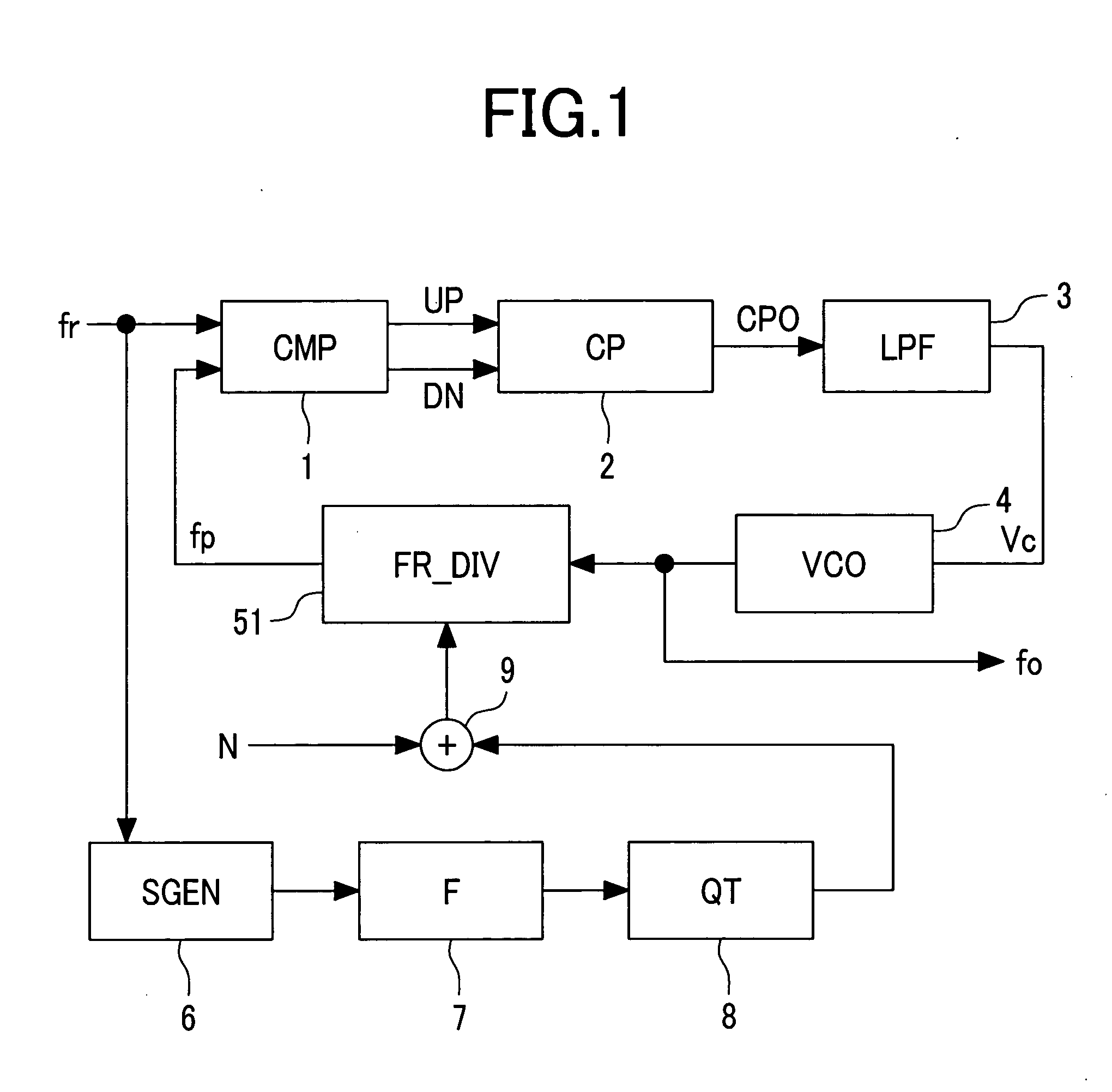
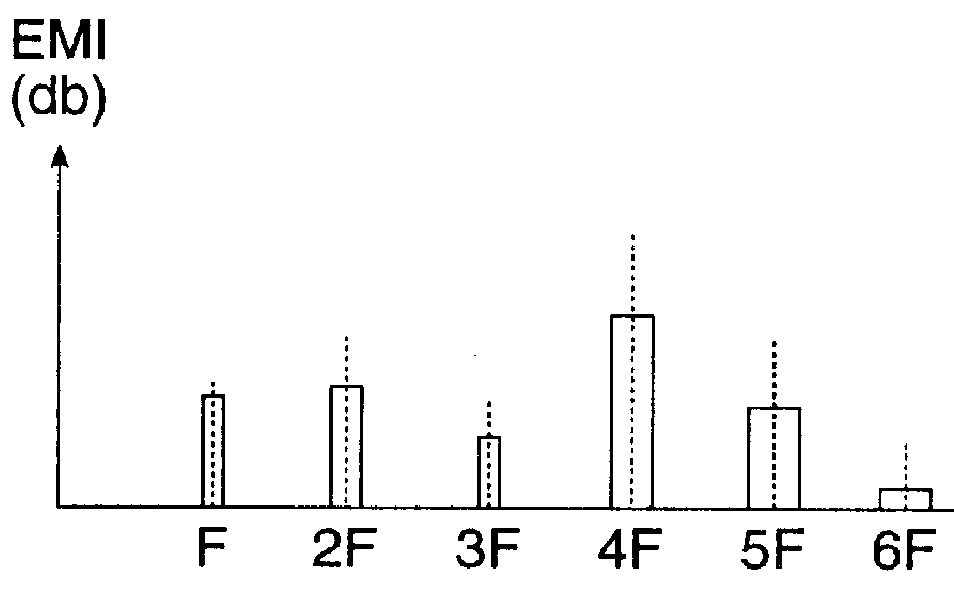
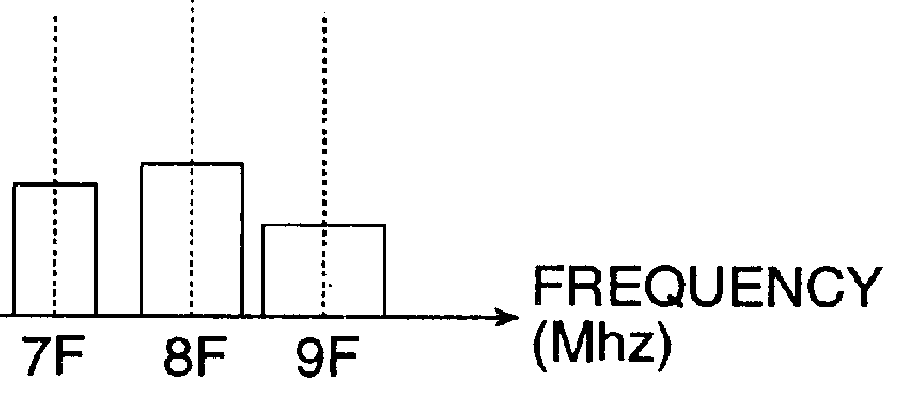
The present invention provides a spread spectrum clock generator that is capable of preventing phase jumps and jitters and suppressing the occurrence of Electro Magnetic Interference components and that can easily be applied to large scale integrated circuits. The spread spectrum clock generator can be configured with a filter, quantizer, fractional divider, and other elements. Also, this clock generator circuitry can be configured by combination of a delta-sigma ΔΣ quantizer and factional divider so that sine wave modulation and random number modulation can be realized. Thereby, control with digital values can be performed. This clock generator prevents precipitous phase variations in the output high frequency clock and makes fine phase control possible. Consequently, EMI reduction by 20-30 dB can be expected.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
System and method for providing noise suppression utilizing null processing noise subtraction
Systems and methods for noise suppression using noise subtraction processing are provided. The noise subtraction processing comprises receiving at least a primary and a secondary acoustic signal. A desired signal component may be calculated and subtracted from the secondary acoustic signal to obtain a noise component signal. A determination may be made of a reference energy ratio and a prediction energy ratio. A determination may be made as to whether to adjust the noise component signal based partially on the reference energy ratio and partially on the prediction energy ratio. The noise component signal may be adjusted or frozen based on the determination. The noise component signal may then be removed from the primary acoustic signal to generate a noise subtracted signal which may be outputted.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for reducing radiated electromagnetic emissions from harmonic frequencies for electronic equipment
InactiveUS6014063AReadily availablePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorFrequency spectrumHarmonic
A system of spreading the energy of higher harmonic frequencies in digital circuits to lower the interference to bandpass receivers is disclosed. A set of passive, impedance-regulated circuits, preferably housed in a standard enclosure, comprises a power restoring unit, a modulating signal generator, an internal oscillator and an impedance spreading unit. The circuits are equivalent to passive resonators such as crystal resonators used in standard oscillators. Any existing standard oscillator that uses common crystal resonators can be transformed into a spectrum-spread oscillator by replacing the crystal resonator with the disclosed circuit, whereby a tightly controlled small frequency spreading occurs in the fundamental clock frequency. Further an active oscillator is disclosed wherein a spreading circuit spreads the frequency of the clock signal originally generated by the oscillator based on a sequence of processing the original clock signal. The processing includes the use of a plurality of delay elements based on a certain topology, the comparisons between the clock signal and a set of predefine parameters so as to create a frequency offset. The spreading circuit, without using additional clocking sources, spreads the frequency of the clock signal with respect to the comparisons.
Owner:QUIET SOLUTION
Method and system of reducing electromagnetic interference emissions
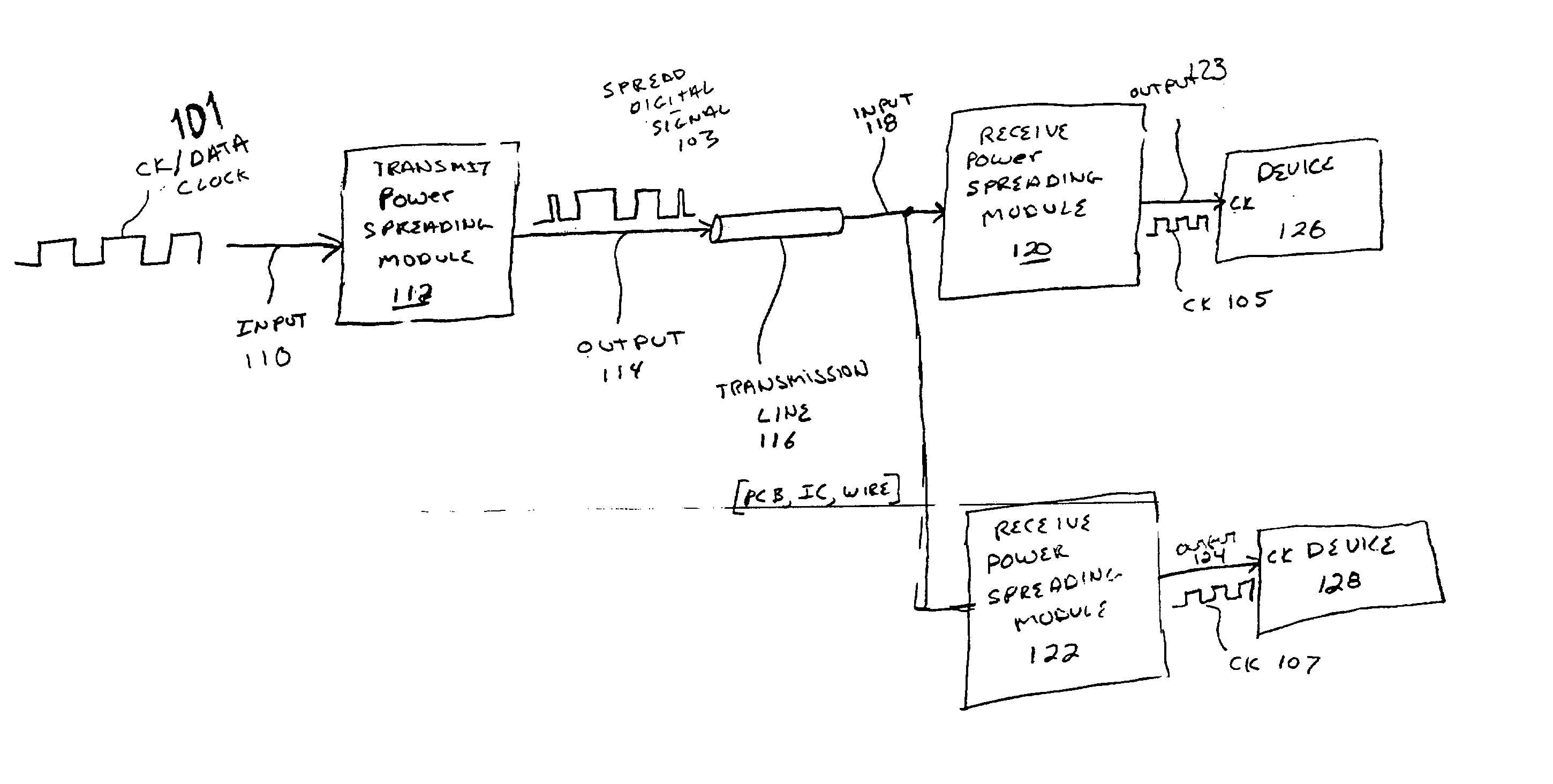
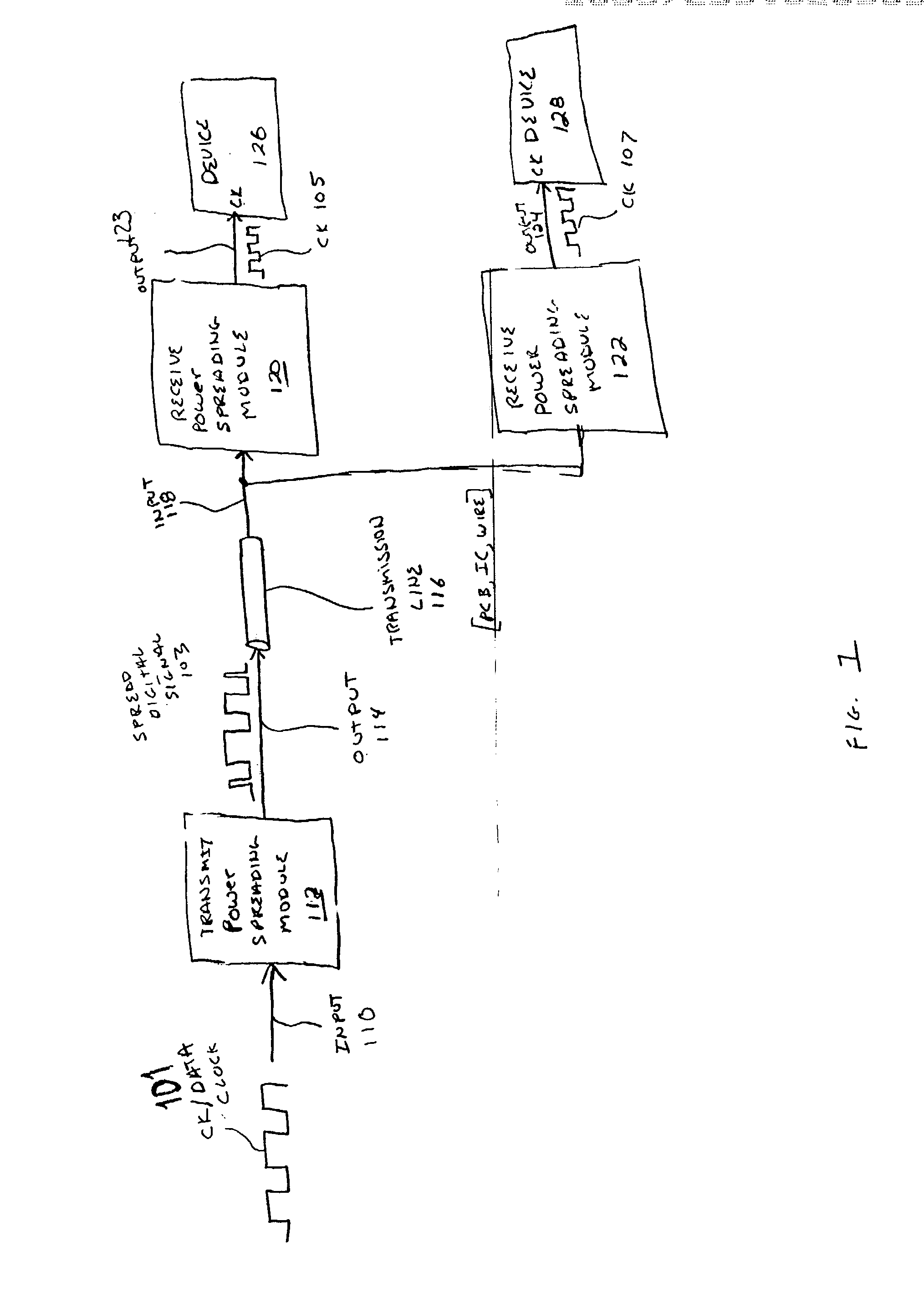
InactiveUS20040001533A1Code division multiplexDigital processing power distributionElectromagnetic interferenceDigital signal
A method and system is disclosed for spreading the power associated with digital signals being transmitted to lower electromagnetic interference (EMI) emissions. After being transmitted across a transmission line, a representation of the original digital signal is recovered and provided to a destination device.
Owner:XEMI
Transmitter with a Variable Sampling Rate
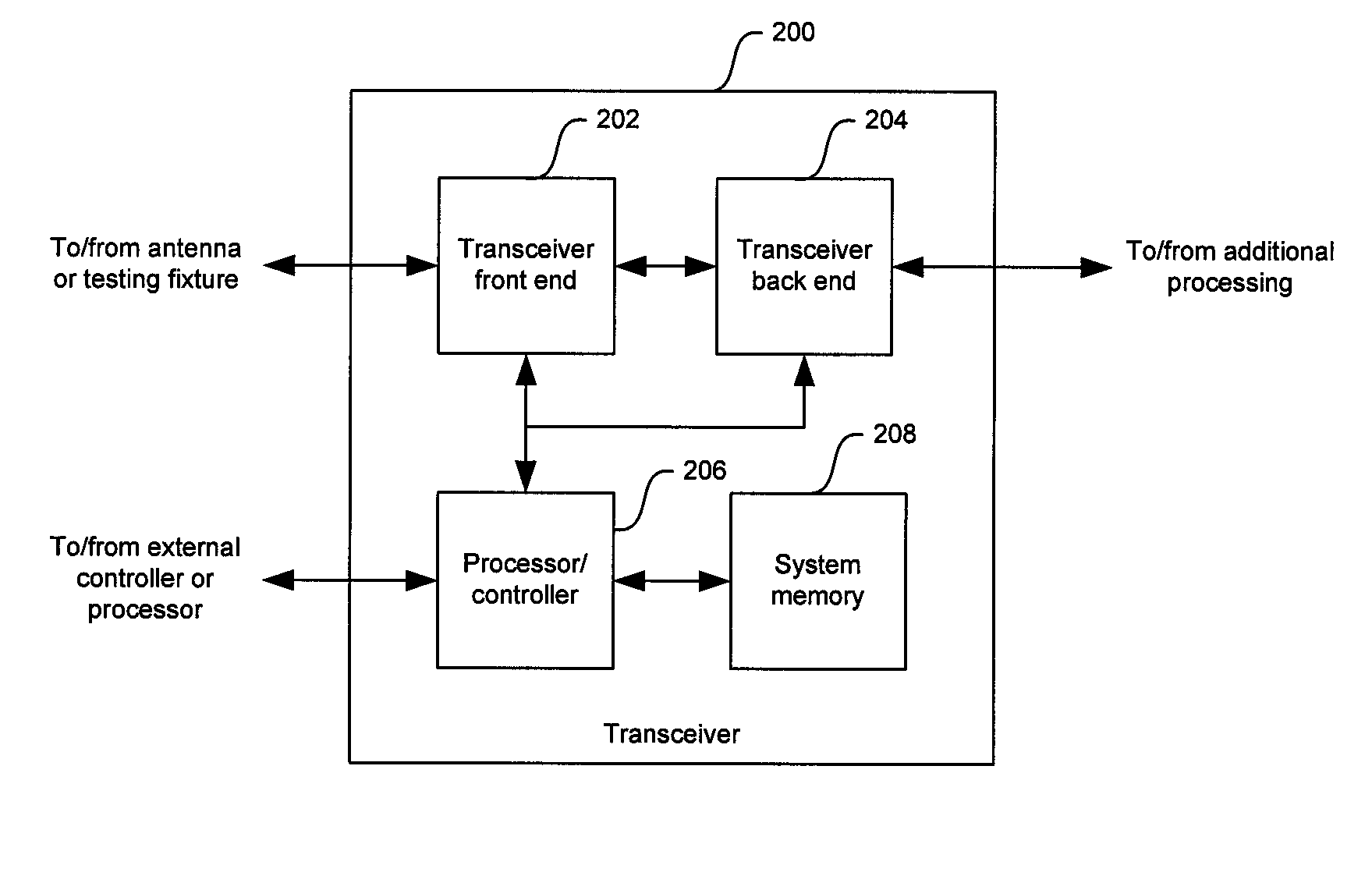
ActiveUS20130016761A1Reduce the impactReduce impactSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionDuplex signal operationTransceiverHarmonic
The present invention presents a method and a system for mitigating effects of clock harmonics in the receiver. The receiving signal may be monitored in such a way that the interfering harmonic component is tracked. When the interfering frequency is found out, the system determines the clock or clocks in the transceiver which are contributing to the interfering spurious tone. After that, the contributing clock(s) frequency is selected so that the effect of the spurious tone in the receiving passband is minimized or mitigated. This is performed by selecting a suitable clock frequency resulting in the spurious tones all falling outside the receiver passband; or in an OFDM system, by choosing a clock frequency deriving the spurious tone straight onto a subcarrier signal frequency.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Portable telephone apparatus with camera
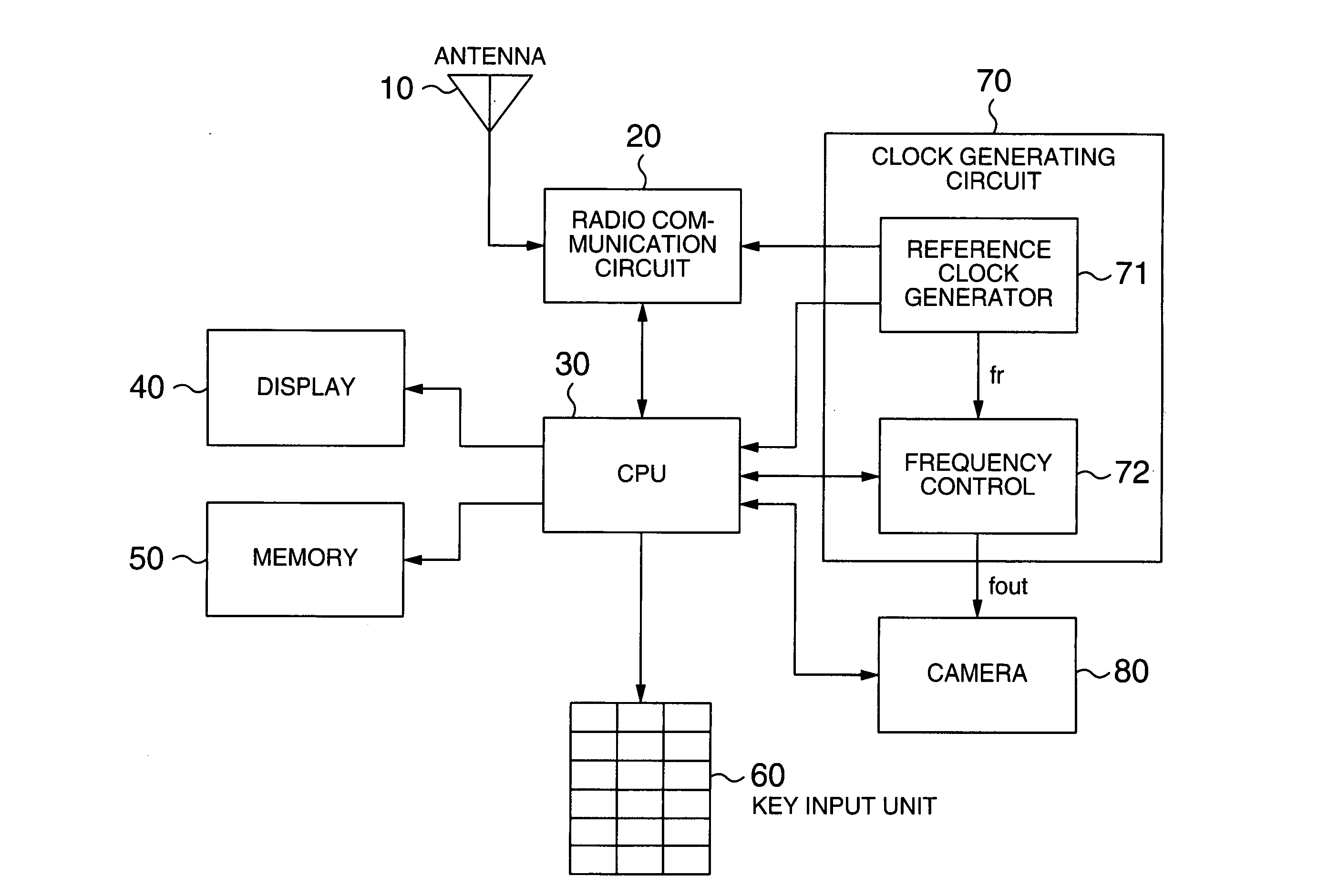
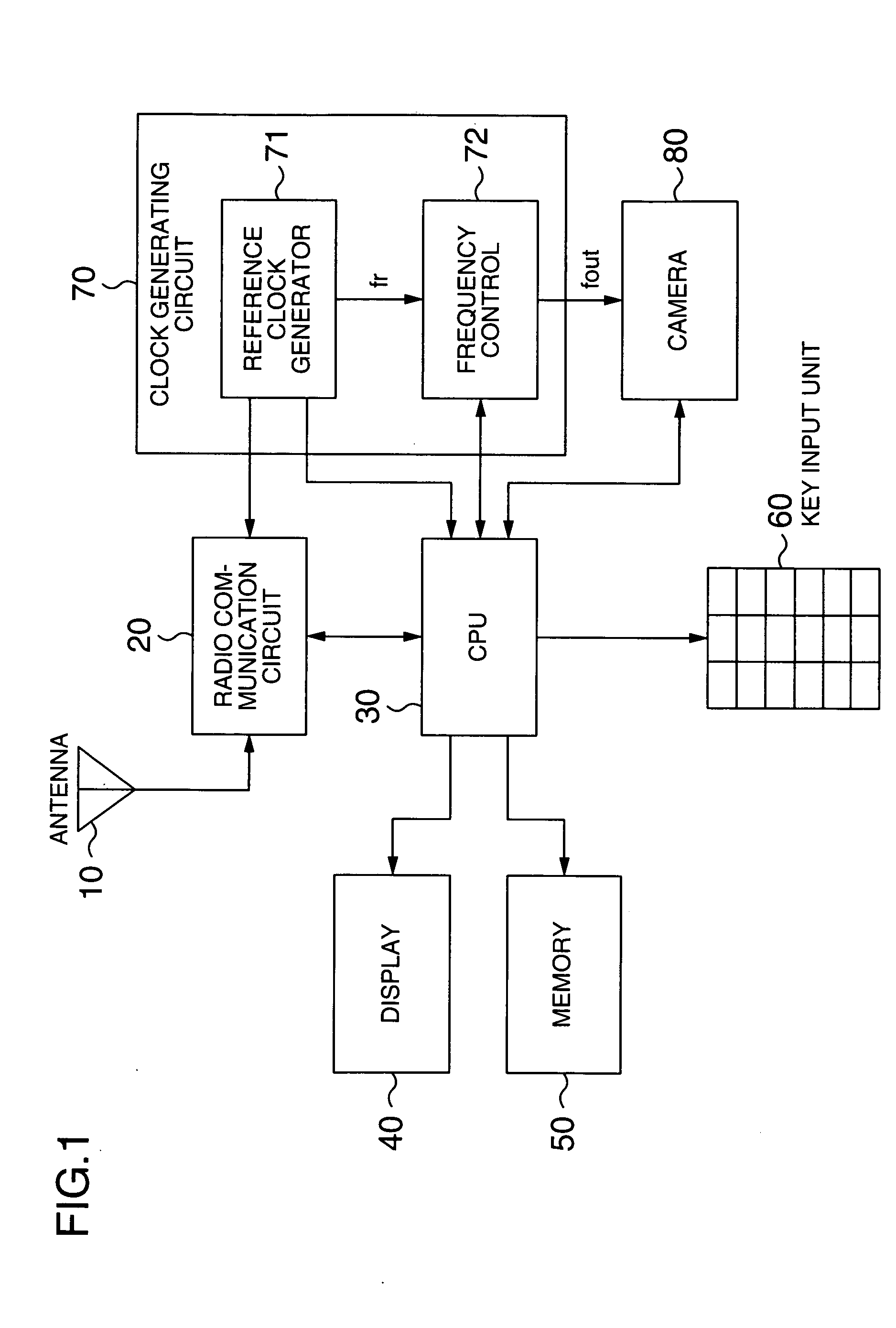
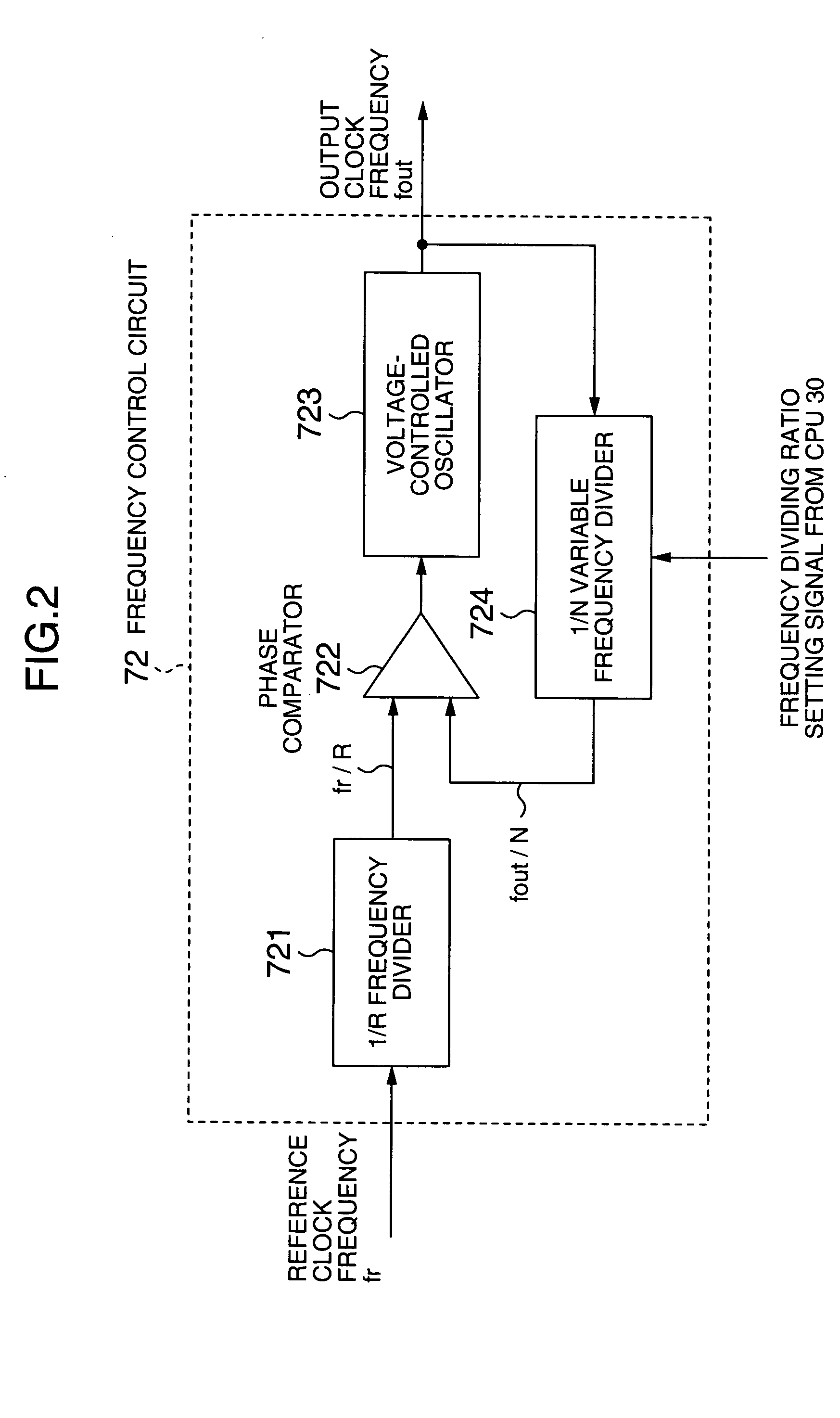
ActiveUS20050255881A1Reduce frequencyReduce distractionsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHarmonicEngineering
A portable telephone apparatus with camera is disclosed, in which the interference between the harmonic component generated from the camera and the receiving frequency band for radio communication can be reduced. The apparatus comprises a radio communication circuit for conducting the radio communication with an external device, a clock signal generating circuit capable of controlling the output clock signal frequency, a camera operated with the output clock signal as an operating clock signal and a control circuit. The control circuit, based on the receiving frequency band information acquired from the radio communication circuit, controls the clock signal of the clock signal generating circuit in such a manner that the harmonic components of the clock signal frequency are not superposed on the receiving frequency band for conducting the radio communication.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
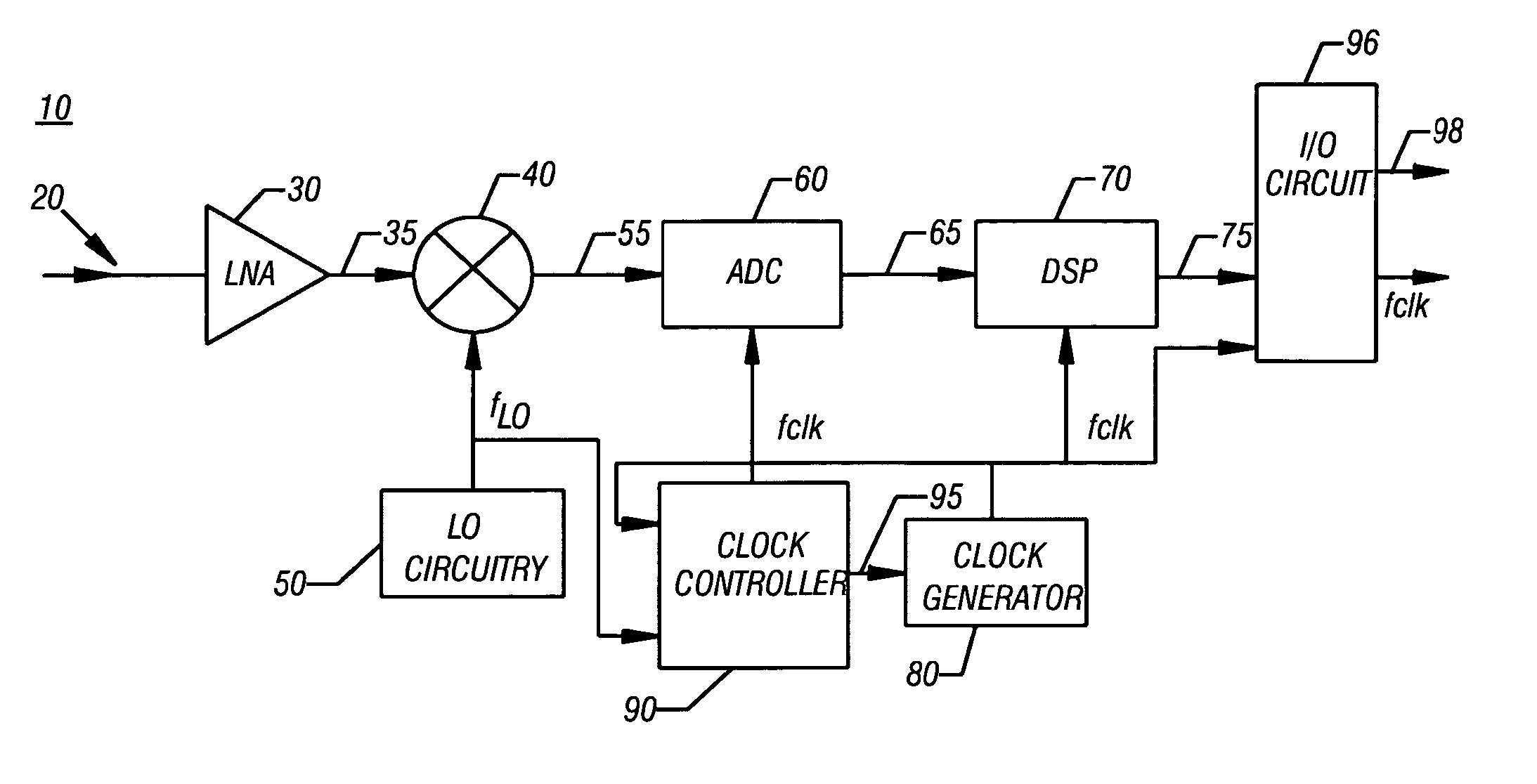
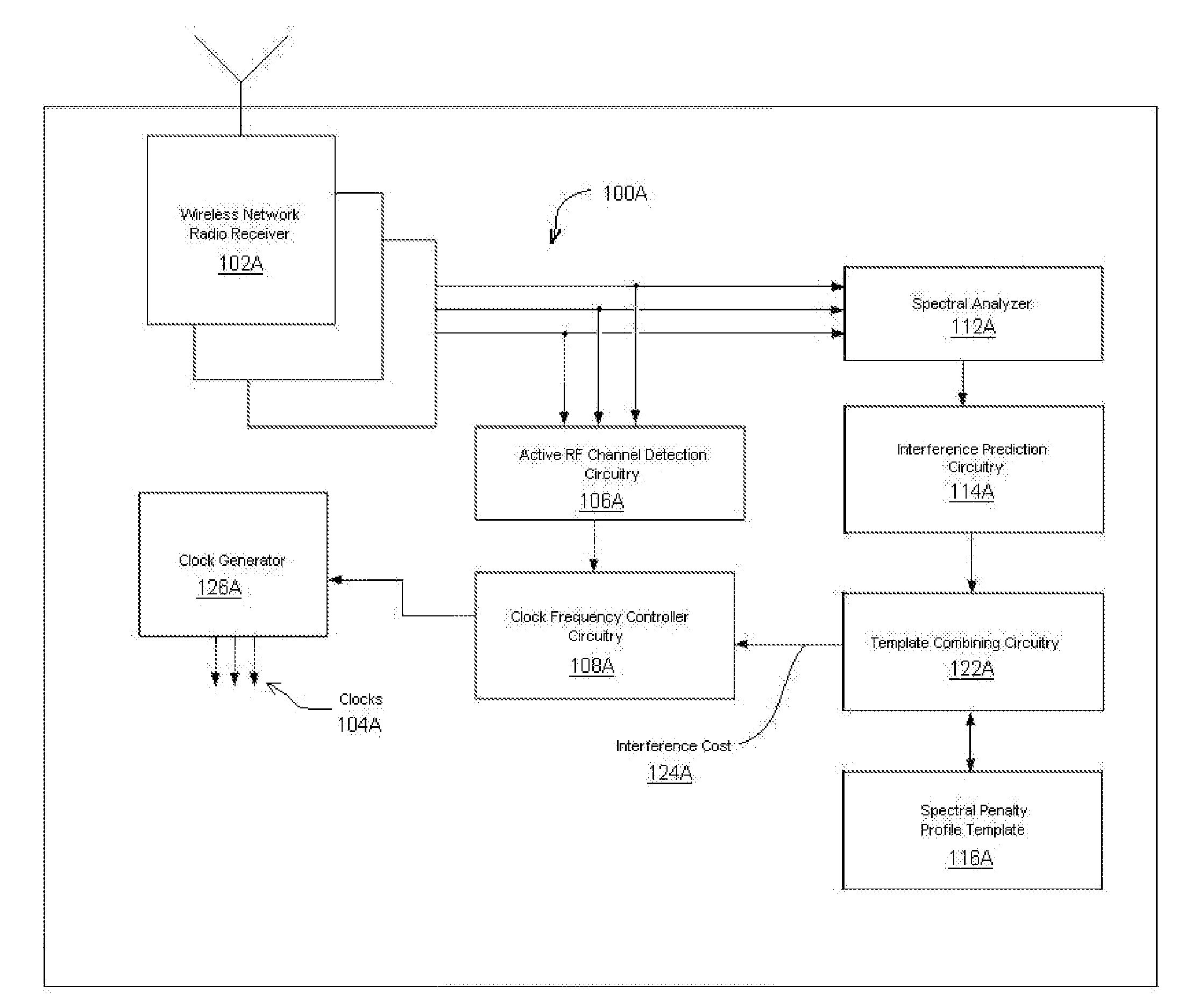
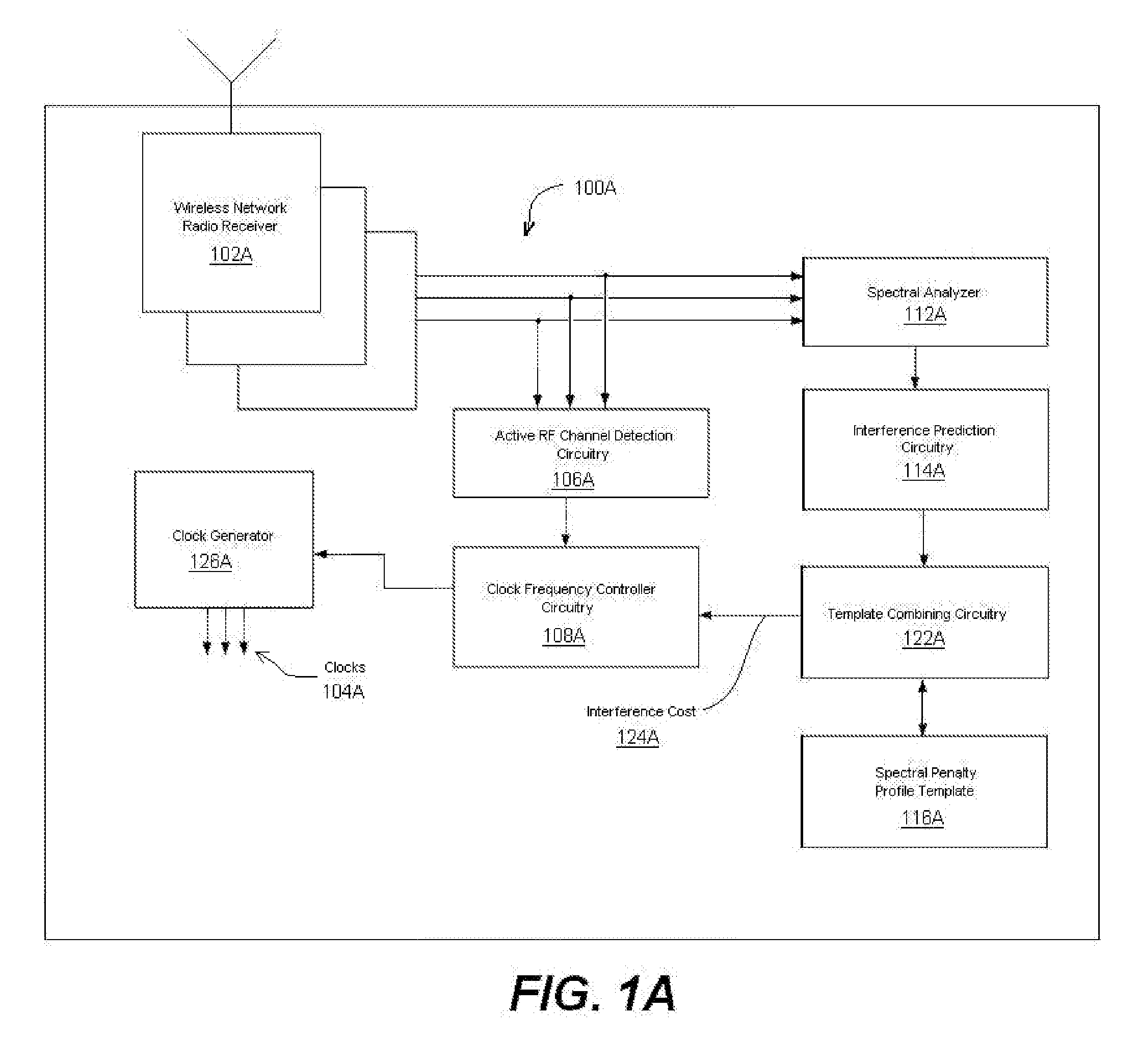
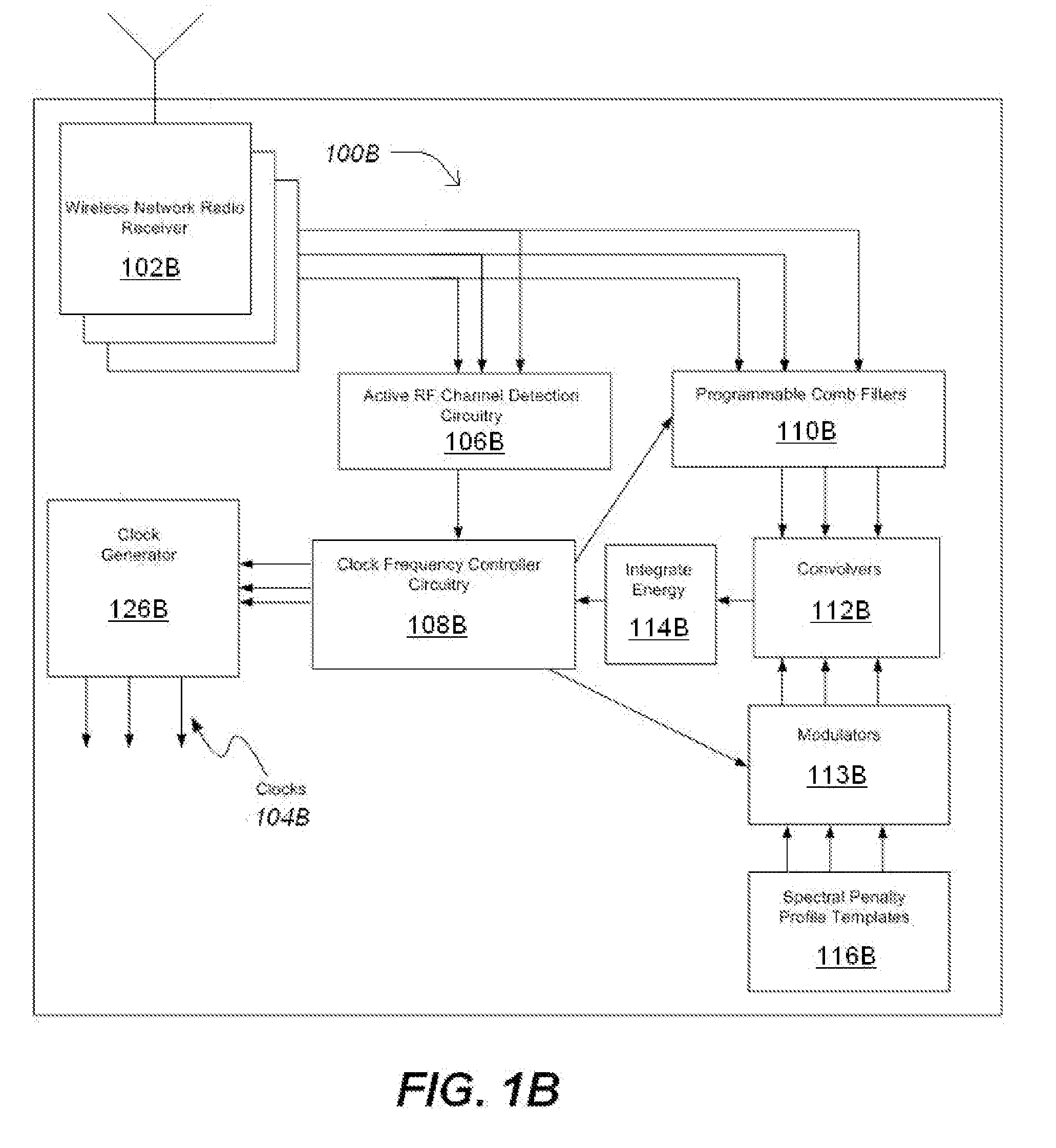
Closed Loop Adaptive Clock RFI Mitigation
A method according to one embodiment for mitigating radio frequency interference by identifying system clocks, identifying active radio channels, measuring clock harmonics in or near the active radio channels, determining potential interference occurring if the clocks were moved to new fundamental frequencies, and shifting clock fundamental frequencies to reduce interference to the active radio channels based on existing interference and the potential interference of a plurality of new fundamental frequencies. Of course, many alternatives, variations, and modifications are possible without departing from this embodiment.
Owner:INTEL CORP
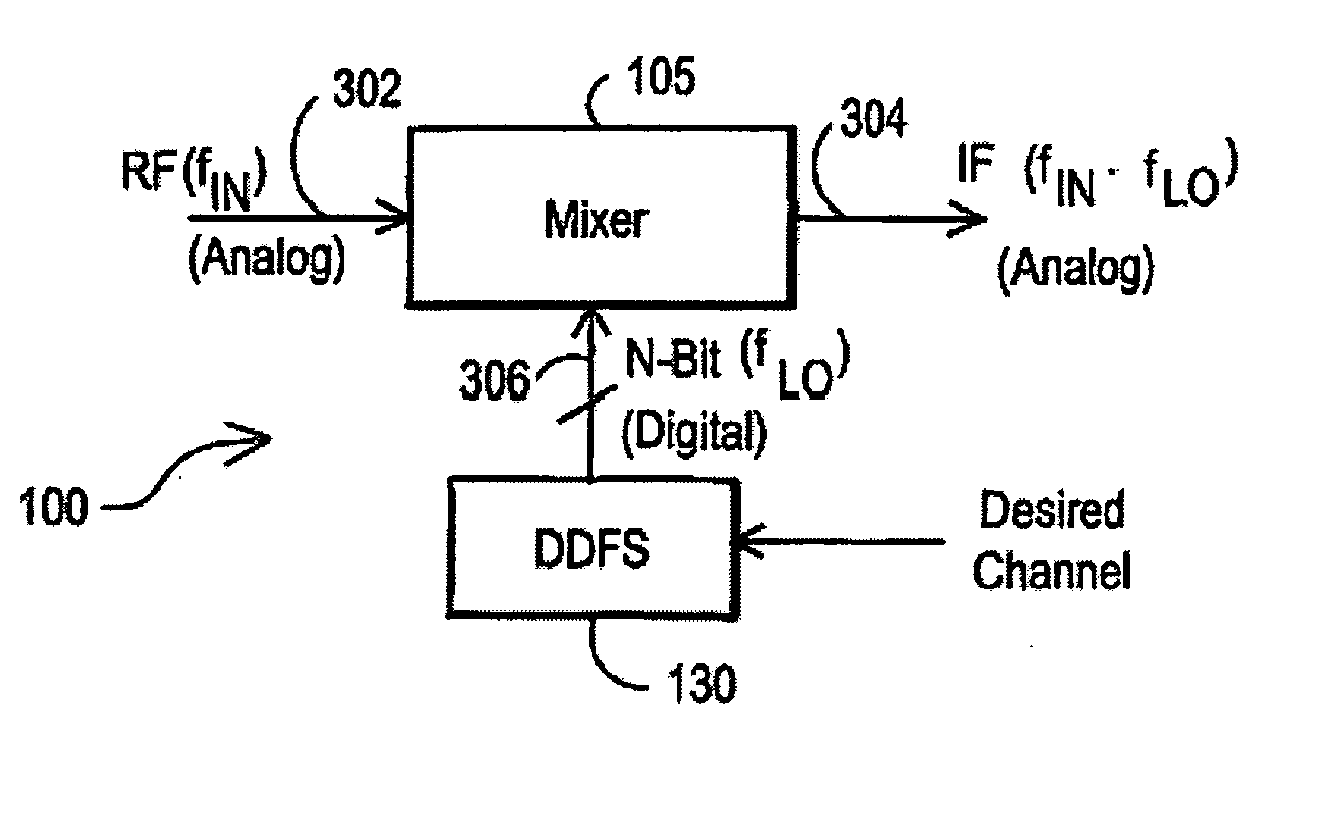
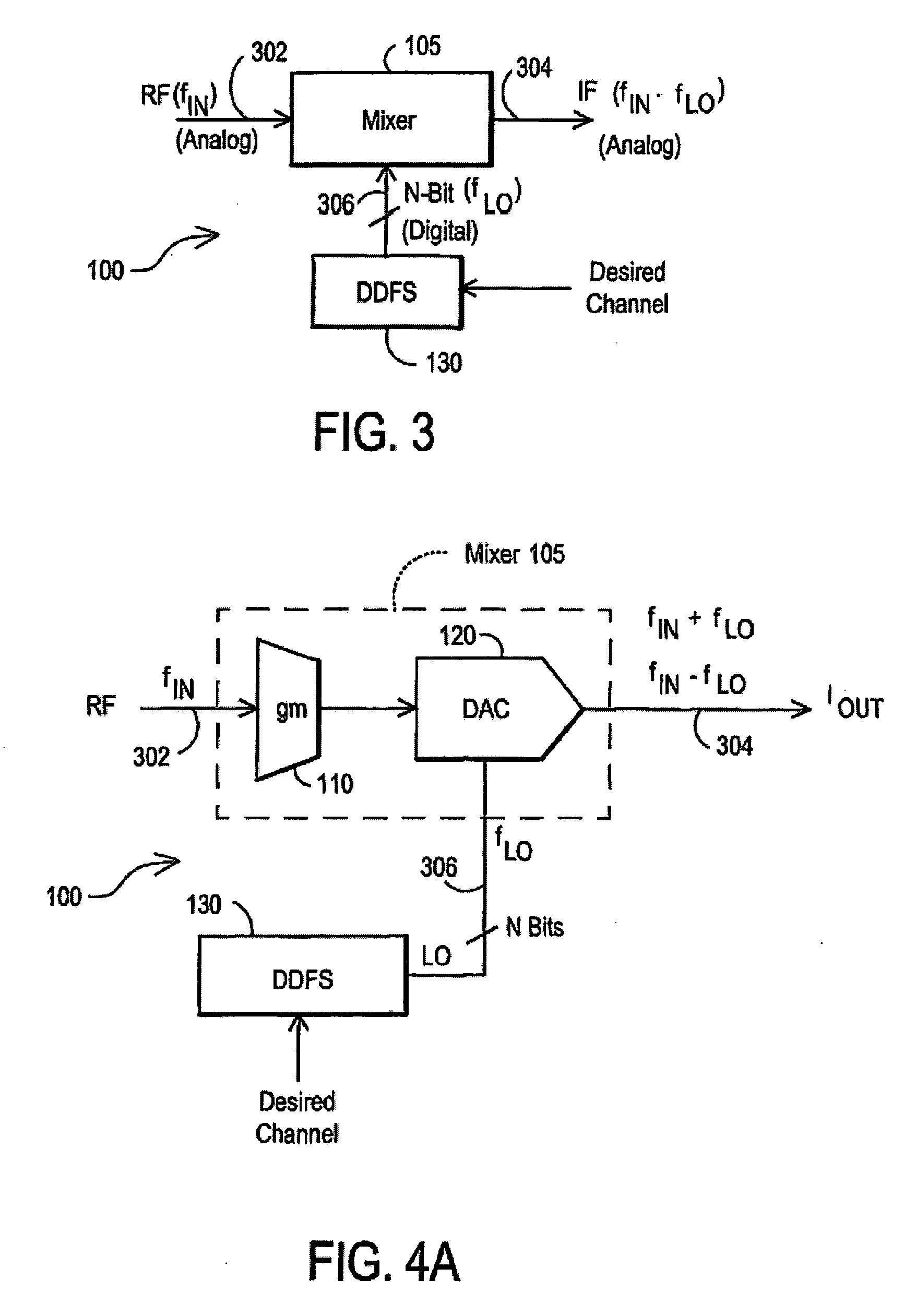
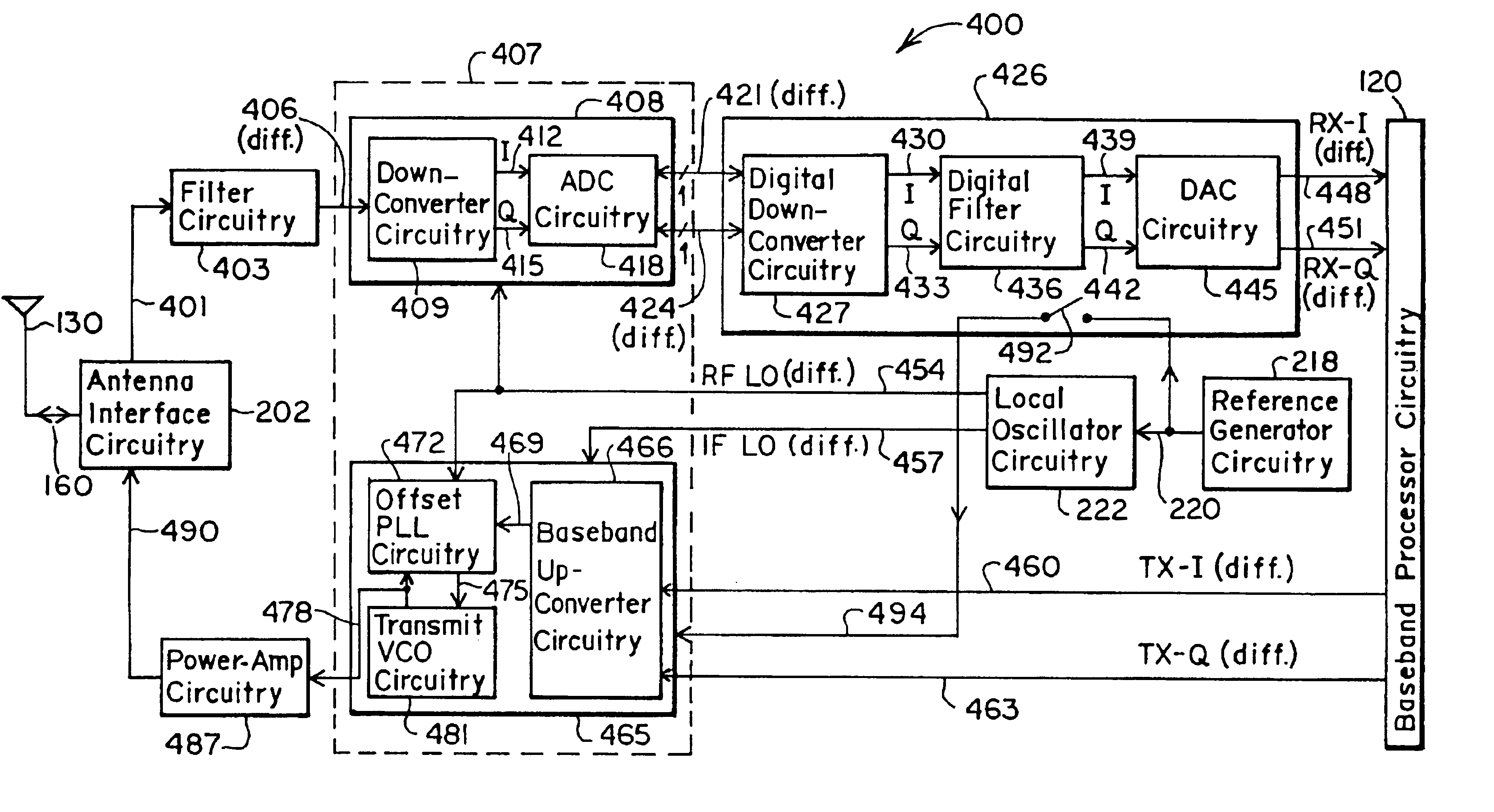
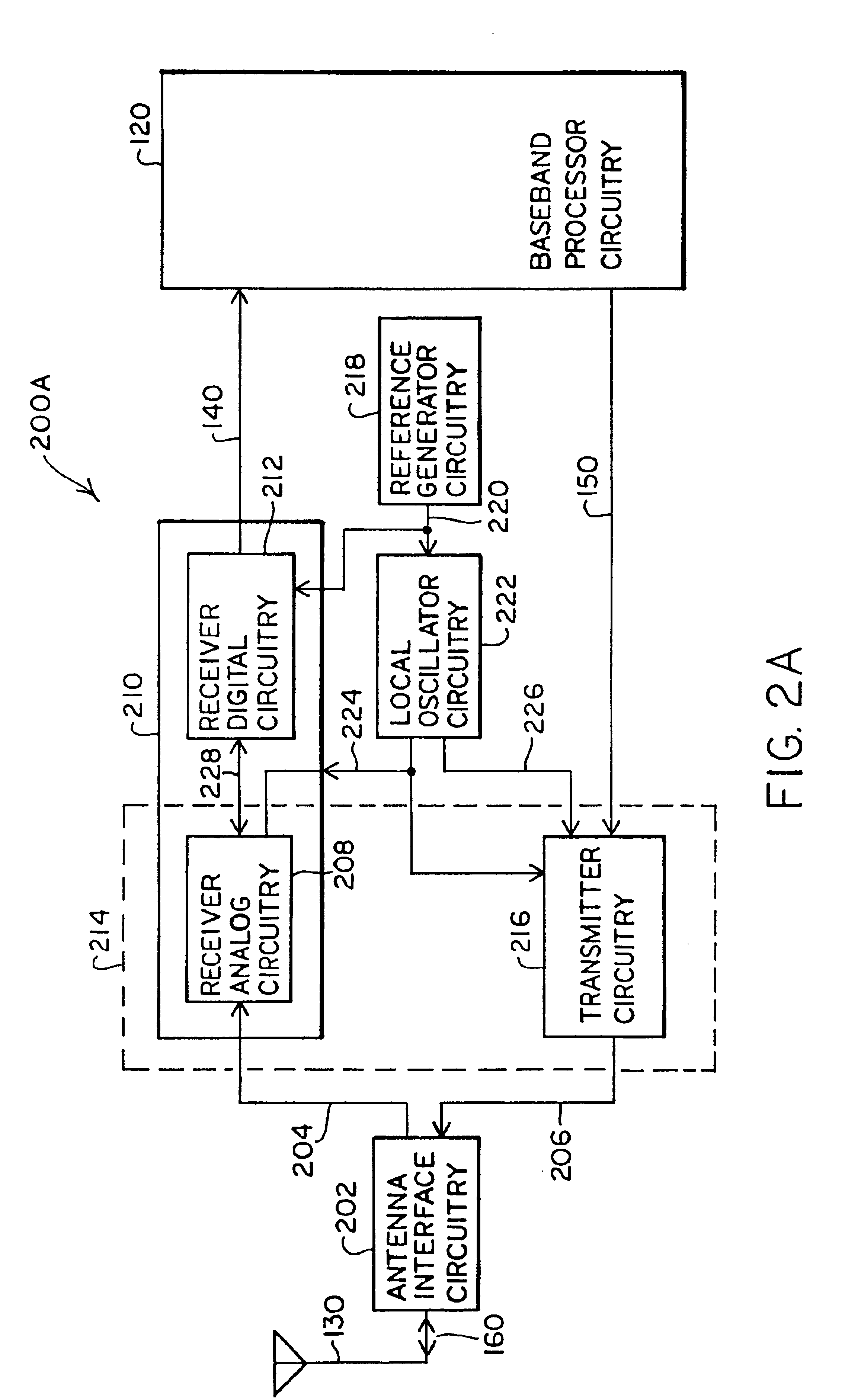
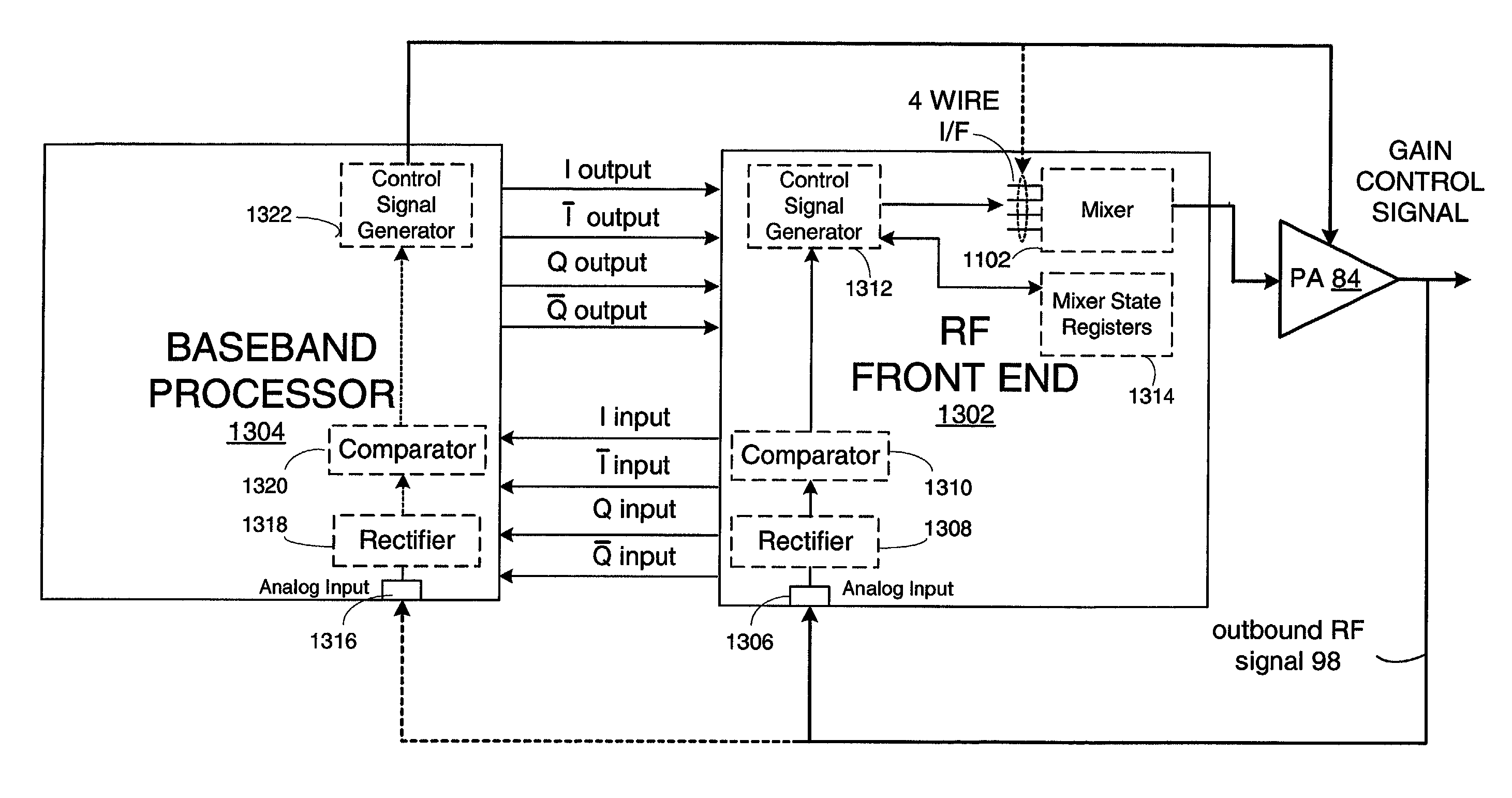
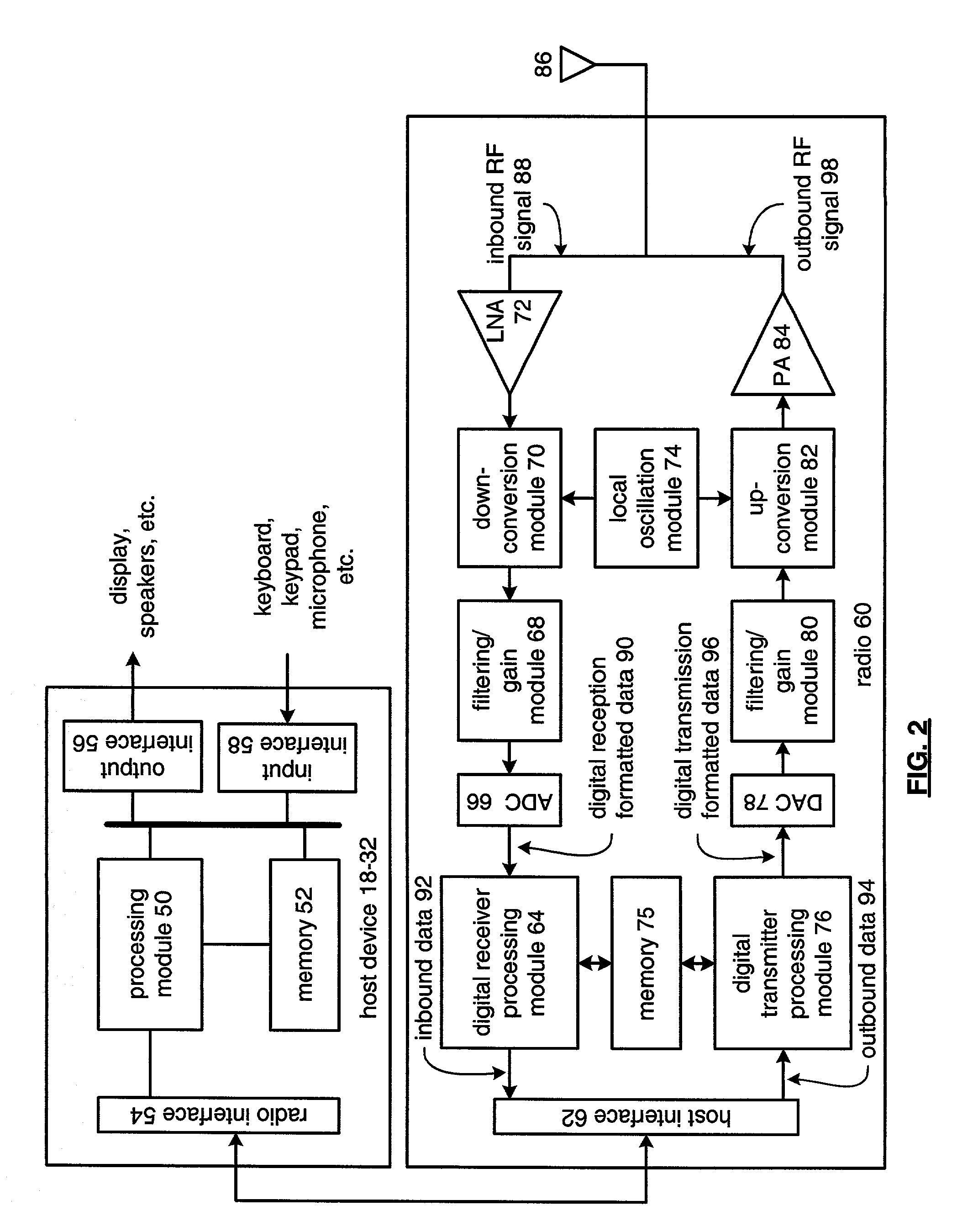
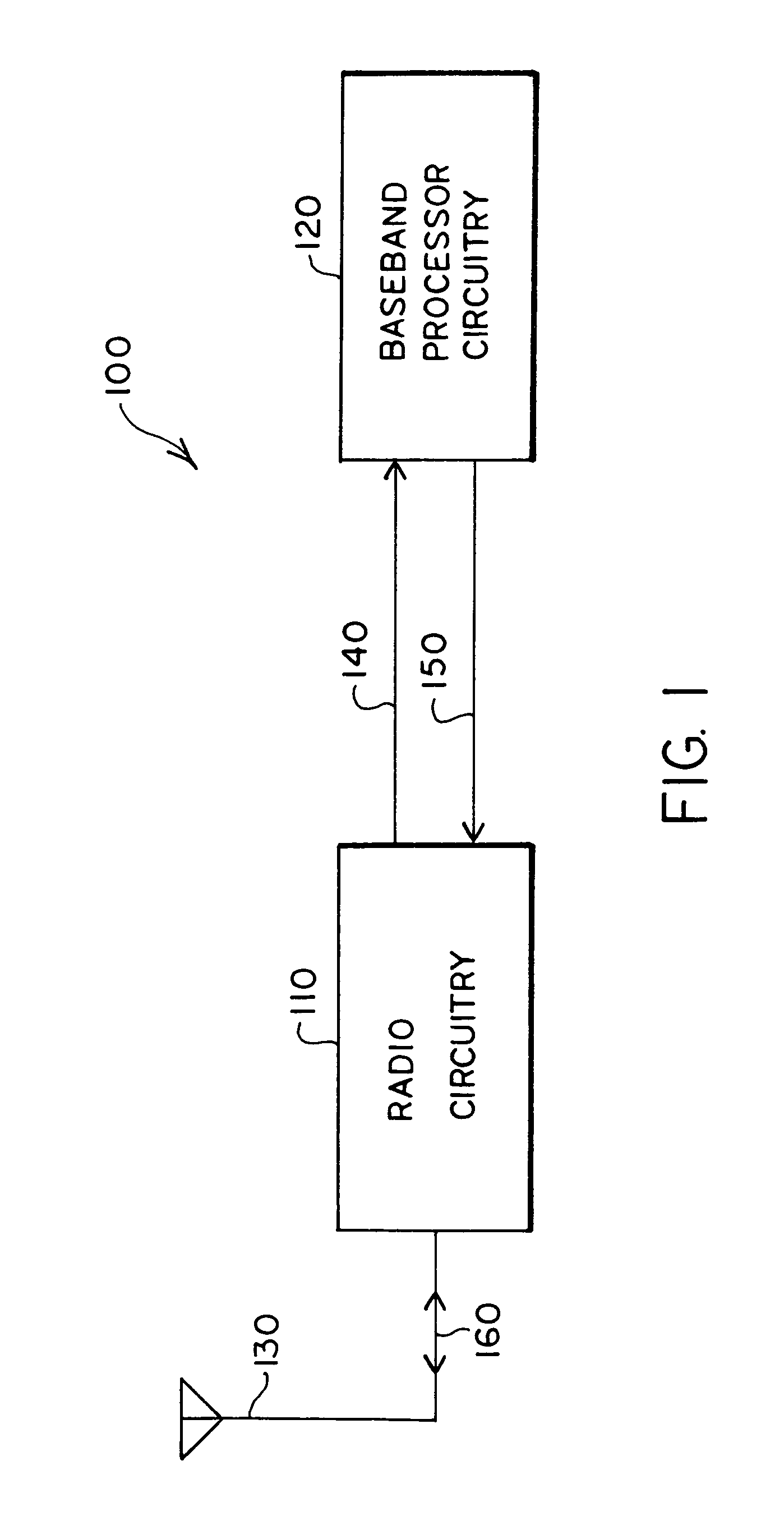
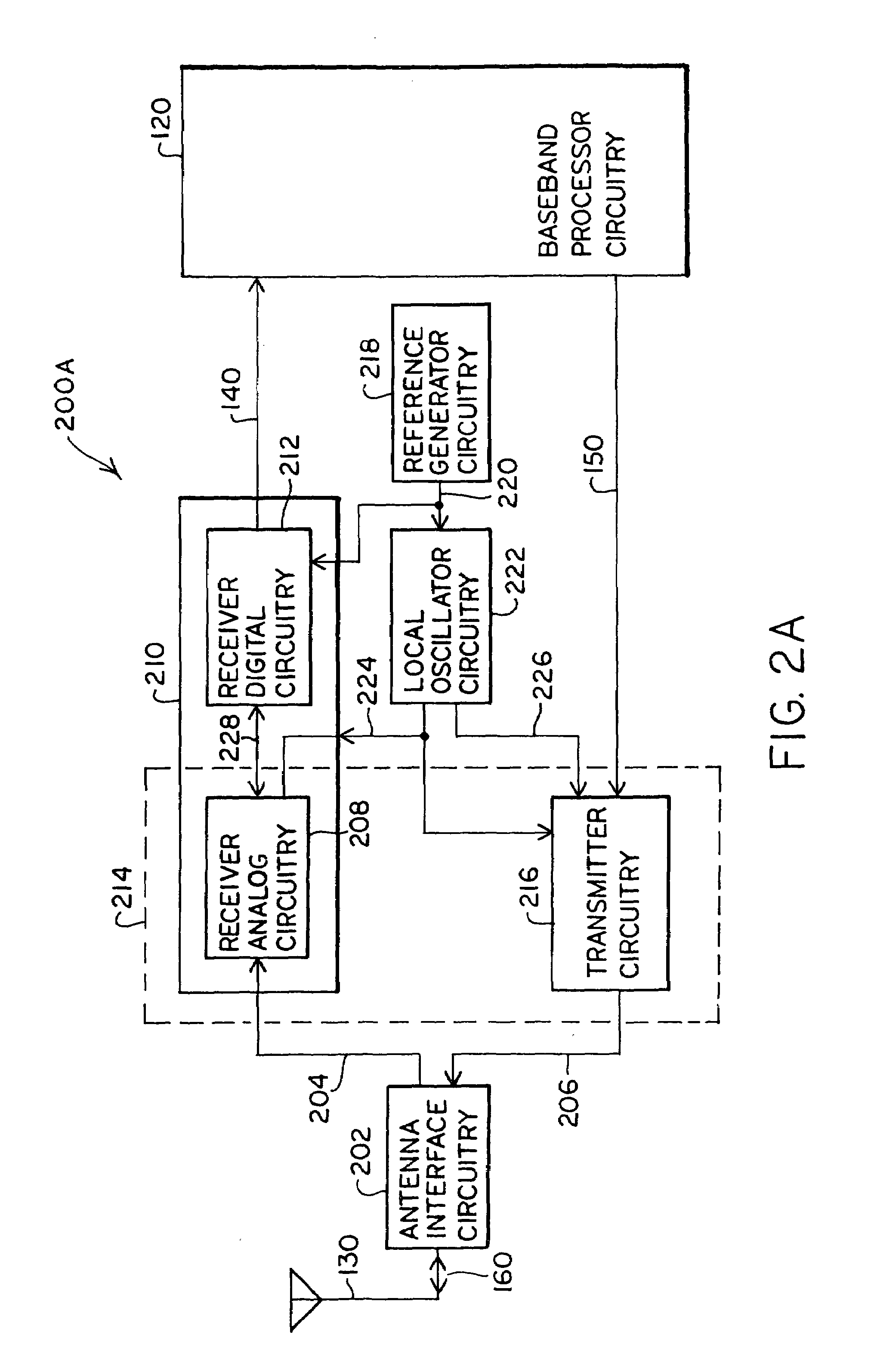
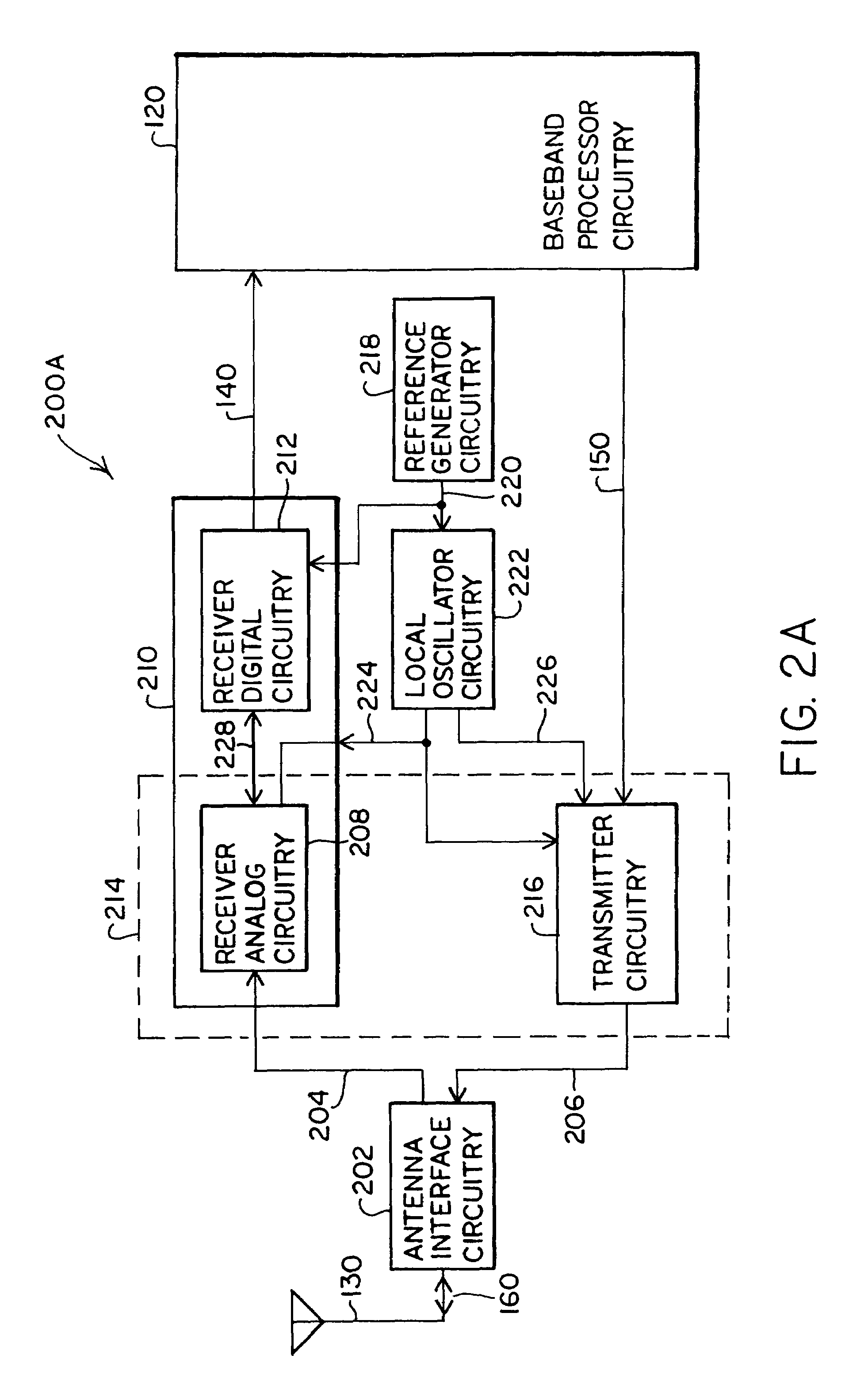
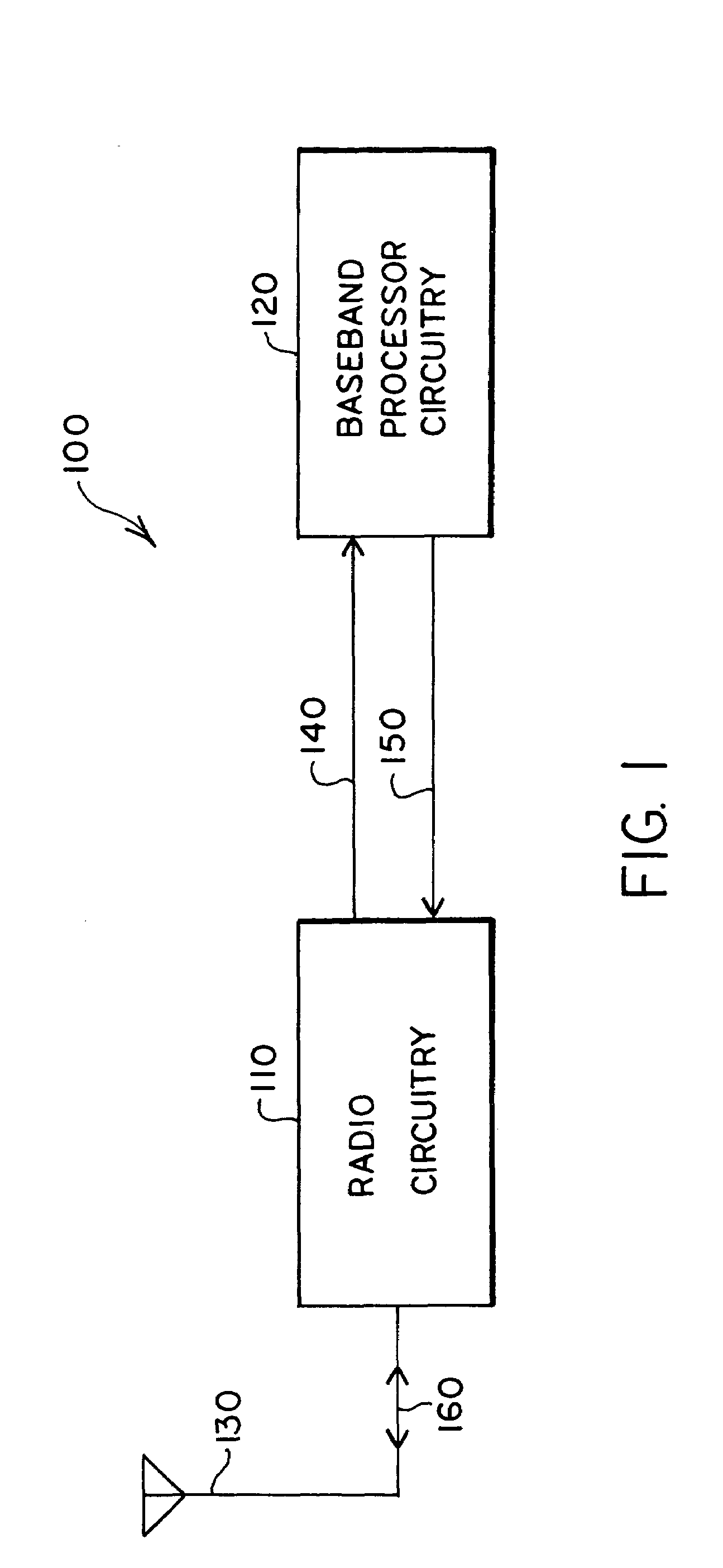
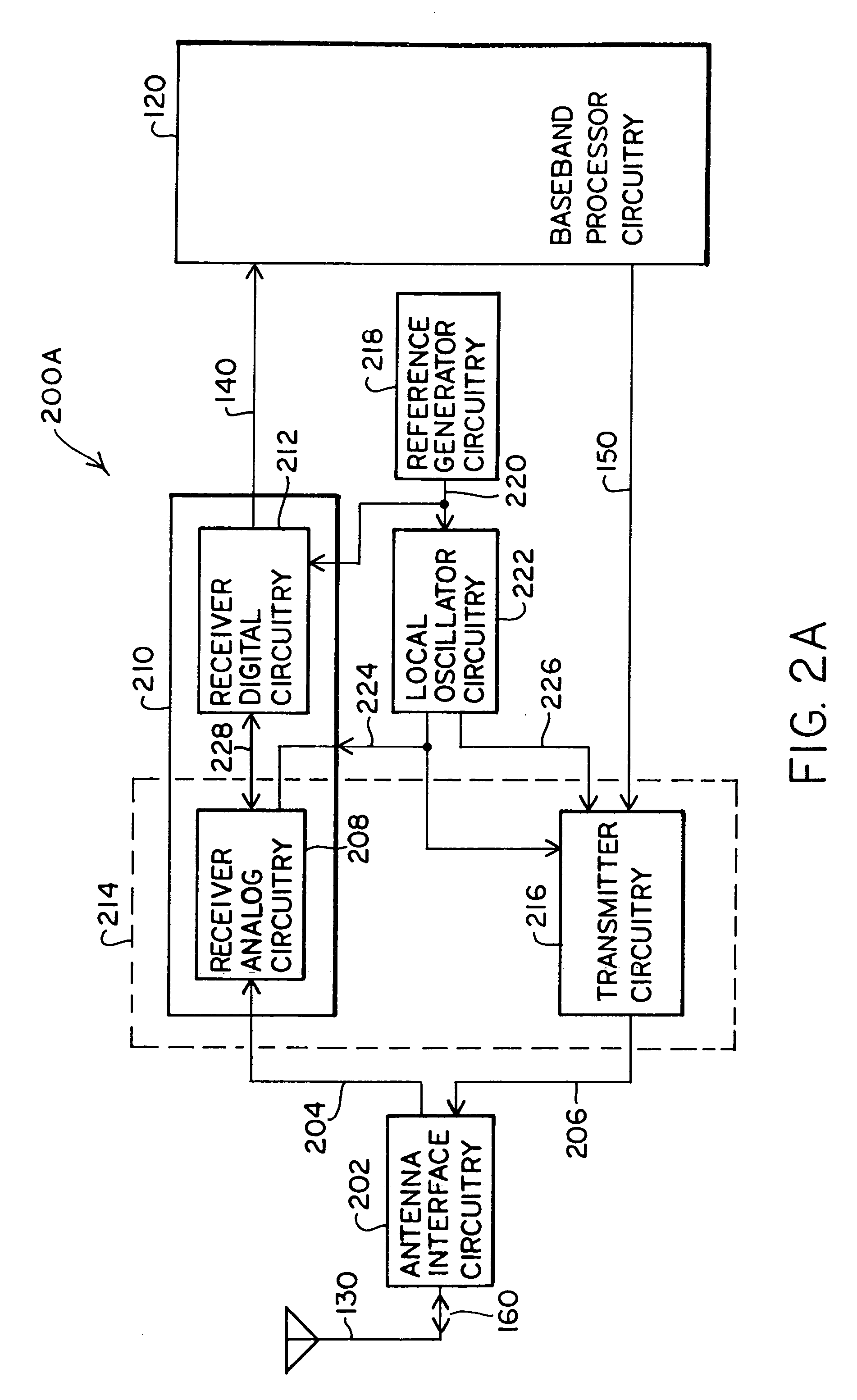
Digital architecture for radio-frequency apparatus and associated methods
InactiveUS6970717B2Substation equipmentSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionFrequency changerDigital down converter
A radio-frequency (RF) receiver includes a receiver analog circuitry and a receiver digital circuitry. The receiver analog circuitry resides within a first integrated circuit and the receiver digital circuitry resides within a second integrated circuit. The second integrated circuit couples to the first integrated circuit via a one-bit digital interface. The receiver analog circuitry receives an RF signal and processes the received RF signal to generate a digital signal. The receiver analog circuitry provides the digital signal to the receiver digital circuitry. The receiver digital circuitry includes a digital down-converter circuitry that mixes the digital signal with an intermediate frequency (IF) local oscillator (LO) signal to generate a digital down-converted signal. The receiver digital circuitry also includes a digital filter circuitry that filters the digital down-converted signal to generate a filtered digital signal.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Radio frequency integrated circuit
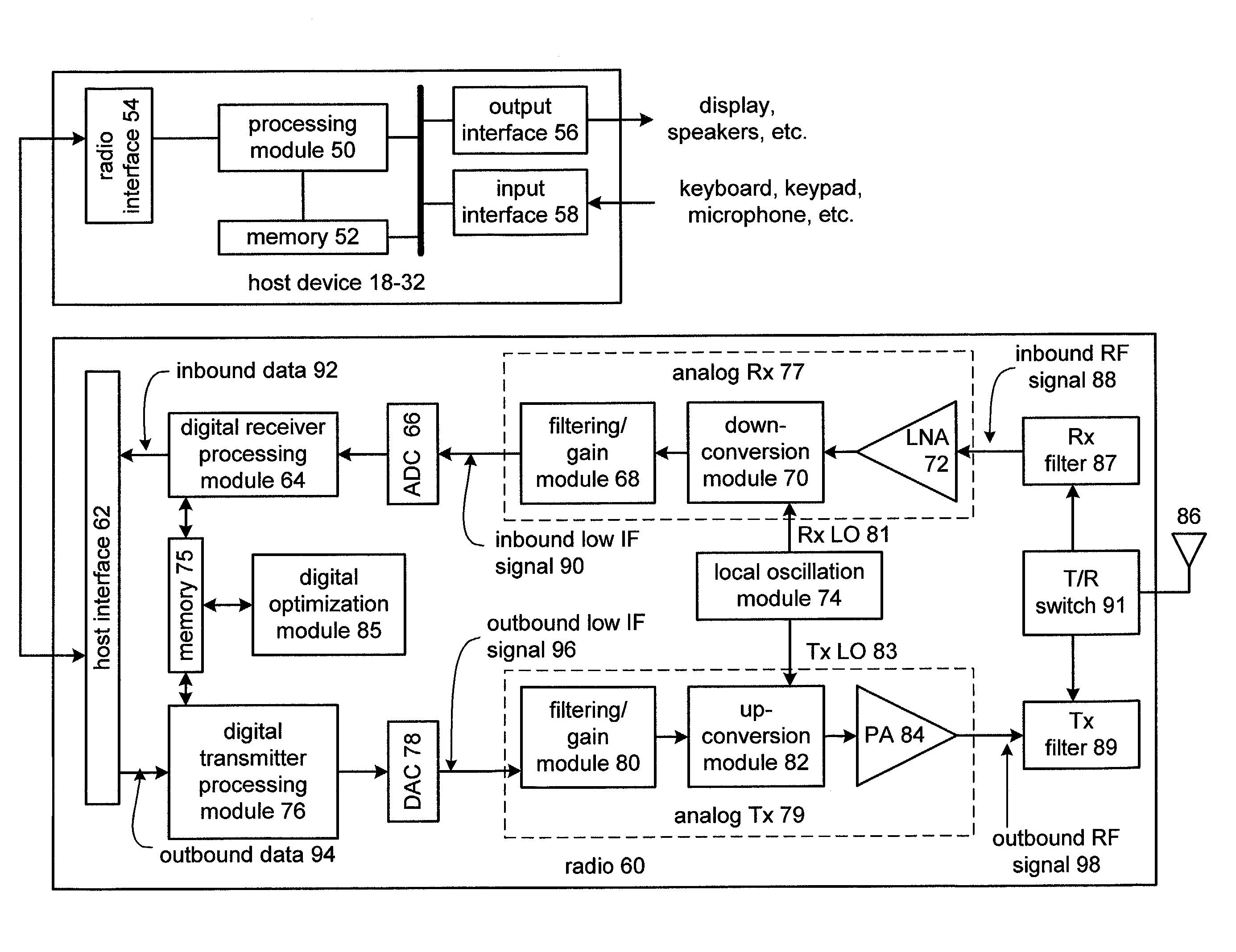
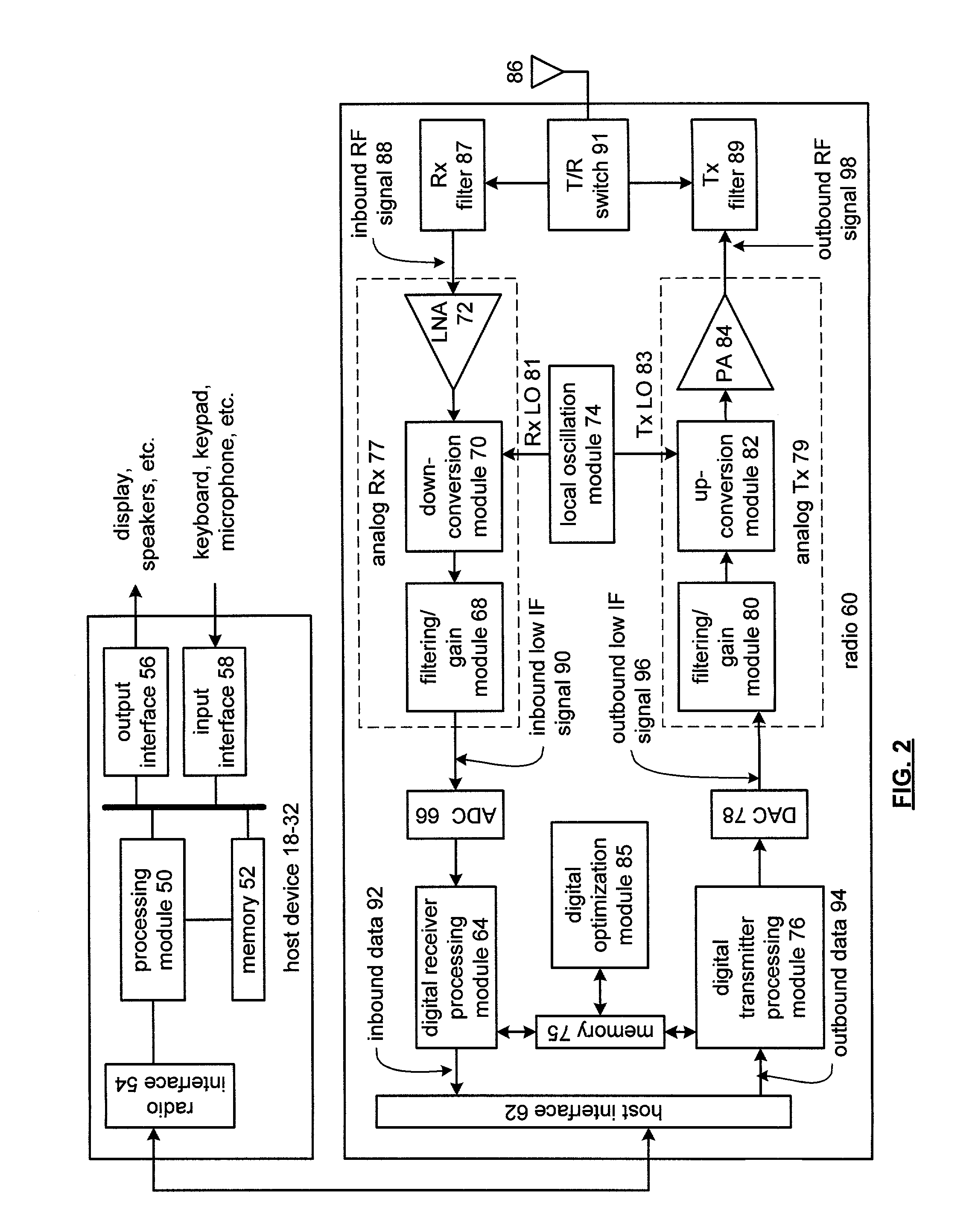
InactiveUS6980774B2Highly integratedImprove performanceResonant long antennasAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsRadio receiverRadio reception
A radio frequency (RF) integrated circuit (IC) includes a local oscillation module, analog radio receiver, analog radio transmitter, digital receiver module, digital transmitter module, and digital optimization module. The local oscillation module is operably coupled to produce at least one local oscillation. The analog radio receiver is operably coupled to directly convert inbound RF signals into inbound low intermediate frequency signals based on the local oscillation. The digital receiver module is operably coupled to process the inbound low IF signals in accordance with one of a plurality of radio transceiving standards to produce inbound data. The digital transmitter is operably coupled to produce an outbound low intermediate frequency signal by processing outbound data in accordance with the one of the plurality of radio transceiving standards. The analog radio transmitter is operably coupled to directly convert the outbound low IF signals into outbound RF signals based on the local oscillation. The digital optimization module is operably coupled to the local oscillation module, the analog radio receiver and / or the analog radio transmitter to optimize performance of at least one aspect of the local oscillation module, the analog radio receiver and / or the analog radio transmitter for the given radio transceiving standard being implemented.
Owner:BELL NORTHERN RES LLC
Programmable mixer for reducing local oscillator feedthrough and radio applications thereof
InactiveUS6970689B2Reduce imbalanceReduce leakageResonant long antennasModulation transferenceLocal oscillatorBlocking oscillator
A state of a programmable mixer is set during a calibration phase to minimize local oscillator feedthrough. During a calibration phase, inputs to the programmable mixer are set to zero, or to a known state and the local oscillator is set to a calibration frequency. Then, one of a plurality of known calibration states of the programmable mixer is entered and the local oscillator feedthrough is measured. For each of a plurality of operating states an amplified output of the programmable mixer is measured. In one operation, the state of the programmable mixer in which the programmable mixer operates during a next operation phase is the state that produces minimal local oscillator feedthrough. In another operation, operation continues until a state is found that produces a local oscillation feedthrough that meets an operating criteria and that state is used during the next operation phase. After these operations are complete, programmable mixer calibration operations are completed until the next calibration phase commences.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
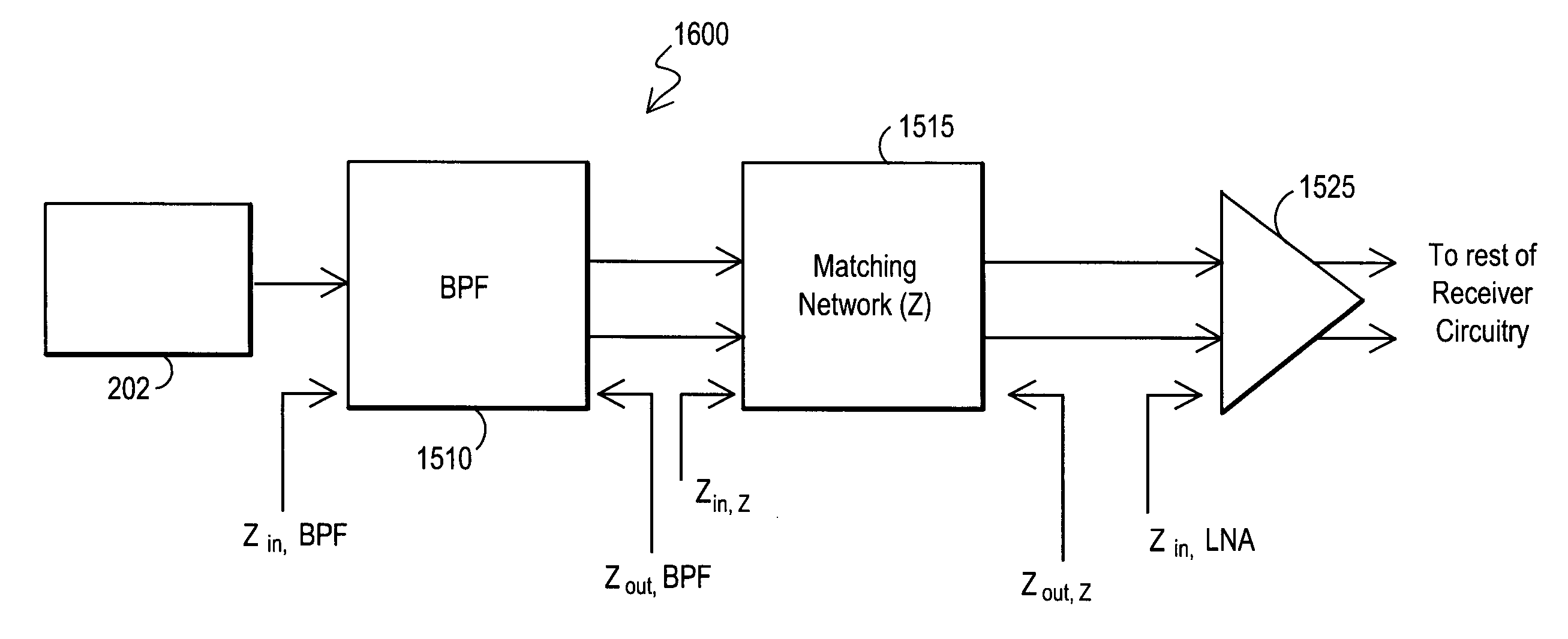
Apparatus and method for front-end circuitry in radio-frequency apparatus
InactiveUS7035611B2Guaranteed interference effectReduce the impact of interferenceMultiple-port networksRadio transmissionSignal processing circuitsInput impedance
A radio-frequency (RF) apparatus includes front-end circuitry. The front-end circuitry includes a filter circuitry and an impedance matching circuitry. The filter circuitry has a differential output that has an output impedance. The filter circuitry filters signals outside a signal band of interest. The impedance matching network has a differential input coupled to the output of the filter circuitry. The impedance matching network also has a differential output coupled to a signal processing circuitry. The signal processing circuitry has an input impedance. The impedance matching network matches the input impedance of the signal processing circuitry to the output impedance of the filter circuitry.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
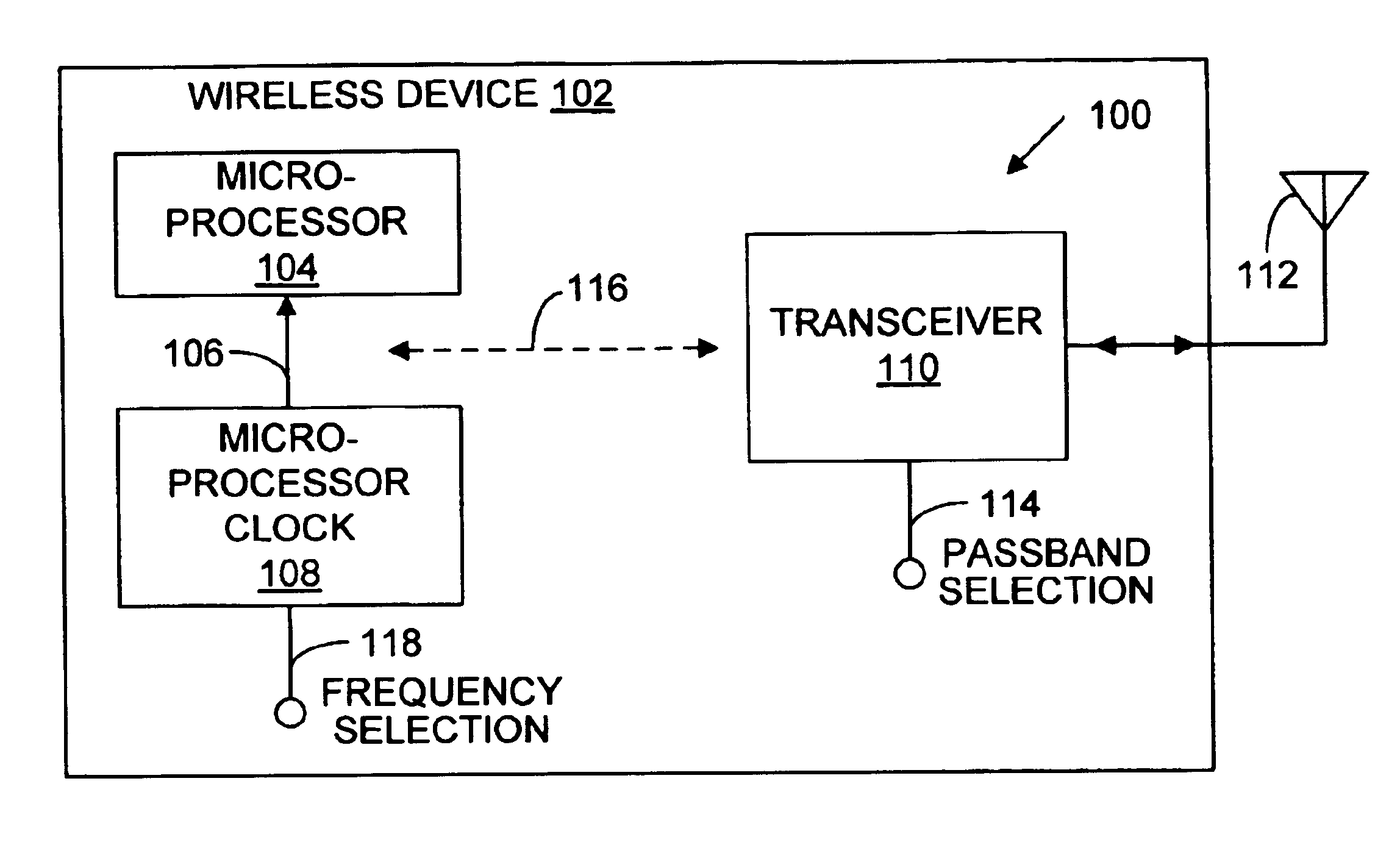
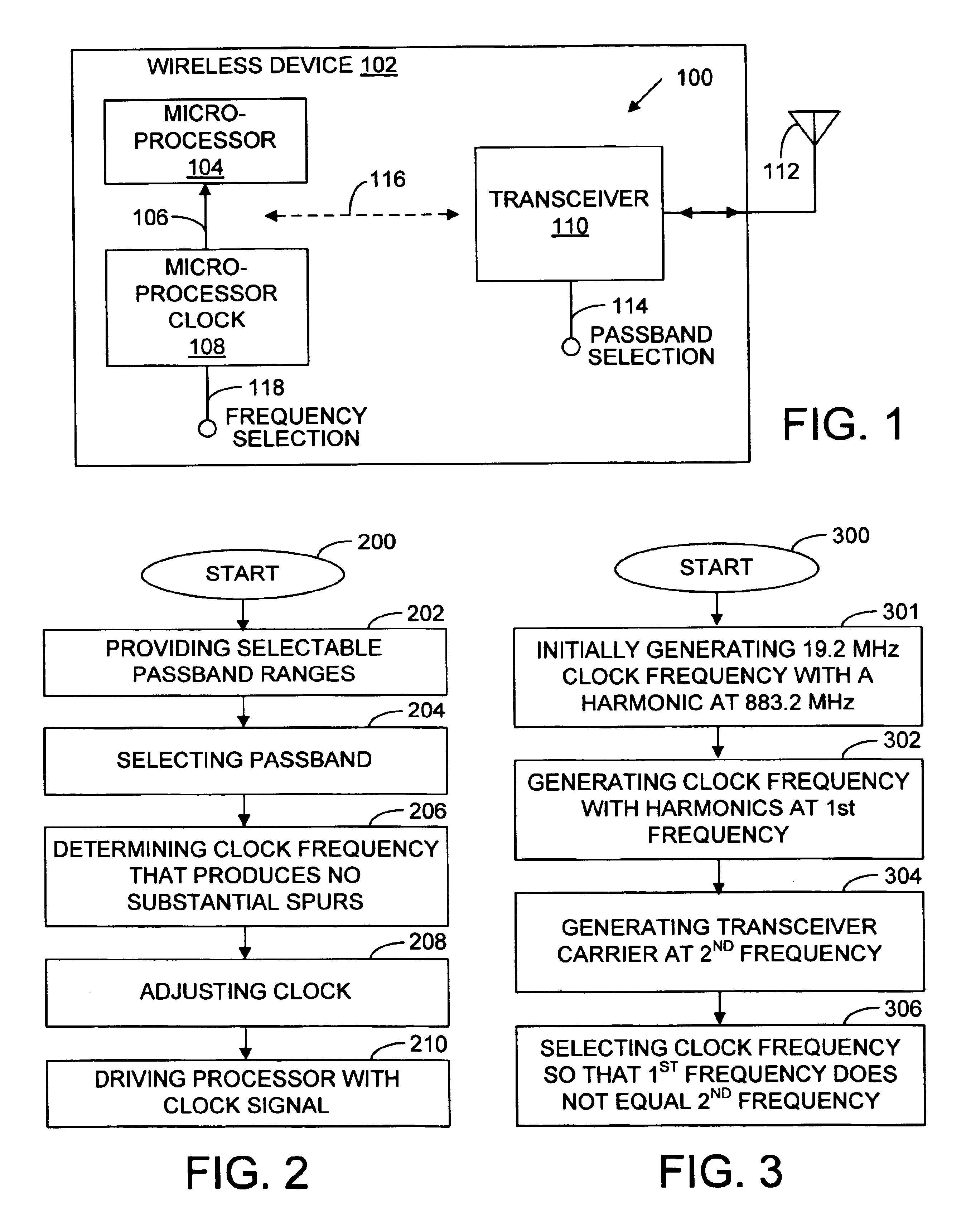
System and method for reducing the effects of clock harmonic frequencies
InactiveUS6999723B2Reduce impactError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTransceiverClock rate
A system and a method are provided for reducing the effects of spurious frequencies in a wireless communications device. The system comprises a processor having a reference frequency input and a clock having an output connected to the processor input. The clock supplies a clock frequency, or reference frequency, to the processor. The reference frequency is the frequency at which the processor operates. The clock also has an input for selecting a reference frequency to provide to the processor. The system also includes a transceiver having a plurality of selectable communications passbands. If the wireless communications device is a telephone, for example, the transceiver frequency (passband) may change as a function of the mode in which the phone is operating (AMPS, PCS, GSM, CDMA, or W-CDMA). In response to changing operating modes (transceiver passband), the clock frequency is adjusted. The clock frequency is selected so that harmonic frequencies associated with the clock frequency do not substantially interfere with the transceiver passband.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Apparatus for generating multiple radio frequencies in communication circuitry and associated methods
InactiveUS6993314B2Guaranteed interference effectReduce the impact of interferenceResonant long antennasPulse automatic controlRadio frequencyTransmitter
A radio-frequency (RF) apparatus capable of transmitting RF signals includes transmitter path circuitry. The transmitter path circuitry includes a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) circuitry. The VCO circuitry generates a first signal that has a first frequency. A divider circuitry couples to the VCO circuitry and, in response to the first signal, the divider circuitry generates a second signal that has a second frequency. The frequency of the second signal equals the frequency of the first signal divided by a number.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
System and method of eliminating or minimizing LO-related interference from tuners
Disclosed are systems and methods of eliminating or reducing interference resulting from harmonics of local oscillator frequencies of mixers. In one embodiment, a determination is made as to a zone or zones in which harmonics result in undesired spur generation. Inter-tuner spurs and intra-tuner spurs may be identified such that frequency information of the identified spurs may be utilized to define a plurality of exclusion zones. LO frequencies may subsequently be efficiently selected in view of the exclusion zone information. Embodiments may also determine a score for identified spurs which may be used to optimally select from within a set of spur-generating local oscillator frequencies.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Partitioning of radio-frequency apparatus
Components of a radio-frequency (RF) apparatus including transceiver circuitry and frequency modification circuitry of a crystal oscillator circuit that generates a reference signal with adjustable frequency may be partitioned in a variety of ways, for example, as one or more separate integrated circuits. The frequency modification circuitry may be implemented as part of a crystal oscillator circuit that includes digitally controlled crystal oscillator (“DCXO”) circuitry and a crystal. The frequency modification circuitry may include at least one variable capacitance device and may be employed to generate a reference signal with adjustable frequency. The adjustable reference signal may be provided to other components of the RF apparatus and / or the RF apparatus may be configured to provide the adjustable reference signal to baseband processor circuitry. Automatic frequency control (AFC) circuitry may be integrated with other components of RF circuitry and may generate frequency control signals for the frequency modification circuitry based on, for example, a signal received from a temperature sensor. Digital-to-analog converter (DAC) circuitry may be integrated with other components of RF circuitry to enable all-digital frequency control communications from baseband processor circuitry to RF circuitry.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Popular searches
Pulse combined modulation Time interval measurement without driving mechanism Electric variable regulation Transducer acoustic reaction prevention Speech recognition Transducer casings/cabinets/supports Pulse shaping Oscillations generators Pulse generation by logic circuits Electrial characteristics varying frequency control
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com