Patents
Literature
36 results about "Spurious tone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
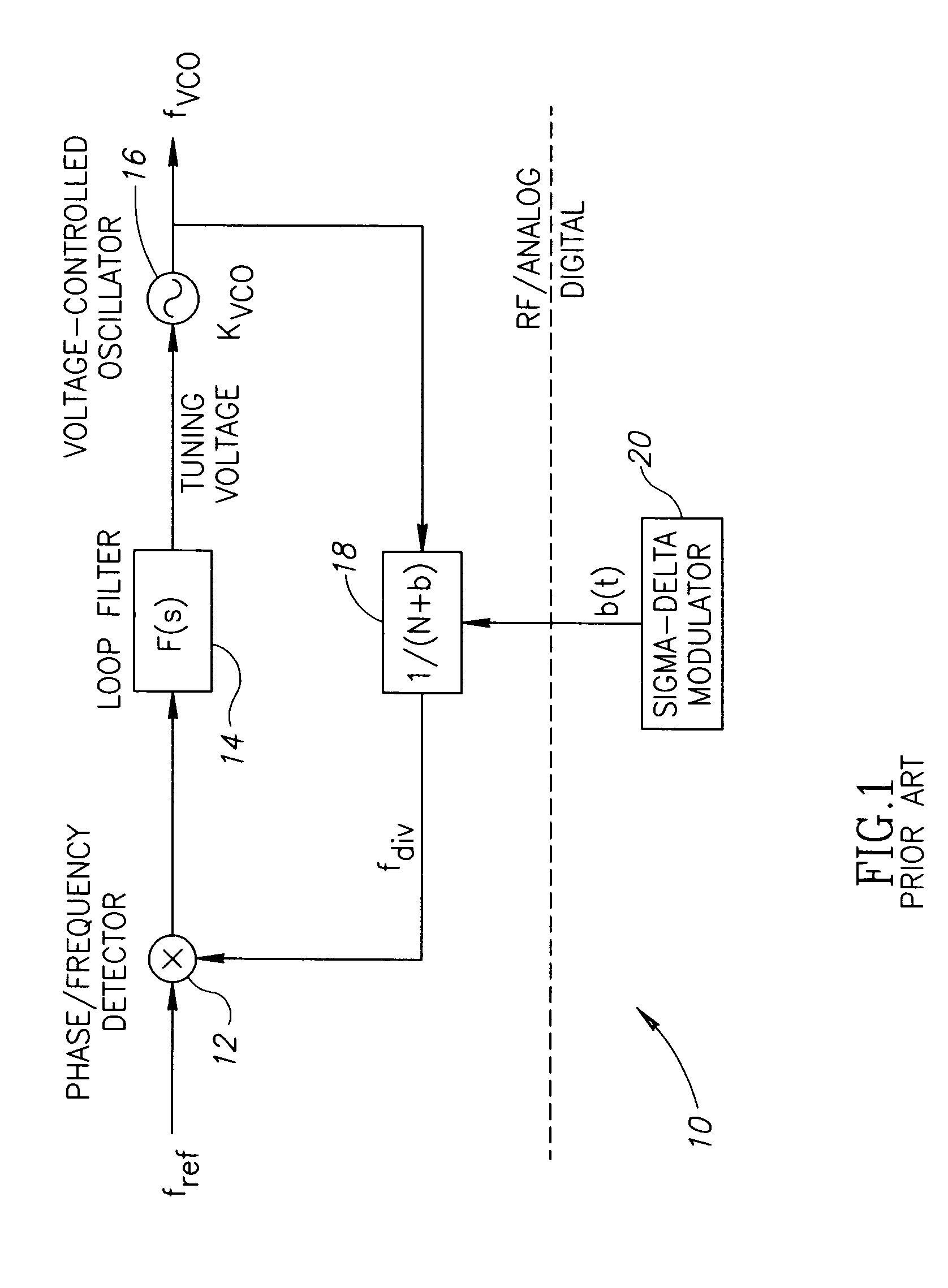
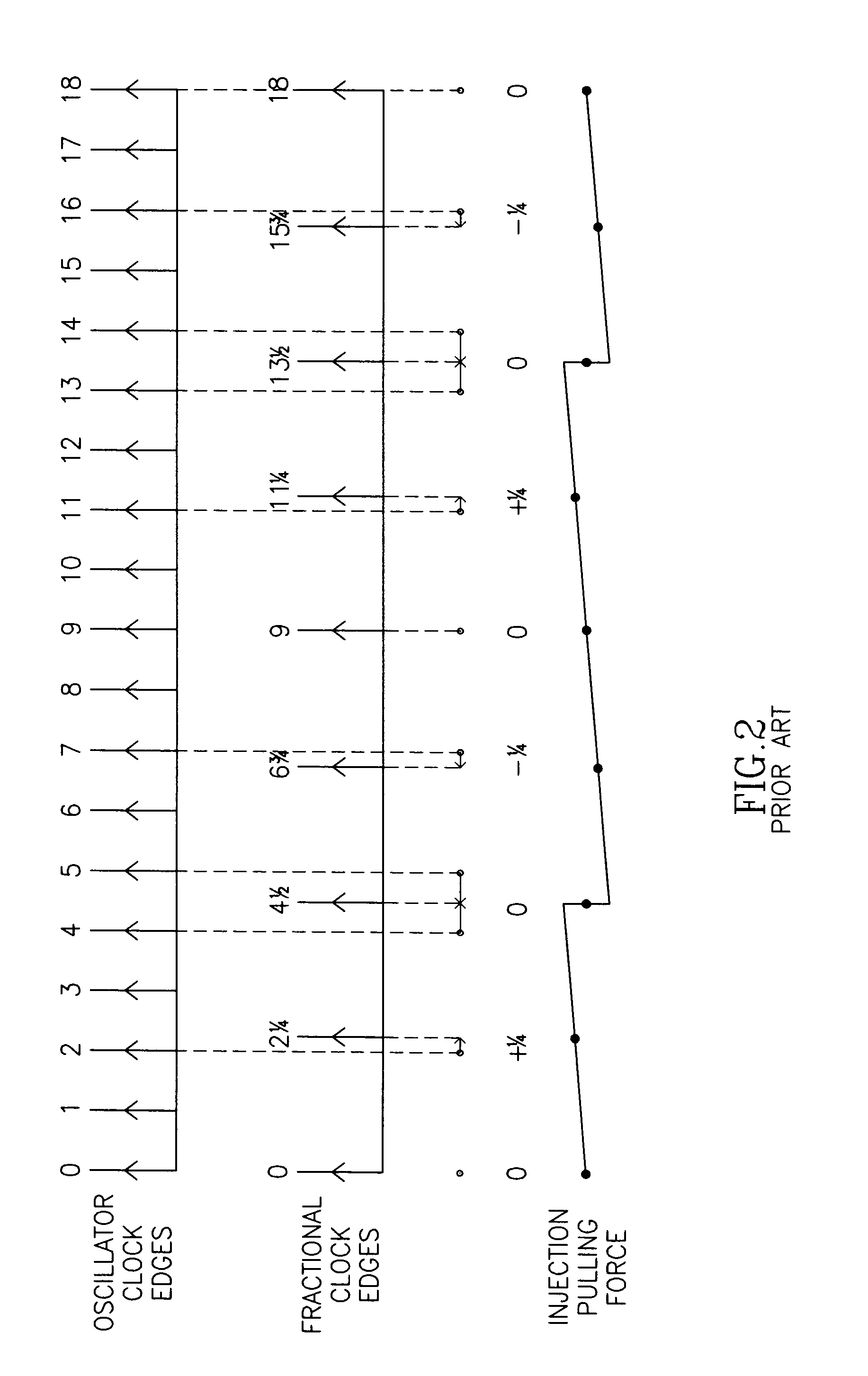
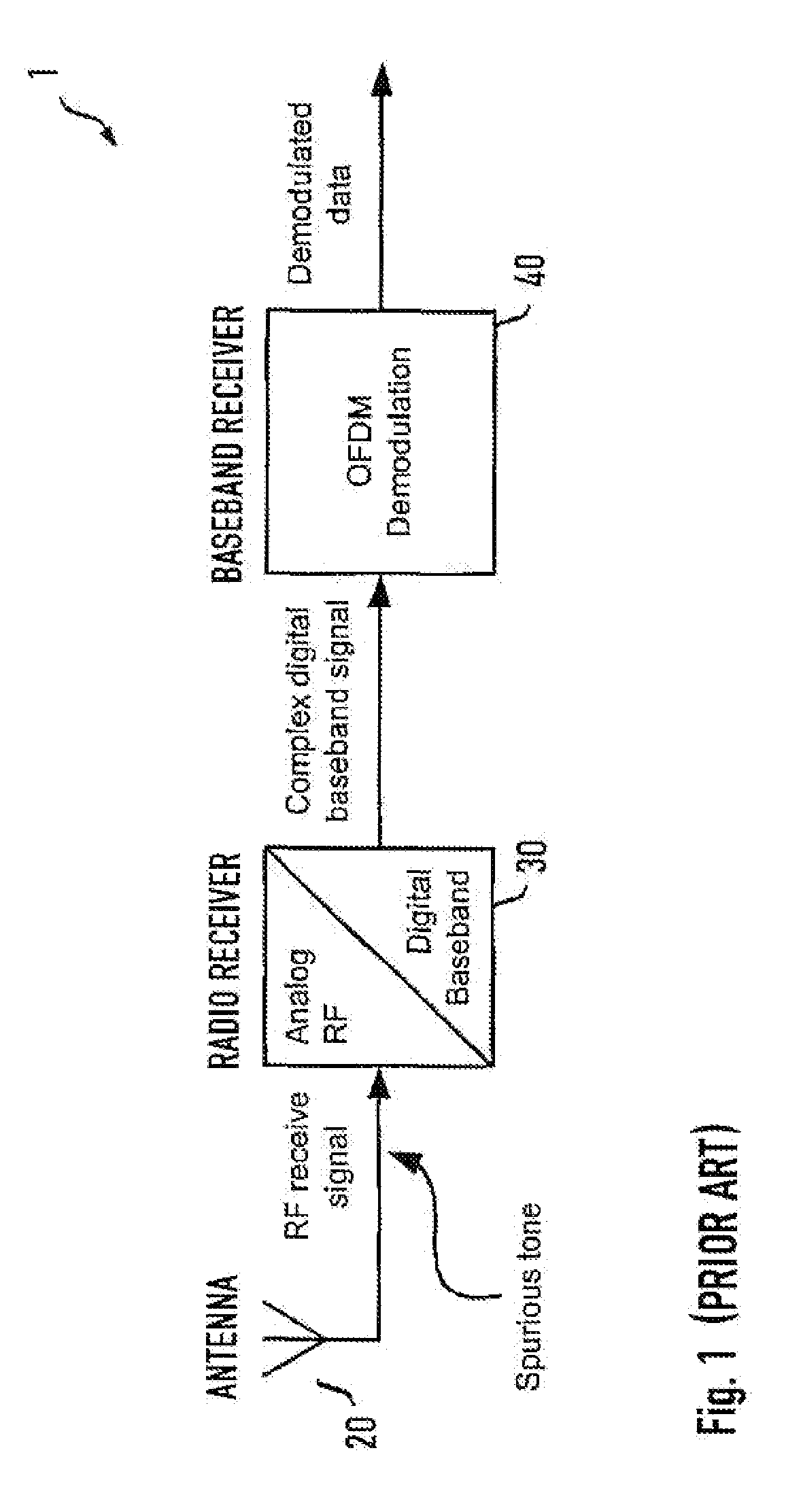
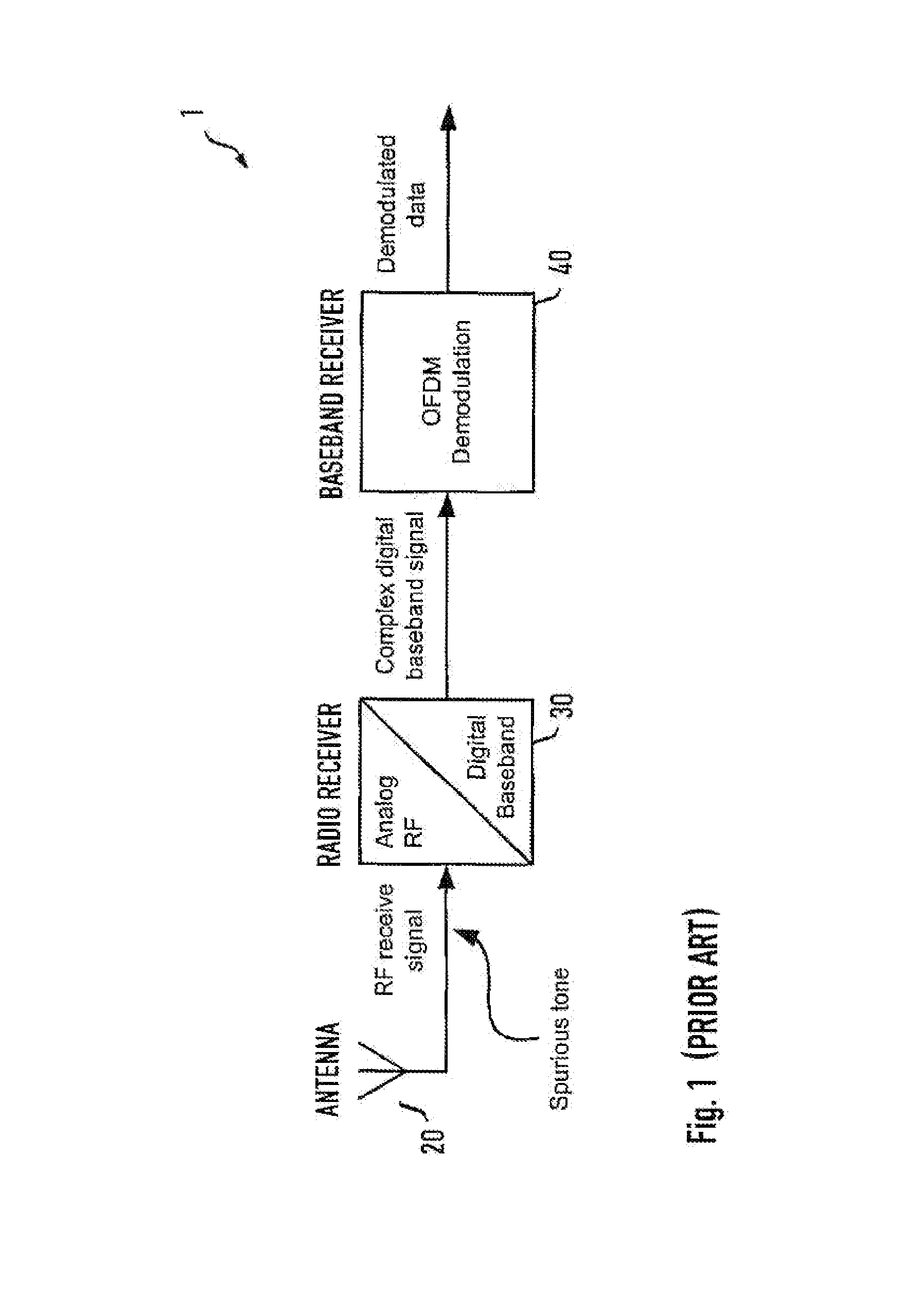
In electronics (radio in particular), a spurious tone (also known as an interfering tone, a continuous tone or a spur) denotes a tone in an electronic circuit which interferes with a signal and is often masked underneath that signal. Spurious tones are any tones other than a fundamental tone or its harmonics. They also include tones generated within the back-to-back connected transmit and receive terminal or channel units, when the fundamental is applied to the transmit terminal or channel-unit input.
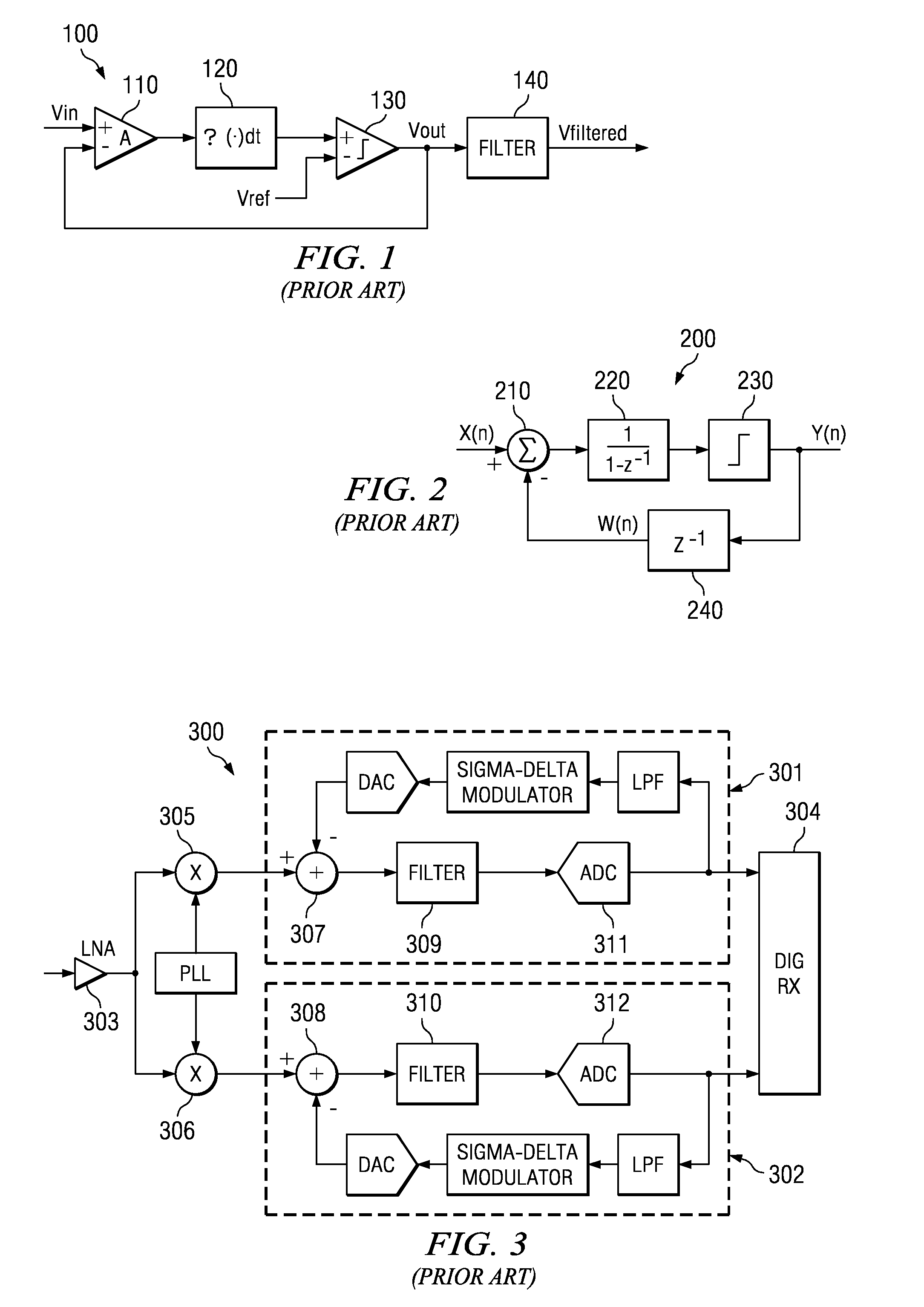
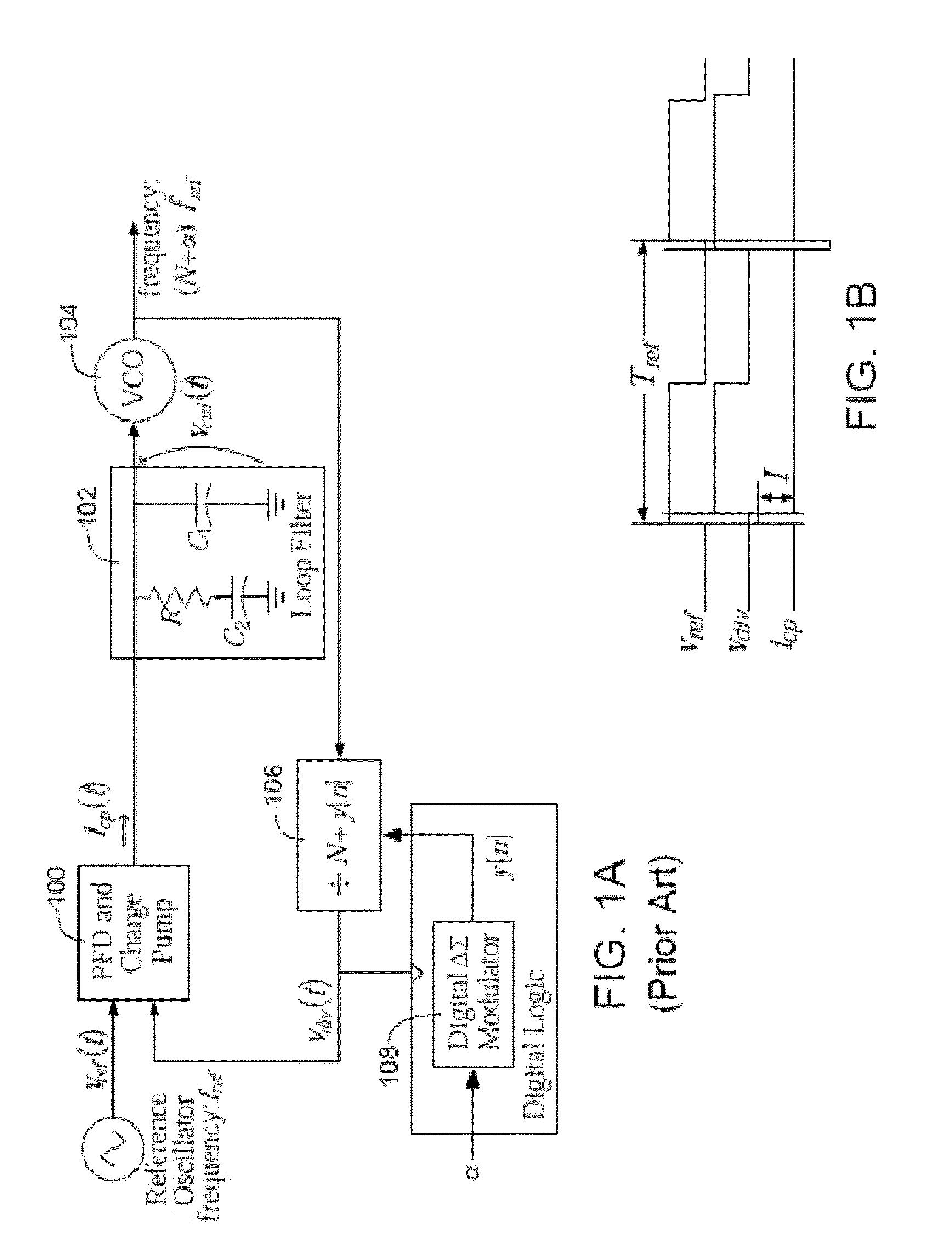
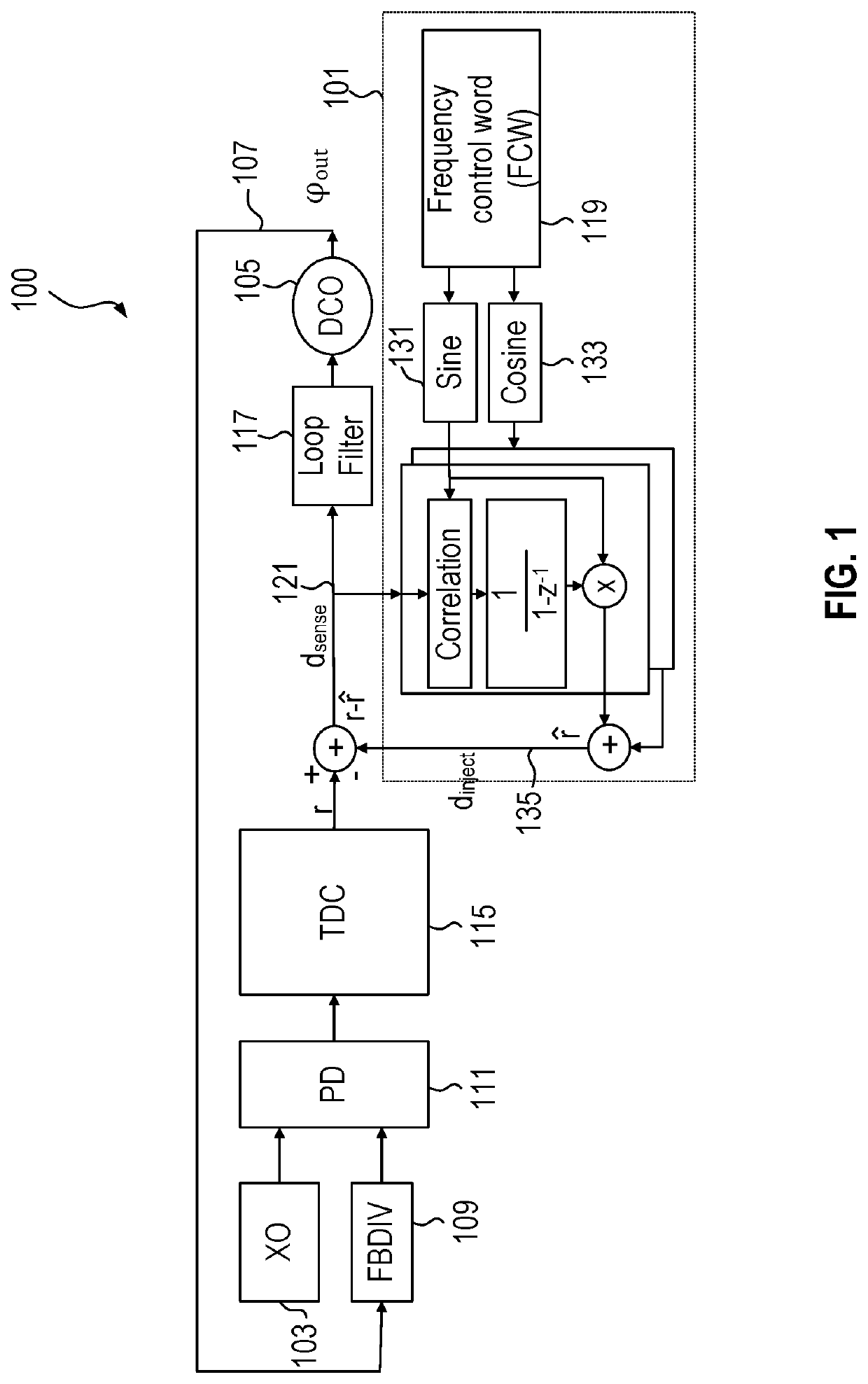
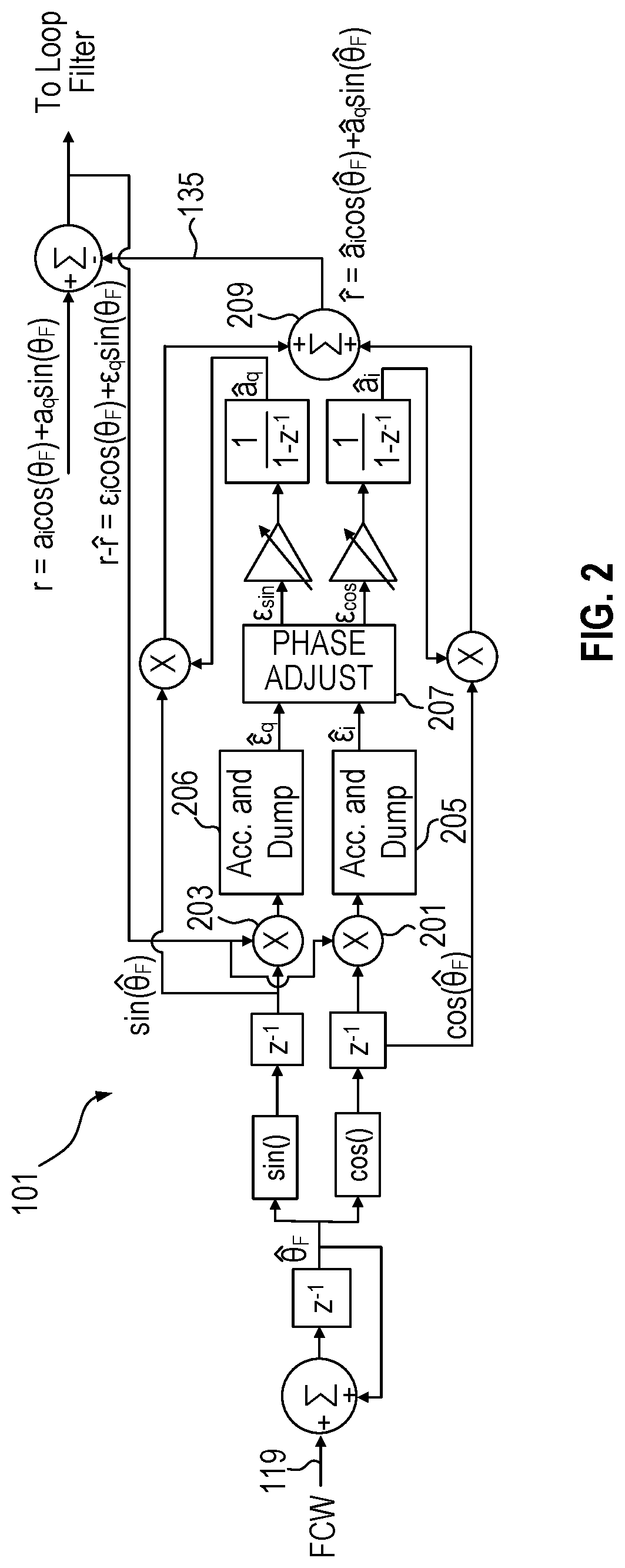
Apparatus for and method of noise suppression and dithering to improve resolution quality in a digital RF processor
InactiveUS20050186920A1Cancel noiseAvoid it happening againPulse automatic controlAngle modulationImage resolutionEngineering
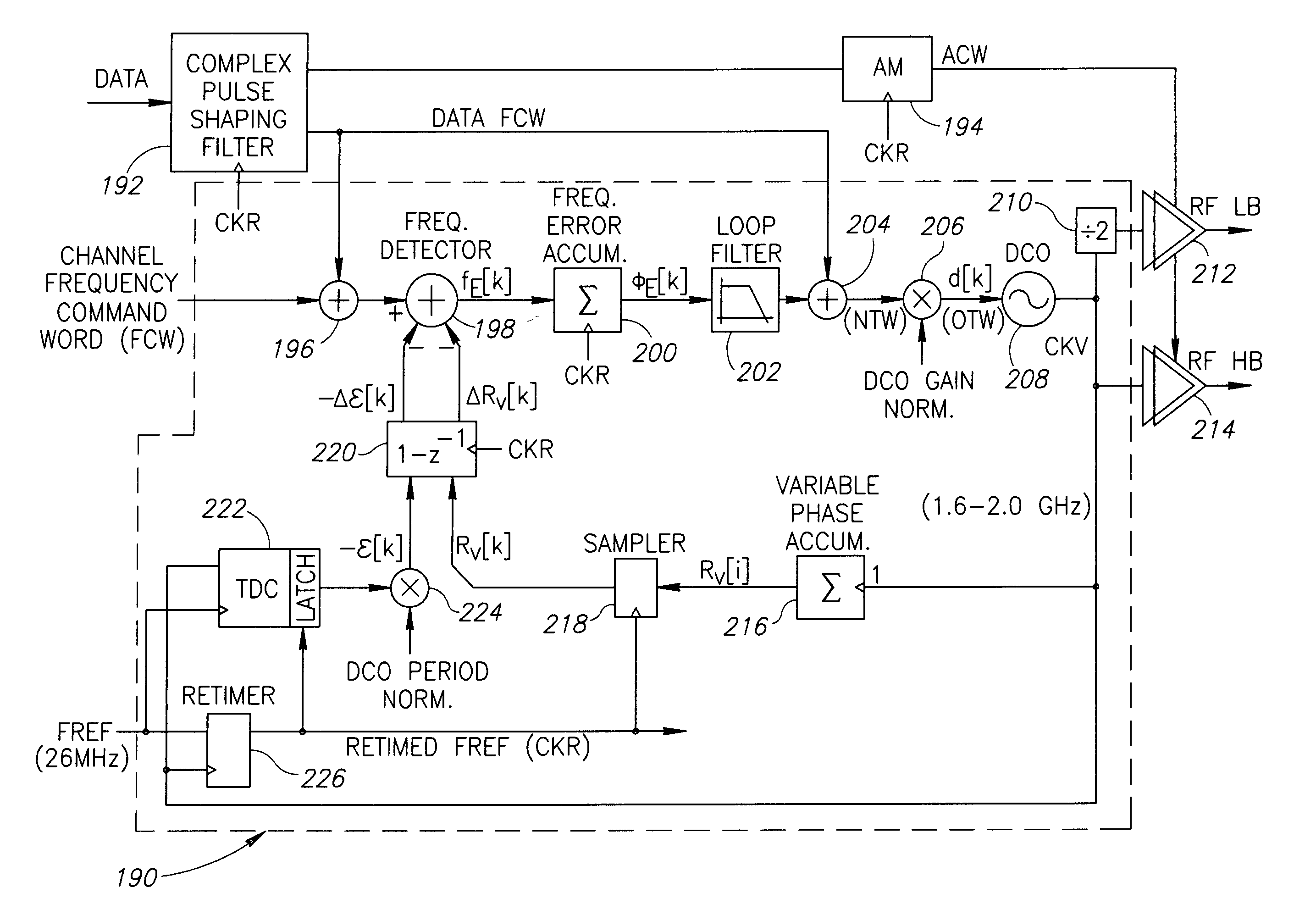
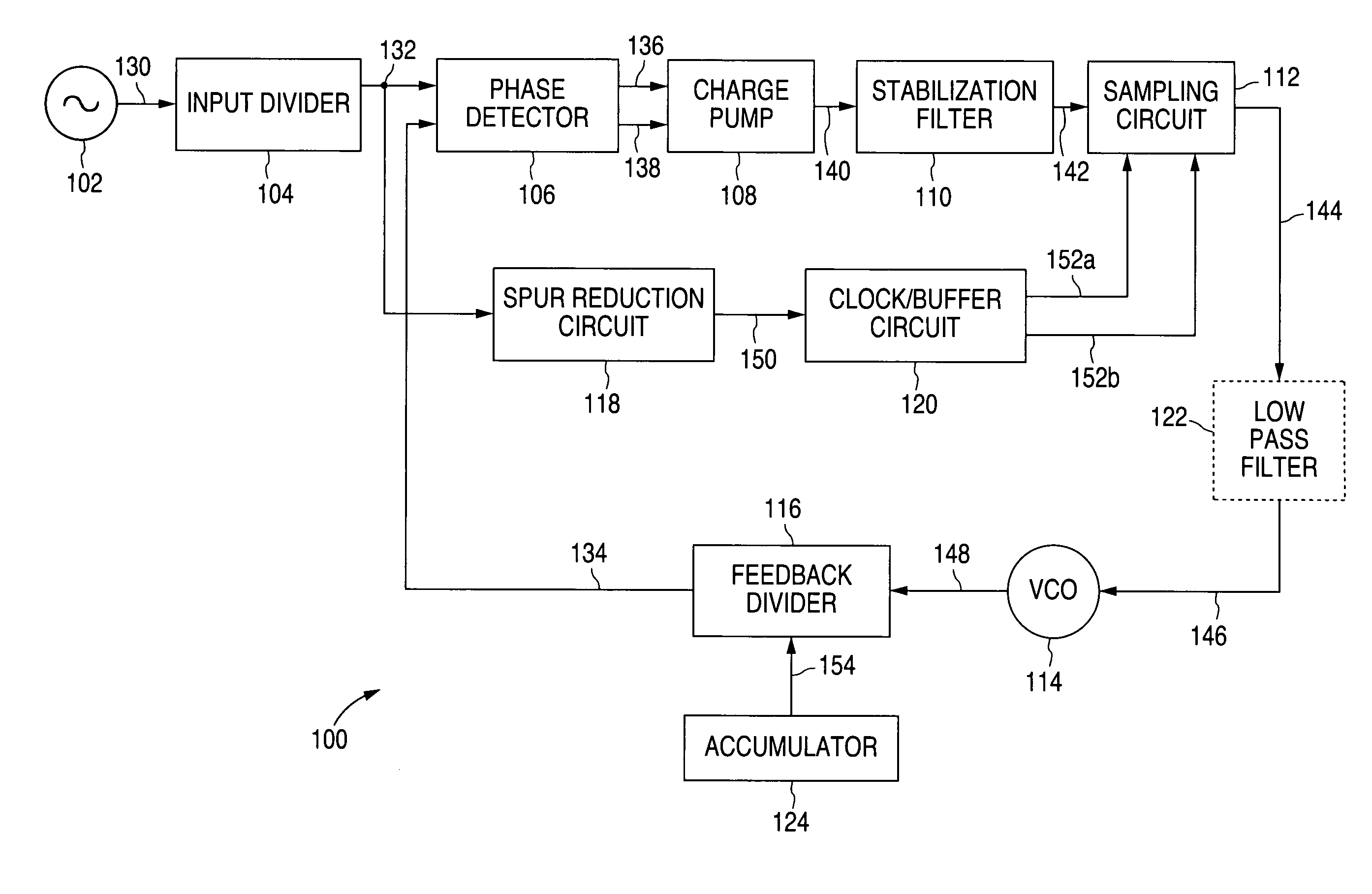
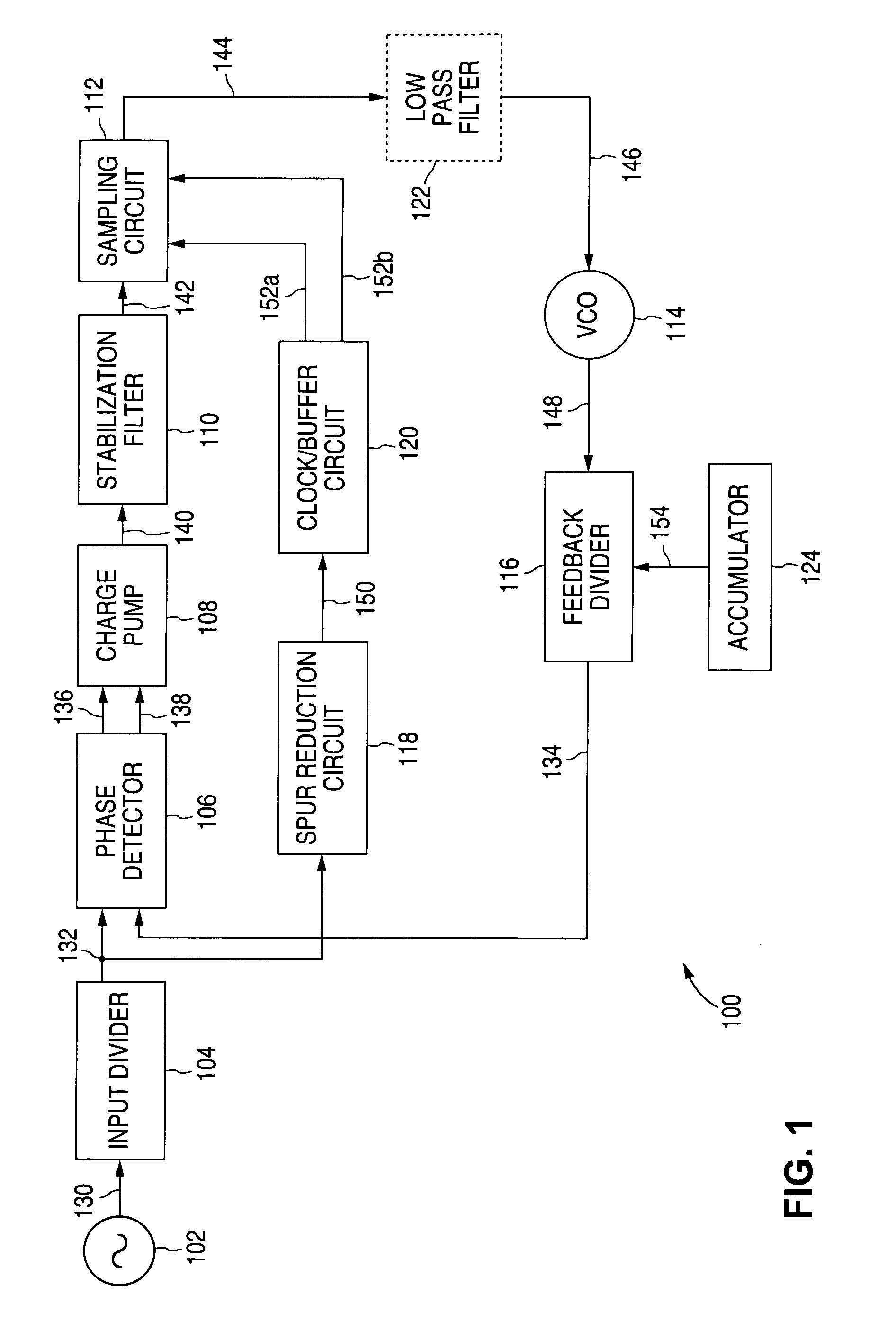
A novel apparatus for and a method of noise and spurious tones suppression in a digital RF processor (DRP). The invention is well suited for use in highly integrated system on a chip (SoC) radio solutions that incorporate a very large amount of digital logic circuitry. The noise suppression scheme eliminates the noise caused by various on chip interference sources transmitted through electromagnetic, power, ground and substrate paths. The noise suppression scheme permits an all digital PLL (ADPLL) to operate in such a way to avoid generating the spurs that would normally be generated from the injection pulling effect of interfering sources on the chip. The frequency reference clock is retimed to be synchronous to the RF oscillator clock and used to drive the entire digital logic circuitry of the DRP. This ensures that the different clock edges throughout the system will not exhibit mutual drift. A method of improving the resolution quality of a time to digital converter within the ADPLL is also taught. The method dithers the reference clock by passing it through a delay circuit that is controlled by a sigma-delta modulator. The dithered reference clock reduces the affect on the phase noise at the output of the ADPLL due to ill-behaved quantization of the TDC timing estimation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
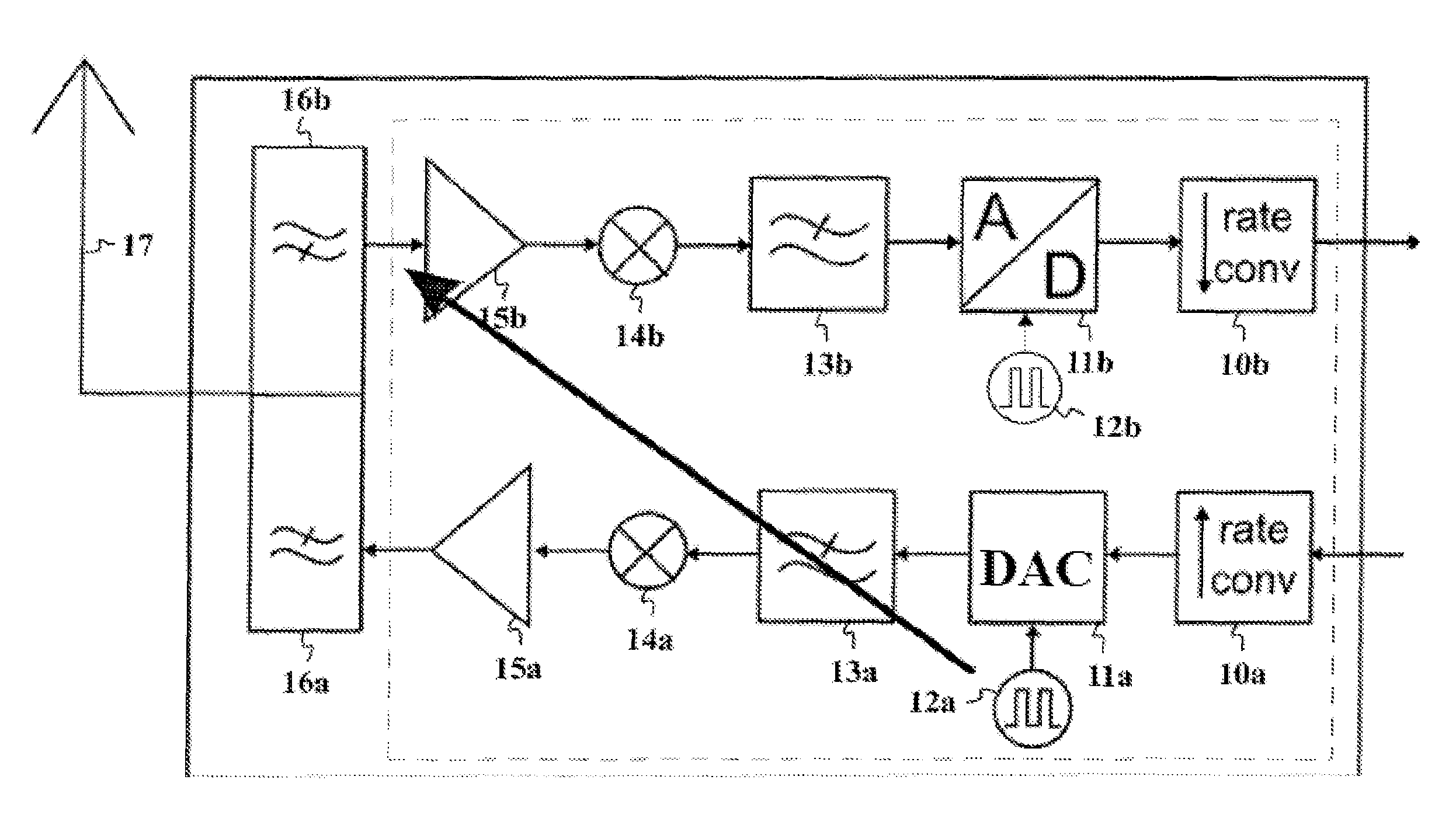
Transmitter with a Variable Sampling Rate
ActiveUS20130016761A1Reduce the impactReduce impactSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionDuplex signal operationTransceiverHarmonic
The present invention presents a method and a system for mitigating effects of clock harmonics in the receiver. The receiving signal may be monitored in such a way that the interfering harmonic component is tracked. When the interfering frequency is found out, the system determines the clock or clocks in the transceiver which are contributing to the interfering spurious tone. After that, the contributing clock(s) frequency is selected so that the effect of the spurious tone in the receiving passband is minimized or mitigated. This is performed by selecting a suitable clock frequency resulting in the spurious tones all falling outside the receiver passband; or in an OFDM system, by choosing a clock frequency deriving the spurious tone straight onto a subcarrier signal frequency.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for providing a phase-locked loop with reduced spurious tones
ActiveUS7038509B1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionComputer sciencePhase-locked loop
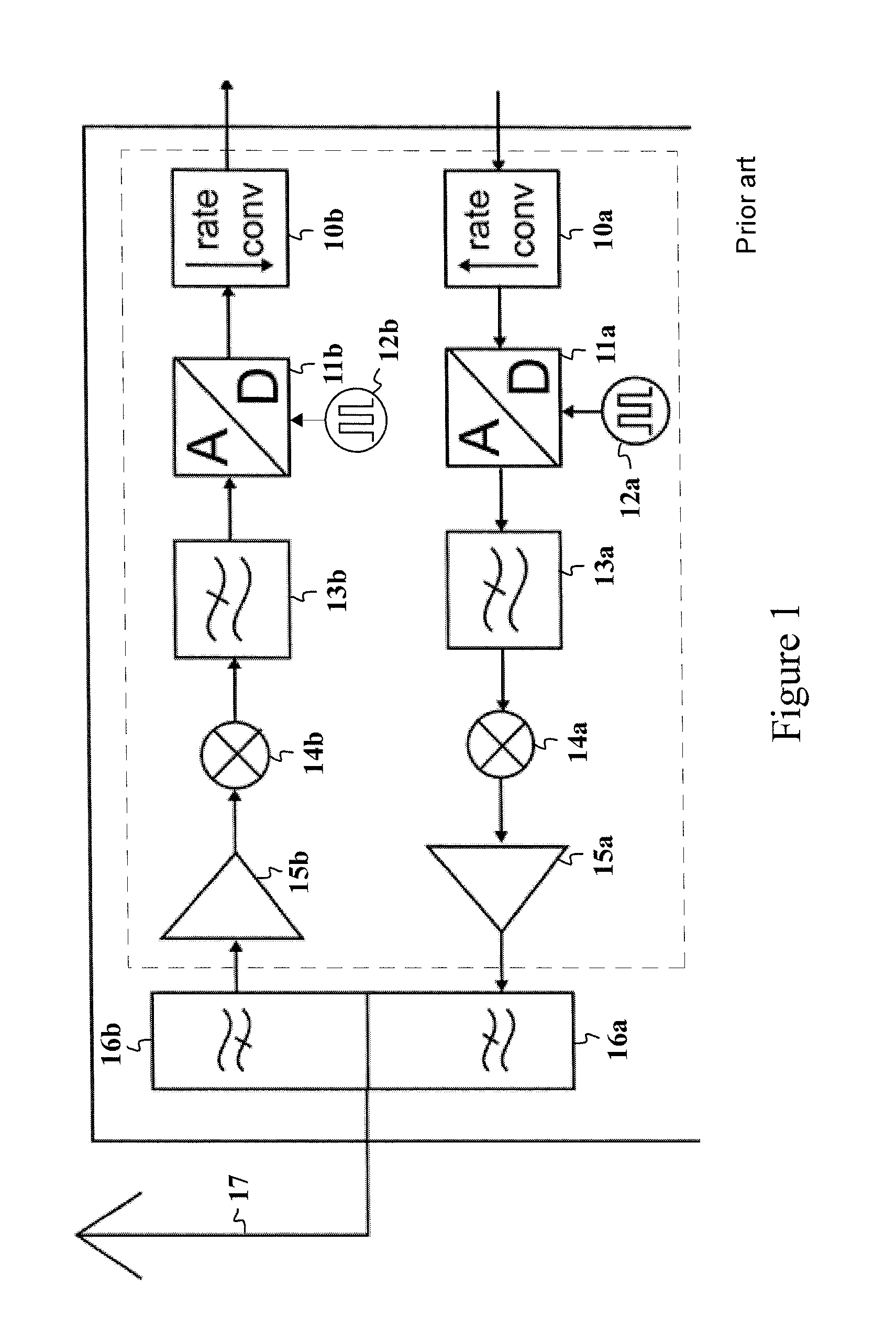
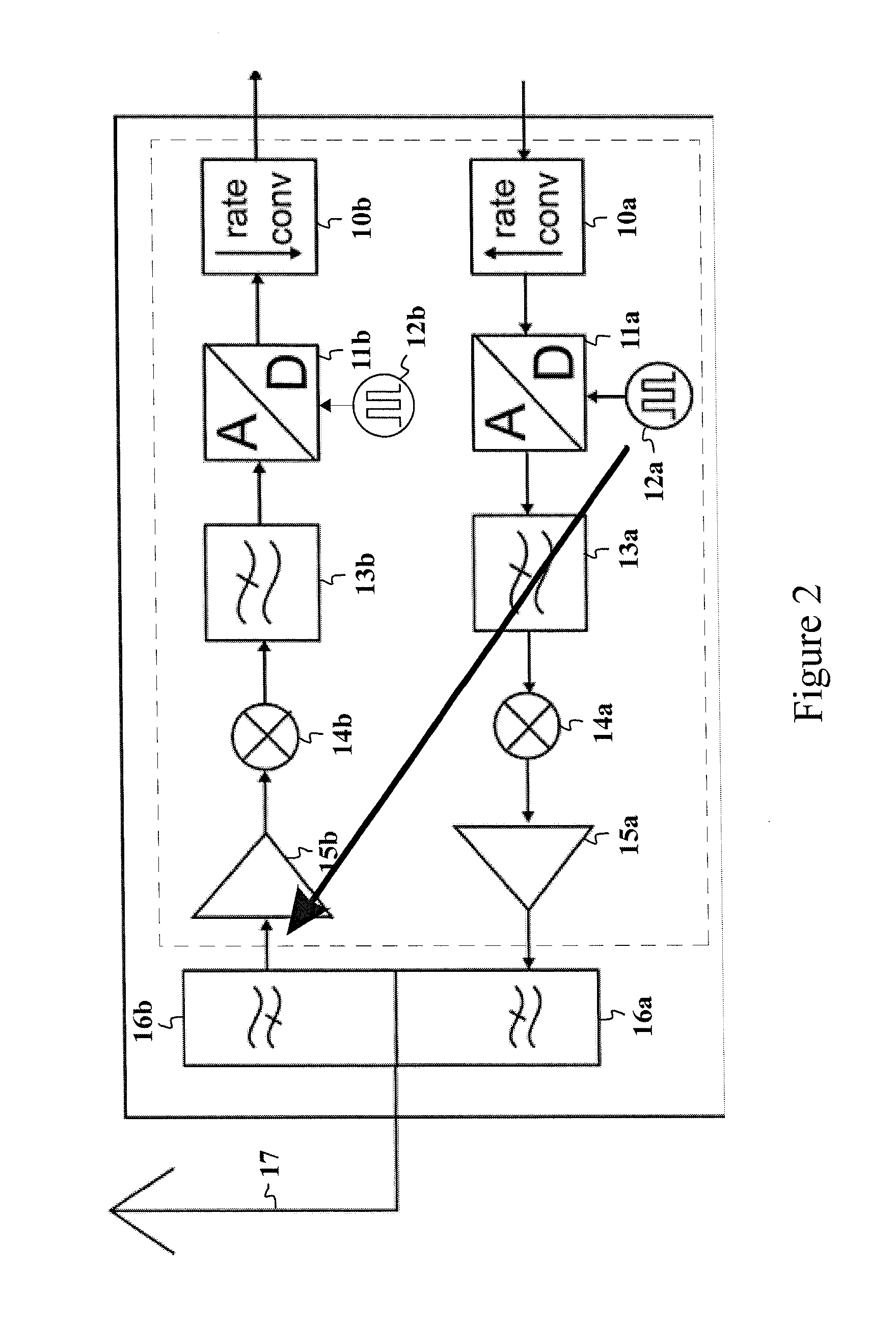
A method for providing a phase-locked loop with reduced spurious tones is provided that includes comparing a reference clock signal to an internal clock signal to generate a first signal. The first signal is sampled based on a sampling clock signal to generate a second signal. The sampling clock signal is reduced with respect to the reference clock signal. The internal clock signal is generated based on the second signal.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
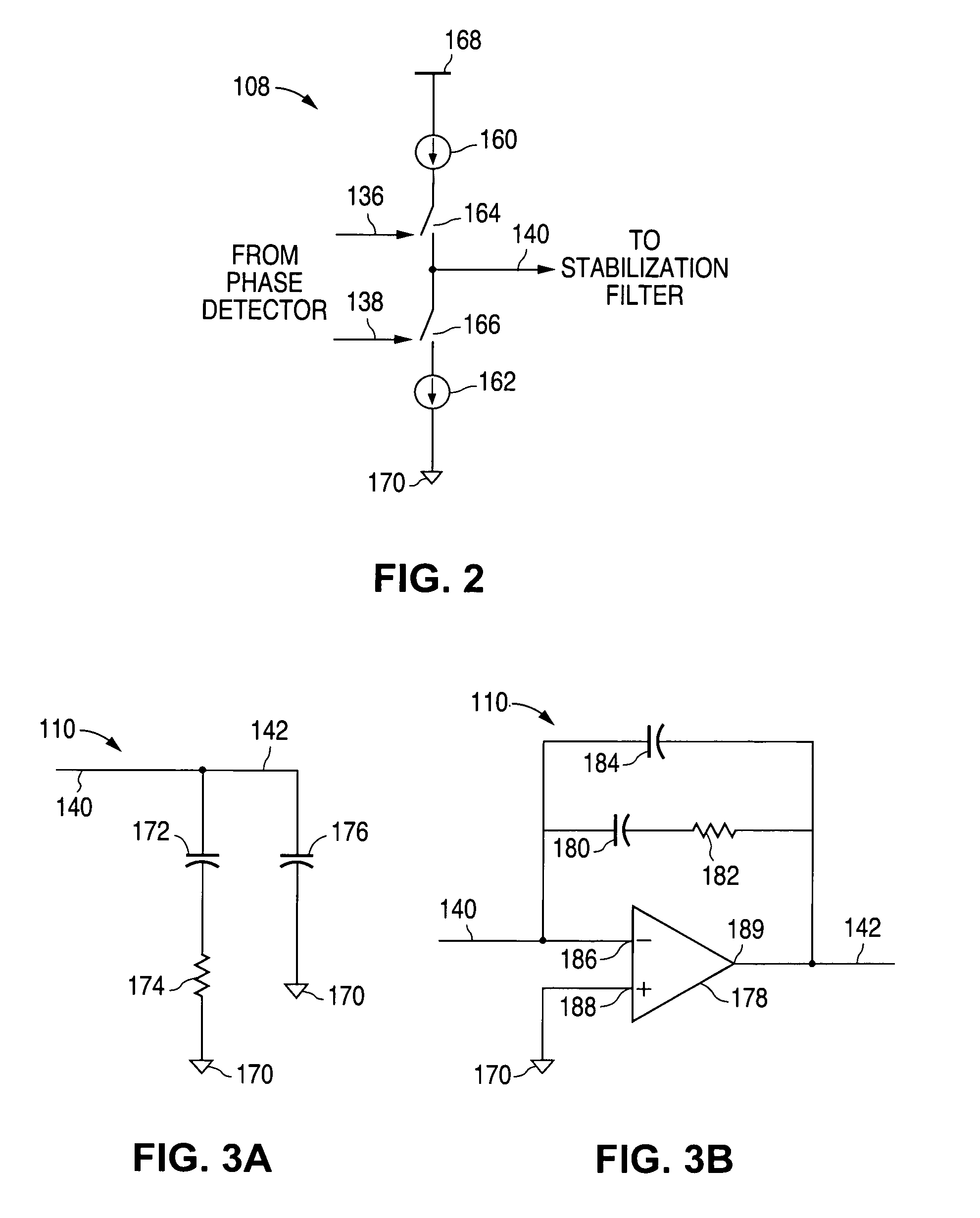
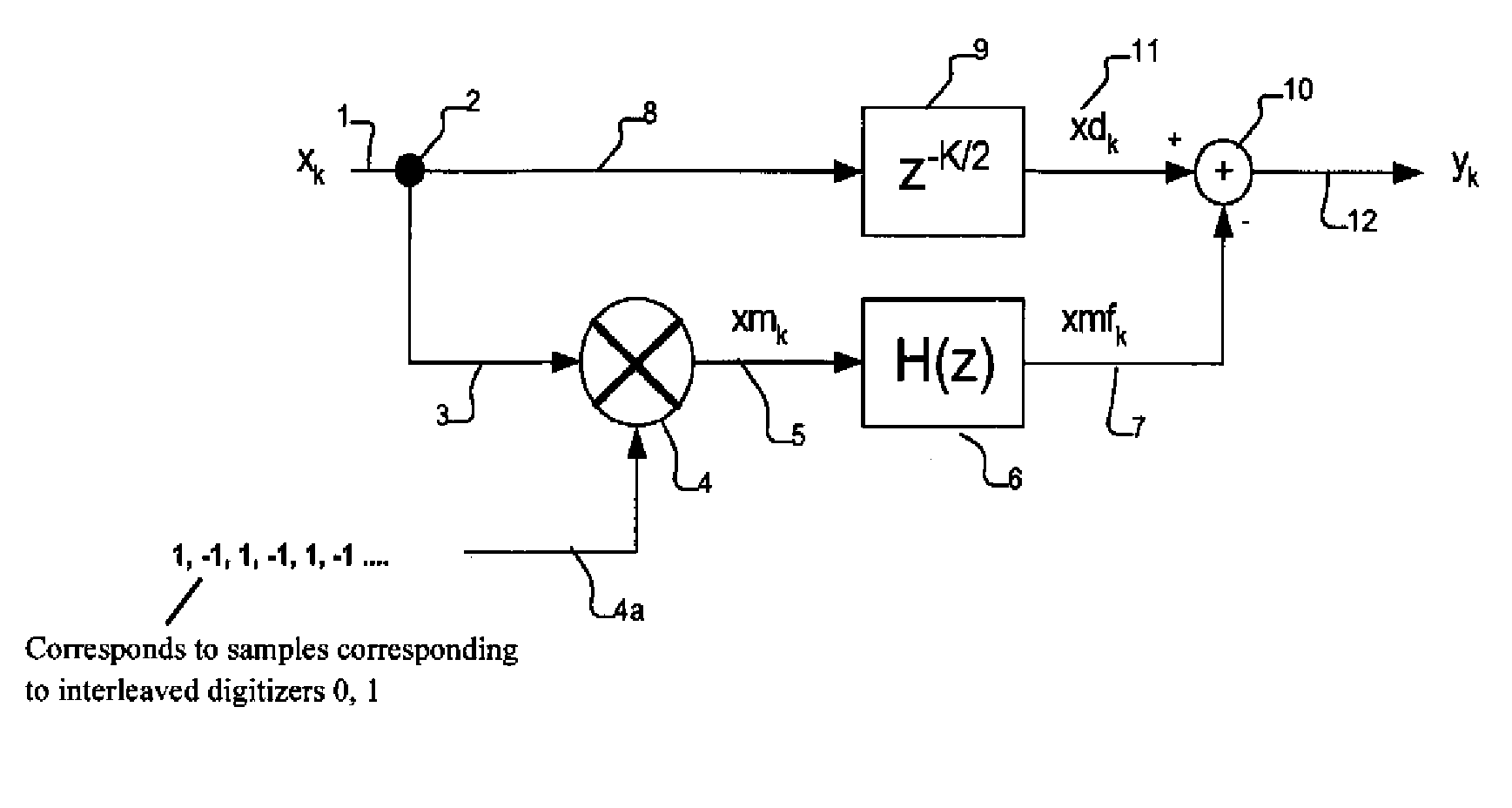
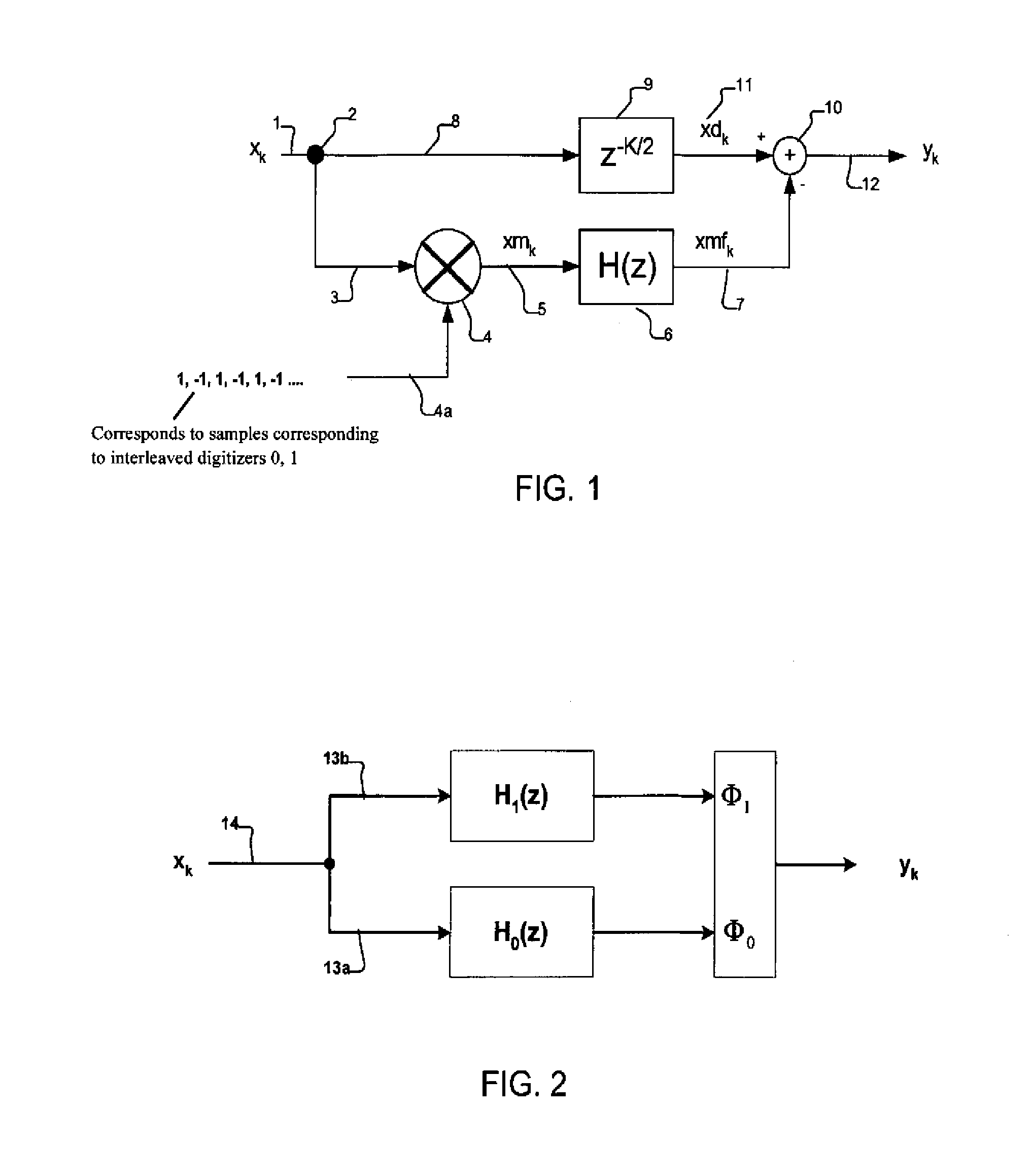
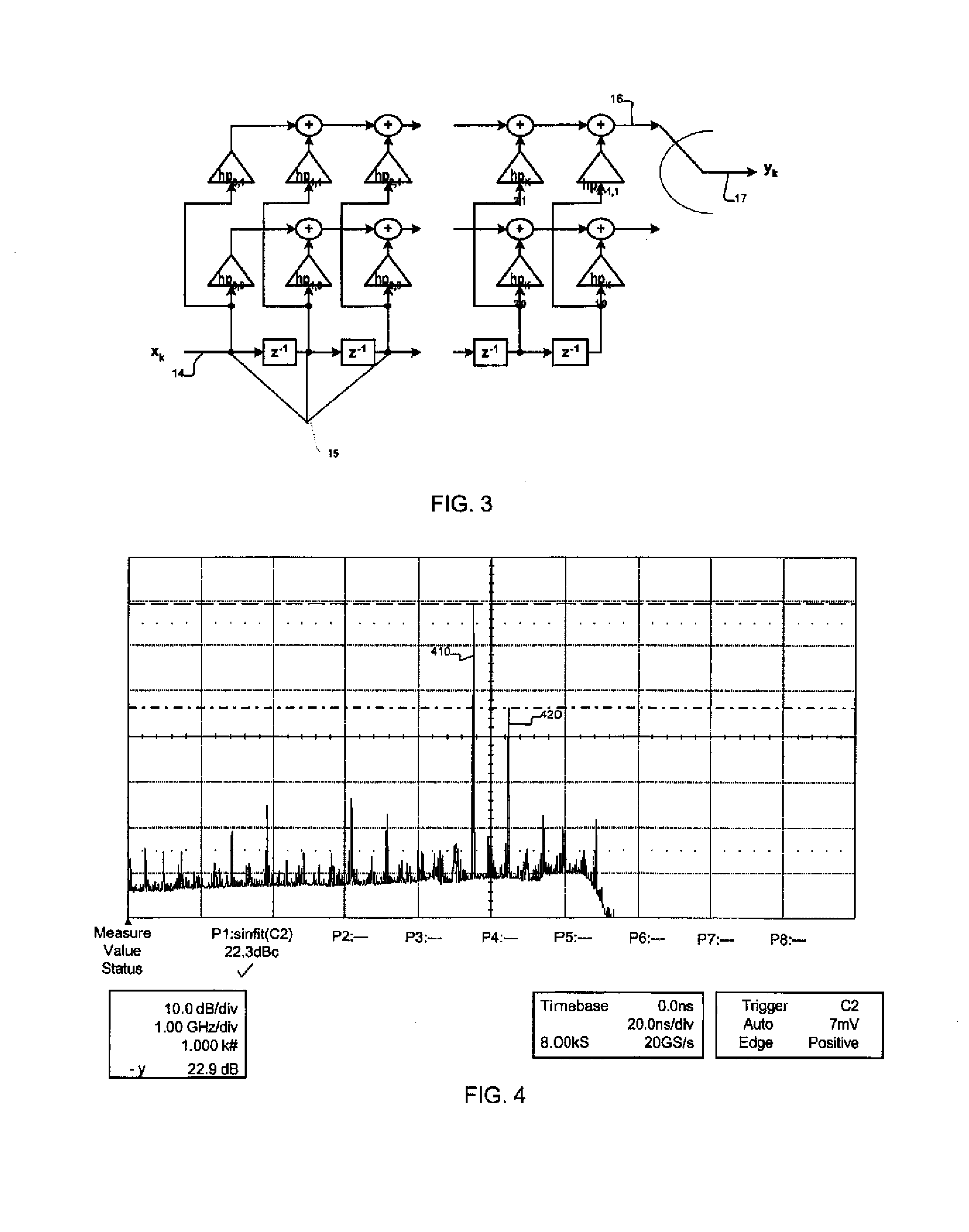
Method and apparatus for artifact signal reduction in systems of mismatched interleaved digitizers
ActiveUS7386409B2Eliminate artifactsReduce and eliminate errorAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsSignal correctionDigital converter
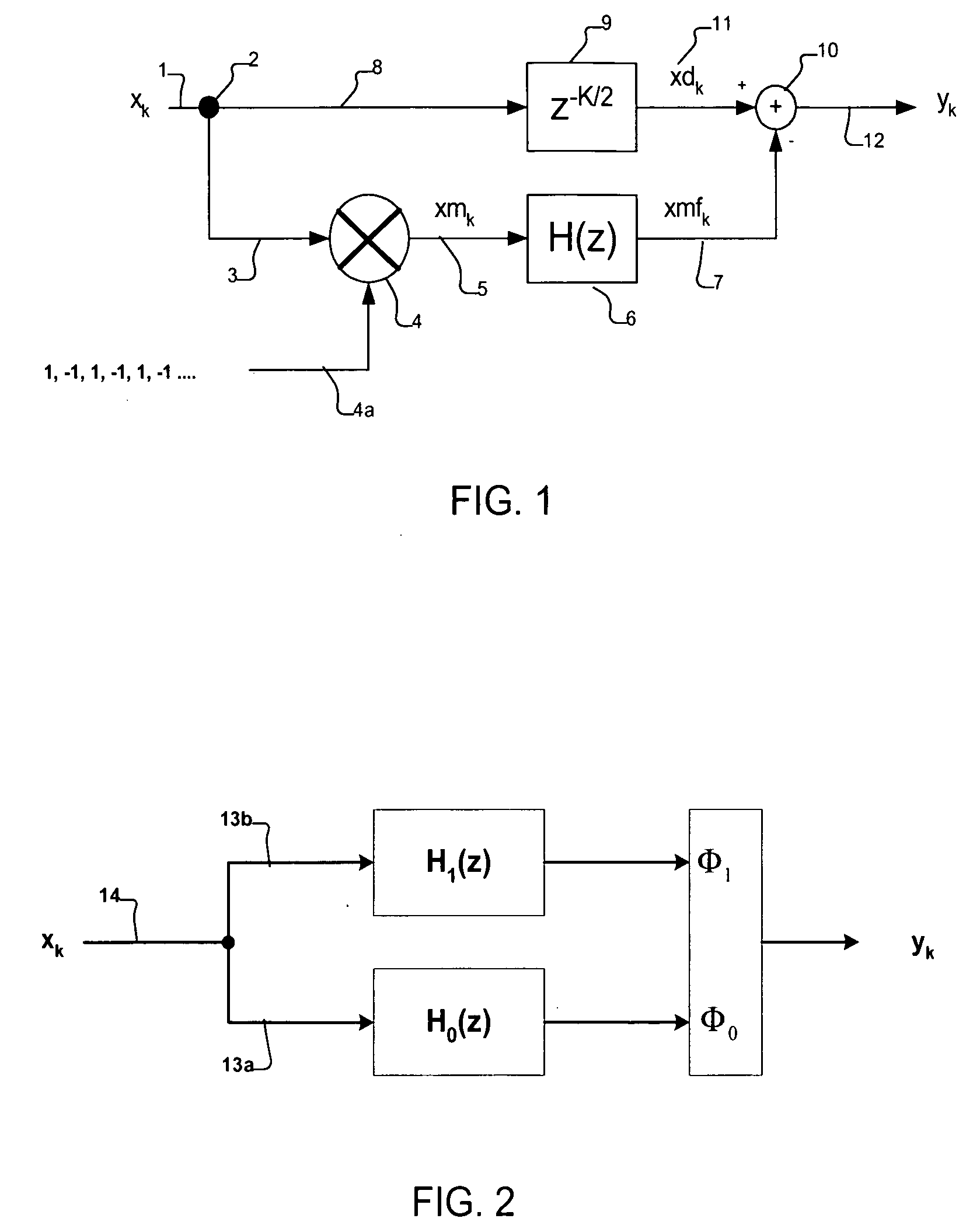
An artifact signal correction system may include a mixing component to generate a waveform corresponding to an artifact such as an error tone, whereupon that waveform may be combined with the input waveform to substantially eliminate the artifact. In preferred embodiments, a method and apparatus for reducing spurious tones in systems of mismatched interleaved digitizers due to interleave error is provided. In various embodiments the method may include reversing the frequency content of an input signal, converting the reversed signal into interleave artifact content, delaying the input signal along a parallel path, and then subtracting the interleave content from the delayed input signal.
Owner:TELEDYNE LECROY
Variable frequency circuit controller
ActiveUS20120242379A1Network traffic/resource managementPulse automatic controlEngineeringRadio frequency
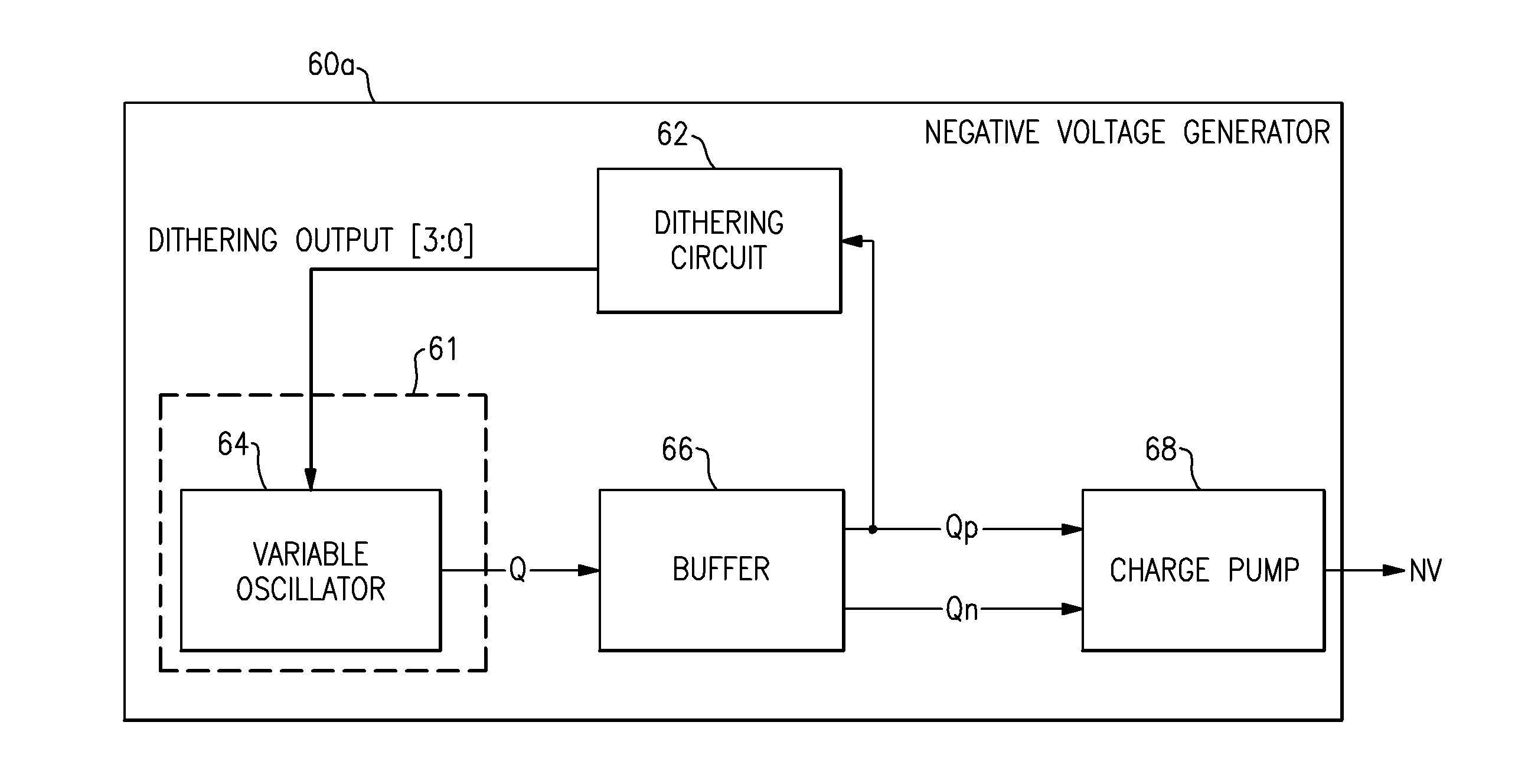
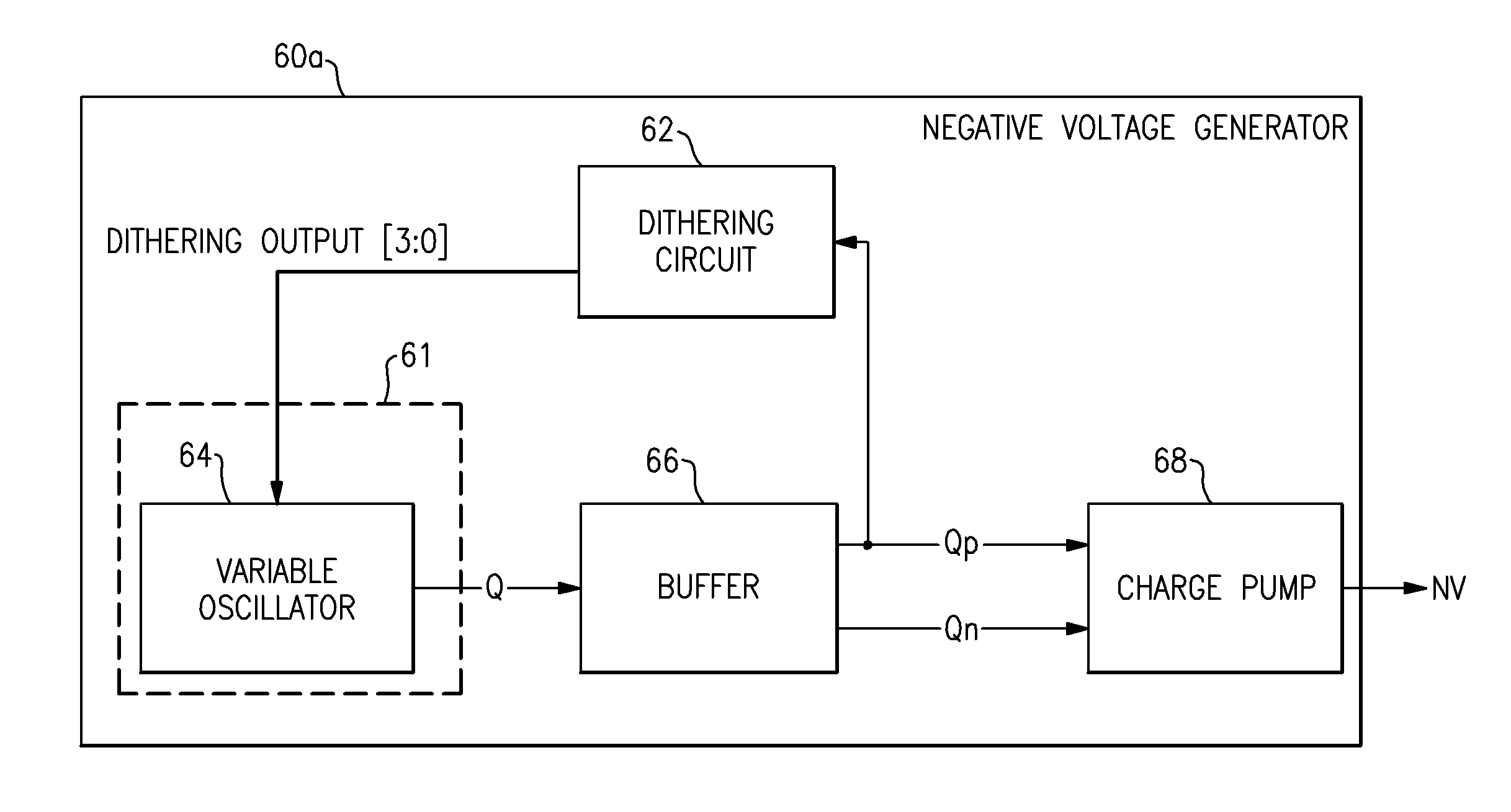
Apparatus and methods for distributing spurious tones through the frequency domain are disclosed. One such apparatus can include a dithering circuit configured to generate a sequence of numbers that exhibit statistical randomness and a variable frequency circuit configured to adjust a frequency of an output based on the sequence of numbers so as to spread energy of spurious tones in a frequency response of the output to lower a noise floor. In one example, spurious tones can be reduced in a negative voltage generator of a radio frequency (RF) attenuator.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
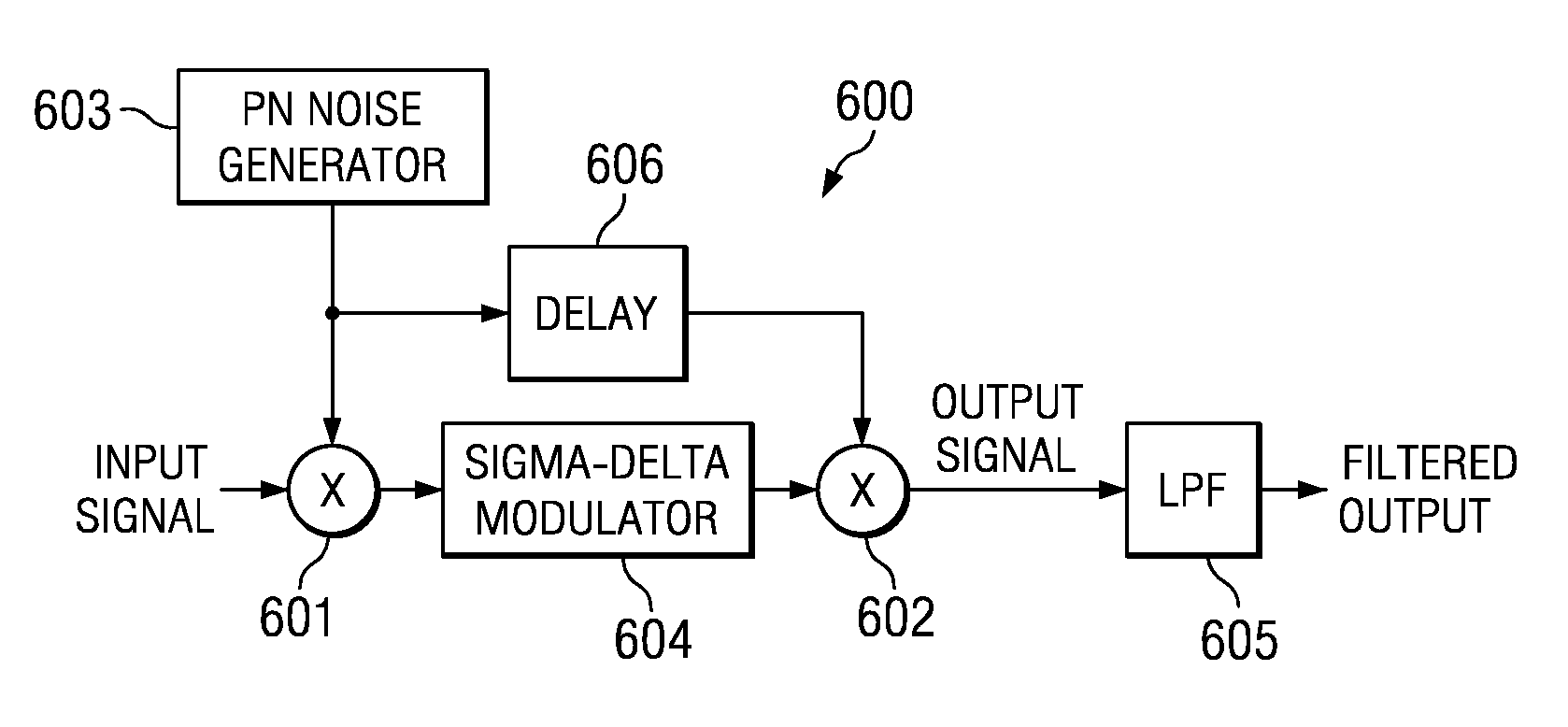
Apparatus and method for dithering a sigma-delta modulator
A signal processor includes a sigma-delta modulator. The input signal to the signal-delta modulator may contain a dc component that generates spurious tones in the modulator output. An input signal to the signal processor is multiplied by an output of a waveform generator to produce an up-converted signal prior to processing by the sigma-delta modulator. Preferably, the waveform generator produces a random signal, which may be a pseudorandom signal. However, other waveforms such as a bipolar binary waveform can also be used. The output of the waveform generator is delayed and multiplied by the output of the sigma-delta modulator to produce a down-converted signal with reduced spurious tones. The delay matches the delay of the sigma-delta modulator. The down-converted signal is filtered with a low-pass filter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
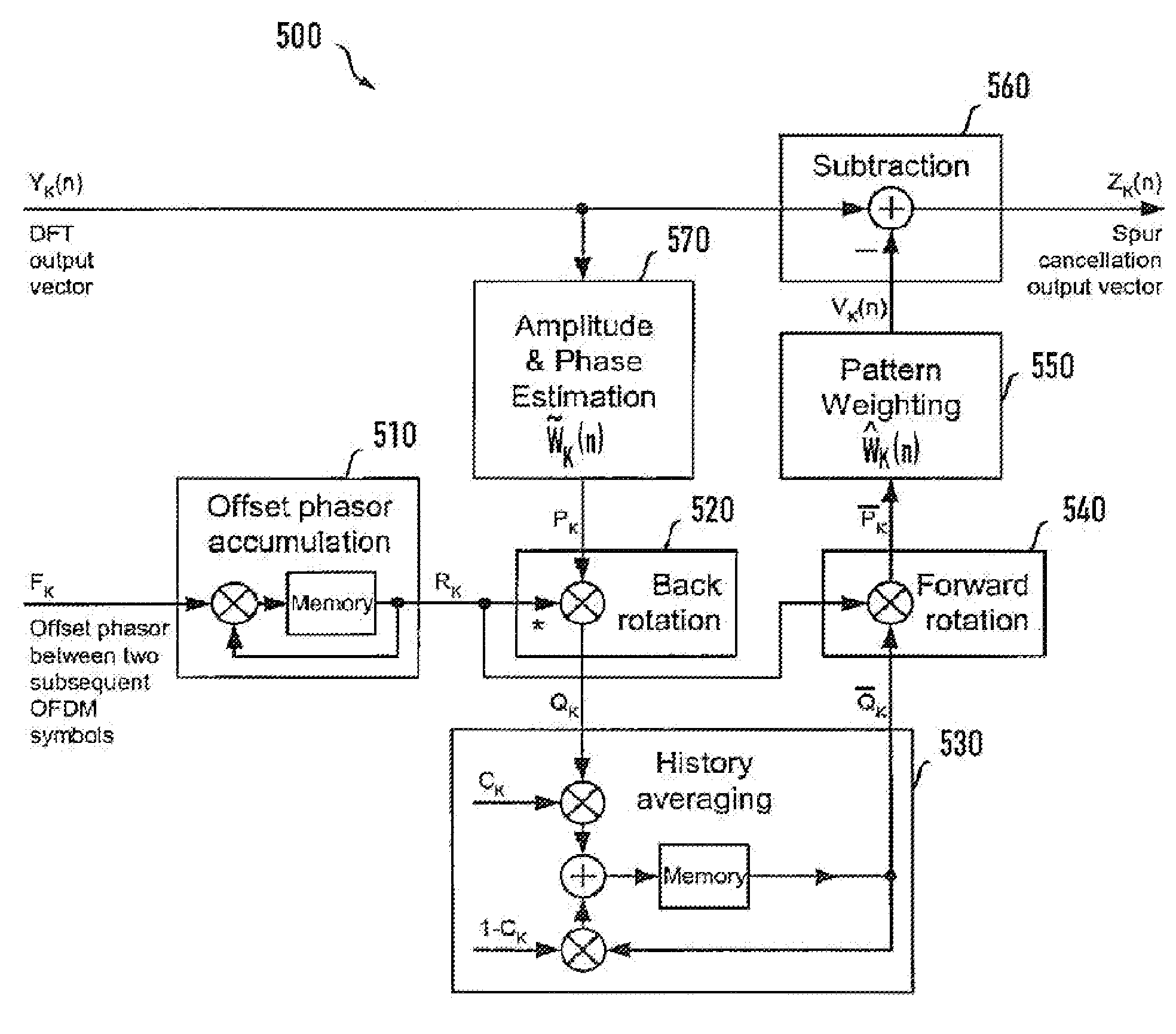
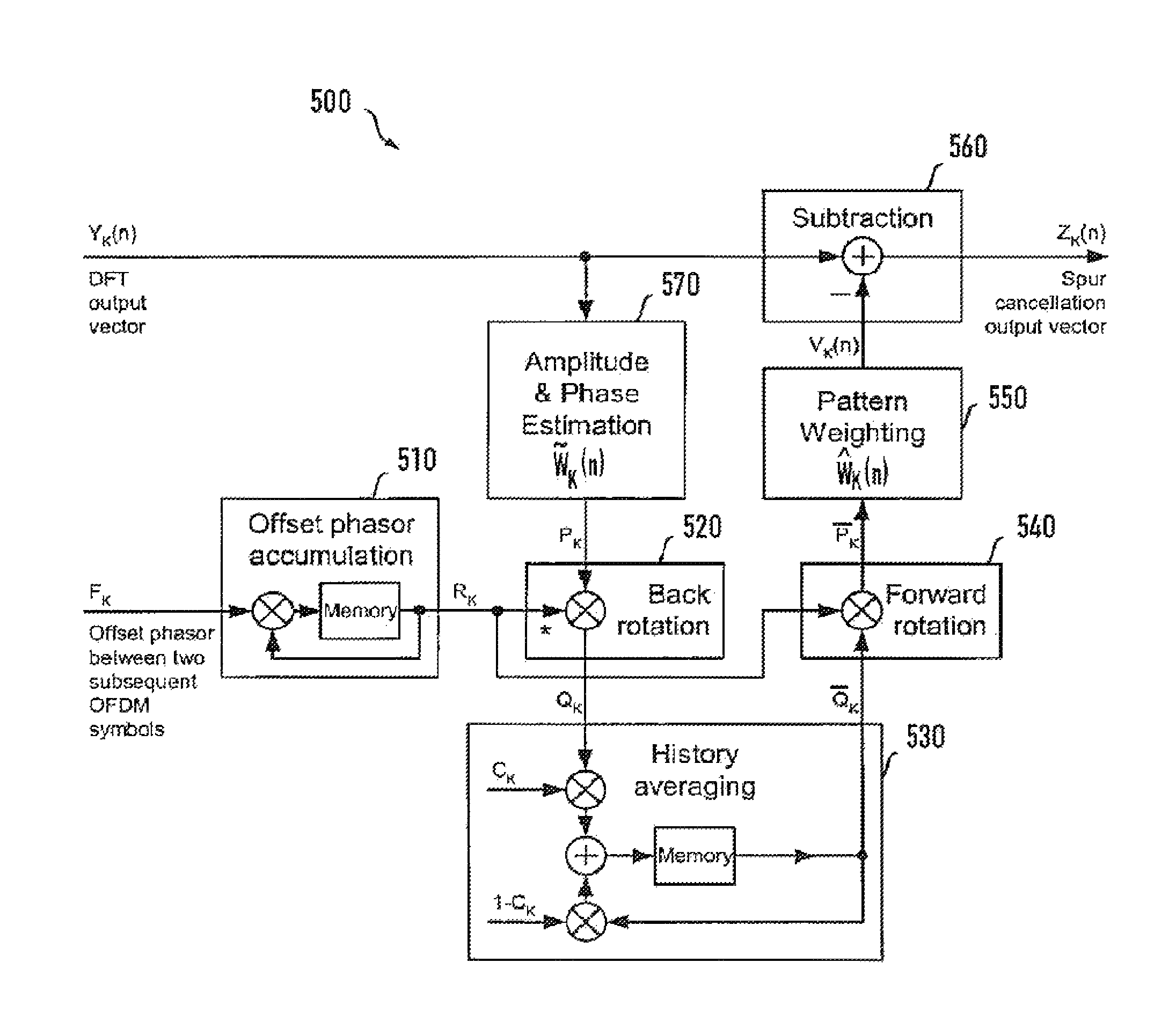
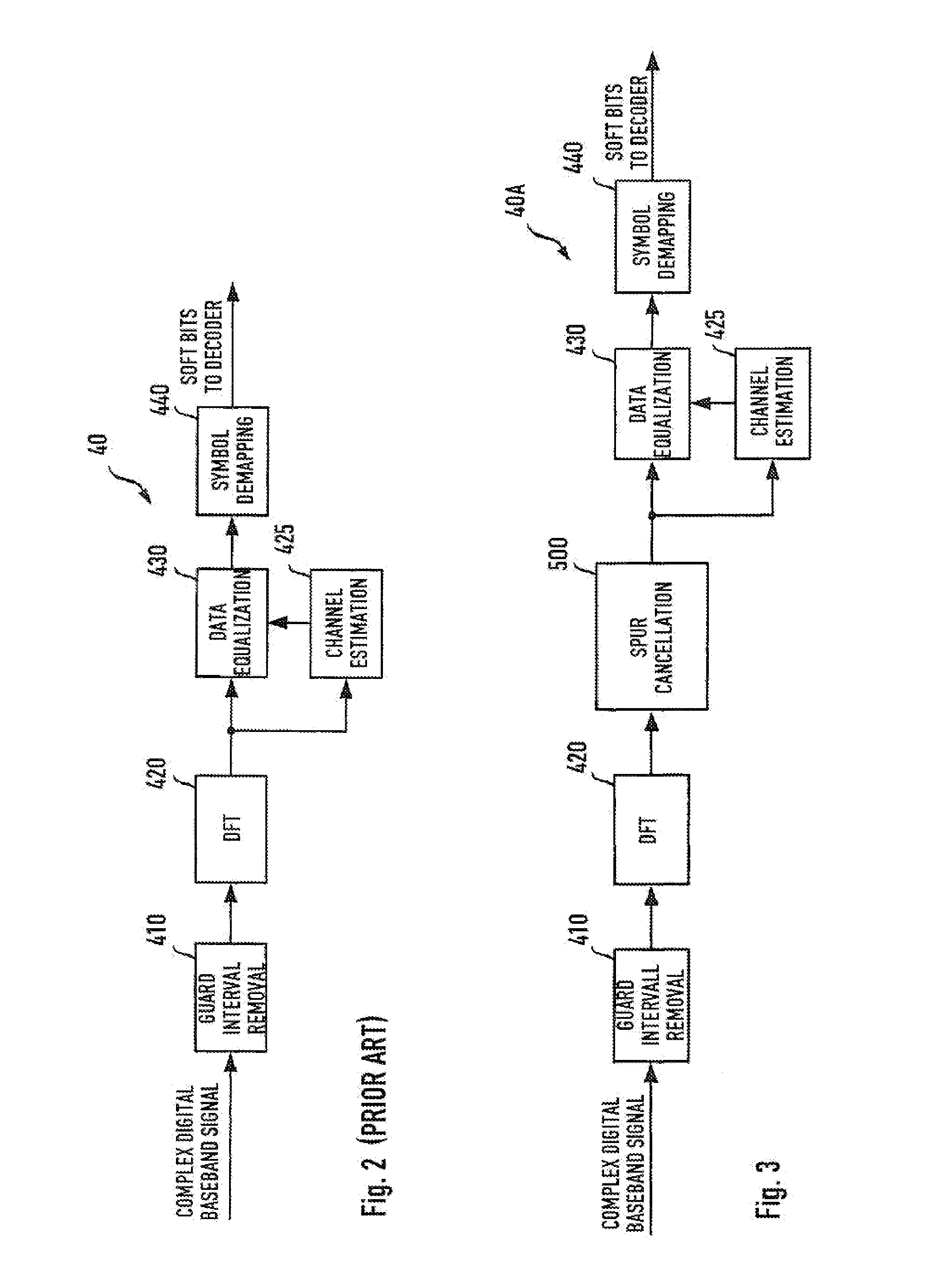
Method and apparatus to cancel additive sinusoidal disturbances in OFDM receivers
ActiveUS20100296568A1Avoid desensitizationReduce complexityPolarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionHarmonicEngineering
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) has become a popular transmission method for high speed wireless radio transmission, due to its potential for low complexity of transmitters and receivers. A method and apparatus are contemplated for cancelling additive sinusoidal disturbances of a known frequency in OFDM receivers which arise e.g. from clock signals that are present for frequency reference, mixer control, and A / D converter control, as well as harmonics and mixing products of those periodic signals, coupling into some point in the receiver chain and appearing as rotating complex exponentials superimposed to complex baseband receive signals. According to the inventive method and apparatus an estimation of an amplitude and phase of a disturbing superimposed tone with a known frequency is obtained and the amplitude and phase estimation is used to cancel the spurious tone preventing a degradation of receiver sensitivity while achieving low implementation complexity.
Owner:NXP BV
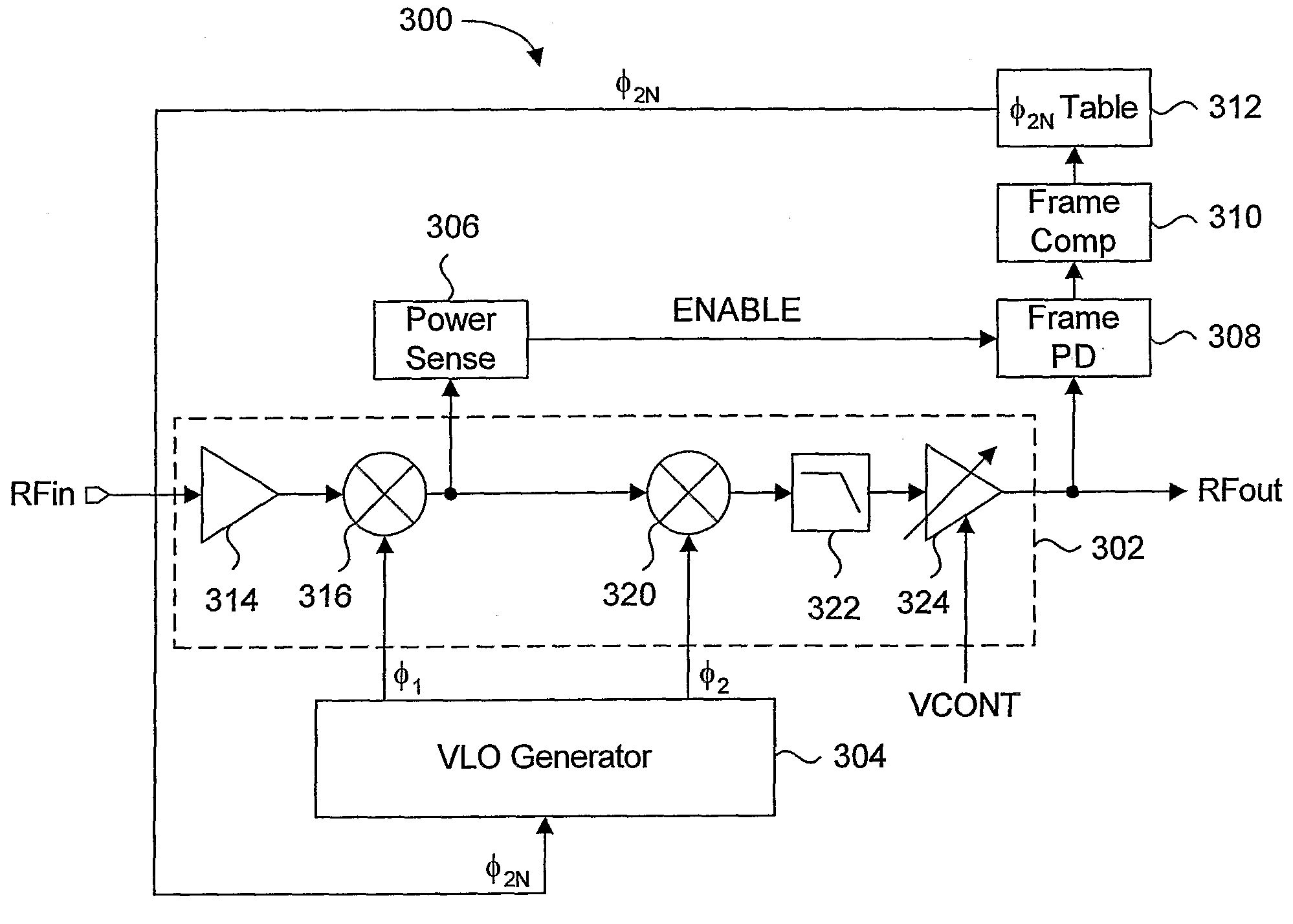
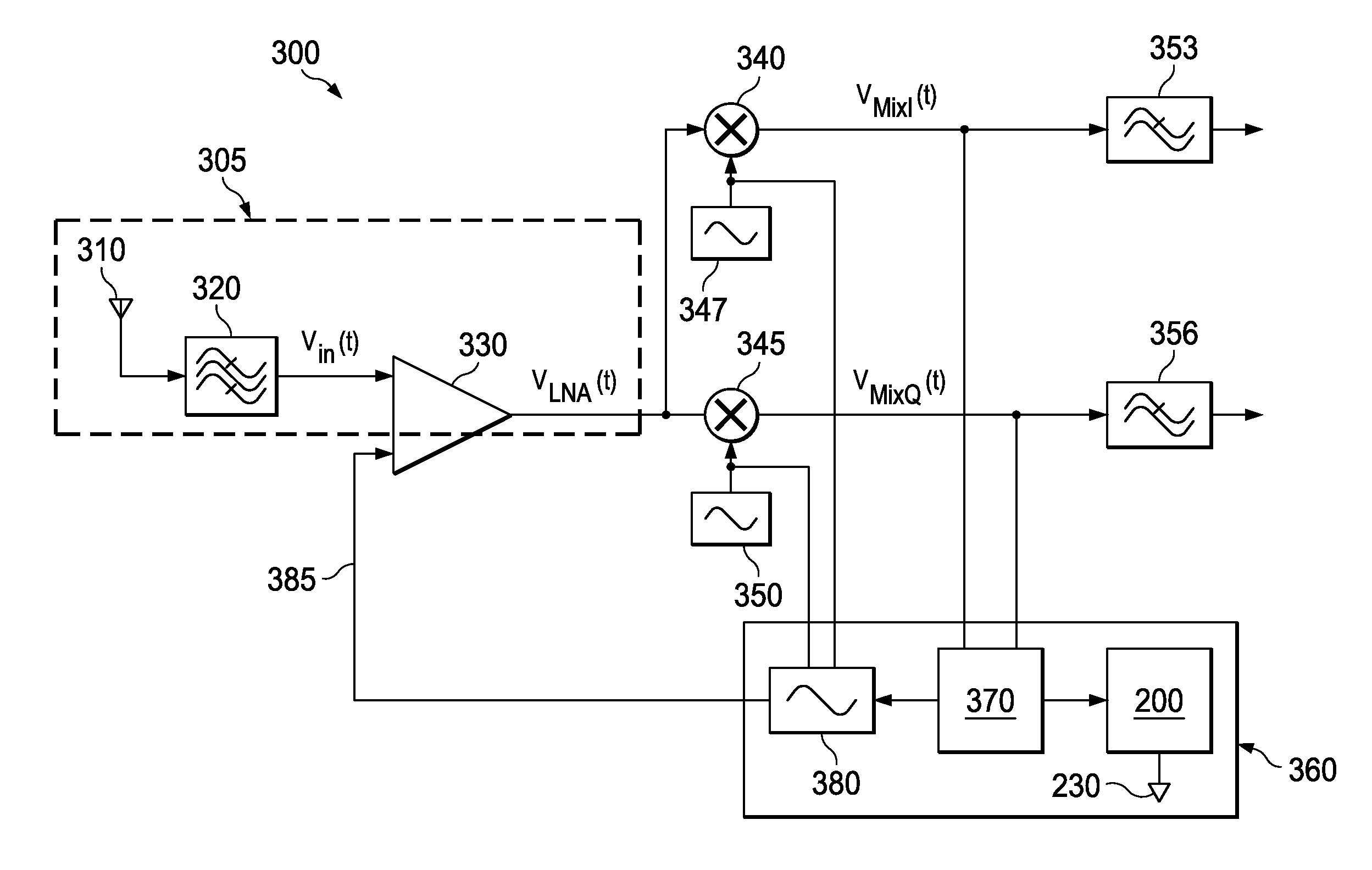
Method And System For Spurious Signal Control In Receivers
ActiveUS20080014894A1Modulation transferenceSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionFrequency mixerLocal oscillator
A method and system for dynamically shifting spurious tones away from the desired frequency in a virtual local oscillator receiver, such that any undesired signal residing at such spurious tones are effectively delineated from the desired signal and removed from the RF input signal. The system detects the presence of potential undesired blocker signals in the RF input signal, and initiates an iterative power comparison and mixer signal adjustment loop. As the virtual local oscillator uses two mixer signals, the frequency of one of the mixer signals is adjusted during the loop until the power of the down-converted signal is minimized to a predetermined level. Minimized power in the down-converted signal is indicative of the absence of the blocker signal, since the presence of a relatively high power signal is indicative of a blocker signal overlapping with a desired signal.
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
Variable frequency circuit controller
ActiveUS8823459B2Angle modulation by variable impedenceElectric signal transmission systemsEngineeringRadio frequency
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Method and apparatus for artifact signal reduction in systems of mismatched interleaved digitizers
ActiveUS20060195301A1Eliminate artifactsReduce and eliminate error toneAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsSignal correctionDigital converter
An artifact signal correction system may include a mixing component to generate a waveform corresponding to an artifact such as an error tone, whereupon that waveform may be combined with the input waveform to substantially eliminate the artifact. In preferred embodiments, a method and apparatus for reducing spurious tones in systems of mismatched interleaved digitizers due to interleave error is provided. In various embodiments the method may comprise reversing the frequency content of an input signal, converting the reversed signal into interleave artifact content, delaying the input signal along a parallel path, and then subtracting the interleave content from the delayed input signal.
Owner:TELEDYNE LECROY
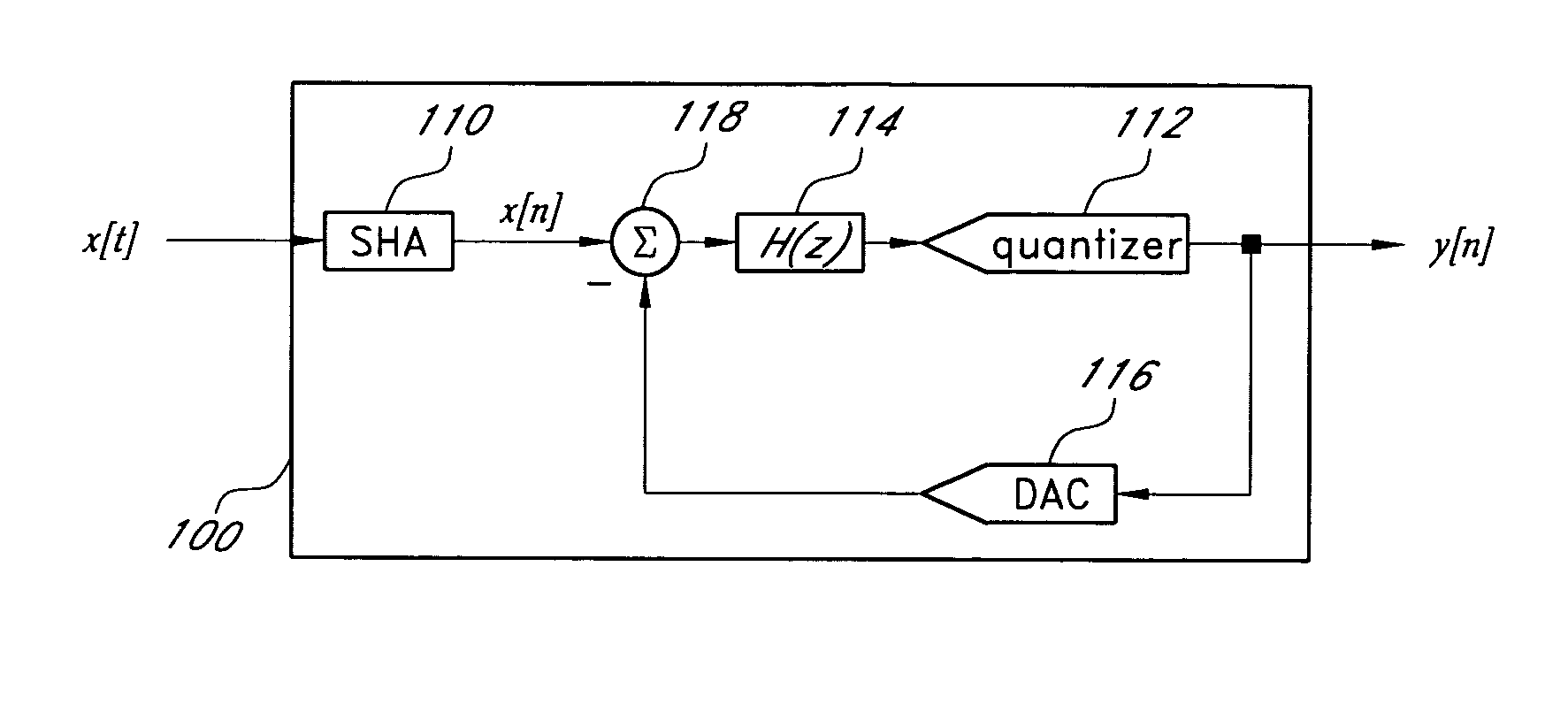
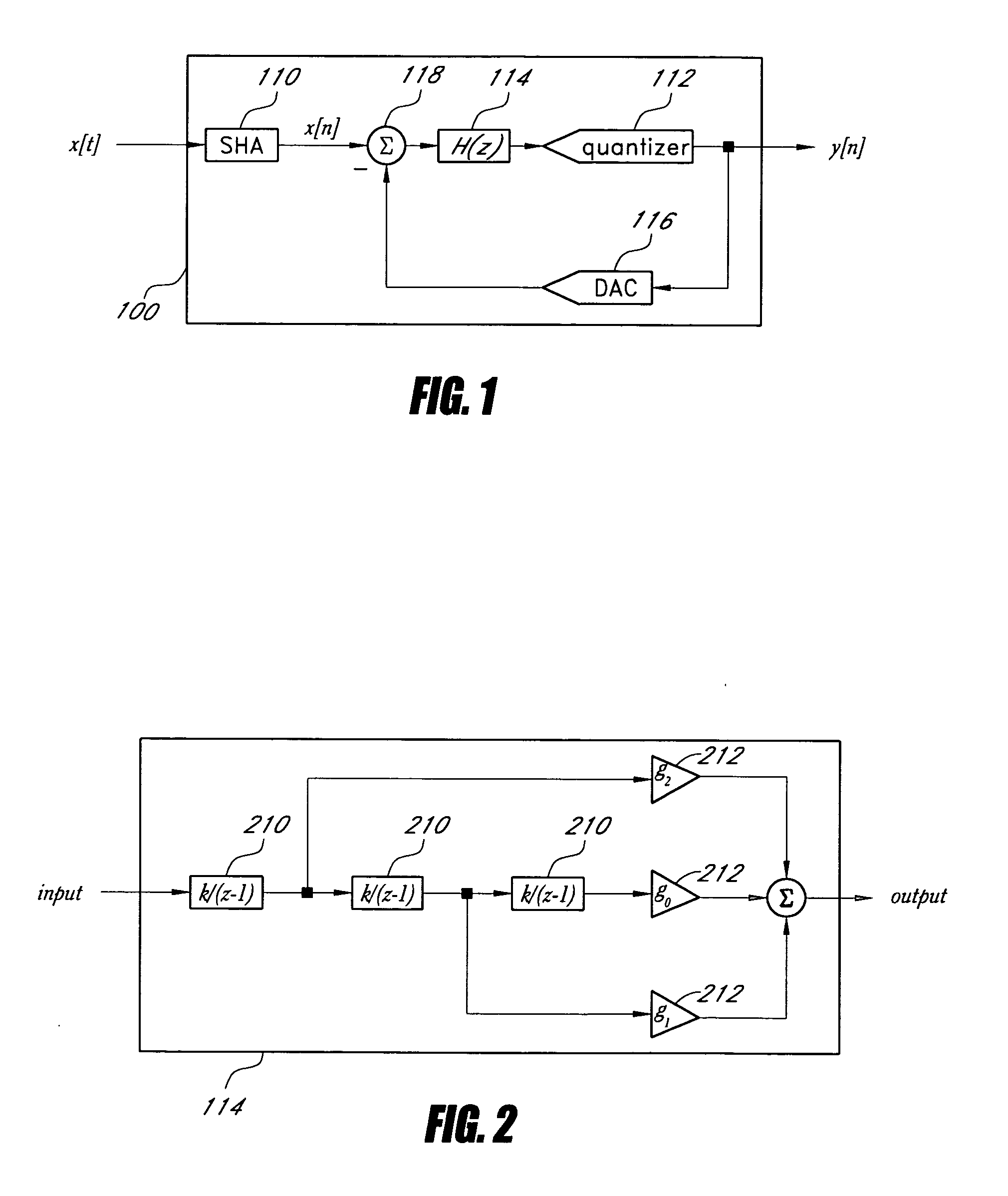
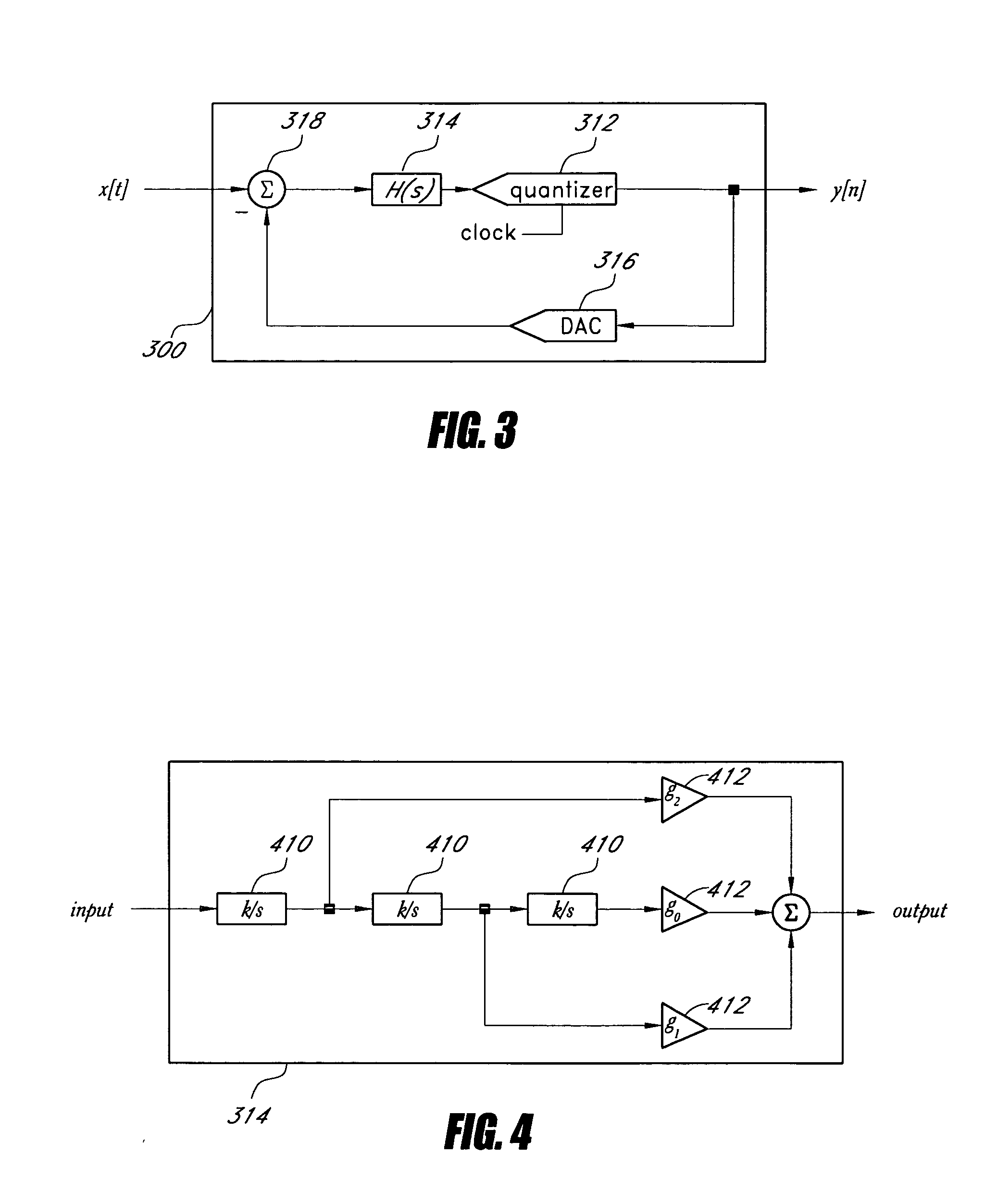
Low-pass filter based delta-sigma modulator
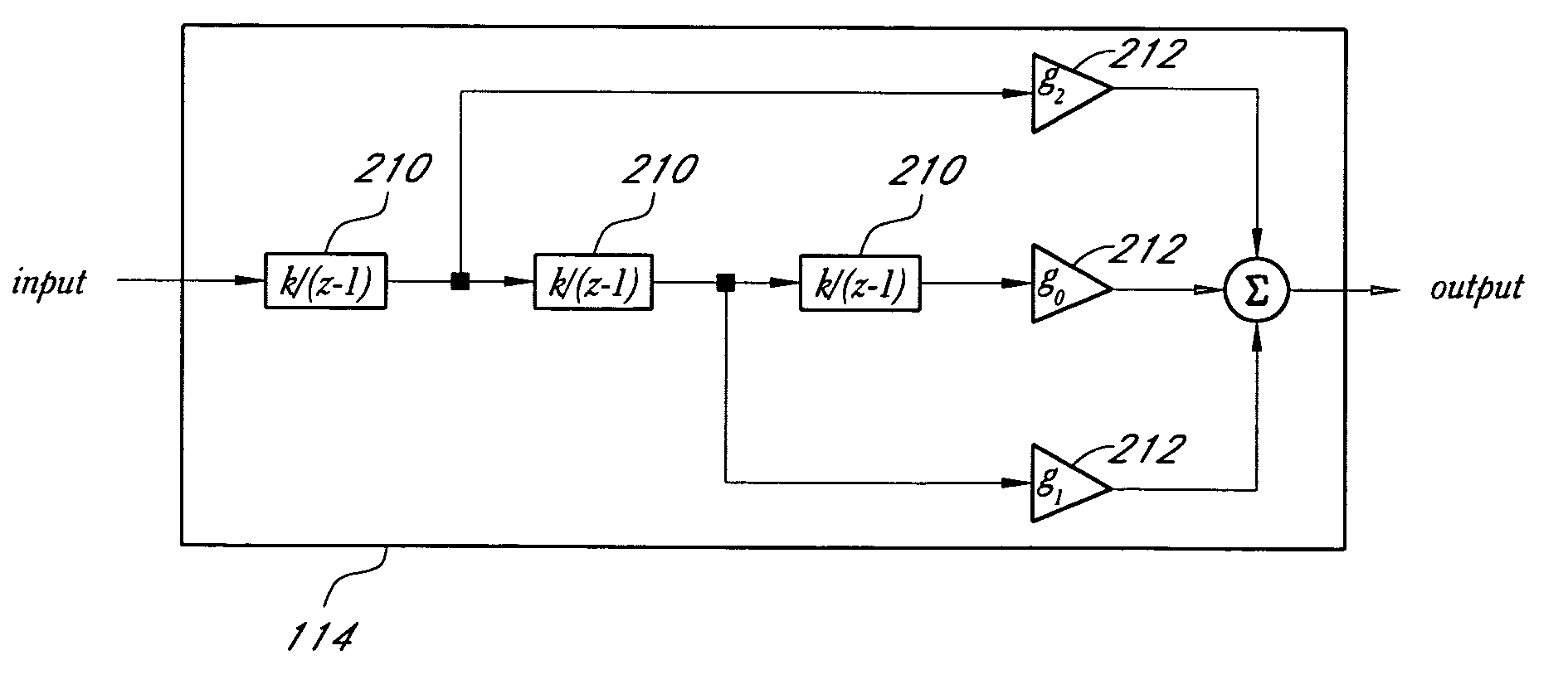
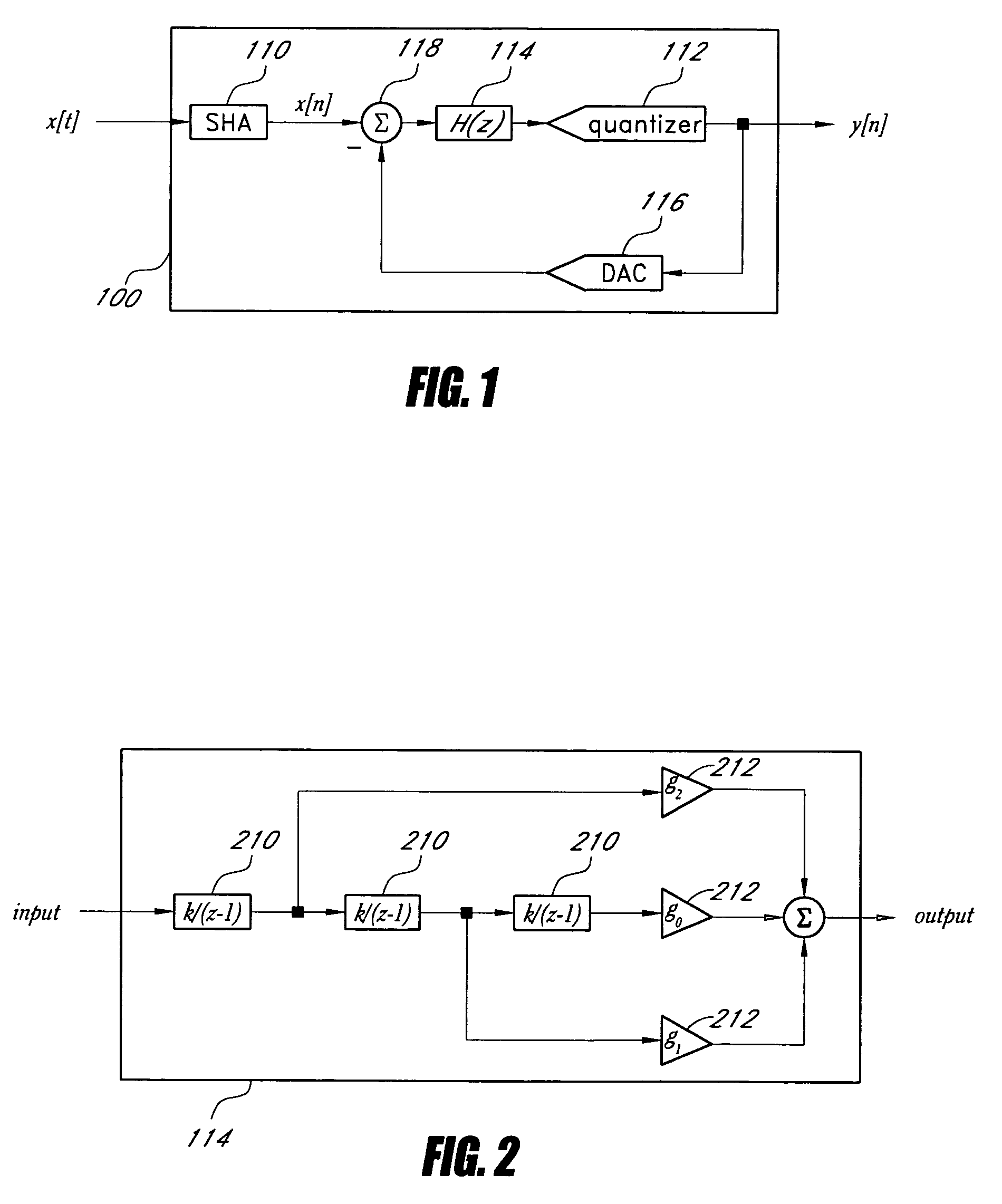
In an embodiment, a delta-sigma modulator is constructed from one or more stages of a first order low-pass filter, which has a modest gain compared to the integrator used in other embodiments of delta-sigma modulators. Delta-sigma modulators can be converted into low-pass filter based delta-sigma modulators according to an embodiment of the invention by replacing the ideal integrator building block with a first order low-pass filter and adjusting other loop parameters, such as gain factors, accordingly.In an embodiment, a dithering technique to suppress spurious tones can be used with the low-pass filter based, ideal integrator based, or near ideal integrator based delta-sigma modulator. In another embodiment, a noise cancellation technique can also be used to cancel the dithering noise.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
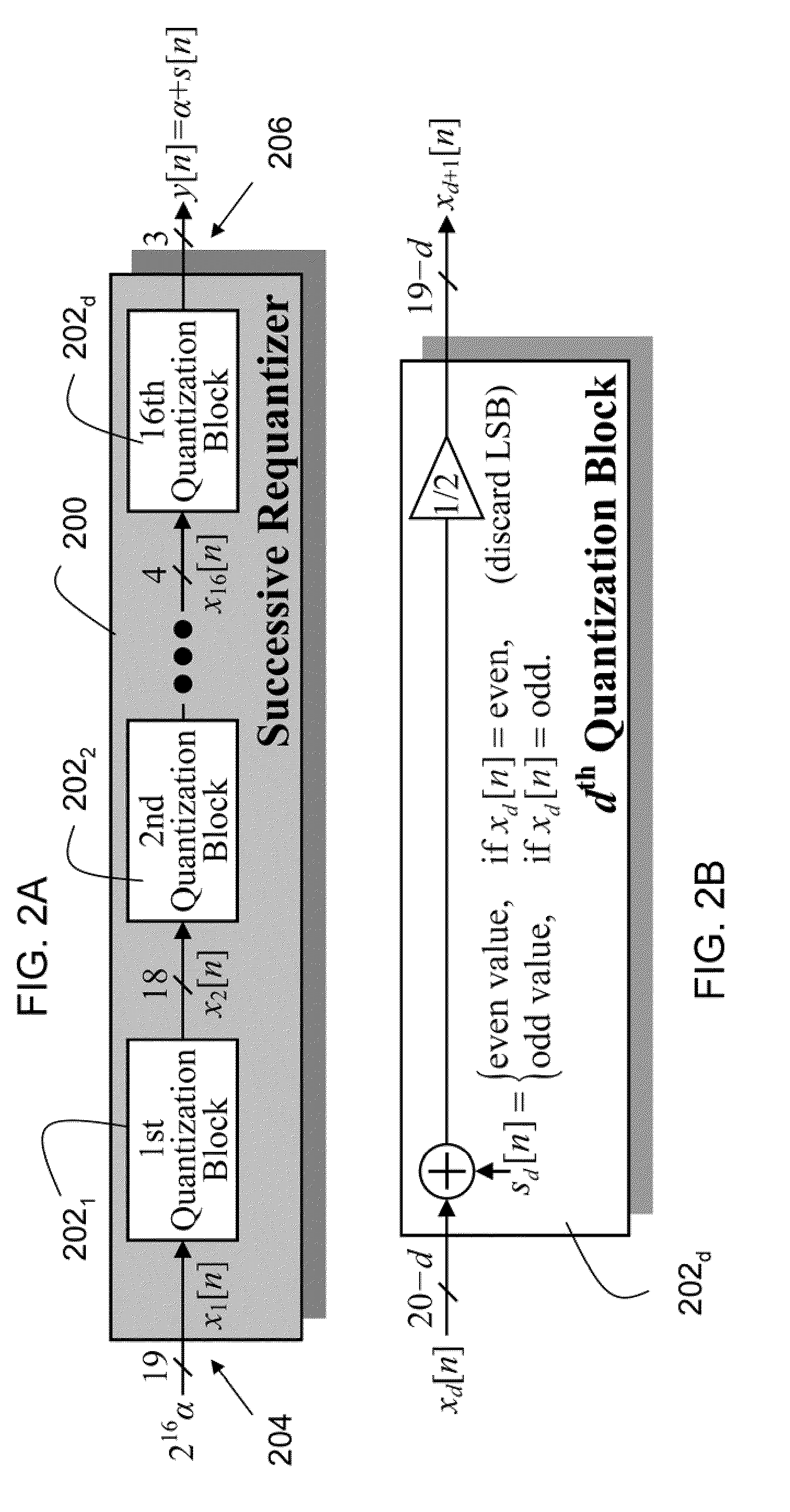
Nonlinearity robust successive requantizer
ActiveUS20100166084A1Reduce consumptionLow costPulse automatic controlAnalogue conversionTransceiverCommunications system
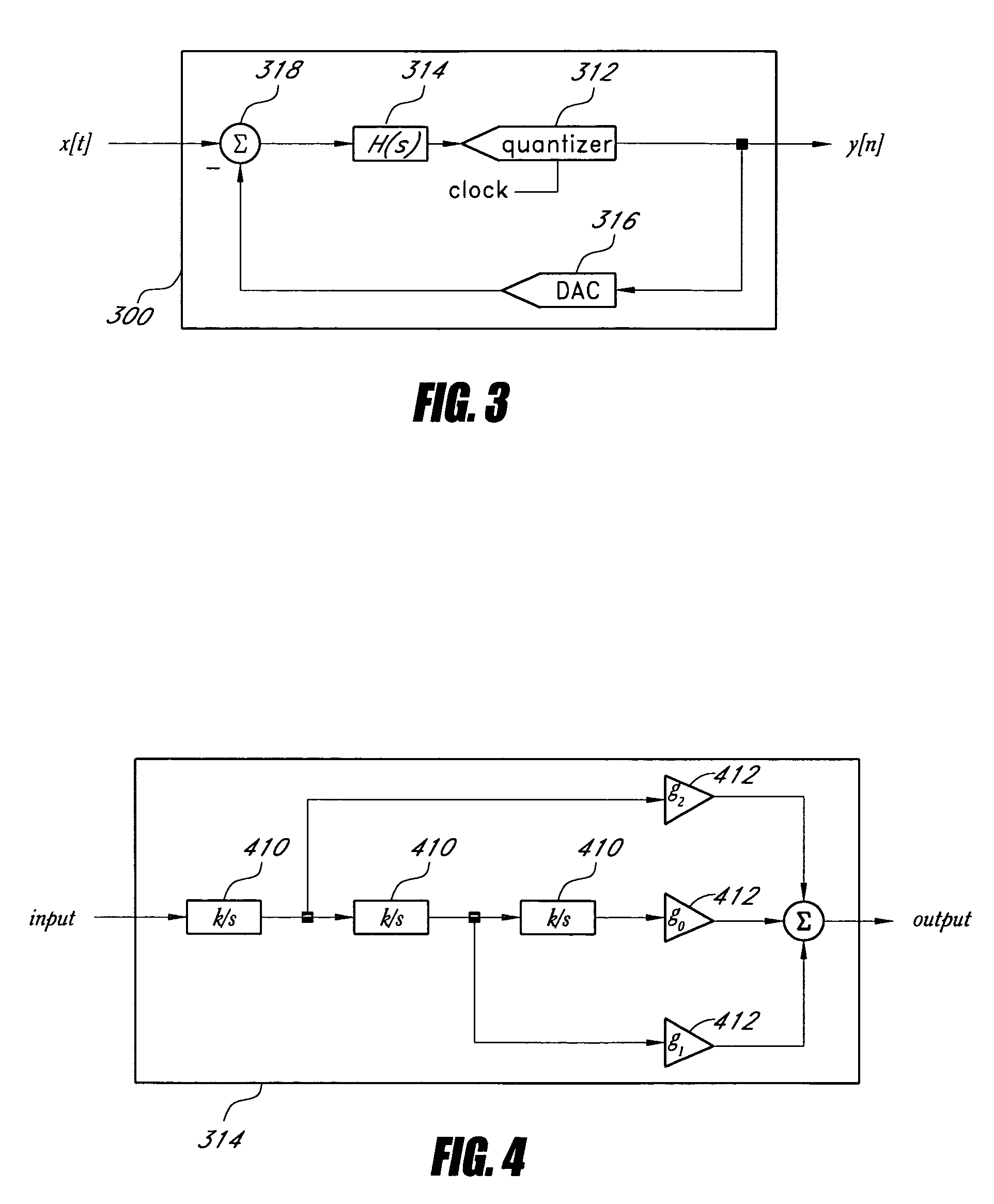
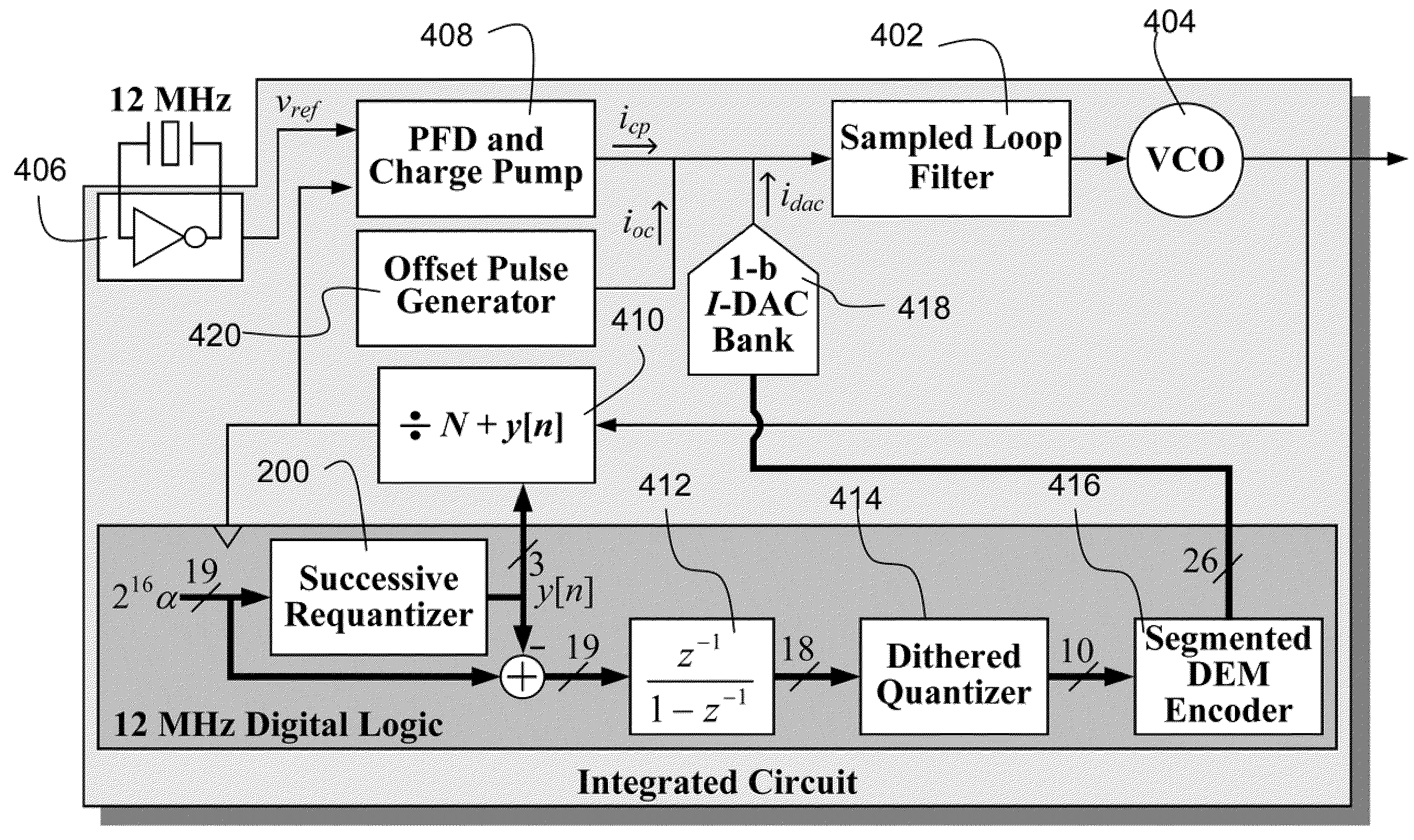
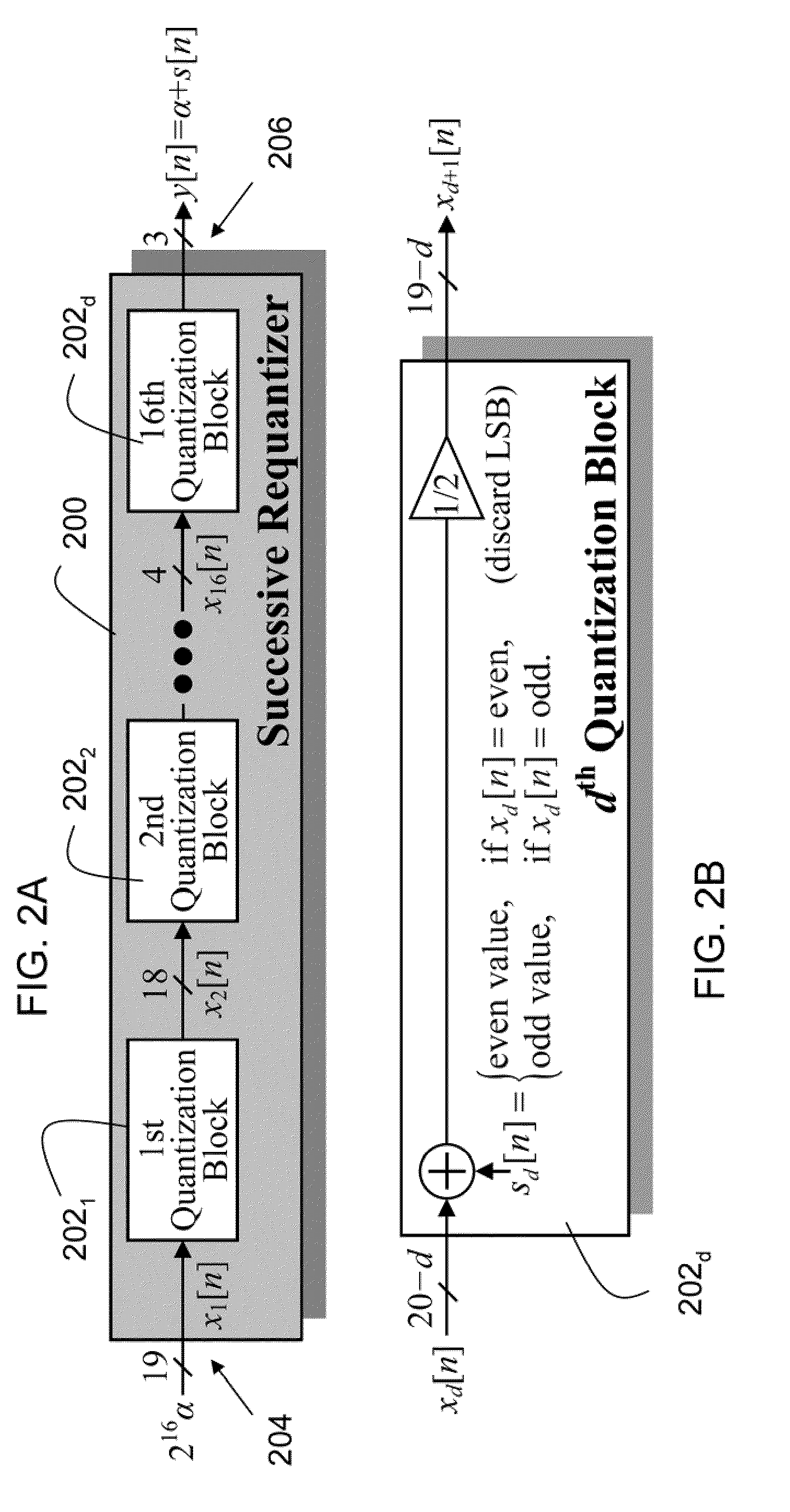
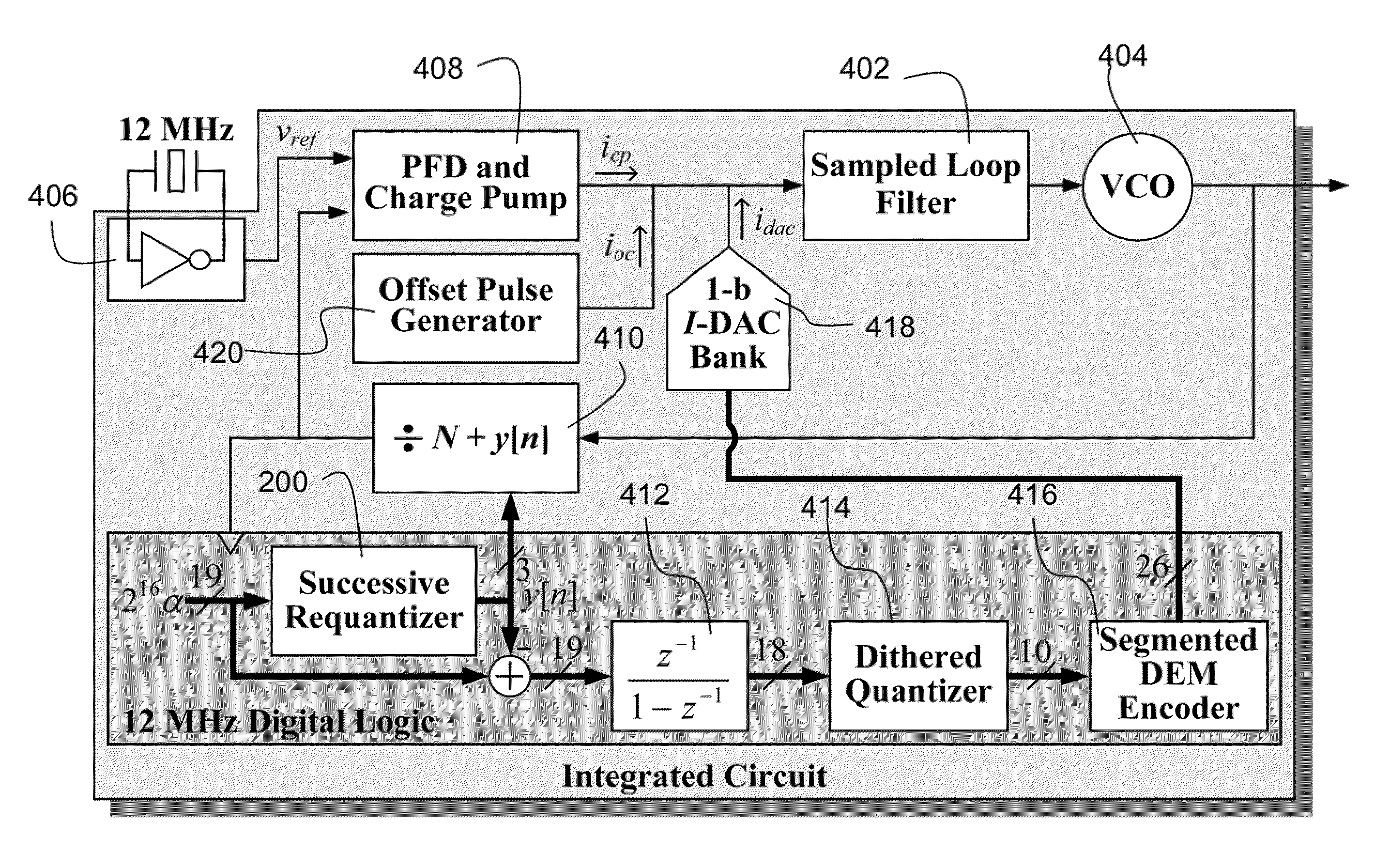
An embodiment of the invention is a successive requantizer, which serves as a replacement for a ΔΣ modulator in a fractional-N PLL or a DAC, and avoids the above-mentioned spurious tone problem, thereby circumventing the tradeoffs that result from reliance on common approach of making highly linear analog circuitry to avoid spurious tones. A successive requantizer fractional-N PLL of the invention has the potential to reduce power consumption and the cost of commercial communication devices. A successive requantizer of the invention performs digital quantization one bit at a time in such a way that the quantization noise can be engineered to have desirable properties such as non-linearity robustness. The invention is applicable to most high-performance digital communication systems, such as cellular telephone handsets and wireless local and metropolitan area network transceivers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dithering noise cancellation for a delta-sigma modulator
ActiveUS20070090980A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionIntegratorLow-pass filter
In an embodiment, a delta-sigma modulator is constructed from one or more stages of a first order low-pass filter, which has a modest gain compared to the integrator used in other embodiments of delta-sigma modulators. Delta-sigma modulators can be converted into low-pass filter based delta-sigma modulators according to an embodiment of the invention by replacing the ideal integrator building block with a first order low-pass filter and adjusting other loop parameters, such as gain factors, accordingly. In an embodiment, a dithering technique to suppress spurious tones can be used with the low-pass filter based, ideal integrator based, or near ideal integrator based delta-sigma modulator. In another embodiment, a noise cancellation technique can also be used to cancel the dithering noise.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
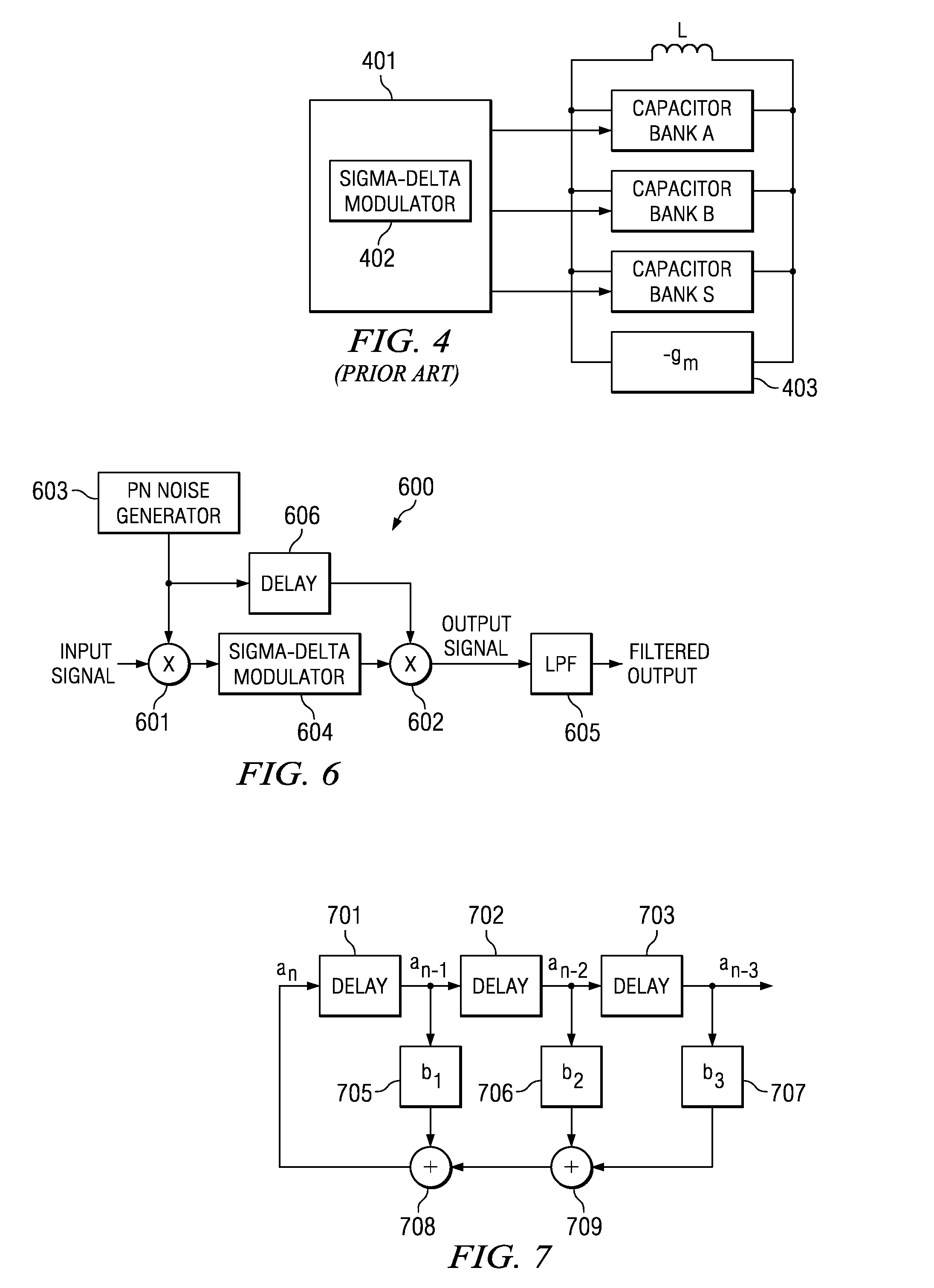
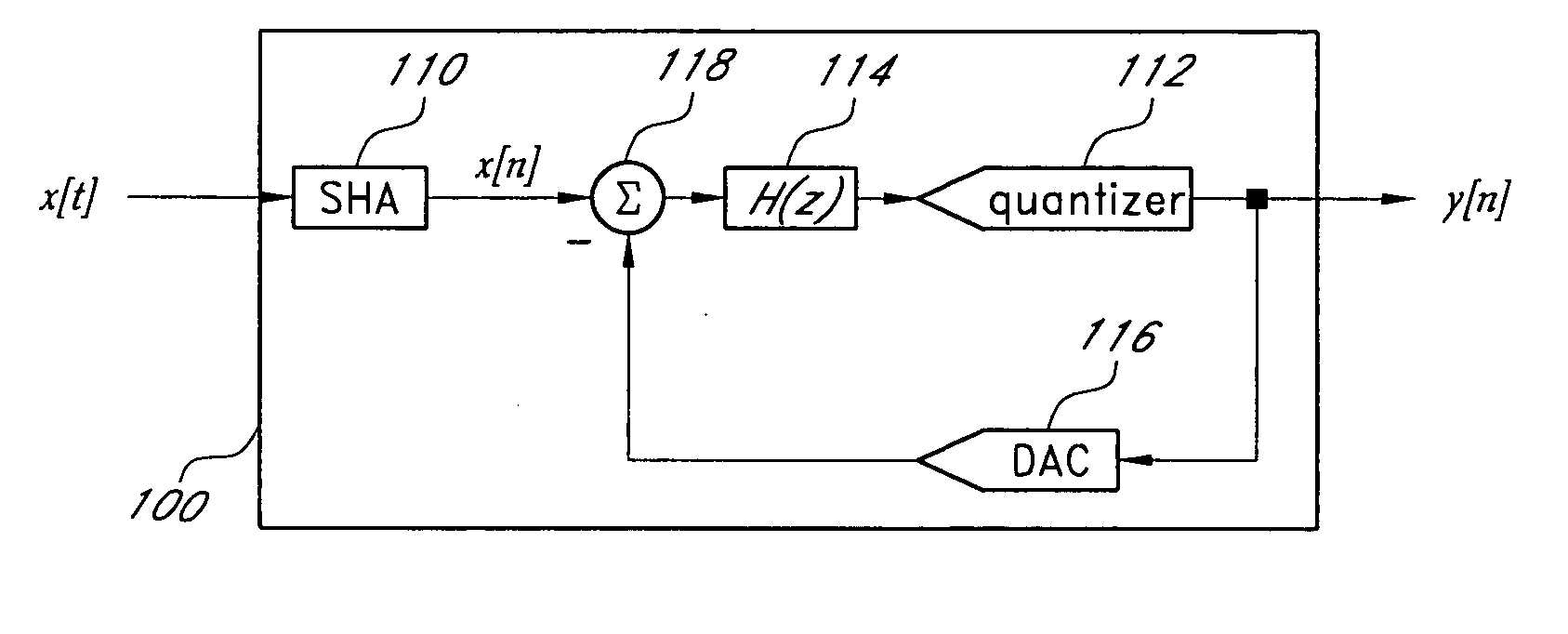
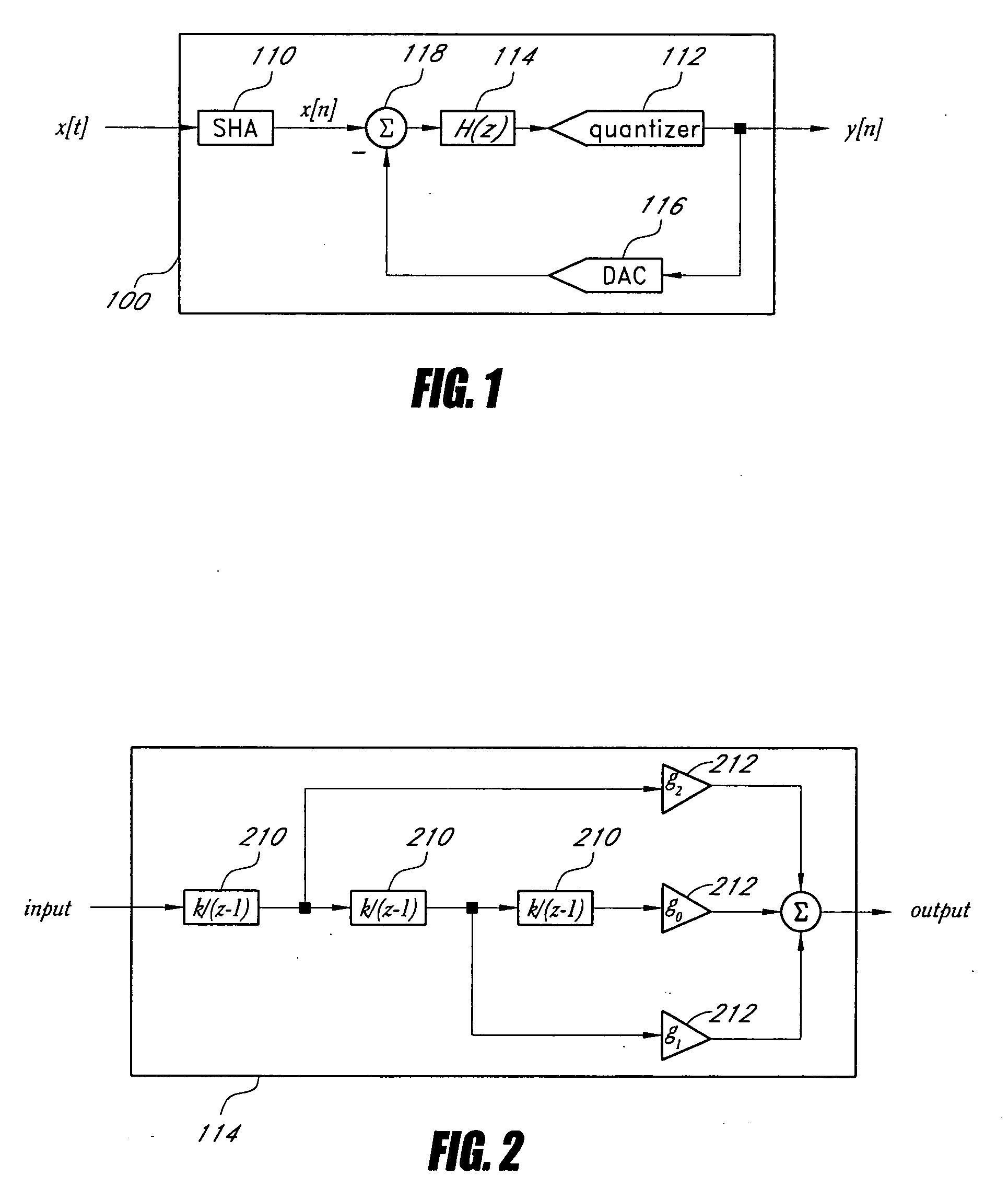
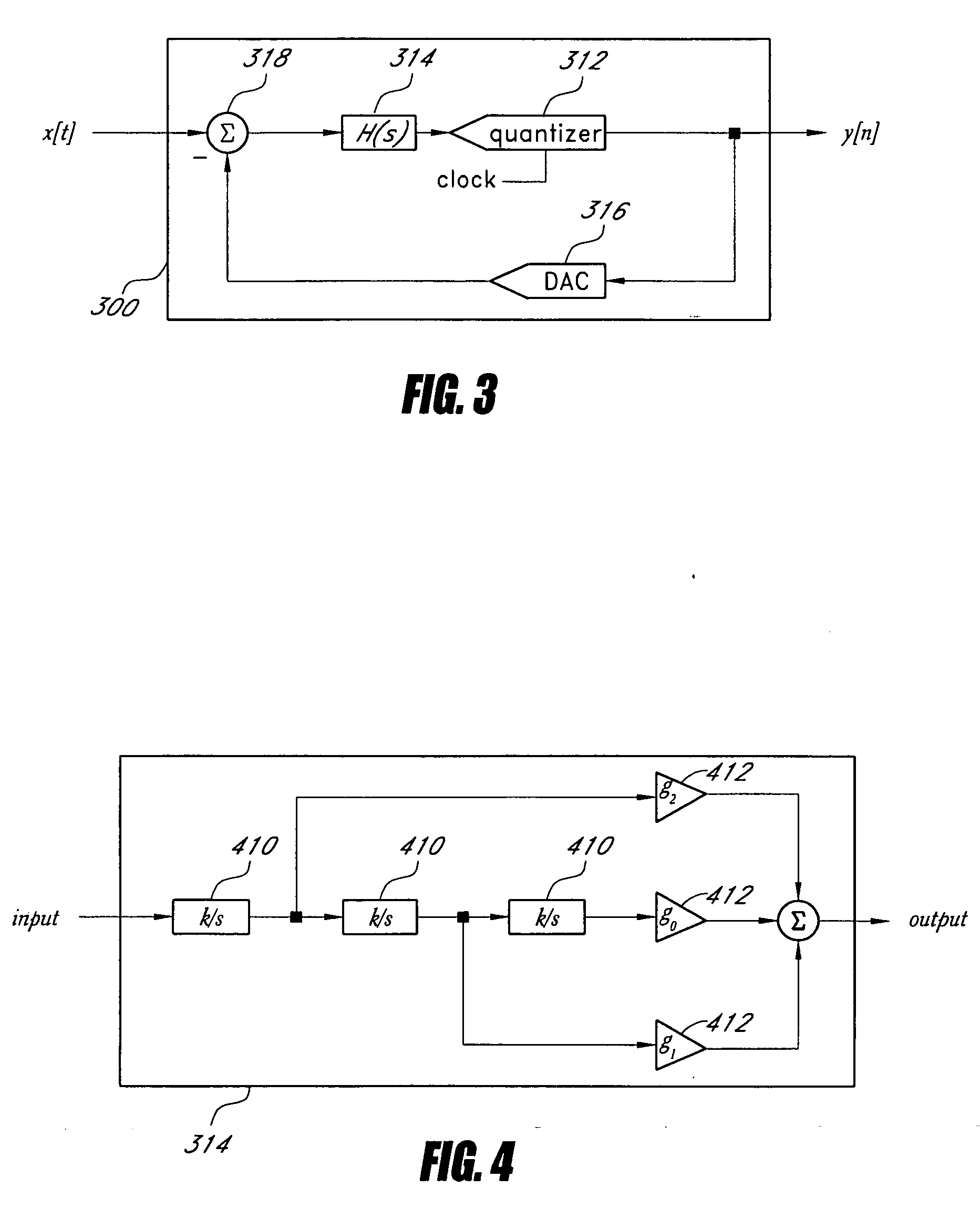
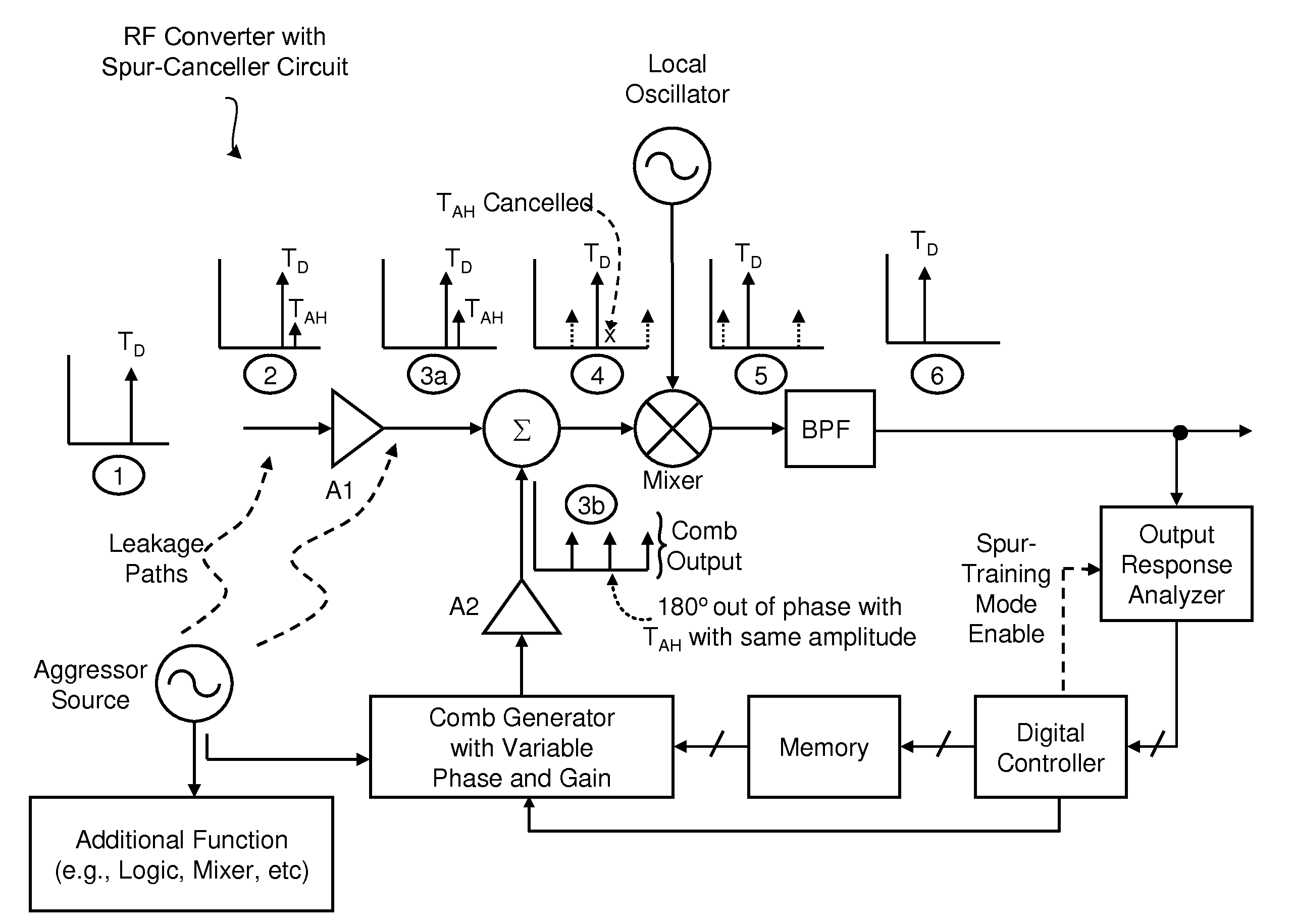
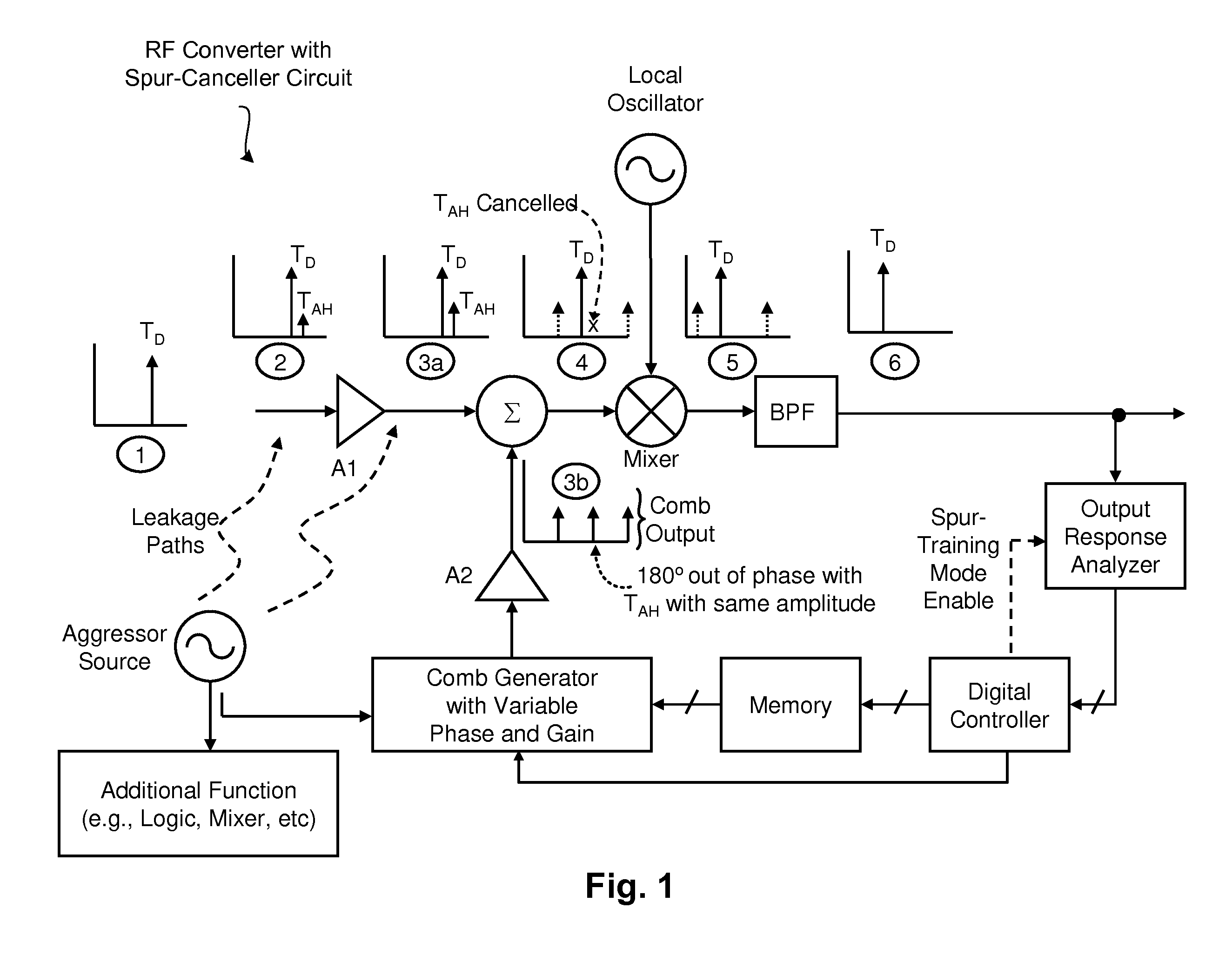
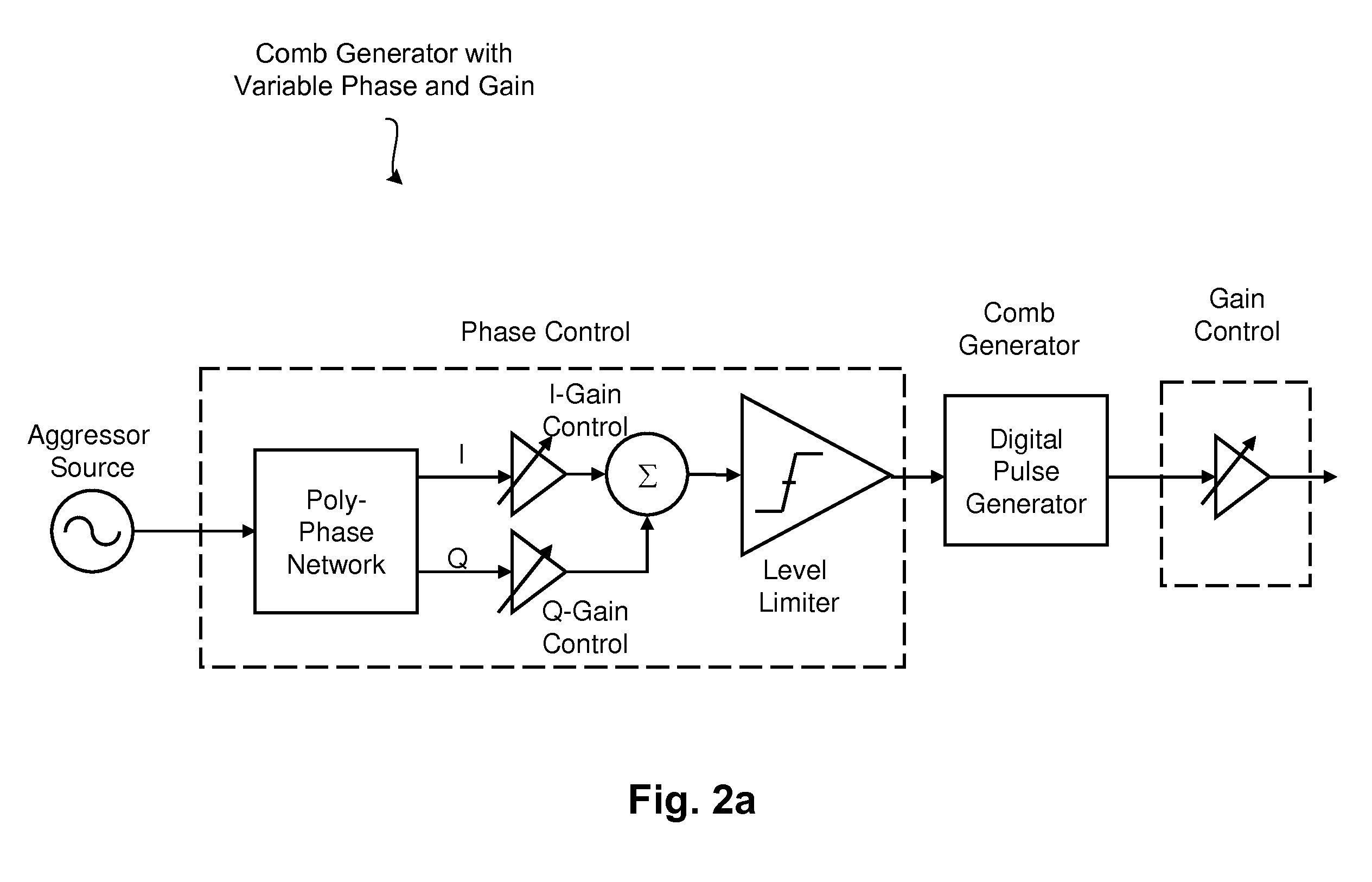
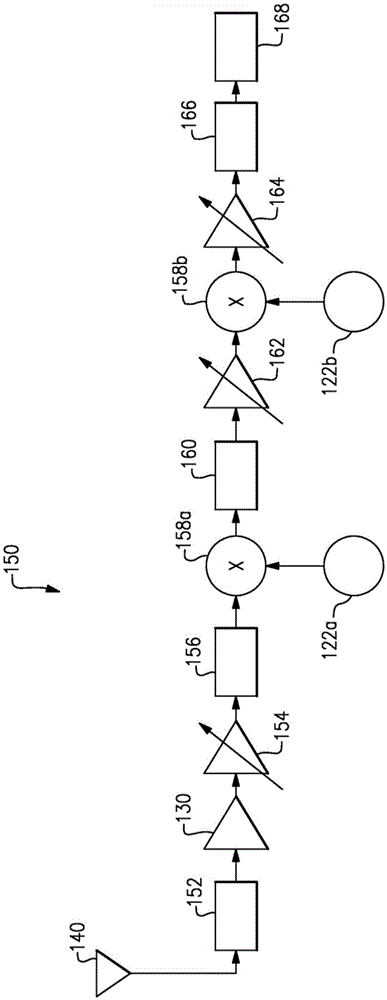
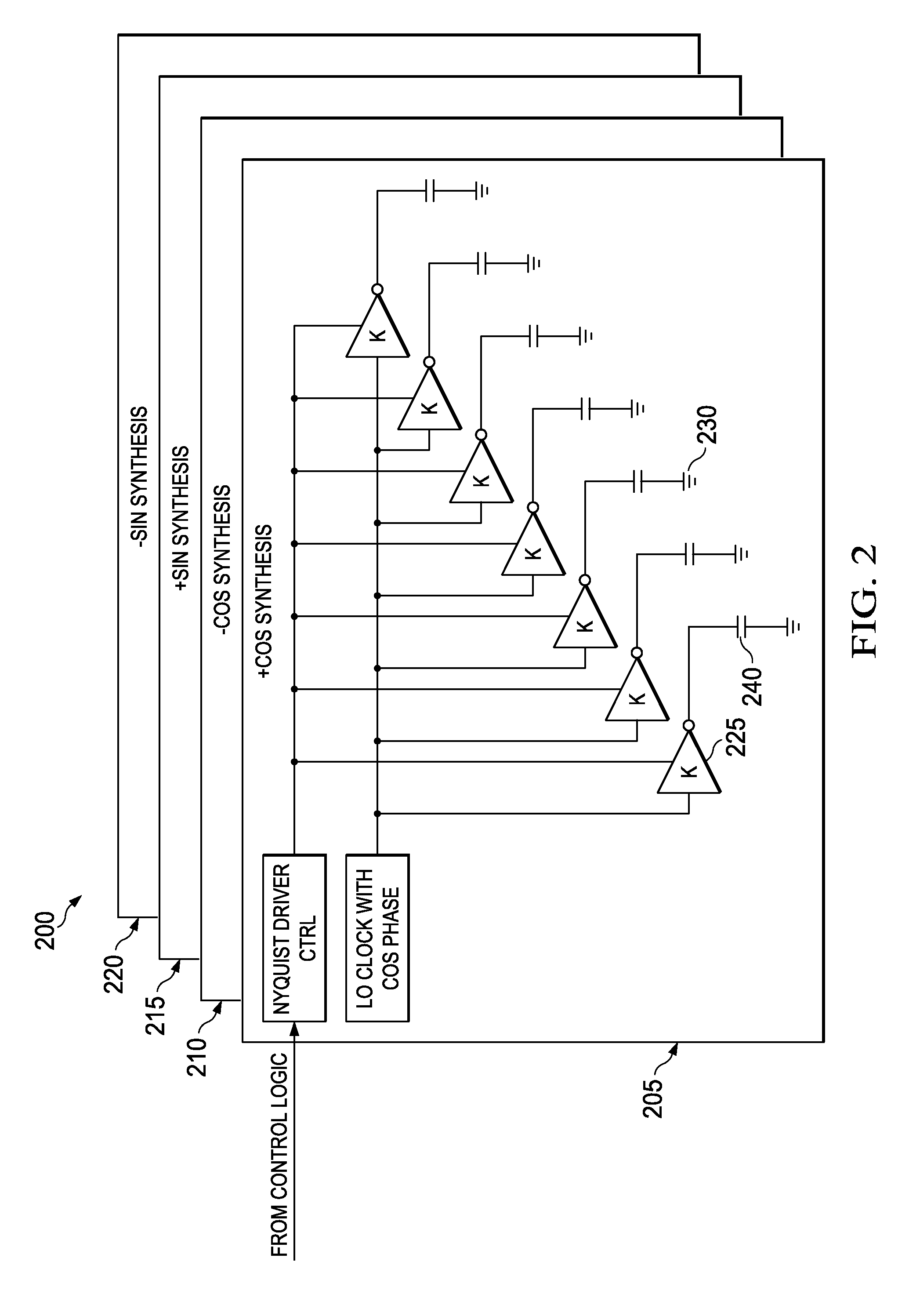
Integrated Cancellation Circuit for RF Converter Spurious Tones
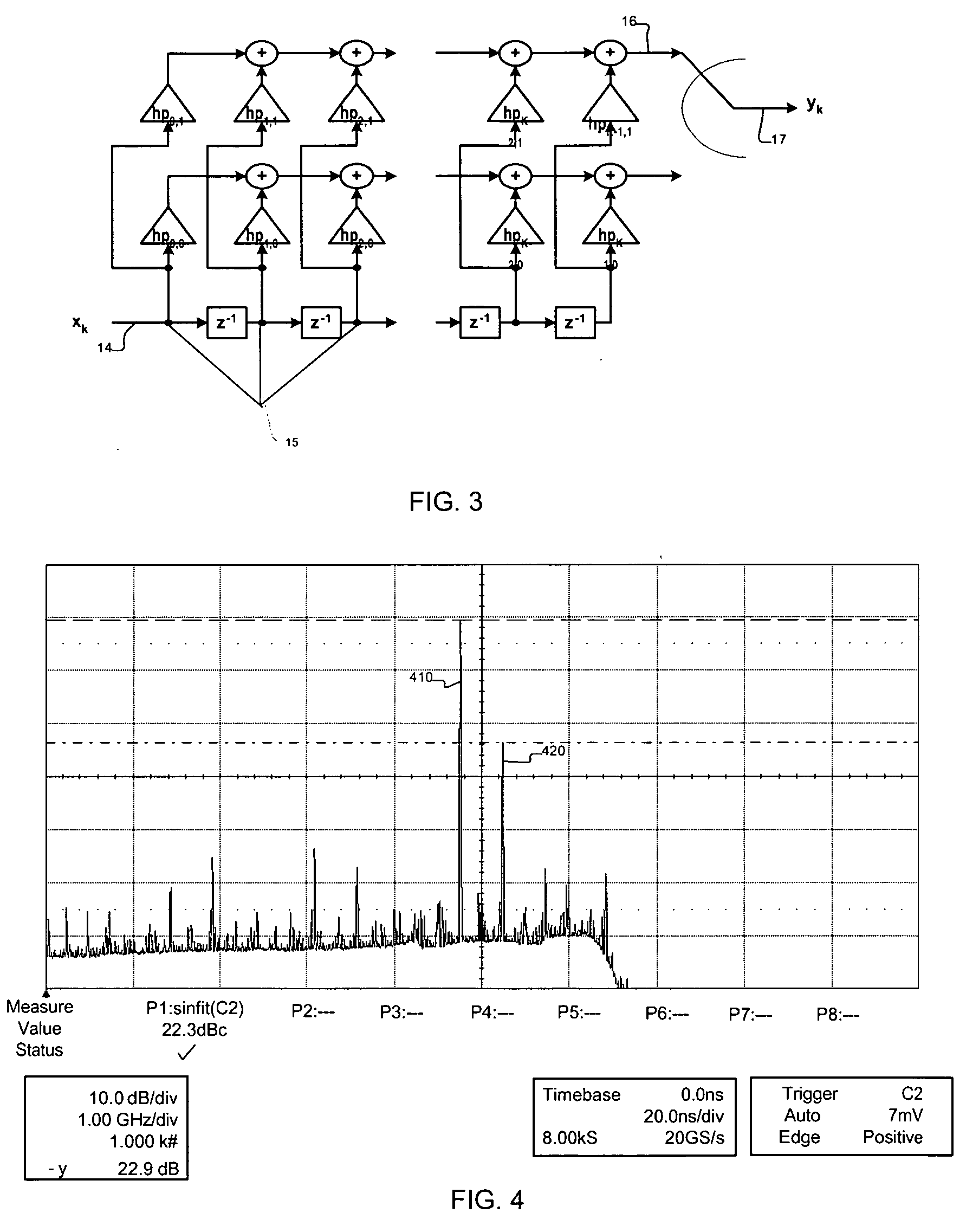
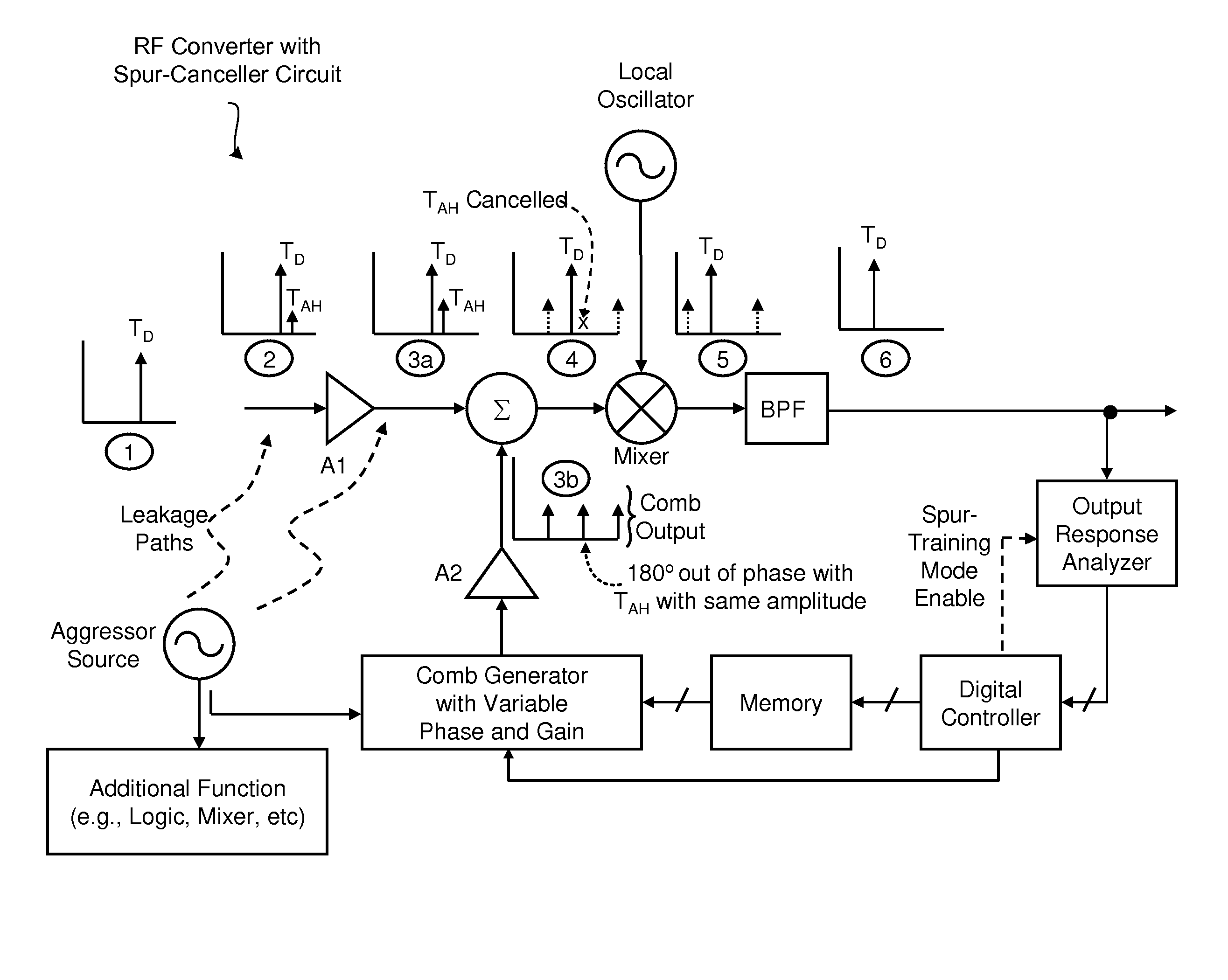
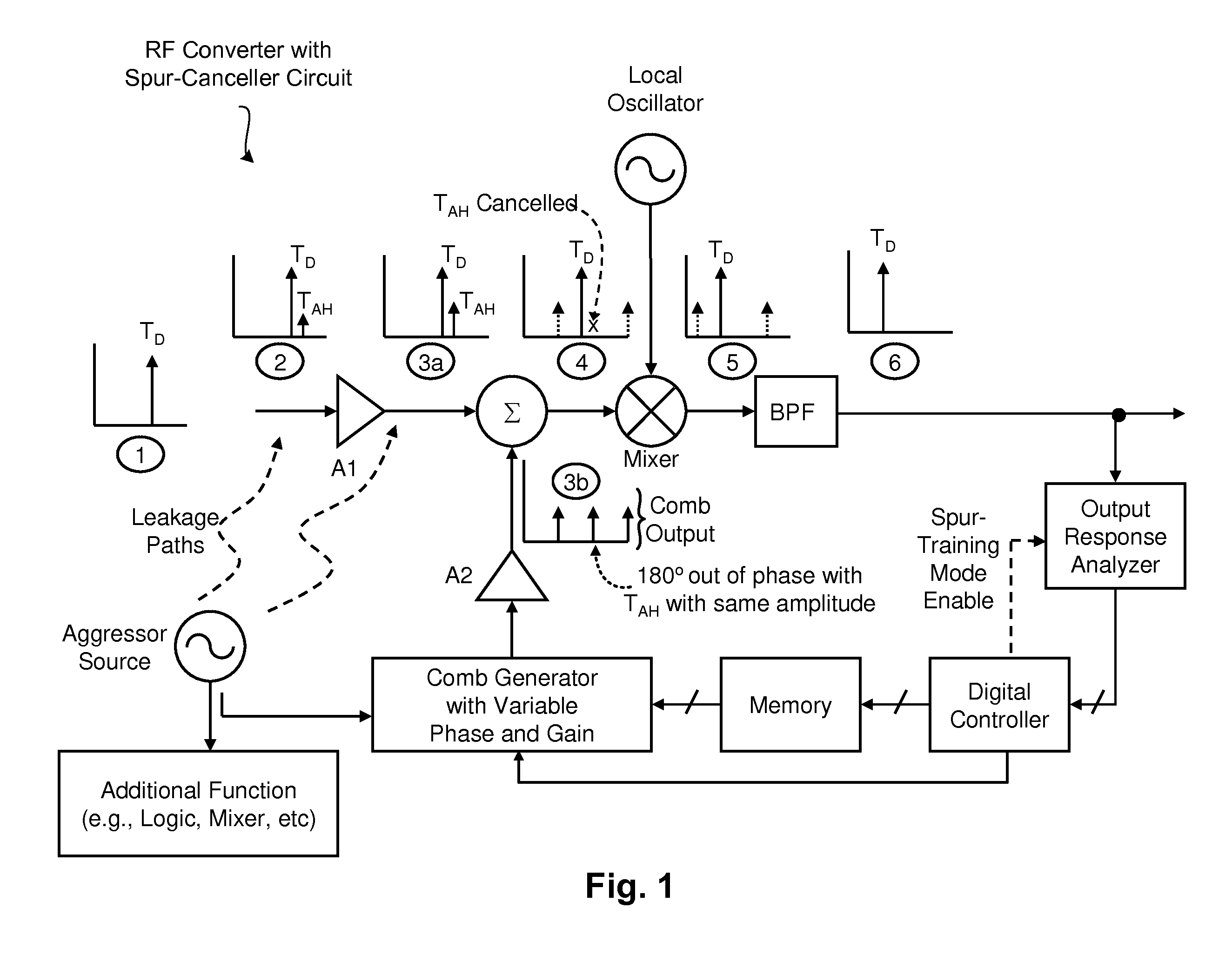
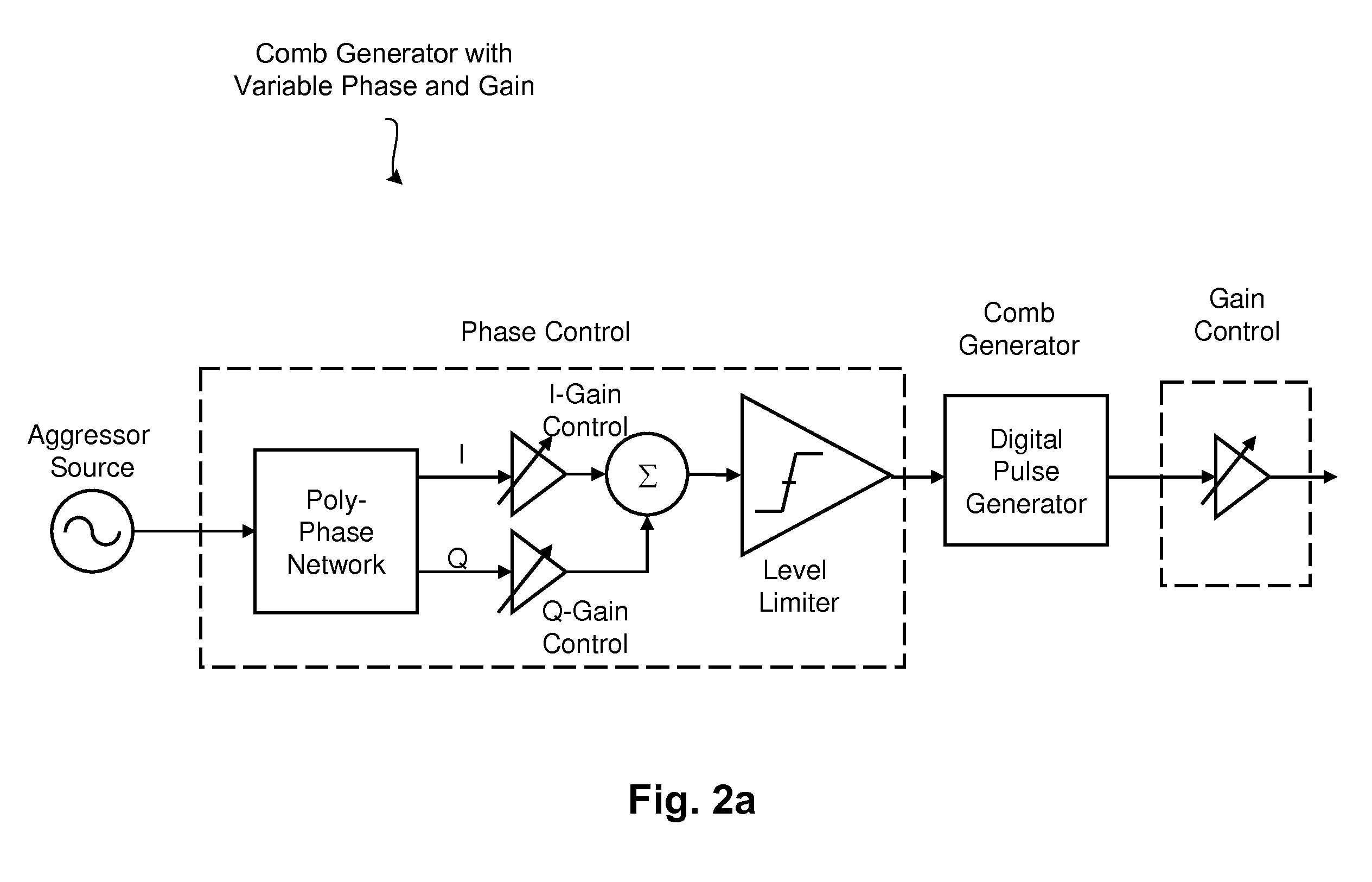
Techniques are disclosed for eliminating or otherwise sufficiently suppressing spurious signals. The techniques are particularly useful in applications such as those that employ aggressor frequency sources along with a frequency conversion or mixing function, and especially applications implemented as a system-on-chip. In the spur-training mode, a spur-canceller circuit identifies spurious tones associated with the host system to neutralize those tones when running in a normal mode. The tones are neutralized using a comb generator with variable phase and gain by way of cancellation with comb output signals having substantially the same amplitude and a phase that is 180° out of phase with the aggressor tone to be cancelled.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method and system for spurious signal control in receivers
ActiveUS7715814B2Modulation transferenceSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionFrequency mixerLocal oscillator
A method and system for dynamically shifting spurious tones away from the desired frequency in a virtual local oscillator receiver, such that any undesired signal residing at such spurious tones are effectively delineated from the desired signal and removed from the RF input signal. The system detects the presence of potential undesired blocker signals in the RF input signal, and initiates an iterative power comparison and mixer signal adjustment loop. As the virtual local oscillator uses two mixer signals, the frequency of one of the mixer signals is adjusted during the loop until the power of the down-converted signal is minimized to a predetermined level. Minimized power in the down-converted signal is indicative of the absence of the blocker signal, since the presence of a relatively high power signal is indicative of a blocker signal overlapping with a desired signal.
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
Spurious tone suppressor and method of operation thereof
The present invention provides a spurious tone suppressor for use with a power supply system. In one embodiment, the spurious tone suppressor includes an error signal generator configured to provide a spur error signal proportional to a spur signal associated with the power supply system. Additionally, the spurious tone suppressor also includes an adaptive spur cancellation engine coupled to the error signal generator and configured to adaptively process the spur error signal and generate a corresponding anti-spur signal that is injected into the power supply system to suppress the spur signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Digital fractional-N PLL based upon ring oscillator delta-sigma frequency conversion
ActiveUS10158366B2Improve performanceReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementDigital down converterDual mode
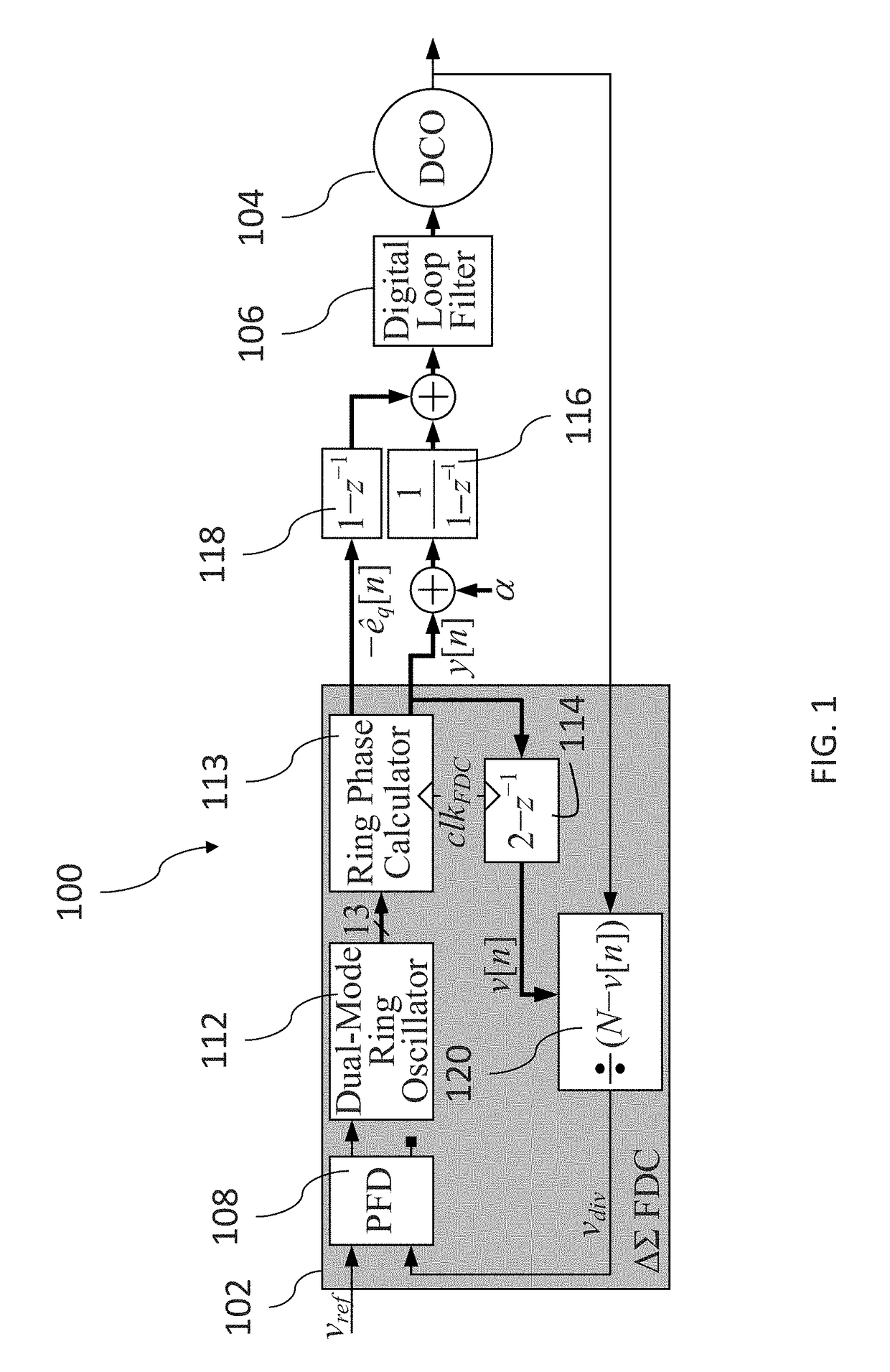
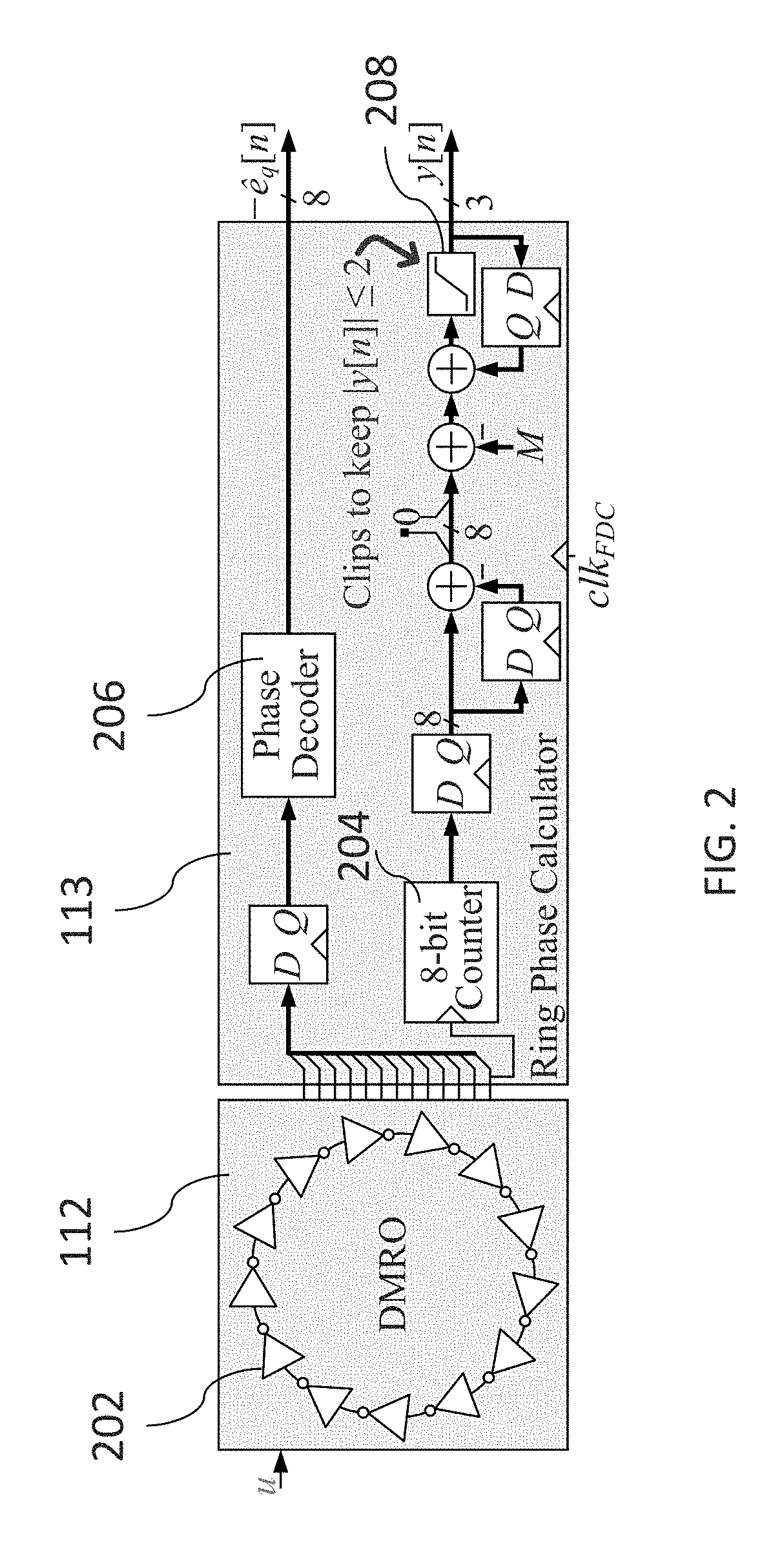
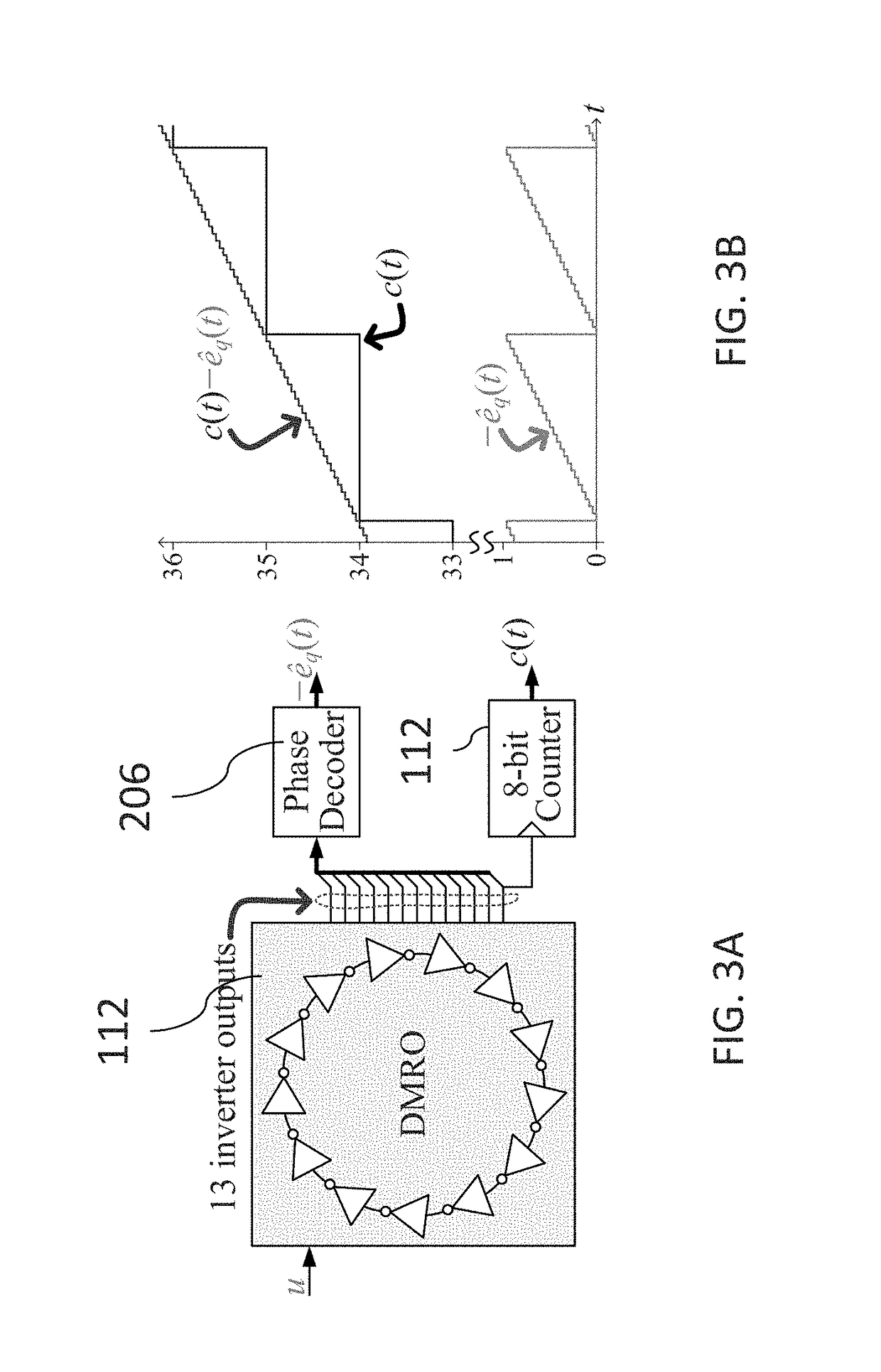
A frequency-to-digital-converter based PLL (FDC-PLL) that implements the functionality of a charge pump and analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with a dual-mode ring oscillator (DMRO) and digital logic. Preferred embodiments of the invention include circuit-level techniques that provide better spurious tone performance and very low phase noise with lower power dissipation and supply voltage than prior digital PLLs known to the inventors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nonlinearity robust successive requantizer
ActiveUS7986250B2Reduce consumptionLow costEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlTransceiverCommunications system
A successive requantizer, which serves as a replacement for a ΔΣ modulator in a fractional-N PLL or a DAC, and avoids spurious tone problems, thereby circumventing the tradeoffs that result from reliance on the common approach of making highly linear analog circuitry to avoid spurious tones. A successive requantizer fractional-N PLL of the invention has the potential to reduce power consumption and the cost of commercial communication devices. The successive requantizer performs digital quantization one bit at a time in such a way that the quantization noise can he engineered to have desirable properties such as non-linearity robustness. The successive requantizer is applicable to most high-performance digital communication systems, such as cellular telephone handsets and wireless local and metropolitan area network transceivers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dither-less error feedback fractional-n frequency synthesizer systems and methods
ActiveCN105556848ASmall static errorModulated-carrier systemsPulse automatic controlControl theoryStatic error
The invention provides dither-less error feedback fractional-n frequency synthesizer systems and methods. A fractional-N divider of a frequency synthesizer is driven by a dither-less error feedback modulator to alleviate fractional spurious tones introduced by the cyclic train of division ratios from deita-sigma modulators. A first feedback loop generates the feedback signal. A second feedback loop disrupts fractional spurious tones and a third feedback loop provides approximately zero static error.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
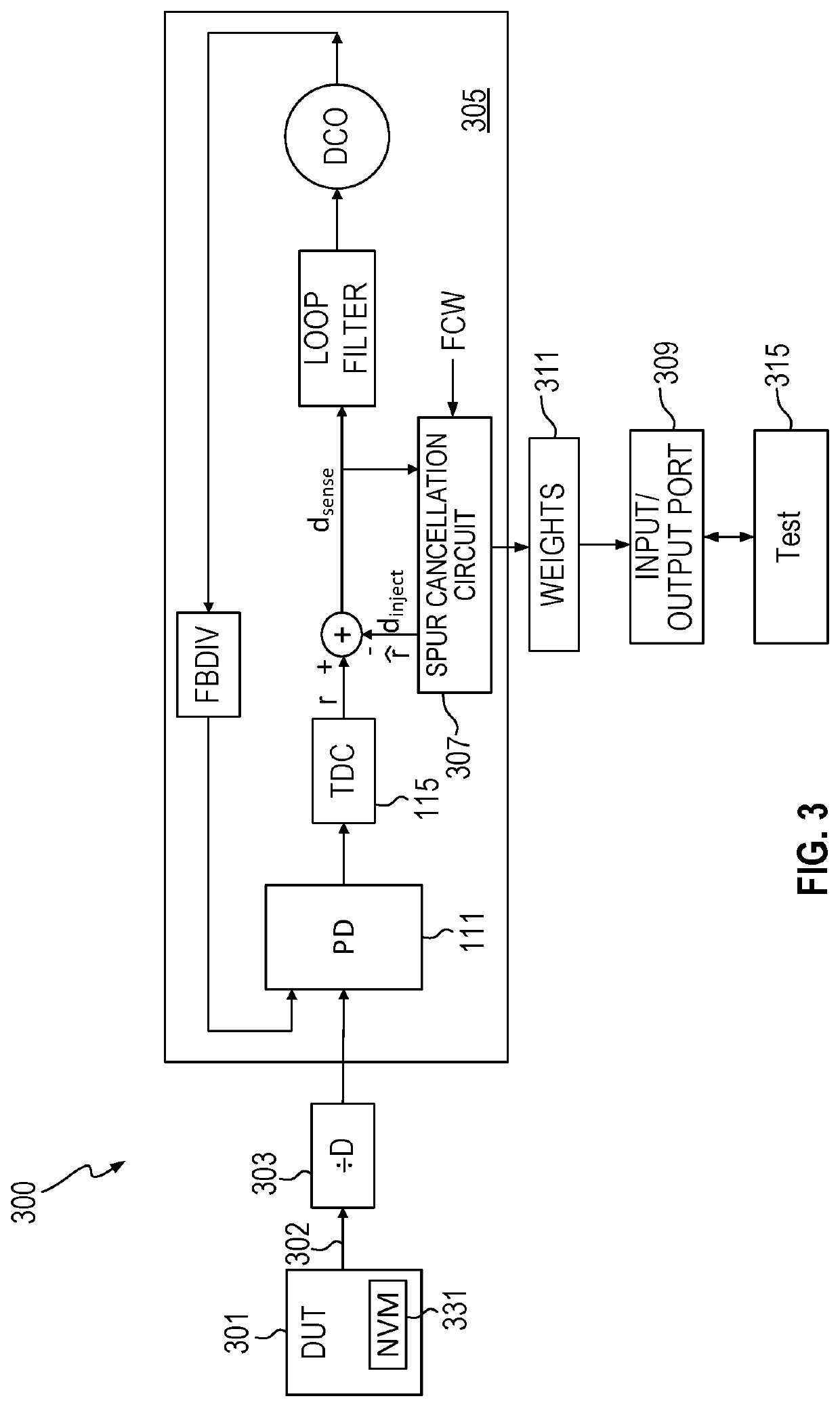
Spur cancellation for spur measurement
ActiveUS11095295B2Digital circuit testingNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementTelecommunicationsEquipment under test
A spur measurement system uses a first device with a spur cancellation circuit that cancel spurs responsive to a frequency control word identifying a spurious tone of interest. A device under test generates a clock signal and supplies the clock signal to the first device through an optional divider. The spur cancellation circuit in the first device generates sine and cosine weights at the spurious tone of interest as part of the spur cancellation process. A first magnitude of the spurious tone in a phase-locked loop in the first device is determined according to the sine and cosine weights and a second magnitude of the spurious tone in the clock signal is determined by the first magnitude divided by gains associated with the first device.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
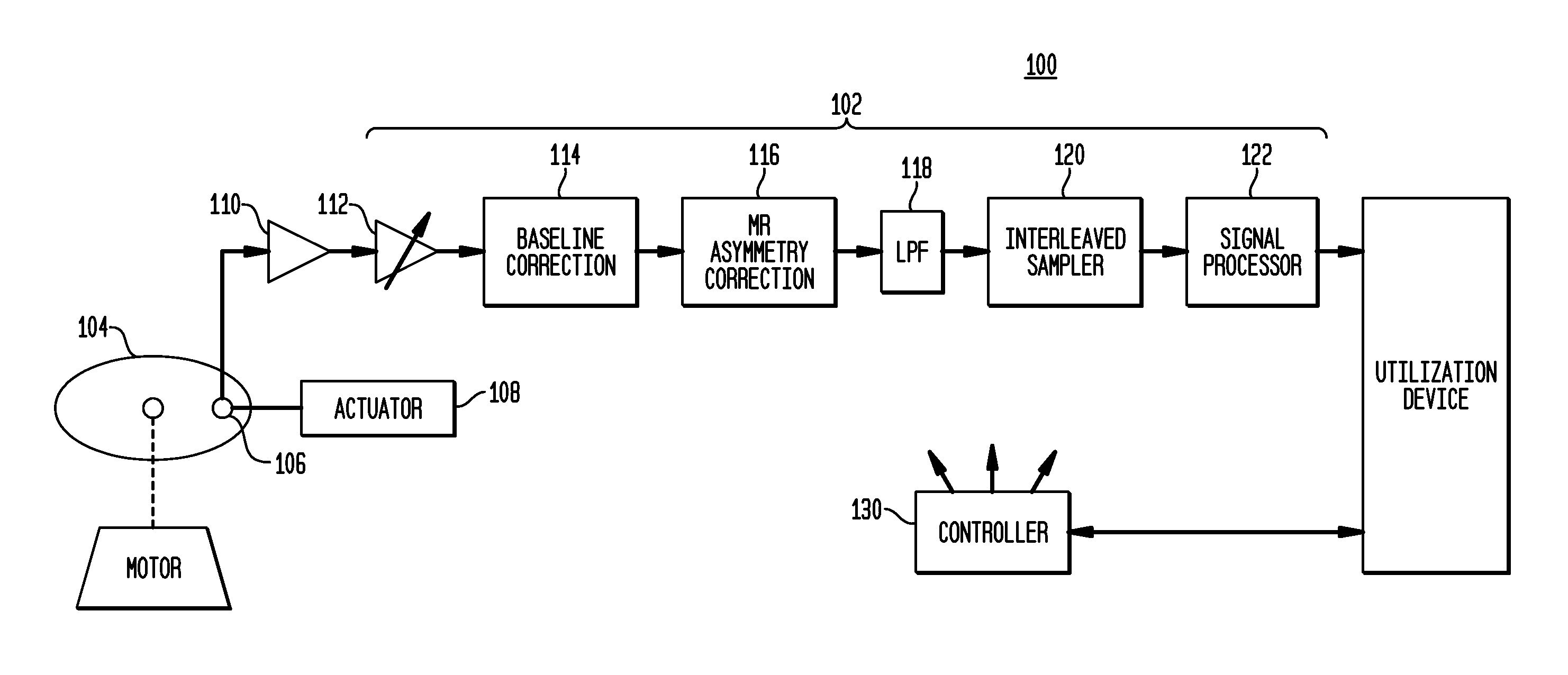
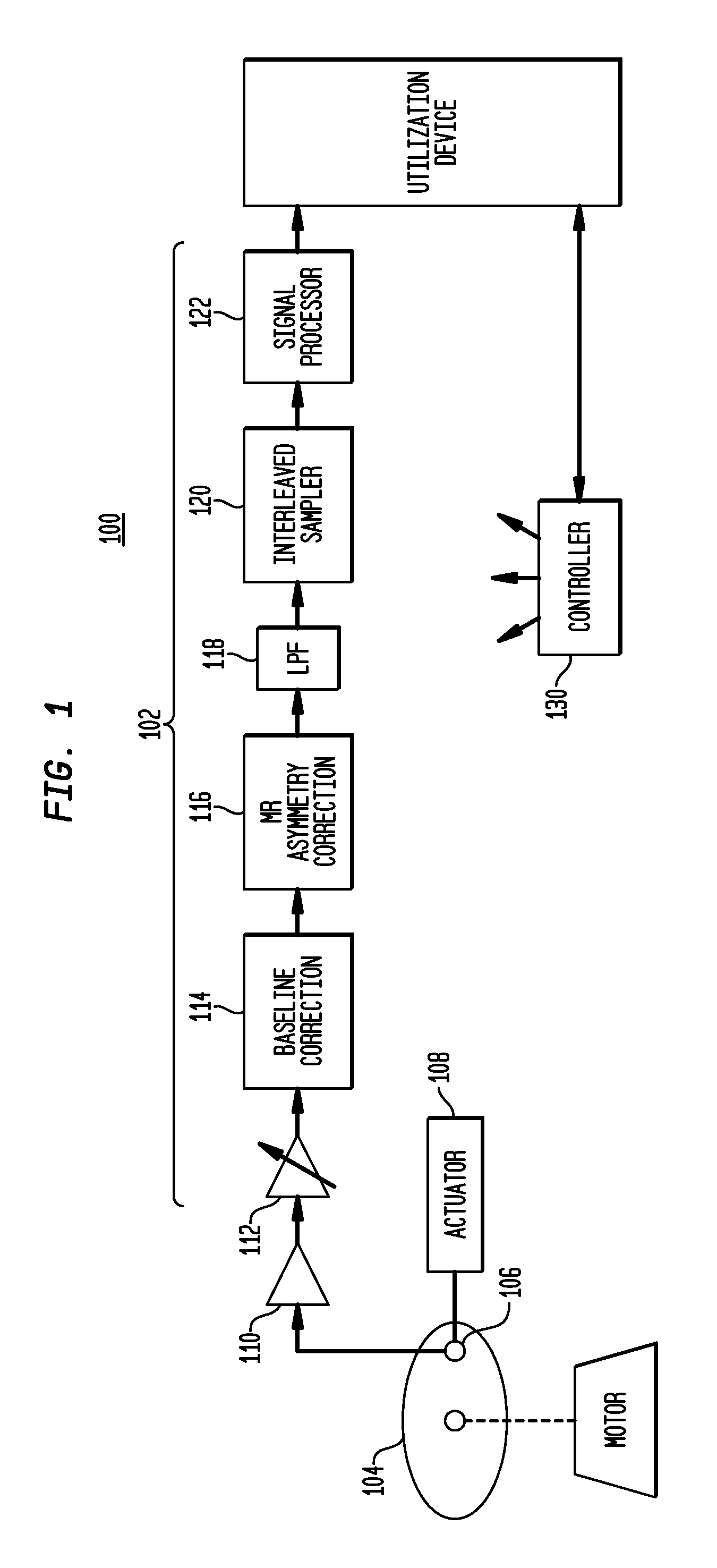
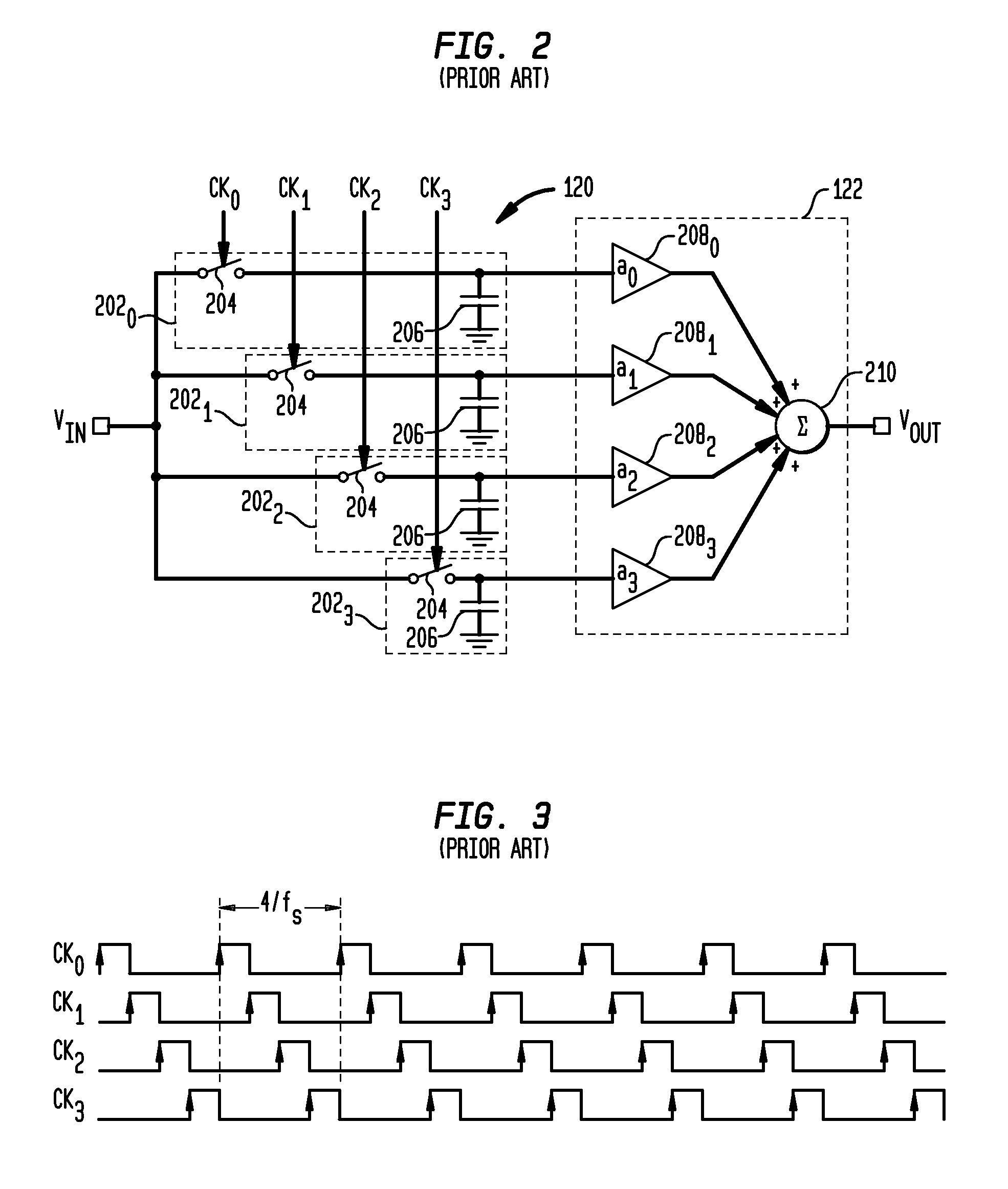
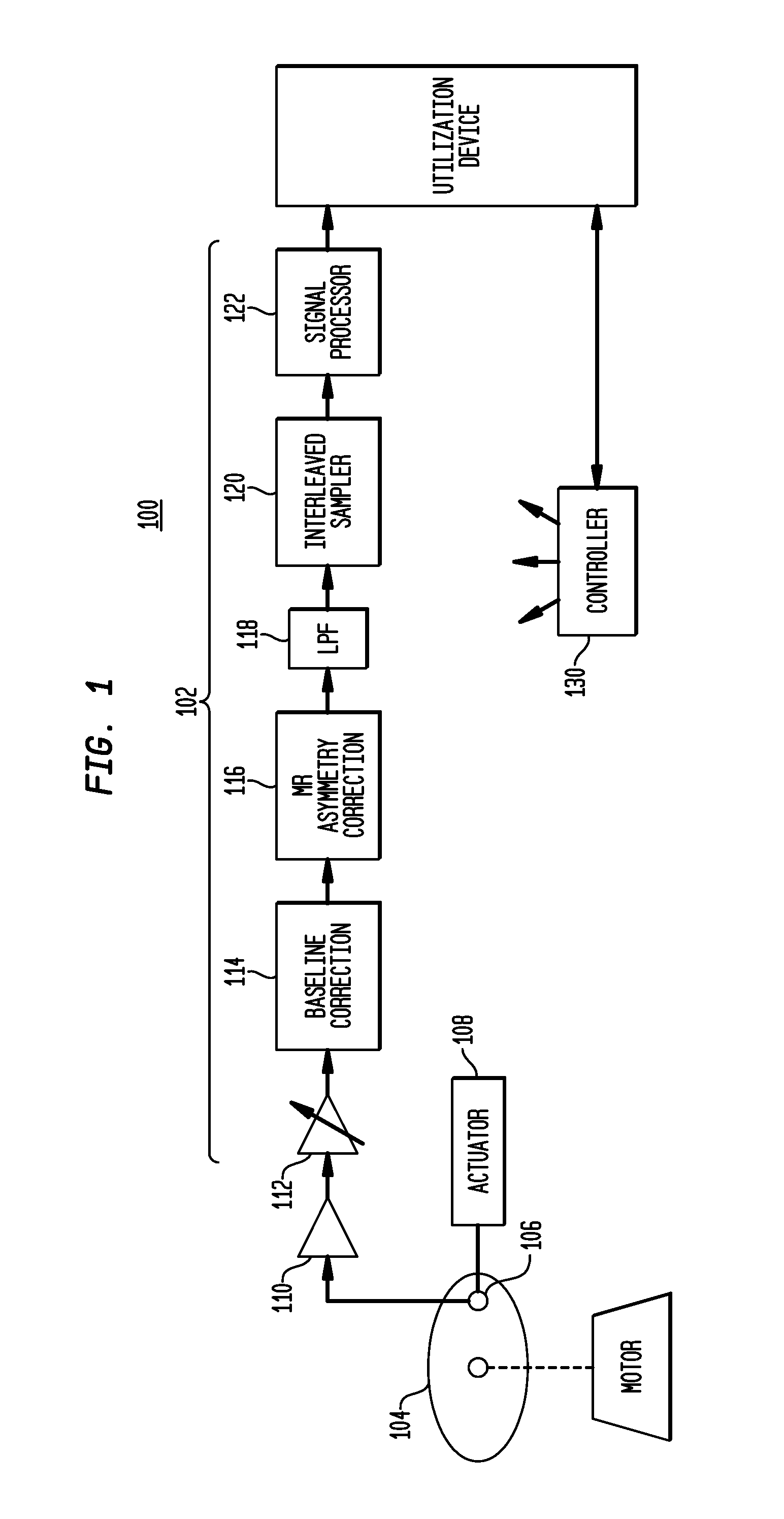
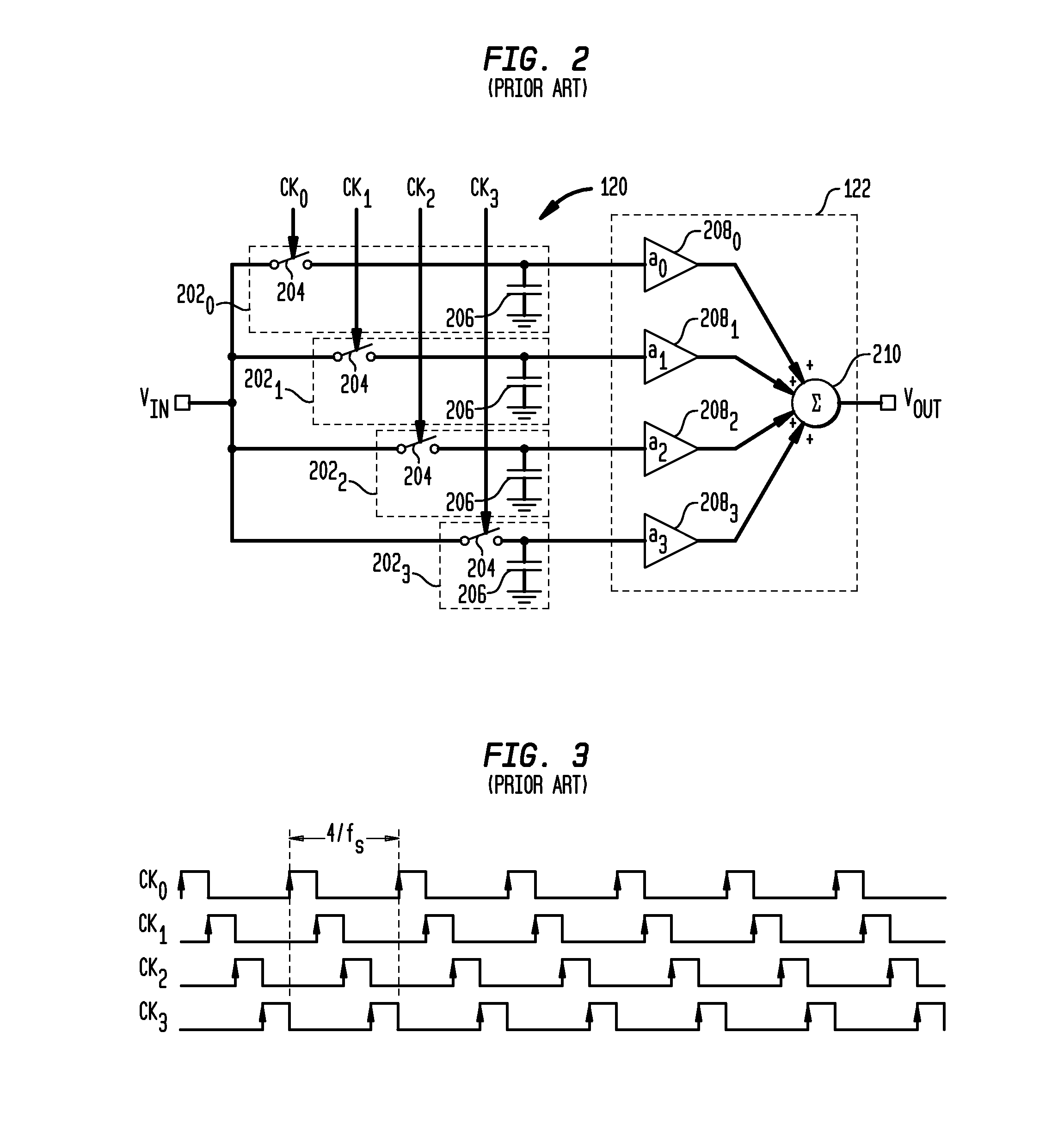
Offset-induced signal cancellation in an interleaved sampling system
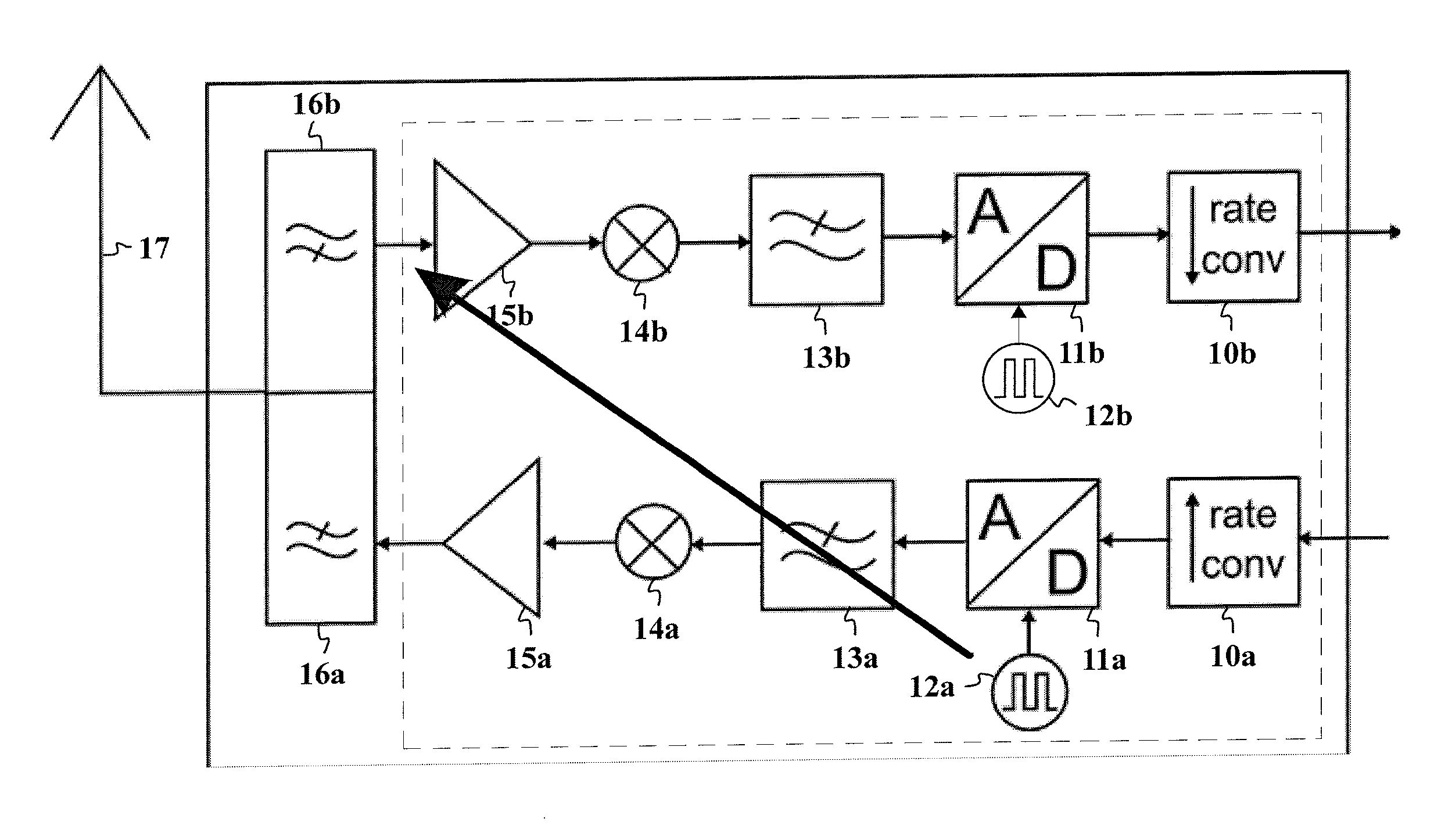
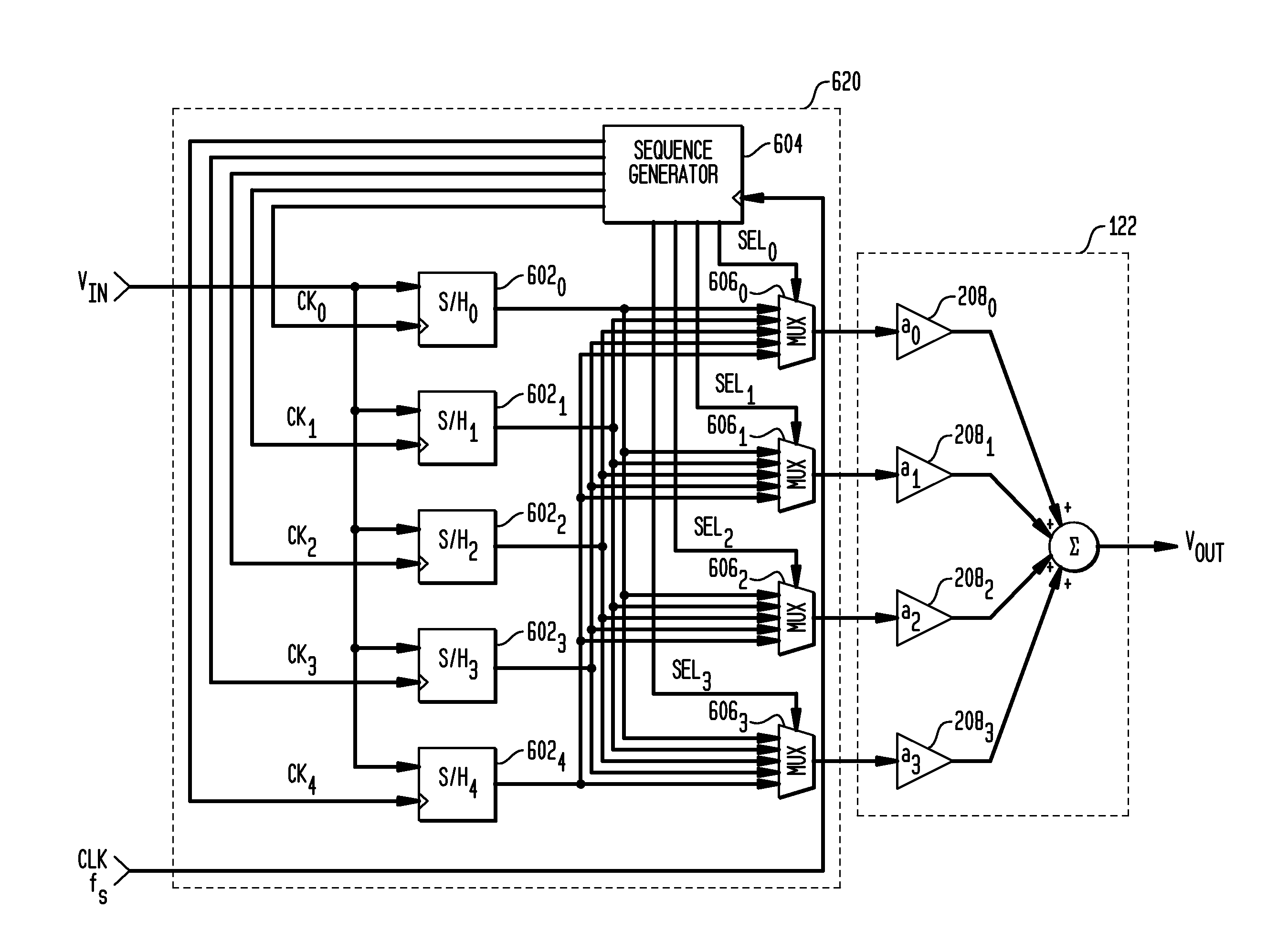
Described embodiments provide an interleaved sampler having N sample and hold circuits for sampling an input signal, and M multiplexers. Each multiplexer is adapted to couple all N of the plurality of sample and hold circuits to a respective output of the interleaved sampler. The interleaved sampler samples at a sample rate of fs, has an interleaved sampling period of M / fs, where M is greater than one and less than N. Because there are more sample and hold circuits than there are samples taken during an interleaved sampling period, different combinations of the sample and hold circuits are used from interleaved sample period to interleaved sample period. This reduces spurious tones generated from offset voltages when using interleaved sample and hold circuits. The order of the sample and hold circuits are clocked might be random, pseudorandom, or a fixed pattern longer than the interleaved sampling period.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low-pass filter based delta-sigma modulator
ActiveUS20070090979A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionIntegratorLow-pass filter
In an embodiment, a delta-sigma modulator is constructed from one or more stages of a first order low-pass filter, which has a modest gain compared to the integrator used in other embodiments of delta-sigma modulators. Delta-sigma modulators can be converted into low-pass filter based delta-sigma modulators according to an embodiment of the invention by replacing the ideal integrator building block with a first order low-pass filter and adjusting other loop parameters, such as gain factors, accordingly. In an embodiment, a dithering technique to suppress spurious tones can be used with the low-pass filter based, ideal integrator based, or near ideal integrator based delta-sigma modulator. In another embodiment, a noise cancellation technique can also be used to cancel the dithering noise.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Linearity of an RF receive path by spurious tone suppression
A method of increasing linearity of an RF signal receive path includes measuring a signal amplified by the receive path. The receive path has a local oscillator operating at an LO frequency and a ground. An error signal is determined from the amplified signal, the error signal being representative of the nonlinearity. An anti-spur tone is injected into the ground. The anti-spur tone has a frequency about equal to the LO frequency and an amplitude and phase that are determined to increase the linearity of the receive path.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus to cancel additive sinusoidal disturbances in OFDM receivers
ActiveUS8611443B2Avoid desensitizationReduce complexityPolarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionHarmonicFrequency mixer
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) has become a popular transmission method for high speed wireless radio transmission, due to its potential for low complexity of transmitters and receivers. A method and apparatus are contemplated for cancelling additive sinusoidal disturbances of a known frequency in OFDM receivers which arise e.g. from clock signals that are present for frequency reference, mixer control, and A / D converter control, as well as harmonics and mixing products of those periodic signals, coupling into some point in the receiver chain and appearing as rotating complex exponentials superimposed to complex baseband receive signals. According to the inventive method and apparatus an estimation of an amplitude and phase of a disturbing superimposed tone with a known frequency is obtained and the amplitude and phase estimation is used to cancel the spurious tone preventing a degradation of receiver sensitivity while achieving low implementation complexity.
Owner:NXP BV
Integrated cancellation circuit for RF converter spurious tones
Techniques are disclosed for eliminating or otherwise sufficiently suppressing spurious signals. The techniques are particularly useful in applications such as those that employ aggressor frequency sources along with a frequency conversion or mixing function, and especially applications implemented as a system-on-chip. In the spur-training mode, a spur-canceller circuit identifies spurious tones associated with the host system to neutralize those tones when running in a normal mode. The tones are neutralized using a comb generator with variable phase and gain by way of cancellation with comb output signals having substantially the same amplitude and a phase that is 180° out of phase with the aggressor tone to be cancelled.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Offset-induced signal cancellation in an interleaved sampling system
ActiveUS20140049853A1Well formedAnalogue/digital conversionElectric analogue storesMultiplexerSignal cancellation
Described embodiments provide an interleaved sampler having N sample and hold circuits for sampling an input signal, and M multiplexers. Each multiplexer is adapted to couple all N of the plurality of sample and hold circuits to a respective output of the interleaved sampler. The interleaved sampler samples at a sample rate of fs, has an interleaved sampling period of M / fs, where M is greater than one and less than N. Because there are more sample and hold circuits than there are samples taken during an interleaved sampling period, different combinations of the sample and hold circuits are used from interleaved sample period to interleaved sample period. This reduces spurious tones generated from offset voltages when using interleaved sample and hold circuits. The order of the sample and hold circuits are clocked might be random, pseudorandom, or a fixed pattern longer than the interleaved sampling period.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Transmitter with a variable sampling rate
ActiveUS8750350B2Reduce impactError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTransceiverHarmonic
The present invention presents a method and a system for mitigating effects of clock harmonics in the receiver. The receiving signal may be monitored in such a way that the interfering harmonic component is tracked. When the interfering frequency is found out, the system determines the clock or clocks in the transceiver which are contributing to the interfering spurious tone. After that, the contributing clock(s) frequency is selected so that the effect of the spurious tone in the receiving passband is minimized or mitigated. This is performed by selecting a suitable clock frequency resulting in the spurious tones all falling outside the receiver passband; or in an OFDM system, by choosing a clock frequency deriving the spurious tone straight onto a subcarrier signal frequency.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Electrical circuit for filtering a local oscillator signal and harmonic rejection mixer
PendingCN111971896AIncrease delayMany design optionsModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesDigital technique networkFinite impulse responseLocal oscillator signal
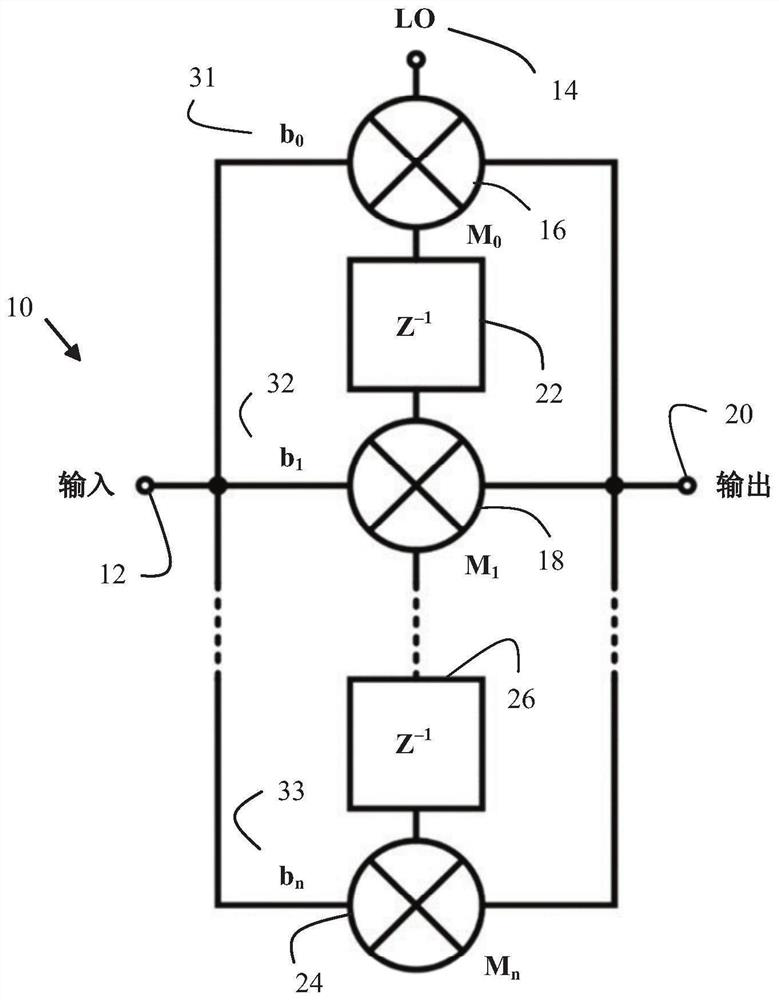
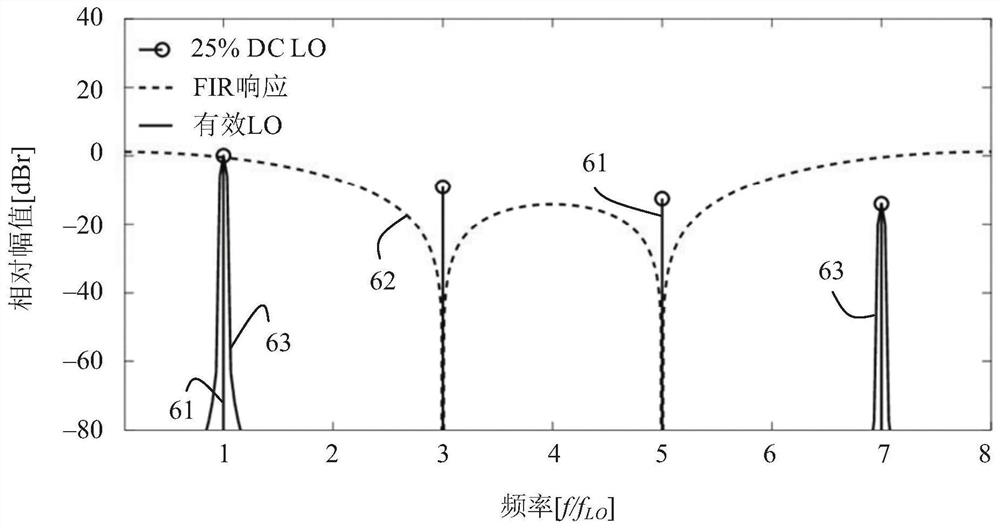
An electrical circuit (10) is provided. The electrical circuit can have an input terminal (12) to receive an input signal and an output terminal (20) at which an output signal can be provided. The electrical circuit further comprises, a local oscillator (14), a first mixer (16), a second mixer (18), and a delay element (22). In the electrical circuit the first mixer is configured to receive an input signal from the input terminal and to mix the input signal with a local oscillator signal. Also, the second mixer is configured to receive said input signal from the input terminal and to mix the input signal with a delayed local oscillator signal, where the delayed local oscillator signal is said local oscillator signal fed via the delay element to the second mixer. The electrical circuit is configured to combine the output signal from the first mixer with the output signal from the second mixer to form an output signal at the output terminal. Hereby, an electrical circuit is provided thatcan efficiently handle the non-idealities of a local oscillator, LO, signal in receivers or transmitters. This is achieved by the electrical circuit that uses a form of finite impulse response, FIR,filter mixer. For example, in receivers, the electrical circuit can be used to filter harmonic components of a pulse-shaped LO signal, resulting in attenuation of the unwanted harmonic down-conversionproducts. The electrical circuit can also be used in other applications, such as but not limited to, filtering of the quantization noise or spurious tones of a digitally generated LO signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Dither-free error feedback fractional-n frequency synthesizer system and method
ActiveCN105556848BSmall static errorModulated-carrier systemsPulse automatic controlControl theoryStatic error
The fractional-N divider of the synthesizer is driven by a jitter-free error feedback modulator to mitigate the fractional spurt introduced by the cyclic string of the division ratio from the incremental accumulation modulator. The first feedback loop generates a feedback signal. The second feedback loop destroys the fractional spurious tone and the third feedback loop provides approximately zero static error.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
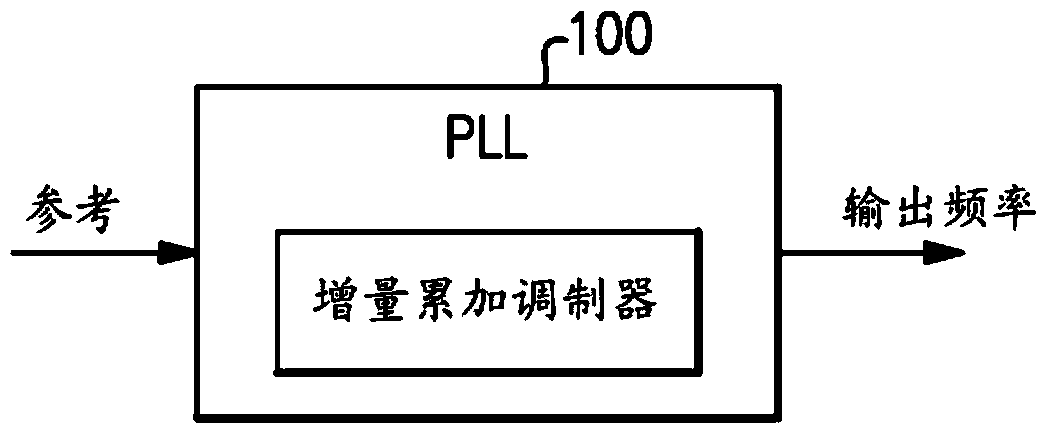
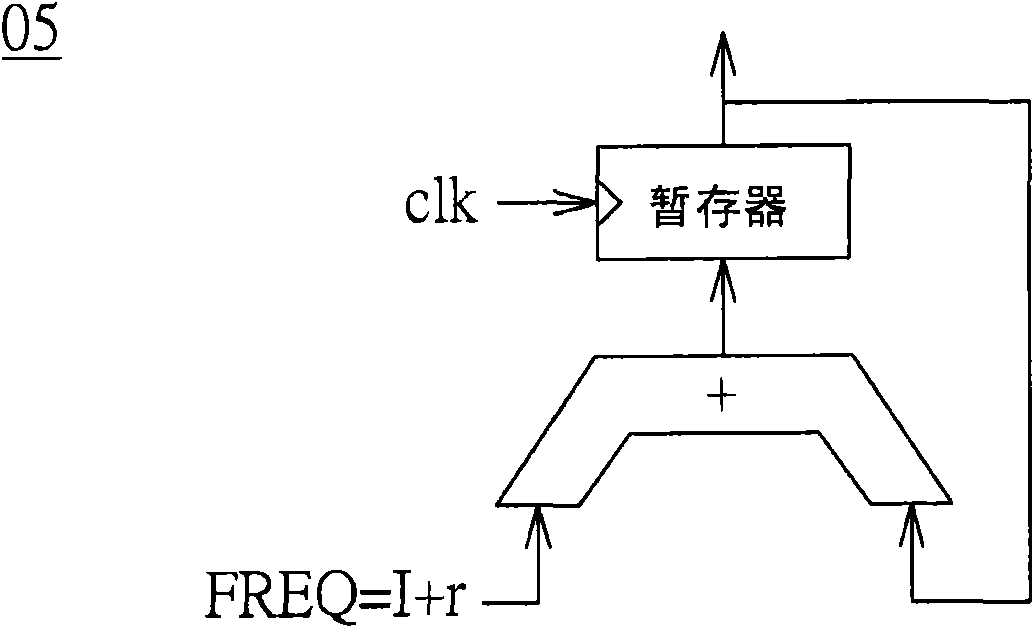
Frequency synthesizer and frequency synthesis method for converting spurious tone to noise
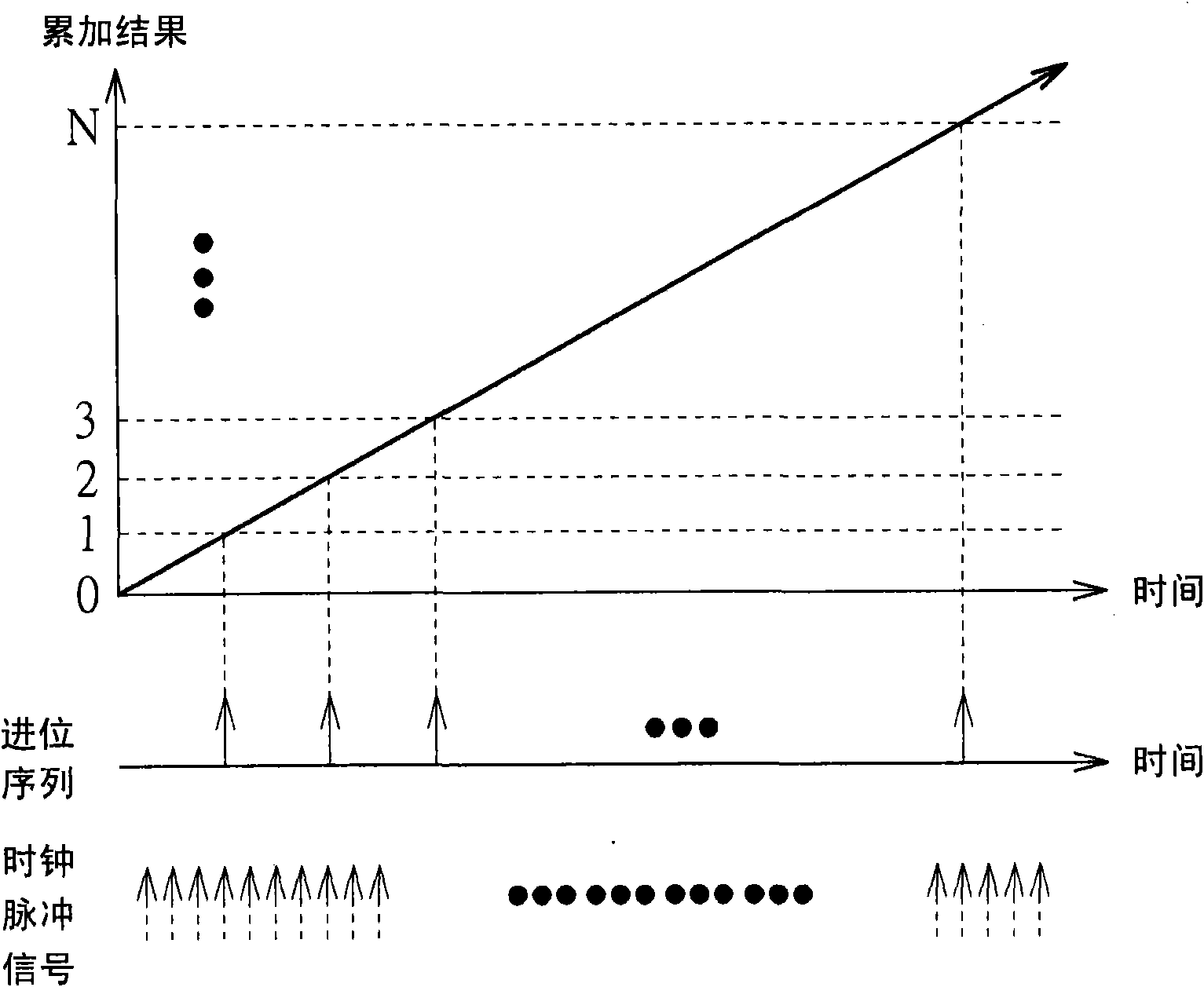
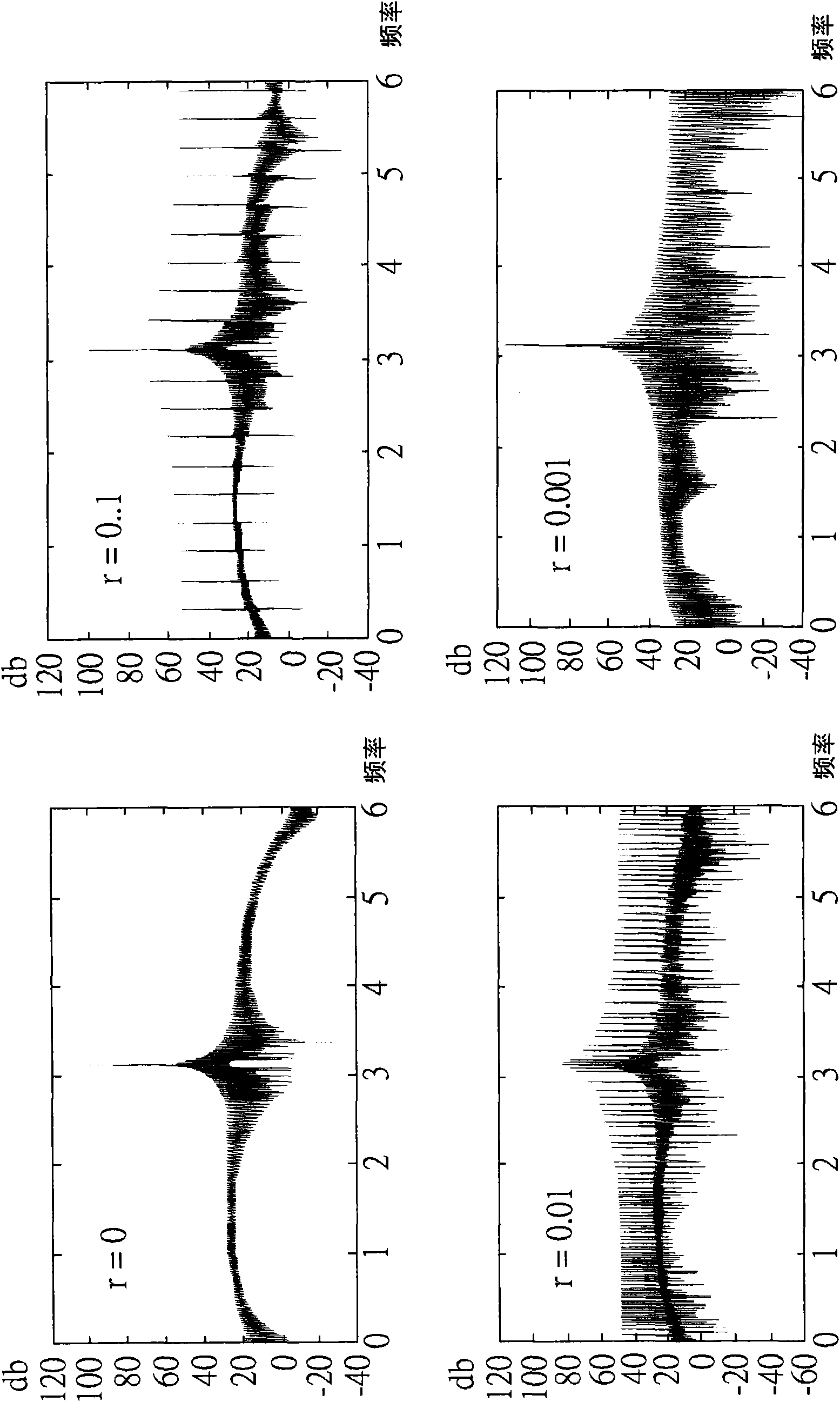
The invention provides a frequency synthesizer and a frequency synthesis method for converting a spurious tone to noise. One of the advantages of a direct frequency synthesis technology (such as flying-adder architecture) is that the technology produces arbitrarily variable frequencies through the concept of time average frequency. At an output end of the frequency synthesized by direct frequency, a period with a single type is replaced by a period with two types. Different from a traditional frequency with the period with a single type, wherein the frequency energy is focused on the design frequency, a frequency based on time average frequency spreads a part of the energy to the spurious tone that may be harmful in some application. The spurious tone is resulted from the periodic carrysequence of a fraction adder in the frequency synthesizer. The invention provides the method and the device to break the periodicity and to convert the spurious tone to wide band noise.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com