Patents
Literature
1260 results about "System on a chip" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
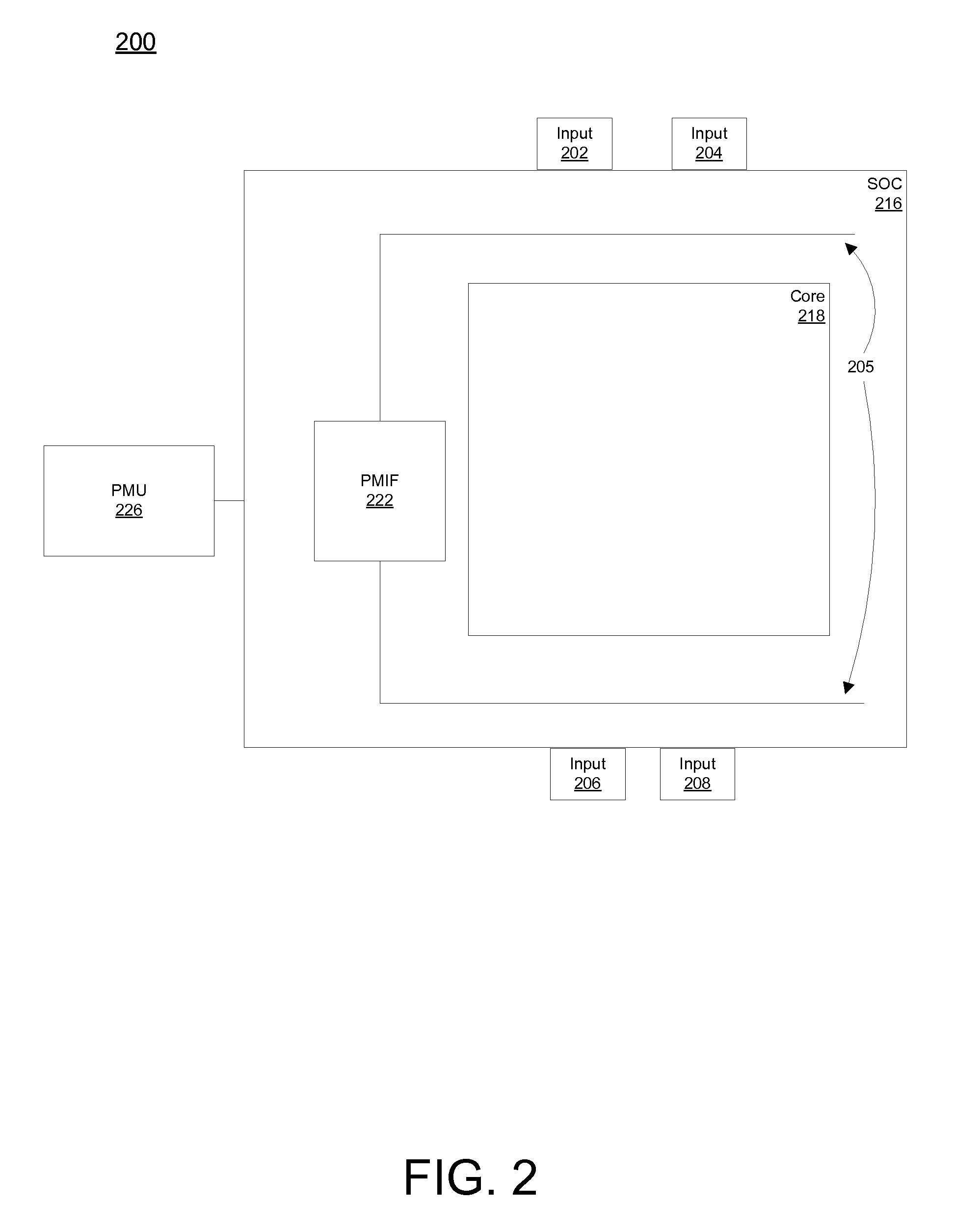
A system on a chip (SoC /ˌɛsˌoʊˈsiː/ es-oh-SEE or /sɒk/ sock) is an integrated circuit (also known as a "chip") that integrates all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components typically (but not always) include a central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output ports and secondary storage – all on a single substrate or microchip, the size of a coin. It may contain digital, analog, mixed-signal, and often radio frequency signal processing functions, depending on the application. As they are integrated on a single substrate, SoCs consume much less power and take up much less area than multi-chip designs with equivalent functionality. Because of this, SoCs are very common in the mobile computing (such as in Smartphones) and edge computing markets. Systems on chip are commonly used in embedded systems and the Internet of Things.
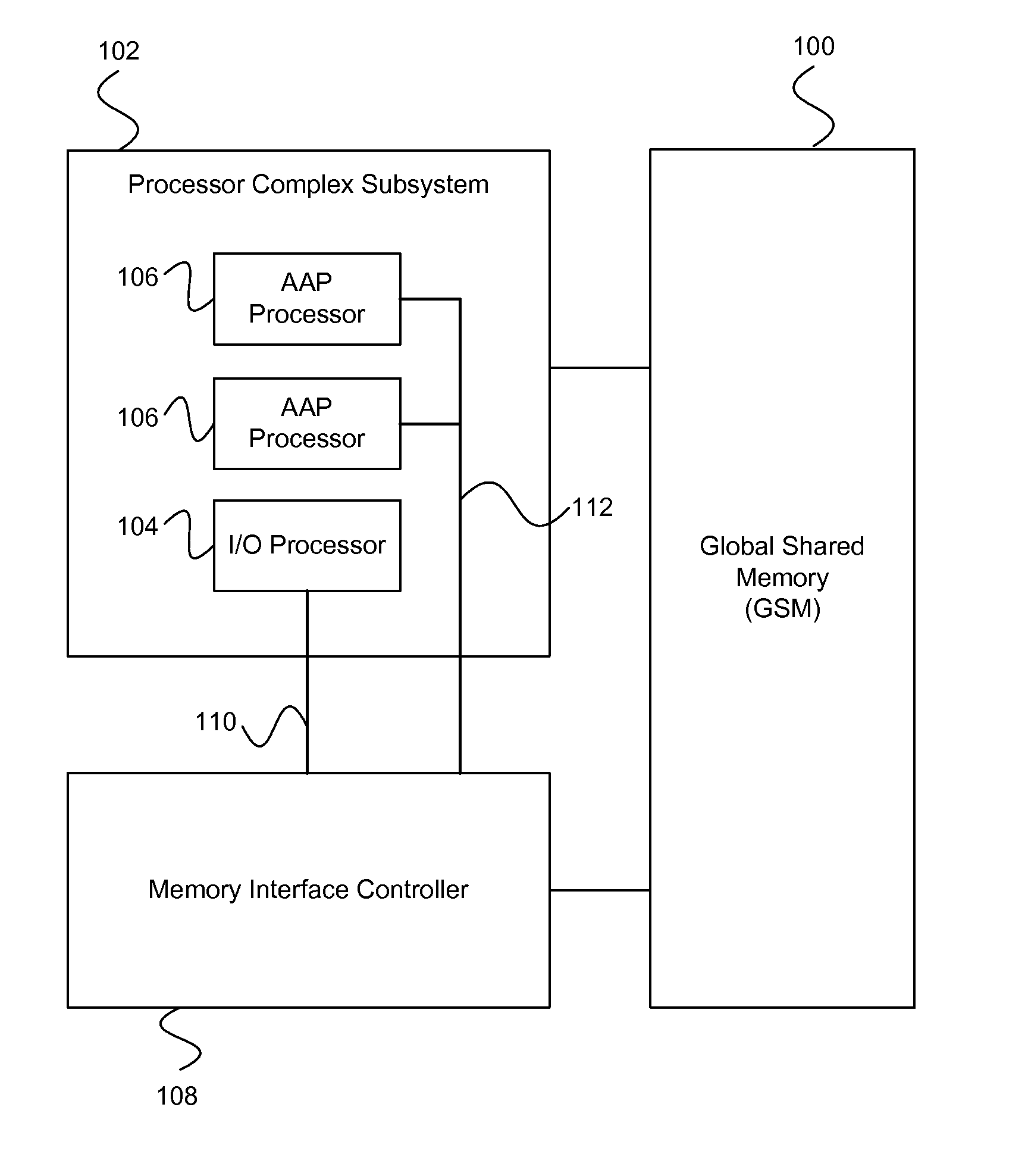
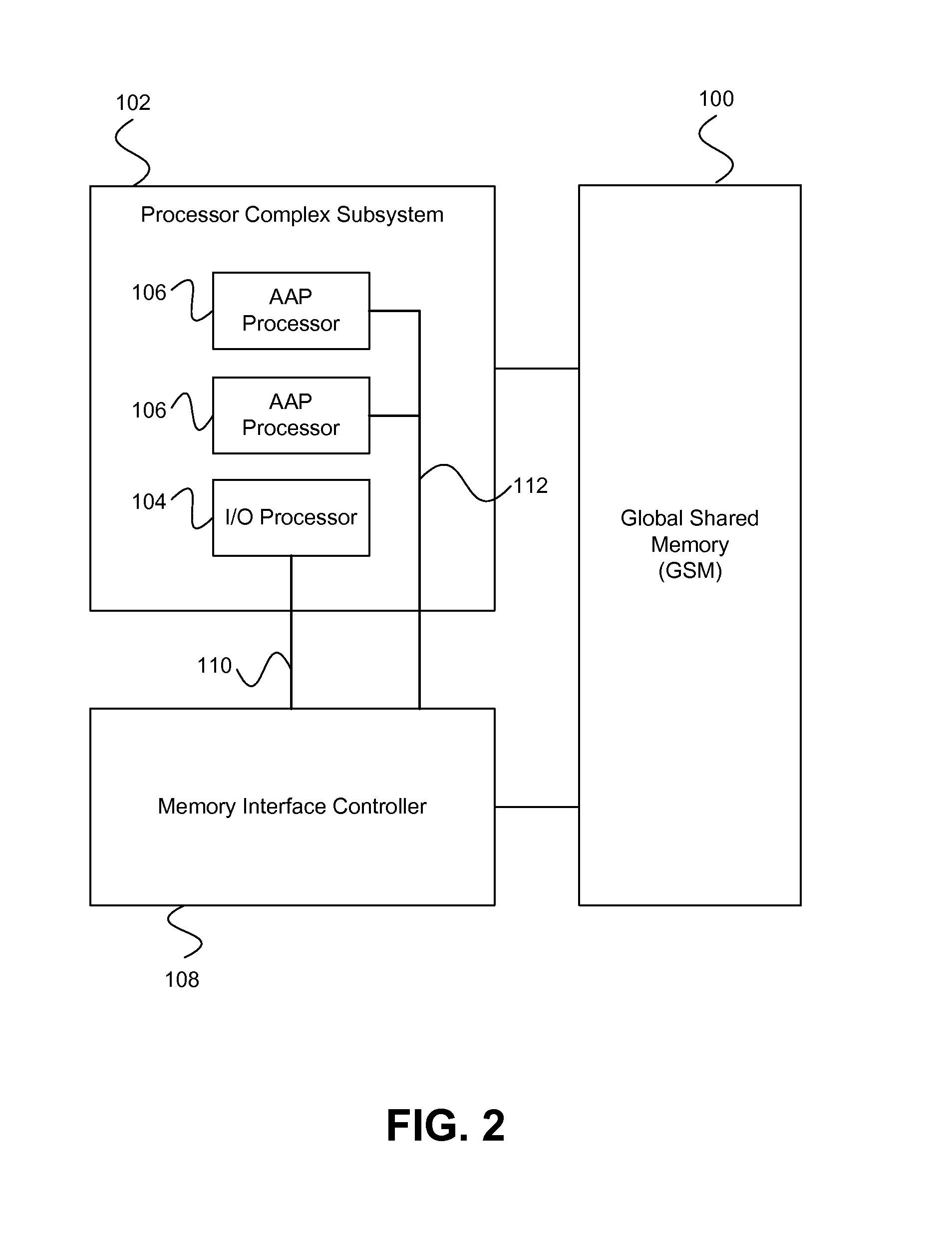
On-chip shared memory based device architecture
ActiveUS7743191B1Reduce disadvantagesLow costRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsRecord information storageExtensibilityRAID
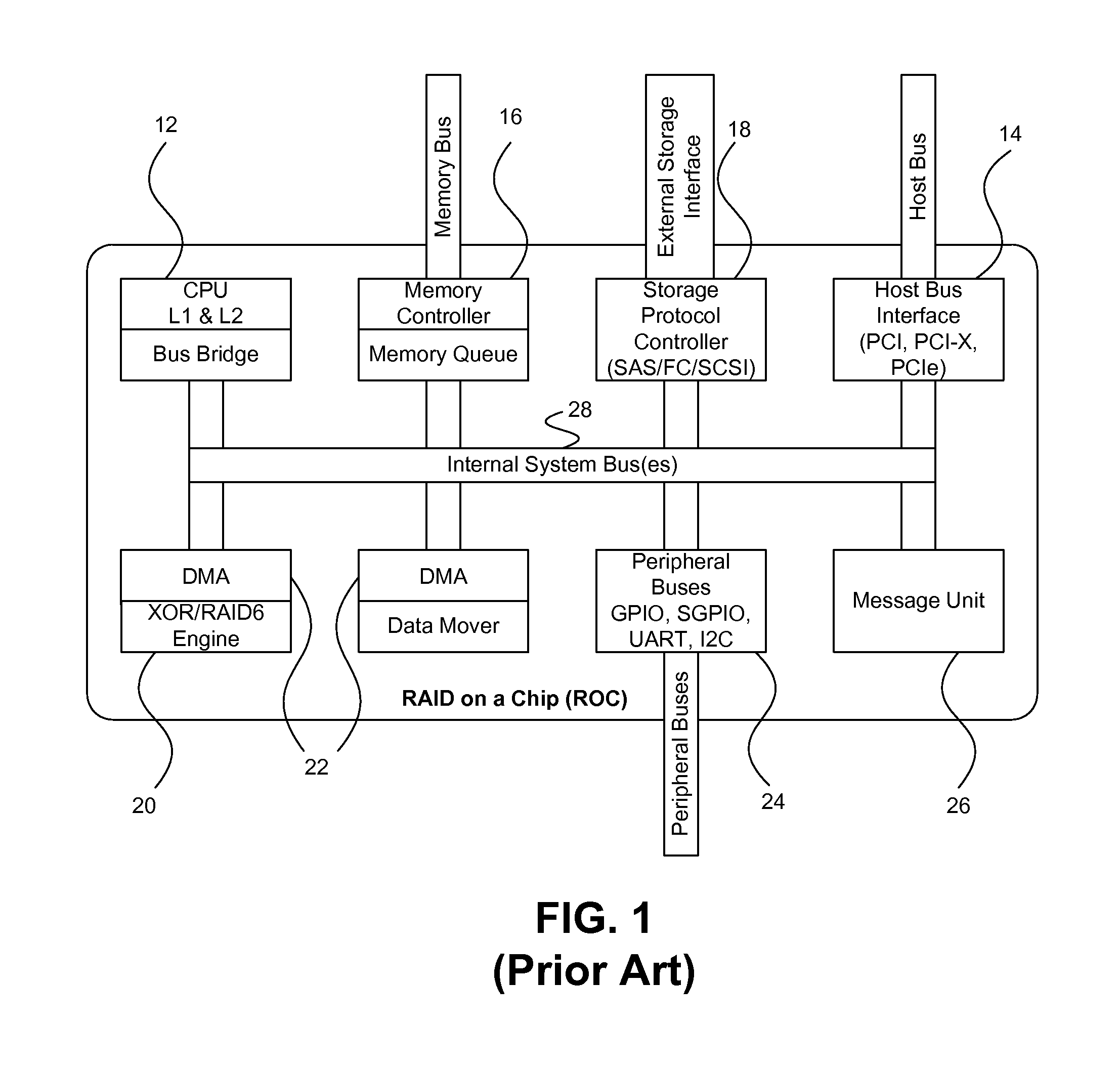
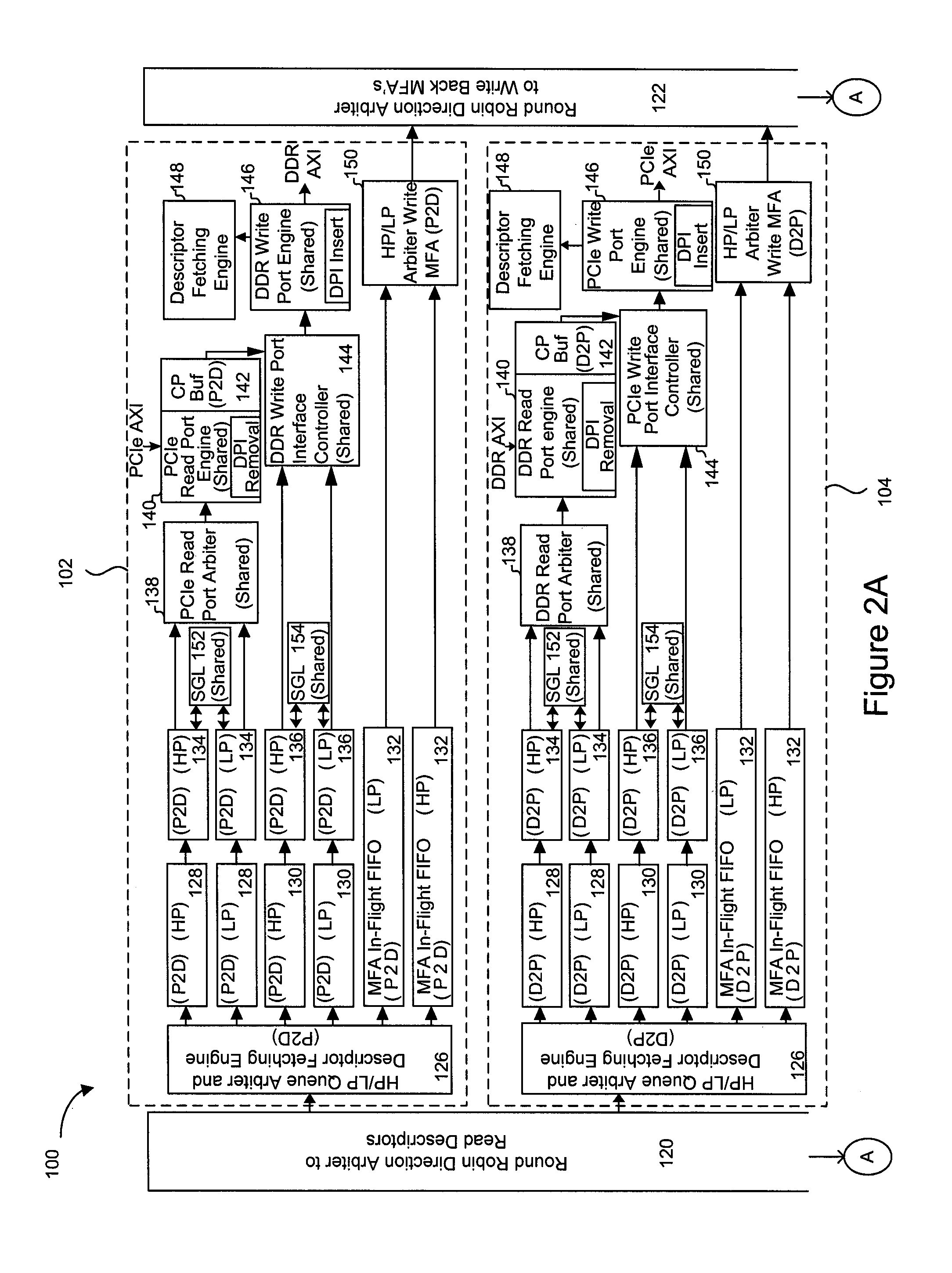
A method and architecture are provided for SOC (System on a Chip) devices for RAID processing, which is commonly referred as RAID-on-a-Chip (ROC). The architecture utilizes a shared memory structure as interconnect mechanism among hardware components, CPUs and software entities. The shared memory structure provides a common scratchpad buffer space for holding data that is processed by the various entities, provides interconnection for process / engine communications, and provides a queue for message passing using a common communication method that is agnostic to whether the engines are implemented in hardware or software. A plurality of hardware engines are supported as masters of the shared memory. The architectures provide superior throughput performance, flexibility in software / hardware co-design, scalability of both functionality and performance, and support a very simple abstracted parallel programming model for parallel processing.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Novel massively parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS20090259713A1Low costReduced footprintError preventionProgram synchronisationSupercomputerPacket communication
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
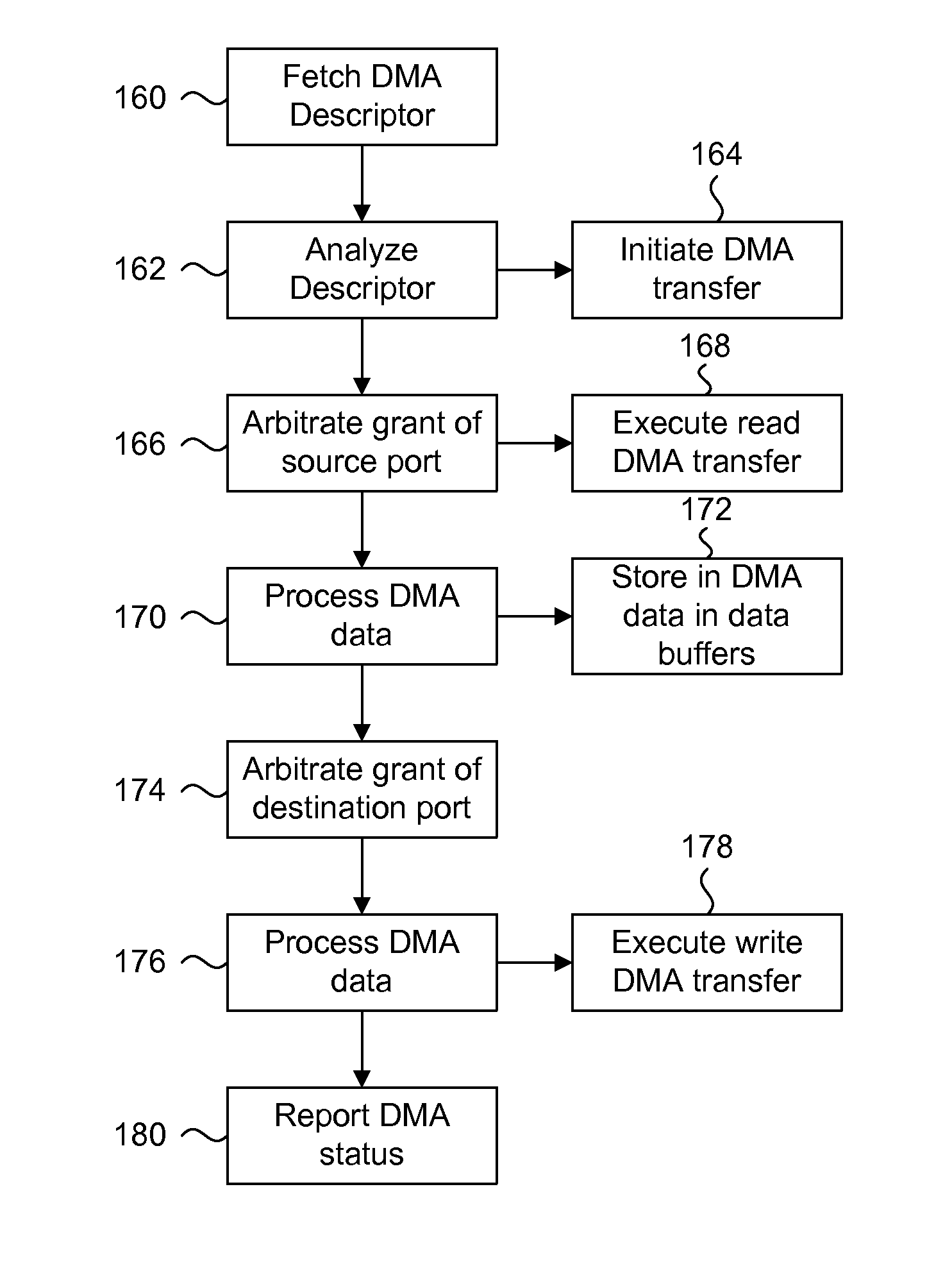
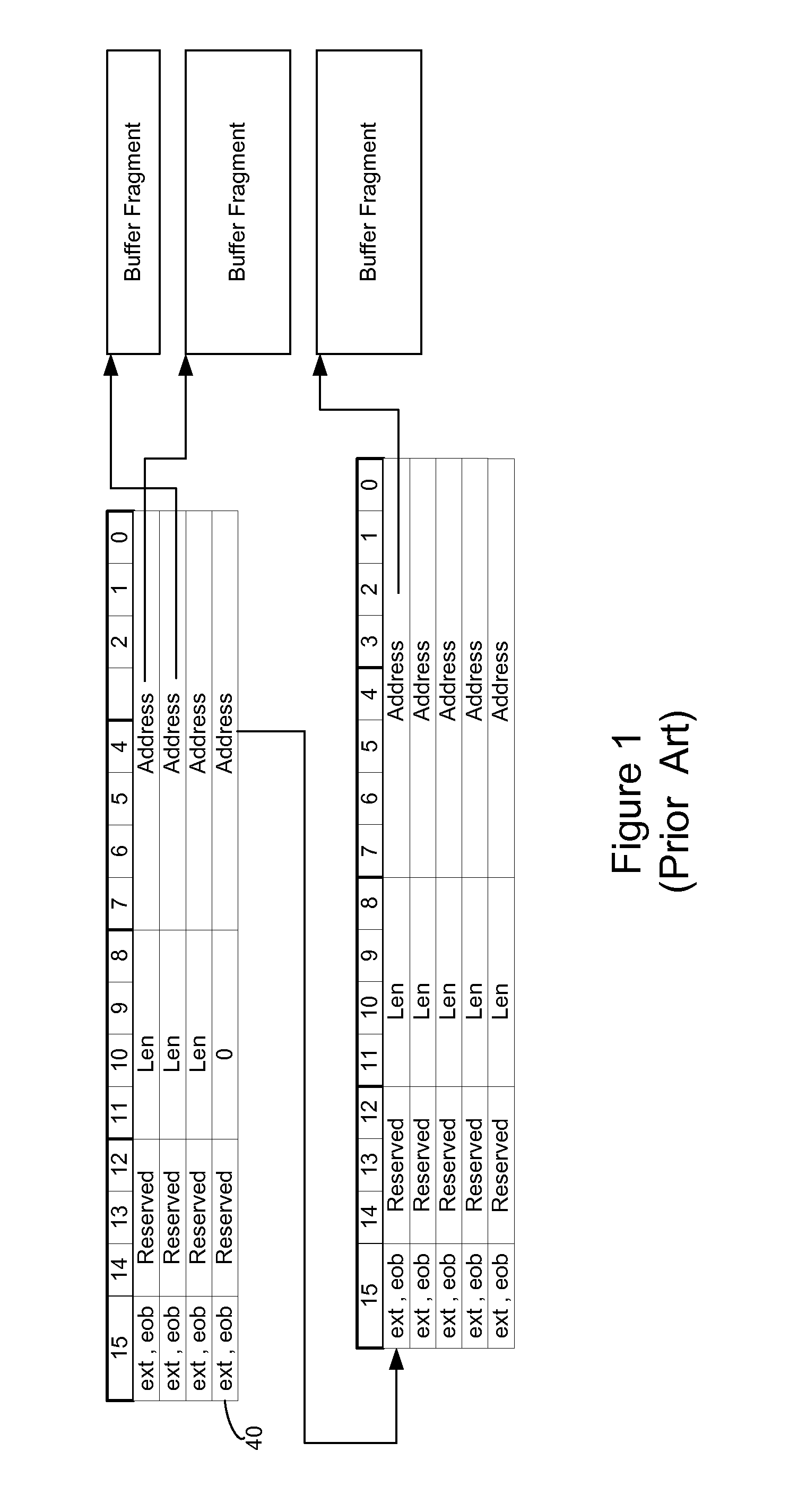
Logical address direct memory access with multiple concurrent physical ports and internal switching
A DMA engine is provided that is suitable for higher performance System On a Chip (SOC) devices that have multiple concurrent on-chip / off-chip memory spaces. The DMA engine operates either on logical addressing method or physical addressing method and provides random and sequential mapping function from logical address to physical address while supporting frequent context switching among a large number of logical address spaces. Embodiments of the present invention utilize per direction (source-destination) queuing and an internal switch to support non-blocking concurrent transfer of data on multiple directions. A caching technique can be incorporated to reduce the overhead of address translation.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOLUTIONS (US) INC
Simultaneous real-time trace and debug for multiple processing core systems on a chip
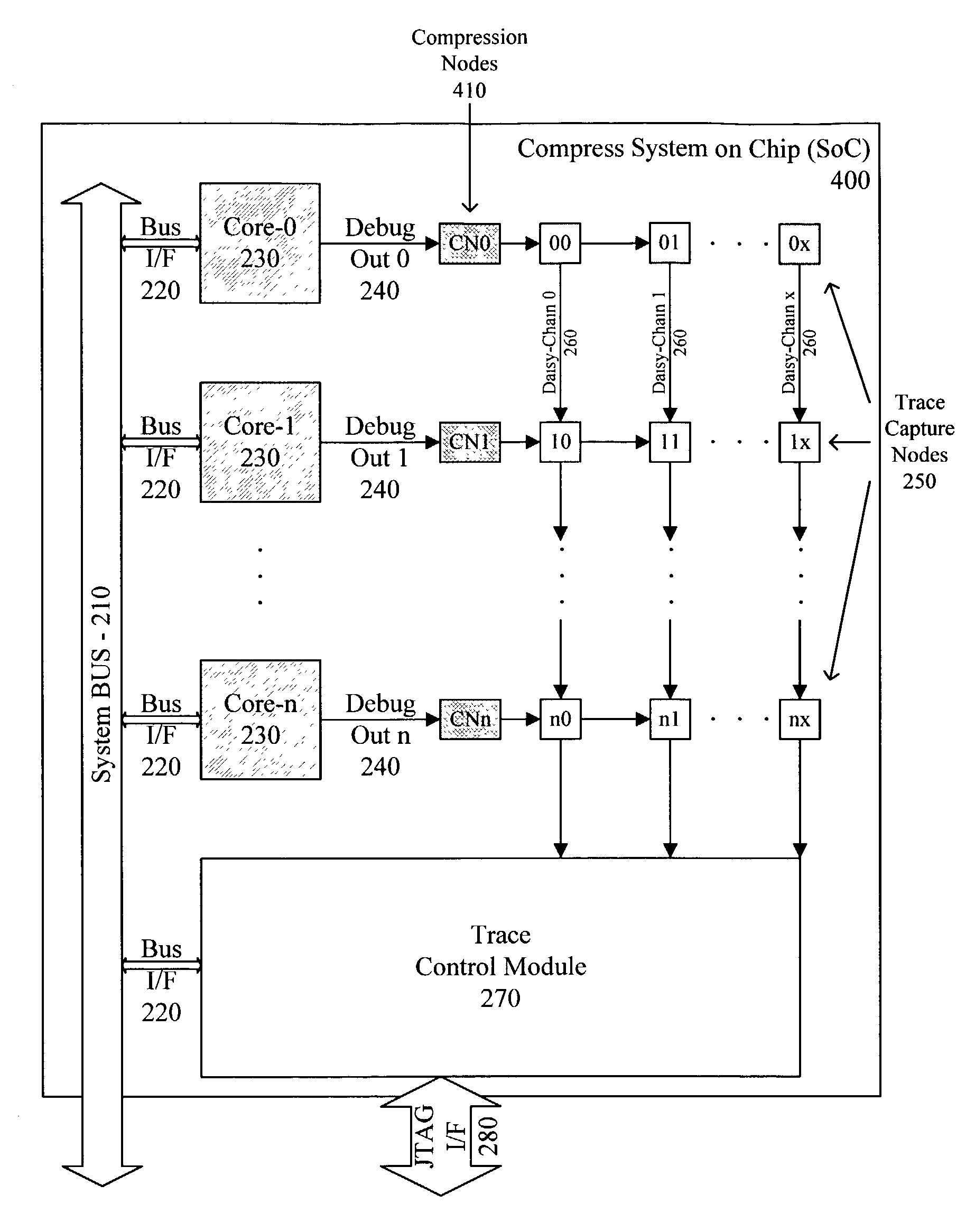
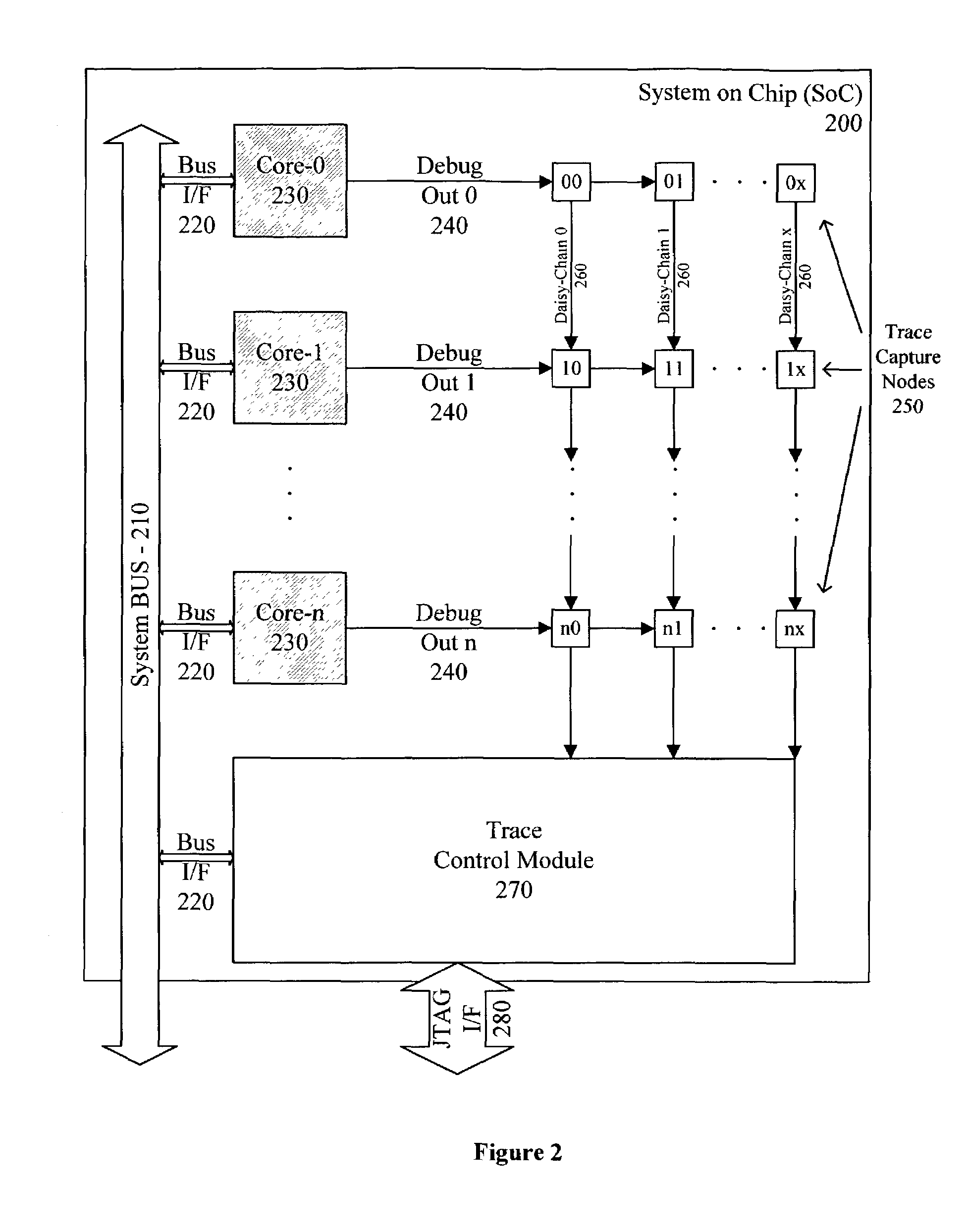
A system for providing simultaneous, real-time trace and debug of a multiple processing core system on a chip (SoC) is described. Coupled to each processing core is a debug output bus. Each debug output bus passes a processing core's operation to trace capture nodes connected together in daisy-chains. Trace capture node daisy-chains terminate at the trace control module. The trace control module receives and filters processing core trace data and decides whether to store processing core trace data into trace memory. The trace control module also contains a shadow register for capturing the internal state of a traced processing core just prior its tracing. Stored trace data, along with the corresponding shadow register contents, are transferred out of the trace control module and off the SoC into a host agent and system running debugger hardware and software via a JTAG interface.
Owner:TENSILICA
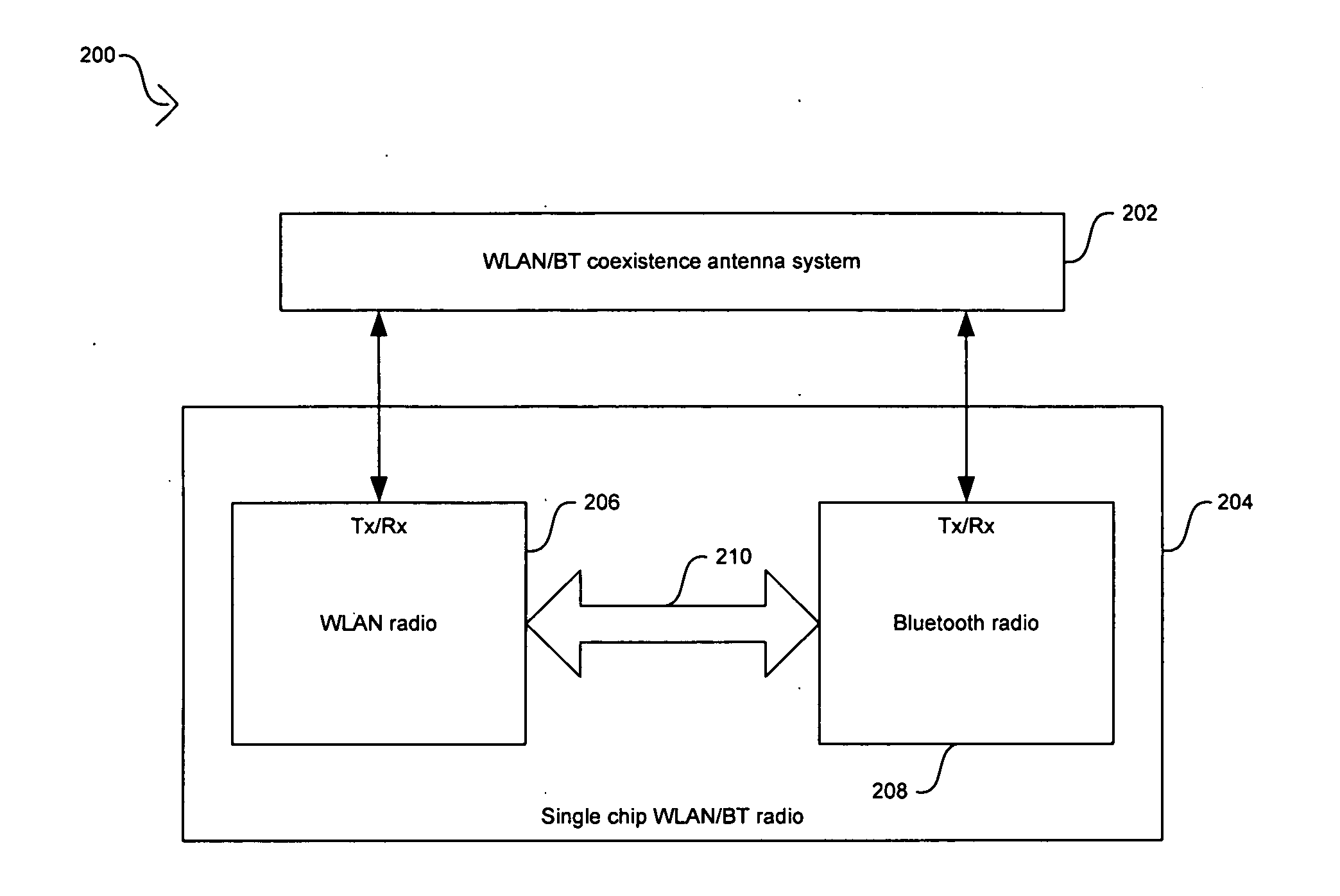
Method and system for antenna and radio front-end topologies for a system-on-a-chip (SOC) device that combines bluetooth and IEEE 802.11 b/g WLAN technologies
Certain embodiments of the invention may be found in a method and system for antenna and radio front-end topologies for a system-on-a-chip (SOC) device that combines Bluetooth and IEEE 802.11 b / g WLAN technologies. A single chip radio device that supports WLAN and Bluetooth technologies receives a WLAN signal in a WLAN processing circuitry of the radio front-end and in a Bluetooth processing circuitry of the radio front-end. Signals generated by the WLAN processing circuitry and the Bluetooth processing circuitry from the received WLAN signal may be combined in a diversity combiner that utilizes selection diversity gain combining or maximal ratio combining (MRC). When a generated signal is below a threshold value, the signal may be dropped from the combining operation. A single antenna usage model may be utilized with the single chip radio device front-end topology to support WLAN and Bluetooth communications.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
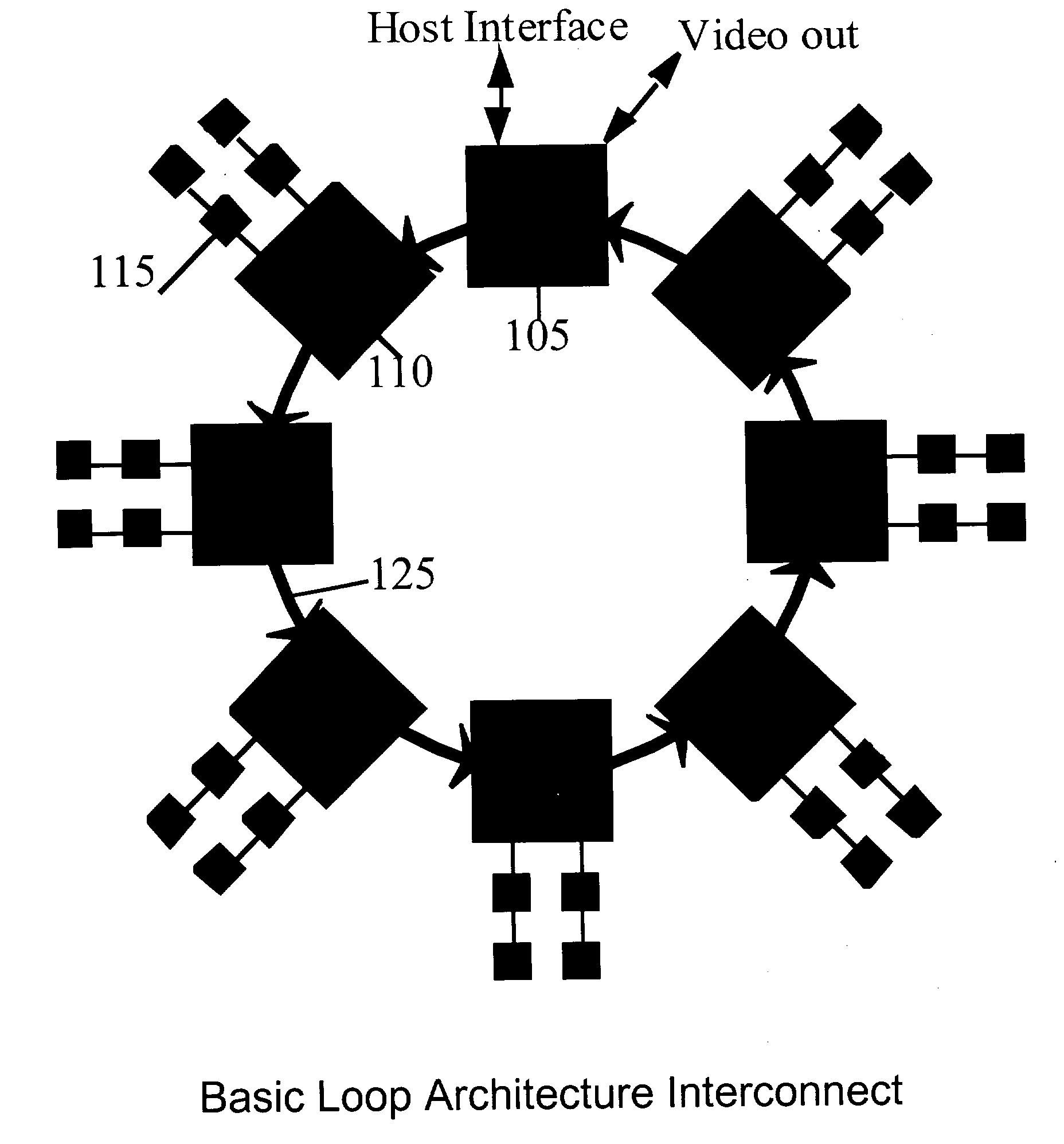
Scalable high performance 3d graphics
InactiveUS20040012600A1Minimizes cost and riskEasy to scaleImage enhancementImage memory managementGraphicsHigh bandwidth
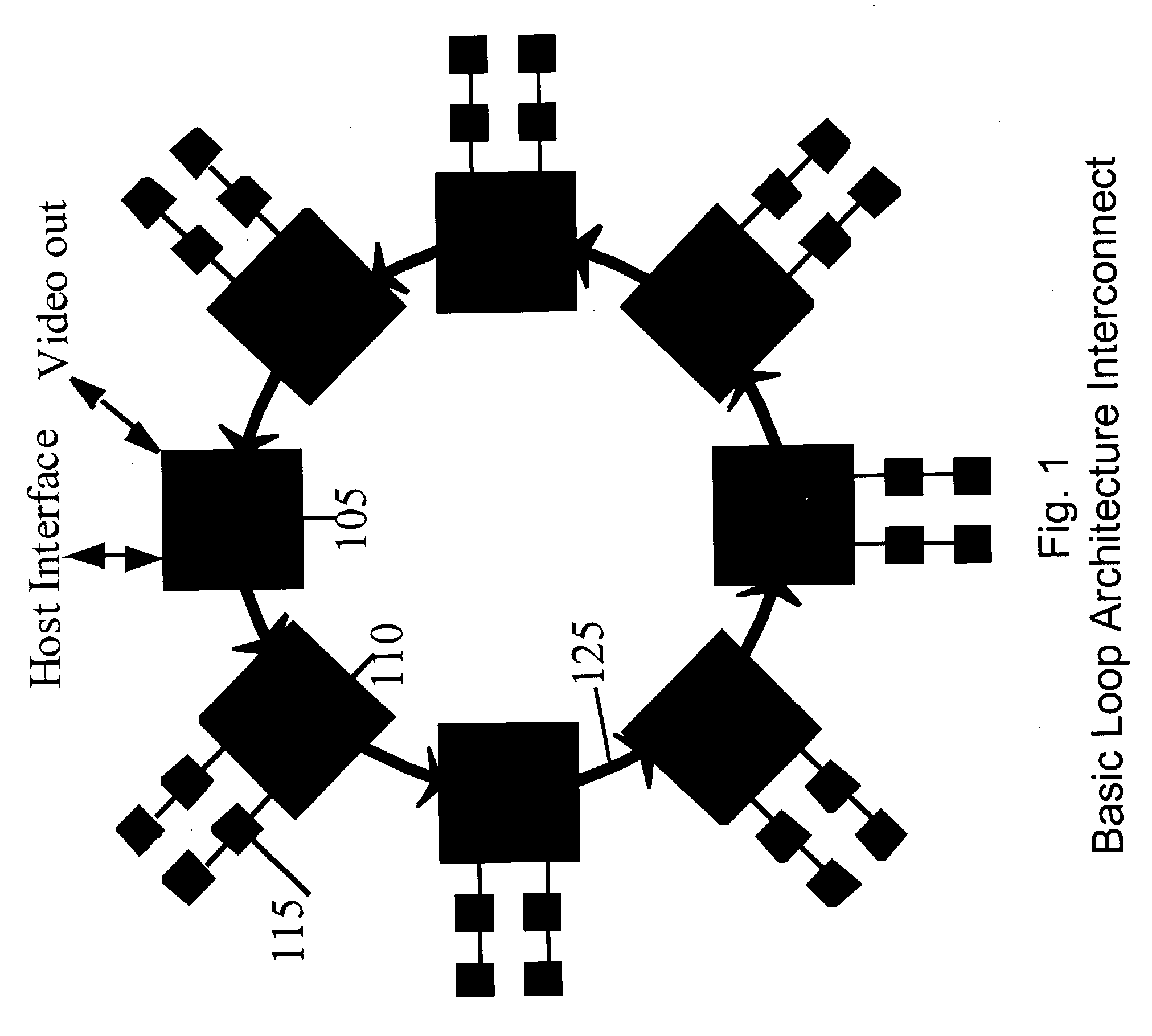
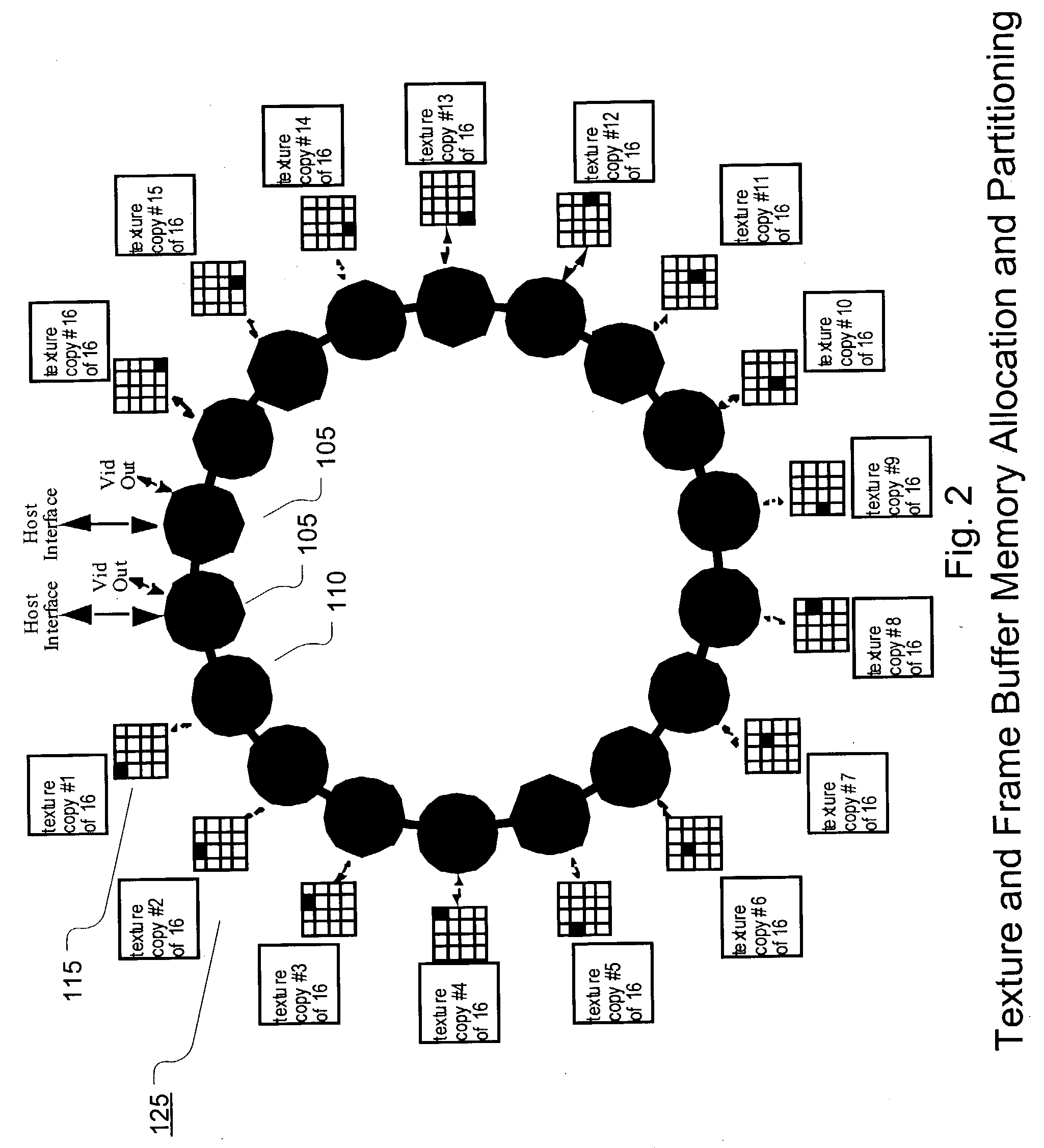
A high-speed ring topology. In one embodiment, two base chip types are required: a "drawing" chip, LoopDraw, and an "interface" chip, LoopInterface. Each of these chips have a set of pins that supports an identical high speed point to point unidirectional input and output ring interconnect interface: the LoopLink. The LoopDraw chip uses additional pins to connect to several standard memories that form a high bandwidth local memory sub-system. The LoopInterface chip uses additional pins to support a high speed host computer host interface, at least one video output interface, and possibly also additional non-local interconnects to other LoopInterface chip(s).
Owner:DEERING MICHAEL F +2
Authenticated Communication Between Security Devices
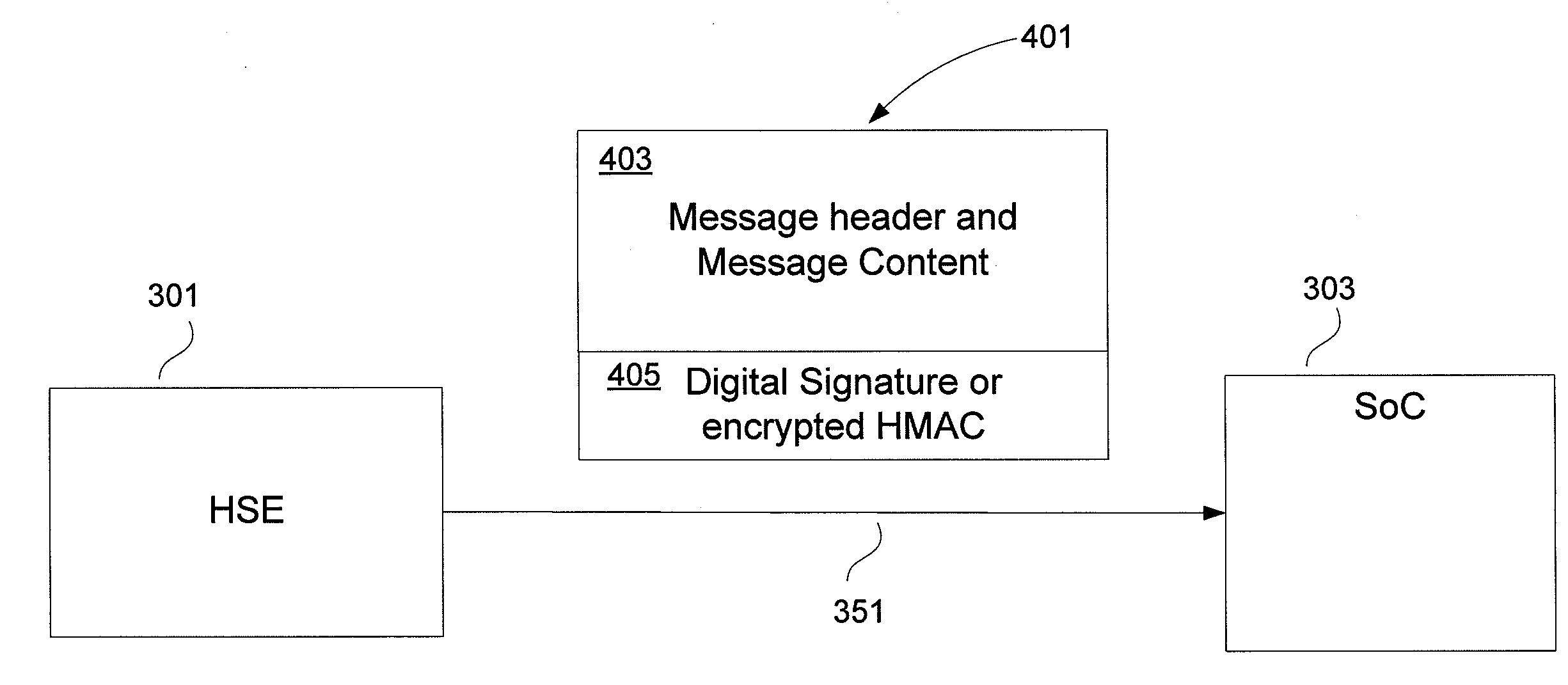
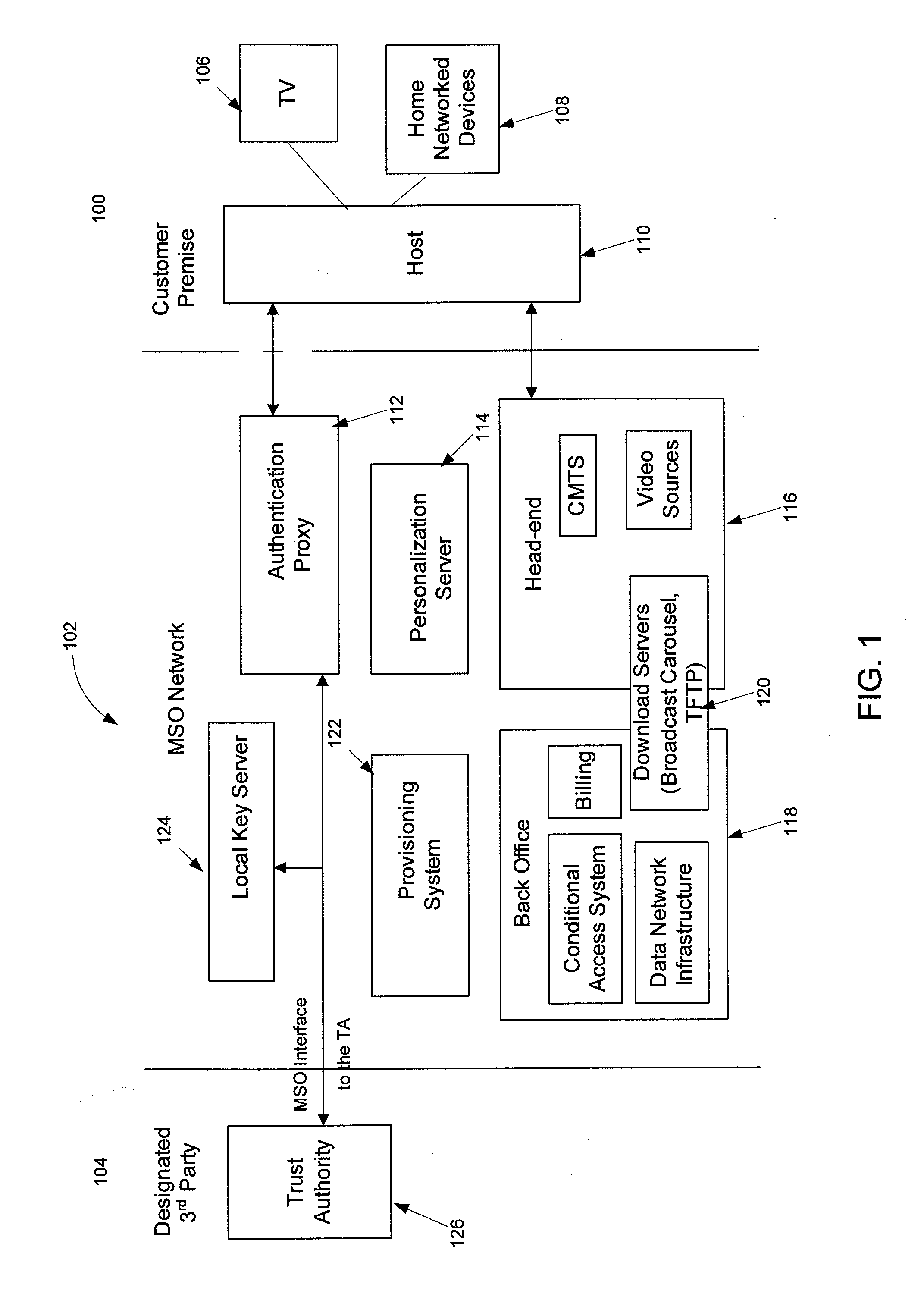
ActiveUS20100217985A1User identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsConditional access systemsDigital signature
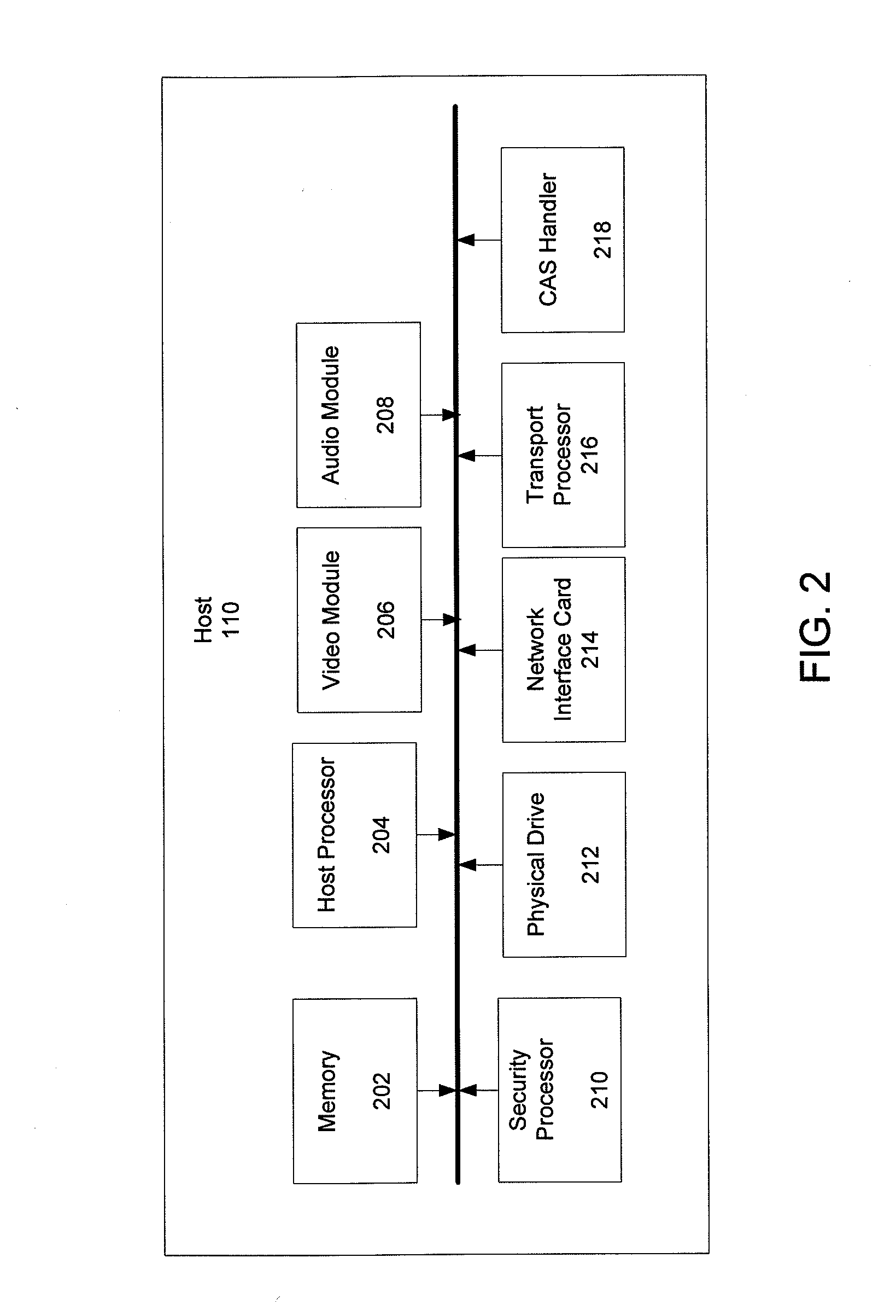
Apparatuses, computer readable media, and methods establishing and maintaining trust between security devices for distributing media content are provided. Two security devices bind to establish an initial trust so that security information can be exchanged. Subsequently, trust is refreshed to verify the source of a message is valid. In an embodiment, the security devices may comprise a security processor and a system on a chip (SoC) in a downloadable conditional access system. Trust may be refreshed by a security device inserting authentication information in a message to another security device, where authentication information may assume different forms, including a digital signature (asymmetric key) or a hash message authentication code (HMAC). Trust may also be refreshed by extracting header information from the message, determining state information from at least one parameter contained in the header information, and acting on message content only when the state information is valid.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Analysis engine and database for manipulating parameters for fluidic systems on a chip
InactiveUS20060281183A1Reduce workloadImprove system efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansComputer scienceSystem on a chip
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Apparatus for and method of noise suppression and dithering to improve resolution quality in a digital RF processor
InactiveUS20050186920A1Cancel noiseAvoid it happening againPulse automatic controlAngle modulationImage resolutionEngineering
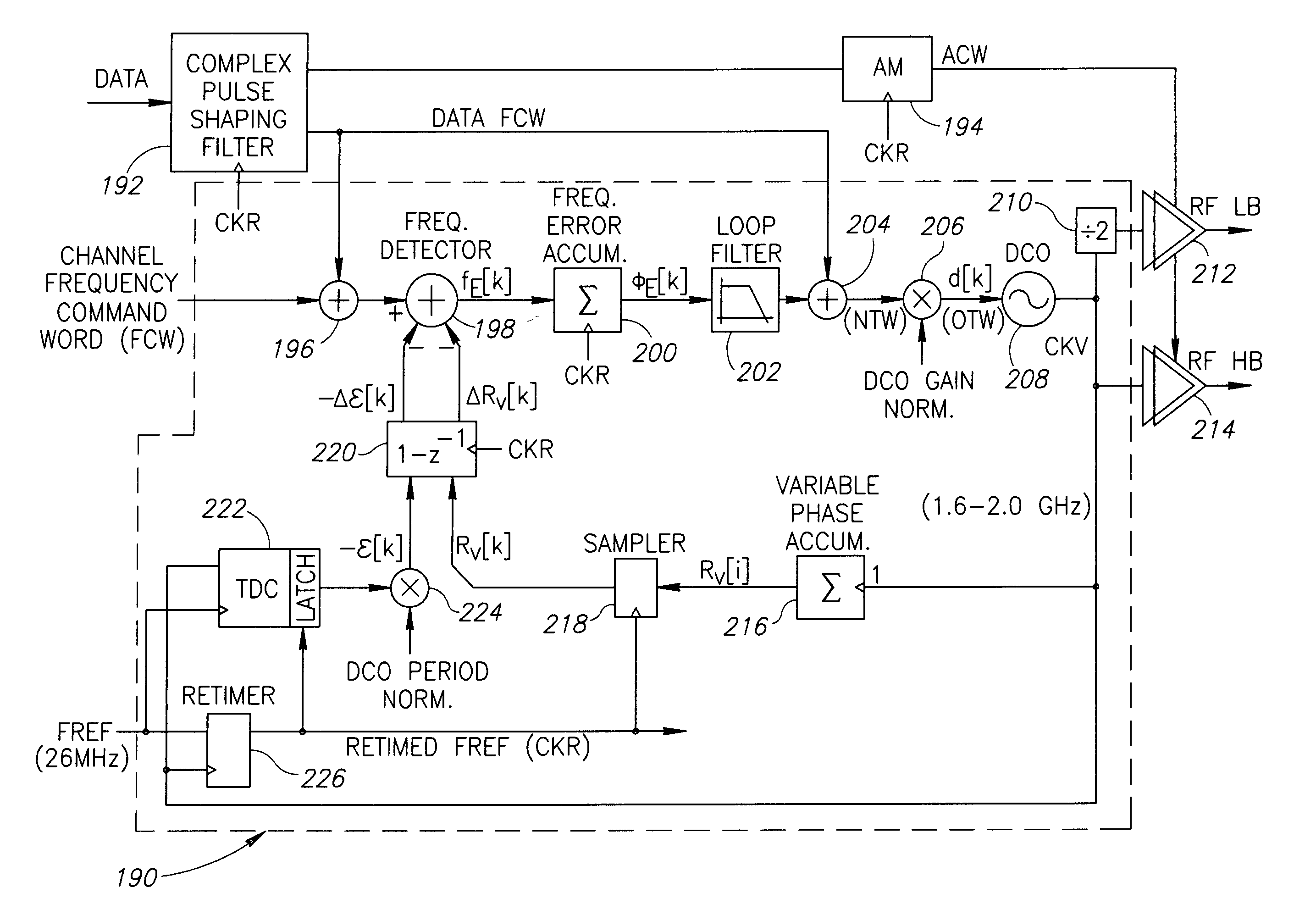
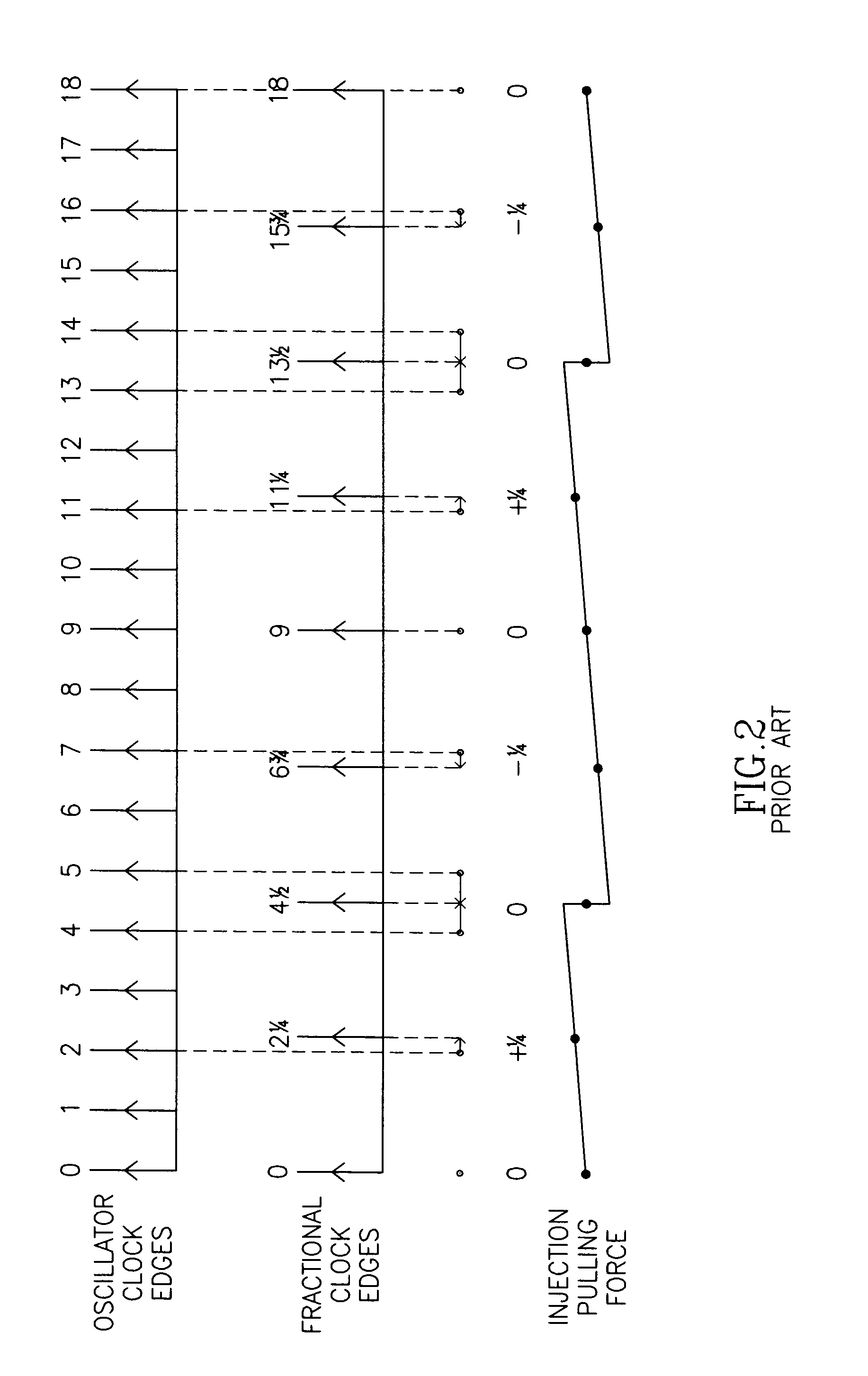
A novel apparatus for and a method of noise and spurious tones suppression in a digital RF processor (DRP). The invention is well suited for use in highly integrated system on a chip (SoC) radio solutions that incorporate a very large amount of digital logic circuitry. The noise suppression scheme eliminates the noise caused by various on chip interference sources transmitted through electromagnetic, power, ground and substrate paths. The noise suppression scheme permits an all digital PLL (ADPLL) to operate in such a way to avoid generating the spurs that would normally be generated from the injection pulling effect of interfering sources on the chip. The frequency reference clock is retimed to be synchronous to the RF oscillator clock and used to drive the entire digital logic circuitry of the DRP. This ensures that the different clock edges throughout the system will not exhibit mutual drift. A method of improving the resolution quality of a time to digital converter within the ADPLL is also taught. The method dithers the reference clock by passing it through a delay circuit that is controlled by a sigma-delta modulator. The dithered reference clock reduces the affect on the phase noise at the output of the ADPLL due to ill-behaved quantization of the TDC timing estimation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
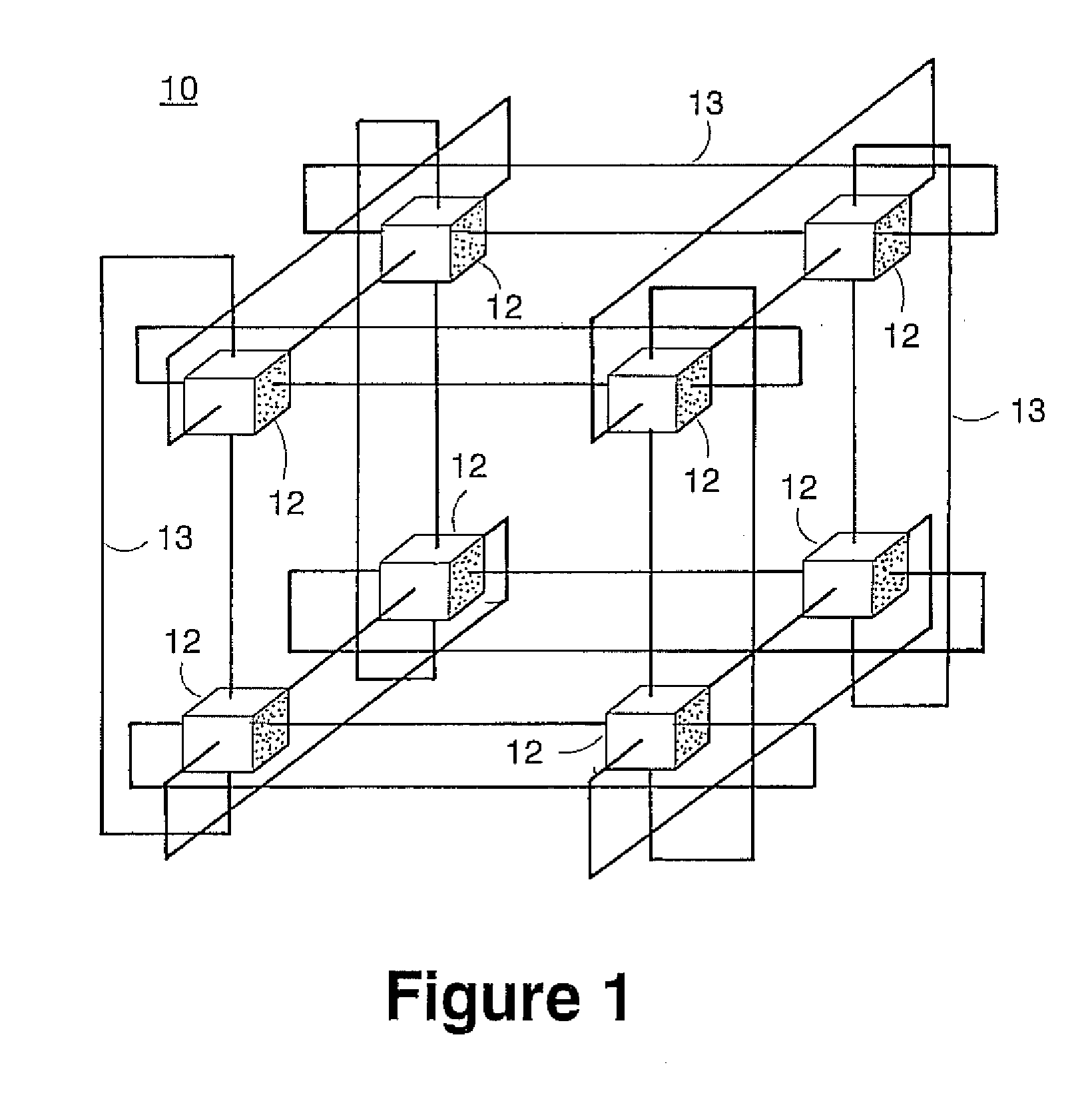
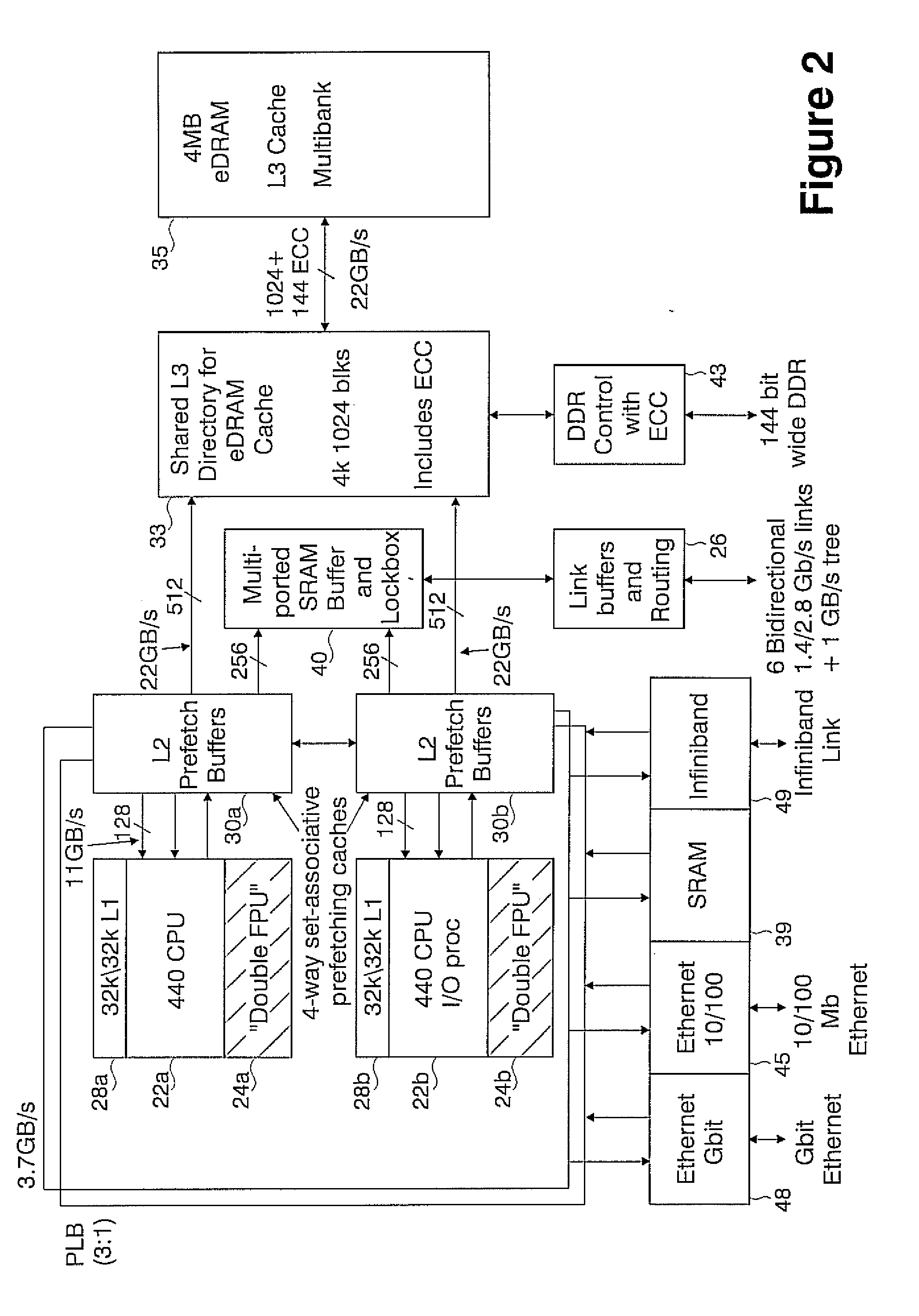
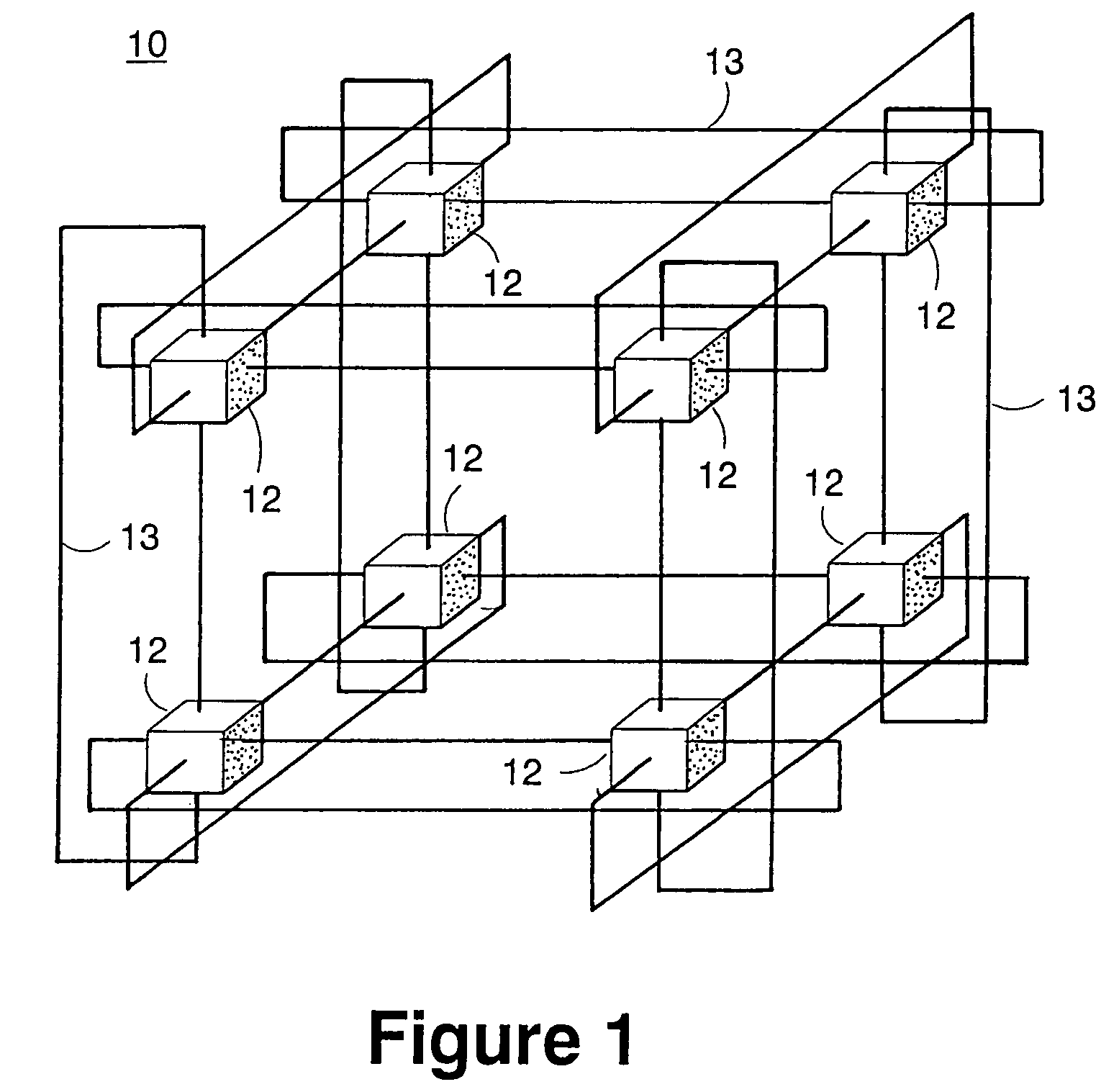
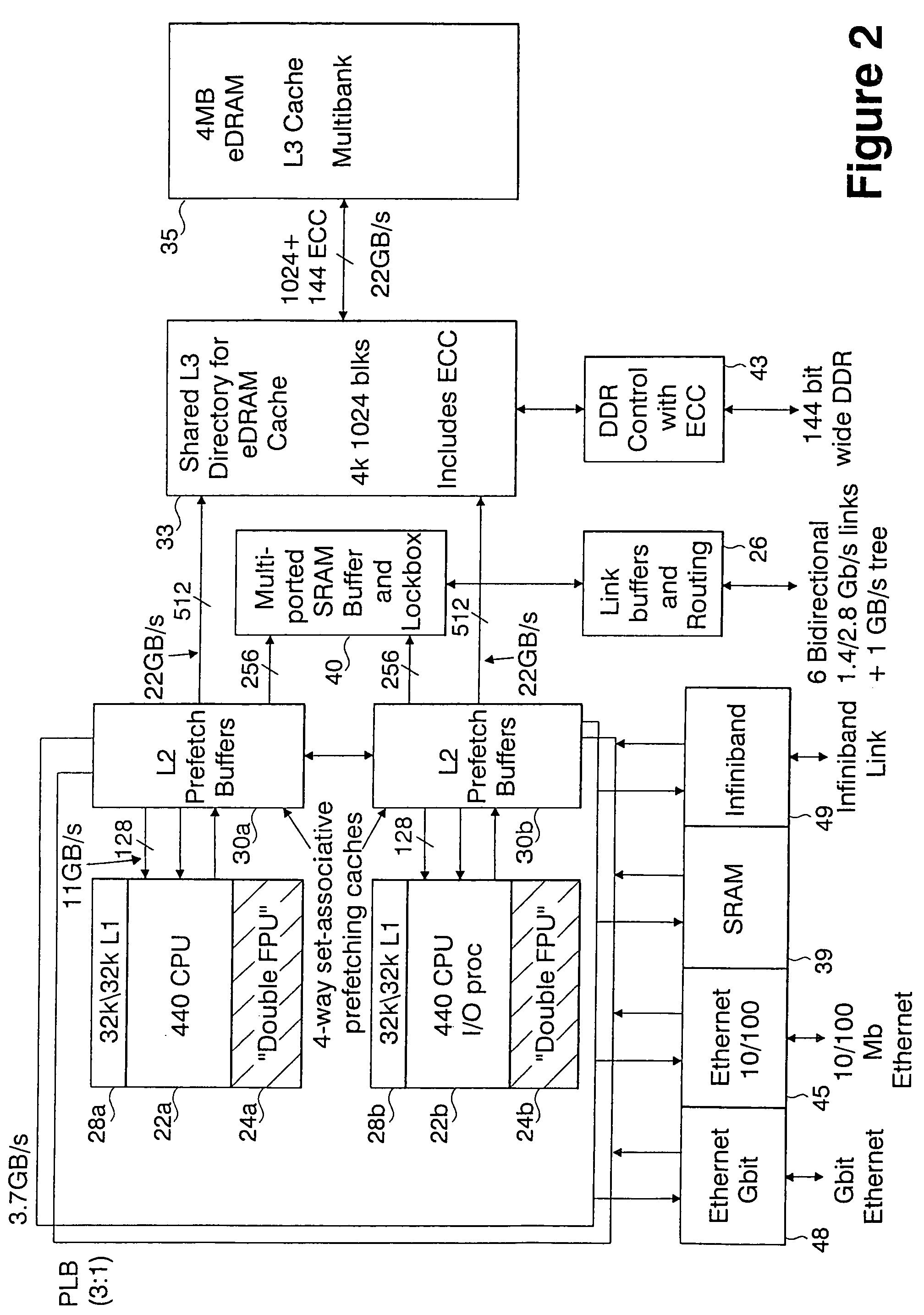
Massively parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS7555566B2Massive level of scalabilityUnprecedented level of scalabilityError preventionProgram synchronisationPacket communicationSupercomputer
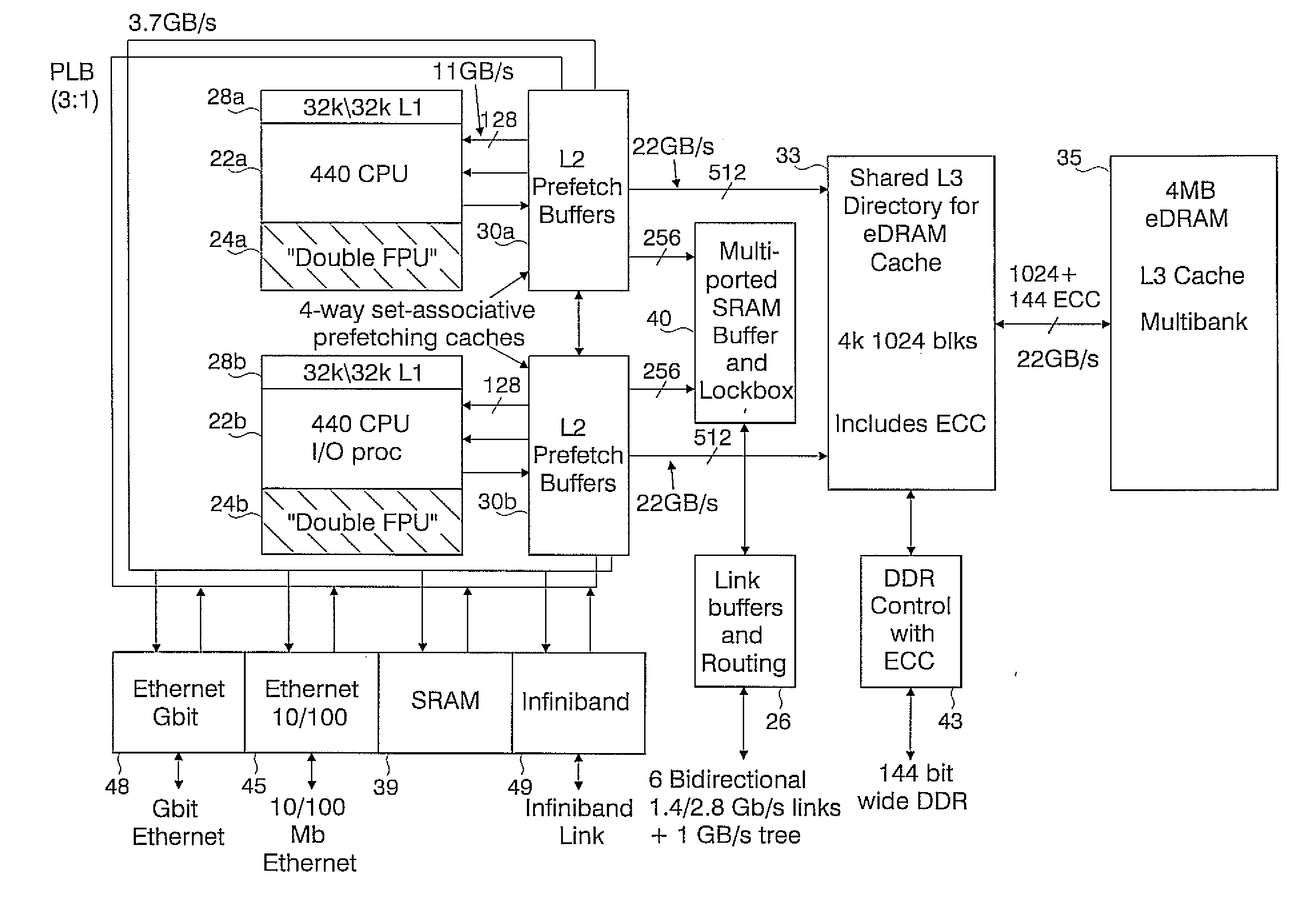
A novel massively parallel supercomputer of hundreds of teraOPS-scale includes node architectures based upon System-On-a-Chip technology, i.e., each processing node comprises a single Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC). Within each ASIC node is a plurality of processing elements each of which consists of a central processing unit (CPU) and plurality of floating point processors to enable optimal balance of computational performance, packaging density, low cost, and power and cooling requirements. The plurality of processors within a single node may be used individually or simultaneously to work on any combination of computation or communication as required by the particular algorithm being solved or executed at any point in time. The system-on-a-chip ASIC nodes are interconnected by multiple independent networks that optimally maximizes packet communications throughput and minimizes latency. In the preferred embodiment, the multiple networks include three high-speed networks for parallel algorithm message passing including a Torus, Global Tree, and a Global Asynchronous network that provides global barrier and notification functions. These multiple independent networks may be collaboratively or independently utilized according to the needs or phases of an algorithm for optimizing algorithm processing performance. For particular classes of parallel algorithms, or parts of parallel calculations, this architecture exhibits exceptional computational performance, and may be enabled to perform calculations for new classes of parallel algorithms. Additional networks are provided for external connectivity and used for Input / Output, System Management and Configuration, and Debug and Monitoring functions. Special node packaging techniques implementing midplane and other hardware devices facilitates partitioning of the supercomputer in multiple networks for optimizing supercomputing resources.
Owner:IBM CORP
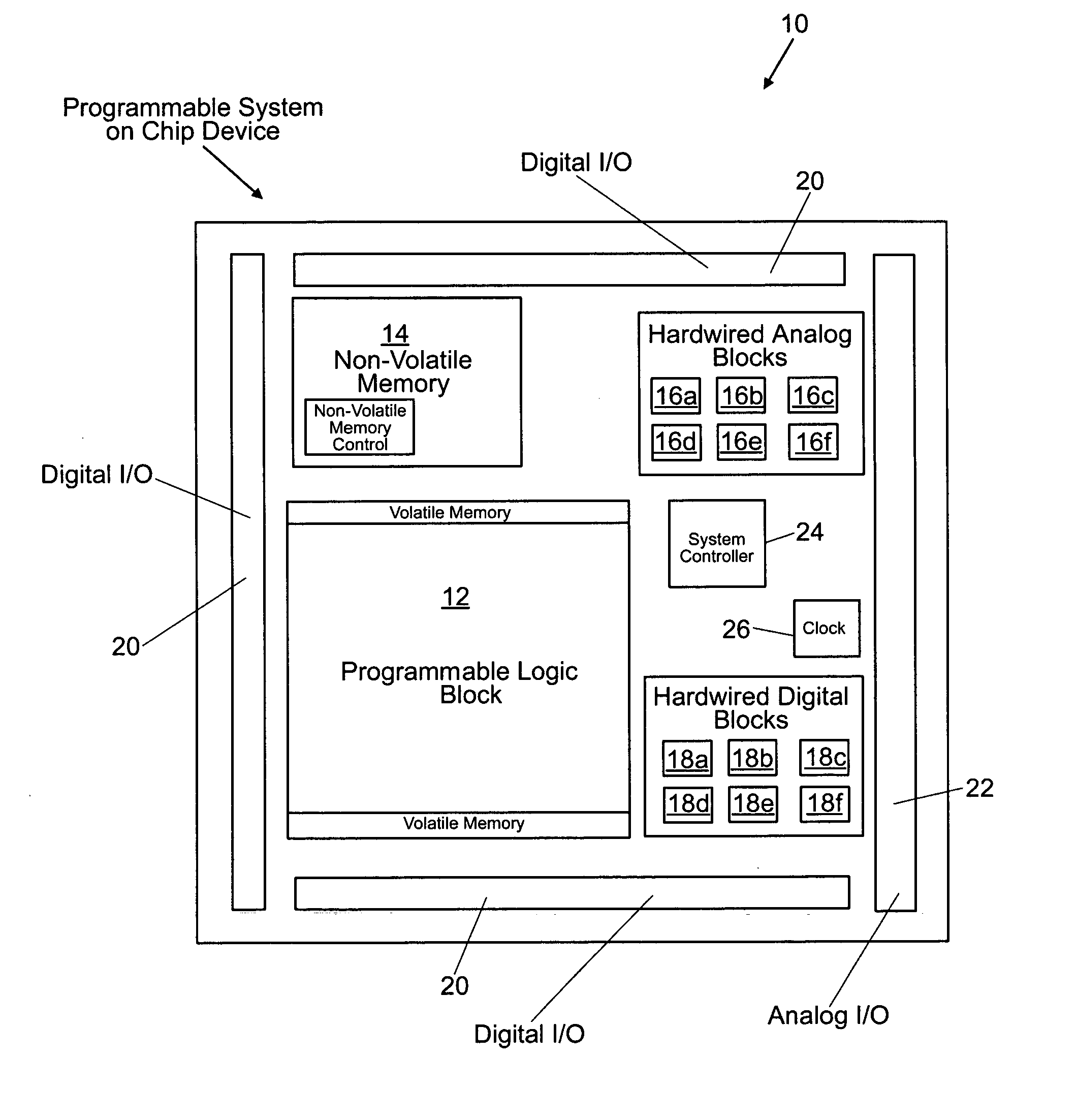
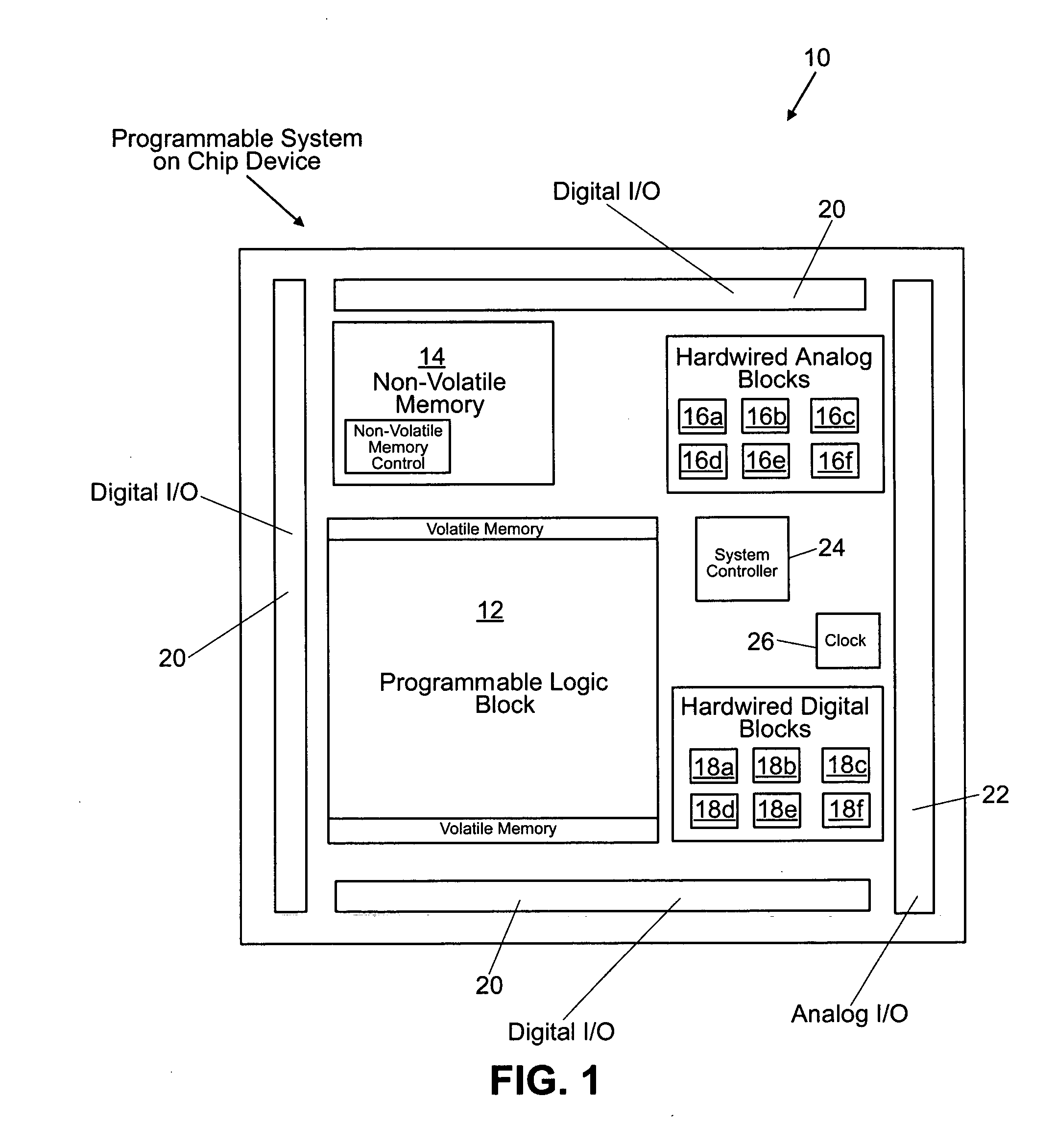
Programmable system on a chip
ActiveUS20050237083A1Thermometers using electric/magnetic elementsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A programmable system-on-a-chip integrated circuit device comprises a programmable logic block, a non-volatile memory block, an analog sub-system, an analog input / output circuit block, and a digital input / output circuit block. A programmable interconnect architecture includes programmable elements and interconnect conductors. Ones of the programmable elements are coupled to the programmable logic block, the non-volatile memory block, the analog sub-system, the analog input / output circuit block, the digital input / output circuit block, and to the interconnect conductors, such that inputs and outputs of the programmable logic block, the non-volatile memory block, the analog sub-system, the analog input / output circuit block, and the digital input / output circuit block can be programmably coupled to one another.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
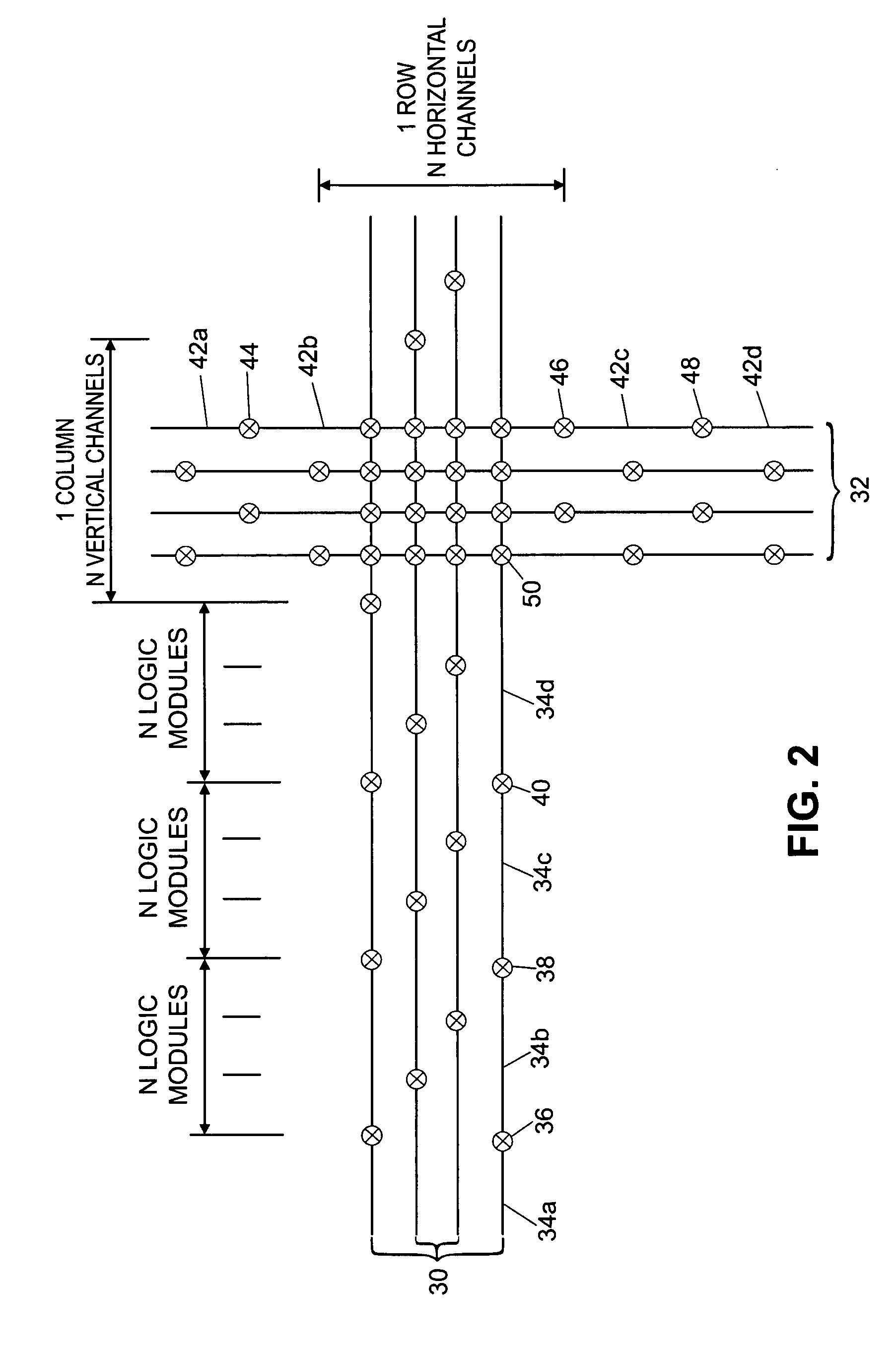
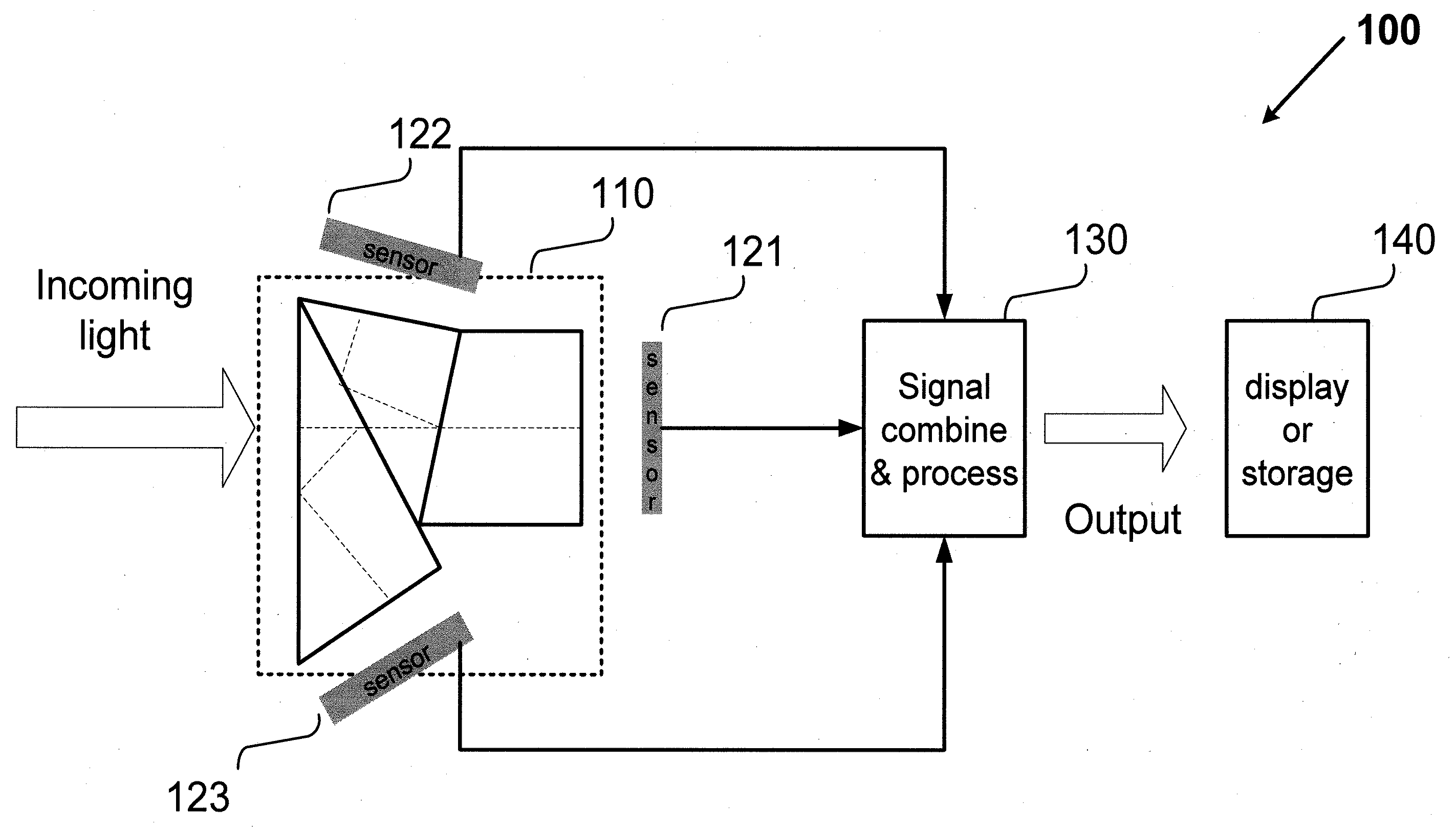
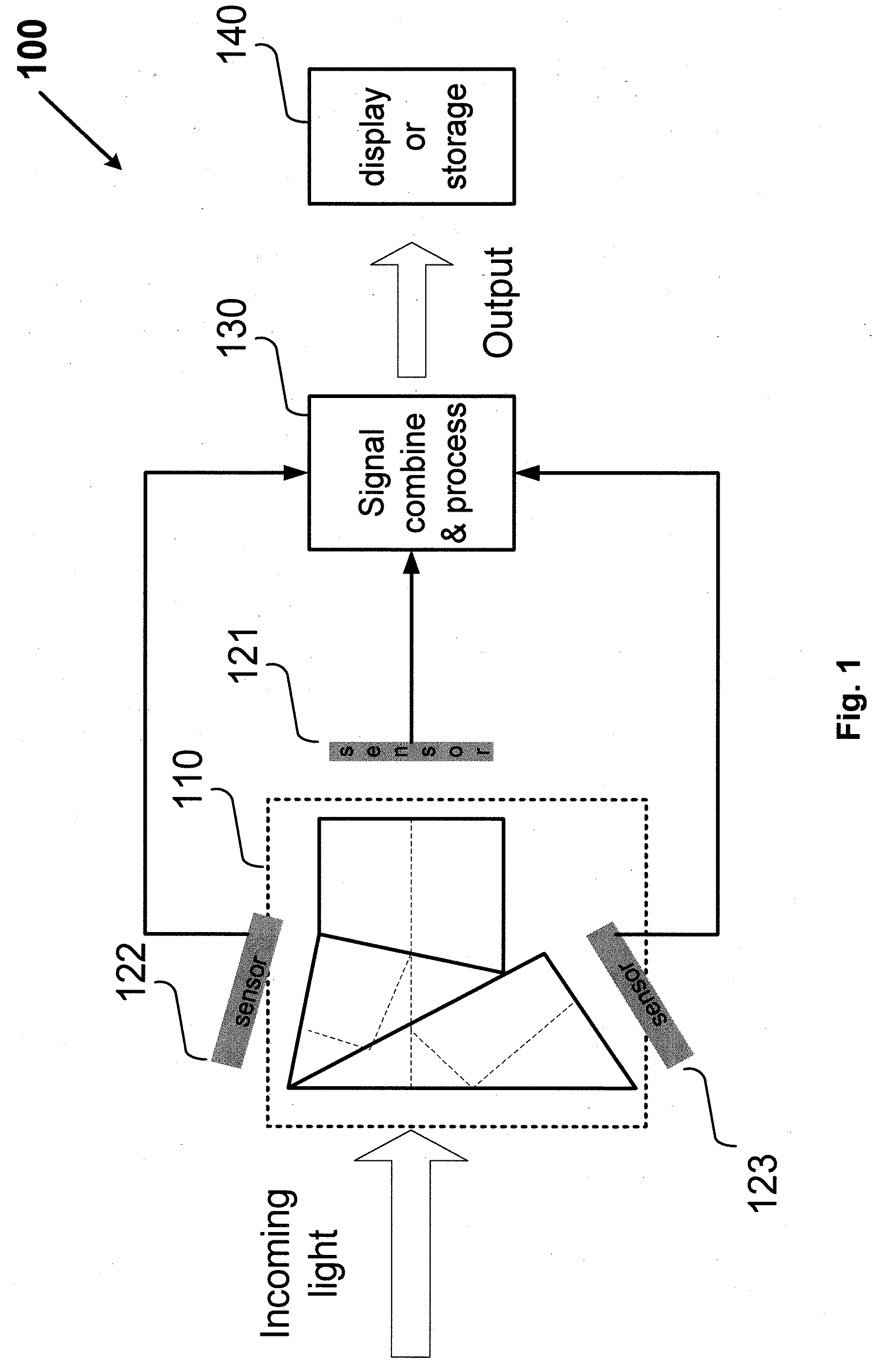
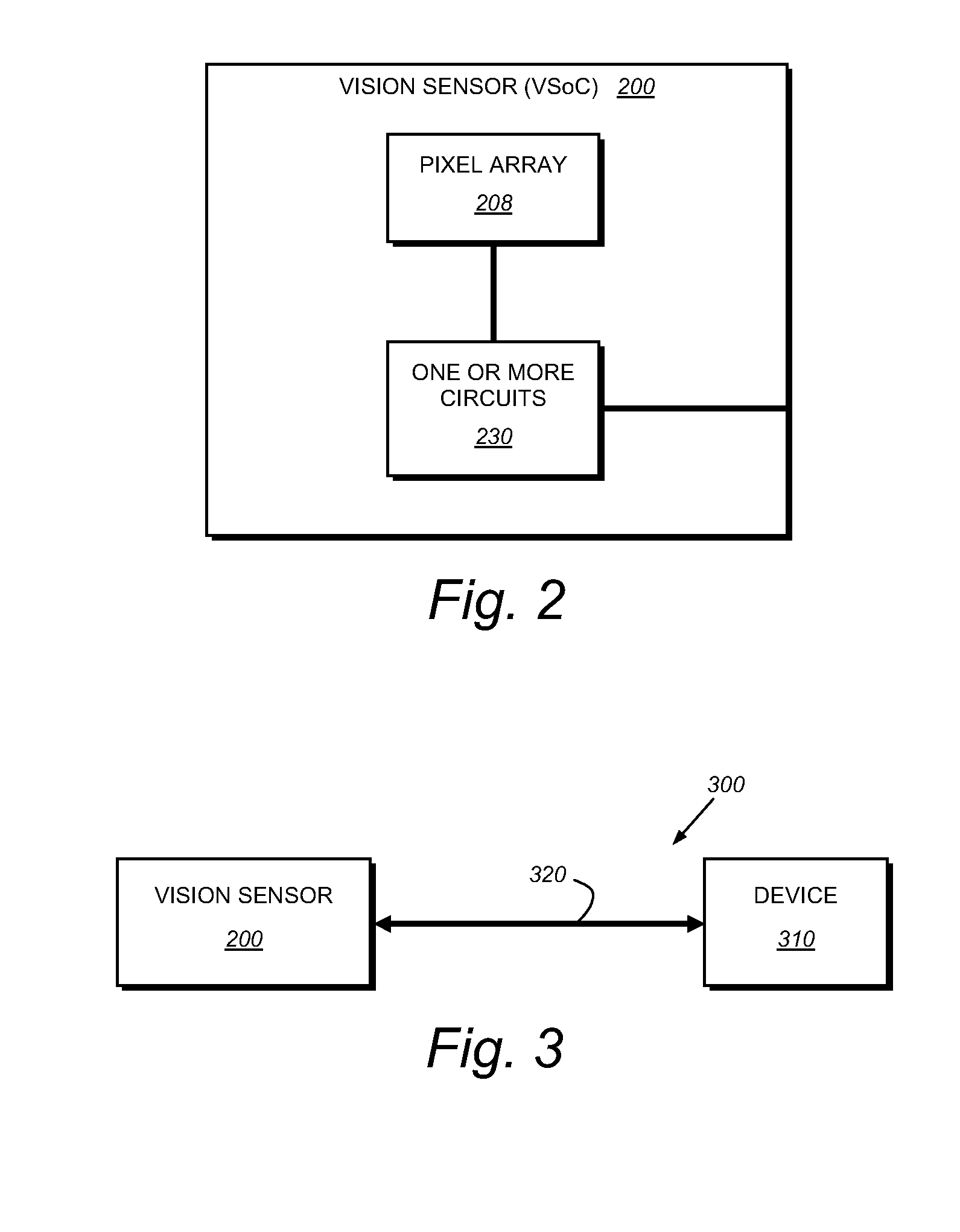
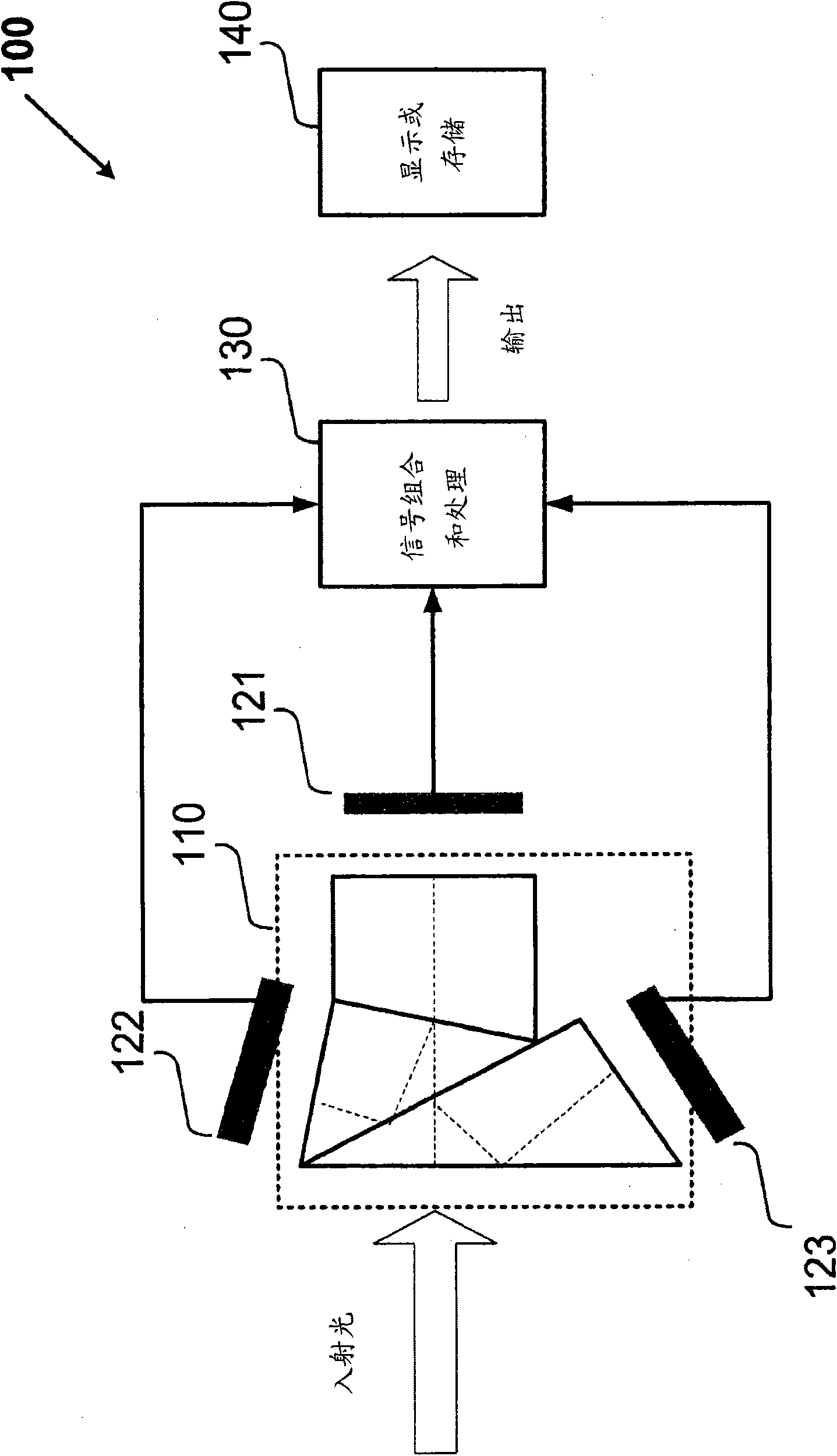
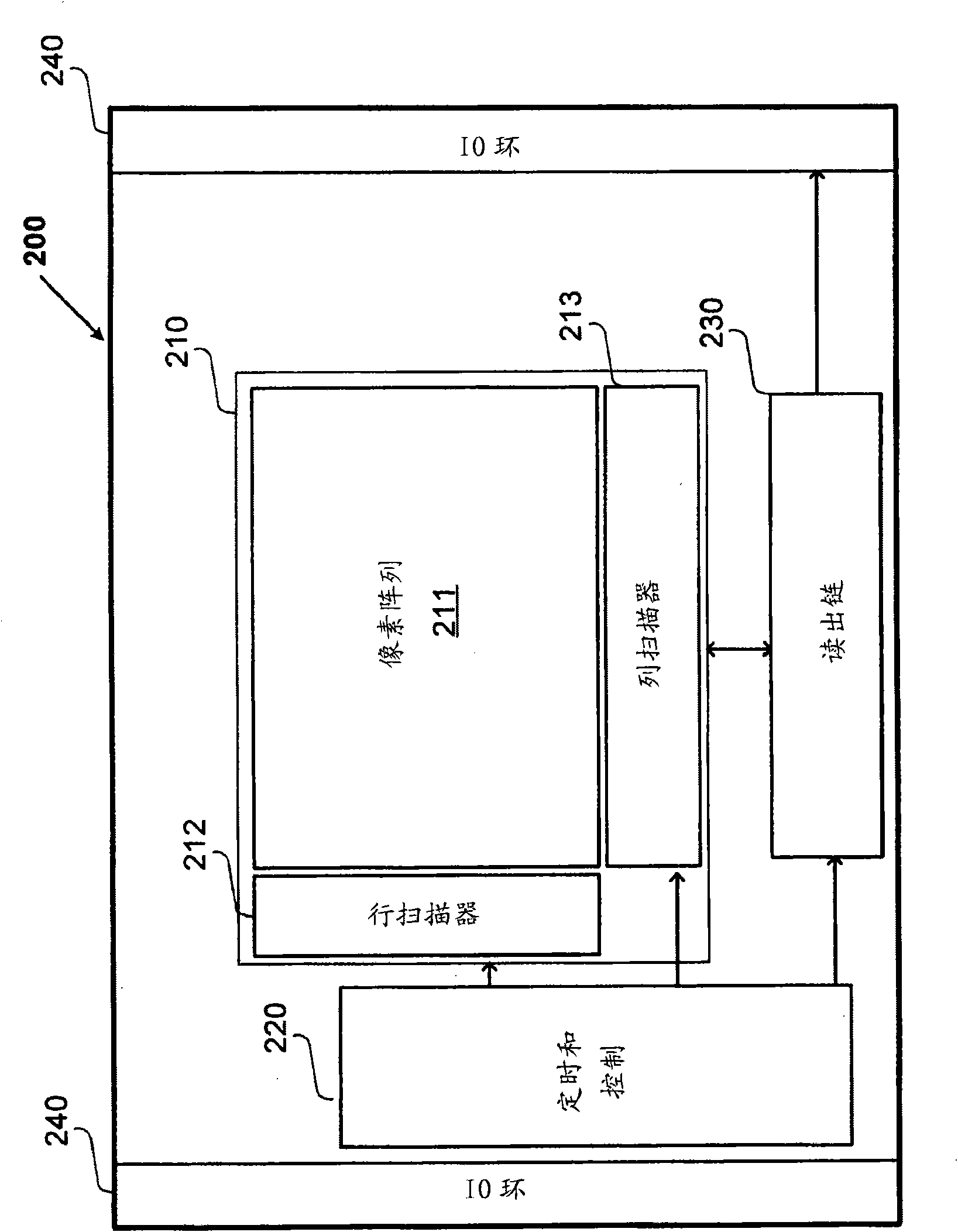
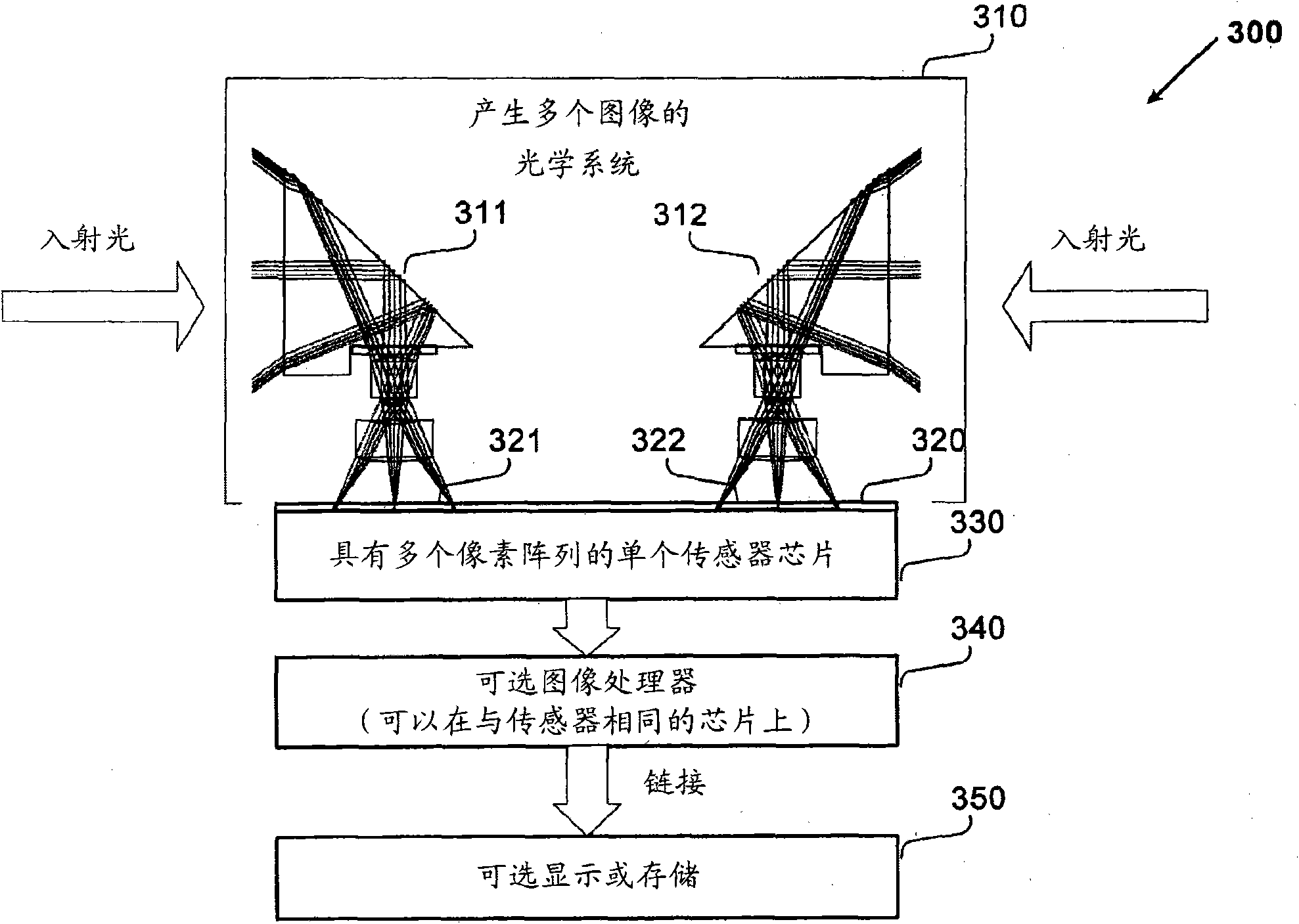
Camera system with multiple pixel arrays on a chip
ActiveUS20090135245A1Compact designEasy to makeTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelecommunications linkDigital storage
A camera system uses one or more image sensor IC chips each having multiple pixel arrays on the same semiconductor substrate (i.e., “multiple pixel arrays on a chip”). In one embodiment, such a camera system includes: (a) optical components that create multiple images in close physical proximity of each other (e.g., within a few millimeters or centimeters); and (b) a single sensor substrate (“chip”) containing multiple 2-dimensional pixel arrays that are aligned to capture these multiple images, so as to convert the multiple images into electrical signal. The pixel arrays can be manufactured using a CCD or a CMOS compatible process. For manufacturing reasons, such a chip is typically two centimeters or less on a side. However, large chips can also be made. Optional electronic components for further signal processing of the captured images may be formed either on the sensor chip (i.e., in a “system-on-a-chip” implementation), or in a separate back-end application specific integrated circuit (ASIC). In addition, digital storage components, display elements, and wired or wireless communication links may also be included in any suitable combination to allow review and further processing of the captured images.
Owner:CAPSO VISION INC
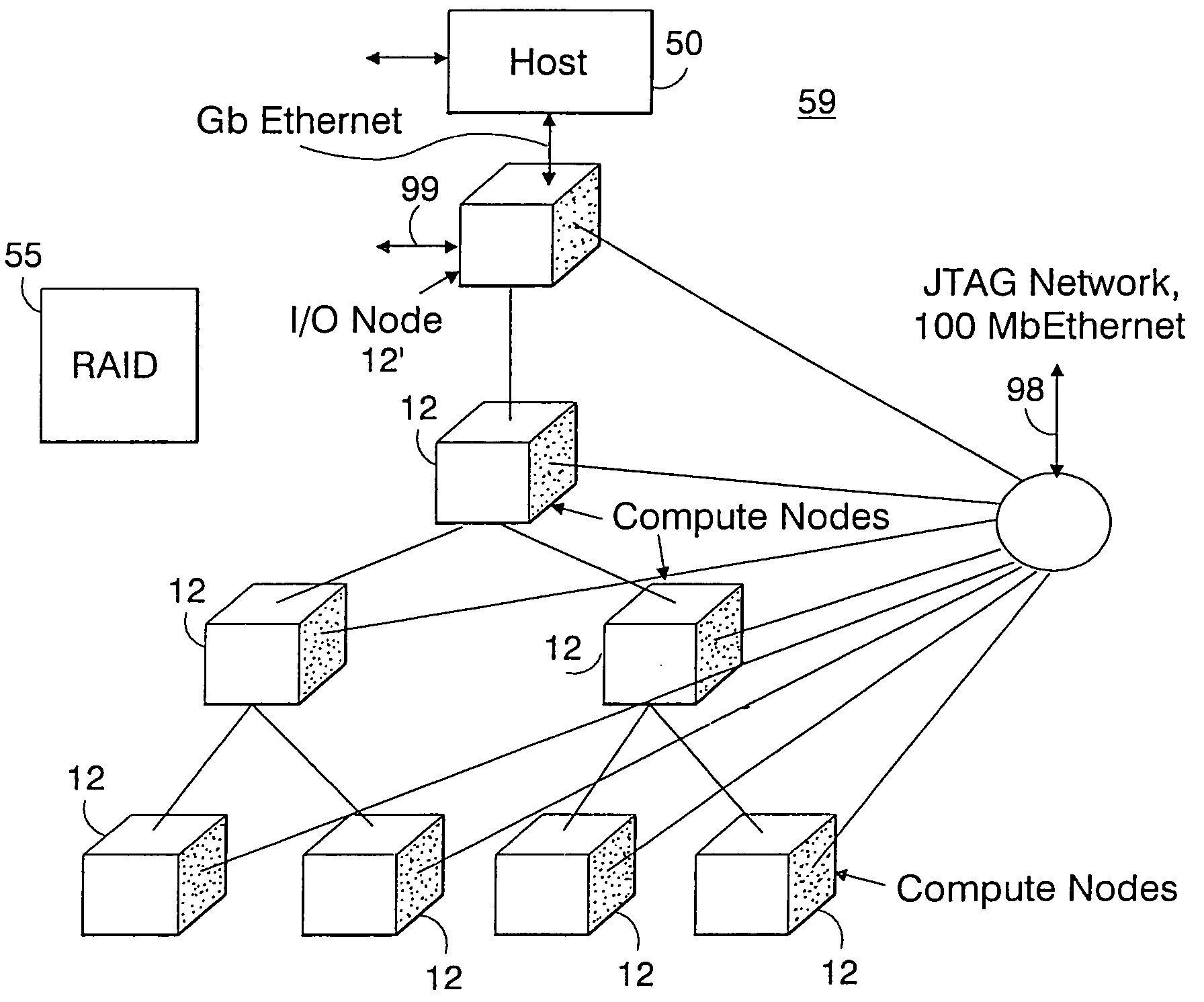
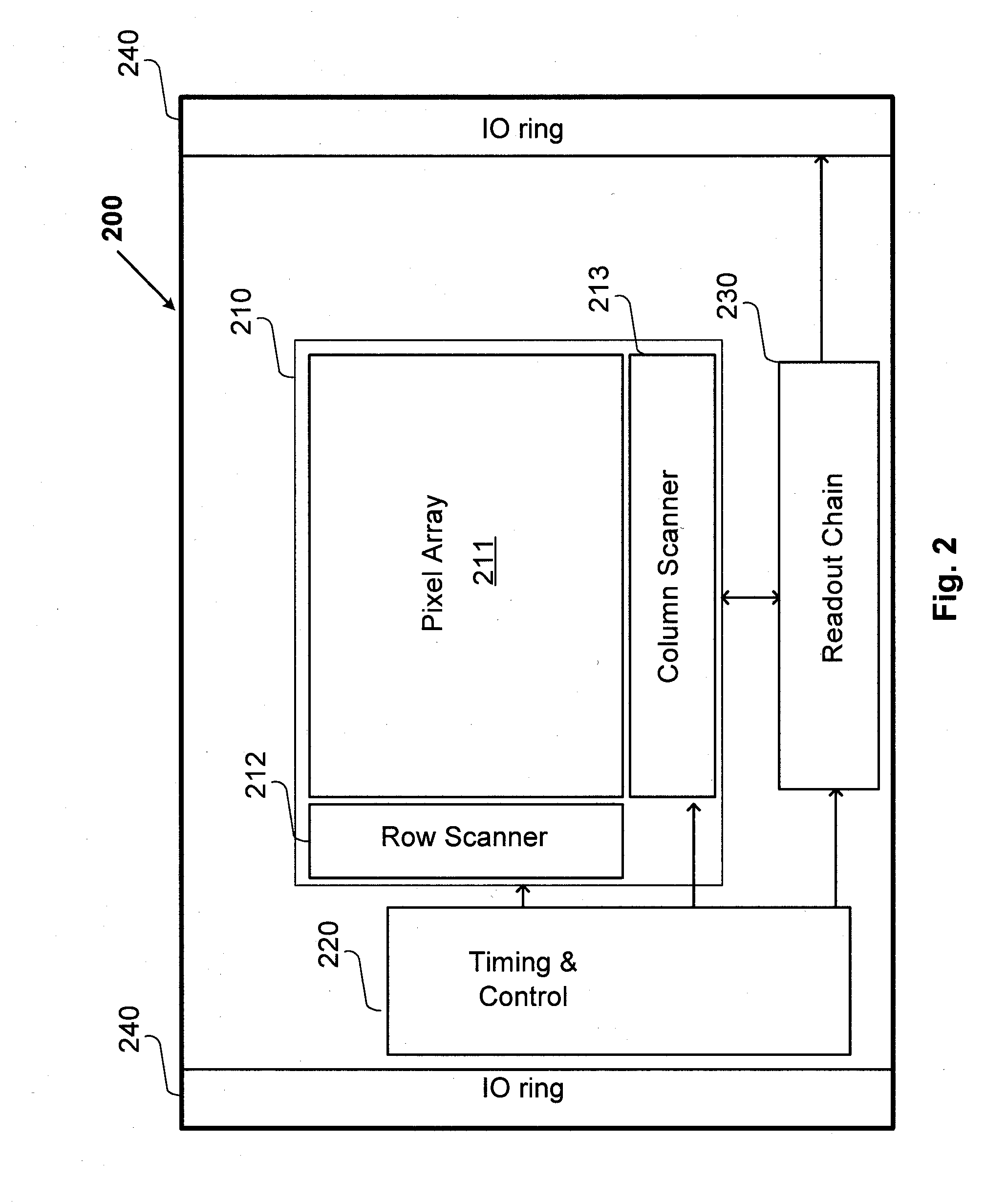
Computer system and method to dynamically generate system on a chip description files and verification information
InactiveUS7100133B1Facilitates efficient and effective creation and modification and verificationConvenience to mergeCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureTest platform
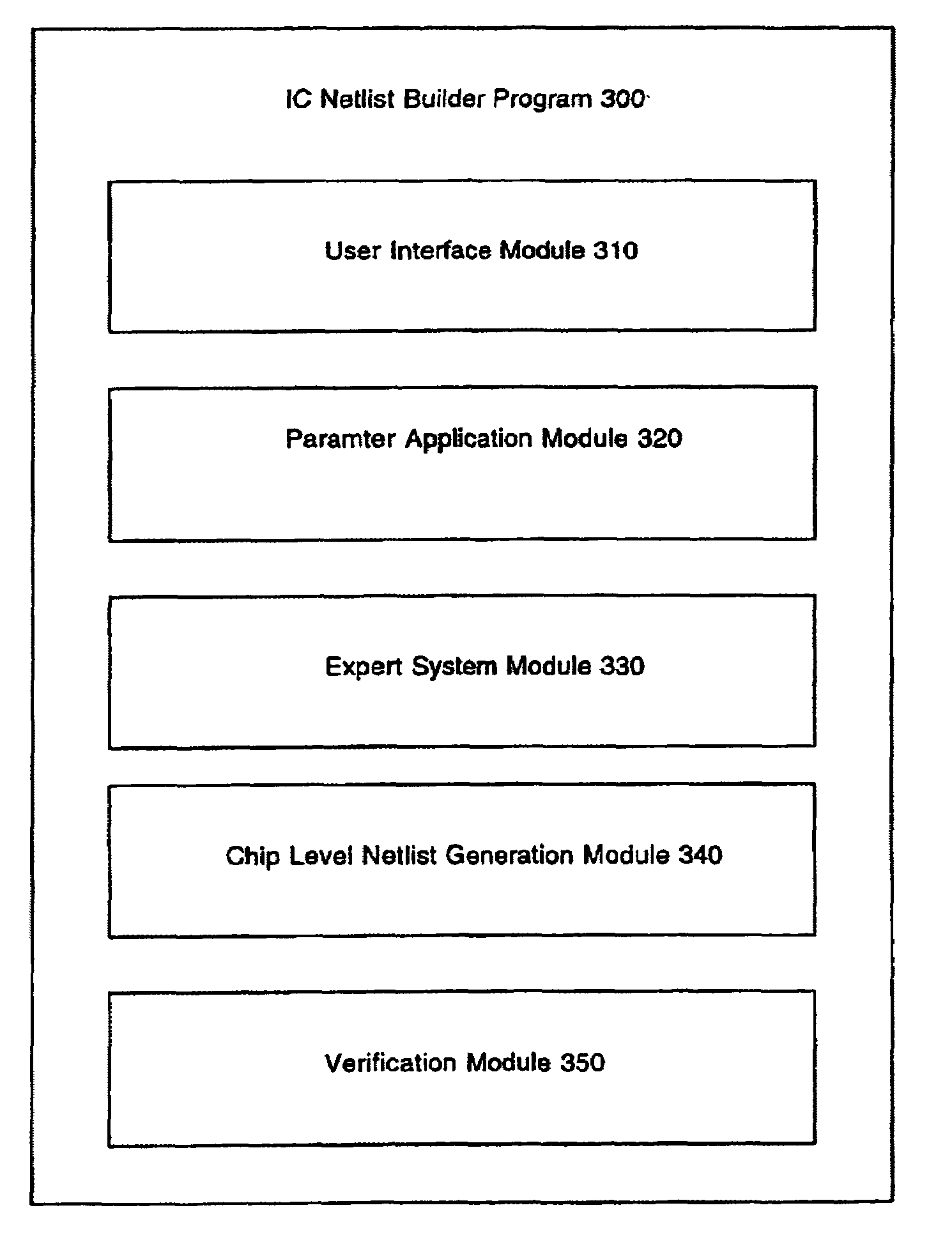
The present invention facilitates automation of system on a chip (SoC) design, manufacture and verification in a convenient and efficient manner. In one embodiment, a SoC netlist builder and verification computer system of the present invention includes a user interface module, a parameter application module, an expert system module and a chip level netlist generation module. The user interface module provides user friendly and convenient interfaces that facilitate easy entry and modification of user selections and parameters. The parameter application module interprets information supplied by the user module and the expert system module and creates directions (e.g., command lines) passed to other modules for execution. The expert system module analyzes information and automatically provides SoC building and verification data including automated addition of default architectural features, automated insertion of default parameters, and automated input of information to the verification module. The chip level netlist generation module automatically generates a chip level netlist, including the instantiation of internal IC devices and connections between the circuit blocks for internal signals. The verification module automatically generates a test bench and a logical verification environment including simulation models (e.g., a chip model and a system level model).
Owner:NXP BV
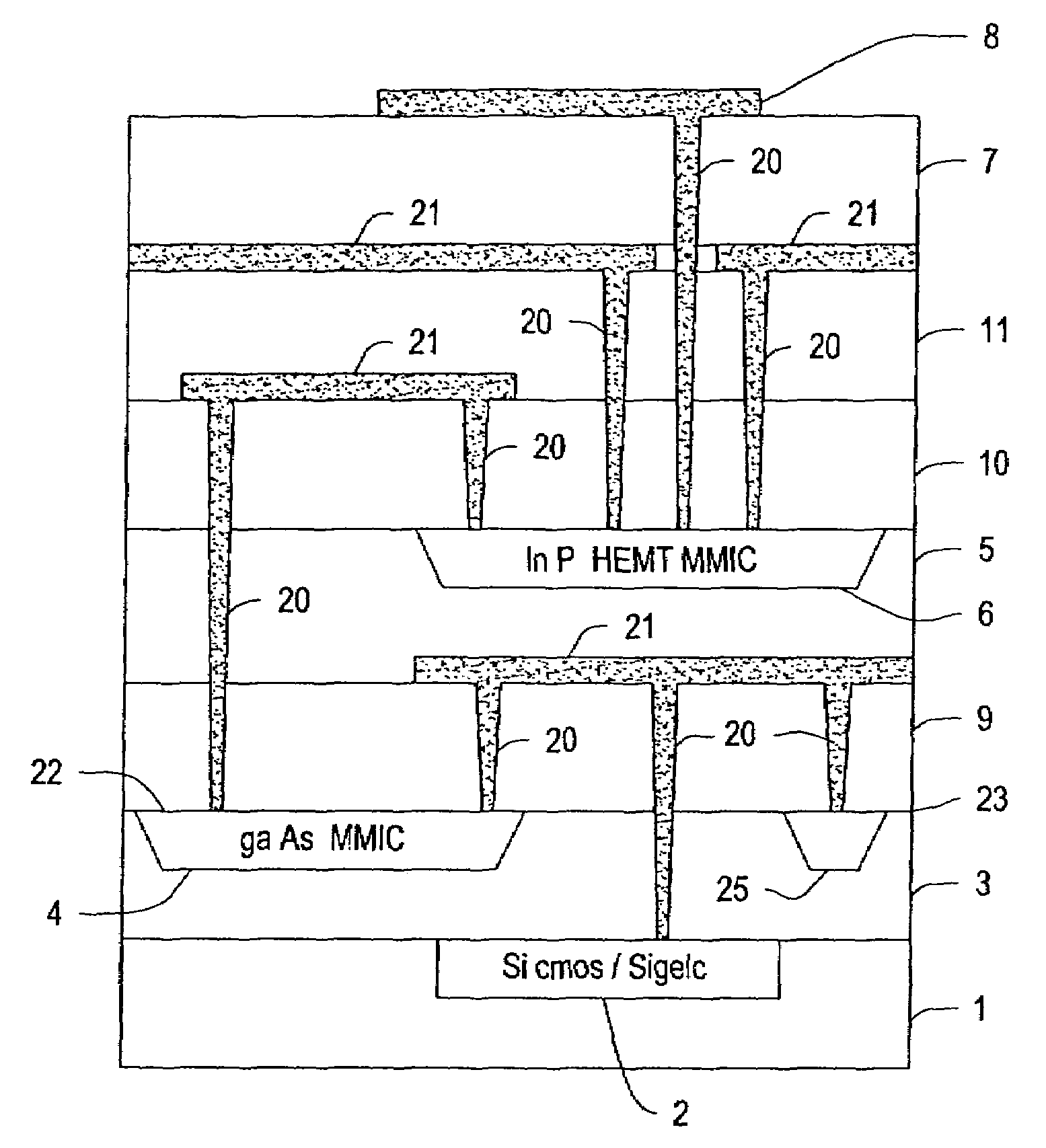
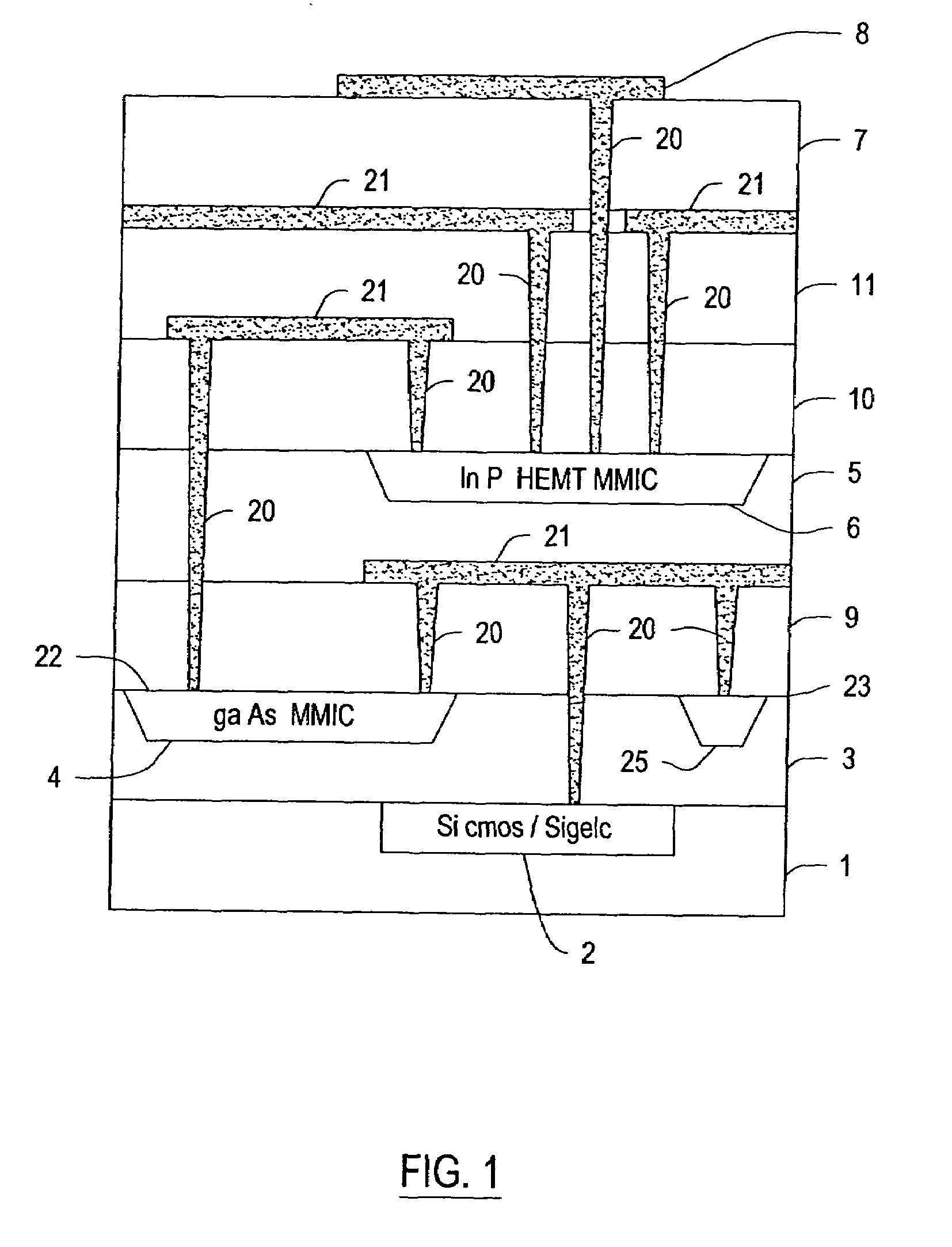
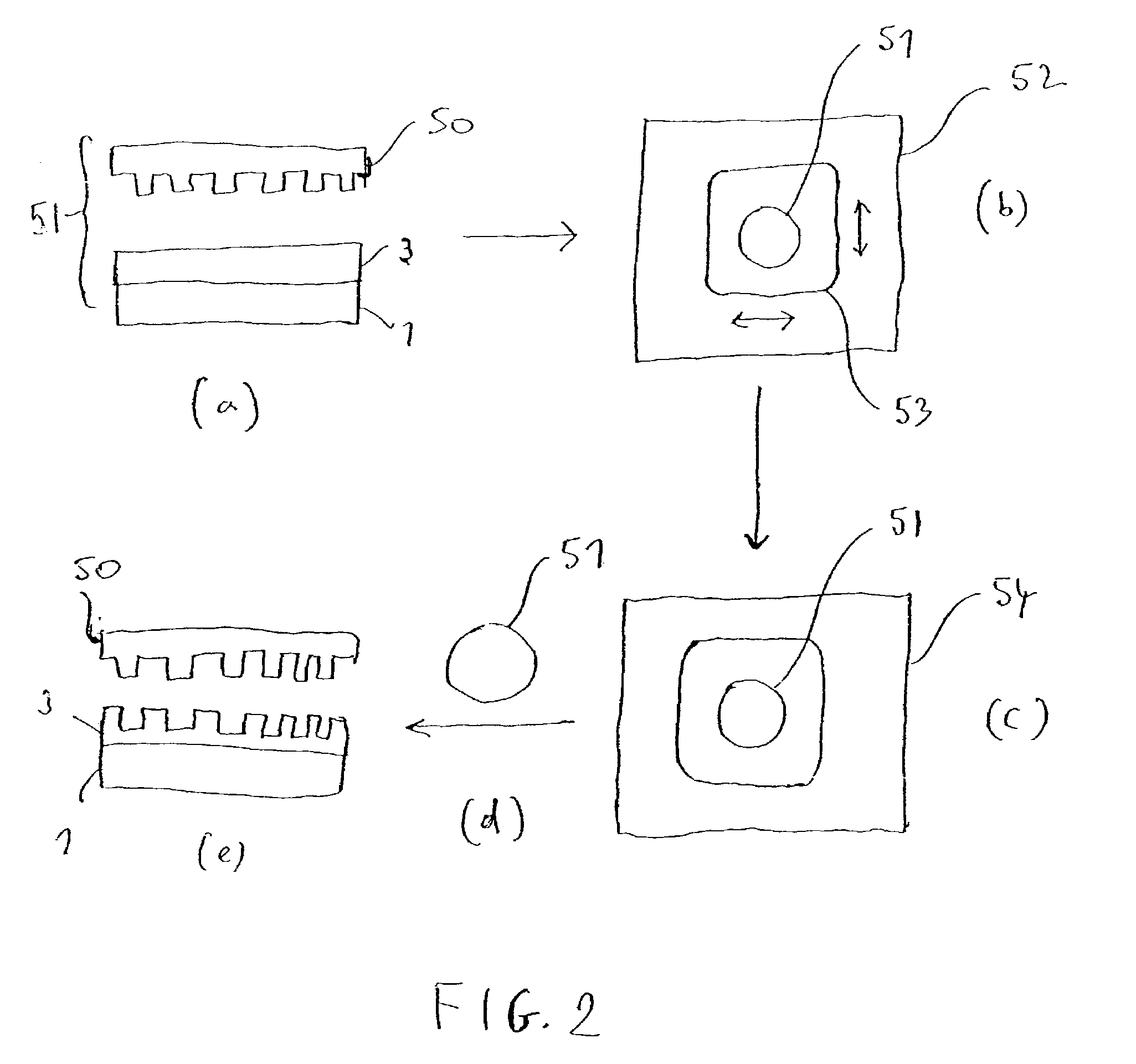
Process for assembling three-dimensional systems on a chip and structure thus obtained
InactiveUS7253091B2Function increaseEasy to manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronic systemsEngineering
A method for assembling an electronic system with a plurality of layers. Recesses in formed in one or more dielectric layers and electronic components are positioned within the recesses. One or more layers containing the components are placed on a host substrate containing host circuits. Electrical interconnects are provided between and among the electronic components in the dielectric layers and the host circuits. The layers containing the components may also be provided by growing the electronic devices on a growth substrate. The growth substrate is then removed after the layer is attached to the host substrate.
Owner:HRL LAB
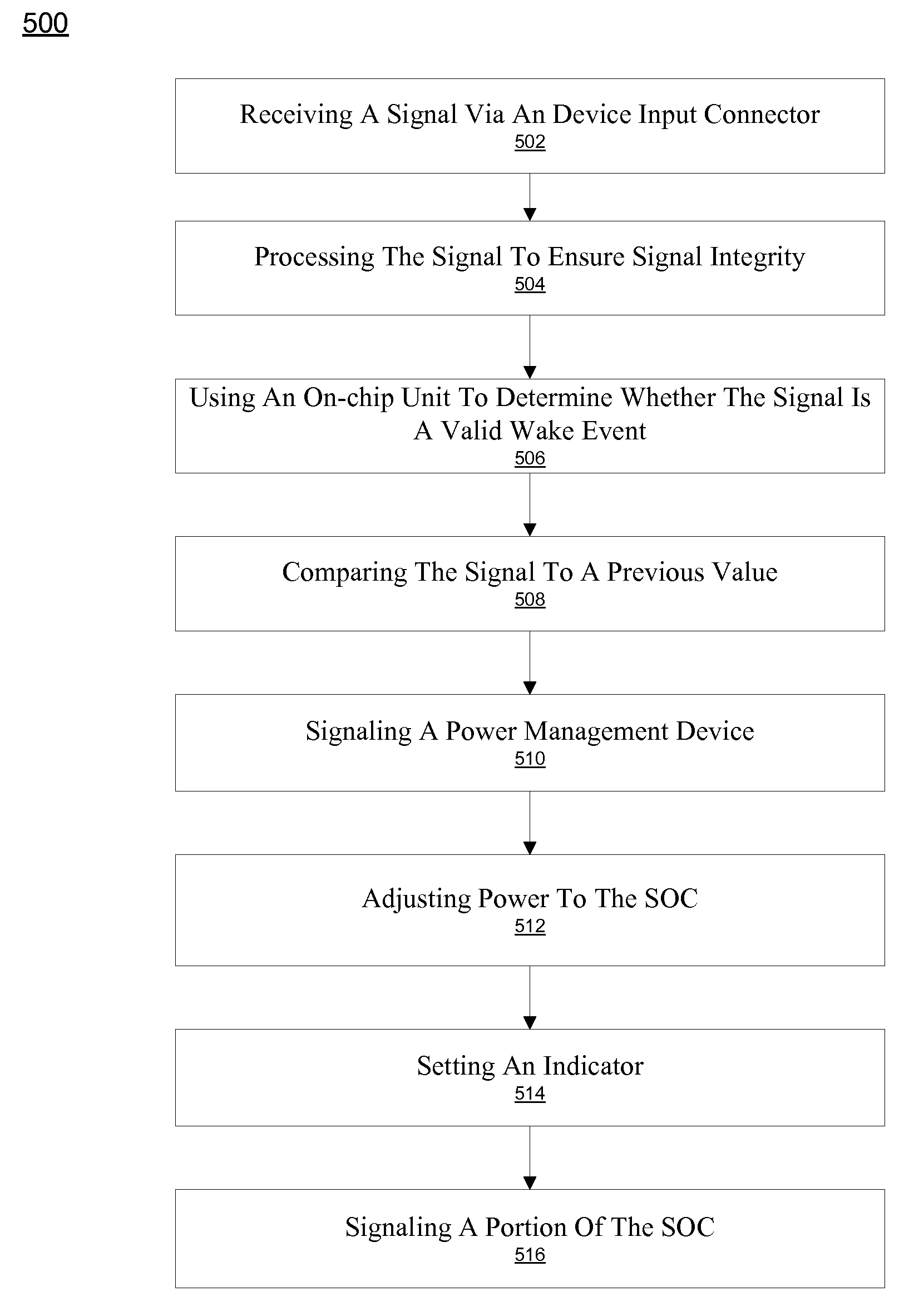
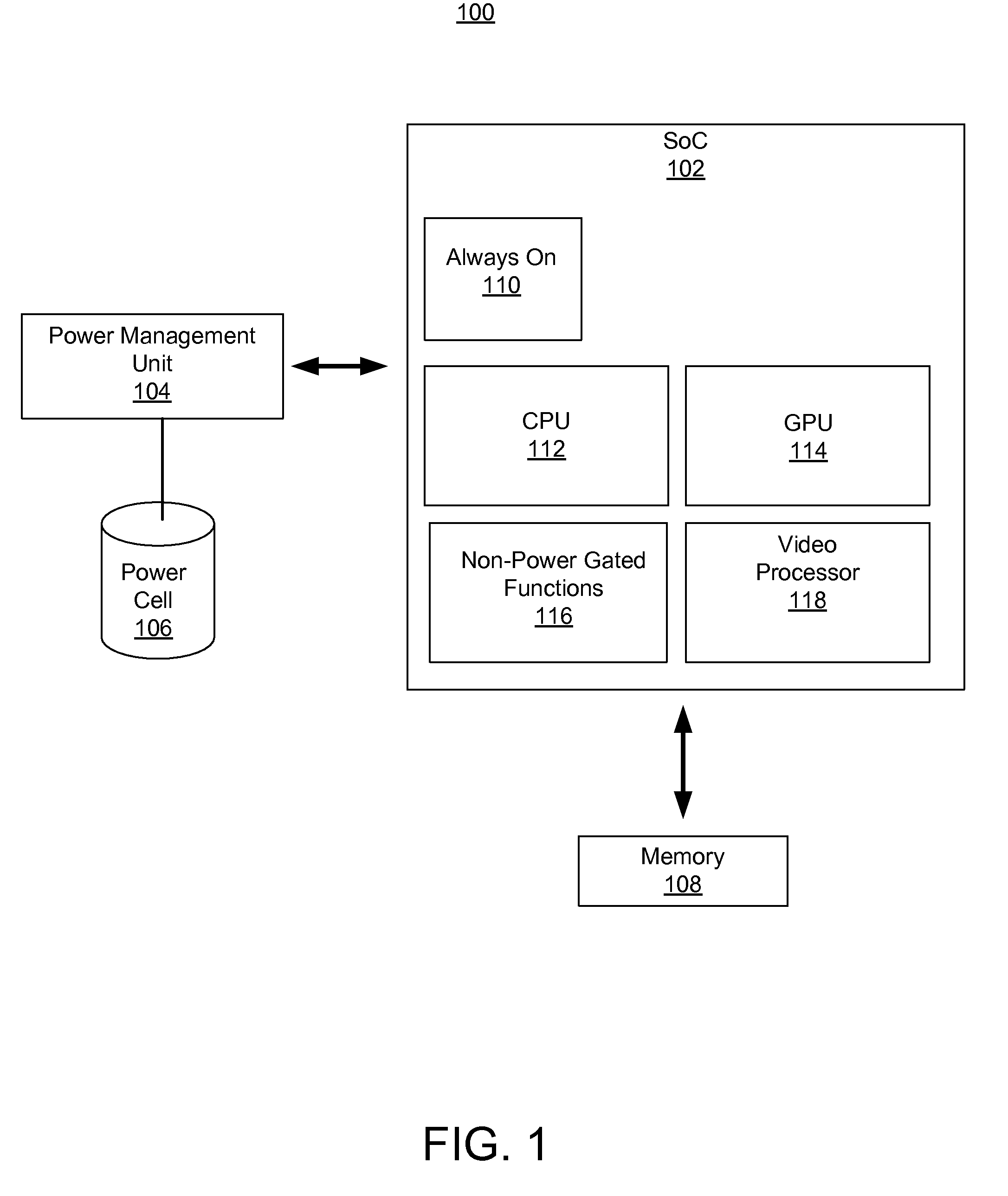
System and method for using inputs as wake signals
InactiveUS20090204834A1Facilitate low power and sleep stateReduce leakagePower supply for data processingEnergy efficient computingControl powerPower Management Unit
A system and method for waking up a portion of a programmable system on a chip (SoC). The system includes a power management unit for controlling power levels to the SoC and one or more inputs for receiving inputs from a coupled device. The system further includes a power management interface coupled to the one or more inputs. The power management interface signals the power management unit to adjust power levels to the SoC in response to receiving a signal via the one or more inputs corresponding to a wake event.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
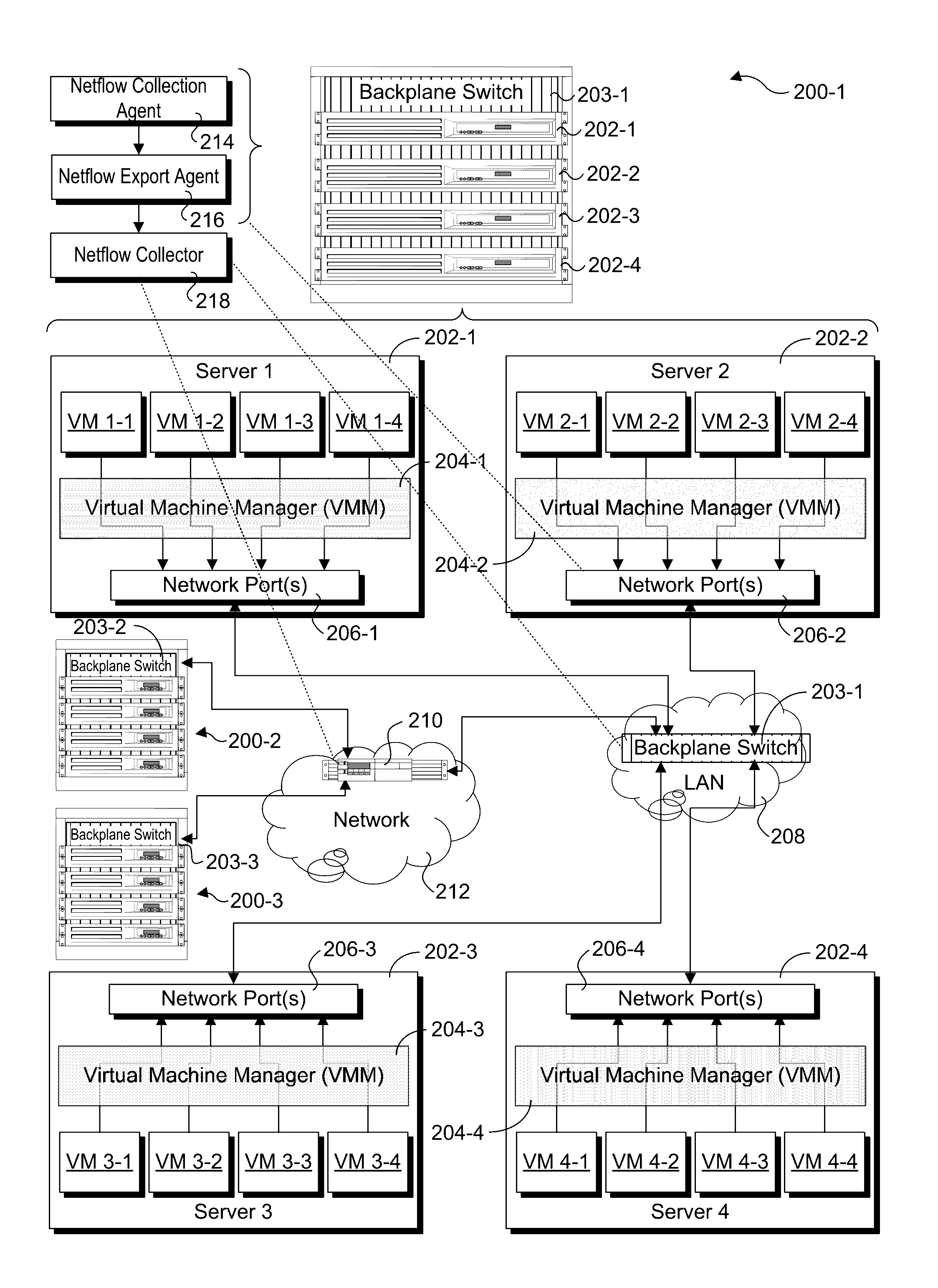
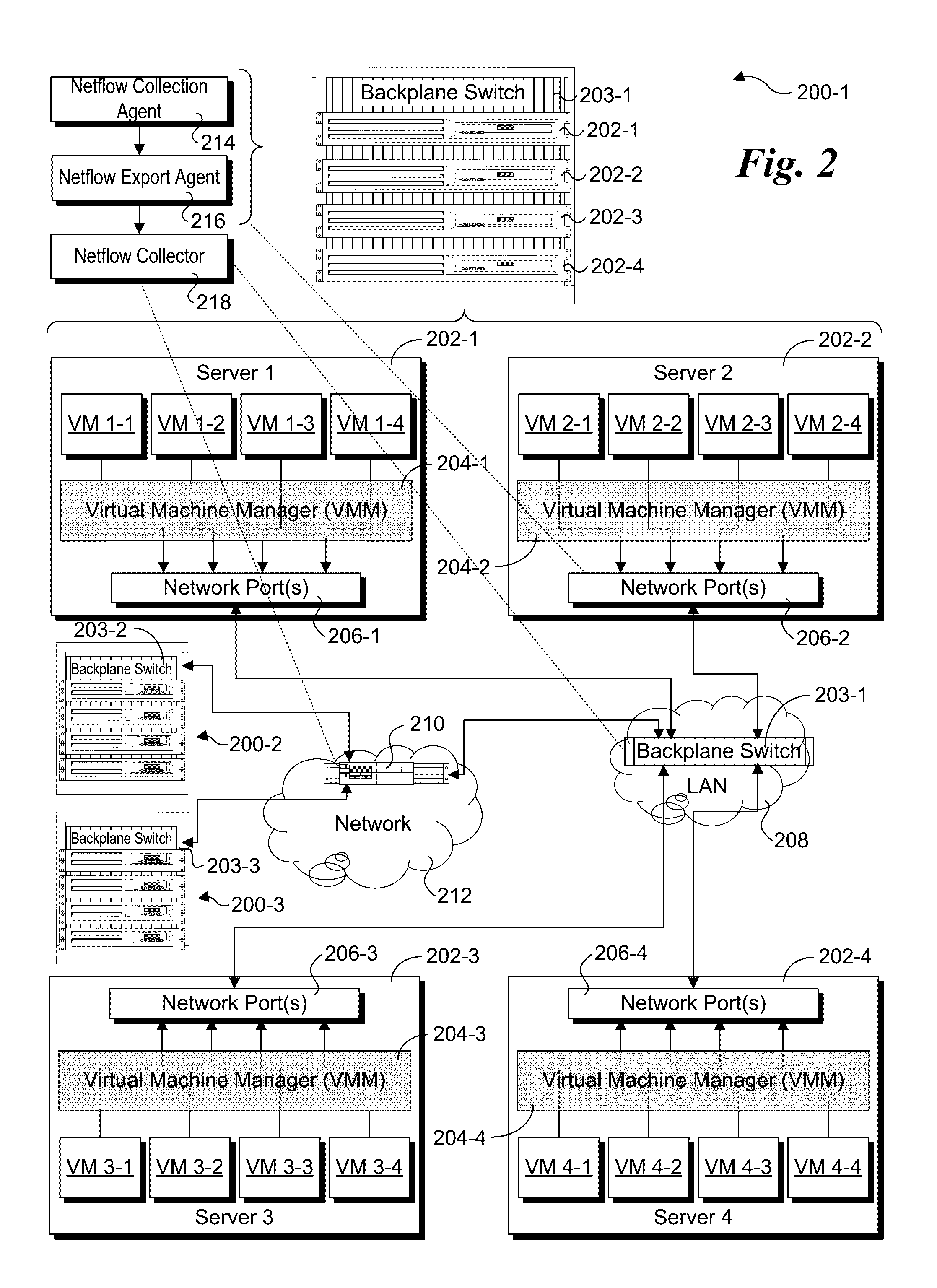
Netflow collection and export offload using network silicon
Methods and apparatus for collection of Netflow data and export offload using network silicon. In accordance with aspects of the embodiments, the Netflow export and collection functions are offloaded to the network silicon in the chipset, System on a Chip (SoC), backplane switch, disaggregated switch, virtual switch (vSwitch) accelerator, and Network Interface Card / Controller (NIC) level. For apparatus implementing virtualized environments, one or both of the collection and export functions are implemented at the Physical Function (PF) and / or Virtual Function (VF) layers of the apparatus.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Intra-body communication (IBC) device and a method of implementing the IBC device
ActiveUS8131334B2Near-field systems using receiversDiagnostic recording/measuringSystem on a chipCommunication device
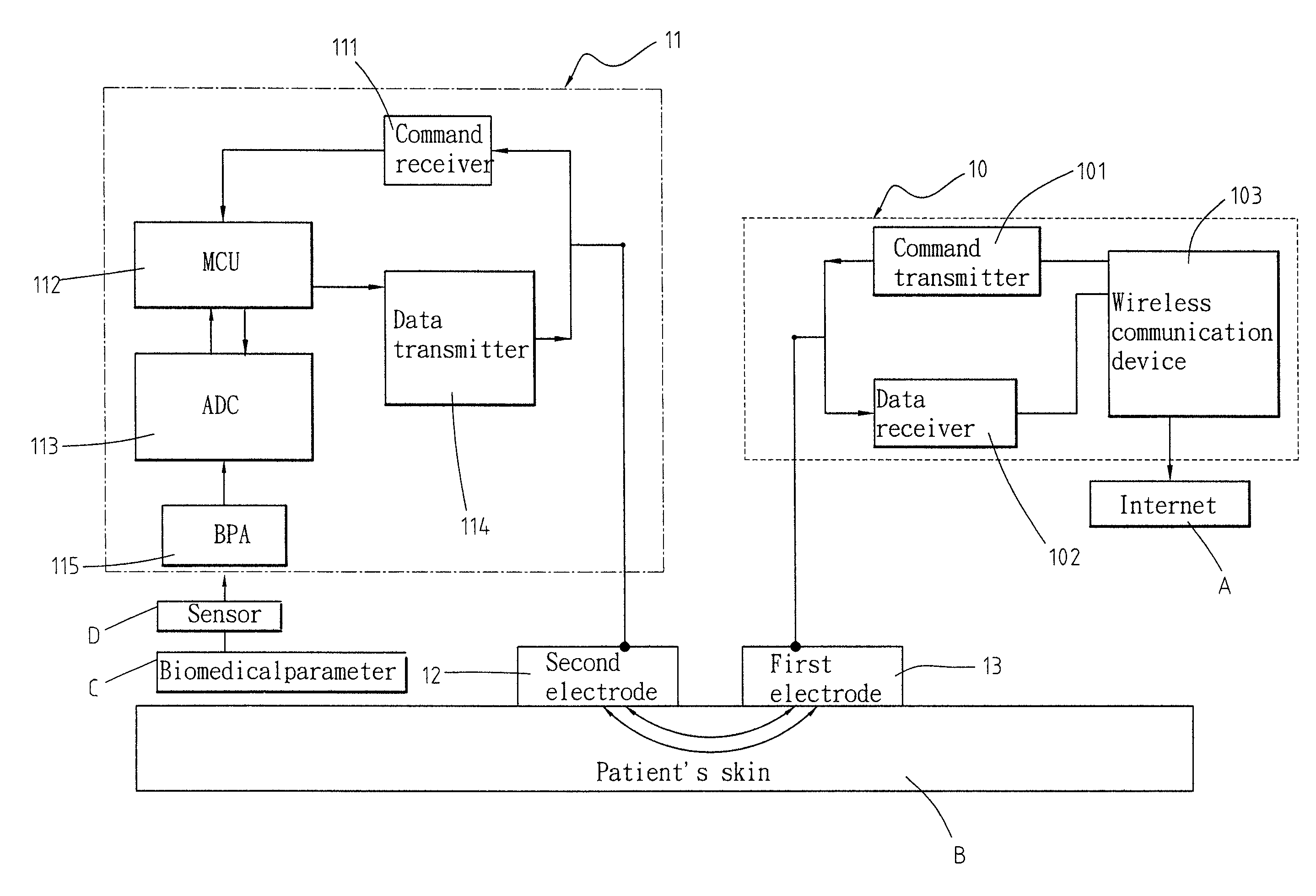
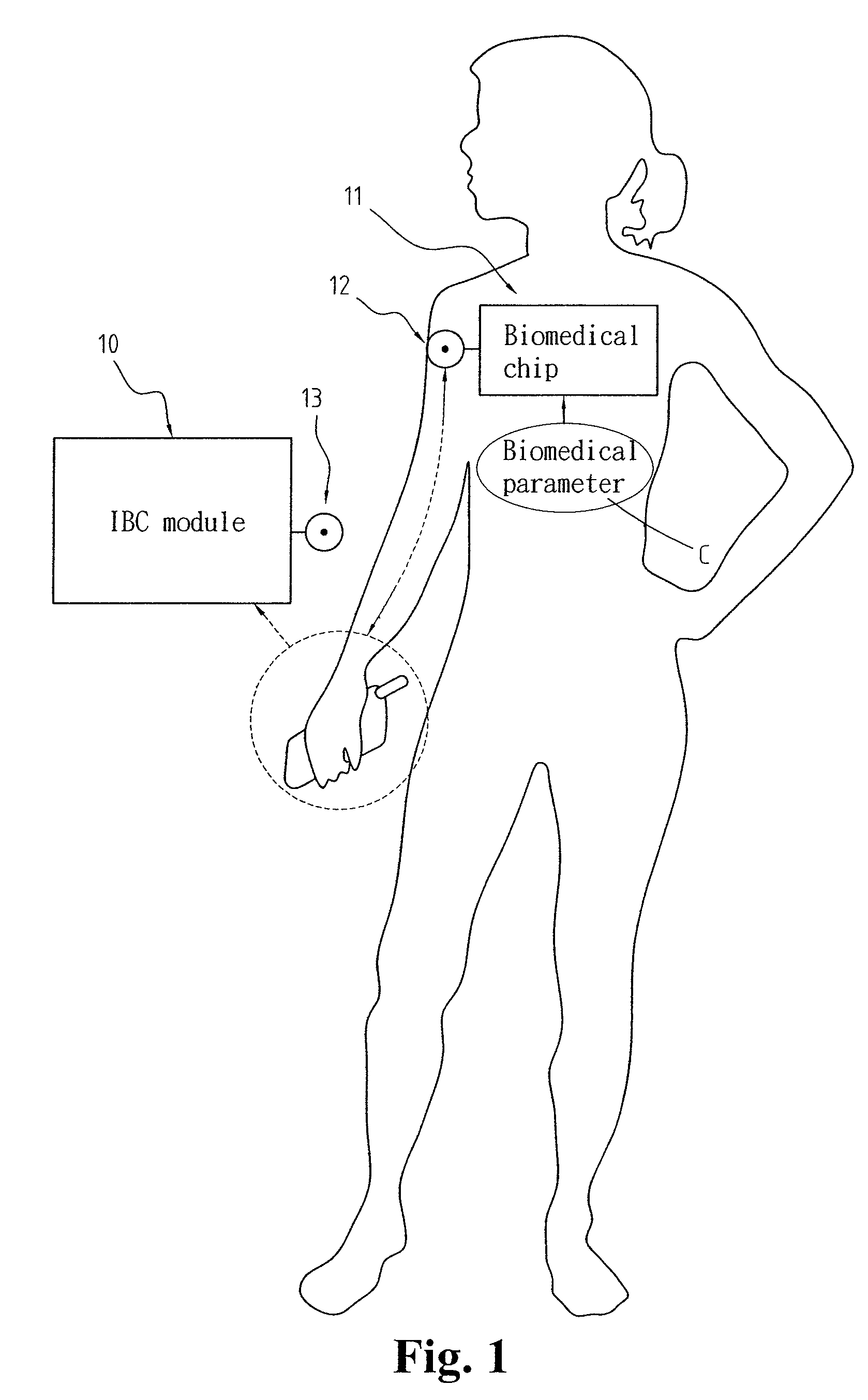
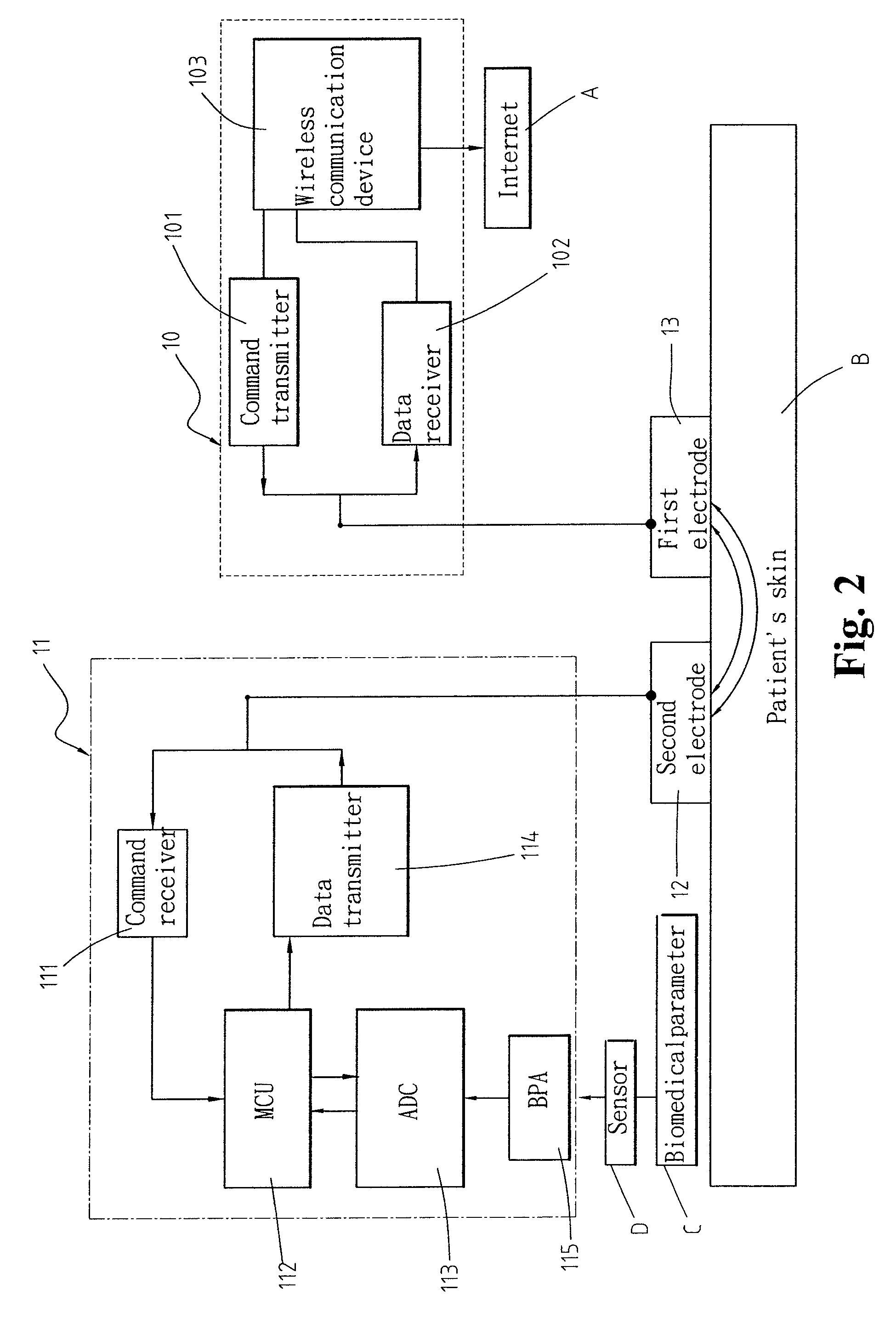
The present invention relates to an intra-body communication (IBC) device and a method of implementing the IBC device. The IBC device is fabricated as a system-on-a-chip (SOC) and comprises a first electrode, a second electrode, an IBC module and a biomedical chip. The first electrode is connected to a patient's skin. The second electrode is connected to the patient's skin. The IBC module is connected to the first electrode and comprises a wireless communication device. The biomedical chip is connected to the second electrode and communicates with the IBC module through the patient's skin to receive external commands and transmit sensed biomedical parameters to a faraway location.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
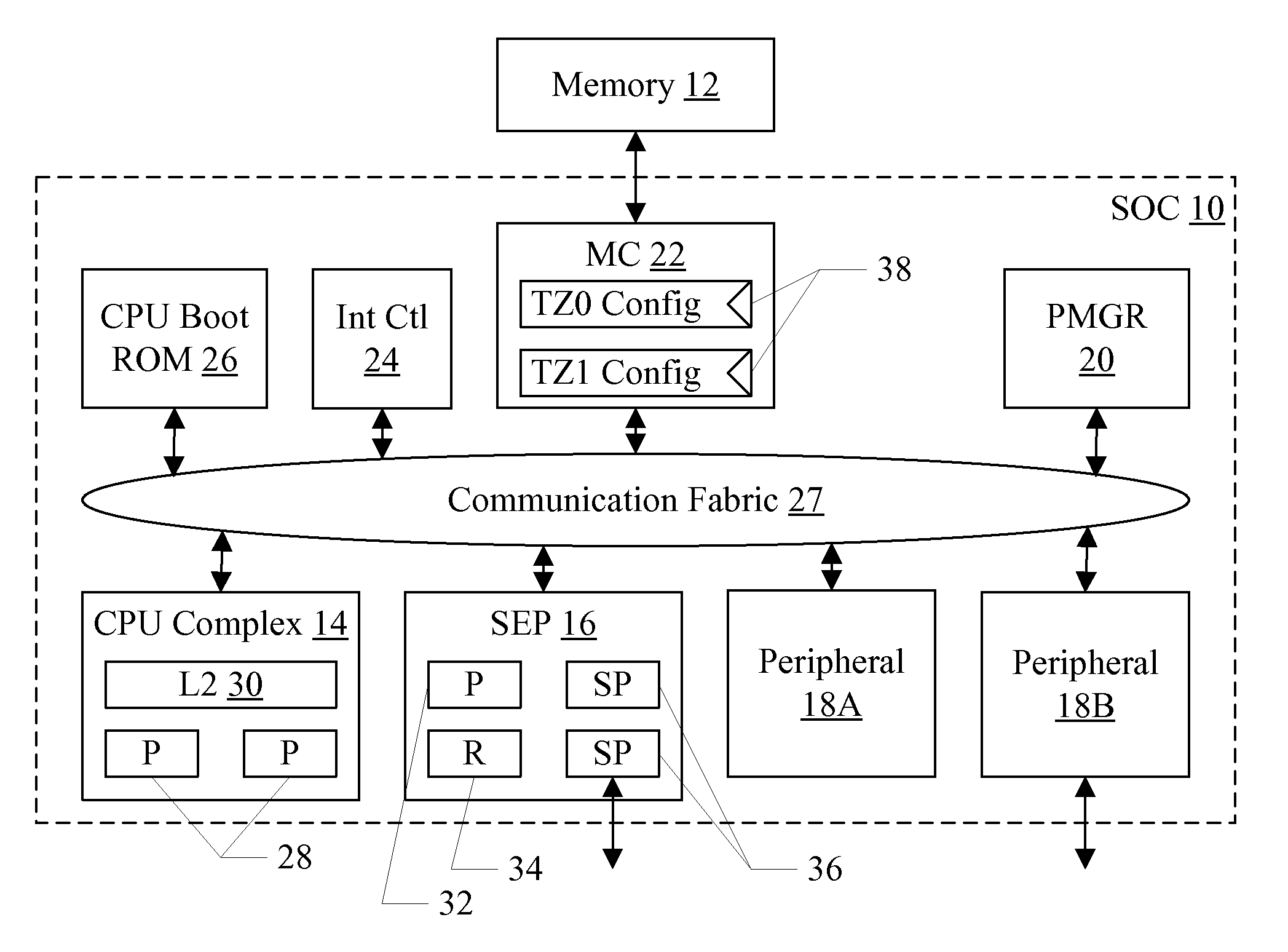
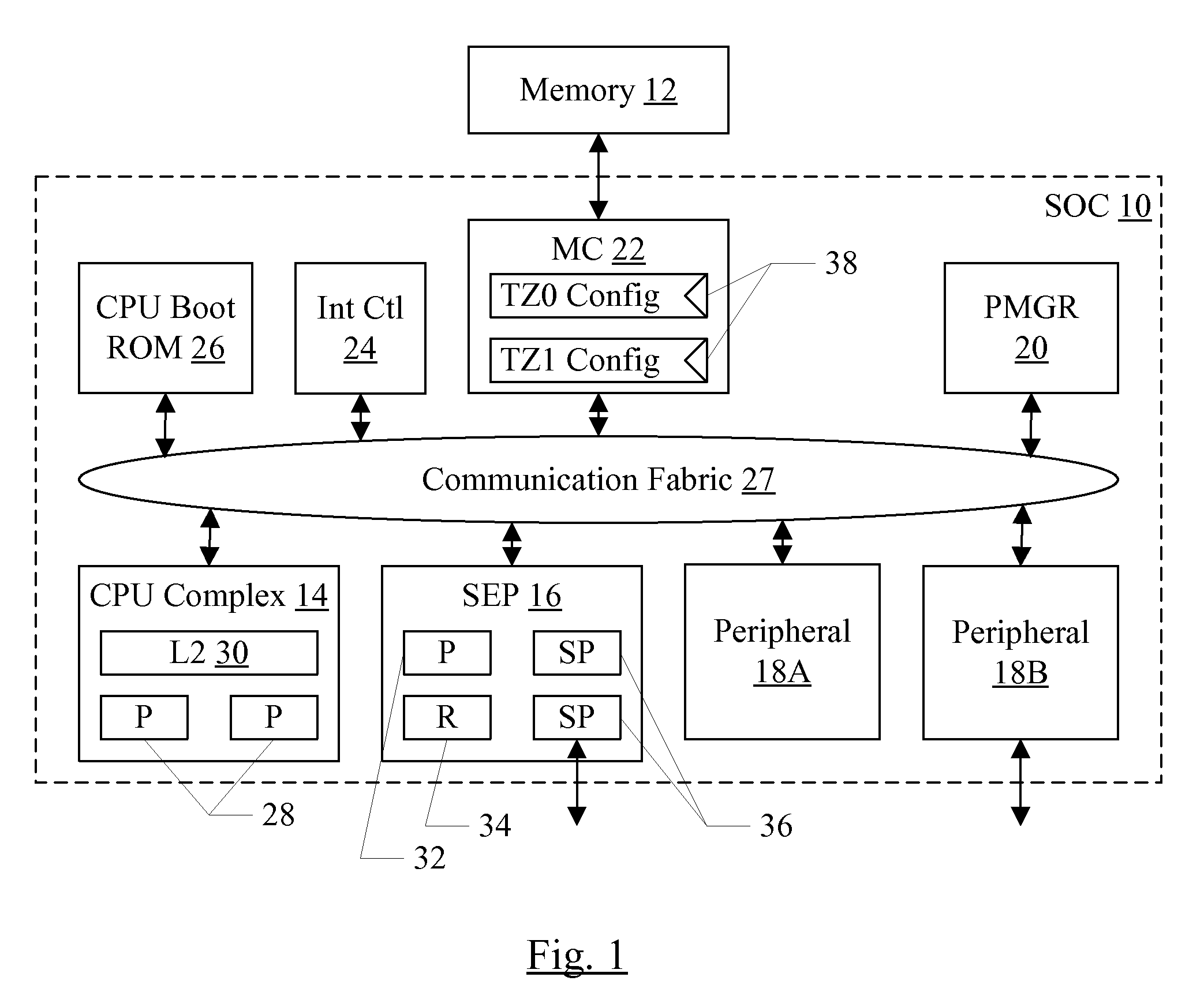
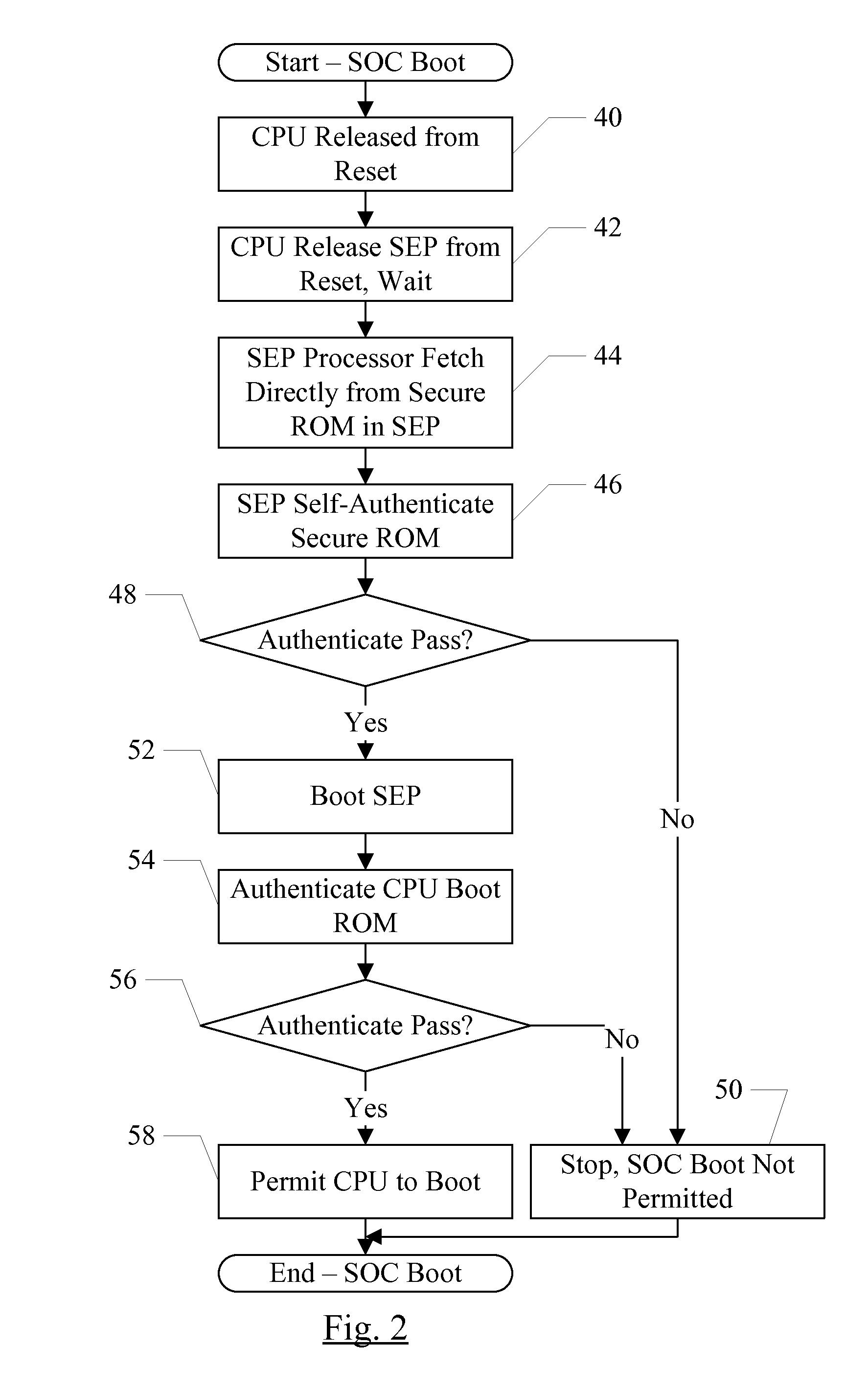
Security enclave processor for a system on a chip
ActiveUS8832465B2Prevent copyingMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionApplication processorSystem on a chip
Owner:APPLE INC
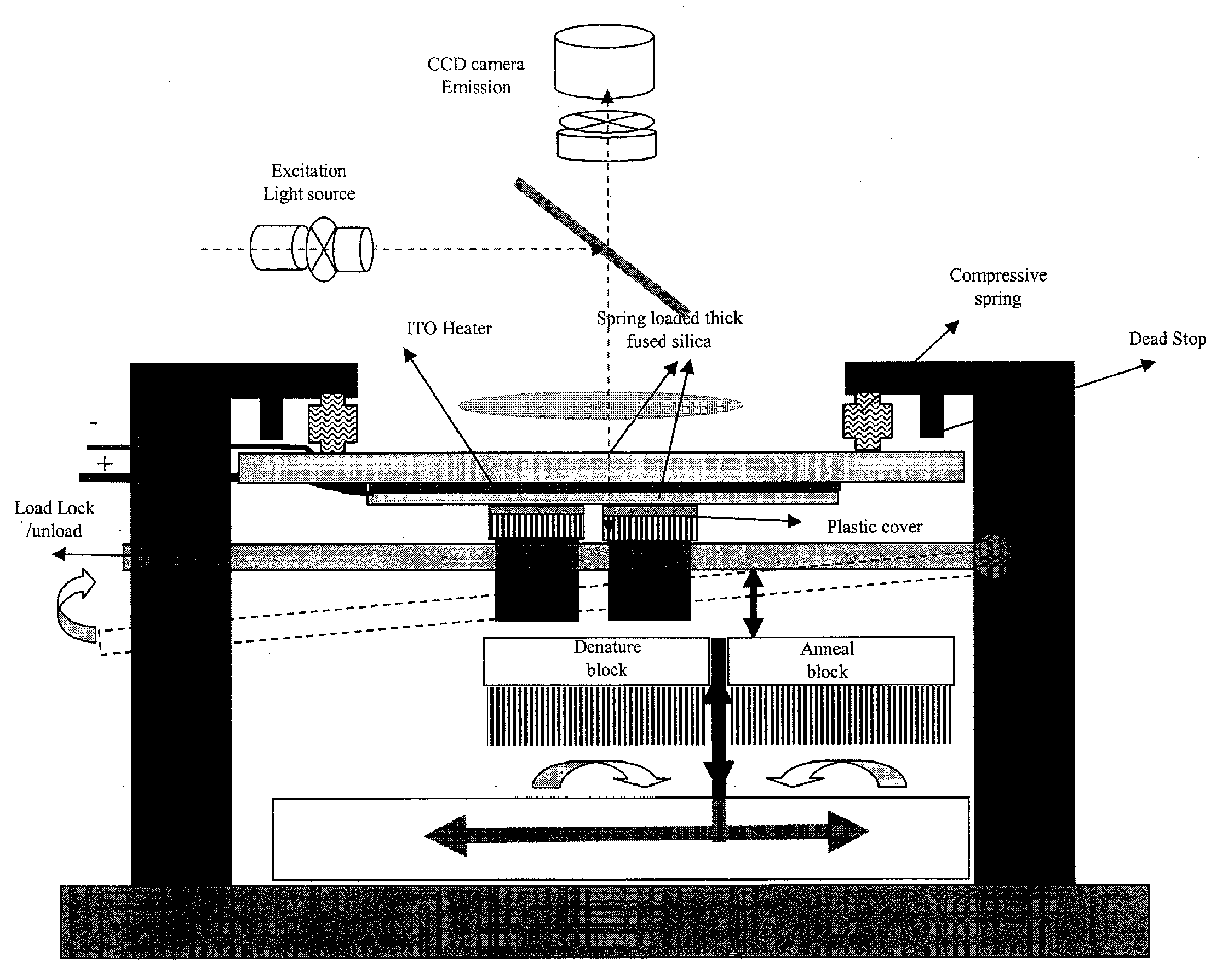
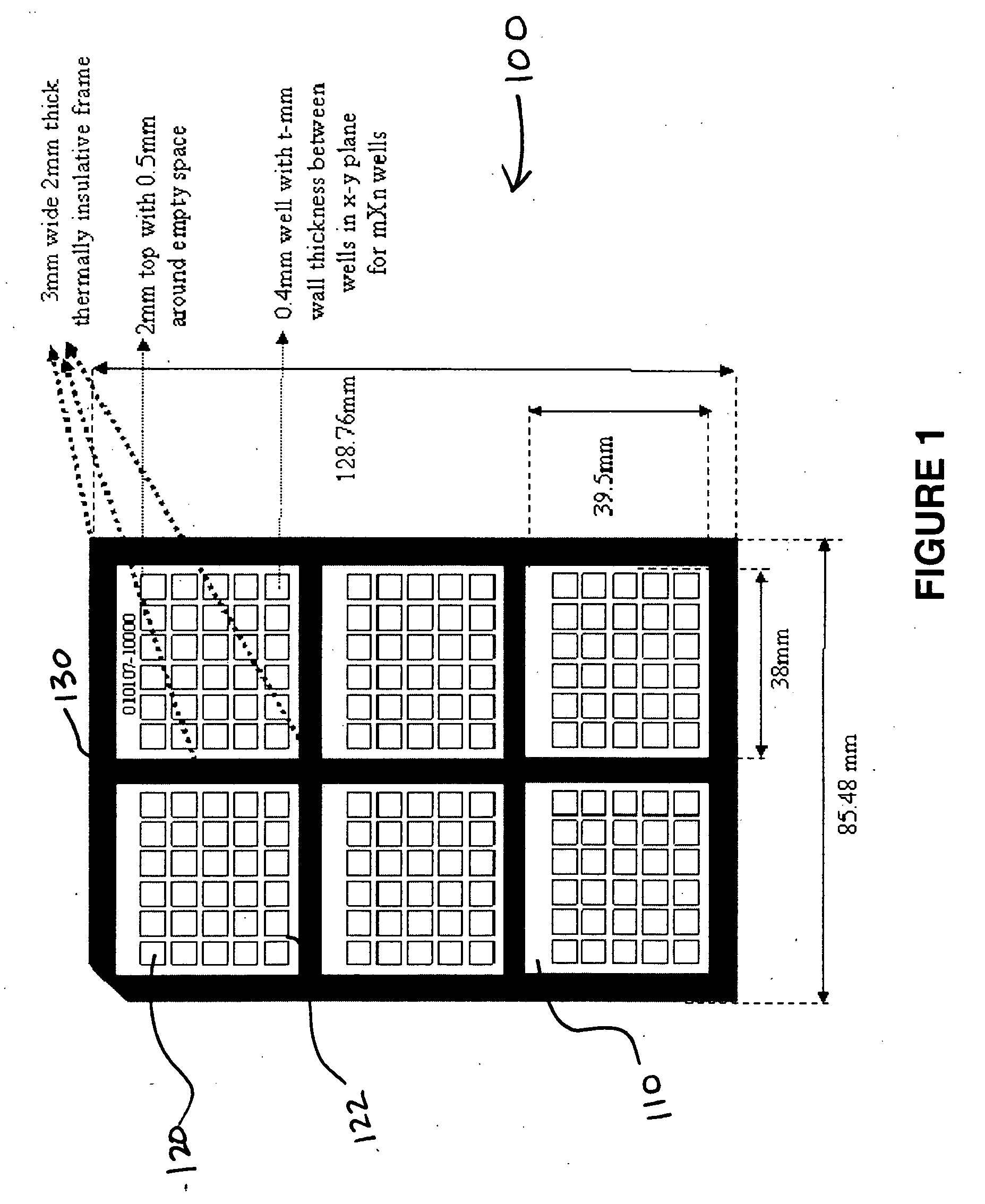
Apparatus for high throughput chemical reactions
ActiveUS20080176290A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionReaction temperature
Apparatus, systems, chips, and methods of performing a large number of simultaneous chemical reactions are provided herein. The chips of the invention comprise addressable units that can be addressed according to the temperature of the reaction to be run. The subject apparatus, systems, and chips are particularly suited for performing polymerase chain reactions on thousands of nucleic acid sequences, up to and including sequences of an entire genome of an organism of interest.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
System on a Chip Using Integrated MEMS and CMOS Devices
ActiveUS20110265574A1Easy to useHigh device yieldVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCmos memsSystem on a chip
An integrated MEMS system in which CMOS and MEMS devices are provided to form an integrated CMOS-MEMS system. The system can include a silicon substrate layer, a CMOS layer, MEMS and CMOS devices, and a wafer level packaging (WLP) layer. The CMOS layer can form an interface region, one which any number of CMOS MEMS devices can be configured.
Owner:MOVELLA INC
System on a Chip with On-Chip RF Shield
ActiveUS20100078779A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
Structures of a system on a chip are disclosed. In one embodiment, the system on a chip (SoC) includes an RF component disposed on a first part of a substrate, a semiconductor component disposed on a second part of the substrate, the semiconductor component and the RF component sharing a common boundary, and a conductive cage disposed enclosing the RF component. The conductive cage shields the semiconductor component from electromagnetic radiation originating from the RF circuit.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
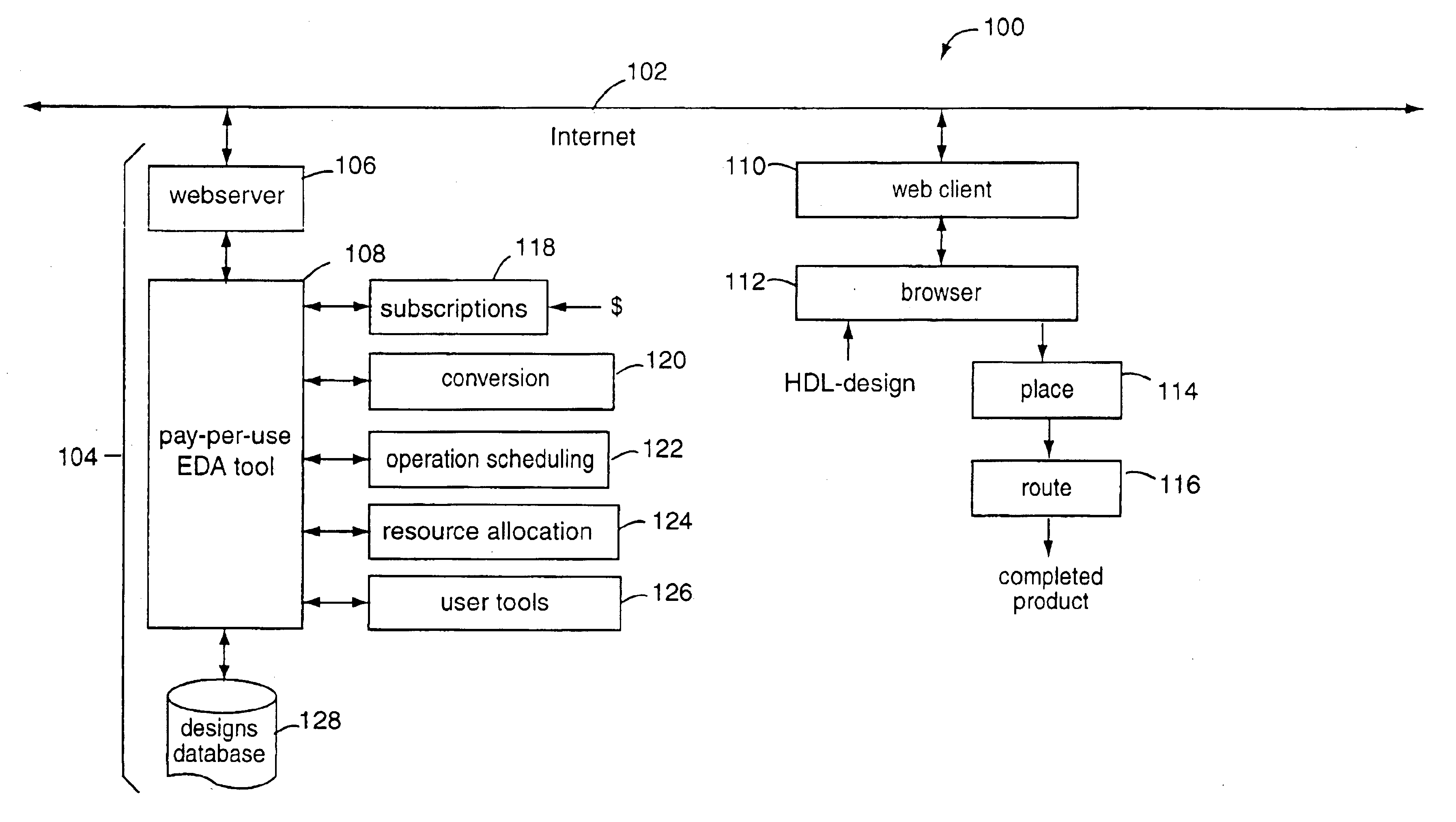
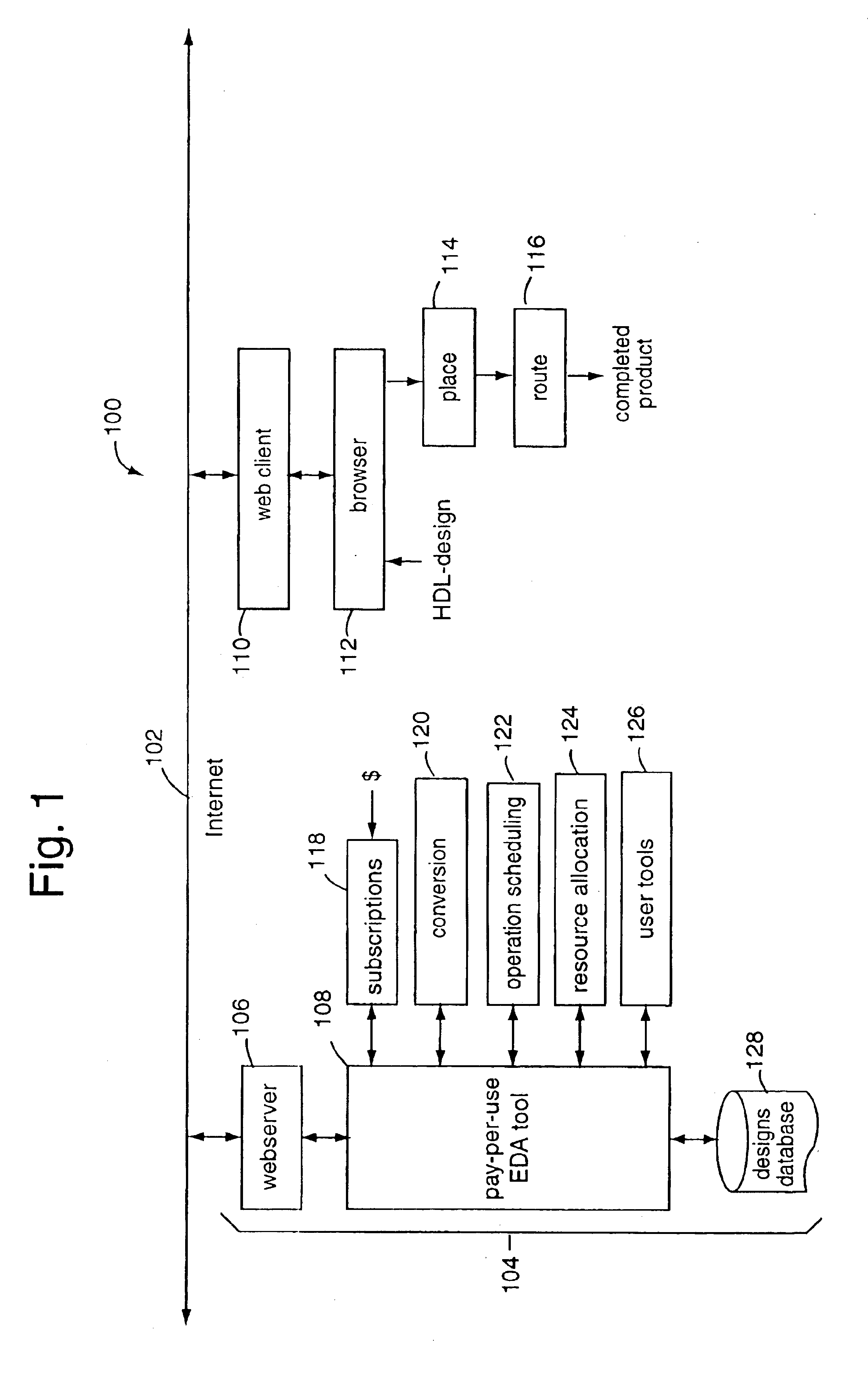
Behavioral-synthesis electronic design automation tool business-to-business application service provider
InactiveUS6782511B1Distributed efficiently and easilyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationWeb serviceIntellectual property
A business-to-business application service provider includes an Internet website and webserver with EDA-on-demand solutions for system-on-a-chip designers. Such website allows electronic designs in hardware description language to be uploaded into a front-end EDA design environment. A behavioral model simulation tool hosted privately on the webserver tests and validates the design. Such tool executes only in the secure environment of the business-to-business application service provider. The validated solution is then downloaded back over the Internet for a pay-per-use fee to the customer, and in a form ready to be placed and routed by a back-end EDA tool. Such validated design solutions are also downloadable to others in exchange for other designs, or available in technology libraries. The intellectual property created can be re-used, sold, shared, exchanged, and otherwise distributed efficiently and easily from a central for-profit clearinghouse.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
On-Chip RF Shields with Through Substrate Conductors
ActiveUS20100078771A1Magnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorEngineering
Structures of a system on chip and methods of forming a system on chip are disclosed. In one embodiment, the system on a chip includes an RF component disposed on a first part of a substrate, a semiconductor component disposed on a second part of the substrate, the semiconductor component and the RF component sharing a common boundary. The system on chip further includes through substrate conductors disposed in the substrate, the through substrate conductors coupled to a ground potential node, the through substrate conductors disposed around the RF component forming a fence around the RF circuit.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
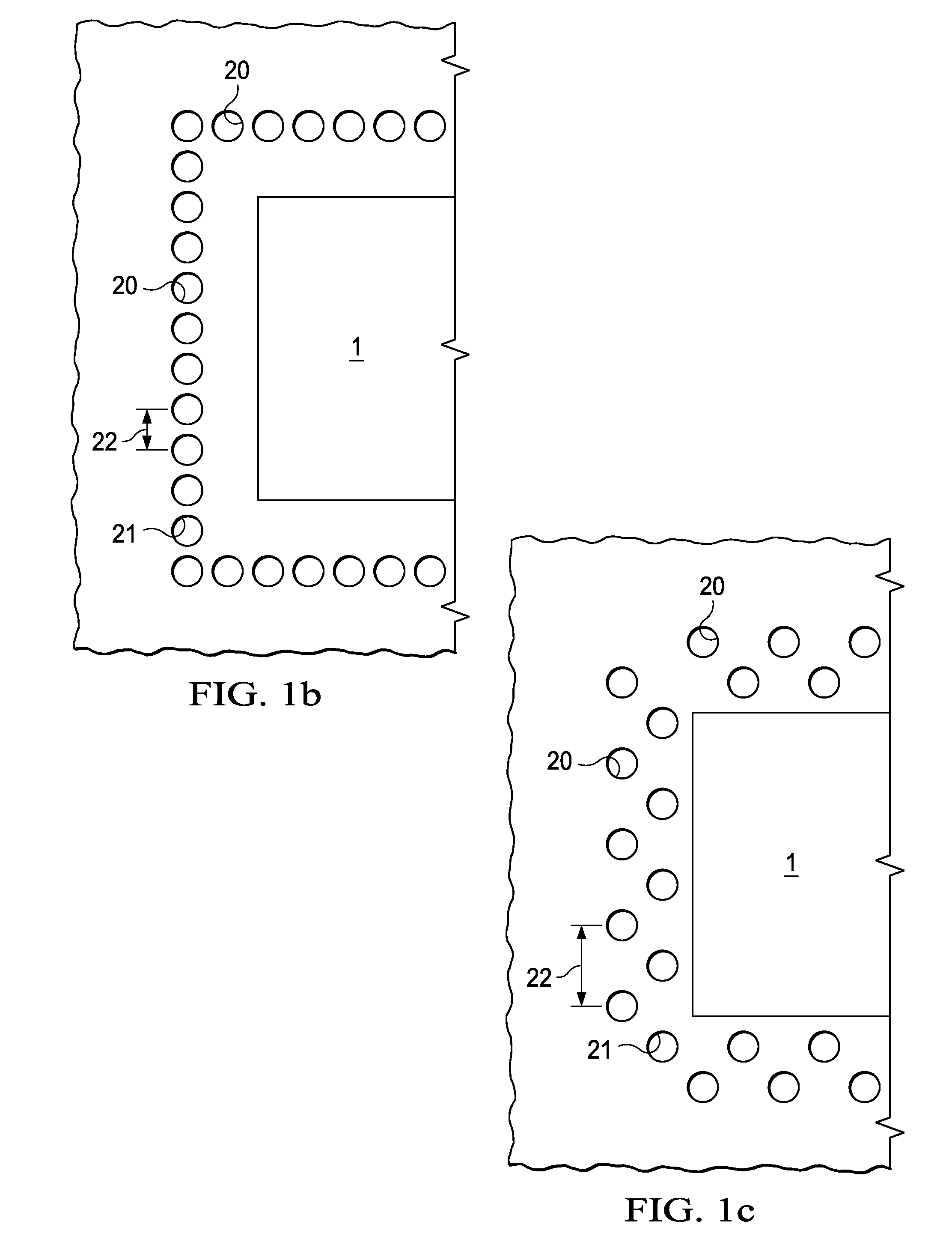
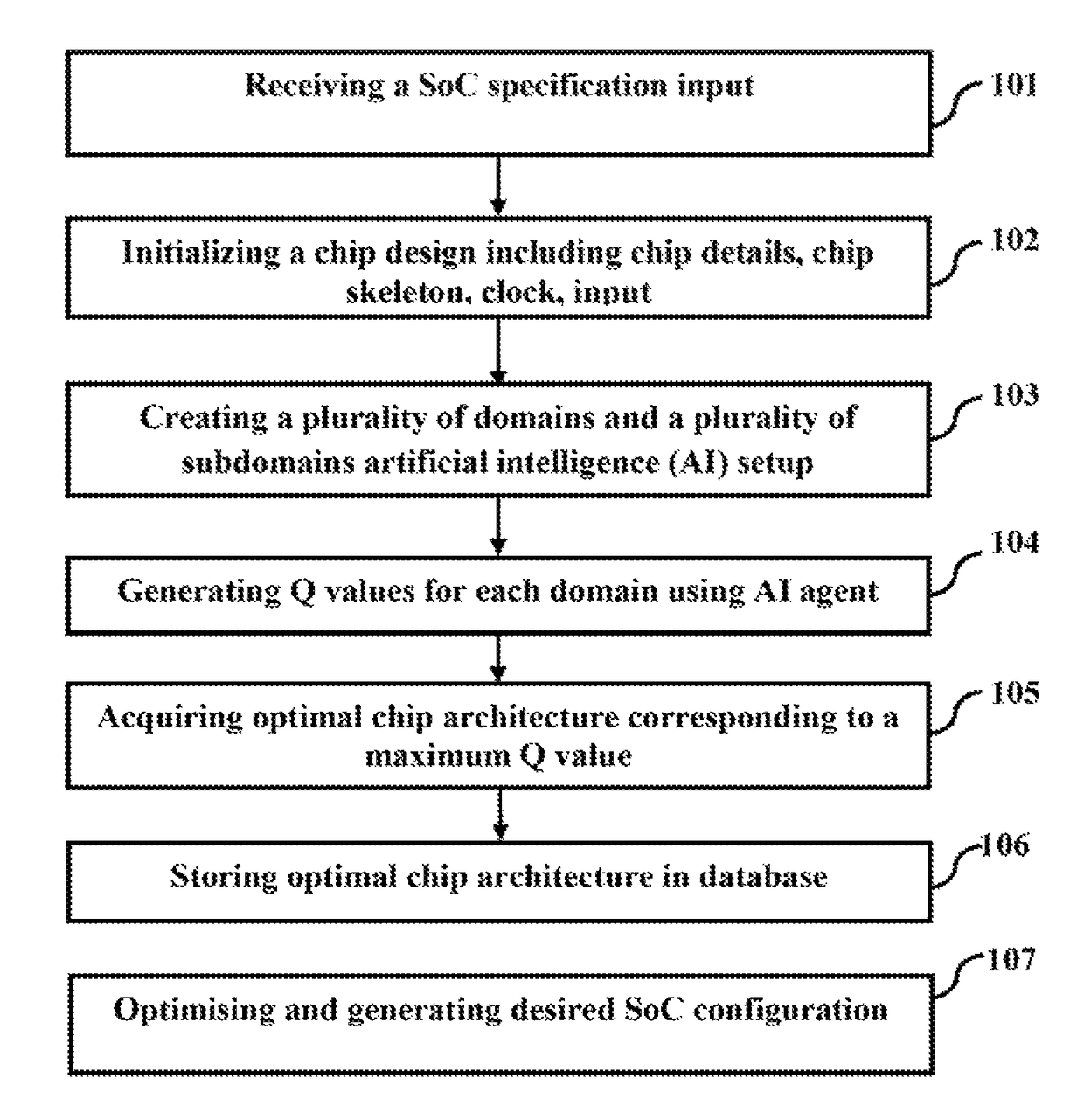
System and method for designing system on chip (SoC) circuits through artificial intelligence and reinforcement learning
ActiveUS9792397B1Reduce complexityGood decisionDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designComputer architectureRelevant information
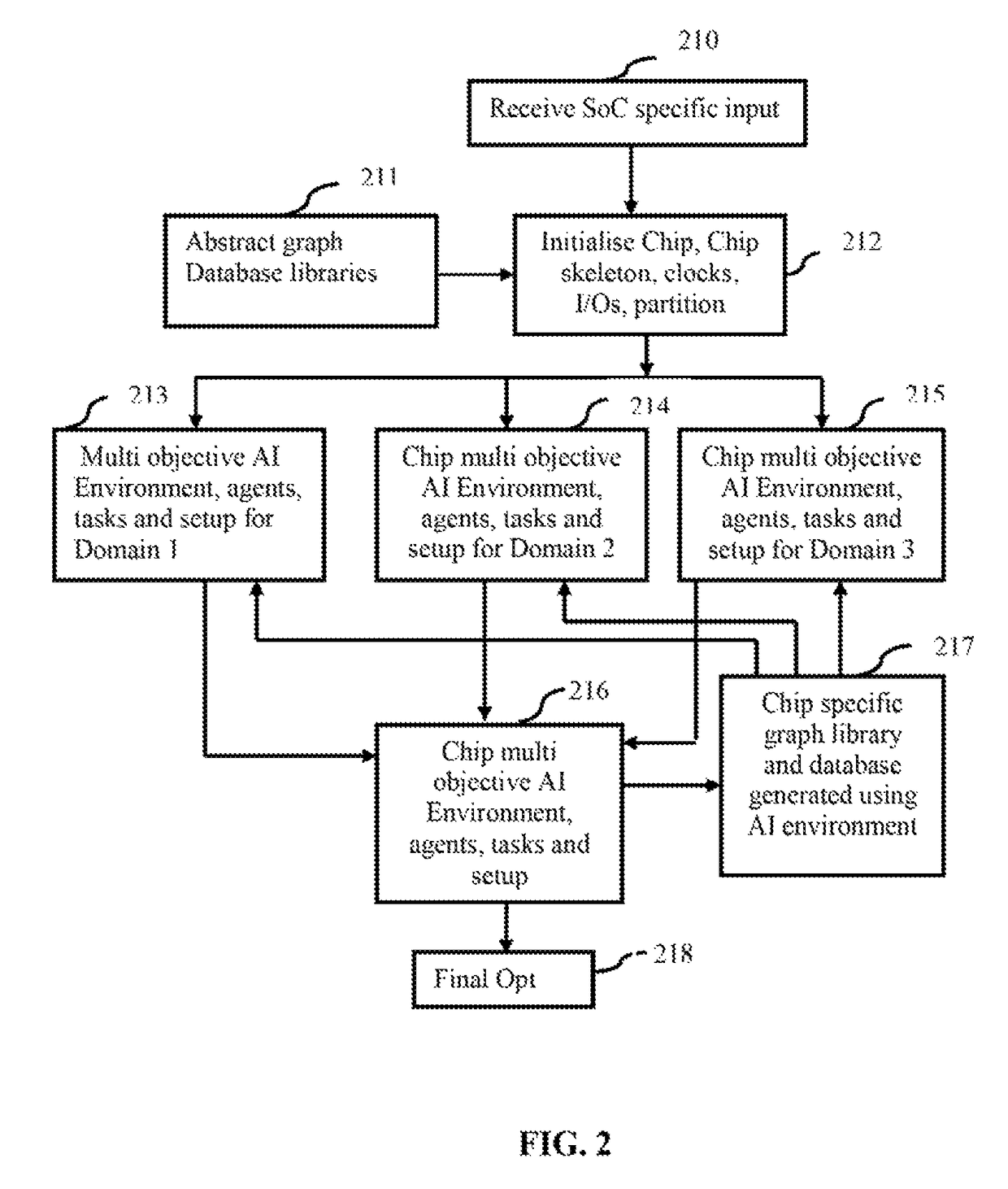
The embodiments herein discloses a system and method for designing SoC using AI and Reinforcement Learning (RL) techniques. Reinforcement Learning is done either hierarchically in several steps or in a single-step comprising environment, tasks, agents and experiments, to have access to SoC (System on a Chip) related information. The AI agent is configured to learn from the interaction and plan the implementation of a SoC circuit design. Q values generated for each domain and sub domain are stored in a hierarchical SMDP structure in a form of SMDP Q table in a big data database. An optimal chip architecture corresponding to a maximum Q value of a top level in the SMDP Q table is acquired and stored in a database for learning and inference. Desired SoC configuration is optimized and generated based on the optimal chip architecture and the generated chip specific graph library.
Owner:ALPHAICS CORP
System and method for IDDQ measurement in system on a chip (SOC) design
ActiveUS7282905B2Short test timeReduce chip areaMarginal circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingElectricityEngineering
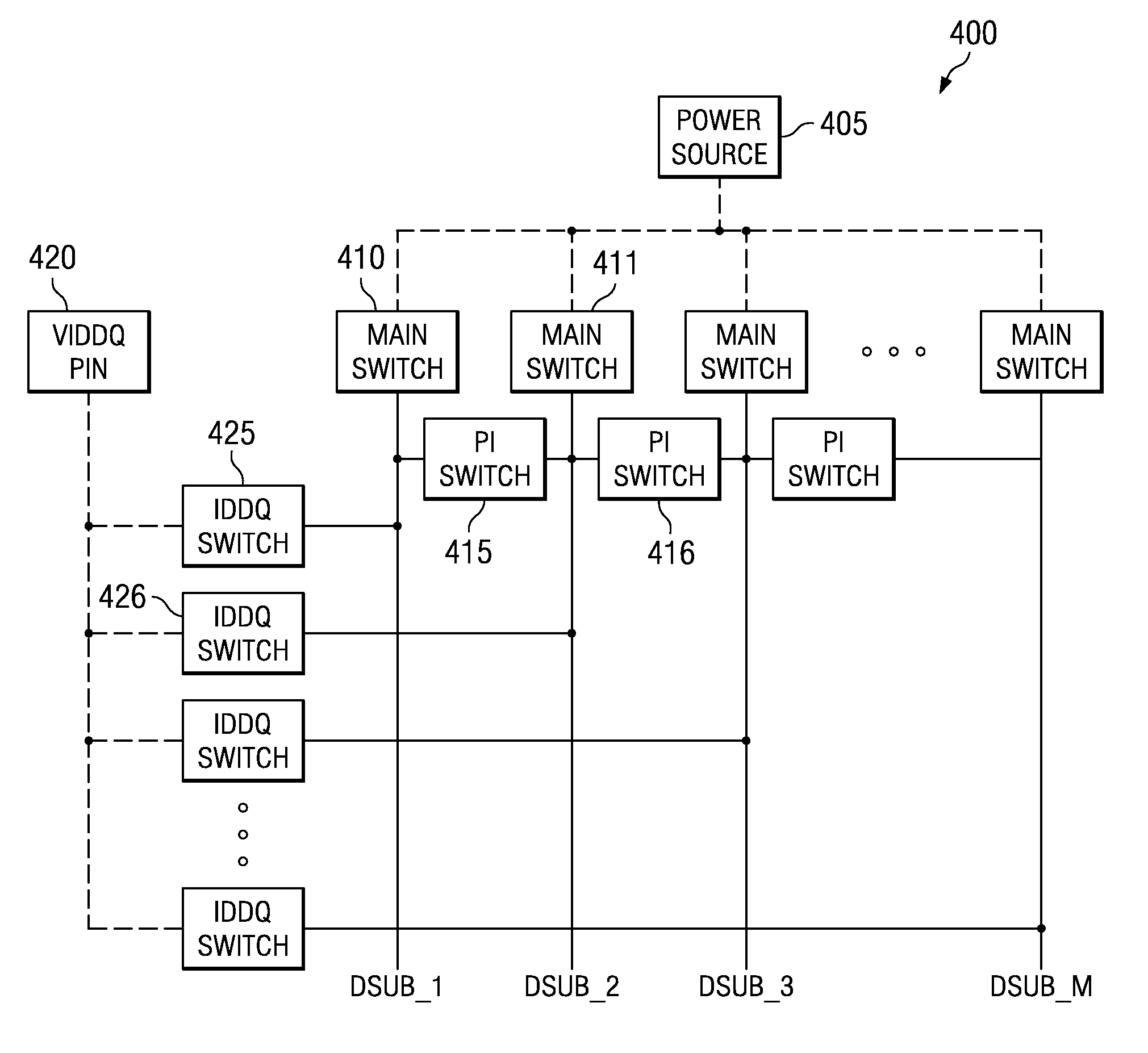
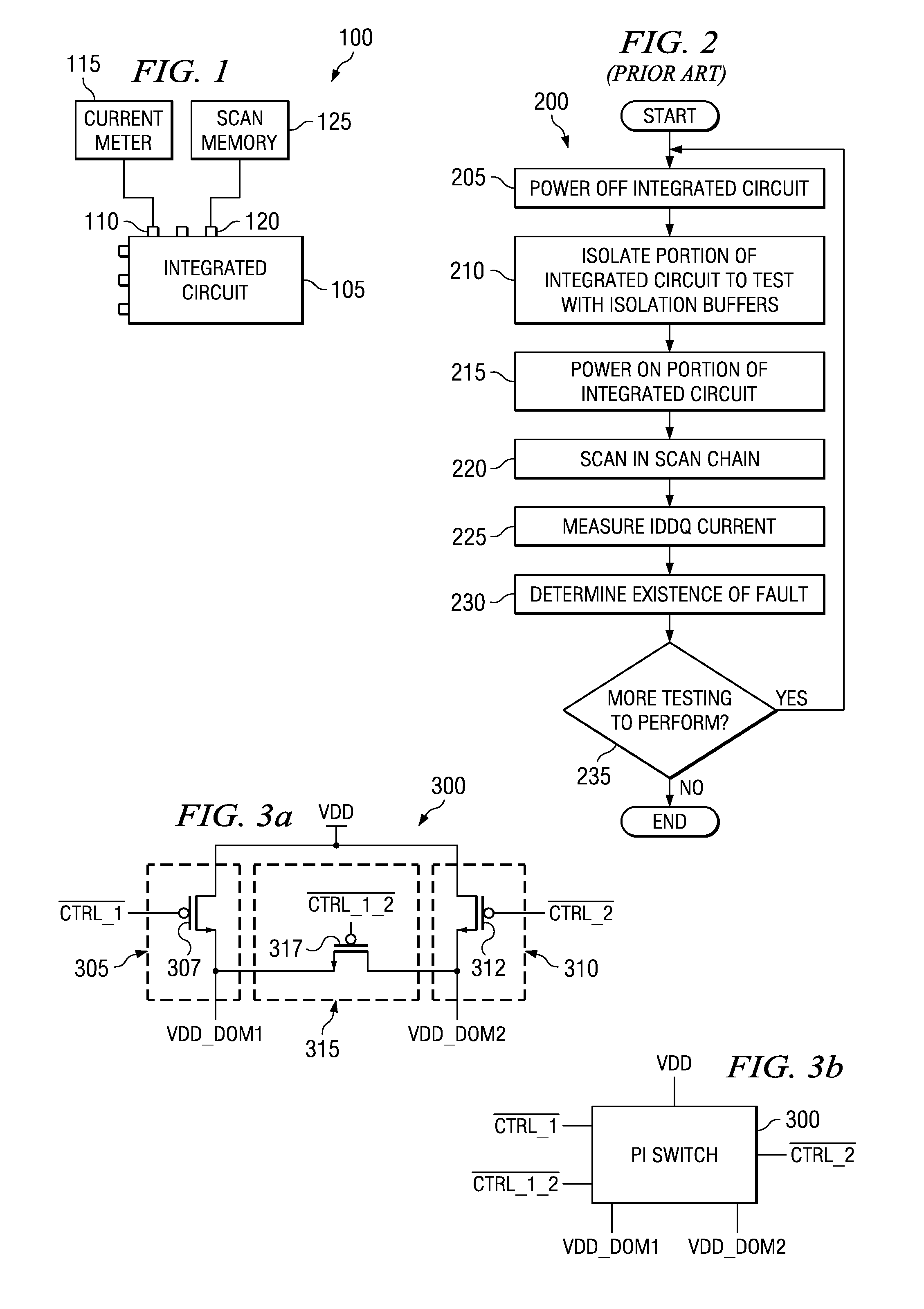
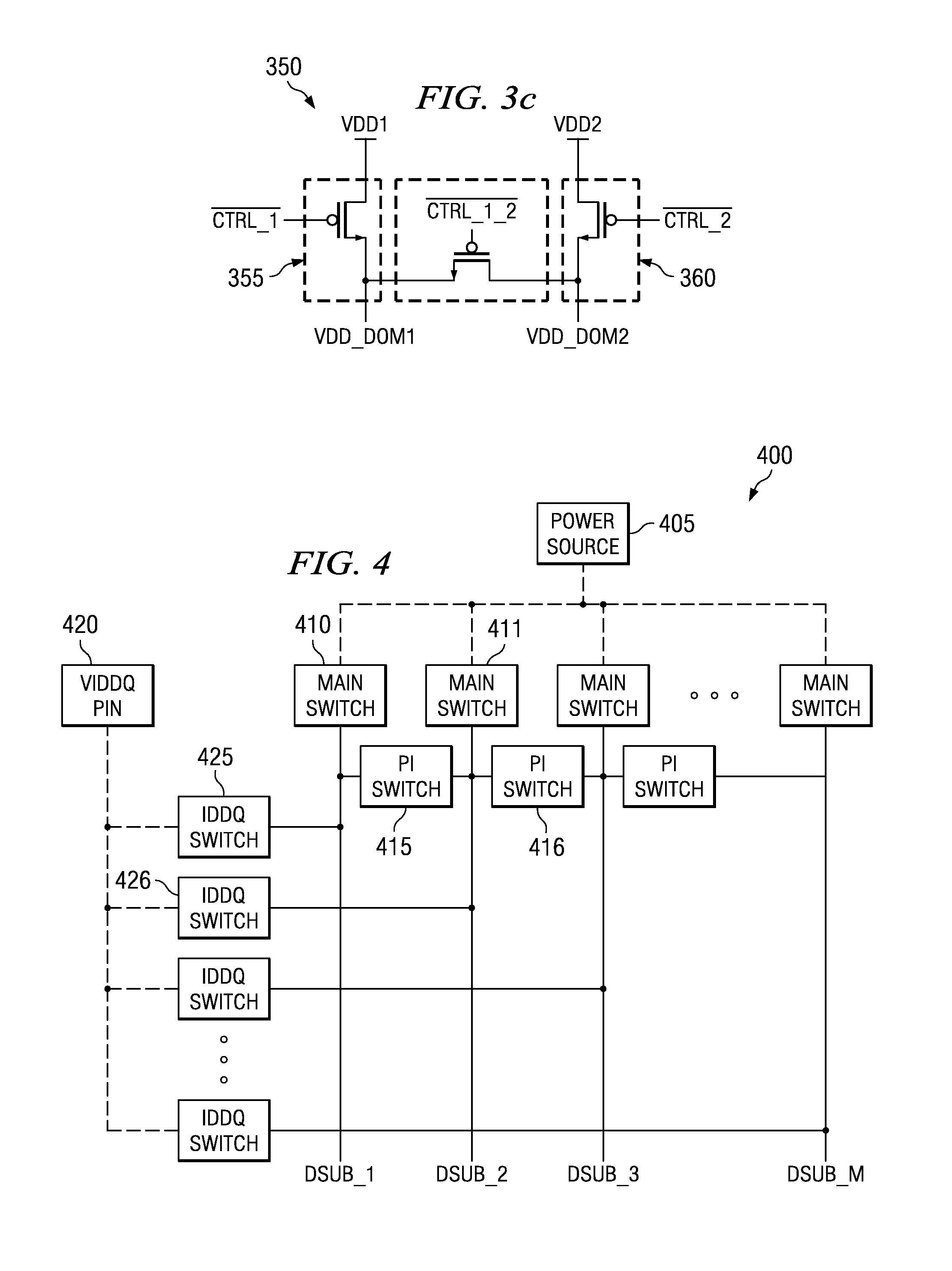
System and method for detecting transistor failure in large-scale integrated circuits by measuring IDDQ. A preferred embodiment comprises a switch structure for an integrated circuit made up of a plurality of main switches (such as main switch 410) selectively coupling a power sub-domain to a power source pin, a plurality of pi-switches (such as pi-switch 415) selectively coupling pairs of power sub-domains, and a plurality of IDDQ switches (such as IDDQ switch 425) selectively coupling the power sub-domains to a VIDDQ pin. The pi-switches can decouple the power sub-domains while the IDDQ switches can enable the measurement of the quiescent current in the power sub-domains. The use of pi-switches and IDDQ switches can permit the measurement of the quiescent current in the power sub-domains without requiring the use of isolation buffers and needed to powering on and off the integrated circuit between current measurements in the different power sub-domains.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for capturing and detecting symbology features and parameters
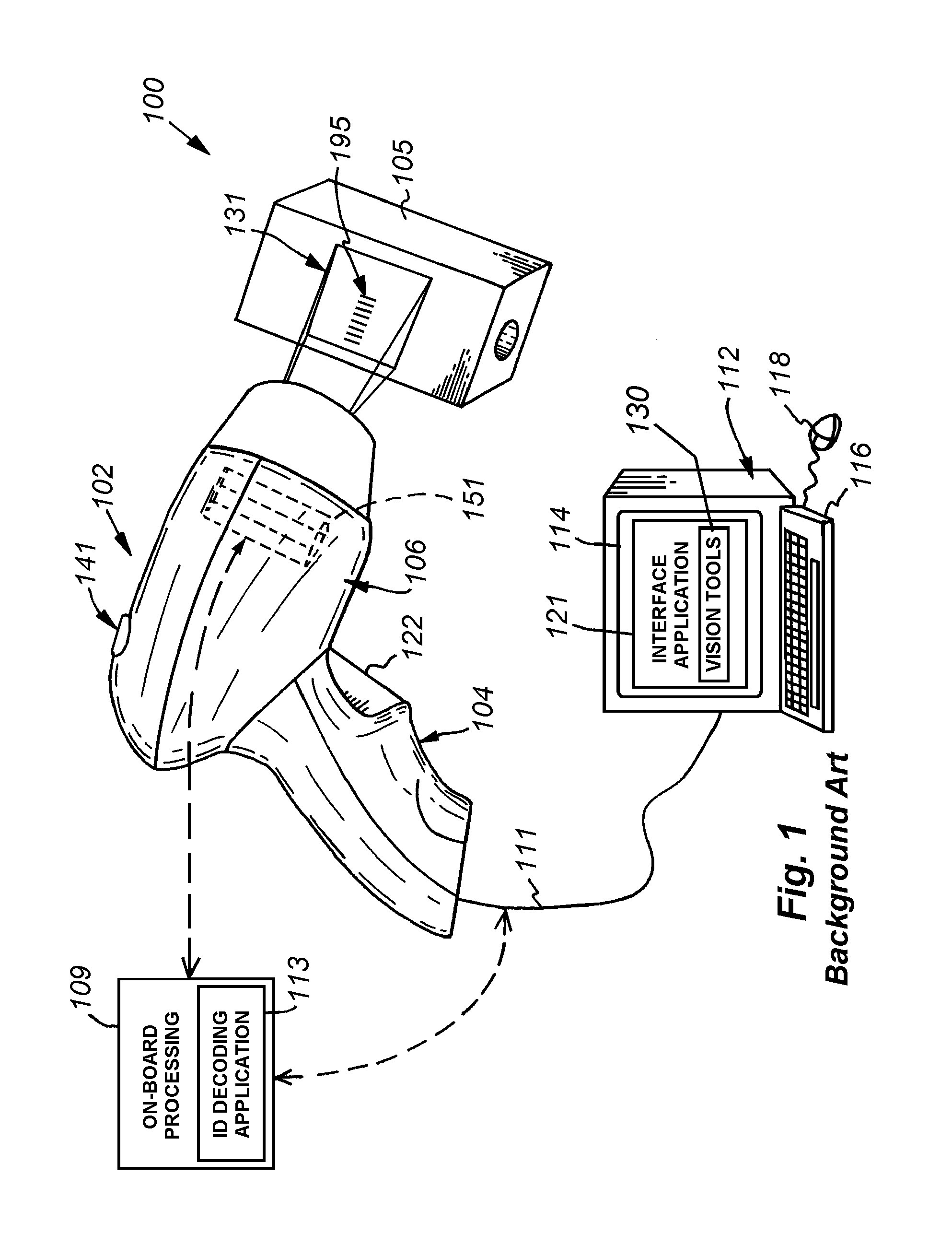
ActiveUS20100200660A1Overcome disadvantagesSensing by electromagnetic radiationSymbolic SystemsFeature set
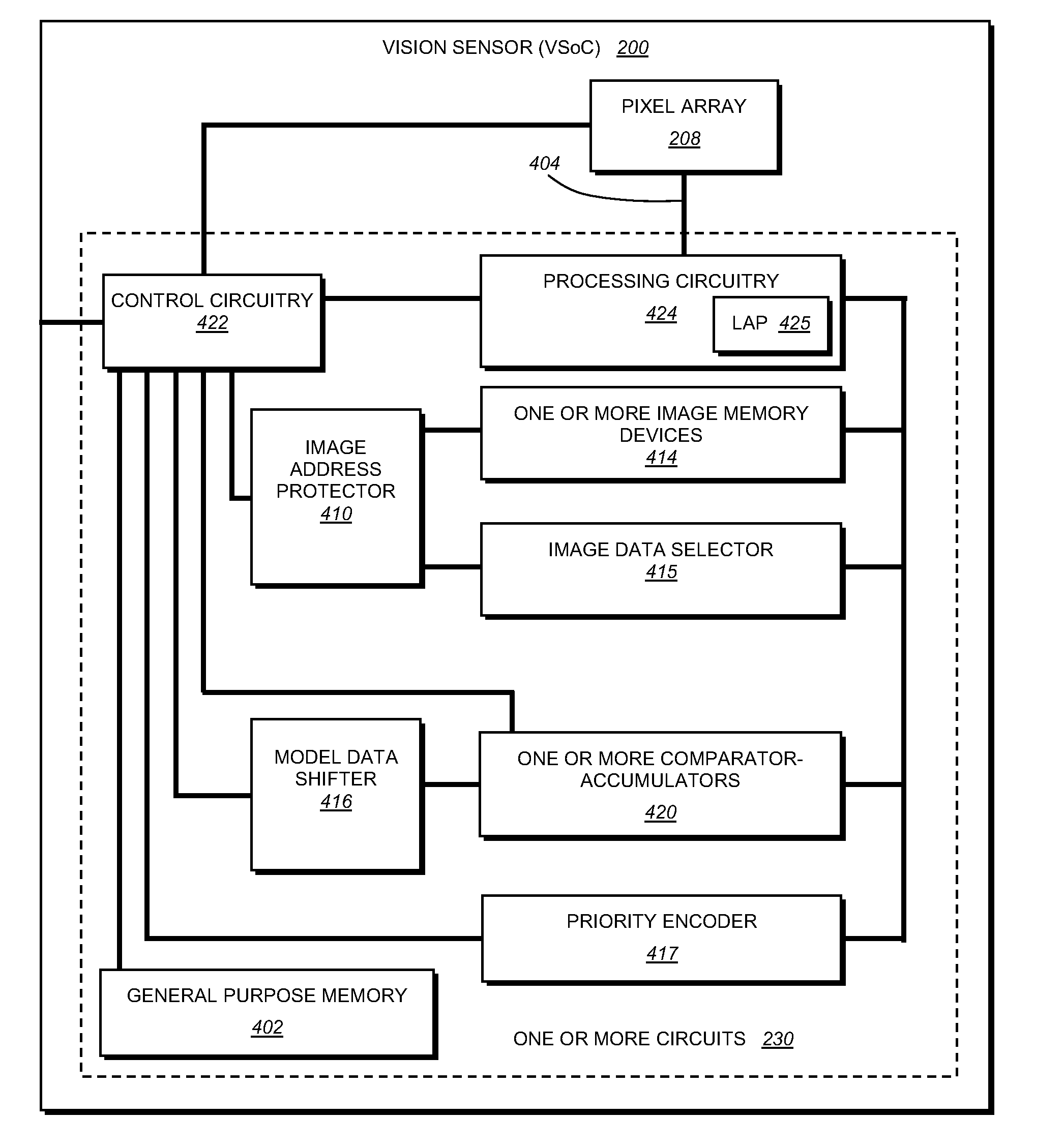
This invention provides a system and method for capturing, detecting and extracting features of an ID, such as a 1D barcode, that employs an efficient processing system based upon a CPU-controlled vision system on a chip (VSoC) architecture, which illustratively provides a linear array processor (LAP) constructed with a single instruction multiple data (SIMD) architecture in which each pixel of the rows of the pixel array are directed to individual processors in a similarly wide array. The pixel data are processed in a front end (FE) process that performs rough finding and tracking of regions of interest (ROIs) that potentially contain ID-like features. The ROI-finding process occurs in two parts so as to optimize the efficiency of the LAP in neighborhood operations—a row-processing step that occurs during image pixel readout from the pixel array and an image-processing step that occurs typically after readout occurs. The relative motion of the ID-containing ROI with respect to the pixel array is tracked and predicted. An optional back end (BE) process employs the predicted ROI to perform feature-extraction after image capture. The feature extraction derives candidate ID features that are verified by a verification step that confirms the ID, creates a refined ROI, angle of orientation and feature set. These are transmitted to a decoding processor or other device.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
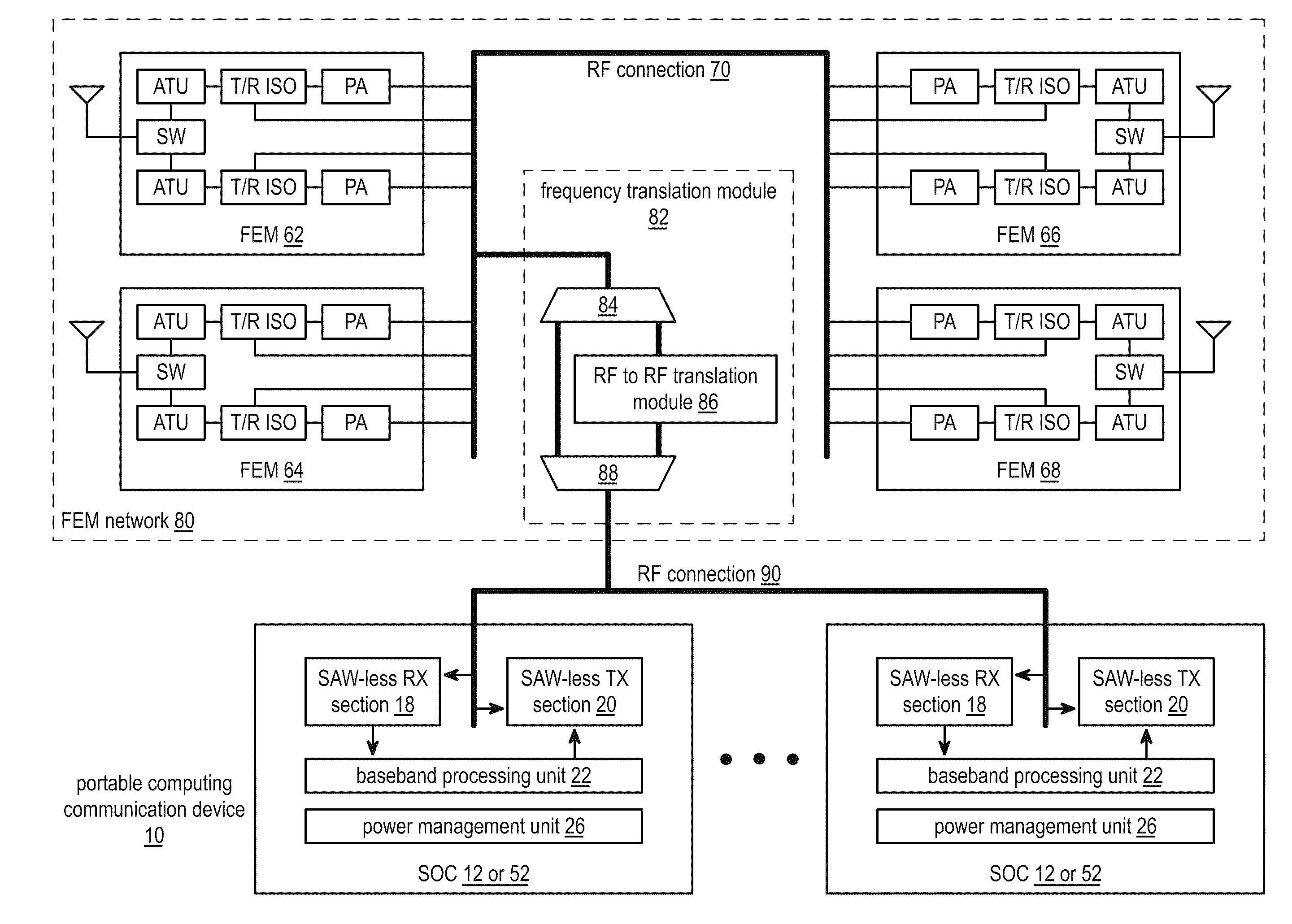
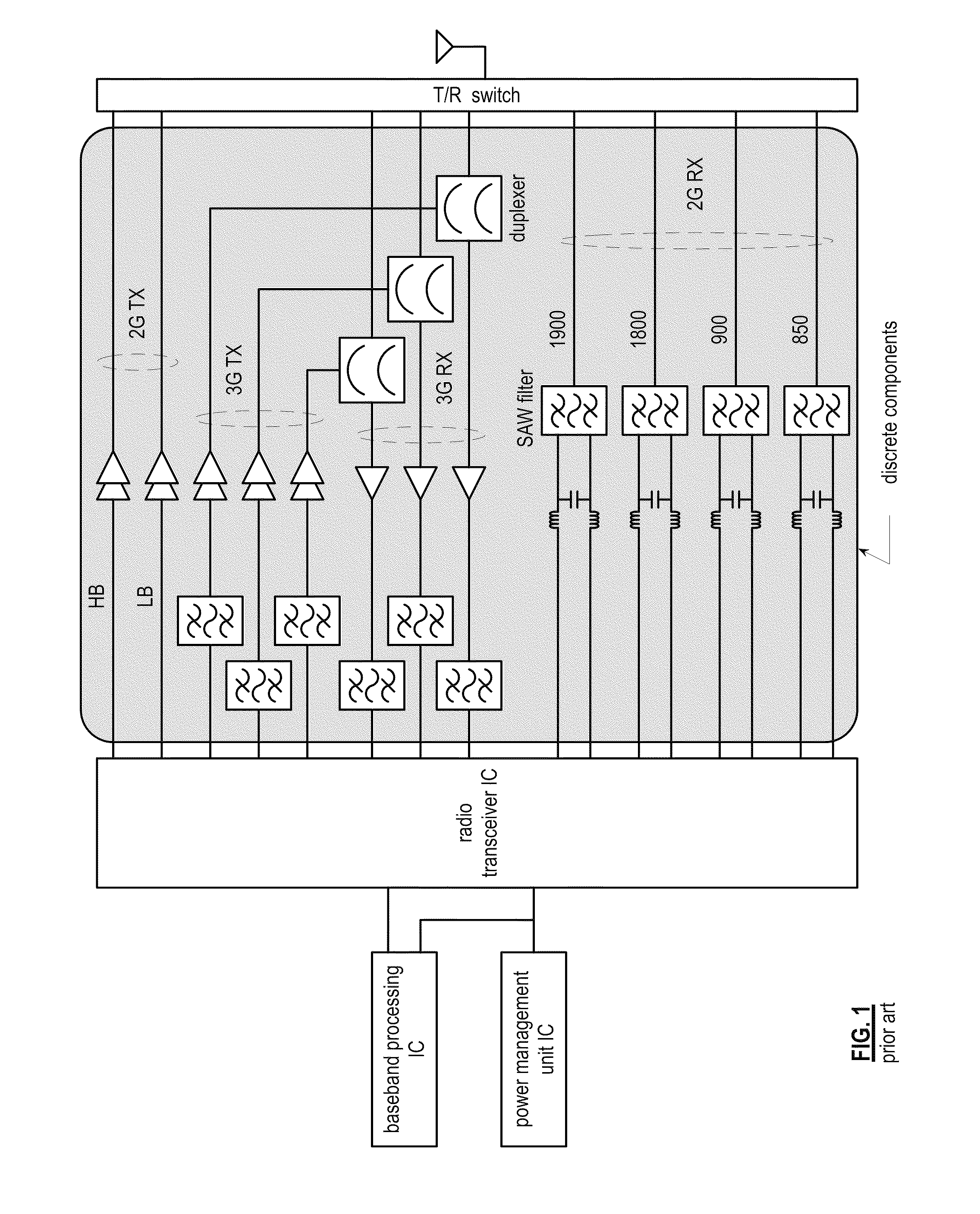
Front-end module network
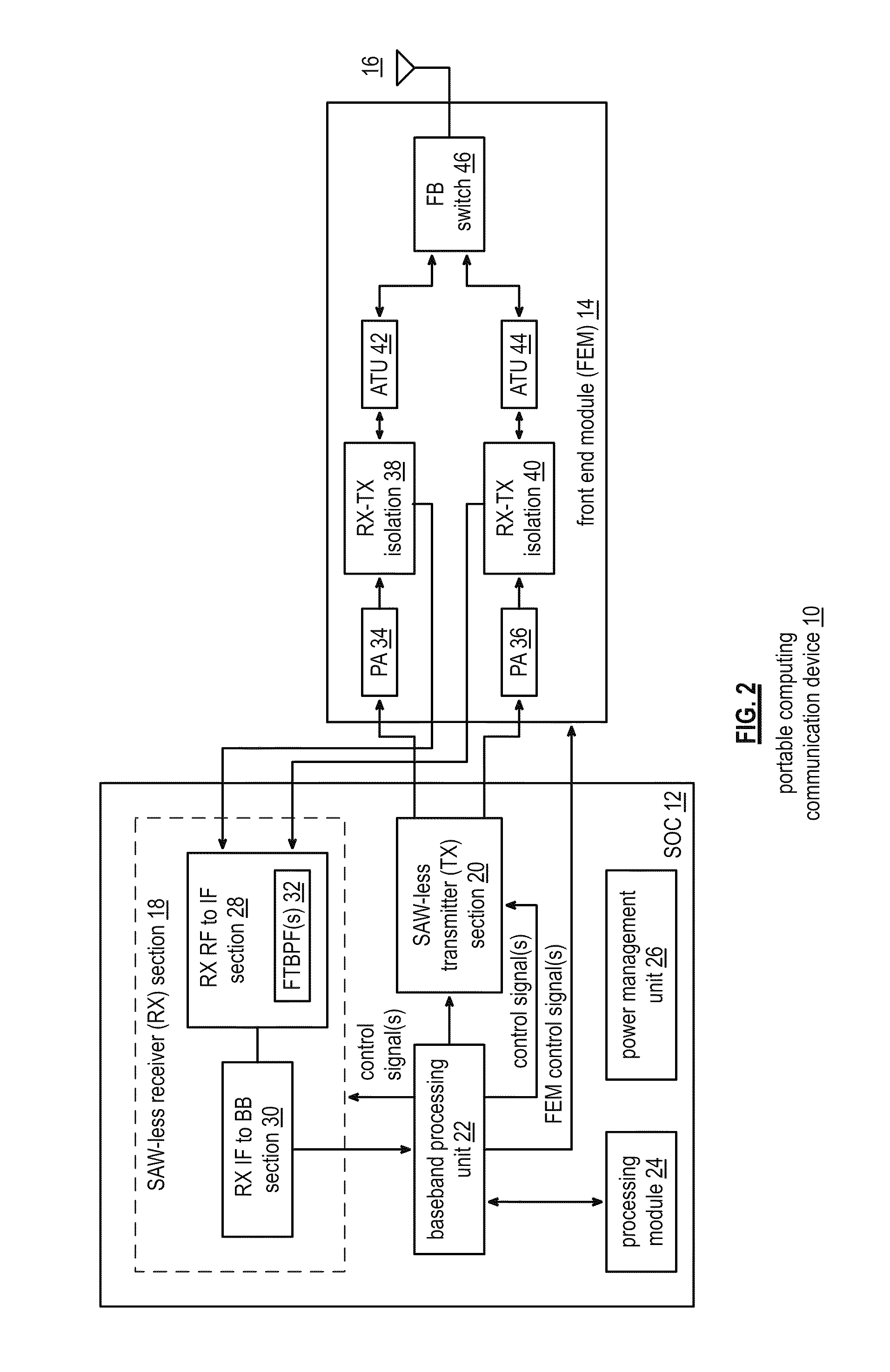
A wireless communication device includes a front-end module (FEM) network coupled to a system on a chip (SOC) via an RF connection. The FEM network includes a plurality of FEMs, wherein, when activated, one or more of the plurality of FEMs is operable to: output an outbound RF signal to one or more antennas; receive an inbound RF signal from the one or more antennas; and isolate the inbound RF signal from the outbound RF signal. The SOC is operable to activate the one or more of the plurality of FEMs; convert outbound data into the outbound RF signal; and convert the inbound RF signal into inbound data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for monitoring power consumption
InactiveUS20100167659A1Improved and accurate power consumptionMore timely awareness of consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusElectrical conductorTransformer
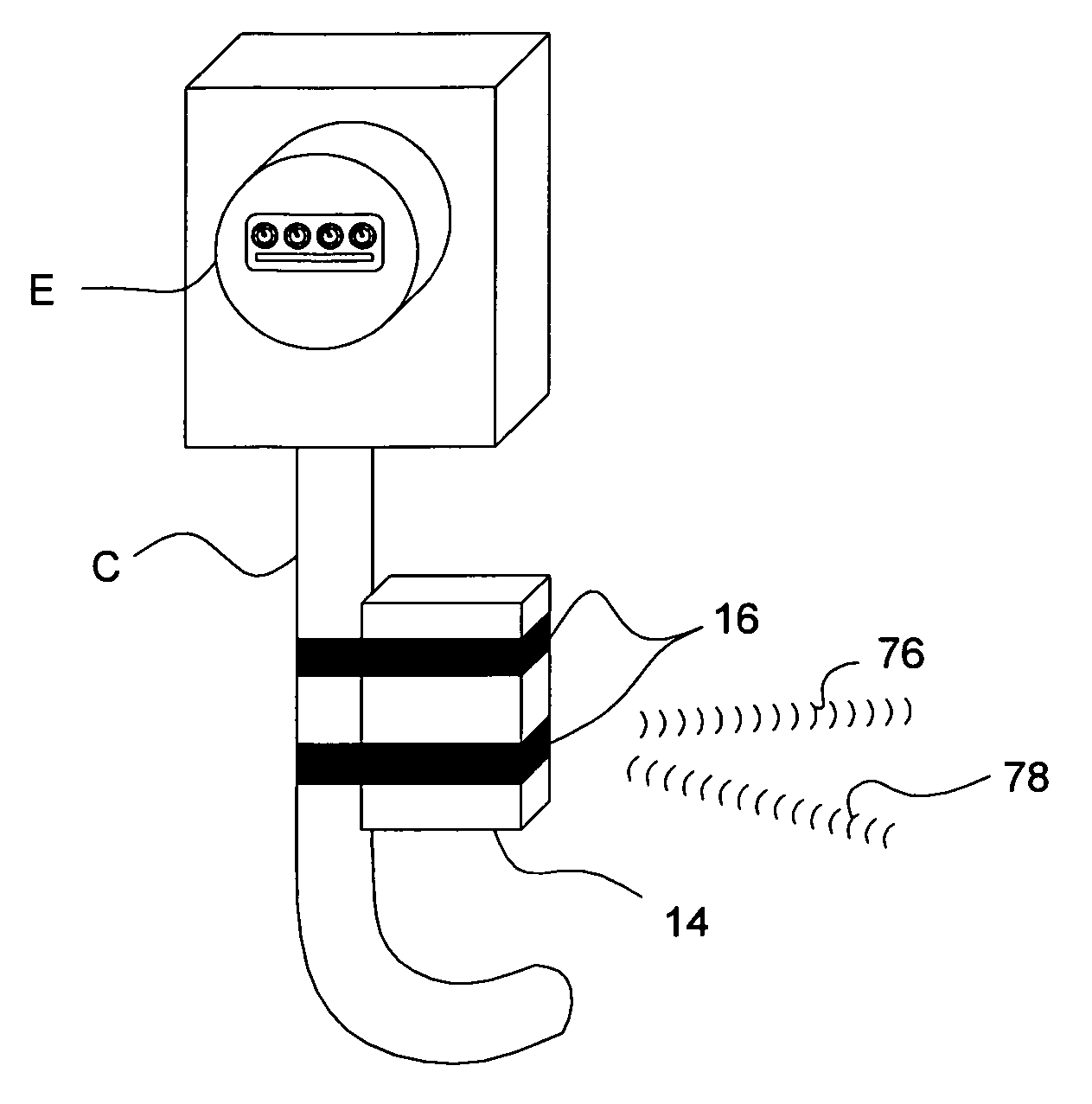
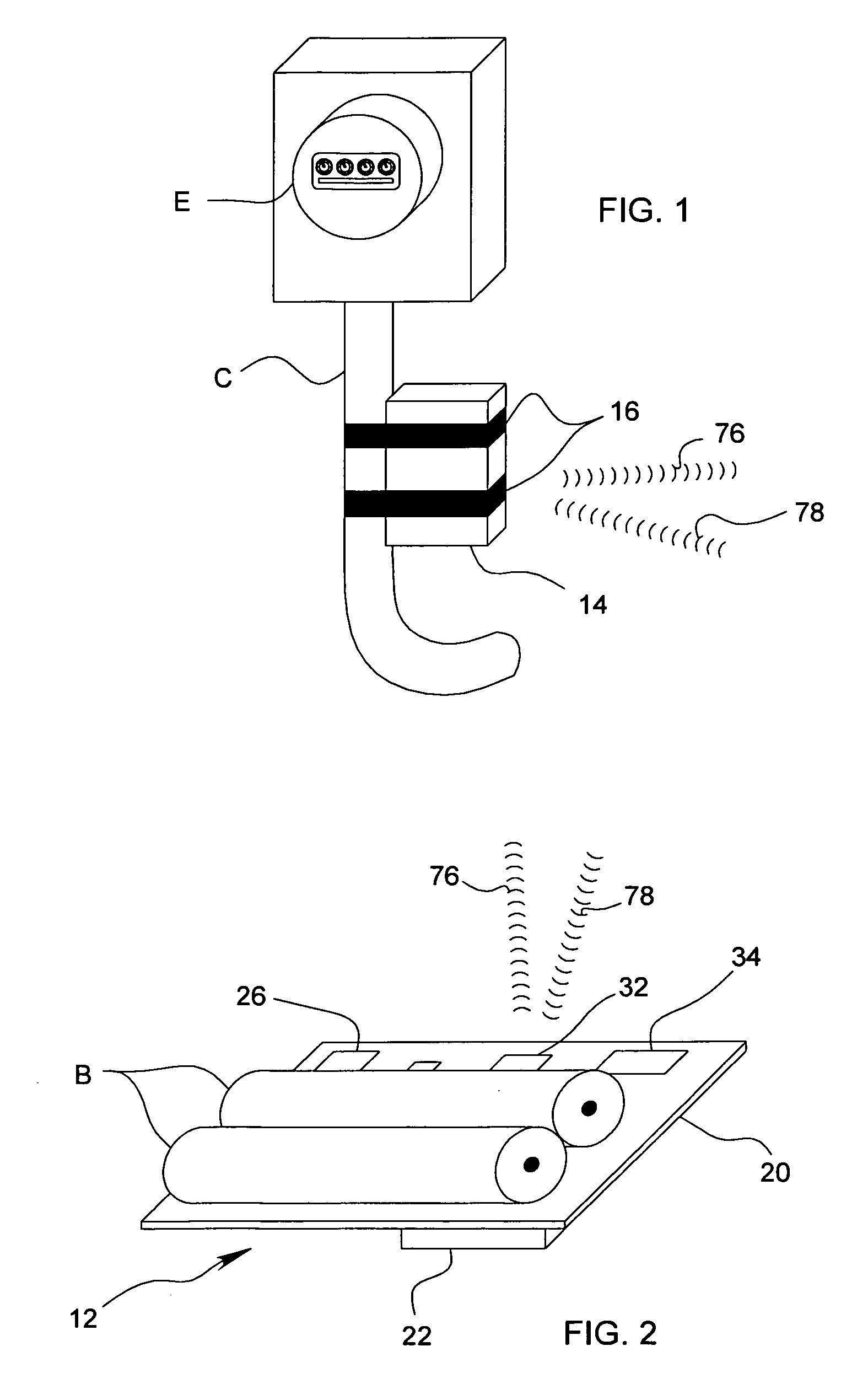
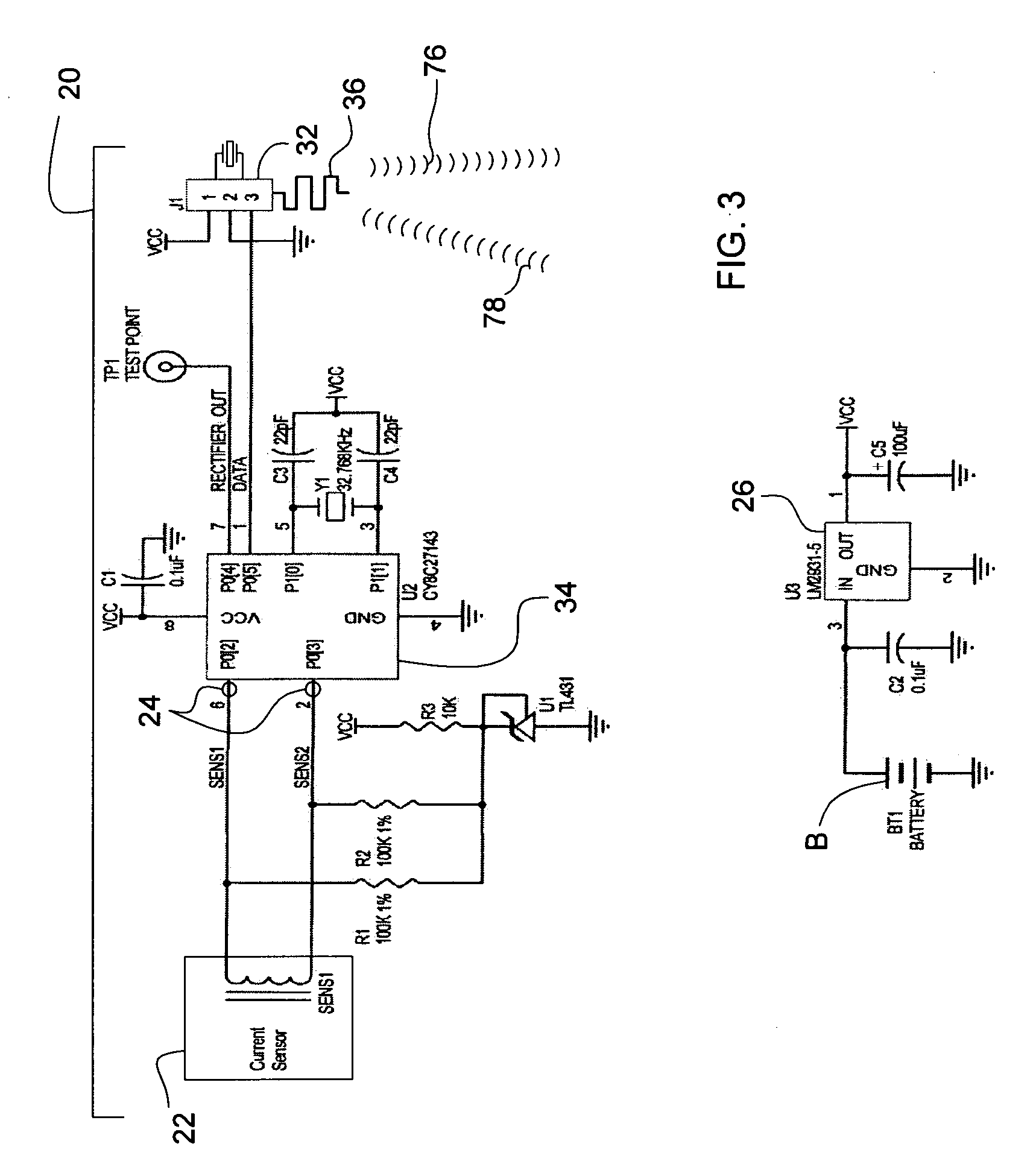
A power consumption monitor, system, and method for monitoring power consumed by equipment, appliances, devices, buildings, and campuses is accomplished by passive sensors (12, 40) that detect power transmitted by individual conductors (C), and which include a current to voltage transformer with a passive, open-circuit electromagnetic force concentrator (22) positioned near the conductor (C). The sensor (22) generates an amplitude signal proportional to the power passing through the conductor (C). Programmable radios on a chip (32, 62, 72) and systems on a chip (34, 64, 74) are used to transmit the amplitude signal to a monitor (50) that displays the power being consumed along with actual and estimated cost and historical information. Software programs are implemented across the sensors (12, 40) and monitors (50) and a remote computer (80) to enable real-time monitoring power consumption with a resolution that spans from entire campuses down to single devices.
Owner:POWERKUFF
Camera system with multiple pixel arrays on chip
ActiveCN101926171AAllow browsingTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionElectronic componentApplication-specific integrated circuit
A camera system uses one or more image sensor IC chips each having multiple pixel arrays on the same semiconductor substrate (i.e., ''multiple pixel arrays on a chip''). In one embodiment, such a camera system includes: (a) optical components that create multiple images in dose physical proximity of each other (e.g., within a few millimeters or 10 centimeters); and (b) a single sensor substrate (''chip'') containing multiple 2 -dimensional pixel arrays that are aligned to capture these multiple images, so as to convert the multiple images into electrical signal. The pixel arrays can be manufactured using a CCD or a CMOS compatible process. Such a chip is typically two centimeters or less on a side. Optional electronic components for further signal processing of the captured images may be formed either on the sensor chip (i.e., in a ''system-on-a-chip'' implementation), or in a separate back-end application specific integrated circuit (ASIC).
Owner:CAPSO VISION INC
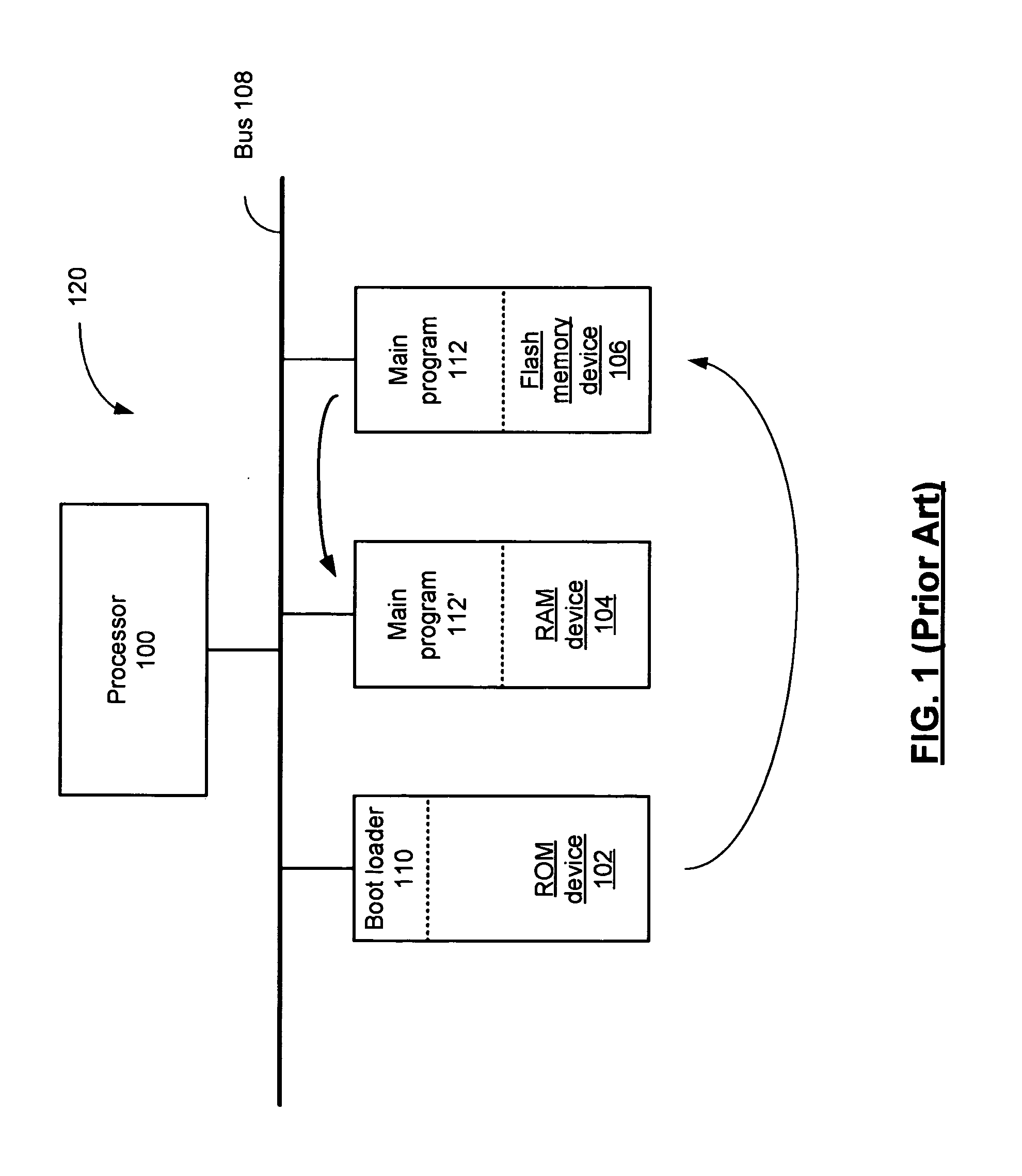
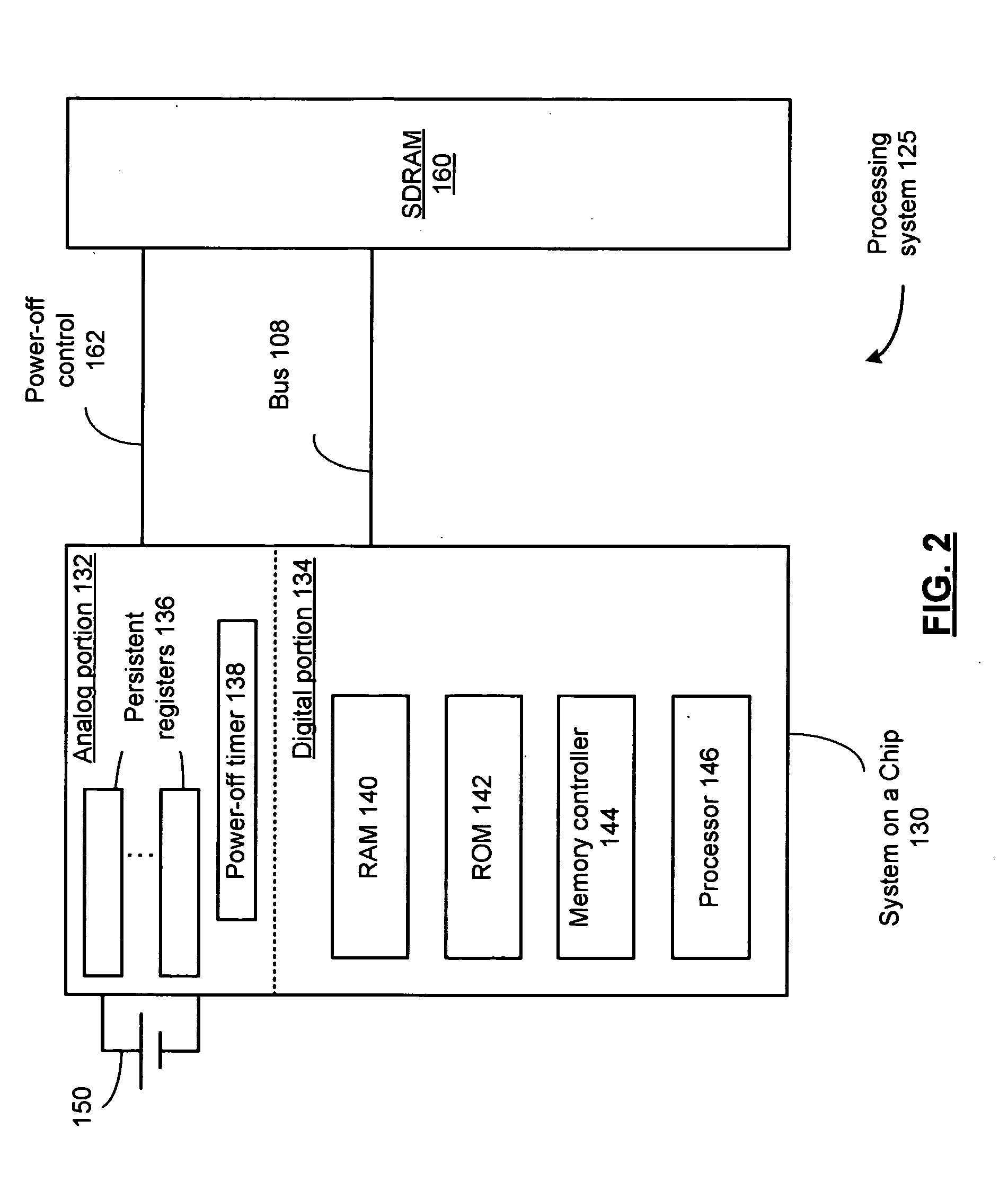
System on a chip integrated circuit, processing system and methods for use therewith
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com