Patents
Literature
2634results about "Single output arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
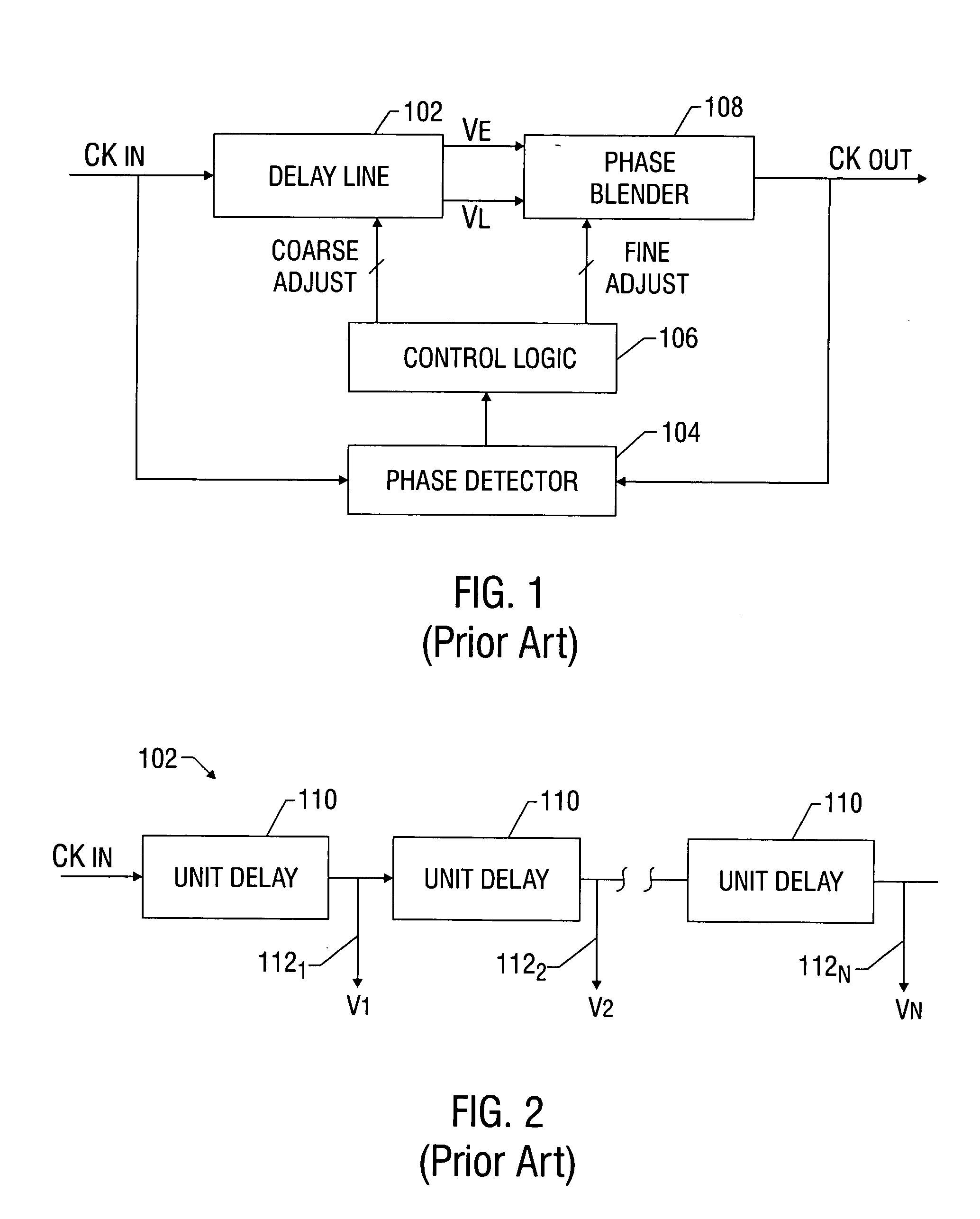
Signal loss detector for high-speed serial interface of a programmable logic device
InactiveUS7996749B2Multiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionPattern matchingProgrammable logic device
Owner:ALTERA CORP
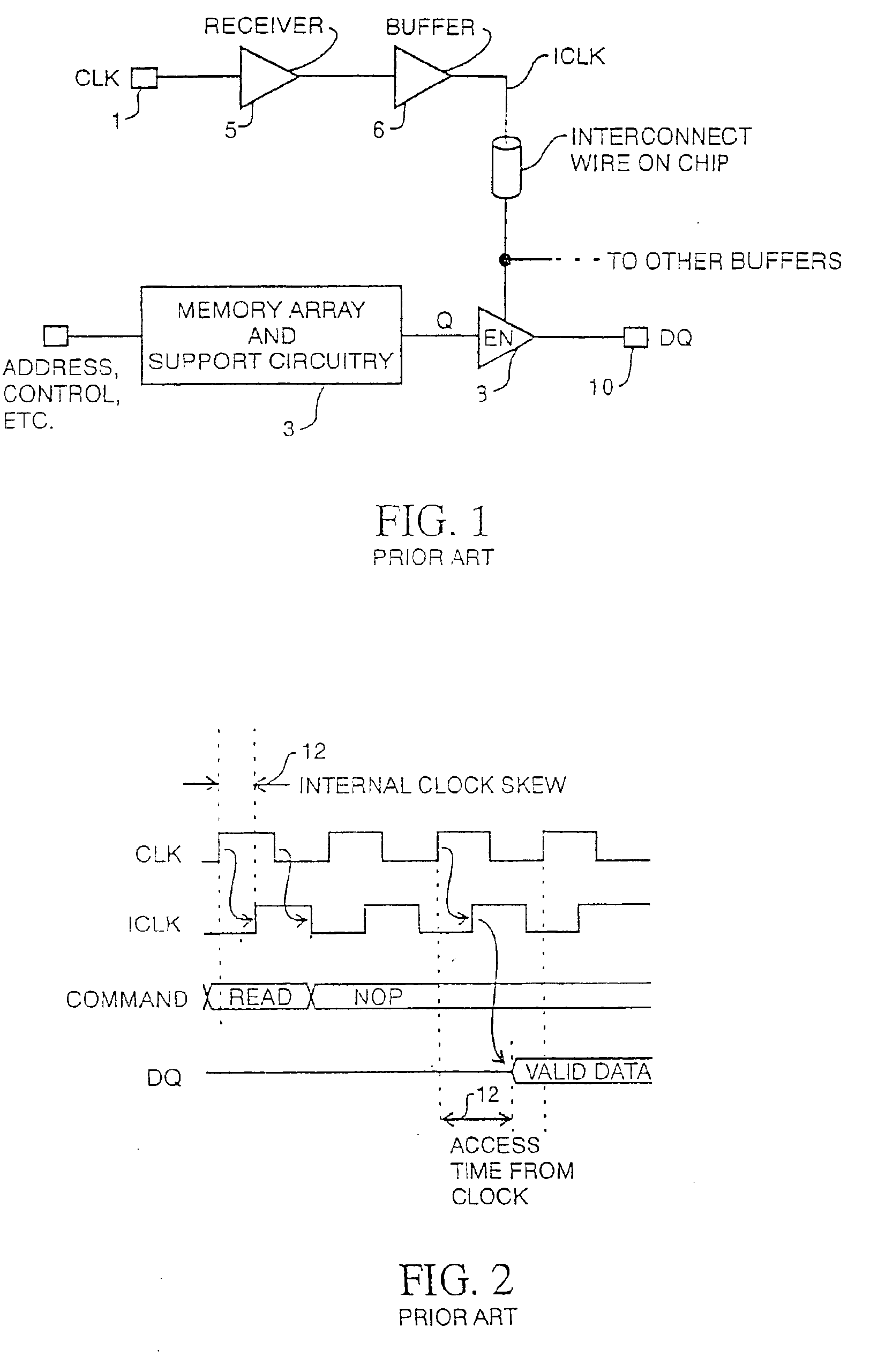
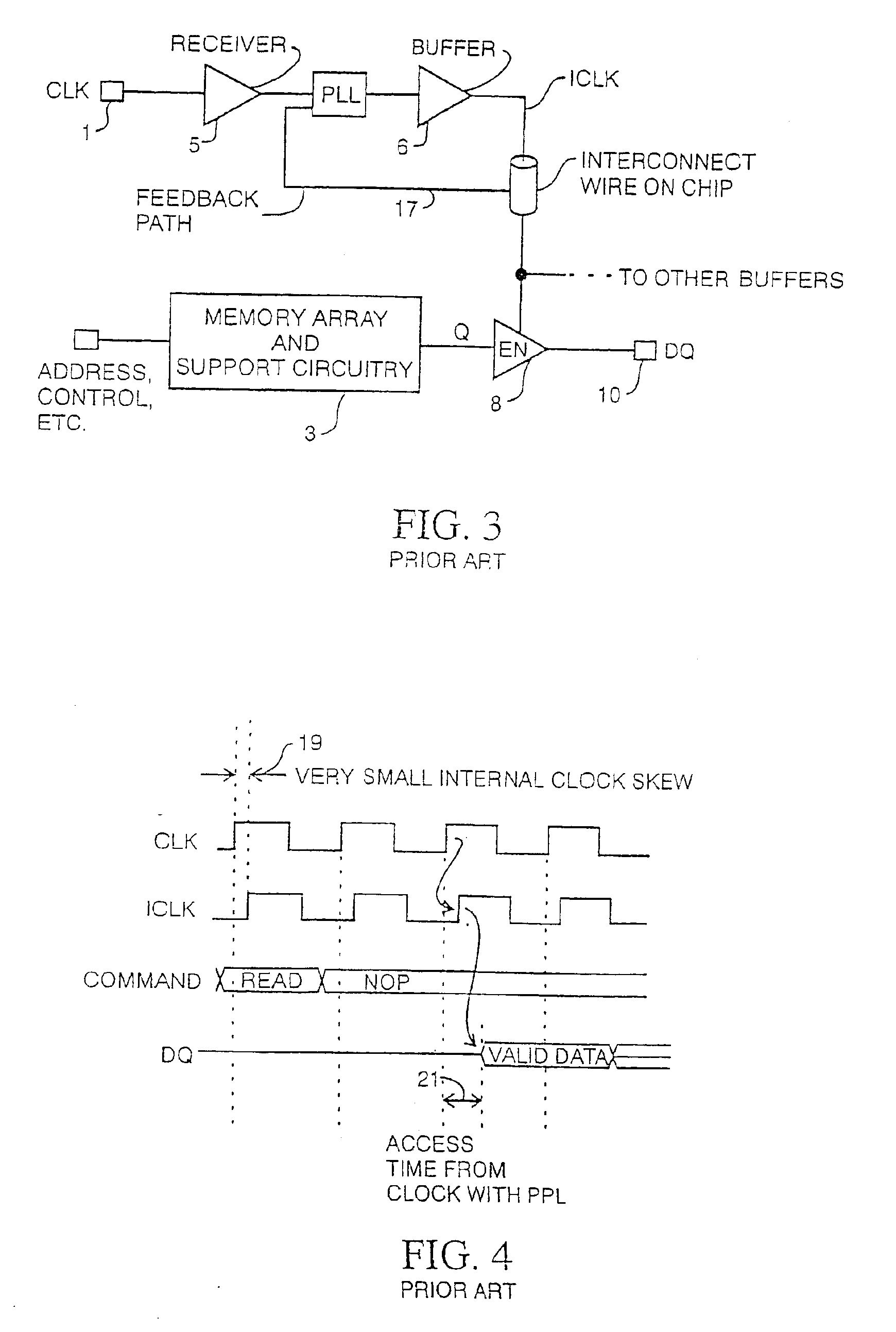
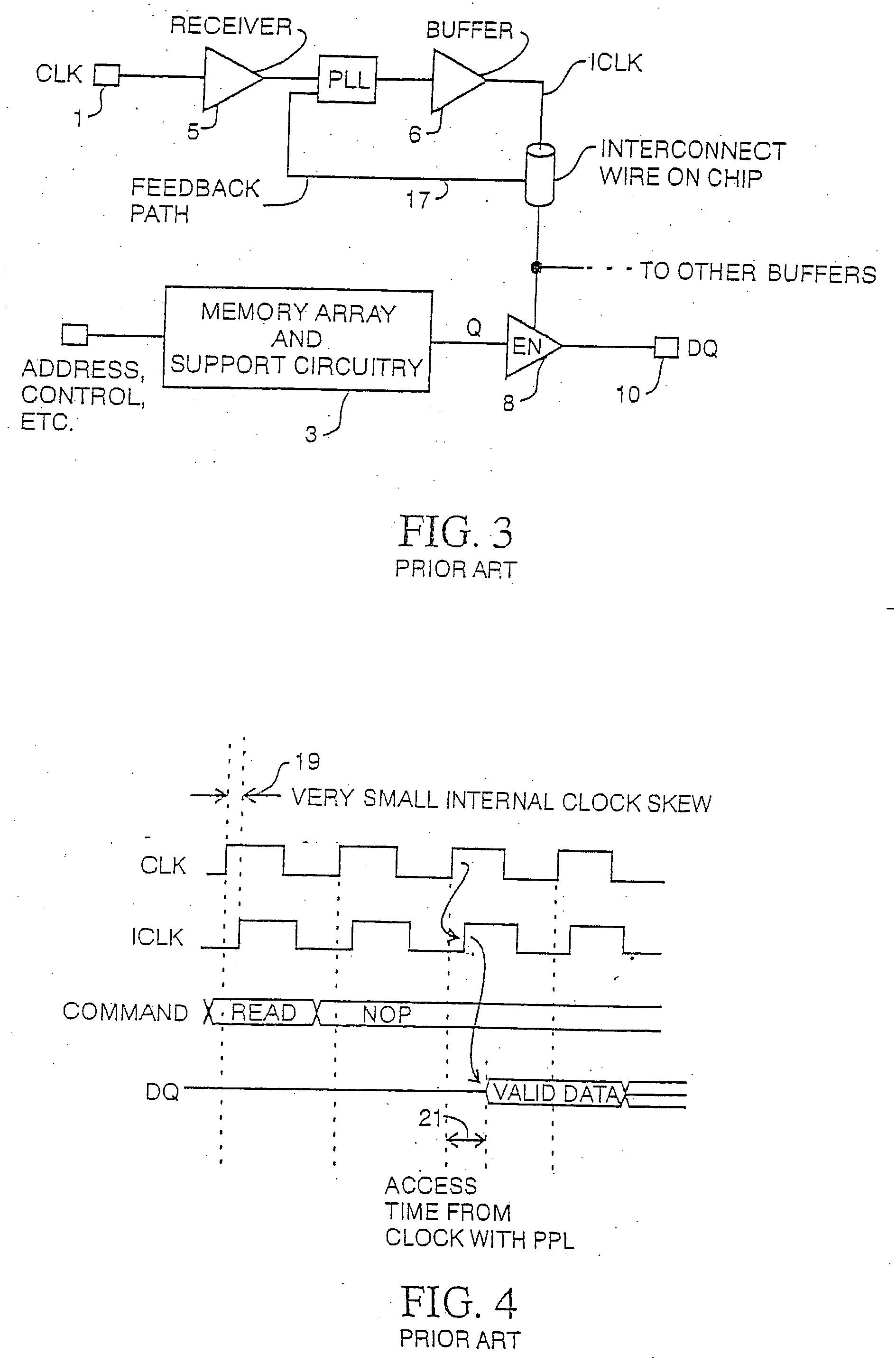
Integrated circuit with timing adjustment mechanism and method
InactiveUS6950956B2Multiple-port active networksModulated-carrier systemsComputer scienceIntegrated circuit
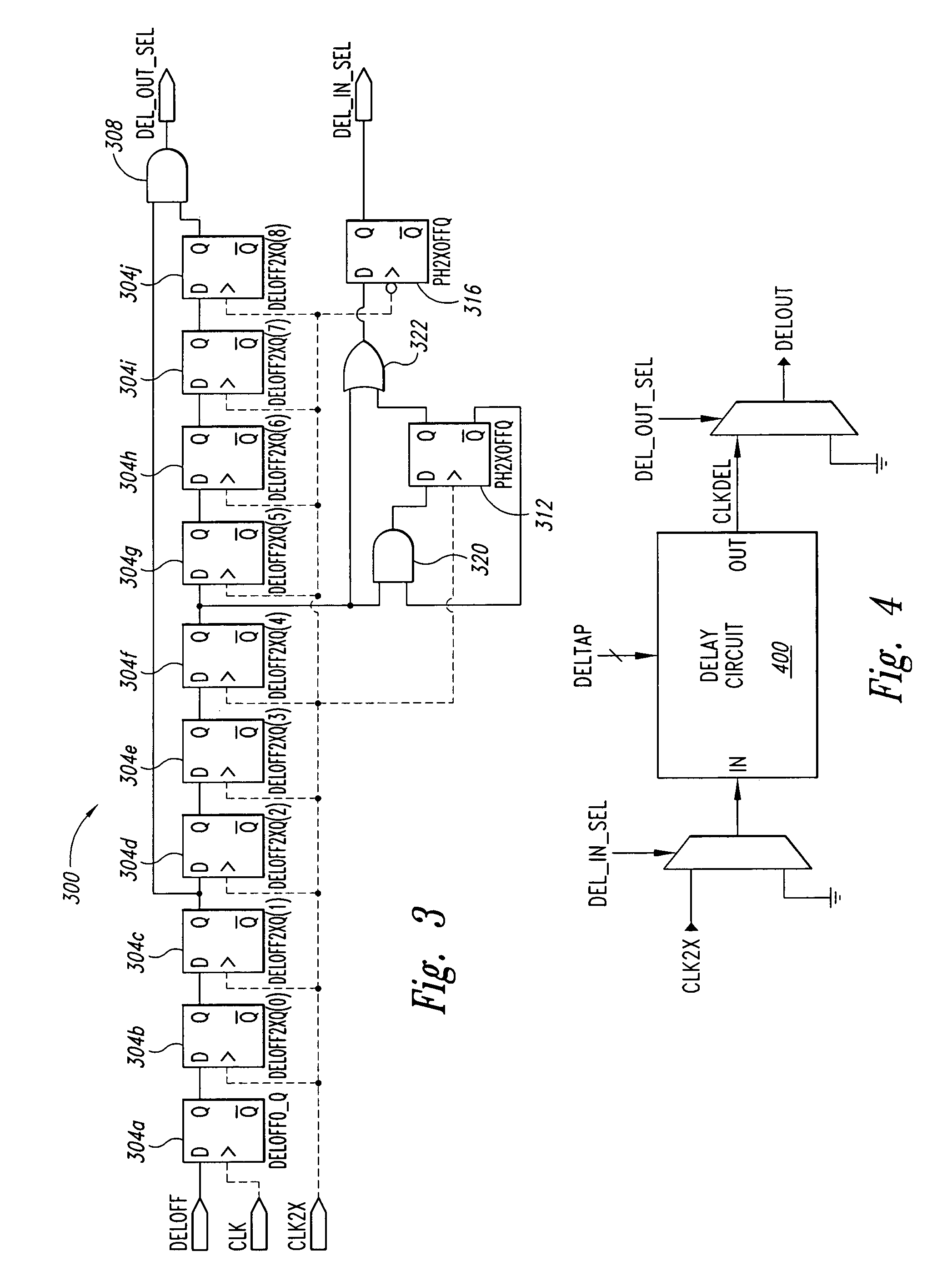
An integrated circuit device includes a receiver, a register and a clock circuit. The receiver samples data from an external signal line in response to an internal clock signal. The register stores a value that represents a timing offset to adjust the time at which the data is sampled. The clock circuit generates the internal clock signal such that the internal clock signal maintains a controlled timing relationship with respect to an external clock signal. The clock circuit includes an interpolator that phase mixes a set of reference clock signals such that the internal clock signal is phase offset in accordance with the value.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
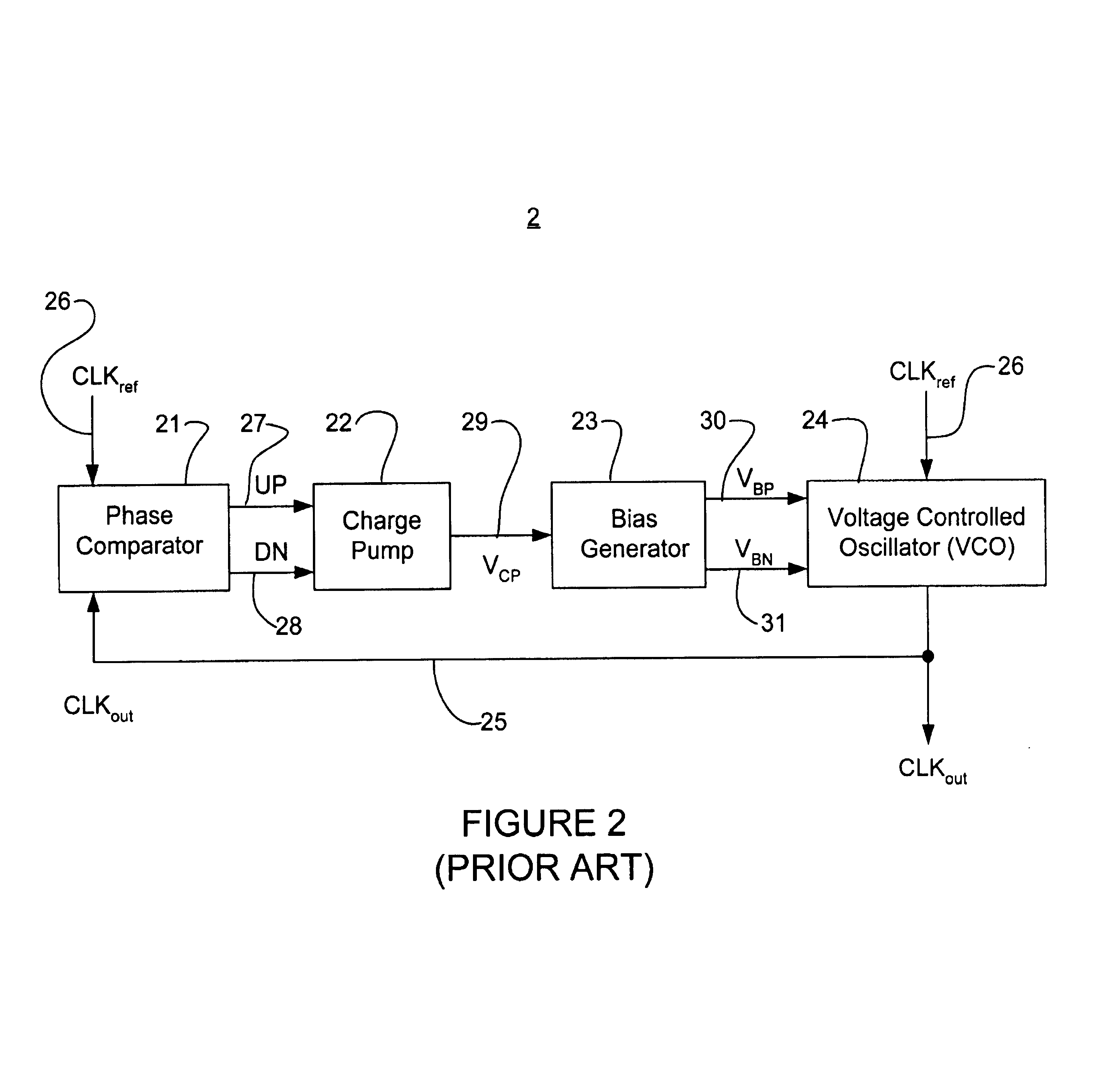
Clock alignment circuit having a self regulating voltage supply
InactiveUS6928128B1Wide range of operationsReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsAudio power amplifierEngineering
Clock alignment circuits and techniques for reducing power dissipation, increasing power supply noise immunity, decreasing process and temperature variation sensitivity, and providing a wide operating range. A power supply generator generates an isolated supply voltage for a delay line used in a clock alignment circuit. The delay line generates a delayed clock from a reference clock. A comparator detects a correction information (i.e., delay or phase error) between the delayed clock and the reference clock and generates error information representative of the correction information. A charge pump circuit converts the error information into a voltage signal, wherein the voltage signal is a scaled representation of the error information. The power supply generator includes an amplifier having a first input coupled to the voltage signal and an output to provide the supply voltage and a capacitor coupled between the supply voltage and a ground voltage, wherein the amplifier tracks the voltage signal level to regulate the supply voltage.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
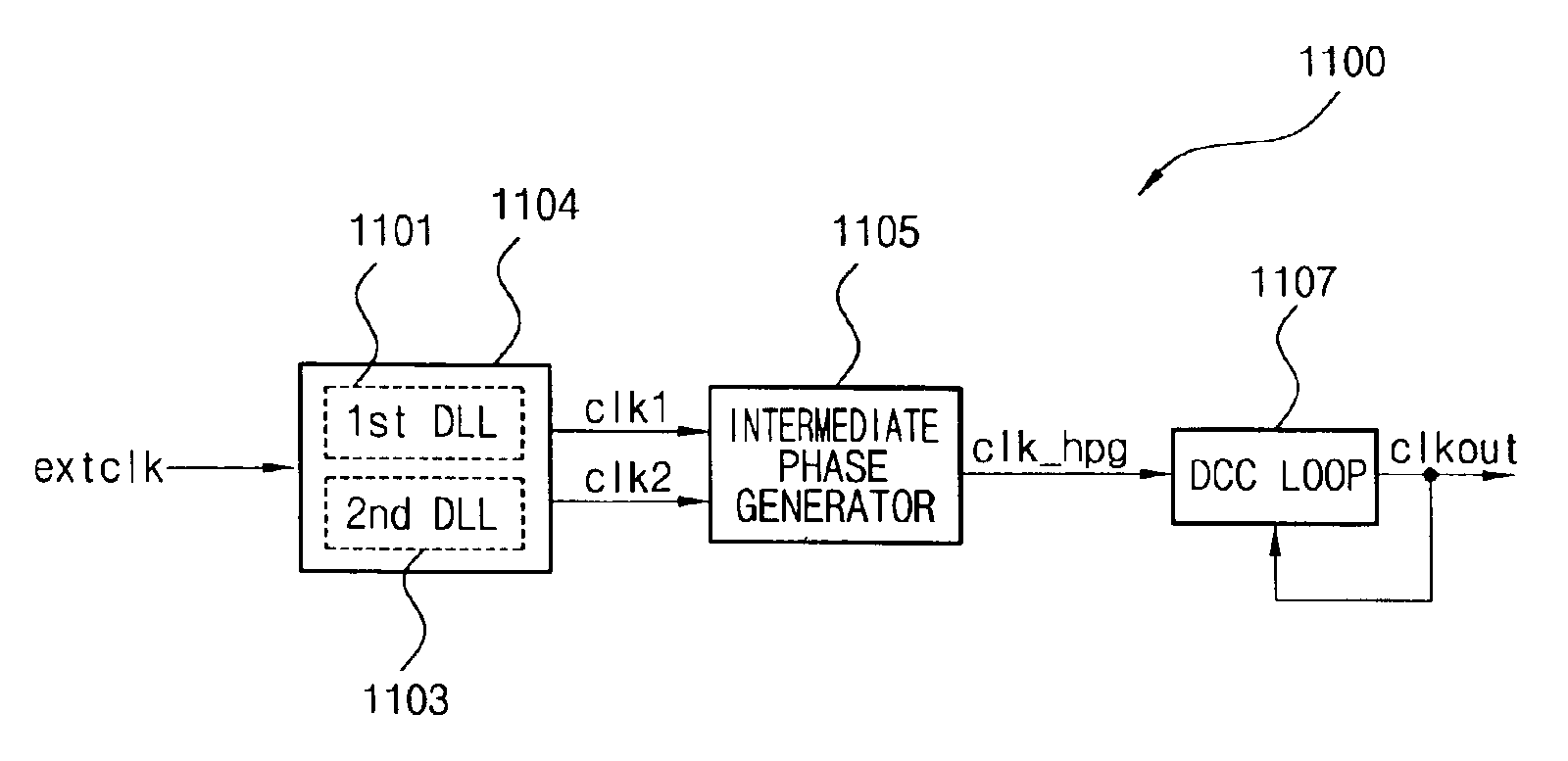
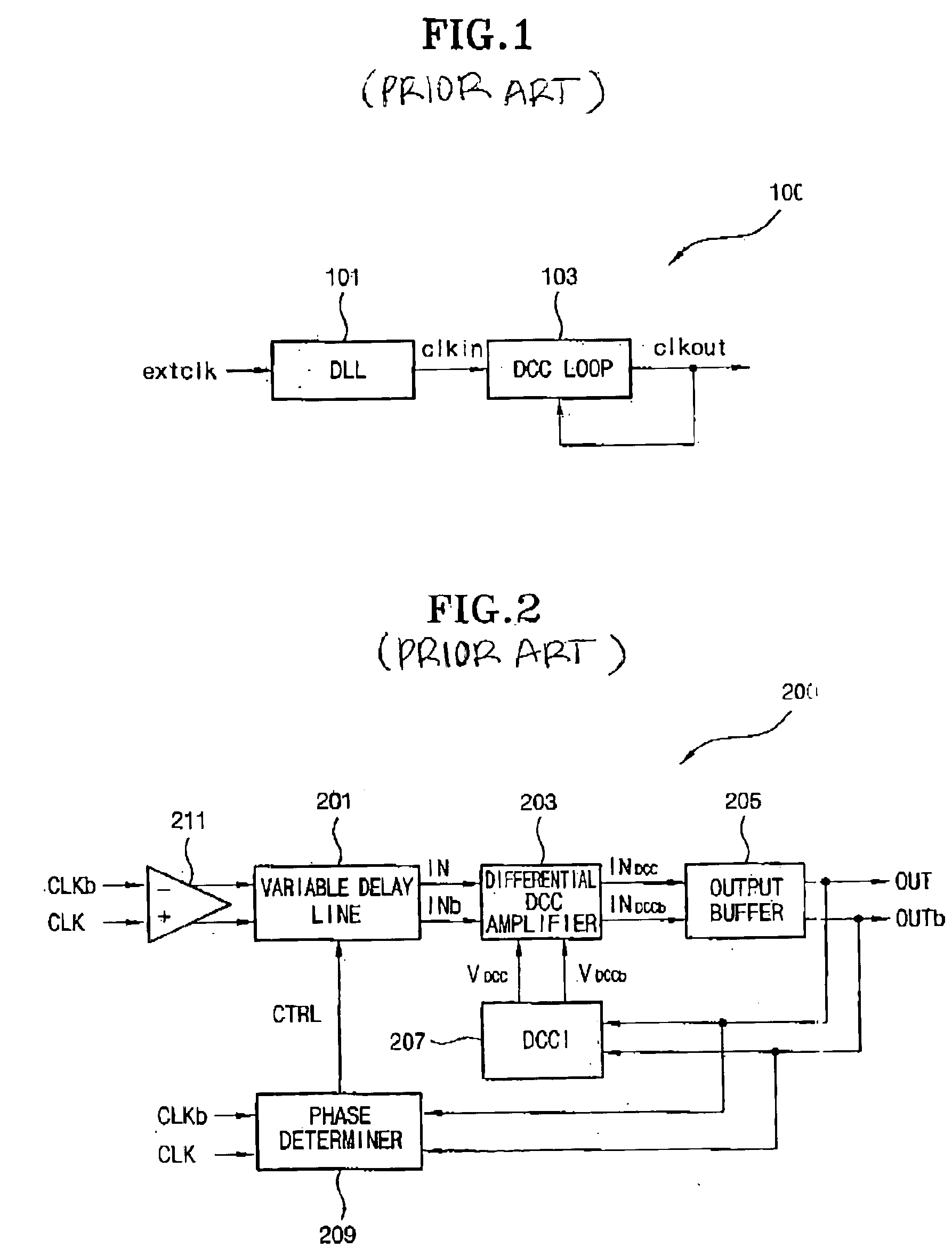
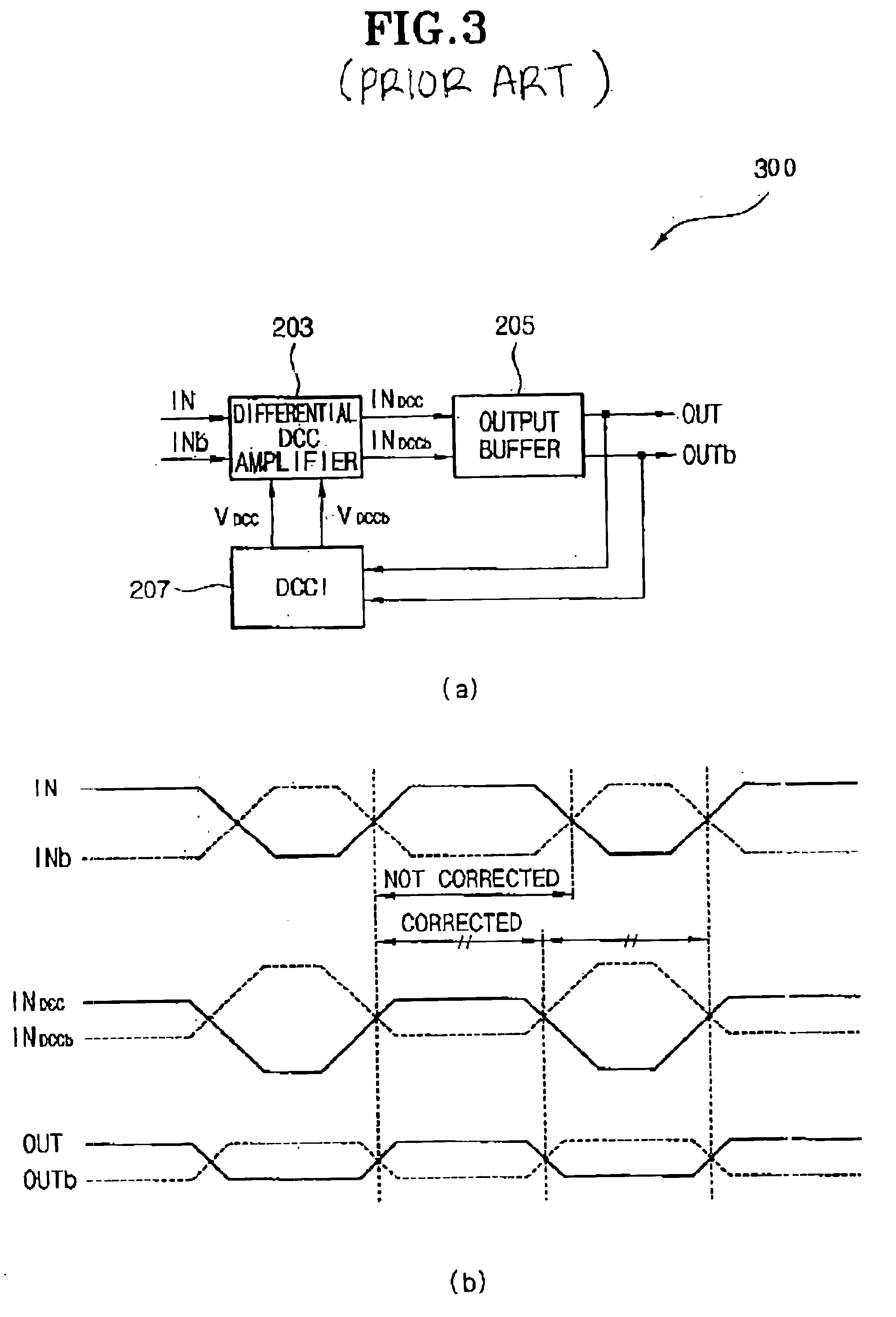
Delay locked loop circuit with duty cycle correction function
InactiveUS6853225B2Improve accuracyShort lock timePulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationNegative feedbackDelay-locked loop
A delay locked loop (DLL) circuit having a structure in which a method of performing duty cycle correction (DCC) using two DLLs and an intermediate phase composer and a method of performing DCC by forming a closed loop using a negative feedback are combined with each other is provided. The DLL circuit includes a first DLL for receiving an external clock signal and generating a first clock signal and a second DLL for receiving an external clock signal and generating a second clock signal. The first clock signal and the second clock signal are synchronized with an external clock signal. The DLL circuit further includes an intermediate phase generation circuit for receiving the first and second clock signals and generating an intermediate phase clock signal and a DCC loop for receiving the intermediate phase clock signal and generating an output clock signal. The intermediate phase clock signal has an intermediate phase between the phases of the first and second clock signals. The output clock signal is generated through correction of the duty cycle of the intermediate phase clock signal using a value obtained by integrating the output clock signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method and apparatus for implementing precision time delays
Owner:TDC ACQUISITION HLDG
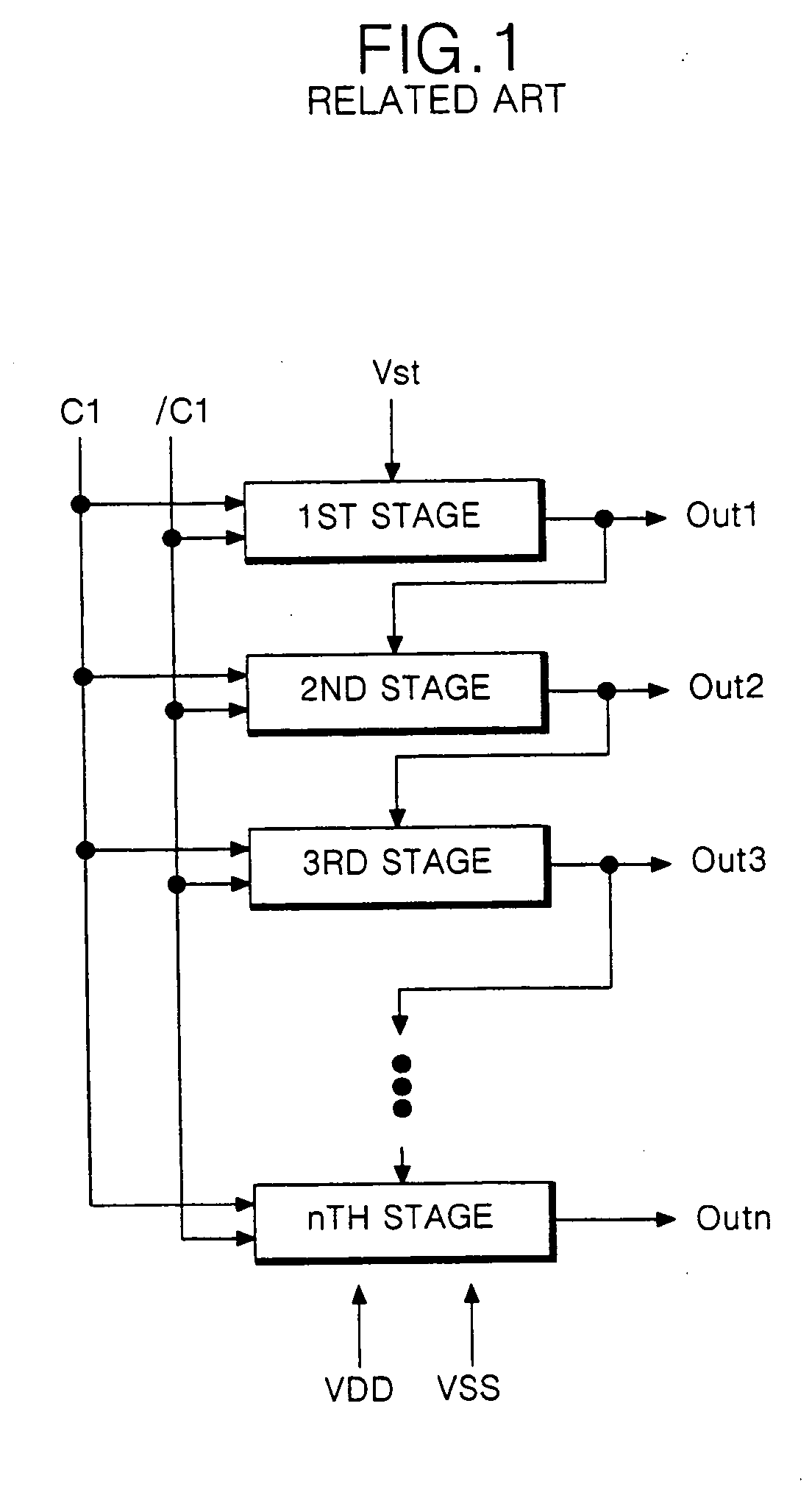
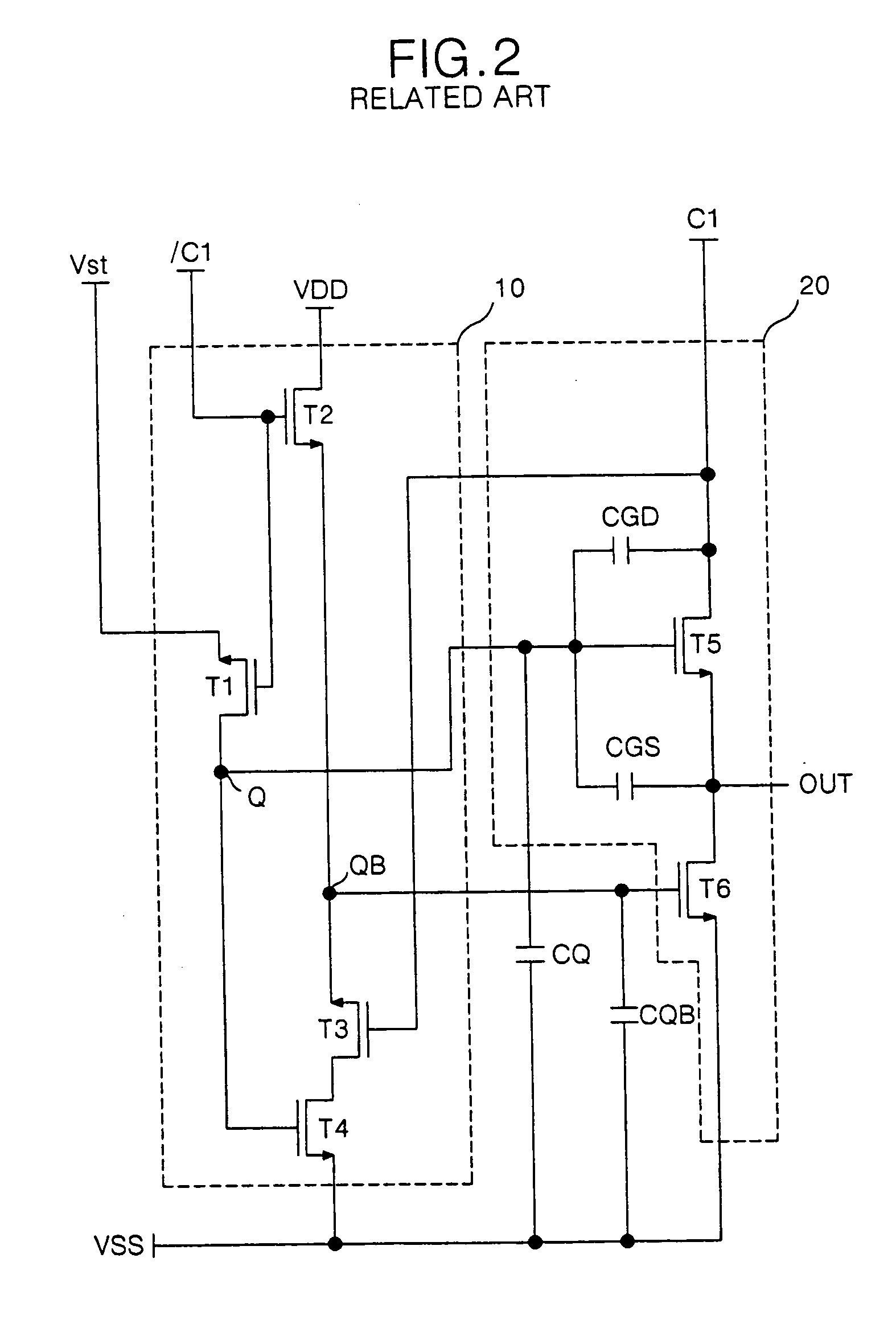
Shift registrer and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20050220263A1Static indicating devicesCounting chain synchronous pulse countersShift registerCapacitor
A shift register having a plurality of stages for shifting a start pulse and outputting a shifted start pulse to a next stage, each of the plurality of stages includes a pull-up transistor controlled by a first node to apply a first clock signal to an output line, a first pull-down transistor controlled by a second node to apply a first driving voltage to the output line, a controller for controlling the first and second nodes, and a compensating capacitor connected between the first node and an input line of a second clock signal, the second clock signal being different from the first clock signal.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Power management apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20110022859A1Precise processingDc network circuit arrangementsVolume/mass flow measurementControl powerIntegrated circuit
Power management integrated circuits (PMICs) and related methods. In one aspect a PMIC which is operable to provide a plurality of PMIC power states is arranged to provide a predetermined delay before a power state transition. The delay is applied after receipt by the PMIC control circuitry of a power state transition command. Applying a delay allows time for the system powered by the PMIC to perform any necessary shut-down procedures and terminate active processes before power is removed, preventing corruption of the system. The delay is preferably configurable. The PMIC may also be arranged to control power converters which are external to the PMIC. In another aspect the PMIC has translation circuitry for providing the control settings of one power block, e.g. power converter, with any necessary modifications to be used by another power block. This means that only one set of control settings needs to be updated to change the output of both power blocks simultaneously.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Phase shifters deposited en masse for an electronically scanned antenna
ActiveUS7324043B2Increase processing costPatterning of backsideSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectricEngineering
A system and method for an electronically scanned antenna is provided in which phase shifters are deposited en masse along with other electronically scanned antenna components on a wafer scale substrate using a thin film process. Alternative wafer scale sizes may be utilized to furnish a required antenna aperture area. Significant processing costs for radar and communication systems are saved utilizing the present invention as compared with contemporary discrete phase shifters that are individually mounted on an antenna. In an aspect, the phase shifter is made up of a base electrode, a barium strontanate titanate (BST) ferroelectric varactor and a top electrode. The BST ferroelectric material is a voltage variable dielectric, which generates a radiation phase. The radiation phase is regulated by a phase shifter control. The radiation phase generates an electromagnetic field about a radiating element and electromagnetic radio waves are radiated from the radiating element.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
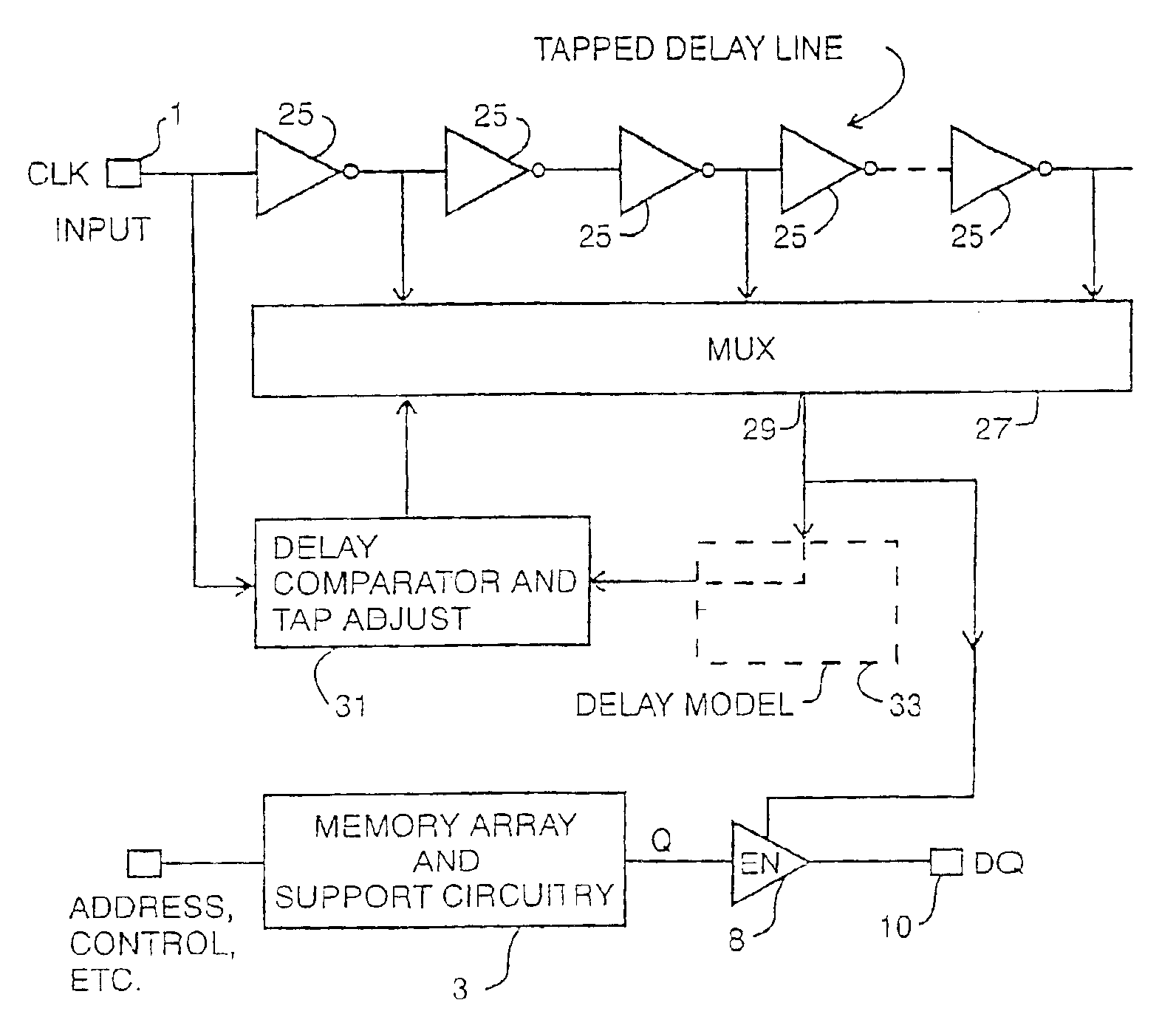
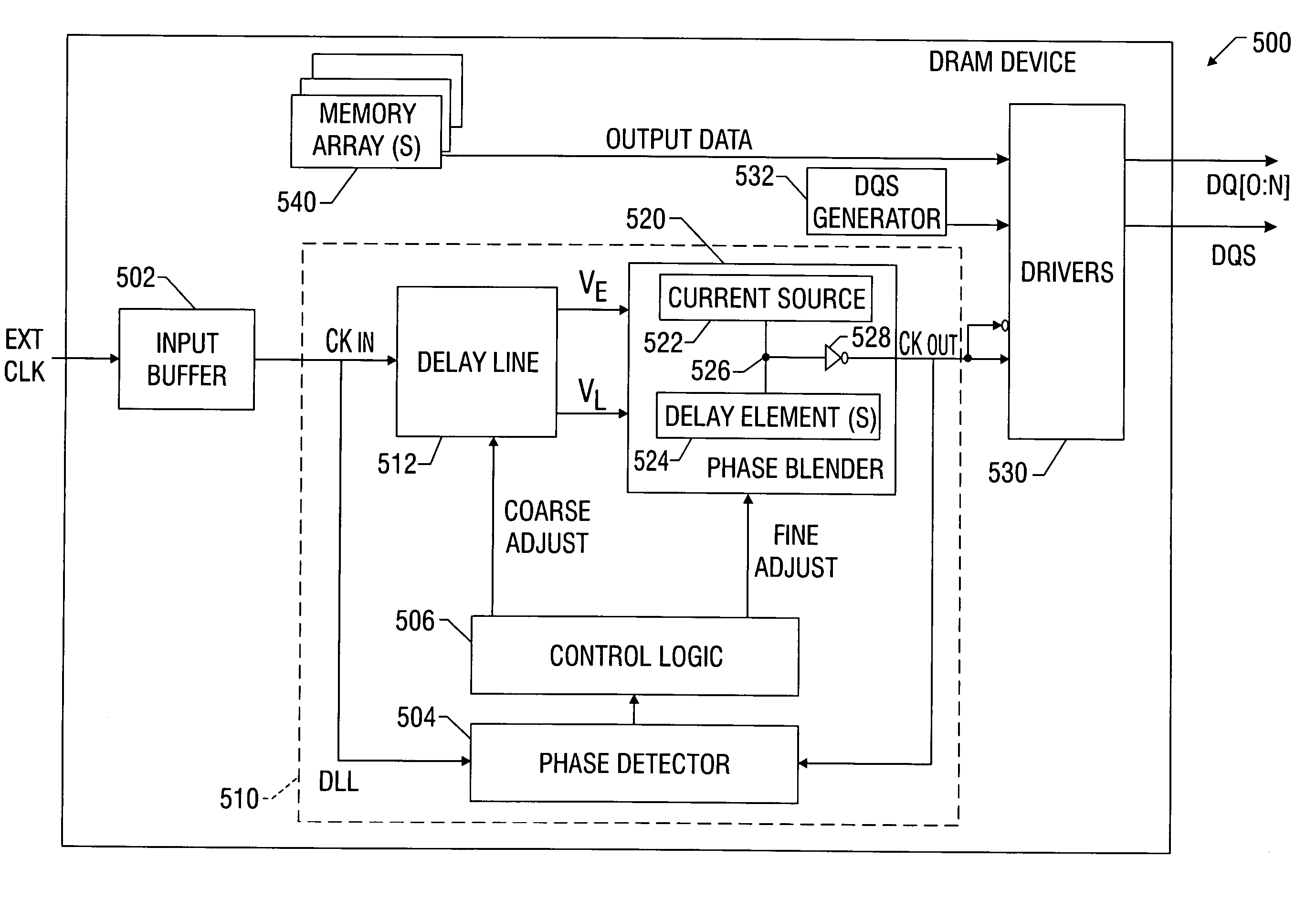
Delay locked loop implementation in a synchronous dynamic random access memory
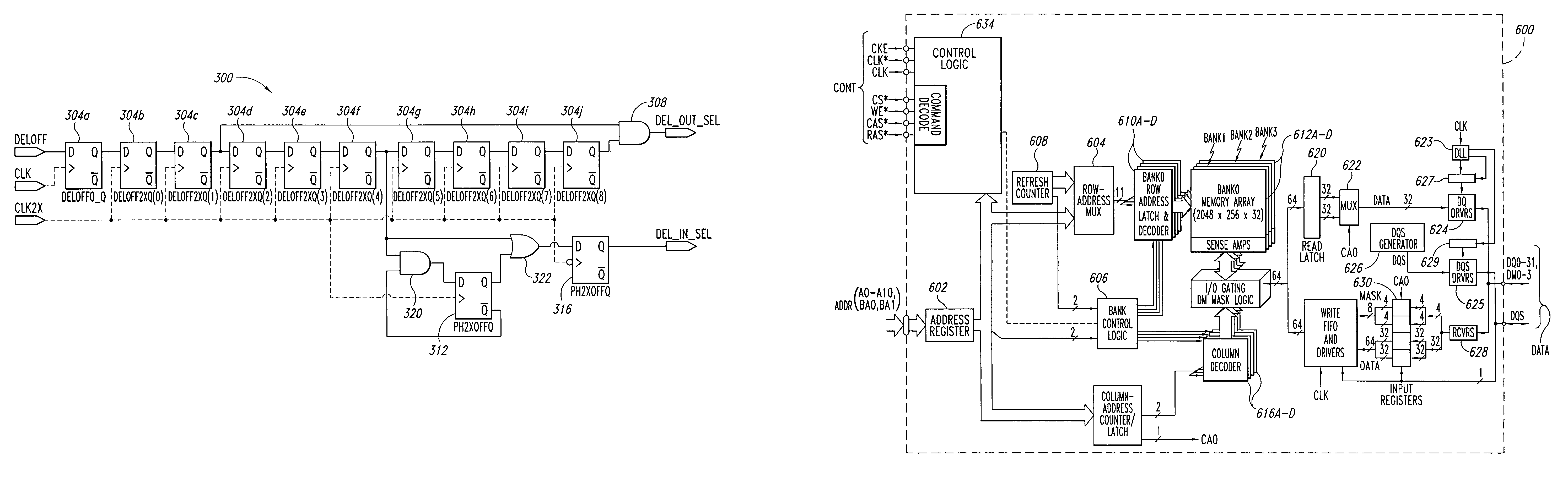
InactiveUS6992950B2High operating requirementsLess standby current and start-up timePulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsRandom access memoryDelay-locked loop
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Integrated circuit logic with self compensating block delays
ActiveUS20050189604A1Reduce logic path variabilityMinimize fabrication parameter variationTransistorSolid-state devicesField-effect transistorCell delay
An integrated circuit (IC) including at least one combinational logic path. The combinational logic path includes two types of logic blocks cells that compensate each other for fabrication parameter effects on cell transistors. The two types may be dense cells with field effect transistor (FET) gates on contacted pitch and isolated cells with FET gates on wider than contacted pitch. Dense cell delay changes from the FET gates being printed out of focus are offset by isolated cell delay changes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
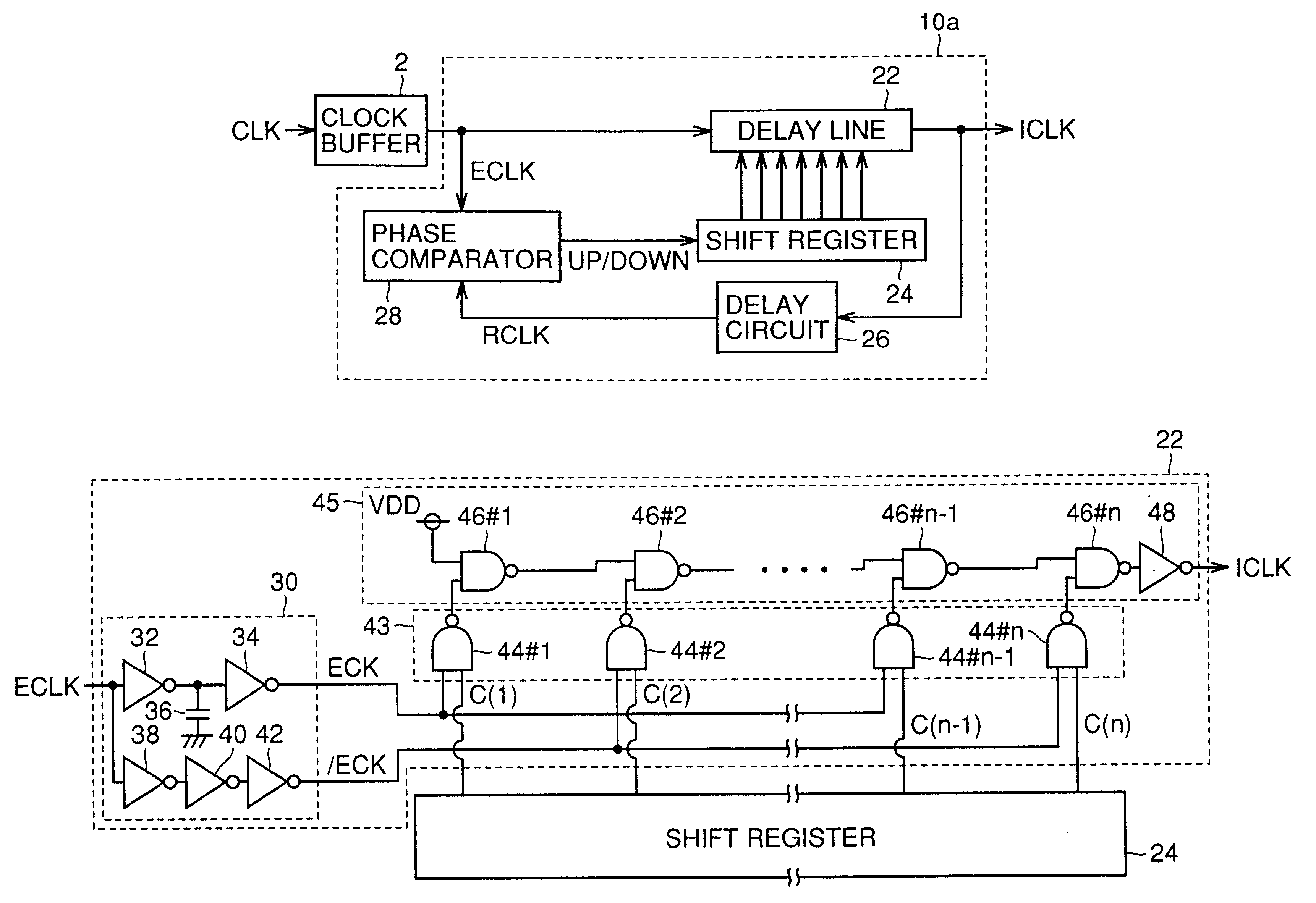
Semiconductor device capable of generating highly precise internal clock
A DLL circuit includes a delay line having a configuration with delay stages receiving alternate complementary clock signals ECK and / ECK having an adjusted phase difference therebetween. A capacitor can be used to adjust the phase difference between signals ECK and / ECK to allow the delay line to provide an amount of delay varying minutely. Preferably, for a fast clock, delay adjustment starts with a shift register having an initial value providing an intermediate amount of delay, and for a slow clock, delay adjustment starts with the shift register having an initial value providing a minimal amount of delay. There can be provided a semiconductor device provided with a DLL circuit accommodating a fast clock with reduced jitter.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
High resolution pulse width modulator
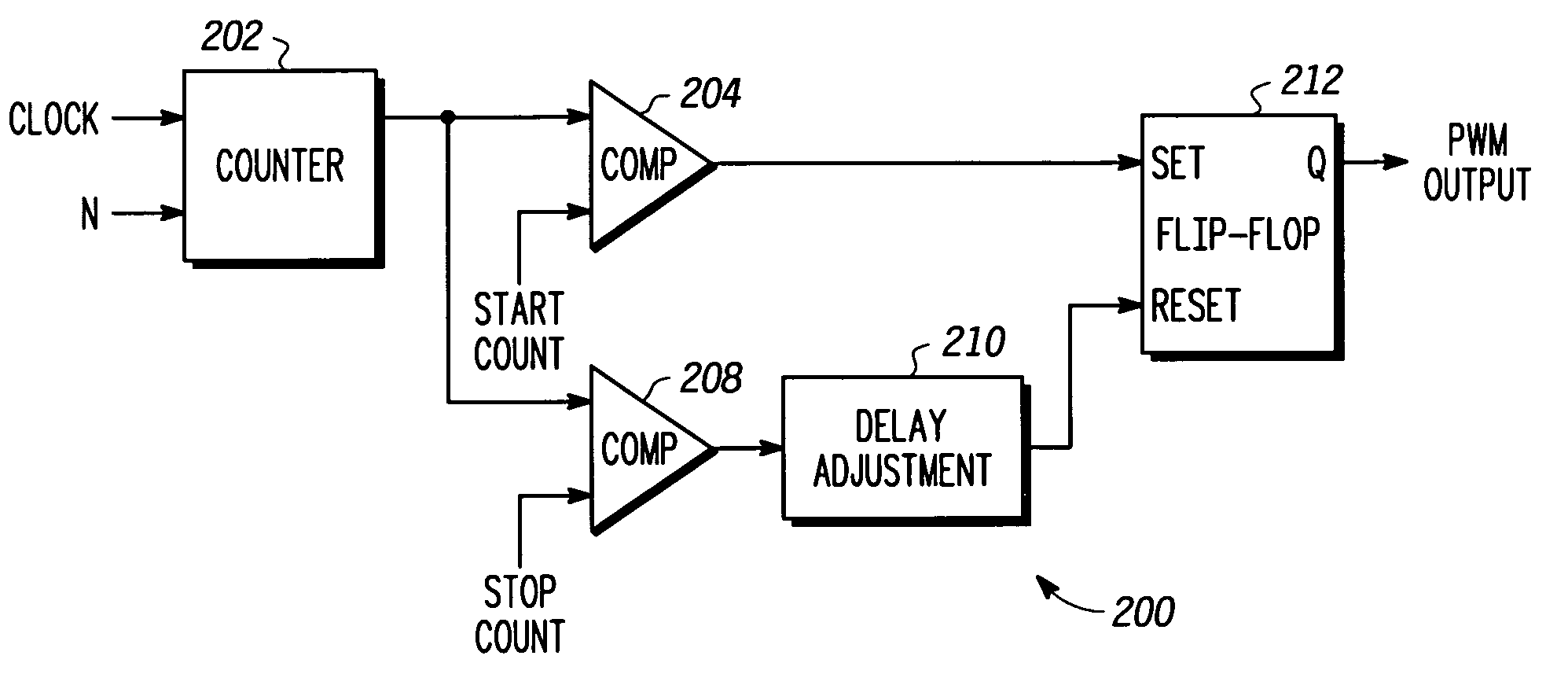
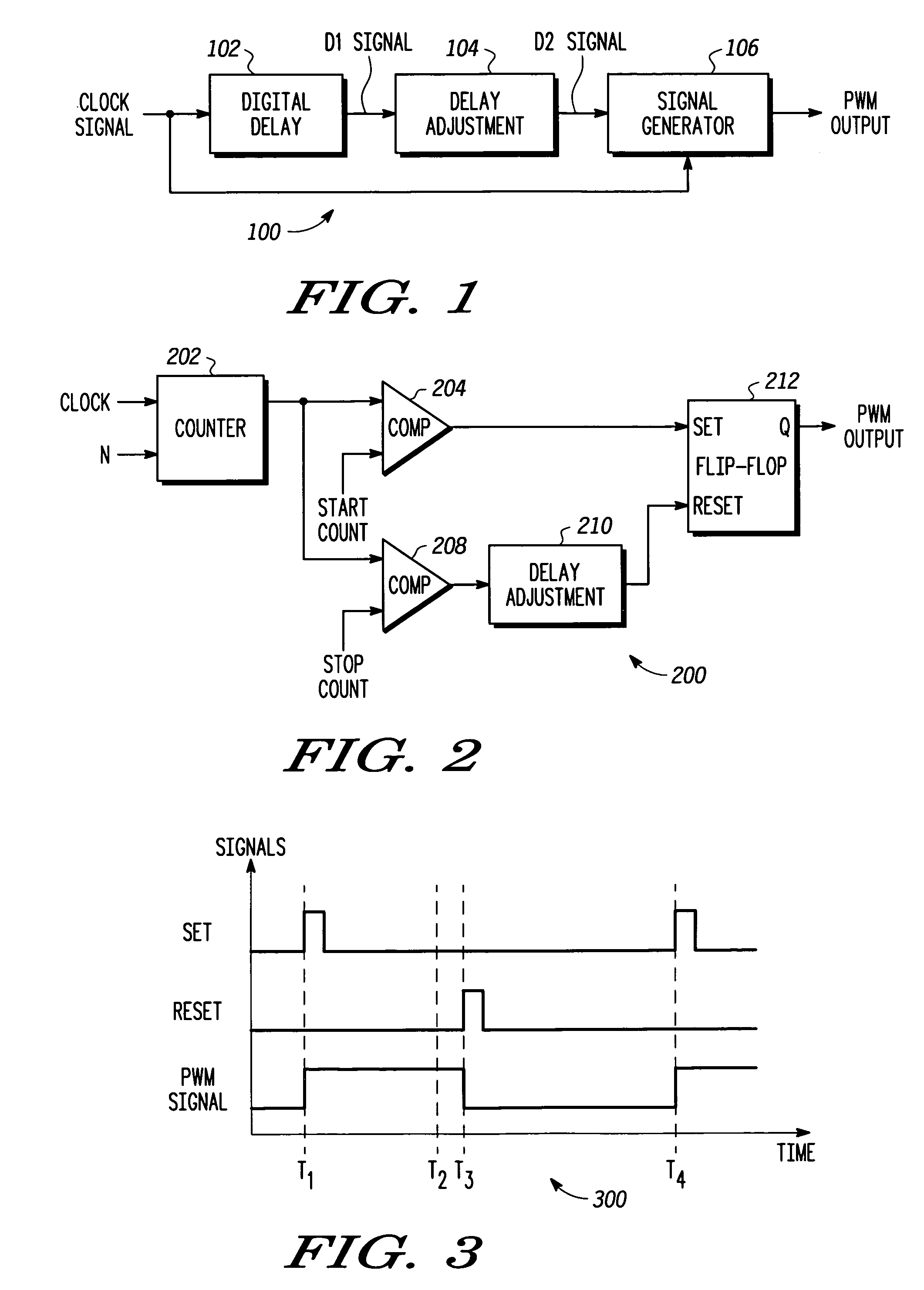
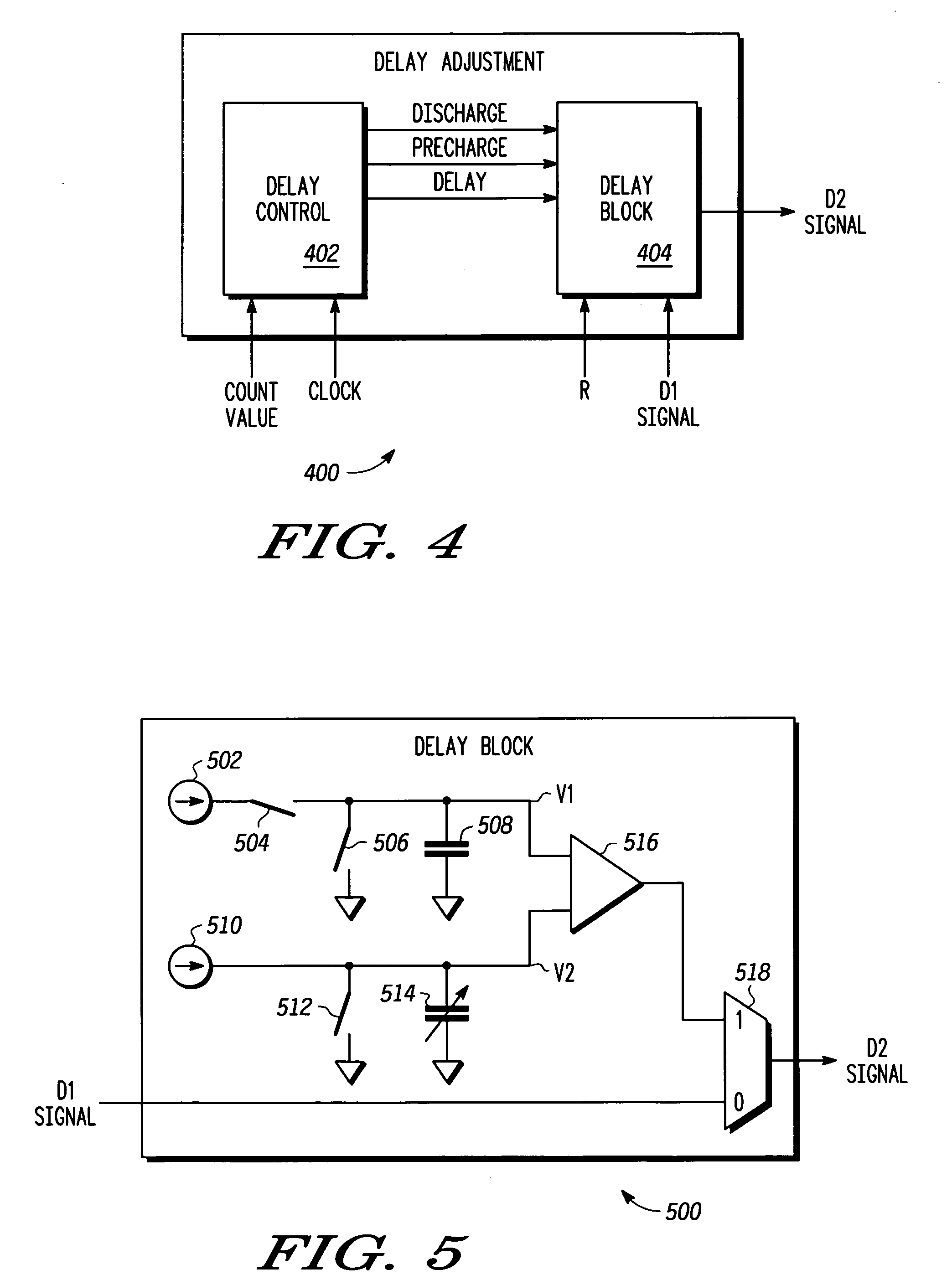
A pulse width modulator (100) and method that facilitates high resolution pulse width modulation is provided. The pulse width modulator (100) creates a pulse width modulated signal having a duty cycle that is proportional to a controllable delay in the modulator. The pulse width modulator combines a first digitally controllable delay (102) with a delay adjustment (104) to provide the controllable delay. In one embodiment, a digital counter (202) is used to provide coarse delay, with the delay adjustment device (210) coupled to the digital counter (202) to provide the fine, high resolution, delay control. Together the digital counter (202) and delay adjustment device (210) provide high resolution pulse width modulation. In one particular implementation, the analog delay adjustment device (100) comprises a delay block (500) designed to provide delay adjustment that is selectively controllable by changing a capacitance in the device.
Owner:APPLE INC
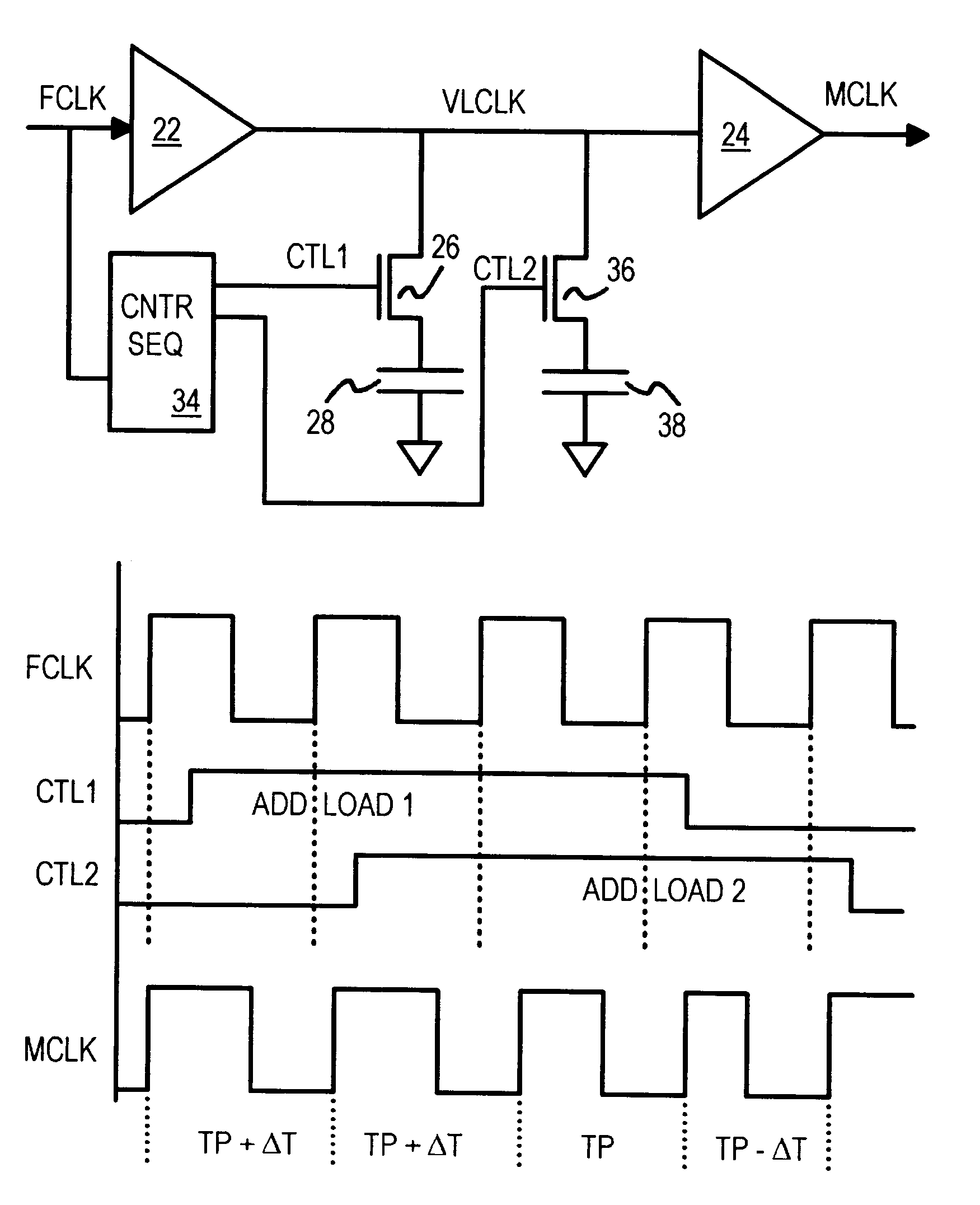
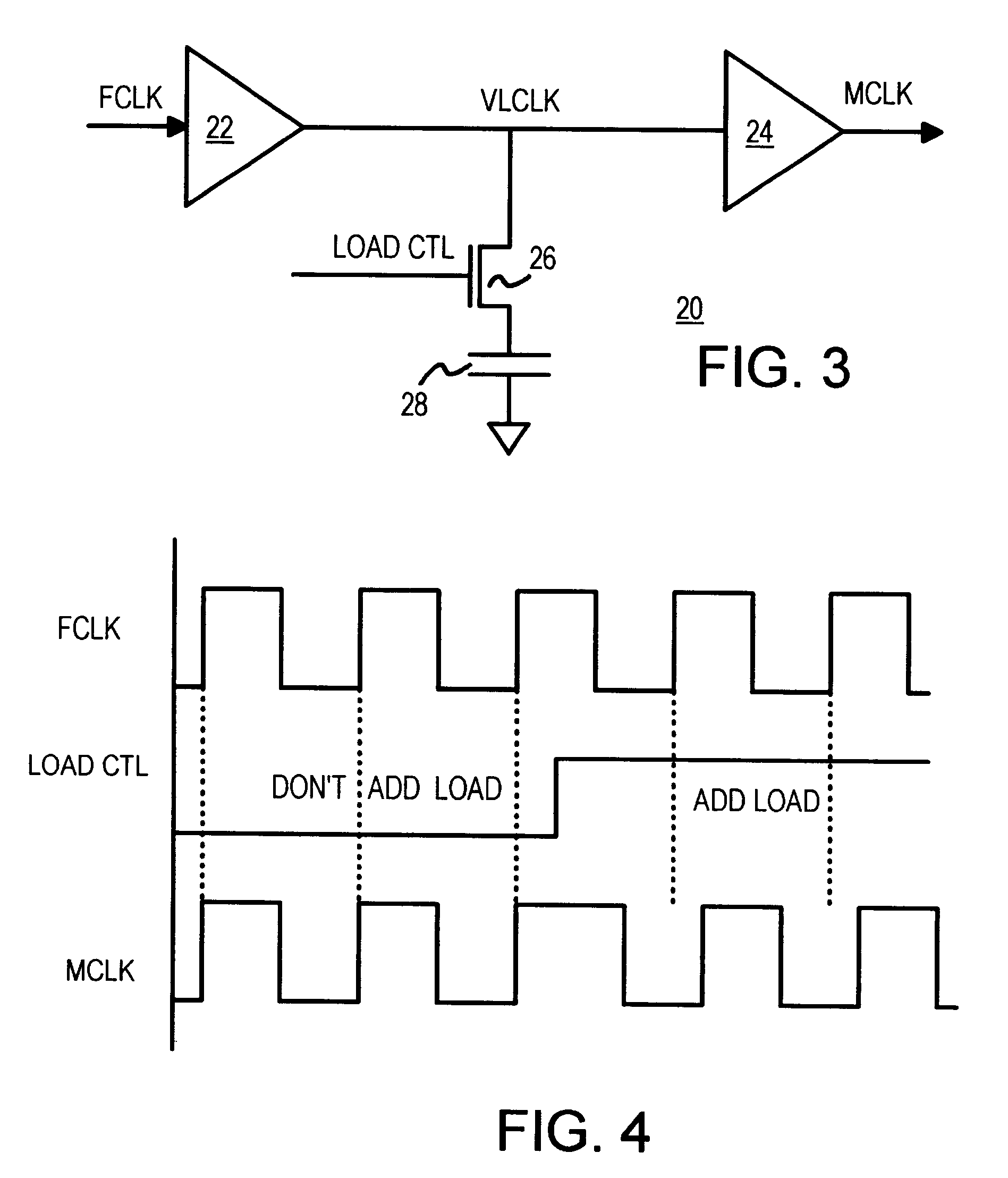
Spread-spectrum clock buffer/driver that modulates clock period by switching loads
A clock modulator spreads the frequency spectrum of an input clock to generate an output clock. A capacitor is connected to an intermediate clock node by a load-switching transistor. When the transistor is turned on, the capacitor increases the loading on the intermediate clock node, increasing delay. When the transistor is turned off, the delay is reduced. Output clock cycle periods are extended when delay is added, and reduced when the transistor turns off. A counter or sequencer is clocked by the input clock and drives the load-switching transistor. The transistor is turned on and off for alternate cycles when the counter is a toggle flip-flop, spreading the frequency over two frequencies every two clock cycles. Two capacitors of different sizes, connected to the intermediate clock node by two transistors, can be switched by a 2-bit sequencer, spreading the output clock over 7 frequencies every 7 clock cycles.
Owner:DIODES INC
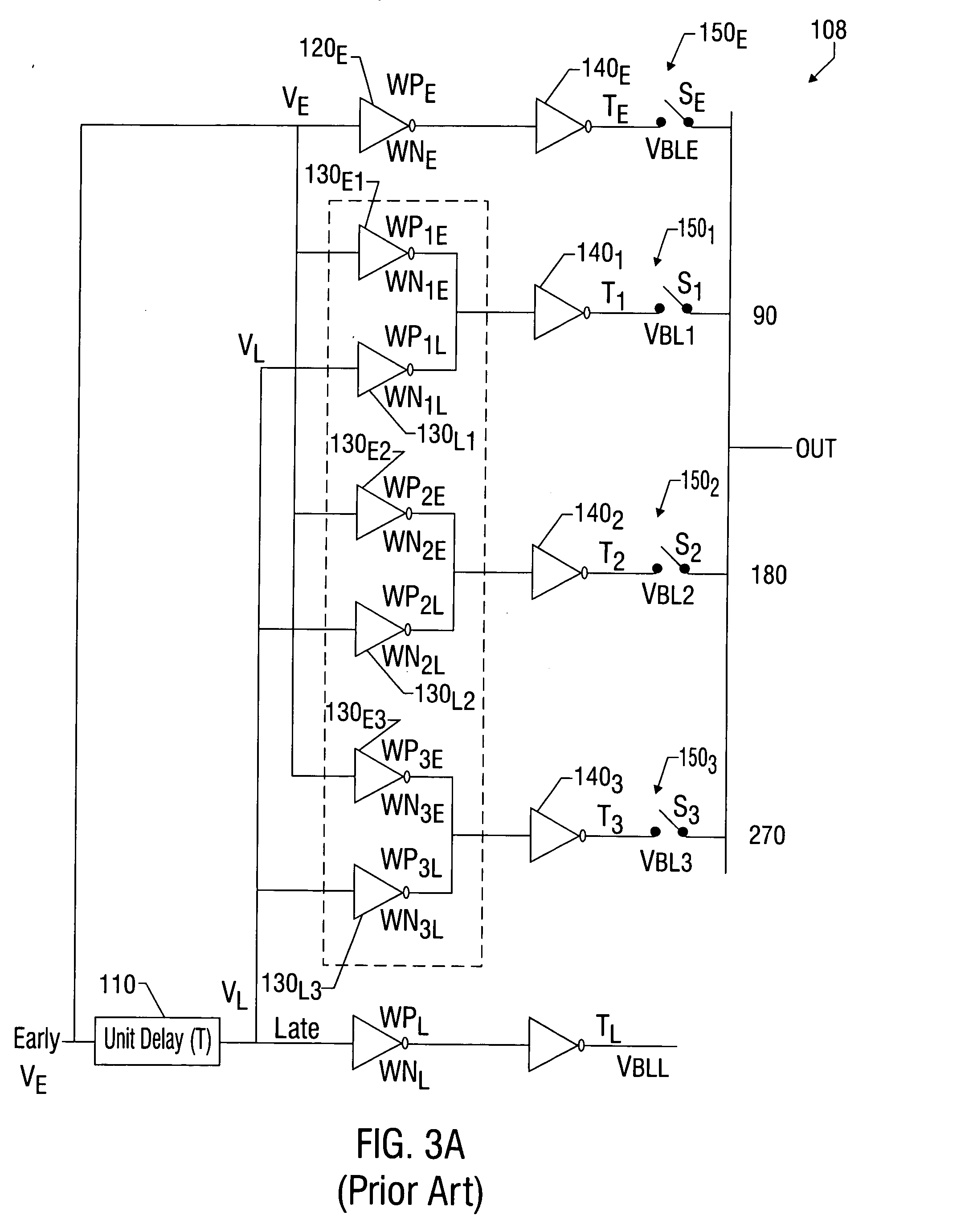
Delay locked loop phase blender circuit
InactiveUS20050093594A1Pulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsDelay-locked loopEngineering
Techniques and circuit configurations for fine phase adjustments, for example, in a delay-locked loop (DLL) circuit are provided. Multiple phase signals may be generated from a single current source by selectively coupling one or more delay elements to an output node of the current source. The delay elements may vary the timing of a signal generated by switching the current source.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
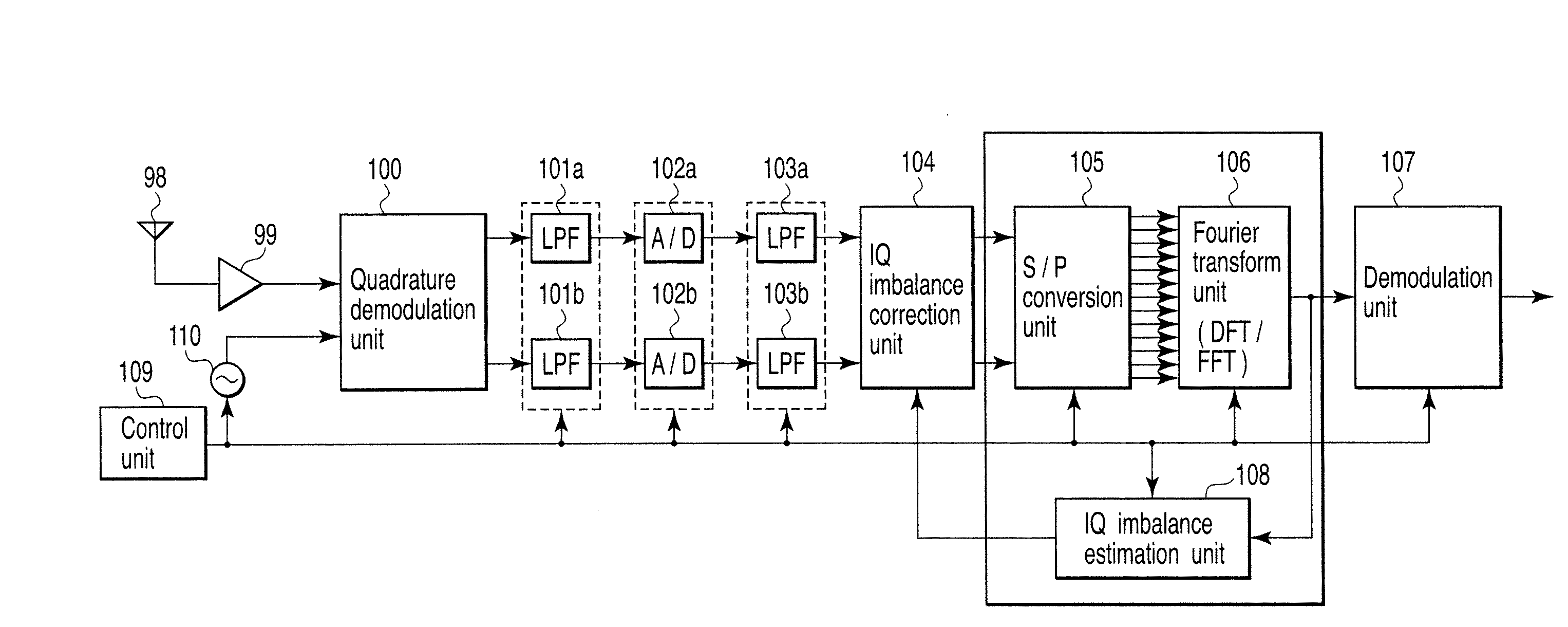
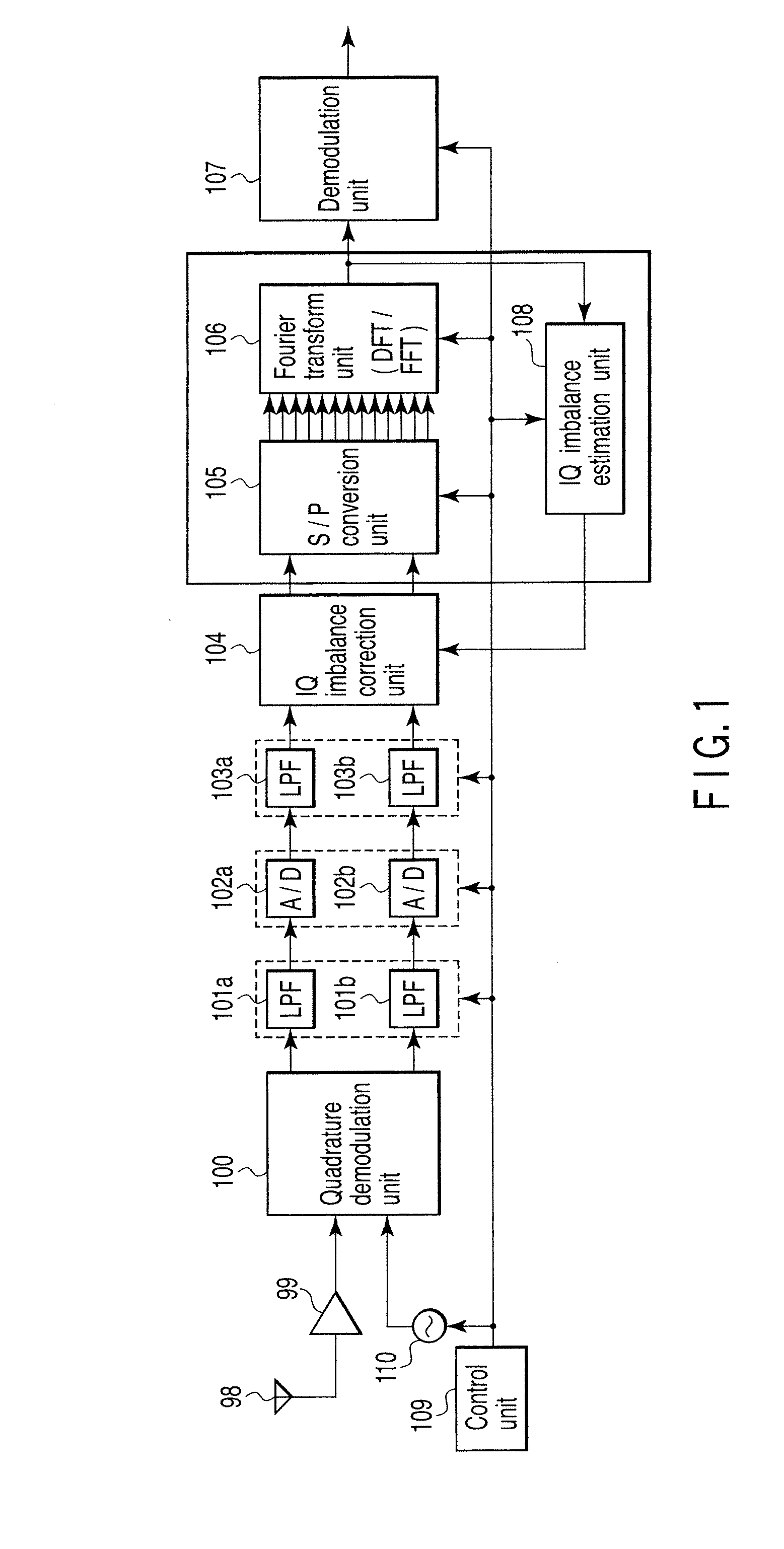
Wireless communication apparatus and receiving method
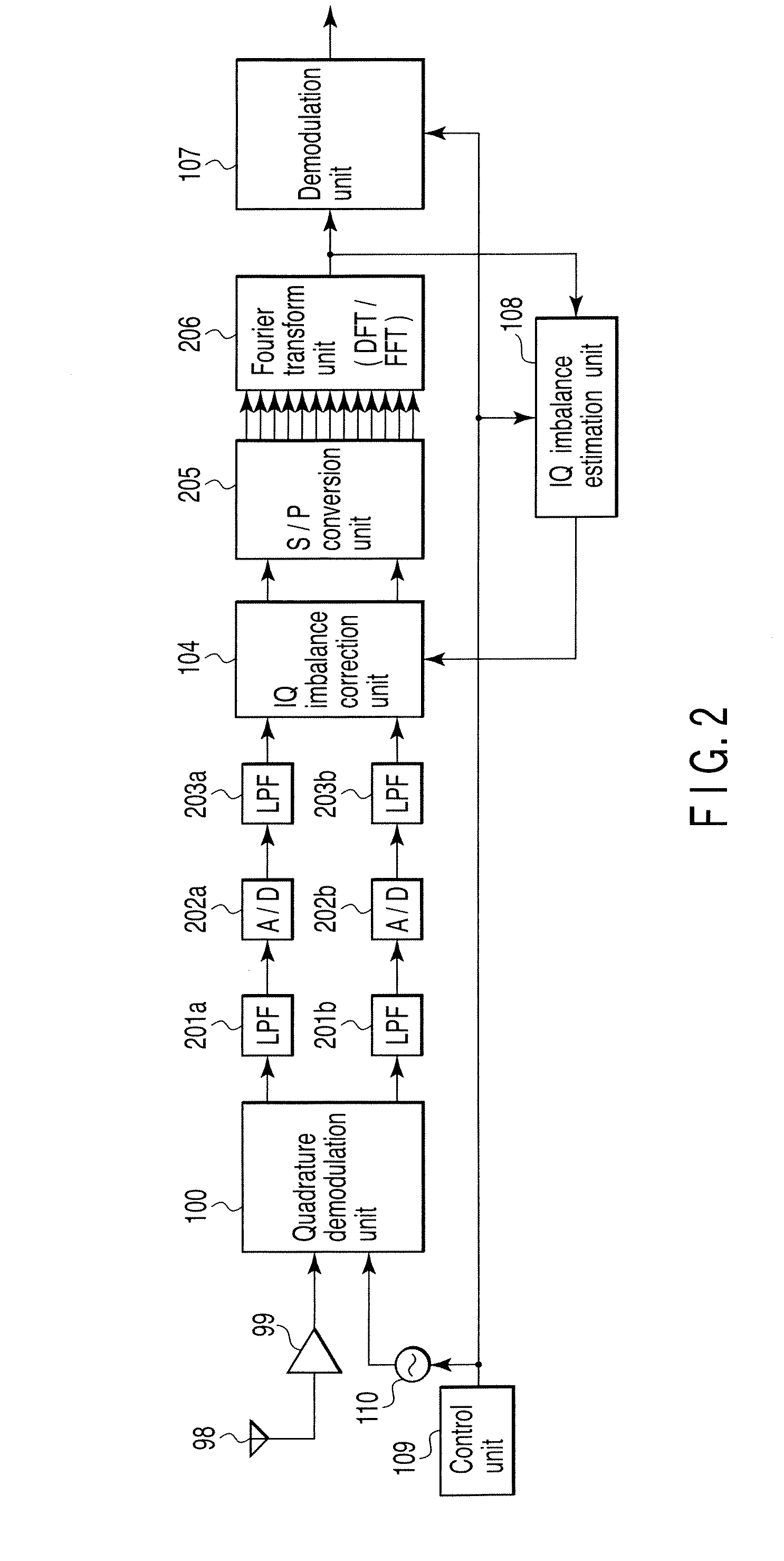
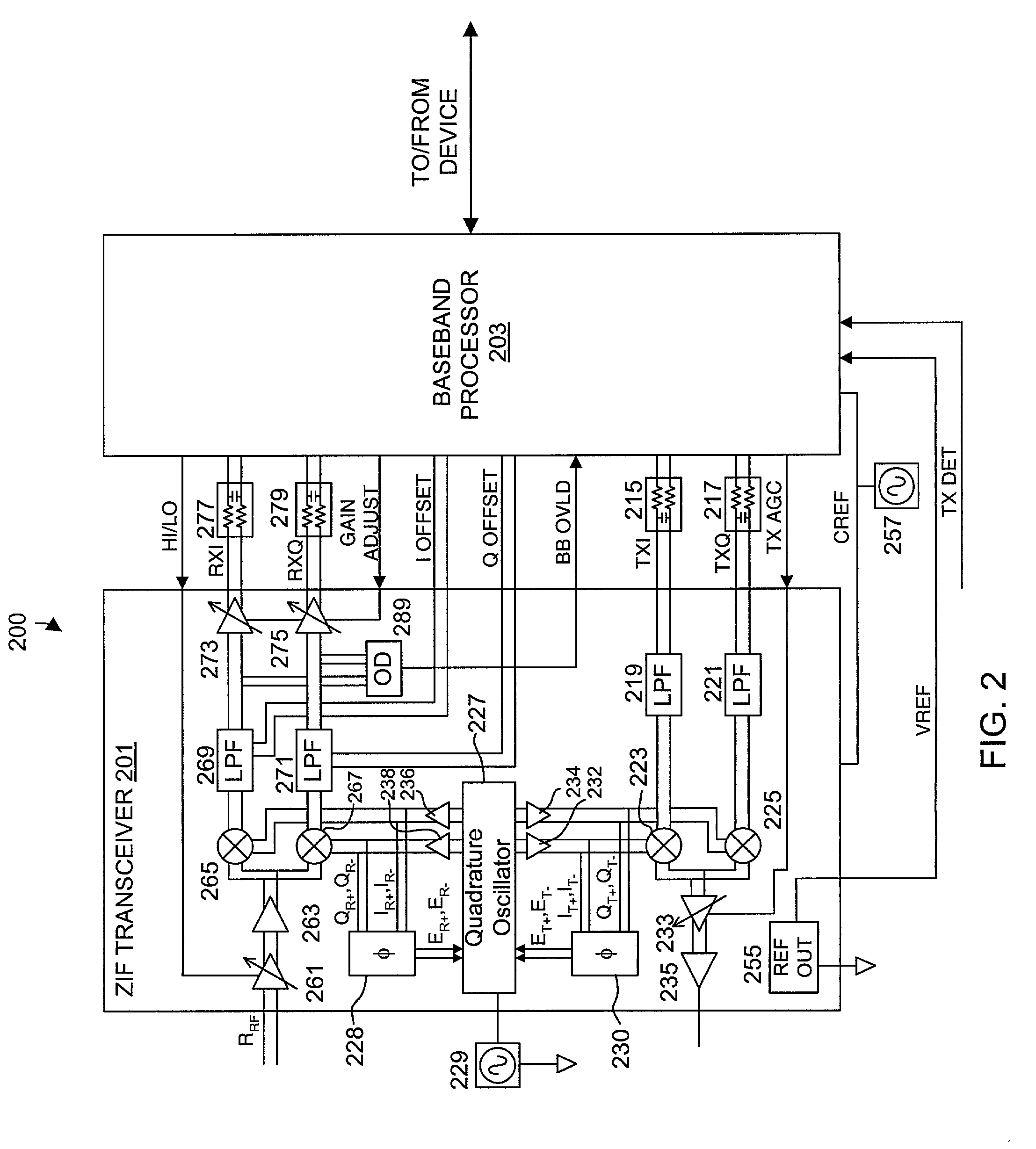
InactiveUS20080159442A1Single output arrangementsElectric pulse generatorAmplitude distortionTelecommunications
A wireless communication apparatus receives an quadrature modulated signal, generate a local signal having a frequency different from a center frequency of the quadrature modulated signal, performs quadrature demodulation on the quadrature modulated signal by using the local signal, to obtain an I channel signal and a Q channel signal, performs Fourier transform on the I channel signal and the Q channel signal, to obtain signals in a frequency domain, and calculates a first correction coefficient for correcting phase distortion and amplitude distortion caused by the quadrature demodulation by using pairs of signals among the signals, each of the pairs are located at symmetrical frequency positions with respect to the frequency of the local signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
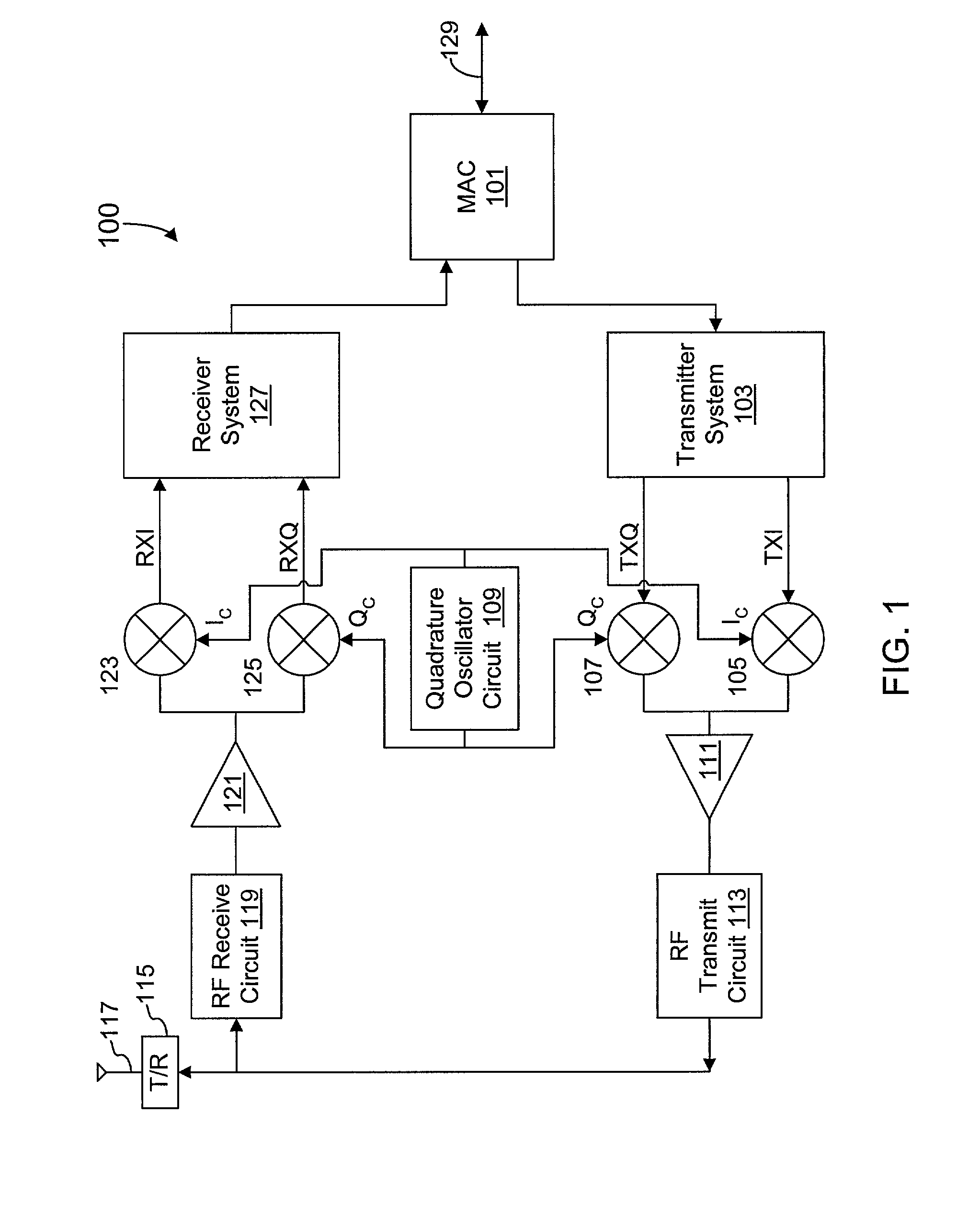
Adaptive radio transceiver with CMOS offset PLL
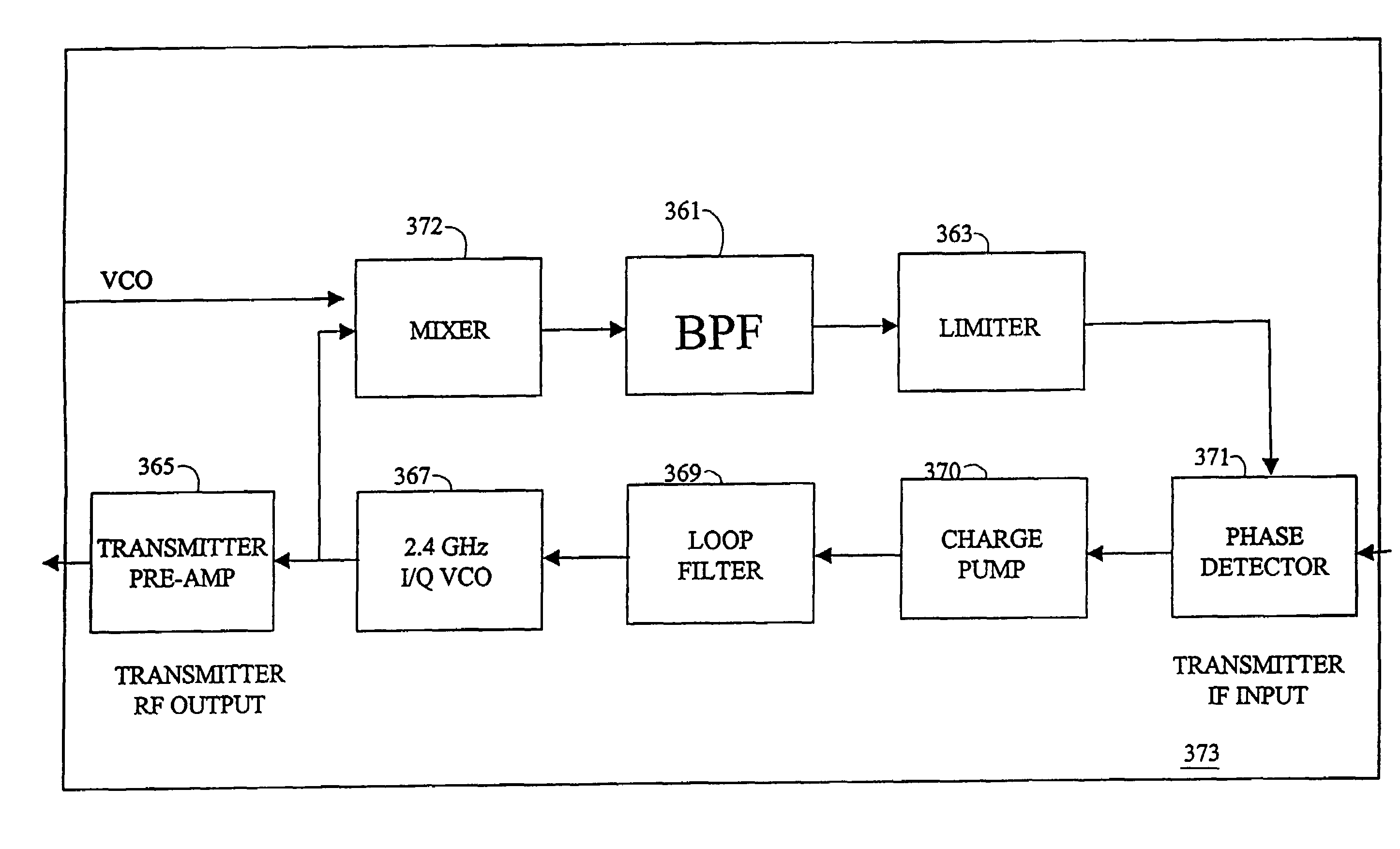
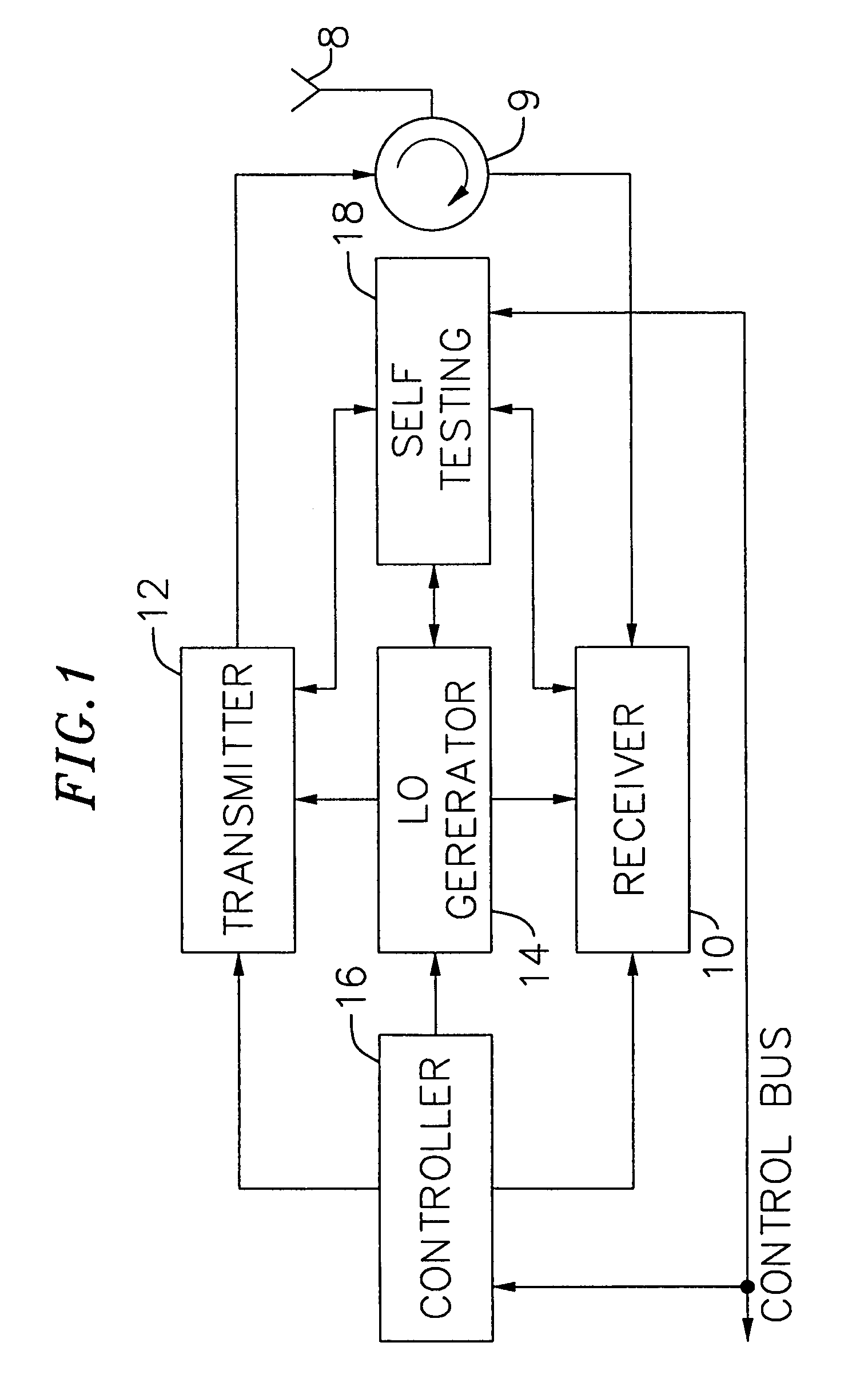
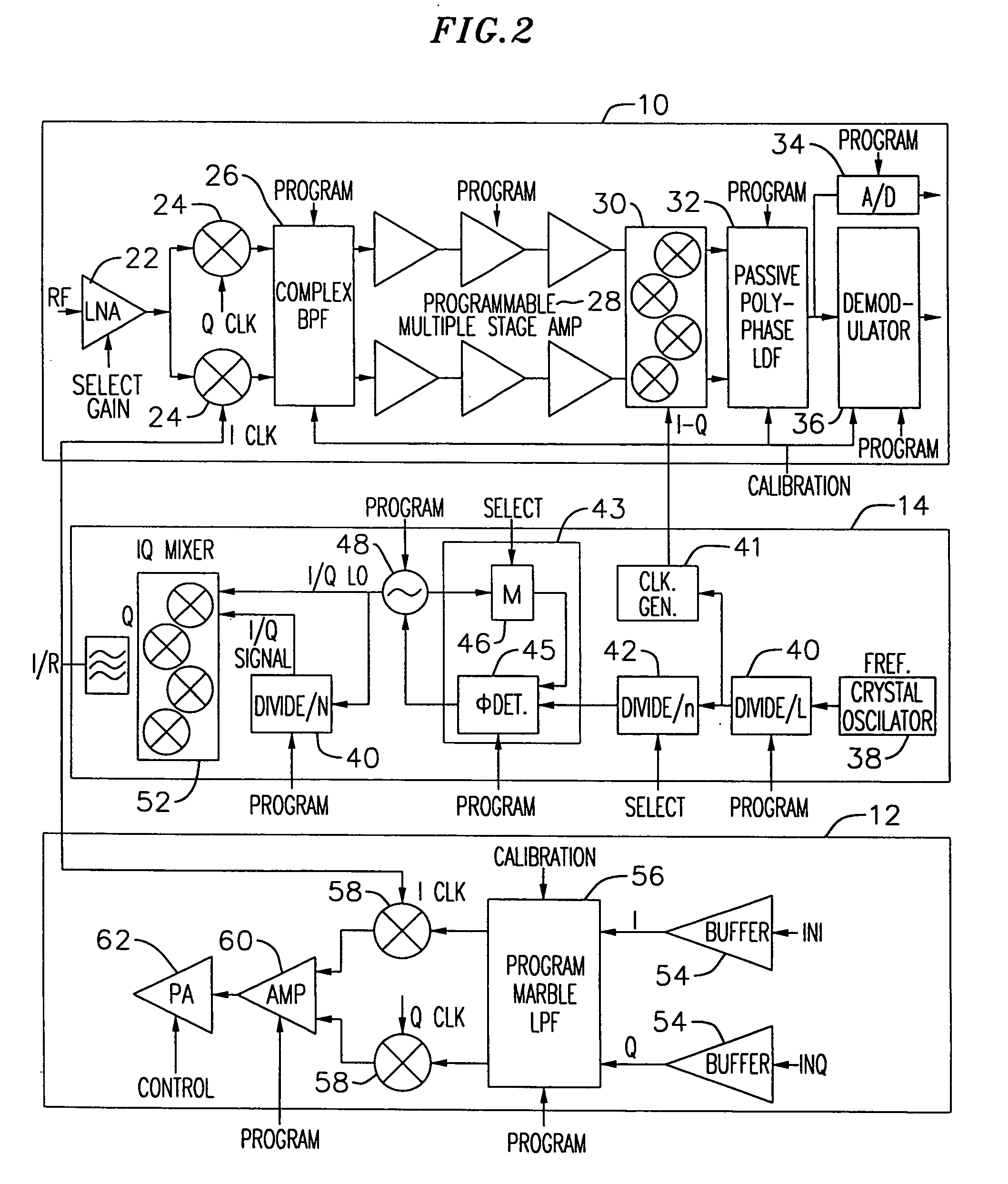
InactiveUS7082293B1Minimize adverse effectsReduce power consumptionTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringCMOSAdaptive programming
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
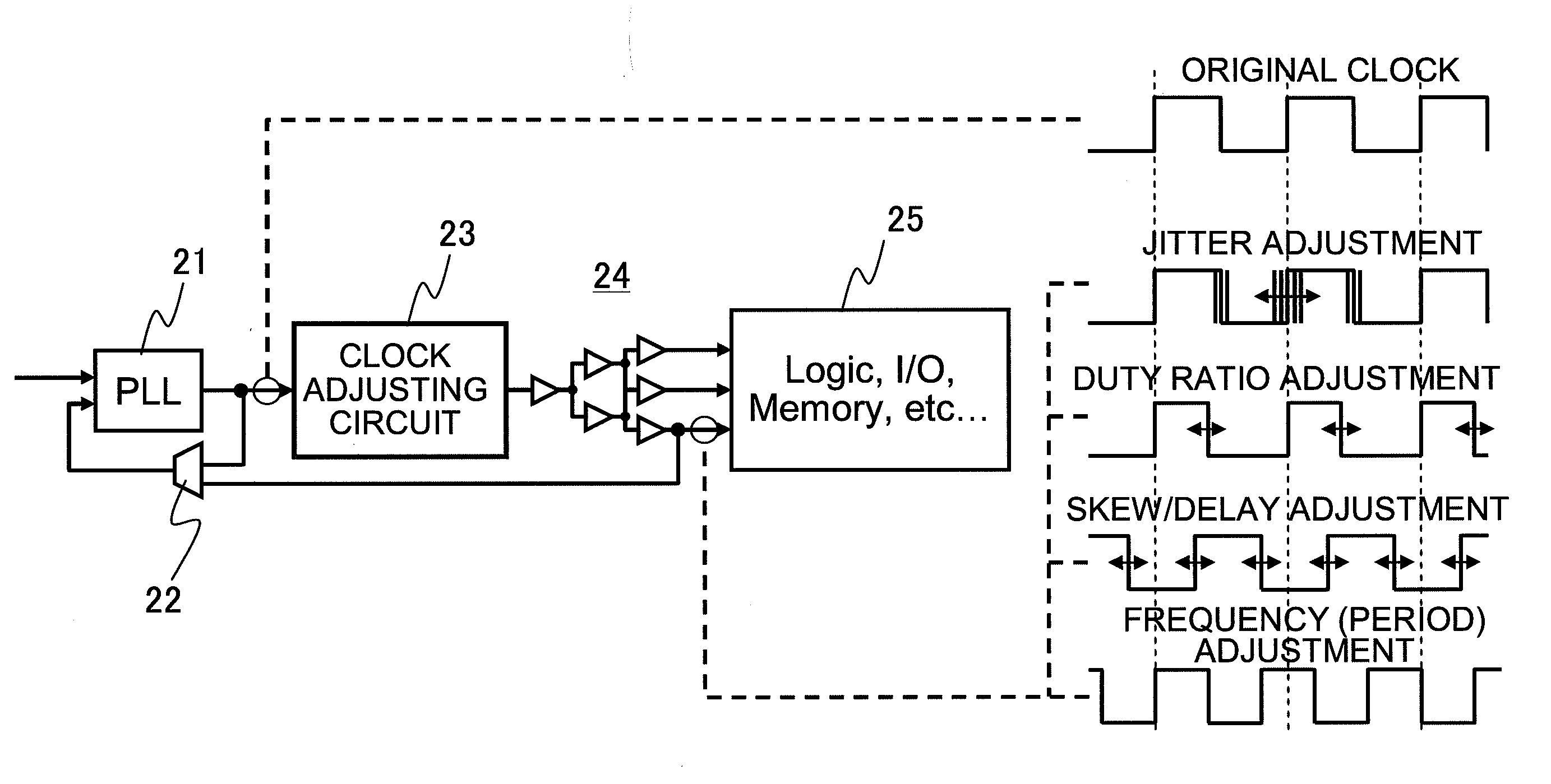
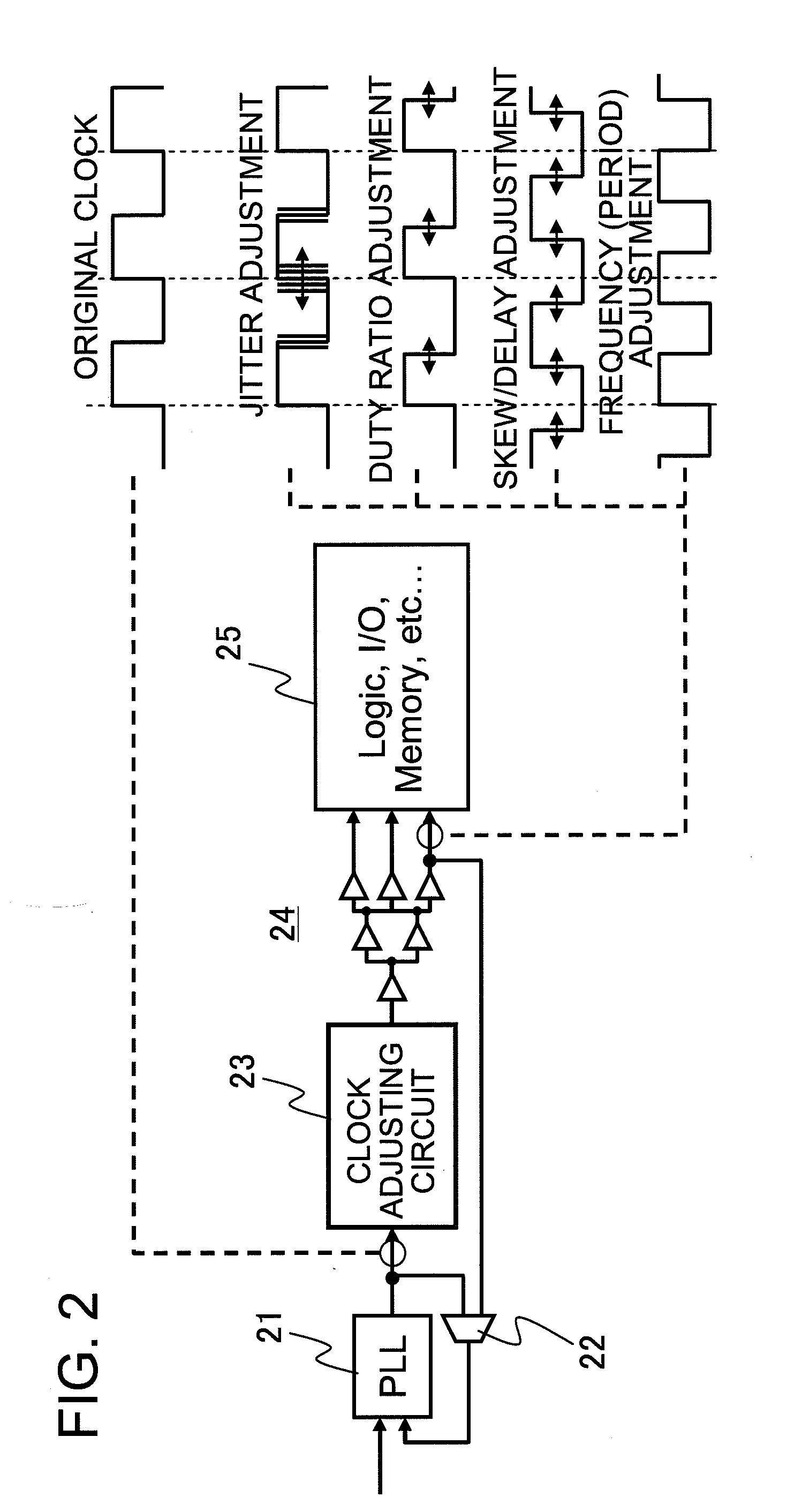
Clock adjusting circuit and semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20100039157A1Improve reliabilityLarge marginPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsControl signalControl circuit
Disclosed is a clock adjusting circuit comprising a phase shifter that receives a clock signal and variably shifts, based on a control signal, respective timing phases of a rising edge and a falling edge of the clock signal; and a control circuit that supplies the control signal to the phase shifter circuit before each edge is output; wherein the clock signal, in which at least one of a period, a duty ratio, jitter and skew / delay of the input clock signal is changed over an arbitrary number of clock cycles, is output.
Owner:NEC CORP
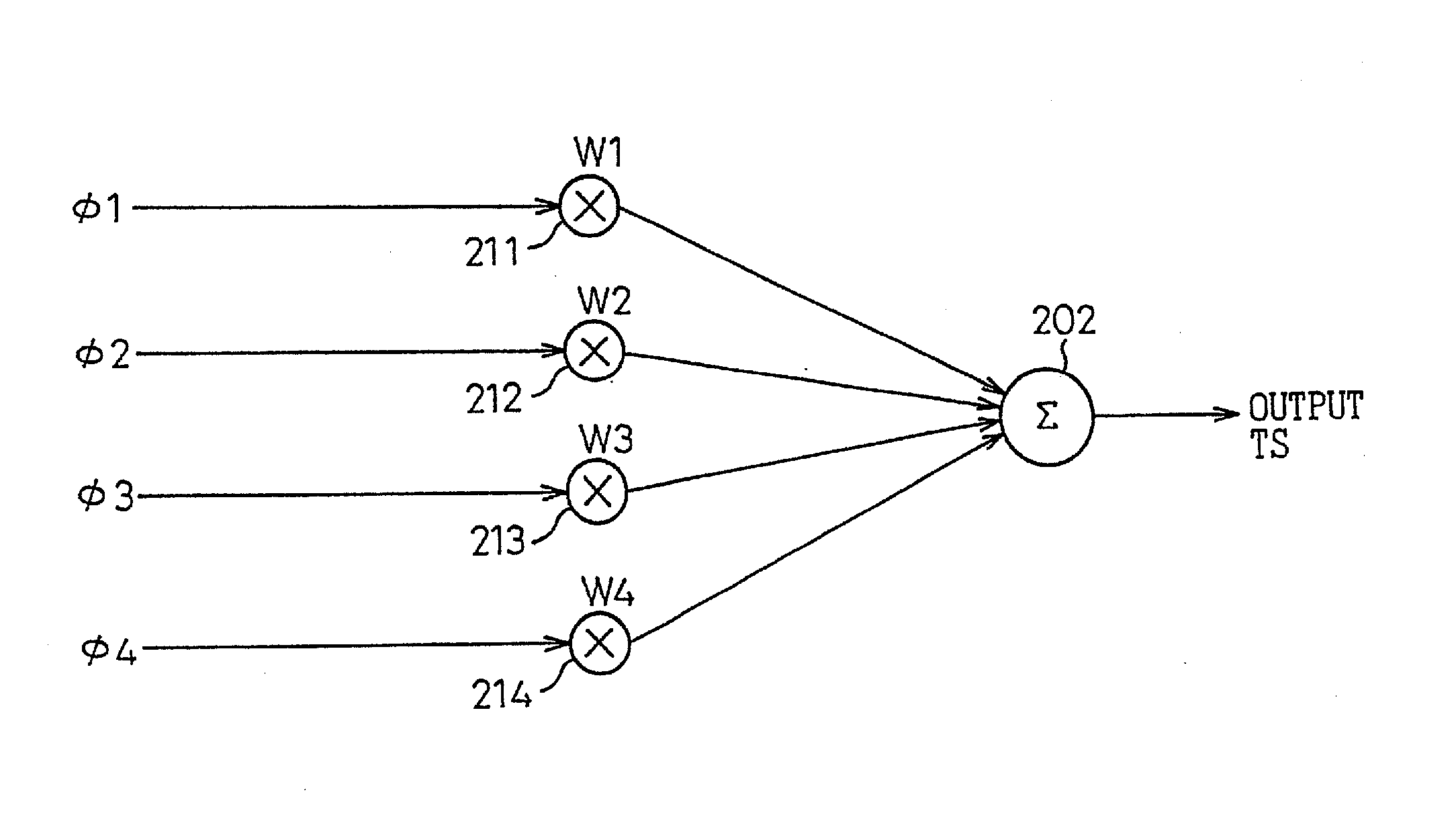
Phase-combining circuit and timing signal generator circuit for carrying out a high-speed signal transmission
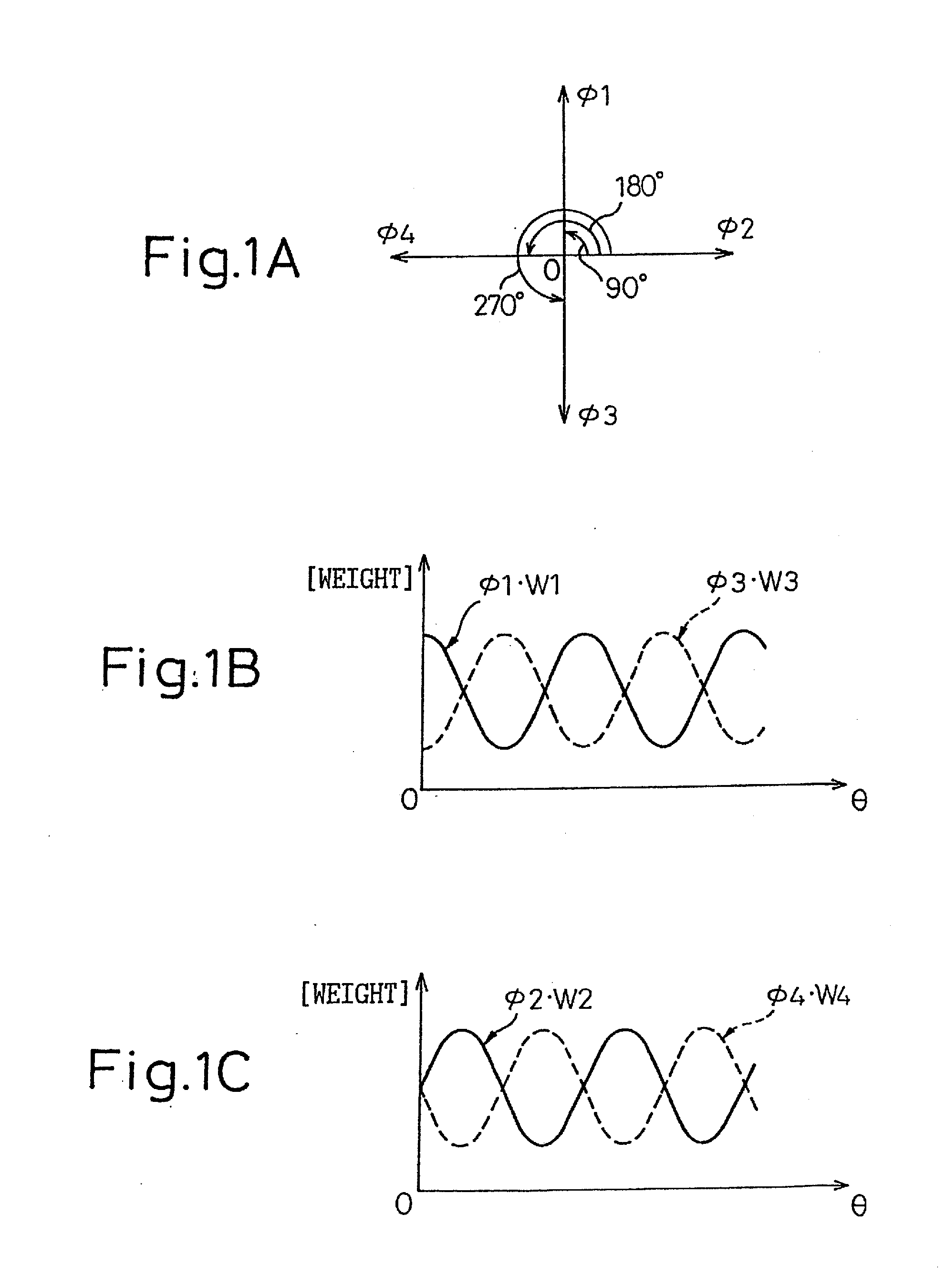
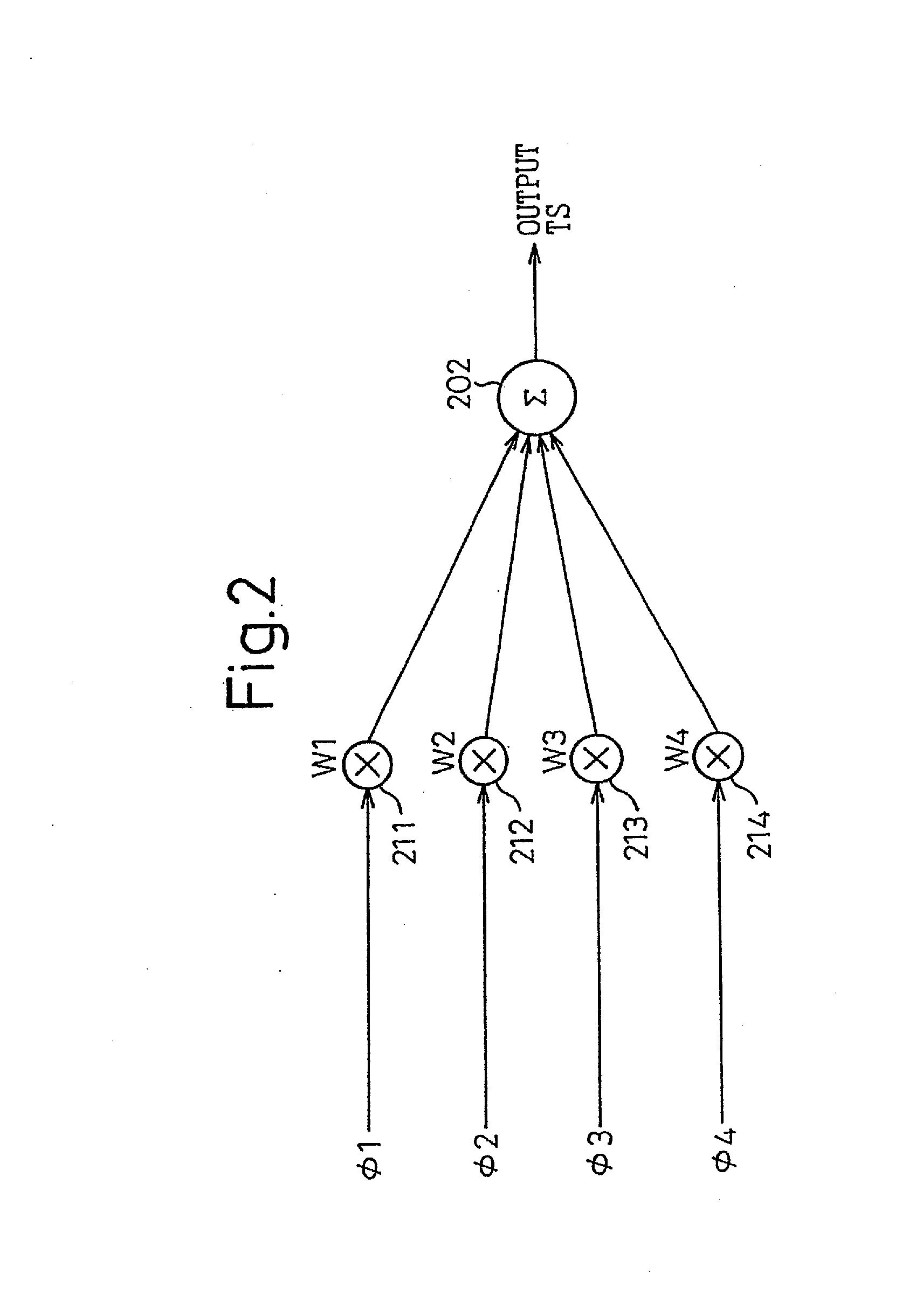
InactiveUS20130314142A1Simple structureError minimizationPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsControl signalPhase control
A phase-combining circuit for combining cyclic timing waveforms that have been phase-controlled by control signals based on three or more input signals of different phases, has a weight signal generating circuit and a weighting circuit. The weight signal generating circuit generates weights according to the control signals, and the weighting circuit gives the weights to the respective input signals, with a positive or negative polarity for each one signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Signal transmission circuit and method for equalizing disparate delay times dynamically, and data latch circuit of semiconductor device implementing the same
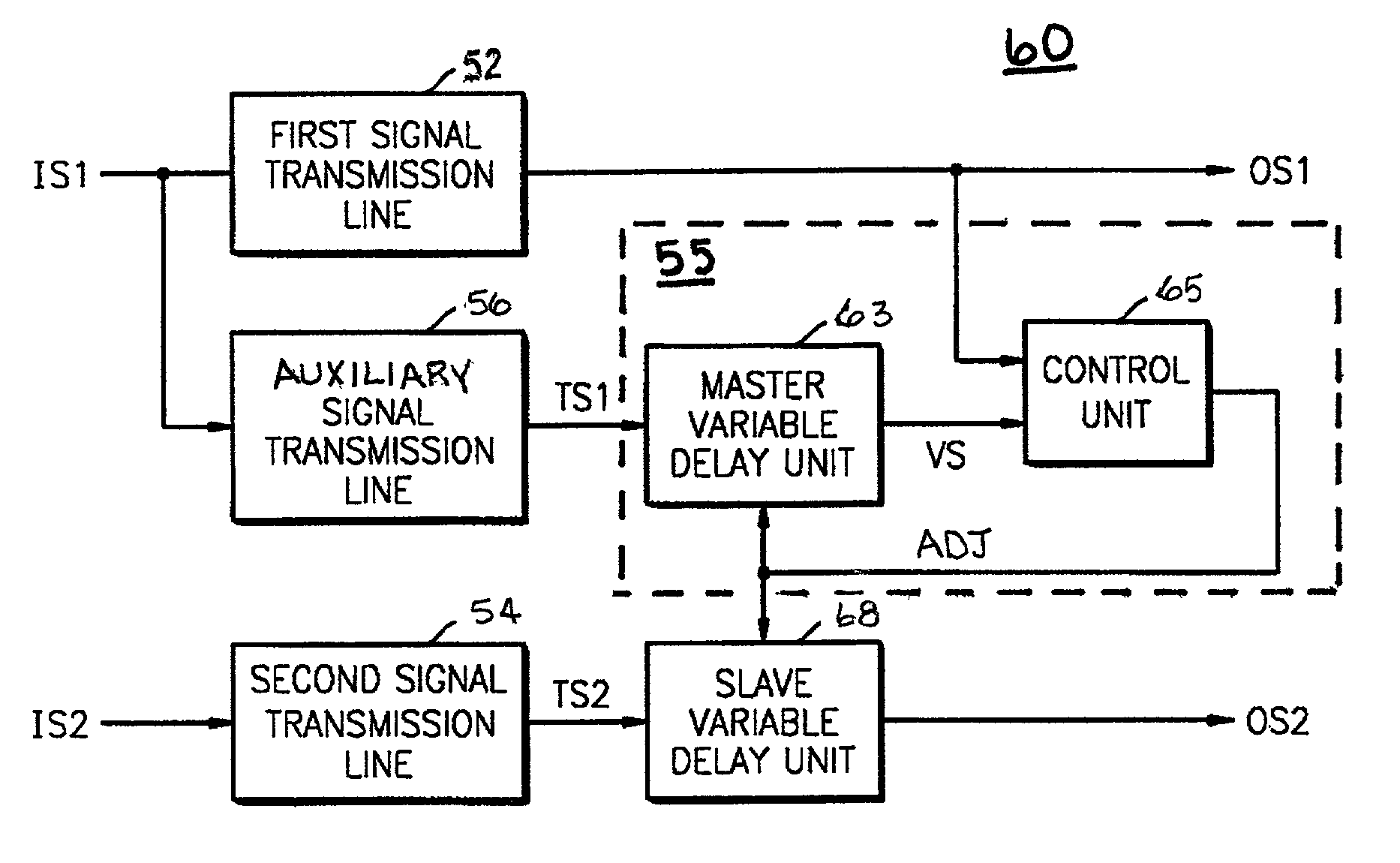
InactiveUS7085336B2Accurate compensationKeep in syncChannel dividing arrangementsError preventionDelayed timeDatapath
A signal transmission circuit and a method equalize differential delay characteristics of two signal transmission lines. A controllable delay unit is connected serially to the second line, so as to compensate by adding its internal delay. An auxiliary signal transmission line replicates the second transmission line, while it processes the input signal of the first. A controlling unit compares the output signal of the first transmission line and the of the auxiliary signal transmission line, and adjusts dynamically the internal delay of the controllable delay unit, to attain continuous synchronization. A data latch circuit synchronizes the delays of data paths by having one controllable delay units in each of the data paths.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Architecture of single substrate ultrasonic imaging devices, related apparatuses, and methods
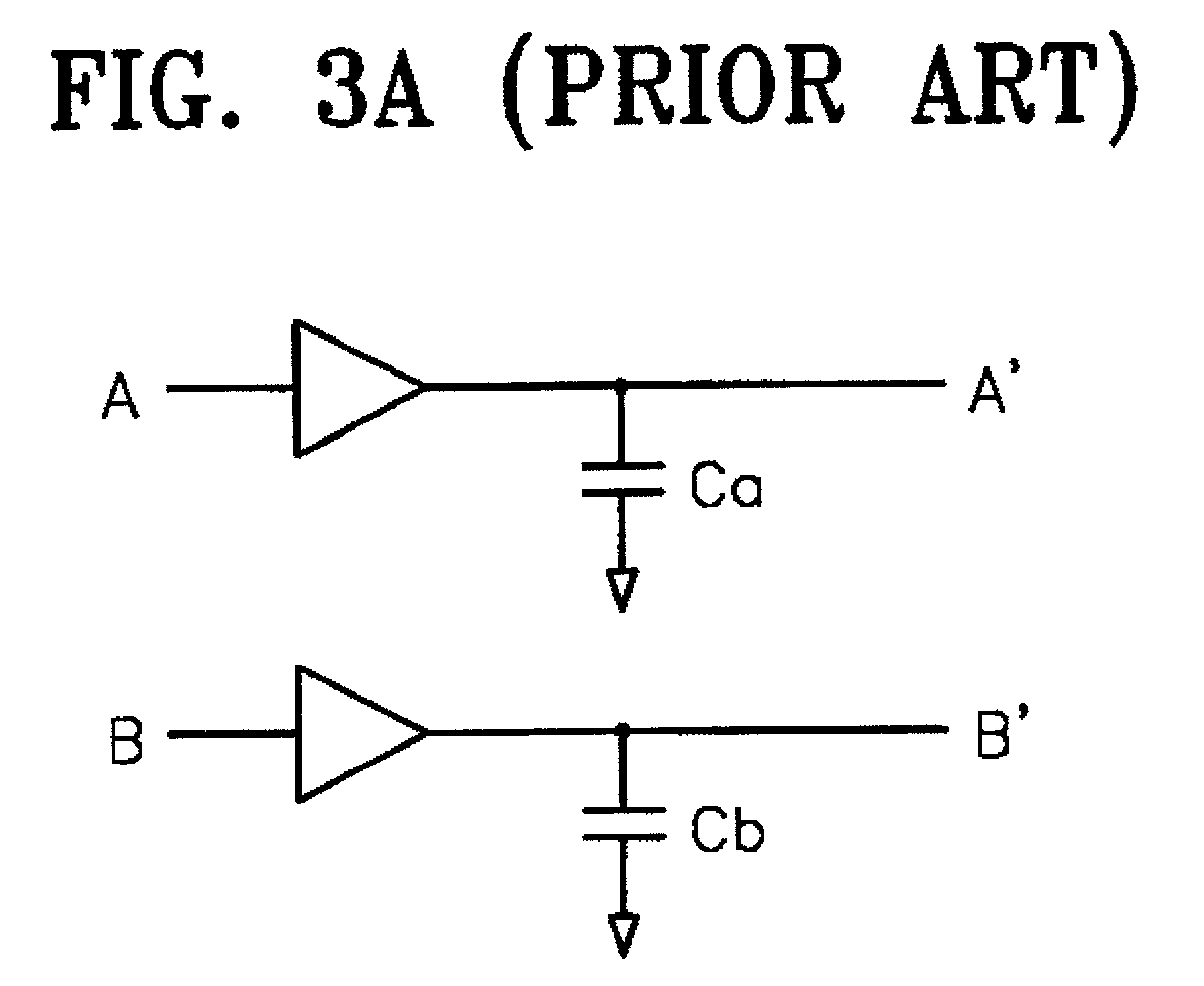
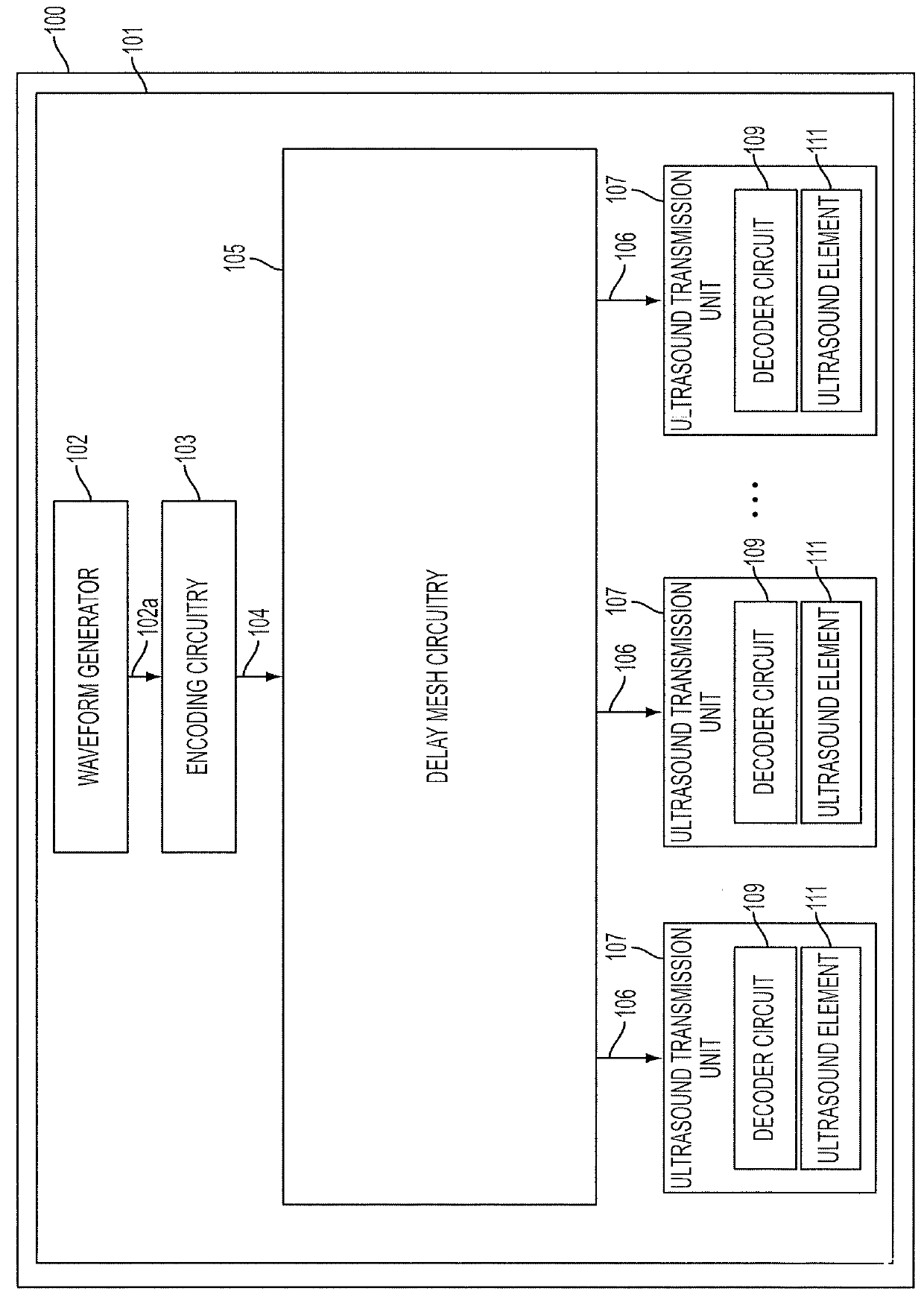
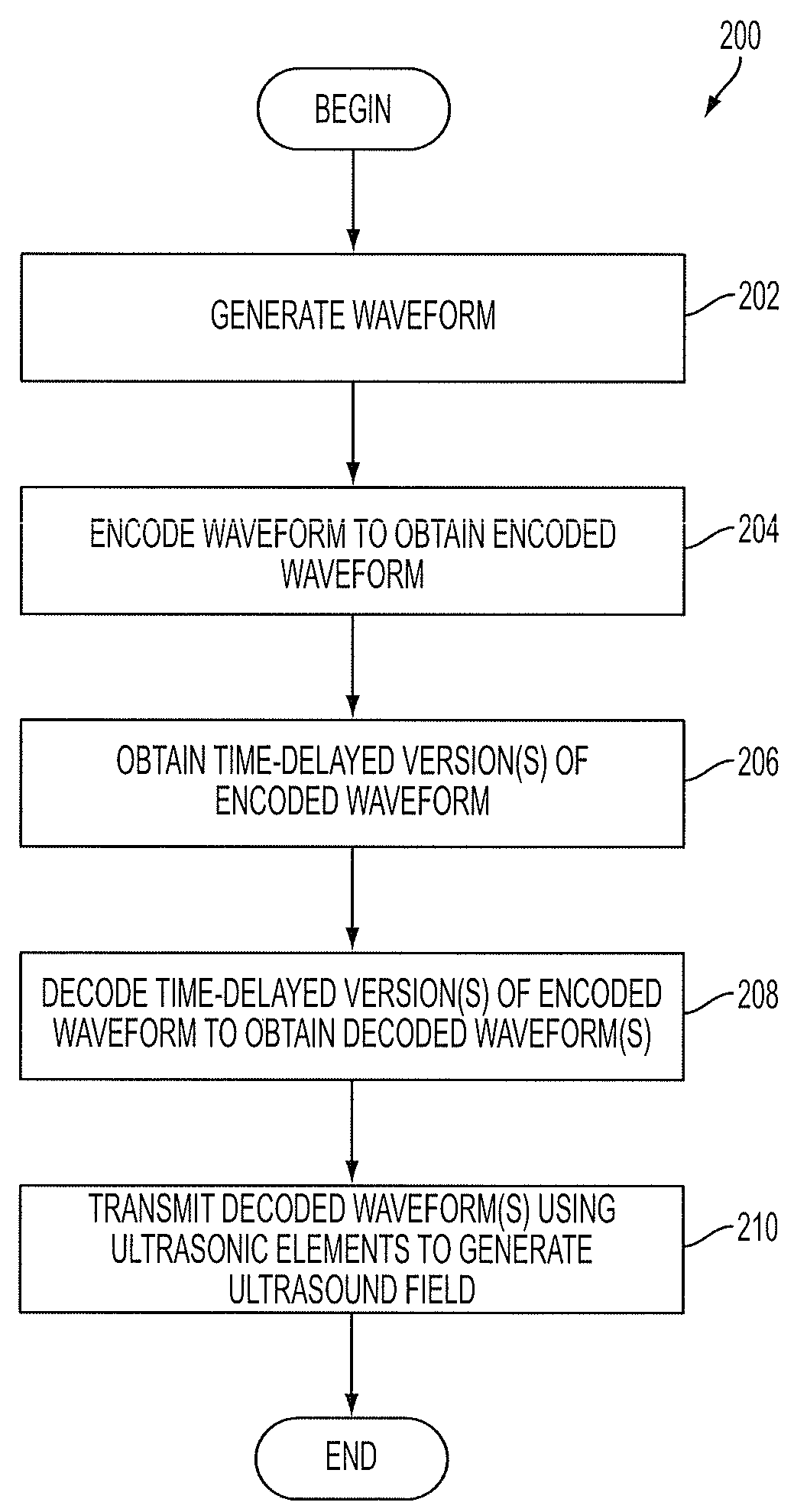
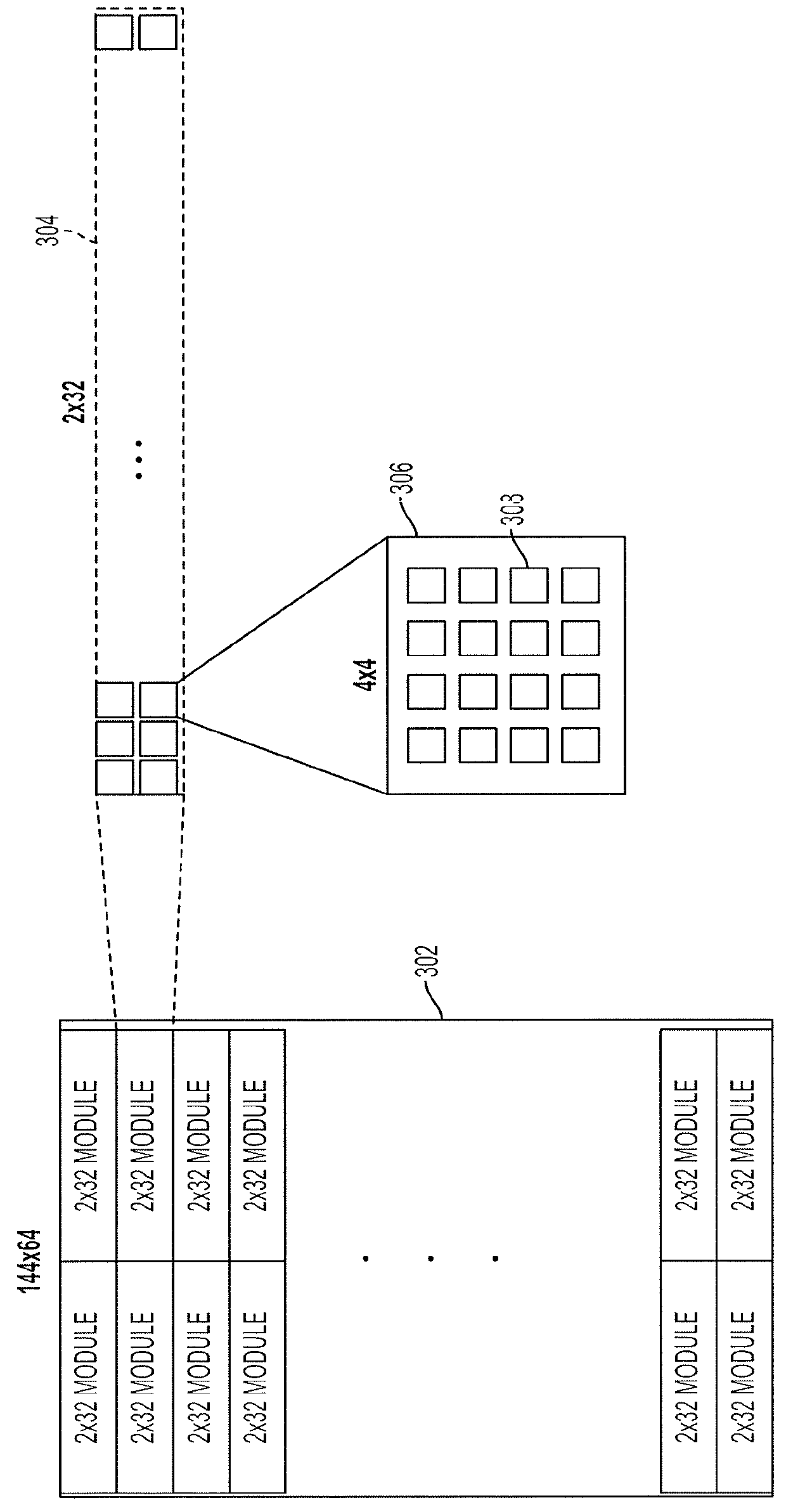
ActiveUS9229097B2Single output arrangementsMechanical vibrations separationUltrasound deviceSonification
Aspects of the technology described herein relate to ultrasound device circuitry as may form part of a single substrate ultrasound device having integrated ultrasonic transducers. The ultrasound device circuitry may facilitate the generation of ultrasound waveforms in a manner that is power- and data-efficient.
Owner:BFLY OPERATIONS INC
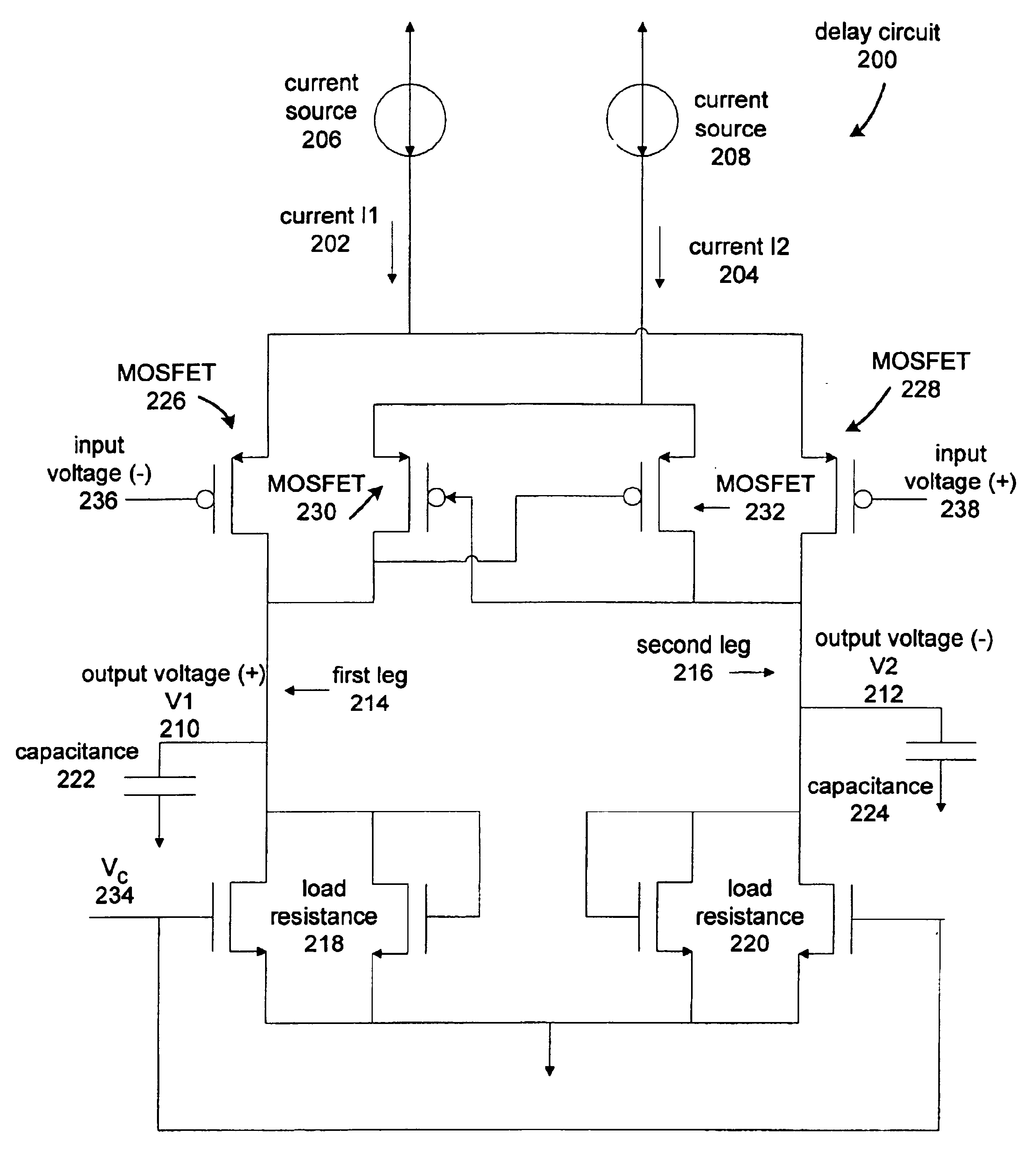
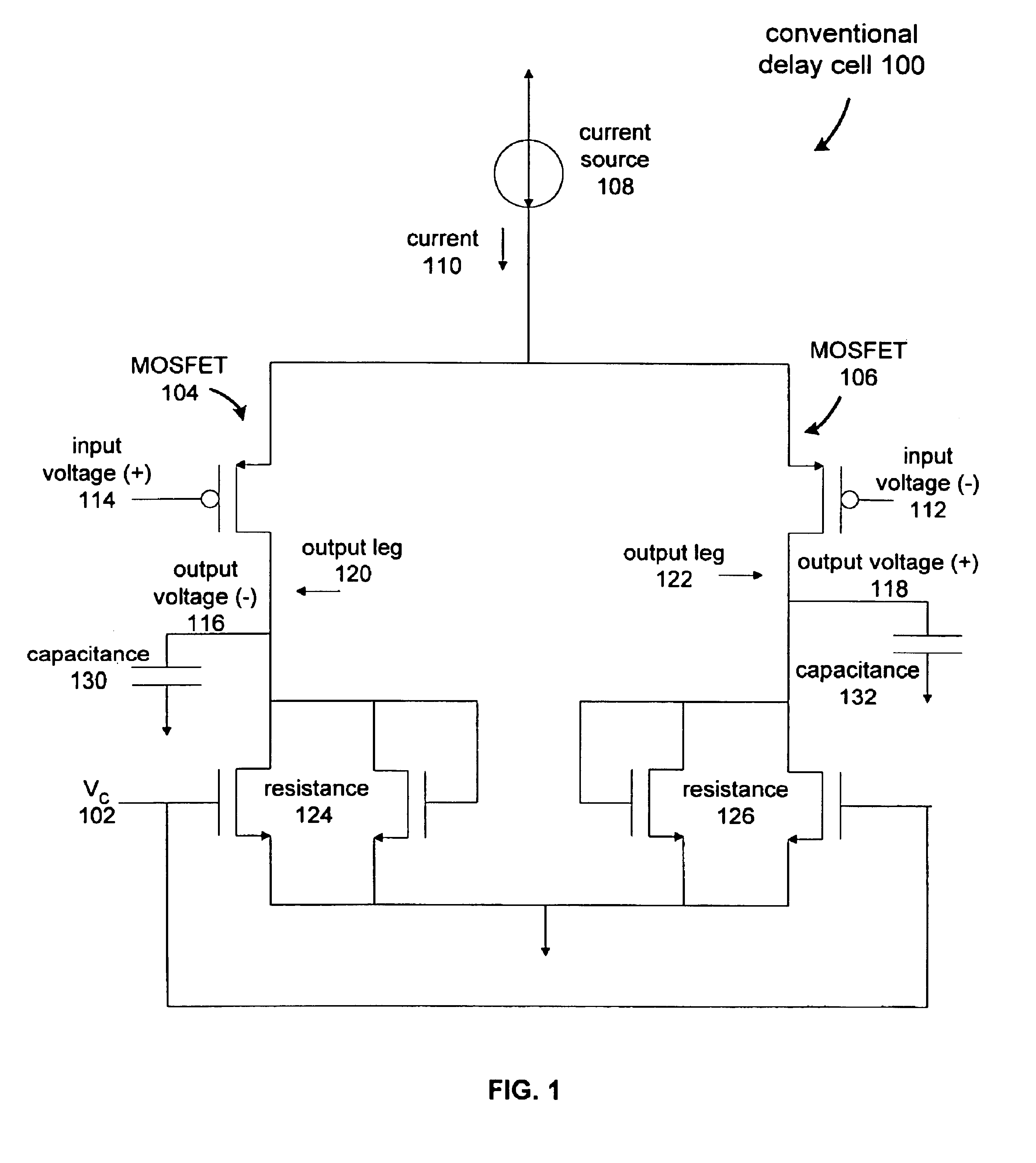
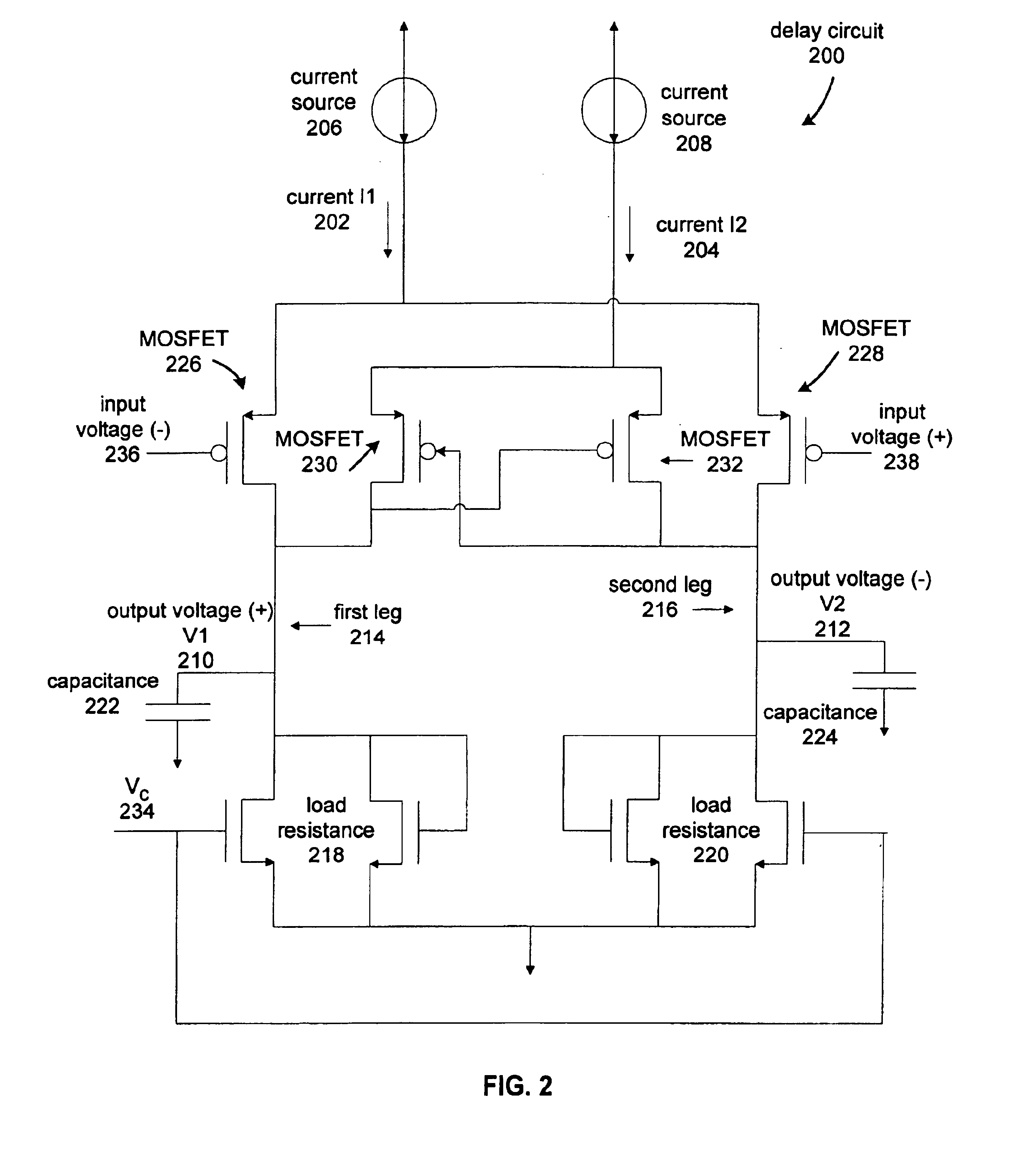
Current controlled delay circuit
A current controlled delay circuit is disclosed. Two currents of constant sum are generated to control the delay of the circuit. The circuit includes a differential pair to switch one of the two currents from one leg of the circuit to another leg of the circuit. The circuit includes a cross-coupled pair to switch the other of the two currents from one leg of the circuit to another leg of the circuit. The circuit may include a fixed or variable load.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
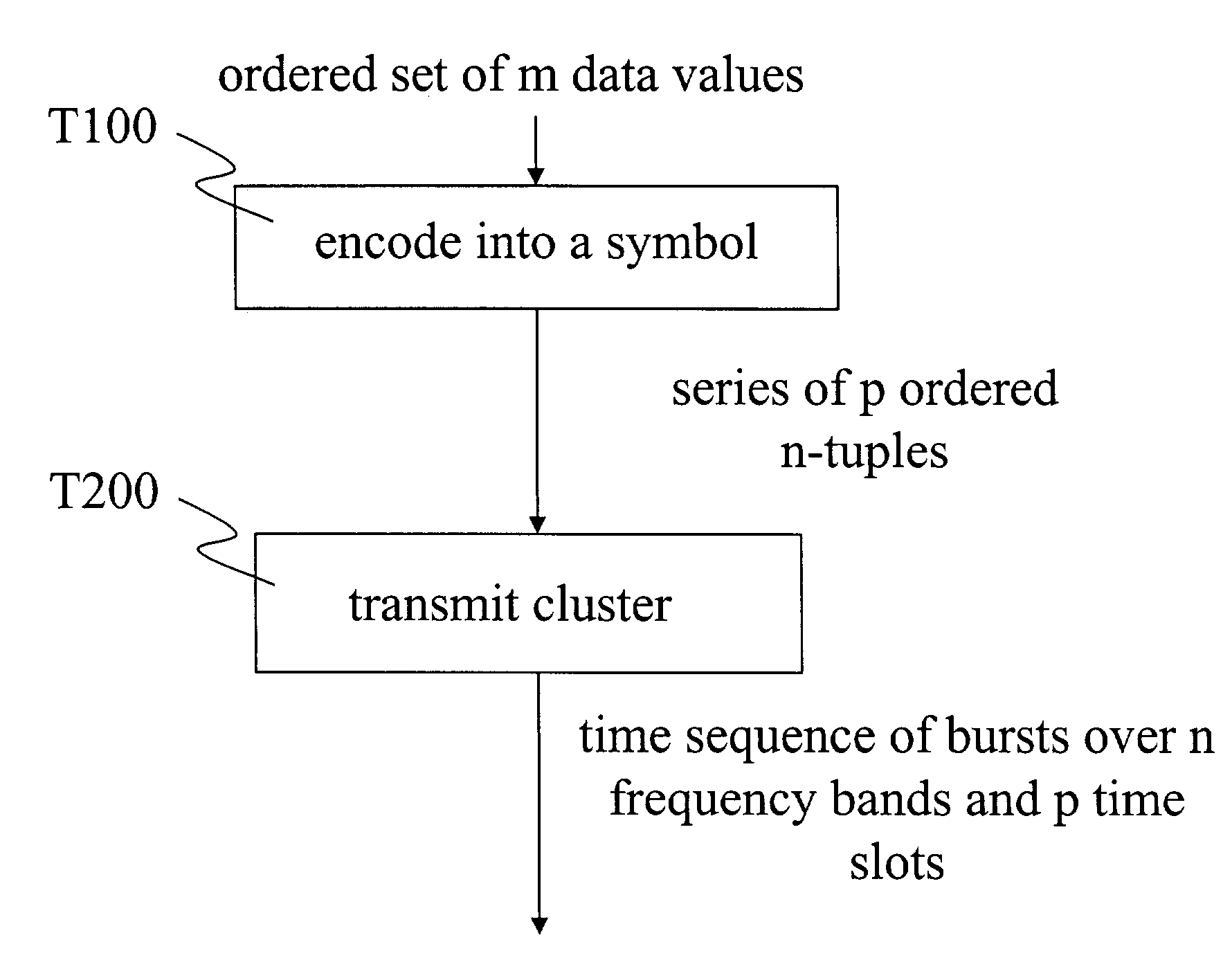
Method and apparatus for data transfer using a time division multiple frequency scheme supplemented with polarity modulation
A method of data transmission according to one embodiment of the invention includes encoding a set of data values to produce a corresponding series of ordered n-tuples. The method also includes transmitting, according to the series of ordered n-tuples, a plurality of bursts over a plurality n of frequency bands. Specifically, for each of the plurality of bursts, a frequency band occupied by the burst is indicated by the order within its n-tuple of an element corresponding to the burst. A bandwidth of at least one of the plurality of bursts is at least two percent of the center frequency of the burst. Information is encoded into a polarity of at least one of the plurality of bursts.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Advanced real-time grid monitoring system and method
ActiveUS20100213925A1Efficient and robustIncreased computational burdenCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage-current phase anglePower qualityElectric power system
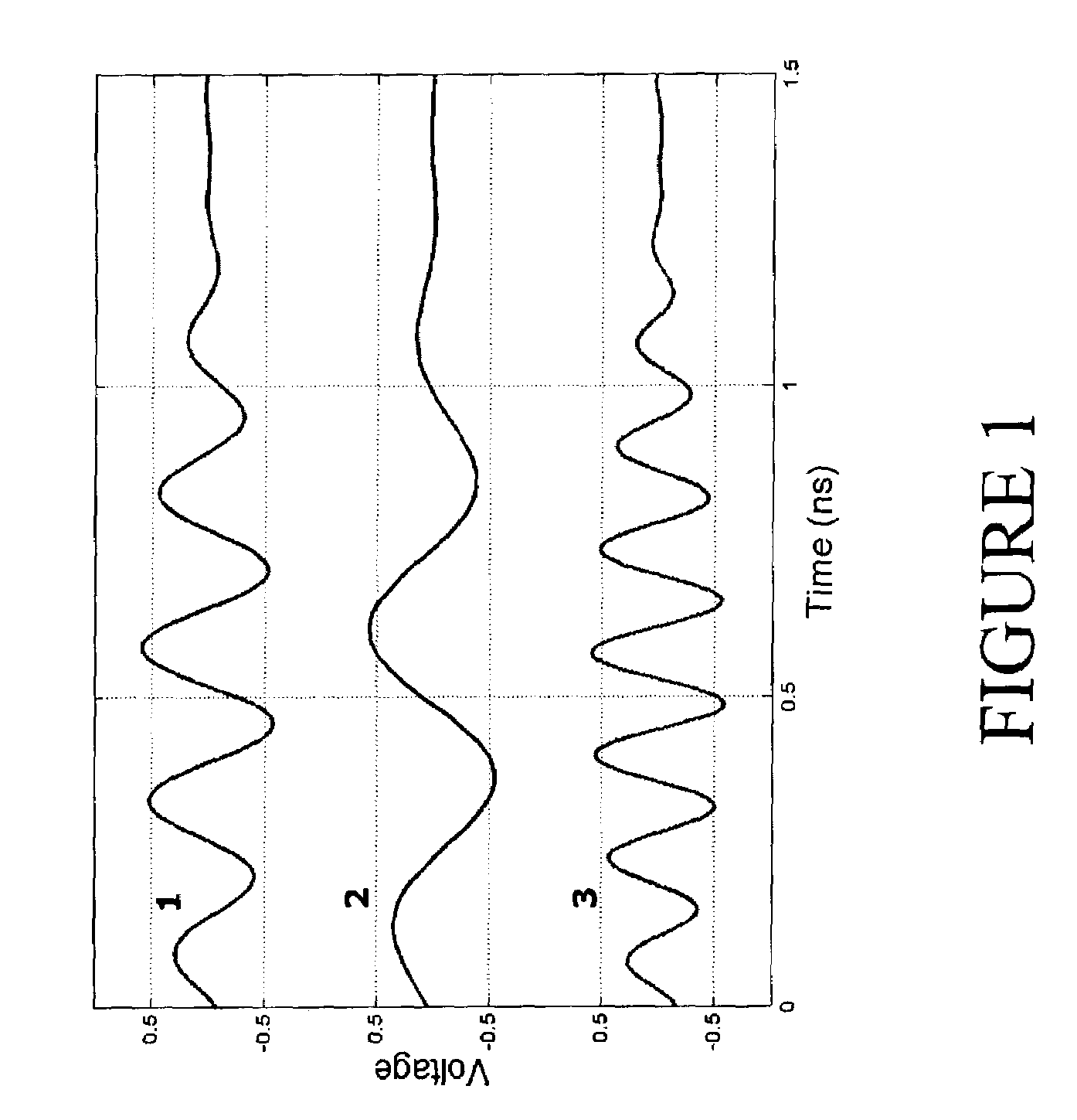
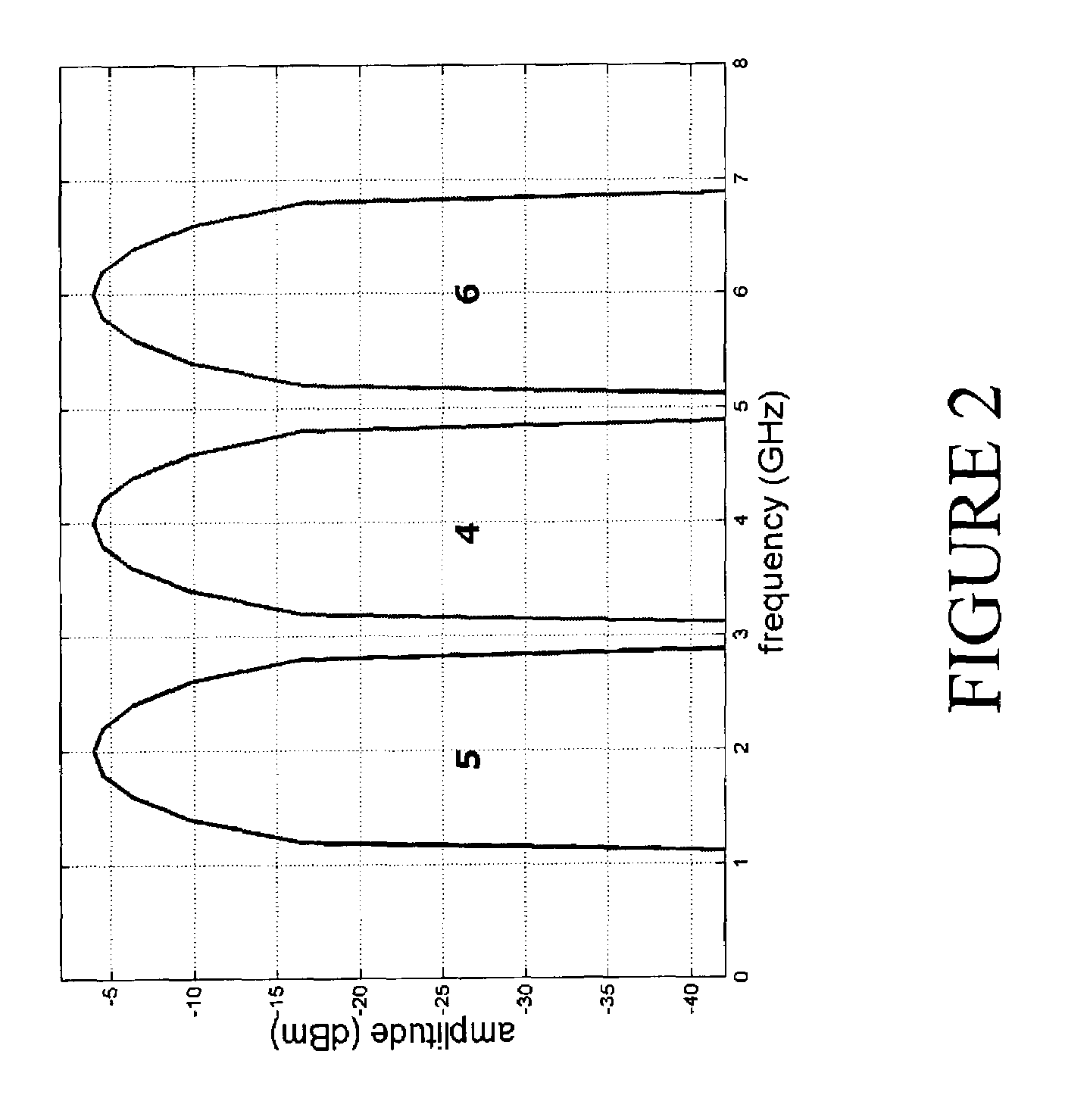
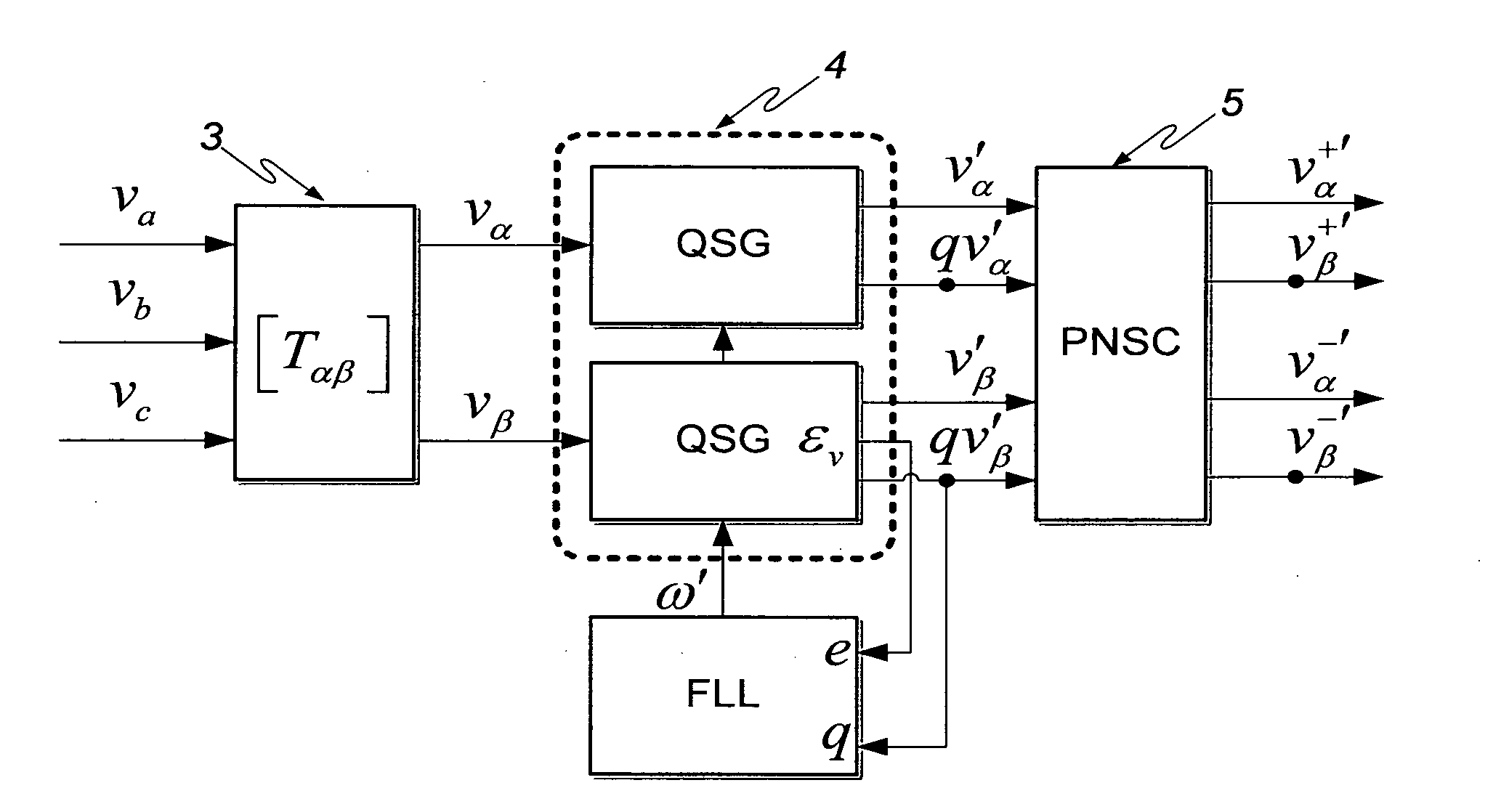
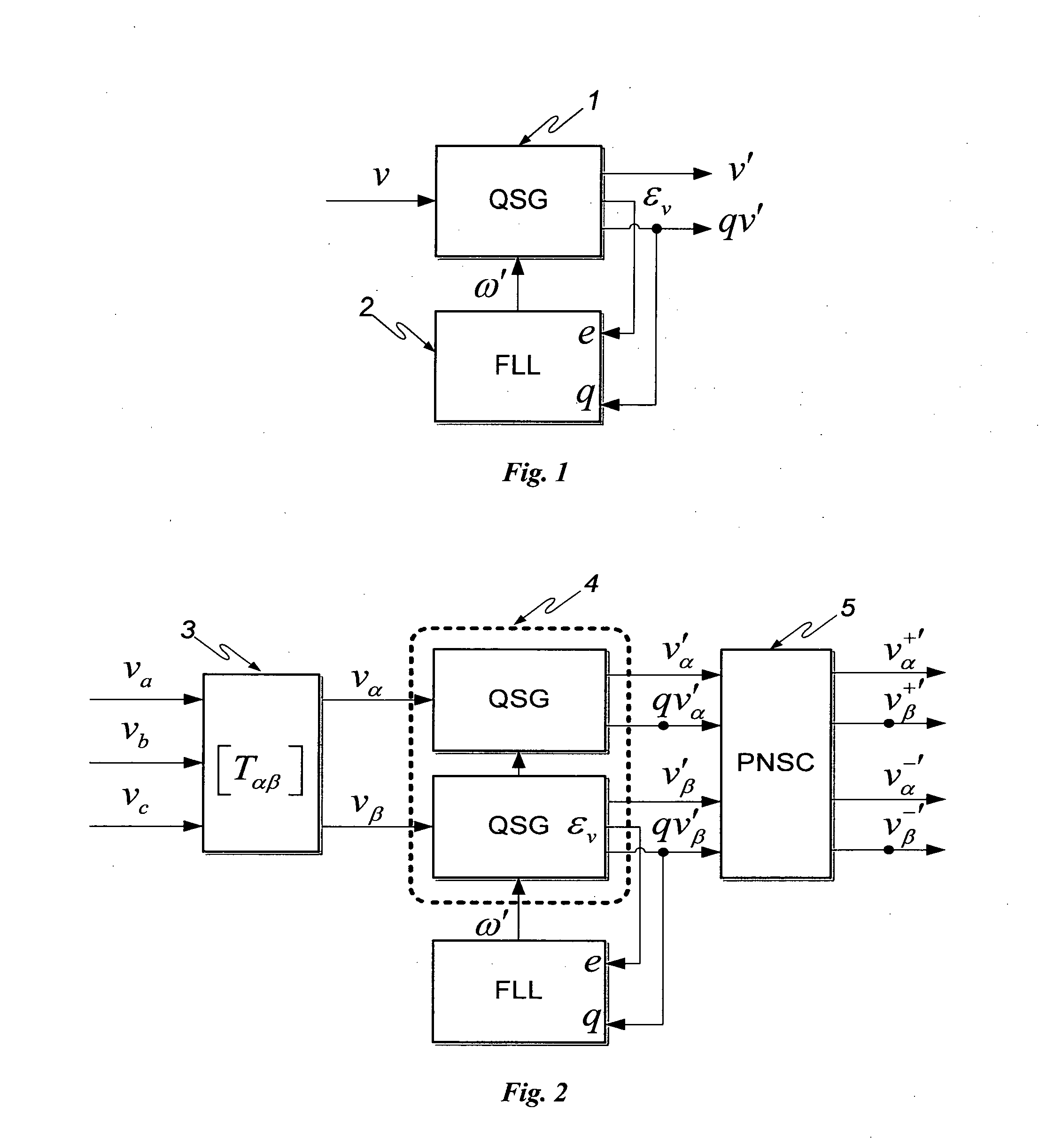
This invention deals with an advanced Real-time Grid Monitoring System (RTGMS) suitable for both single-phase and three-phase electric power systems. This invention provides an essential signal processing block to be used as a part of complex systems either focused on supervising and diagnosing power systems or devoted to control power processors interacting with the grid. This invention is based on a new algorithm very suitable for real-time characterization of the grid variables under distorted and unbalanced grid conditions. The main characteristic of this invention is the usage of a frequency-locked loop, based on detecting the grid frequency, for synchronizing to the grid variables. It results in a very robust system response in relation to existing technique based on the phase-angle detection since grid frequency is much more stable variable than the grid voltage / current phase-angle, mainly during grid faults. Moreover, the algorithm supporting this invention is very efficient and can be implemented in regular industrial microprocessors. These features make the RTGMS object of this invention ideal to be applied in the control of distributed generation systems (DGS), flexible AC transmission systems (FACTS), power quality conditioners (PQC) and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). In all these systems, the fast and precise real time detection of the voltage and / or current sequence components under grid fault conditions is a crucial matter.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Low-skew single-ended to differential converter
InactiveUS7119602B2Reduce offsetReduce static power consumptionTransistorSingle output arrangementsTransmission gateEngineering
A single-ended to differential converter uses a cross-coupled latch that maximizes the output zero-crossing symmetry and is self compensating over PVT variations. An in-phase driving signal is provided by an always-on transmission gate coupled to the input. An out-of-phase driving signal is provided by an inverter coupled to the input. The in-phase and out-of-phase driving signals each drive an input of the cross-coupled latch. The in-phase driving signal from the always-on transmission gate starts to bring the cross-coupled latch into conduction, and when the out-of-phase driving signal arrives, the simultaneous driving of the cross-coupled latch causes a rapid and symmetric transition of both outputs of the cross-coupled latch.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Delay line synchronizer apparatus and method
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Clock and data recovery circuit and clock control method
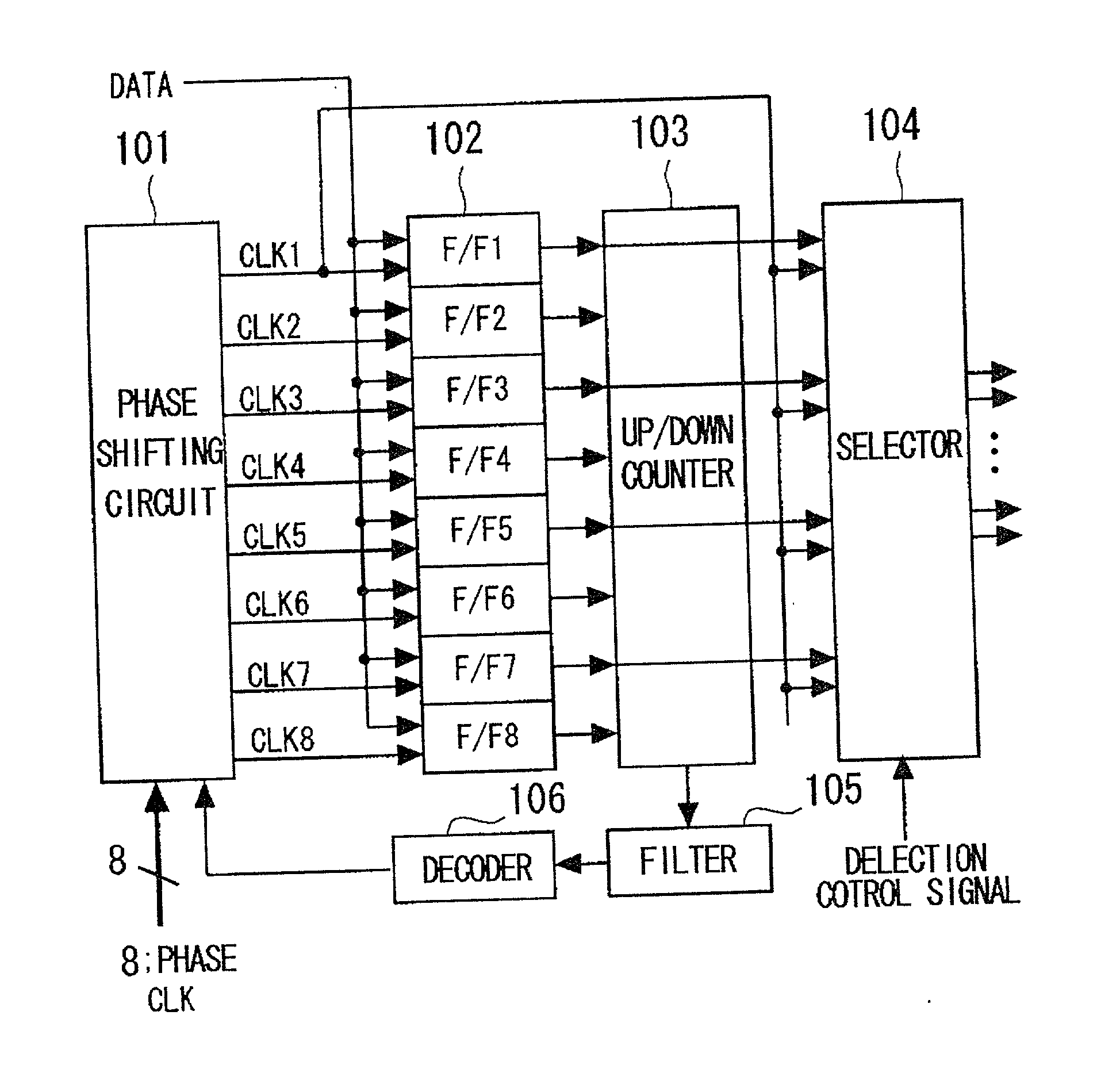
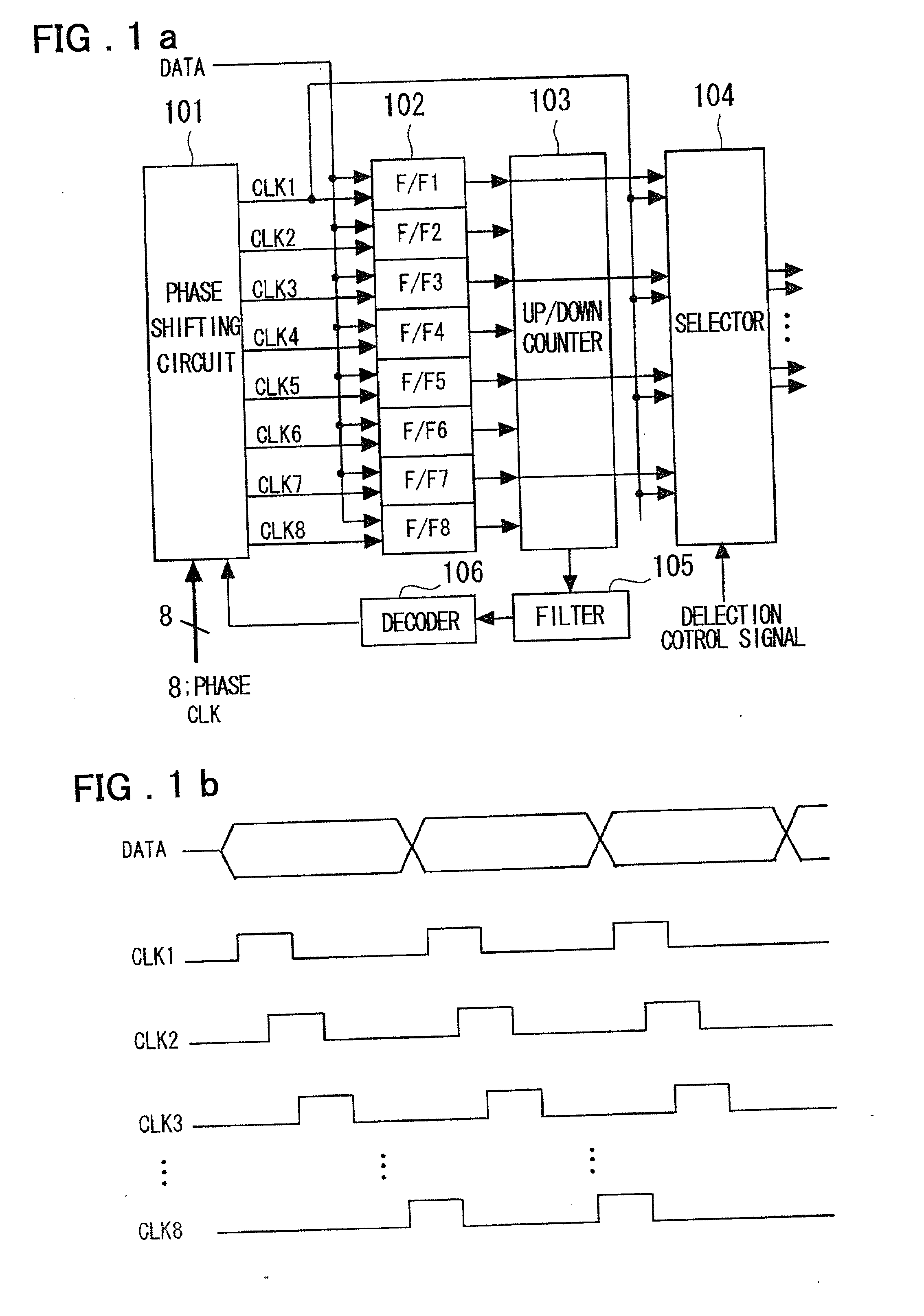
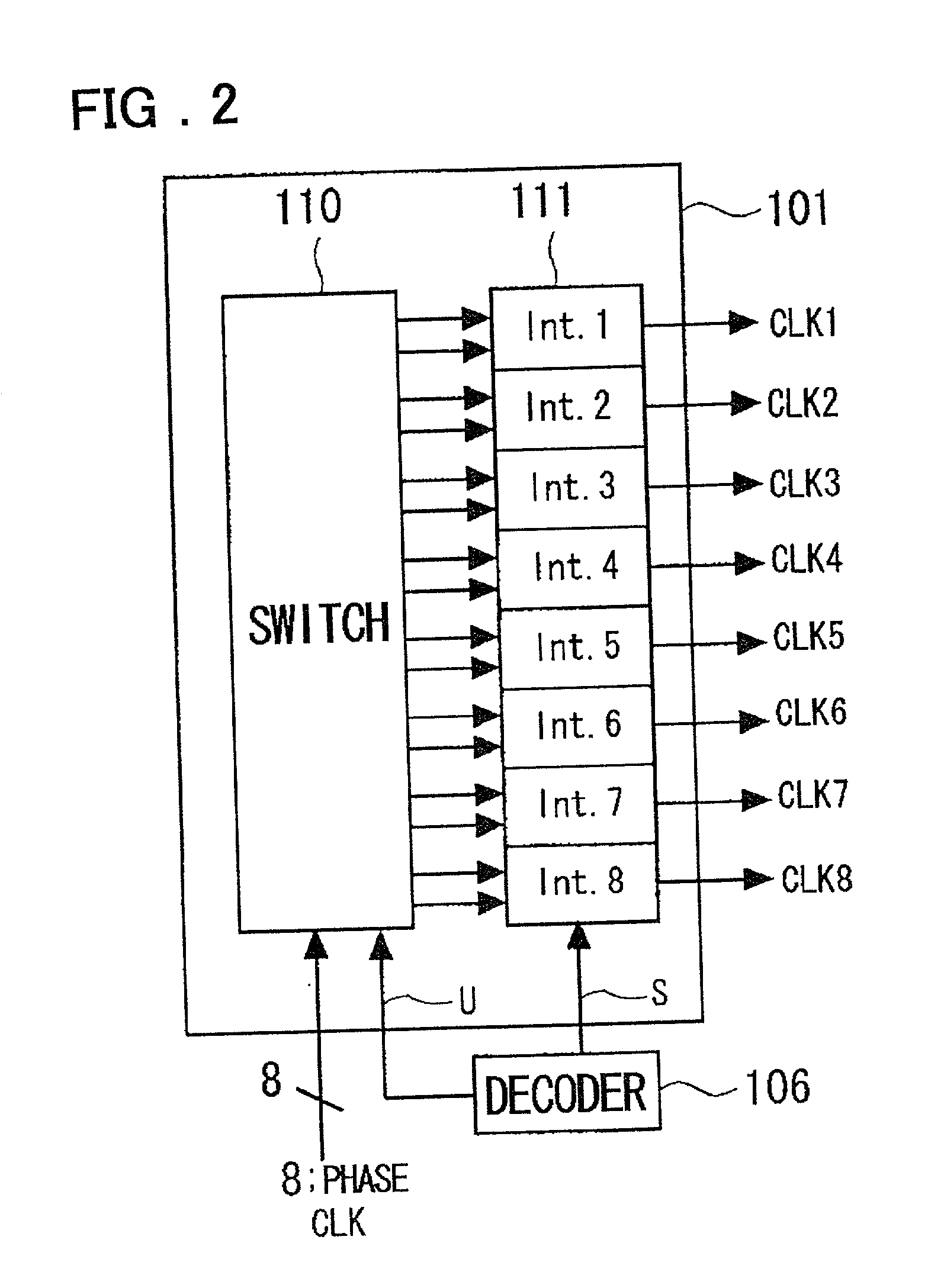
InactiveUS20020079938A1Easy to characterizeFacilitate change of frequencyPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase shiftedPhase difference
To provide a clock and data recovery circuit which facilitates alteration of the frequency range and adjustment of characteristics. The clock and data recovery circuit includes a phase shift circuit 101 having a switch receiving as inputs multi-phase clocks for selecting and outputting plural sets of the paired clocks from the input multi-phase clocks and a plural number of interpolators receiving the plural number of clock pairs output from the switch to output signals having the delay prescribed by the time corresponding to interior division of the phase difference of the clock pairs, a plural number of latch circuits 102 for latching the input data based on the signals output from the phase shift circuit 101, a counter 103 for counting the outputs of the plural latch circuits, a filter 105 for averaging the counter output over a preset time, a decoder 106 for decoding an output of the filter and a selection circuit 104 fed with a plural number of sets of data output by the plural latch circuits and clocks output from a preset one of the plural interpolators to select pairs of output data and clocks.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
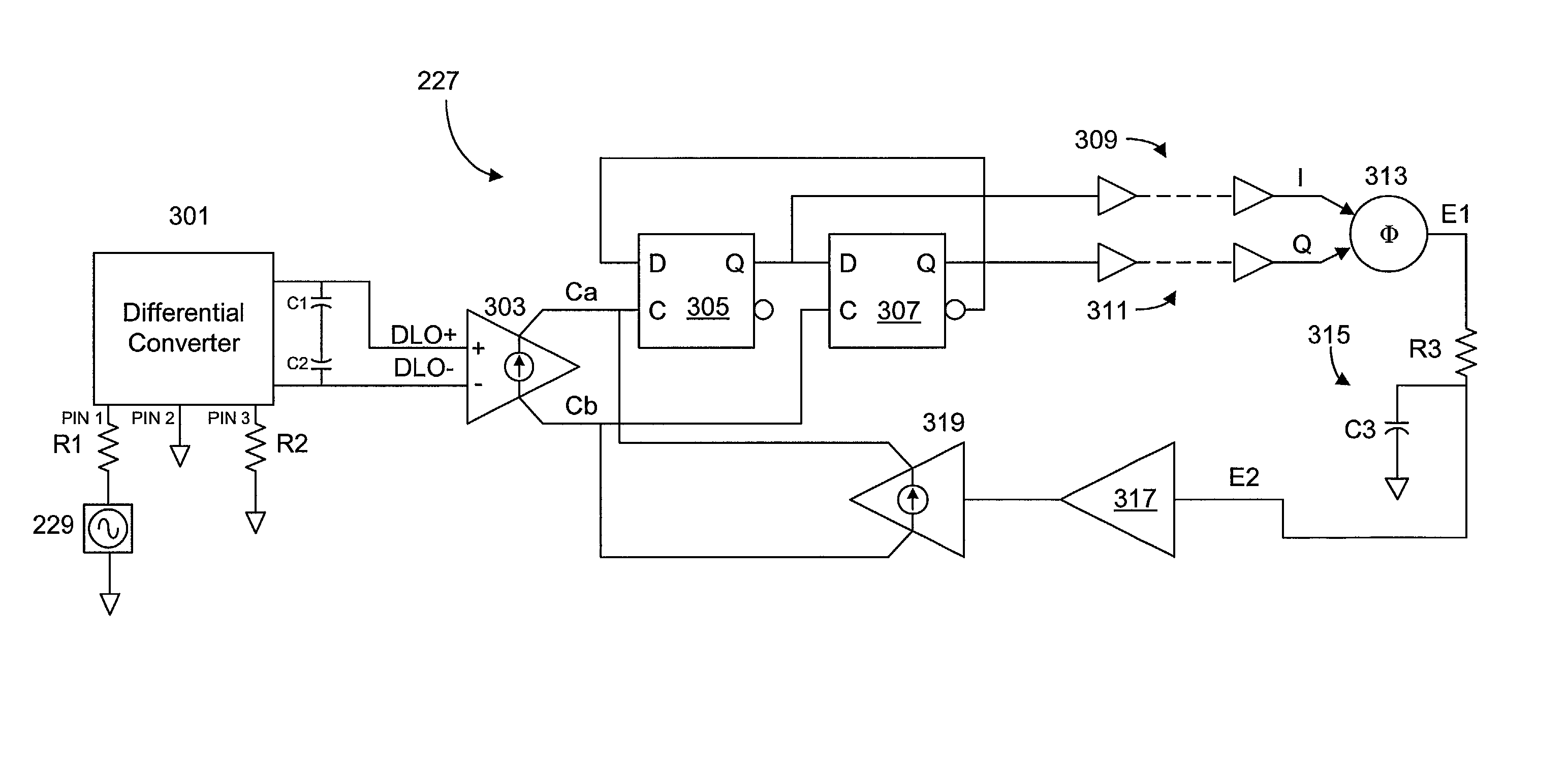
Quadrature oscillator with phase error correction
InactiveUS20020039052A1Increase volumePulse automatic controlGain controlPhase detectorAudio power amplifier
A quadrature oscillator with phase error correction including a local oscillator that generates a single-ended clock signal, a single-ended to differential converter that converts the clock signal to a differential clock signal, a quadrature generator that converts the differential clock signal into I and Q carrier signals, a phase error detector that measures a phase error between the I and Q carrier signals, and a feedback amplifier that modifies the differential clock signal based on measured phase error. The feedback amplifier applies the measured phase error as a DC offset to an AC differential clock signal. A transconductor converts the differential clock voltage signal into two pairs of differential current clock signals, where the quadrature generator generates I and Q current signal outputs from the two pairs of differential current clock signals. The phase error detector generates a phase error voltage, and the feedback amplifier includes a transconductance stage that converts phase error voltage into a DC correction current and that adds the correction current to each of the two pairs of AC differential current clock signals.
Owner:M RED INC
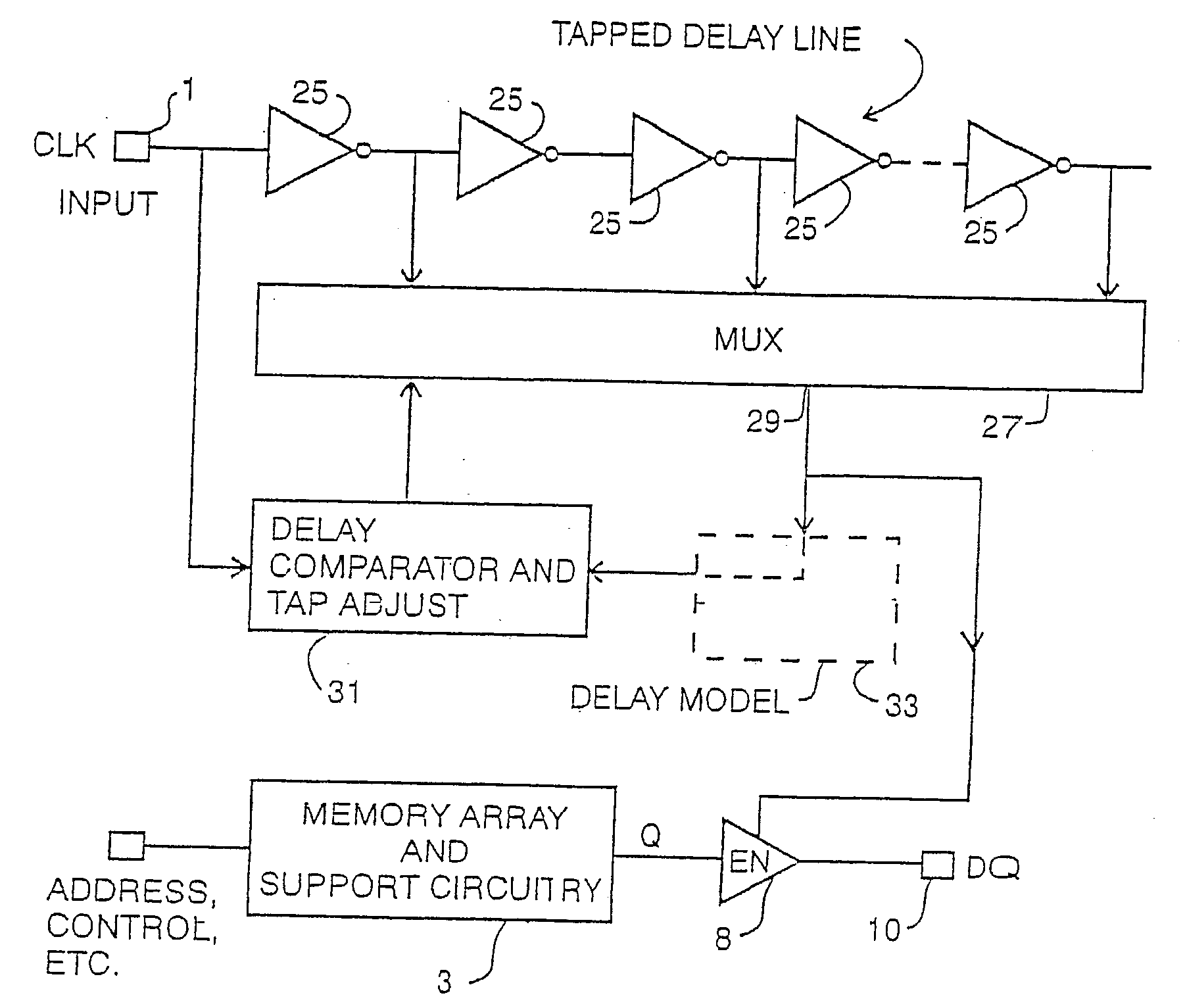
Delay locked loop implementation in a synchronous dynamic random access memory
InactiveUS20050265506A1Minimizes elapsed timeHigh clock frequency operationPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsRandom access memoryDelay-locked loop
A clock applying circuit for a synchronous memory is comprised or a clock input for receiving a clock input signal, apparatus connected to the synchronous memory for receiving a driving clock signal, and a tapped delay line for receiving the clock input signal and for delivering the clock driving signal to the synchronous memory in synchronism with but delayed from the clock input signal, the delay being a small fraction of the clock period or the clock input signal.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Single particle upset and single particle transient pulse resisiting D trigger
InactiveCN101499788ASingle event upsetCapable of single-event transient pulse performanceSingle output arrangementsElectronic switchingMultiway switchingRadiation resistance
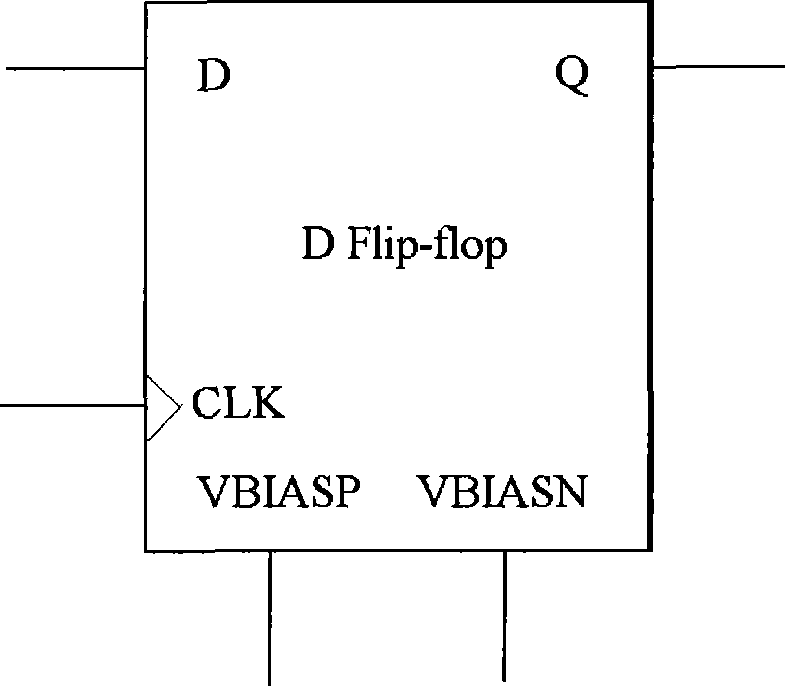
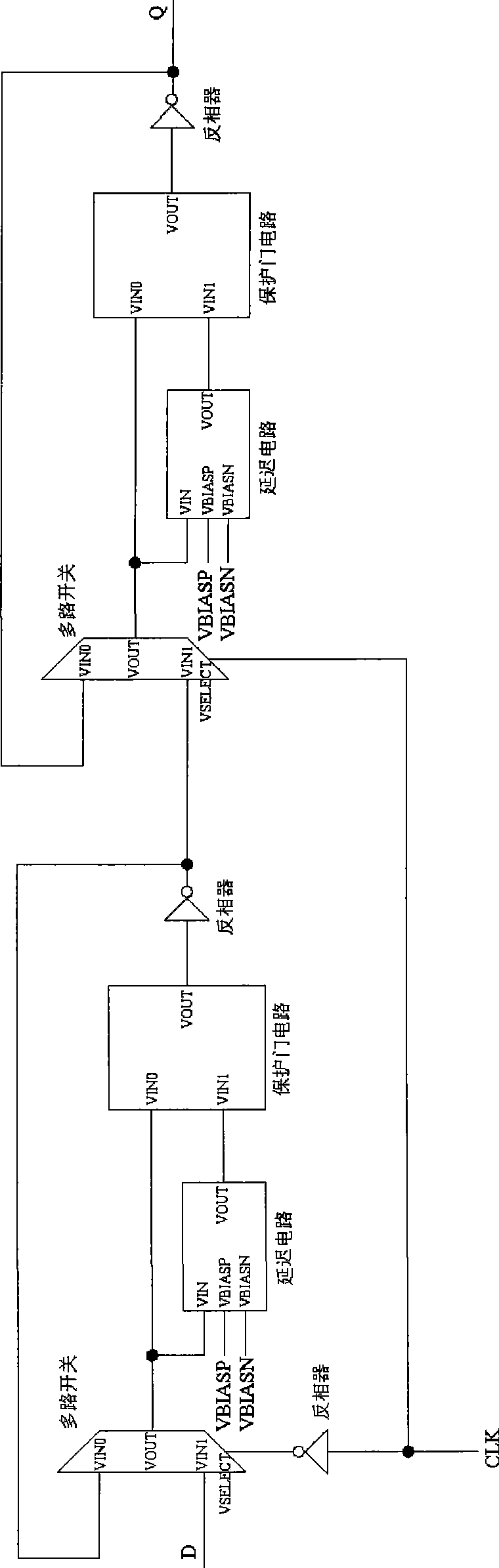
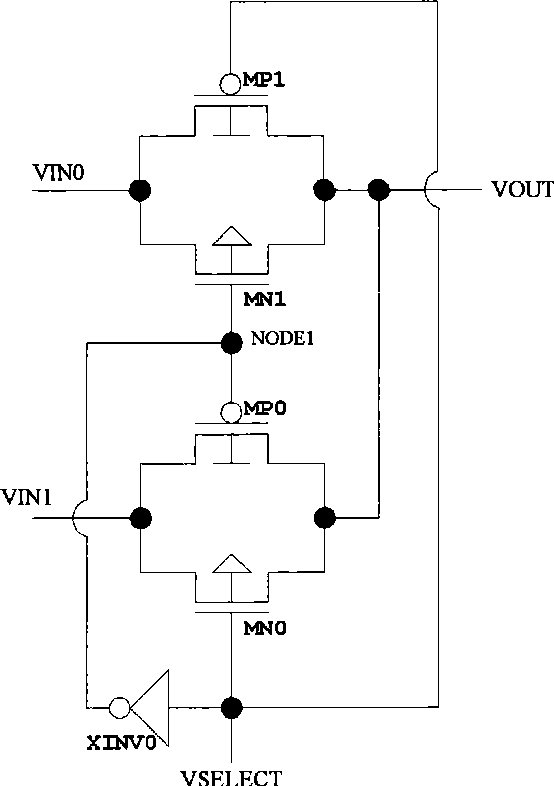
The invention relates to a D trigger used for single particle upsetting resistance and single particle transient pulse in the technical filed of an integrated circuit, comprising two multichannel switches, two delay circuits, two protecting gate circuits and three inverters; wherein, the multichannel switches are used for forming a feedback loop for latching data; the delay circuits are used for generating signals in delay modes; the protecting gate circuits are used for filtering voltage transient fluctuation of the input signals; in the feedback loop of the D trigger, data input signal D and the delayed mode thereof enter the protecting gate circuit; and the output signals of the protecting gate circuit filter the delayed voltage transient fluctuation of the data input signal D and the width of the voltage transient fluctuation is not wider than the delay of the delay circuit. The invention can be applied to application occasions needing higher radiation resistance, leads the single particle upsetting resistance and single particle transient pulse performance of D trigger to reach the same level as a time sampling D trigger; and simultaneously, the increasing of the unit area is less than that of the time sampling D trigger and the working speed is superior to that of the time sampling D trigger.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Delay circuit, voltage-controlled delay circuit, voltage-controlled oscillation circuit, delay adjustment circuit, DLL circuit, and PLL circuit
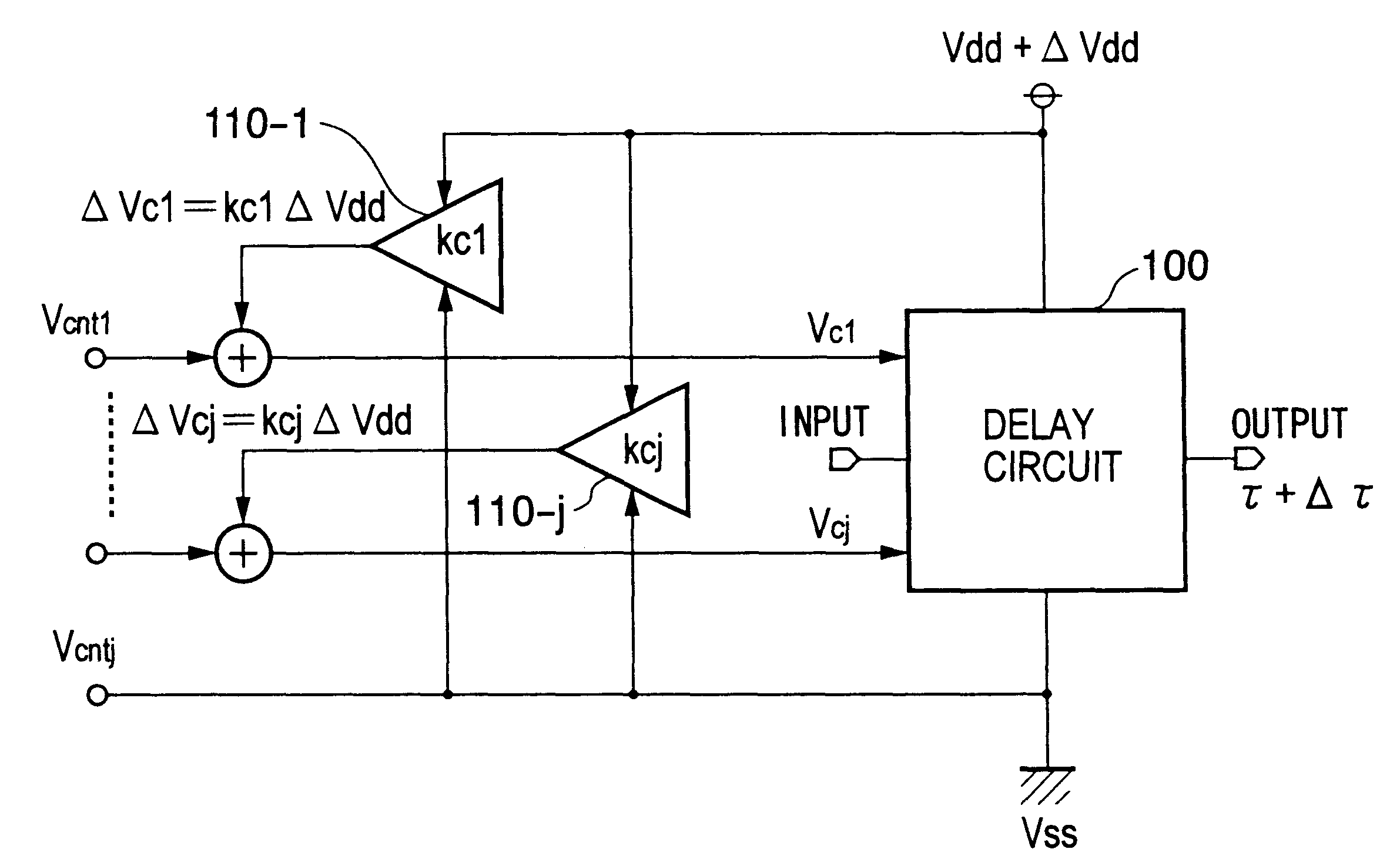
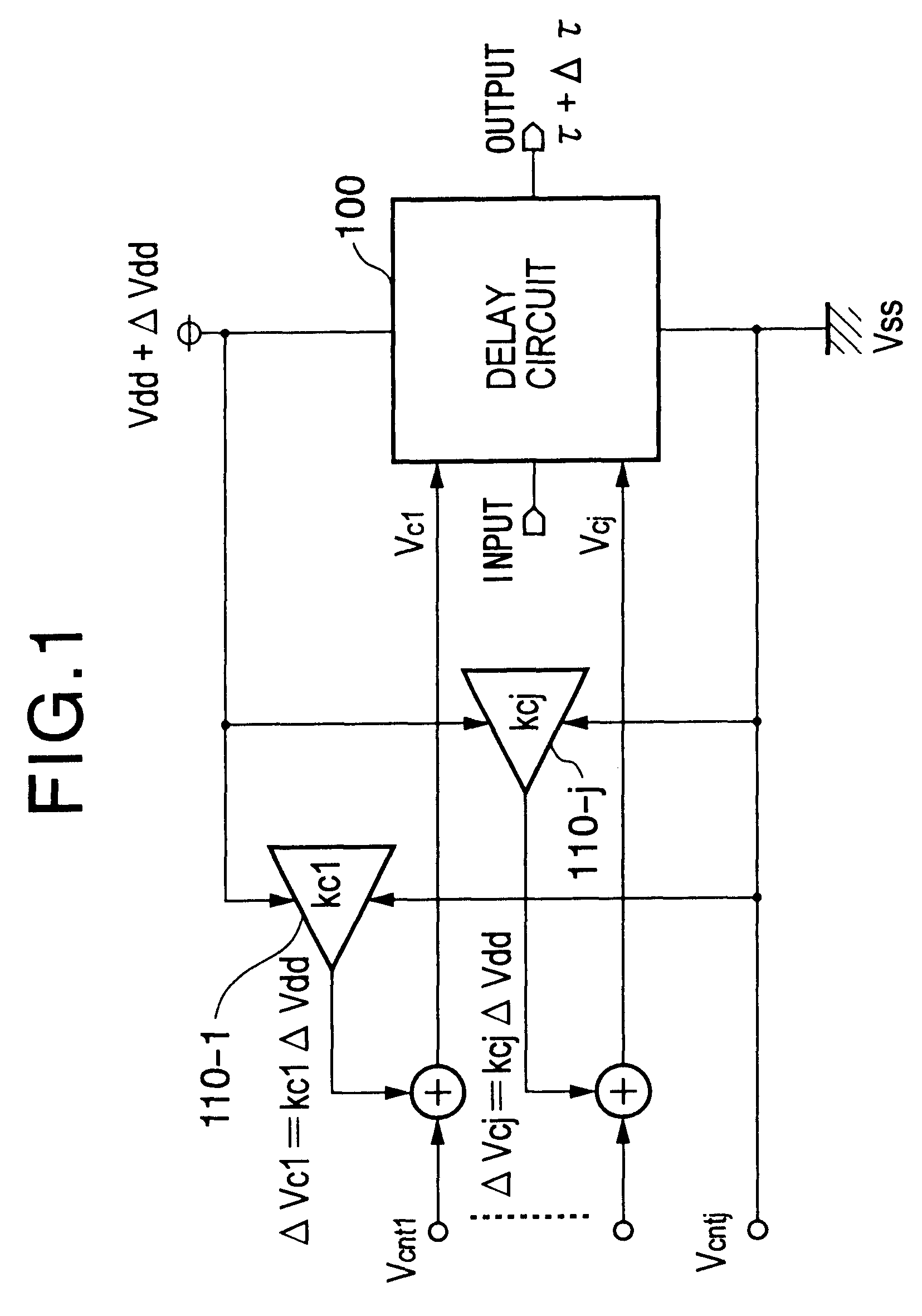
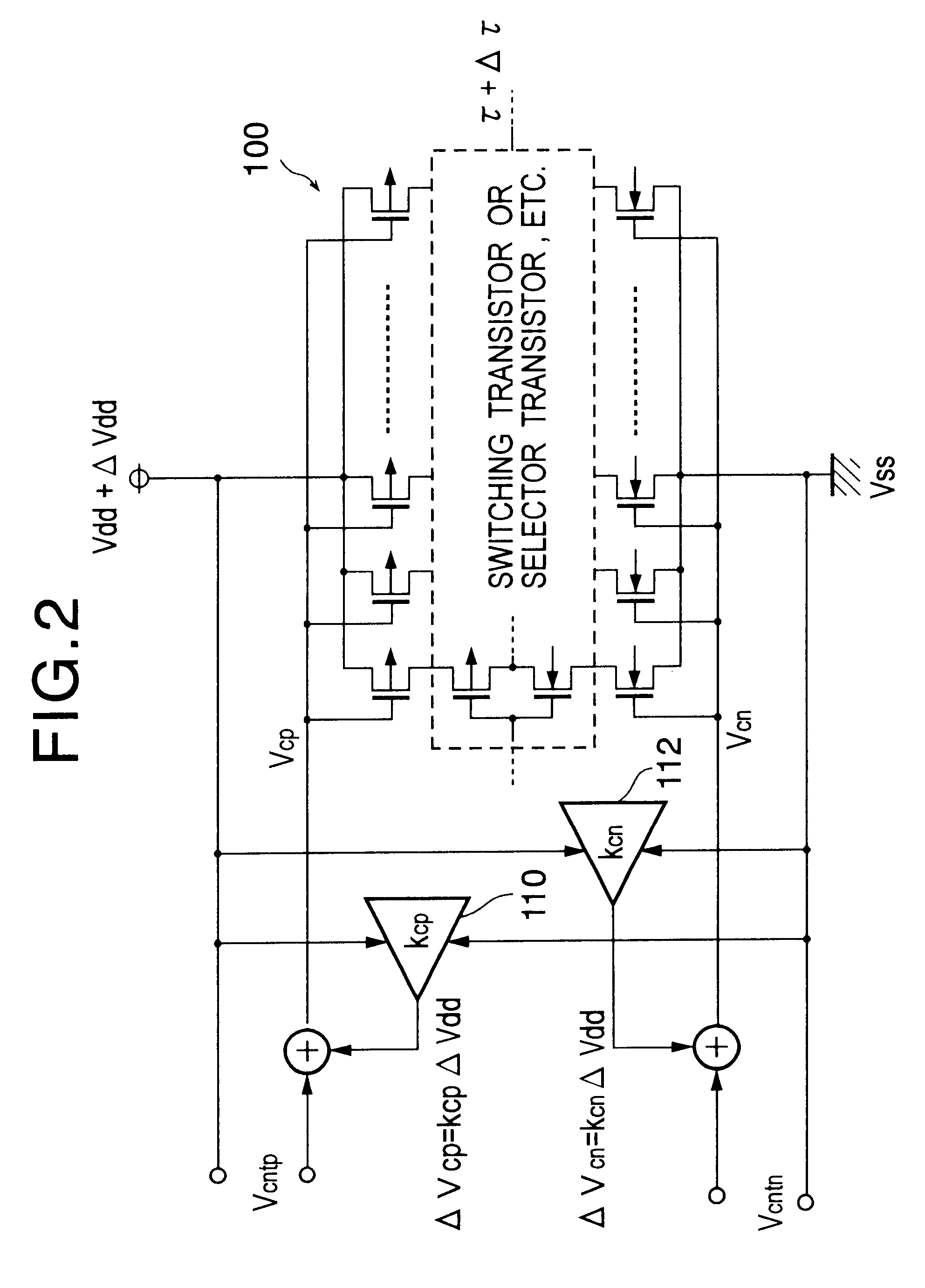
An inverter type delay circuit, voltage-controlled oscillation circuit, and voltage-controlled delay circuit capable of realizing simplification of circuit configuration, reduction of an effect of power source noise, and reduction of jitter, wherein a delay circuit, voltage-controlled oscillation circuit, and voltage-controlled delay circuit comprised of a plurality of delay stages controlled in drive current in accordance with a bias voltage or a control voltage and determined in delay time by the drive current, adding a change of a power source voltage to the above bias voltage or control voltage by a predetermined ratio and supplying a result of the addition to the above delay stages to suppress the power source voltage dependencies of the delay times of the delay stages, or connecting by a predetermined ratio a plurality of delay stages having different power source voltage dependencies, for example, power source voltage dependencies of opposite delay times, to suppress the power source voltage dependencies of delay times of the delay stages are realized.
Owner:SONY CORP
Popular searches
Code conversion Transmission monitoring Phase shifting networks Synchronous/start-stop systems Color television details Digital storage Television signal transmission by single/parallel channels Memory architecture accessing/allocation Color television with pulse code modulation Color television with bandwidth reduction
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com