Patents
Literature
879 results about "Combinational logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
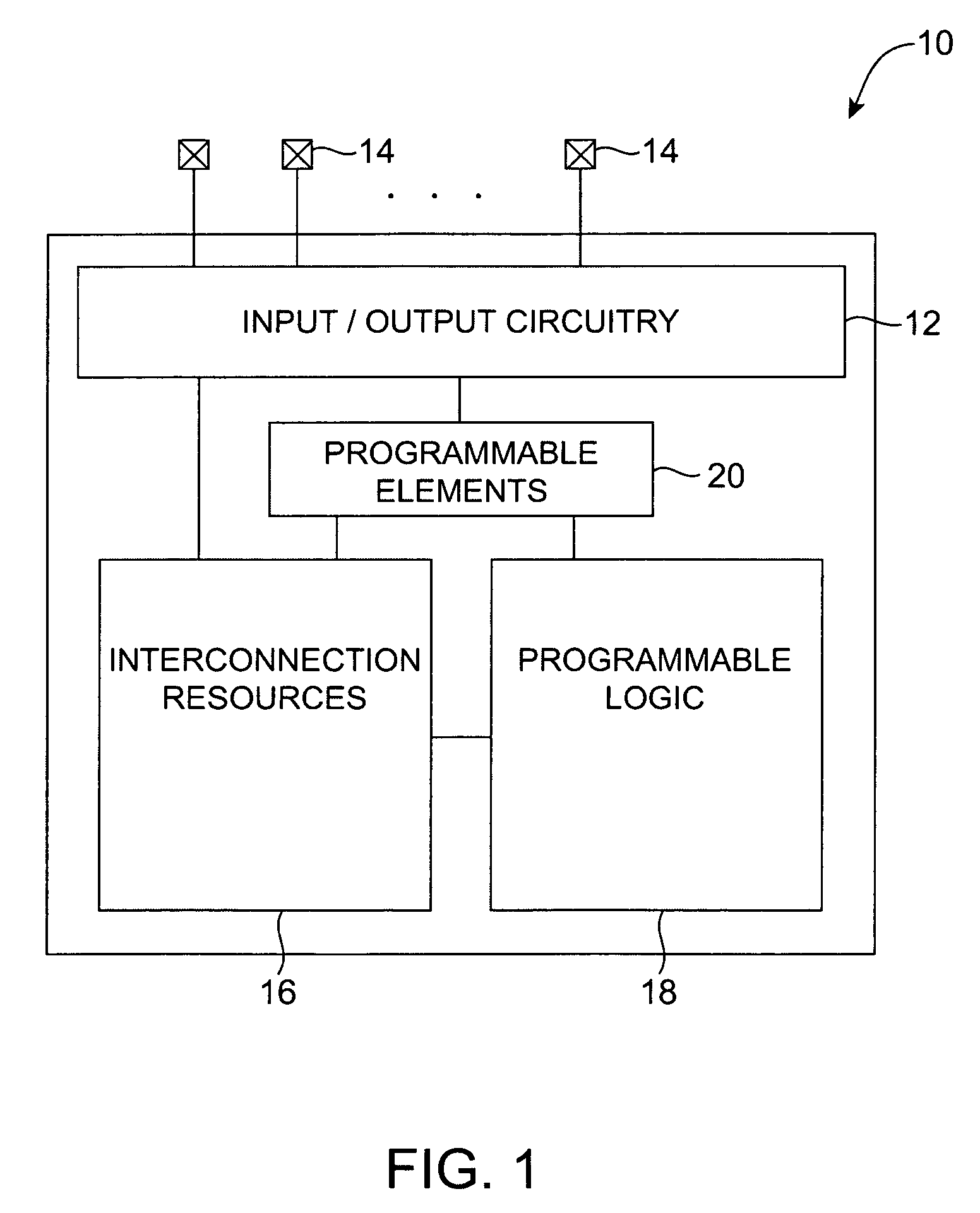
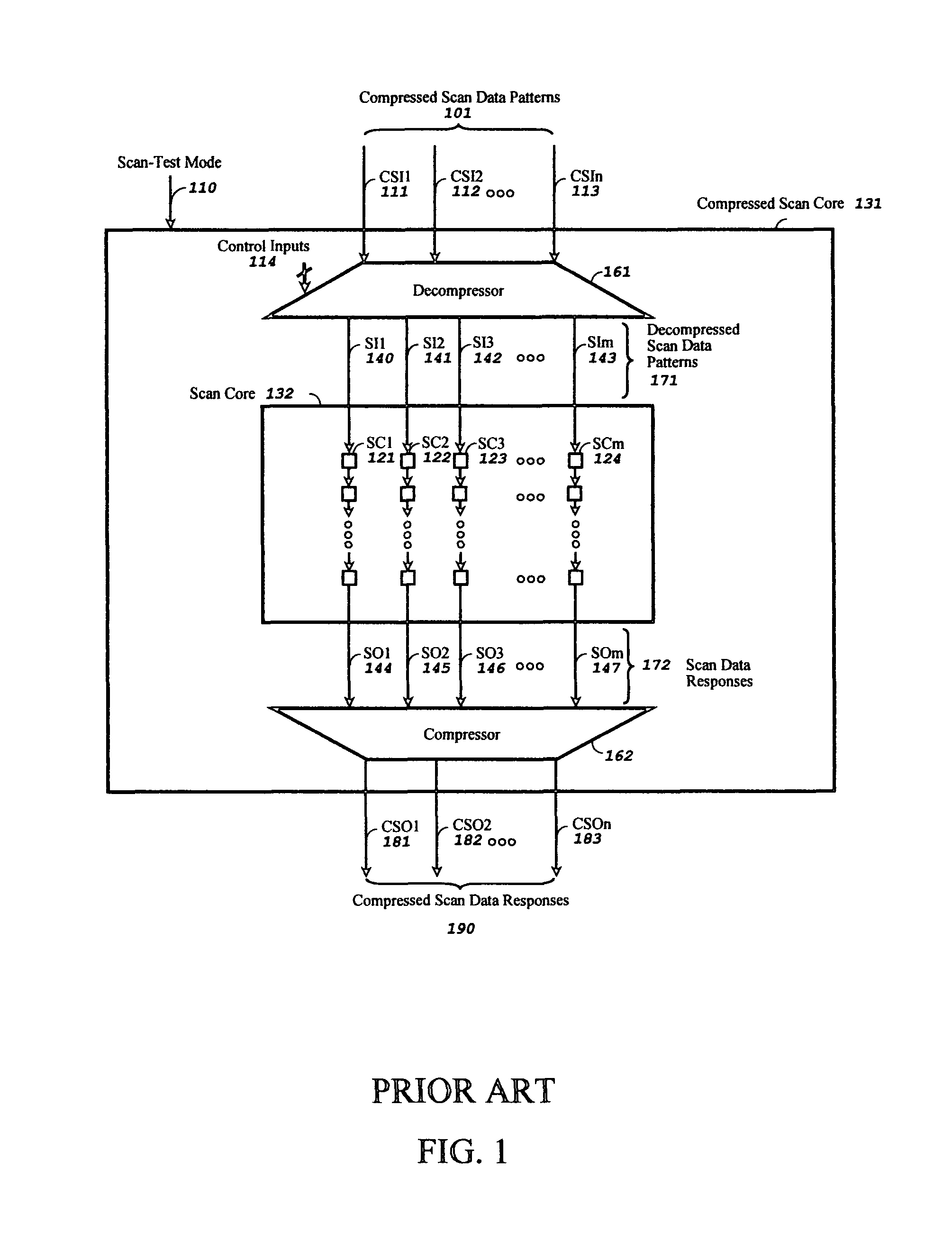
In digital circuit theory, combinational logic (sometimes also referred to as time-independent logic ) is a type of digital logic which is implemented by Boolean circuits, where the output is a pure function of the present input only. This is in contrast to sequential logic, in which the output depends not only on the present input but also on the history of the input. In other words, sequential logic has memory while combinational logic does not.
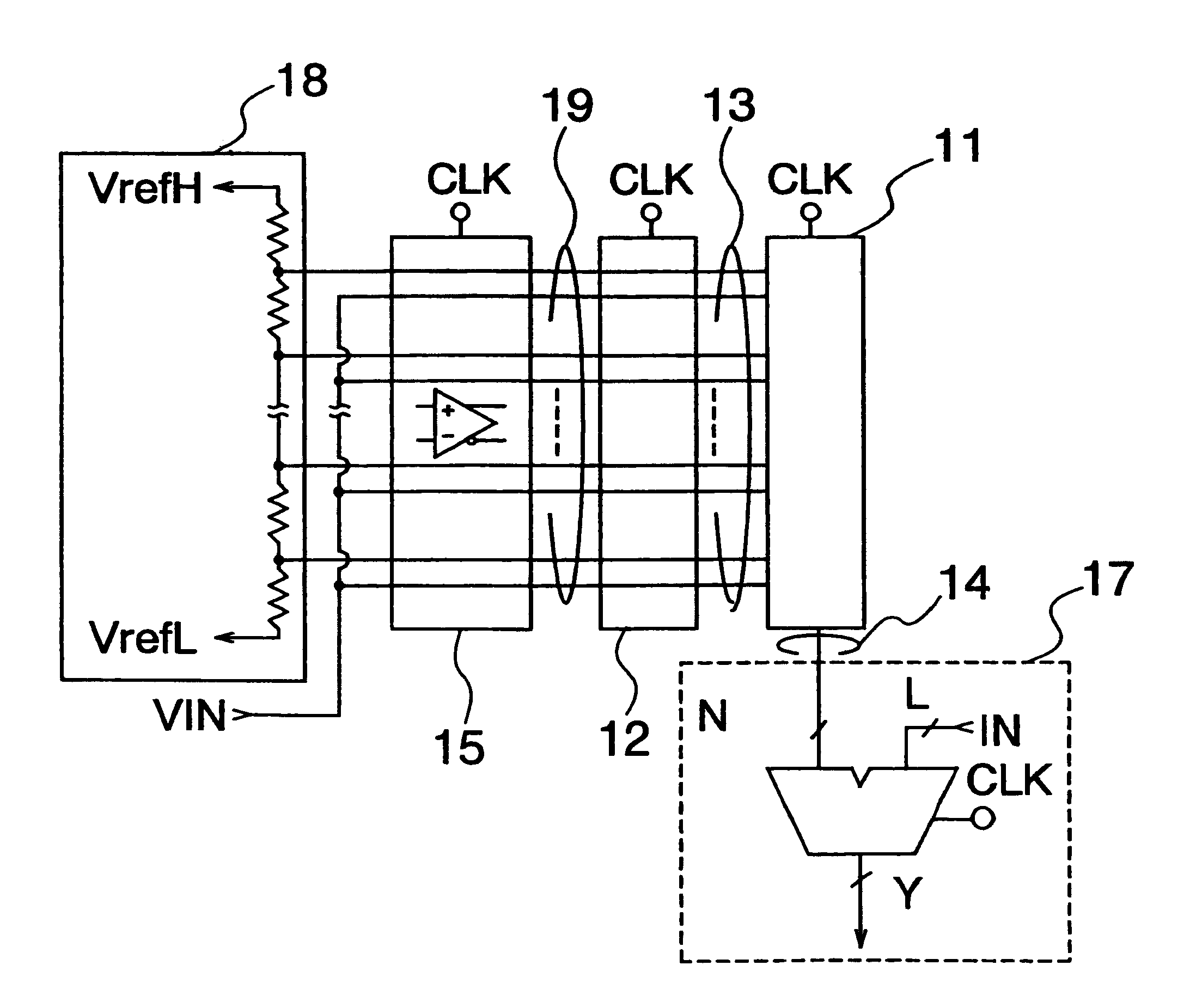
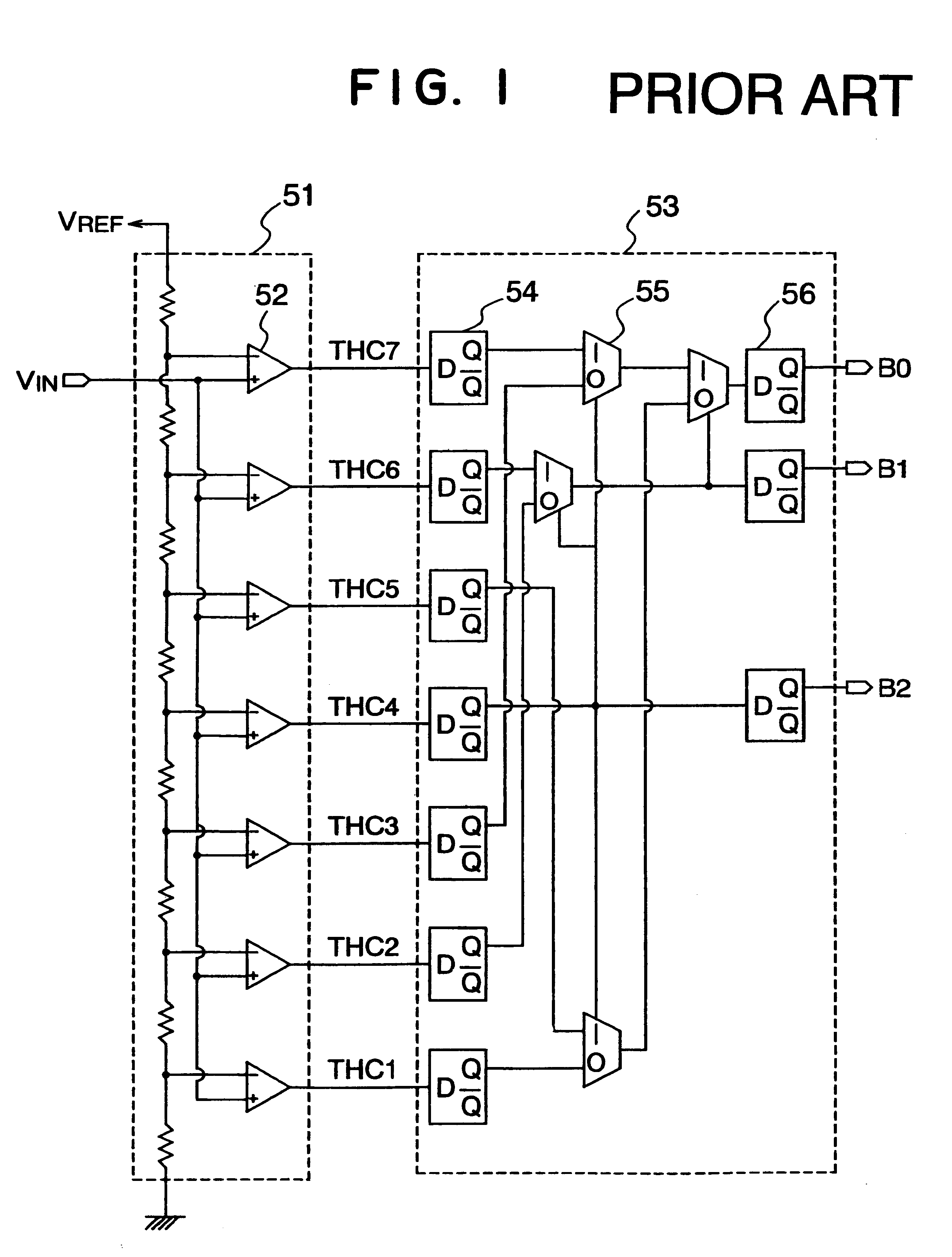
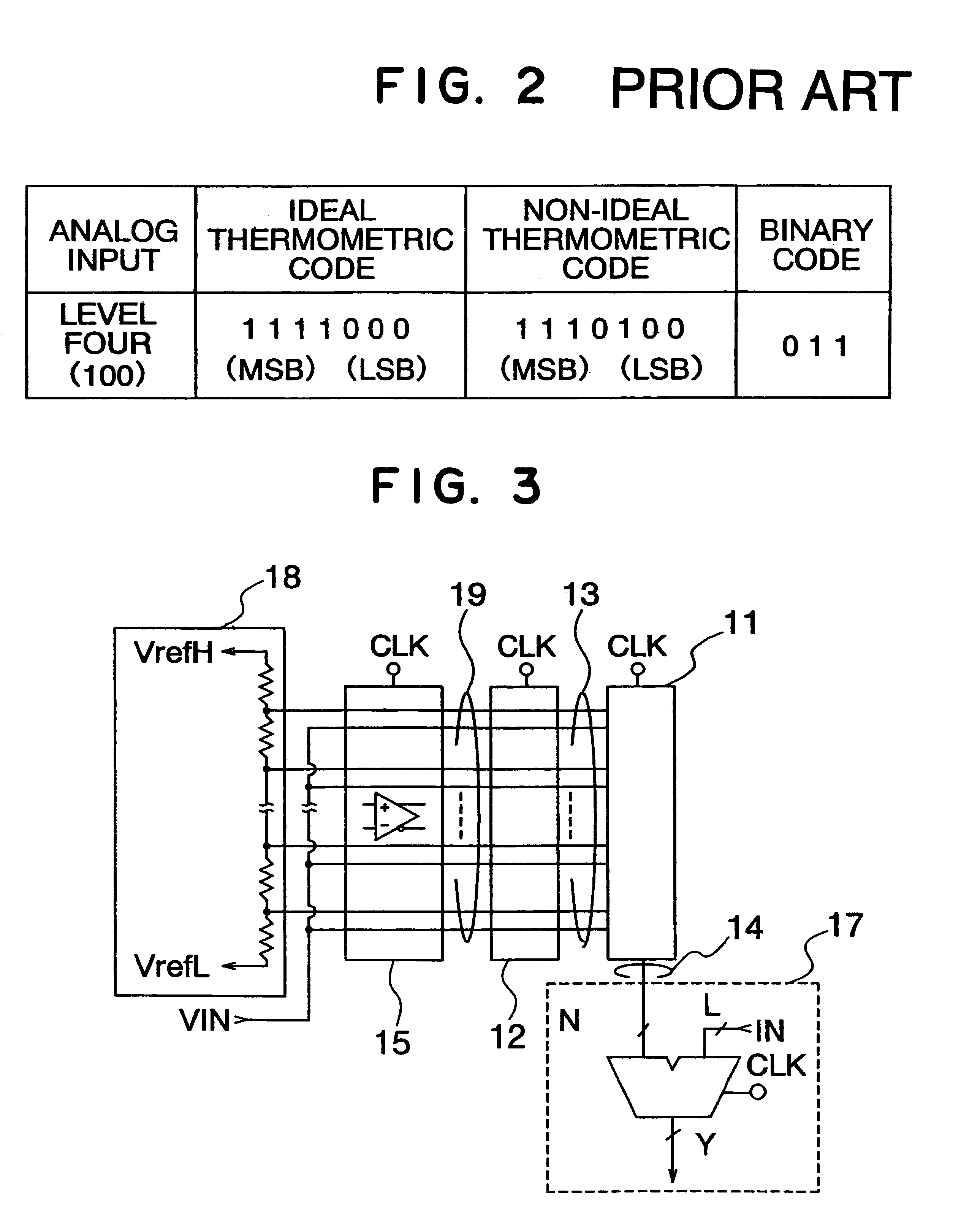
A/D converter having a dynamic encoder
InactiveUS6232908B1Increase speedReduce circuit sizeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersBuck converterA d converter
An A / D converter includes a resistor ladder for generating a plurality of reference potentials, a comparing section for comparing each of the reference potentials against an input analog signal to output a thermometric code, and a dynamic encoder composed of a combinational circuit to encode the thermometric code to a binary code by responding a clock signal. The A / D conversion is finished in a single clock cycle at a high speed, with a reduced number of elements and reduced power dissipation.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Register retiming technique
InactiveUS7120883B1High frequencySimple designCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTrade offsEmbedded system
An electronic automation system performs register retiming on a logic design, which may be a logic design for a programmable logic integrated circuit. Register retiming is a moving or rearranging of registers across combinatorial logic in a design in order to improve a maximum operating frequency or fmax. In one implementation, the system includes machine-readable code, which may be stored on a computer-readable medium such as a disk, executing on a computer. The system balances timing in order to trade off delays between critical and noncritical paths. Register retiming may make changes to a design at a gate level.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Integrated circuit logic with self compensating block delays
ActiveUS20050189604A1Reduce logic path variabilityMinimize fabrication parameter variationTransistorSolid-state devicesField-effect transistorCell delay
An integrated circuit (IC) including at least one combinational logic path. The combinational logic path includes two types of logic blocks cells that compensate each other for fabrication parameter effects on cell transistors. The two types may be dense cells with field effect transistor (FET) gates on contacted pitch and isolated cells with FET gates on wider than contacted pitch. Dense cell delay changes from the FET gates being printed out of focus are offset by isolated cell delay changes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
False lock protection in a delay-locked loop (DLL)
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG KANGDE XIN OPTRONICS MATERIAL +1
Programmable logic device latch circuits
InactiveUS7088136B1Logic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsComputation using denominational number representationEngineeringProgrammable logic array
Latch circuitry is provided for programmable logic regions on integrated circuits such as programmable logic device integrated circuits. A programmable logic device may have programmable logic regions based on programmable combinational logic circuits. Latch circuitry in a logic region may be provided between an output of a programmable combinational logic circuit in the logic region and an output of the logic region. When the latch circuitry is enabled, the latch circuitry performs the functions of a level-sensitive latch. When the latch circuitry is disabled, the latch circuitry acts as a passive data path. The passive data path may include only a single driver so that the latch circuitry adds essentially zero additional delay to the data produced by the combinational logic.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
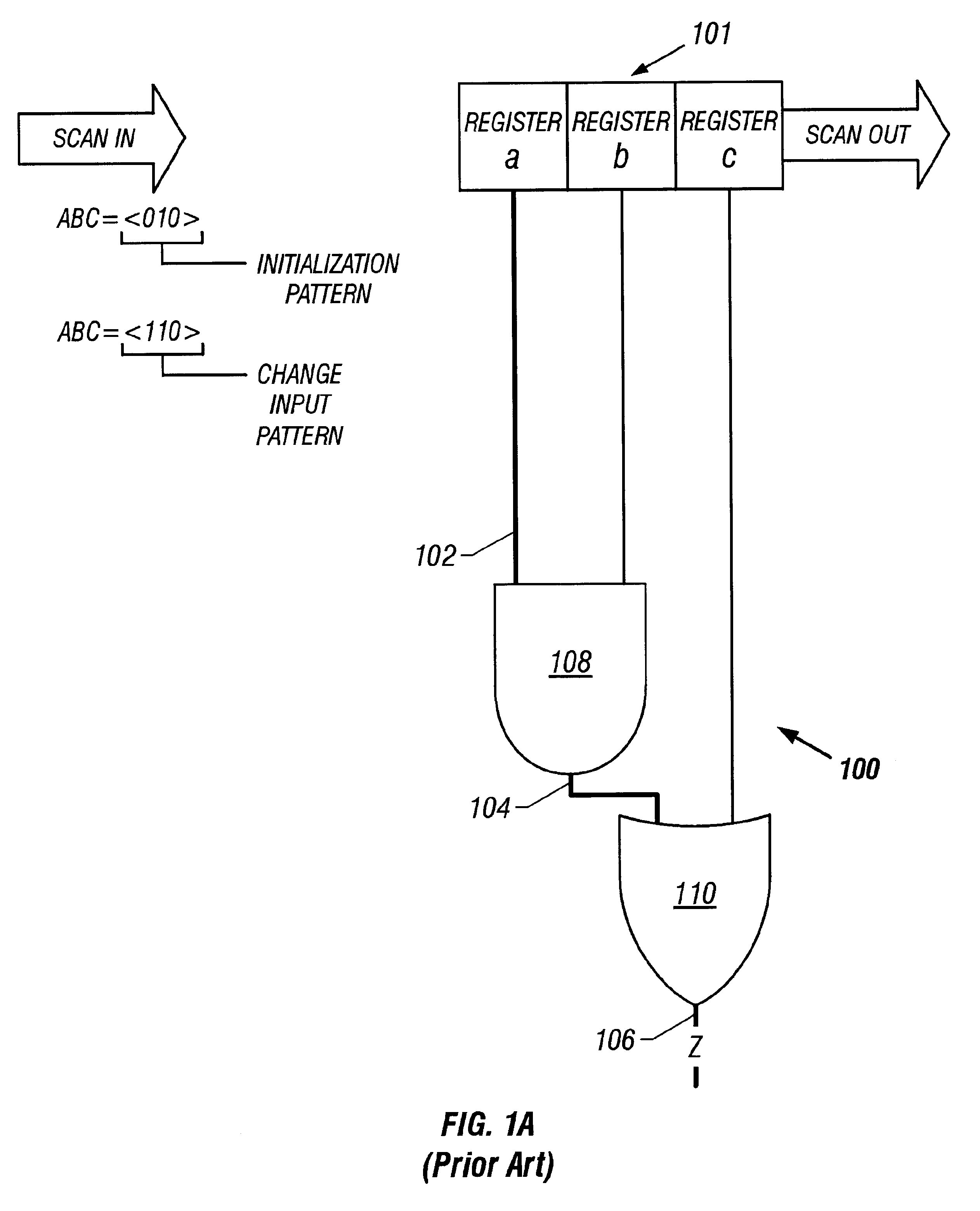
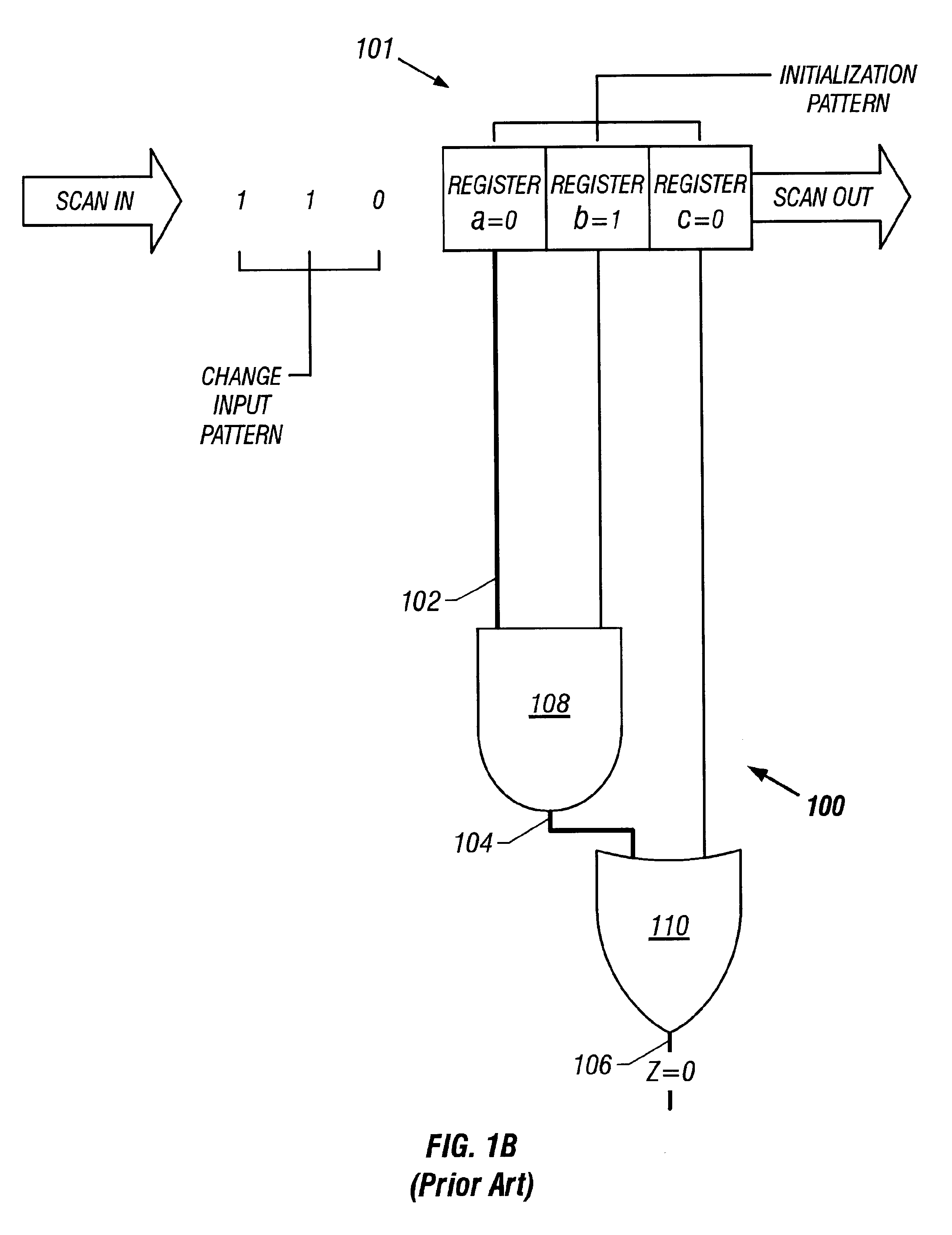
Combinational test pattern generation method and apparatus
InactiveUS6480980B2Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionPattern generationEngineering
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS AMERICA
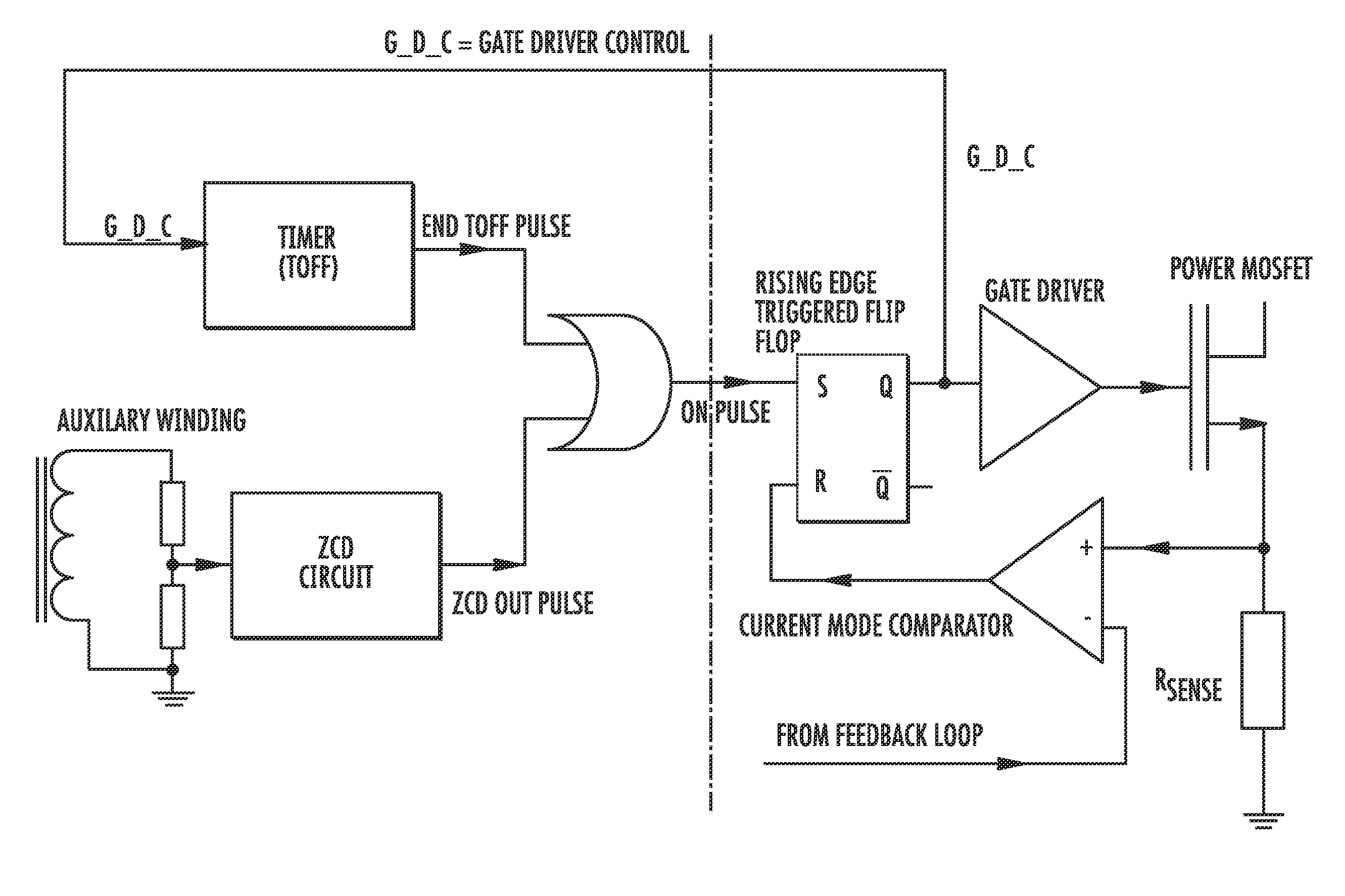
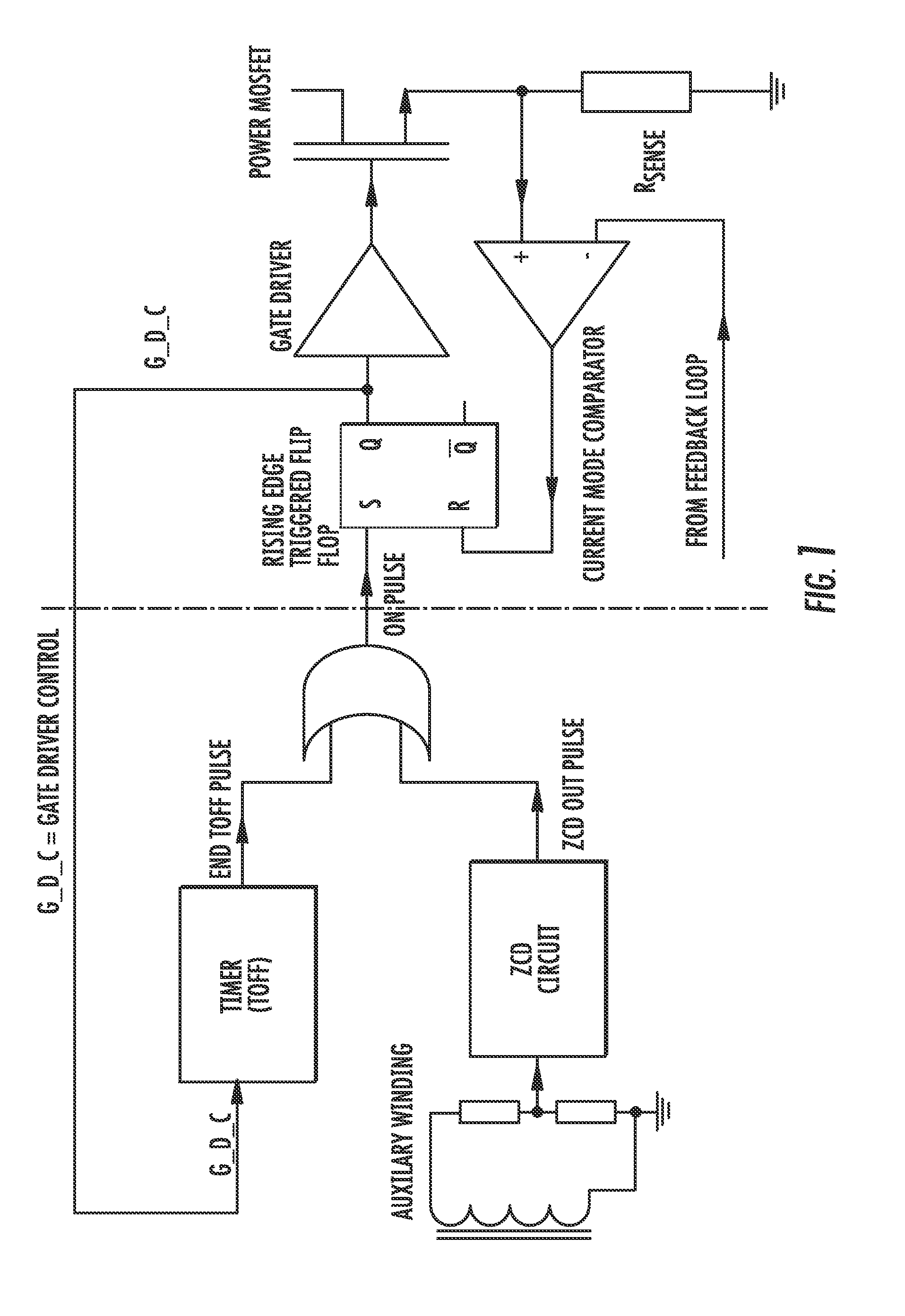
Dual mode flyback converter and method of operating it
ActiveUS20110149614A1Reduce lossesImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDetector circuitsDual mode
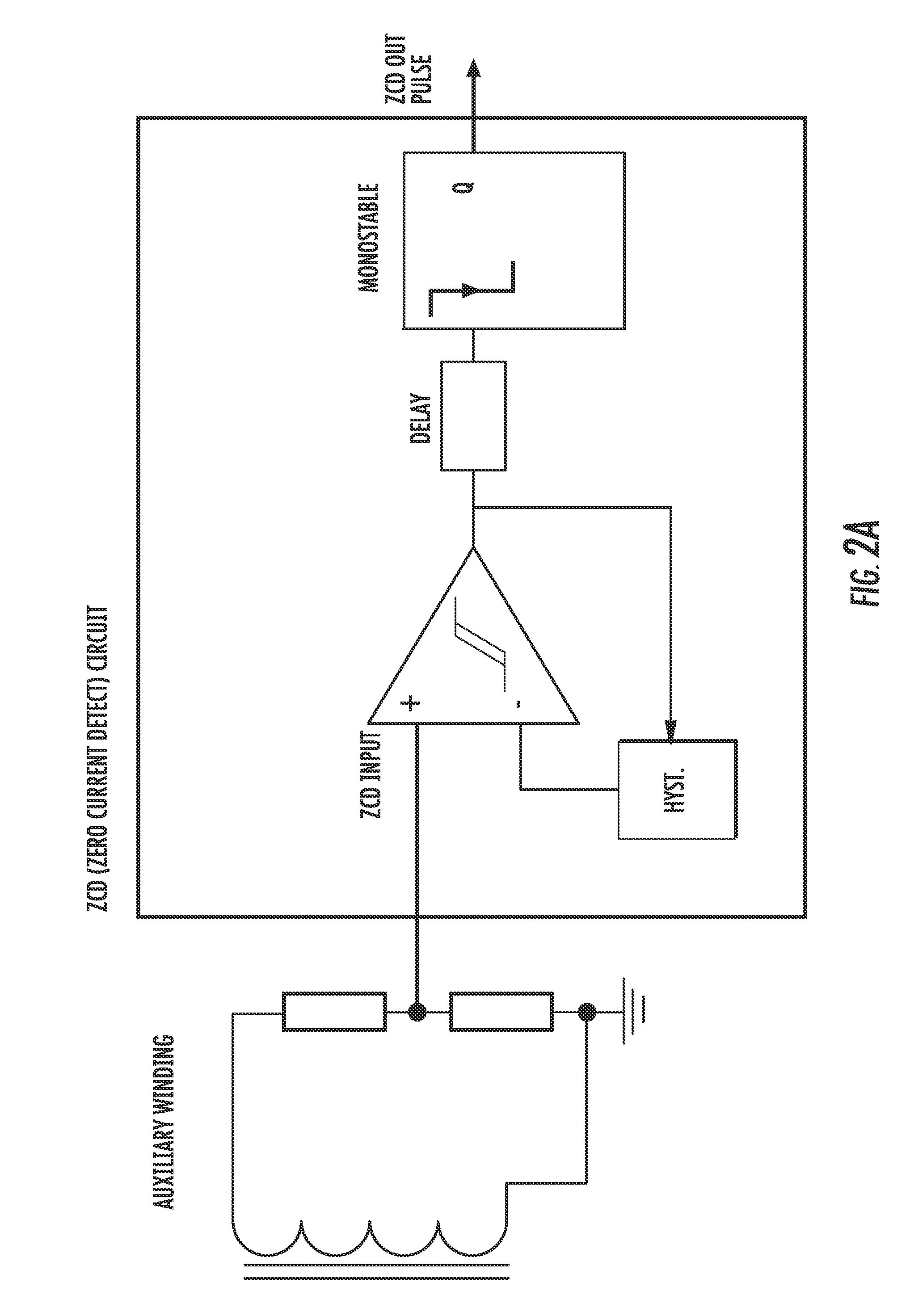
A DC-DC converter includes a power switching device and a mode control logic circuit to control the power switching device and generate an ON-pulse. A flip-flop is configured to be set by the mode control logic circuit. A current mode comparator is configured to reset the flip-flop and to compare a signal based upon current flowing through the power switching device with a signal based upon an output voltage of the dual mode flyback DC-DC converter. A transformer is driven by the current mode comparator. The mode control logic circuit includes a timer starting when a gate driver control signal applied to the power switching device turns the power switching device off and configured to generate a pulse when an off time interval elapses, a zero current detector circuit configured to sense a voltage on the transformer and generate a pulse when the voltage drops below a trigger threshold, and a combinatory logic circuit configured to compare pulse signals generated by the timer and the zero current detector circuit and generate the ON-pulse based thereupon.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
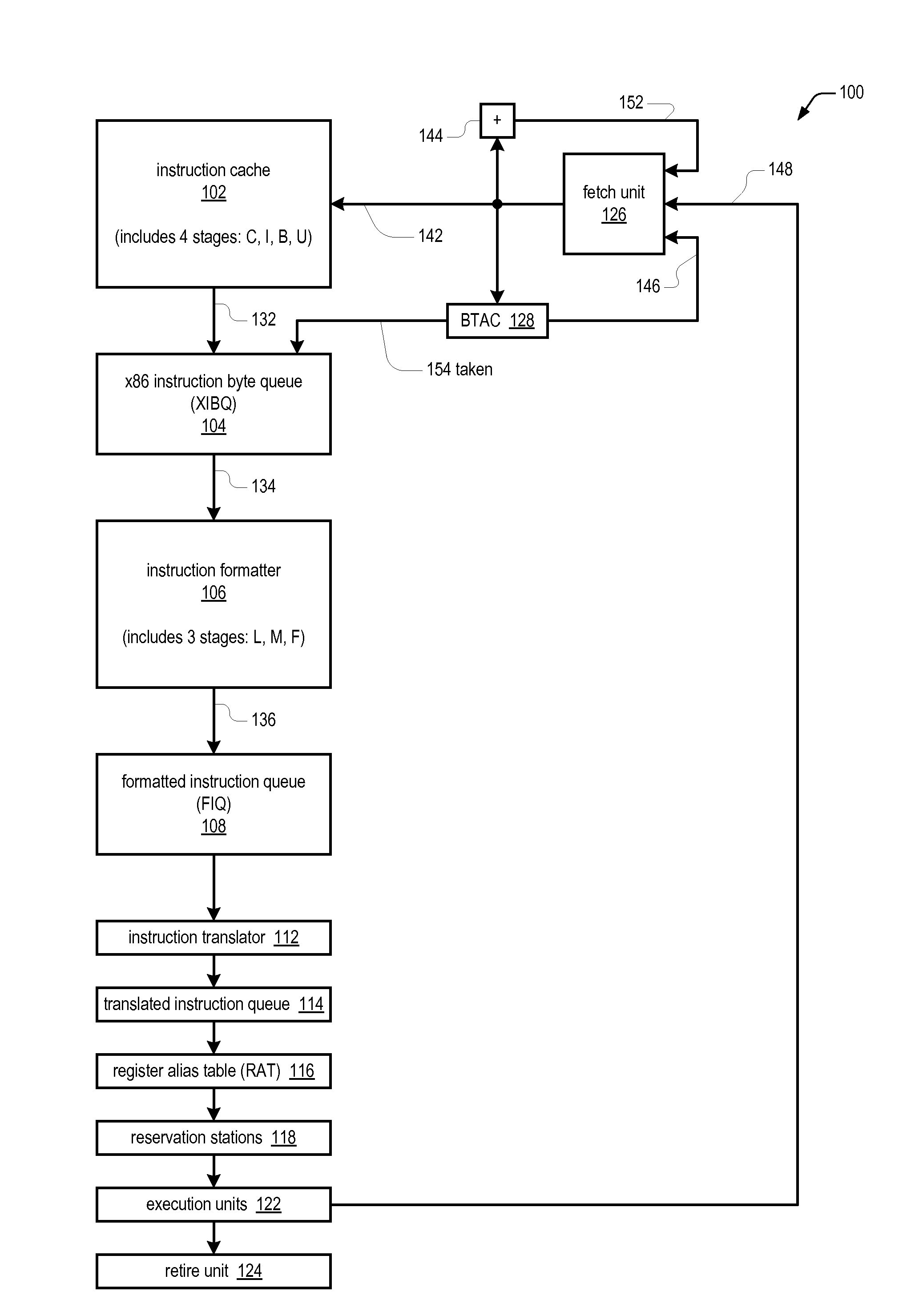
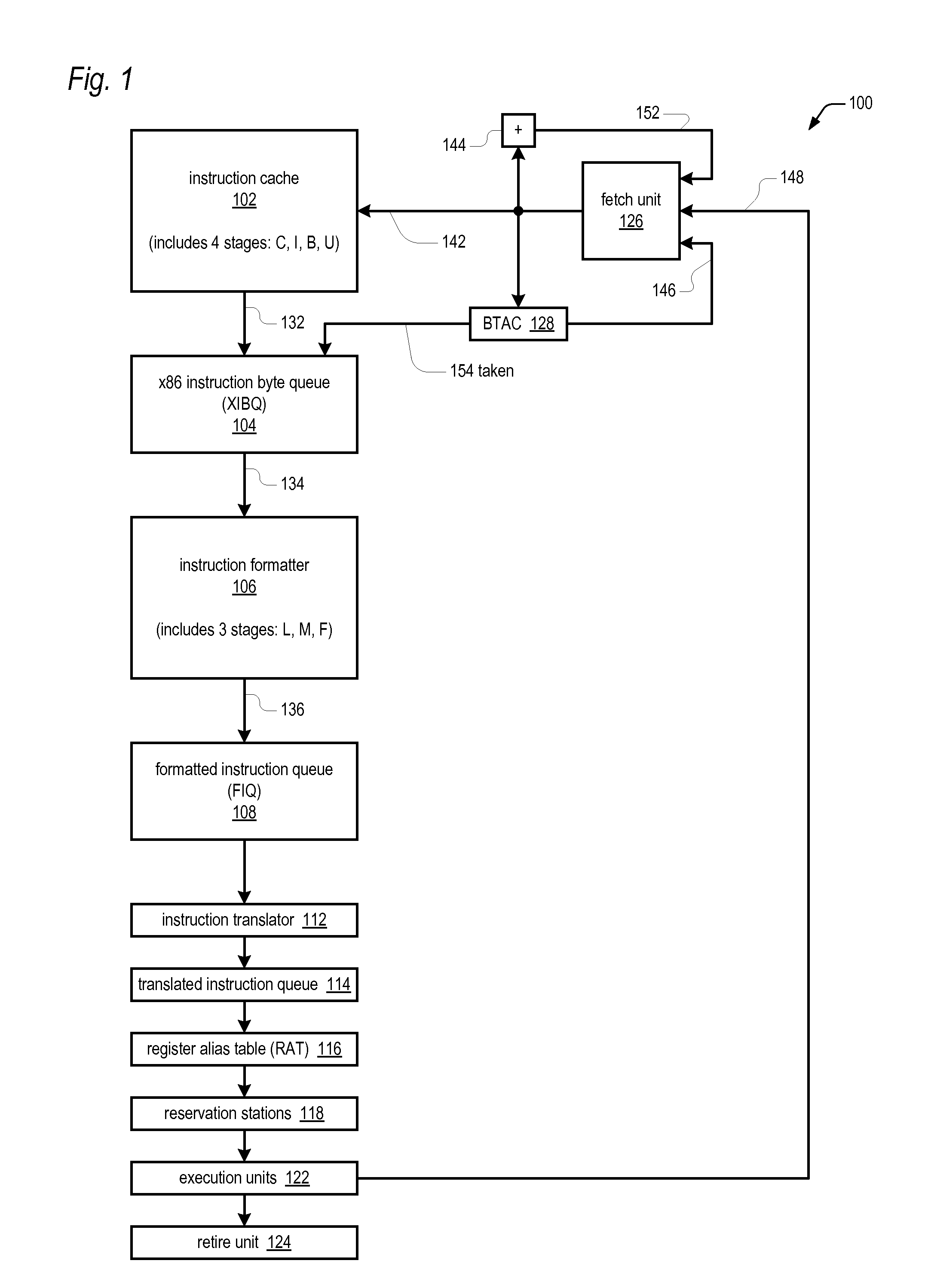
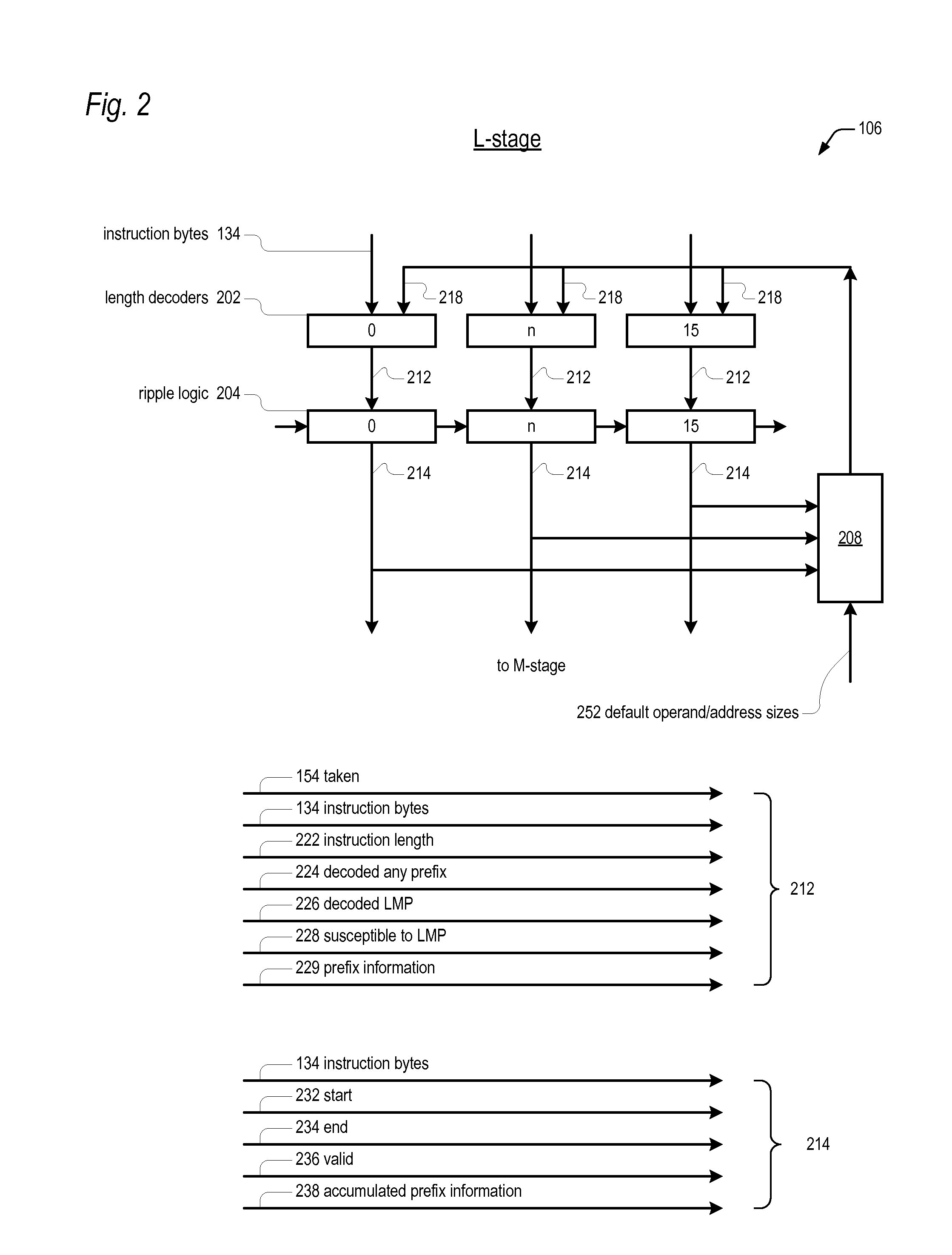
Apparatus for efficiently determining instruction length within a stream of x86 instruction bytes
ActiveUS20100299497A1Efficiently determinedMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital computer detailsByteCombinational logic
An apparatus efficiently determines the length of an instruction within a stream of instruction bytes processed by a microprocessor having a variable instruction length instruction set architecture. The apparatus includes combinatorial logic associated with each instruction byte of the stream, each configured to receive the associated instruction byte and the next instruction byte of the stream and to generate in response thereto a first length, a second length, and a select control. A multiplexor associated with each of the combinatorial logic selects and outputs one of the following inputs based on the select control received from the combinatorial logic: a zero input and the second length received from the combinatorial logic associated with each of the next three instruction bytes of the stream. An adder associated with each of the combinatorial logic and multiplexor adds the first length and the output of the multiplexor to generate the length of the instruction.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Noise mitigating microphone system and method
ActiveUS20070047744A1Effectively mitigatedRemove and mitigatesMicrophonesMicrophones signal combinationEngineeringCombinational logic
A microphone system has a base coupled with first and second microphone apparatuses. The first microphone apparatus is capable of producing a first output signal having a noise component, while the second microphone apparatus is capable of producing a second output signal. The system also has combining logic operatively coupled with the first microphone apparatus and the second microphone apparatus. The combining logic uses the second output signal to remove at least a portion of the noise component from the first output signal.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Electronic circuitry protected against transient disturbances and method for simulating disturbances
ActiveUS20060220716A1Improve protectionElectrical testingElectric pulse generatorPropagation timeEngineering
The circuitry comprises successive stages, each comprising a combinatory logic circuit connected to the input of a first latch. Staggered clock signals are respectively associated with the first latches of the odd and even stages. Means for detecting a transient disturbance affecting the first latch of a stage and liable to propagate downstream, compare, in each stage, a value present on the output of the first latch of the stage considered at an observation time with a value present on the input of said first latch at a predetermined observation time taking account of the various propagation times.
Owner:IROC TECH
Programmable application specific integrated circuit and logic cell
A field programmable gate array includes a programmable routing network, a programmable configuration network integrated with the programmable routing network; and a logic cell integrated with the programmable configuration network. The logic cell includes four two-input AND gates, two six-input AND gates, three multiplexers, and a delay flipflop. The logic cell is a powerful general purpose universal logic building block suitable for implementing most TTL and gate array macrolibrary functions. A considerable variety of functions are realizable with one cell delay, including combinational logic functions as wide as thirteen inputs, all boolean transfer functions for up to three inputs, and sequential flipflop functions such as T, JK and count with carry-in.
Owner:QUICKLOGIC
Method For Optimized Automatic Clock Gating
ActiveUS20080301594A1Reduce Switching Power ConsumptionConsumes less powerCAD circuit designMulti-objective optimisationComputer architectureCombinational logic
A method of optimizing clock-gated circuitry in an integrated circuit (IC) design is provided. A plurality of signals which feed into enable inputs of a plurality of clock gates is determined, where the clock gates gate a plurality of sequential elements in the IC design. Combinational logic which is shared among the plurality of signals is identified. The clock-gated circuitry is transformed into multiple levels of clock-gating circuitry based on the shared combinational logic.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
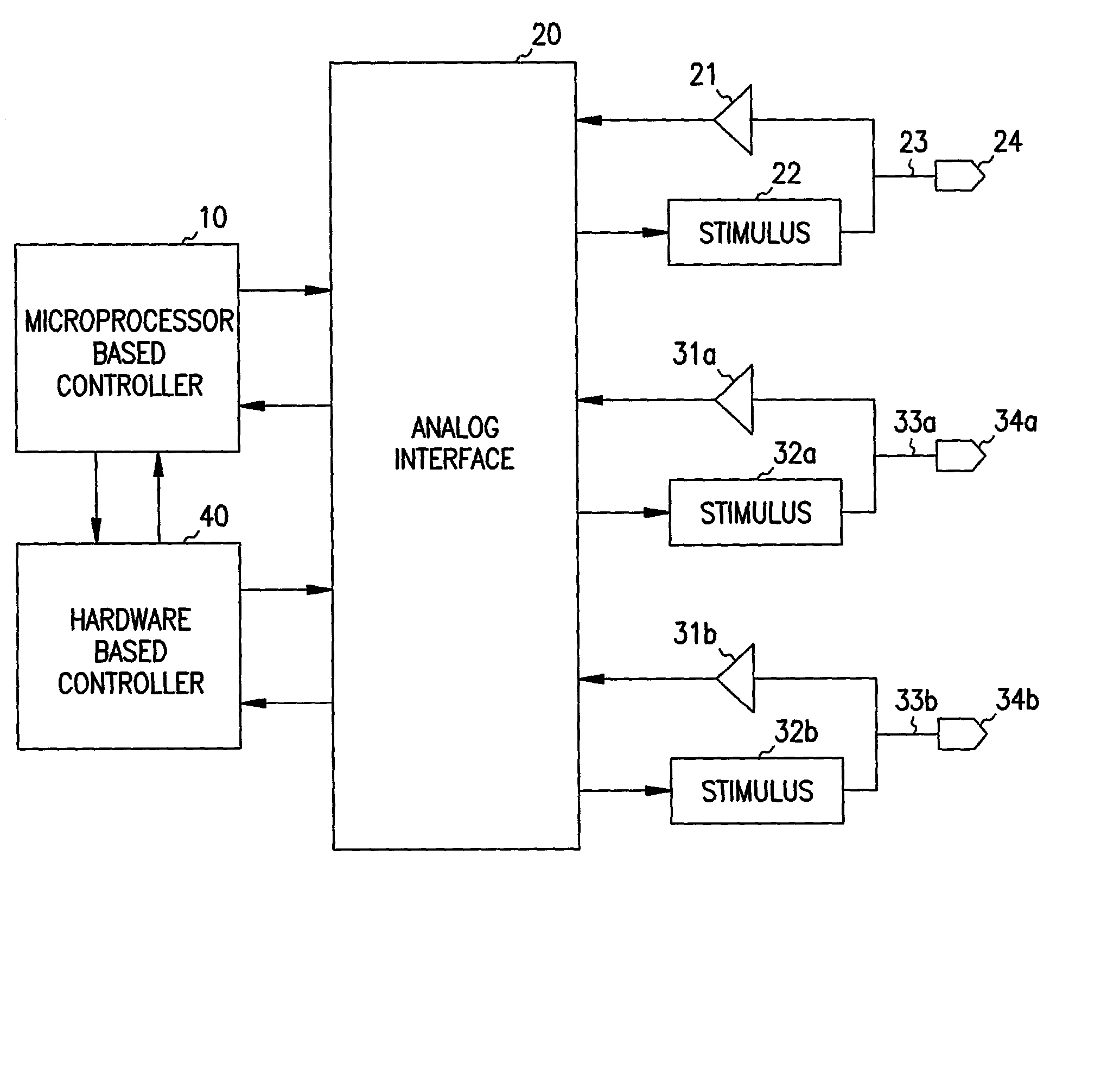
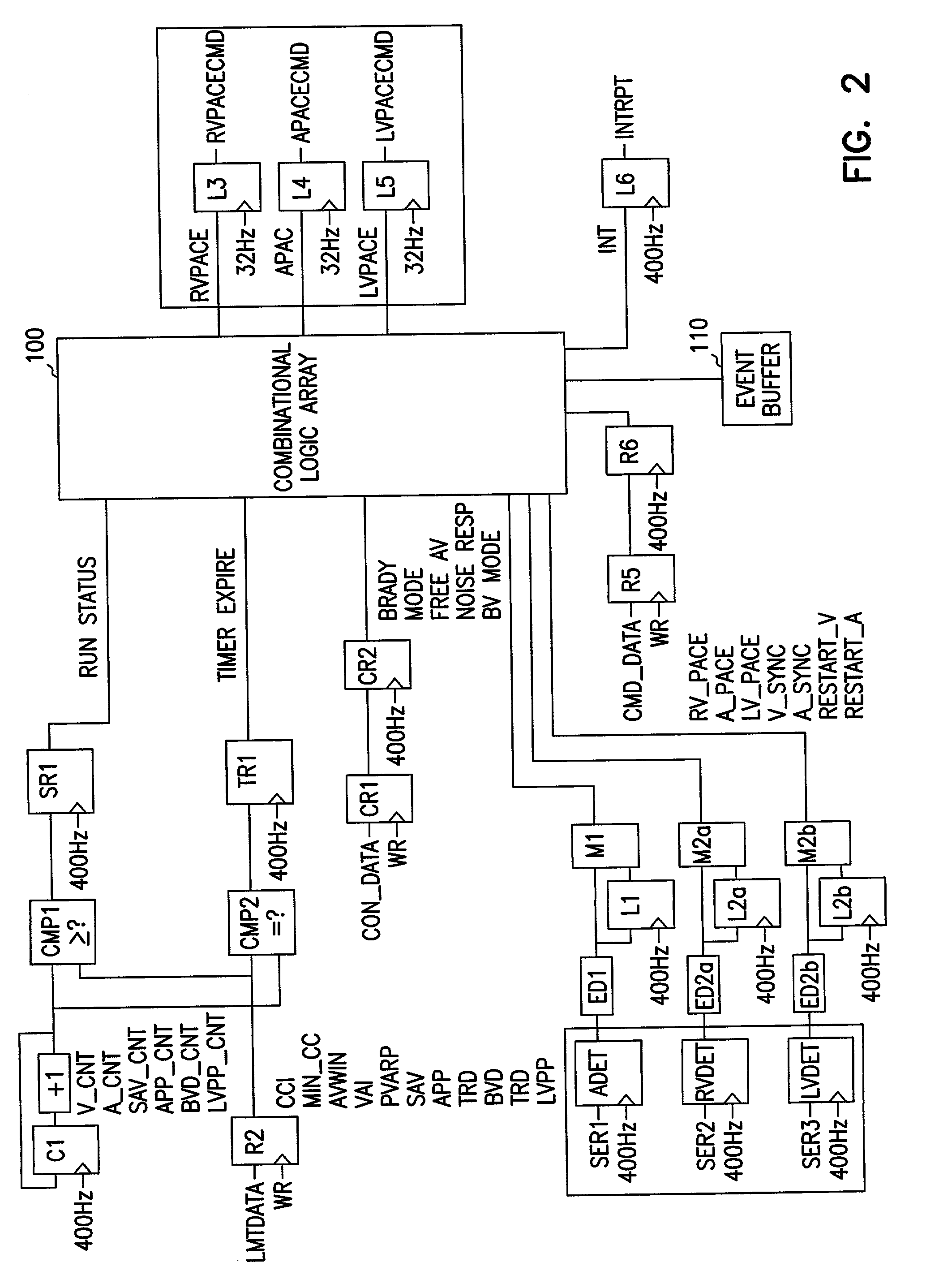
Multi-site hybrid hardware-based cardiac pacemaker
A hybrid cardiac pacemaker in which the operation of the device is controlled by hardware-based controller as supervised by a microprocessor-based controller. The hardware-based controller comprises a plurality of timers that expire when they reach timer limit values stored in registers updatable by the microprocessor, and a combinational logic array for causing the device to generate pace outputs in accordance with timer expirations and sense signals. The combinational logic array may operate the pacemaker in a number of programmed modes in accordance with a mode value stored in a mode control register by the microprocessor.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
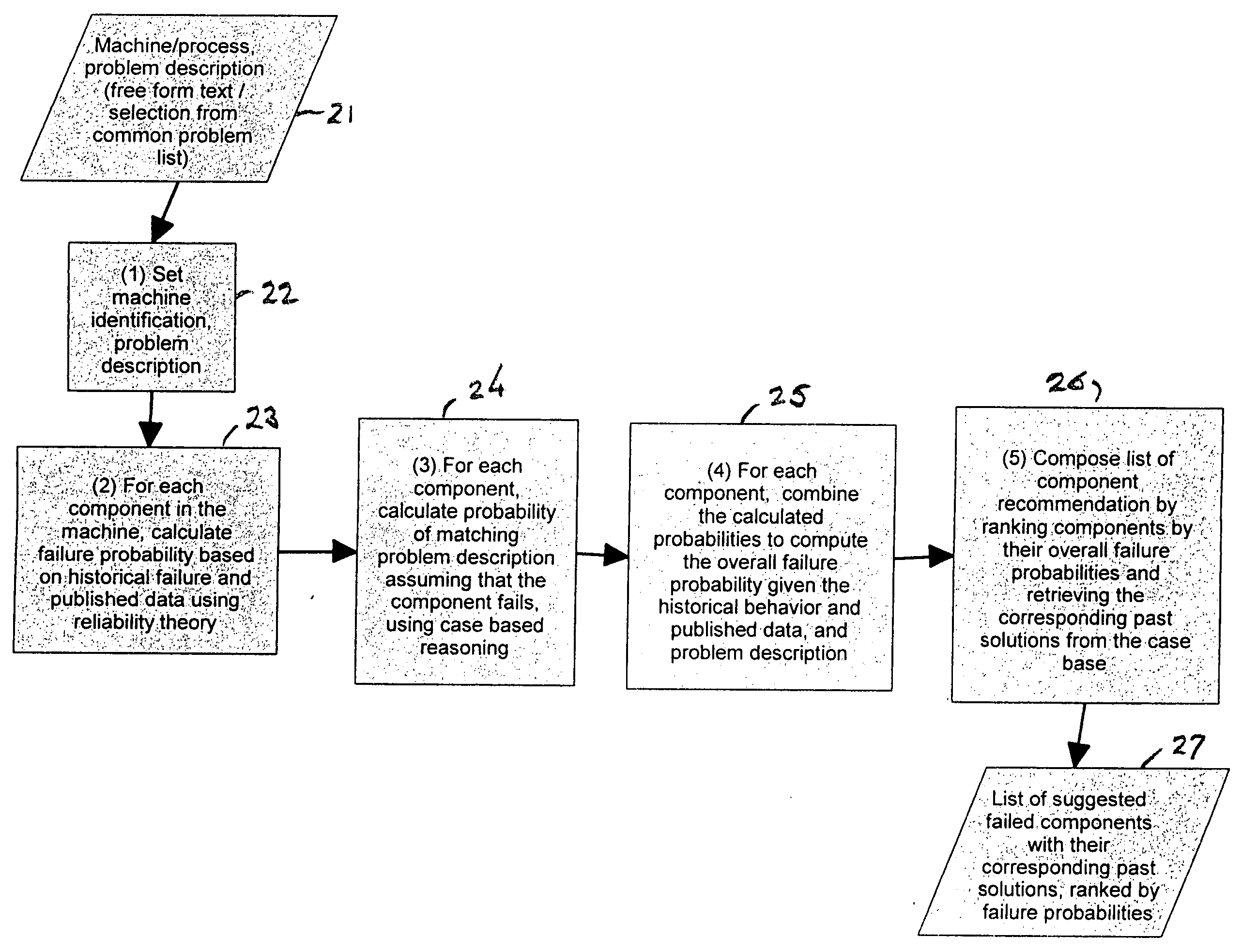
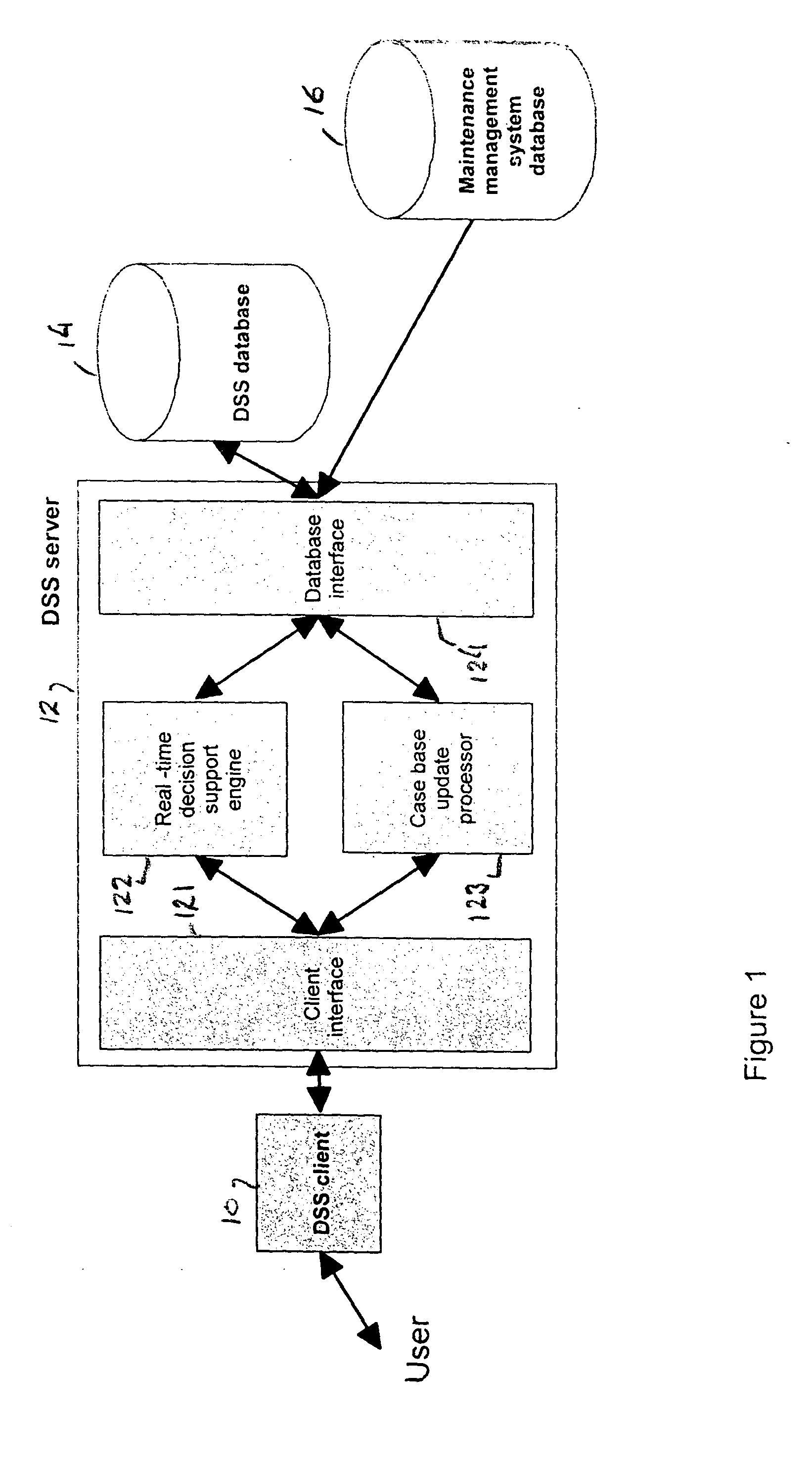
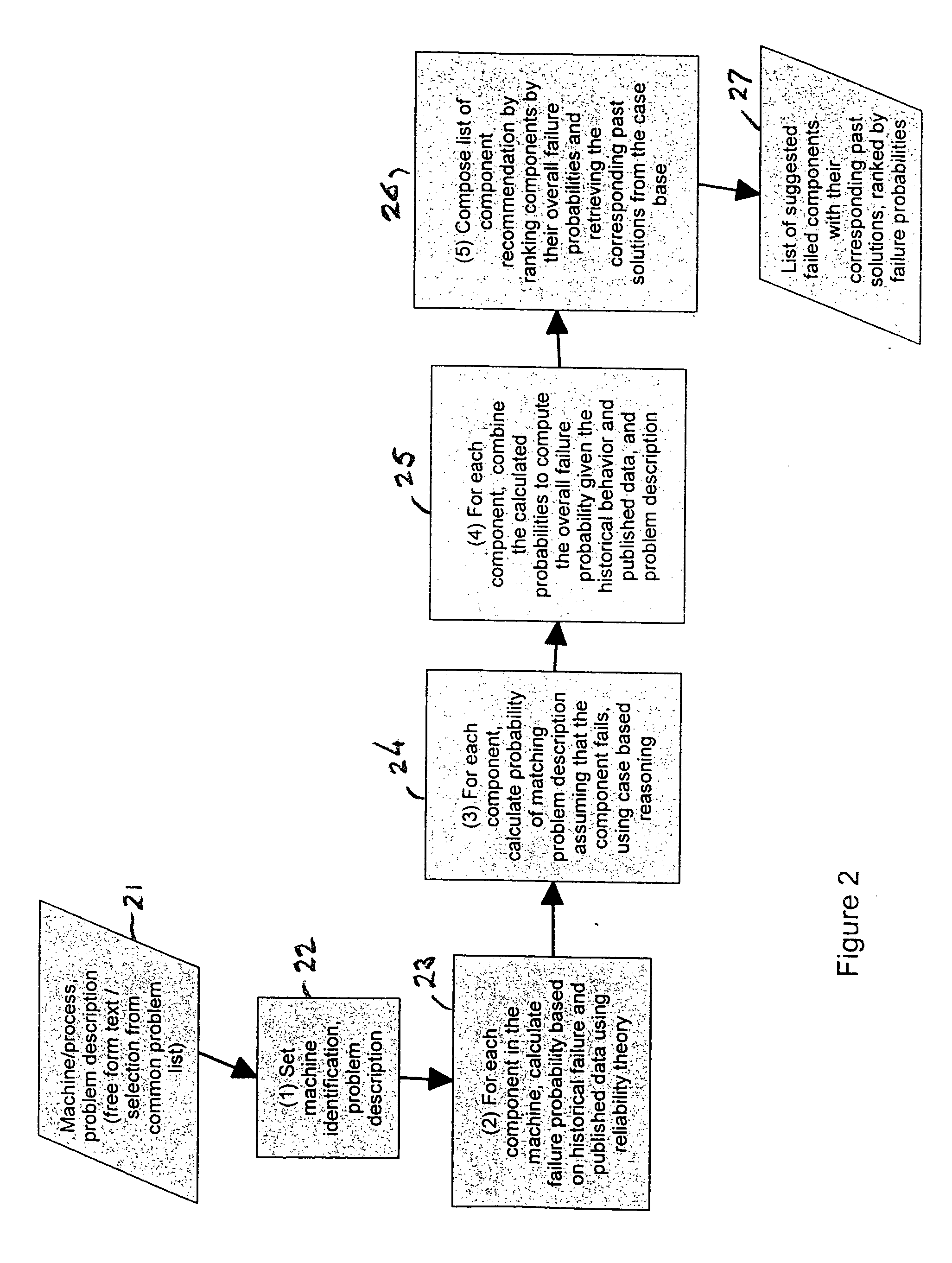
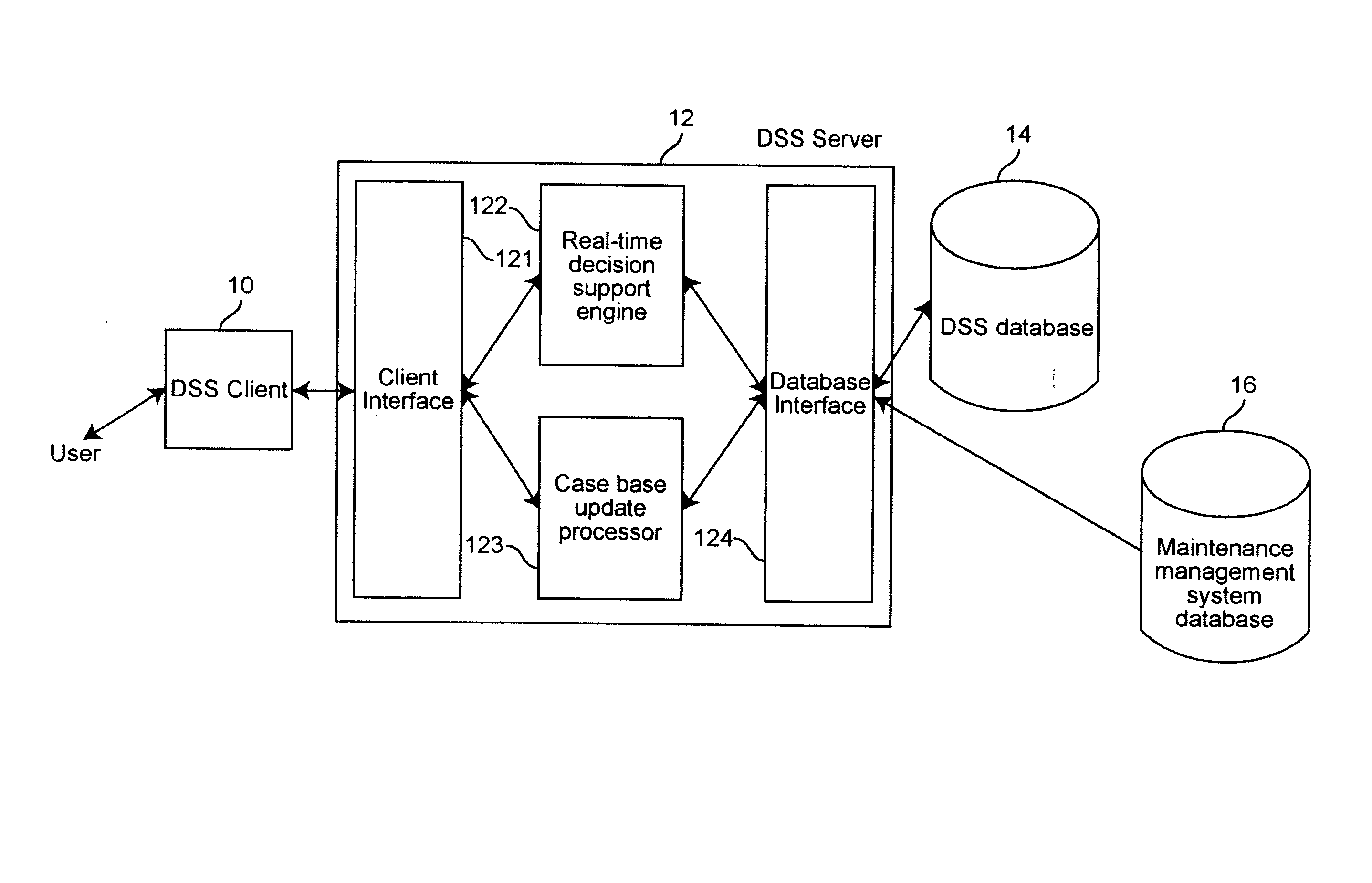
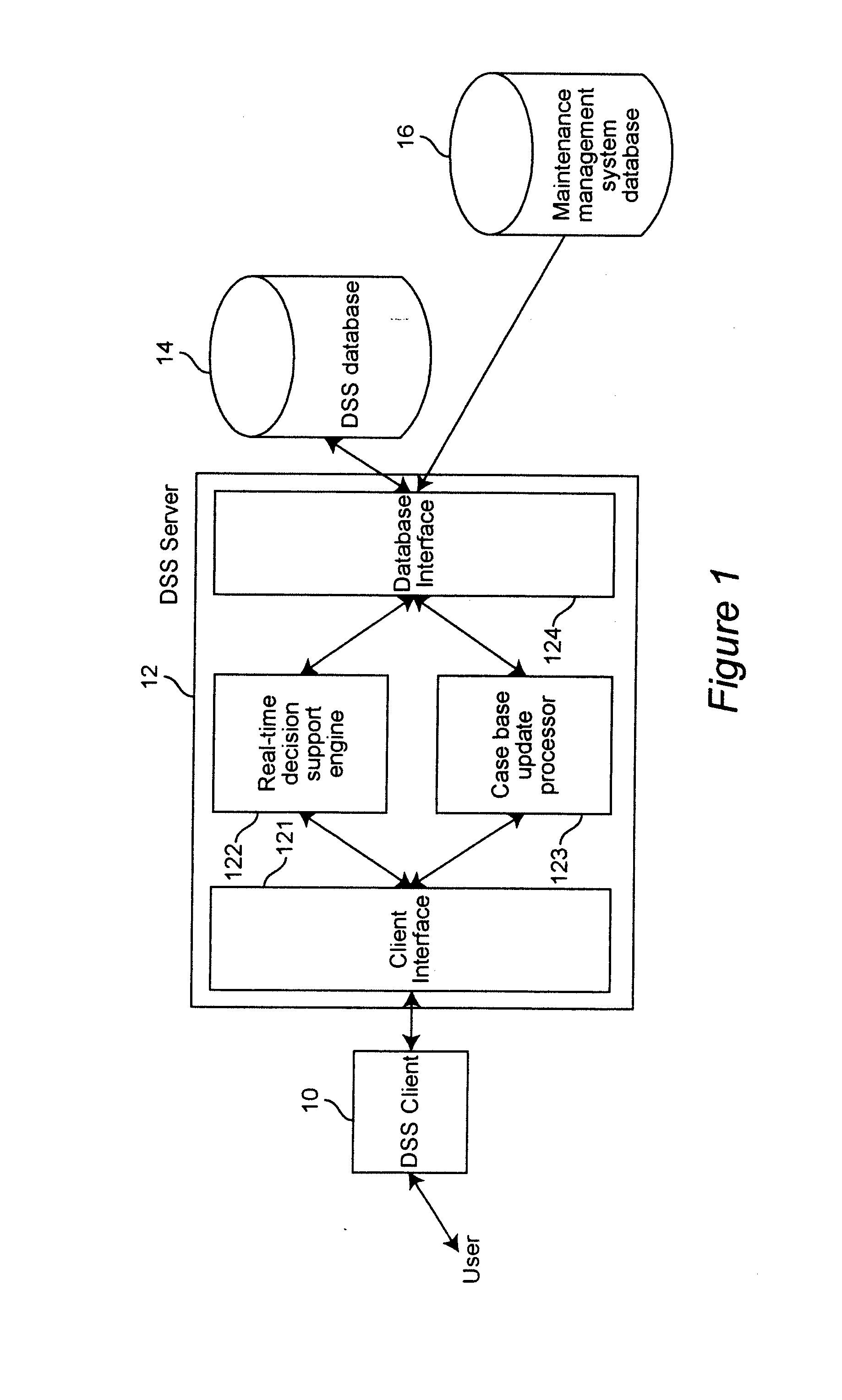
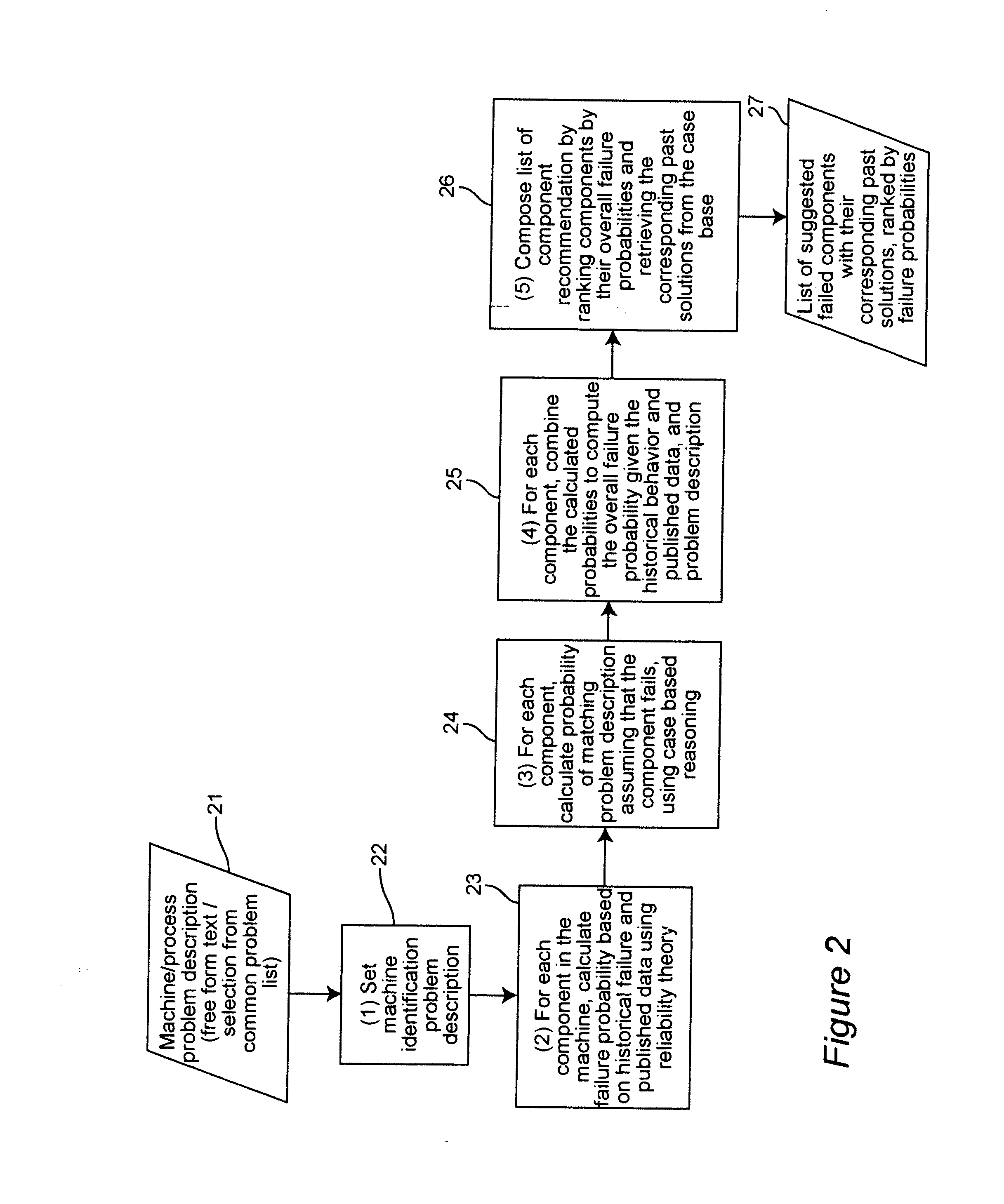
Diagnosis of equipment failures using an integrated approach of case based reasoning and reliability analysis
InactiveUS20050060323A1Shorten diagnostic timeIncrease probabilityData processing applicationsElectric testing/monitoringComputer scienceFailure probability
Equipment failures are diagnosed using an integrated approach of case-based reasoning (CBR) and statistical reliability analysis. The method outputs a single list of suggested failed components, ranked by an overall probability of failure, and their associated past solutions from the case base. The overall probability of failure is calculated using the combined logic of case based reasoning and statistical reliability analysis. The method is typically used in a real-time decision support system to aid equipment diagnosis by a maintenance technician working in the field.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
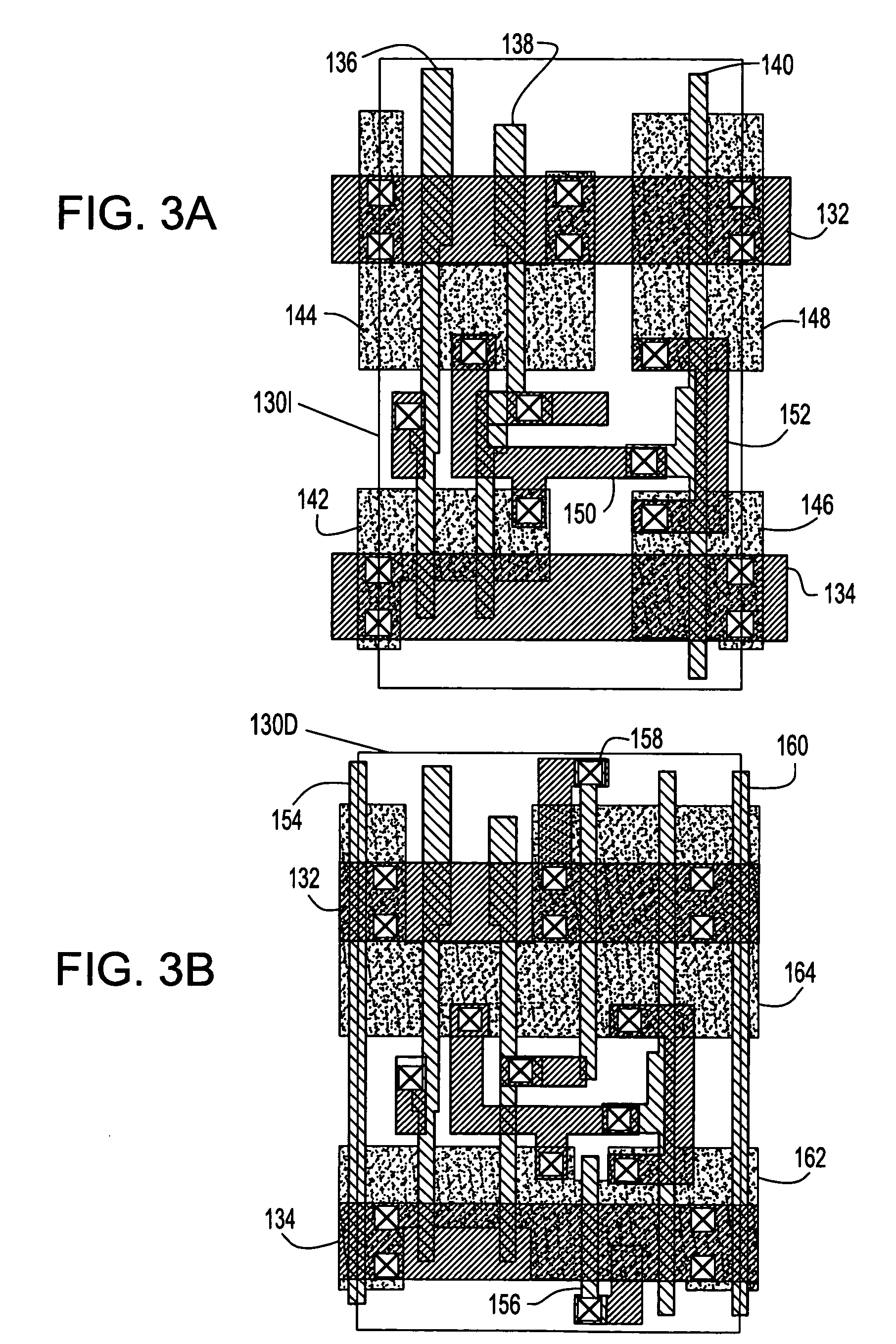
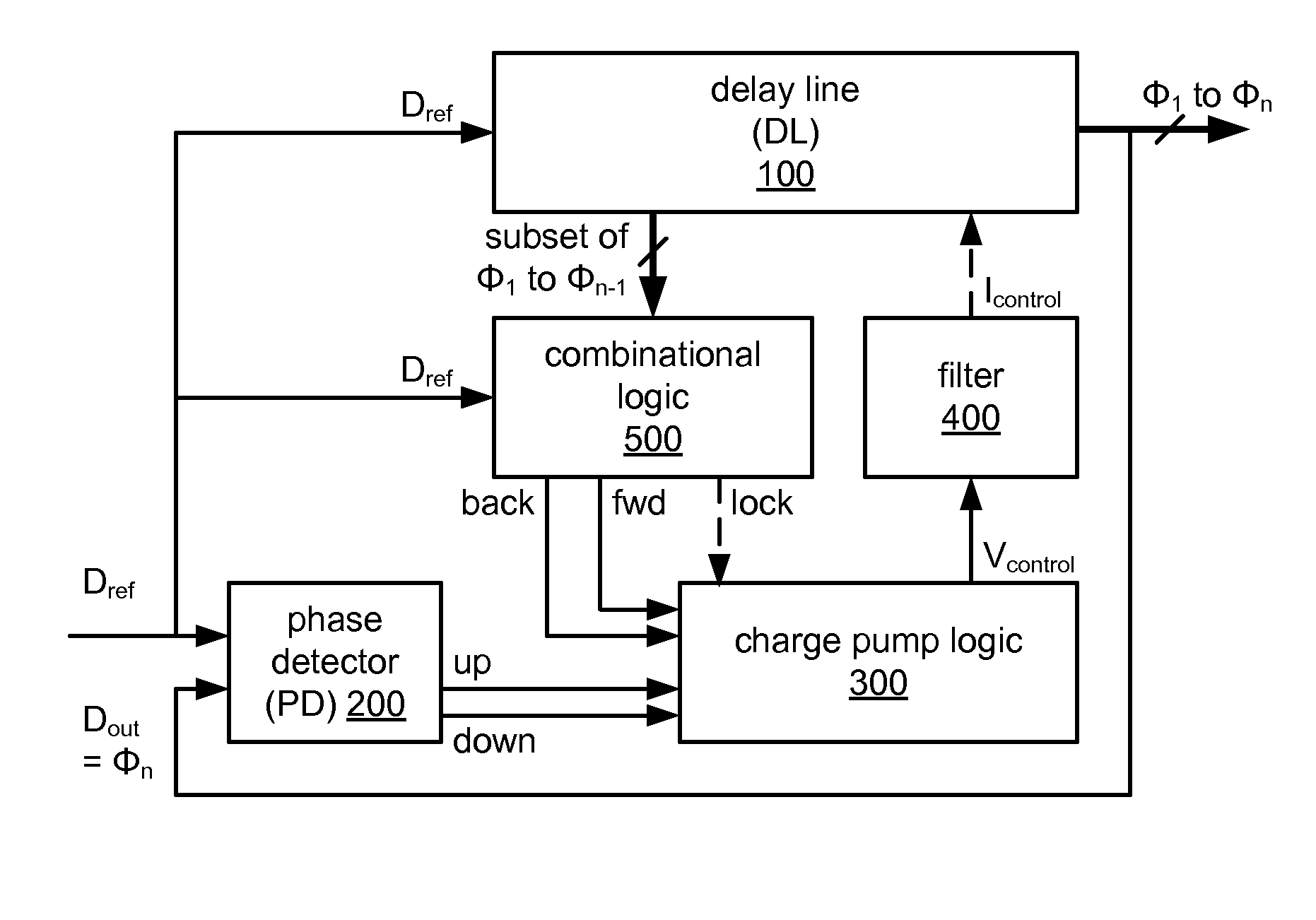
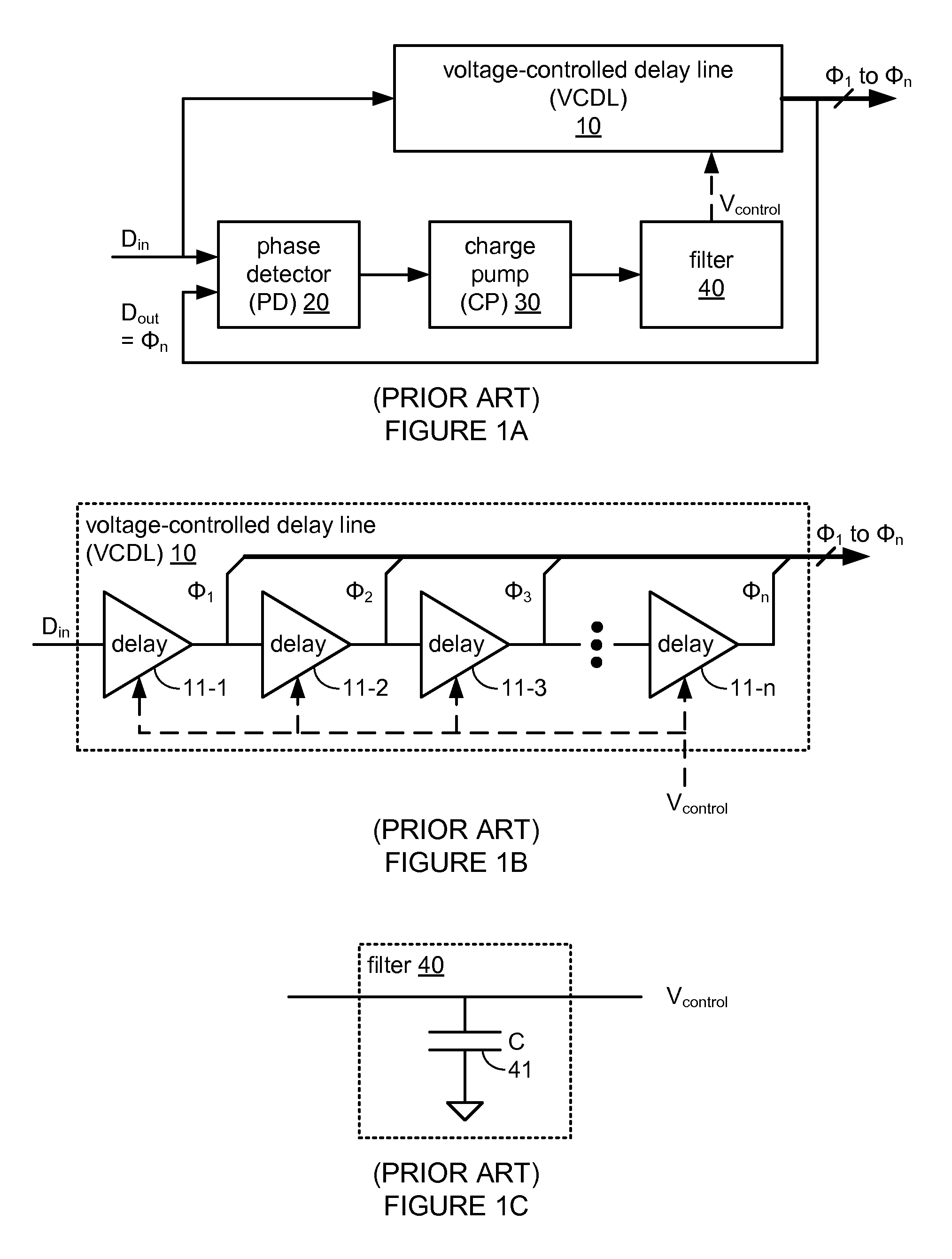
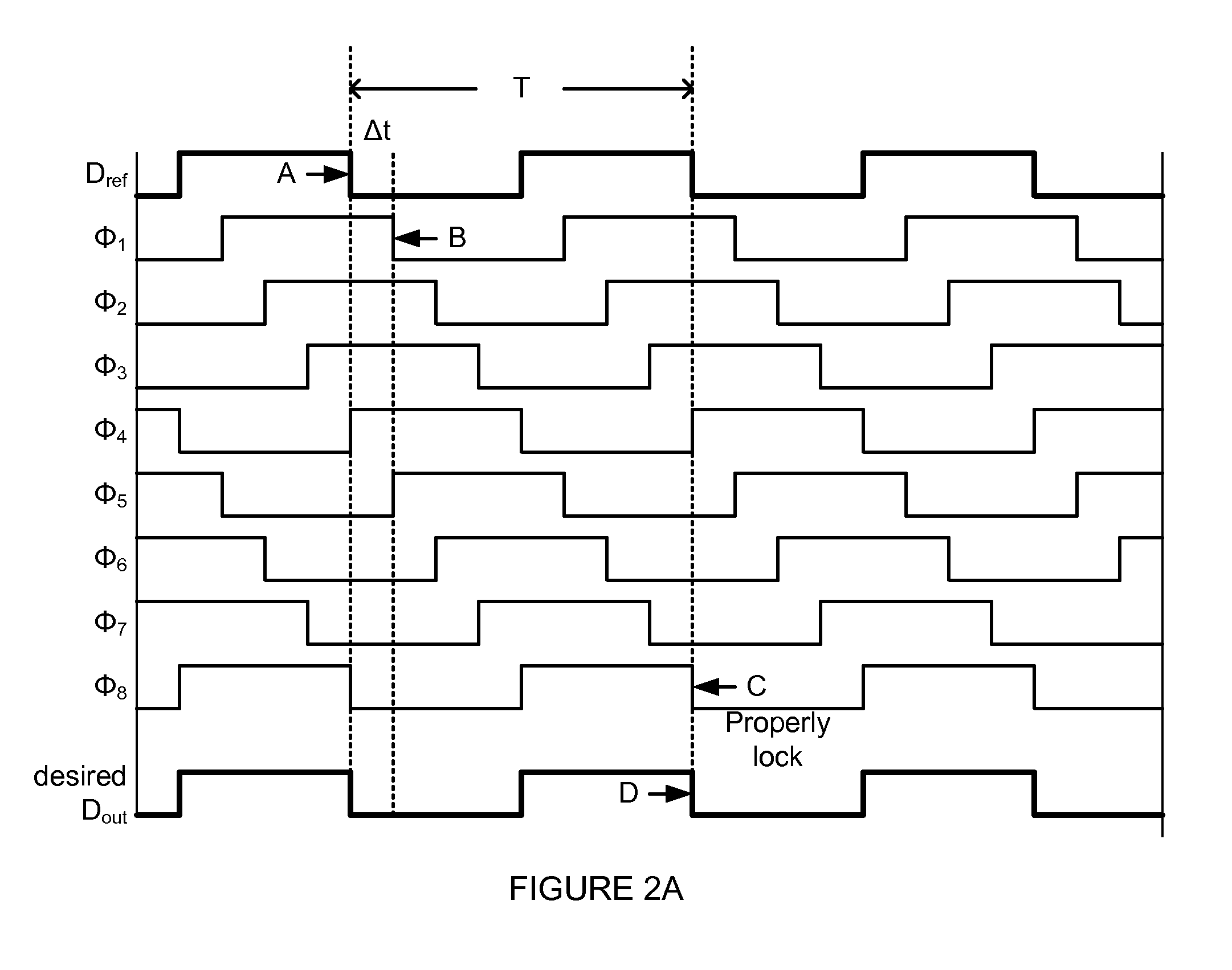
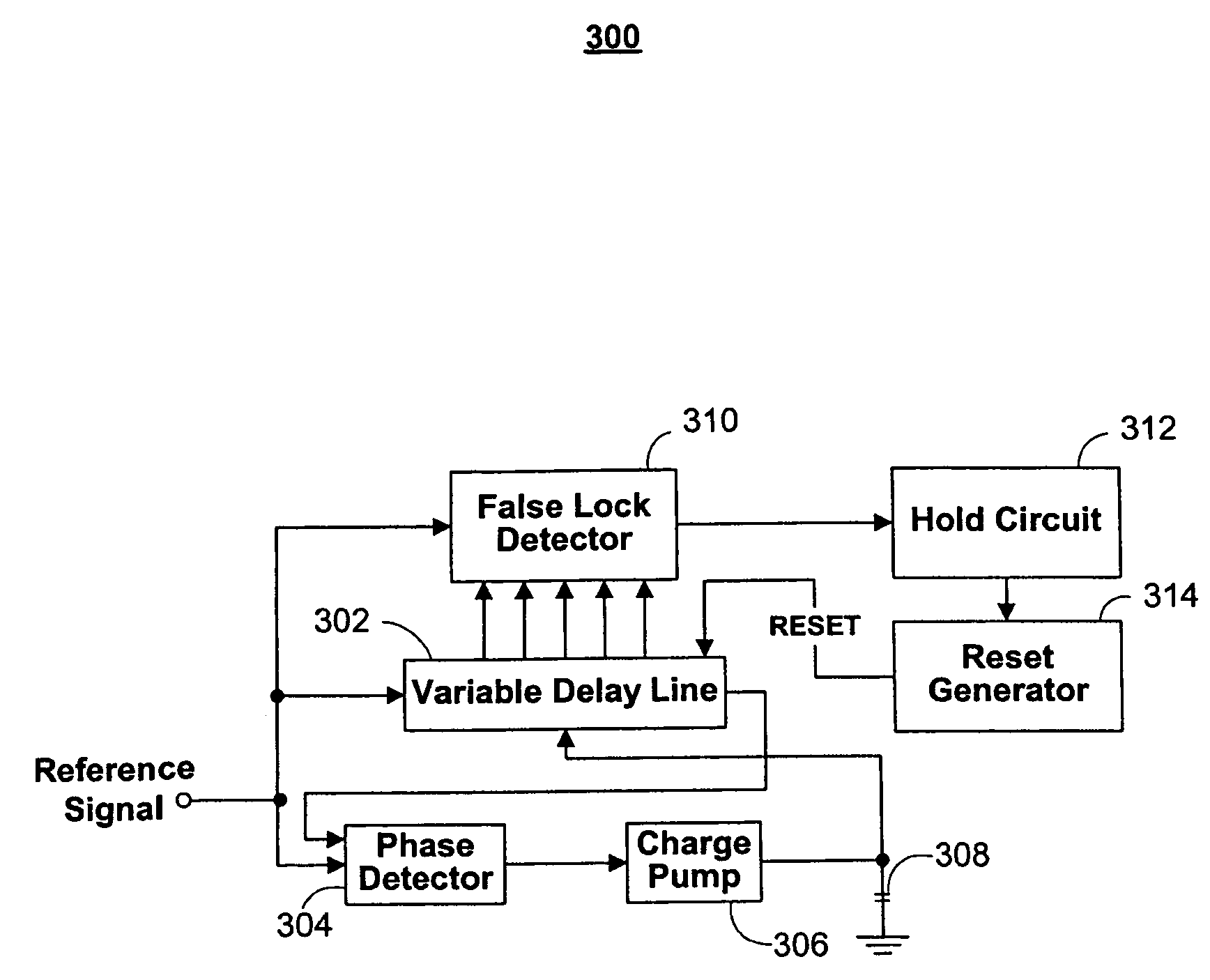
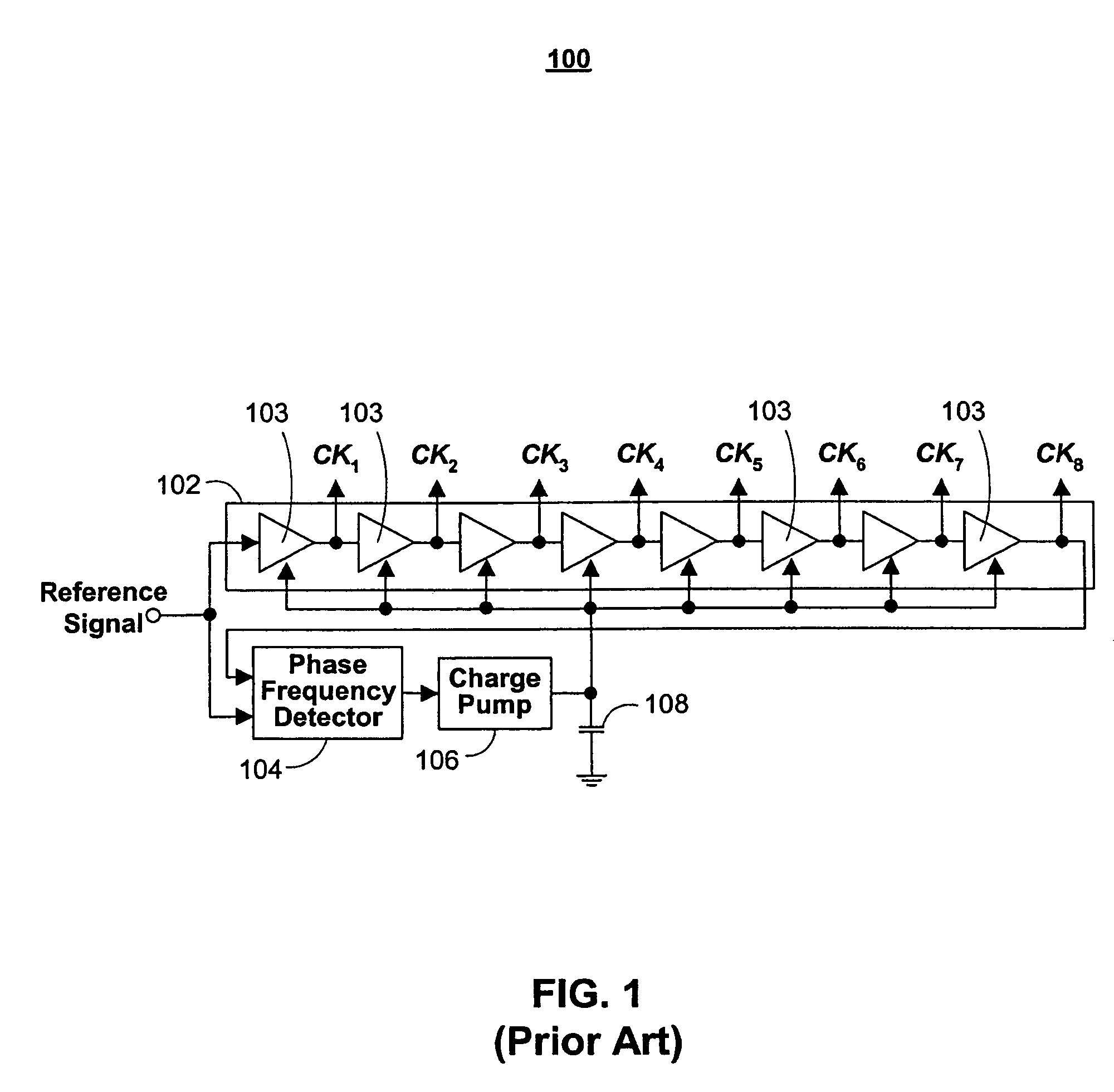
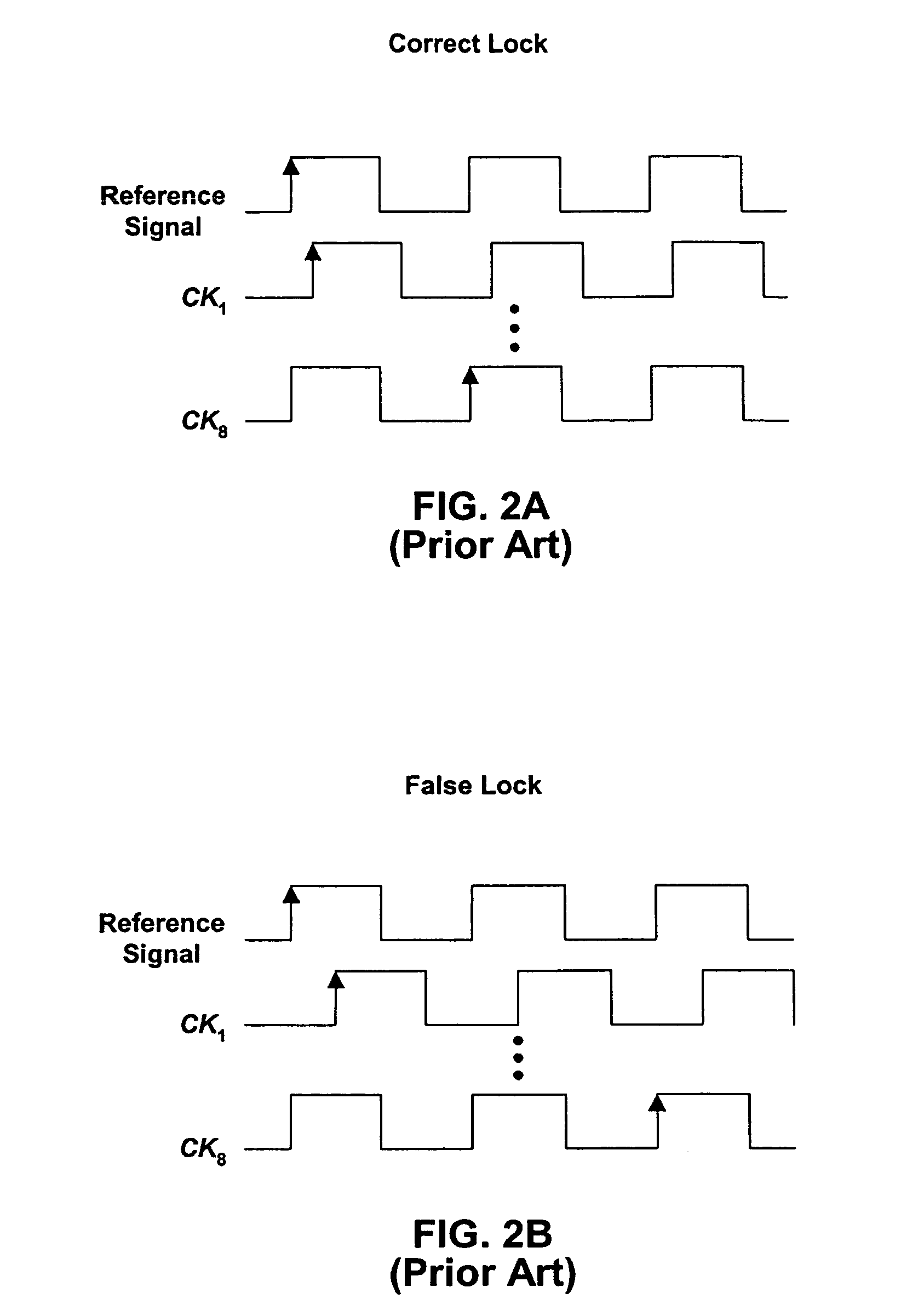
Circuitry for eliminating false lock in delay-locked loops
A delay-locked loop (DLL) acquires correct lock when the delay line on the DLL delays a reference signal by one clock period. False lock occurs when the delay line delays the reference signal by more than one clock period. False lock may be detected by a false lock detector. The false lock detector may include (1) flip-flops to take samples of the delay line outputs and (2) combinational logic for detecting patterns in the samples that may indicate false lock. Once false lock has been detected, a hold circuit may ensure that false lock persists for at least the amount of time required by the DLL to acquire lock (i.e., to prevent reset of the DLL before it has acquired lock). After this determination is made, a reset generator may produce a reset signal for resetting the DLL.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Diagnosis of equipment failures using an integrated approach of case based reasoning and reliability analysis
InactiveUS20070288795A1Increase probabilityReduce needData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsComputer scienceFailure probability
Equipment failures are diagnosed using an integrated approach of case-based reasoning (CBR) and statistical reliability analysis. The method outputs a single list of suggested failed components, ranked by an overall probability of failure, and their associated past solutions from the case base. The overall probability of failure is calculated using the combined logic of case based reasoning and statistical reliability analysis. The method is typically used in a real-time decision support system to aid equipment diagnosis by a maintenance technician working in the field.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Fault tolerant asynchronous circuits
ActiveUS7505304B2Reliability increasing modificationsDigital storageAsynchronous circuitMemory circuits
Owner:ACHRONIX SEMICON CORP
System, apparatus, and method for adaptive weighted interference cancellation using parallel residue compensation
InactiveUS7706430B2Reduce Algorithmic ComplexityEasy to solveError preventionBroadcast transmission systemsMean squareRound complexity
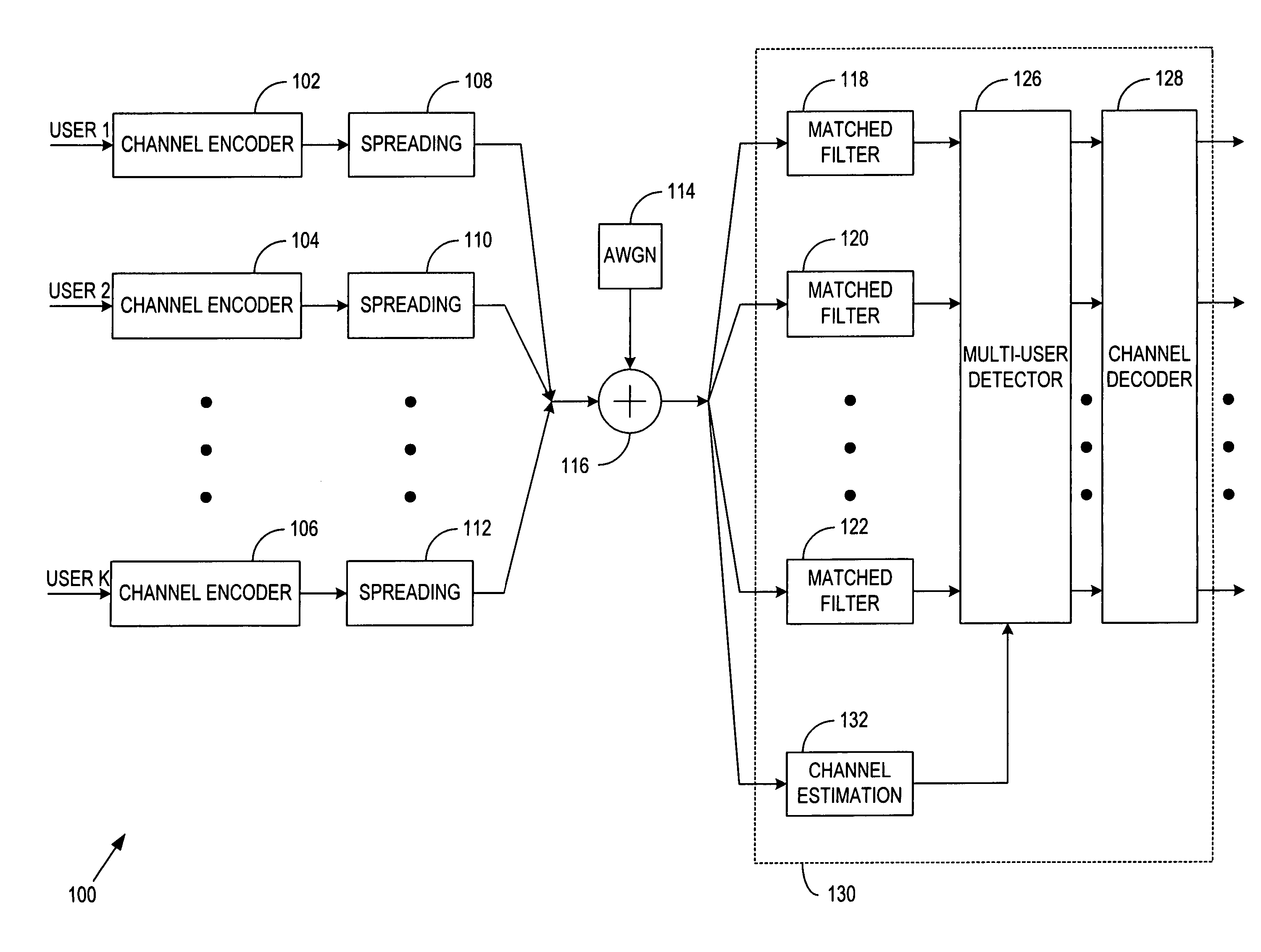
A system, apparatus and method for a multi-stage Parallel Residue Compensation (PRC) receiver for enhanced suppression of the Multiple Access Interference (MAI) in Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) systems. The accuracy of the interference estimation is improved with a set of weights computed from an adaptive Normalized Least Mean Square (NLMS) algorithm. In order to reduce complexity, the commonality of the multi-code processing is extracted and used to derive a structure of PRC to avoid direct interference cancellation. The derived PRC structure reduces the interference cancellation architecture from a complexity that is proportional to the square of the number of users to a complexity that is linear with respect to the number of users. The complexity is further reduced by replacing dedicated multiplier circuits with simple combinational logic.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
Fault tolerant asynchronous circuits
ActiveUS20070262786A1Reliability increasing modificationsFail-safe circuitsAsynchronous circuitMemory circuits
New and improved methods and circuit designs for asynchronous circuits that are tolerant to transient faults, for example of the type introduced through radiation or, more broadly, single—event effects. SEE-tolerant configurations are shown and described for combinational logic circuits, state-holding logic circuits and SRAM memory circuits.
Owner:ACHRONIX SEMICON CORP
Single-cycle hardware implementation of crypto-function for high throughput crypto-processing
InactiveUS20020101985A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSecret communicationComputer hardwareProcessor register
A hardware implementation of a crypto-function is realized using combinational logic performing computation iterations of the crypto-function on data in a single hardware cycle. Only combinational logic is used to implement the entire cryptographic algorithm, and registers are used only to store input or output from the combinational logic, leading to a very high speed implementation of the crypto-function.
Owner:IBM CORP
Detection method and detector applied to integrated circuit for detecting electromagnetic fault injection attack
ActiveCN105391542AAchieve protectionSimple structureEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationInformation securitySafety design
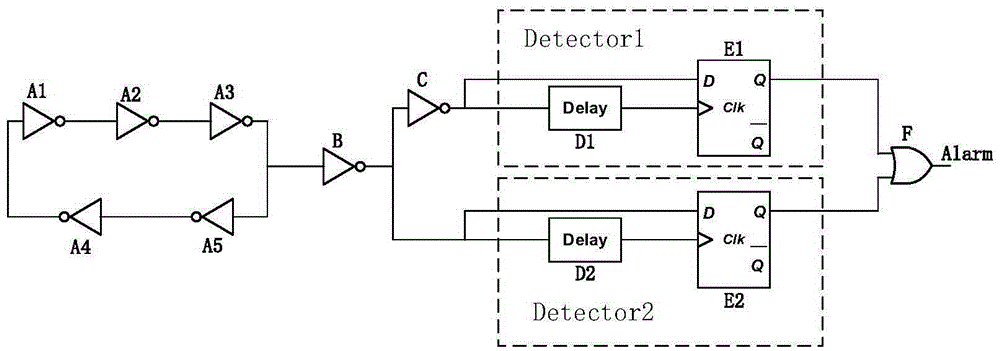
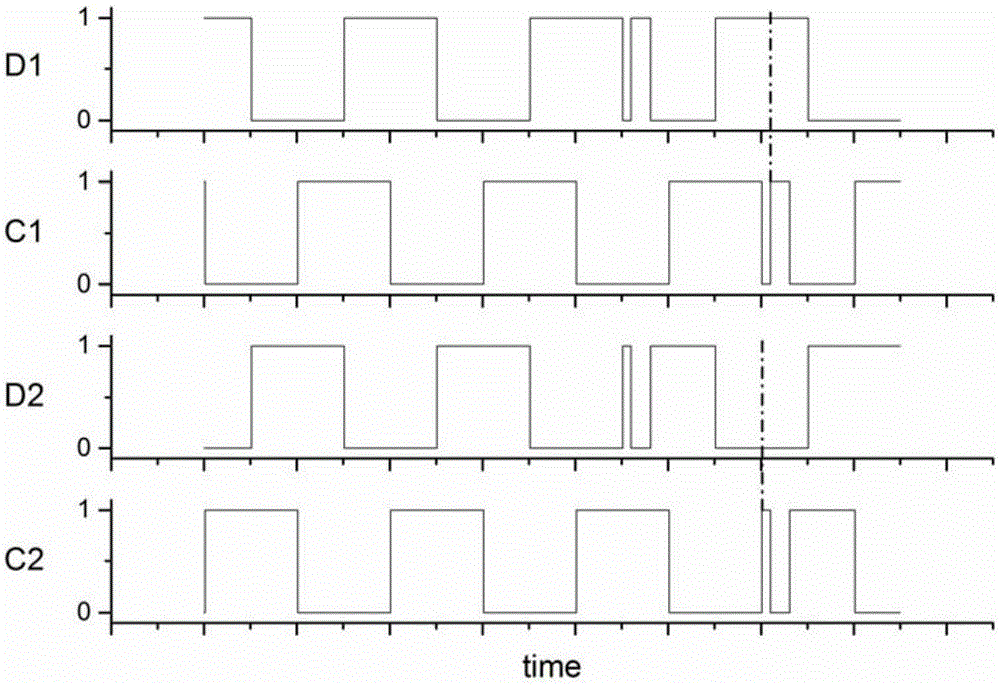
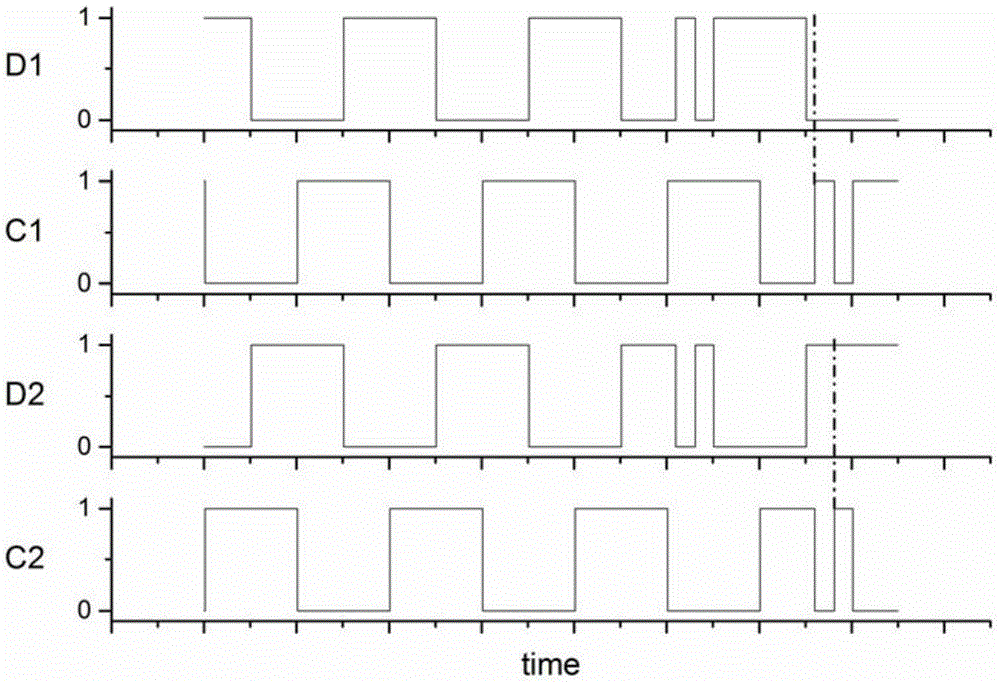
The invention relates to the field of information security, cryptography and encrypted circuits, provides detection on electromagnetic fault injection attack for information security related integrated circuits such as the encrypted circuit, and ensures to respond timely when the attack happens. Therefore, the invention adopts the technical scheme that: the structure of a detector applied to an integrated circuit for detecting electromagnetic fault injection attacks comprises phase inverters A1, A2, A3, A4 and A5, wherein the phase inverters are cascaded to form a ring oscillator, the ring oscillator is buffered through a phase inverter B and outputs a channel of oscillation signals directly input to a combinational logic delay comparative structure Detector1, another channel of oscillation signals is input to another combinational logic delay comparative structure Detector2 through the reverse action of a phase inverter C; and an input signal of each of the two Detectors is output to a clock input end of a trigger of the corresponding Detector through the combinational logic of the Detector. The detection method and the detector are mainly applied to safety design of the integrated circuit.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Fault tolerant asynchronous circuits
ActiveUS20070253240A1Reliability increasing modificationsDigital storageAsynchronous circuitHemt circuits
New and improved methods and circuit designs for asynchronous circuits that are tolerant to transient faults, for example of the type introduced through radiation or, more broadly, single-event effects. SEE-tolerant configurations are shown and described for combinational logic circuits, state-holding logic circuits and SRAM memory circuits.
Owner:ACHRONIX SEMICON CORP
Self-adaptive continuous erasure decoding method and architecture based on polarization code
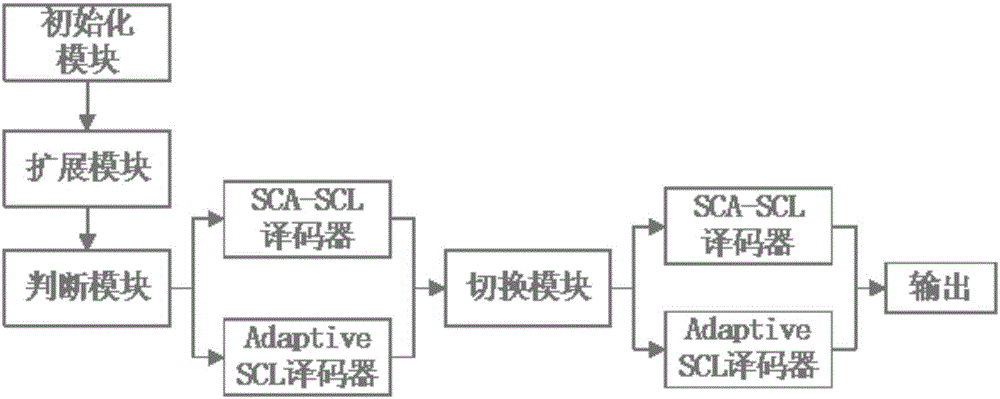
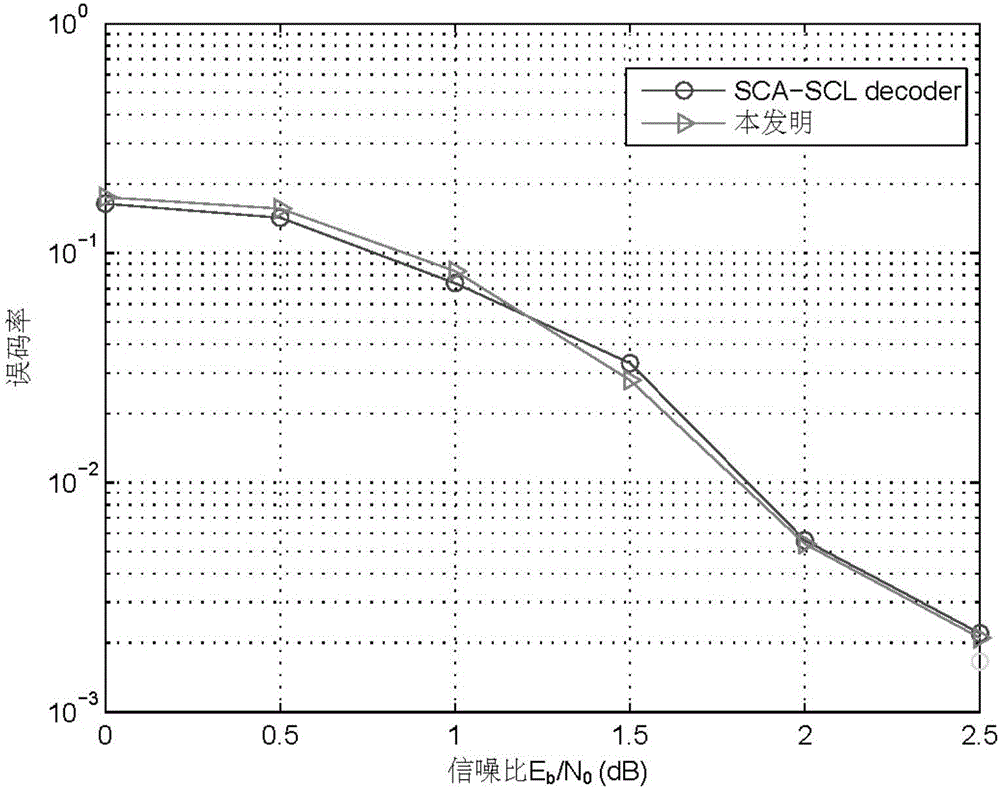
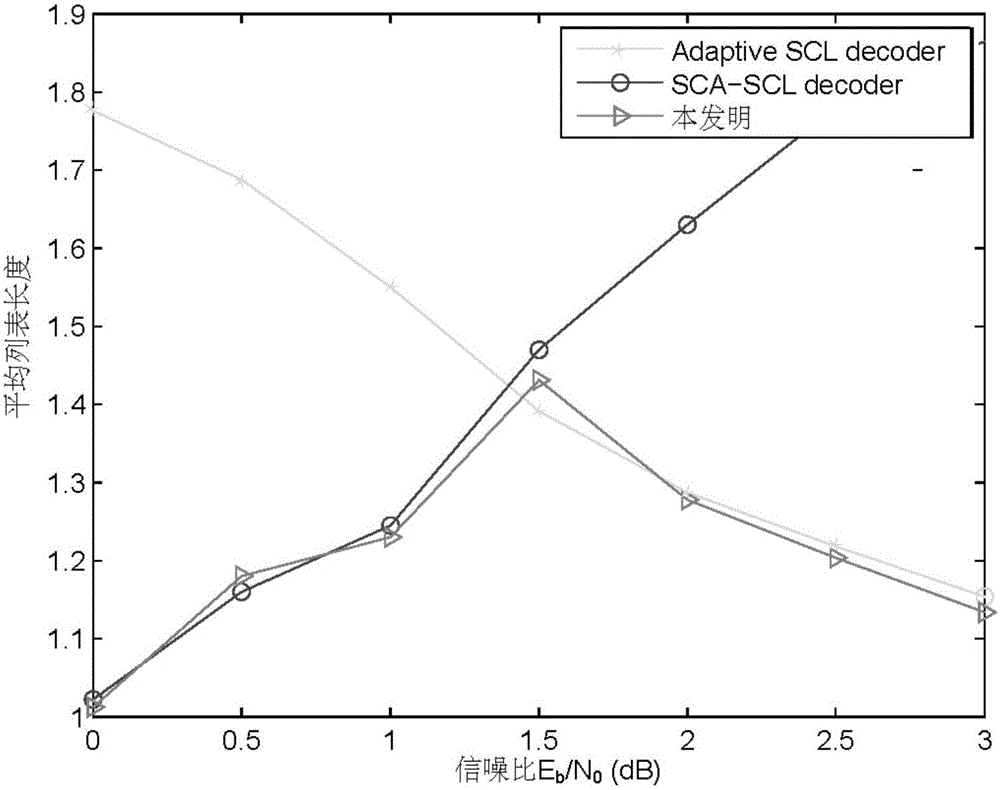
InactiveCN106656212AGuaranteed performanceReduce computational complexityError correction/detection using linear codesError detection onlyDecoding methodsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a self-adaptive continuous erasure decoding method and architecture based on a polarization code. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a SCA-SCL decoder when a signal to noise ratio (SNR) is less than a specific threshold value, or selecting an adaptive SCL decoder; and performing the decoder conversion by use of a switching mechanism when a list length is greater than the specific threshold value. By use of the method disclosed by the invention, the optimal condition of two decoder working modes is selected, and the existing combined logic circuit architecture is not greatly changed, so that the architecture is universal and general, popular and easy to understand; not only is the performance of the decoder improved, but also is the complexity of the decoder lowered.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Low power scan flip-flop cell
ActiveUS20140040688A1Eliminate unnecessary switchingReduce unnecessary power consumptionElectronic circuit testingMultiplexerEngineering
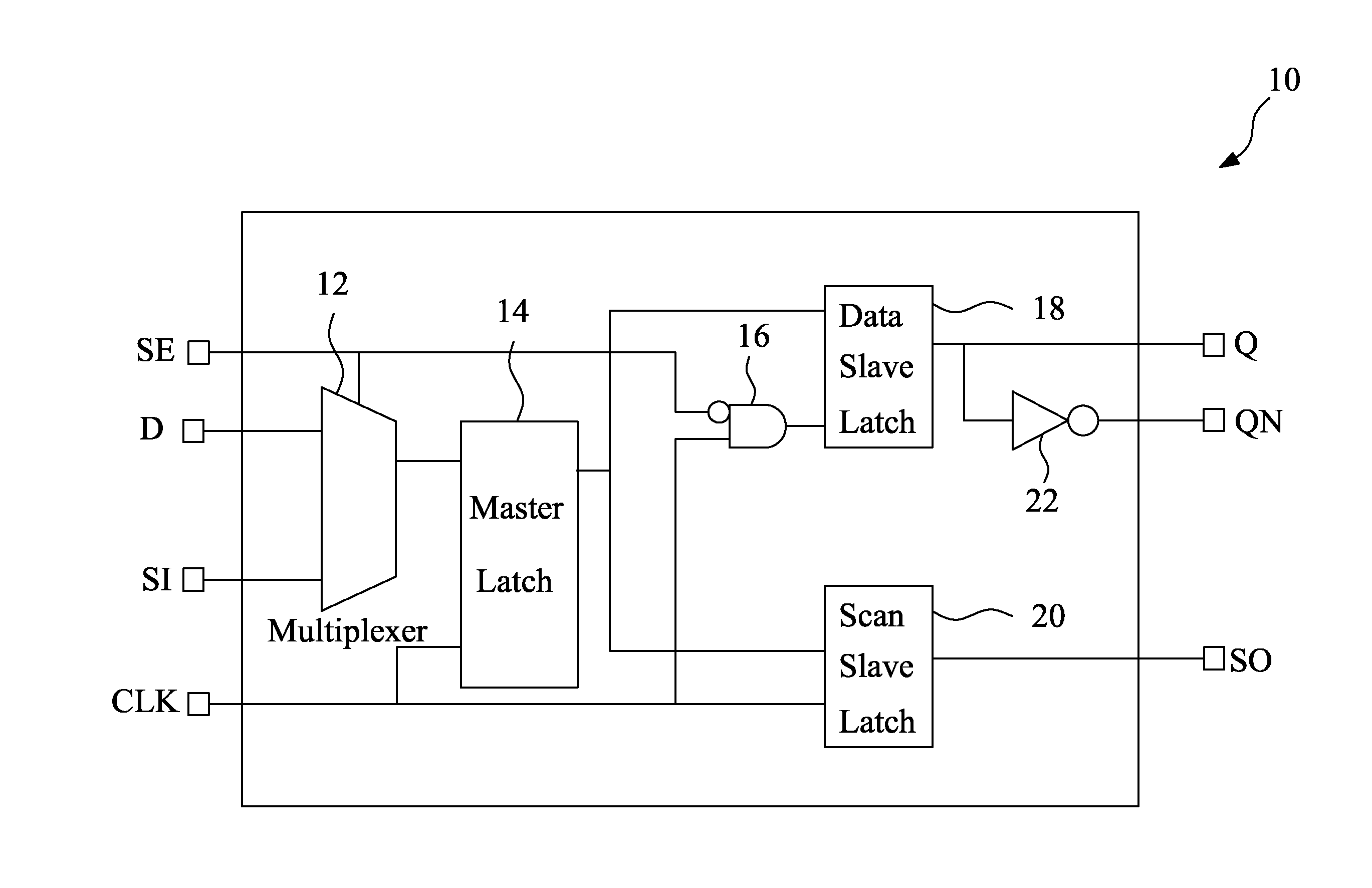
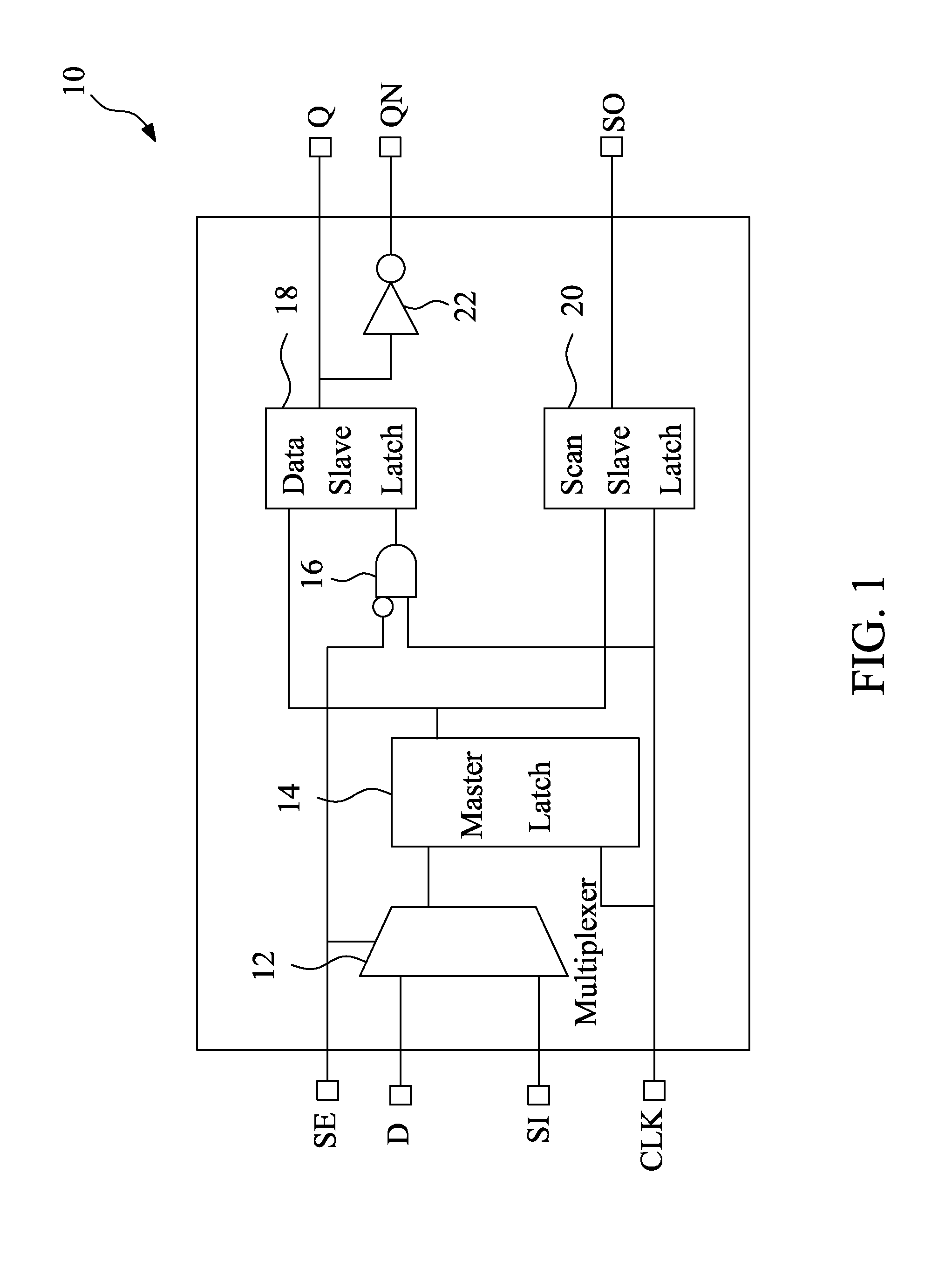
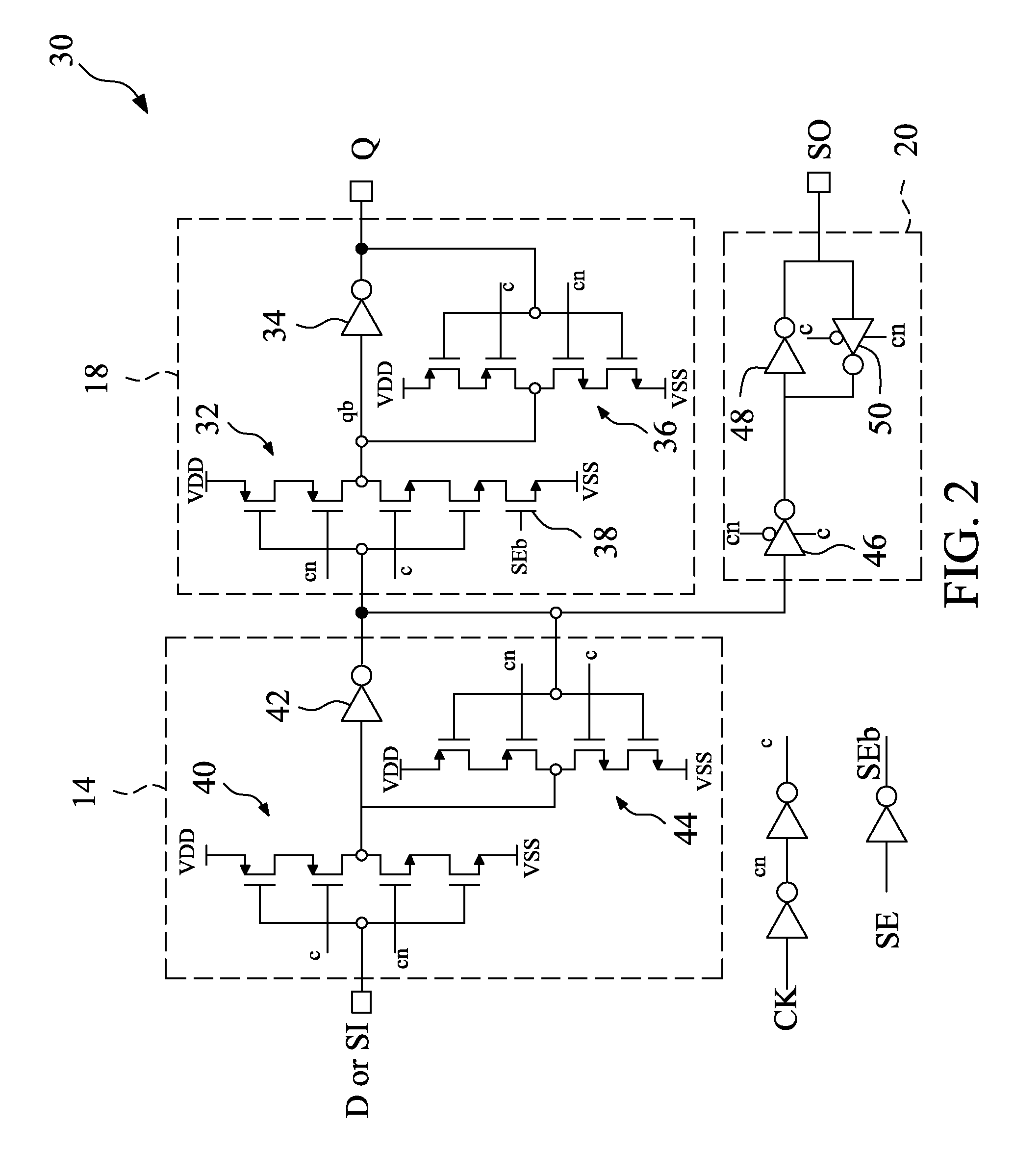
A low power scan flip-flop cell includes a multiplexer, a master latch, a scan slave latch and a data slave latch. The master latch is connected to the multiplexer, and used for generating a first latch signal. The scan slave latch is connected to the master latch, and generates a scan output (SO) signal. The data slave latch is connected to the master latch, and generates a Q output depending on a scan enable (SE) input signal and the first latch signal. The Q output is maintained at a predetermined level during scan mode, which eliminates unnecessary switching of combinational logic connected to the scan flip-flop cell and thus reduces power consumption.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Versatile logic element and logic array block
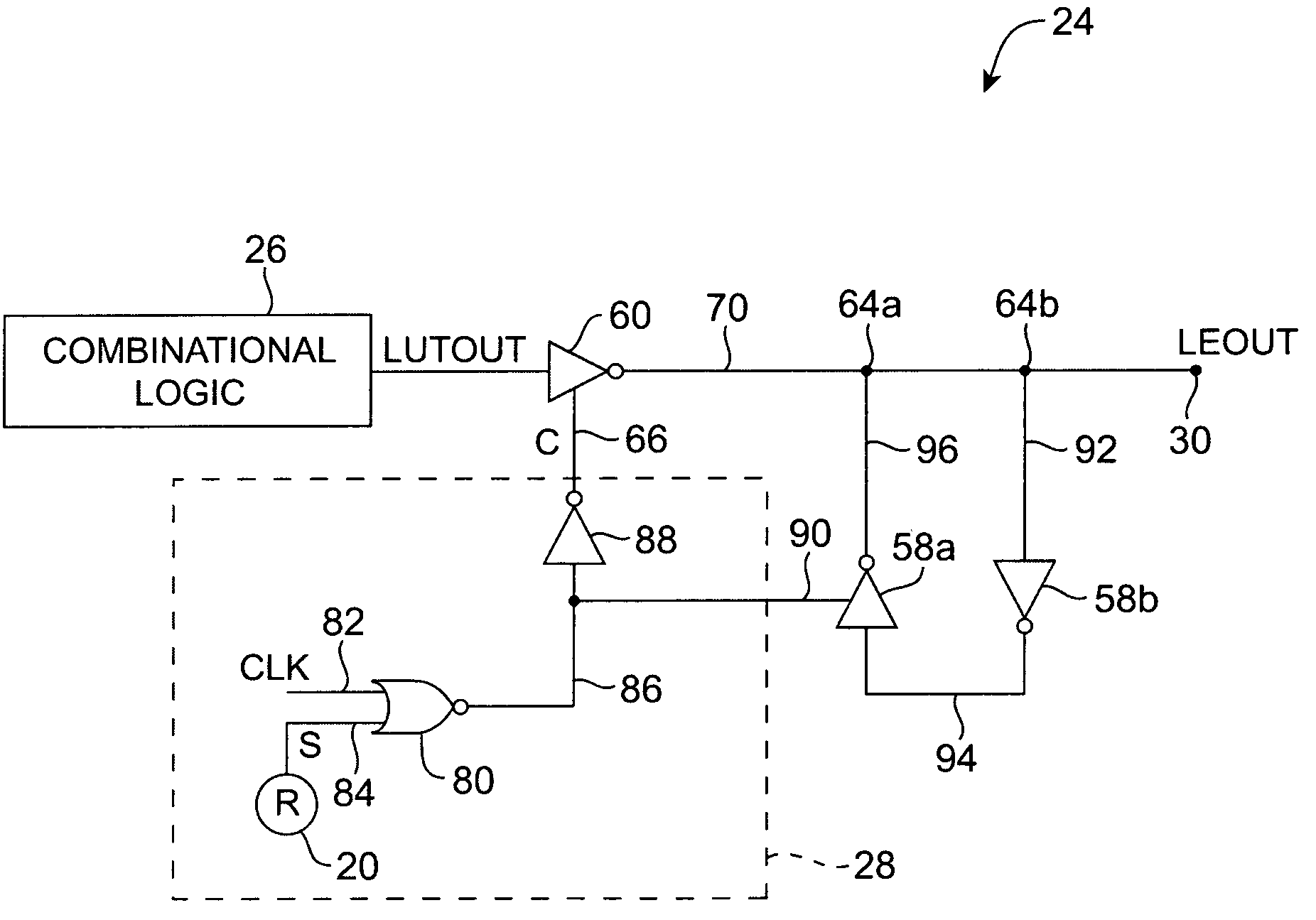
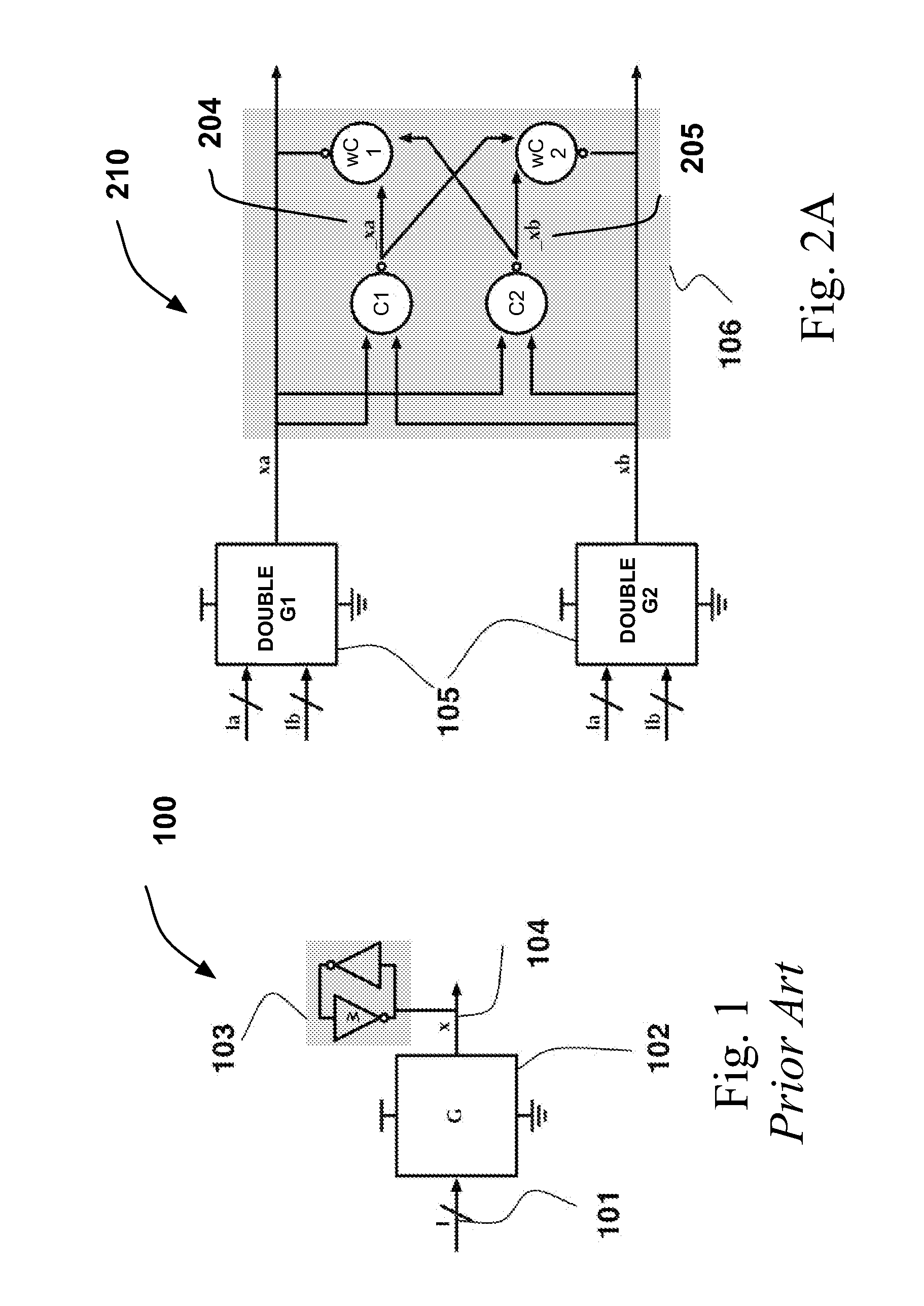
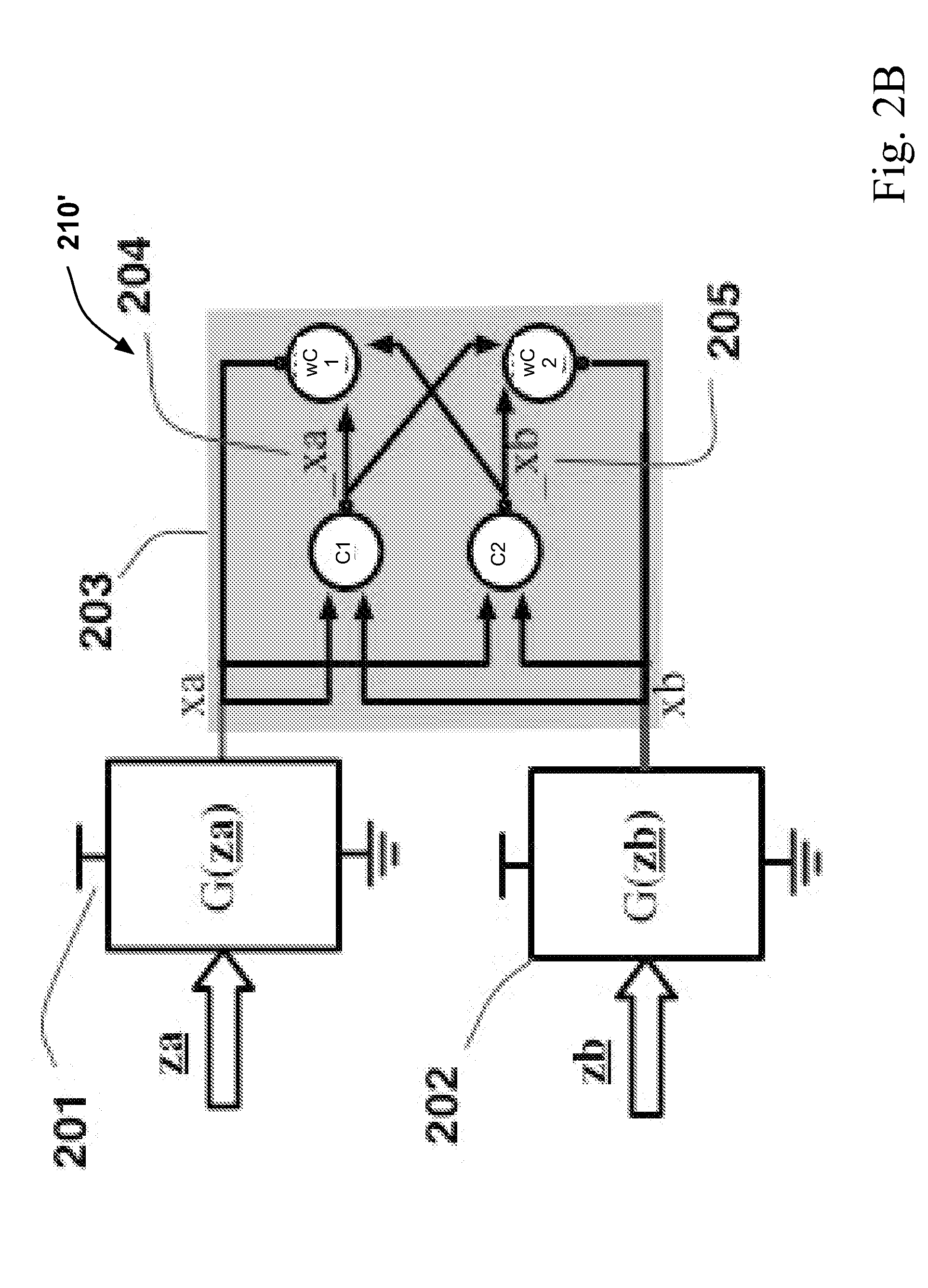
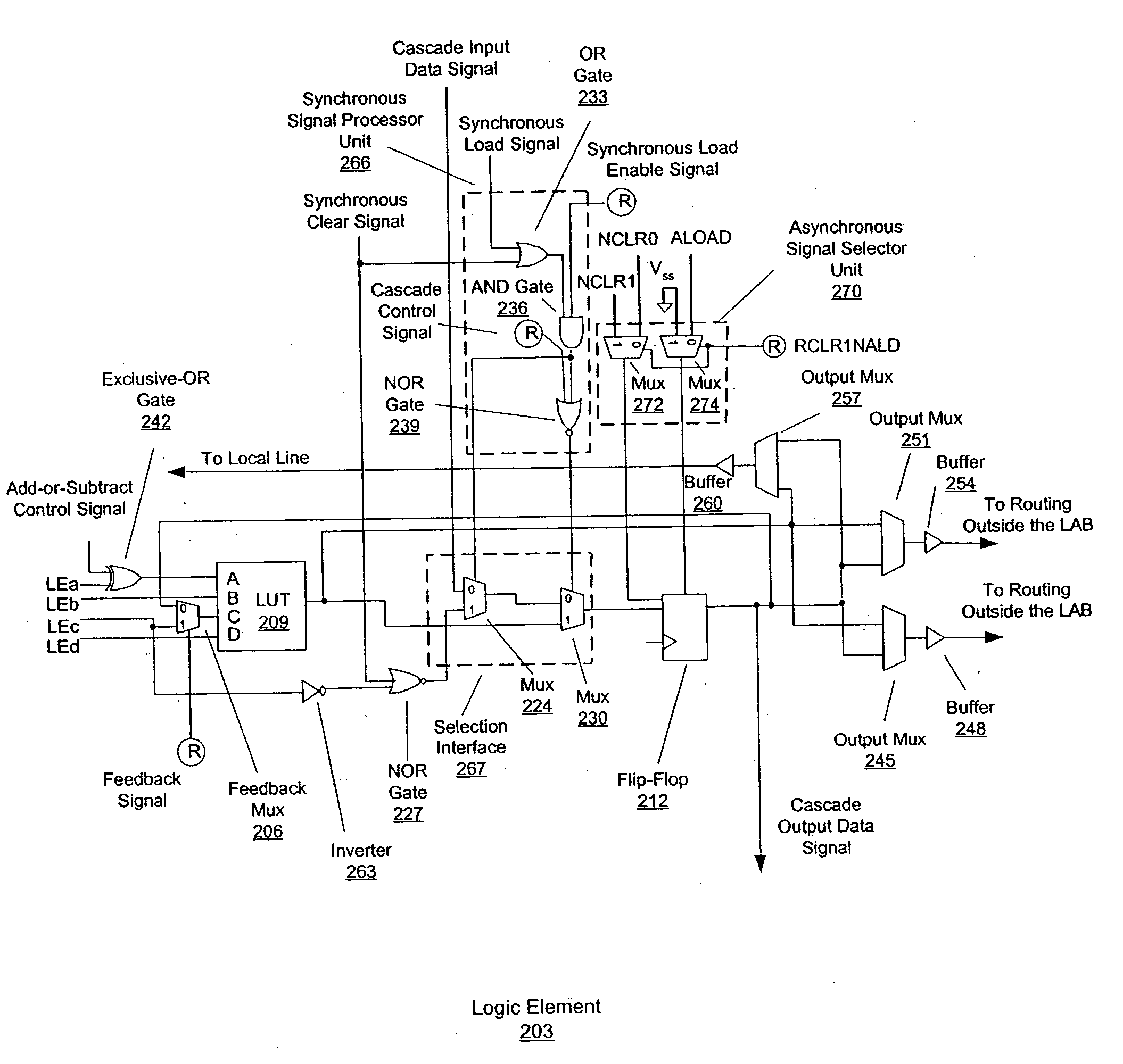
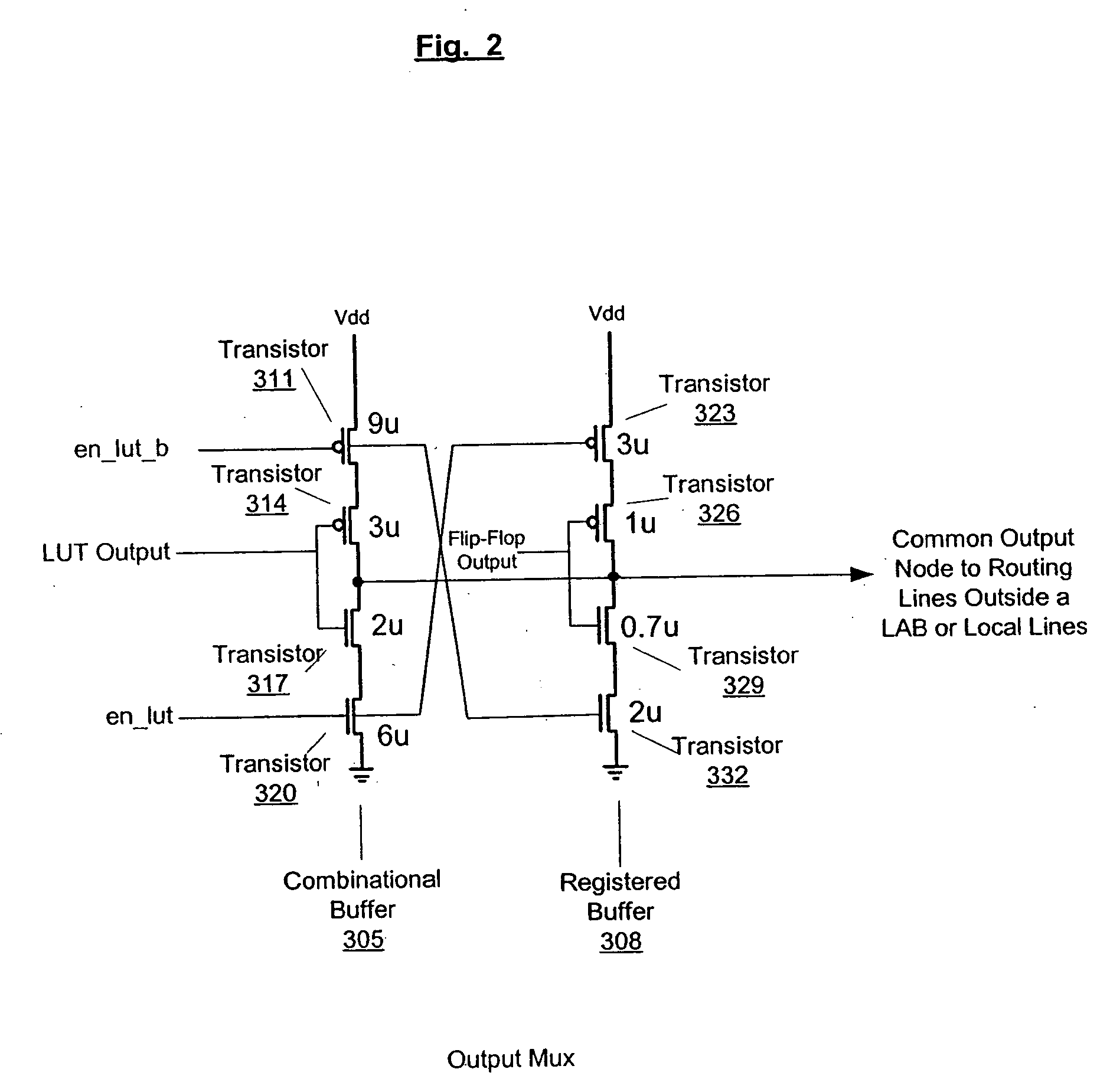
InactiveUS20050127944A1Reliability increasing modificationsSolid-state devicesMultiplexerControl signal
An embodiment of this invention pertains to a versatile and flexible logic element and logic array block (“LAB”). Each logic element includes a programmable combinational logic function block such as a lookup table (“LUT”) and a flip-flop. Within the logic element, multiplexers are provided to allow the flip-flop and the LUT to be programmably connected such that either the output of the LUT may be connected to the input of the flip-flop or the output of the flip-flop may be connected to the input of the LUT. An additional multiplexer allows the output of the flip-flop in one logic element to be connected to the input of a flip-flop in a different logic element within the same LAB. Output multiplexers selects between the output of the LUT and the output of the flip-flop to generate signals that drive routing lines within the LAB and to routing lines external to the LAB. These output multiplexers are constructed such that the combinational output (output from the LUT) is faster than the output from the flip-flop. A collection of routing lines and multiplexers within the LAB are used to provide inputs to the LUTs. Each of the input multiplexers for each logic element is connected to a subset of the routing lines within the LAB using a specific pattern of connectivity of multiplexers to associated wires that maximizes the efficiency of use of the routing wires. Control signals for the set of logic elements within the LAB are generated using a secondary signal generation unit that minimizes contention for shared signals. One of the control signals is an “add-or-subtract control signal” that allows all of the LEs in a LAB to perform either addition or subtraction under the control of a logic signal. In a PLD supporting redundancy, the carry chain for the LABs is arranged in the same direction that redundancy shifts to remap defective LABs and a multiplexer on the carry input of a LAB is used to select the appropriate carry output from another LAB depending on whether redundancy is engaged.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
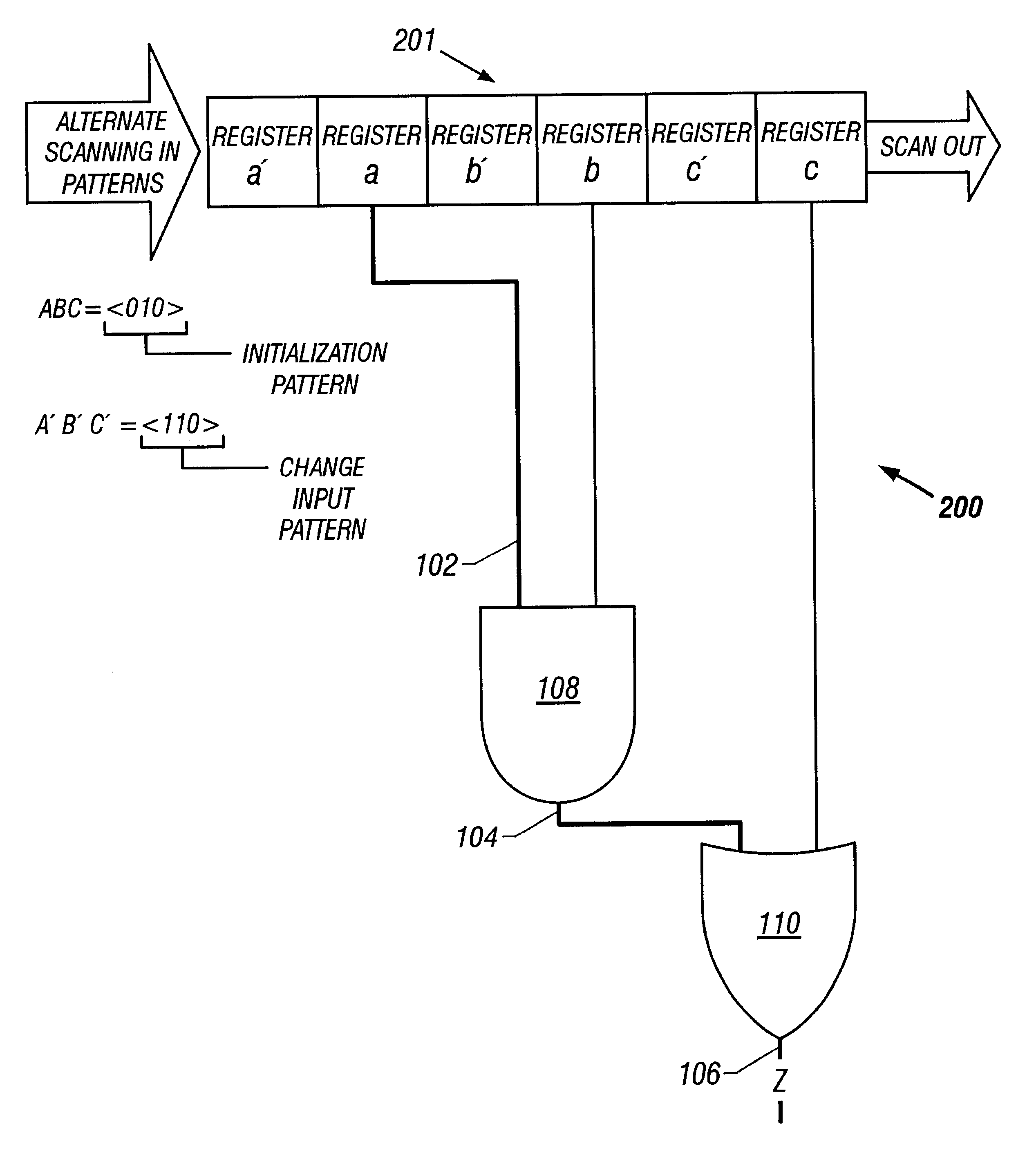
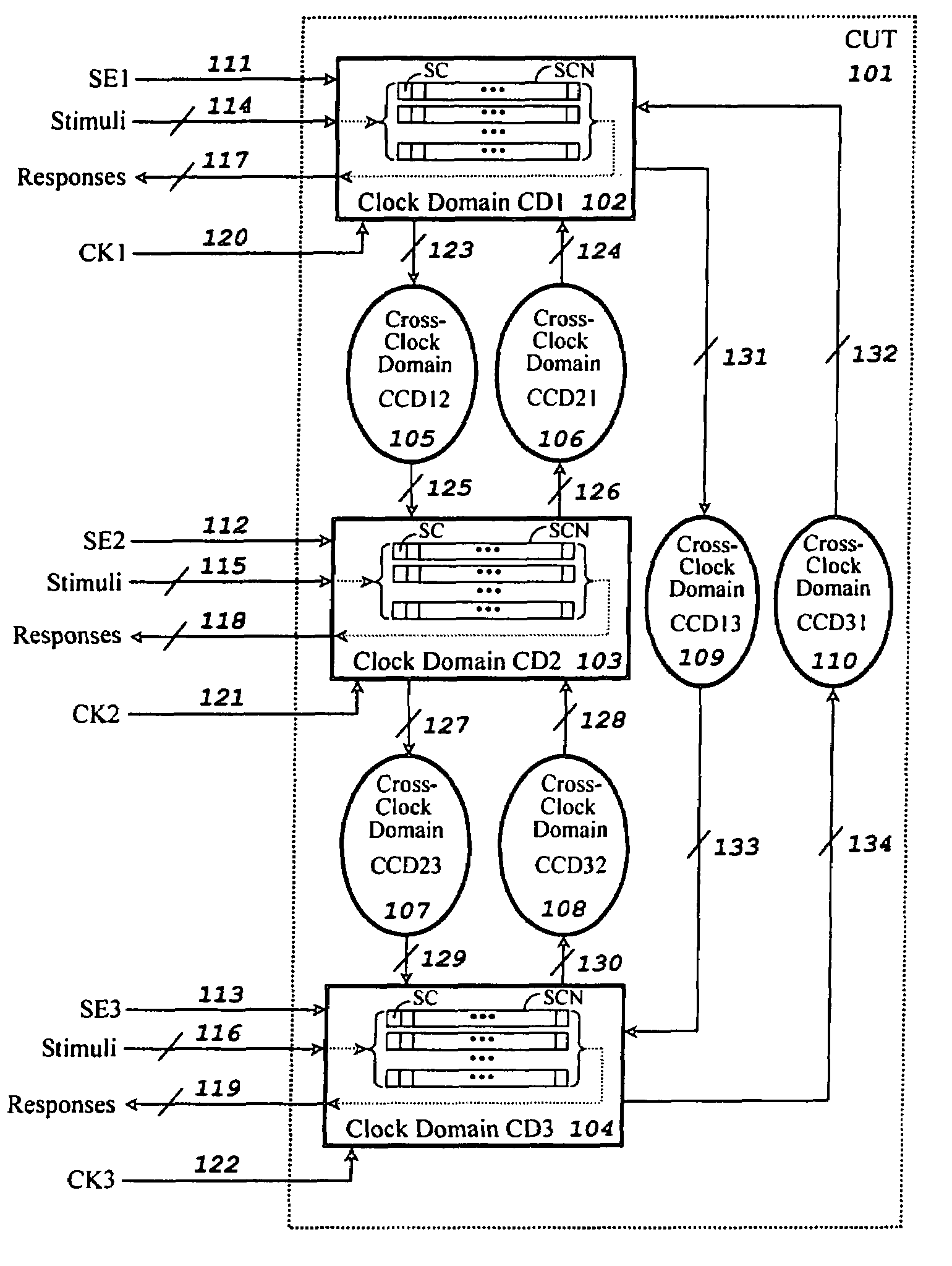
Smart capture for ATPG (automatic test pattern generation) and fault simulation of scan-based integrated circuits
InactiveUS7124342B2Improve performanceHigh simulationError detection/correctionMarginal circuit testingHemt circuitsAutomatic test pattern generation
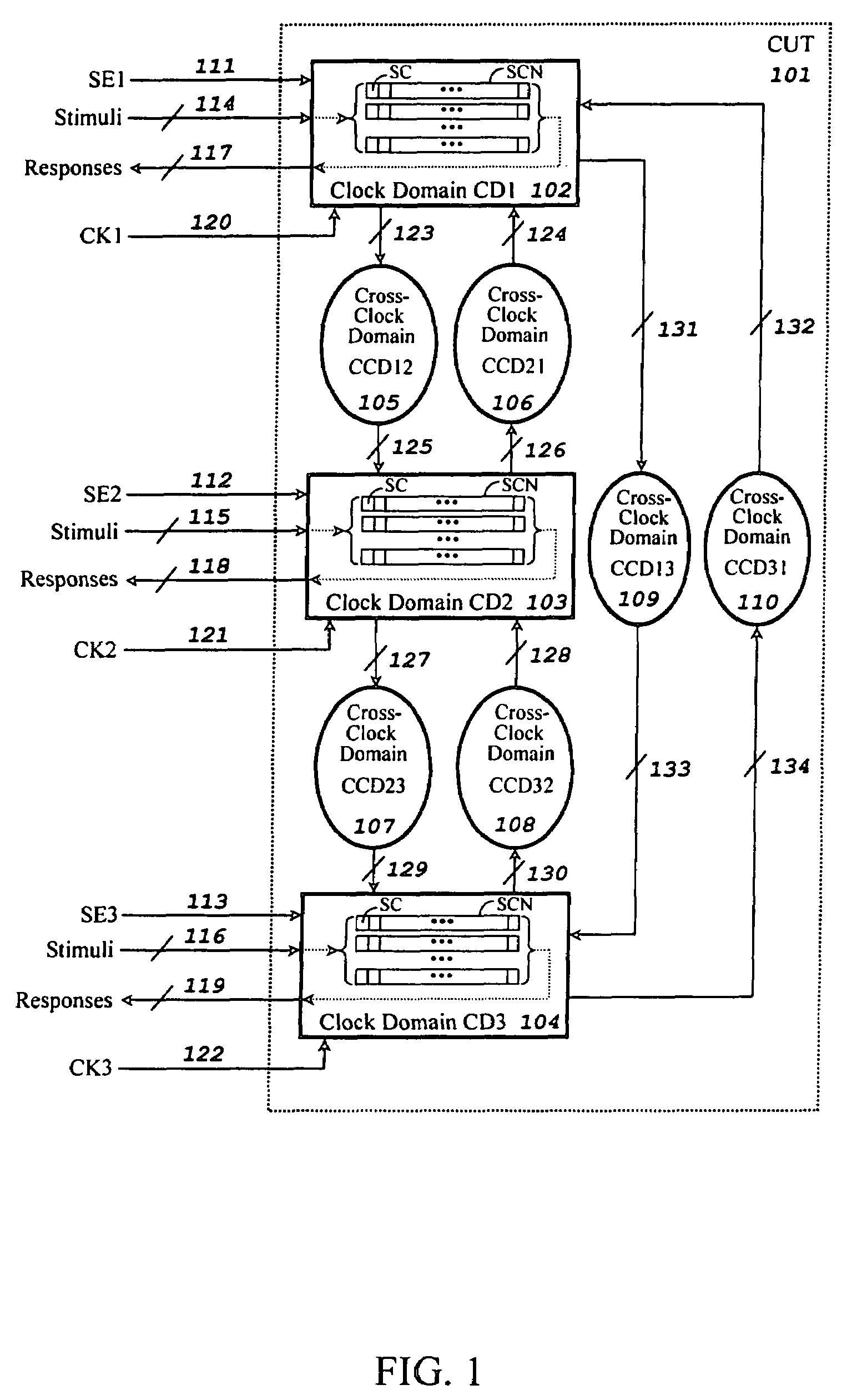
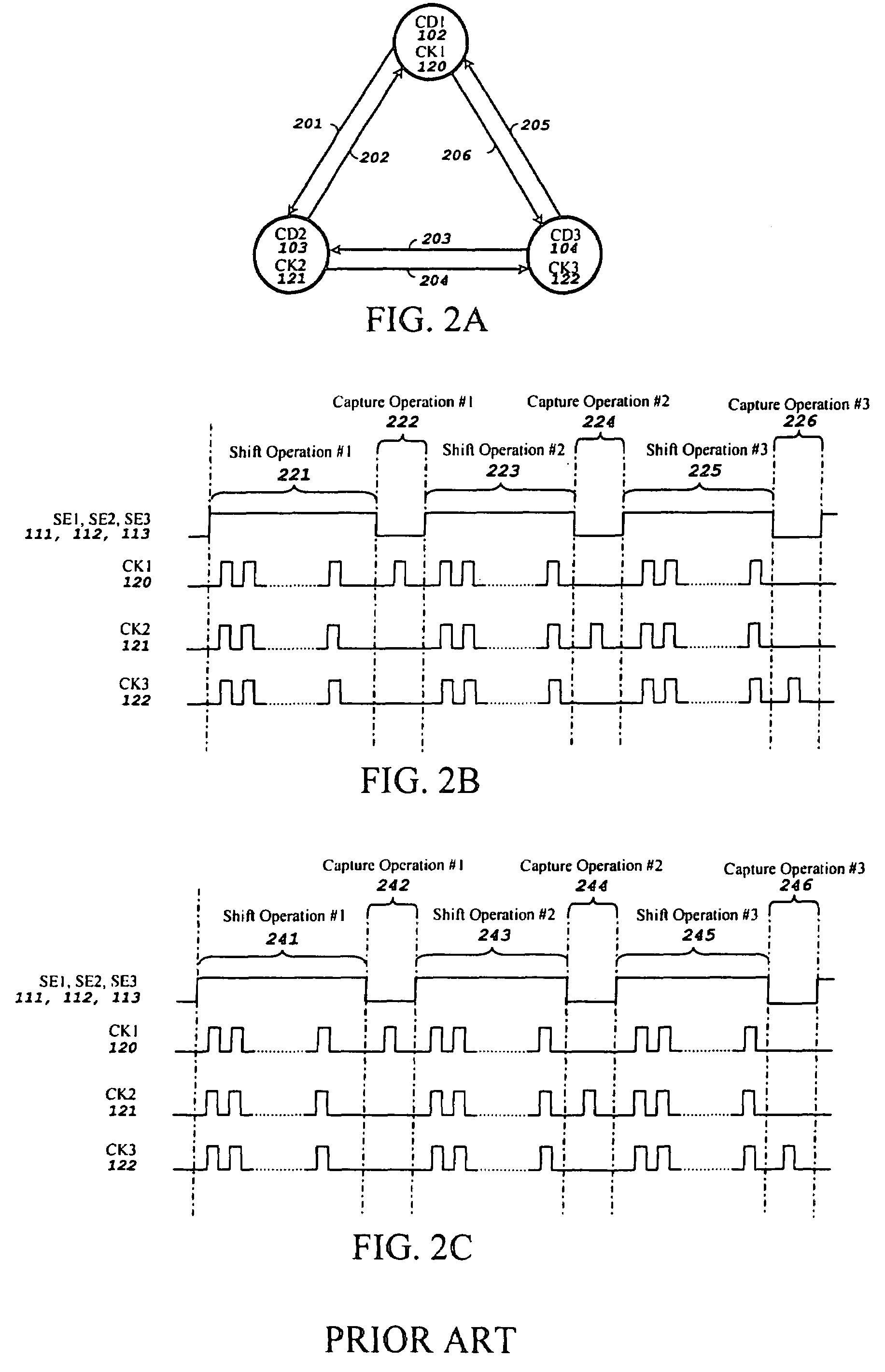
A method for generating stimuli and test responses for testing faults in a scan-based integrated circuit in a selected scan-test mode or a selected self-test mode, the scan-based integrated circuit containing a plurality of scan chains, N clock domains, and C cross-clock domain blocks, each scan chain comprising multiple scan cells coupled in series, each clock domain having one capture clock, each cross-clock domain block comprising a combinational logic network. The method comprises compiling the scan-based integrated circuit into a sequential circuit model; specifying input constraints on the scan-based integrated circuit during a shift and capture operation; specifying a clock grouping to map the N clock domains into G clock domain groups, where N>G>1; transforming the sequential circuit model into an equivalent combinational circuit model according to the input constraints and the clock grouping; and generating the stimuli and test responses on the equivalent combinational circuit model according to the input constraints.
Owner:SYNTEST TECH
Soft Error Hard Electronic Circuit and Layout
ActiveUS20100264953A1Reliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionCombinational logicSoft error
This invention comprises a layout method to effectively protect electronic circuits against soft errors (non-destructive errors) and circuit cells, which are protected against soft errors. The invention applies a layout method to sequential and combinational logic to generate specific circuit cells with netlists and layouts which are hardened against single event generated soft-errors. It also devices methods of how two or more such cells should be laid out and placed relative to each other, in order to have the best global soft-error protection.
Owner:RCI EURO AB
Semiconductor circuit and methodology for in-system scan testing
ActiveUS20140047293A1Quantity minimizationEasy to reuseElectronic circuit testingAddress spacePrinted circuit board
A semiconductor circuit comprising a digital circuit portion, which comprises a combinatorial logic block. The semiconductor circuit further comprises a scan chain for loading and applying a predefined digital test pattern to inputs of the combinatorial logic block. A bi-directional communication port is adapted for writing incoming data to an address space of the digital circuit portion. Scan control hardware comprises a plurality of individually addressable scan control registers which are mapped to the address space of the bi-directional communication port. A method of testing the digital circuit portion involves, using the scan chain, writing bit values to inputs of the individually addressable scan control registers, and reading bit values from at least one output of an individually addressable scan control register. The method and semiconductor circuit allow thorough testing and diagnosing of failing semiconductor devices, including core logic thereof, while mounted on a printed circuit board.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
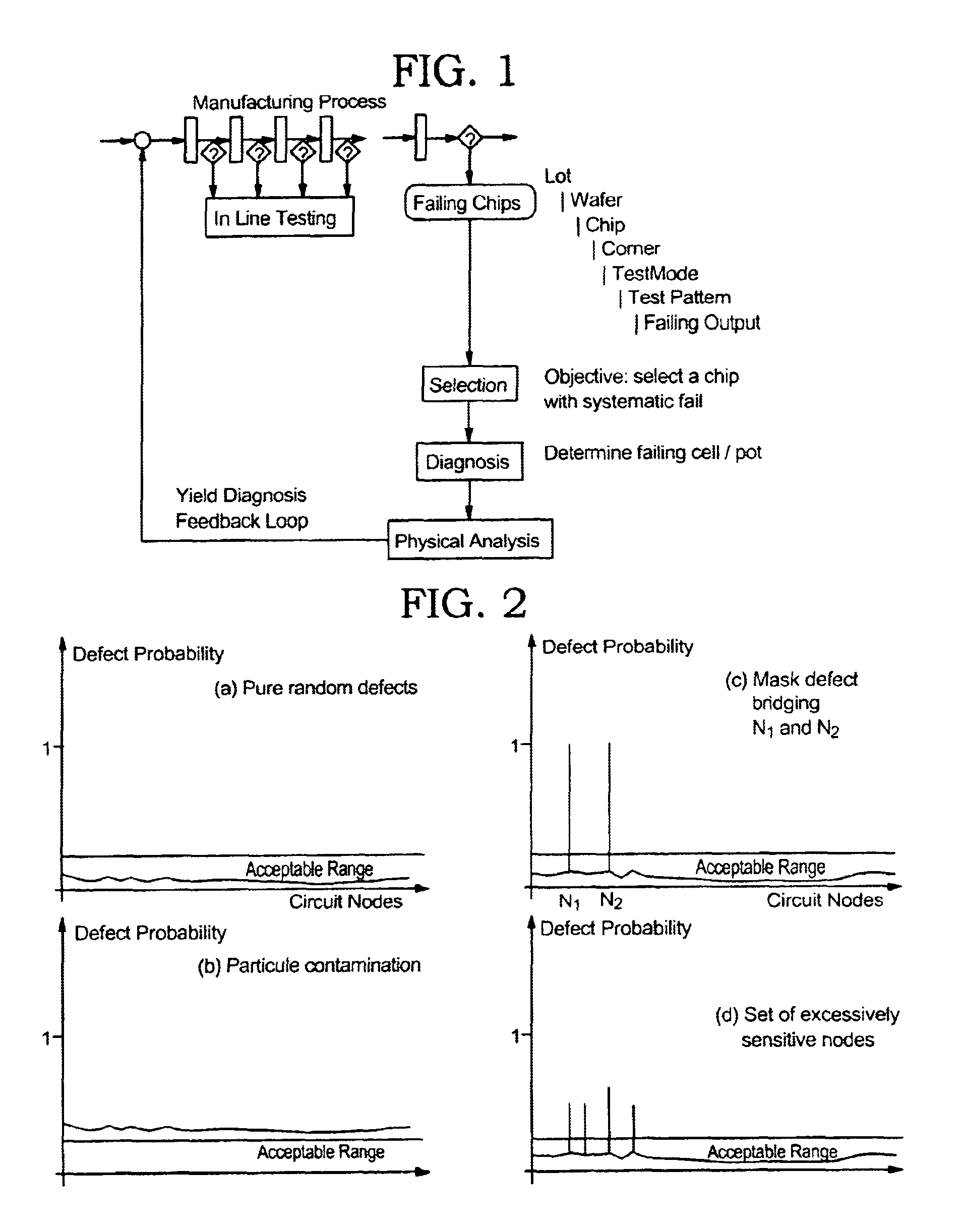
Method to detect systematic defects in VLSI manufacturing
InactiveUS6880136B2Improve manufacturing yieldGood choiceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty computer hardwareEngineeringCombinational logic
Defects in manufacturing of IC devices are analyzed by testing the devices for defects using results of LSSD technology to find at least one failing pattern that contains incorrect values. The failing latches are used as a starting point to trace back through combinational logic feeding the failing latches, until controllable latches are encountered. A decision is then made to continue the back tracing or not depending on whether the latter latches were clocked during the application of one of the failing patterns or not.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
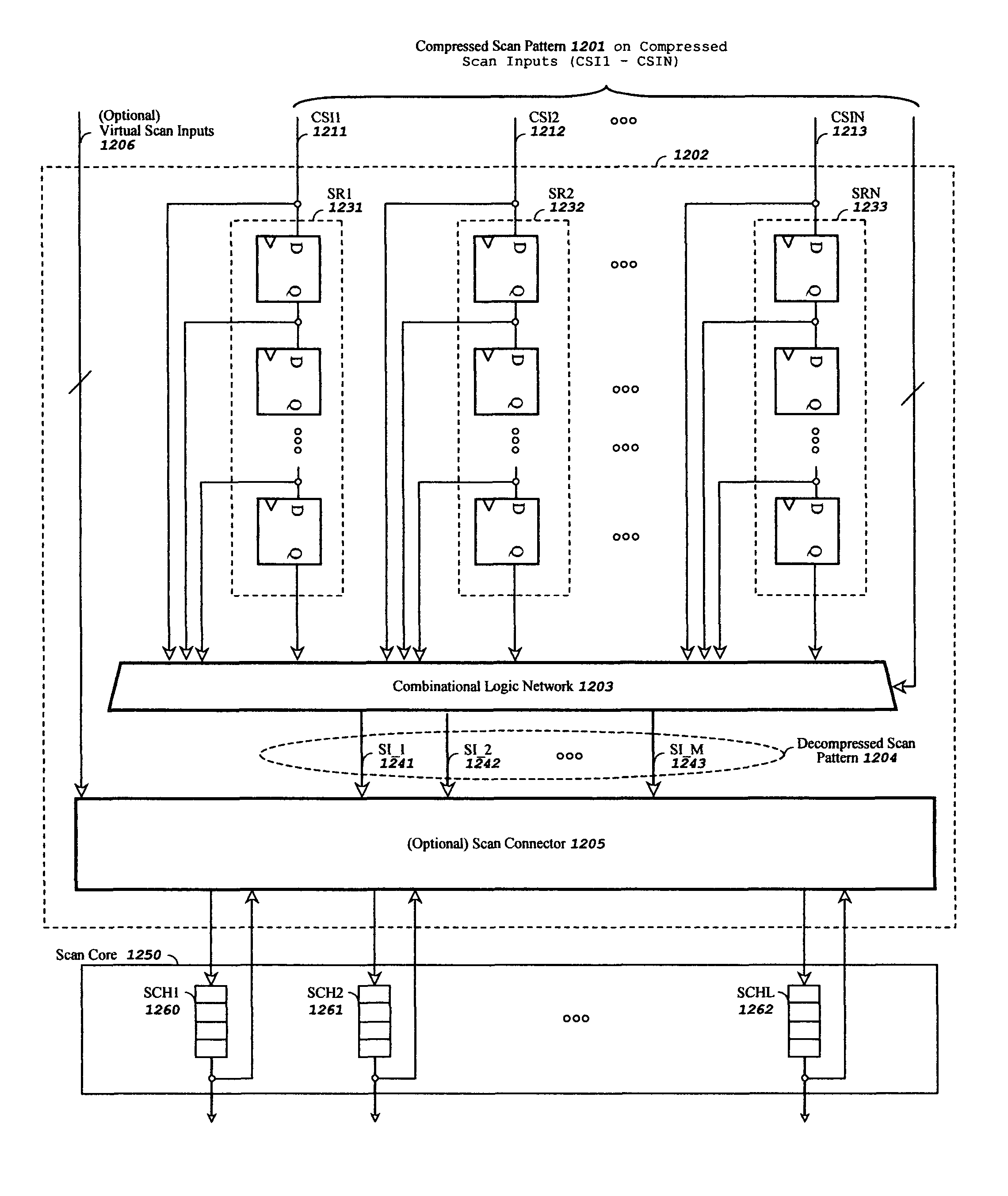
Method and apparatus for pipelined scan compression
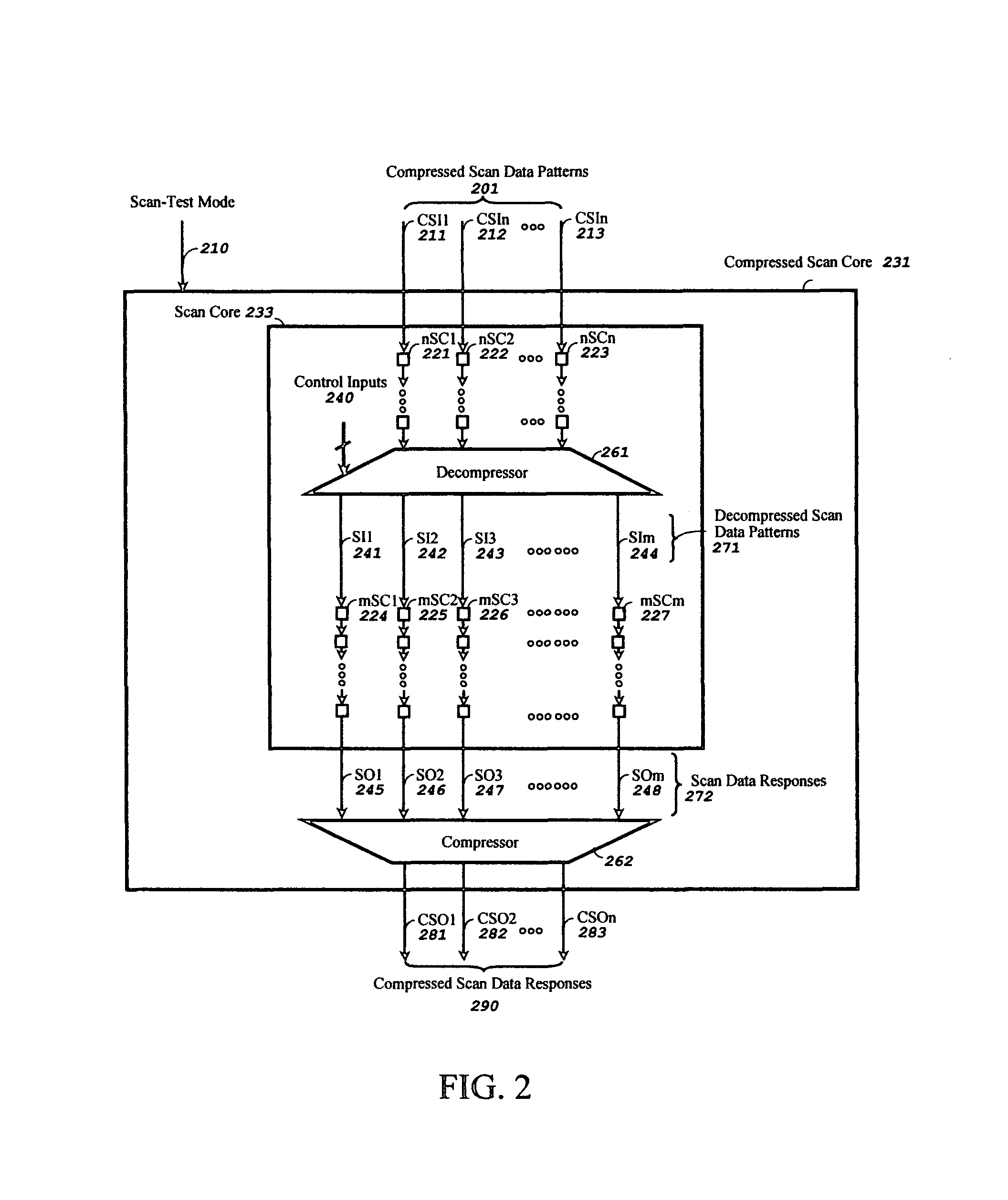
InactiveUS7945833B1Reduce loadImprove balanceElectronic circuit testingPower supply testingShift registerEngineering
A pipelined scan compression method and apparatus for reducing test data volume and test application time in a scan-based integrated circuit without reducing the speed of the scan chain operation in scan-test mode or self-test mode. The scan-based integrated circuit contains one or more scan chains, each scan chain comprising one or more scan cells coupled in series. The method and apparatus includes a decompressor comprising one or more shift registers, a combinational logic network, and an optional scan connector. The decompressor decompresses a compressed scan pattern on its compressed scan inputs and drives the generated decompressed scan pattern at the output of the decompressor to the scan data inputs of the scan-based integrated circuit. Any input constraints imposed by said combinational logic network are incorporated into an automatic test pattern generation (ATPG) program for generating the compressed scan pattern for one or more selected faults in one-step.
Owner:SYNTEST TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com