Patents
Literature
4404results about How to "Easy to reuse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
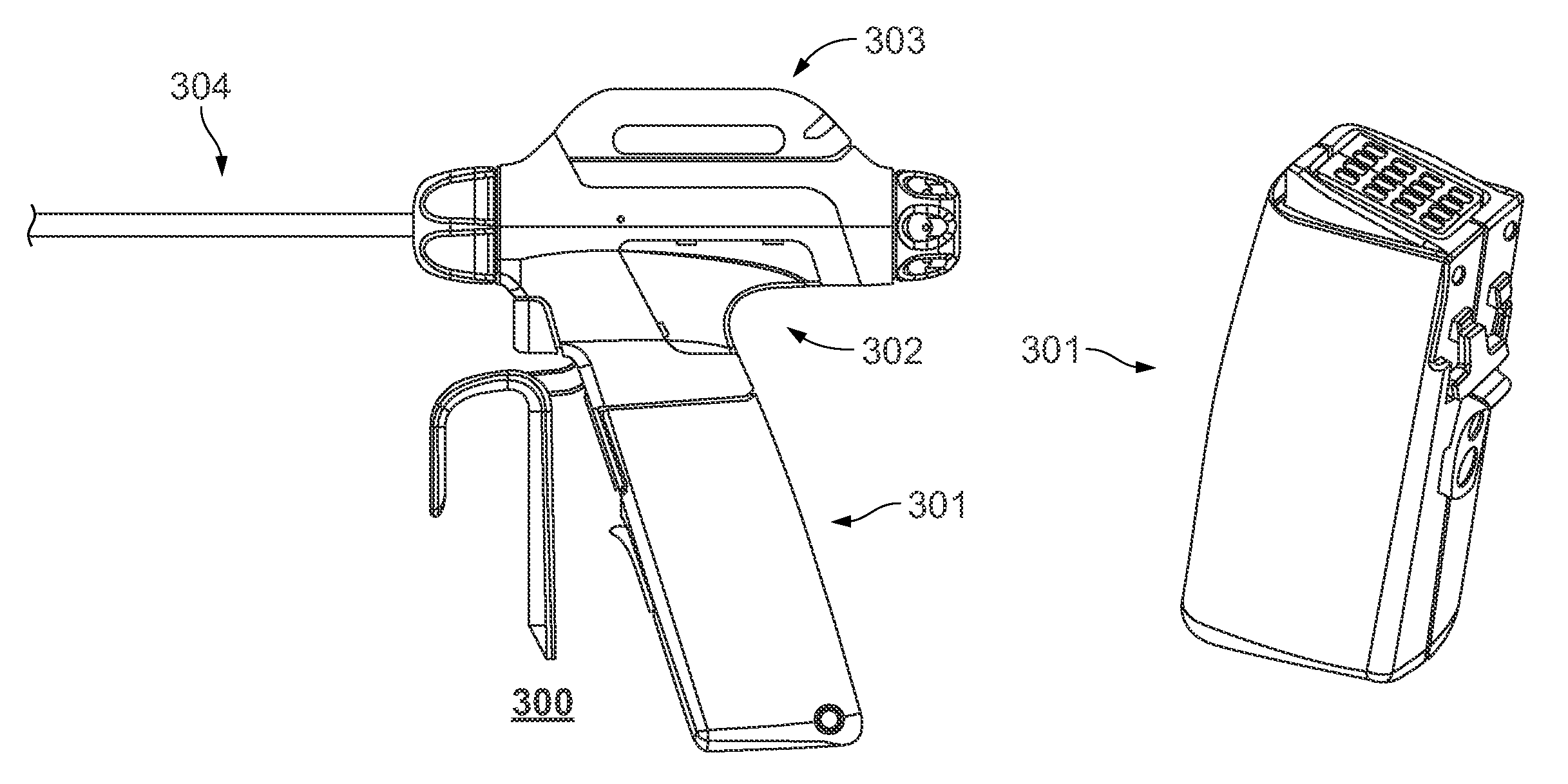
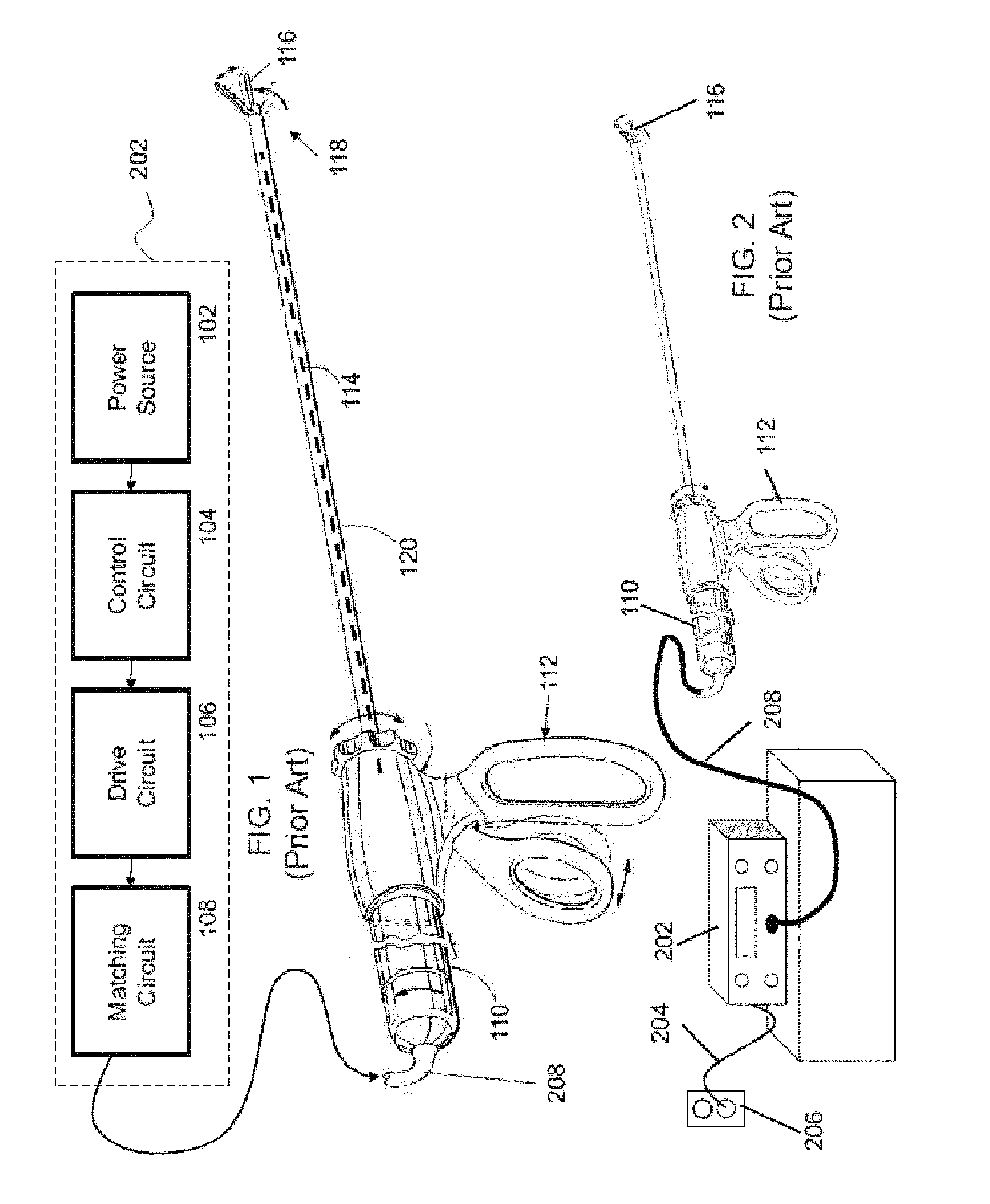
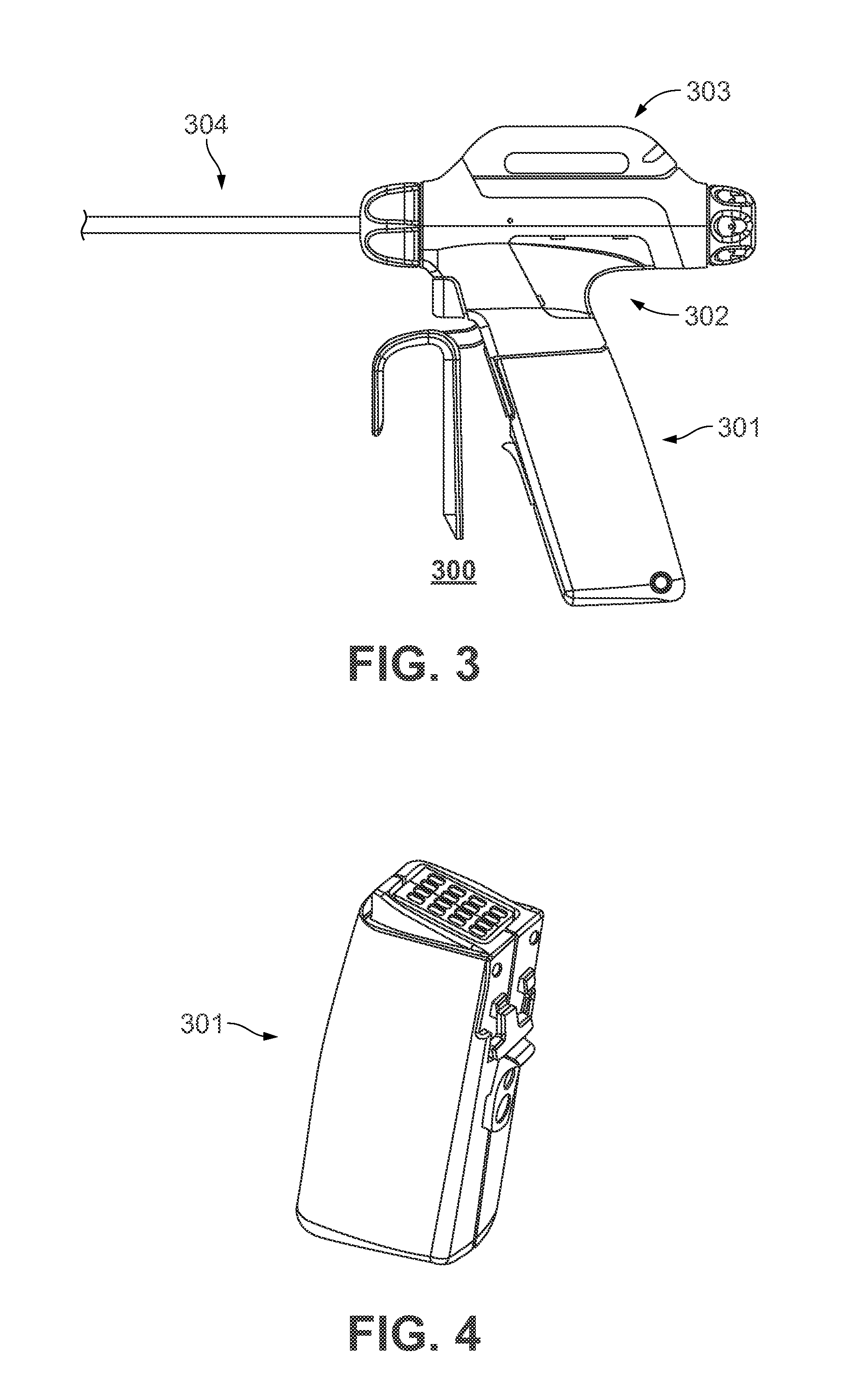
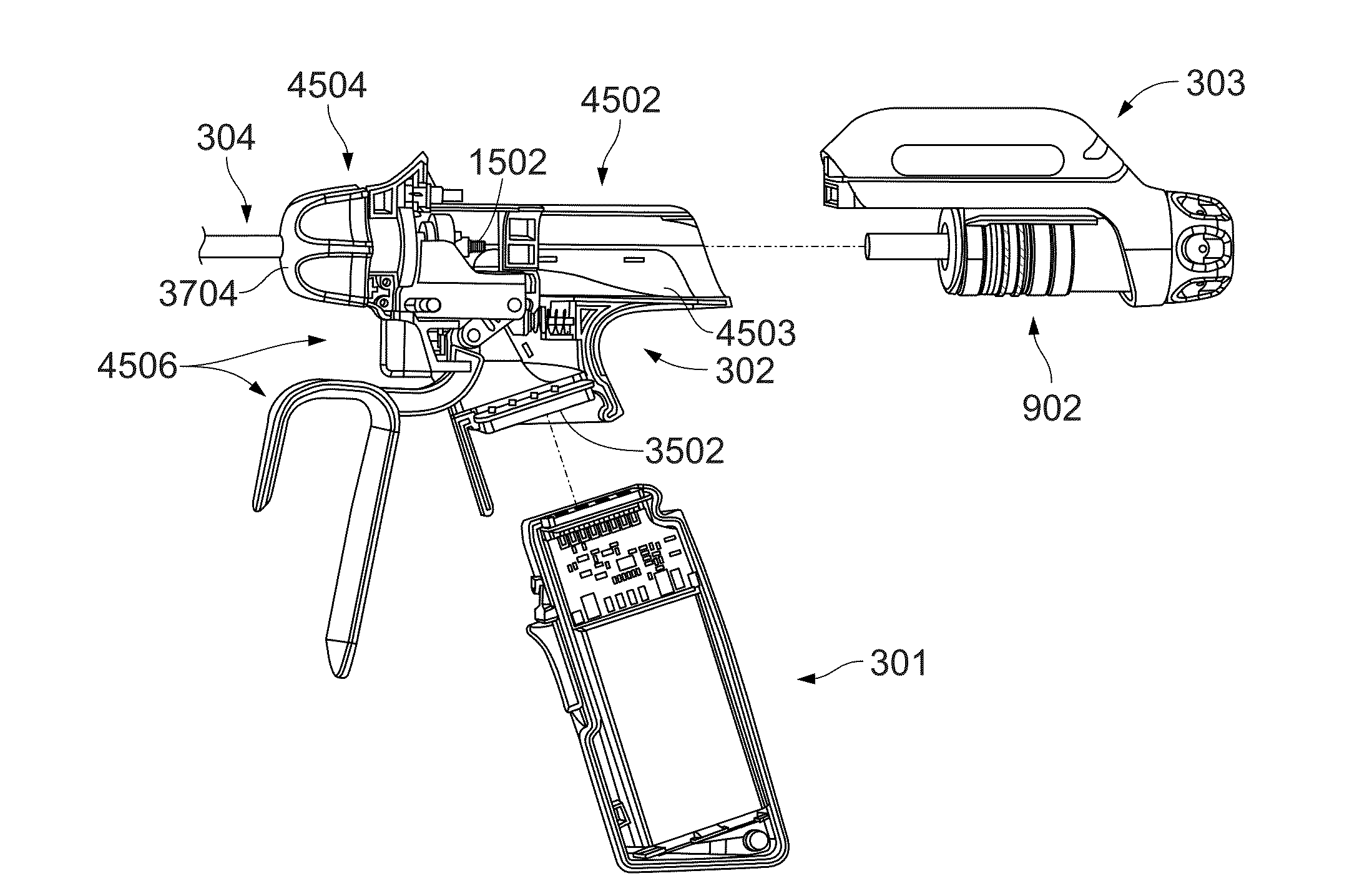
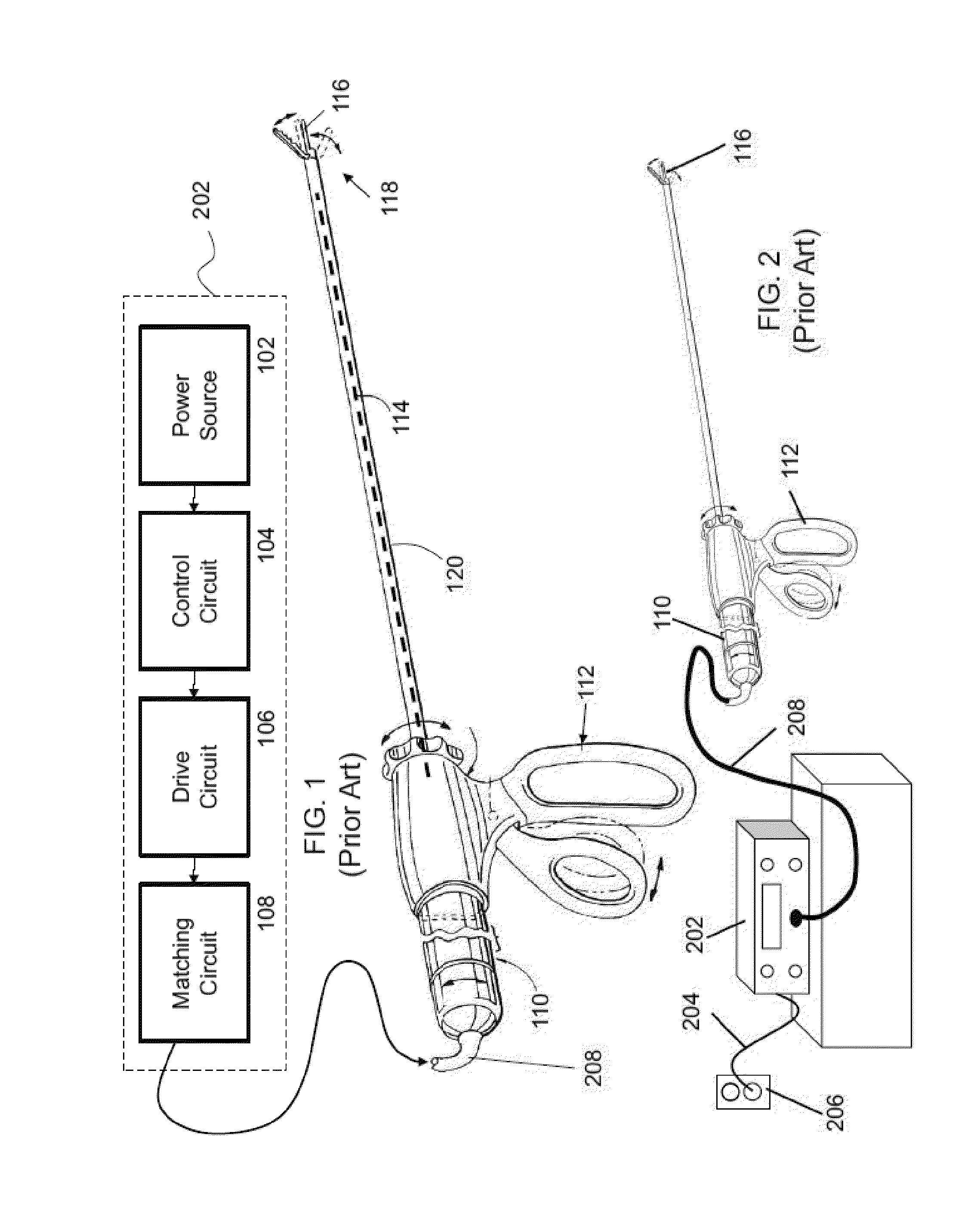
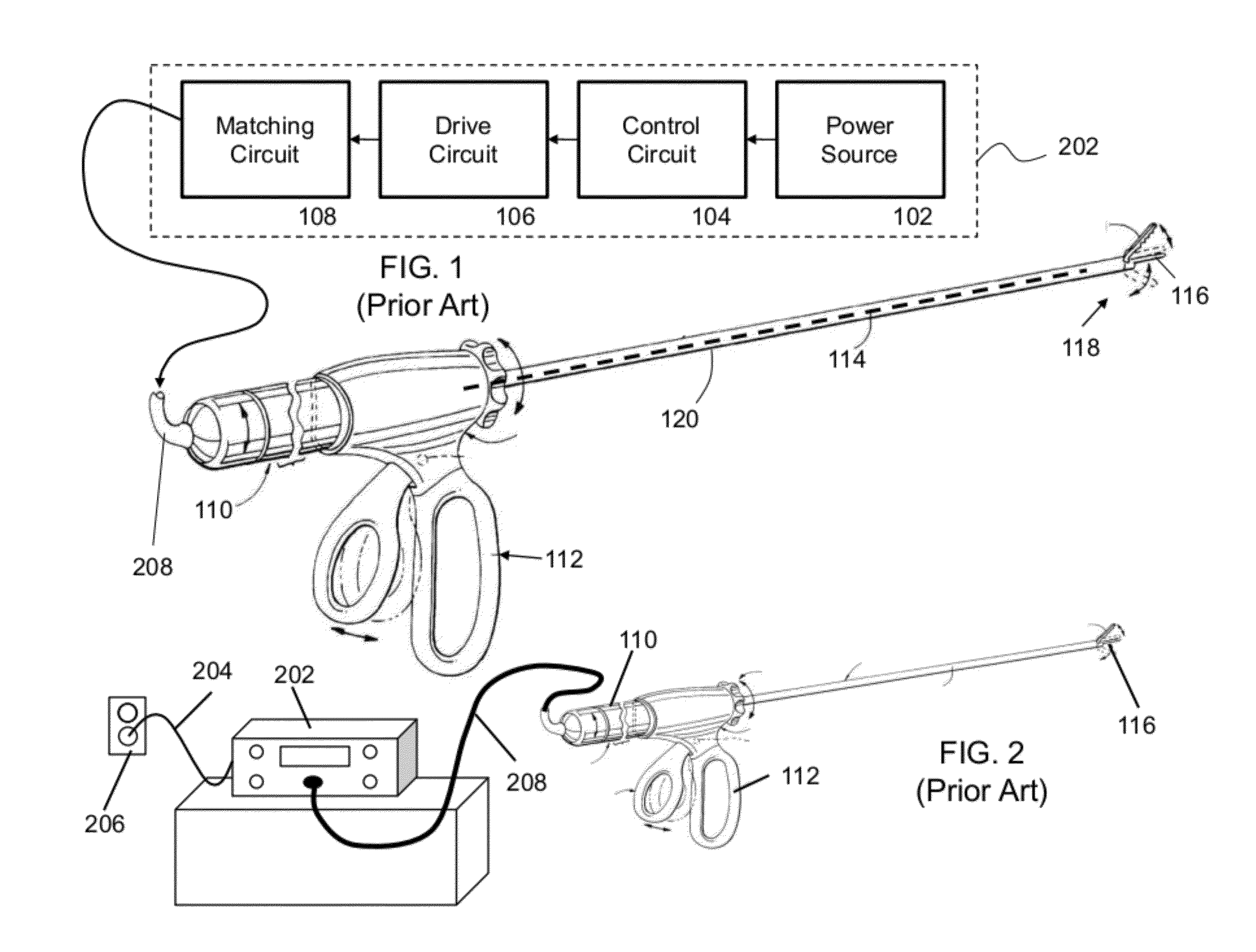
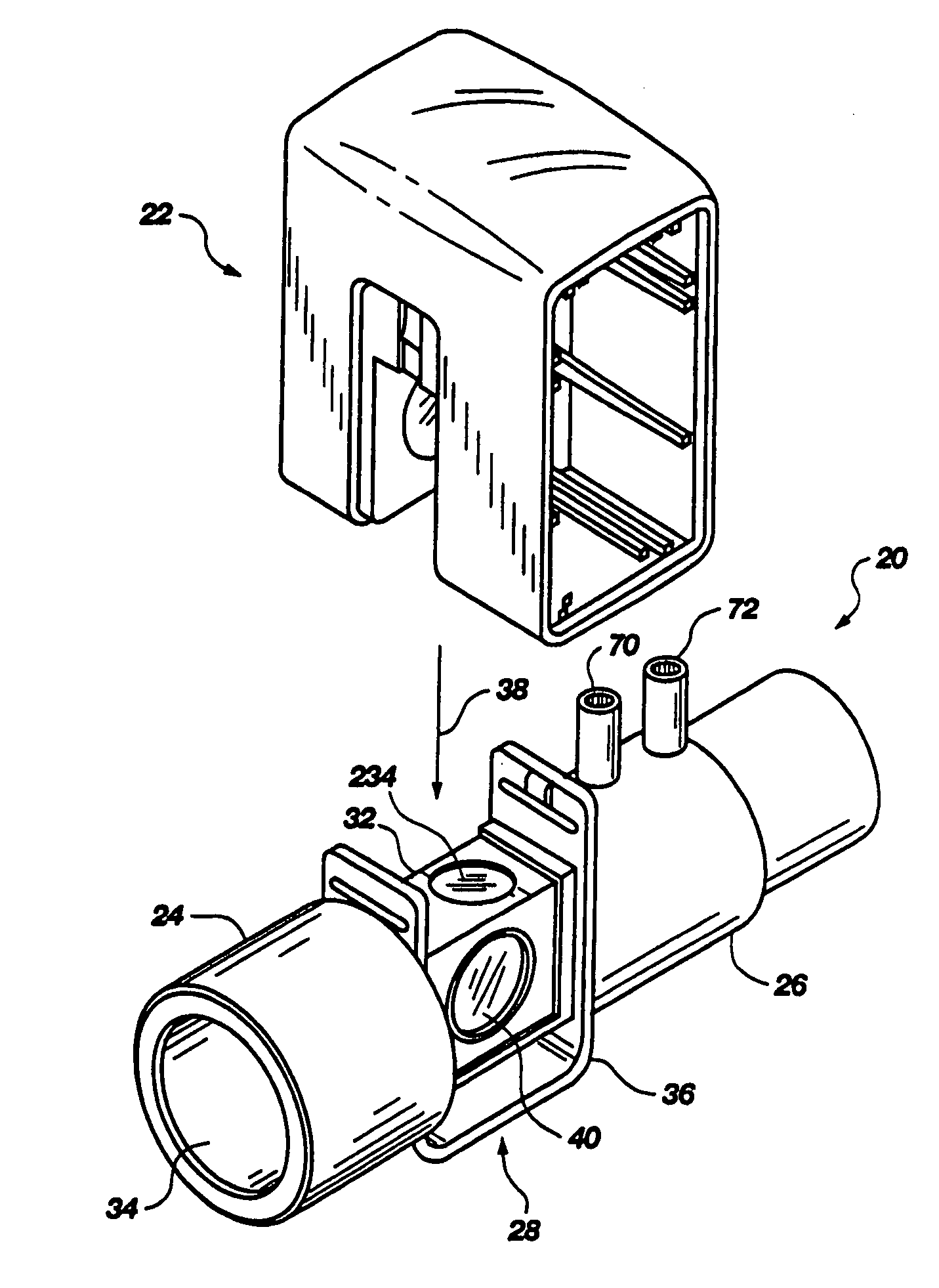
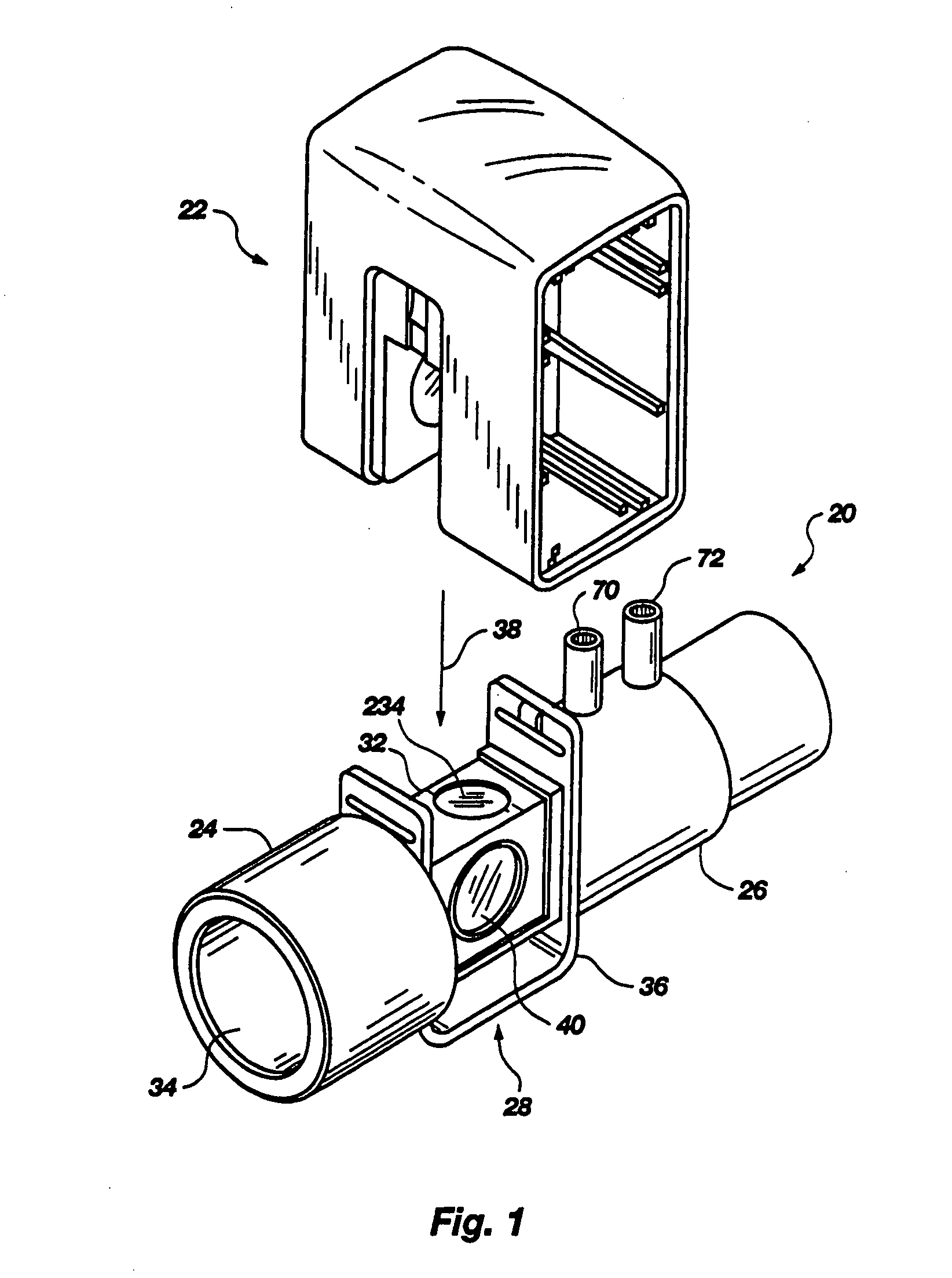
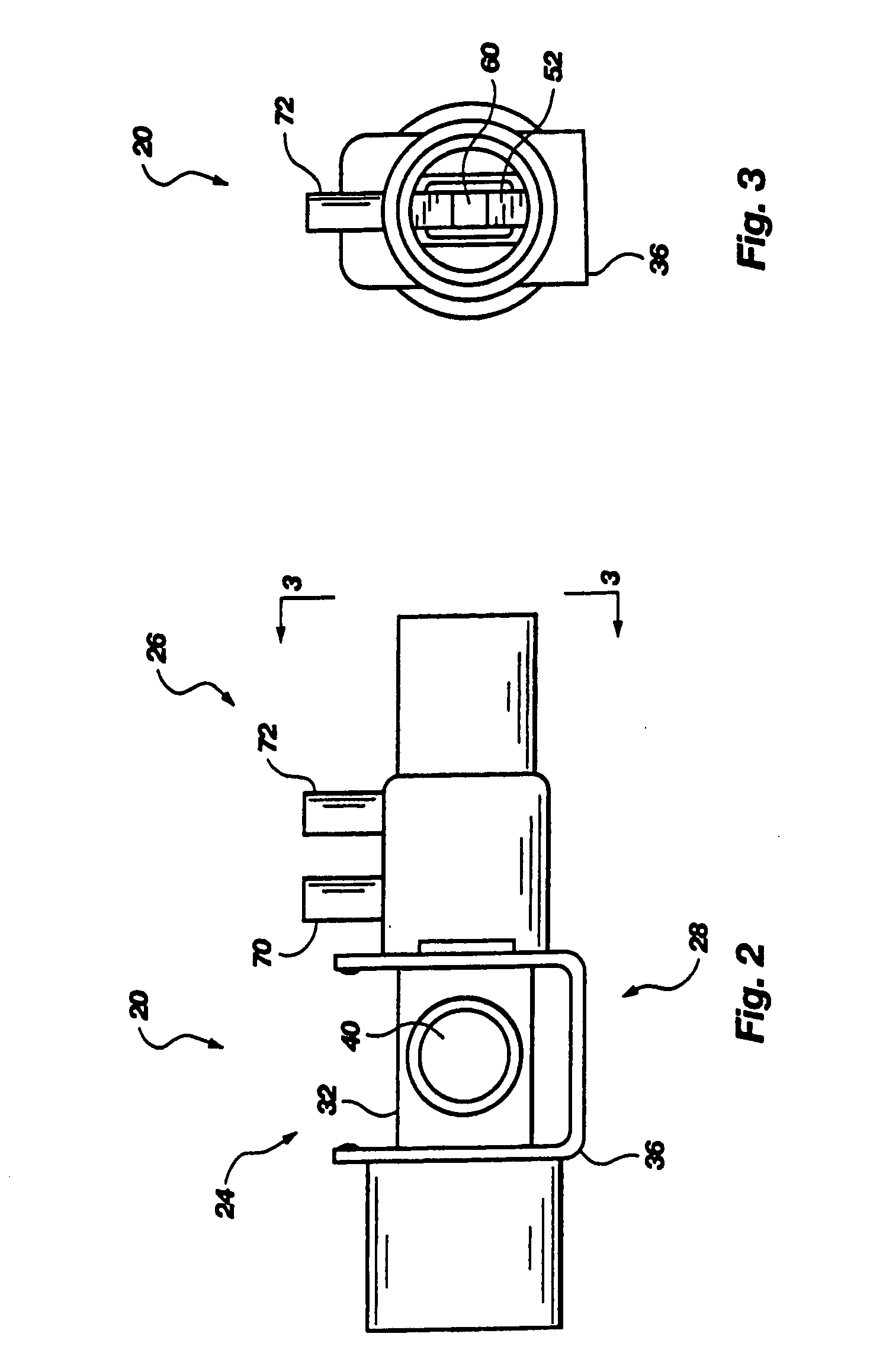
Battery-powered hand-held ultrasonic surgical cautery cutting device
ActiveUS9107690B2Alter functionAlter performanceBatteries circuit arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsReal-time clockElectrical battery
A battery assembly for use with a surgical device having a battery terminal and operational parameters includes a housing having a shape formed to removably connect with the terminal. The housing contains a modular battery operable to supply power to the device at the terminal and has a control circuit with a microprocessor, a memory, and a real-time clock. The control circuit is communicatively coupled to the battery and is operable to detect an identity of the surgical device, to determine at least one piece of information pertaining to at least one of the operational parameters of the surgical device based upon the detected identity, to record the piece of information at least in the memory, and to selectively allow or prevent the battery from supplying power to the surgical device dependent upon the piece of information.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Battery-powered hand-held ultrasonic surgical cautery cutting device
ActiveUS9314261B2Alter functionAlter performanceSurgical furnitureMechanical vibrations separationElectrical batteryHand held
A battery-powered, modular surgical device comprising an electrically powered surgical instrument that requires a pre-determined minimum amount of electrical energy to complete a surgical procedure, and a power module assembly that has a battery that powers the surgical instrument and has a current state of electrical charge, and a control circuit that is electrically coupled to the battery and the surgical instrument and has a memory and a microprocessor. The microprocessor determines the current state of electrical charge of the battery, compares the current state of electrical charge to the pre-determined minimum amount of electrical energy, permits the battery to discharge if the current state of electrical charge is above the pre-determined minimum amount of electrical energy, and maintains the battery in a non-discharge state if the current state of electrical charge is below the pre-determined minimum amount of electrical energy.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
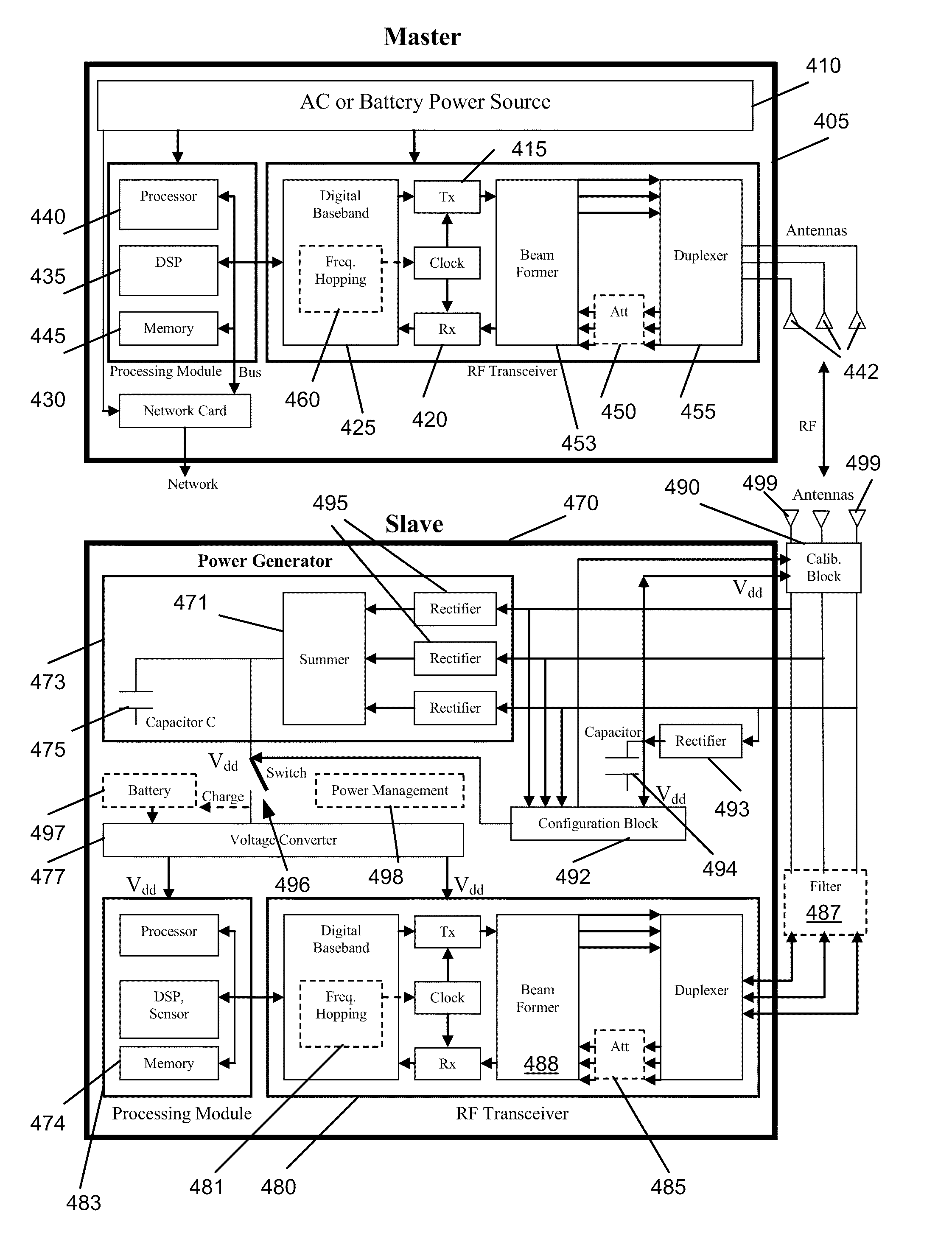
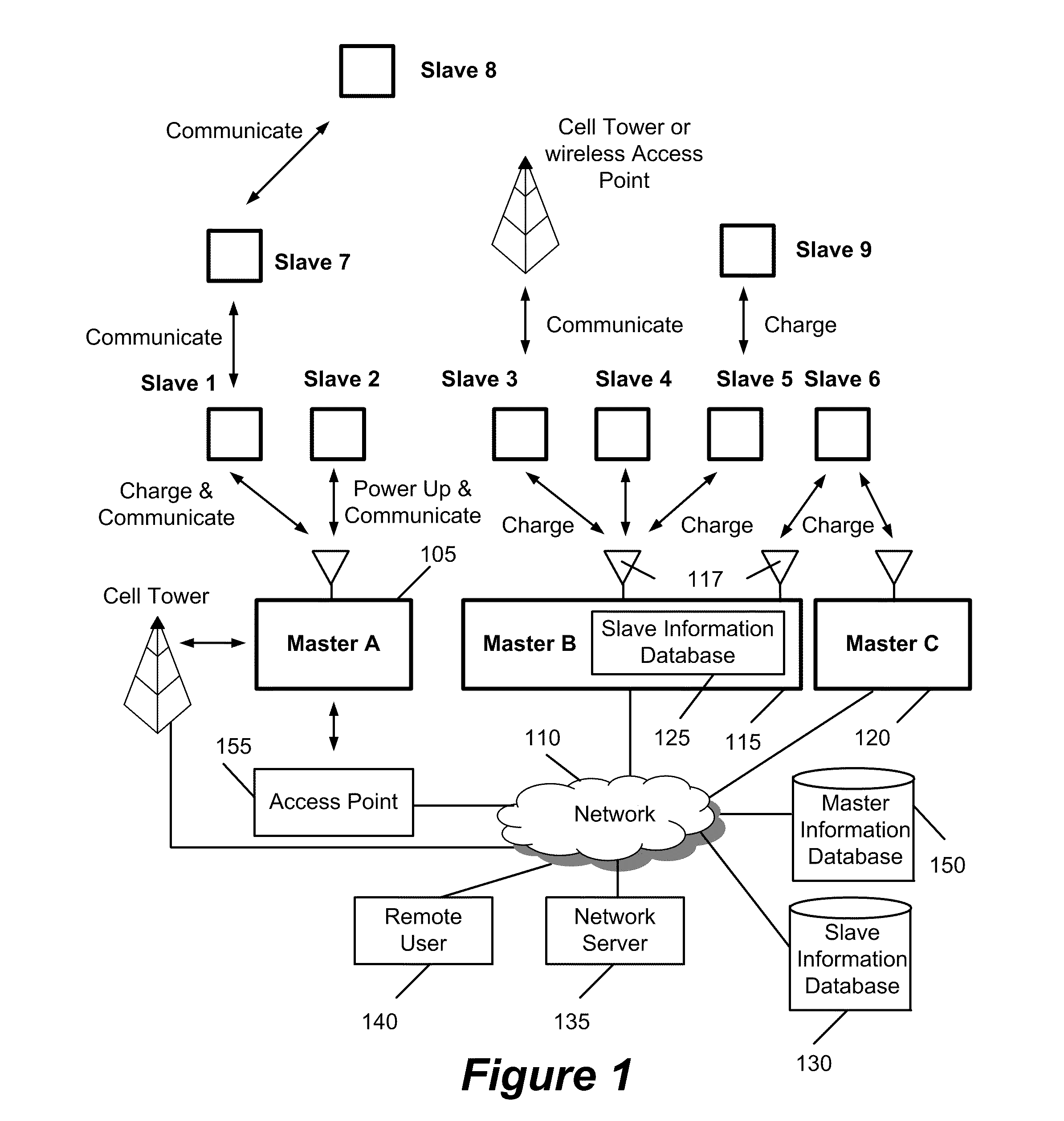
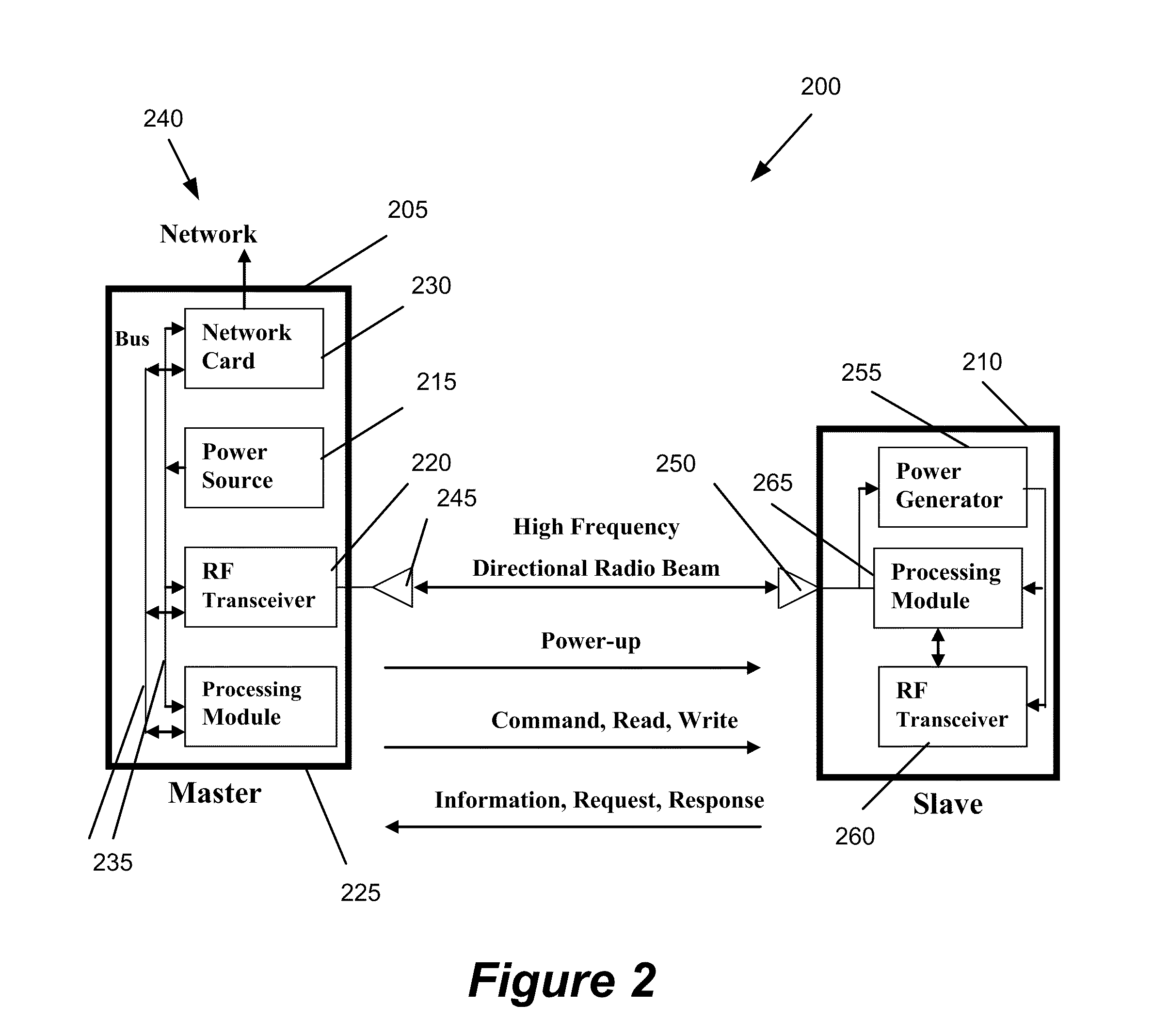
Method and apparatus for wirelessly transferring power and communicating with one or more slave devices
InactiveUS20110156640A1Improve communication efficiencyImprove power efficiencyCircuit authenticationElectromagnetic wave systemWireless transmissionDirectional antenna
Some embodiments provide a system for charging devices. The system includes a master device and a slave device. Some embodiments provide a method for charging devices in a system that includes a slave device and a master device. The slave device includes (1) an antenna to receive a radio frequency (RF) beam and (2) a power generation module connected to the antenna that converts RF energy received by the slave antenna to power. The master device includes (1) a directional antenna to direct RF power to the antenna of the slave device and (2) a module that provides power to the directional antenna of the master device.
Owner:CREEKVIEW IP LLC
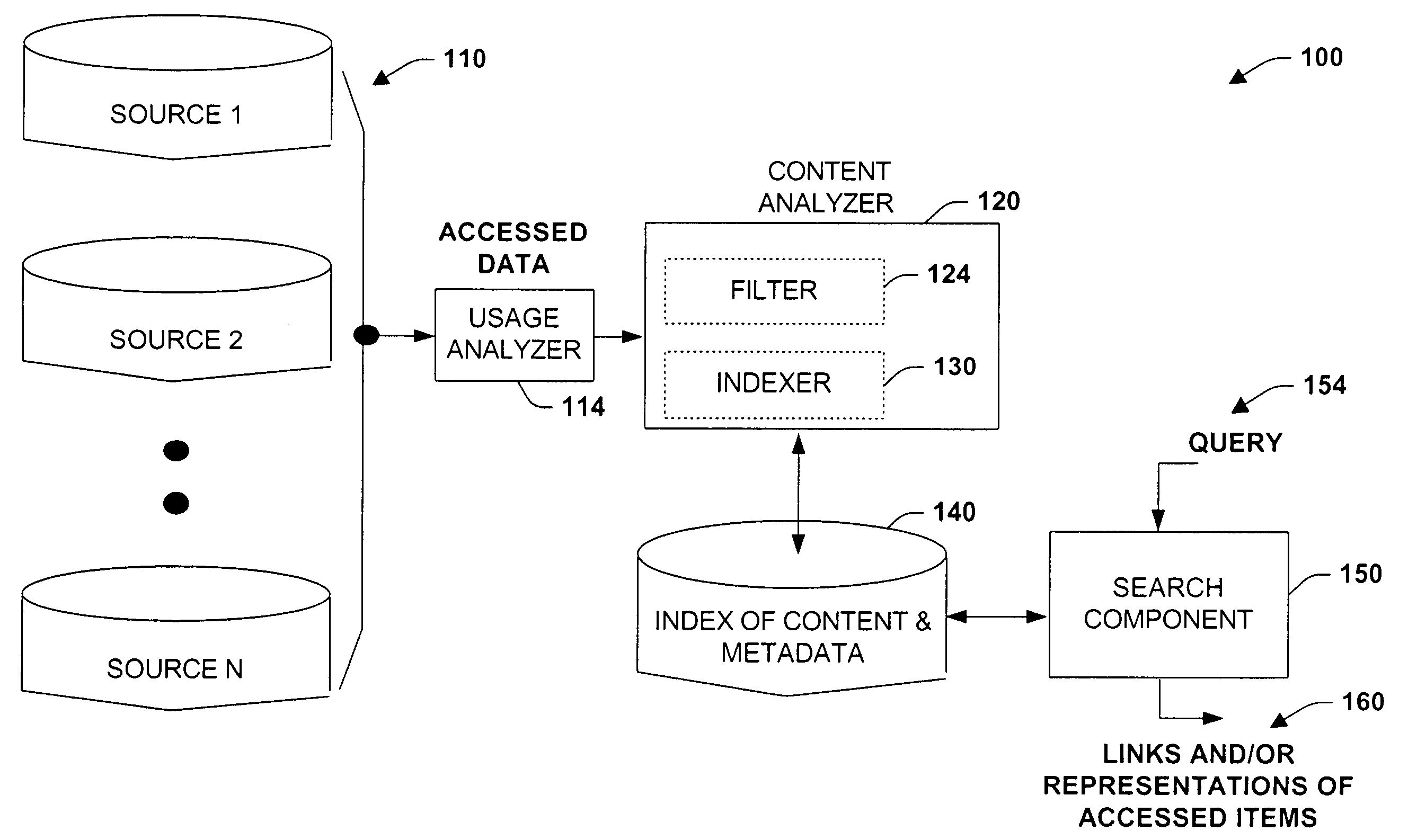
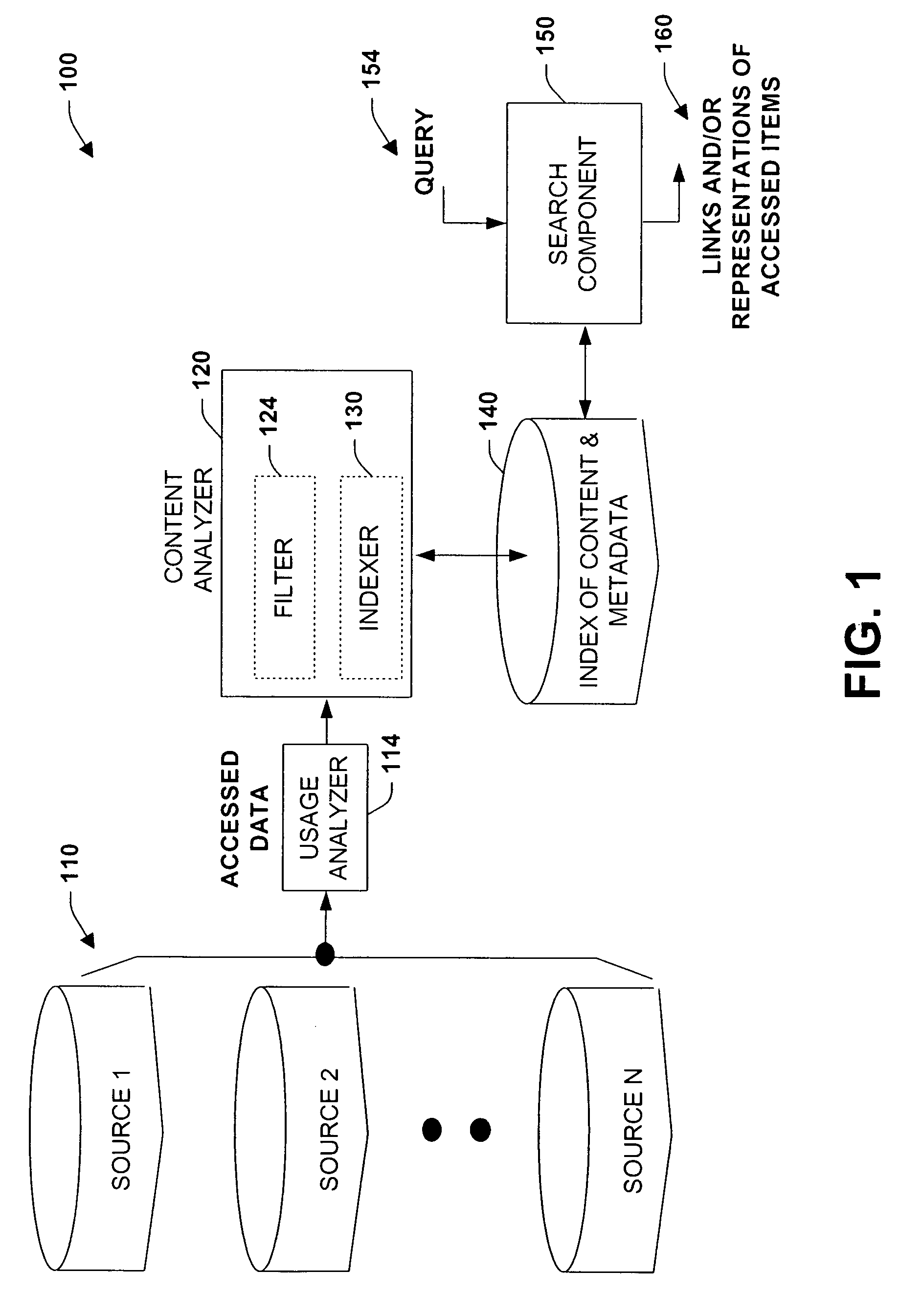
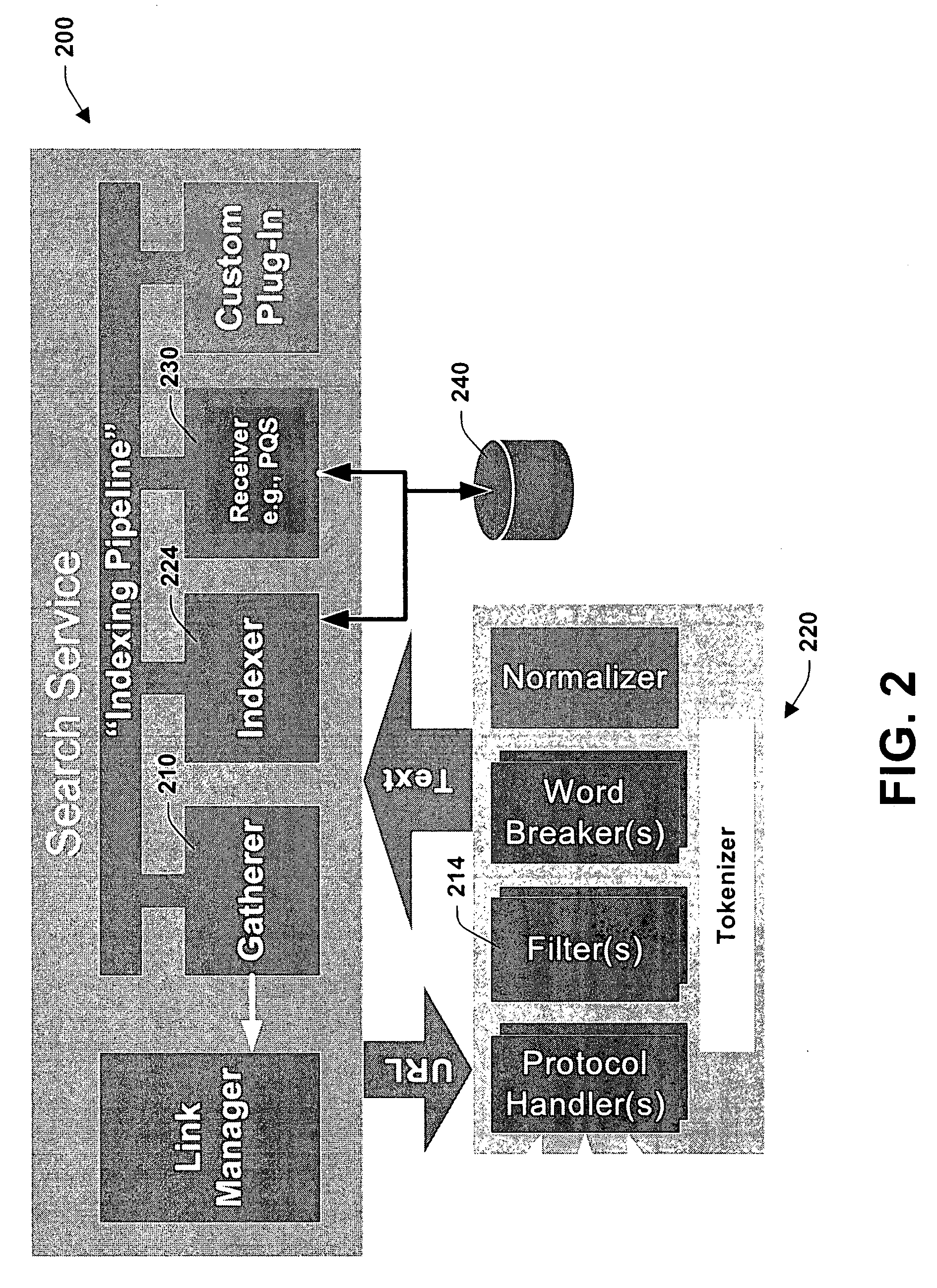
Method and system for usage analyzer that determines user accessed sources, indexes data subsets, and associated metadata, processing implicit queries based on potential interest to users
InactiveUS7162473B2Useful purposeFacilitate search for informationData processing applicationsText database indexingData accessContent analytics
The present invention relates to systems and methods providing content-access-based information retrieval. Information items from a plurality of disparate information sources that have been previously accessed or considered are automatically indexed in a data store, whereby a multifaceted user interface is provided to efficiently retrieve the items in a cognitively relevant manner. Various display output arrangements are possible for the retrieved information items including timeline visualizations and multidimensional grid visualizations. Input options include explicit, implicit, and standing queries for retrieving data along with explicit and implicit tagging of items for ease of recall and retrieval. In one aspect, an automated system is provided that facilitates concurrent searching across a plurality of information sources. A usage analyzer determines user accessed items and a content analyzer stores subsets of data corresponding to the items, wherein at least two of the items are associated with disparate information sources, respectively. An automated indexing component indexes the data subsets according to past data access patterns as determined by the usage analyzer. A search component responds to a search query, initiates a search across the indexed data, and outputs links to locations of a subset and / or provides sparse representations of the subset.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
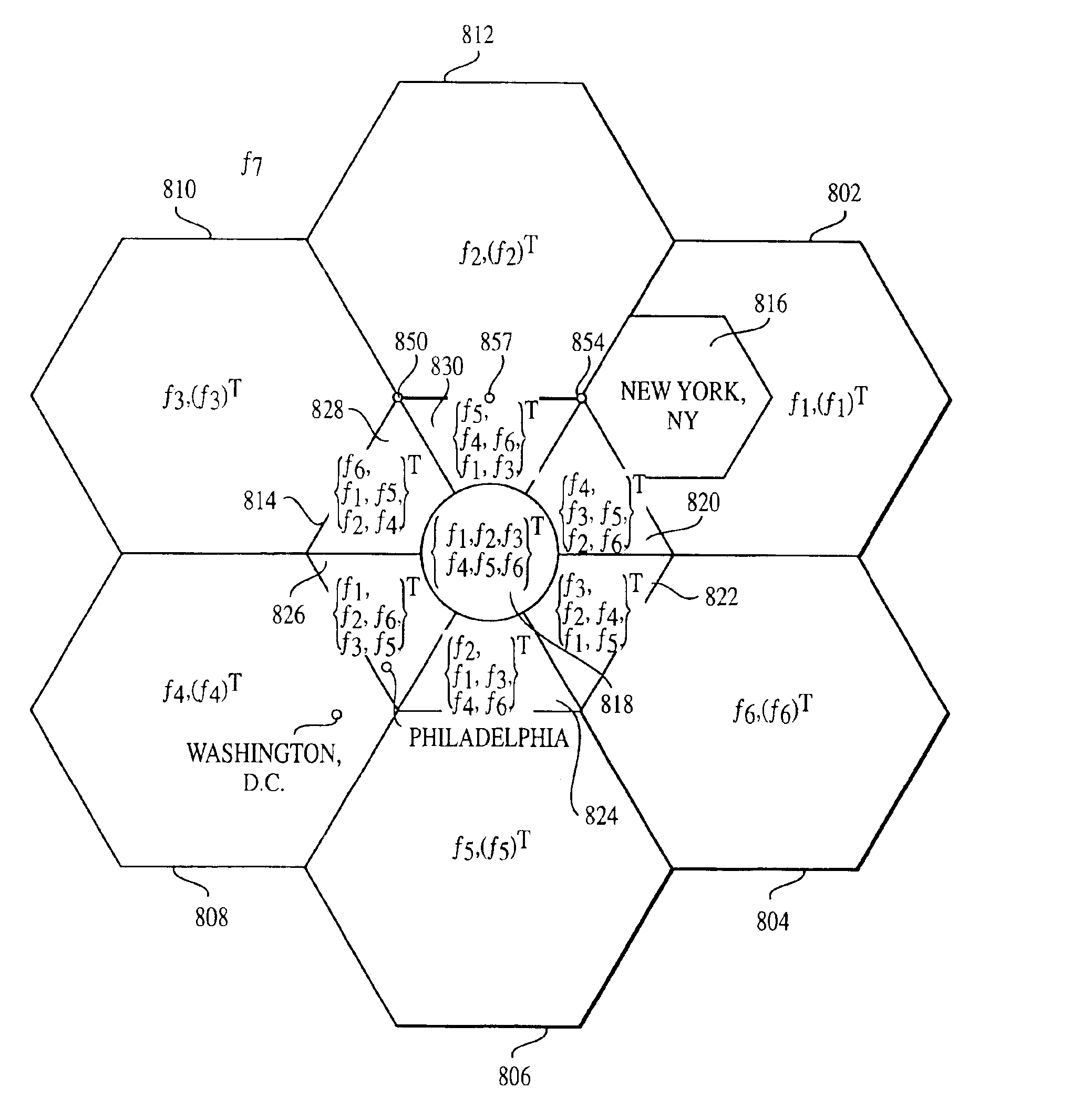
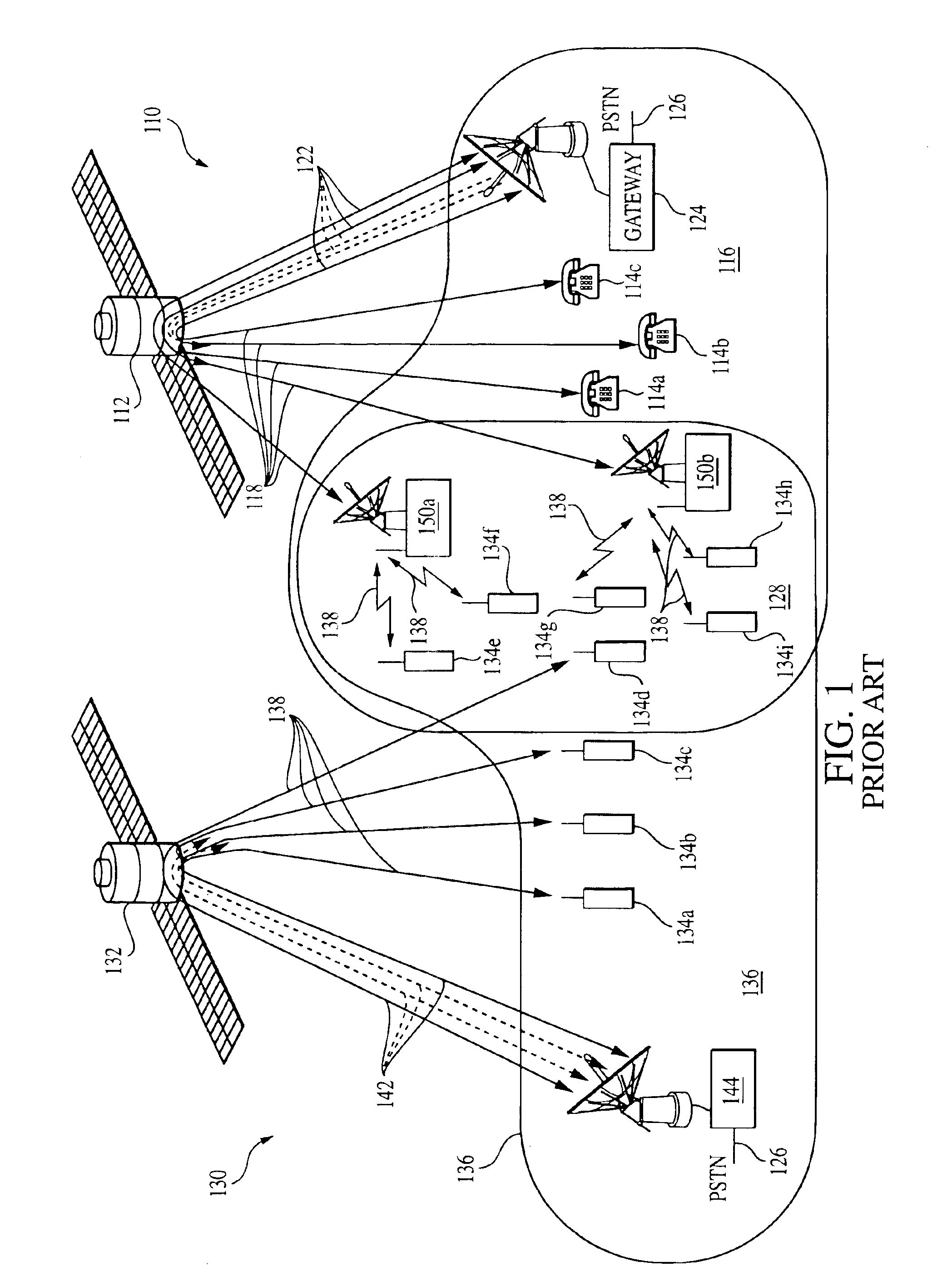
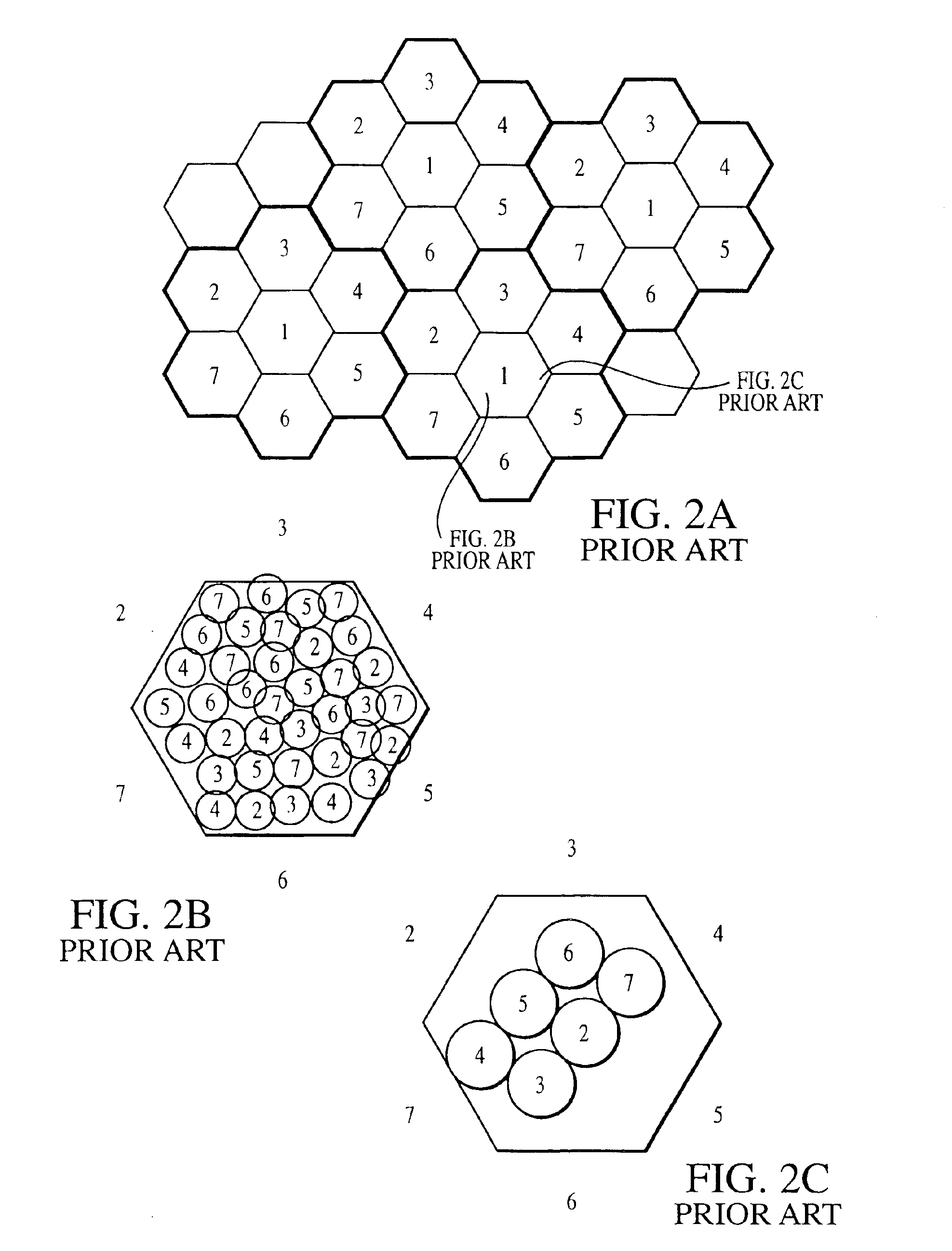
Coordinated satellite-terrestrial frequency reuse
InactiveUS6892068B2Facilitates assignmentEasy to shareRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumFrequency reuse
A system and method of operation for efficiently reusing and / or sharing at least a portion of the frequency spectrum between a first satellite spot beam and a second satellite spot beam, and / or an underlay terrestrial network associated with a second satellite spot beam. The spectrum is efficiently reused and / or shared between respective spot beams and / or associated underlay terrestrial systems in a manner minimizes interference between the respective satellite and terrestrial systems.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Battery-Powered Hand-Held Ultrasonic Surgical Cautery Cutting Device
ActiveUS20120078278A1Alter functionAlter performanceBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsProtective switchesReal-time clockElectrical battery
A battery assembly for use with a surgical device having a battery terminal and operational parameters includes a housing having a shape formed to removably connect with the terminal. The housing contains a modular battery operable to supply power to the device at the terminal and has a control circuit with a microprocessor, a memory, and a real-time clock. The control circuit is communicatively coupled to the battery and is operable to detect an identity of the surgical device, to determine at least one piece of information pertaining to at least one of the operational parameters of the surgical device based upon the detected identity, to record the piece of information at least in the memory, and to selectively allow or prevent the battery from supplying power to the surgical device dependent upon the piece of information.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Method of time multiplexing a programmable logic device
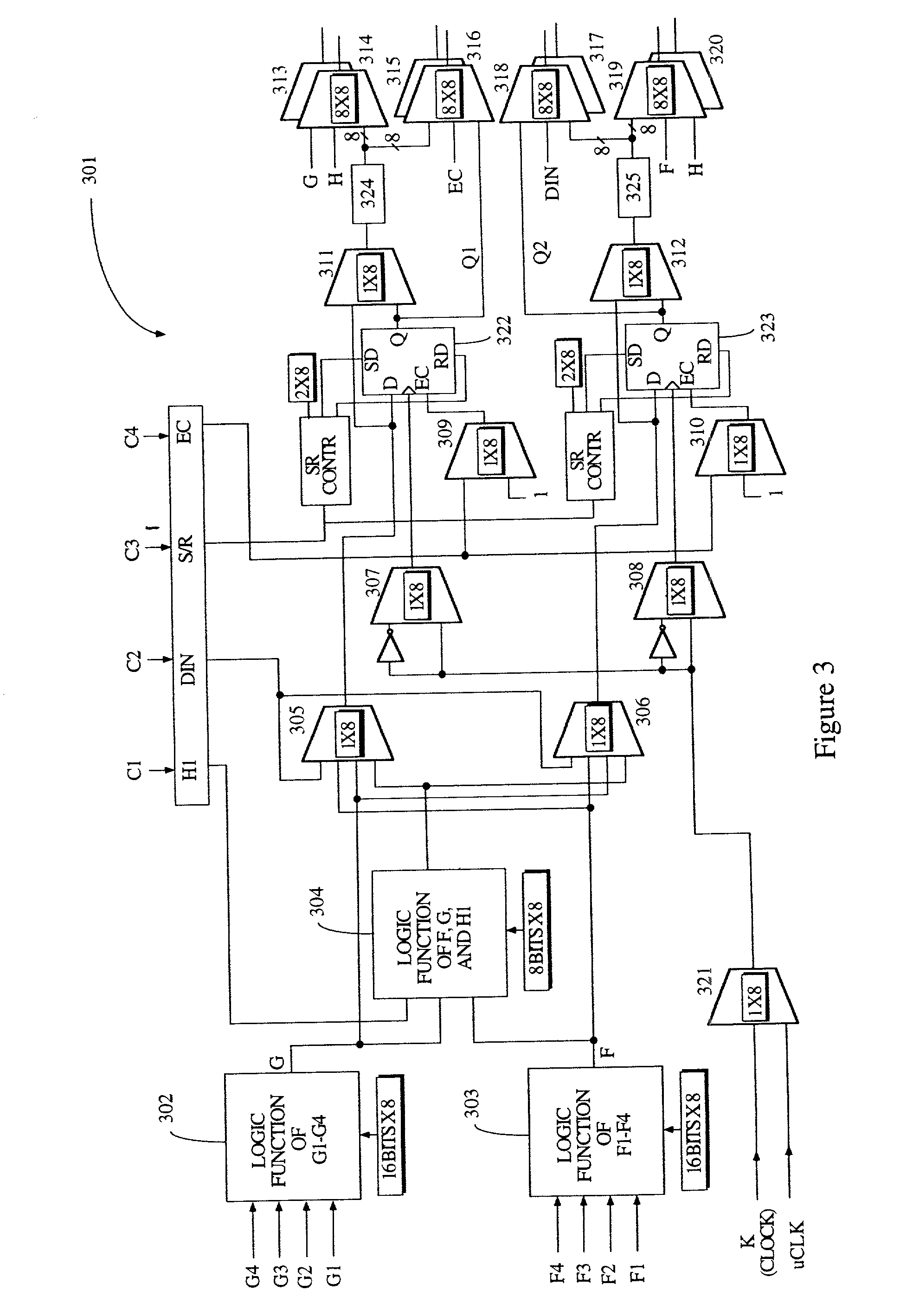
InactiveUS20020010853A1Reduce in quantityEasy to reuseDigital computer detailsData resettingProgrammable logic deviceLogic element
A programmable logic device (PLD) comprises at least one configurable element, and a plurality of programmable logic elements for configuring the configurable element(s). Alternatively, a PLD comprises an interconnect structure and a plurality of programmable logic elements for configuring the interconnect structure. In either embodiment, at least one of the programmable logic elements includes N memory cells. A predetermined one of the N memory cells forms part of a memory slice, wherein at least a portion of each slice of the programmable logic device is allocated to either configuration data or user data memory. Typically, one memory slice provides one configuration of the programmable logic device. In accordance with one embodiment, a memory access port is coupled between at least one of the N memory cells and either one configurable element or the interconnect, thereby facilitating loading of new configuration data into other memory slices during the one configuration. The new configuration data may include off-chip or on-chip data. The present invention typically allocates at least one slice to user data memory and includes means for disabling access to at least one of the N memory cells.
Owner:XILINX INC
Generic, multi-instance method and GUI detection system for tracking and monitoring computer applications
ActiveUS20070083813A1Facilitates code reuse and modular packagingPromote publicationError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsObject structureClient-side
Presented is a system and method for monitoring events derived from a computer target application presentation layer including the steps of providing, independent of recompiling the target application's source code, a script running at a level within the target application. The script scans run-time instantiations of objects of the target application, and allocates structures in real-time to the object instantiations. These allocated structures are adapted to create a reflection of the target application structure, which is used along with detected object instantiations that match a predetermined object structure to capture a portion of an environmental spectrum of the detected object. Further, the system can process state machine events occurring on at least one of a server machine and a client / localized machine, correlate the state machine events with the environmental spectrum, and deduce a user experience based on the correlated state machine events.
Owner:KNOA SOFTWARE INC
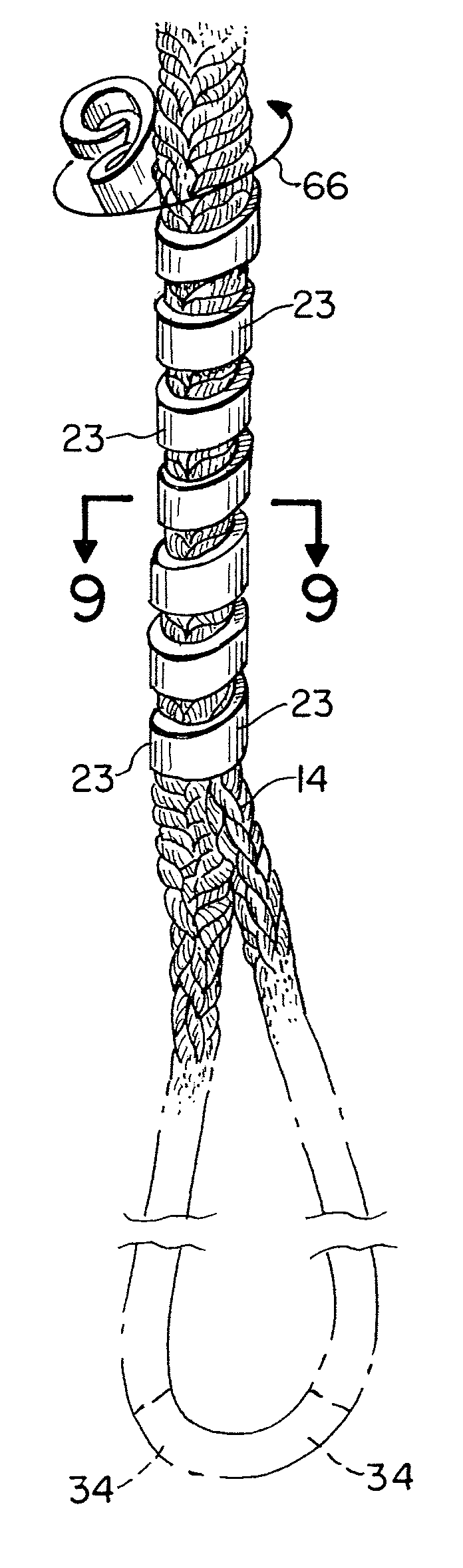
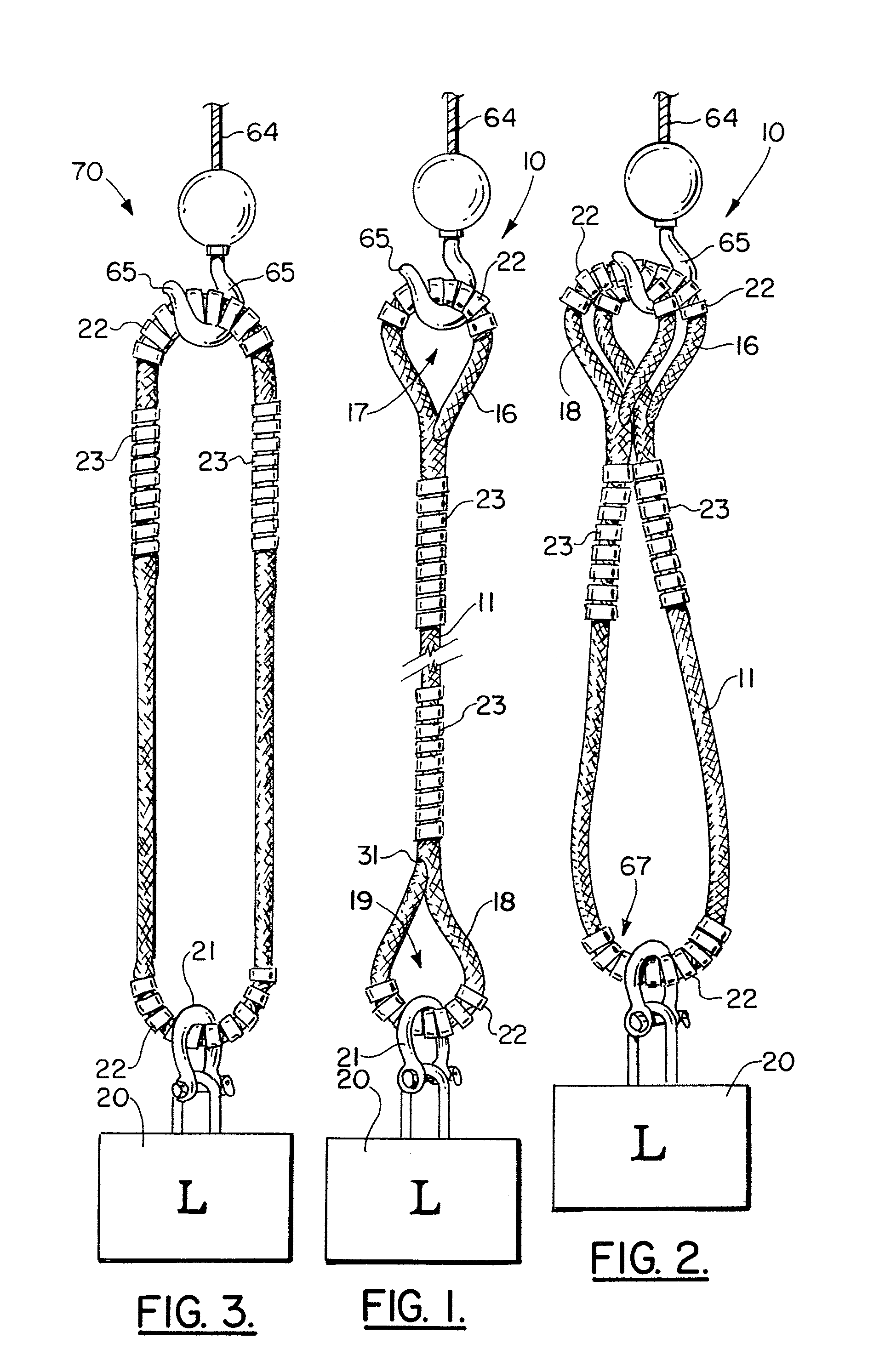
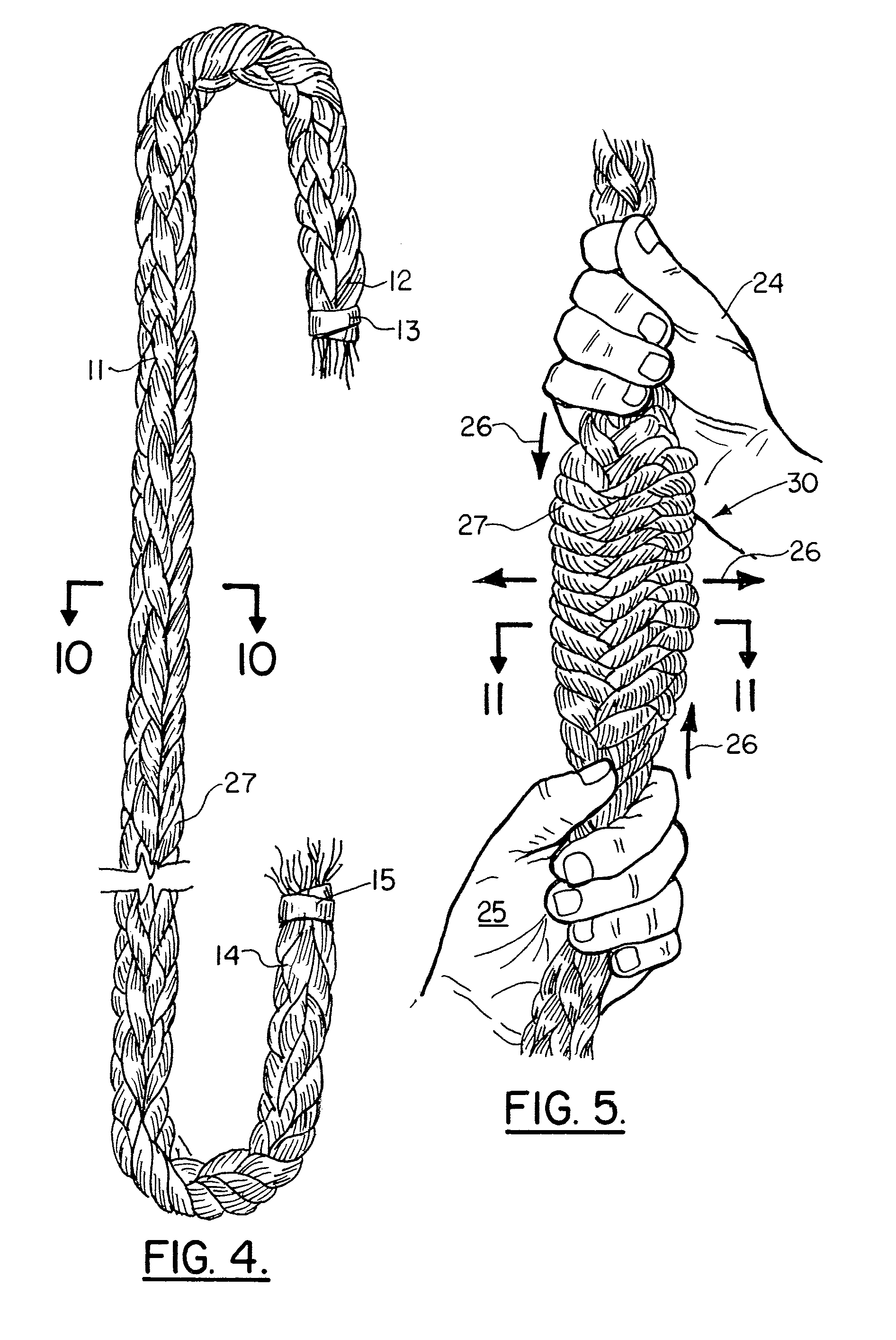
Lifting sling
ActiveUS7399018B1Avoid abrasionsPrevent rapid wearTextile cablesLoad-engaging elementsFiberEngineering
A lifting sling and a lifting grommet are disclosed which can be fabricated of a high tensile strength polymeric material, preferably a woven polymer such as liquid crystal polymer fibers, that are woven in a rope or cable configuration. The apparatus features an elongated woven material length of cable that is spliced. Plastic, preferably polyurethane spring cut tube sleeves are positioned as a grip on the splices to allow for handling in the field without concern for the splice becoming disassembled or undone. The sling and grommet of the present invention can each be provided with a clear cover spring cut tube that serves as a flexible protective cover for minimizing abrasion and maintaining the slings appearance.
Owner:VERSABAR
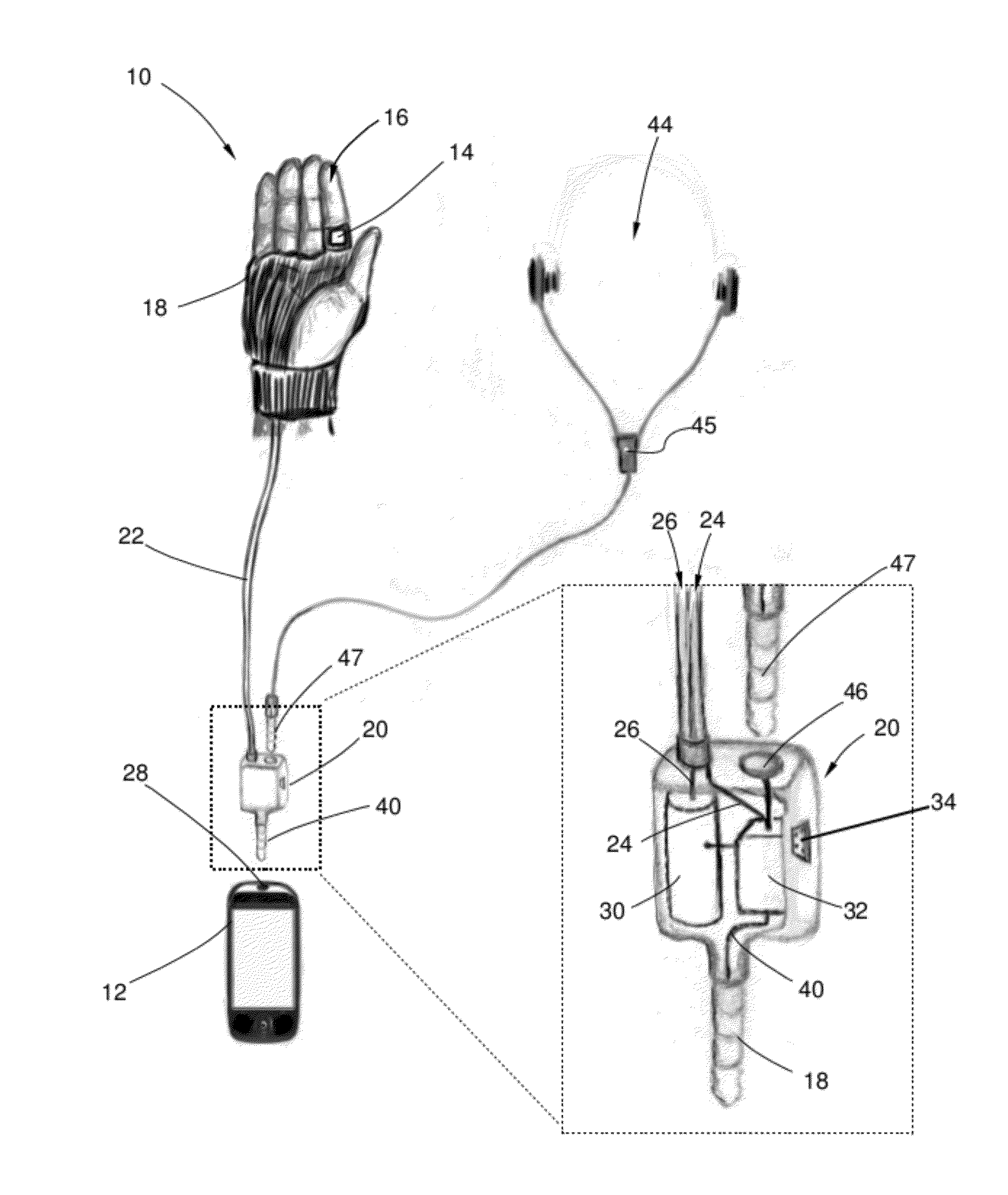
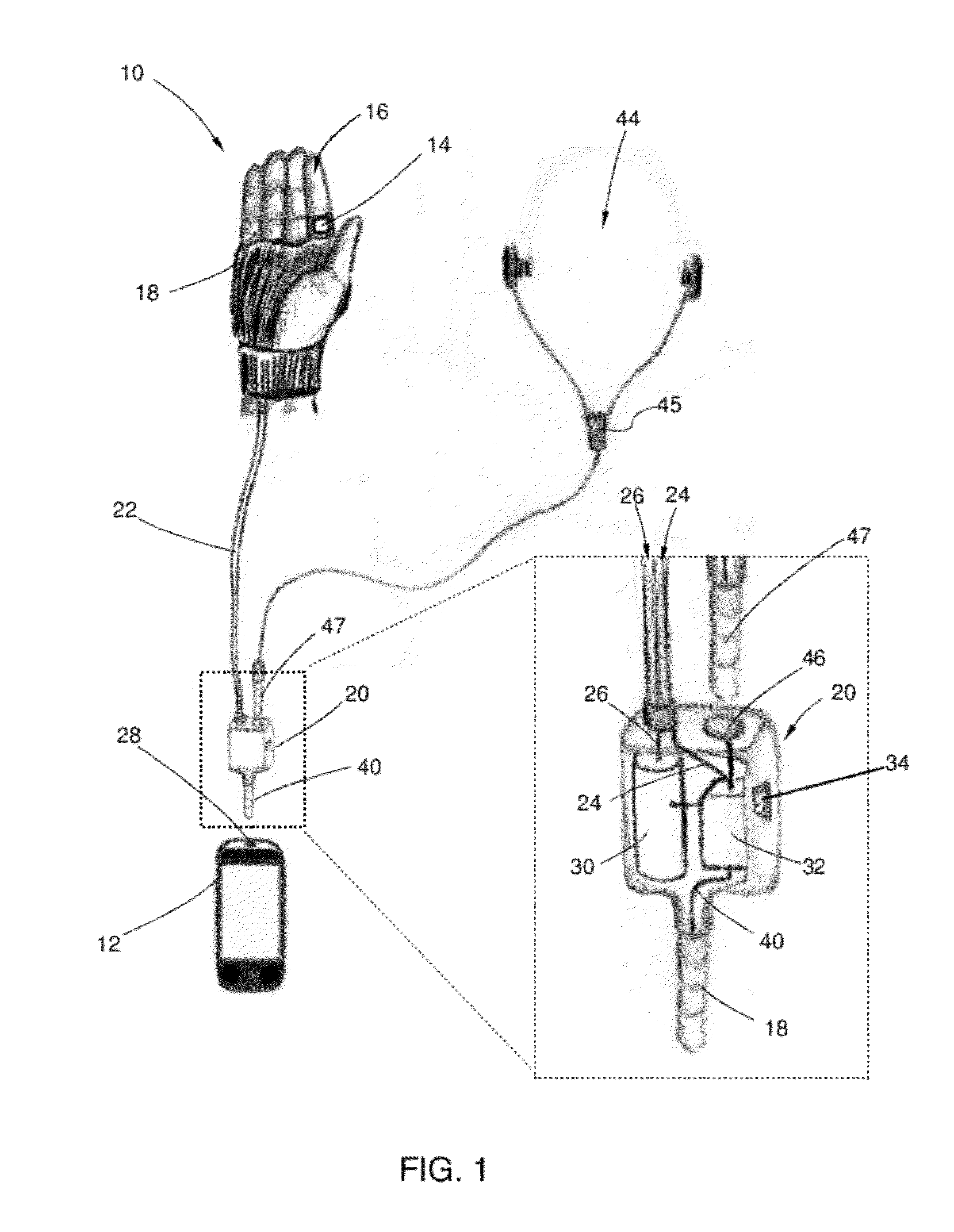
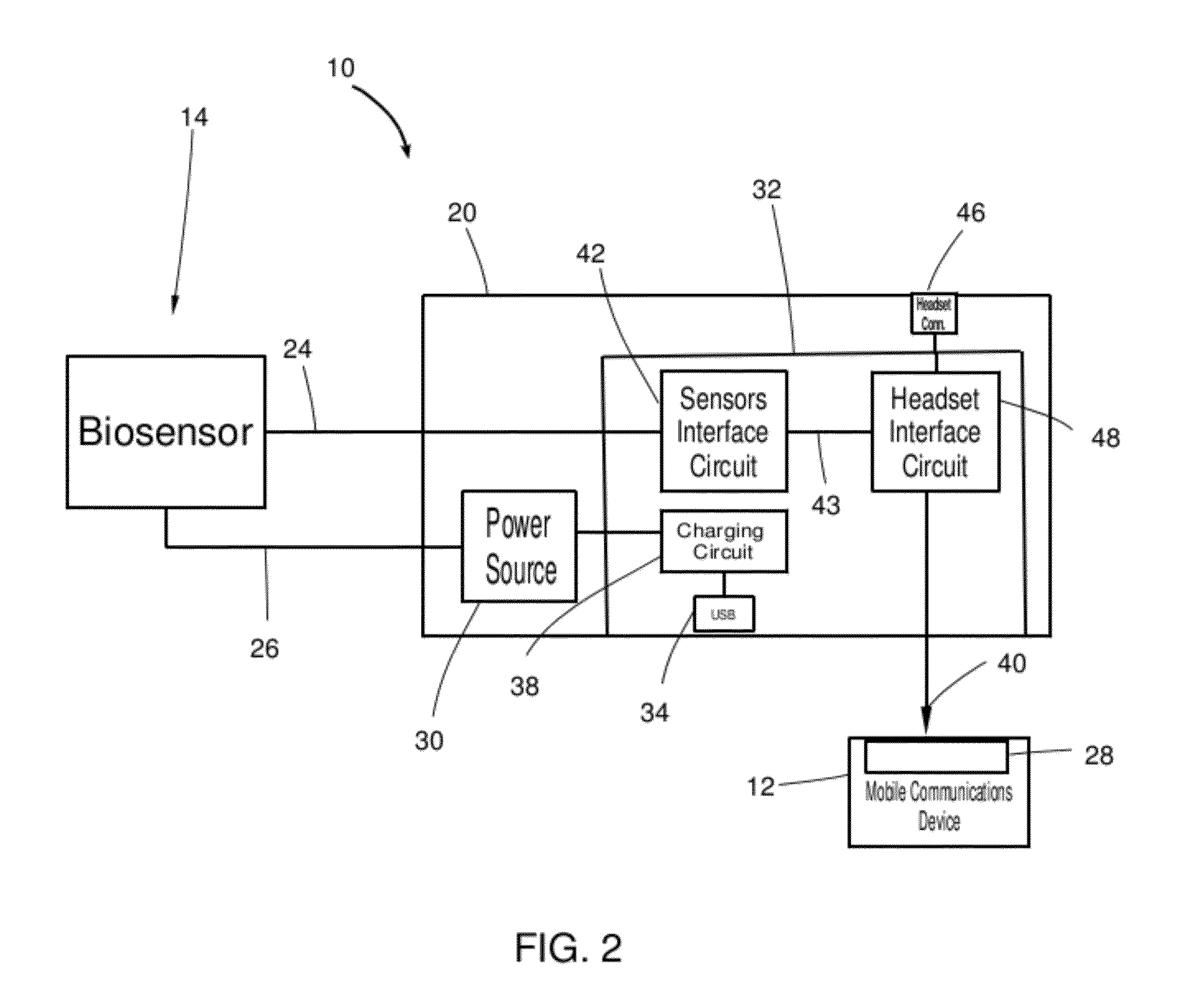
Biosensor Interface Apparatus for a Mobile Communication Device
ActiveUS20120156933A1Advanced technologySimple and inexpensiveSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersCouplings bases/casesElectricityElectrical connector
A bio sensor interface apparatus that utilizes pre-existing or standard electrical connectors of mobile devices such as smart phones, mobile media players, and tablets. The interface device transforms the input bio sensor signals to compatible electrical signals for input to one or more of the mobile's connectors. That signals are then conducted via one or more input conductors in the connectors to the mobile's microprocessor, which may display or transmit the biosensor signals and derive further measurements from them.
Owner:KALLOWS ENG INDIA PVT
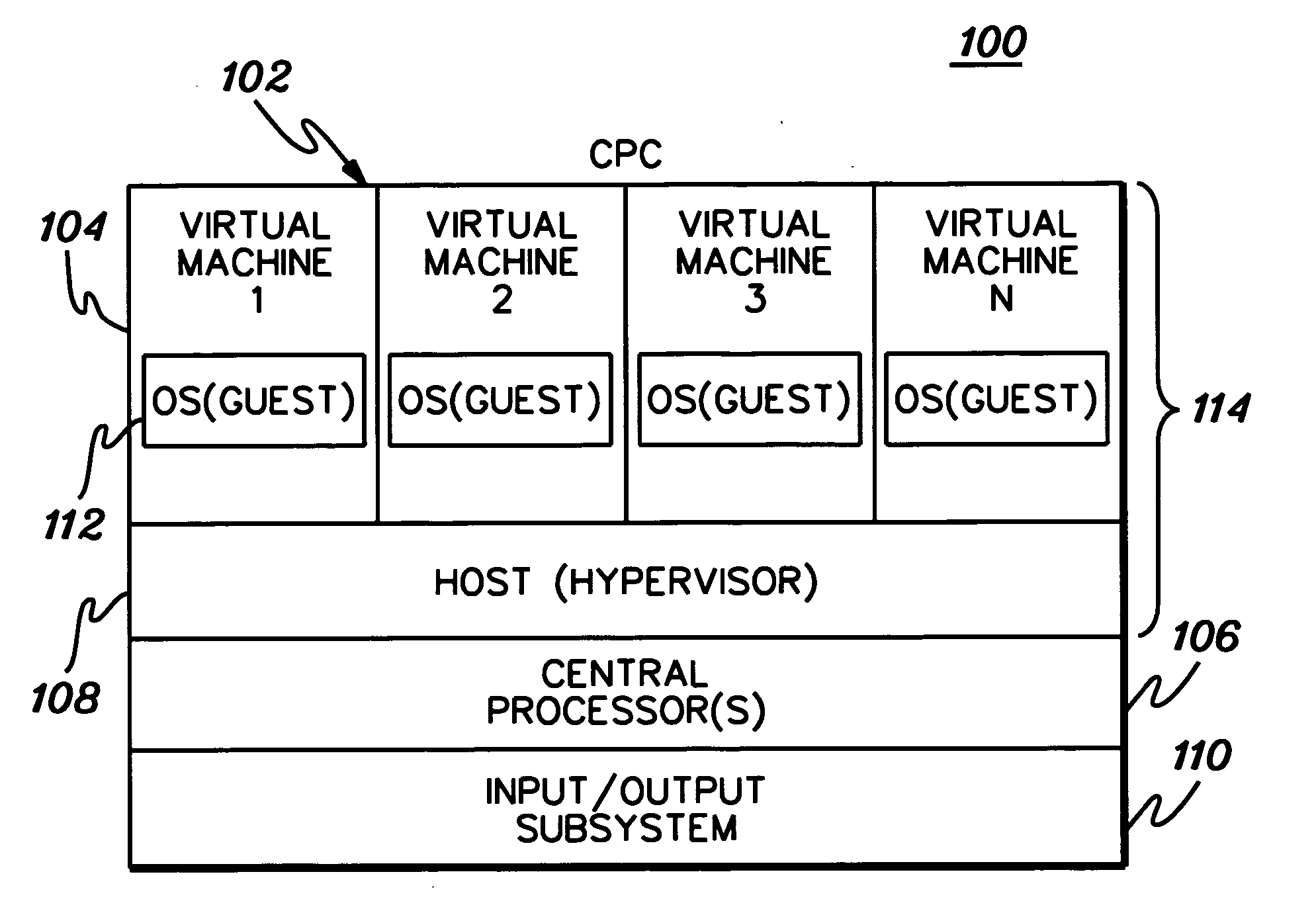
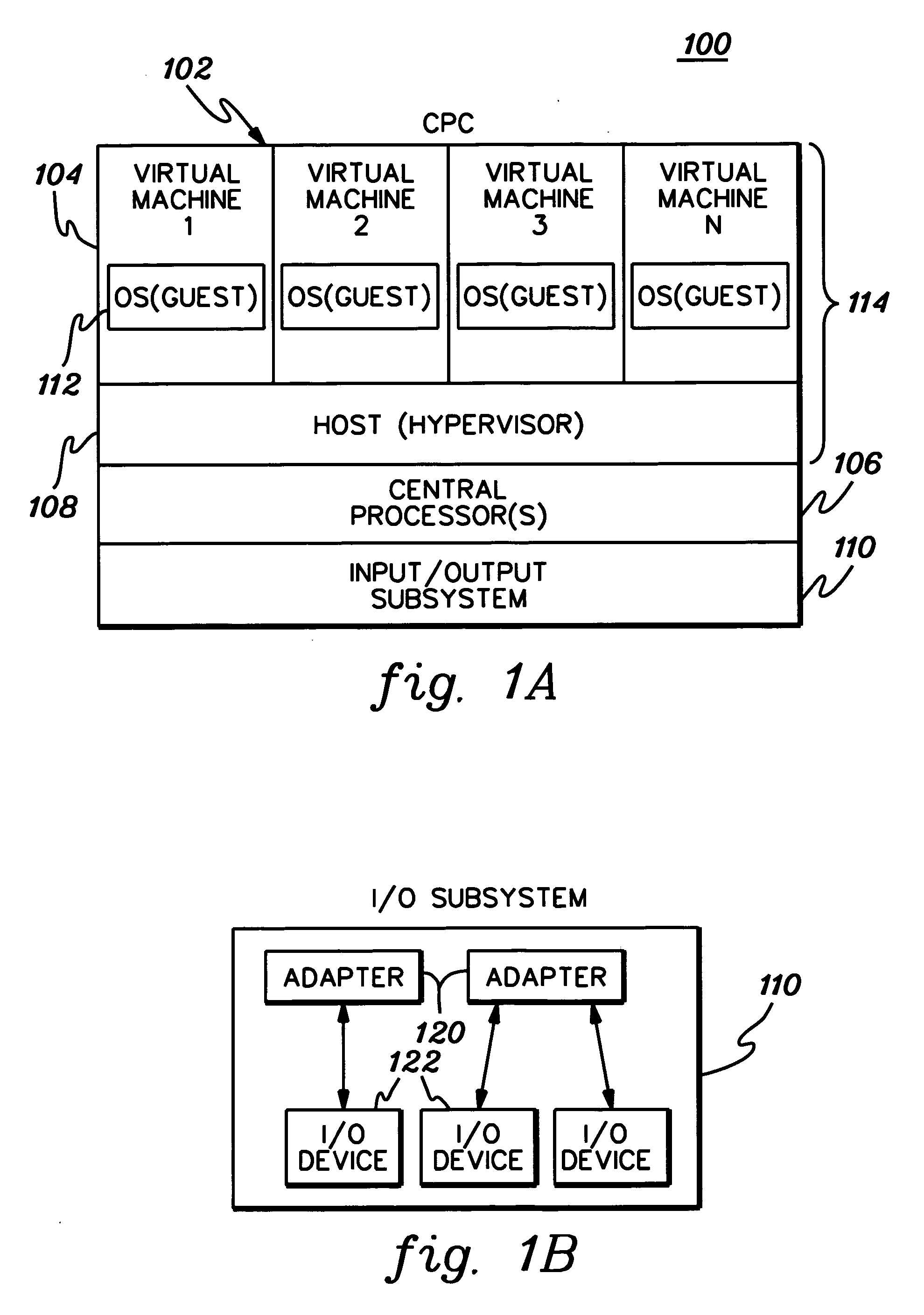
Facilitating processing within computing environments supporting pageable guests
ActiveUS20070016904A1Overcomes shortcomingEnhanced advantageMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPagingHost memory
Processing within a computing environment that supports pageable guests is facilitated. Processing is facilitated in many ways, including, but not limited to, associating guest and host state information with guest blocks of storage; maintaining the state information in control blocks in host memory; enabling the changing of states; and using the state information in management decisions. In one particular example, the guest state includes an indication of usefulness and importance of memory contents to the guest, and the host state reflects the ease of access to memory contents. The host and guest state information is used in managing memory of the host and / or guests.
Owner:IBM CORP
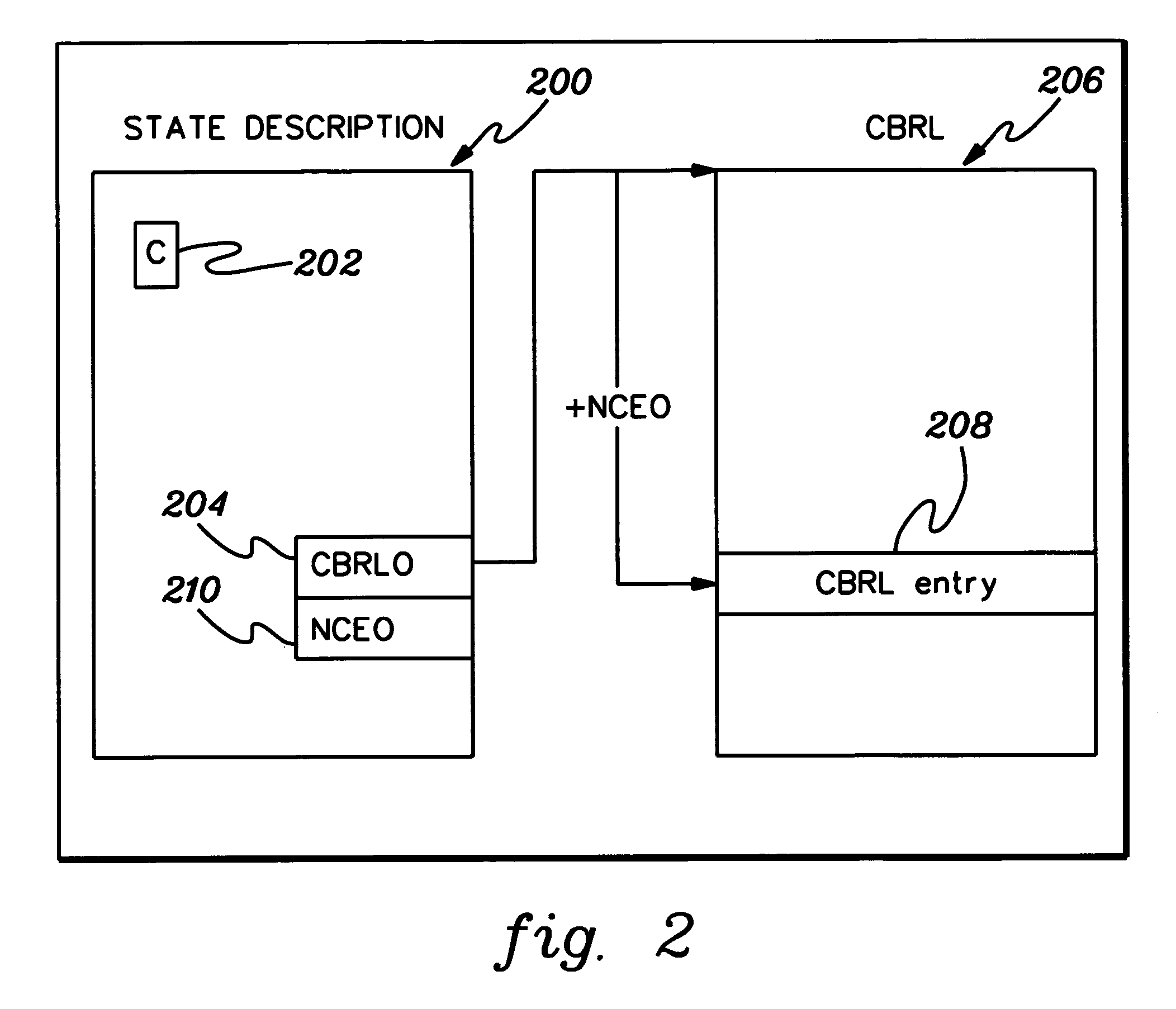
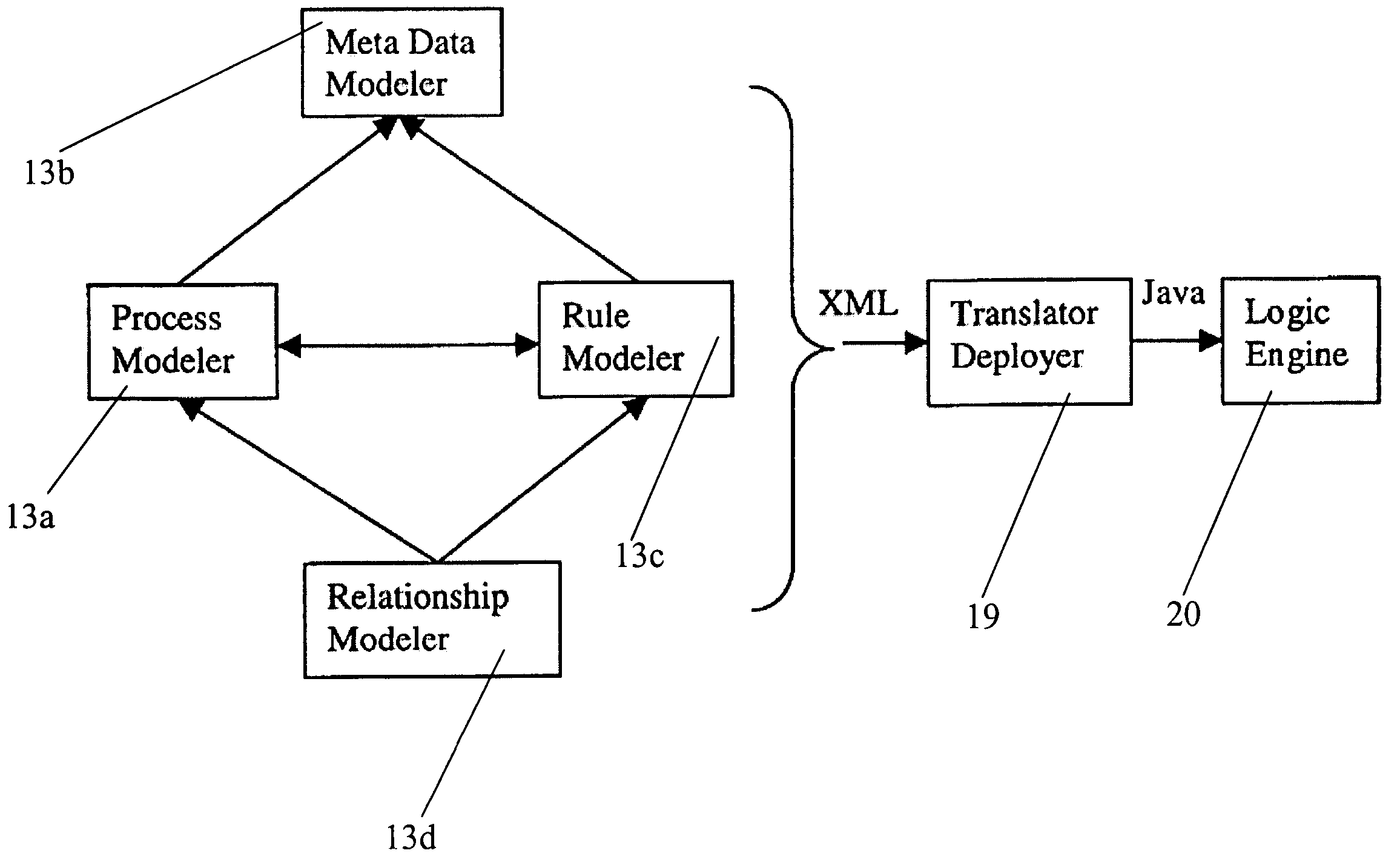
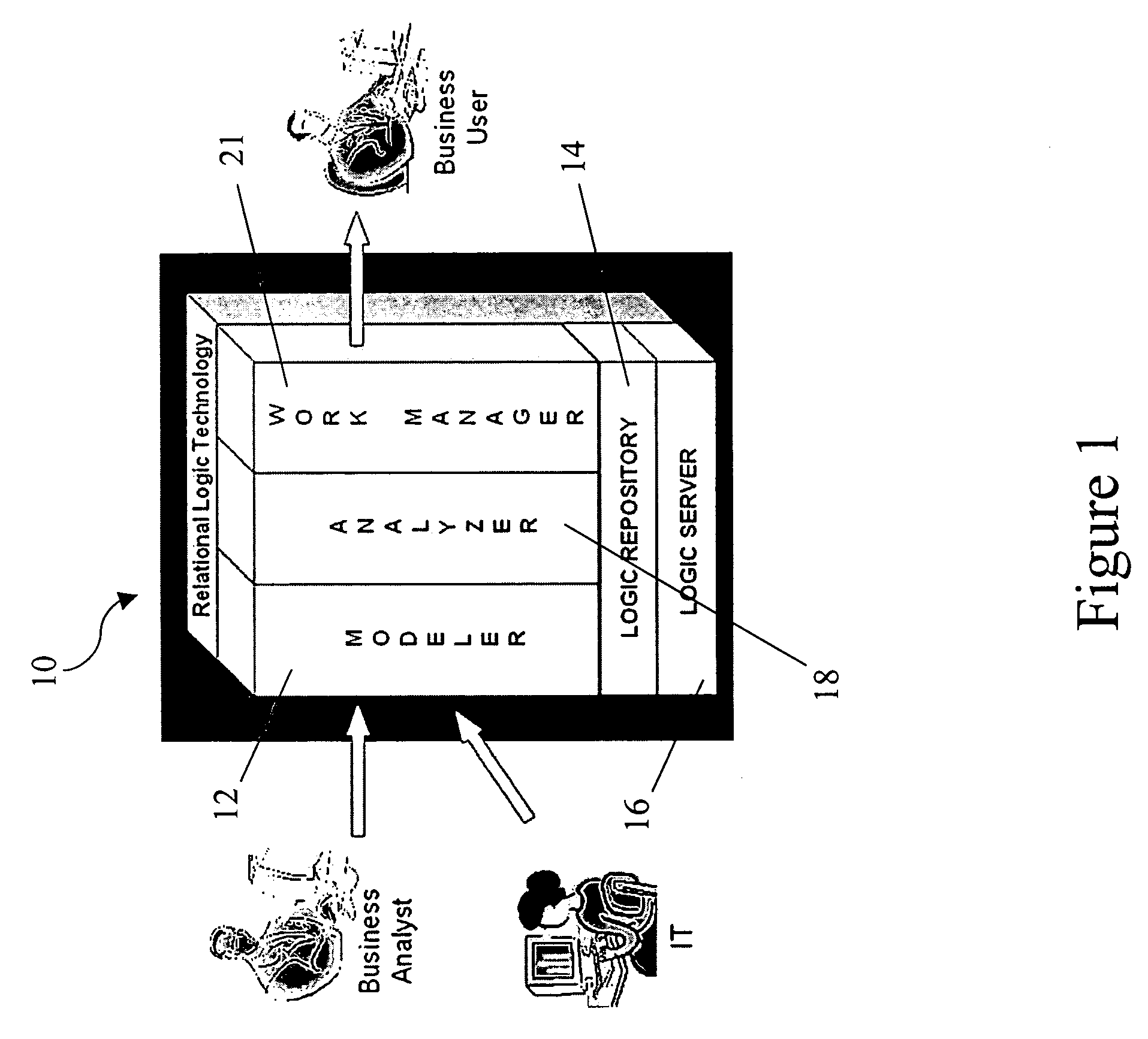
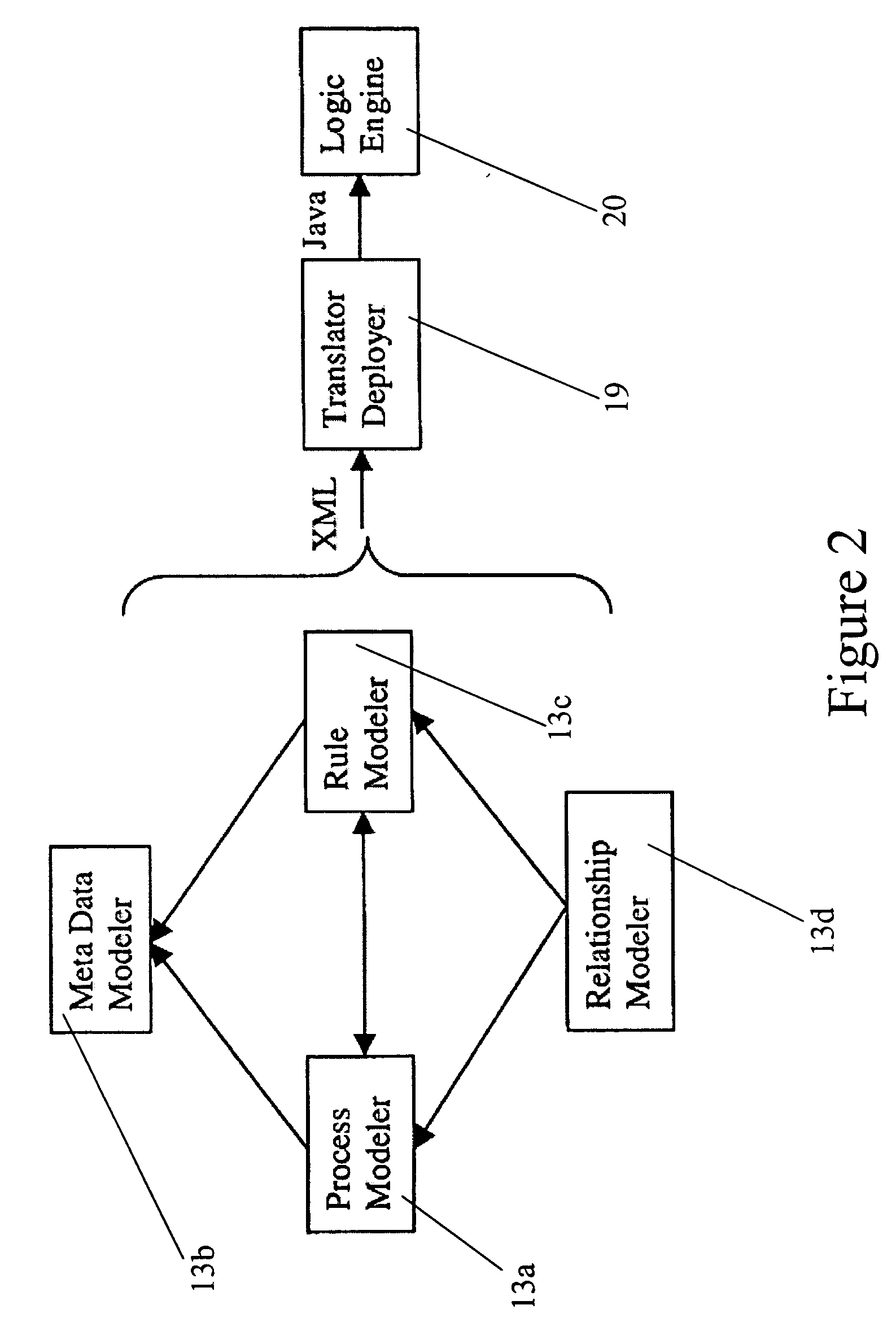
Relational logic management system
ActiveUS20050038764A1Analysis can be performedPromote reuseKnowledge representationResourcesMulti valuedMany-valued logic
In one aspect, the invention relates to a method to propagate relations between a first rule set and a second rule set wherein the first and second rule sets are invoked by a common workflow model. The method includes tracing paths forward through the workflow model from the first rule set to the second rule set. Enumerating relations that extend forward from the first rule set to the second rule set is another step in the method. Additionally, using multi-valued logic, calculating the effects on the relations of control flow through the workflow model from the first rule set to the second rule set, tracing paths backward through the workflow model from the second rule set to the first rule set, enumerating relations that extend backward from the second rule set to the first rule set, and using multi-valued logic, calculating the effects on the relations of control flow backwards through the workflow model from the second rule set to the first rule set are also steps in the method.
Owner:FAIR ISAAC & CO INC
Method of accessing data and logic on existing systems through dynamic construction of software components
InactiveUS6931623B2Easy to reuseMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftware maintainance/managementBinary informationApplication software
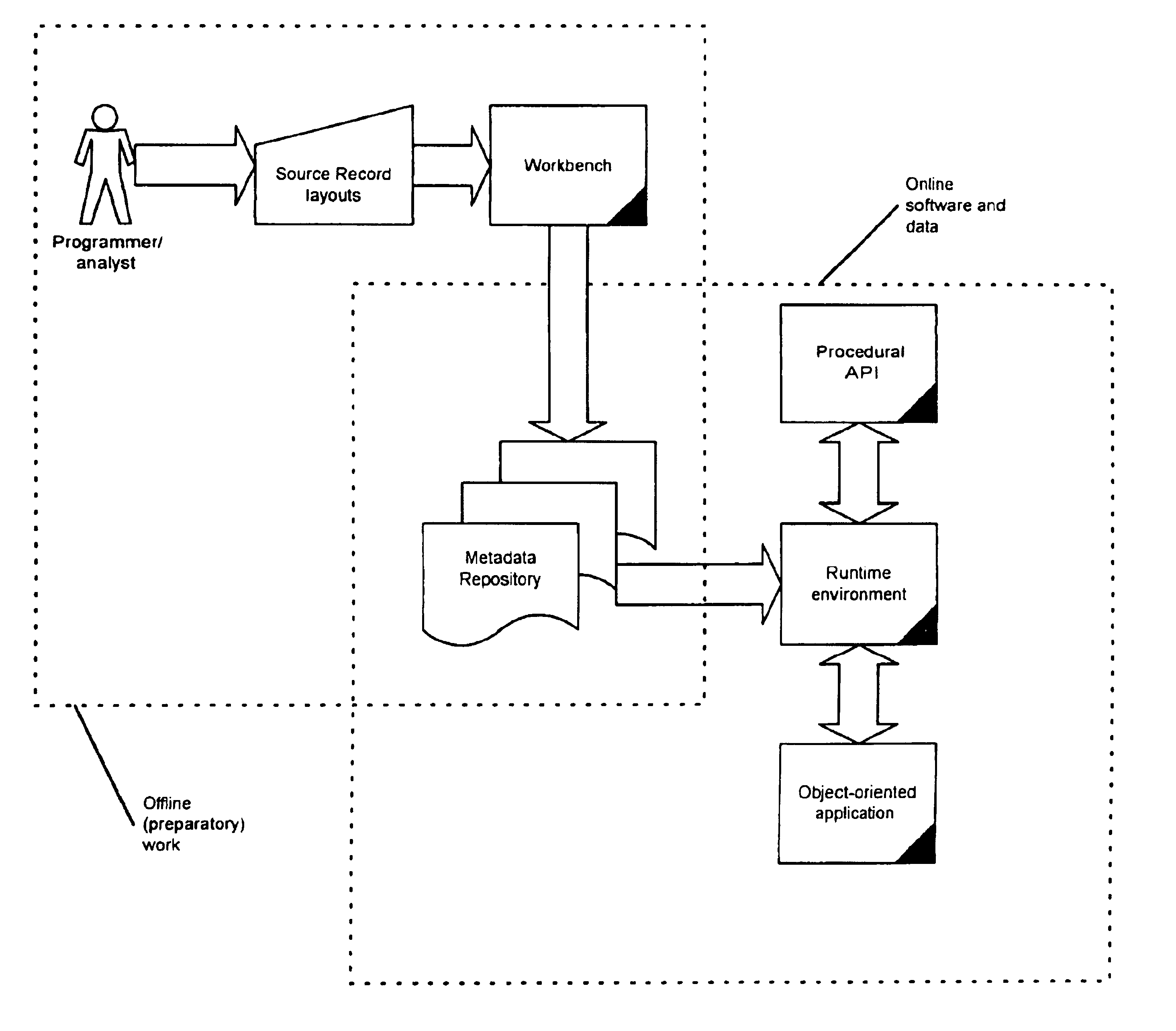
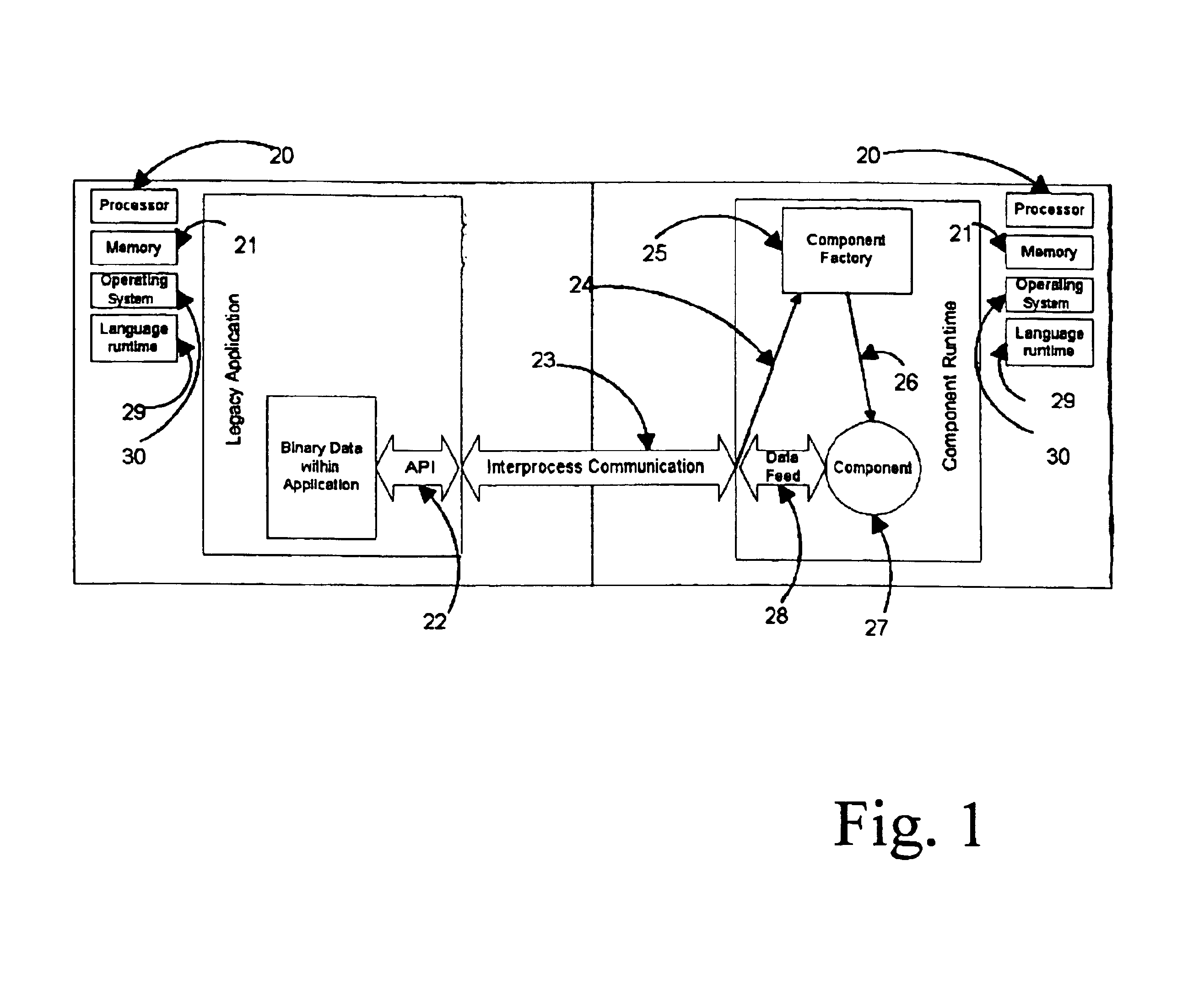
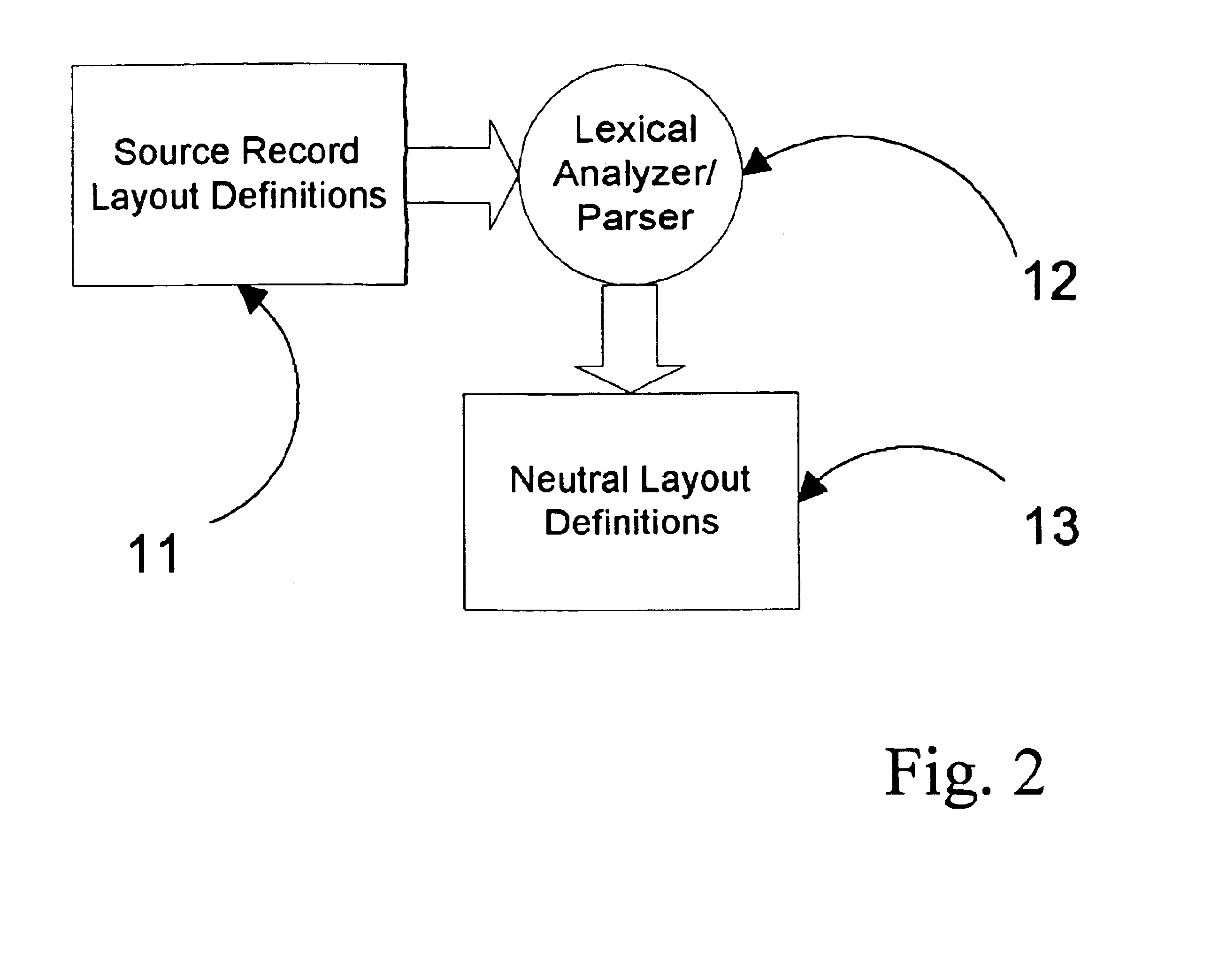
A record layout in a legacy application is defined by the record definition in the source code of the language in which the application was written. For each record in a legacy application, the layout of the record is saved in a language-neutral and architecture neutral format in preparation for a runtime invocation. During runtime, for each record, the legacy application can send architecture-specific binary information as it exists in memory on the legacy computer to a component runtime environment that will construct a compatible object-oriented instance of a class to manipulate the information. Once the information is manipulated, the updated information can be represented to the original legacy application in an architecture-specific binary record layout.
Owner:TOUCHNET INFORMATION SYST
Computer system and computer implemented process for representing software system descriptions and for generating executable computer programs and computer system configurations from software system descriptions
InactiveUS7017146B2Accurately and completely describeEasy to reuseSoftware designSpecific program execution arrangementsArchitecture description languageSoftware system
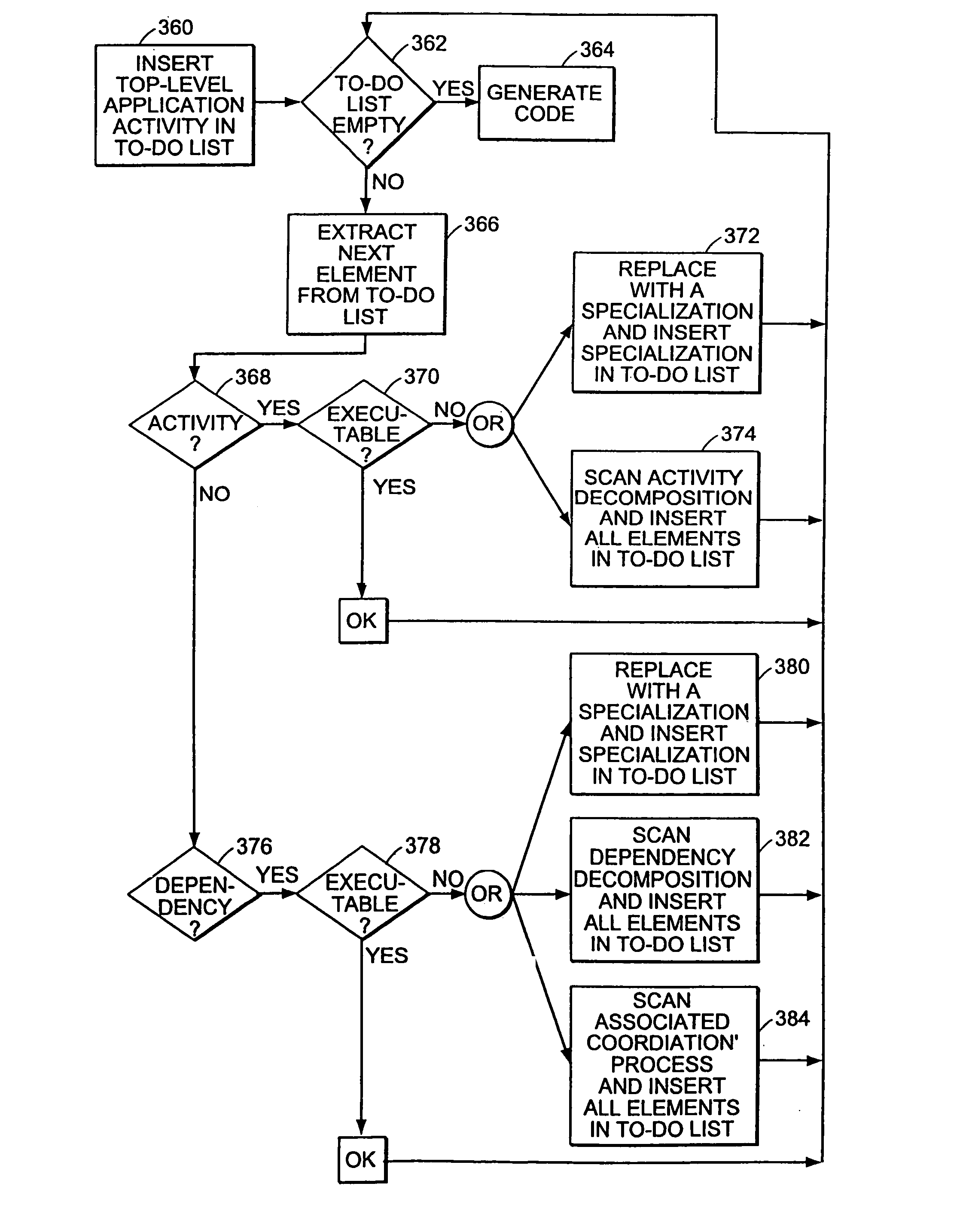
A computer-implemented method for automatically generating computer code for a software system from a representation of the software system. An architectural description language is used to represent activities and dependencies between activities as separate entities. Dependencies are managed by coordination processes associated with the dependency. Activities and dependencies are connected through ports which encode interfaces between activities and coordination processes. At least one associated computer program is identified for each activity and dependency for implementing the activity or managing the dependency, wherein the representation is defined by activities, dependencies and ports through which activities are connected to dependencies. The associated computer programs are combined to provide the computer code for the software system.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
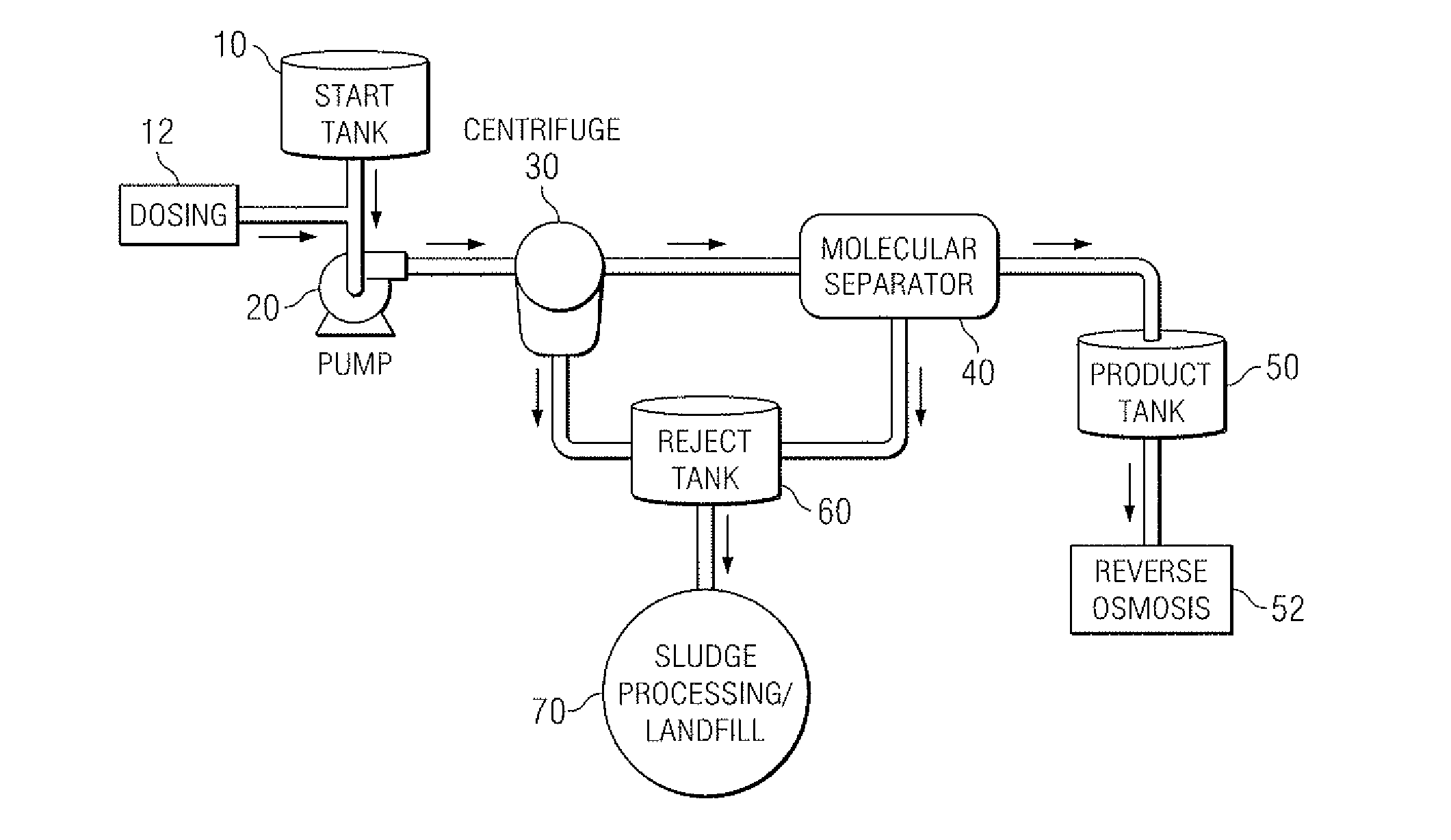
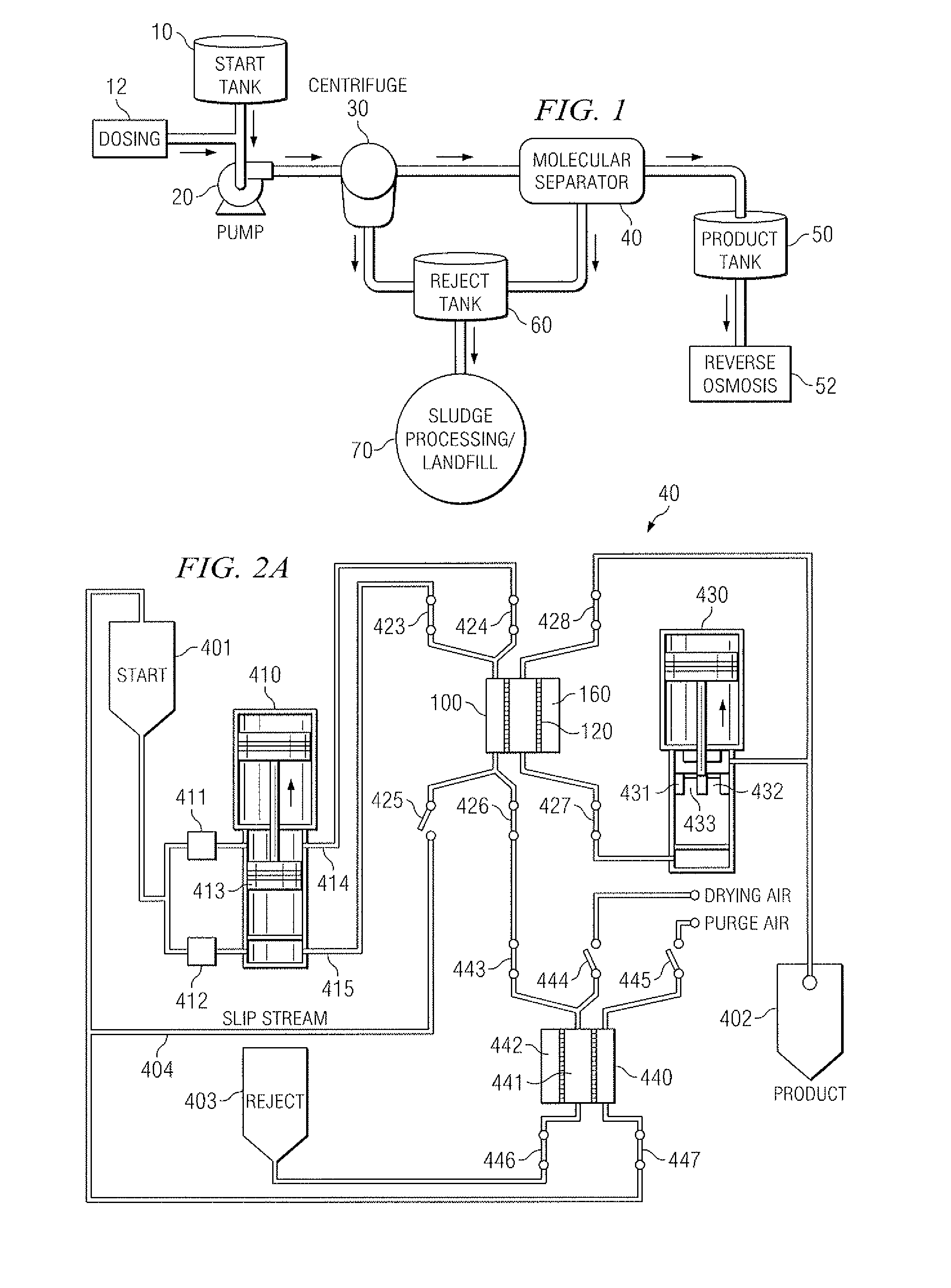
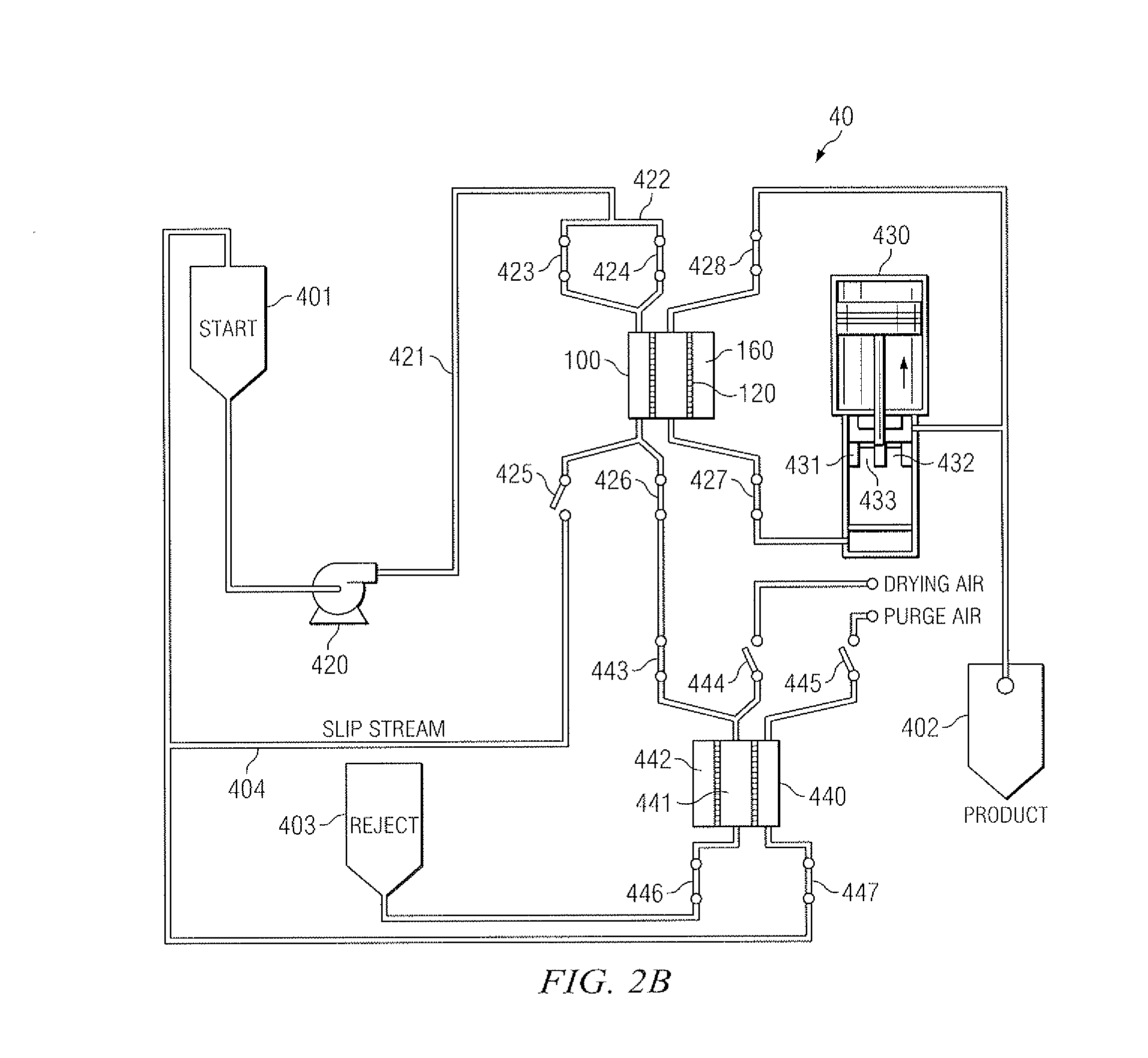
Produced water treatment method and apparatus
InactiveUS20080156709A1Improve filtration efficiencyEnhanced cavitationUltrafiltrationLoose filtering material filtersCavitationWaste collection
The present invention discloses a method and apparatus for separating particles and dissolved matter from a produced water fluid stream. Specifically, the present invention includes a first pressure source which transports untreated produced water or contaminated aqueous fluid into a separator annulus with a filter element disposed therein. The untreated fluid is placed under appropriate pressure sufficient to produce turbulent flow, increased particle kinetics and / or cavitation allowing the desired fluid to penetrate and pass into and through the filter media. The treated fluid is then transported to a collection tank. The contaminant matter retained by the filter media may be removed by the nearly instantaneous reverse pressurization of the separator annulus by a second pressure source thereby removing the contaminant particles away from contact with the filter media, and which may then be transported to a waste collection tank or a separator for further treatment.
Owner:TERVITA +1
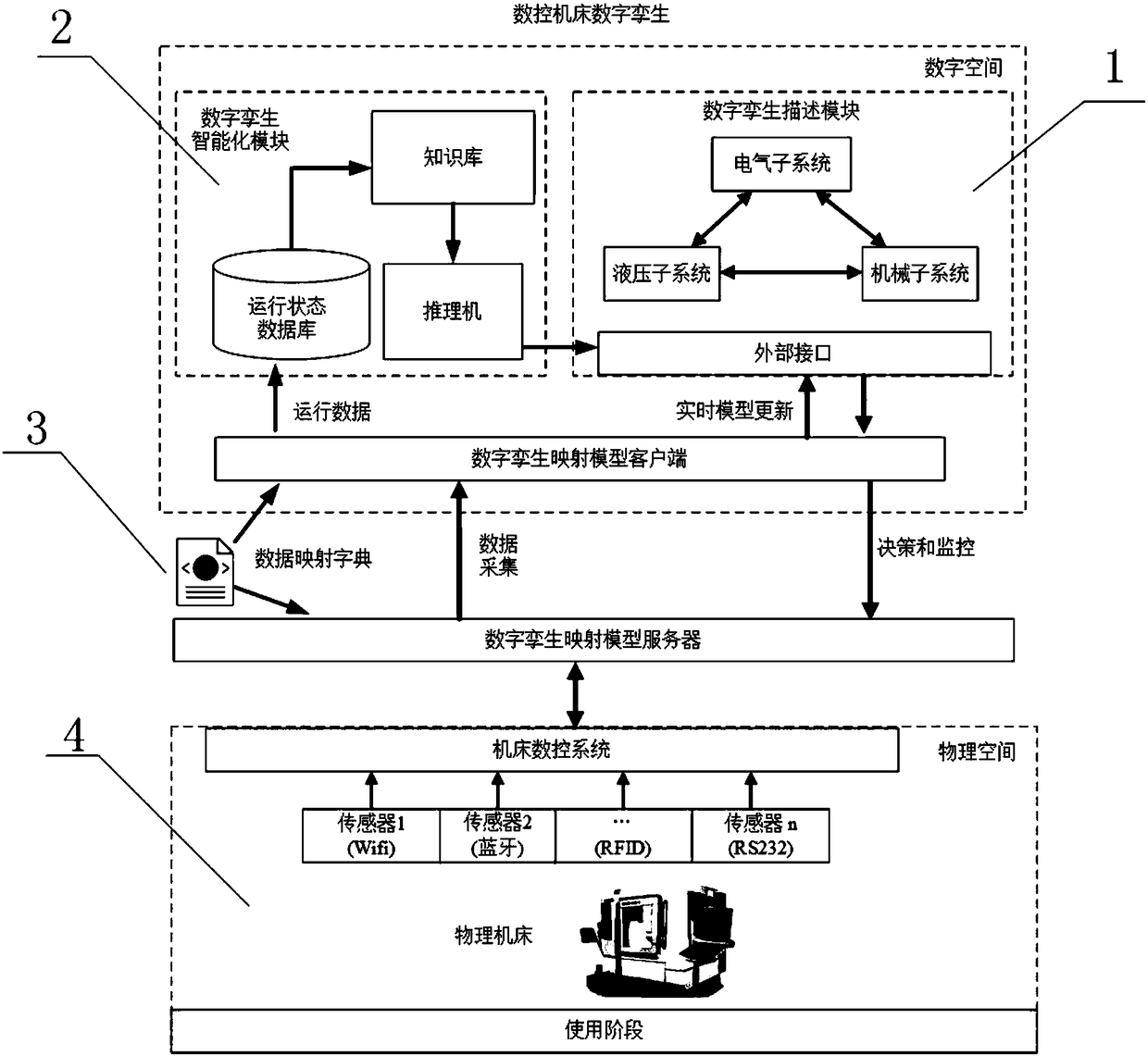
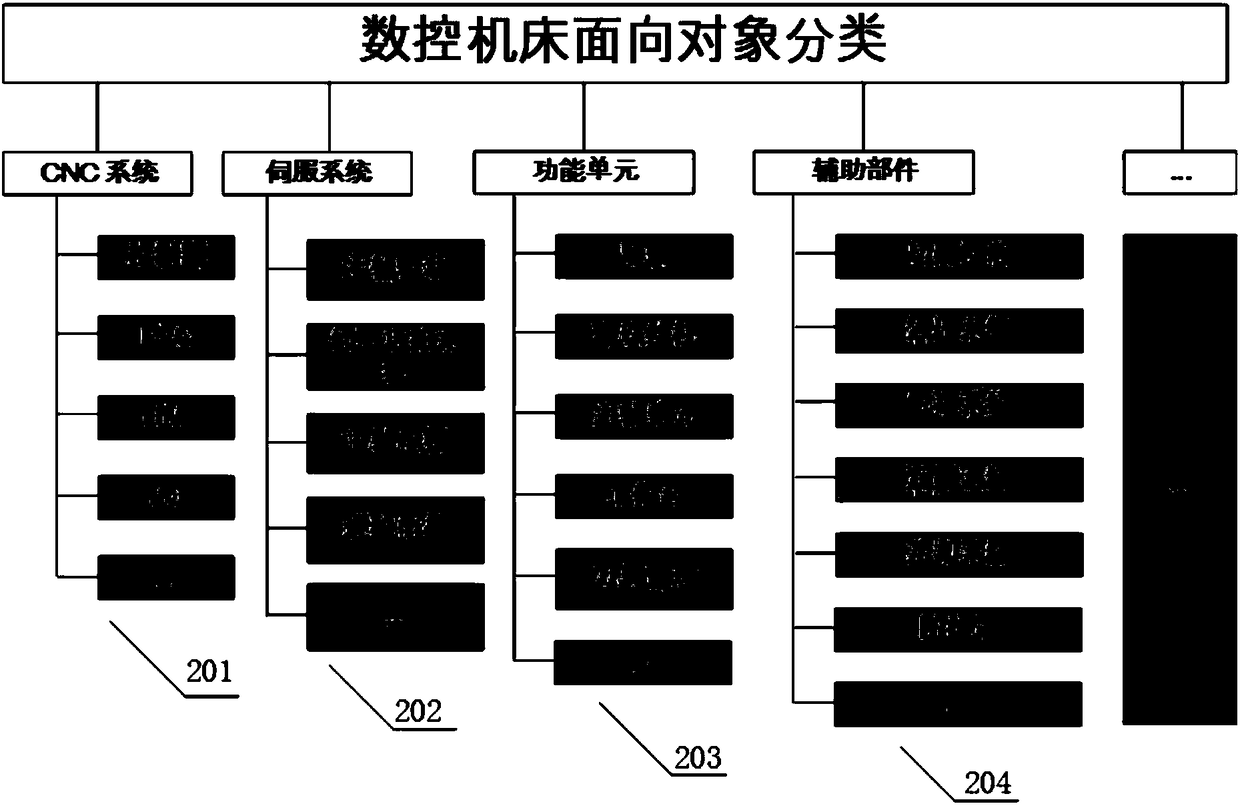
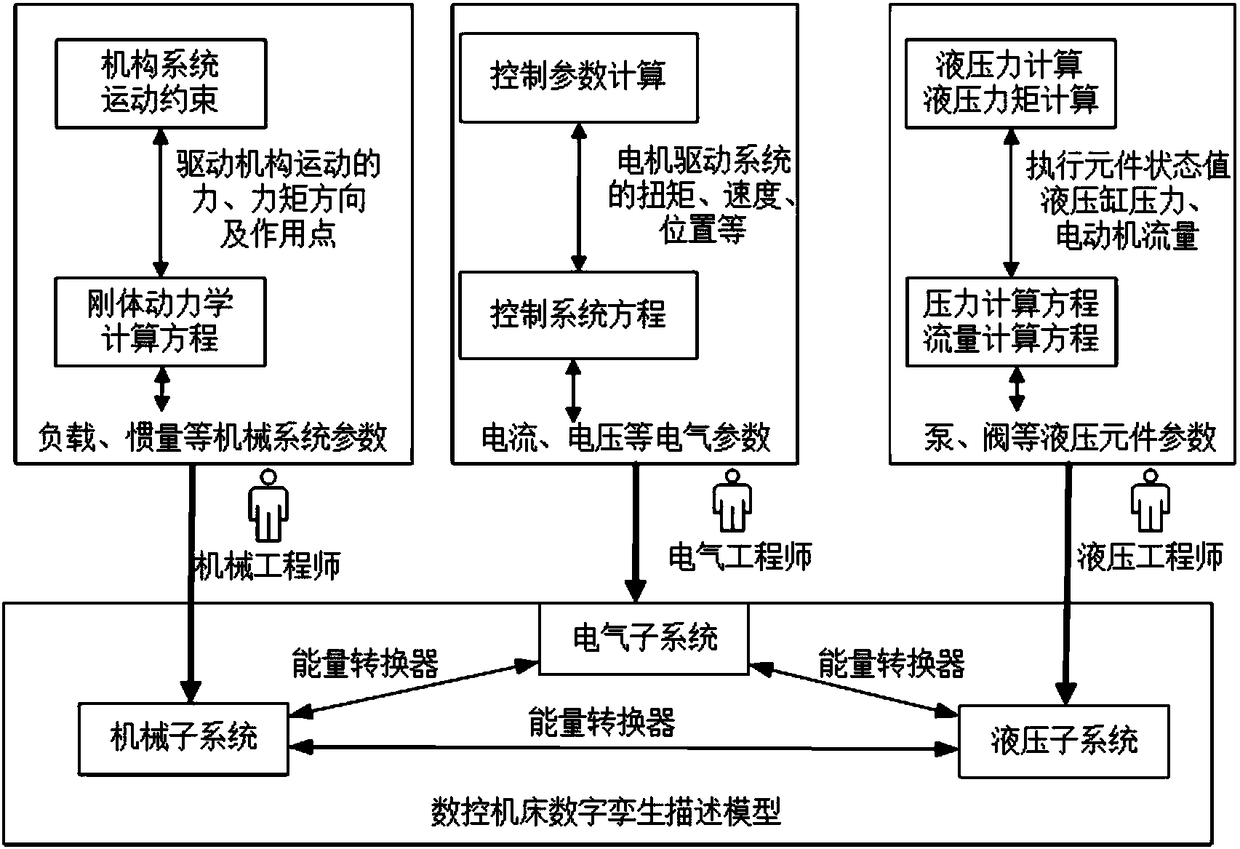
Numerical control machine tool digital twinning modeling method
ActiveCN108107841AConducive to reuseRich data scalabilityProgramme controlComputer controlMulti fieldDynamo
The present invention relates to a numerical control machine tool digital twinning modeling method. A physical space, a digital twinning digital space and a digital twinning mapping model are provided. The digital twinning digital space is connected with the physical space through the digital twinning mapping model; a data sensor is installed on a numerical control machine tool, the data sensor isconnected with a numerical control system through different data interfaces, the numerical control system performs related data collection and protocol analysis through the digital twinning mapping model; the digital twinning digital space comprises a digital twinning description model and a digital twinning intelligent model, and the digital twinning intelligent model achieves intelligent service of numerical control machine tool digital twinning through data analysis and decision. The modeling method employs multi-field uniform modeling language Modelica to allow the established digital twinning description model to have features of multi-field uniform modeling, mathematics equations and object-orientation, and can more really reflect the constitutive relation of a complex dynamo-electric system.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Metabolic measurements system including a multiple function airway adapter
InactiveUS20070225612A1Easy to reusePromote generationRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsAnesthetic AgentRespiratory flow
A system for measuring a metabolic parameter. The system includes an integrated airway adapter capable of monitoring any combination of respiratory flow, O2 concentration, and concentrations of one or more of CO2, N2O, and an anesthetic agent in real time, breath by breath. Respiratory flow may be monitored with differential pressure flow meters under diverse inlet conditions through improved sensor configurations which minimize phase lag and dead space within the airway. Molecular oxygen concentration may be monitored by way of luminescence quenching techniques. Infrared absorption techniques may be used to monitor one or more of CO2, N2O, and anesthetic agents.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
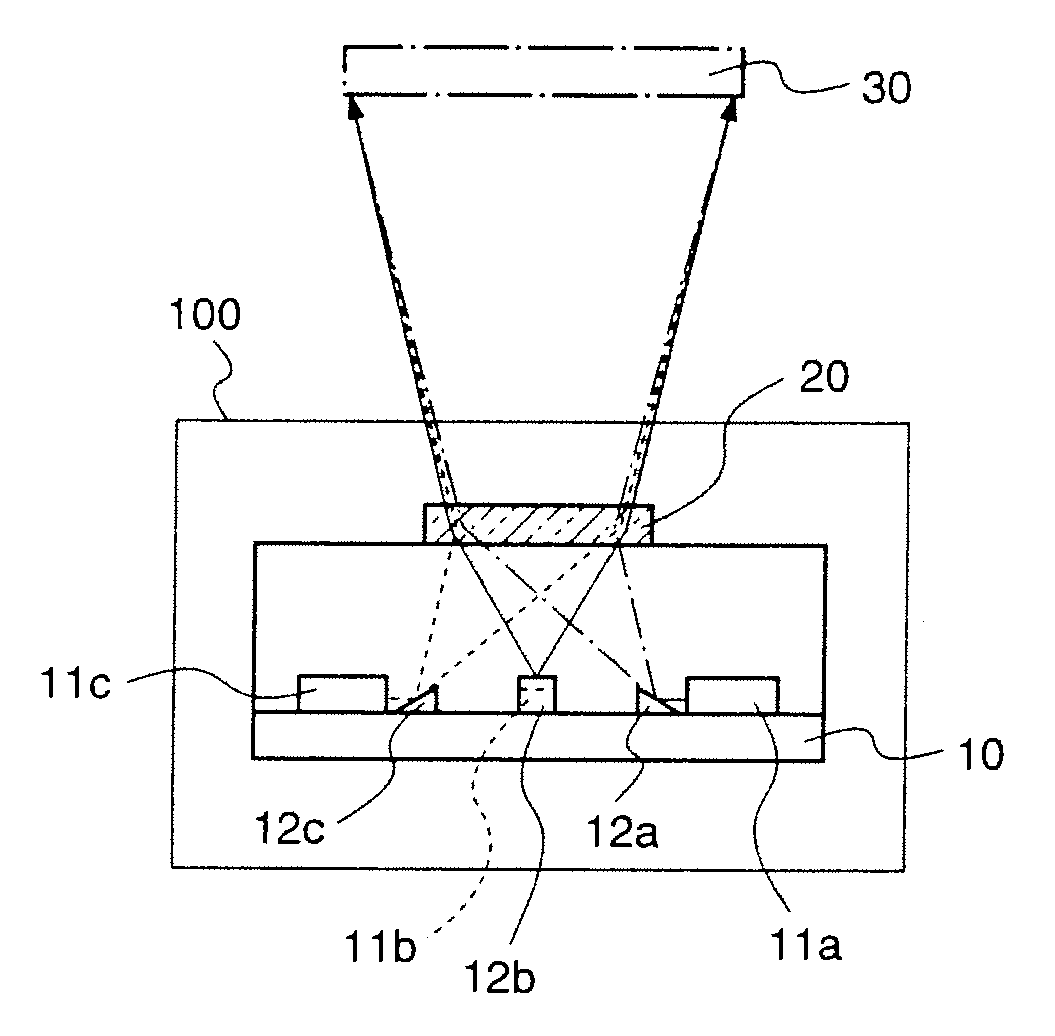
Light source device, and two-dimensional image display device
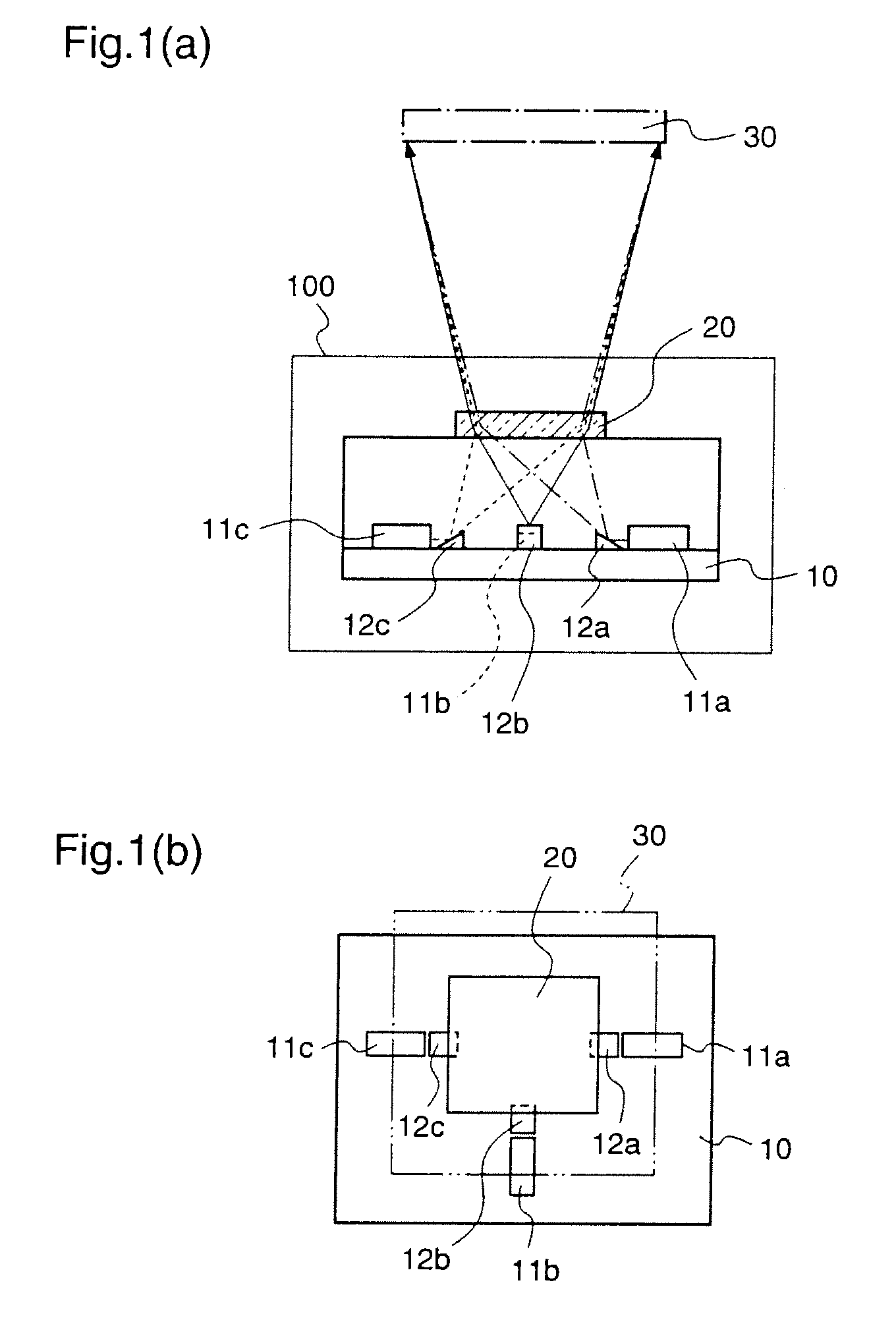
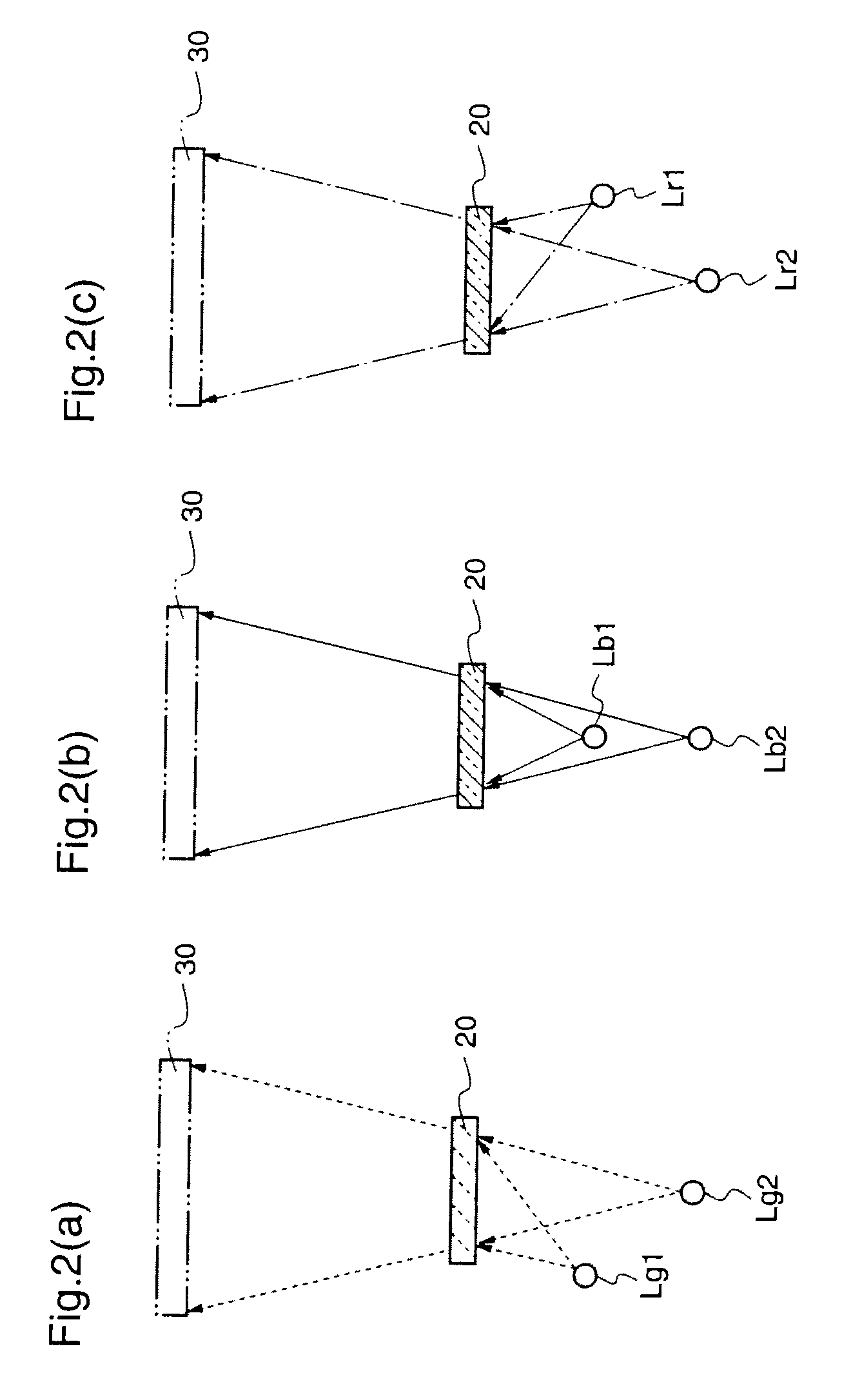
There is provided a light source device which can miniaturize a two-dimensional image display device as small as possible. The light source device is provided with three coherent light sources (11a), (11b), and (11c) corresponding to red, blue, and green; prisms (12a) and (12c) for reflecting lights emitted from the coherent light sources (11a) and (11c); and a diffraction part (20) comprising a single volume hologram on which plural gratings are multiply-formed, which gratings diffract the light emitted from the coherent light source (11b), and the lights that are emitted from the coherent light sources (11a) and (11c) and reflected by the prisms (12a) and (12b) so that these lights propagate in the same optical path.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
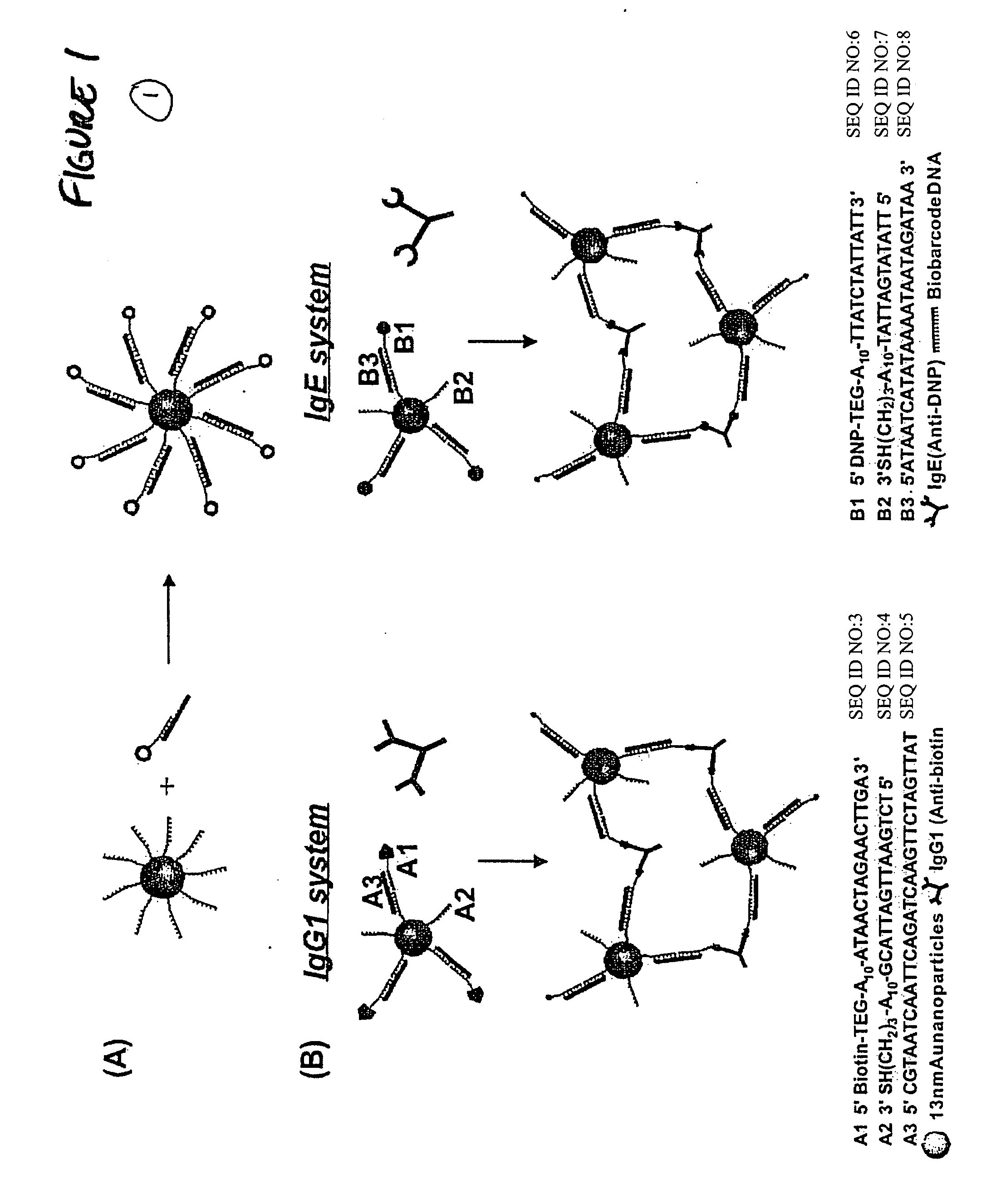
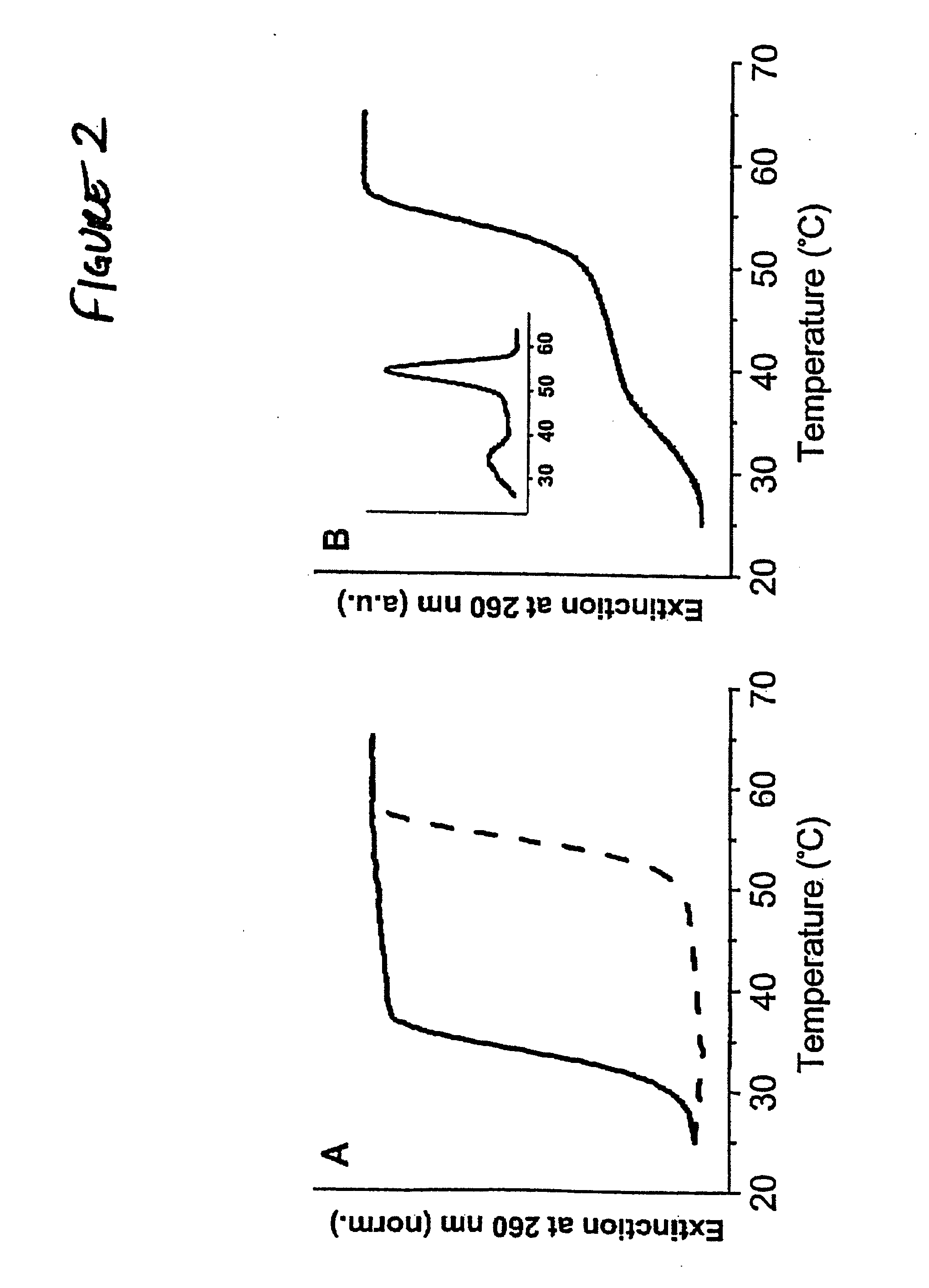
Bio-barcode based detection of target analytes
InactiveUS20060040286A1Long complexityKeep for a long timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTarget analysisAnalyte
The present invention relates to screening methods, compositions, and kits for detecting for the presence or absence of one or more target analytes, e.g. biomolecules, in a sample. In particular, the present invention relates to a method that utilizes reporter oligonucleotides as biochemical barcodes for detecting multiple protein structures or other target analytes in a solution.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Generic, multi-instance method and GUI detection system for tracking and monitoring computer applications
ActiveUS20120066378A1Facilitates code reuse and modular packagingPromote publicationHardware monitoringMultiple digital computer combinationsObject structureFrequency spectrum
Presented is a system and method for monitoring events derived from a computer target application presentation layer including the steps of providing, independent of recompiling the target application's source code, a script running at a level within the target application. The script scans run-time instantiations of objects of the target application, and allocates structures in real-time to the object instantiations. These allocated structures are adapted to create a reflection of the target application structure, which is used along with detected object instantiations that match a predetermined object structure to capture a portion of an environmental spectrum of the detected object. Further, the system can process state machine events occurring on at least one of a server machine and a client / localized machine, correlate the state machine events with the environmental spectrum, and deduce a user experience based on the correlated state machine events.
Owner:KNOA SOFTWARE INC
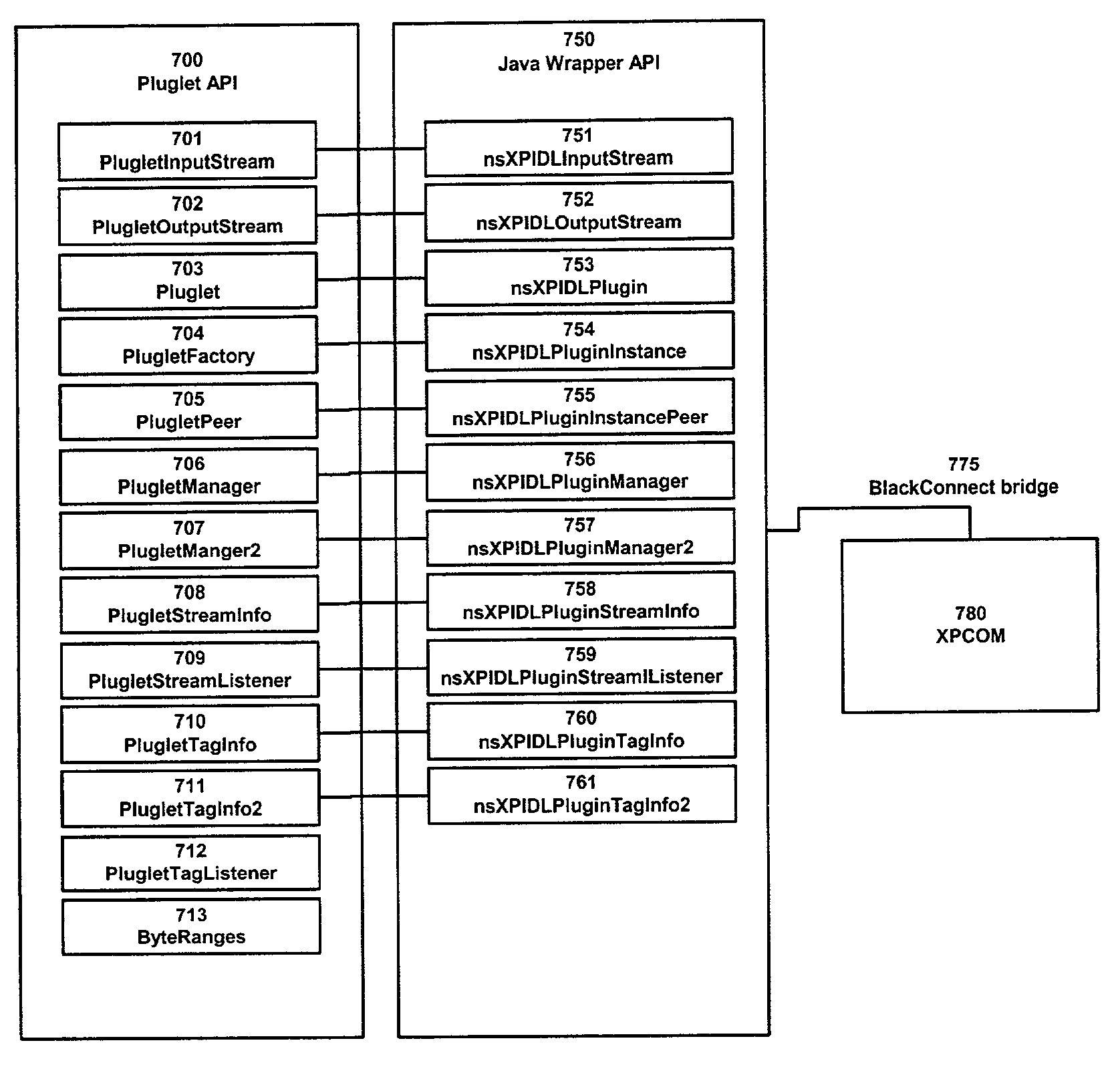
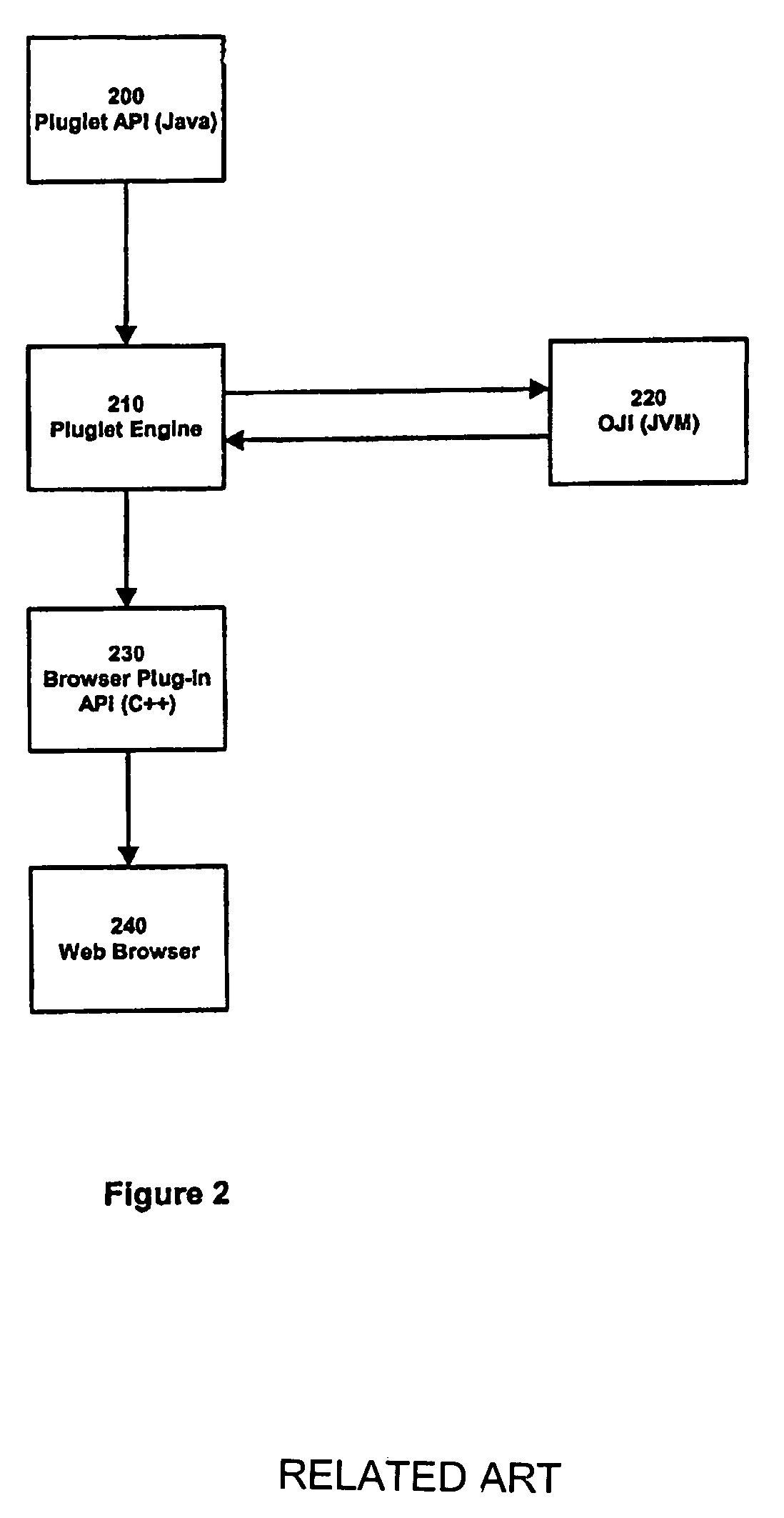
Application programming interface for connecting a platform independent plug-in to a web browser
InactiveUS7069562B2Promotes component reuseSimplify development workMultiprogramming arrangementsExecution paradigmsWeb browserApplication programming interface
Embodiments of the present invention relate to the implementation of an Application Programming Interface (API) that enables platform independent plug-ins to work with browser applications. In one or more embodiments of the present invention, the API allows platform independent plug-ins to use XPCOM (Cross Platform Component Object Model), a technology that allows software components of different various programming languages to communicate. In one or more embodiments of the present invention, the API enables platform independent plug-ins to take advantage of existing BlackConnect and Scriptable Plug-In API technologies to integrate with the native plug-in API. Embodiments of the present invention ensures backward code compatibility by allowing the current platform independent plug-in API and browser API to remain unchanged. Furthermore, embodiments of the present invention enables platform independent plug-ins to communicate and use components created in native programming languages such as C++. This promotes component reuse and eases the development effort.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
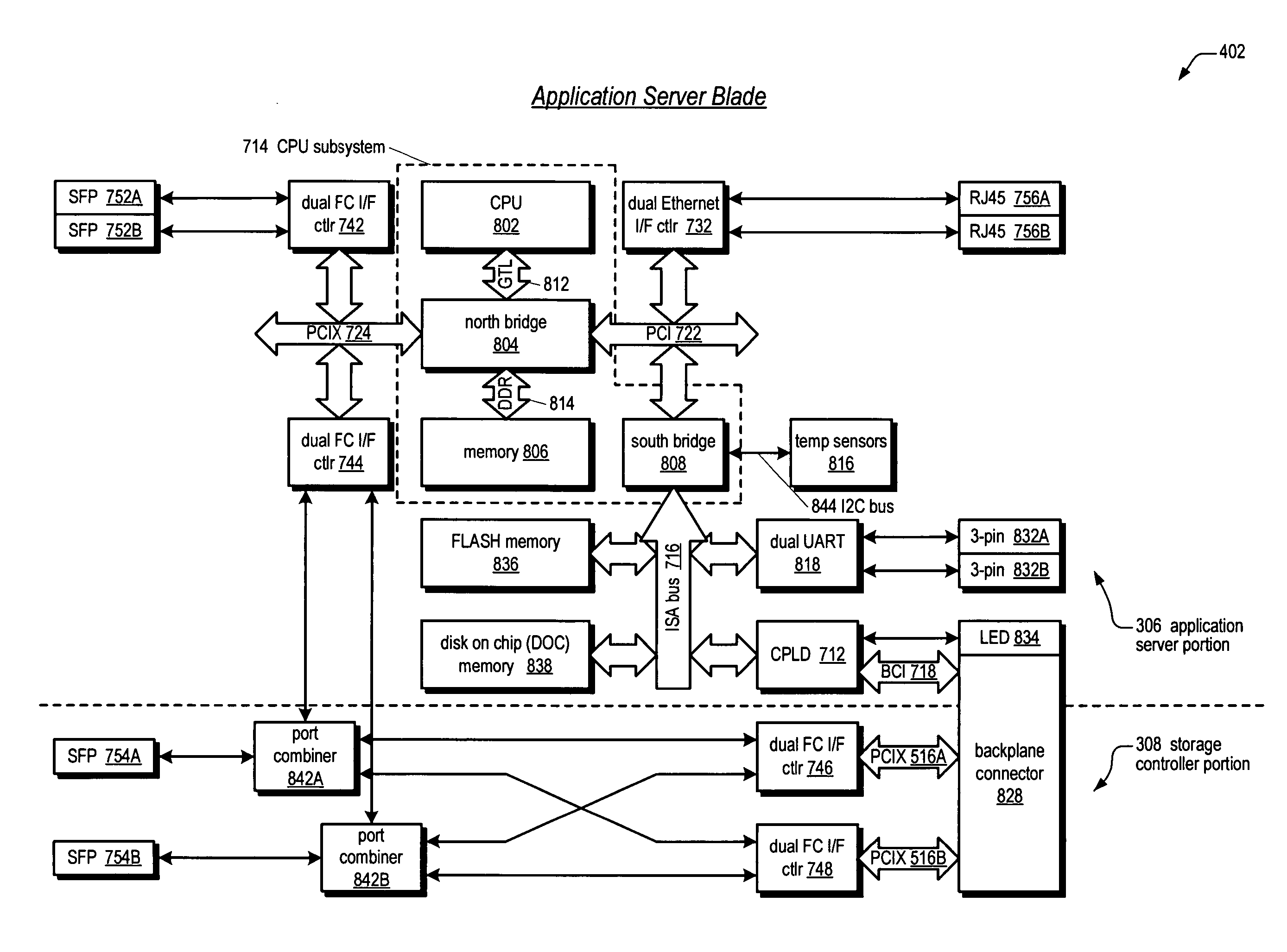
Application server blade for embedded storage appliance
ActiveUS20050010709A1Little and no software developmentEasy to reuseInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsData packApplication server
An application server blade for an embedded storage appliance is disclosed. The blade includes a printed circuit board (PCB) with a connector for connecting to a chassis backplane including a local bus. Affixed on the PCB is a server, a portion of a storage controller, and an I / O link coupling the server and storage controller portion. The server transmits packets on the I / O link to the storage controller portion. The packets include commands to transfer data to a storage device controlled by the storage controller. The storage controller portion receives the packets from the server on the I / O link and forwards the commands on the backplane local bus to another portion of the storage controller affixed on a separate PCB also enclosed in the chassis. The blade also includes a removal mechanism for hot-replacement of the blade in the chassis. The blade architecture facilitates software reuse.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
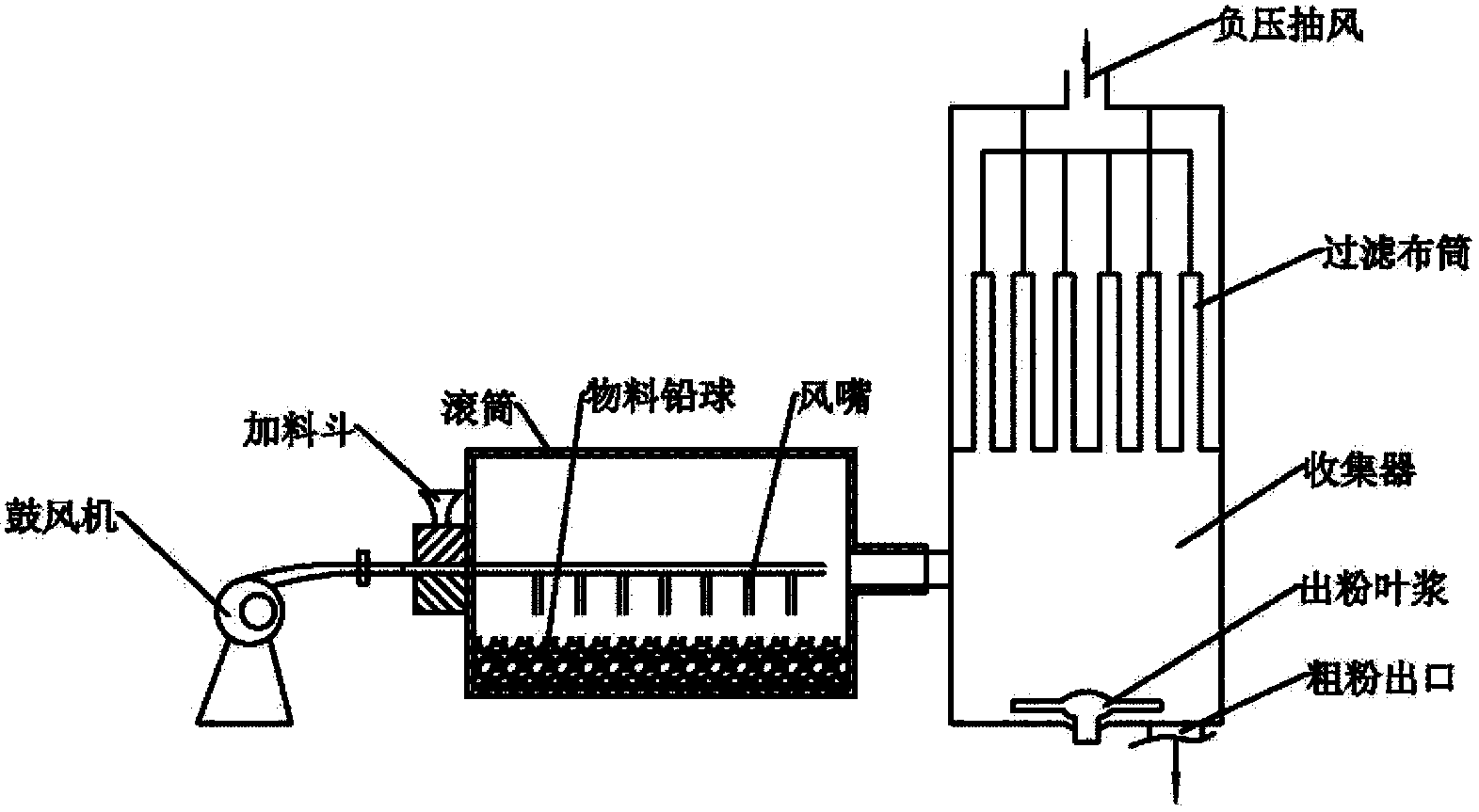
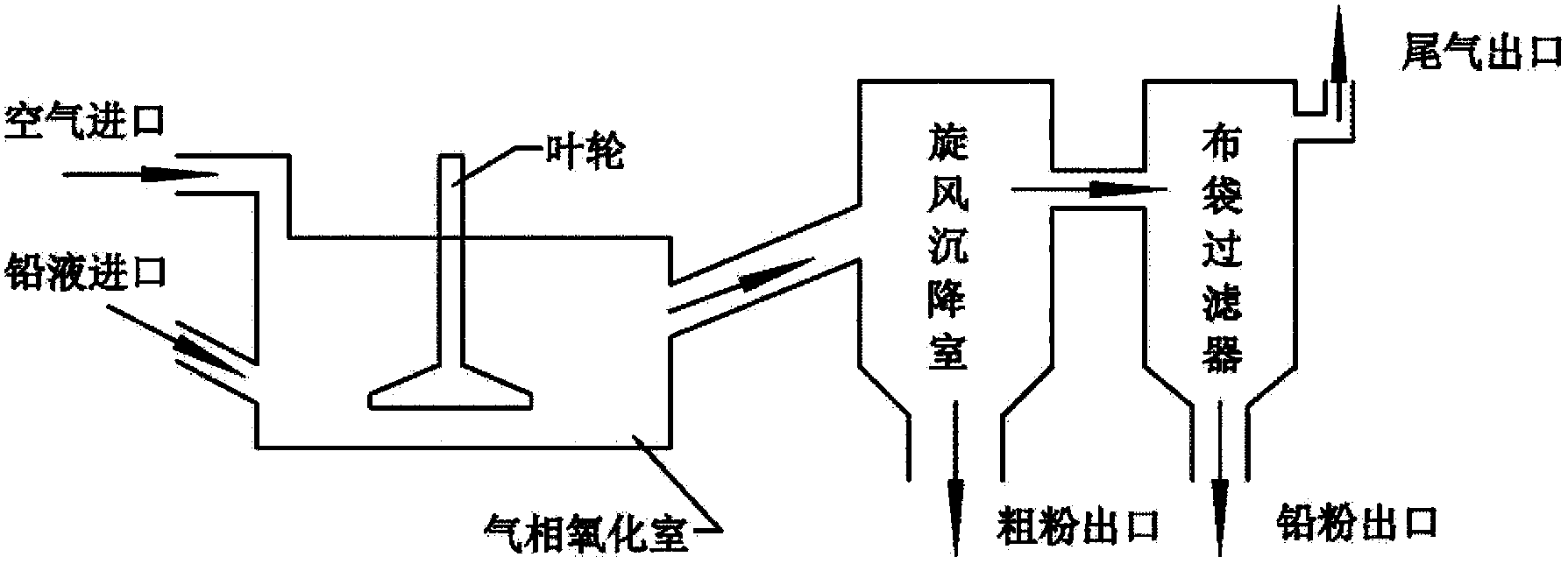
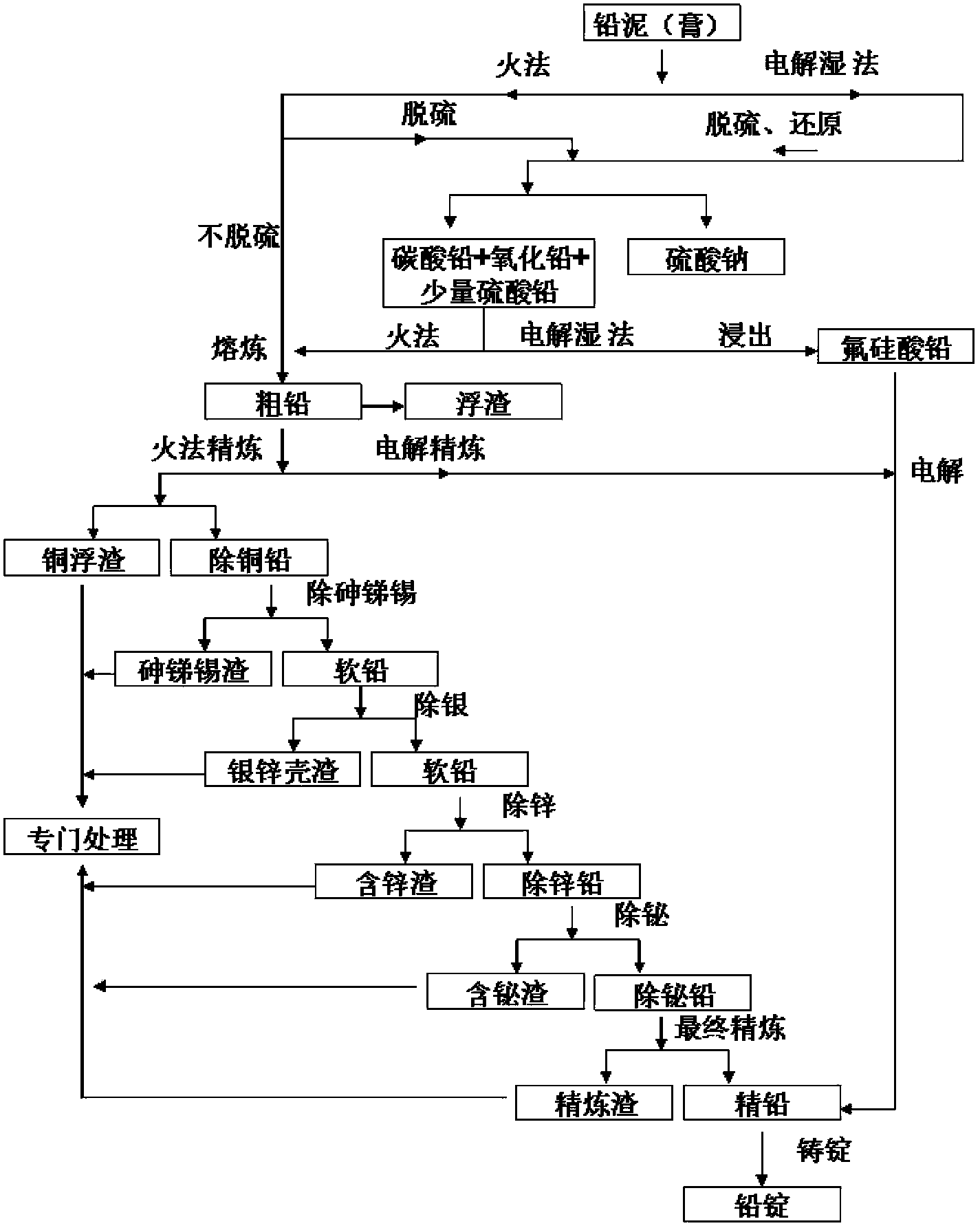
Methods and equipment for recovering waste diachylon by wet method and manufacturing electrode active material of high performance lead acid battery by wet method
ActiveCN103509949AIncrease profitLarge particle sizeWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementElectrical batteryEngineering
The invention discloses methods and equipment for recovering waste diachylon by a wet method and manufacturing an electrode active substance material of a high performance lead acid battery by the wet method. The equipment comprises device required for a technology process by a chemical method, a chemical machinery method or an electrochemical machinery method. The active substance material provided by the invention can substantially raises an utilization rate of the active substance of the lead acid battery, specific energy of the battery and charging capability of the battery, simultaneously avoids generation and discharge of harmful substances such as lead gas, lead smoke, lead dust and SO2, raises a lead utilization rate in a production process, is beneficial for treating and recycling lead compounds and lead-containing liquid generated in a lead gas recovering process in a plate casting or welding technology, and reduces cost.
Owner:杨春晓
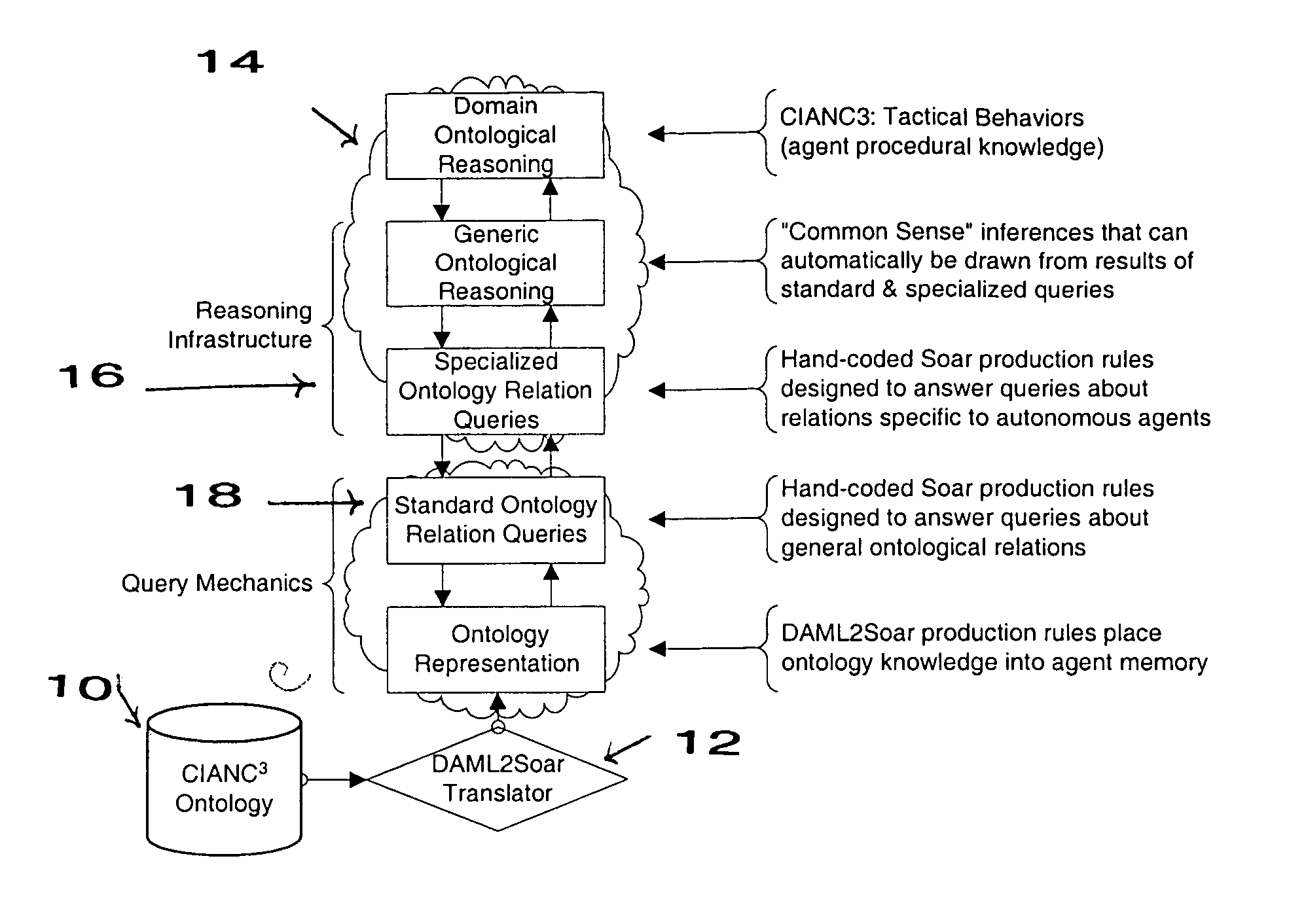
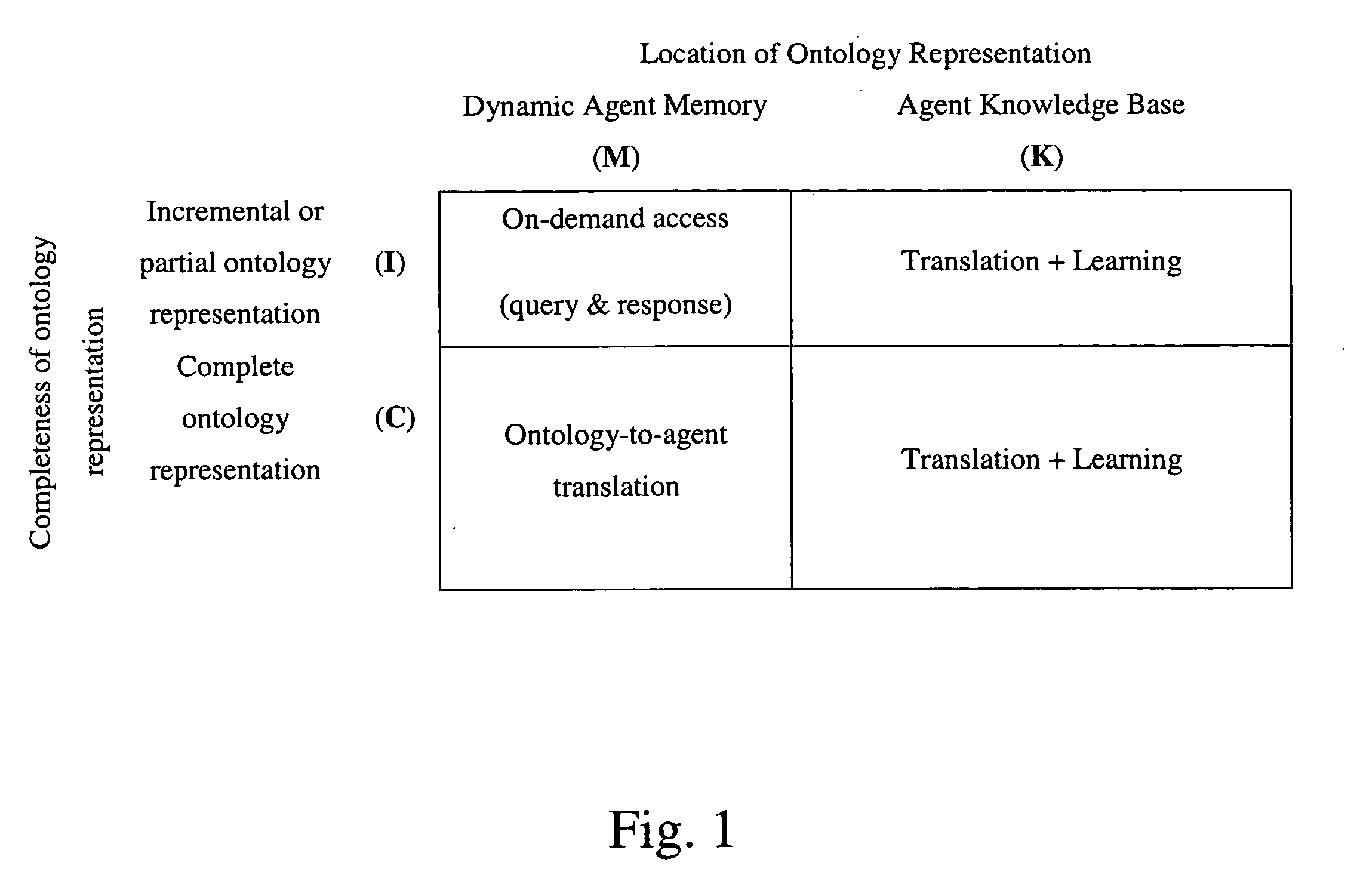
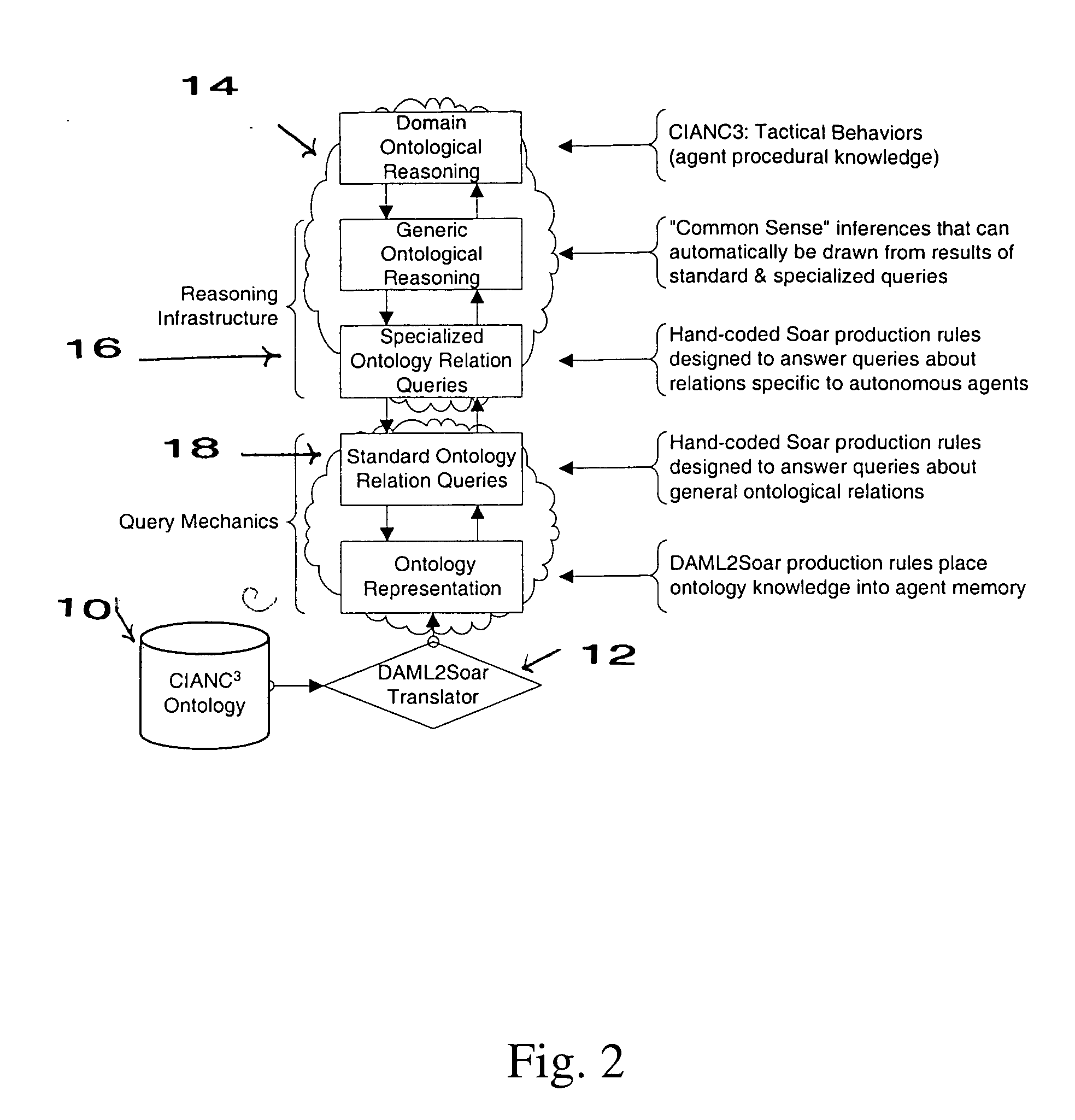
Method and apparatus for providing rule-based, autonomous software agent with ontological information
InactiveUS20050197991A1Eliminate needImprove applicabilityKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware agentData mining
Autonomous systems require efficient run-time performance. In agents optimized for performance, control structures and domain knowledge are often intertwined, providing efficient execution but brittle knowledge bases that scale poorly. Combining ontology representations and agents optimized for performance can capitalize the strengths of individual approaches and reduce individual weaknesses. Automatic translators are to convert ontological representations, hand-coded procedures for ontological inference, and explanation-based learning to cache inference.
Owner:CHENG TING TECH
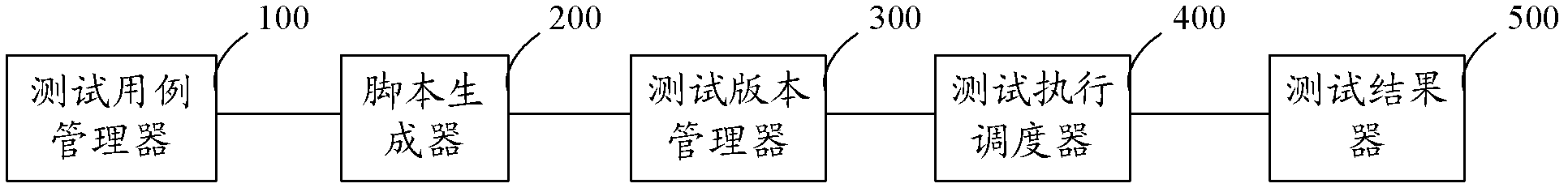
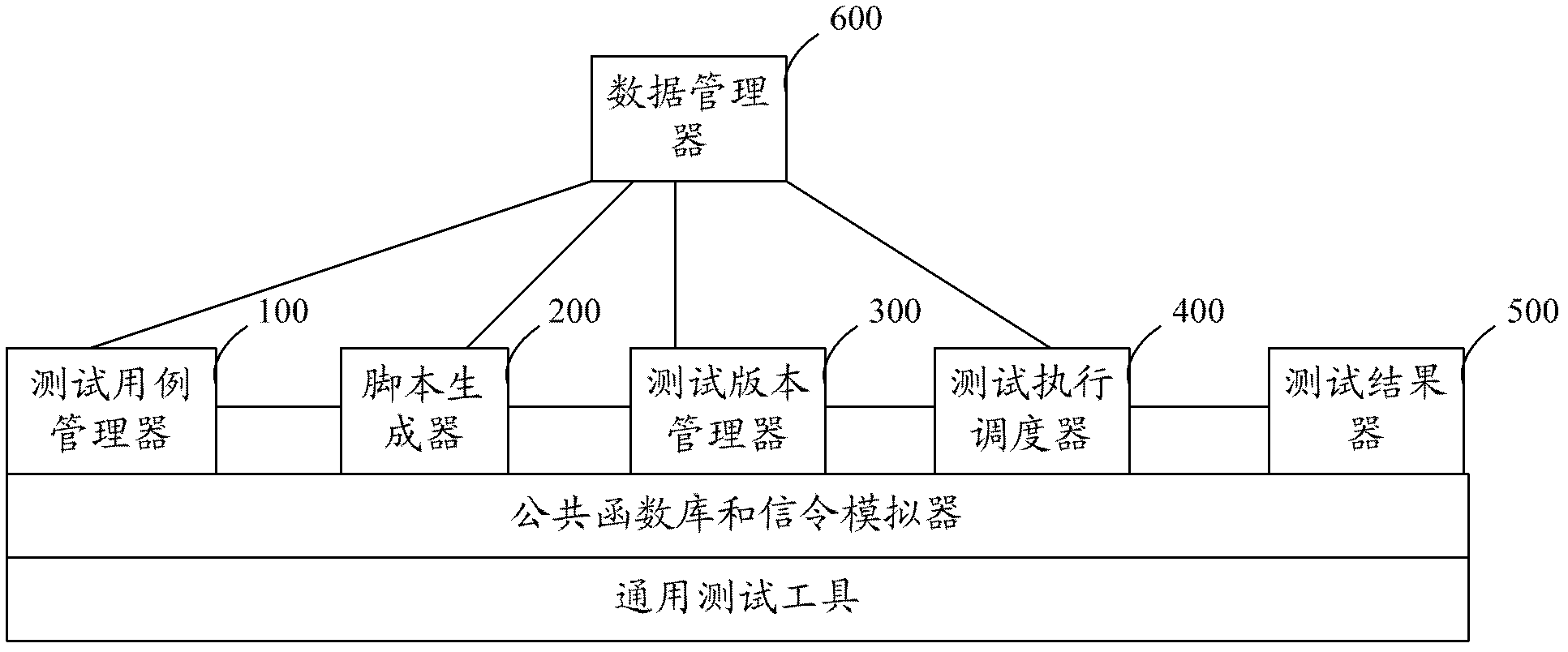
Automatic testing method and system
ActiveCN103150249ABoth correctnessEasy to reuseSoftware testing/debuggingComputer hardwareChoice test
The invention discloses an automatic testing method and an automatic testing system. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a testing case manager sets the service verification function and testing data of a testing case, wherein the testing data include a signaling parameter and a service parameter; 2, a script generator generates a script of the testing case; 3, a testing version manager selects a testing case used by a testing version according to a service scene, sets the executing sequence of the testing case, and configures a corresponding value of testing data of the testing case; 4, a testing execution scheduler executes the script of a testing case in a specified testing version; and 5, a testing result generator generates a testing report according to an execution result of the testing execution scheduler. According to the method and the system, functionally influencing testing can be prevented from being omitted.
Owner:BEIJING FEINNO COMM TECH
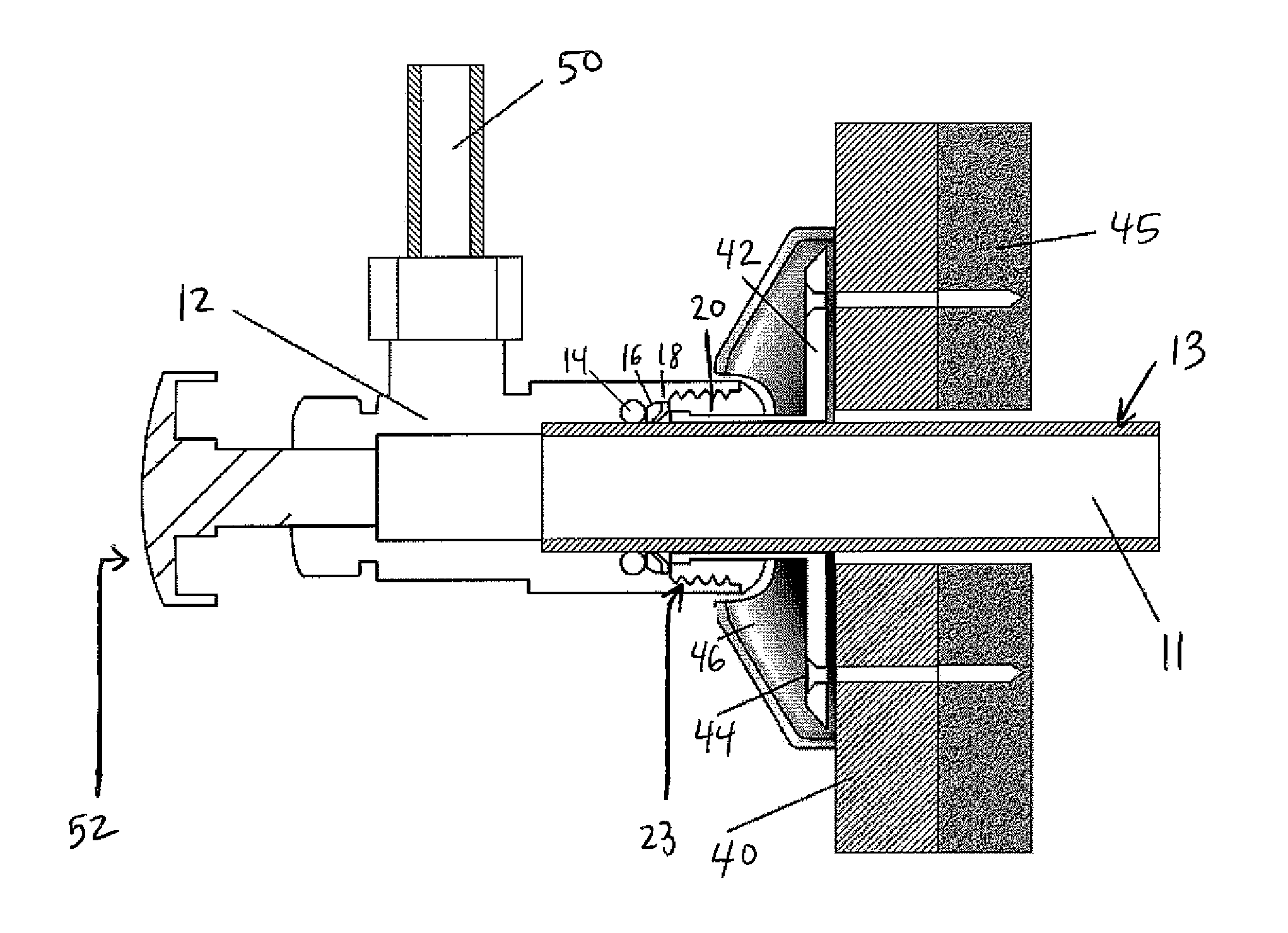
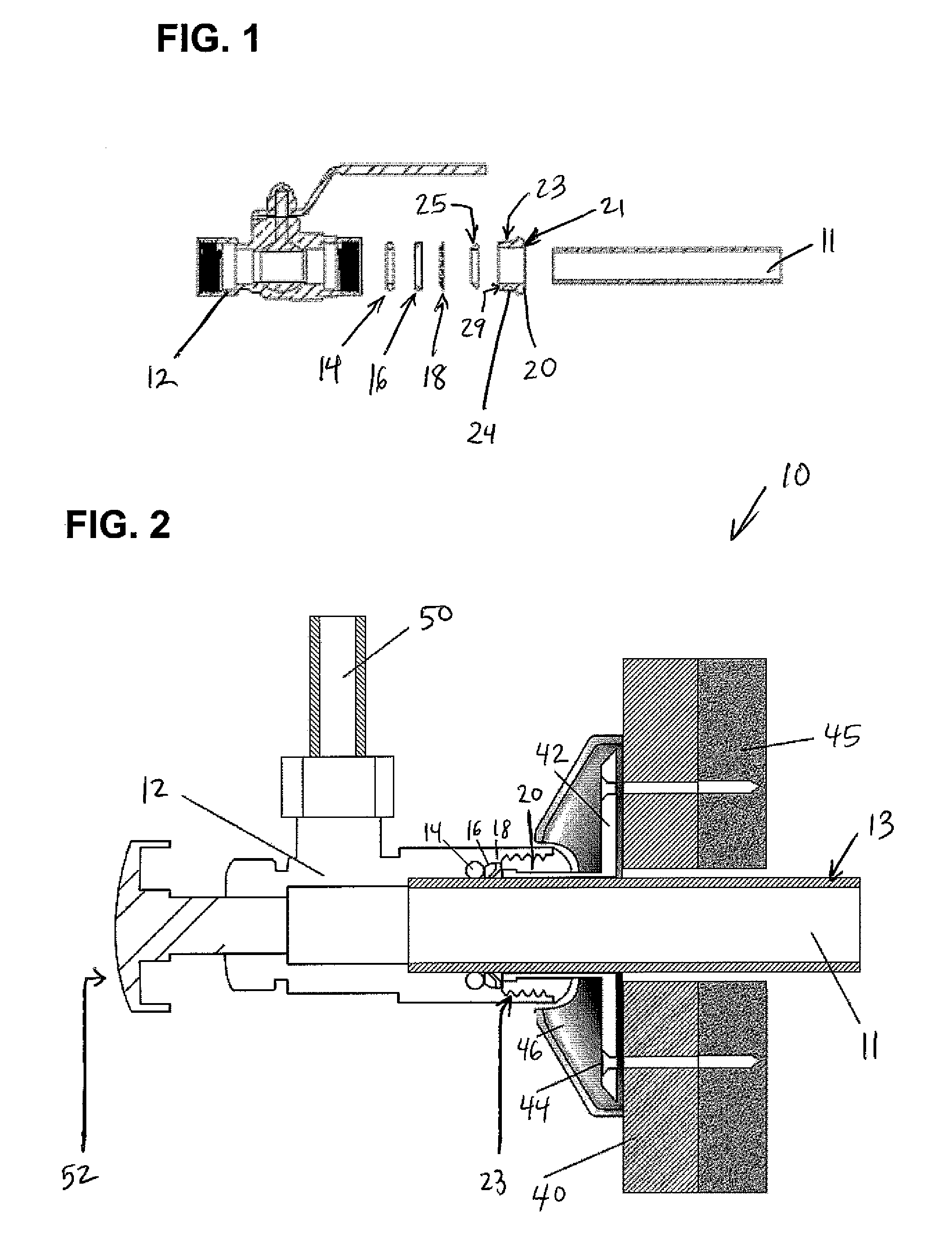
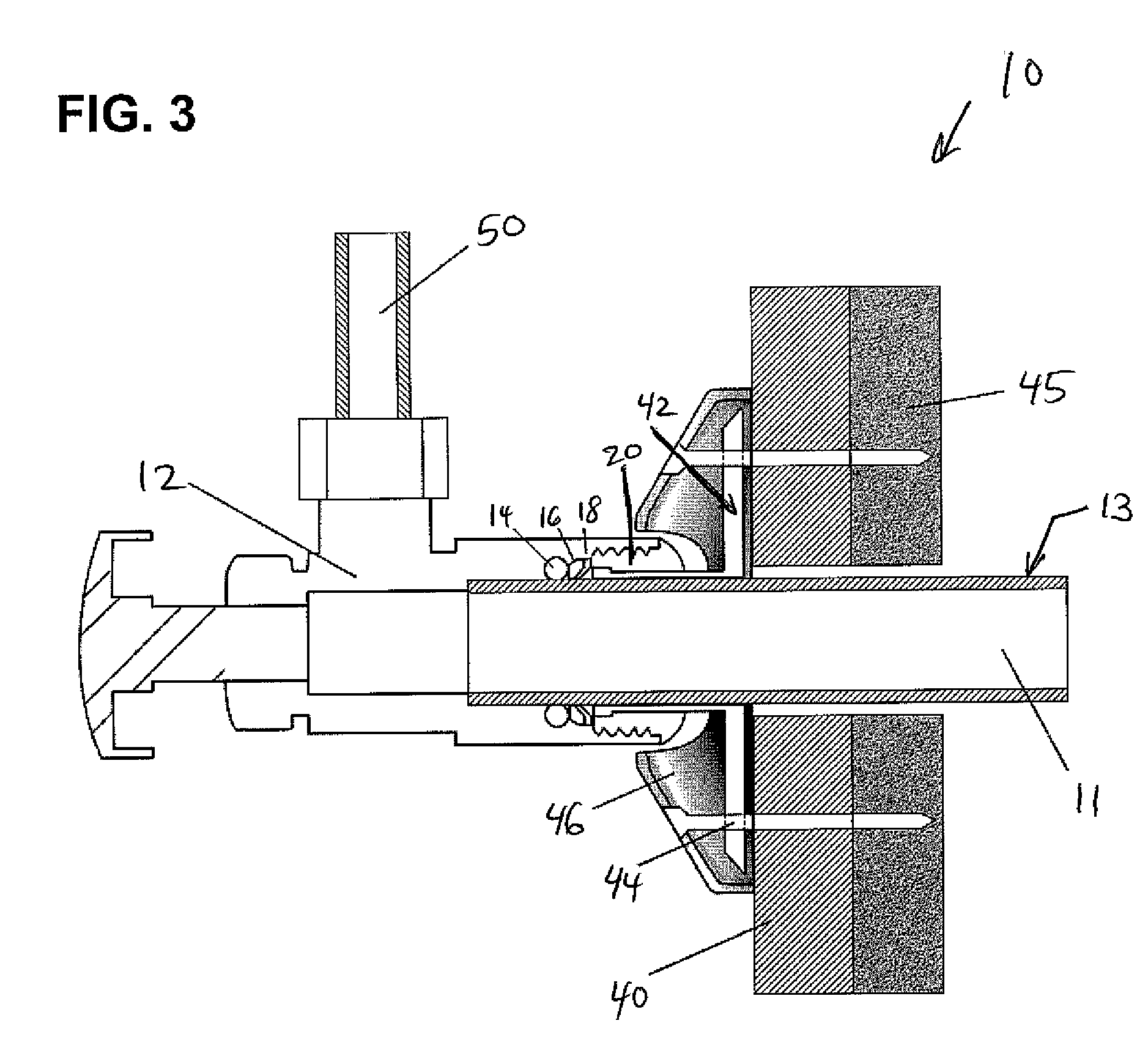
Push-fit valve with integrated mounting assembly
The present invention provides an integrated valve, push connection and push release components, and a valve mounting assembly for use on fluid, air or gas applications. The invention allows for the installation of the valve by sliding the valve over the supply tube / piping or pushing the tube / piping into the valve. Once connected, an o-ring seals the connection, a packing gland applies energy to the o-ring seal maintaining constant, even pressure across the seal, and a grip ring applies opposing energy to prevent the disconnection of the assembly. The quick connection assembly is retained by a retaining cap, which applies constant, positive force on the sealing surface.
Owner:QUICK FITTING
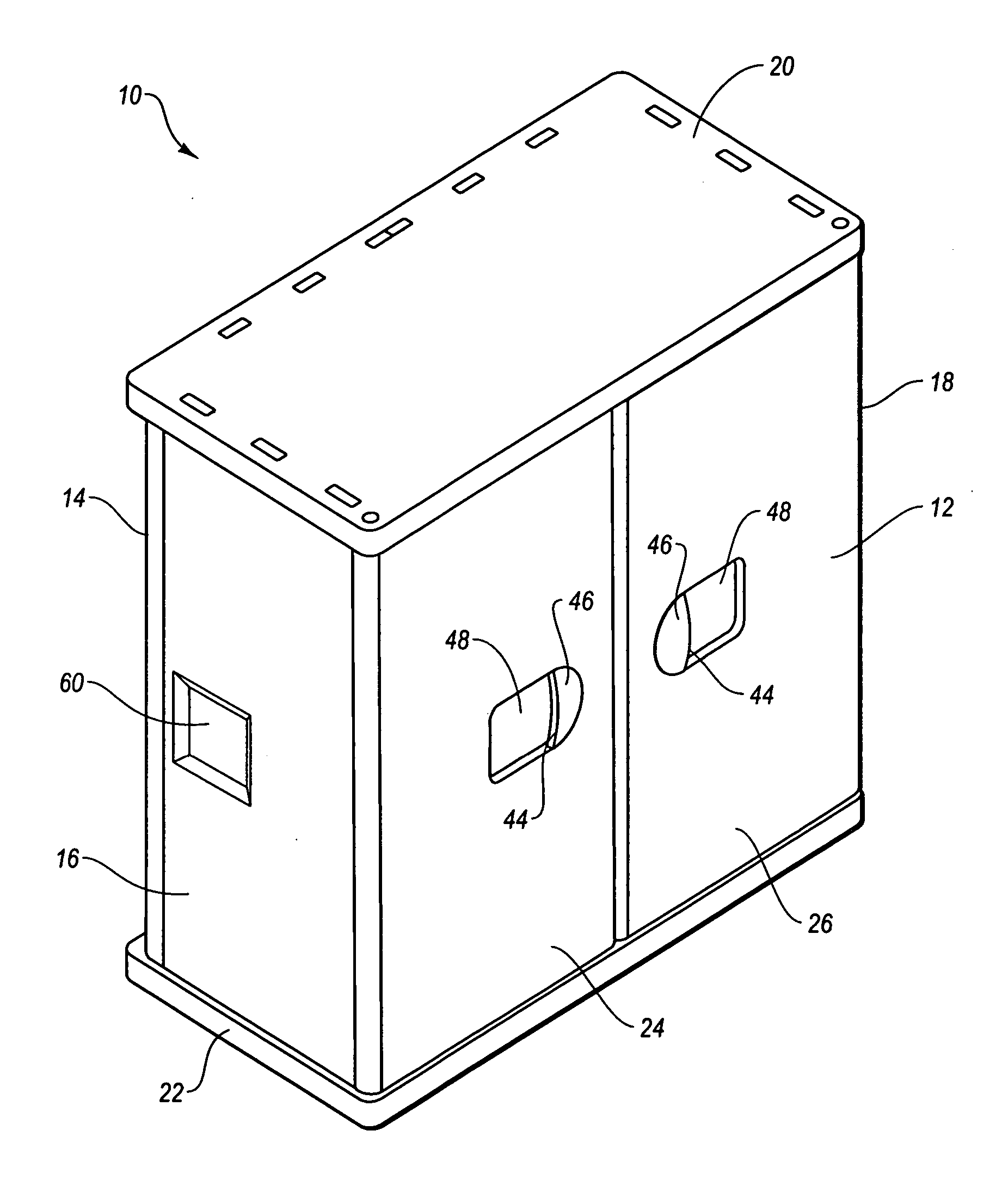
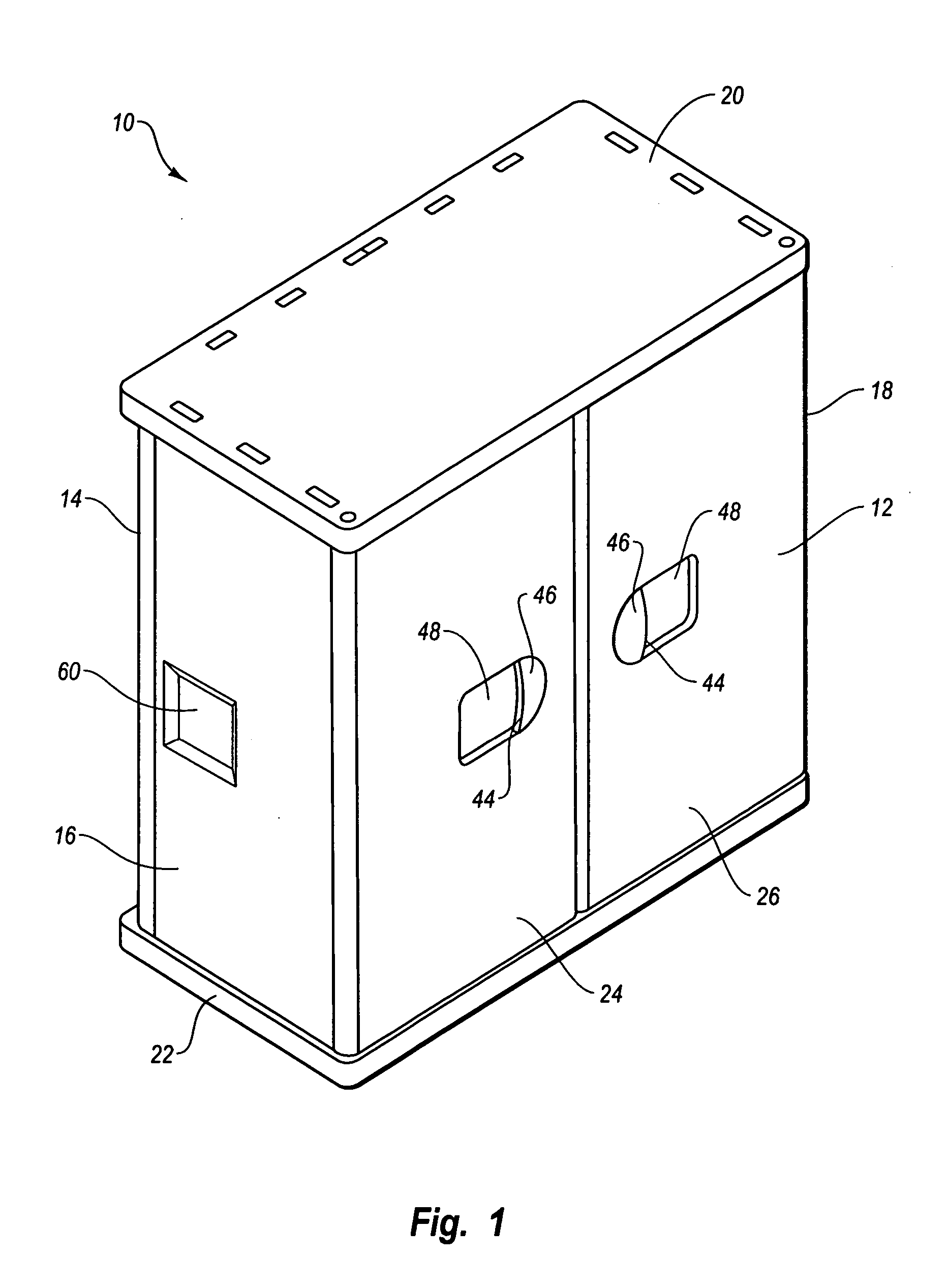
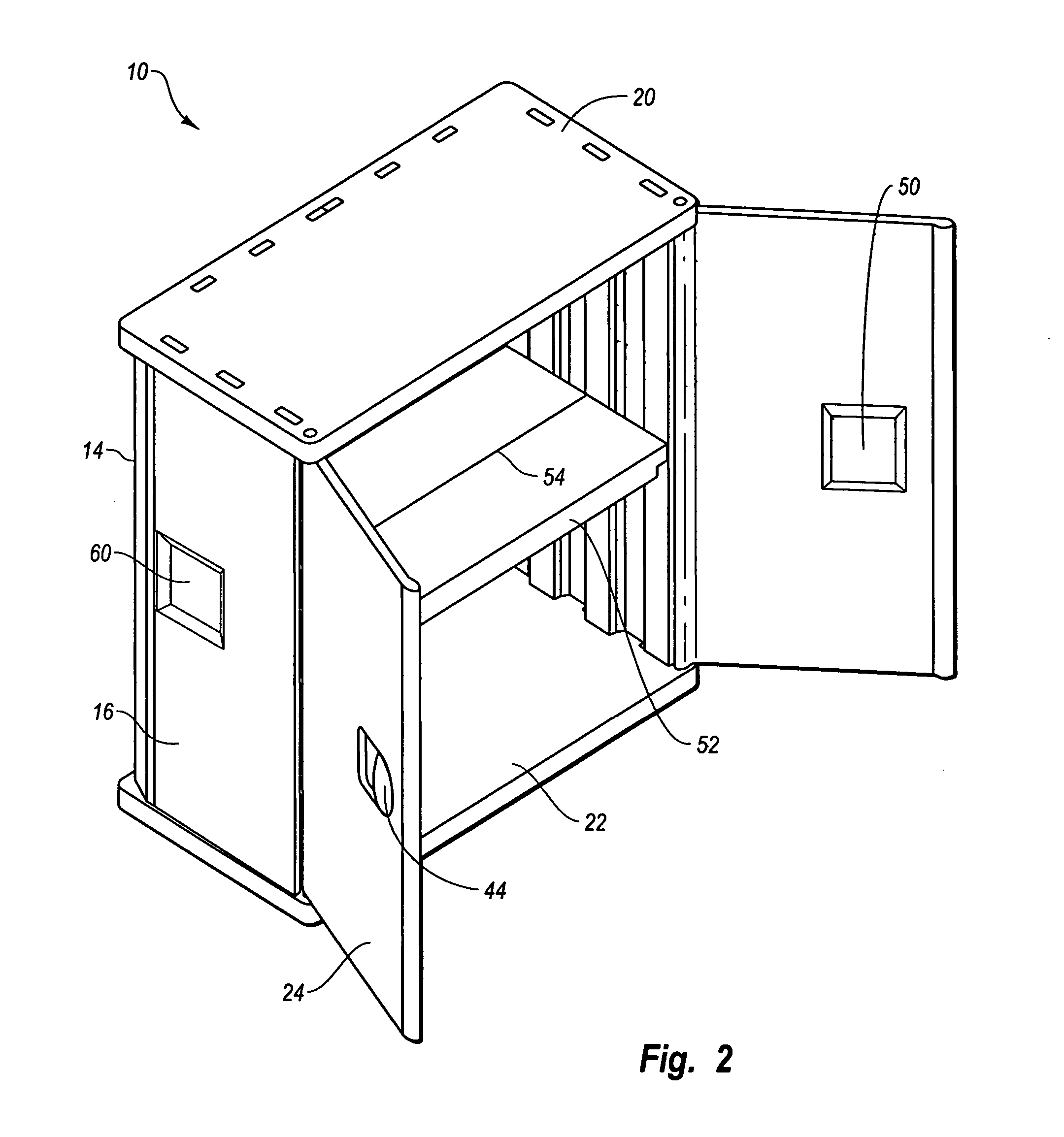
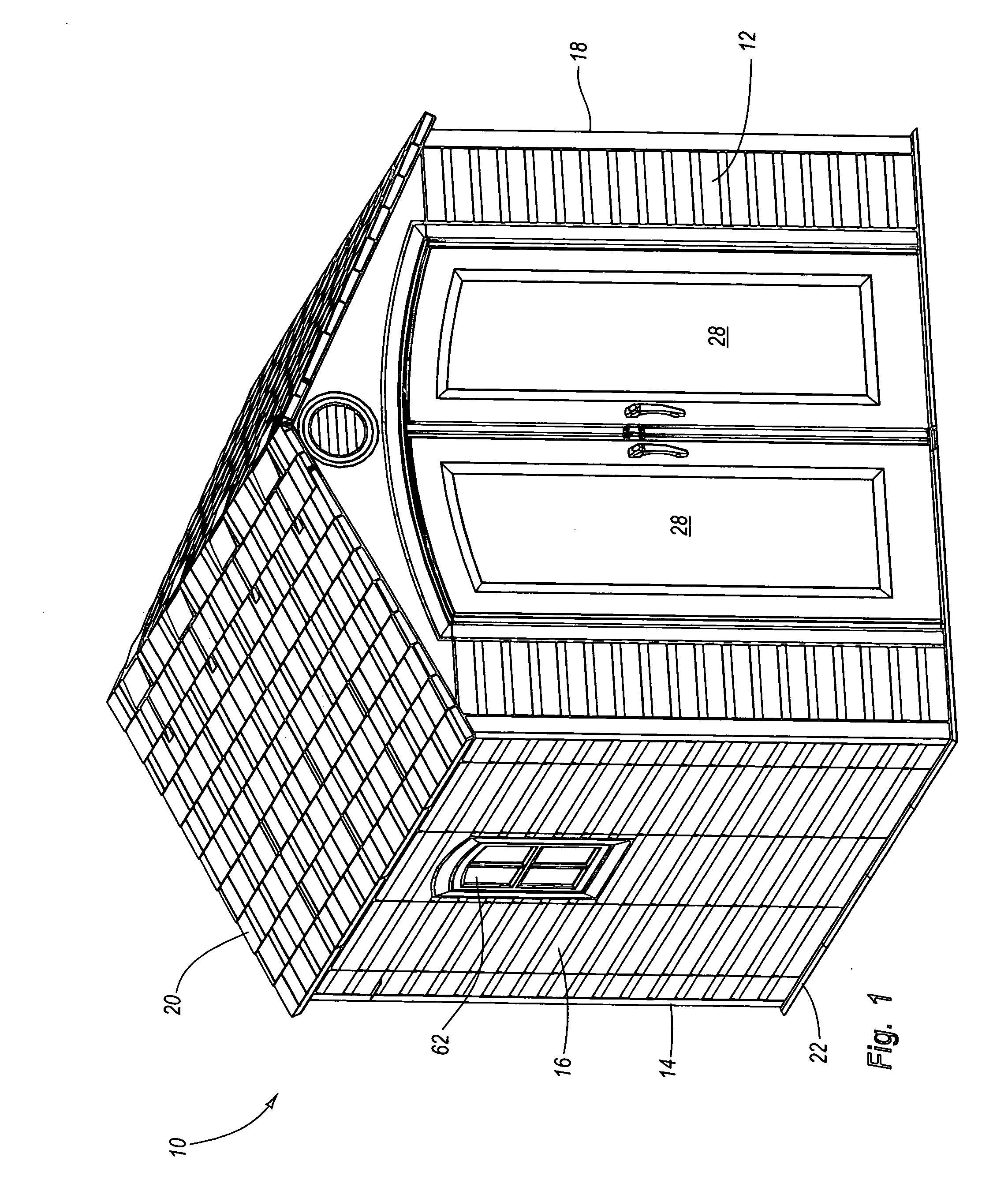
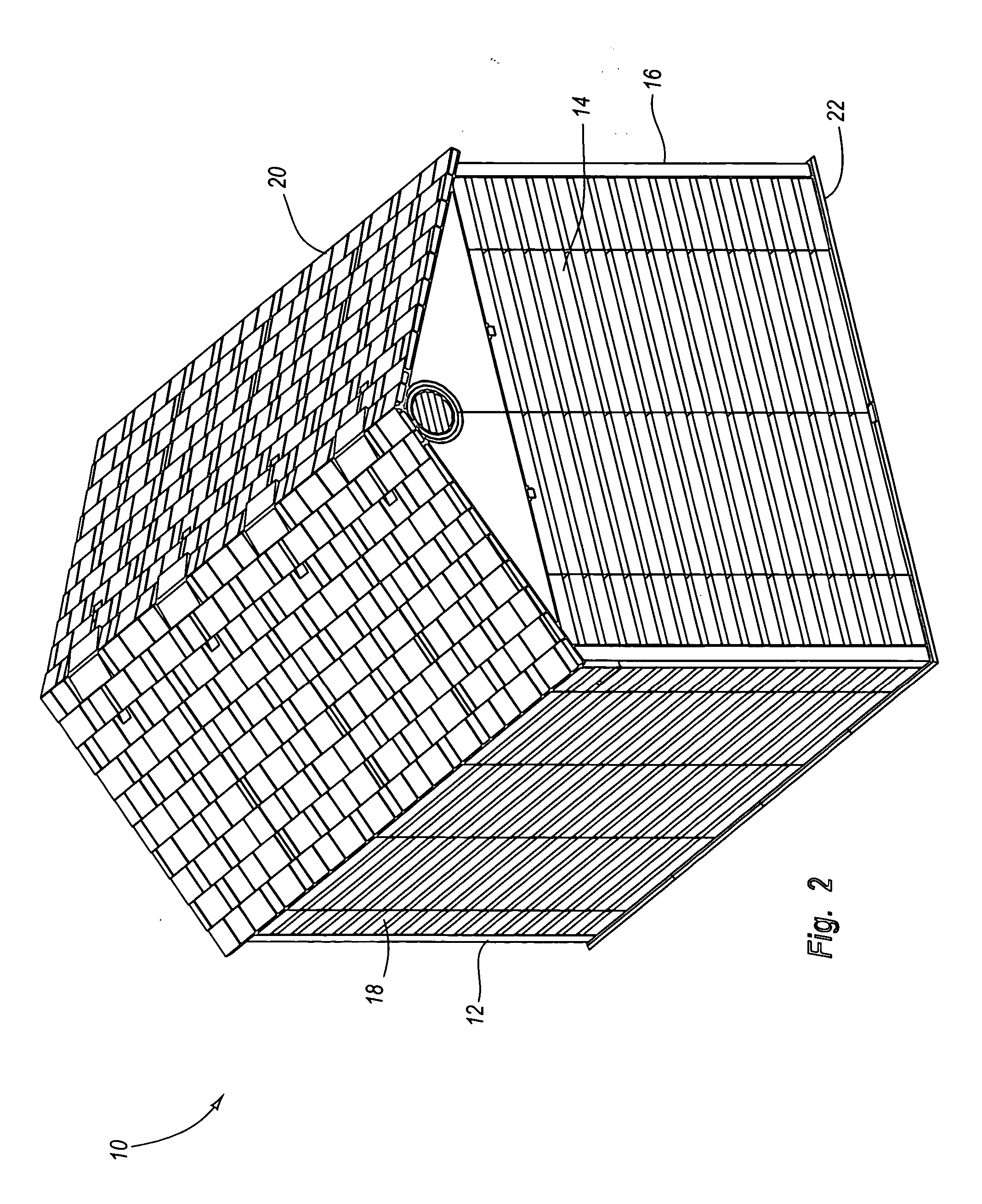
Storage enclosure
InactiveUS20060108899A1Quickly and easily assembleIncrease strength and rigidityKitchen cabinetsFolding cabinetsComputer caseEngineering
A storage enclosure may include a number of components, such as floor panels, wall panels and roof panels, which may be interconnected to form a structure such as a storage cabinet. The storage enclosure may include wall panels with outwardly extending projections that are sized and configured to allow the wall panels to be connected to floor panels and roof panels. The storage enclosure may also include one or more living hinges, which may facilitate storage and / or shipping of the storage enclosure.
Owner:LIFETIME PRODUCTS
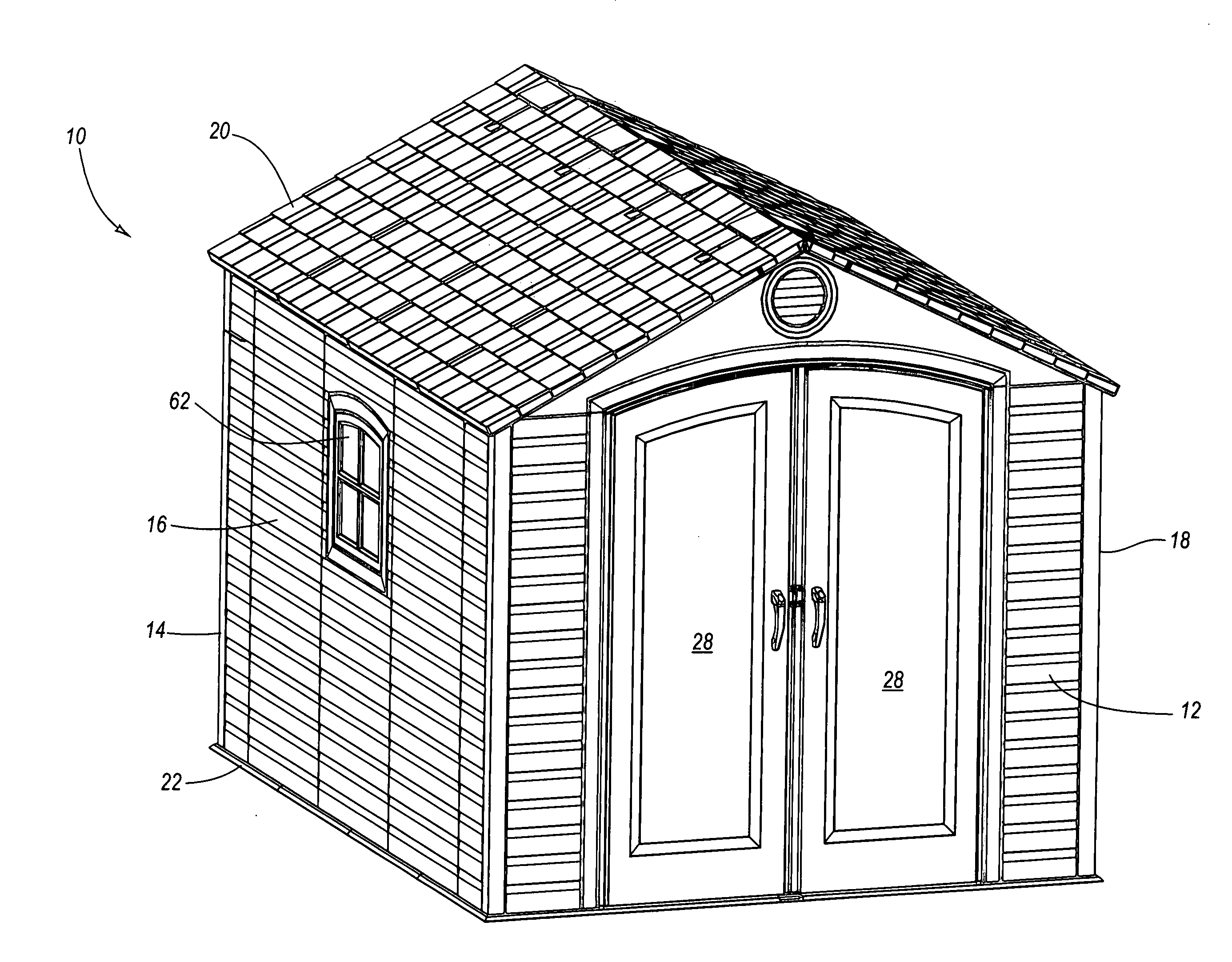
Modular enclosure with offset panels
ActiveUS20050223655A1Quickly and easily connected and disconnectedEasily reconfigured and repaired and replacedPublic buildingsSpecial buildingModularityLiving hinge
A modular enclosure, such as a shed, may include a number of components. For example, the enclosure may include roof panels, floor panels and wall panels that are connected to the roof and / or floor panels. Preferably, the wall panels span the seams disposed between the roof and / or floor panels. In addition, the wall panels are preferably offset from the roof and / or floor panels. Further, the roof panels, wall panels and floor panels desirably have a substantially similar width. The enclosure may also include one or more corner panels and the corner panels may have a living hinge that generally divides the corner panel in half. Advantageously, the offset connection of the roof panels, wall panels and floor panels may facilitate construction of an enclosure with increased strength and functionality.
Owner:LIFETIME PRODUCTS
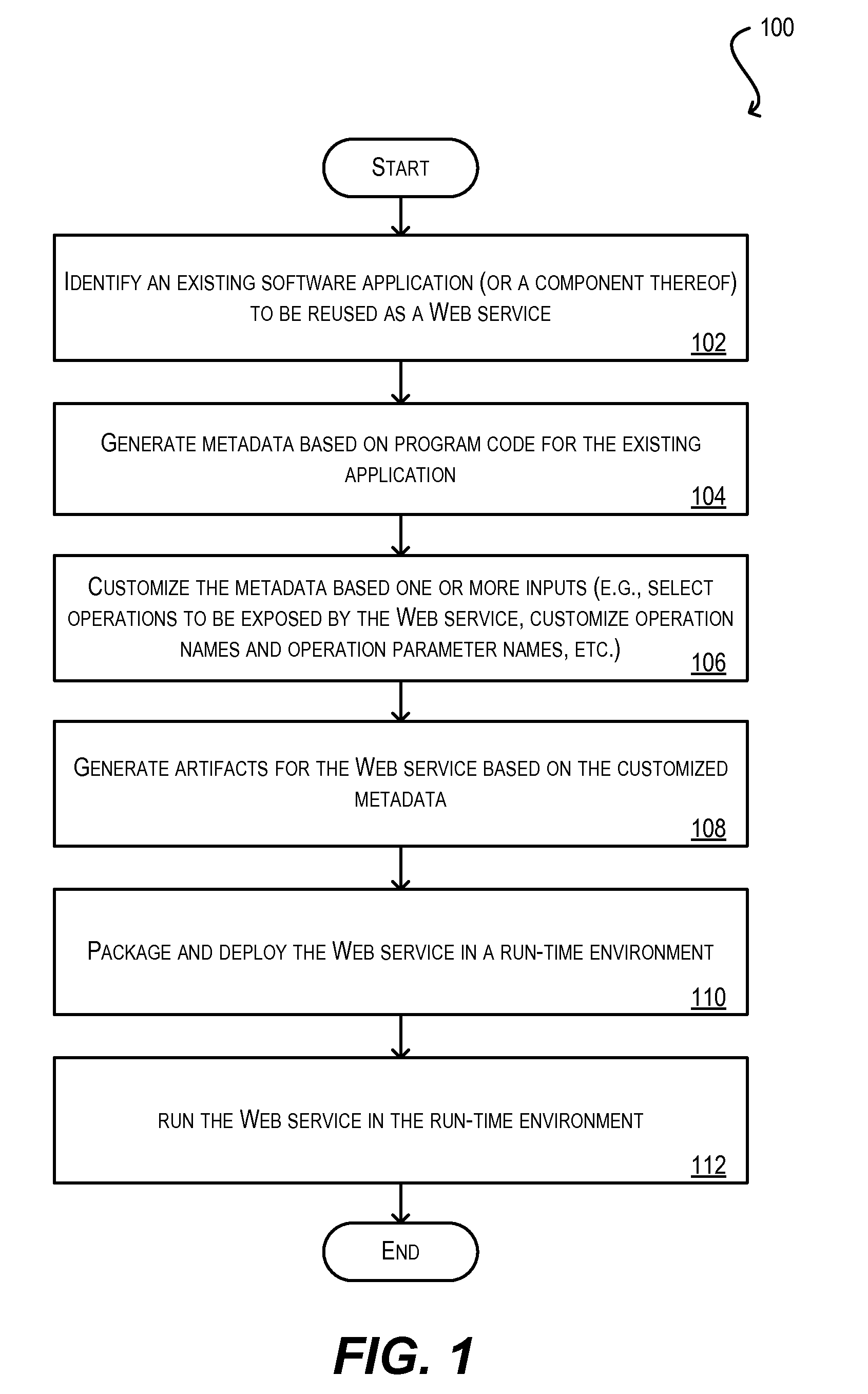
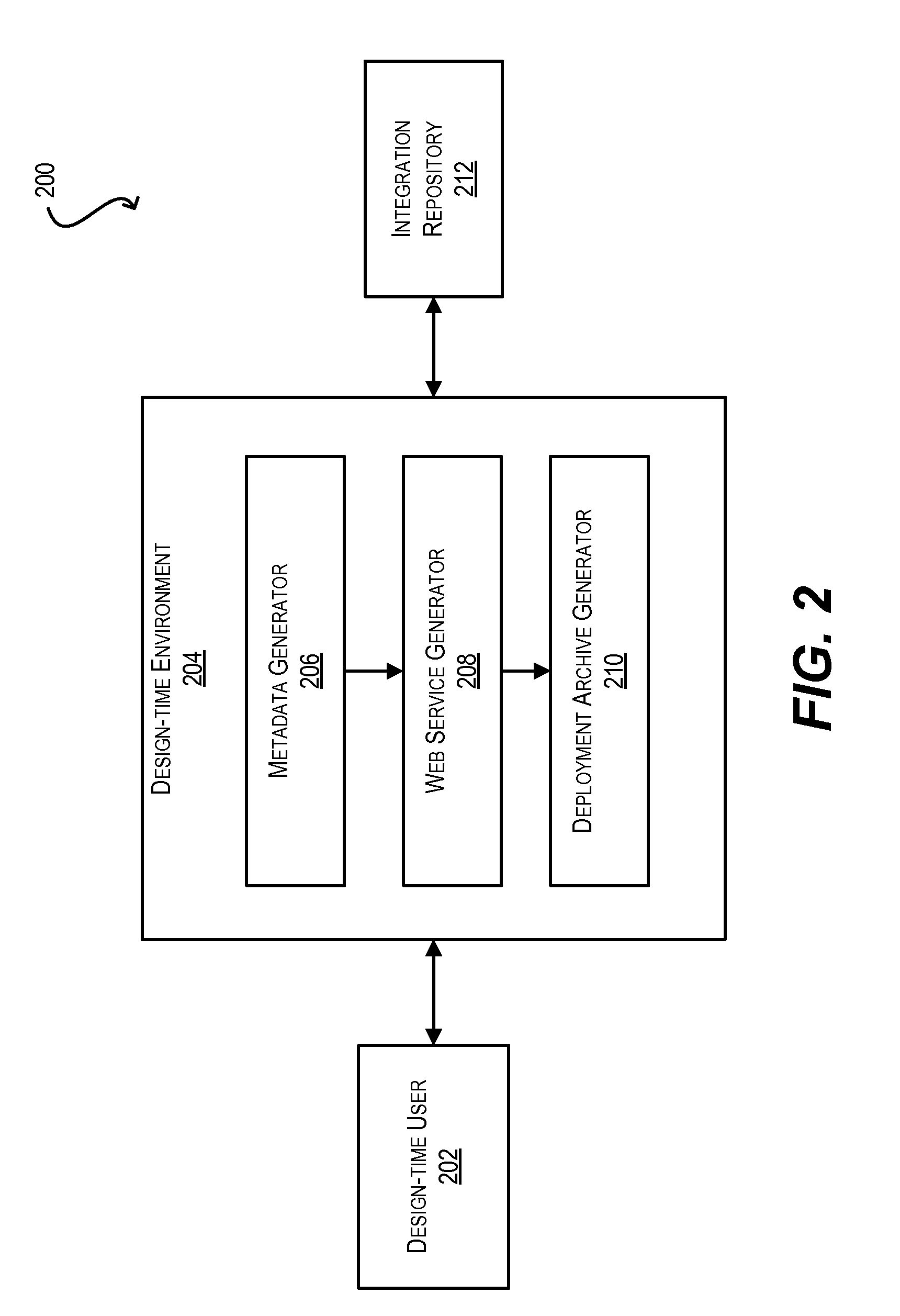
System and method for meta-data driven, semi-automated generation of web services based on existing applications
ActiveUS20100082556A1Promote reuseEasy to reuseDigital data processing detailsCode refactoringApplication softwareMetadata
Techniques for reusing logic implemented in an existing software application such that the logic can be exposed as a Web service or in any other service-oriented context. In one set of embodiments, a design-time technique is provided that comprises, inter alia, receiving program code for an existing software application, generating metadata based on the program code, and customizing the metadata to align with an intended Web service. Artifacts for the Web service are then generated based on the customized metadata. In another set of embodiments, a run-time technique is provided that comprises, inter alia, receiving a payload representing an invocation of a Web service operation of the generated Web service, processing the payload, and, based on the processing, causing the existing software application to execute an operation in response to the invocation of the Web service operation.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Multifunctional automatic dumpling machine
InactiveCN102726671AGood synchronizationSimple designFood shapingFood preparationSkin rollingBiomedical engineering
The invention discloses a multifunctional automatic dumpling machine, comprising a rack, a skin rolling mechanism, a skin conveyer belt, a punching skin conveying mechanism, a stuffing filling unit, a die closing unit, an encircling intermittent movement dumpling forming template, a disk conveying mechanism, a placement mechanism, an intermittent driving unit and a stepping motor, wherein the punching skin conveying mechanism structurally has a structure that blanking holes on upper and lower side synchronous belts are vertically alignment, the stuffing filling unit realizes multi-hole quantification and synchronization stuffing filling; the contact surface between the skin and the template is reduced by 90% by using the structure of a movable template on the encircling intermittent movement dumpling forming template; protrusion ribs have certain gradients, thus the skins do not adhere to the template and can smoothly enter the forming die; and die assembly can be complete by the projection and concave cavity, thus the produced dumpling has beautiful appearance, and the advantages of firm bonding and low cost are achieved.
Owner:朱景超
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com