Patents
Literature
592 results about "Anesthetic Agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A drug or other substance that causes a loss of feeling or awareness. Local anesthetics cause a loss of feeling in one small area of the body. Regional anesthetics cause a loss of feeling in a part of the body, such as an arm or leg. General anesthetics cause a loss of feeling and a complete loss of awareness that feels like a very deep sleep.
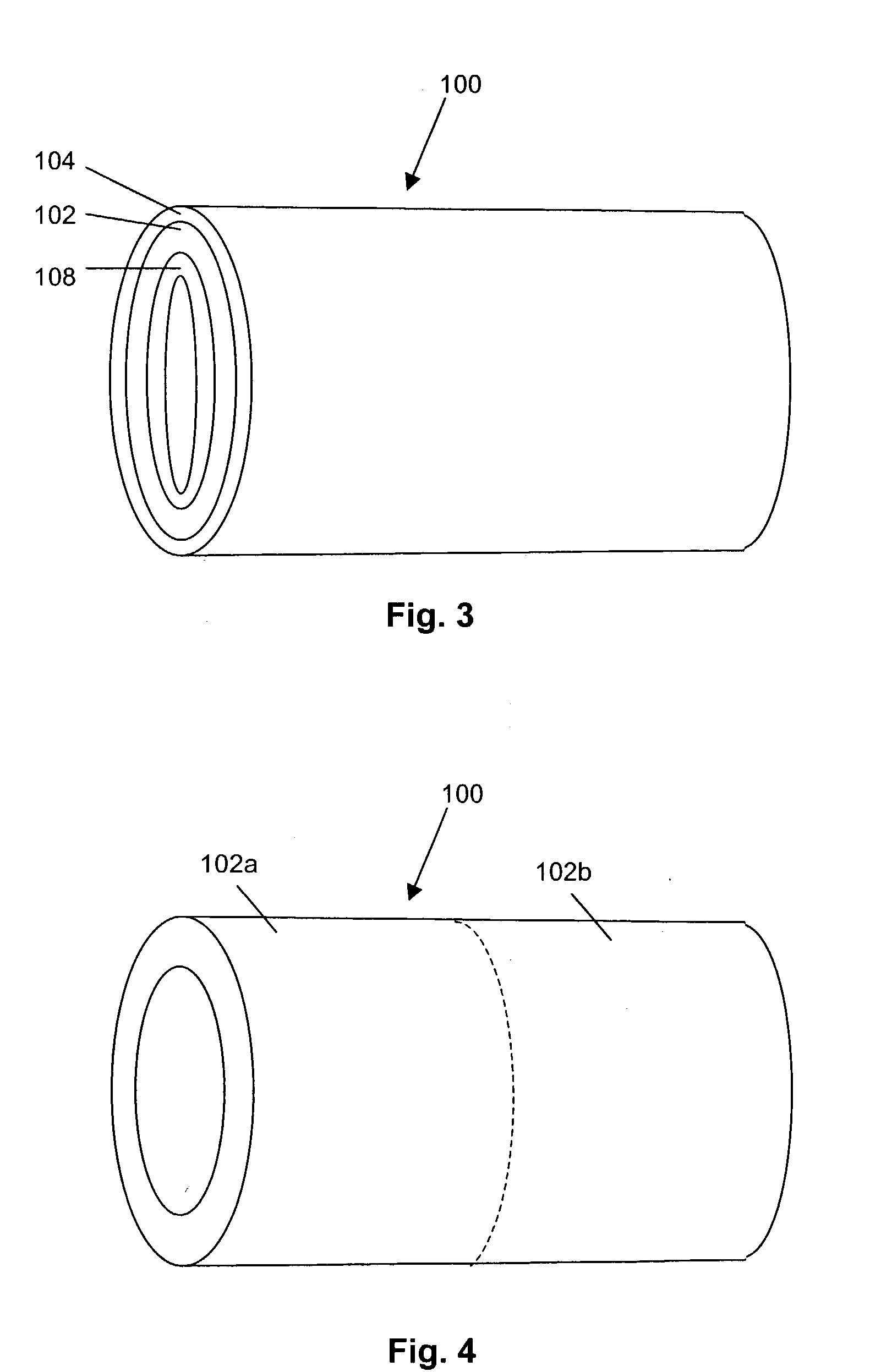
Particulate acellular tissue matrix
A method of processing an acellular tissue matrix to give a particulate acellular tissue matrix includes: cutting sheets of dry acellular tissue matrix into strips; cryofracturing the dry acellular tissue matrix strips at cryogenic temperatures; separating the resulting particles by size at cryogenic temperatures; and freeze drying the fraction of particles desired size to remove any moisture that may have been absorbed to give a dry particulate acellular tissue matrix. Rehydration of the dry particulate acellular tissue matrix may take place just prior to use. The particulate acellular tissue may be applied to a recipient site, by way of injection, spraying, layering, packing, in-casing or combinations thereof. The particulate acellular tissue may further include growth and stimulating agents selected from epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, nerve growth factor, keratinocyte growth factor, platelet derived growth factor, vasoactive intestinal peptide, stem cell factor, bone morphogetic proteins, chondrocyte growth factor and combinations thereof. Other pharmaceutically active compounds may be combined with the rehydrated particulate material including: analgesic drugs; hemostatic drugs; antibiotic drugs; local anesthetics and the like to enhance the acceptance of the implanted particulate material. The particulate material product may also be combined with stem cells selected from mesenchymal stem cells, epidermal stem cells, cartilage stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells and combinations thereof.
Owner:LIFECELL
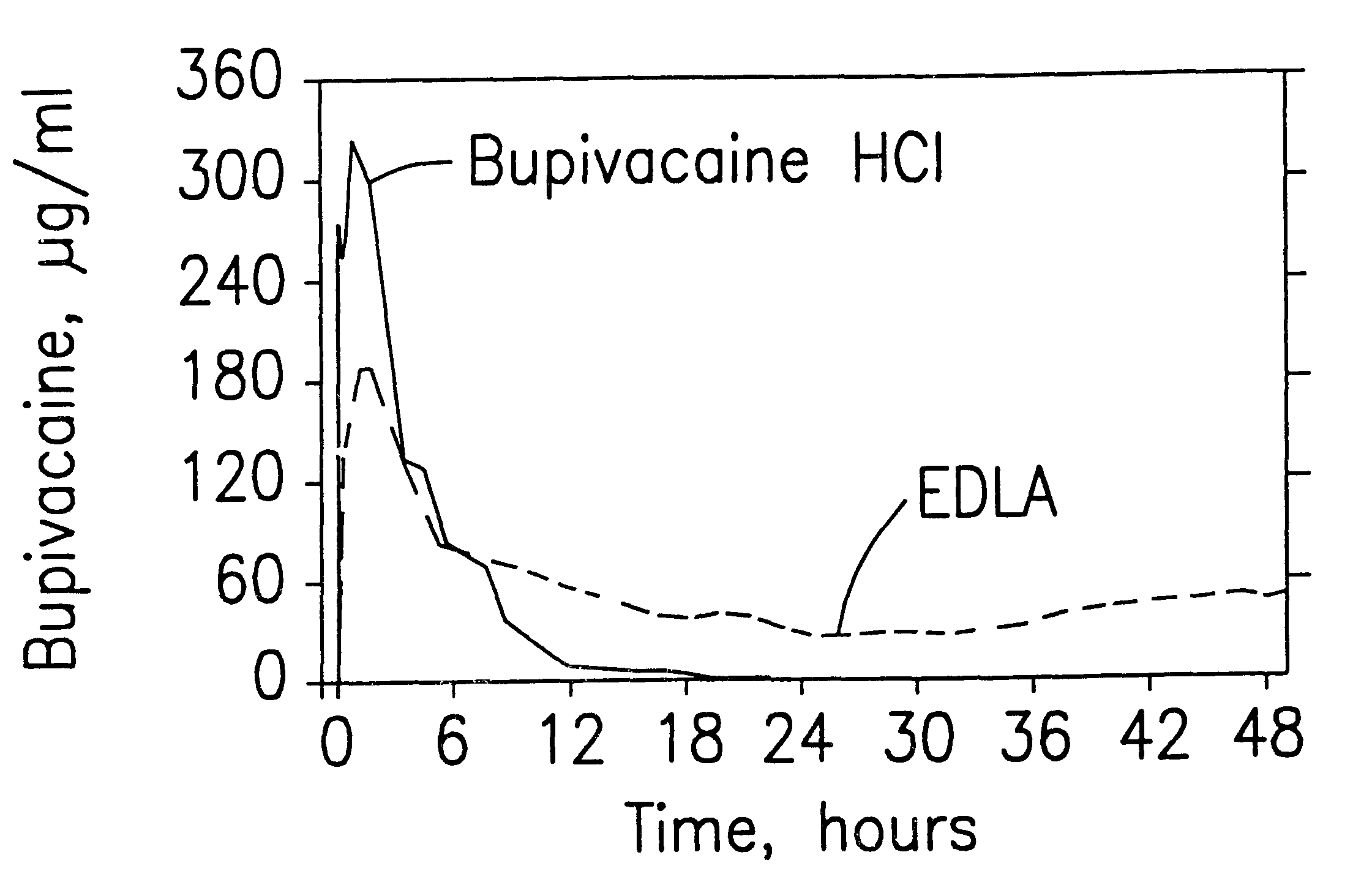
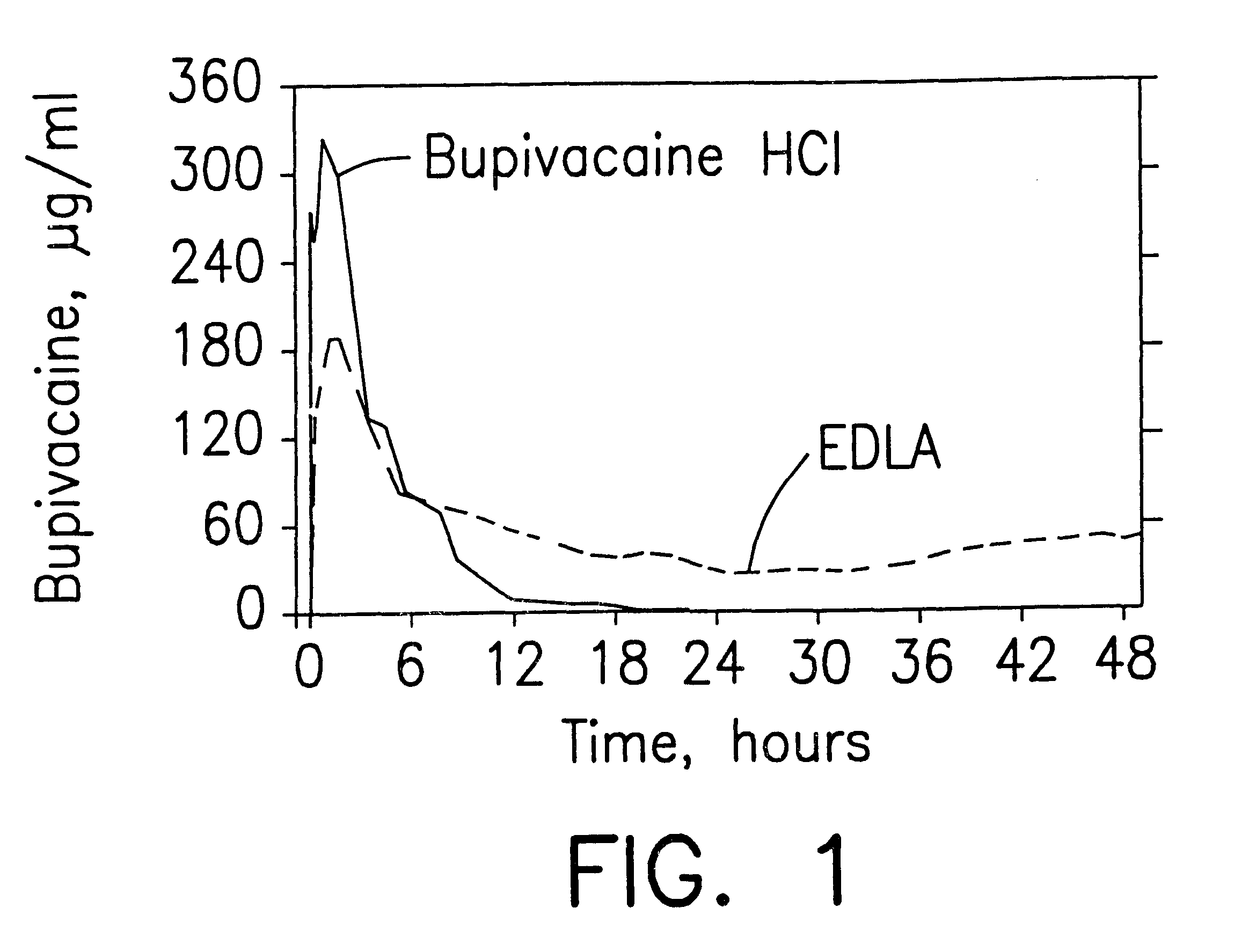
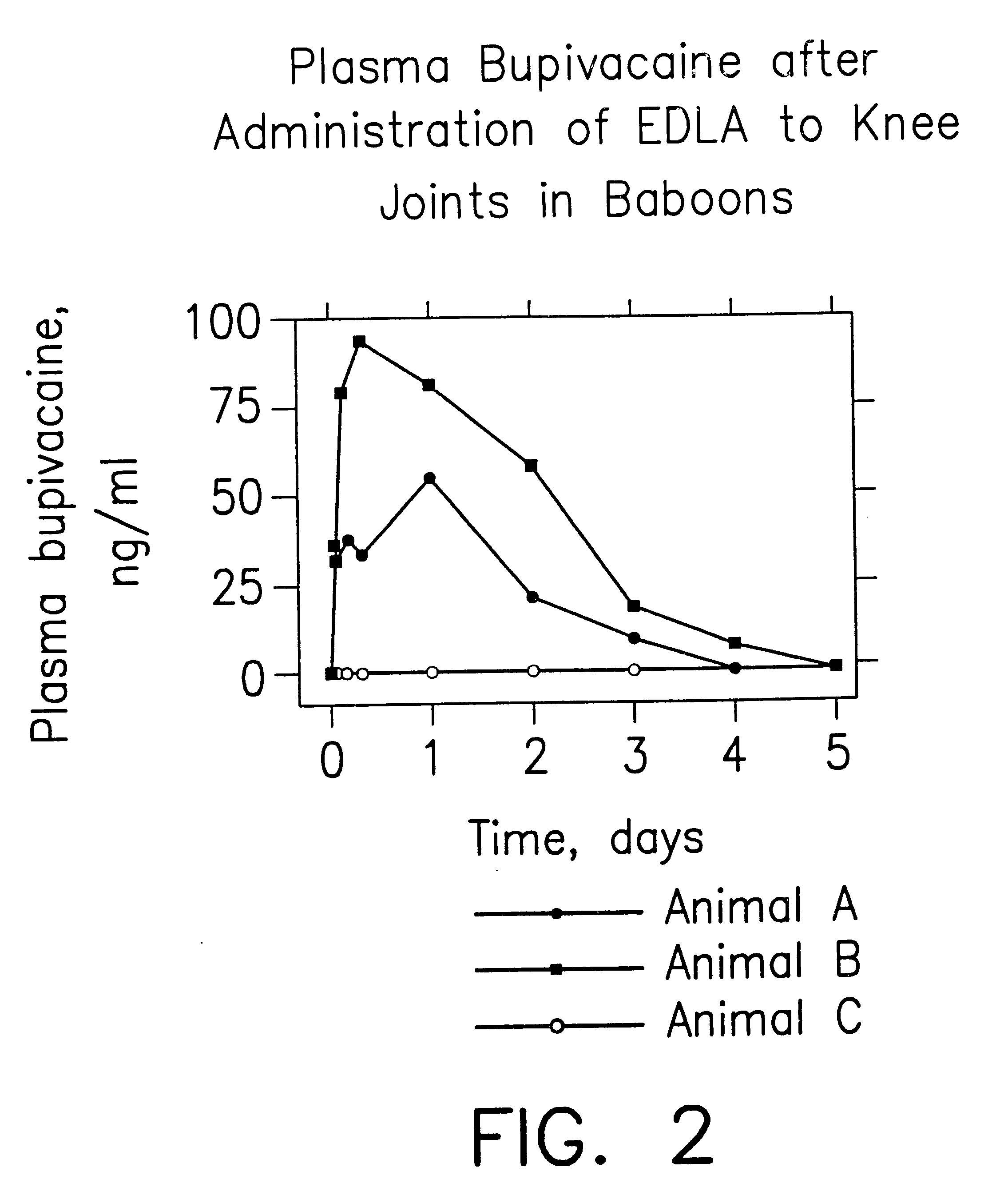
Prolonged anesthesia in joints and body spaces
InactiveUS6248345B1Enhance and prolong local anesthesiaImprovement in administrationInorganic non-active ingredientsAnaestheticsAnesthetic AgentPharmaceutical medicine
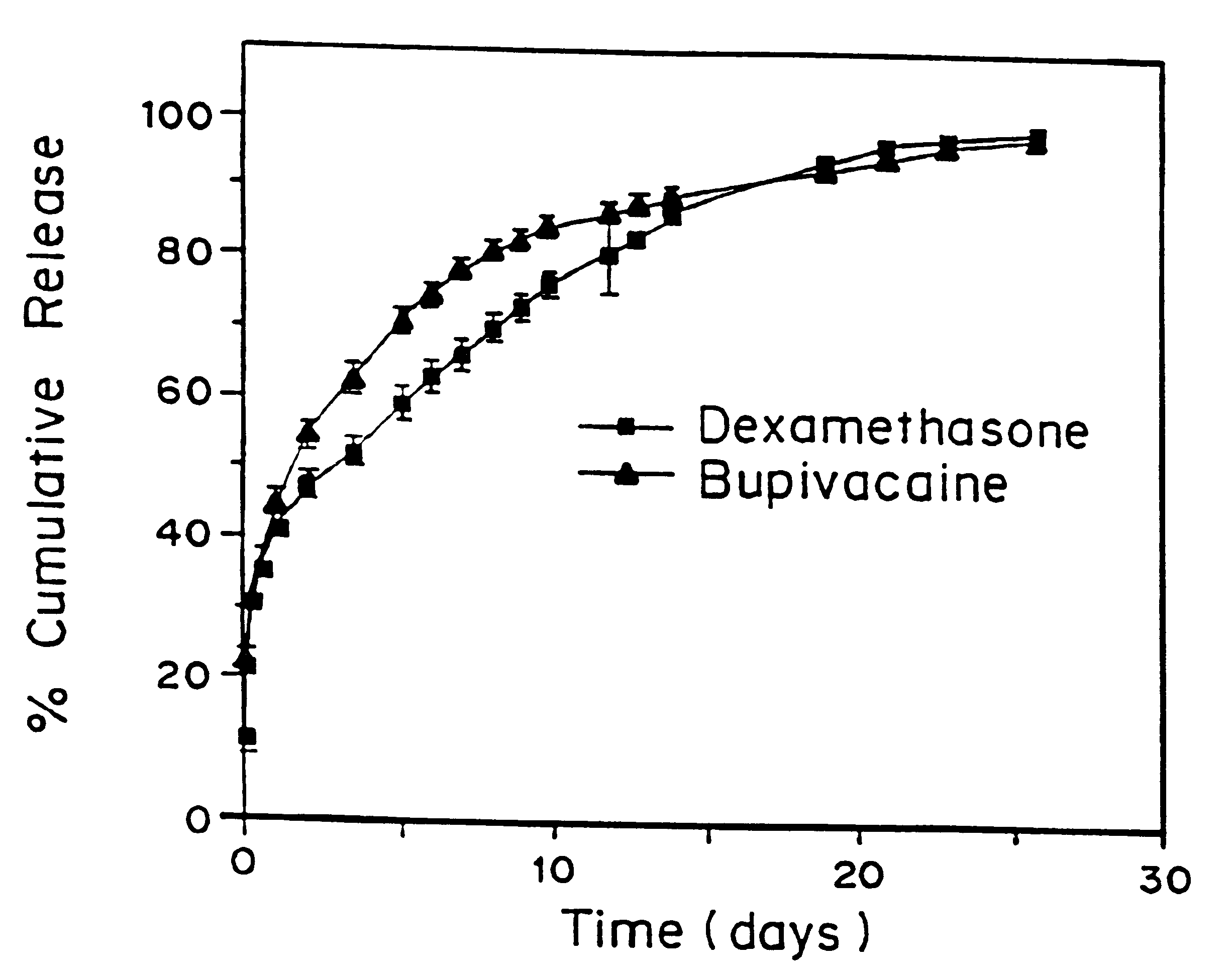
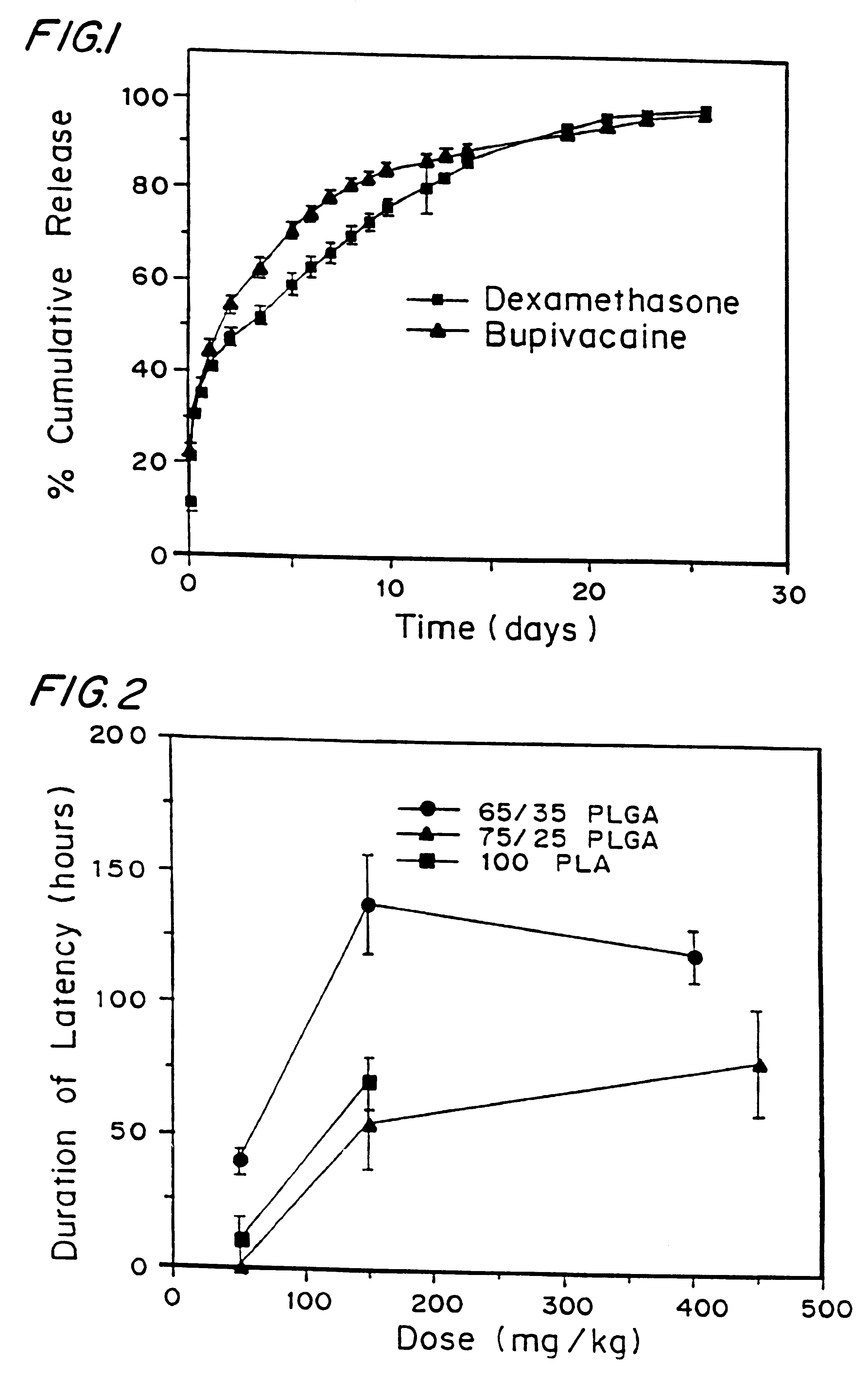
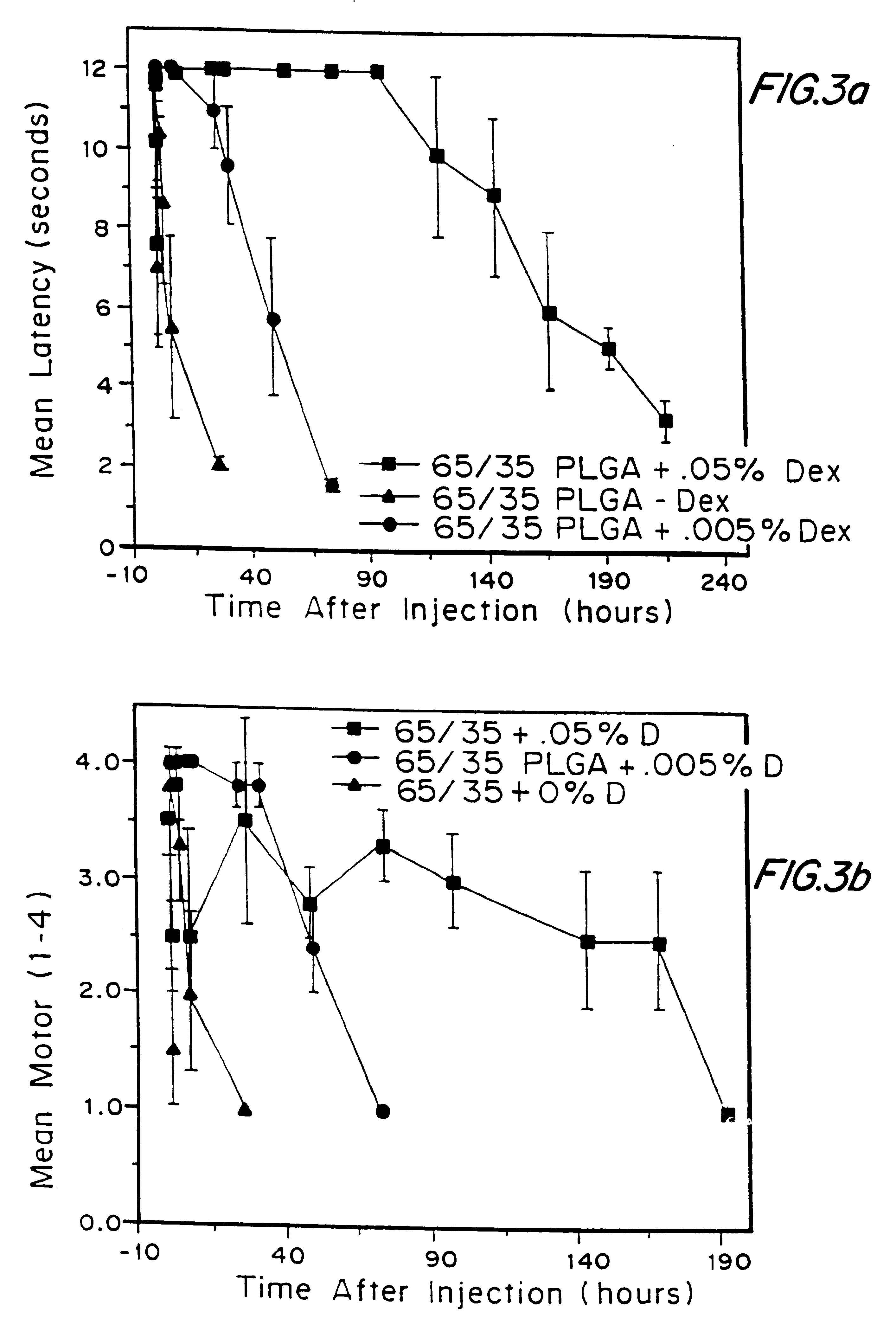
Sustained release local anesthetic formulations are administered intra articularly and / or into body spaces / cavities. The formulation is preferably a plurality of injectable microparticles including a local anesthetic and an effective amount of a biocompatible, biodegradable, sustained release material prolonging the release of the local anesthetic and optionally and a pharmaceutically acceptable, i.e., non-toxic, augmenting agent effective to prolong the duration of the local anesthesia for a time period longer than that obtainable without the augmenting agent.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
High load formulations and methods for providing prolonged local anesthesia
A formulation for inducing sustained local anesthesia in a patient comprising a substrate comprising a high load of local anesthetic by weight and an effective amount of a biocompatible, controlled release material to obtain a. reversible nerve blockade or anesthesia effect when implanted or injected in a patient, and a non-toxic glucocorticosteroid agent effective to prolong the duration of the local anesthesia for a time period longer than that obtainable from the substrate without the glucocorticosteroid agent.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Skin resurfacing and treatment using biocompatible materials
InactiveUS20050059940A1Eliminate the problemAvoid infectionSurgeryMedical devicesHuman bodyCarrier fluid
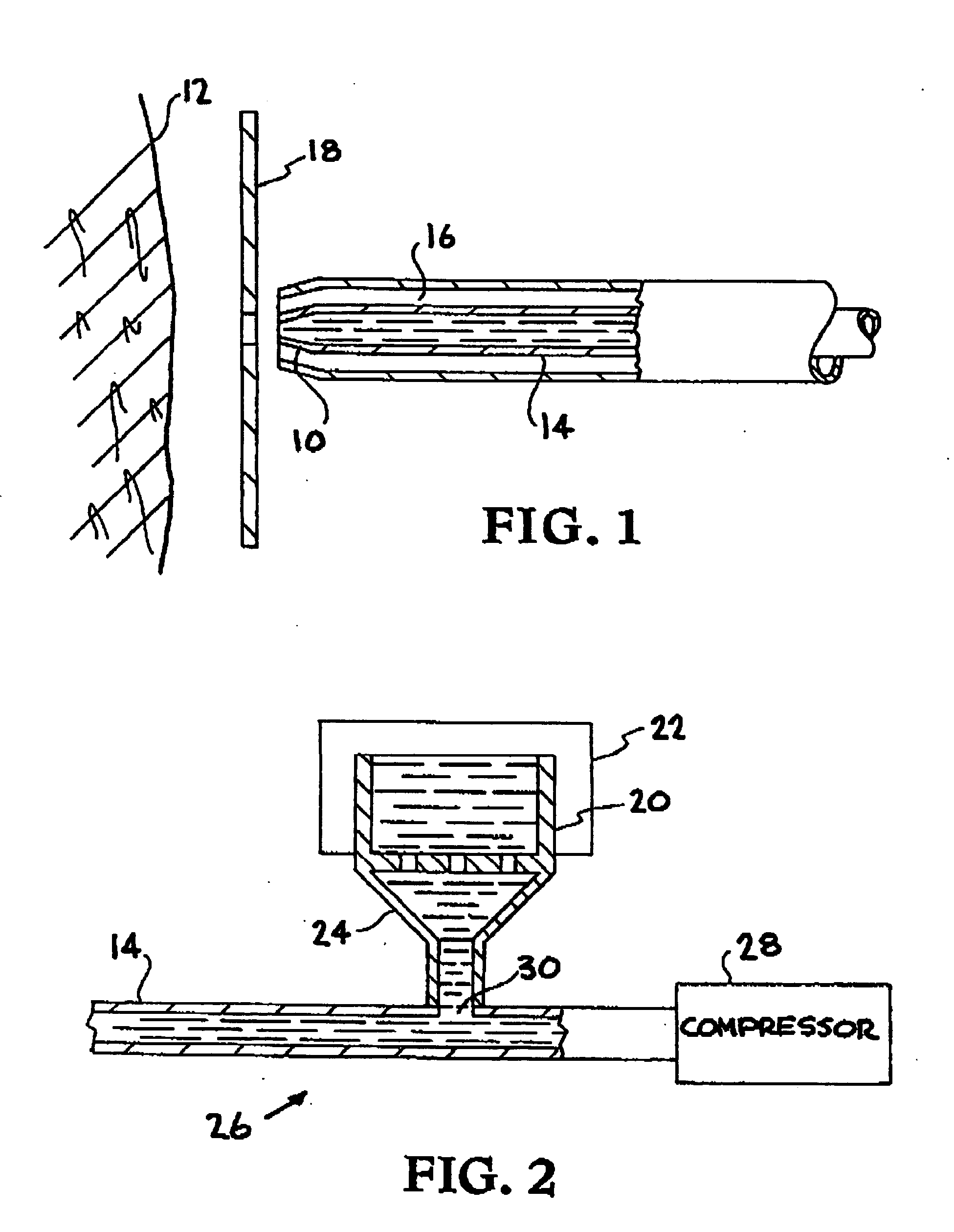
Biocompatible materials are propelled at the skin with sufficient velocity to cause desired resurfacing of skin layers to the desired penetration depth. The materials, such as dry ice or water ice, are harmonious with the human body and thus eliminate foreign body reactions. Various materials may be used in combination, including local anesthetics and vasoconstrictors in solid or liquid form. The biocompatible solid or liquid particles are suspended in a cold carrier fluid and propelled through an insulated delivery system to the surface of the skin. The treatment of diseased skin lesions may be accomplished using the present invention as a drug delivery system.
Owner:PEARL TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Implantable or insertable medical devices for controlled drug delivery
Implantable or insertable medical devices are provided, which comprises: (a) a biocompatible polymer; and (b) at least one therapeutic agent selected from an anti-inflammatory agent, an analgesic agent, an anesthetic agent, and an antispasmodic agent. The medical devices are adapted for implantation or insertion at a site associated with pain or discomfort upon implantation or insertion. In many embodiments, the therapeutic will be selected from at least one of (i) ketorolac and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof (e.g., ketorolac tromethamine) and (ii) 4-diethylamino-2-butynylphenylcyclohexyl glycolate and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof (e.g., oxybutynin chloride). Also provided are uses for the implantable or insertable medical devices, which uses comprise reducing pain or discomfort accompanying the implantation or insertion of such devices. Further uses may comprise reducing microbial buildup along the device. Methods for manufacturing implantable or insertable medical devices are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
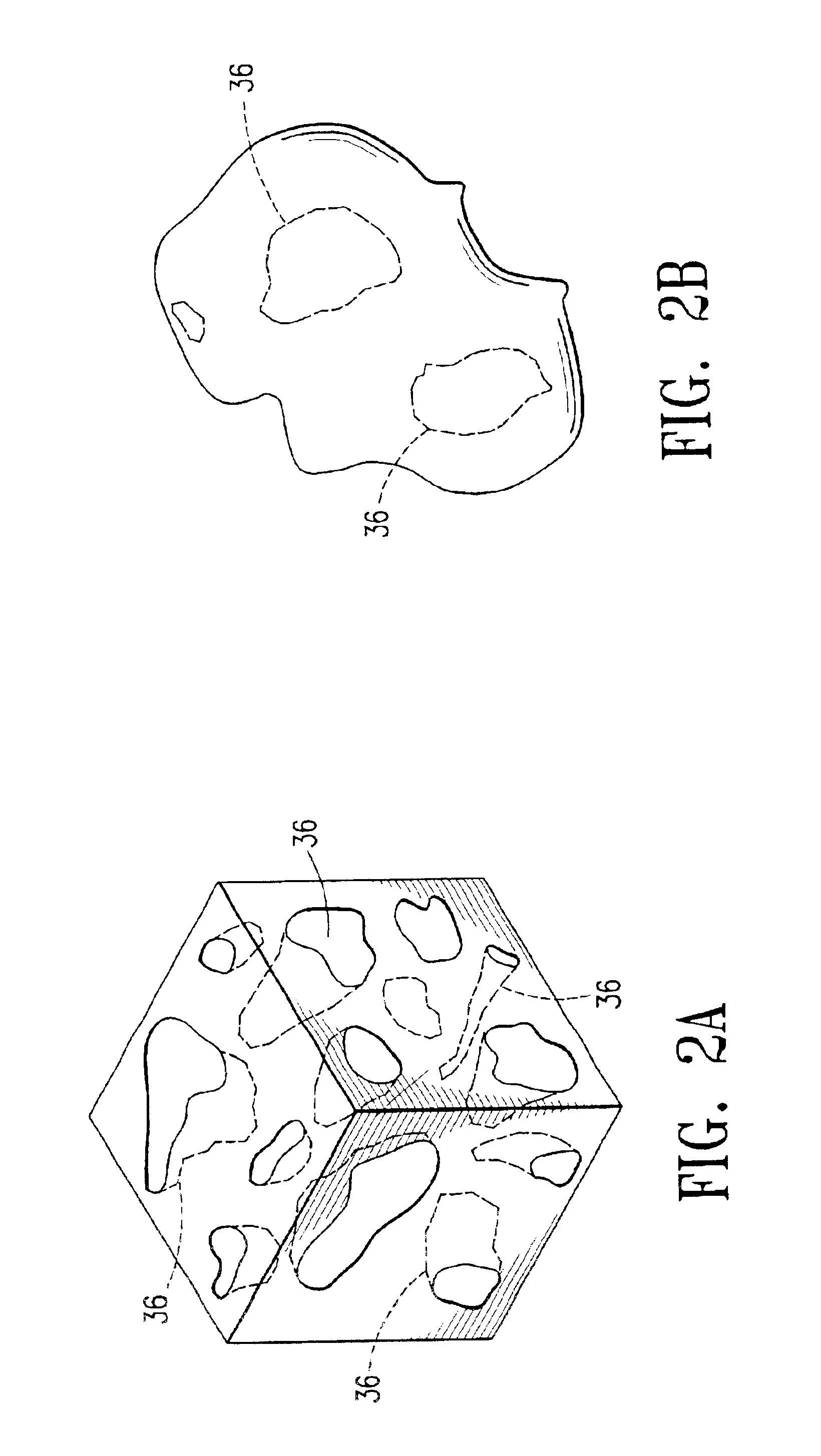
Cavity-filling biopsy site markers
InactiveUS6862470B2Easy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesAnesthetic AgentMaximum dimension
The invention provides materials, devices and methods for marking biopsy sites for a limited time. The biopsy-marking materials are ultrasound-detectable bio-resorbable powders, with powder particles typically between about 20 microns and about 800 microns in maximum dimension, more preferably between about 300 microns and about 500 microns. The powders may be formed of polymeric materials containing cavities sized between about 10 microns and about 500 microns, and may also contain binding agents, anesthetic agents, hemostatic agents, and radiopaque markers. Devices for delivering the powders include tubes configured to contain the powders and to fit within a biopsy cannula, the powders being ejected by action of a syringe. Systems may include a tube containing powder, and a syringe containing sterile saline. The tube may be configured to fit within a biopsy cannula such as a Mammotome® or SenoCor 360™ cannula.
Owner:SENORX
Formulations and methods for providing prolonged local anesthesia
InactiveUS6451335B1Slow in-vitro releaseRelease the local anestheticAnaesthesiaGranular deliveryControlled releaseAnesthetic Agent
A formulation for inducing sustained regional local anesthesia in a patient comprising a substrate comprising a local anesthetic and an effective amount of a biocompatible, biodegradable, controlled release material prolonging the release of the local anesthetic from the substrate to obtain a reversible local anesthesia when implanted or injected in a patient, and a non-toxic augmenting agent effective to prolong the duration of the local anesthesia for a time period longer than that obtainable from the substrate without the augmenting agent. In preferred embodiments, the controlled release material is a low molecular weight, acid-terminated polymer. A further aspect of the invention is directed to such formulations which release the local anesthetic in two phases, the first a rapid "bolus" to initiate anesthesia and a second, slower release to maintain anesthesia.
Owner:EURO-CELTIQUE SA
Sterile, breathable patch for treating wound pain
InactiveUS20030082225A1Not further irritate the wound upon removalBiocideNervous disorderAnesthetic AgentIntact skin
An intradermal patch having a permeable backing coated with a polyvinylpyrrolidone-based hydrogel and containing one or more local anesthetics. The patch is breathable, non-irritating upon application and removal, soothing, and sterile. The patch is useful for treating the pain associated with non-intact skin indications.
Owner:EPICEPT CORP
Effervescent granules and methods for their preparation
InactiveUS6488961B1Improve stabilityParticular regionPowder deliveryBiocideAnesthetic AgentHYDROMORPHONE HYDROCHLORIDE
Disclosed here are effervescent granules having a controllable rate of effervescence. In some embodiments, the such granules comprise an acidic agent, an alkaline agent, a pharmacologically active agent, hot-melt extrudable binder capable of forming a eutectic mixture with the acidic agent and, optionally, a plasticizer. The effervescent granules are made by a hot-melt extrusion process. The present invention also provides a thermal heat process for preparing a pharmacologically active agent containing effervescent granule. In certain aspects, the granules contain pharmacologically active agents such as narcotics, antidiarrheal agents, antiviral agents, anxiolytic agents, a cholesterol lowering agent, an alpha adrenergic blocking agent, a phenanthrene derivative. By way of example, some of the narcotics that may be included in the granules and in the process of preparing the granules include, by way of example: phenanthrene derivatives (e.g., morphine sulfate), and morphine derivatives (e.g., hydromorphone hydrochloride).
Owner:ETHYPHARM SA
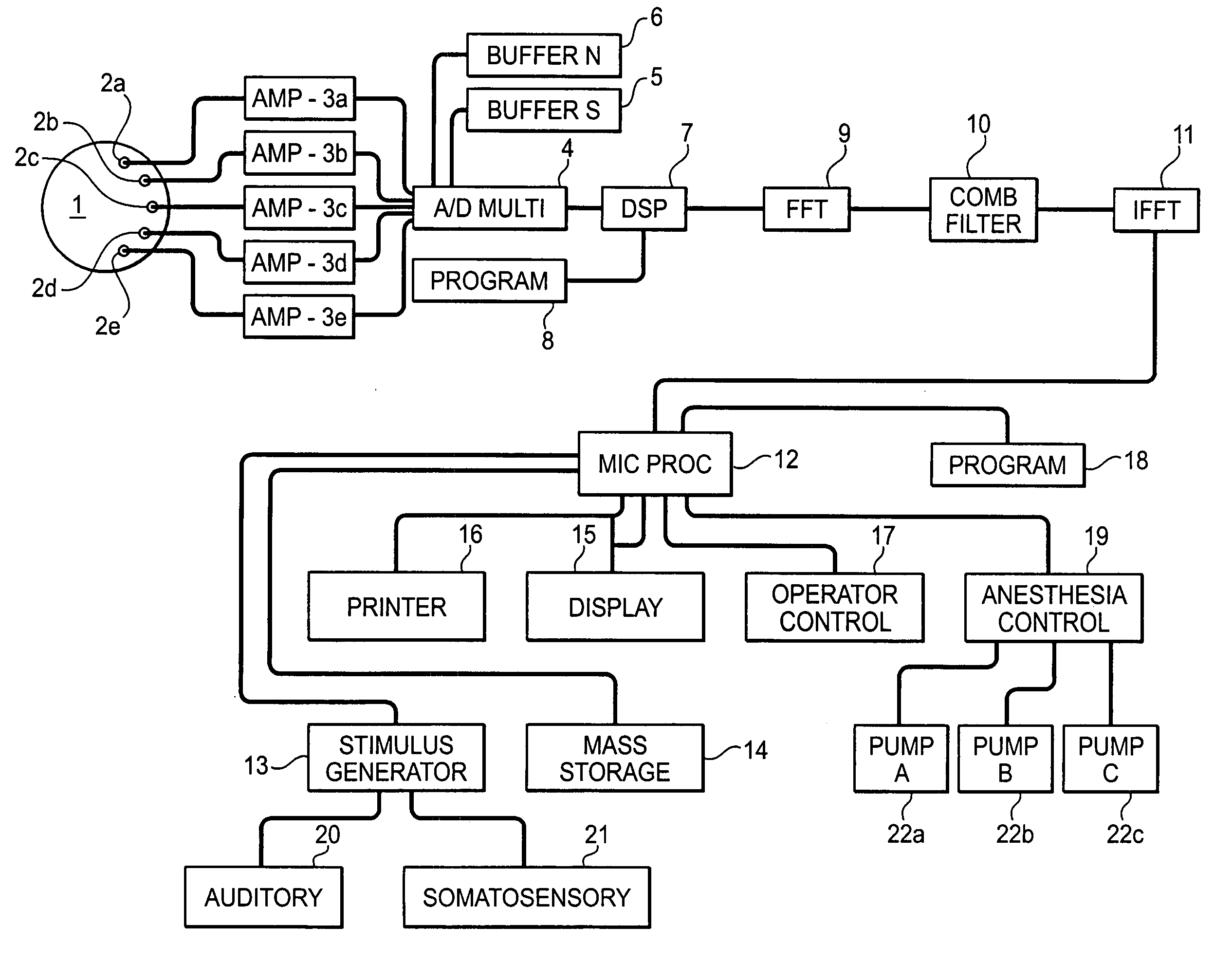
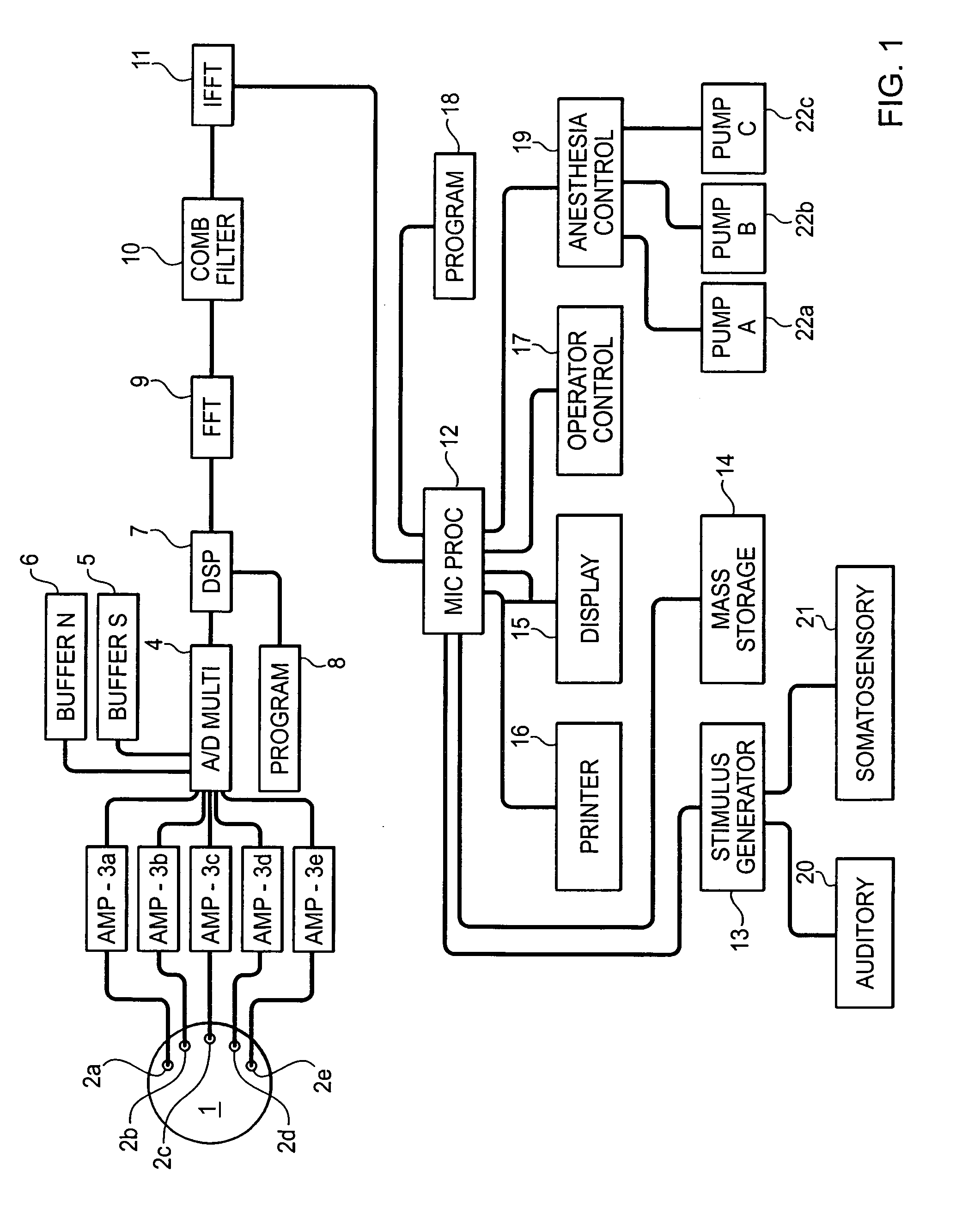
Method and apparatus for monitoring respiratory gases during anesthesia
InactiveUS6981947B2Good correlationCost-effective and frequent mannerRespiratorsMedical devicesAnesthetic AgentMetabolite
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
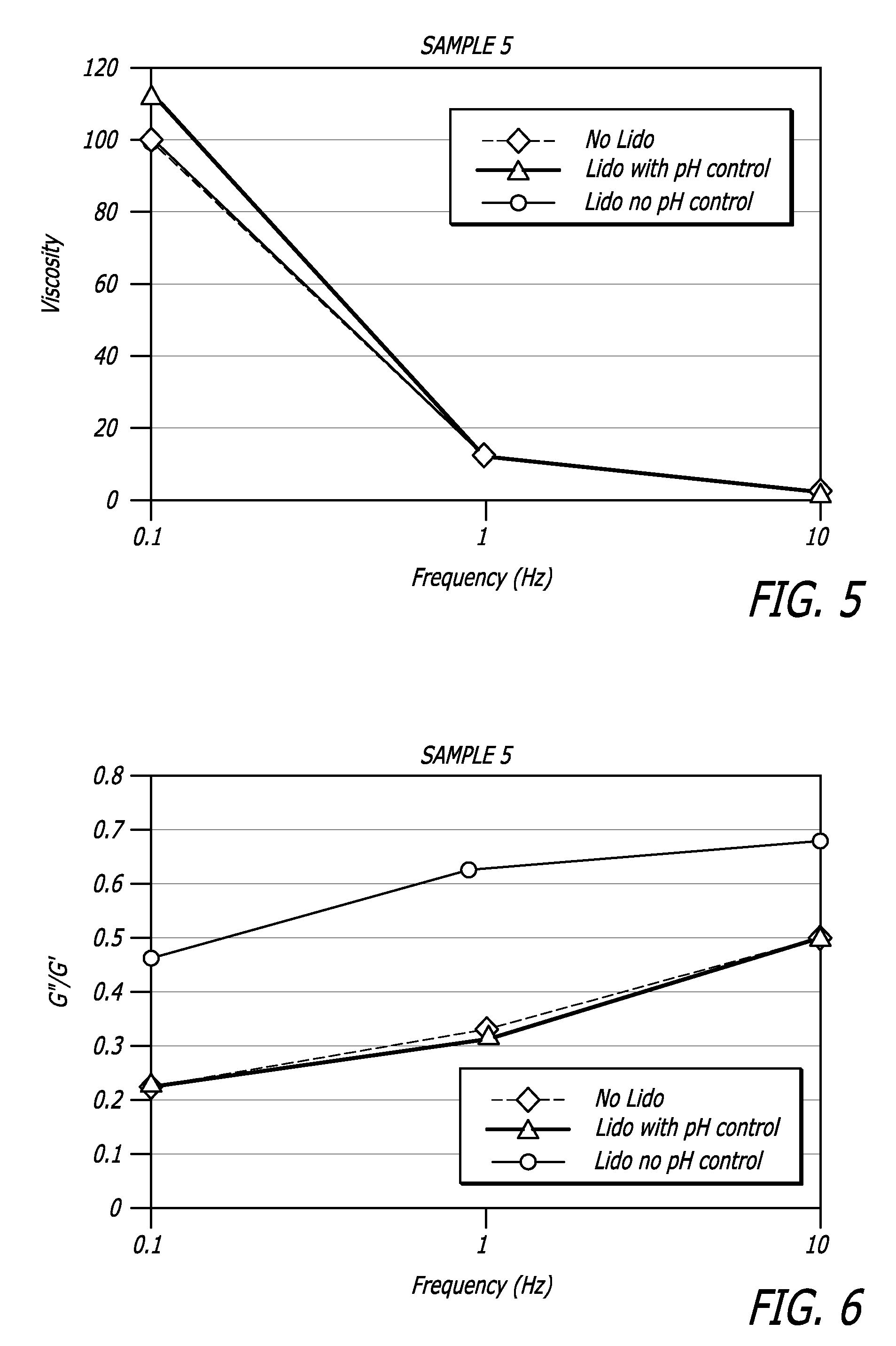
Hyaluronic acid-based gels including lidocaine
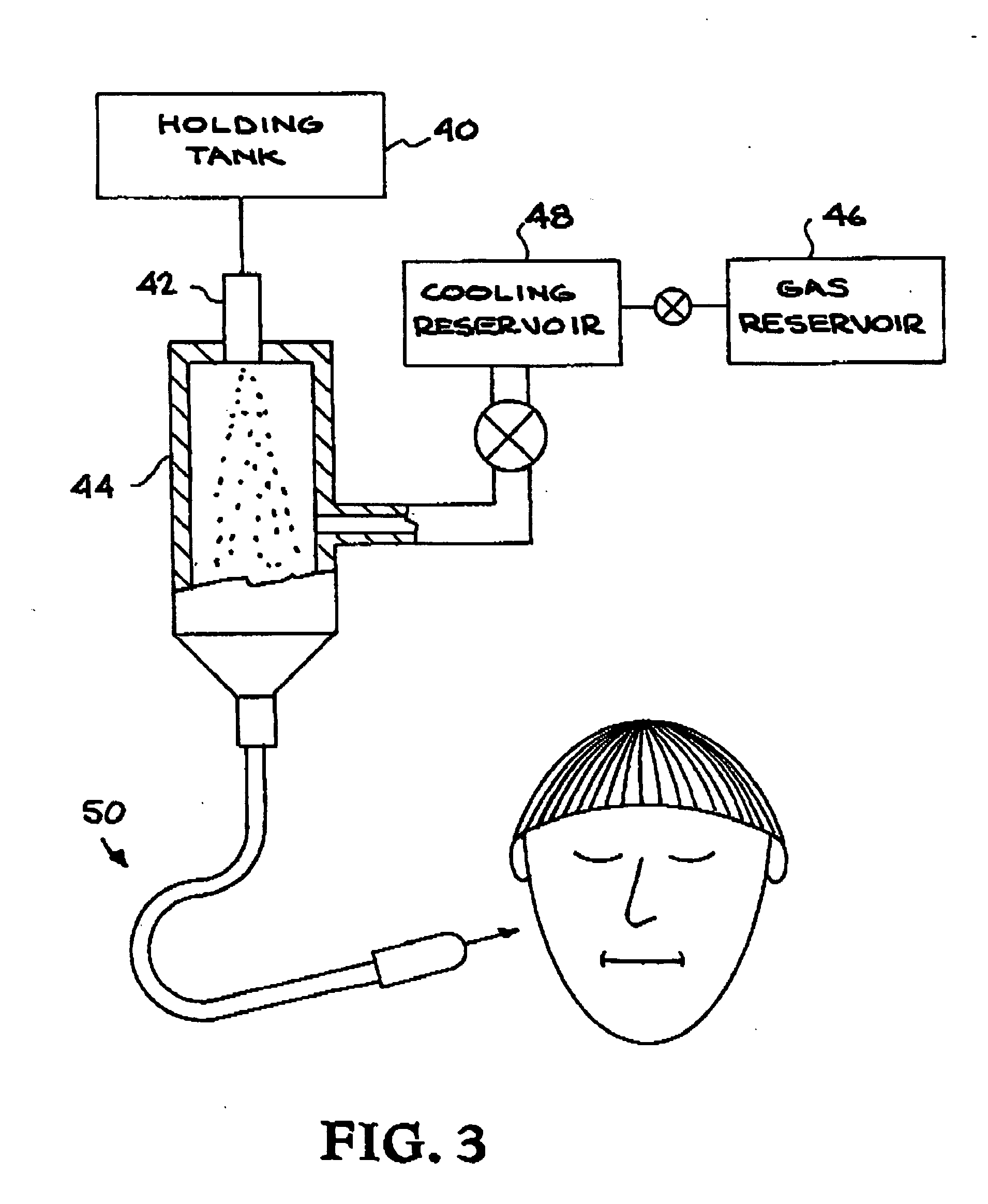
Disclosed herein are cohesive soft tissue fillers, for example, dermal and subdermal fillers, based on hyaluronic acids and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. In one aspect, hyaluronic acid-based compositions described herein include a therapeutically effective amount of at least one anesthetic agent, for example, lidocaine. The present hyaluronic acid-based compositions including lidocaine have an enhanced stability and cohesivity, relative to conventional compositions including lidocaine, for example when subjected to sterilization techniques or when stored for long periods of time. Methods and processes of preparing such hyaluronic acid-based compositions are also provided.
Owner:ALLERGAN IND
Apparatus for locating and anesthetizing nerve groups
InactiveUS20030167021A1Cost-efficient to useEasy to transportInternal electrodesMedical devicesAnesthetic AgentElectricity
An apparatus for locating and anesthetizing a nerve enables an anesthesiologist to perform a nerve blockade procedure without an assistant. An anesthetic-filled syringe is releasably mounted to a hands-free, foot-actuated, hydraulic syringe controller. An electric current generator is mounted to the syringe controller and operatively connected to a needle of the syringe. A hands-free, foot-actuated current generator controller determines an amperage of an electrical stimulus output to the needle. The current generator includes audible and visual displays for informing the anesthesiologist of the output amperage. Because the syringe controller and current generator controller allow hands-free operation, an anesthesiologist can continuously use both hands to manipulate and hold the needle in a patient.
Owner:SHIMM PETER B
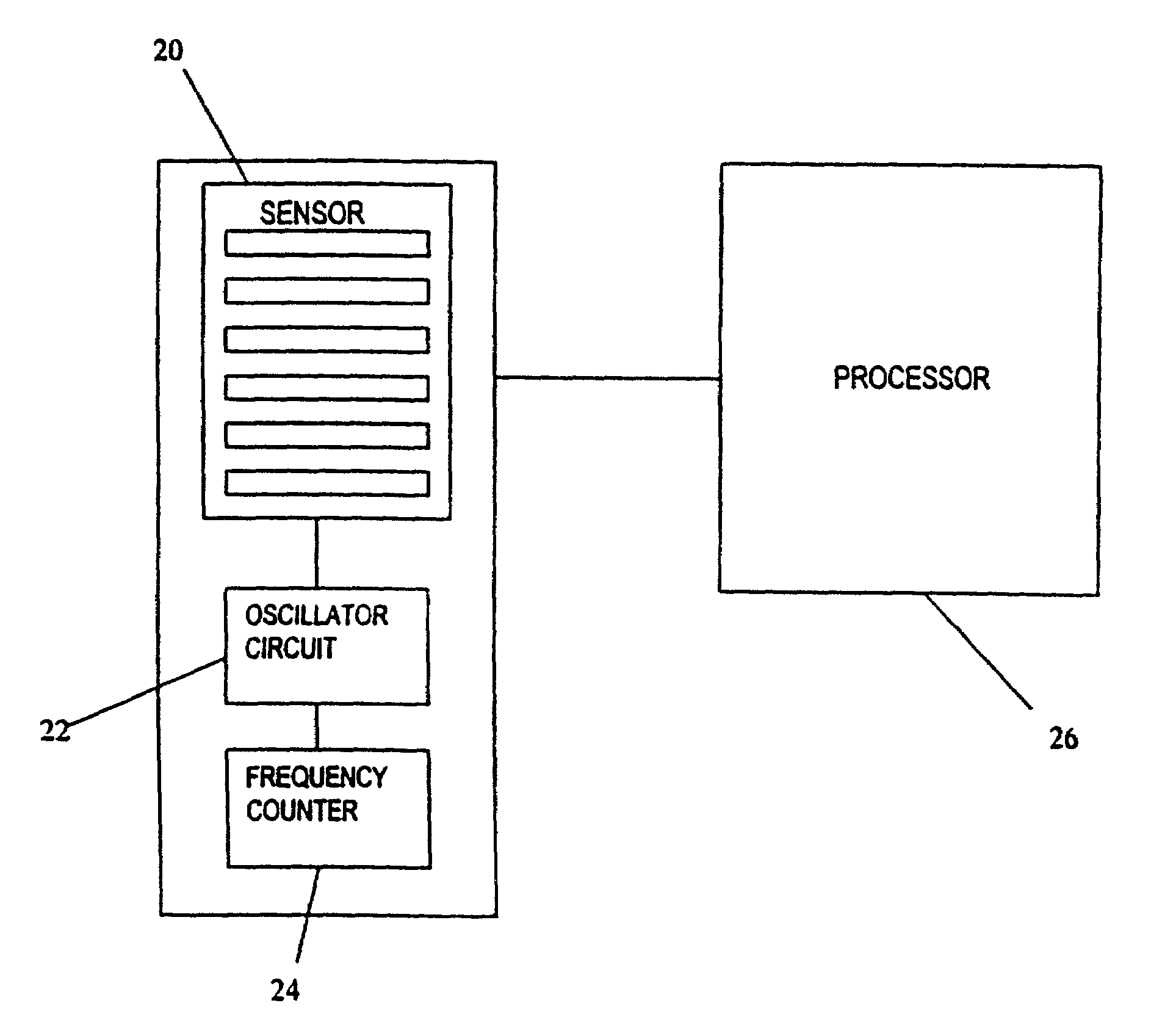
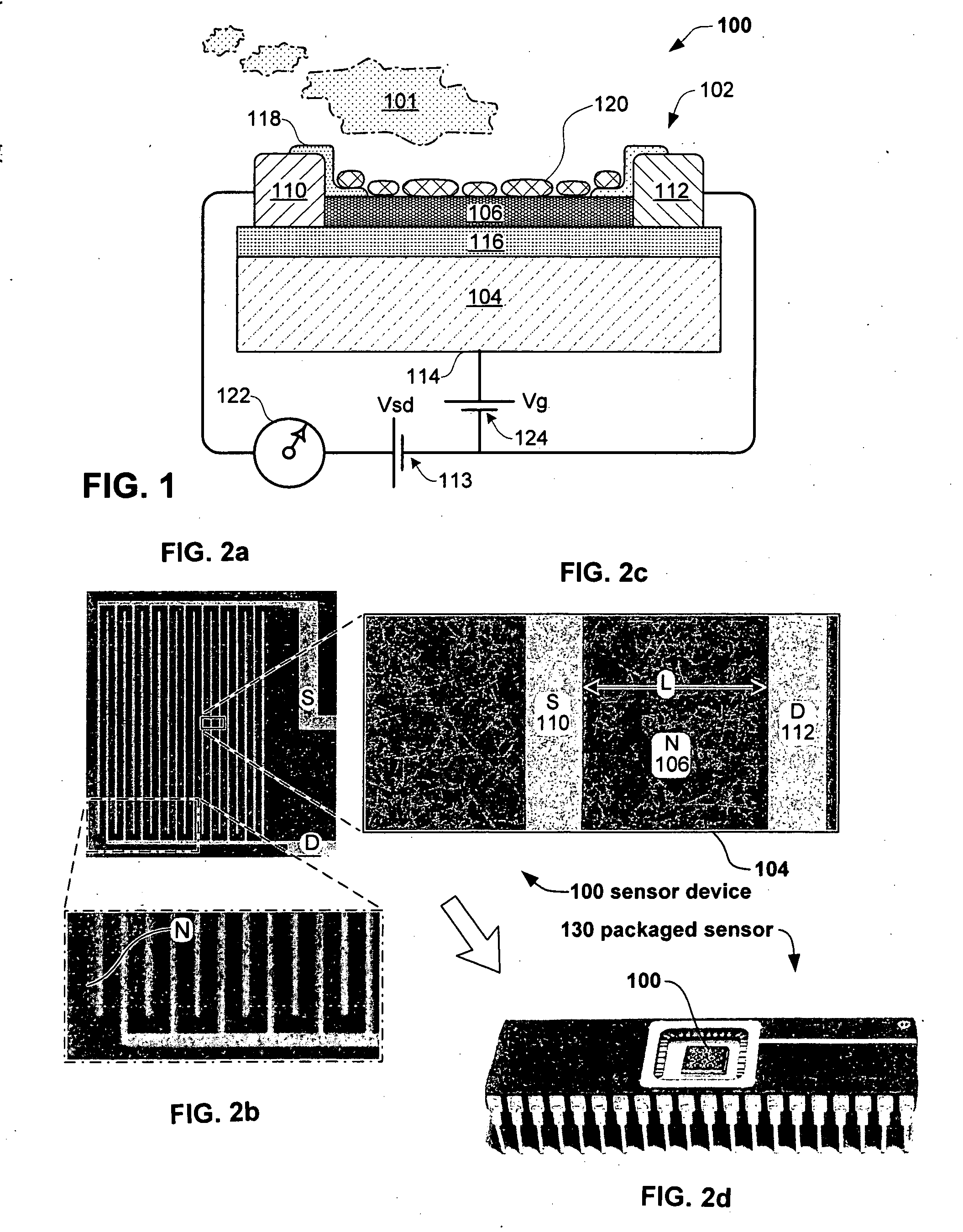
Anesthesia monitor, capacitance nanosensors and dynamic sensor sampling method
InactiveUS20080021339A1Inexpensively identifyMore cost-effectiveMaterial nanotechnologyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsCapacitanceAnesthetic Agent
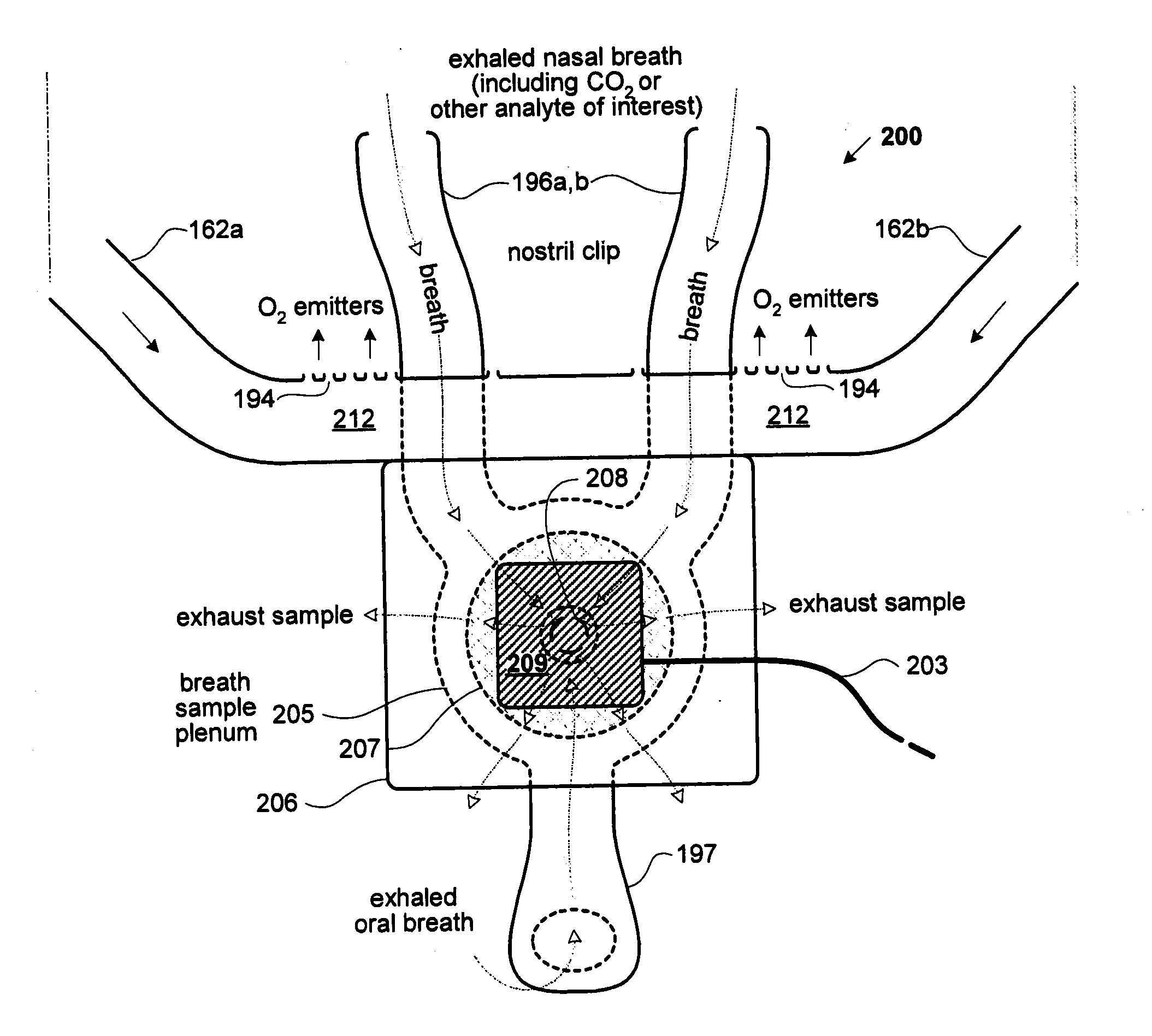
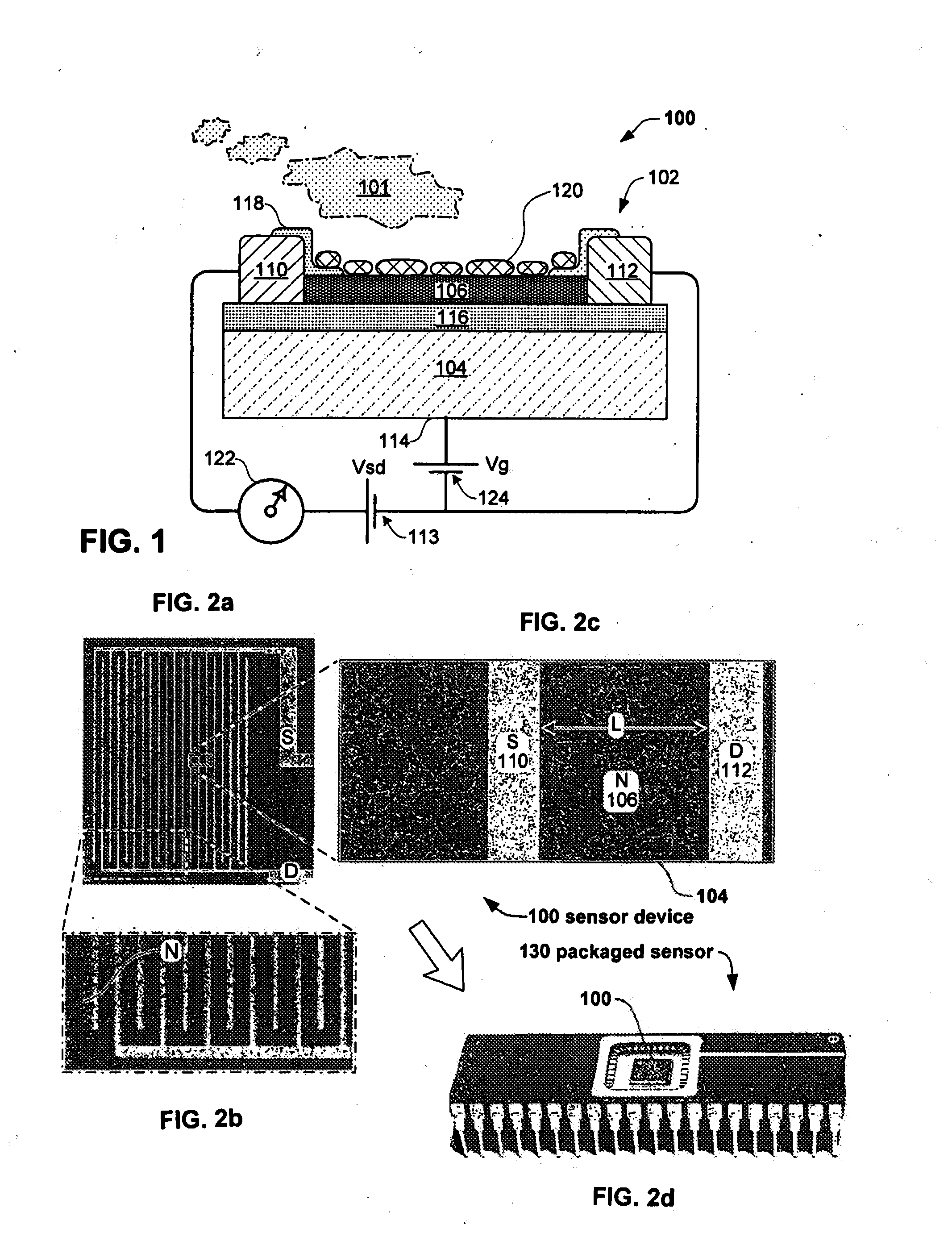
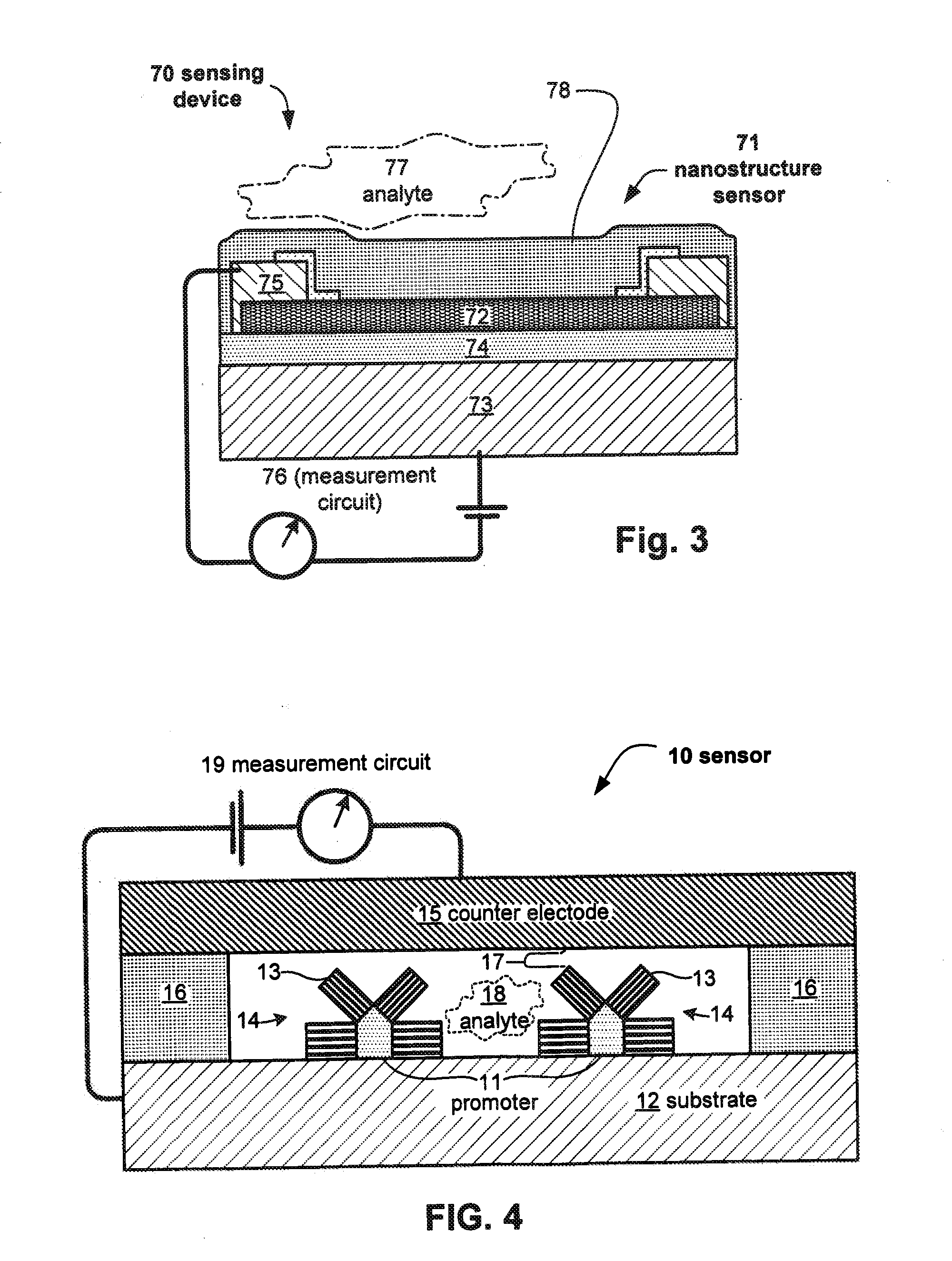
Embodiments of nanoelectronic sensors are described, including sensors for detecting analytes such as anesthesia gases, CO2 and the like in human breath. An integrated monitor system and disposable sensor unit is described which permits a number of different anesthetic agents to be identified and monitored, as well as concurrent monitoring of other breath species, such as CO2. The sensor unit may be configured to be compact, light weight, and inexpensive. Wireless embodiments provide such enhancements as remote monitoring. A simulator system for modeling the contents and conditions of human inhalation and exhalation with a selected mixture of a treatment agent is also described, particularly suited to the testing of sensors to be used in airway sampling.
Owner:NANOMIX
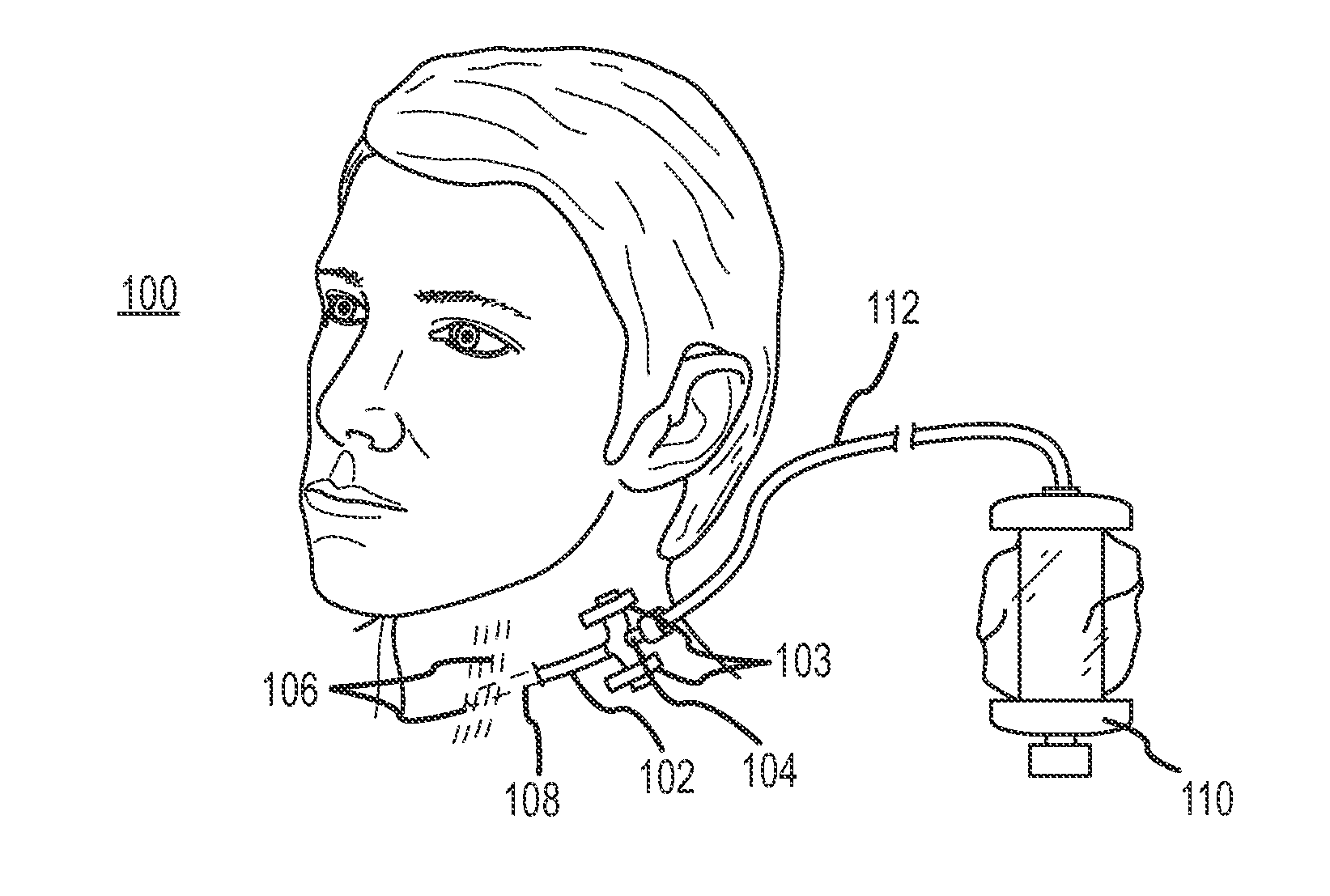
Metabolic measurements system including a multiple function airway adapter
InactiveUS20070225612A1Easy to reusePromote generationRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsAnesthetic AgentRespiratory flow
A system for measuring a metabolic parameter. The system includes an integrated airway adapter capable of monitoring any combination of respiratory flow, O2 concentration, and concentrations of one or more of CO2, N2O, and an anesthetic agent in real time, breath by breath. Respiratory flow may be monitored with differential pressure flow meters under diverse inlet conditions through improved sensor configurations which minimize phase lag and dead space within the airway. Molecular oxygen concentration may be monitored by way of luminescence quenching techniques. Infrared absorption techniques may be used to monitor one or more of CO2, N2O, and anesthetic agents.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for monitoring respiratory gases during anesthesia
A method and system is provided for monitoring delivery of anesthesia (inhalational and intravenous) and detecting the depth of anesthesia wherein at least one anesthetic agent is absorbed in patient's bloodstream during the administration of anesthesia, which includes sampling inspired and expired gas; analyzing the gas for concentration of at least one substance indicative of the anesthetic agent using sensor technology such as free (unmetabolized) anesthetic agent or its metabolites; determining the effect of the agent based on that concentration; and determining depth of anesthesia based thereon.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
System and methods for detection and identification of chemical substances
InactiveUS20050077476A1MinimizesHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAnesthetic AgentSpectrograph
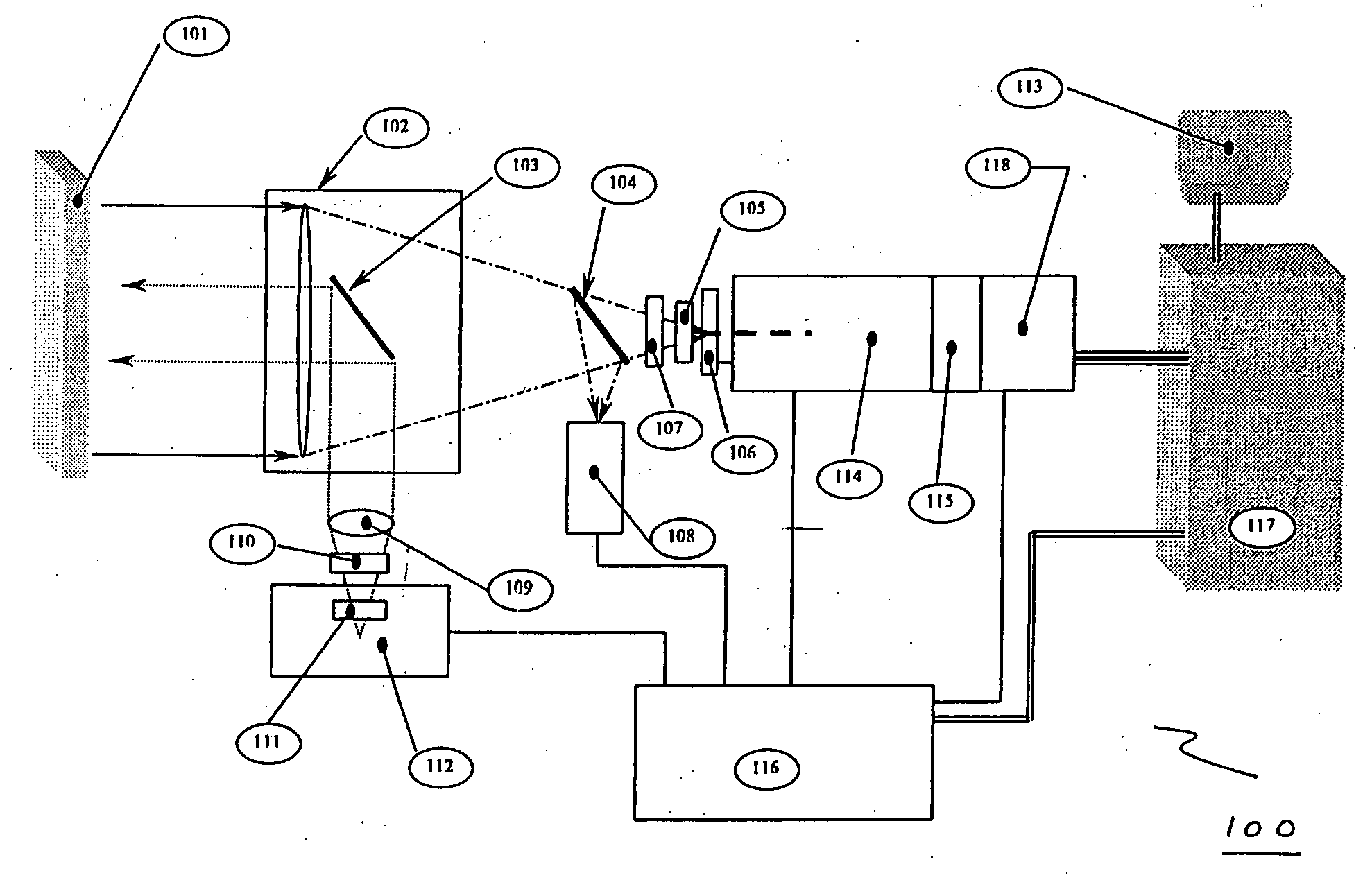
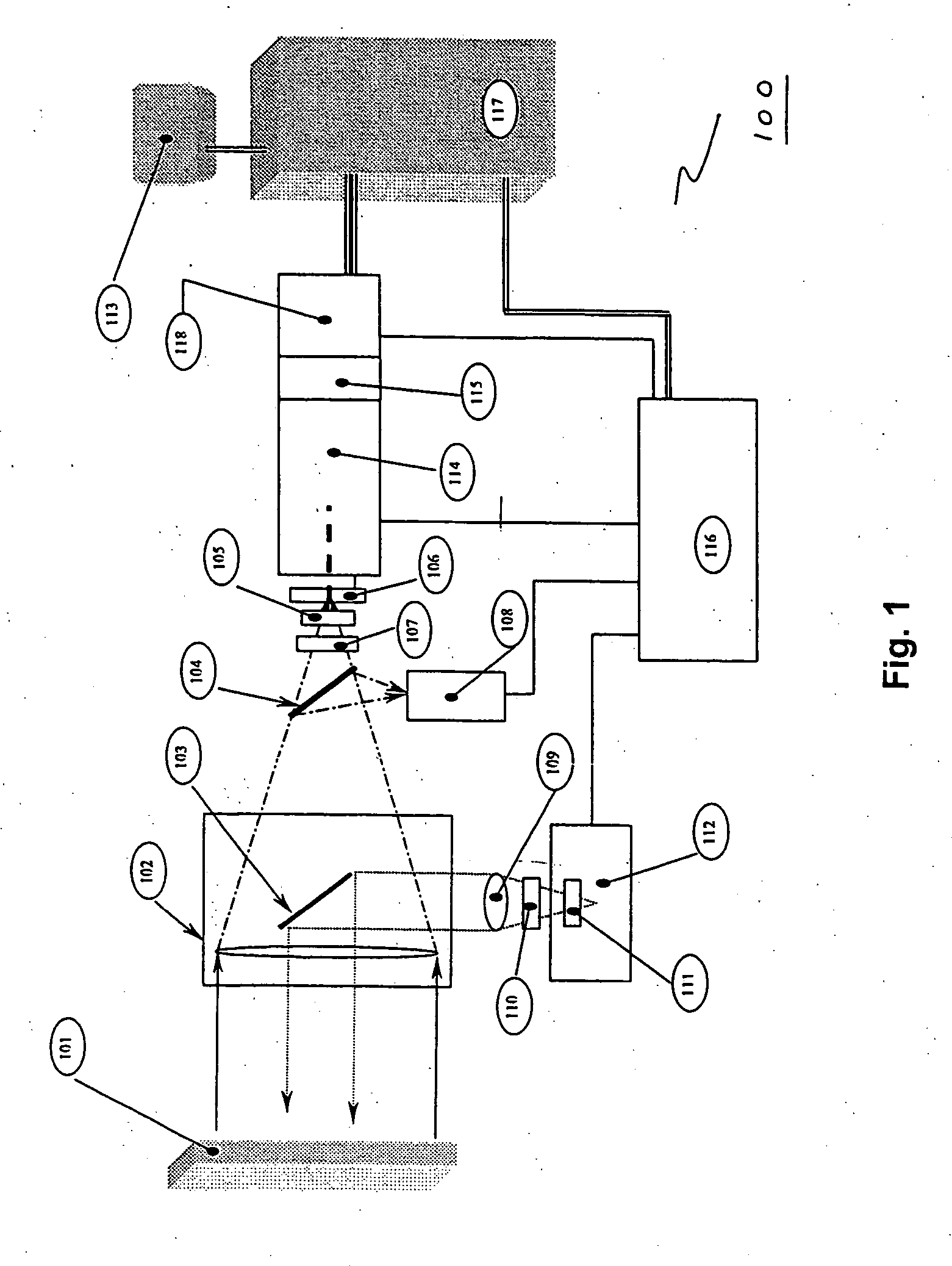
The invention provides a system and method utilizing, among other things, fluorescence spectroscopy in the ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to determine chemical species and concentrations. The basic measuring system includes optics, a spectrograph, a detector, and an energy source (“head” components), along with a computer and control electronics and power source capable of generating and detecting unique fluorescence signatures for individual and unique mixtures of chemical substances including, for example, prescribed and / or compounded medications, alcohol products, food types, synthetic drugs, narcotics, perfumes, liquids, and the like.
Owner:CDEX
Methods for providing safe local anesthesia
InactiveUS6699908B2Reduce riskImproved therapeutic indexBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAnesthetic AgentControlled release
Methods and formulations for inducing substantially safer local anesthesia in a patient are provided. The methods comprise administering, to a patient in need thereof, a substrate containing a local anesthetic and an effective amount of a biocompatible, biodegradable, controlled release material to safely obtain a reversible nerve blockade when implanted or injected in a patient.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
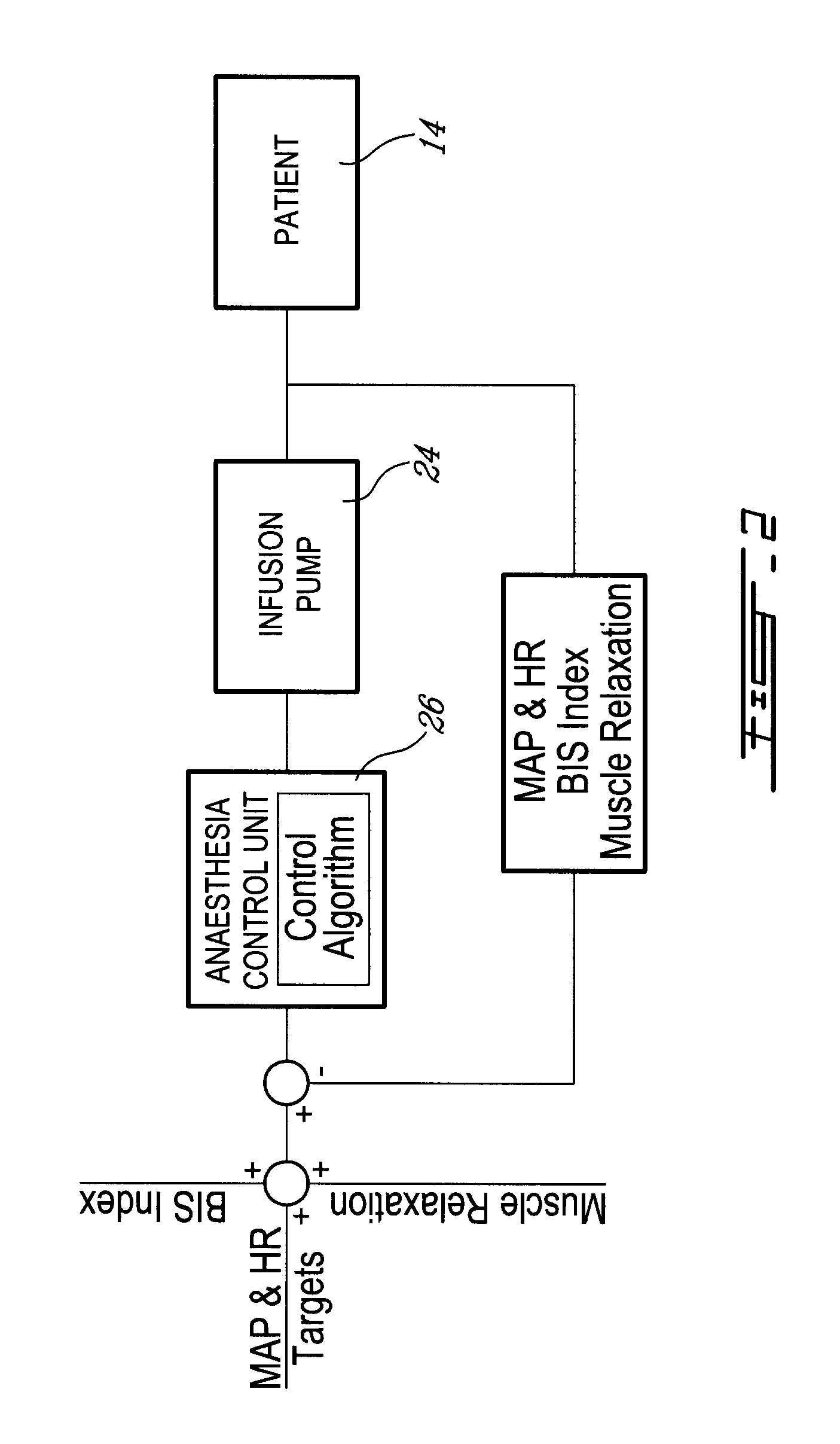
Method and system for administering an anaesthetic
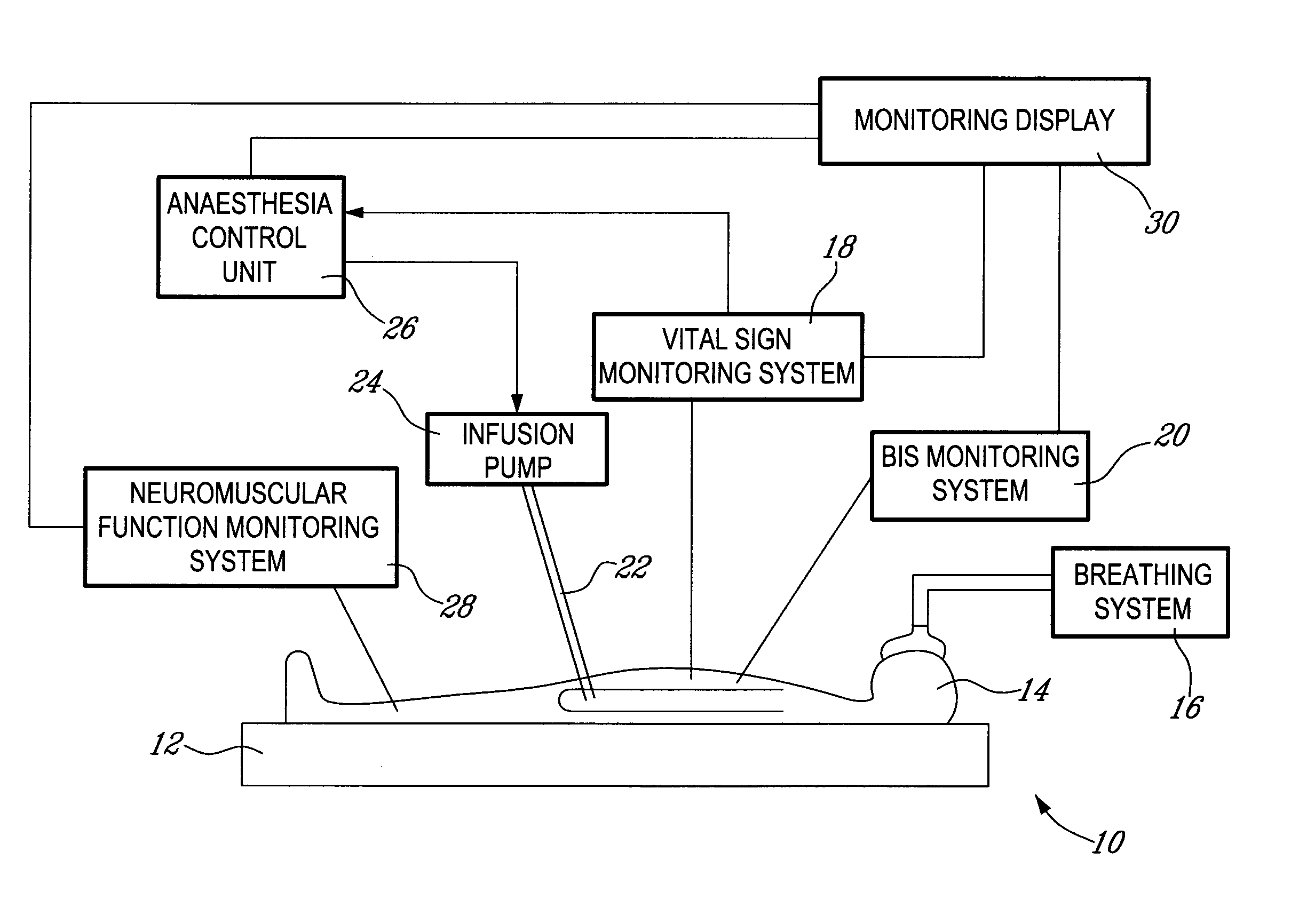
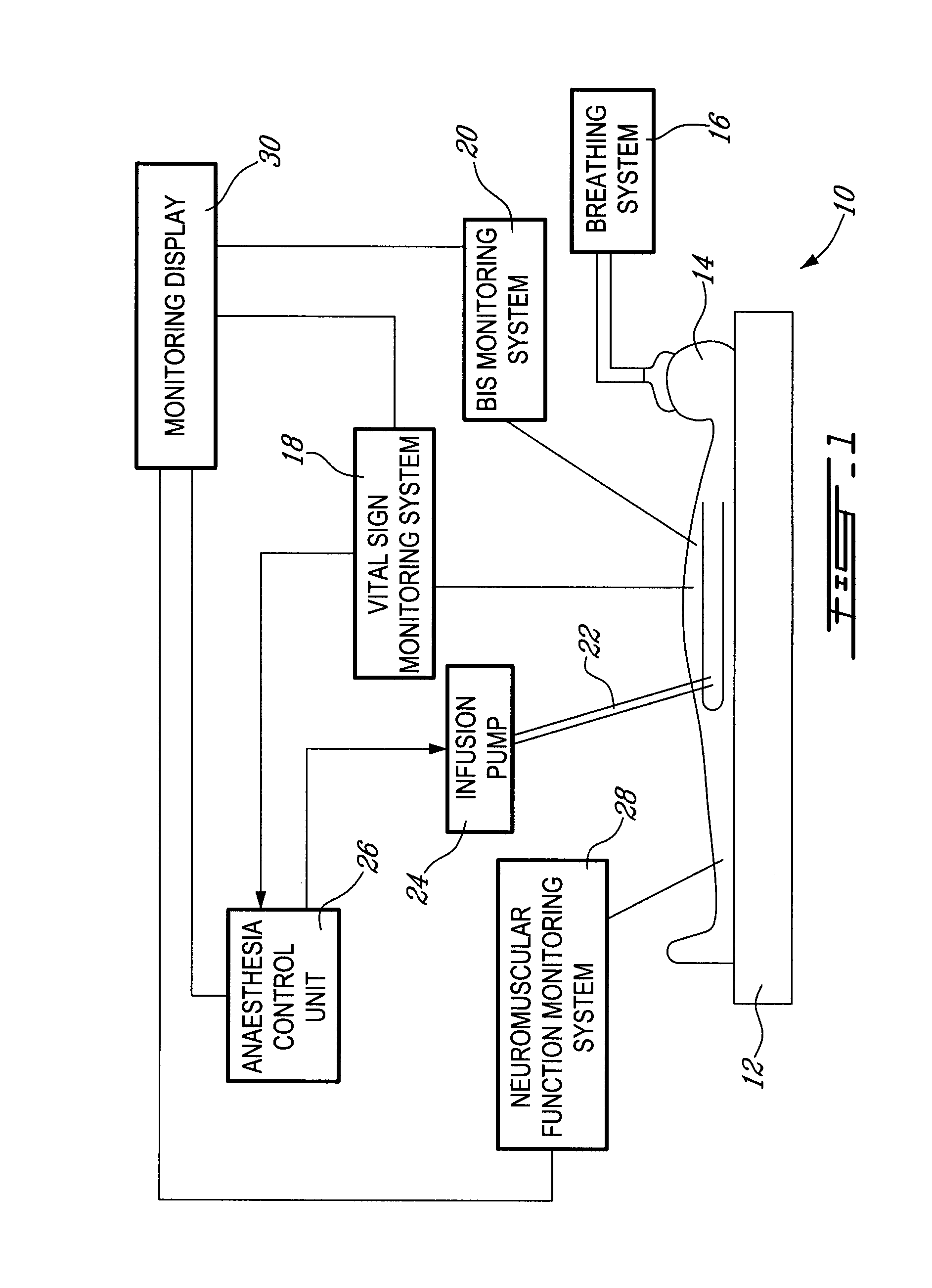
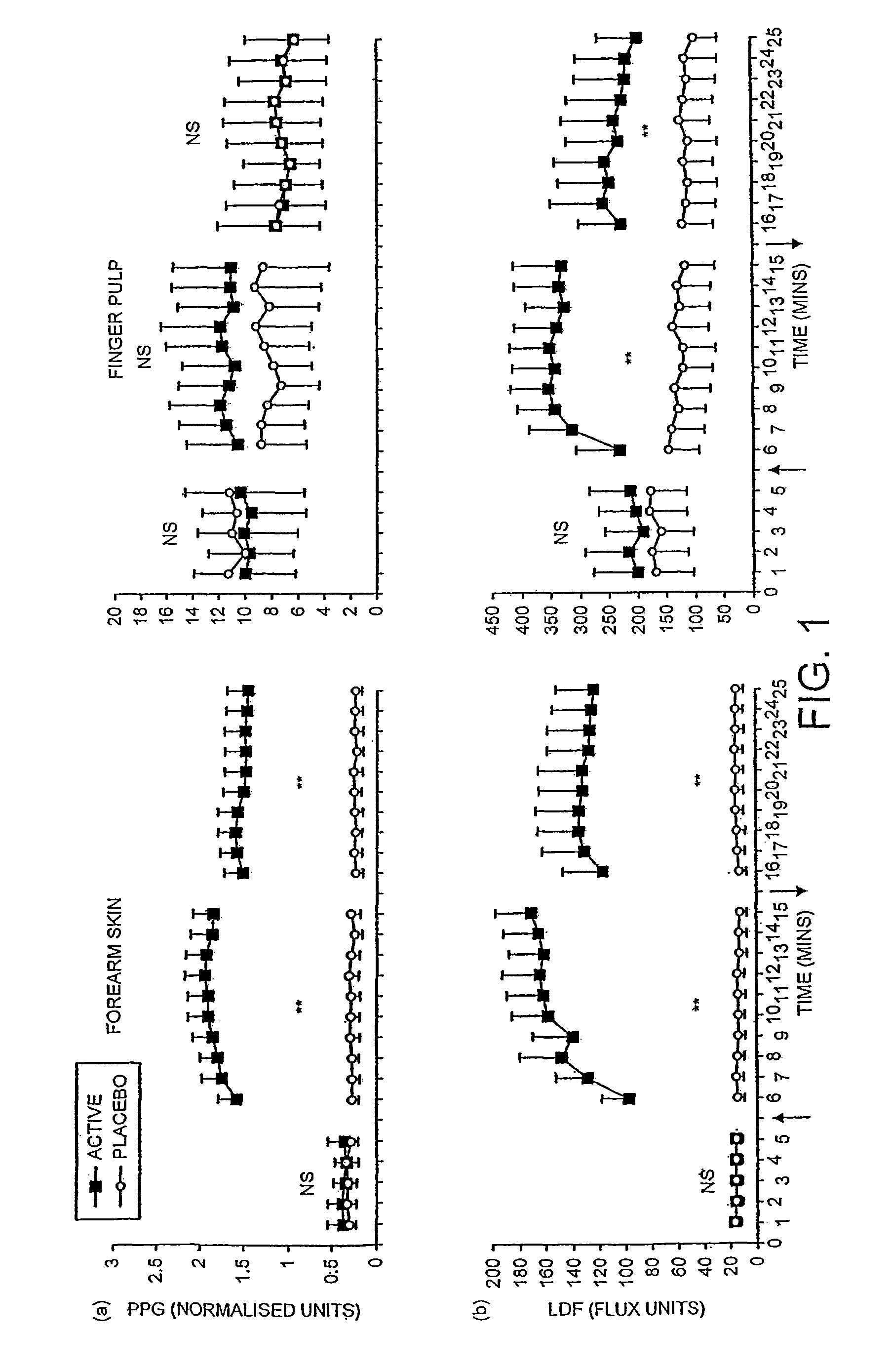
A method and system for objectively scoring intra-operative pain during general anaesthesia based on the patient's mean arterial pressure and heart rate. The index is used for closed-loop control of the intra-operative analgesia through adjustment of the drug infusion level according to fuzzy logic. It is further displayed along with other components of anaesthesia and important patient data on a monitoring display for presentation to medical staff.
Owner:HEMMERLING THOMAS +4
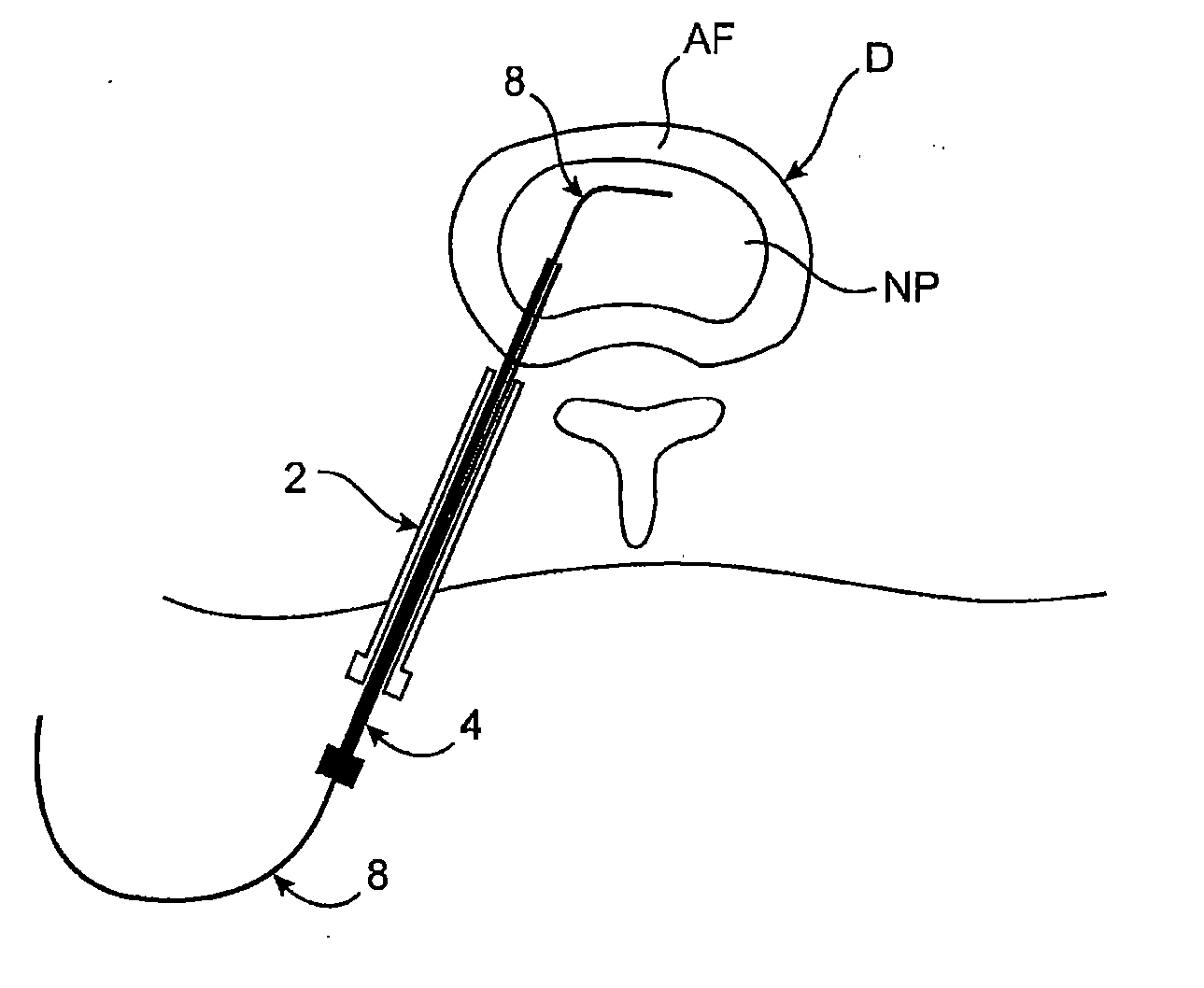
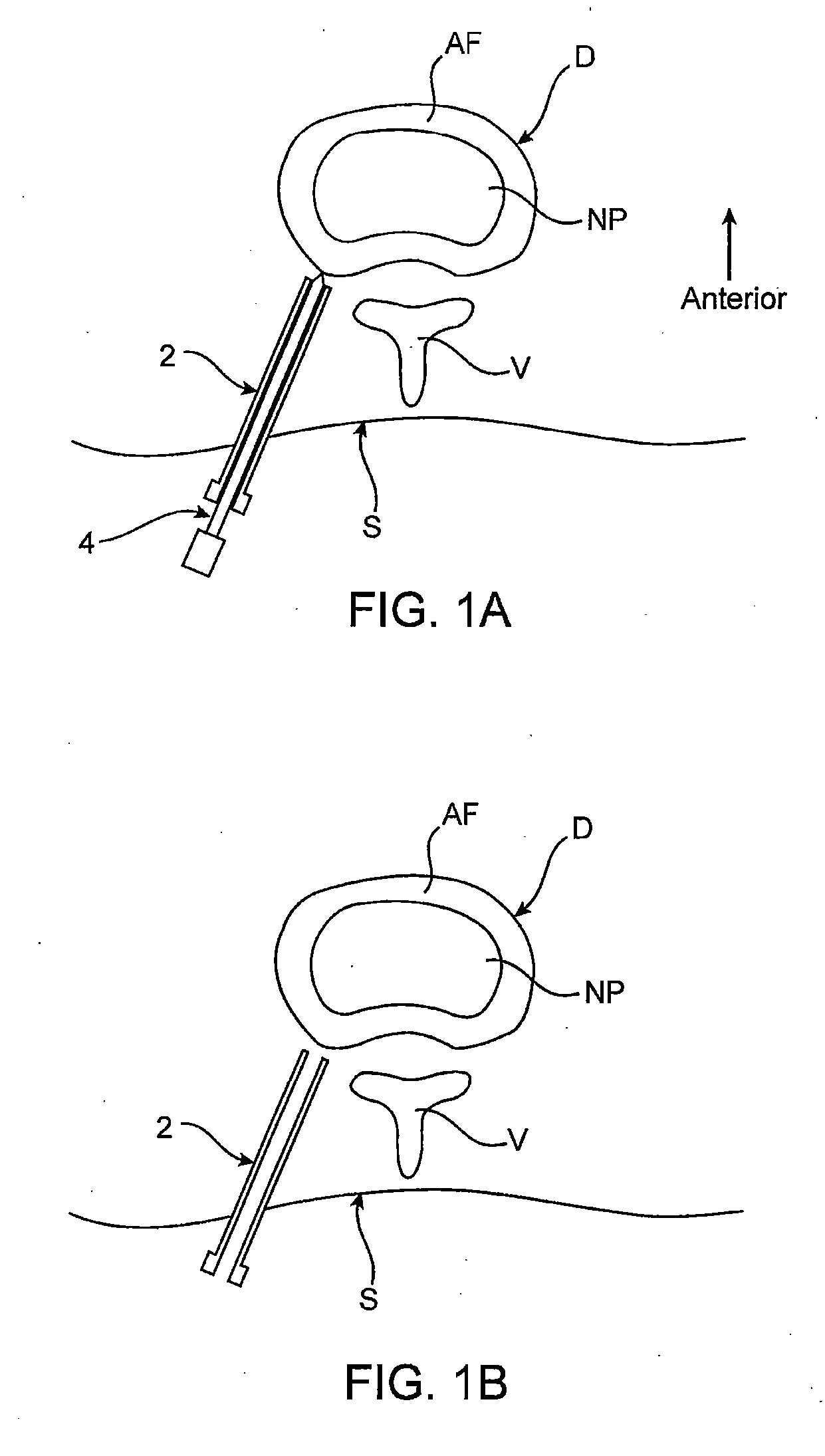
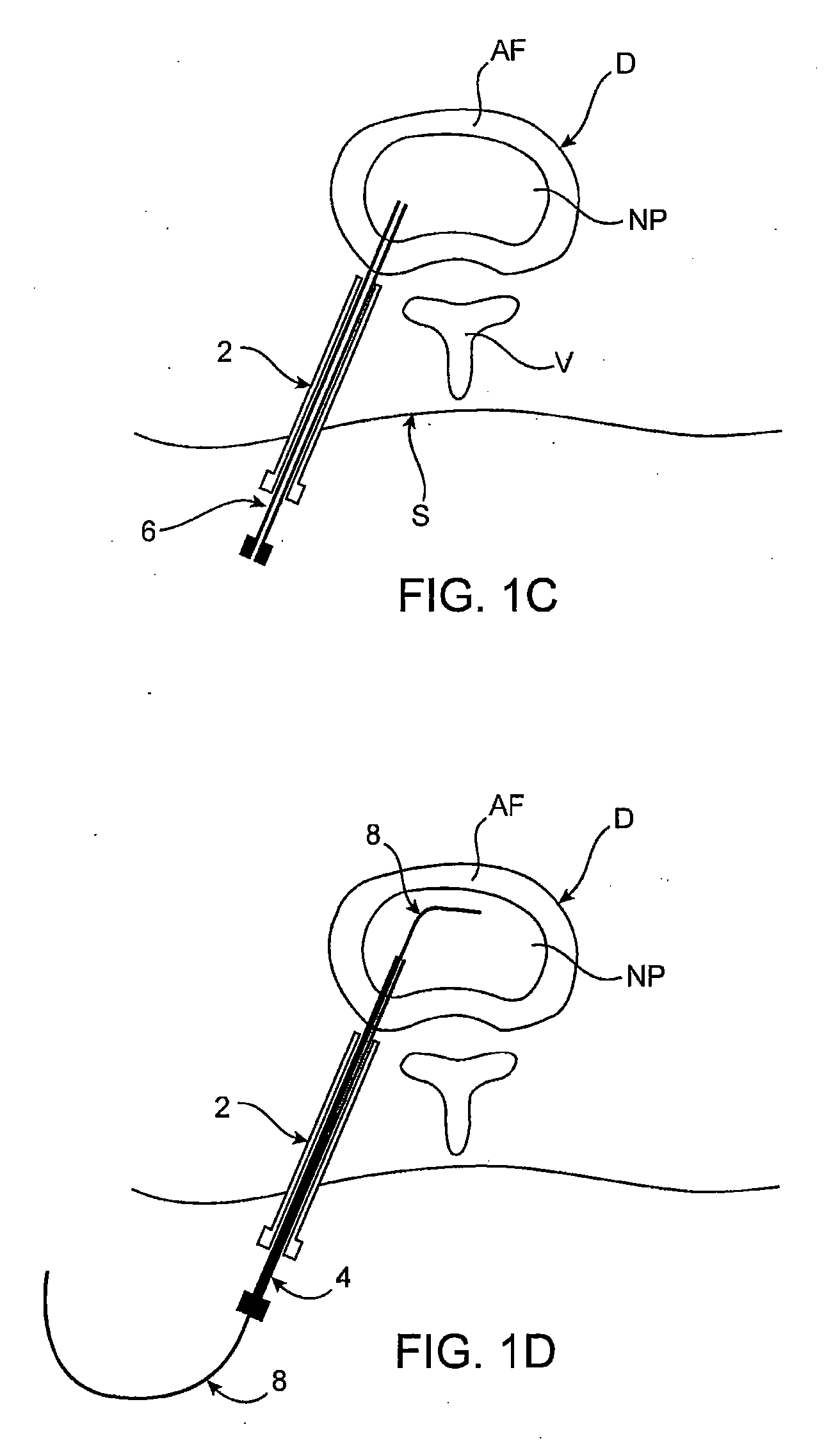
Spinal diagnostic methods and apparatus
ActiveUS20080009826A1Easy diagnosisRelieve painCannulasSurgical needlesSpinal columnAnesthetic Agent
Methods, devices and systems facilitate diagnosis, and in some cases treatment, of back pain originating in intervertebral discs. Methods generally involve introducing one or more substances into one or more discs using a catheter device. In one embodiment, a patient assumes a position that causes back pain, and a substance such as an anesthetic or analgesic is introduced into the disc to determine whether the substance relieves the pain. Injections into multiple discs may optionally be performed, to help pinpoint a disc as a source of the patient's pain. In some embodiments, the catheter device is left in place, and possibly coupled with another implantable device, to provide treatment of one or more discs. A catheter device includes at least one anchoring member for maintaining a distal portion of the catheter within a disc.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
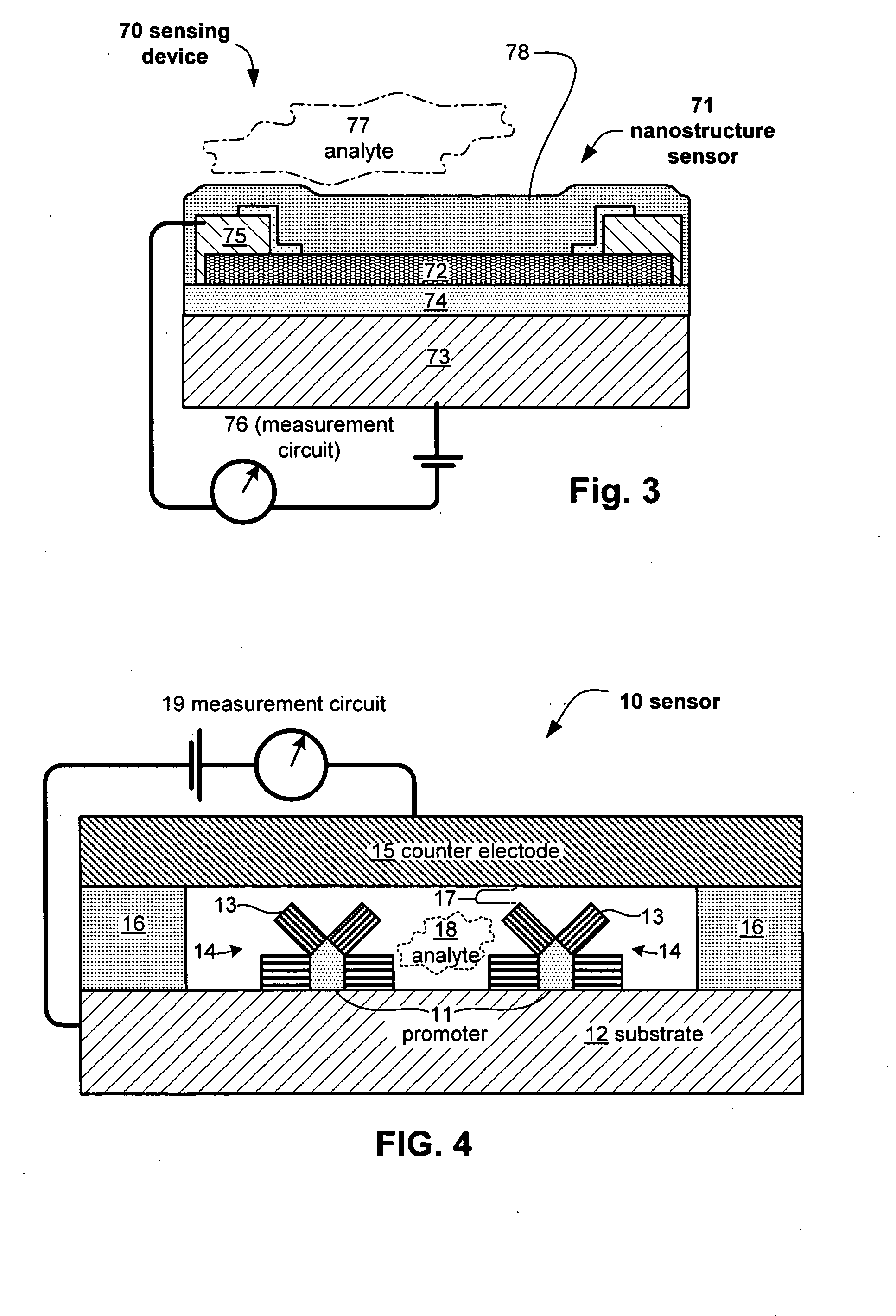
System and method for guidance of anesthesia, analgesia and amnesia
A method for monitoring anesthetization of a patient, includes the steps of removably connecting a plurality of electrodes to the scalp of the patient and administering sufficient anesthesia to the patient so that the patient attains a plane of anesthesia selected by an operator. The brain waves of the patient are then amplified and digitized after the patient has been anesthetized, before beginning the medical procedure, to obtain a first set of digital data. The brain waves of the patient are then amplified and digitized during the medical procedure to provide a second set of digital data and the first and second sets of digital data are analyzed in at least one of a time domain and a frequency domain. Separate trajectories are then computed from the data analysis trajectories for at least two different indices of an anesthetic state of the patient during the medical procedure, the indices being selected from a group including a Depth Index (DI), a Memory Index (MI) and a Pain Index (PI). A system for providing anesthesia to a patient, includes a plurality of electrodes, a first arrangement allowing an operator to administer anesthesia to the patient until the patient has attained a selected plane of anesthesia and a second arrangement coupled to the electrodes for amplifying and digitizing brain waves of the patient after the patient has been anesthetized, before the medical procedure has been begun to obtain a first set of digital data, the second arrangement amplifying and digitizing ongoing brain waves of the patient during the medical procedure to provide a second set of digital data in combination with a third arrangement analyzing the first and second sets of digital data in at least one of a time domain and a frequency domain, a fourth arrangement computing from the data analysis separate trajectories for at least two different indices of a state of the patient during the medical procedure, the indices being selected from a group including a Depth Index (DI), a Memory Index (MI) and a Pain Index (PI), a fifth arrangement providing control signals when any of the trajectories indicates that the patient is deviating from the selected plane of anesthesia and a sixth arrangement automatically adjusting two different anesthetic agents administered to the patient based on the control signal to restore the patient to the selected plane of anesthesia.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Multiple function airway adapter
InactiveUS7335164B2Promote generationEasy to measureAnalysis using chemical indicatorsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRespiratory flowAirway adaptor
An integrated airway adapter capable of monitoring any combination of respiratory flow, O2 concentration, and concentrations of one or more of CO2, N2O, and an anesthetic agent in real time, breath by breath. Respiratory flow may be monitored with differential pressure flow meters under diverse inlet conditions through improved sensor configurations which minimize phase lag and dead space within the airway. Molecular oxygen concentration may be monitored by way of luminescence quenching techniques. Infrared absorption techniques may be used to monitor one or more of CO2, N2O, and anesthetic agents.
Owner:NTC TECH
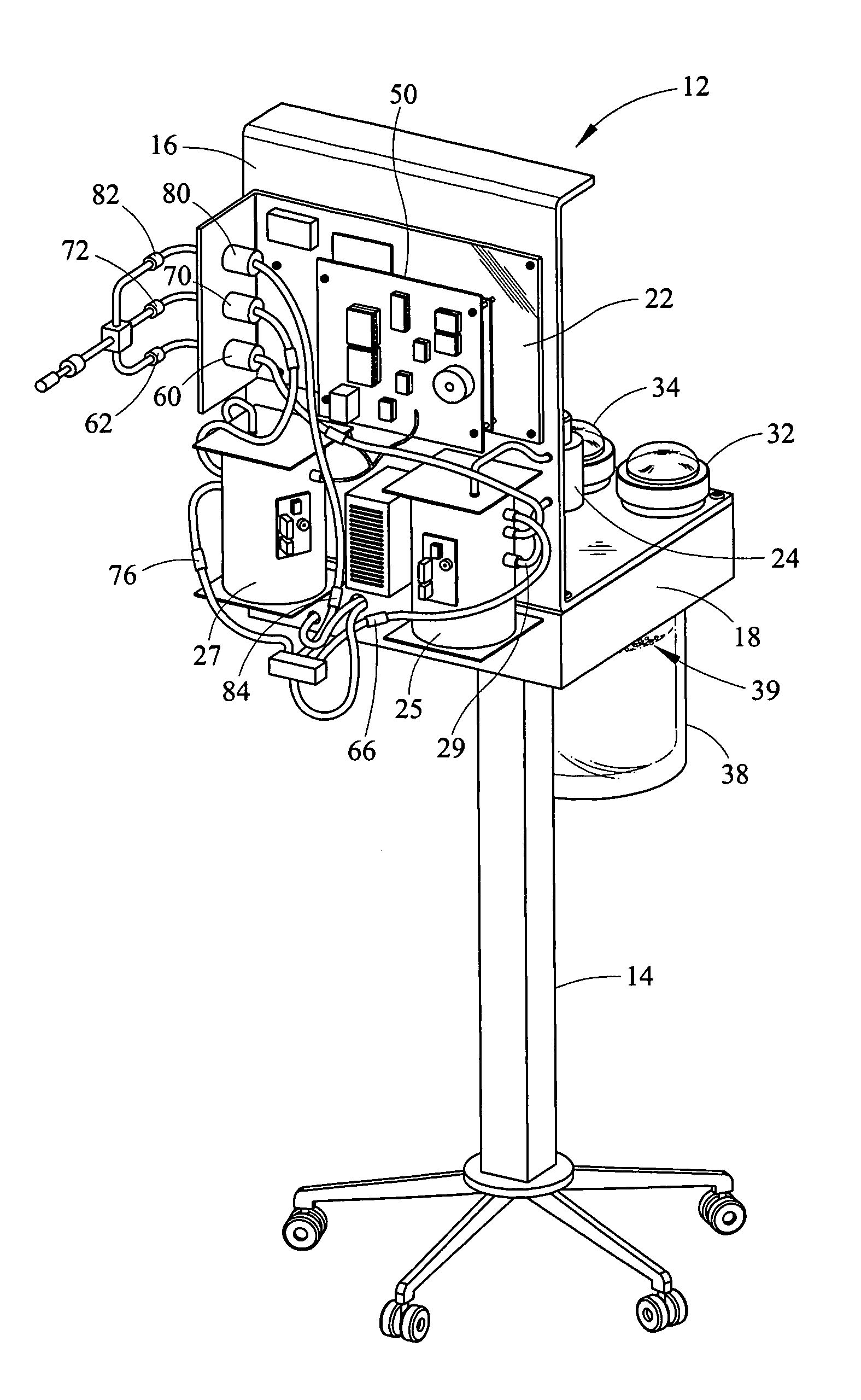
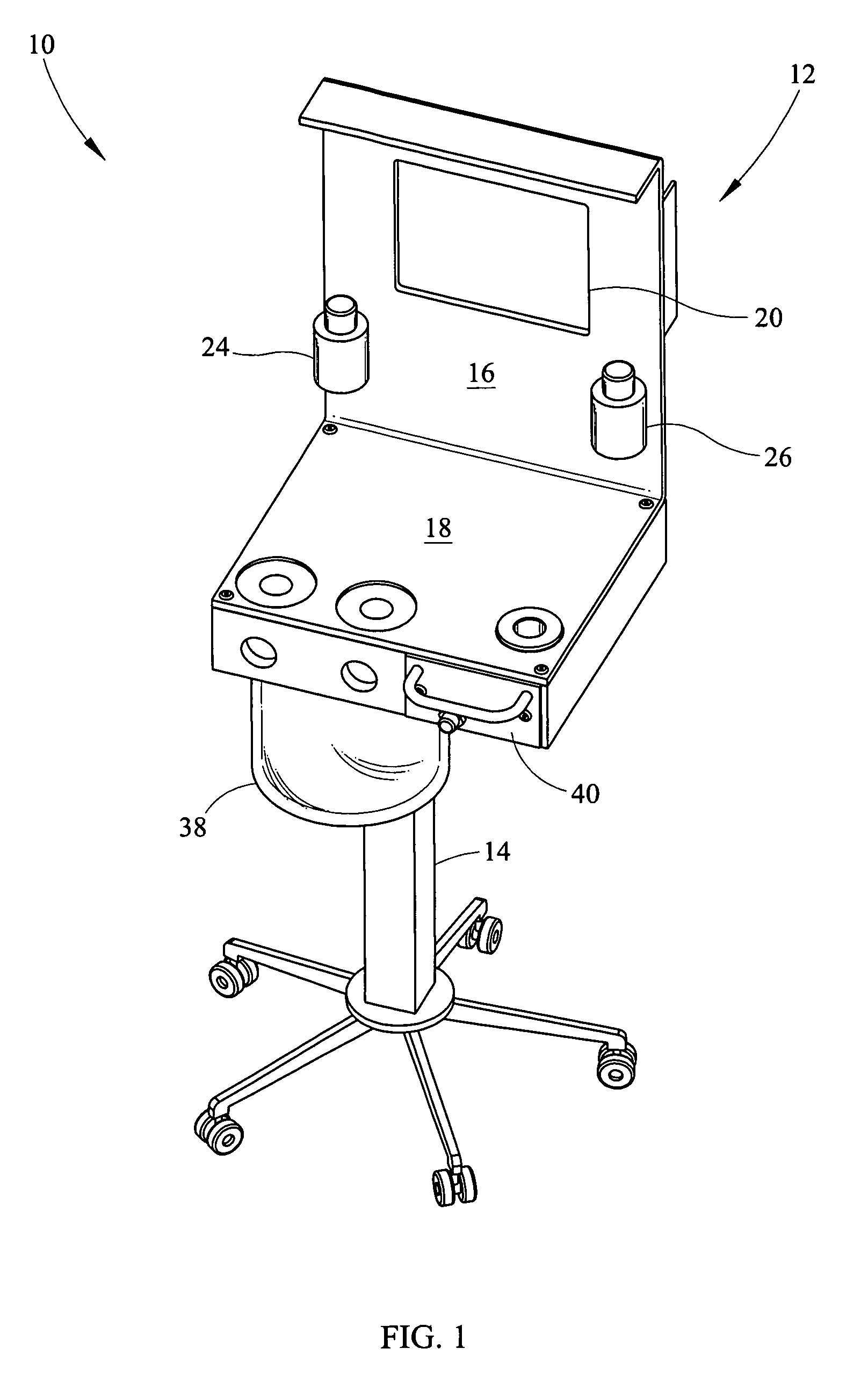
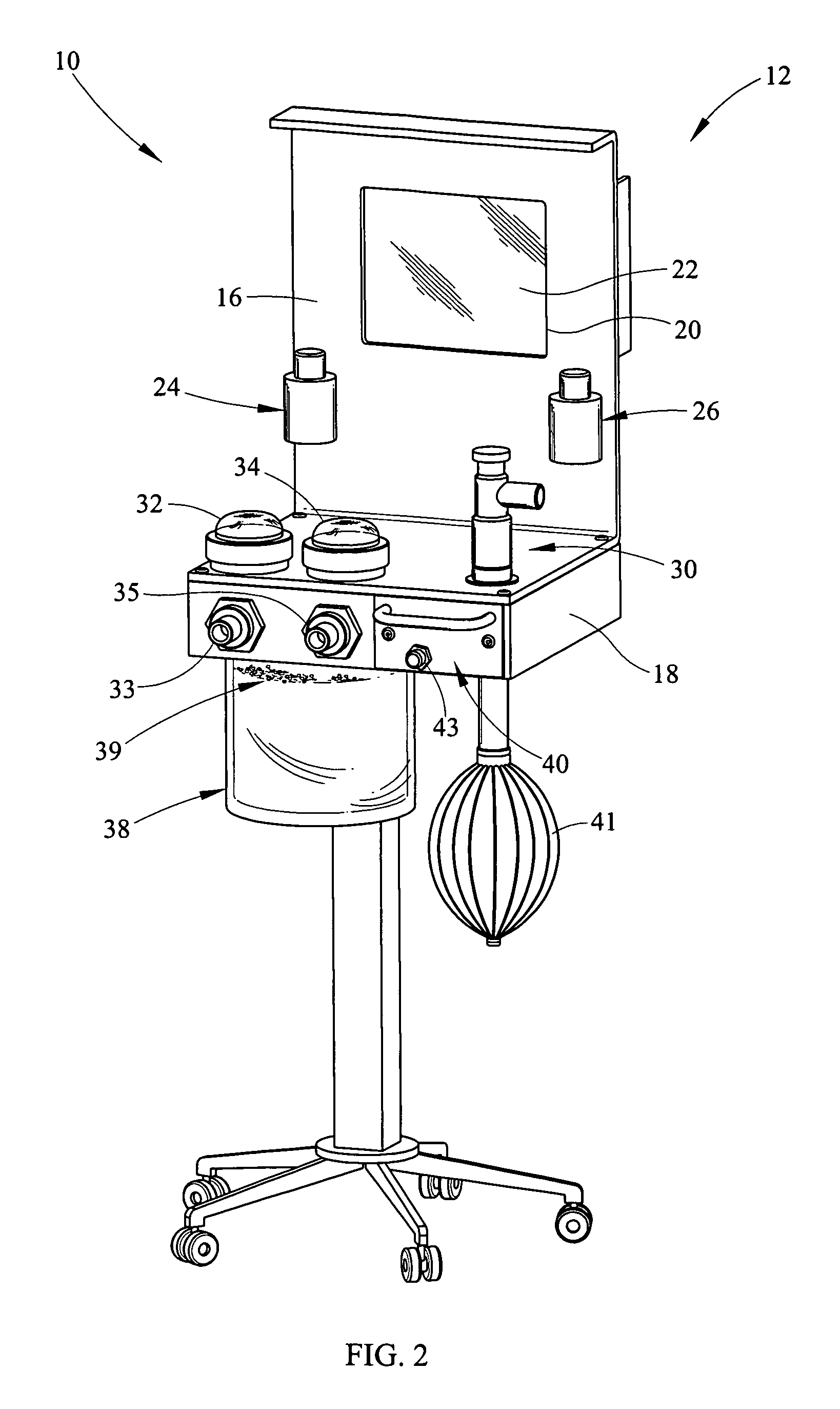
Portable field anesthesia machine and control therefore
InactiveUS7438072B2Overcomes drawbackFacilitate casualty careRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsAnesthetic AgentProduct gas
A portable anesthetic machine comprises a chassis having a cradle which removably receives a vaporizer, a control panel and a support member. The control panel and support member are pivotal relative to each other to selectively change the machine between carrying and use configurations. The control panel includes a gas flow path having gas inputs connectable to sources of carrier gases, a manifold which combines the gases, a carrier gas outlet and inlet connectable to the vaporizer input and outlet, respectively, a common gas port, and flow control devices to control the carrier gas flow rate and to control the anesthetic and carrier gas mixture. A controller is also provided which controls the flow of gas into and around the vaporizer to maintain a substantially constant concentration of anesthetic agent in the gas stream delivered to the patient without the need to adjust the flow of gases from the gas supply sources.
Owner:IZUCHUKWU JOHN I
Cavity-filling biopsy site markers
InactiveUS20050143656A1Easy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesAnesthetic AgentMaximum dimension
The invention provides materials, devices and methods for marking biopsy sites for a limited time. The biopsy-marking materials are ultrasound-detectable bio-resorbable powders, with powder particles typically between about 20 microns and about 800 microns in maximum dimension, more preferably between about 300 microns and about 500 microns. The powders may be formed of polymeric materials containing cavities sized between about 10 microns and about 500 microns, and may also contain binding agents, anesthetic agents, hemostatic agents, and radiopaque markers. Devices for delivering the powders include tubes configured to contain the powders and to fit within a biopsy cannula, the powders being ejected by action of a syringe. Systems may include a tube containing powder, and a syringe containing sterile saline. The tube may be configured to fit within a biopsy cannula such as a Mammotome® or SenoCor 360™ cannula.
Owner:SENORX
Transdermal pharmaceutical delivery compositions
A pharmaceutically delivery system and method of use therefor are described comprising a pharmaceutically active agent and acidified nitrite as an agent to produce local production of nitric oxide at the skin surface. The dosage form may be in any pharmaceutically acceptable carrier means and comprises an acidifying agent adapted to reduce the pH at the environment. In one embodiment, a barrier consisting of a membrane allows diffusions of the anaesthetic and nitrite ions while preventing direct contact of the skin and acidifying agent.
Owner:QUEEN MARY UNIV OF LONDON
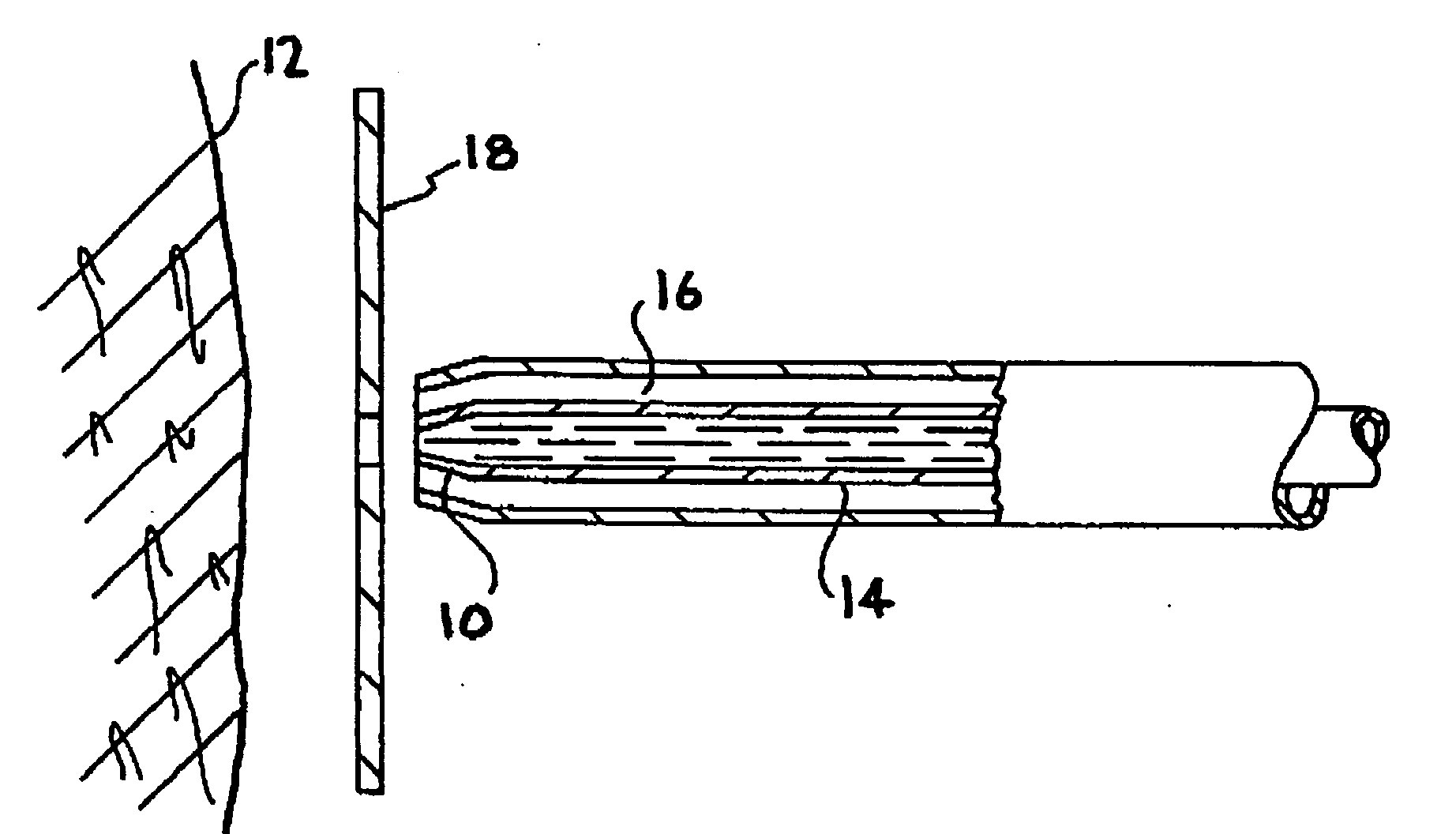
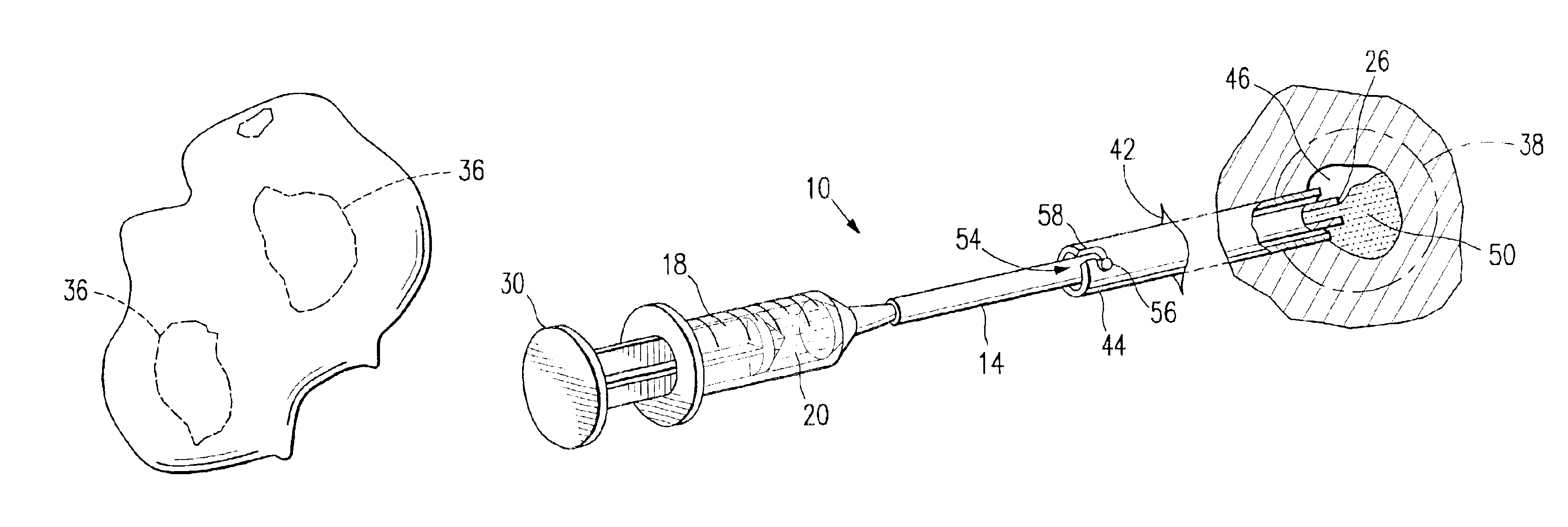
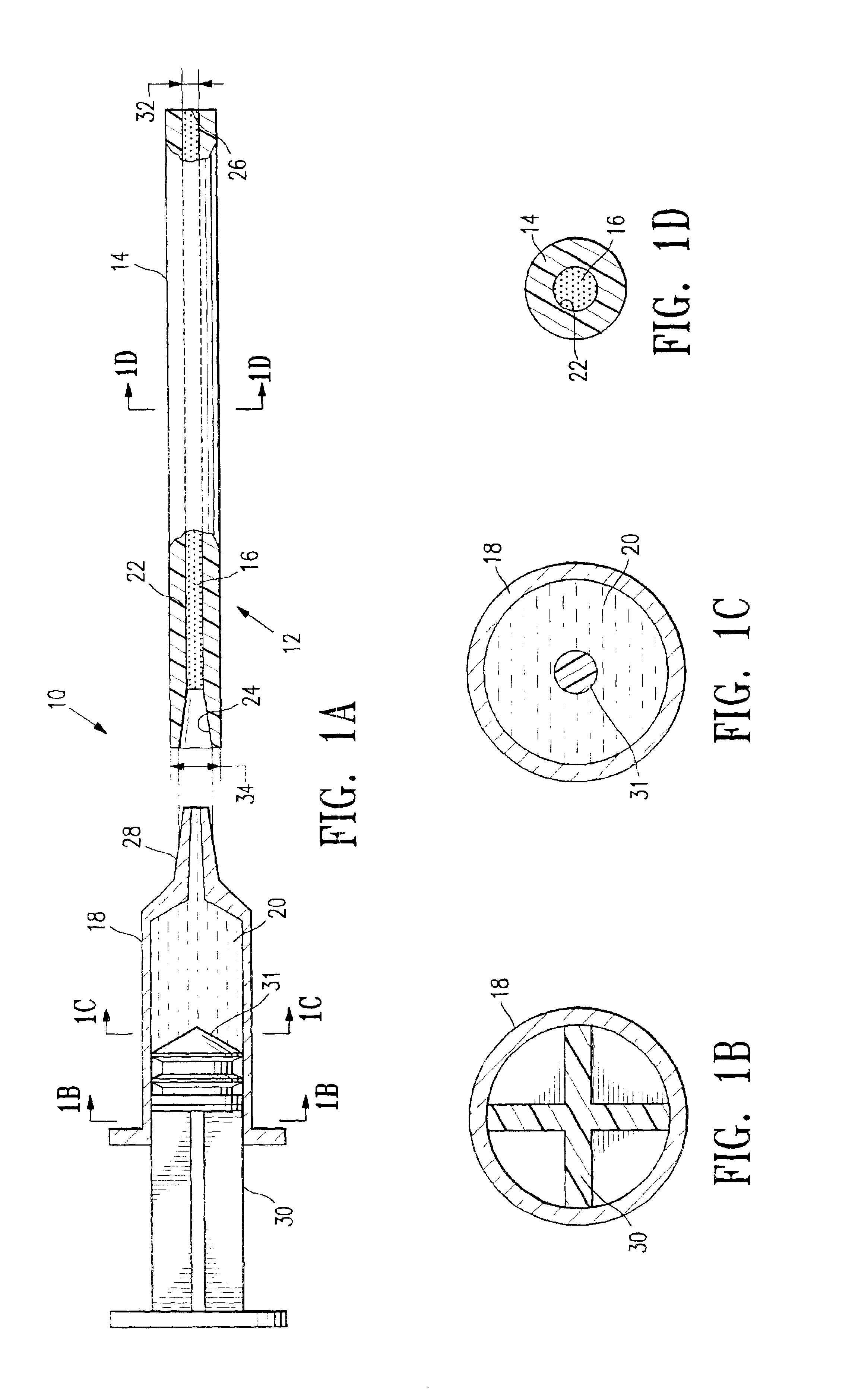
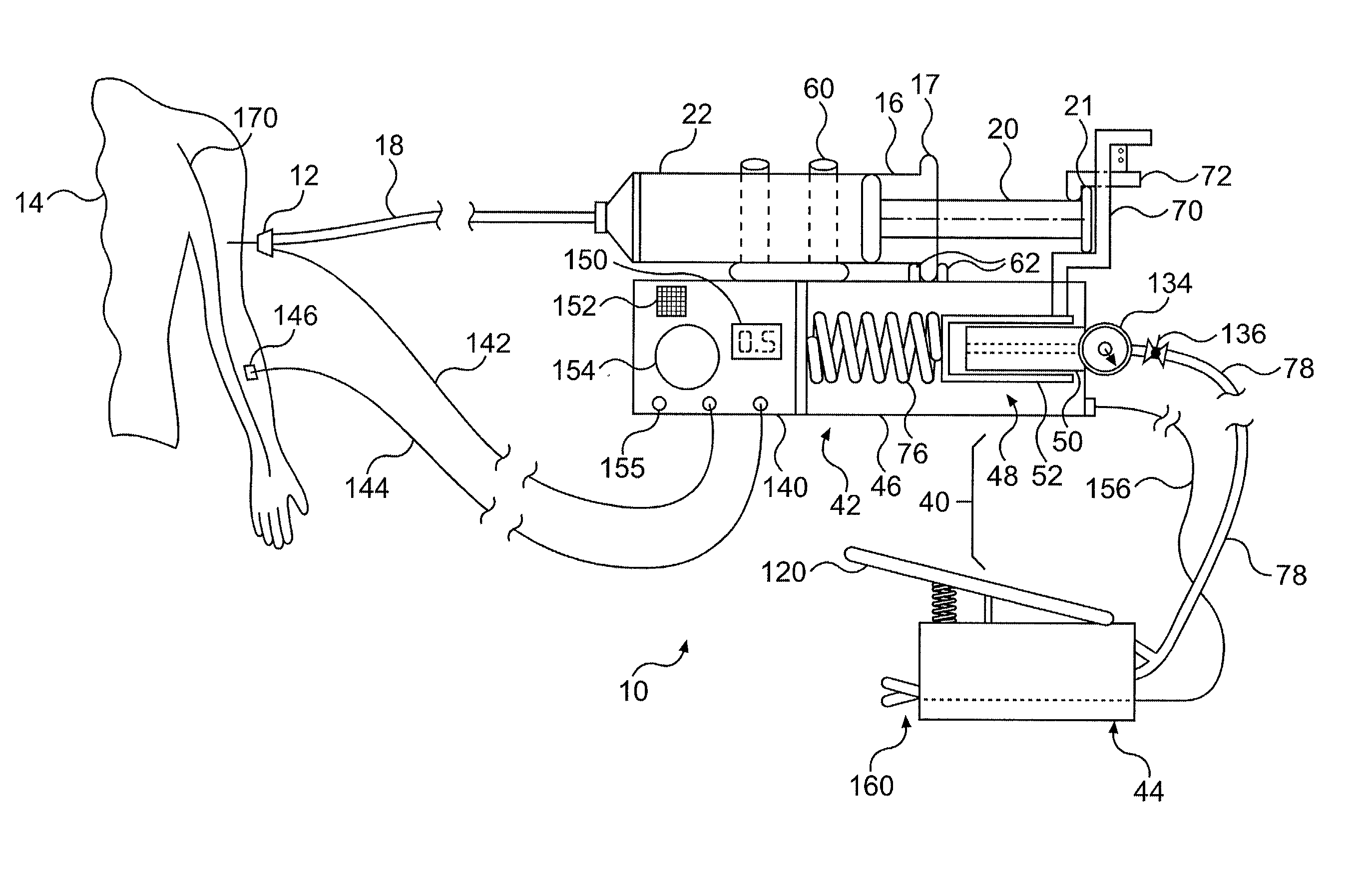
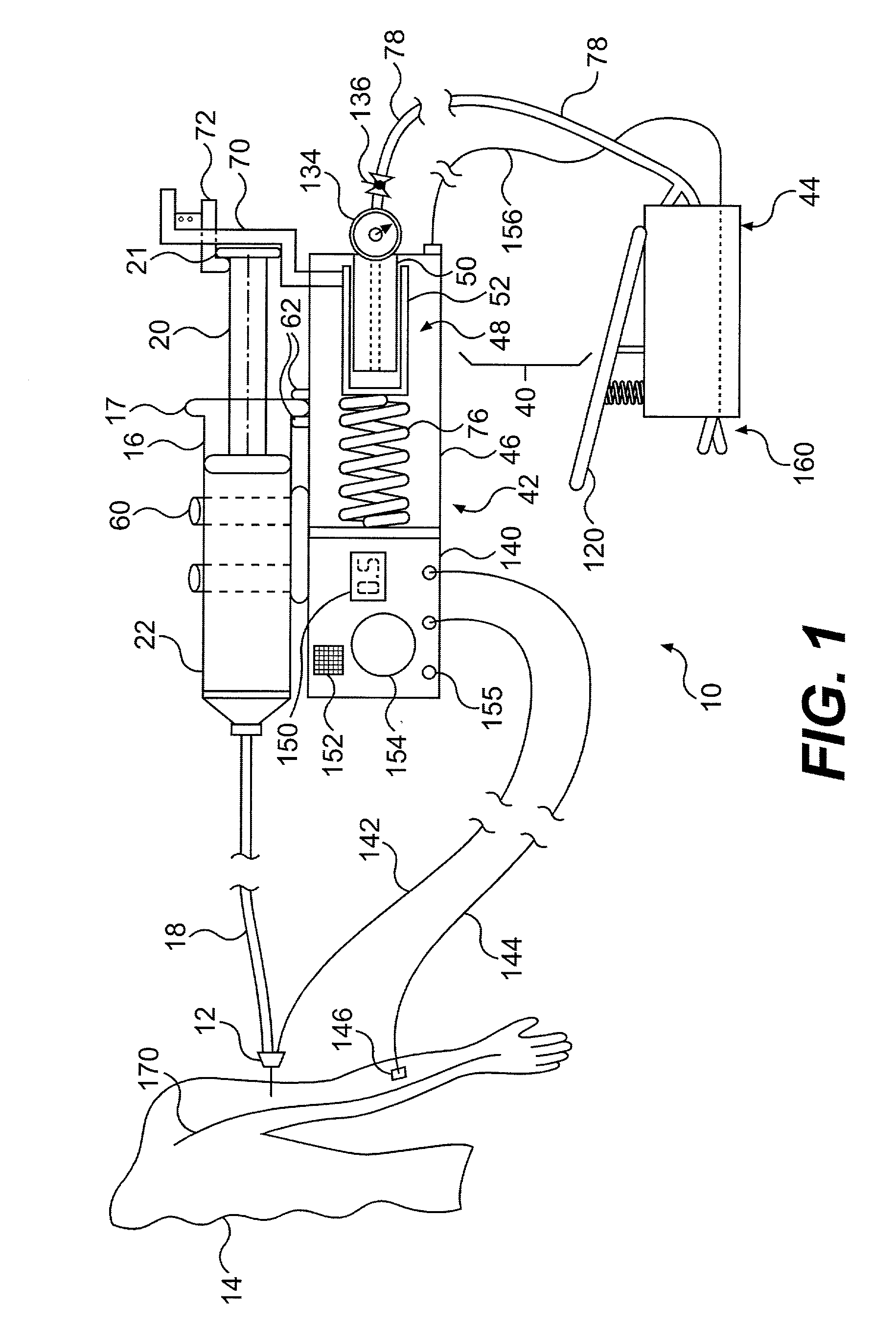
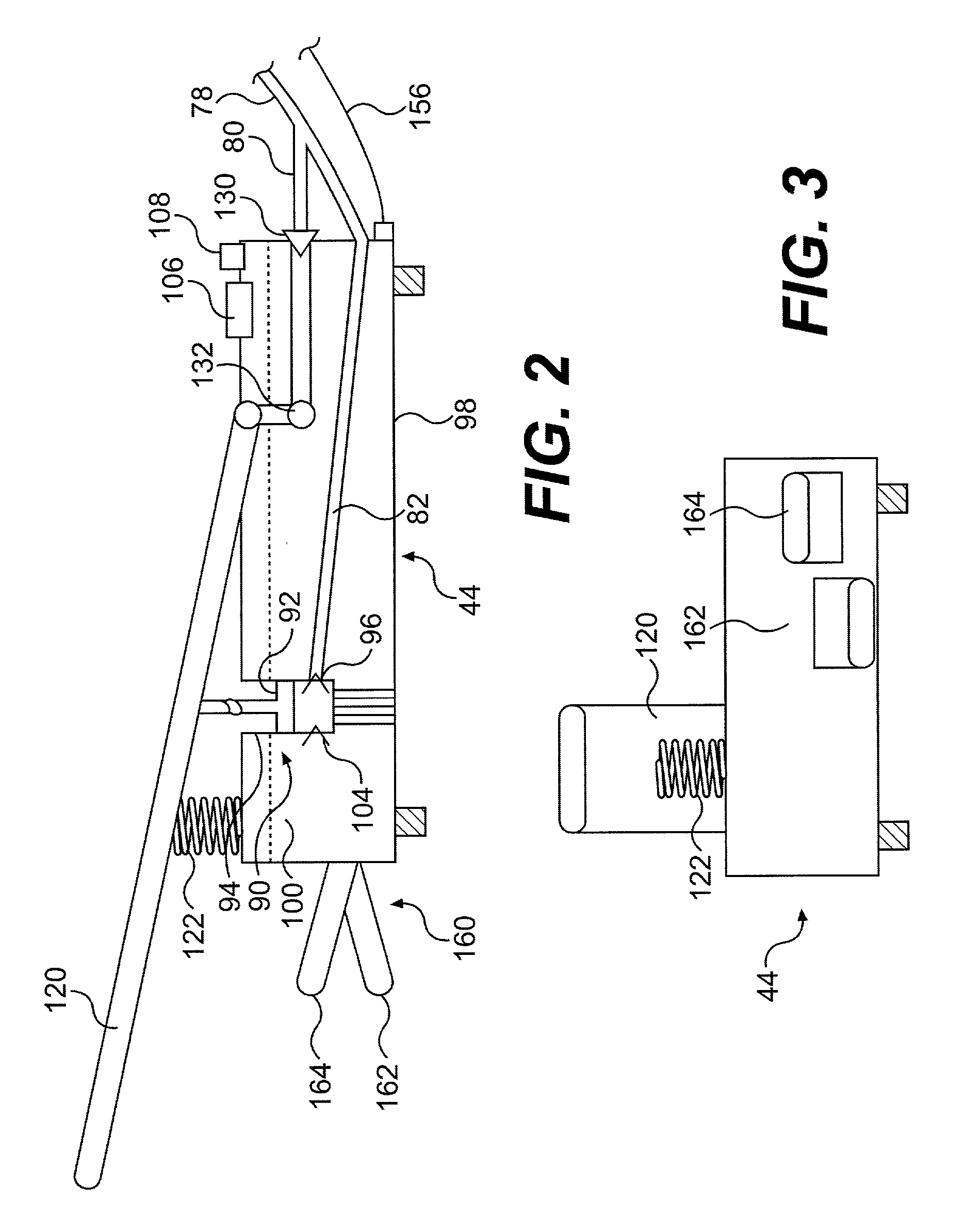
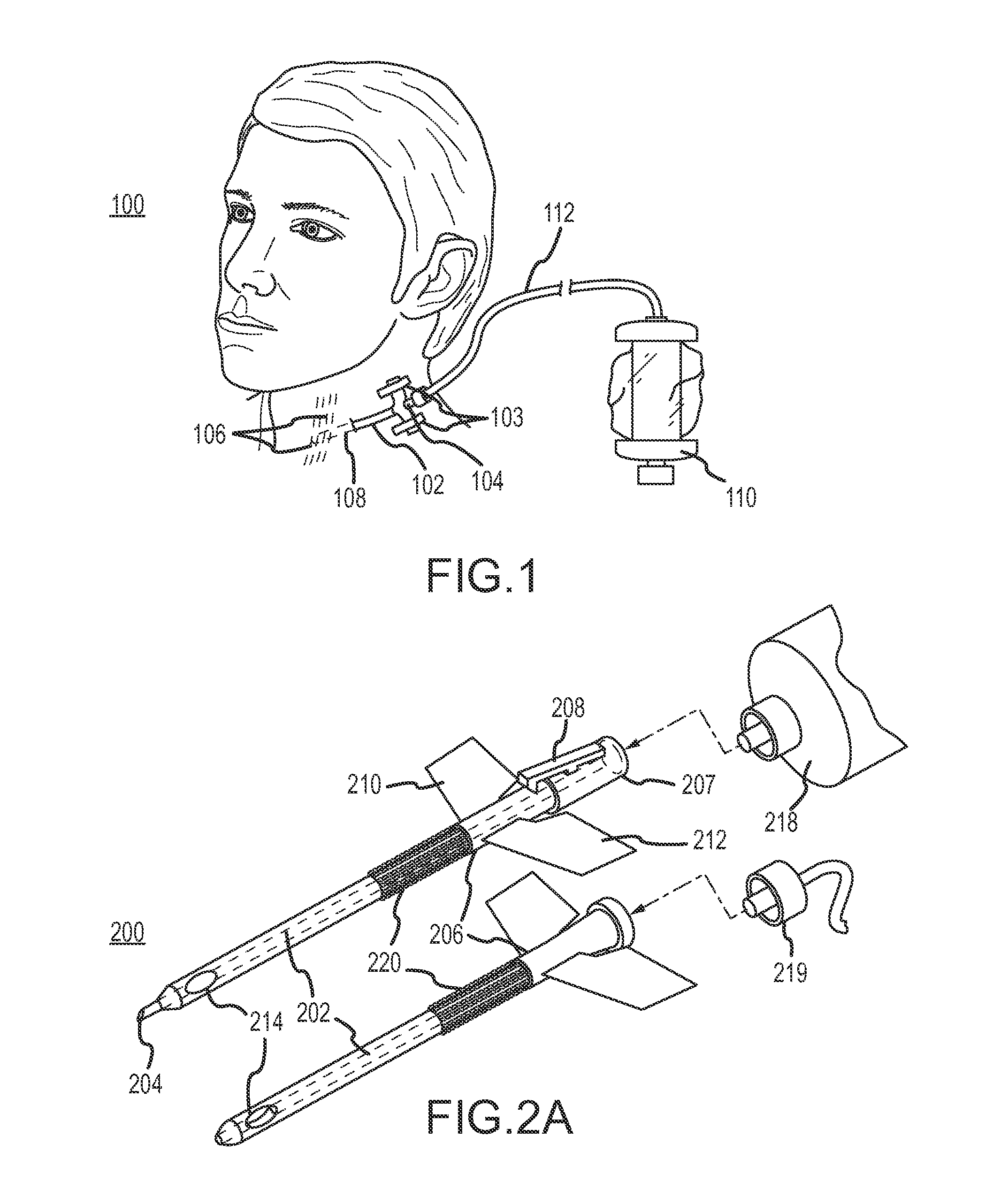
Continuous anesthesia nerve conduction apparatus and method
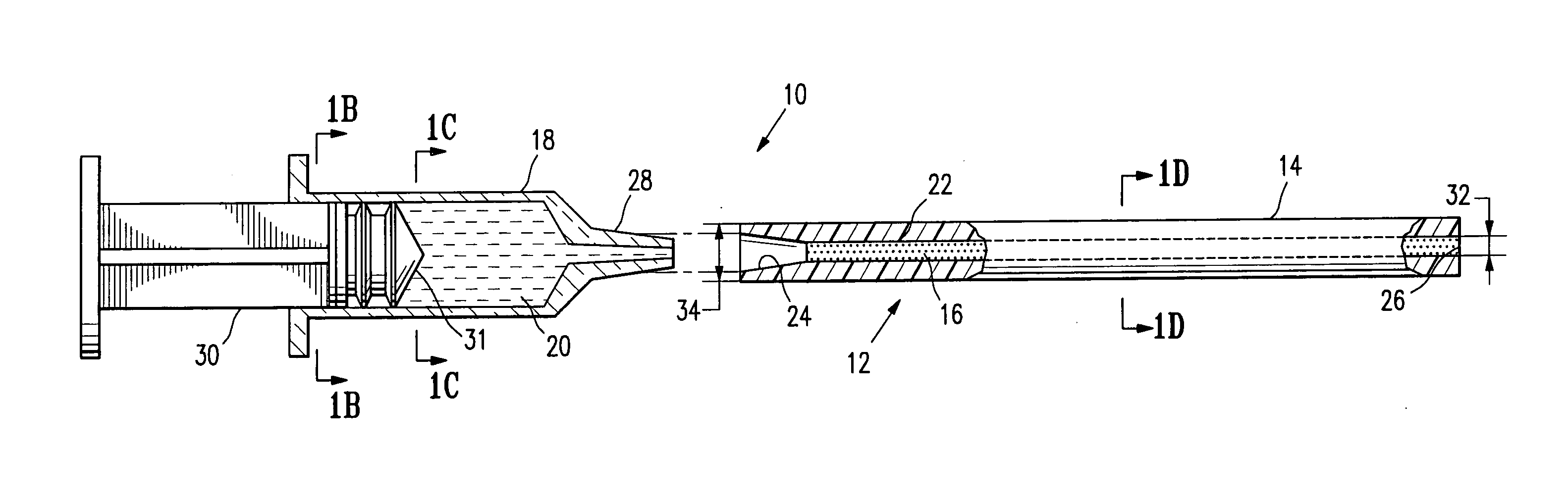
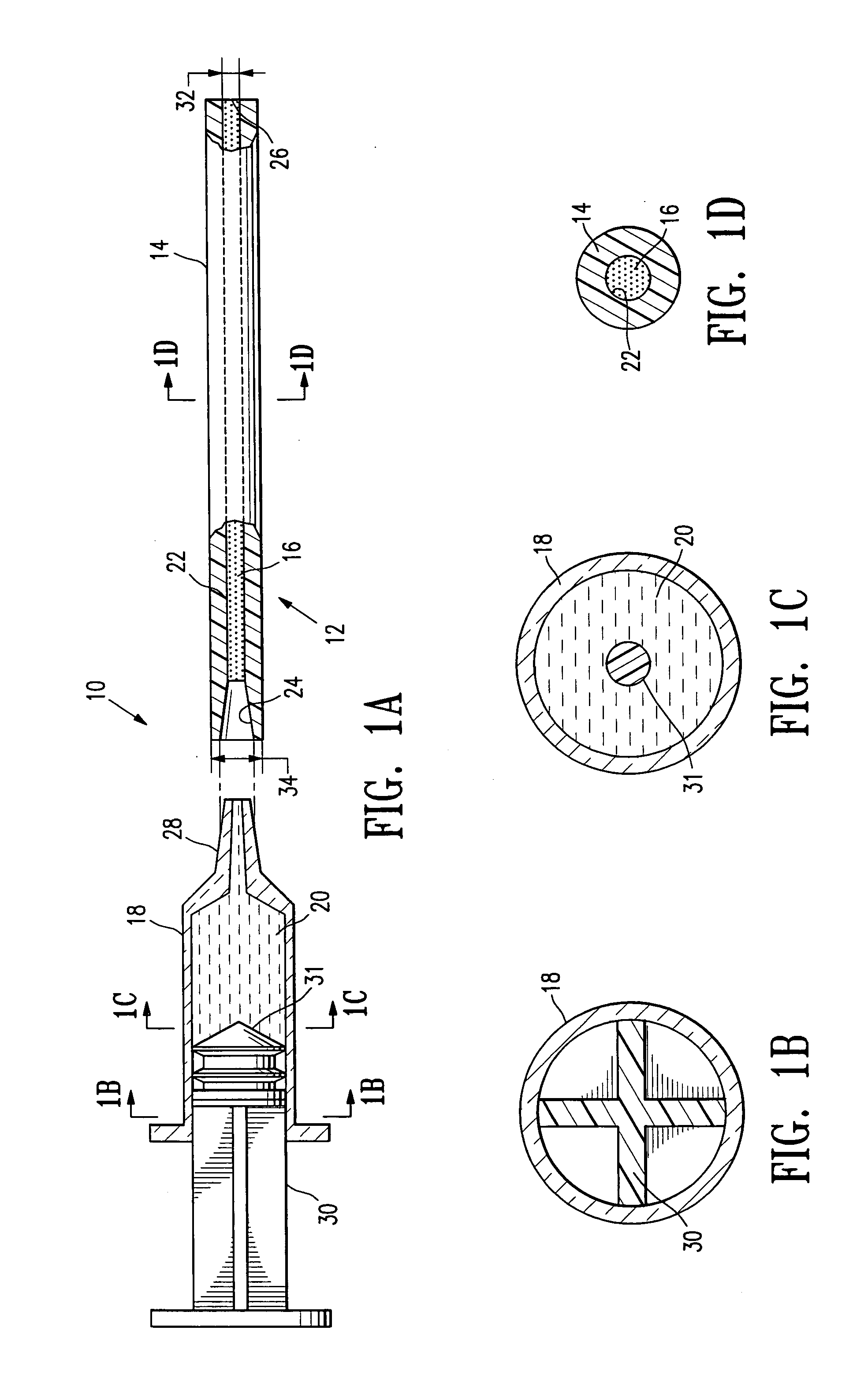
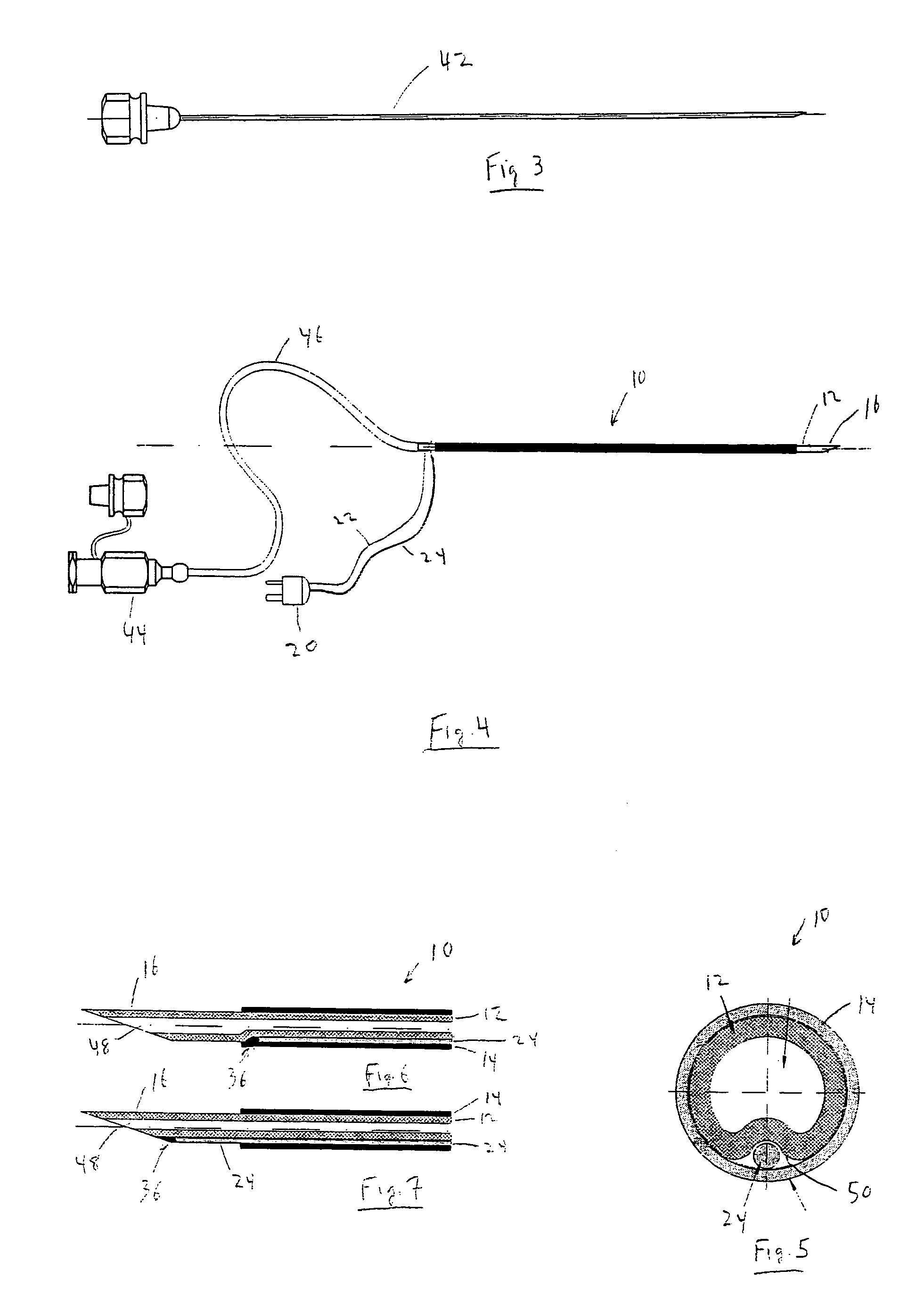
The invention generally relates to a continuous anesthesia nerve conduction apparatus and method thereof, and more particularly to a method and system for use in administering a continuous flow or intermittent bolus of anesthetic agent to facilitate a continuous or prolonged nerve block. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a sheath having a proximal end, a distal end and at least one lumen extending from the proximal end to the distal end. The sheath also includes an embedded conductive element for transmitting an electrical signal from a proximal portion of the sheath to a distal portion of the sheath. A cannula is arranged in the at least one lumen of the sheath and has a distal end protruding from a distal portion of the sheath. The cannula is electrically coupled to at least a portion of the embedded conductive element and is configured to provide nerve stimulation.
Owner:SOLODEX LLC
Method and apparatus for monitoring intravenous (IV) drug concentration using exhaled breath
InactiveUS7104963B2Good correlationCost-effective and frequentRespiratorsRespiratory organ evaluationAnesthetic AgentMetabolite
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Anesthesia monitor, capacitance nanosensors and dynamic sensor sampling method
InactiveUS20100085067A1Inexpensively identifyMore cost-effectiveMaterial nanotechnologyResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceAnesthetic Agent
Embodiments of nanoelectronic sensors are described, including sensors for detecting analytes such as anesthesia gases, CO2 and the like in human breath. An integrated monitor system and disposable sensor unit is described which permits a number of different anesthetic agents to be identified and monitored, as well as concurrent monitoring of other breath species, such as CO2. The sensor unit may be configured to be compact, light weight, and inexpensive. Wireless embodiments provide such enhancements as remote monitoring. A simulator system for modeling the contents and conditions of human inhalation and exhalation with a selected mixture of a treatment agent is also described, particularly suited to the testing of sensors to be used in airway sampling.
Owner:NANOMIX INC
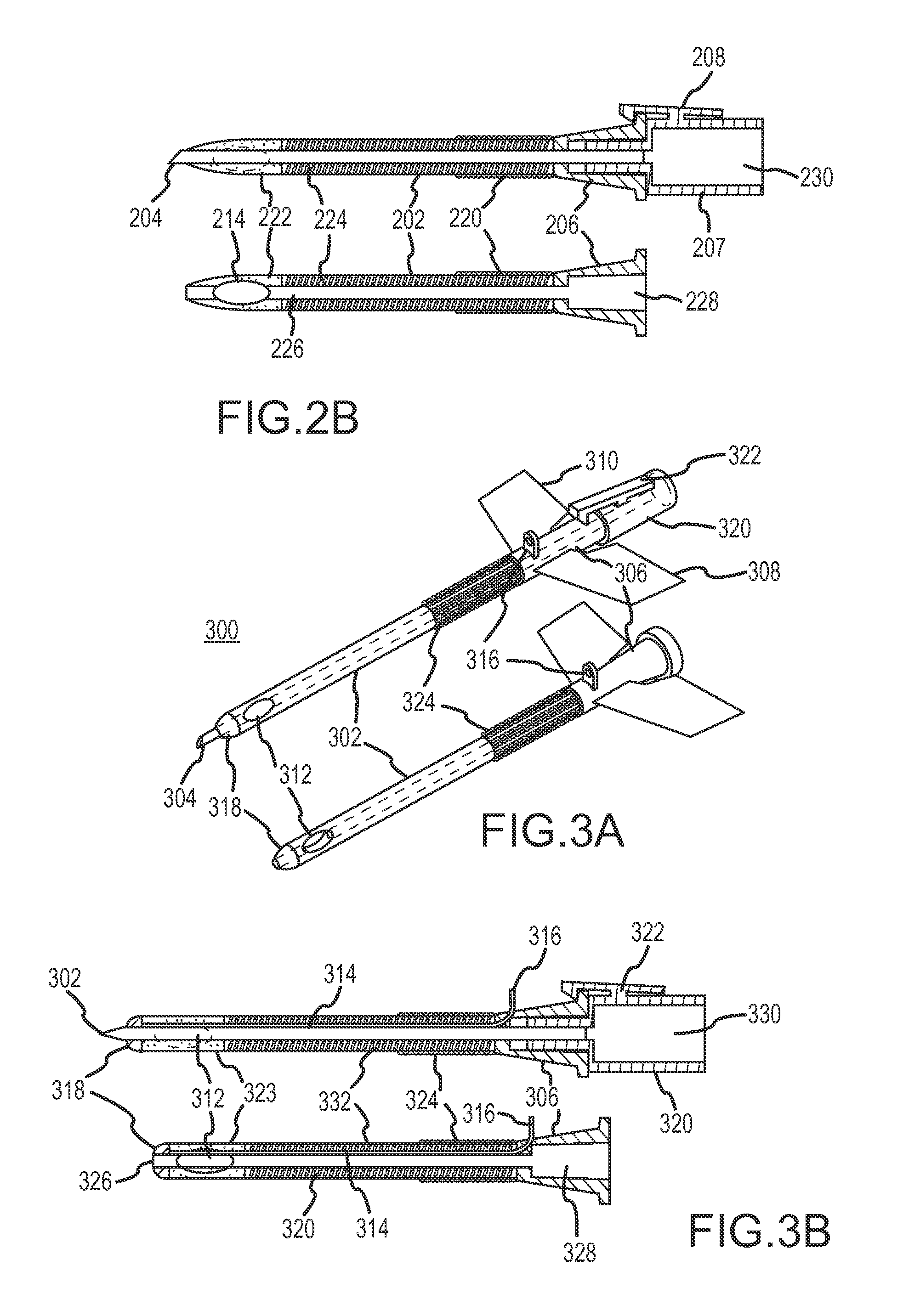
Continuous anesthesia nerve conduction apparatus, system and method thereof
ActiveUS20140025039A1Shorten operation timeEasy to handleSpinal electrodesGuide needlesElectricityAnesthetic Agent
The invention generally relates to a continuous anesthesia nerve conduction apparatus and method thereof, and more particularly to a method and system for use in administering a continuous flow or intermittent bolus of anesthetic agent to facilitate a continuous or prolonged nerve block. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a sheath having a proximal end, a distal end and at least one lumen extending from the proximal end to the distal end. The sheath also includes an embedded conductive element for transmitting an electrical signal from a proximal portion of the sheath to a distal portion of the sheath. A cannula is arranged in the at least one lumen of the sheath and has a distal end protruding from a distal portion of the sheath. The cannula is electrically coupled to at least a portion of the embedded conductive element and is configured to provide nerve stimulation.
Owner:SOLODEX LLC
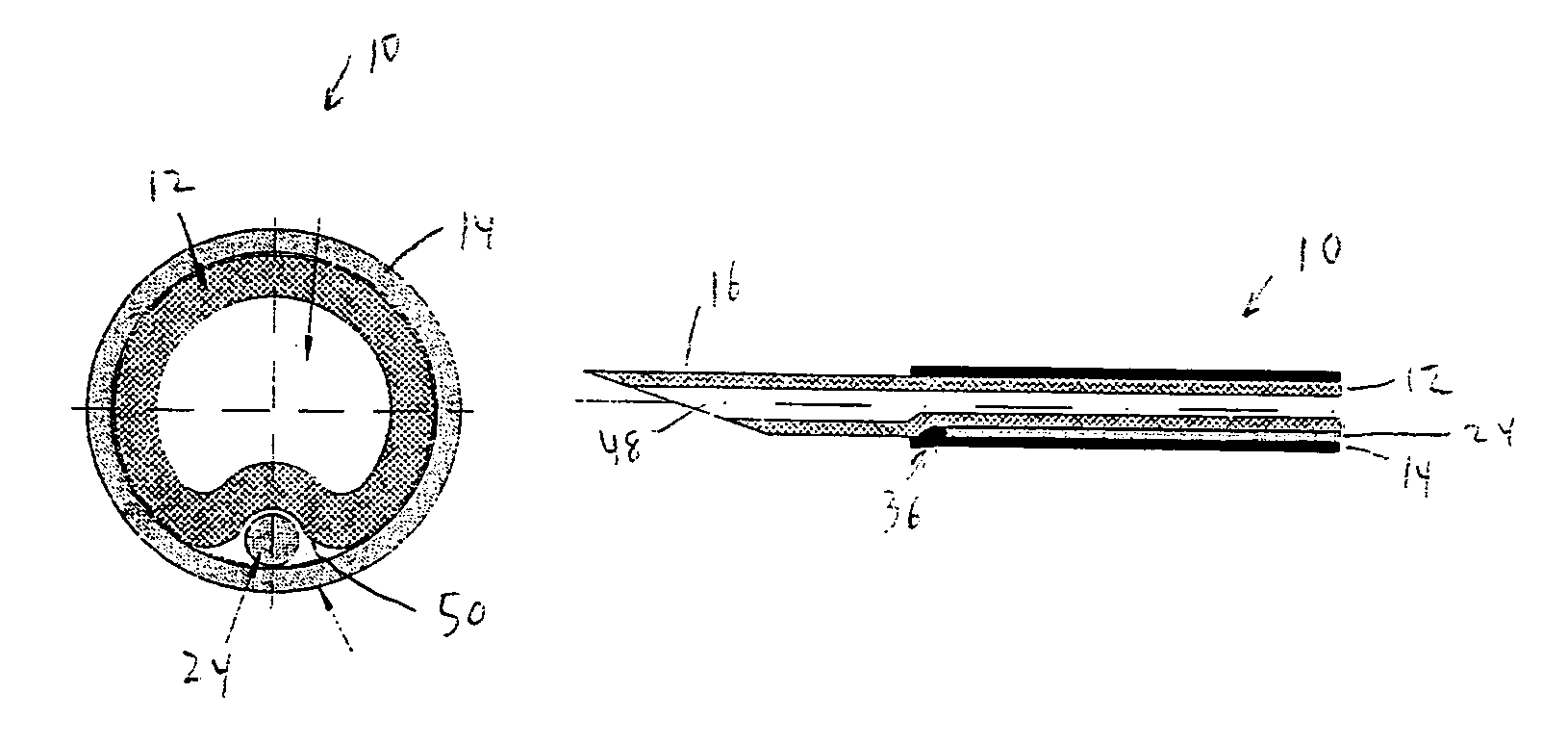
Hybrid cannula/electrode medical device and method
InactiveUS7318822B2Simplify surgical proceduresReduce complicationsCannulasSurgical needlesAnesthetic AgentInsulation layer
A cannula having a hollow metal tube for injection of liquids such as an anesthetic, or RF energy, into a patient. A thermocouple or other temperature sensor is located at the bare tip of the cannula, and a wire for the temperature sensor extends along the length of the cannula, preferably in a groove formed in the tube, or through a passageway formed in the tube. An outer insulation layer covers the tube and wire. Thus, a single device serves as both a cannula and an electrode.
Owner:DIROS TECH
Electronic anesthesia delivery apparatus
An electronic anesthesia delivery apparatus having a chassis including a first anesthetic agent chamber and a second anesthetic agent chamber, each of the first and second chambers including an anesthetic agent therein. At least one electronically controlled valve is in fluid communication with each of the first agent chamber and the second agent chamber and an oxygen source. The oxygen source is in fluid communication with each of the at least one electronically controlled valves. A touchscreen graphic display having controls corresponding to each of the at least one electronically controlled valves for controlling flow rate and concentration of anesthesia.
Owner:VETLAND MEDICAL SALES & SERVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com