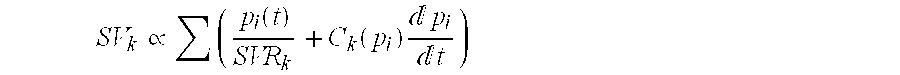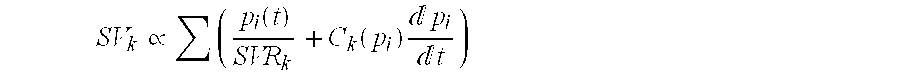Patents
Literature
82 results about "Mean arterial pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In medicine, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) is an average blood pressure in an individual during a single cardiac cycle.
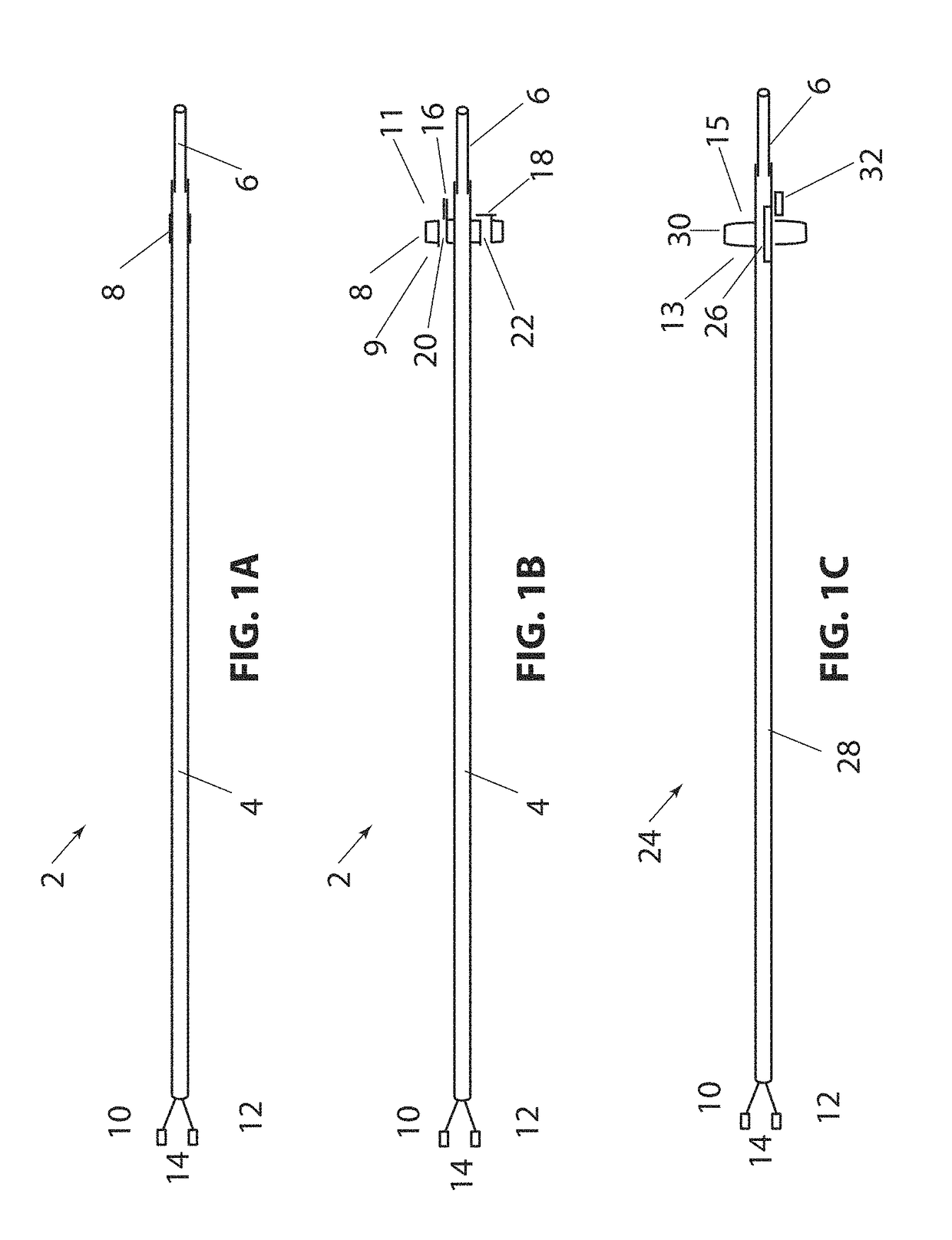
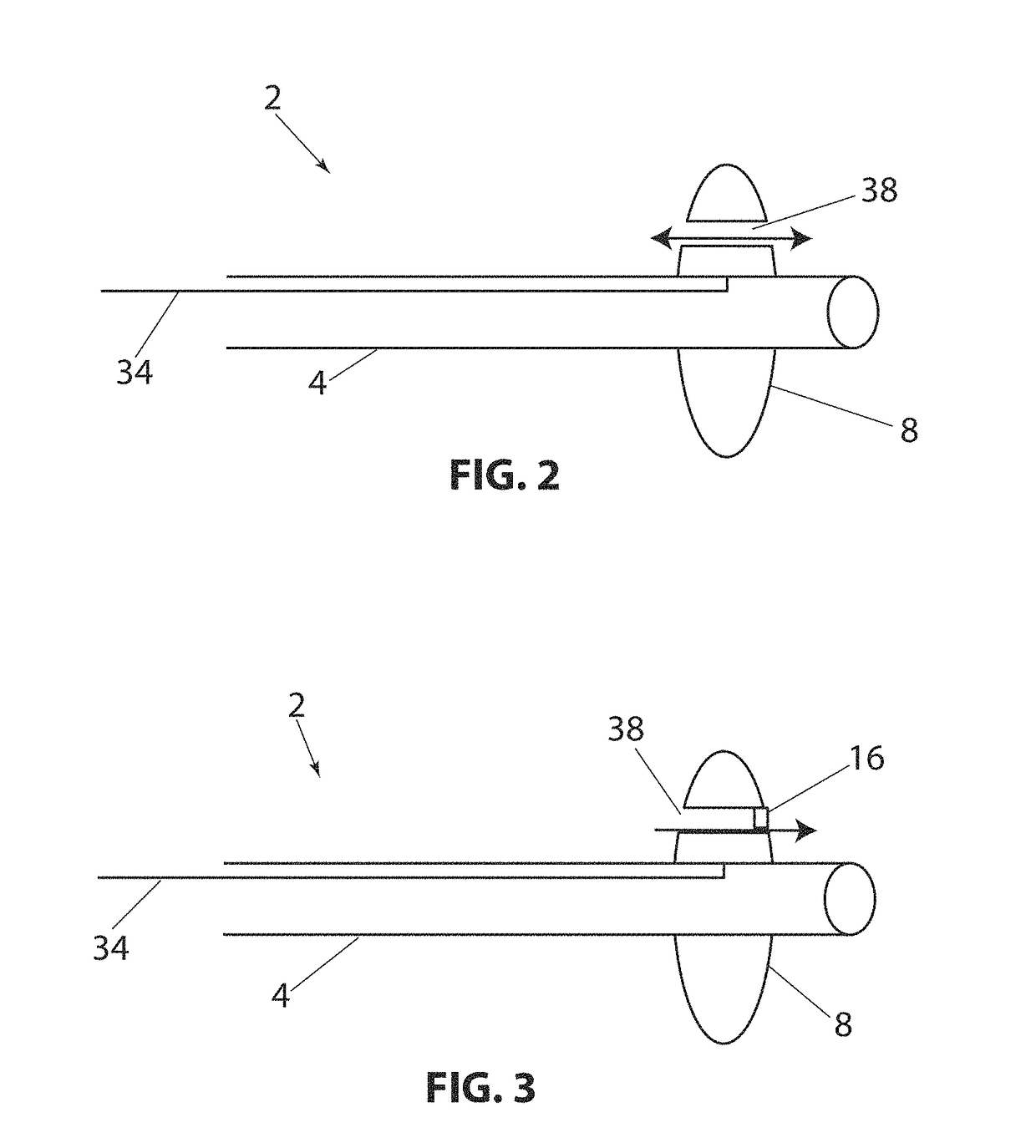
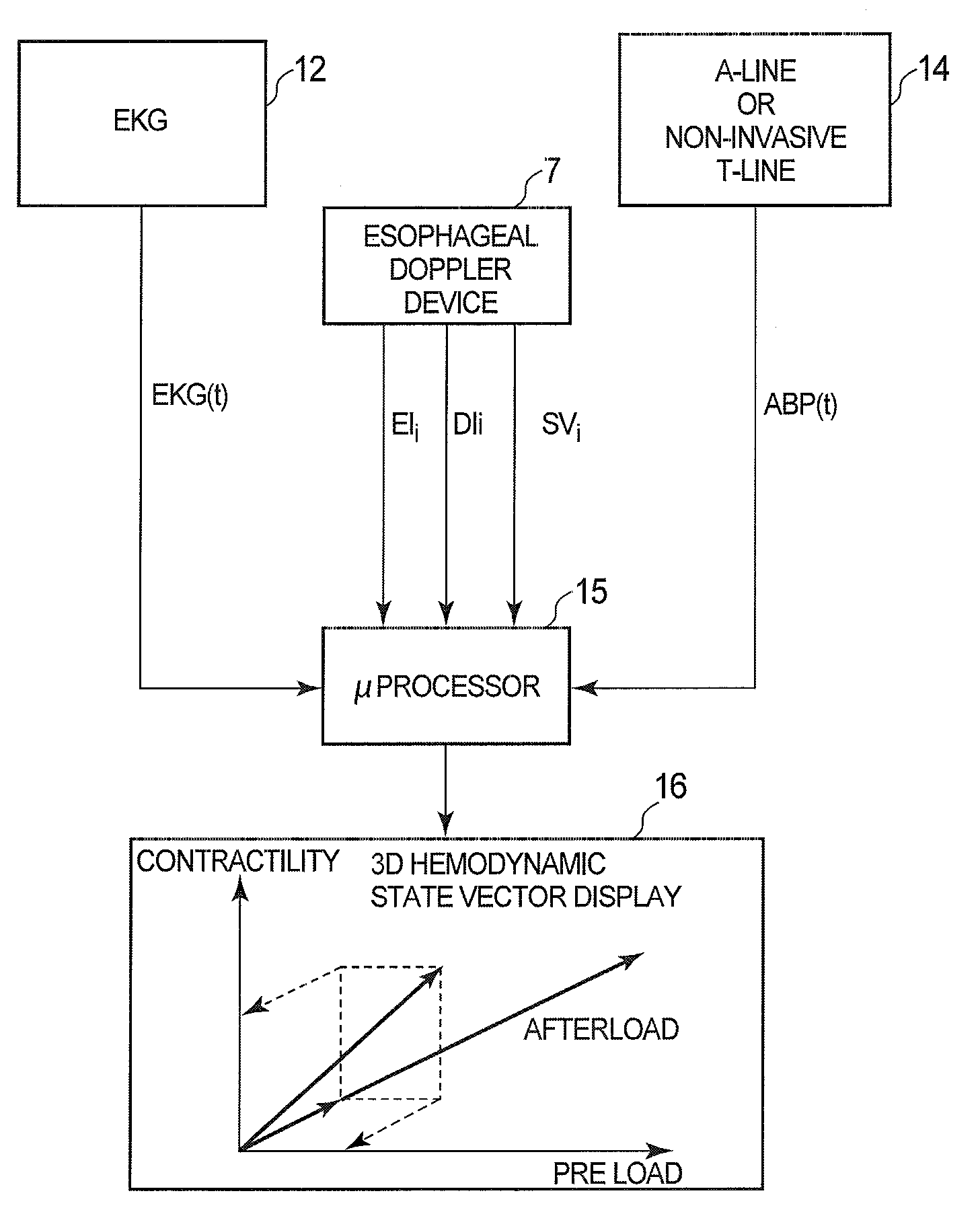
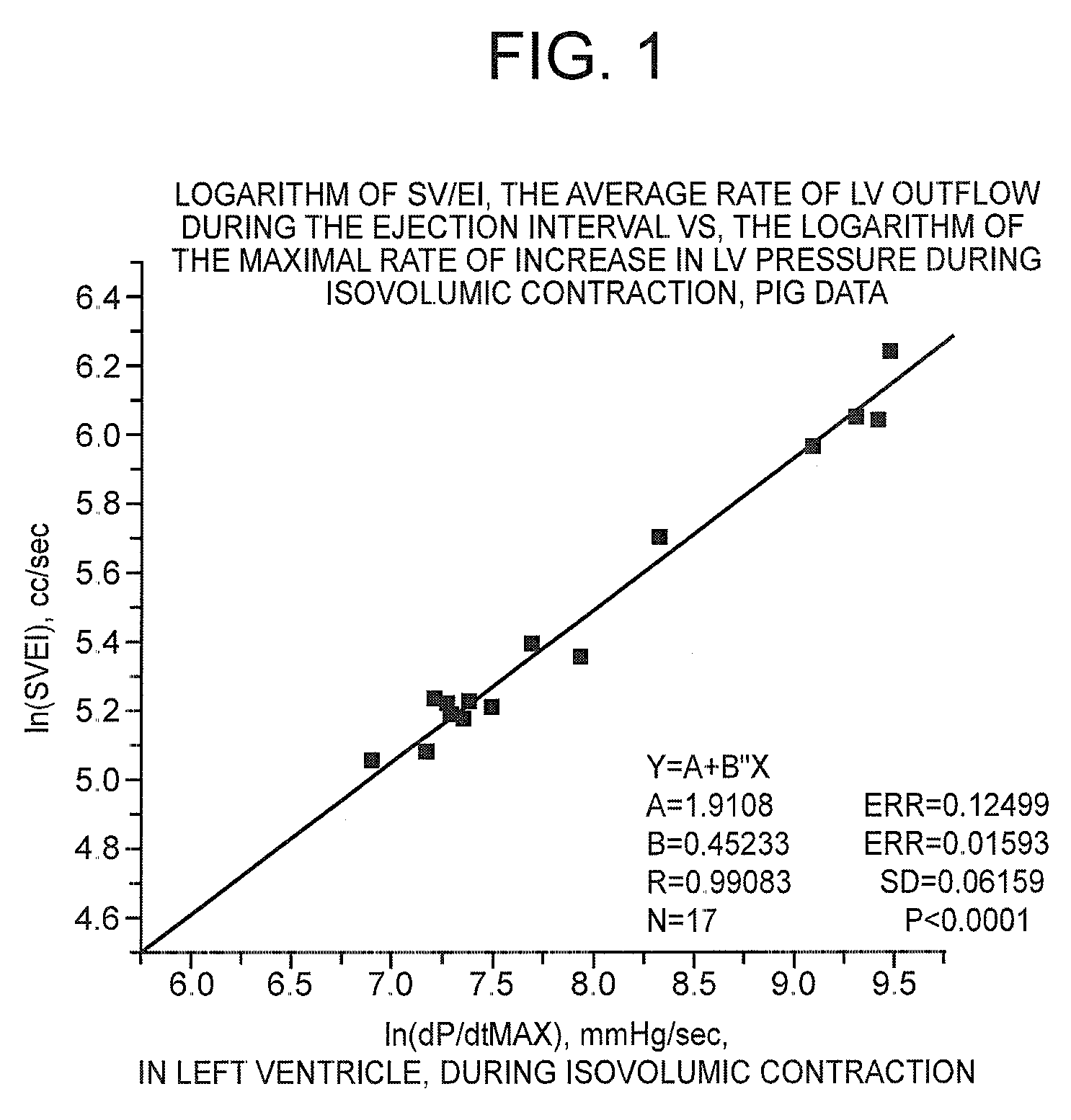
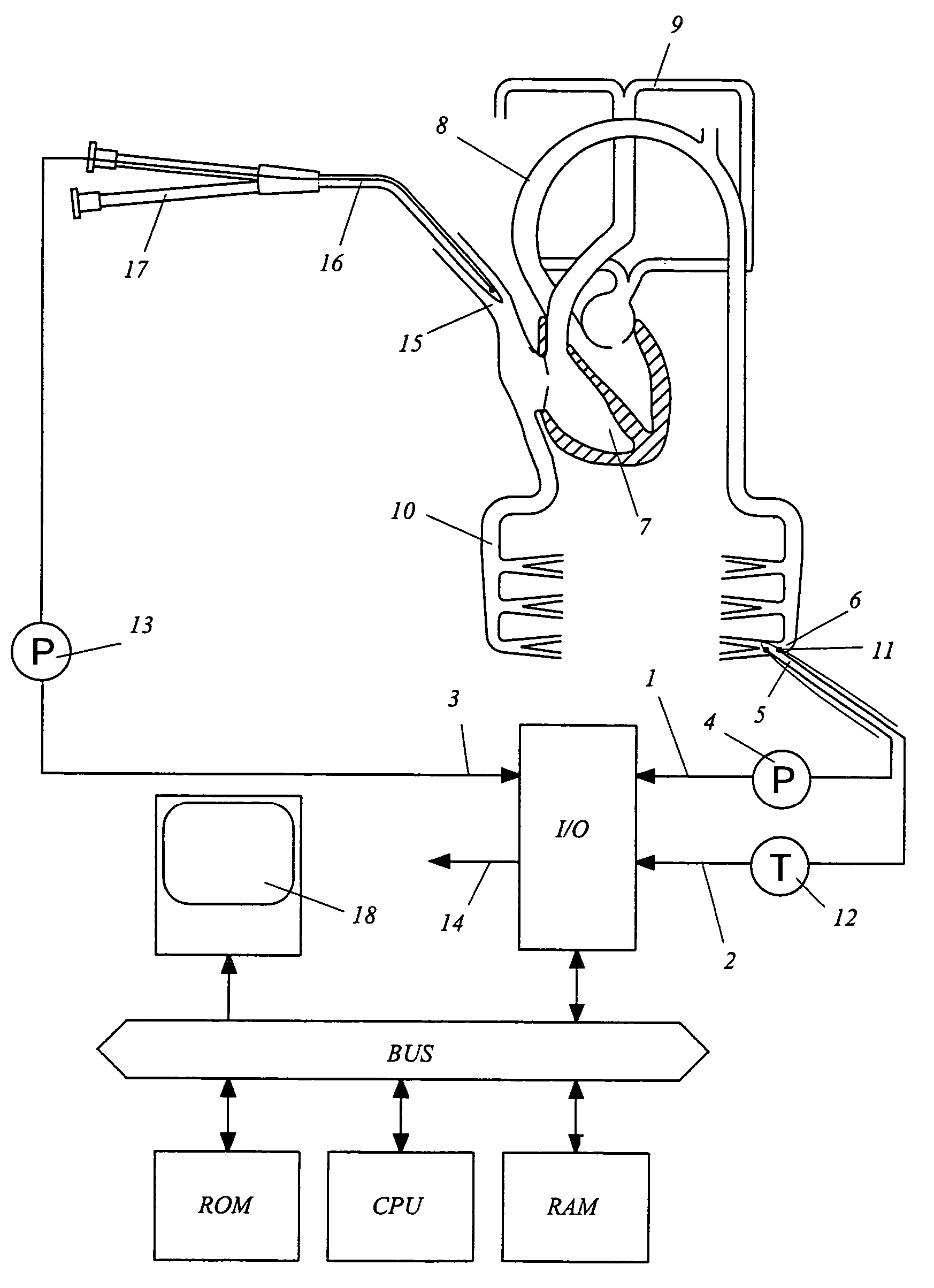
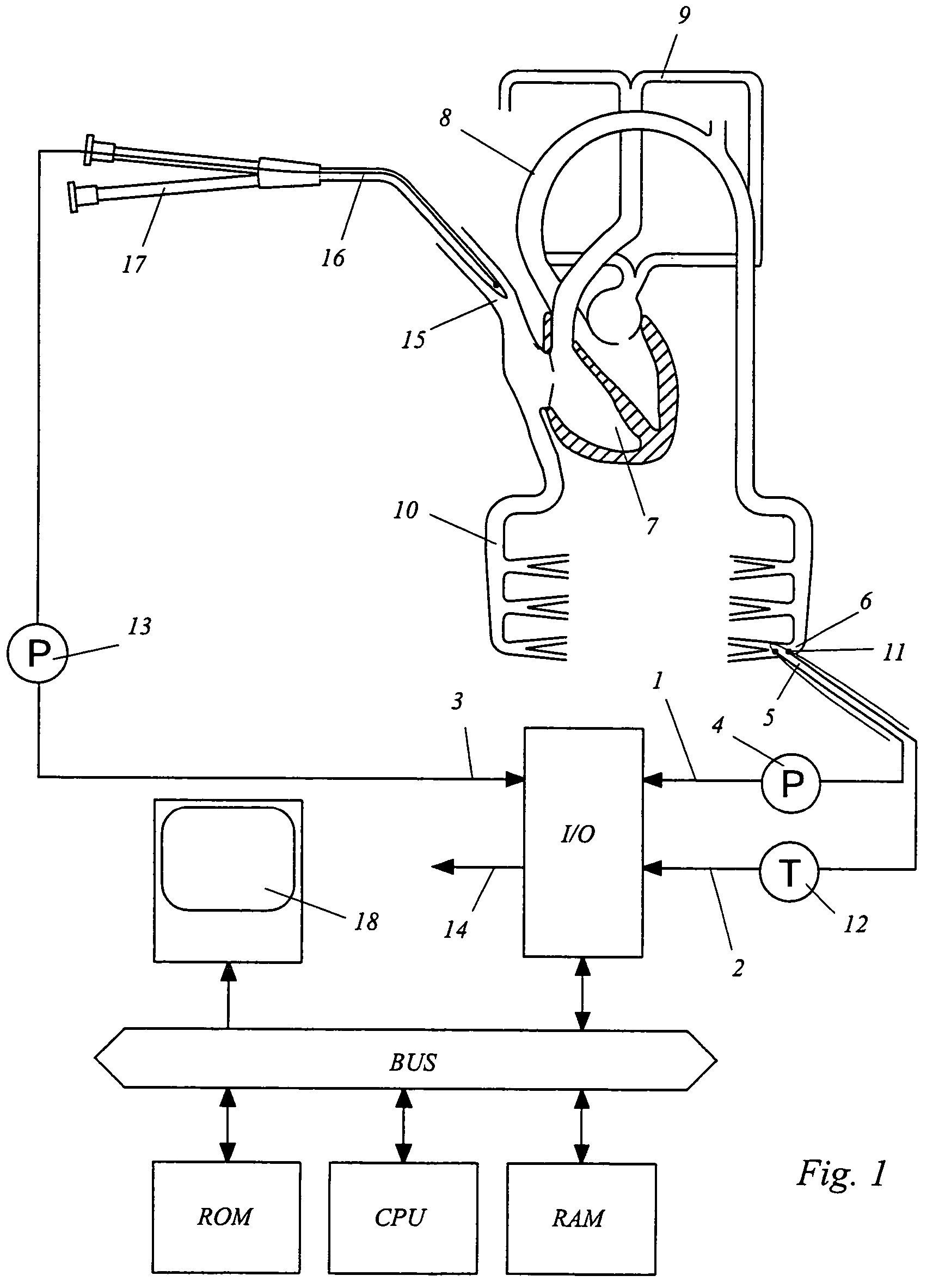
Non-invasive method and device to monitor cardiac parameters
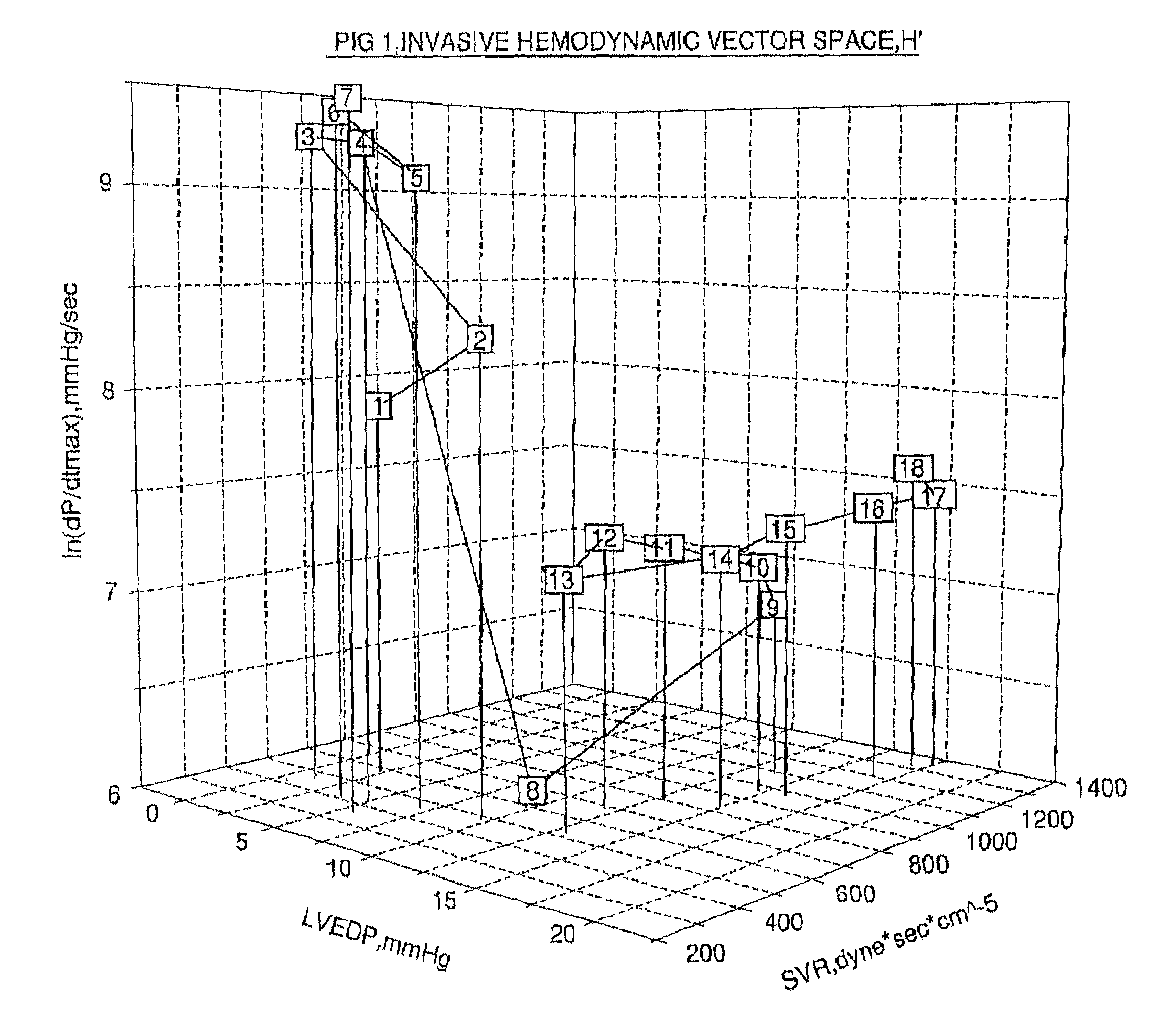
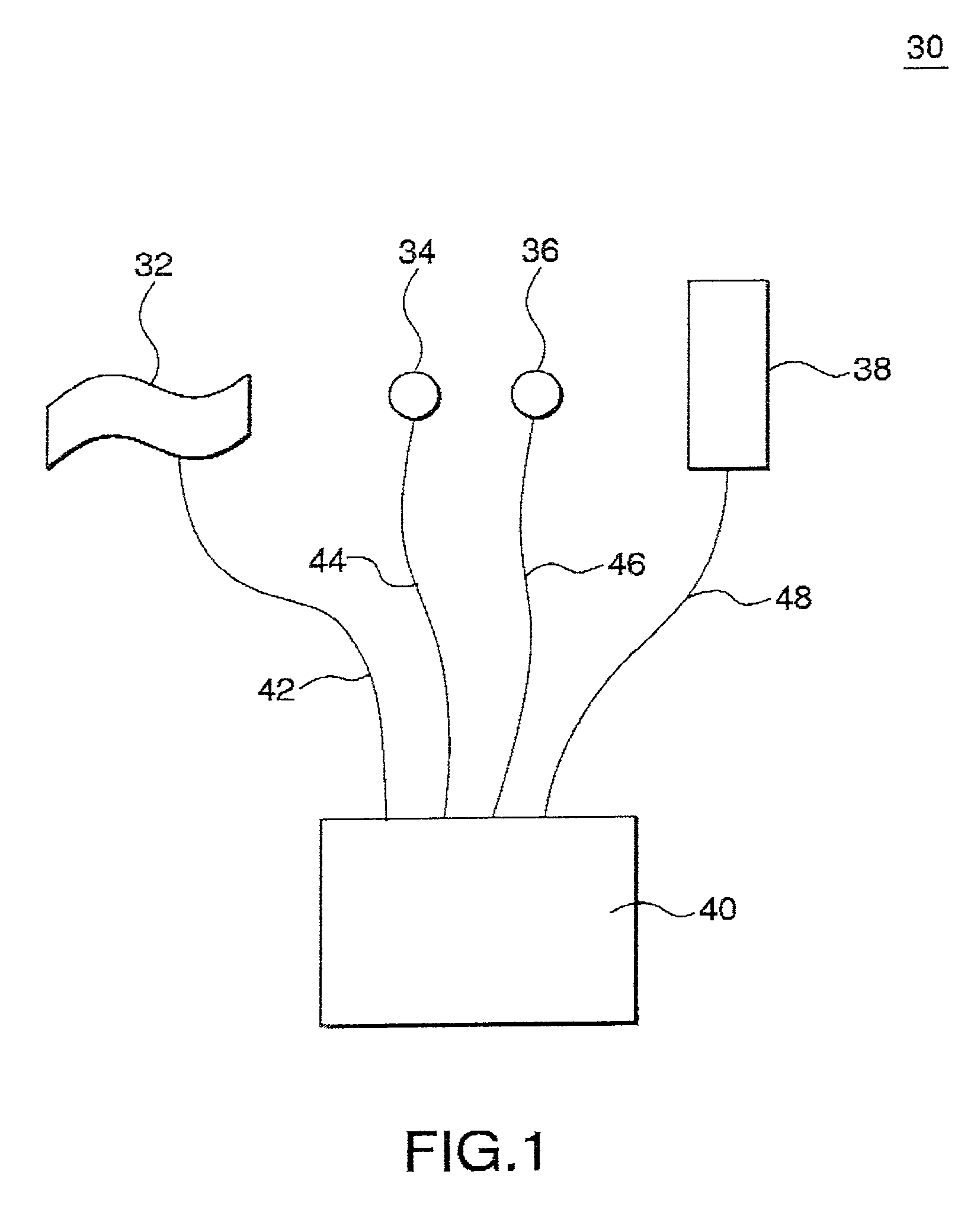
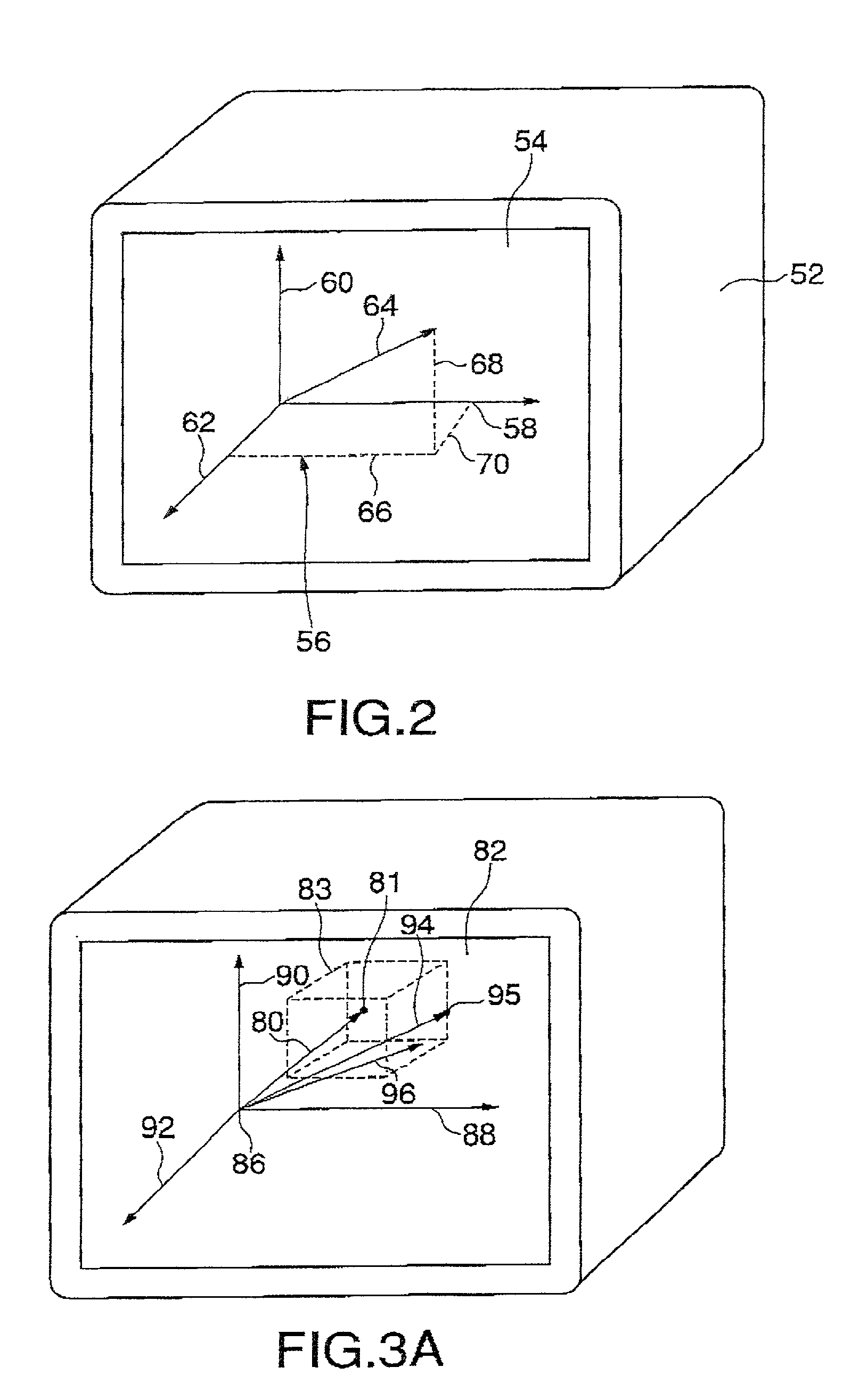
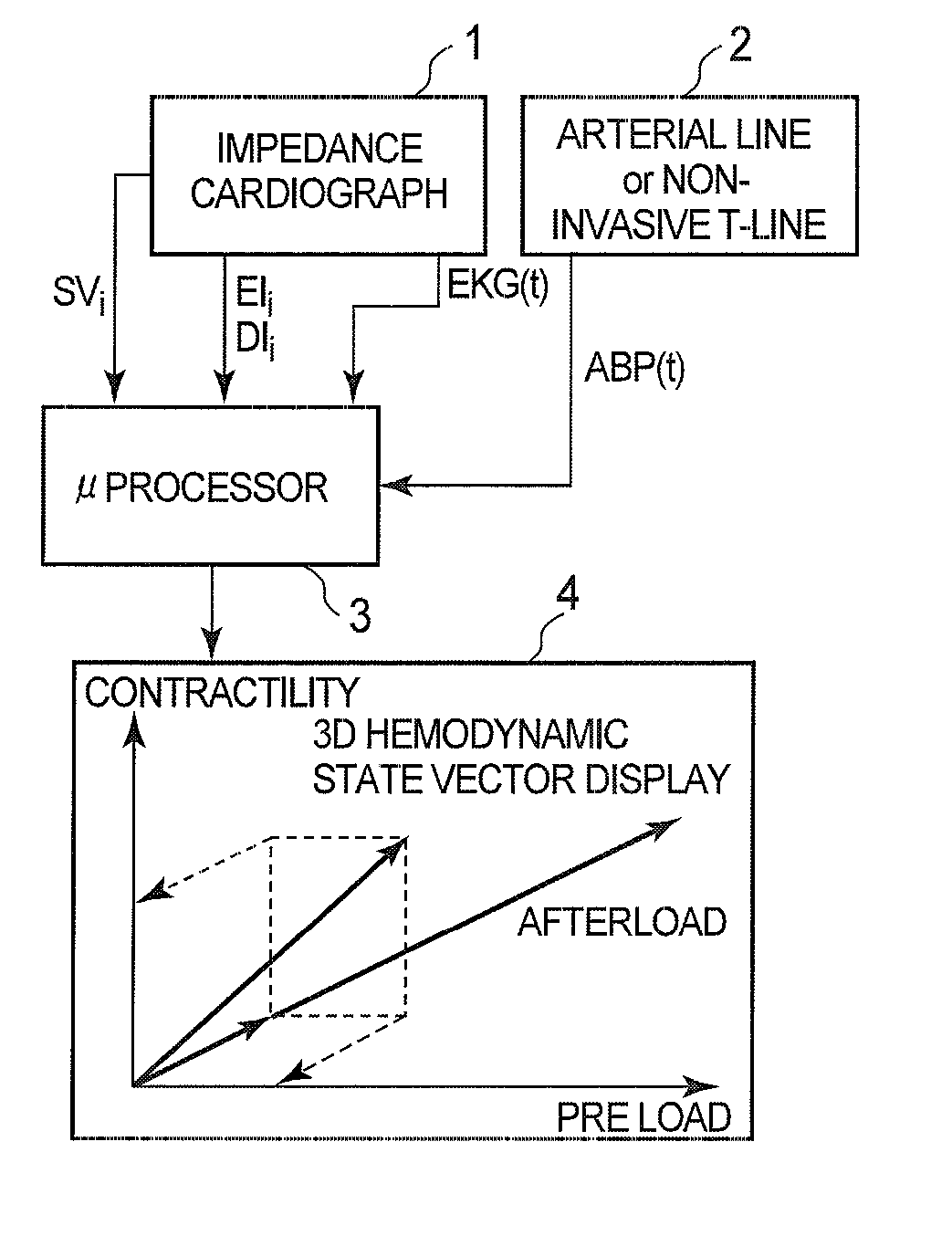
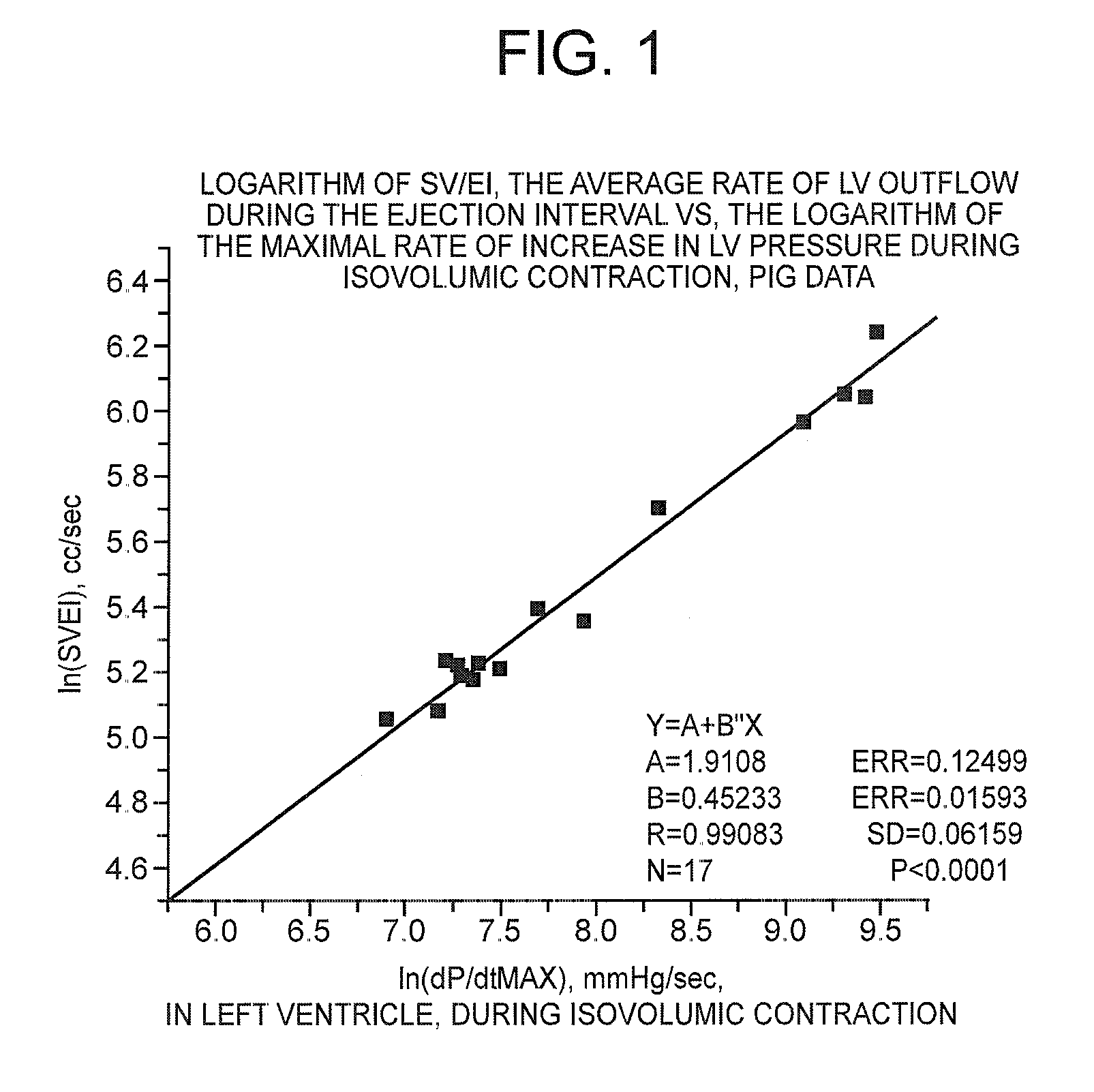
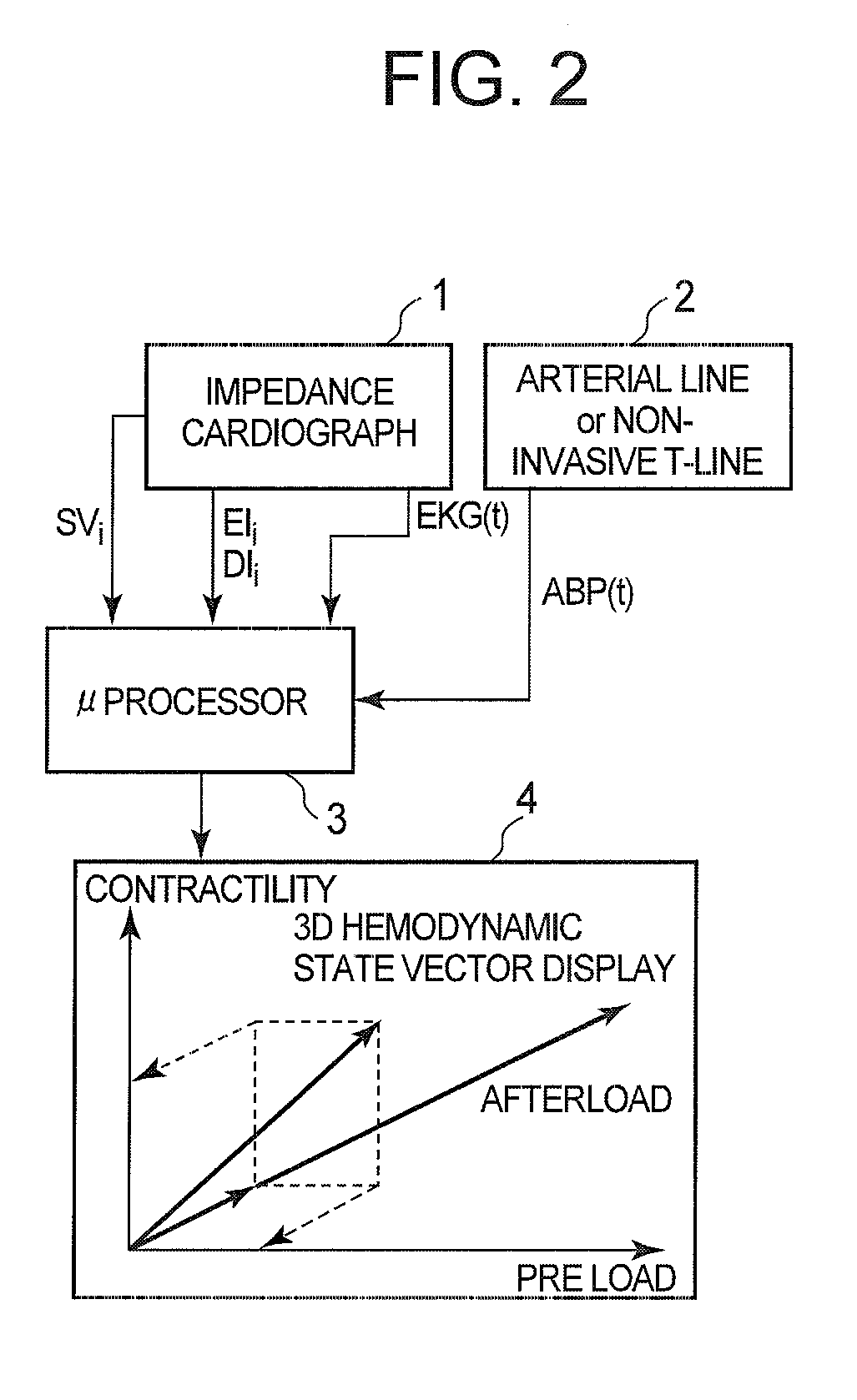
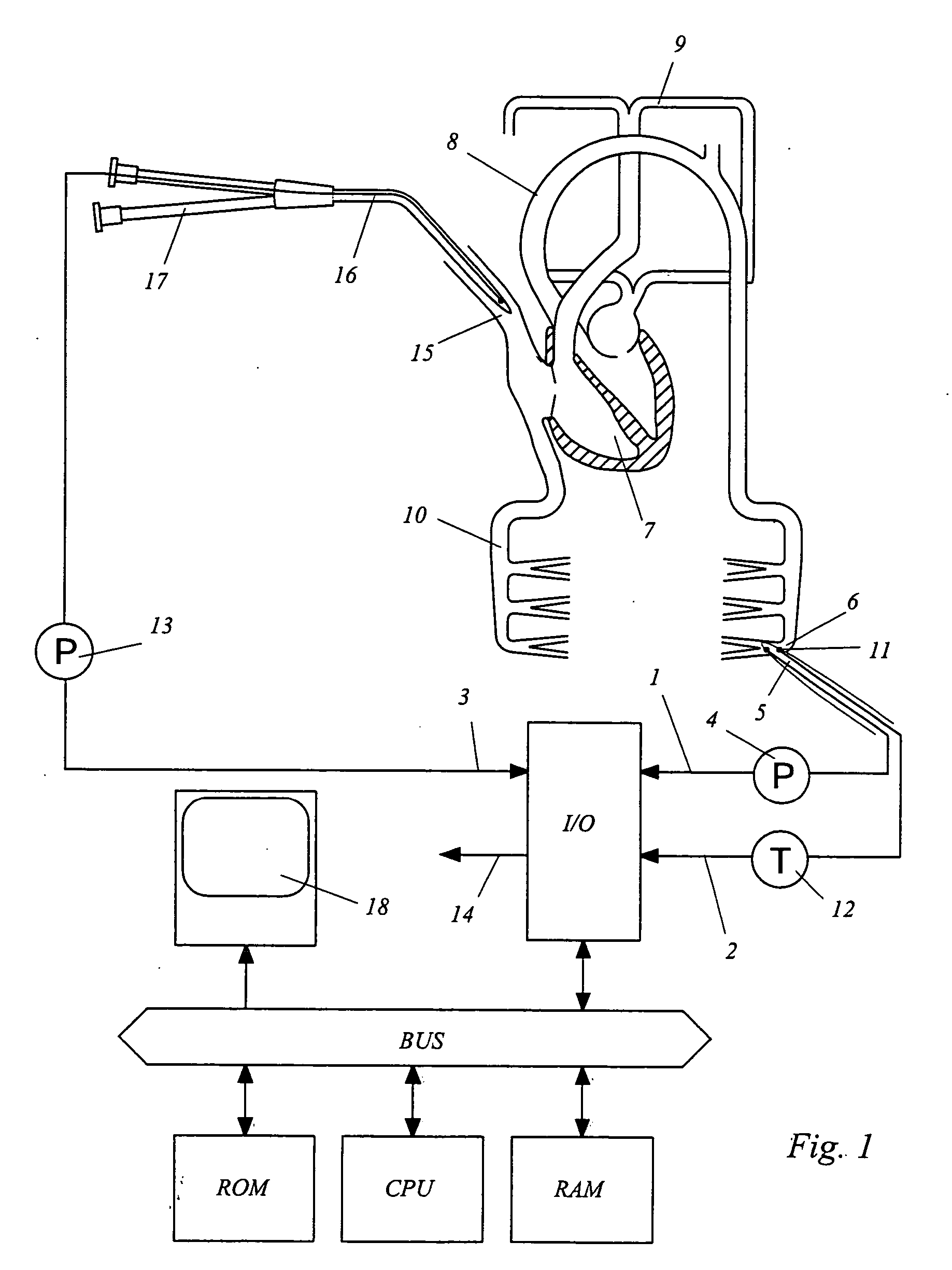
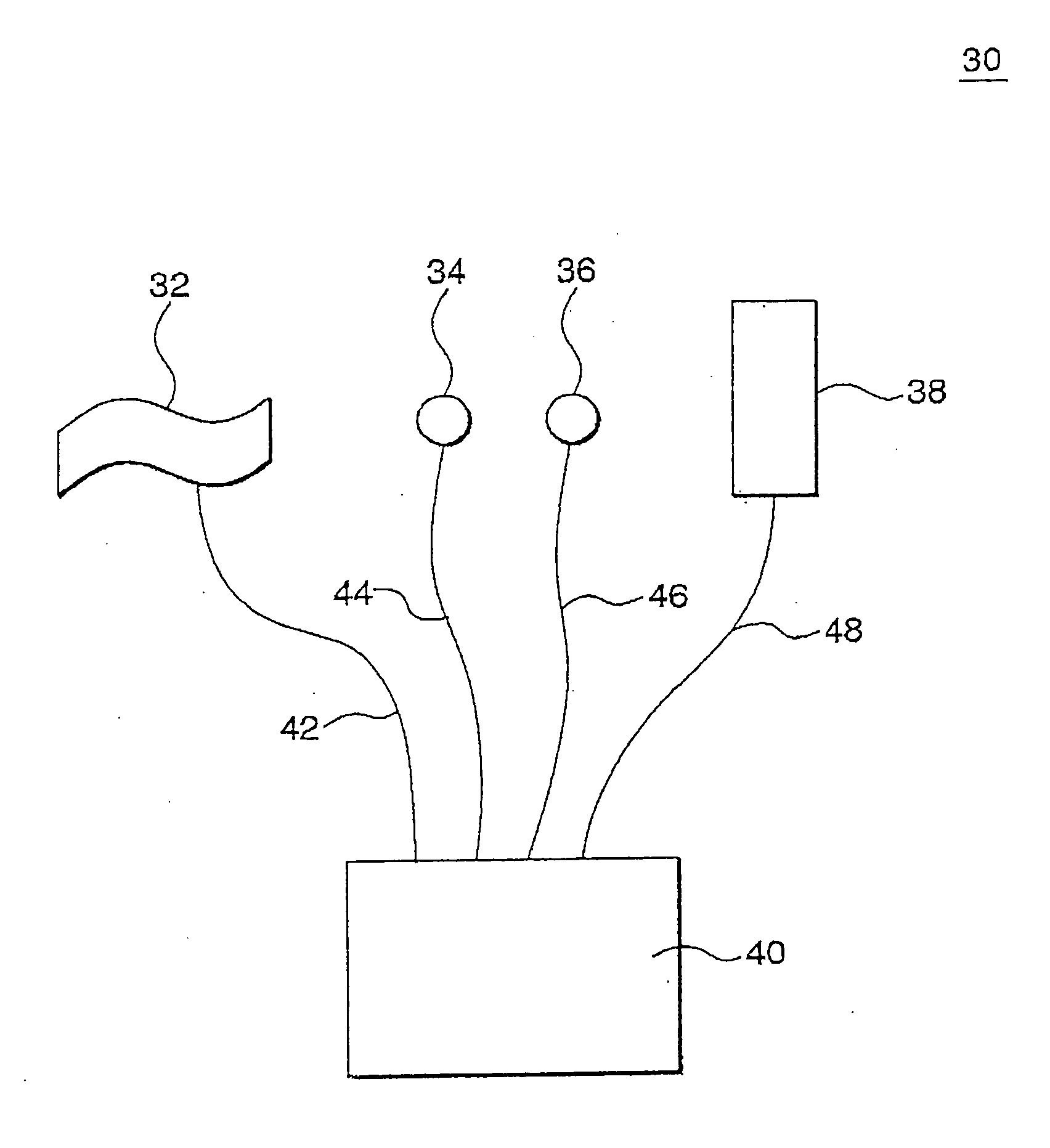
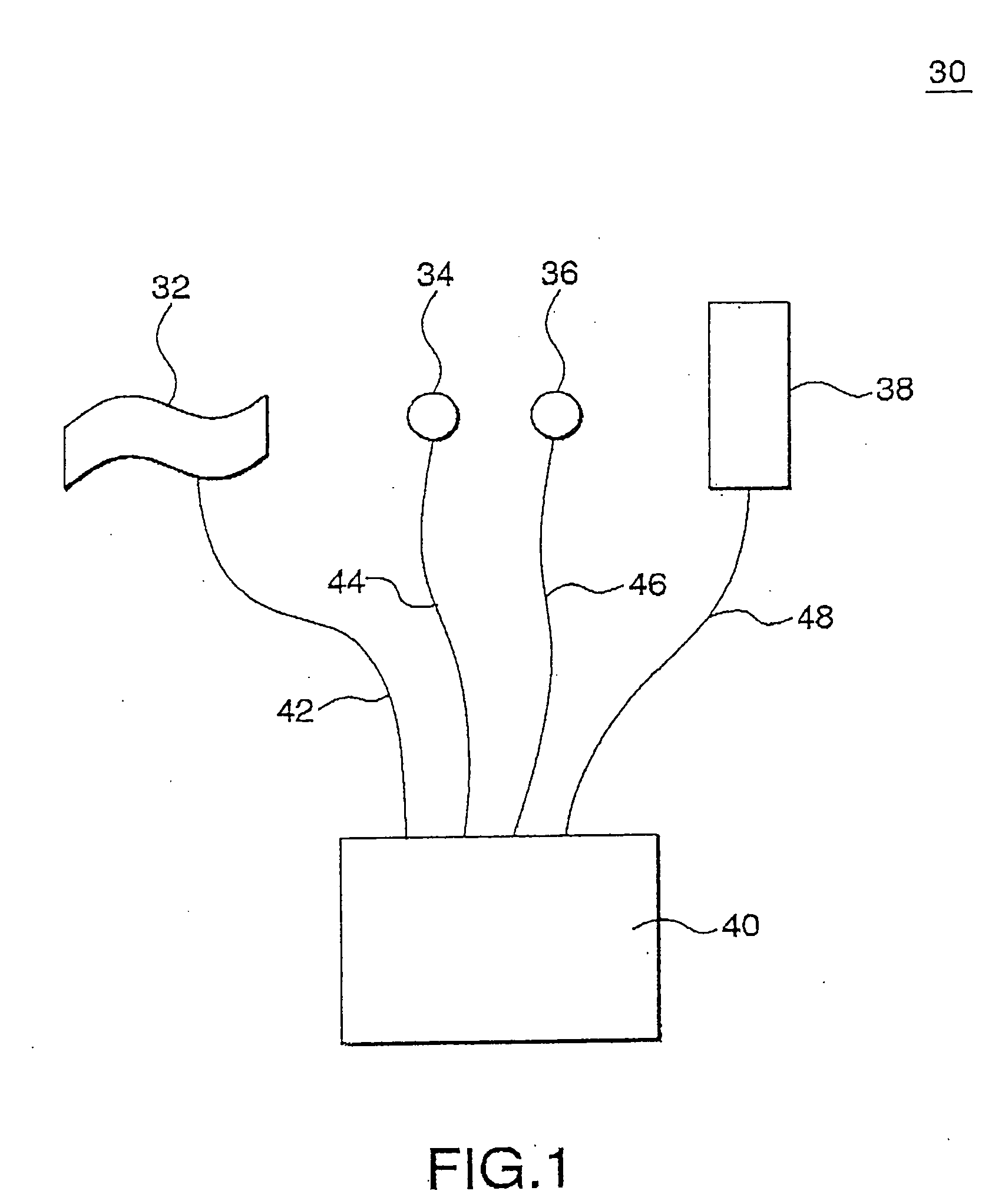
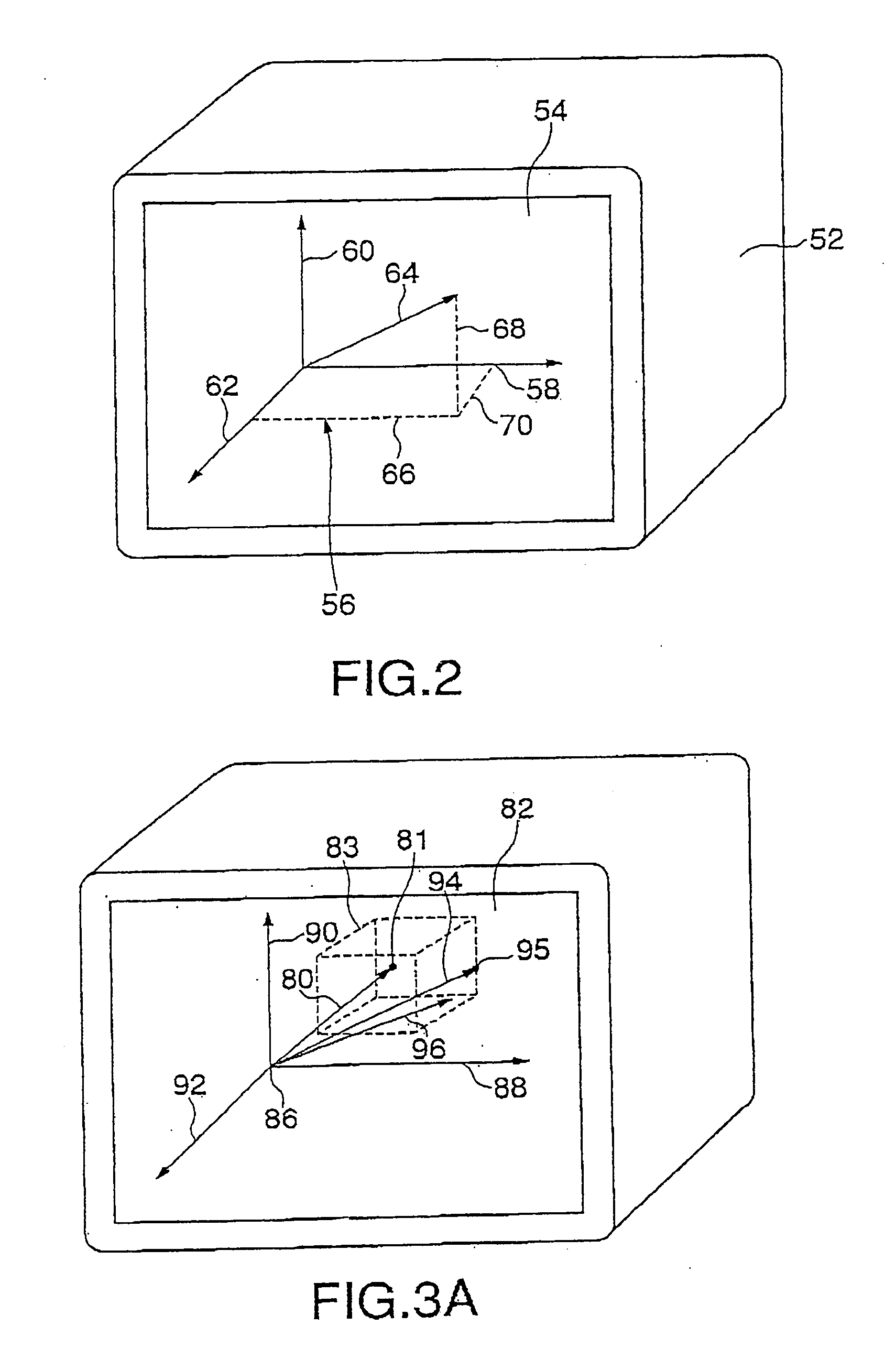
A method of and a device for non-invasively measuring the hemodynamic state of a subject or a human patient involve steps and units of non-invasively measuring cardiac cycle period, electrical-mechanical interval, mean arterial pressure, and ejection interval and converting the measured electrical-mechanical interval, mean arterial pressure and ejection interval into the cardiac parameters such as Preload, Afterload and Contractility, which are the common cardiac parameters used by an anesthesiologist.The converted hemodynamic state of a patient is displayed on a screen as a three-dimensional vector with each of its three coordinates respectively representing Preload, Afterload and Contractility. Therefore, a medical practitioner looks at the screen and quickly obtains the important and necessary information.
Owner:HIRSH ROBERT
Method and device to administer anesthetic and or vosactive agents according to non-invasively monitored cardiac and or neurological parameters
InactiveUS20090124867A1Efficiently safely teachingPumping capacity is overwhelmedMedical simulationRespiratorsCardiac cycleWhole body
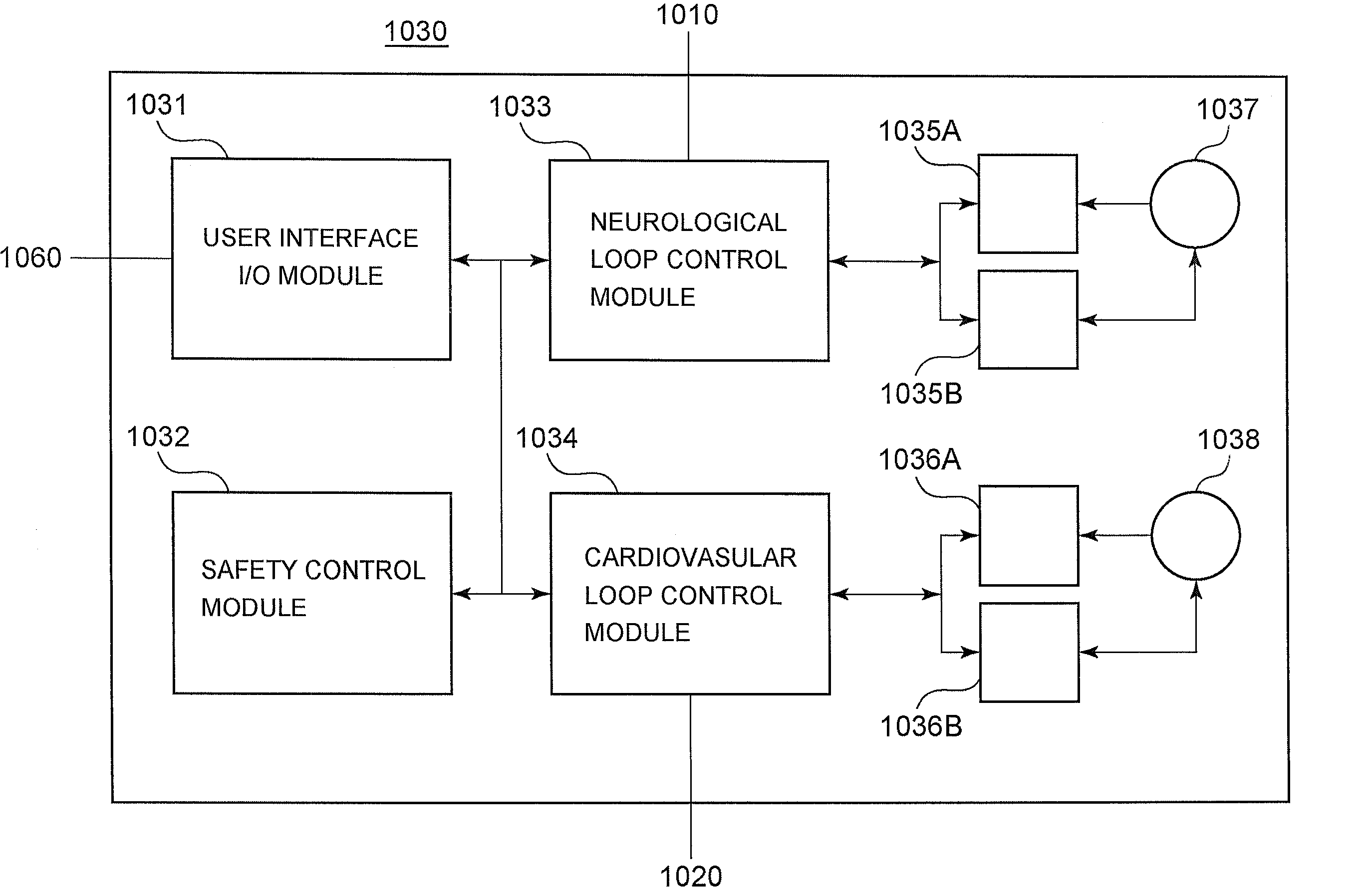
A method of and a device for non-invasively measuring the neurological depressed state and the hemodynamic state of a human patient and involving steps and units of non-invasively measuring EEG, cardiac cycle period, electrical-mechanical interval, mean arterial pressure, and ejection interval and converting the EEG into a neurological index as well as converting the measured electrical-mechanical interval, mean arterial pressure and ejection interval into the cardiac parameters such as Preload, Afterload and Contractility, which are the common cardiac parameters used by an anesthesiologist. A general anesthetic is administered based upon the converted neurological index. A vasoactive agent is independently administered based upon the converted cardiac parameters as necessary in order to restore cardiovascular homeostasis in the patient. The converted neurological and hemodynamic state of a patient are displayed on a screen as an index value and a three-dimensional vector with each of its three coordinates respectively representing Preload, Afterload and Contractility. Therefore, a medical practitioner looks at the screen and quickly obtains the important and necessary information.
Owner:THE COOPER HEALTH SYST
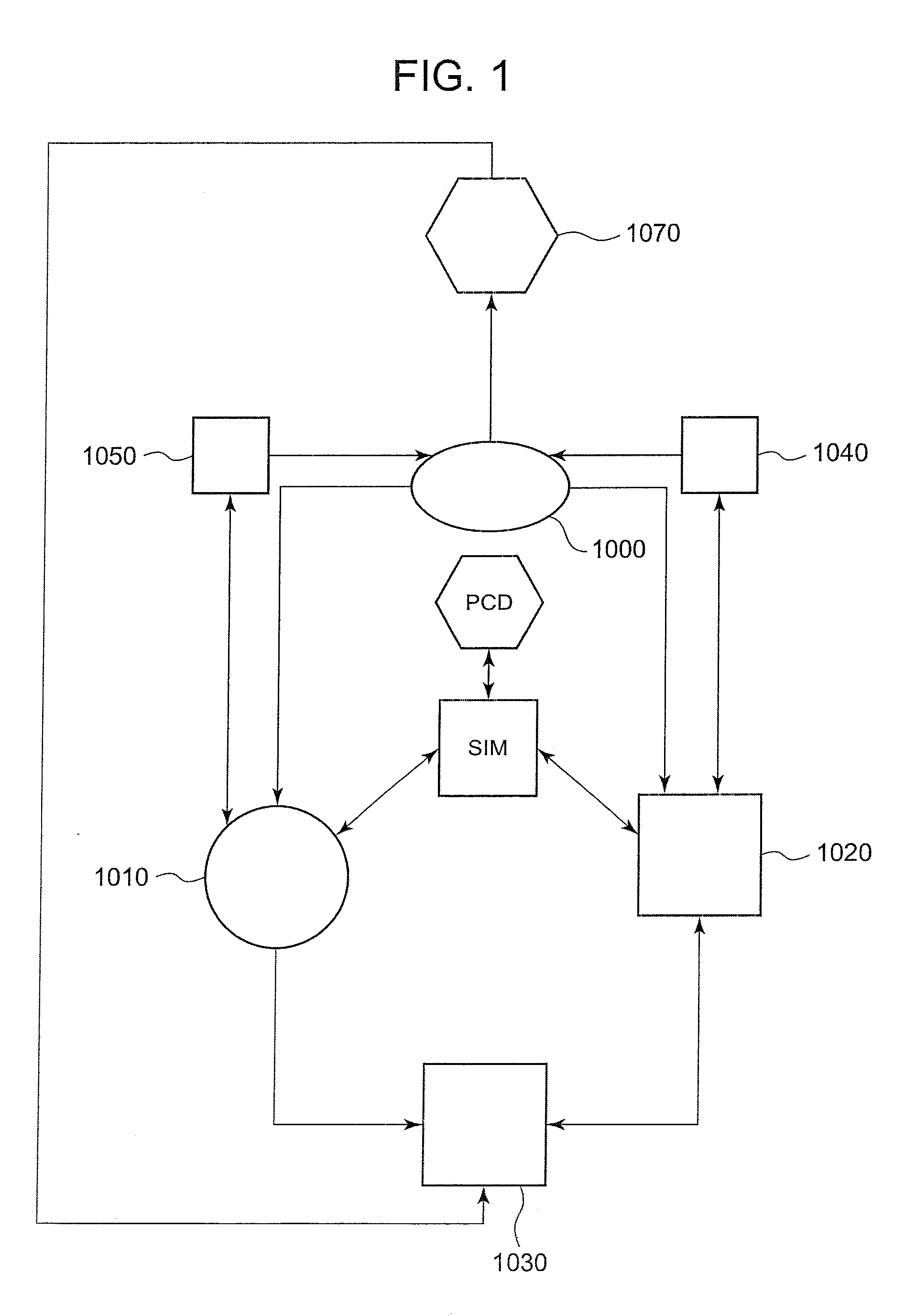
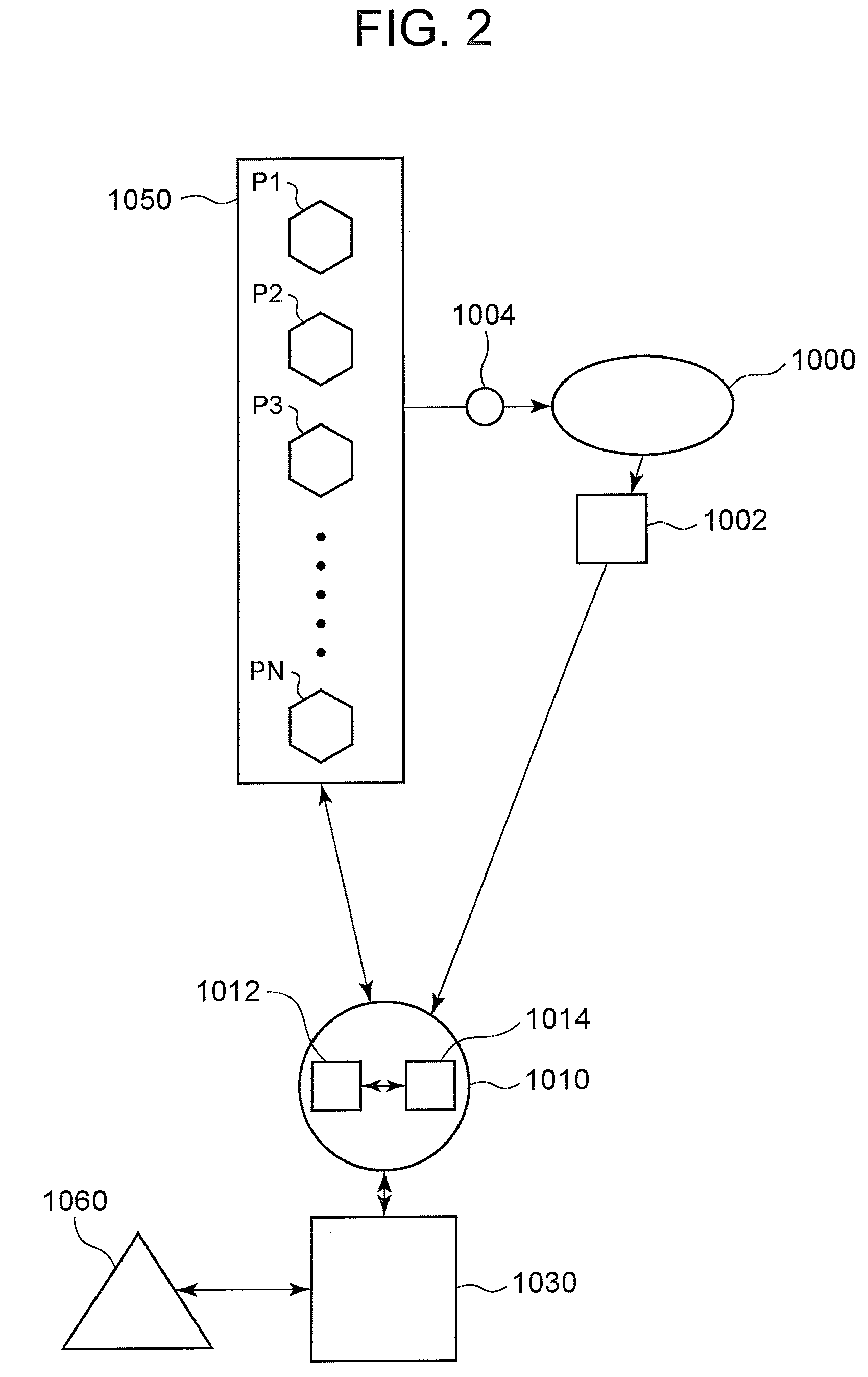
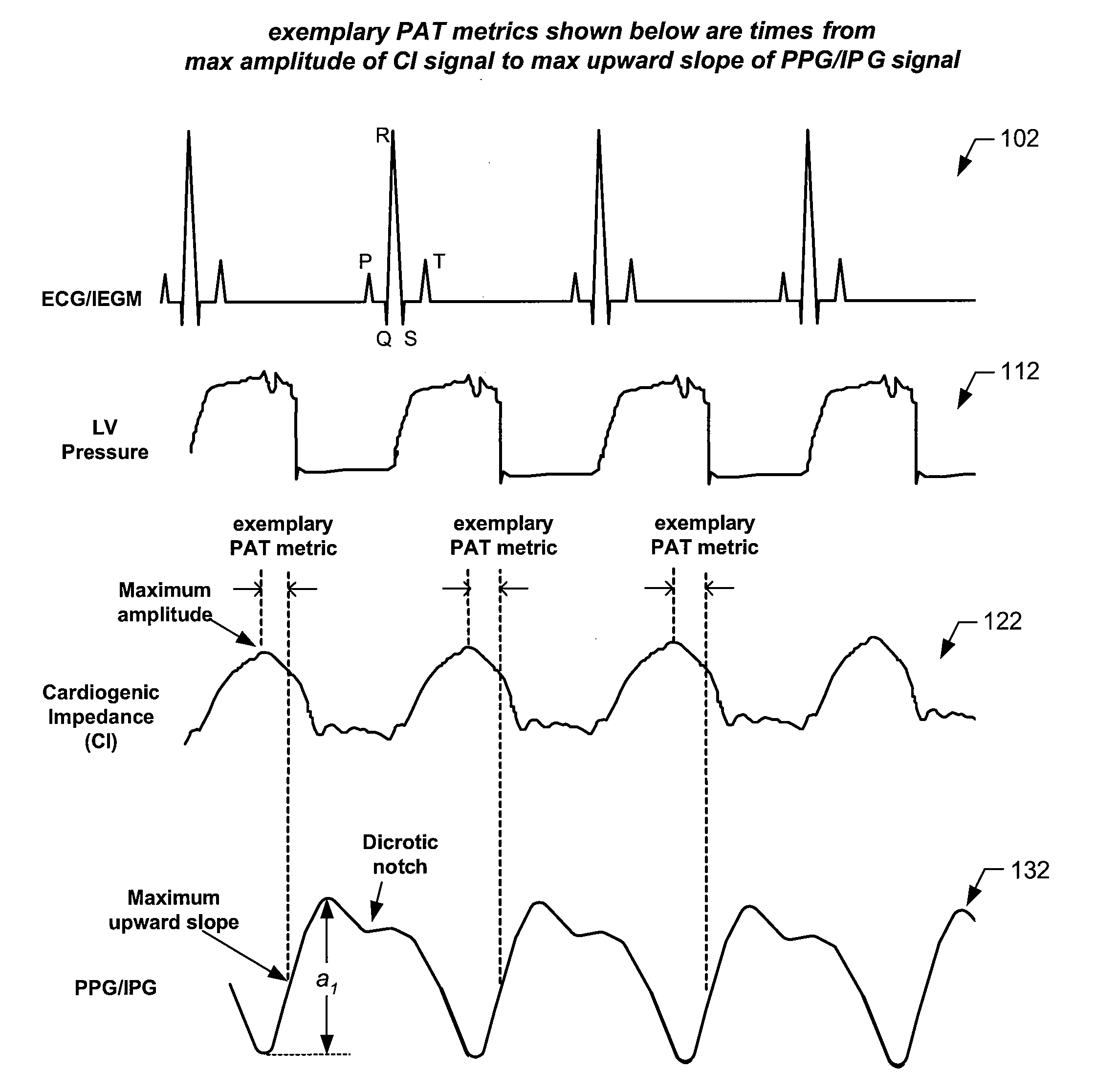
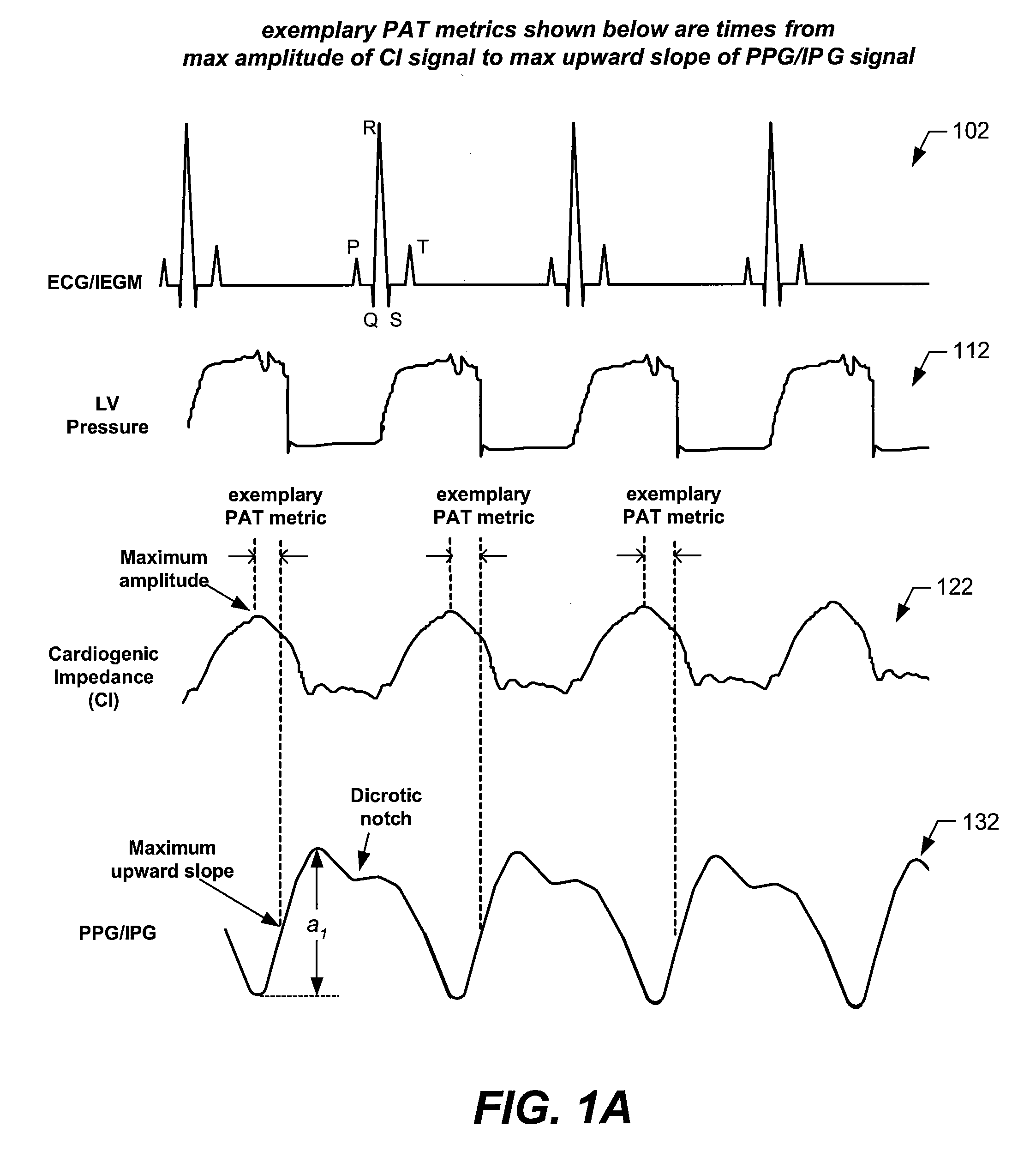
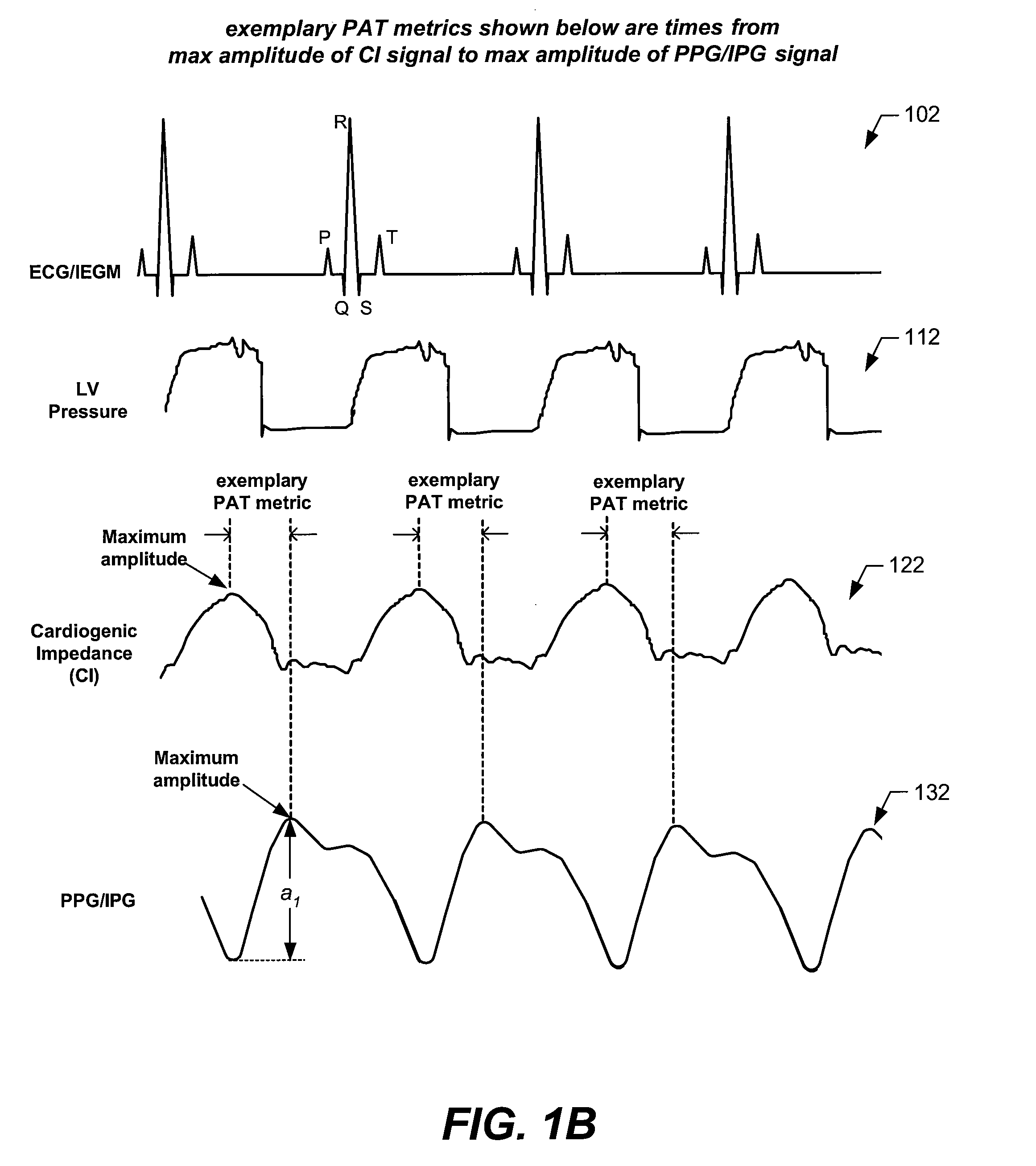
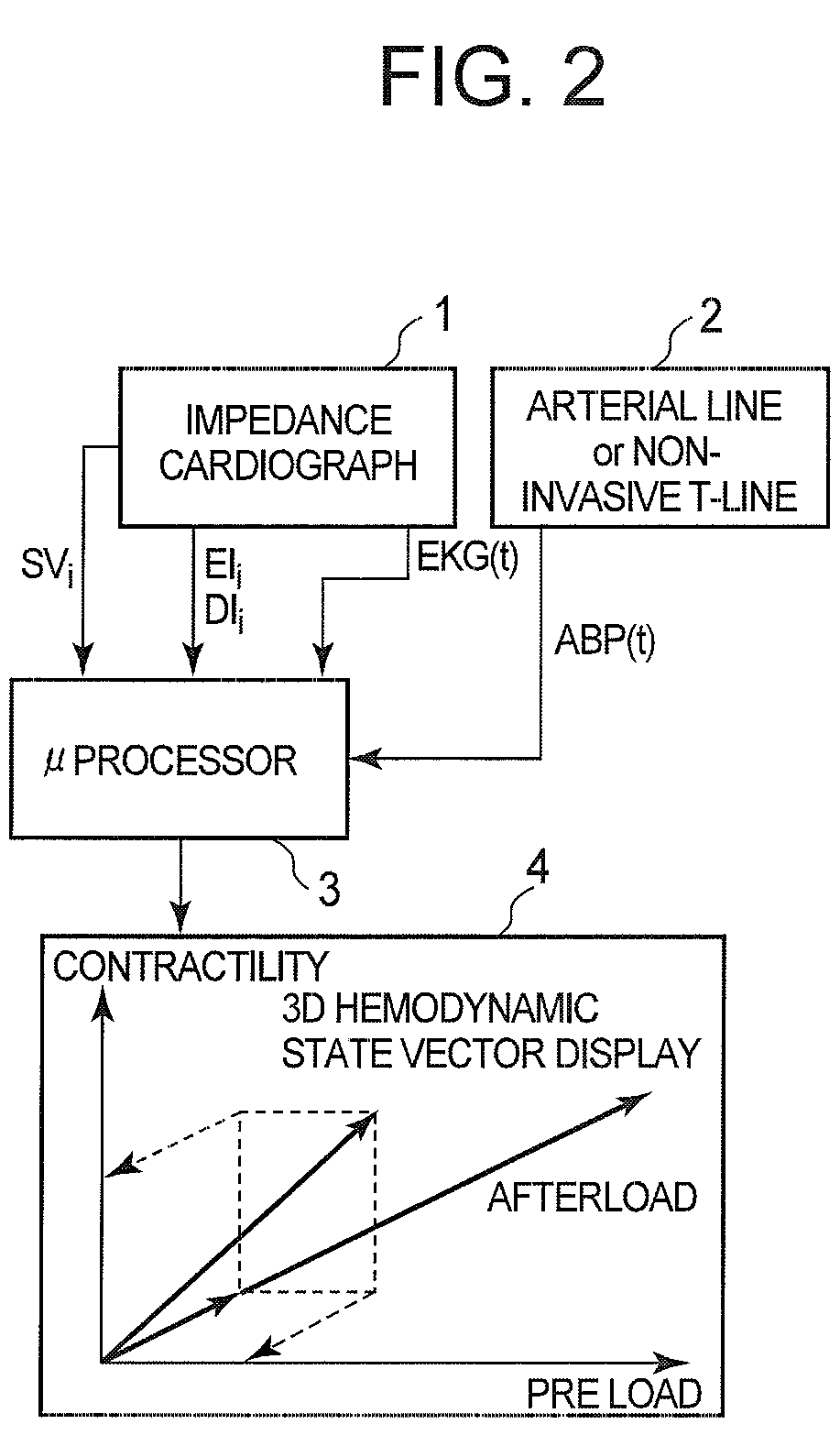
Arterial blood pressure monitoring devices, systems and methods using cardiogenic impedance signal
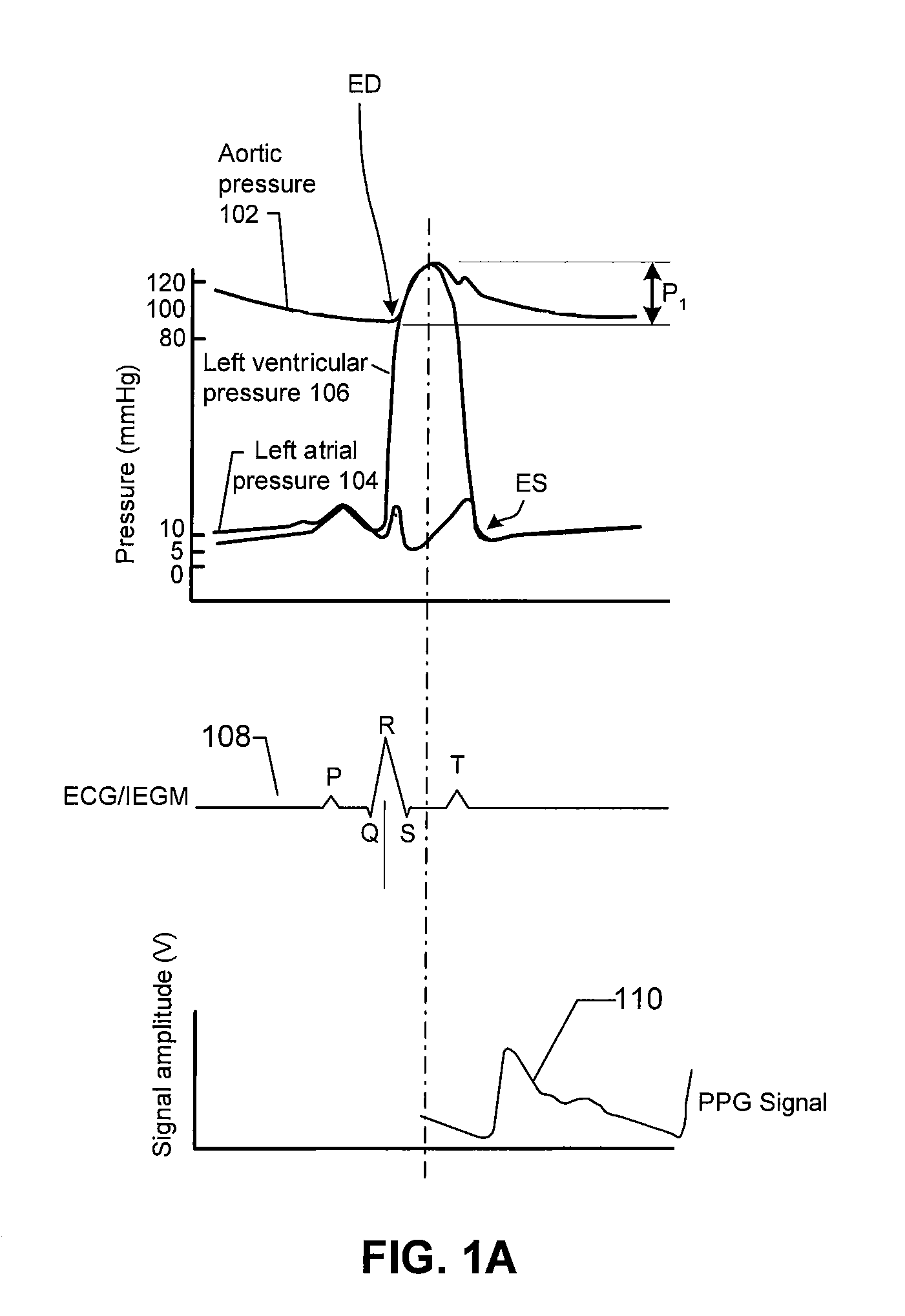
Provided herein are implantable systems, and methods for use therewith, for monitoring a patient's arterial blood pressure. Electrode(s) implanting within and / or on the patient's heart are used to obtain a cardiogenic impedance (CI) signal indicative of cardiac contractile activity. Additionally, a signal (e.g., PPG or IPG signal) indicative of changes in arterial blood volume remote from the patient's heart is obtained using a sensor or electrodes that are implanted remote from the patient's heart. One or more metrics indicative of pulse arrival time (PAT) are determined, where each metric can be determined by determining a time from one of the detected features of the CI signal to one of the detected features of the signal indicative of changes in arterial blood volume. Based on at least one of the metric(s) indicative of PAT, arterial blood pressure is estimated, which can include determining values indicative of systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, pulse pressure and / or mean arterial blood pressure, and / or changes in such values.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
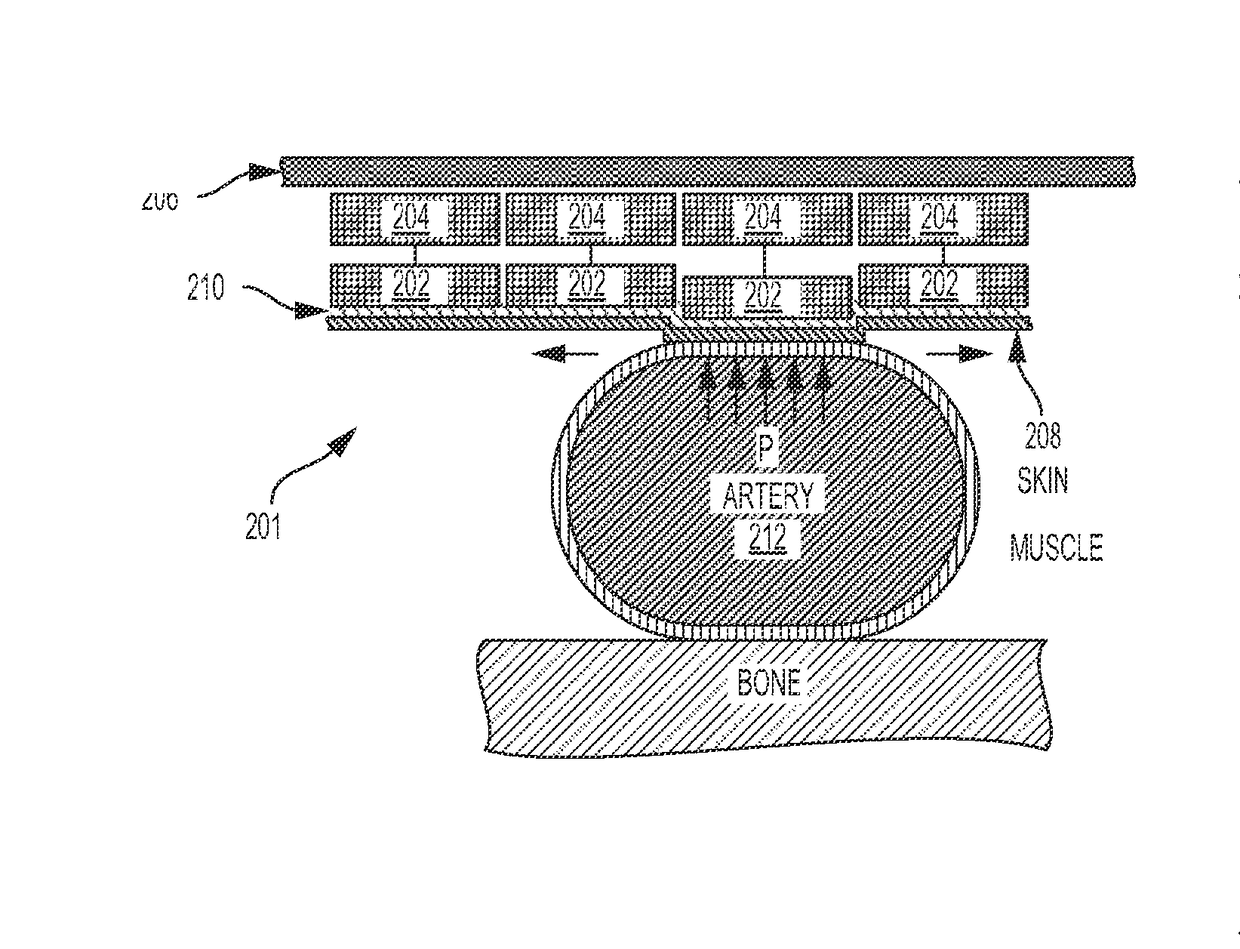
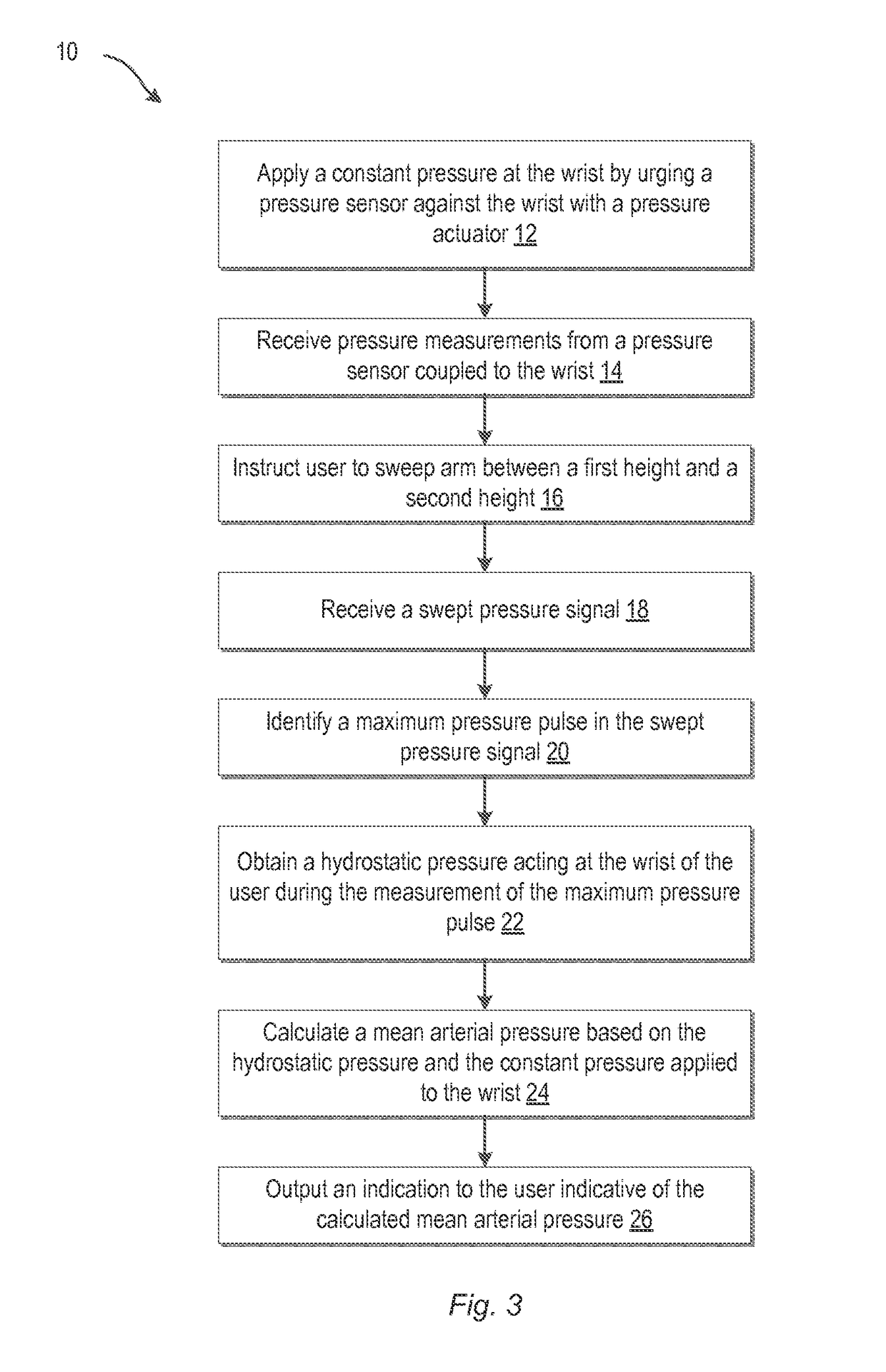
Systems, devices, and methods for measuring blood pressure of a user
ActiveUS20170360306A1Diagnostics using pressureEvaluation of blood vesselsElectricityMonitor blood pressure
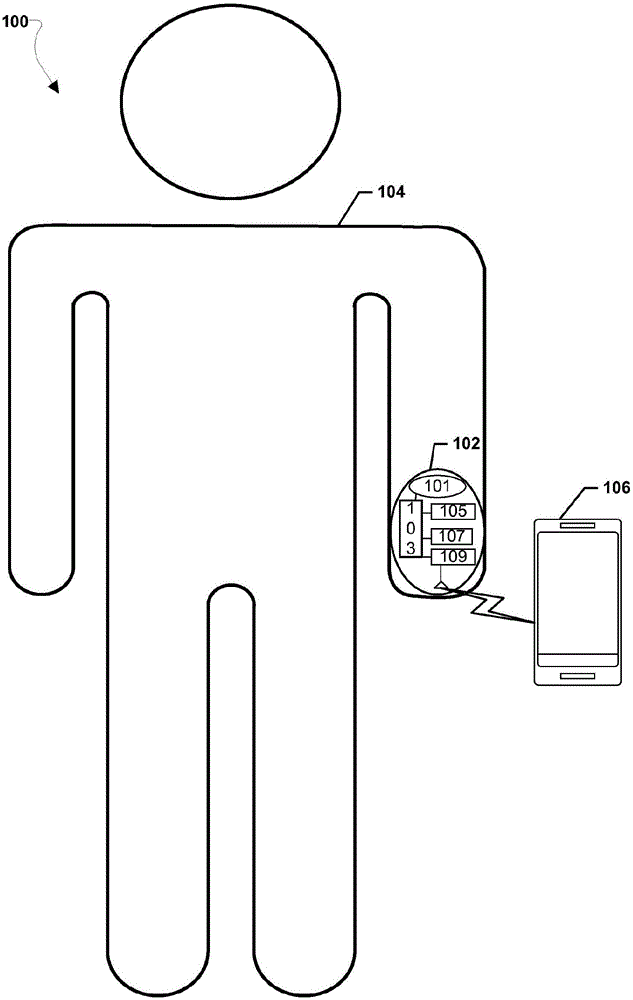
The present invention generally relates to blood pressure monitoring. In some embodiments, methods and devices of measuring a mean arterial pressure are provided and / or monitoring blood pressure changes. A wrist-worn device may include a plurality of sensors backed by a plurality of actuators. Subsets of the plurality of sensors may be selectively actuateable against a wrist of a user using one or more of the plurality of actuators. A preferred sensor and location may be identified based on pressure signals received from each of the sensors. In some embodiments, devices may use a fluid bladder coupled with piezoelectric film sensors. A fluid bladder pressure sensor may be used to calibrate the piezoelectric film signal to provide a static and dynamic pressure reading. In yet another embodiment, a mean arterial pressure may be calculated by processing a swept pressure signal obtained as a sensor is swept through different heights.
Owner:APPLE INC
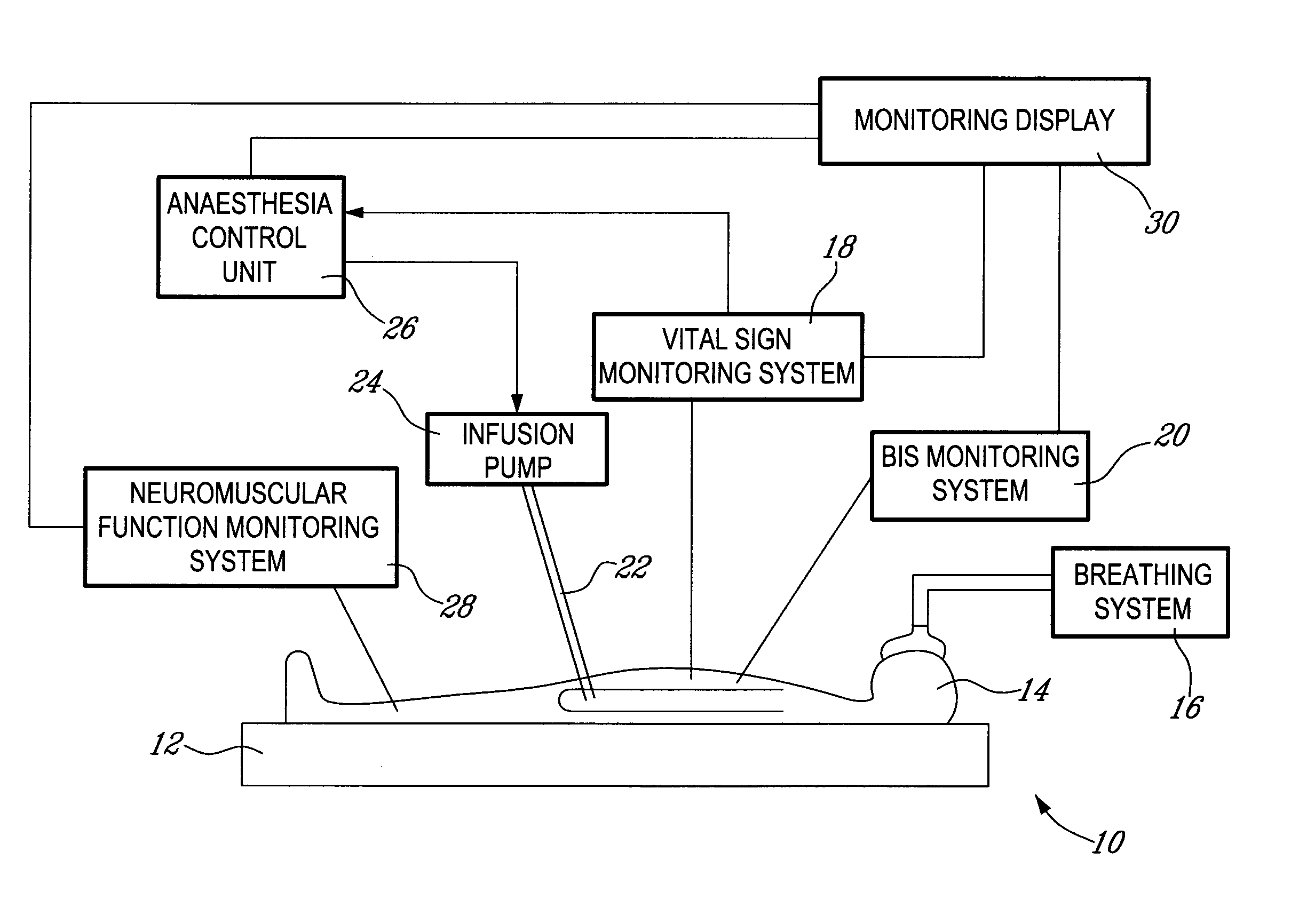
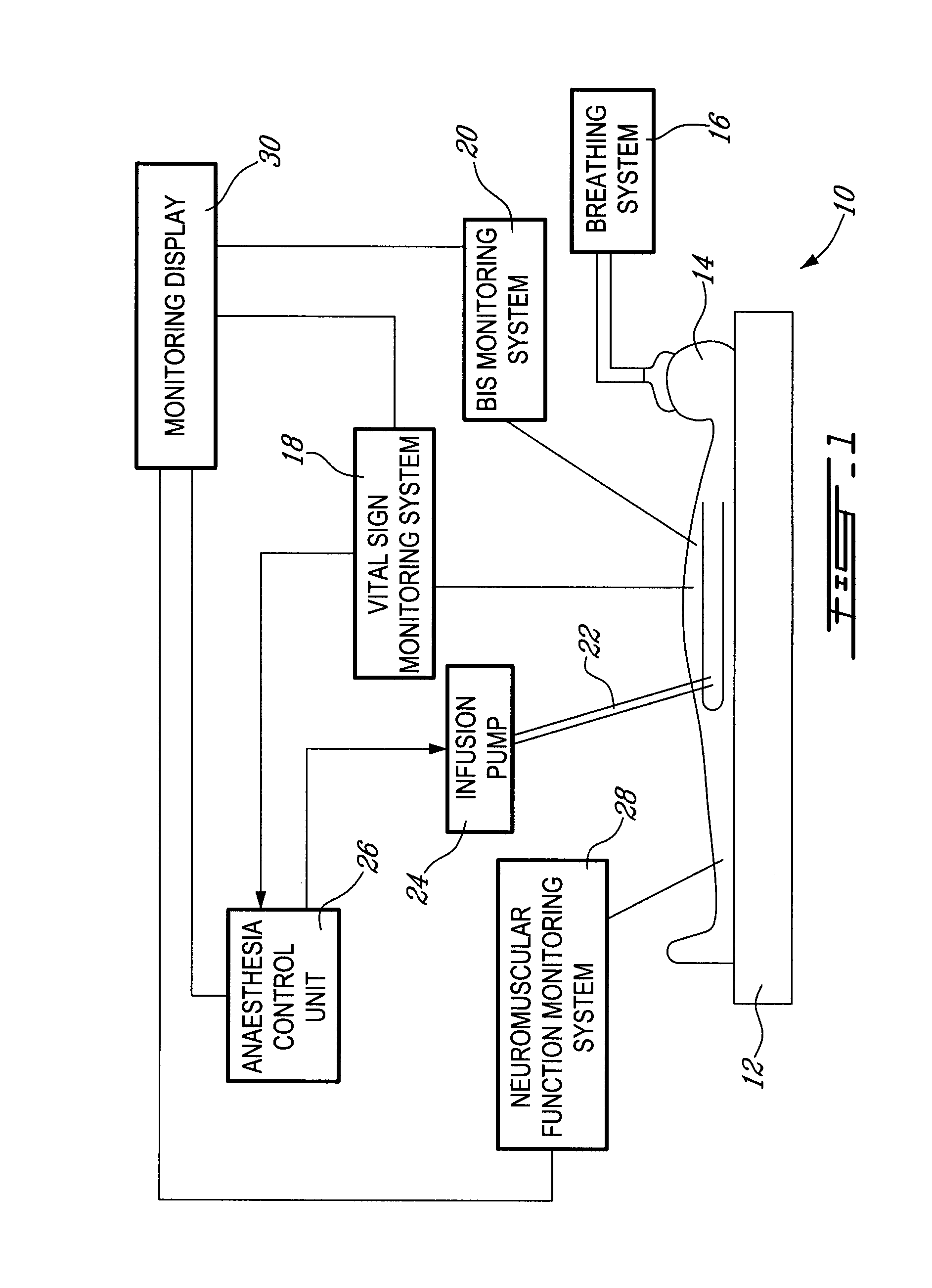
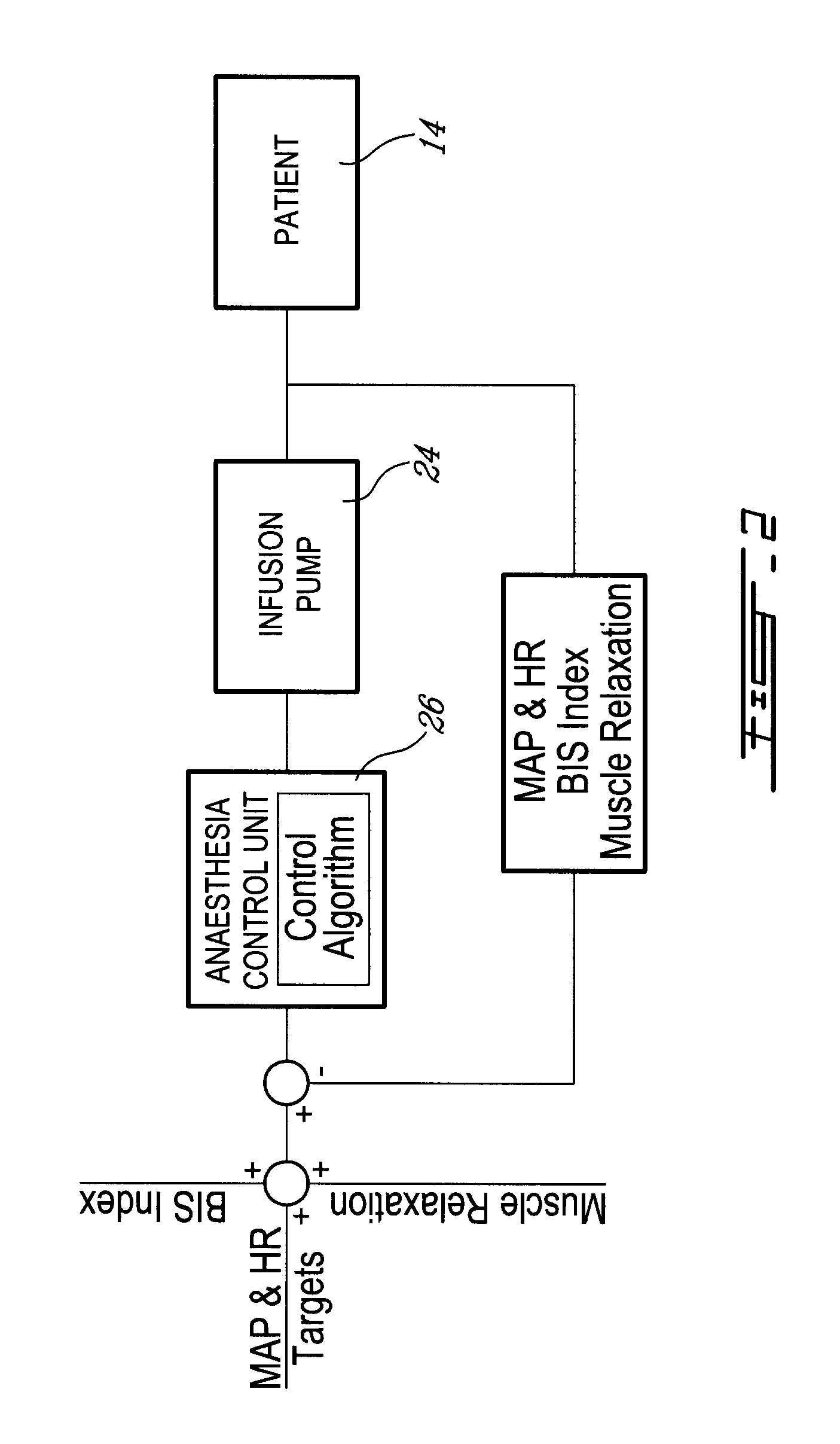
Method and system for administering an anaesthetic
A method and system for objectively scoring intra-operative pain during general anaesthesia based on the patient's mean arterial pressure and heart rate. The index is used for closed-loop control of the intra-operative analgesia through adjustment of the drug infusion level according to fuzzy logic. It is further displayed along with other components of anaesthesia and important patient data on a monitoring display for presentation to medical staff.
Owner:HEMMERLING THOMAS +4
Non-invasive method and device to monitor cardiac parameters without use of electrical-mechanical interval
InactiveUS20070191724A1Easy to measureSimple processElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesDiastolic intervalCardiac cycle
A method of and a device for non-invasively measuring the hemodynamic state of a subject or a human patient involve steps and units of non-invasively or minimally invasively measuring cardiac cycle period, mean arterial pressure, stroke volume, diastolic interval and ejection interval and converting the measured mean arterial pressure, stroke volume, diastolic interval and ejection interval into the cardiac parameters such as Preload, Afterload and Contractility, which are the common cardiac parameters used by an anesthesiologist. In the current invention, the use of electrical-mechanical interval has been eliminated for various advantageous reasons. The converted hemodynamic state of a patient is displayed on a screen as a three-dimensional vector with each of its three coordinates respectively representing Preload, Afterload and Contractility. Therefore, a medical practitioner looks at the screen and—quickly obtains the important and necessary information.
Owner:HIRSH ROBERT
Electronic hemomanometer and blood pressure measuring method of electronic hemomanometer
InactiveUS20050119578A1Improve accuracyReduce necessityEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterOscillometryPulse wave
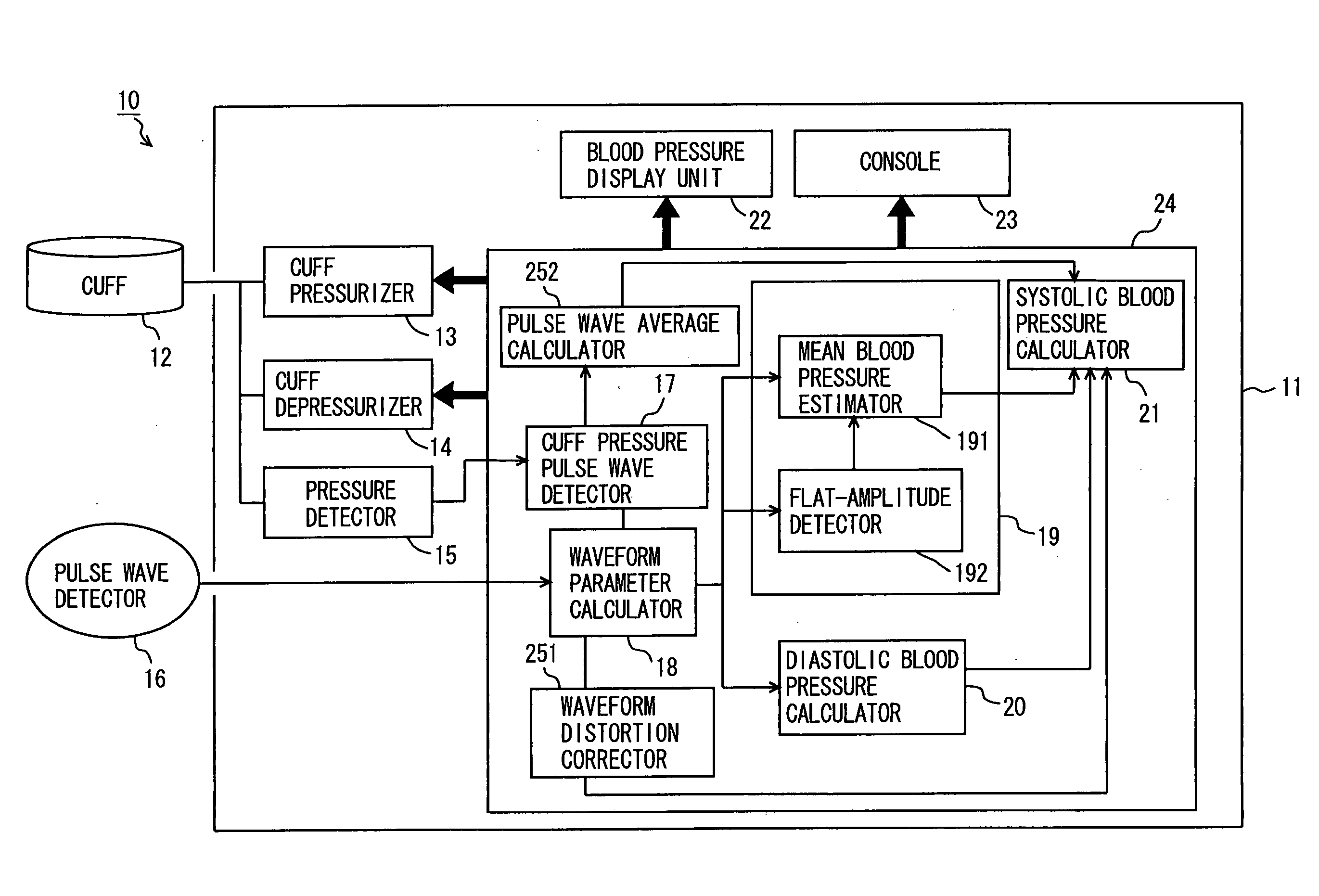
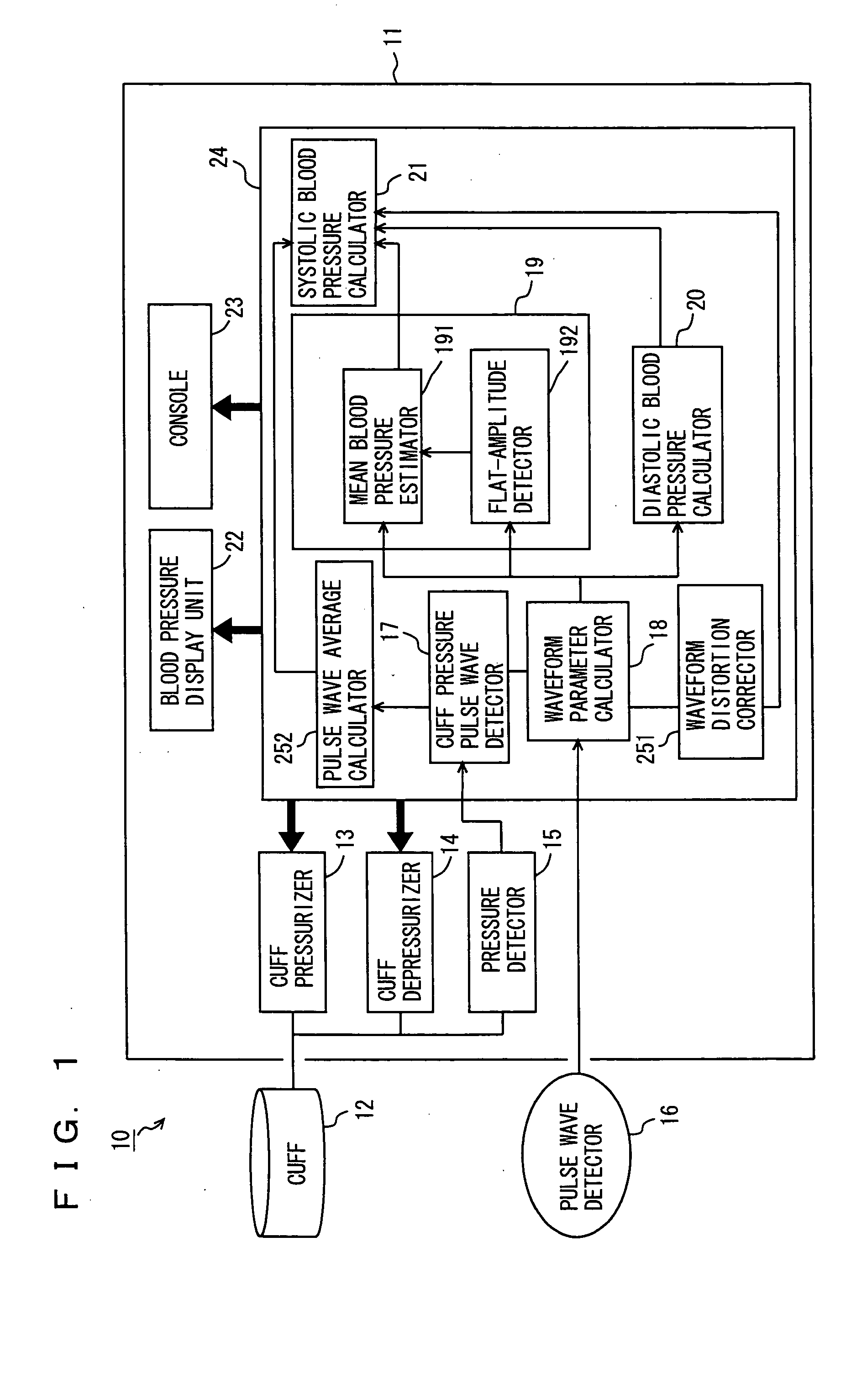
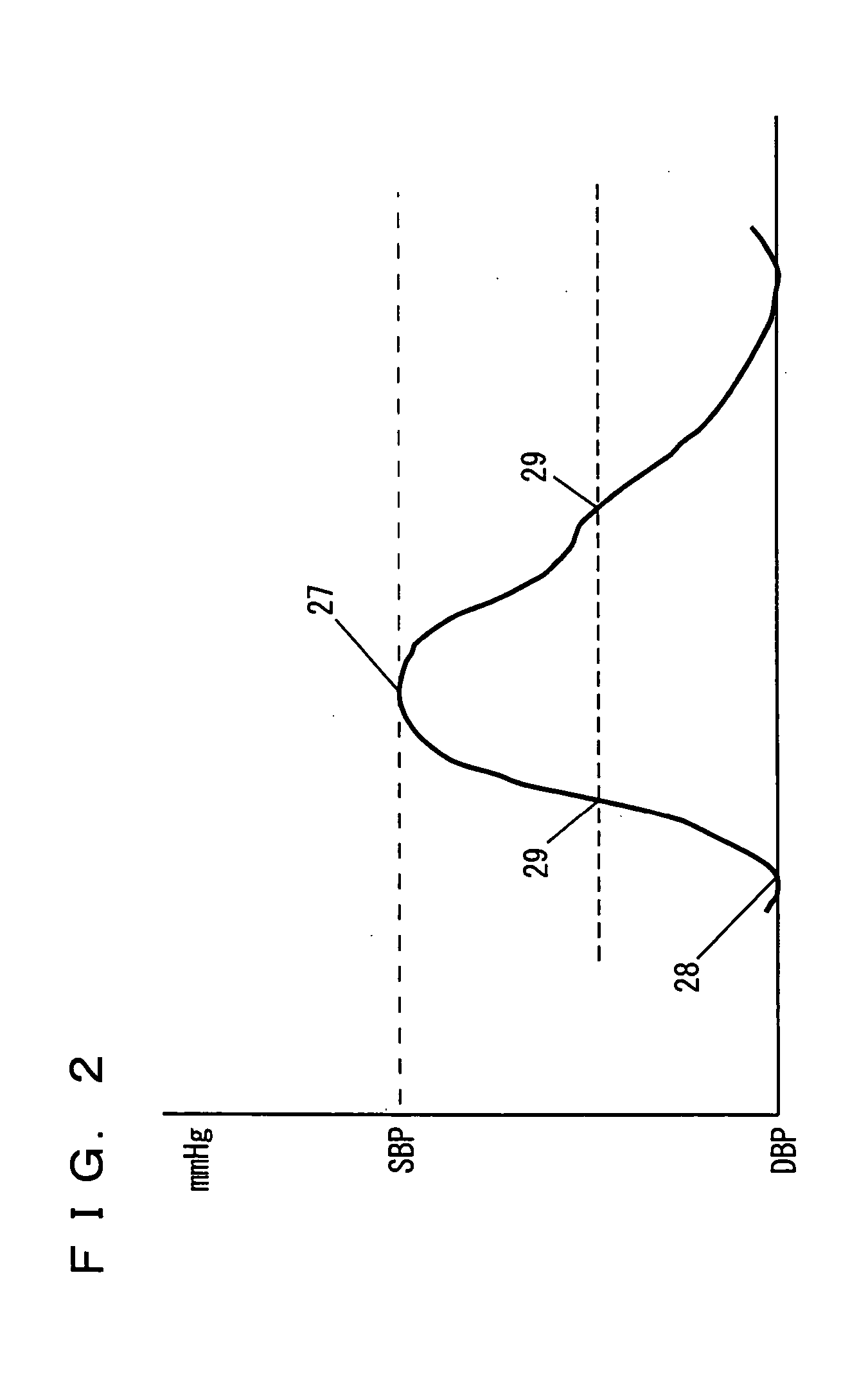
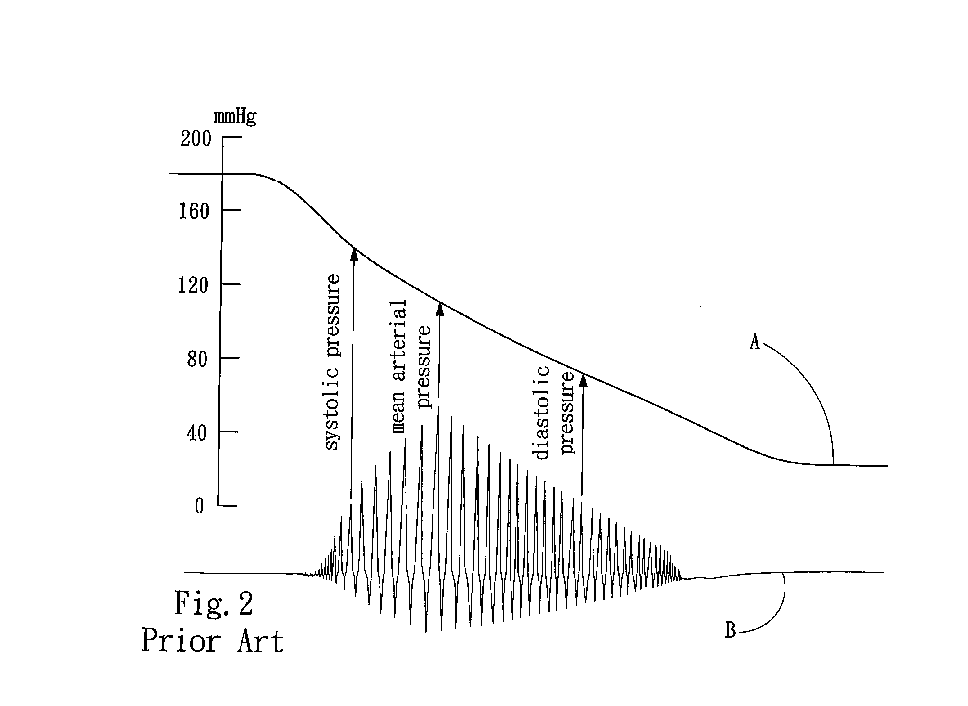
Oscillometry or another method is employed to initially determine a mean blood pressure and a diastolic blood pressure. There is a similarity between an intra-arterial pressure waveform exactly representing blood pressure and a pulse wave form generated when a cuff occludes a site to be measured. This similarity is utilized to obtain blood pressure. More specifically, the cuff occludes a site to be measured, while a pulse wave is detected. From the detected pulse wave's maximum amplitude an estimated mean arterial pressure is obtained. The obtained estimated mean arterial pressure and the pulse wave's minimum value are regarded as a mean blood pressure and a diastolic blood pressure, respectively. From the pulse wave's maximum value a systolic blood pressure is obtained by an arithmetic operation.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Apparatus for evaluating cardiovascular functions
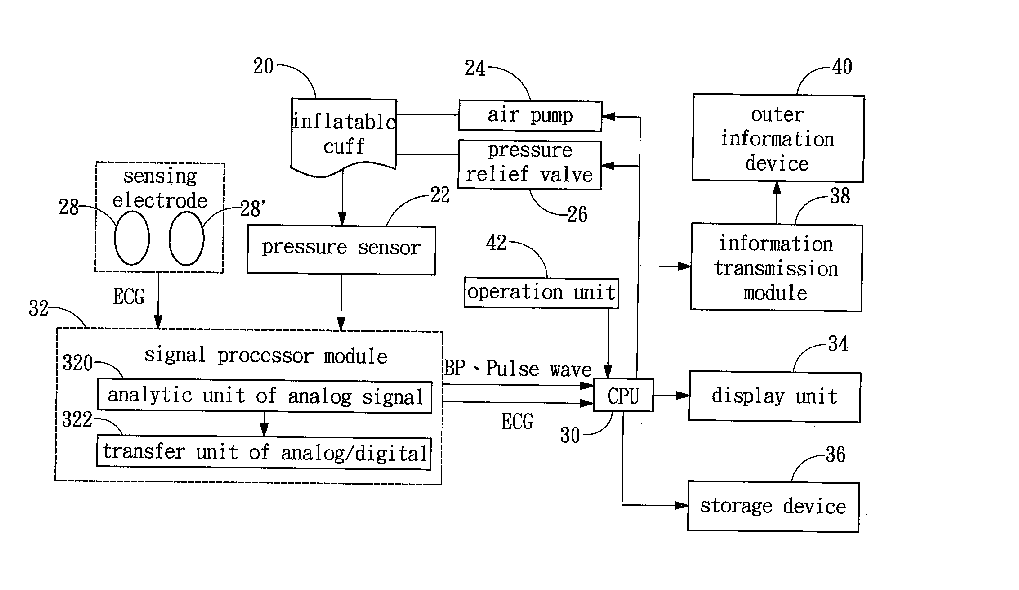
An apparatus is provided for evaluating cardiovascular functions. The apparatus combines the principles of measuring pressure and pulse signals, and monitors blood pressure, pulse wave velocity and electrocardiogram (ECG) signals simultaneously. An inflatable cuff measures blood pressure and pulse wave velocity. The apparatus also calculates systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, mean arterial pressure and other parameters related to blood pressure. The apparatus not only calculates vascular Stiffness Index (SI), vascular Reflection Index (RI) and other arterial related parameters but also Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV), heartbeat, QRS interval, ST segment, and other ECG parameters.
Owner:DAILYCARE BIOMEDICAL
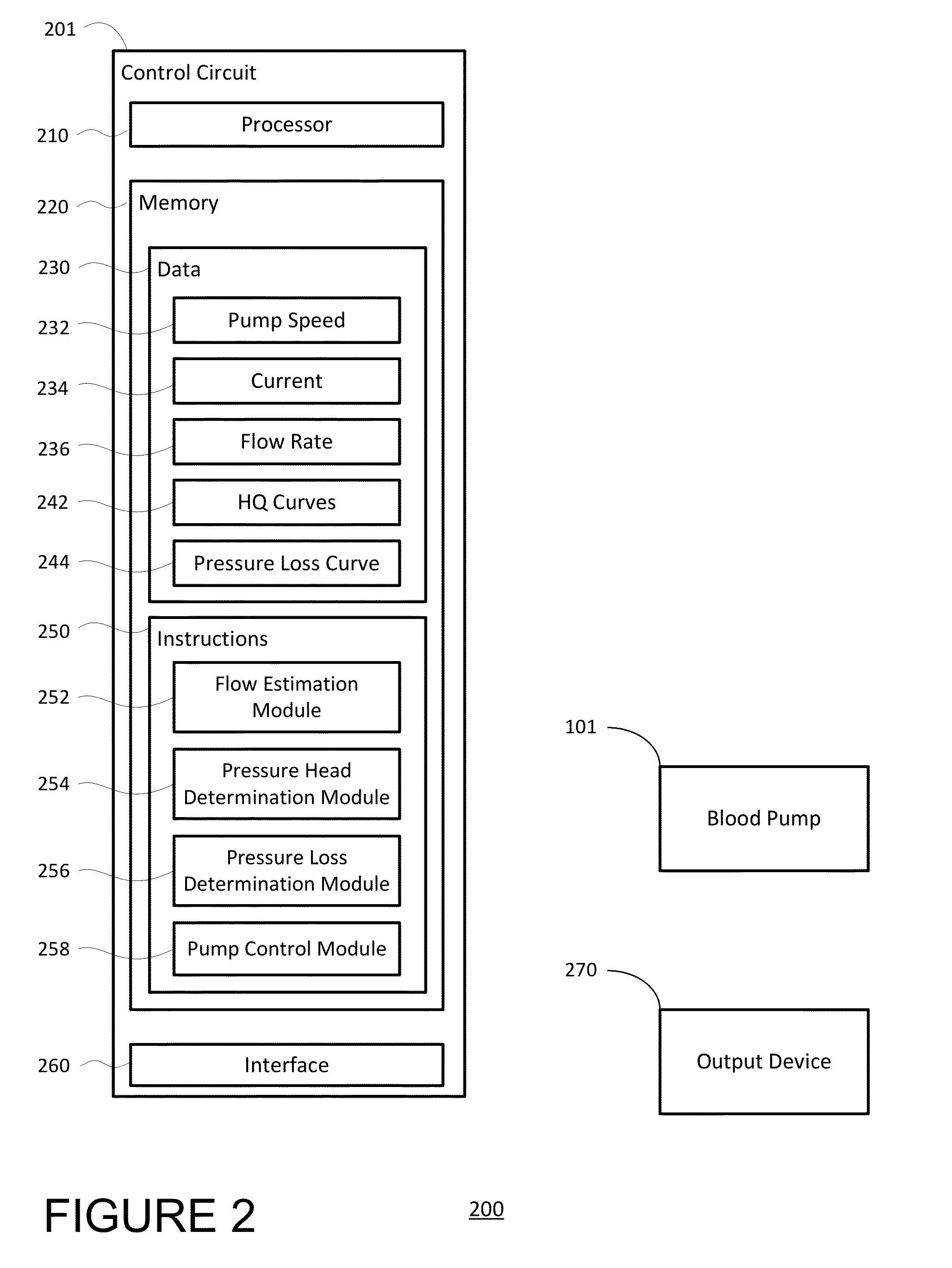
Mean arterial pressure estimation
The present disclosure provides for a method of monitoring the mean arterial pressure of a patient having a blood pump. The method may involve identifying a segment of time associated with diastole of the patient's cardiac cycle, determining a first parameter of the blood pump corresponding to the identified segment of time, and estimating the mean arterial pressure of the patient based at least in part on the first parameter.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Devices and methods for low pressure tumor embolization
ActiveUS9844383B2Increase the number ofLow pressureBalloon catheterMedical devicesAnatomical structuresTransarterial embolization
Owner:EMBOLX
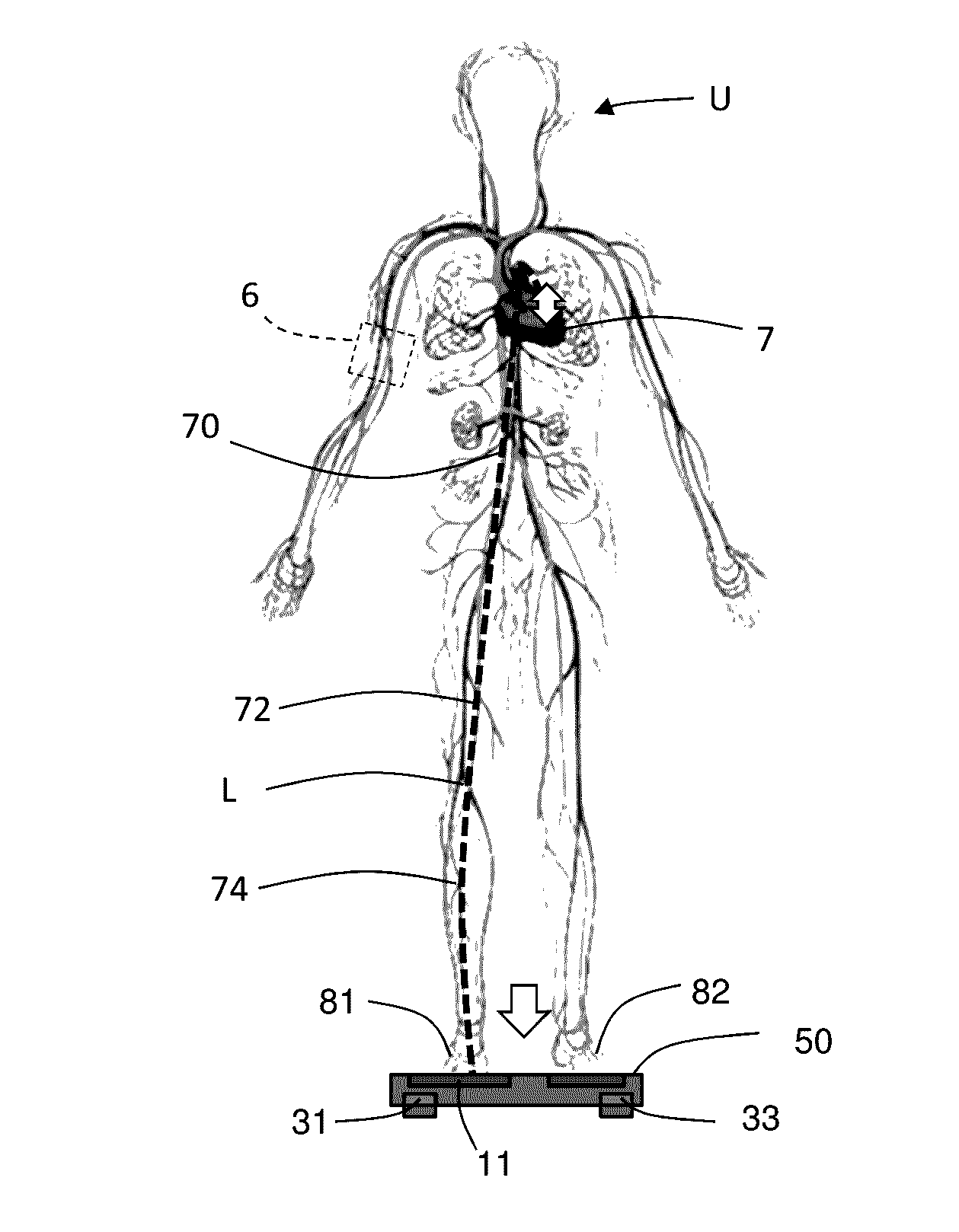
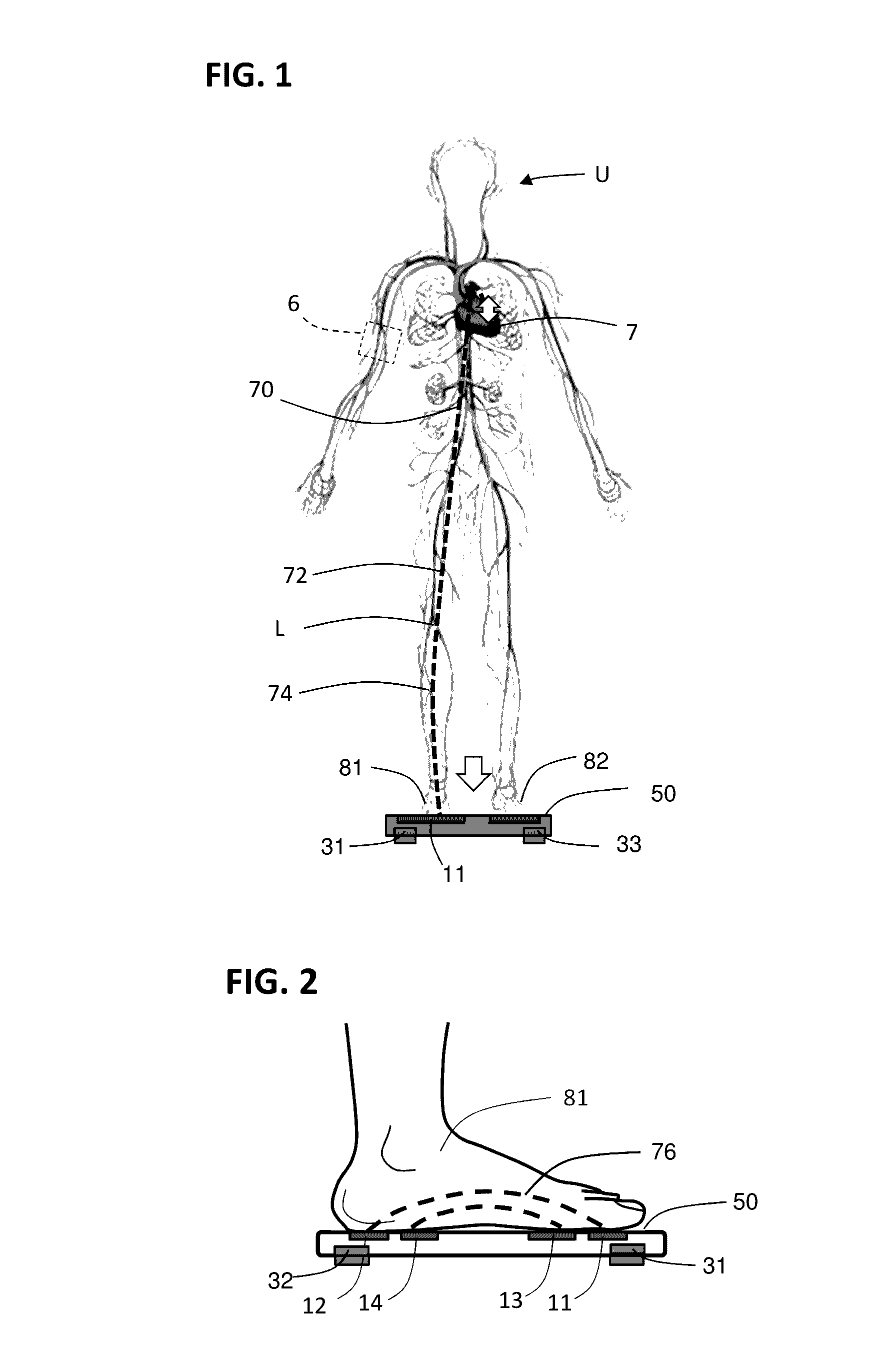
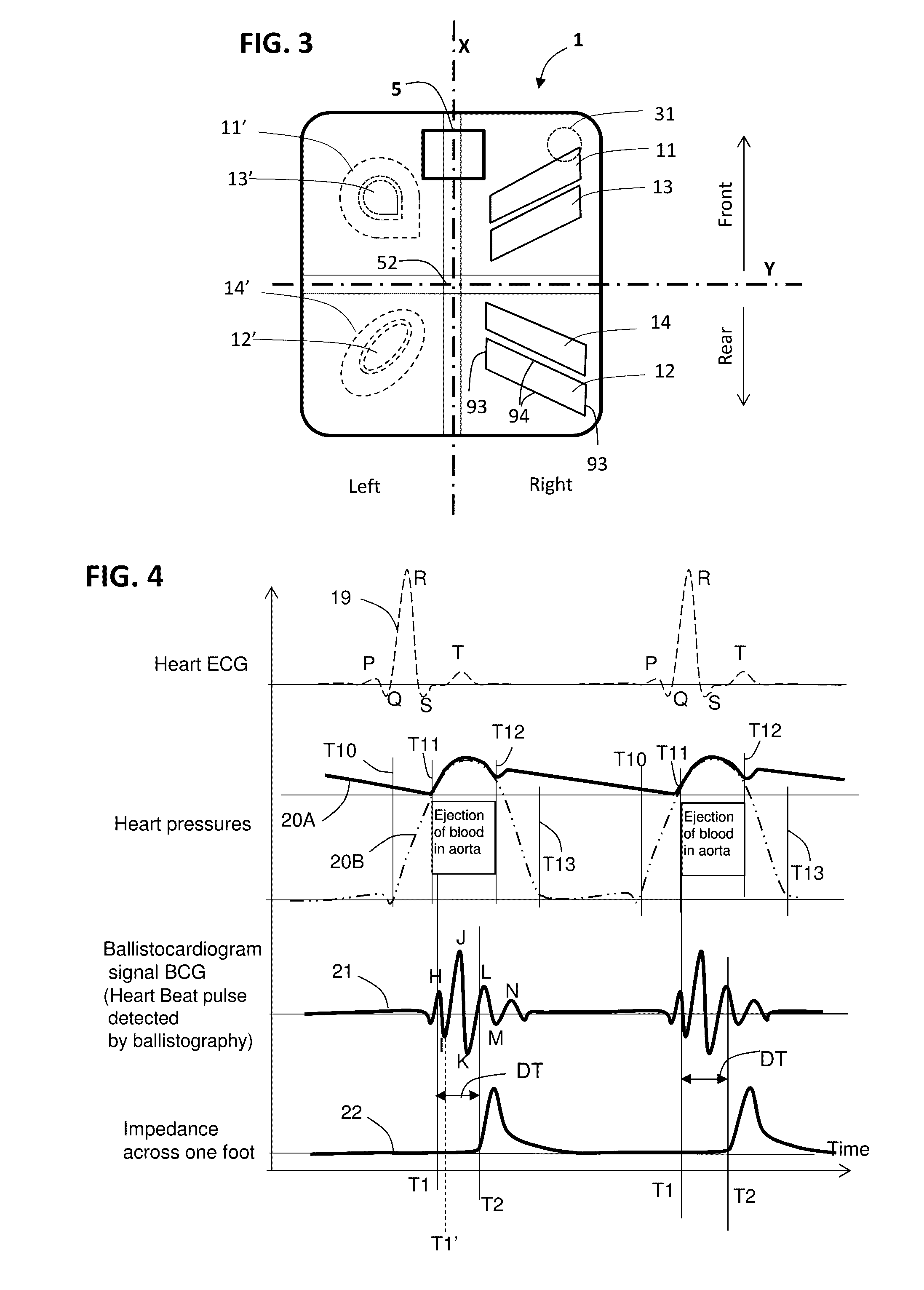
Weighing scale with extended functions
Methods of determination of the blood pressure, determination of a heart stroke volume, determination of the state of stress or relaxation of a user, with use of a ballistocardiogram signal reflecting the user's heart beats, with a measure of characteristic amplitude of ballistocardiogram signal, and measure for each couple of consecutive heart beats, beat time intervals DeltaHB(i) between successive heart beats, extracted from a ballistocardiogram signal or from an impedance plethysmography signal measured at the user's foot, leading to determination of a heart rate variability index, over at least six successive heart beats, leading to determination of mean arterial pressure, leading to determination of state of relaxation or stress of the user.
Owner:WITHINGS SAS
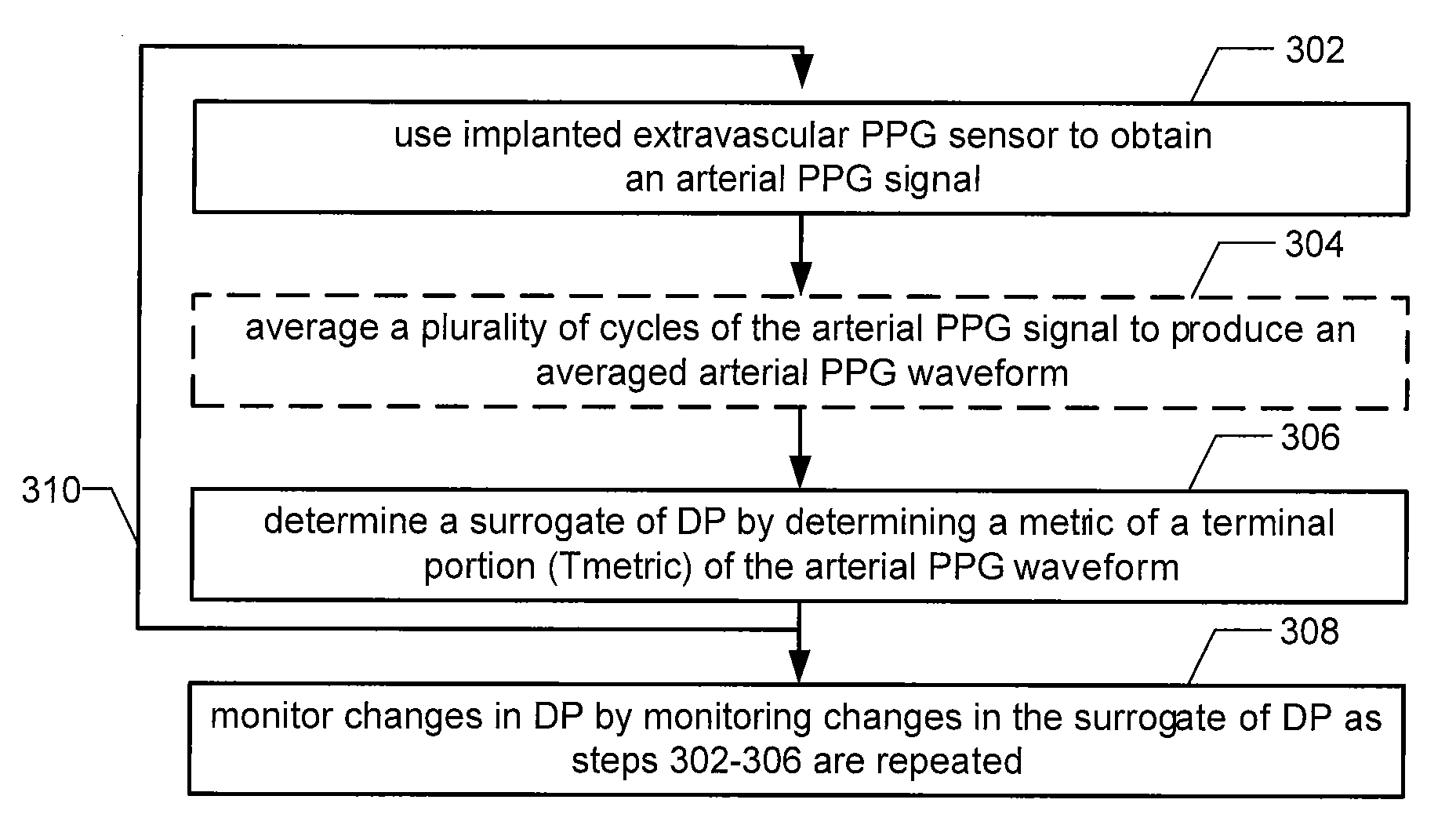
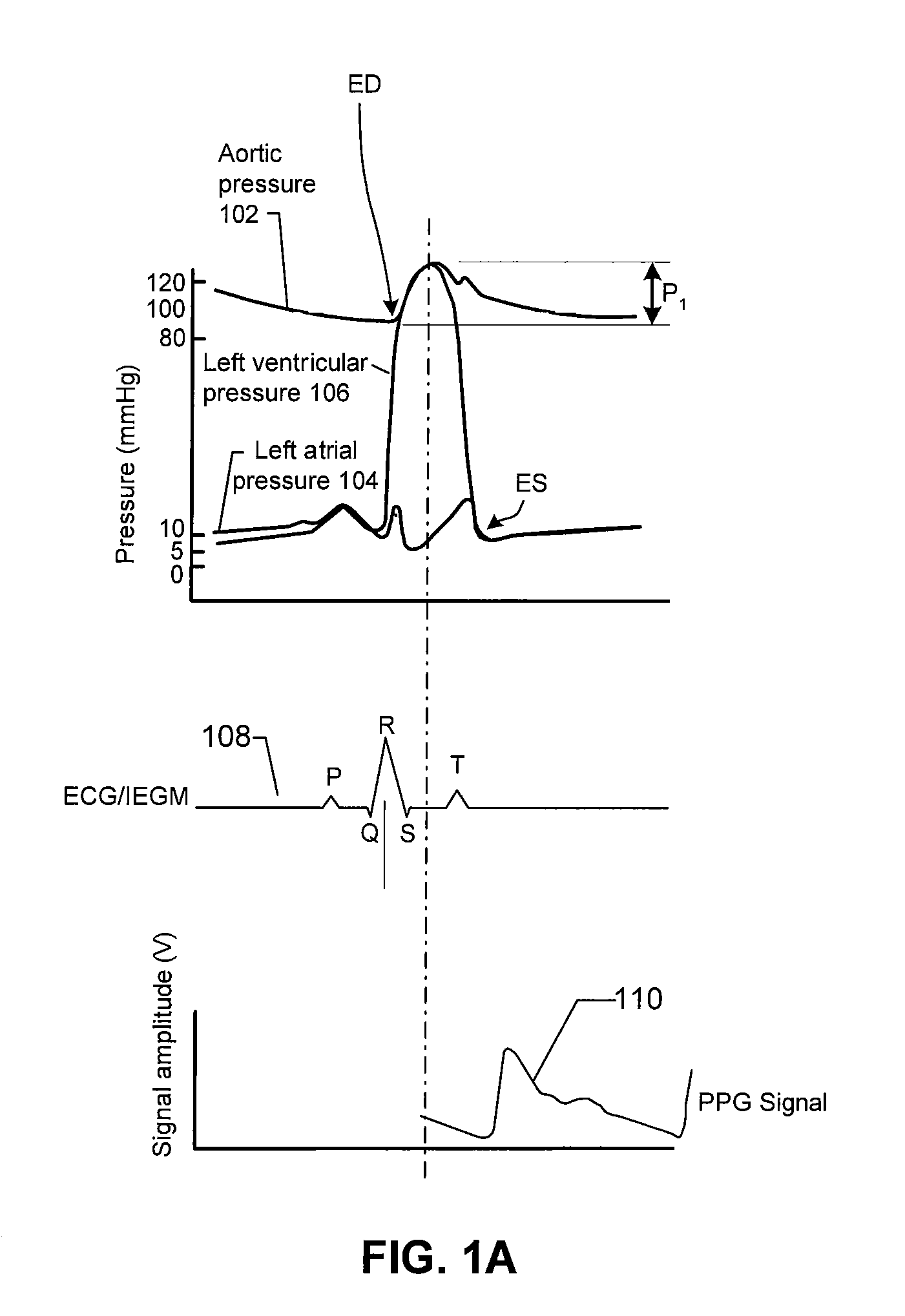
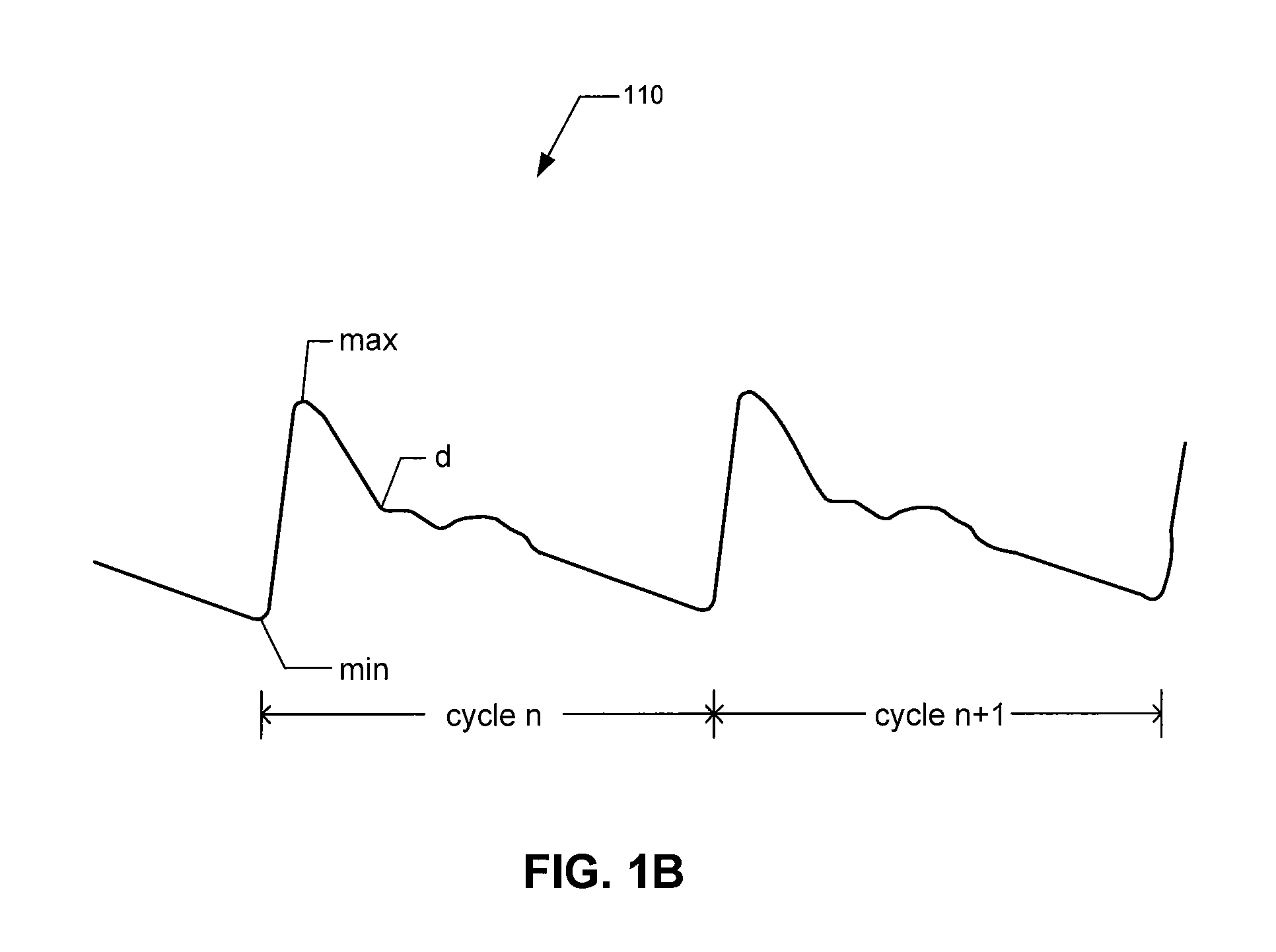
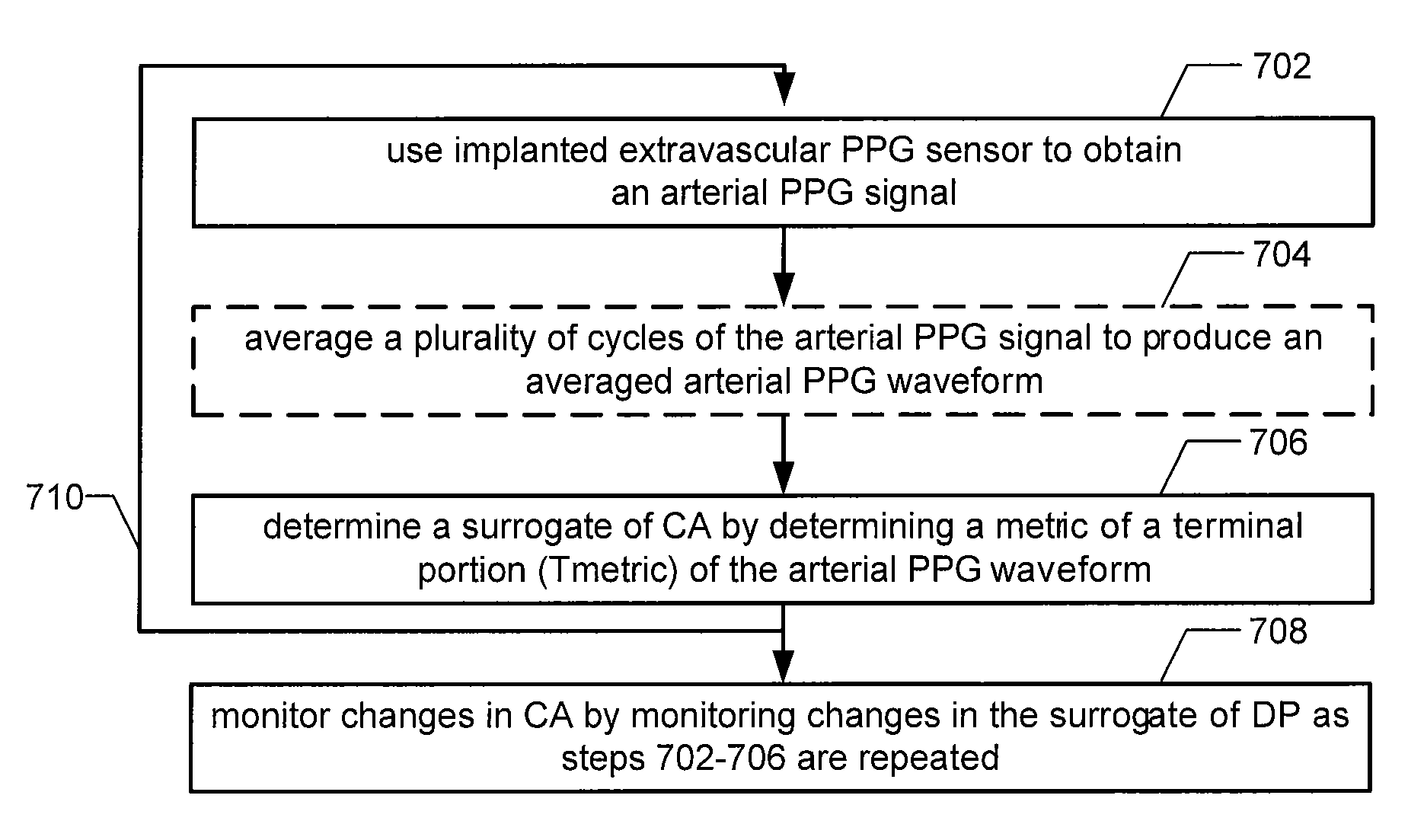
Implantable hemodynamic monitor and methods for use therewith
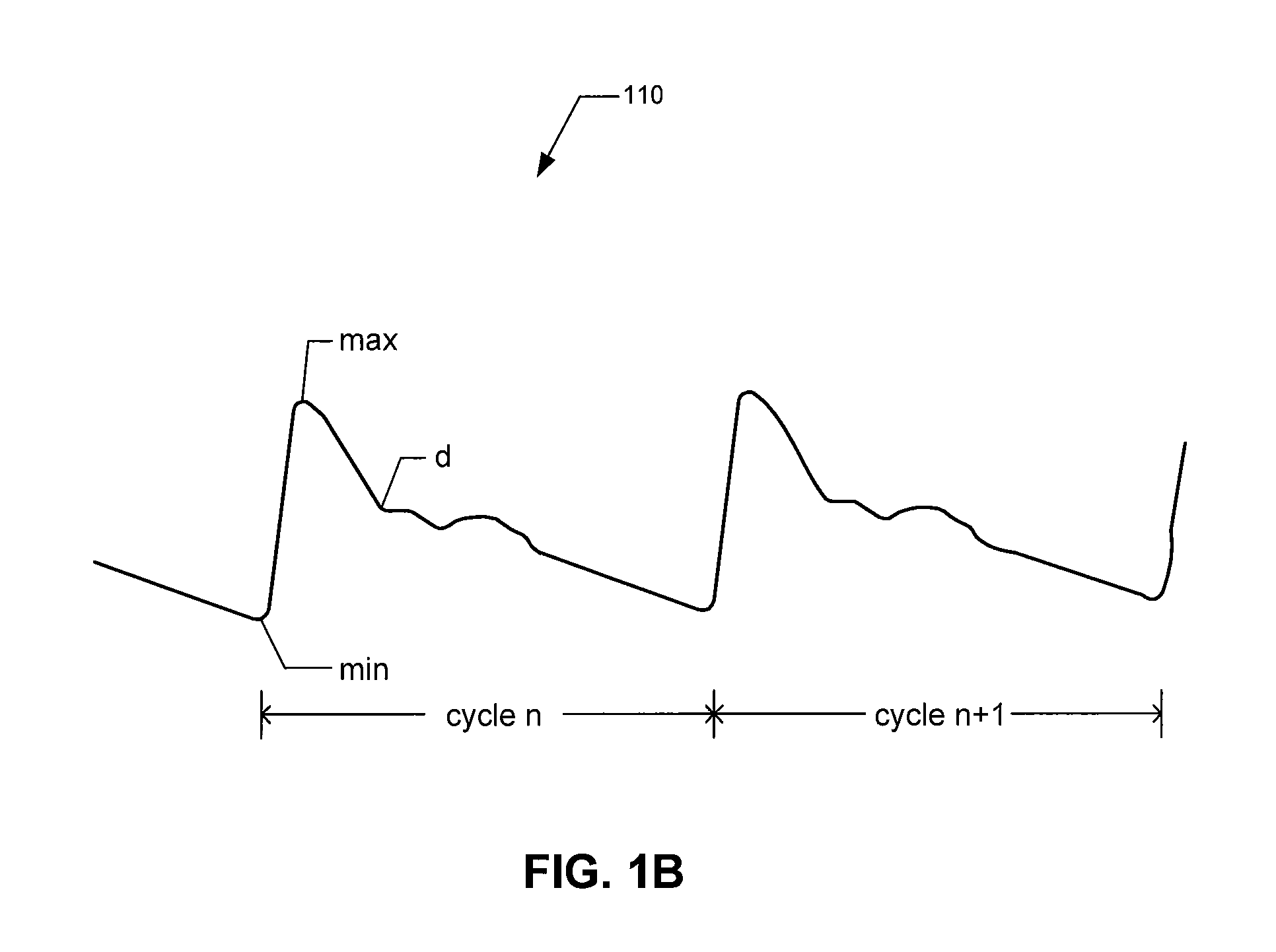
Provided herein are implantable systems that include an implantable photoplethysmography (PPG) sensor, which can be used to obtain an arterial PPG waveform. In an embodiment, a metric of a terminal portion of an arterial PPG waveform is determined, and a metric of an initial portion of the arterial PPG waveform is determined, and a surrogate of mean arterial pressure is determined based on the metric of the terminal portion and the metric of the initial portion. In another embodiment, a surrogate of diastolic pressure is determined based on a metric of a terminal portion of an arterial PPG waveform. In a further embodiment, a surrogate of cardiac afterload is determined based on a metric of a terminal portion of an arterial PPG waveform.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for automatic, non-invasive diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension and measurement of mean pulmonary arterial pressure
InactiveUS20100094122A1Optimize workflowAnalyze moreMagnetic measurementsEvaluation of blood vesselsSystoleCardiac cycle
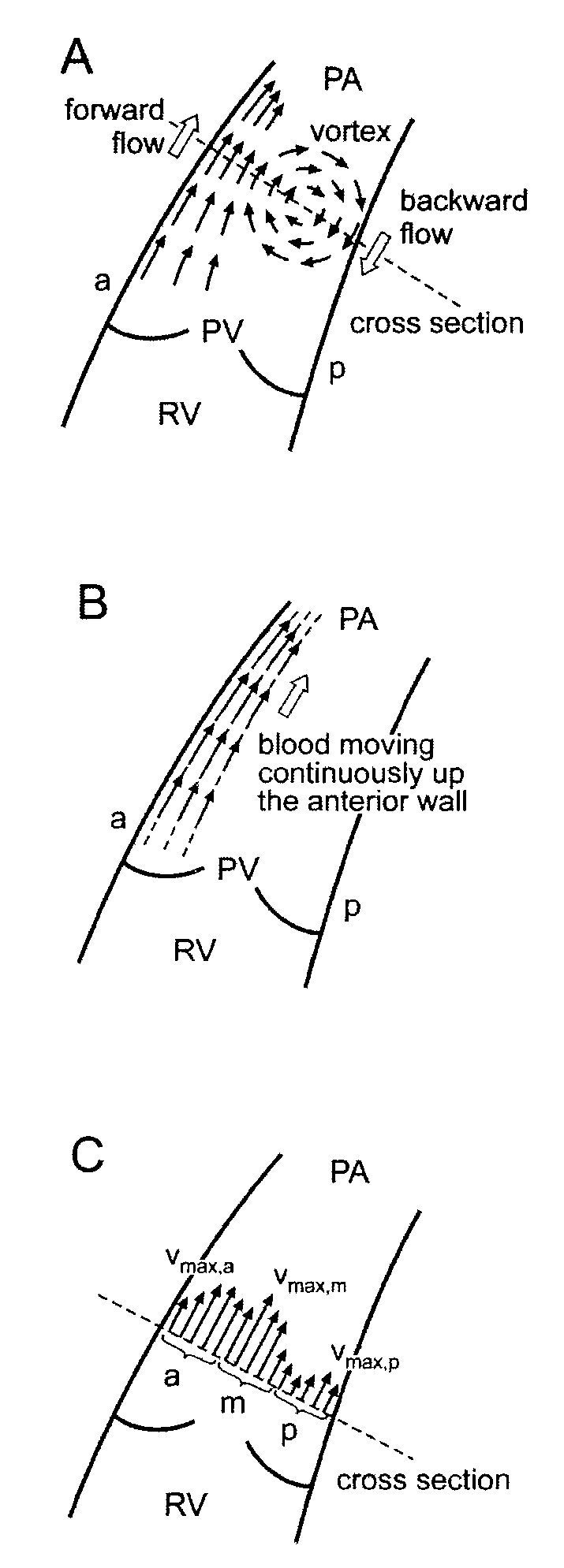
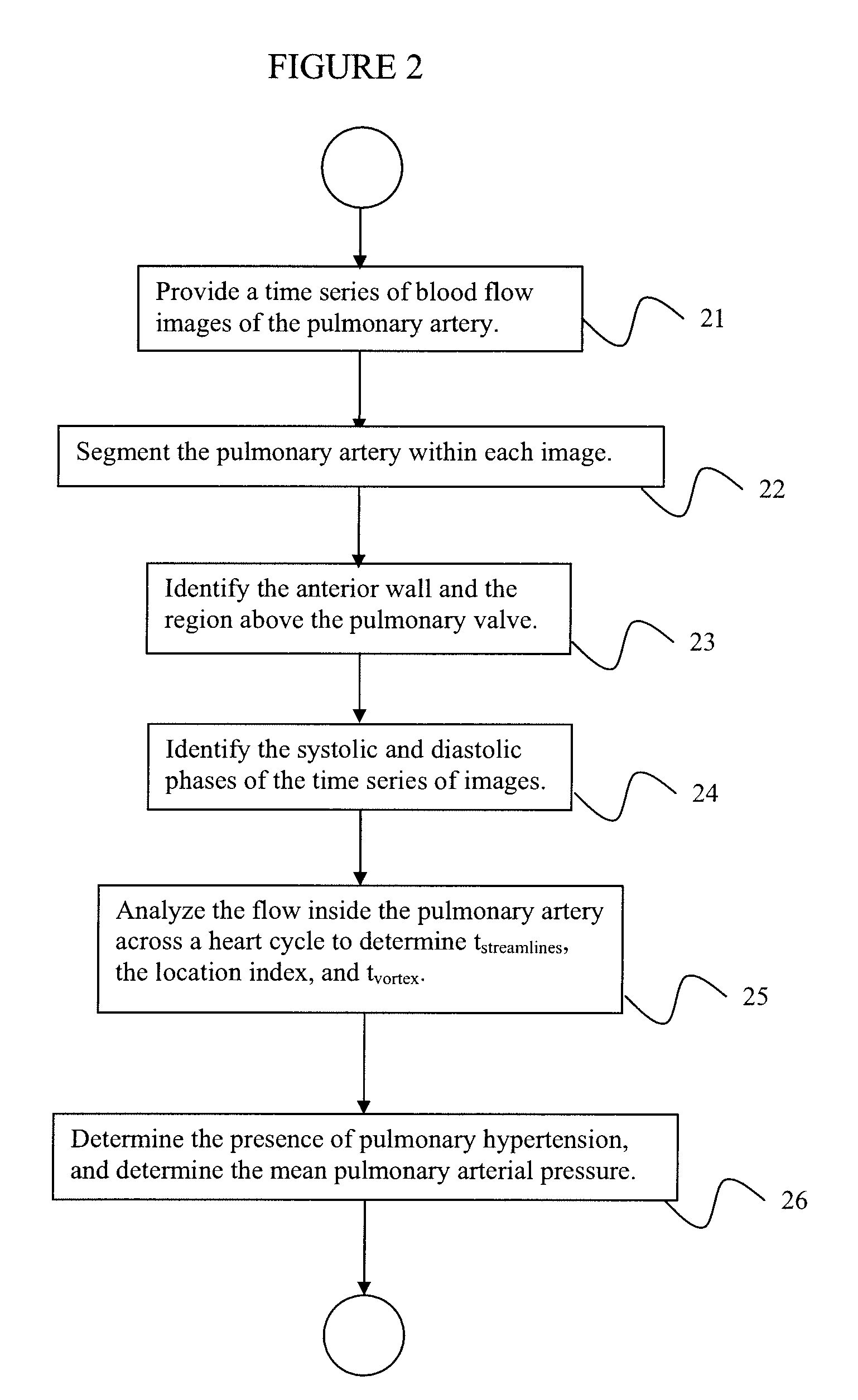
A method for diagnosing pulmonary hypertension from phase-contrast magnetic resonance (MR) images includes providing a time series of one or more magnetic resonance (MR) flow images of a patient's mediastinum during one or more cardiac cycles, segmenting the pulmonary artery within each image of the times series of images, identifying the anterior wall and pulmonary valve within the segmented pulmonary artery, analyzing blood flow during a diastolic phase of the one or more cardiac cycles to determine a relative duration of blood flow, tstreamlines, during the diastolic phase, analyzing blood flow during a latter portion of a systolic phase and a subsequent diastolic phase of the one or more cardiac cycles to detect the presence and duration tvortex of a vortex, and diagnosing the presence of pulmonary hypertension from tstreamlines and tvortex.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Device for determining a hemodynamic parameter
Owner:PULSION MEDICAL SYSTEMS SE
Non-invasive cardiac output detecting methods and apparatus based on sphygmus wave
InactiveCN101176663ARealize non-invasive cardiac output detectionCatheterMeasuring/recording heart/pulse ratePulse waveEngineering
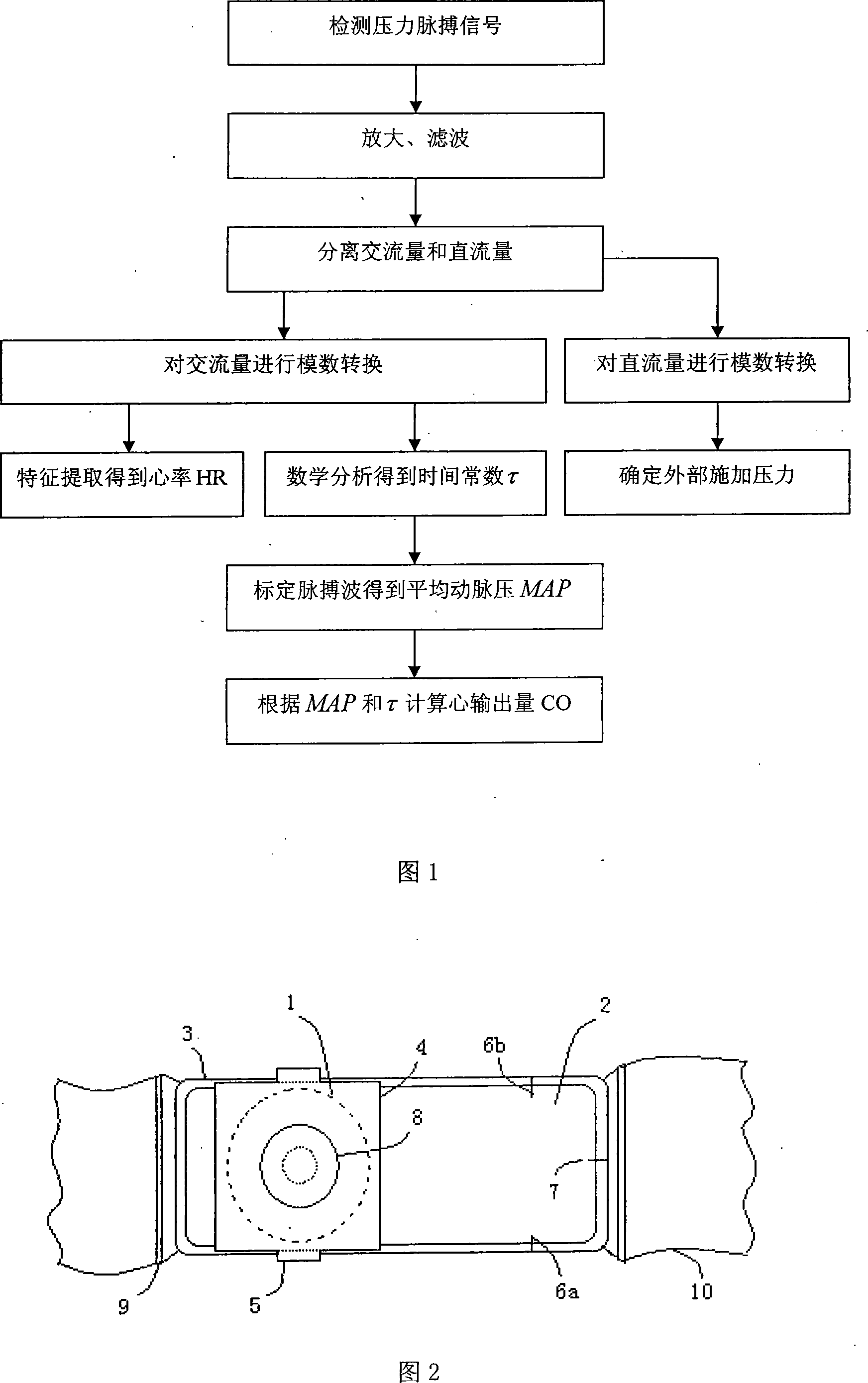
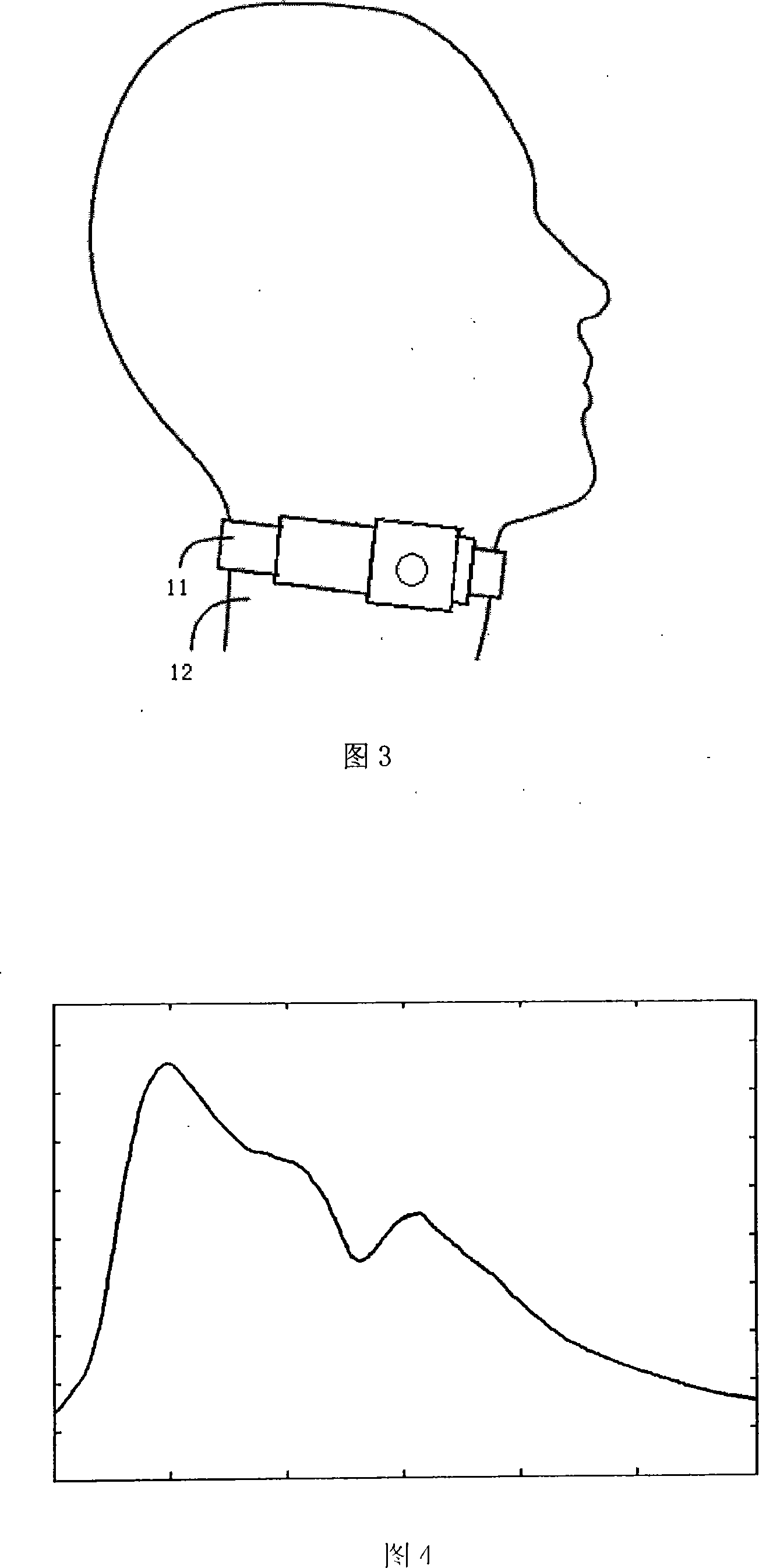
The invention provides a non-invasive cardiac output detection method and apparatus based on a pulse wave; wherein, the detection method comprises the following steps: firstly, amplifying and filtering the pressure pulse signals, and detaching the alternating current and direct current by means of amplifying and filtering; secondly, modulus conversion for the alternating current and direct current, and resampling the digital signals converted; fixing heart rate via the feature points on the waveform of the pulse; and fixing the external pressurizing force via calibrating the separated direct current; thirdly, using mathematical analyzing method to estimate time constant Tau for the separated alternating current; fourthly, calibrating the pulse wave to get mean arterial pressure MAP; fifthly, according to the MAP and Tau, calculating the cardiac output. The detecting apparatus comprises a pulse wave detection device, a detection circuit, a cardiac output estimation device and a display unit. The invention has the advantages of obtaining the cardiac output via a mathematical analyzing of the pulse wave on the non-invasive detection and realizing the non-invasive cardiac output detection.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for monitoring the efficacy of fluid resuscitation
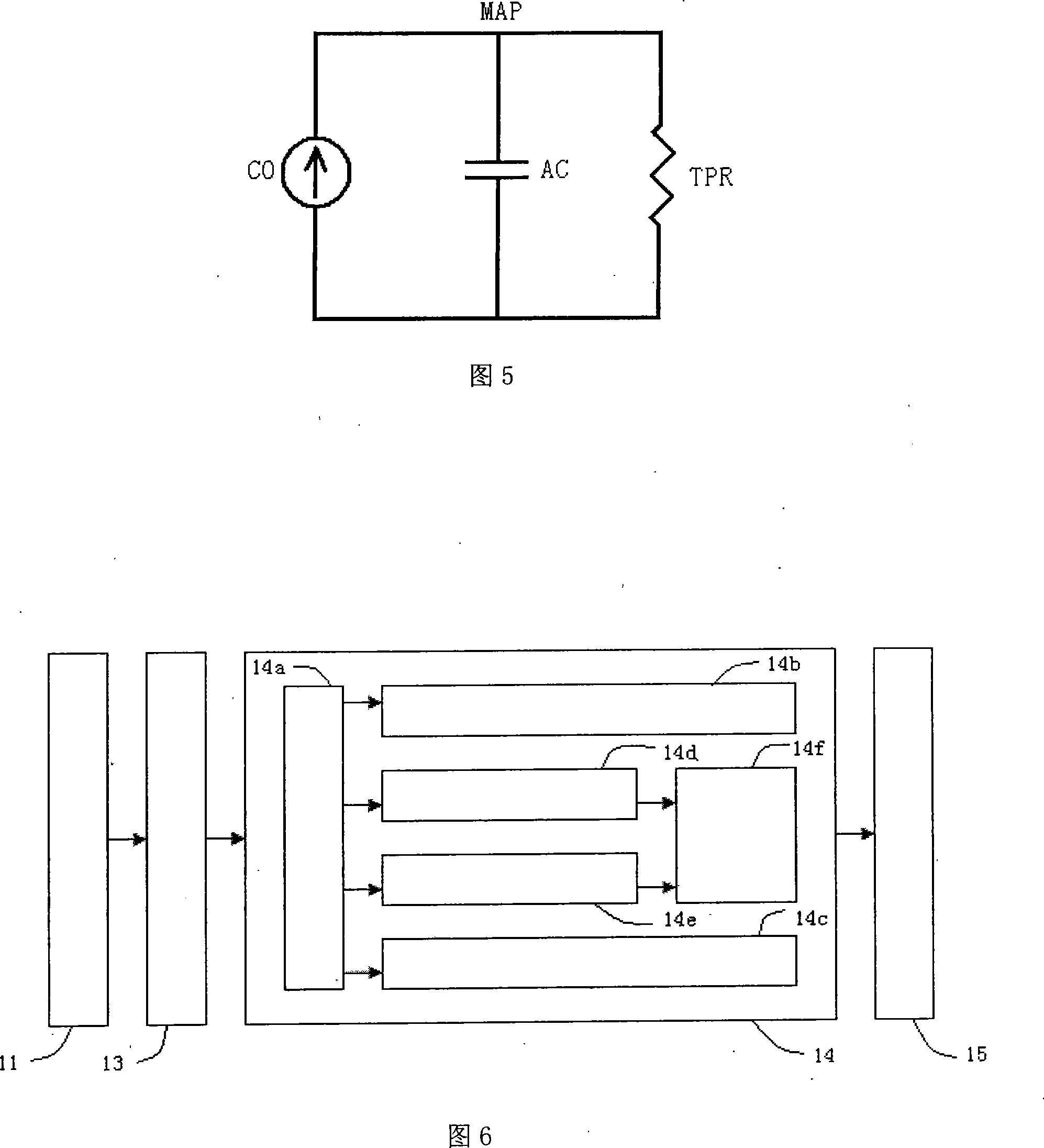
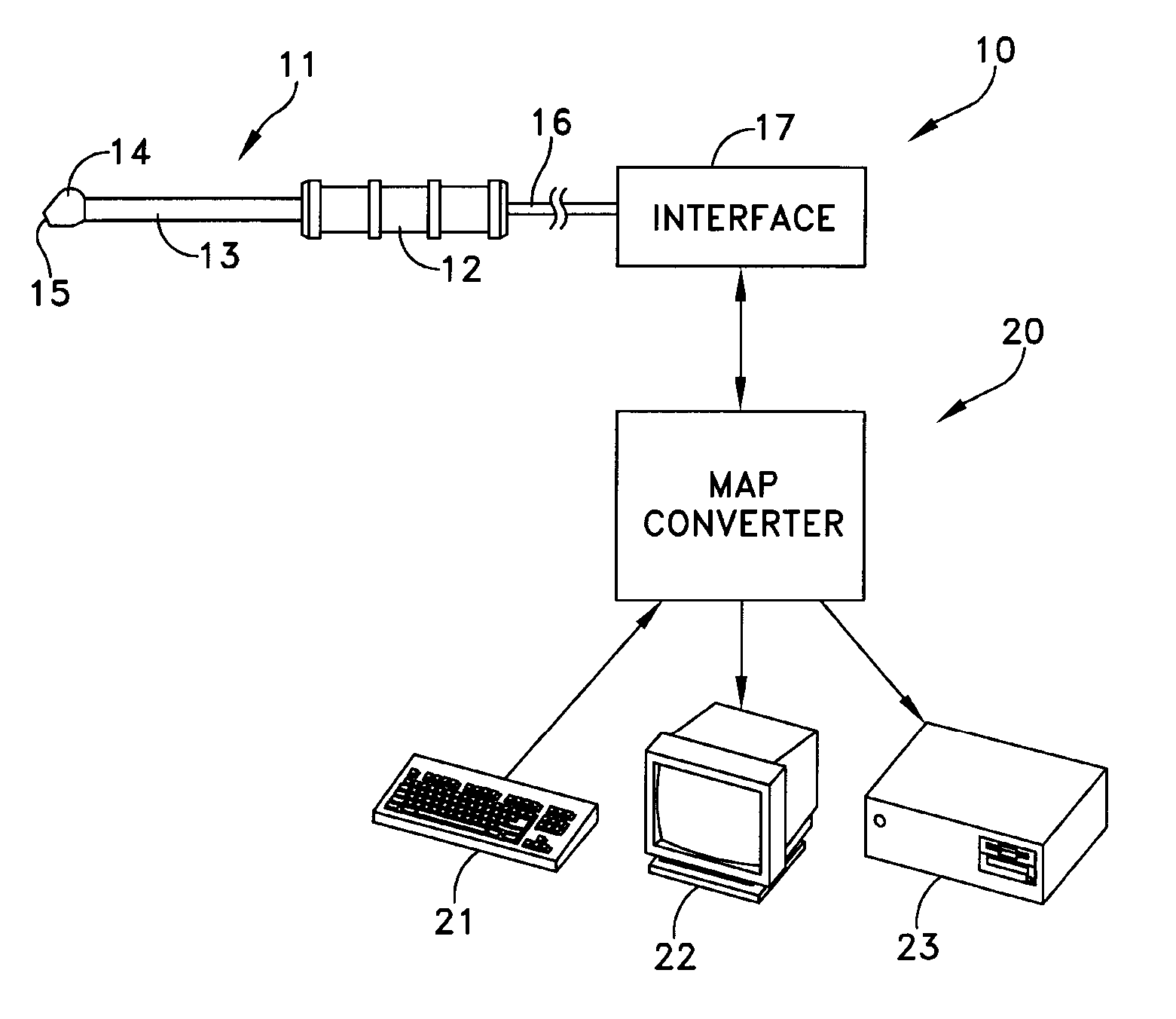
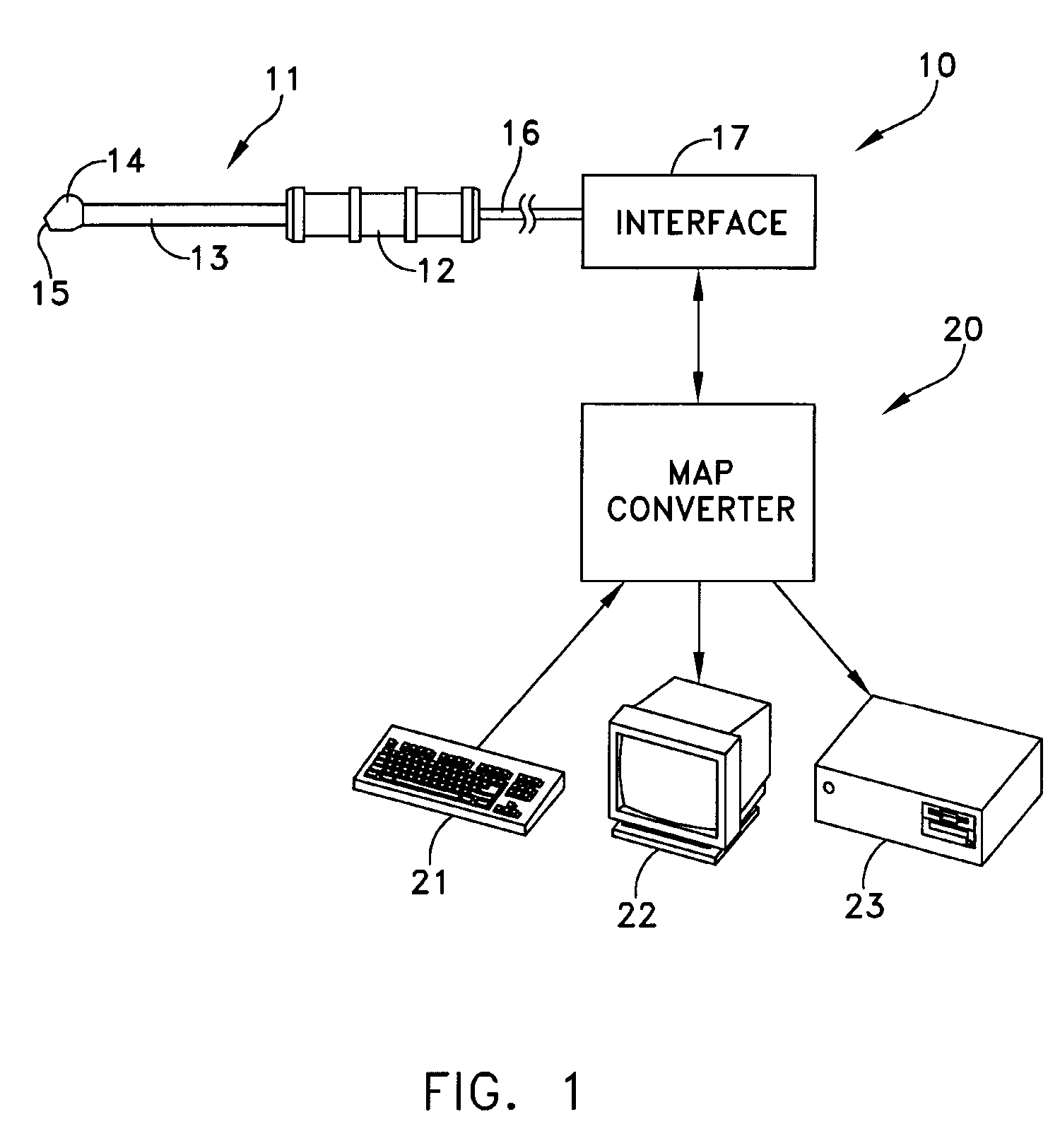
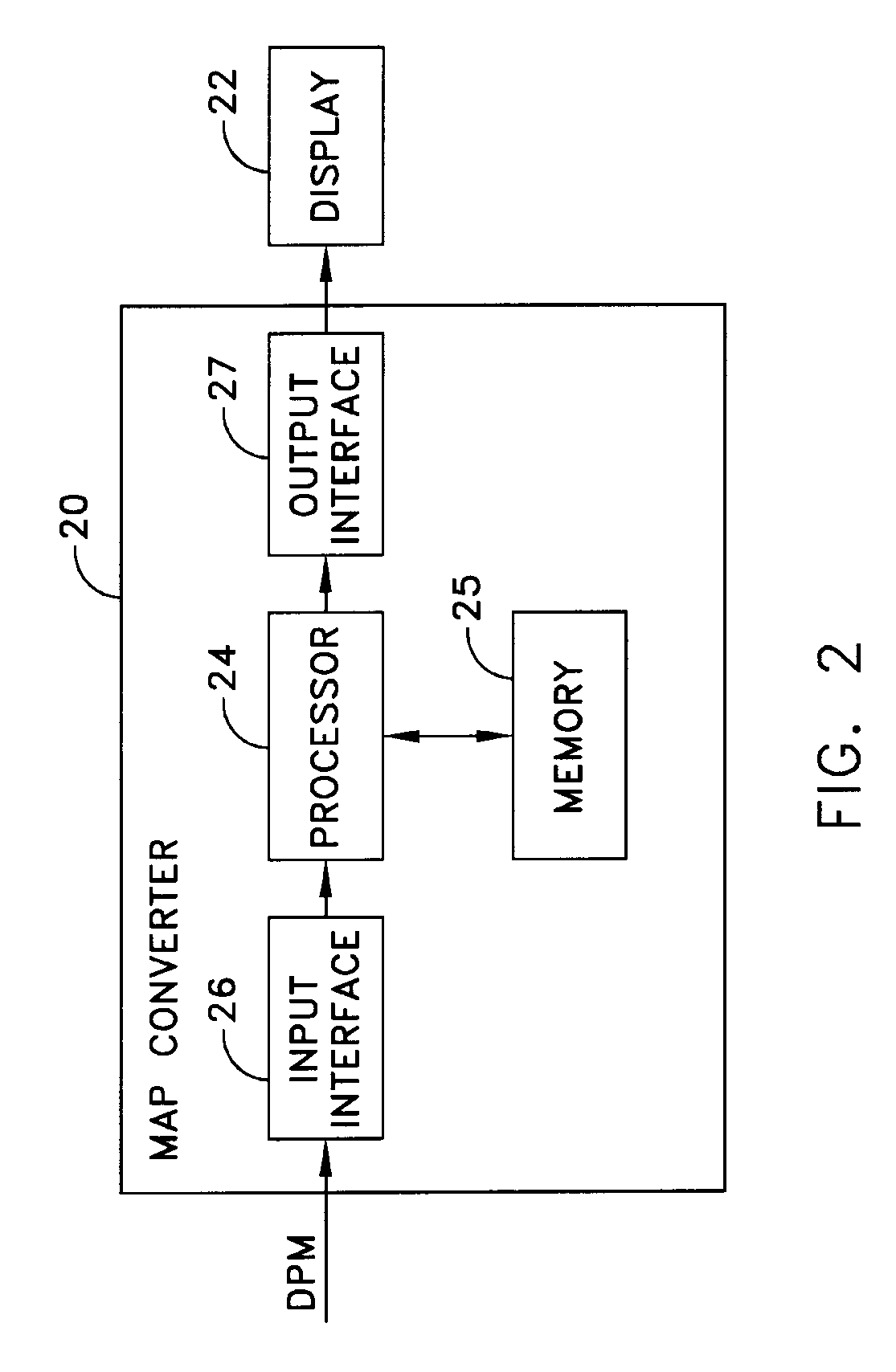
Relative Mean Arterial Pressure values are obtained non-invasively using a probe to obtain moisture measurements at a selected site on a subject. A control collects data samples. A converter produces a relative value of Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) in response to the collected data (DPM) in accordance with a correlation defined by:MAP=(DPM−DPM(0)) / K(I).
Owner:NOVA TECH CORP
Application of penehyclidine hydrochloride in preparing medicament for treating haemorrhagic shock
The invention discloses application of penehyclidine hydrochloride in preparation of a medicine for treating a hemorrhagic shock disease. Hemorrhagic shock has a pathological change that the central venous pressure, the peripheral mean arterial pressure and the cardiac output are all obviously reduced and the middle-light microcirculatory disturbance appears, the medicine for treating the hemorrhagic shock disease can be liquid and can also be solid, and the mass percent concentration of the penehyclidine hydrochloride in the medicine is between 0.01 and 2 percent. The application effect is proved through the influence of a penehyclidine hydrochloride water solution on a canine hemorrhagic shock model.
Owner:CHENGDU LIST PHARMA
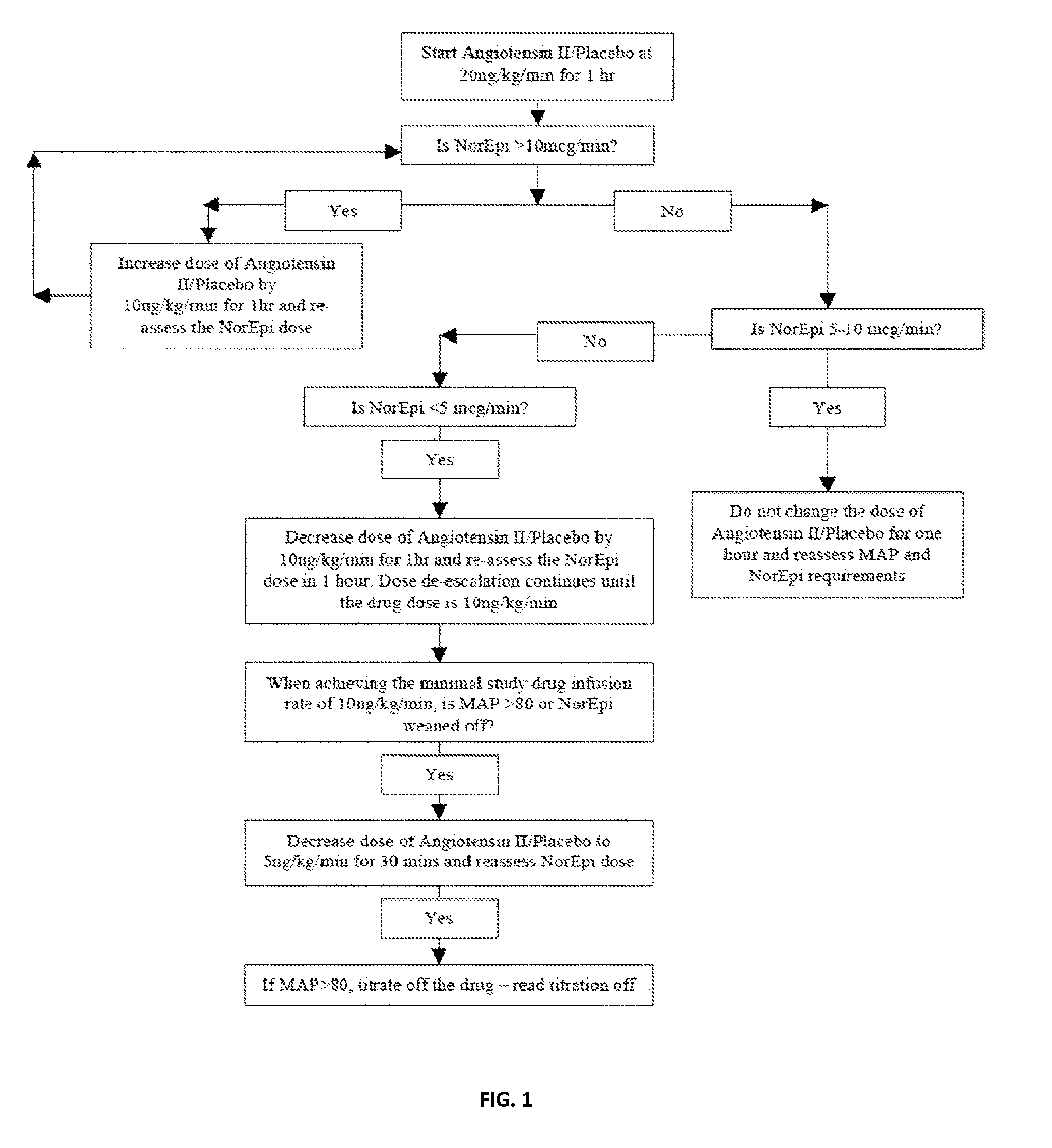
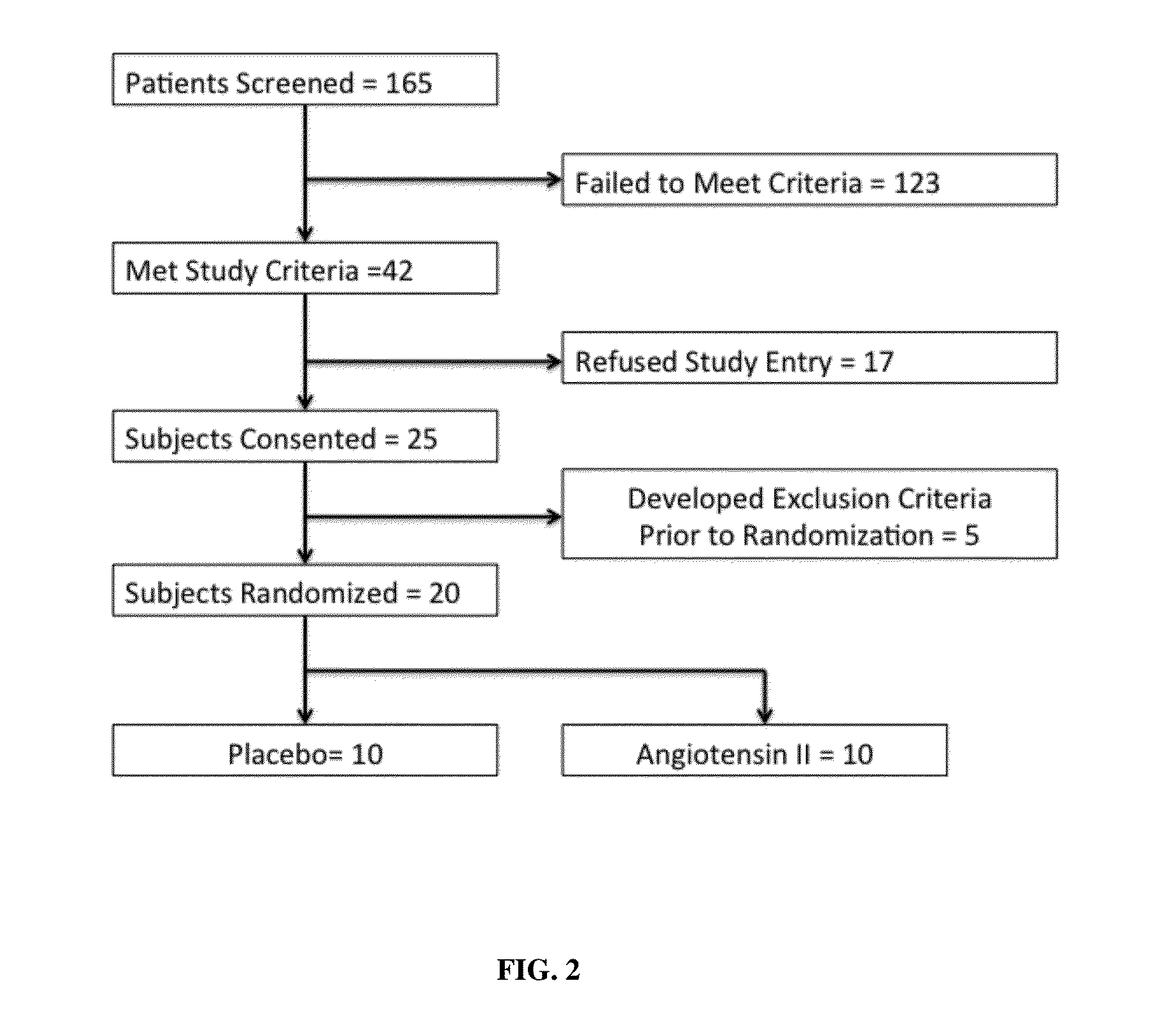
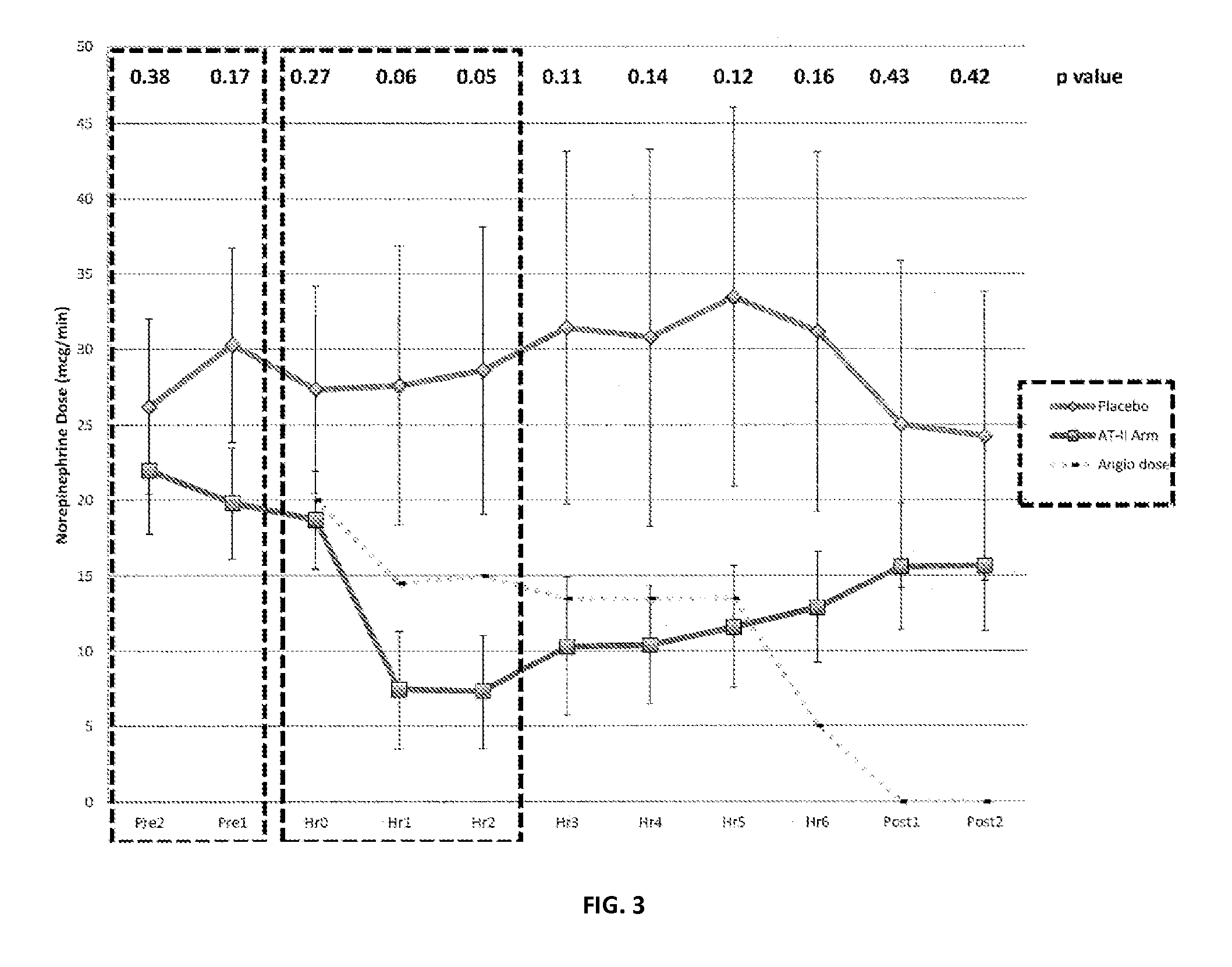
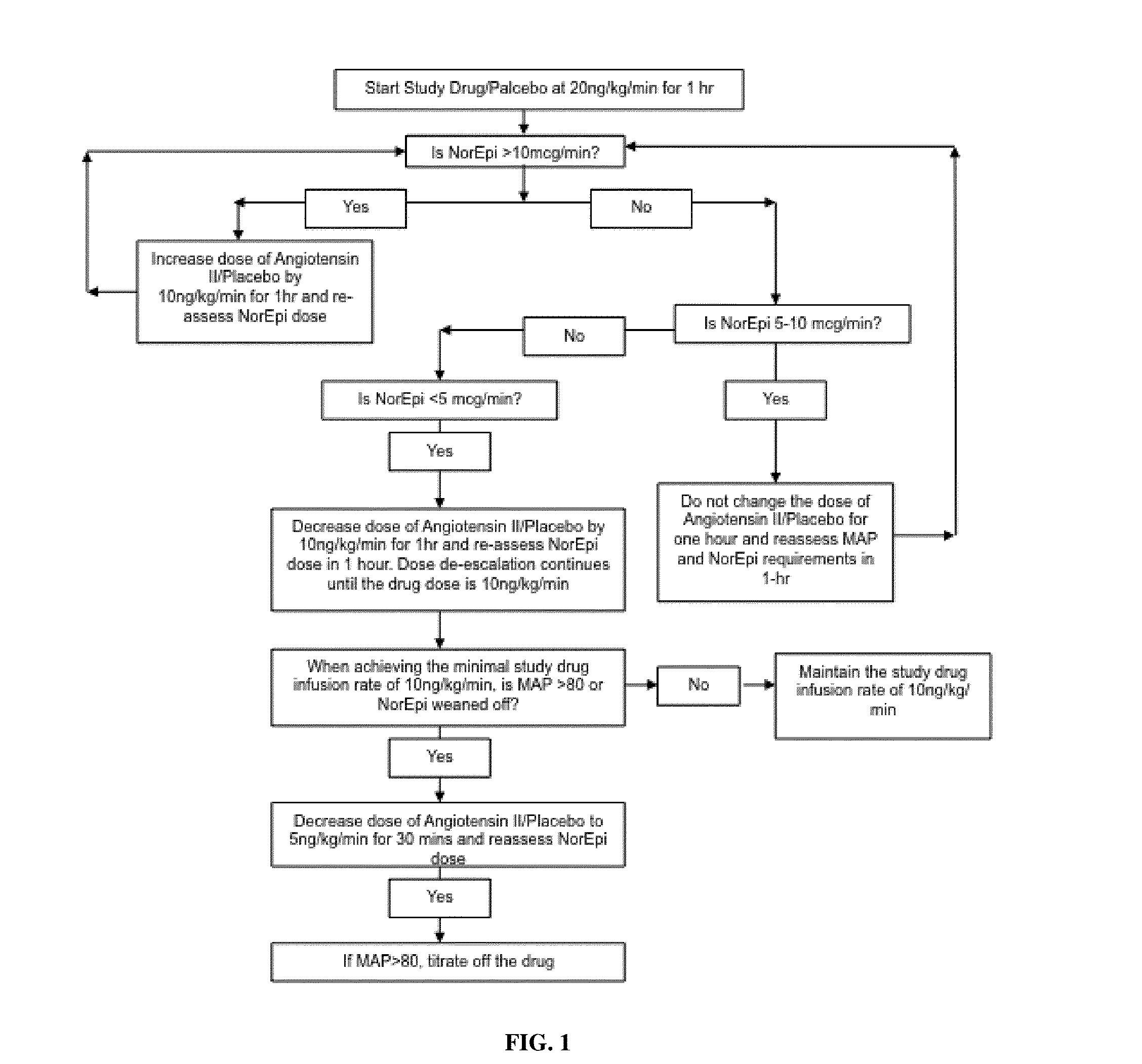
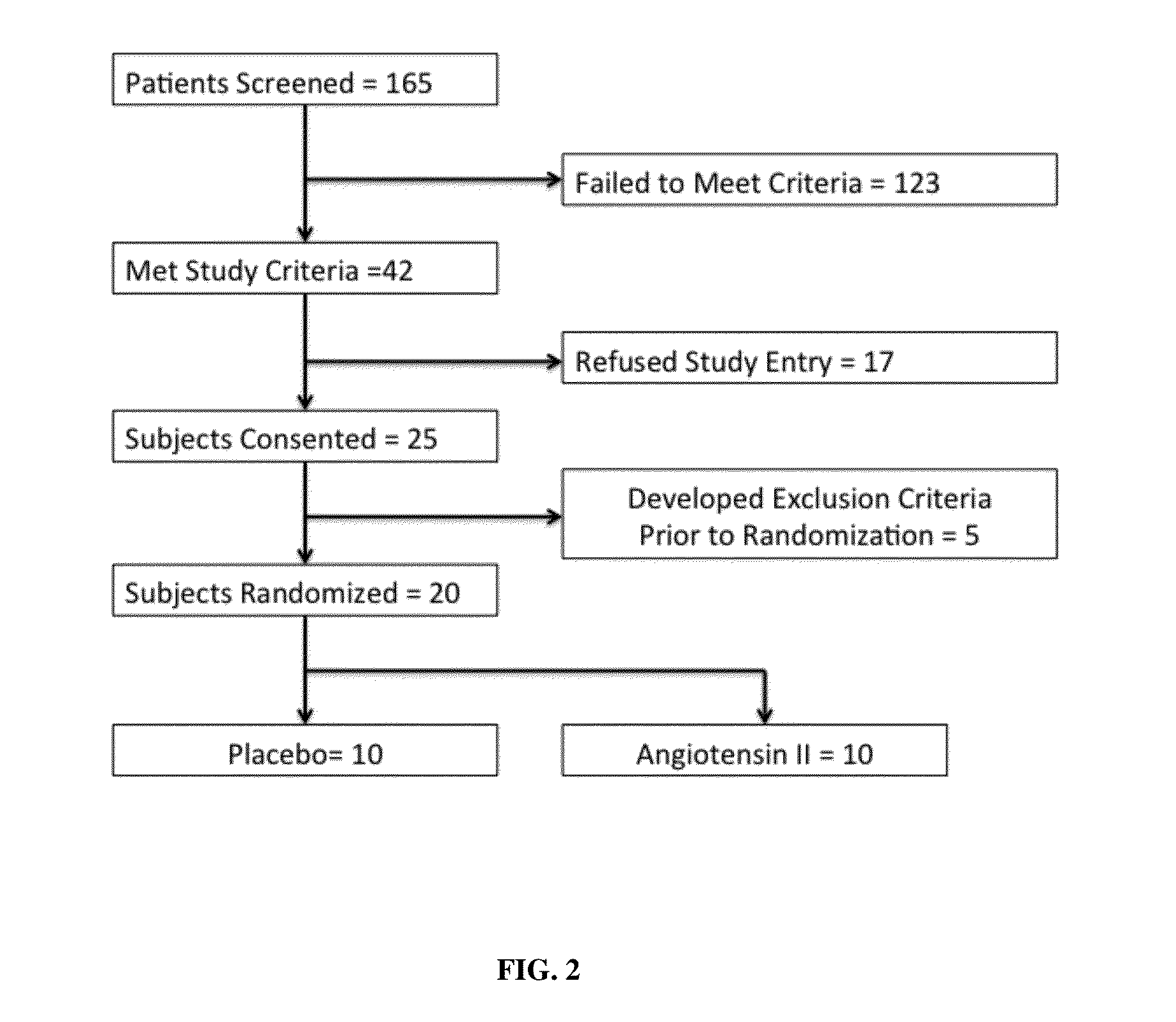
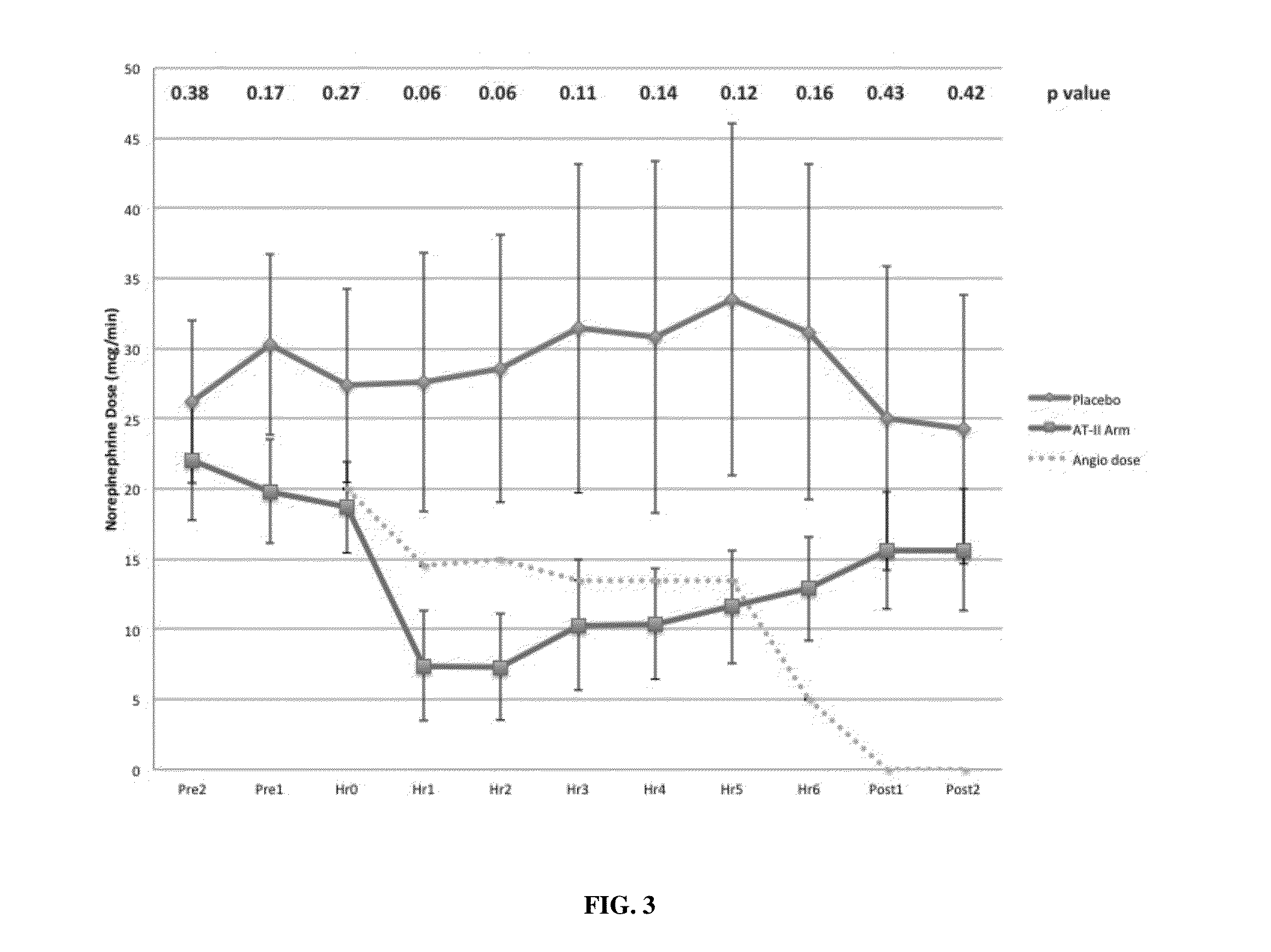
Angiotensin II alone or in combination for the treatment of hypotension
The present invention relates, inter alia, to a method comprising administering to a subject having high output shock and undergoing treatment with a catecholamine at a dose equivalent to at least about 0.2 mcg / kg / min of norepinephrine a dose of angiotensin II which is effective to raise the blood pressure of the subject to a mean arterial pressure (MAP) of about 65 mm Hg or above, and which is effective to reduce the dose of the catecholamine required to maintain a MAP of about 65 mm Hg to the equivalent of about 0.05-0.2 mcg / kg / min norepinephrine or less, or to the equivalent of about 0.05 mcg / kg / min norepinephrine or less.
Owner:THE GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIV A CONGRESSIONALLY CHARTERED NOT FOR PROFIT CORP
Blood pressure measurement apparatus
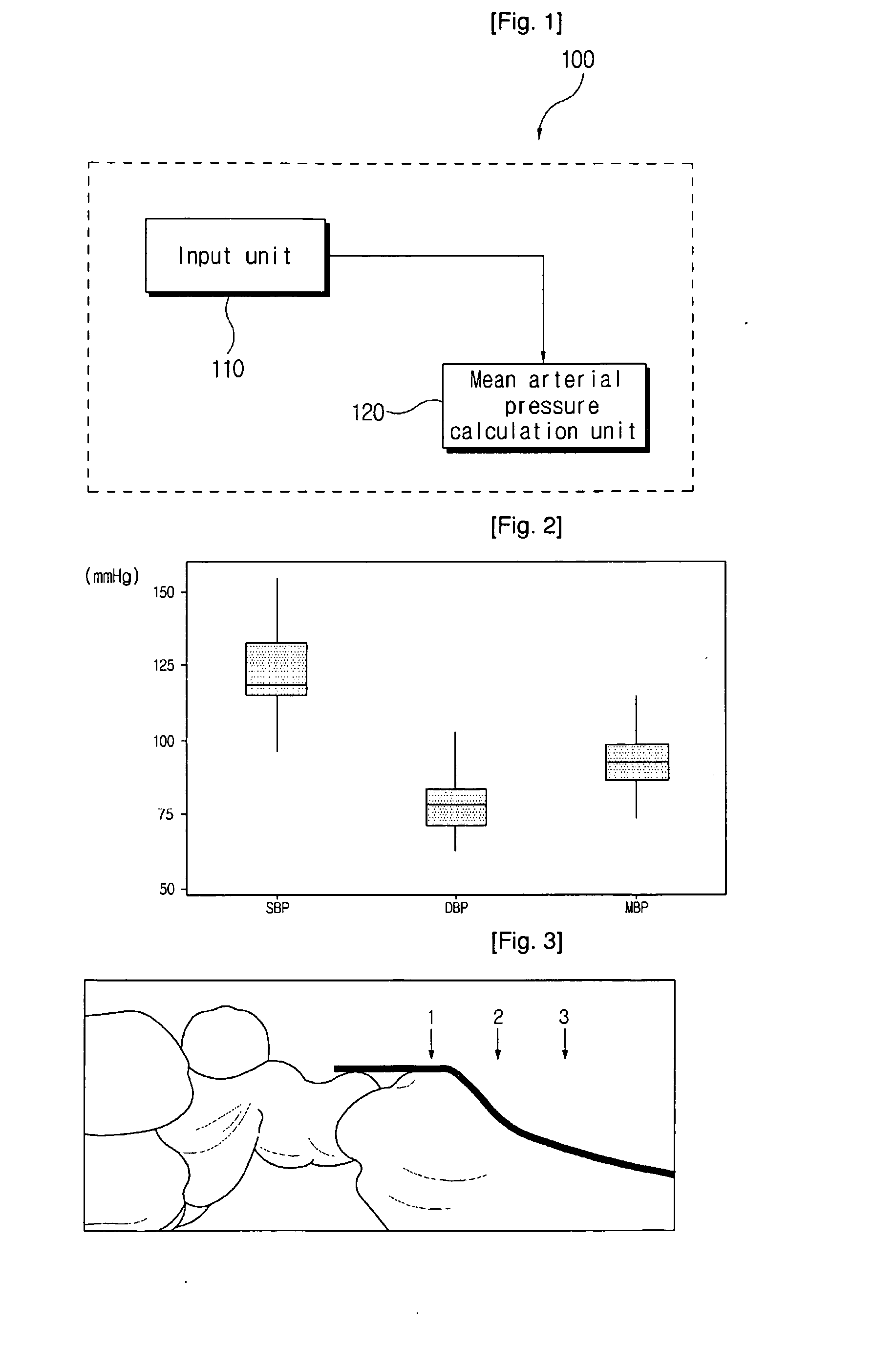
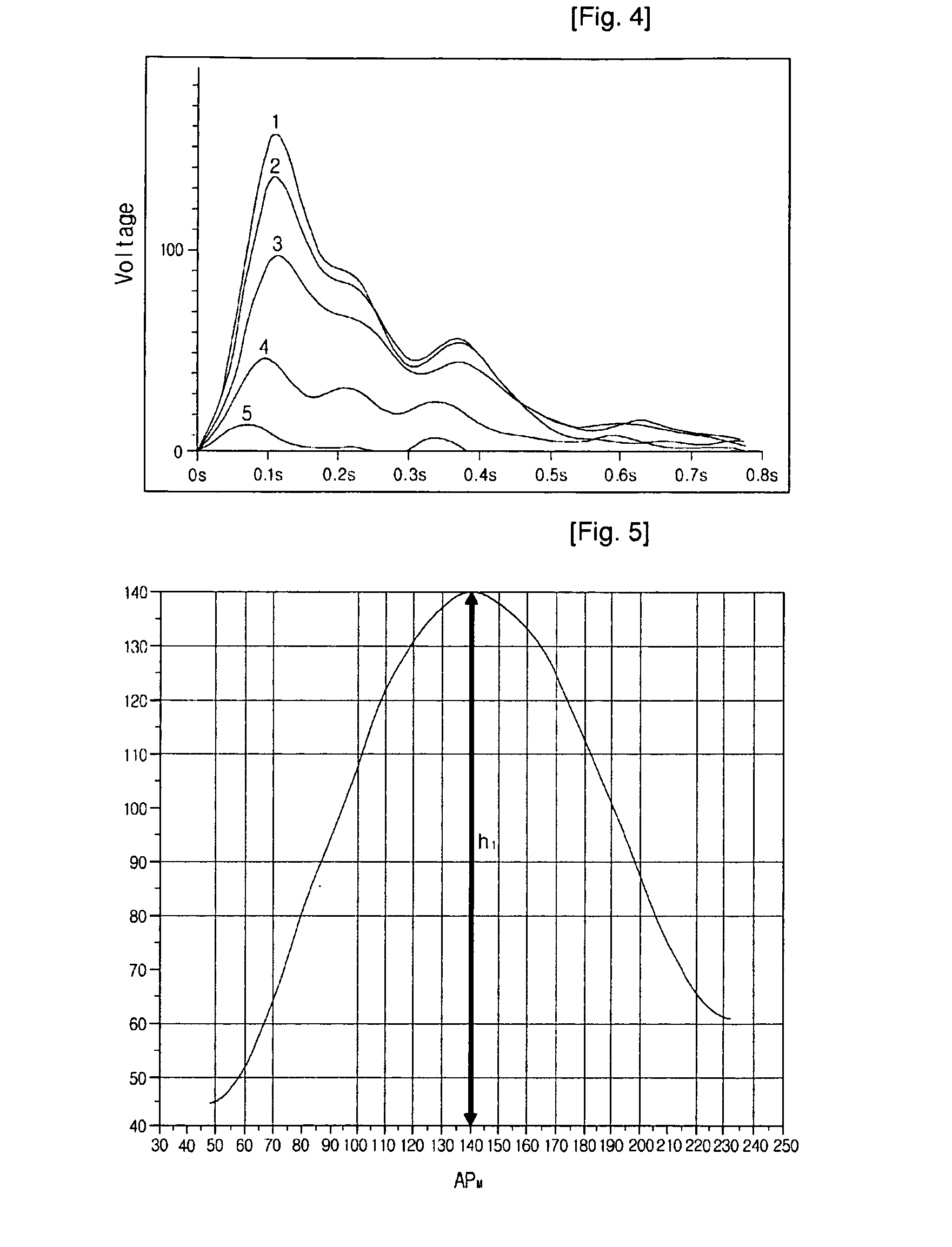
The present invention relates to a blood pressure measurement apparatus comprising: an input unit where at least one value selected from the maximum applied pressure, which is the applied pressure at which the maximum pulse pressure is attained during the pulse pressure measurement at the measurement part, the maximum pulse pressure, which is the pulse pressure at the maximum applied pressure, the depth of blood vessel at the measurement part measured by a pressure sensor, the elasticity of skin tissue at the measurement part and the elasticity of blood vessel at the measurement part is inputted; and a mean arterial press calculation unit where the mean arterial pressure is calculated from the input values of the maximum applied pressure, the depth of blood vessel and the elasticity of skin tissue. The present invention offers more effective and reliable blood pressure measurement apparatus.
Owner:DAEYO MEDI
Non-invasive method and device to monitor cardiac parameters without use of electrical-mechanical interval
InactiveUS7761141B2Easy to measureSimple processElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesDiastolic intervalCardiac cycle
A method of and a device for non-invasively measuring the hemodynamic state of a subject or a human patient involve steps and units of non-invasively or minimally invasively measuring cardiac cycle period, mean arterial pressure, stroke volume, diastolic interval and ejection interval and converting the measured mean arterial pressure, stroke volume, diastolic interval and ejection interval into the cardiac parameters such as Preload, Afterload and Contractility, which are the common cardiac parameters used by an anesthesiologist. In the current invention, the use of electrical-mechanical interval has been eliminated for various advantageous reasons. The converted hemodynamic state of a patient is displayed on a screen as a three-dimensional vector with each of its three coordinates respectively representing Preload, Afterload and Contractility. Therefore, a medical practitioner looks at the screen and—quickly obtains the important and necessary information.
Owner:HIRSH ROBERT
Devices and methods for low pressure tumor embolization
ActiveUS20160310148A1Increase the number ofLow pressureBalloon catheterMedical devicesAnatomical structuresTransarterial embolization
A method of transarterial embolization agent delivery at a low pressure is provided. The method comprises advancing a delivery device with an occlusion structure in a retracted non-occlusive configuration through a supply artery to a vascular position in the supply artery that is in the vicinity of a target anatomical structure, the target structure having terminal capillary beds, expanding the occlusion structure from the retracted non-occlusive configuration to an expanded occlusive configuration, lowering a mean arterial pressure in a vascular space distal to the expanded occlusion structure, redirecting fluid flow from the collateral vessels toward the lowered pressure vascular space and into the target anatomical structure, injecting an embolization agent through the delivery device and into the lowered pressure vascular space, and delivering the embolization agent from the lowered pressure vascular space into the target anatomical structure. Other catheter assemblies and methods of use are also disclosed.
Owner:EMBOLX
Closed-loop external chest compression system
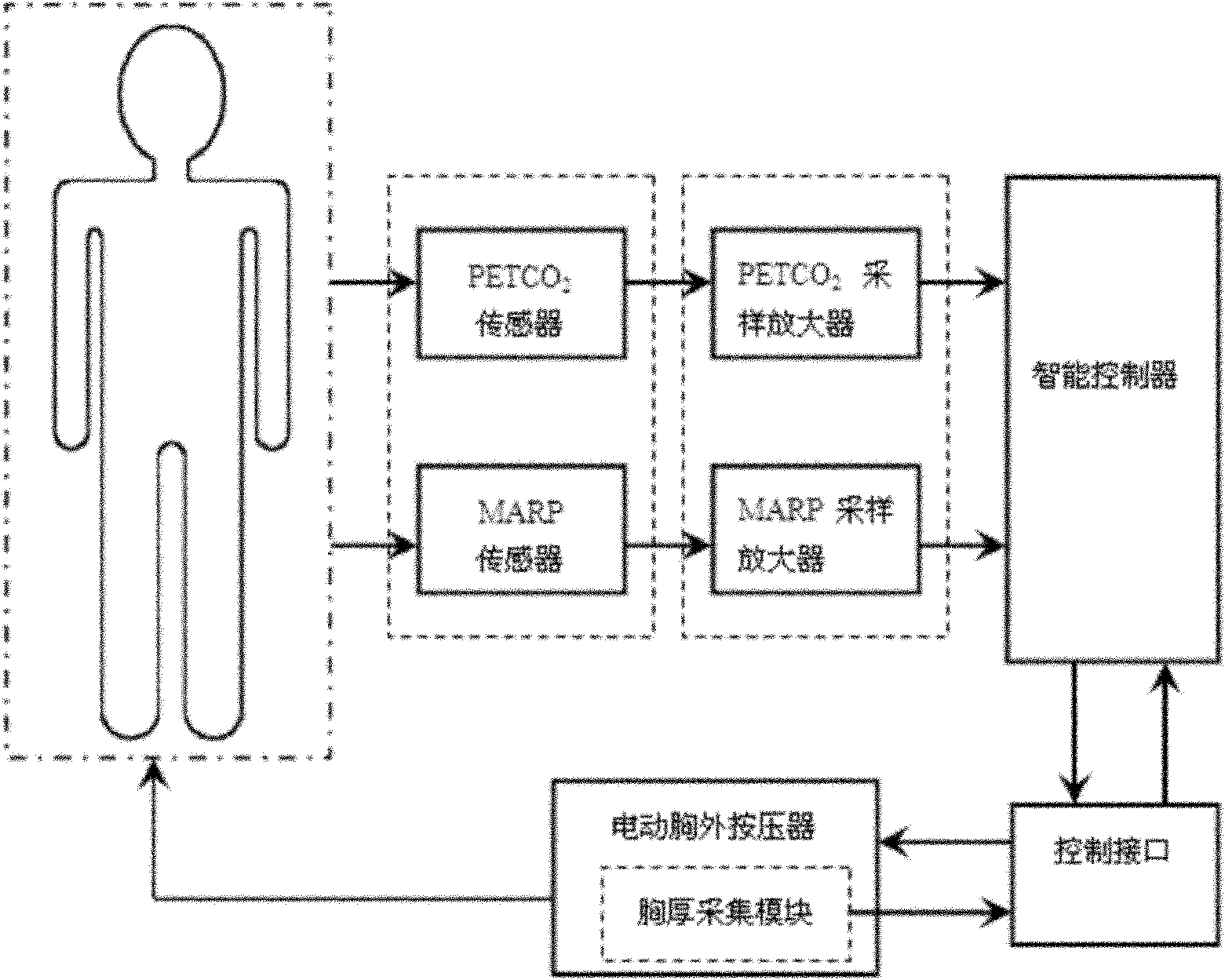
InactiveCN102119908AImproved quality of chest compressionsElectrotherapyArtificial respirationProportional integral differentialControl signal
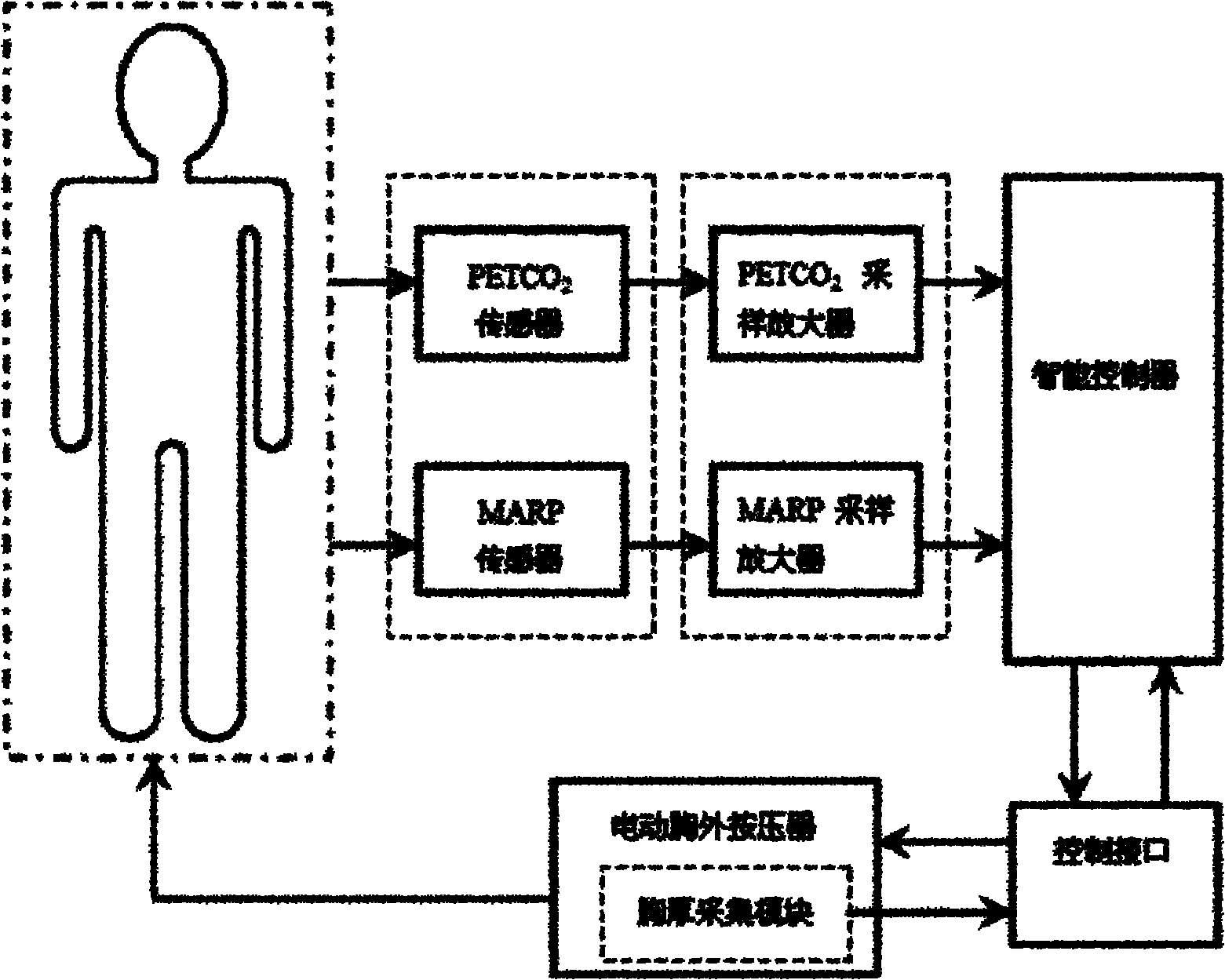
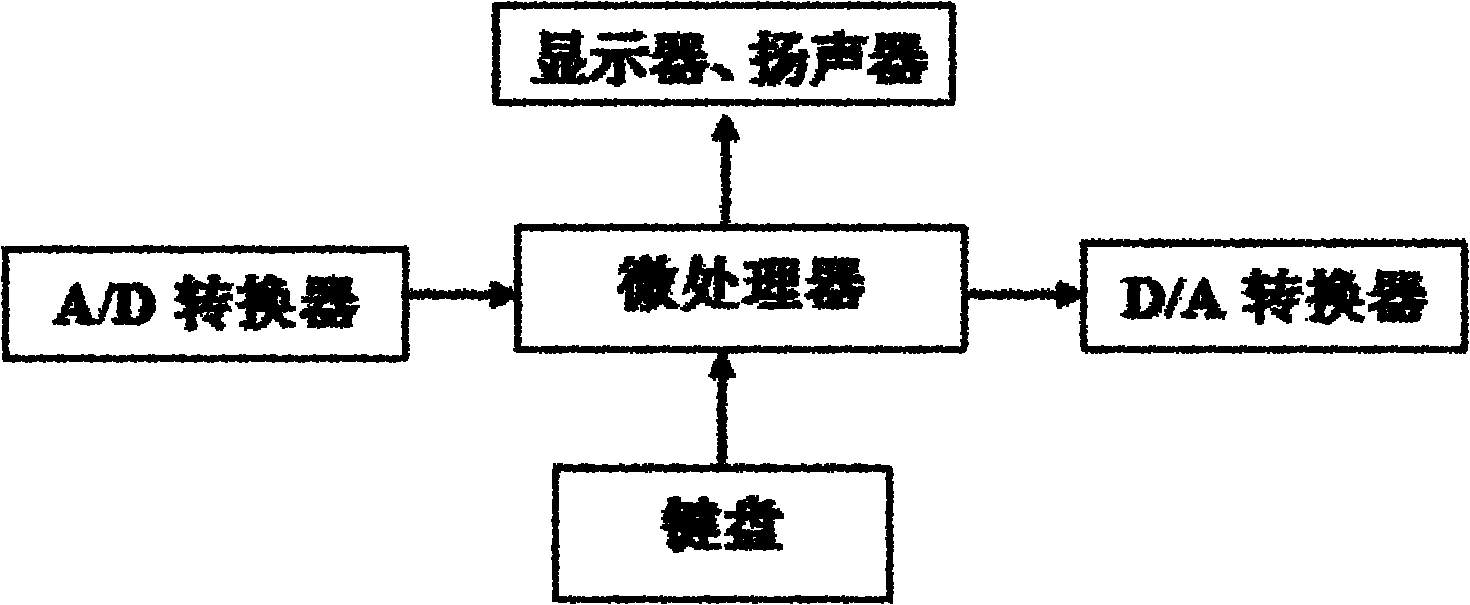
The invention discloses a closed-loop external chest compression system. The system comprises a feedback physiological signal acquiring module, a postprocessing and amplifying module, an intelligent controller, a control interface, an electrical external chest compressor and a chest thickness signal acquiring module, wherein the intelligent controller samples an analogue signal which comes from the postprocessing and amplifying module and a patient chest thickness signal which is sampled by the chest thickness signal acquiring module, compares the analogue signal which reflects actual feedback physiological information with a target physiological signal, and generates the depth and frequency control signal of the external chest compression to be implemented, which can accord with the target physiological signal, by combining a fuzzy control algorithm or a fuzzy proportional integral differential (PID) control algorithm. By continuously monitoring partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide (PETCO2) and mean arterial pressure (MARP) in real time and using the feedback physiological signal, the closed-loop control over the depth and the frequency of the external chest compression is performed on the basis of the fuzzy control algorithm or the fuzzy PID control algorithm. The closed-loop external chest compression system is suitable for pre-hospital emergency treatment and continuous treatment of patients with sudden cardiac arrest.
Owner:SANITARY EQUIP INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI PLA
Method and apparatus for non-invasive determination of cardiac output
InactiveUS20140303509A1Easy and simpler and accurate and non invasiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEvaluation of blood vesselsMicrocomputerNon invasive
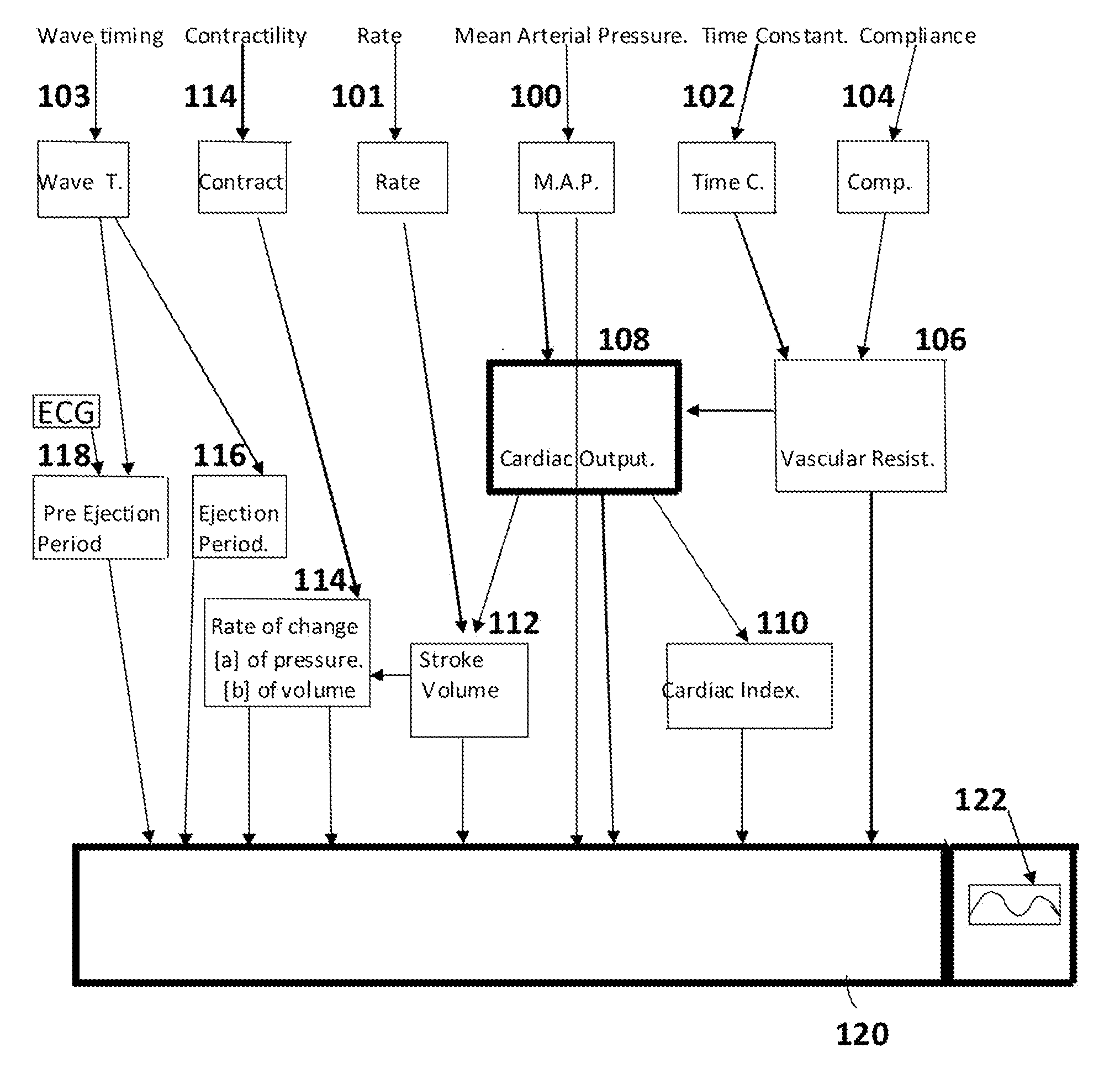
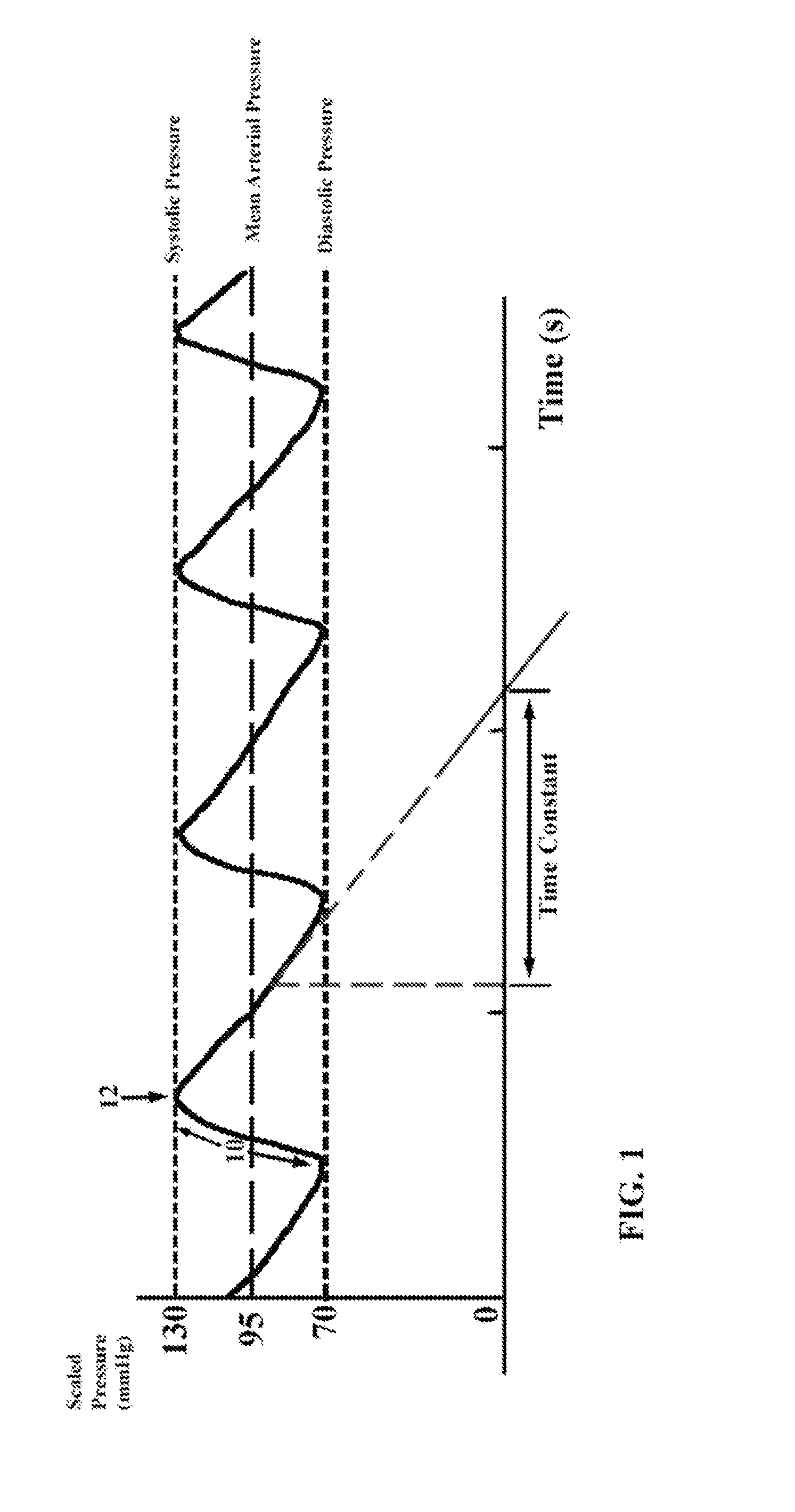
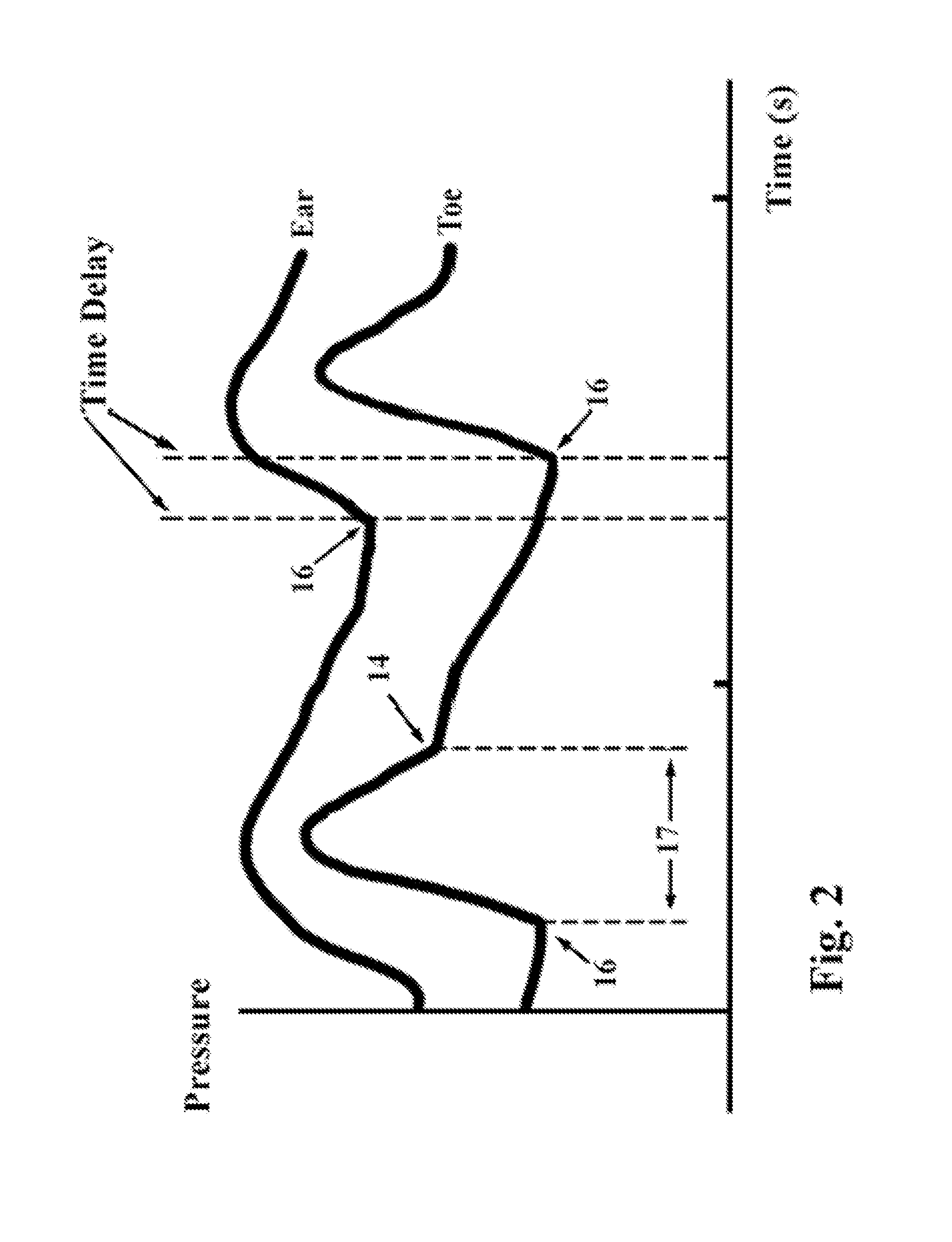
A non-invasive method and apparatus determines continuously cardiac output by first analysing the trace obtained from an optical sensor which has been scaled and calibrated using an electronic sphygmomanometer. From this the mean arterial pressure and time constant are determined. Compliance is determined from the pulse delay between two other optical sensors at well separated sites. Cardiac output is the product of mean arterial pressure and compliance divided by the time constant. A microcomputer provides the necessary calculations.
Owner:DUNCAN CAMPBELL INVESTMENTS
Device for determining a hemodynamic parameter
Owner:PULSION MEDICAL SYSTEMS SE
Continuous calibration of a blood pressure measurement device
Systems, methods, and devices of the various embodiments enable continuous non-invasive monitoring of blood pressure with a minimum of interference. The various embodiments may provide a method for adaptation for the calibration for continuous measurements of blood pressure, wherein the measured quantity may be related to an arterial lumen or arterial cross sectional area comprising calibrating the conversion for incremental variations of arterial properties and absolute value adaptation by exploitation of the exponential decay during the diastole. In various embodiments, continuous calibration of a non-interfering blood pressure measurement device may be initiated based on a change in mean arterial pressure being greater than a threshold value, such as a pressure value associated with an actual measured distension of a patient's artery.
Owner:PHILIPS HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS INC
Angiotensin ii alone or in combination for the treatment of hypotension
The present invention relates, inter alia, to a method comprising administering to a subject having high output shock and undergoing treatment with a catecholamine at a dose equivalent to at least about 0.2 mcg / kg / min of norepinephrine a dose of angiotensin II which is effective to raise the blood pressure of the subject to a mean arterial pressure (MAP) of about 65 mm Hg or above, and which is effective to reduce the dose of the catecholamine required to maintain a MAP of about 65 mm Hg to the equivalent of about 0.05-0.2 mcg / kg / min norepinephrine or less, or to the equivalent of about 0.05 mcg / kg / min norepinephrine or less.
Owner:THE GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIV A CONGRESSIONALLY CHARTERED NOT FOR PROFIT CORP
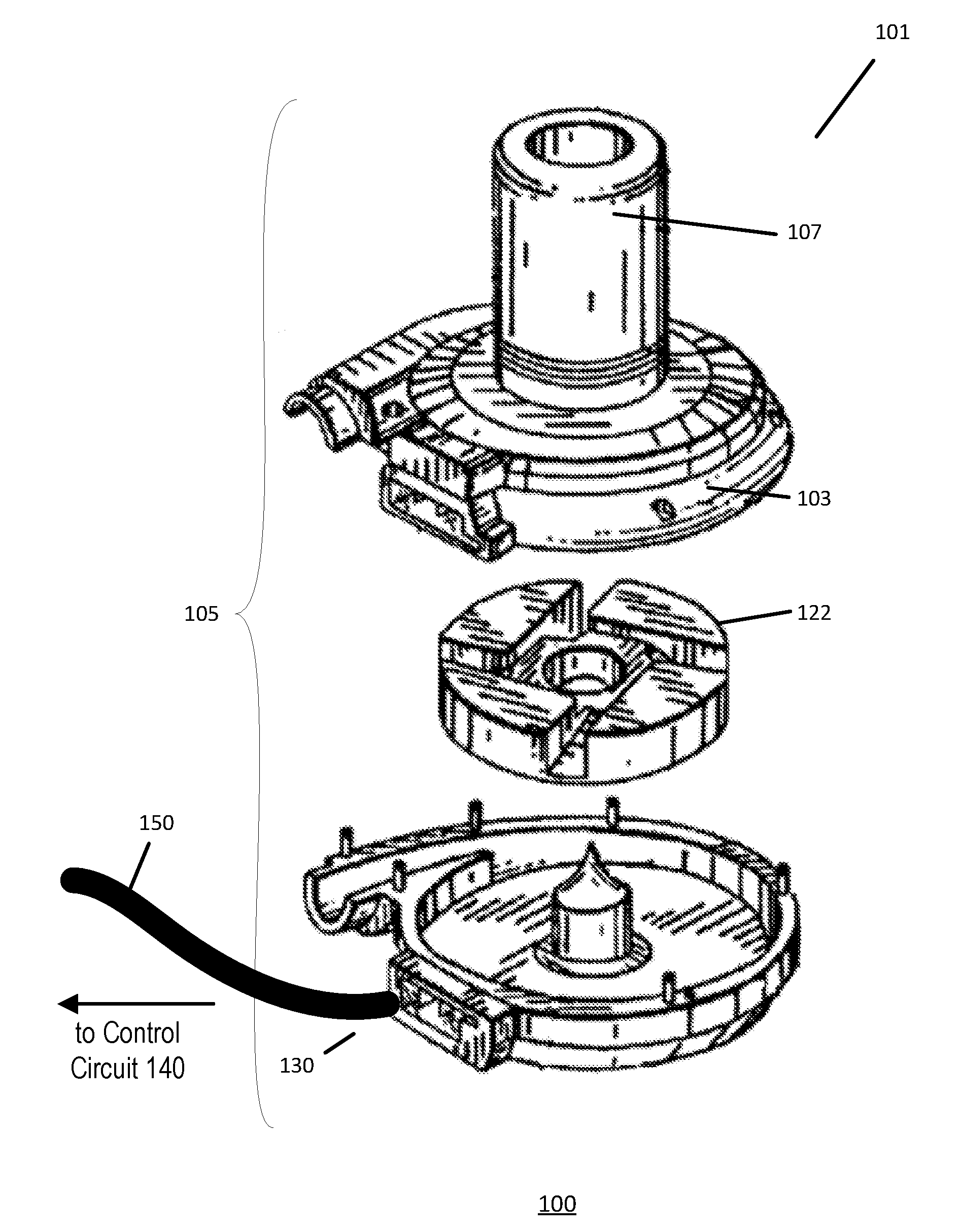
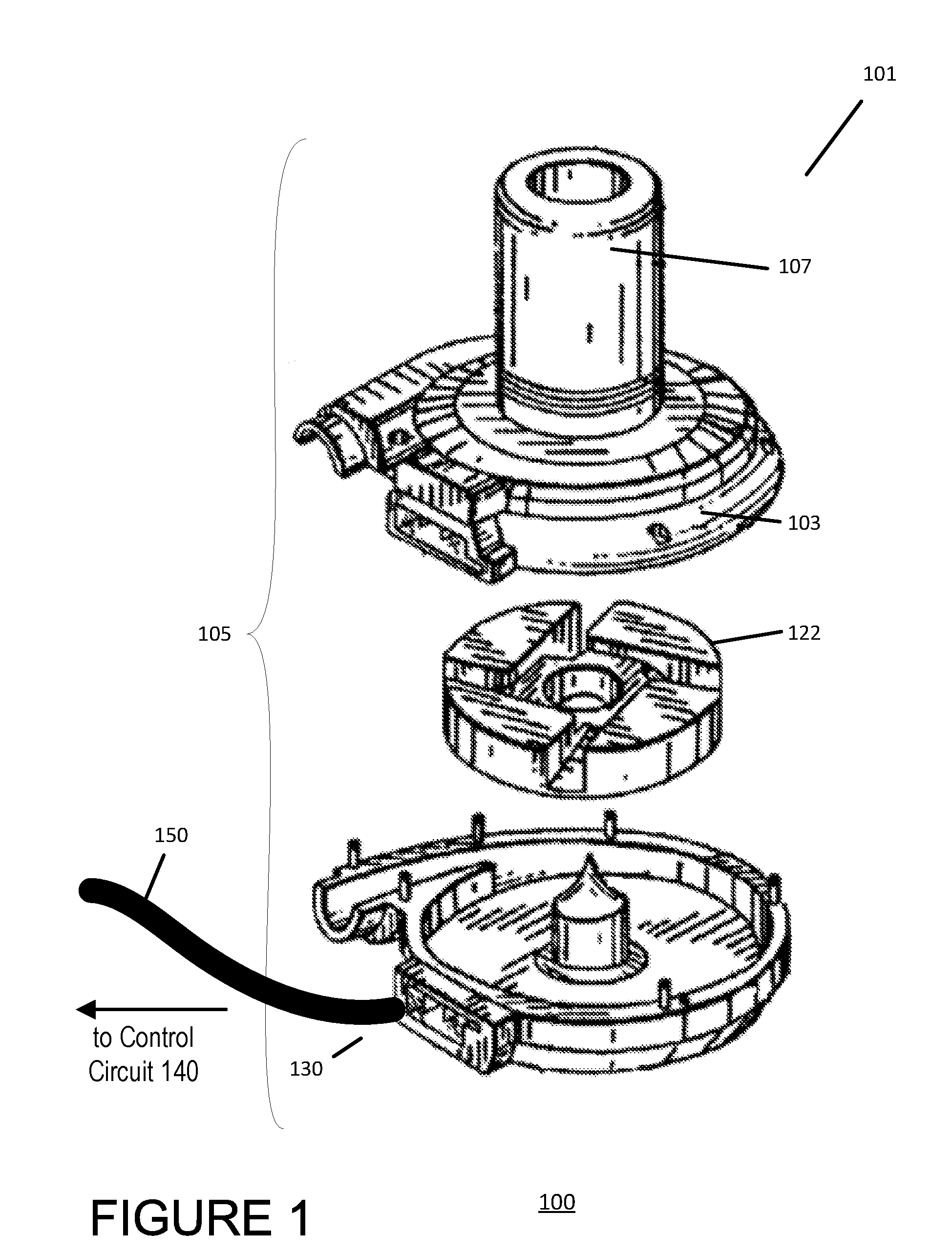
Non-invasive method and device to monitor cardiac parameters
A method of and a device for non-invasively measuring the hemodynamic state of a subject or a human patient involve steps and units of non-invasively measuring cardiac cycle period, electrical-mechanical interval, mean arterial pressure, and ejection interval and converting the measured electrical-mechanical interval, mean arterial pressure and ejection interval into the cardiac parameters such as Preload, Afterload and Contractility, which are the common cardiac parameters used by an anesthesiologist. The converted hemodynamic state of a patient is displayed on a screen as a three-dimensional vector with each of its three coordinates respectively representing Preload, Afterload and Contractility. Therefore, a medical practitioner looks at the screen and quickly obtains the important and necessary information.
Owner:HIRSH ROBERT
Apparatus and methods for computing cardiac output of a living subject via applanation tonometry
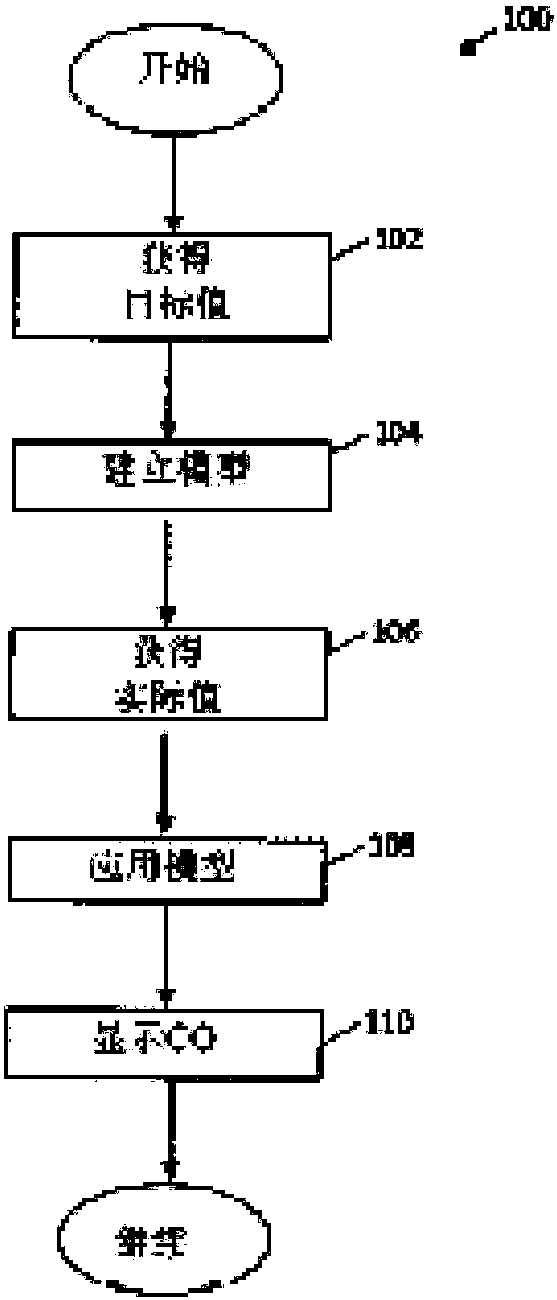
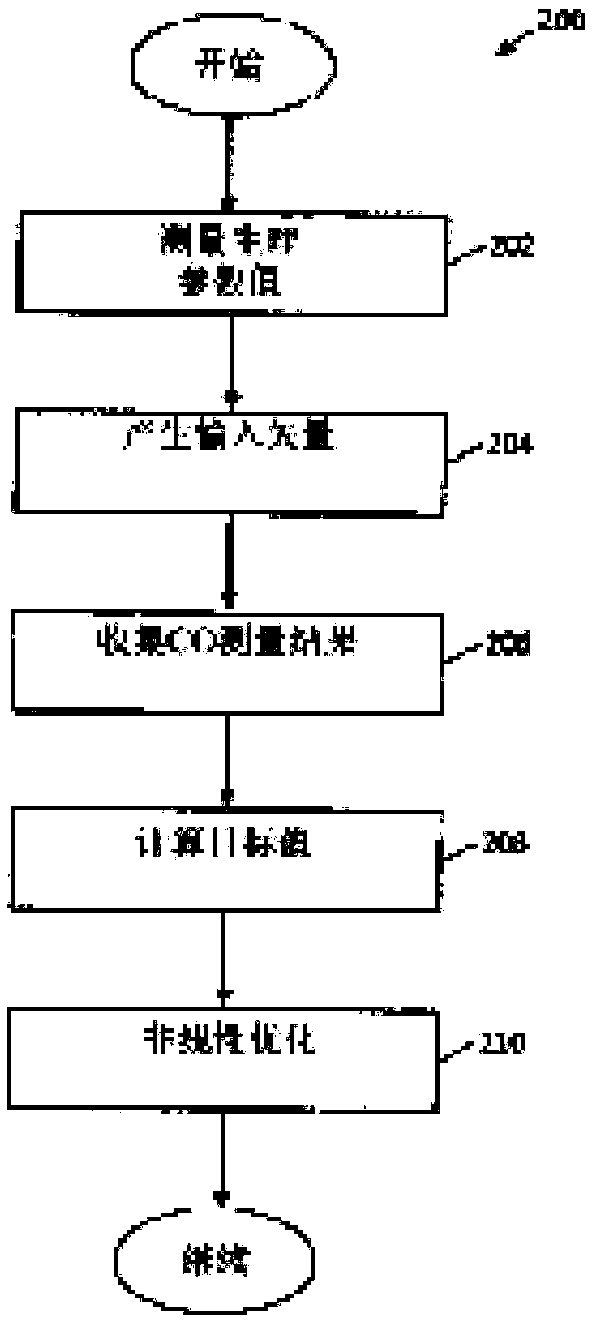
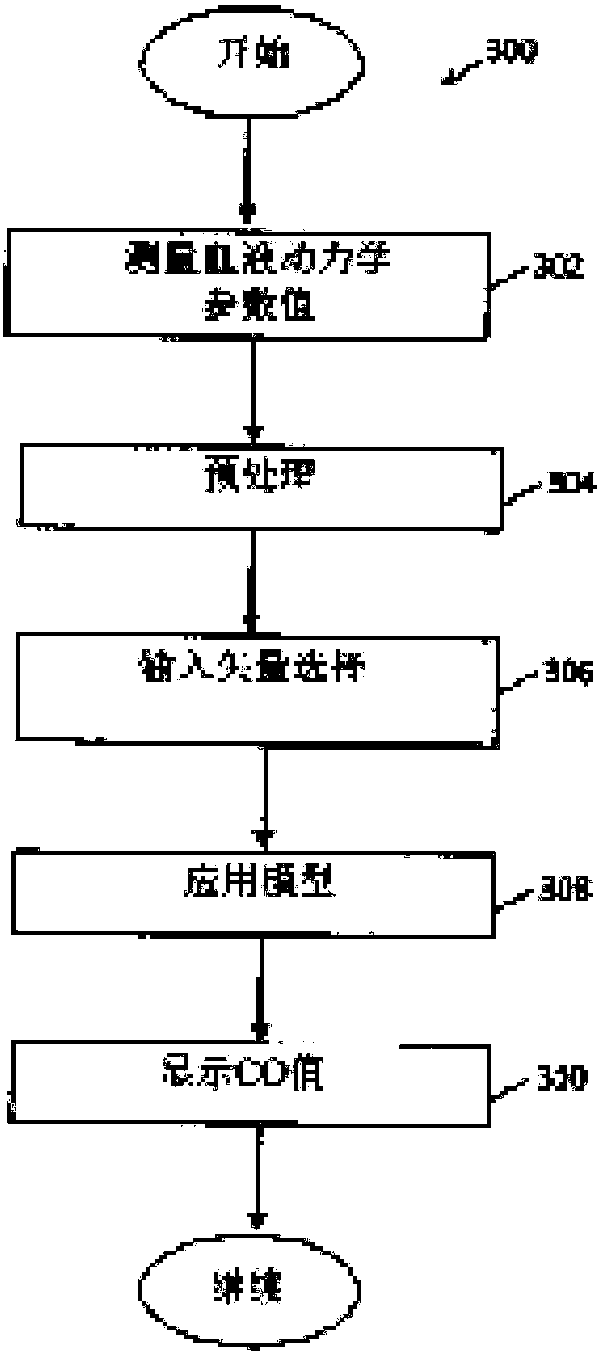
Apparatus and methods for calculating cardiac output (CO) of a living subject using applanation tonometry measurements. In one embodiment, the apparatus and methods build a nonlinear mathematical model to correlate physiologic source data vectors to target CO values. The source data vectors include one or more measurable or derivable parameters such as: systolic and diastolic pressure, pulse pressure, beat-to-beat interval, mean arterial pressure, maximal slope of the pressure rise during systole, the area under systolic part of the pulse pressure wave, gender (male or female), age, height andweight. The target CO values are acquired using various methods, across a plurality of individuals. Multidimensional nonlinear optimization is then used to find a mathematical model which transformsthe source data to the target CO data. The model is then applied to an individual by acquiring physiologic data for the individual and applying the model to the collected data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHANSHI BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL DEVICES (SHANGQIU) CO LTD
Compositions and methods for treating a damaged cardiovascular element
InactiveUS20070012323A1Reduce thrombosisReduce severityNervous disorderAntipyreticProphylactic treatmentHypotension shock
In the present invention, the applicants describe methods and compositions of treating damaged cardiovascular elements and cardiovascular conditions including hypotension, atherosclerotic lesions, vulnerable plaque, and acute myocardial infarct. The applicants demonstrate the ability of a biomembrane sealing agent to accumulate on the walls of damaged blood vessels and help improving mean arterial pressure following tissue injury. The applicants describe the use of formulations comprising at least one biomembrane sealing agent and one bioactive agent for prophylactic treatment such as they could be administered concurrently to an invasive therapeutic intervention or after the insult (i.e. post-injury or post-surgery). Alternatively, these methods and compositions could be used to reduce the severity of cardiovascular diseases after onset.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Implantable hemodynamic monitor and methods for use therewith
Provided herein are implantable systems that include an implantable photoplethysmography (PPG) sensor, which can be used to obtain an arterial PPG waveform. In an embodiment, a metric of a terminal portion of an arterial PPG waveform is determined, and a metric of an initial portion of the arterial PPG waveform is determined, and a surrogate of mean arterial pressure is determined based on the metric of the terminal portion and the metric of the initial portion. In another embodiment, a surrogate of diastolic pressure is determined based on a metric of a terminal portion of an arterial PPG waveform. In a further embodiment, a surrogate of cardiac afterload is determined based on a metric of a terminal portion of an arterial PPG waveform.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com