Patents
Literature
47 results about "Systolic phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
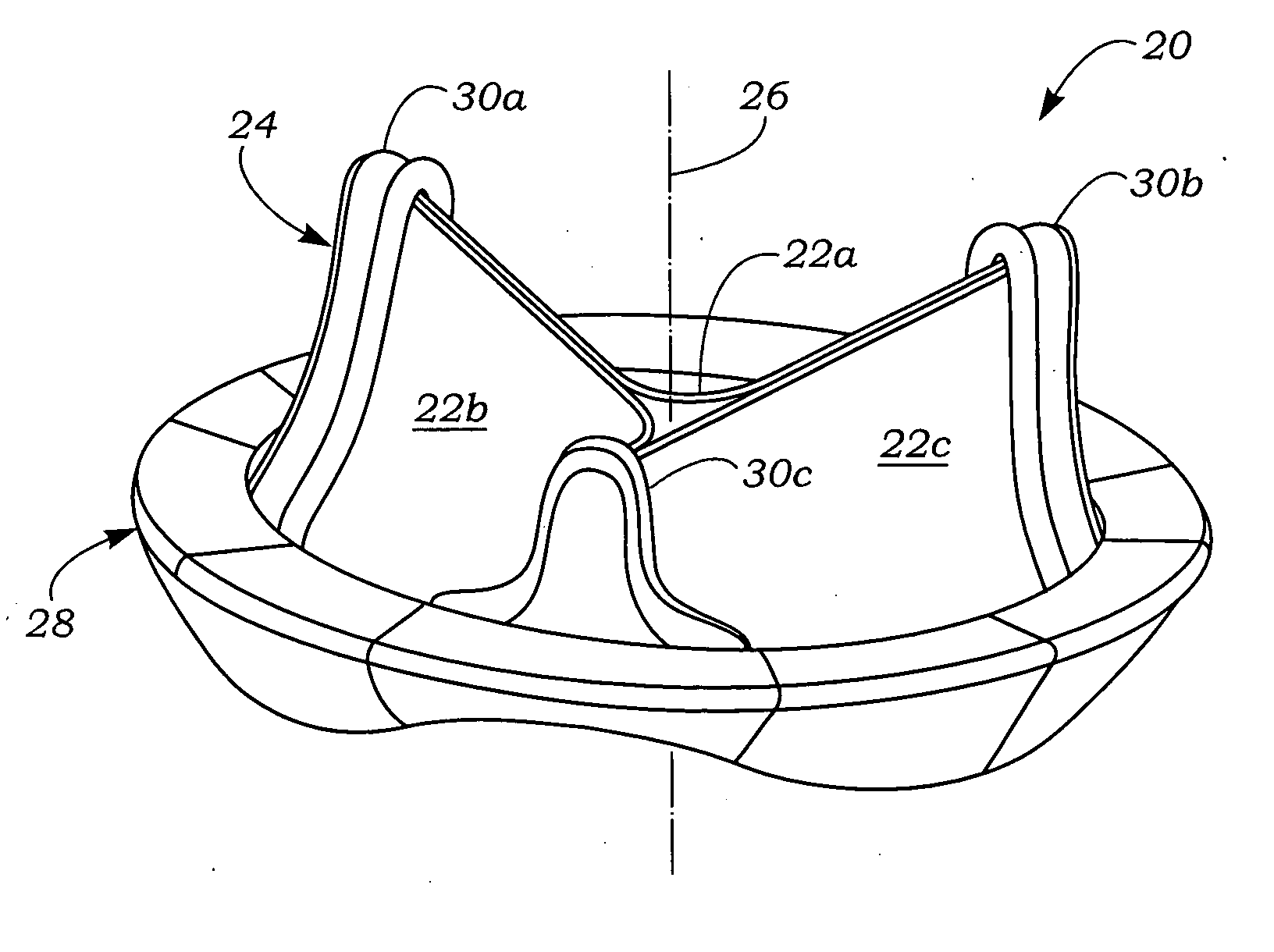
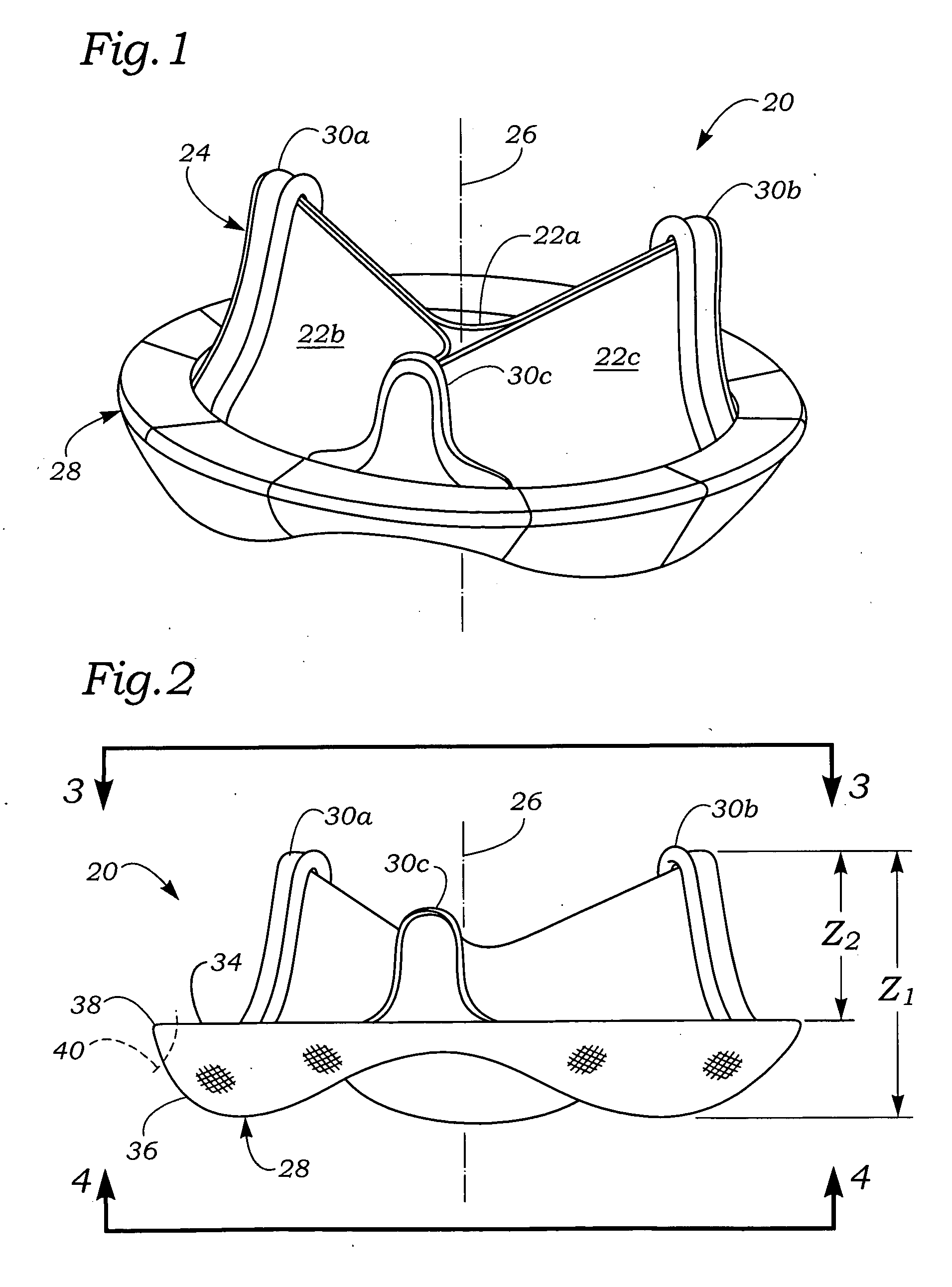
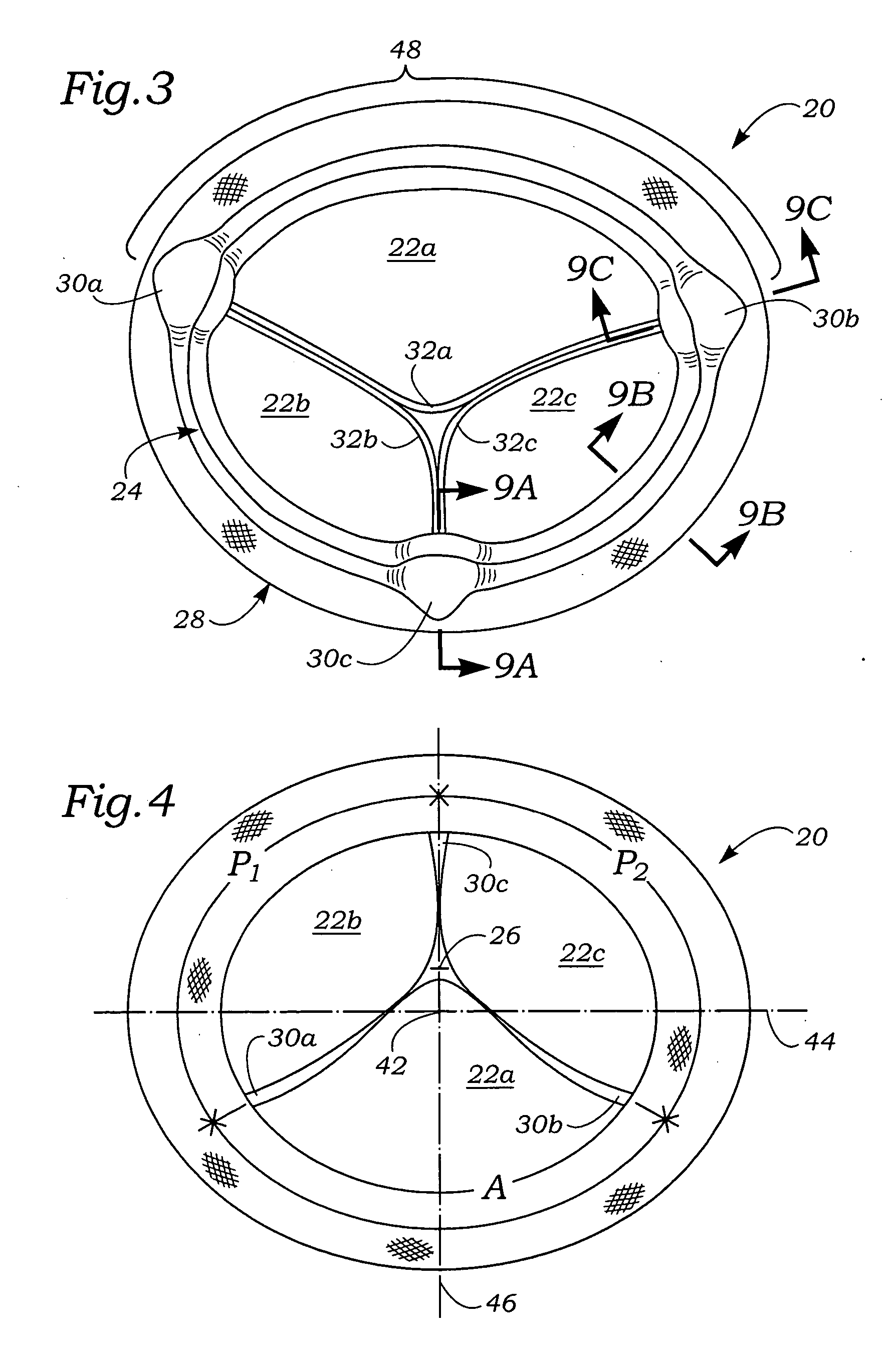
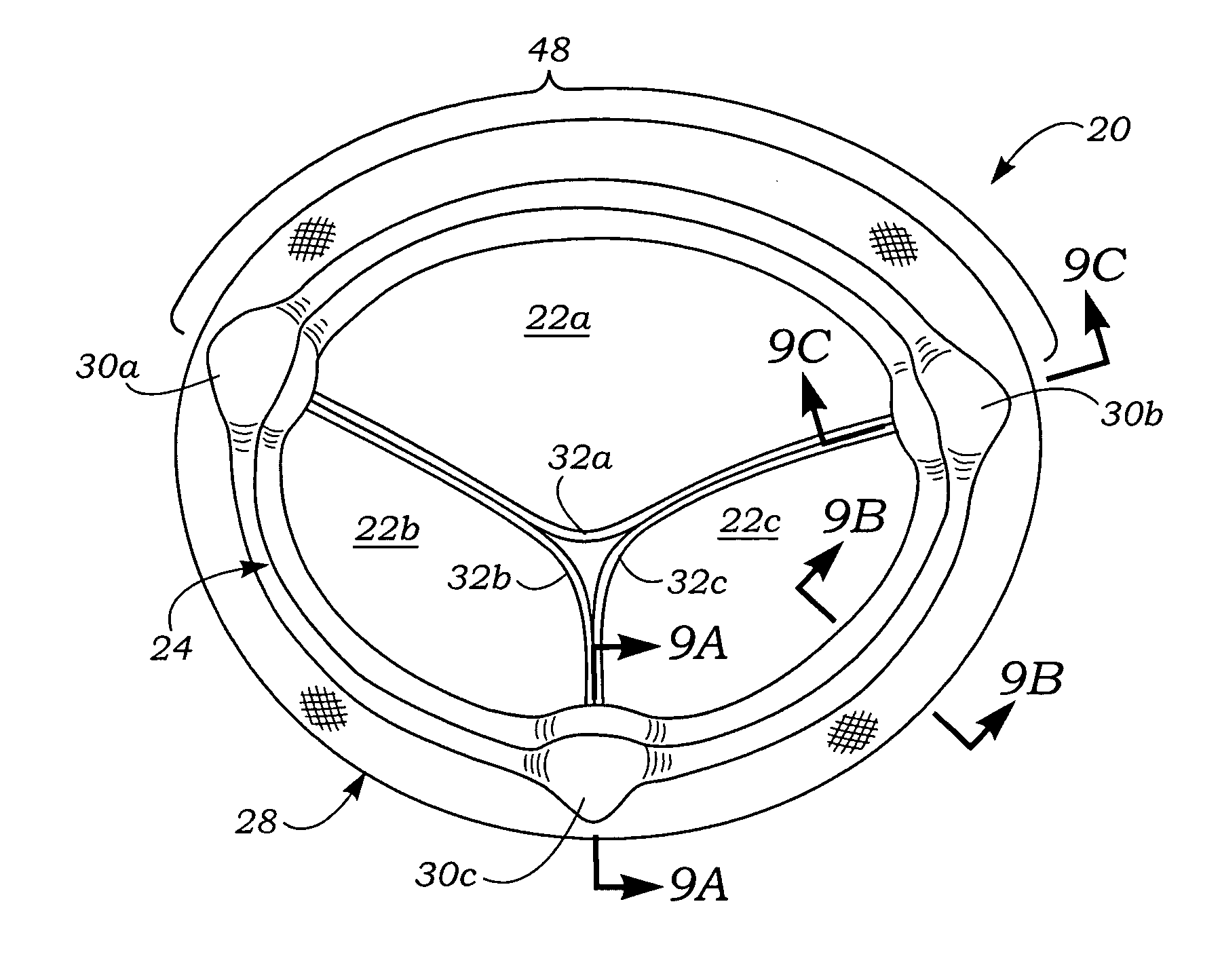
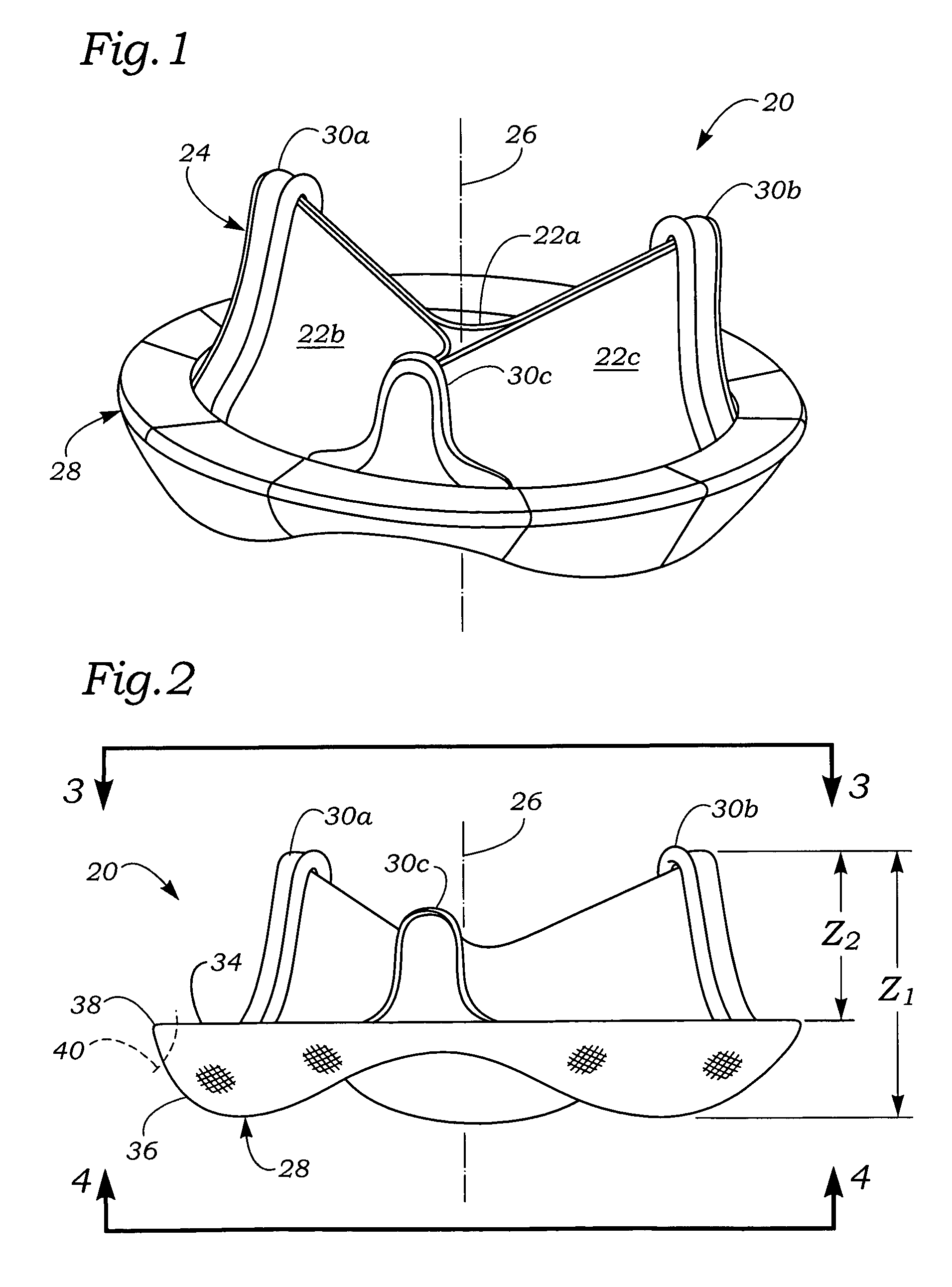
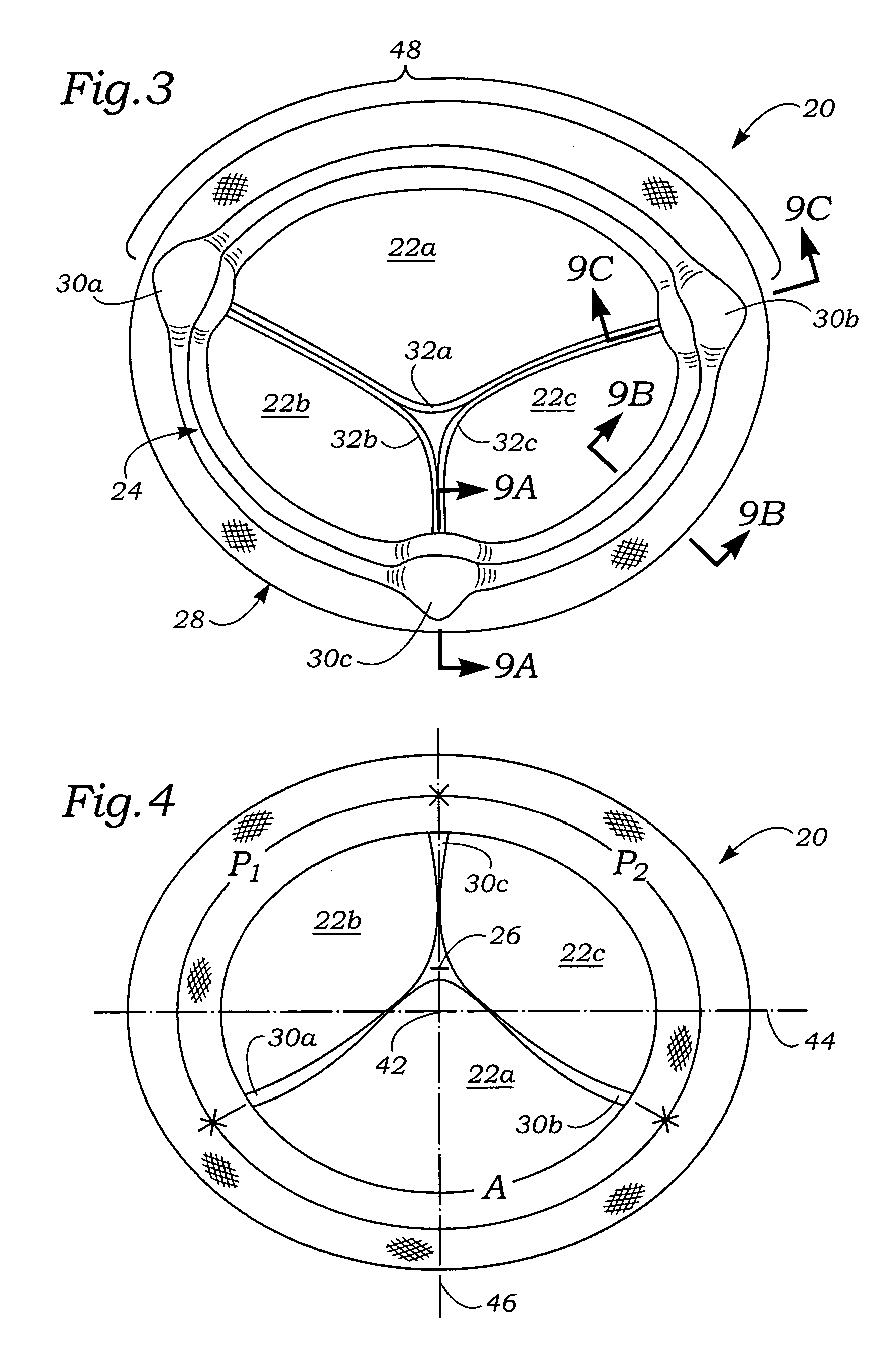
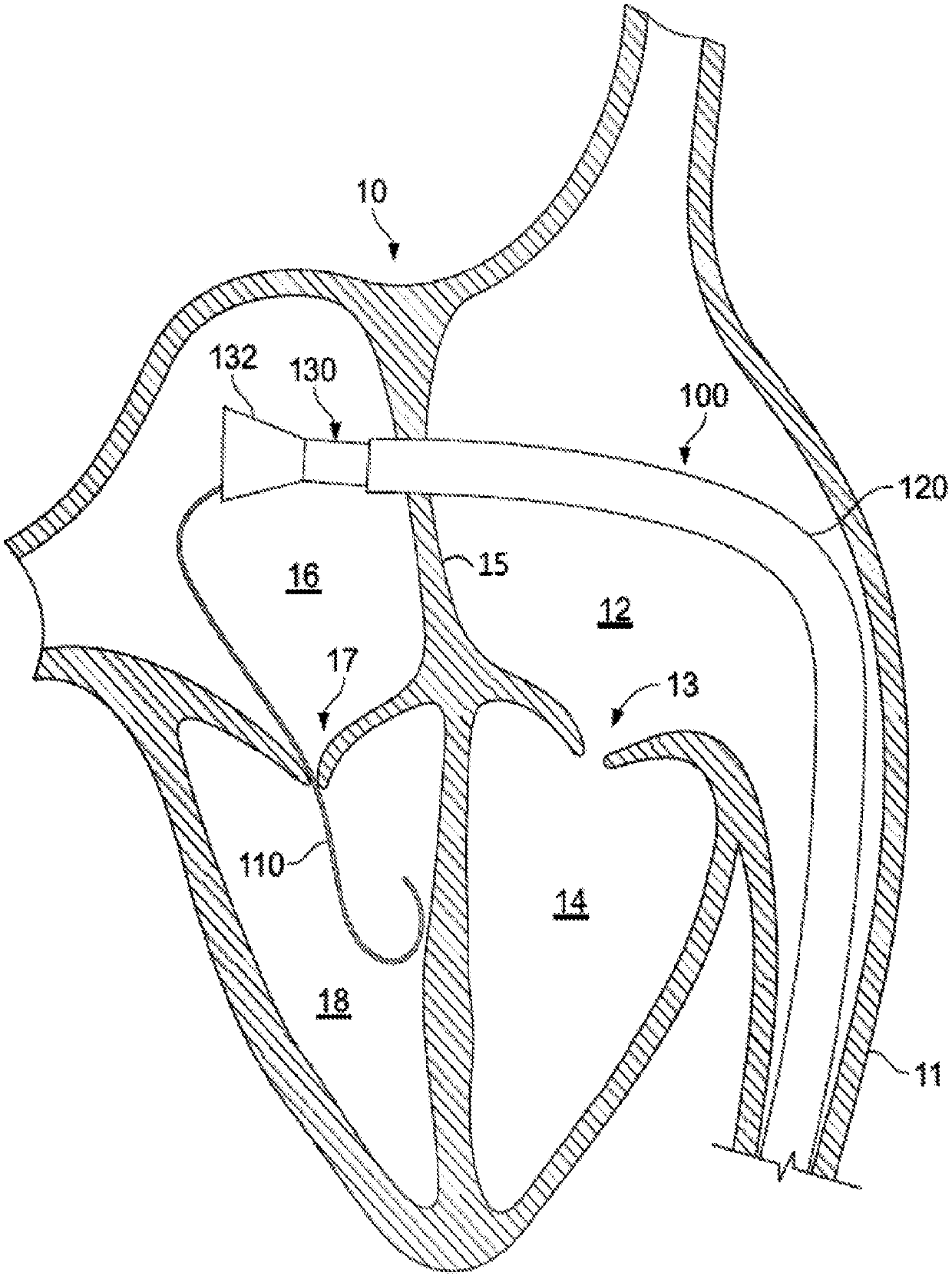
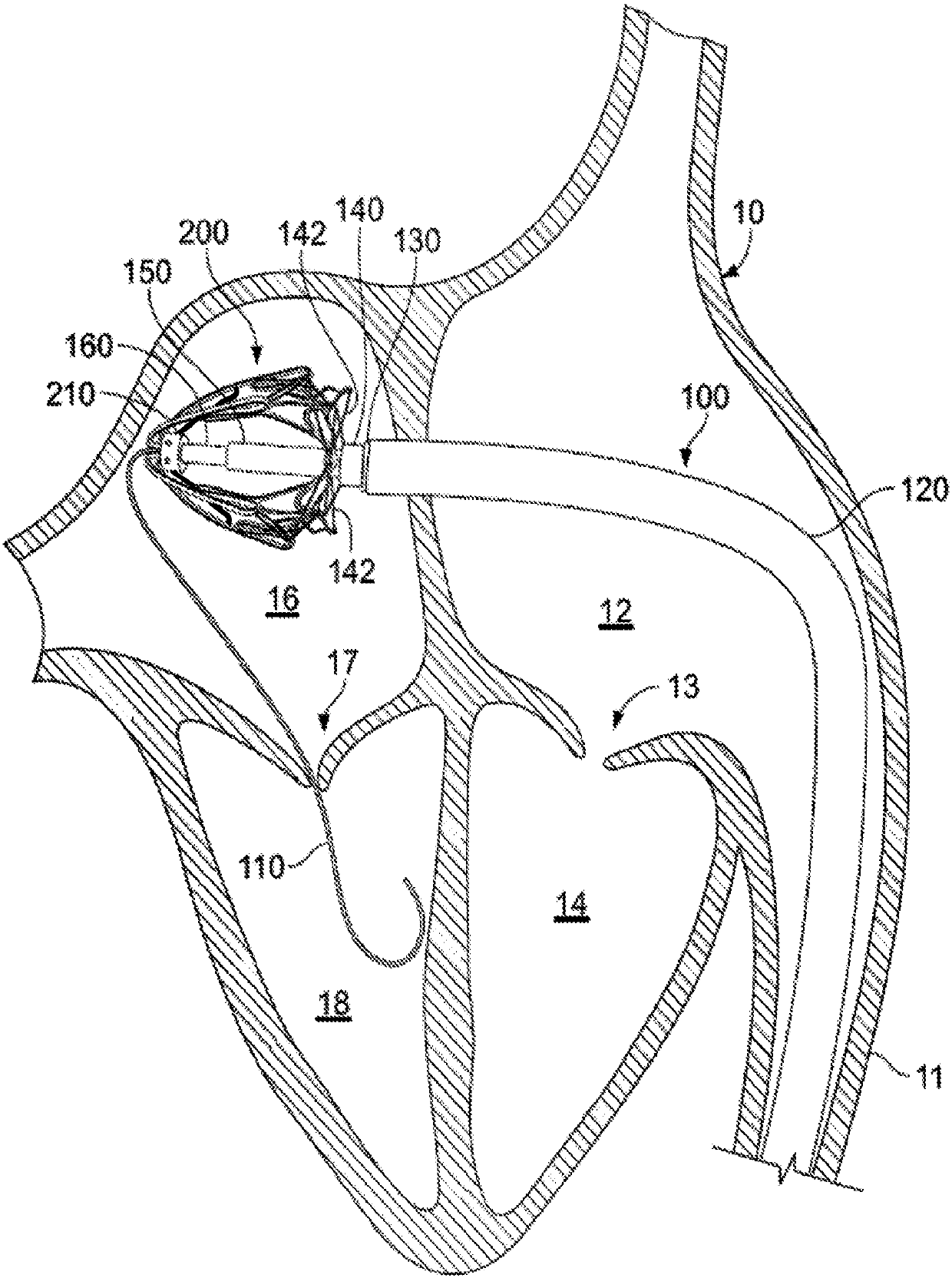
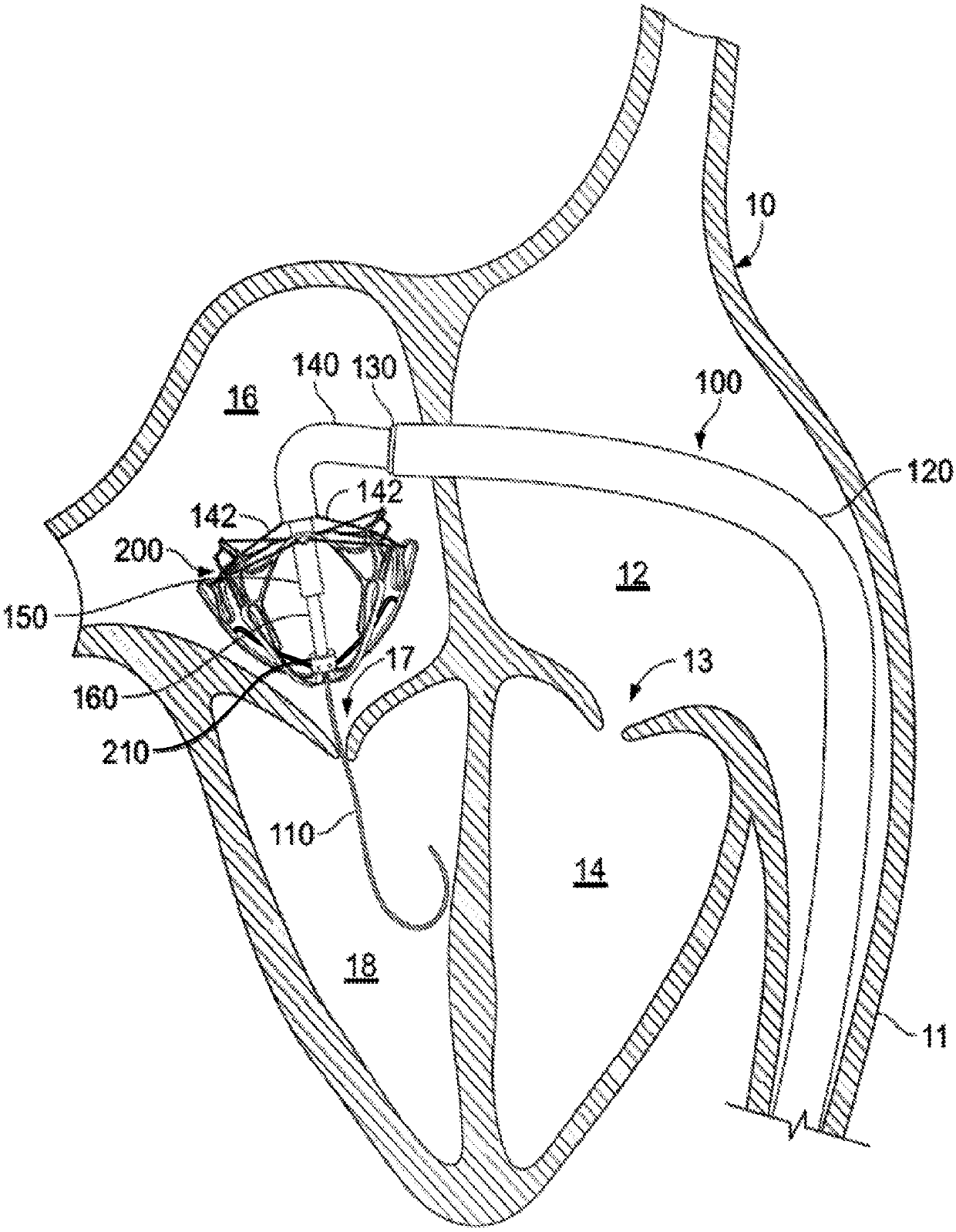
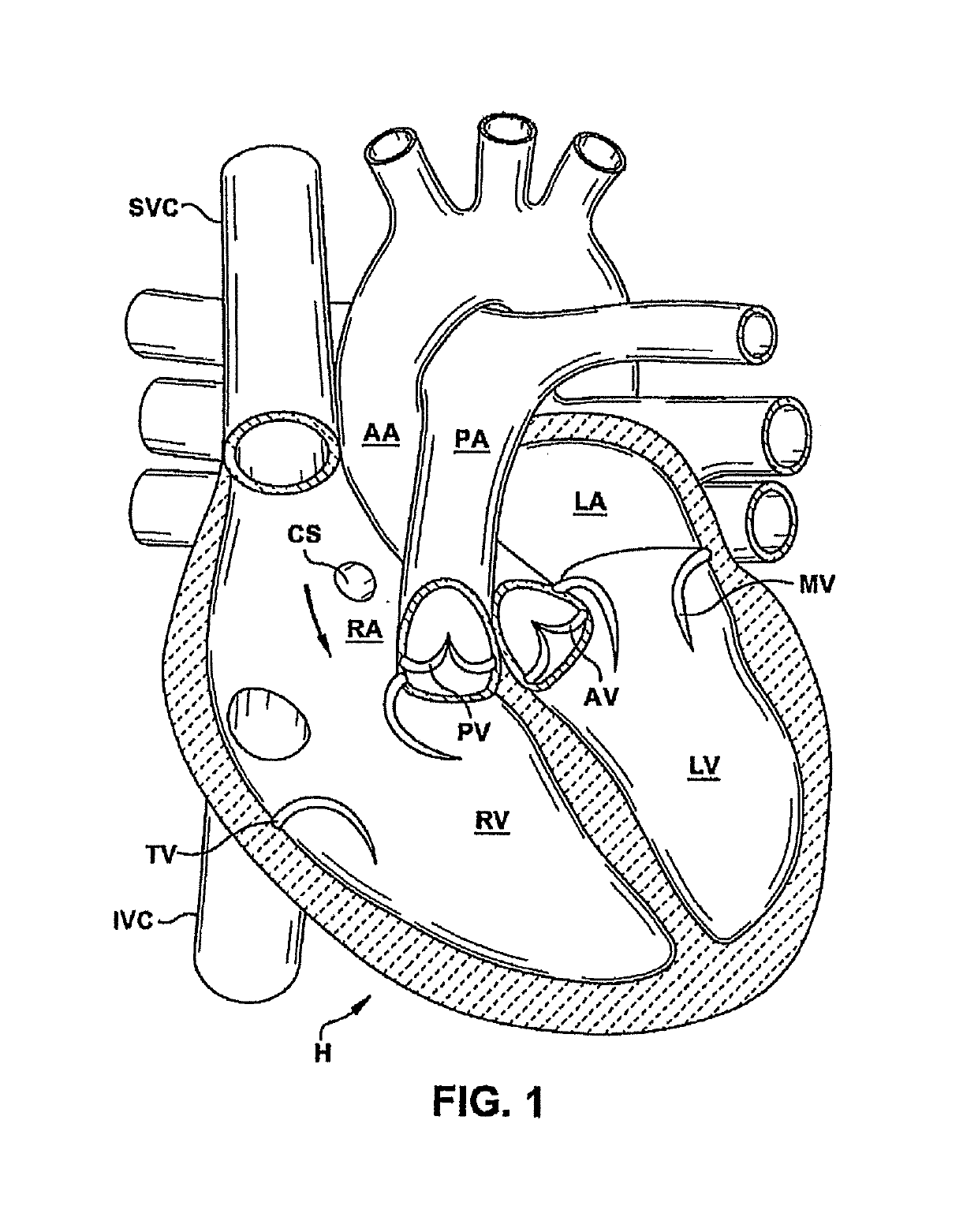
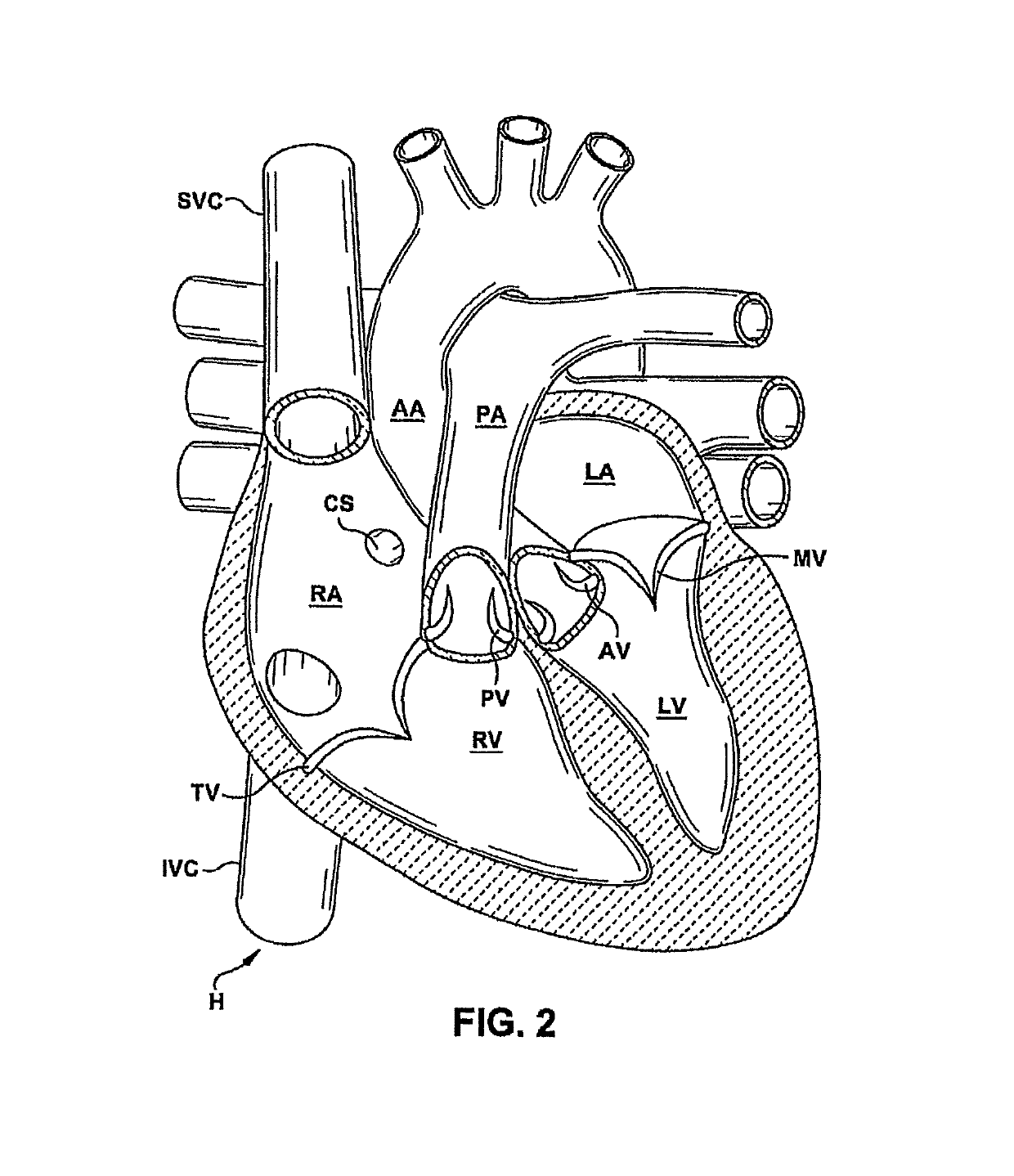
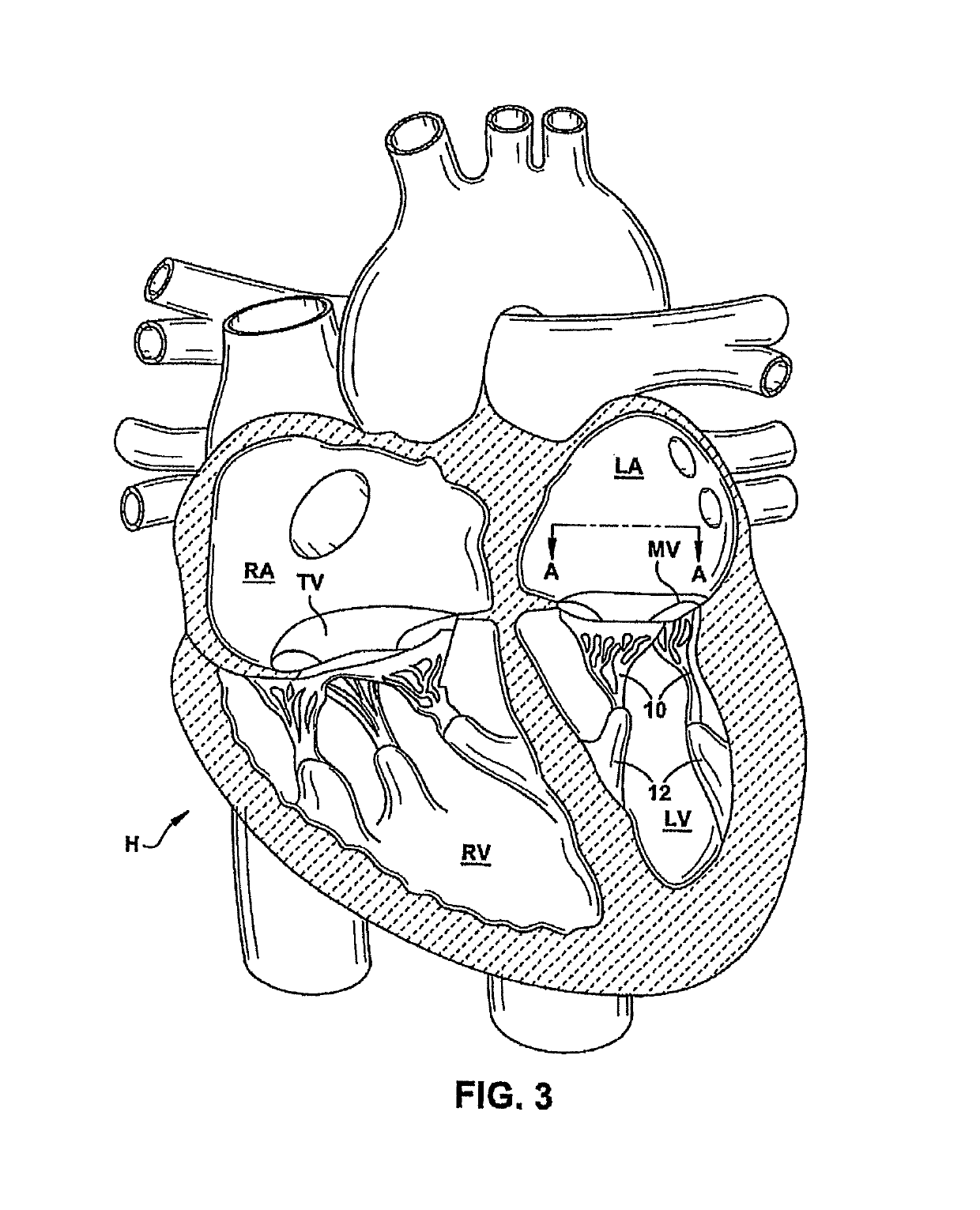
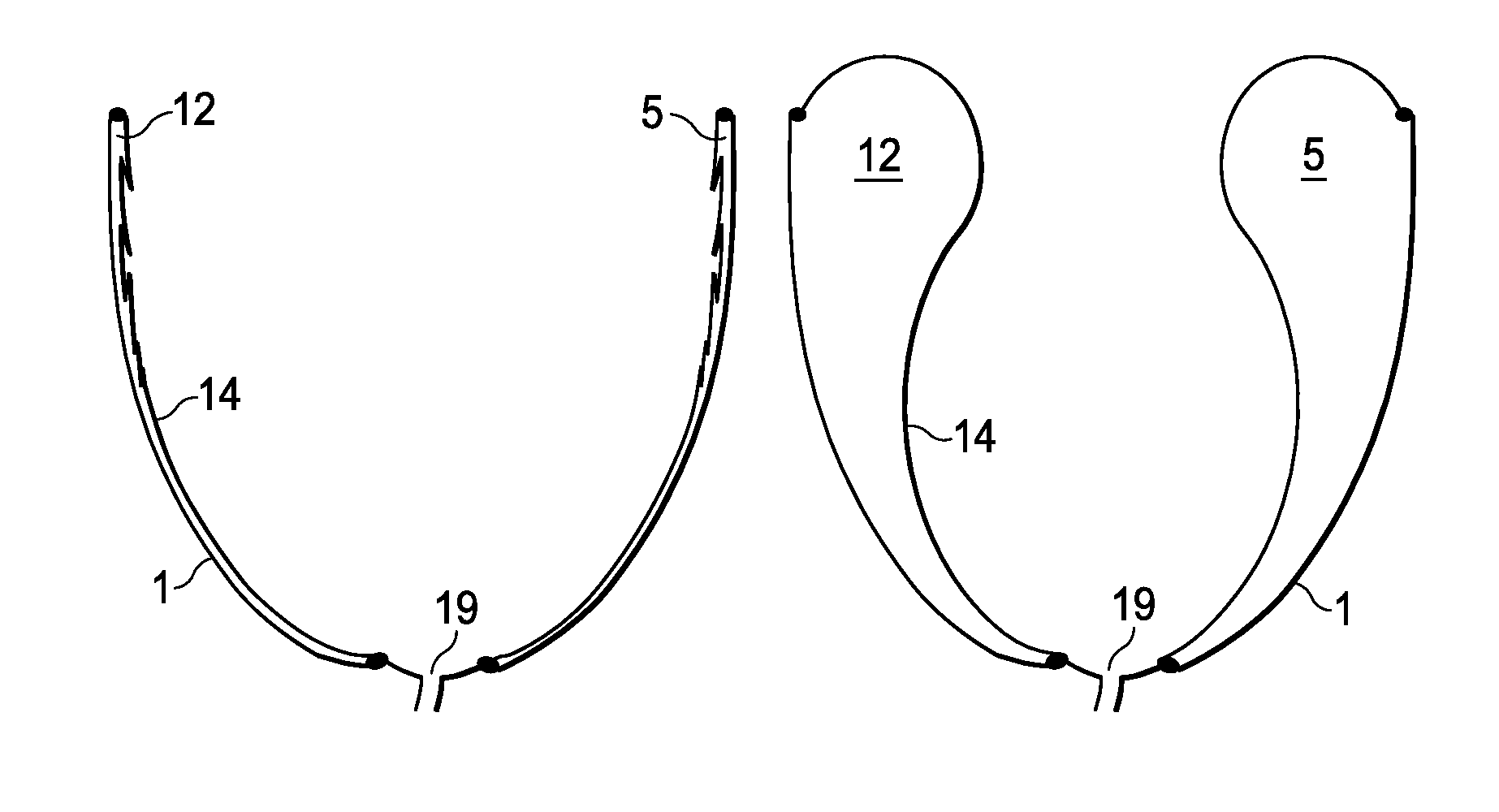
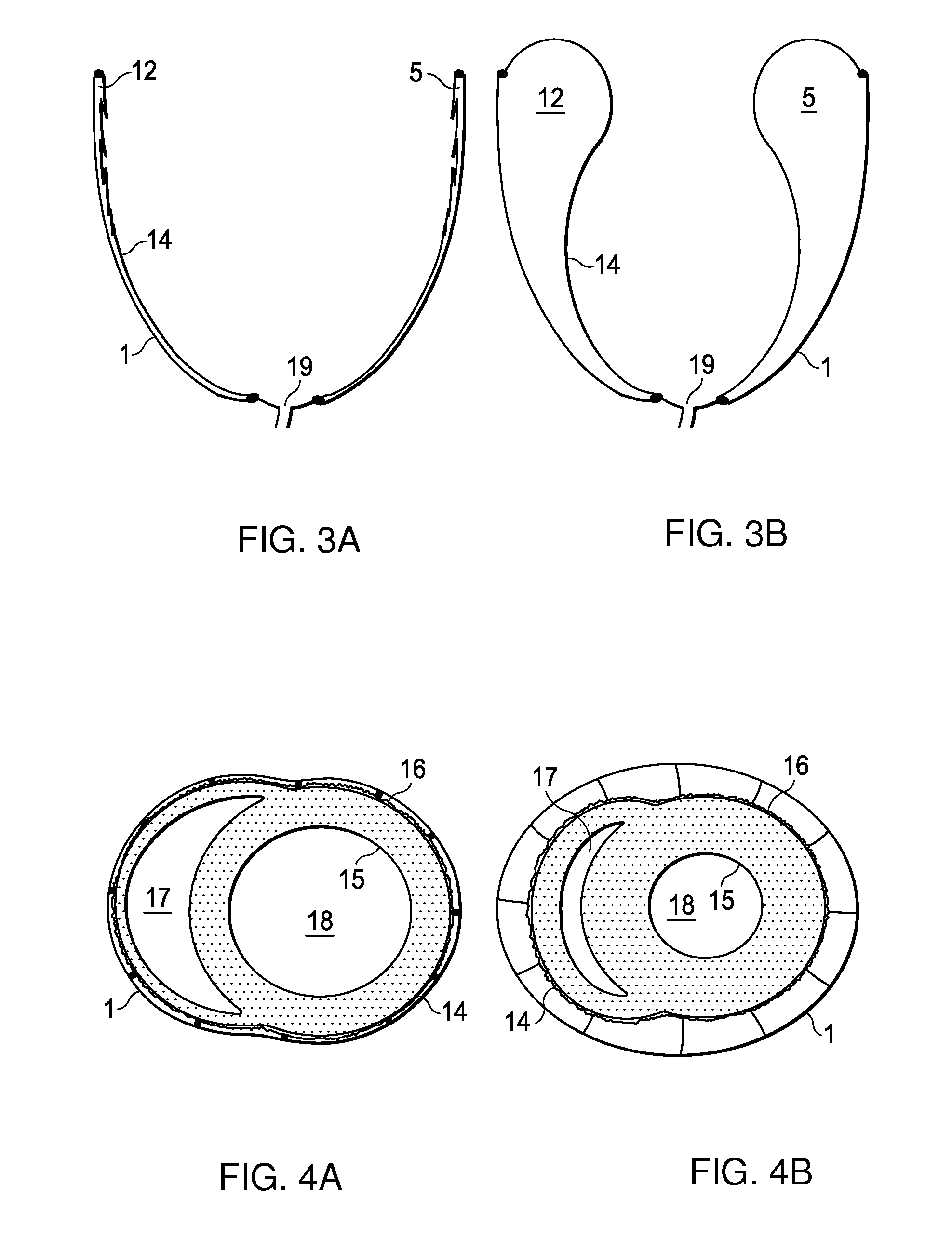
Anatomically approximate prosthetic mitral heart valve
ActiveUS20060293745A1Increase the areaReduce the overall heightAnnuloplasty ringsAnterior leafletMitral annulus
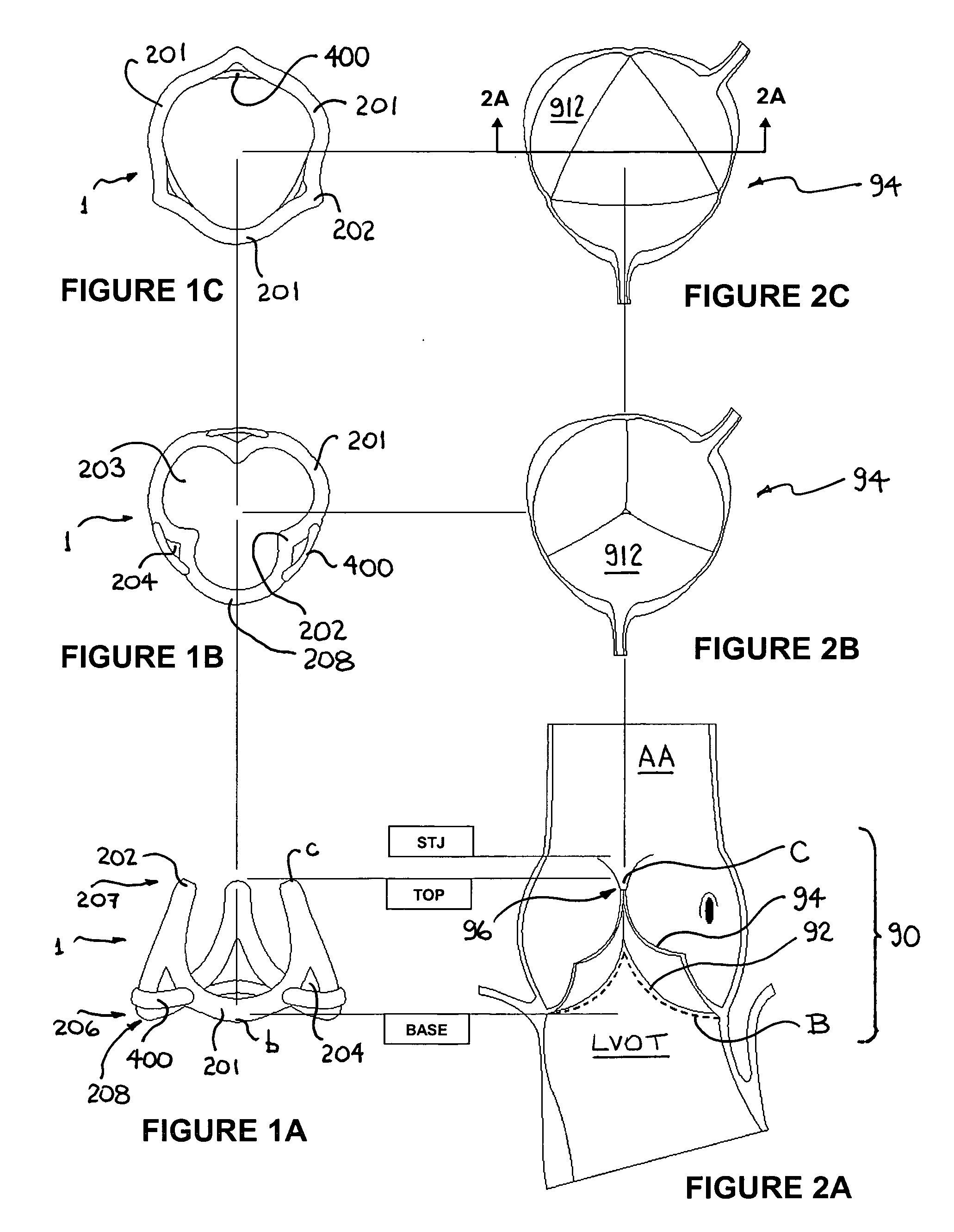
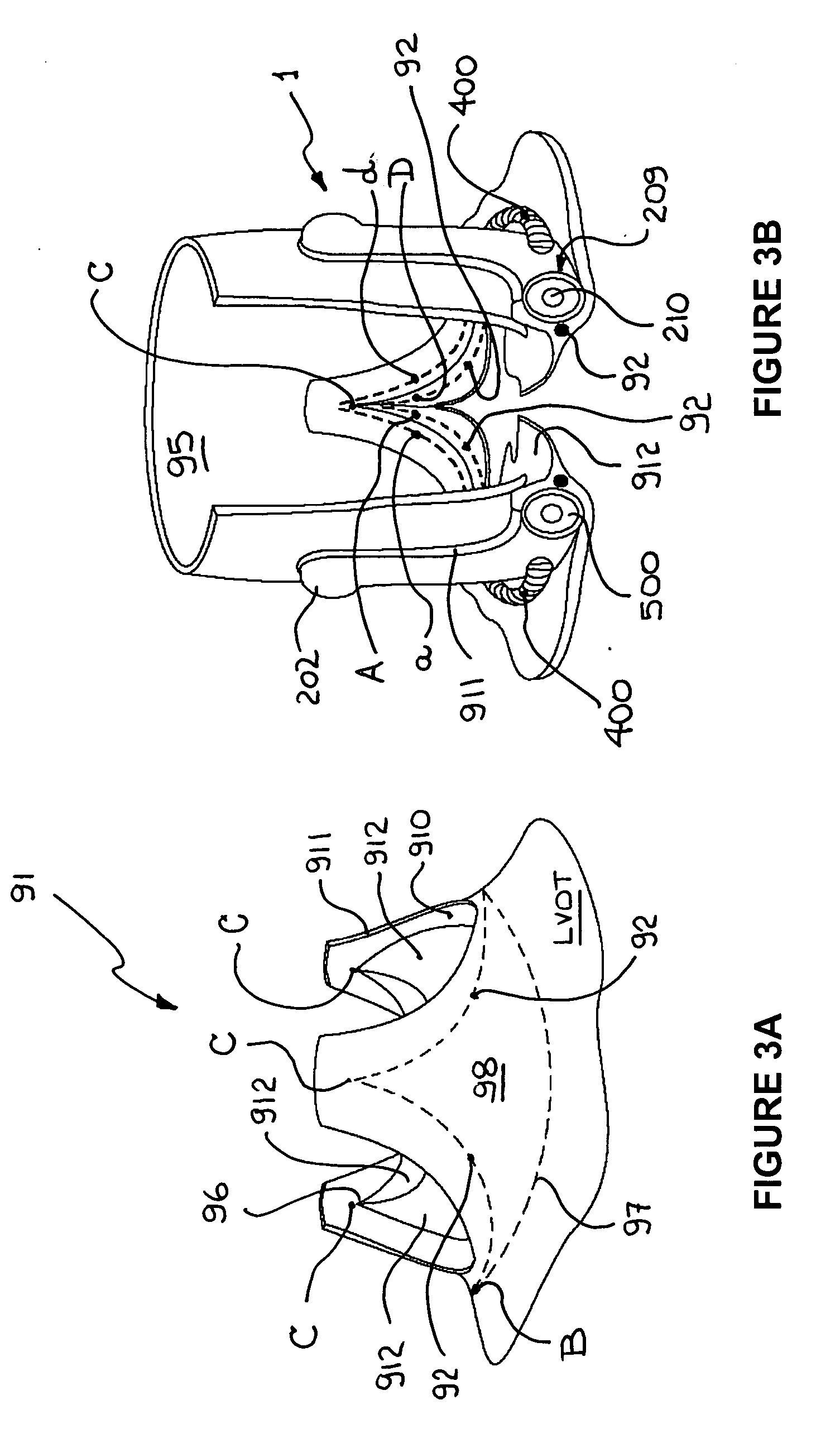
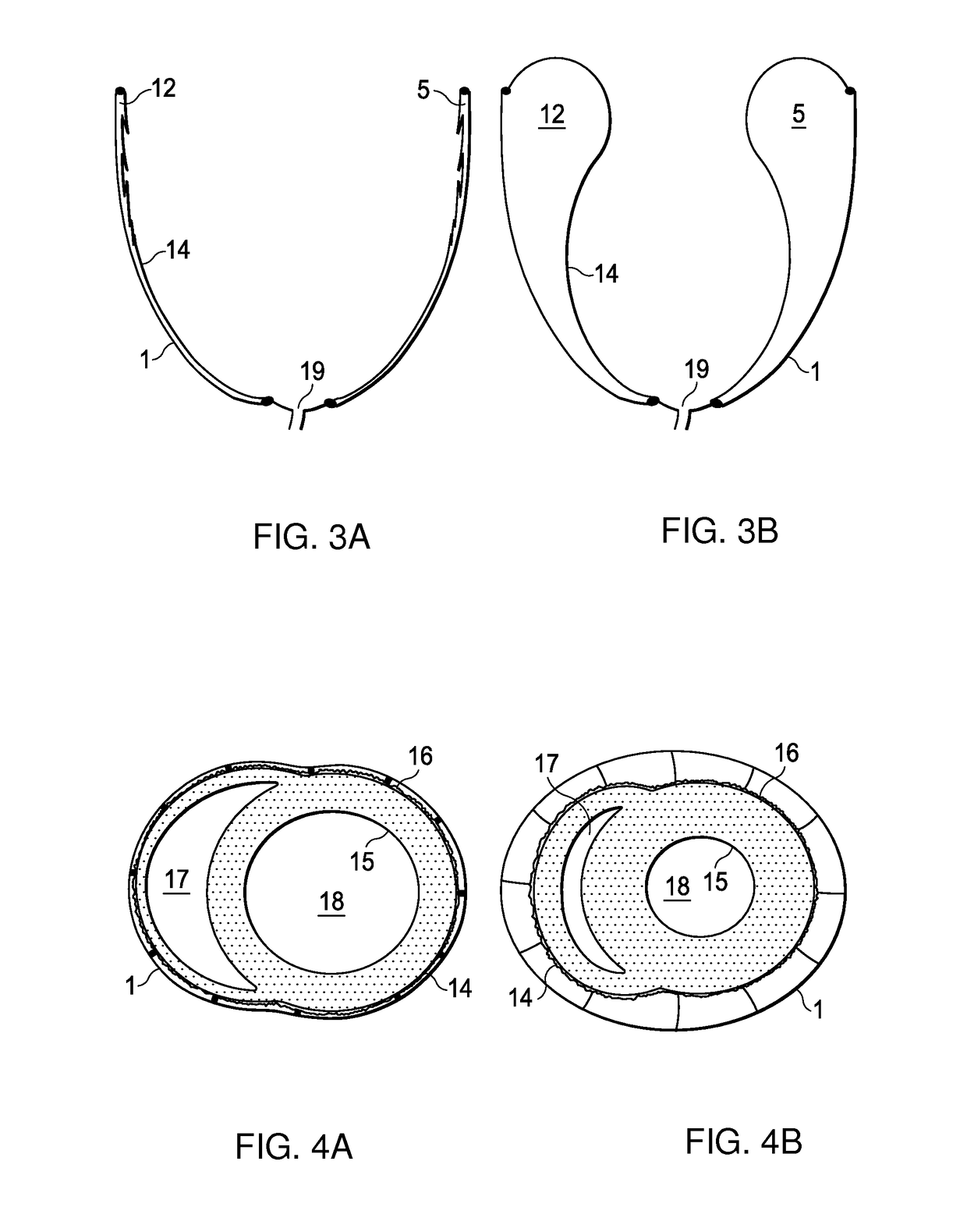
An anatomically approximate prosthetic heart valve includes dissimilar flexible leaflets, dissimilar commissures and / or a non-circular flow orifice. The heart valve may be implanted in the mitral position and have one larger leaflet oriented along the anterior aspect so as to mimic the natural anterior leaflet. Two other smaller leaflets extend around the posterior aspect of the valve. A basic structure providing peripheral support for the leaflets includes two taller commissures on both sides of the larger leaflet, with a third, smaller commissure between the other two leaflets. The larger leaflet may be thicker and / or stronger than the other two leaflets. The base structure defines a flow orifice intended to simulate the shape of the mitral annulus during the systolic phase. For example, the flow orifice may be elliptical. A relatively wide sewing ring has a contoured inflow end and is attached to the base structure in such a way that the valve can be implanted in an intra-atrial position and the taller commissures do not extend too far into the left ventricle, therefore avoiding injury to the ventricle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Aortic annuloplasty ring
ActiveUS20060015179A1Preserve and restore normal aortic rootPreserve and restore and valve leafletAnnuloplasty ringsBlood vesselsCardiac cycleAnnuloplasty rings
An annuloplasty ring to resize a dilated aortic root during valve sparing surgery includes a scalloped space frame having three trough sections connected to define three crest sections. The annuloplasty ring is mounted outside the aortic root, and extends in height between a base plane and a spaced apart commissure plane of the aortic root. At least two adjacent trough sections are coupled by an annulus-restraining member or tether that limits the maximum deflection of the base of the annuloplasty ring. In use, the tether is preferably located in proximity to the base plane of the aortic root. The annuloplasty ring is movable between a first, substantially conical configuration occurring during a diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle, and a second, substantially cylindrical configuration occurring during a systolic phase of the cardiac cycle. The attachment of the annuloplasty ring in proximity to the cardiac valve annulus allows the ring to regulate the dimensions of a dynamic aortic root during the different phases of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:CORONEO
Contraction status assessment
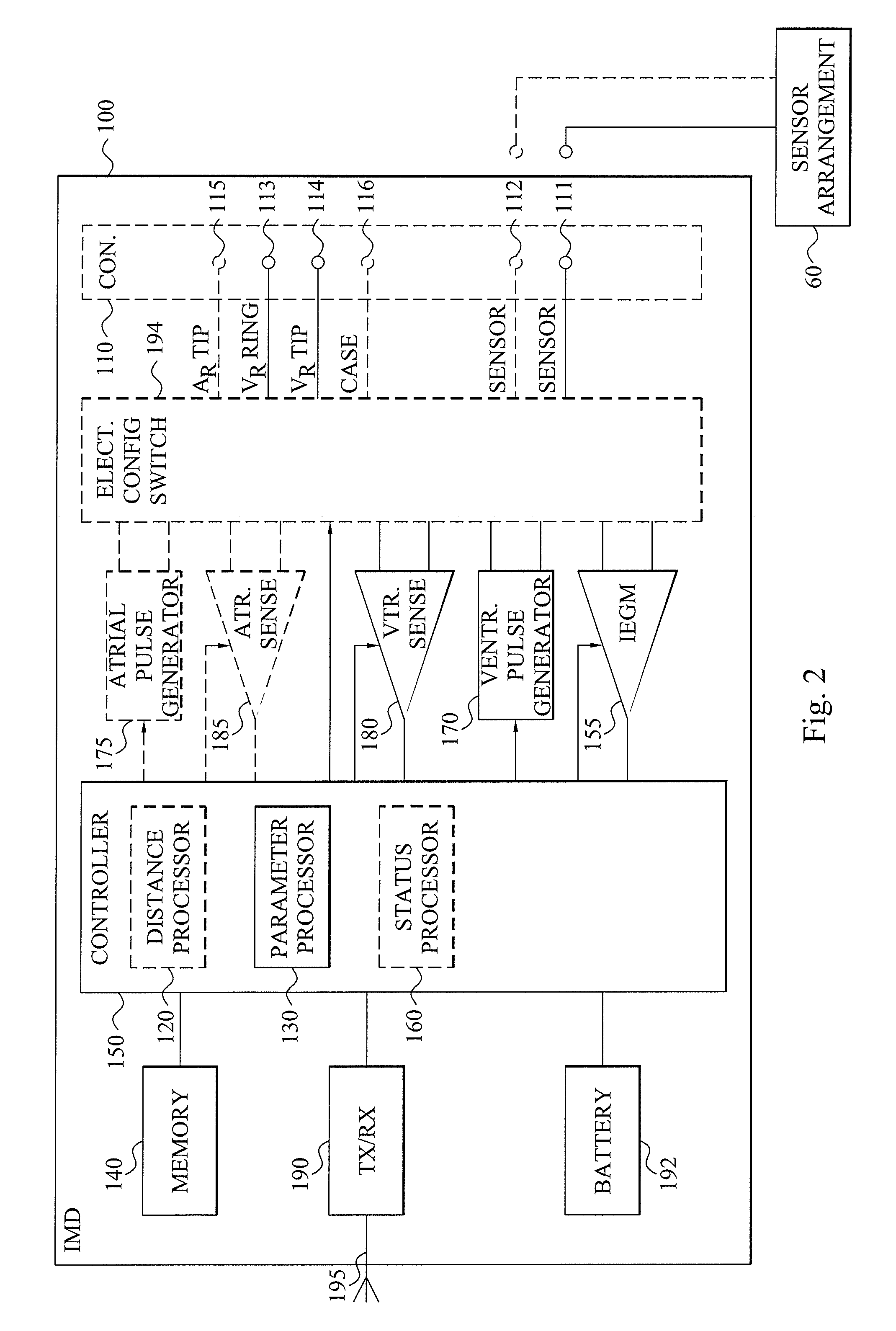
An implantable medical device receives at least one sensor signal representing inter-movement between a basal region of a heart ventricle and a ventricle apex during at least a portion of a systolic phase of a cardiac cycle. A parameter processor calculates a contraction status parameter value based on the at least one sensor signal. This contraction status parameter value represents an elongation of the ventricle following onset of ventricular activation during a cardiac cycle. The contraction status parameter value is stored in a memory as a diagnostic parameter representing a current contraction status of a subject's heart.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Anatomically Approximate Prosthetic Mitral Valve
ActiveUS20110015731A1Increase the areaReduce the overall heightAnnuloplasty ringsProsthetic heartLeft ventricle wall
An anatomically approximate prosthetic heart valve includes dissimilar flexible leaflets, dissimilar commissures and / or a non-circular flow orifice. The heart valve may be implanted in the mitral position and have one larger leaflet oriented along the anterior aspect so as to mimic the natural anterior leaflet. Two other smaller leaflets extend around the posterior aspect of the valve. A basic structure providing peripheral support for the leaflets includes two taller commissures on both sides of the larger leaflet, with a third, smaller commissure between the other two leaflets. The larger leaflet may be thicker and / or stronger than the other two leaflets. The base structure defines a flow orifice intended to simulate the shape of the mitral annulus during the systolic phase. For example, the flow orifice may be elliptical. A relatively wide sewing ring has a contoured inflow end and is attached to the base structure in such a way that the valve can be implanted in an intra-atrial position and the taller commissures do not extend too far into the left ventricle, therefore avoiding injury to the ventricle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Anatomically approximate prosthetic mitral heart valve
ActiveUS7871435B2Increase the areaReduce the overall heightAnnuloplasty ringsProsthetic heartLeft ventricle wall
An anatomically approximate prosthetic heart valve includes dissimilar flexible leaflets, dissimilar commissures and / or a non-circular flow orifice. The heart valve may be implanted in the mitral position and have one larger leaflet oriented along the anterior aspect so as to mimic the natural anterior leaflet. Two other smaller leaflets extend around the posterior aspect of the valve. A basic structure providing peripheral support for the leaflets includes two taller commissures on both sides of the larger leaflet, with a third, smaller commissure between the other two leaflets. The larger leaflet may be thicker and / or stronger than the other two leaflets. The base structure defines a flow orifice intended to simulate the shape of the mitral annulus during the systolic phase. For example, the flow orifice may be elliptical. A relatively wide sewing ring has a contoured inflow end and is attached to the base structure in such a way that the valve can be implanted in an intra-atrial position and the taller commissures do not extend too far into the left ventricle, therefore avoiding injury to the ventricle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
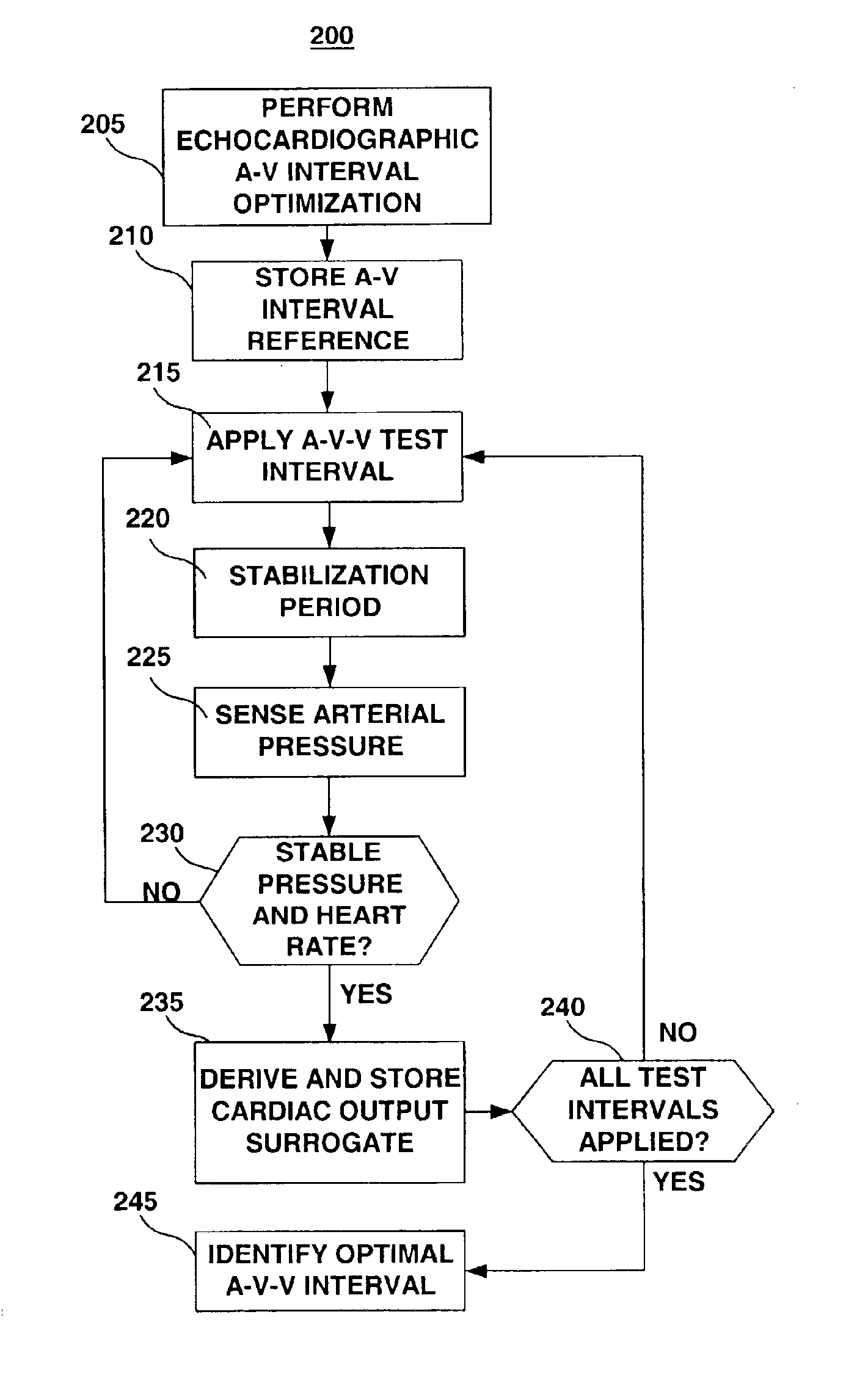
Method and apparatus for optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy
InactiveUS6871088B2Shorten the timeLower requirementCatheterHeart stimulatorsBlood flowBlood pressure
A method and apparatus for optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy are provided. An iterative optimization procedure is performed to test the systolic hemodynamic effects of varying A-V-V timing schemes. The hemodynamic effect is assessed based on a surrogate of stroke volume. The stroke volume surrogate is derived from a sensor signal proportional to the blood pressure in the aorta or a major artery. The A-V-V timing scheme corresponding to the greatest stroke volume, as indicated by the stroke volume surrogate, is identified and automatically programmed to maintain optimal A-V-V settings acutely and chronically.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac pump with speed adapted for ventricle unloading
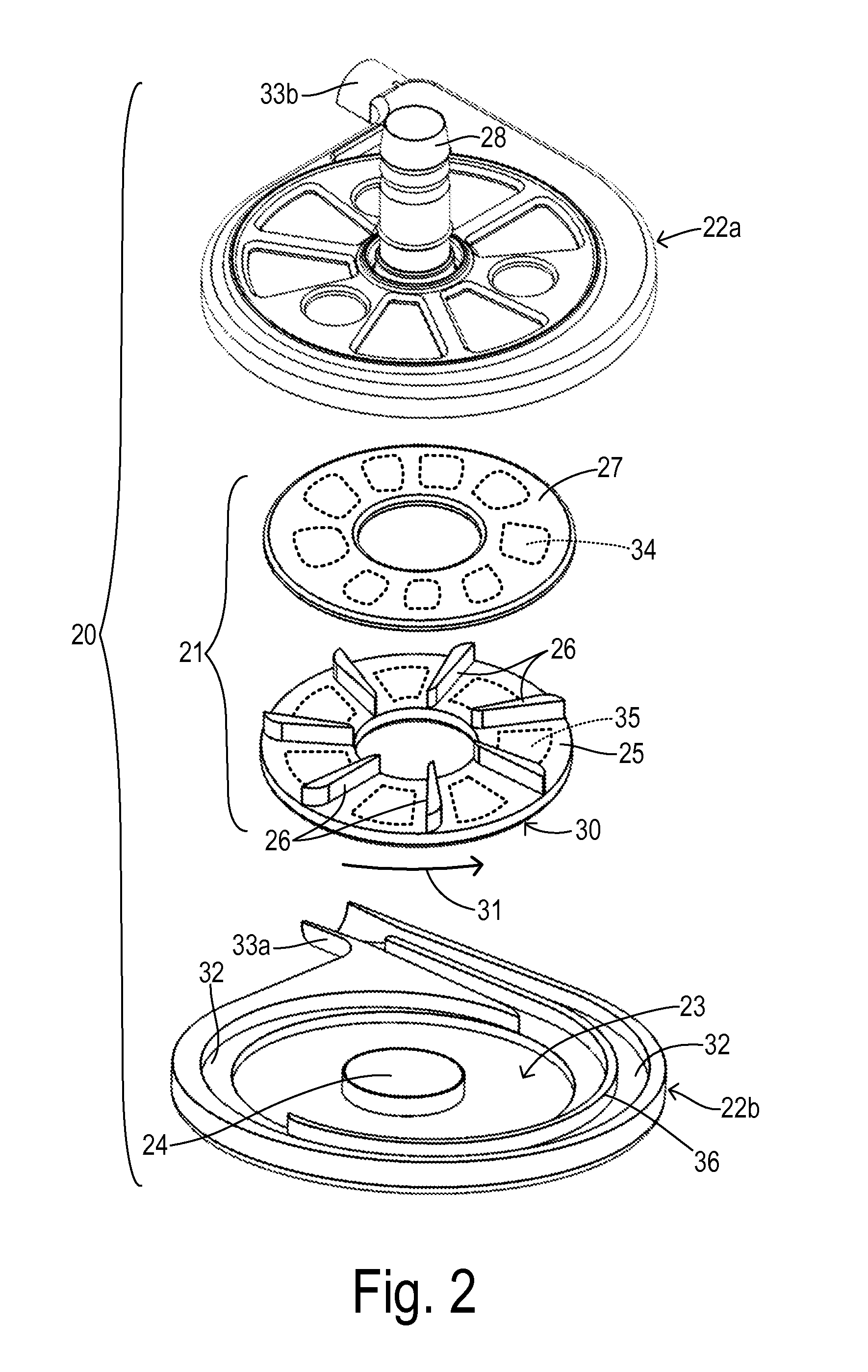
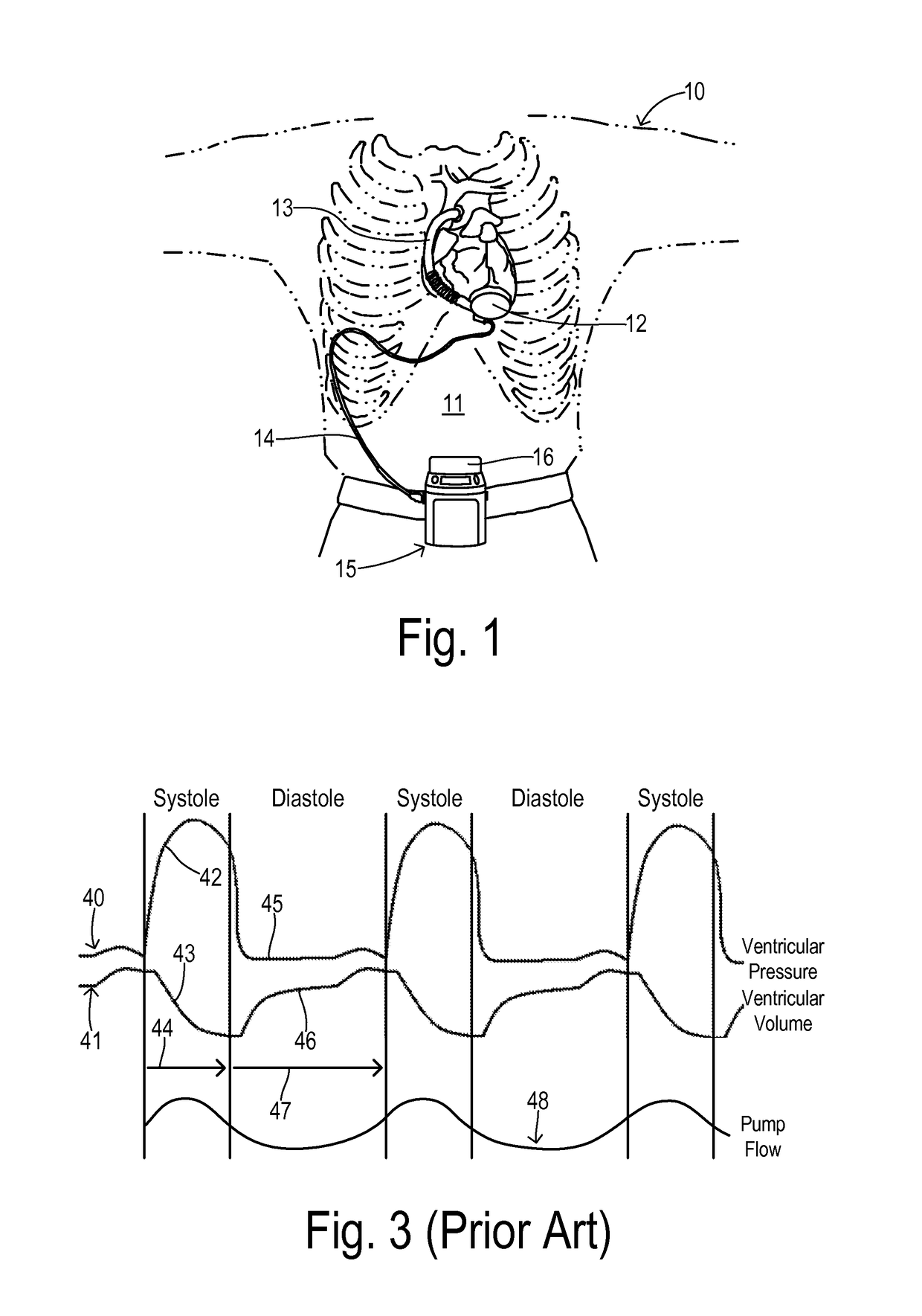
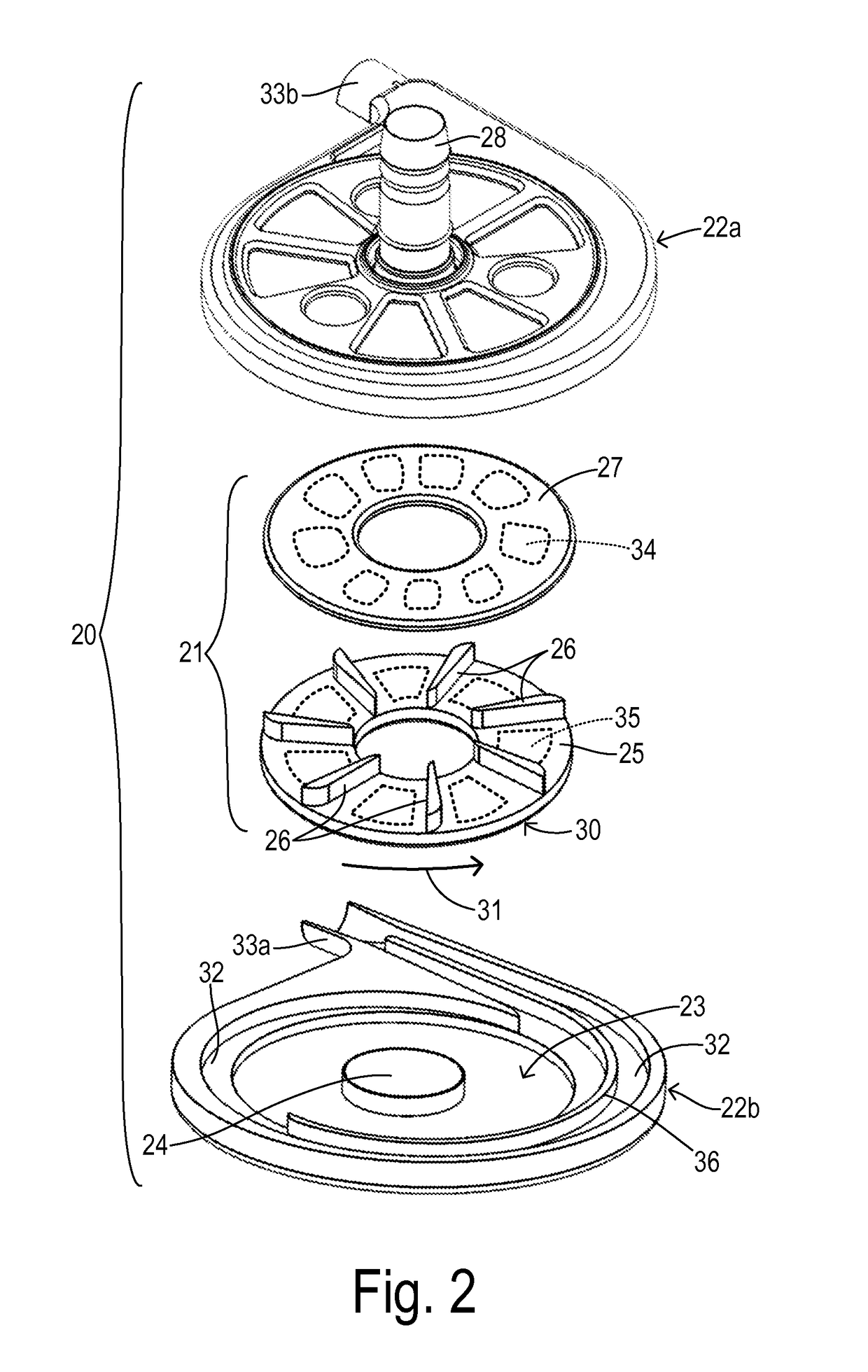
ActiveUS20140323796A1Readily contractedReduce resistanceControl devicesBlood pumpsImpellerPump chamber
A blood pump system is implantable in a patient for ventricular support. A pumping chamber has an inlet for receiving blood from a ventricle of the patient. An impeller is received in the pumping chamber. A motor is coupled to the impeller for driving rotation of the impeller. A motor controller is provided for tracking systolic and diastolic phases of a cardiac cycle of the patient and supplying a variable voltage signal to the motor in a variable speed mode to produce a variable impeller speed linked to the cardiac cycle. The impeller speed comprises a ramping up to an elevated speed during the diastolic phase in order to reduce a load on the ventricle at the beginning of the systolic phase.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Cardiac pump with speed adapted for ventricle unloading
A blood pump system is implantable in a patient for ventricular support. A pumping chamber has an inlet for receiving blood from a ventricle of the patient. An impeller is received in the pumping chamber. A motor is coupled to the impeller for driving rotation of the impeller. A motor controller is provided for tracking systolic and diastolic phases of a cardiac cycle of the patient and supplying a variable voltage signal to the motor in a variable speed mode to produce a variable impeller speed linked to the cardiac cycle. The impeller speed comprises a ramping up to an elevated speed during the diastolic phase in order to reduce a load on the ventricle at the beginning of the systolic phase.
Owner:TC1 LLC
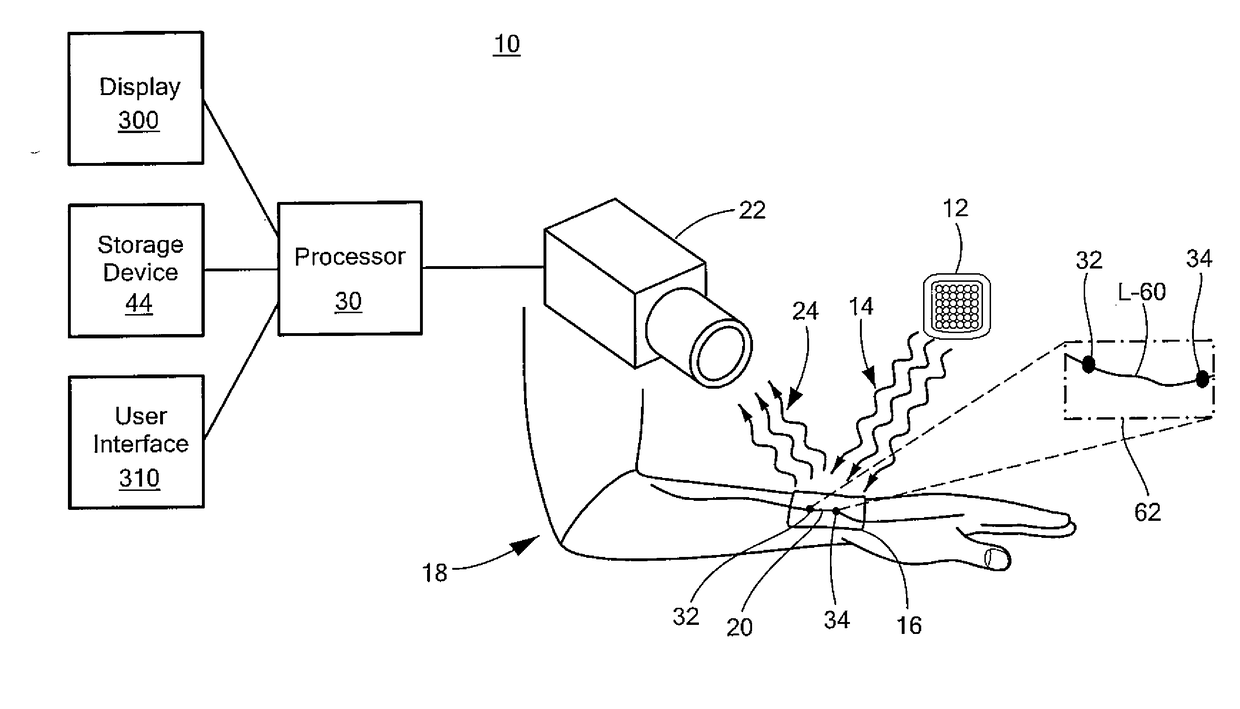
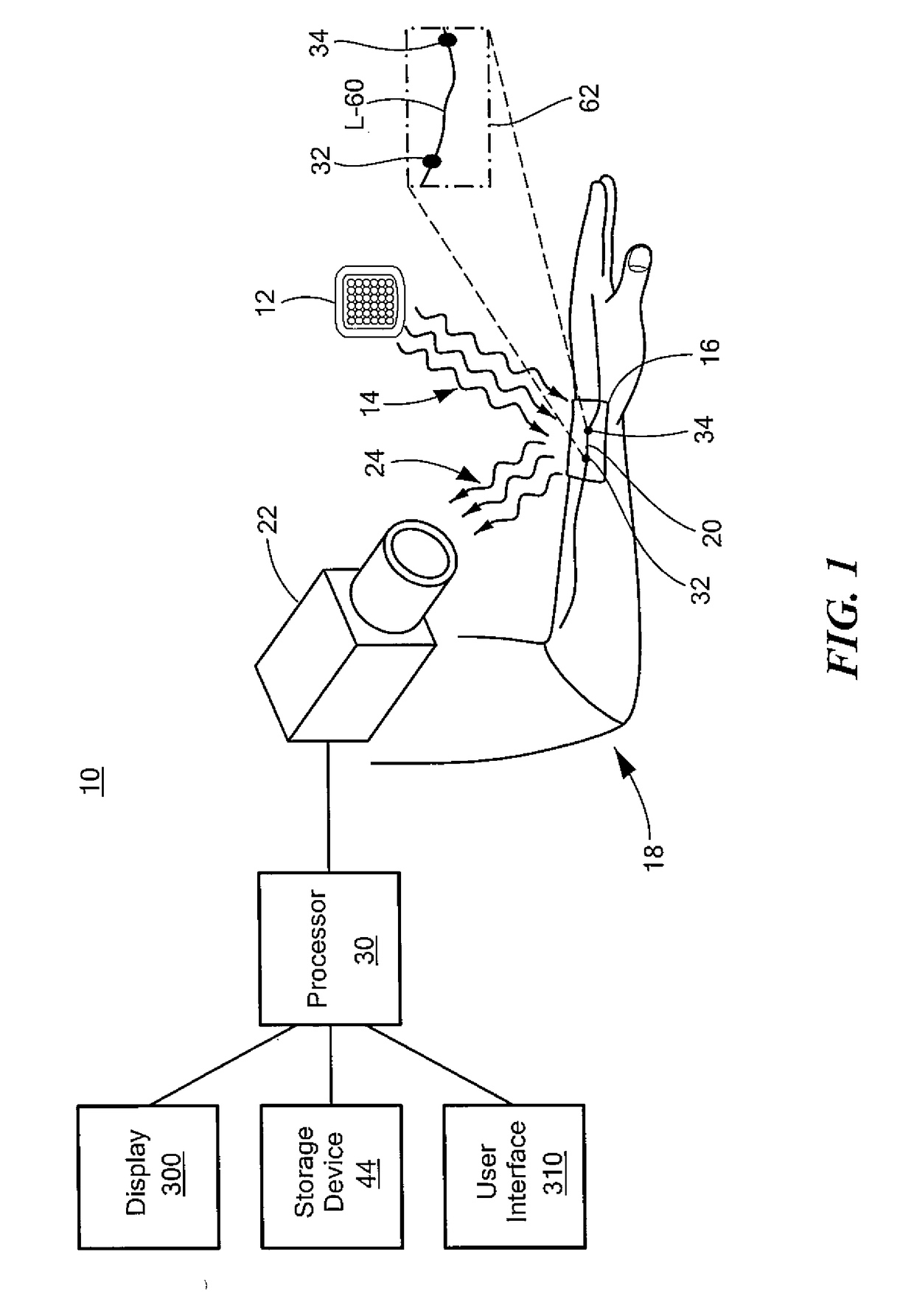
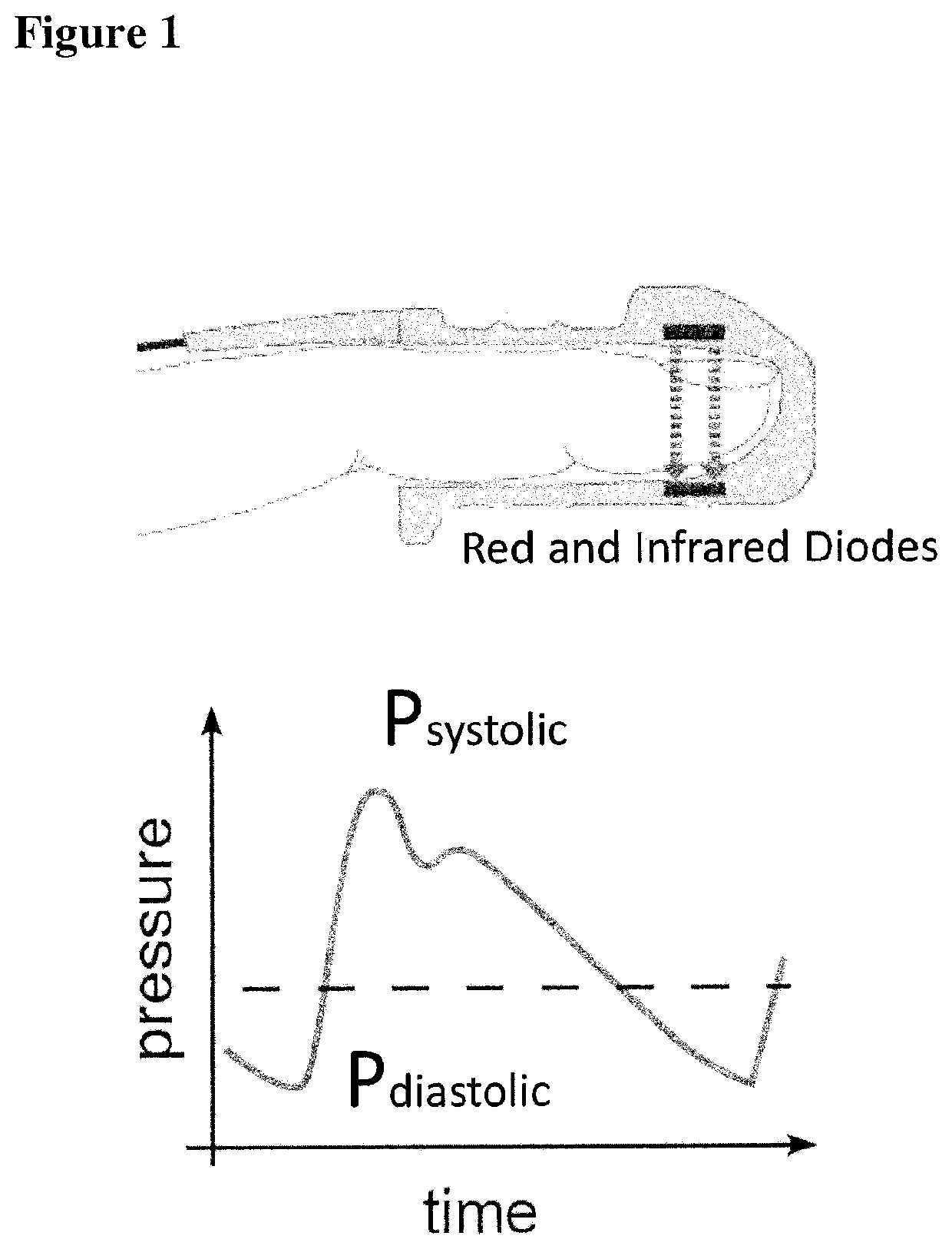
Contactless System and Method For Measuring and Continuously Monitoring Arterial Blood Pressure
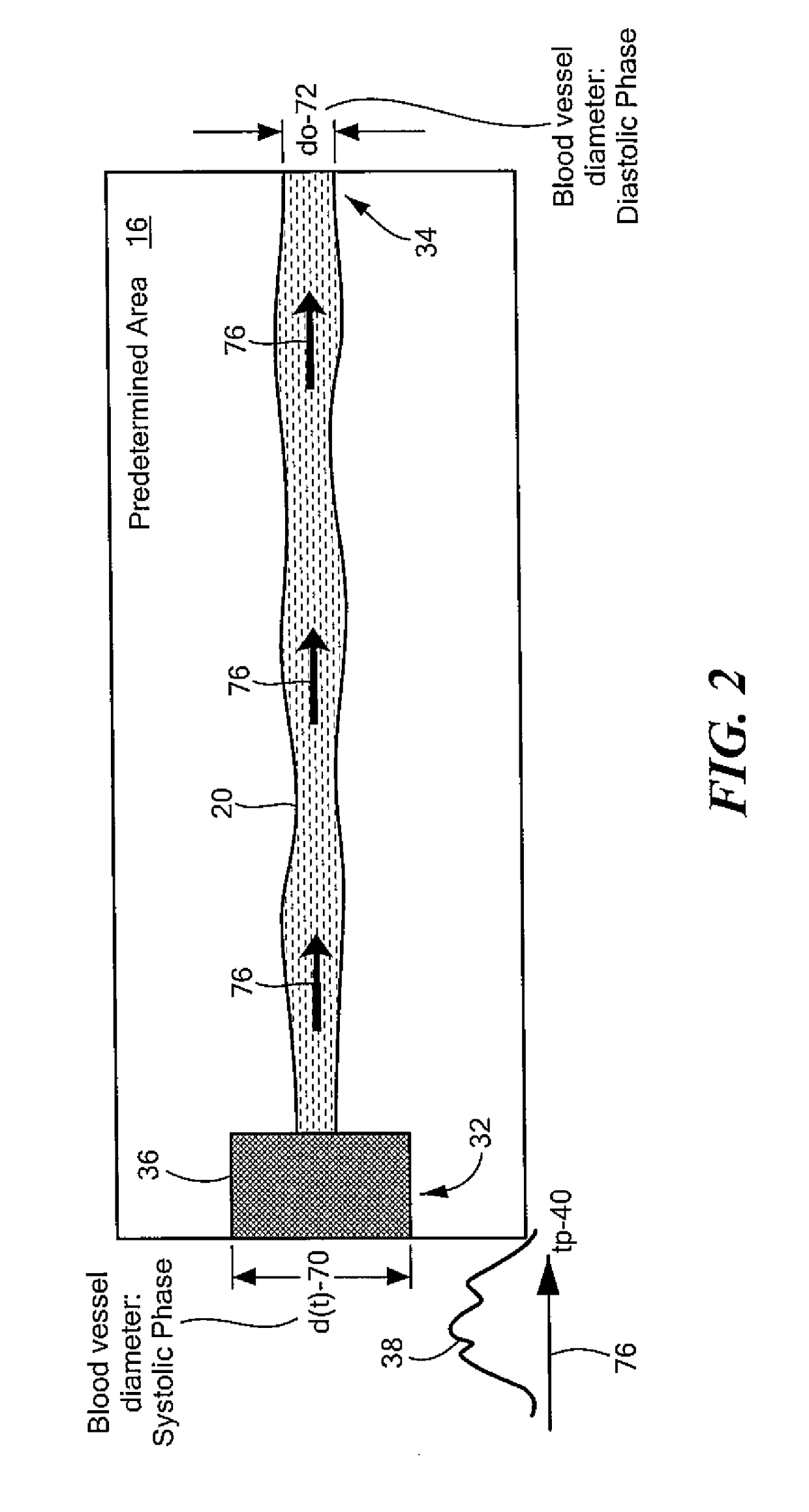
A contactless system for measuring and continuously monitoring arterial blood pressure includes a light source configured to illuminate light having at least one predetermined wavelength at a predetermined area of a human subject having an artery therein. A detector responsive to reflected light from the predetermined area is configured to continuously acquire images of the artery in the predetermined area. A processor is configured to process the images and determine: when an image at a proximal location of the predetermined area is darker indicating transition of a pulse wave into the artery at the proximal location and at a proximal time and when an image at a distal location of the predetermined area is darker indicating transition of the pulse wave into the artery at a distal location at a distal time, determine the difference in time between the distal time and the proximal time to calculate a pulse transit time (PTT), determine a length between the proximal location and the distal location, determine a diameter of the artery during a systolic phase of a cardiac pulse, determine a diameter of the artery during a diastolic phase of a cardiac pulse, calculate a pulse wave velocity of the pulse wave, calculate pulse pressure (ΔP), calculate an elastic modulus (E) of the artery, and contactlessly and continuously calculate the arterial blood pressure for each cardiac cycle of the human subject.
Owner:VIVONICS
Systems and methods for heart valve therapy
ActiveCN107613908AReduced risk of cloggingReduce adverse health conditionsStentsHeart valvesAnatomical structuresBlood flow
Prosthetic mitral valves described herein can be deployed using a transcatheter mitral valve delivery system and technique to interface and anchor in cooperation with the anatomical structures of a native mitral valve. This document describes prosthetic heart valve designs and techniques to manage blood flow through the left ventricular outflow tract. For example, this document describes prosthetic heart valve designs and techniques that reduce or prevent obstructions of the left ventricular outflow tract that may otherwise result from systolic anterior motion of an anterior leaflet of the native mitral valve.
Owner:CAISSON INT LLC
Heart valve sealing devices and delivery devices therefor
A valve repair device for repairing a native heart valve of a patient includes a pair of clasps, where each clasp is configured to attach to native valve leaflet. The ends of the pair of clasps can move away from one another to a partially open position when the native valve leaflets open during a diastolic phase of a cardiac cycle, and the ends of the pair of clasps can move toward one another when the native valve leaflets close during a systolic phase of a cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
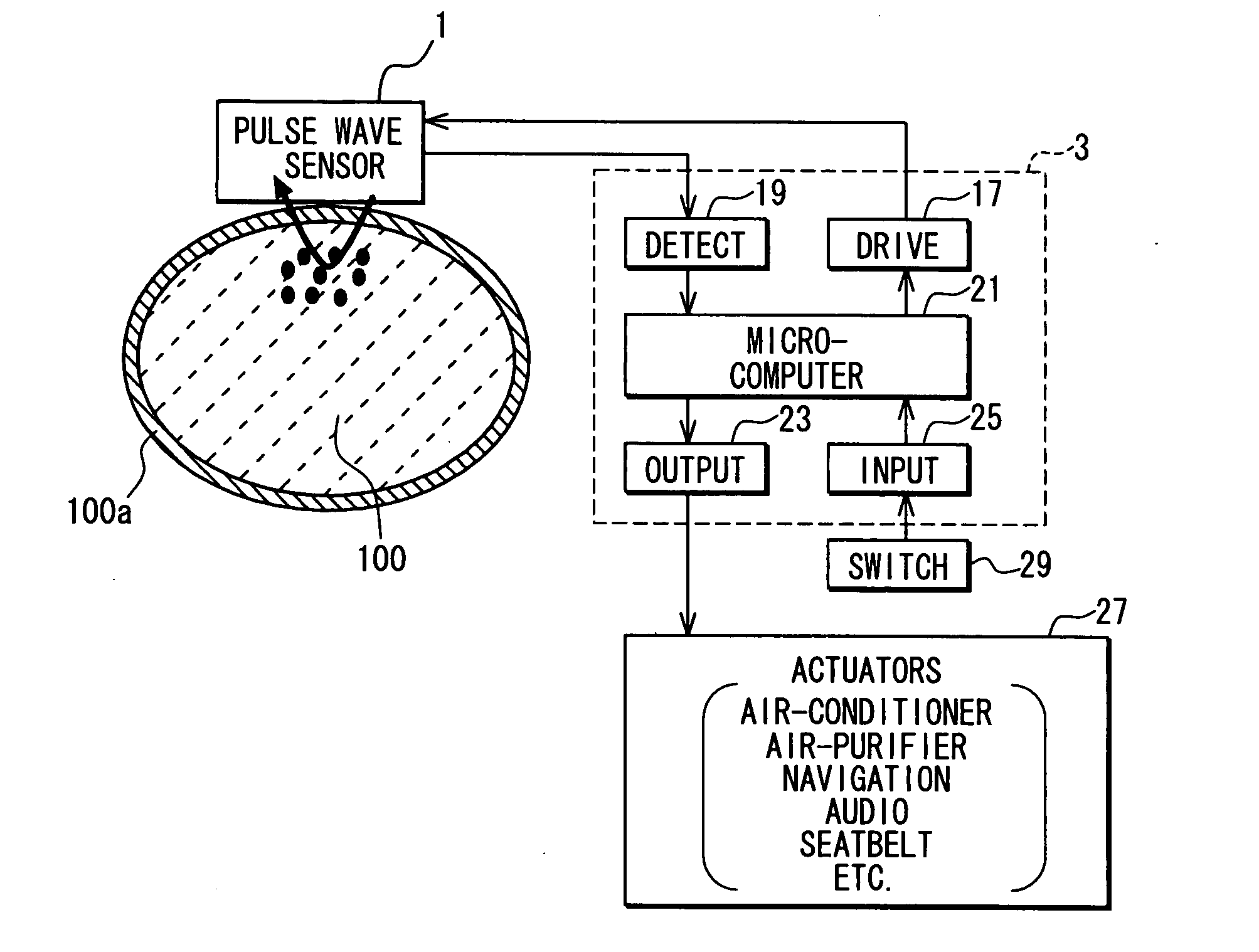
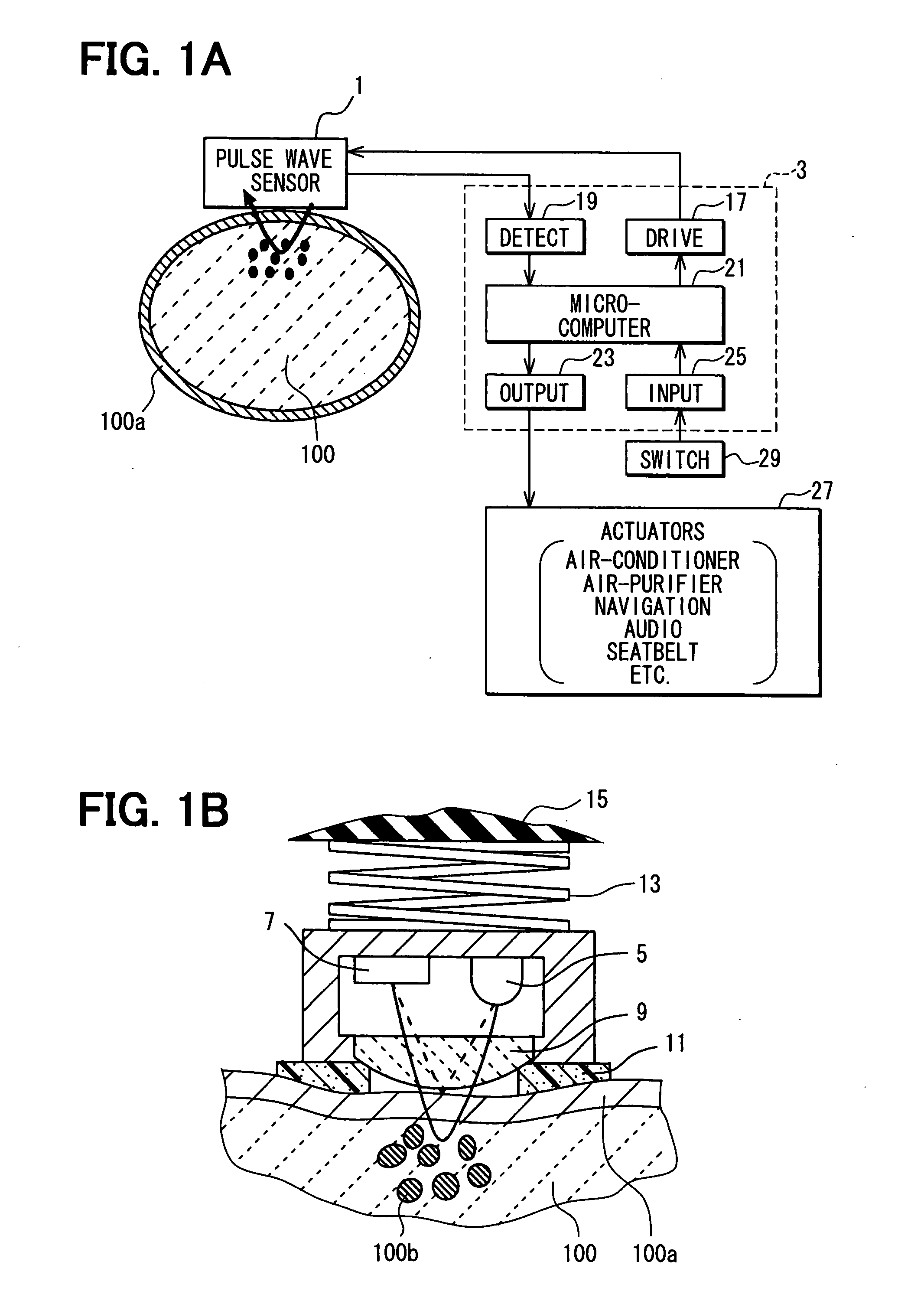
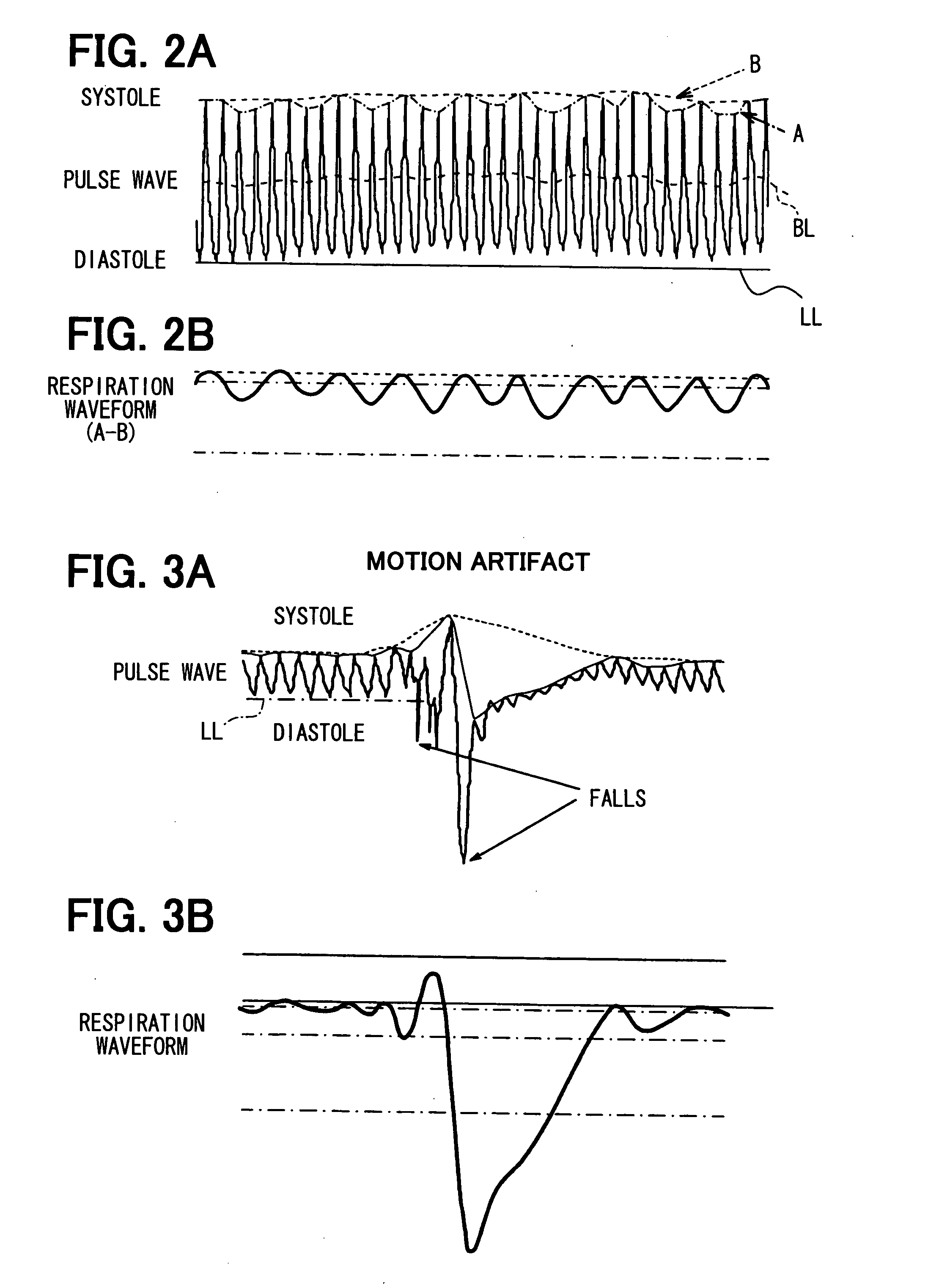
Apparatus for detecting vital functions, control unit and pulse wave sensor
ActiveUS20070282227A1Simple methodAccurate measurementDiagnostics using lightPerson identificationYawnPulse wave
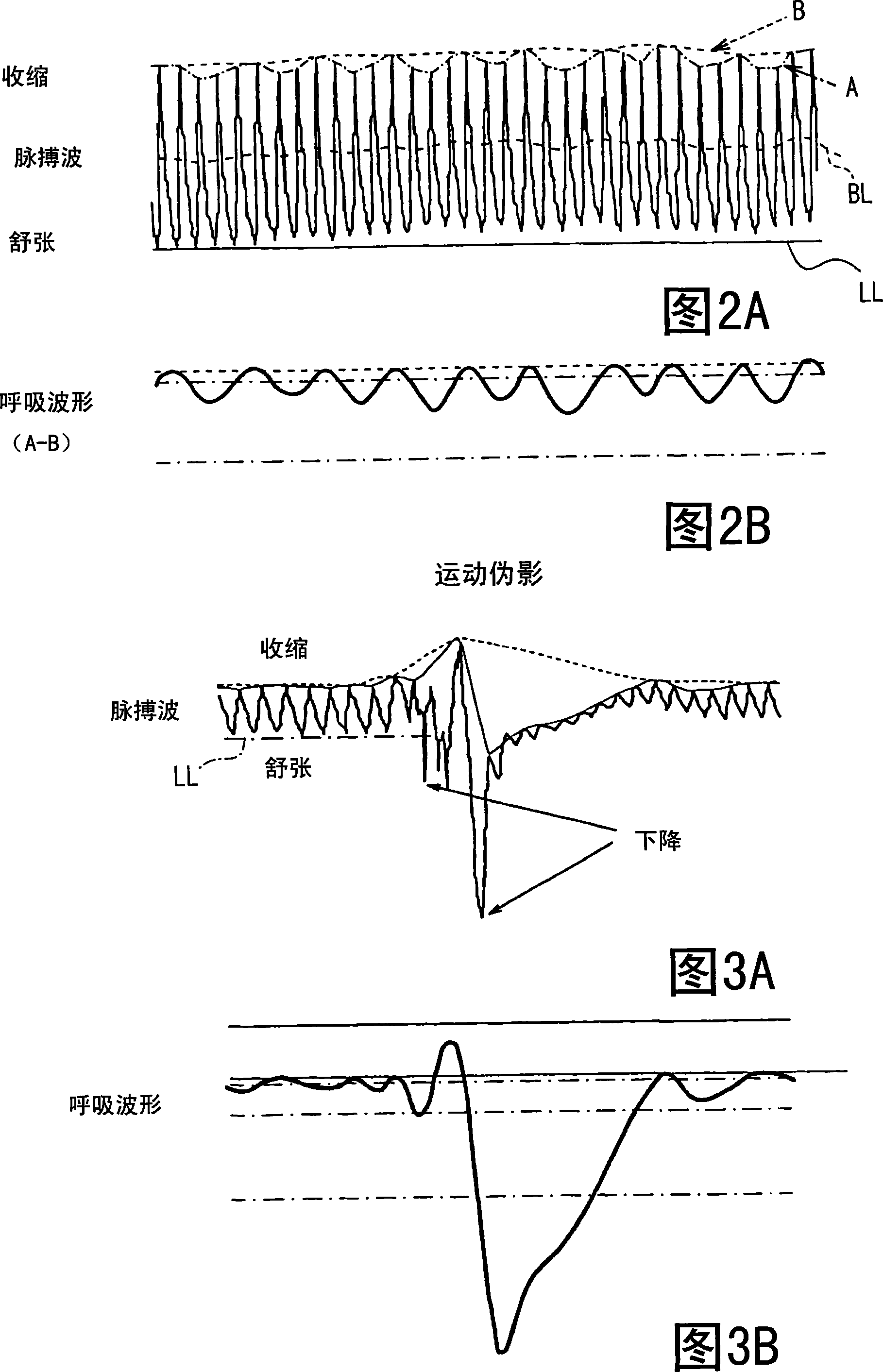
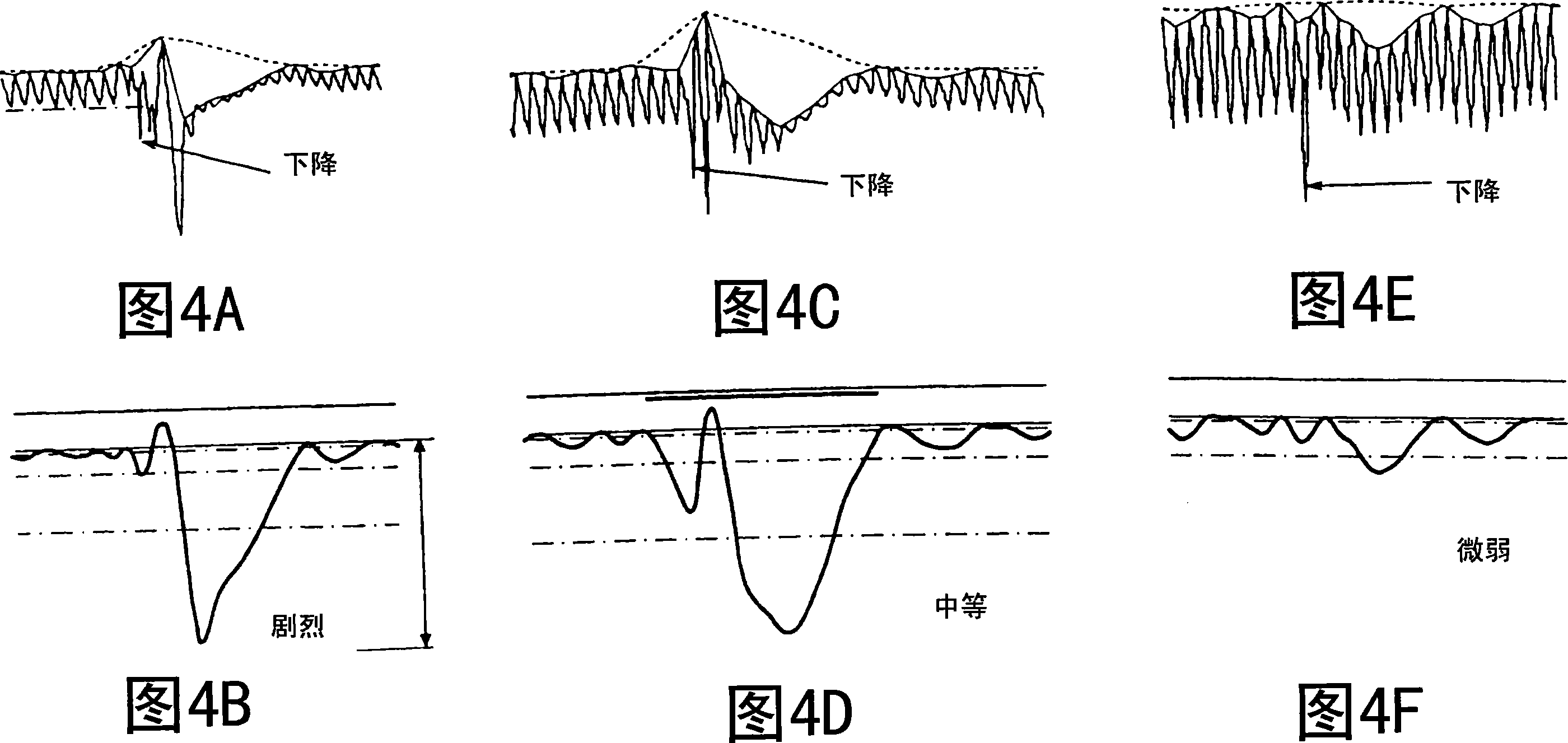
An apparatus for detecting vital functions has a pulse wave sensor attachable to a body and a control unit. The control unit checks if amplitude of pulse wave signals produced from the pulse wave sensor varies. The control unit further checks if a large change in the amplitude during a systolic phase of a pulse wave corresponding to the systolic phase of the heart. If a first large change in the amplitude during a diastolic phase of a pulse wave corresponding to the diastolic phase of the heart, it is highly probable that a motion artifact has occurred. Therefore, a motion artifact flag is set. Next, it is checked if the amplitude in the next diastole is changing by more than 30%. If it is presumed that the occurrence of cough is highly probable, a cough flag is set. If it is neither the motion artifact nor the cough, then a yawn flag is set.
Owner:SHIOMI TOSHIAKI +1
Apparatus and method for diagnosing ischemic heart disease
A region of interest is set at a thin layer on the inside of the left ventricular wall for ecocardiographical apical long-axis tomographic images obtained while at rest, and the strain rate of the set region of interest is calculated. The value of a discriminant function is determined on the basis of a plurality of strain rates of an intermediate portion of the systolic phase. Ischemic heart disease is then diagnosed according to the value of the discriminant function.
Owner:KAKIHARA RI ICHIRO
Apparatus for detecting vital functions, control unit and pulse wave sensor
InactiveCN101081167AEasy to detectImprove coughDiagnostics using lightRespiratory organ evaluationYawnPulse wave
An apparatus for detecting vital functions has a pulse wave sensor (1)attachable to a body and a control unit(3). The control unit checks if amplitude of pulse wave signals produced from the pulse wave sensor (1)varies. The control unit further checks if a large change in the amplitude during a systolic phase of a pulse wave corresponding to the systolic phase of the heart. If a first large change in the amplitude during a diastolic phase of a pulse wave corresponding to the diastolic phase of the heart, it is highly probable that a motion artifact has occurred. Therefore, a motion artifact flag is set. Next, it is checked if the amplitude in the next diastole is changing by more than 30%. If it is presumed that the occurrence of cough is highly probable, a cough flag is set. If it is neither the motion artifact nor the cough, then a yawn flag is set.
Owner:盐见利明
Ventricular assist device and related computer program product
InactiveUS20080045779A1Easily repairableEasily replaceableControl devicesFlexible member pumpsVentricular assistanceDiastolic phase
Owner:NEWCORTEC
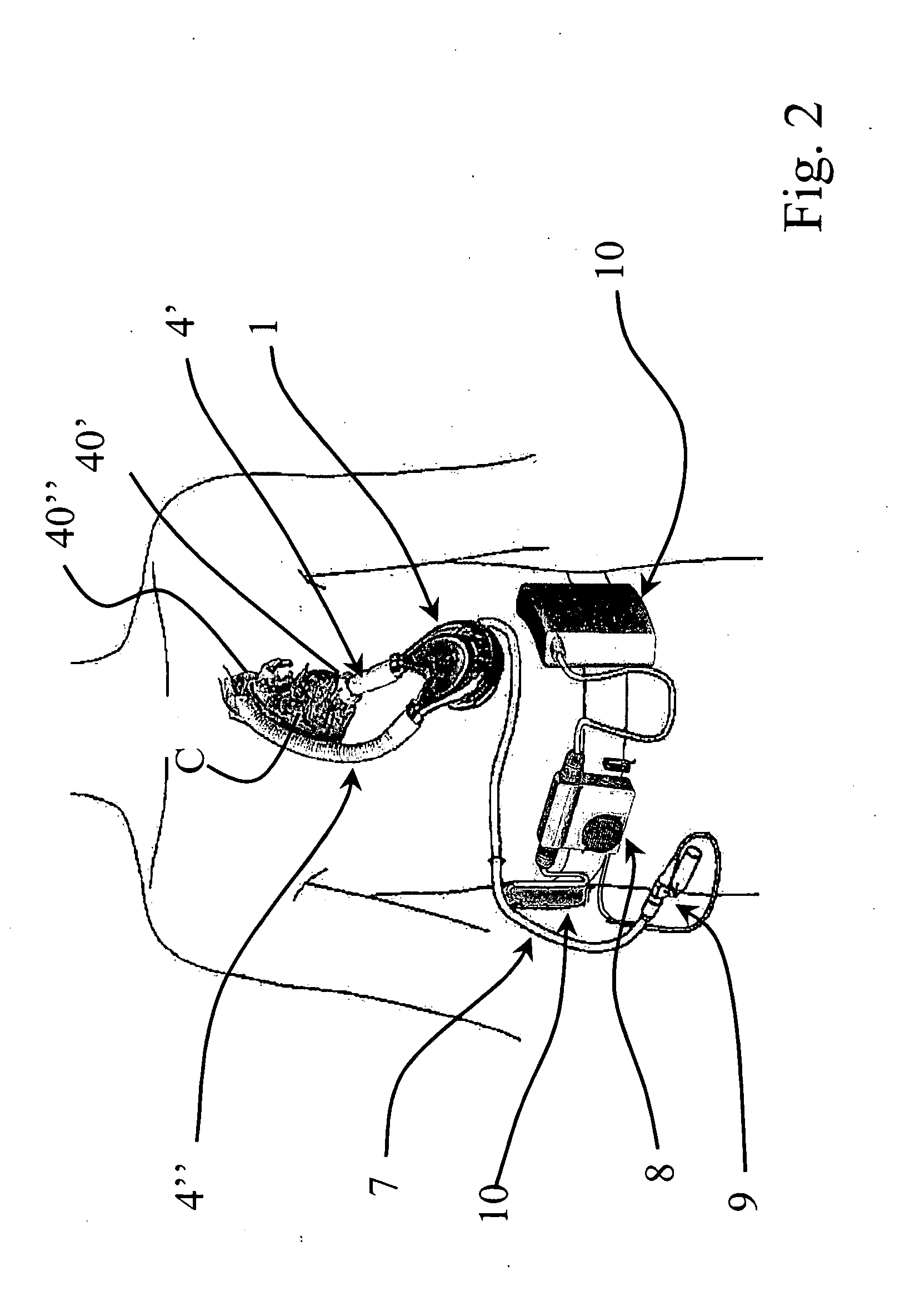
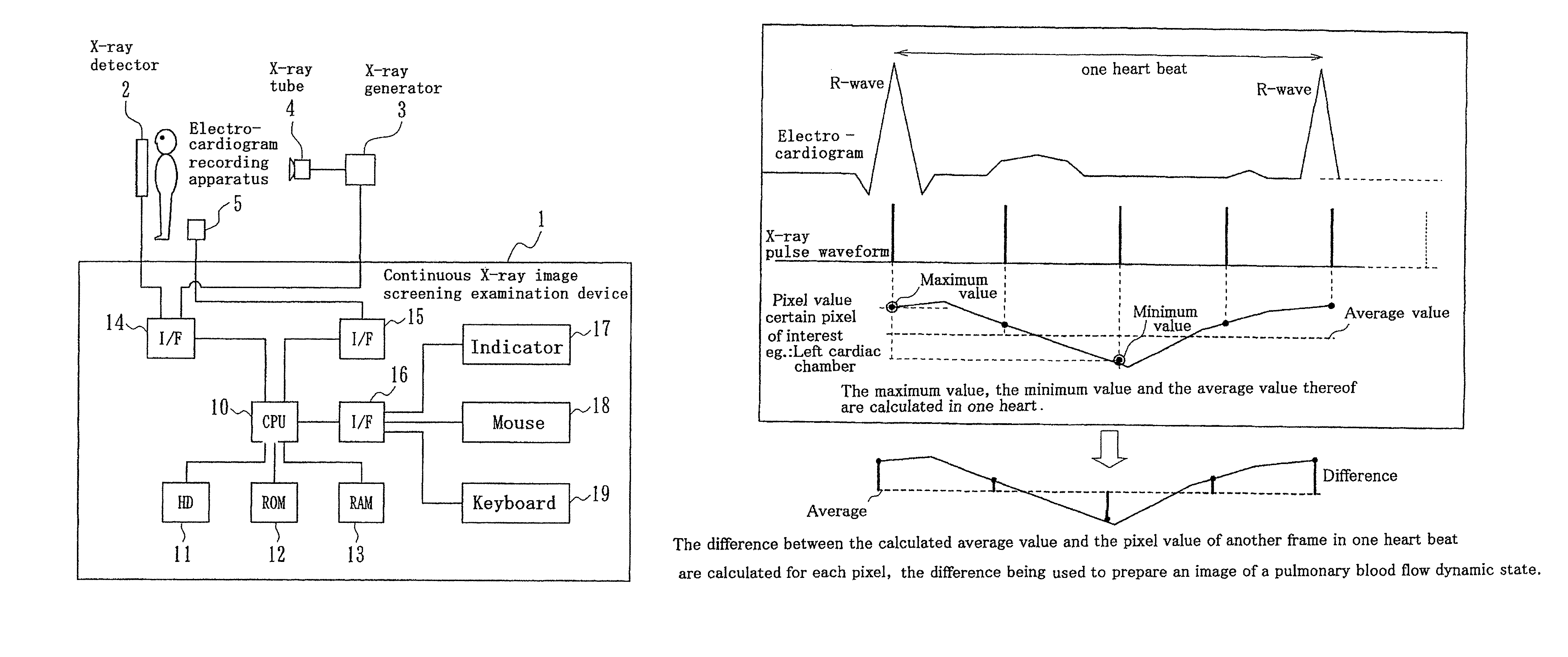
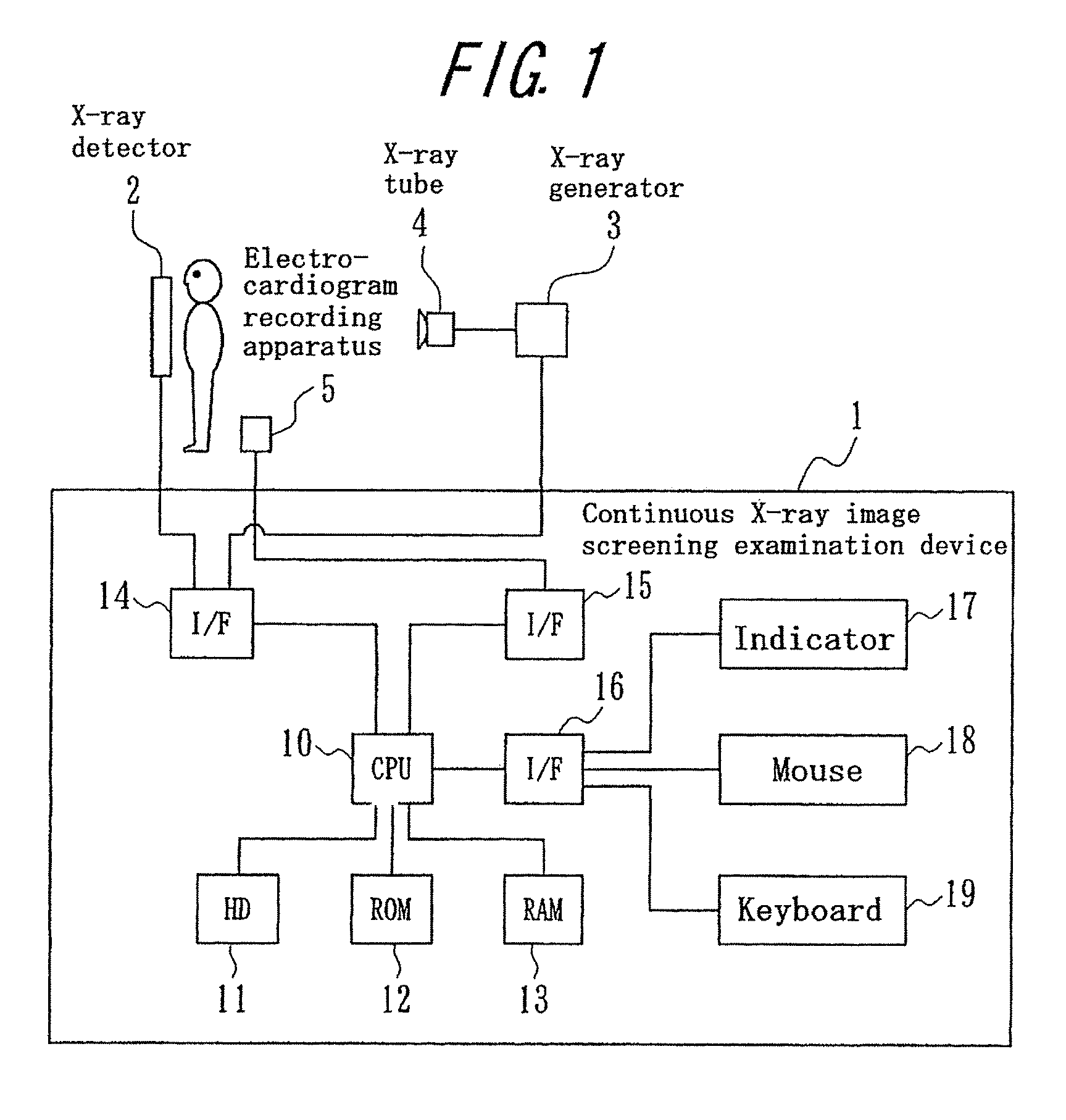
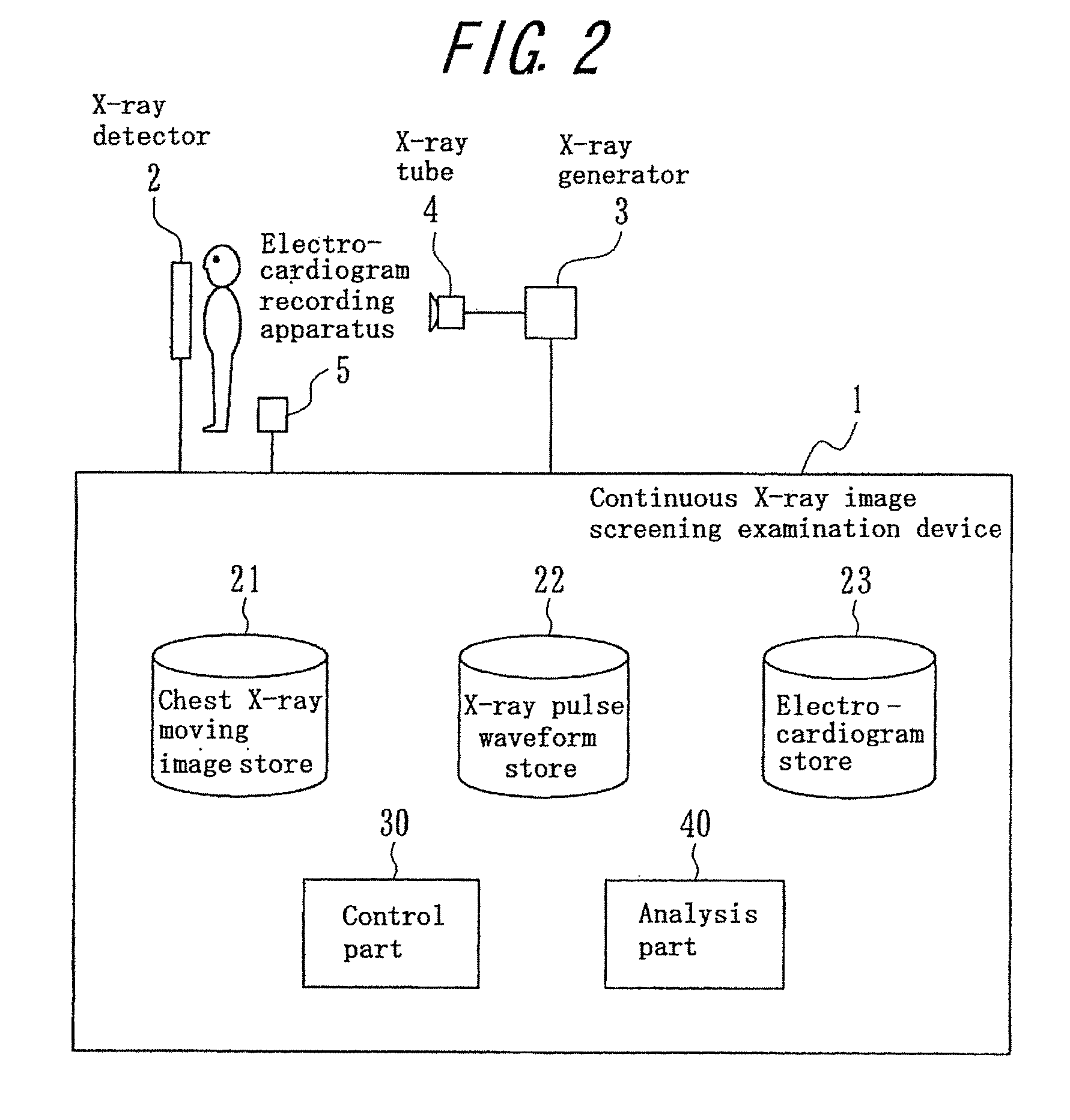
Continuous X-ray image screening examination device, program, and recording medium
InactiveUS8300912B2Simple and convenient generationEffectively utilizableImage enhancementElectrocardiographyX-rayScreening Examination
Using nature that a pixel value in a lung of a chest X-ray moving image varies due to heart beat, the variation information on the pixel value is effectively used for diagnosis such as of a lung embolism or a heart disease, considering the variation information as lung blood flow information. A continuous X-ray image screening examination device receives a chest X-ray moving image from an X-ray detector and receives an electrocardiogram to become original information on a heart beat variation from an electrocardiogram recording apparatus. From the dynamic state of the heart wall measured by the electrocardiograph or the chest X-ray moving image, the heart dynamic state during the cardiac chamber systolic and diastolic phases is grasped, and information such as the variation of the pixel value of the chest X-ray moving image due to increase (lung blood flow increase) of the blood flow from the heart to the lung during the cardiac chamber systolic phase is generated.
Owner:KANAZAWA UNIV
Diastolic recoil method and device for treatment of cardiac pathologies
ActiveUS20150165104A1Improve diastolic recoilOptimize mechanical environmentHeart valvesMedical devicesHeart diseaseDiastole
The present invention provides methods and direct cardiac contact device to improve the diastole phase and the systolic phase of a heart and includes a biocompatible film pneumatic locked to the heart to aid in heart compression and relaxation.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
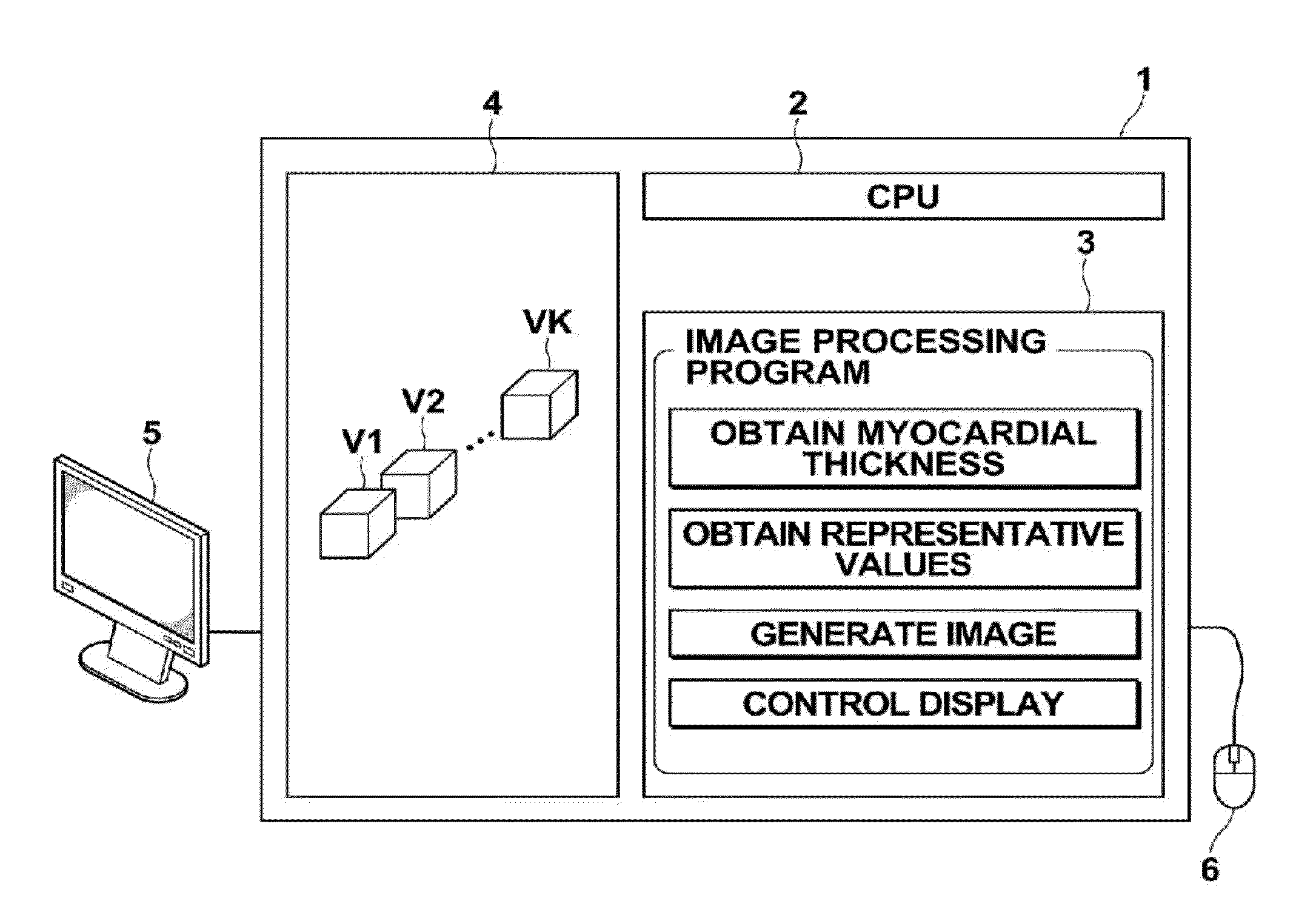
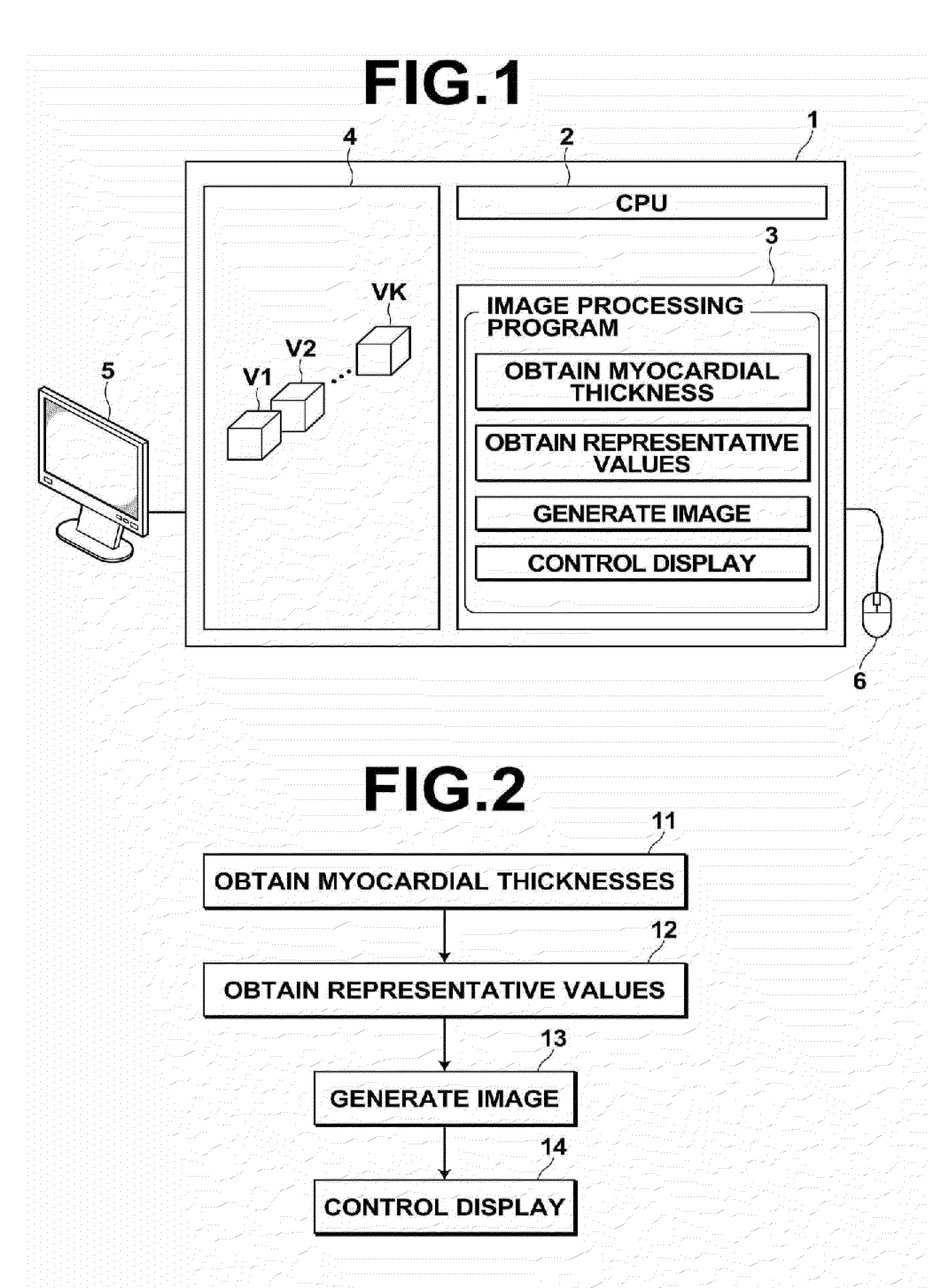
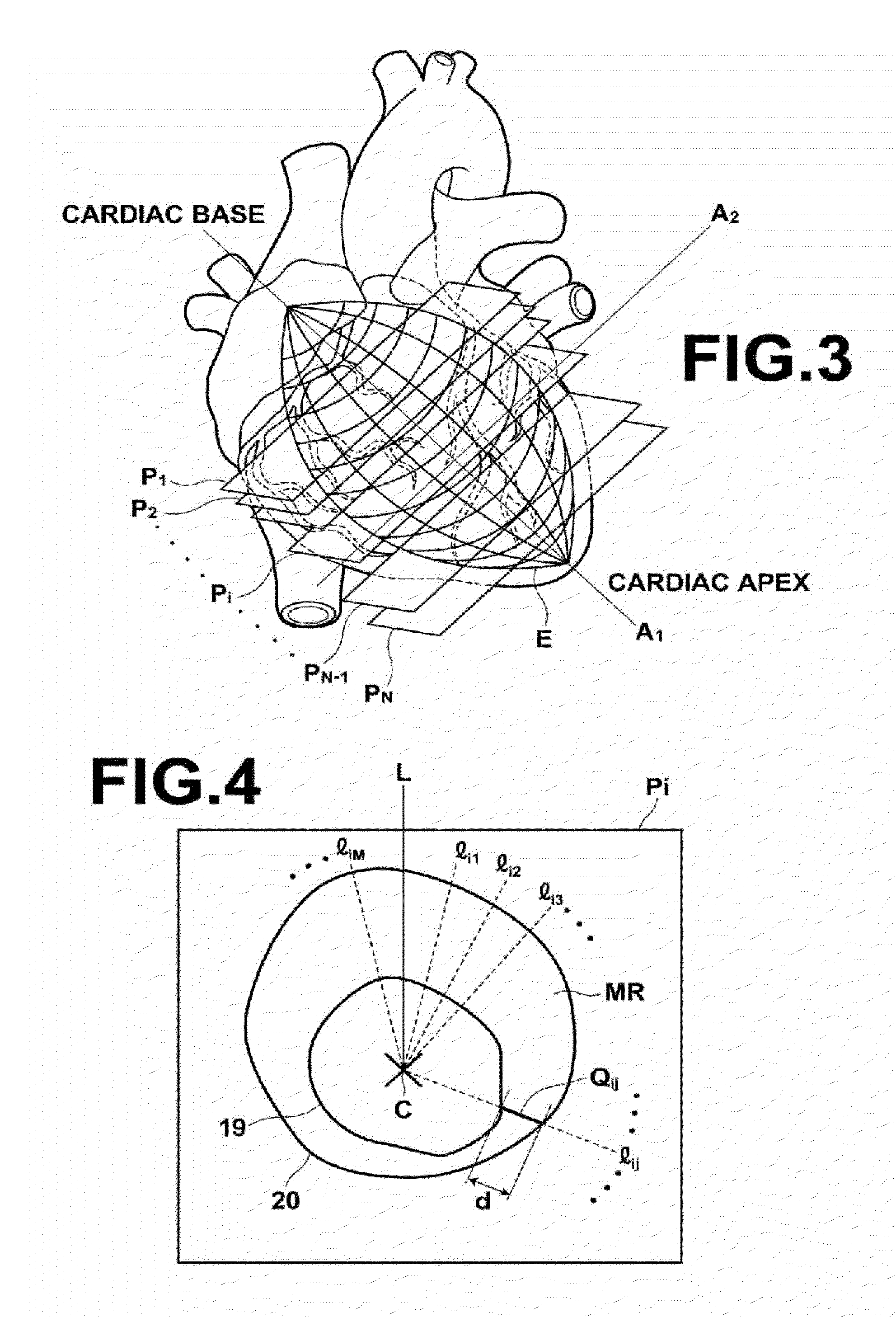
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program
ActiveUS20120065530A1Easy to analyzeEase of evaluationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingCardiac cycle
The systolic timings of myocardia at various positions of a heart are analyzed and evaluated. An image processing apparatus 1 obtains myocardial thicknesses at various positions of a heart within a plurality of three dimensional images V1 through VK, obtained by imaging a heart at a plurality of temporal phases within a single cardiac cycle, at each of the temporal phases. The image processing apparatus 1 obtains representative values that represent the systolic phase of the myocardia at each position, based on the obtained myocardial thicknesses at each temporal phase, and outputs the obtained representative values.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
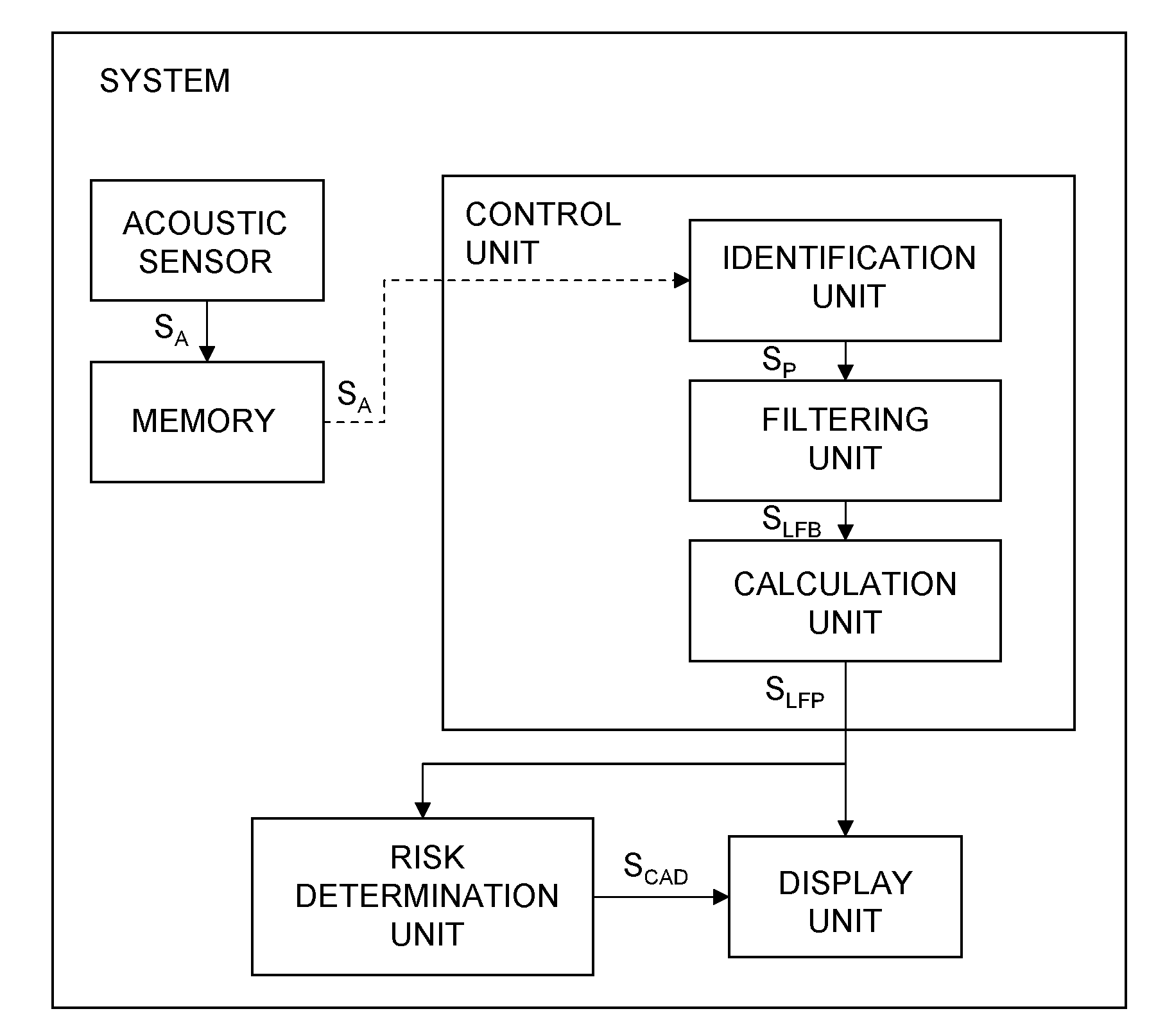
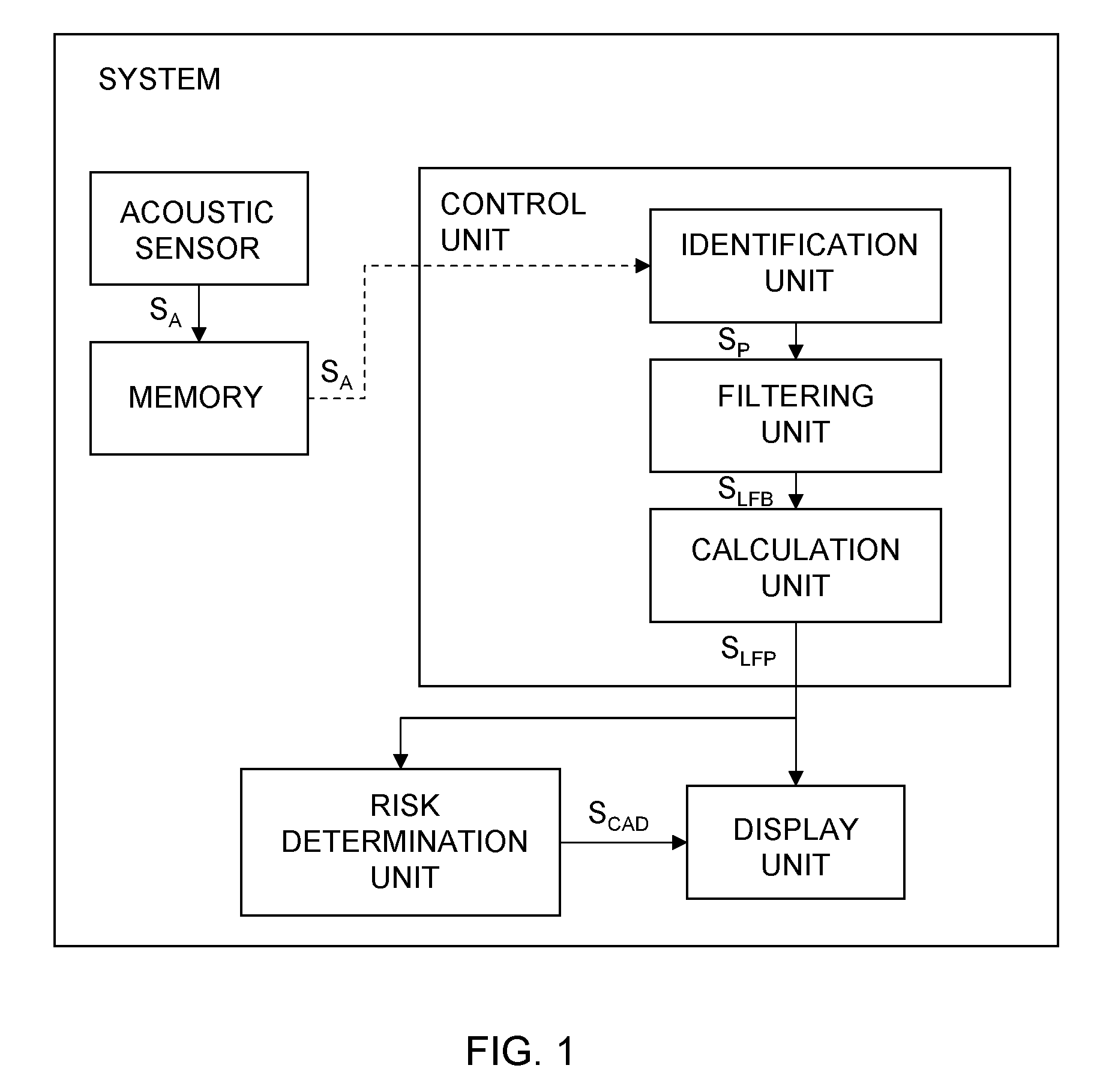
System, stethoscope and method for indicating risk of coronary artery disease
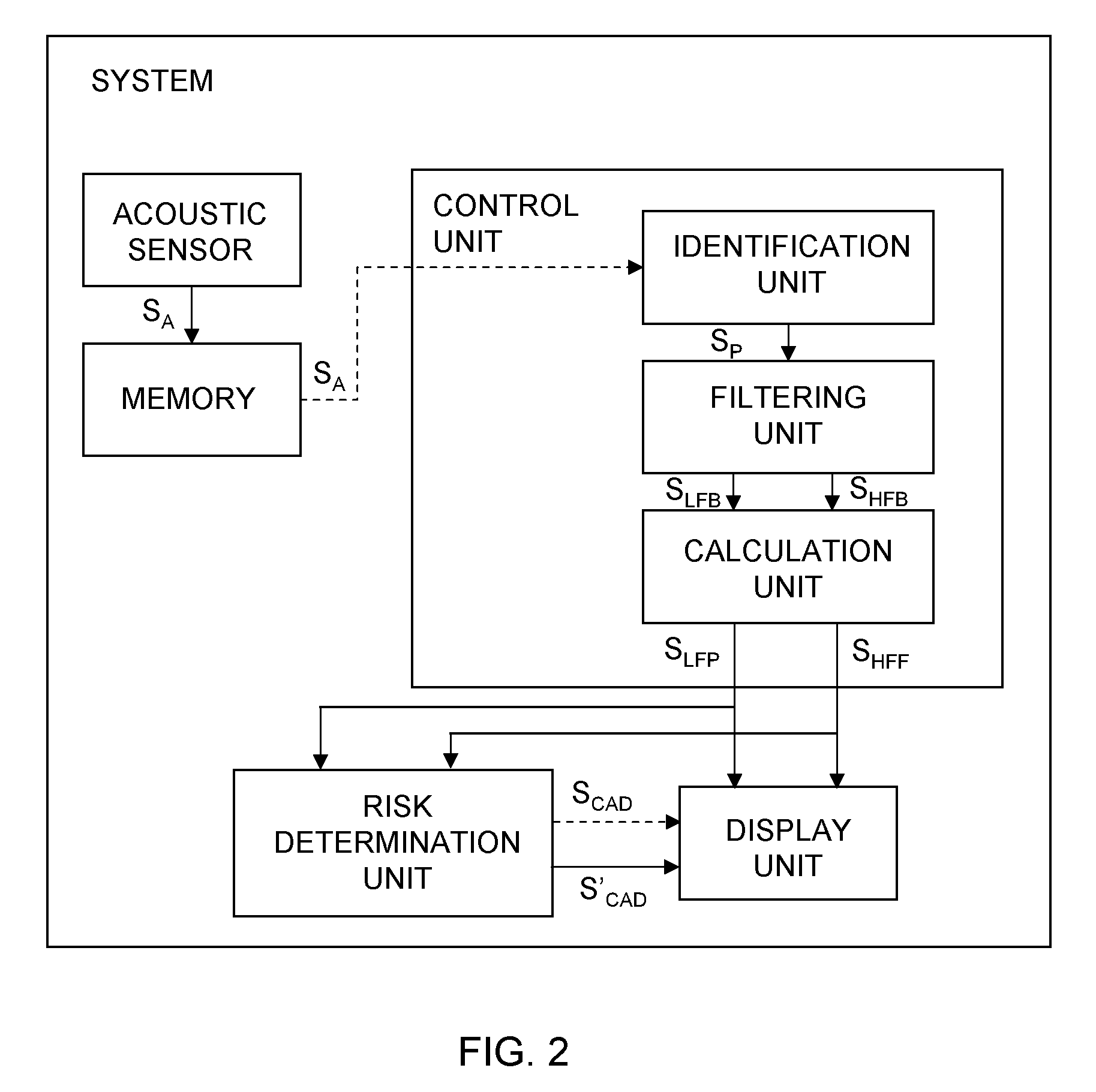
A system for detection of frequency power for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD), comprising: an acoustic sensor to be placed on the chest of a patient to generate acoustic signals SA: a memory adapted to store acoustic signals SA; a control unit adapted to receive said acoustic signals SA; the control unit comprising: an identification unit to identify diastolic or systolic periods in a predetermined time period and to generate a period signal SP, a filtering unit adapted to apply a filter to said identified periods to generate a low frequency band signal SLFB indicating low frequency bands of identified periods; a calculation unit to estimate the power in said low frequency band of identified periods, to calculate a low frequency power measure and to generate a low frequency power measure signal SLFP. The invention also relates to a stethoscope and a method for detection of low frequency power.
Owner:ACARIX AS
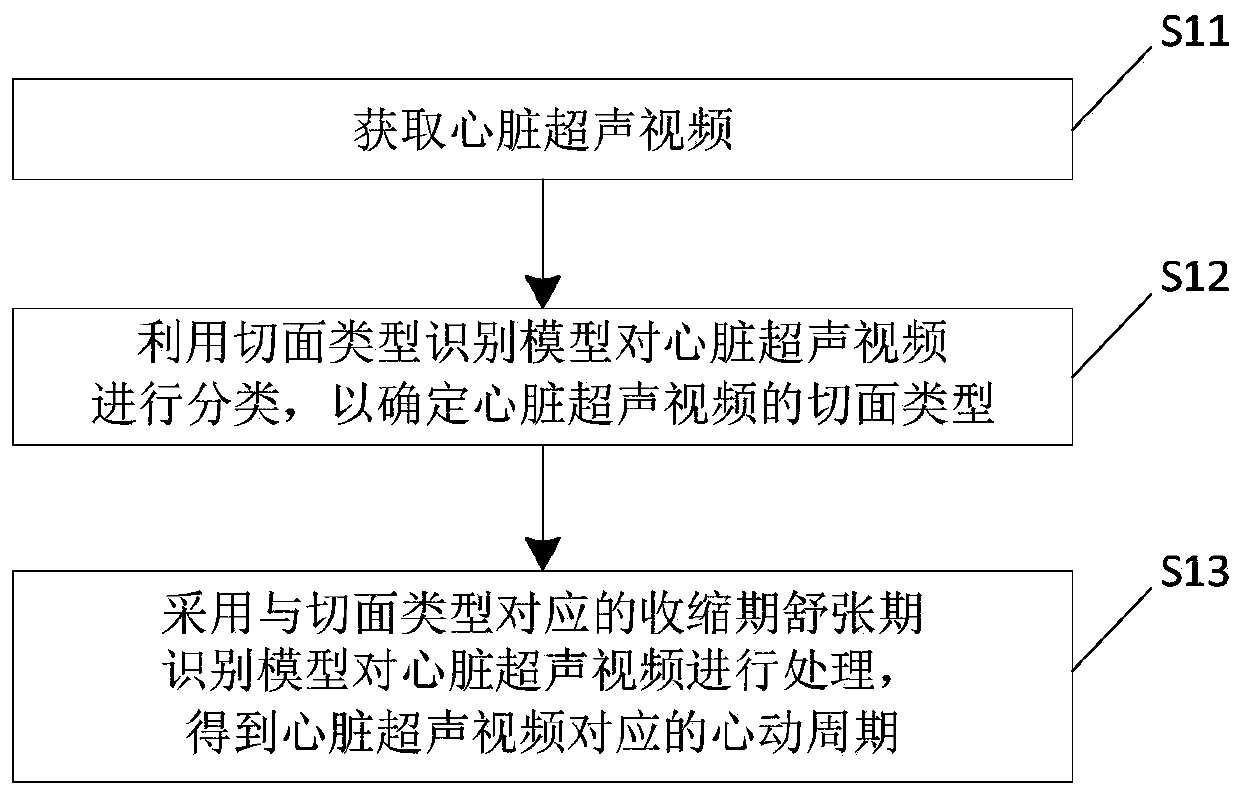
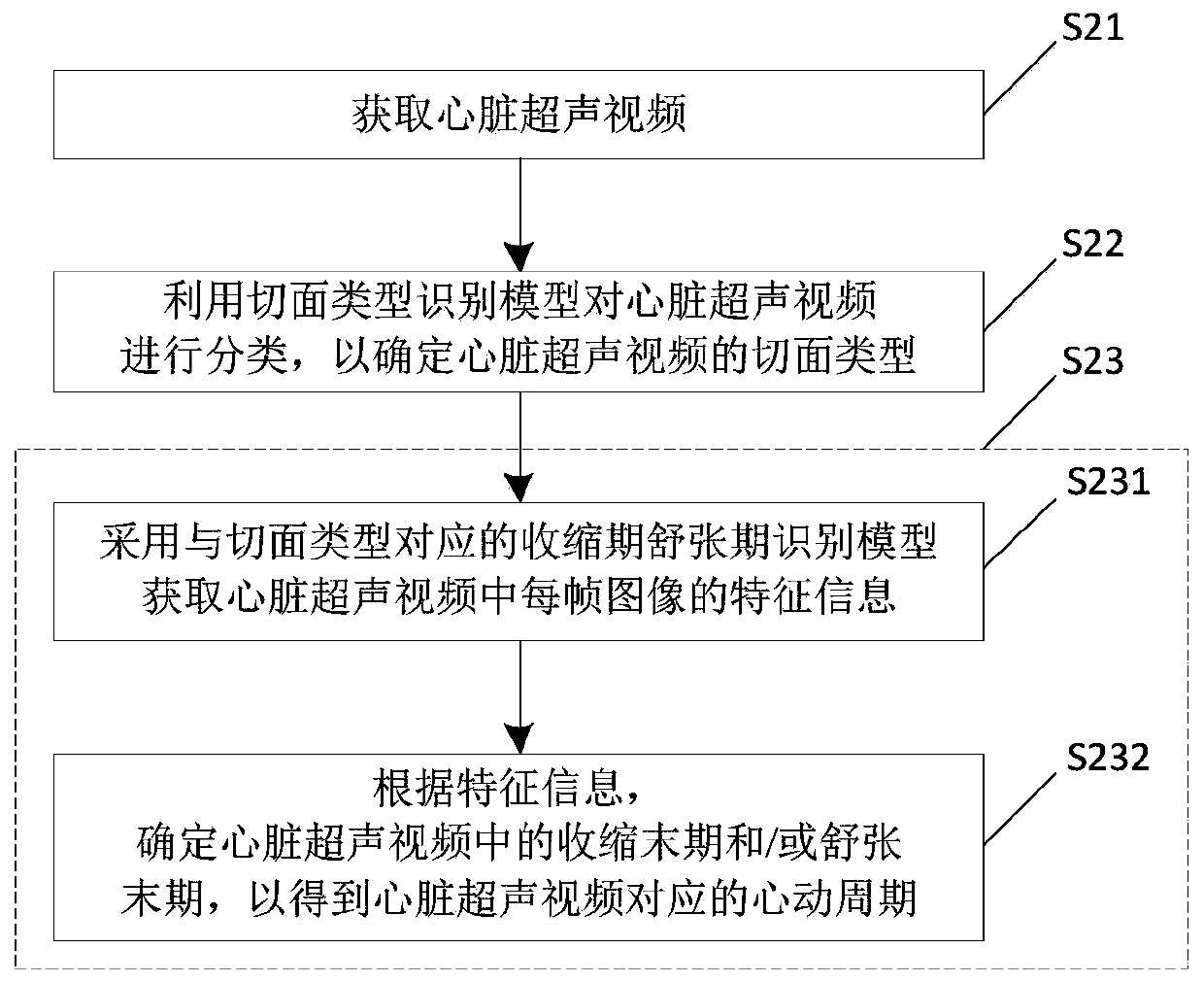
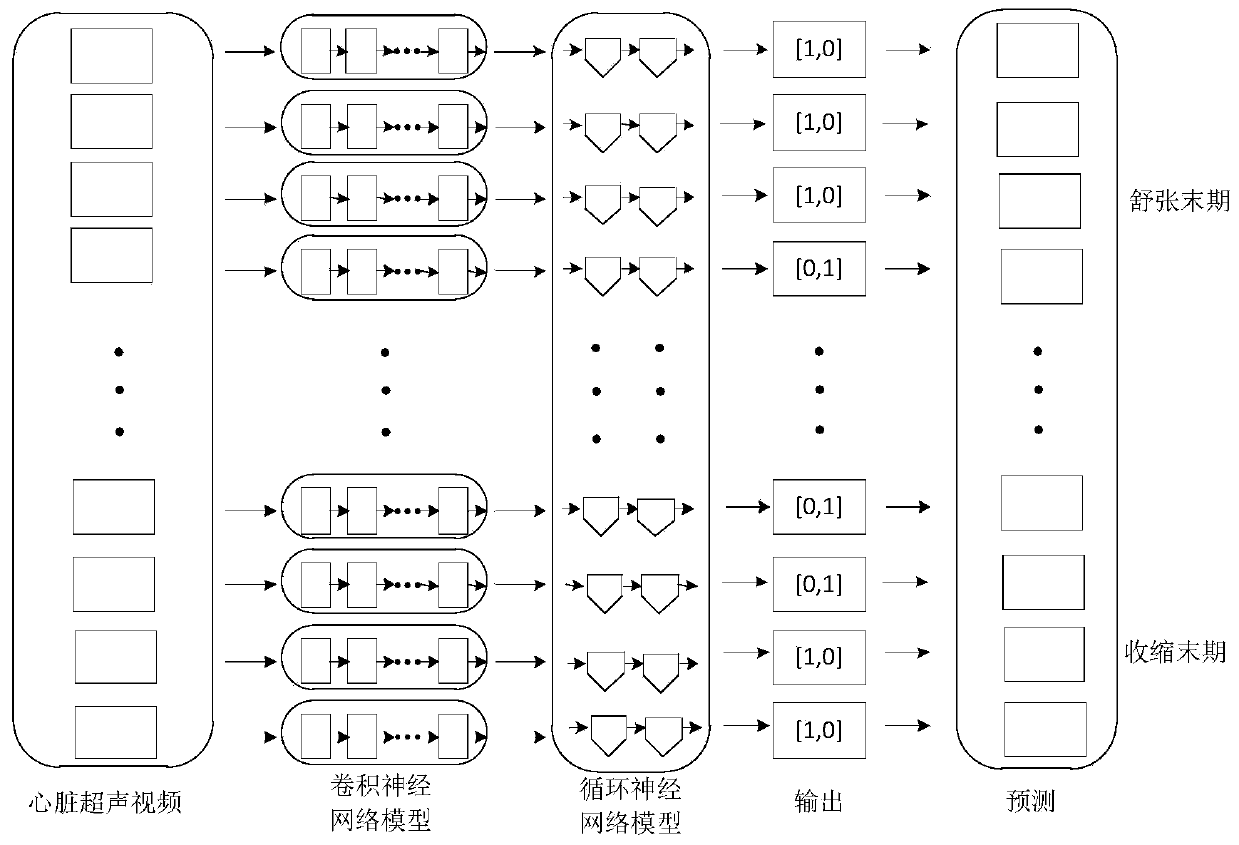
Determination method of cardiac cycles and ultrasonic equipment
ActiveCN110742653AEasy to detectRealize real-time detectionImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac cycleEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of image treatment, in particular to a determination method of cardiac cycles and ultrasonic equipment. The determination method comprises the steps that cardiac ultrasonic videos are obtained; the cardiac ultrasonic videos are classified by using a section-type recognition model to determine the section types of the cardiac ultrasonic videos; and the cardiac ultrasonic videos are processed by adopting systolic and diastolic period recognition models corresponding to the section types, and the cardiac cycles corresponding to the cardiac ultrasonic videos are obtained. Models are adopted to process the cardiac ultrasonic videos to detect the corresponding cardiac cycles. Through a mode of model detection, the use of an electrocardiograph can be avoided, and the detection of the cardiac cycles can be simplified; and furthermore, the real-time detection of the cardiac cycles in the process of cardiac ultrasound can be achieved.
Owner:CHISON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
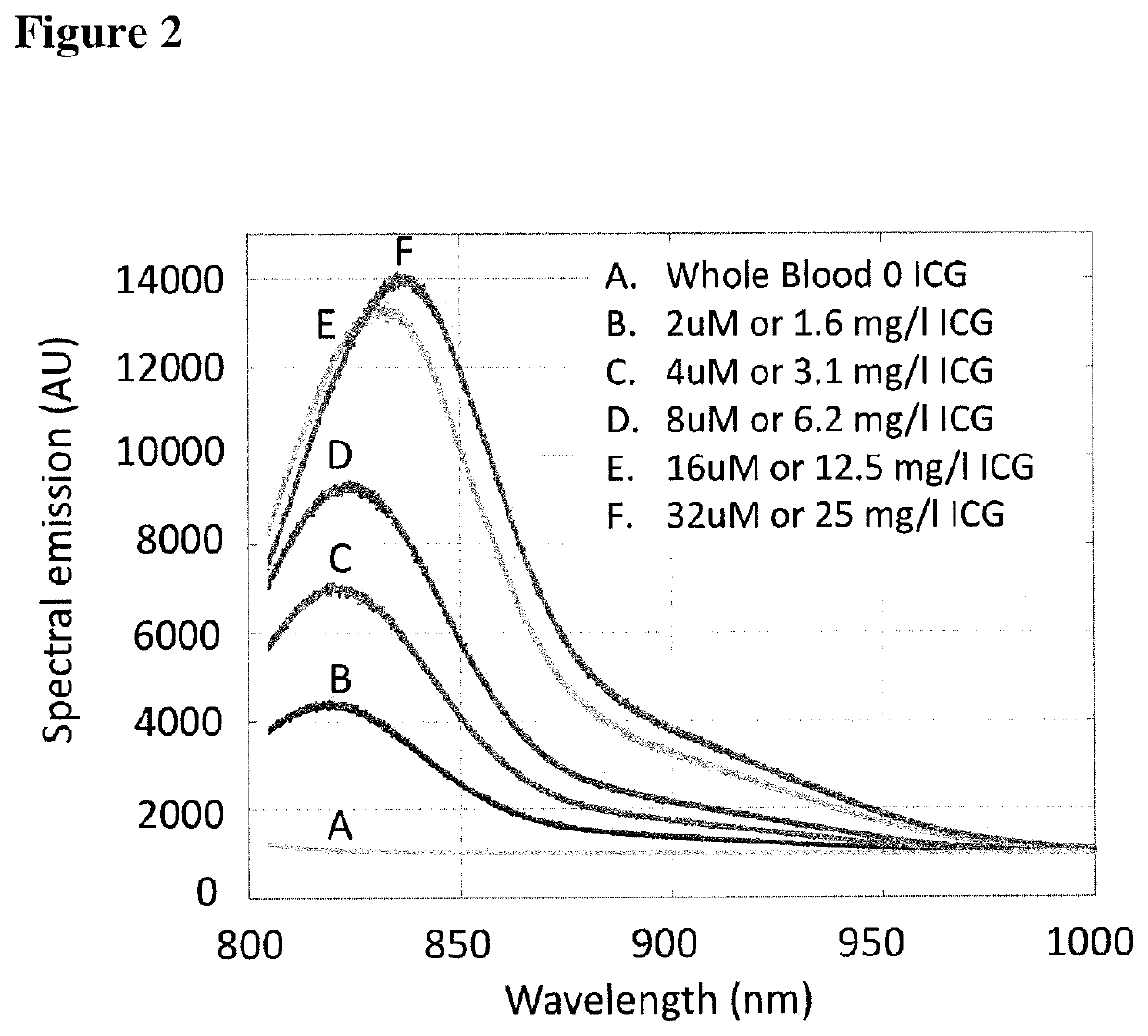
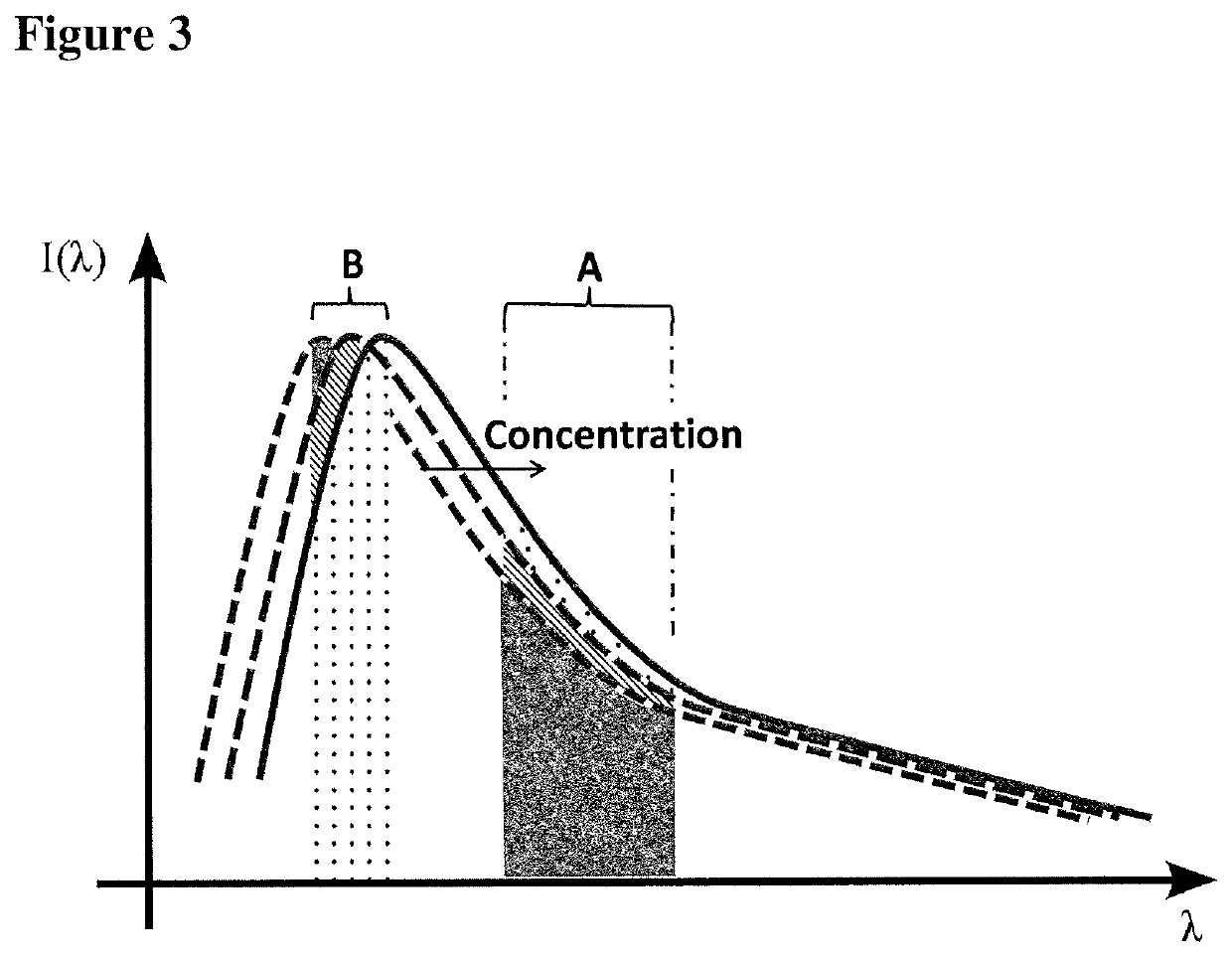
Quantification of absolute blood flow in tissue using fluorescence-mediated photoplethysmography
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
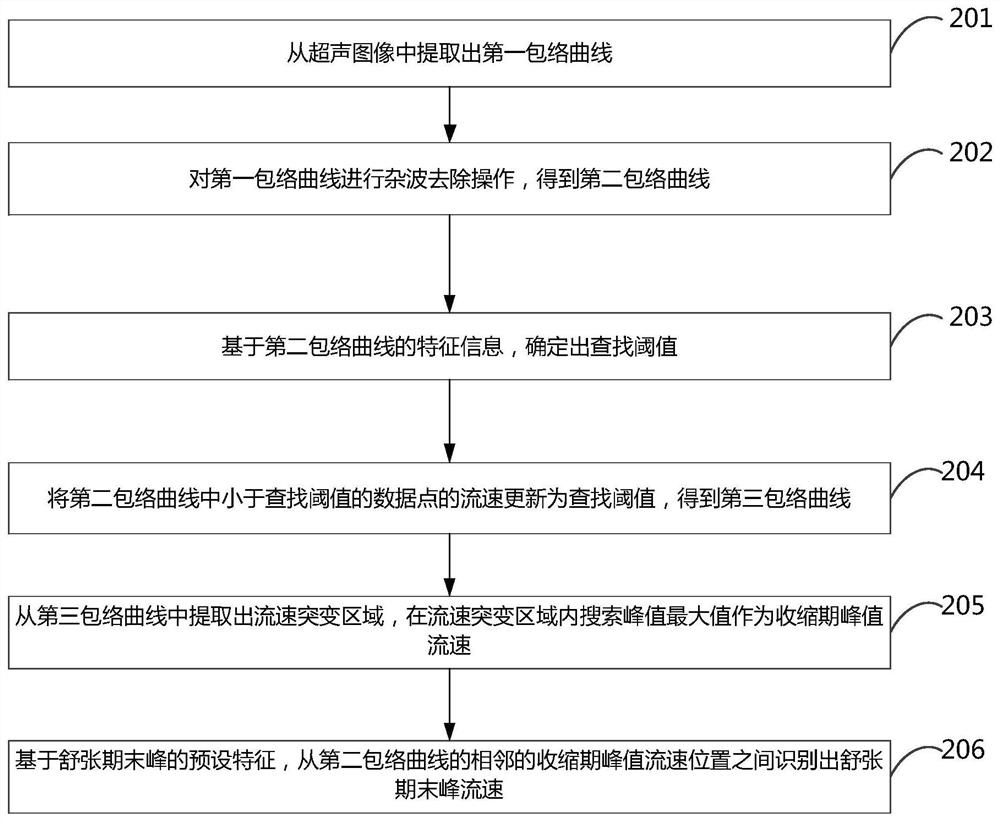
Fluid Doppler parameter determination method and electronic equipment
The invention discloses a fluid Doppler parameter determination method and electronic equipment. In the embodiment of the invention, the clutter is firstly removed through the clutter removal operation, and then the feature information of the envelope curve of the fluid is adopted to obtain the search threshold suitable for the envelope curve, so that the determination of the search threshold can conform to the own features of the envelope curve, the search threshold can be passed without prior information, and a fluid mutation region from the envelope curve is accurately extracted. Then, a systolic period peak flow velocity position can be extracted in the fluid mutation area, and a diastolic period end peak flow velocity position is further extracted from the envelope curve in combination with preset features of a diastolic period end peak. In the application, the preset feature of the end peak of the diastolic period is obtained through data analysis and expert experience, and can be suitable for the characteristics of the fluid, so that the flow velocity position of the end peak of the diastolic period can be accurately extracted based on the feature.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MEDICAL EQUIP
Method and Apparatus for Measuring Blood Pressure
ActiveUS20140316288A1Easy to adjustMinimize complexityEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterPeripheral pulsesDiastolic phase
Embodiments of the present invention provide an improved transformation method whereby the peripheral pulse waveform is filtered to separate different phases which make up the waveform. The separate phases are transformed before being re-combined to provide an estimated intra-arterial transfer function. For example, in one embodiment the peripheral pulse waveform is filtered by a first high pass filter, and a copy of the peripheral pulse waveform filtered by a second high pass filter, having a different cut-off frequency. The two filtered waveforms may then be further processed, for example by being added back to original wave-form, and are then multiplexed together in a time division manner to provide a final waveform. For example, the part of the first filtered waveform corresponding to the systolic phase may be combined with the part of the second filtered waveform corresponding to the diastolic phase to produce the final waveform, and the respective filter cut-off frequencies may be chosen to extract characteristics of the respective phases of the heart.
Owner:SUNTECH MEDICAL
A high-flow pulsating electromagnetic blood pump and a left ventricular counterpulsation assisting system including the same
InactiveCN109157686AIncrease powerIncrease afterloadElectrocardiographyOther blood circulation devicesMagnetic tension forceLeft ventricular size
The invention discloses a high-flow pulsating electromagnetic blood pump, which comprises a mounting bracket. At least two magnetic pushing devices mounted on the support surface, the magnetic pushingdevices comprising a drive coil, a permanent magnet piston, a two-way joint, an inner bag and a magnetic shielding cylinder; At least one set of linkage assemblies for linkage of permanent magnet pistons in two of the magnetic propulsion devices of the same set reciprocating alternately; A processor for controlling a control circuit of the driving coil by a set rhythm or according to an electrocardiogram signal of a human body surface; And an electrocardiogram electrode for detecting and transmitting a body surface electrocardiogram signal of the human body to the processor. The invention integrates a plurality of magnetic pushing devices and is linked by the linkage components in two groups, thereby effectively reducing heat generation, increasing the power of the whole machine in multiple, simultaneously increasing the flow rate, and effectively improving the working condition. It can also be controlled according to extracorporeal electrocardiogram signals, which can avoid increasing the afterload of myocardium in systolic phase.
Owner:SHANGHAI YANGPU SHIDONG HOSPITAL
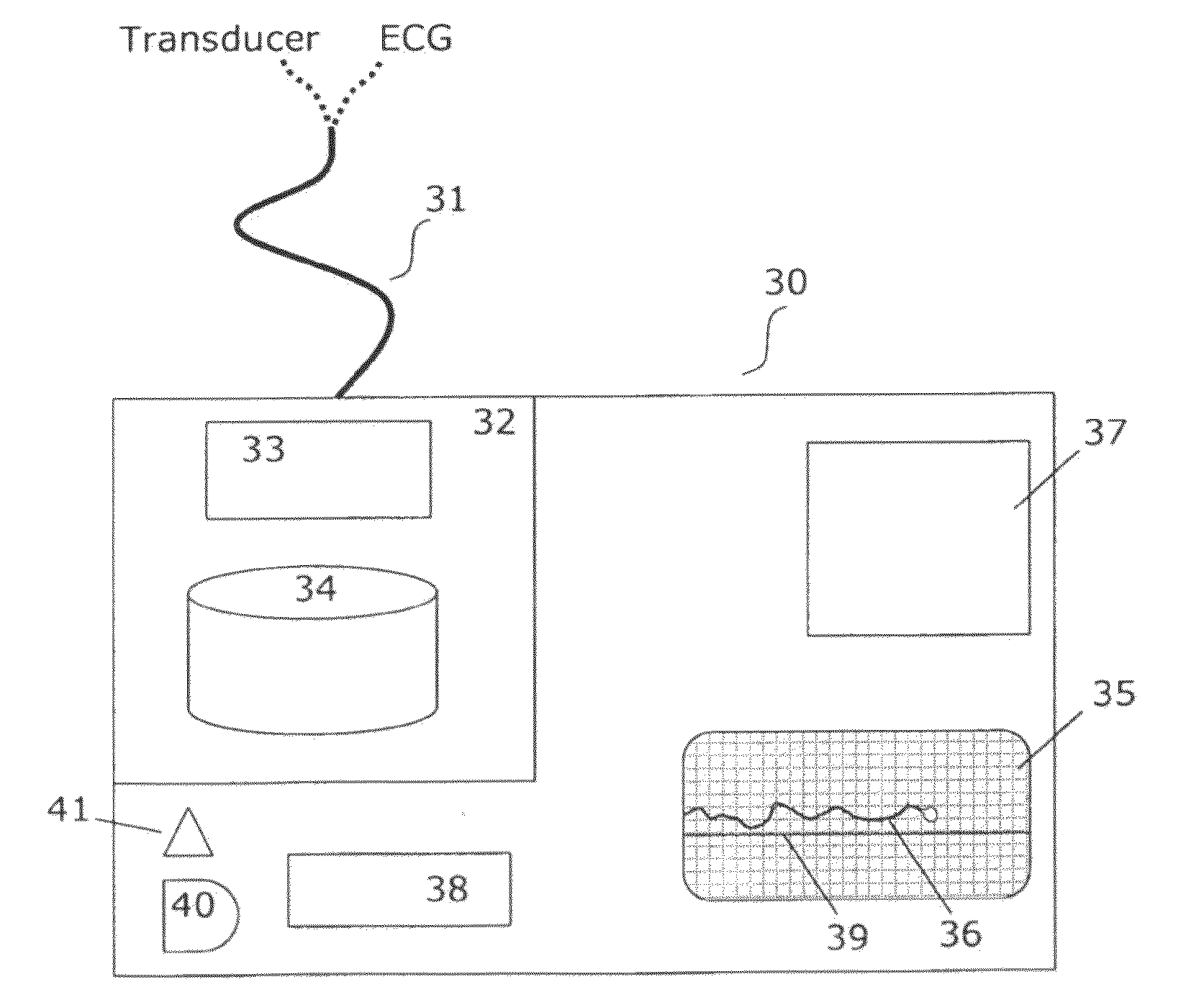
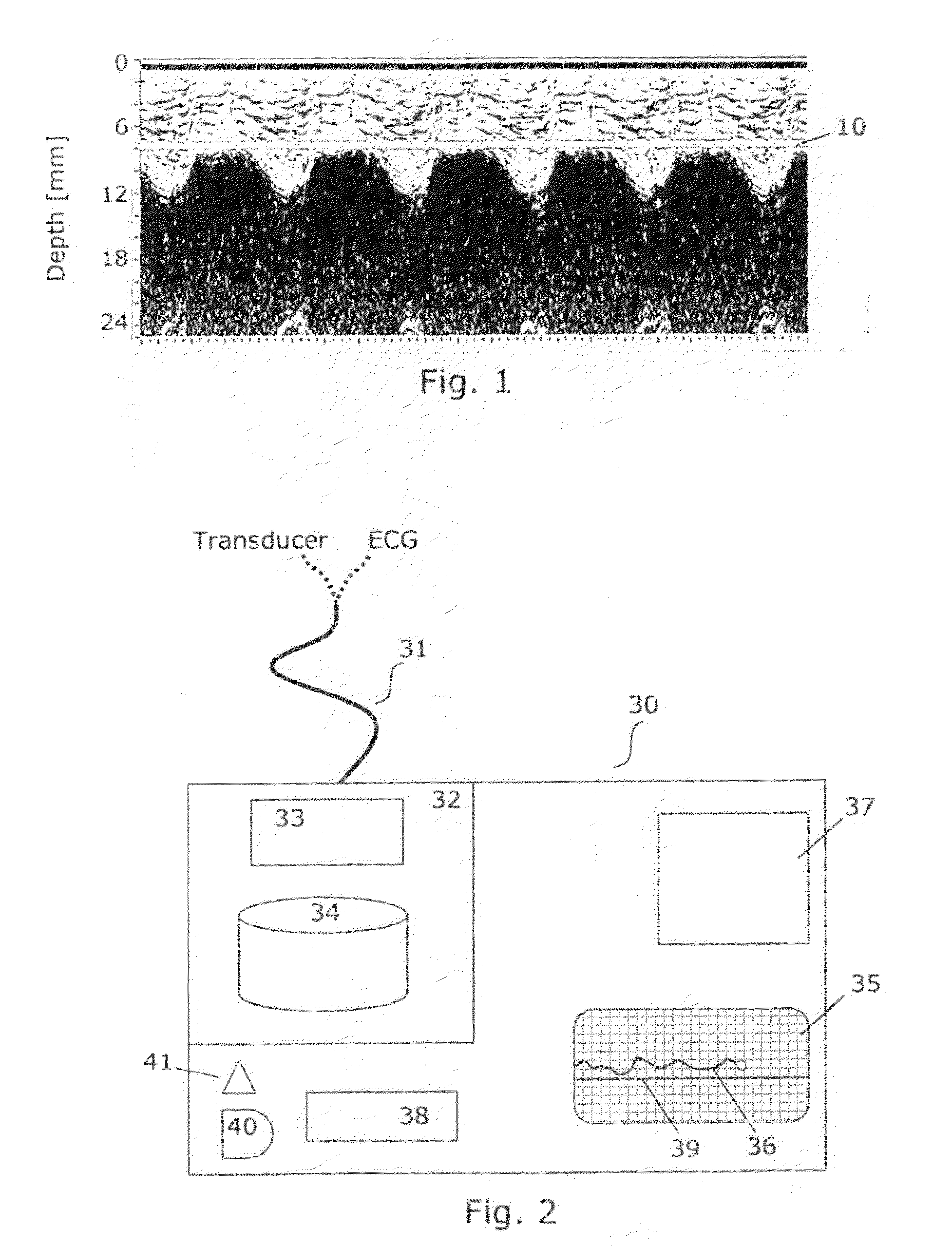
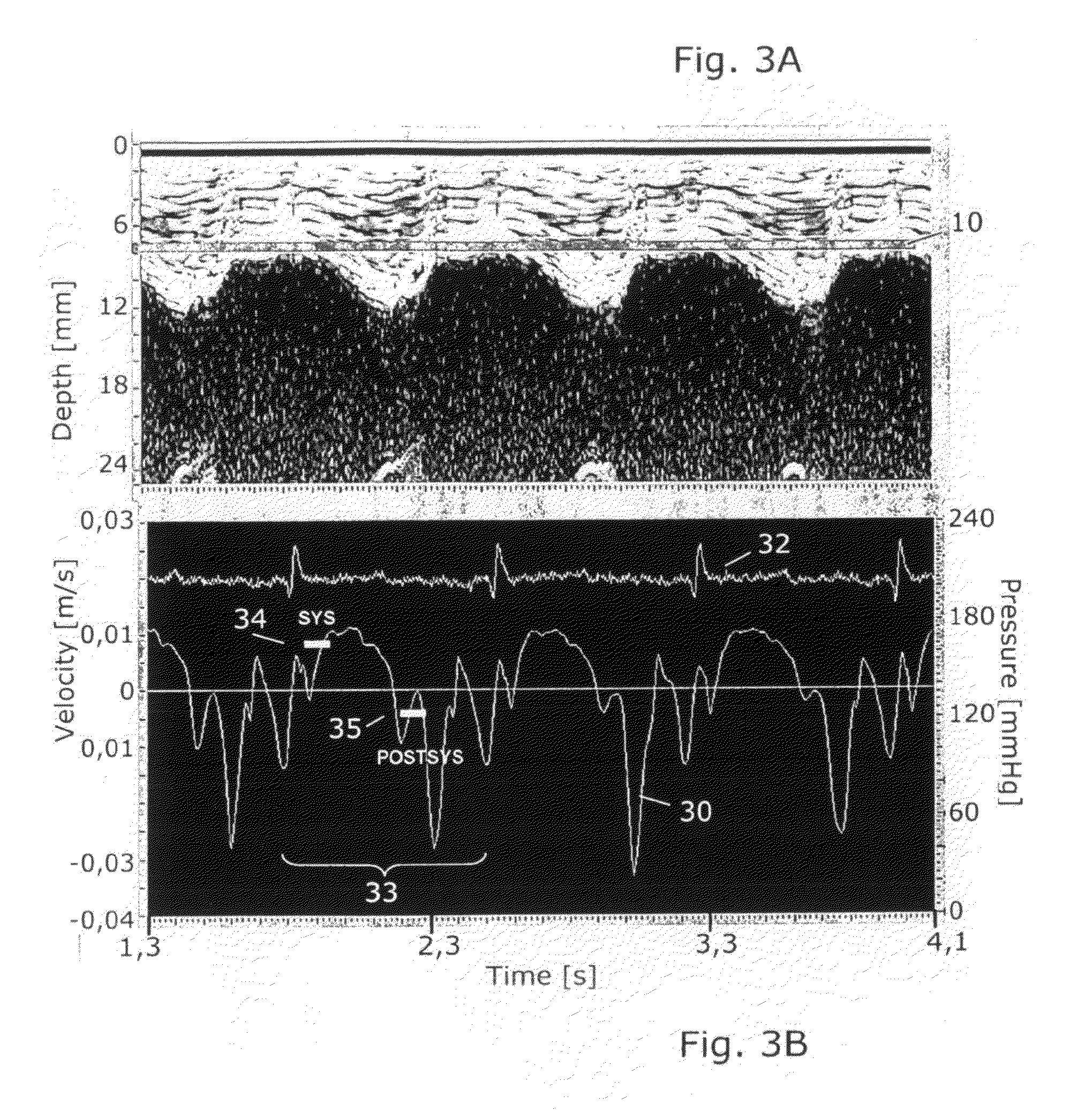
Automated monitoring of myocardial function by ultrasonic transducers positioned on the heart
InactiveUS20110046488A1Promote contractionInduce ischaemiaDiagnostic probe attachmentCatheterCardiac ischaemiaUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a method and a post-operative care unit for analysing and quantifying an ultrasound tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) signal from a transducer fastened on the myocardium to obtain a parameter indicating regional cardiac ischaemia or correlates with global hypokinetic heart function. This has the advantage over manually operated probes that it can be automated and used continuously over long time. According to the method, a TDI signal trace corresponding to at least one of tissue velocity, strain or strain rate is extracted and correlated with an electrocardiogram to define subsections within a cardiac cycle in the extracted trace corresponding to the early systolic phase and the post-systolic phase. Then, a velocity, strain or strain rate is read in at least the post-systolic phase of the extracted trace, and a parameter which is a function of one of these readings and which indicates ischaemia or global hypokinetic function is generated.
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
Method and device for screening diastolic and systolic images based on cardiac ultrasound video
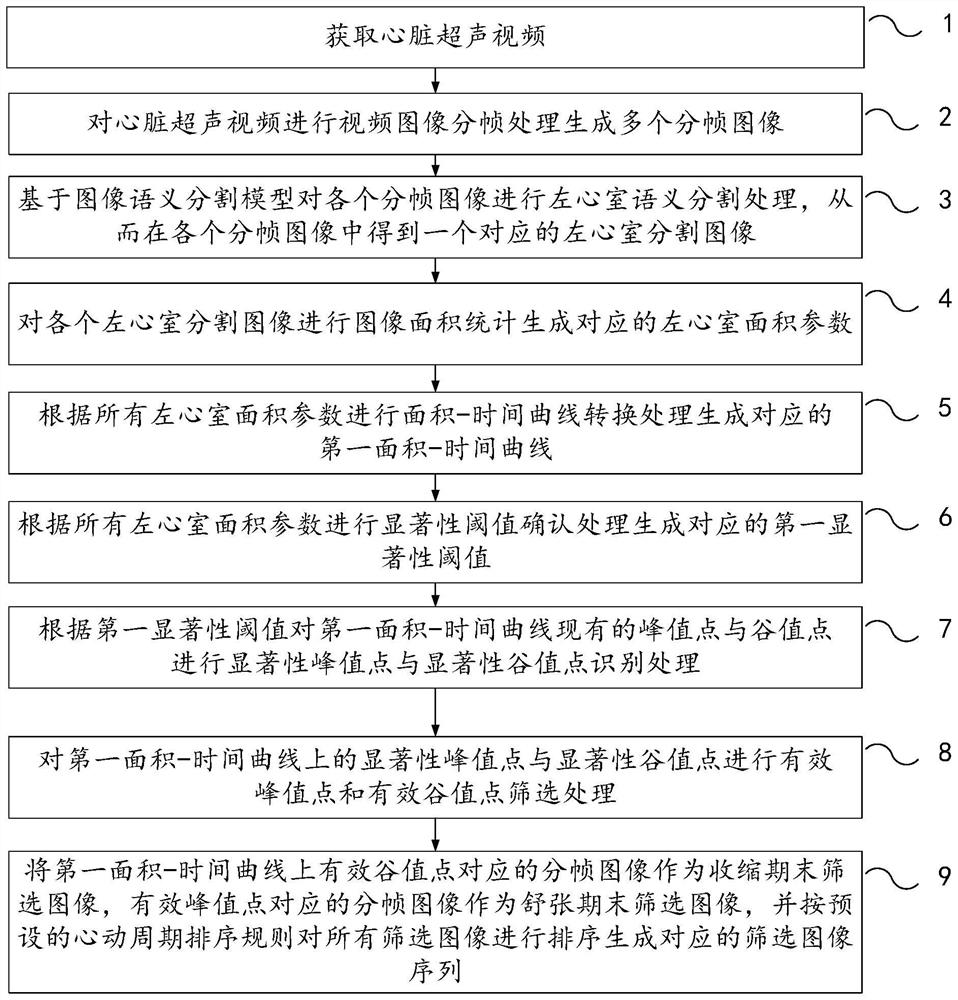
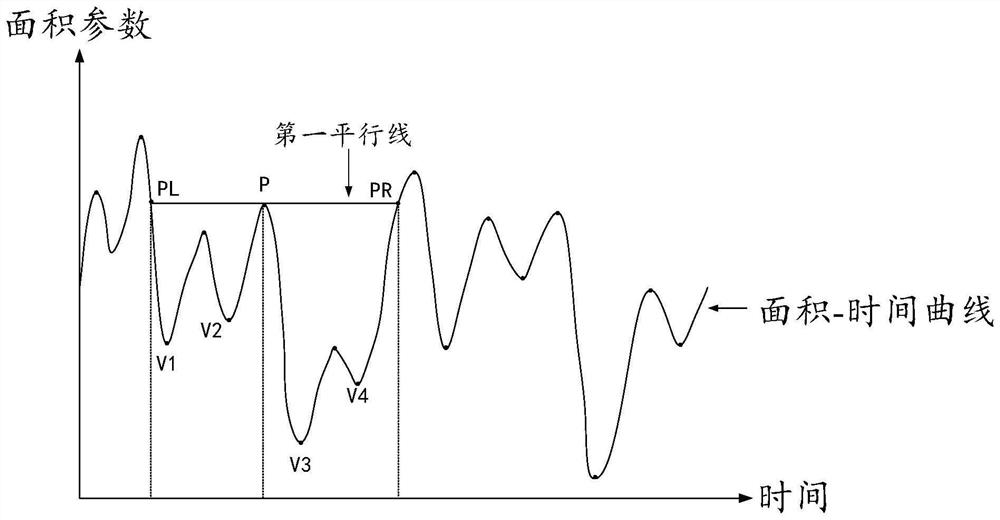
PendingCN114419500AImprove screening accuracyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisLeft ventricular sizeVideo image
The embodiment of the invention relates to a method and device for screening diastolic and systolic images based on a cardiac ultrasound video. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the cardiac ultrasound video; performing video image framing to generate a plurality of framed images; performing left ventricle semantic segmentation on each framed image to obtain a corresponding left ventricle segmented image; performing image area statistics to generate corresponding left ventricular area parameters; performing area-time curve conversion to generate a first area-time curve; performing significance threshold confirmation to generate a first significance threshold; carrying out saliency peak and valley value point identification on the existing peak and valley value points of the first area-time curve; performing effective peak and valley value point screening on the significant peak and valley value points; and taking the framed image corresponding to the effective valley point as a screening image at the end of a contraction period, taking the framed image corresponding to the effective peak point as a screening image at the end of a relaxation period, and sorting all the screening images to generate a screening image sequence. According to the invention, the image screening quality stability can be ensured.
Owner:LEPU MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Coronary artery stenosis visualization quantification method and device based on multi-channel heart sound
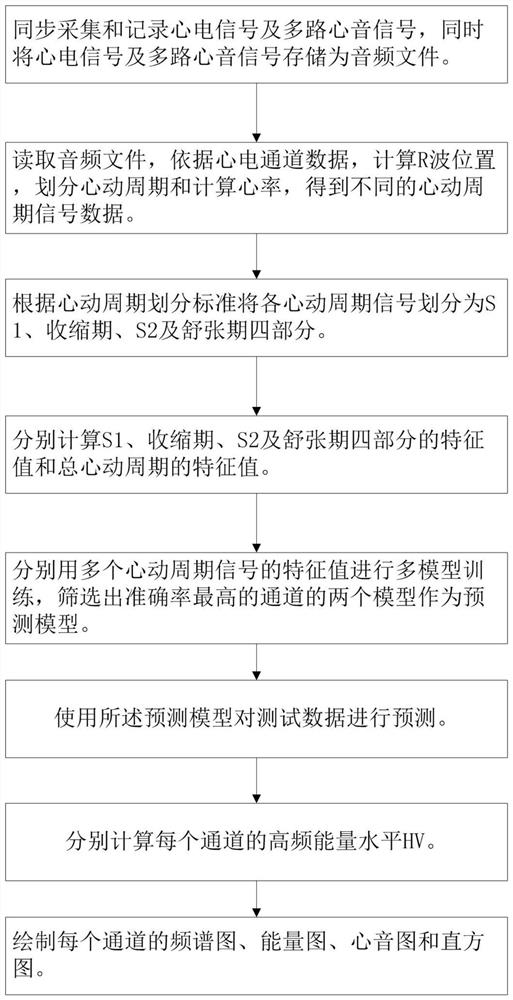
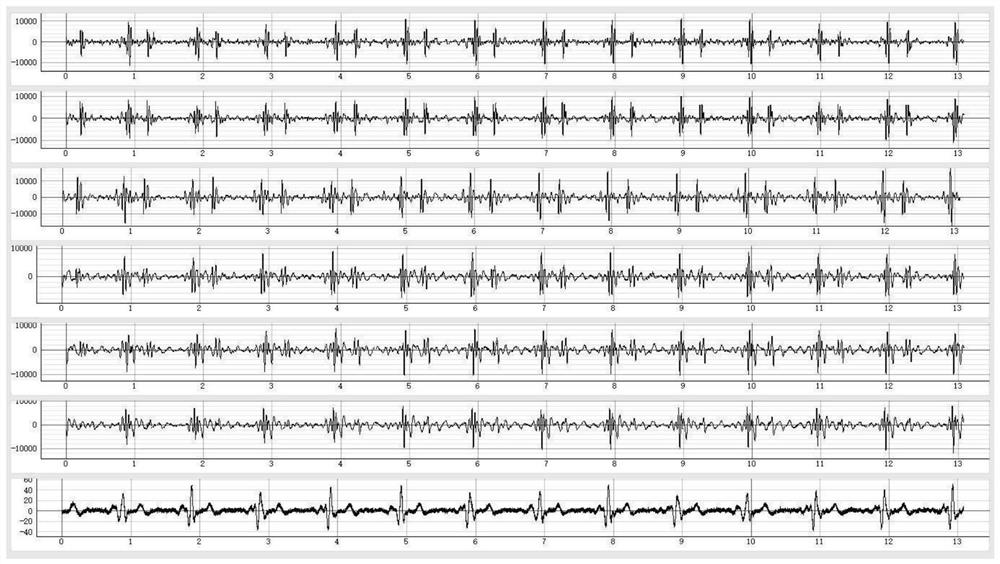
ActiveCN112494000AImprove forecast accuracyIntuitively reflect the health statusCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringCoronary arteriesHistogram
The invention discloses a coronary artery stenosis visualization quantification method and device based on multi-channel heart sound, and is suitable for the field of analysis of cardiophonogram electrocardiograms. The method comprises the steps of synchronously collecting and recording electrocardiosignals and multi-channel heart sound signals, and storing the electrocardiosignals and the multi-channel heart sound signals as audio files; segmenting heartbeat cycle signal data into S1, a systolic period, S2 and a diastolic period by using R waves and heart sound characteristics; respectively calculating characteristic values of each section of the heartbeat cycle and the total heartbeat cycle; performing stenosis degree risk prediction by adopting multi-model prediction and decision rules;and representing the coronary artery stenosis risk degree by adopting columnar graphs with different colors and heights. According to the method, various characteristics are extracted, heartbeat cycle characteristics are reflected in all directions, and the model prediction accuracy is improved through the multi-machine learning model and the use of decision rules. The health condition of the coronary artery is visually reflected in the forms of the energy spectrogram and the histogram.
Owner:河北德睿健康科技有限公司
System for performing an analysis of pressure-signals derivable from pressure measurements on or in a body
InactiveUS20070060836A1Reduce pressureEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterDigital dataVisual presentation
A system for performing an analysis of pressure-signals derivable from pressure measurements on or in a body of a human being or animal, includes a communication interface for receiving a set of digital pressure sample values, a memory for storing these values, and a processor capable of performing the analysis, the processor having means to identify features related to single pressure waves in the pressure signals based on input of the digital data into the processor, and the processor further having determination means which based on the features is configured to a) determine a minimum pressure value related to diastolic minimum value and a maximum pressure value related to systolic maximum value, b) determine at least one parameter of the single wave parameters elected from the group of: pressure amplitude=ΔP=[(maximum pressure value)−(minimum pressure value)], latency (AT), rise time or rise time coefficient=ΔP / ΔT, and wavelength of the single wave, c) determine number of the single pressure waves occurring during a given time sequence, including determination of the number of single pressure waves with pre-selected values of one or more of the single pressure wave parameters during the given time sequence, and d) determine number of single pressure waves with pre-selected combinations of two or more of the single pressure wave parameters during the given time sequence. Further, the system has a display for visual presentation of the result of analysis performed by the processor.
Owner:SENSOMETRICS AS (NO)
Ultrasonic equipment, ultrasonic image processing method and storage medium
ActiveCN112656445AOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesVentricular volumeCardiac cycle
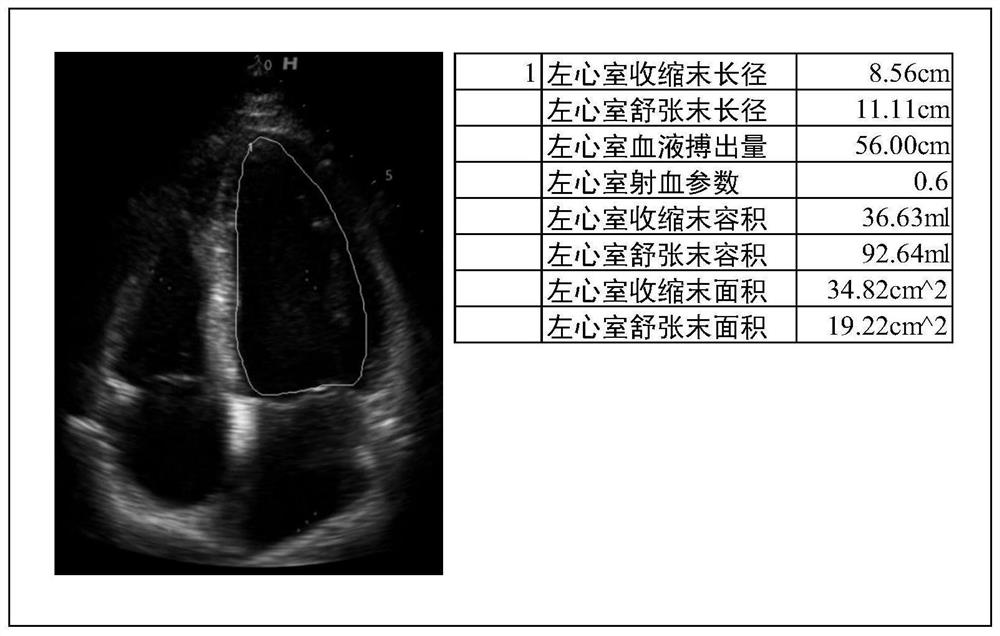
The invention discloses ultrasonic equipment, an ultrasonic image processing method and a storage medium, which are used for automatically measuring heart state parameters and improving the measurement accuracy. The equipment comprises a processor and a display. The processor obtains an image sequence composed of ultrasonic images from the continuously collected ultrasonic image information of the heart; the ventricular volume corresponding to each frame of ultrasonic image in the image sequence is determined to obtain a ventricular volume sequence; the end-diastolic volume corresponding to the central ventricular end diastolic phase of at least one cardiac cycle and the end-systolic volume corresponding to the ventricular end-systolic phase is determined according to the change trend of the central ventricular volume of the ventricular volume sequence; and heart state parameters can be determined according to the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume. The ventricular volume is determined according to the ultrasonic images in the acquired image sequence, so that the ventricular volume is determined quickly and accurately; the heart state parameters are determined according to the determined end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume, so that the accuracy of the heart state parameters is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MEDICAL EQUIP
Diastolic recoil method and device for treatment of cardiac pathologies
ActiveUS9642957B2Optimize mechanical environmentSmall sizeElectrotherapyHeart valvesHeart diseaseDiastole
The present invention provides methods and direct cardiac contact device to improve the diastole phase and the systolic phase of a heart and includes a biocompatible film pneumatic locked to the heart to aid in heart compression and relaxation.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com