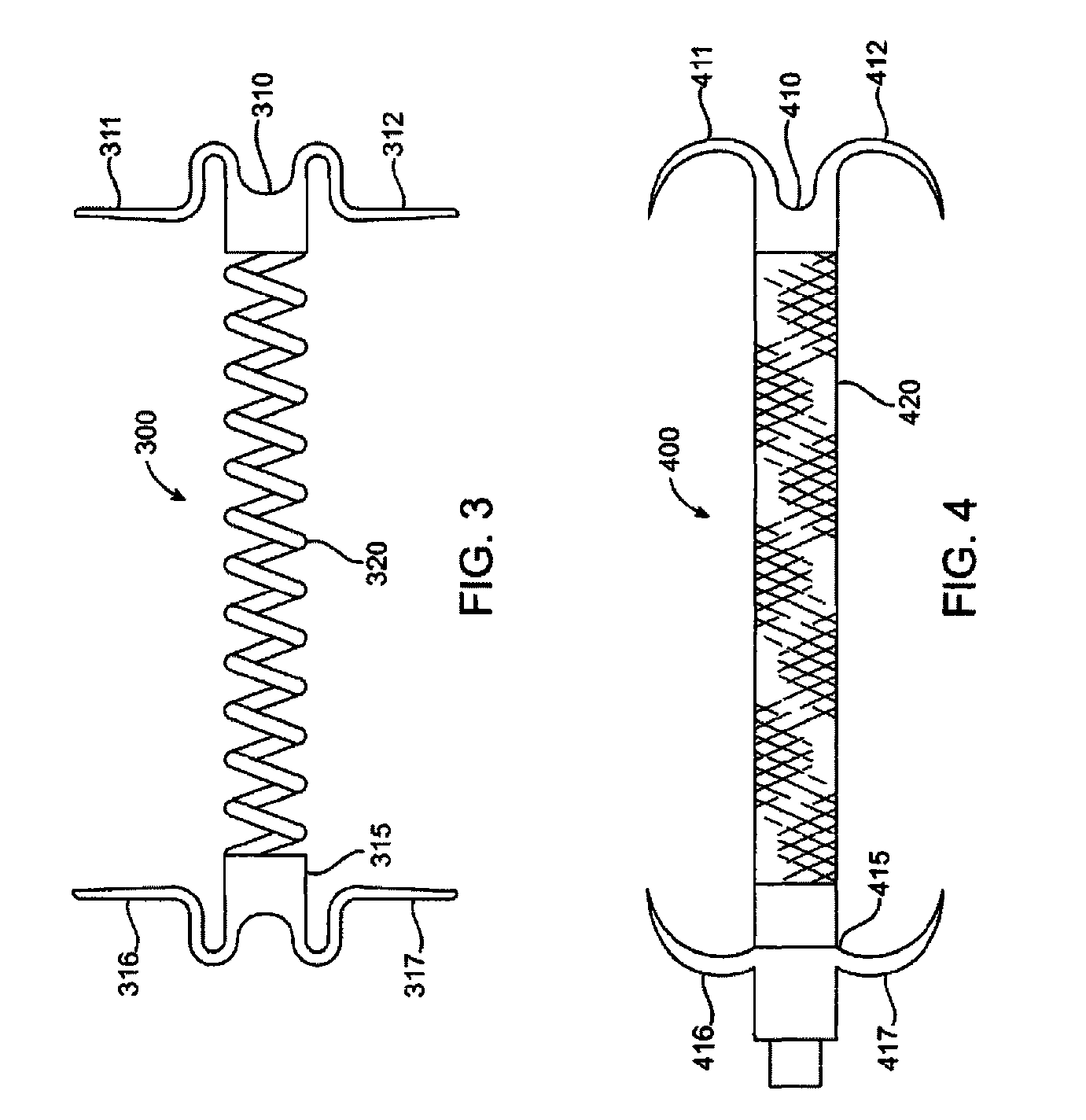
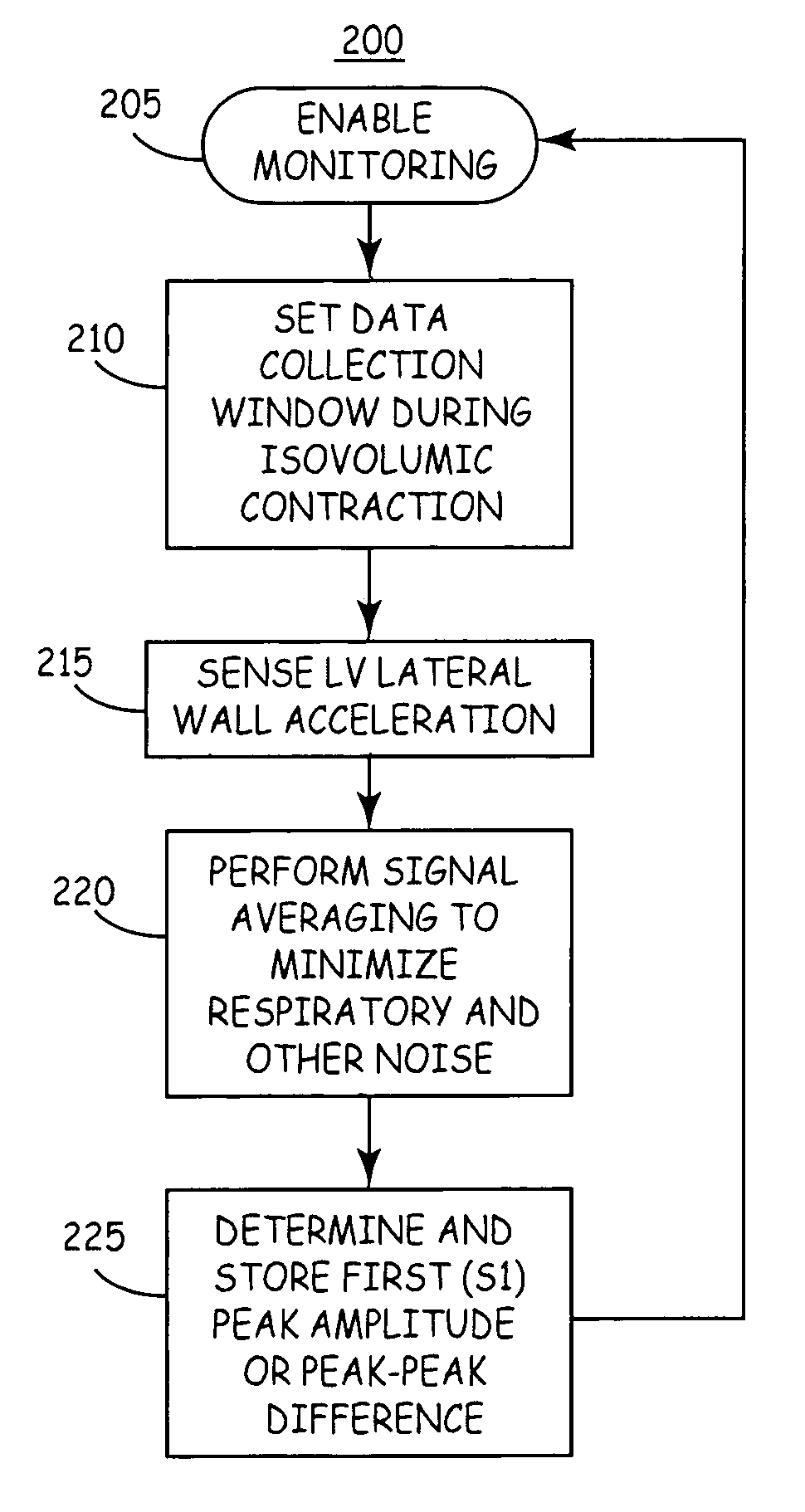
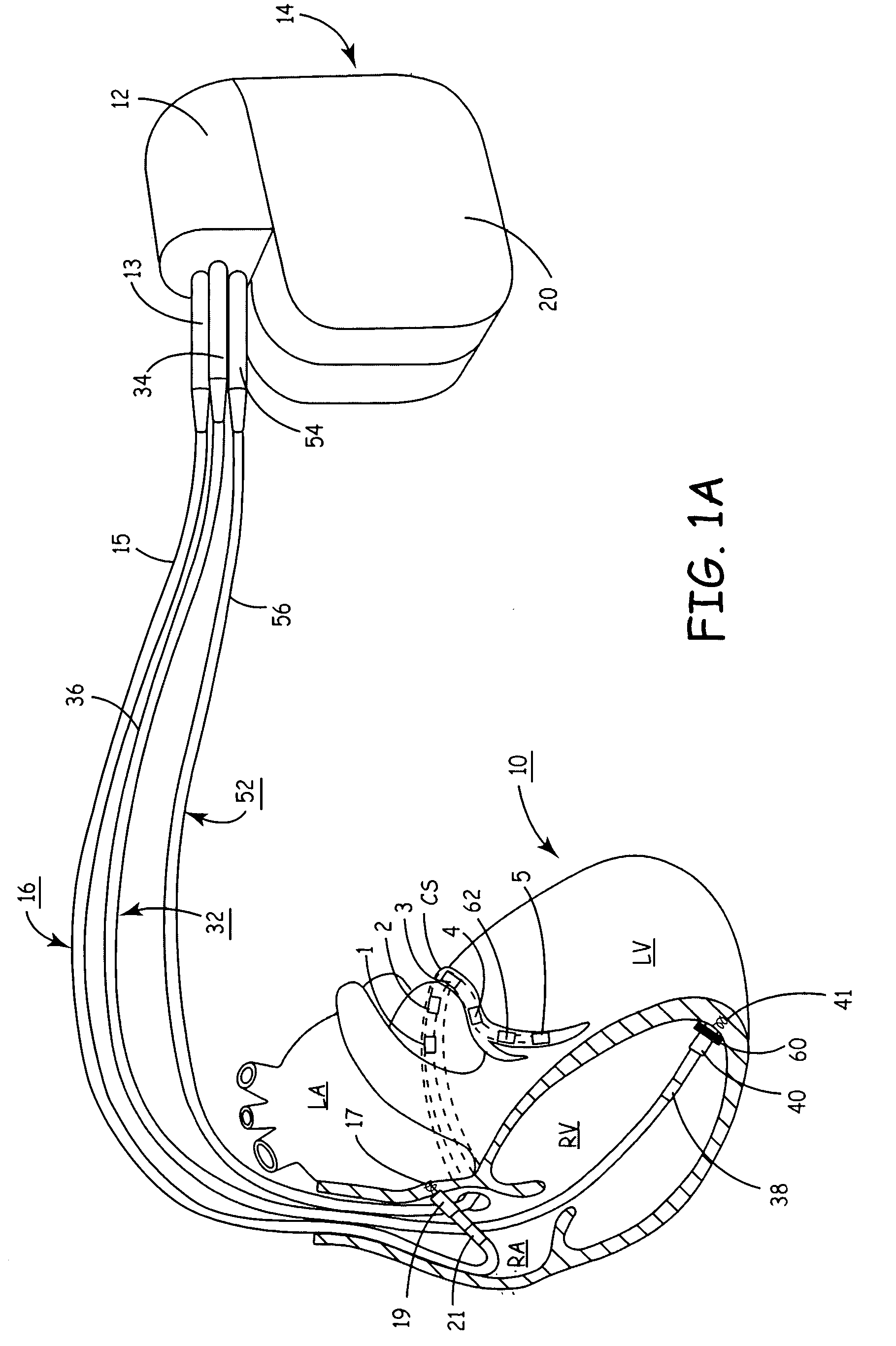
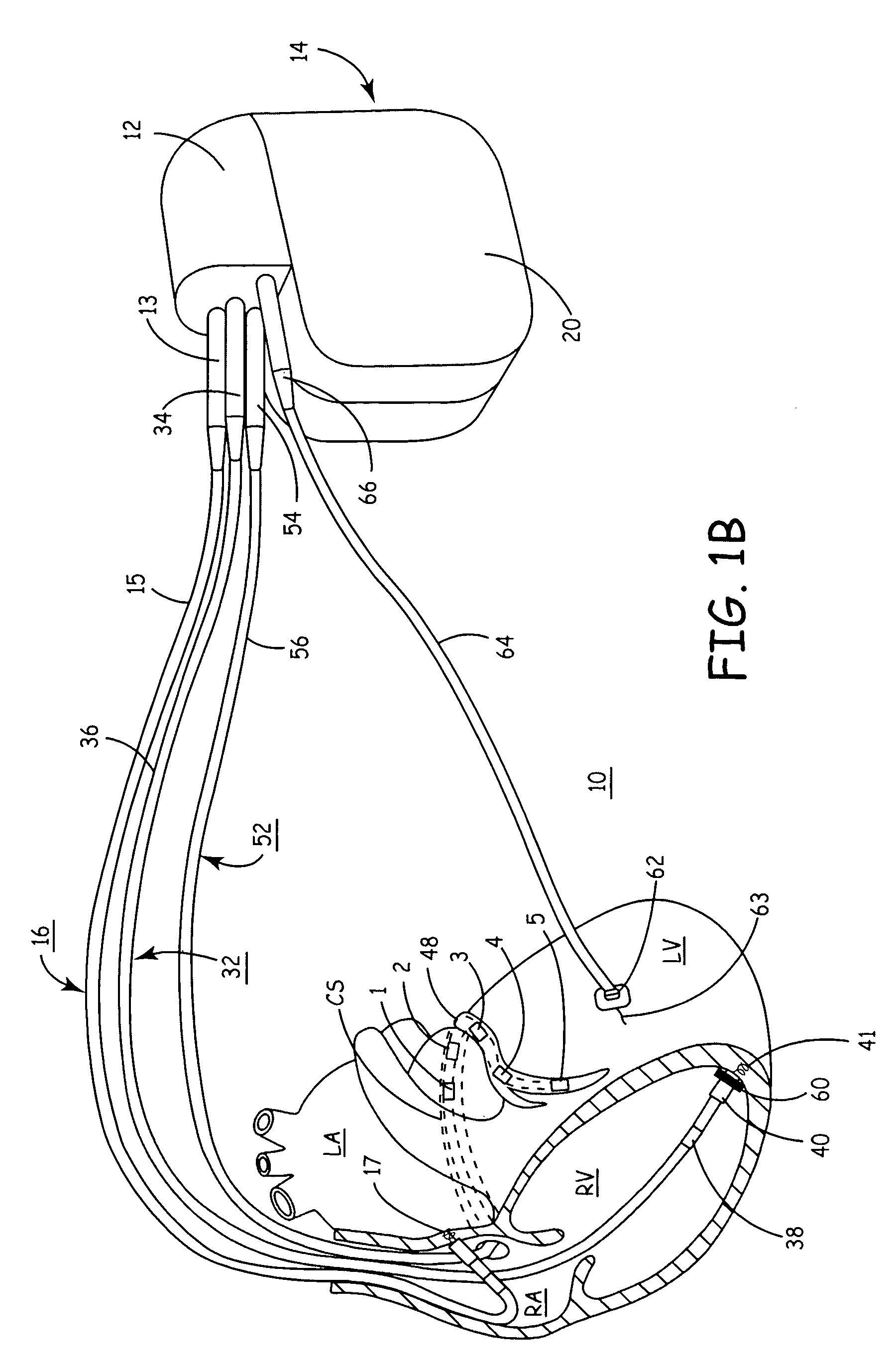
Patents
Literature
873 results about "Left ventricle wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
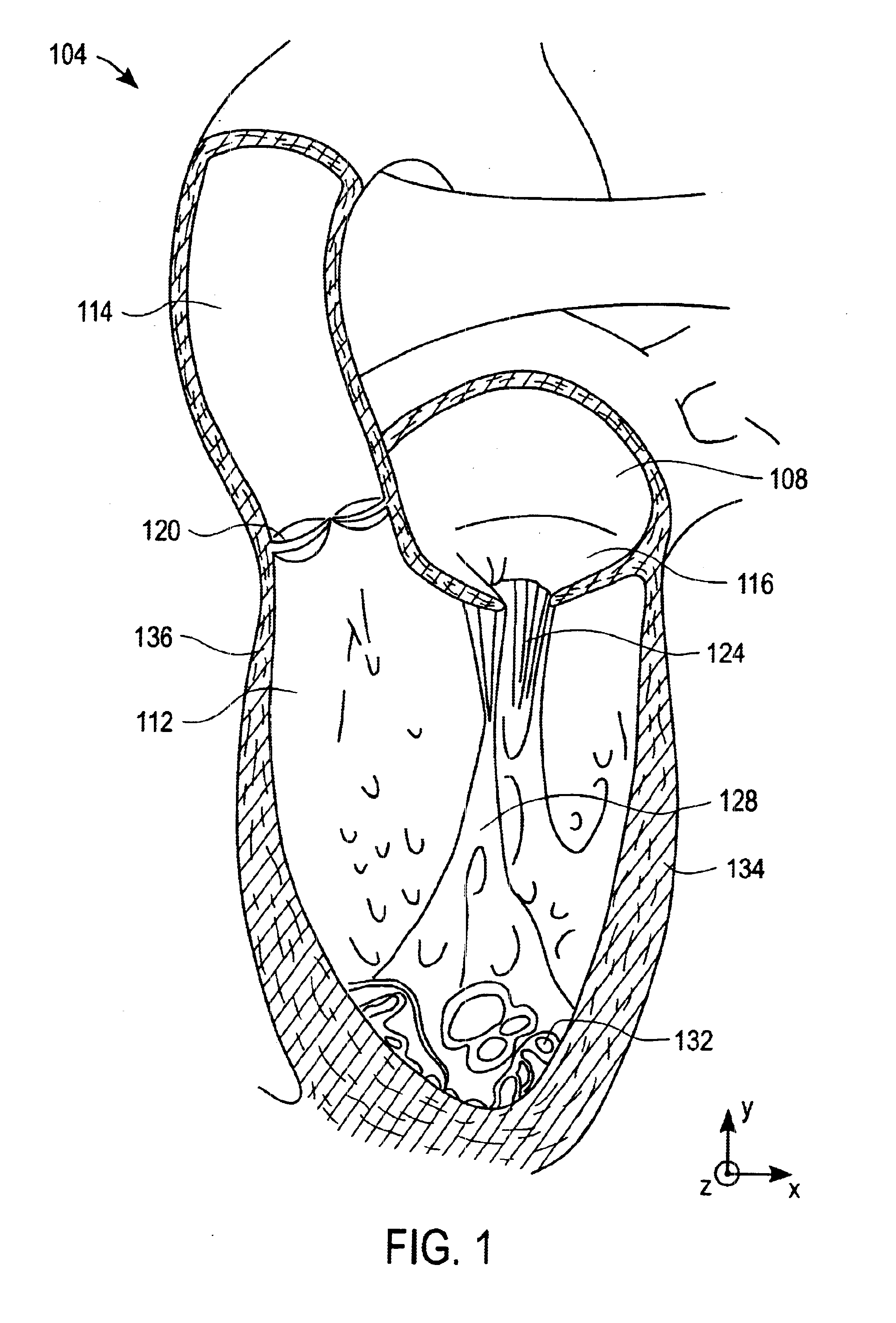
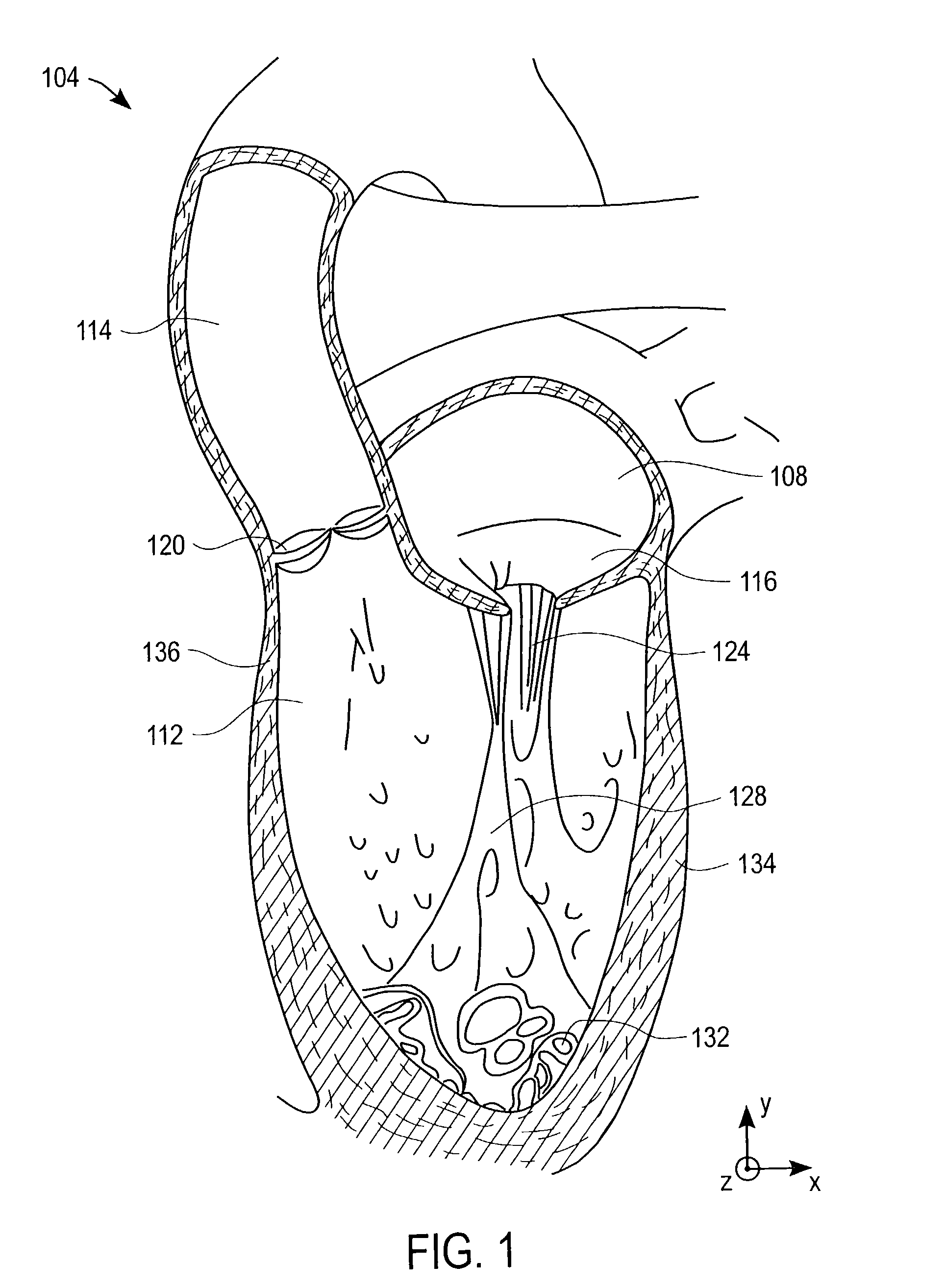
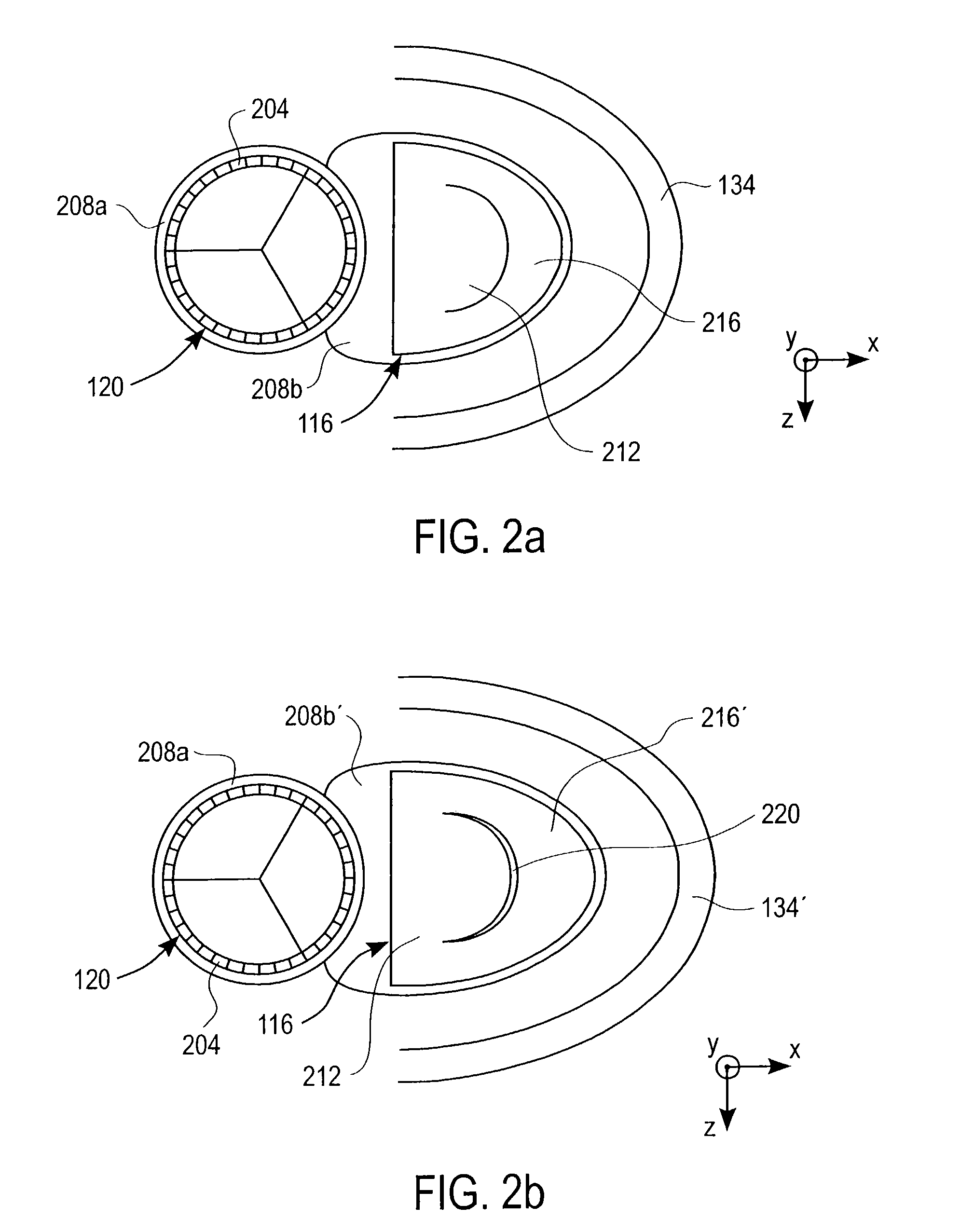
The left ventricle is thicker and more muscular than the right ventricle because it pumps blood at a higher pressure. The right ventricle is triangular in shape and extends from the tricuspid valve in the right atrium to near the apex of the heart. Its wall is thickest at its base and thins towards the atrium.
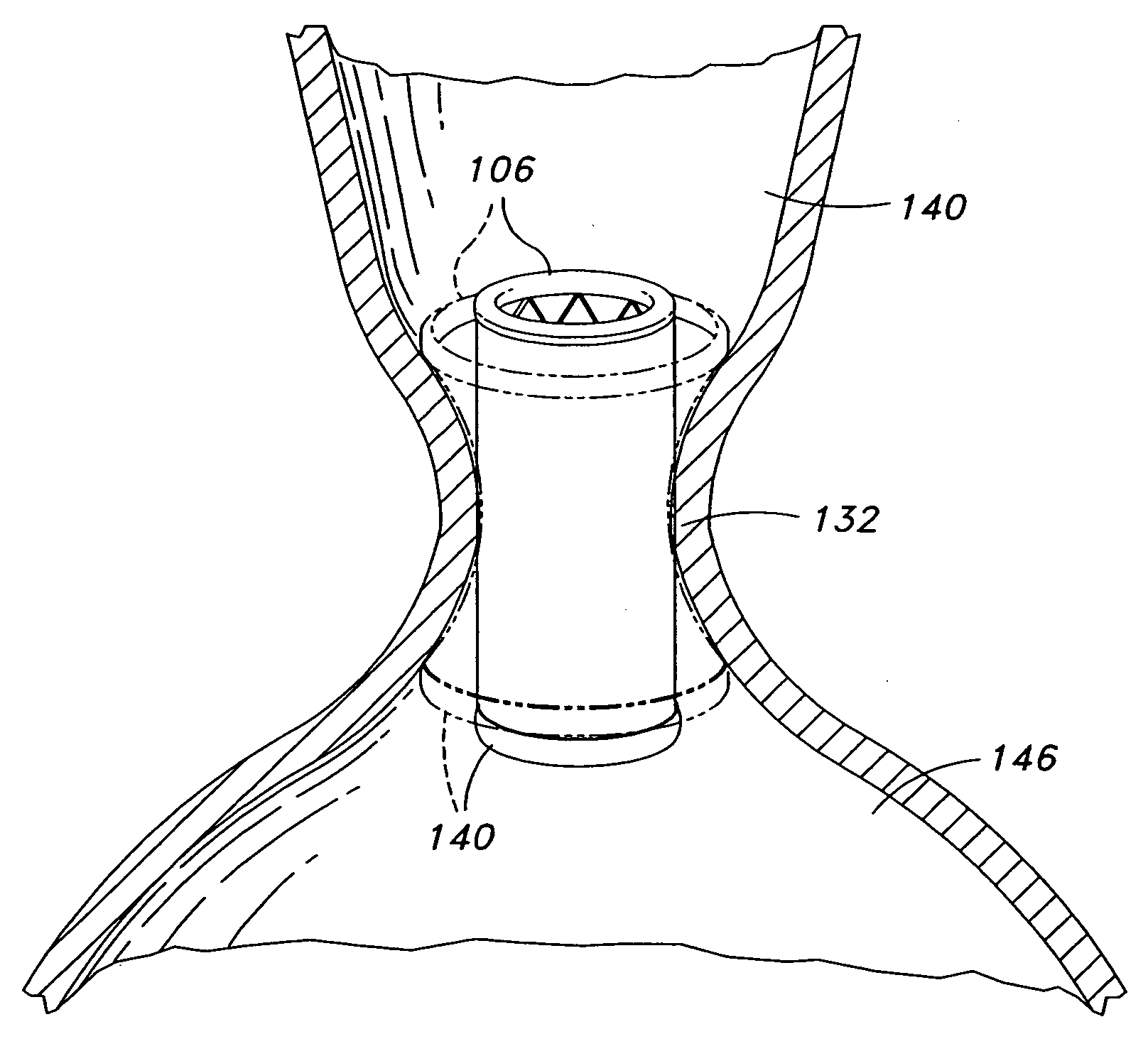
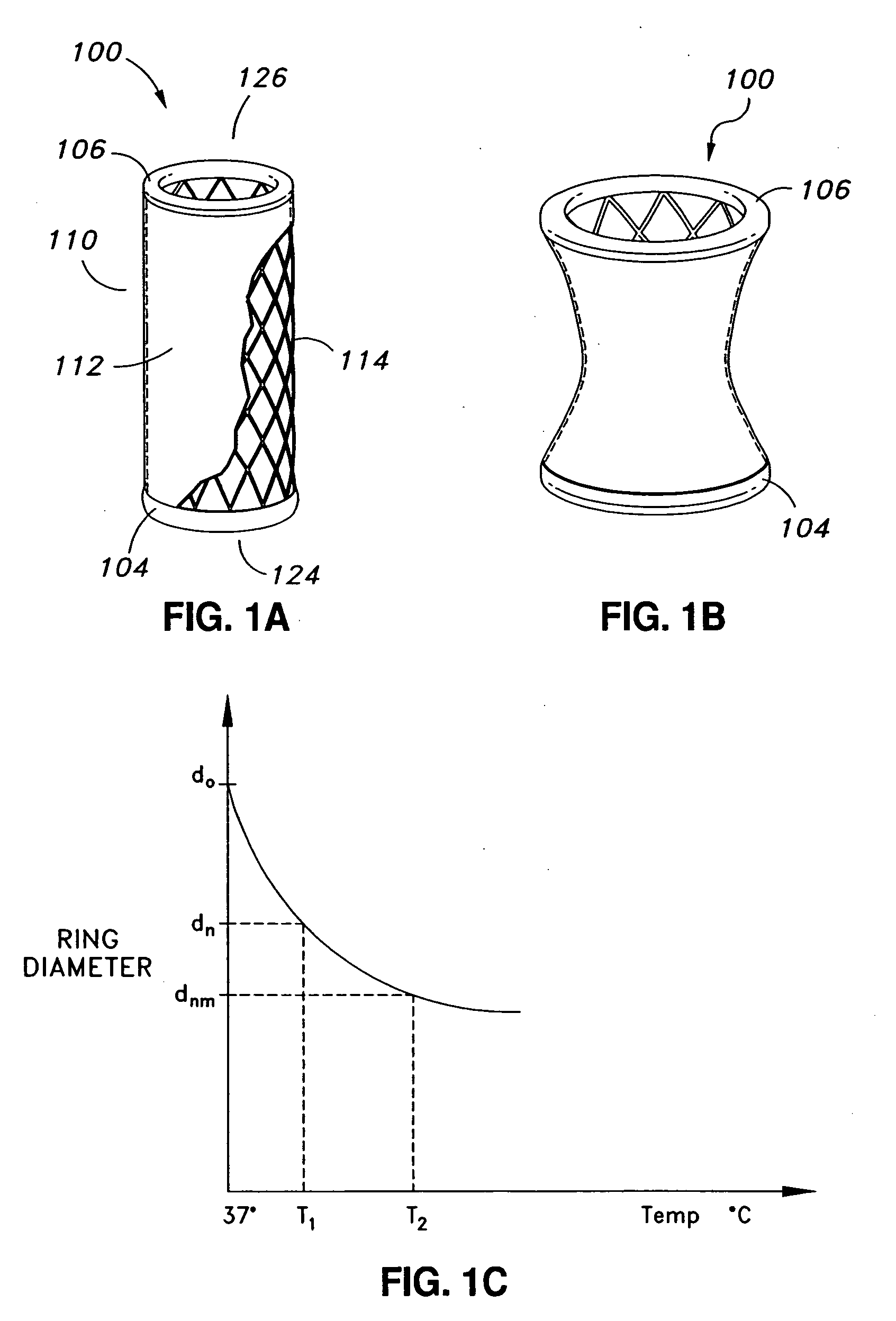
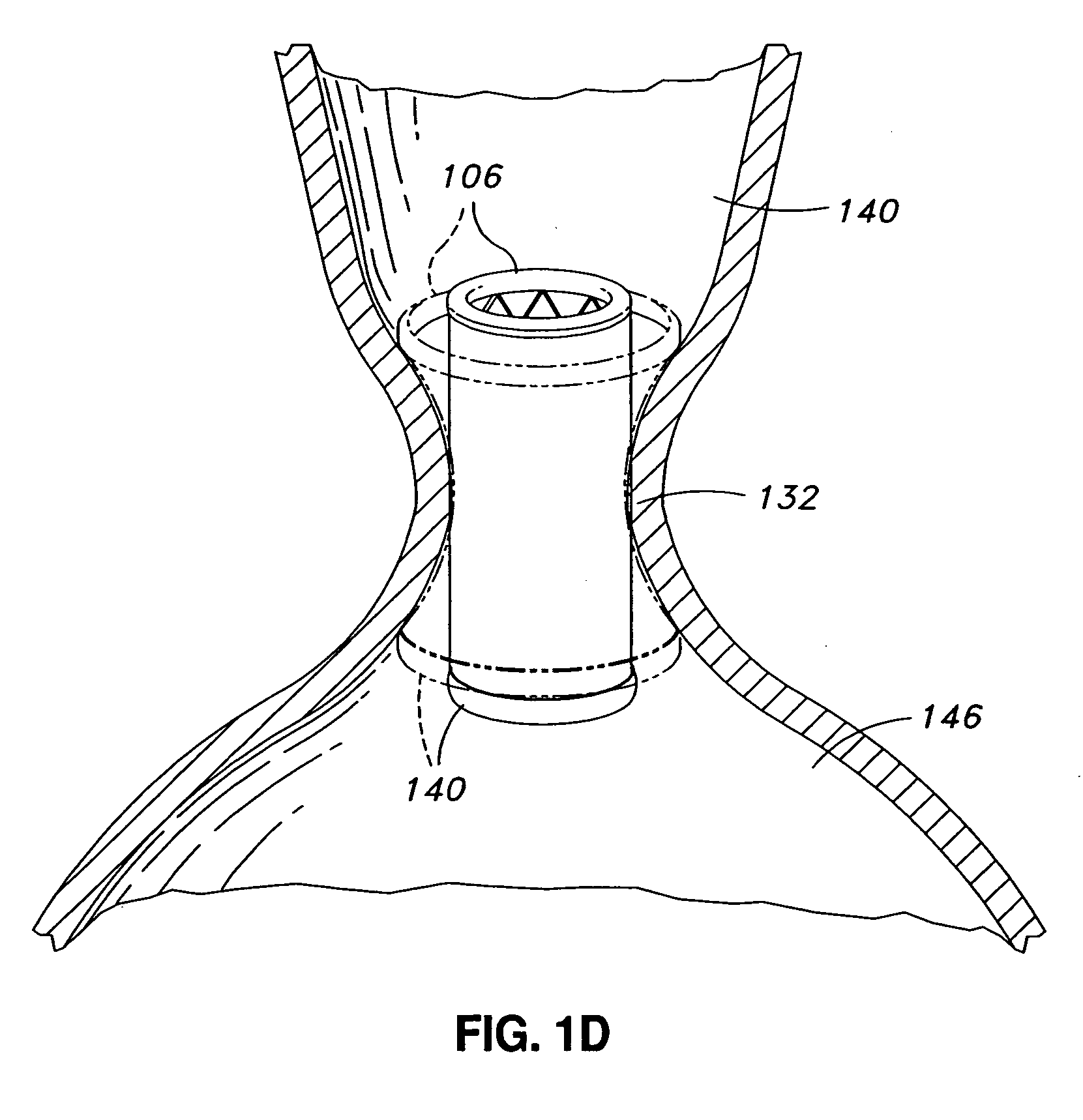
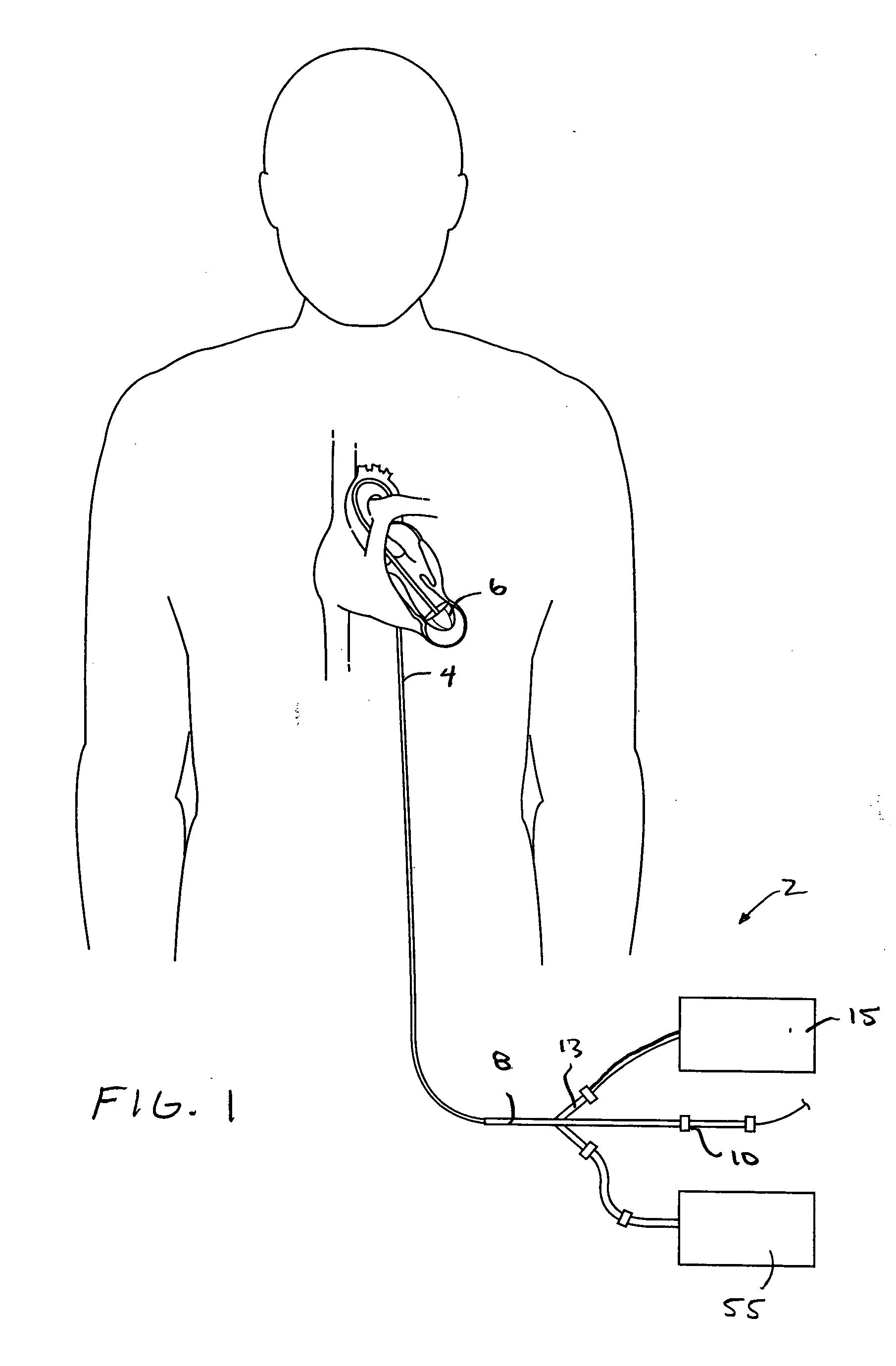
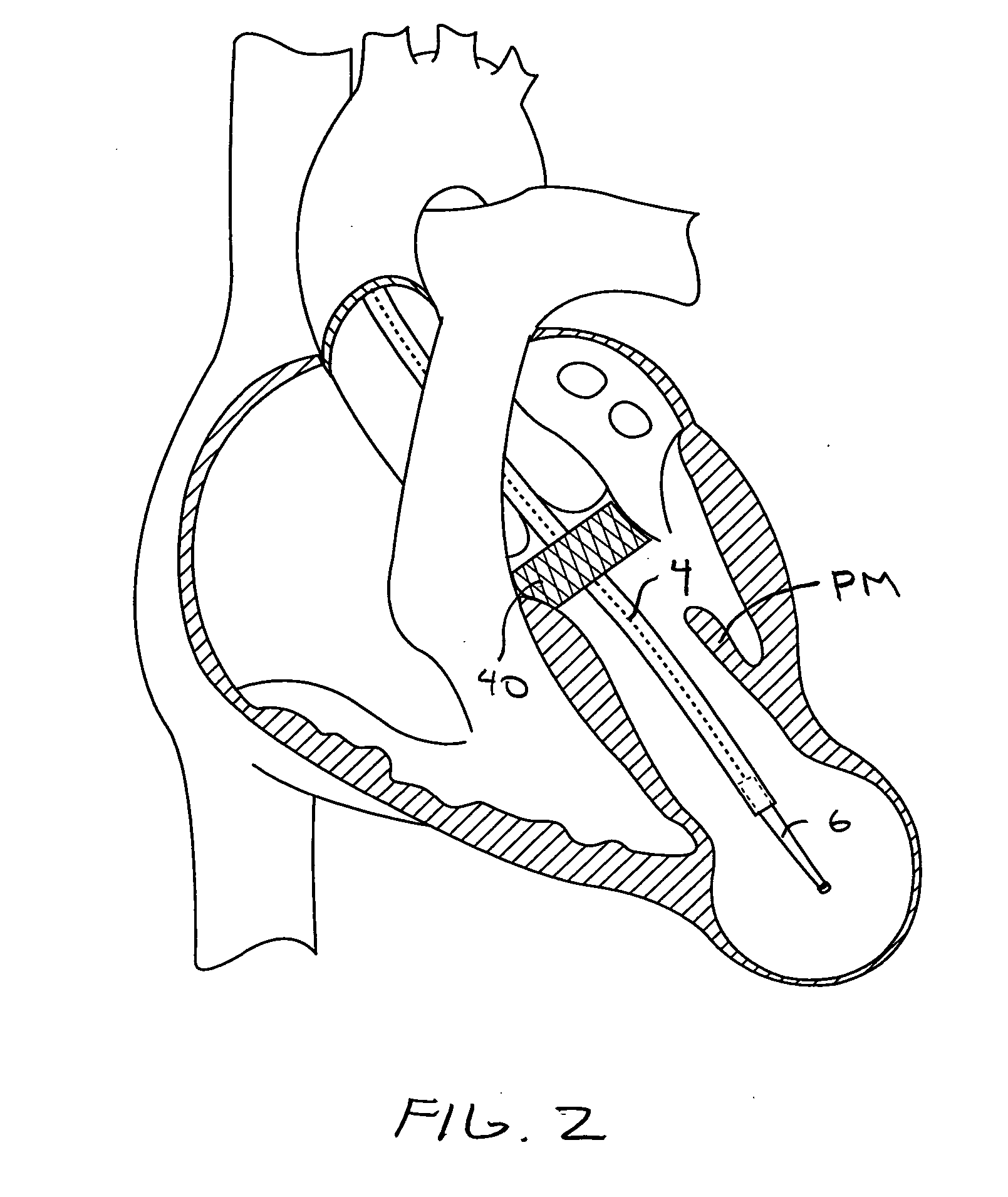
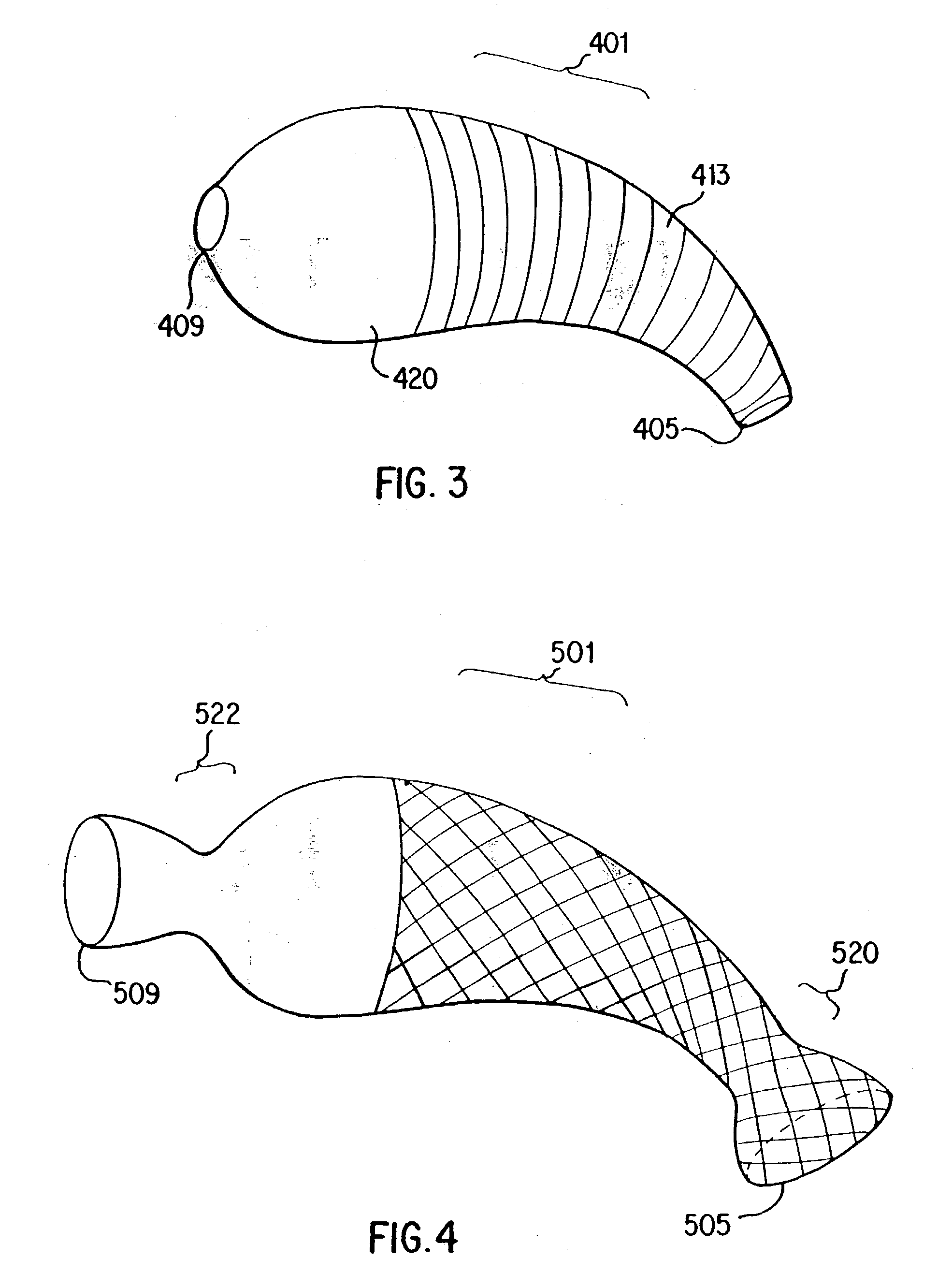
Transapical heart valve delivery system and method
ActiveUS20070112422A1Facilitate positioning of valveHelp positioningStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic heartLeft ventricular apex
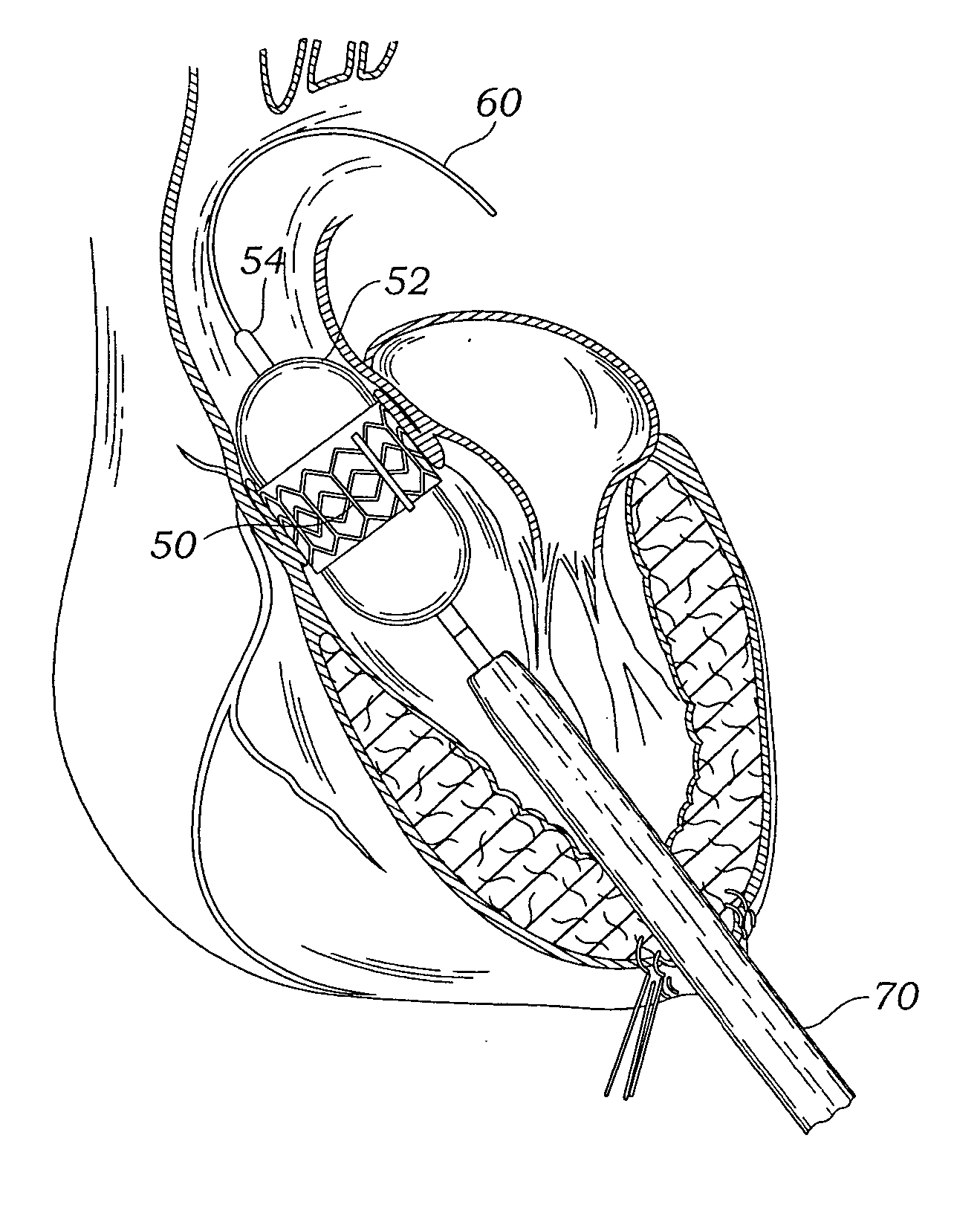
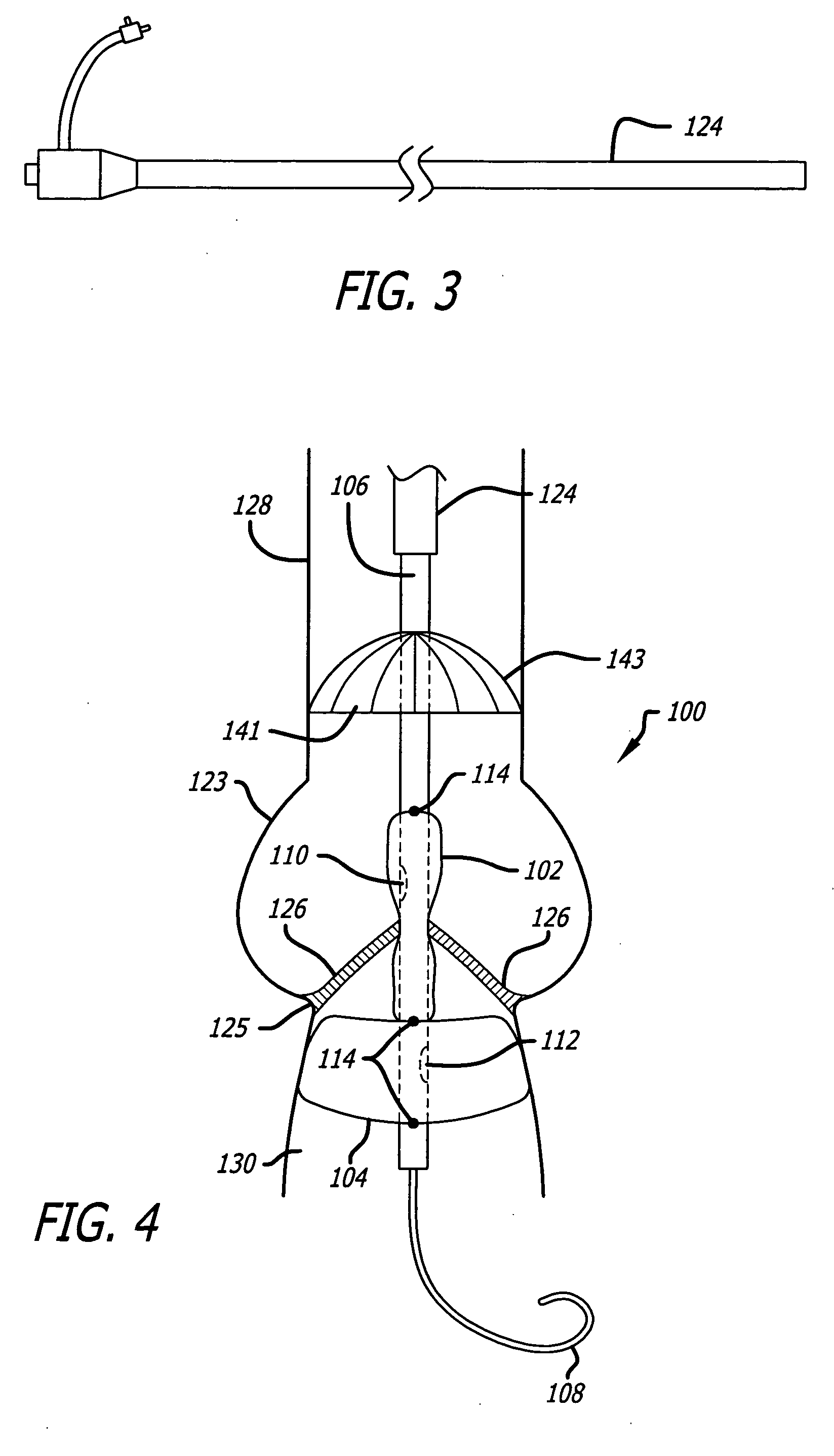
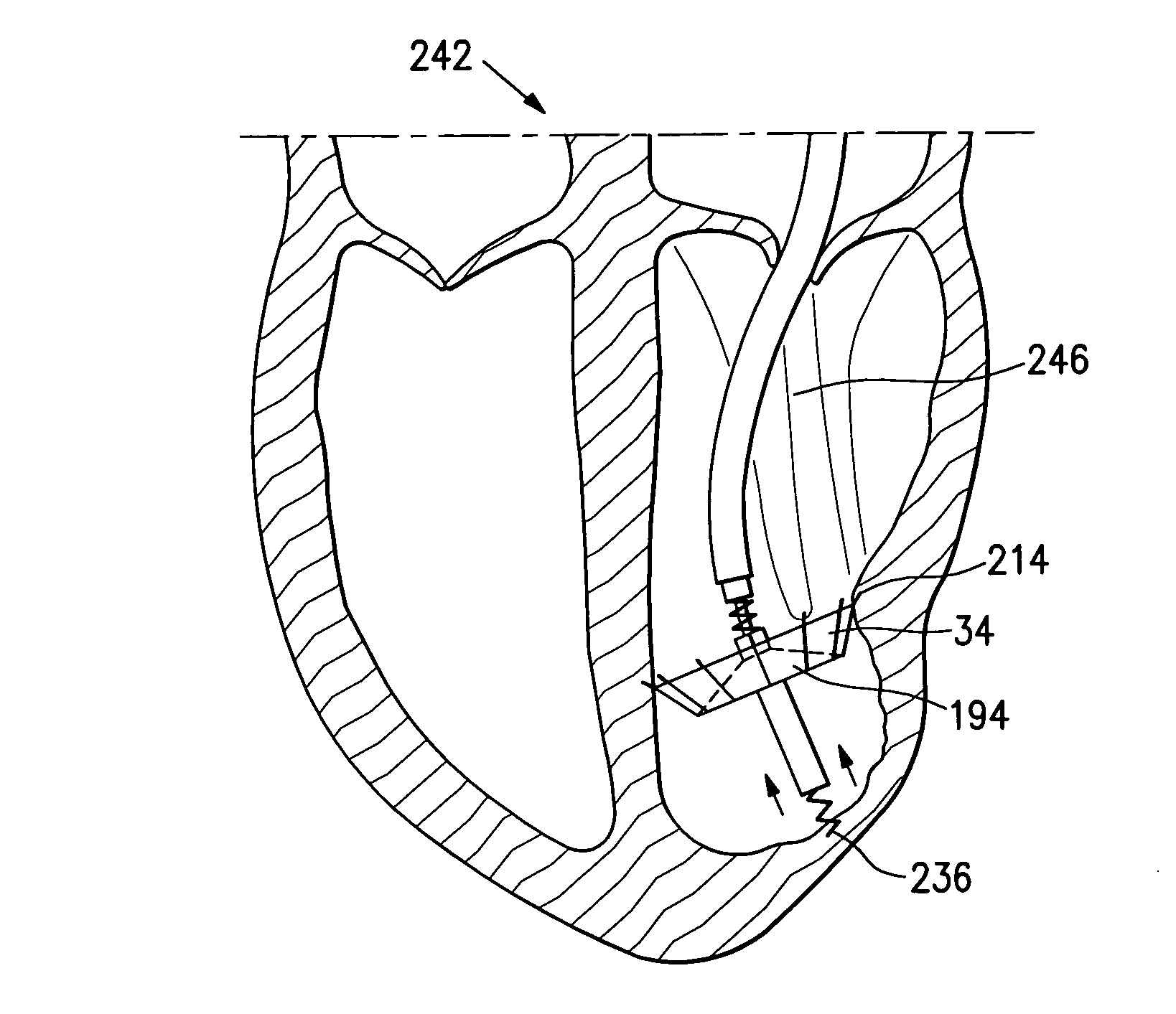
A delivery system and method for delivering a prosthetic heart valve to the aortic valve annulus. The system includes a balloon catheter having a steering mechanism thereon for delivering a balloon-expandable prosthetic heart valve through an introducer in an antegrade fashion to the aortic annulus. The balloon catheter passes through an introducer that accesses the left ventricle through its apex and a small incision in the chest wall. The balloon catheter includes a deflecting segment just proximal to the distal balloon to facilitate positioning of the prosthetic heart valve in the proper orientation within the aortic annulus. A slider in a deflection handle may be coupled to a deflection wire that actuates the deflecting segment. The method includes using two concentric rings of purse-string sutures around the puncture in the left ventricular apex to maintain a good seal around instruments passed therethrough. The prosthetic heart valve may be installed over the existing calcified leaflets, and a pre-dilation valvuloplasty procedure may also be utilized.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for replacing mitral valve
InactiveUS20090276040A1Prevent movementRelieve pressureSuture equipmentsStentsNative tissueProsthesis
A prosthetic mitral valve assembly and method of inserting the same is disclosed. In certain disclosed embodiments, the prosthetic mitral valve assembly has a flared upper end and a tapered portion to fit the contours of the native mitral valve. The prosthetic mitral valve assembly can include a stent or outer support frame with a valve mounted therein, The assembly can be adapted to expand radially outwardly and into contact with the native tissue to create a pressure fit. One embodiment of a method includes positioning the mitral valve assembly below the annulus such that the annulus itself can restrict the assembly from moving in an upward direction towards the left atrium. The mitral valve assembly is also positioned so that the leaflets of the mitral valve hold the assembly to prevent downward movement of the assembly towards the left ventricle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
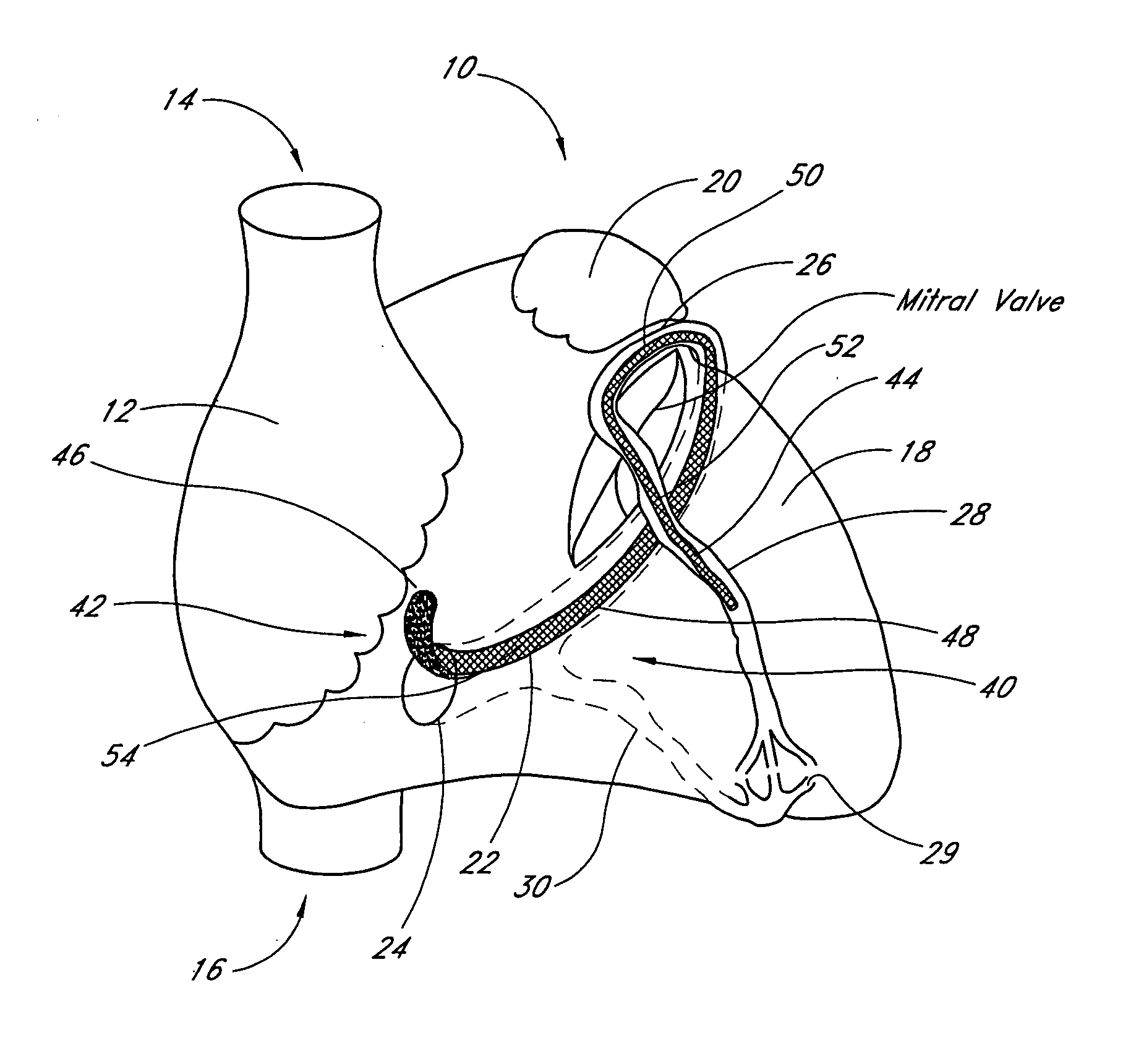
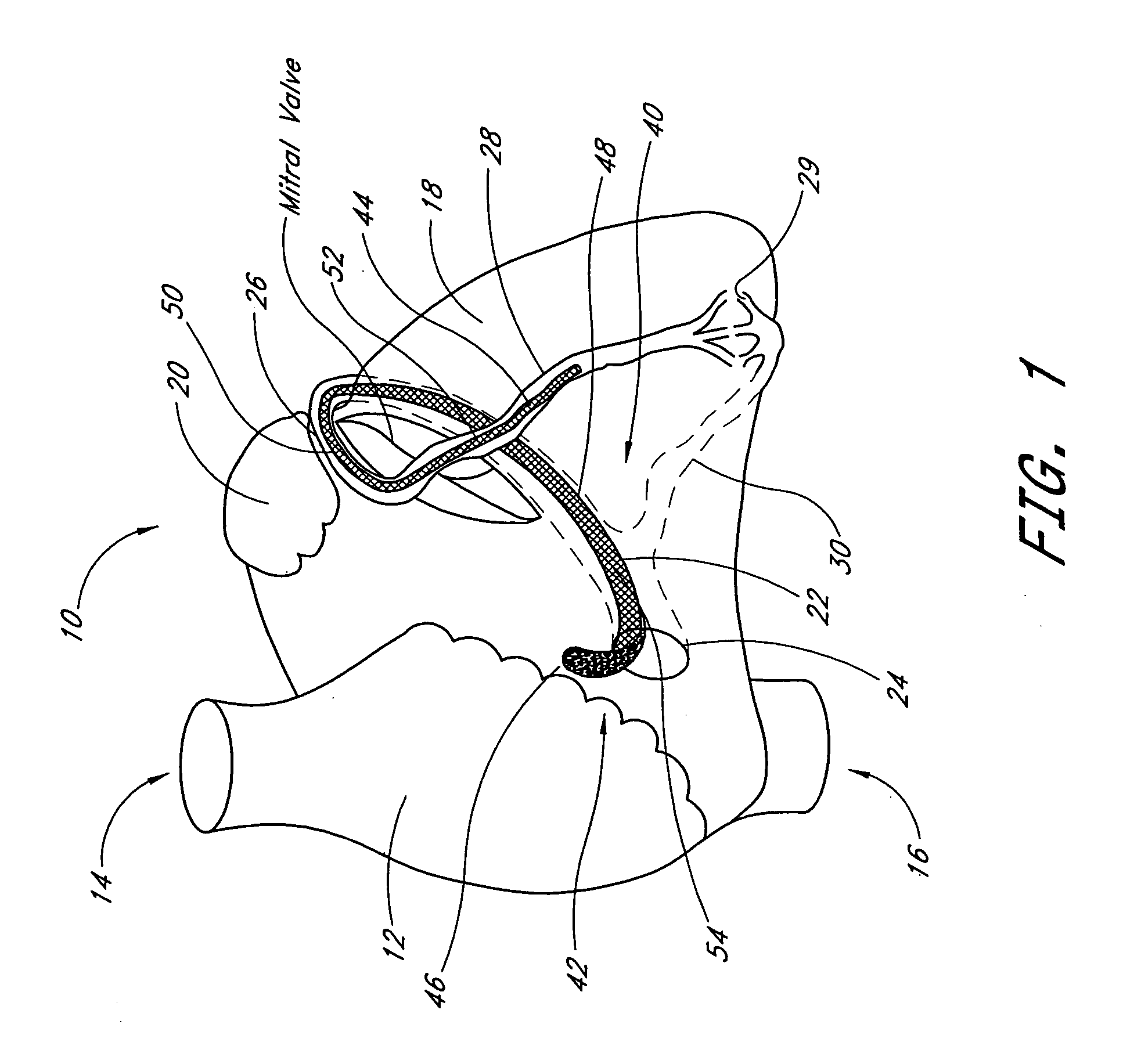
Method and apparatus for catheter-based annuloplasty
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for treatment of heart valve regurgitation
In one embodiment, the present invention provides a prosthesis that can be implanted within a heart to at least partially block gaps that may be present between the two mitral valve leaflets. In one preferred embodiment, the prosthesis includes an anchoring ring that expands within the left atrium to anchor the prosthesis and a pocket member fixed to the anchoring ring. The pocket member is positioned within the mitral valve, between the leaflets so that an open end of the pocket member is positioned within the left ventricle. When the mitral valve is open, blood flows past the pocket member, maintaining the pocket member in a collapsed state. When the mitral valve closes, the backpressure of the blood pushes into the pocket member, expanding the pocket member to an inflated shape. The mitral valve leaflets contact the expanded pocket member, allowing the prosthesis to block at least a portion of the openings between the leaflets, thereby minimizing regurgitated blood flow into the left atrium.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Adjustable prosthetic valve implant
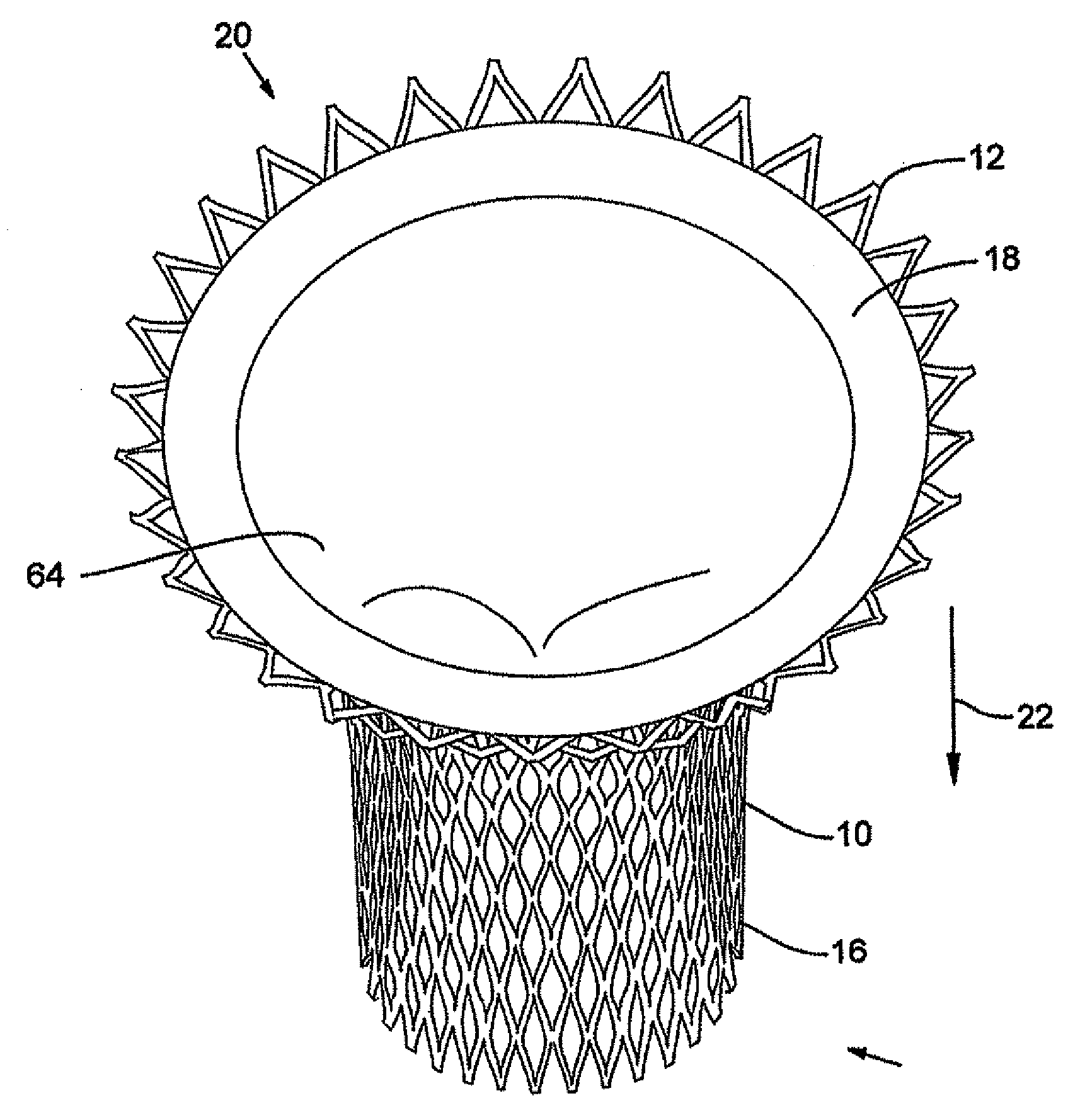
A prosthetic implant for treating a diseased aortic valve is described. The prosthetic implant includes a substantially tubular body configured to be positioned in an aorta of a patient, at or near the patient's aortic valve. The body includes a lumen extending through the body from a proximal end to a distal end of the body; and an adjustable frame surrounding the lumen. The prosthetic implant further includes at least one adjustable element located in or on the body and extending at least partially around a circumference of the lumen. The at least one adjustable element includes a shape memory material and is transformable, in response to application of an activation energy, from a first configuration to a second configuration, wherein the first configuration and second configuration differ in a size of at least one dimension of the at least one adjustable element. The at least one adjustable element may engage at least one of a root of the aorta, an annulus of the aortic valve, and the patient's left ventricle, when the at least one adjustable element is in the second configuration.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
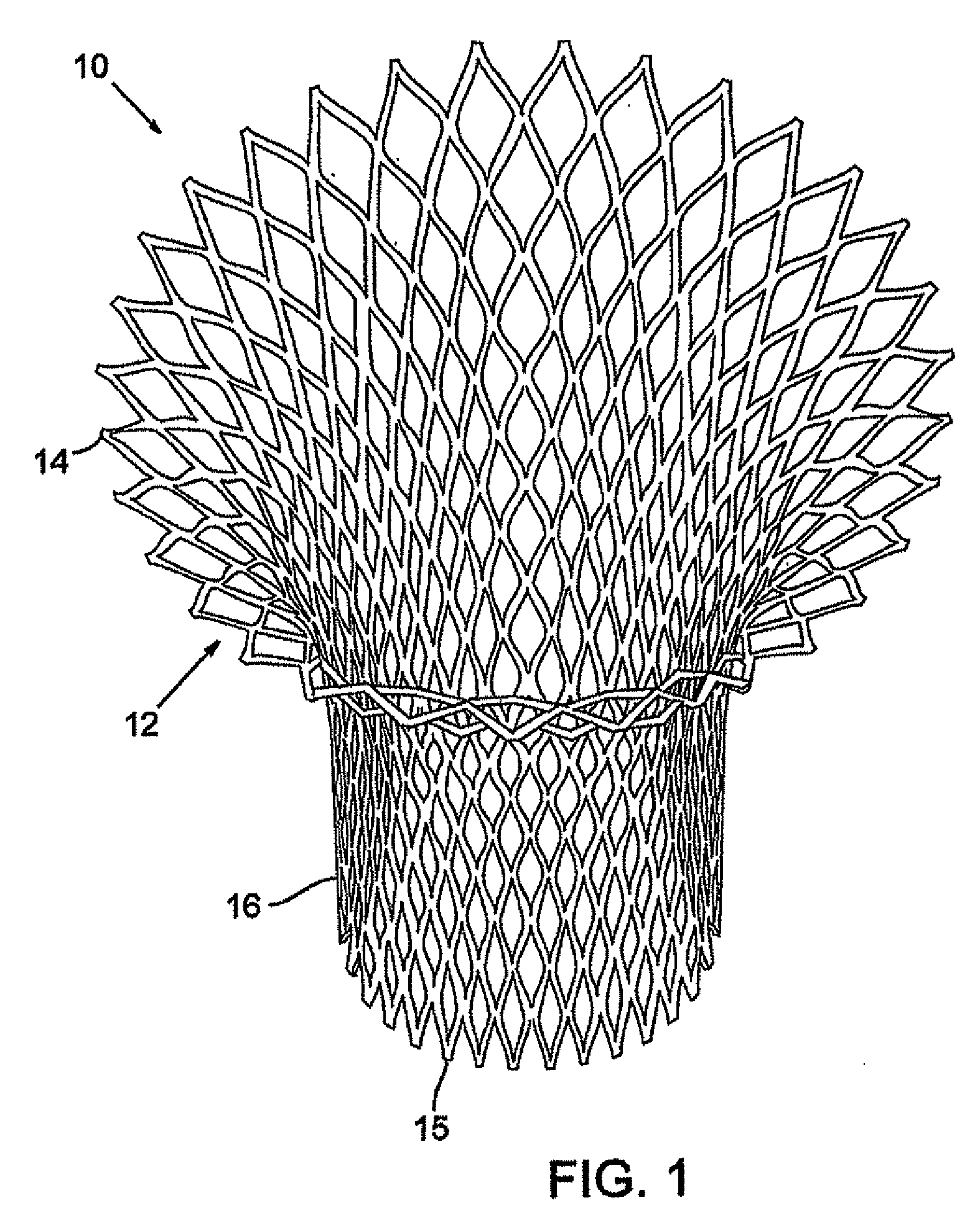
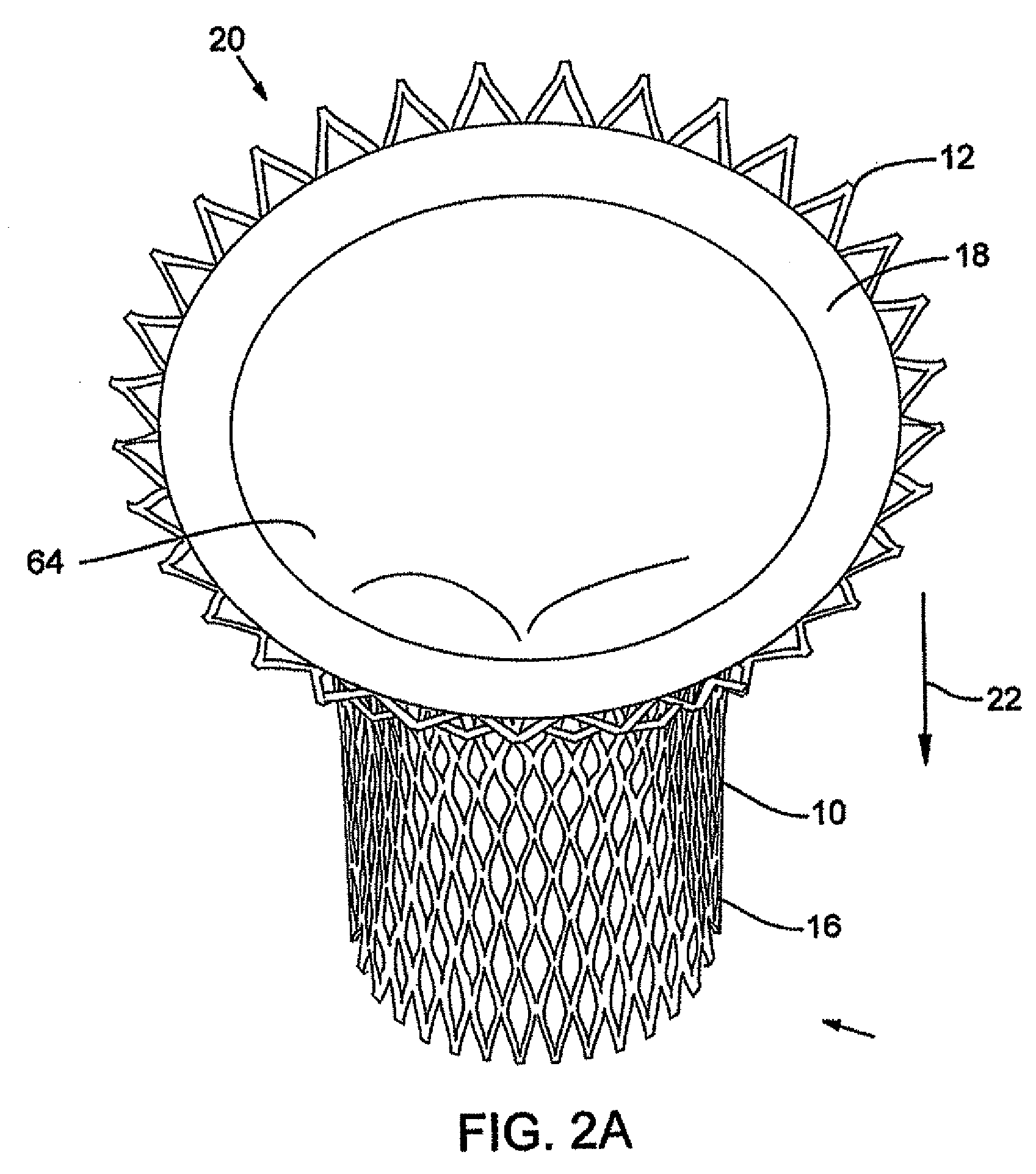
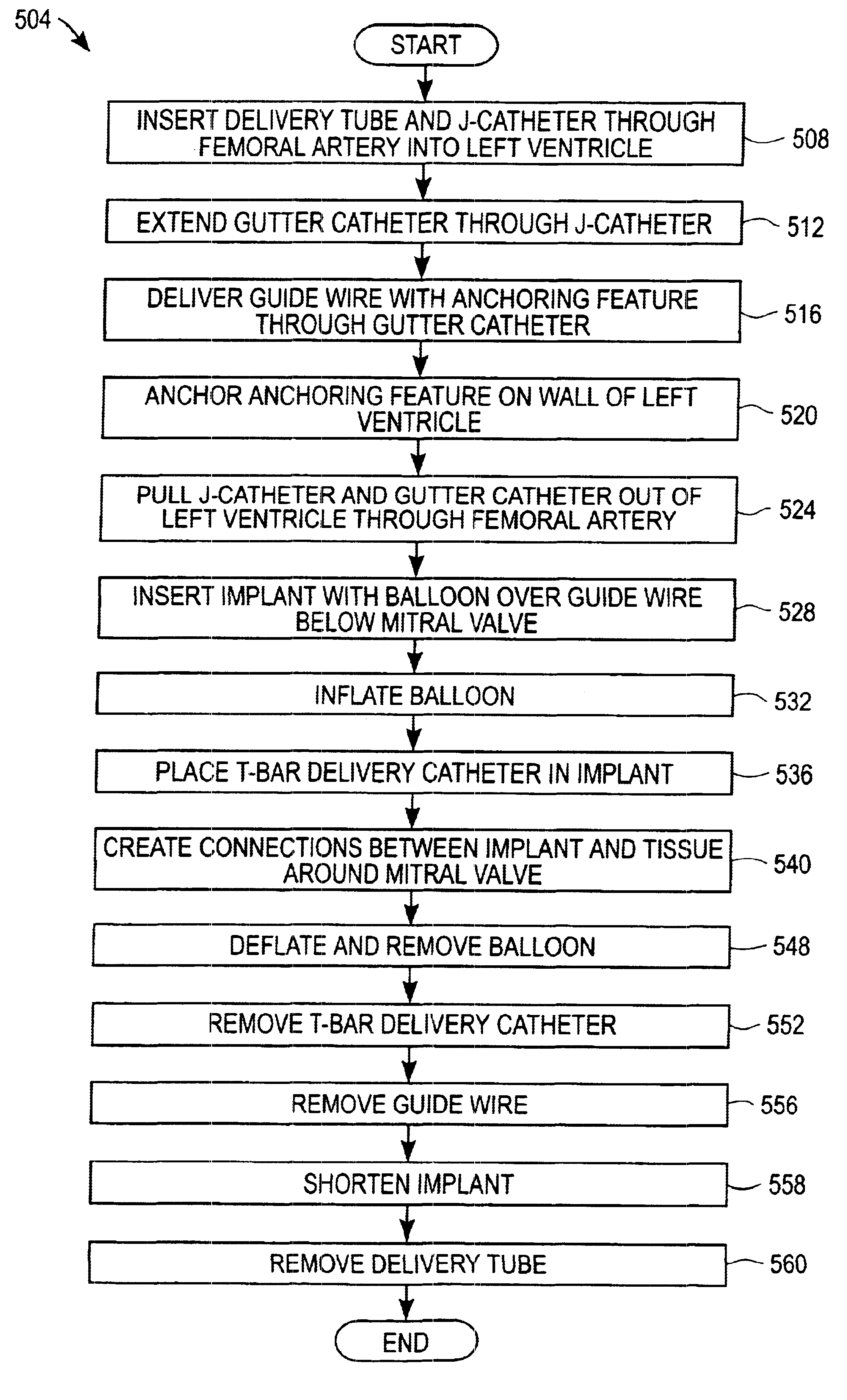
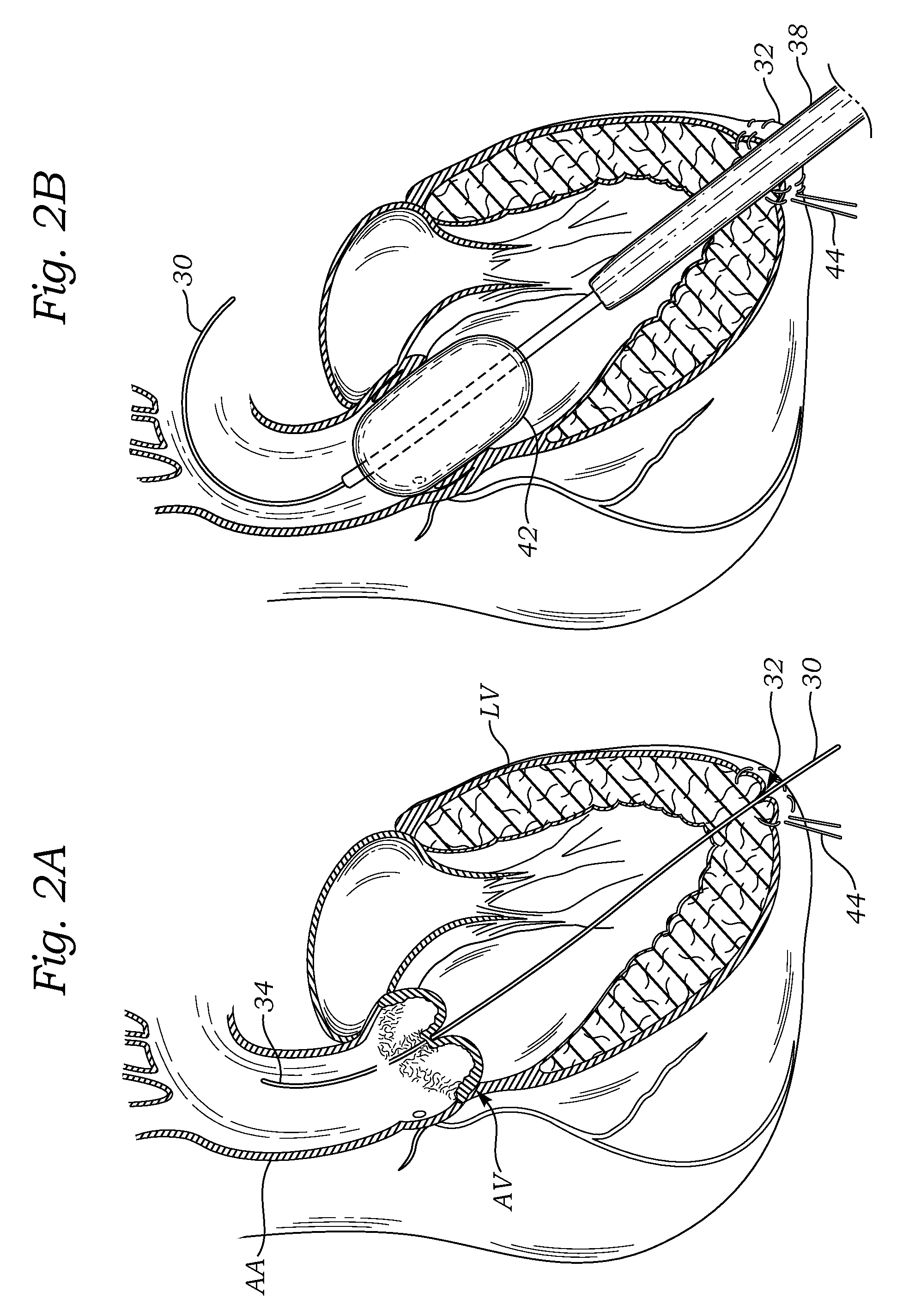
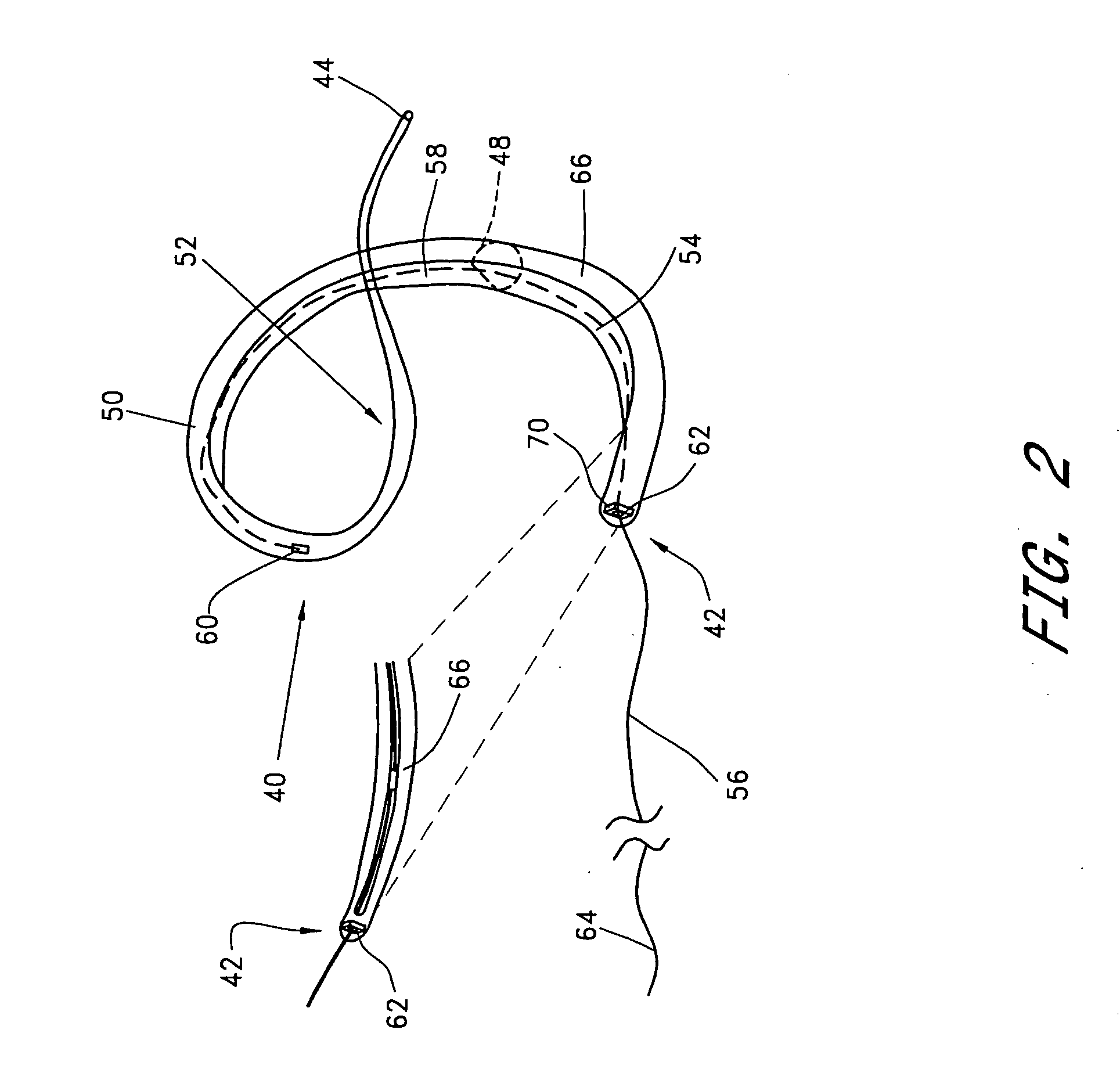
Method and apparatus for catheter-based annuloplasty using local plications
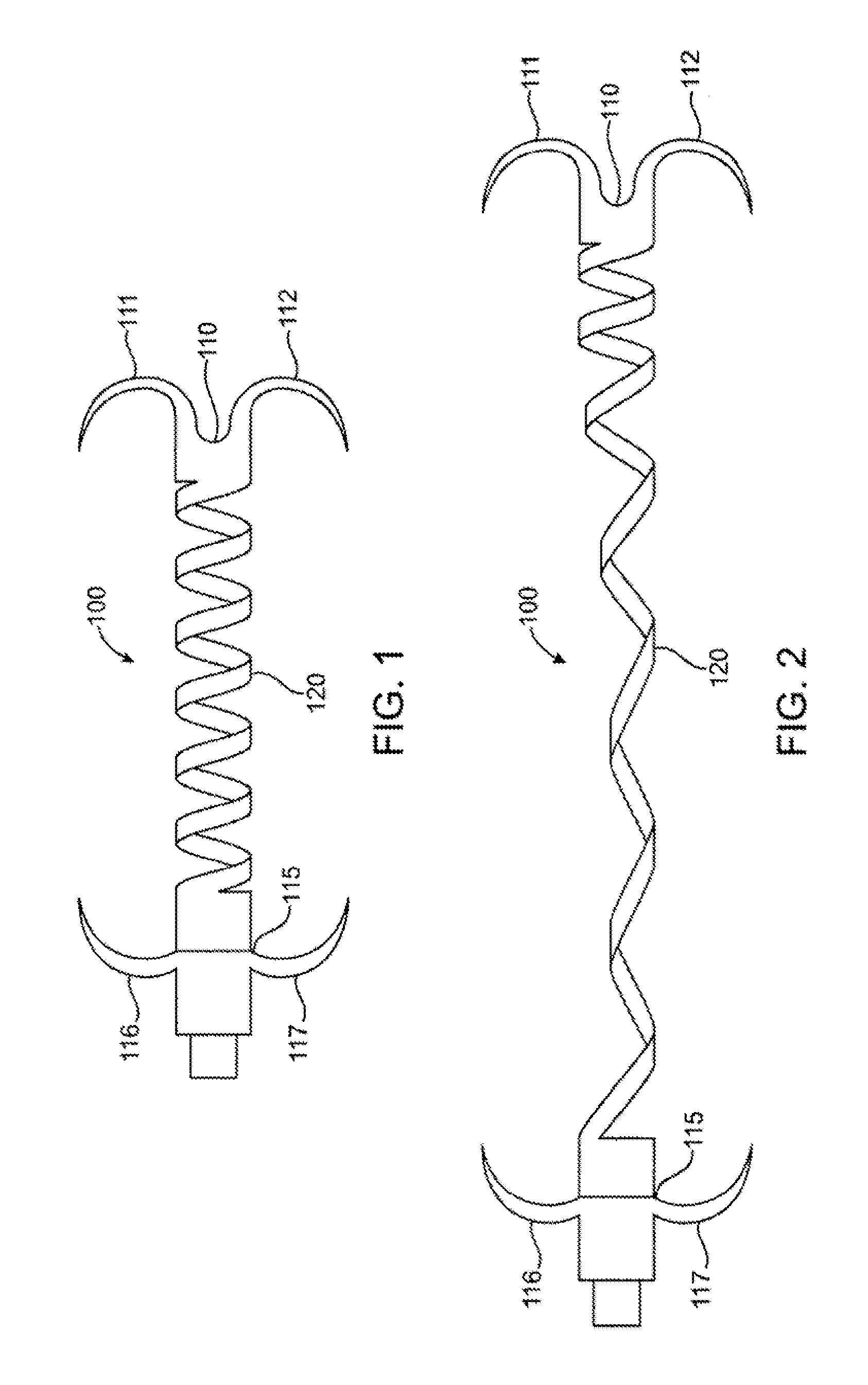
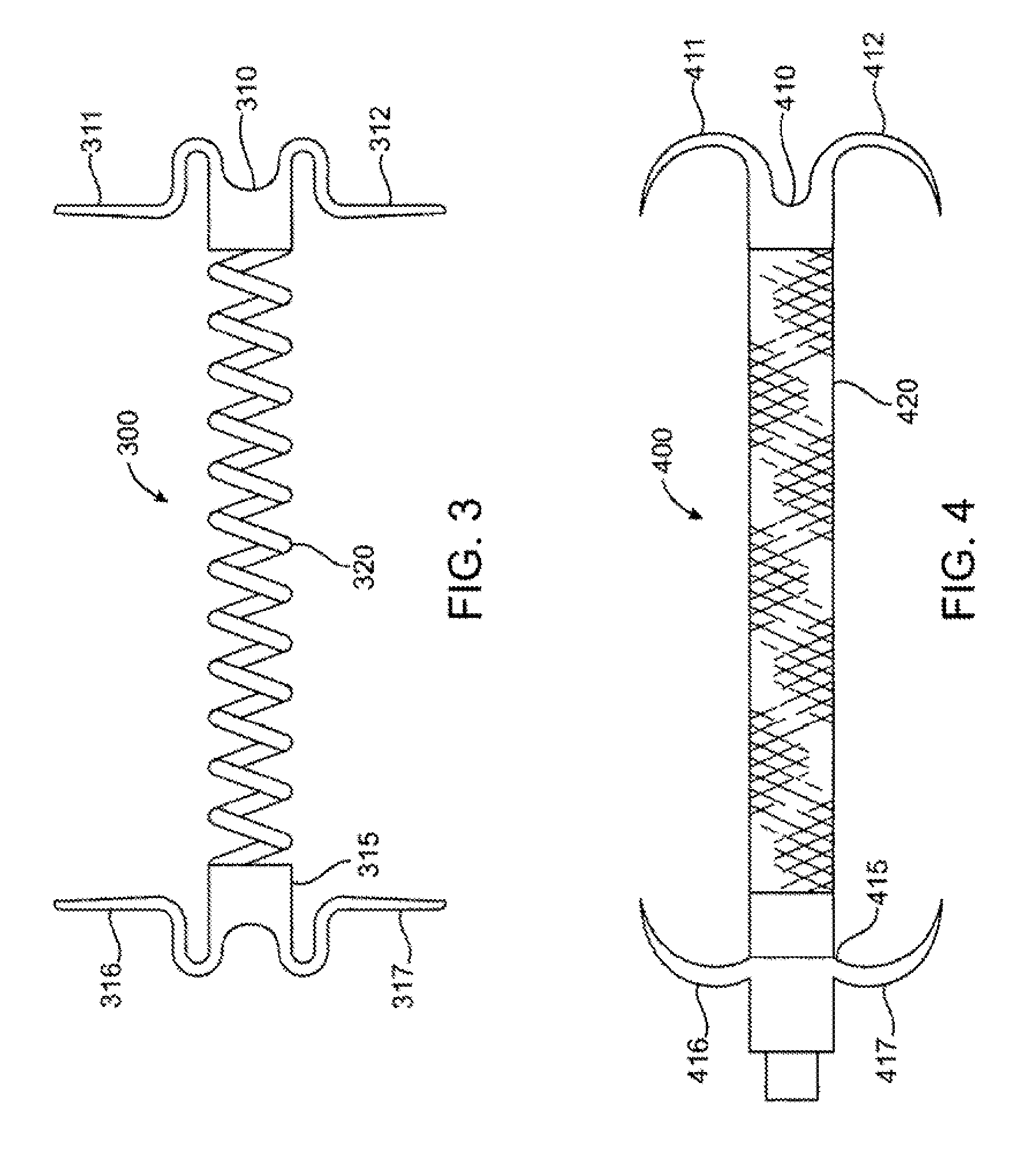
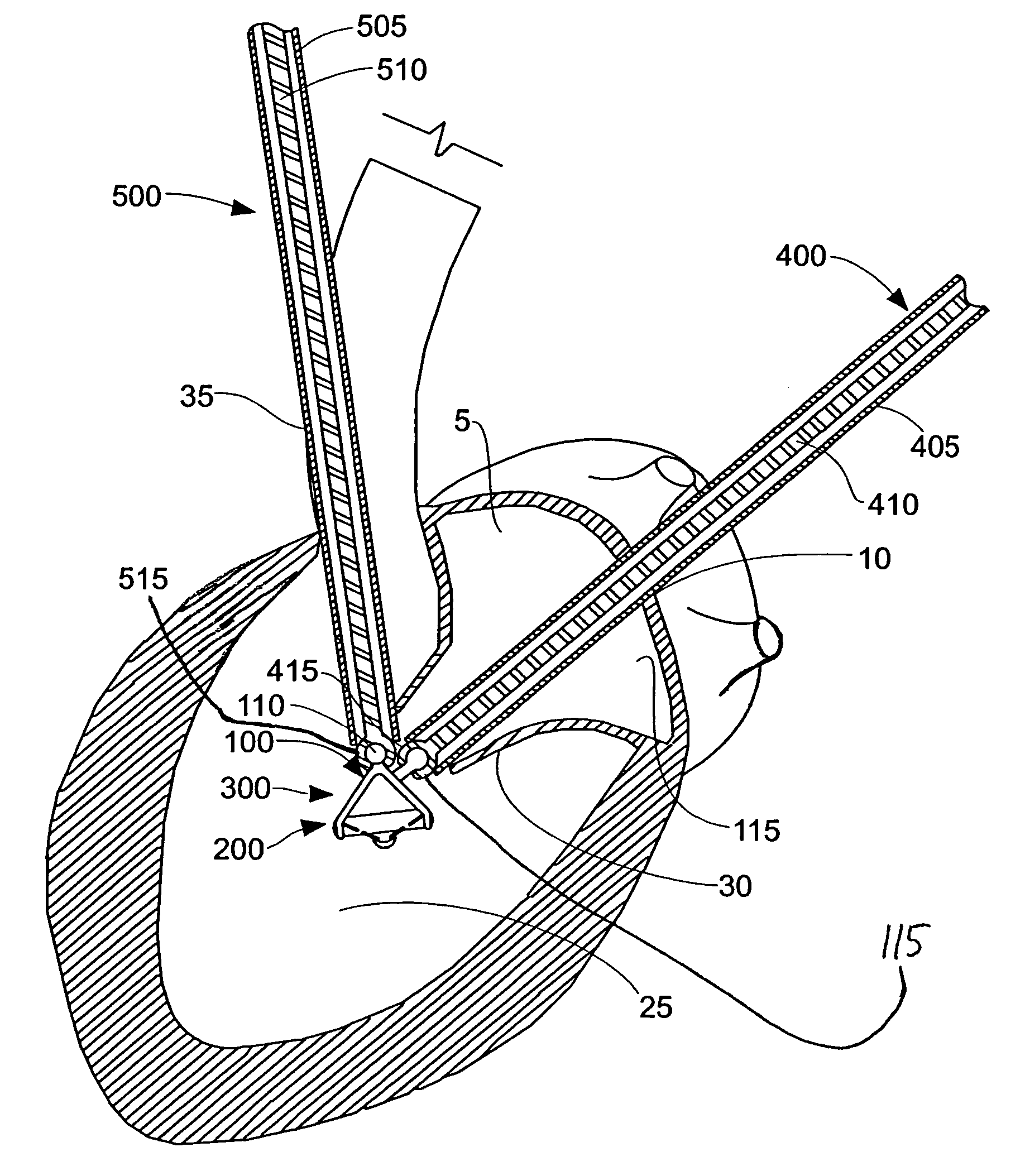
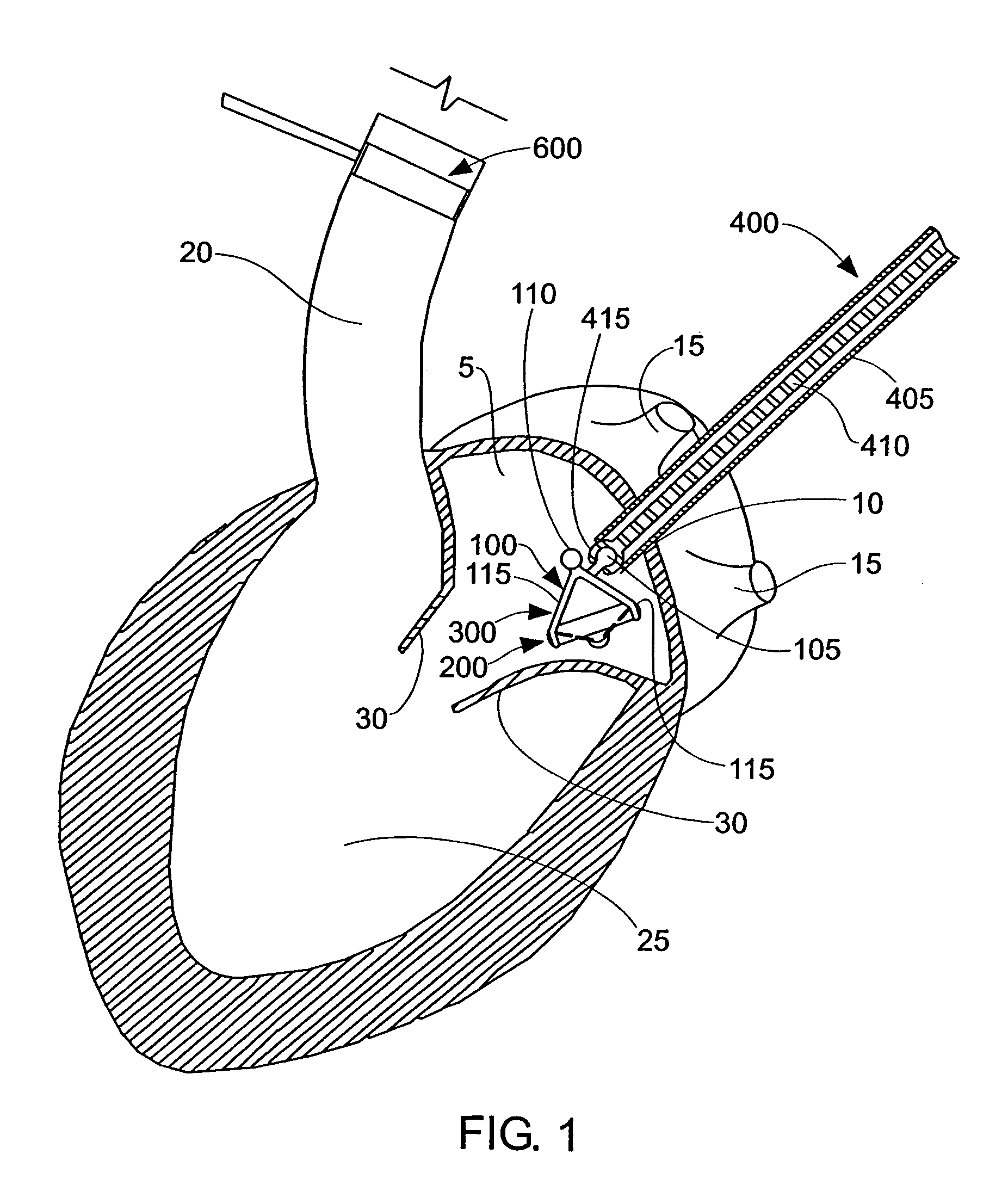
InactiveUS7037334B1Complicated surgical procedure can be avoidedImprove the quality of lifeSuture equipmentsBone implantMitral valve leafletLeft ventricle wall
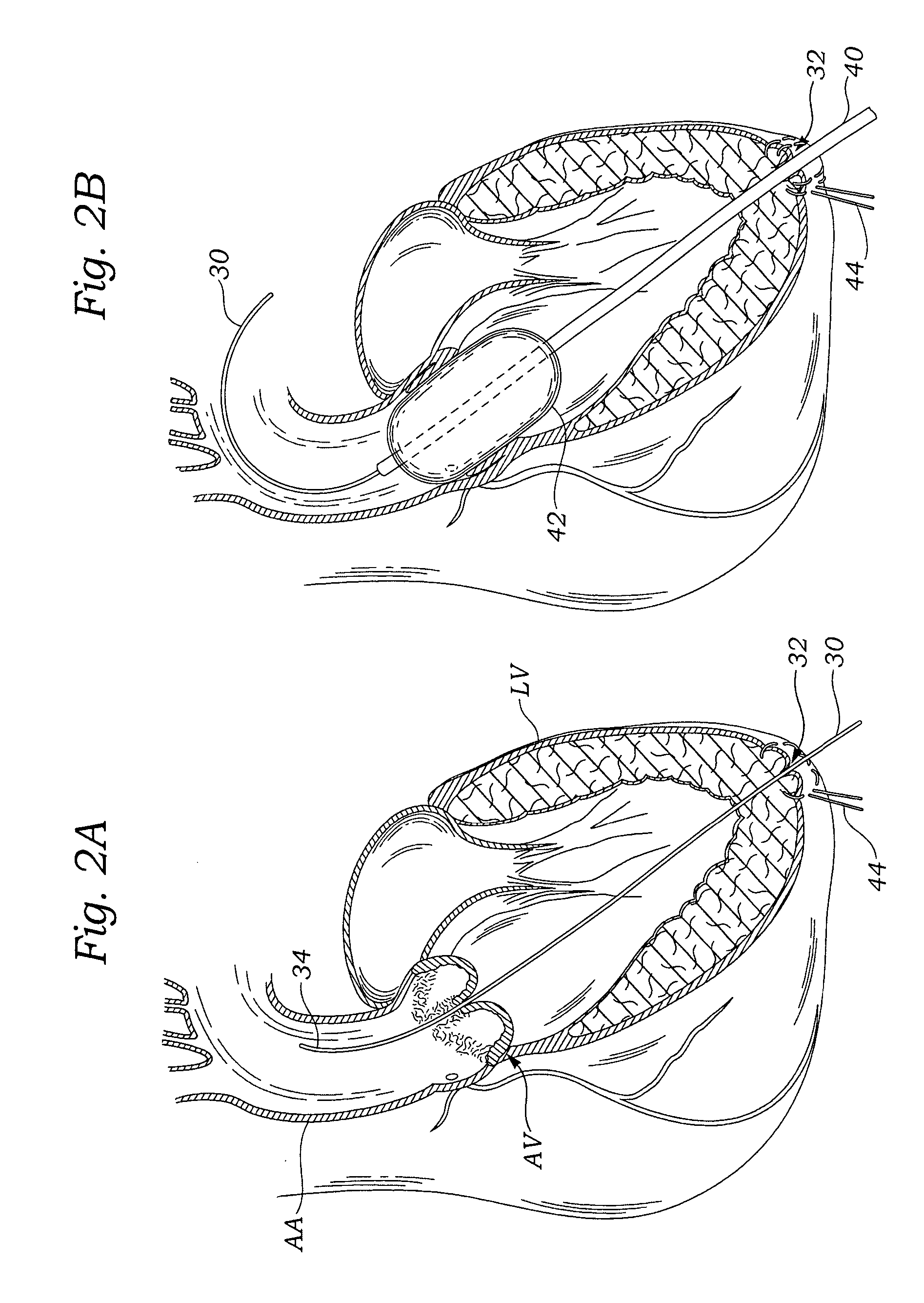
The present invention relates to a minimally invasive method of performing annuloplasty. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method for performing annuloplasty includes accessing a left ventricle of a heart to provide a discrete plication element to the left ventricle, and engaging the plication element to tissue near a mitral valve of the heart. Engaging the plication element includes causing the plication element to gather a portion of the tissue to create a plication. In one embodiment, accessing the left ventricle of the heart to provide the plication element includes accessing the left ventricle of the heart using a catheter arrangement.
Owner:MITRALIGN INC
Valvuloplasty devices and methods
ActiveUS20050090846A1Stable positionAvoid structureBalloon catheterCannulasAortic valvuloplastyAortic sinus
The present invention provides an aortic valvuloplasty catheter which, in one preferred embodiment, has a tapered distal balloon segment that anchors within the left ventricle outflow track of the patient's heart and a rounded proximal segment which conforms to the aortic sinuses forcing the valve leaflets open. In addition, this embodiment of the valvuloplasty catheter includes a fiber-based balloon membrane, a distal pigtail end hole catheter tip, and a catheter sheath.
Owner:INTERVALVE MEDICAL INC
Transapical delivery system for heart valves
ActiveUS20110015729A1Facilitate positioning of valveHelp positioningStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic valveProsthetic heart
A delivery system and method for delivering a prosthetic heart valve to the aortic valve annulus. The system includes a delivery catheter having a steering mechanism thereon for delivering a balloon-expandable prosthetic heart valve to the aortic annulus in an antegrade fashion through an introducer passing into the left ventricle through its apex. The introducer may have a more floppy distal section than a proximal section to reduce trauma to the heart wall while preserving good operating field stability. The delivery catheter includes a deflecting segment just proximal to a distal balloon to facilitate positioning of the prosthetic heart valve in the proper orientation within the aortic annulus. A trigger in a catheter handle may be coupled to a deflection wire that actuates the deflecting segment, while a slider in the handle controls retraction of a valve pusher. The prosthetic heart valve may be installed over the existing calcified leaflets, and a pre-dilation valvuloplasty procedure may also be utilized.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
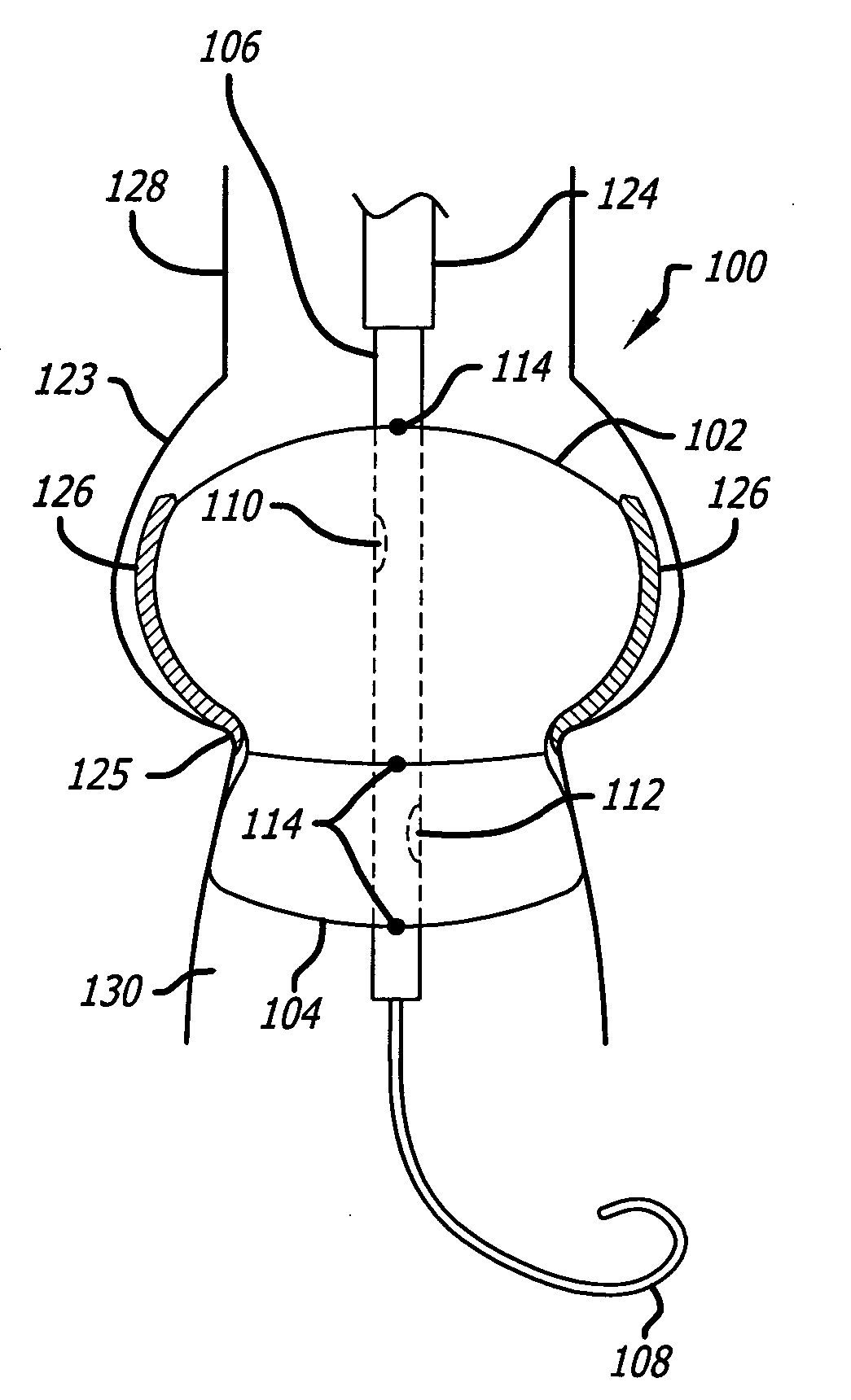
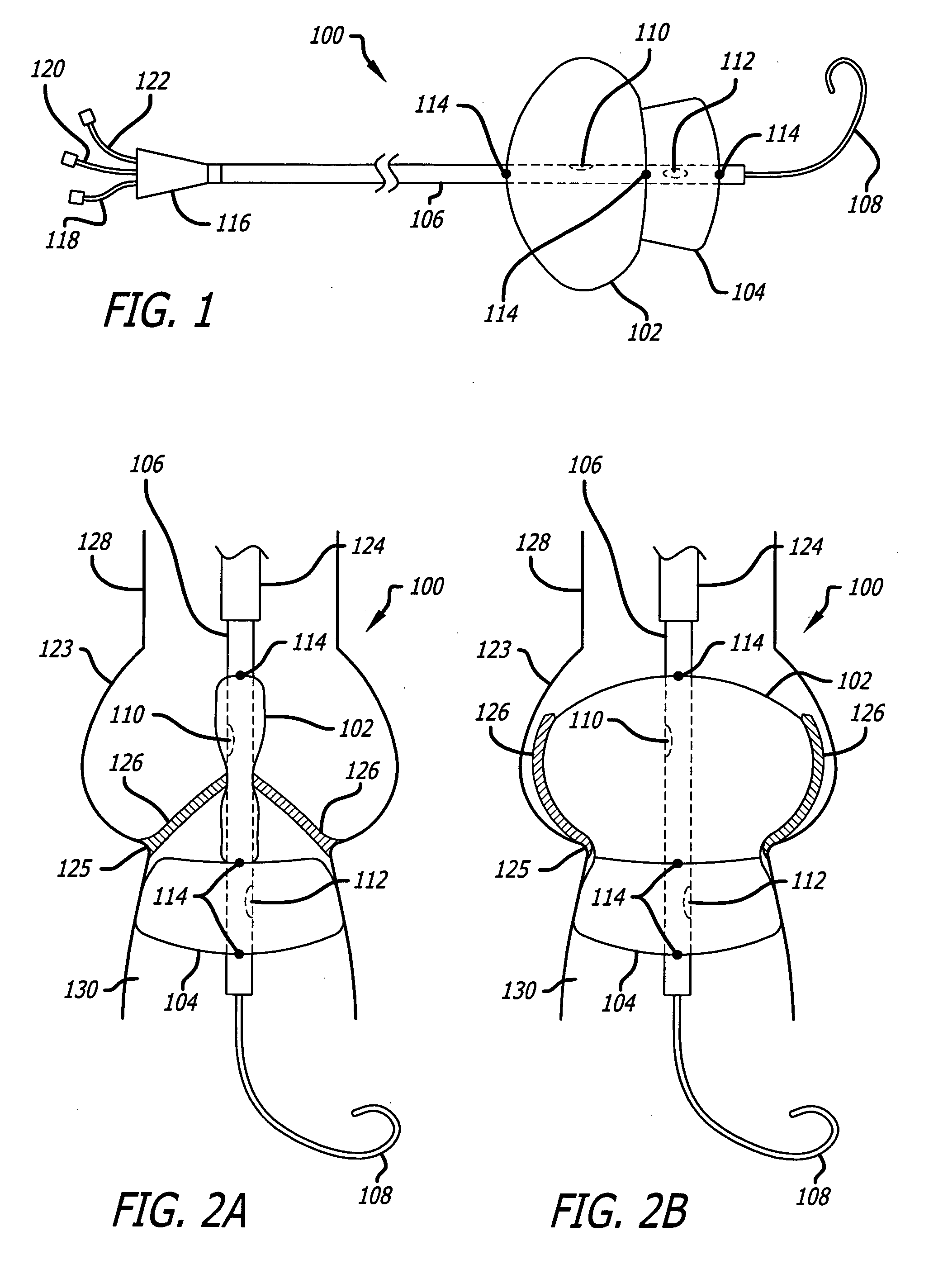
Transluminal mitral annuloplasty
A mitral annuloplasty and left ventricle restriction device is designed to be transvenously advanced and deployed within the coronary sinus and in some embodiments other coronary veins The device places tension on adjacent structures, reducing the diameter and / or limiting expansion of the mitral annulus and / or limiting diastolic expansion of the left ventricle. These effects may be beneficial for patients with dilated cardiomyopathy.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Device for treating mitral valve regurgitation
InactiveUS20070066863A1Reduce lateral distanceReduce fatigueSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberTonicity
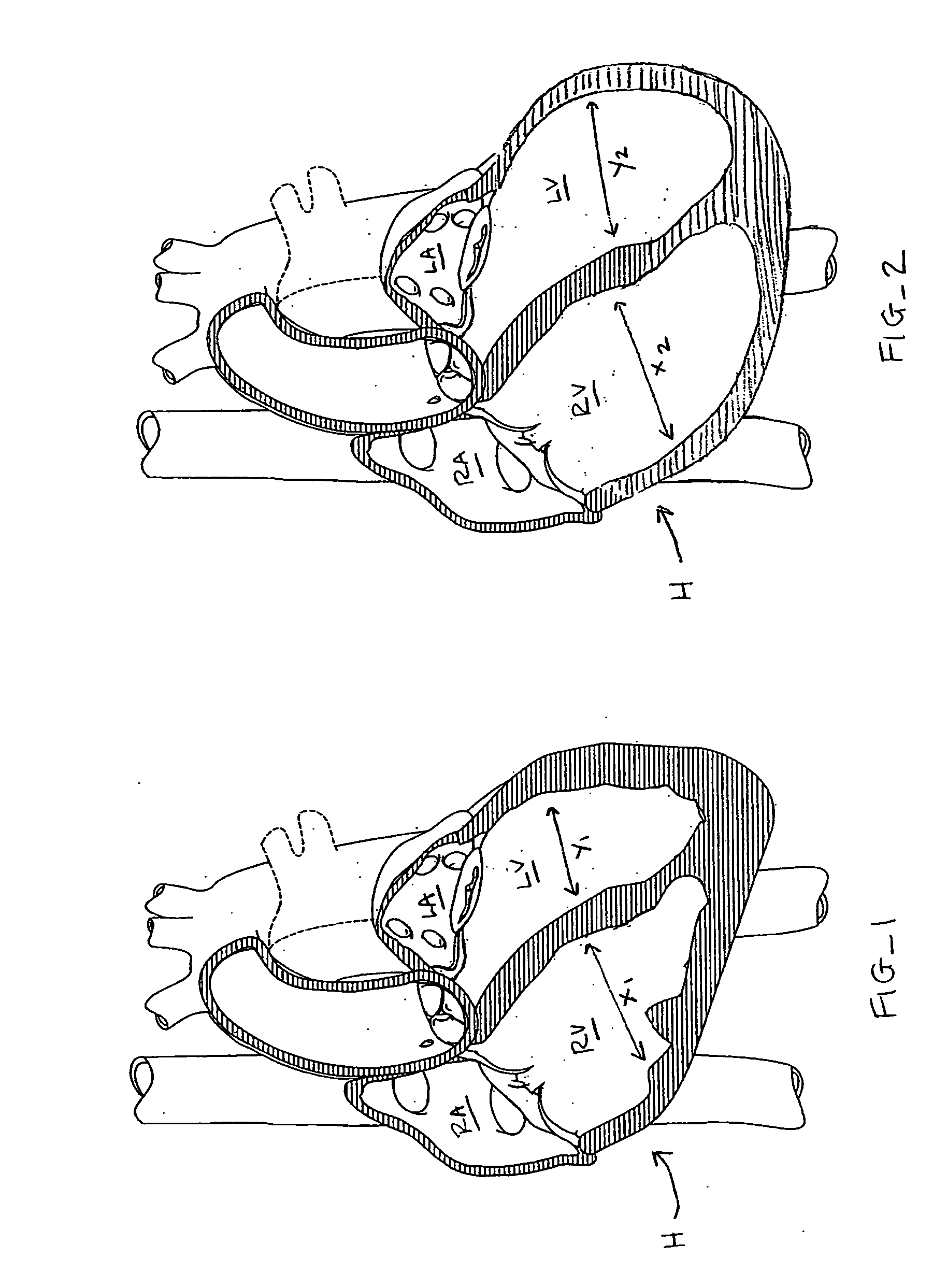
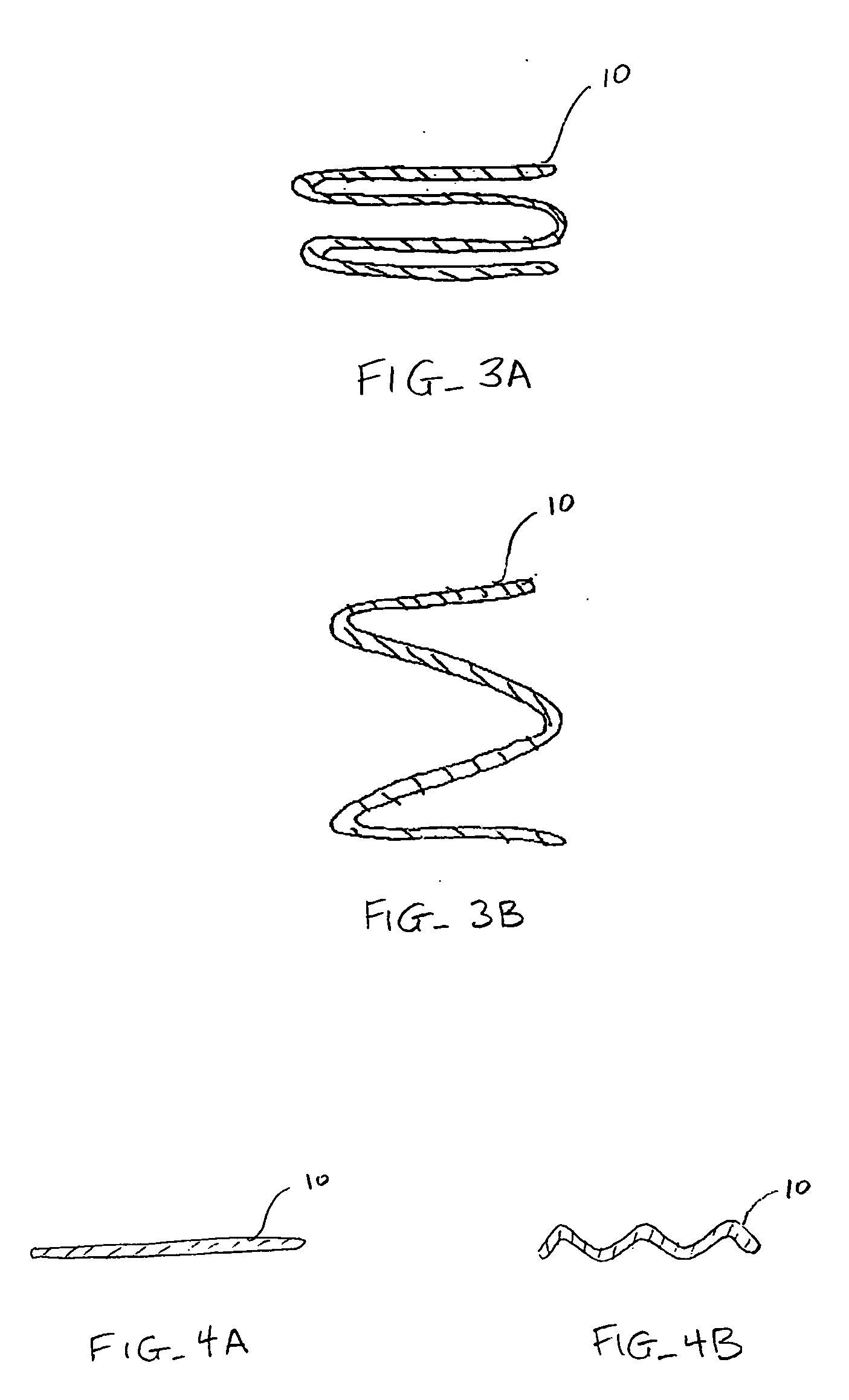
A system for treating mitral valve regurgitation comprises tensioning device that can be deployed using a delivery catheter. The device includes tension member linking a proximal anchor and distal anchor. The device is constructed from a material having suitable elastic properties such that the device applies a constant tension force between the anchors, while stretching or flexing in response to a heartbeat when positioned across a chamber of a heart. The anchors may include a plurality of arms. In some embodiments, the arms may also flex in response to a heart beat. When positioned across the left ventricle of a heart, the device can reduce the lateral distance between the walls of the ventricle and thus allow better coaption of the mitral valve leaflets thereby reducing mitral regurgitation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
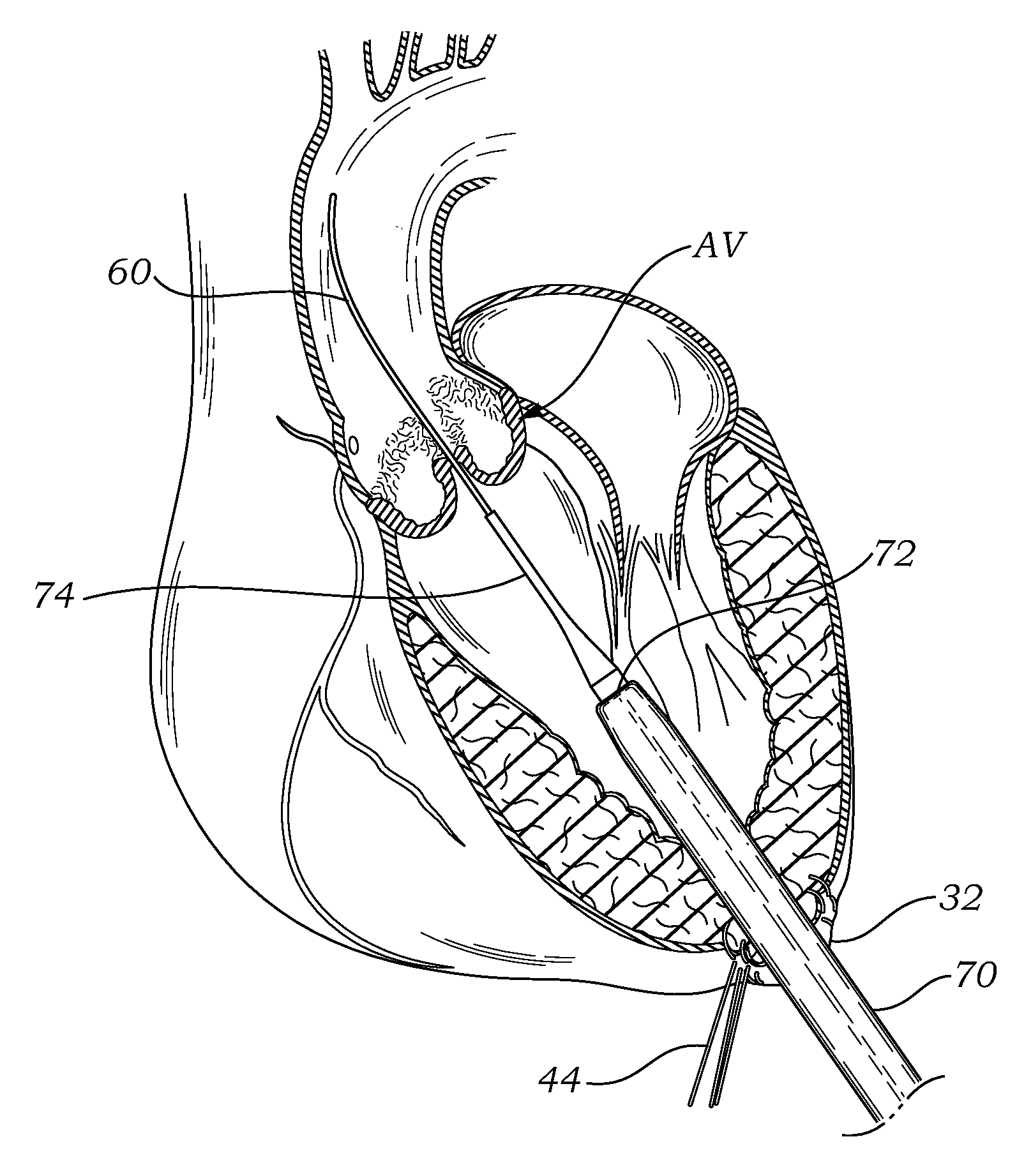
Method and apparatus for resecting and replacing an aortic valve
InactiveUS7544206B2Risk minimizationAccurate placementEar treatmentCannulasMitral valve leafletLeft atrium
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Magnetic devices and methods for reshaping heart anatomy
InactiveUS20060015003A1Improve shrinkageIncreased total stroke volumeElectrotherapyHeart valvesCardiac surfaceHeart Part
Systems, methods and devices are provided for treating heart failure patients suffering from various levels of heart dilation. Heart dilation treated by reshaping the heart anatomy with the use of magnetic forces. Such reshaping changes the geometry of portions of the heart, particularly the right or left ventricles, to increase contractibility of the ventricles thereby increasing the stroke volume which in turn increases the cardiac output of the heart. The magnetic forces are applied with the use of one or more magnetic elements which are implanted within the heart tissue or attached externally and / or internally to a surface of the heart. The various charges of the magnetic forces interact causing the associated heart tissue areas to readjust position, such as to decrease the width of the ventricles. Such repositioning is maintained over time by the force of the magnetic elements, allowing the damaging effects of heart dilation to slow in progression or reverse.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
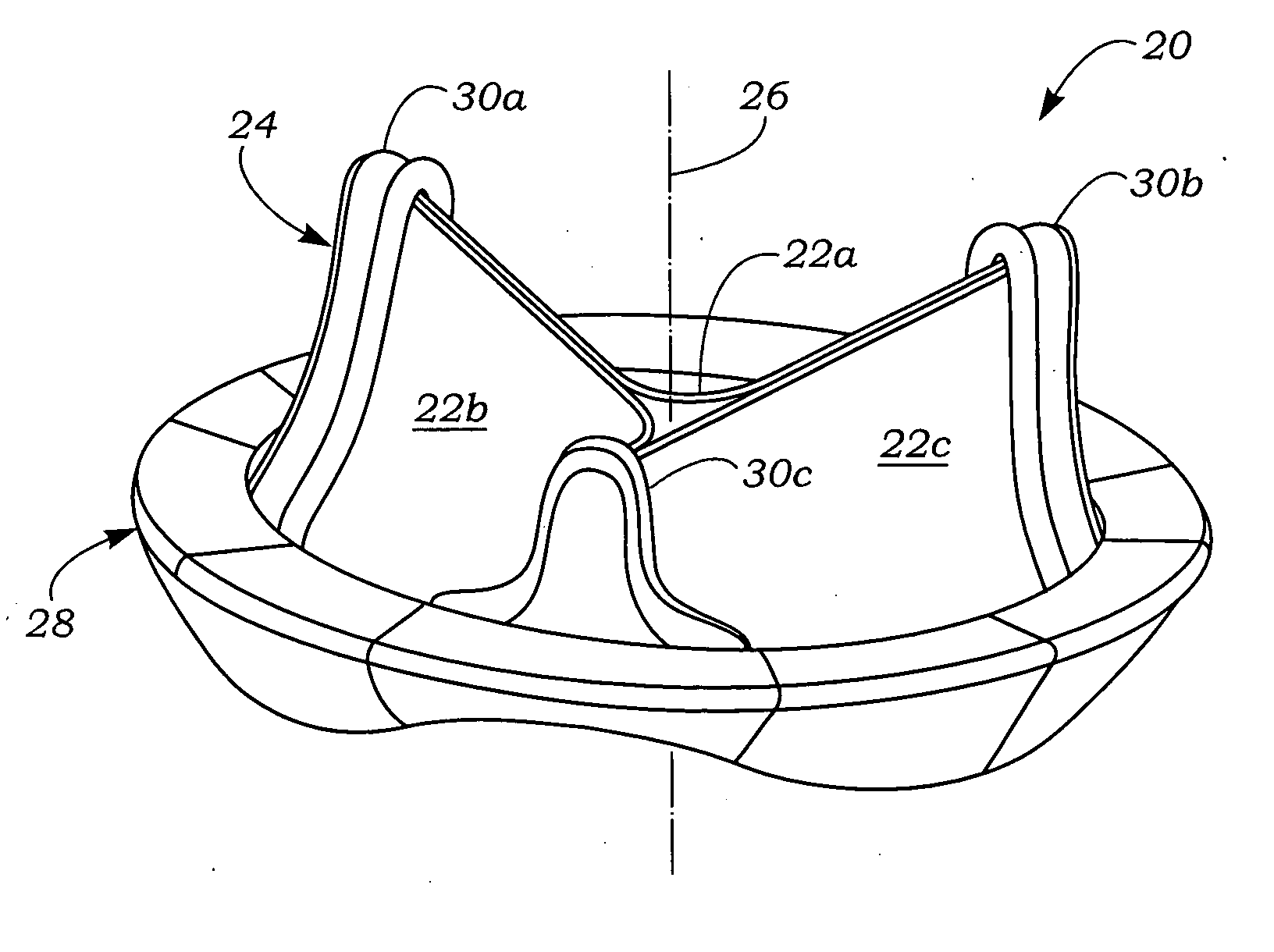
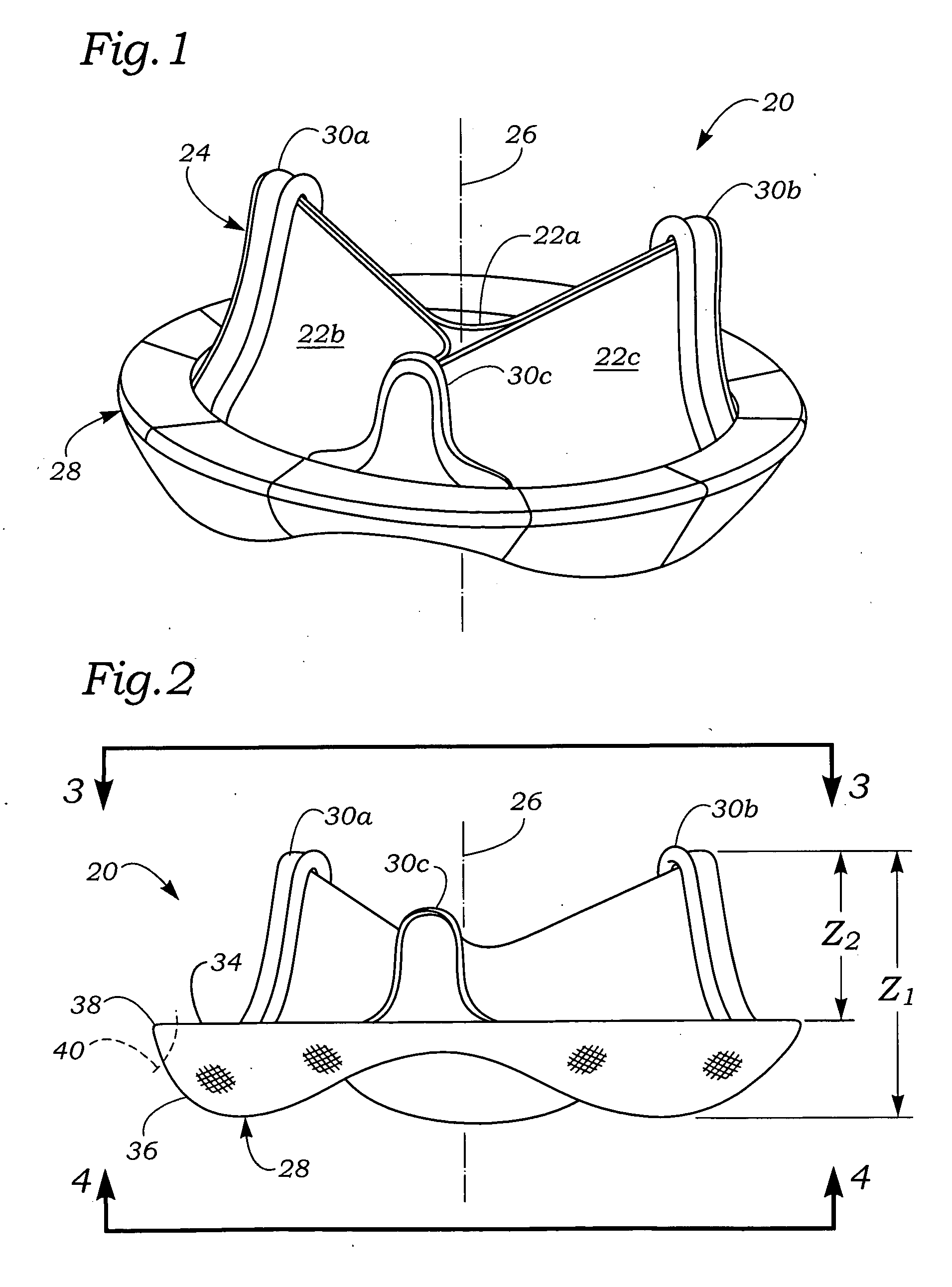
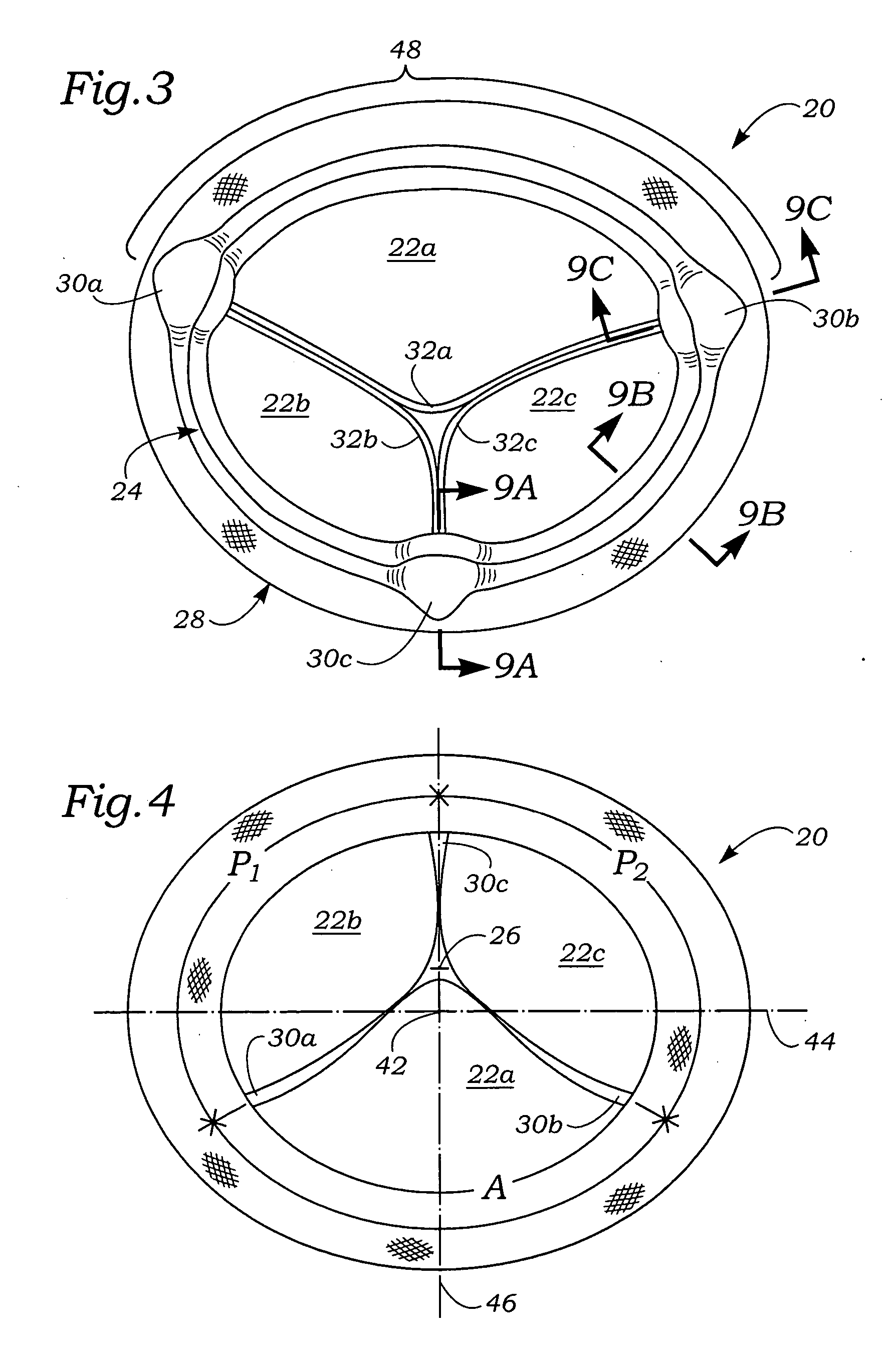
Anatomically approximate prosthetic mitral heart valve
ActiveUS20060293745A1Increase the areaReduce the overall heightAnnuloplasty ringsAnterior leafletMitral annulus
An anatomically approximate prosthetic heart valve includes dissimilar flexible leaflets, dissimilar commissures and / or a non-circular flow orifice. The heart valve may be implanted in the mitral position and have one larger leaflet oriented along the anterior aspect so as to mimic the natural anterior leaflet. Two other smaller leaflets extend around the posterior aspect of the valve. A basic structure providing peripheral support for the leaflets includes two taller commissures on both sides of the larger leaflet, with a third, smaller commissure between the other two leaflets. The larger leaflet may be thicker and / or stronger than the other two leaflets. The base structure defines a flow orifice intended to simulate the shape of the mitral annulus during the systolic phase. For example, the flow orifice may be elliptical. A relatively wide sewing ring has a contoured inflow end and is attached to the base structure in such a way that the valve can be implanted in an intra-atrial position and the taller commissures do not extend too far into the left ventricle, therefore avoiding injury to the ventricle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for treatment of heart valve regurgitation
In one embodiment, the present invention provides a prosthesis that can be implanted within a heart to at least partially block gaps that may be present between the two mitral valve leaflets. In one preferred embodiment, the prosthesis includes an anchoring ring that expands within the left atrium to anchor the prosthesis and a pocket member fixed to the anchoring ring. The pocket member is positioned within the mitral valve, between the leaflets so that an open end of the pocket member is positioned within the left ventricle. When the mitral valve is open, blood flows past the pocket member, maintaining the pocket member in a collapsed state. When the mitral valve closes, the backpressure of the blood pushes into the pocket member, expanding the pocket member to an inflated shape. The mitral valve leaflets contact the expanded pocket member, allowing the prosthesis to block at least a portion of the openings between the leaflets, thereby minimizing regurgitated blood flow into the left atrium.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Method and apparatus for catheter-based annuloplasty
The present invention relates to a minimally invasive method of performing annuloplasty. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method for performing a procedure on a mitral valve of a heart includes inserting an implant into a left ventricle and orienting the implant in the left ventricle substantially below the mitral valve. The implant and tissue around the mitral valve are connected and tension is provided to the implant, in one embodiment, in order to substantially reduce an arc length associated with the mitral valve. In another embodiment, the implant is inserted into the left ventricle through the aorta and the aortic valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and device for surgical ventricular repair
InactiveUS20060025800A1Relieve pressureImproved surgical outcomeHeart valvesSurgeryTunica intimaCatheter
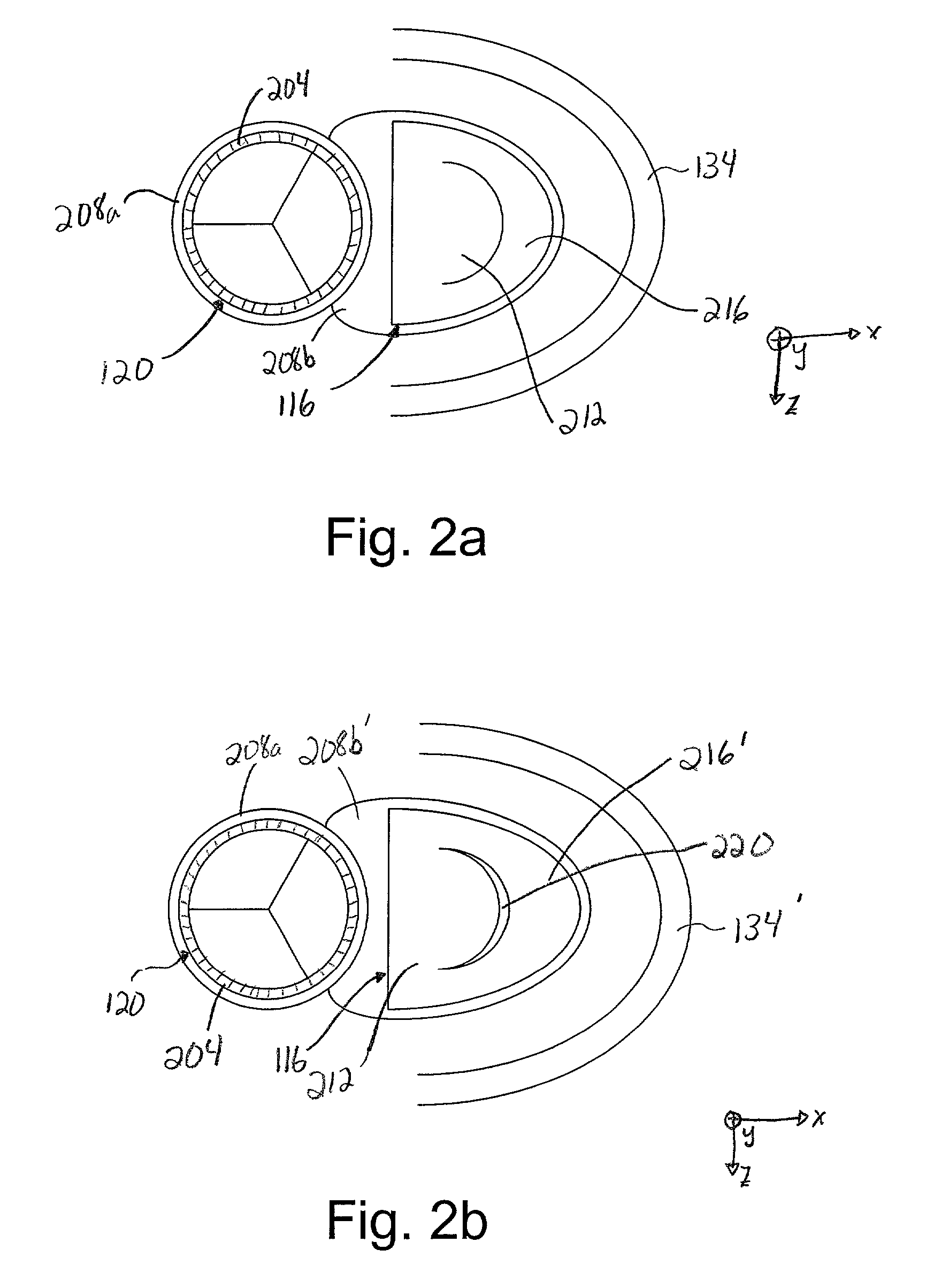
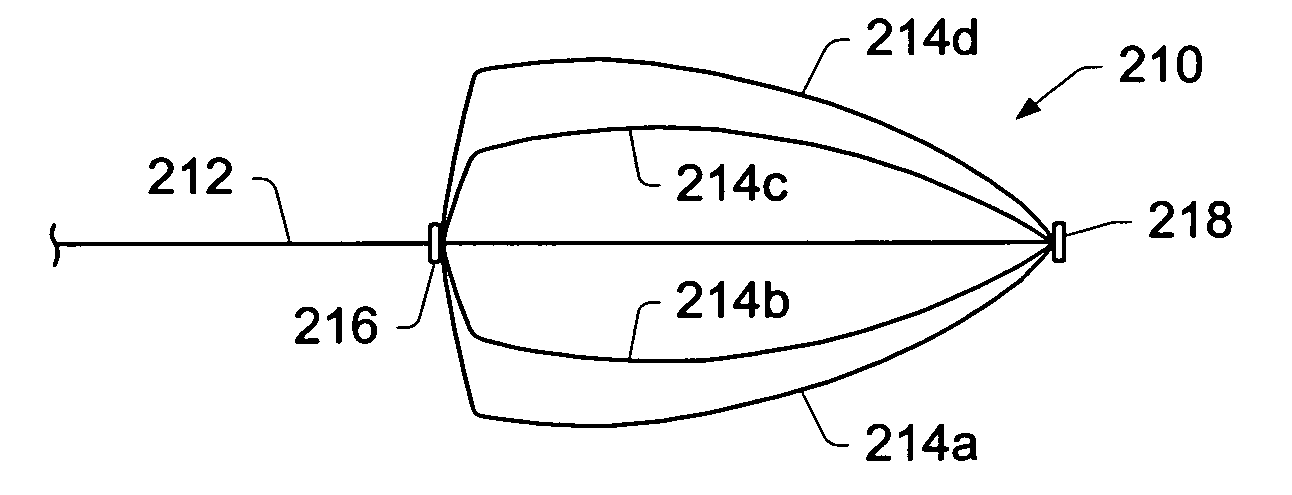
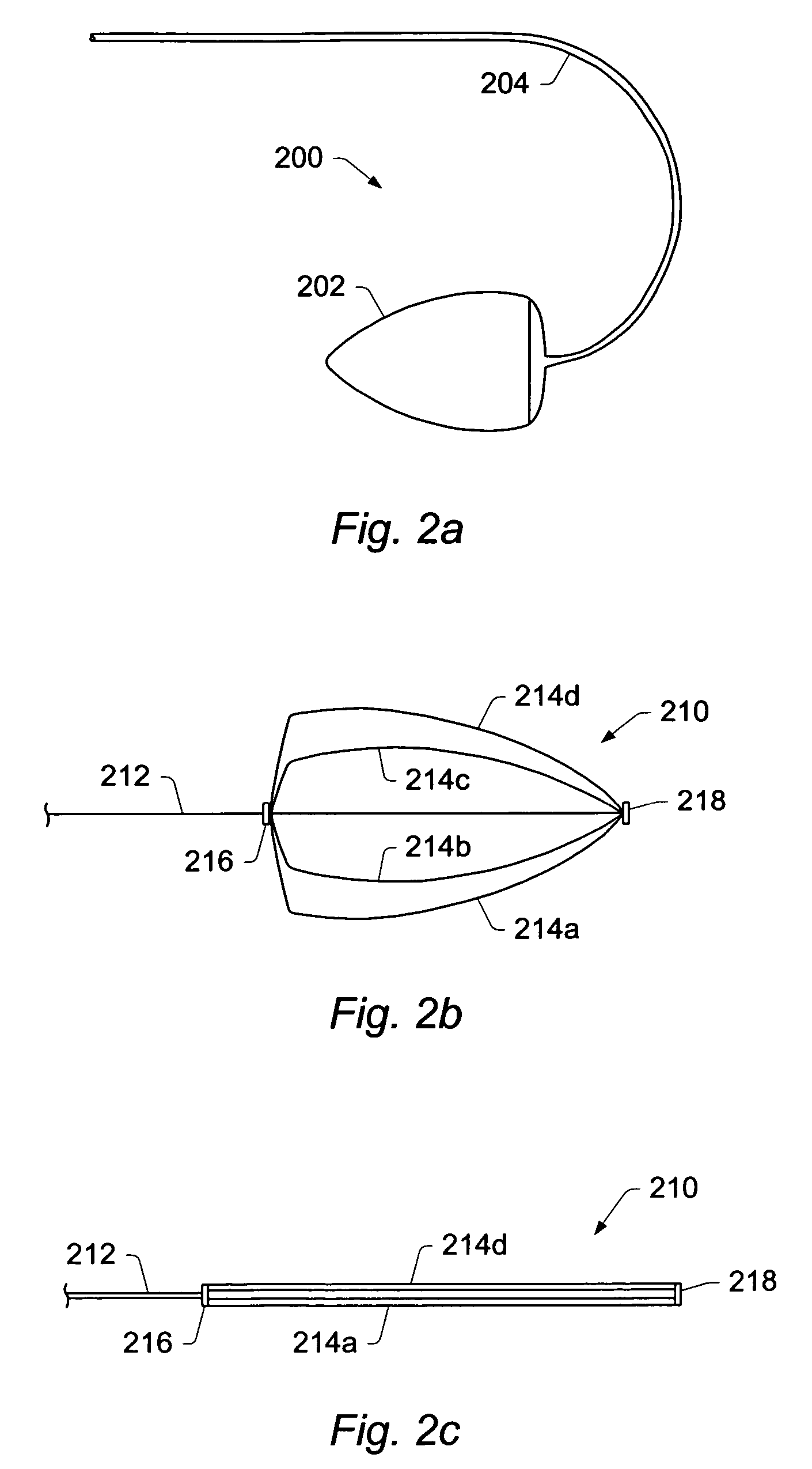
Embodiments disclose a method for repairing a heart of a human. A method may include introducing a collapsed reinforcing element through the skin into the vascular system of the human. The method may include delivering the reinforcing element into a left ventricle through the arteries. Once inside the left ventricle, the reinforcing element may be expanded to an expanded shape. In certain embodiments, a reinforcing element may be used to structurally reinforce a portion of an endocardial surface of a heart. The reinforcing element may include a preshaped patch and / or a plurality of preshaped flexible conduits. The method may include deploying the reinforcing element soon after a myocardial infarction to inhibit naturally occurring remodeling of the heart. The reinforcing element may be deployed with or without the use of a shaper. In some embodiments, a reinforcement element may be positioned on / coupled to an external surface of a human heart. In some embodiments, a reinforcing element may include an externally positioned apparatus configured to substantially reshape a portion of an interior chamber of a heart.
Owner:CAPITAL SOUTHWEST
Devices and methods for accelerometer-based characterization of cardiac synchrony and dyssynchrony
InactiveUS20080021336A1Easy to identifyReduce power consumptionStentsElectrotherapyAccelerometerCardiac muscle
Systems and methods according to the invention employ an acceleration sensor to characterize the synchrony or dyssynchrony of the left ventricle. Patterns of acceleration related to myocardial contraction can be used to assess synchrony or dyssynchrony. Time-frequency transforms and coherence are derived from the acceleration. Information and numerical indices determined from the acceleration time frequency transforms and coherence can be used to find the optimal pacing location for cardiac resynchronization therapy. Similarly, the information can be used to optimize timing intervals including V to V and A to V timing.
Owner:CARDIOSYNC
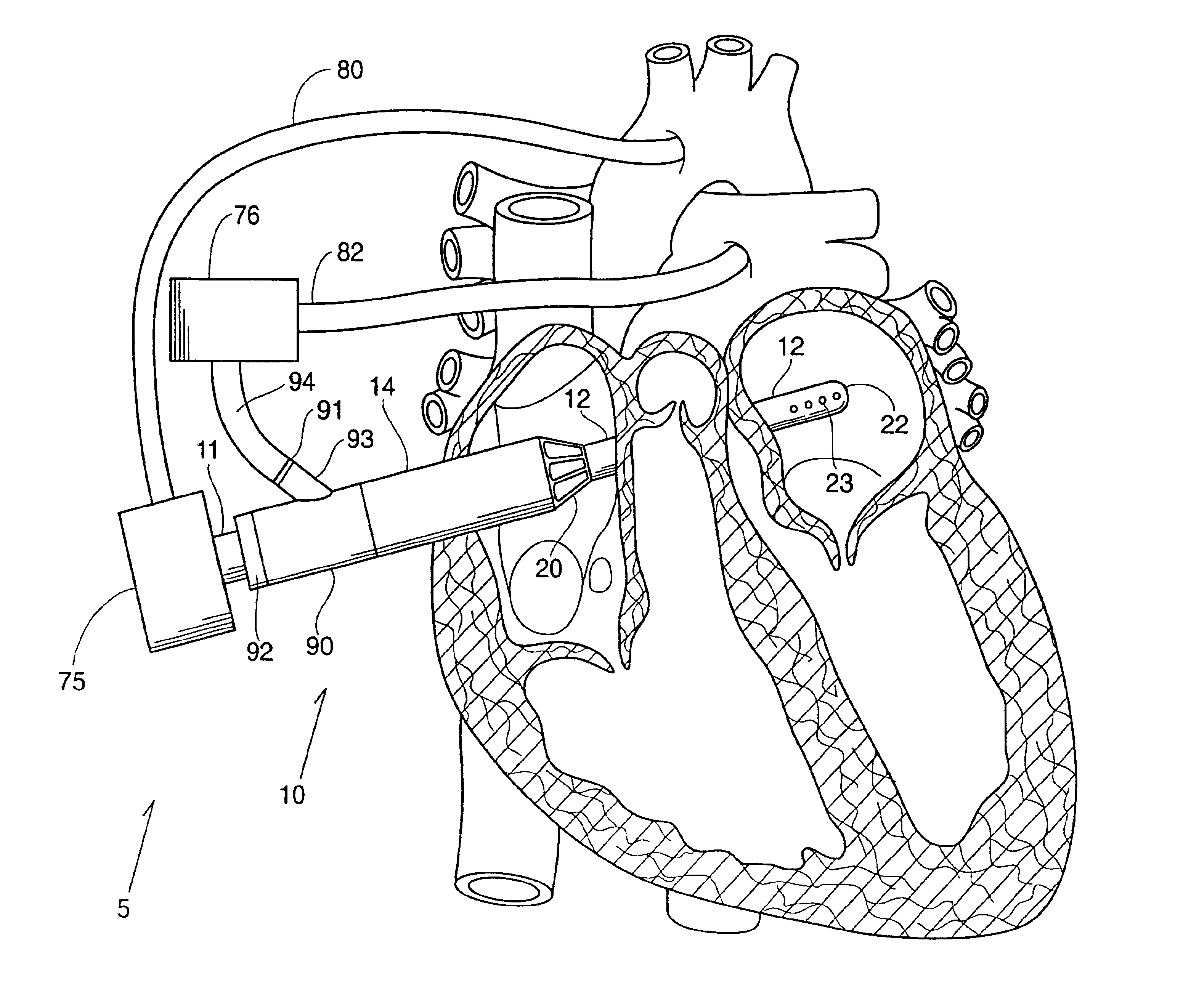
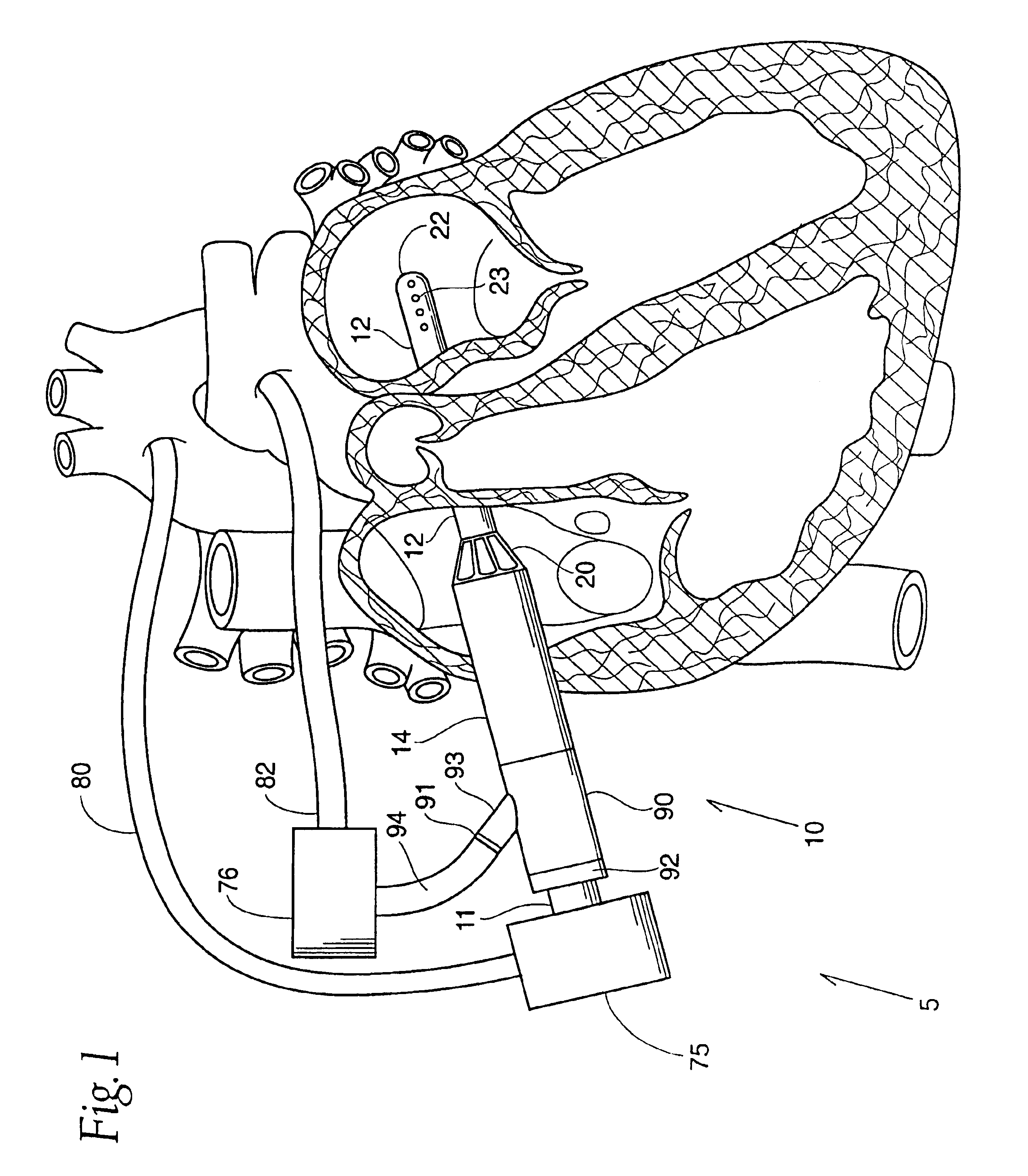
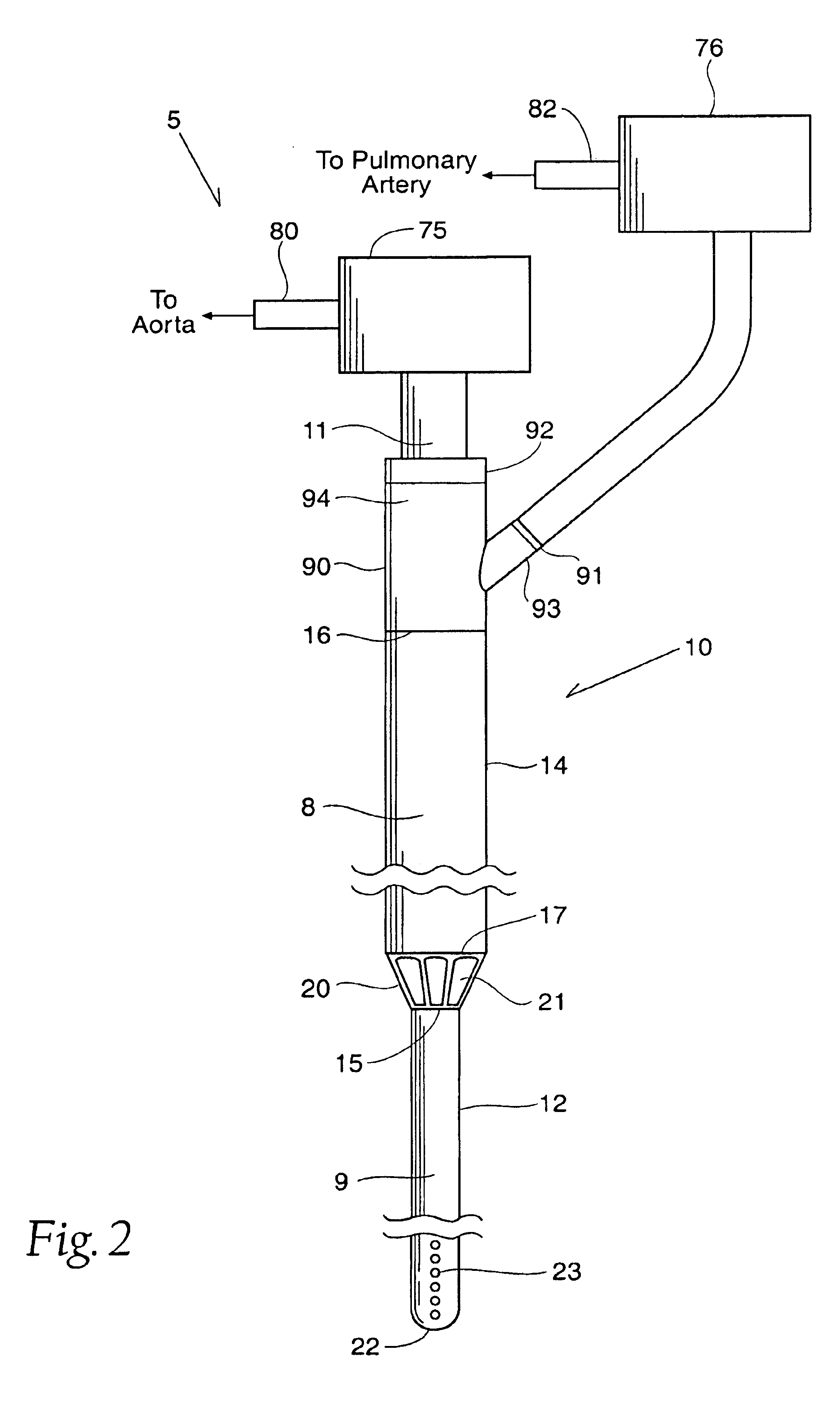
Methods and devices for altering blood flow through the left ventricle
ActiveUS20050015109A1Lower the volumeInefficient geometry for pumpingHeart valvesDilatorsBlood flowMaterial Perforation
An element is expanded in the left ventricle to isolate part of the left ventricle. The element has a generally convex outer surface and an apex which together define a desired geometry of the left ventricle. The isolated part of the wall of the left ventricle may be left so that the wall naturally forms around the element or the isolated portion of the ventricle may be evacuated and / or filled. The element may also be used to isolate part of the left ventricle containing a ventricular septal defect or other perforation or opening in the ventricular wall.
Owner:KARDIUM
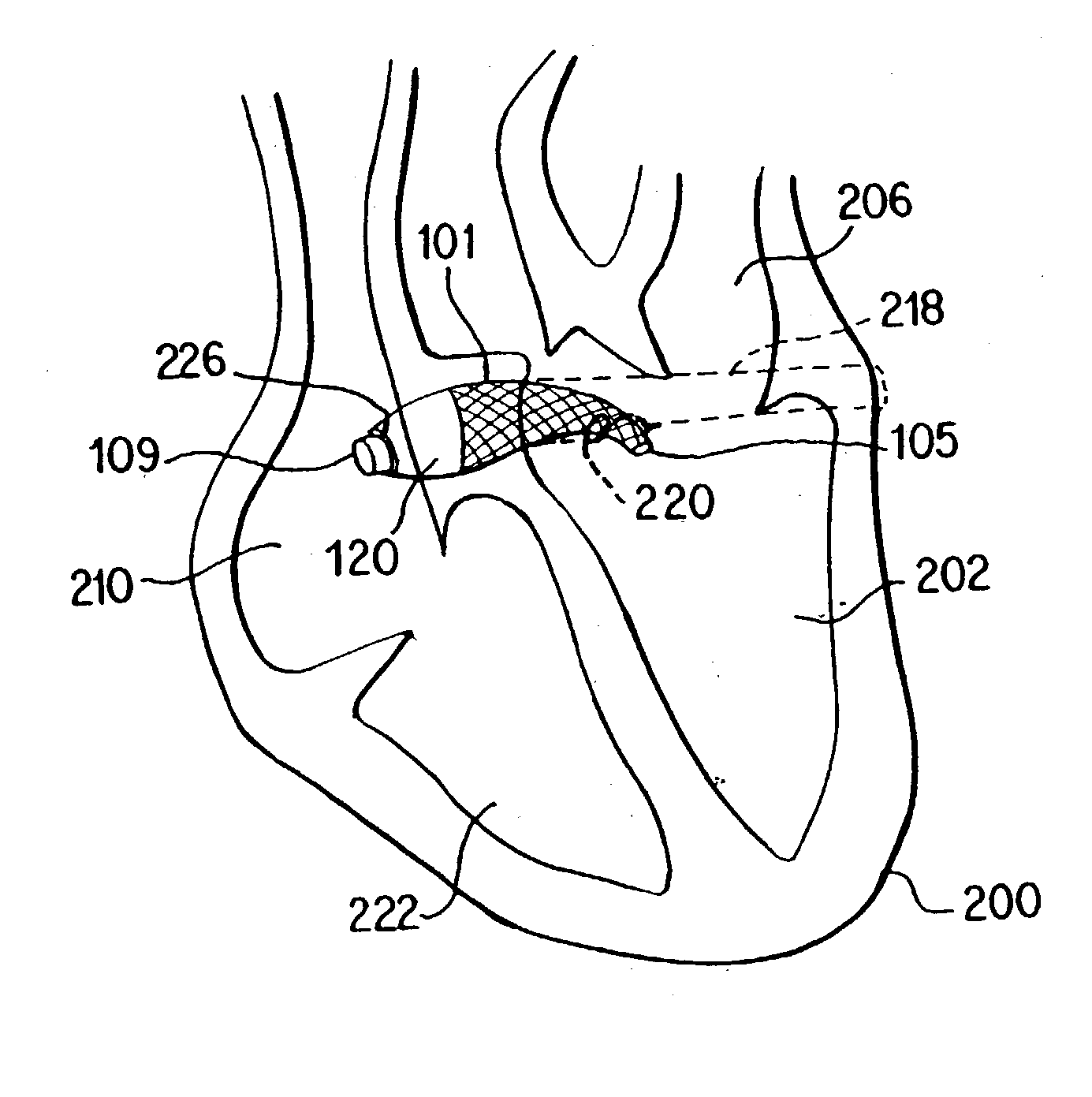
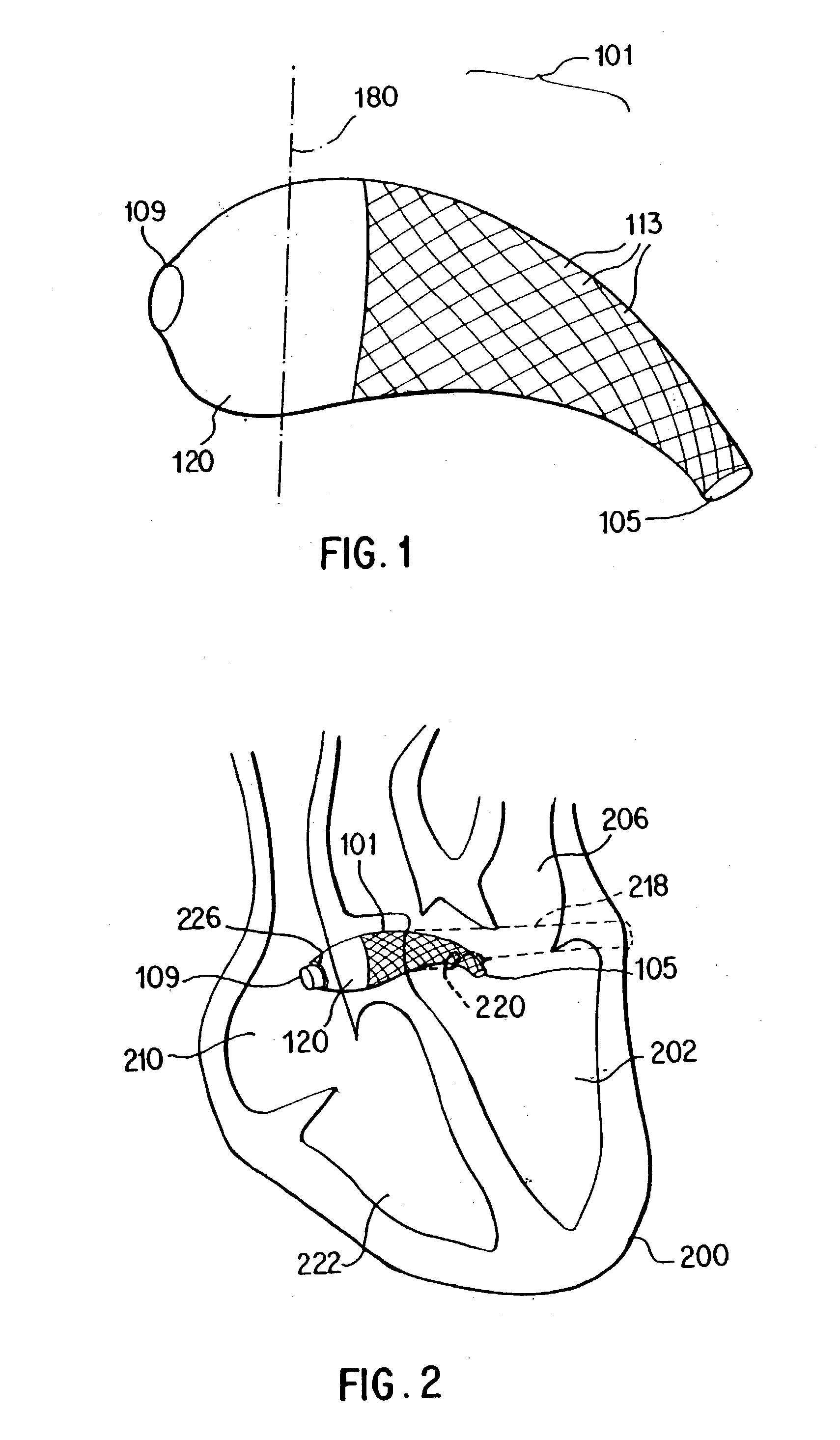
Stent for arterialization of the coronary sinus and retrograde perfusion of the myocardium
The present invention concerns a novel stent and a method for communicating oxygenated blood directly from the left ventricle to the coronary sinus to provide retrograde perfusion to the myocardium. The stent is placed substantially within the coronary sinus with its trailing end protruding into the right atrium and the leading end protruding into the left ventricle. The stent has a smaller passageway at or near the trailing (right ventricular) end and at or near the leading (left ventricle) end, and has a covering at the trailing end. The smaller passageway and the cover at the trailing end to promote retrograde flow into the venous system of the hear and specifically the myocardium of the left ventricle and to reduce a significant left-to-right shunt.
Owner:MARTIN ERIC C
Left and right side heart support
InactiveUS6926662B1Lower the volumeReduce the amount requiredOther blood circulation devicesBlood pumpsOuter CannulaRight atrium
A cannulation system for cardiac support uses an inner cannula disposed within an outer cannula. The outer cannula includes a fluid inlet for placement within the right atrium of a heart. The inner cannula includes a fluid inlet extending through the fluid inlet of the outer cannula and the atrial septum for placement within at least one of the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. The cannulation system also employs a pumping assembly coupled to the inner and outer cannulas to withdraw blood from the right atrium for delivery to the pulmonary artery to provide right heart support, or to withdraw blood from at least one of the left atrium and left ventricle for delivery into the aorta to provide left heart support, or both.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
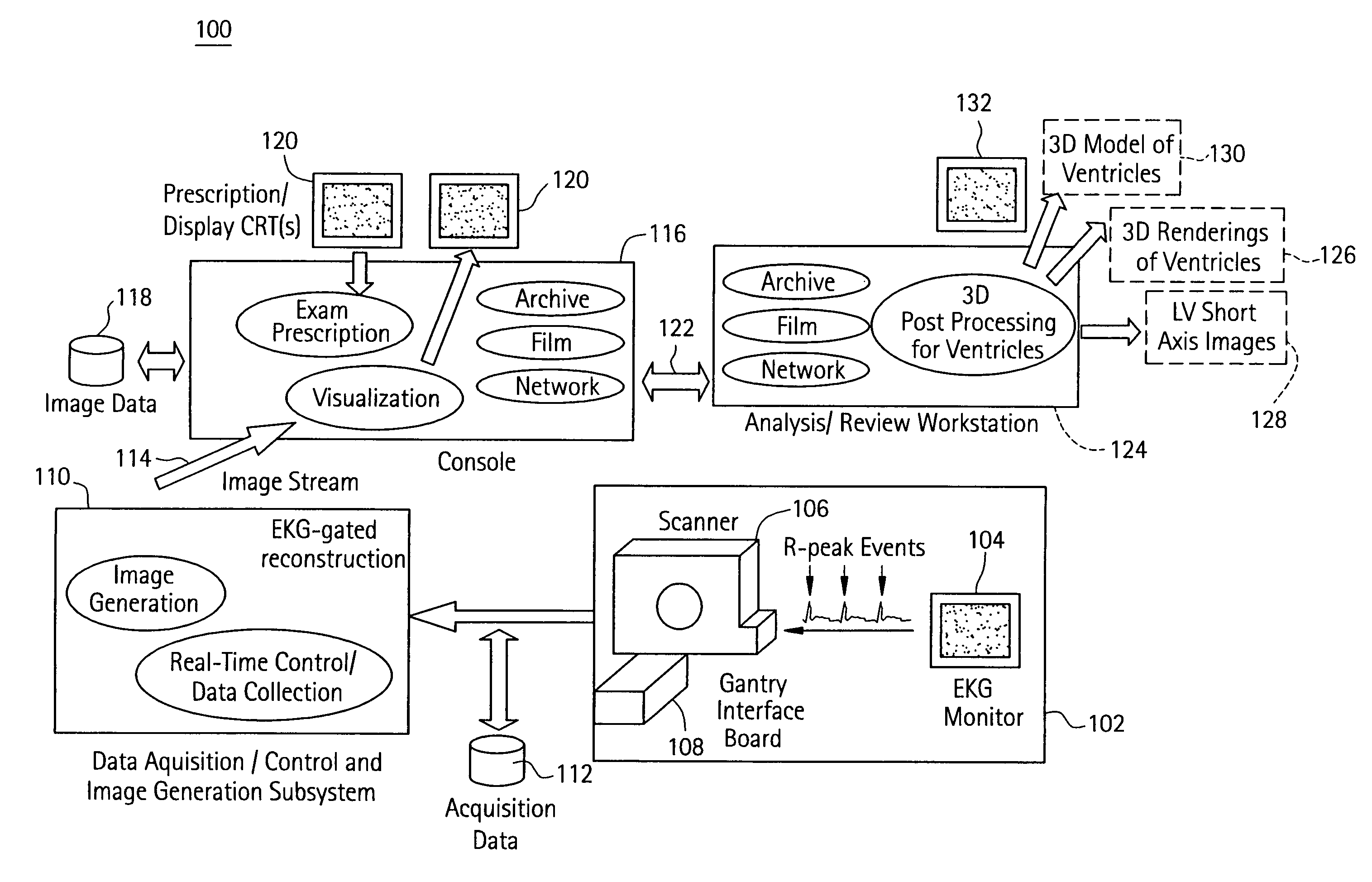
Cardiac imaging system and method for quantification of desynchrony of ventricles for biventricular pacing
A method for quantifying cardiac desynchrony of the right and left ventricles includes obtaining cardiac acquisition data from a medical imaging system, and determining a movement profile from the cardiac acquisition data. The movement profile is directed toward identifying at least one of a time-based contraction parameter for a region of the left ventricle (LV), and a displacement-based contraction parameter for a region of the LV. The determined movement profile is visually displayed by generating a 3D model therefrom.
Owner:APN HEALTH +1
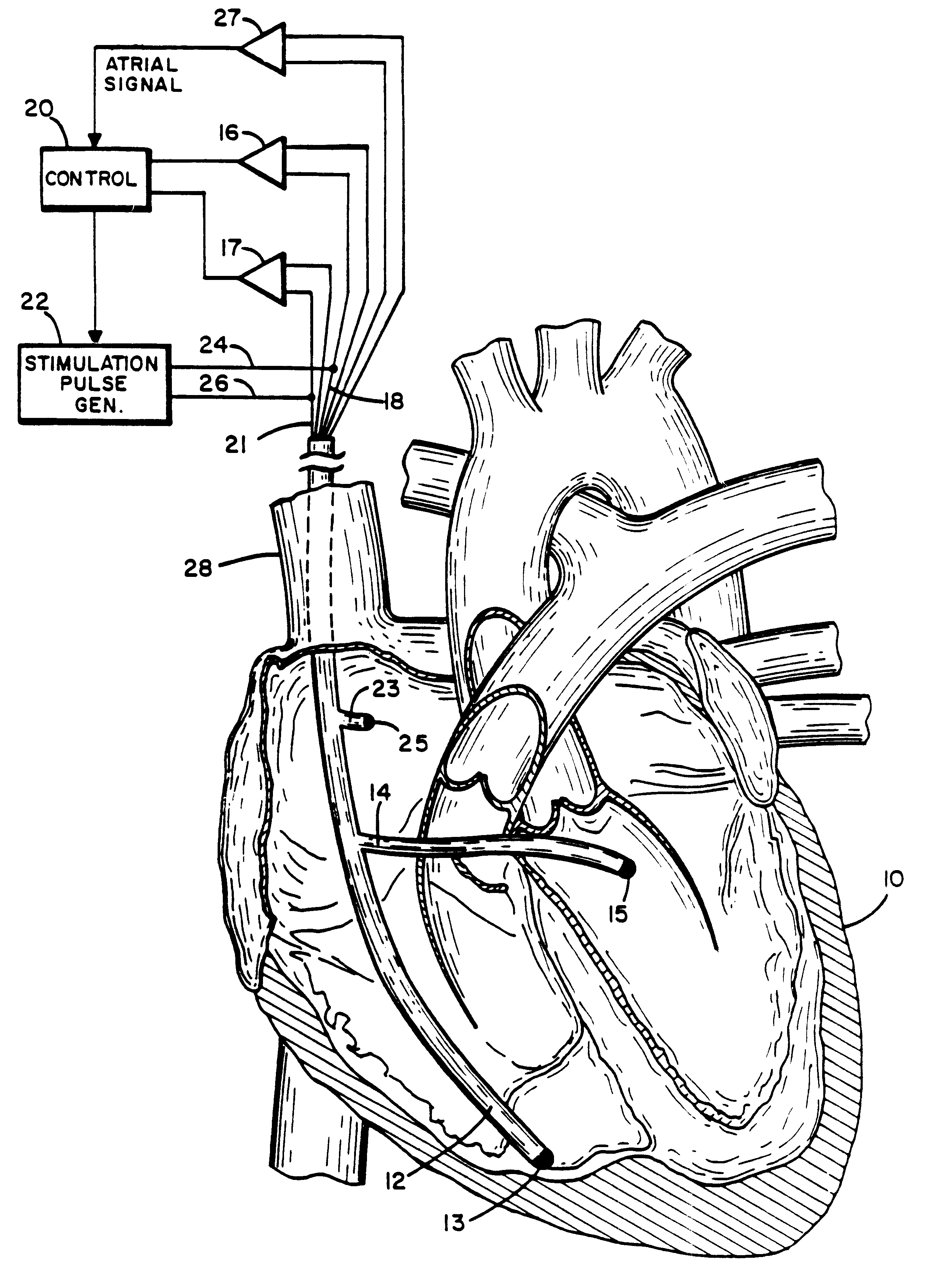
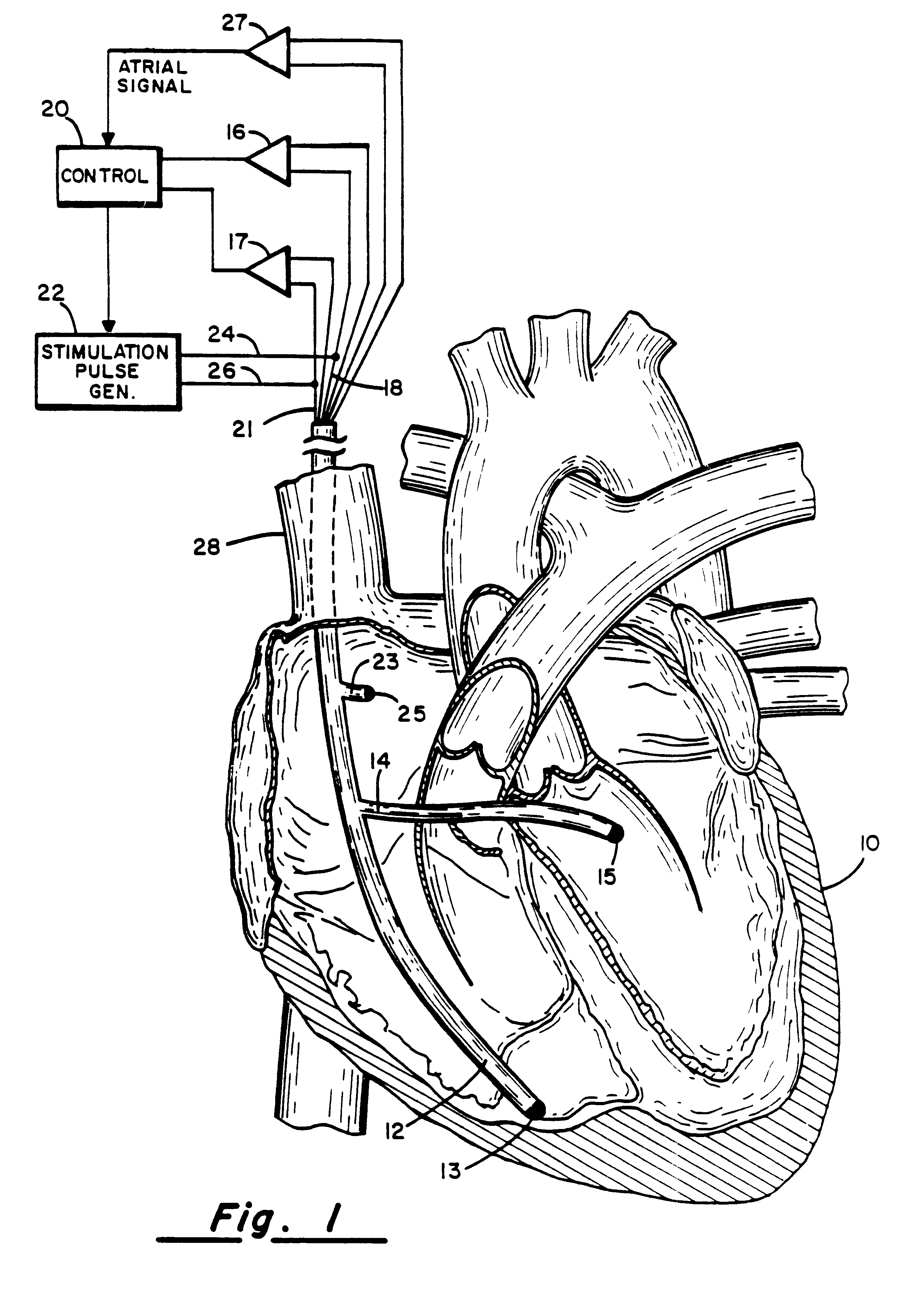
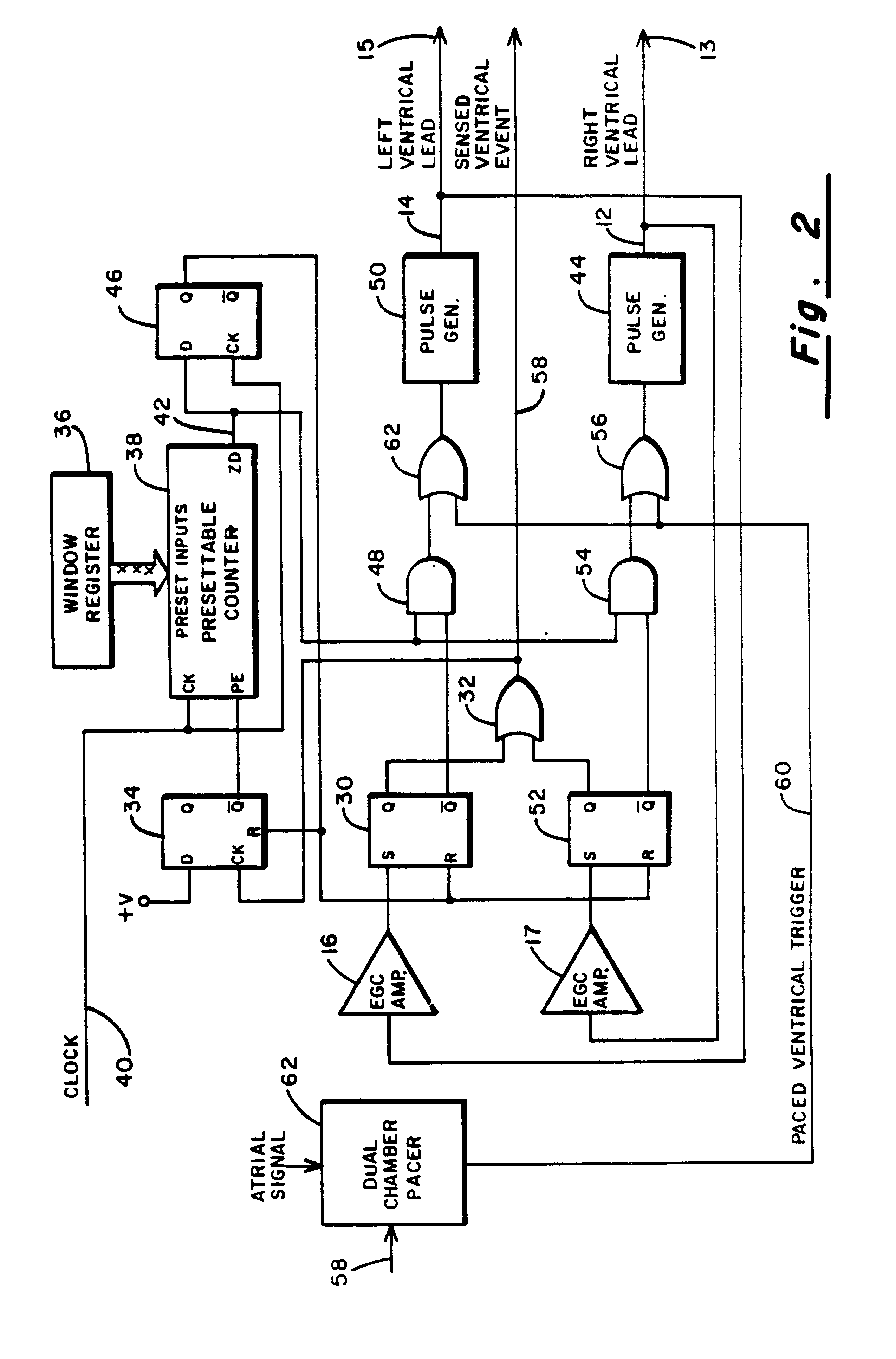
Method and apparatus for treating hemodynamic disfunction
A method of treating hemodynamic disfunction by simultaneously pacing both ventricles of a heart. At least one ECG amplifier is arranged to separately detect contraction of each ventricle and a stimulator is then activated for issuing stimulating pulses to both ventricles in a manner to assure simultaneous contraction of both ventricles, thereby to assure hemodynamic efficiency. A first ventricle is stimulated simultaneously with contraction of a second ventricle when the first fails to properly contract. Further, both ventricles are stimulated after lapse of a predetermined A-V escape interval. One of a pair of electrodes, connected in series, is placed through the superior vena cava into the right ventricle and a second is placed in the coronary sinus about the left ventricle. Each electrode performs both pacing and sensing functions. The pacer is particularly suitable for treating bundle branch blocks or slow conduction in a portion of the ventricles.
Owner:MIROWSKI FAMILY VENTURES LLC
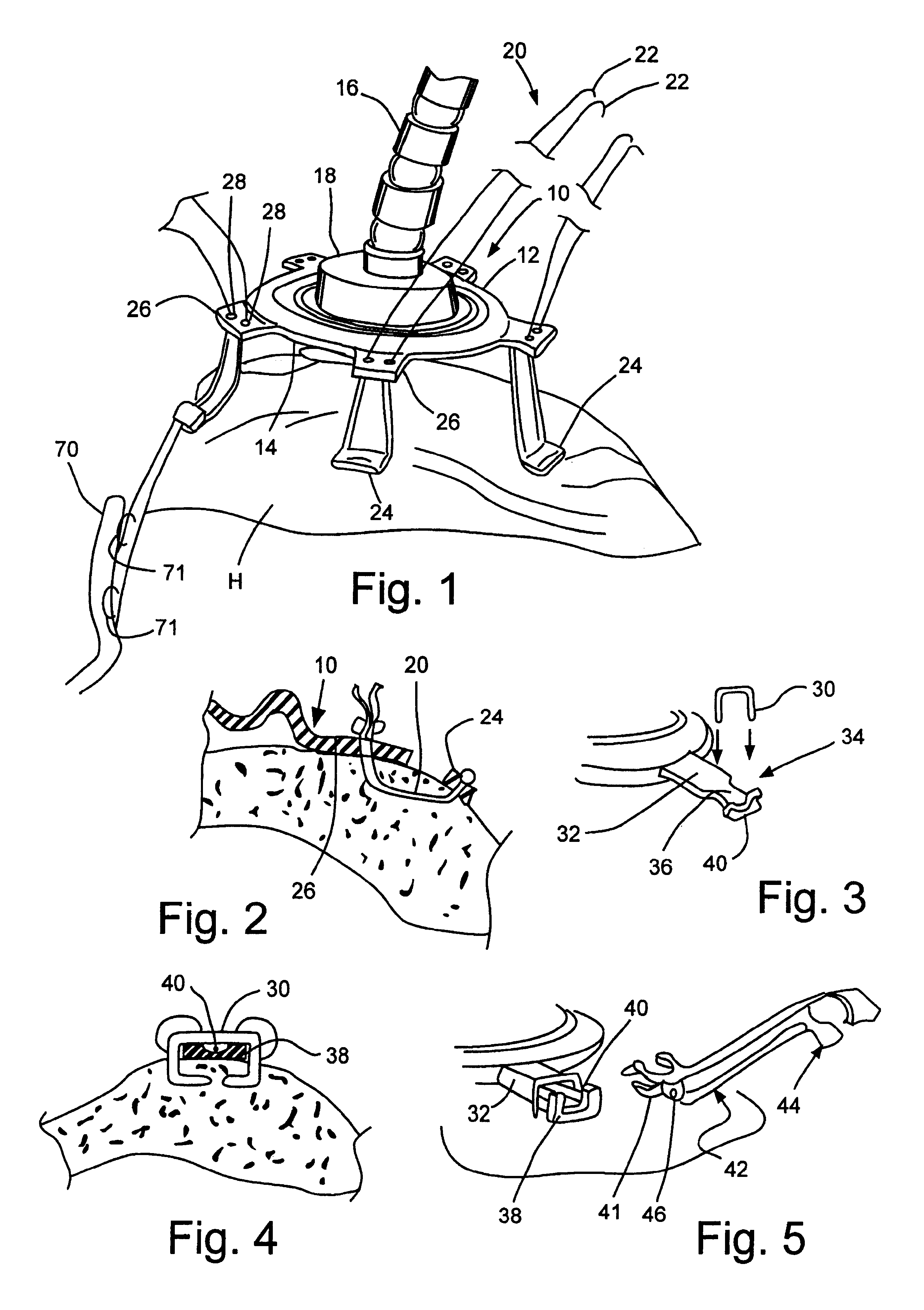
System to permit offpump beating heart coronary bypass surgery
InactiveUS6390976B1Improve performanceImprove system performanceSuture equipmentsStaplesAdhesiveCardiac muscle
A system for manipulating and supporting a beating heart during cardiac surgery, including a gross support element for engaging and supporting the heart (the gross support element preferably including a head which is sized and shaped to cradle the myocardium of the left ventricle), a suspension head configured to exert lifting force on the heart when positioned near the apical region of the heart at a position at least partially overlying the right ventricle, and a releasable attachment element for releasably attaching at least one of the gross support element and the suspension head to the heart. The releasable attachment element can be a mechanical element (such as one or more staples or sutures) or an adhesive such as glue. Alternatively, the system includes a suspension head and a releasable attachment element for releasably attaching it to the heart, but does not include a gross support element.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Ventricular assist device for intraventricular placement
A ventricular assist device includes a pump such as an axial flow pump, an outflow cannula connected to the outlet of the pump, and an anchor element. The anchor element is physically connected to the pump, as by an elongate element. The pump is implanted within the left ventricle with the outflow cannula projecting through the aortic valve but desirably terminating short of the aortic arch. The anchor element is fixed to the wall of the heart near the apex of the heart so that the anchor element holds the pump and outflow cannula in position.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
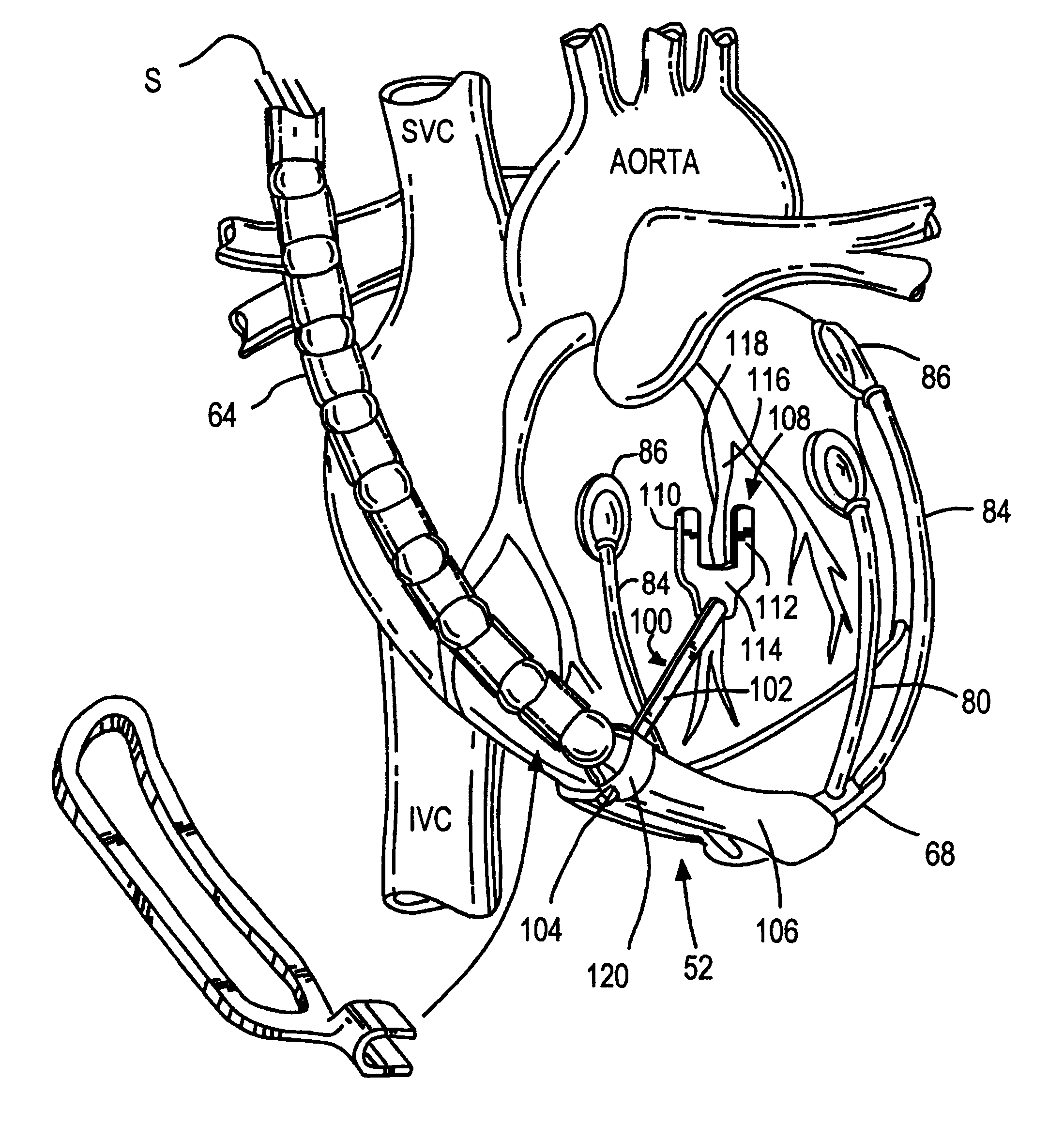
Method and apparatus for resecting and replacing an aortic valve
InactiveUS20090164004A1Risk minimizationAccurate placementHeart valvesSurgeryMitral valve leafletLeft atrium
A method and apparatus for delivering a device to a given location within a heart, the method and apparatus being adapted for: passing a first catheter through the left atrium of the heart, through the mitral valve and into the left ventricle, and passing a second catheter through the aorta toward the heart, one or the other of the first catheter and the second catheter, with the device attached thereto, forming a device-carrying assembly for engagement with the remaining catheter; causing the device-carrying assembly and the remaining catheter to engage one another so as to form a connection therebetween; and retracting one of the device-carrying assembly and the remaining catheter in a direction opposite to the other of the device-carrying assembly and the remaining catheter so as to position the device relative to the given location within the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Shape memory devices and methods for reshaping heart anatomy
InactiveUS20060015002A1Improve shrinkageReduce widthSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCardiac surfaceHeart anatomy
Systems, methods and devices are provided for treating heart failure patients suffering from various levels of heart dilation. Such heart dilation is treated by reshaping the heart anatomy with the use of shape memory elements. Such reshaping changes the geometry of portions of the heart, particularly the right or left ventricles, to increase contractibility of the ventricles thereby increasing the stroke volume which in turn increases the cardiac output of the heart. The shape memory elements have an original shape and at least one memory shape. The elements are implanted within the heart tissue or attached externally and / or internally to a surface of the heart when in the original shape. The elements are then activated to transition from the original shape to one of the at least one memory shapes. Transitioning of the elements cause the associated heart tissue areas to readjust position, such as to decrease the width of the ventricles. Such repositioning is maintained over time by the elements, allowing the damaging effects of heart dilation to slow in progression or reverse.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
Device for Treating Mitral Valve Regurgitation
InactiveUS20070078297A1Reduce lateral distanceEasy to deploySuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberTension member
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Reconfigurable, fault tolerant multiple-electrode cardiac lead systems
InactiveUS20050090870A1Easy to detectEfficient deliveryElectrocardiographyEpicardial electrodesLead systemVentricular tissue
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for assessing ventricular function on a chronic basis using a plurality of electrodes disposed on or about a left ventricle and / or a right ventricle—and optionally, at least one mechanical or metabolic sensor—all operatively electrically coupled to an implantable medical device. The plurality of electrodes are preferably spaced-apart so that at least one electrode is disposed electrical communication with a discrete volume of ventricular tissue. In one embodiment, the discrete volume of tissue is defined by multiple longitudinal and axial planes as known and used in the medical arts. Thus, according to the present invention, at least one electrode couples to appropriate sensing circuitry and essentially provides a localized electrogram (EGM) that, when compared to other EGMs, provides for configurable, localized delivery of therapeutic pacing stimulus, diverse impedance-sensing vectors, various diagnostic information regarding myocardial function and / or anti-tachycardia pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System for improving cardiac function
ActiveUS20060264980A1Improve heart functionOcculdersSurgical staplesCardiac functioningCardiac muscle
A system for improving cardiac function is provided. A foldable and expandable frame having at least one anchoring formation is attached to an elongate manipulator and placed in a catheter tube while folded. The tube is inserted into a left ventricle of a heart where the frame is ejected from the tube and expands in the left ventricle. Movements of the elongate manipulator cause the anchor to penetrate the heart muscle and the elongate manipulator to release the frame. The installed frame minimizes the effects of an akinetic portion of the heart forming an aneurysmic bulge.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
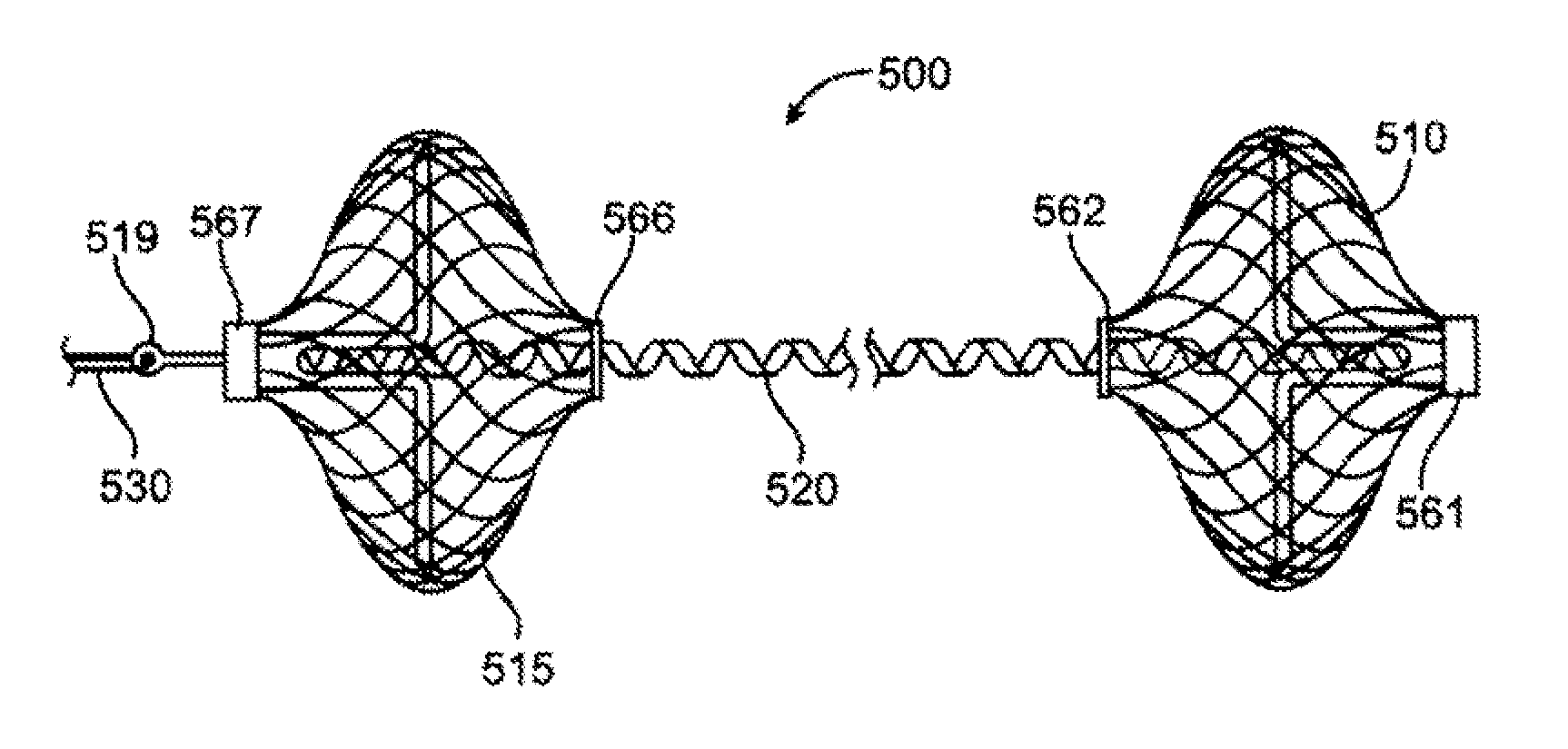
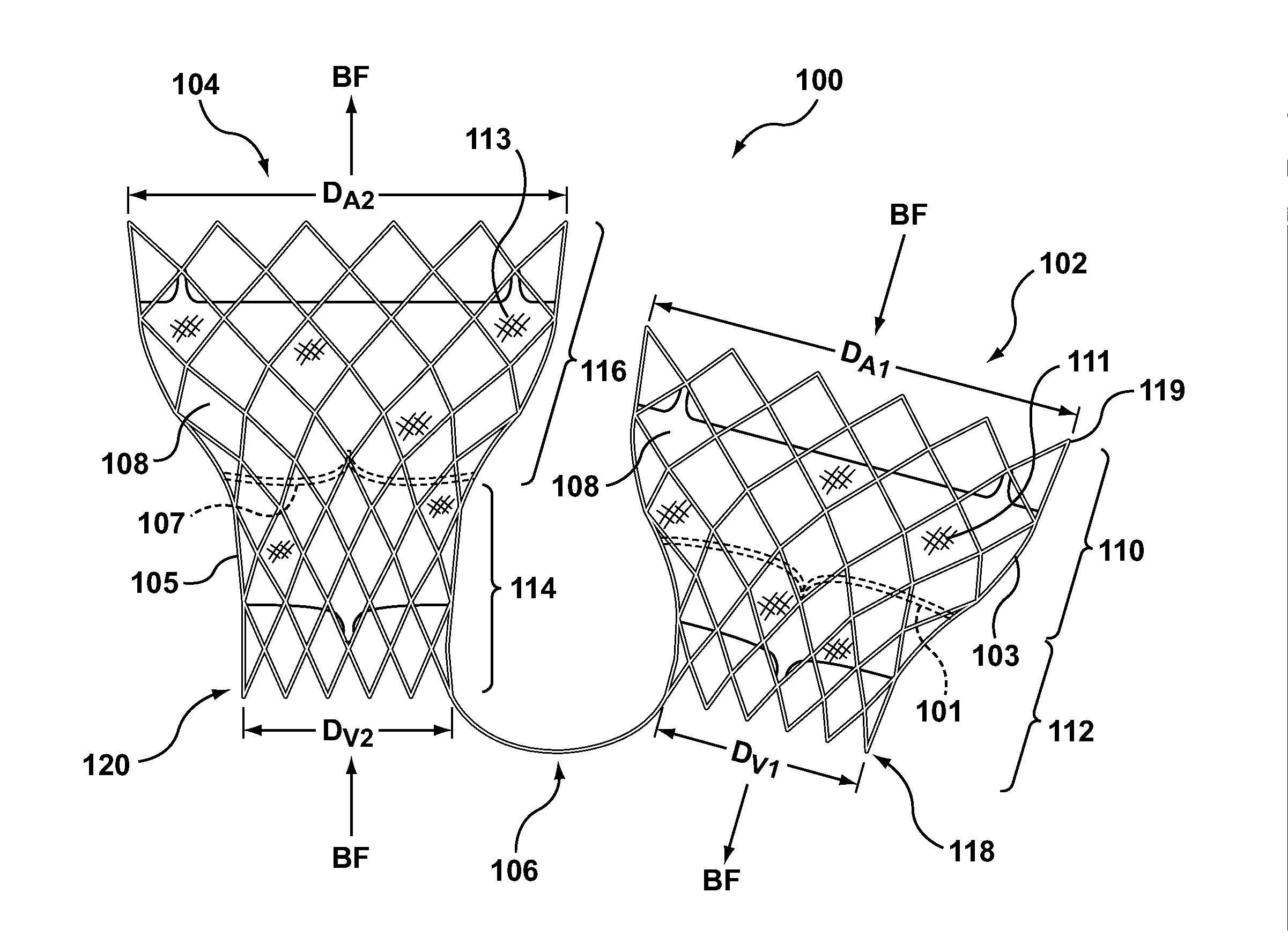
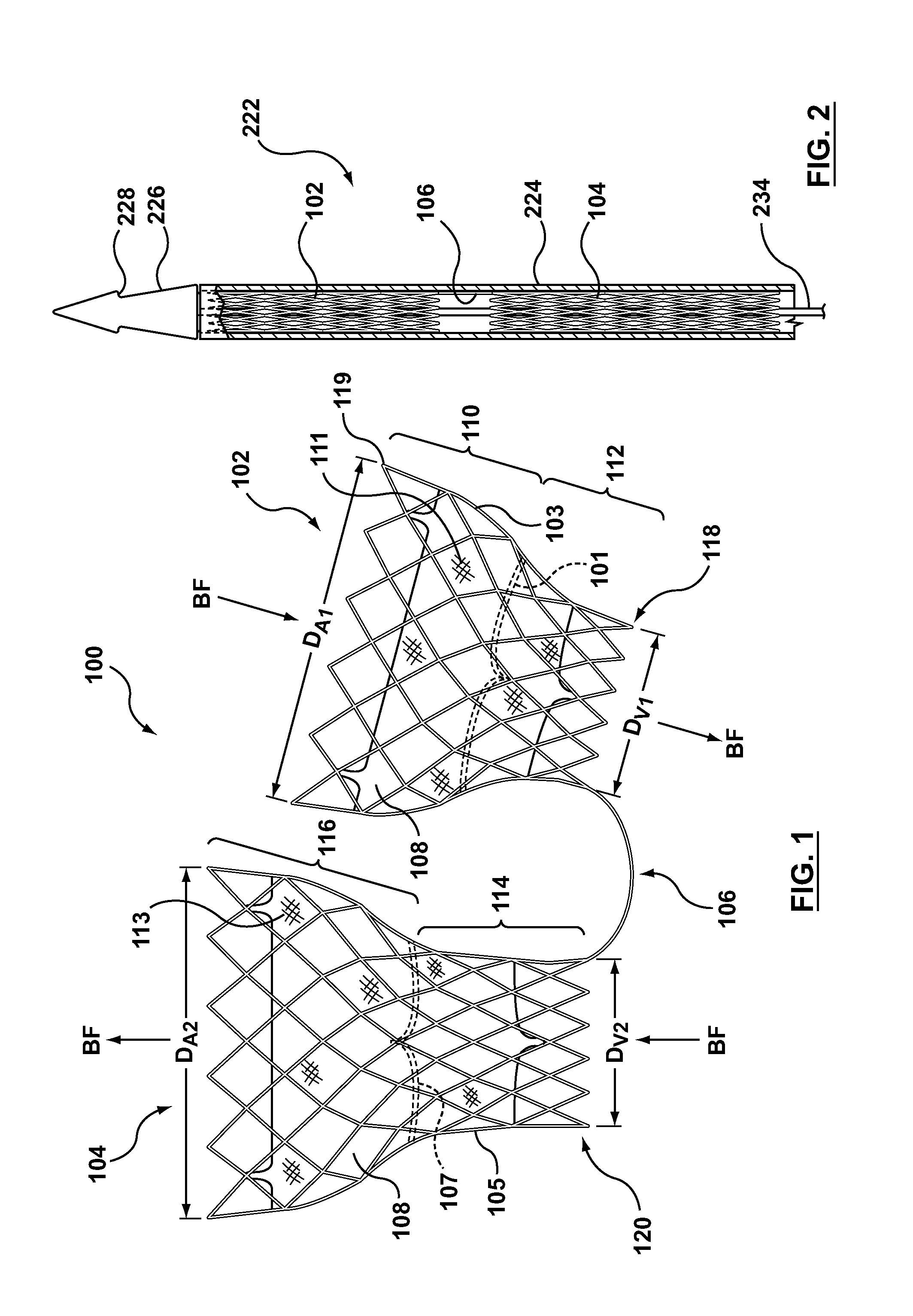
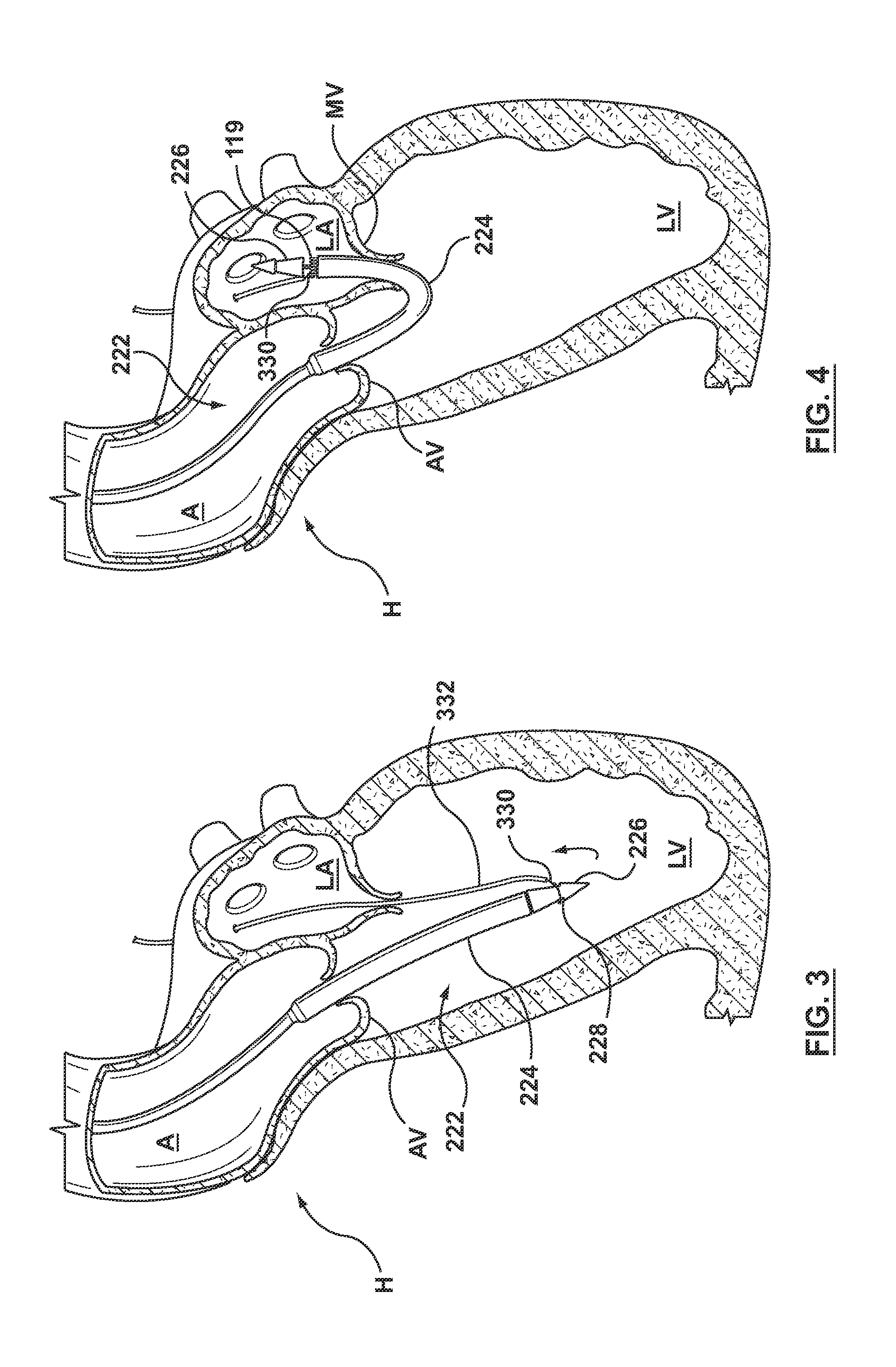
Dual Valve Prosthesis for Transcatheter Valve Implantation
A dual valve prosthesis having first and second prosthetic valve components with a linkage that connects the first and second prosthetic valve components together is disclosed. Each of the first and second prosthetic valve components includes a stent structure with a prosthetic valve secured therein. In a disclosed method, the first and second prosthetic valve components include prosthetic mitral and aortic valves, respectively, and the dual heart valve prosthesis is configured to replace both the native mitral and aortic valves of the heart in a single transcatheter heart valve implantation procedure. The linkage between the first and second prosthetic valve components is configured to secure the anterior mitral valve leaflet against a wall of the left ventricle when the dual valve prosthesis is implanted within the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com