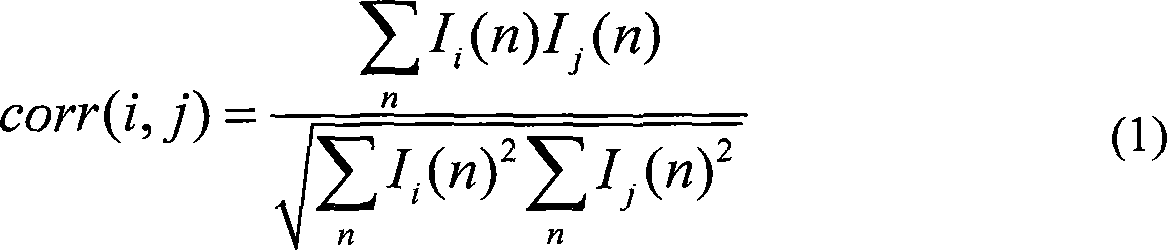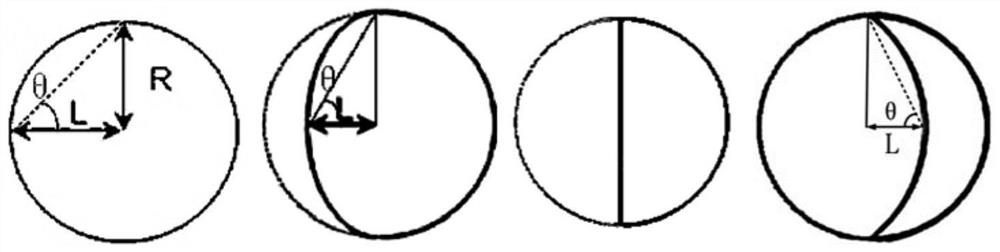Patents
Literature
53 results about "Heart Part" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
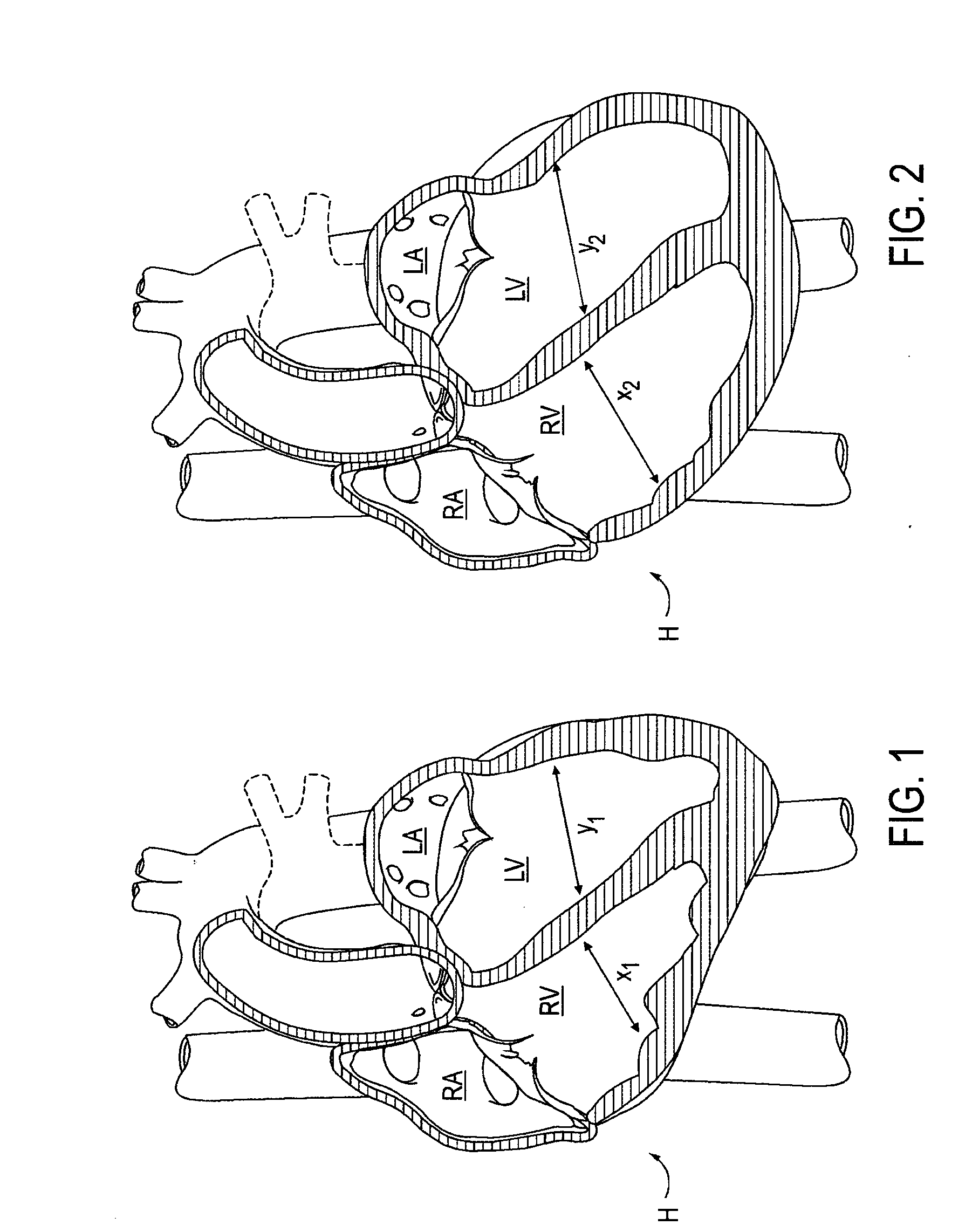
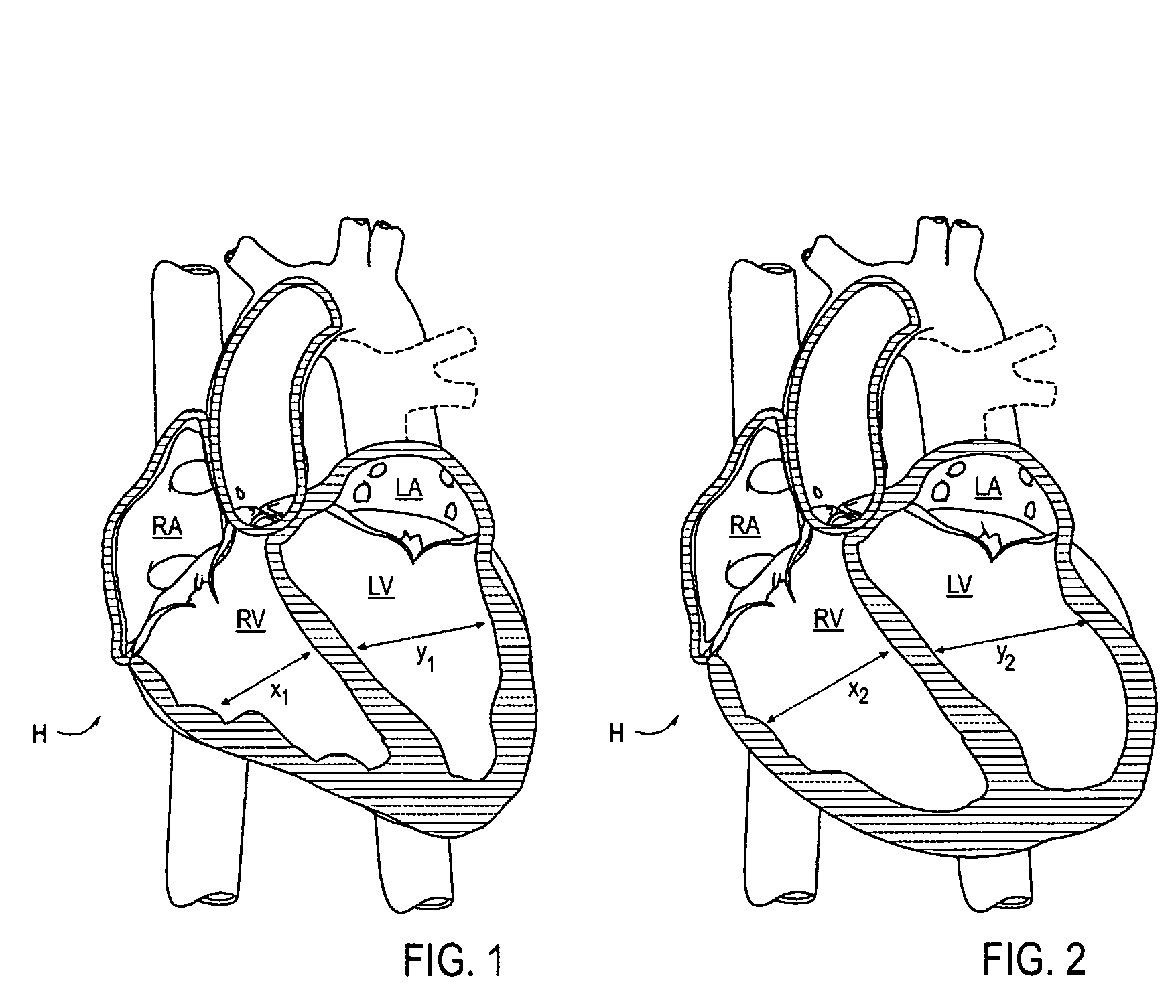
Any component of the organ which receives blood from the veins and ejects it into the arteries.
Performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia
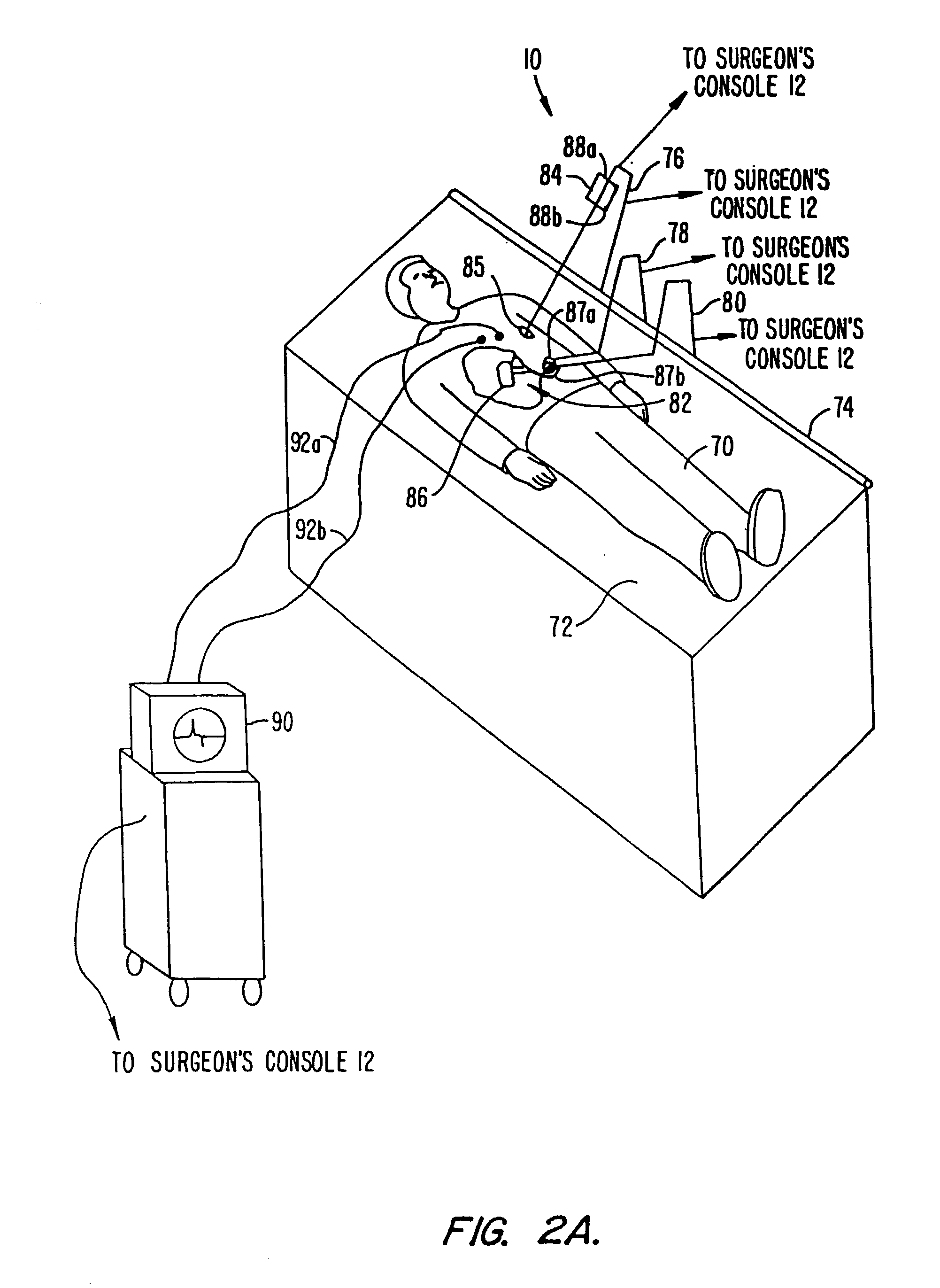
InactiveUS6468265B1Improve abilitiesEasy to controlSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsForcepsMotion tracking system
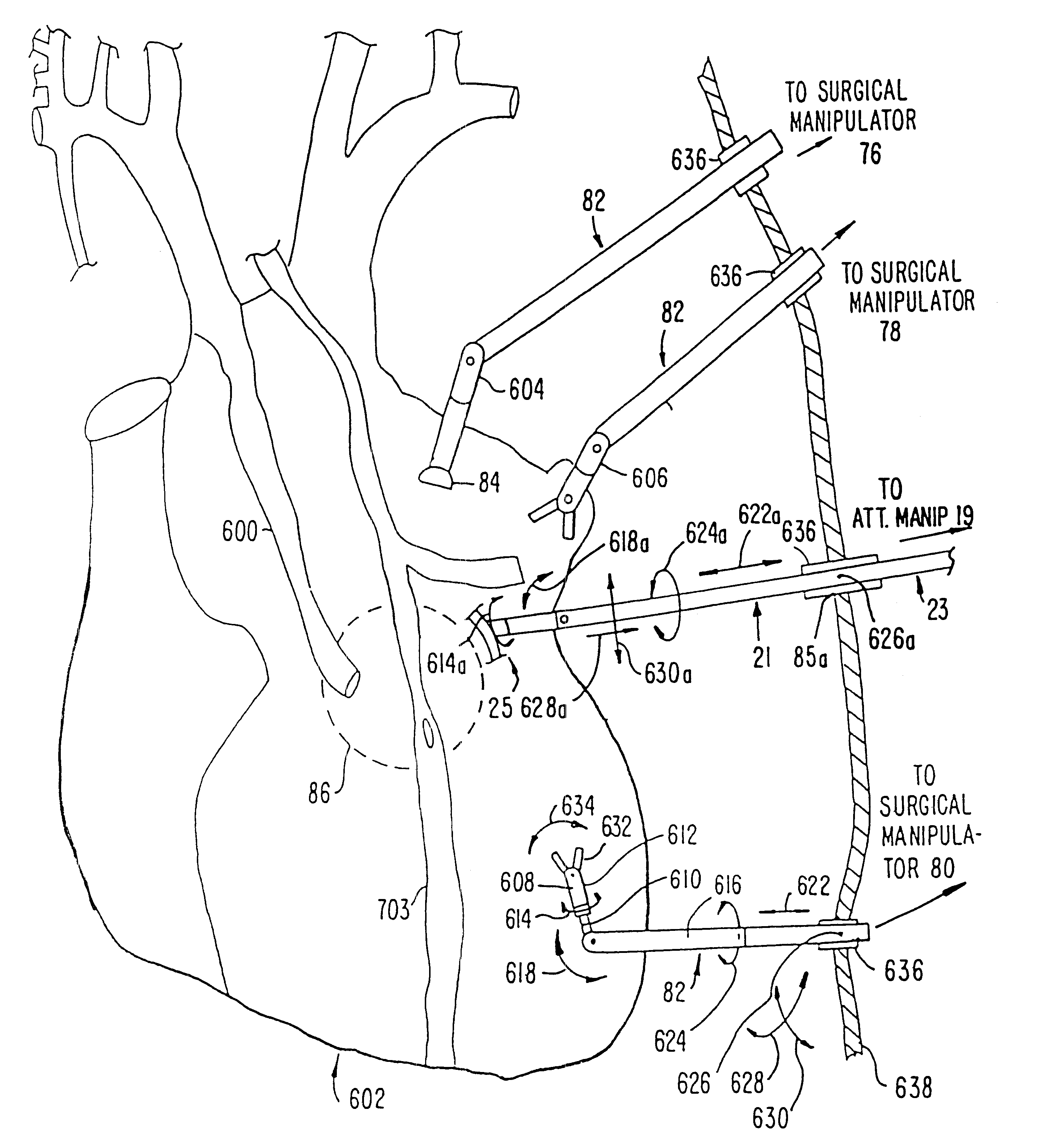
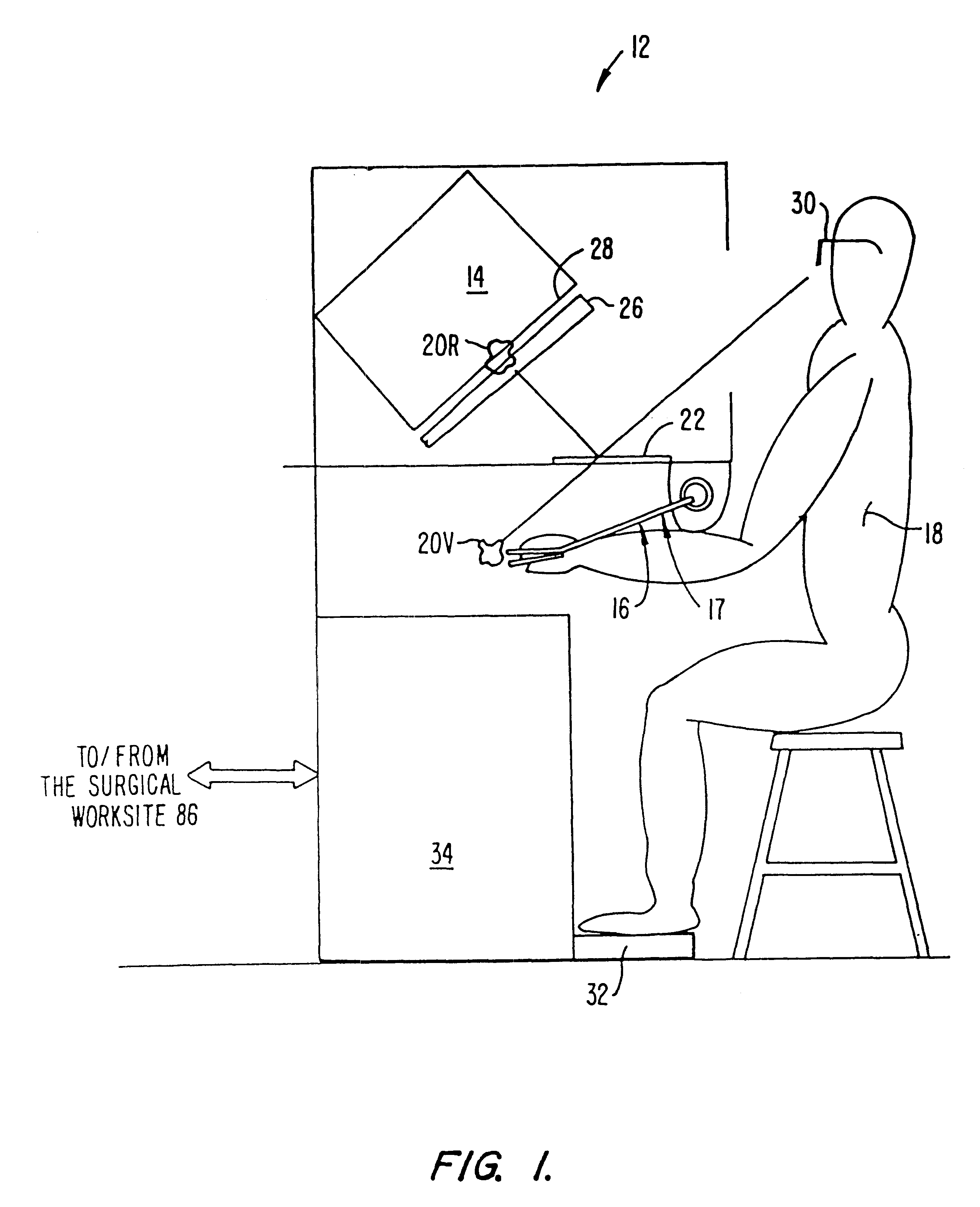
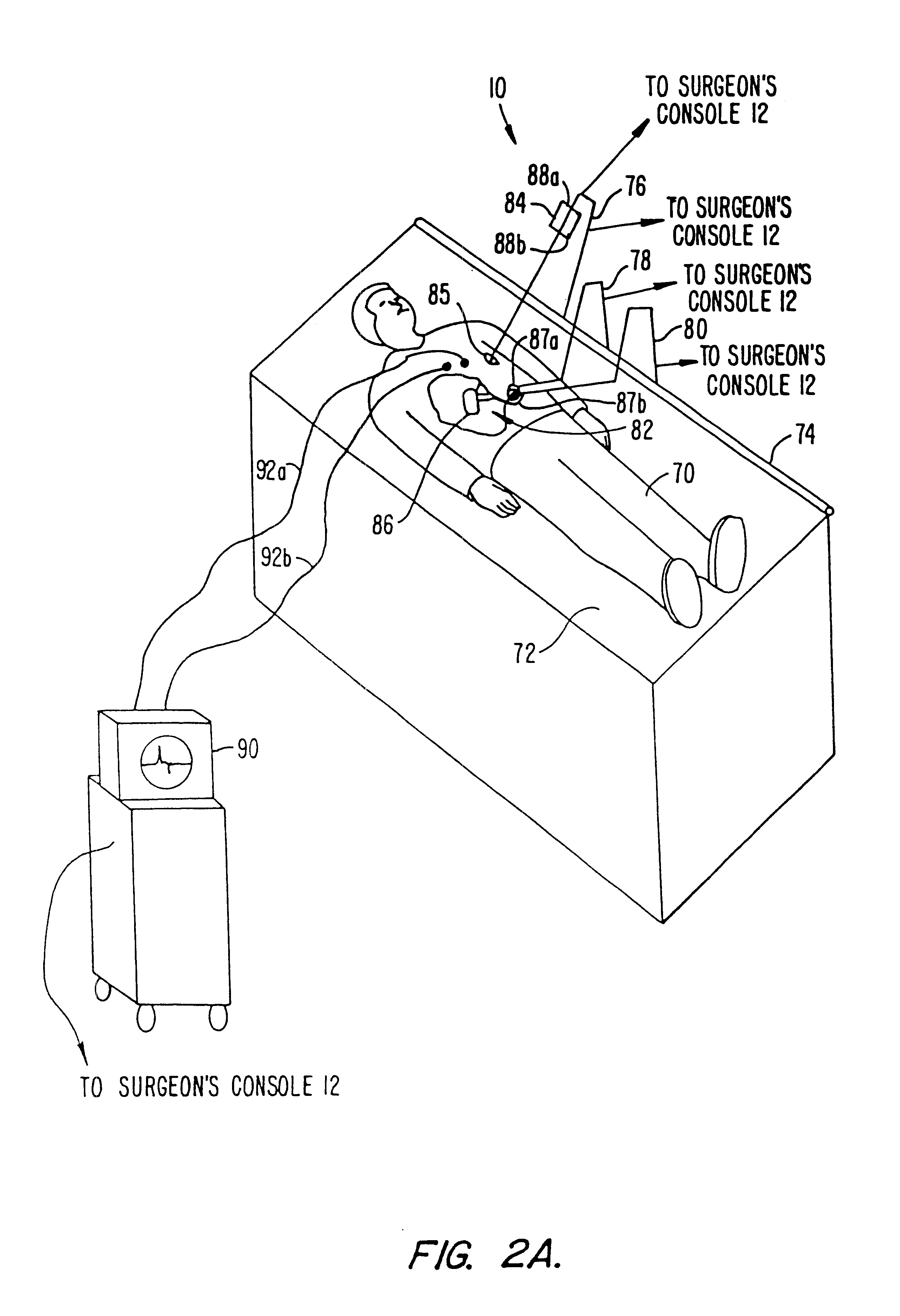
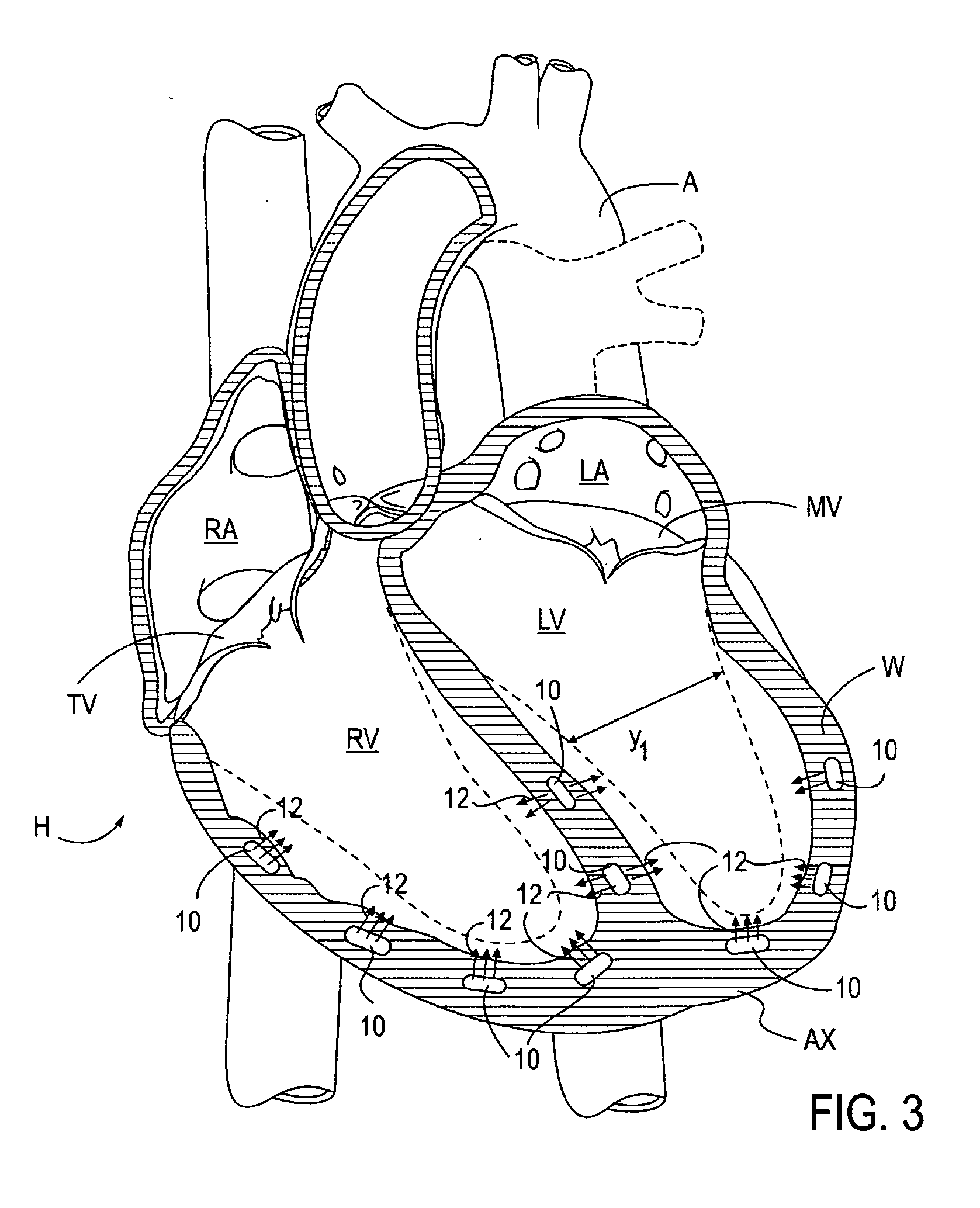
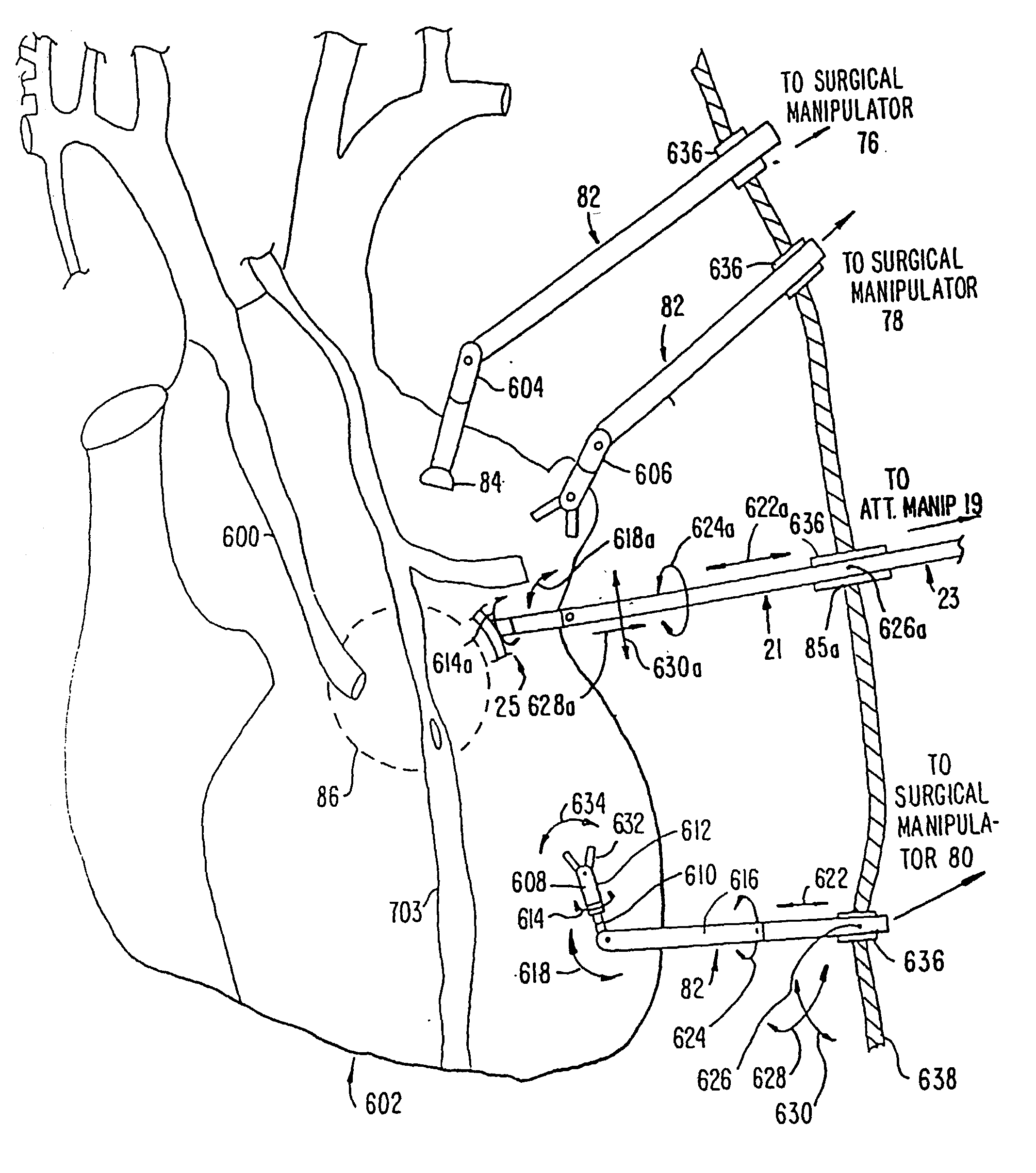
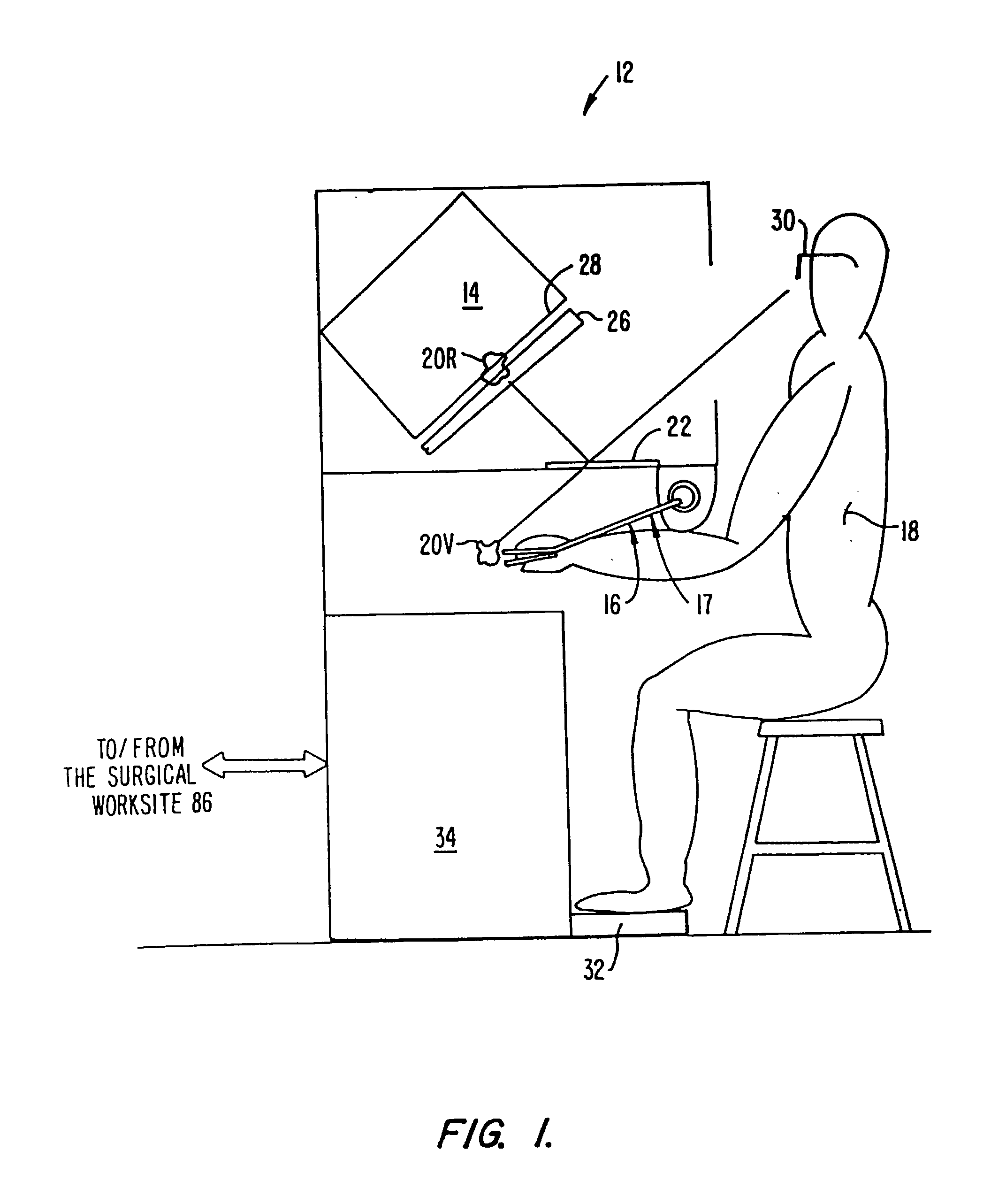
A surgical system or assembly for performing cardiac surgery includes a surgical instrument; a servo-mechanical system engaged to the surgical instrument for operating the surgical instrument; and an attachment assembly for removing at least one degree of movement from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. The surgical system or assembly also includes a motion tracking system for gathering movement information on a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. A control computer is engaged to the attachment assembly and to the motion tracking system and to the servo-mechanical system for controlling movement of the attachment assembly and for feeding gathered information to the servo-mechanical system for moving the surgical instrument in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite such that a relative position of the moving surgical instrument with respect to the resultant surgical cardiac worksite is generally constant. A video monitor is coupled to the control computer; and an input system is coupled to the servo-mechanical system and to the control computer for providing a movement of the surgical instrument. The video monitor displays movement of the surgical instrument while the resultant surgical cardiac worksite appears substantially stationary, and while a relative position of the surgical instrument moving in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite, as a result from the movement information gathered by the motion tracking system, remains generally constant. A method of performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia comprising removing at least one degree of movement freedom from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce at least a partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite while allowing a residual heart section, generally separate from the at least partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite, to move as a residual moving heart part. Cardiac surgery is performed on the at least partially stationary cardiac worksite with a surgical instrument such as needle drivers, forceps, blades and scissors.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Magnetic devices and methods for reshaping heart anatomy
InactiveUS20060015003A1Improve shrinkageIncreased total stroke volumeElectrotherapyHeart valvesCardiac surfaceHeart Part
Systems, methods and devices are provided for treating heart failure patients suffering from various levels of heart dilation. Heart dilation treated by reshaping the heart anatomy with the use of magnetic forces. Such reshaping changes the geometry of portions of the heart, particularly the right or left ventricles, to increase contractibility of the ventricles thereby increasing the stroke volume which in turn increases the cardiac output of the heart. The magnetic forces are applied with the use of one or more magnetic elements which are implanted within the heart tissue or attached externally and / or internally to a surface of the heart. The various charges of the magnetic forces interact causing the associated heart tissue areas to readjust position, such as to decrease the width of the ventricles. Such repositioning is maintained over time by the force of the magnetic elements, allowing the damaging effects of heart dilation to slow in progression or reverse.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
Performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia
InactiveUS20030055410A1Improve abilitiesEasy to controlSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsForcepsMotion tracking system
A surgical system or assembly for performing cardiac surgery includes a surgical instrument; a servo-mechanical system engaged to the surgical instrument for operating the surgical instrument; and an attachment assembly for removing at least one degree of movement from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. The surgical system or assembly also includes a motion tracking system for gathering movement information on a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. A control computer is engaged to the attachment assembly and to the motion tracking system and to the servo-mechanical system for controlling movement of the attachment assembly and for feeding gathered information to the servo-mechanical system for moving the surgical instrument in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite such that a relative position of the moving surgical instrument with respect to the resultant surgical cardiac worksite is generally constant. A video monitor is coupled to the control computer; and an input system is coupled to the servo-mechanical system and to the control computer for providing a movement of the surgical instrument. The video monitor displays movement of the surgical instrument while the resultant surgical cardiac worksite appears substantially stationary, and while a relative position of the surgical instrument moving in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite, as a result from the movement information gathered by the motion tracking system, remains generally constant. A method of performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia comprising removing at least one degree of movement freedom from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce at least a partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite while allowing a residual heart section, generally separate from the at least partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite, to move as a residual moving heart part. Cardiac surgery is performed on the at least partially stationary cardiac worksite with a surgical instrument such as needle drivers, forceps, blades and scissors.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Shape memory devices and methods for reshaping heart anatomy
InactiveUS20060015002A1Improve shrinkageReduce widthSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCardiac surfaceHeart anatomy
Systems, methods and devices are provided for treating heart failure patients suffering from various levels of heart dilation. Such heart dilation is treated by reshaping the heart anatomy with the use of shape memory elements. Such reshaping changes the geometry of portions of the heart, particularly the right or left ventricles, to increase contractibility of the ventricles thereby increasing the stroke volume which in turn increases the cardiac output of the heart. The shape memory elements have an original shape and at least one memory shape. The elements are implanted within the heart tissue or attached externally and / or internally to a surface of the heart when in the original shape. The elements are then activated to transition from the original shape to one of the at least one memory shapes. Transitioning of the elements cause the associated heart tissue areas to readjust position, such as to decrease the width of the ventricles. Such repositioning is maintained over time by the elements, allowing the damaging effects of heart dilation to slow in progression or reverse.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
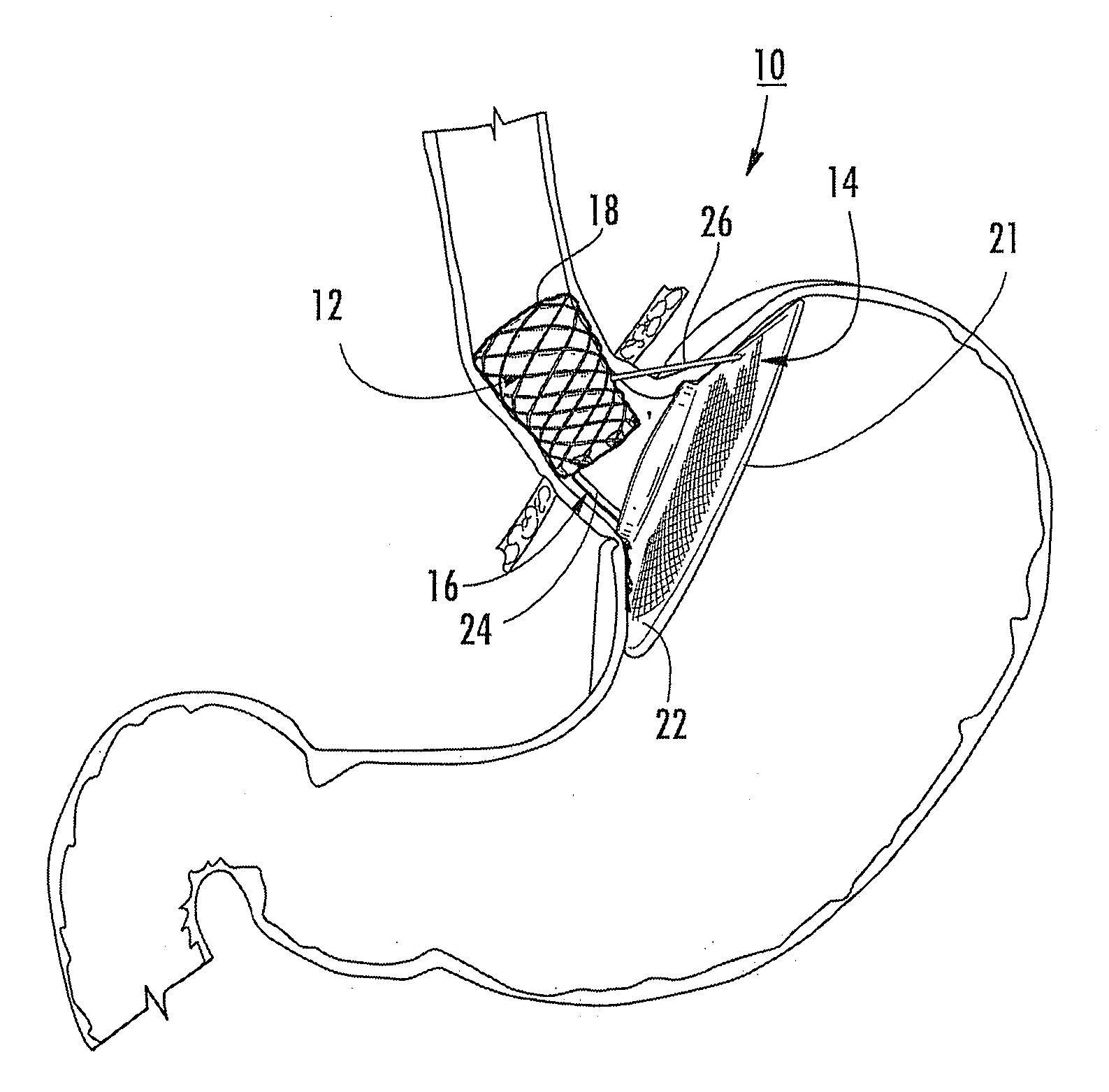
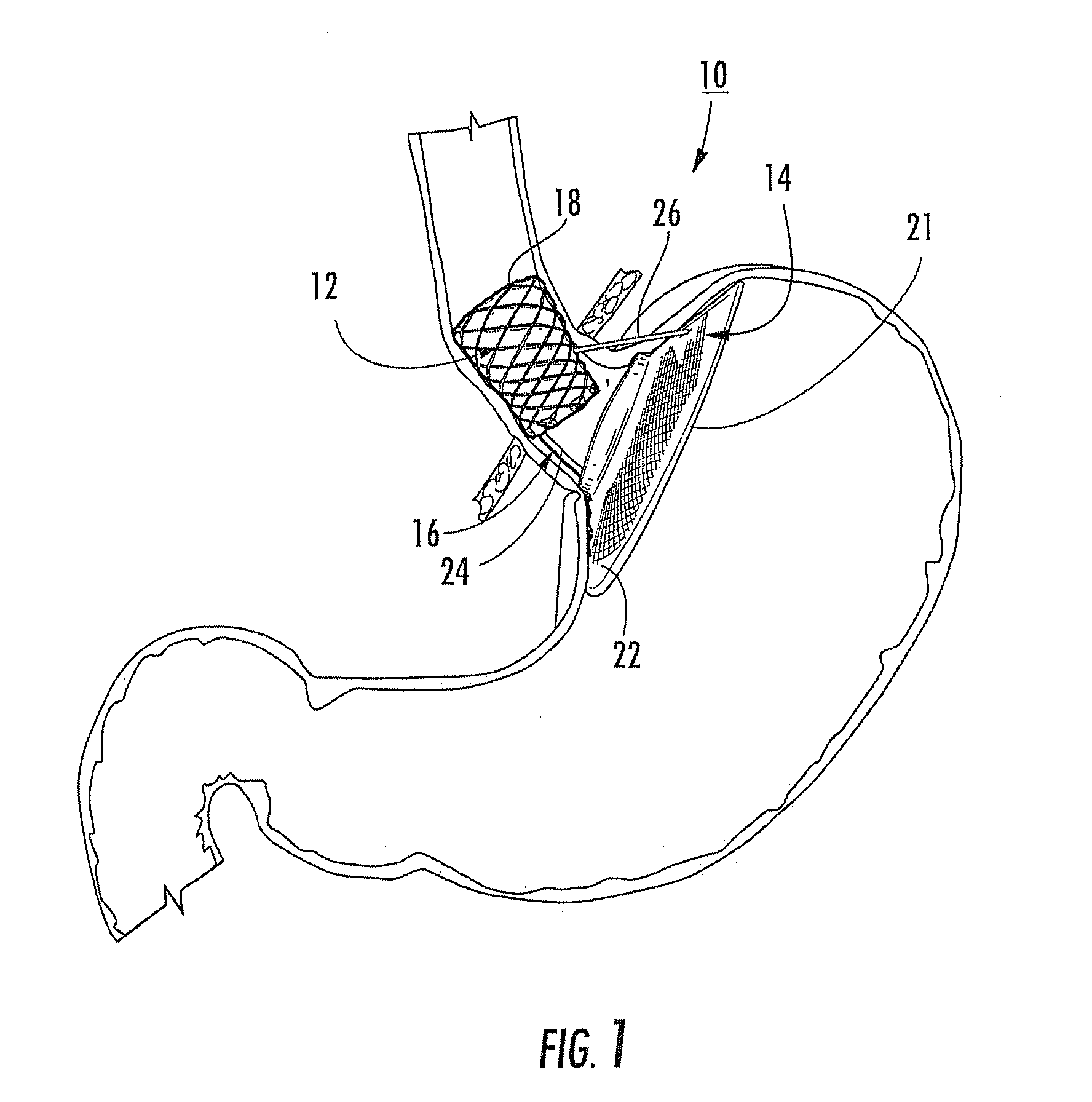
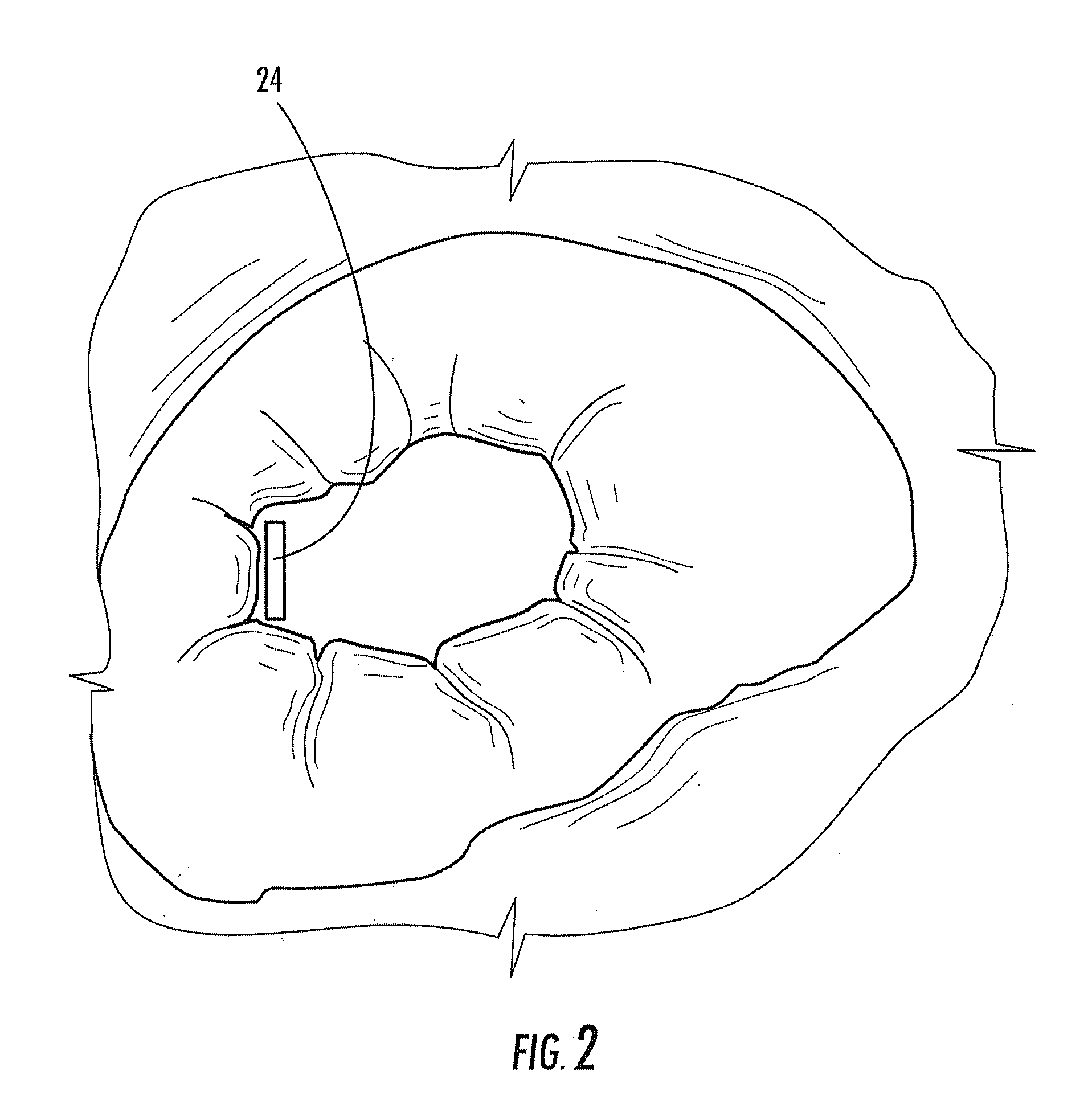
Bariatric device and method
ActiveUS20100030017A1Effective and invasive mannerEffective and minimally invasiveSuture equipmentsDilatorsCardiac surfaceHeart Part
A bariatric device and method of causing weight loss in a recipient includes providing a bariatric device having an esophageal member, a cardiac member and a connector connected with the esophageal member and the cardiac member. The esophageal member has an esophageal surface that is configured to generally conform to the shape and size of a portion of the esophagus. The cardiac member has a cardiac surface that is configured to generally conform to the shape and size of a portion of the cardiac portion of the stomach. The esophageal surface is positioned at the esophagus. The cardiac surface is positioned at the cardiac portion of the stomach. The bariatric device stimulates receptors in order to influence a neurohormonal mechanism in the recipient.
Owner:BFKW
Shape memory devices and methods for reshaping heart anatomy
InactiveUS7285087B2Improve shrinkageReduce widthSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCardiac surfaceHeart Part
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
Minimally invasive cardiac surgery procedure
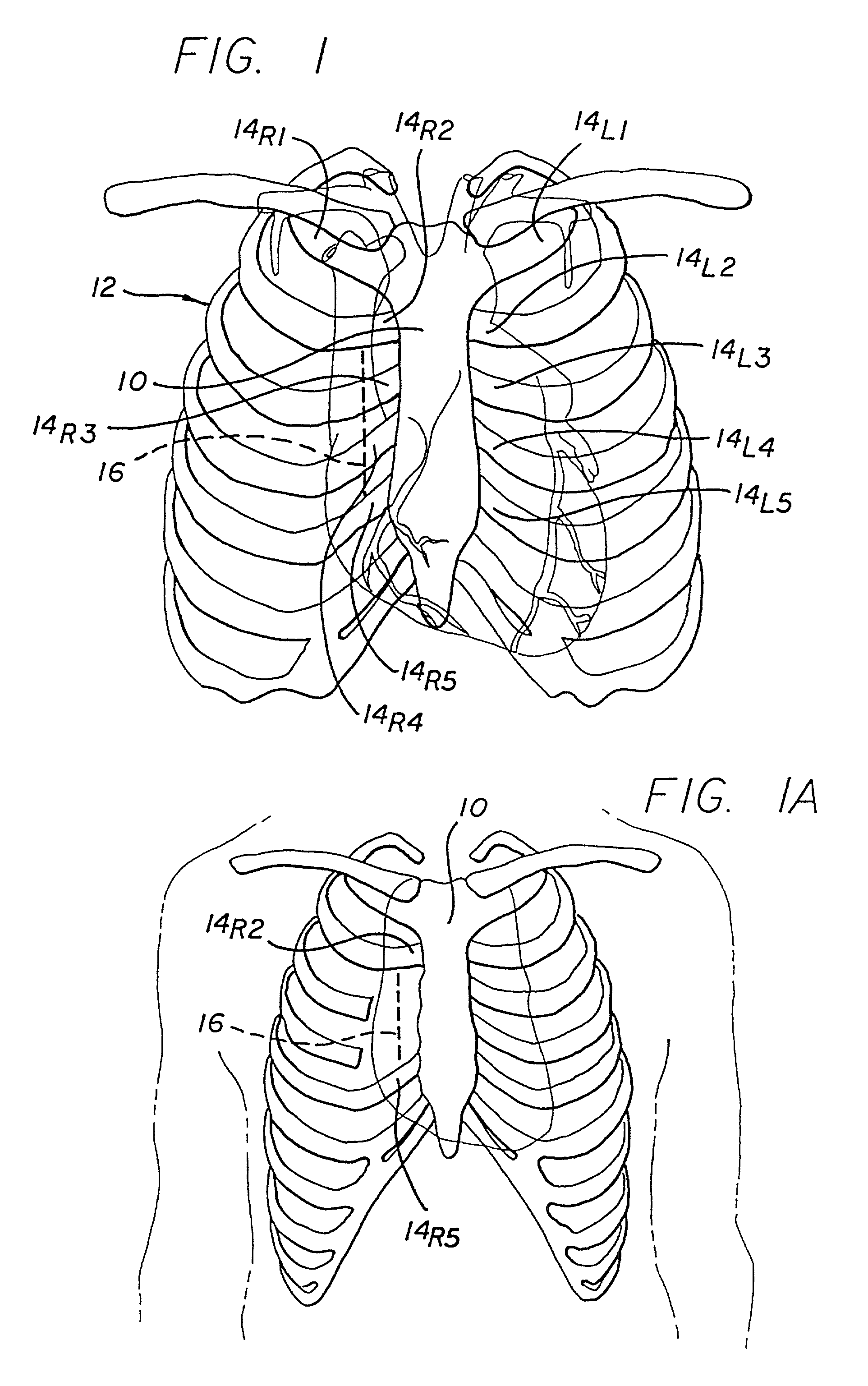
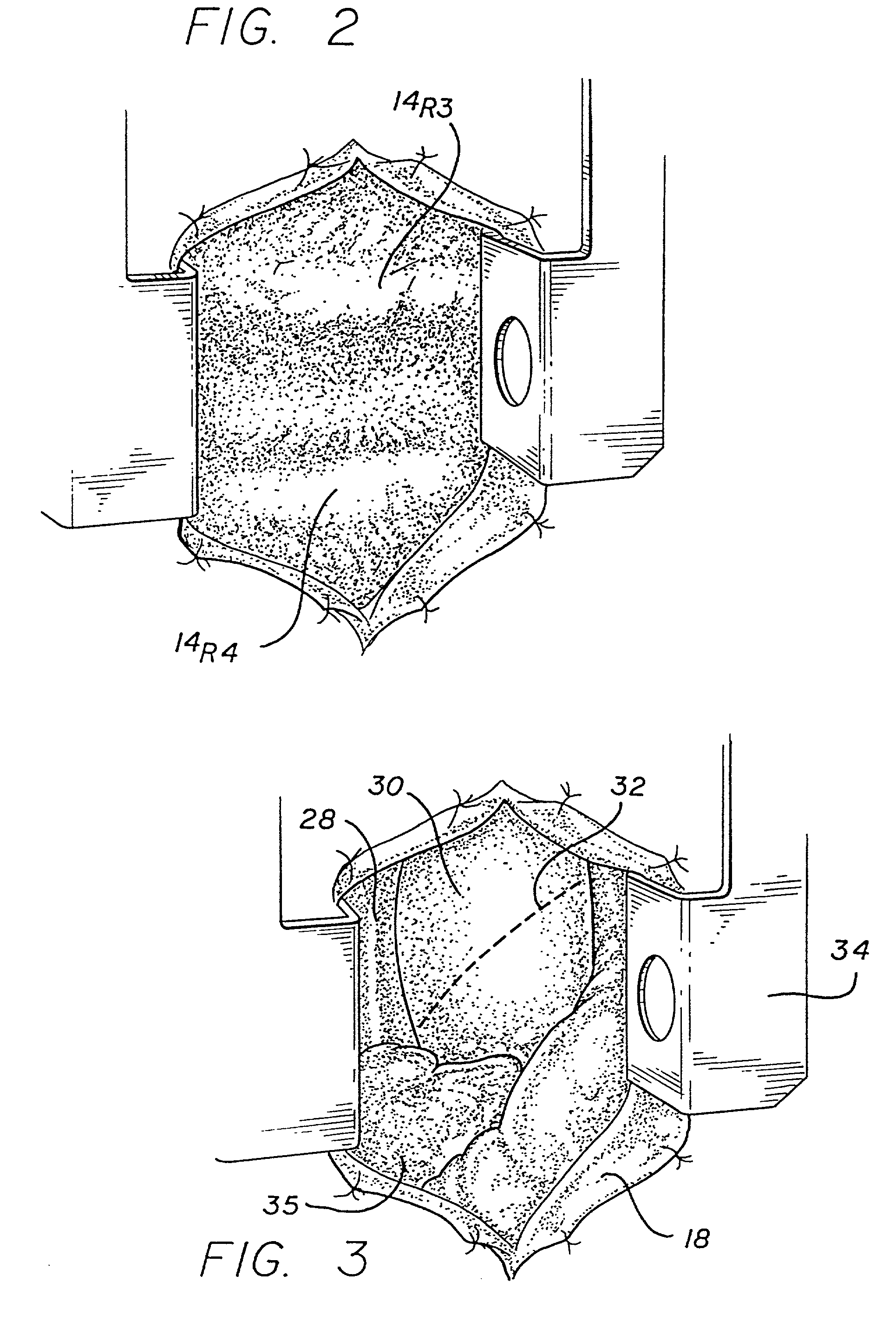
A minimally invasive approach for surgery on portions of the heart and great vessels. A parasternal incision is made extending across a predetermined number of costal cartilages, e.g., a right parasternal incision extending from the lower edge of the second costal cartilage to the superior edge of the fifth costal cartilage. One or more costal cartilages, e.g., the third and fourth, are then excised to provide access to the portion of the heart or great vessels of interest, for example between a point approximately three centimeters above supra annular ridge and the mid ventricular cavity, and a desired procedure completed. A minimally invasive procedure for repair or replacement of the aortic valve is disclosed that includes making a transverse incision of about 10 cm in length over the second or third intercostal space in the thorax of the patient, dividing the sternum transversely following the incision, retracting the transversely divided sternum, exposing the ascending aorta, and incising the ascending aorta to provide access to an area adjacent the aortic valve.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
Materialized heart 3D model manufacturing method capable of achieving internal and external structures
ActiveCN104462650AClear and complete structureIncrease success rateSpecial data processing applications3D modellingDICOMMedical imaging data
The invention relates to a materialized heart 3D model manufacturing method capable of achieving internal and external structures. The method can overcome the defects in the prior art. The method includes the steps that (1) the heart part of a patient is scanned to obtain medical image data to form a DICOM file; (2) the DICOM file obtained in the step (1) is identified through Mimics software and stored to form a computer-identified .mcs file; (3) different data templates are extracted from the software; (4) the templates, with cavity structures or incomplete images or unclear boundaries, obtained in the step (3) are processed to be made clear and complete; (5) a needed template is formed by adding or deleting or separating or combining the templates; (6) a 3D image formed in the step (5) is processed to enable the exterior of the 3D image to be smooth and interior image templates to be complete to form an STL file; (7) data processed in the step (6) are input in a 3D laser printer, and accordingly a heart model is printed. According to the method, heart models with clear and complete structures can be obtained, and the success rate of heart operations can be greatly increased.
Owner:河南龙光三维生物工程有限公司
Magnetic devices and methods for reshaping heart anatomy
InactiveUS7402134B2Improve shrinkageIncrease volumeHeart valvesSurgical needlesCardiac surfaceHeart Part
Systems, methods and devices are provided for treating heart failure patients suffering from various levels of heart dilation. Heart dilation treated by reshaping the heart anatomy with the use of magnetic forces. Such reshaping changes the geometry of portions of the heart, particularly the right or left ventricles, to increase contractibility of the ventricles thereby increasing the stroke volume which in turn increases the cardiac output of the heart. The magnetic forces are applied with the use of one or more magnetic elements which are implanted within the heart tissue or attached externally and / or internally to a surface of the heart. The various charges of the magnetic forces interact causing the associated heart tissue areas to readjust position, such as to decrease the width of the ventricles. Such repositioning is maintained over time by the force of the magnetic elements, allowing the damaging effects of heart dilation to slow in progression or reverse.
Owner:MICARDIA CORP
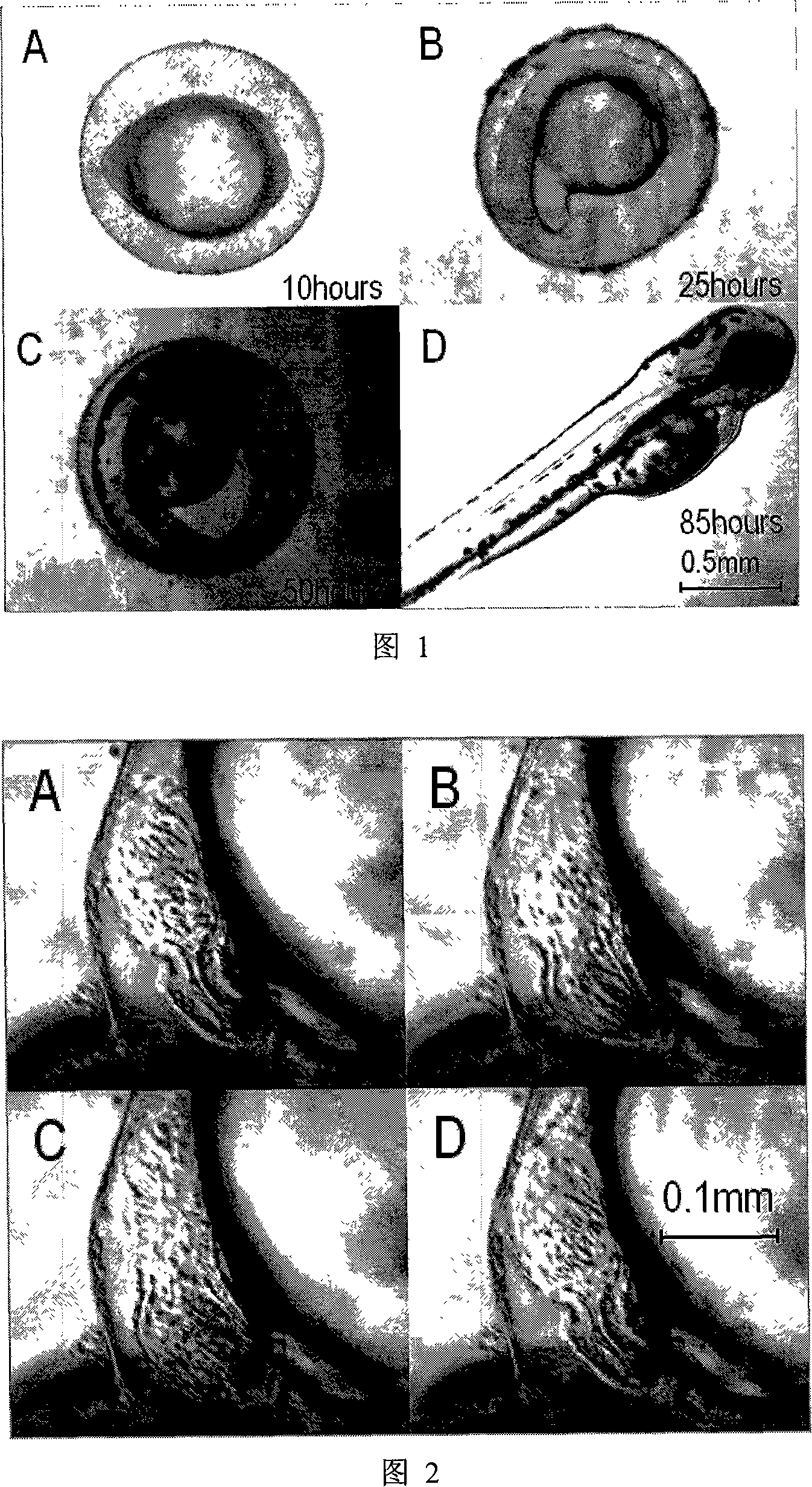
Method for measuring the heart rate of zebra fish by using high-speed CCD
InactiveCN101112307AConvenient and accurateIncrease credibilityDiagnostics using lightMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateBiological bodyPattern recognition
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology measurement, in particular to a method of measuring the heart rate of the zebra fish by utilizing a high-speed CCD. The method comprises that the heart part of the zebra fish is imaged and a video file is collected by the high-speed CCD, then the correlated image process to the obtained video file is carried out, namely an interested image with one frame is chosen as a reference image, the other images and the reference image are calculated in a correlation way, then the data of the heart rate of the zebra fish is obtained. The method of the invention belongs to a non-contact measurement and improves the reliability of the research data without any damage to the creature.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Whole heart extracting method based on heart CT image
InactiveCN103985122ARealize remote auxiliary diagnosisAdaptableImage enhancementImage analysisThoracic structureThoracic cavity
A whole heart extracting method based on a heart CT image comprises the steps of obtaining the heart CT image, removing the lung part, the descending aorta part, the thoracic cavity wall part and the vertebra part of the heart CT image to obtain a middle image, and removing the noise part in the middle image. The whole heart extracting method based on the heart CT image gradually removes the non-heart parts such as the thoracic cavity wall, the lung, the vertebra and the descending aorta in an reverse angle mode to achieve the purpose of extracting the whole heart, has the advantages of being high in self-adaptation performance, high in operation efficiency, accurate in extraction effect and the like, can be rapidly embedded in an existing medical network, and achieves remote auxiliary diagnosis.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
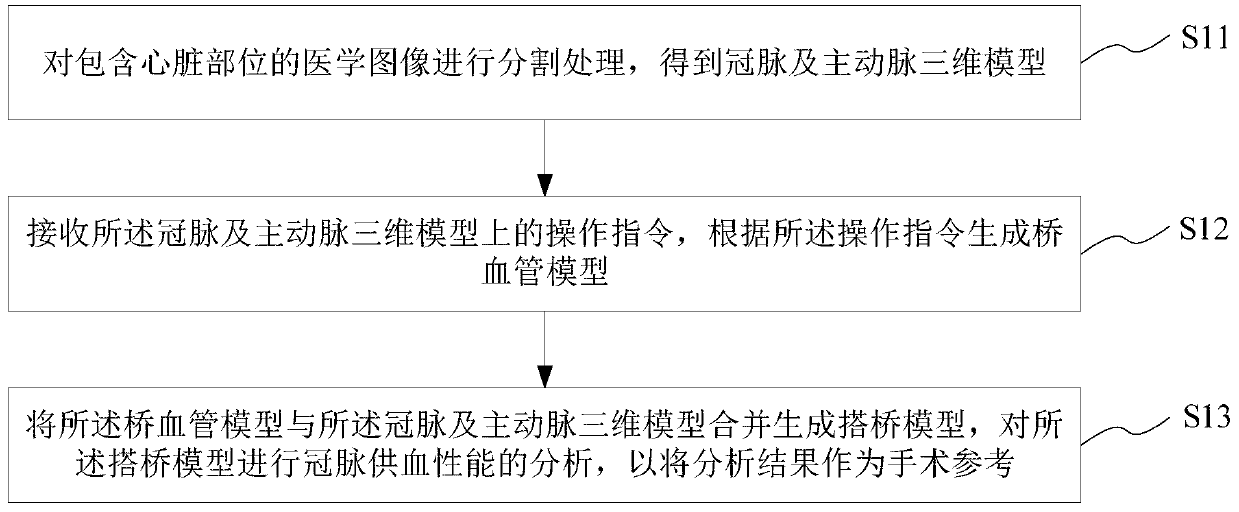
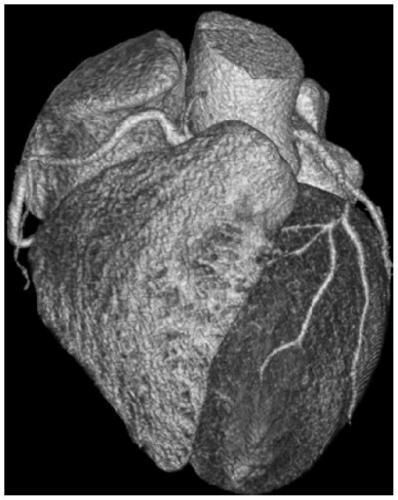
Virtual coronary artery operation bypass analysis method and system, medium and equipment
InactiveCN111312375ARational choice of surgical procedureMedical simulationImage enhancementCoronary arteriesHeart Part
The invention provides a virtual coronary artery operation bypass analysis method and system, a medium and equipment, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the segmentation of a medical image comprising a heart part, and obtaining a coronary artery and aorta three-dimensional model; receiving an operation instruction on the coronary artery and aorta three-dimensional model, and generating a saphenous vein bypass graft according to the operation instruction; and combining the saphenous vein bypass graft model with the coronary artery and aorta three-dimensional model to generate a bypass model, and performing coronary artery blood supply performance analysis on the bypass model so as to take an analysis result as an operation reference. According to the invention, a coronary artery bypass surgery type reference can be provided for doctors from multiple angles of the bypass position and the length of the saphenous vein bypass graft.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGMAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
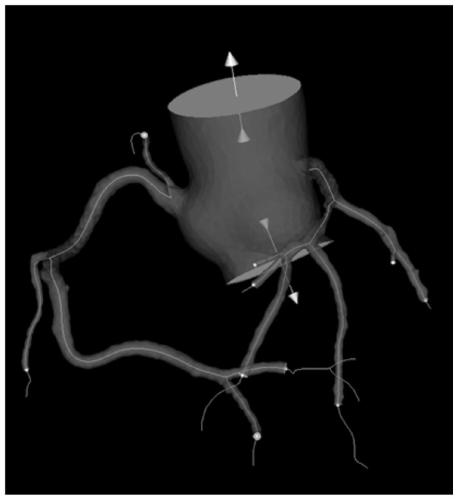
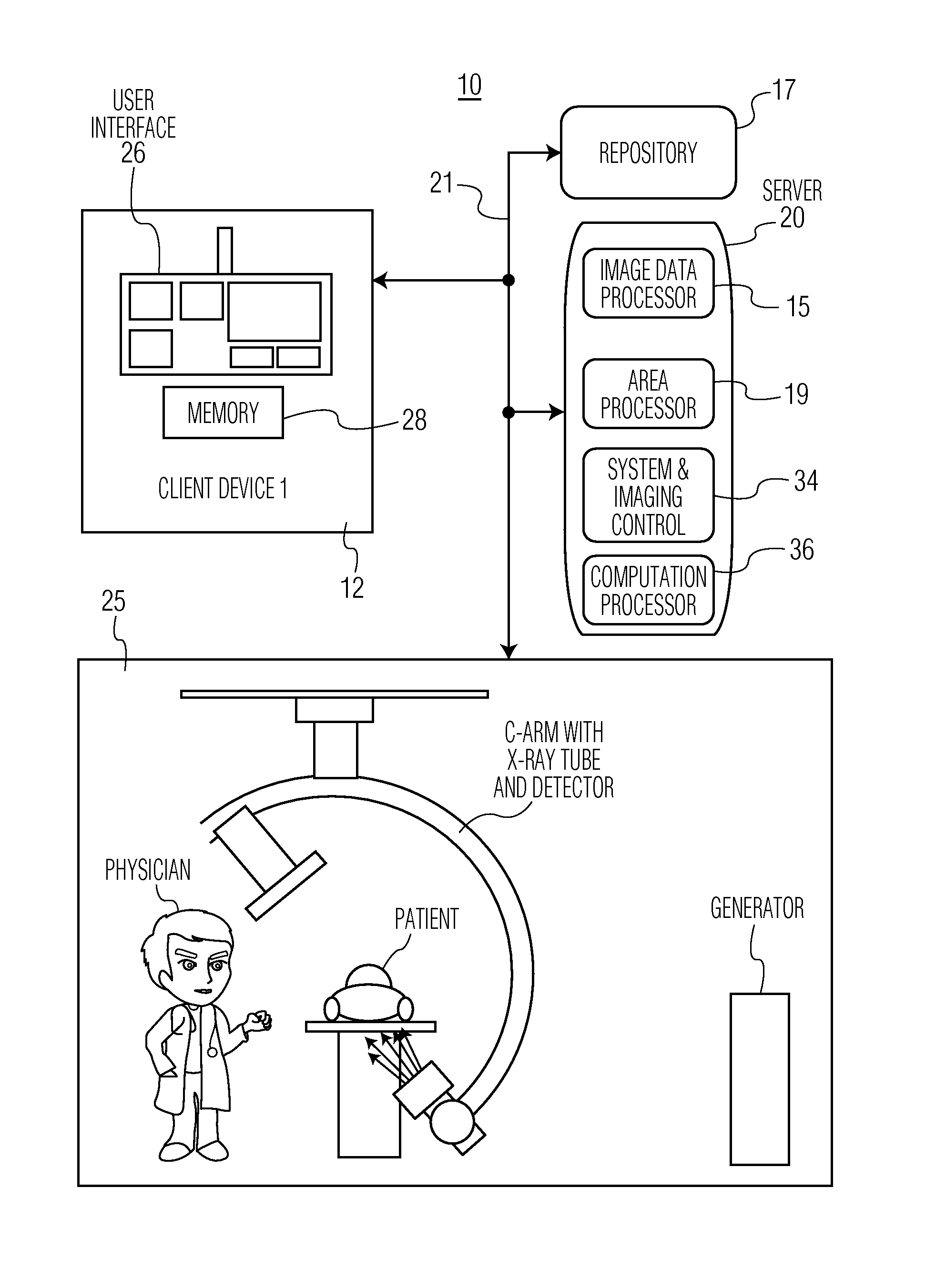
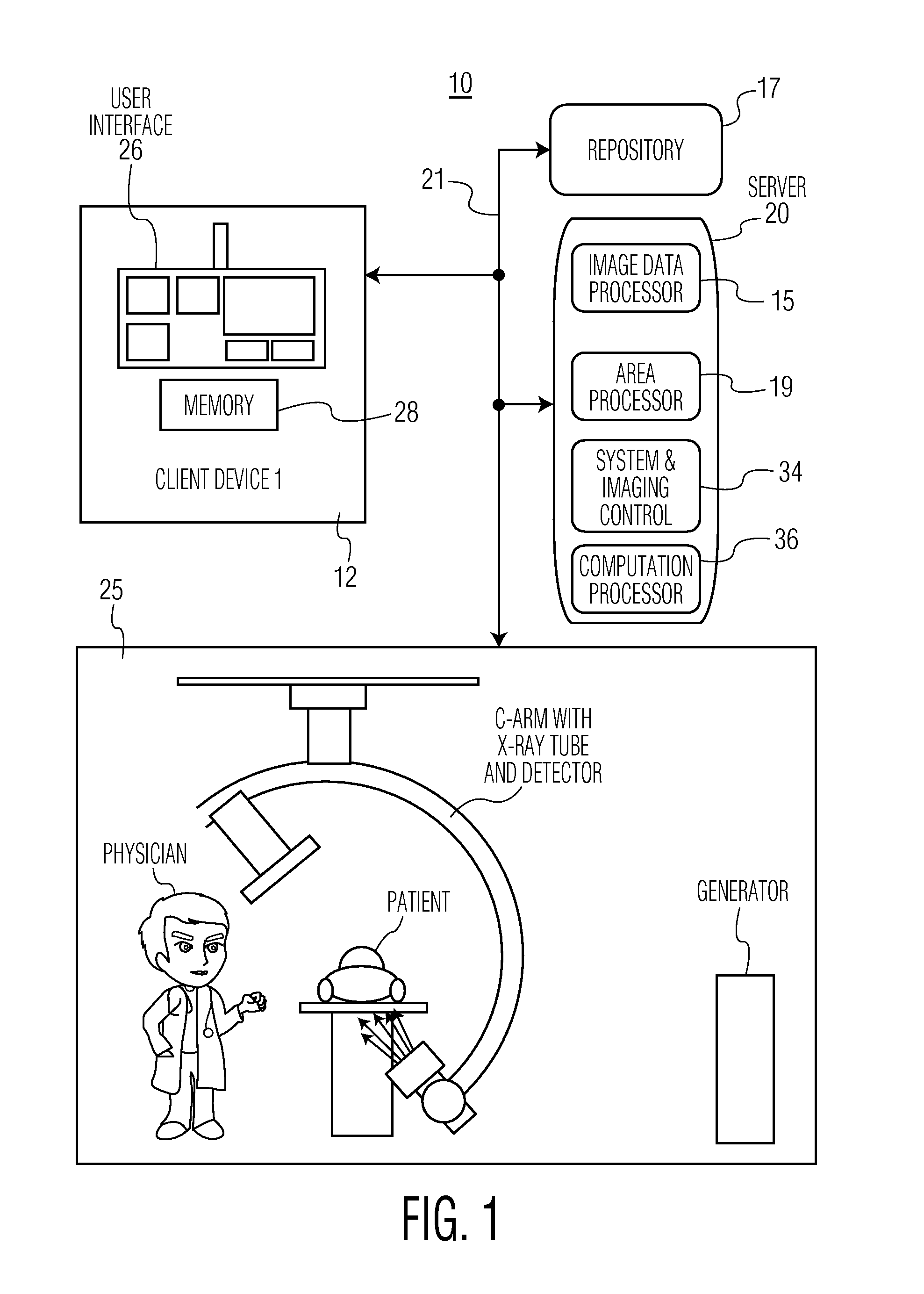
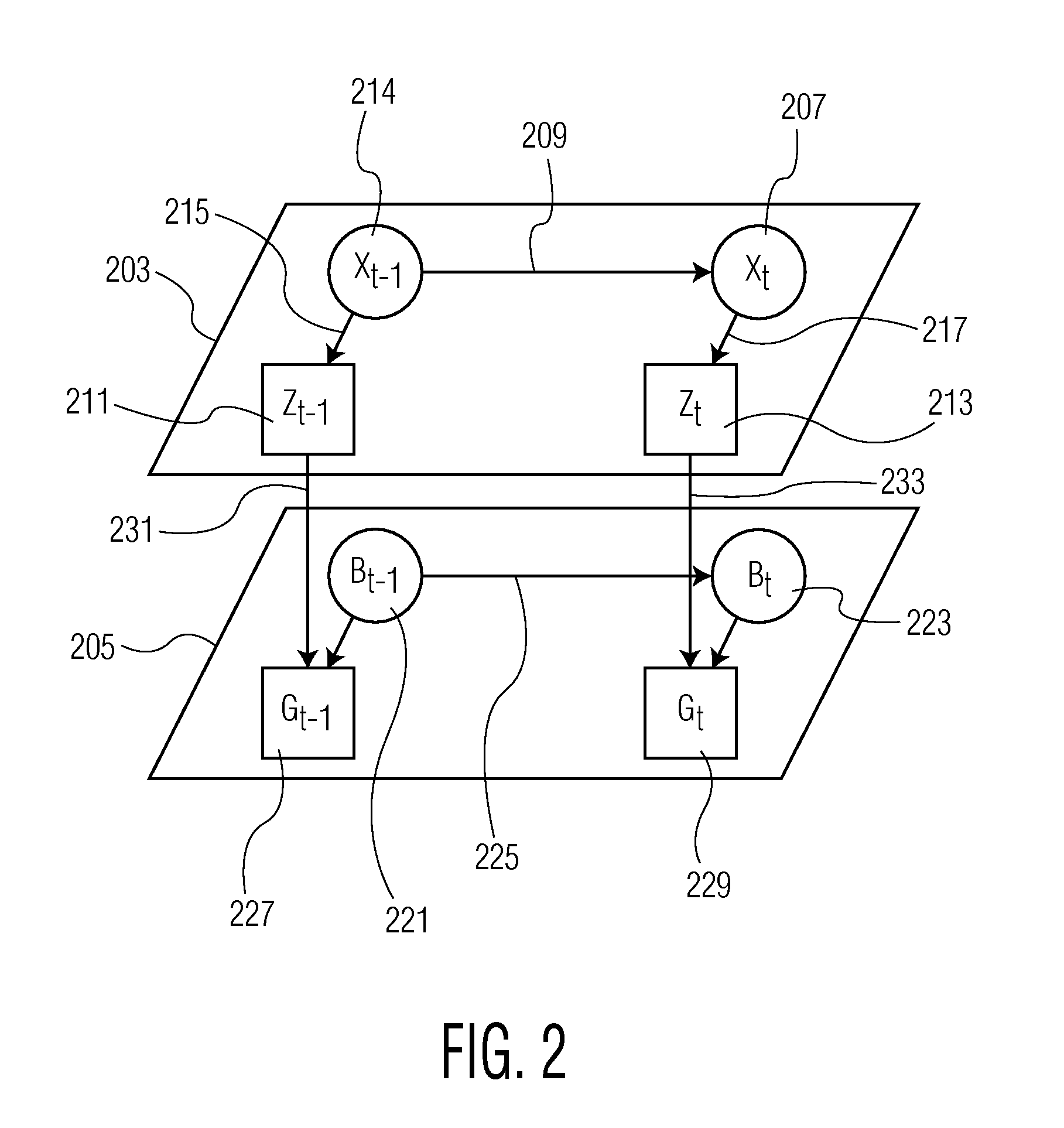
System for Determining Patient Heart related Parameters for use in Heart Imaging
A system uses integrated spatio-temporal analysis in X-ray angiography, for example, by using spatial information within each image frame and temporal information between image frames to provide robust and accurate estimation of stroke area and volume, two and three dimensional ejection fraction and to accommodate patient heart variation. A system determines patient heart related parameters for use in patient heart imaging examination. An image data processor processes data representing multiple cardiac images of a patient over multiple heart beat cycles of the patient to derive data representing a distribution curve of a heart section area over multiple heart beat cycle times and indicating heart section area change over a heart beat cycle. An area processor determines a heart section area in response to user command. Also a computation processor determines a heart function parameter in response to the determined heart section area and the indicated heart section area change.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Cardio-pulmonary resuscitator for medical treatment in emergency department
The invention relates to a cardio-pulmonary resuscitator for medical treatment in an emergency department. The cardio-pulmonary resuscitator comprises a resuscitator casing, wherein an operating handle is arranged on one side of the resuscitator casing; a pressing frame adopting an I-shaped structure is arranged in the resuscitator casing; an elastic pad is arranged on the lower surface of the pressing frame; a rotary shaft is arranged between the pressing frame and the resuscitator casing; a cam is arranged on the rotary shaft; a first return spring and a second return spring are arranged between the pressing frame and the resuscitator casing; a handle cover is arranged on the operating handle; an operating button is arranged on one side of the operating handle. When the cardio-pulmonary resuscitator is used, the elastic pad on the lower side of the pressing frame is put on the heart part of the body of a patient, then the cam rotates at a high speed and drives the pressing frame to vibrate at a high speed in the longitudinal direction under the action of the first return spring and the second return spring, the heart is pressed, the size is small, the operation is convenient, and the practicability is good.
Owner:马俊
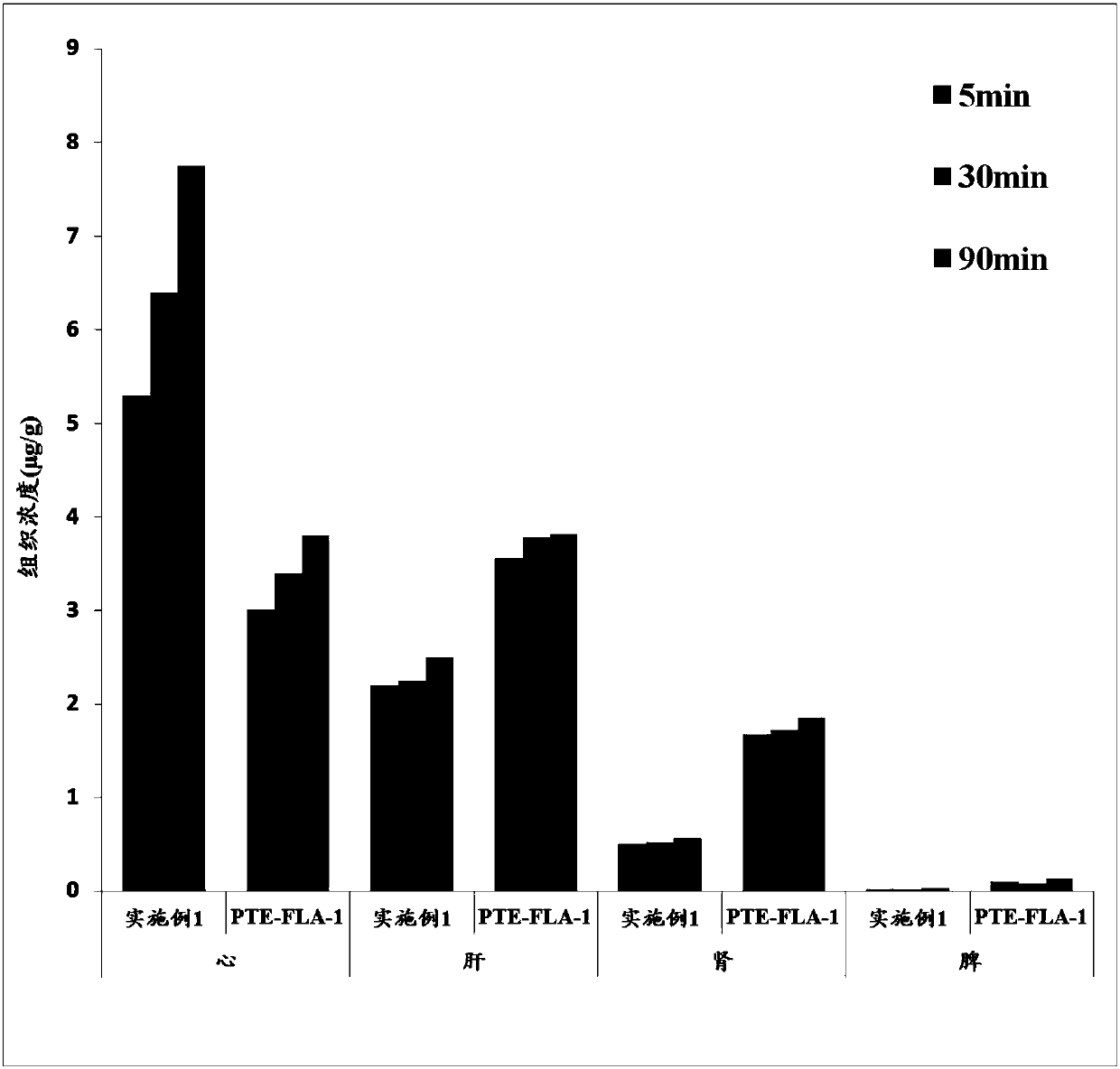
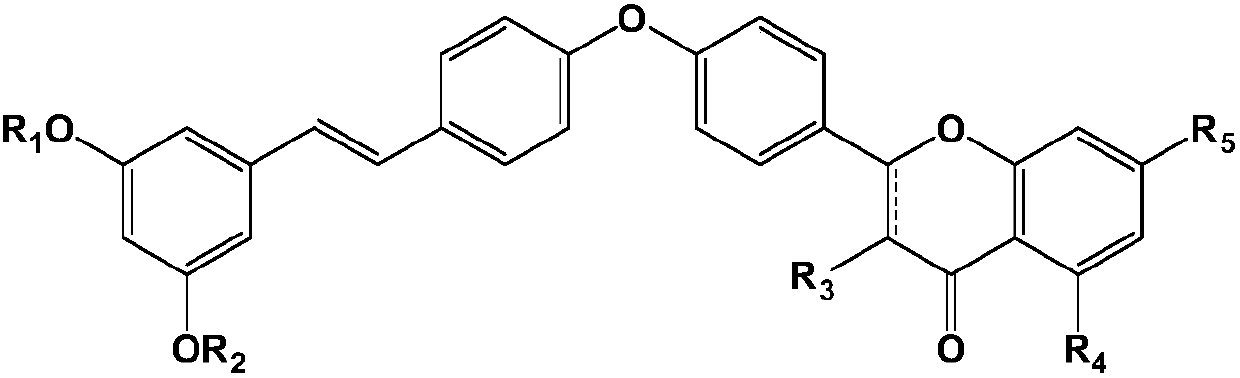
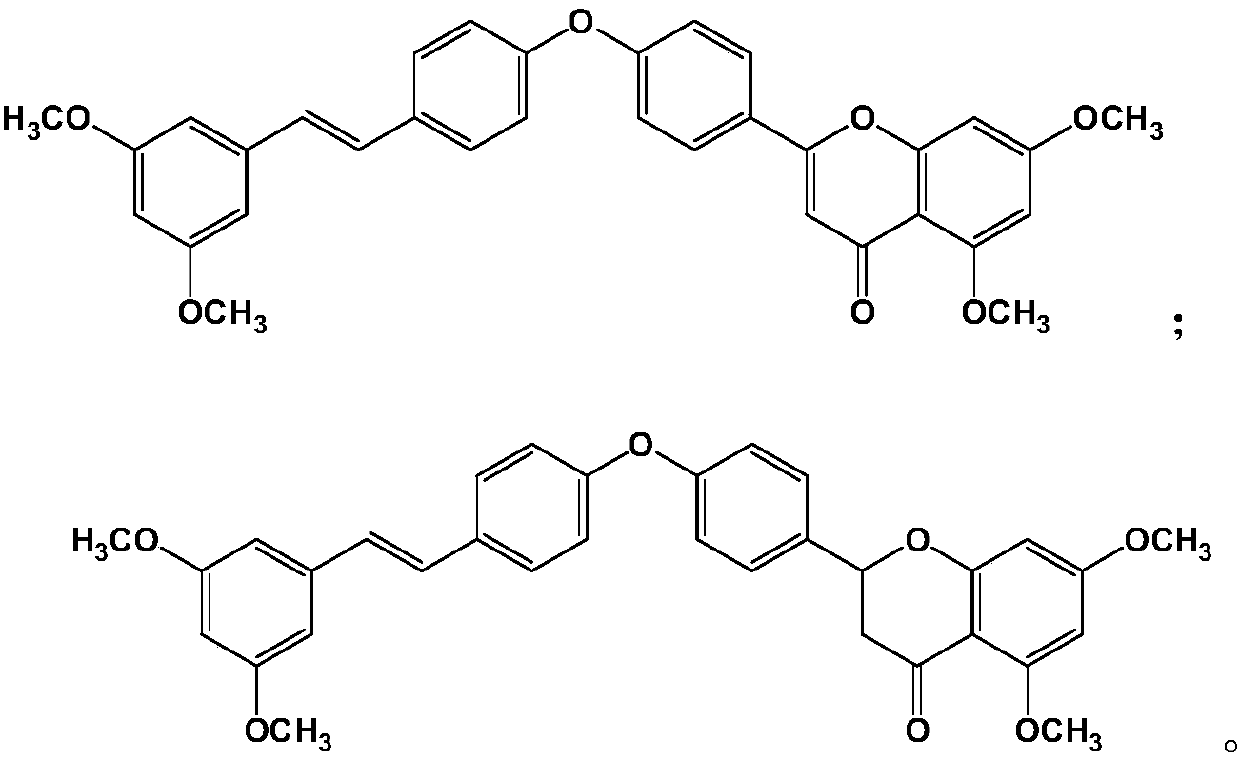
Pterostilbene compound myocardium targeted preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN108309935AIncrease concentrationReduce dosageOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide effectHalf-life
The invention relates to a myocardium targeted preparation containing a pterostilbene compound. Specifically, the pterostilbene compound includes pterostilbene and analogues thereof. Because of structural modification optimization, pterostilbene analogues have more prominent effect than pterostilbene in the aspect of preventing myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. After intravenous injection, the myocardium targeted preparation can enable slow release of pterostilbene compound so as to prolong the half-life period in blood plasma, at the same time can concentrate the pterostilbene compoundat the heart part relatively, thereby increasing the concentration in myocardium, improving the effect of the pterostilbene compound on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury, especially diabetic myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury, also the drug dosage can be reduced, and the drug concentration of other tissue parts in the whole body can be reduced relatively, therefore the toxic and side effects are reduced.
Owner:董少红
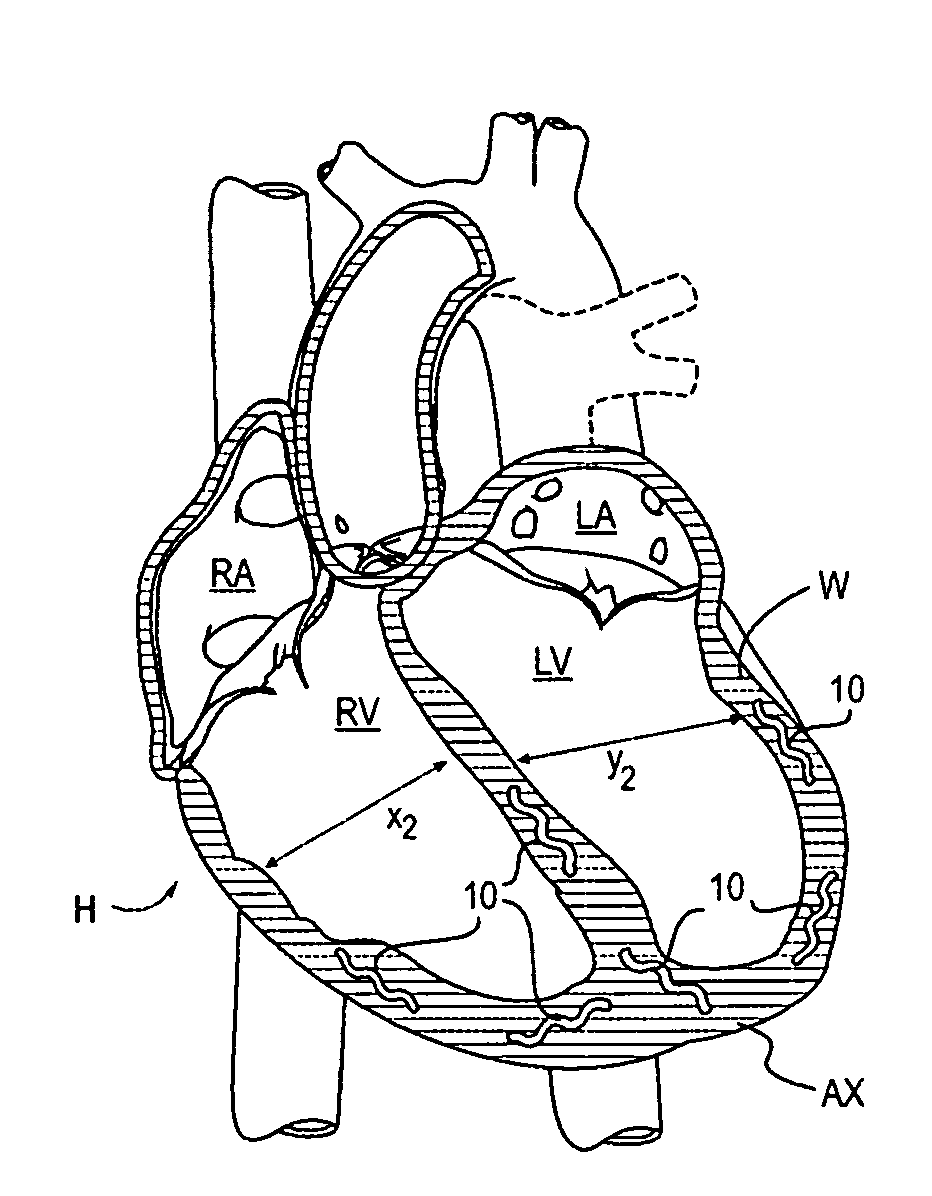
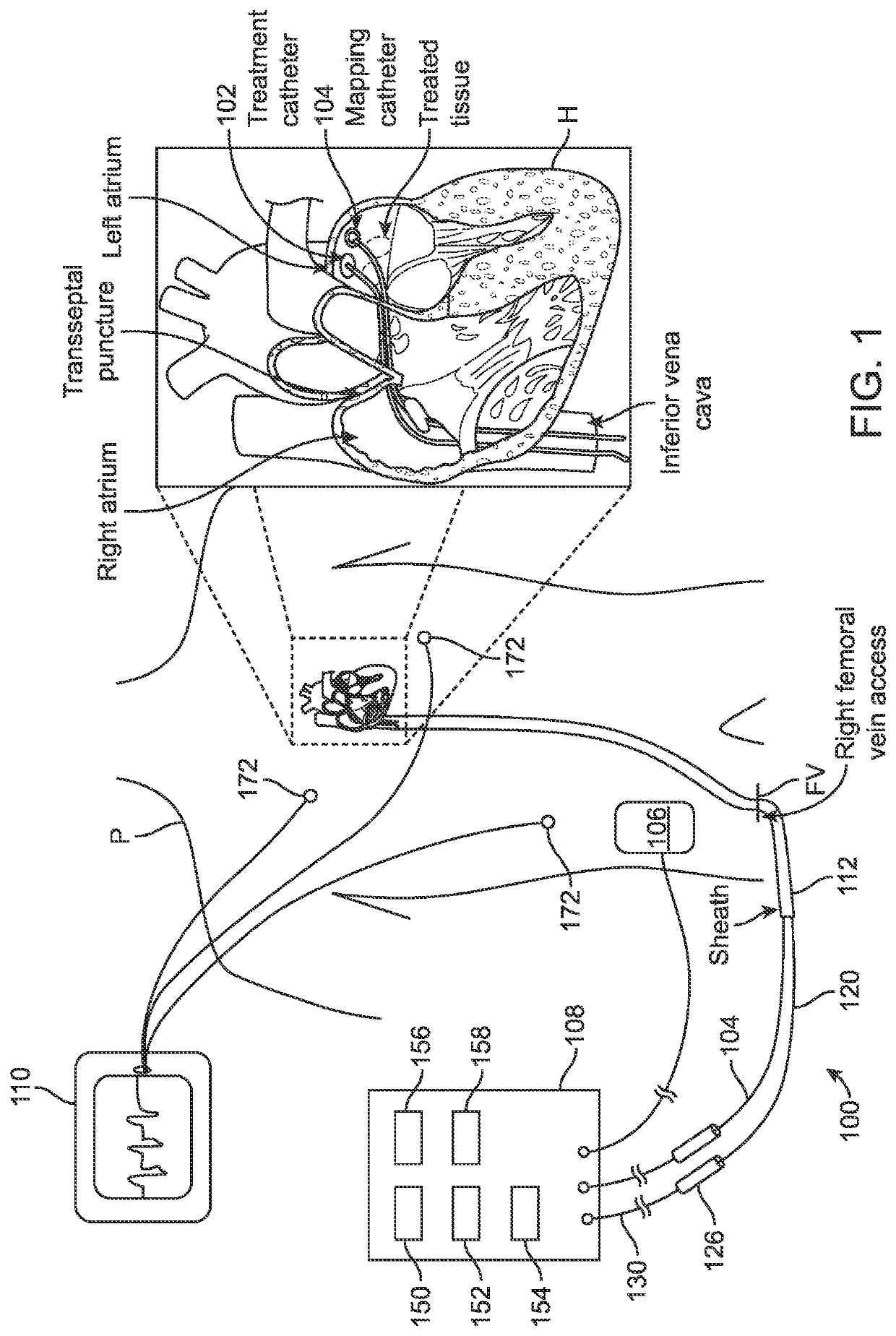
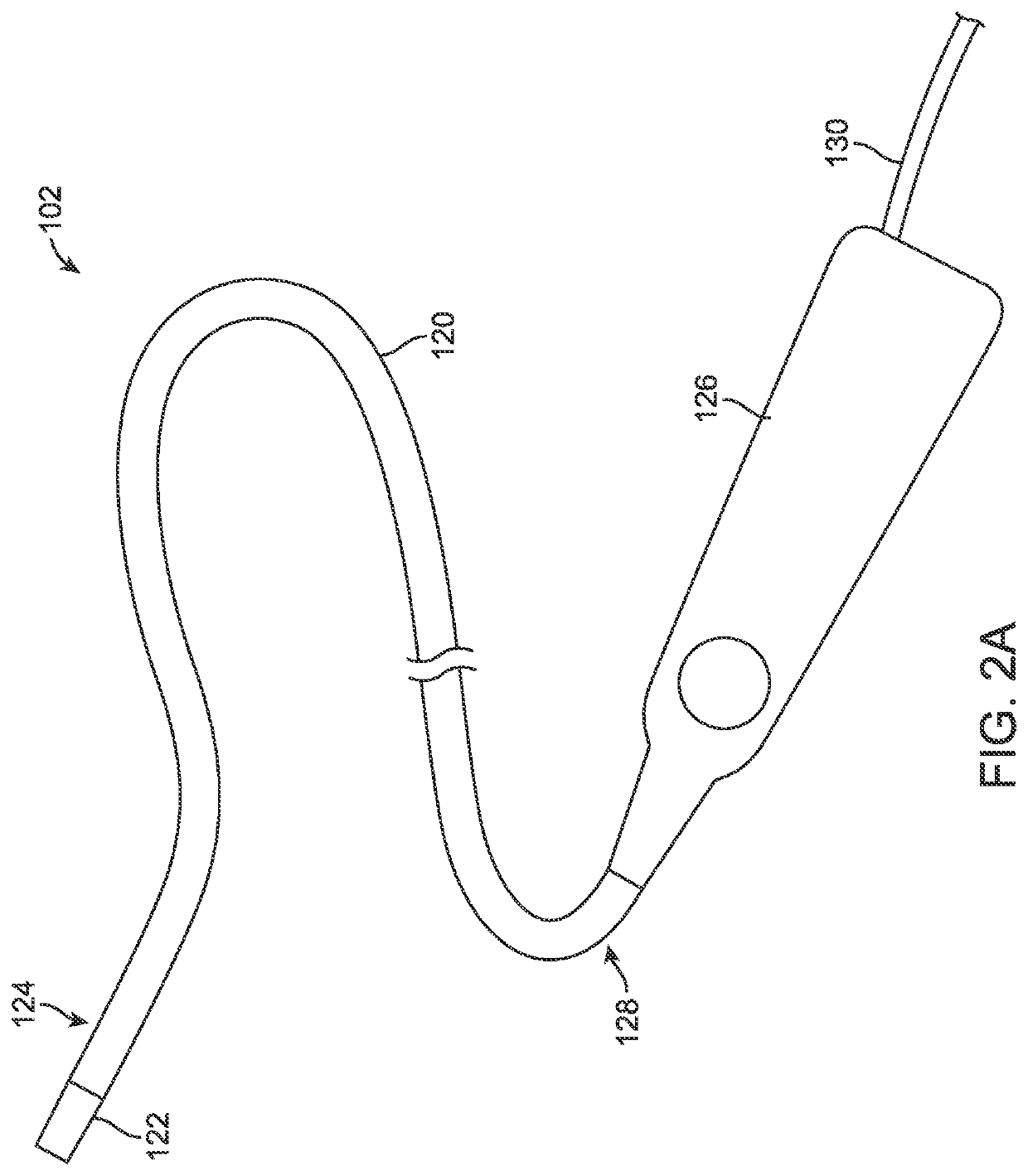
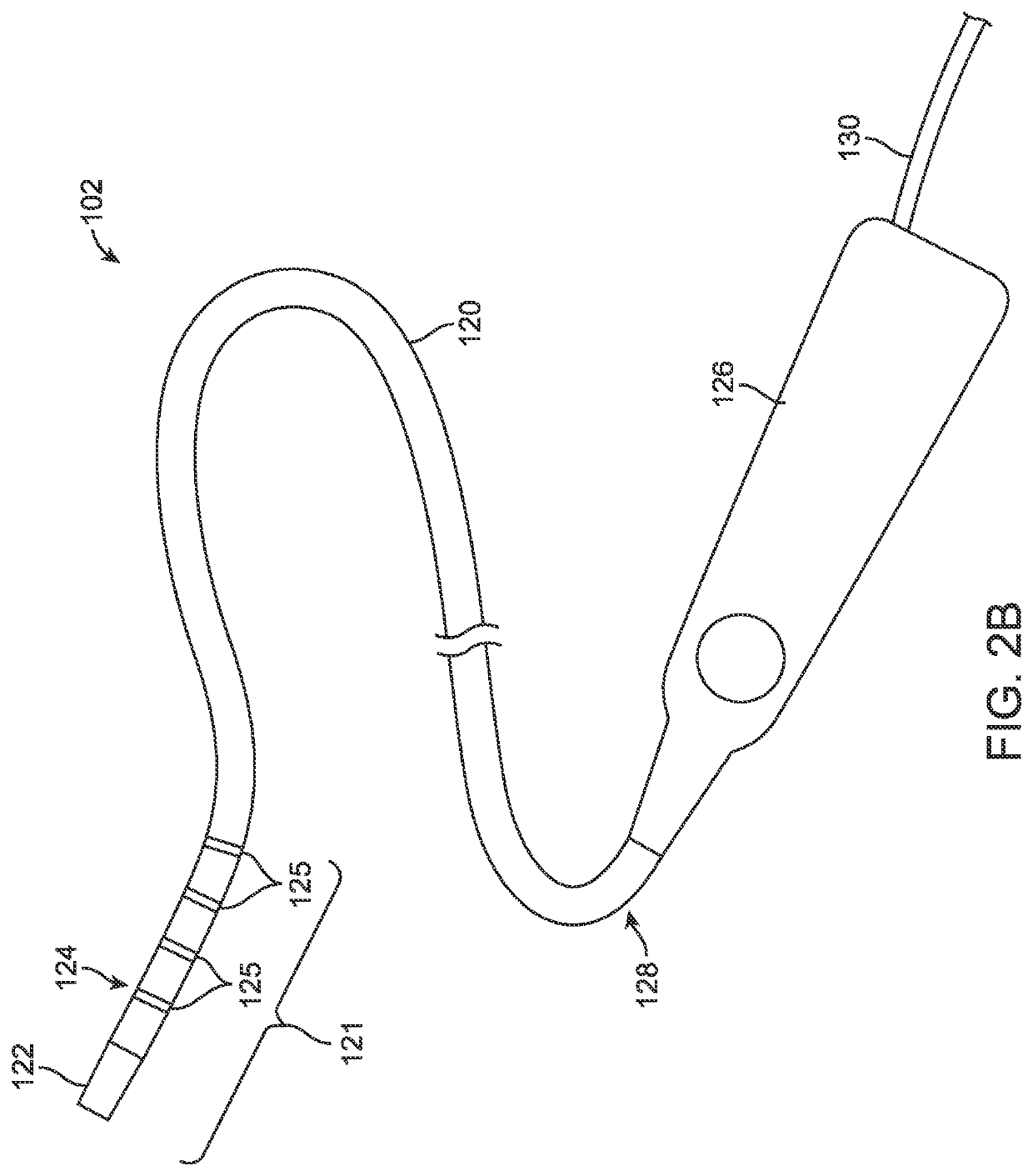
Treatment of cardiac tissue with pulsed electric fields
PendingUS20210393327A1High voltage energyWeaken energyDiagnosticsTemperature sensorsCatheterCardiac arrhythmia
Devices, systems and methods are provided for treating conditions of the heart, particularly the occurrence of arrhythmias. The devices, systems and methods deliver therapeutic energy to portions the heart to provide tissue modification, such as to the entrances to the pulmonary veins in the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Generally, the tissue modification systems include a specialized catheter, a high voltage waveform generator and at least one distinct energy delivery algorithm. Other embodiments include conventional ablation catheters and system components to enable use with a high voltage waveform generator. Example catheter designs include a variety of delivery types including focal delivery, “one-shot” delivery and various possible combinations. In some embodiments, energy is delivered in a monopolar fashion. However, it may be appreciated that a variety of other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:GALVANIZE THERAPEUTICS INC
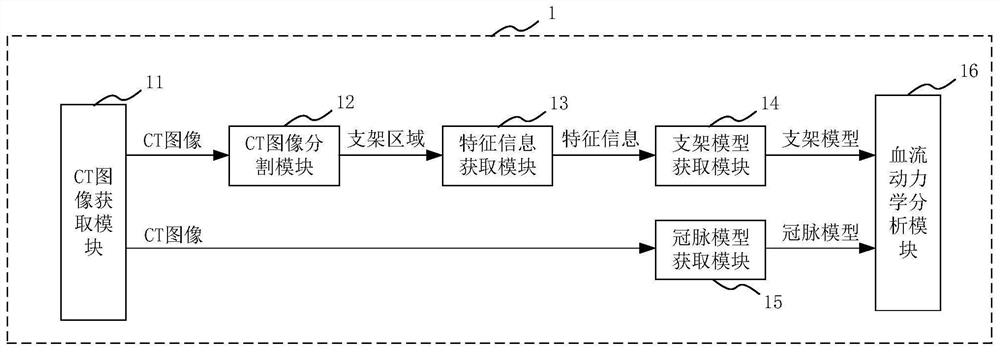
Hemodynamic analysis device and method, medium and electronic equipment
PendingCN113397579AAccurate hemodynamic analysis resultsComputerised tomographsDesign optimisation/simulationCoronary arteriesImage segmentation
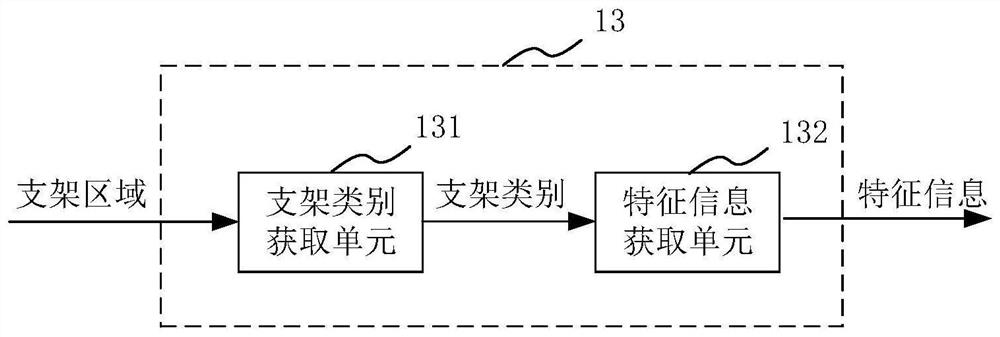
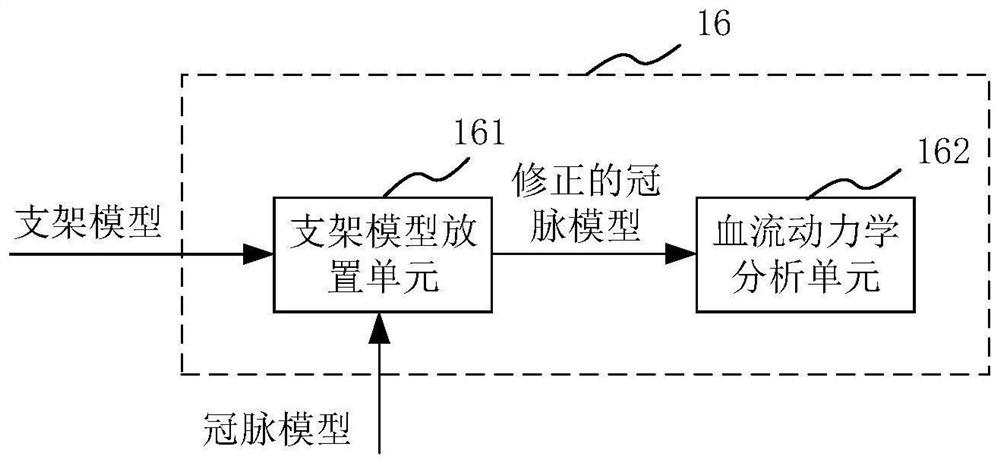
The invention provides a hemodynamic analysis device and method, a medium and electronic equipment. The hemodynamic analysis device comprises a CT image acquisition module, a CT image segmentation module, a feature information acquisition module, a stent model acquisition module, a coronary artery model acquisition module and a hemodynamic analysis module, and the CT image acquisition module is used for acquiring a CT image of a heart part of a patient; the CT image segmentation module is used for segmenting the CT image to obtain a stent area in the CT image; the feature information acquisition module is used for acquiring feature information of a stent according to the stent area; the stent model acquisition module is used for acquiring a stent model according to the feature information of the stent; the coronary artery model acquisition module is used for acquiring a coronary artery model of the patient according to the CT image; and the hemodynamic analysis module is used for performing hemodynamic analysis according to the coronary artery model and the stent model. The hemodynamic analysis device can obtain a more accurate hemodynamic analysis result.
Owner:上海友脉科技有限责任公司
Heart 3D printing system and printing method thereof
ActiveCN110310364ASimple structureReasonable designBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDetails involving processing stepsGraphicsBiological cell
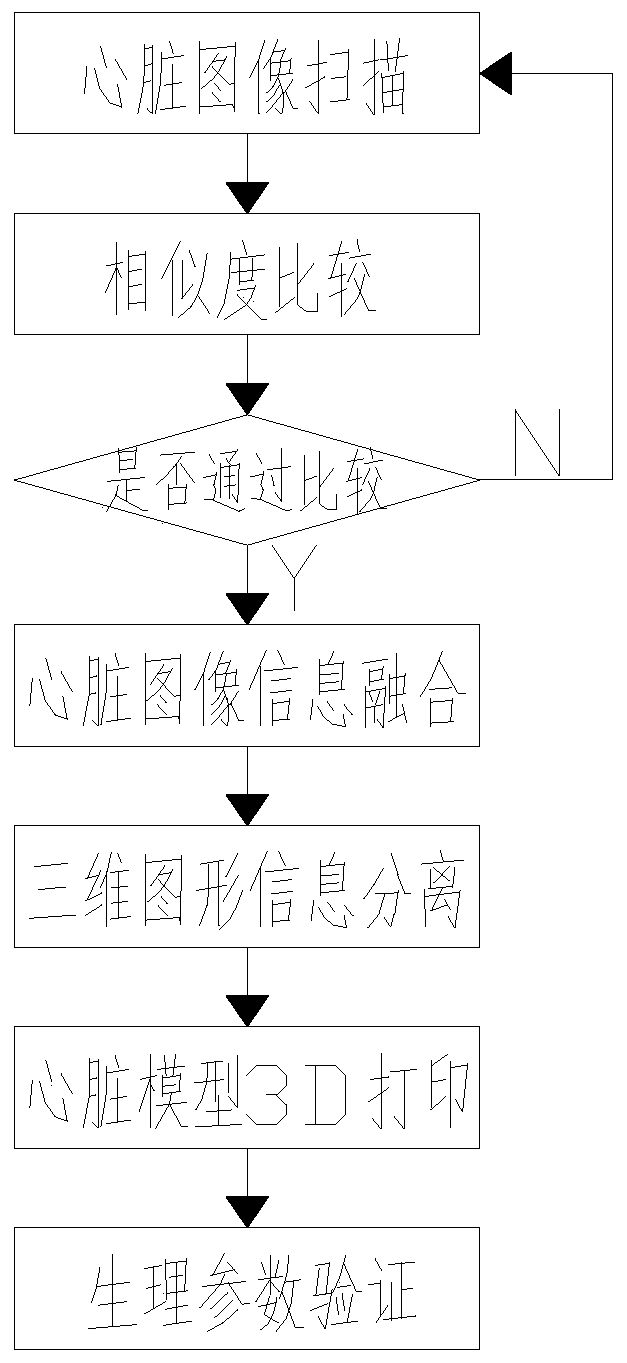
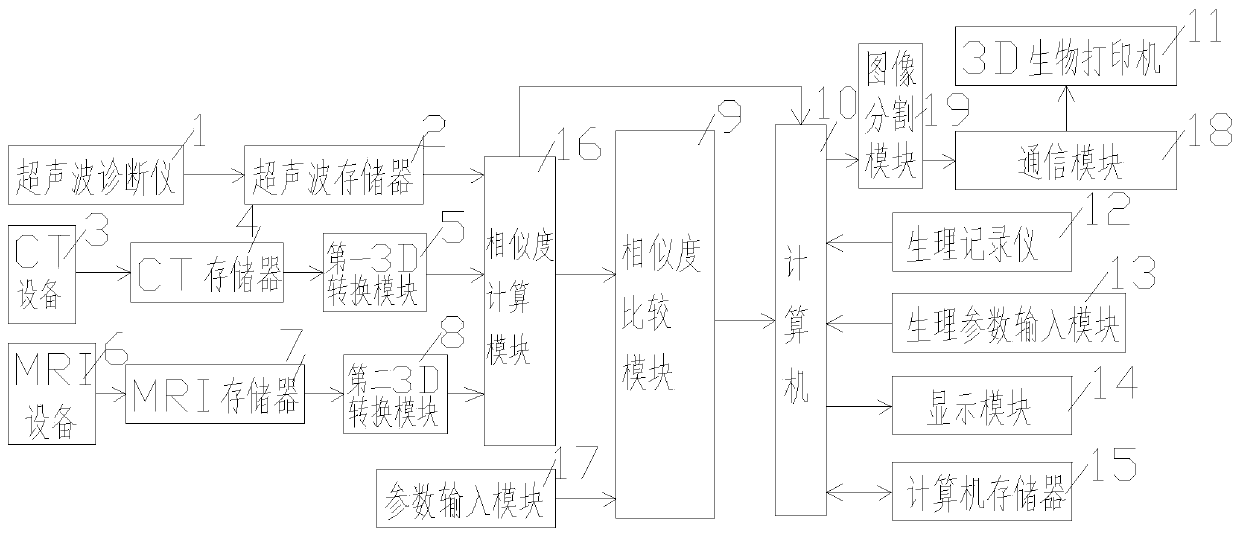
The invention discloses a heart 3D printing system. The system comprises a computer, an ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus, a CT device, an MRI device and a 3D biological printer. The input end of the computer is connected with a similarity comparison module, a physiological recorder and a physiological parameter input module, the output end of the computer is connected with a display module and an image segmentation module, and the image segmentation module is connected with a communication module; the similarity comparison module is connected with a similarity calculation module and a parameterinput module, and the similarity calculation module is connected with a first 3D conversion module, a second 3D conversion module and an ultrasonic memory. According to the invention, three imaging devices are combined to carry out fusion establishment of the three-dimensional graphs on the heart, the imaging precision is improved, and the errors are reduced; during the process of generating a heart 3D model, in order to avoid that the biological cells on the heart 3D model cannot realize synchronous contraction, the blood vessels at the heart part are independently subjected to 3D printing,a clear blood vessel pipeline is provided for a blood pumping function in the later period, and the technical support is provided for improving the synchronous contraction of the biological cells.
Owner:王寅
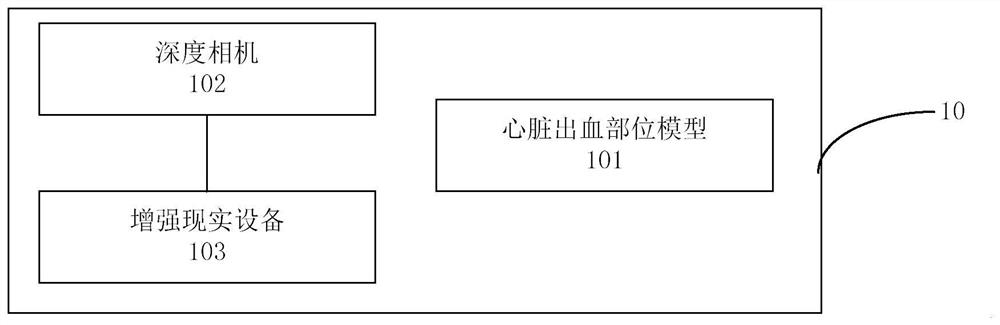
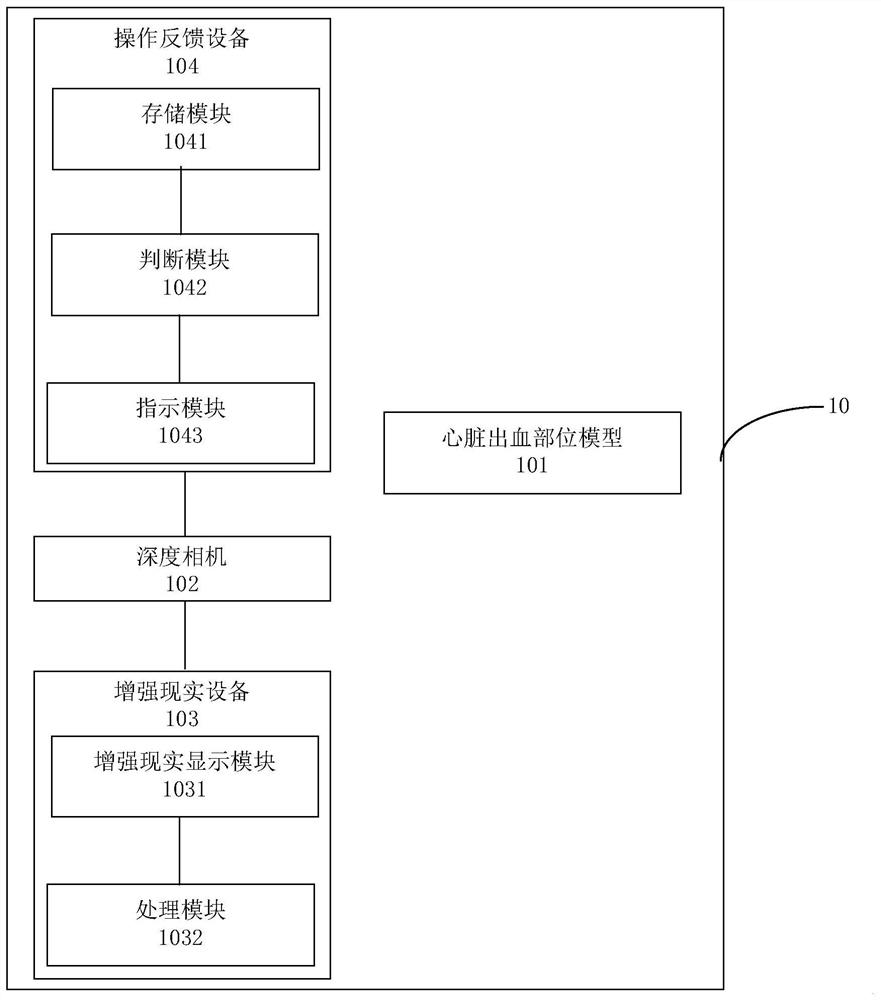
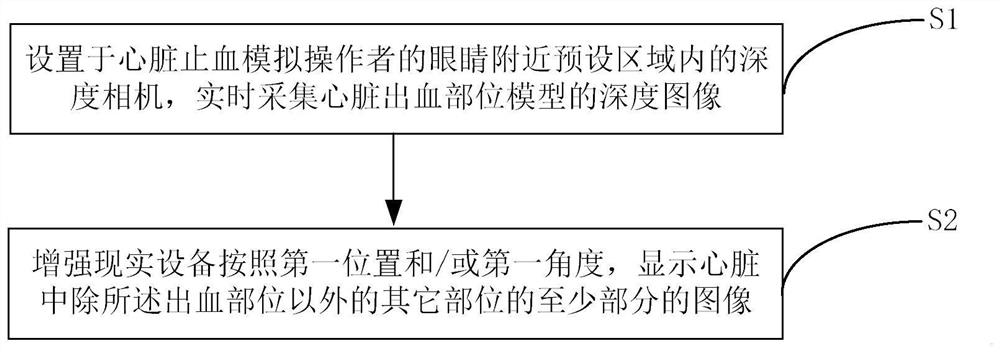
Cardiac hemorrhage and hemostasis model simulation system and method based on augmented reality
ActiveCN113761776AReduce manufacturing costShorten production timeVirtual/augmented realityDesign optimisation/simulationHeart PartRat heart
The invention provides a cardiac hemorrhage and hemostasis model simulation system and method based on augmented reality, and belongs to the technical field of medical analog simulation. The system comprises: a cardiac hemorrhage site model manufactured by using a three-dimensional model forming device, the cardiac hemorrhage site model comprising a model of one or more hemorrhage sites of the heart and used for performing cardiac hemostasis simulation operation; a depth camera, which is used for collecting a depth image of the cardiac hemorrhage part model in real time and is arranged in a preset area near eyes of a cardiac hemostasis simulation operator; and an augmented reality device, which is used for displaying at least part of images of other parts except the bleeding part in the heart according to the first position and / or the first angle, the first position and / or the first angle are / is determined according to the depth image, and the heart part displayed by the augmented reality device is associated with the heart part in the depth image. Entity-based hemostasis simulation operation can be realized, the simulation effect is good, and the manufacturing cost and the manufacturing time of the three-dimensional model can be reduced.
Owner:THE FIRST MEDICAL CENT CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL
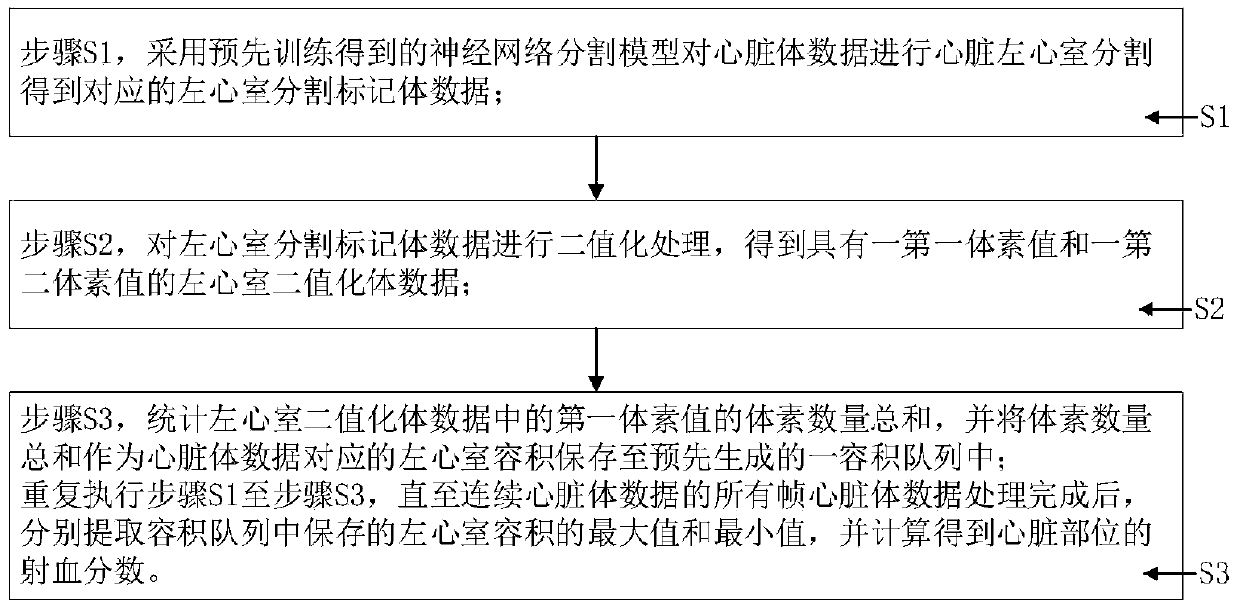
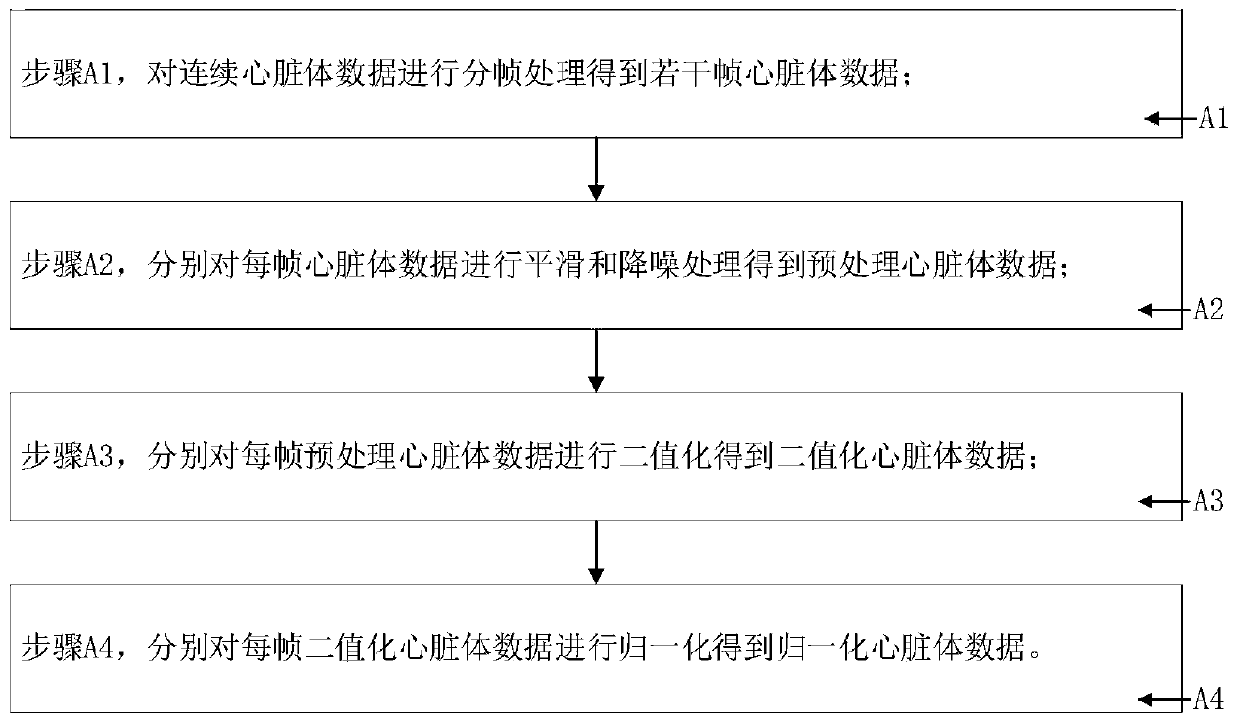
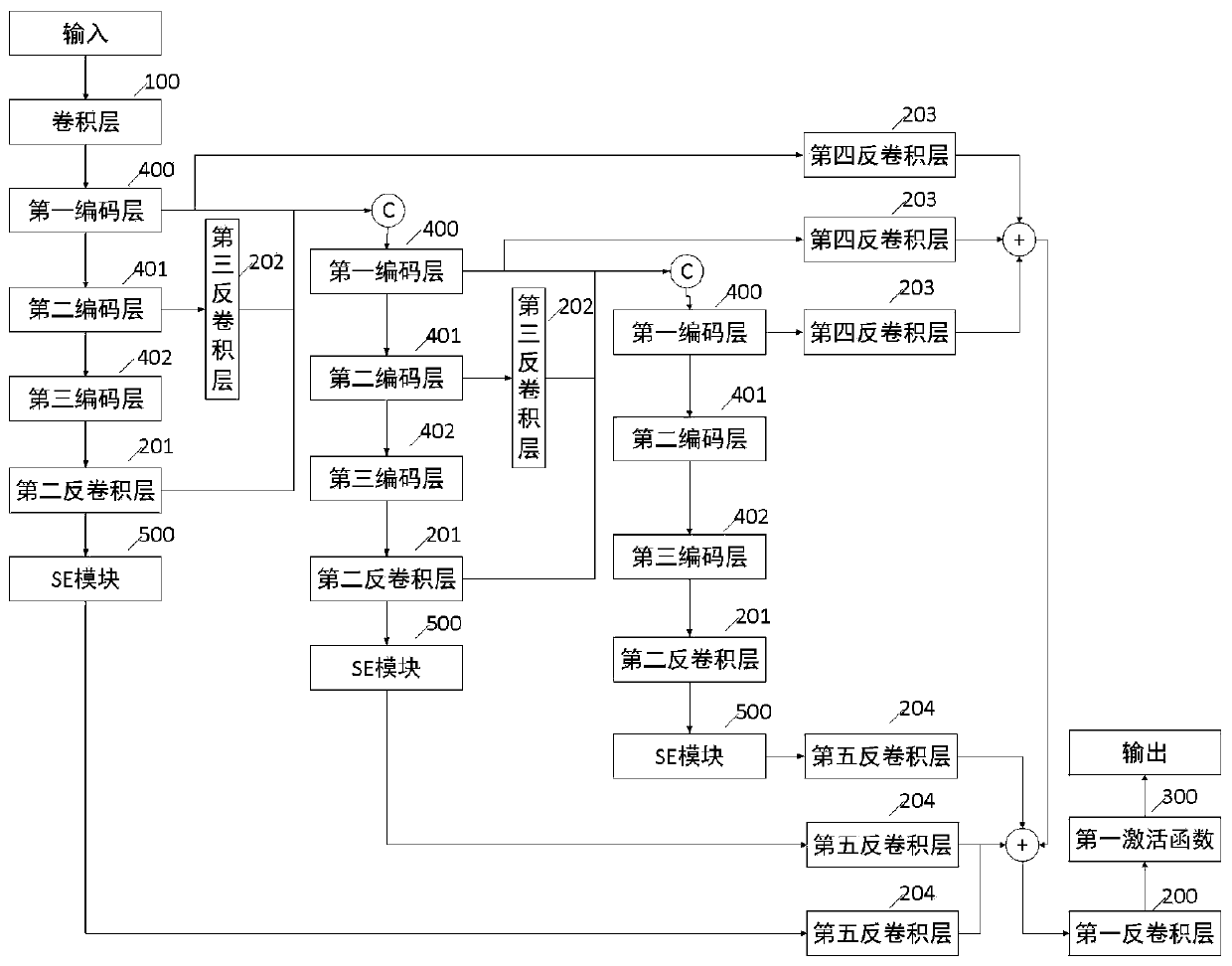
Deep learning-based ejection fraction calculation method and system
ActiveCN111466894AImprove work efficiencyAvoid human errorOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterVoxelLeft ventricular size
The invention provides a deep learning-based ejection fraction calculation method and system, and relates to the technical field of deep learning. The method comprises the steps: carrying out heart left ventricle segmentation on heart body data through a pre-trained neural network segmentation model to obtain corresponding left ventricle segmentation marker data; performing binarization processingon the left ventricle segmentation marker data to obtain left ventricle binarization body data with first voxel values and second voxel values; counting the voxel quantity sum of the first voxel values in the left ventricle binarization body data, and storing the voxel quantity sum as the left ventricle volume corresponding to the heart body data into a pre-generated volume queue; and after all frames of heart body data of the continuous heart body data are processed, respectively extracting the maximum value and the minimum value of the left ventricular volume stored in the volume queue, andperforming calculation to obtain the ejection fraction of the heart part. The method has the beneficial effects of effectively improving the calculation accuracy and improving the working efficiencyof medical personnel.
Owner:上海深至信息科技有限公司
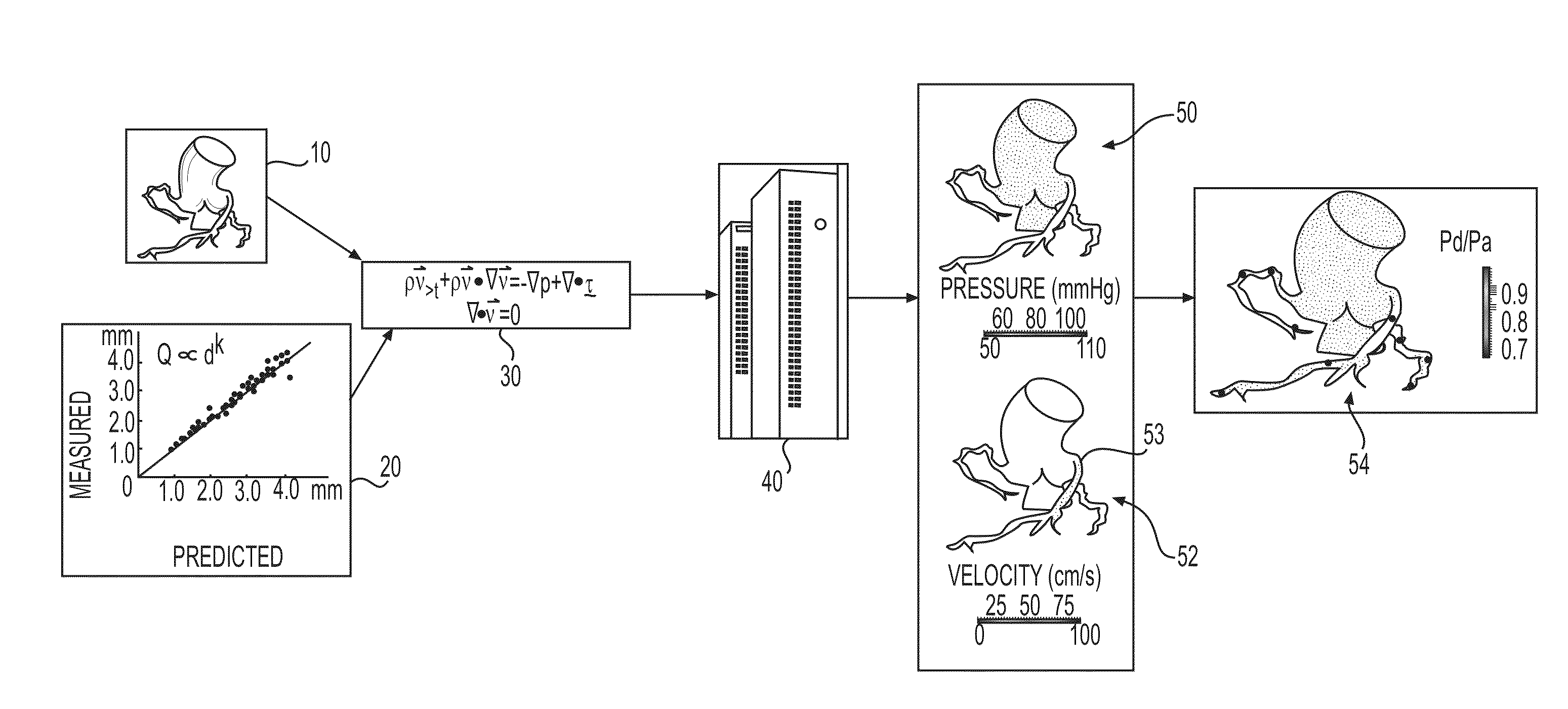
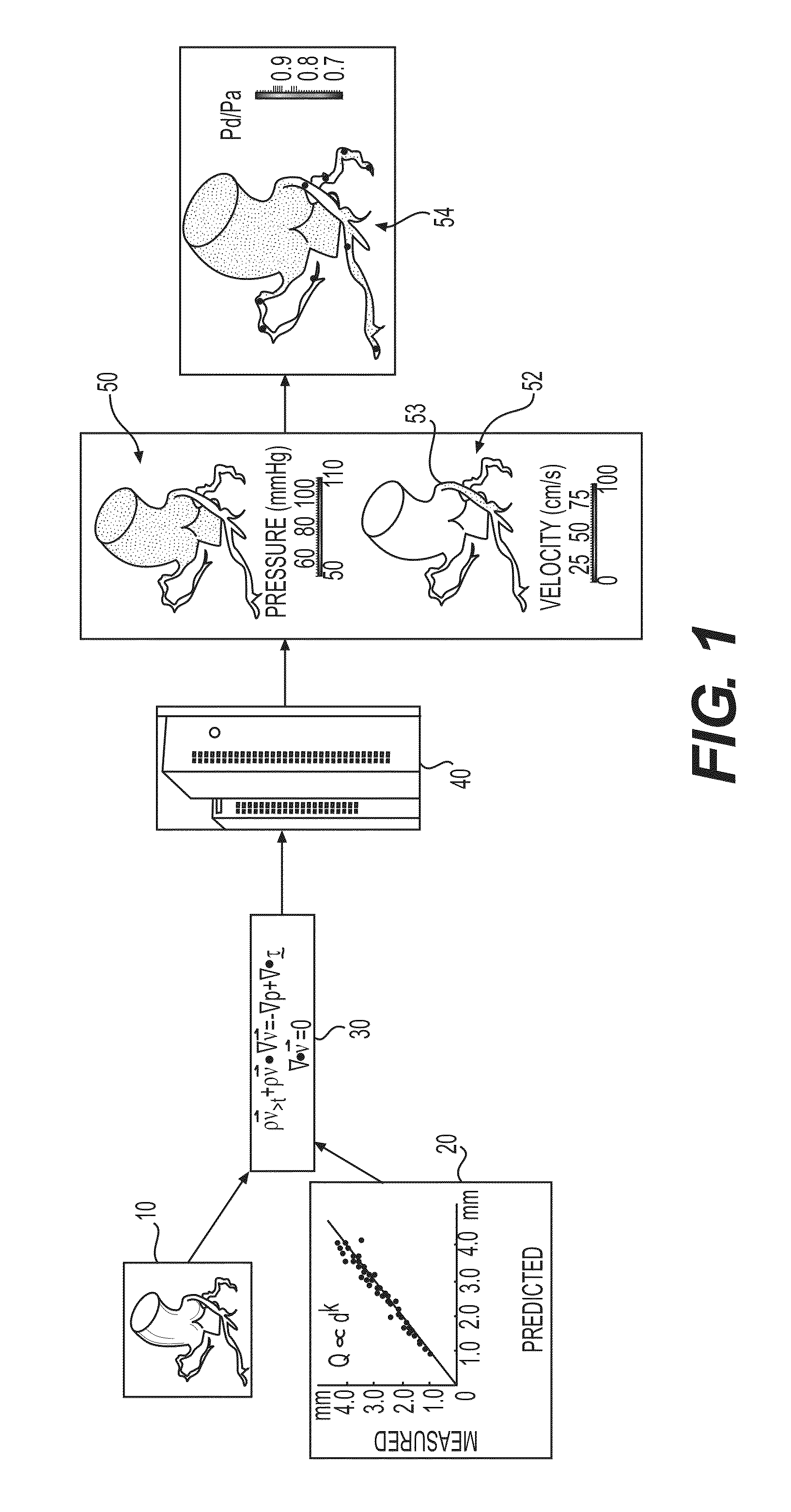
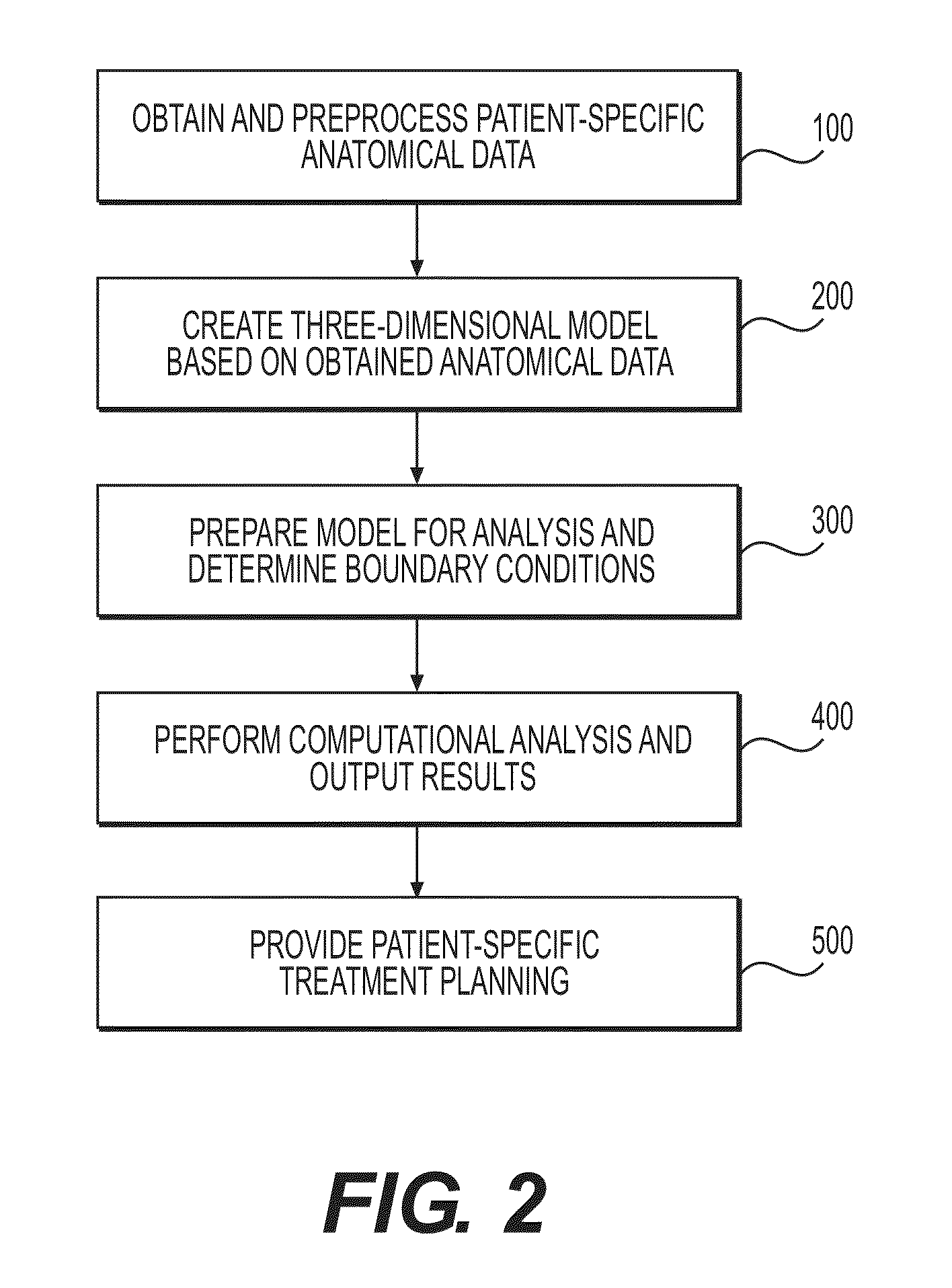
Method and system for determining treatments by modifying patient-specific geometrical models
Systems and methods are disclosed for evaluating cardiovascular treatment options for a patient. One method includes creating a three-dimensional model representing a portion of the patient's heart based on patient-specific data regarding a geometry of the patient's heart or vasculature; and for a plurality of treatment options for the patient's heart or vasculature, modifying at least one of the three-dimensional model and a reduced order model based on the three-dimensional model. The method also includes determining, for each of the plurality of treatment options, a value of a blood flow characteristic, by solving at least one of the modified three-dimensional model and the modified reduced order model; and identifying one of the plurality of treatment options that solves a function of at least one of: the determined blood flow characteristics of the patient's heart or vasculature, and one or more costs of each of the plurality of treatment options.
Owner:HEARTFLOW
Light emitting diode (LED) necklace lamp
InactiveCN102425728AUnique shapeLow costLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLED lamp
The invention discloses a light emitting diode (LED) necklace lamp which comprises a lamp body, a lamp source and a hanging chain. The LED necklace lamp is characterized in that the lamp body is integrally in a heart shape; the lamp body is symmetrically divided into two half-heart parts along the central axis of the heart shape; a rotating shaft is arranged in the middle of the central axis; the two half-heart parts are respectively provided with a circuit connection point at mutually corresponding positions at the upper side or lower side of the rotating shaft; an LED lamp, a power supply and a circuit board are arranged in the lamp body; and the lamp body is made from a light transparent material. The LED necklace lamp provided by the invention has special formation, can be used as an ornamental necklace at the same time, is simple in structure and beautiful in appearance, and is easy to produce and manufacture.
Owner:SUZHOU JINGLEI PHOTOELECTRIC LIGHTING TECH
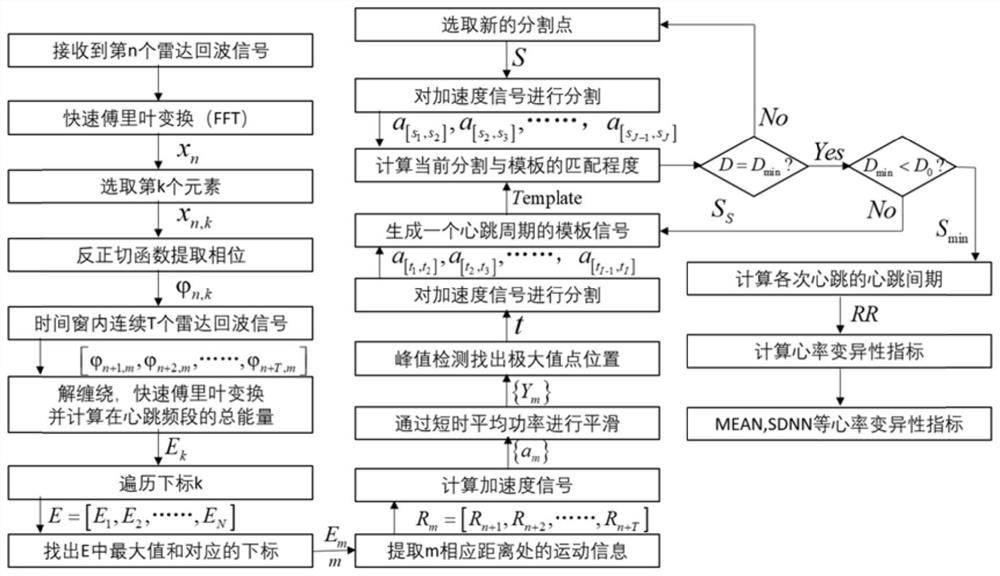
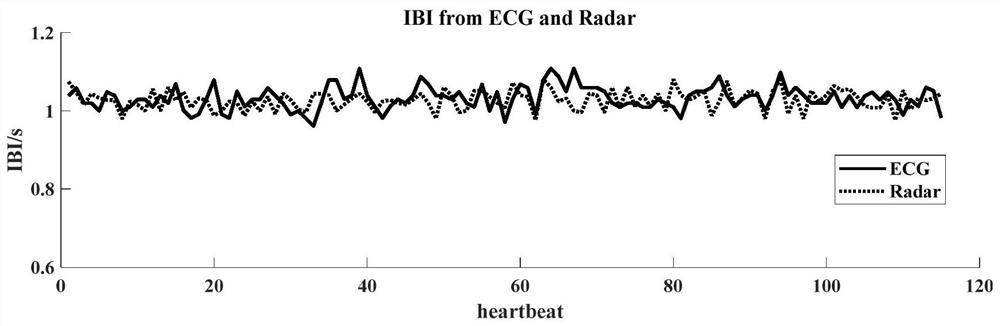
Non-contact heart rate variability monitoring method based on frequency modulated continuous wave radar
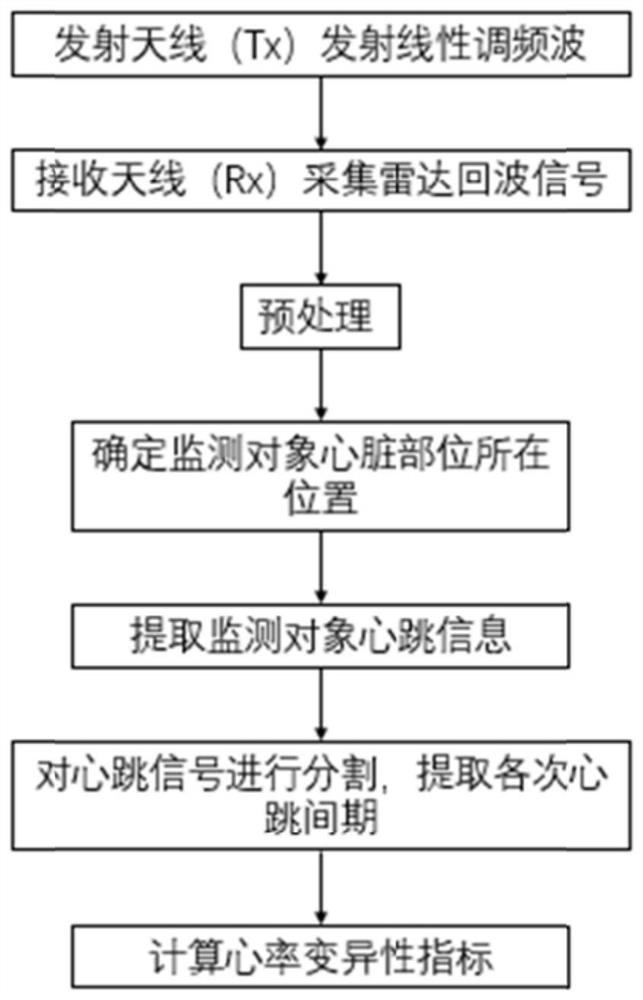
PendingCN114732390AStrong penetrating powerImprove anti-interference abilitySensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateEngineeringFetal Heart Rate Variability
The invention discloses a non-contact heart rate variability monitoring method based on a frequency modulated continuous wave radar, and the method specifically comprises the steps: transmitting a periodic linear frequency modulated wave to an area where a monitored object is located, and collecting a radar echo signal; the radar echo signals are preprocessed through frequency mixing and FFT in sequence; then extracting the position of the heart part of the monitored object; adopting a phase correlation method to extract motion information of a heart part of a monitored object, and calculating an acceleration signal according to the motion information; smoothing the obtained acceleration signal, and estimating the position of a segmentation point between each heartbeat through a peak detection method; and generating an acceleration template signal of a single heartbeat, carrying out precise segmentation on the acceleration signal to obtain a heartbeat interval of each heartbeat, and calculating a heart rate variability index. According to the invention, microwaves are adopted as a detection medium, and the system has the advantages of strong anti-interference capability, strong penetrating power to non-metal obstacles, high integration level, low power consumption, high measurement precision, strong robustness and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
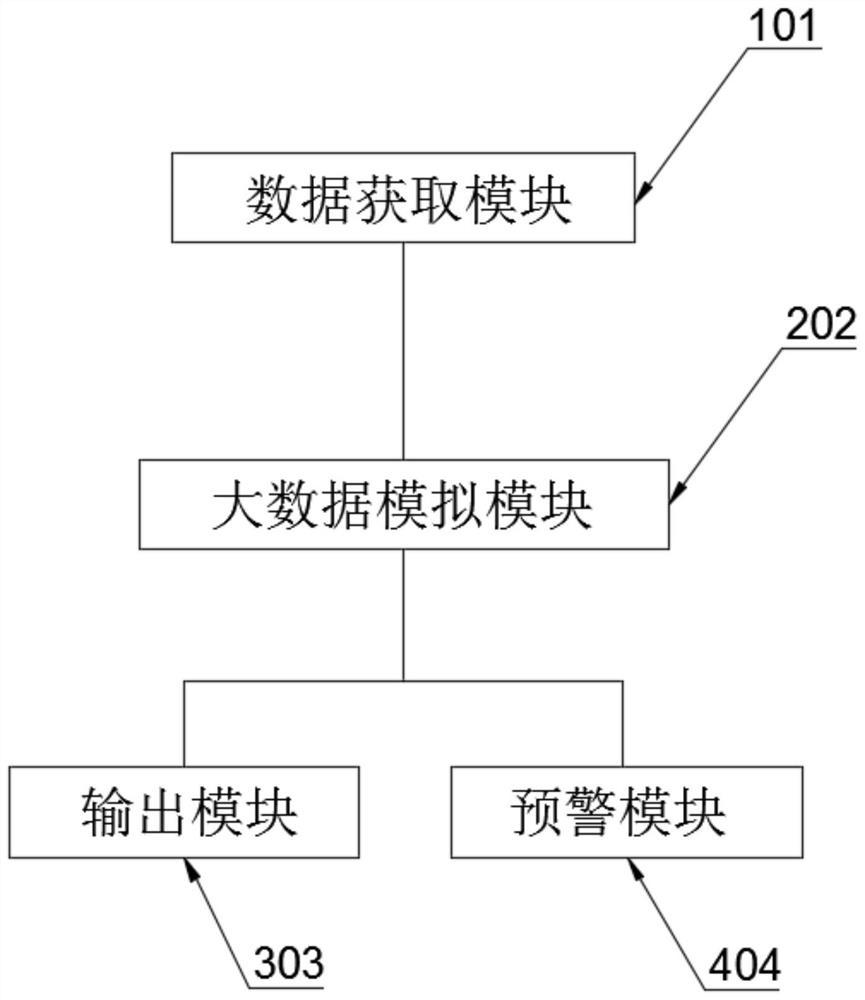
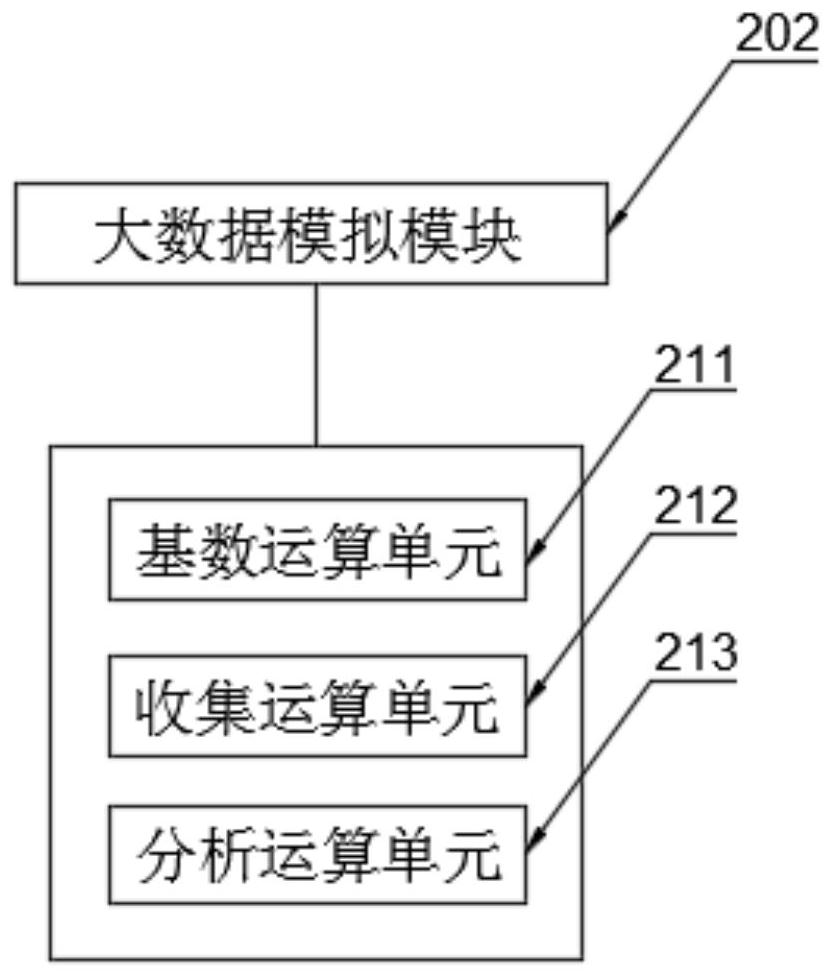
Heart health quality early warning system and early warning method thereof
PendingCN111710419AEarly detectionReduce riskMedical data miningHealth-index calculationData informationData acquisition
The invention discloses a heart health quality early warning system and an early warning method thereof, and specifically relates to the technical field of heart health early warning. The system comprises: a data acquisition module which is specifically a data acquisition module based on a hospital database and an intelligent system and is used for acquiring data information related to the body health of a user from the database of the system and completing acquisition of data information of a heart part according to a heart information weight part in a data information flow; and a big data simulation module which is specifically a big data operation module based on a Storm framework and is used for establishing a heart quality index model of the user according to the acquired heart data of the user. According to the method, the heart quality of healthy and sub-healthy individuals and heart disease individuals can be analyzed and predicted, heart quality events can be found as soon aspossible, preventive measures are put forward, and therefore the risk of the heart events is reduced.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
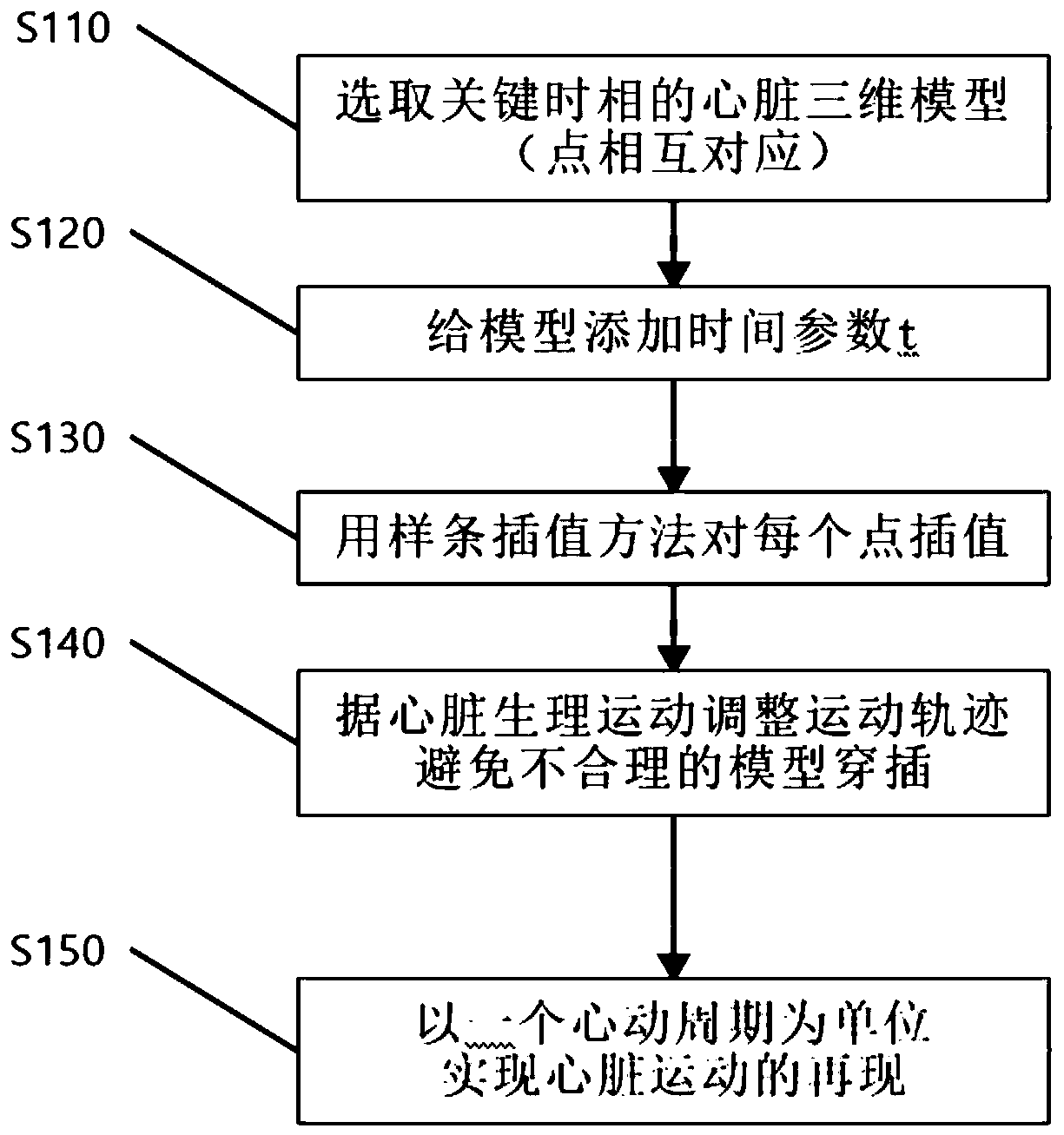
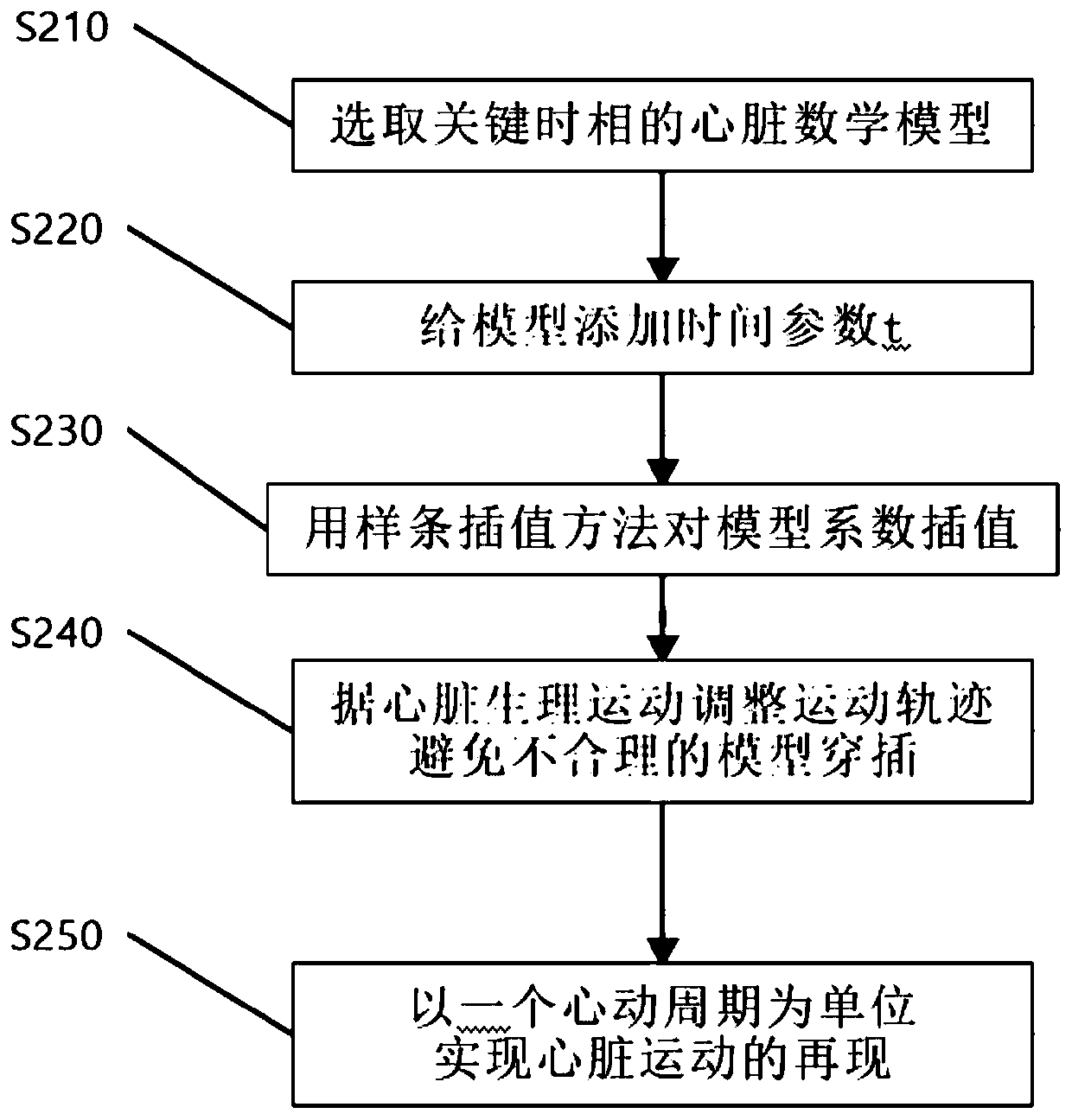
Reconstruction method of dynamic heart three-dimensional model
The invention provides a reconstruction method of a dynamic heart three-dimensional model. The method comprises the steps of selecting a heart model of an import time phase in a cardiac cycle; addinga time parameter in a mathematical model expression of the step 1, thereby representing a heart model in a four-dimensional space; performing interpolation for fitting the movement track of each pointon the heart model which is represented by the step 2; checking a model interpenetration part which does not accord with common sense in an interpolation process, and modifying unreasonable parts; dynamically displaying heart motion through using one cardiac cycle as a unit, thereby obtaining dynamic heart three-dimensional model. According to the reconstruction method, the dynamic three-dimensional heart model with medical value can be established for reproducing the physiological motion of the heart in the cardiac cycle. The heart model comprises a left atrium, a right atrium, a left ventricle, a right ventricle, a left ventricle outer wall and all heart parts of the whole heart chamber outer wall. Based on the reconstruction method, comprehensive analysis for the motion characteristicof the heart can be realized, and furthermore whether a heart physiological function abnormity exists is checked.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Quick-release preparation for targeted treatment of heart failure
ActiveCN111973623AHigh affinityGood biocompatibilityInorganic active ingredientsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsHydroxyethyl starchNitric oxide gas
The invention provides a quick-release preparation for targeted treatment of a heart failure. The quick-release preparation is composed of a basic solution and drug-loaded microbubbles, wherein the basic solution comprises the following components: poloxamer and hydroxyethyl starch; the mass ratio of the poloxamer to the hydroxyethyl starch is 1: 10; the drug-loaded microbubbles are composed of nitric oxide microbubbles carrying basic fibroblast growth factors; the nitric oxide microbubbles are vesicles formed by wrapping nitric oxide gas with hydrogenated soyabean lecithin and heparin-poloxamer as bubble film materials; the mass ratio of the hydrogenated soyabean lecithin to the heparin-poloxamer is 1: 2; the molar mass of the basic fibroblast growth factors is equal to the molar mass ofthe heparin-poloxamer; the basic fibroblast growth factor is adhered to the surfaces of the nitric oxide microbubbles; the particle size range of the drug-loaded microbubbles is 2-5 microns; and the concentration of the drug-loaded microbubbles is 6 * 10<6>-9 * 10<6> / mL. According to the invention, after intravenous injection of the quick-release preparation for targeted treatment of the heart failure, accurate positioning and targeted delivery of a heart part are realized through an ultrasonic mediation technology, and the quick-release preparation is used for treatment of the heart failure.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Method and system for modelling a human heart and atria
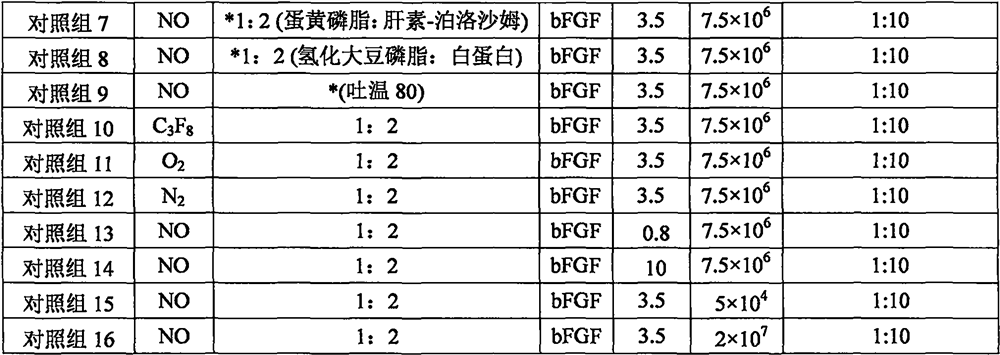
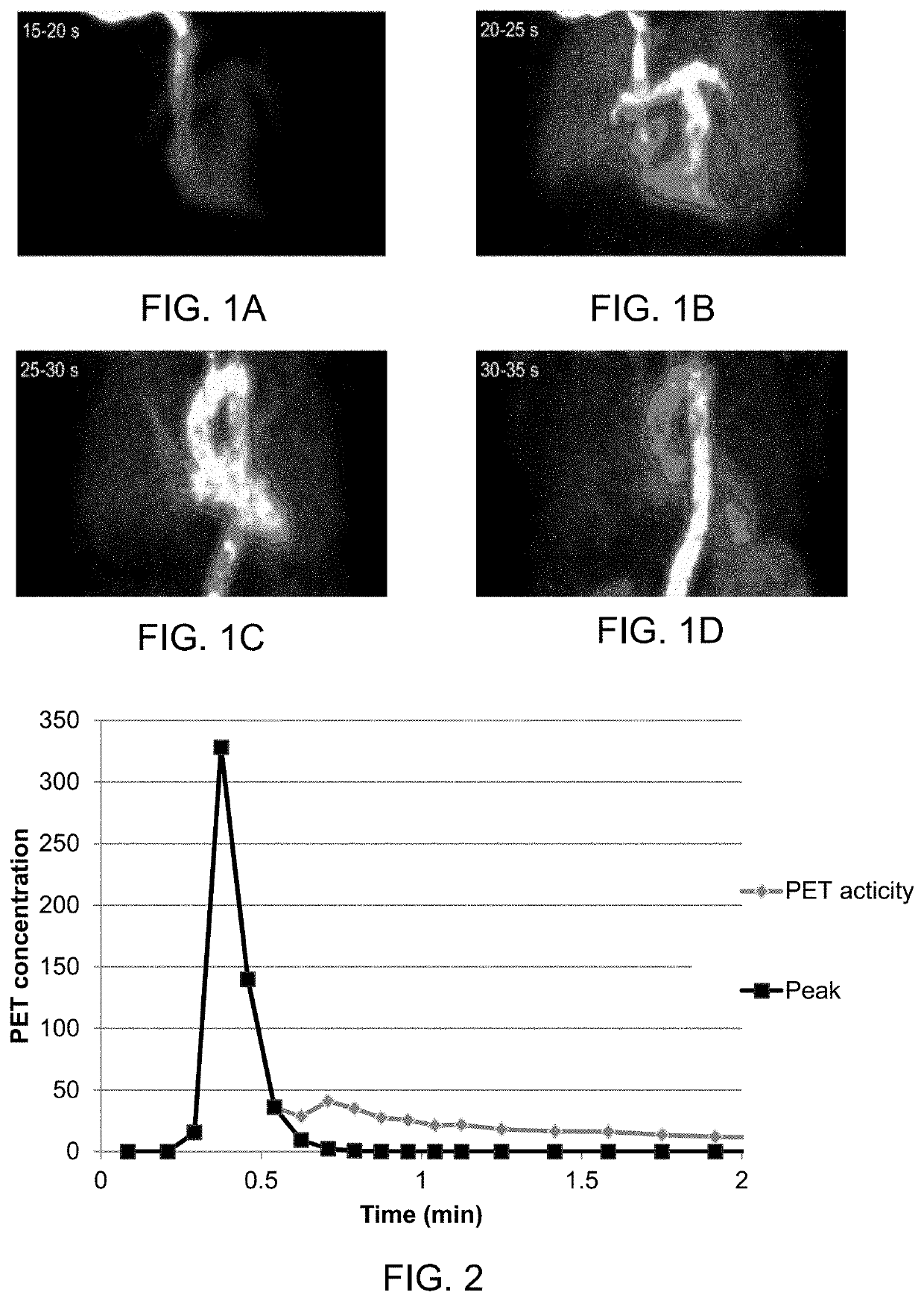
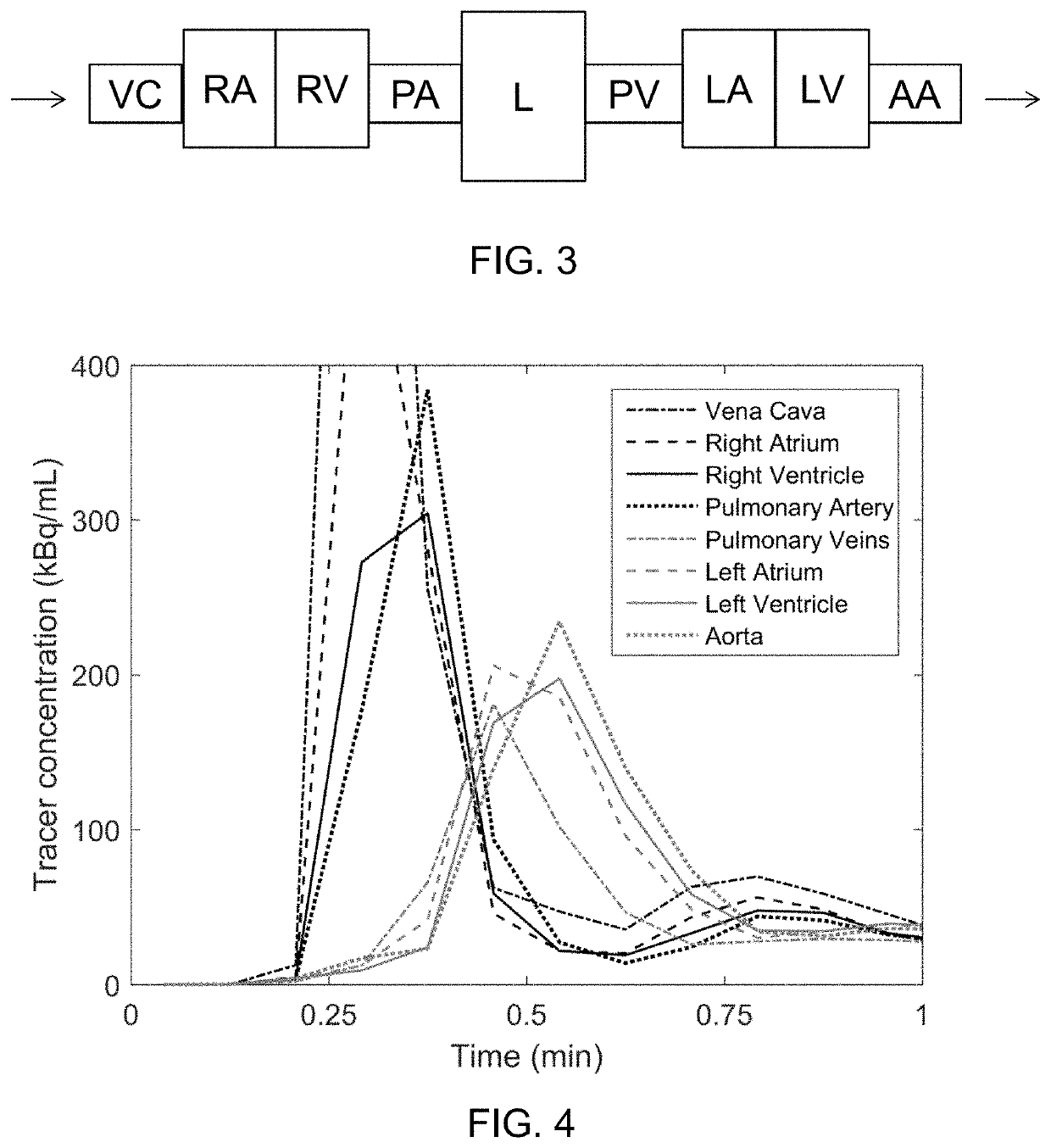
A method and a system for modelling a human heart based on a plurality of emission tomography images representing concentrations of a tracer that has been injected at a specific time is presented. The method comprising: extracting time activity curves of a tracer that has been injected for a plurality of pixels and / or voxels; identifying first-pass peaks of the time activity curves corresponding to an arrival time of the injected tracer at the corresponding pixel / voxel; defining a model comprising at least two portions of the heart; and arranging the at least two portions in relation to each other by comparing the arrival times of the first-pass peaks. The method and model may be used to obtain an estimate of the volume of the left or right atrium of the human heart.
Owner:MEDTRACE AS
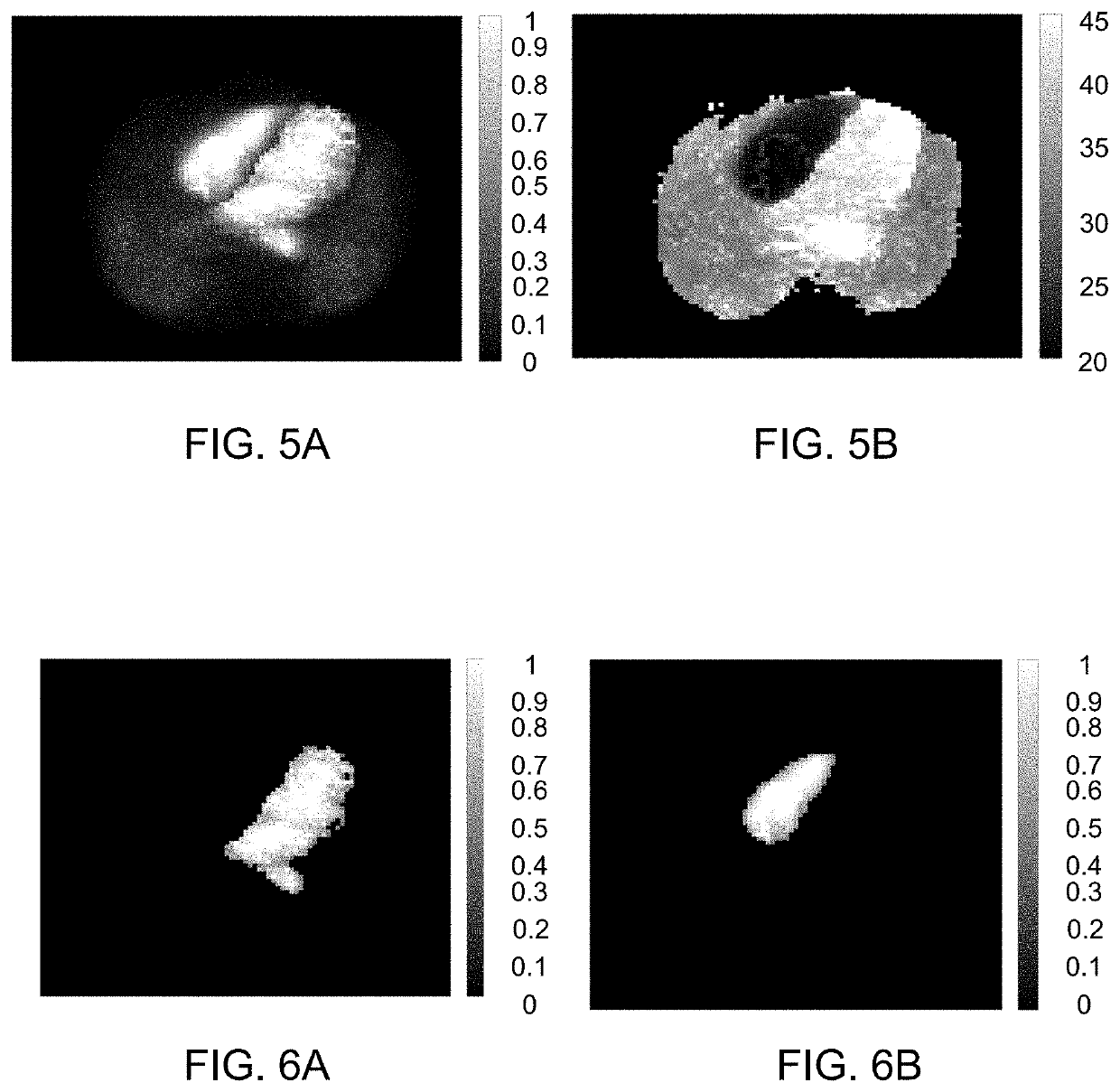
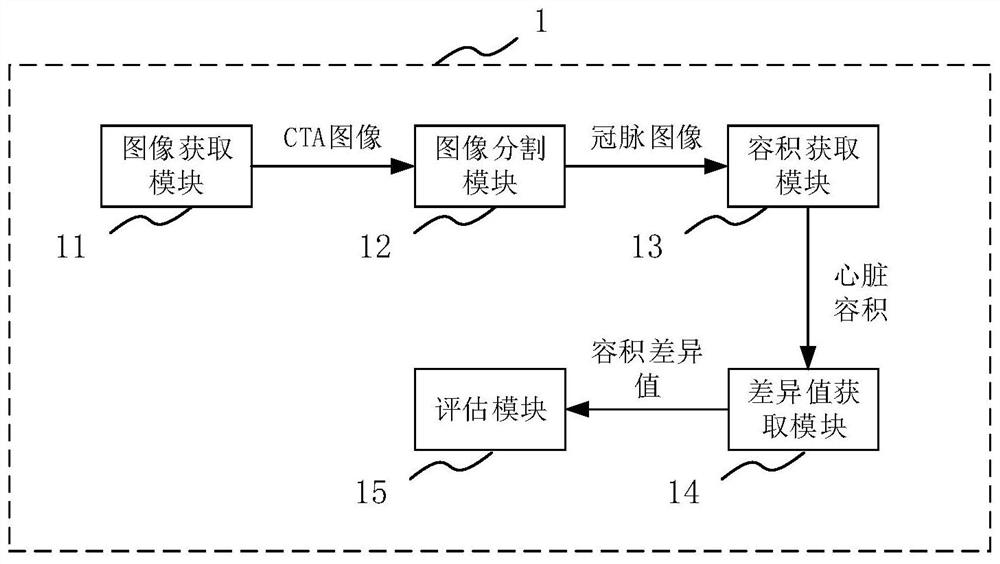
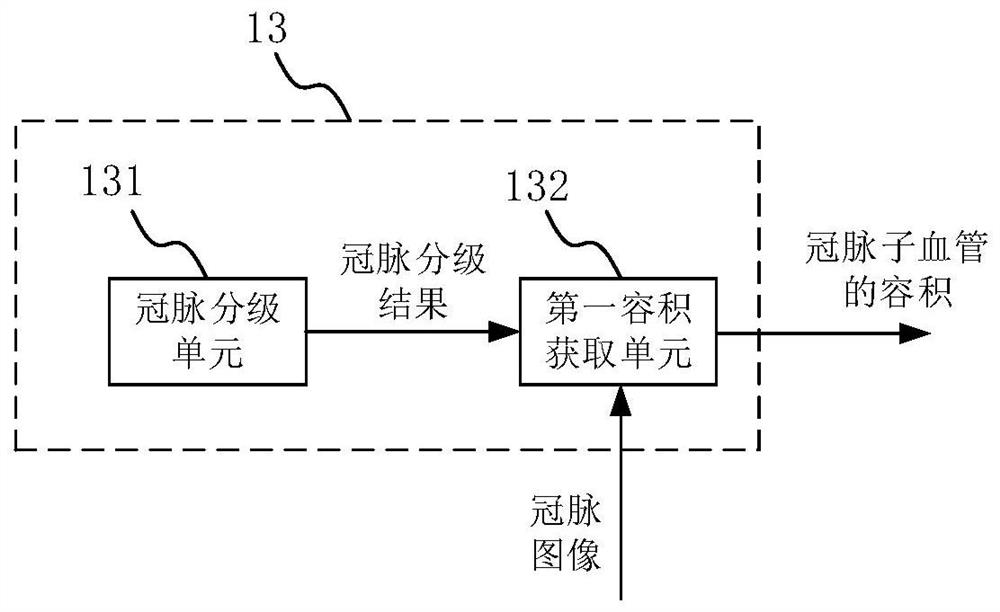
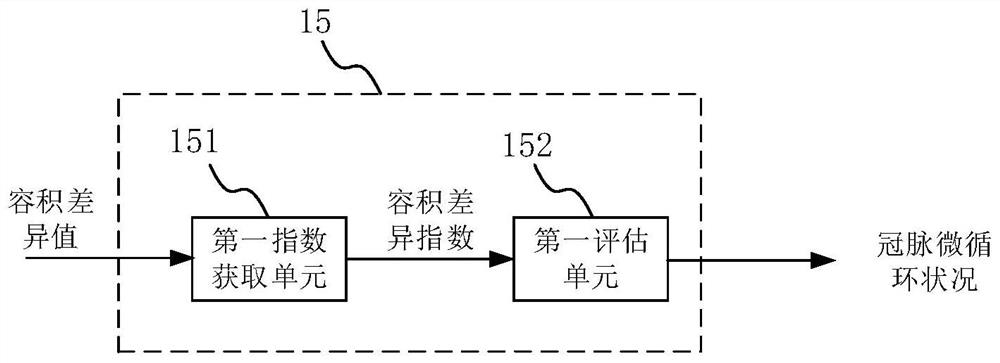
Coronary artery microcirculation condition evaluation device and method
ActiveCN112381780AEasy to operateEasy to implementImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesSystole
The invention provides a coronary artery microcirculation condition evaluation device and method. The coronary artery microcirculation condition evaluation device comprises an image acquisition moduleused for acquiring a CTA image of a heart part of a patient; an image segmentation module which is used for segmenting the CTA image to obtain a coronary artery image in a systolic period and a coronary artery image in a diastolic period; a volume acquisition module which is used for acquiring the volume of the systolic period and the volume of the diastolic period according to the coronary artery image of the systolic period and the coronary artery image of the diastolic period; a difference value acquisition module which is used for acquiring a volume difference value according to the volume of the systolic period and the volume of the diastolic period; and an evaluation module which is used for obtaining the coronary artery microcirculation condition of the patient according to the volume difference value. According to the coronary artery microcirculation condition evaluation device, the coronary artery microcirculation condition of the patient can be obtained by processing the CTAimage only by obtaining the CTA image of the heart part of the patient, and the coronary artery microcirculation condition evaluation device is easy to operate and easy to implement.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL +1
Large ablation head and ablation device
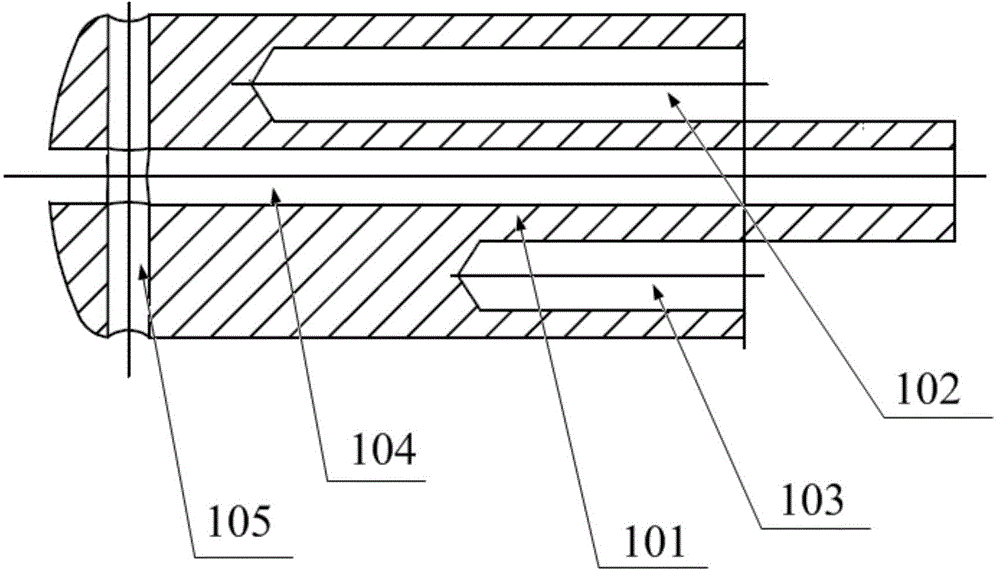
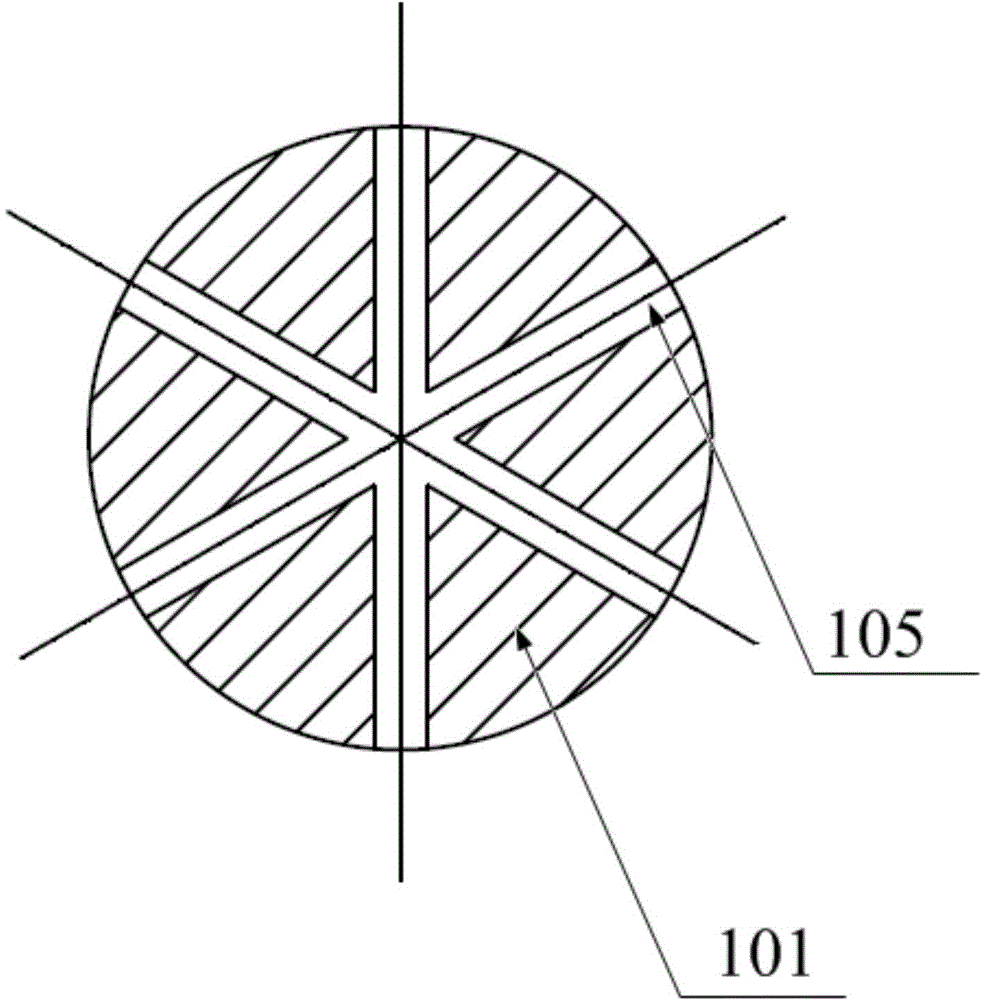
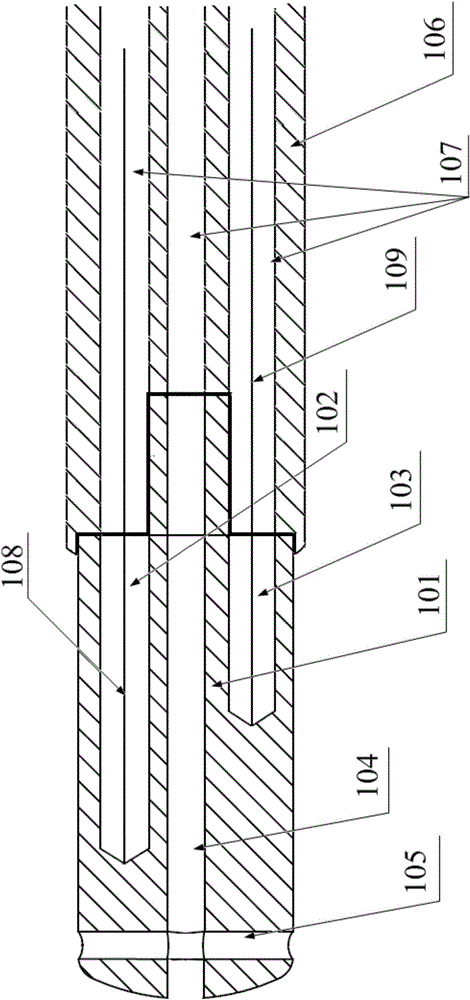
InactiveCN104825226APerfusion does not affectHigh trafficInfusion syringesSurgical instruments for heatingTemperature controlHeart Part
The invention relates to the field of surgical instruments, in particular to a large ablation head and an ablation device. The large ablation head comprises a large ablation head main body, wherein a temperature control wire hole, a stay wire hole and a liquid hole of which the axes are parallel to one another are formed in the large ablation head main body; a plurality of outflow holes are further formed in one end of the large ablation head main body; the liquid hole penetrates through the large ablation head main body; the overflow holes are communicated with the liquid hole; the diameter of the liquid hole is 0.5-0.7mm; the diameter of each overflow hole is 0.55-0.65mm. Through the large ablation head provided by the invention, a contrast medium can be injected into a special heart part of a human body for radiography, and cold brine can be injected into the heart in an ablation process; during a surgery, the large ablation head needs to be put to a designated position through a vascular access, the quantity of the surgical instruments is decreased, the surgical steps are simplified, and the surgical time is shortened.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Interventricular septum offset parameter determination device and electronic equipment
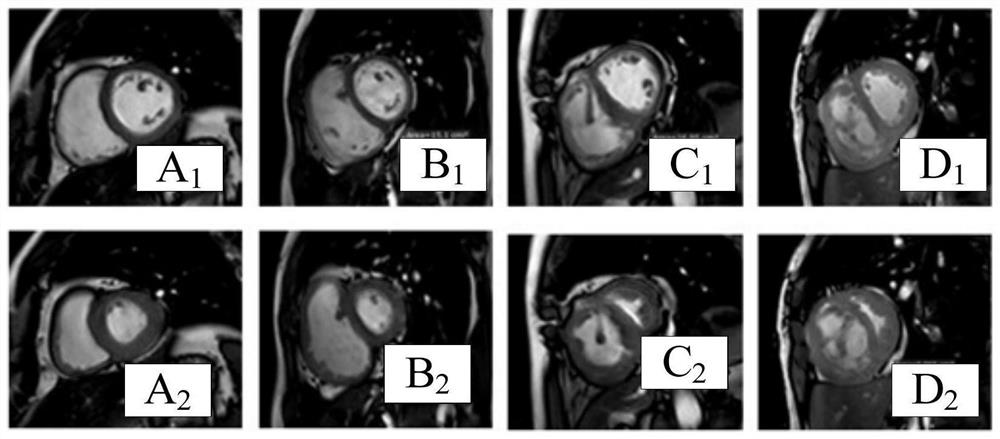
The invention discloses a ventricular septum offset parameter determination device and electronic equipment, relates to the technical field of medical image processing, and aims to solve the problems of health damage caused by adopting an invasive detection mode on a patient and high requirement on the experience level of a doctor when pulmonary artery pressure is evaluated. The device comprises an obtaining module used for obtaining a biological heart image; the processing module is used for determining geometric parameters of at least one ventricle based on the biological heart part image; and a determination module for determining an actual offset parameter of the ventricular septum based on the geometric parameter of at least one of the ventricles. The readable storage medium for the ventricular offset parameters and the electronic equipment are provided by the technical scheme. The ventricular offset parameter determination device provided by the invention is used for measuring biological pulmonary arterial pressure.
Owner:JEDICARE MEDICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com