Patents
Literature
414 results about "Thorax" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans and various other animals located between the neck and the abdomen. The thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ thorax "breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via Latin: thorax.
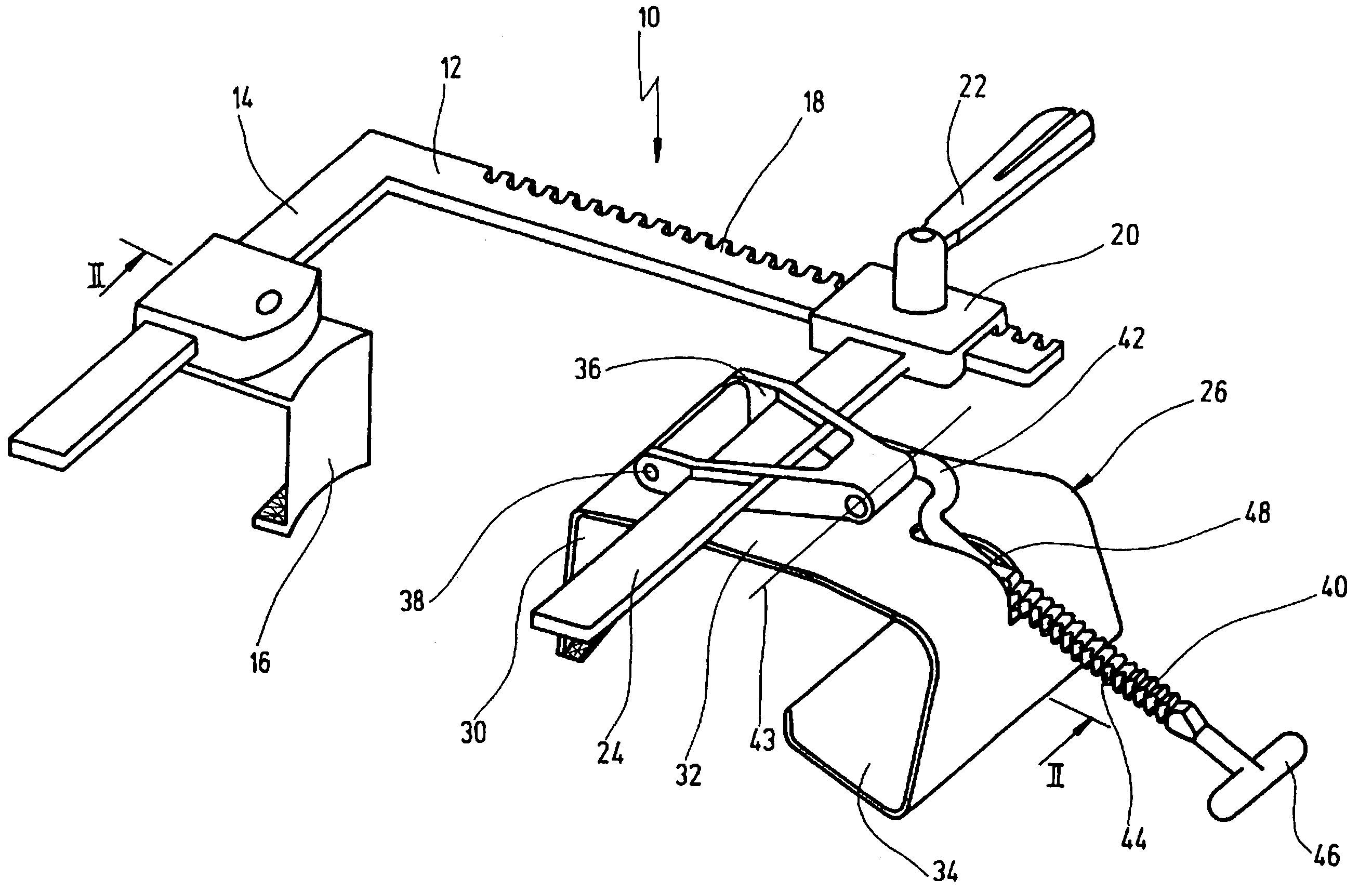
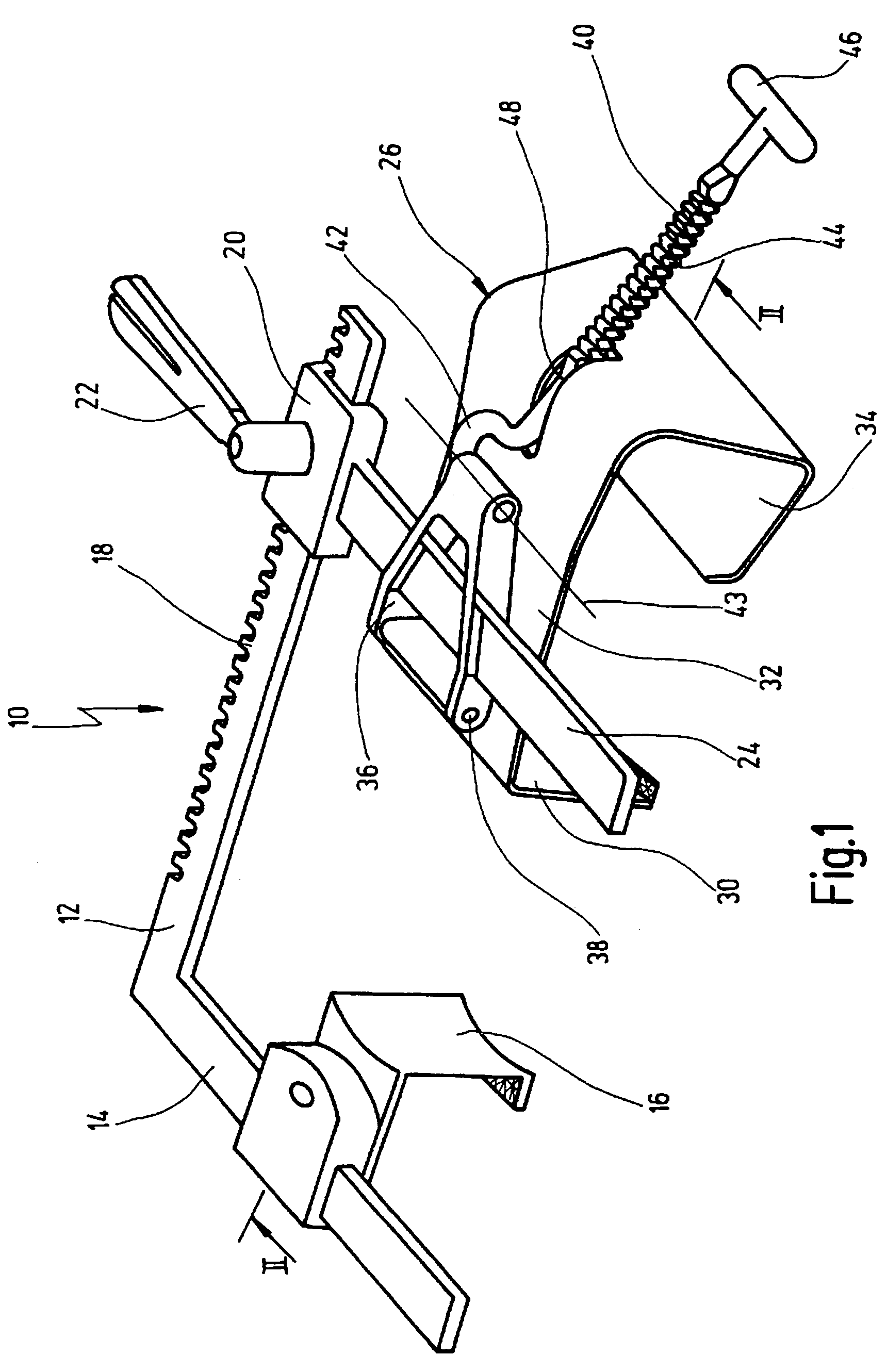
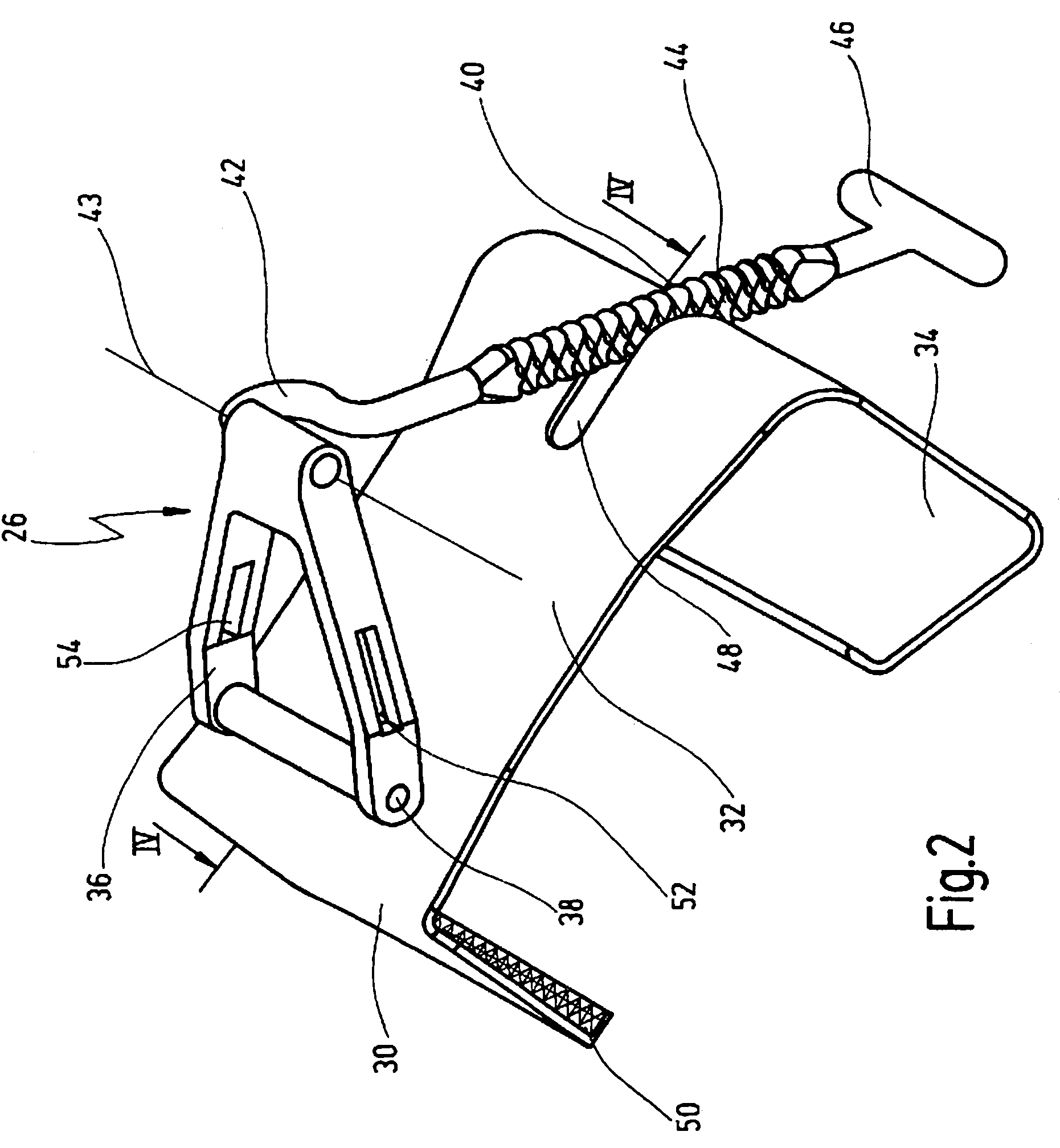
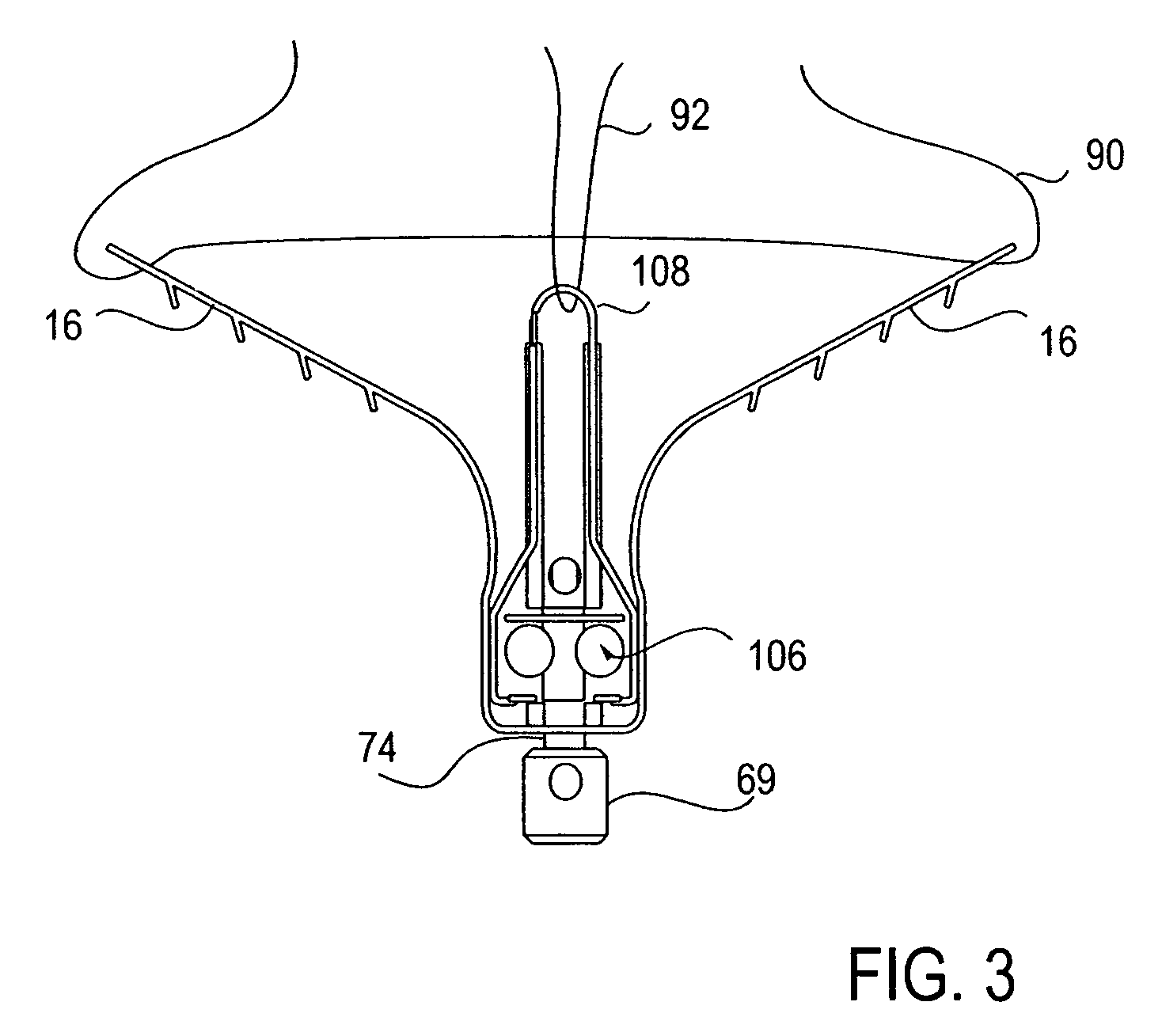
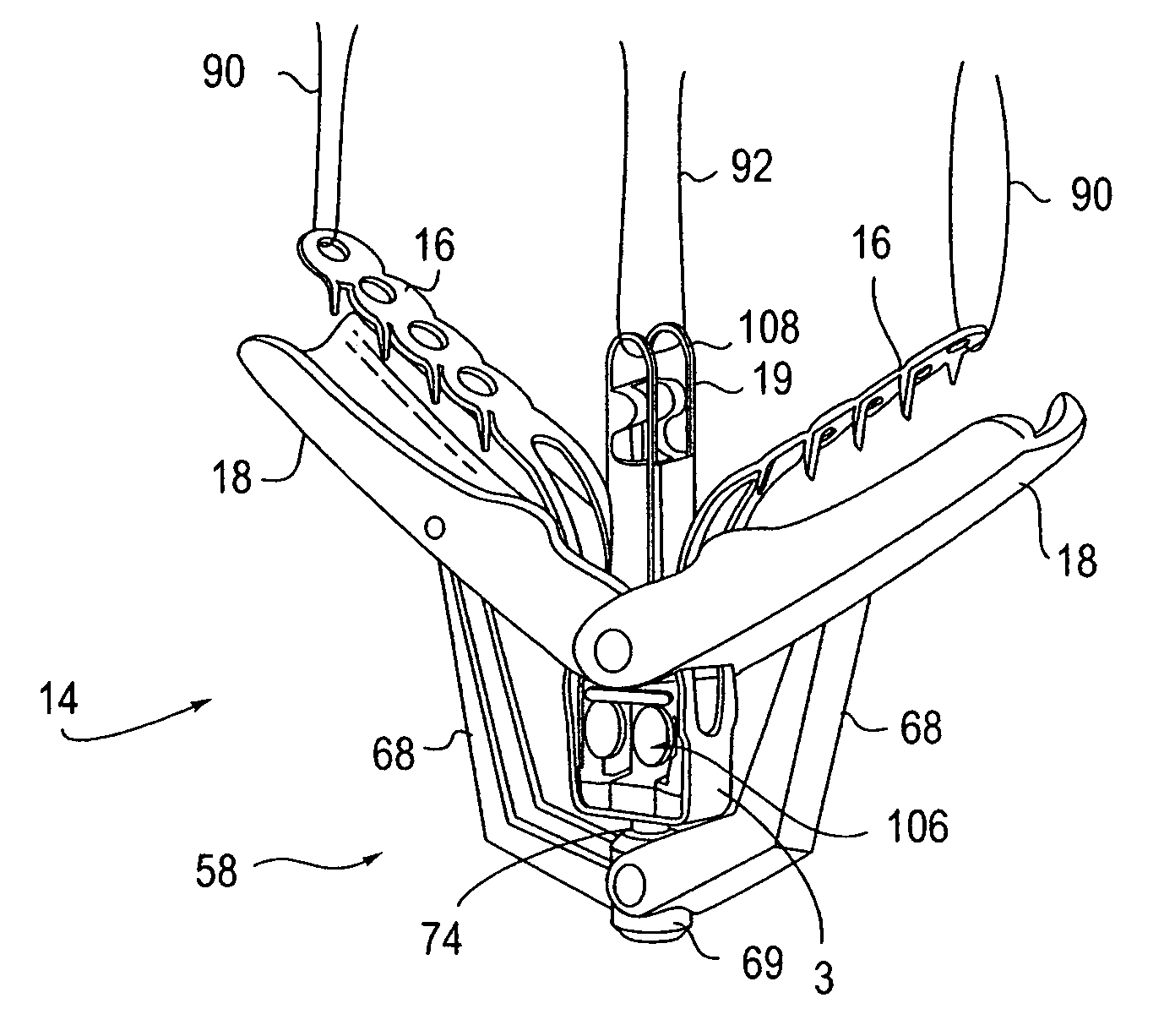
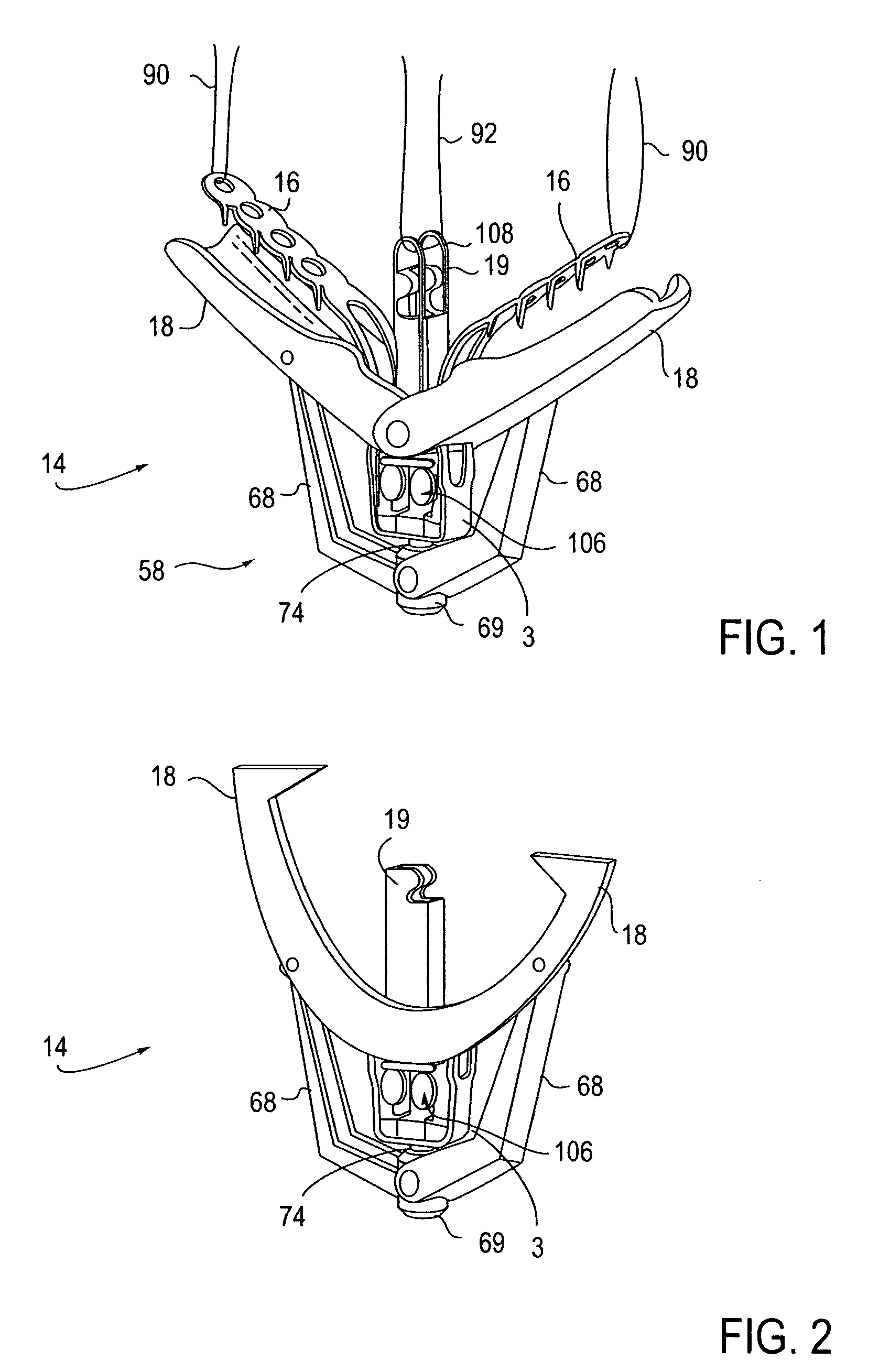
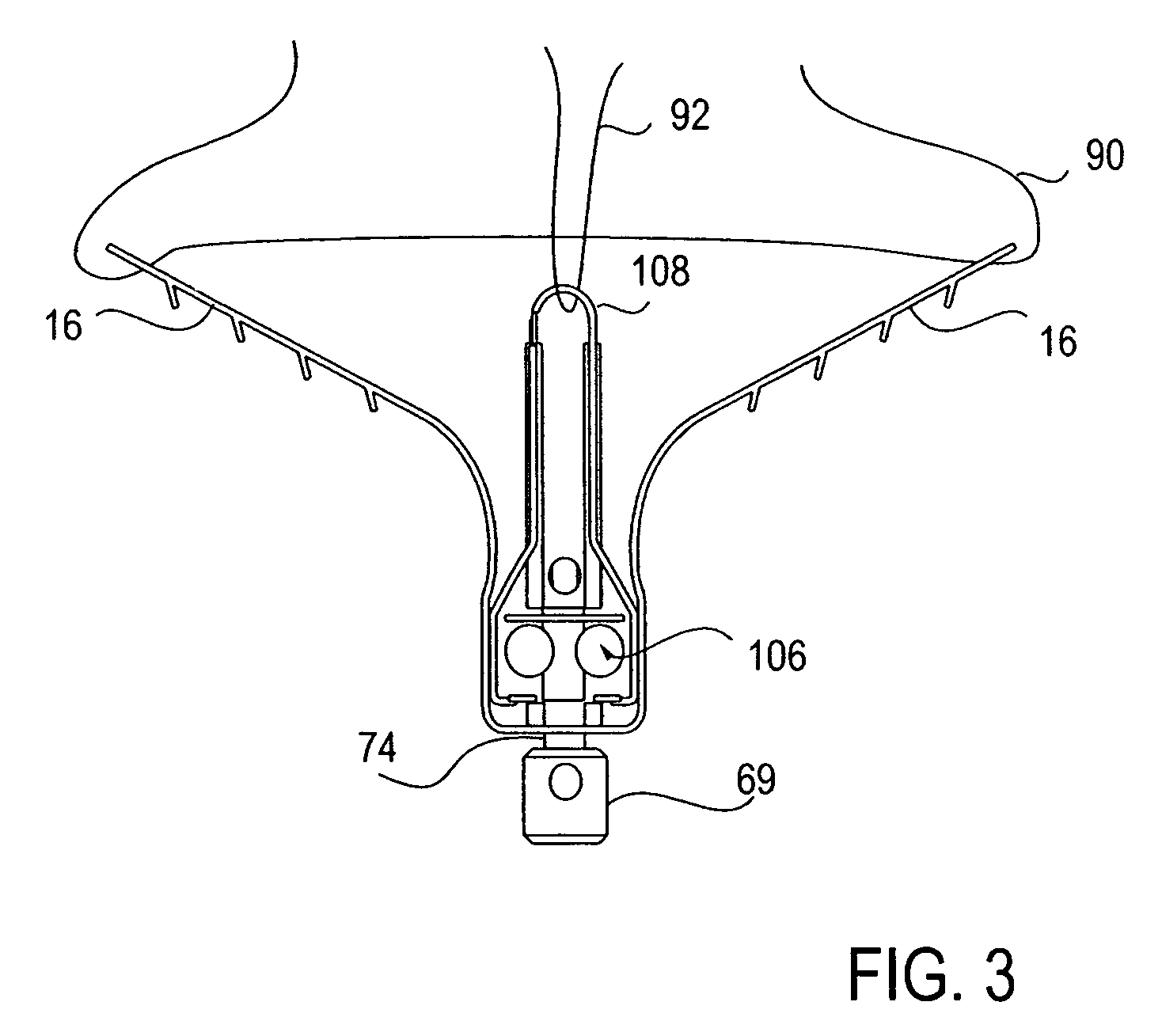
Retractor for performing heart and thorax surgeries
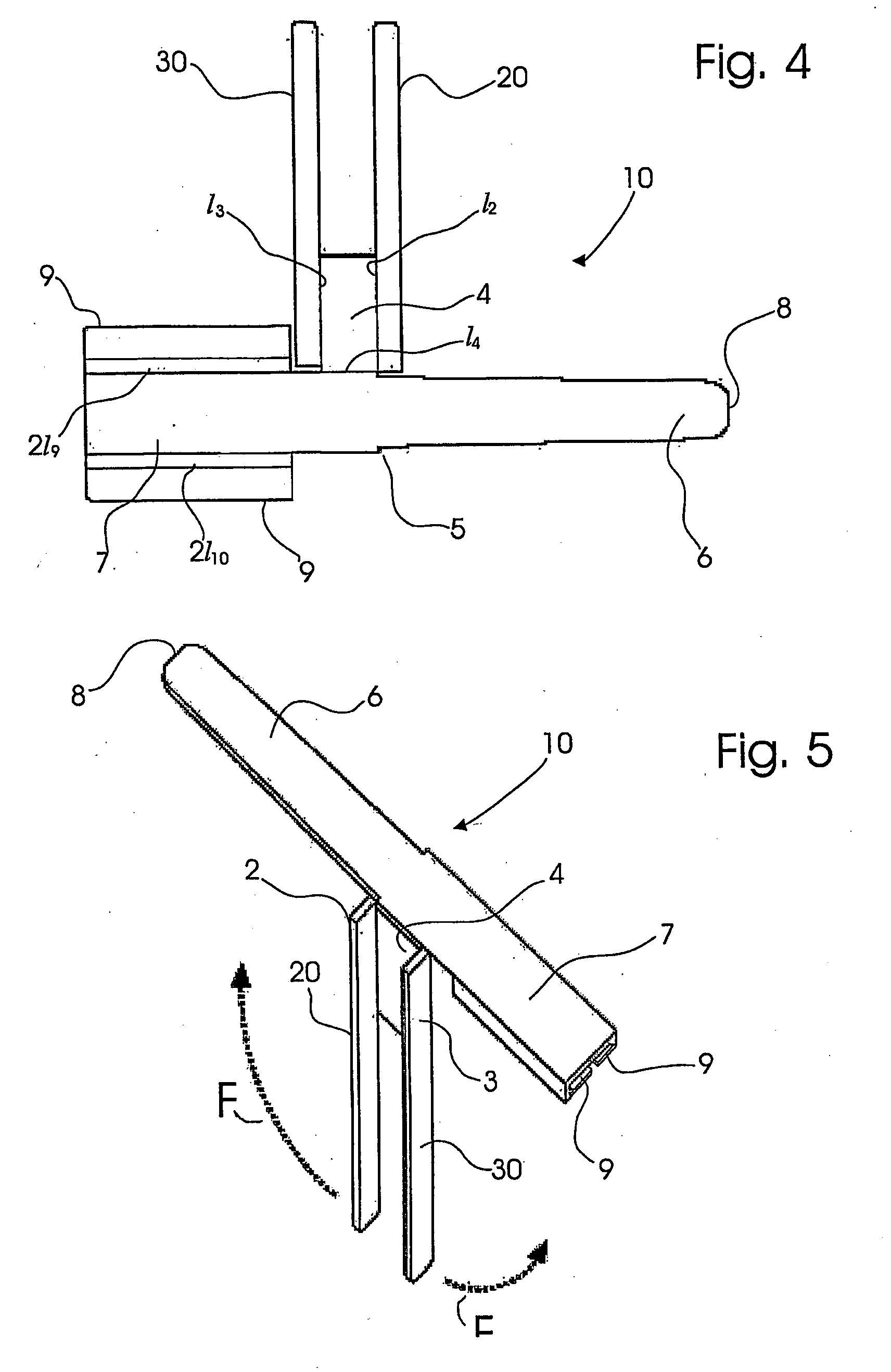
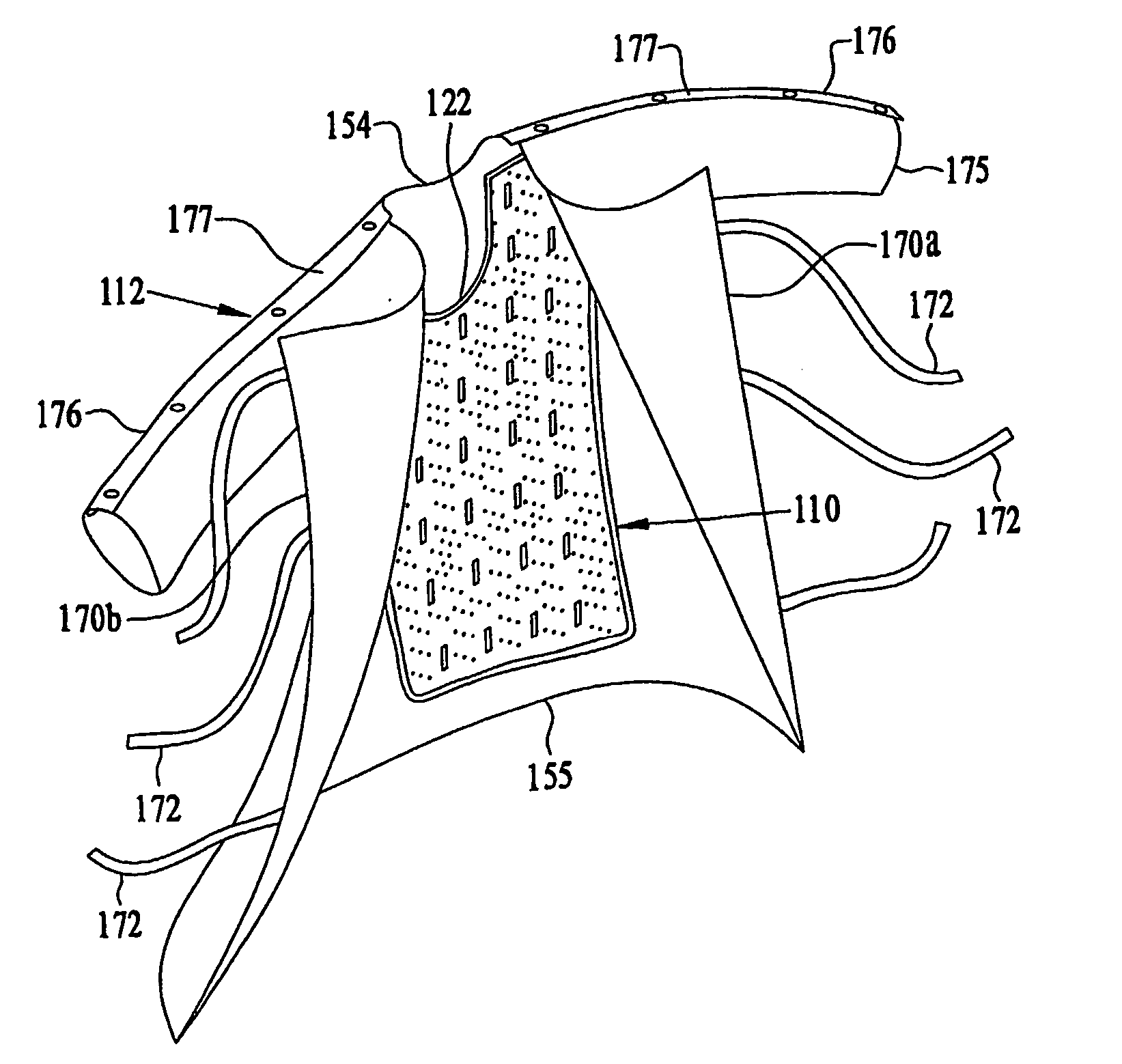
A retractor has a rail, a first holding arm protruding from this rail at an angle at a second holding arm extending approximately parallel to the first holding arm. A distance between the two arms being modifiable. At least one functional element is mounted on one of these holding arms, which functional element has a section extending transversely to the holding arms and a swivel bracket protruding from this transverse section. The functional element being pivotable about a pin extending roughly parallel to the arms via the swivel bracket, a swiveled position can be set by grasping the function element with a hand. A locking mechanism serves for locking the functional element in a swiveled position.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Apparatus and methods of bioelectrical impedance analysis of blood flow
InactiveUS6095987AAccurately and non-invasively and continuously measuring cardiac outputCatheterSensorsBioelectrical impedance analysisCardiac pacemaker electrode
Apparatus and methods are provided for monitoring cardiac output using bioelectrical impedance techniques in which first and second electrodes are placed in the trachea and / or bronchus in the vicinity of the ascending aorta, while an excitation current is injected into the thorax via first and second current electrodes, so that bioelectrical impedance measurements based on the voltage drop sensed by the first and second electrodes reflect voltage changes induced primarily by blood flow dynamics, rather than respiratory or non-cardiac related physiological effects. Additional sense electrodes may be provided, either internally, or externally, for which bioelectrical impedance values may be obtained. Methods are provided for computing cardiac output from bioelectrical impedance values. Apparatus and methods are also provided so that the measured cardiac output may be used to control administration of intravenous fluids to an organism or to optimize a heart rate controlled by a pacemaker.
Owner:ECOM MED
Locking mechanisms for fixation devices and methods of engaging tissue
InactiveUS20060020275A1Reduce frictional contactRestrict movementSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsEngineeringThoracic cavity
Devices, systems and methods are provided for tissue approximation and repair at treatment sites. In particular, fixation devices are provided comprising a pair of elements each having a first end, a free end opposite the first end, and an engagement surface therebetween for engaging the tissue, the first ends being moveable between an open position wherein the free ends are spaced apart and a closed position wherein the free ends are closer together with the engagement surfaces generally facing each other. The fixation devices also include a locking mechanism coupled to the elements for locking the elements in place. The devices, systems and methods of the invention will find use in a variety of therapeutic procedures, including endovascular, minimally-invasive, and open surgical procedures, and can be used in various anatomical regions, including the abdomen, thorax, cardiovascular system, heart, intestinal tract, stomach, urinary tract, bladder, lung, and other organs, vessels, and tissues. The invention is particularly useful in those procedures requiring minimally-invasive or endovascular access to remote tissue locations, where the instruments utilized must negotiate long, narrow, and tortuous pathways to the treatment site.
Owner:EVALVE
Locking mechanisms for fixation devices and methods of engaging tissue
InactiveUS7604646B2Prevent movementReduce frictional contactSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsEngineeringSurgical department
Owner:EVALVE
Single or multi-mode cardiac activity data collection, processing and display obtained in a non-invasive manner
InactiveUS7043292B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioEasy to identifyElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorCardiac surface
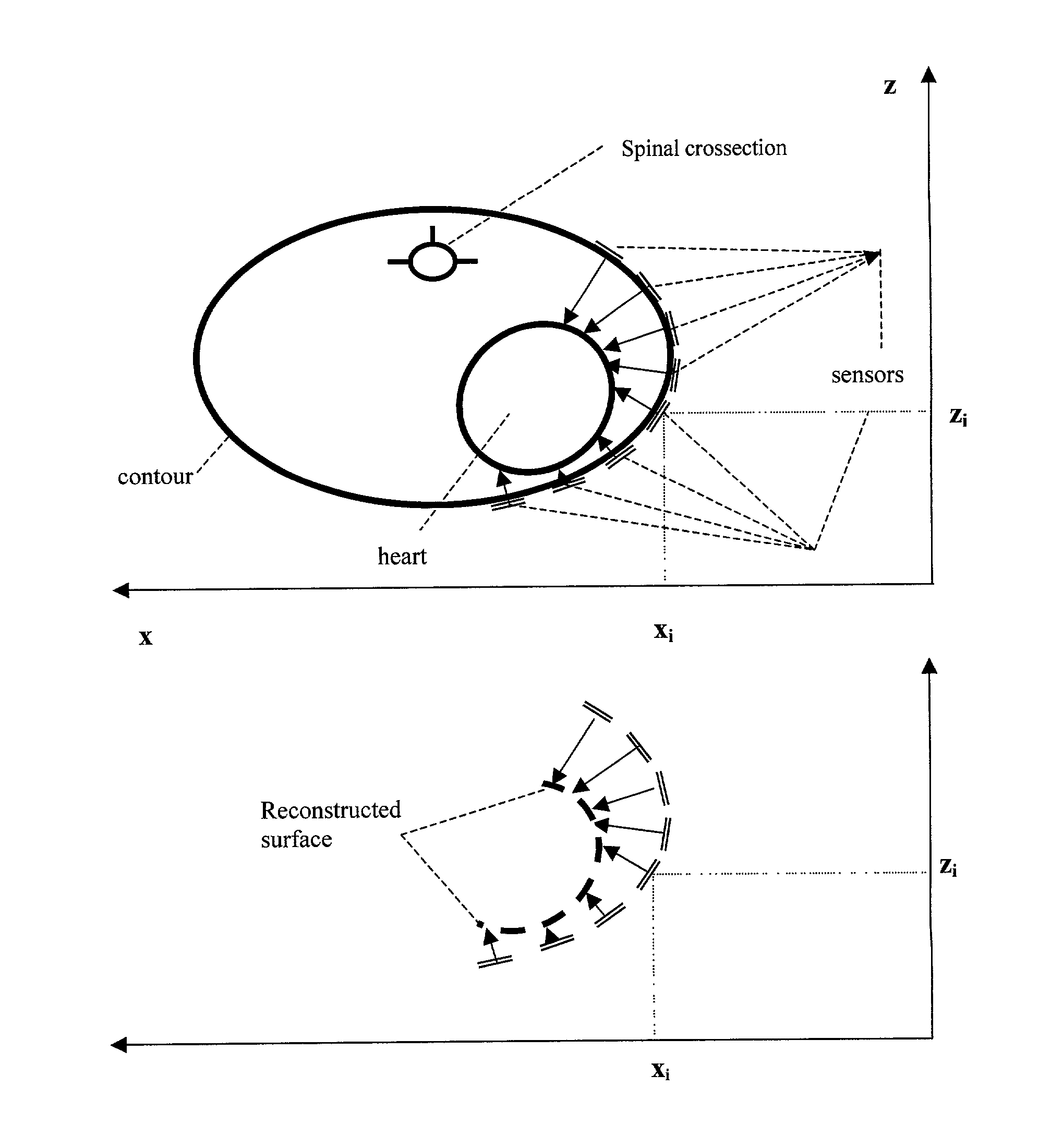
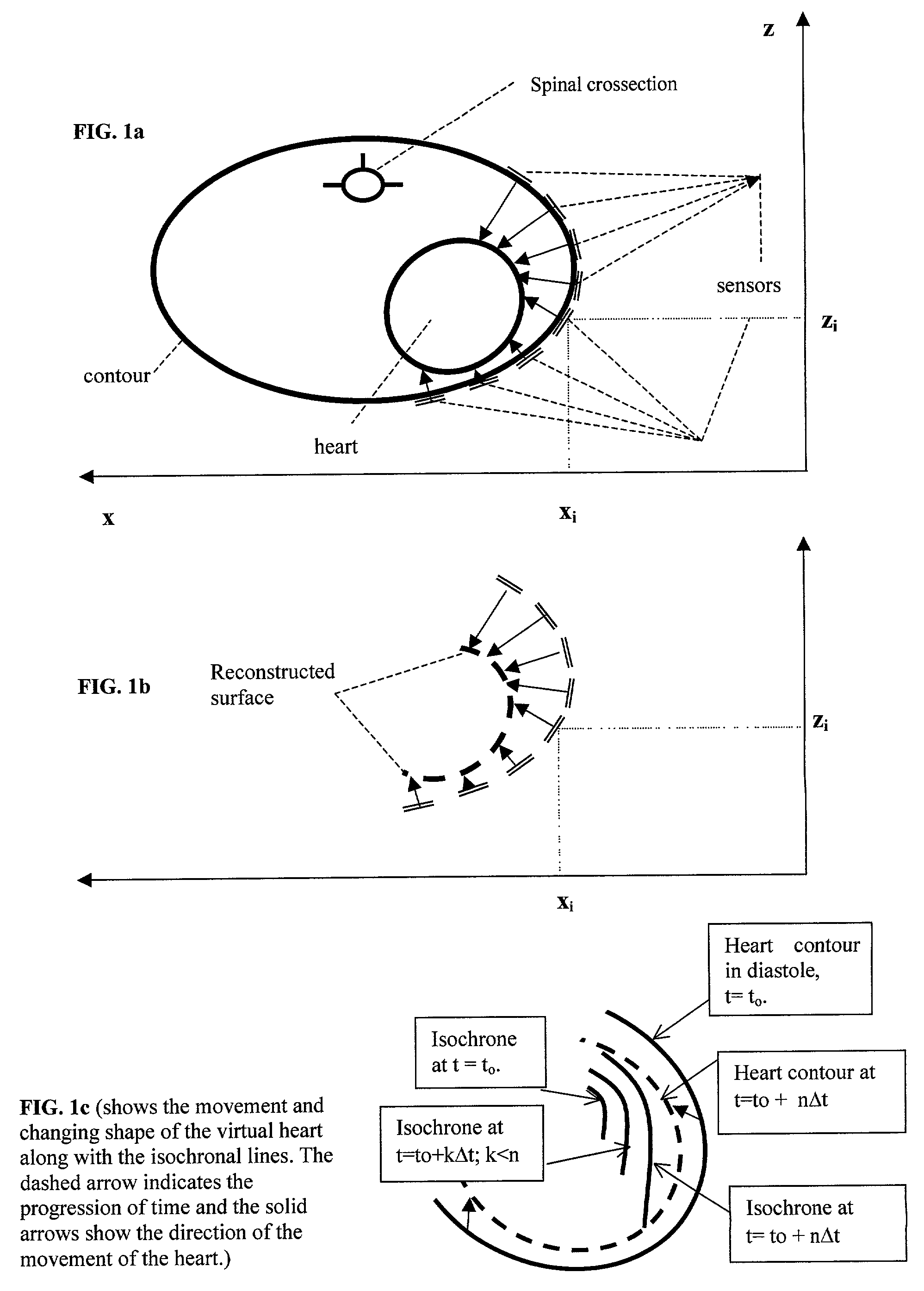
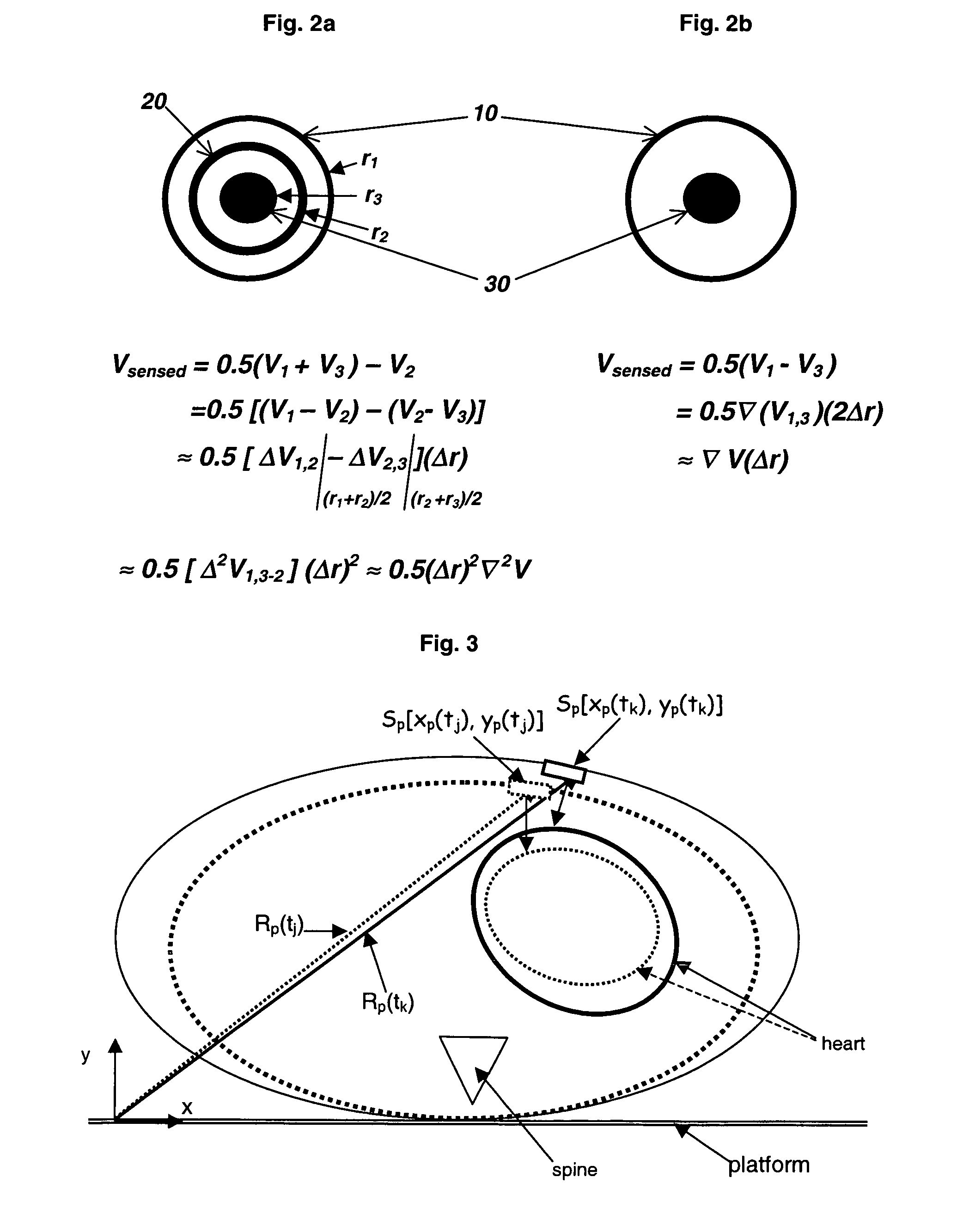
The method of presenting concurrent information about the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart using non-invasively obtained electrical and mechanical cardiac activity data from the chest or thorax of a patient comprises the steps of: placing at least three active Laplacian ECG sensors at locations on the chest or thorax of the patient; where each sensor has at least one outer ring element and an inner solid circle element, placing at least one ultrasonic sensor on the thorax where there is no underlying bone structure, only tissue, and utilizing available ultrasound technology to produce two or three-dimensional displays of the moving surface of the heart and making direct measurements of the exact sites of the sensors on the chest surface to determine the position and distance from the center of each sensor to the heart along a line orthogonal to the plane of the sensor and create a virtual heart surface; updating the measurements at a rate to show the movement of the heart's surface; monitoring at each ultrasonic sensor site and each Laplacian ECG sensor site the position and movement of the heart and the passage of depolarization wave-fronts in the vicinity; treating those depolarization wave-fronts as moving dipoles at those sites to create images of their movement on the image of the beating heart's surface; and, displaying the heart's electrical activity on the dynamically changing image of the heart's surface with the goal to display an approximation of the activation sequence on the beating virtual surface of the heart
Owner:TARJAN PETER P +2
Steerable epicardial pacing catheter system placed via the subxiphoid process
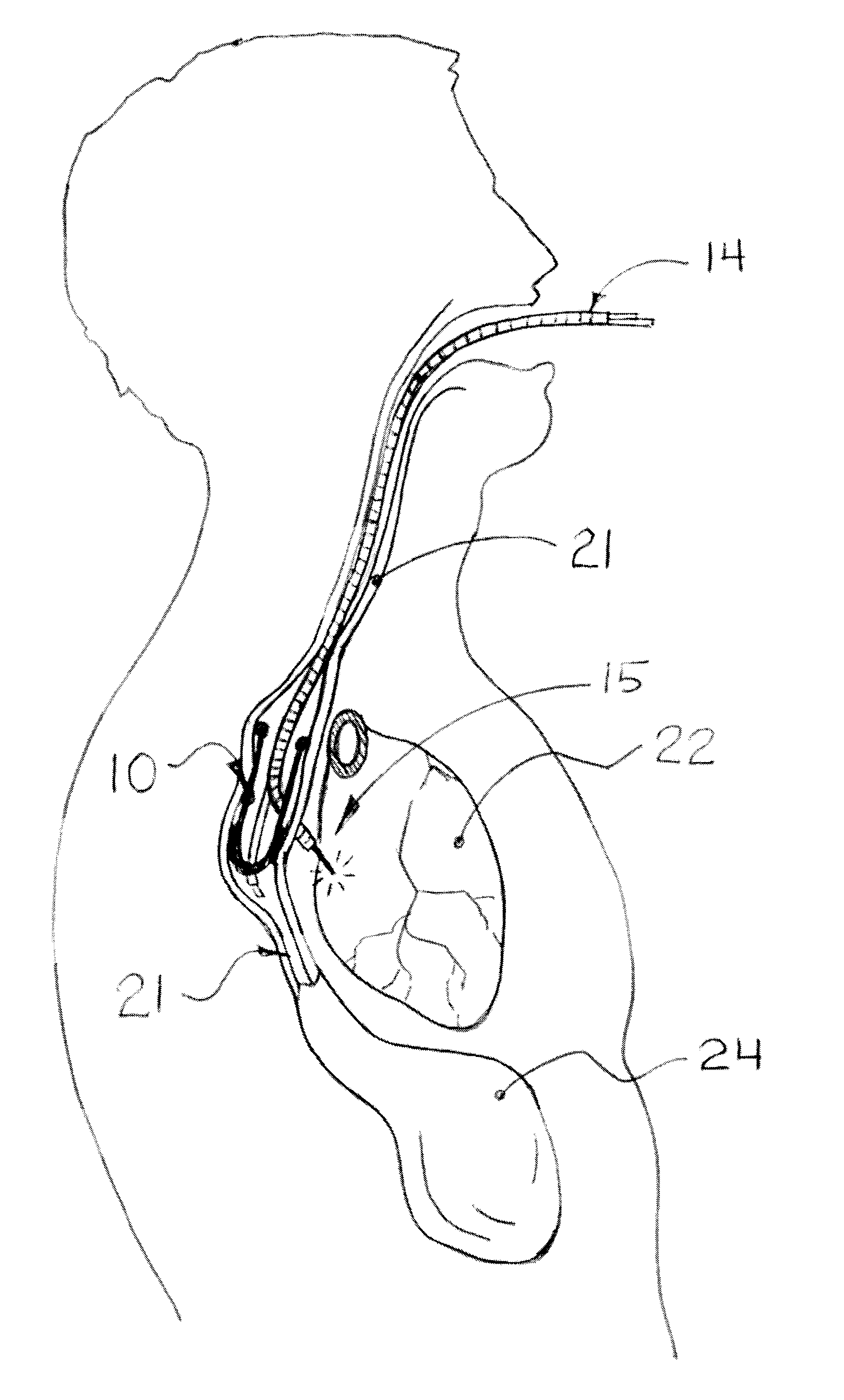
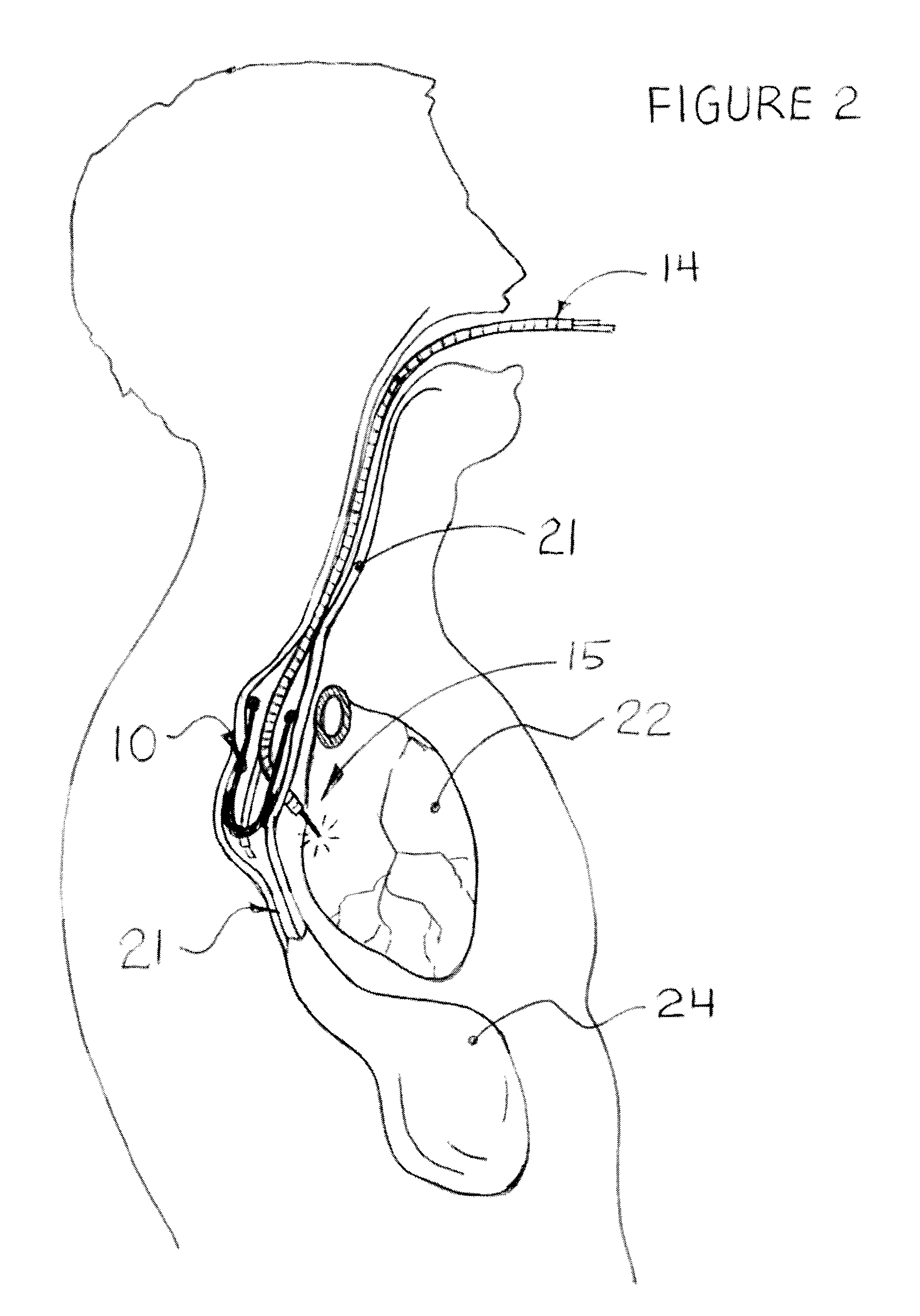
InactiveUS20100241185A1Free from damageEpicardial electrodesDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresThoracic cavity
The epicardial pacing system and related method includes an epicardial catheter configured to be disposed in the middle mediastinum of the thorax of a subject for use in electrical pacing of the heart at one or more locations on the epicardial surface. The epicardial pacing catheter may include at least one electrode whereby the electrode is insulated on at least one side to allow pacing of the heart without damage to adjacent anatomical structures.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
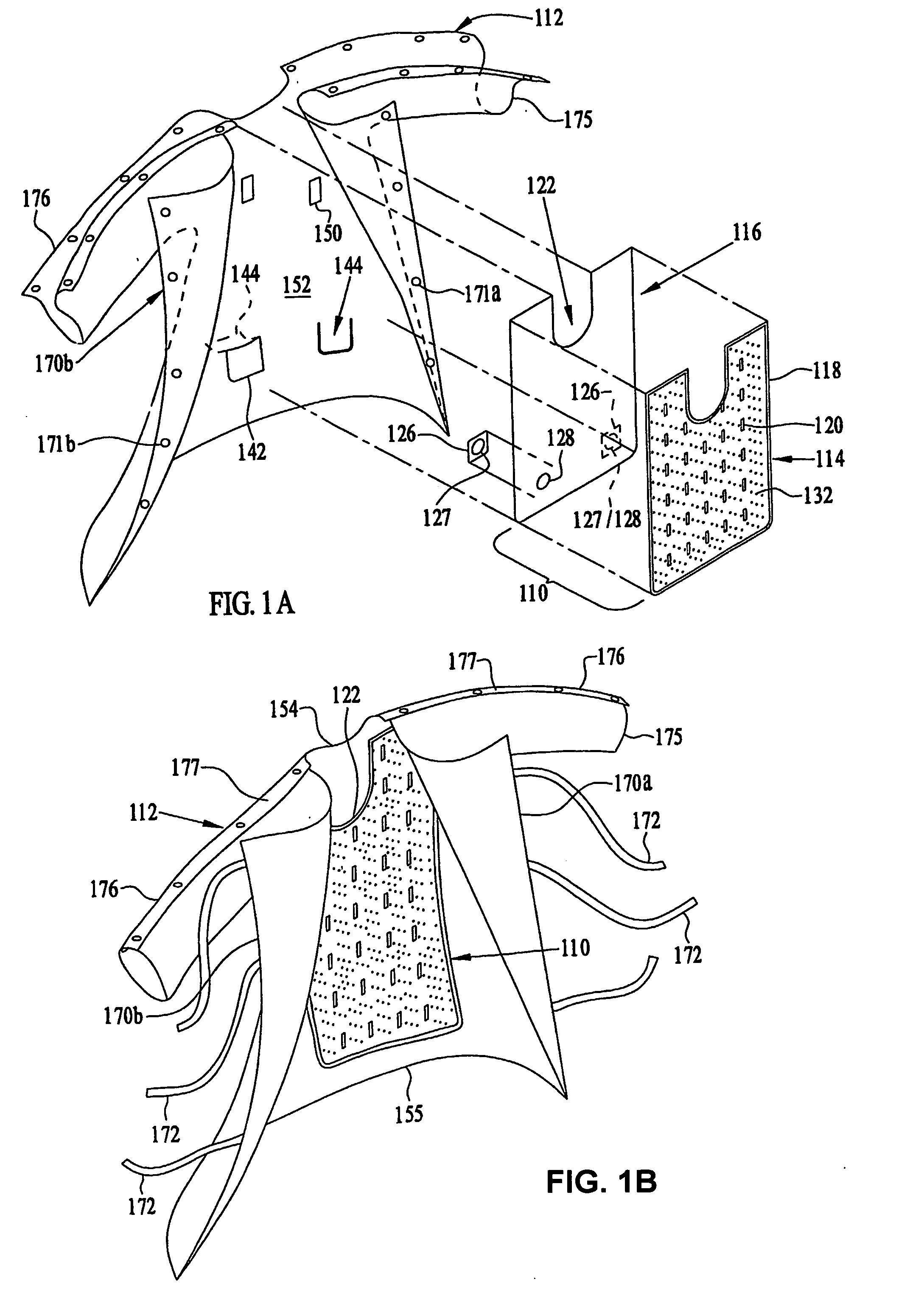
Sternum Reinforcing Device to be Used After a Sternotomy or a Sternal Fracture
ActiveUS20080221578A1High risk of damageInternal osteosythesisBone implantSternal fractureEngineering
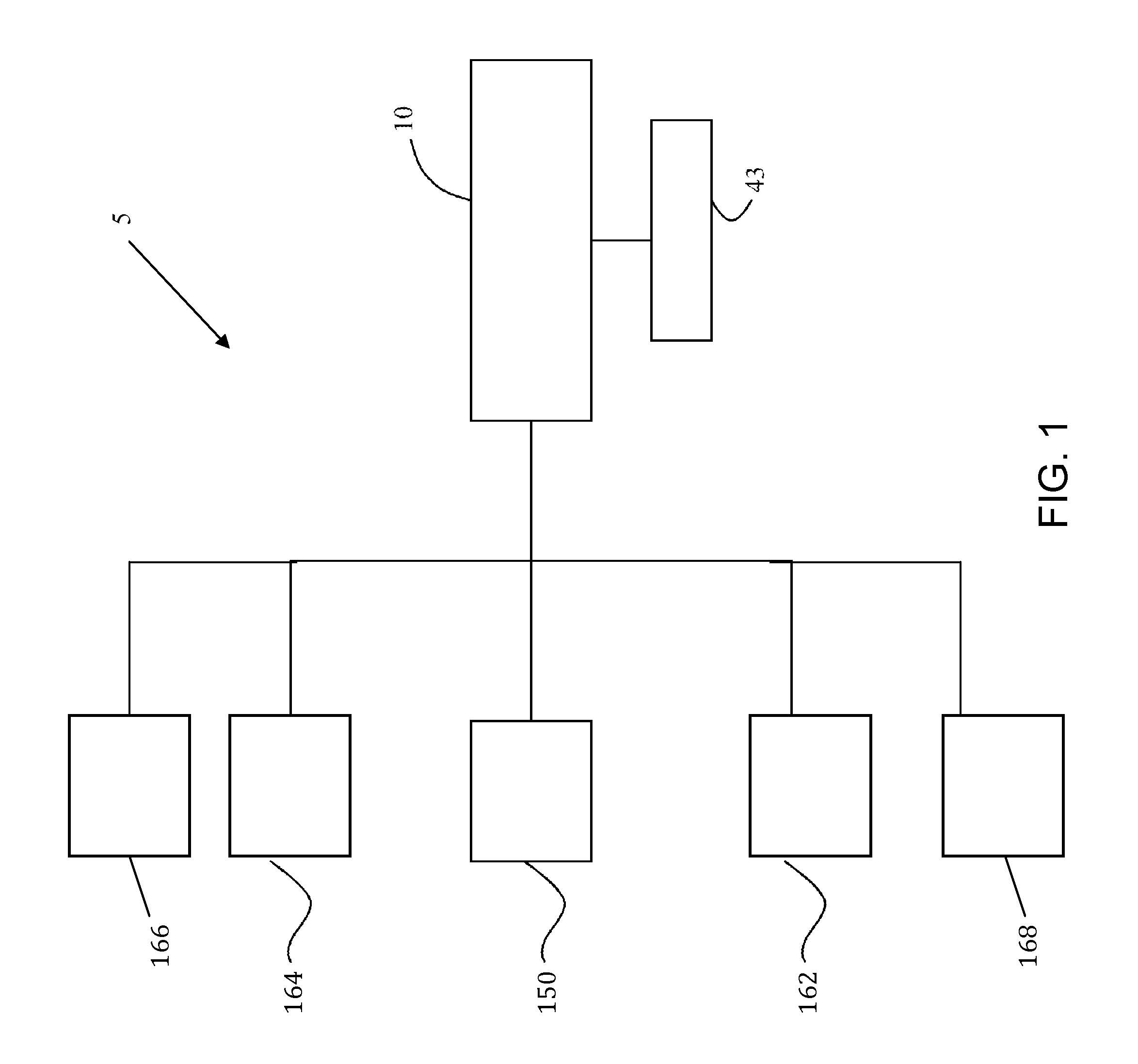
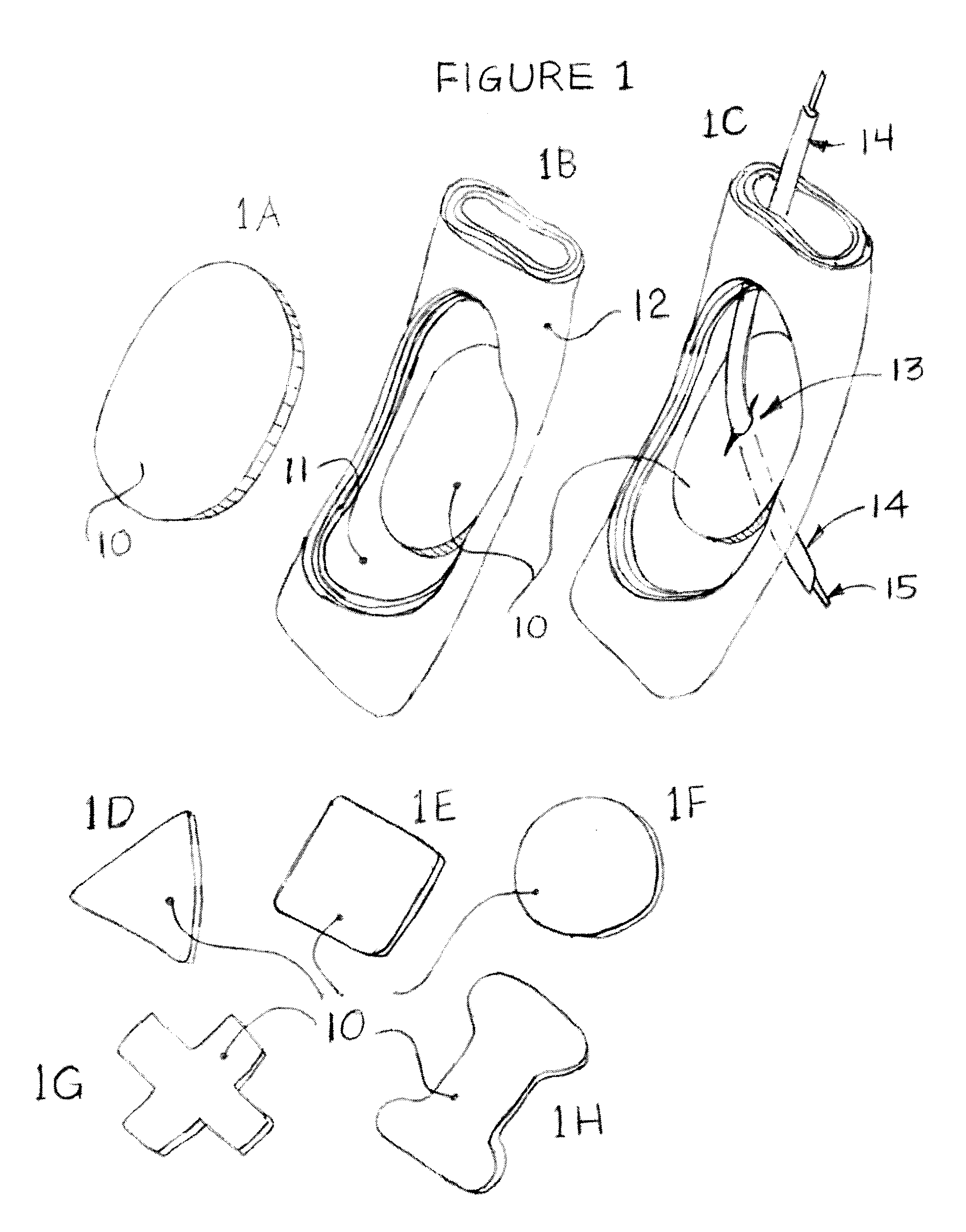
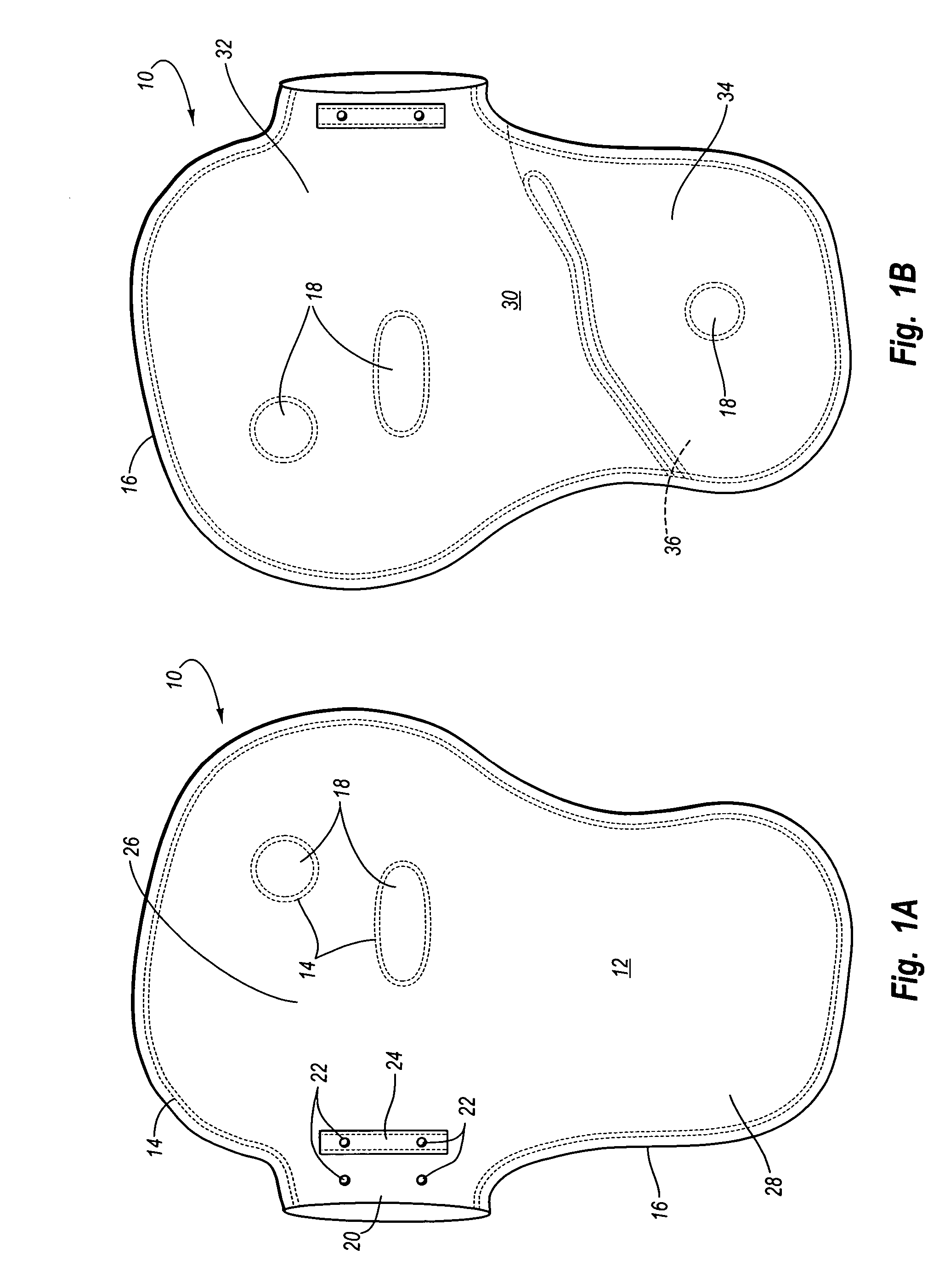
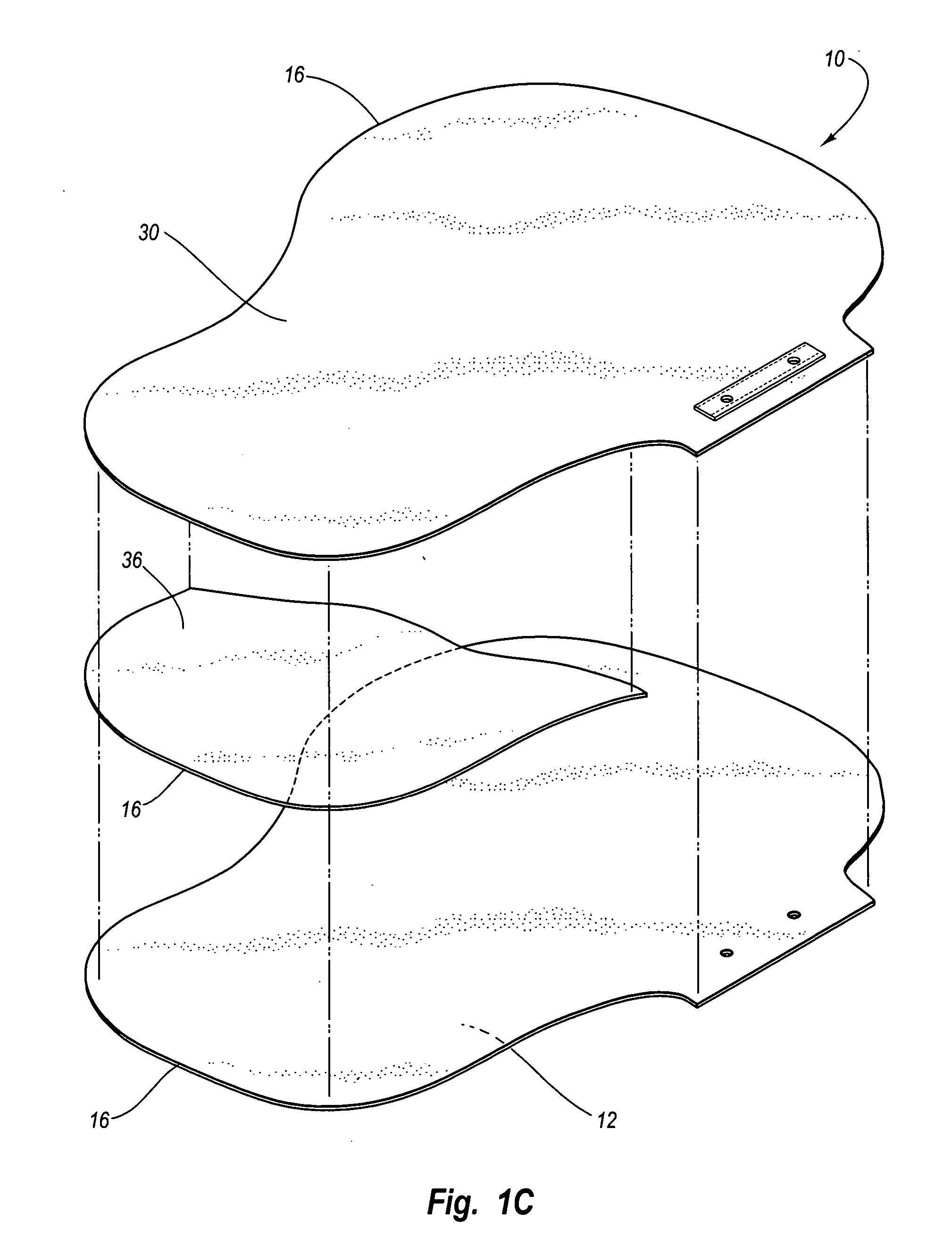
A sternum reinforcing device to be used after a sternotomy or a sternal fracture, made of a biocompatible material, comprises an elongated modular member (10) with a pair of legs (20, 30), that are joined each other by a body portion (4), and a pair of arms (6, 7). The legs (20, 30) can be fitted in an intercostal space of the thorax of a patient, laterally to the sternum, and can be bent in a mutually opposite direction, on the internal side of the thorax, after being fitted therein. The arms (6, 7), extending from one side to the other of the body portion (4) and orthogonally to the pair of legs (20, 30), constitute a male part and a female part, respectively, of a prismatic type coupling for consecutive modular members.
Owner:SIC BREVETTI SRL
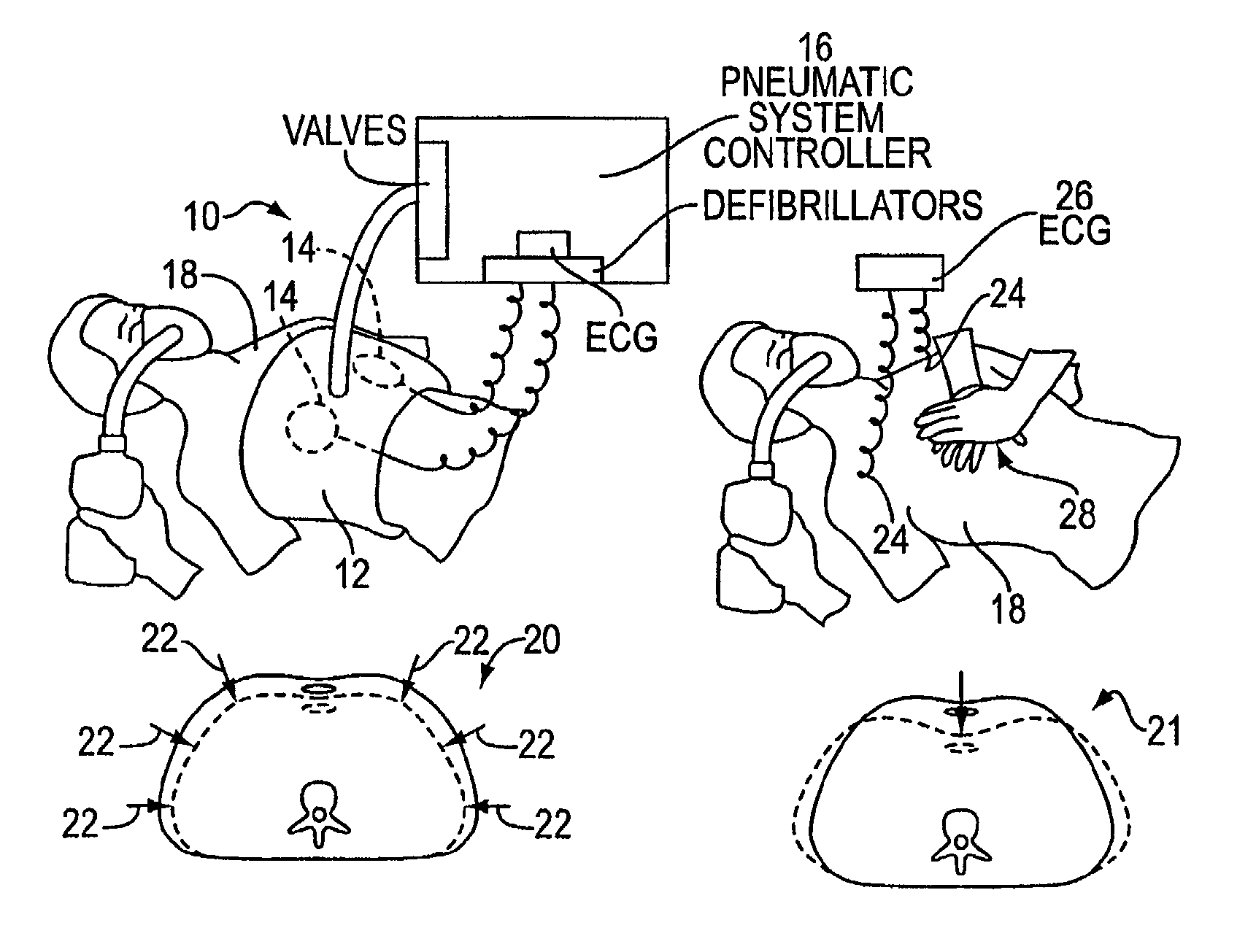
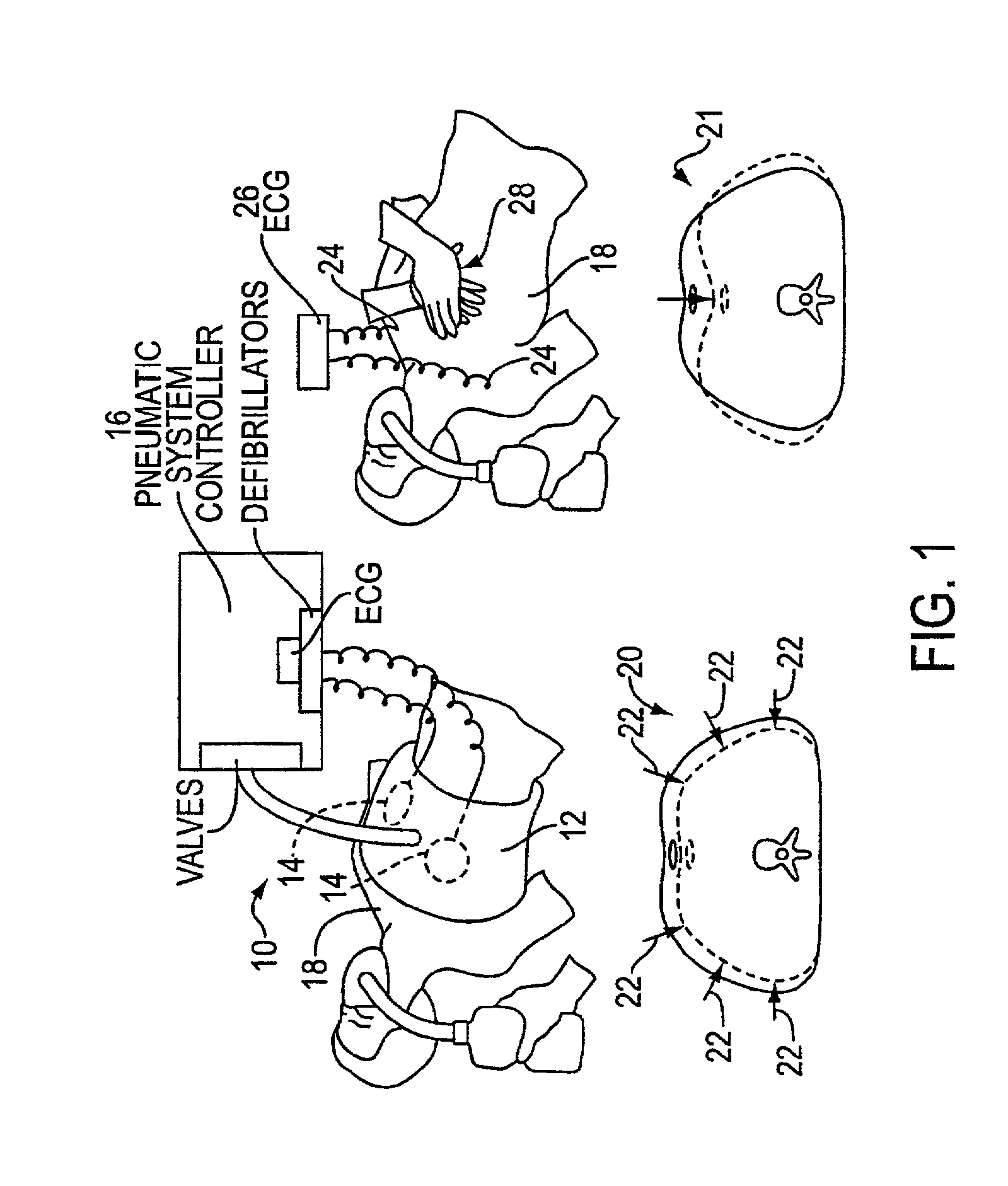
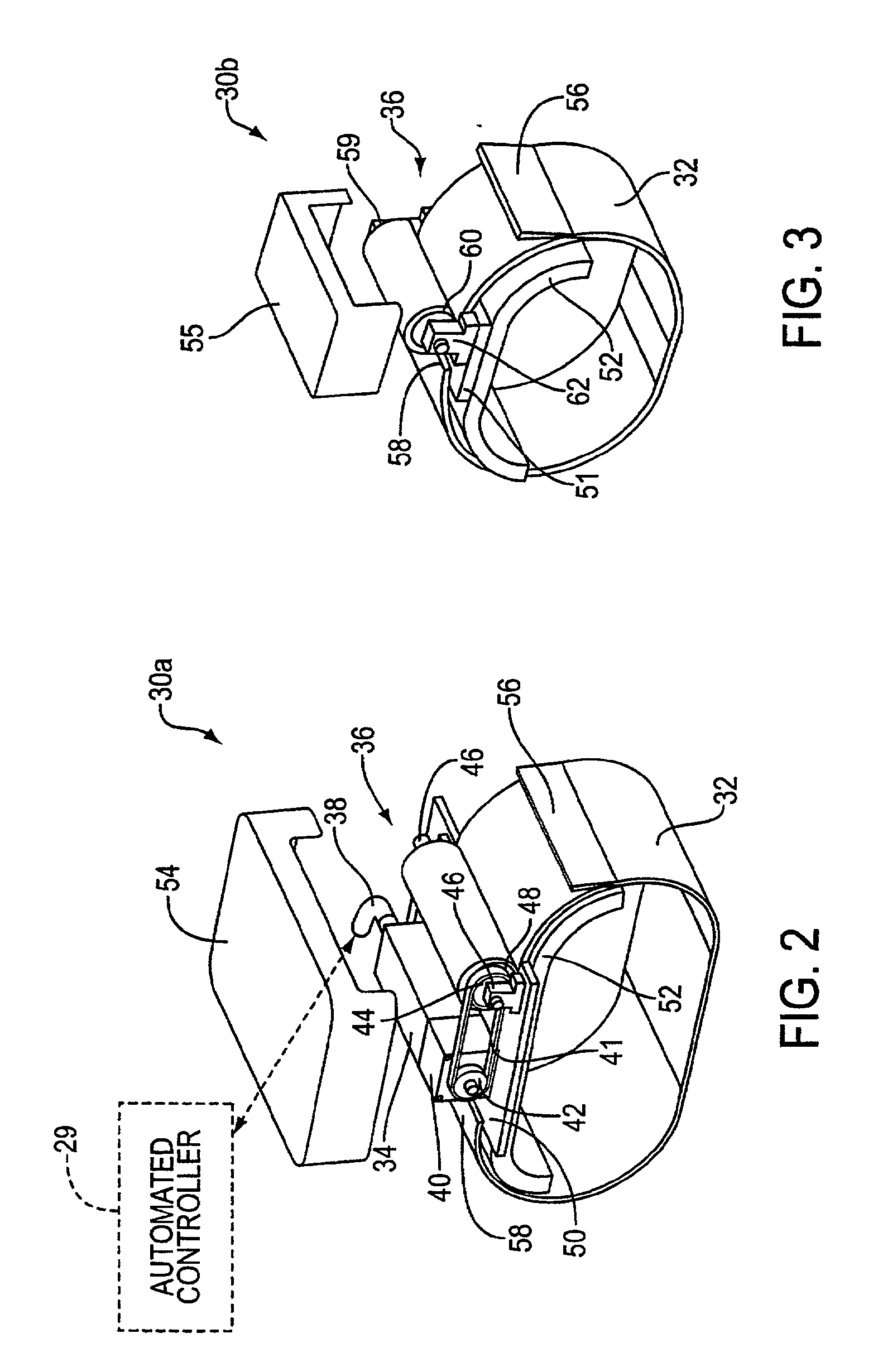
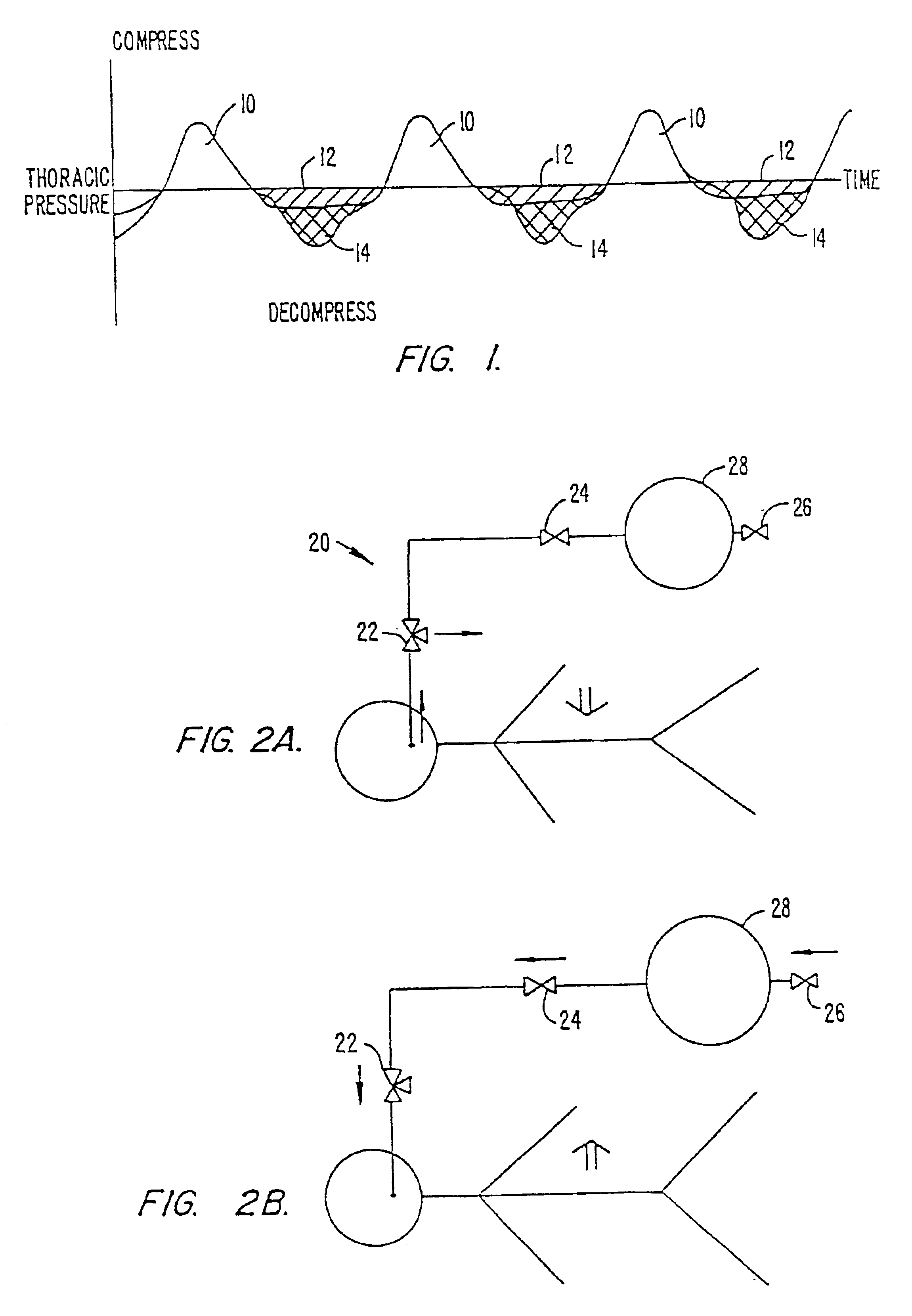
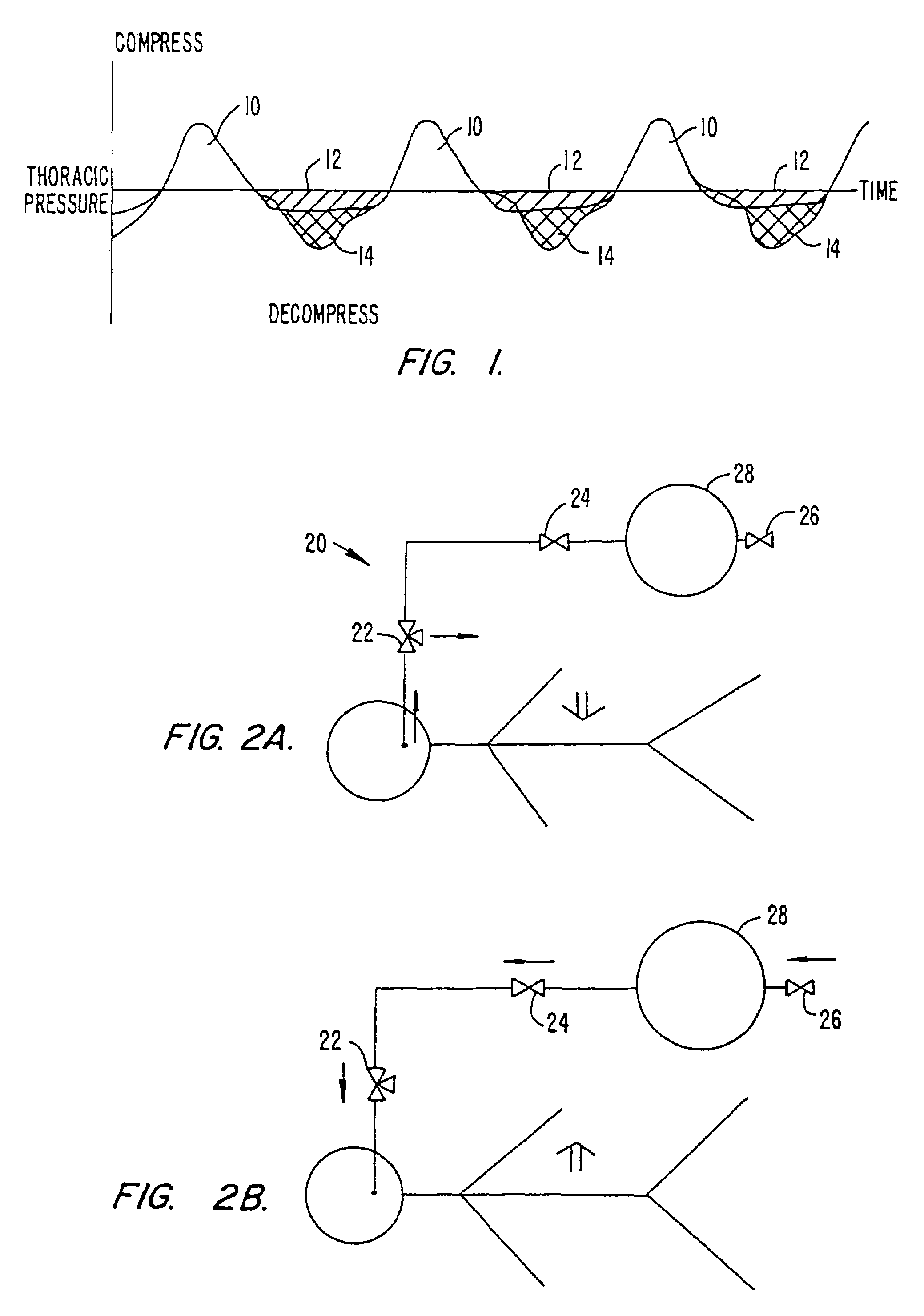
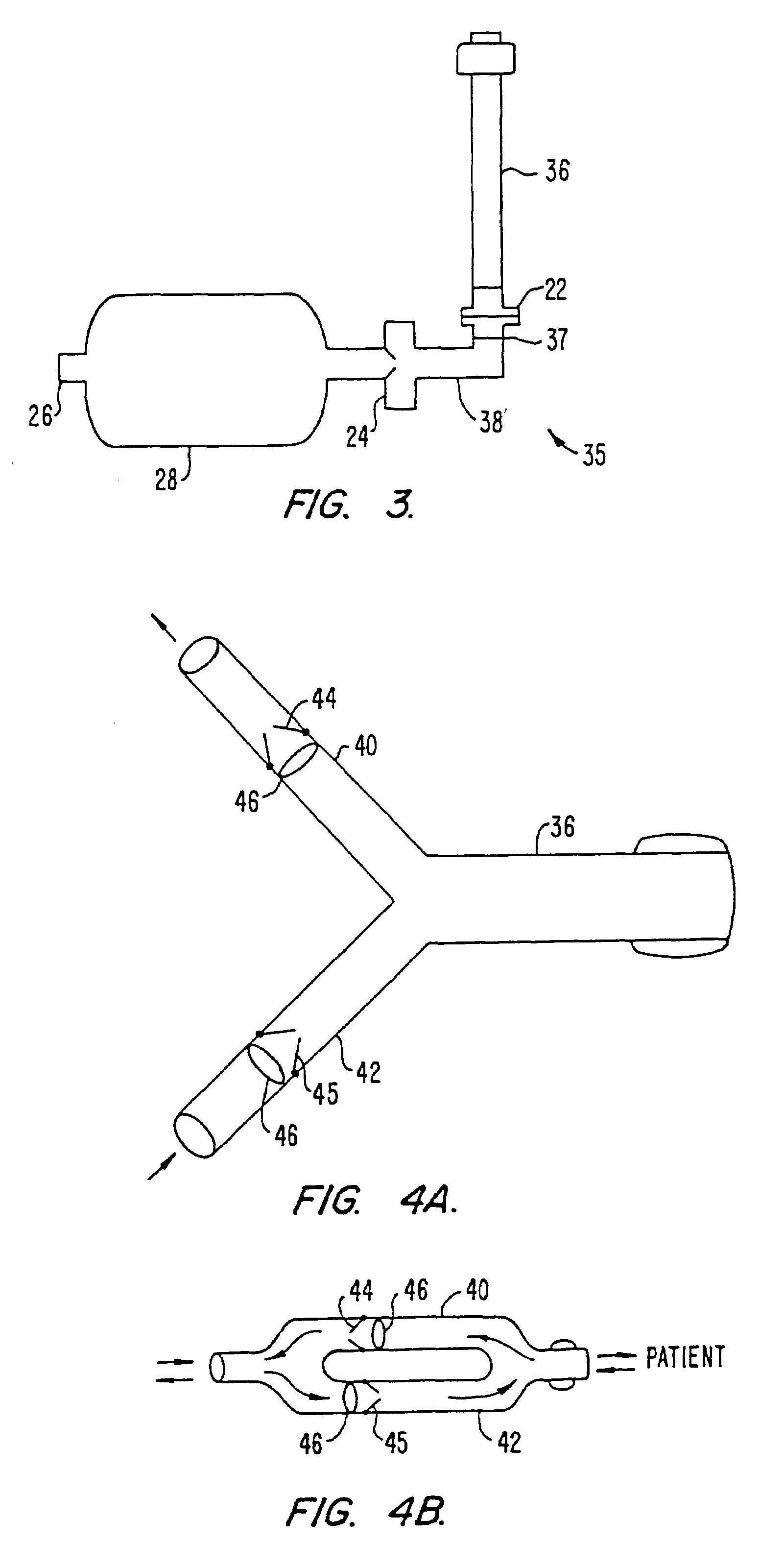
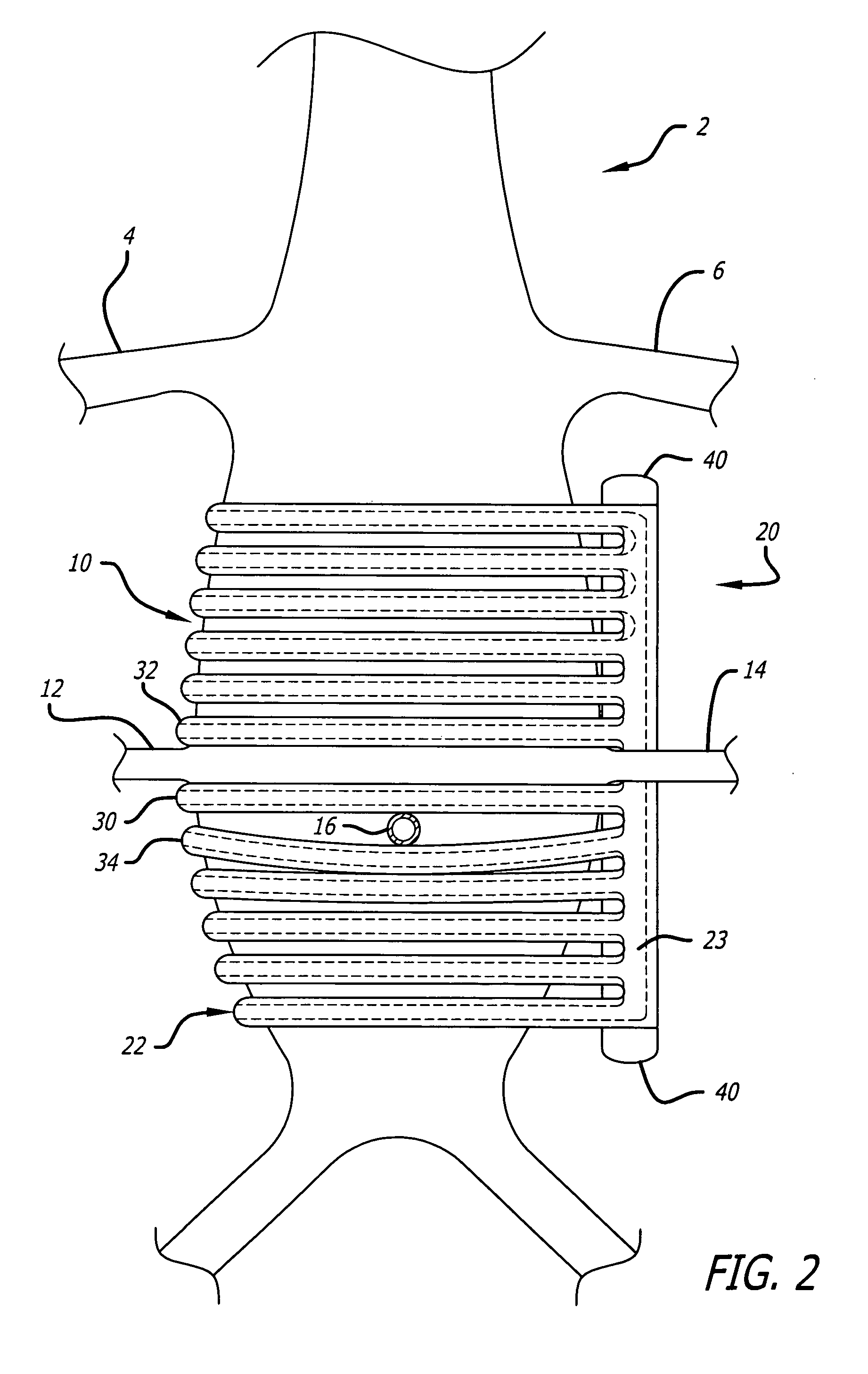
Automated chest compression apparatus
A system applies cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to a recipient. An automated controller is provided together with a compression device which periodically applies a force to a recipient's thorax under control of the automated controller. A band is adapted to be placed around a portion of the torso of the recipient corresponding to the recipient's thorax. A driver mechanism shortens and lengthens the circumference of the band. By shortening the circumference of the band, radial forces are created acting on at least lateral and anterior portions of the thorax. A translating mechanism may be. provided for translating the radial forces to increase the concentration of anterior radial forces acting on the anterior portion of the thorax. The driver mechanism may comprise a tension device for applying a circumference tensile force to the band. The driver mechanism may comprise an electric motor, a pneumatic linear actuator, or a contracting mechanism defining certain portions of the circumference of the band. The contracting mechanism may comprise plural fluid-receiving cells linked together along the circumference of the band. The width of each of the fluid-receiving cells becomes smaller as each cell is filled with a fluid. This causes the contraction of the band and a resulting shortening of the circumference of the band.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Methods and apparatus for transesophageal microaccess surgery
The current invention describes methods of transesophageal access to the neck and thorax to perform surgical interventions on structures outside the esophagus in both the cervical and the thoracic cavity. It describes a liner device made of a complete or partial tubular structure, or a flat plate, the liner having means to facilitate creation of a side opening, which may include a valve. The liner with its side opening form a port structure inside the esophageal lumen. The port structure allows elongated surgical devices to pass through a perforation across the full thickness of the esophageal wall to outside location, in a controlled way. The elongated surgical devices can be diagnostic scopes, therapeutic scopes, manual elongated surgical devices, robotic arms or the like. After being deployed outside the esophagus, the surgical devices can access structures outside the esophagus, in the neck and thorax in 360 degrees of freedom around the esophageal circumference. These structures can be bony, cartilaginous, spinal, vascular, soft tissue, deep tissues, lymph nodal, cardiac, pulmonary, tracheal, nervous, muscular or diaphragmatic, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the neck, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the anterior chest wall, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the skin of the back, and skin and layers of the breast.
Owner:MICROACCESS
Patient comfort apparatus and system
InactiveUS20050143796A1Easily remove or adjustSimple to manufactureGarment special featuresCouplingsHospital gownThermal treatment
Apparatus and a system for thermally comforting a patient include pneumatic, convective providing thermal treatment for persons or animals, which is adapted for use in combination with a clinical garment such as a hospital gown, robe, bib, and other equivalents. The pneumatic convective device provides convective warming focused or directly primarily on the thorax or body core. The pneumatic convective device includes at least one inlet for being accessed through a clinical garment, a region in distribution with the inlet for distributing a stream of pressurized, thermally treated air, and a permeable member for emitting pressurized, thermally treated air from the distribution region.
Owner:GEN ELECTRIC CAPITAL +1
Positive pressure systems and methods for increasing blood pressure and circulation
InactiveUS20050165334A1Enhance blood flow blackEnhances vital organ circulationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyBlood flowPositive pressure
In one embodiment, the invention provides a medical method for treating a person and comprises repeatedly compressing the person's chest. While repeatedly compressing the person's chest, the method further includes repeatedly delivering a positive pressure breath to the person and extracting respiratory gases from the person's airway using a vacuum following the positive pressure breath to create an intrathoracic vacuum to lower pressures in the thorax and to enhance blood flow back to the heart.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
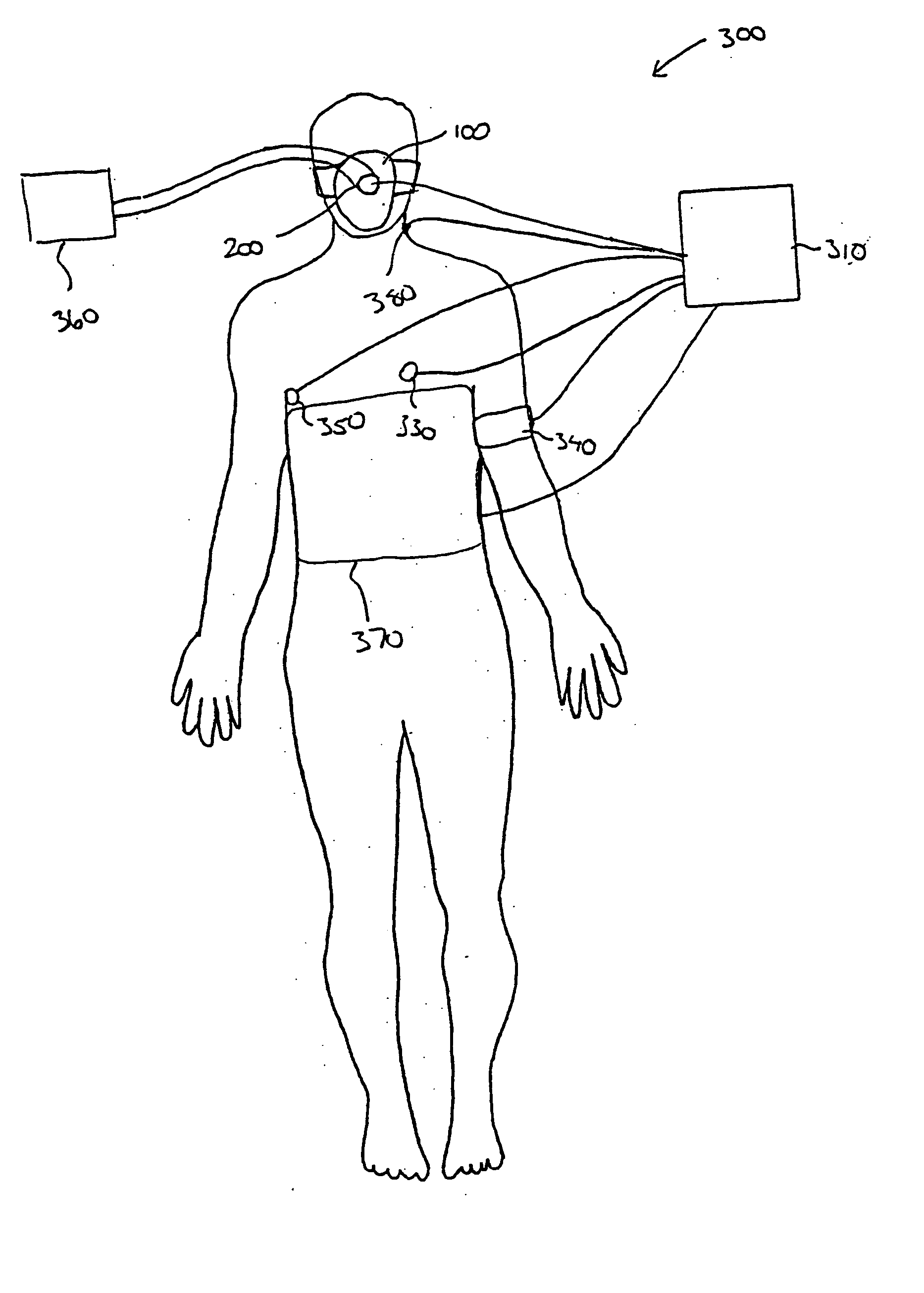
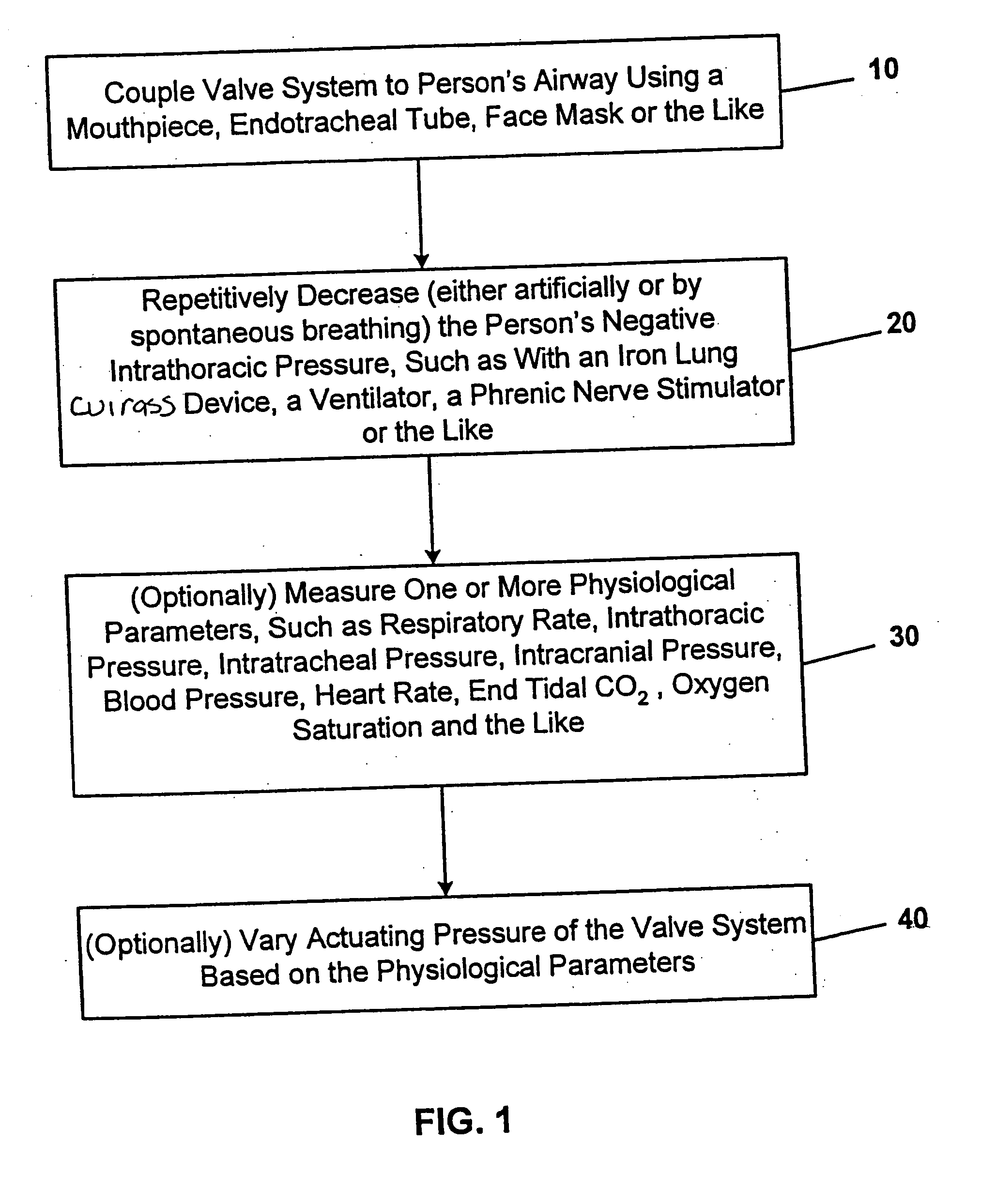
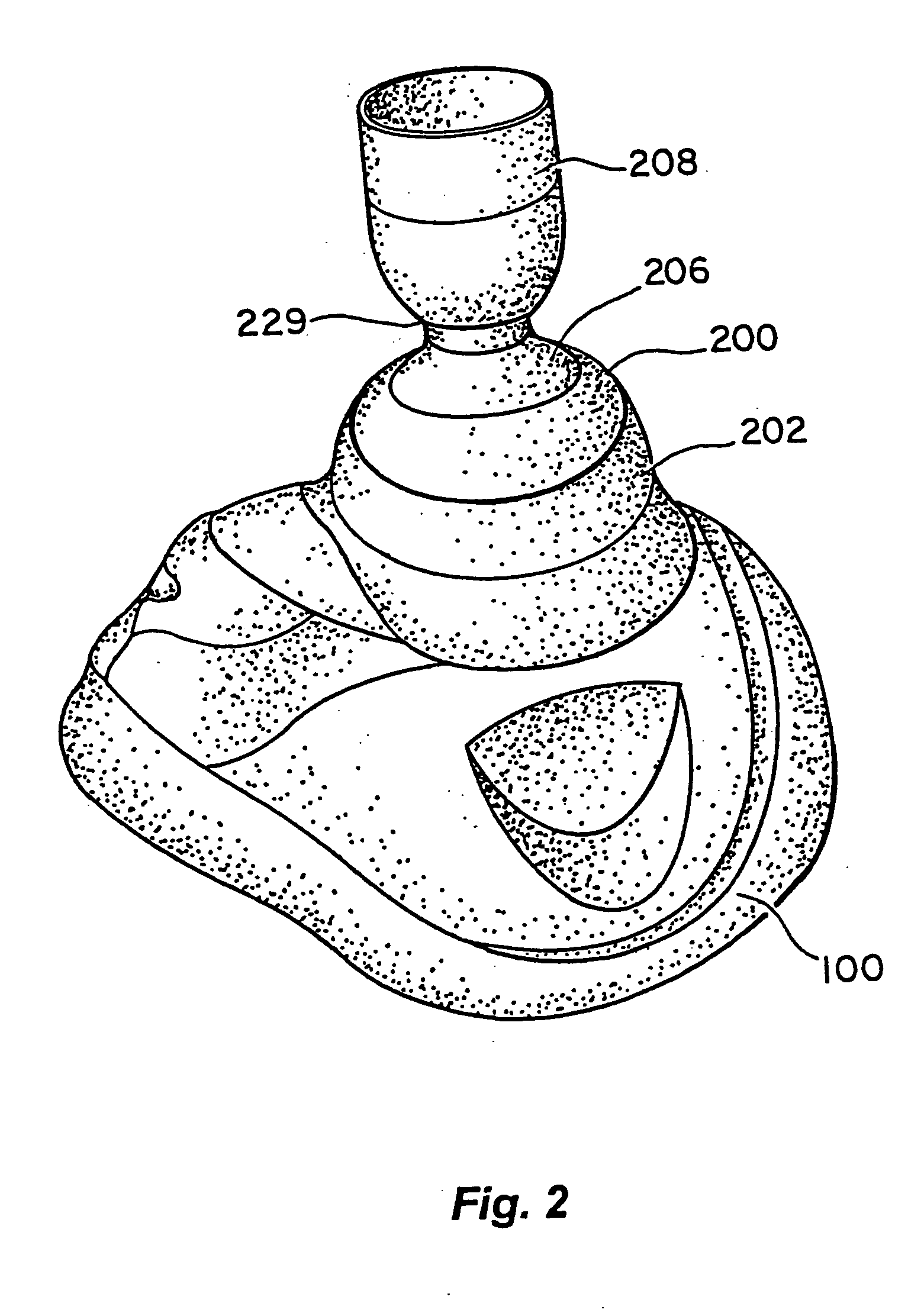
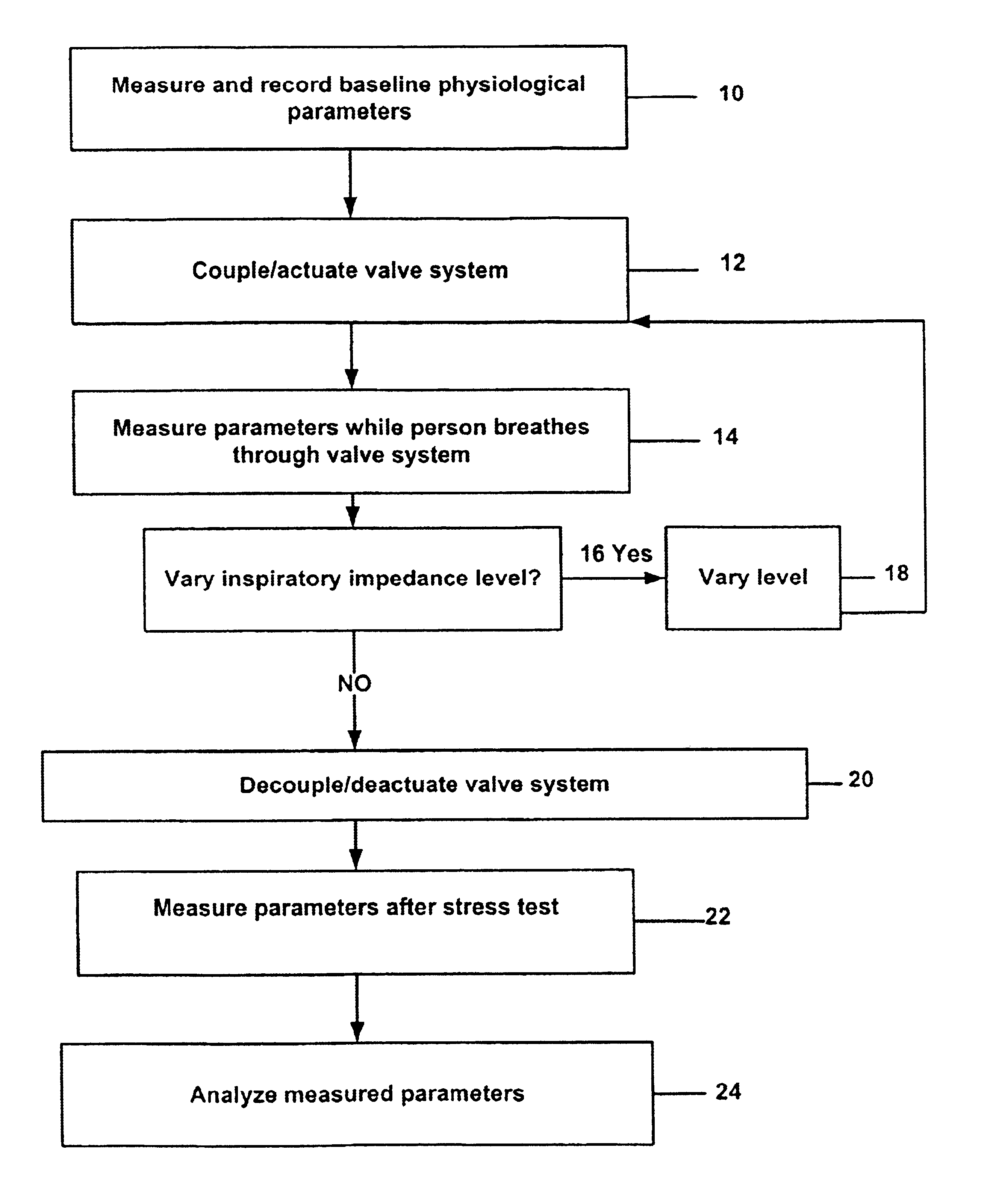
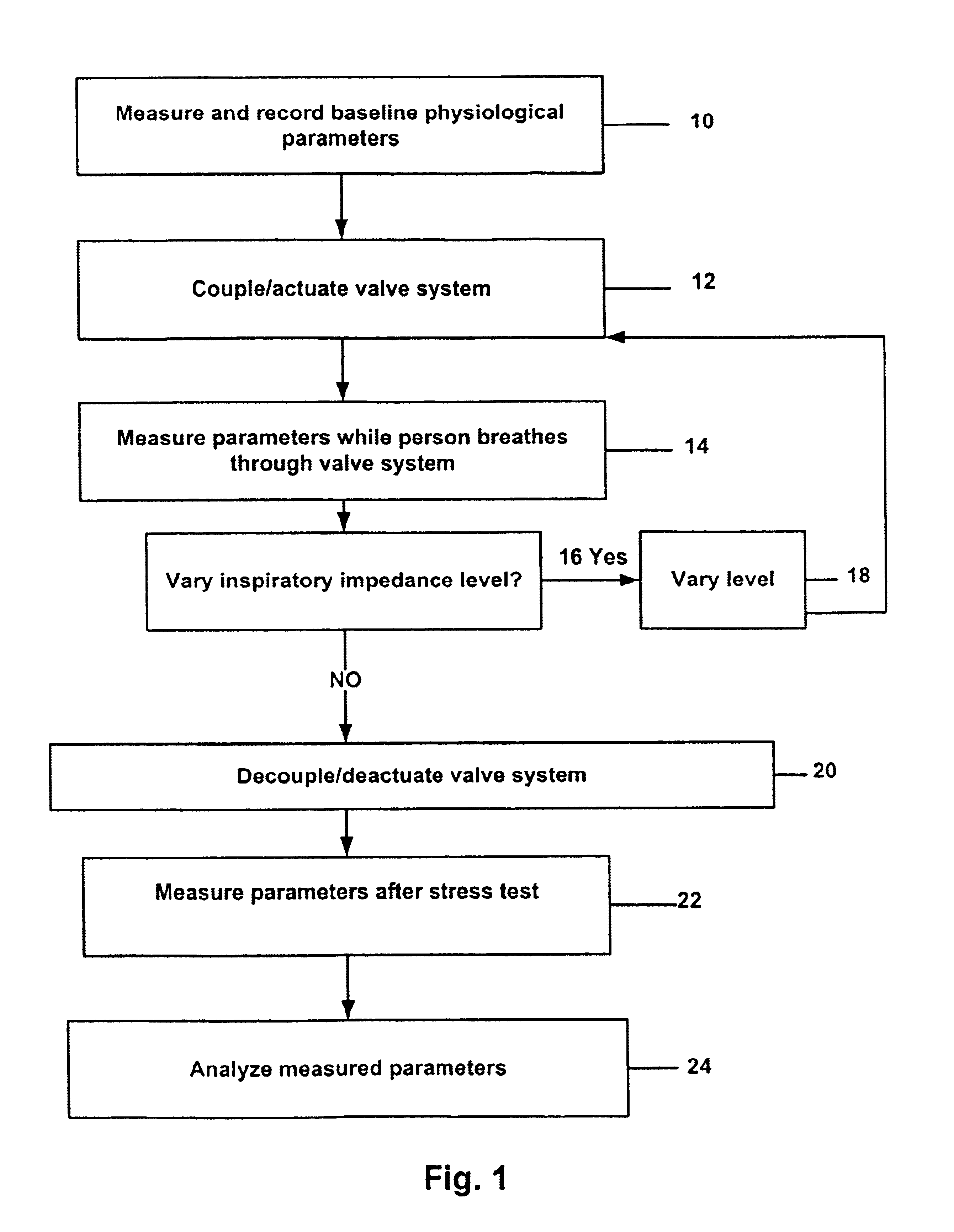
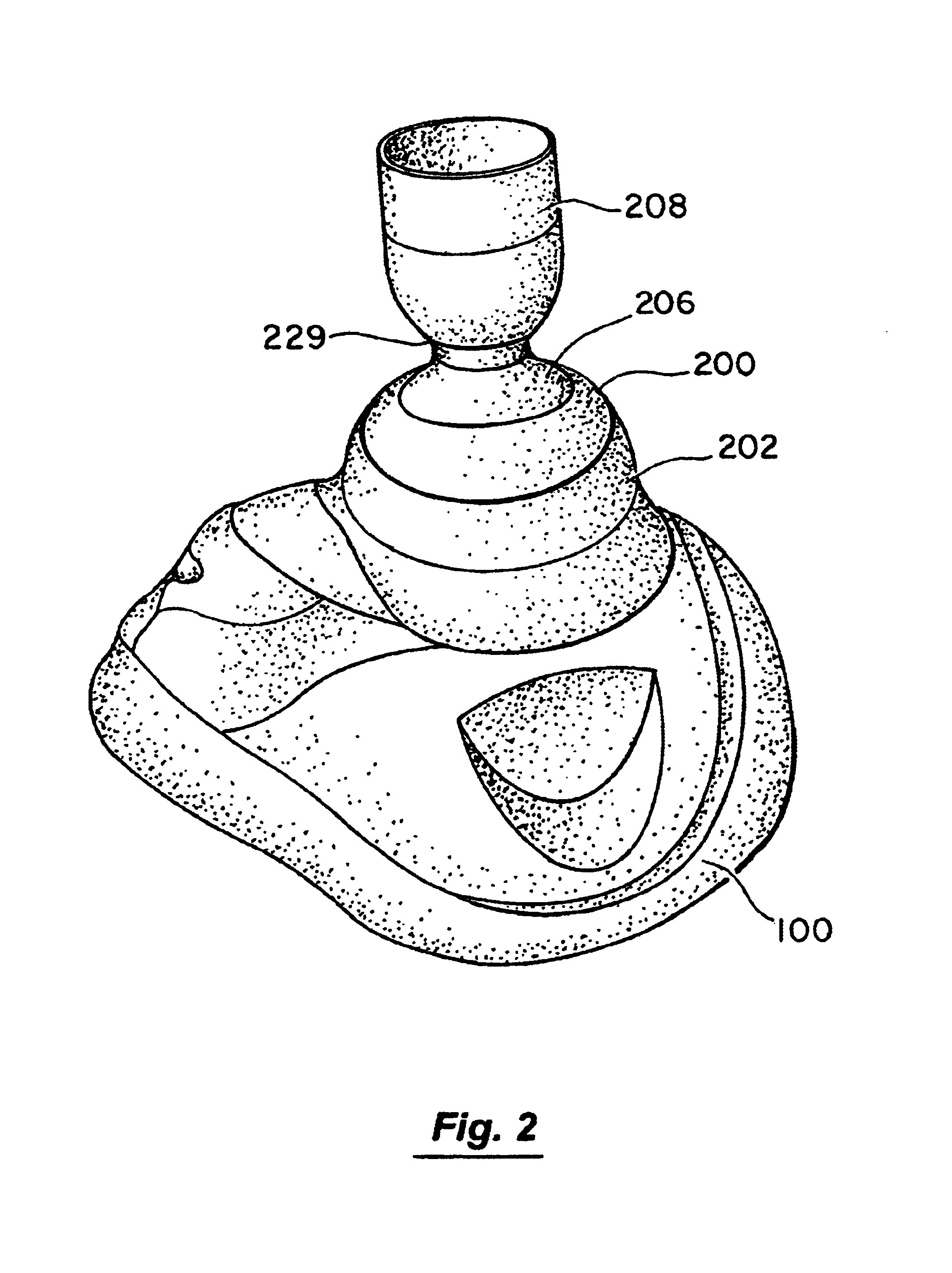
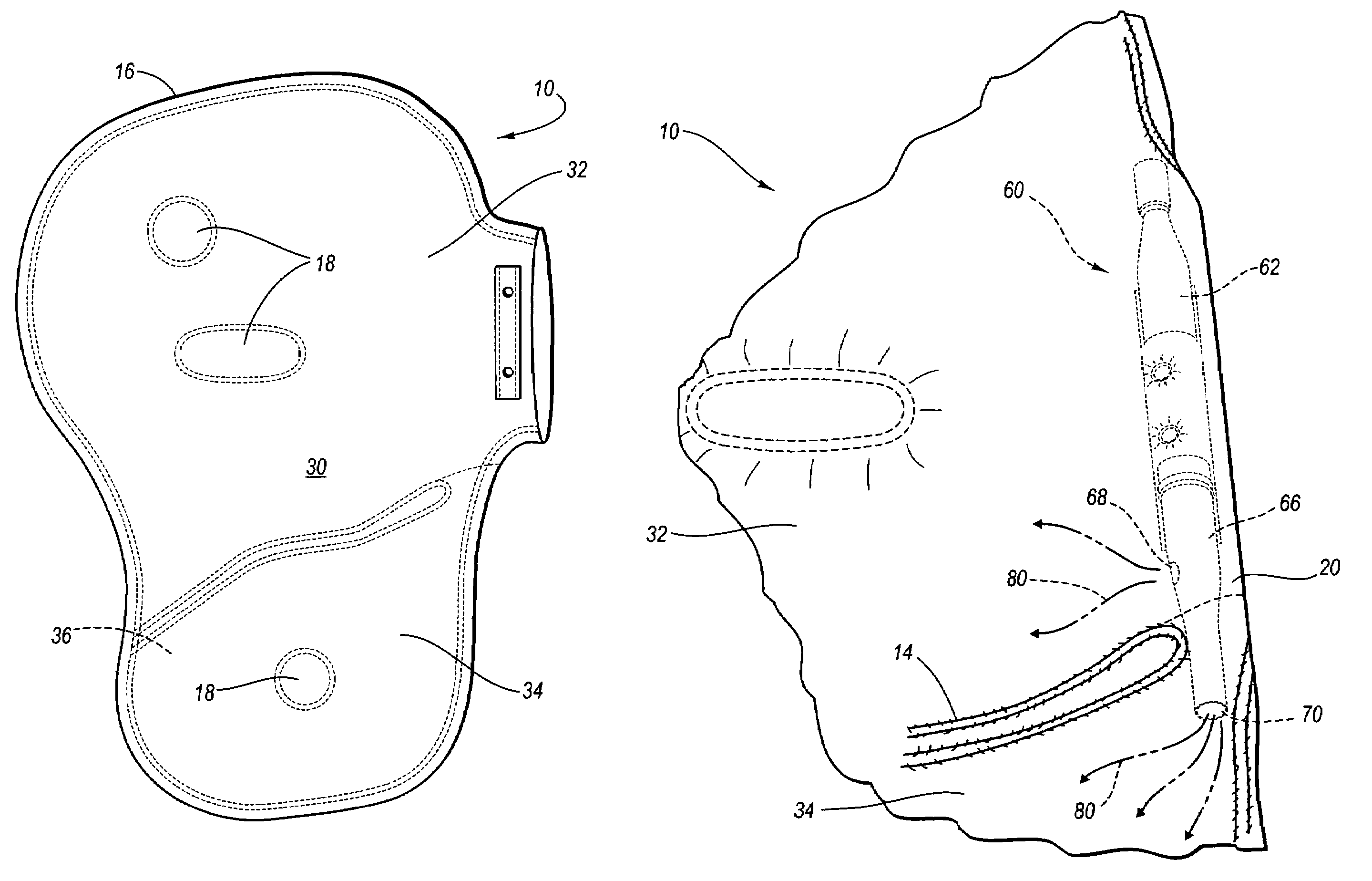
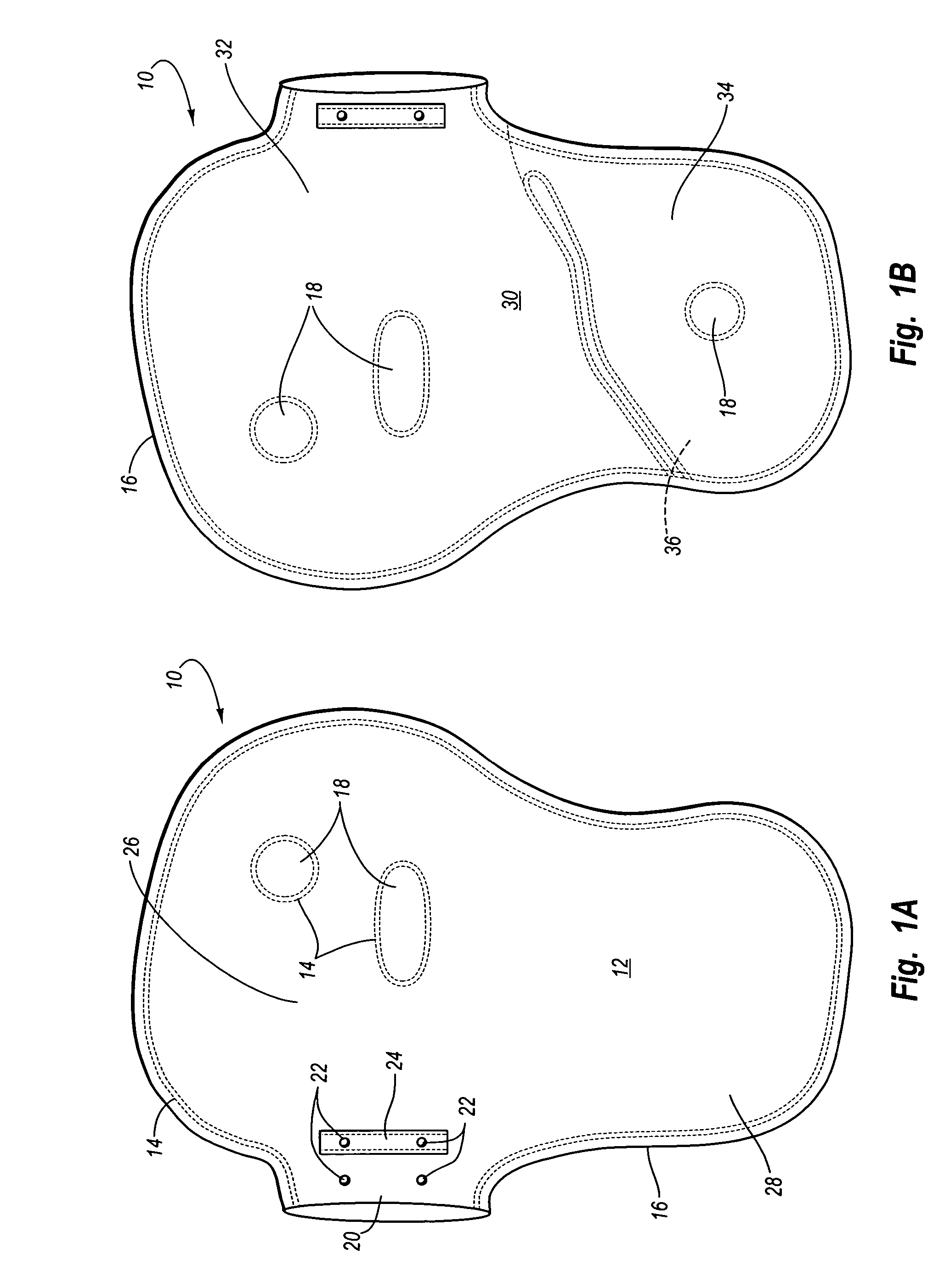
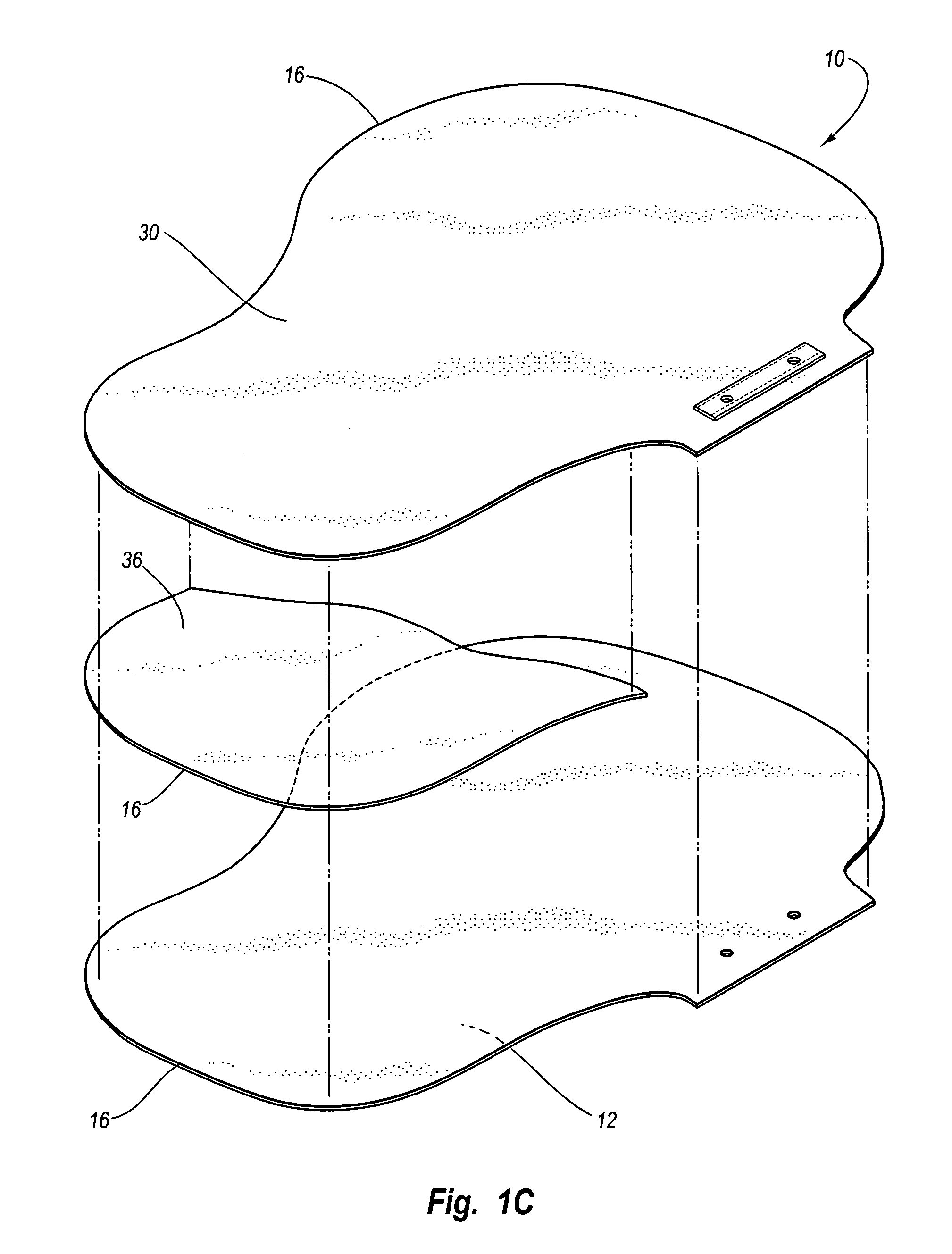
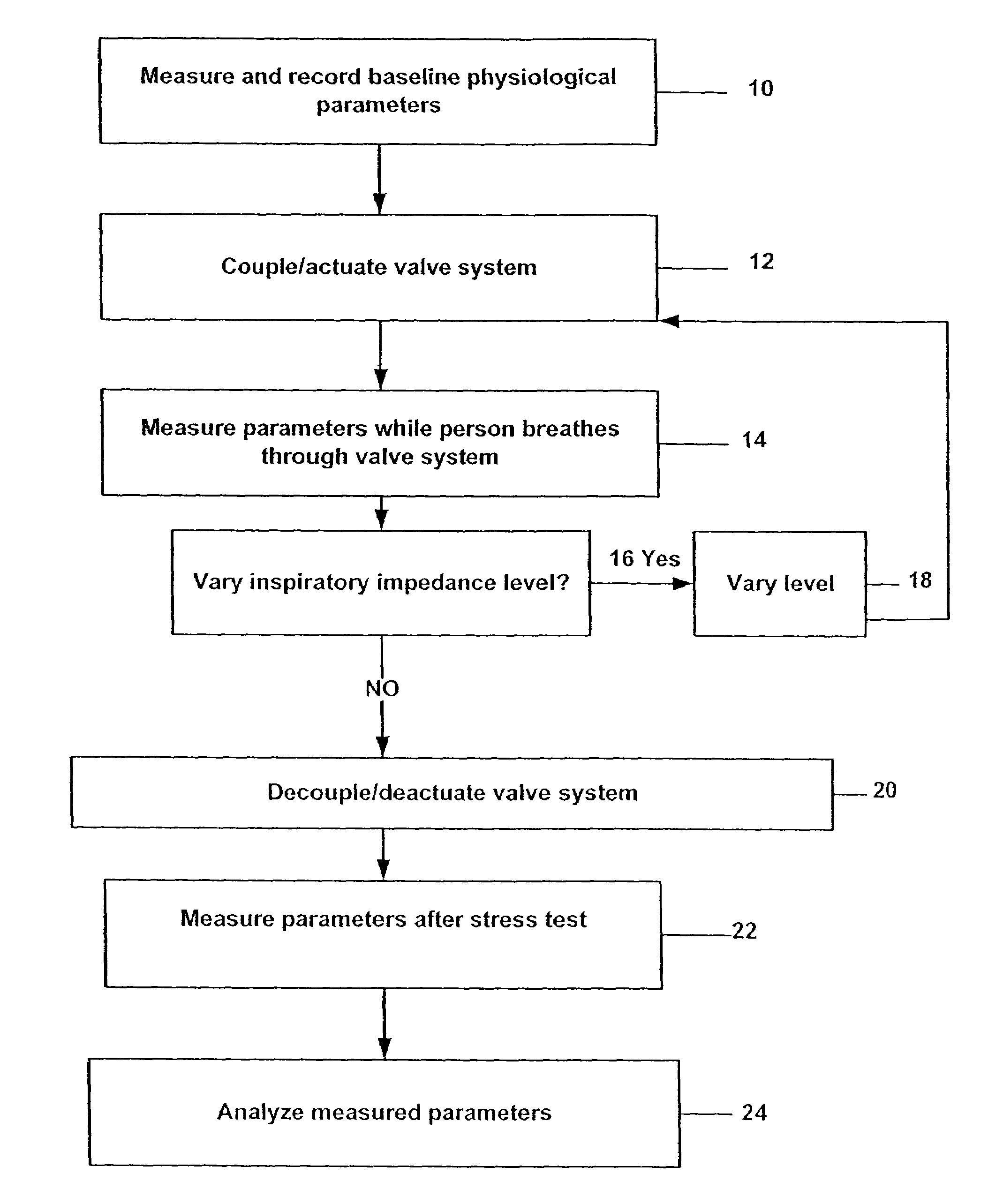
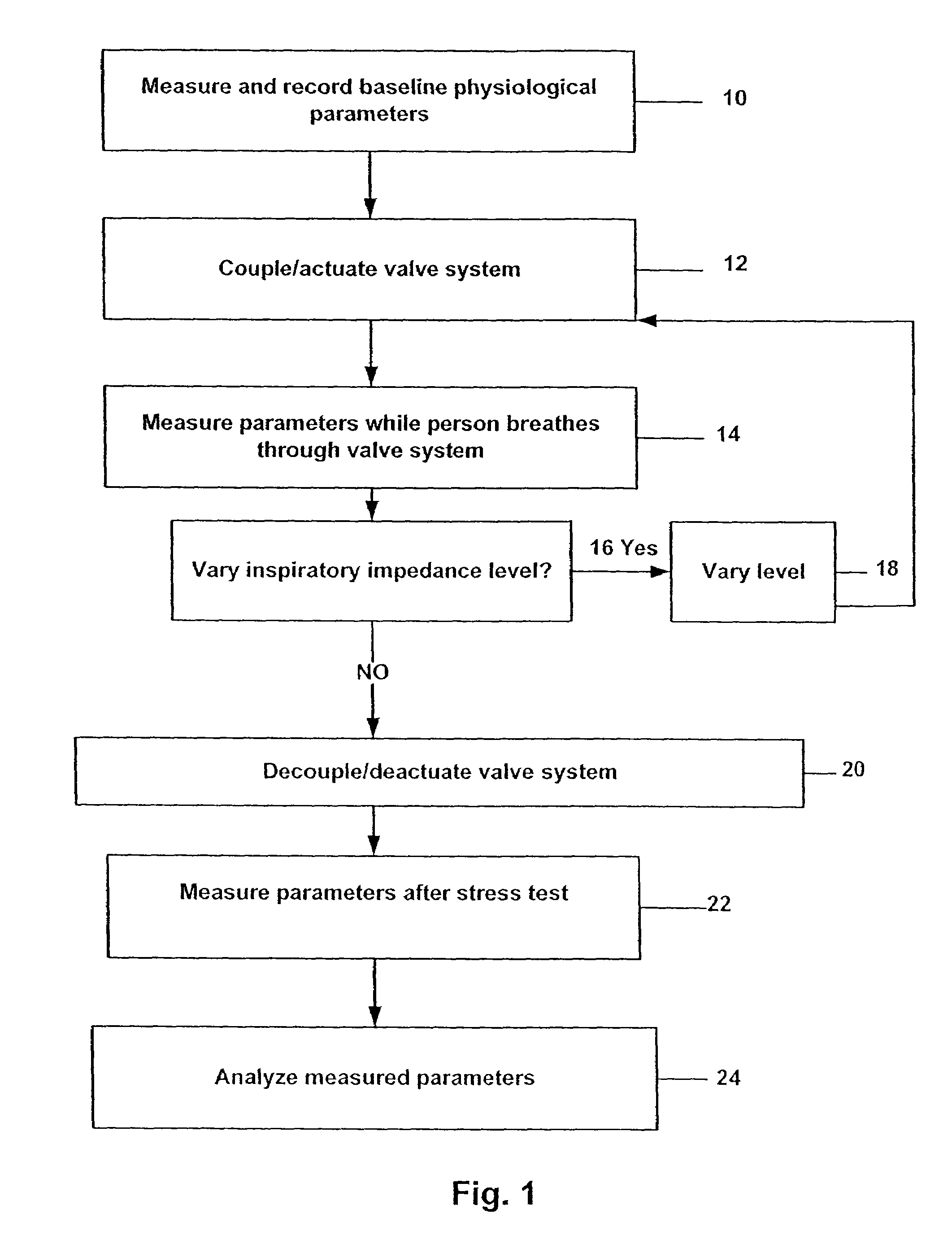
Stress test devices and methods
InactiveUS6863656B2Good effectLower blood pressureCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationHeart rightInhalation
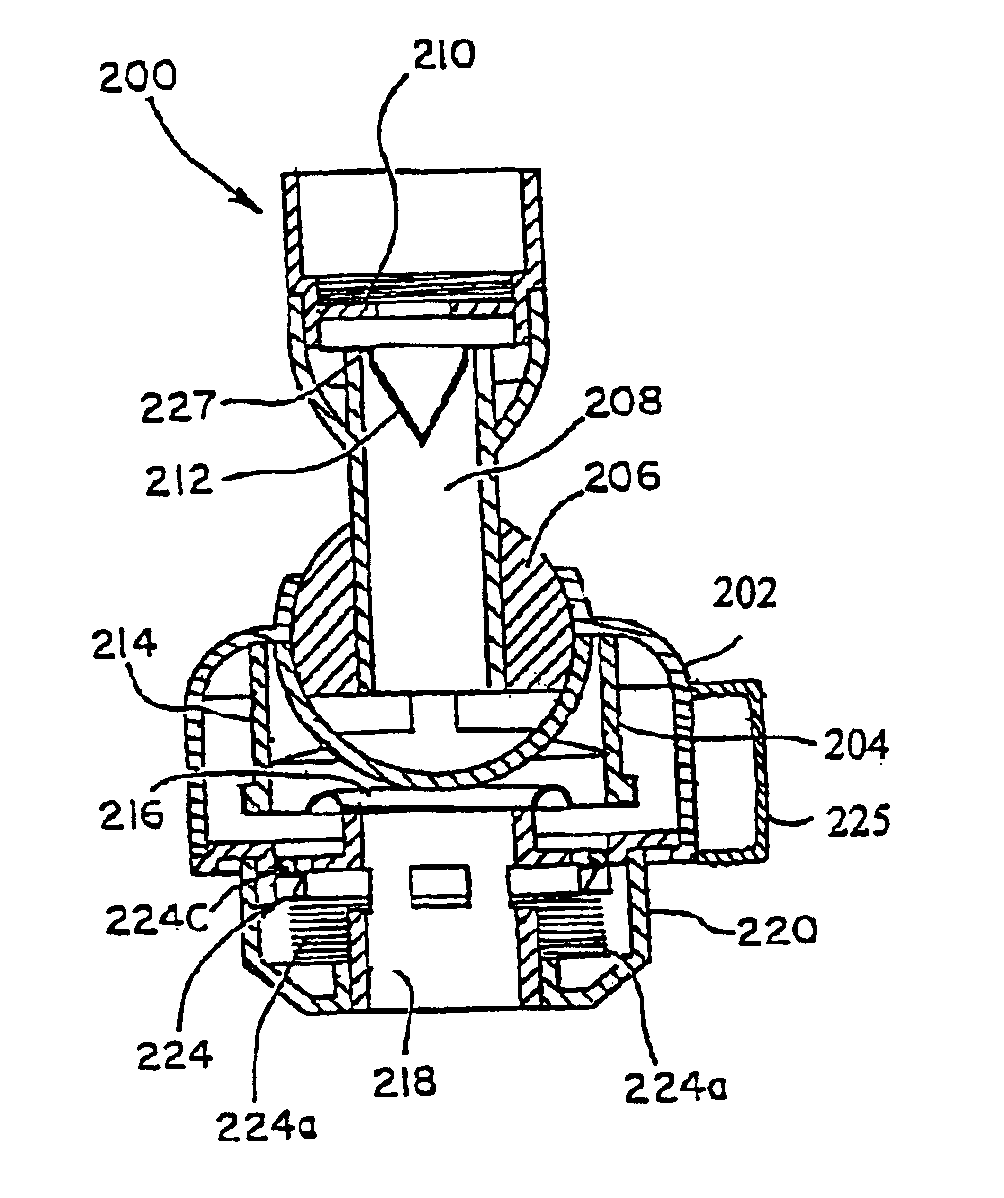
One method for diagnosing a cardiovascular-related condition in a breathing person comprises interfacing a valve system to the person's airway. The valve system is configured to decrease or prevent respiratory gas flow to the person's lungs during at least a portion of an inhalation event. The person is permitted to inhale and exhale through the valve system. During inhalation, the valve system functions to produce a vacuum within the thorax to increase blood flow back to the right heart of the person, thereby increasing blood circulation and blood pressure. Further, at least one physiological parameter is measured while the person inhales and exhales through the valve system. The measured parameter is evaluated to diagnose a cardiovascular condition.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
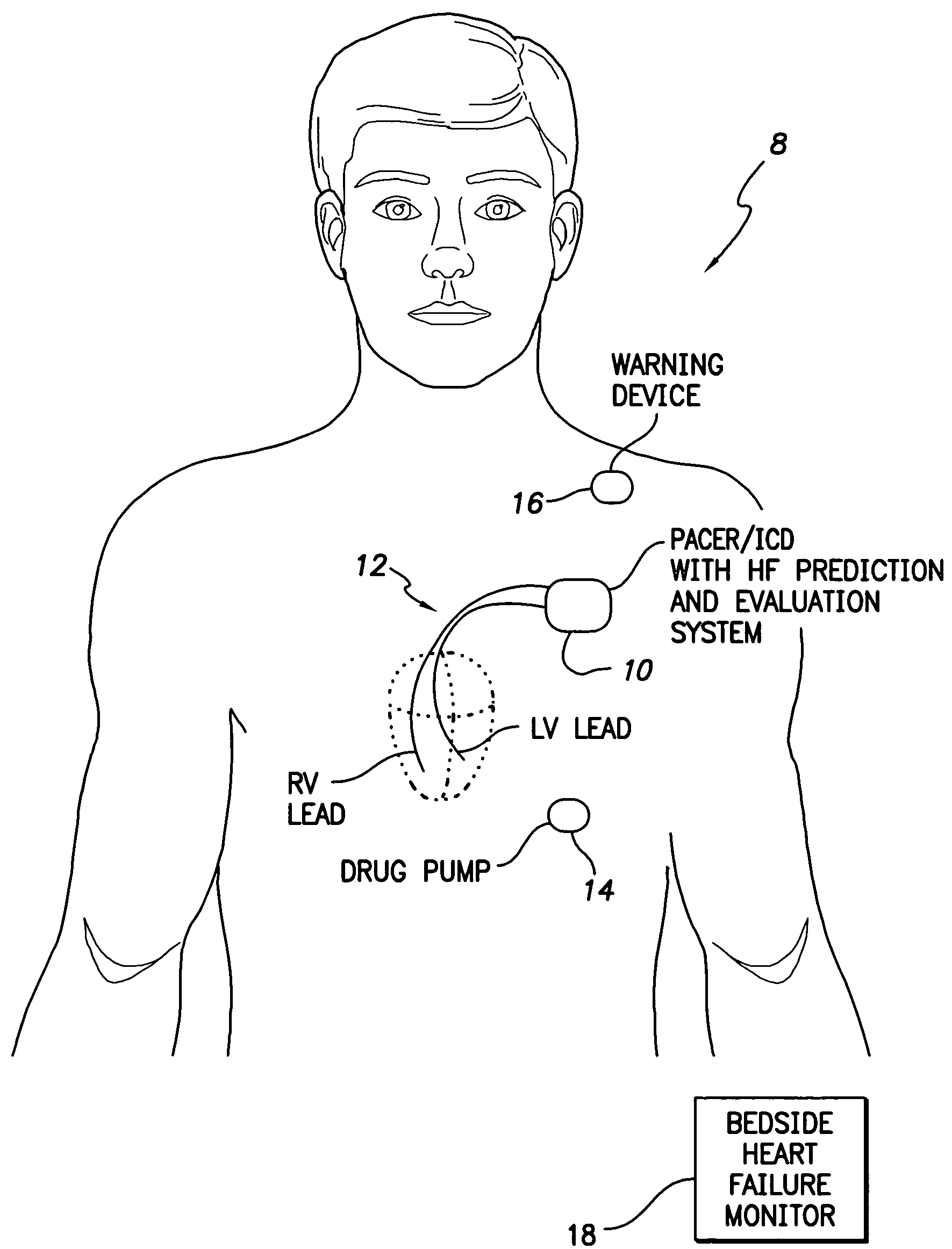
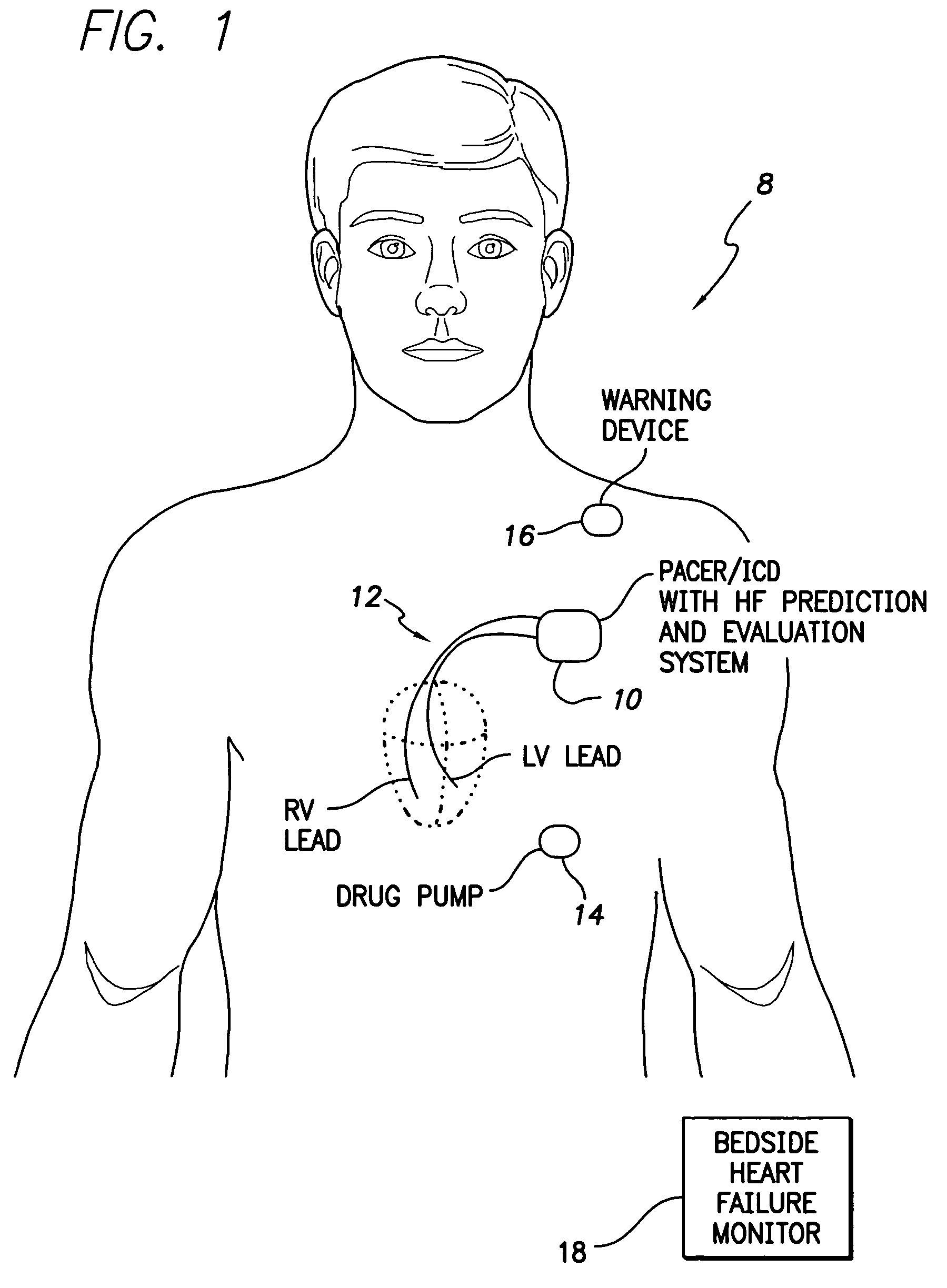
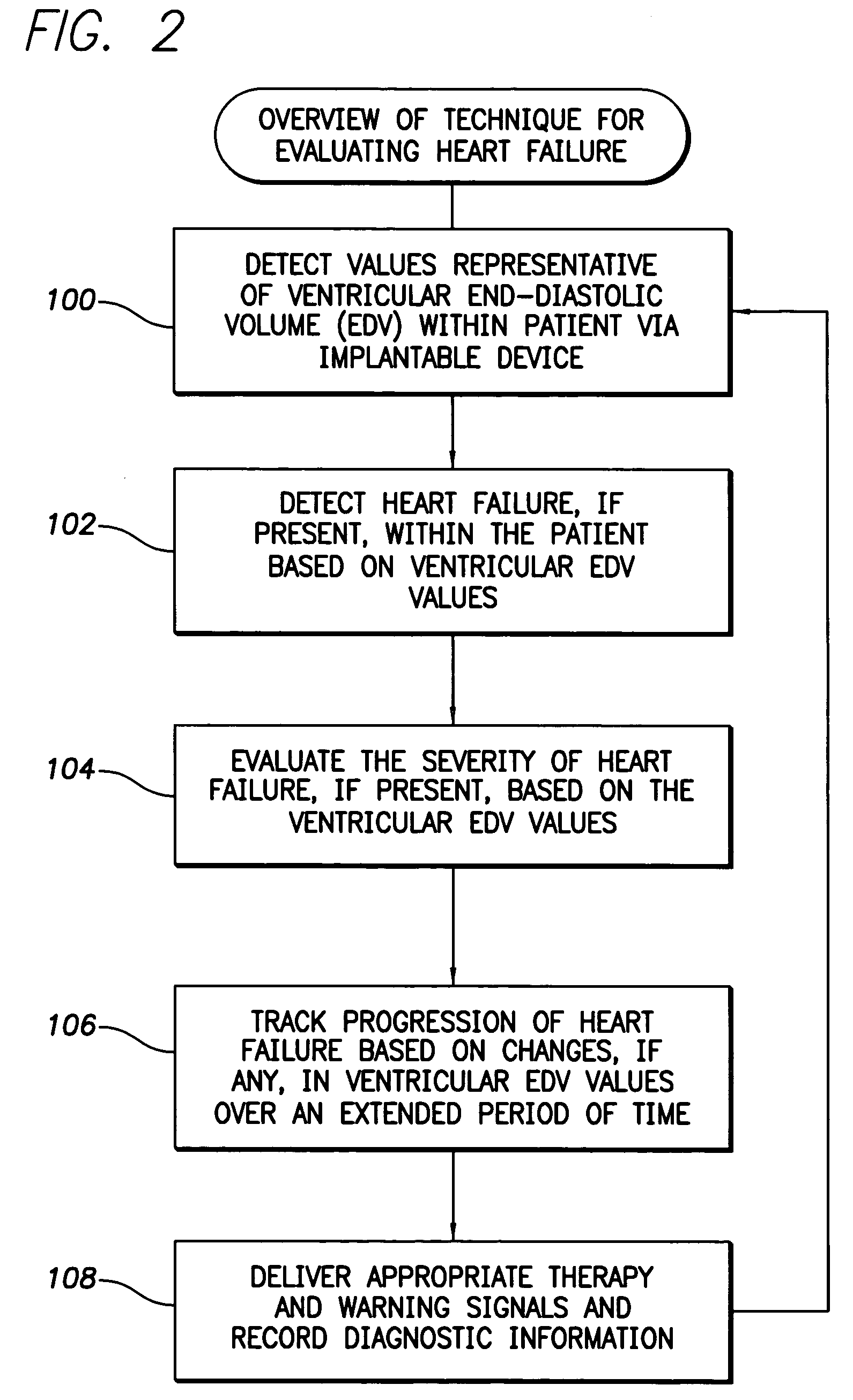
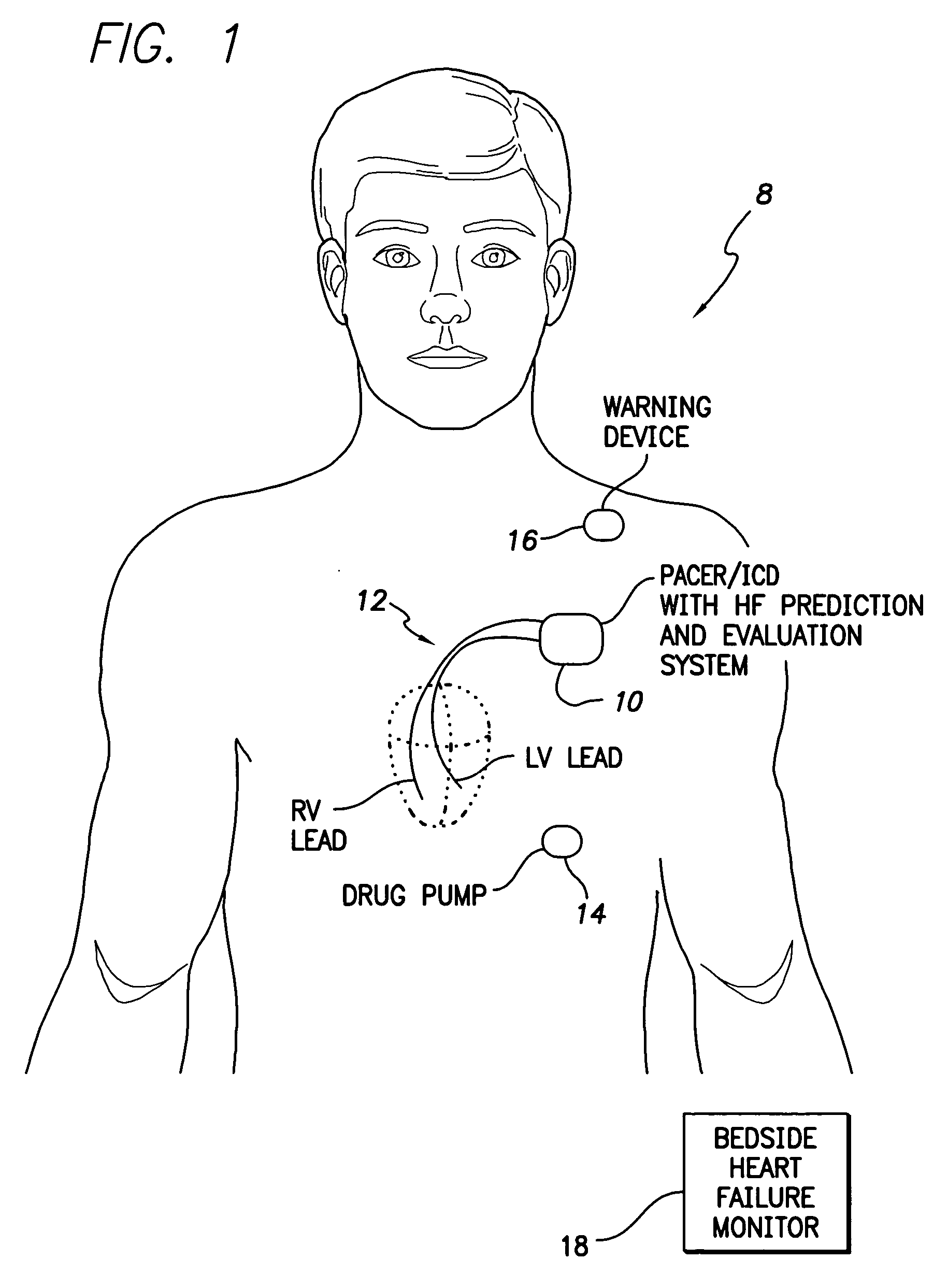
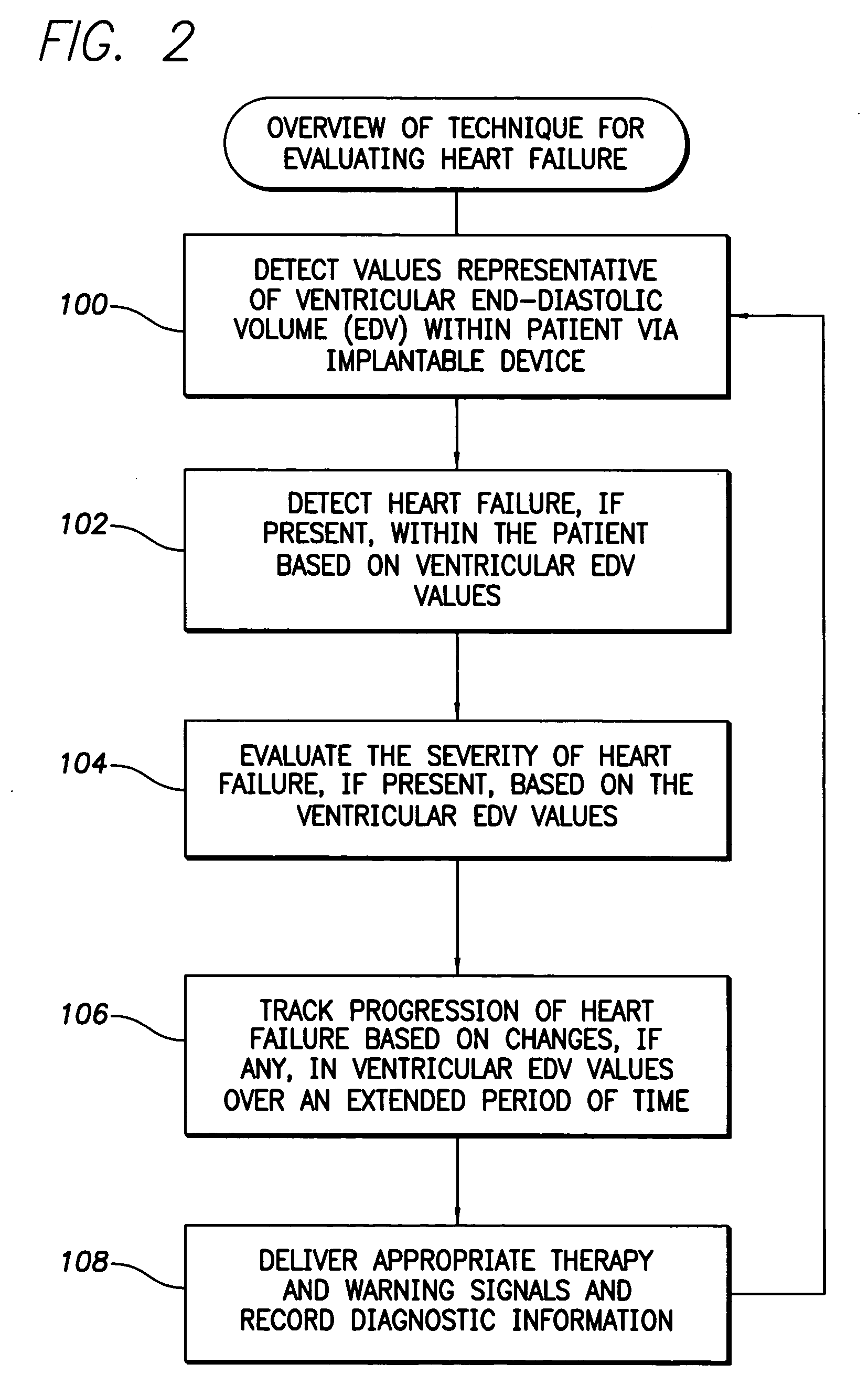
System and method for predicting a heart condition based on impedance values using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7272443B2Reliably predict onset of heart conditionHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringPulmonary edemaThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for predicting the onset of a heart condition within a patient based on impedance measurements. Briefly, overloads in fluid levels in the thorax and in ventricular myocardial mass within the patient are detected based on impedance signals sensed using implanted electrodes. The onset of certain heart conditions is then predicted based on the overloads. For example, pulmonary edema arising due to diastolic heart failure is predicted based on the detection of on-going overloads in both fluid levels and ventricular mass. Ventricular hypertrophy is detected based on an on-going ventricular mass overload without a sustained fluid overload. Various other heart conditions may also be predicted based on specific combinations of recent or on-going overloads. Evoked response is exploited to corroborate the predictions. Appropriate warning signals are generated and preemptive therapy is initiated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
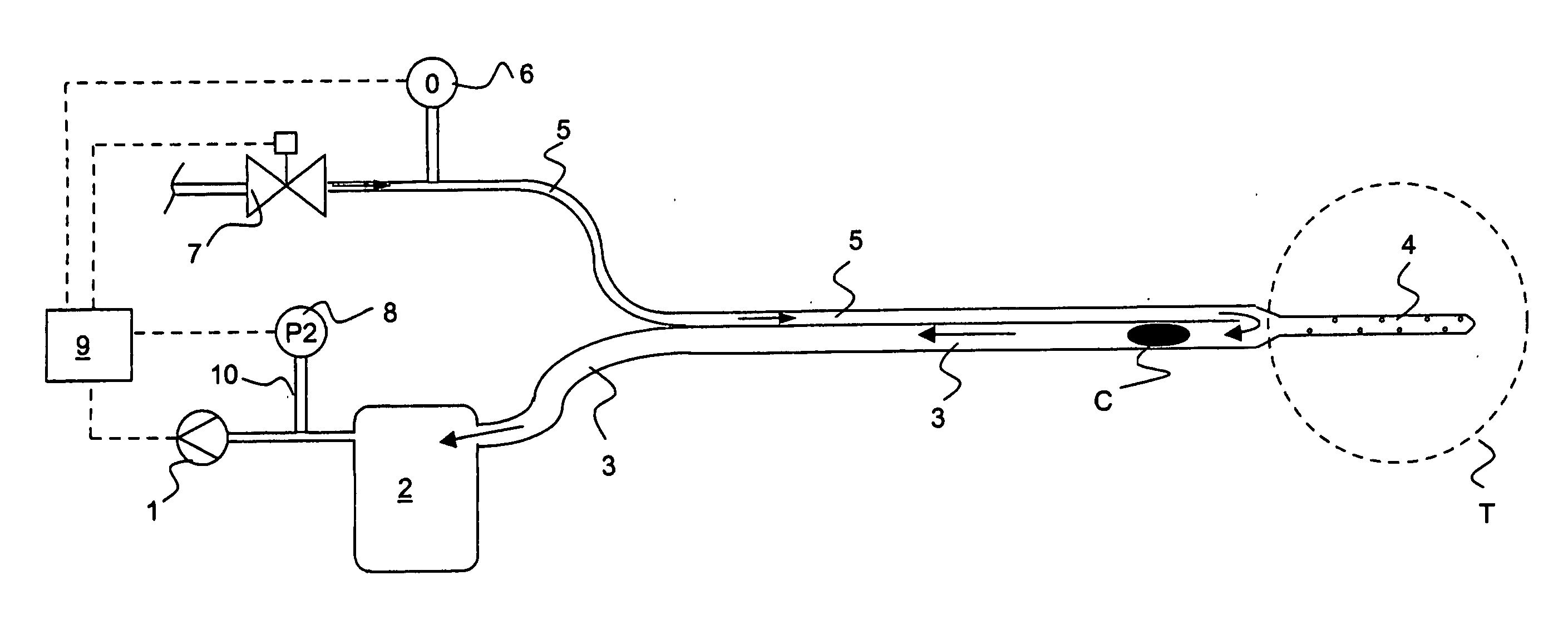
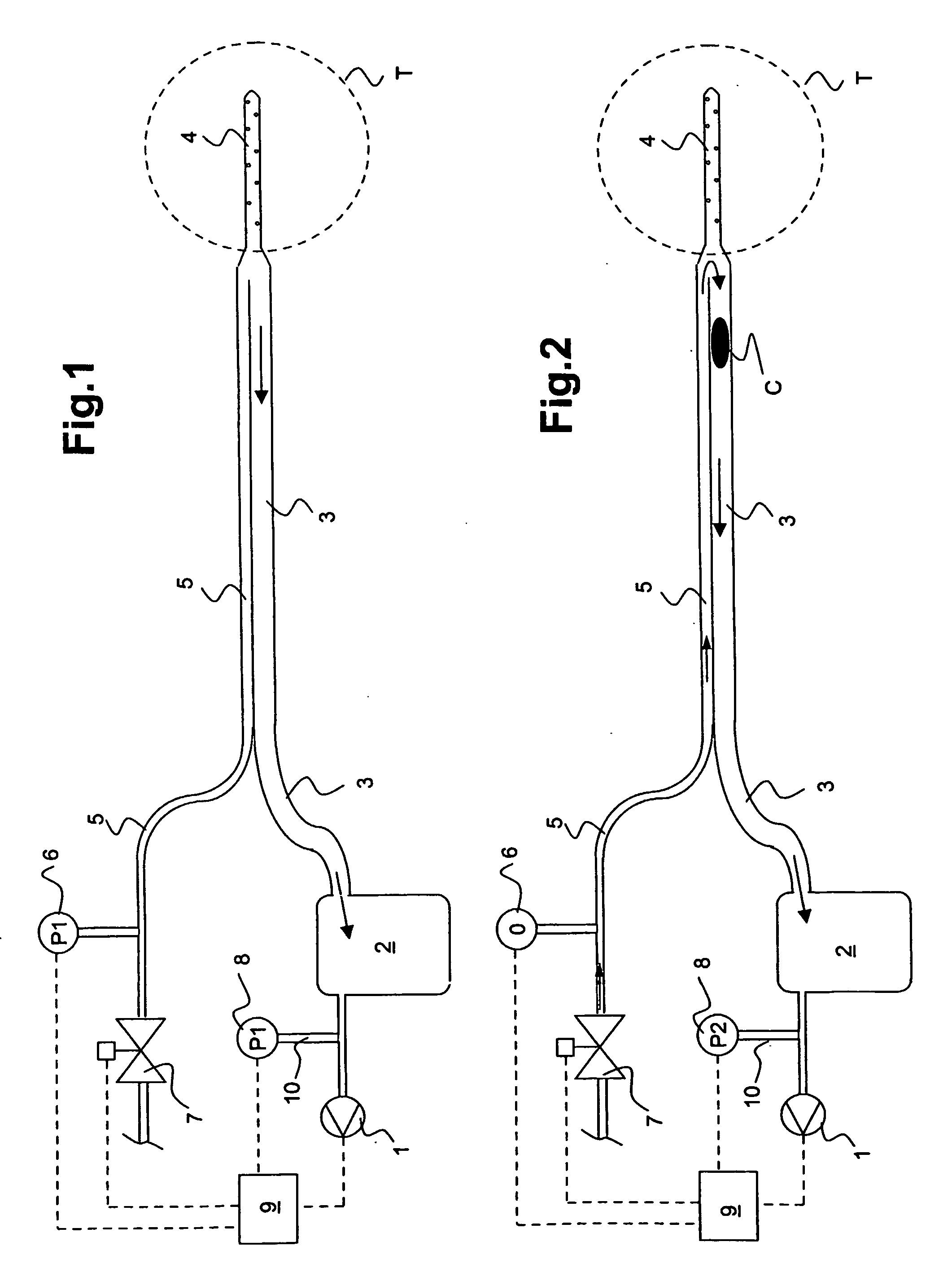
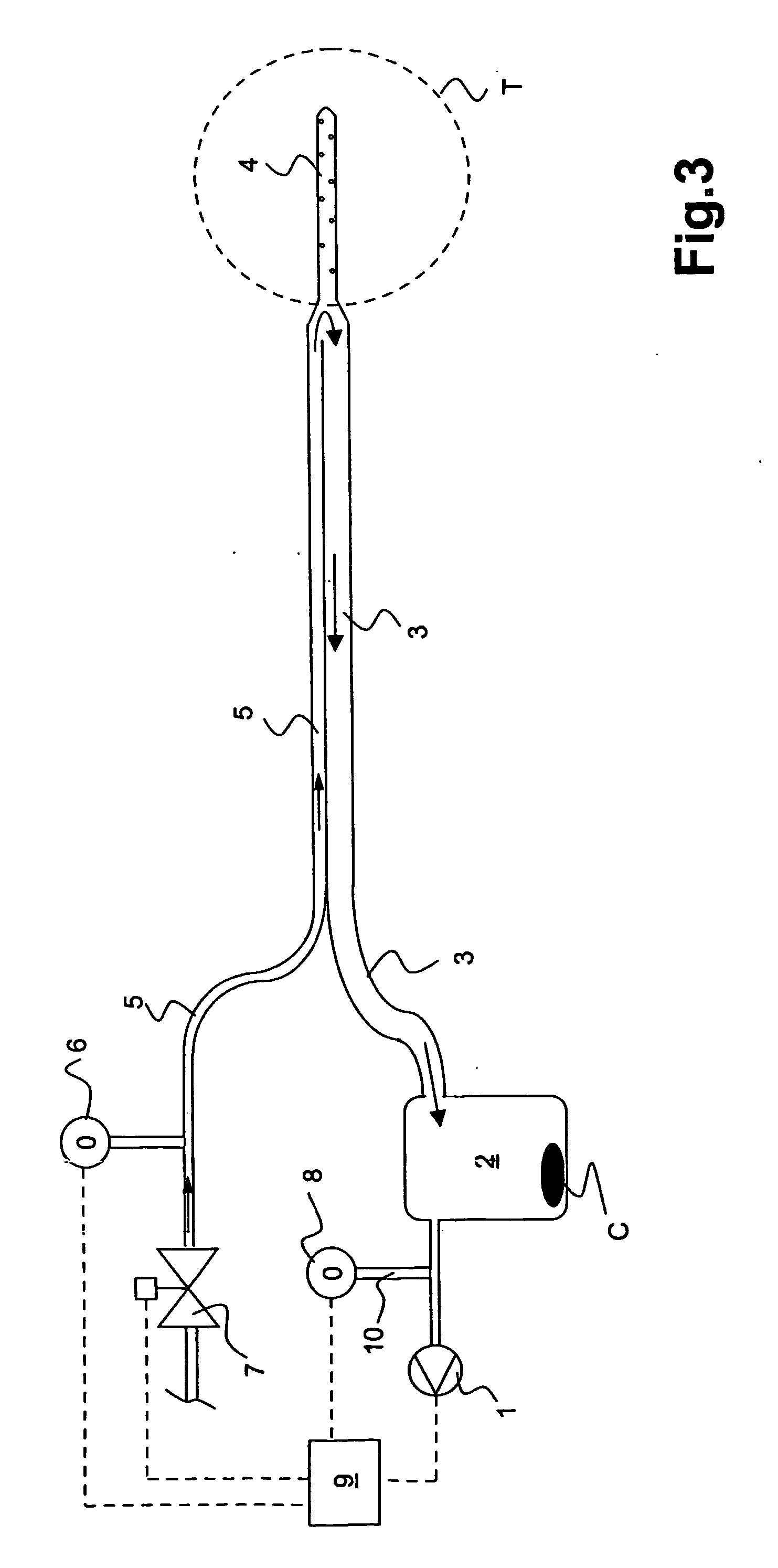
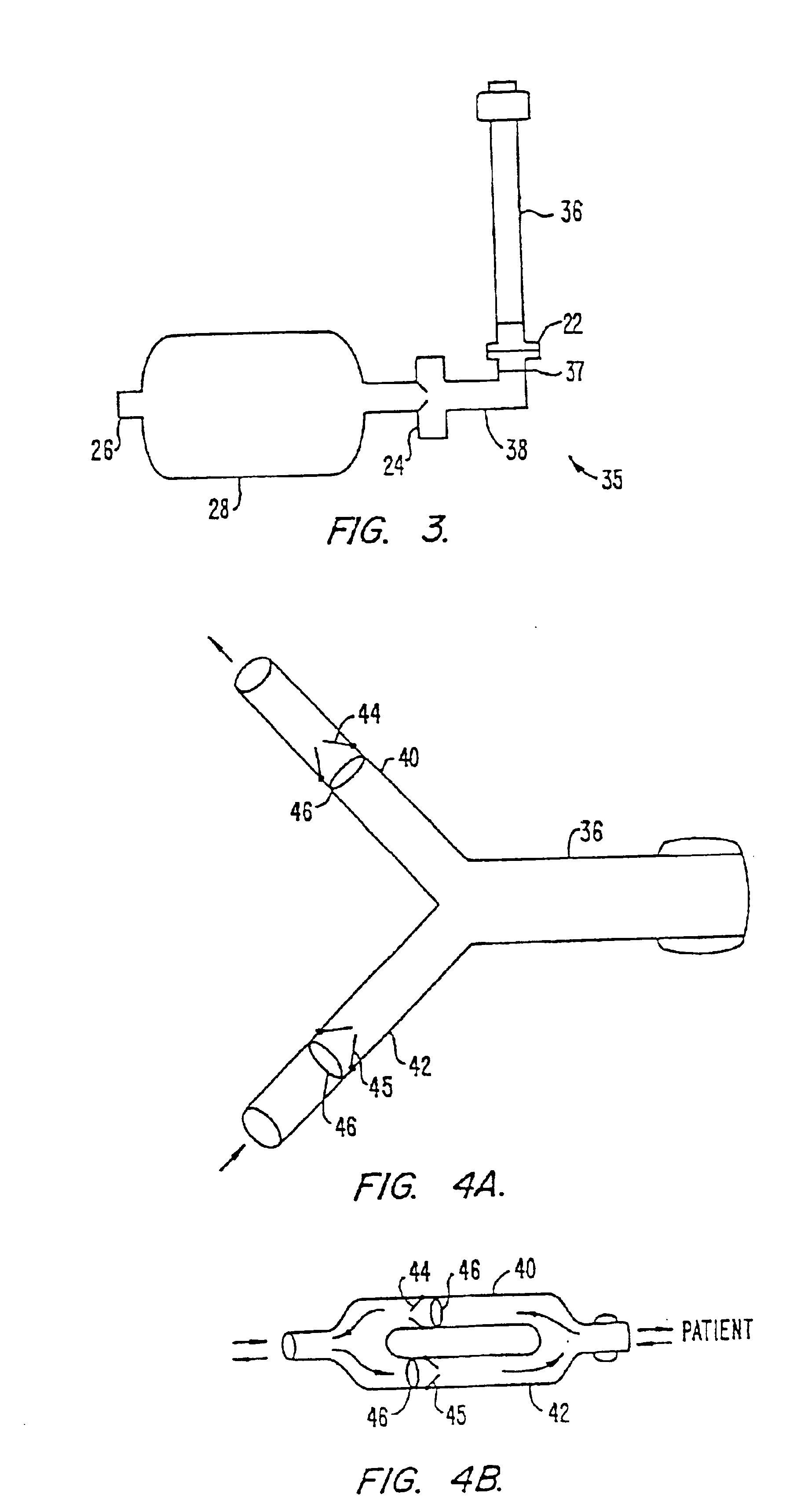
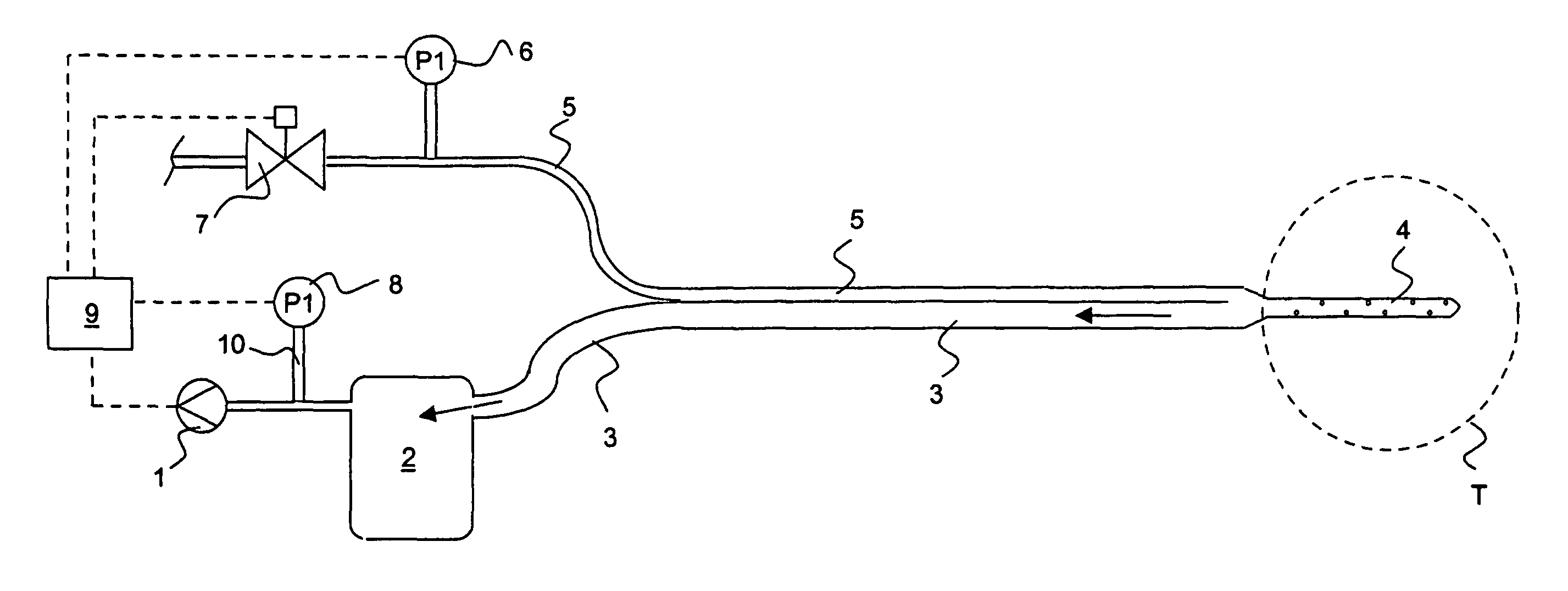
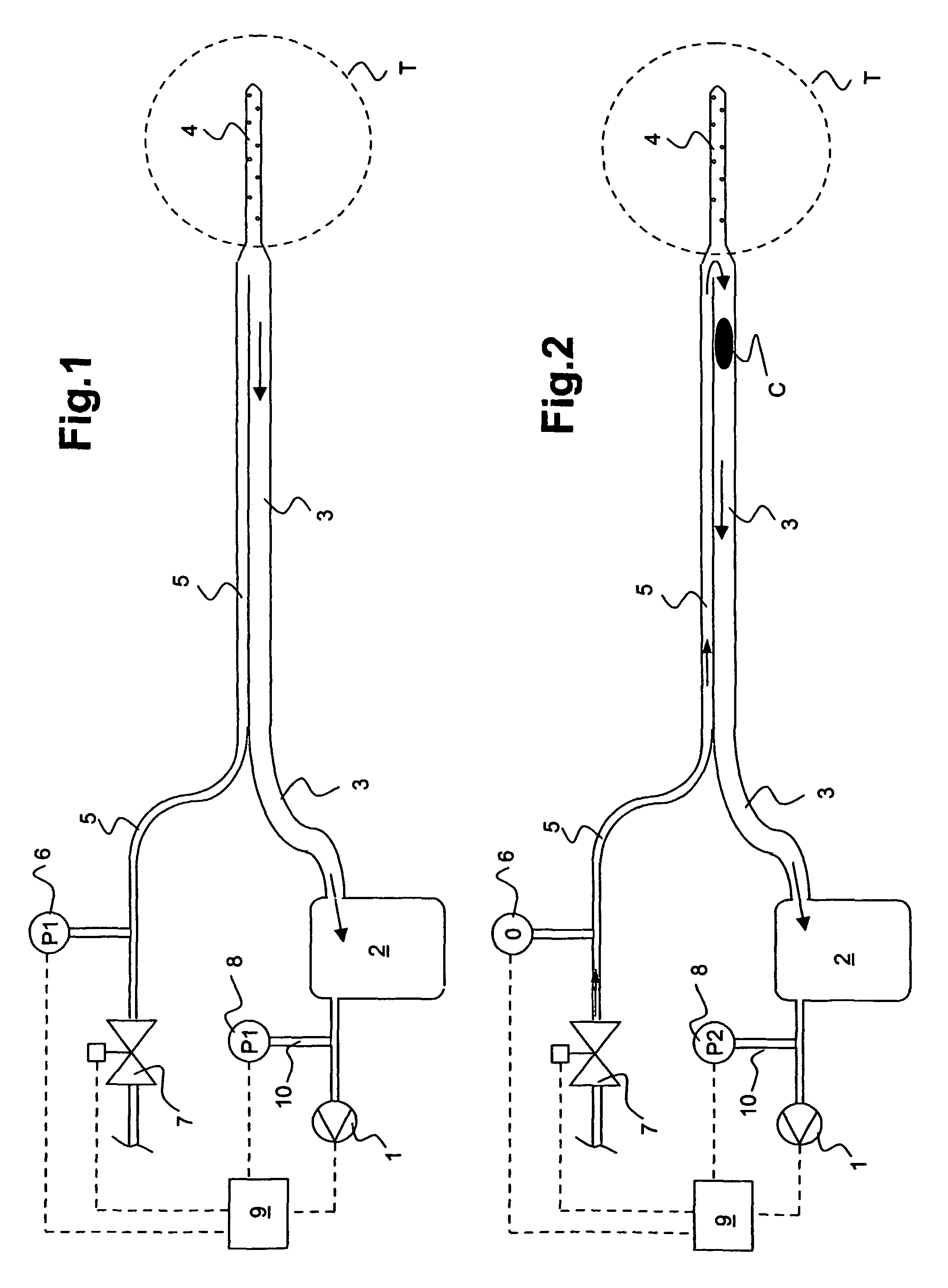
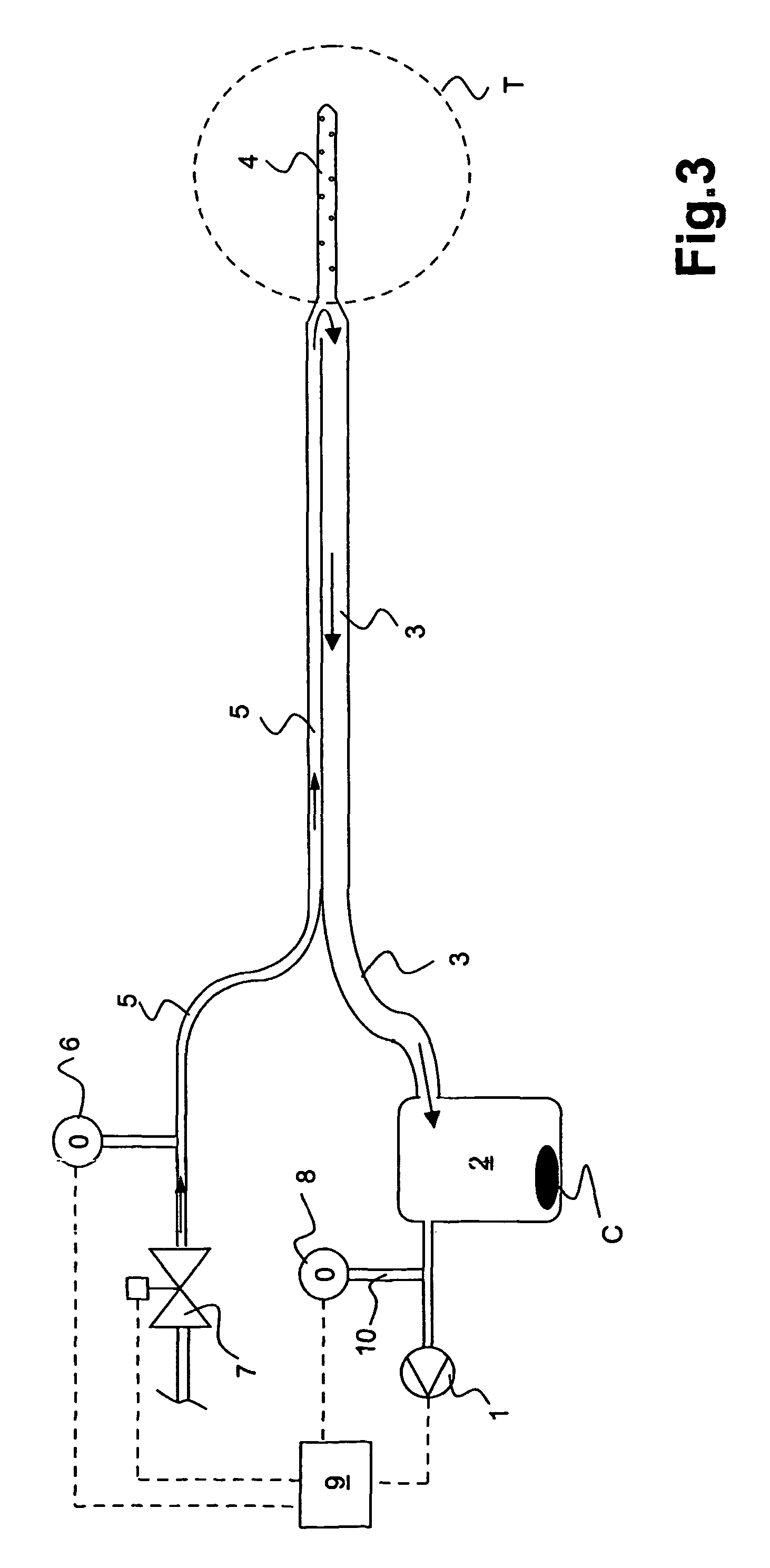
Drainage apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070078444A1The process is simple and convenientGreat suctionInfusion syringesSurgeryThoracic cavityPressure difference
An apparatus for removing body fluids from a body cavity by suction, such as a thorax, gastric or any other human body cavity or a wound, comprises means (9) to increase the pressure difference between a pressure in a drainage lumen (3) and a pressure in the atmosphere when an auxiliary lumen (5) is open. The apparatus enables removal of clots or other plugs of the catheter and drainage tube in an efficient and not patient disturbing way.
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
Systems and methods for enhancing blood circulation
InactiveUS6986349B2Increase loopDecrease and prevent flowCompressorElectrotherapyHeart rightInhalation
A method for increasing circulation in a breathing person utilizes a valve system that is interfaced to the person's airway and is configured to decrease or prevent respiratory gas flow to the person's lungs during at least a portion of an inhalation event. The person is permitted to inhale and exhale through the valve system. During inhalation, the valve system functions to produce a vacuum within the thorax to increase blood flow back to the right heart of the person, thereby increasing cardiac output and blood circulation.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Drainage apparatus and method
InactiveUS7976533B2The process is simple and convenientGreat suctionInfusion syringesWound drainsPressure differenceThoracic cavity
An apparatus for removing body fluids from a body cavity by suction, such as a thorax, gastric or any other human body cavity or a wound, comprises means (9) to increase the pressure difference between a pressure in a drainage lumen (3) and a pressure in the atmosphere when an auxiliary lumen (5) is open. The apparatus enables removal of clots or other plugs of the catheter and drainage tube in an efficient and not patient disturbing way.
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
Inflatable airbag with overlapping chamber
ActiveUS7347444B2Avoid injuryIncrease pressurePedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringThoracic cavity
An inflatable side airbag apparatus having a thorax cushion and an independently inflatable overlapping high pressure pelvic cushion is disclosed. The airbag system provides for rapid deployment of the pelvic cushion. The thorax cushion inflates adjacent to and provides impact protection for an occupant's thorax and pelvis in a lateral collision. The pelvic cushion inflates between the thorax cushion and the side structure of the vehicle and provides impact protection for the occupant's pelvis. The airbag system also includes an inflator having a gas guide that is in fluid communication with both cushions, and inflates the pelvic cushion to a higher pressure than the thorax cushion. The thorax cushion further includes a diffuser hood for diverting inflation gas toward the pelvic region of the cushion, thereby rapidly positioning the pelvic cushion in its intended deployment position.
Owner:AUTOLIV ASP INC
System for sensing, diagnosing and treating physiological conditions and methods
InactiveUS7682312B2Good effectLower blood pressureCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationHeart rightInhalation
One method for diagnosing a cardiovascular-related condition in a breathing person comprises interfacing a valve system to the person's airway. The valve system is configured to decrease or prevent respiratory gas flow to the person's lungs during at least a portion of an inhalation event. The person is permitted to inhale and exhale through the valve system. During inhalation, the valve system functions to produce a vacuum within the thorax to increase blood flow back to the right heart of the person, thereby increasing blood circulation and blood pressure. Further, at least one physiological parameter is measured both prior to and while the person inhales and exhales through the valve system. The measured parameters are evaluated to confirm the initial diagnosis of a cardiovascular condition.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
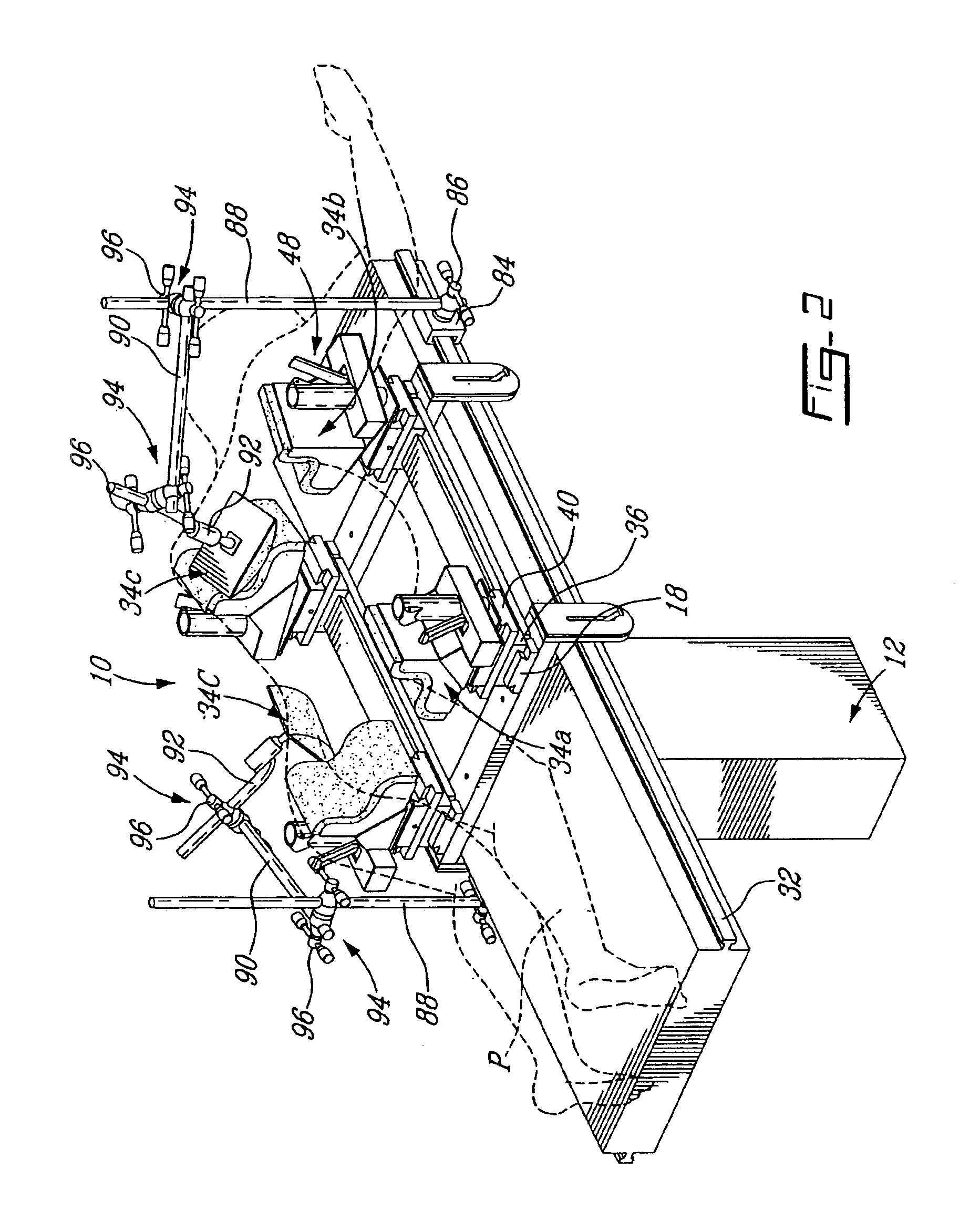
Dynamic frame for prone surgical positioning
ActiveUS6941951B2Improve patient positioningPrecise positioningInternal osteosythesisOperating chairsSurgery procedureSurgical department
Owner:HUBERT LABELLE +6
Diabetes treatment systems and methods
InactiveUS7204251B2Increase loopDecrease and prevent flowCompressorElectrotherapyHeart rightInhalation
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Apnea treatment device
Treatment or control of sleep apnea by achieved using a device or method for stimulation of expiration muscles. Somatic or expiratory muscle stimulation instead of a mask during sleep may regularize breathing. An apnea belt around the thorax may detect respiration by monitoring stretch and provide electrical stimulation to muscles used for expiration.
Owner:RMX
System and method for predicting a heart condition based on impedance values using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20050216067A1Reliably predict onset of heart conditionHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringPulmonary edemaThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for predicting the onset of a heart condition within a patient based on impedance measurements. Briefly, overloads in fluid levels in the thorax and in ventricular myocardial mass within the patient are detected based on impedance signals sensed using implanted electrodes. The onset of certain heart conditions is then predicted based on the overloads. For example, pulmonary edema arising due to diastolic heart failure is predicted based on the detection of on-going overloads in both fluid levels and ventricular mass. Ventricular hypertrophy is detected based on an on-going ventricular mass overload without a sustained fluid overload. Various other heart conditions may also be predicted based on specific combinations of recent or on-going overloads. Evoked response is exploited to corroborate the predictions. Appropriate warning signals are generated and preemptive therapy is initiated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cervical brace
The present invention provides a cervical brace that has a chest plate secured to the thorax of a wearer and a chin strut attached to the chest plate. In a preferred embodiment, the chin strut extends to a point on a chin support of a cervical collar disposed adjacent a wearer's chin so as to provide better support. The chest plate is in the form of a vest or can be comprised of a chest plate and a back plate. In preferred embodiments the chin strut extends in a straight line from the chest plate to the chin support and is adjustable and maybe positioned securely, relative to the chest plate, the cervical brace also has a back plate and an occipital support. In certain embodiments it has a rear strut extending between the occipital support and the back plate. In such embodiments, the back plate and the chest plate are preferably attached to each other around the body. In accordance with one aspect of the present invention, the rear strut is adjustable and further has a strut latch, which is most preferably an eccentric lever for locking one end of the rear strut to a bracket affixed to the back plate. In another embodiment it may have a strap which serves the occipital support to the forehead.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Sleep staging based on cardio-respiratory signals
A method for diagnosis of a sleep-related condition of a patient having a thorax. The method includes receiving physiological signals from sensors coupled to the thorax of the patient, and analyzing the physiological signals, independently of any electroencephalogram (EEG) or electro-oculogram (EOG) signals, in order to identify sleep stages of the patient.
Owner:WIDEMED
Apparatus and method to determine functional lung characteristics
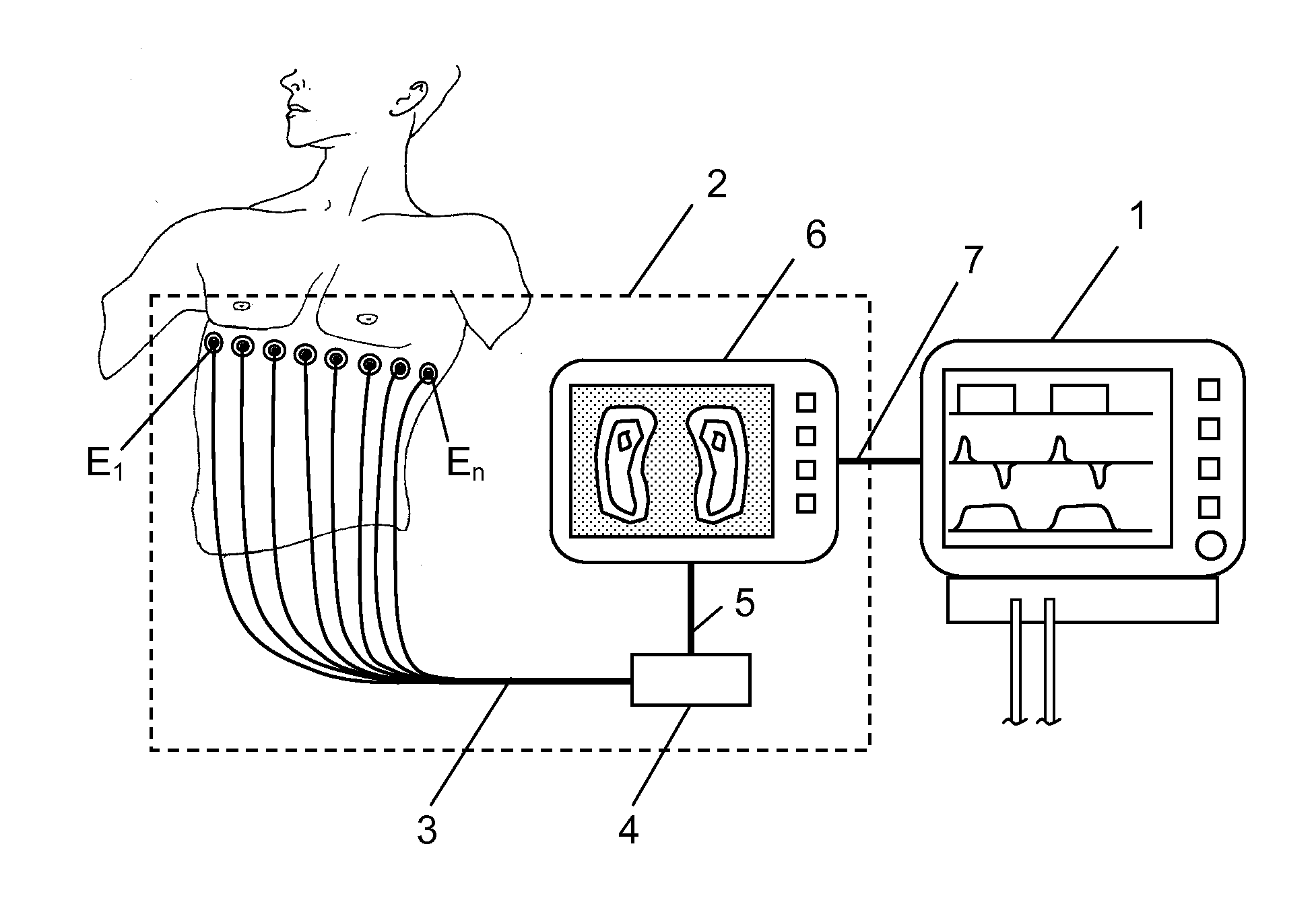
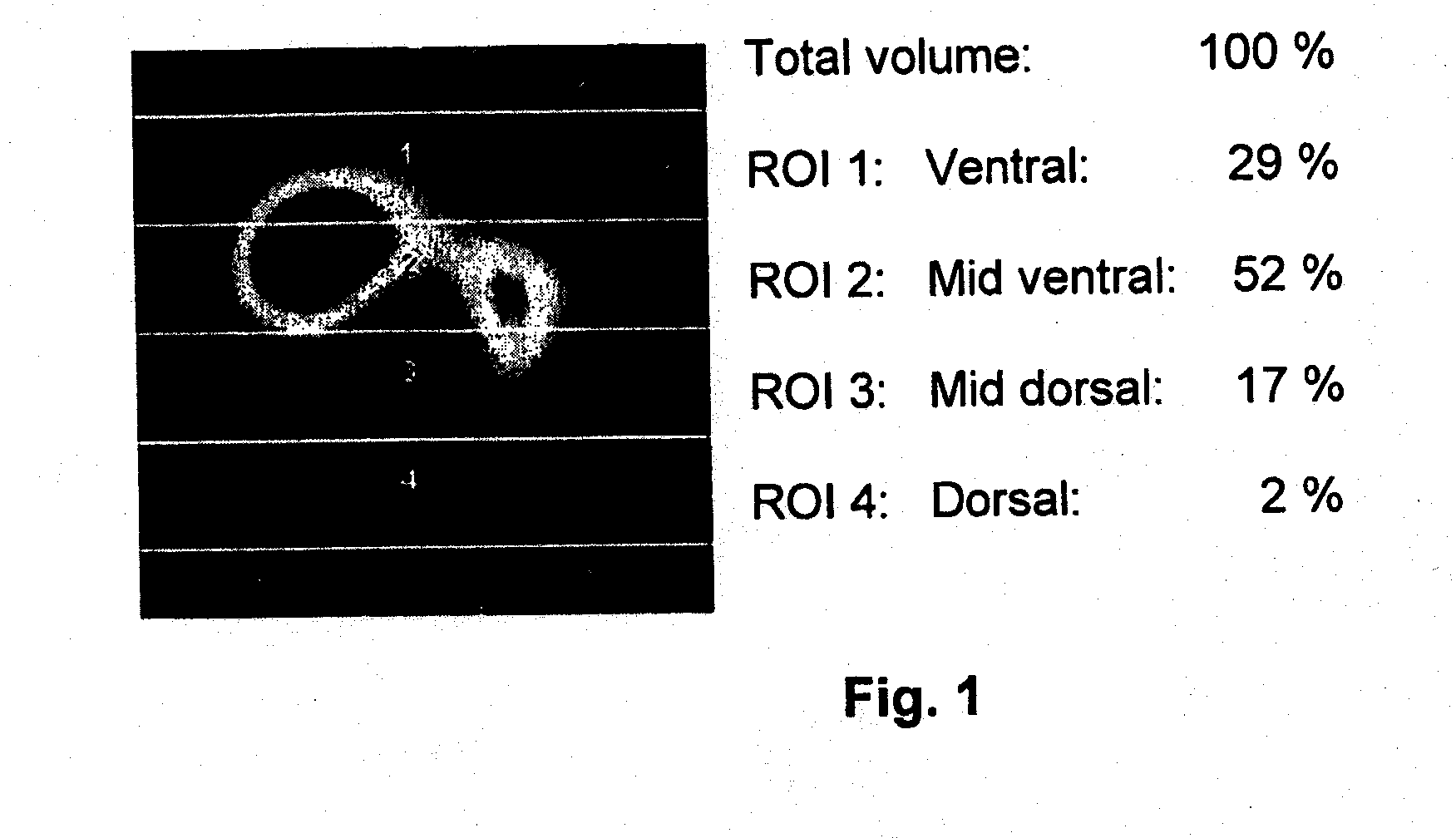
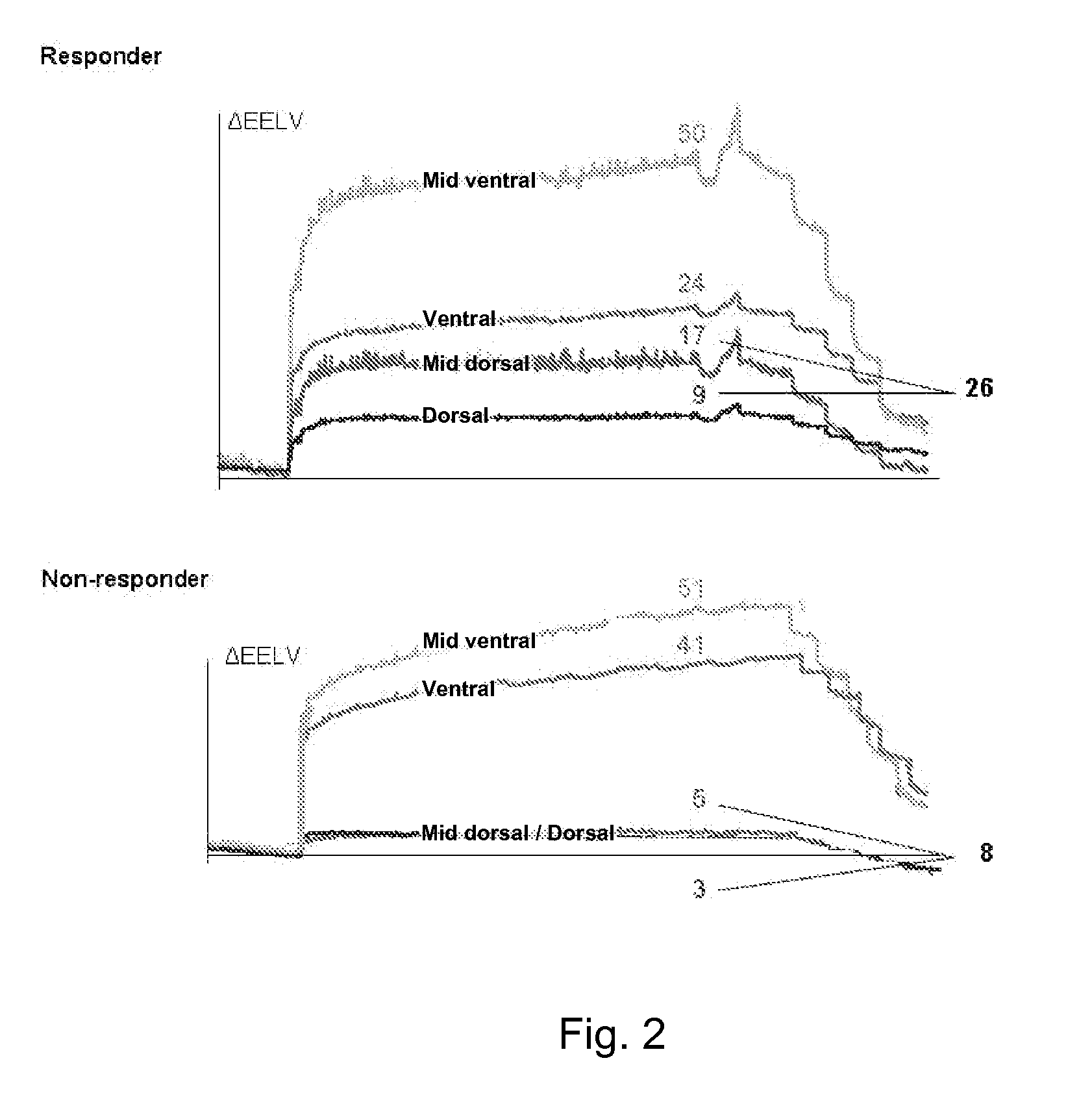
InactiveUS20100228143A1Easy to interpretEasy to perceiveRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesImpedance distributionBreathing cycle
An apparatus for determining functional lung characteristics of a patient includes an electrical impedance tomography (EIT) imaging device adapted to record the impedance distribution within a plane of the thorax of the patient. The EIT imaging device includes a control and analysis unit for performing the impedance measurement and deriving the impedance distribution within the plane of the thorax. The control and analysis unit automatically performs steps including determining a global impedance change, defined as the impedance change with respect to an earlier measured reference impedance distribution integrated over the electrode plane, and recording the global impedance change curve as a function of time, performing breath detection in order to identify a breathing cycle, subdividing each breathing cycle to define a plurality of intratidal intervals, subdividing an EIT image from each interval into a plurality of regions of interest and calculating for each region of interest the ratio of the integrated impedance change within this region of interest to the global impedance change of this EIT image, for each intratidal interval presenting indications of the ratios determined for the regions of interest to provide an intratidal gas distribution representation for each interval.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
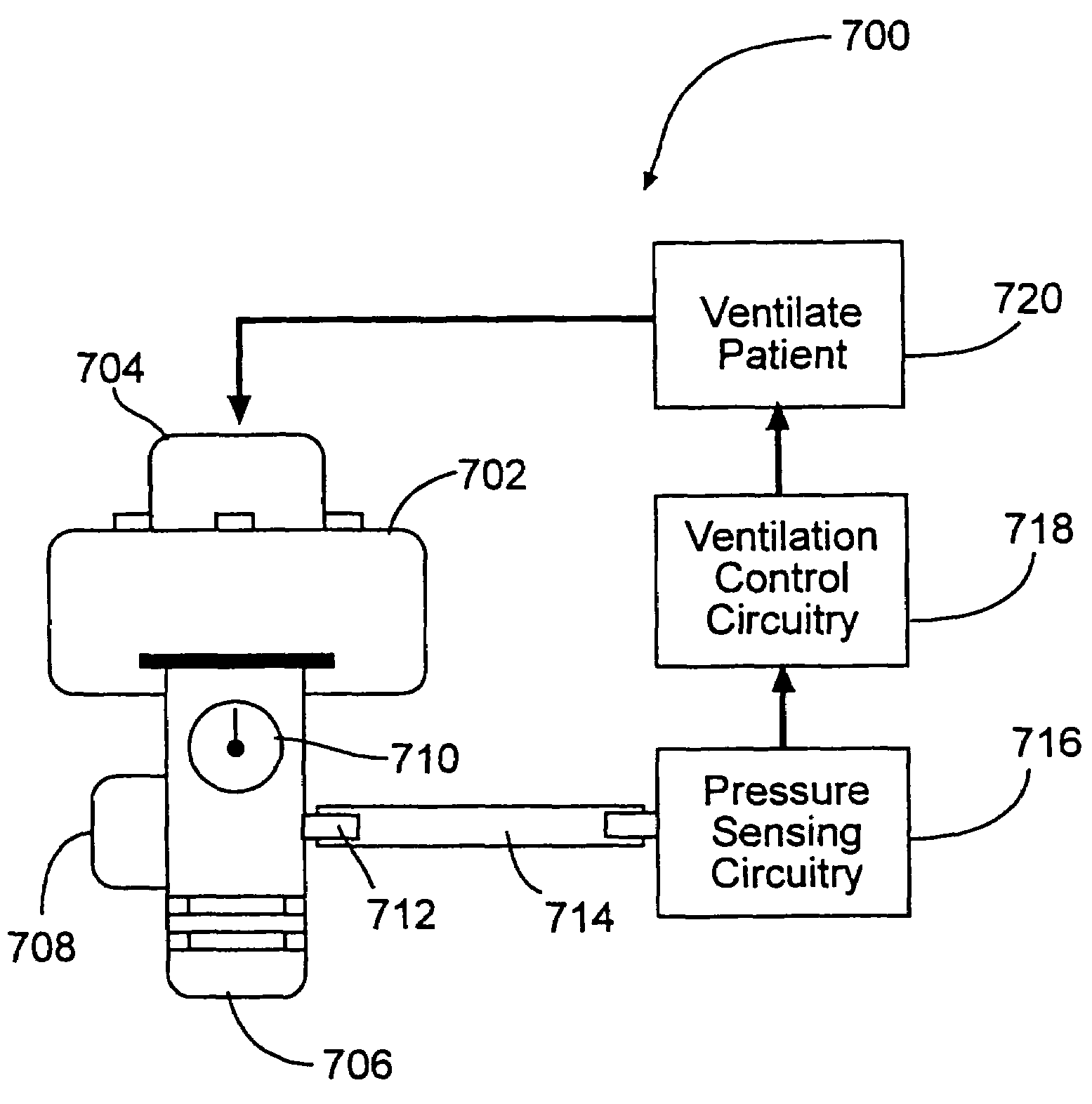
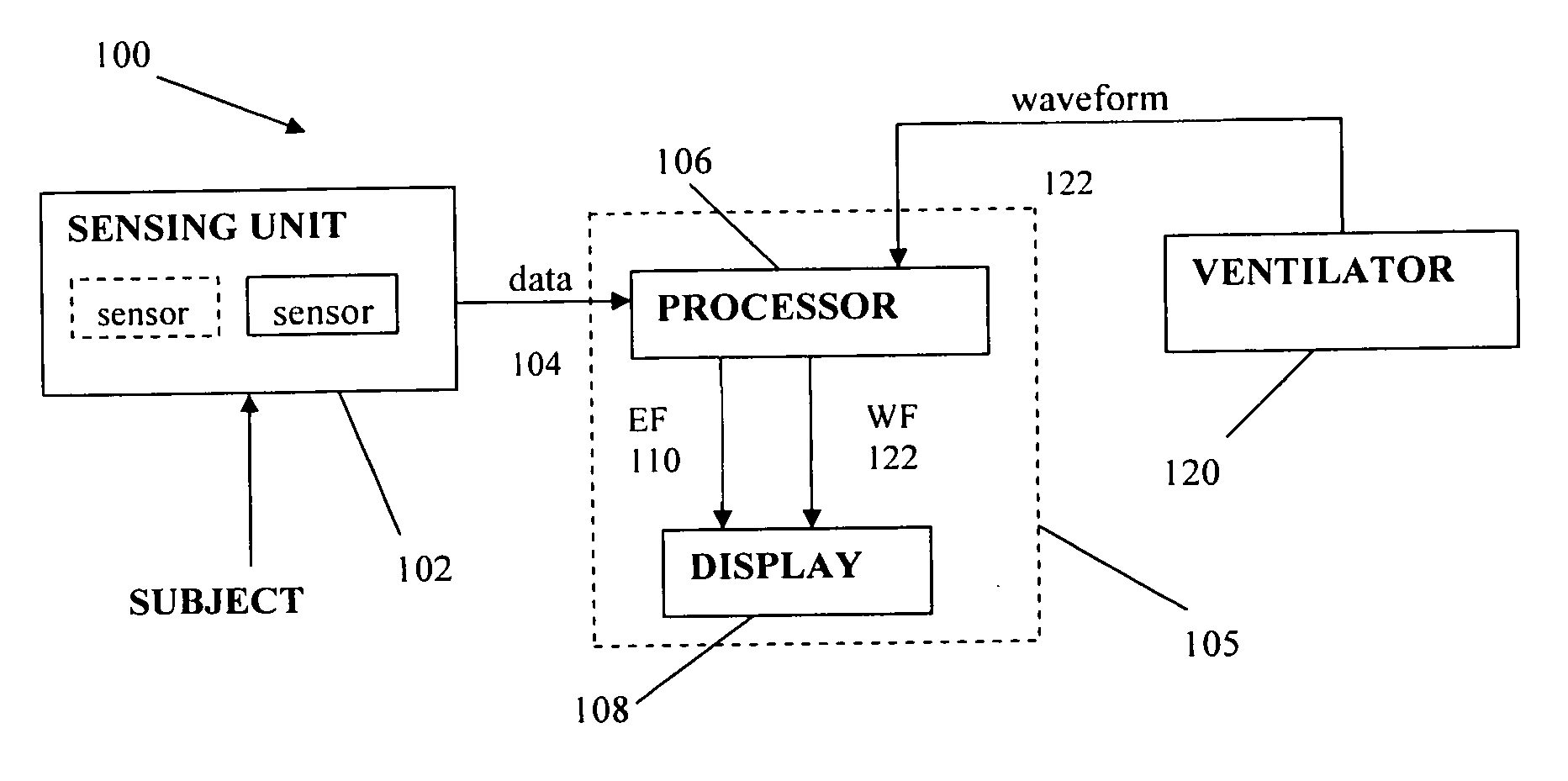
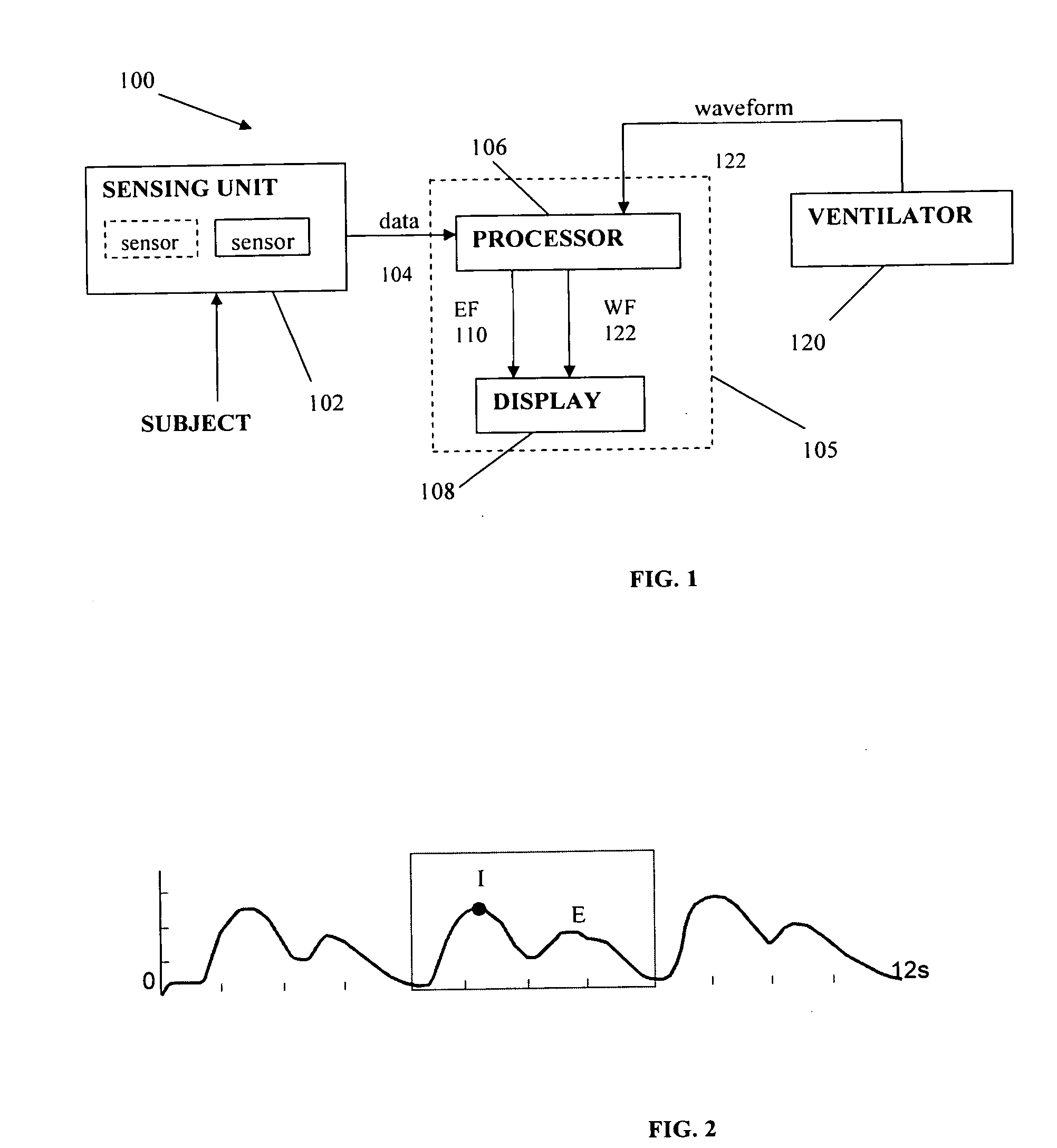
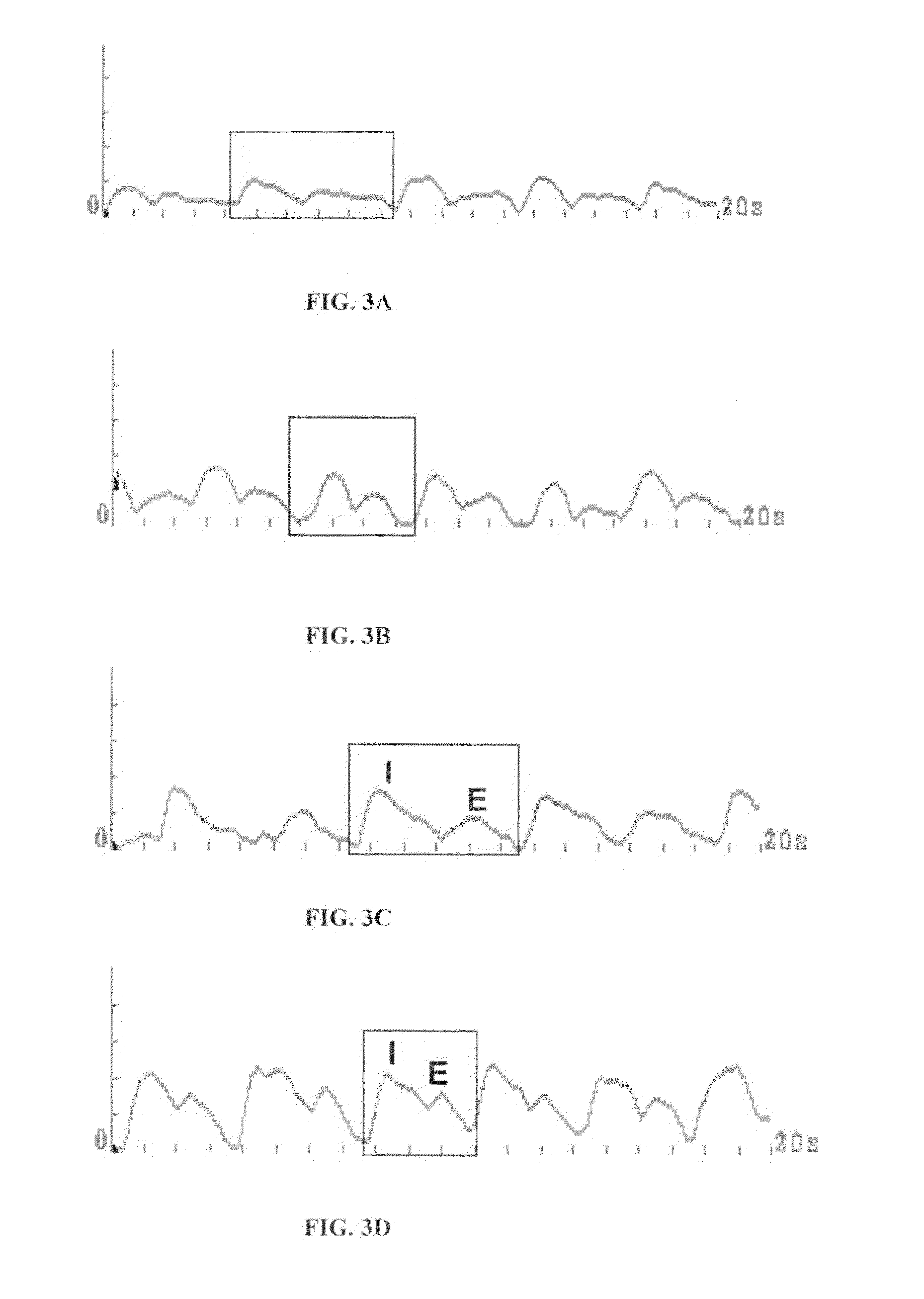
Method and System for Assessing Lung Condition and Managing Mechanical Respiratory Ventilation
The present invention discloses a novel non-invasive, bedside system and method to monitor parameters associated lung changes. A novel approach for monitoring the operation of the respiratory system of a subject is provided. There is also provided a method for objectively evaluating the benefit of one mode of ventilation over another, and for assessing the differences in regional lung vibration during different modes of mechanical ventilation. The method comprises recording one or more signals from the subject, the signal varying in time according to operation of the respiratory system; and; processing the recorded signals to obtain a predetermined functional thereof presenting one or more time-varying energy functions of the subject, an abnormality in the one or more energy functions being indicative of a suspected abnormality in the operation of the respiratory system. The signals may be acoustic signals recorded by a plurality of acoustic sensors placed over the subject's thorax or back, and the at least one time-varying energy function is obtained from one or more specific regions of lung or by summing / averaging the time-dependent acoustic signals of the plurality of sensors indicative of the whole lungs.
Owner:DEEPBREEZE
Aneurysm treatment system and method
InactiveUS20060281966A1Reduce dilationShorten the progressStentsSurgeryAneurysm treatmentBlood vessel
An external aneurysm support scaffold is implanted around an exterior surface of an aneurysm and prevents substantial dilation or progression of the AAA. Minimally invasive delivery is used via port-access, i.e. for aortic aneurysms along the back, abdomen, or thorax, to a location externally adjacent the aneurysm, such as via laparascopic delivery. The scaffold is unwound or unfolded in-situ to extend partially (e.g. about 270 degrees) or completely circumferentially around the aneurysm. Unique delivery devices allow for deployment around the aneurysm. Gaps between an array of transverse fingers of the scaffold may accommodate branch vessels extending from the aneurismal vessel, such as aortic perforators. An agent is injected to treat an aneurysm, such as by providing support, cell retention or recruitment, and / or angiogenesis. Living cells are delivered to treat an aneurysm. An adjustable graft polymerizes in-situ to support an aneurysm conformed therewith.
Owner:EMERGE MEDSYST
Systems and methods to facilitate the delivery of drugs
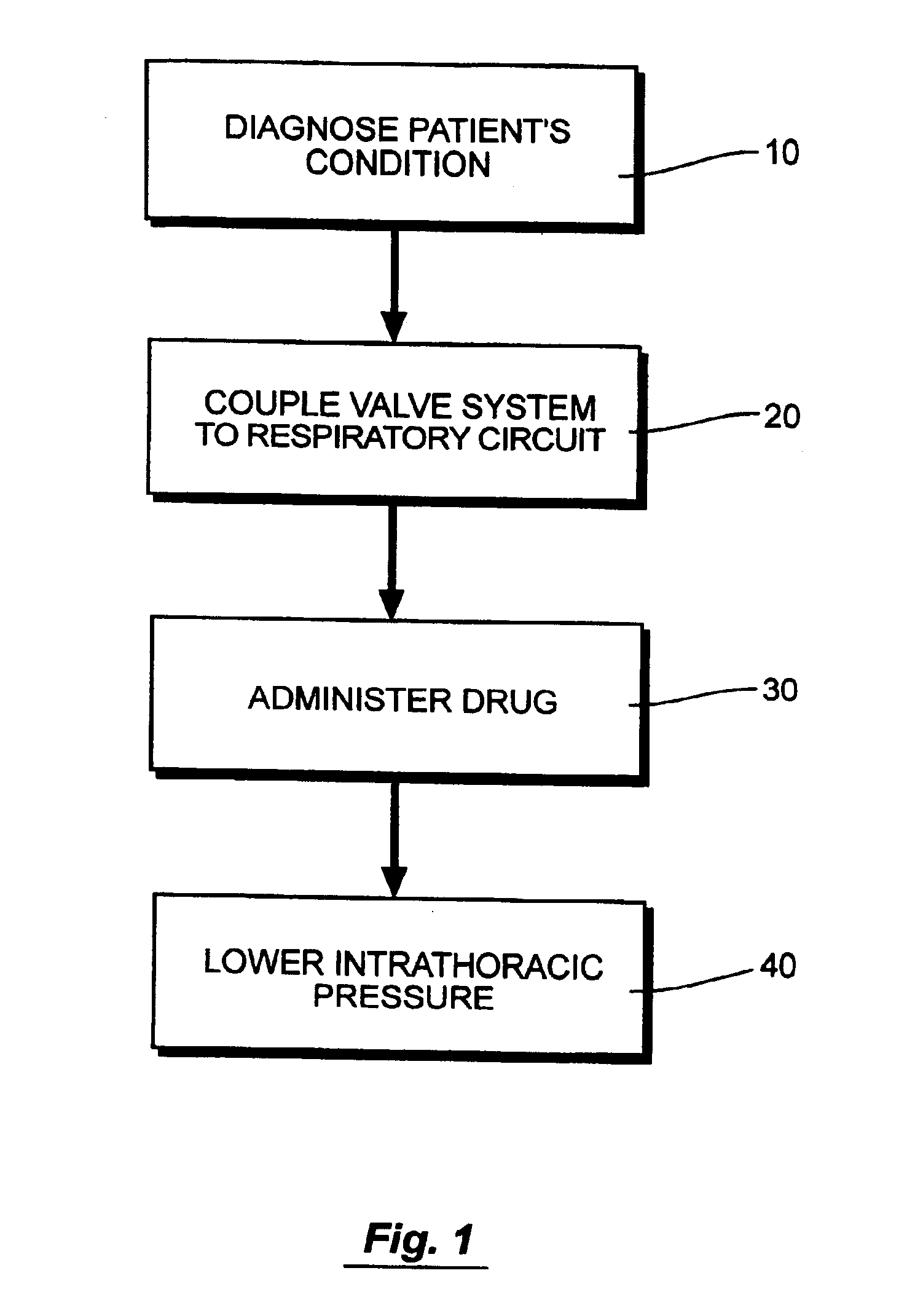
InactiveUS6935336B2Good curative effectLow toxicityRespiratorsElectrotherapyBreathing gasAtmospheric pressure
A method for administering a drug to a patient comprises coupling a valve system to the patient's airway. The valve system is configured to prevent or impede respiratory gases from flowing into the lungs for at least some time such that the intrathoracic pressure is less than atmospheric pressure. A drug is introduced into the patient, and the intrathoracic pressure is lowered using the valve system to cause blood to flow into the thorax and thereby increasing vital organ perfusion to enhance the circulation of the drug.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Noninvasive Ultrasound Cardiac Pacemaker and Defibrillator
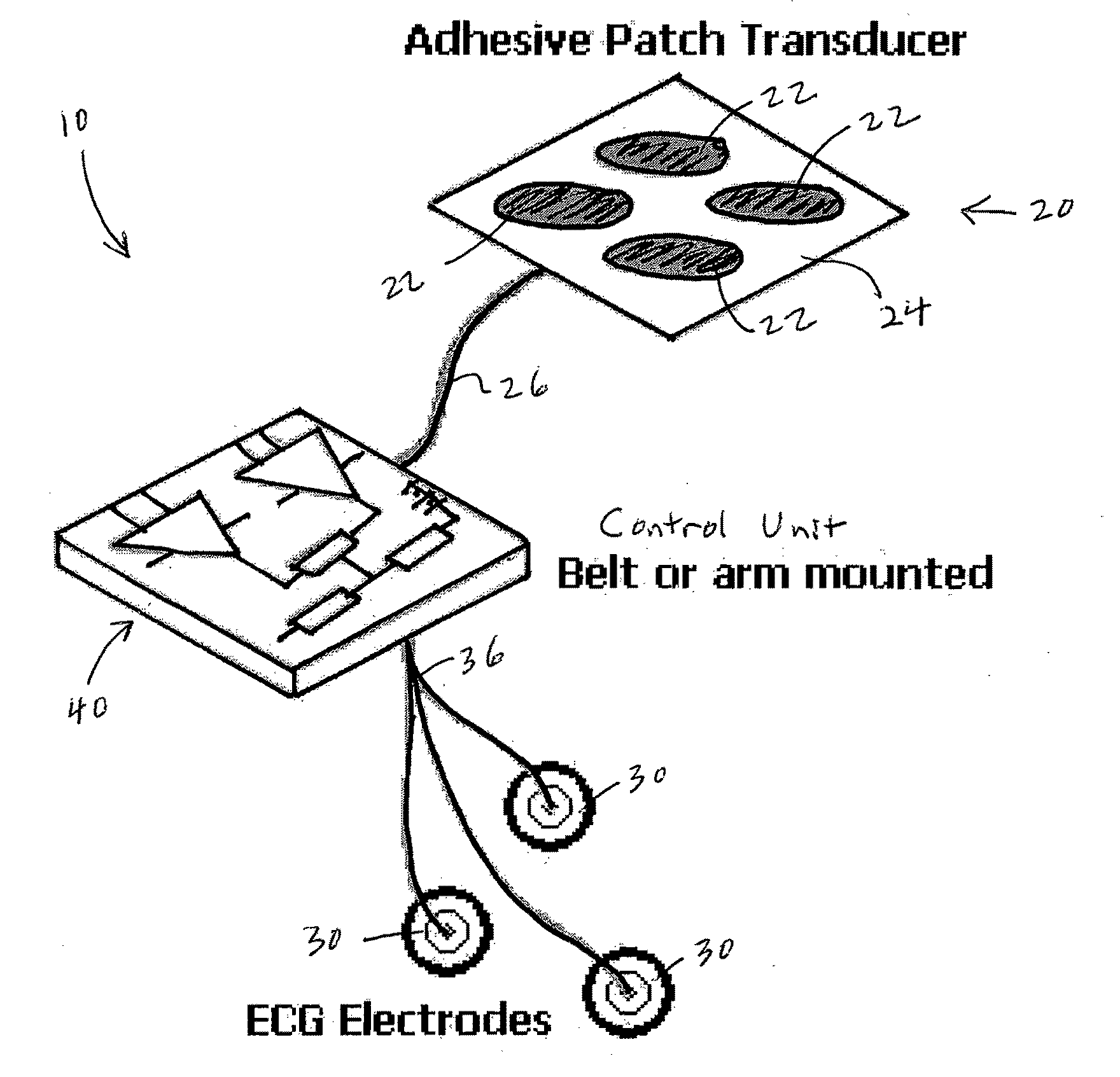
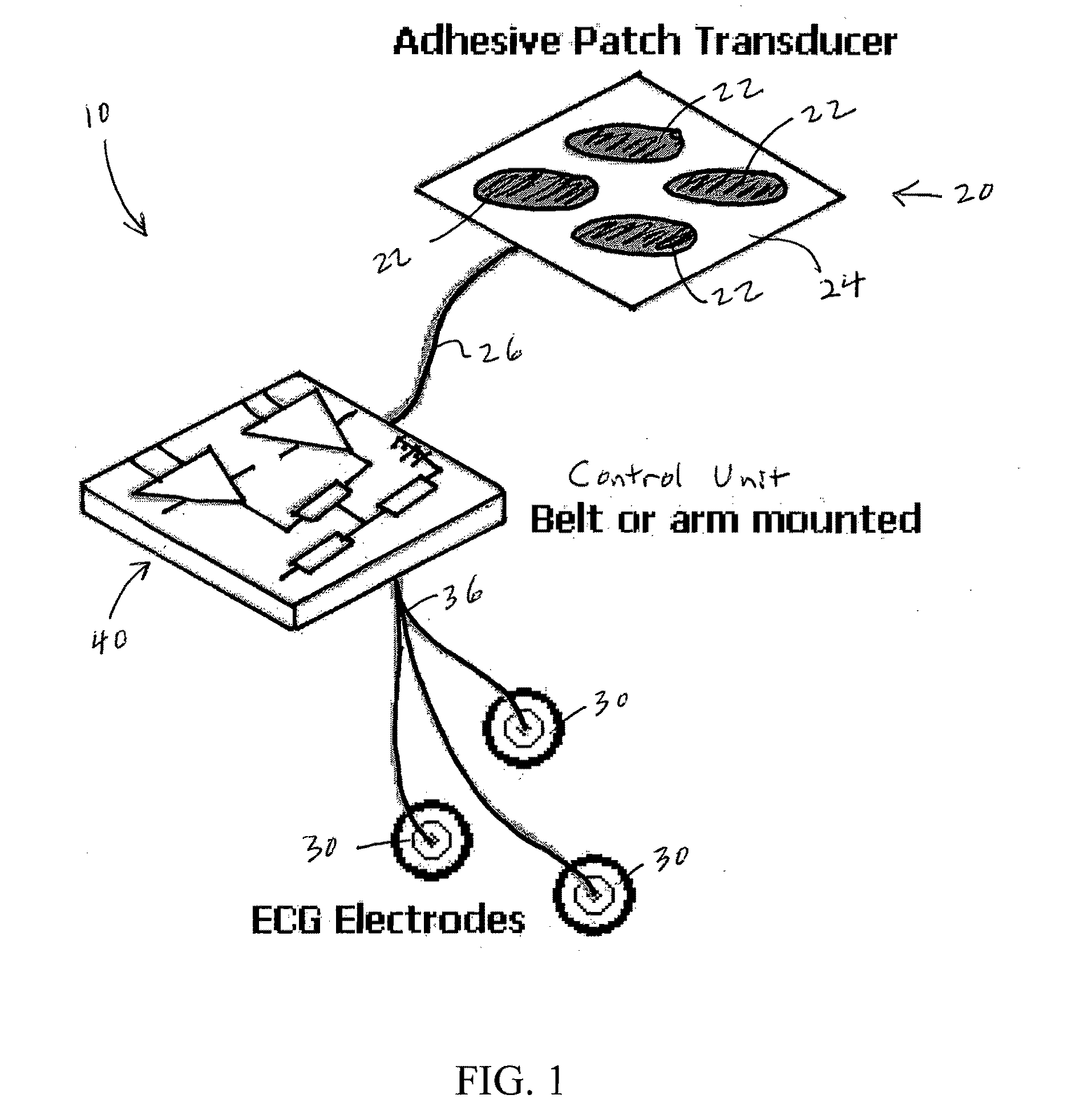
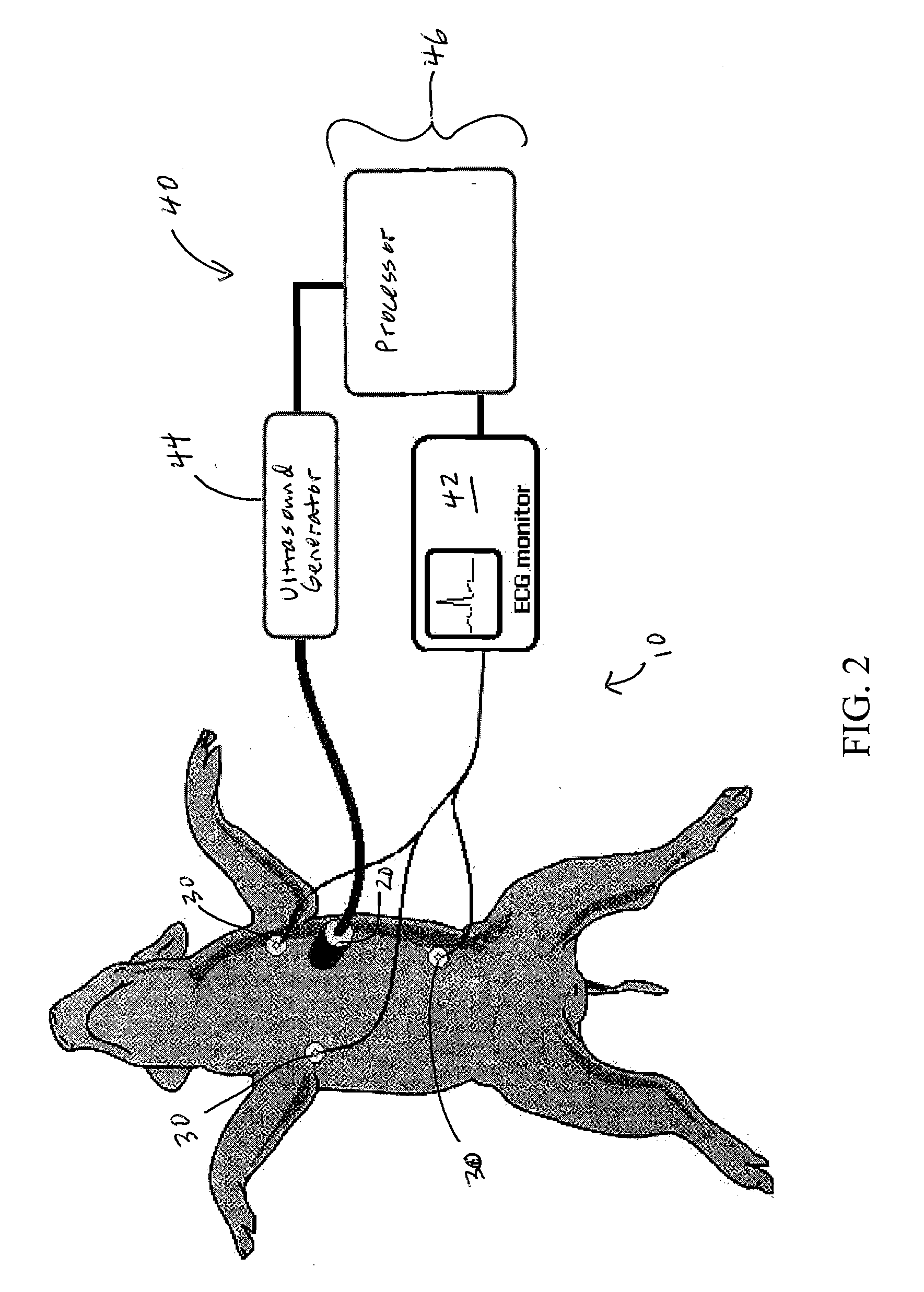
A device for providing extracorporeal cardiac pacing. The device includes an ultrasound transducer mountable to the external thorax of a patient and an ultrasound generator for transmitting ultrasound pulses to the ultrasound transducer. The heart rate of a patient is monitored by the device. A controller evaluates the heartbeat as compared with threshold criteria for stimulation of the heart and causes the ultrasound generator to deliver ultrasound pulses to the ultrasound transducer at a prescribed intensity, frequency, and pulse duration.
Owner:PHILADELPHIA HEALTH & EDUCATION CORP
Inflatable airbag with overlapping chamber
ActiveUS20050248132A1Avoid injuryIncrease pressurePedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringThoracic cavity
An inflatable side airbag apparatus having a thorax cushion and an independently inflatable overlapping high pressure pelvic cushion is disclosed. The airbag system provides for rapid deployment of the pelvic cushion. The thorax cushion inflates adjacent to and provides impact protection for an occupant's thorax and pelvis in a lateral collision. The pelvic cushion inflates between the thorax cushion and the side structure of the vehicle and provides impact protection for the occupant's pelvis. The airbag system also includes an inflator having a gas guide that is in fluid communication with both cushions, and inflates the pelvic cushion to a higher pressure than the thorax cushion. The thorax cushion further includes a diffuser hood for diverting inflation gas toward the pelvic region of the cushion, thereby rapidly positioning the pelvic cushion in its intended deployment position.
Owner:AUTOLIV ASP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com