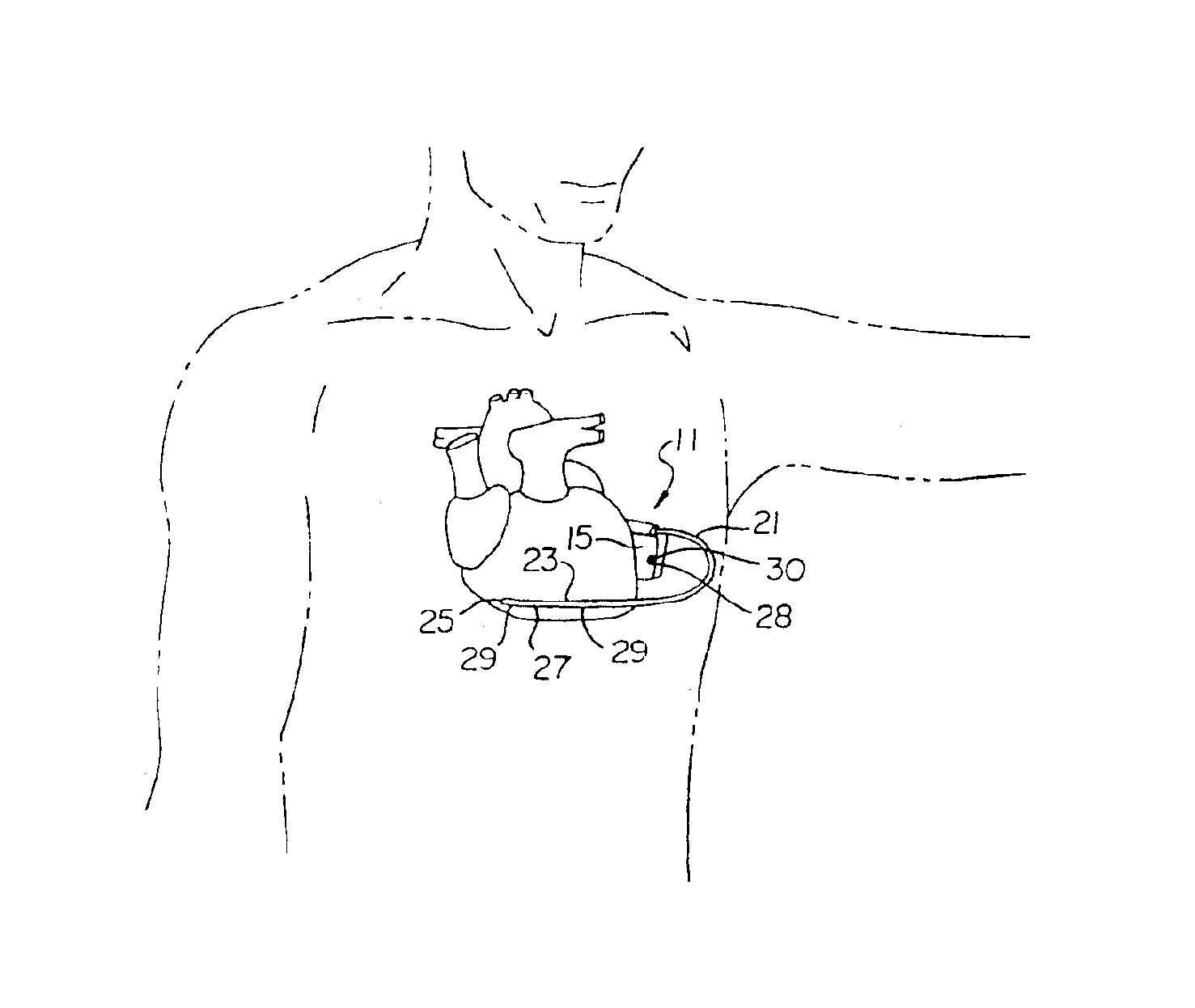
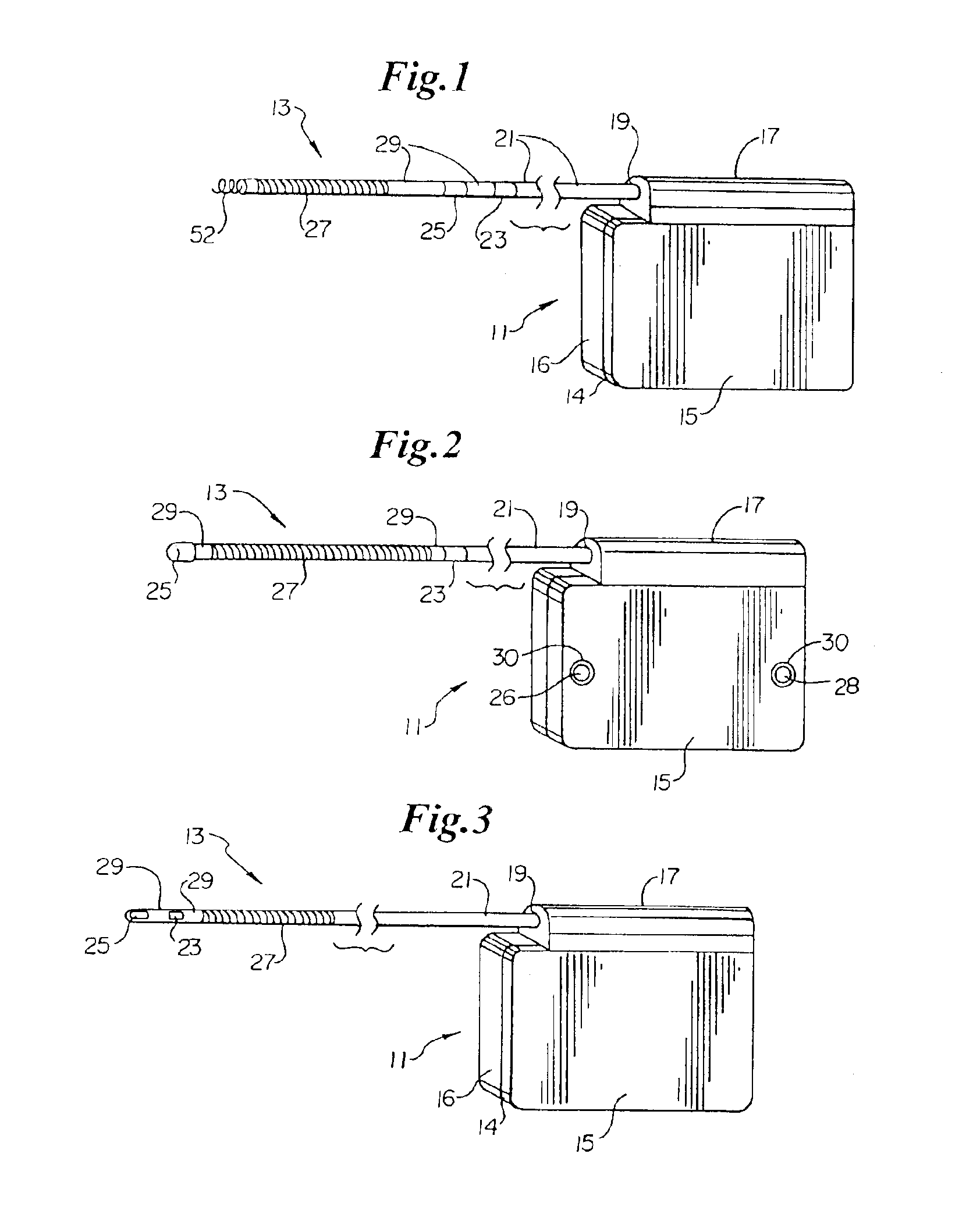
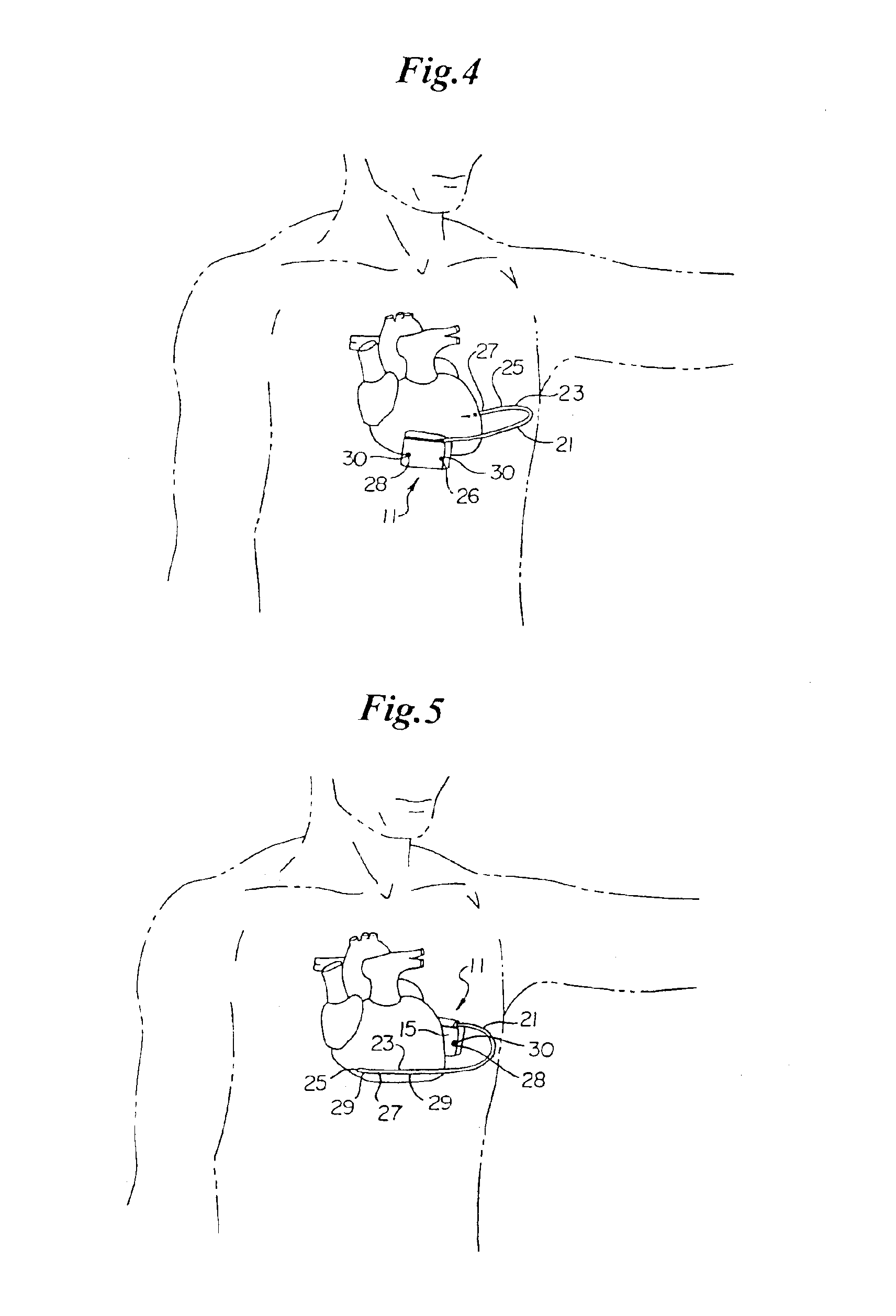
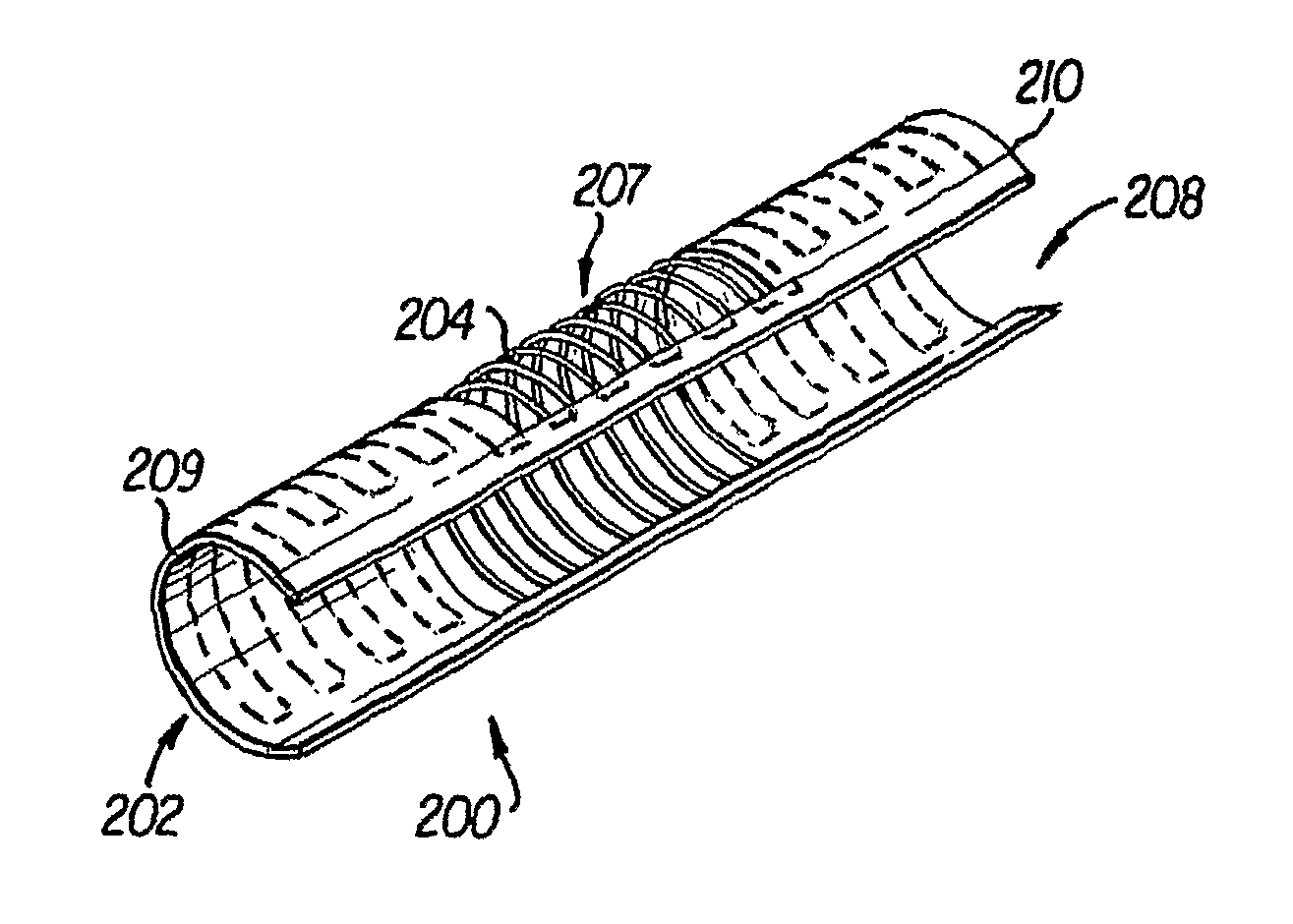
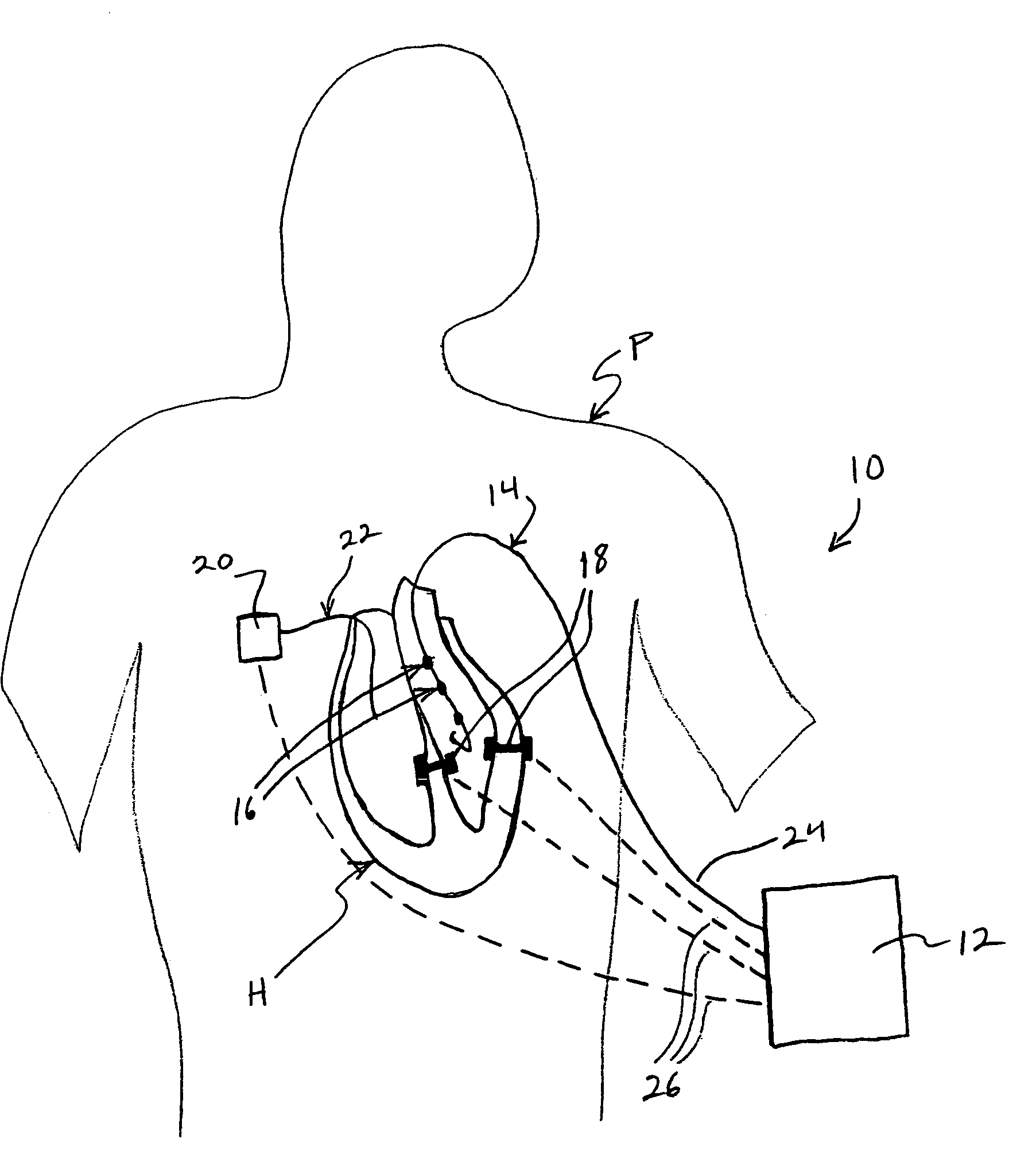
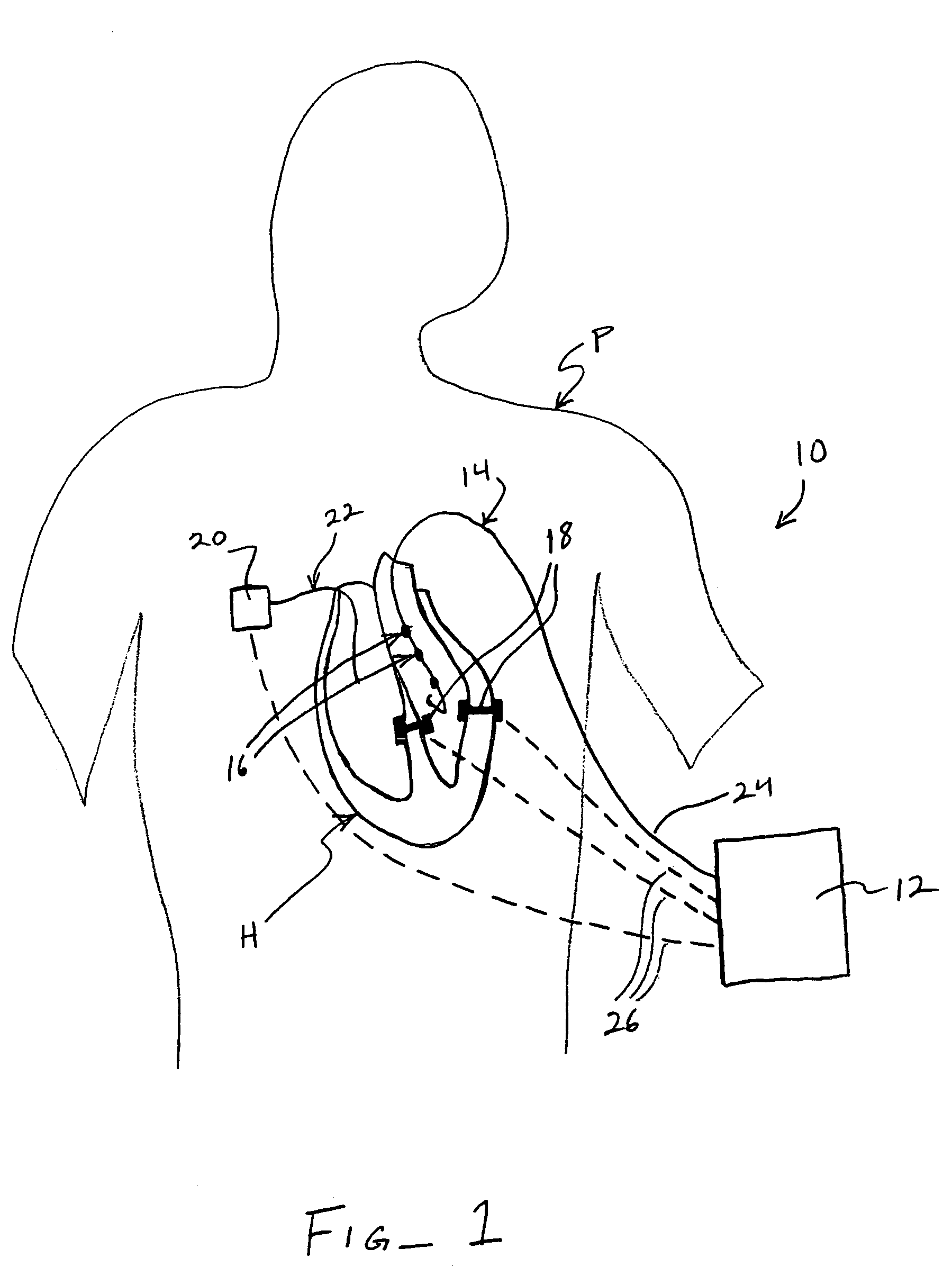
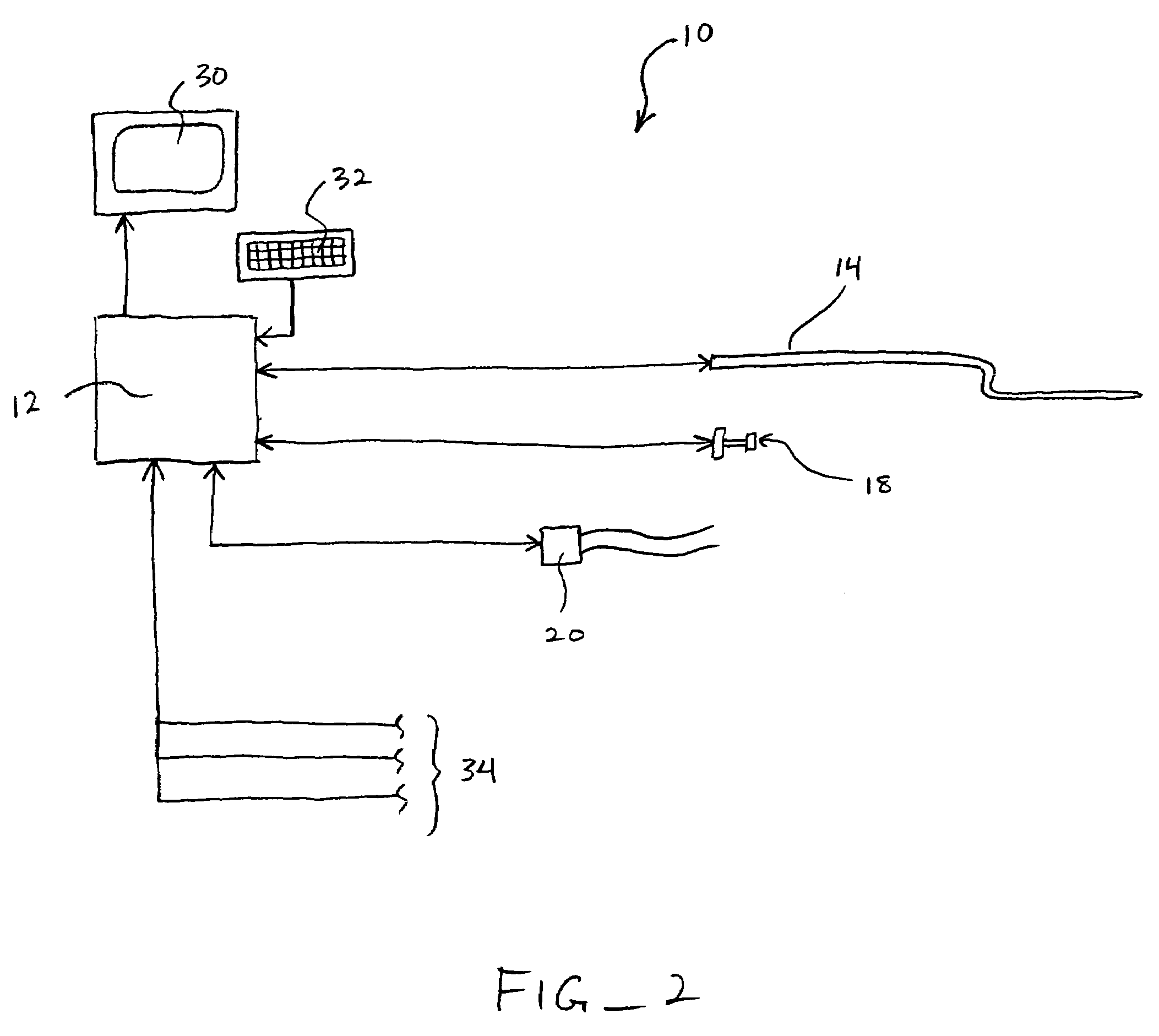
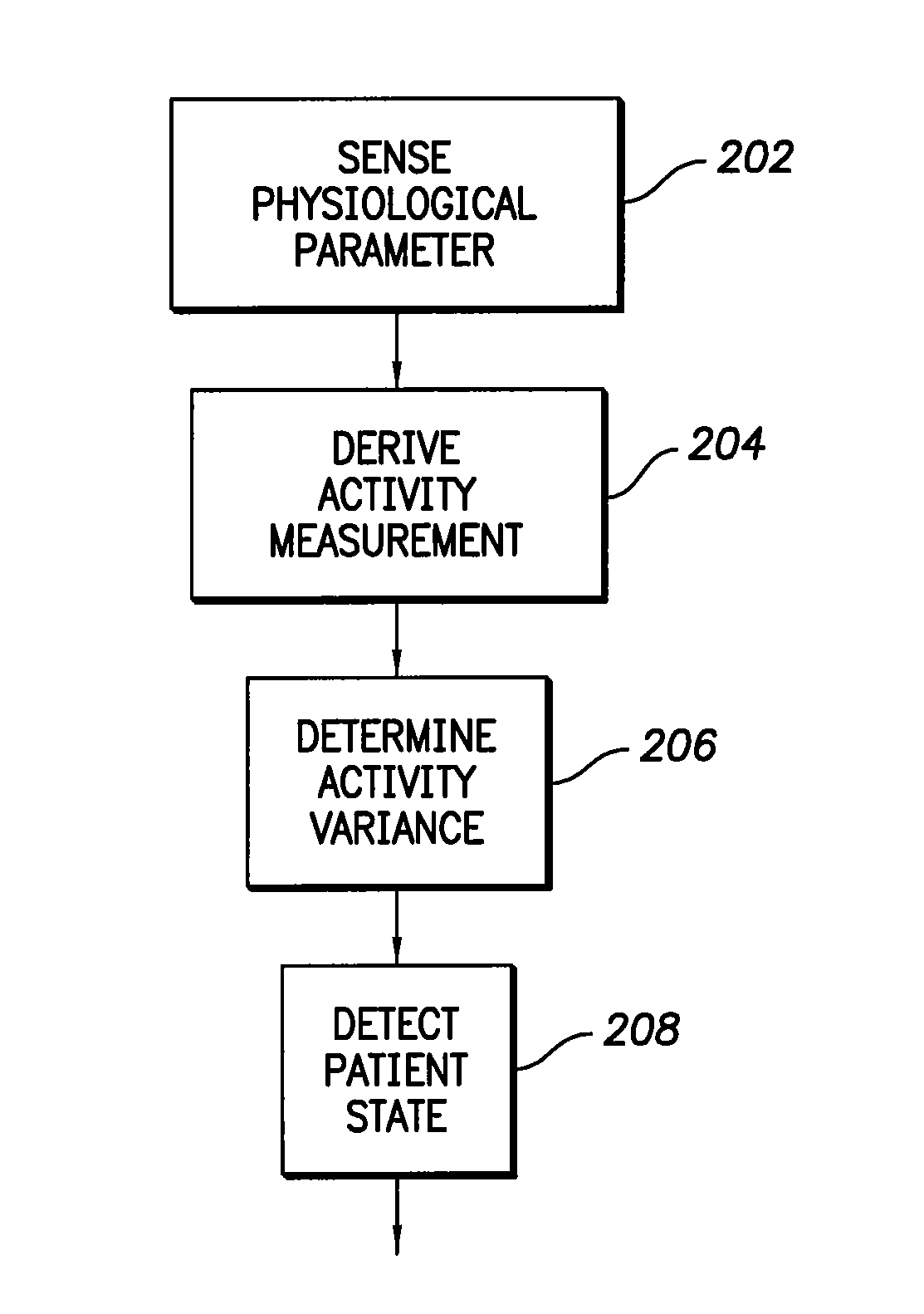
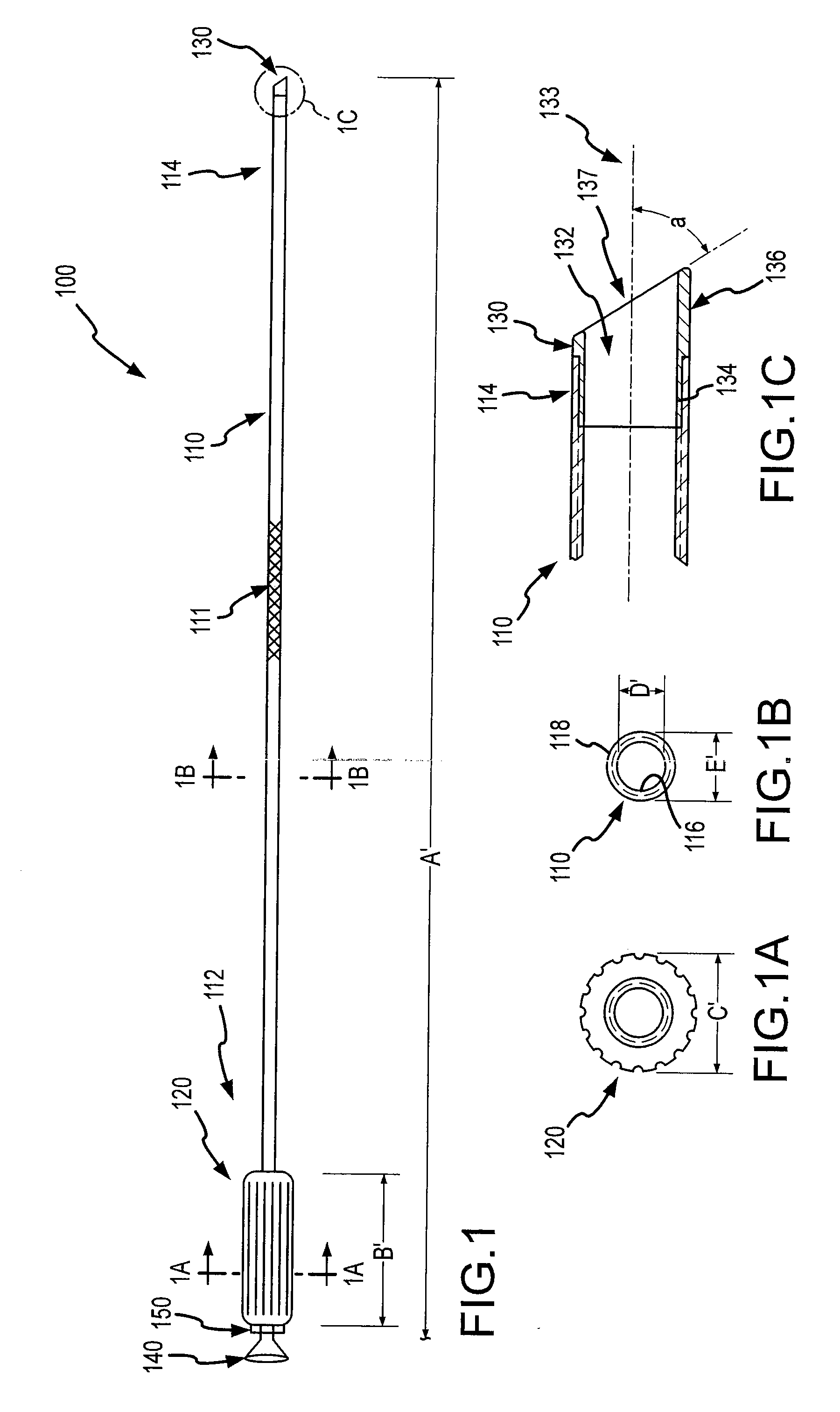
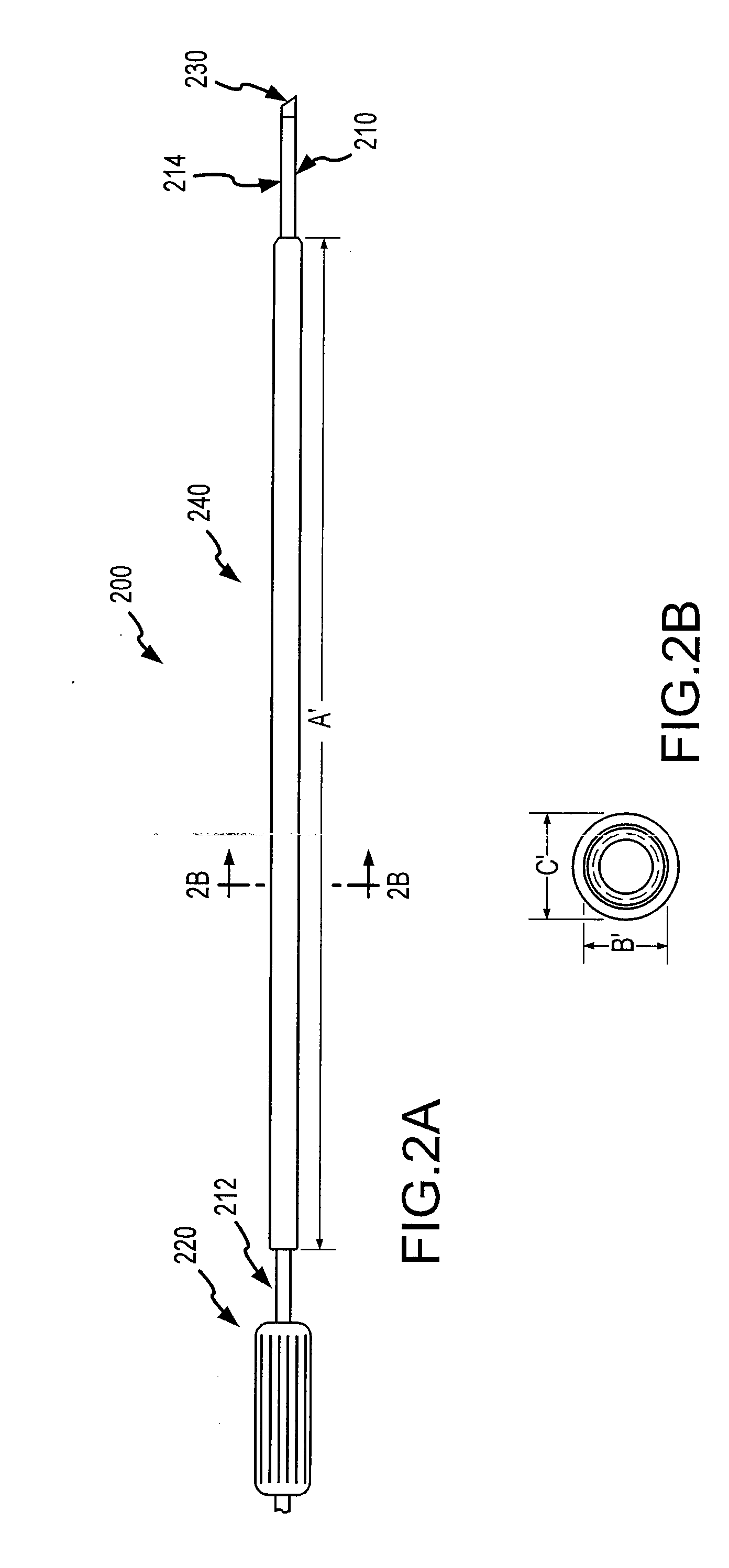
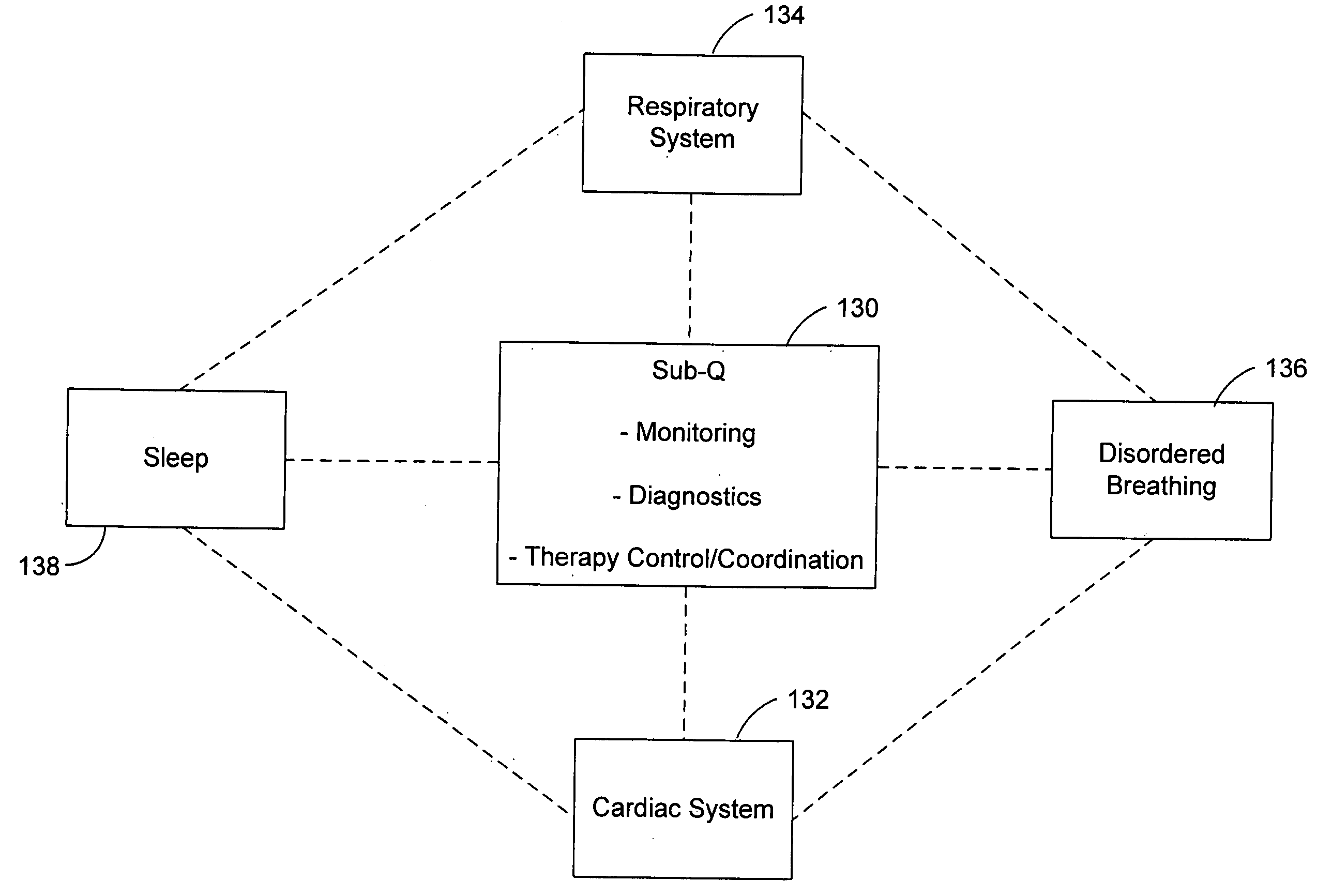
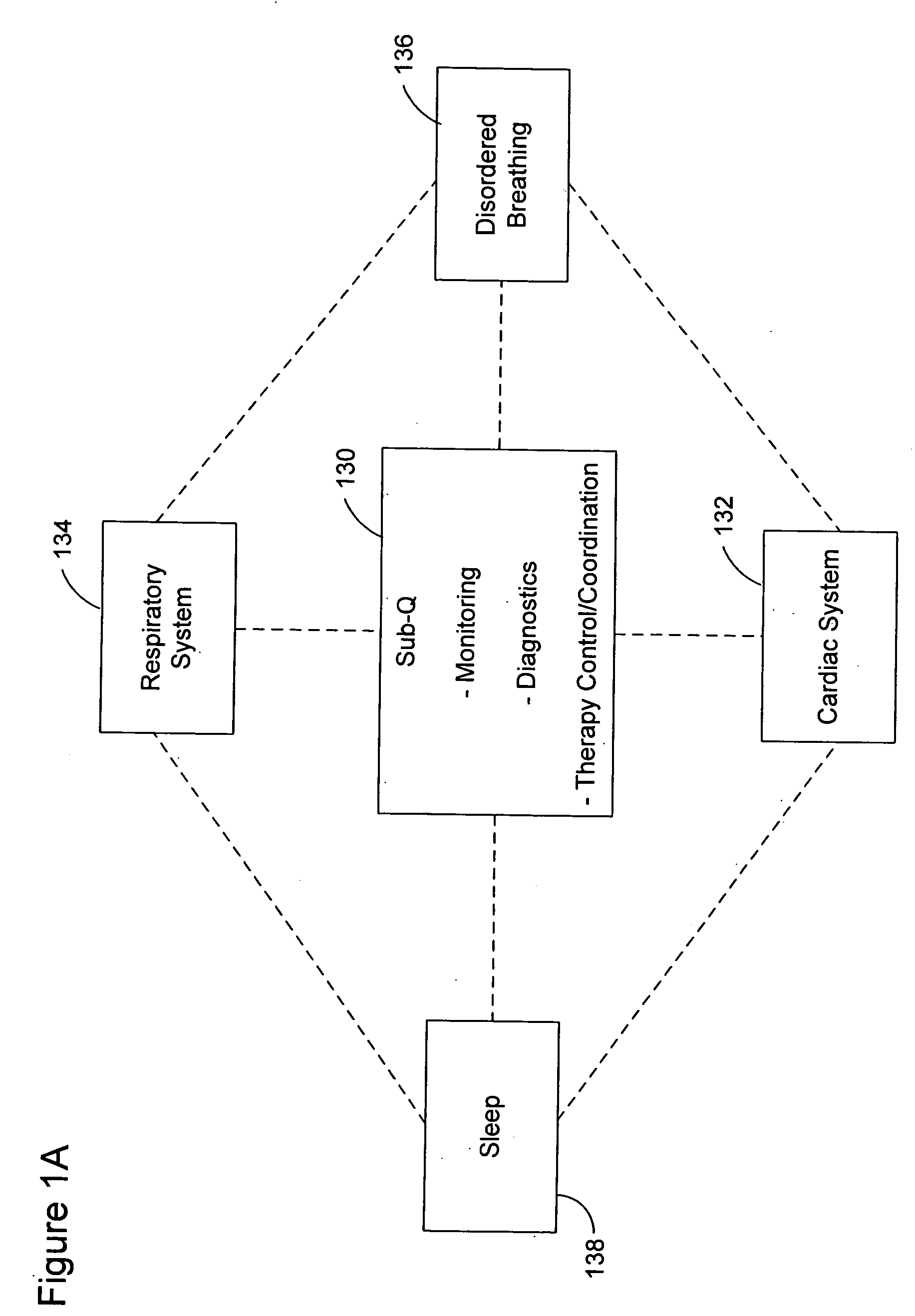
Patents
Literature
383 results about "Cardiac pacing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stimulation device for sleep apnea prevention, detection and treatment
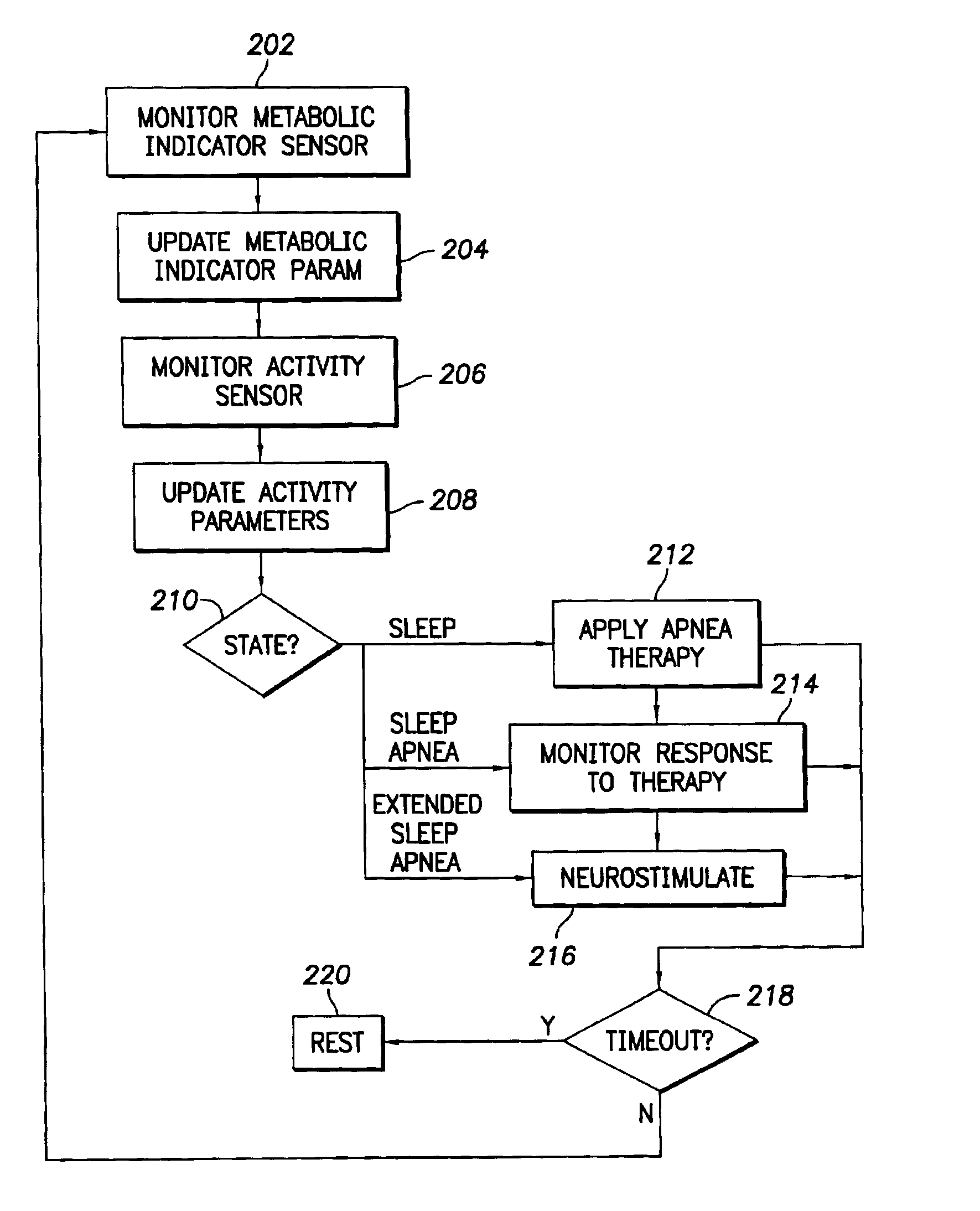
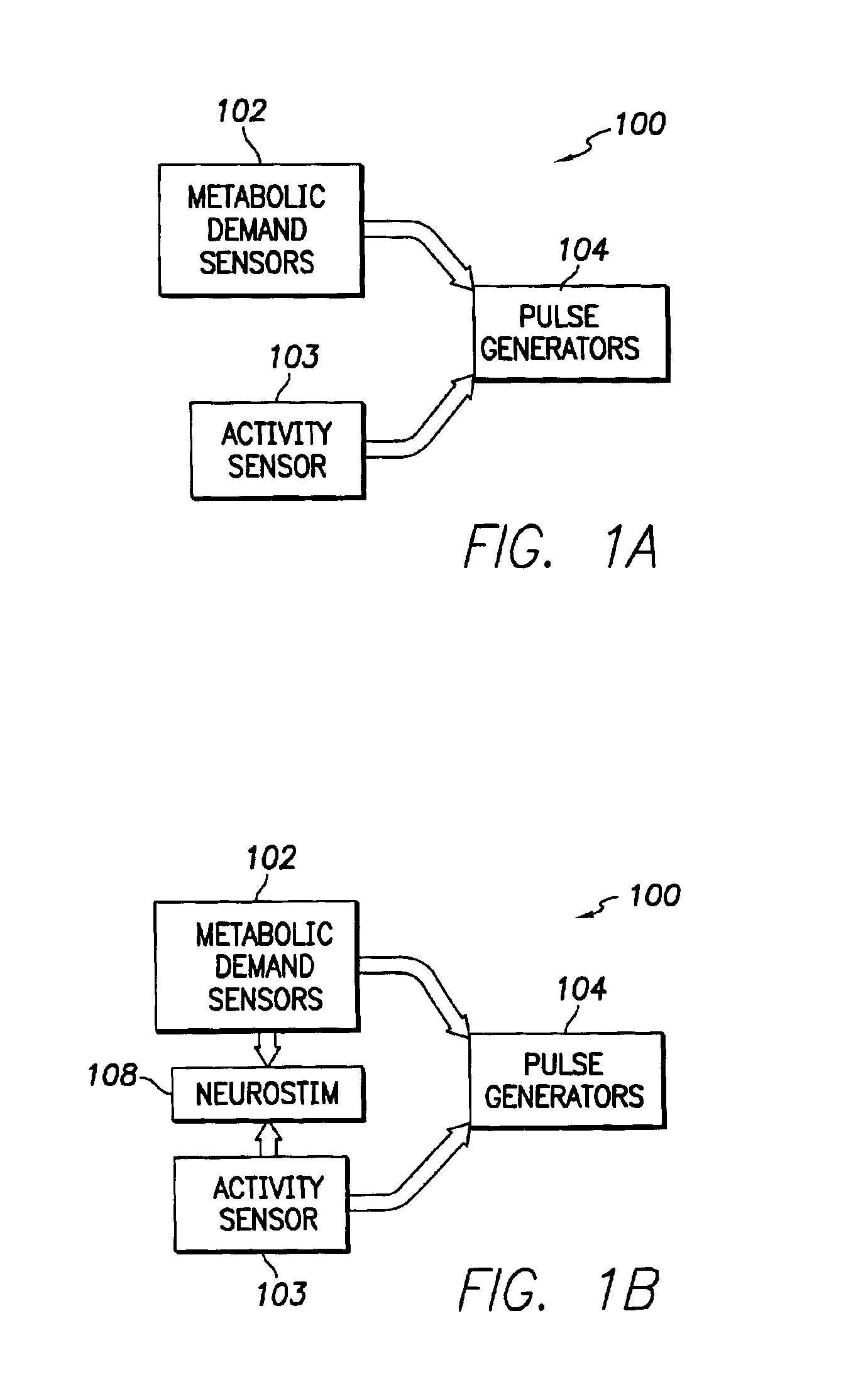
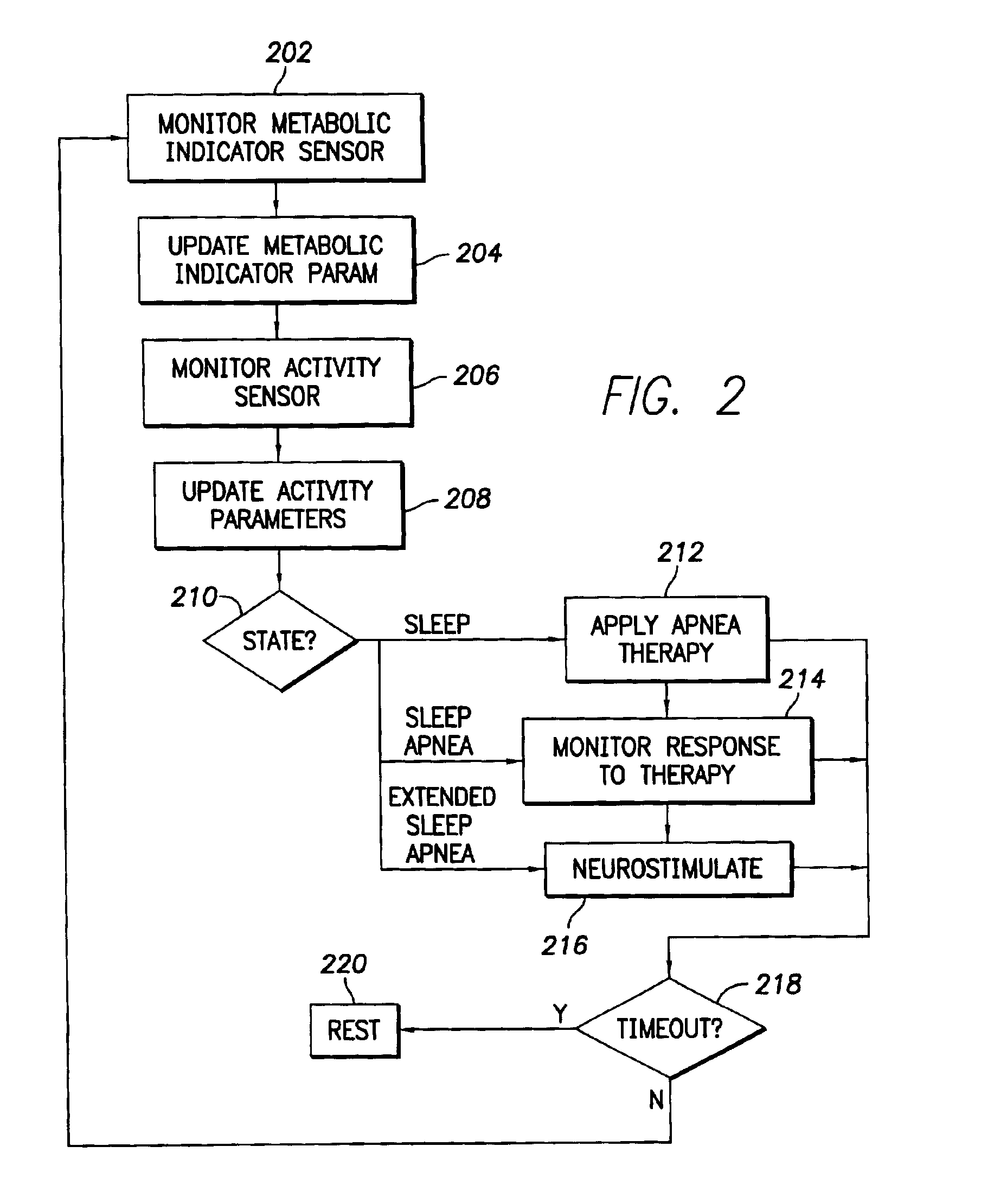
InactiveUS6928324B2Increase oxygen concentrationReduce carbon dioxide concentrationHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationSleep apneaMetabolic demand
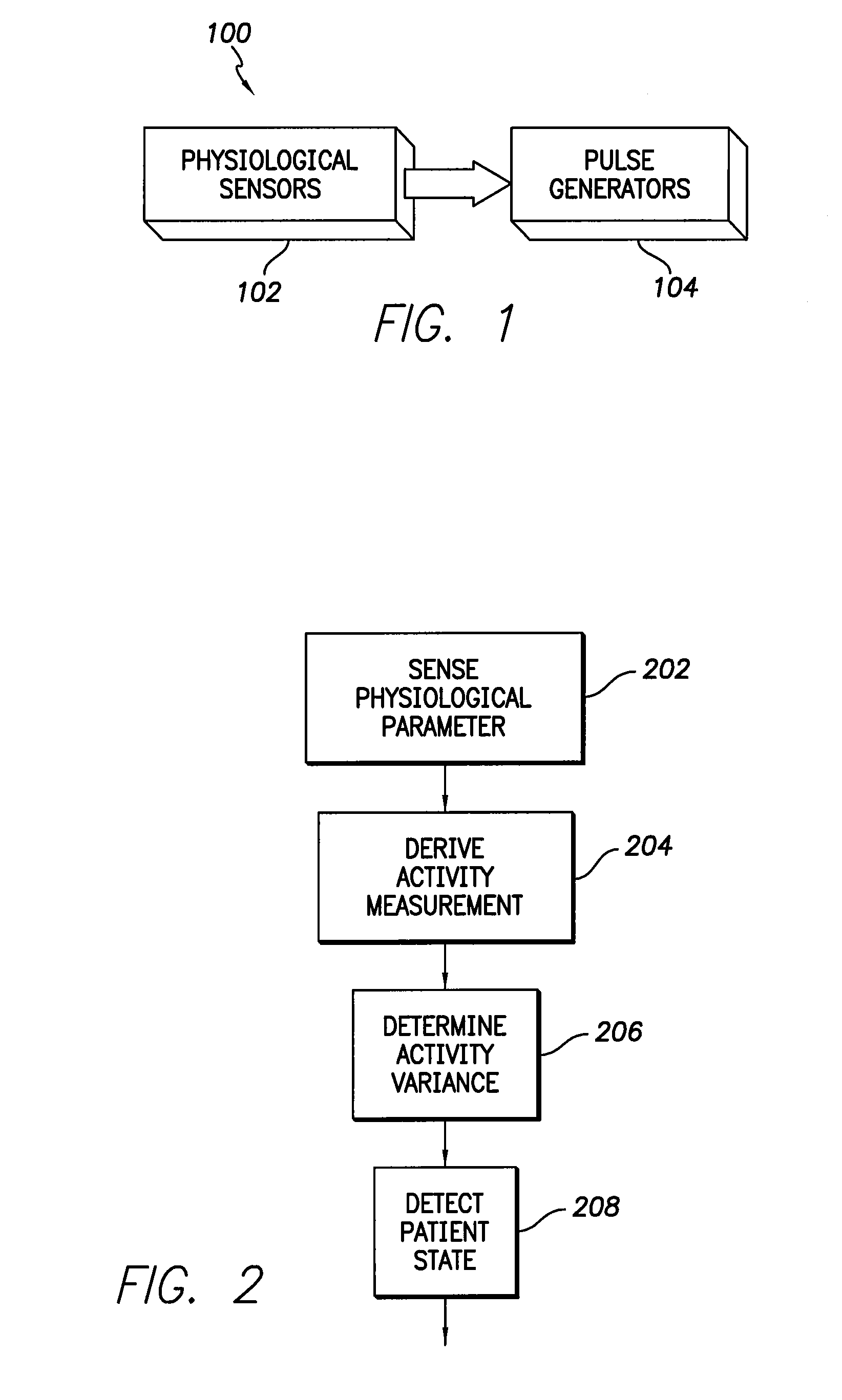
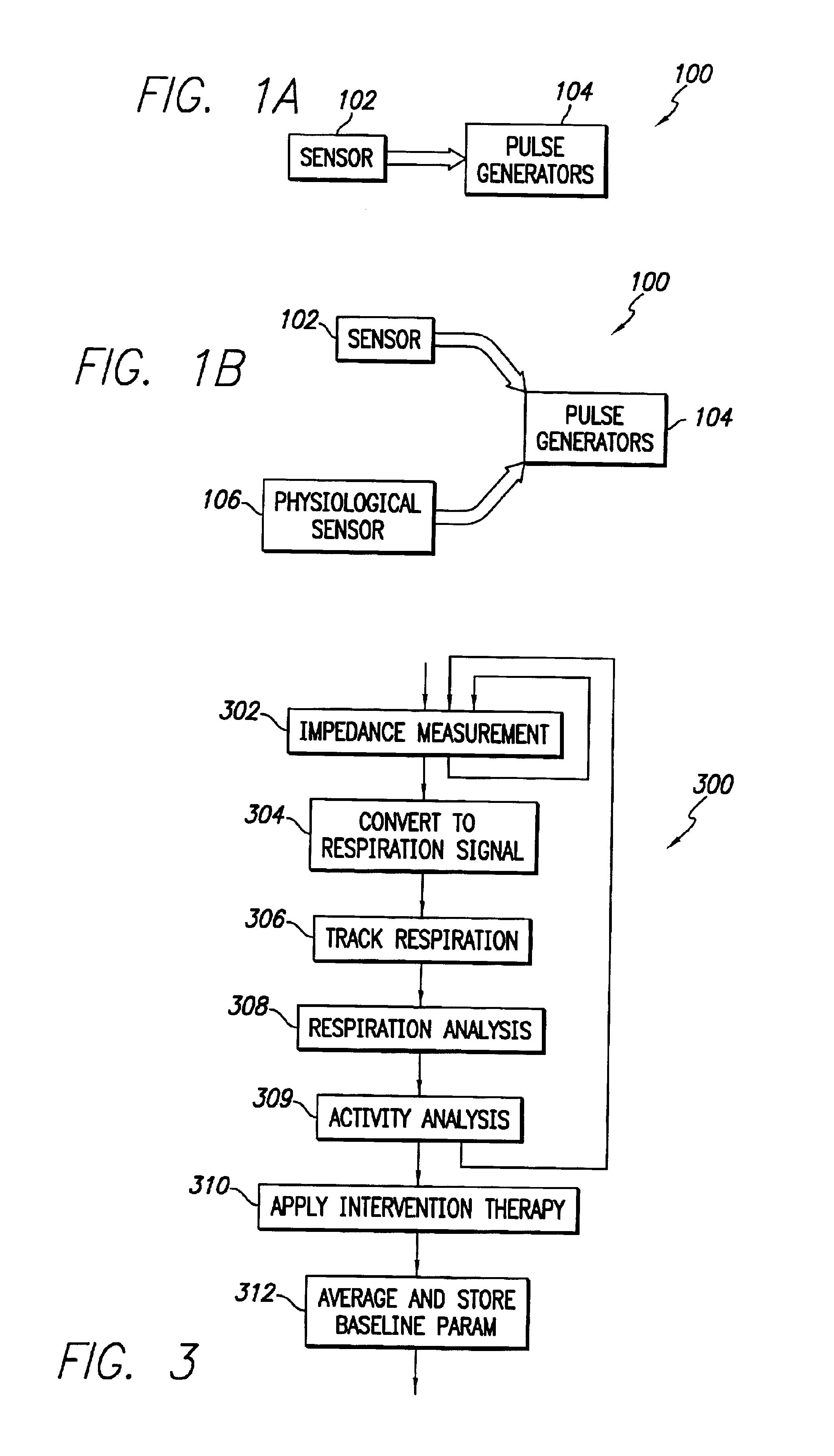
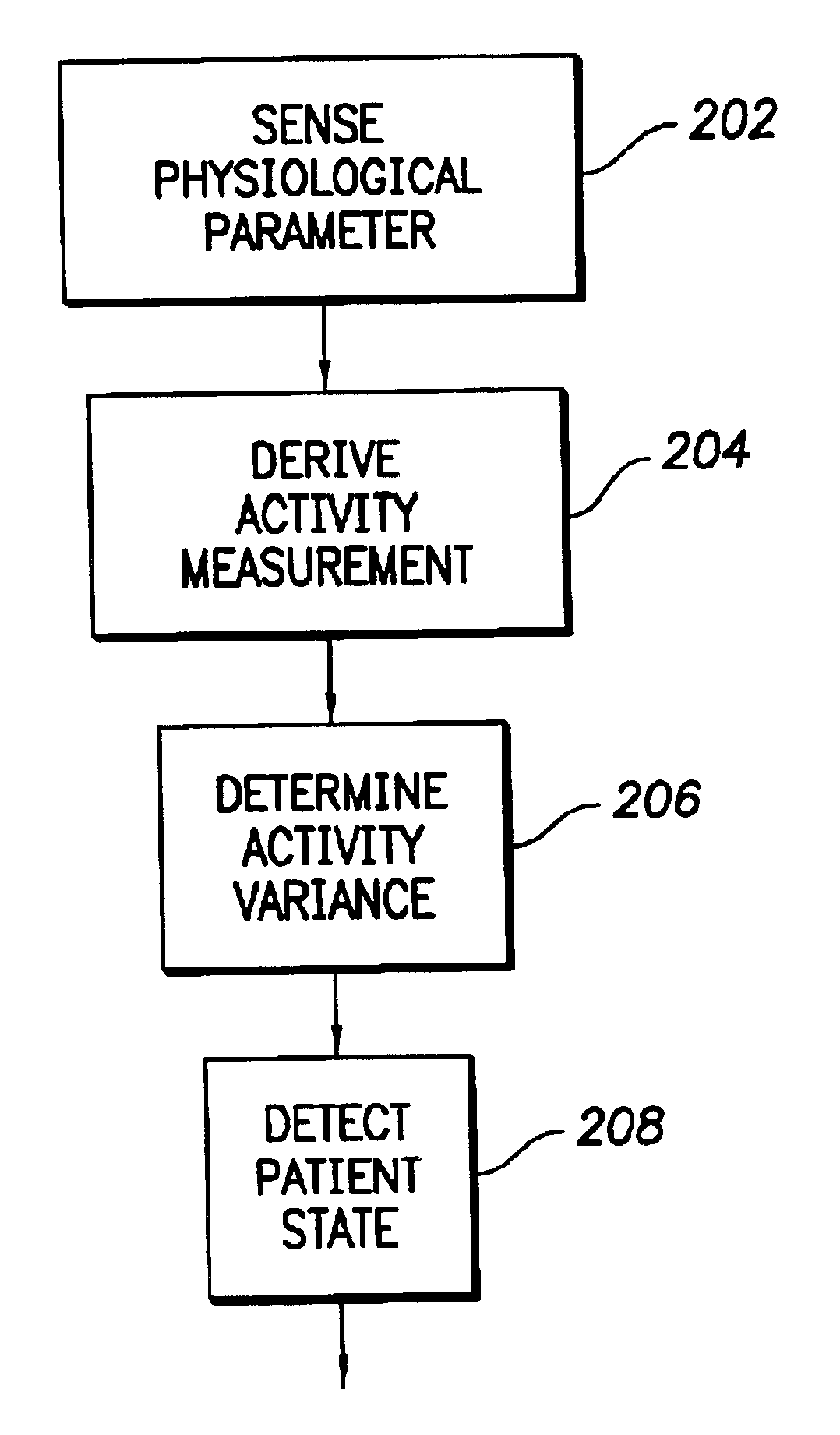
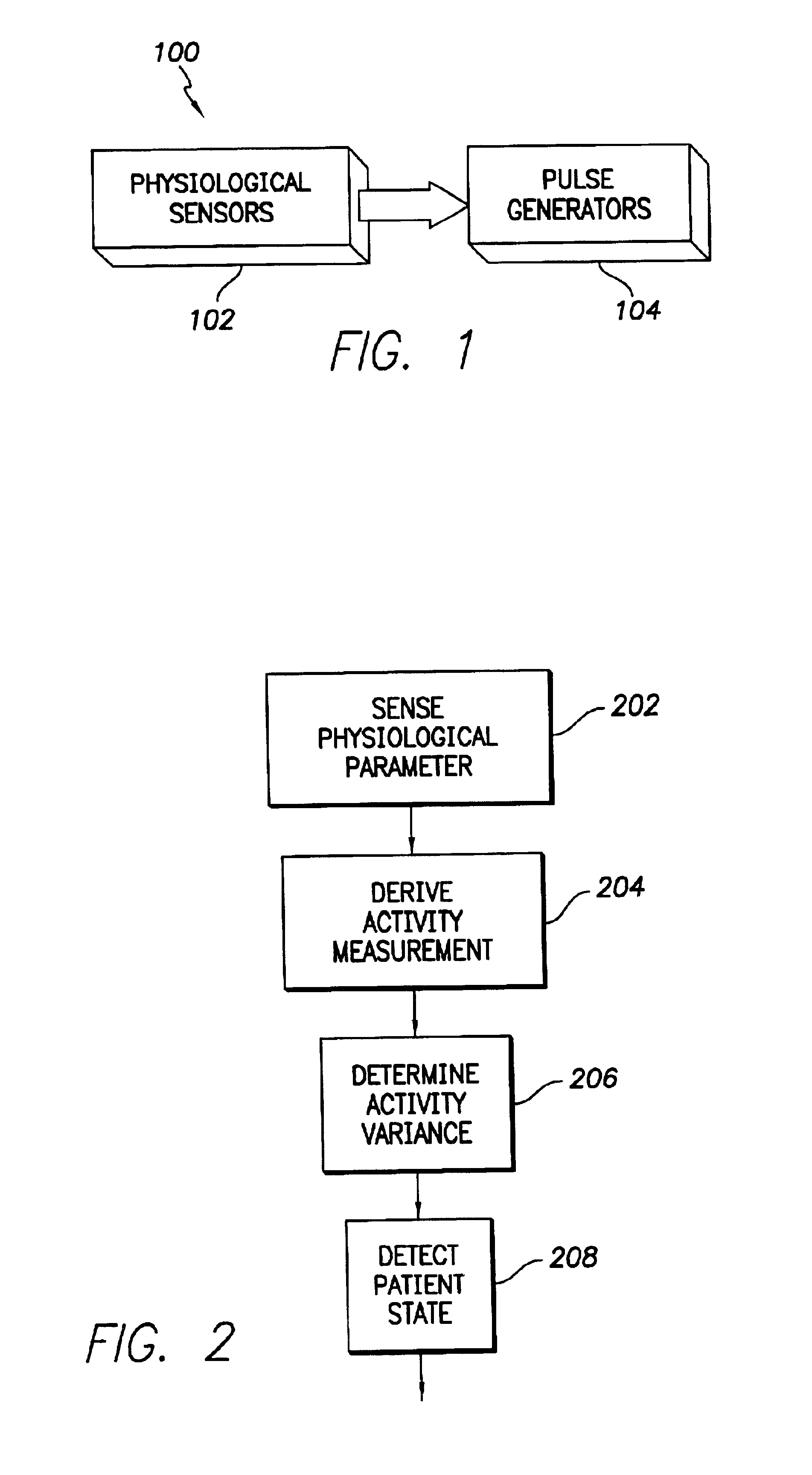
An implantable cardiac stimulation device comprises a metabolic demand sensor, an activity sensor, and one or more pulse generators. The metabolic demand sensor and activity sensor can sense metabolic demand and physical activity parameters, respectively. The pulse generators can generate cardiac pacing pulses with timing based on a comparison of the metabolic demand and physical activity parameters. The timed cardiac pacing pulses can prevent a sleep apnea condition.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
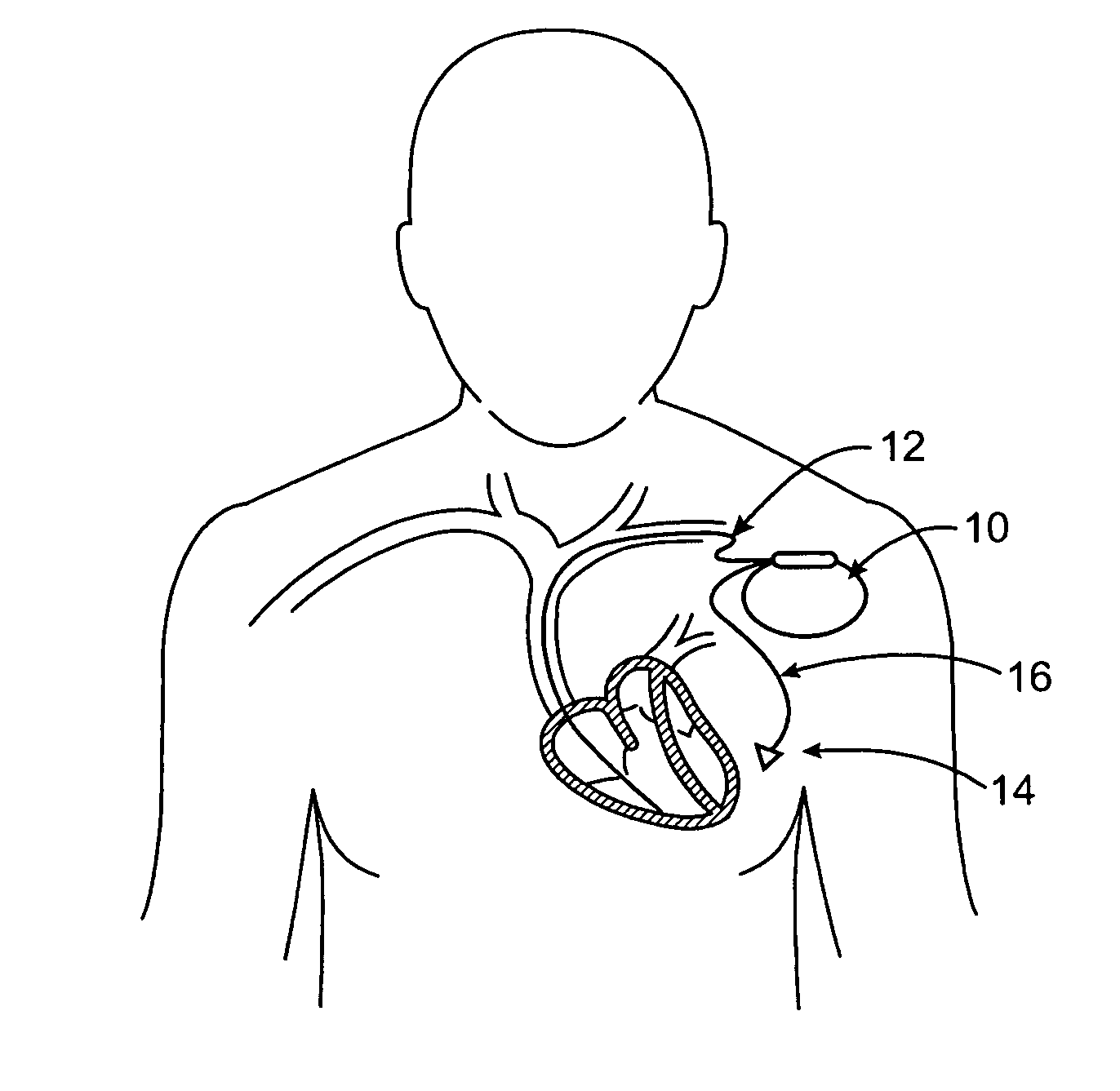
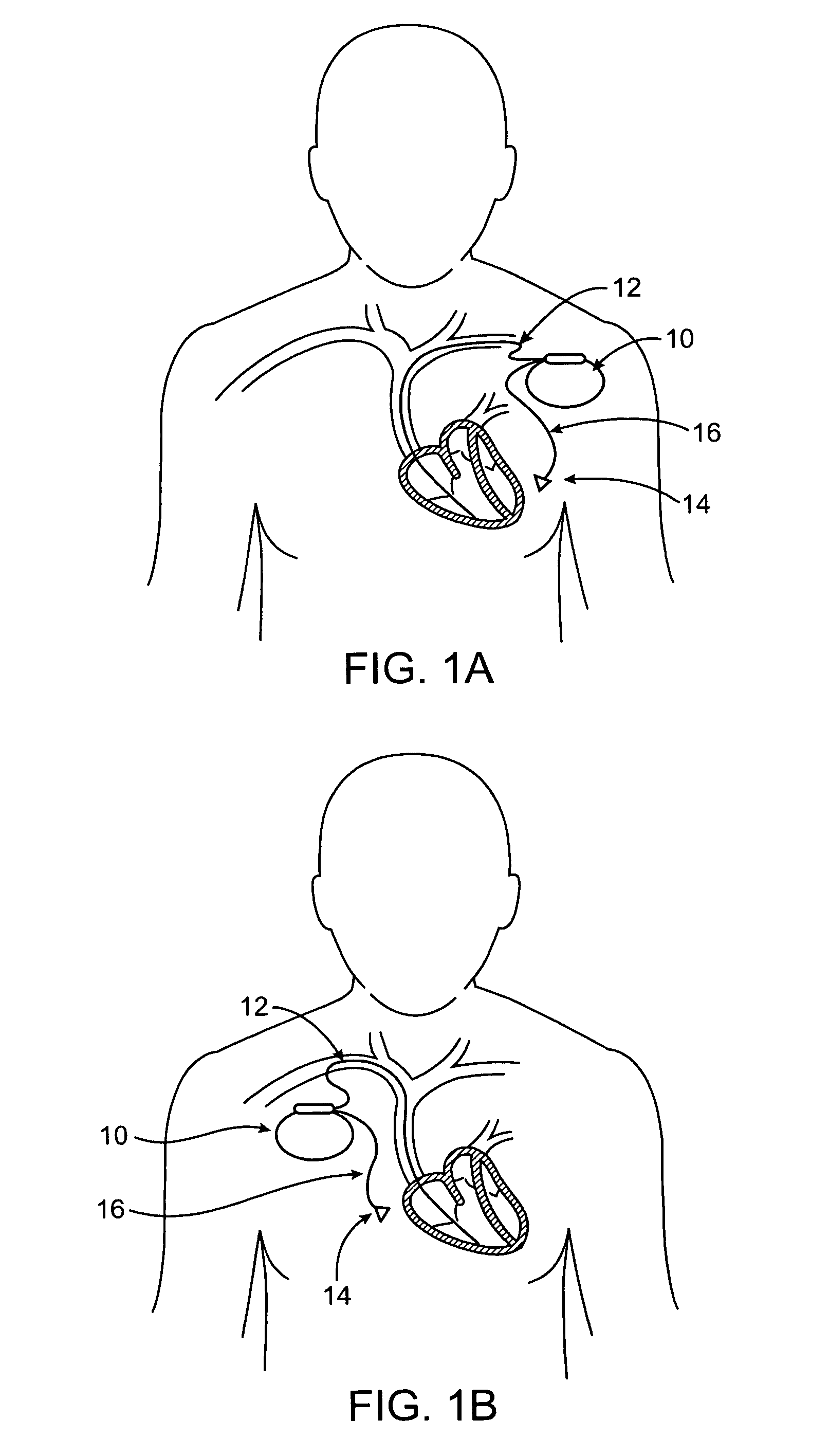
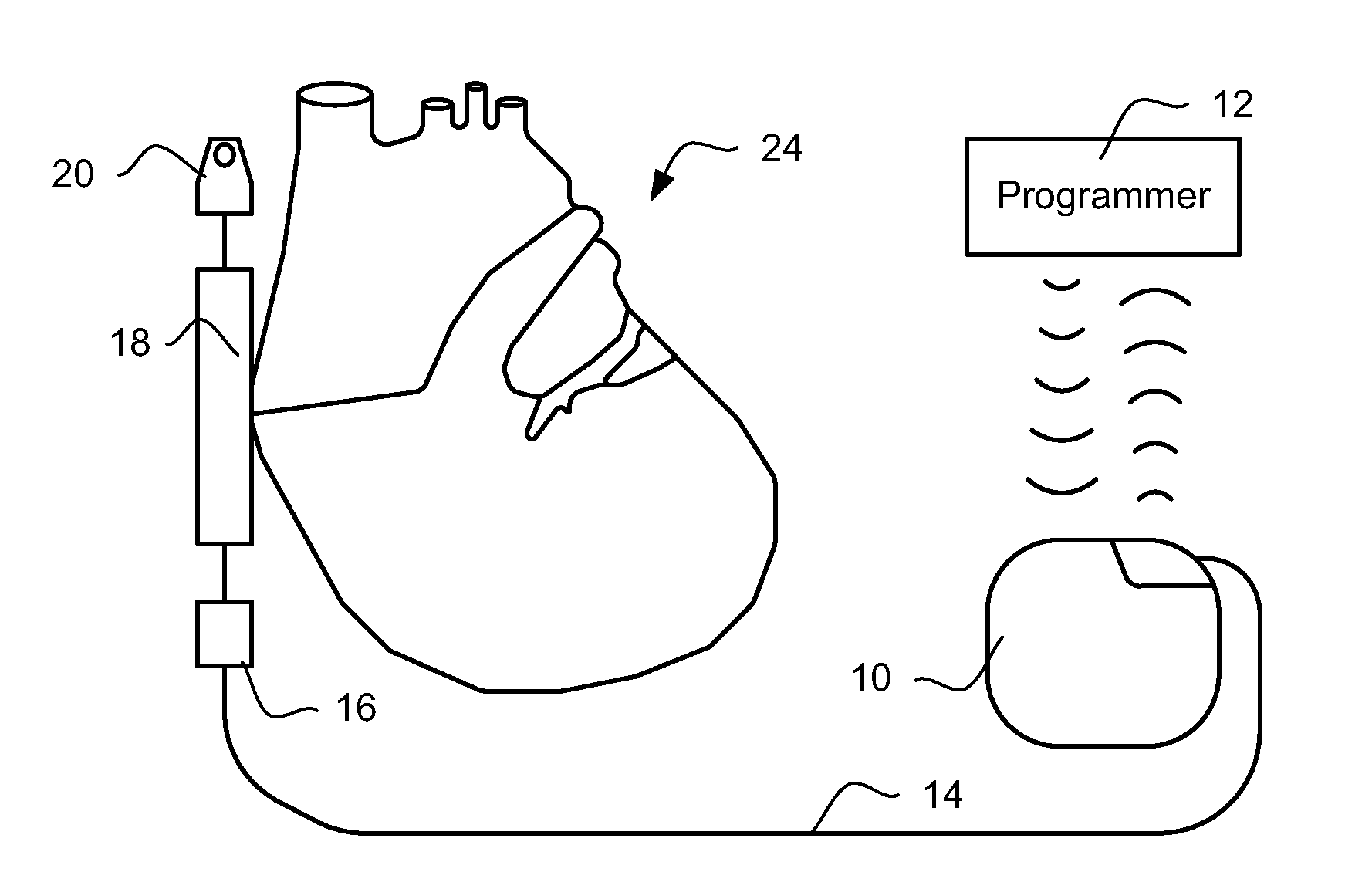
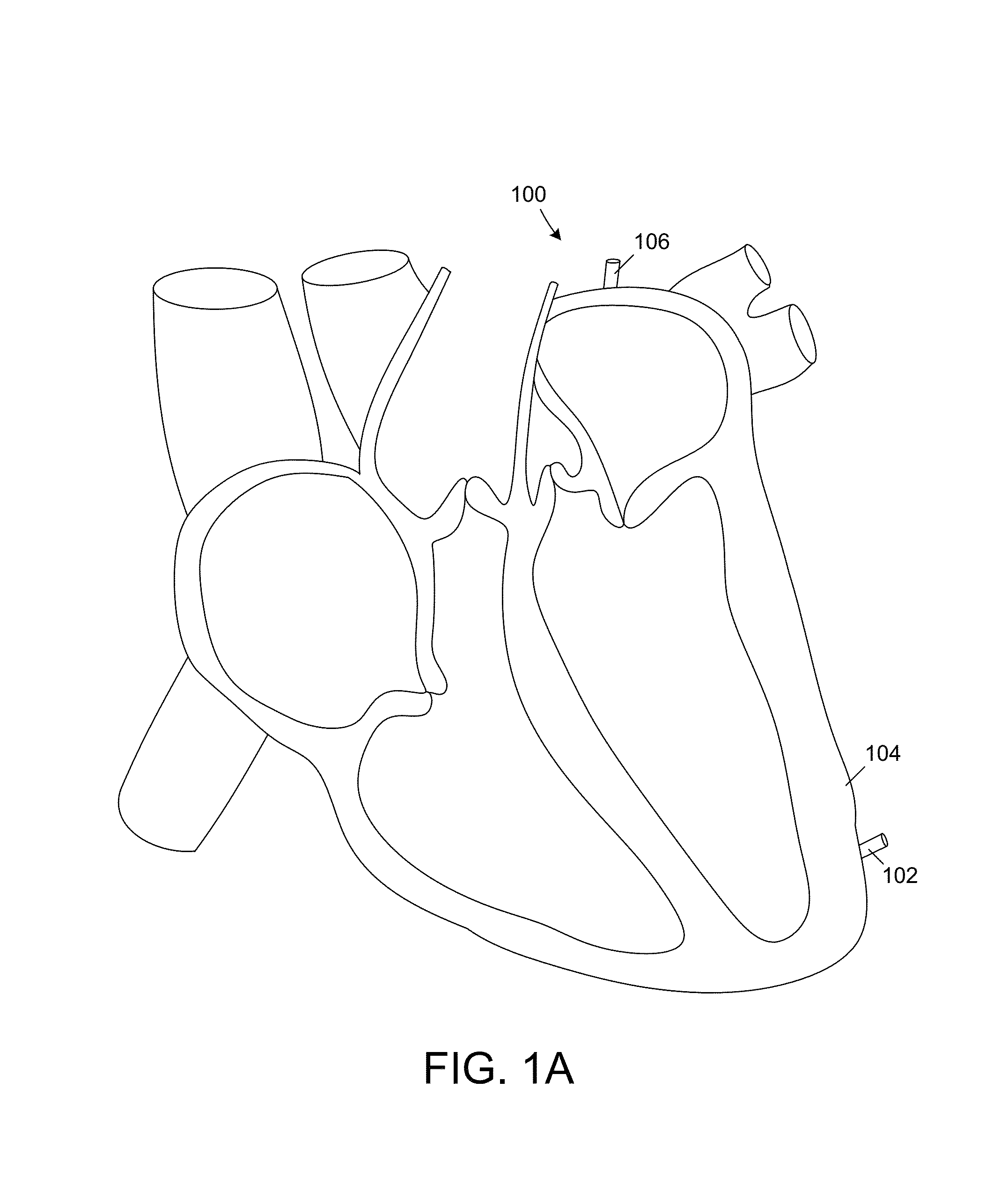
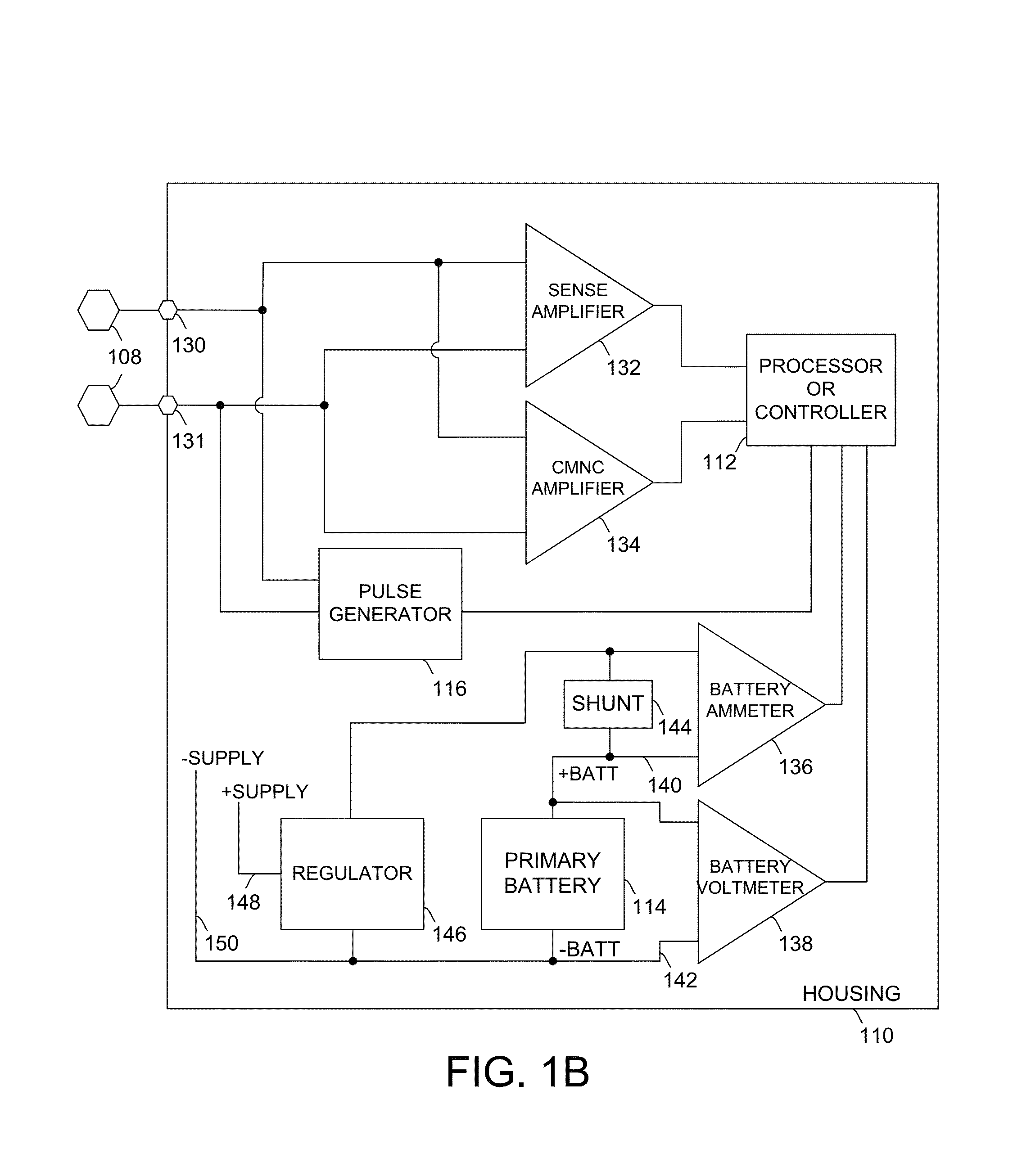
Leadless cardiac pacemaker with conducted communication
ActiveUS20120109236A1Convenient timeHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac pacemaker
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac rhythm management system promoting atrial pacing
InactiveUS6353759B1Promoting atrial pacingReduce the possibilityHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaInfinite impulse response
A cardiac rhythm management system includes an atrial pacing preference (APP) filter for promoting atrial pacing. The APP filter includes an infinite impulse response (IIR) or other filter that controls the timing of delivery of atrial pacing pulses. The atrial pacing pulses are delivered at an APP-indicated pacing rate that is typically at a small amount above the intrinsic atrial heart rate. For sensed beats, the APP indicated rate is increased until it becomes slightly faster than the intrinsic atrial heart rate. The APP-indicated pacing rate is then gradually decreased to search for the underlying intrinsic atrial heart rate. Then, after a sensed atrial beat, the APP filter again increases the pacing rate until it becomes faster than the intrinsic atrial rate by a small amount. As a result, most atrial heart beats are paced, rather than sensed. This decreases the likelihood of the occurrence of an atrial tachyarrhythima, such as atrial fibrillation. The decreased likelihood of atrial tachyarrhythmia, in turn, decreases the likelihood of inducing a ventricular arrhythmia, either as a result of the atrial tachyarrhythmia, or as the result of delivering a defibrillation shock to treat the atrial tachyarrhythmia.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Health monitoring garment
InactiveUS20030212319A1Increase the conductive areaConductivity of contactElectrocardiographyWeft knittingFiberElectricity
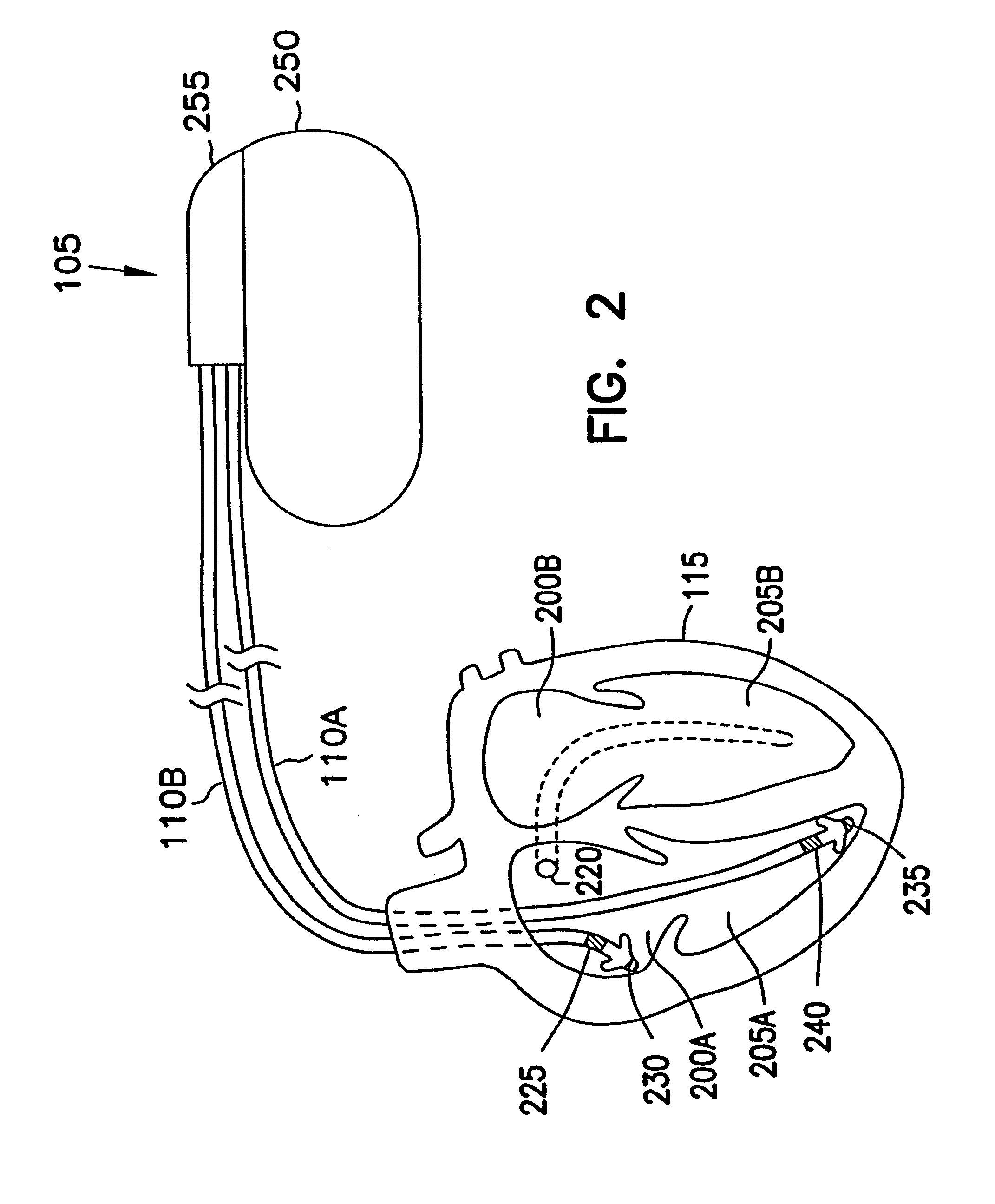
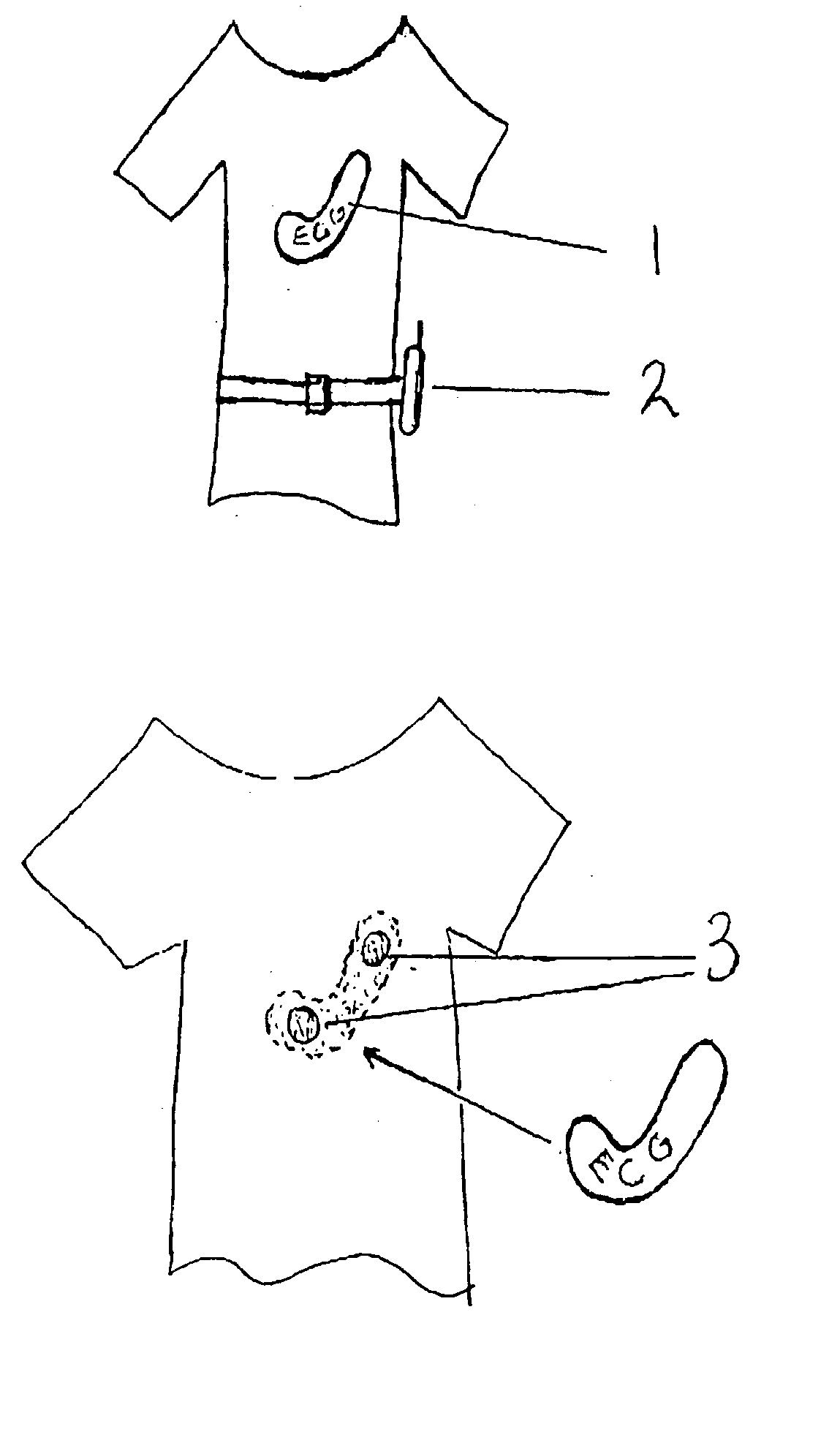
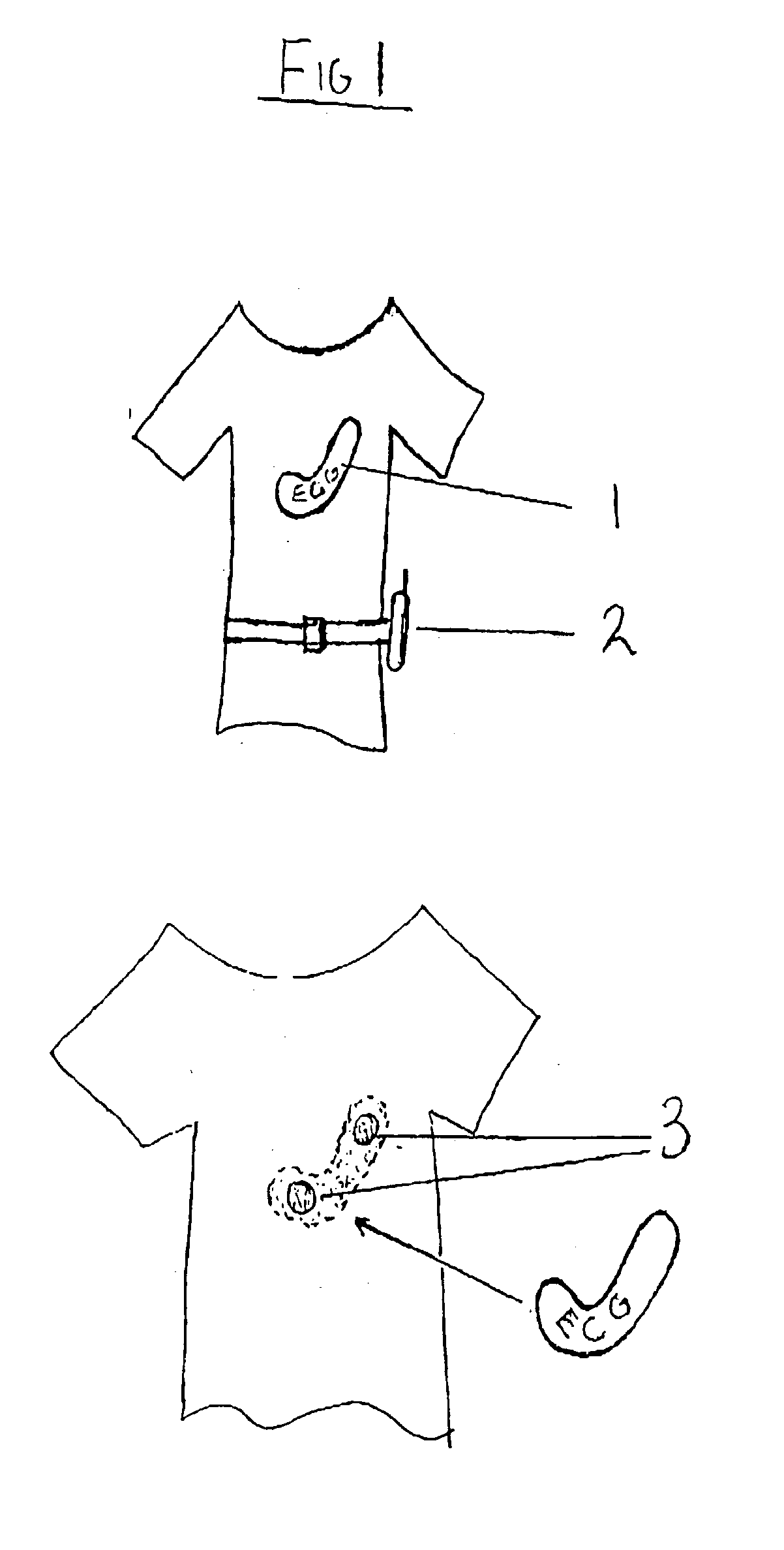
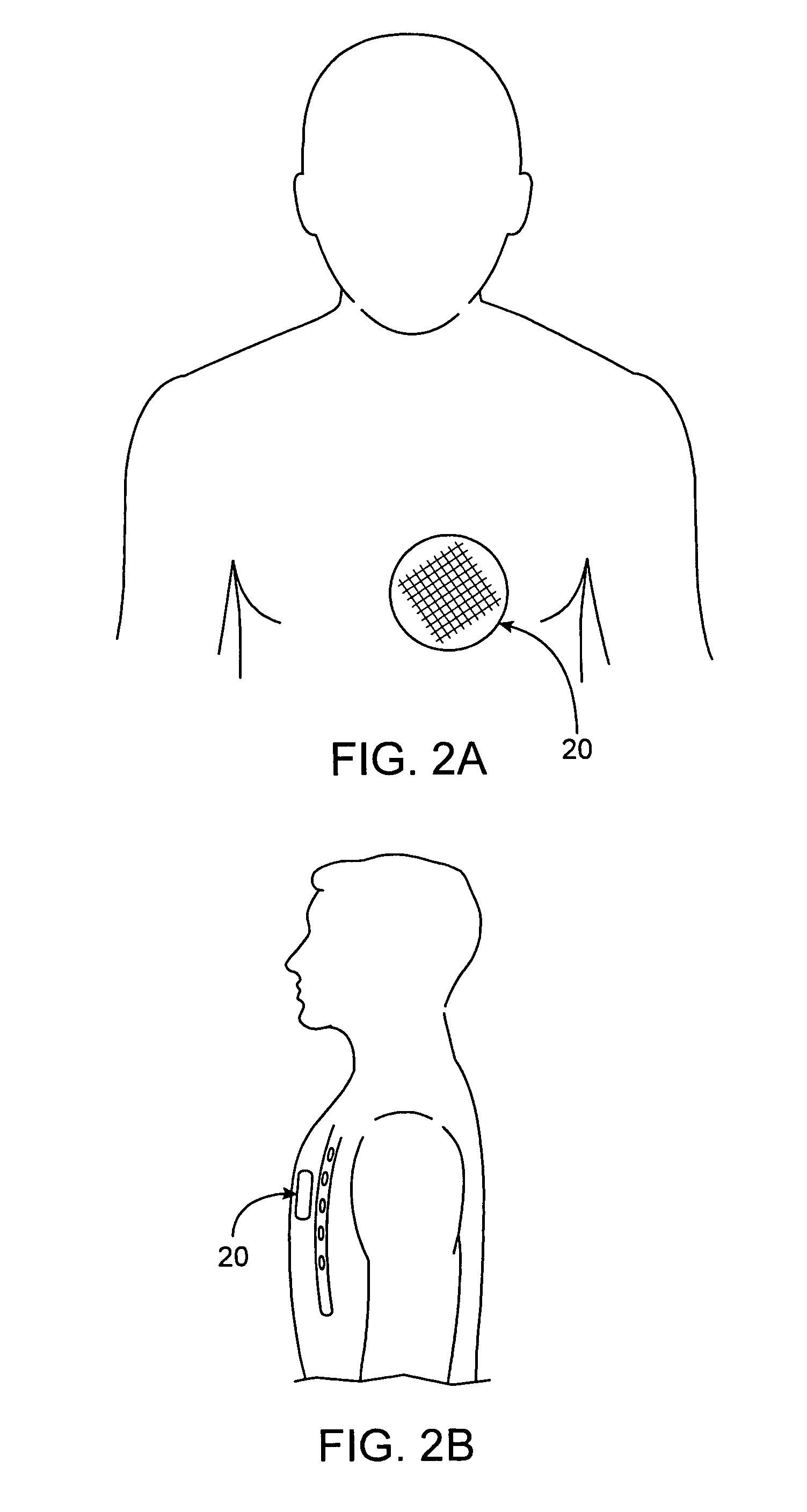
A health monitoring garment which employs a means of conducting electricity from the surface of the skin, through the fibres of a fabric to another fabric which is removably attached to it and contains a microprocessor, telemetry and a power source to monitor and transmit EKG data of a person wearing the clothing, as illustrated in FIG. 2. Removability enables tile garment to be washed and the electronics to be kept separate from the washing and tumble drying process. The same system can be used in reverse to effect cardiac pacing or defibrillation or to deliver other forms of electronically conveyed healing such as tissue repair.
Owner:MAGILL ALAN REMY
Biphasic waveform for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathorasic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Leadless Implantable Intravascular Electrophysiologic Device for Neurologic/Cardiovascular Sensing and Stimulation
ActiveUS20080119911A1Enhances specificity/integrityRestricted blood flowHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesOptical communicationRadio frequency
A leadless intravascular sensor (100, 200) uses the body tissue as a communication medium. The implantable intravascular device has a tubular stent-like structure (102) for intravascular fixation with embedded microcircuits to allow bipolar and unipolar sensing of cardiac and neurologic electrical activity, sensing of other physiologic signals, local electrical stimulation (cardiac pacing and defibrillation; neurologic stimulation and seizure therapy) as well as the ability to communicate with other implanted and non implanted devices via radio frequency and / or optical communication and / or analog signal communication using the body tissue as the conducting medium. The device can also be used in the extravascular or perivascular space. In this form, it has an open / flexible ring that can be adjusted, or self-adjusts to provide no pressure or required contact around the vessel or target region.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
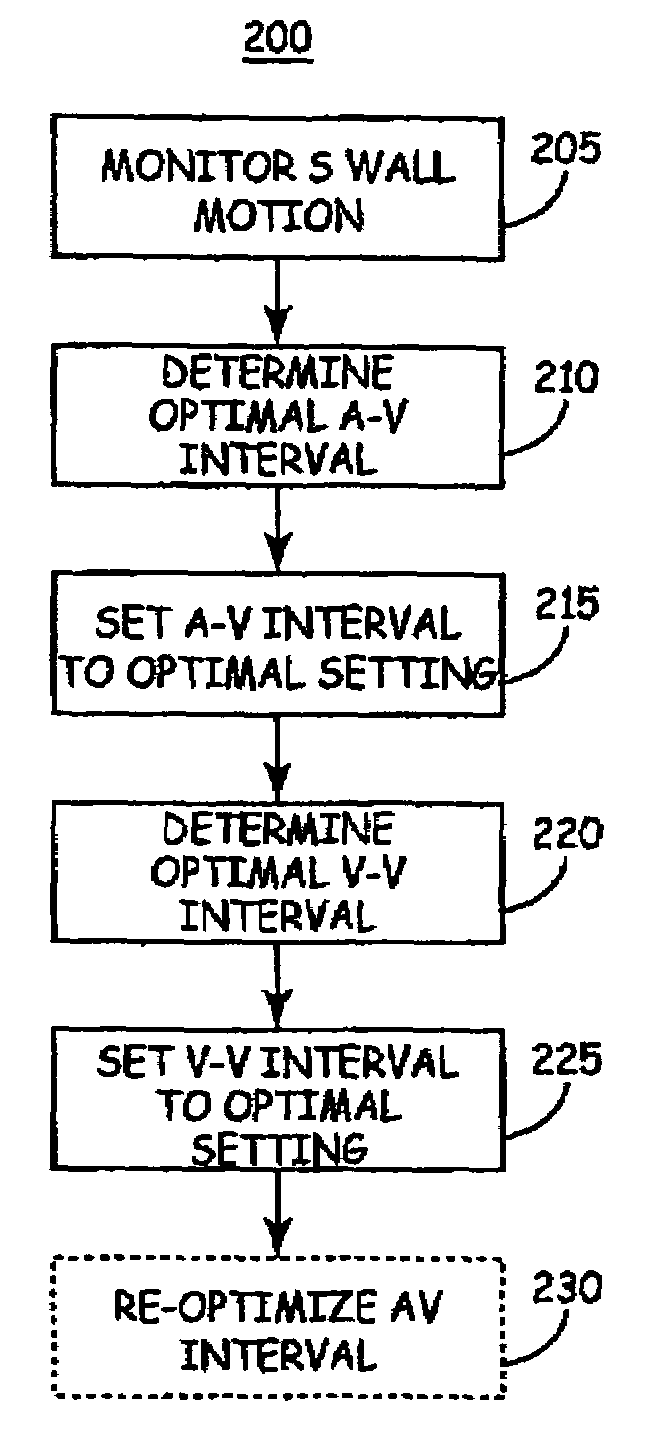
Method of optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy using sensor signals of septal wall motion
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
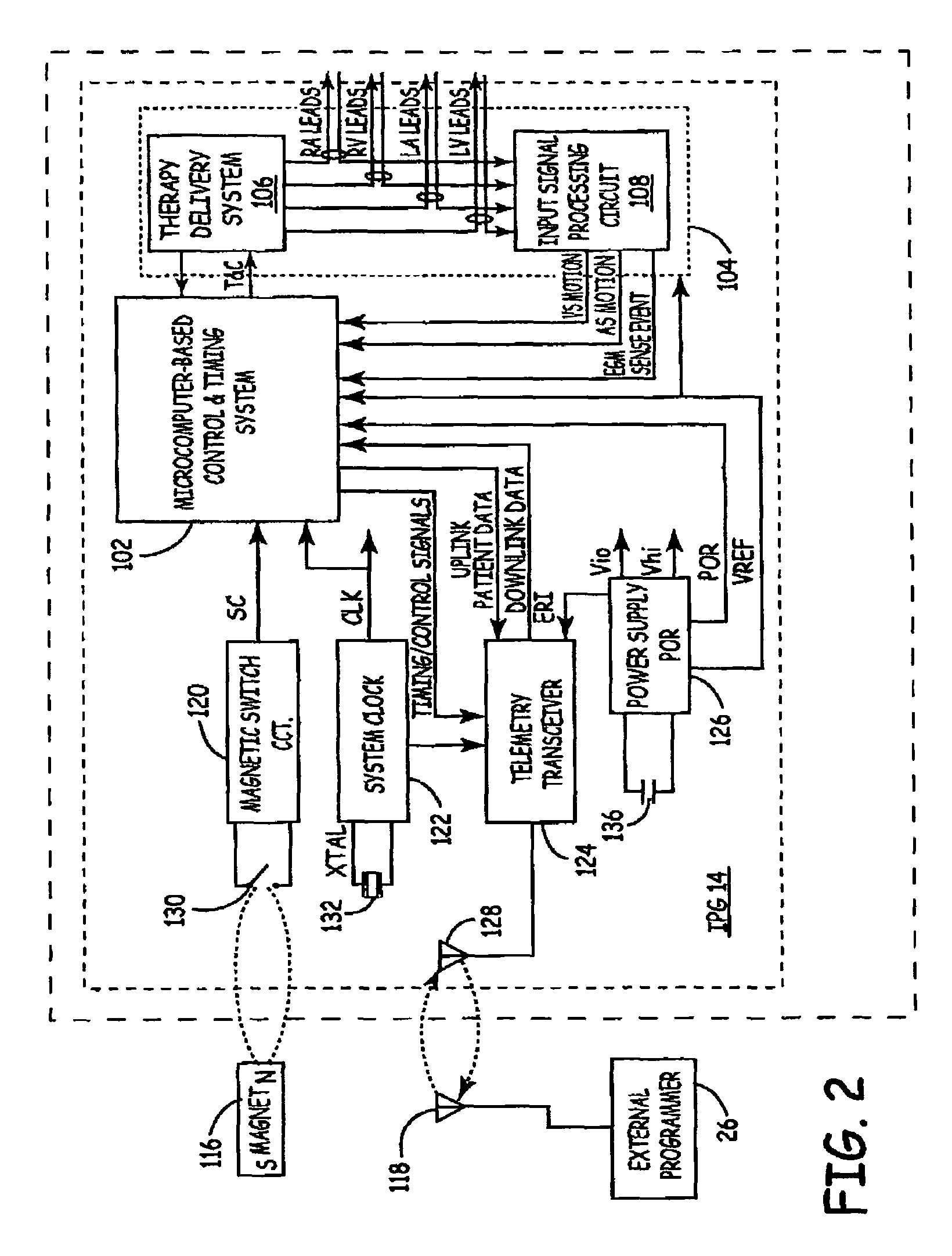
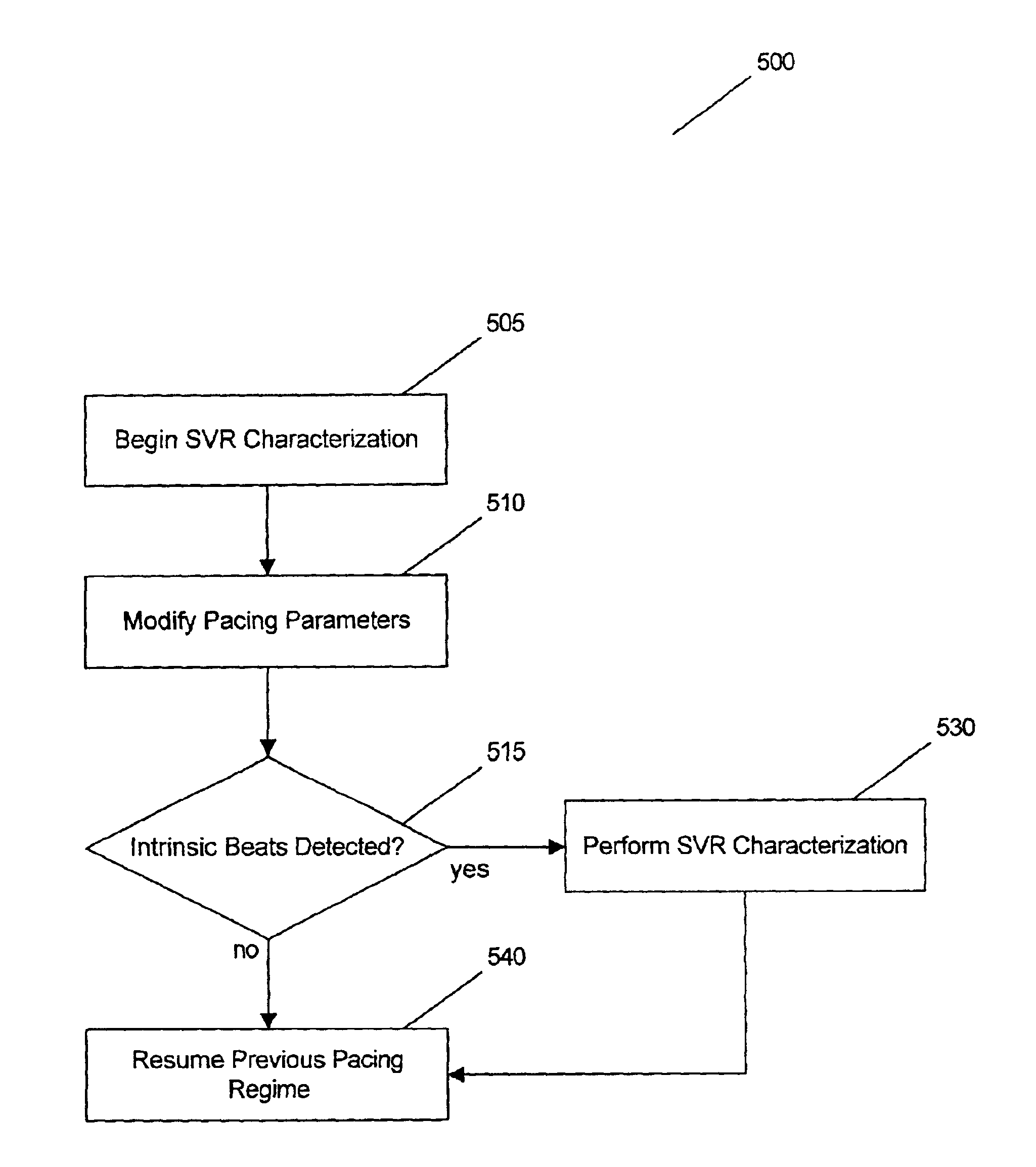
Method and system for characterizing supraventricular rhythm during cardiac pacing
A method and system for generating a characterization of one beat of a patient's supraventricular rhythm (SVR) involves performing such characterization while the heart is being paced. During SVR characterization, various pacing parameters are modified and the patient's supraventricular rhythm is characterized while the pacing parameters are modified. The SVR characterization process is effective in single and multiple chamber pacing modes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC +1
Method and apparatus for enhancing cardiac pacing
ActiveUS7200439B2Realize automatic adjustmentEnhancing cardiac pacingCatheterHeart stimulatorsActuatorHeart wall
Methods, apparatus and systems for enhancing cardiac pacing generally provide for measuring at least one cardiac characteristic, calculating at least one cardiac performance parameter based on the measured characteristic(s), and adjusting at least one functional parameter of a cardiac pacing device. Devices may include at least one catheter (such as a multiplexed catheter with one or more sensors and / or actuators), at least one implant (such as a sensor implantable in a heart wall), or a combination of both. Various cardiac performance parameters and / or pacing device performance parameters may be weighted, and the parameters and their respective weights may be used to determine one or more adjustments to be made to the pacing device. In some instances, the adjustments are made automatically.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
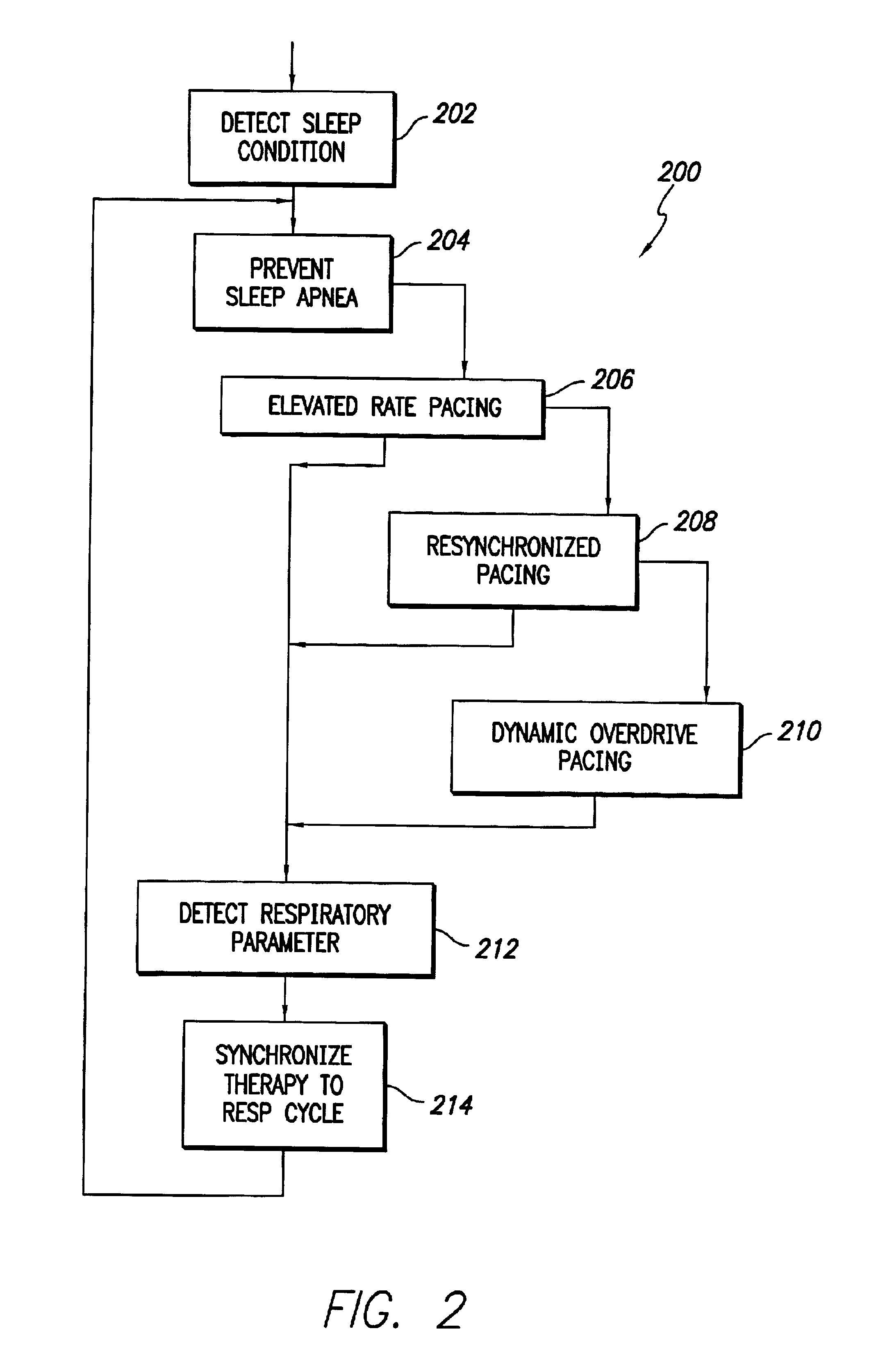
Cardiac stimulation device including sleep apnea prevention and treatment
InactiveUS7212862B2Prevents sleep apneaReduce outputHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationTreatment sleepPulse rate
An implantable cardiac stimulation device comprises a physiologic sensor and one or more pulse generators. The physiologic sensor is capable of sensing a physiologic parameter. The pulse generators can generate cardiac pacing pulses with a timing based on the physiologic parameter. The timed cardiac pacing pulses can prevent a sleep apnea condition. In one example, a cardiac stimulation device has a physiologic sensor and can be configured to pace a patient's heart according to a rest mode of operation. The cardiac stimulation device uses measurements from the physiologic sensor to prevent and treat sleep apnea using a revised rest mode of operation. The revised rest mode operates under a presumption that sleep apnea is primary to a reduced heart rate, rather than secondary, so that pacing at a rate higher than the natural cardiac rate during sleep will prevent sleep apnea.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Sleep apnea therapy device using dynamic overdrive pacing
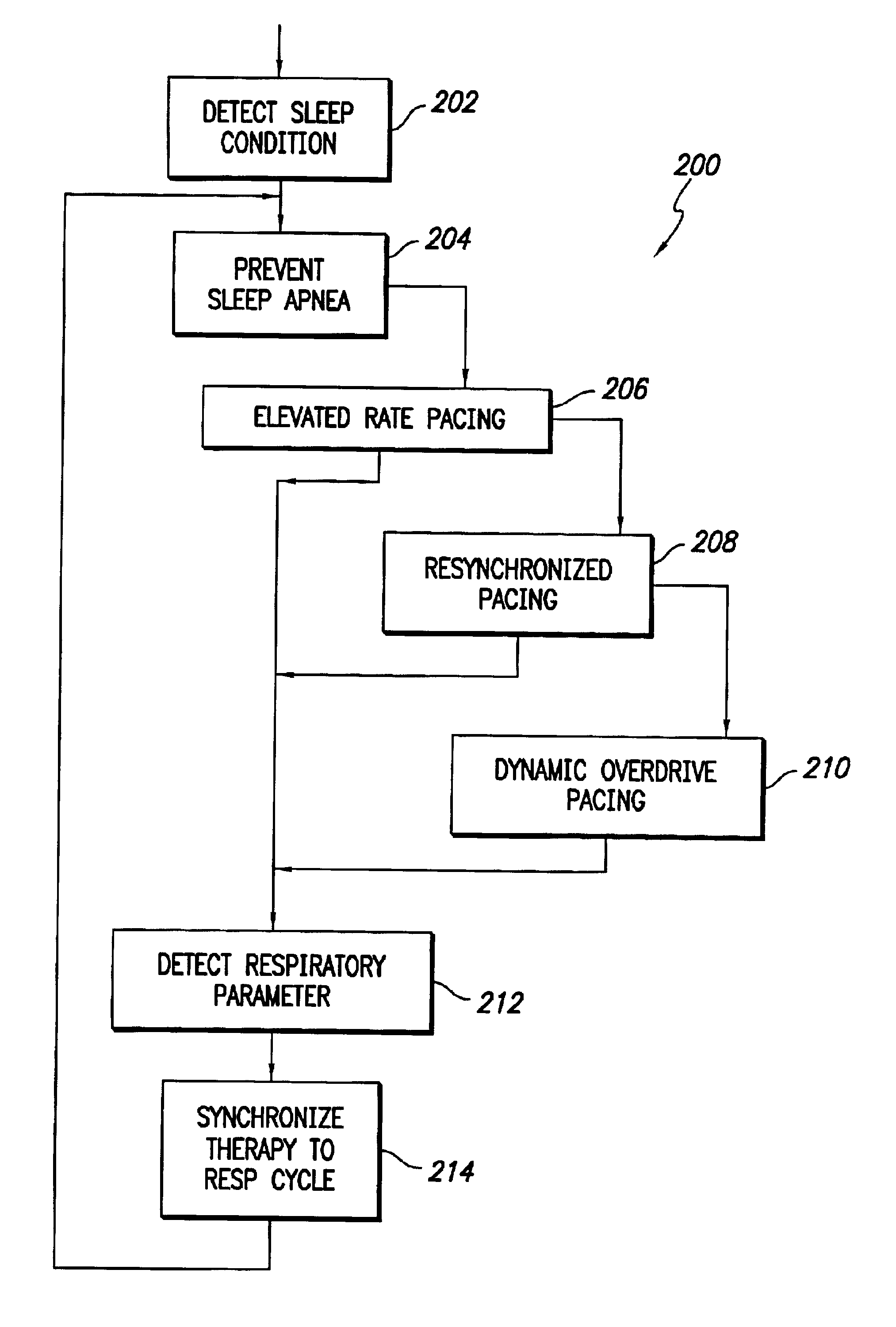
A cardiac stimulation device uses dynamic overdrive pacing to prevent sleep apnea. In another aspect, the device can use dynamic overdrive pacing to terminate sleep apnea after detection. An implantable cardiac stimulation device comprises a sensor and one or more pulse generators. The sensor senses intrinsic cardiac electrical phenomena. The pulse generators can generate cardiac pacing pulses with timing based on the sensed intrinsic cardiac electrical phenomena to dynamically overdrive the intrinsic cardiac electrical phenomena. The timed cardiac pacing pulses can prevent a sleep apnea condition.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac stimulation device including sleep apnea prevention and treatment
InactiveUS6999817B2Prevents sleep apneaAvoid adjustmentHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationTreatment sleepPulse rate
An implantable cardiac stimulation device comprises a physiologic sensor and one or more pulse generators. The physiologic sensor is capable of sensing a physiologic parameter. The pulse generators can generate cardiac pacing pulses with a timing based on the physiologic parameter. The timed cardiac pacing pulses can prevent a sleep apnea condition. In one example, a cardiac stimulation device has a physiologic sensor and can be configured to pace a patient's heart according to a rest mode of operation. The cardiac stimulation device uses measurements from the physiologic sensor to prevent and treat sleep apnea using a revised rest mode of operation. The revised rest mode operates under a presumption that sleep apnea is primary to a reduced heart rate, rather than secondary, so that pacing at a rate higher than the natural cardiac rate during sleep will prevent sleep apnea.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
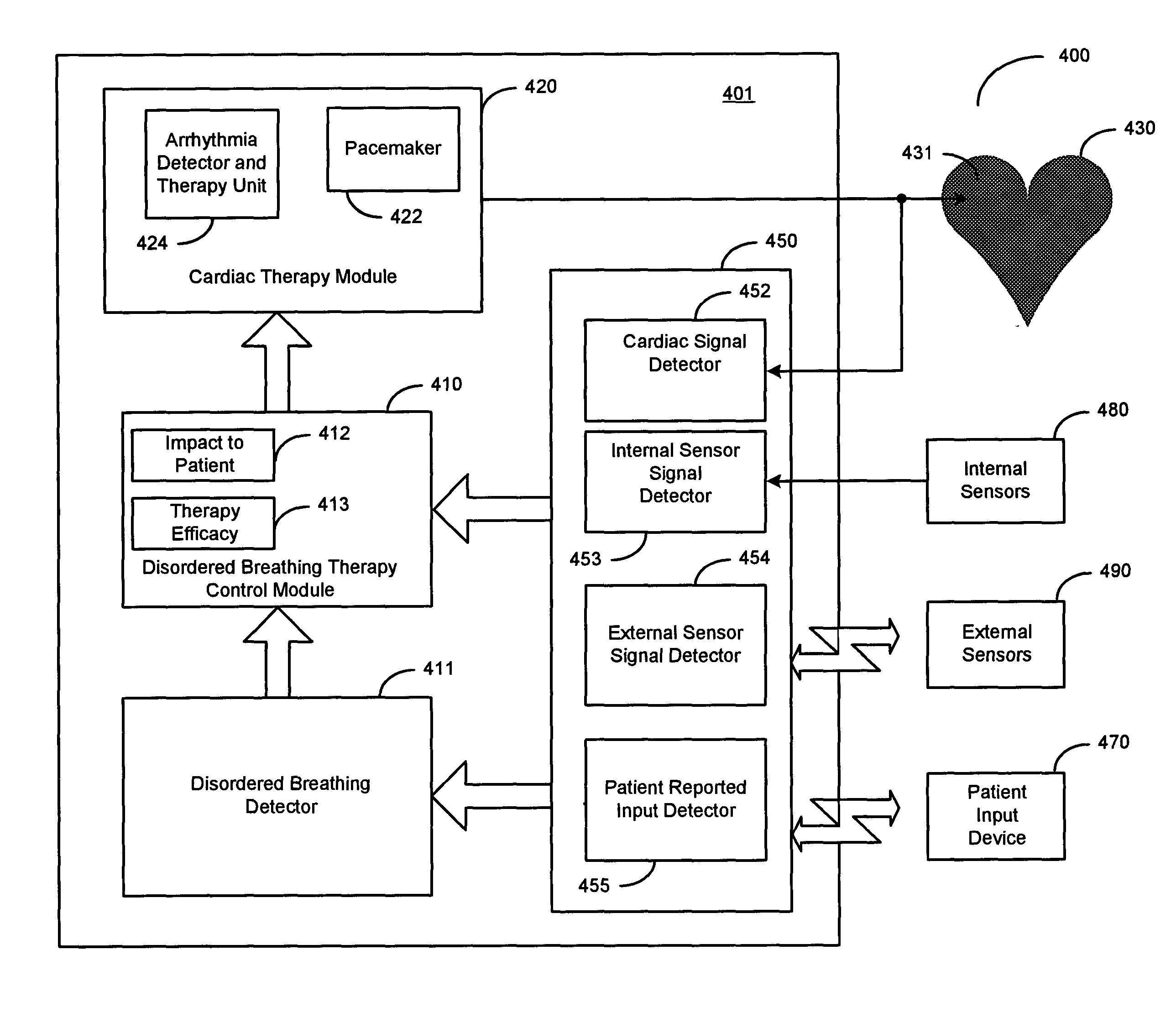
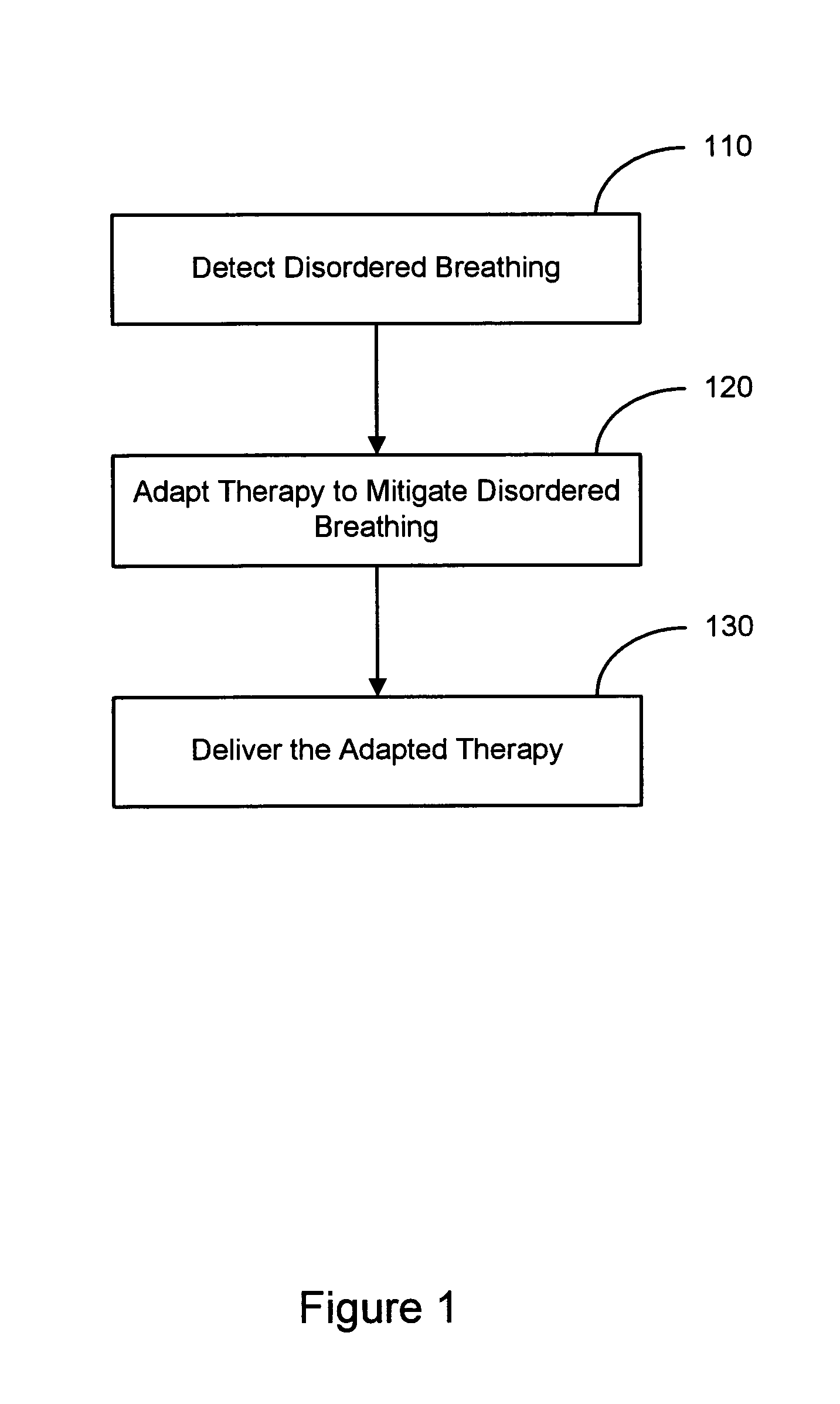
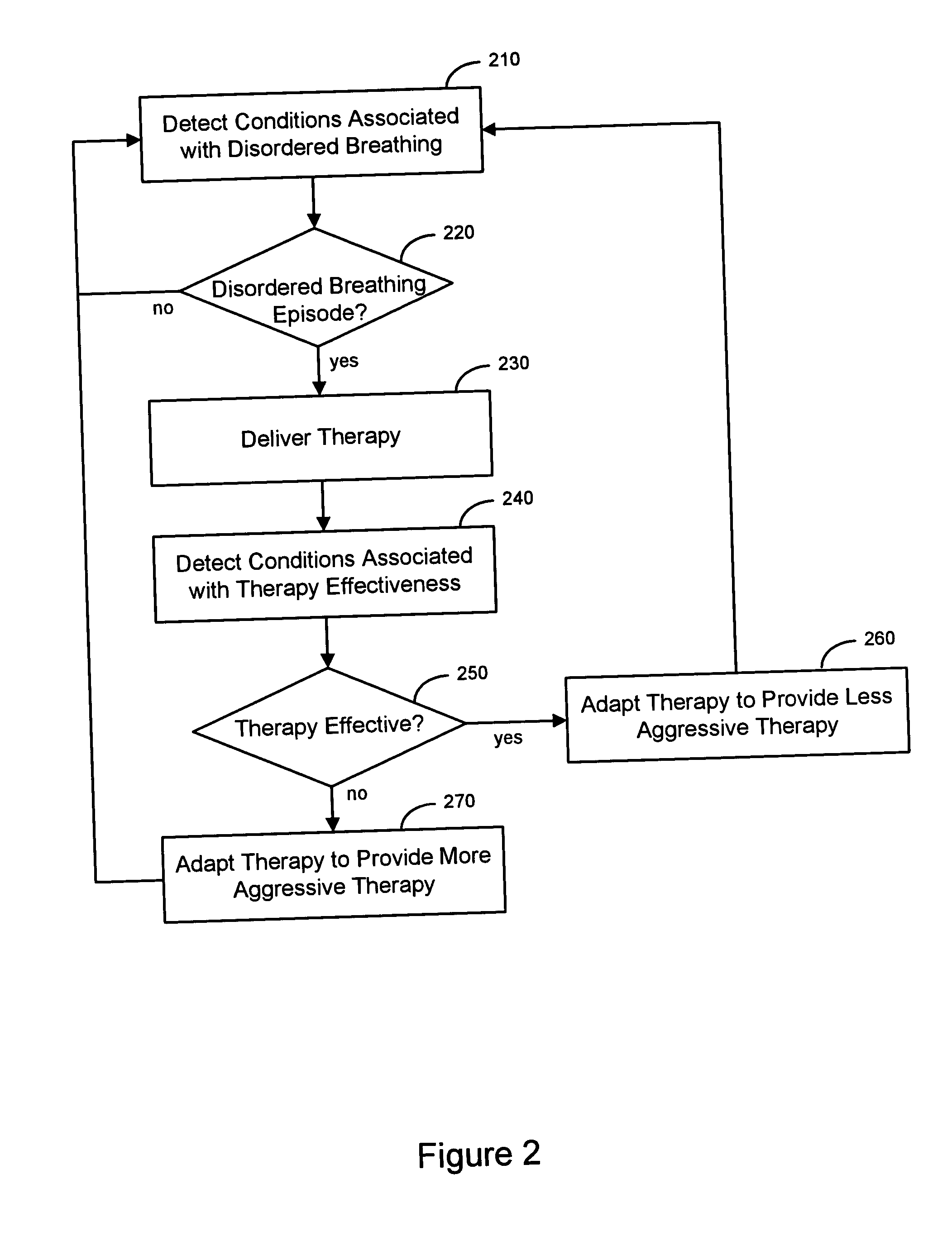
Adaptive therapy for disordered breathing
InactiveUS20050039745A1Mitigate disordered breathingImprove efficiencyRespiratorsFire rescueTherapeutic goalBreathing therapy
An approach to providing disordered breathing therapy includes detecting disordered breathing and adapting a therapy to mitigate the disordered breathing. The therapy may be adapted to enhance therapy effectiveness, to provide therapy that reduces an impact of the therapy on the patient, or to achieve other therapeutic goals. Cardiac electrical therapy to mitigate the disordered breathing may include various cardiac pacing regimens and / or delivery of non-excitatory electrical stimulation to the heart.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
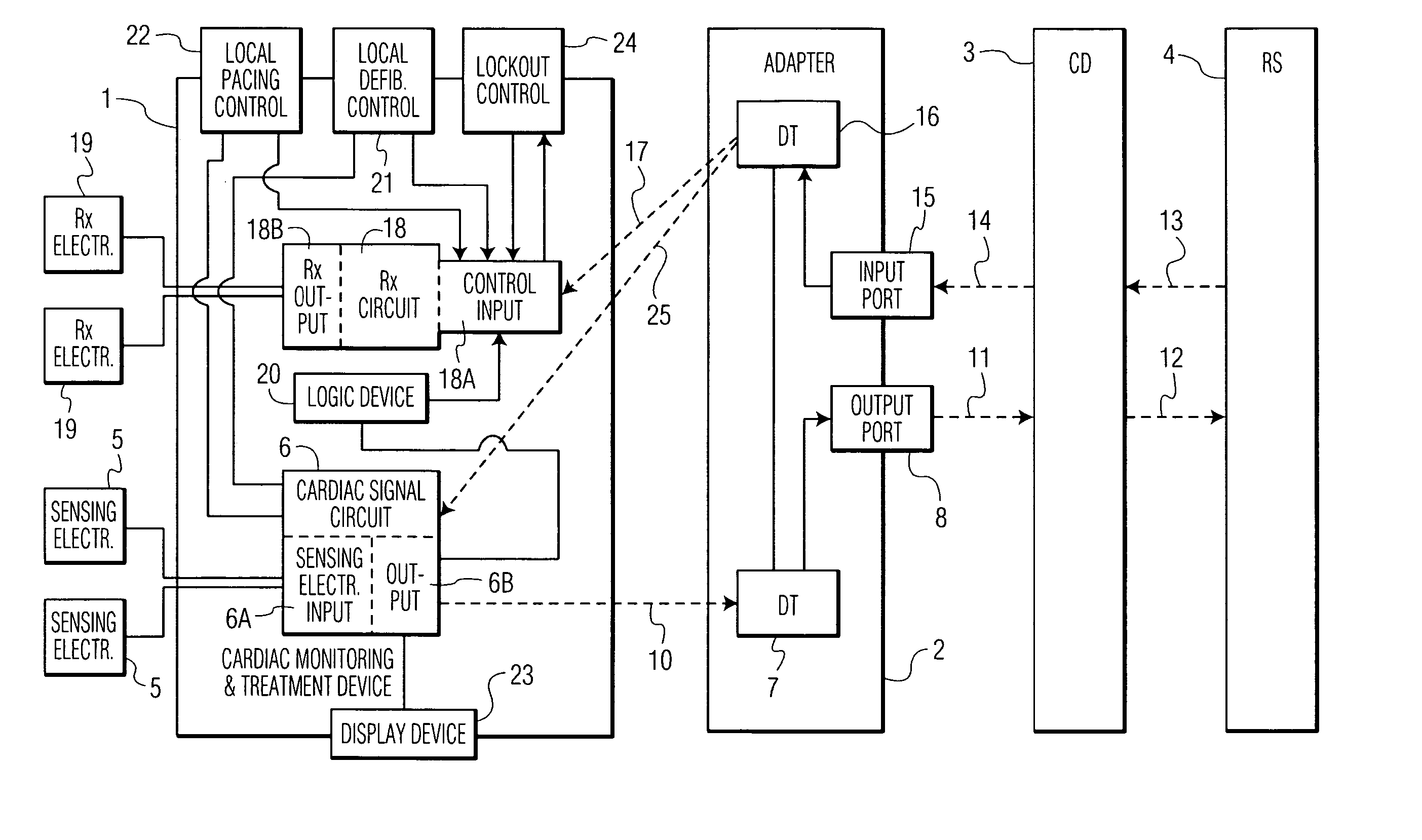
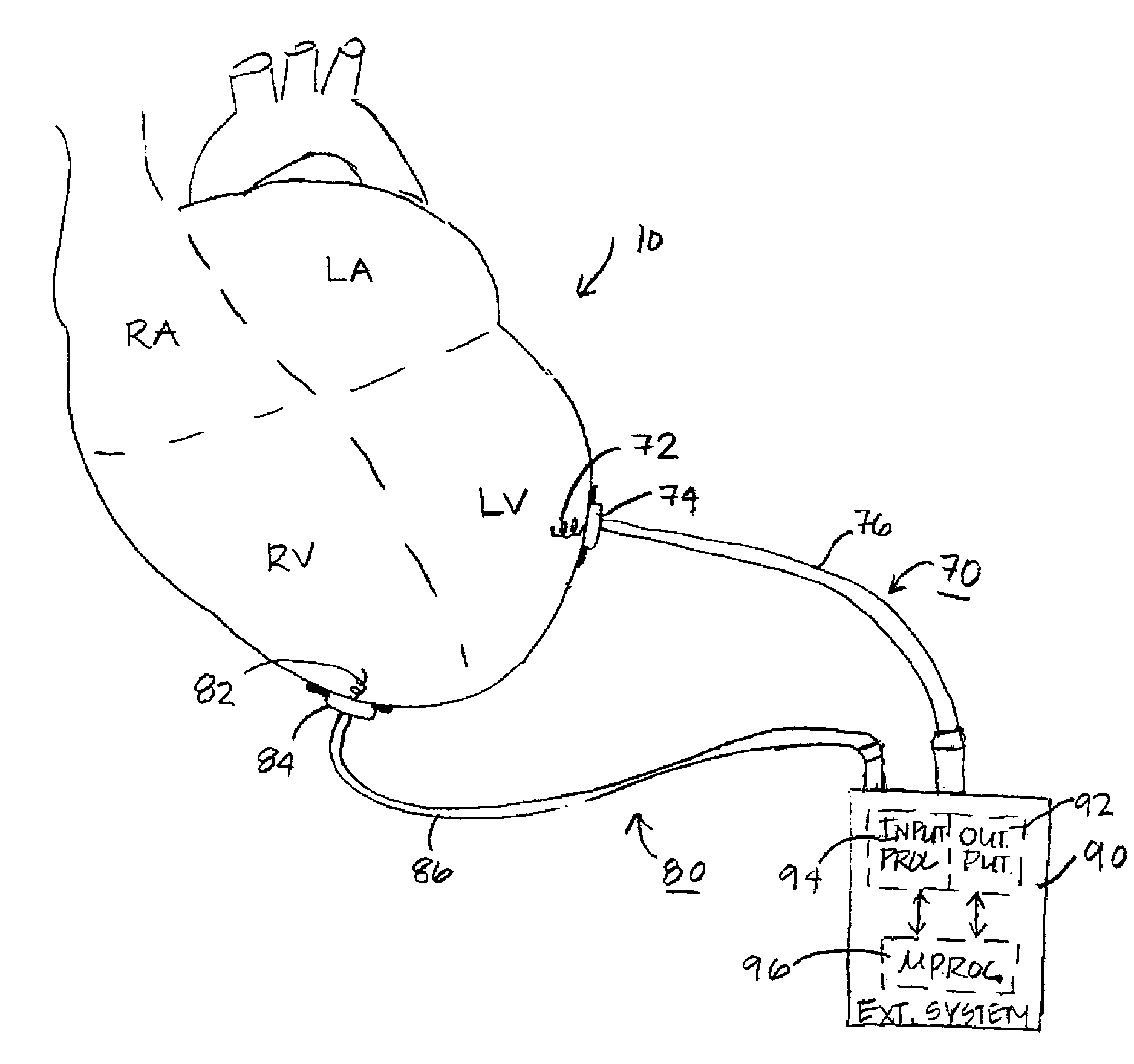
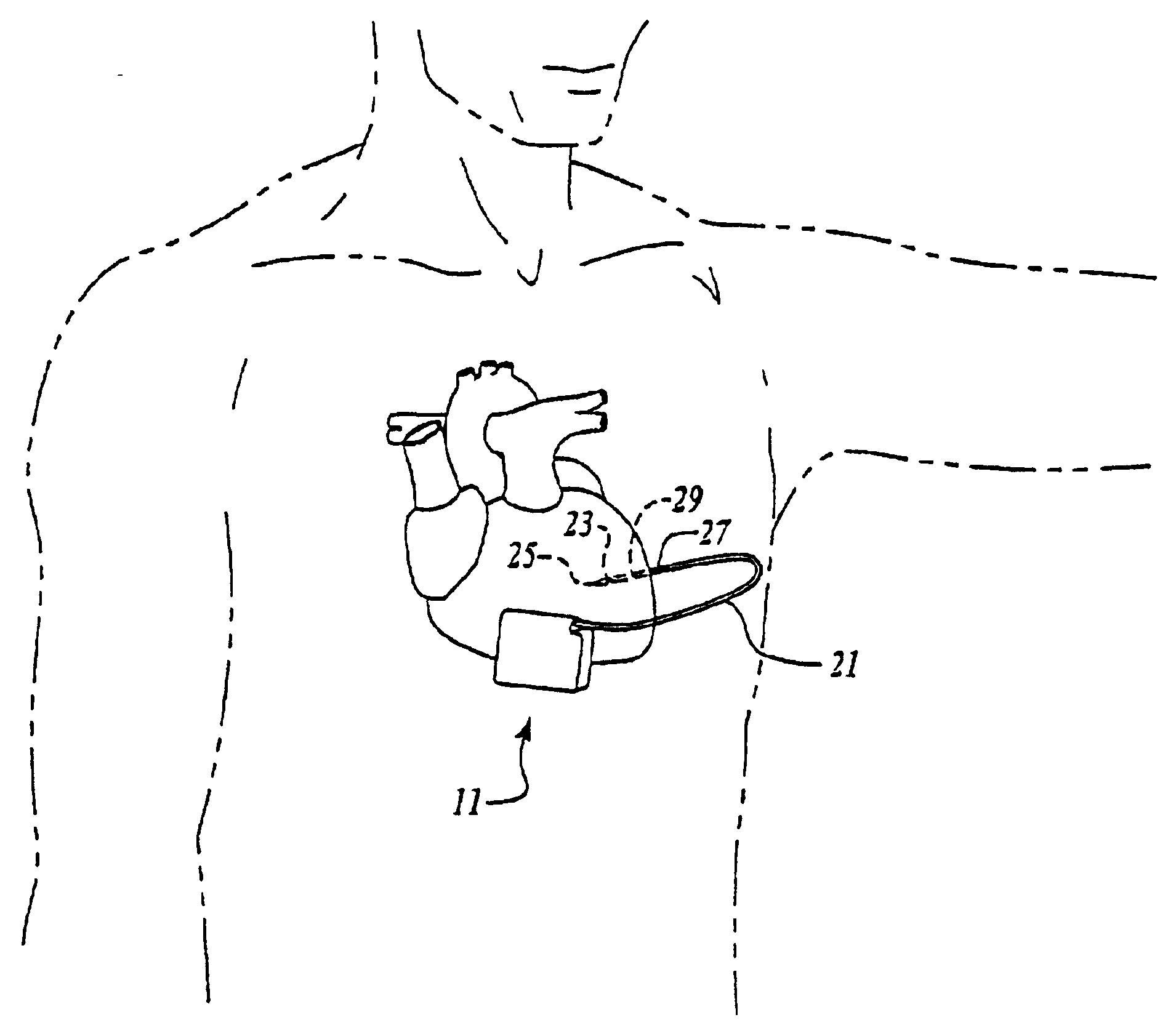
Control of a defibrillator and/or pacemaker
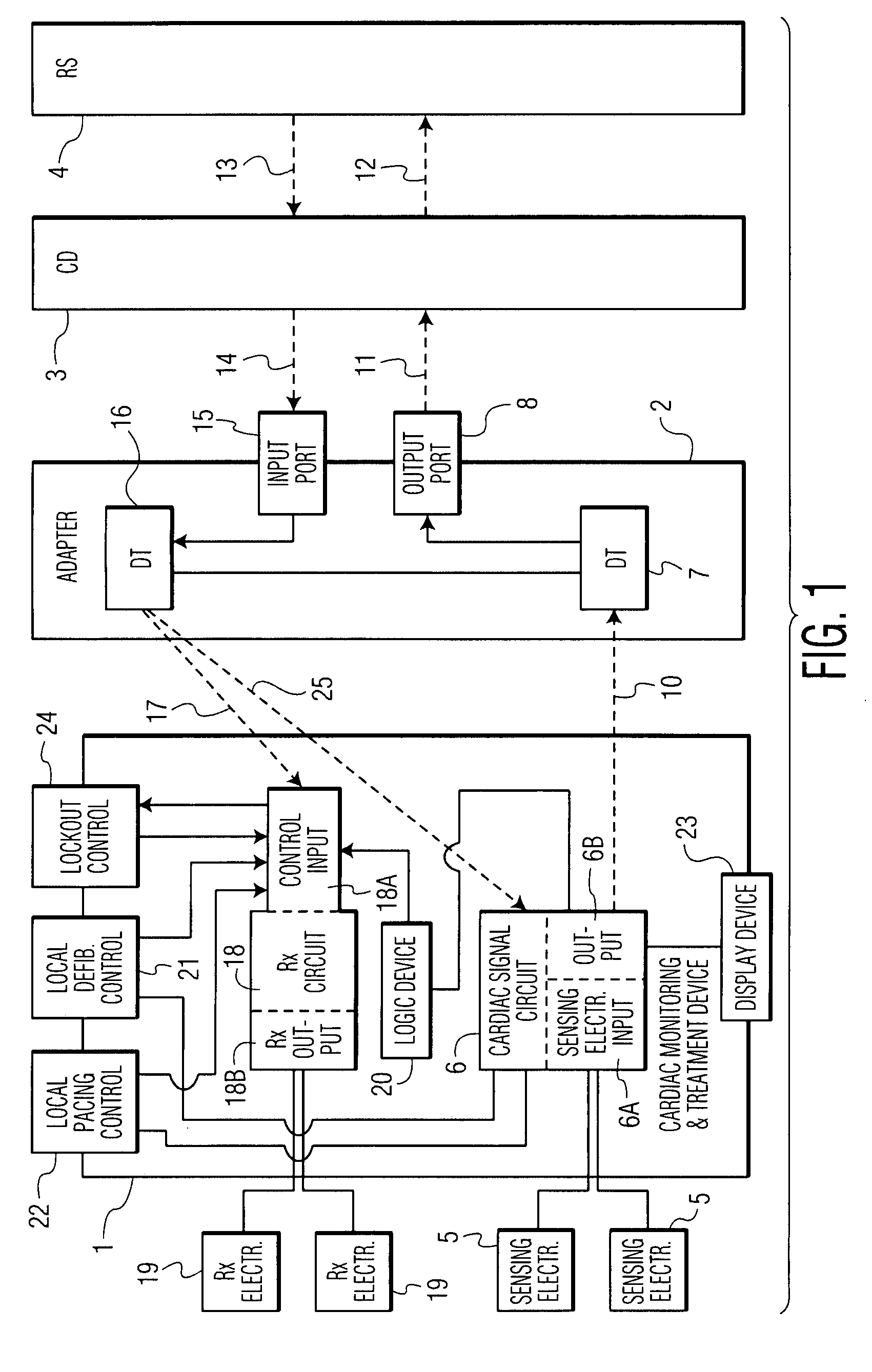
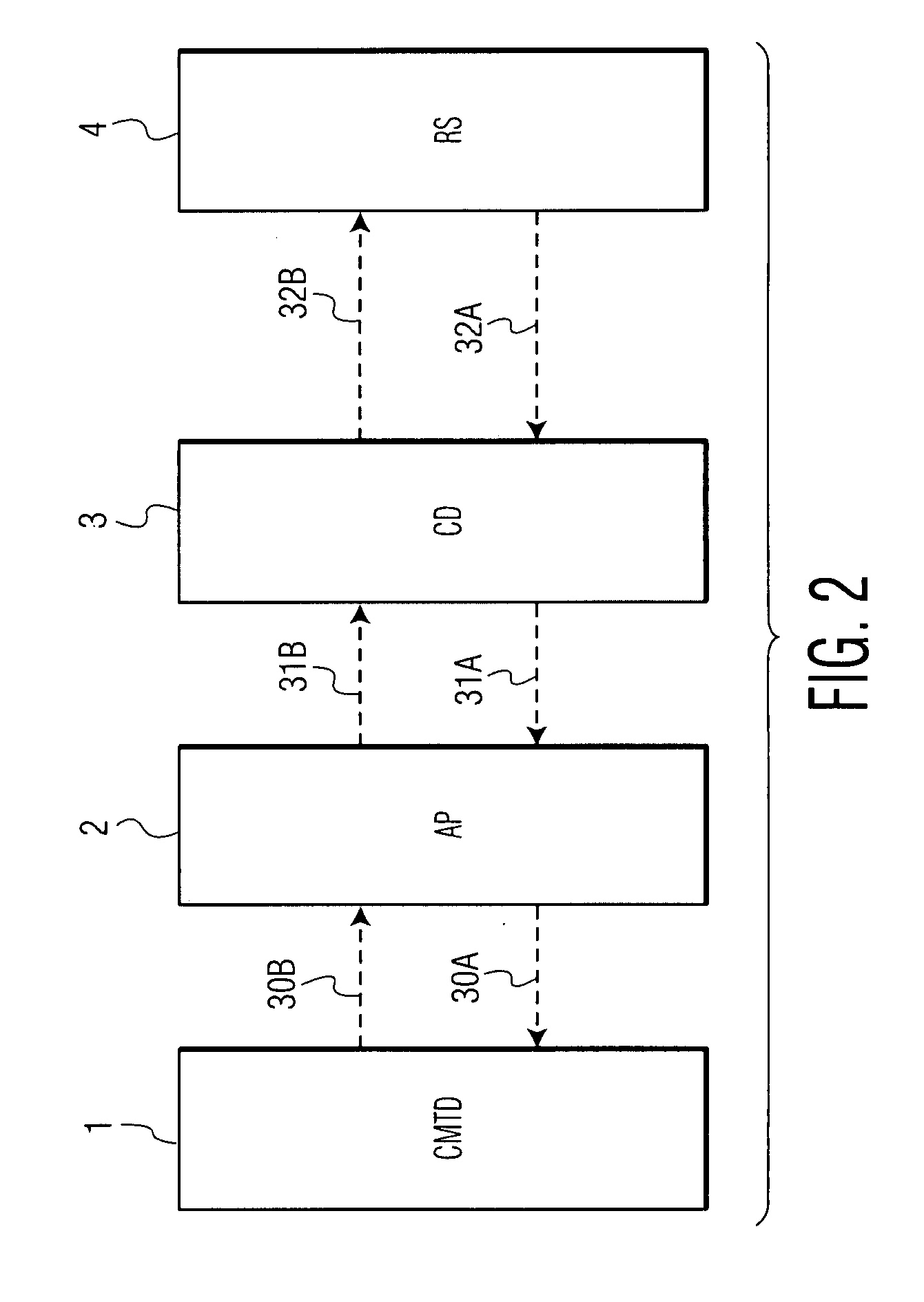
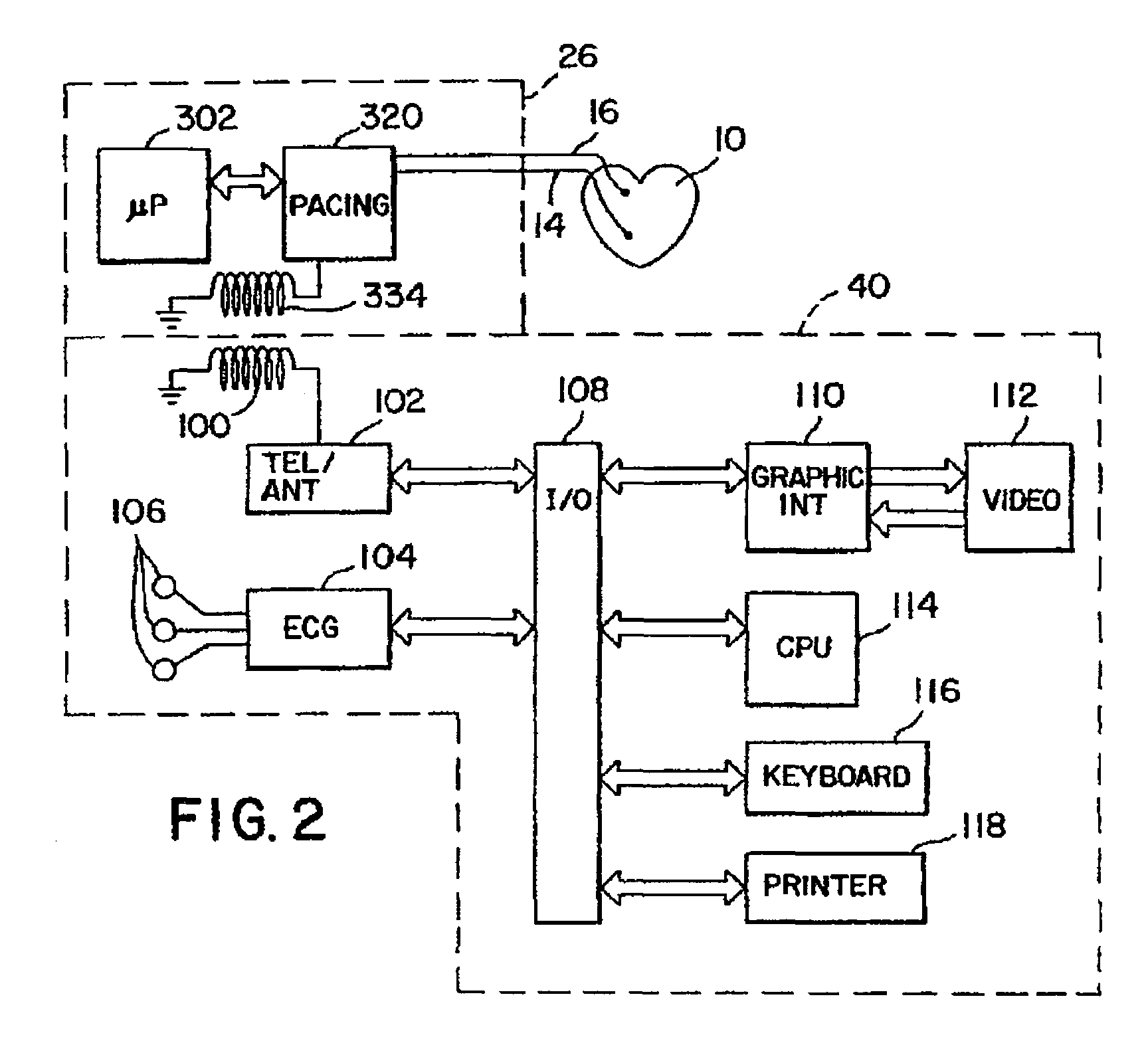
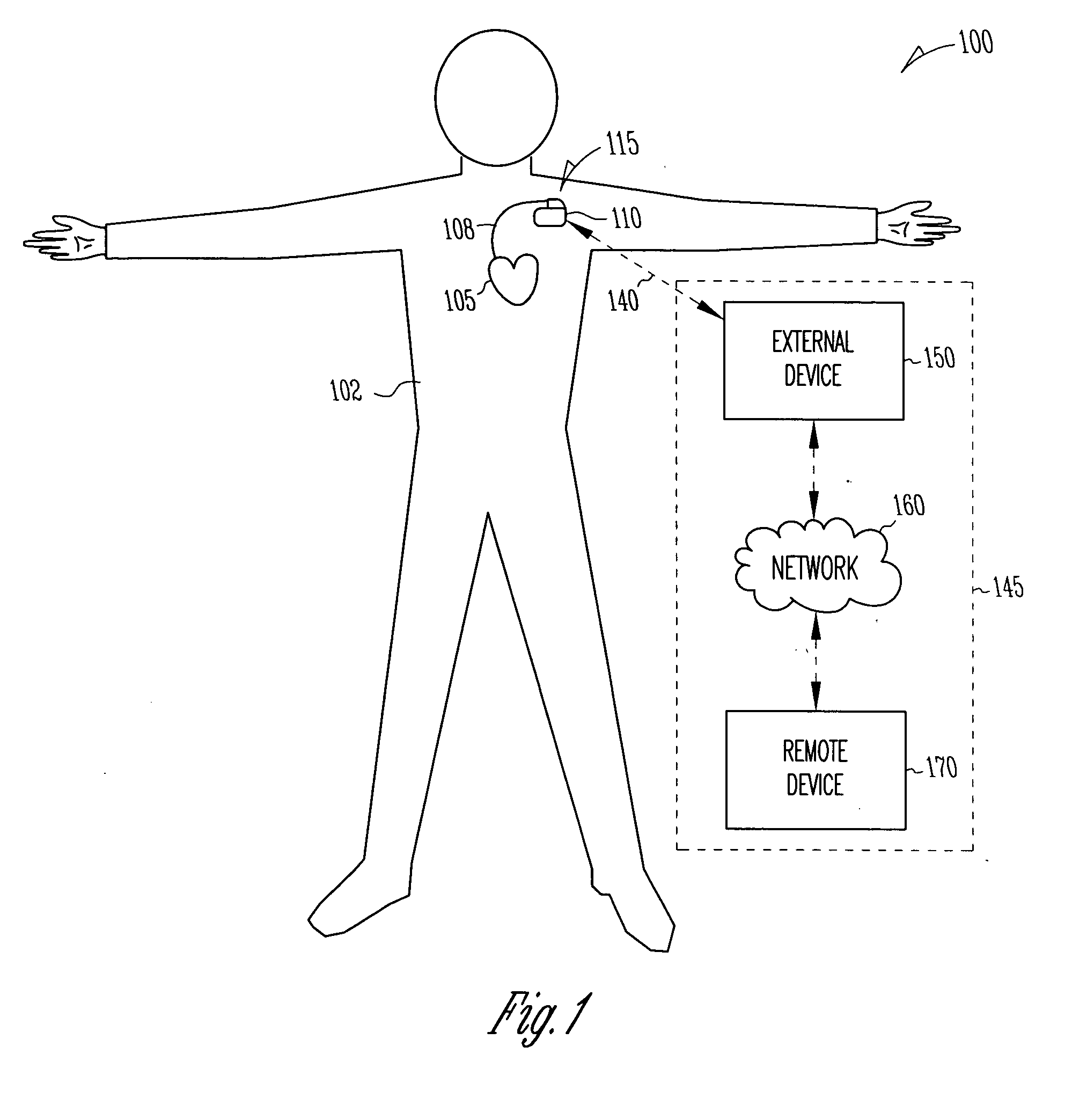
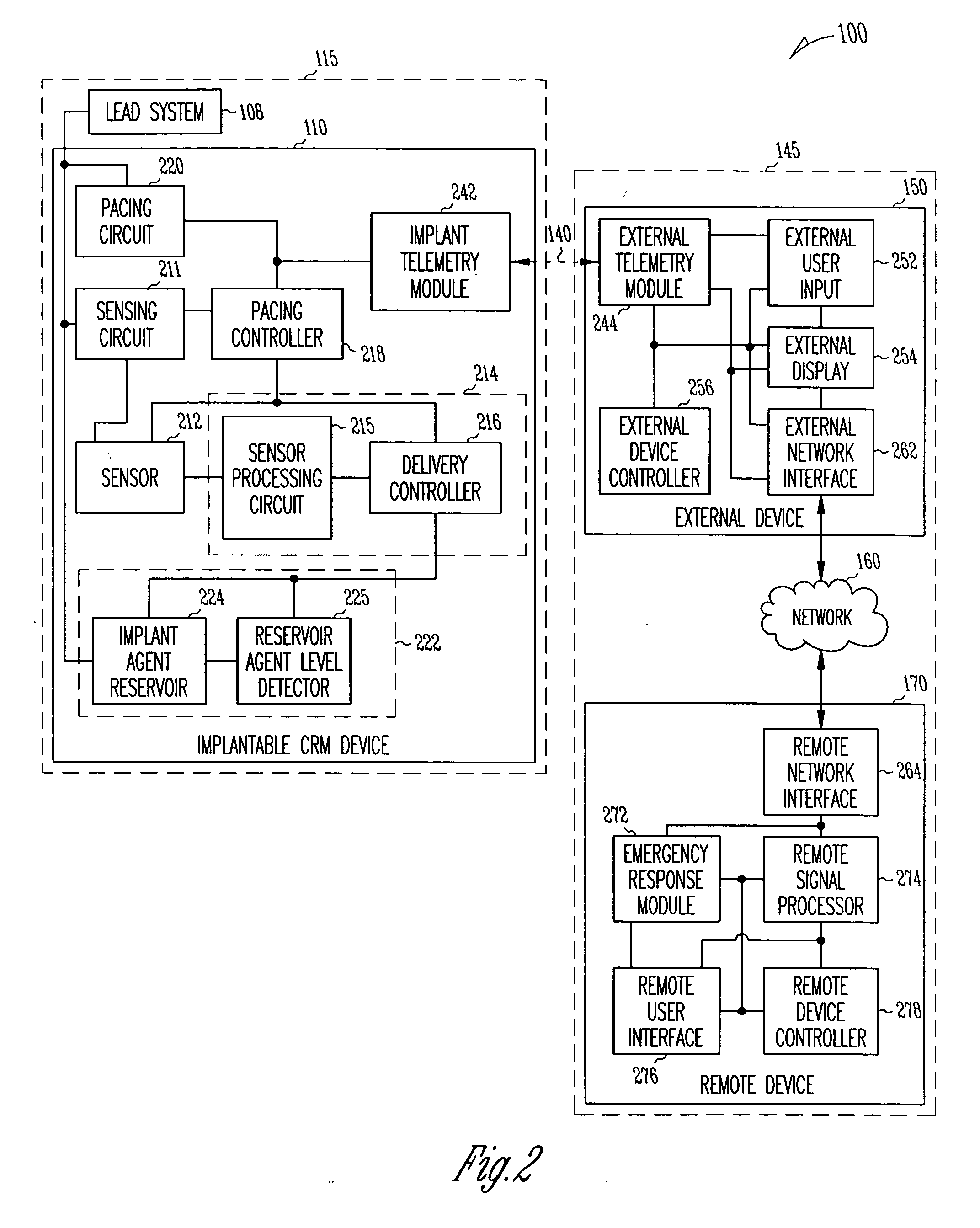
A cardiac monitoring and treatment apparatus allows a victim of a medical emergency access to a medical professional (MP) who can monitor, diagnose and treat the victim from a remote site. The apparatus includes a cardiac monitoring and treatment device (CMTD) coupled to an electronic adaptor designed to communicate with a local, first transmitting / receiving (T / R) device which, in turn, is adapted to electronically communicate with a remote, second transmitting / receiving (T / R) device used by the MP. The CMPD comprises a cardiac treatment circuit for effecting cardiac pacing and / or defibrillation and a cardiac signal circuit for receiving cardiac signals. The cardiac signals are (1) transmitted from the signal circuit to the second T / R device for evaluation by the MP, (2) the MP may transmit a control signal to the treatment circuit, and (3), in response thereto, the treatment circuit may generate one or more electrical pulses for treatment of the victim.
Owner:MATOS JEFFREY A
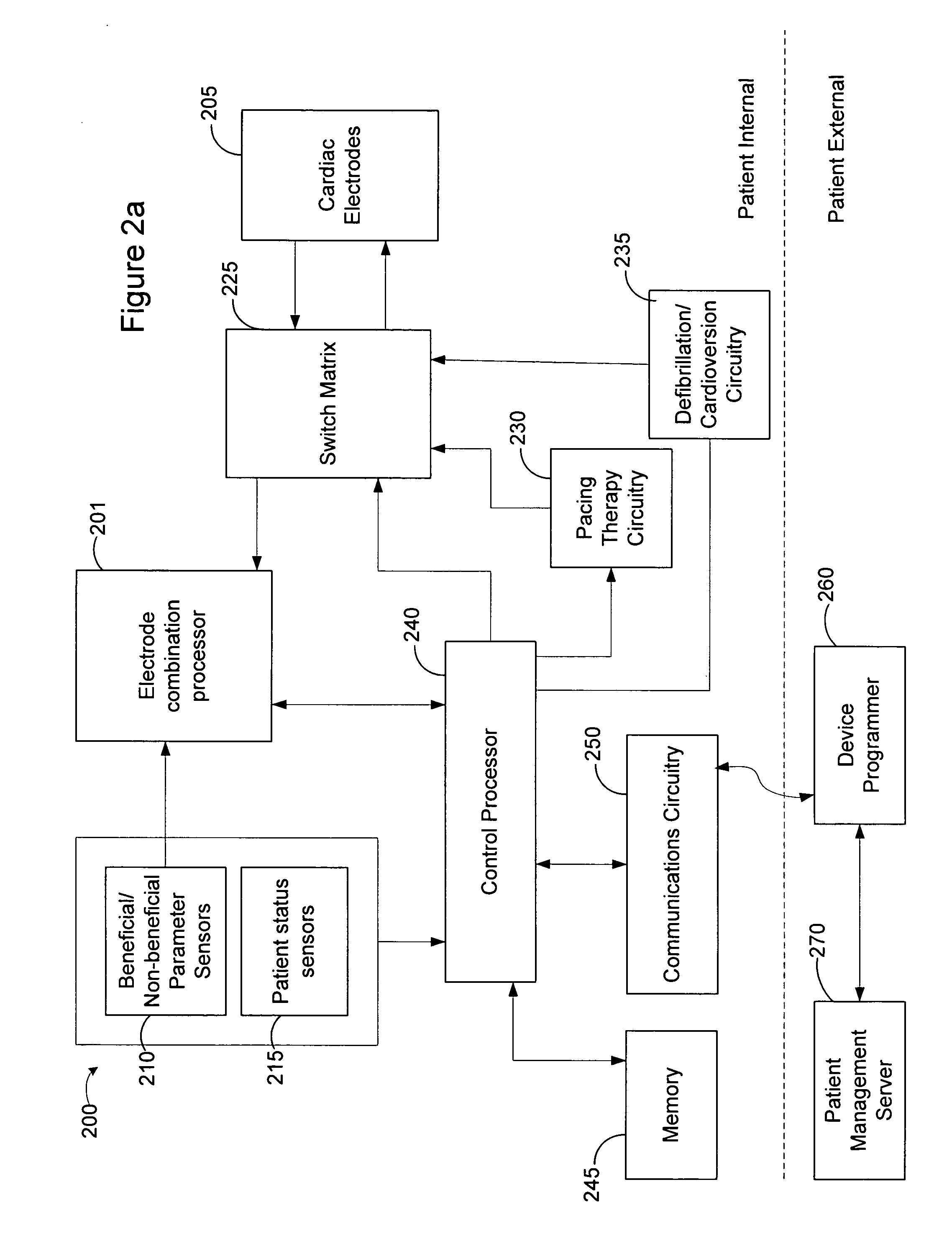
Method and apparatus to perform electrode combination selection
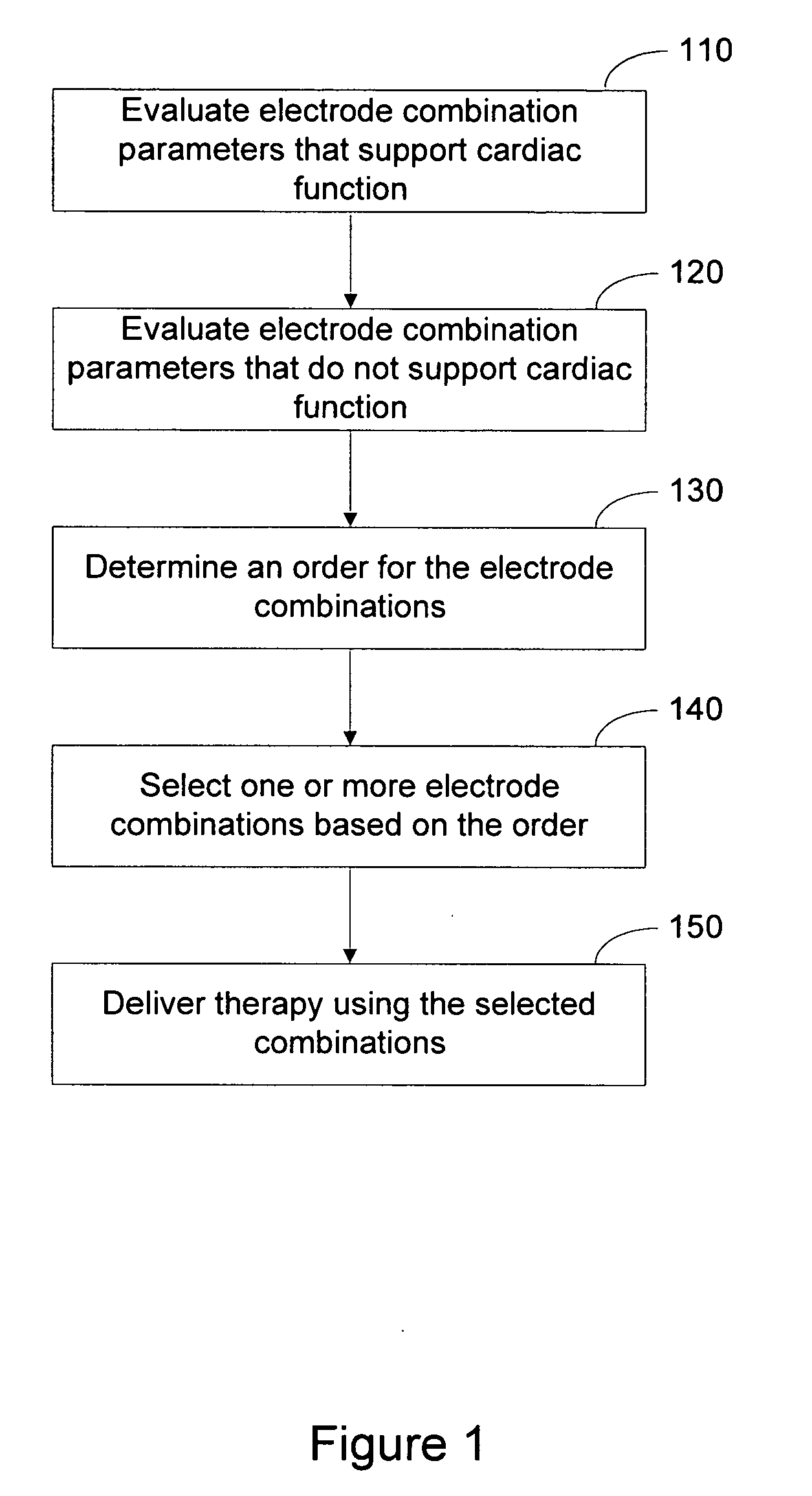
The present invention involves approaches for selecting one or more electrode combinations. Various method embodiments can include implanting a plurality of cardiac electrodes supported by one or more leads in a patient, attaching the one or more leads to a patient external analyzer circuit, delivering electrical stimulation to the patient's heart using the plurality of cardiac electrodes and the analyzer circuit, evaluating, for each electrode combination of a plurality of electrode combinations of the plurality of cardiac electrodes, one or more first parameters and one or more second parameters produced by the electrical stimulation delivered using the electrode combination, the first parameters supportive of cardiac function consistent with a prescribed therapy and the second parameters not supportive of cardiac function consistent with the prescribed therapy, selecting one or more electrode combinations of the plurality of cardiac electrodes based on the evaluation, the one or more electrode combinations selected as being associated with the one or more first parameters and less associated with the one or more second parameters relative to other electrode combinations of the plurality of cardiac electrodes, programming an implantable pacing circuit to deliver a cardiac pacing therapy that preferentially uses the selected one or more electrode combinations relative to other electrode combinations of the plurality of cardiac electrodes, detaching the one or more leads from the analyzer circuit, attaching the one or more leads to the implantable pacing circuit, and implanting the implantable pacing circuit.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
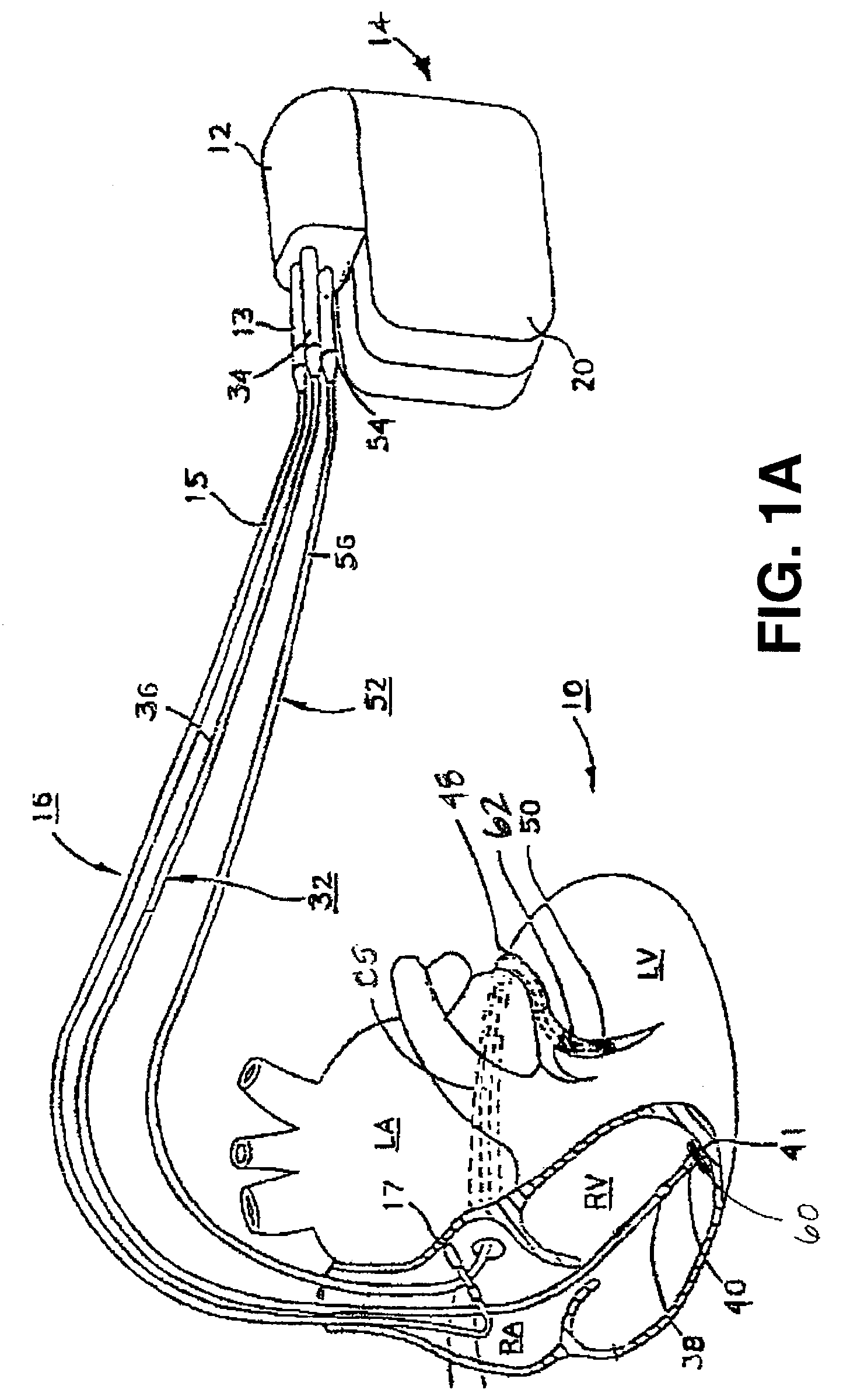
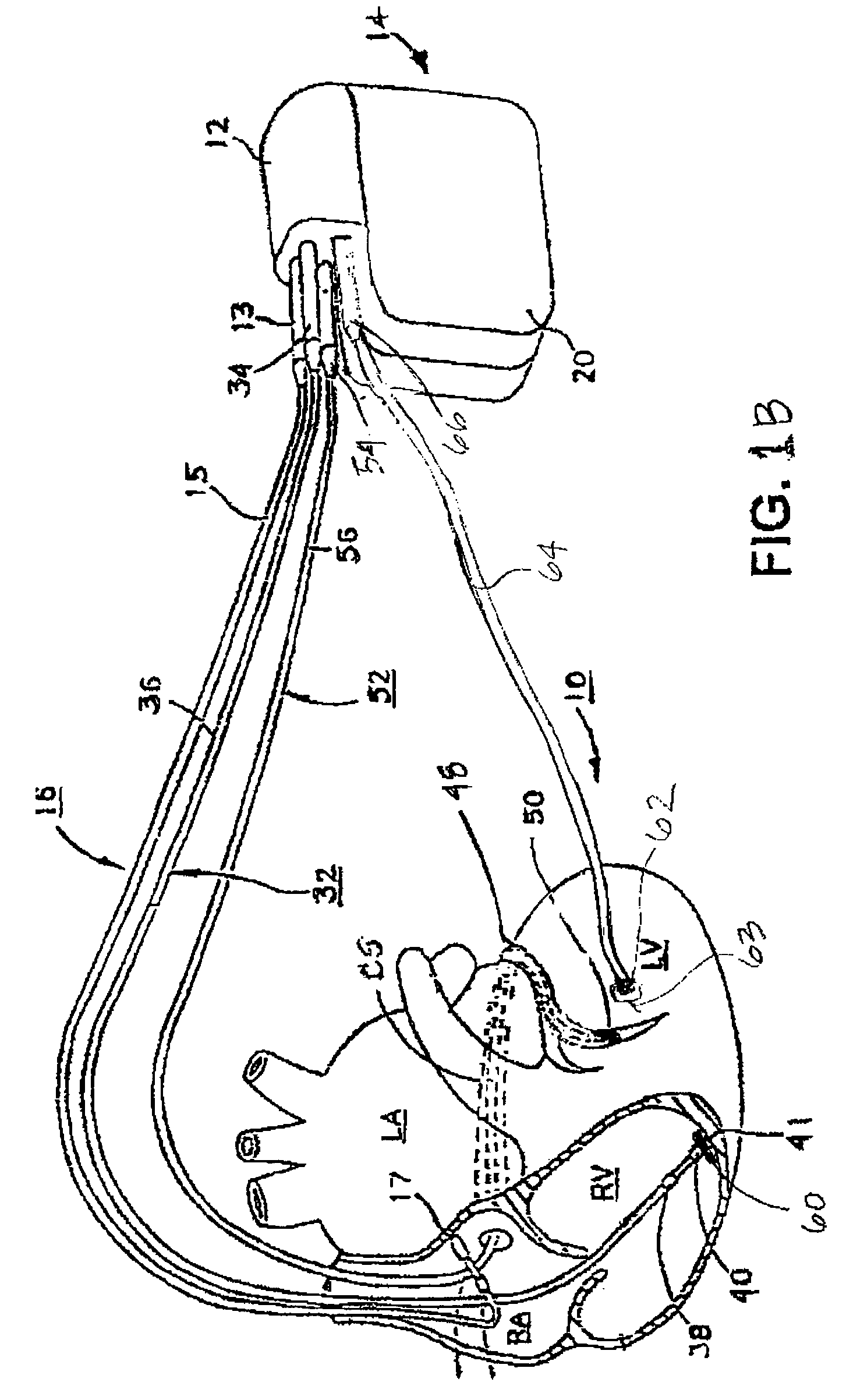
System and method for communicating information using encoded pacing pulses within an implantable medical system
InactiveUS7630767B1Facilitate communicationHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeLeft ventricular size
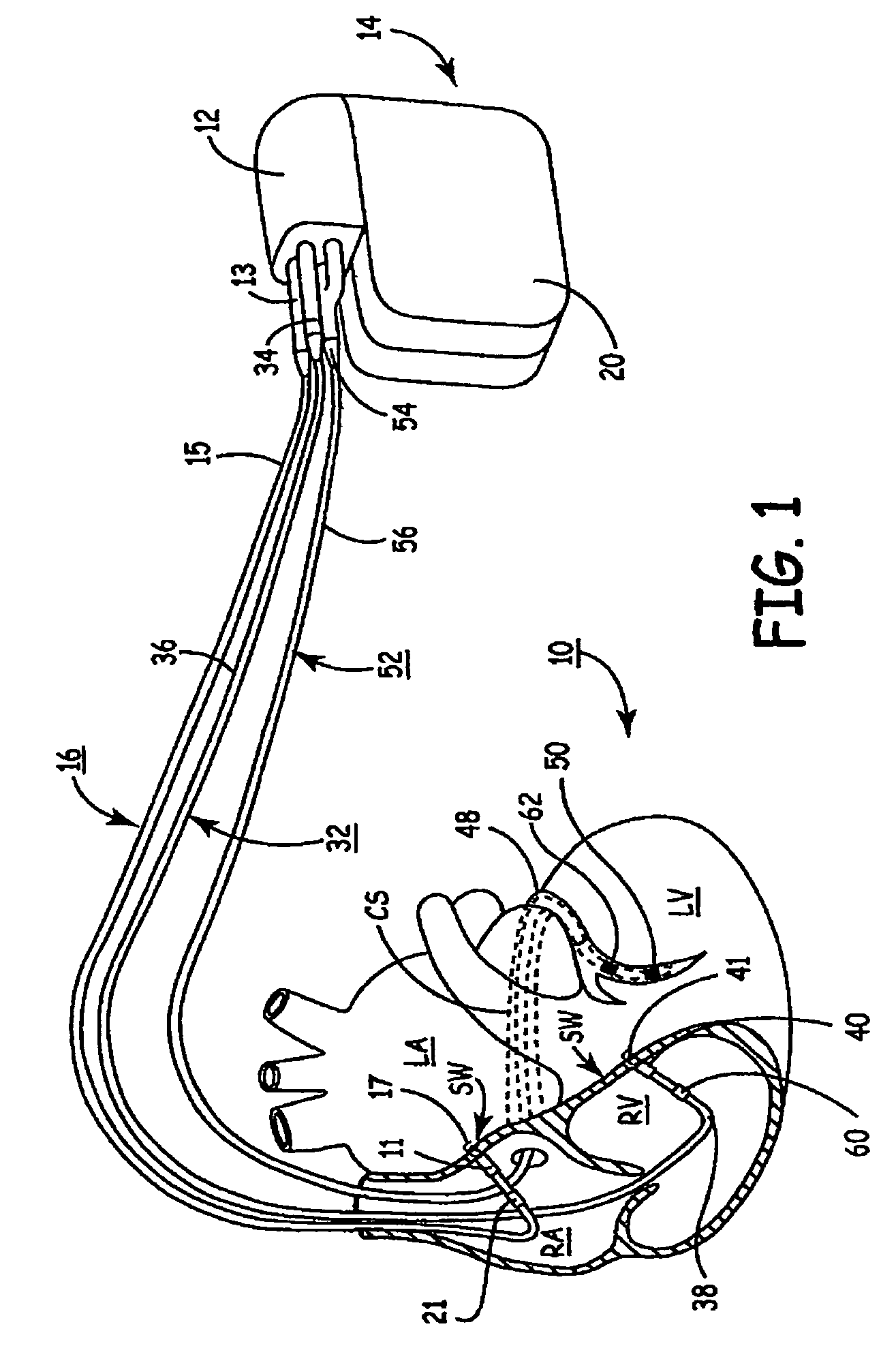
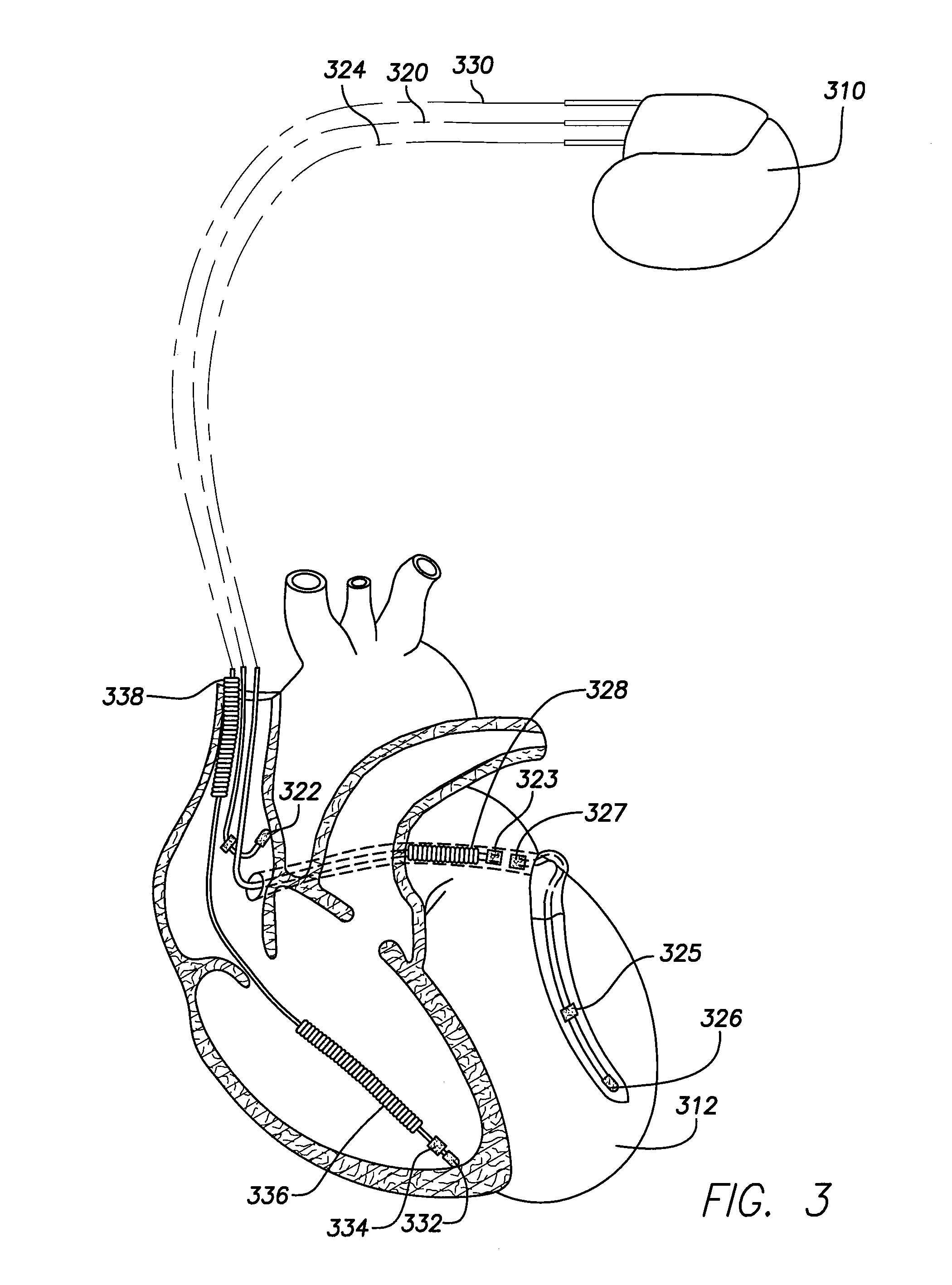
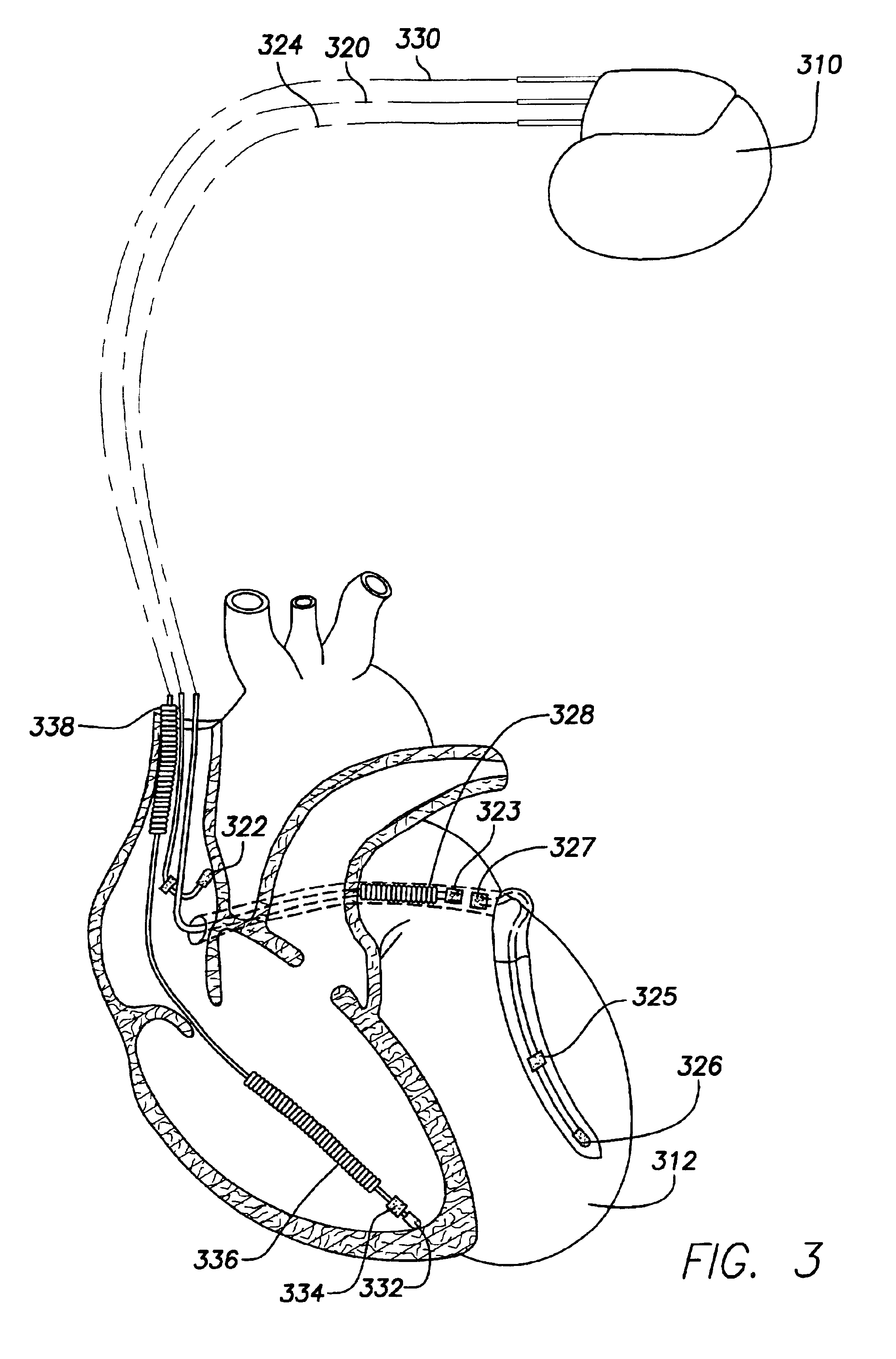
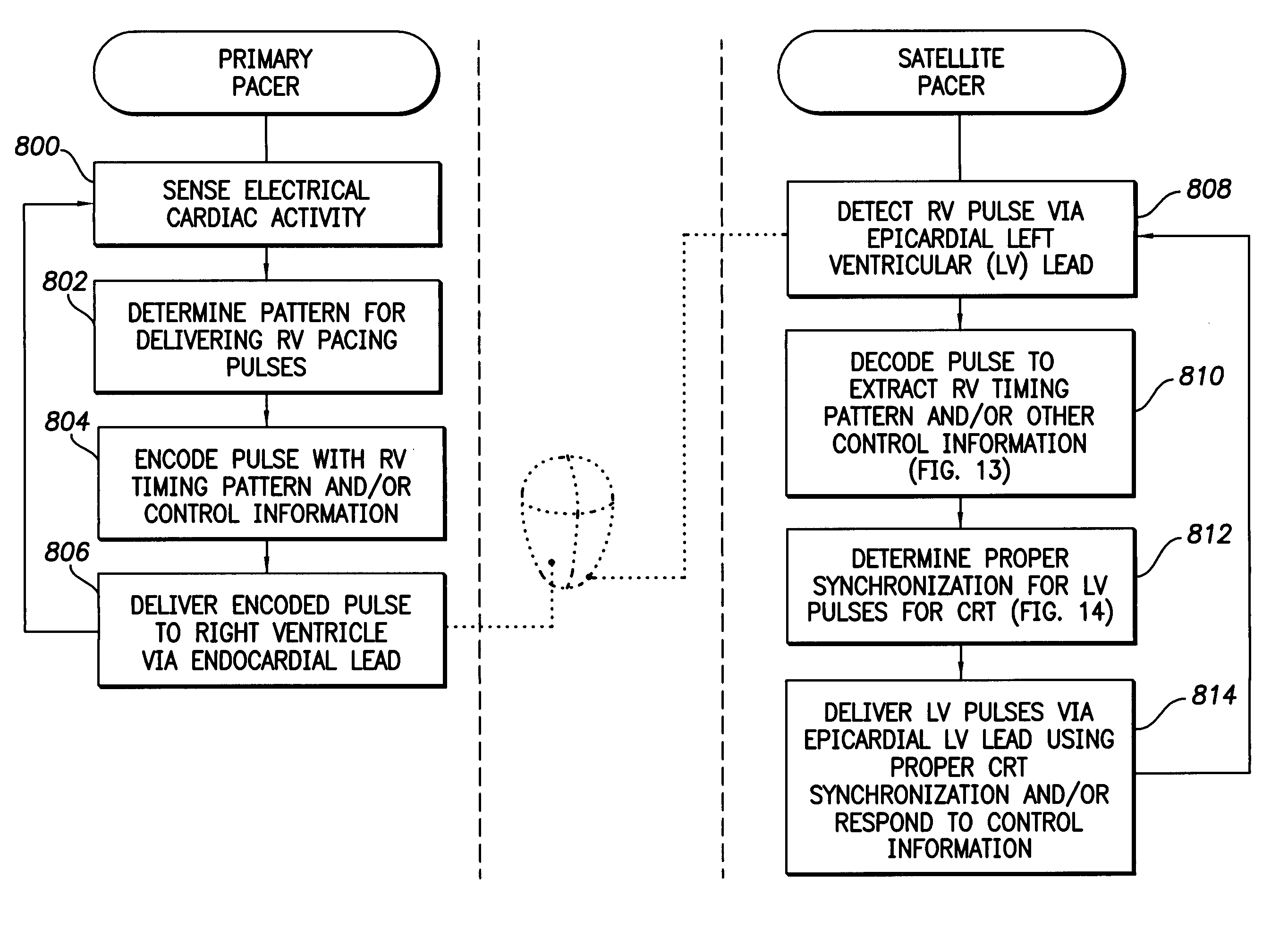
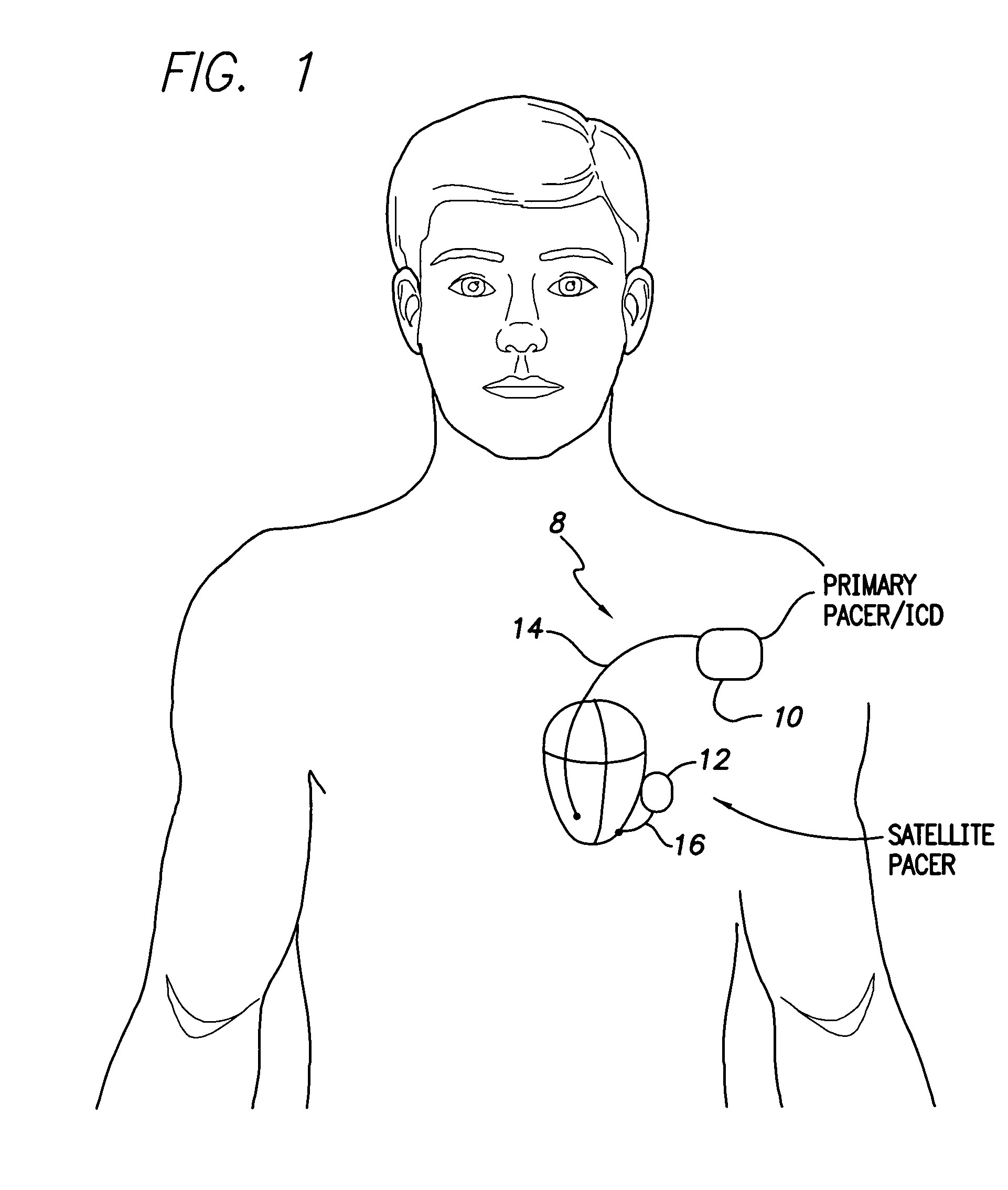
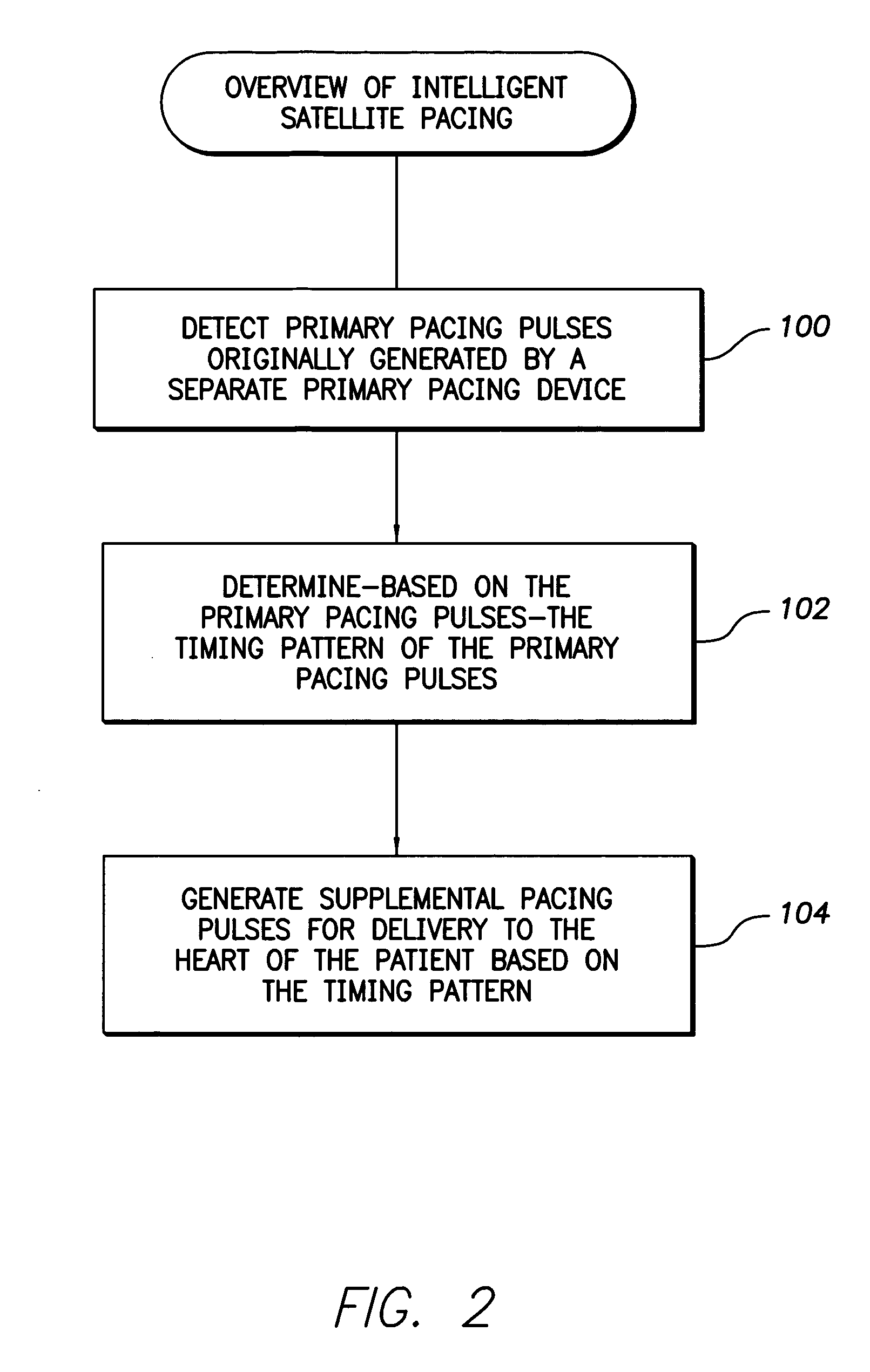
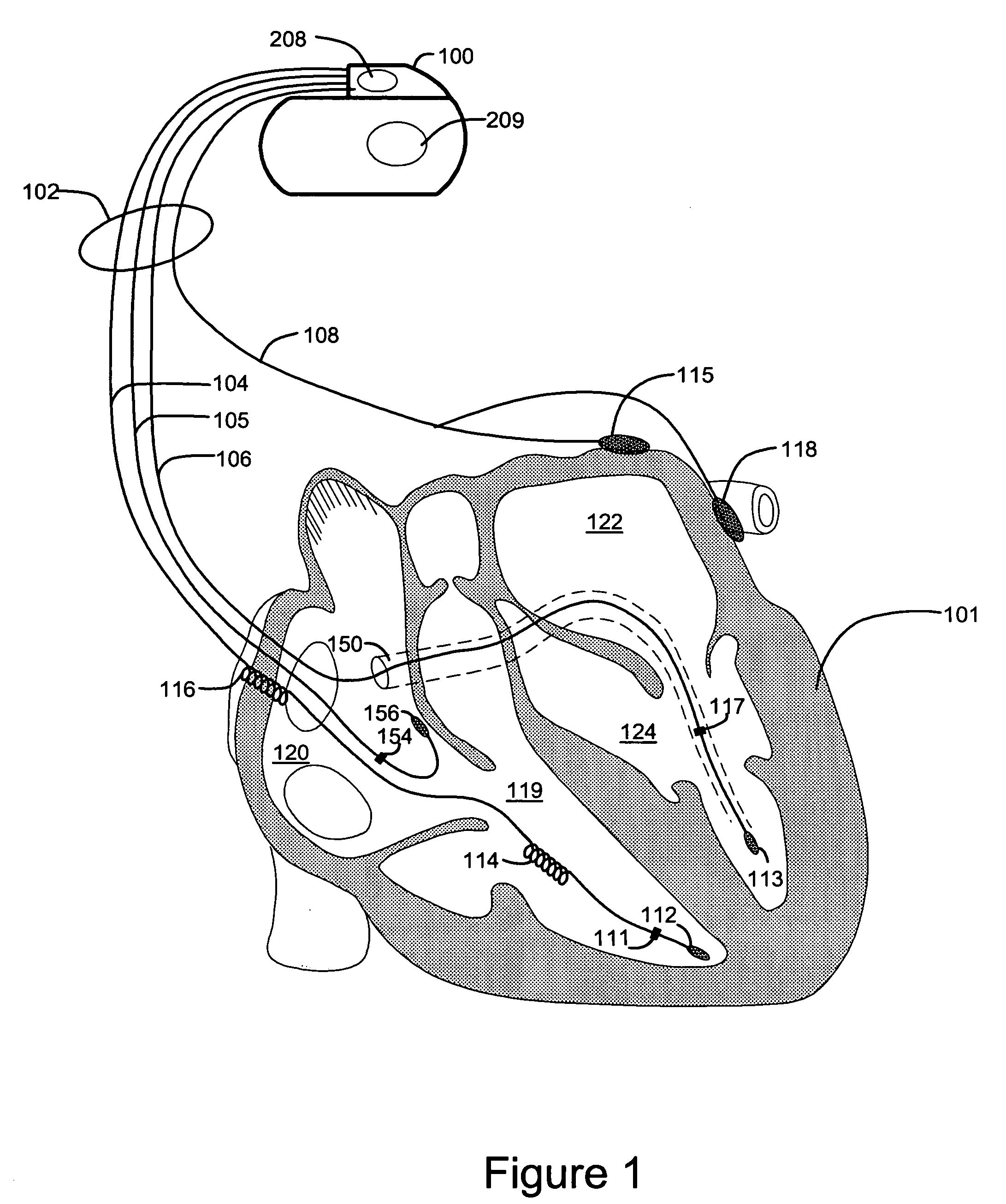
Techniques are provided for delivering cardiac pacing therapy to the heart of a patient using an epicardial left ventricular satellite pacing device in conjunction with primary pacemaker having at least a right ventricular pacing lead. In one embodiment described herein, right ventricular pulses generated by the primary pacemaker are detected by the satellite pacer and analyzed to determine the timing pattern employed by the primary pacemaker. The timing pattern is then used to specify the delivery times of epicardial left ventricular pulses so as to be synchronized with right ventricular pulses. In another embodiment described herein, the primary pacemaker modulates the right ventricular pulses to encode timing information, which is then detected and decoded by the satellite pacemaker. In this manner, biventricular pacing therapy, such as cardiac resynchronization therapy, may be conveniently delivered using a non-biventricular pacemaker in combination with an epicardial satellite pacer.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac pacing apparatus and method for continuous capture management
ActiveUS7831303B2Increase the number ofIncrease incidenceHeart stimulatorsHeart chamberCardiac stimulation
An implantable cardiac stimulation system and method having continuous capture management capabilities are provided. Continuous capture management is realized by continuously monitoring for secondary effects of loss of capture, thereby effectively providing continuous capture management in any heart chamber without encountering the limitations normally associated with evoked response sensing. A pacing threshold search is triggered upon detecting a secondary indicator of loss of capture. Secondary indicators of loss of capture may be lead-related changes, changes related to the occurrence of atrial sensed events, changes related related to the occurrence of ventricular sensed or paced events, and / or changes related to a monitored physiological condition.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus to modulate cellular regeneration post myocardial infarct
InactiveUS20050288721A1Easy to adjustModulate tissue growthMedical devicesPressure infusionCardiac muscleWorkload
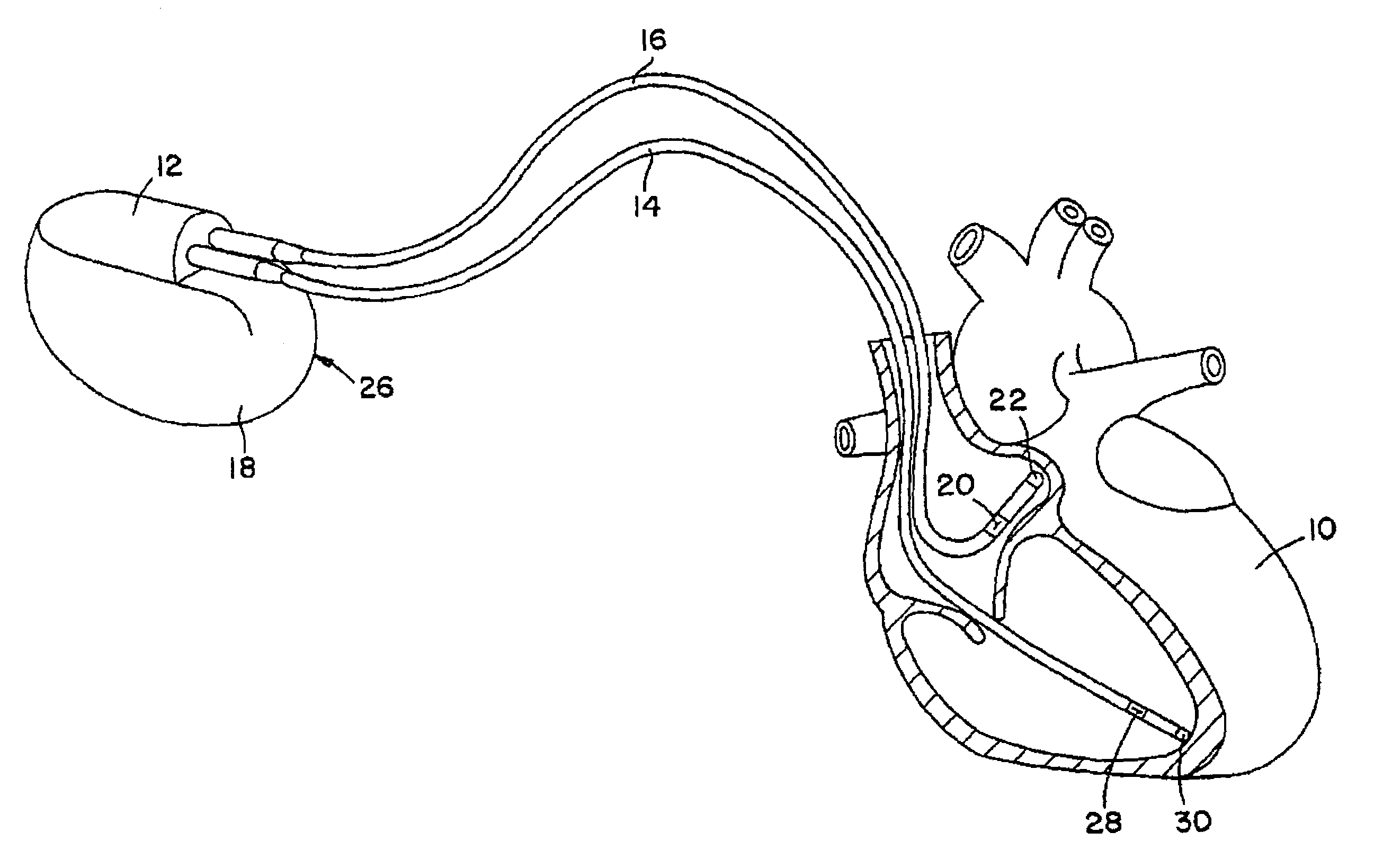
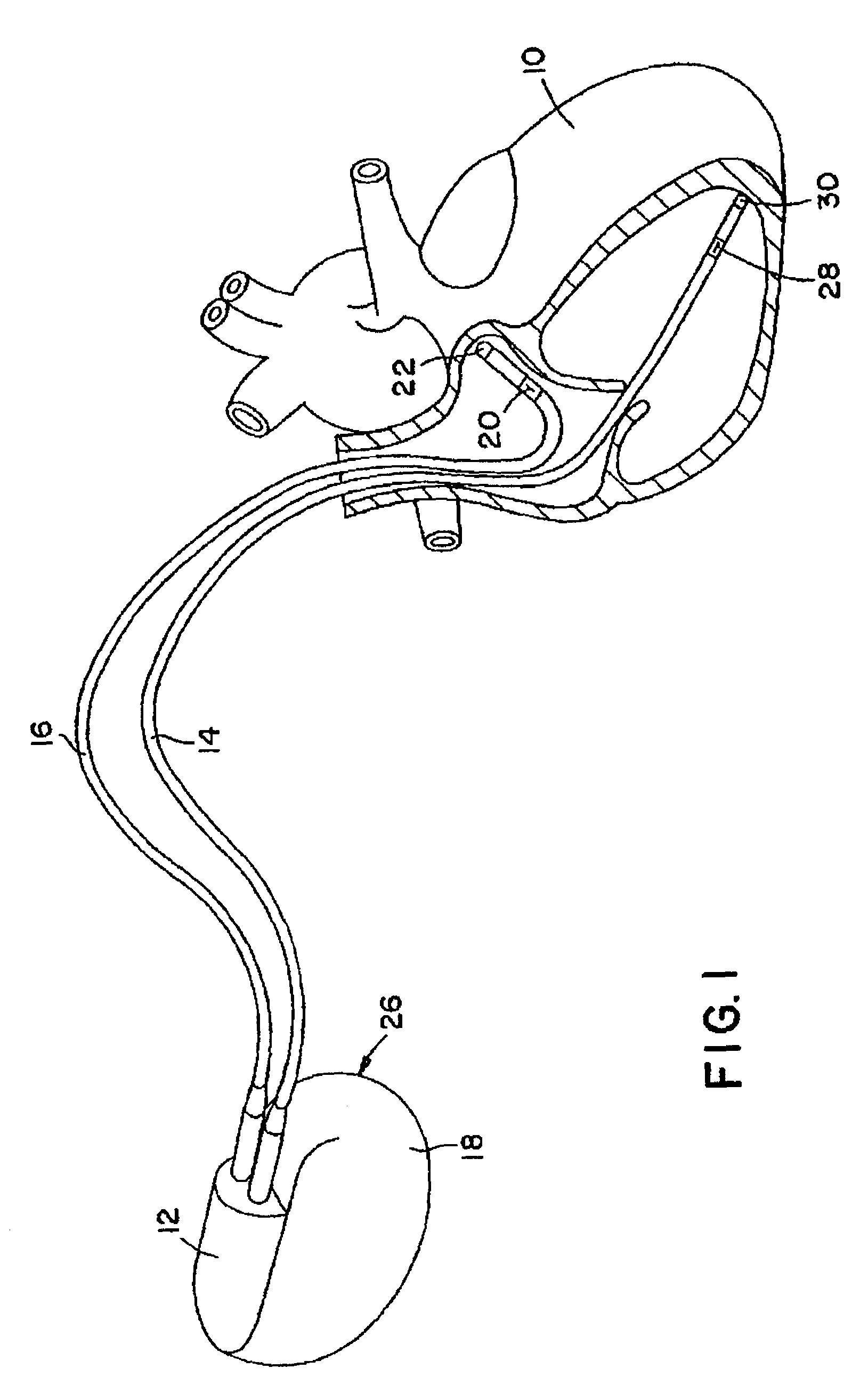
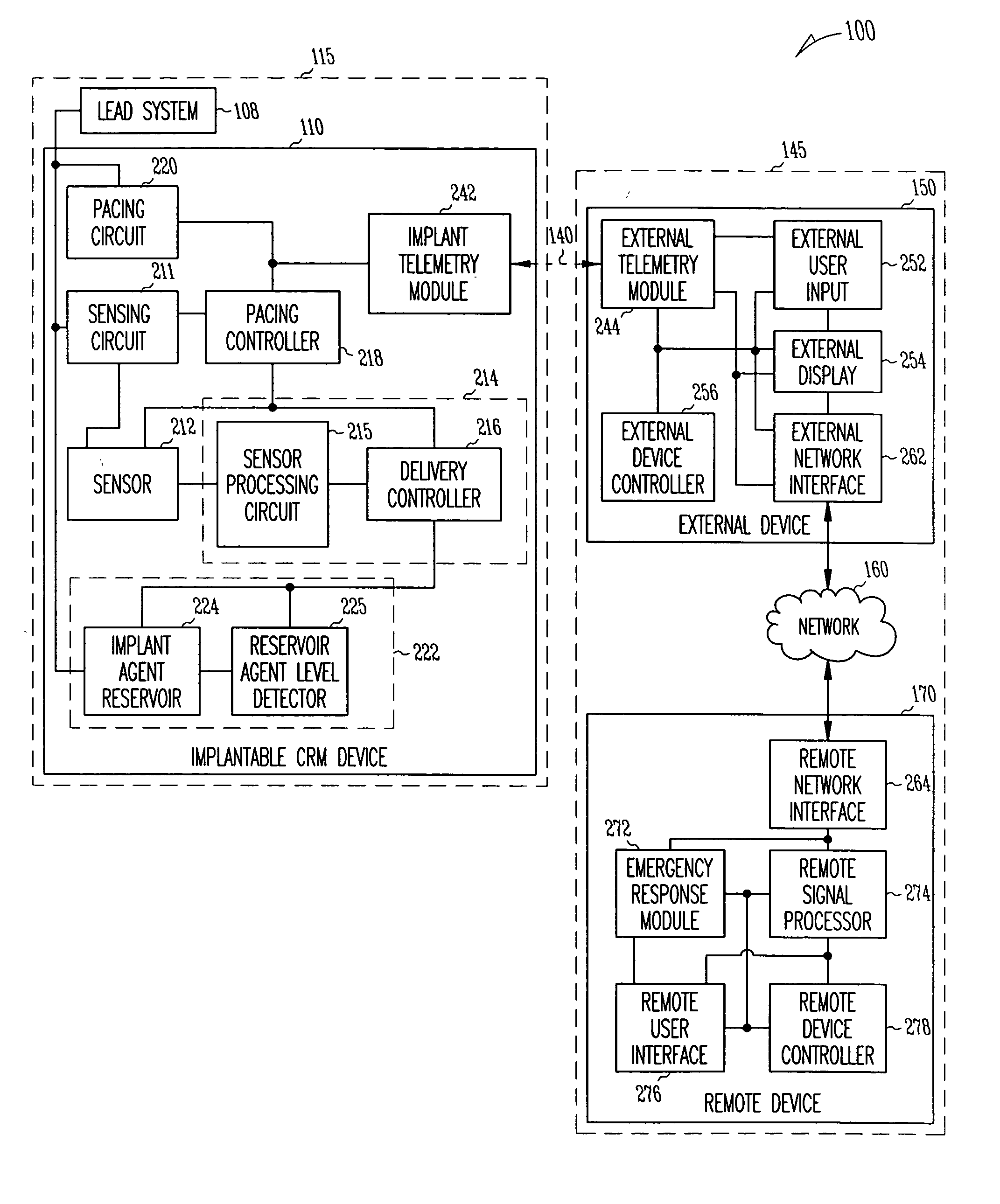
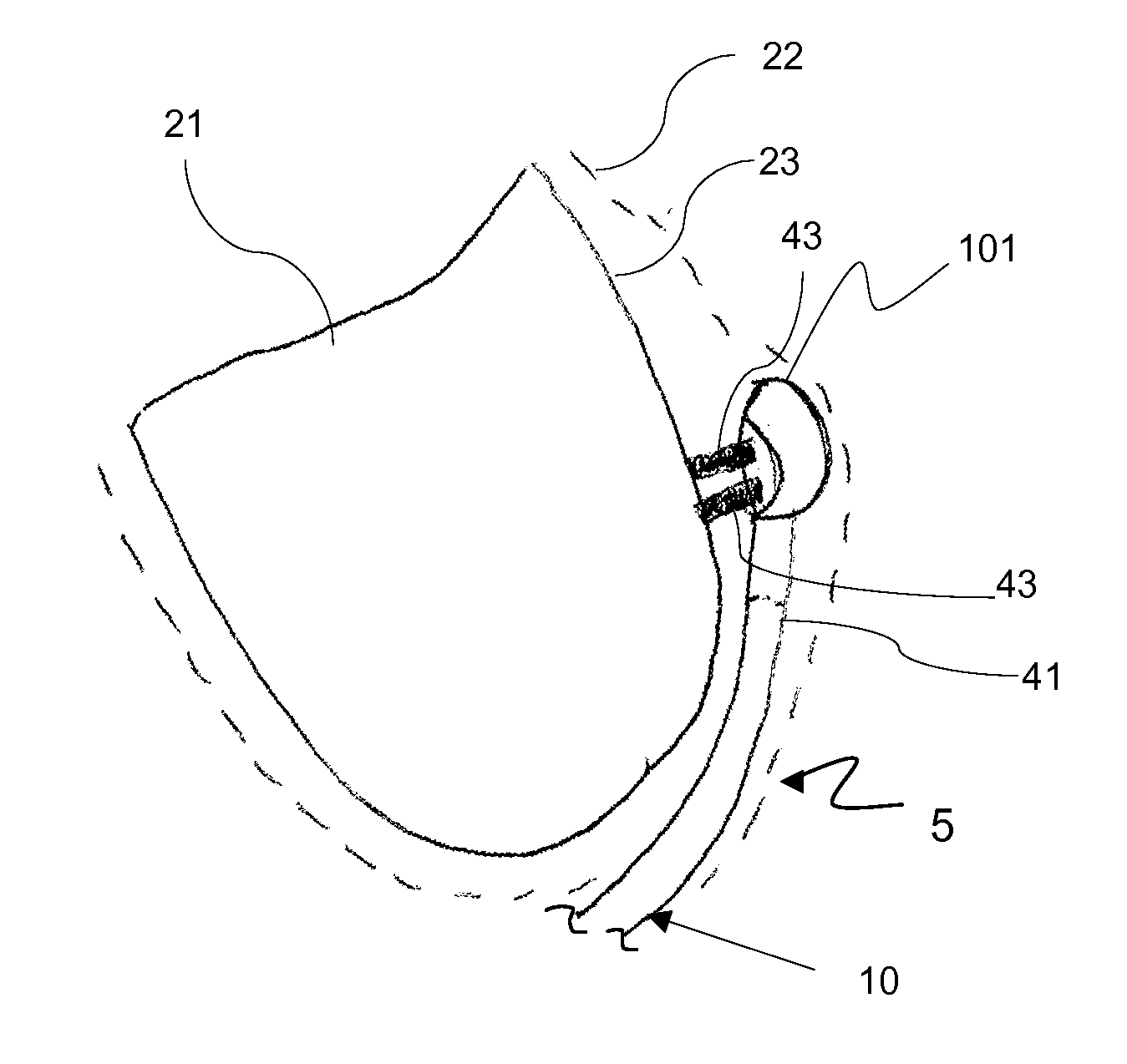
A system delivers cardiac pacing therapy and chemical and / or biological therapy to modulate myocardial tissue growth in a heart after myocardial infarction (MI). The system includes an agent delivery device to release one or more agents to an MI region to modulate myocardial tissue growth in that region, and a cardiac rhythm management (CRM) device to deliver pacing pulses to enhance the effects of the one or more agents by altering myocardial wall stress and cardiac workload. In one embodiment, the system is an implantable system including an implantable agent delivery device and an implantable CRM device.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Steerable epicardial pacing catheter system placed via the subxiphoid process
InactiveUS20100241185A1Free from damageEpicardial electrodesDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresThoracic cavity
The epicardial pacing system and related method includes an epicardial catheter configured to be disposed in the middle mediastinum of the thorax of a subject for use in electrical pacing of the heart at one or more locations on the epicardial surface. The epicardial pacing catheter may include at least one electrode whereby the electrode is insulated on at least one side to allow pacing of the heart without damage to adjacent anatomical structures.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
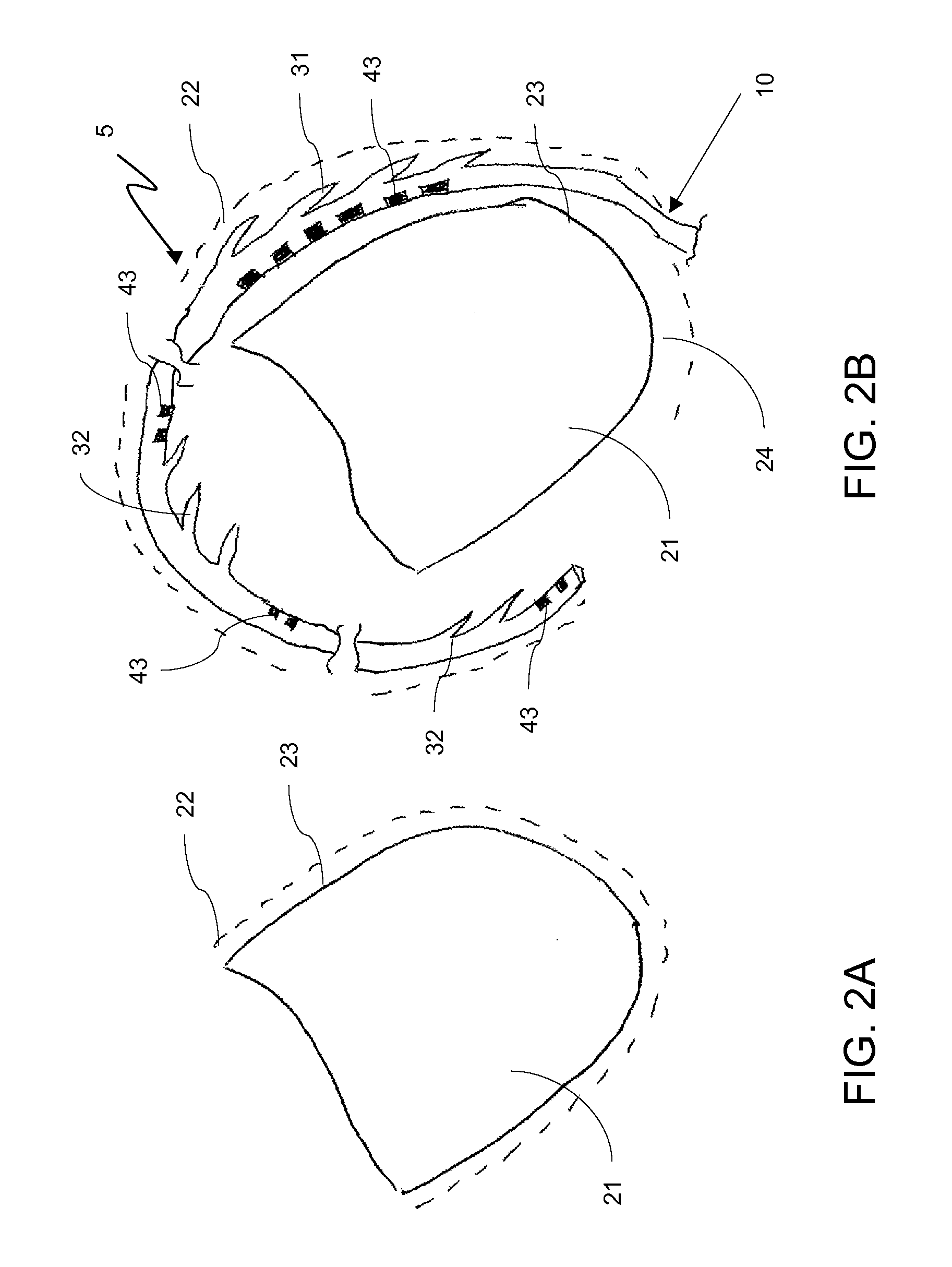
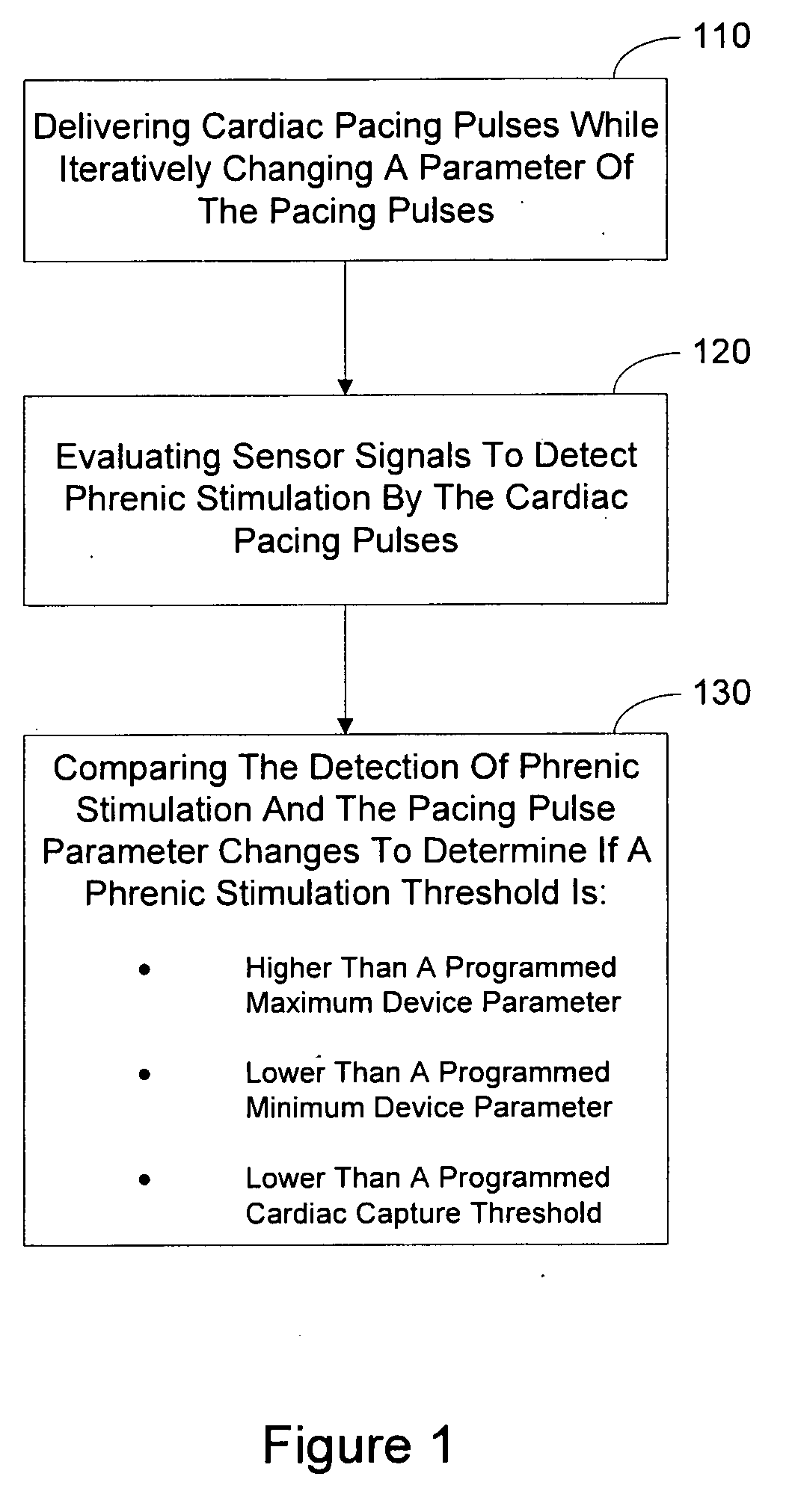
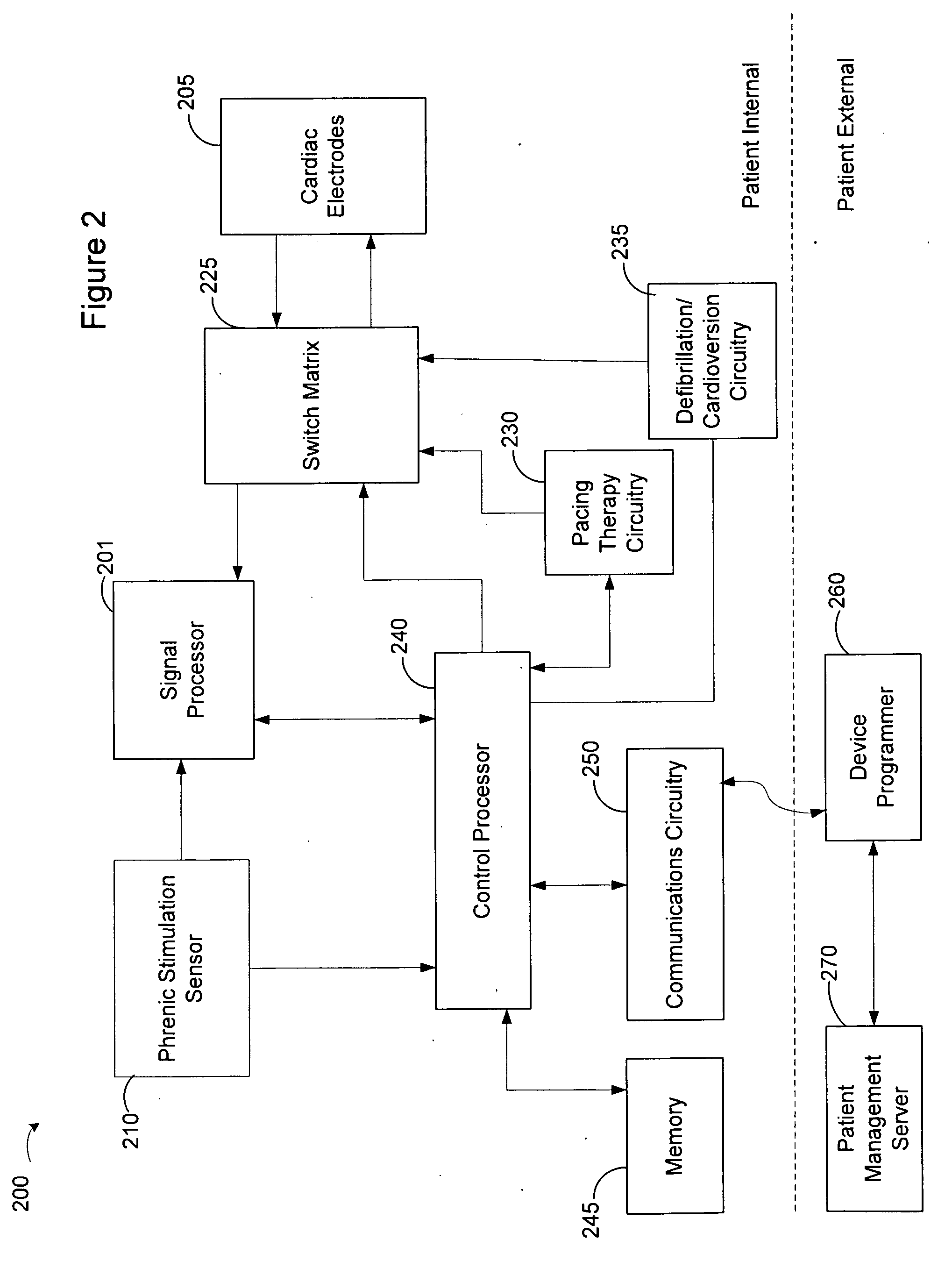
Method and Apparatus for Phrenic Stimulation Detection
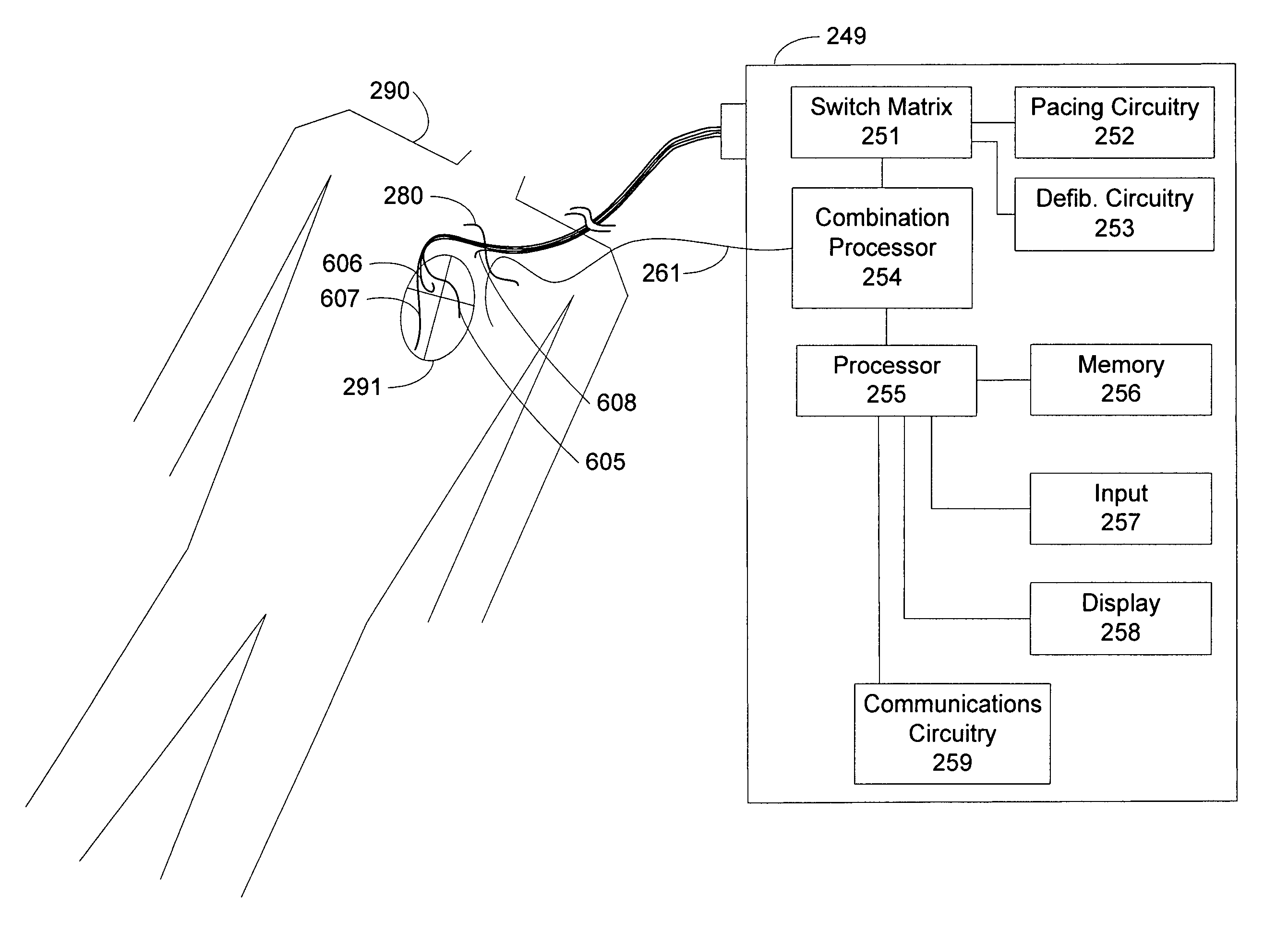
Approaches for characterizing a phrenic stimulation threshold, a cardiac capture threshold, a maximum device parameter, and a minimum device parameter are described. A plurality of cardiac pacing pulses can be delivered by using a cardiac pacing device, a pacing parameter of the plurality of cardiac pacing pulses being changed between delivery of at least some of the pulses. One or more sensor signals can be evaluated to detect stimulation of the phrenic nerve by one or more of the plurality of cardiac pacing pluses. The evaluation of the one or more sensor signals and the pacing parameter can be compared to determine if a phrenic stimulation threshold is at least one of higher than a maximum device parameter and lower than a minimum device parameter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Tissue Separating Systems and Methods
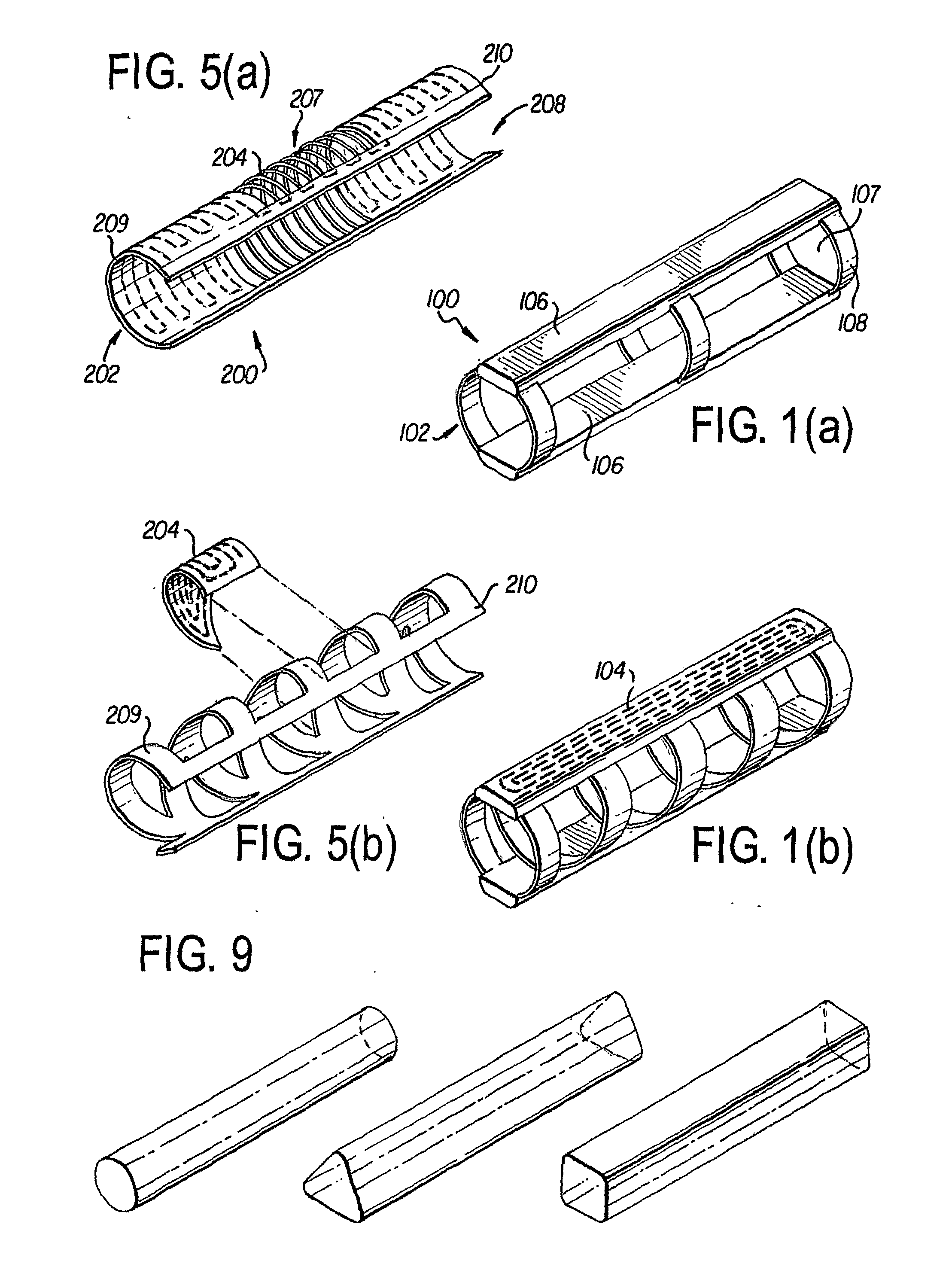
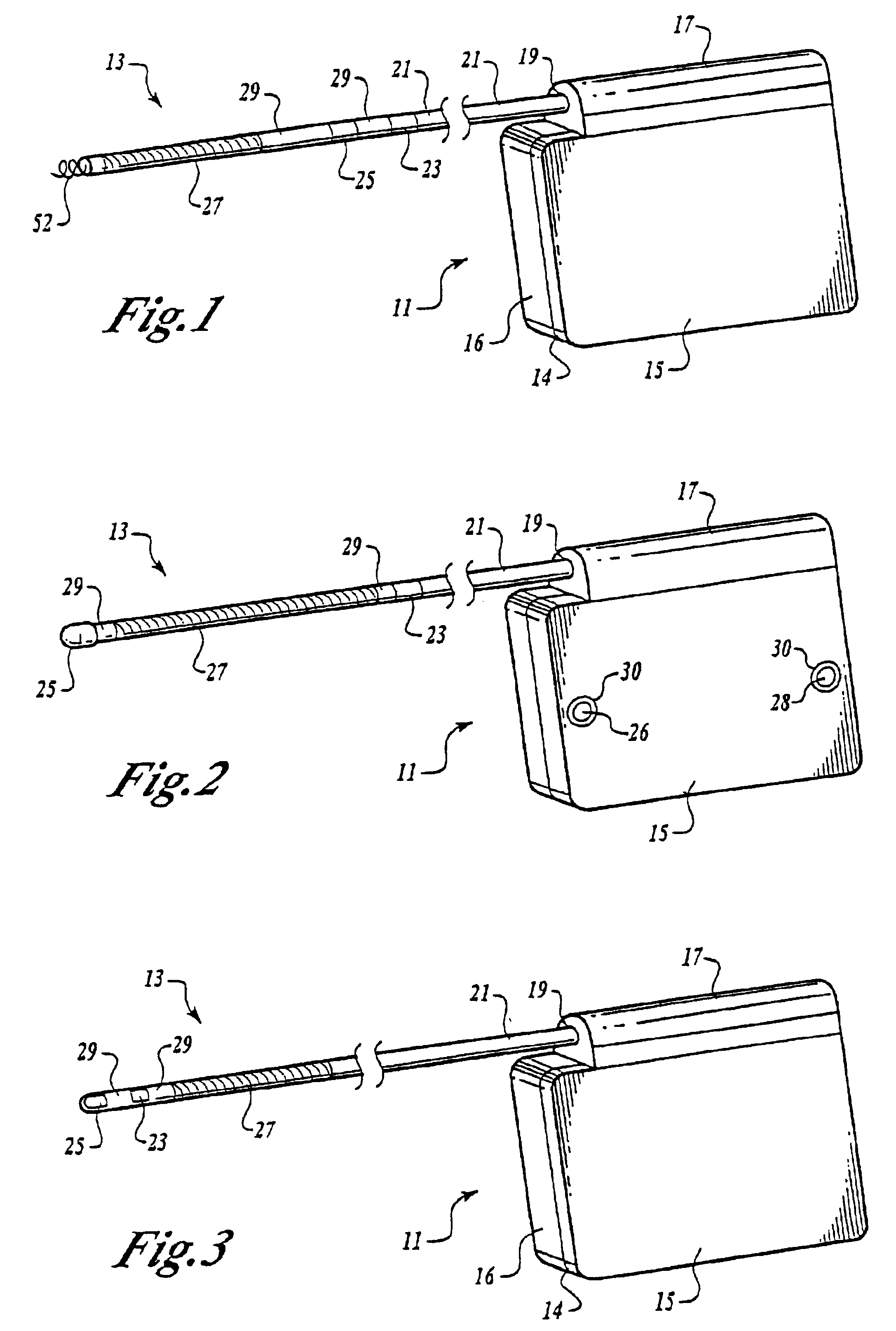
ActiveUS20080154296A1Smooth connectionReduce morbidityTransvascular endocardial electrodesBlunt dissectorsEngineeringBiomedical engineering
Systems and methods for separating an object such as a pacing lead from a patient tissue involve a flexible and torqueable shaft having an internal lumen sized to receive the object, and a hard separating mechanism for separating the object from the tissue. Typically the shaft and separating mechanism are advanced along or toward the object, and the separating mechanism is contacted with the tissue. The shaft is rotated to effect separation between the object and the tissue. The systems and methods are well suited for use in cardiac pacing or defibrillator lead explant procedures.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
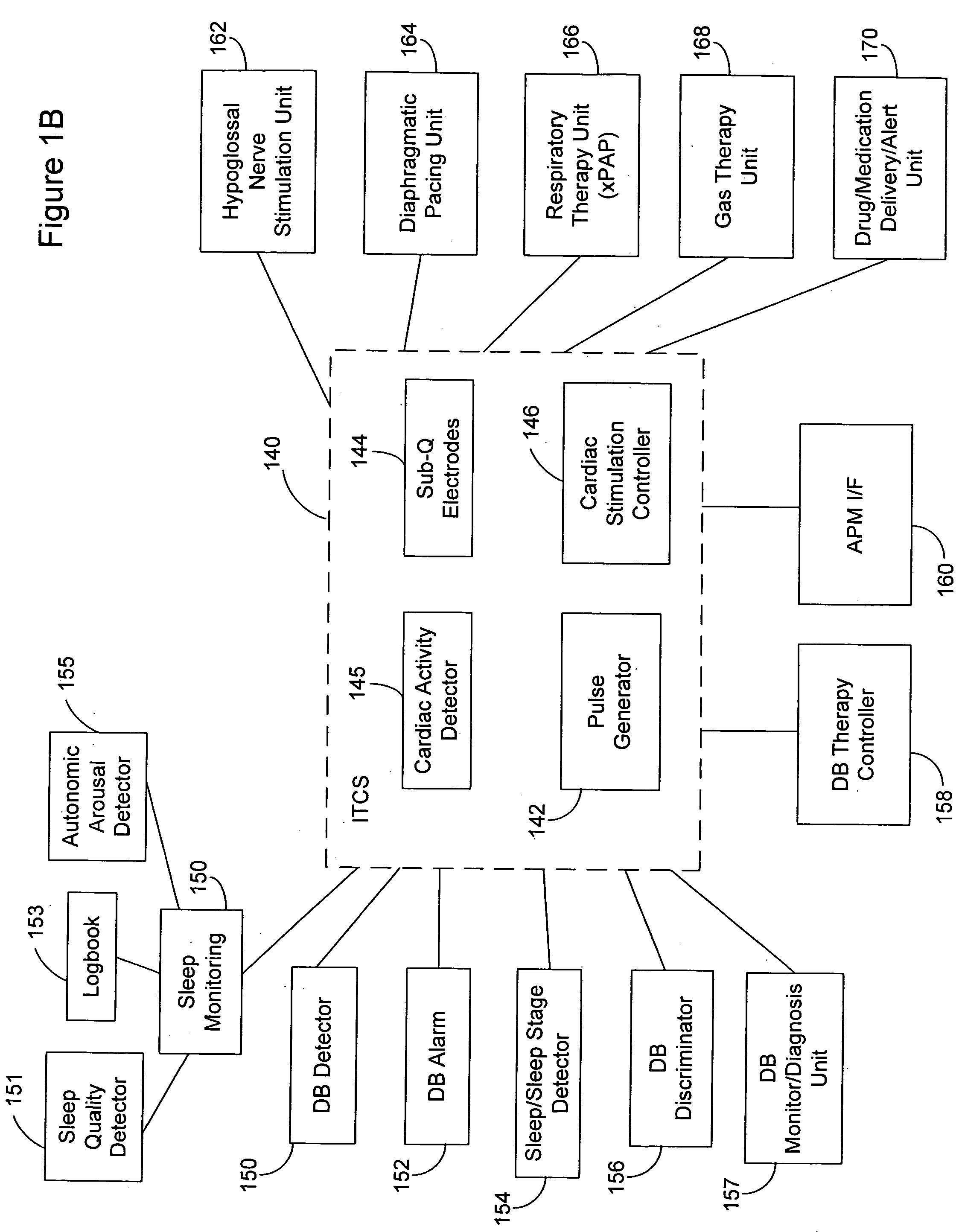
Subcutaneous cardiac rhythm management with disordered breathing detection and treatment
InactiveUS20050107838A1Heart defibrillatorsInertial sensorsPositive airway pressure deviceCardiac activity
A lead system, coupled to an implantable device, is configured for subcutaneous, non-intrathoracic placement relative to a patient's heart. Cardiac activity detection circuitry is coupled to the lead system and configured to detect cardiac rhythms. Disordered breathing detection circuitry is coupled to the lead system and configured to detect disordered breathing. One or both of cardiac therapy circuitry and disordered breathing therapy circuitry may be coupled to the lead system and configured to delivery therapies to treat disordered breathing. Such therapies include cardiac pacing, diaphragmatic pacing, and hypoglossal nerve stimulation therapies. A patient-external respiratory device, such as a positive airway pressure device, may be configured to deliver a disordered breathing therapy. One or more of a patient-internal drug delivery device, a patient-external drug delivery device, or a gas therapy device may be employed to treat disordered breathing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
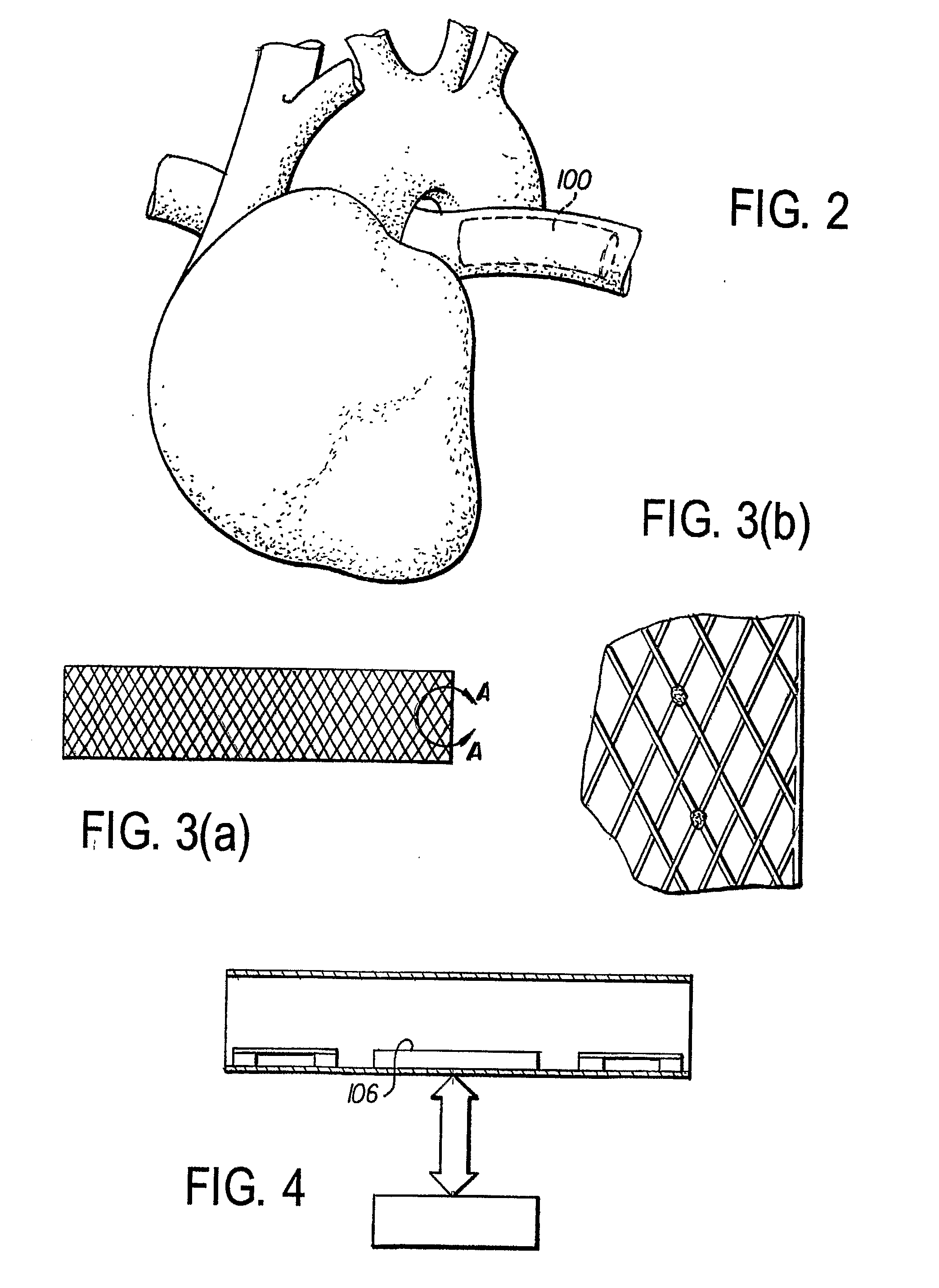
Method and apparatus for assessing left ventricular function and optimizing cardiac pacing intervals based on left ventricular wall motion
A system and method for monitoring left ventricular (LV) lateral wall motion and for optimizing cardiac pacing intervals based on left ventricular lateral wall motion is provided. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads including a left ventricular epicardial or coronary sinus lead equipped with a motion sensor electromechanically coupled to the lateral wall of the left ventricle. The device receives and processes wall motion sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of systolic LV lateral wall motion or acceleration. An automatic pacing interval optimization method evaluates the LV lateral wall motion during varying pacing interval settings, including atrial-ventricular intervals and inter-ventricular intervals and selects the pacing interval setting(s) that correspond to LV lateral wall motion associated with improved cardiac synchrony and hemodynamic performance.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vibrational therapy device used for resynchronization pacing in a treatment for heart failure
Systems for pacing the heart include a vibrational transducer which directs energy at the heart, usually at at least a ventricle, to pace the heart and to promote synchronized contraction of the ventricles. Optionally, additional vibrational and / or electrical stimulation may be provided. The vibrational transducers are usually implantable at a location proximate the heart.
Owner:EBR SYST
Antitachycardia Pacing Pulse from a Subcutaneous Defibrillator
Devices and methods for single therapy pulse (STP) therapy for tachyarrythmia are disclosed. The STP therapy can be delivered from a far-field position to allow a “global” capture approach to pacing. Due to the global capture in STP, a series of pulses, which is indicative of conventional anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) delivered by transvenous systems, becomes unnecessary. One to four pulses at most are needed for STP, and after delivery of the one to four pulses, therapy delivery can be interrupted to determine whether the previously delivered therapy has been successful.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Method and system for optimizing left-heart lead placement
InactiveUS20070055124A1Easy to placePredict successUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac wallBlood flow
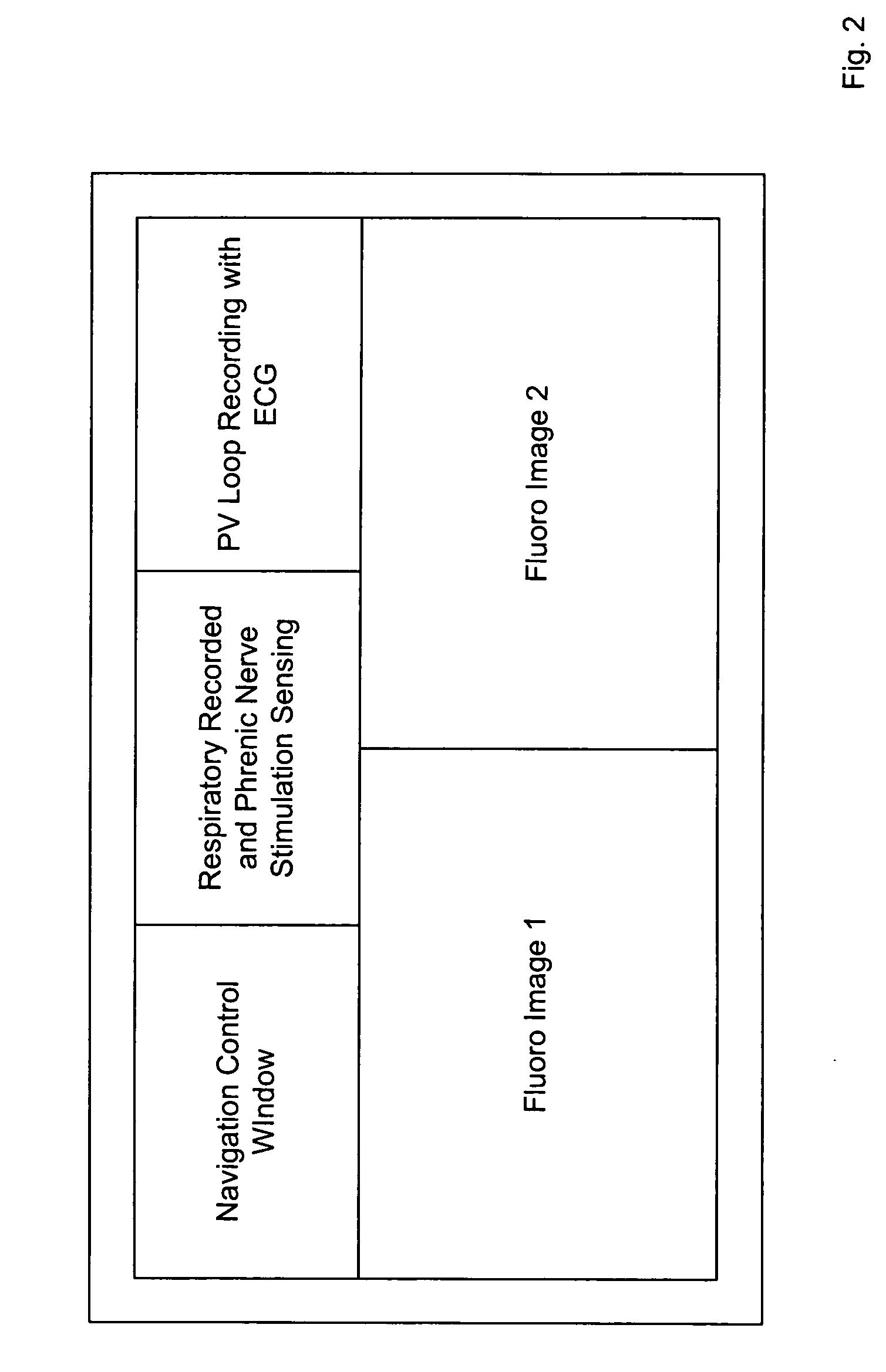
A system for identifying locations for pacing the heart, the system comprising a pacing electrode, a remote navigation system for positioning the pacing electrode at each of a plurality of locations; a system for determining Pressure-Volume loop data resulting from pacing at each location; an ECG system, a phrenic nerve stimulation detection system, and a means of identifying at least one preferred location based upon at least the Pressure-Volume loop, ECG, and phrenic nerve stimulation data at each location. A method of identifying locations for pacing the heart, the method comprising: navigating a pacing electrode to each of a plurality of locations in the heart; pacing the heart at each of the plurality of locations; and assessing the effectiveness of the pacing at each location by measuring cardiac blood flow and cardiac wall strain.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Detection of abnormal and induction of normal heat rate variability
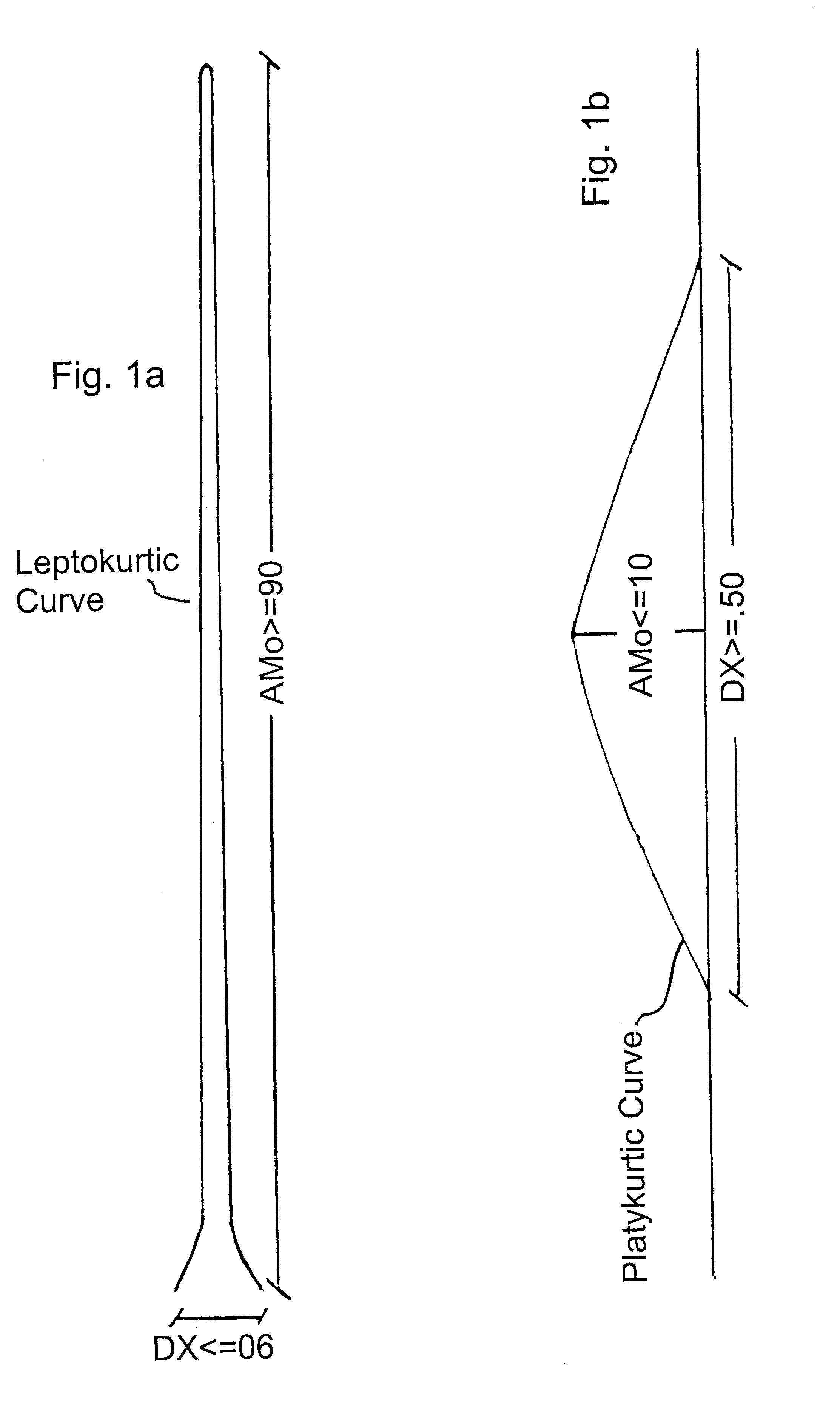
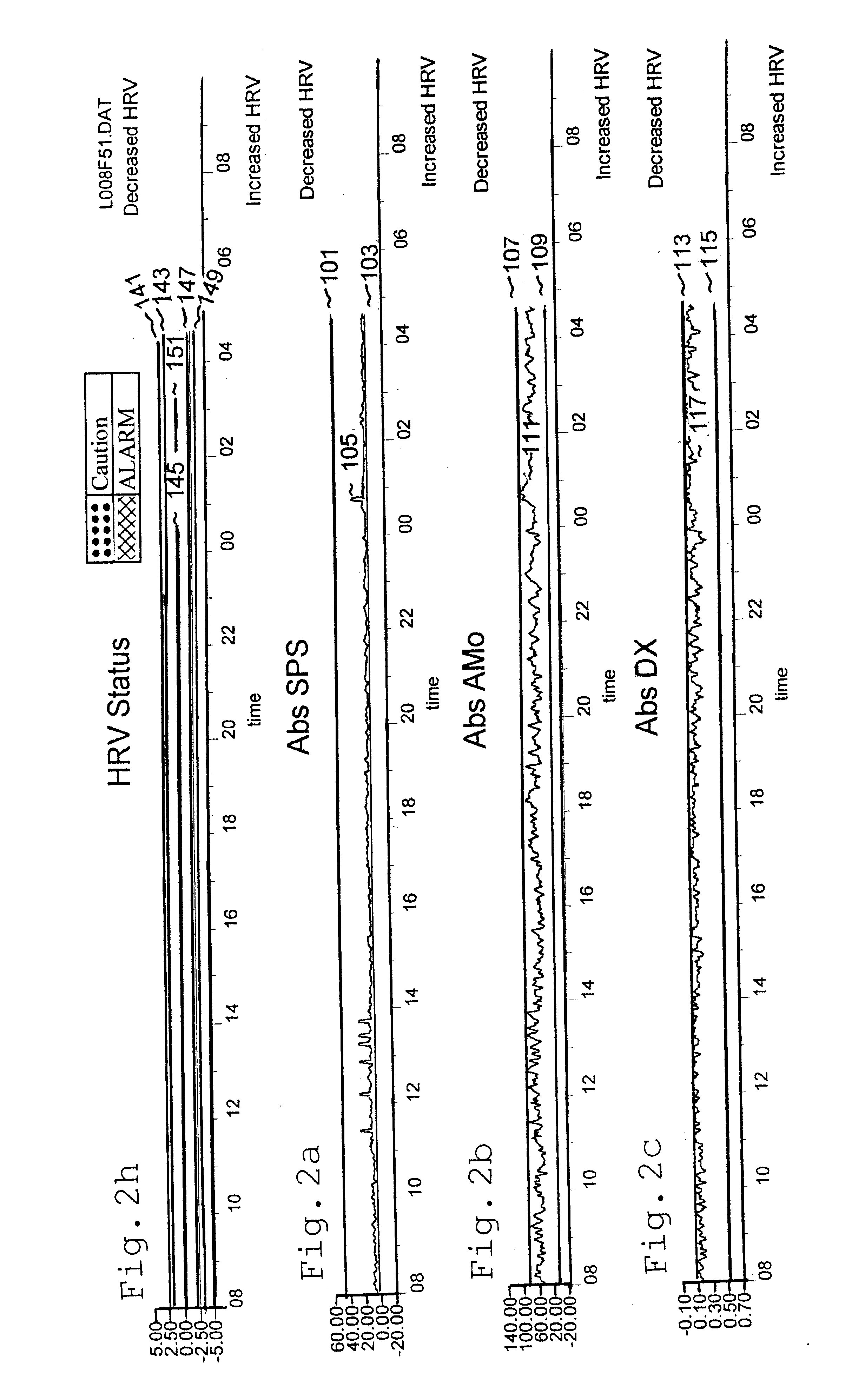
An apparatus and method for predicting potentially fatal arrhythmias up to twenty four hours in advance of the event by employing formulas indicating either too little or too much heart rate variability. A number of these formulas have both predetermined upper and lower limits, which if exceeded for a period of time are a predictor of a potentially fatal arrhythmia. When a patient's ALARM condition is predicted, whether the patient is indoors or outdoors, conscious or unconscious, a redundant protocol is utilized to relay that ALARM condition to a central monitoring station. The central monitoring station informs the patient's doctor, and then uses what ever means are available to transport the patient to the nearest emergency room for treatment. An apparatus and method for pacing the heart in a natural way, once a potentially fatal arrhythmia has been predicted is also disclosed.
Owner:GW SCI
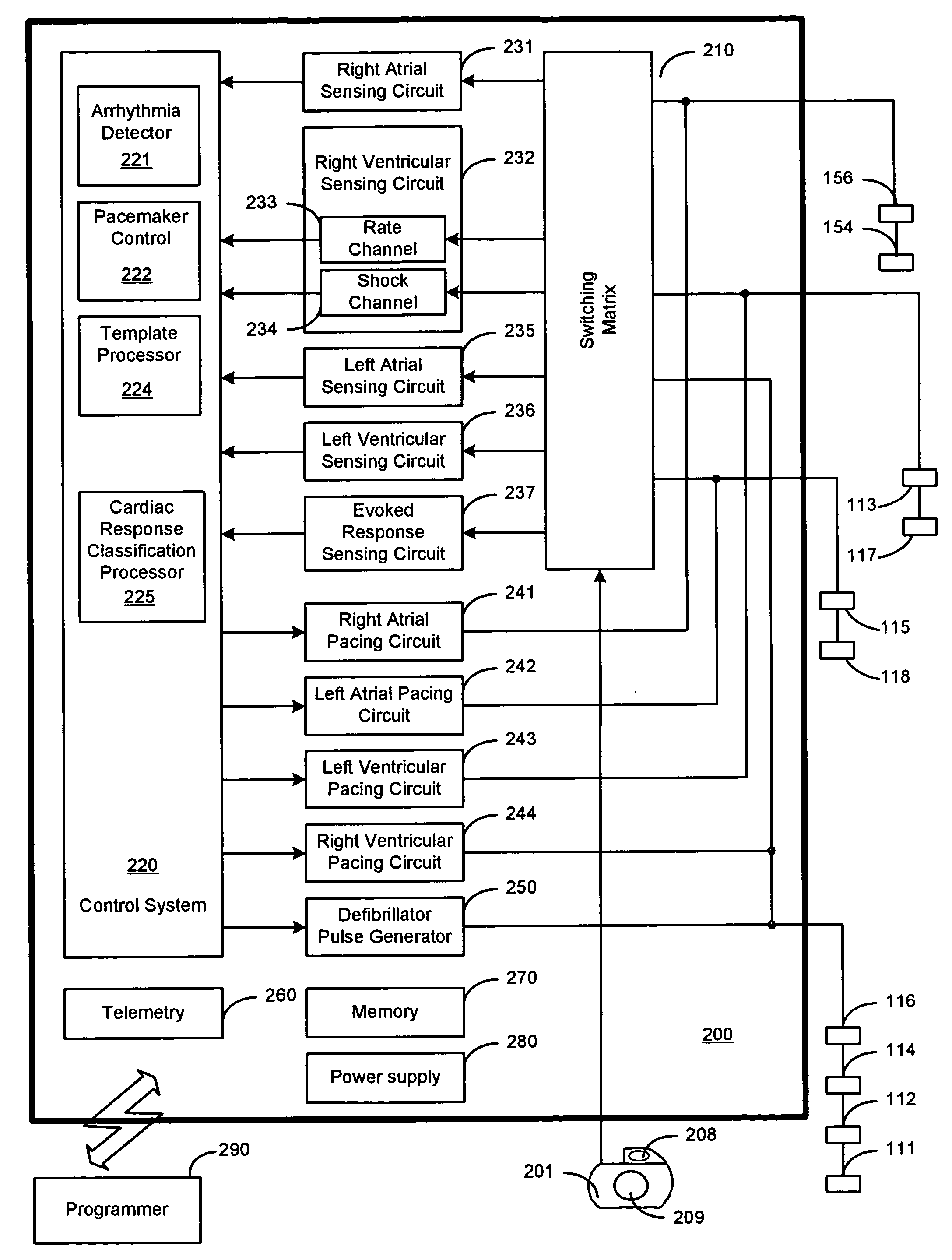
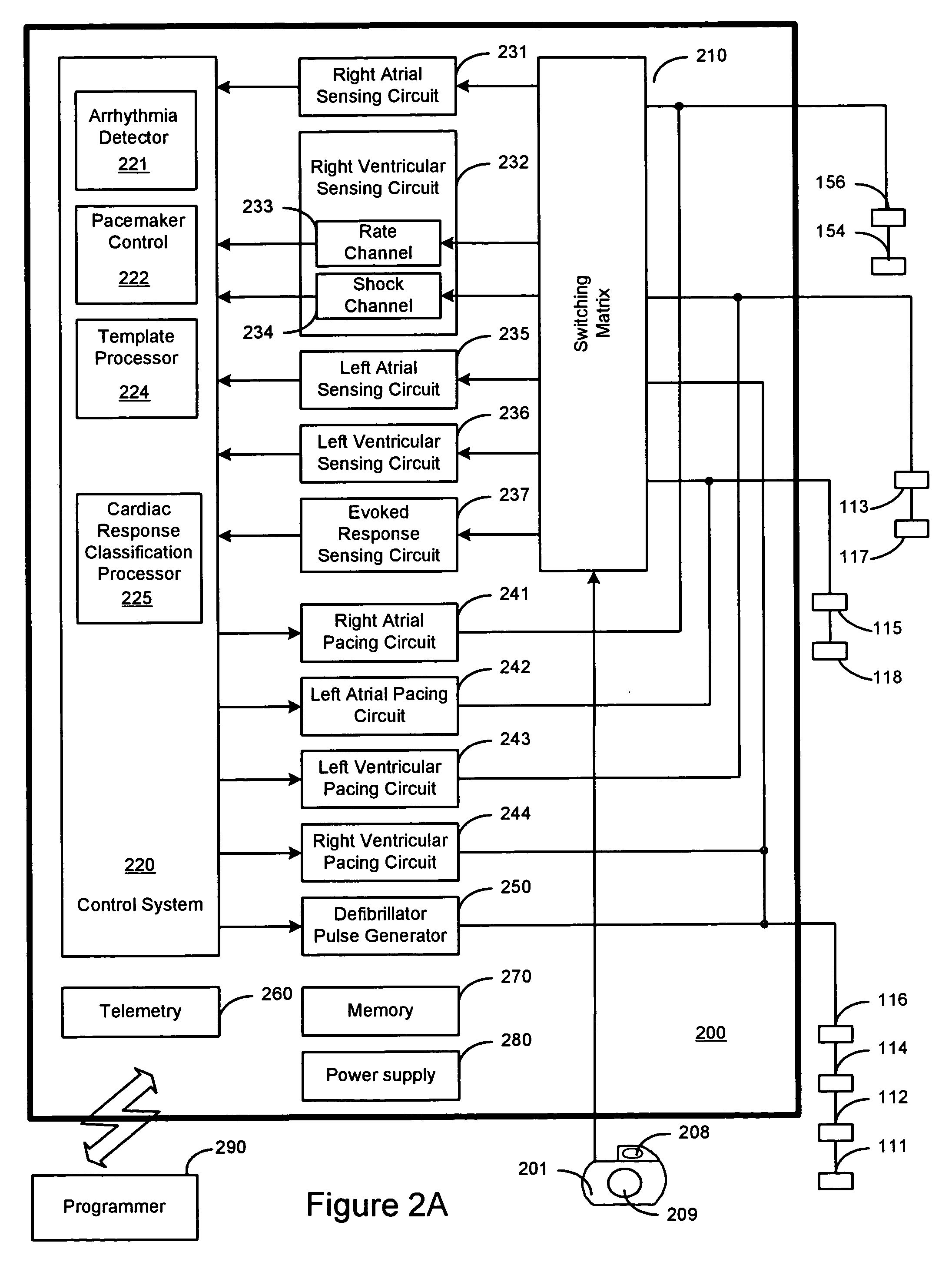
Cardiac response classification using multisite sensing and pacing
Methods and devices for classifying a cardiac pacing response involve using a first electrode combination for pacing and a second electrode combination for sensing a cardiac signal following pacing. The cardiac response to pacing may be classified using the sensed cardiac signal. One process involves using the sensed cardiac signal to detect the cardiac response as a fusion / pseudofusion beat. Another process involves using the sensed cardiac signal to classify the cardiac response to pacing as one of at least three cardiac response types.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Leadless cardiac pacemaker with conducted communication
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Current waveforms for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter- defibrillator
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathoracic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com