Patents
Literature
139 results about "Subcutaneous implantation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
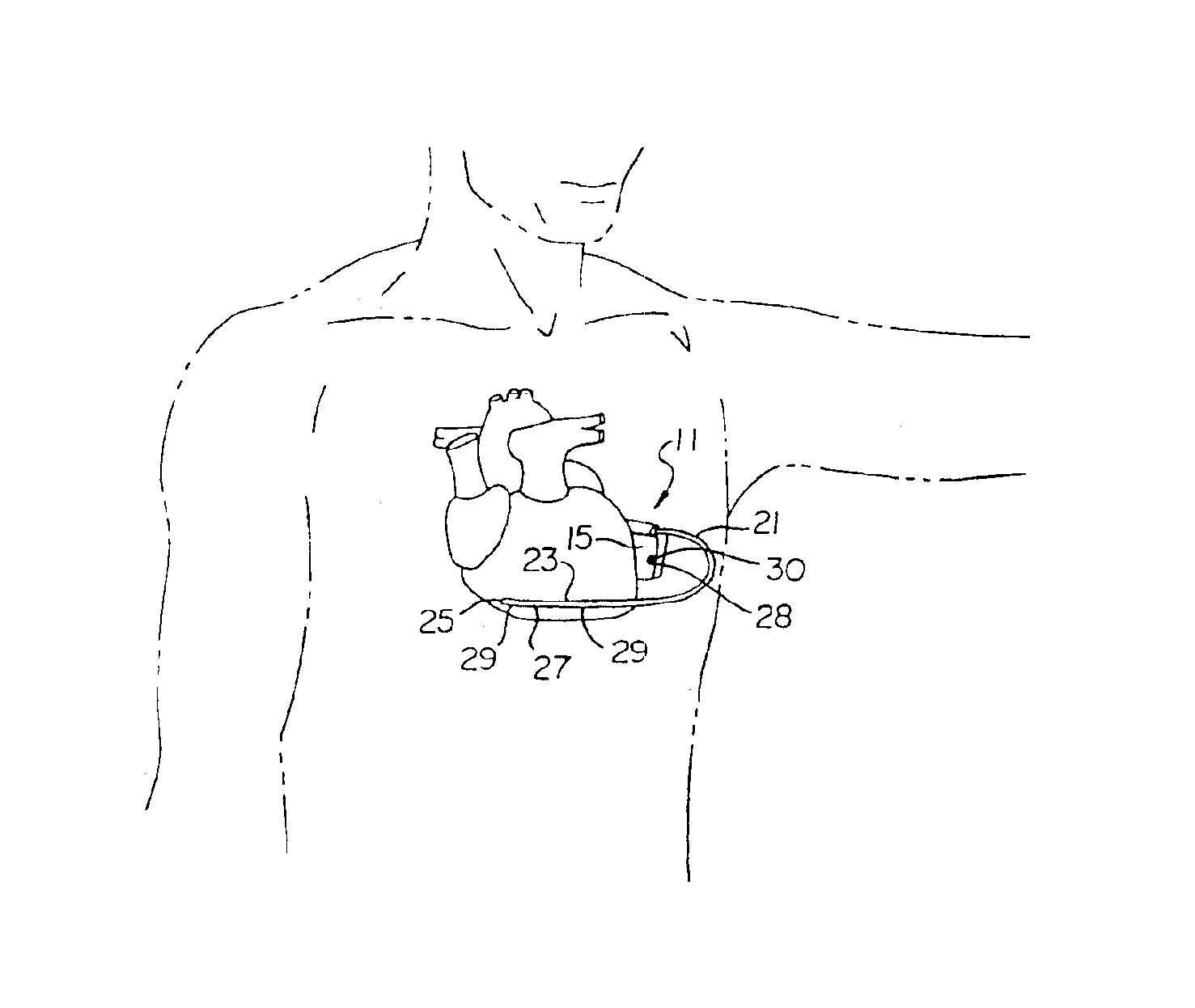
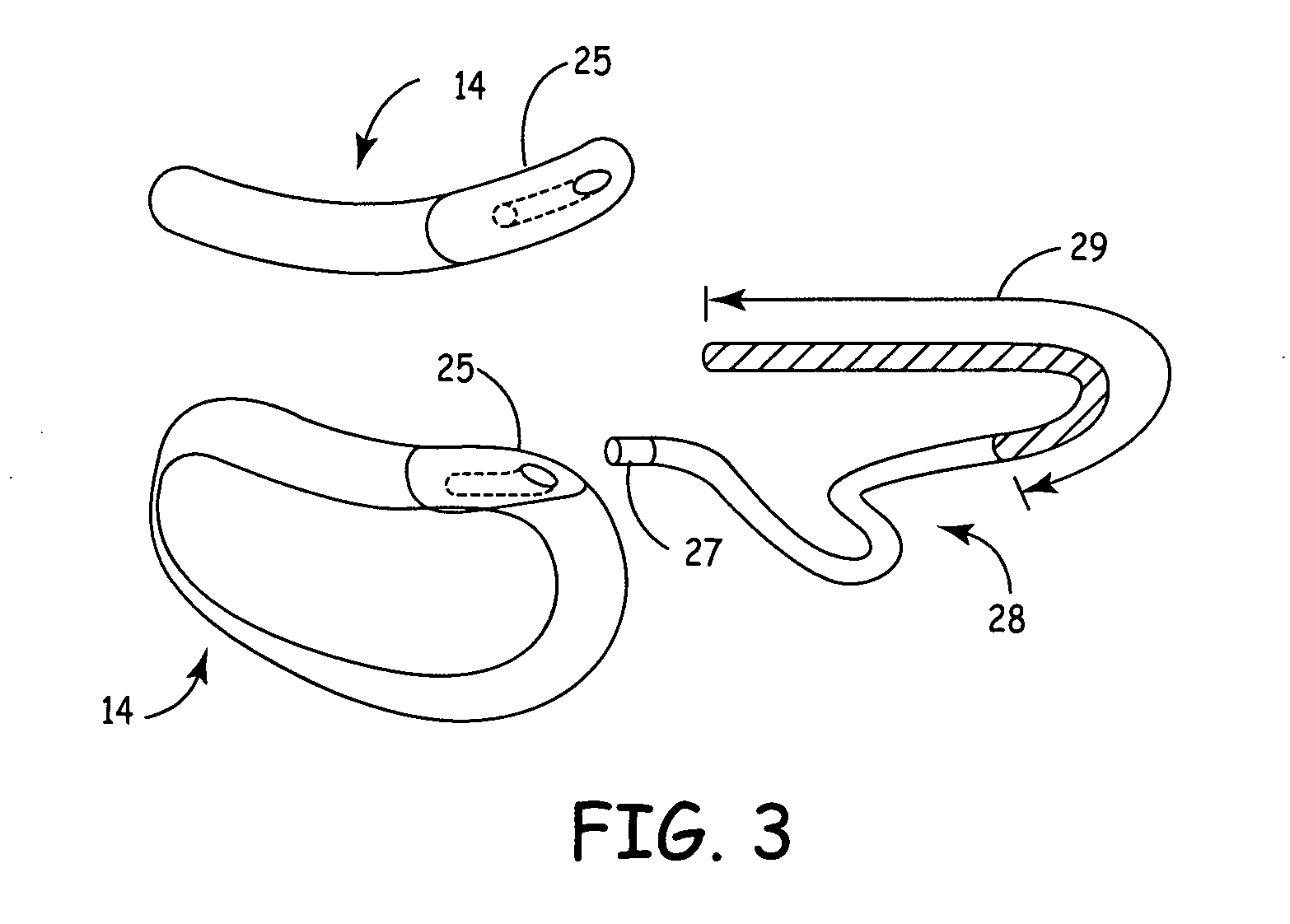
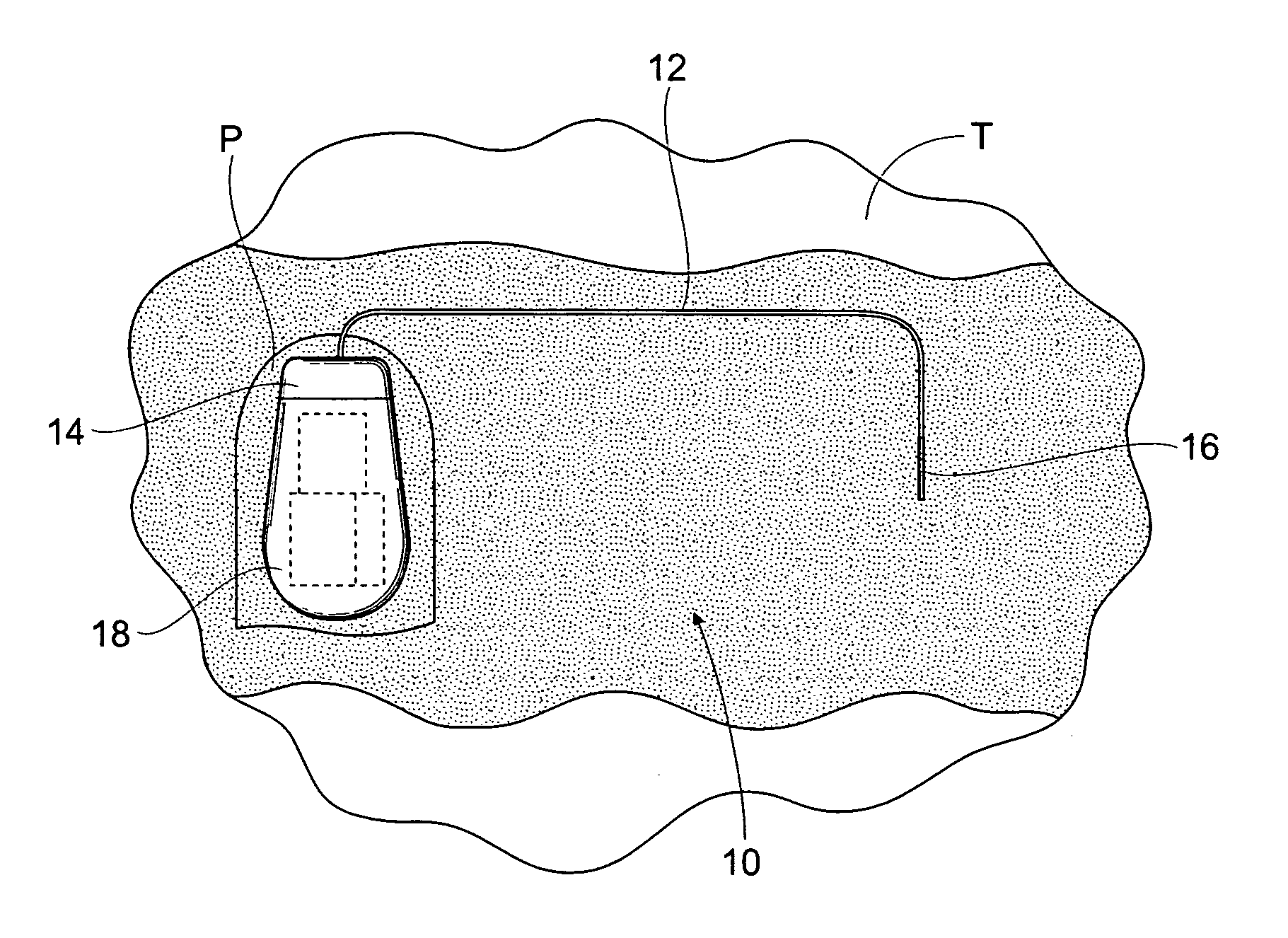
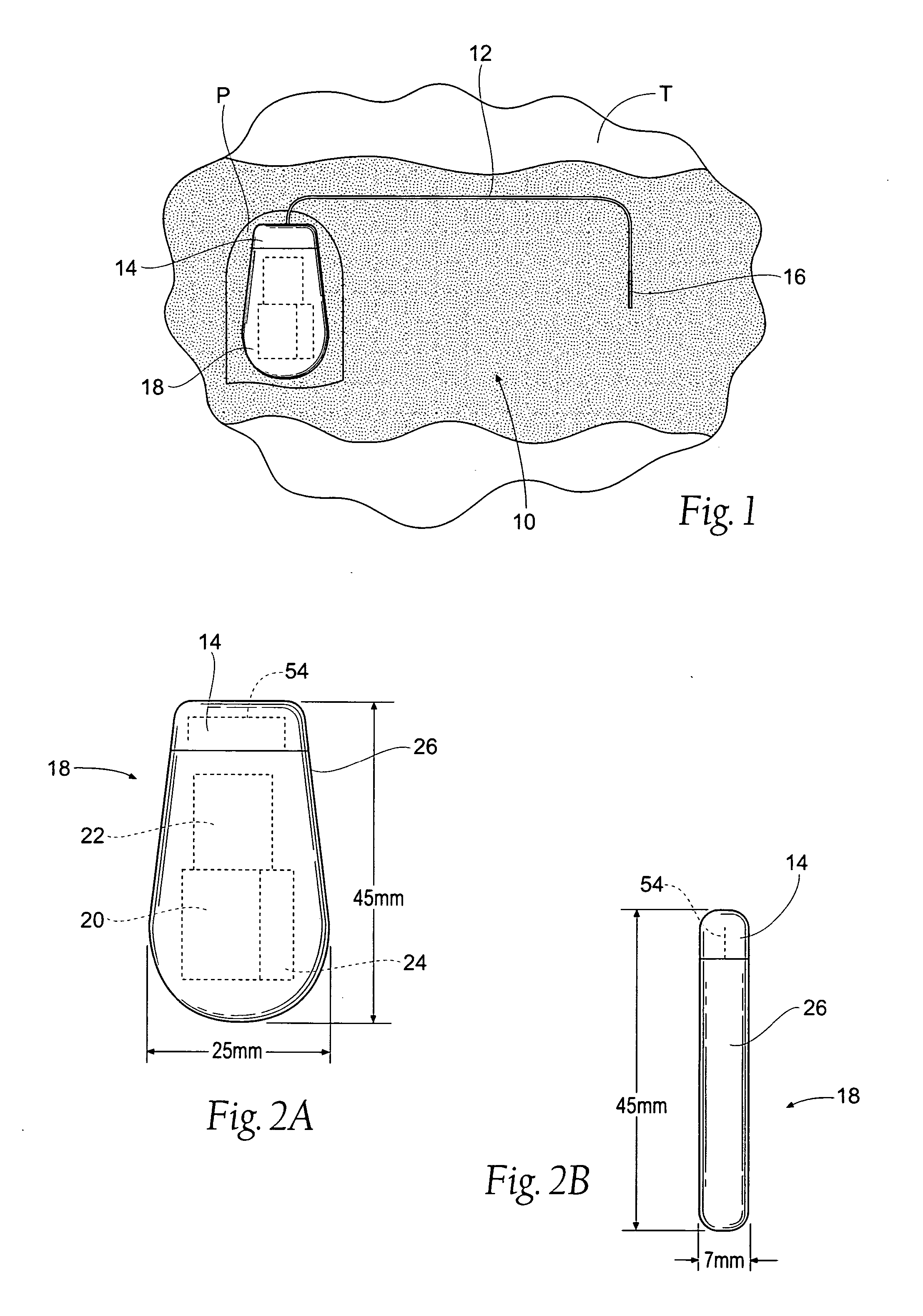
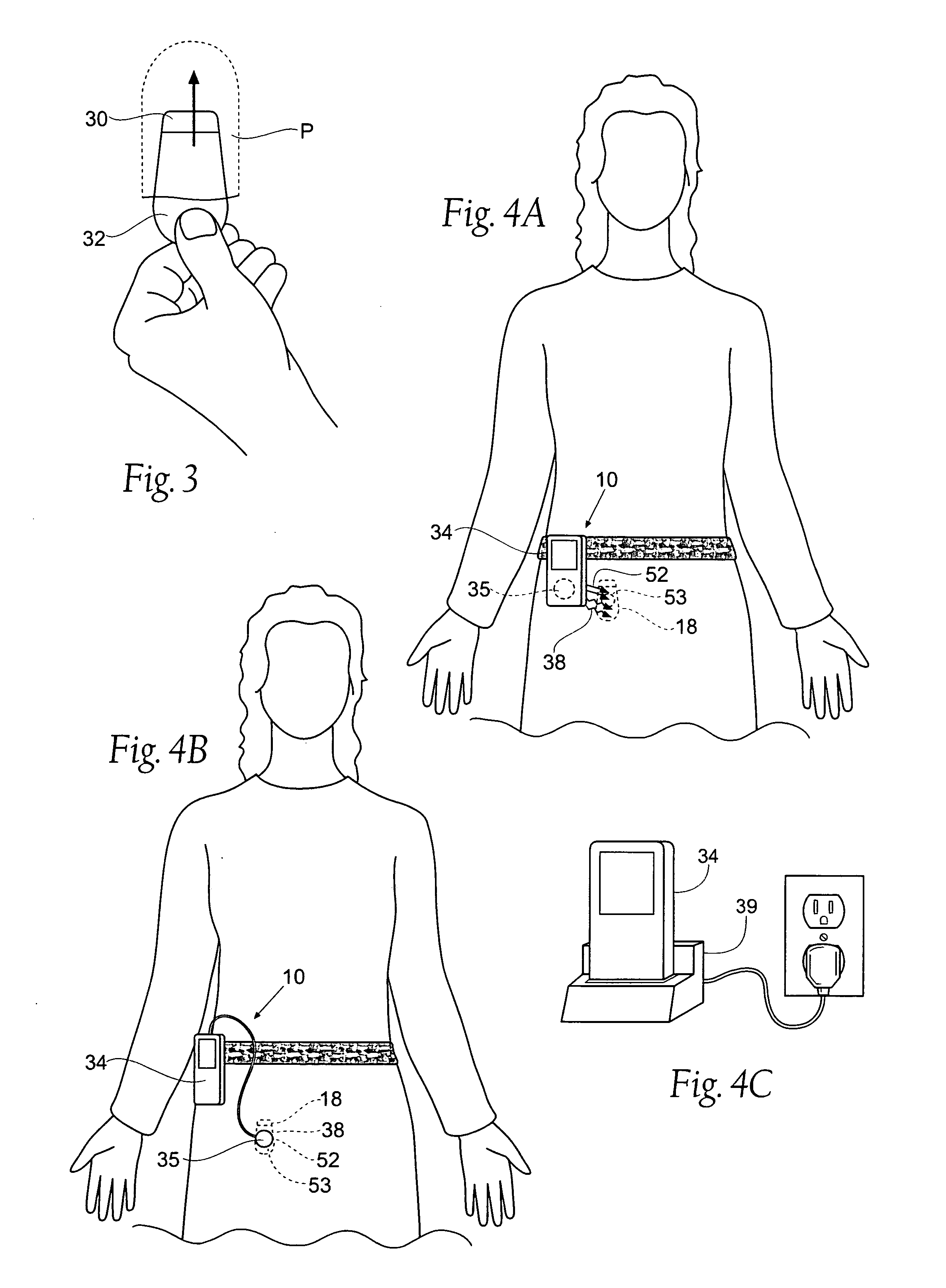
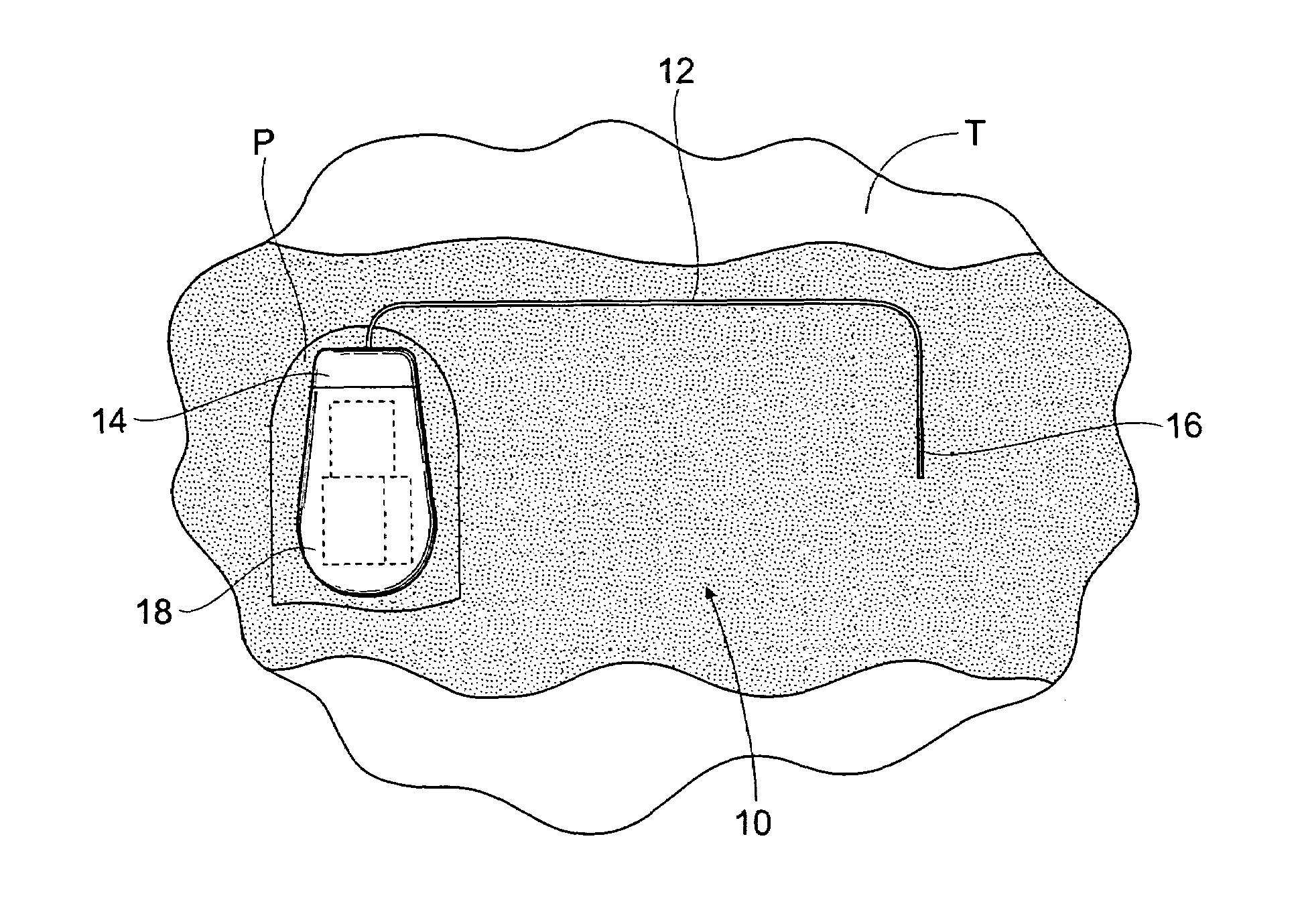
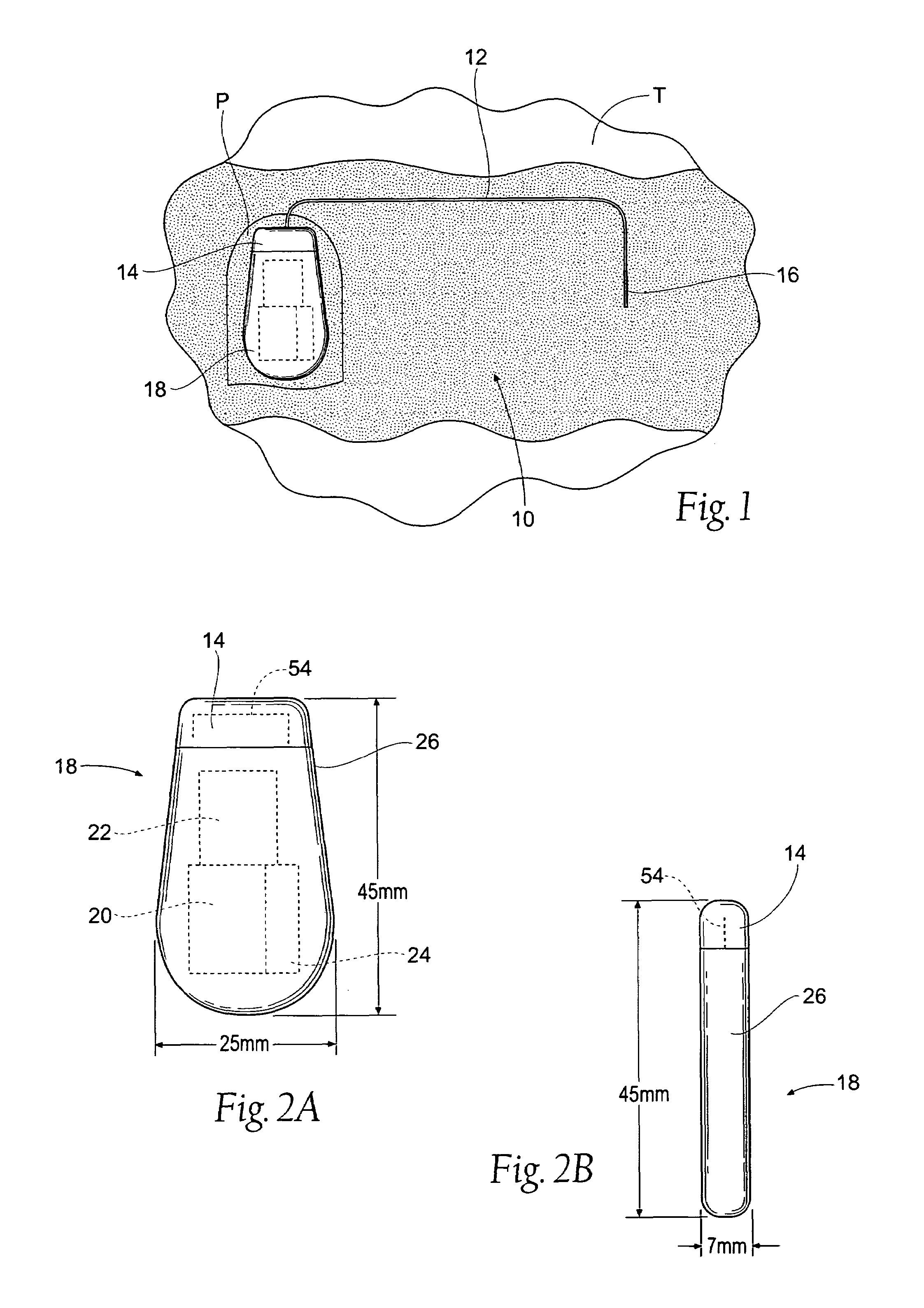
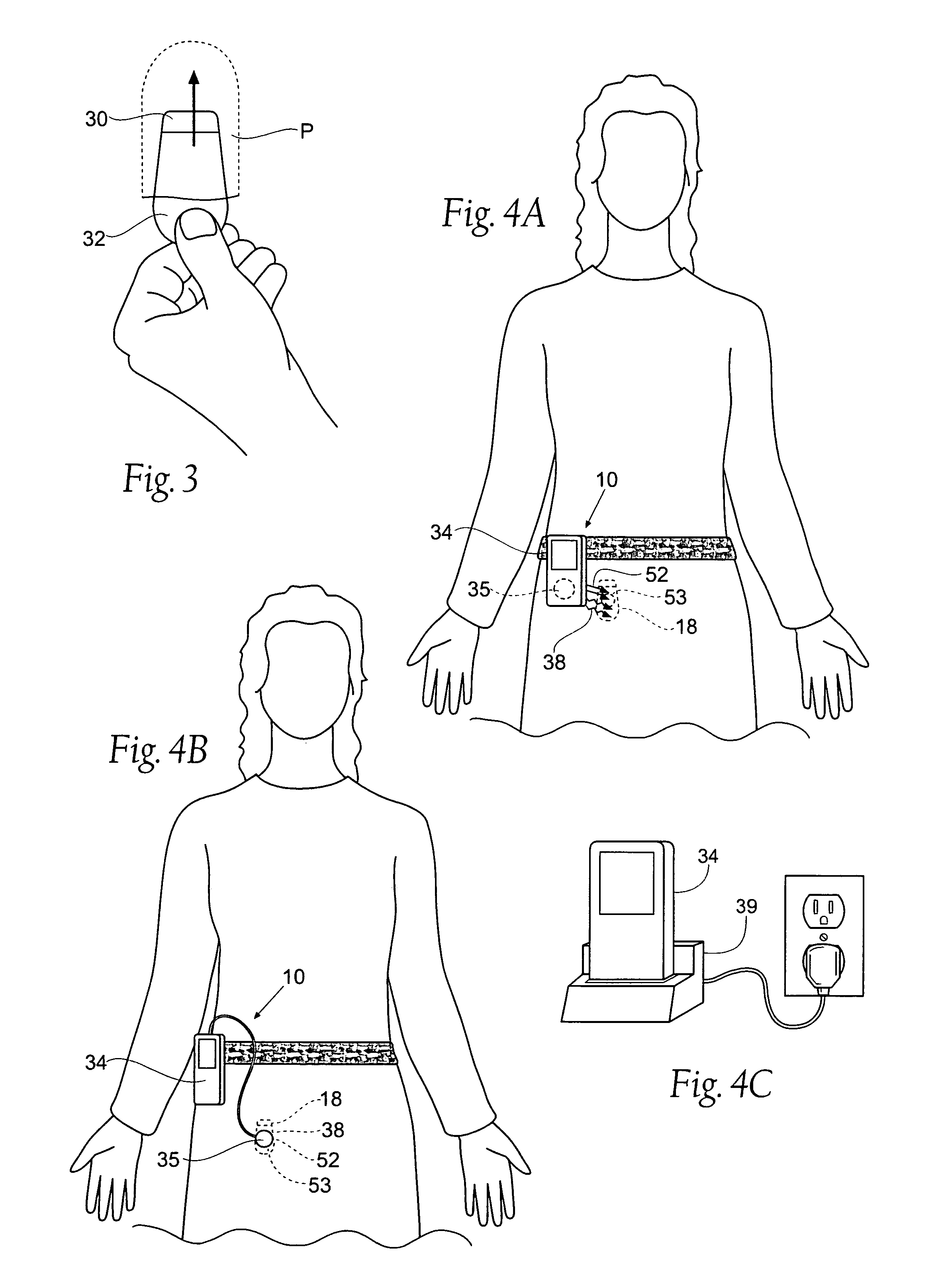
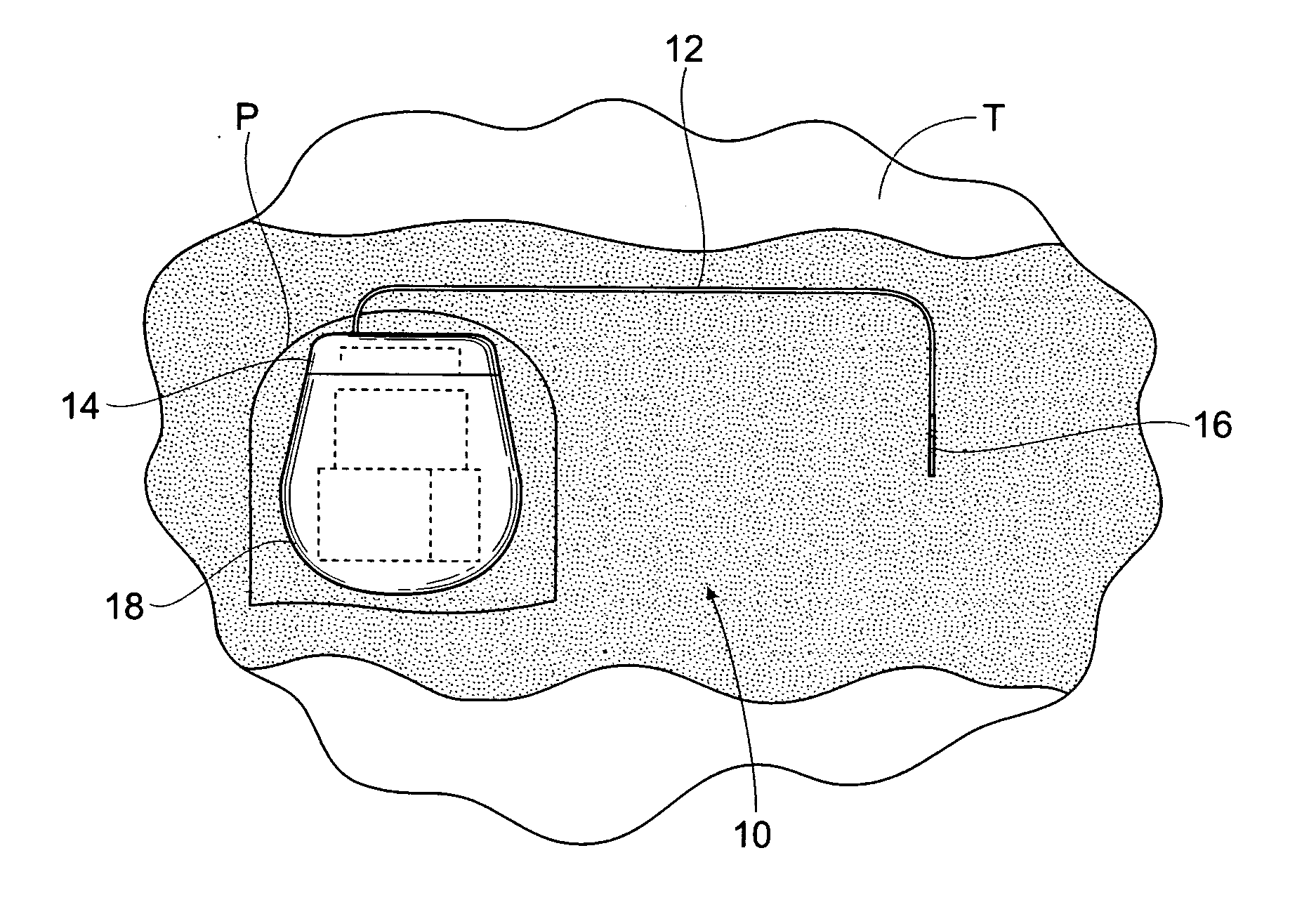
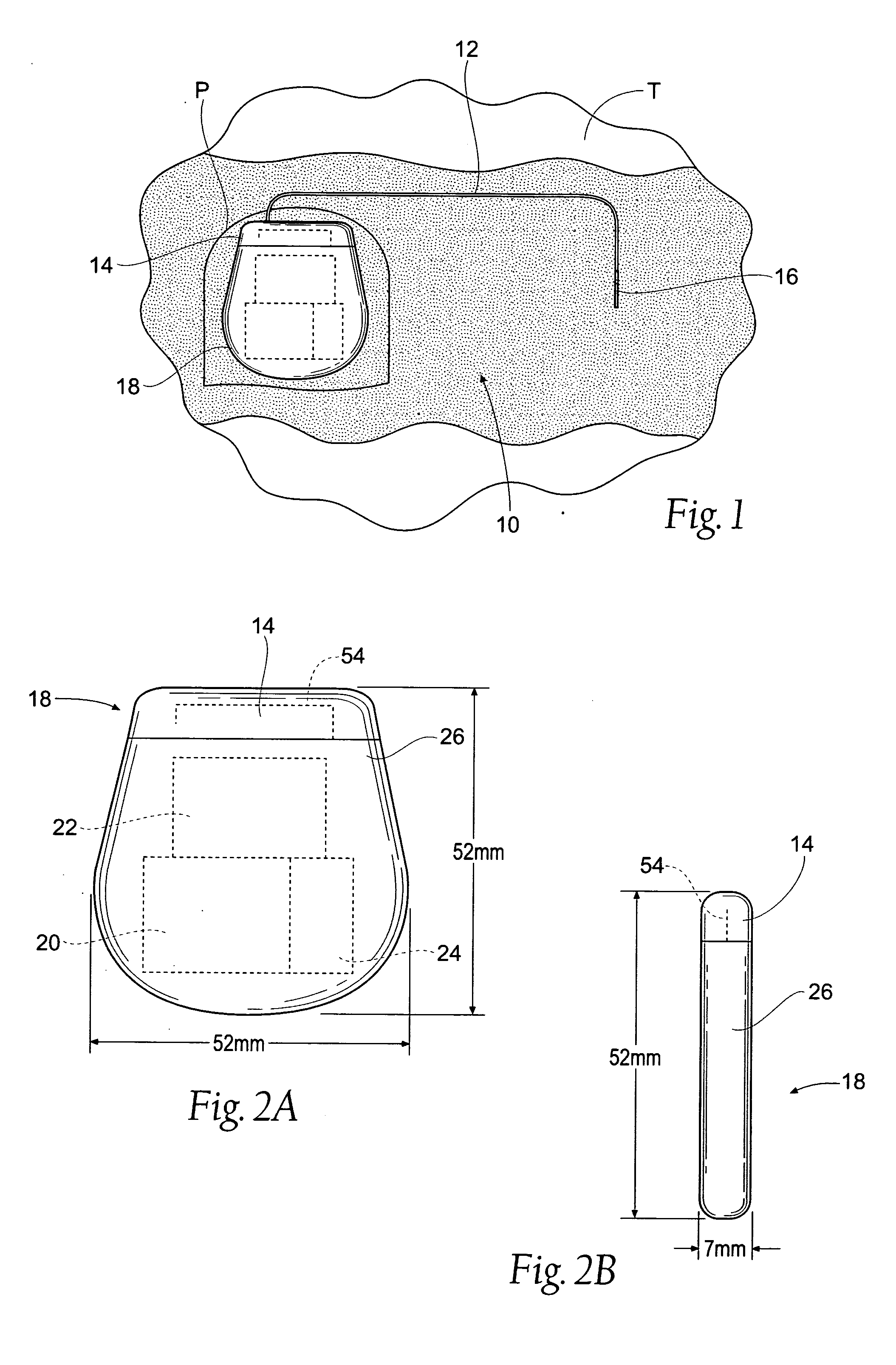
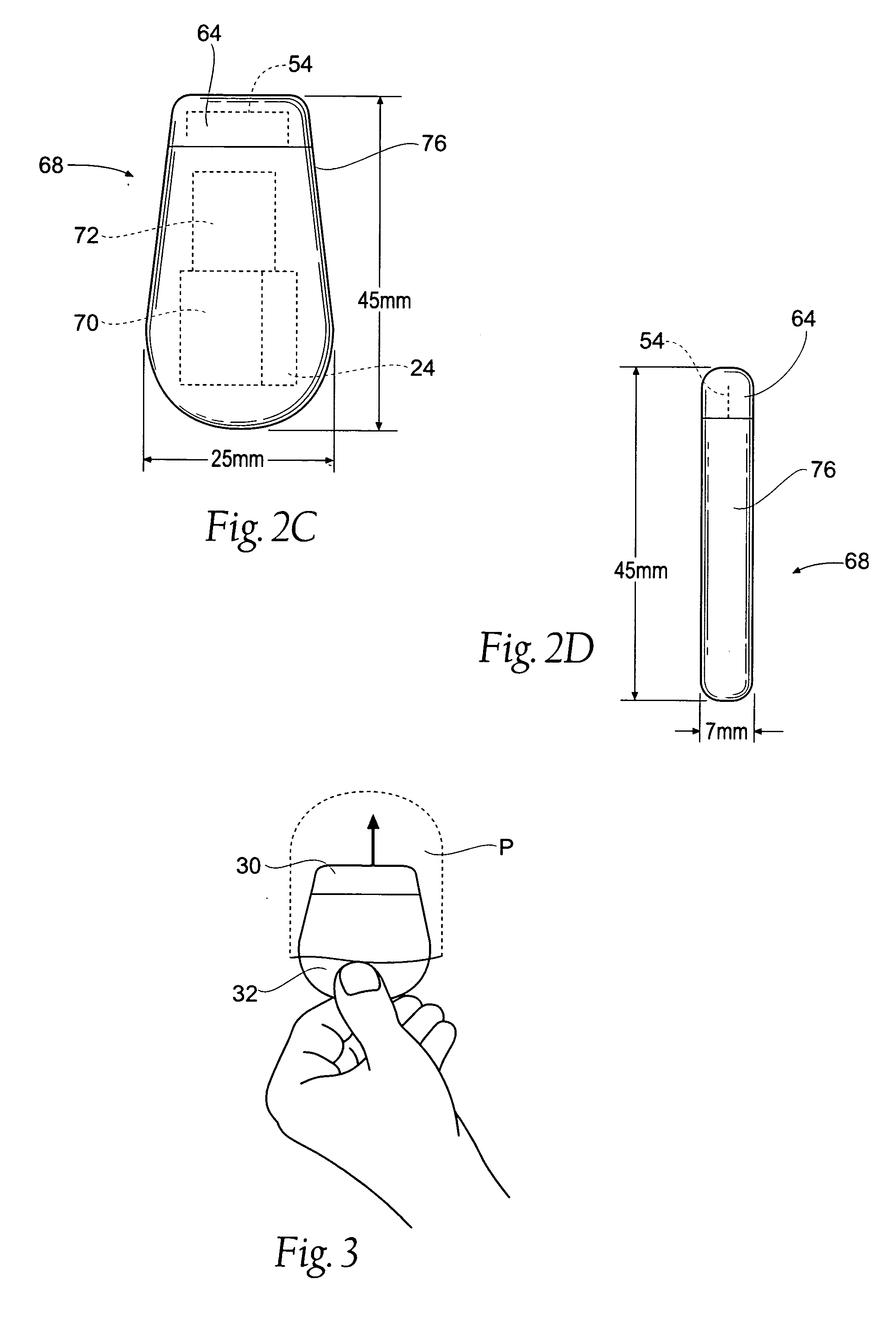
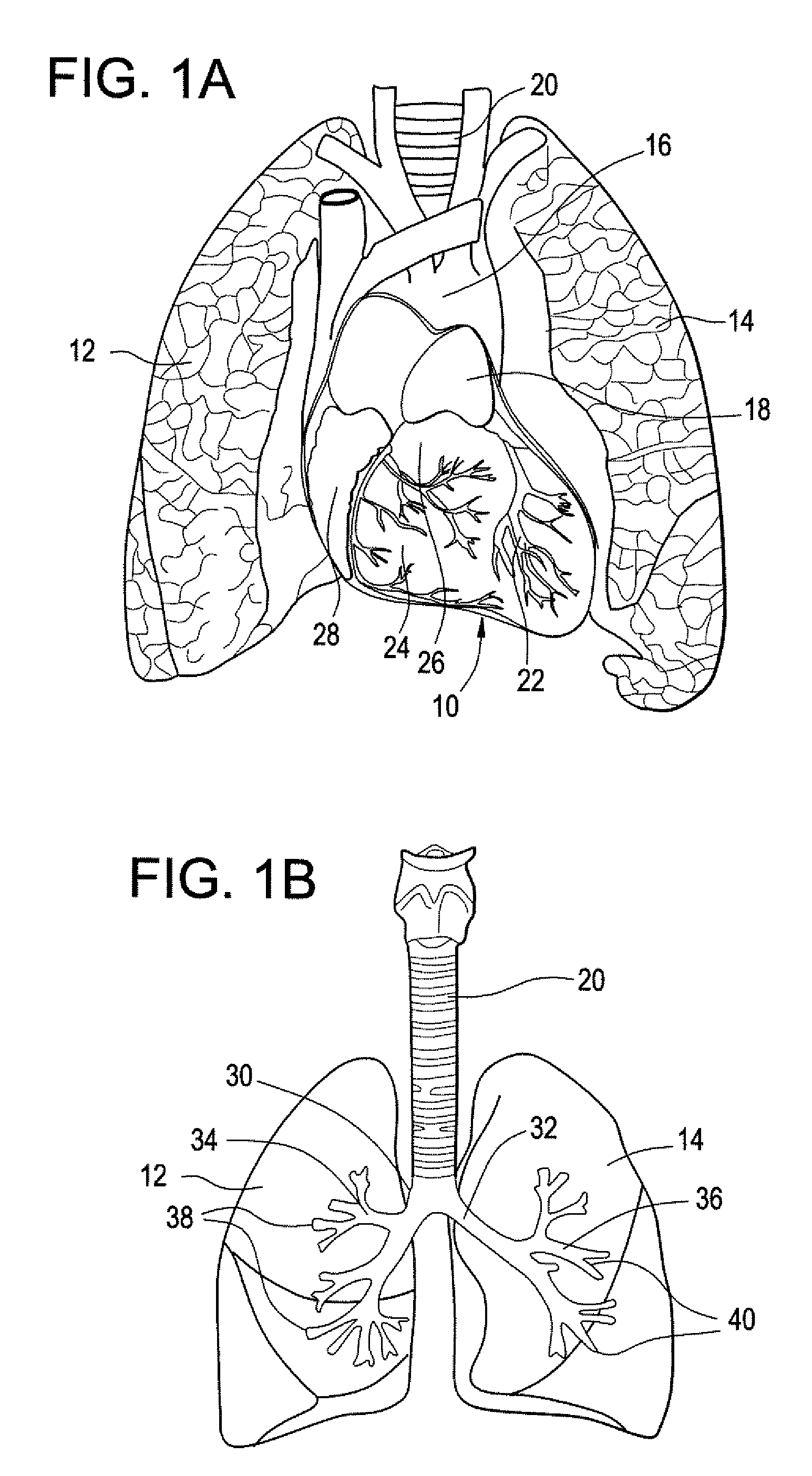
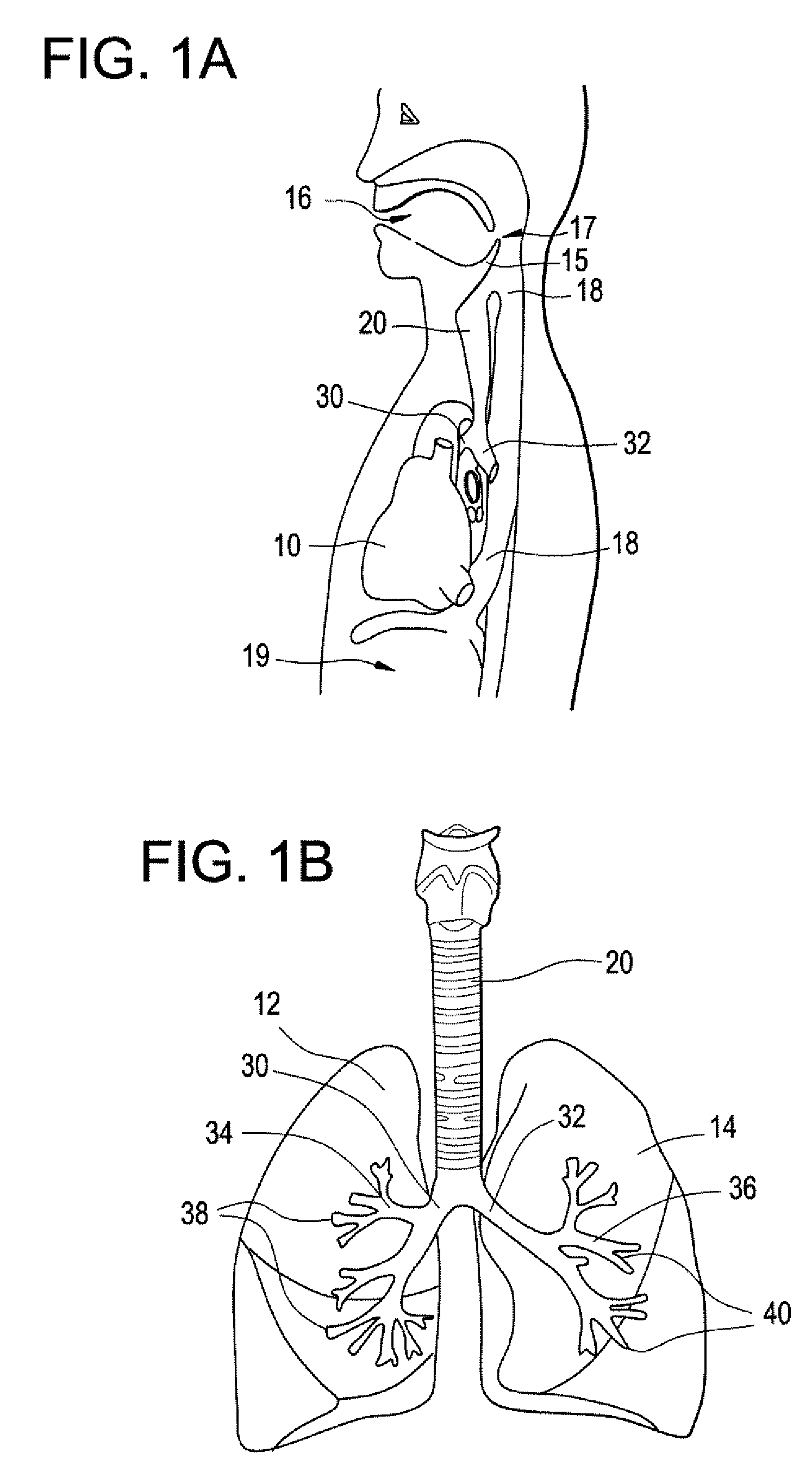
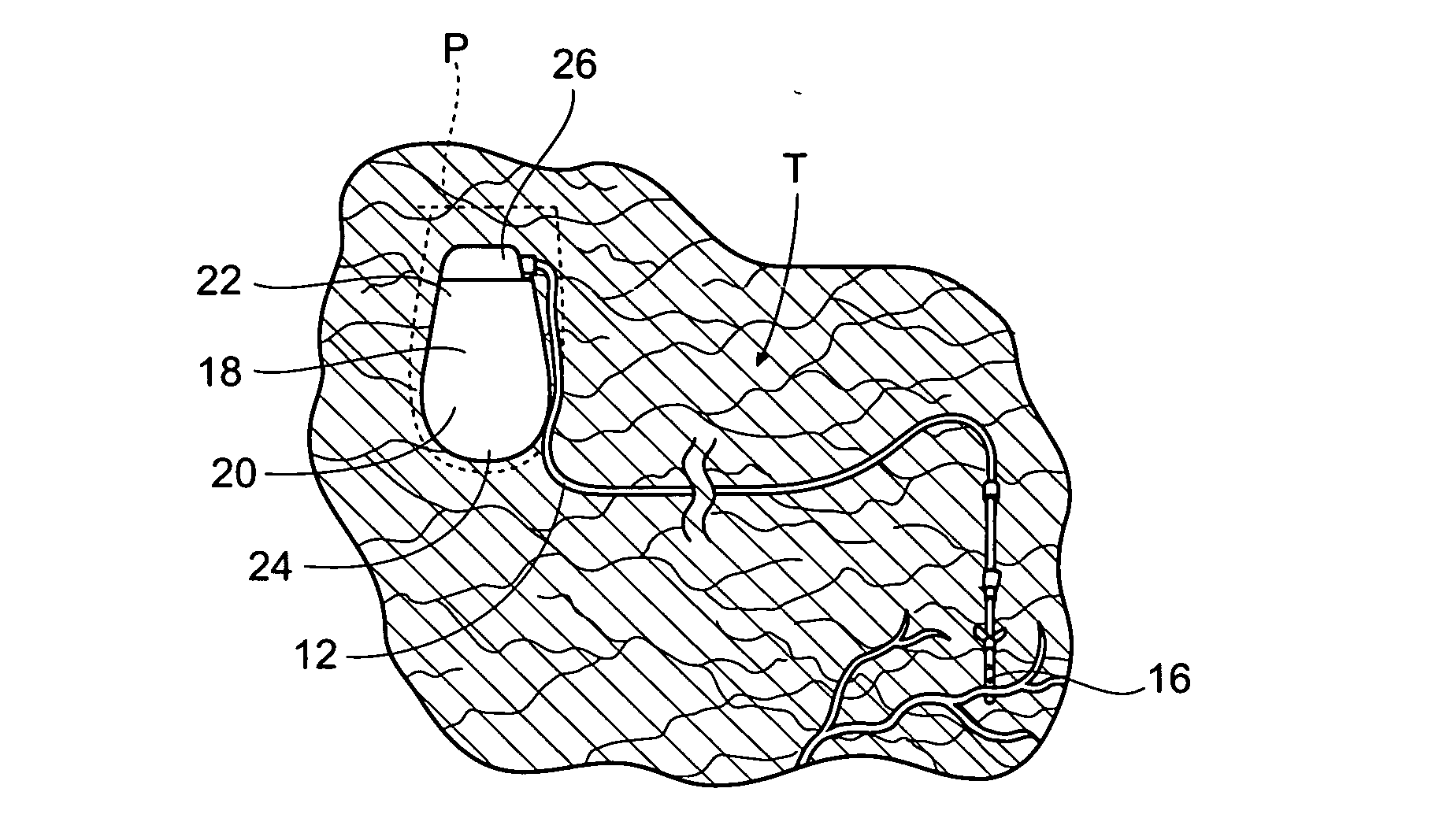
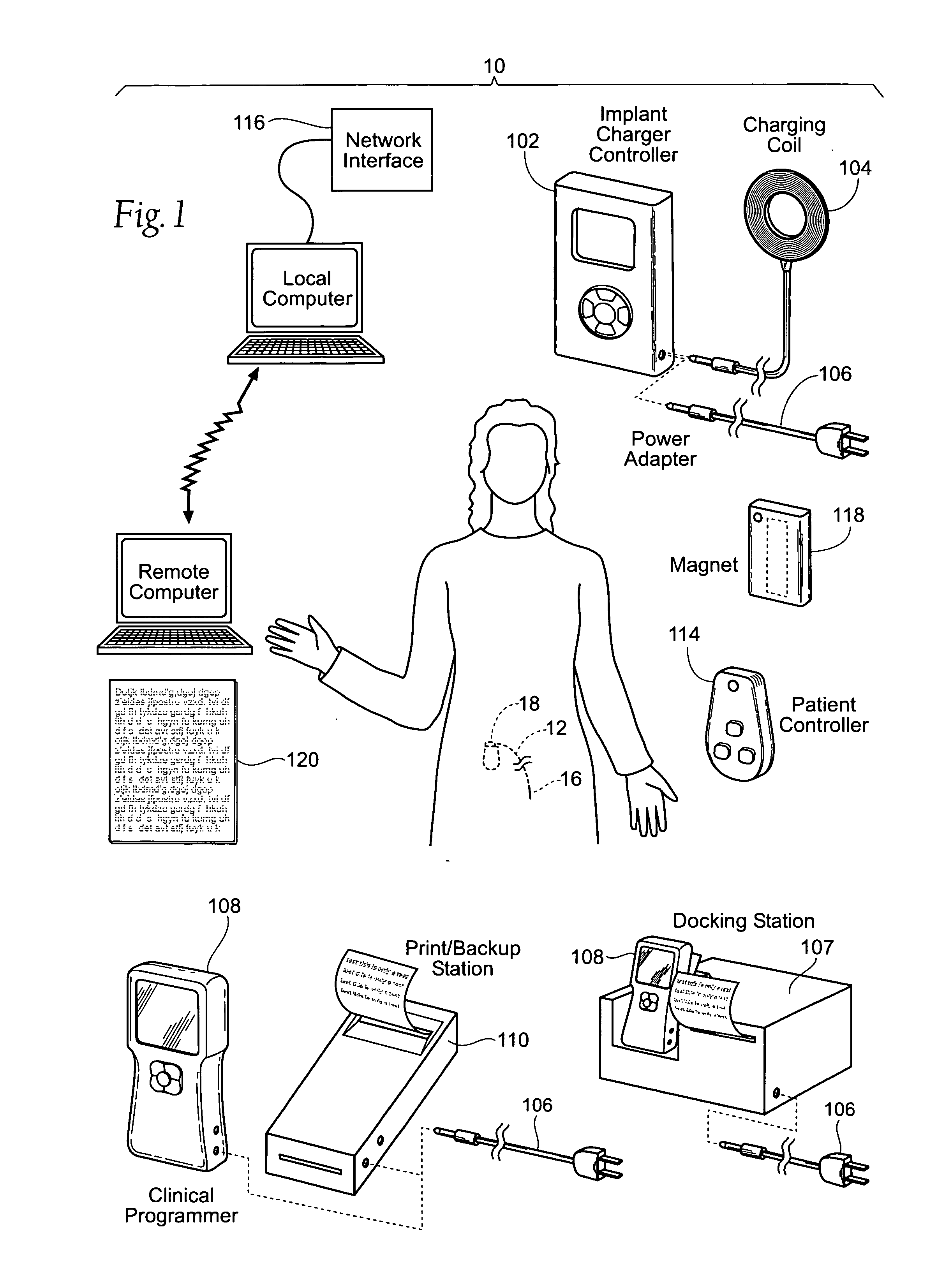
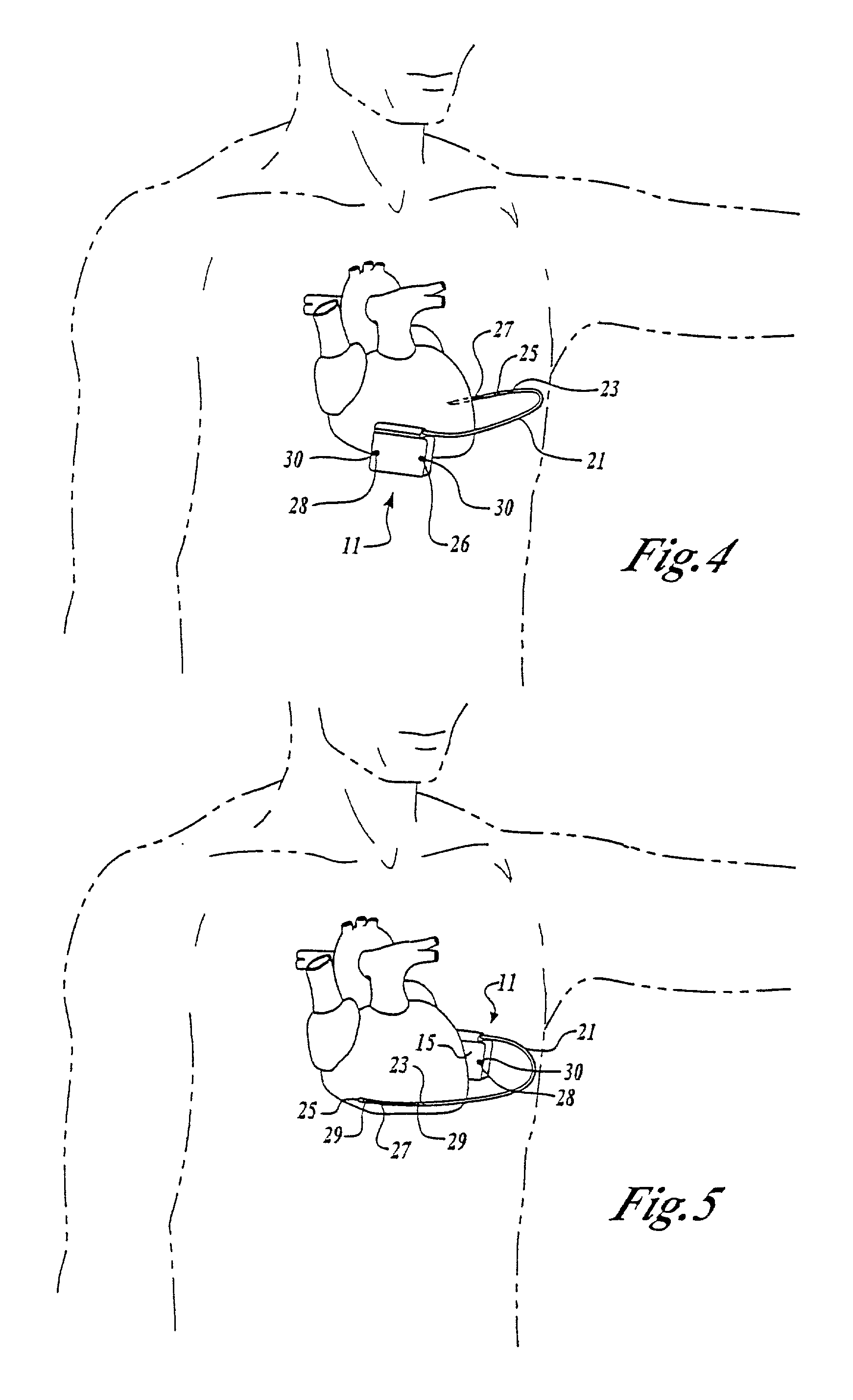
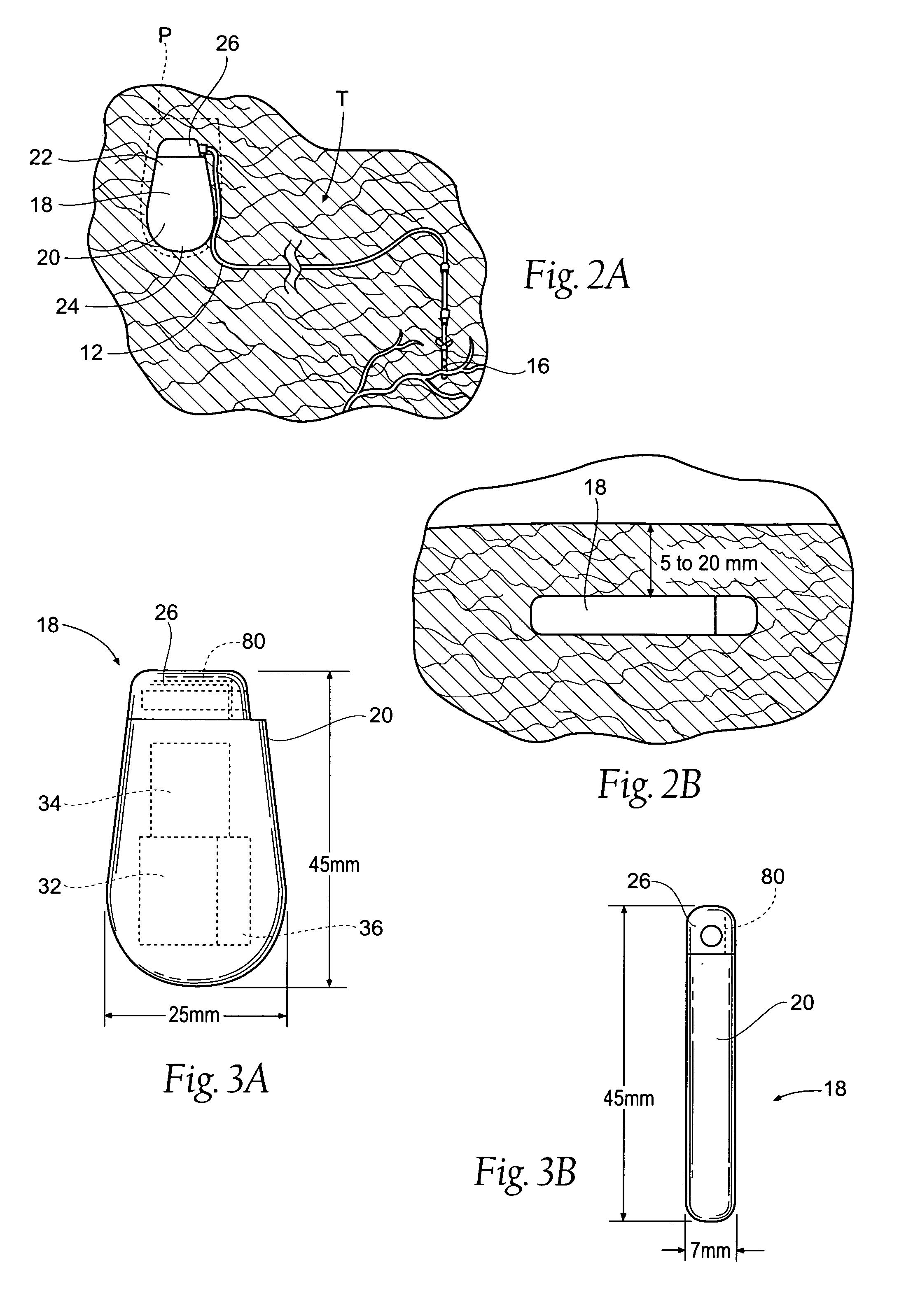
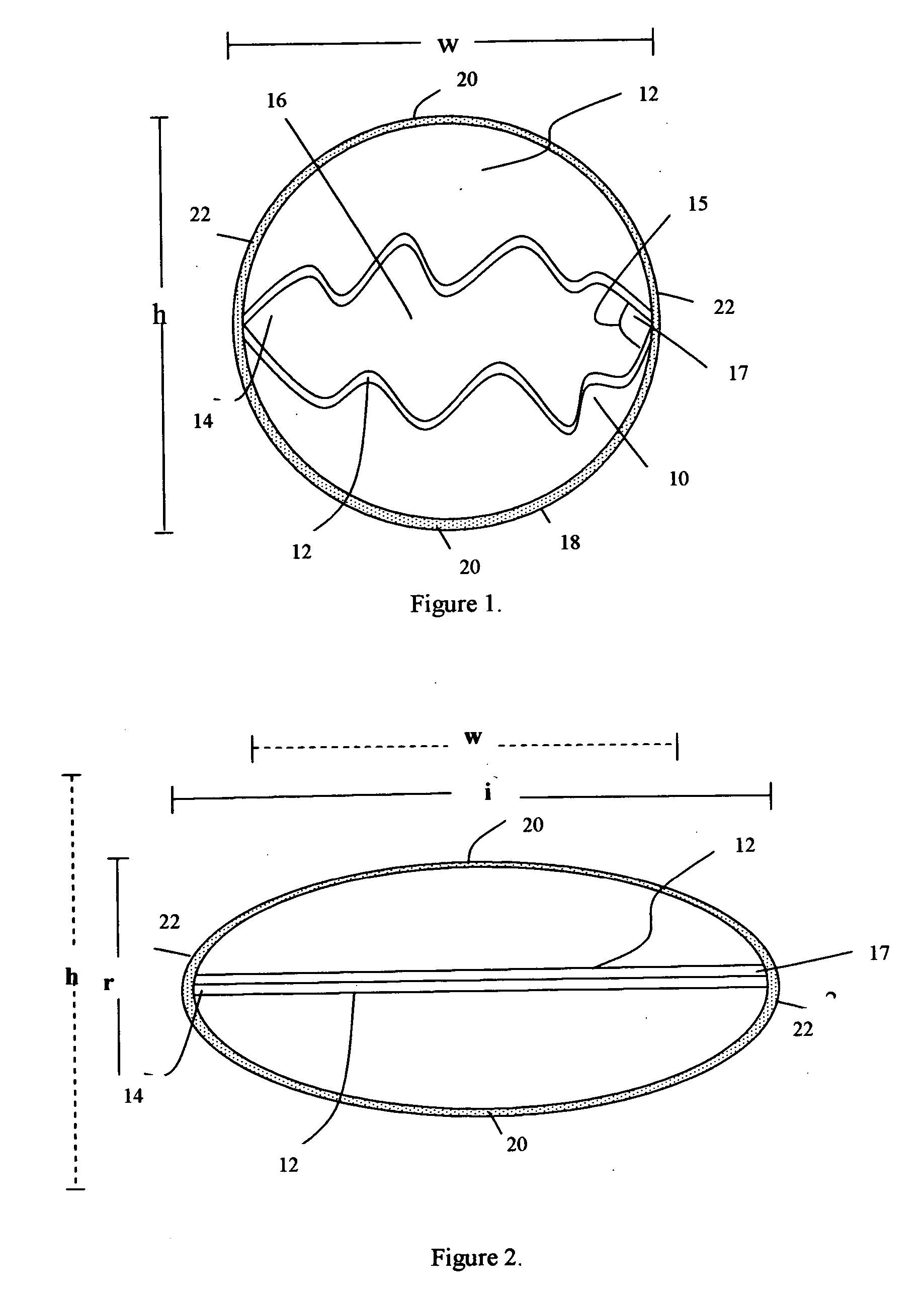
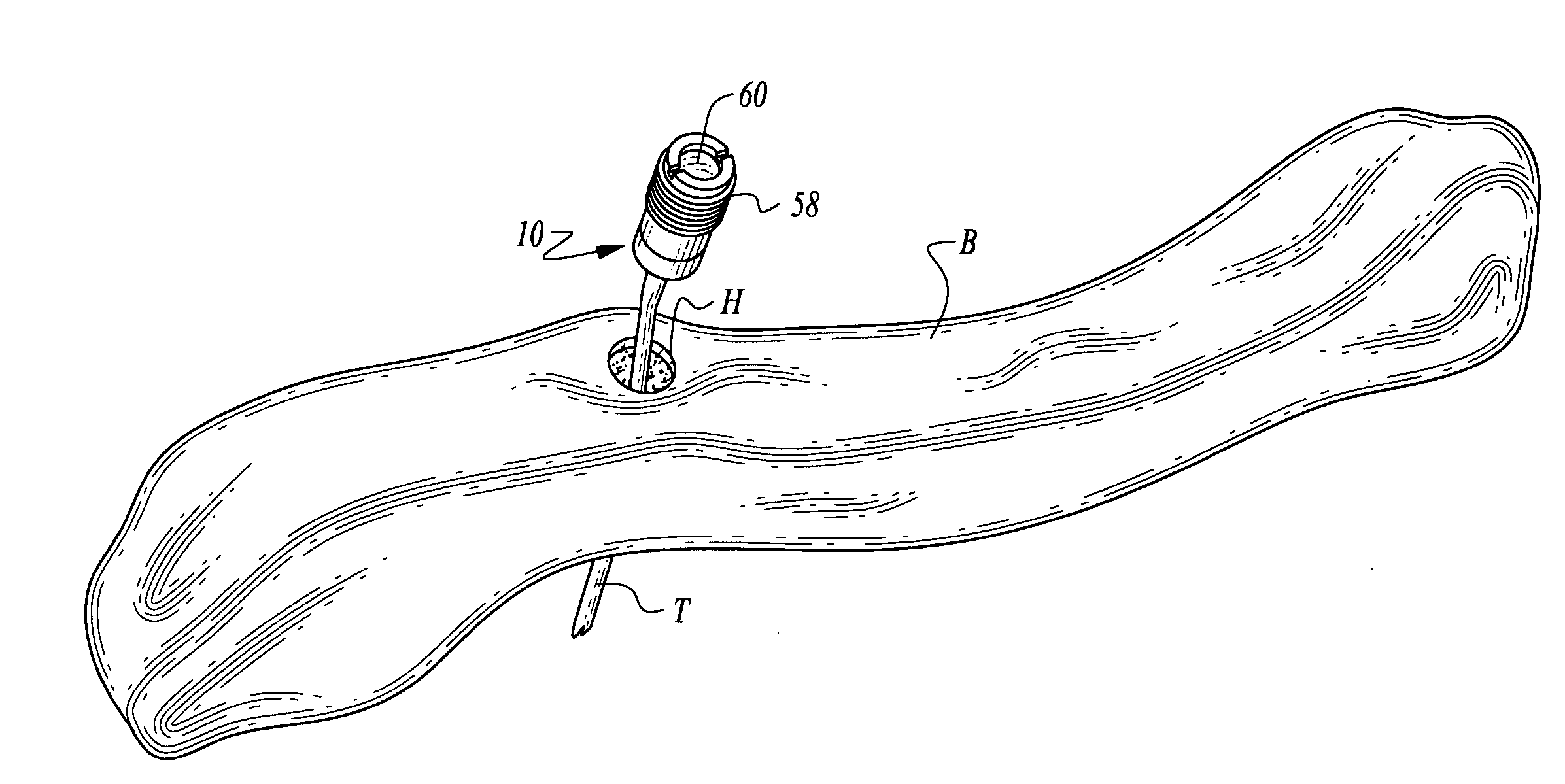
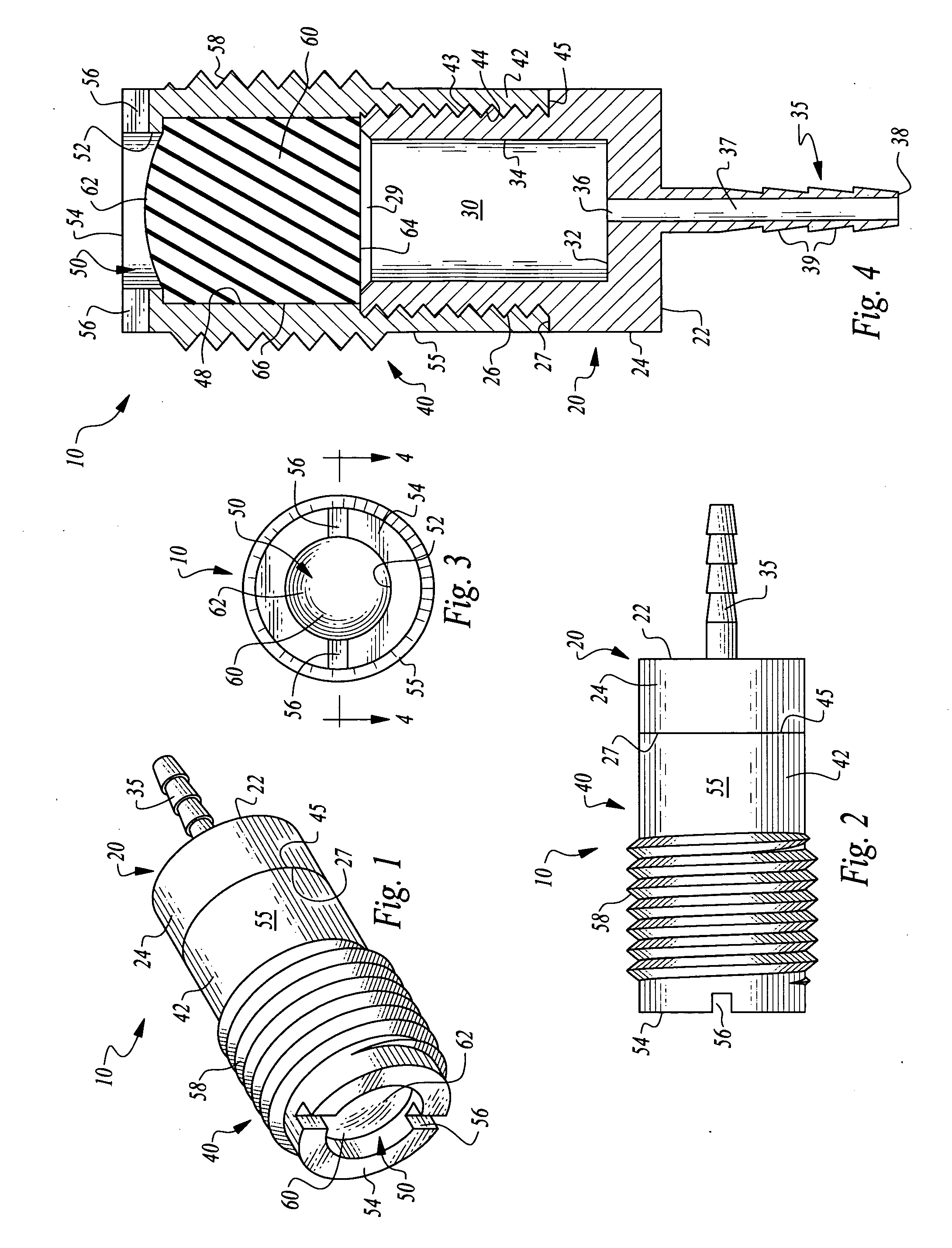
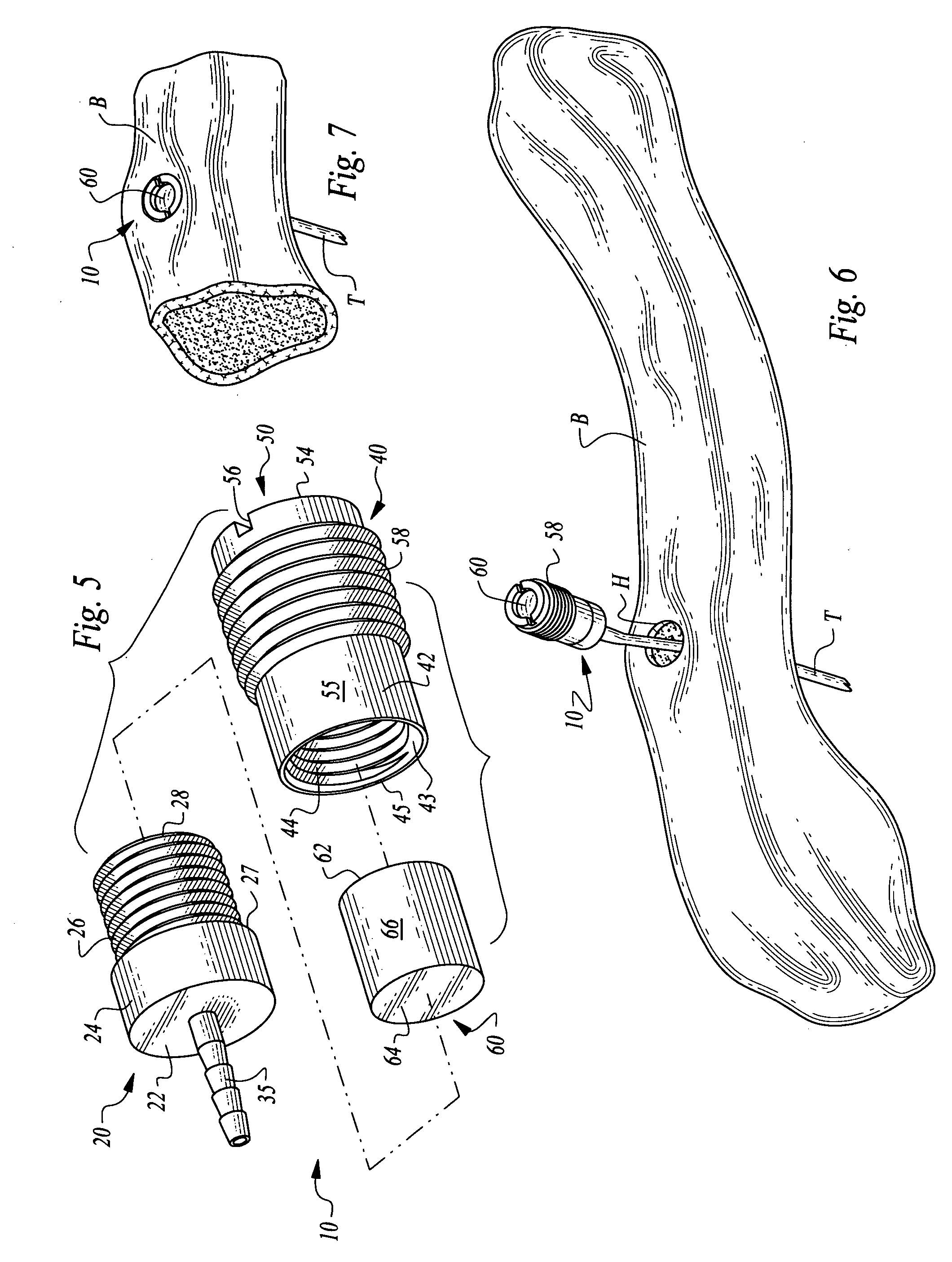
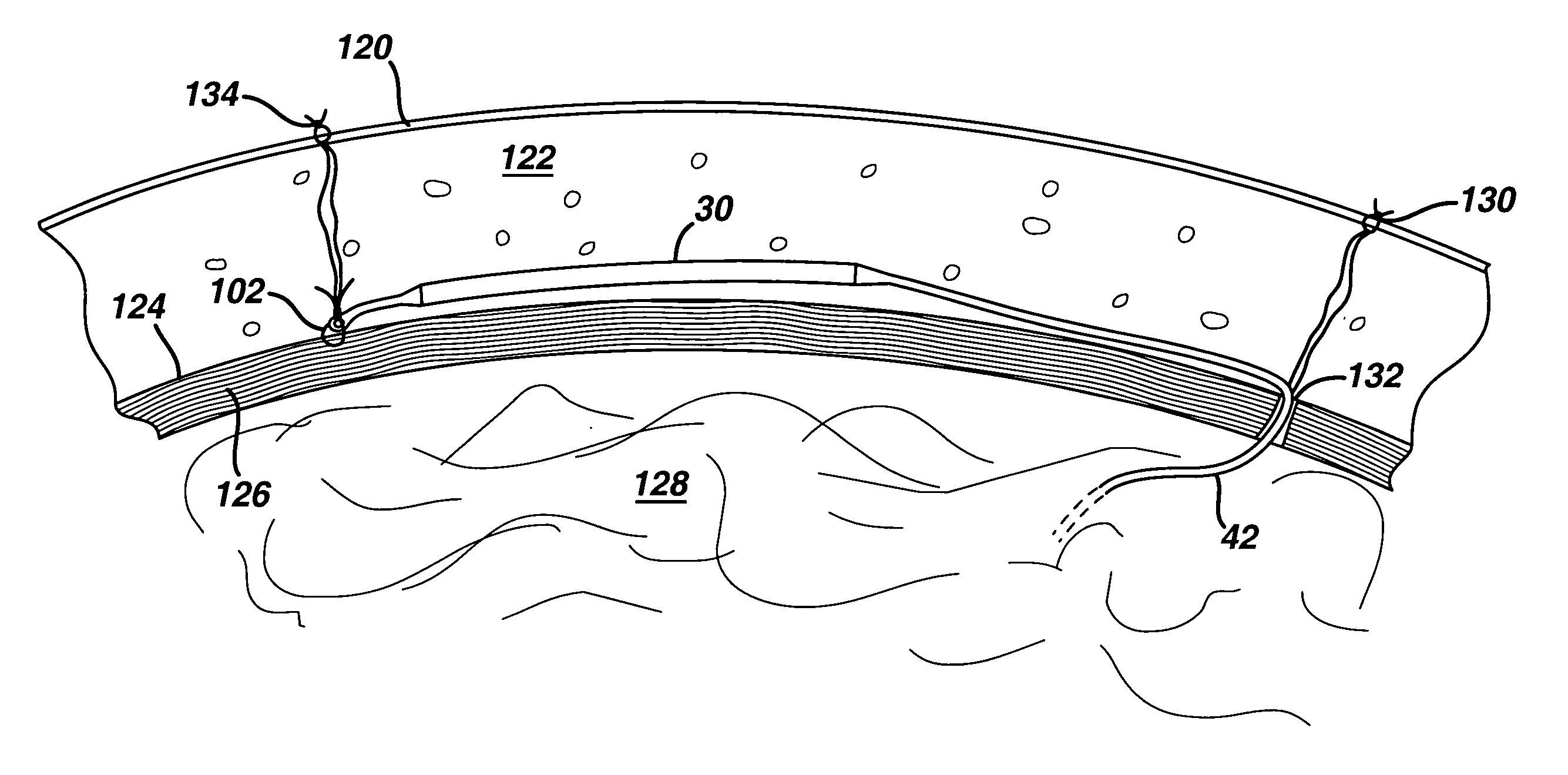
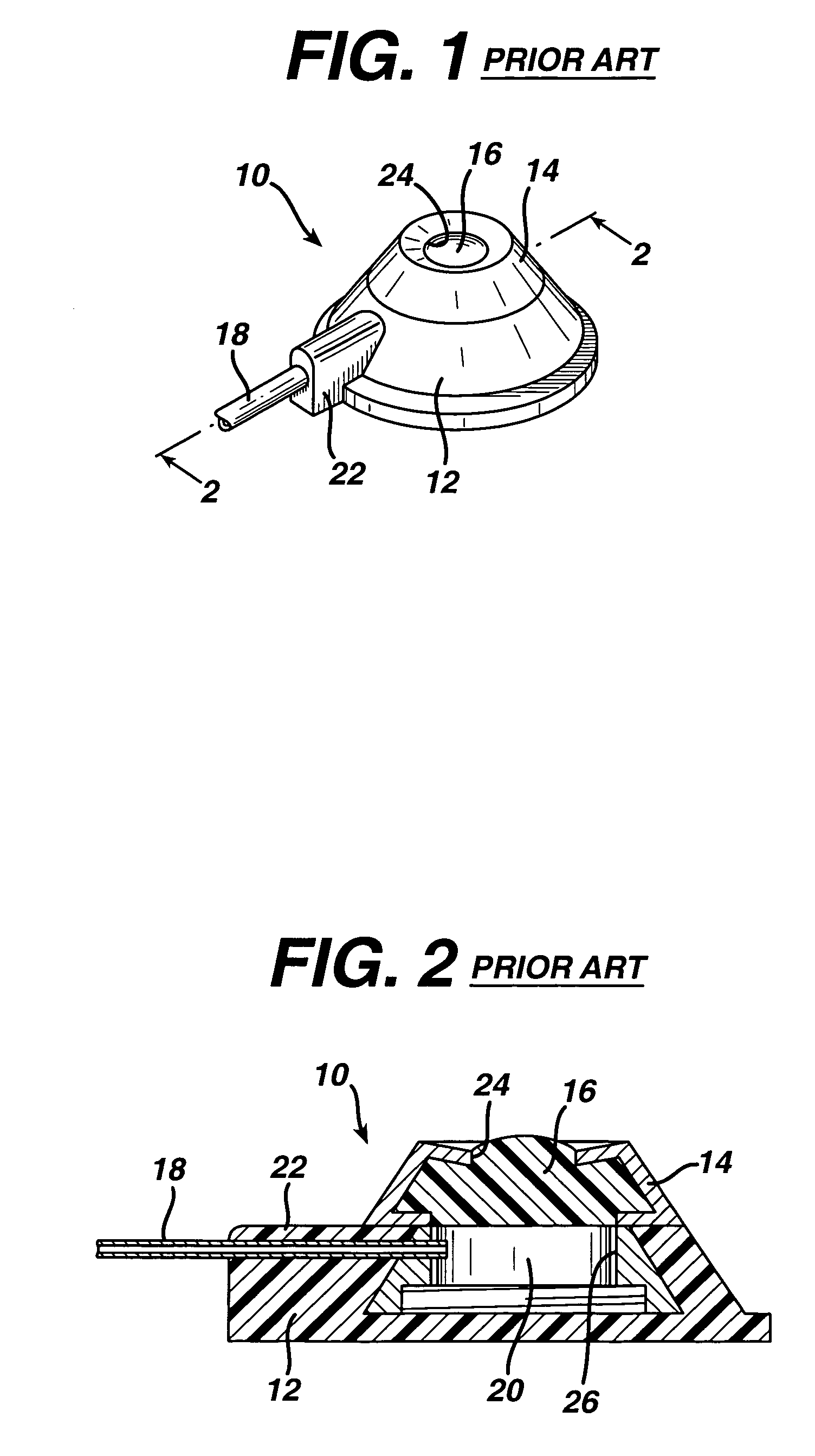
The subcutaneous tissue is the ideal site for implantation of such devices. Implantation often requires a surgical procedure or a specialized injection device. The fact that the device will be in constant contact with the subcutaneous tissue requires that the device materials be biocompatible (e.g.,...
Implantable monitor
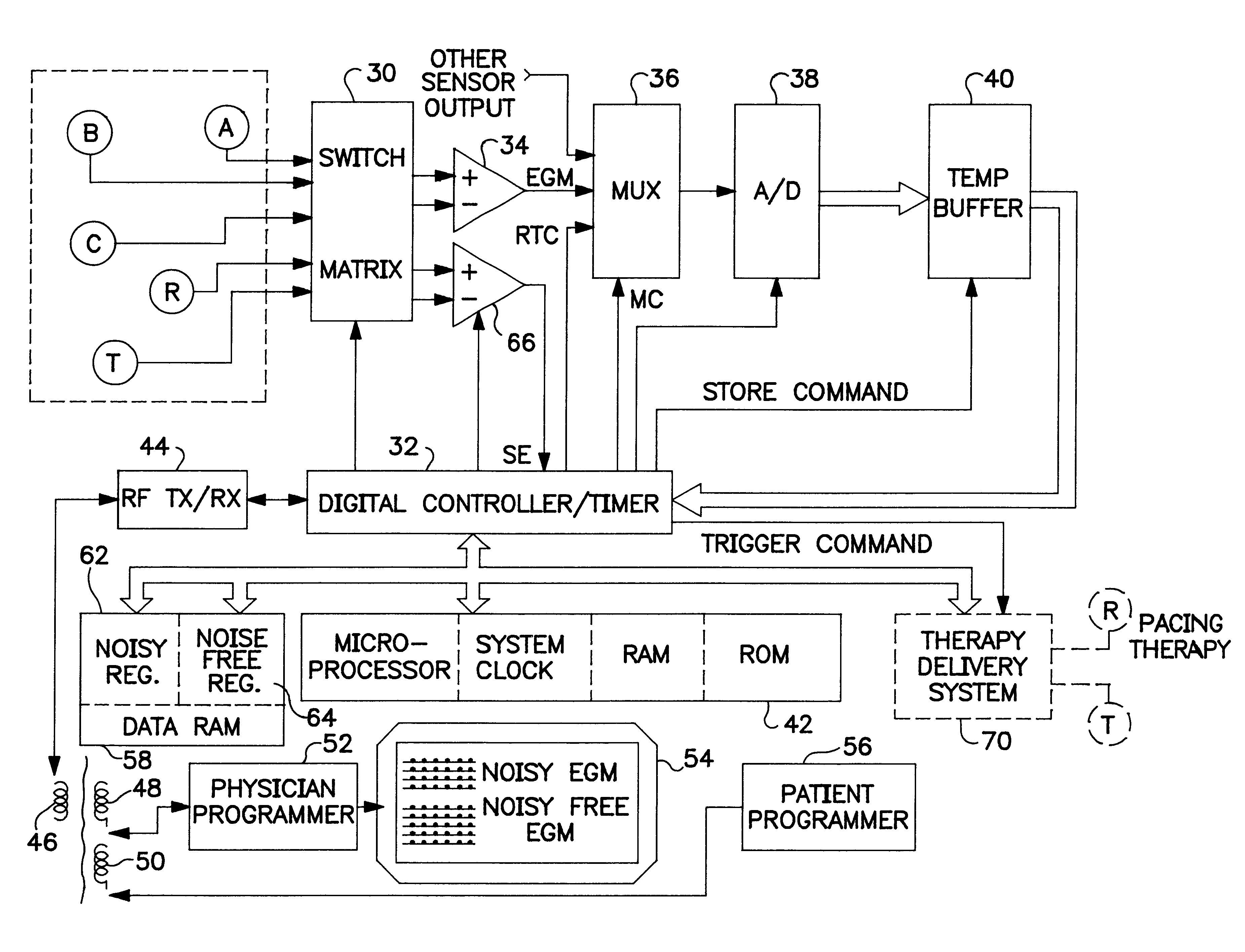
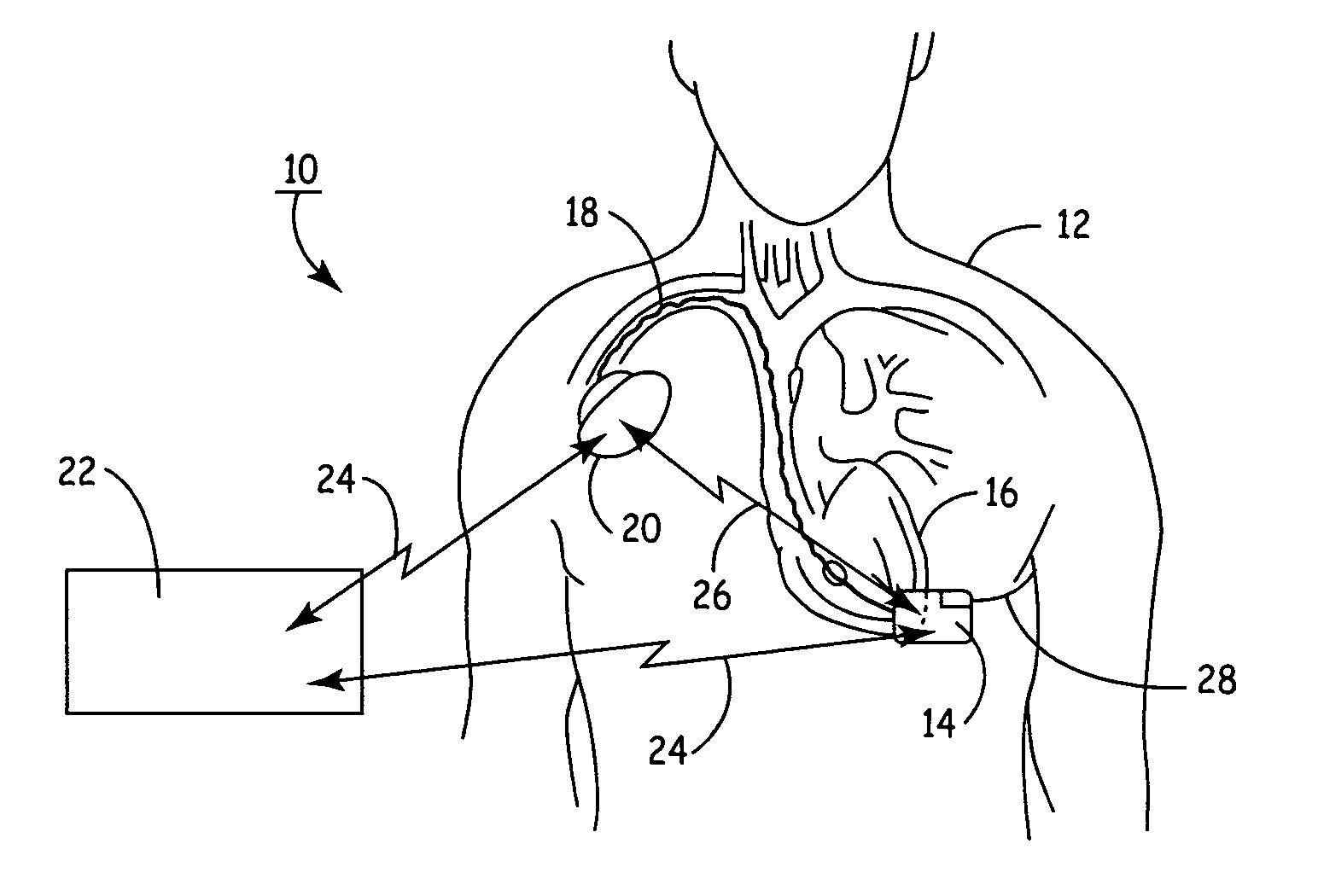
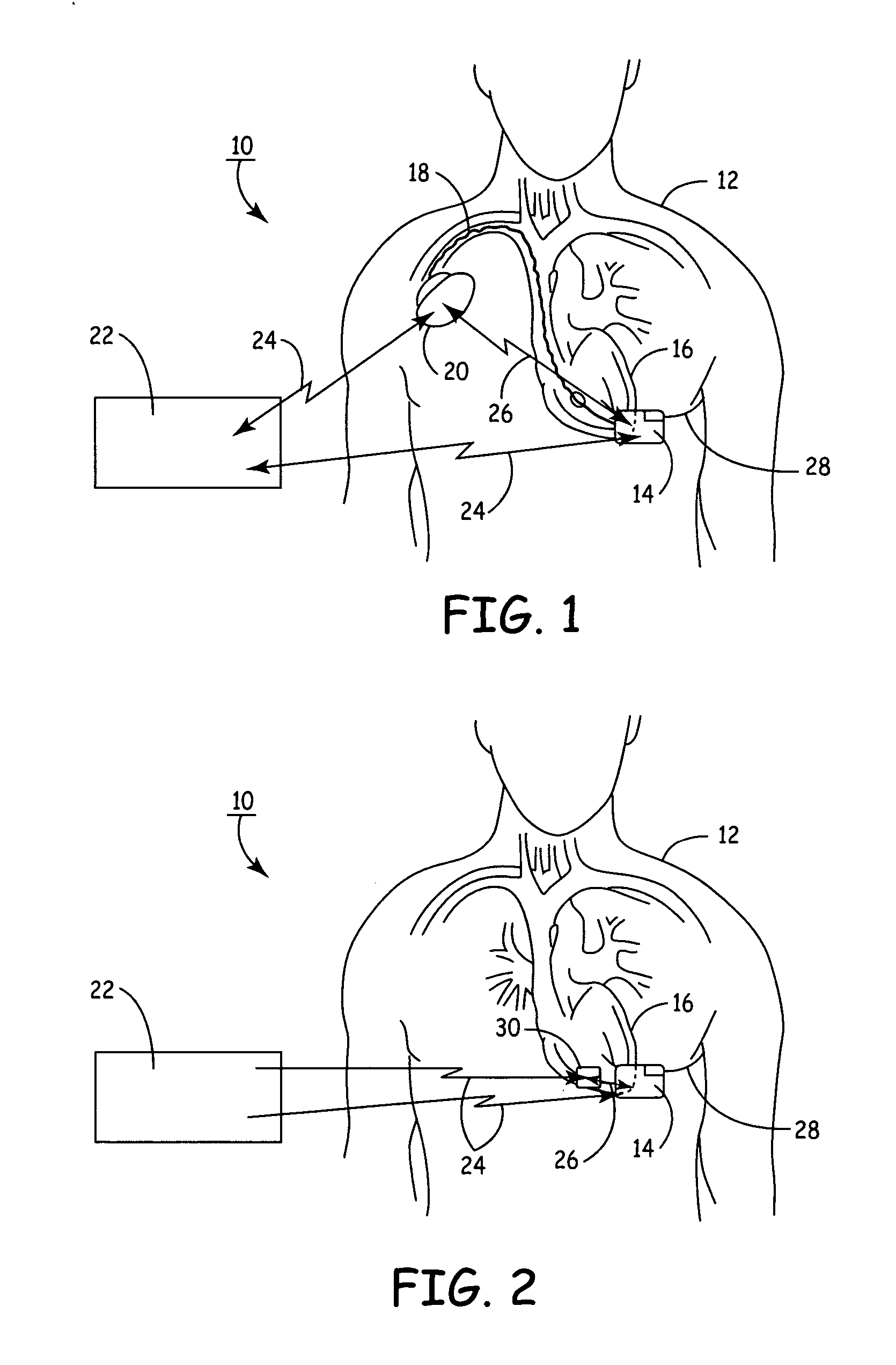
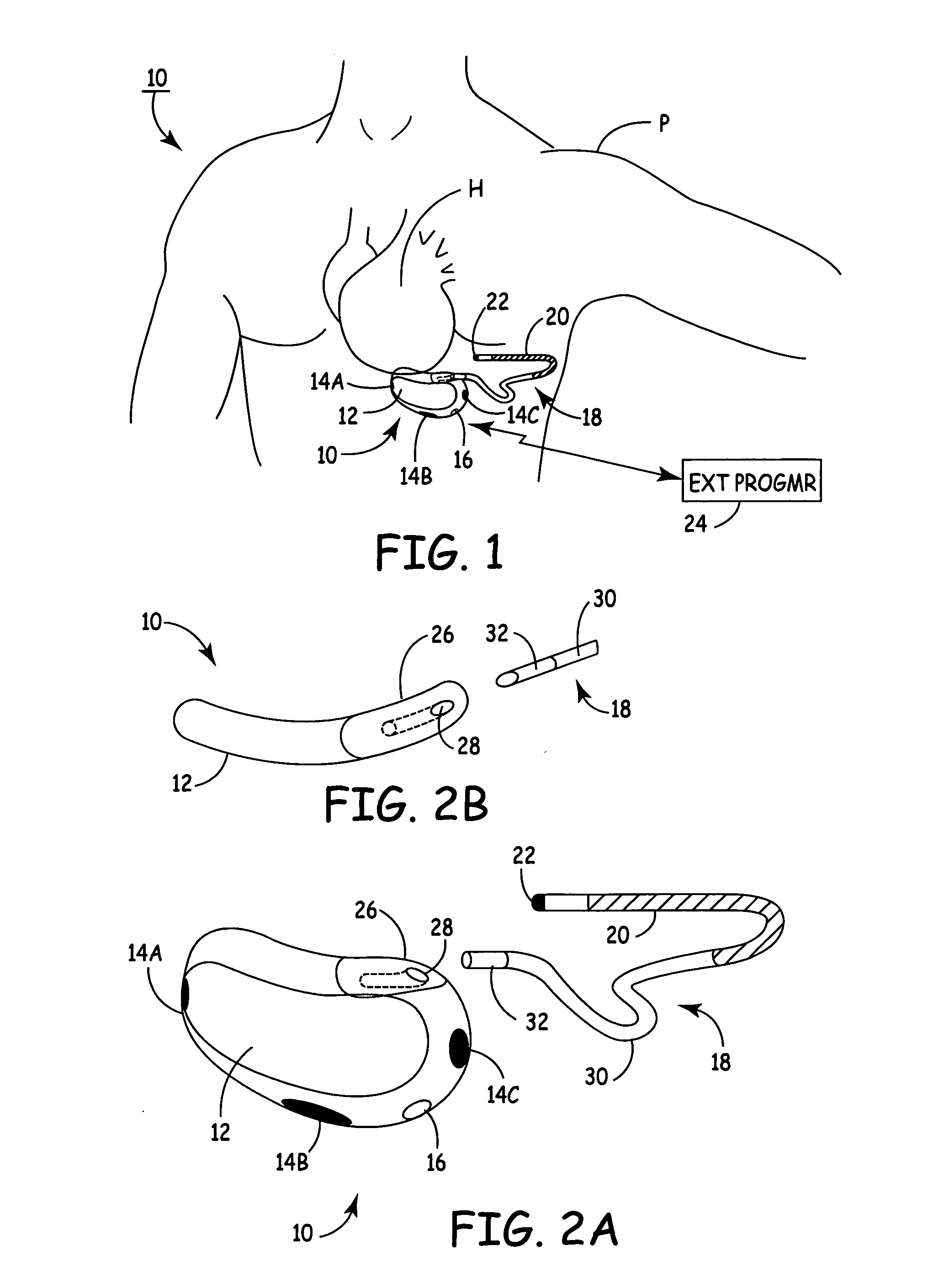
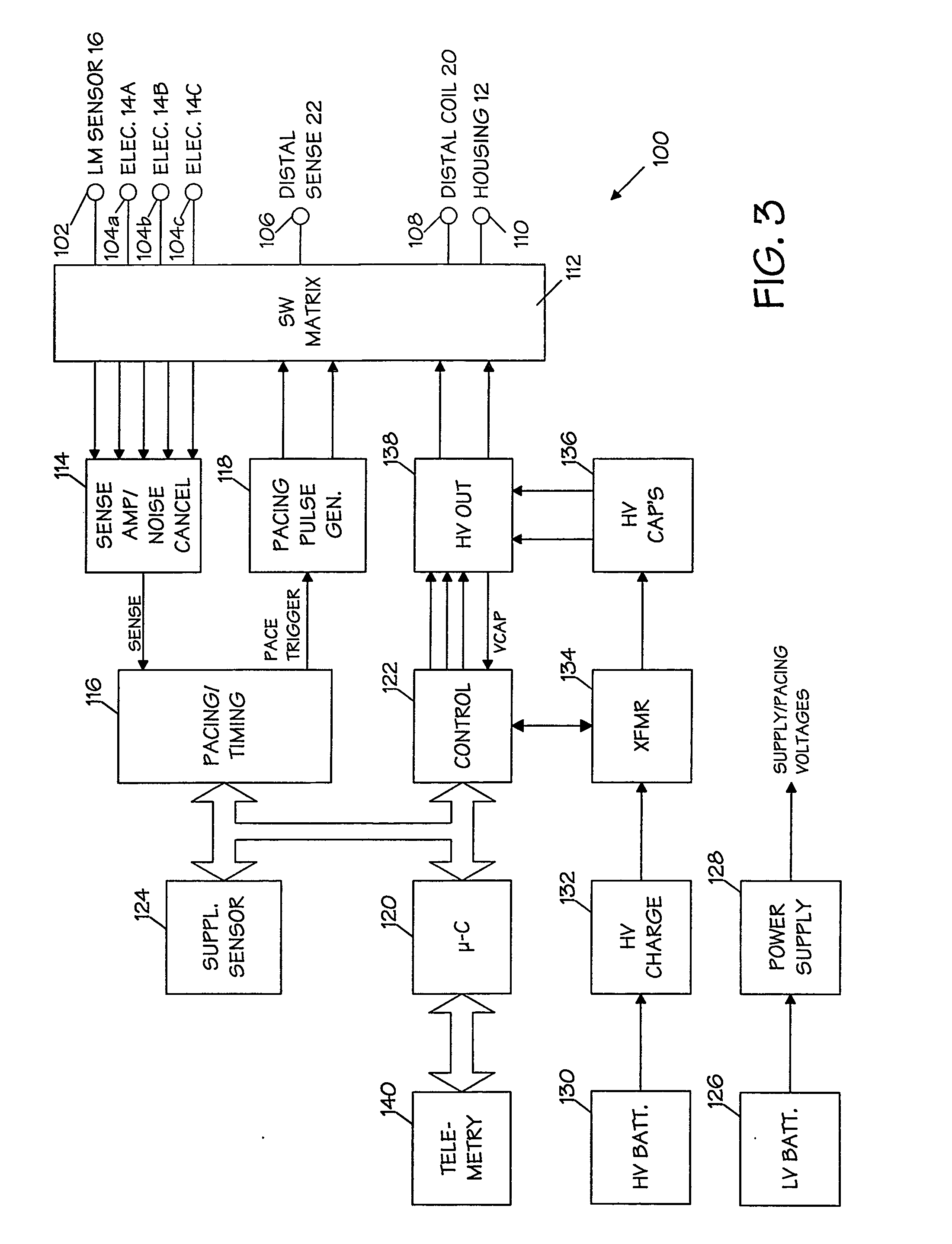
An implantable medical device (IMD) capable of monitoring physiologic data, distinguishing relatively noisy and noise free physiologic data, and recording noisy and relatively noise free segments of physiologic data in separate memory registers of a limited memory for retrieval and analysis at a later time. Preferably the physiologic data comprises the sampled EGM of the heart detected from sense electrode pairs that are implanted in the patient at sites where extraneous electrical noise, e.g., electromyographic signals, are also capable of being detected. The sense electrode pairs can constitute one or both sense electrodes located on or adjacent to the atrial and / or ventricular heart chambers and coupled to the IMD by a lead body or sense electrode pairs that are located remotely from the heart, e.g. at a subcutaneous implantation site of the IMD. A plurality of noisy EGM episode data registers store a corresponding plurality of noisy EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis and another plurality of noise free EGM episode data registers to store a corresponding plurality of relatively noise free EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis. Any form of discrimination of noisy data from relatively noise free data can be employed at the time of recording, but because the stored EGM episode data sets are subsequently viewed and analyzed by a physician, discrimination with absolute certainty is not required, and the physician can alter the detection criteria to fine tune it.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Hypodermic implant device
InactiveUS20030004457A1Avoid spreadingLess-costly disposalMedical devicesInfusion needlesSubcutaneous implantationImplanted device
A hypodermic implant device, comprising a barrel; an upper piston segment engaged with an inner wall of the barrel; an axially aligned needle extendably distally out of the barrel for insertion into an object when the upper piston segment is moved distally within the body; a lower piston segment push rod in alignment with the needle, so that upon distal movement of the lower piston segment, the push rod moves distally through the needle expelling a releasable implant housed in the needle; and a means for retraction of the needle into a needle receptacle in the barrel.
Owner:GRAY PLANT MOOTY MOOTY & BENNETT PA
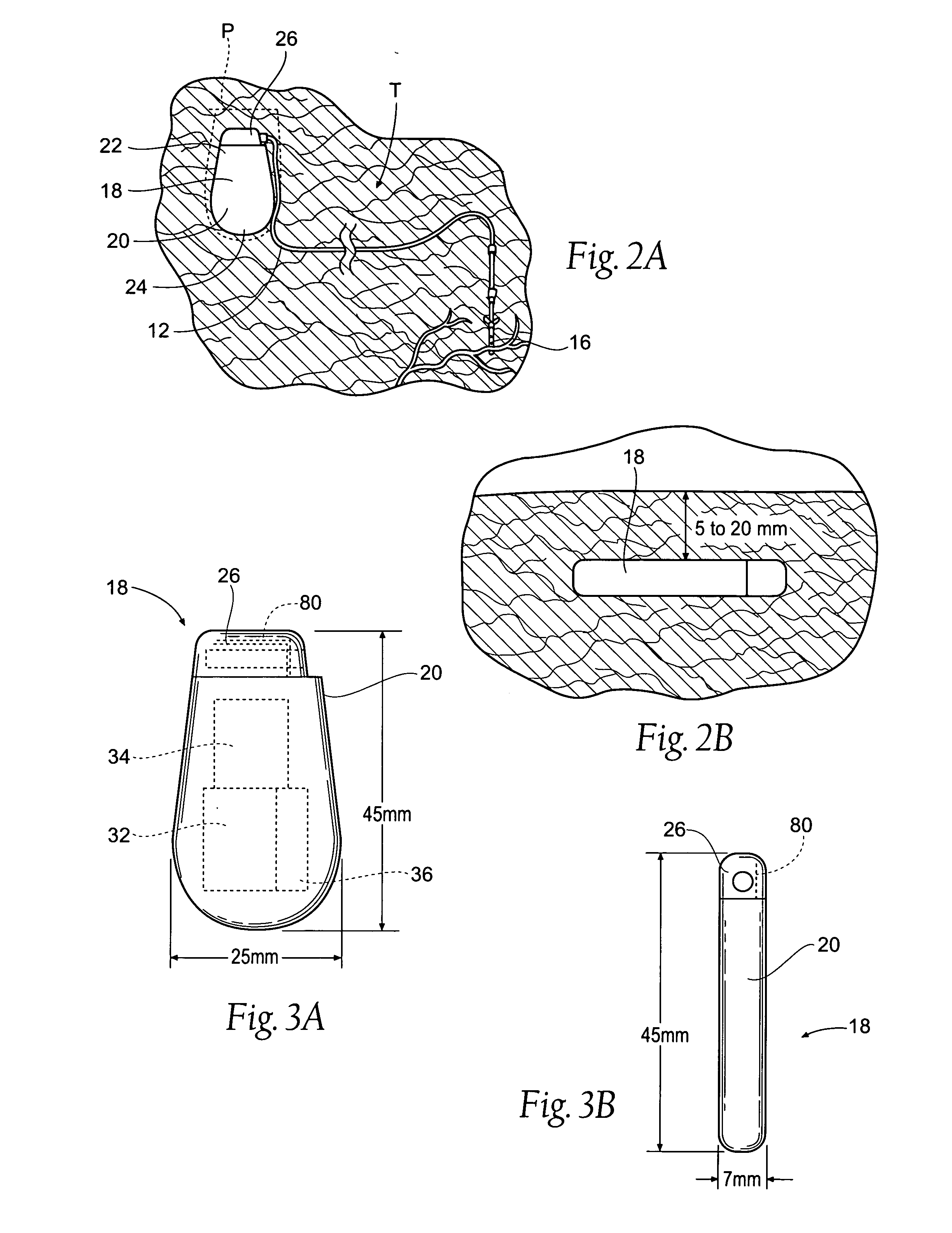
Implantable device for vital signs monitoring
InactiveUS20070016089A1Few suture requirementKeep the distanceElectrocardiographyCatheterSubcutaneous implantationDigital storage
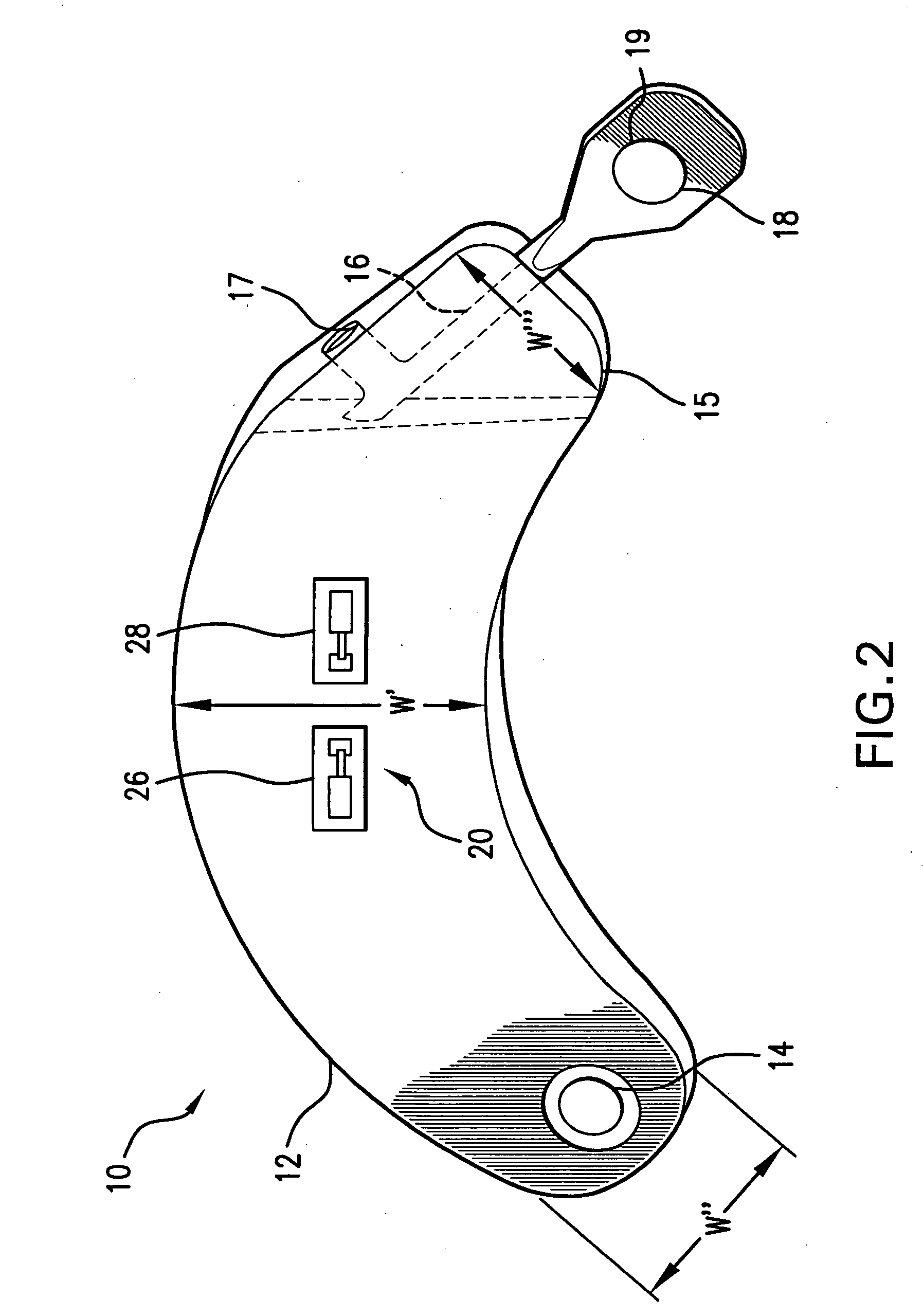
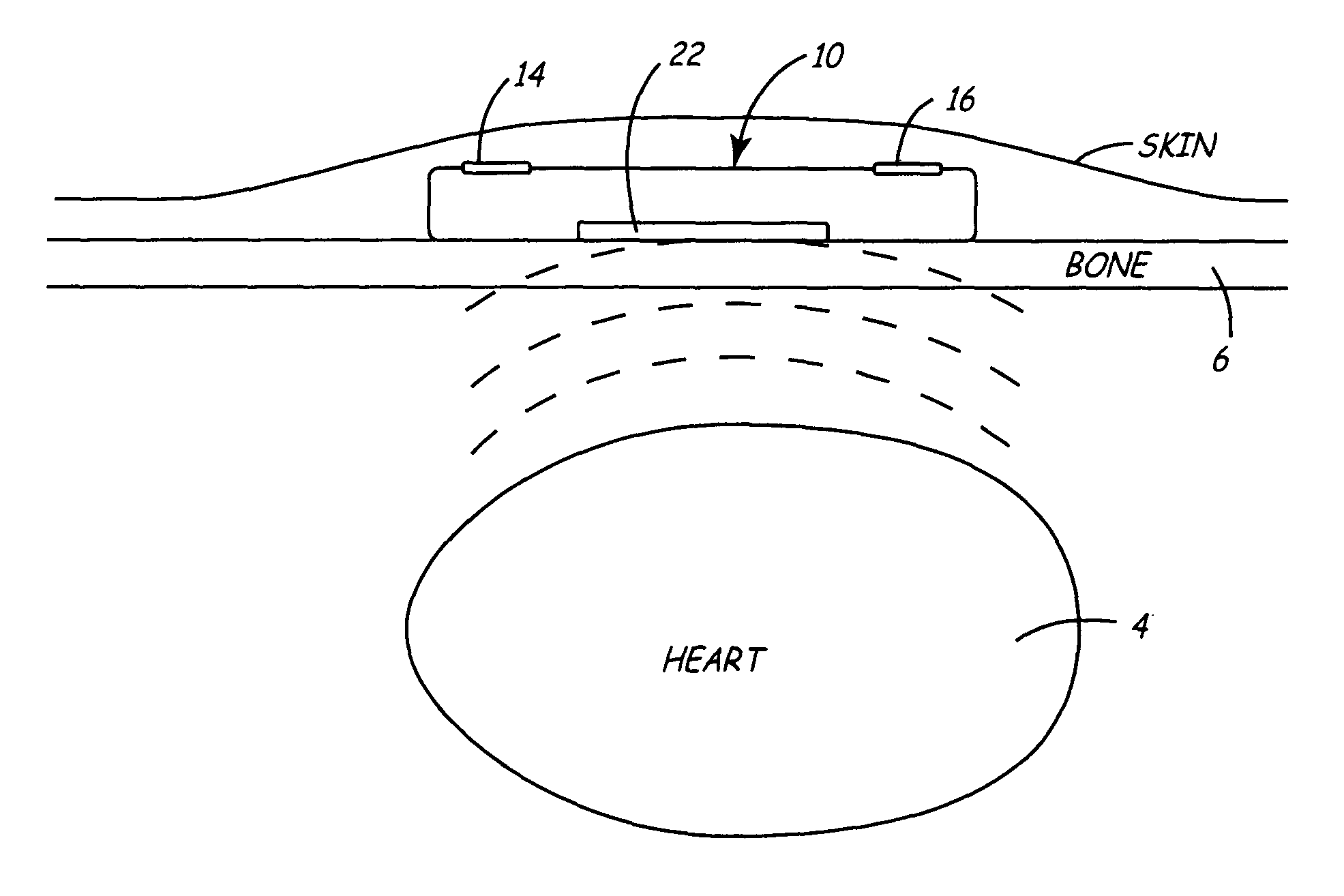
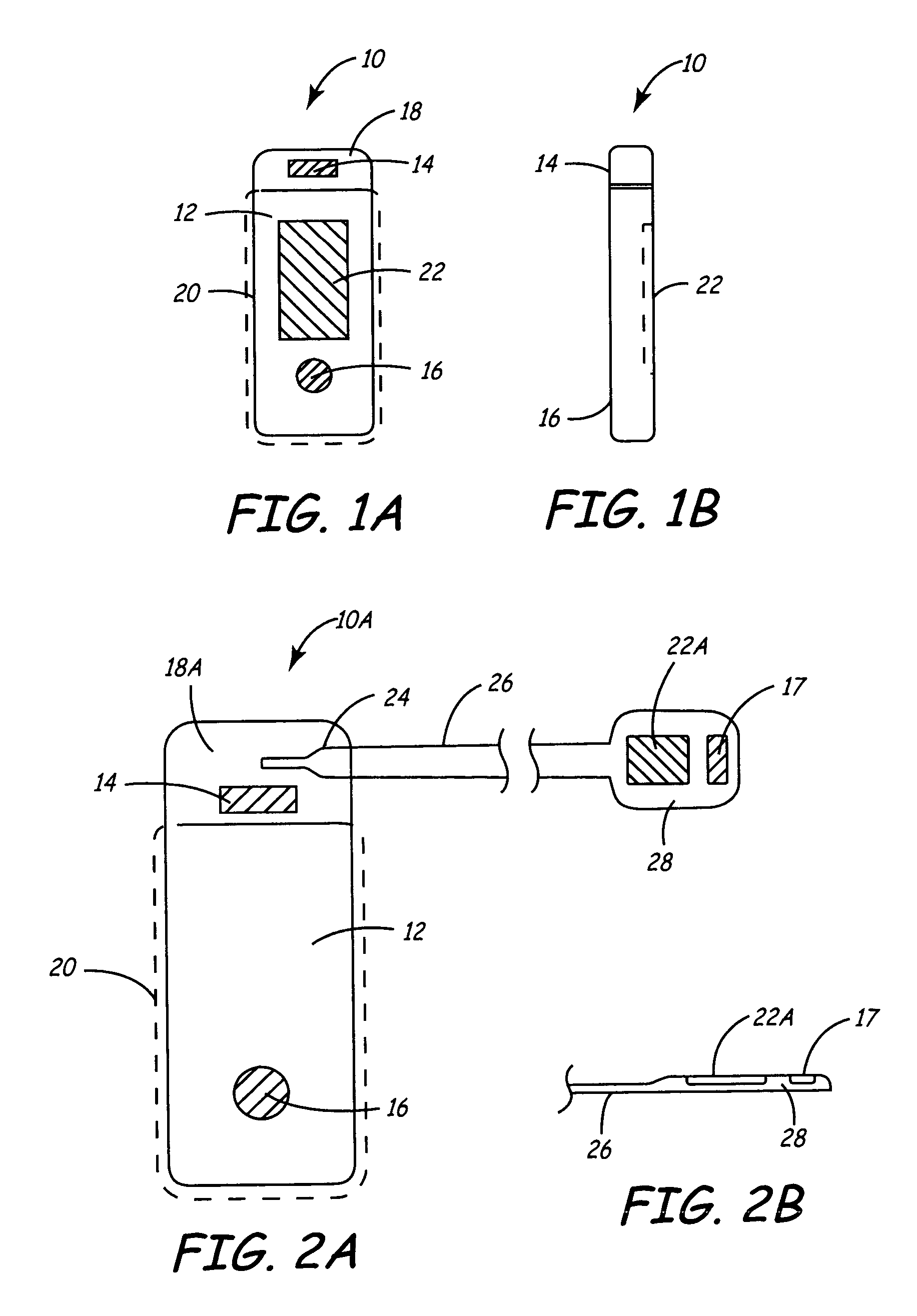
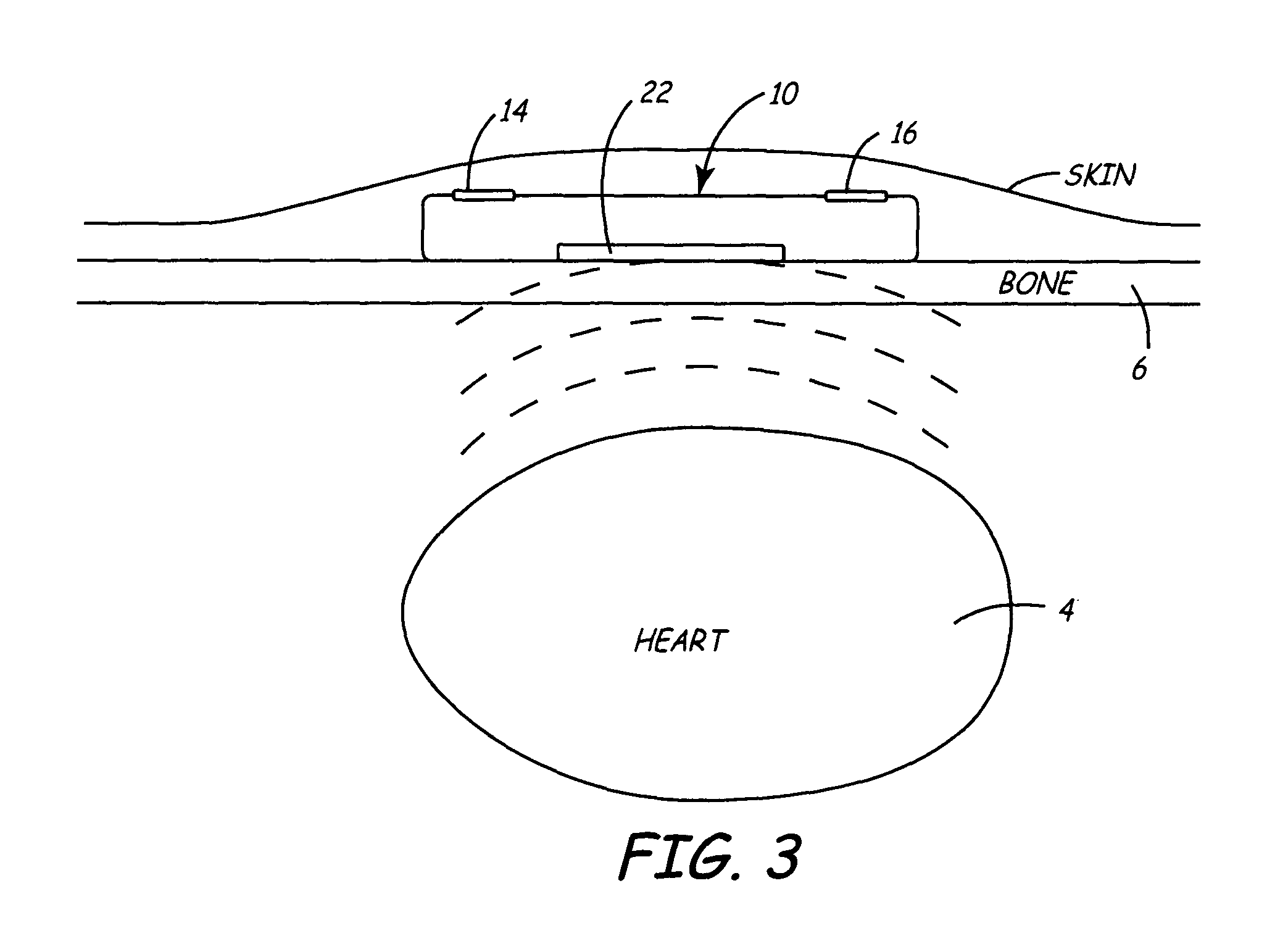
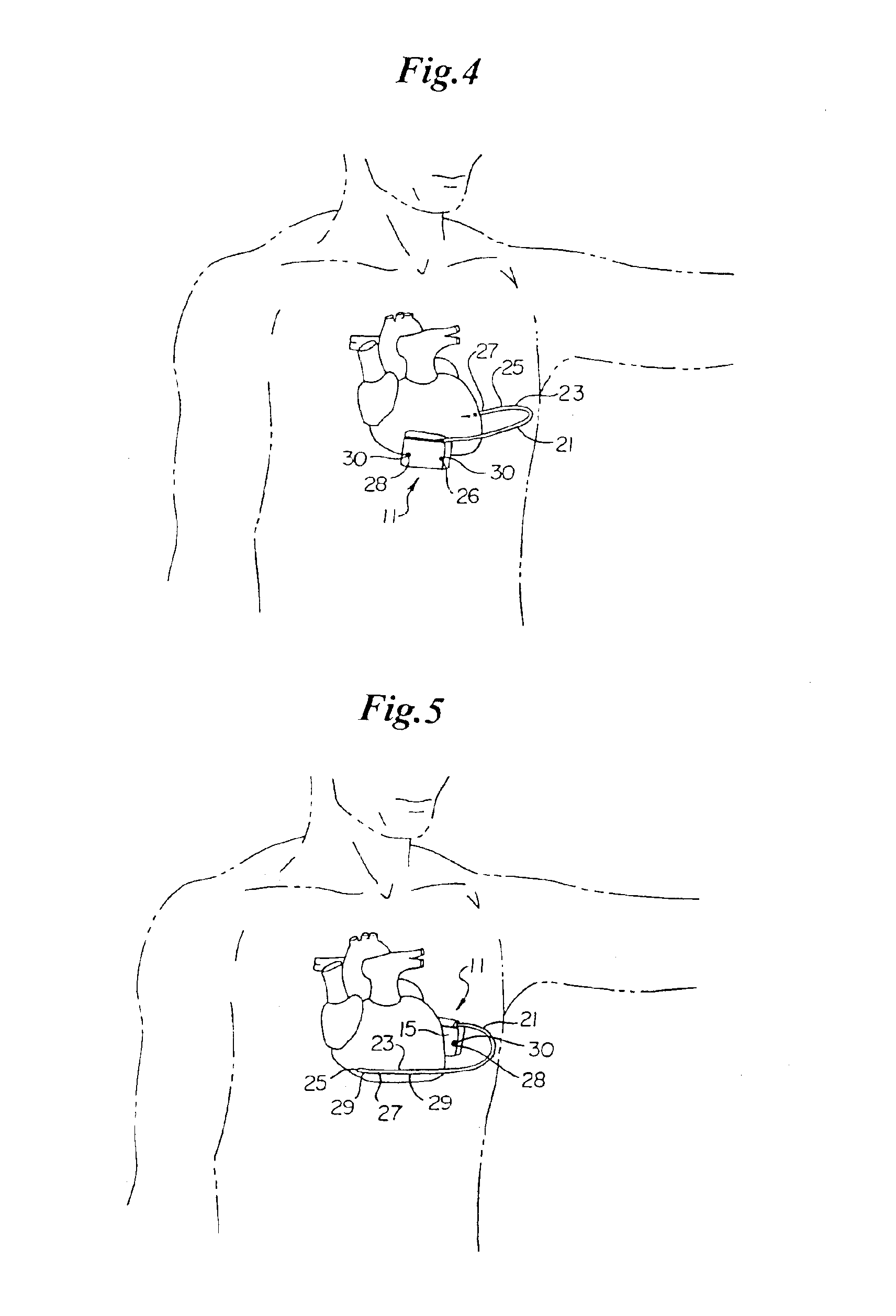
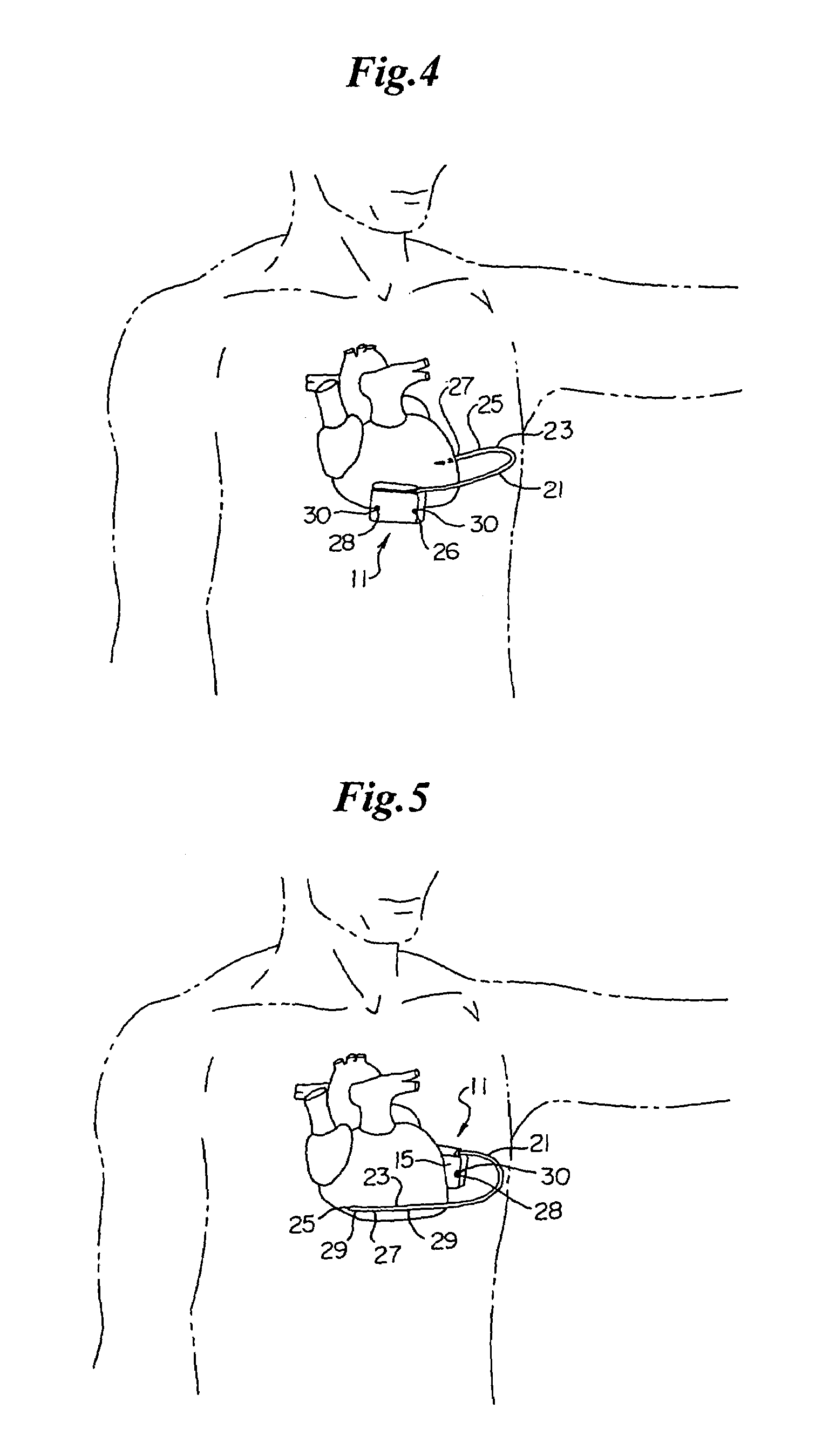
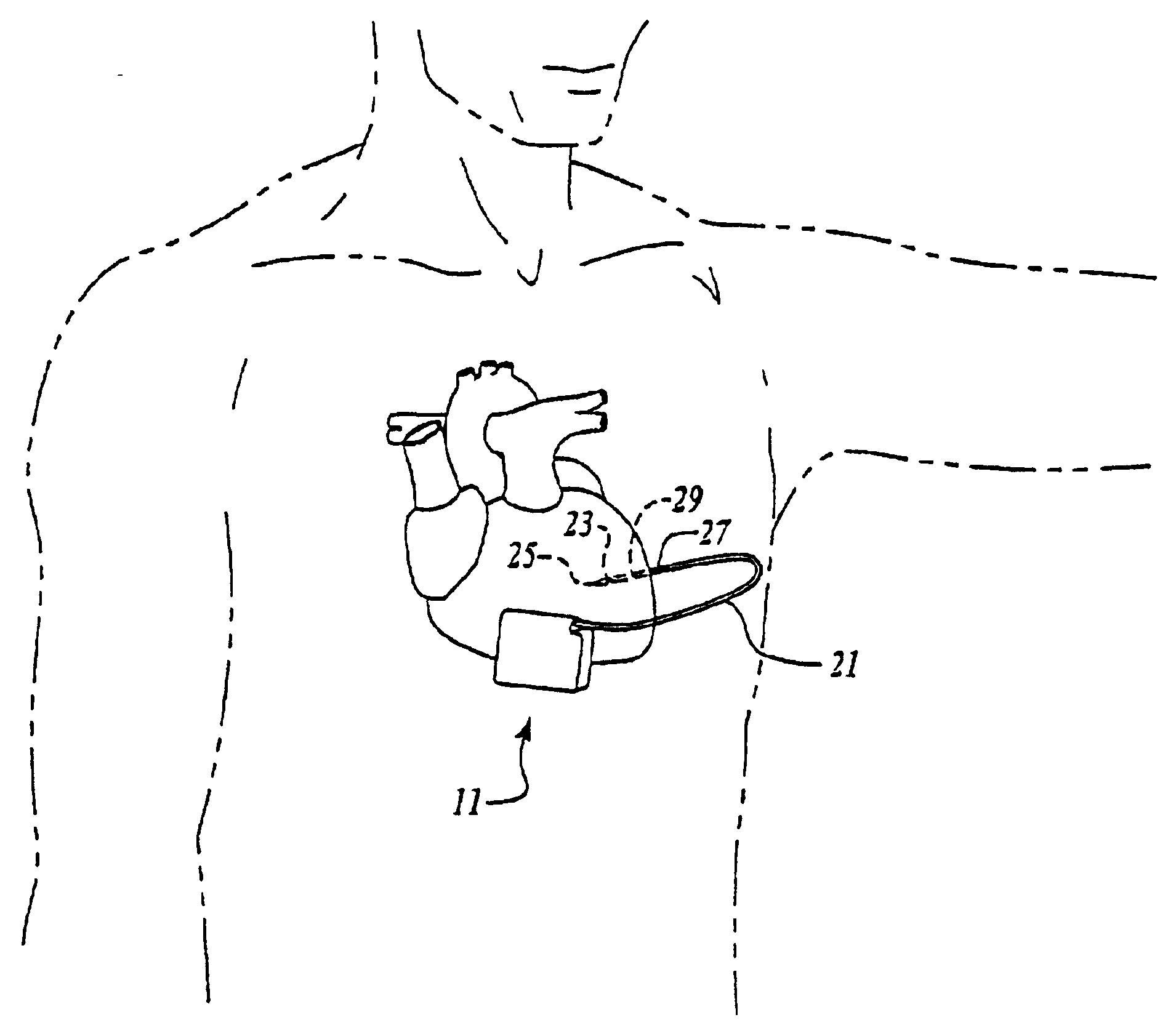
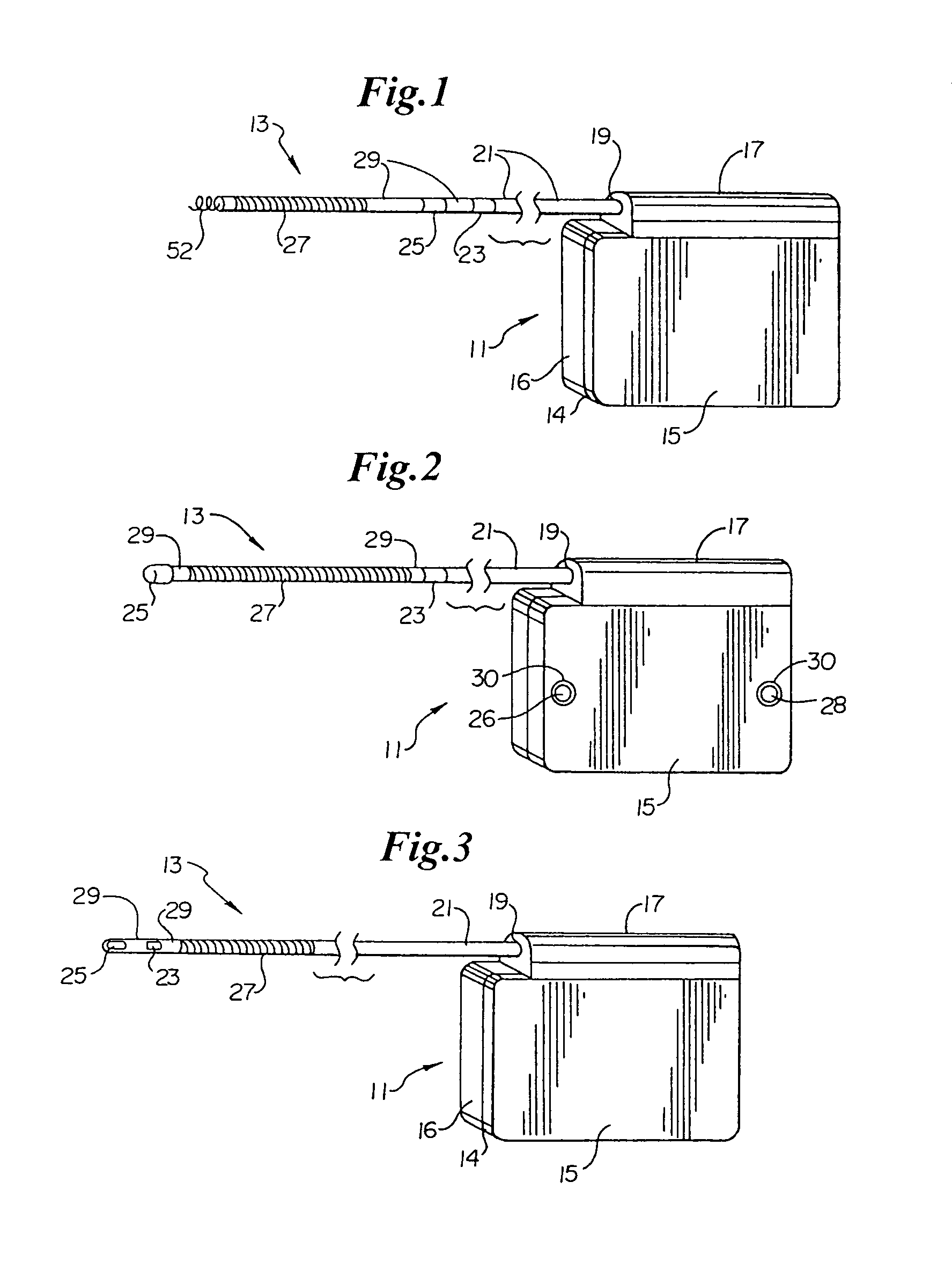
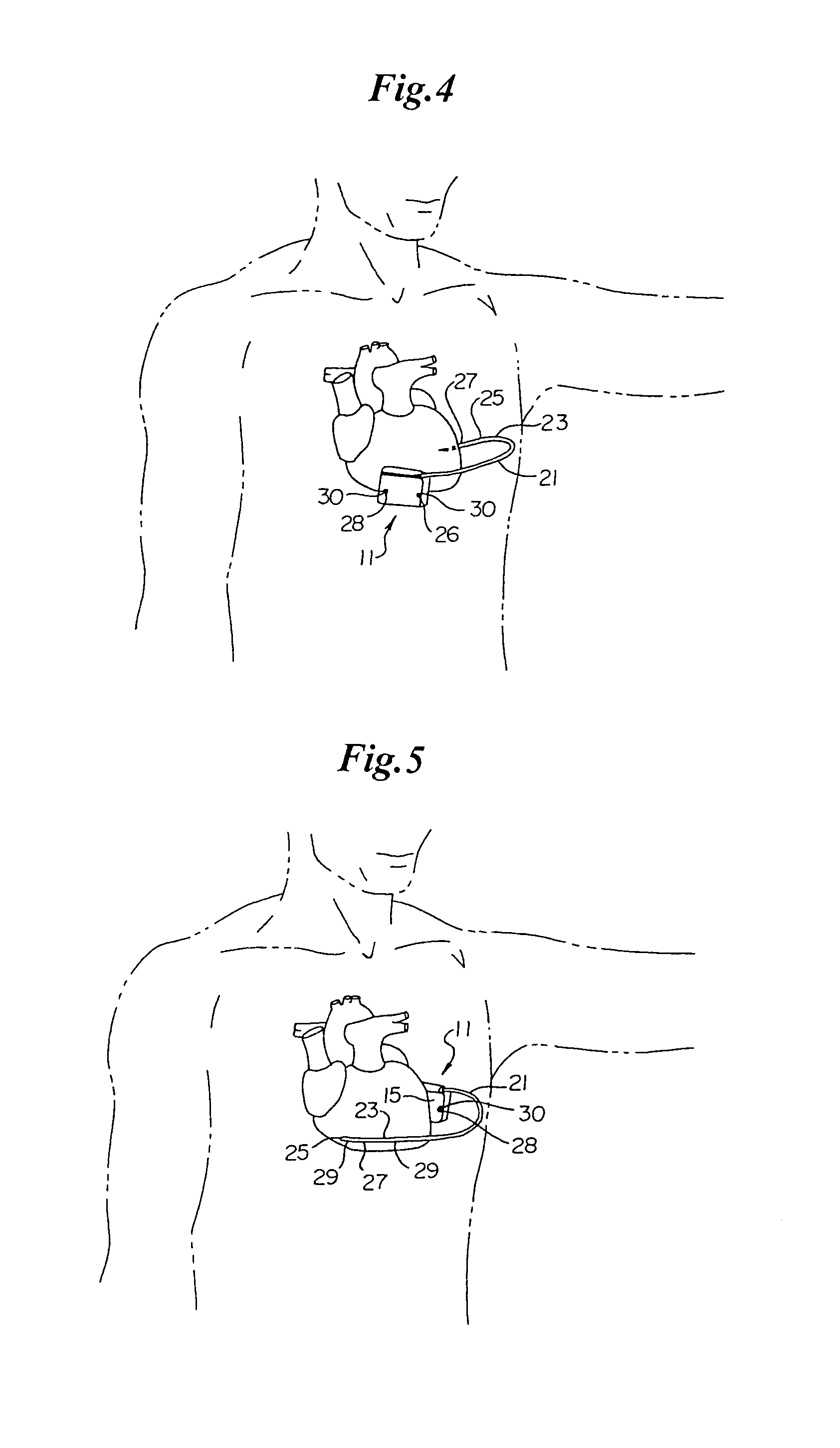
An implantable medical device is provided for subcutaneous implantation within a human being. The implantable medical device includes a pair of electrodes for sensing electrical signals from the human being's heart. Electronic circuitry having digital memory is provided with the electronic circuitry designed to record the electrical signals from the heart. The electronics of the electronic circuitry are housed in a case having a tapered shape to facilitate implantation and removal of the implantable medical device.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST +1
Method and apparatus for monitoring heart function in a subcutaneously implanted device
ActiveUS7035684B2Optimizing received energyRepeatability of measurement madeElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesElectricityLTM - Long-term memory
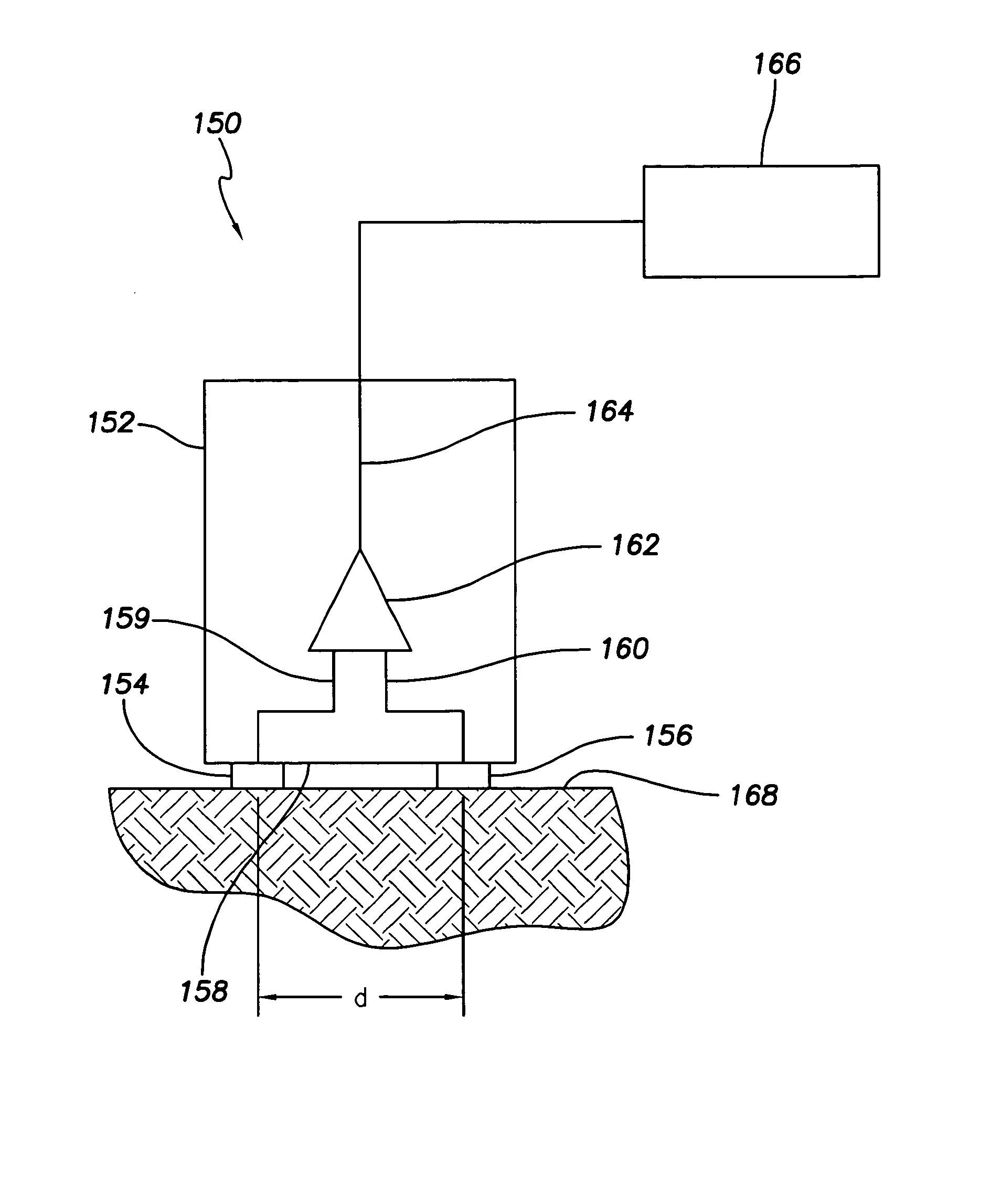
A minimally invasive, implantable monitor and associated method for chronically monitoring a patient's hemodynamic function based on signals sensed by one or more acoustical sensors. The monitor may be implanted subcutaneously or submuscularly in relation to the heart to allow acoustic signals generated by heart or blood motion to be received by a passive or active acoustical sensor. Circuitry for filtering and amplifying and digitizing acoustical data is included, and sampled data may be continuously or intermittently written to a looping memory buffer. ECG electrodes and associated circuitry may be included to simultaneously record ECG data. Upon a manual or automatic trigger event acoustical and ECG data may be stored in long-term memory for future uploading to an external device. The external device may present acoustical data visually and acoustically with associated ECG data to allow interpretation of both electrical and mechanical heart function.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Poly(beta-amino alcohols), their preparation, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130302401A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical structureFibrosis
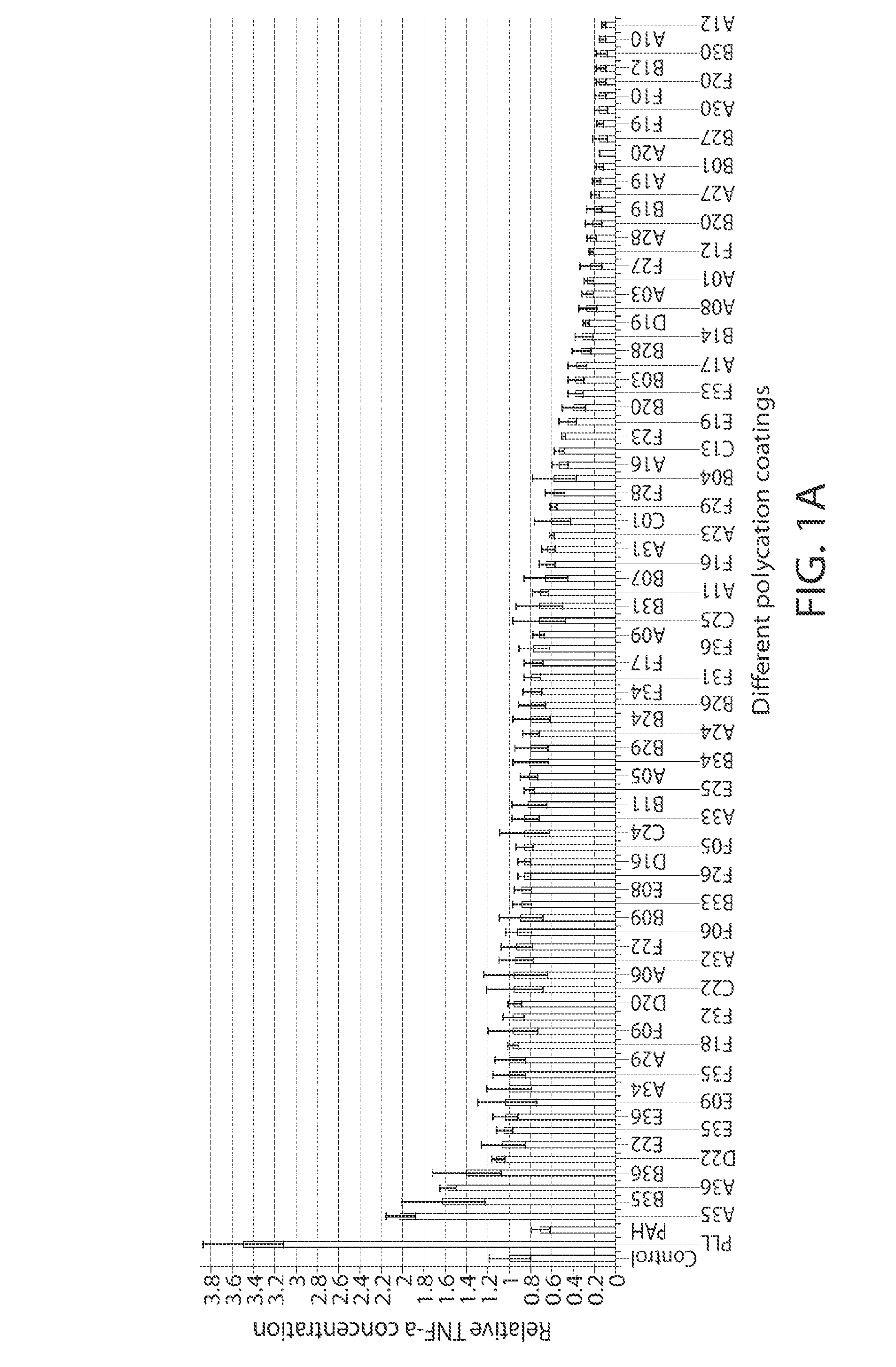
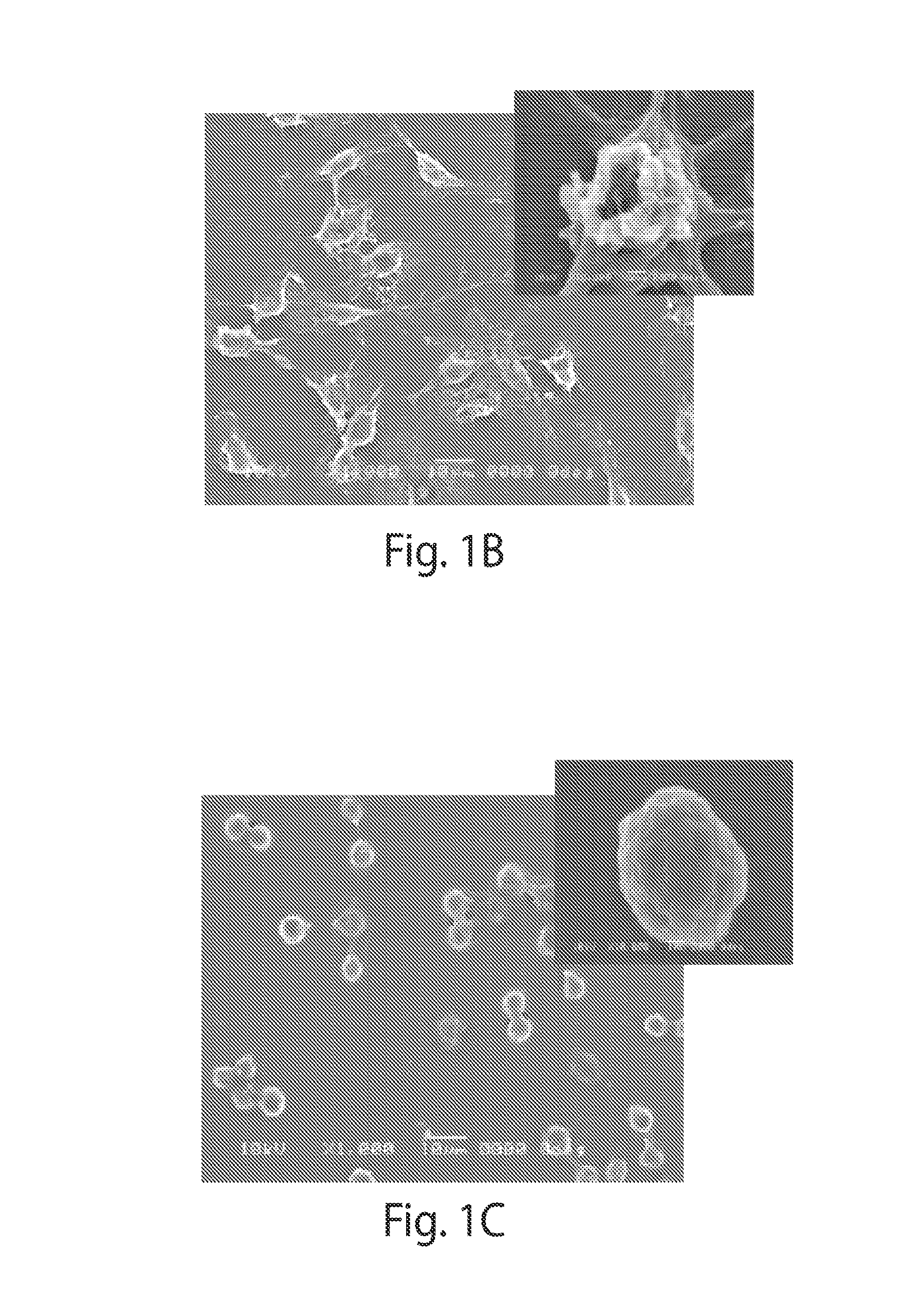
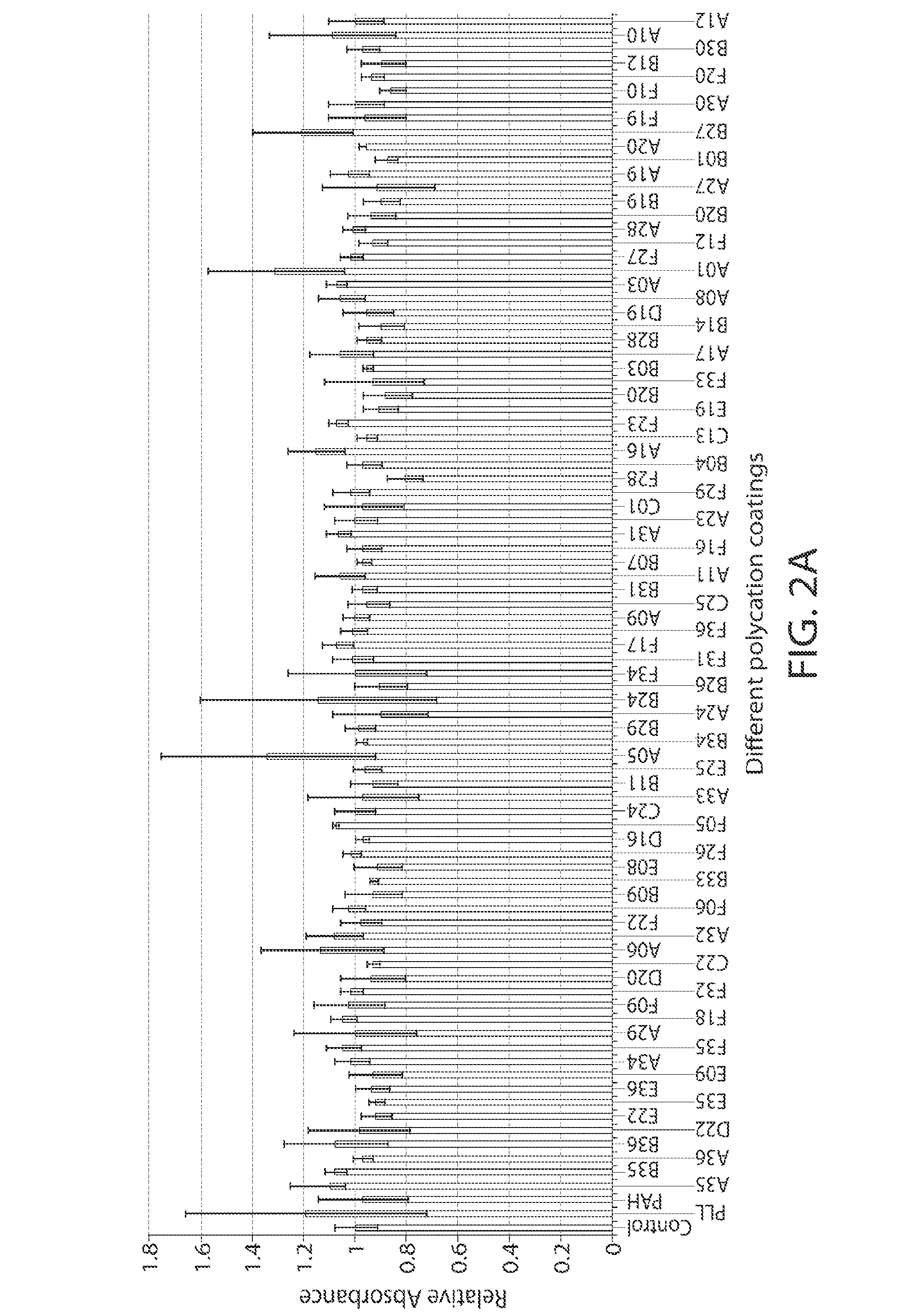
A new class of poly(beta-amino alcohols) (PBAAs) has been prepared using combinatorial polymerization. The inventive PBAAs may be used in biotechnology and biomedical applications as coatings (such as coatings of films or multilayer films for medical devices or implants), additives, materials, excipients, non-biofouling agents, micropatterning agents, and cellular encapsulation agents. When used as surface coatings, these PBAAs elicited different levels of inflammation, both in vitro and in vivo, depending on their chemical structures. The large chemical diversity of this class of materials allowed us to identify polymer coatings that inhibit macrophage activation in vitro. Furthermore, these coatings reduce the recruitment of inflammatory cells, and reduce fibrosis, following the subcutaneous implantation of carboxylated polystyrene microparticles. These polymers may be used to form polyelectrolyte complex capsules for cell encapsulation. The invention may also have many other biological applications such as antimicrobial coatings, DNA or siRNA delivery, and stem cell tissue engineering.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
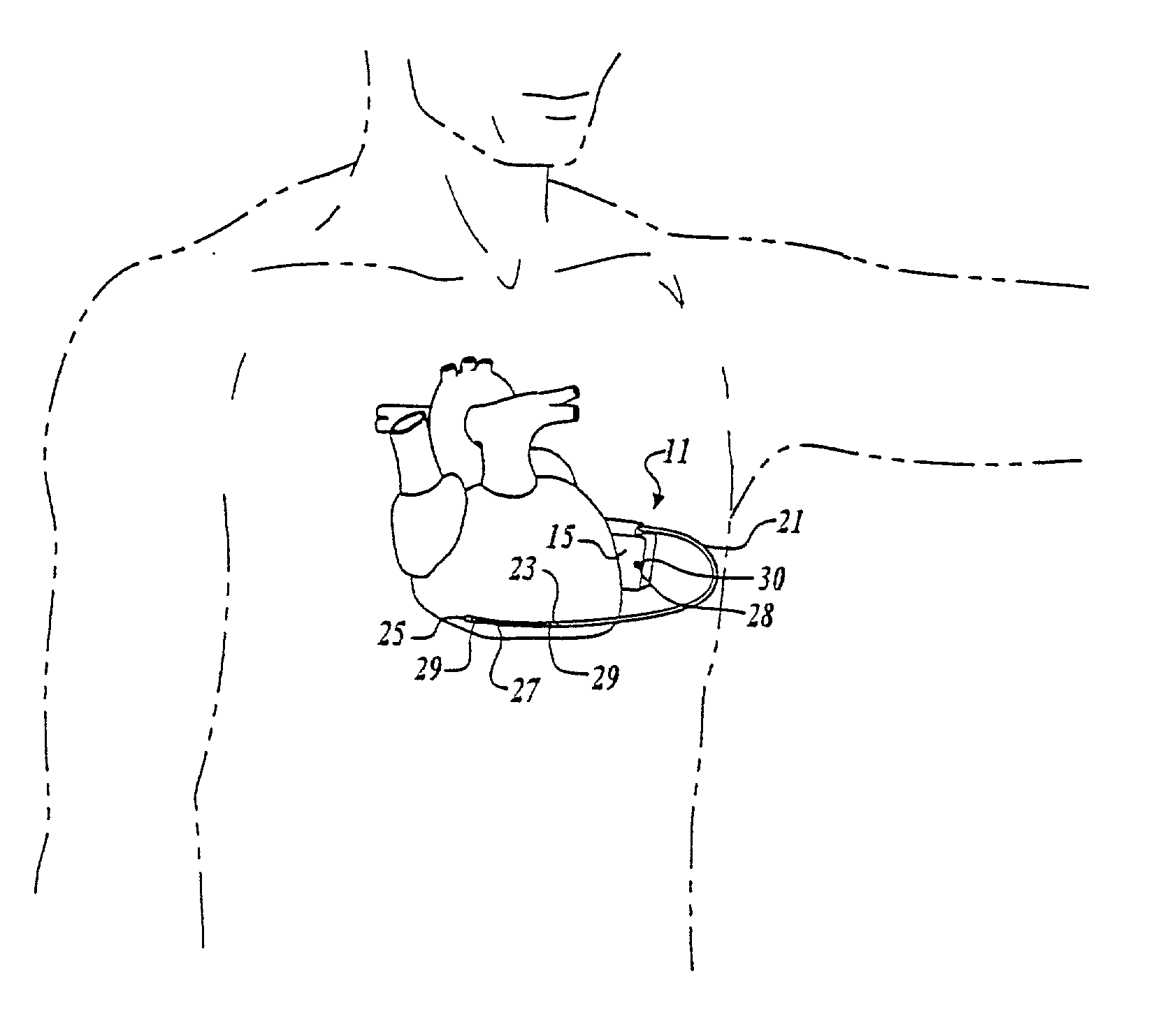
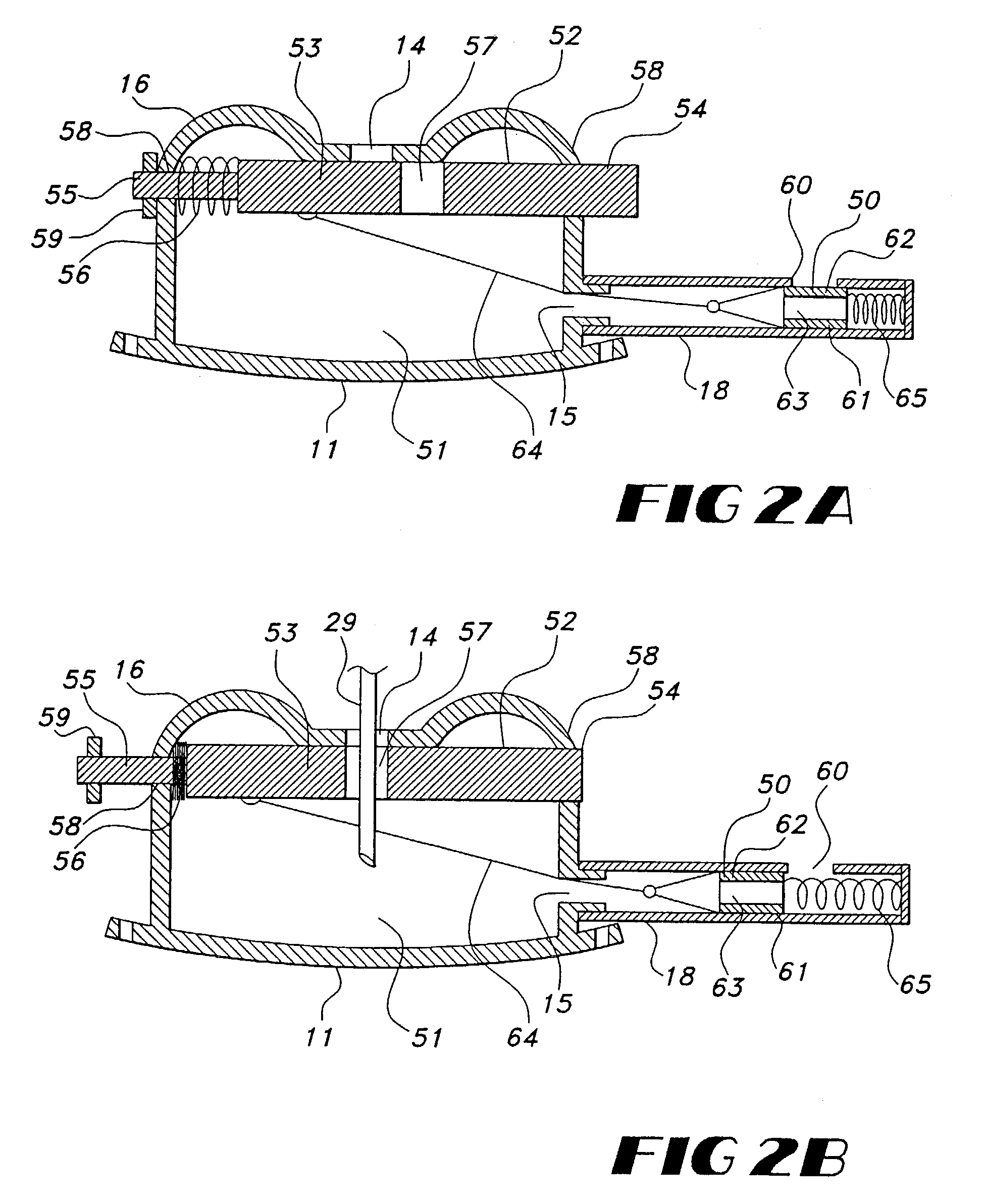
Biphasic waveform for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathorasic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Remotely enabled pacemaker and implantable subcutaneous cardioverter/defibrillator system
ActiveUS20060241701A1Relieve painSafe and effective operationHeart defibrillatorsSubcutaneous implantationCardiac pacemaker electrode
Subcutaneous Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (SubQ ICDS) are disclosed that are entirely implantable subcutaneously with minimal surgical intrusion into the body of the patient and provide distributed cardioversion-defibrillation sense and stimulation electrodes for delivery of cardioversion-defibrillation shock and pacing therapies across the heart when necessary. The SubQ ICD is implemented with other implantable and external medical devices and communicates to provide drugs and therapy in a coordinated and synergistic manner.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
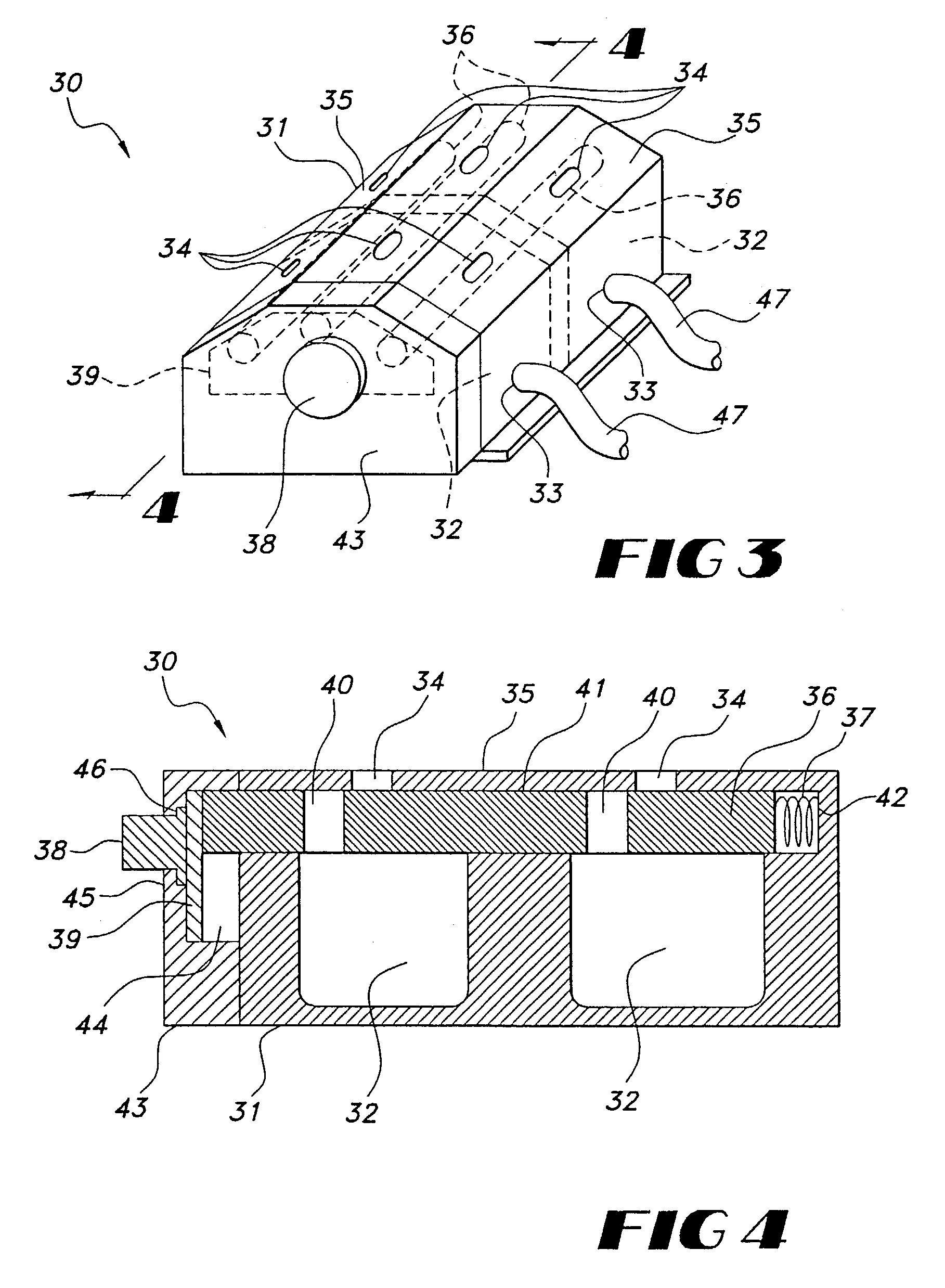
Implantable pulse generator for providing functional and/or therapeutic stimulation of muscles and /or nerves and/or central nervous system tissue
ActiveUS20050277999A1Efficient chargingImprove the quality of lifeElectrotherapyElectromyographyElectricityMicrocontroller
Improved assemblies, systems, and methods provide an implantable pulse generator for prosthetic or therapeutic stimulation of muscles, nerves, or central nervous system tissue, or any combination. The implantable pulse generator is sized and configured to be implanted subcutaneous a tissue region. The implantable pulse generator includes an electrically conductive case of a laser welded titanium material. Control circuitry is located within the case, the control circuitry including a rechargeable power source, a receive coil for receiving an RF magnetic field to recharge the power source, and a microcontroller for control of the implantable pulse generator. Improved assemblies, systems, and methods also provide a stimulation system for prosthetic or therapeutic stimulation of muscles, nerves, or central nervous system tissue, or any combination. The stimulation system provides at least one electrically conductive surface, a lead connected to the electrically conductive surface, and an implantable pulse generator electrically connected to the lead.
Owner:MEDTRONIC URINARY SOLUTIONS
Implantable pulse generator for providing functional and/or therapeutic stimulation of muscles and/or nerves and/or central nervous system tissue
ActiveUS7239918B2Reliable and easy connectionEfficient chargingElectrotherapySurgeryElectricityMicrocontroller
Owner:MEDTRONIC URINARY SOLUTIONS
Subcutaneous ICD with motion artifact noise suppression
A subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator (SubQ ICD) includes a housing carrying electrodes for sensing ECG signals and delivering therapy. A sensor detects local motion in the area of the housing and produces a noise signal related to motion artifact noise contained in ECG signals derived from the electrode array. An adaptive noise cancellation circuit enhances ECG signals based on the local motion noise signal. A therapy delivery circuit delivers cardioversion and defibrillation pulses based upon the enhanced ECG signals.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Subcutaneous electrode with improved contact shape for transthorasic conduction
One embodiment of the present invention provides a lead electrode assembly for use with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator subcutaneously implanted outside the ribcage between the third and twelfth ribs comprising the electrode.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Implantable pulse generator for providing functional and/or therapeutic stimulation of muscles and/or nerves and/or central nervous system tissue
ActiveUS20050278000A1Efficient chargingImprove the quality of lifeElectrotherapyElectromyographyMicrocontrollerPrimary cell
Improved assemblies, systems, and methods provide an implantable pulse generator for prosthetic or therapeutic stimulation of muscles, nerves, or central nervous system tissue, or any combination. The implantable pulse generator is sized and configured to be implanted subcutaneously in a tissue region. The implantable pulse generator includes an electrically conductive laser welded titanium case. Control circuitry is located within the case, and includes a primary cell or rechargeable power source, a receive coil for receiving an RF magnetic field to recharge the rechargeable power source, and a microcontroller for control of the implantable pulse generator. Improved assemblies, systems, and methods also provide a stimulation system for prosthetic or therapeutic stimulation of muscles, nerves, or central nervous system tissue, or any combination. The stimulation system provides at least one electrically conductive surface, a lead connected to the electrically conductive surface, and an implantable pulse generator electrically connected to the lead.
Owner:MEDTRONIC URINARY SOLUTIONS
Current waveforms for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter- defibrillator
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathoracic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
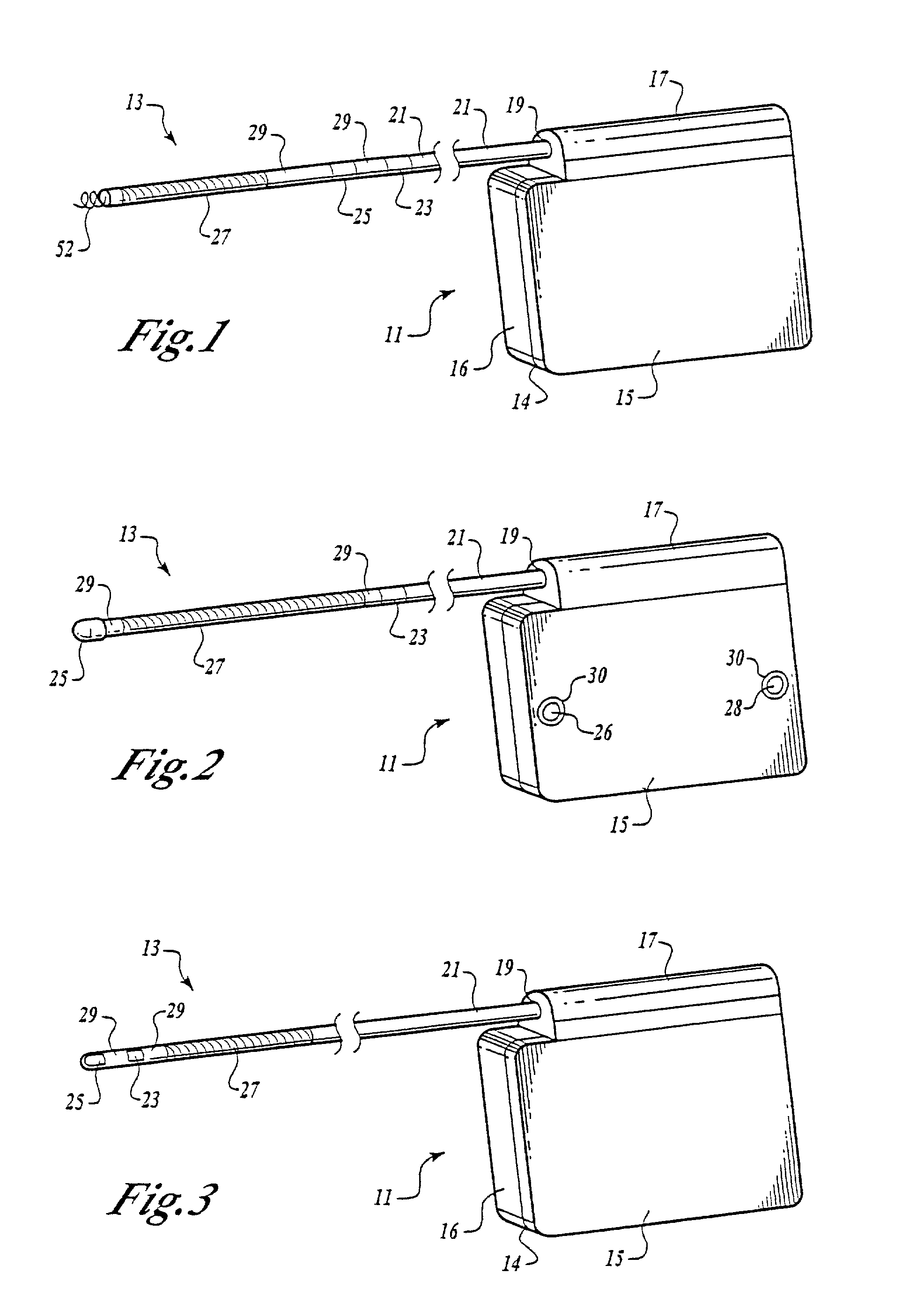
Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator employing a telescoping lead
One embodiment of the present invention provides an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib within a patient, the implantable cardioverter-defibrillator including a housing including a first electrode; a telescoping lead assembly including a second electrode, wherein the telescoping lead assembly is electrically and mechanically coupled to the housing; and an electrical circuit located within and electrically coupled to the housing.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
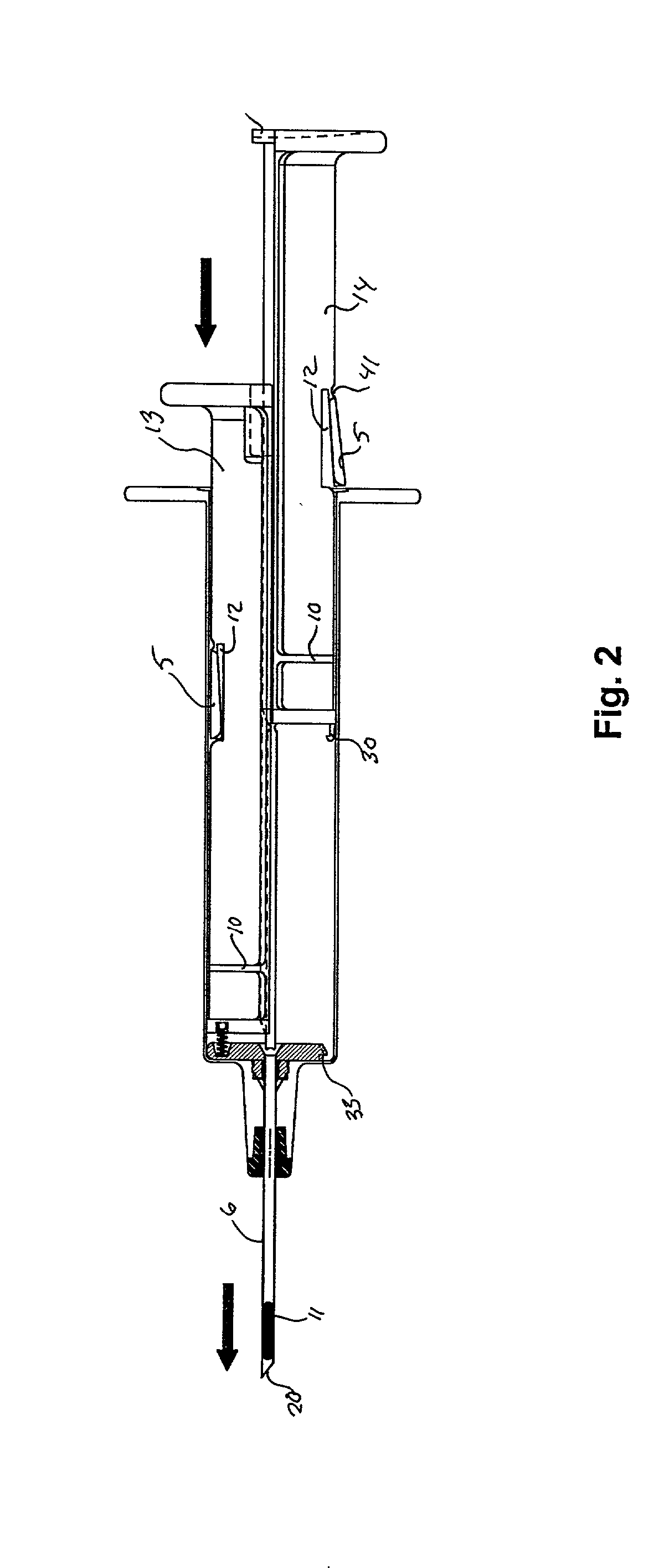
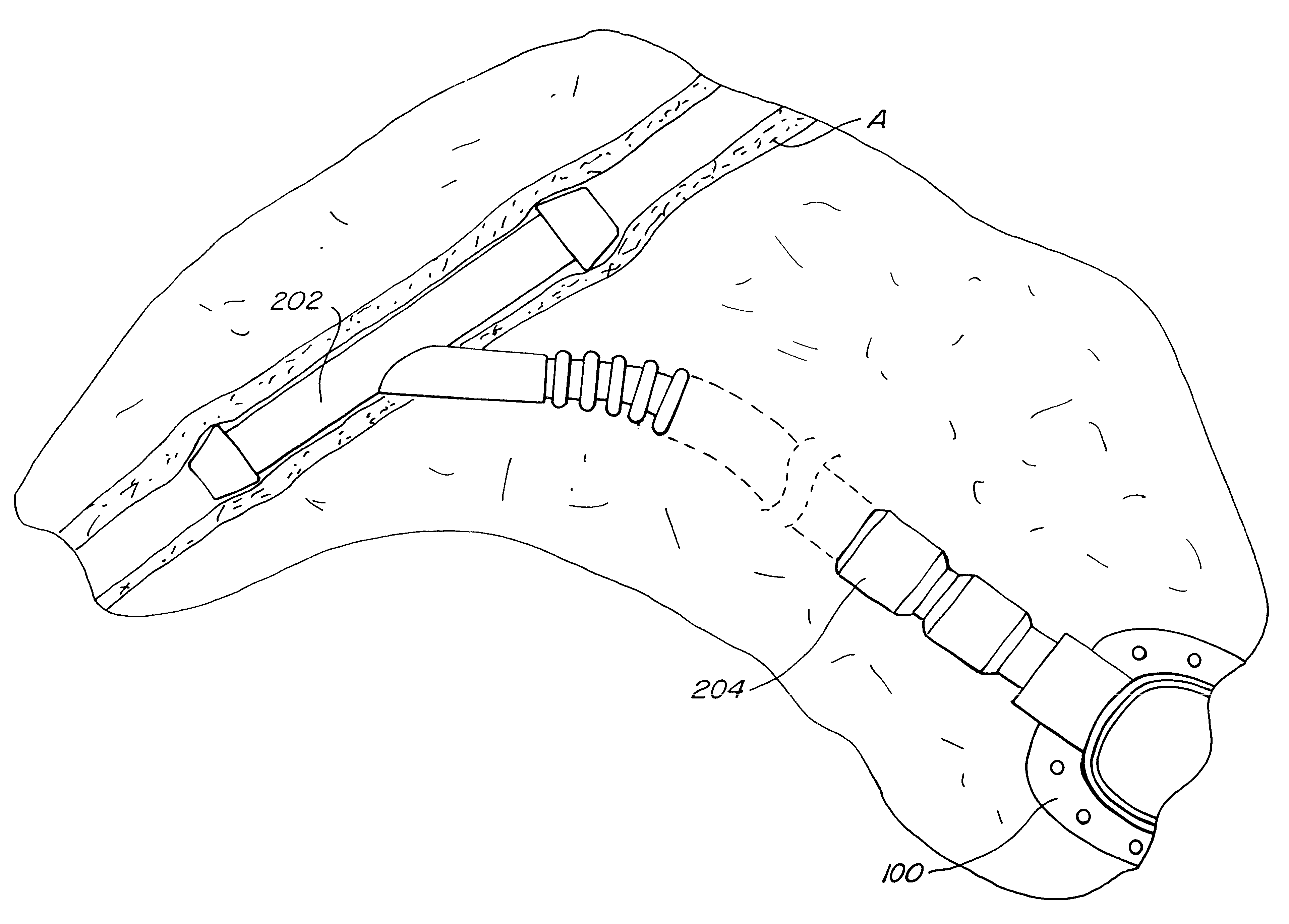
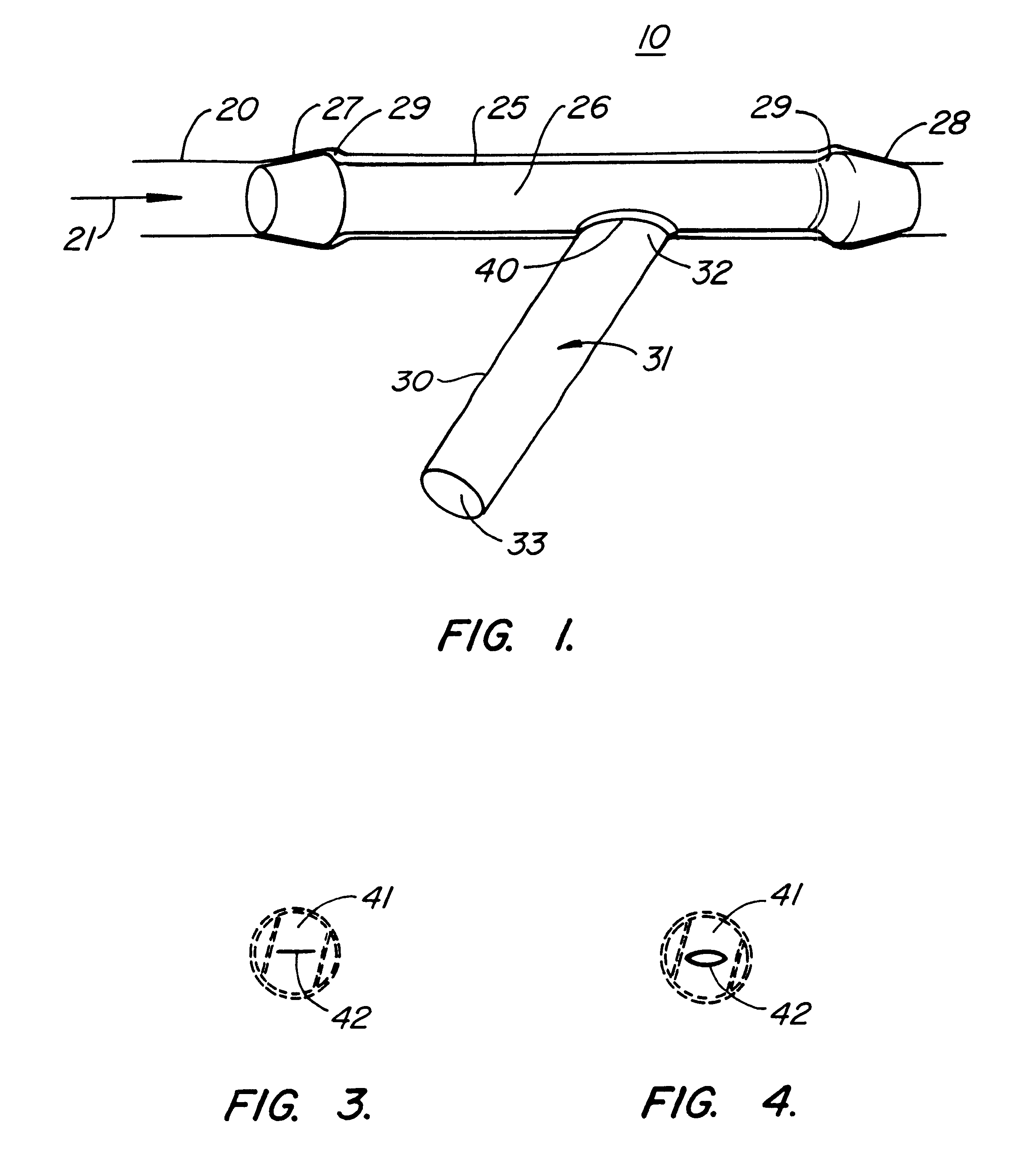
Subcutaneously implanted cannula and method for arterial access
InactiveUS6398764B1Avoid blood lossReduce exerciseMedical devicesCatheterDifferential pressureSubcutaneous implantation
A catheter with valve for implantation in a vascular structure of a living being. The catheter is in the general shape of a "T" with the top of the "T" implanted within the lumen of a vascular structure, and the leg of the "T" extending out of the vascular structure through an incision in the vascular structure. The lumen of the implanted portion of the catheter completely occupies the lumen of the vascular structure, causing all blood flow through the vascular structure to be directed through the implanted portion of the catheter. A valve is placed in the wall of the implanted portion of the catheter which opens into the lumen of the leg of the "T" of the catheter upon application of sufficient differential pressure between the lumens of the two portions of the catheter. The leg of the "T" is connected to the side wall of the implant portion of the catheter at an angle, such that the axis of the lumen of the leg of the "T" intersects the axis of the lumen of the implanted portion of the catheter at approximately a 45 degree angle.
Owner:VASCA
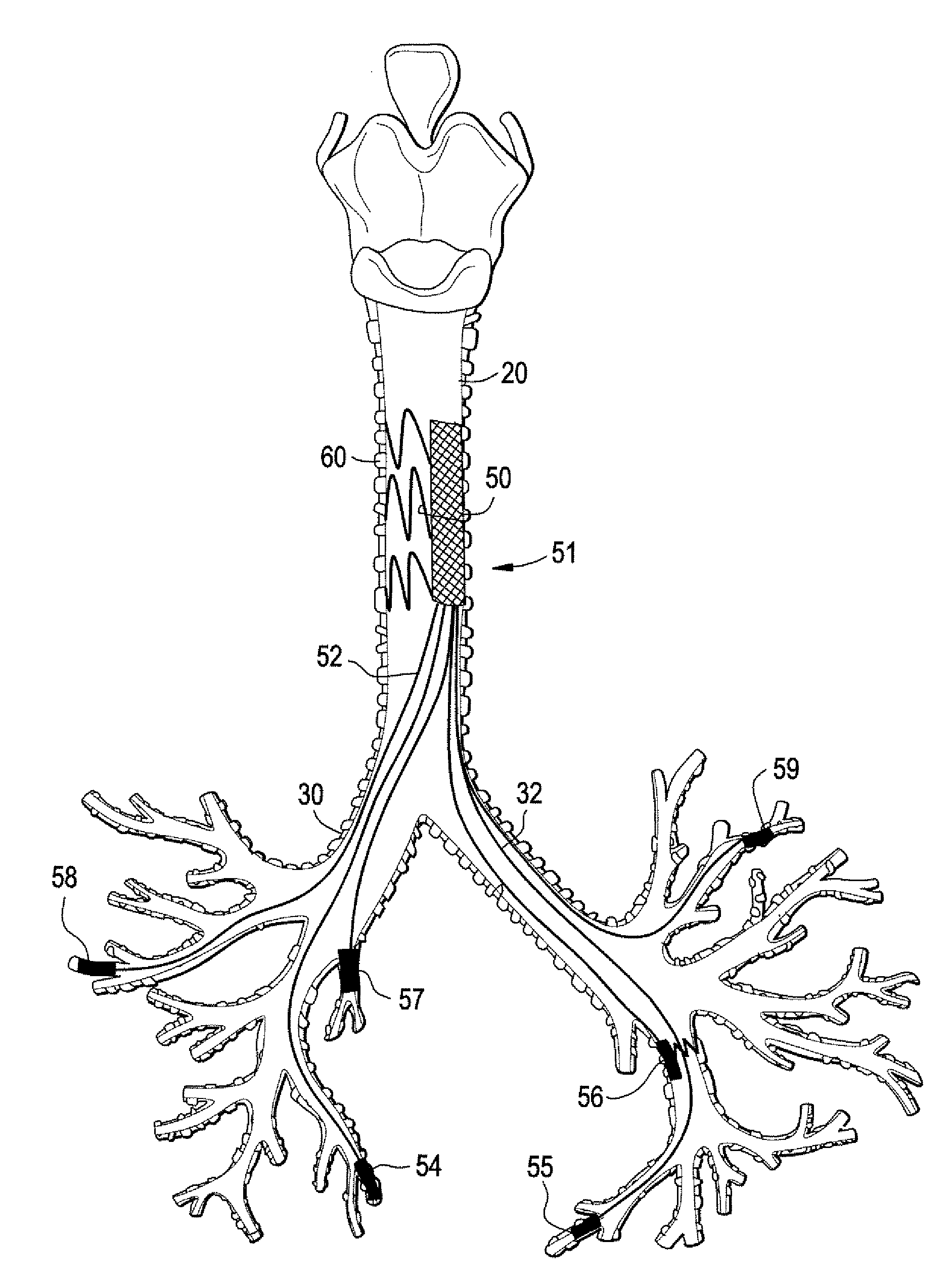
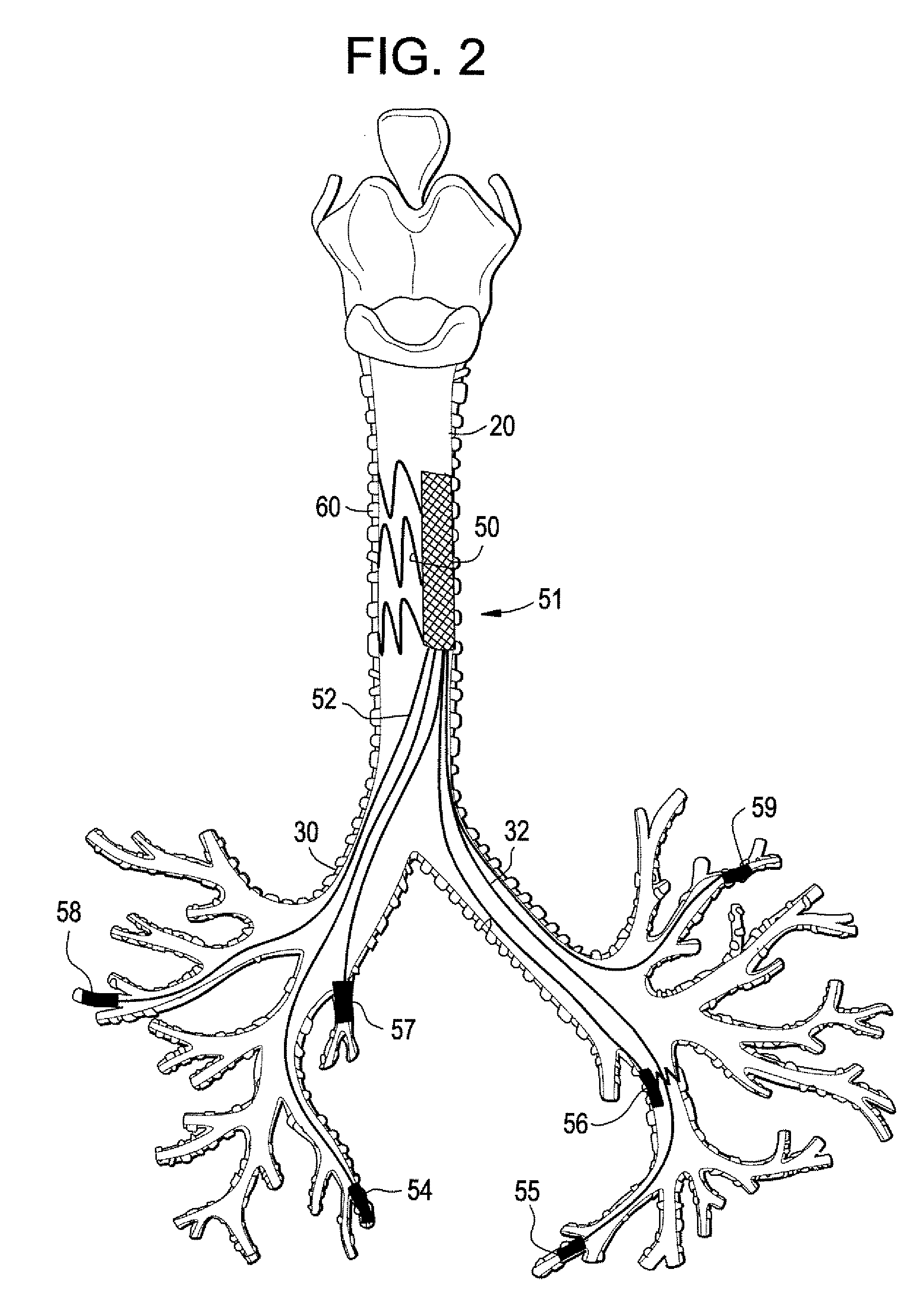
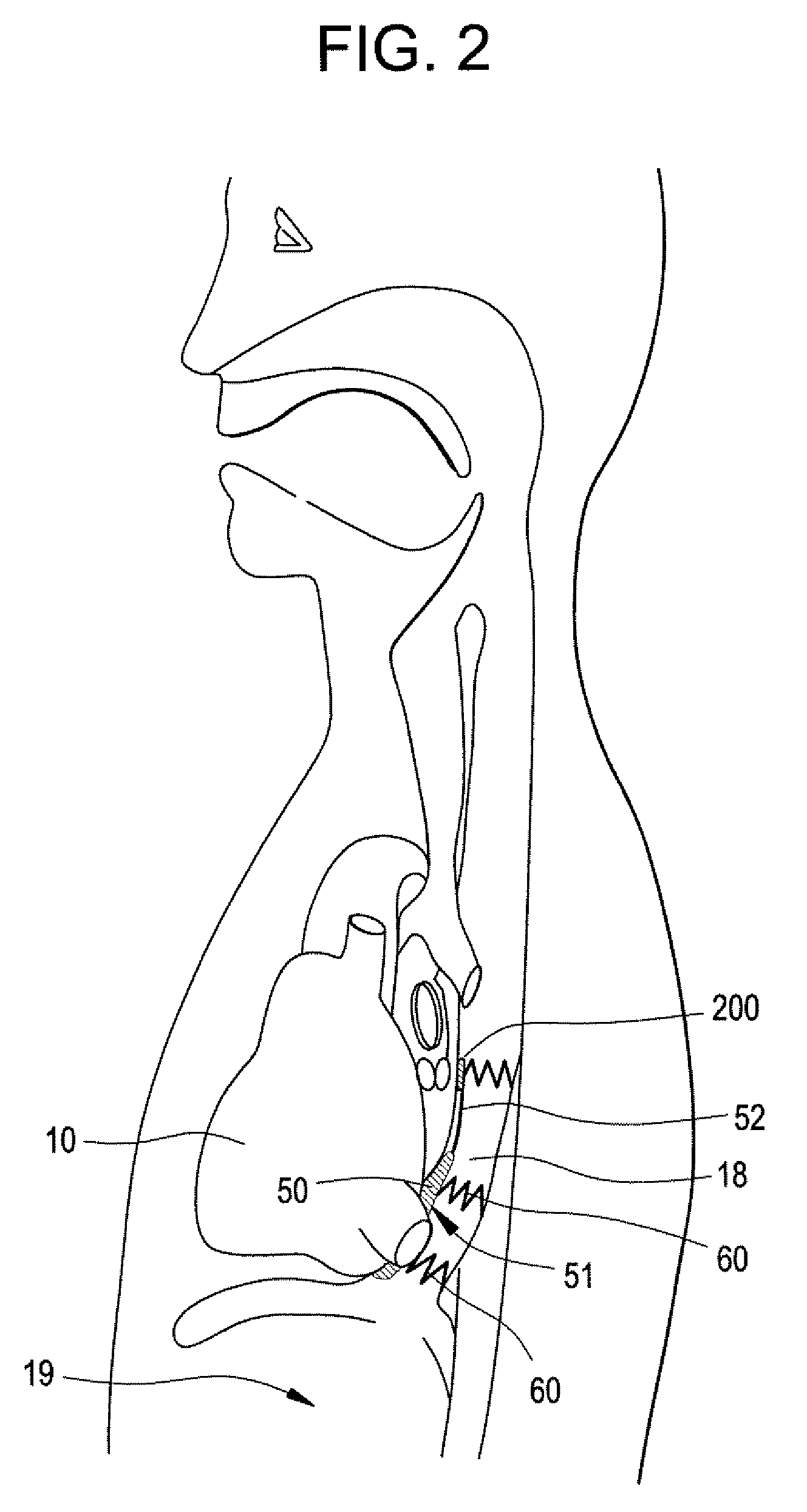
Implantable Devices And Methods For Stimulation Of Cardiac And Other Tissues
An implantable system is provided for stimulation of the heart, phrenic nerve, or other tissue structures accessible via a patient's airway. The stimulation system includes an implantable controller housing which includes a pulse generator; at least one electrical lead attachable to said pulse generator; and at least one electrode carried by the at least one electrical lead, wherein the at least one electrode is positionable and fixable at a selected position within an airway of a patient. The controller housing may be adaptable for implantation subcutaneous, or alternatively, at a selected position within the patient's trachea or bronchus, wherein the controller housing is proportioned to substantially permit airflow through the patient's airway about housing.
Owner:E PACING
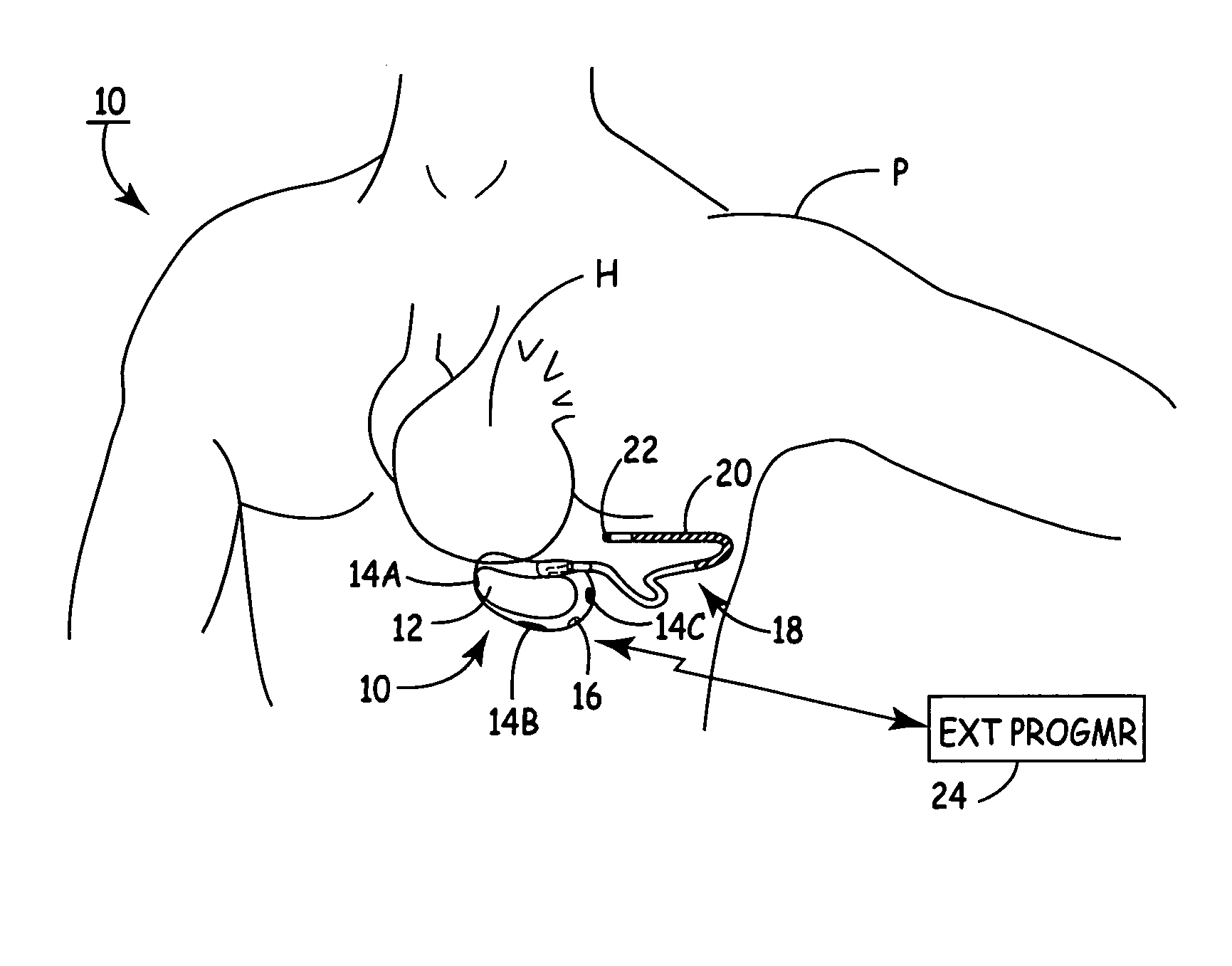
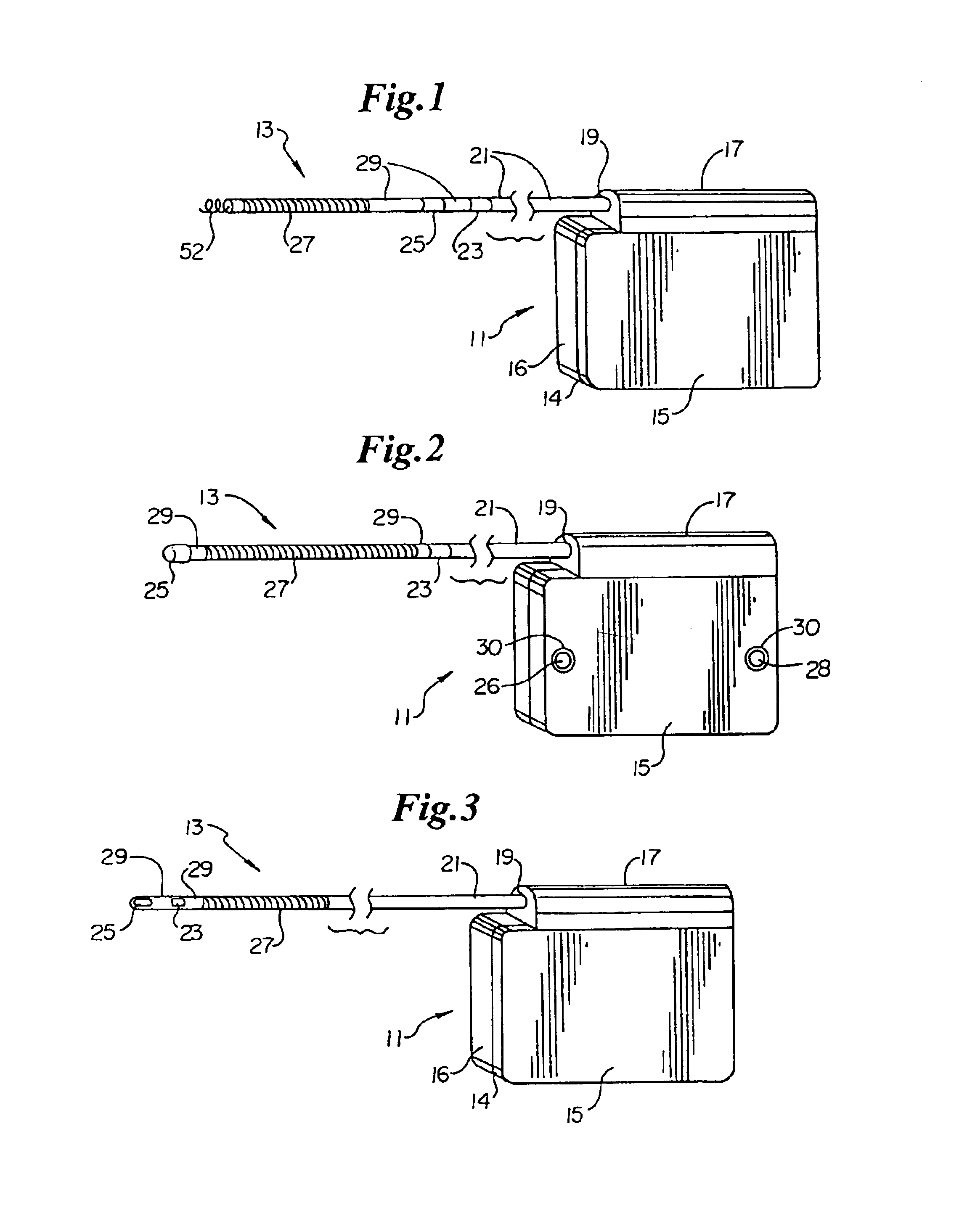
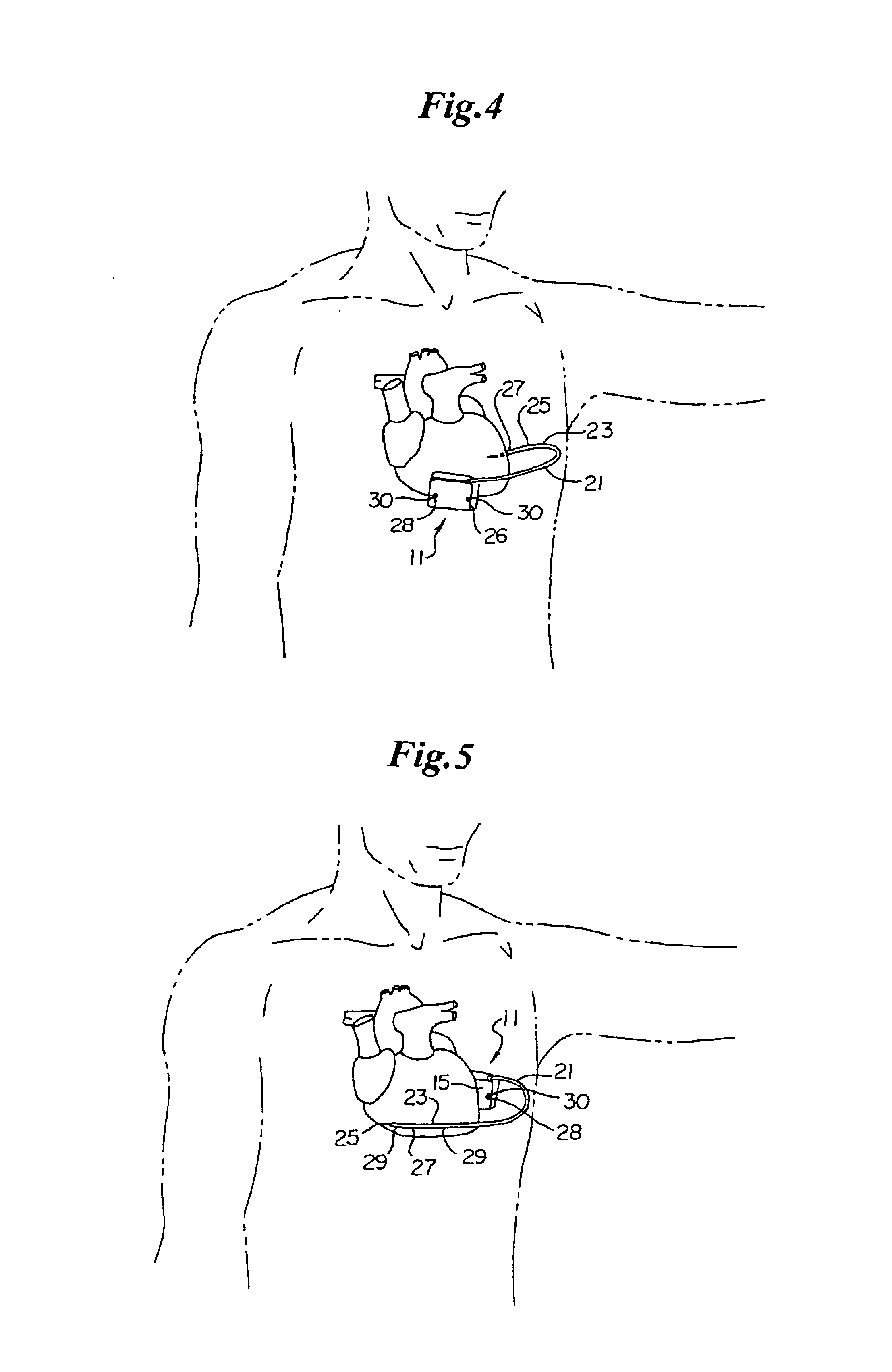
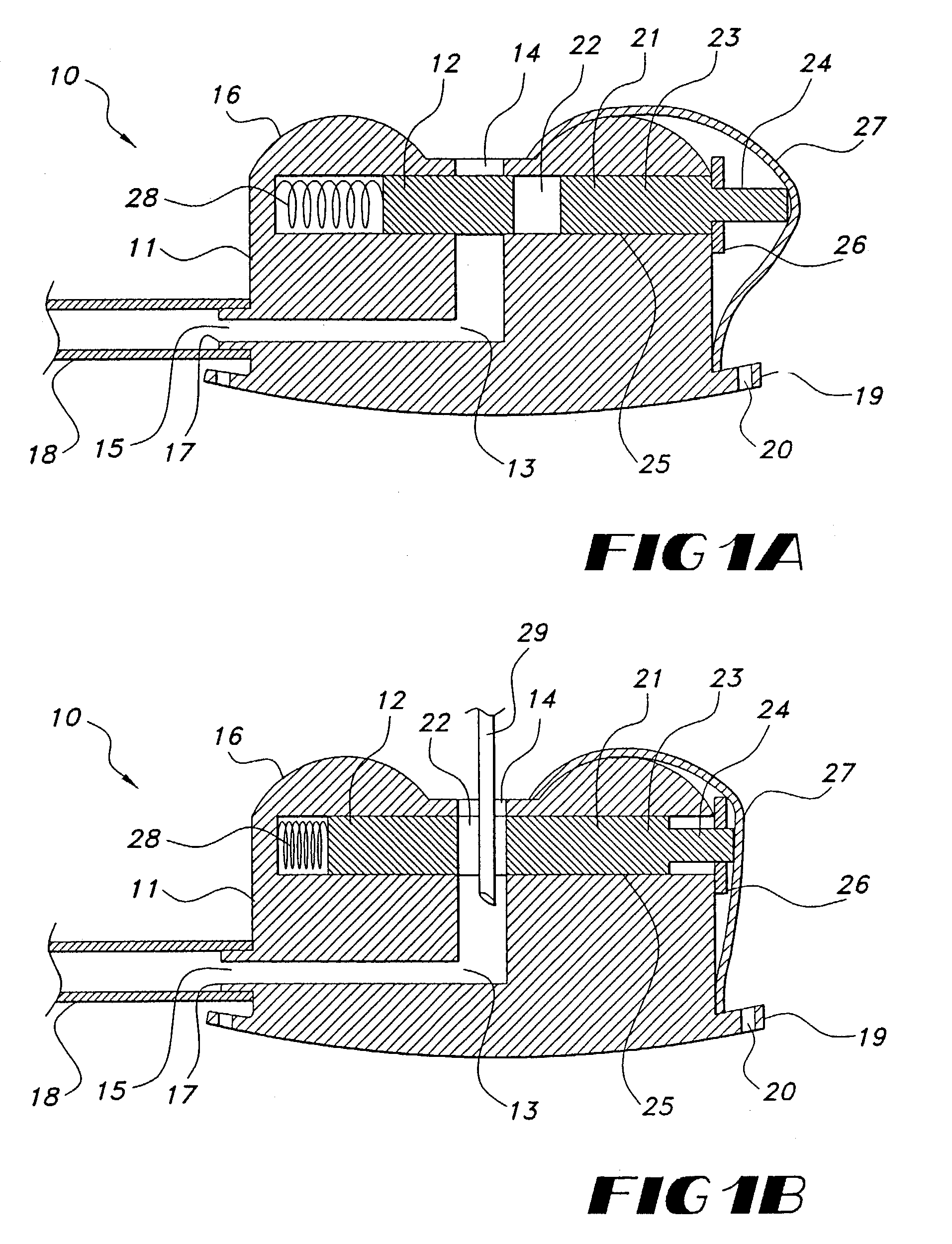
Cardiac event microrecorder and method for implanting same
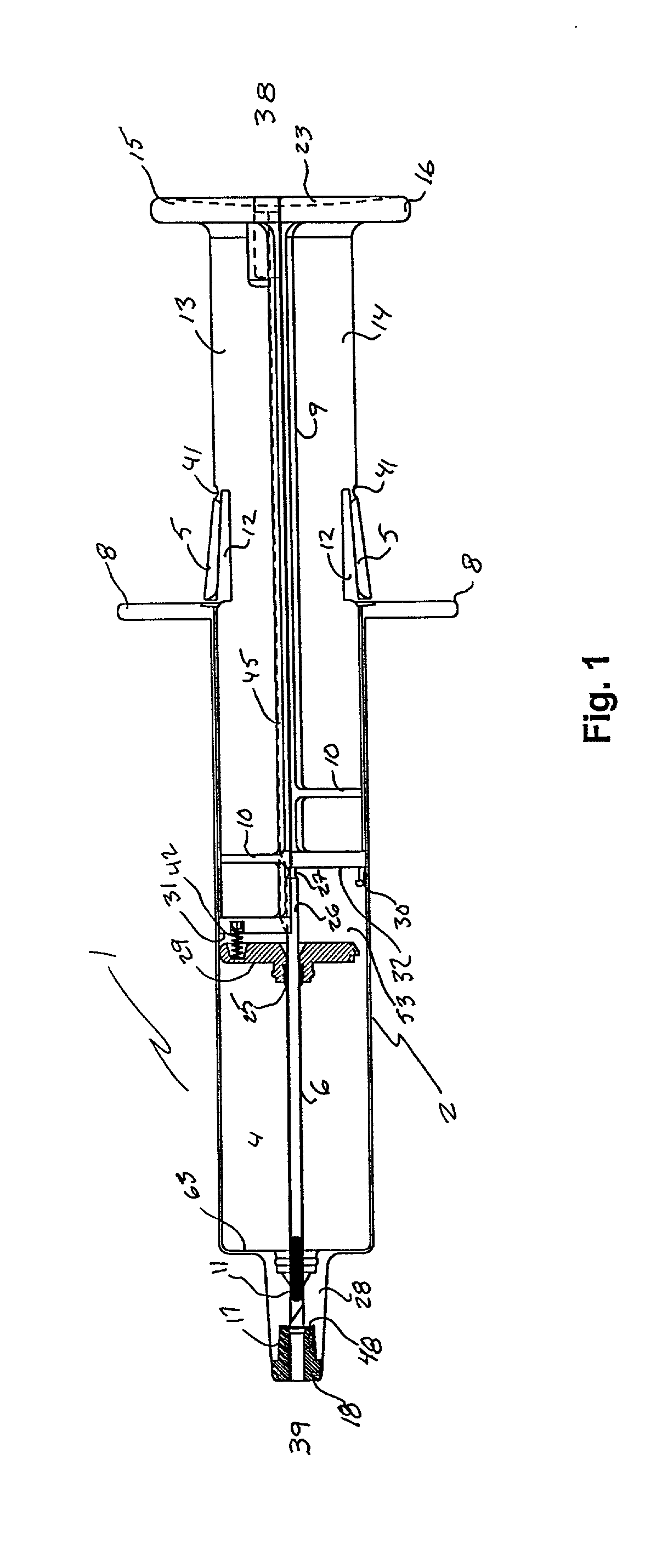
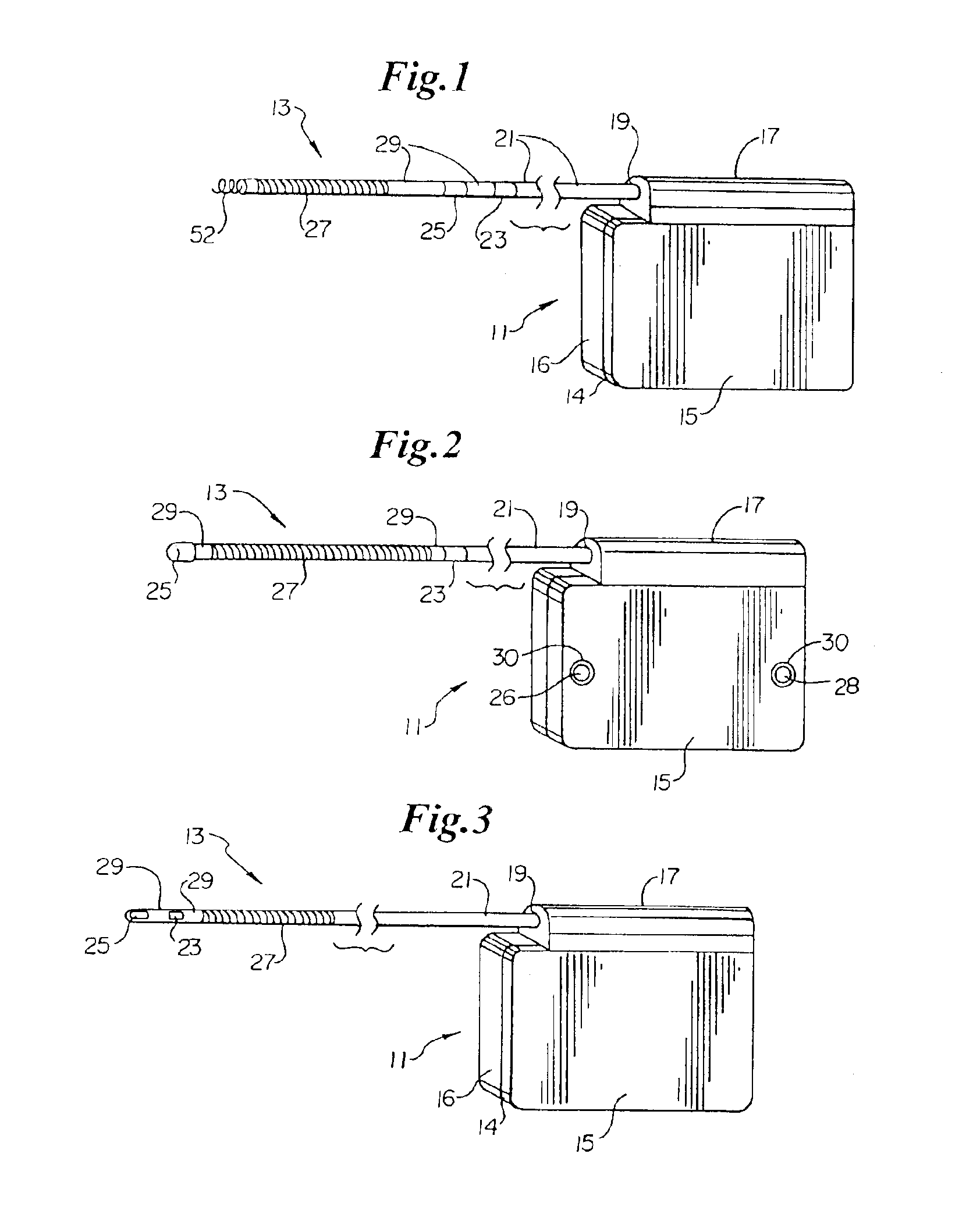
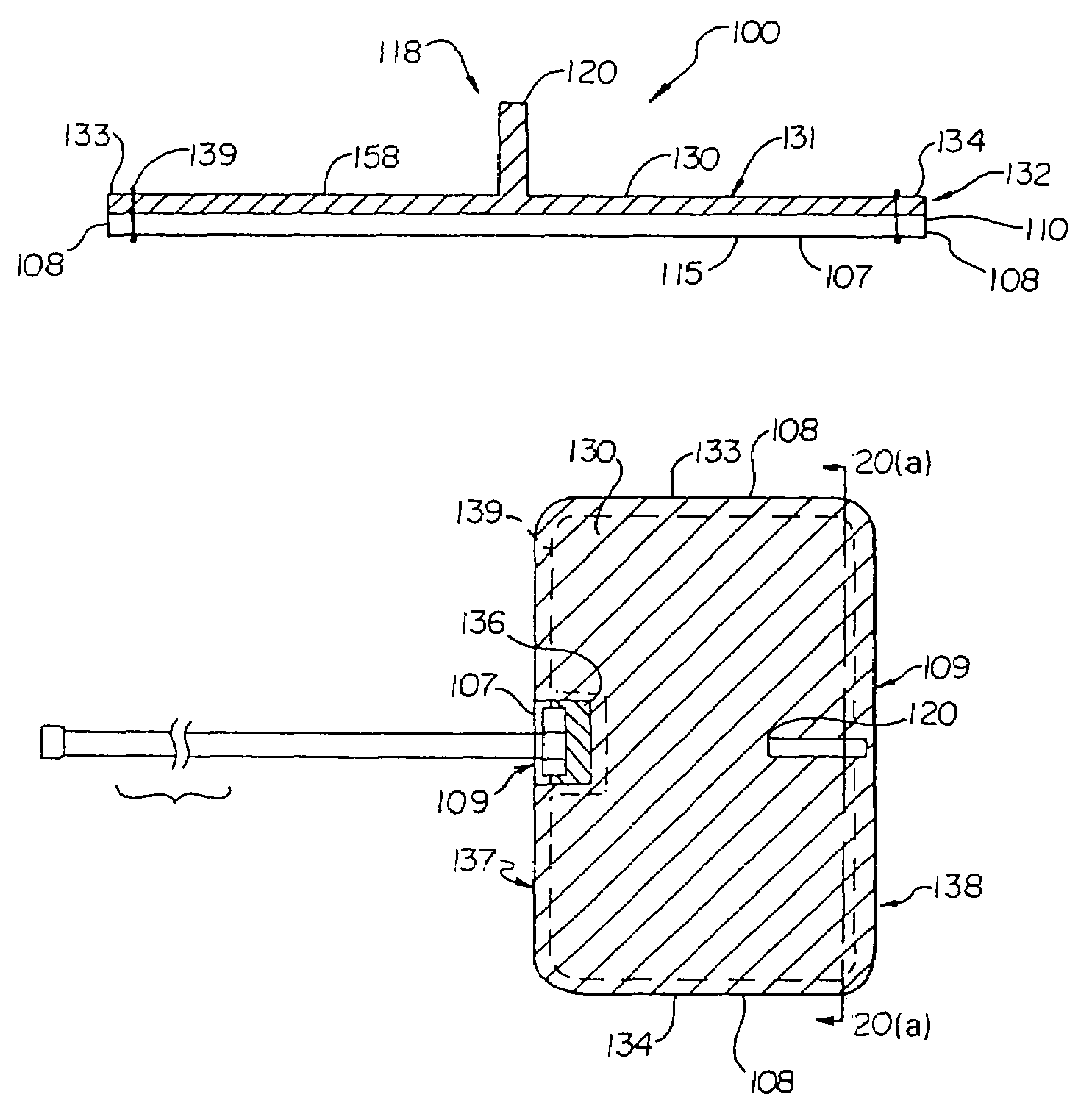
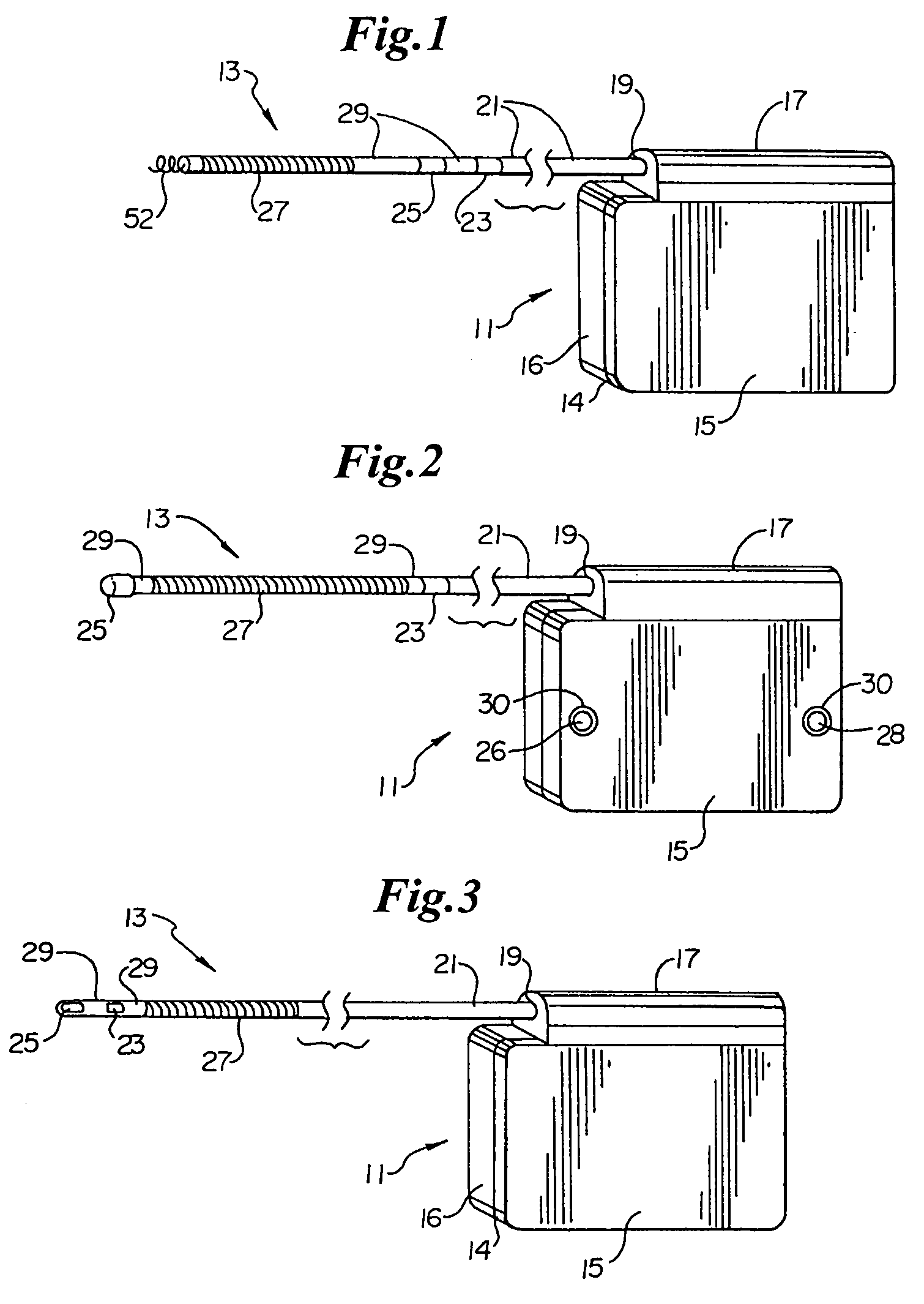
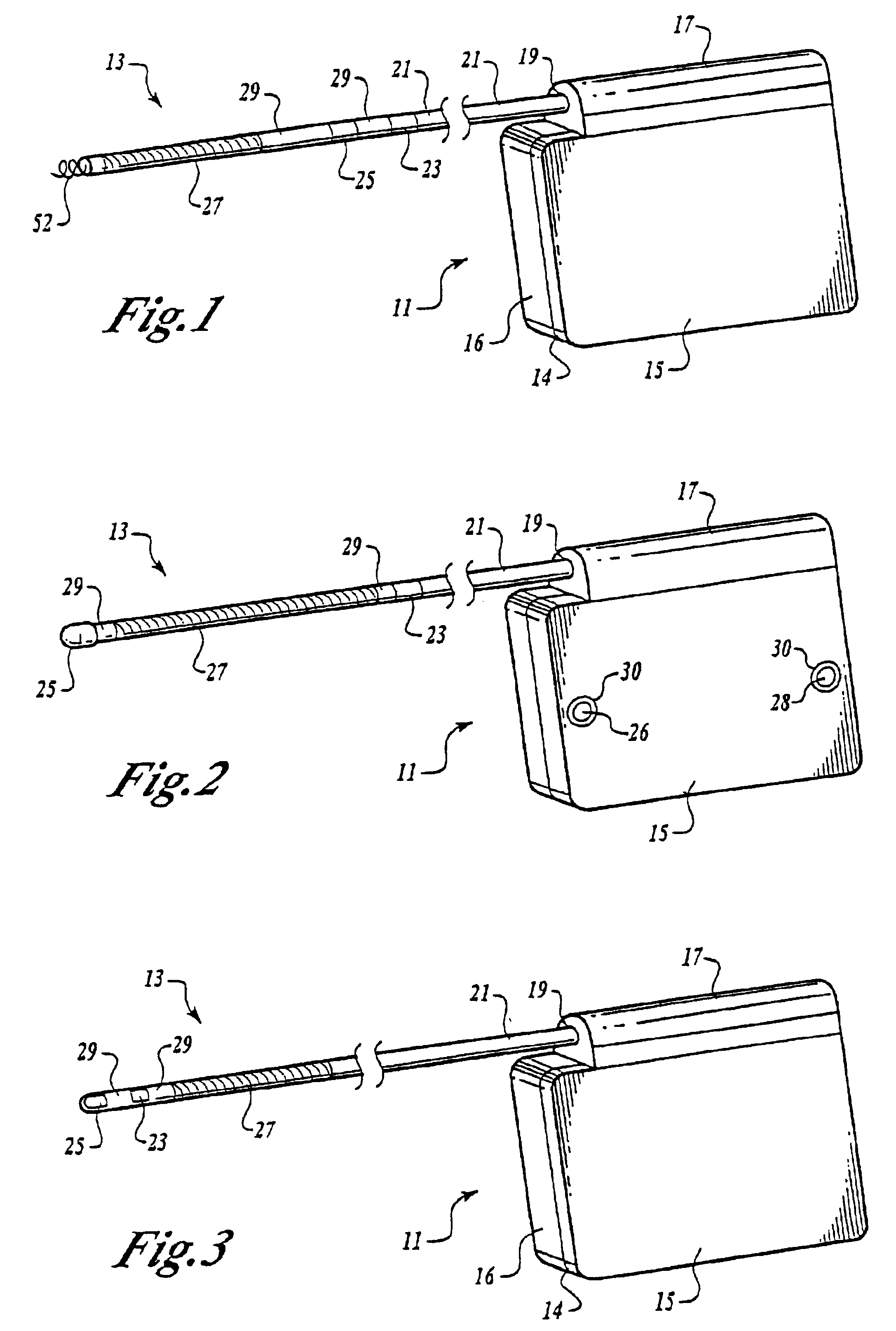
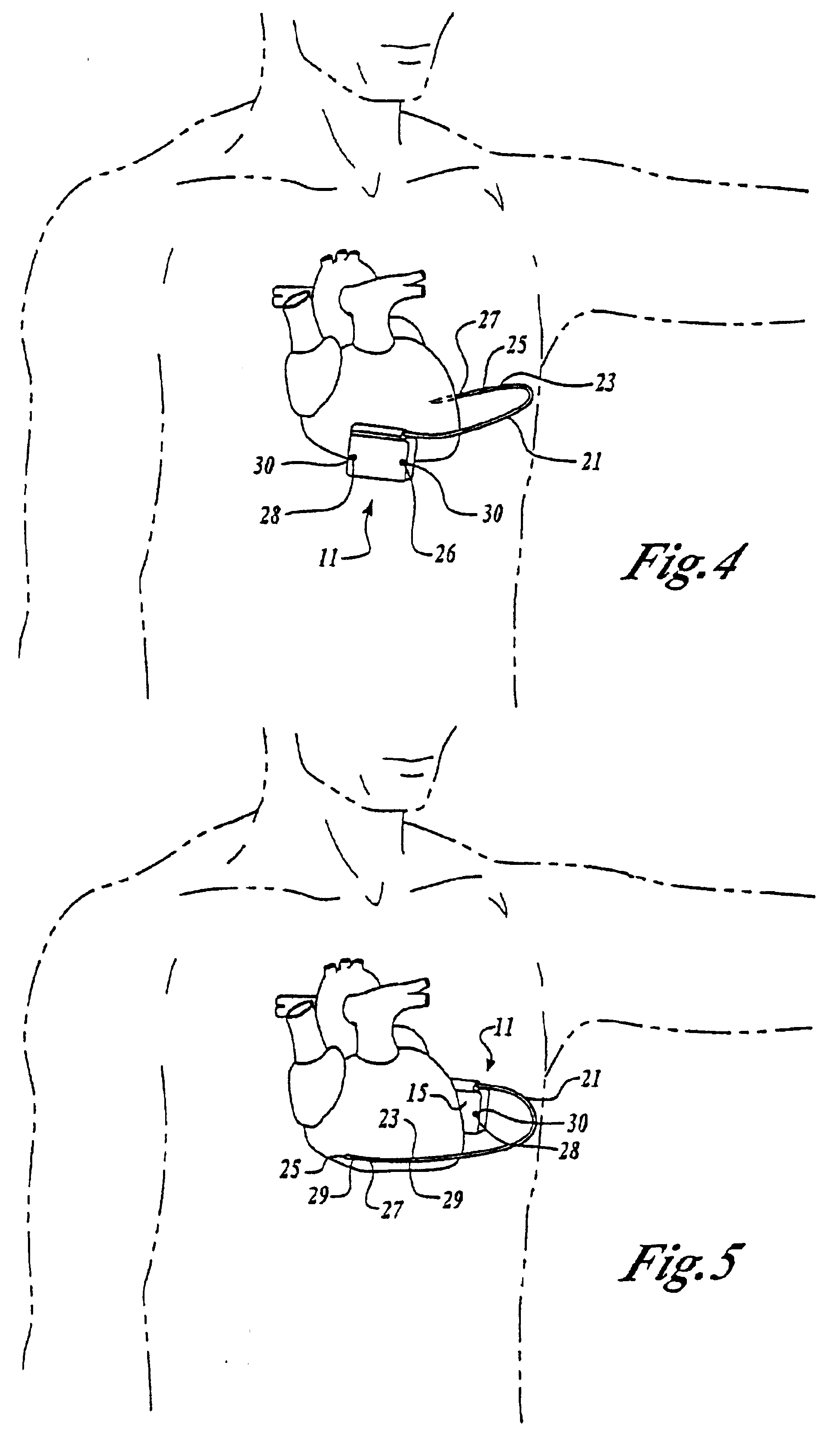
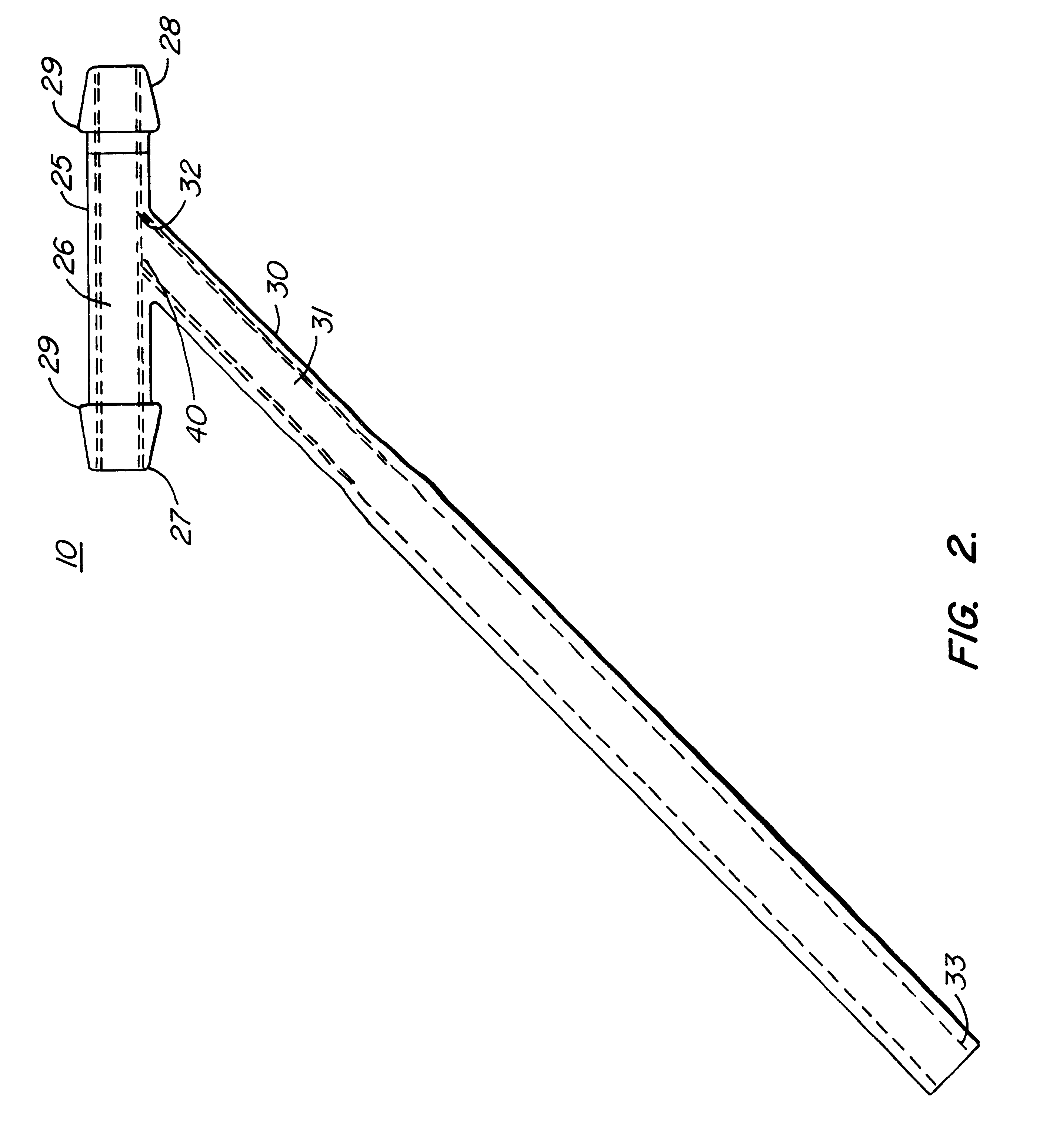
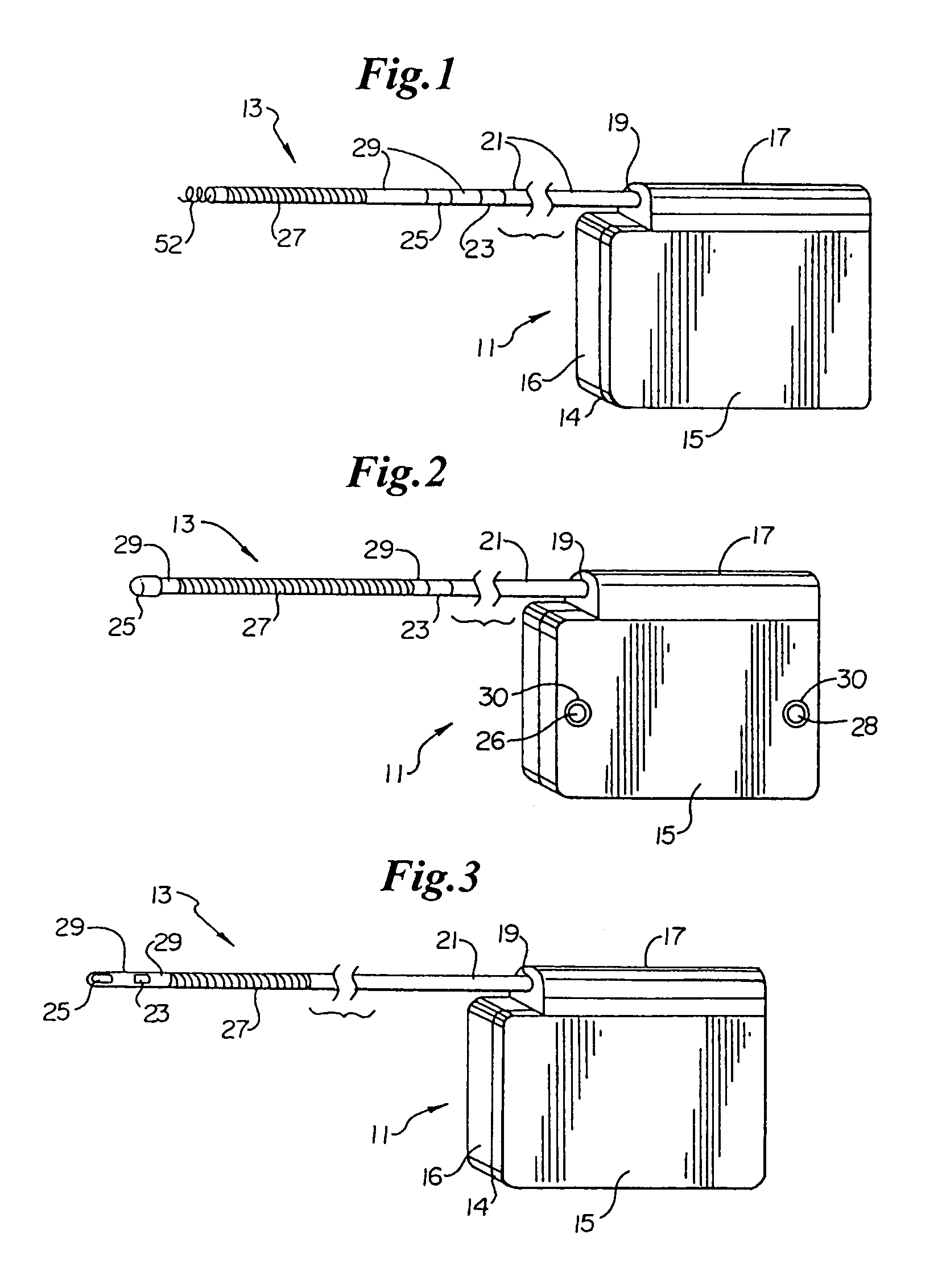
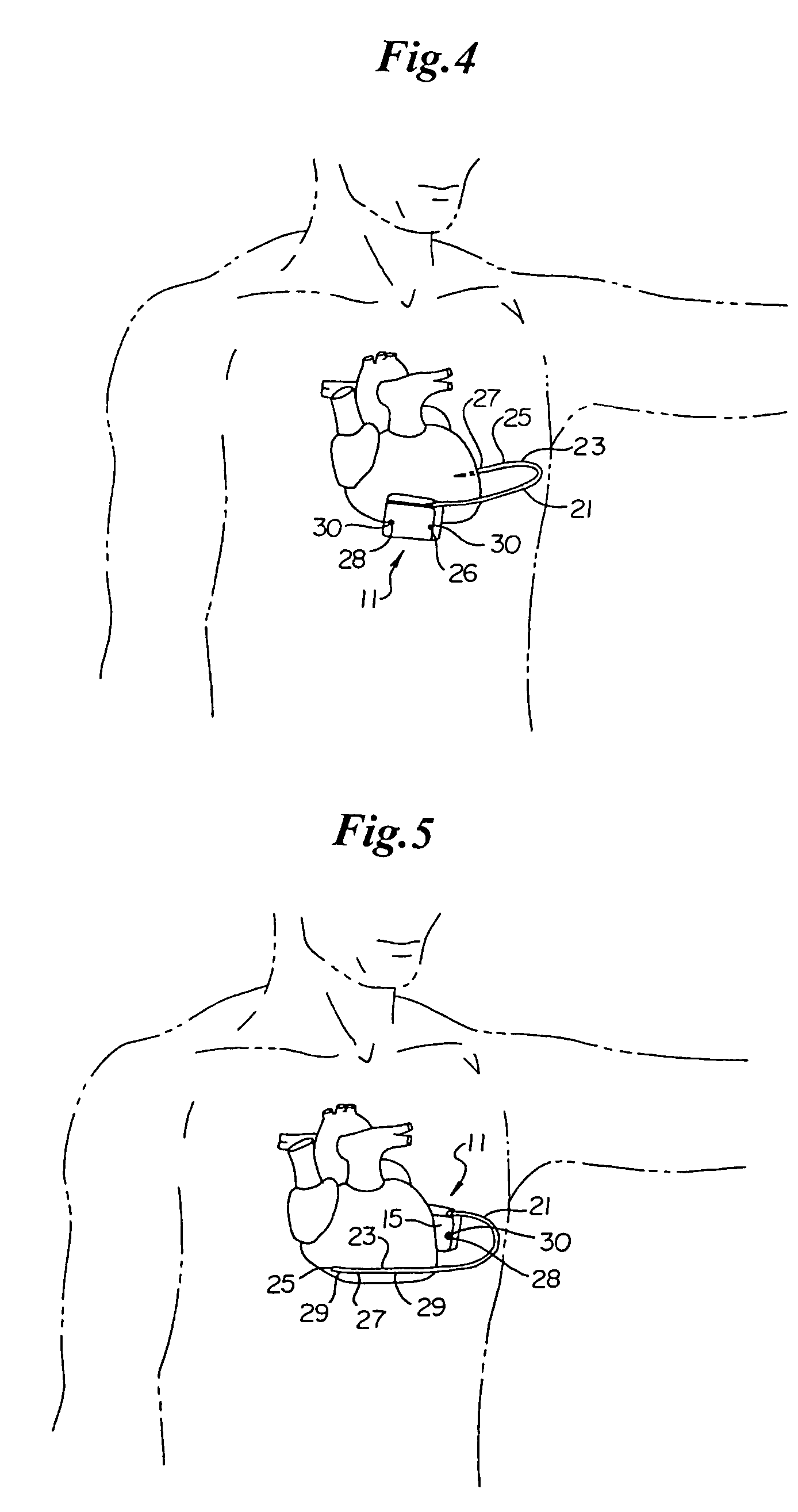
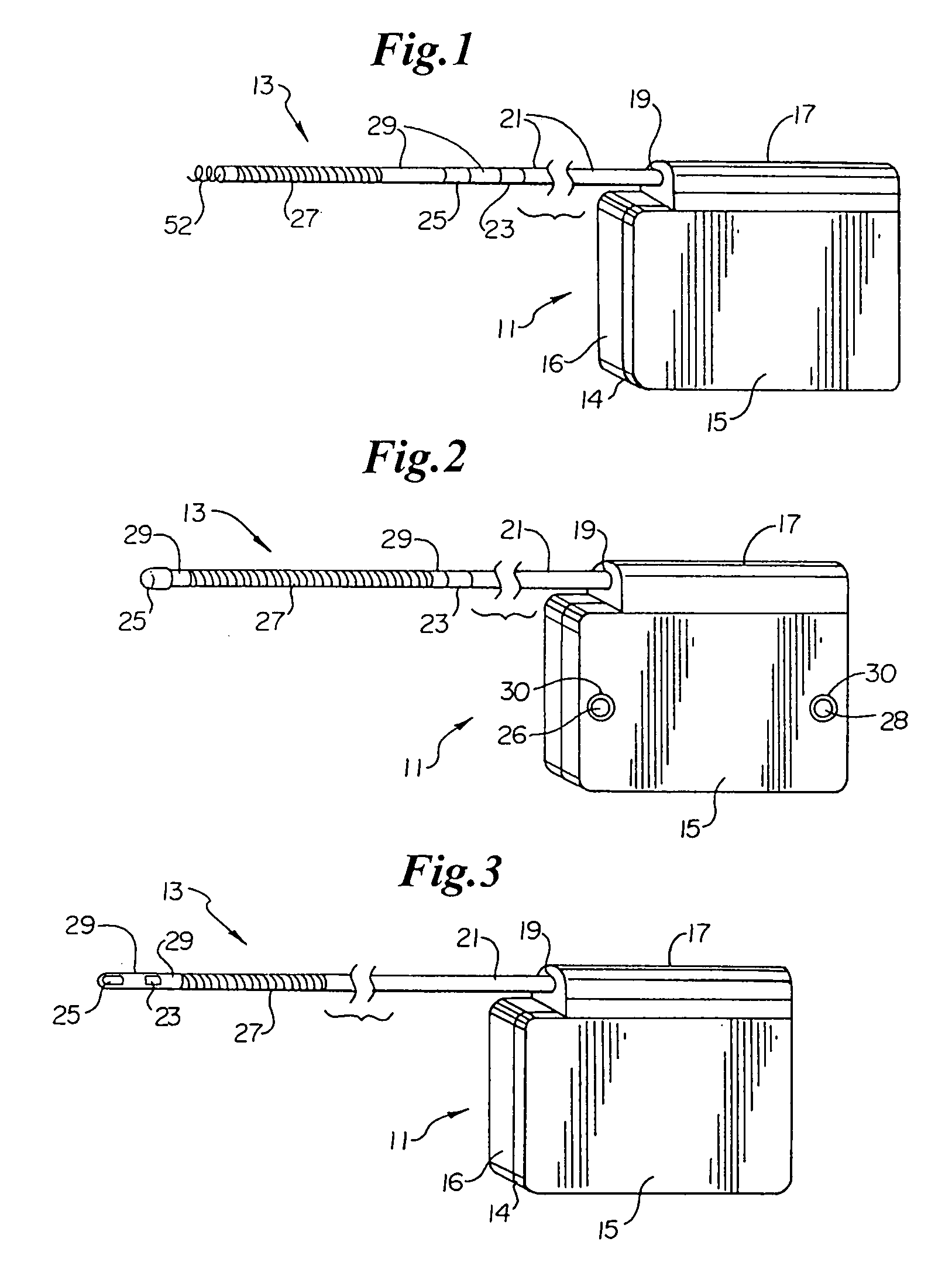
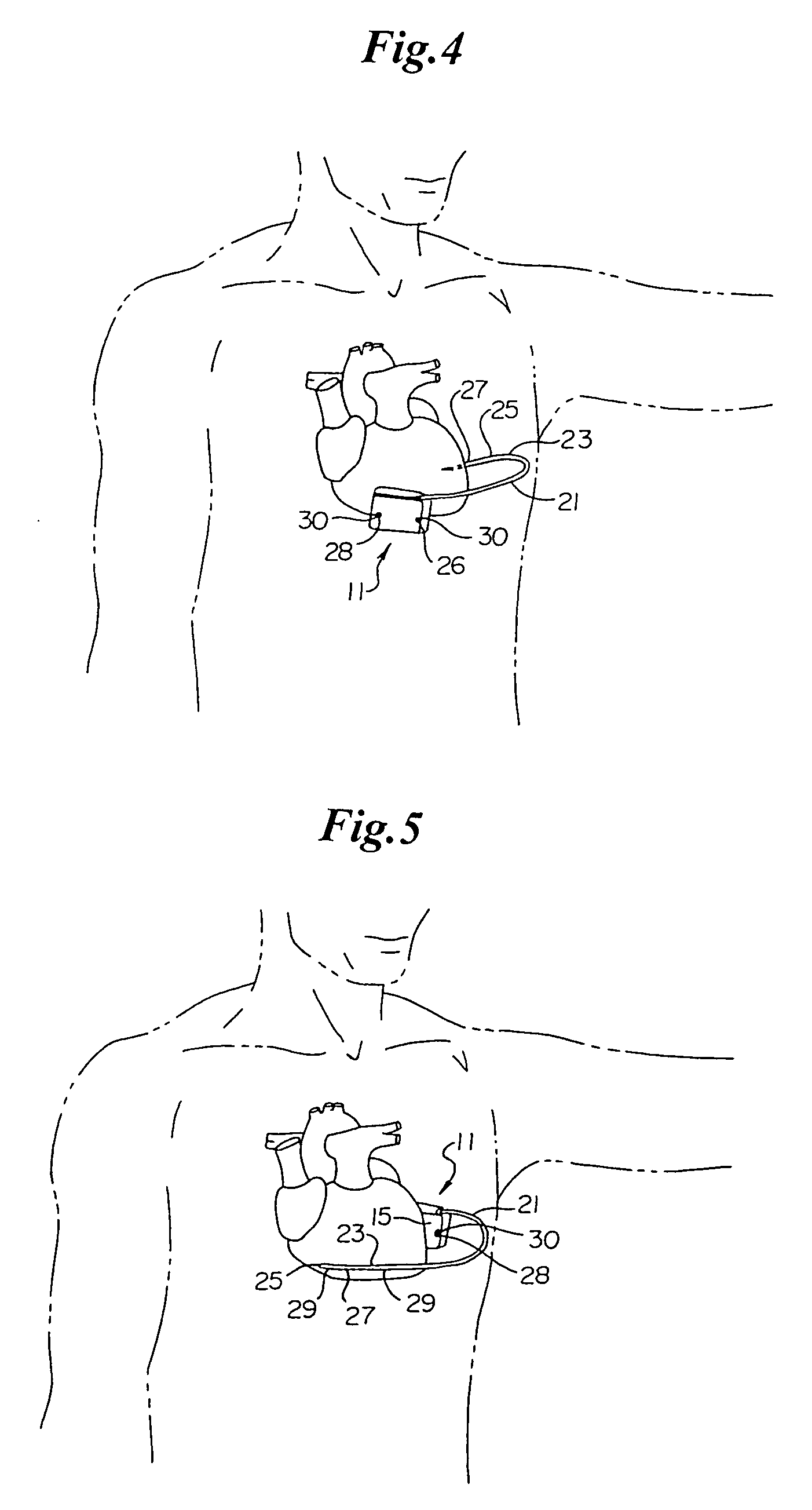
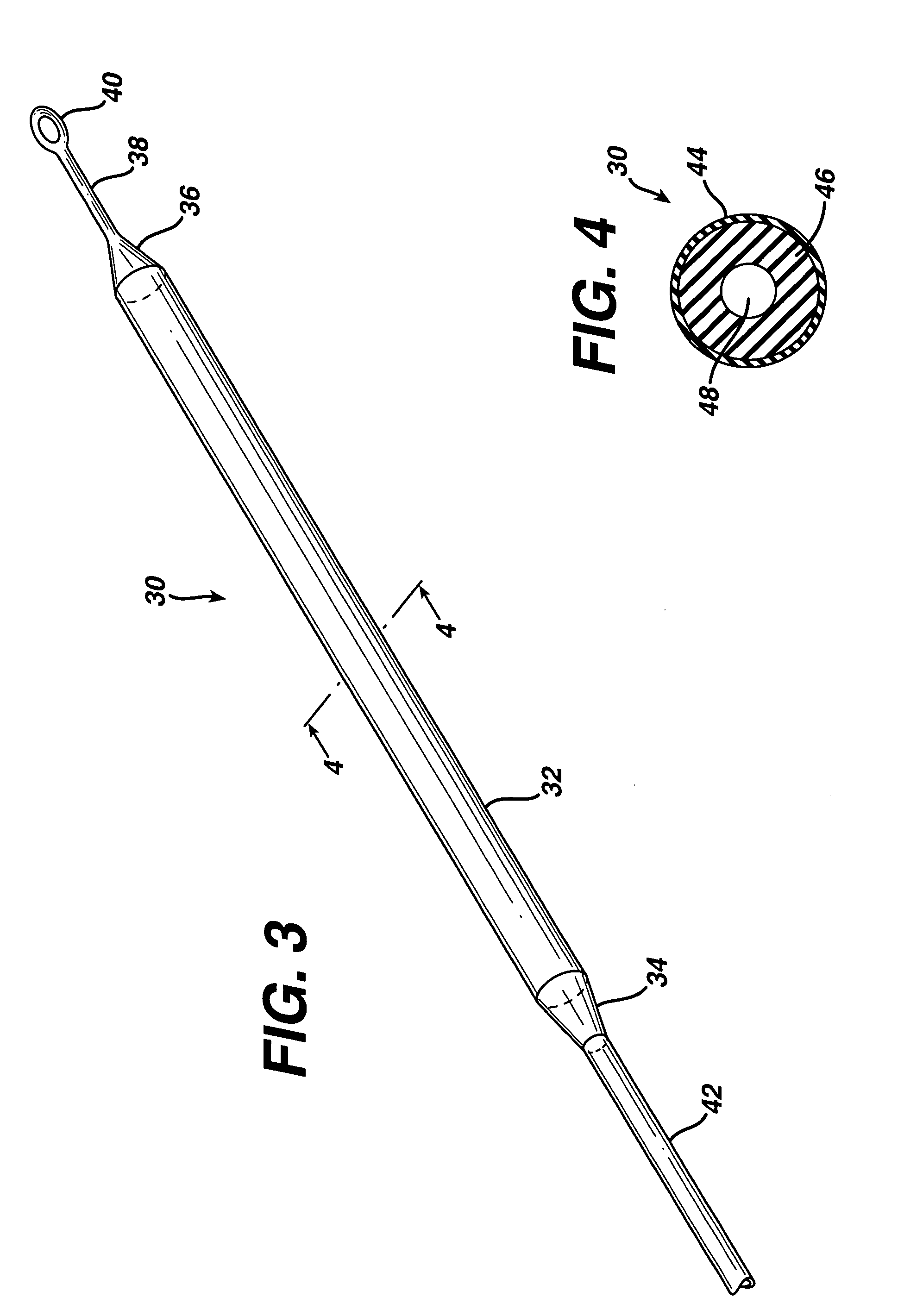
ActiveUS7294108B1Facilitate subcutaneous implantationElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsElectricityHypodermic needle
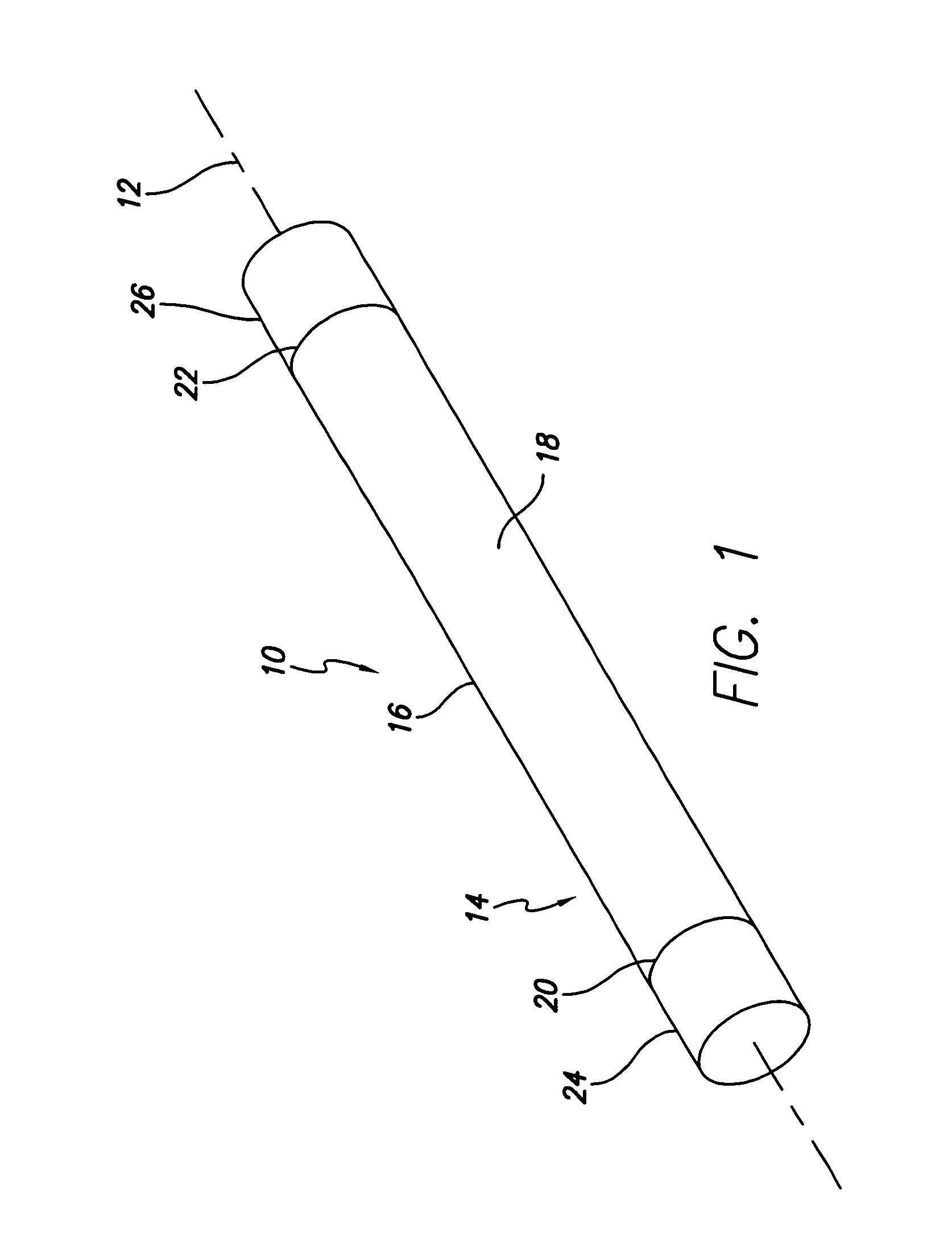
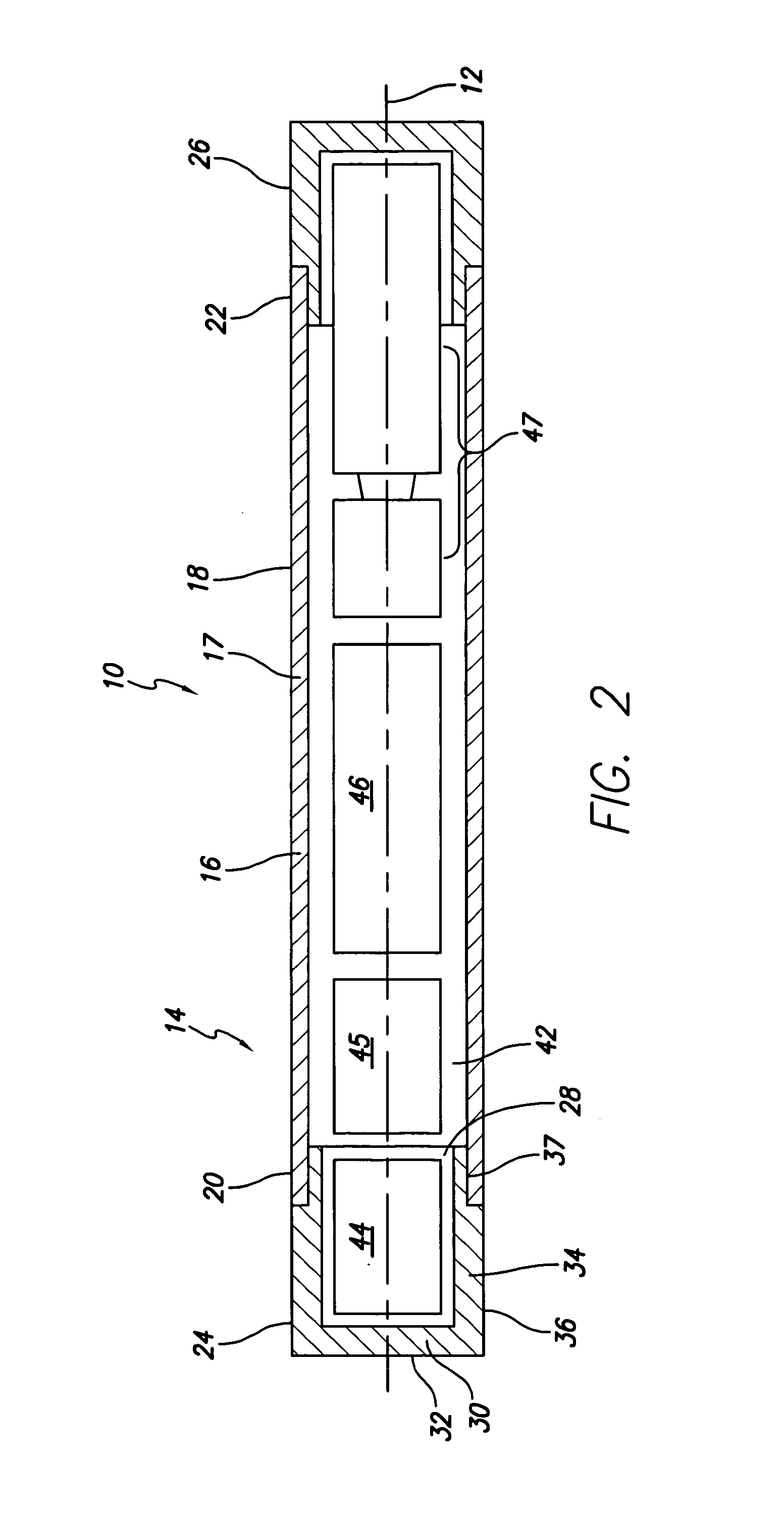
A cardiac event microrecorder comprising a hermetically sealed housing is shaped and dimensioned to facilitate the subcutaneous implantation of the microrecorder in a human patient by injection through the lumen of a hypodermic needle. The housing comprises a tubular central section of an electrically insulating material, the central section having spaced apart extremities. An electrically conductive sense electrode is secured to and seals each extremity. The housing may have an interior enclosing (1) electrical circuitry for processing, storing and telemetering data representing physiologic information detected by the sense electrodes; (2) a primary cell or rechargeable battery for electrically powering the electrical circuitry; and (3) an inductively couplable charger where a rechargeable battery is used. Also disclosed are a method of subcutaneously implanting a cardiac event recorder in a patient's thoracic region, and a handheld mapping device for determining an optimum location and orientation for the cardiac event microrecorder to be implanted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Implantable Devices and Methods for Stimulation of Cardiac or Other Tissues
An implantable stimulation system is provided for stimulation of the heart, phrenic nerve, gastric system, or other tissue structures accessible via a patient's upper gastrointestinal system or airway. The stimulation system includes an implantable controller housing including a pulse generator; at least one electrical lead attachable to the pulse generator; and at least one electrode carried by the electrical lead that is positionable and fixable within the upper gastrointestinal tract or airway. The controller housing may be adaptable for subcutaneous implantation, or within the upper gastrointestinal tract or airway, wherein the controller housing is proportioned to substantially permit fluid and solid flow through the upper gastrointestinal tract or airway about the controller housing. The pulse generator may be operable to deliver one or more electrical pulses effective in cardiac pacing, cardiac defibrillation, cardioversion, cardiac resynchronization therapy, diaphragm pacing, phrenic nerve stimulation, gastric electrical stimulation, or a combination thereof.
Owner:E PACING
Dual well port device
ActiveUS20050171502A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesSubcutaneous implantationThree vessels
A port for implantation within a body, comprises a housing having a proximal surface, a distal surface and a side surface wherein, when the port is implanted within a body in a desired orientation, the proximal surface faces outward toward the skin, the distal surface faces inward away from the skin and the side surface extends between the proximal and distal surfaces and a first well formed within the housing, the first well including a first opening in the proximal surface. A second well is formed in the housing adjacent to the first well and has a second opening formed in the proximal surface. First and second outlet openings formed on the side surface of the port are in fluid communication with the first and second wells, respectively, and are separated from one another by a distance substantially equal to a distance separating lumens of a dual lumen catheter to which the port is to be connected. In addition, a method of infusing fluids to a patient, comprises attaching a dual lumen catheter to a blood vessel of the patient and implanting subcutaneously a port including first and second openings separated by a distance substantially equal to a distance between the dual lumens of the catheter, wherein the first opening is in fluid communication with a first well of the port and the second opening is in fluid communication with a second well of the port. The dual lumen catheter is then connected to the first and second openings of the port and a first fluid is provided to the first well while a second fluid is provided to the second well.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Flexible subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
One embodiment of the present invention provides an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning over a patient's ribcage, the implantable cardioverter-defibrillator including a housing, wherein the housing conforms to the patient's ribcage when subcutaneously positioned; an electrode disposed upon a portion of the housing; and an electrical circuit located within the housing, wherein the electrical circuit is electrically coupled to the electrode.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Subcutaneous electrode for transthoracic conduction with low-profile installation appendage and method of doing same
One embodiment of the present invention provides a lead electrode assembly for subcutaneous implantation including an electrode; a riser coupled to the electrode; and a head coupled to the riser.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Implantable pulse generator systems and methods for providing functional and/or therapeutic stimulation of muscles and/or nerves and/or central nervous system tissue
InactiveUS20070060955A1Spinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsMicrocontrollerElectrical battery
Improved assemblies, systems, and methods provide a stimulation system for prosthetic or therapeutic stimulation of muscles, nerves, or central nervous system tissue, or any combination. The stimulation system may include both external and internal components, with an implantable pulse generator sized and configured to be implanted subcutaneously in a tissue region. The implantable pulse generator includes a welded titanium case. Circuitry and hardware adapted for wireless telemetry is located within the case, and includes a primary cell or rechargeable power source, a microcontroller for control of the implantable pulse generator, and a power receiving coil for receiving an RF magnetic field to recharge the rechargeable power source, the power receiving coil having a maximum outside dimension.
Owner:MEDTRONIC URINARY SOLUTIONS
Monophasic waveform for anti-bradycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Implantable pulse generator systems and methods for providing functional and/or therapeutic stimulation of muscles and/or nerves and/or central nervous system tissue
InactiveUS20070066995A1Spinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsElectricitySubcutaneous implantation
Improved assemblies, systems, and methods provide a stimulation system for prosthetic or therapeutic stimulation of muscles, nerves, or central nervous system tissue, or any combination. The stimulation system may include both external and internal components, with an implantable pulse generator sized and configured to be implanted subcutaneously in a tissue region. A lead having a proximal end and a distal end is coupled to the implantable pulse generator and is adapted for implantation in subcutaneous tissue. The distal end of the lead is adapted to be remote from the pulse generator and capable of extending up to an anatomical furthest distance from the pulse generator. The circuitry carried within the case is operable for generating electrical stimulation pulses and capable of electrically driving the generated electrical stimulation pulses from the pulse generator through the lead extending up to the anatomical furthest distance.
Owner:MEDTRONIC URINARY SOLUTIONS
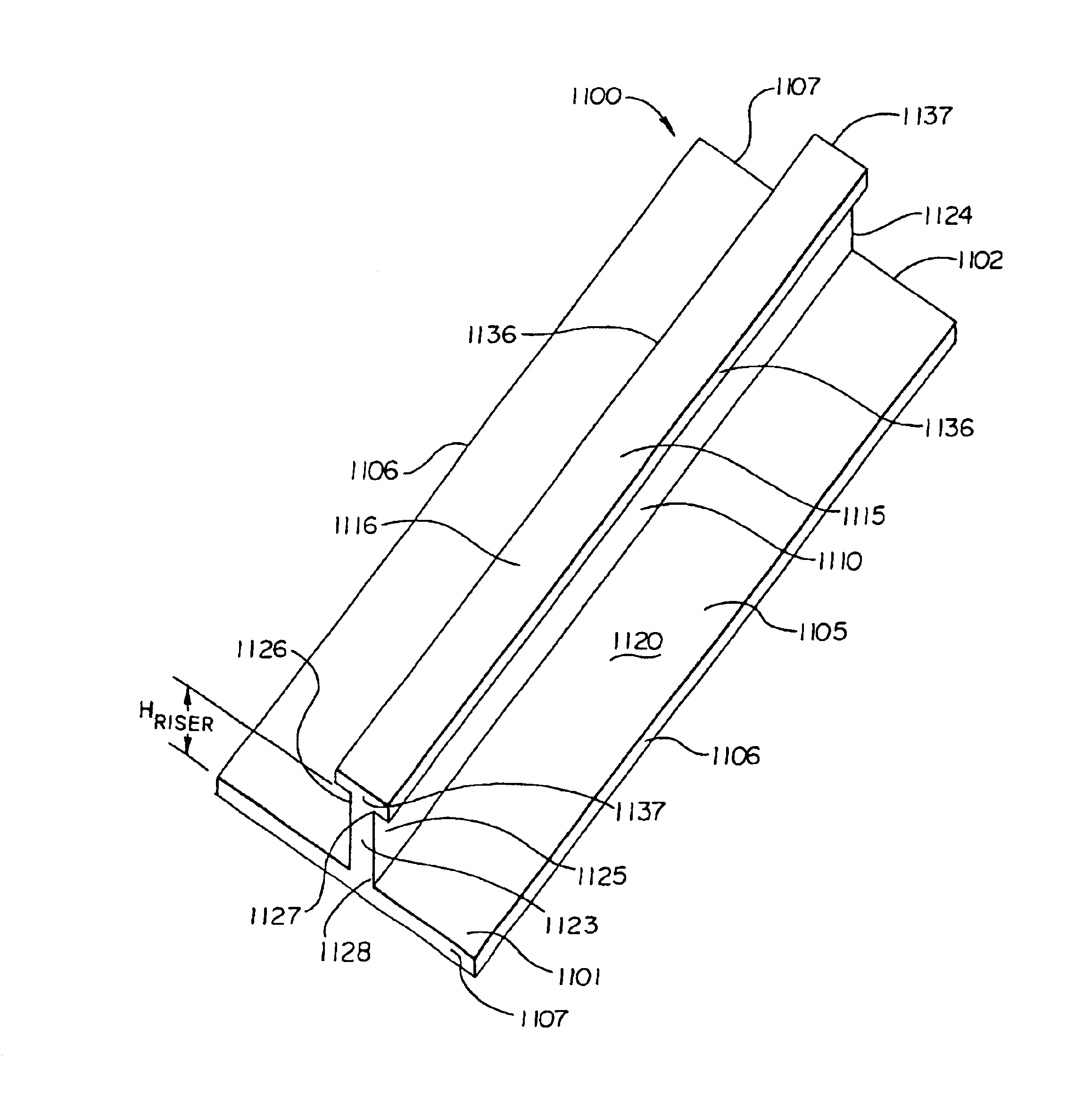
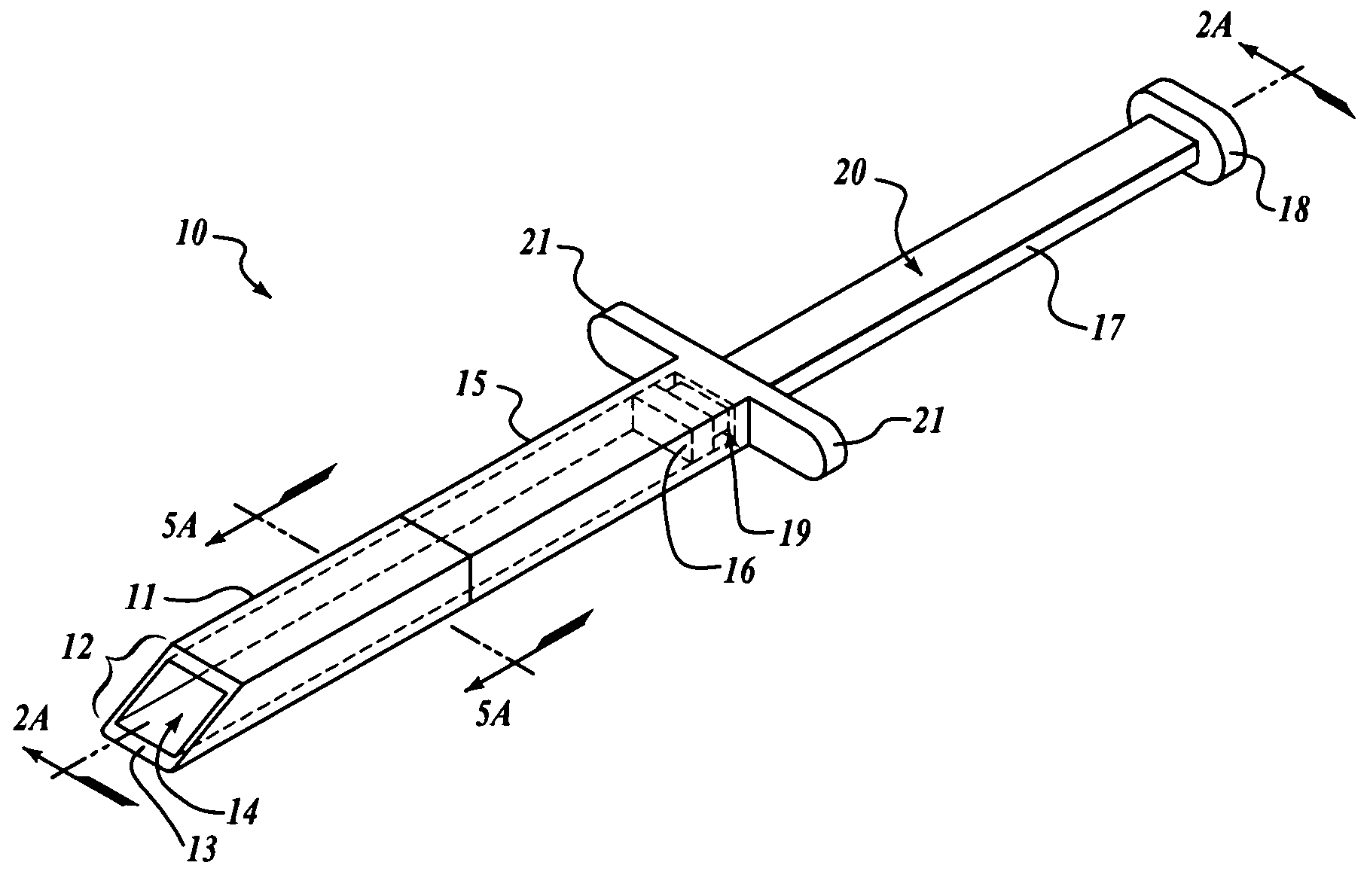
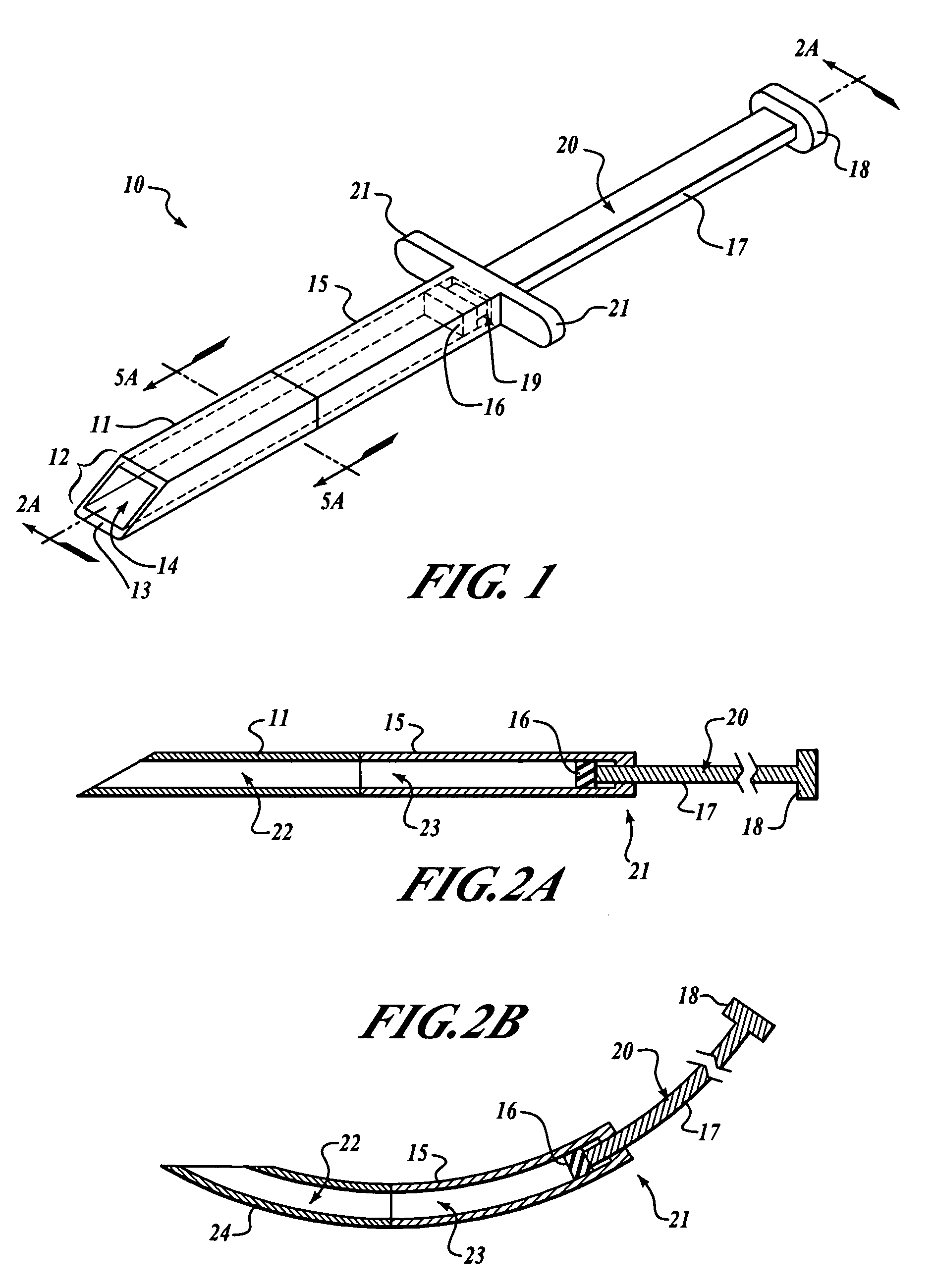
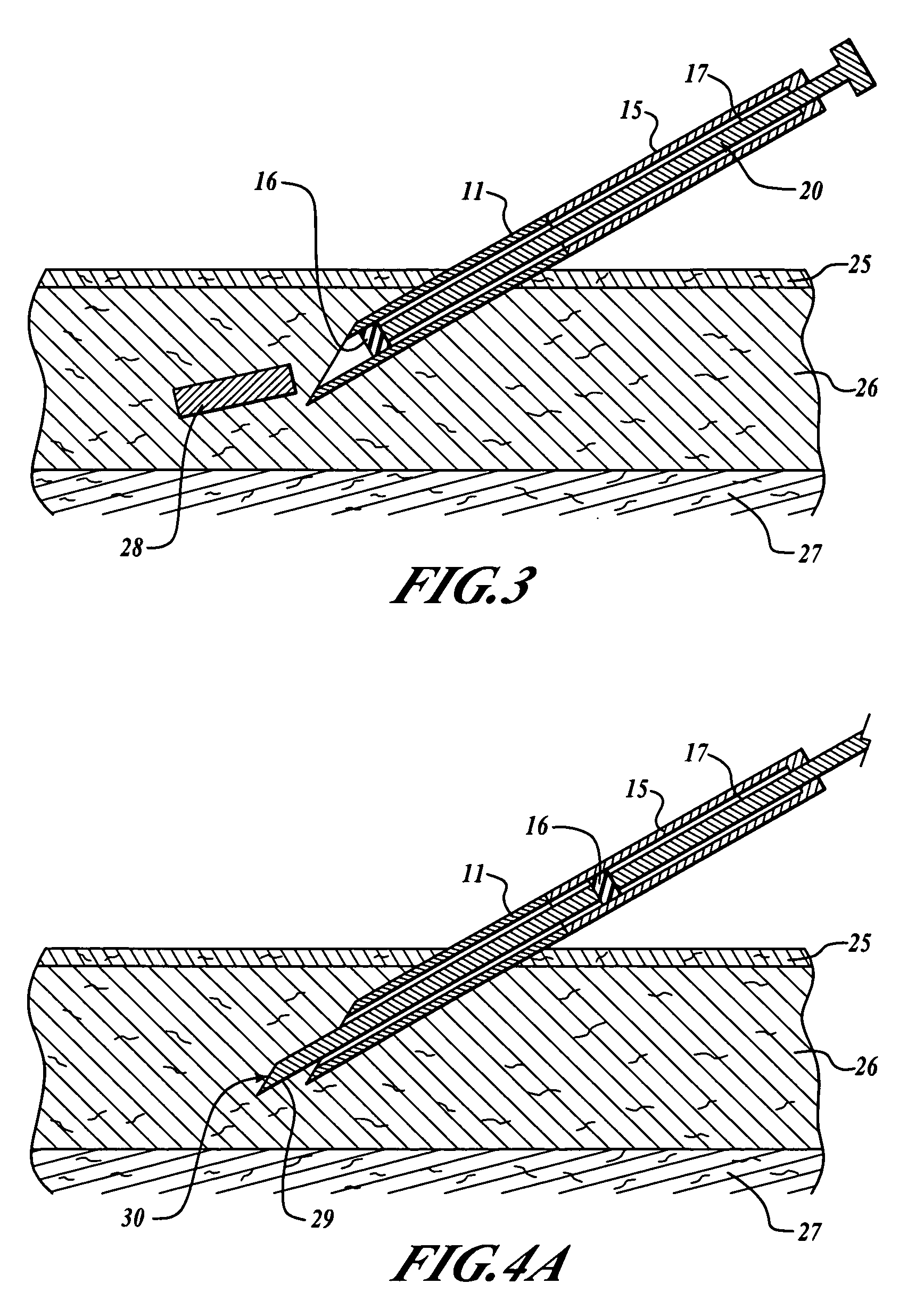
Subcutaneous implantation instrument with dissecting tool and method of construction
A subcutaneous implantation instrument with dissecting tool and method of construction are described. An incising shaft longitudinally defines a substantially non-circular bore continuously formed to communicatively receive an implantable object and further includes a beveled cutting blade formed on a distal end. A dissecting tool includes a needle tip forming a pair of longitudinal cutting edges progressively defined outwardly from the needle tip planar to the beveled cutting blade and removably affixable to the distal end of the incising shaft through a proximal coupling. A delivery mechanism longitudinally defines a substantially non-circular bore formed to deploy the implantable object into the incising shaft. One goal is to reduce the subcutaneous sensor insertion of implantable objects and devices, such as sensors, having non-conforming shapes to be the functional equivalent of an injection.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Implantable vascular access device
InactiveUS7252649B2Increase the number ofWithout deteriorationMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismVascular Access DevicesSubcutaneous implantation
An implantable vascular access device includes a housing having an inlet, an outlet, an interior chamber defined therein and a valve positioned between the inlet and the interior chamber. The valve is subcutaneously manipulated between an open position, in which fluid can flow between the inlet and the interior chamber, and a closed position in which the valve occludes the inlet. The device may include any combination of multiple inlets, outlets and / or interior chambers. In the preferred embodiment, the housing includes two separate interior chambers suitable for the inflow and outflow of a typical hemodialysis procedure. A method for accessing a vascular structure is provided which includes the steps of subcutaneously implanting the device connecting one end of a cannula to the outlet of the device and another end of the cannula to a selected vascular structure. The valve of the device is manipulated to permit fluid communication between the inlet of the device and the selected vascular structure. A needle is introduced through the inlet opening to access the selected vascular structure.
Owner:NAVILYST MEDICAL
Devices and methods for treatment of venous valve insufficiency
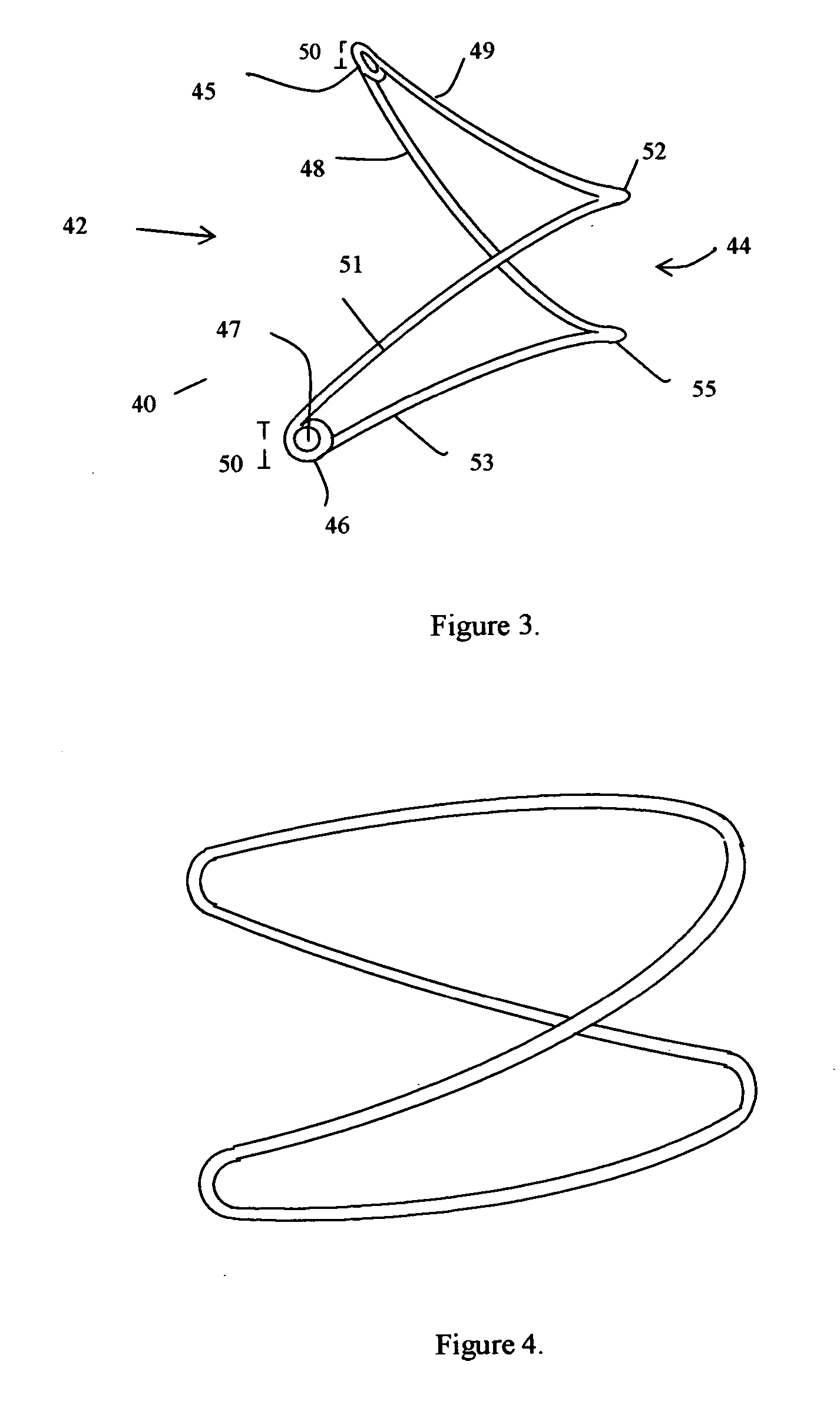
InactiveUS20070112423A1Function increaseIncrease distanceAnnuloplasty ringsVenous valvesVenous ValvesSubcutaneous implantation
Devices and methods for improvement of functioning of a valve of a subject are disclosed. A device exhibiting an outward bias at its proximal end and an outward bias at its distal end, disposed at an angle to the bias at the proximal end is described. A device having a first arm and a second arm separated by a peak and having shoulders is also described. Alternative embodiments which function to decrease the distance between valve leaflets, having a first arm and a second arm biased toward one another are also disclosed. Several embodiments which may have mirror image ends are also disclosed. Any of the devices may have barbs, umbrella structures, sutures, or a variety of spring elements. Devices may be implanted surgically, percutaneously or subcutaneously. Methods and devices for delivery and deployment of devices are disclosed as well as methods for treatment of a valve of a subject.
Owner:CHU JACK F
Anti-bradycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathoracic blood vessels and far providing anti-bradycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-bradycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-bradycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Bone supported vascular access port
InactiveUS20070179456A1Easy to disassembleSecurely holdSurgical needlesMedical devicesVisibilitySubcutaneous implantation
A vascular access port is disclosed for subcutaneous implantation. The port is particularly adapted to be affixed to a bone to securely hold the port in position, to assist medical personnel in finding the port and to decrease a visibility of the port. The port has a chamber therein which is accessed by a needle through a septum adjacent the chamber. The chamber is placed into fluid communication with the vascular structure of the patient, such as through catheter tubing. The chamber is surrounded by a body with an outer surface which is preferably fitted with threads to facilitate secure but removable attachment of the port within a hole in the bone where the port is to be implanted.
Owner:GLENN BRADLEY J
Method for implanting flexible injection port
InactiveUS20050131383A1Shorten the construction periodLess dissectionSurgeryMedical devicesInjection portSubcutaneous implantation
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a method for subcutaneously implanting an injection port for use with an implantable medical device. The method involves providing an injection port comprising an elongated flexible substantially non-rigid body having first and second ends and a wall therebetween, the wall is such that it will self seal after being punctured, the body further including and a fluid reservoir surrounded by the wall and a flexible elongated tubular catheter attached to the body which is in fluid communication with the reservoir. Thereafter, the method involves creating an incision within the patient, accessing the subcutaneous fat layer of the patient through the incision, creating a space in the subcutaneous fat layer and implanting the injection port within the subcutaneous fat layer such that the port can be found externally by palpitation.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com