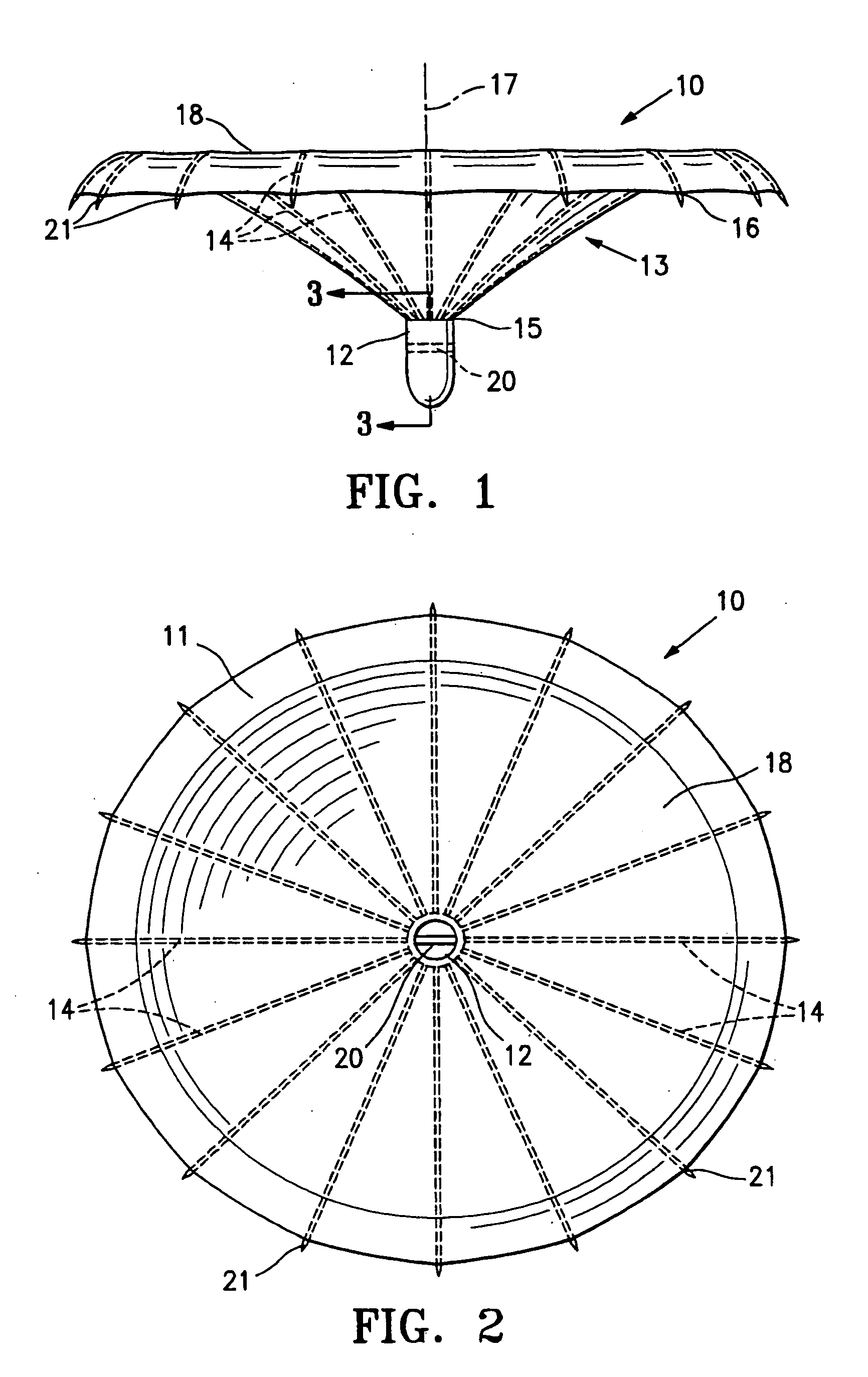
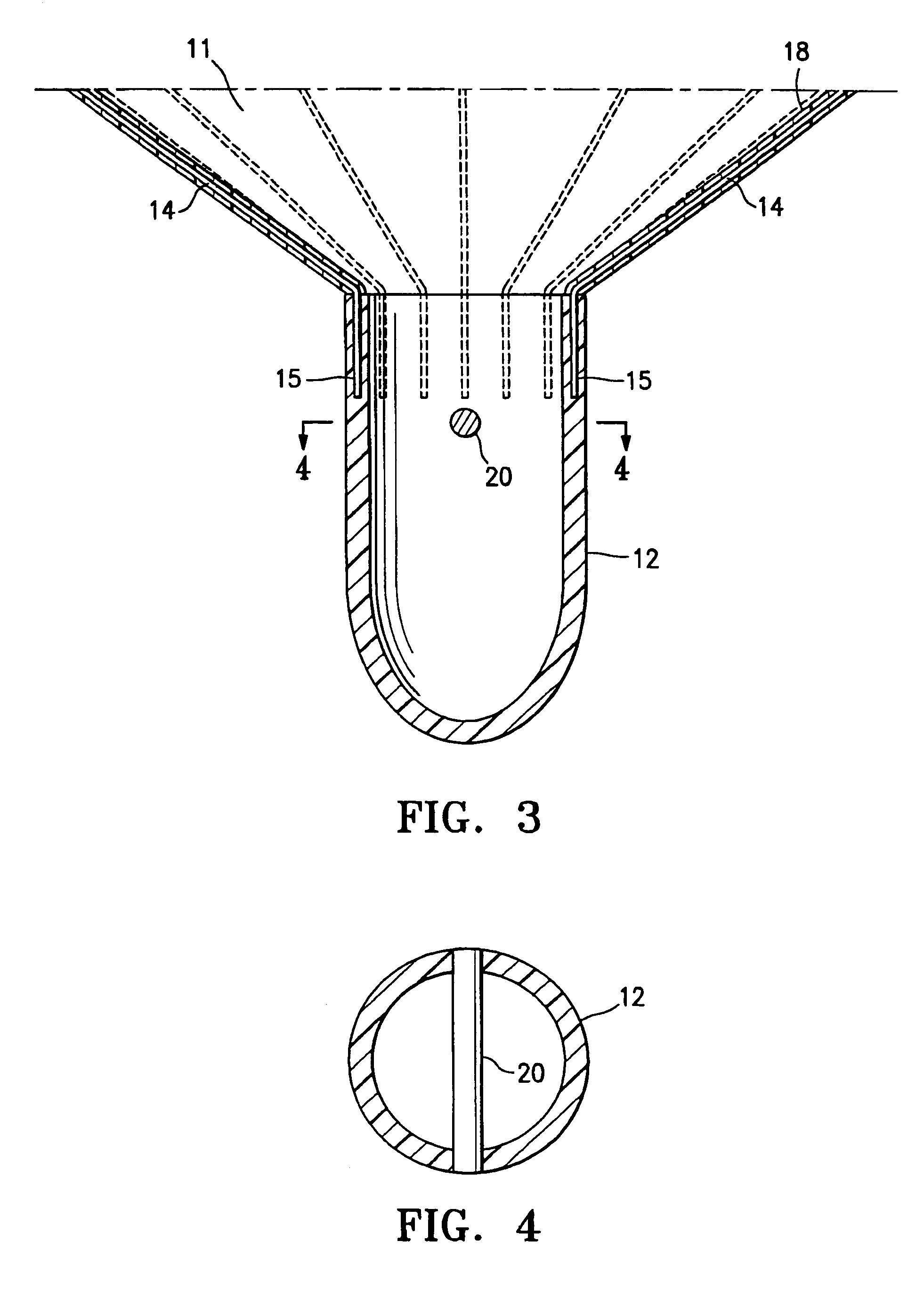
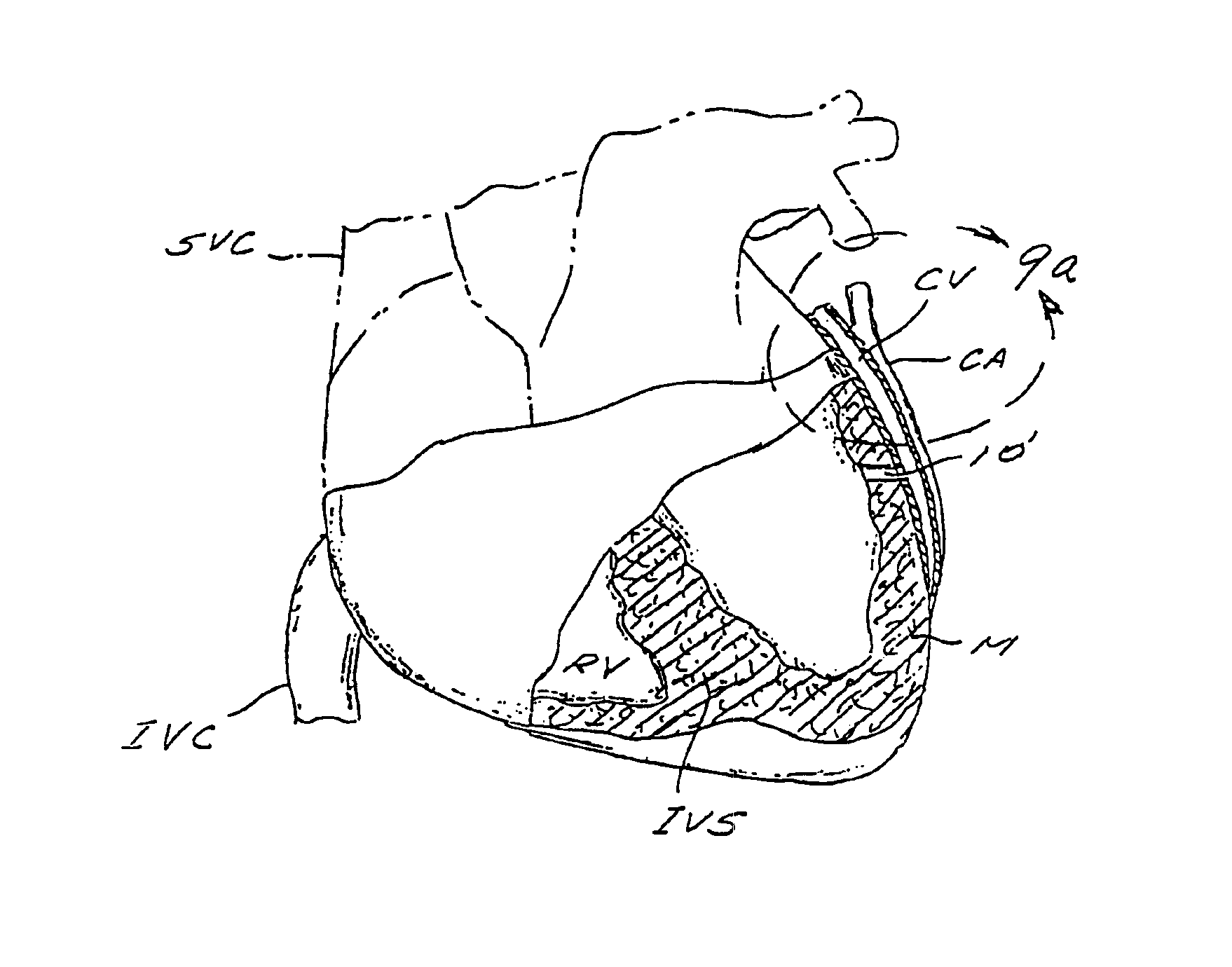
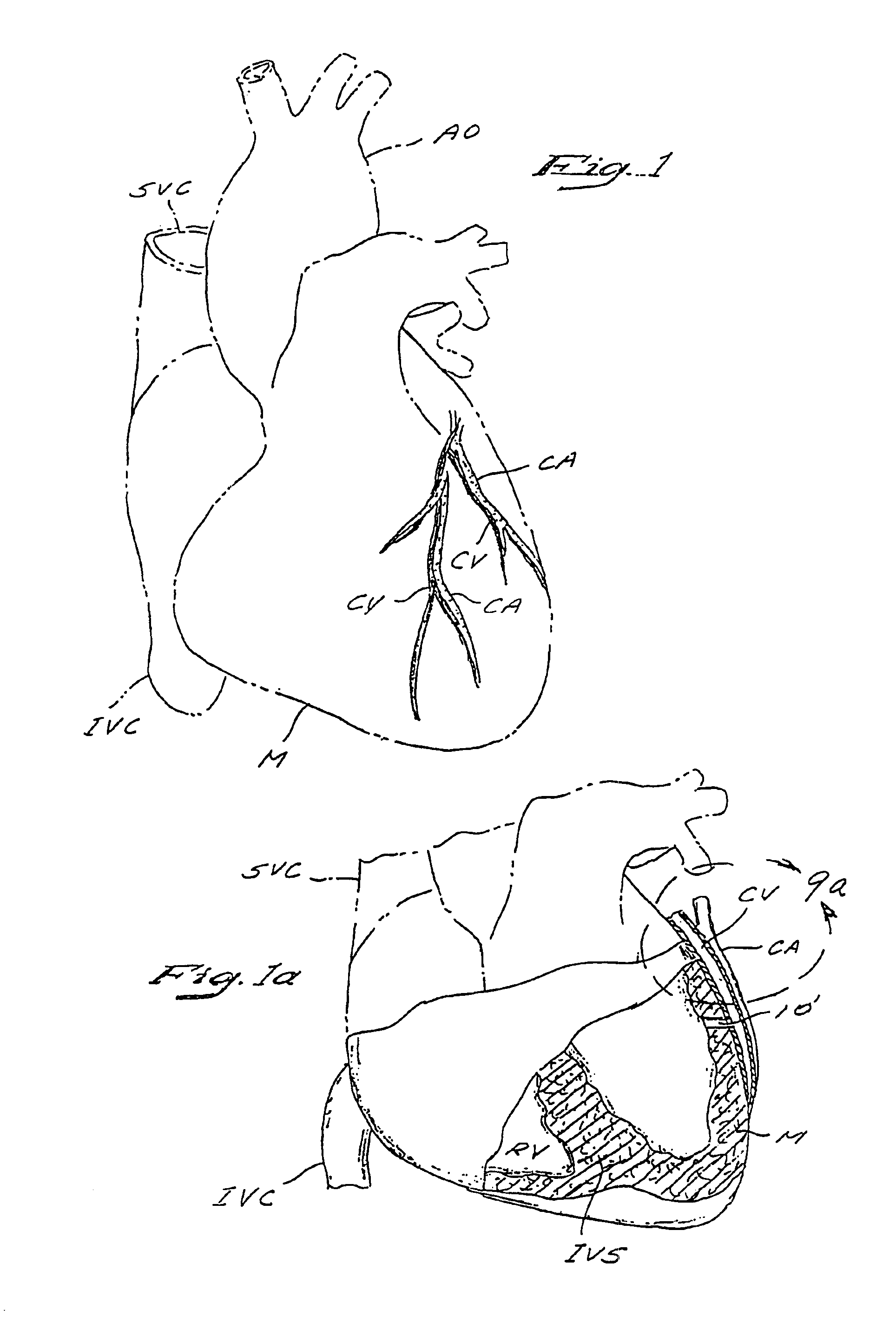
Patents
Literature
231 results about "Heart.chambers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
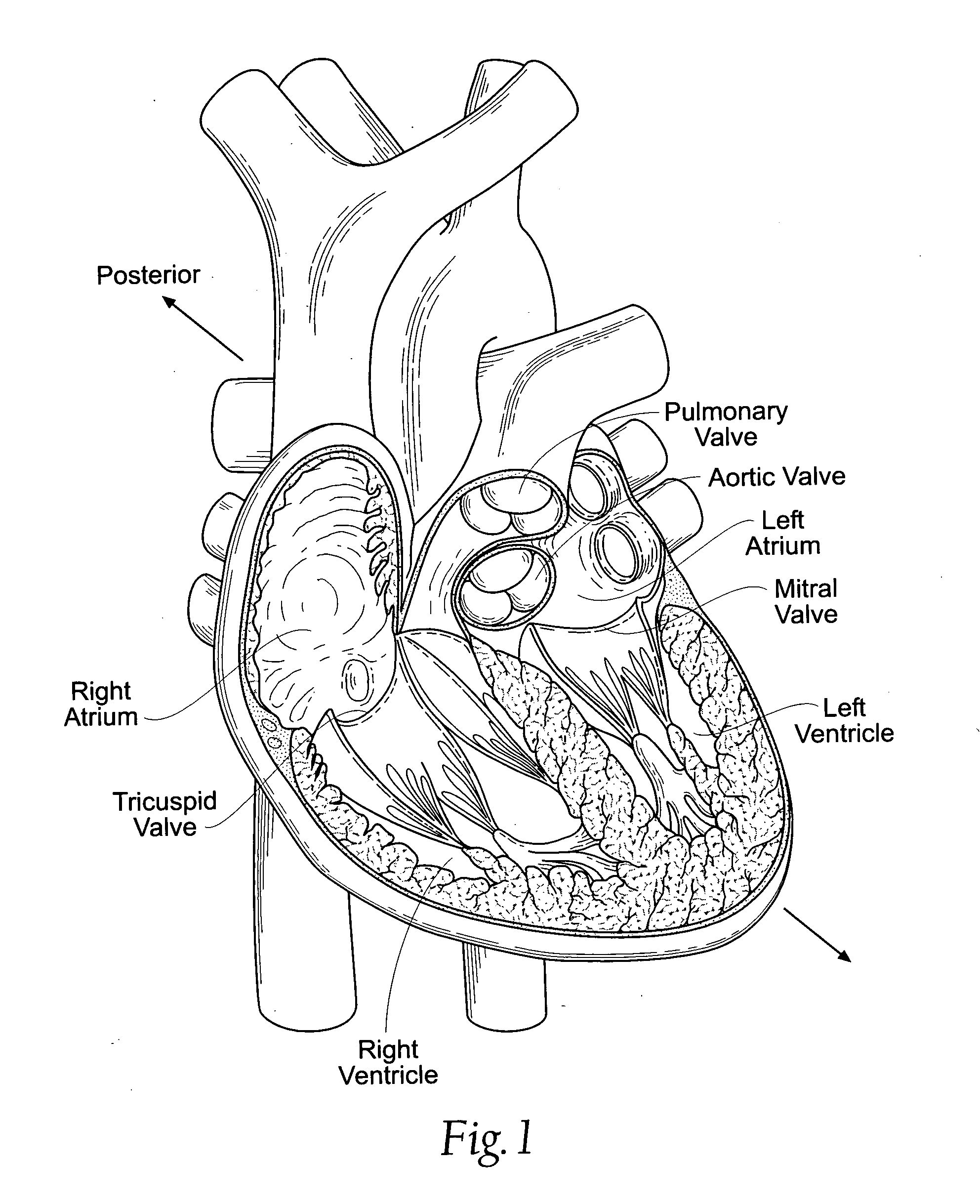
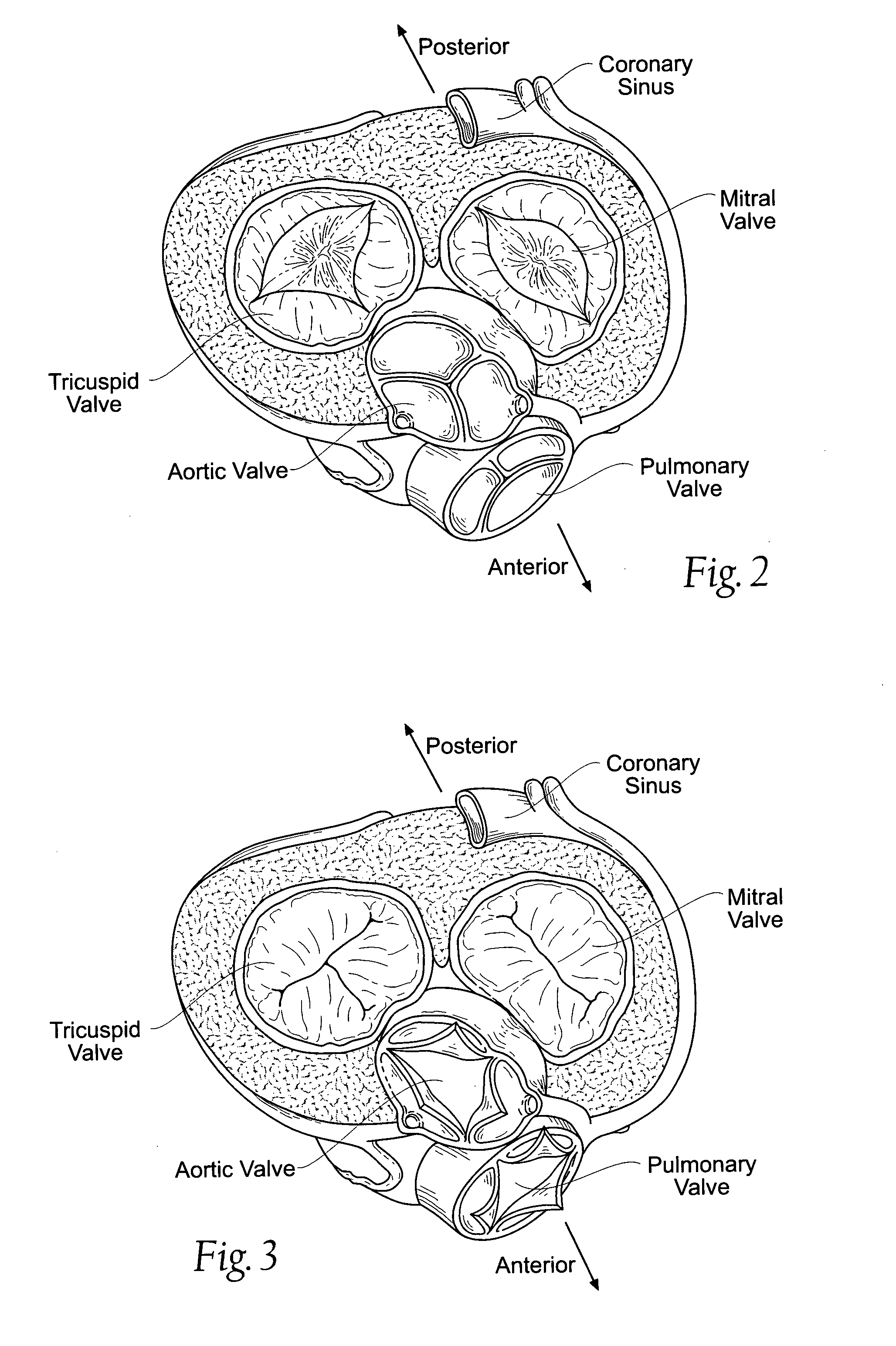
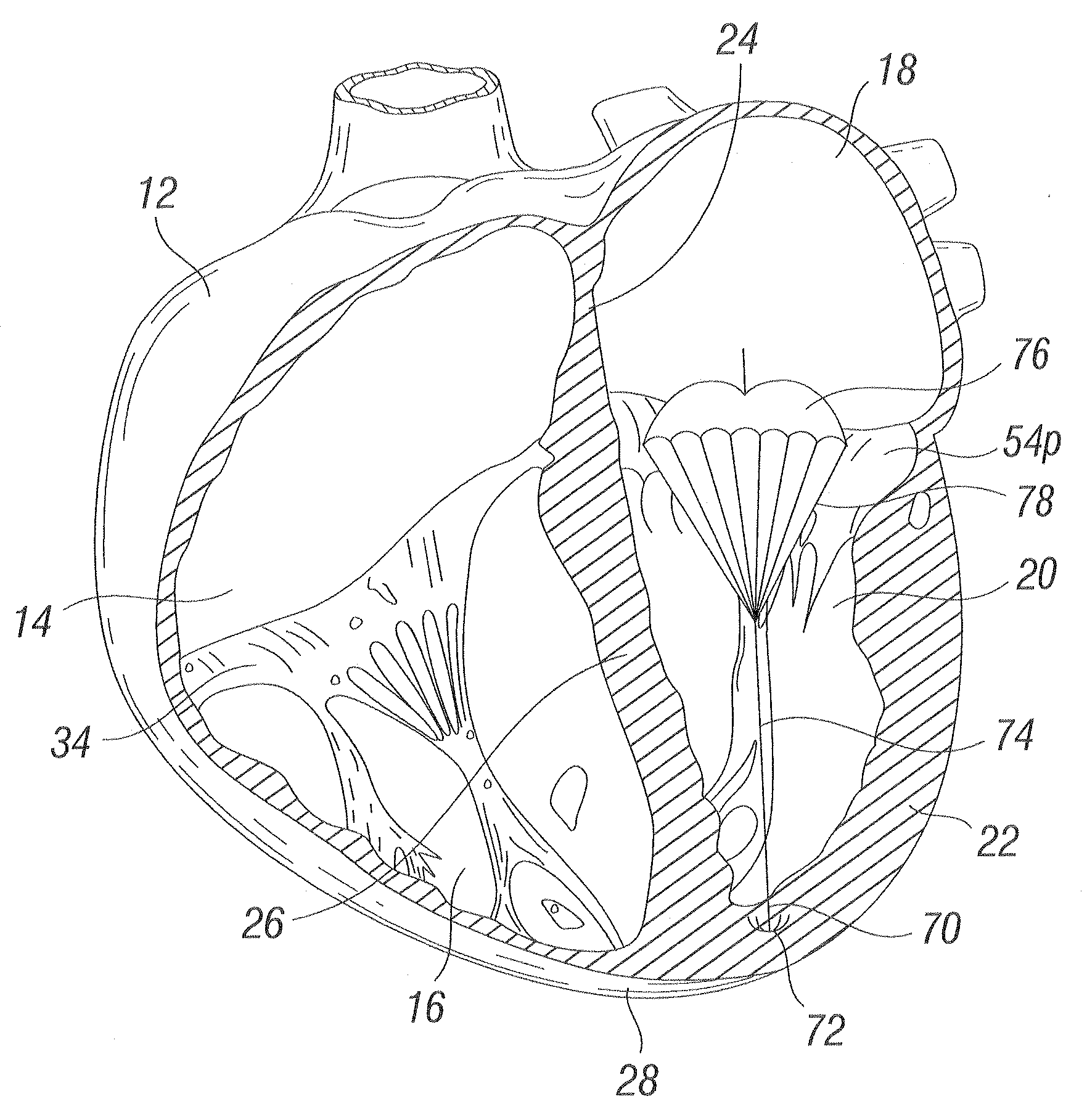
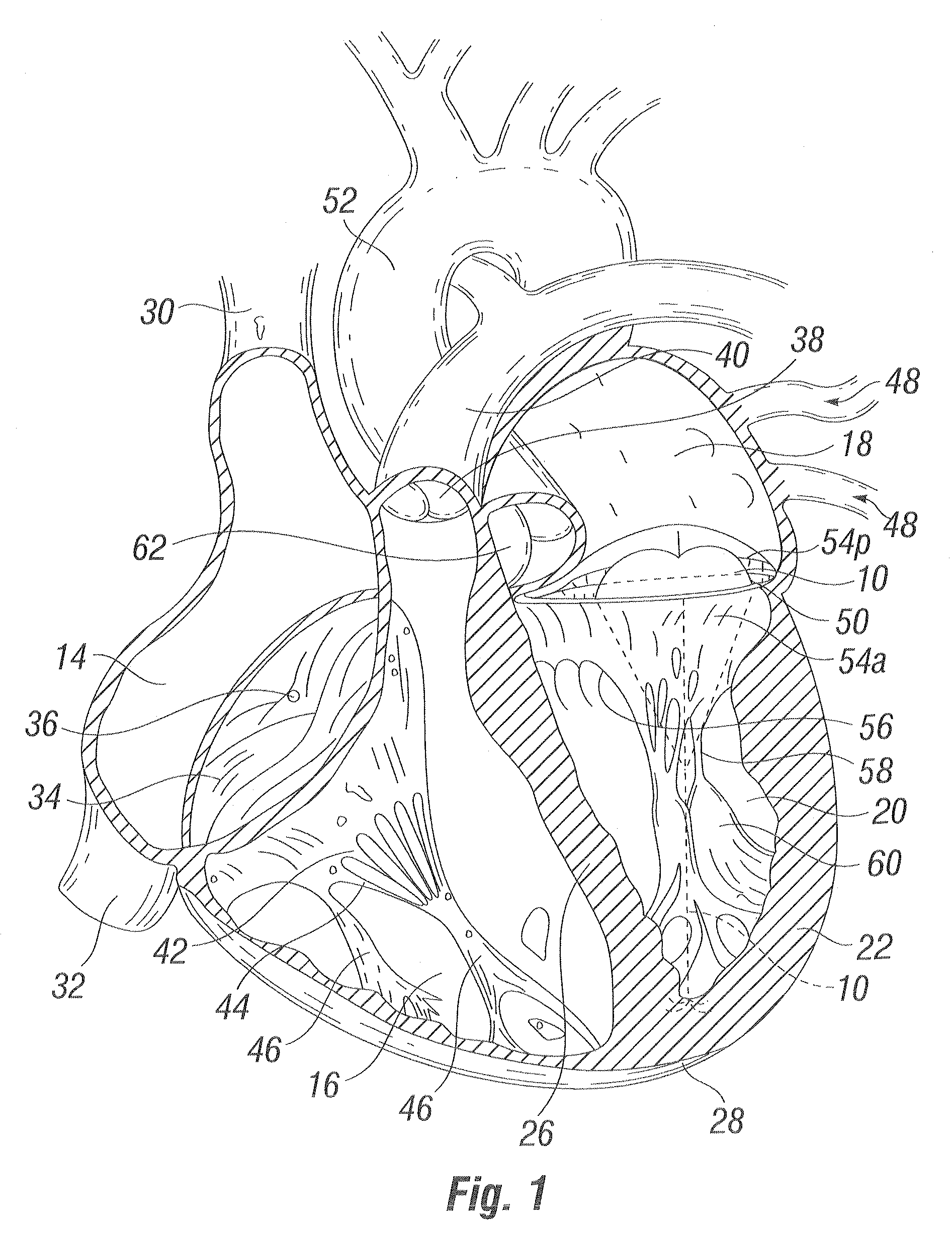
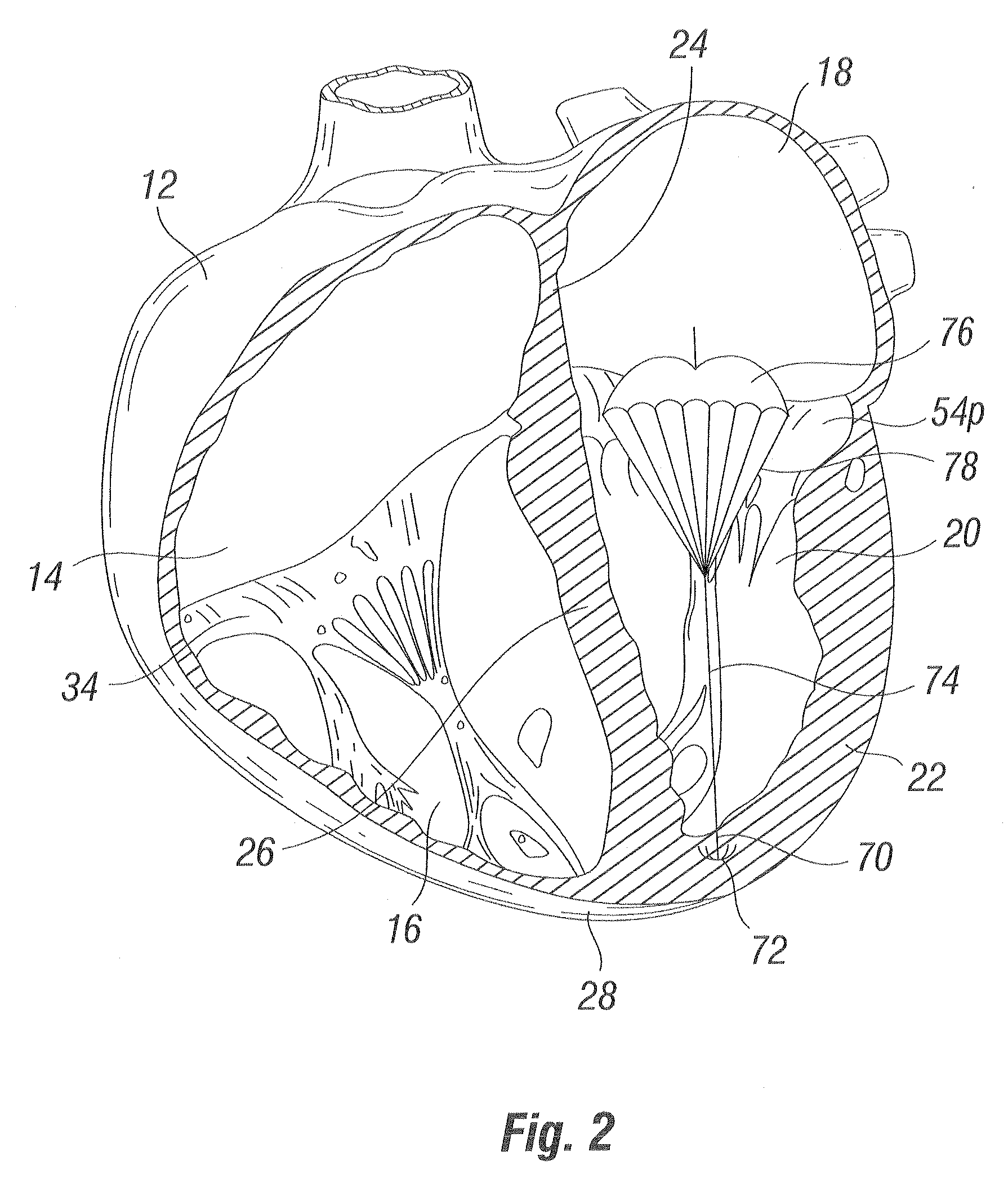
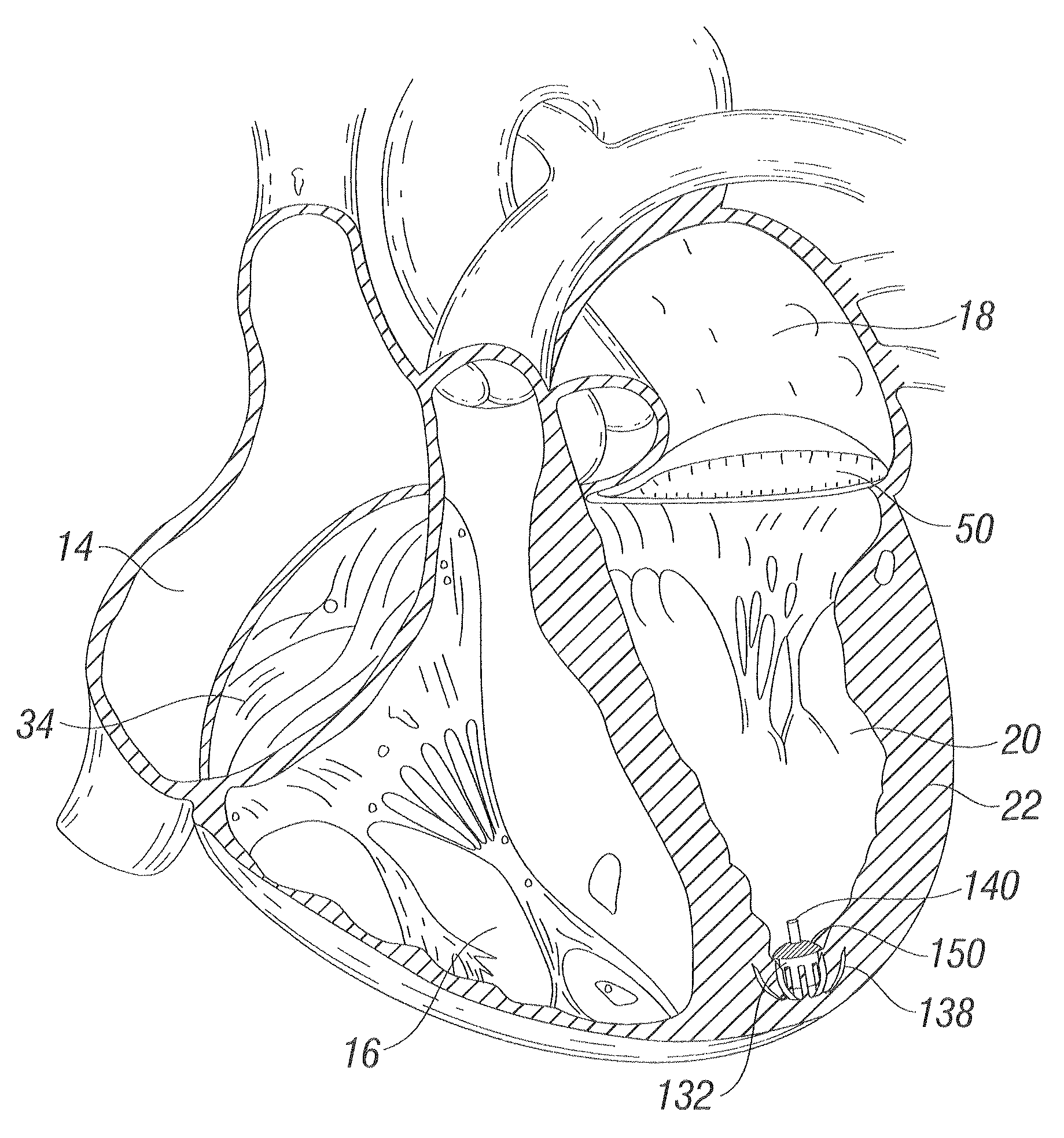
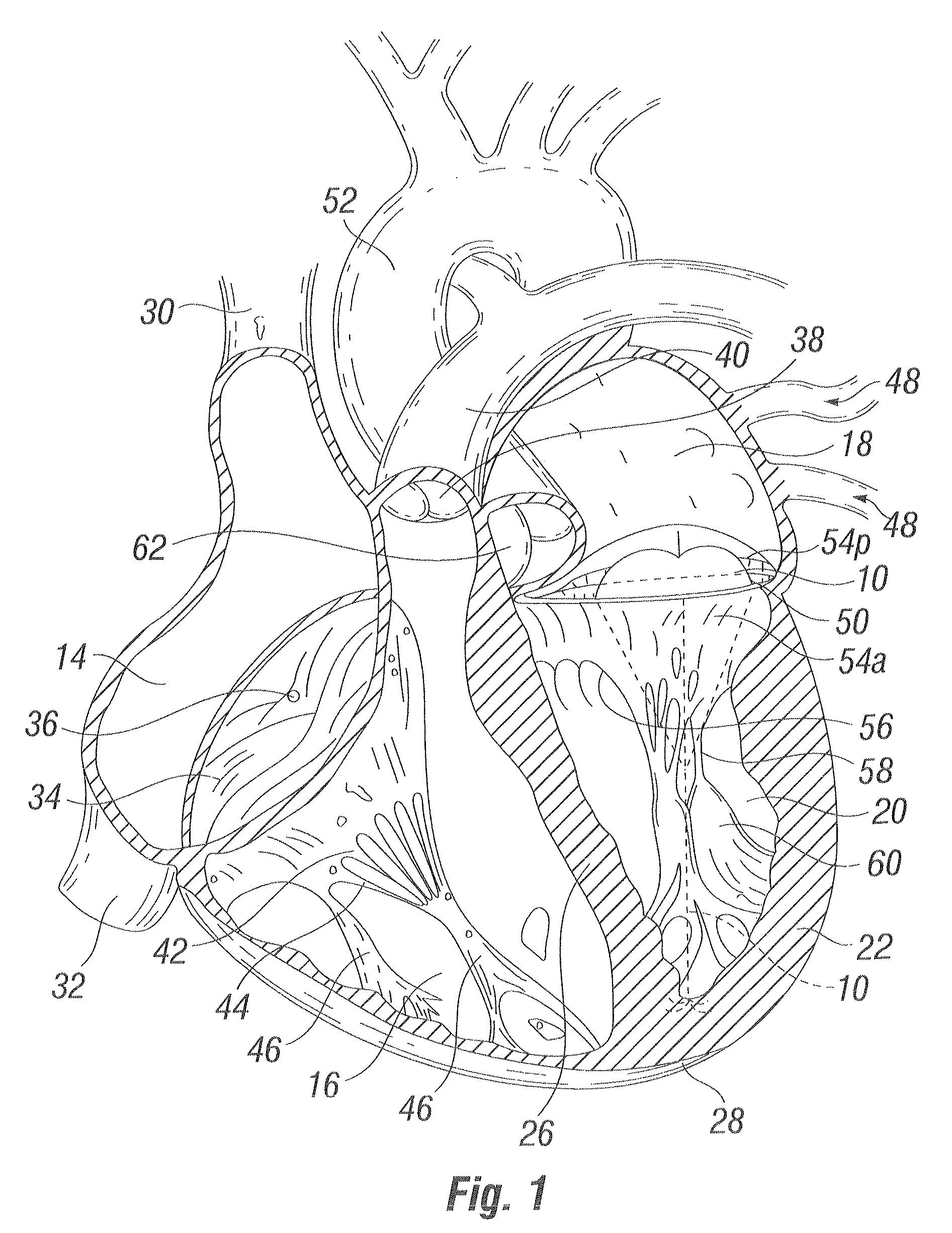
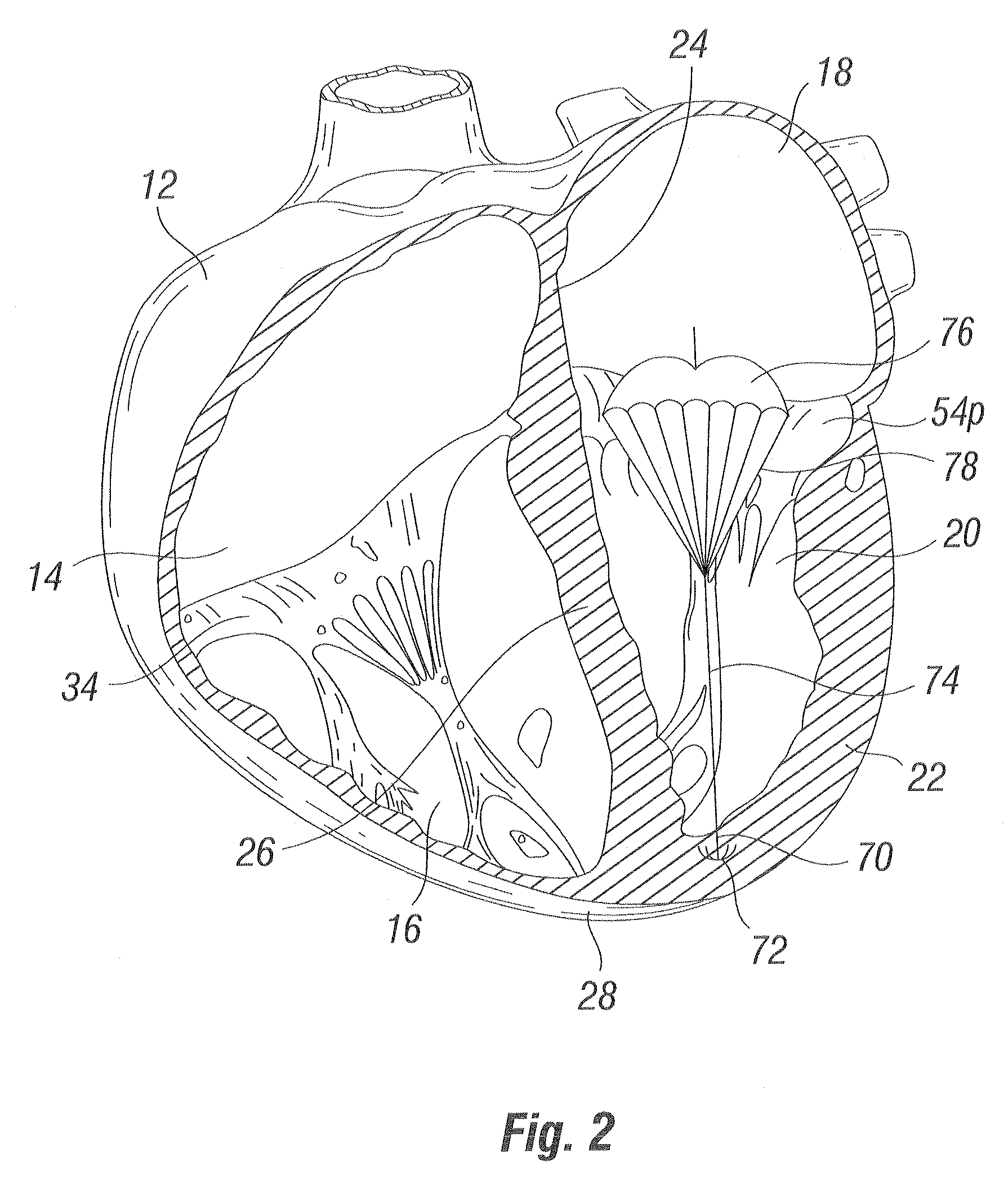
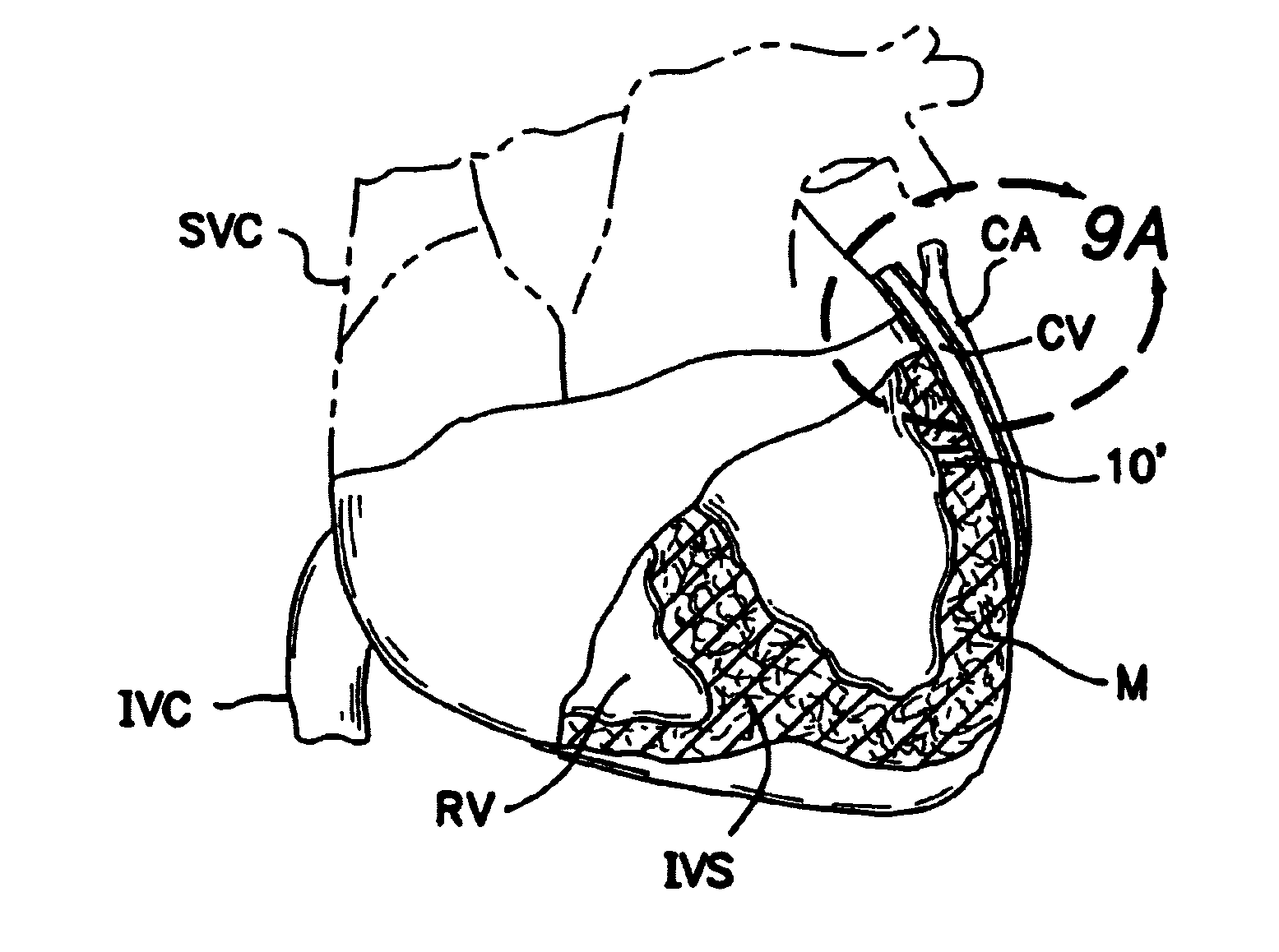
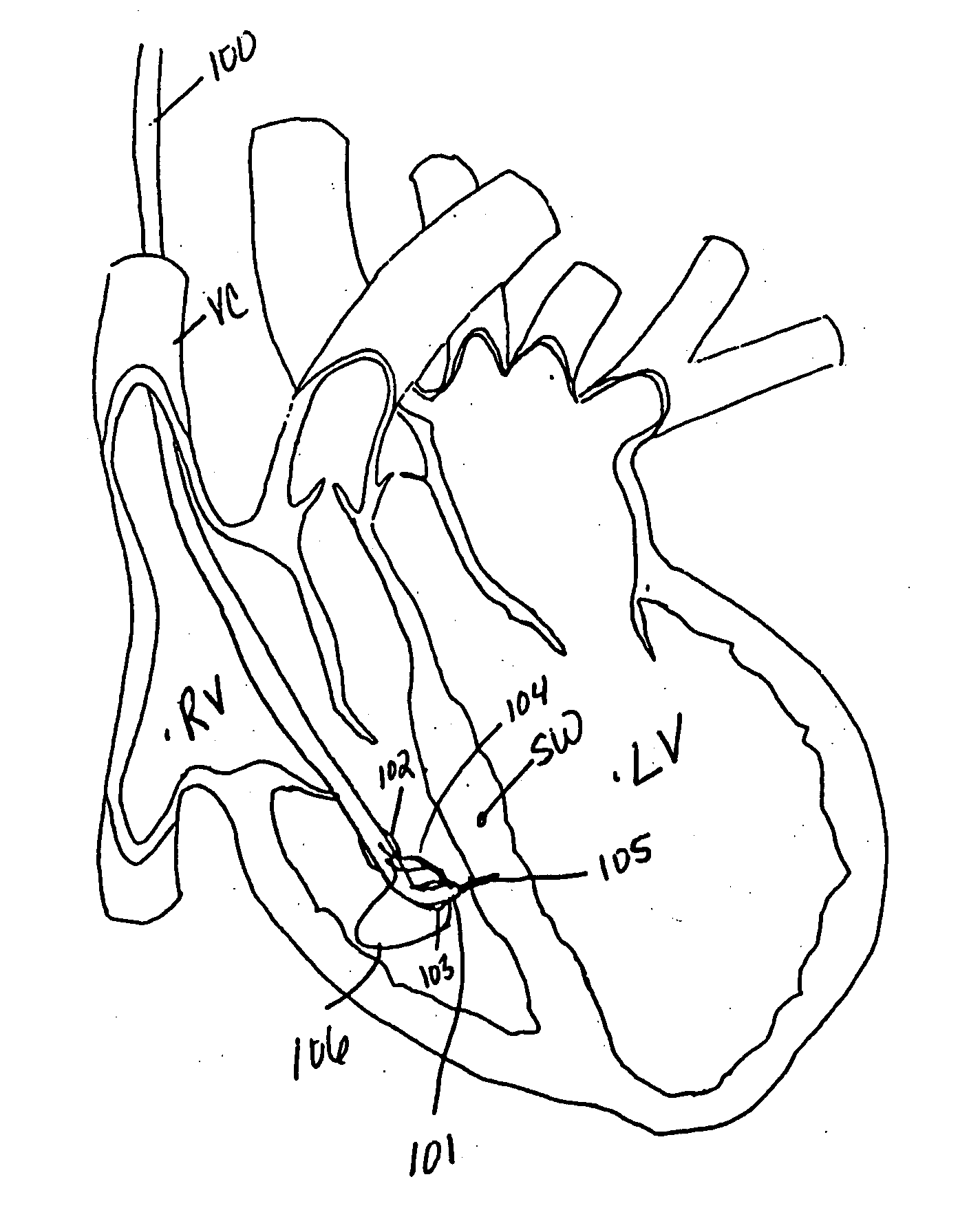
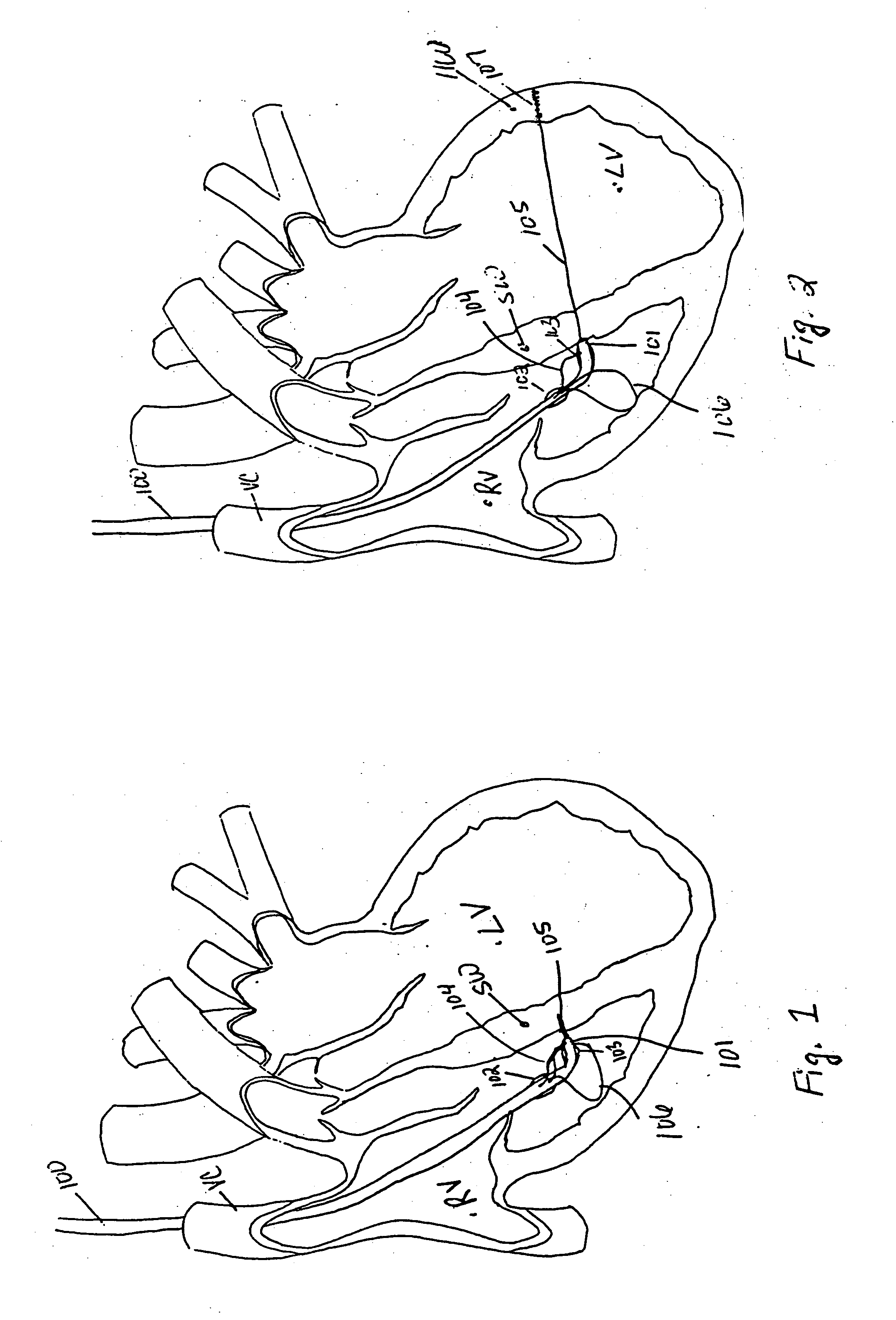
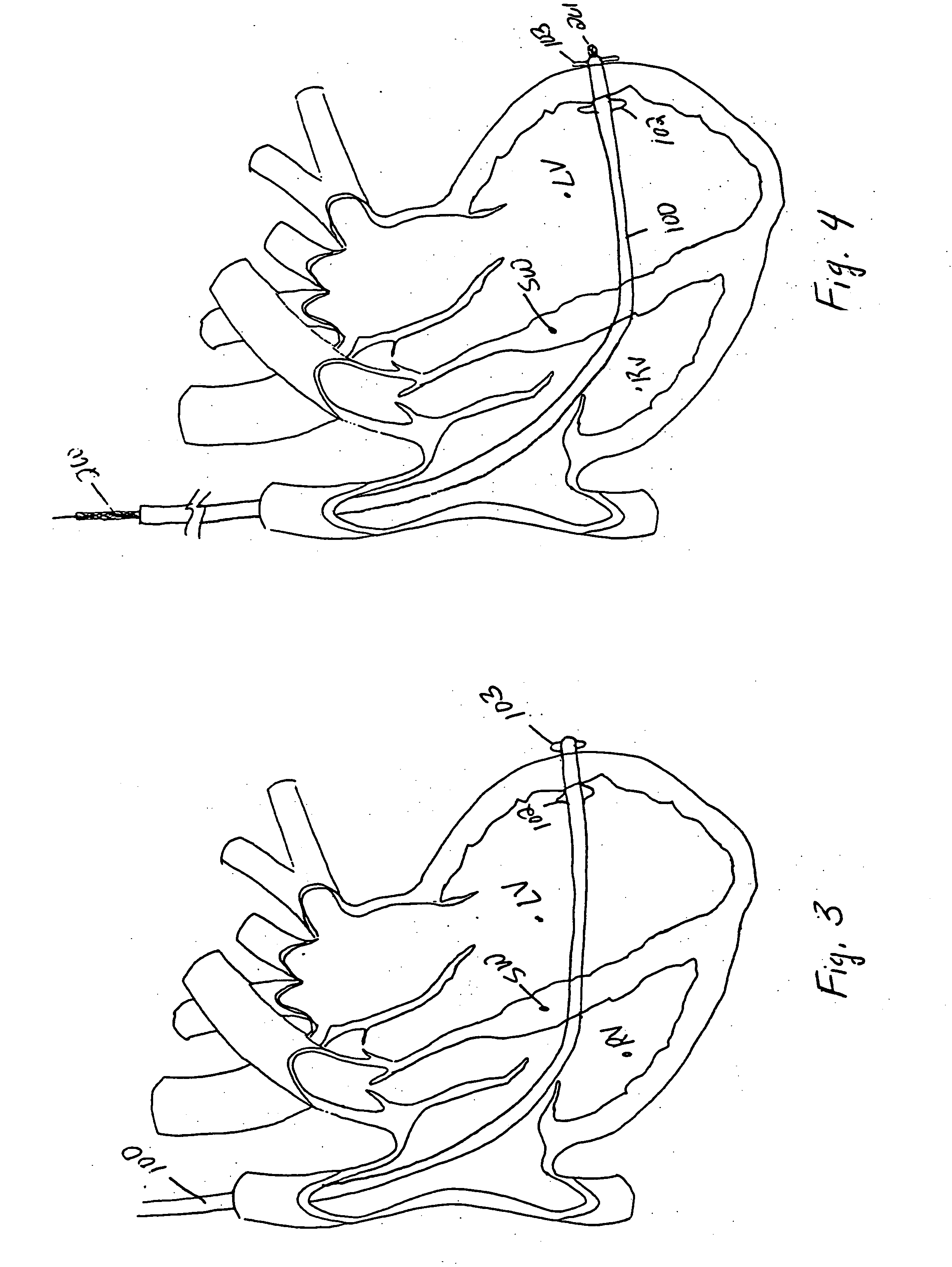
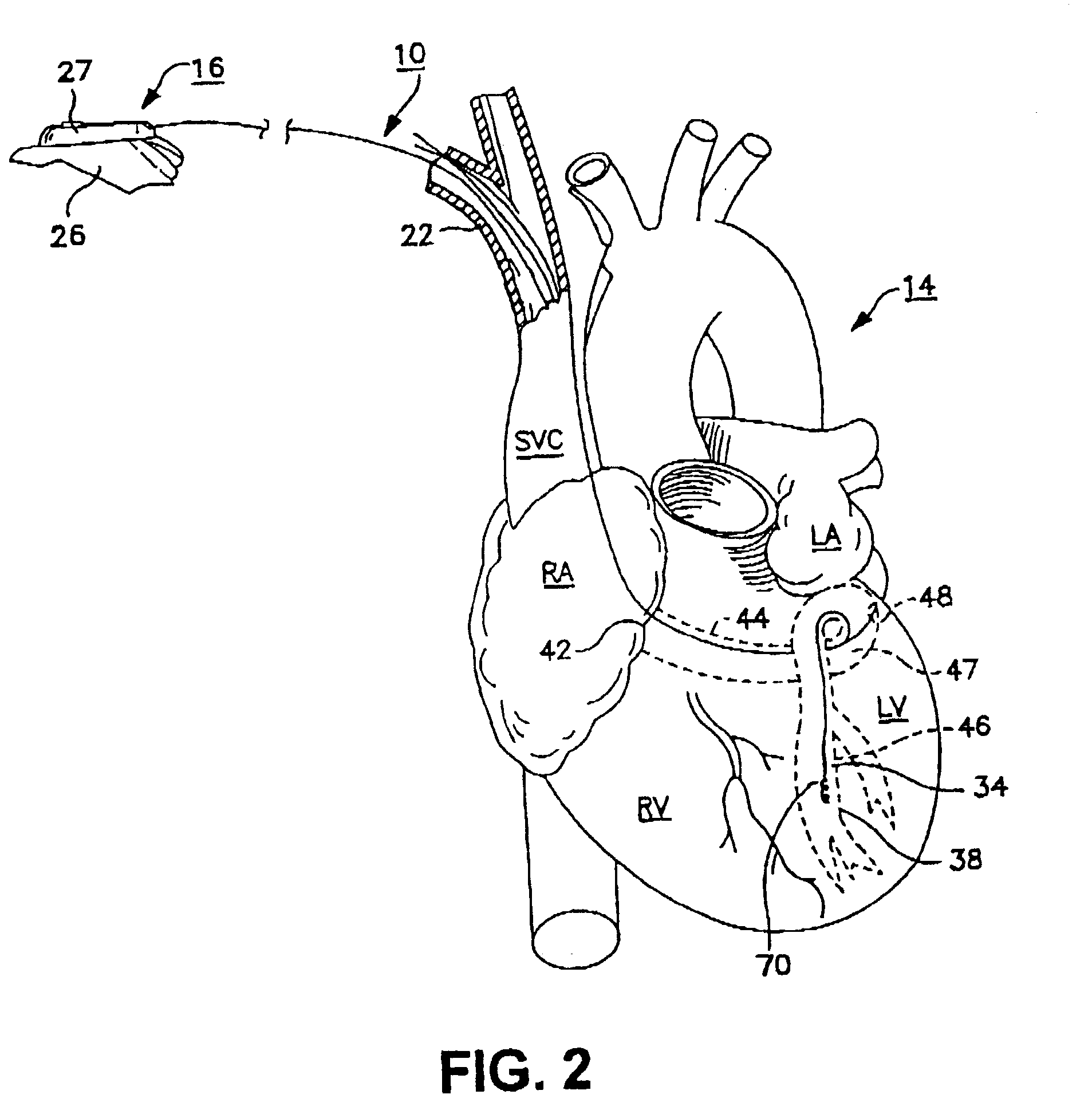
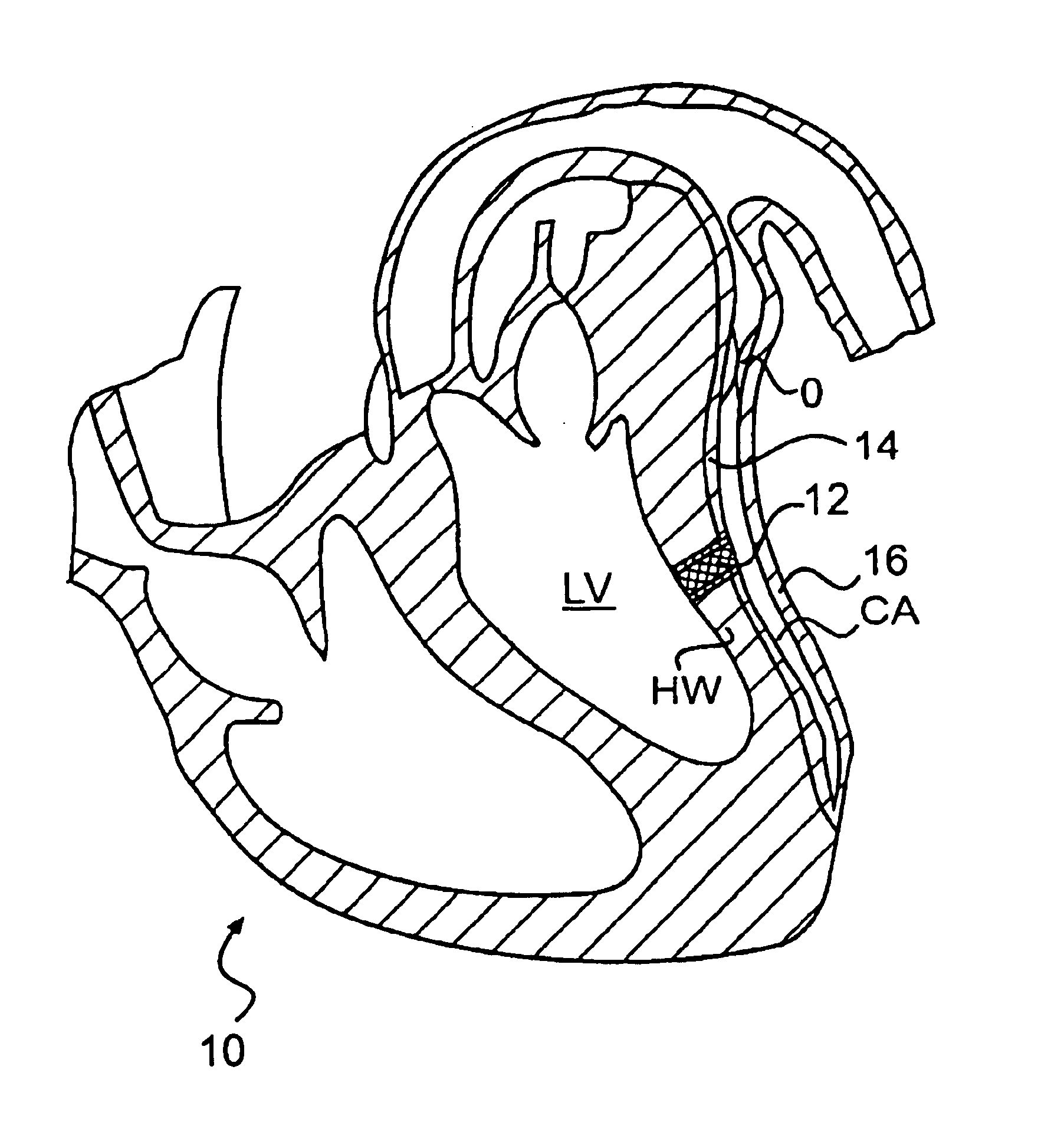
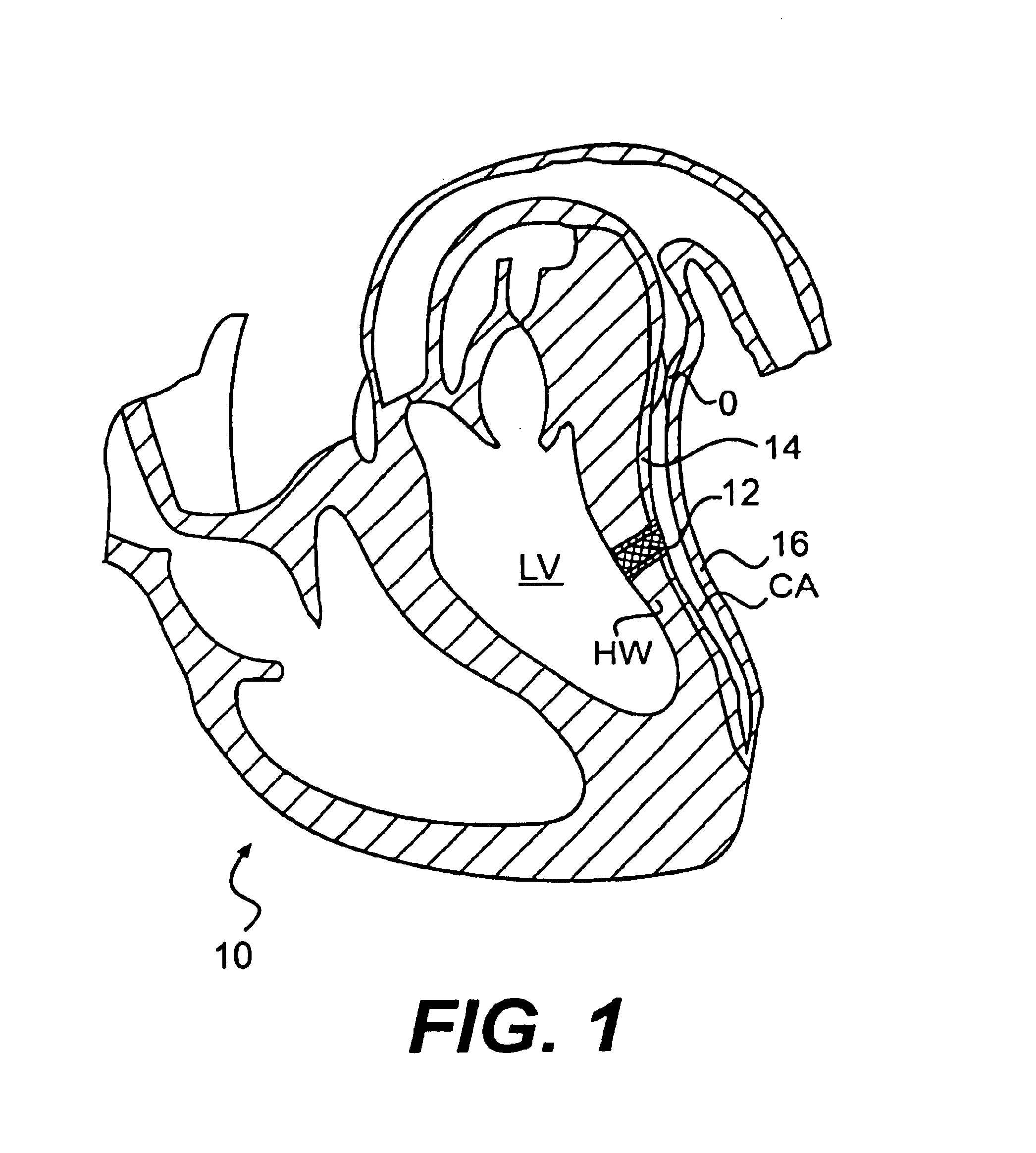
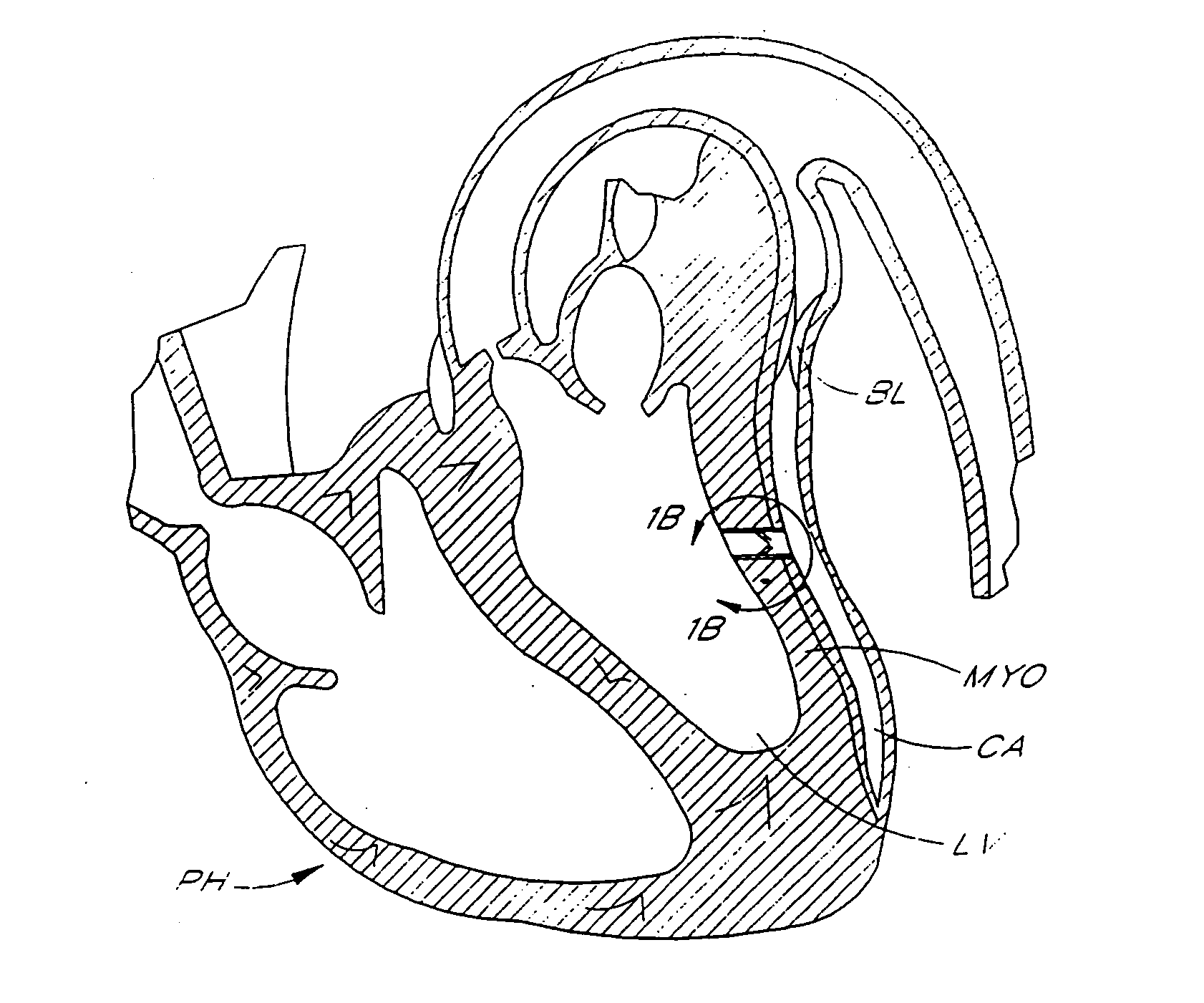
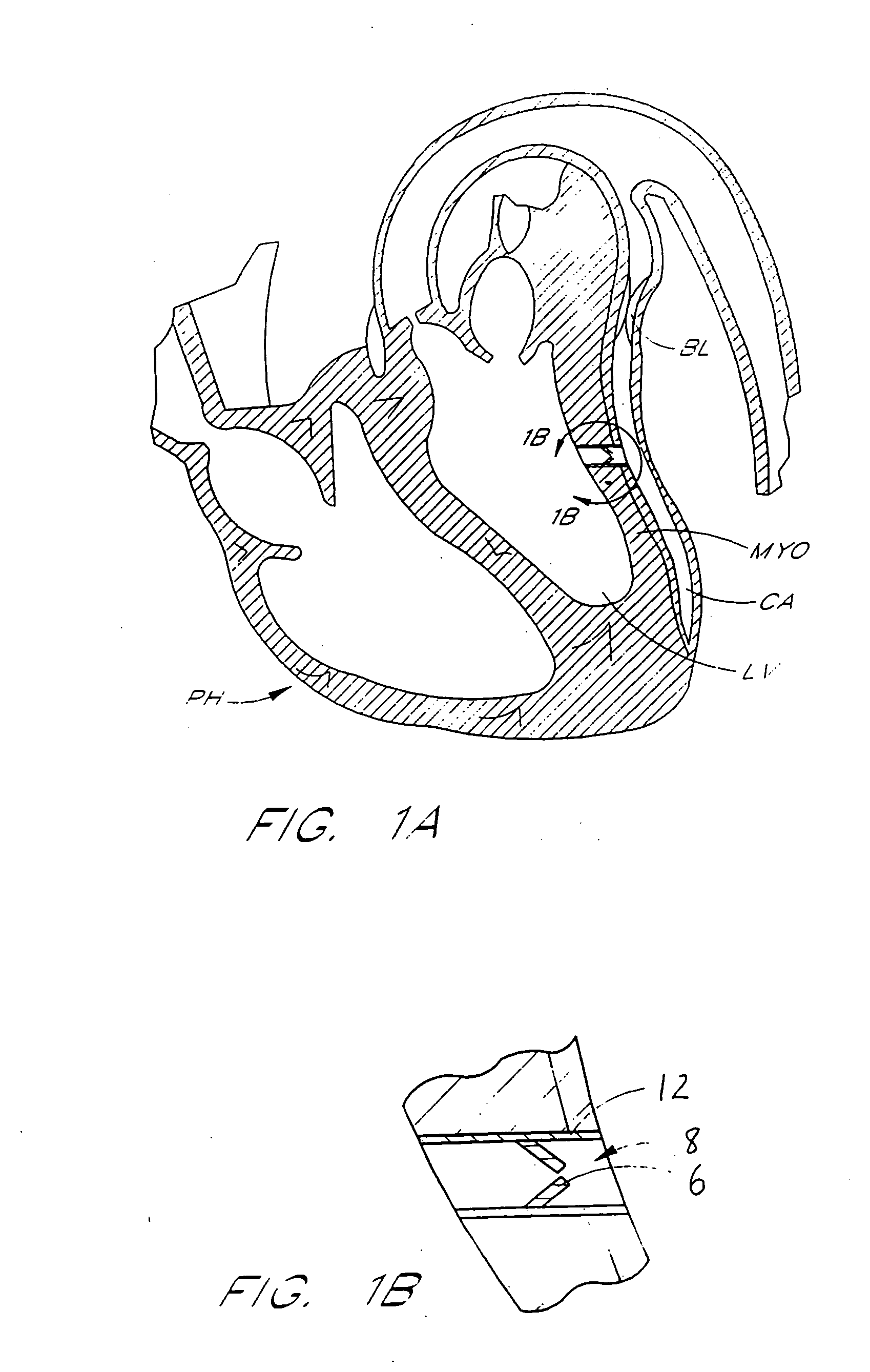
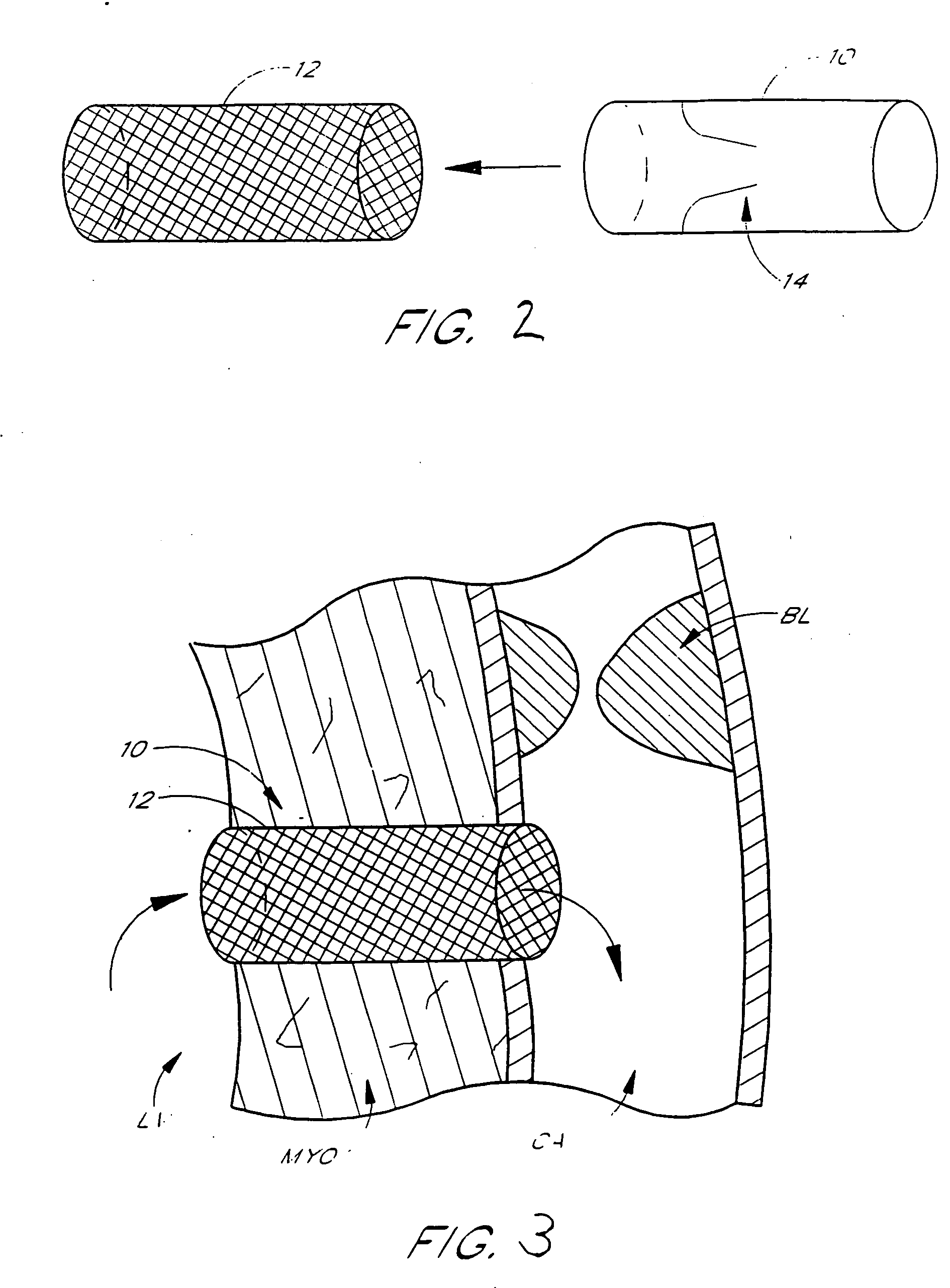
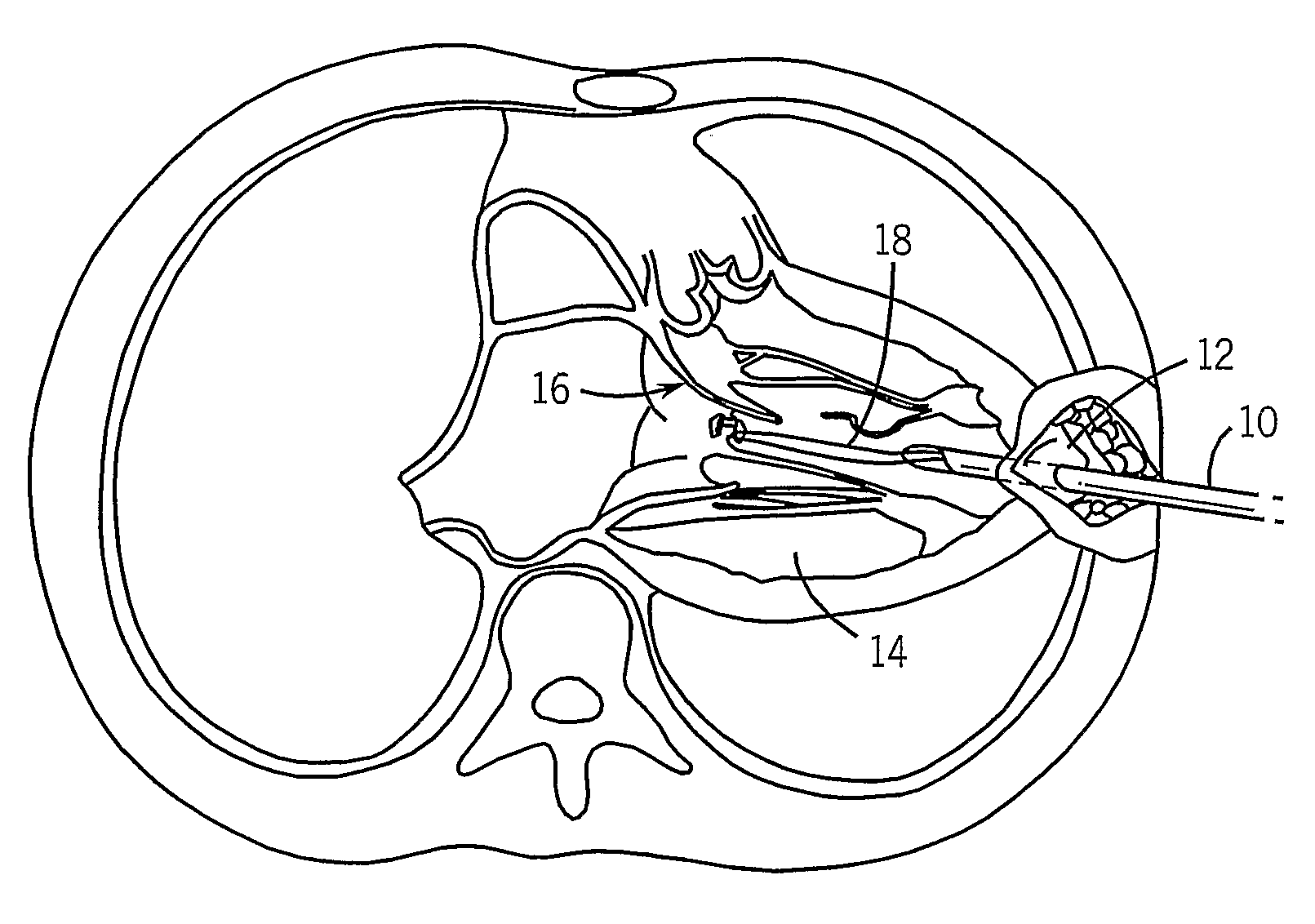
The heart consists of four chambers in which blood flows. Blood enters the right atrium and passes through the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs where it becomes oxygenated.
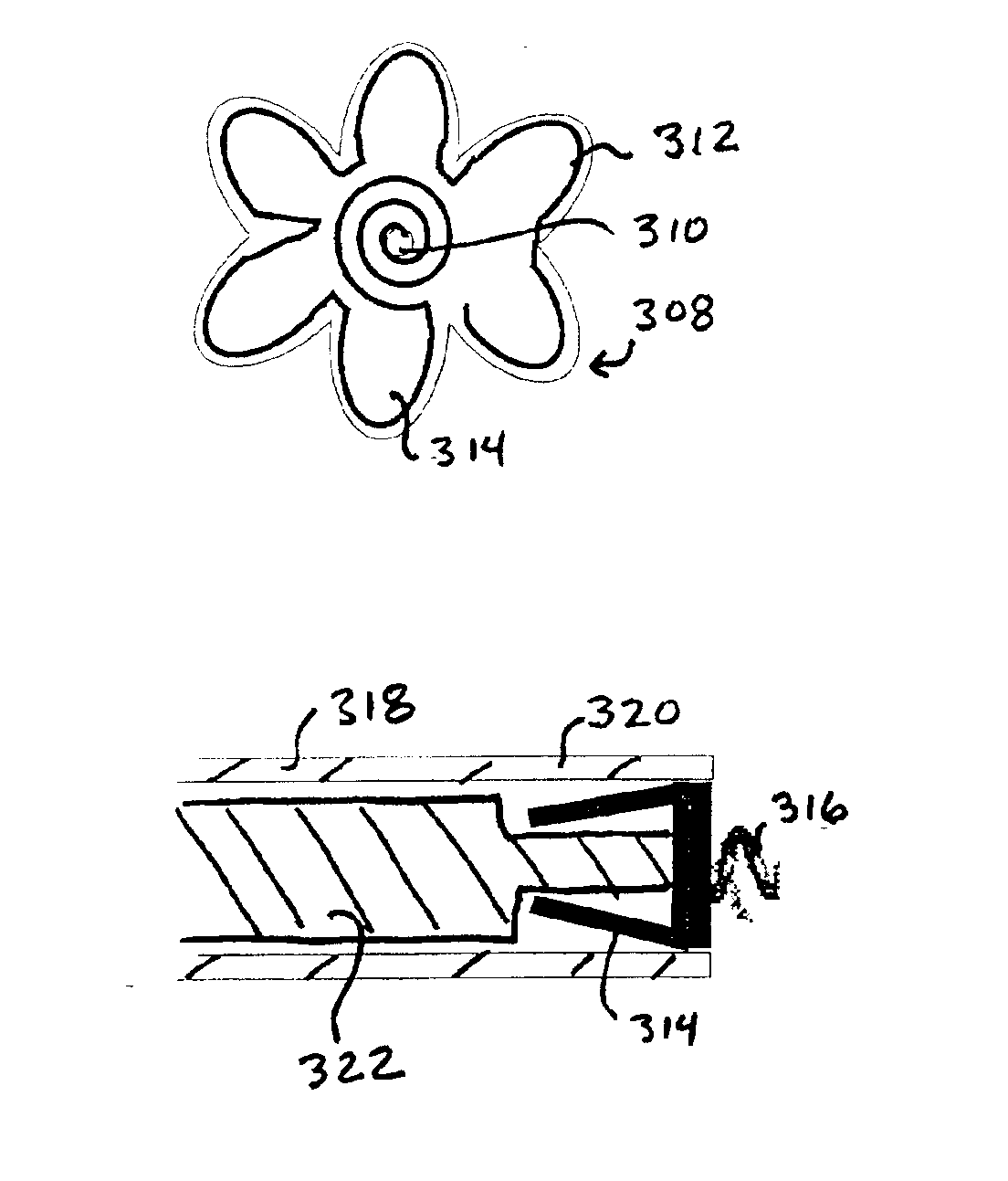
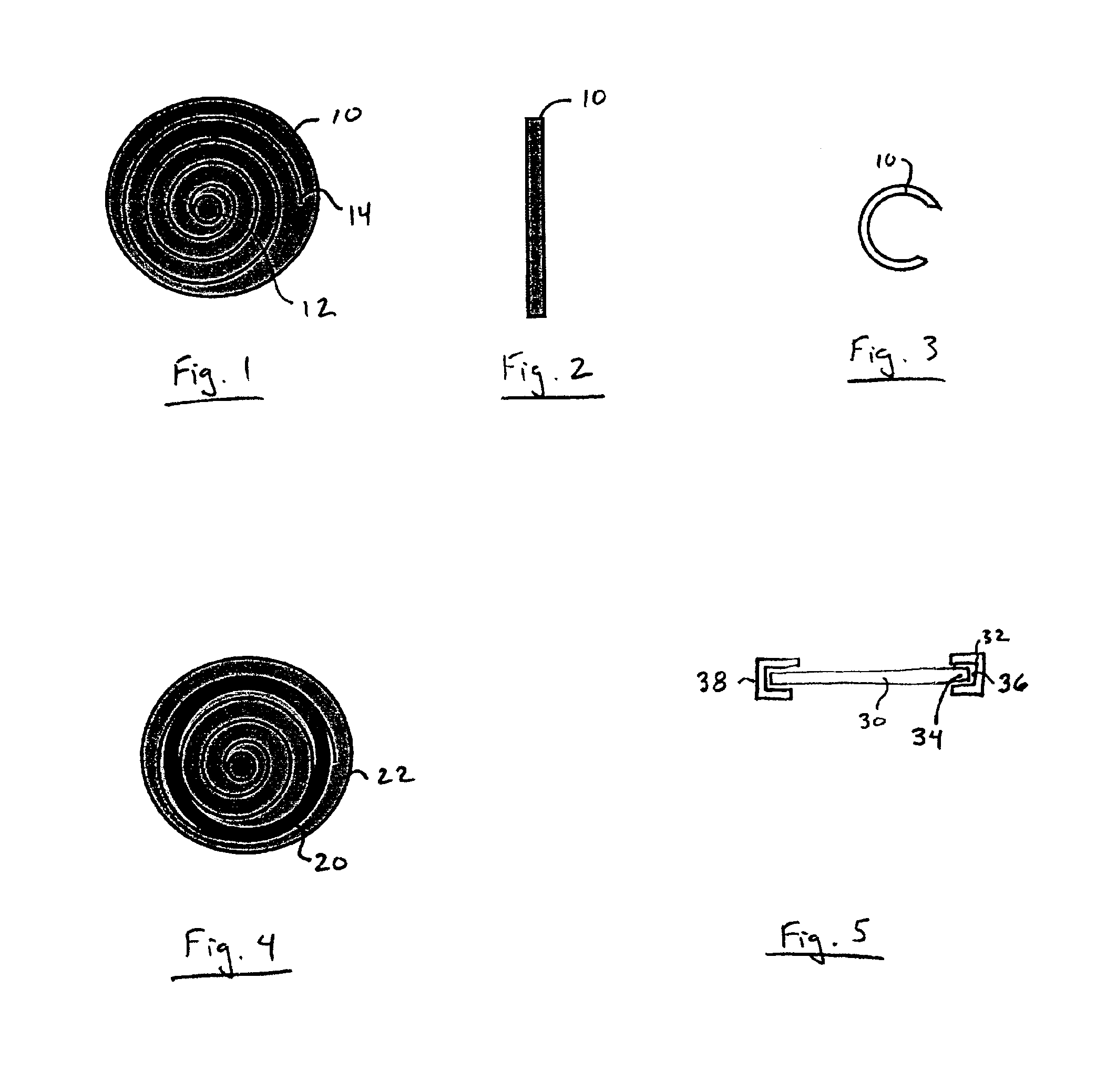
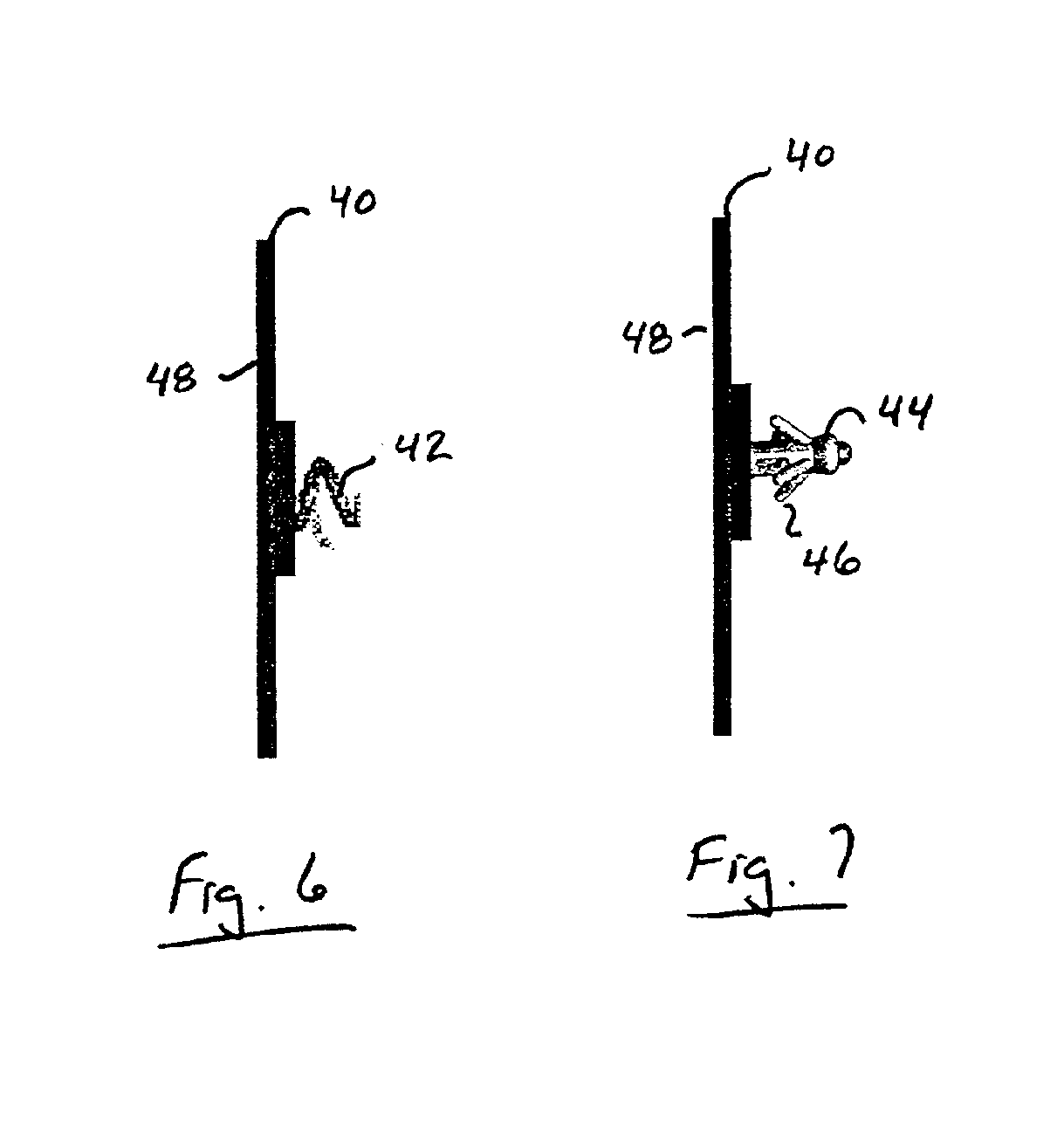
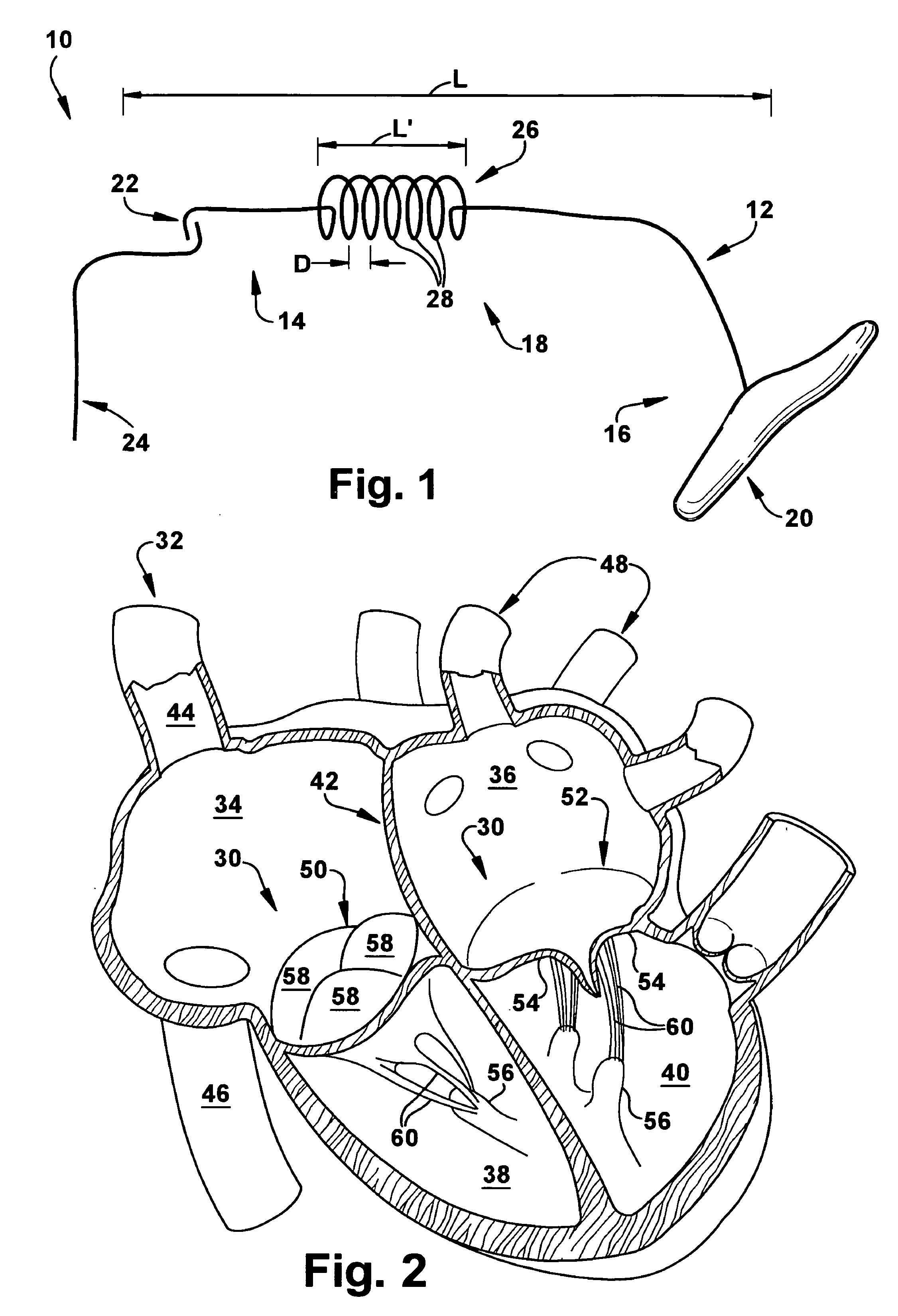
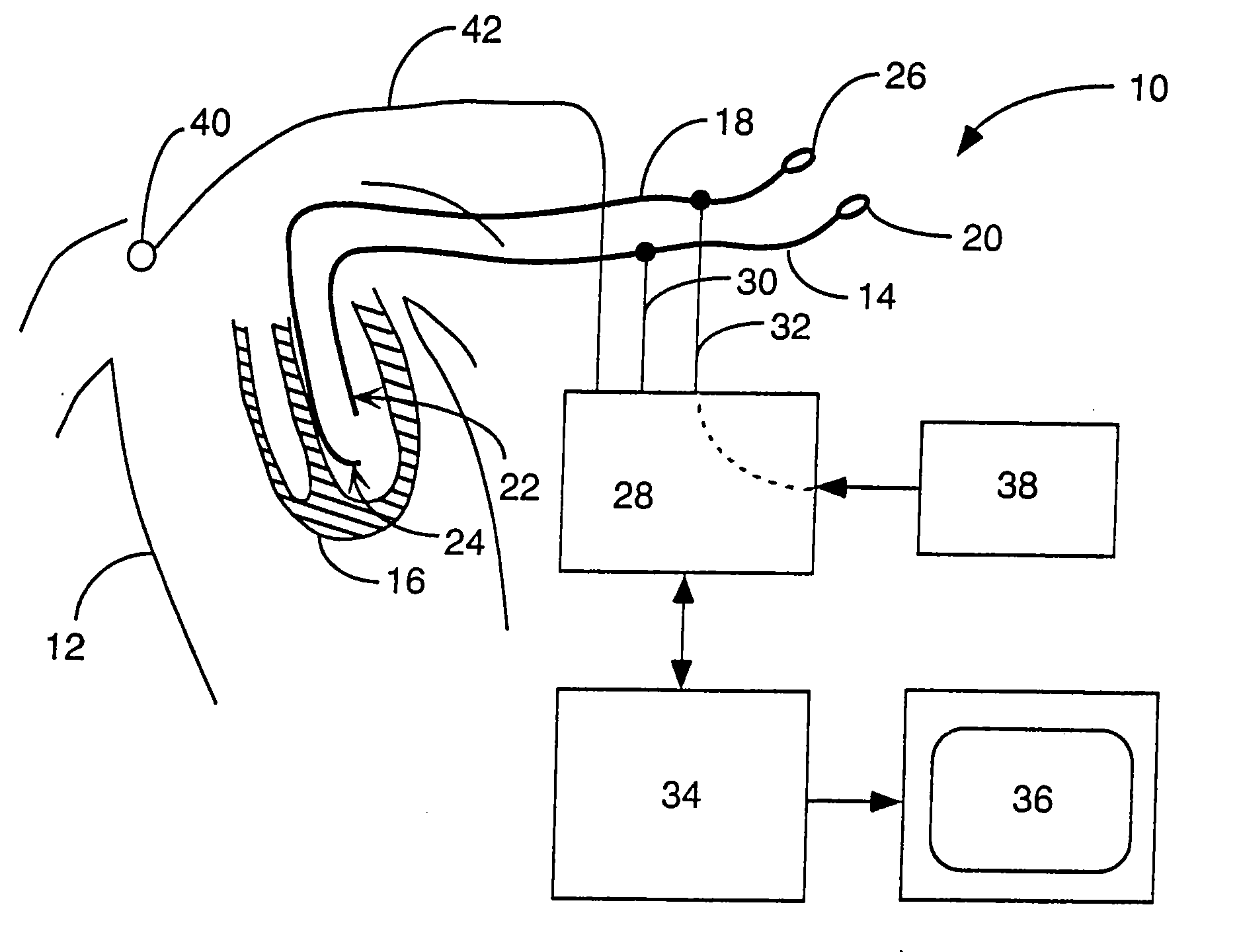
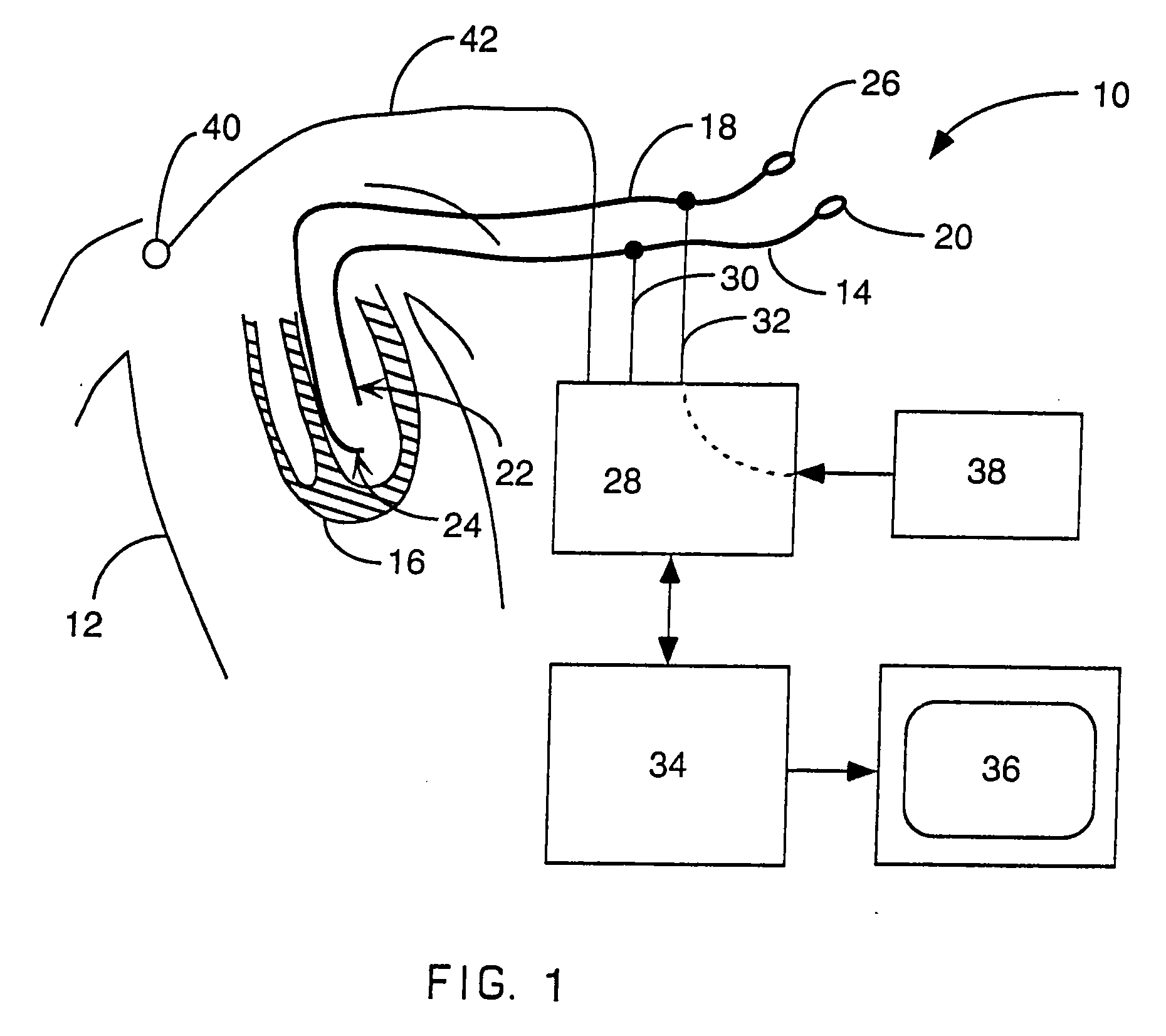
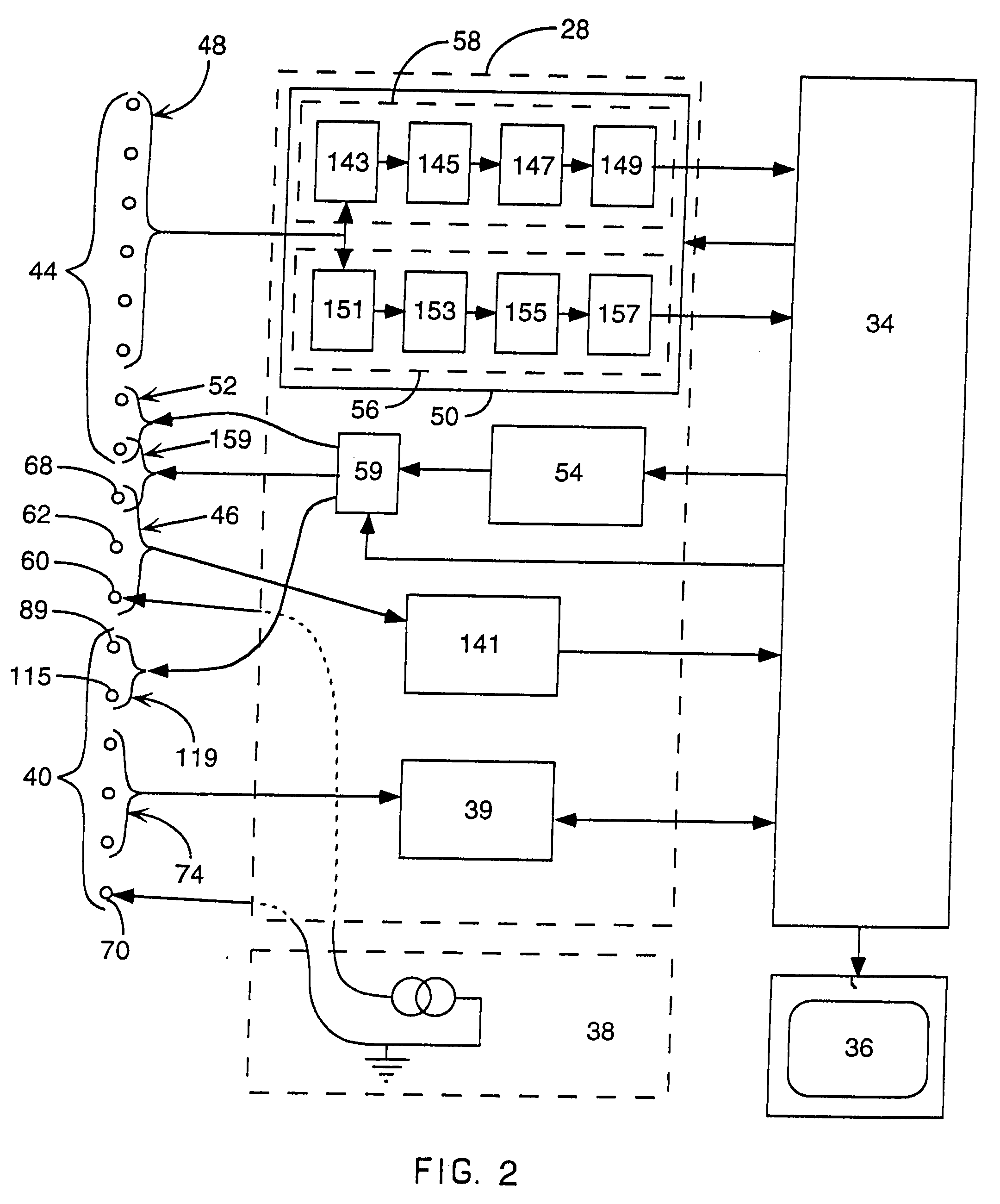
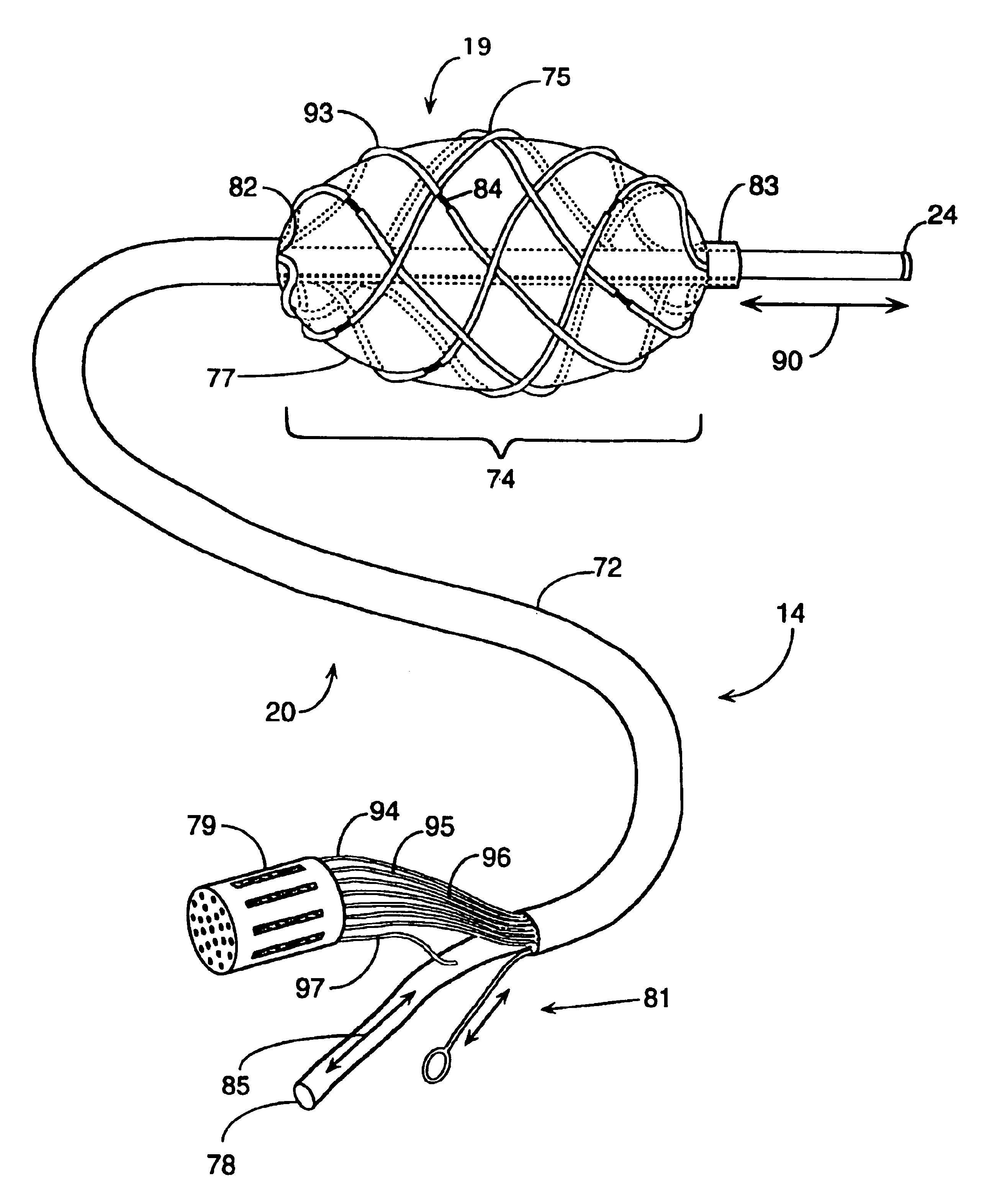
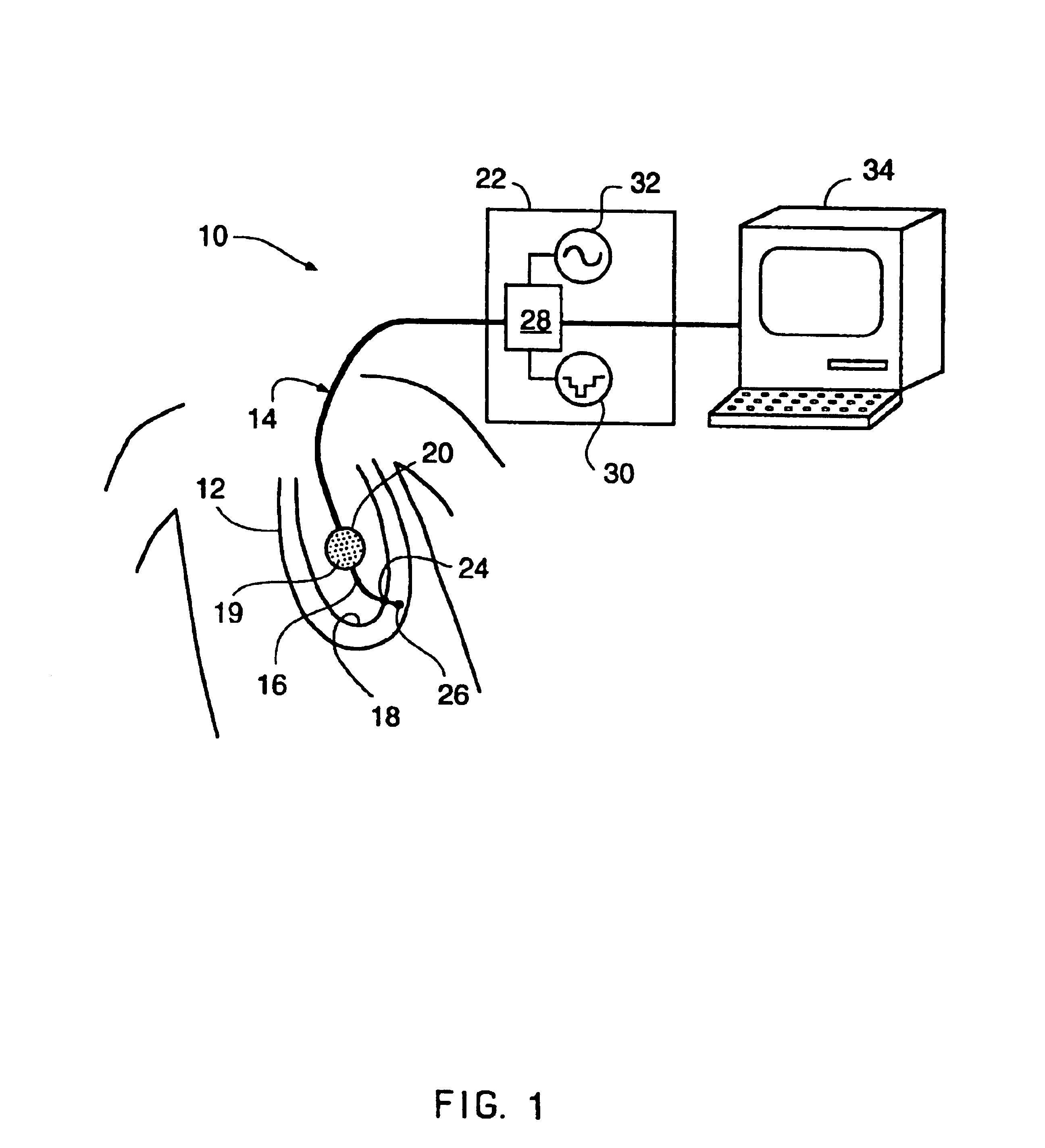
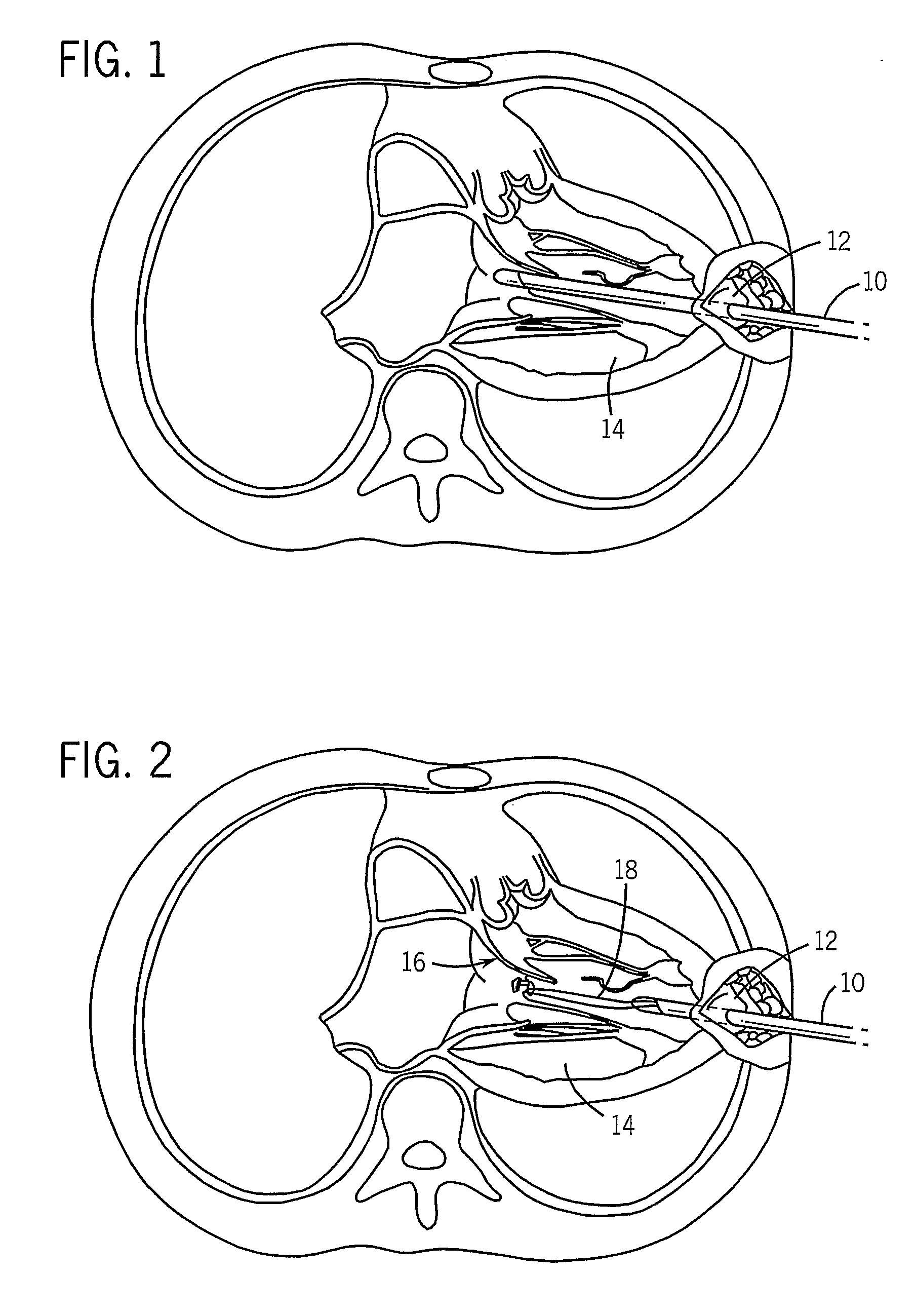
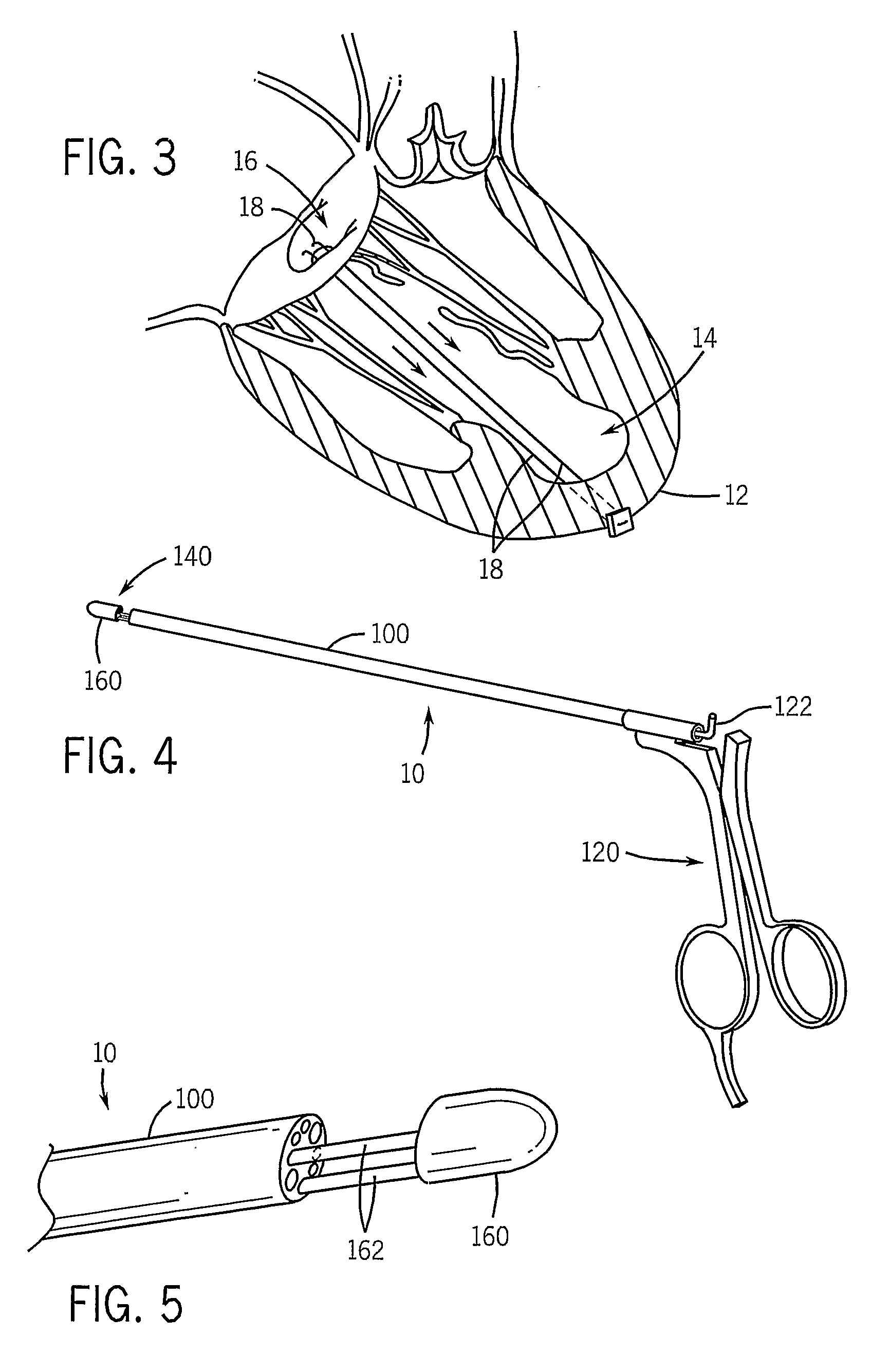
Implantable wireless sensor for pressure measurement within the heart
InactiveUS6855115B2Measure the pressure easily, safely, inexpensively and accuratelyElectrotherapyPerson identificationLine sensorHeart chamber
The progress of a endovascular cardiac repair can be monitored by inserting a pressure transducer sensor using a catheter into a chamber of the heart during endovascular repair and then using a small, hand-held read out device to measure pressure easily, safely, inexpensively and accurately. In one aspect a sensor is introduced into the body by the steps of folding or rolling the sensor into a cylinder, loading it into a catheter, and deploying into the heart chamber by allowing it to unroll or unfold, either by itself or facilitated by the incorporation of a super-elastic alloy component.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
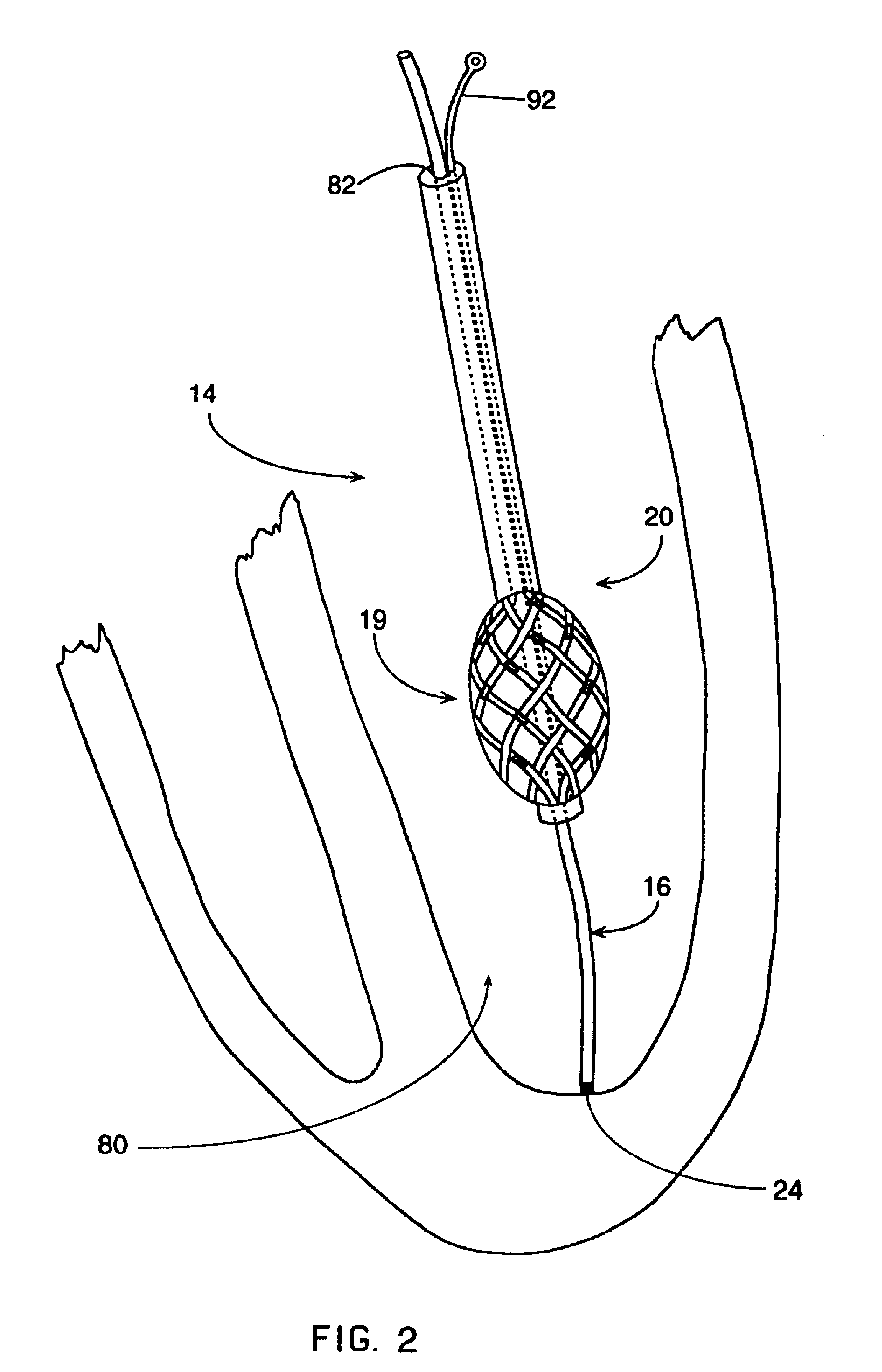
Tensioning device, system, and method for treating mitral valve regurgitation
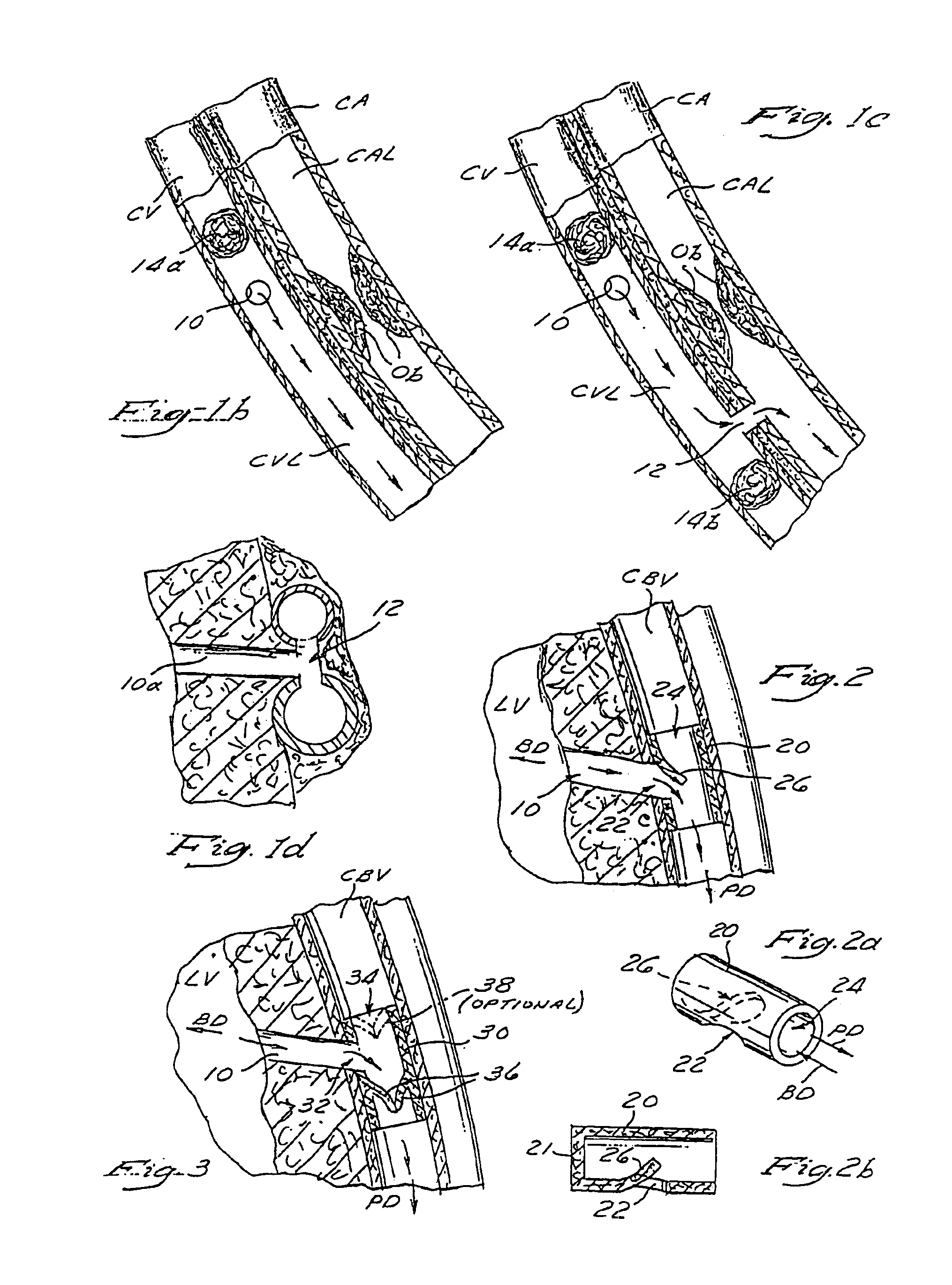
A system for treating mitral valve regurgitation comprises a tensioning device slidably received within a delivery catheter. The tensioning device includes a tether linking proximal an anchoring member and a distal anchoring member. At least one of the anchoring members includes an elastic portion that flexes in response to a heartbeat when the tensioning device is positioned across a chamber of a heart. The tether includes at least one locking member initially positioned between the anchoring members. A method for treating mitral valve regurgitation comprises piercing a first wall of a chamber of a heart, engaging a distal anchoring member with a second wall of the heart chamber, engaging a proximal anchoring member with the first wall, and pulling a locking member affixed to a tether linking the anchoring members from an initial position between the two anchoring members to a locked position proximal the proximal anchoring member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
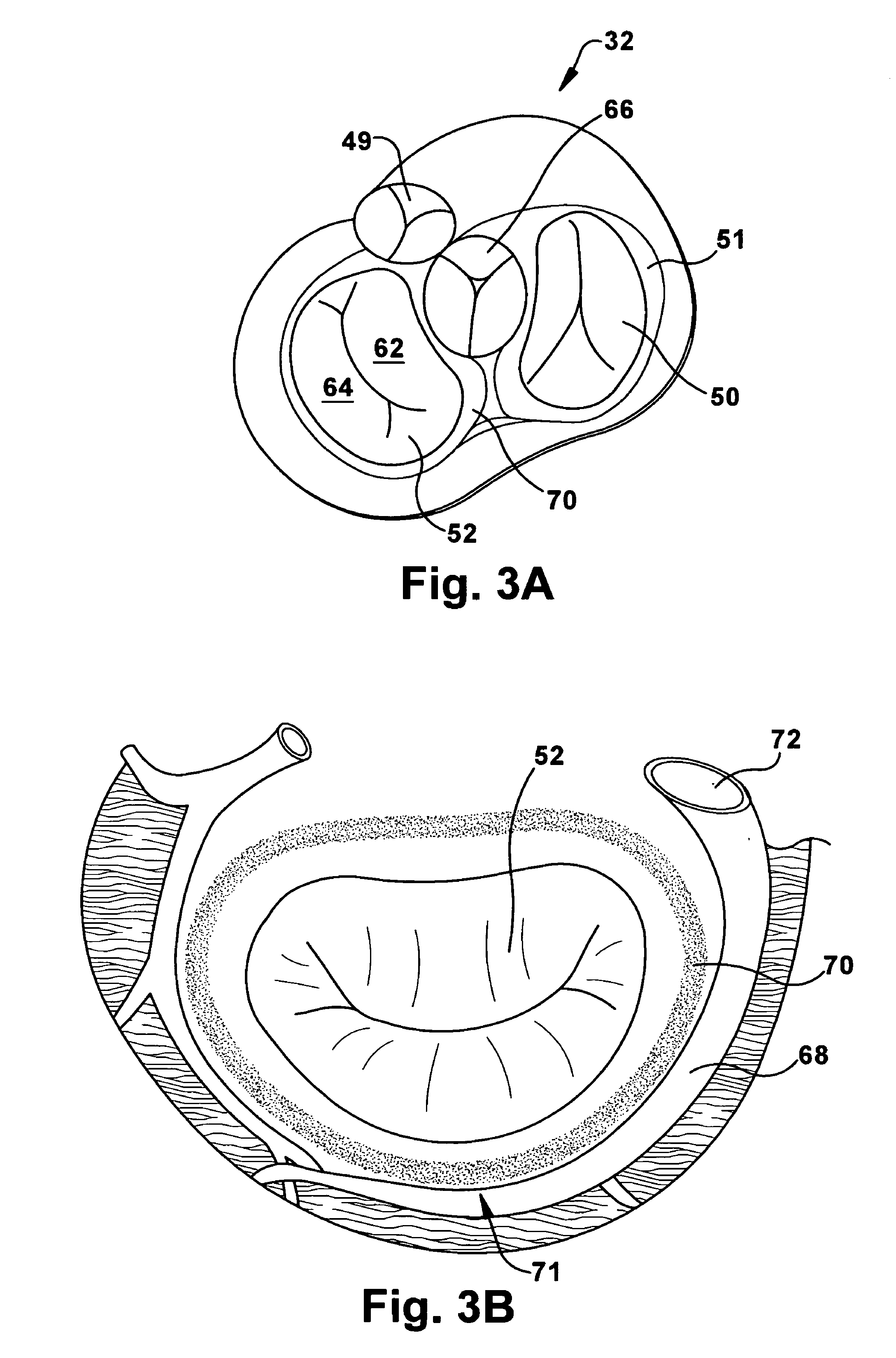
Suspended heart valve devices, systems, and methods for supplementing, repairing, or replacing a native heart valve
InactiveUS20050228495A1Good flexibility and compressibilityImprove foldabilityHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart chamberBlood vessel
A valve prosthesis is sized and configured to rest within a blood path subject to antegrade and retrograde blood flow. A trestle element on the prosthesis extends across the blood path. A leaflet assembly is suspended from the trestle element and extends into the blood path in alignment with blood flow. At least one mobile leaflet member on the leaflet assembly is sized and configured to assume orientations that change according to blood flow direction. The mobile leaflet member has a first orientation that permits antegrade blood flow and a second orientation that resists retrograde blood flow. The valve prosthesis, when implanted in a heart chamber or great vessel, serves to supplement and / or repair and / or replace native one-way heart valve function.
Owner:AM DISCOVERY
Device and method for improving heart valve function
ActiveUS20070270943A1Function increaseInhibit refluxSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac wallHeart chamber
The invention is device and method for reducing regurgitation through a mitral valve. The device and method is directed to an anchor portion for engagement with the heart wall and an expandable valve portion configured for deployment between the mitral valve leaflets. The valve portion is expandable for preventing regurgitation through the mitral valve while allowing blood to circulate through the heart. The expandable valve portion may include apertures for reducing the stagnation of blood. In a preferred configuration, the device is configured to be delivered in two-stages wherein an anchor portion is first delivered and the valve structure is then coupled to the anchor portion. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides a method of forming an anchor portion wherein a disposable jig is used to mold the anchor portion into a three-dimensional shape for conforming to a heart chamber.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP +1
Conduit with valved blood vessel graft
Disclosed is a conduit that provides a bypass around an occlusion or stenosis in a coronary artery. The conduit is a tube adapted to be positioned in the heart wall to provide a passage for blood to flow between a heart chamber and a coronary artery, at a site distal to the occlusion or stenosis. The conduit has a section of blood vessel attached to its interior lumen which preferably includes at least one naturally occurring one-way valve positioned therein. The valve prevents the backflow of blood from the coronary artery into the heart chamber.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC +1
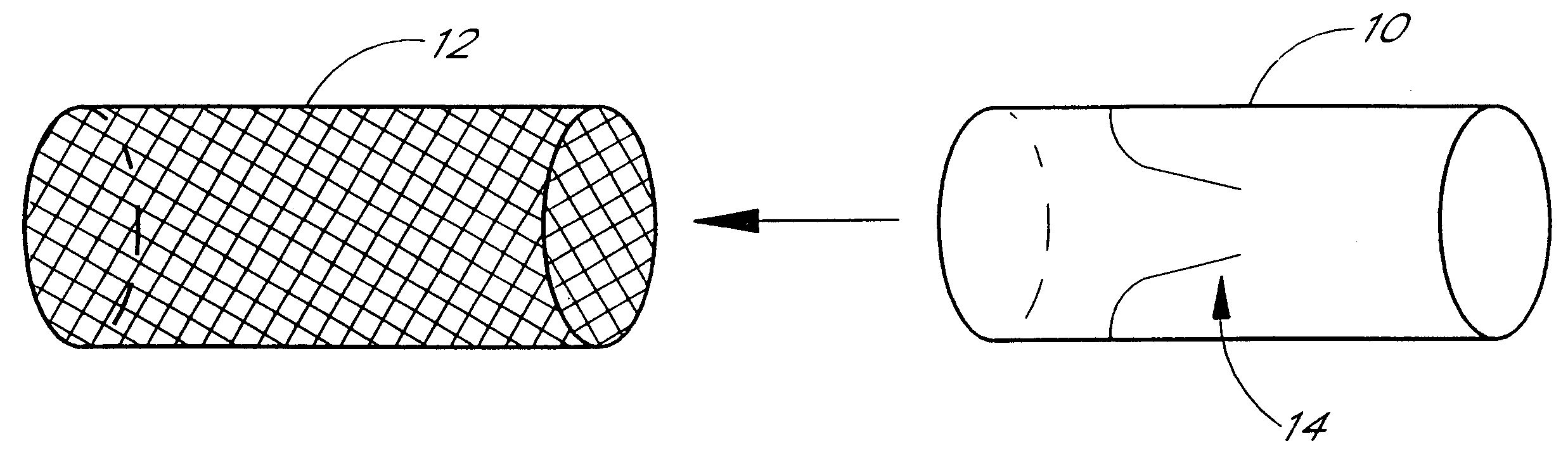
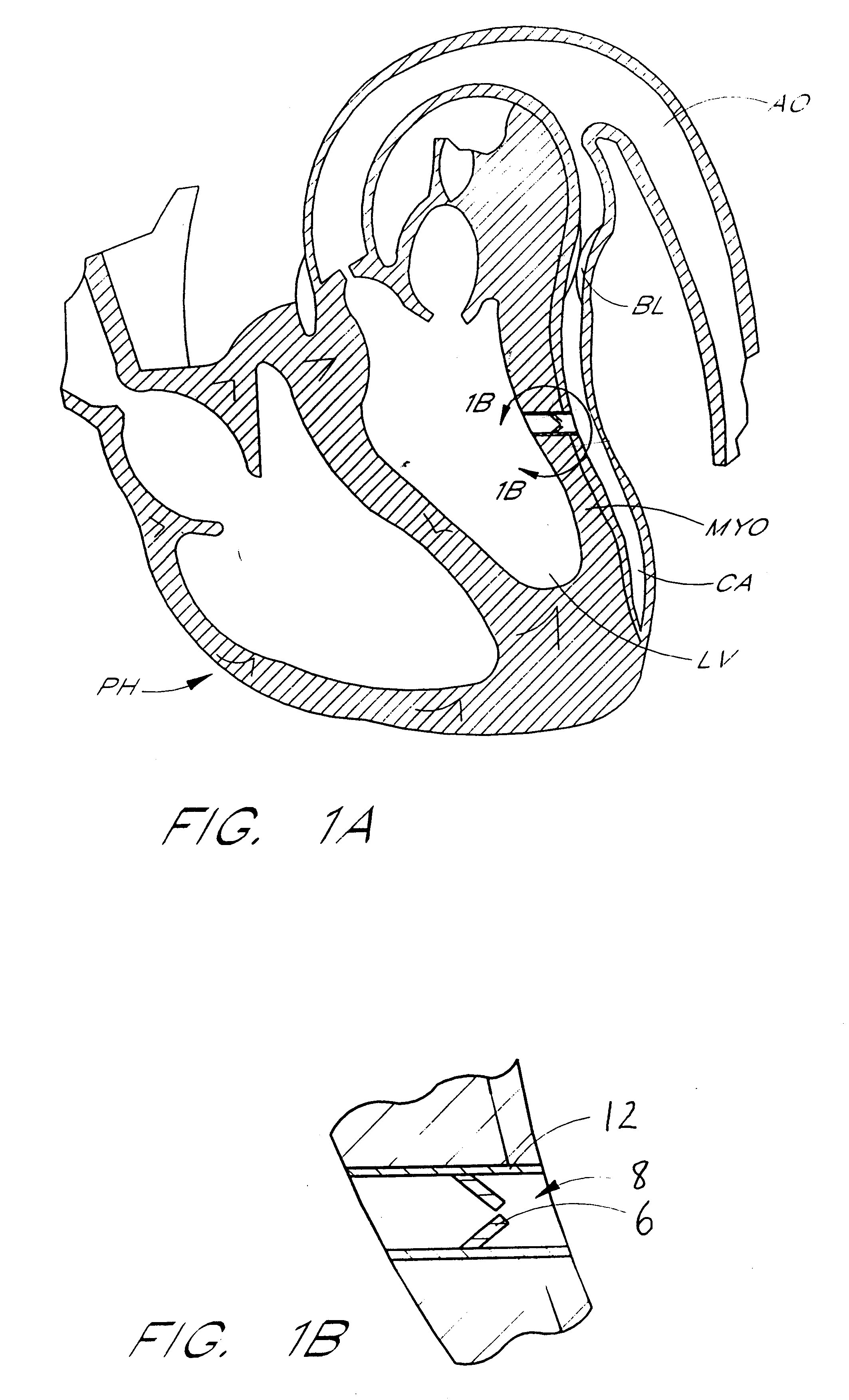
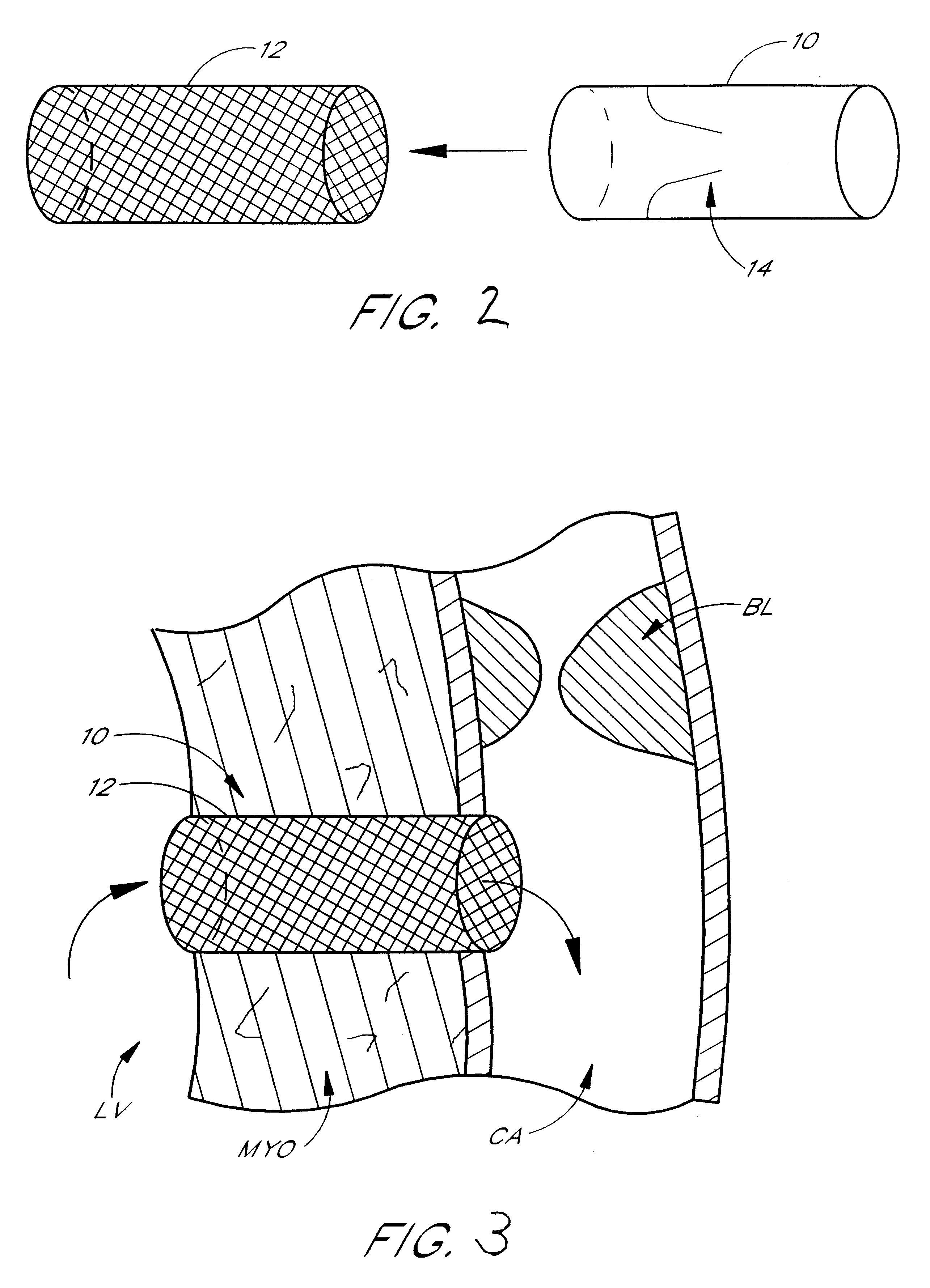
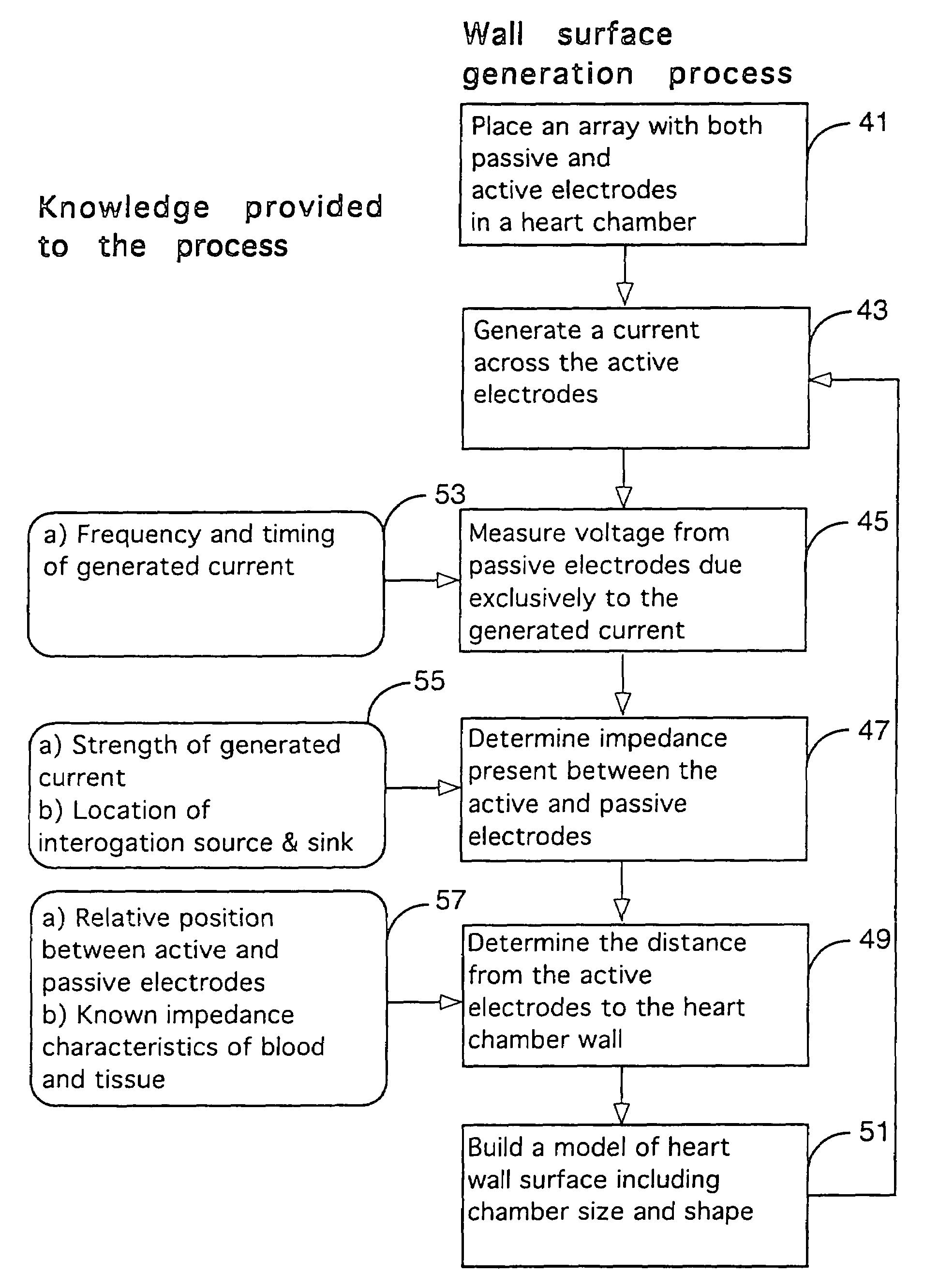
Method for measuring heart electrophysiology
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Implantable medical device for treating cardiac mechanical dysfunction by electrical stimulation
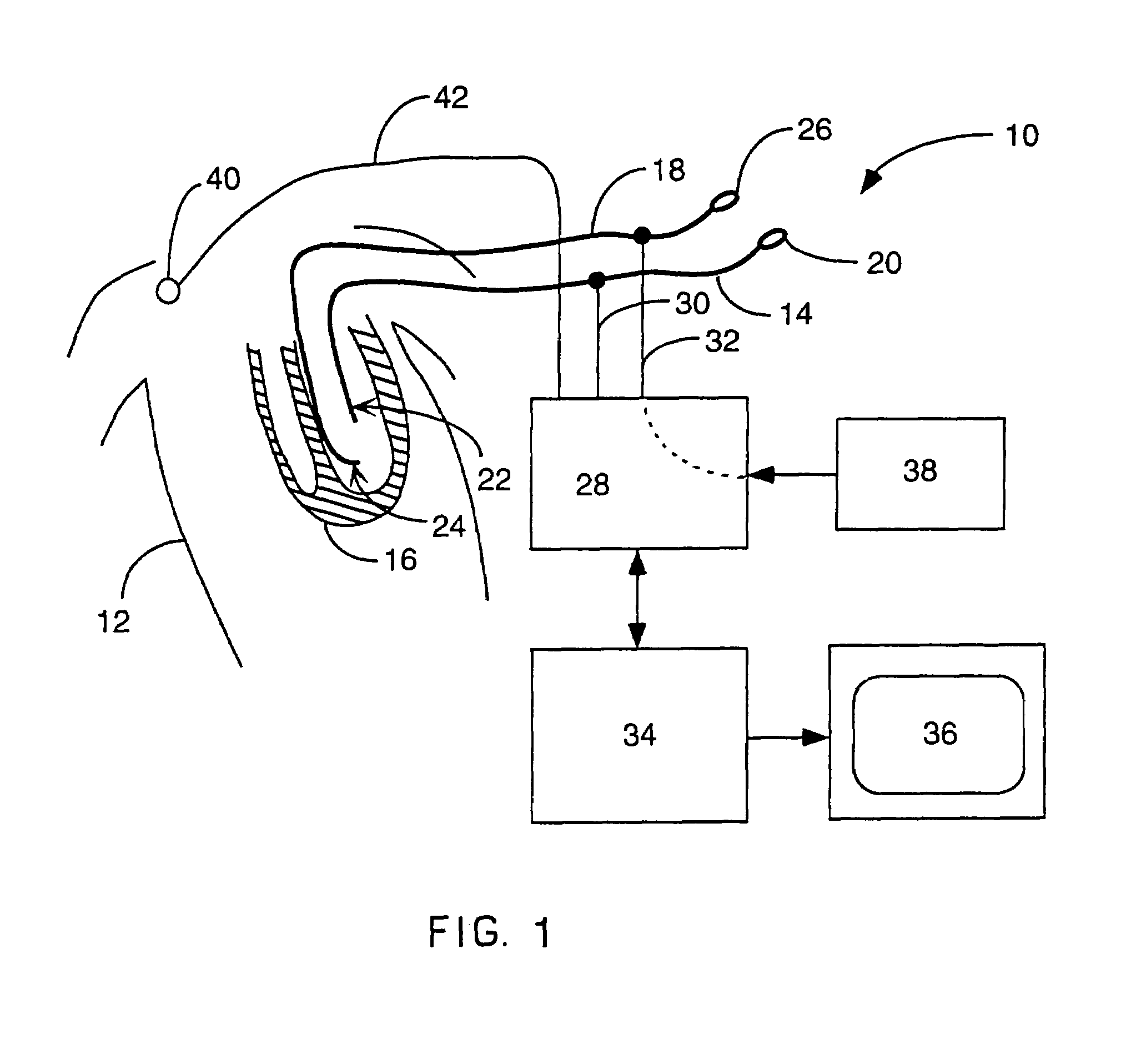
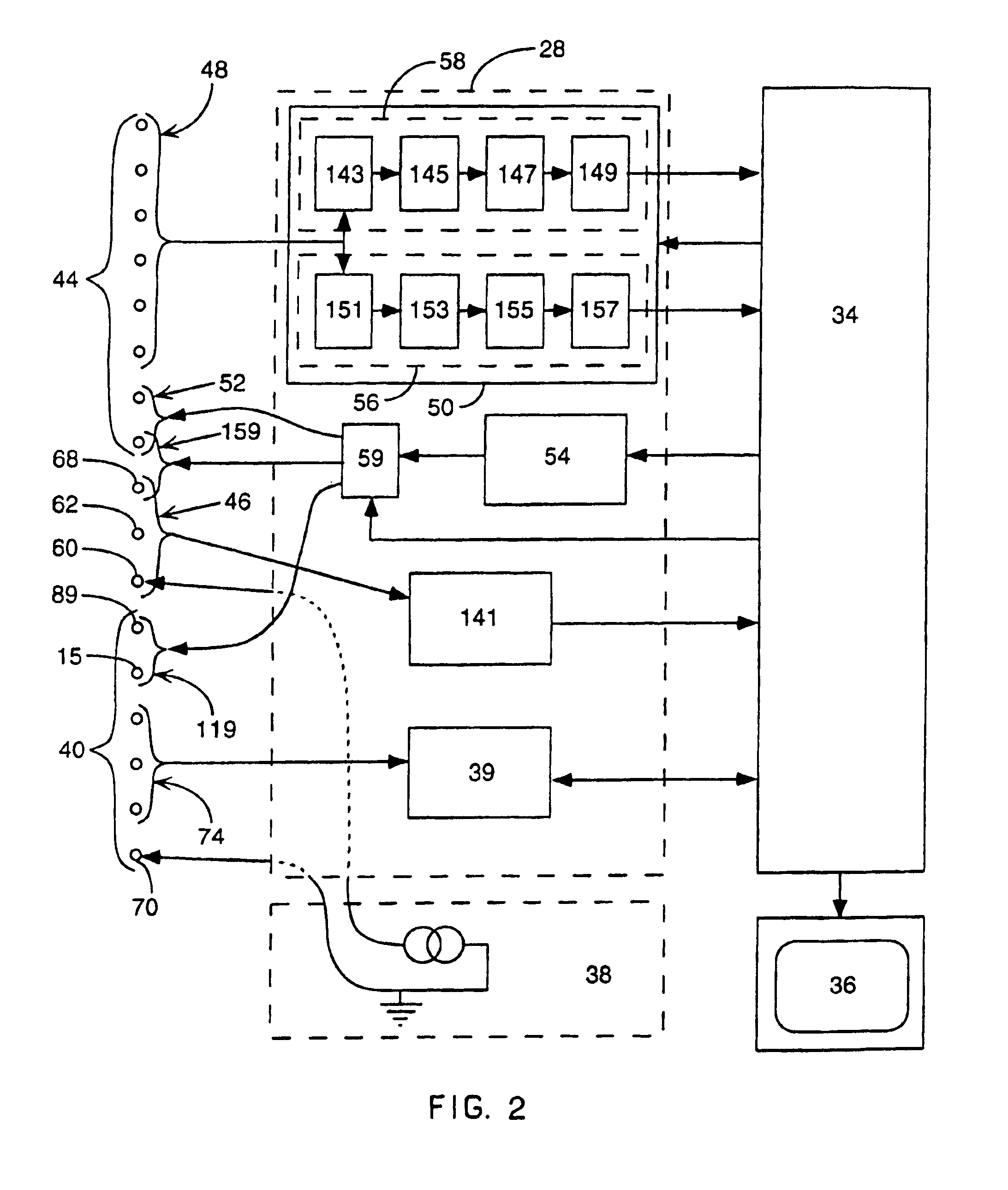
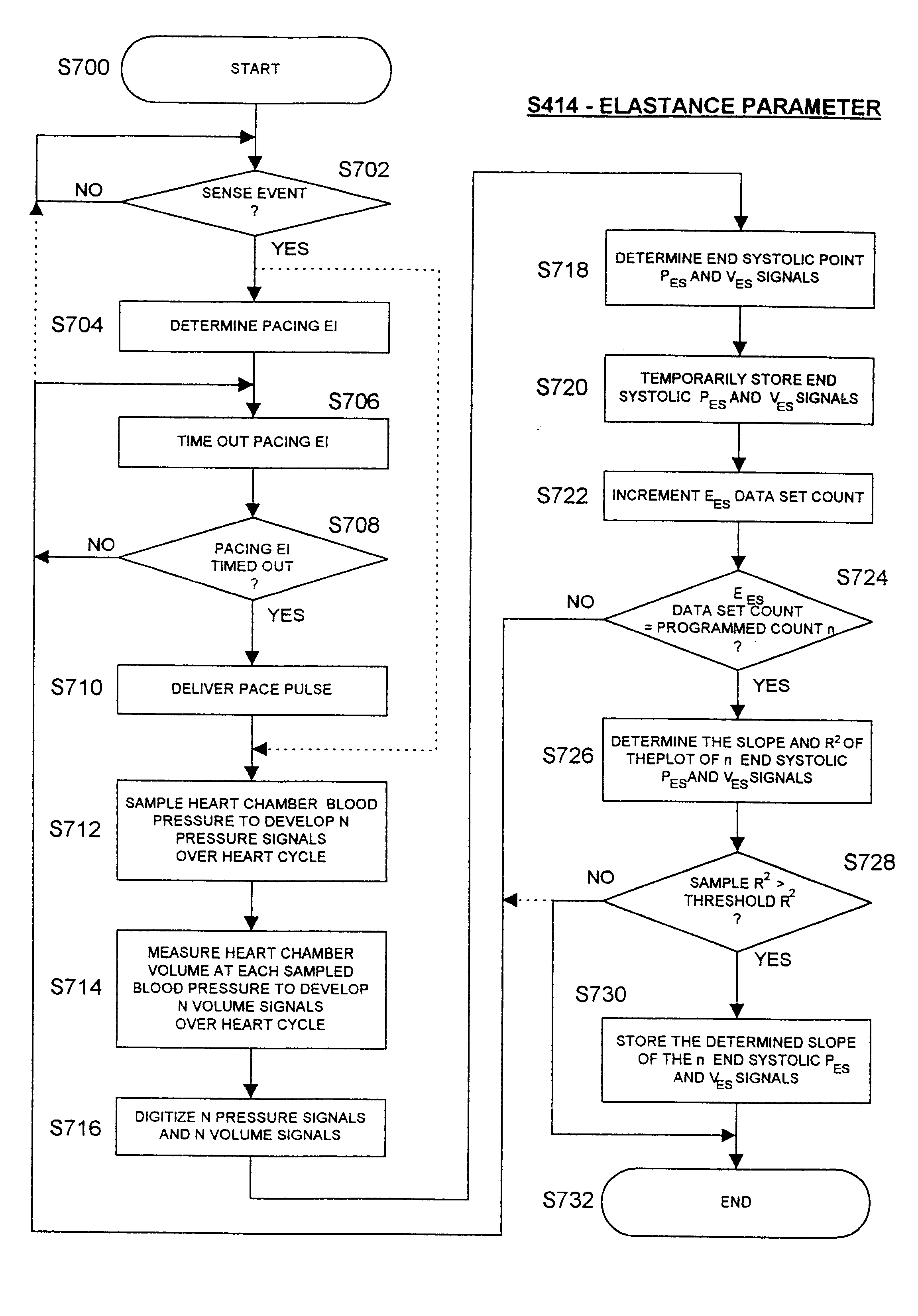
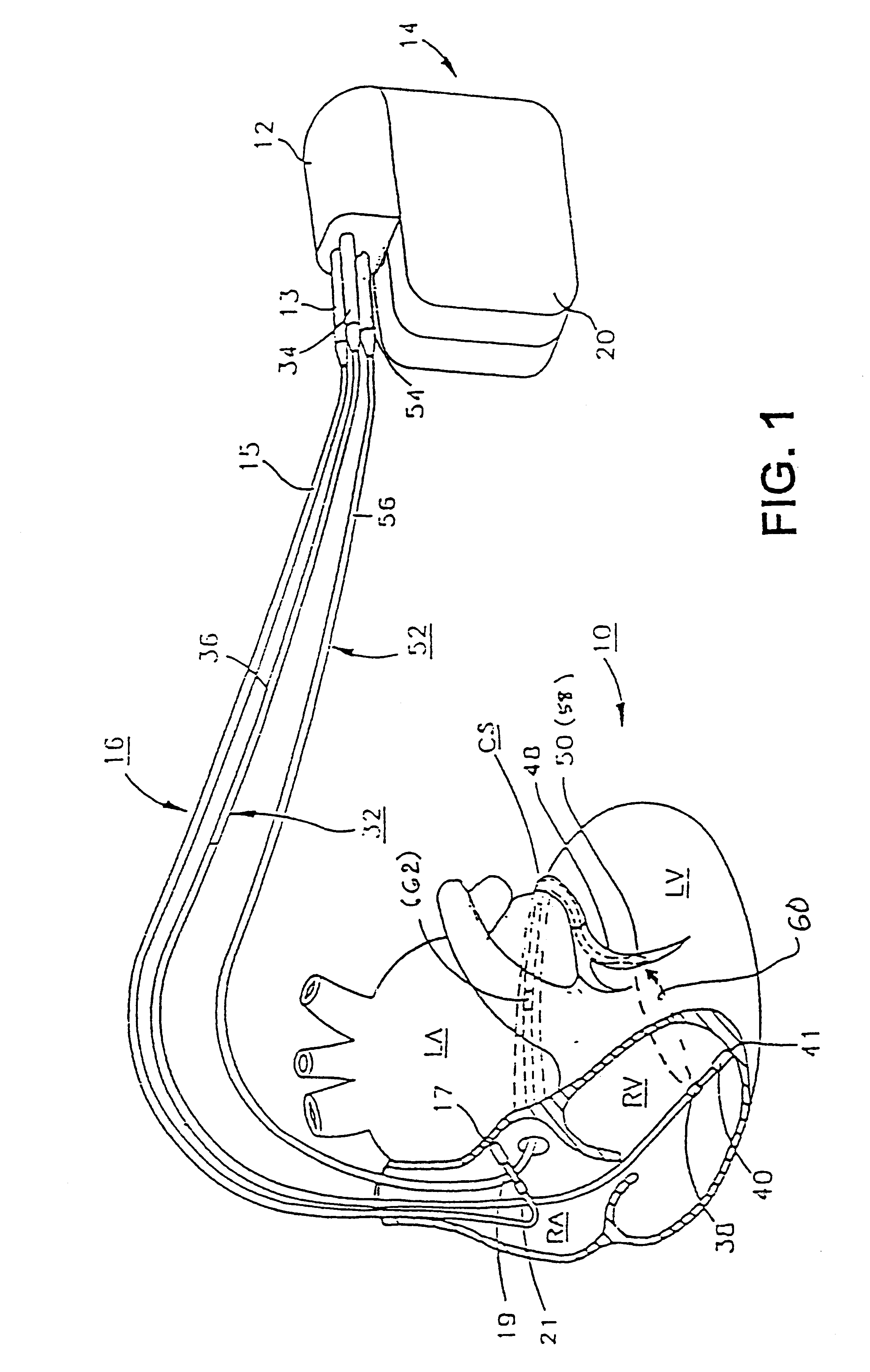
InactiveUS6738667B2Increase contractilityEasy to relaxCatheterHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleHeart chamber
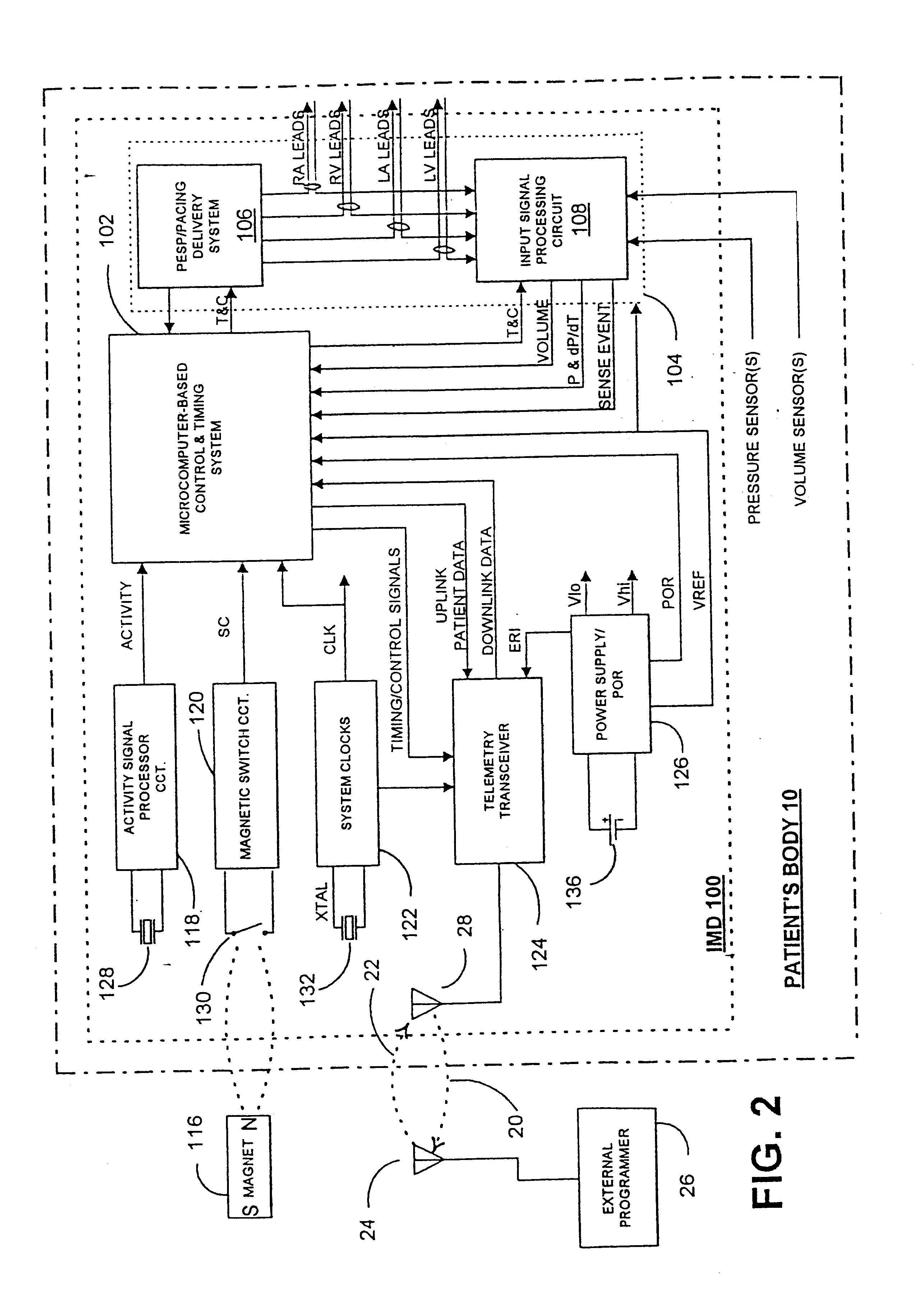
An implantable stimulator and monitor measures a group of heart failure parameters indicative of the state of heart failure employing EGM signals, measures of blood pressure including absolute pressure P, developed pressure (DP=systolic P-diastolic P), and / or dP / dt, and measures of heart chamber volume (V) over one or more cardiac cycles. These parameters include: (1) relaxation or contraction time constant tau (.tau.); (2) mechanical restitution (MR), i.e., the mechanical response of a heart chamber to premature stimuli applied to the heart chamber; (3) recirculation fraction (RF), i.e., the rate of decay of PESP effects over a series of heart cycles; and (4) end systolic elastance (E.sub.ES), i.e., the ratios of end systolic blood pressure P to volume V. These heart failure parameters are determined periodically regardless of patient posture and activity level. The physician can determine whether a particular therapy is appropriate, prescribe the therapy for a period of time while again accumulating the stored patient data for a later review and assessment to determine whether the applied therapy is beneficial or not, thereby enabling periodic changes in therapy, if appropriate. Drug therapies and electrical stimulation therapies, including PESP stimulation, and pacing therapies including single chamber, dual chamber and multi-chamber (bi-atrial and / or bi-ventricular) pacing can be delivered. In patient's prone to malignant tachyarrhythmias, the assessment of heart failure state can be taken into account in setting parameters of detection or classification of tachyarrhythmias and the therapies that are delivered.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for improving ventricular function
InactiveUS7374573B2Easy to operateControl volumeHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsHeart chamberVentricular function
An approach is disclosed for improving ventricular function of a patient's heart. According to one embodiment, the system includes a pouch that defines a chamber dimensioned and configured to simulate at least a portion of a heart chamber. The pouch has a sidewall portion extending from an inflow annulus and terminating in a closed distal end spaced apart from the inflow annulus. A generally cylindrical outflow portion extends from the sidewall portion of the pouch and terminating in an outflow annulus thereof to provide for flow of fluid from the chamber through the outflow annulus. A valve is operatively associated with the inflow annulus of the pouch to provide for substantially unidirectional flow of fluid through the inflow annulus and into the chamber.
Owner:GABBAY SHLOMO
Device and method for improving heart valve function
ActiveUS8932348B2Function increaseInhibit refluxSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberThree dimensional shape
The invention is device and method for reducing regurgitation through a mitral valve. The device and method is directed to an anchor portion for engagement with the heart wall and an expandable valve portion configured for deployment between the mitral valve leaflets. The valve portion is expandable for preventing regurgitation through the mitral valve while allowing blood to circulate through the heart. The expandable valve portion may include apertures for reducing the stagnation of blood. In a preferred configuration, the device is configured to be delivered in two-stages wherein an anchor portion is first delivered and the valve structure is then coupled to the anchor portion. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides a method of forming an anchor portion wherein a disposable jig is used to mold the anchor portion into a three-dimensional shape for conforming to a heart chamber.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP +1
Ventricular partitioning device
InactiveUS20060030881A1Lower the volumeImprove ejection fractionOcculdersSurgical veterinaryHeart chamberNon traumatic
This invention is directed to a partitioning device for separating a patient's heart chamber into a productive portion and a non-productive portion. The device is particularly suitable for treating patients with congestive heart failure. The partitioning device has a frame-reinforced, expandable membrane which separates the productive and non-productive portions of the heart chamber. The proximal ends of the ribs of the frame have tissue penetrating elements about the periphery thereof which are configured to penetrate tissue lining the heart wall at an angle approximately perpendicular to a longitudinal axis of the partitioning device. The partitioning device has a hub with a non-traumatic distal end to engage the ventricular wall.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
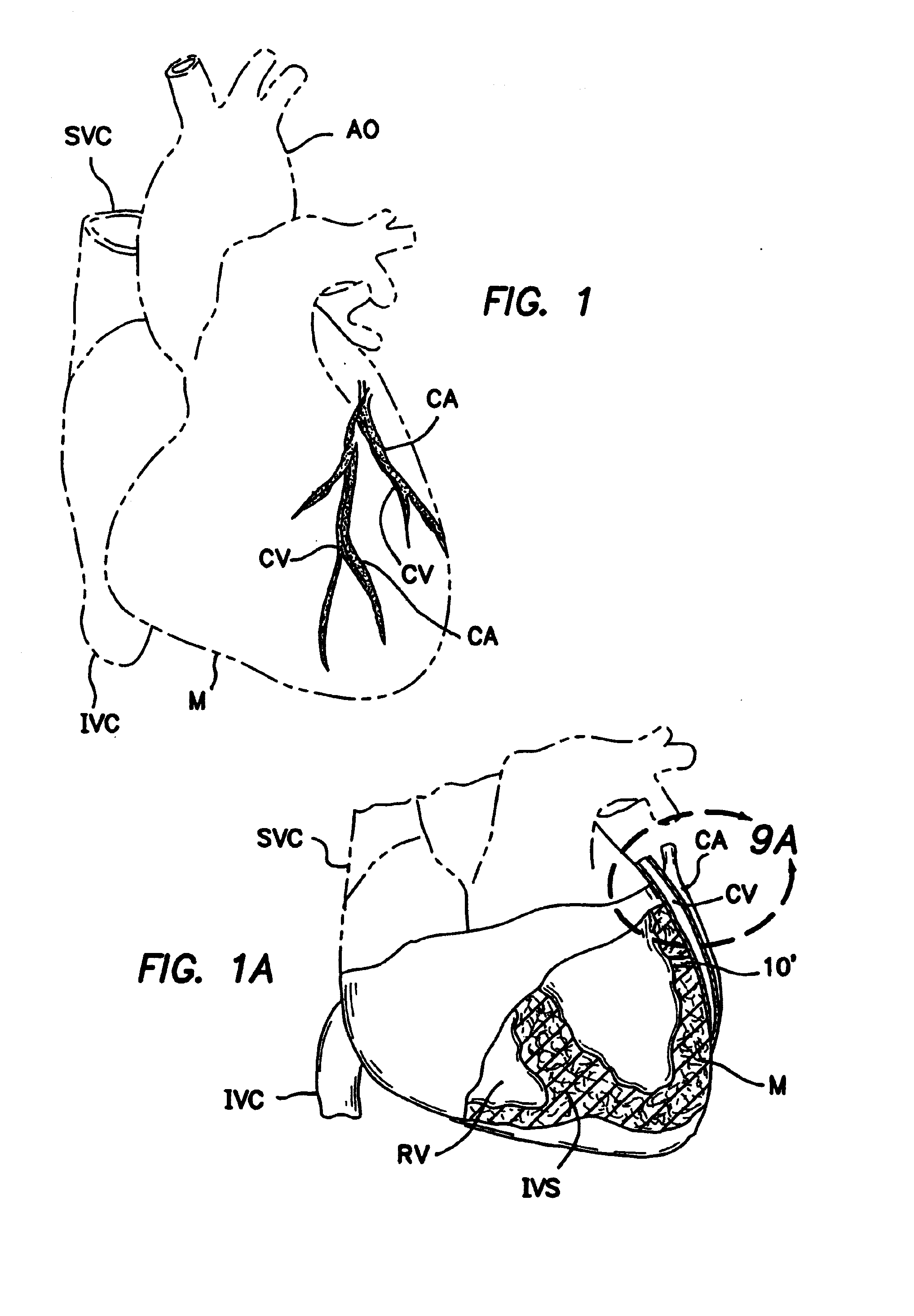
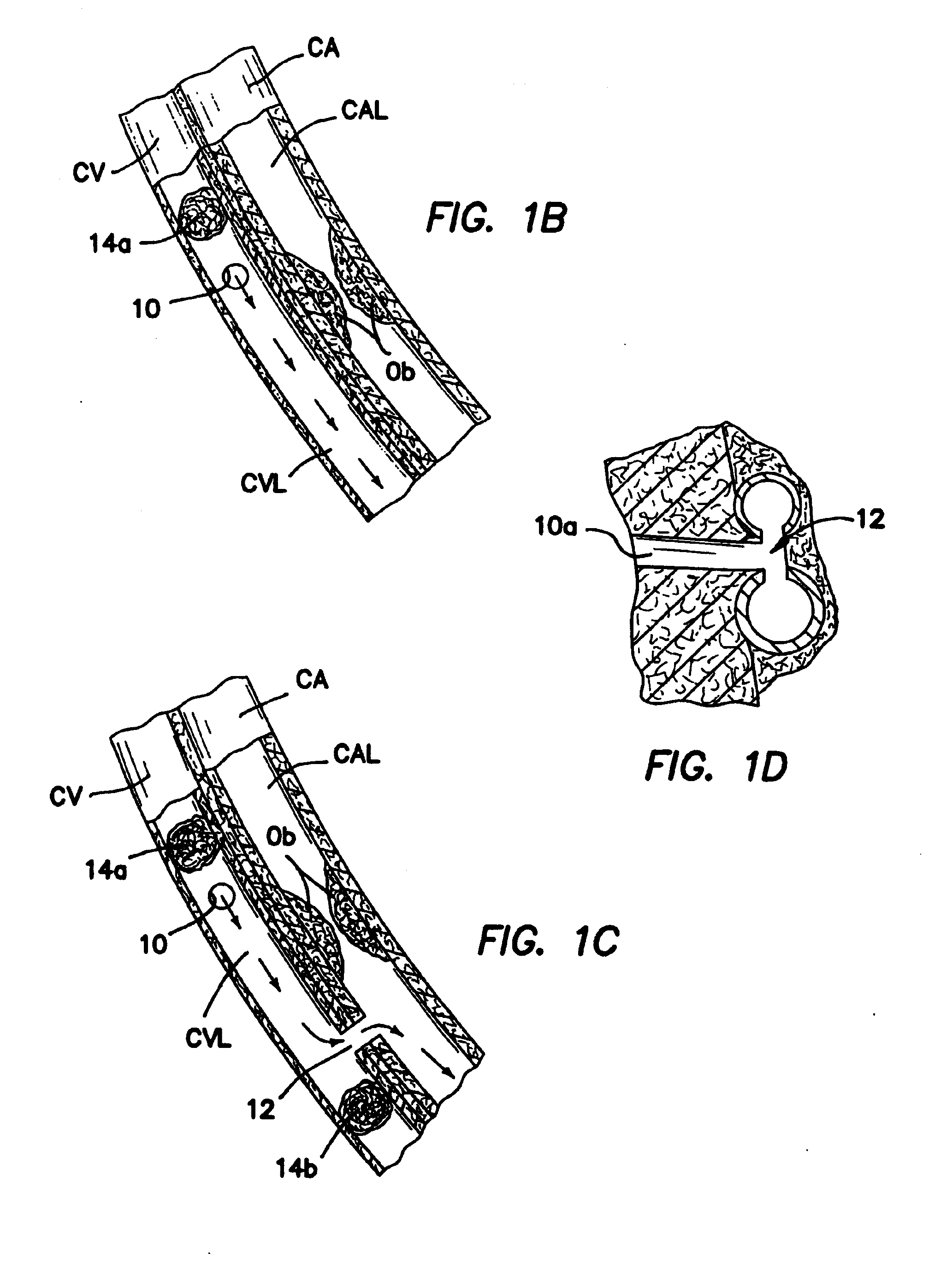
Method and apparatus for transmyocardial direct coronary revascularization
InactiveUS6929009B2Facilitate valvingShortening and thickeningEar treatmentCannulasVeinHeart chamber
Methods and apparatus for direct coronary revascularization wherein a transmyocardial passageway is formed between a chamber of the heart and a coronary blood vessel to permit blood to flow therebetween. In some embodiments, the transmyocardial passageway is formed between a chamber of the heart and a coronary vein. The invention includes unstented transmyocardial passageways, as well as transmyocardial passageways wherein protrusive stent devices extend from the transmyocardial passageway into an adjacent coronary vessel or chamber of the heart. The apparatus of the present invention include protrusive stent devices for stenting of transmyocardial passageways, intraluminal valving devices for valving of transmyocardial passageways, intracardiac valving devices for valving of transmyocardial passageways, endogenous tissue valves for valving of transmyocardial passageways, and ancillary apparatus for use in conjunction therewith.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Coronary bypass implant
InactiveUS6093166AImprove visualizationReduce oxygen requirementStentsDiagnosticsCoronary arteriesHeart chamber
A method and apparatus for performing coronary artery bypass surgery establishes a channel leading directly from a chamber of a heart into a coronary artery. The coronary artery bypass procedure may be performed with or without cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
Methods and devices for placing a conduit in fluid communication with a target vessel
Methods and devices for placing a conduit in fluid communication with a target vessel and a source of blood, such as the aorta or a heart chamber. The device may be actuated using one hand to place the conduit. The invention allows air in the conduit to be removed prior to placement of the conduit. The invention deploys the conduit in the target vessel by moving a sheath in a distal direction and then in a proximal direction. A conduit is provided with a reinforcing member to prevent kinking of the conduit, and a structure for preventing blockage of the conduit by tissue. A vessel coupling may be used to secure a conduit to a target vessel so as to preserve native blood flow through the vessel, and the conduit may be placed in fluid communication with a target vessel via a laparoscopic or endoscopic procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Intra-cardiac mapping and ablation method
ActiveUS20080004534A1Accurate locationMinimize the numberElectrotherapySurgical systems user interfaceHeart chamberCooling effect
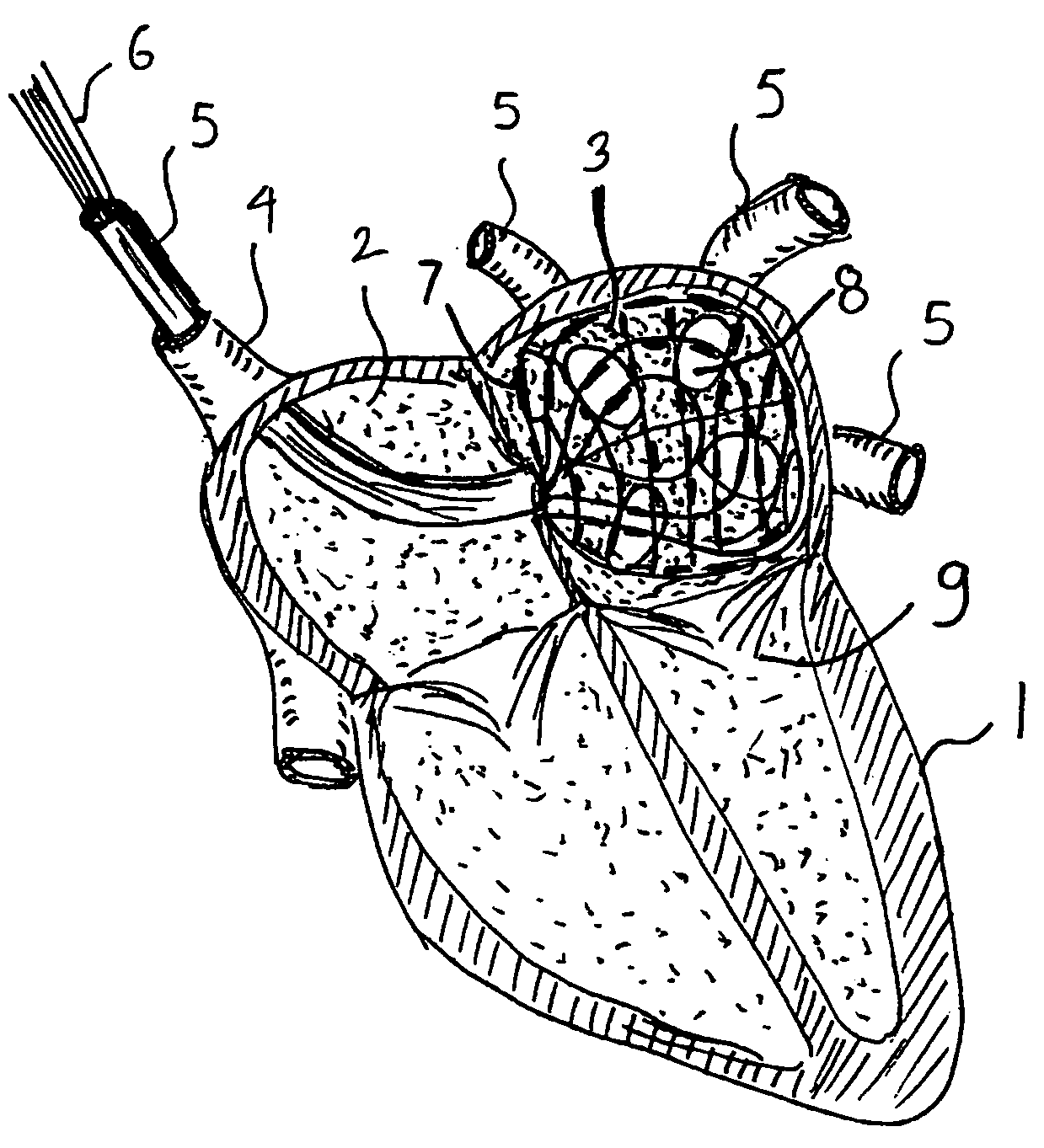
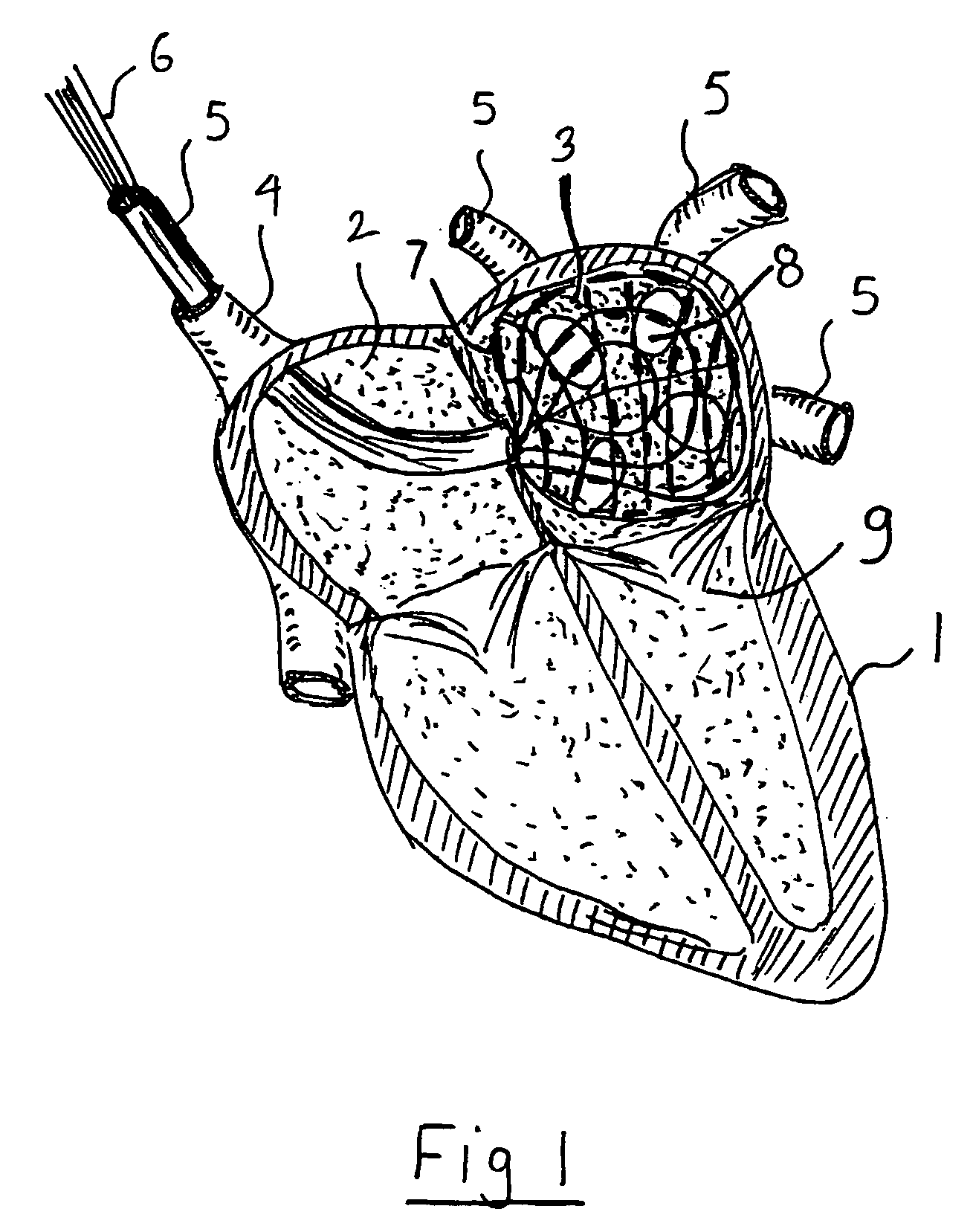
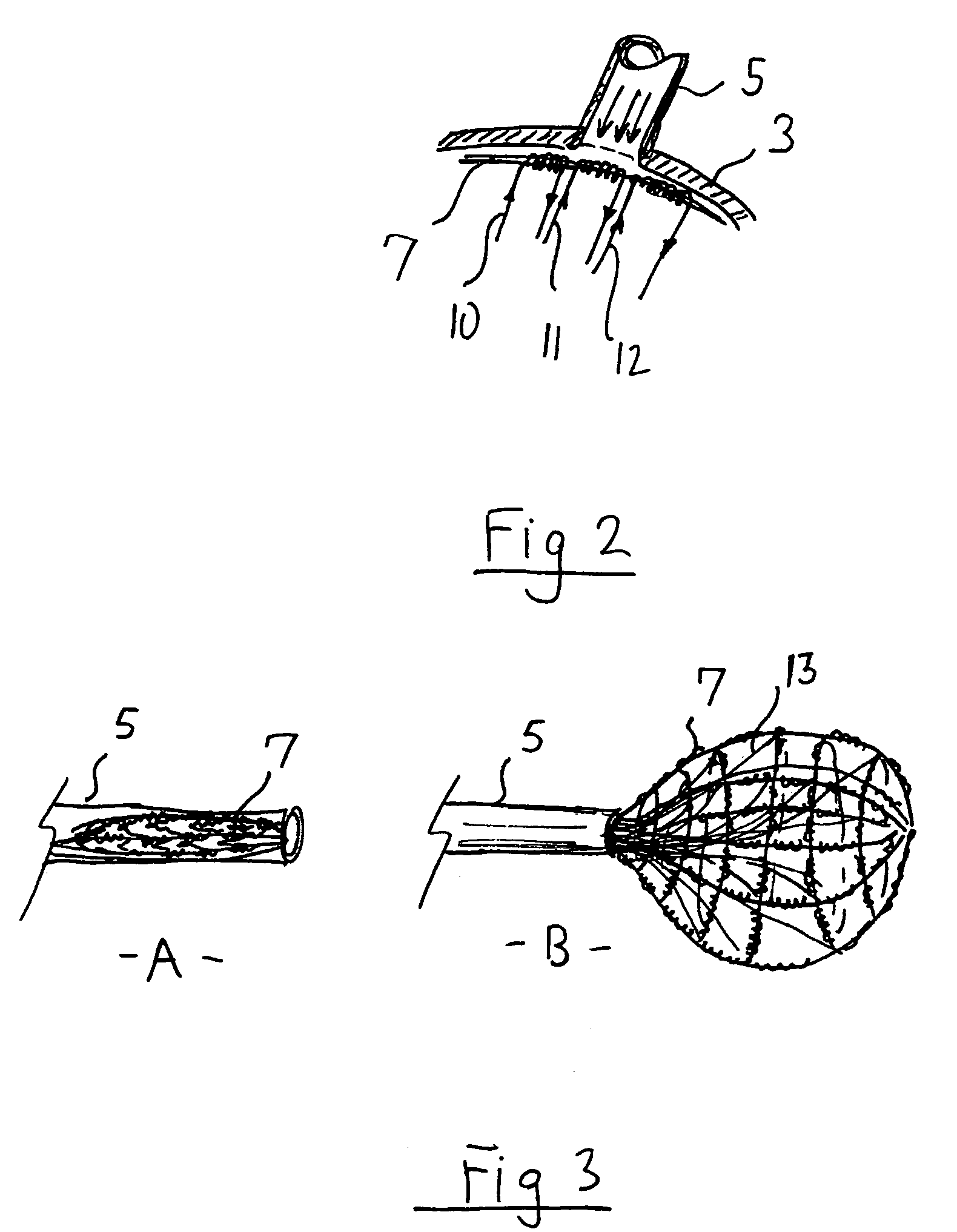
An intra-cardiac mapping system is based on locating the ports through which blood flows in or out the heart chambers. For many procedures, such as ablation to cure atrial fibrillation, locating the pulmonary veins and the mitral valve accurately allows to perform a Maze procedure. The location of the ports and valves is based on using the convective cooling effect of the blood flow. The mapping can be performed by a catheter-deployed expandable net or a scanning catheter. The same net or catheter can also perform the ablation procedure.
Owner:KARDIUM
Methods and apparatus for transmyocardial direct coronary revascularization
InactiveUS7159592B1Easy to movePromote formationEar treatmentCannulasCoronary revascularizationCoronary revascularisation
Methods and apparatus for direct coronary revascularization wherein a transmyocardial passageway is formed between a chamber of the heart and a coronary blood vessel to permit blood to flow therebetween. In some embodiments, the transmyocardial passageway is formed between a chamber of the heart and a coronary vein. The invention includes unstented transmyocardial passageways, as well as transmyocardial passageways wherein protrusive stent devices extend from the transmyocardial passageway into an adjacent coronary vessel or chamber of the heart. The apparatus of the present invention include protrusive stent devices for stenting of transmyocardial passageways, intraluminal valving devices for valving of transmyocardial passageways, intracardiac valving devices for valving of transmyocardial passageways, endogenous tissue valves for valving of transmyocardial passageways, and ancillary apparatus for use in conjunction therewith.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Single port cardiac support apparatus
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Laminar ventricular partitioning device
InactiveUS20080071298A1Lower the volumeReduce stressCeramic shaping apparatusOcculdersHeart chamberNon traumatic
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for trans myocardial revascularization
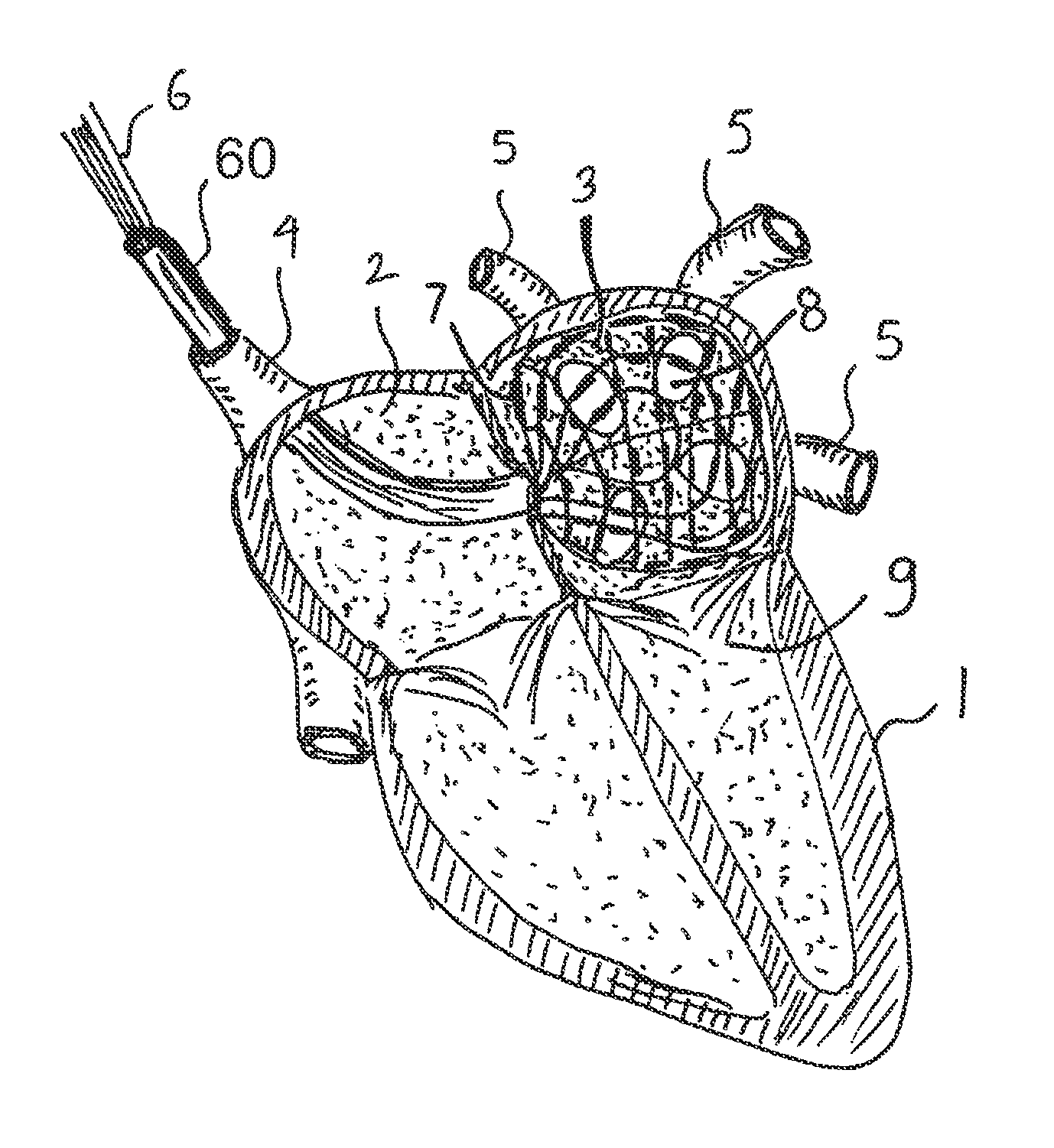
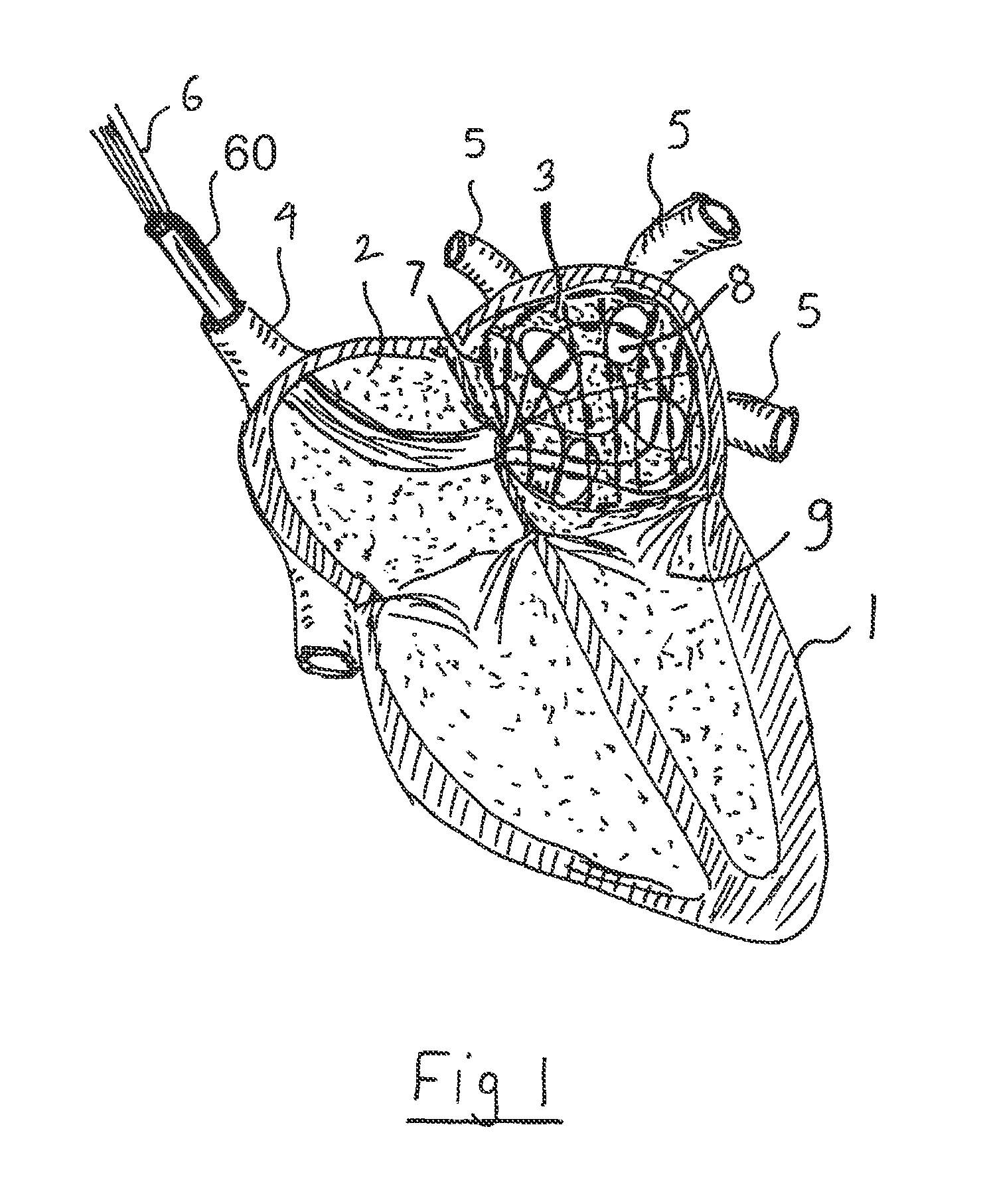
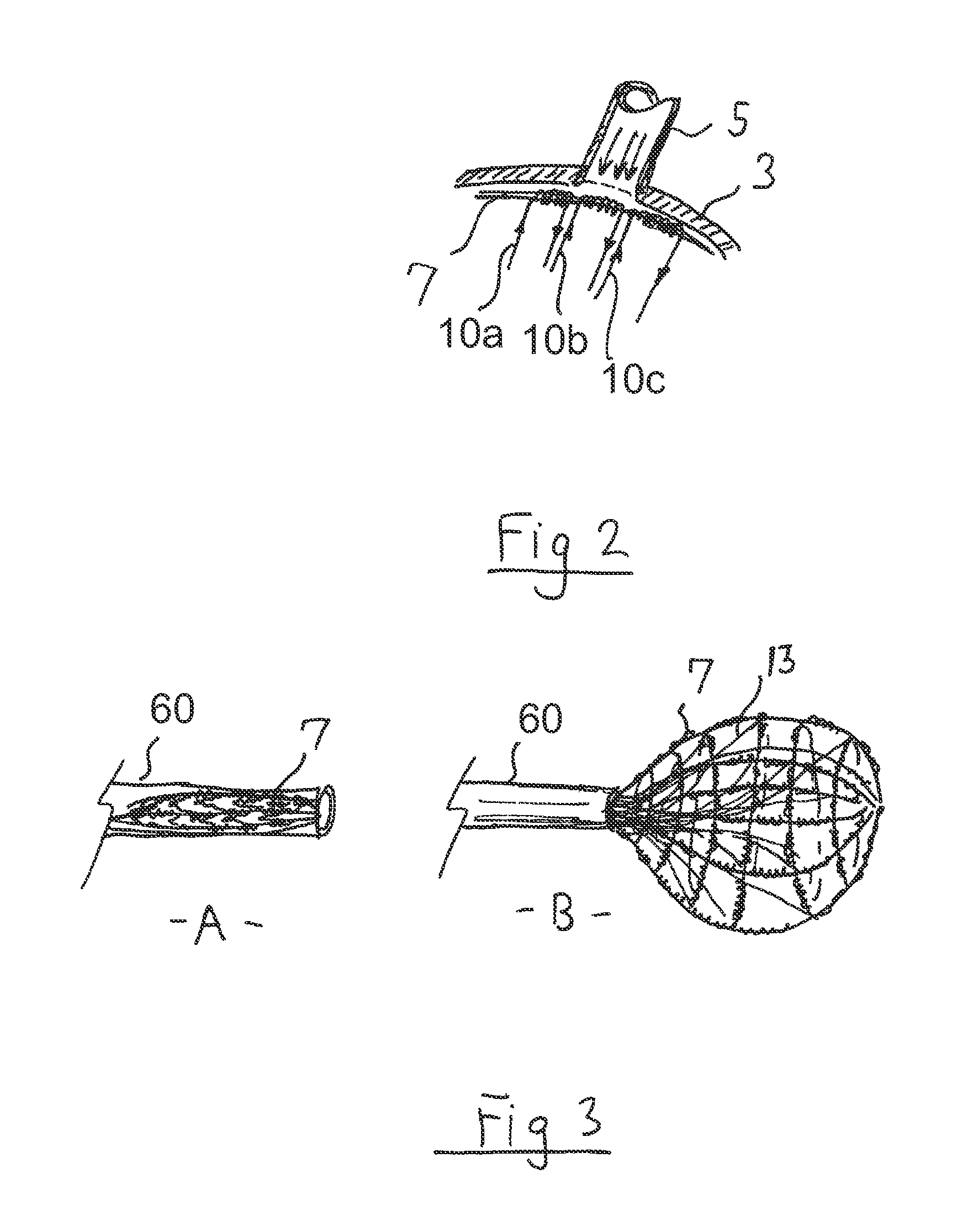
InactiveUS6053924AImprove protectionIncrease supplyEar treatmentHeart valvesCardiac wallHeart chamber
A medical device and method are described for performing Trans Myocardial Revascularization (TMR) in a human heart. The device consists of a myocardial implant and a directable intracardiac catherter that are suited for delivery into a heart wall of the implant. The catheter utilizes a percutaneous, minimally-invasive access to reach the inner surface of the heart chambers. The catheter provides a conduit for advancing multiple myocardial implants to the heart wall. The implant may include anchoring elements or a retainer for holding the implant body into the heart wall. The implant may include a tapered leading end, and can be advanced into the heart wall using a rotational or a pushing technique until the implant is fully deployed. The implant is then released from the catheter, and another implant inserted into the catheter, or the catheter withdrawn from the human body. The myocardial implant is used to stimulate the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) in the treated heart wall, and to result in Trans Myocardial Revascularization of this heart wall.
Owner:HUSSEIN HANY
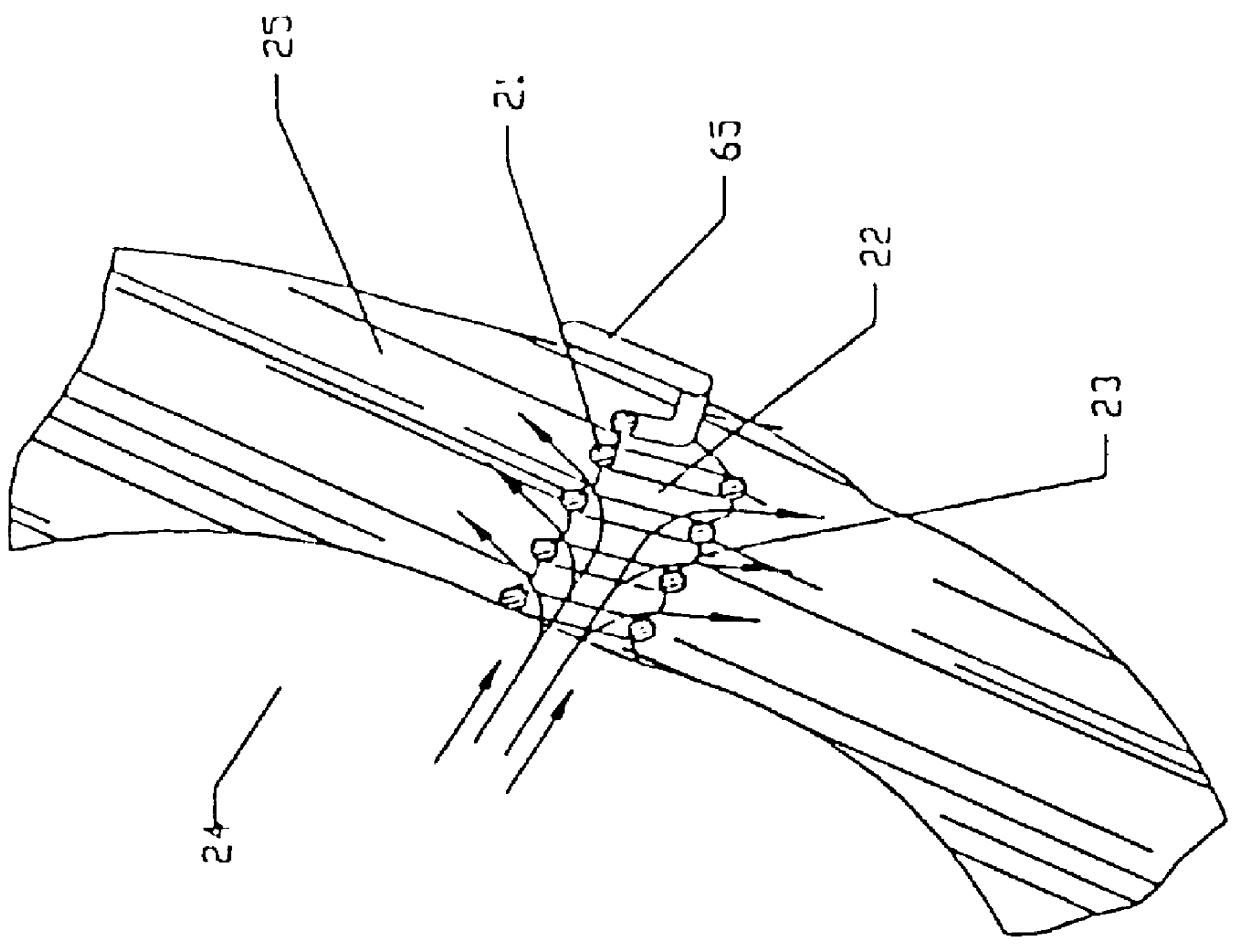
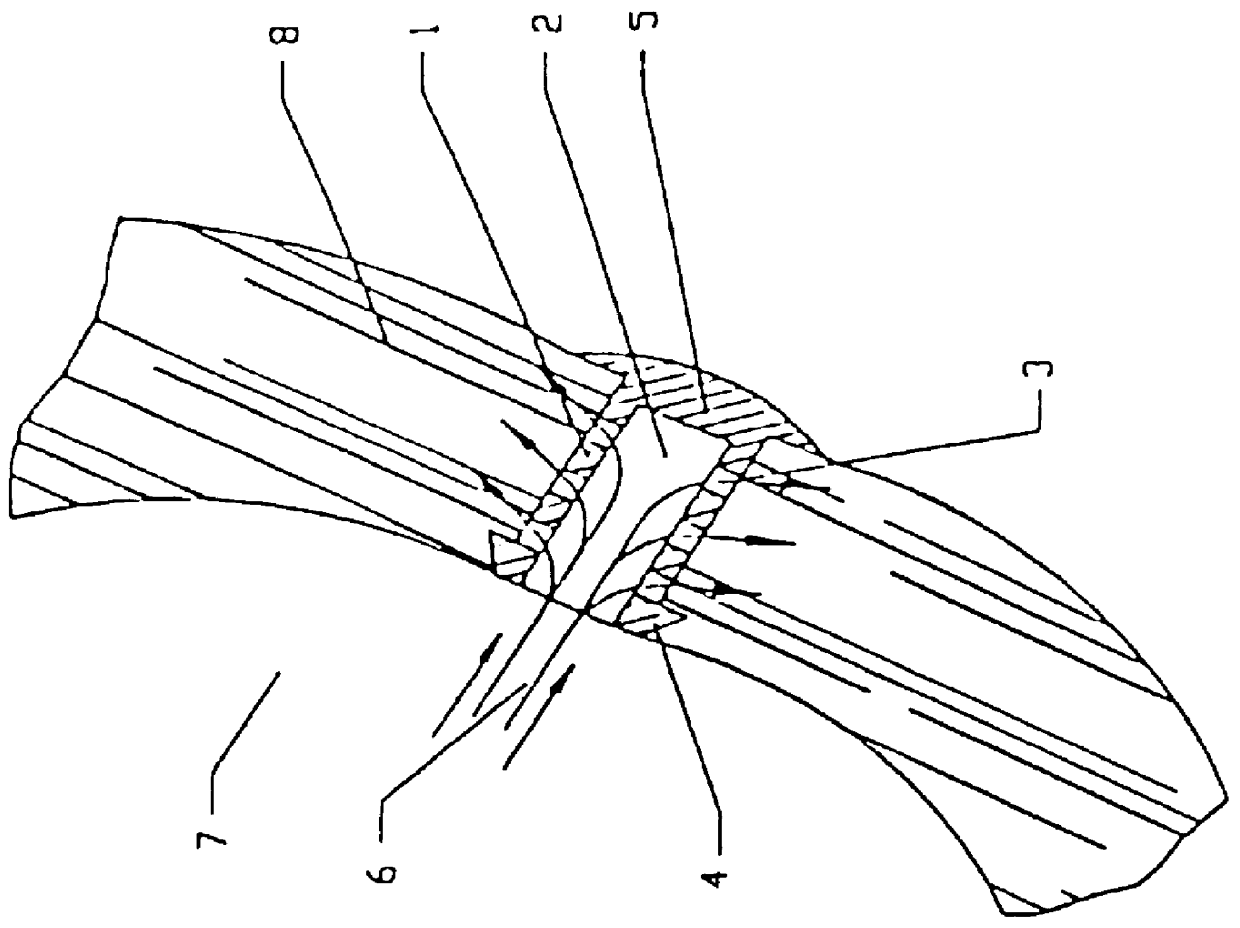
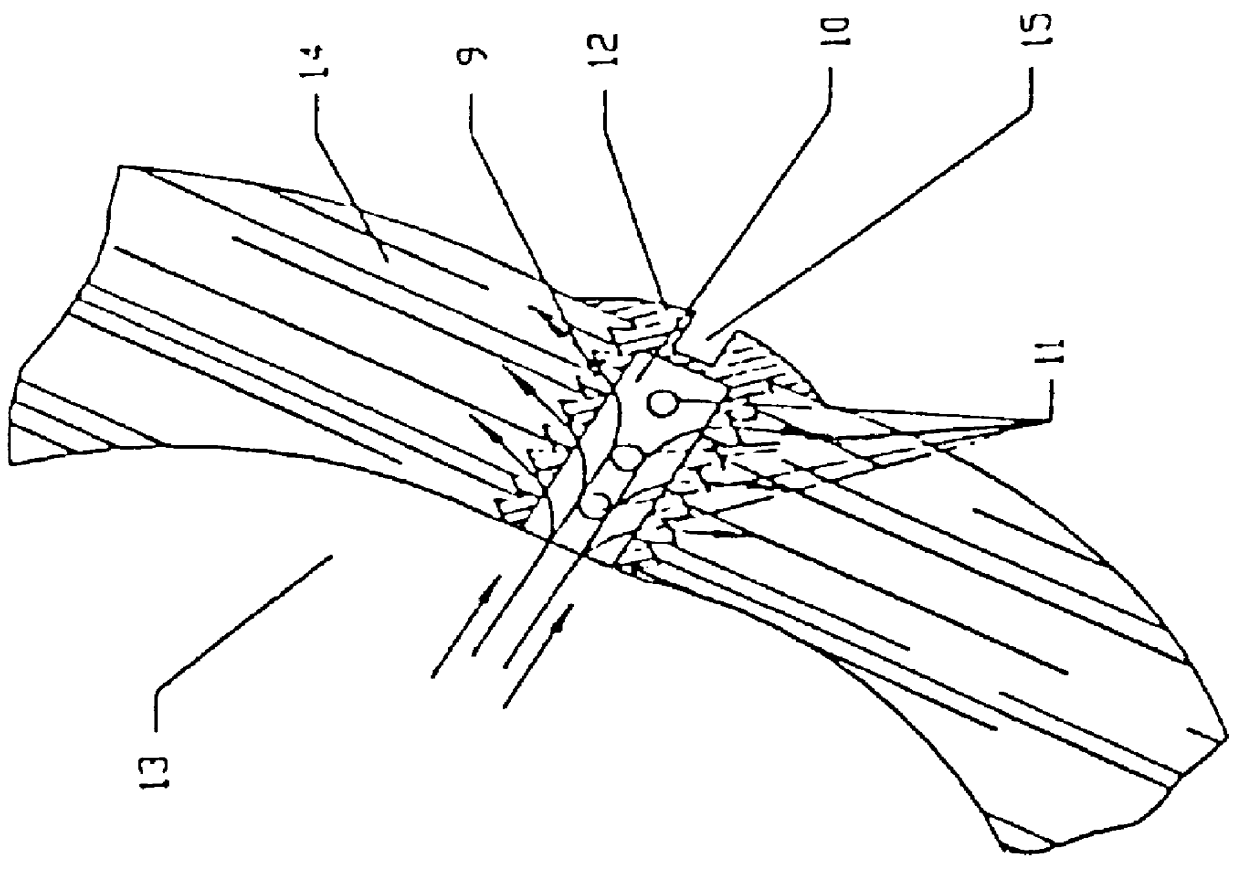
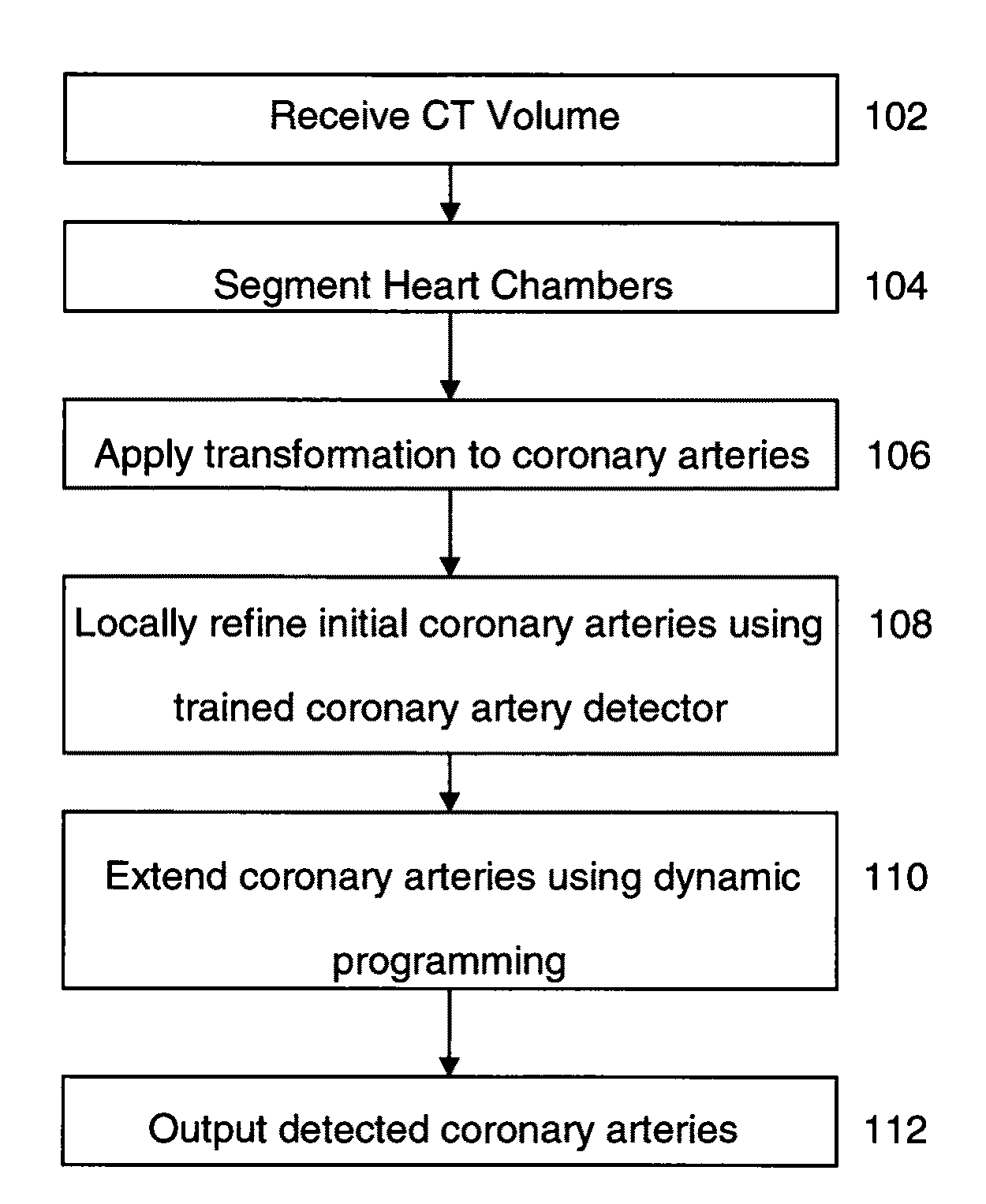
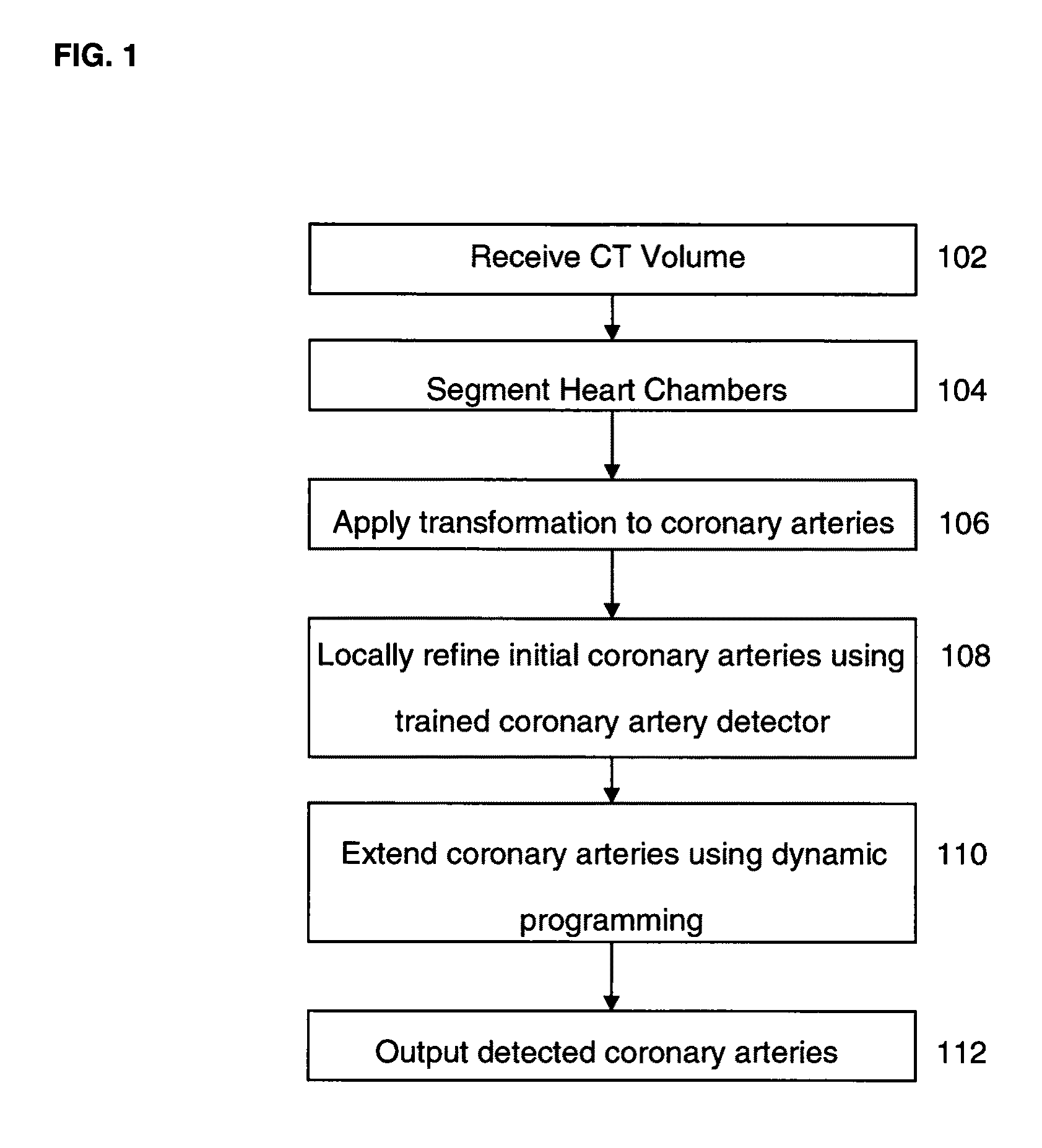
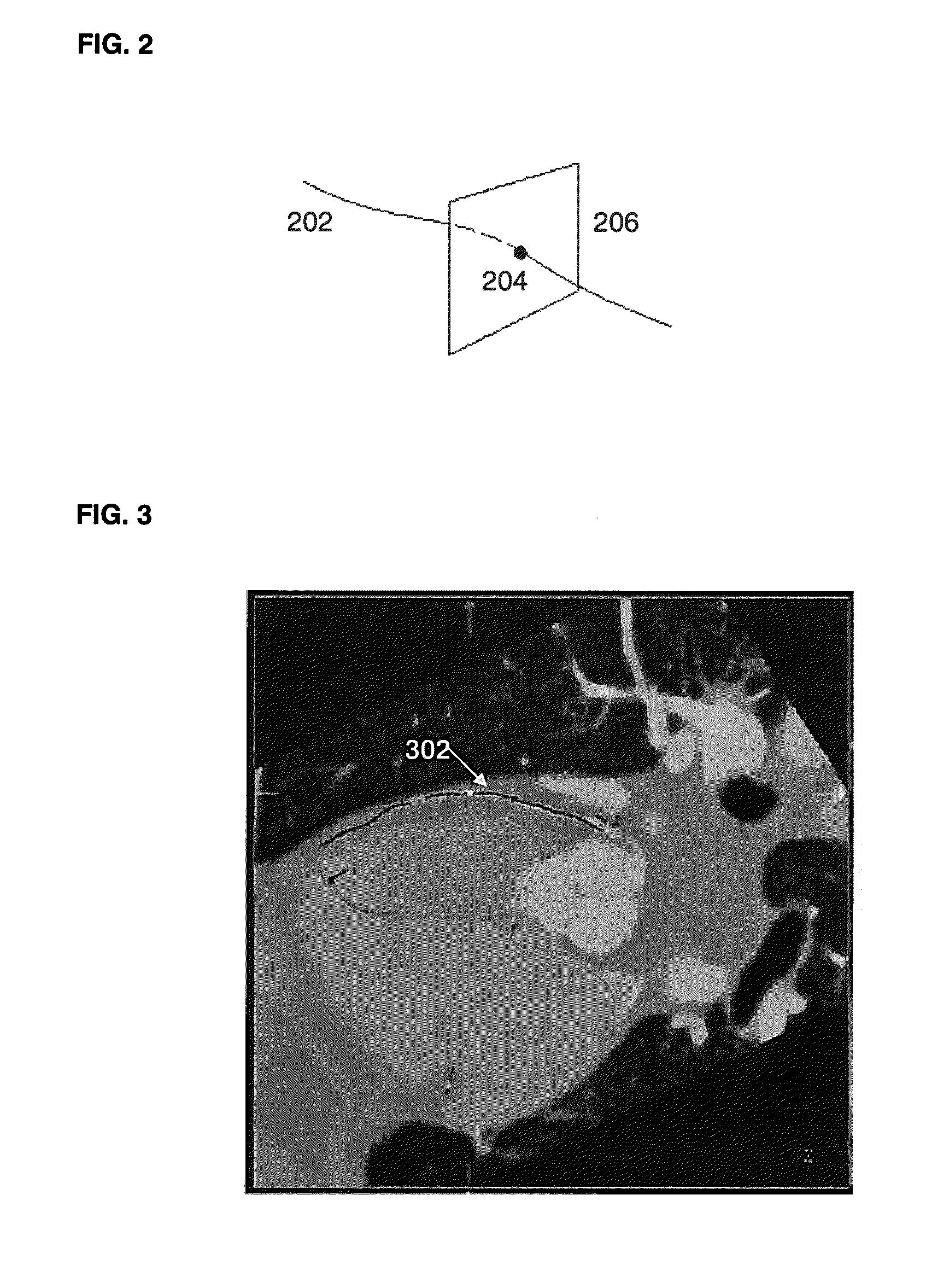
Method and System for Automatic Coronary Artery Detection
ActiveUS20100067760A1Efficiently and robustly detectImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesHeart chamber
A method and system for coronary artery detection in 3D cardiac volumes is disclosed. The heart chambers are segmented in the cardiac volume, and an initial estimation of a coronary artery is generated based on the segmented heart chambers. The initial estimation of the coronary artery is then refined based on local information in the cardiac volume in order to detect the coronary artery in the cardiac volume. The detected coronary artery can be extended using 3D dynamic programming.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Device and method for regulating pressure in a heart chamber
A device for regulating blood pressure in a heart chamber is provided. The device includes a shunt positionable within a septum of the heart. The shunt is designed for enabling blood flow between a left heart chamber and a right heart chamber, wherein the flow rate capacity of the device is mostly a function of pressure in the left heart chamber.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
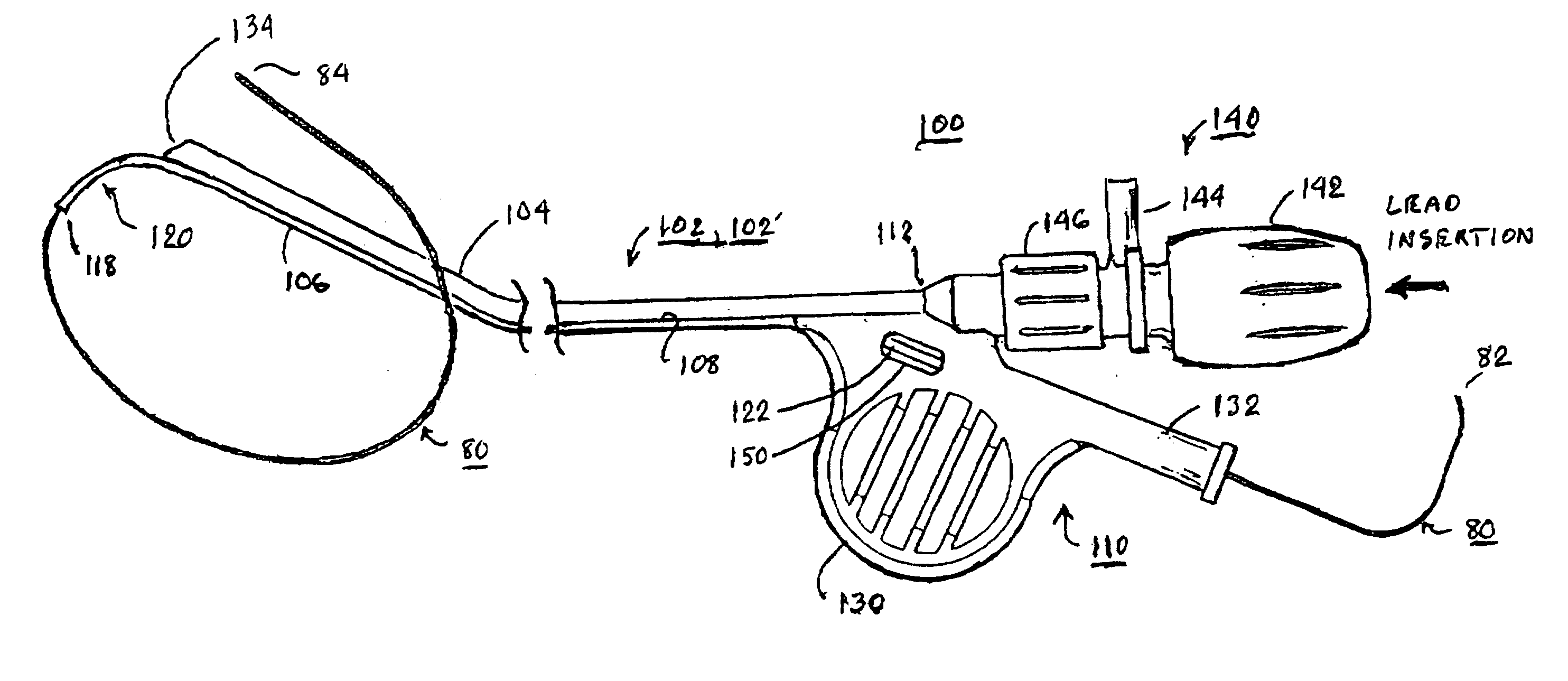
System and method for cardiac valve repair and replacement
A method of delivering a prosthetic mitral valve includes delivering a distal anchor from a delivery sheath such that the distal anchor self-expands inside a first heart chamber on a first side of the mitral valve annulus, pulling proximally on the distal anchor such that the distal anchor self-aligns within the mitral valve annulus and the distal anchor rests against tissue of the ventricular heart chamber, and delivering a proximal anchor from the delivery sheath to a second heart chamber on a second side of the mitral valve annulus such that the proximal anchor self-expands and moves towards the distal anchor to rest against tissue of the second heart chamber. The self-expansion of the proximal anchor captures tissue of the mitral valve annulus therebetween.
Owner:CEPHEA VALVE TECH
Endovascular splinting devices and methods
InactiveUS20070055303A1Less invasiveMore clinical utilitySuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberBlood vessel
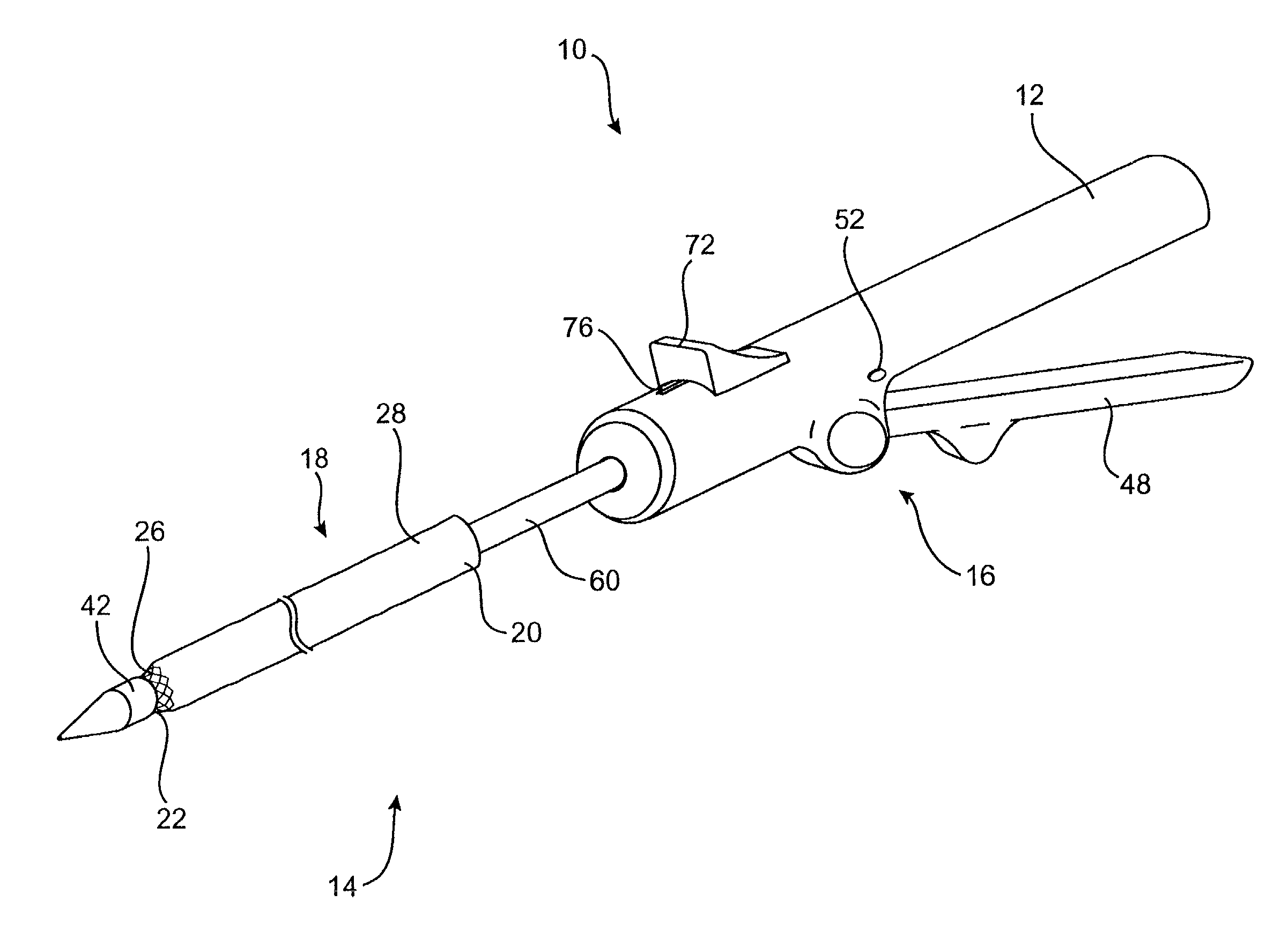
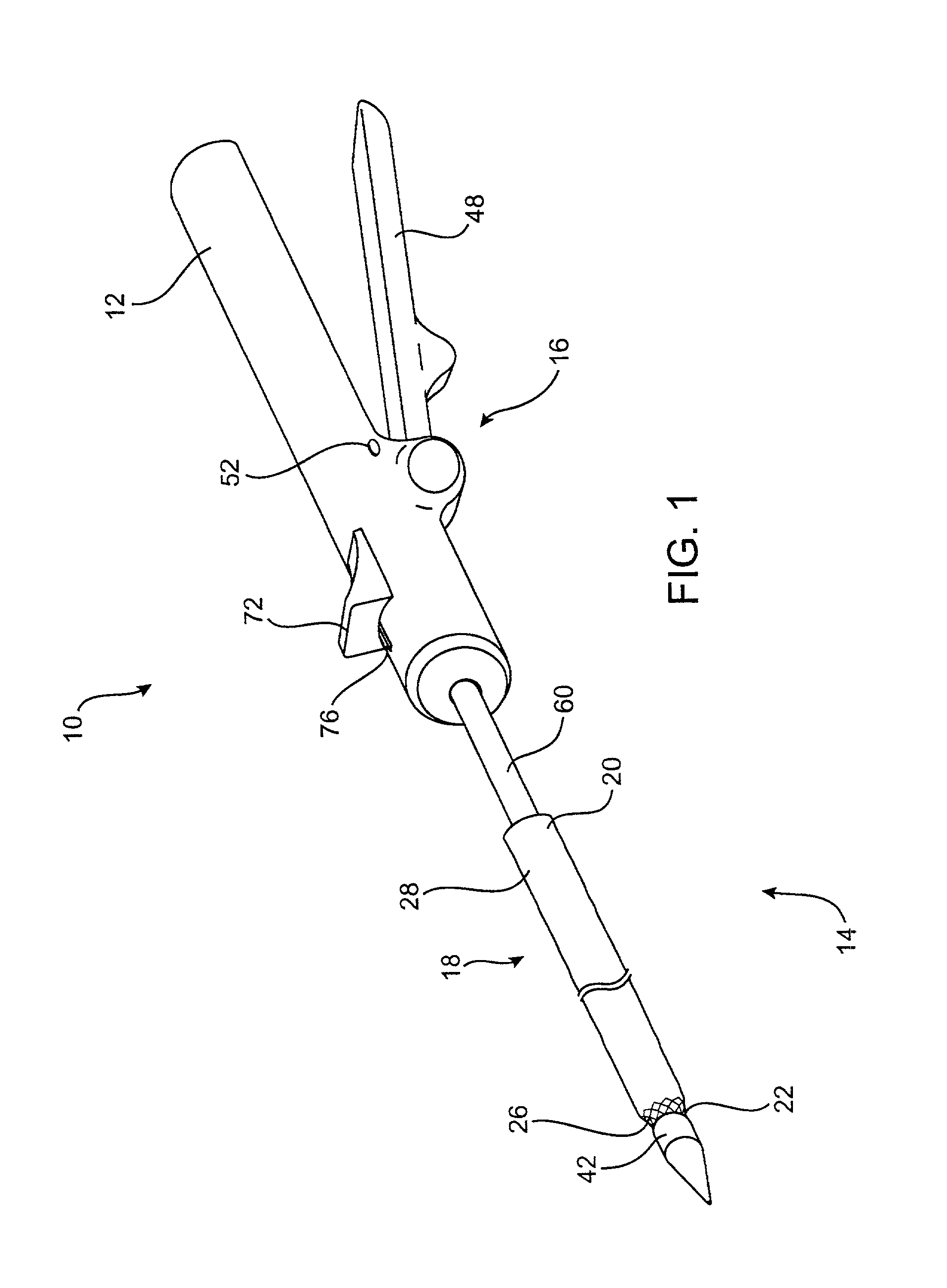
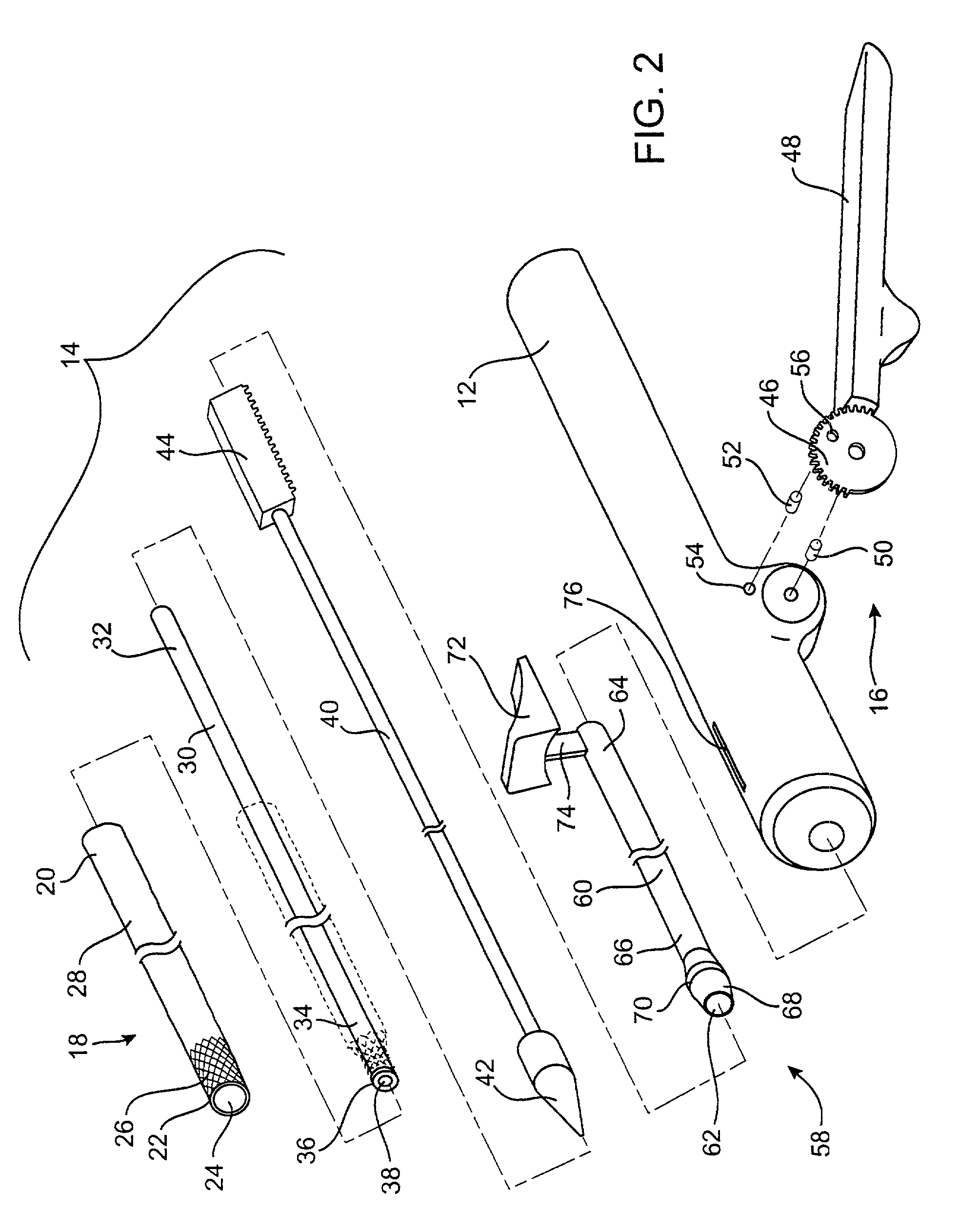
A method for placing a splint assembly transverse a heart chamber includes providing an elongate member having a first end and a second end and a deployable heart-engaging assembly connected to at least the first end. The method includes advancing the elongate member through vasculature structure and into the heart chamber such that the first end of the elongate member extends through a first location of a wall surrounding the heart chamber and the second end extends through a second location of the heart chamber wall substantially opposite the first location. A deployable heart-engaging assembly is deployed such that it engages with a first exterior surface portion of the heart chamber wall adjacent the first location. The elongate member is secured with respect to the heart with a second heart-engaging assembly connected to the second end. The second heart-engaging assembly engages with a second exterior surface portion of the heart chamber wall adjacent the second location. A splint assembly includes an expandable heart-engaging assembly formed partially from portions forming the elongate member of the splint assembly. A delivery tool includes a tubular member configured to be advanced through vasculature structure and has a curved distal end.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Apparatus and method for treating a regurgitant valve
An apparatus for treating regurgitation of blood through a diseased heart valve having at least two leaflets includes an occluding member configured to be positioned within the diseased heart valve so that at least a portion of the occluding member is positioned adjacent to one of the at least two leaflets. The at least one portion of the occluding member contacts at least one surface of the at least one leaflet. The occluding member is dimensioned so that the at least one leaflet abuts the at least one surface of the occluding member. The apparatus further includes a suspending wire operatively attached to the occluding member and configured to facilitate positioning of the occluding member within the heart valve. The suspending wire includes an anchoring portion having a coiled shape. The anchoring portion is configured to secure the suspending wire to at least one of a blood vessel and a heart wall surrounding a heart chamber.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
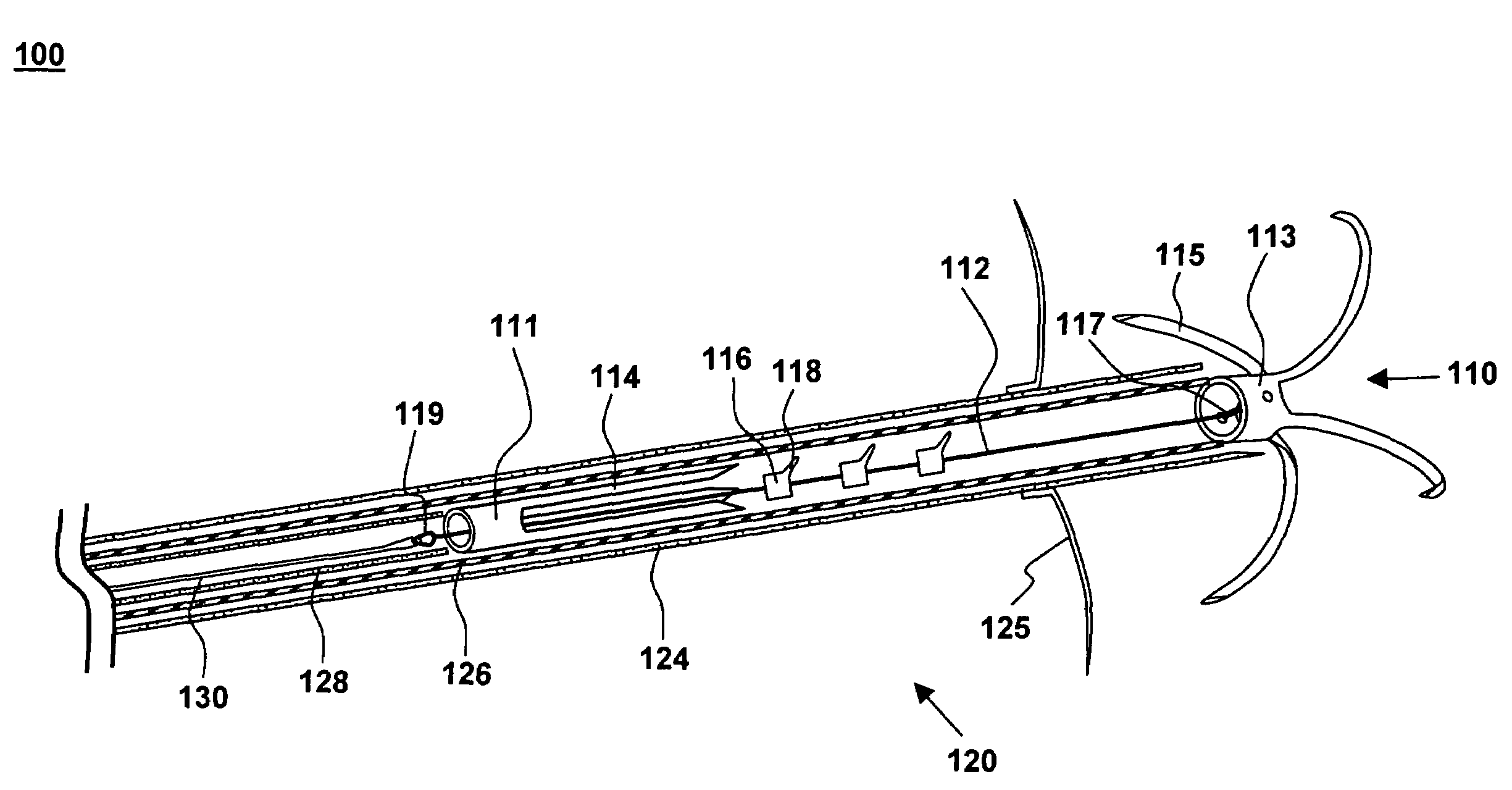
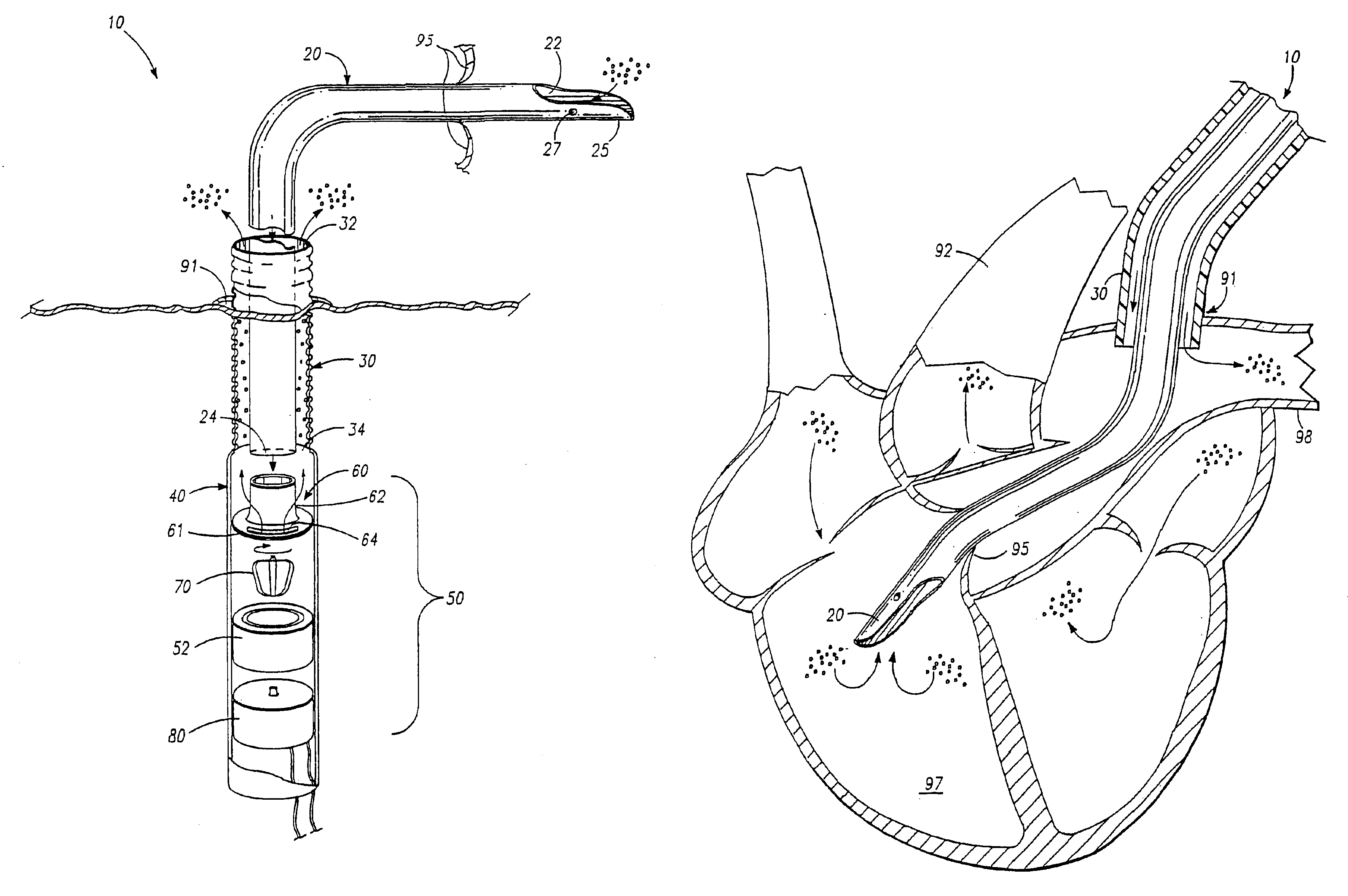
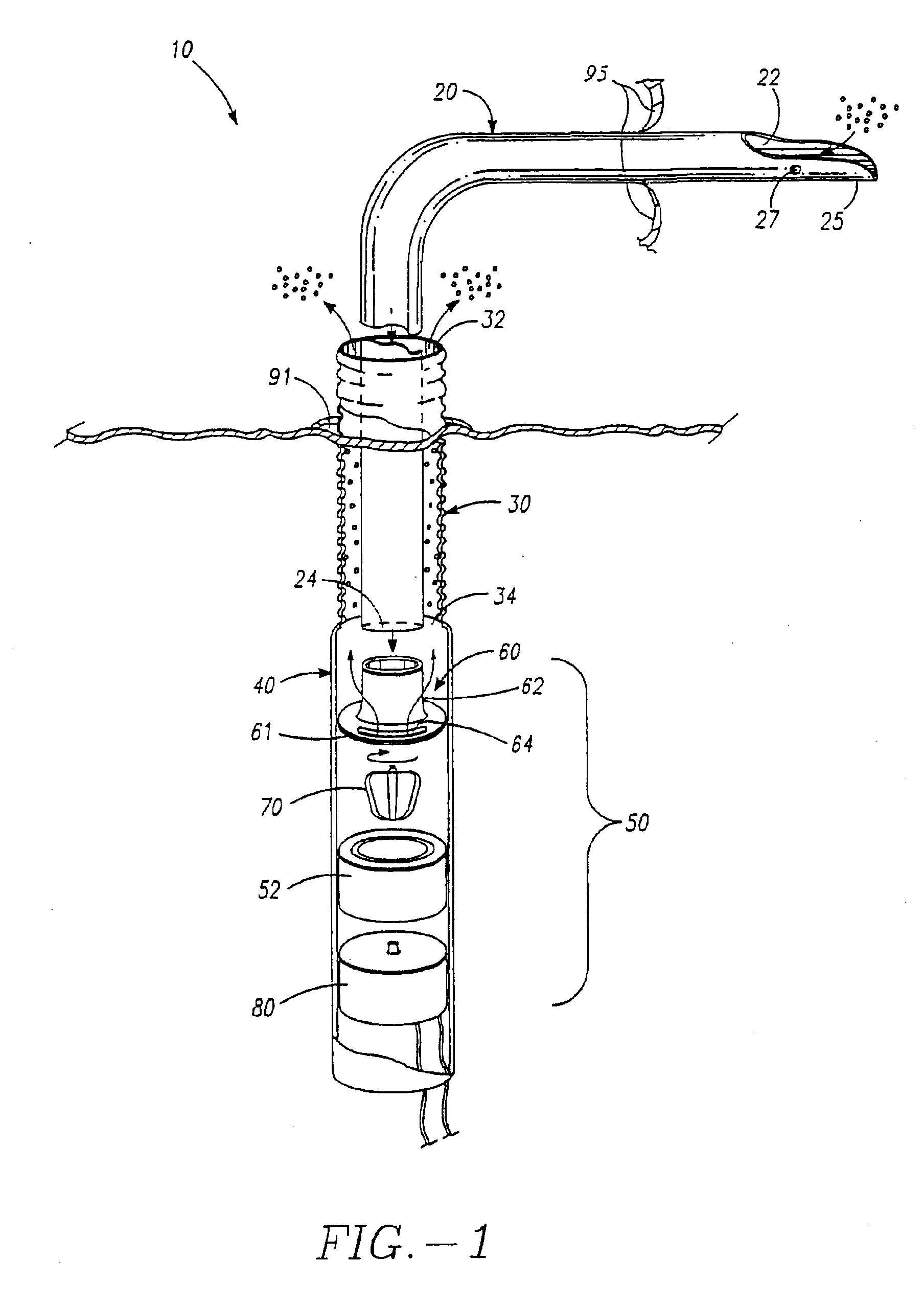
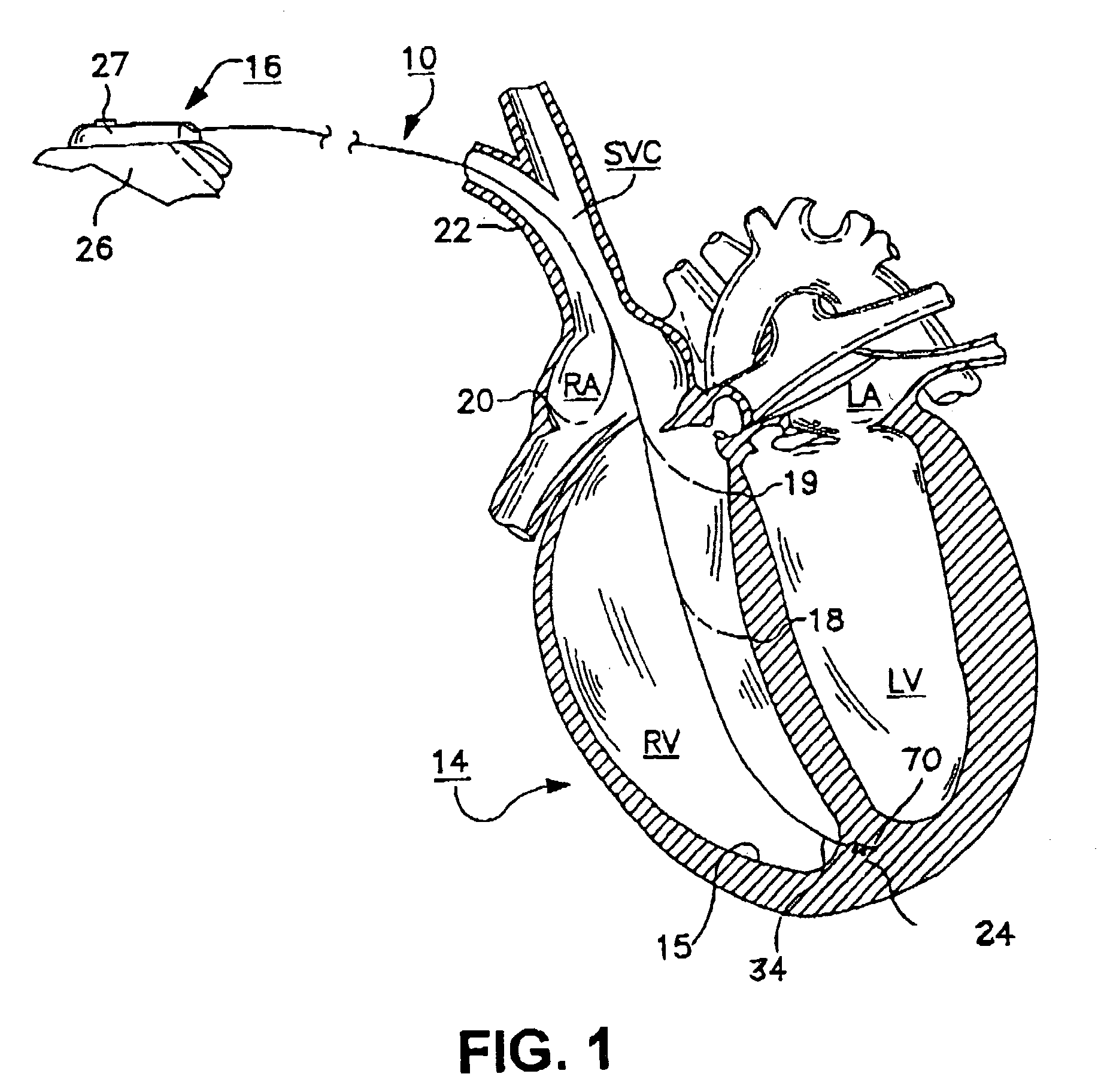
Bilumen guide catheters for accessing cardiac sites
ActiveUS20040116878A1Meet actual needsAdvantageously employedTransvascular endocardial electrodesCatheterHeart chamberElectrical stimulations
Bilumen catheters and methods of using same for facilitating implantation of cardiac leads for applying electrical stimulation to and / or sensing electrical activity of the heart through one or more electrode positioned at an implantation site within a heart chamber or cardiac vessel adjacent a heart chamber, and more particularly to a method and apparatus for introducing such a cardiac lead having low torqueability and pushability through a tortuous pathway to enable attachment of the cardiac lead at the implantation site employing a bilumen guide catheter are disclosed. The bilumen catheter body includes a relatively large diameter delivery lumen to introduce a small diameter cardiac lead and a small diameter guide lumen to receive a stylet or guidewire to locate the guide catheter body distal end at the implantation site. The small diameter lumen within a small diameter guide tube extends distally from the delivery exit port of the delivery lumen.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and devices for delivering a ventricular stent
A method, and related tools for performing the method, of delivering a stent or other like device to the heart to connect the left ventricle to the coronary artery to thereby supply blood directly from the ventricle to the coronary artery may be used to bypass a total or partial occlusion of a coronary artery. The method may include placing a guide device and a dilation device through an anterior wall and a posterior wall of the coronary vessel and through a heart wall between the heart chamber and the coronary vessel. The dilation device may be used to form a passageway in the heart wall at a location defined by the guide device. The method may then include placing a stent within the passageway.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
Electrophysiology Therapy Catheter
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Left ventricular conduit with blood vessel graft
Disclosed is a conduit that provides a bypass around an occlusion or stenosis in a coronary artery. The conduit is a tube adapted to be positioned in the heart wall to provide a passage for blood to flow between a heart chamber and a coronary artery, at a site distal to the occlusion or stenosis. The conduit has a section of blood vessel attached to its interior lumen which preferably includes at least one naturally occurring one-way valve positioned therein. The valve prevents the backflow of blood from the coronary artery into the heart chamber.
Owner:JENAVALVE TECH INC
Endocardial mapping catheter
A mapping catheter is described to map electric field activity in a heart chamber. The catheter has a first grouping of electrodes positioned so that they are not in contact with the patient's heart. The catheter also having a second set of electrodes positioned in contact with the patient's heart.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Apparatus and method for intra-cardiac mapping and ablation
ActiveUS8920411B2Accurate locationMinimize the numberSurgical systems user interfaceCatheterHeart chamberCooling effect
An intra-cardiac mapping system is based on locating the ports through which blood flows in or out the heart chambers. For many procedures, such as ablation to cure atrial fibrillation, locating the pulmonary veins and the mitral valve accurately allows to perform a Maze procedure. The location of the ports and valves is based on using the convective cooling effect of the blood flow. The mapping can be performed by a catheter-deployed expandable net or a scanning catheter. The same net or catheter can also perform the ablation procedure.
Owner:KARDIUM
Thorascopic Heart Valve Repair Method and Apparatus
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com