Endovascular splinting devices and methods
a splinting device and endovascular technology, applied in the field of endovascular splinting devices and methods, can solve the problems of heart failure, significant increase in wall tension and/or stress, and dilatation of the left ventricular chamber, so as to achieve less invasiveness, less risk to the patient, and more clinical utility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
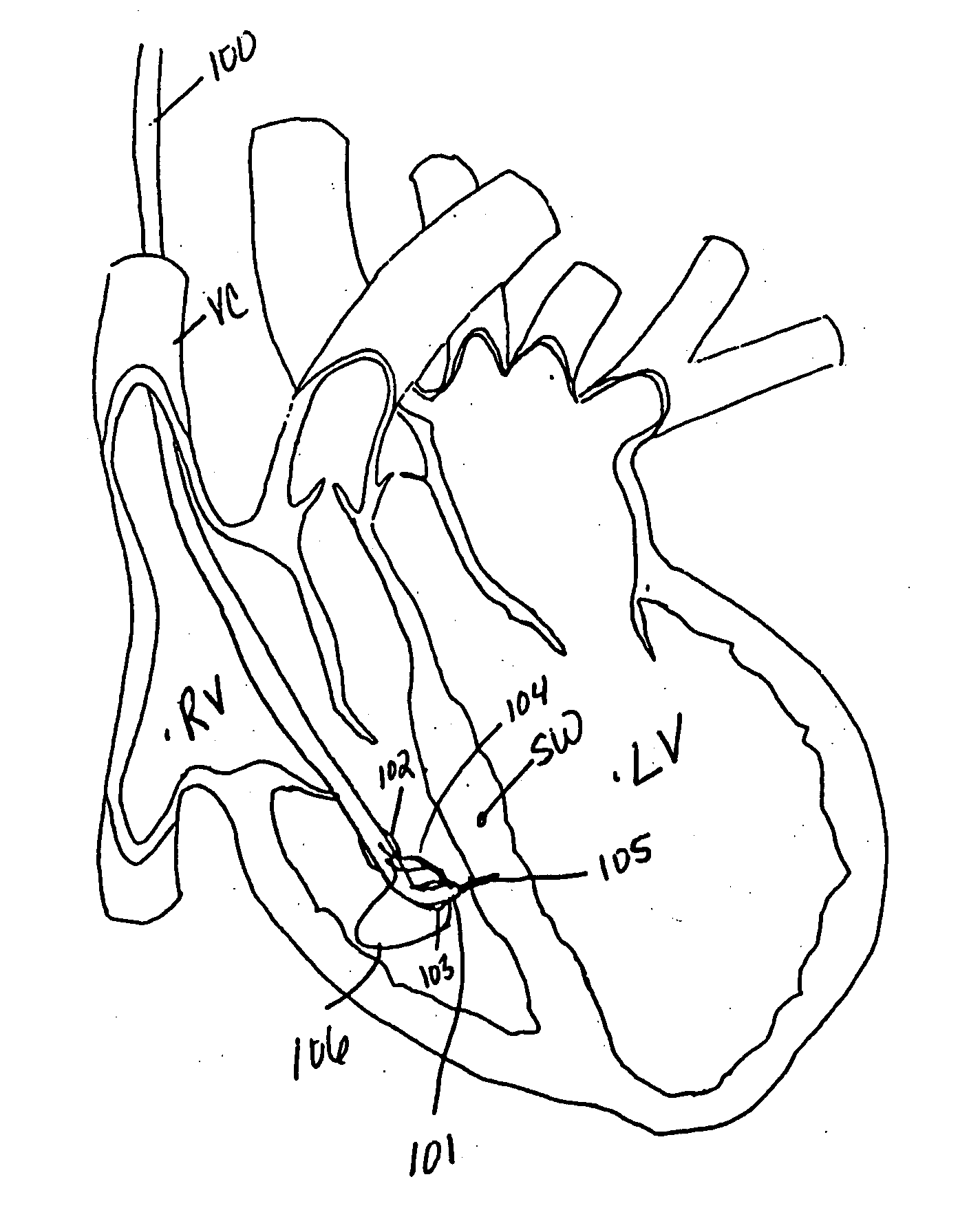
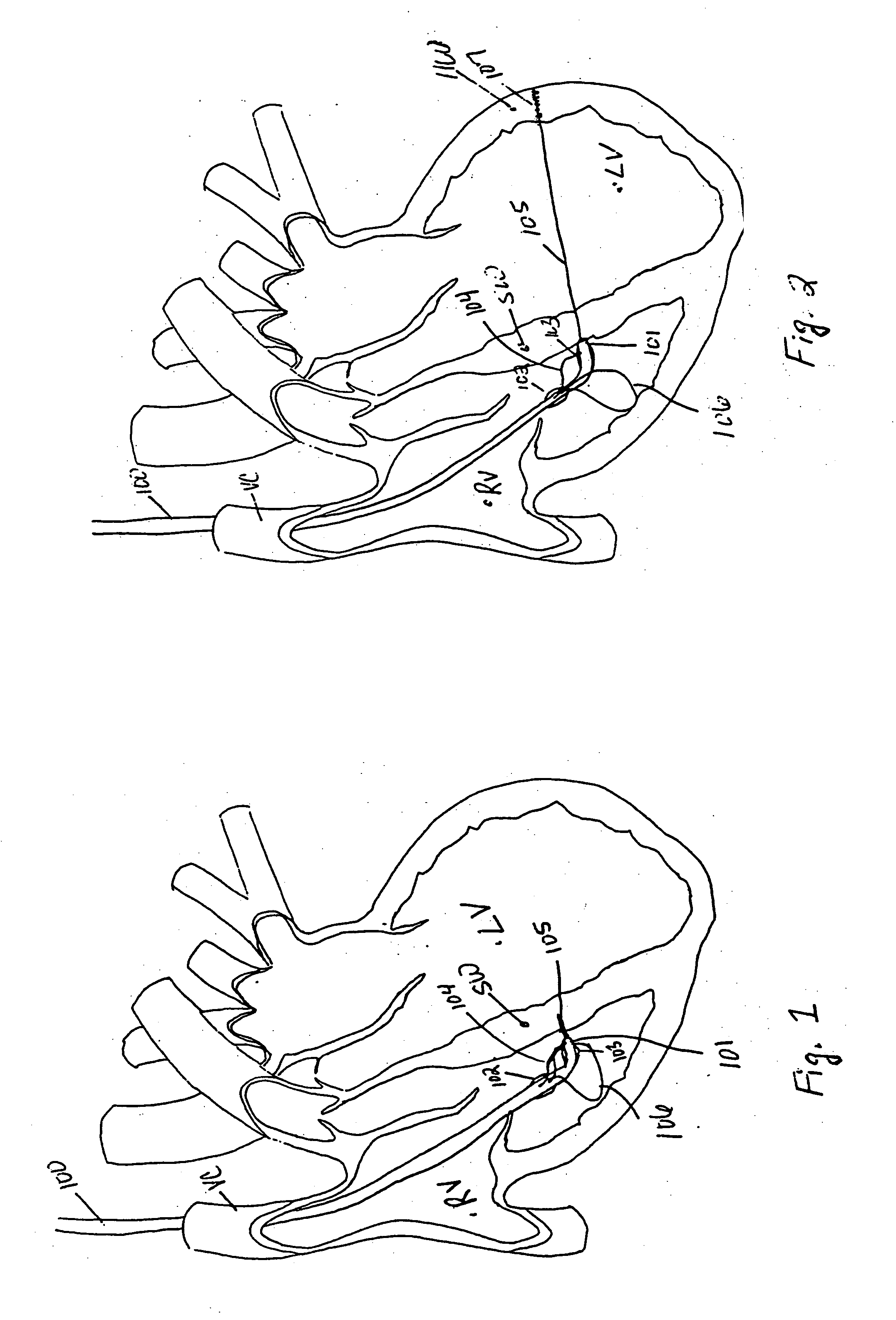
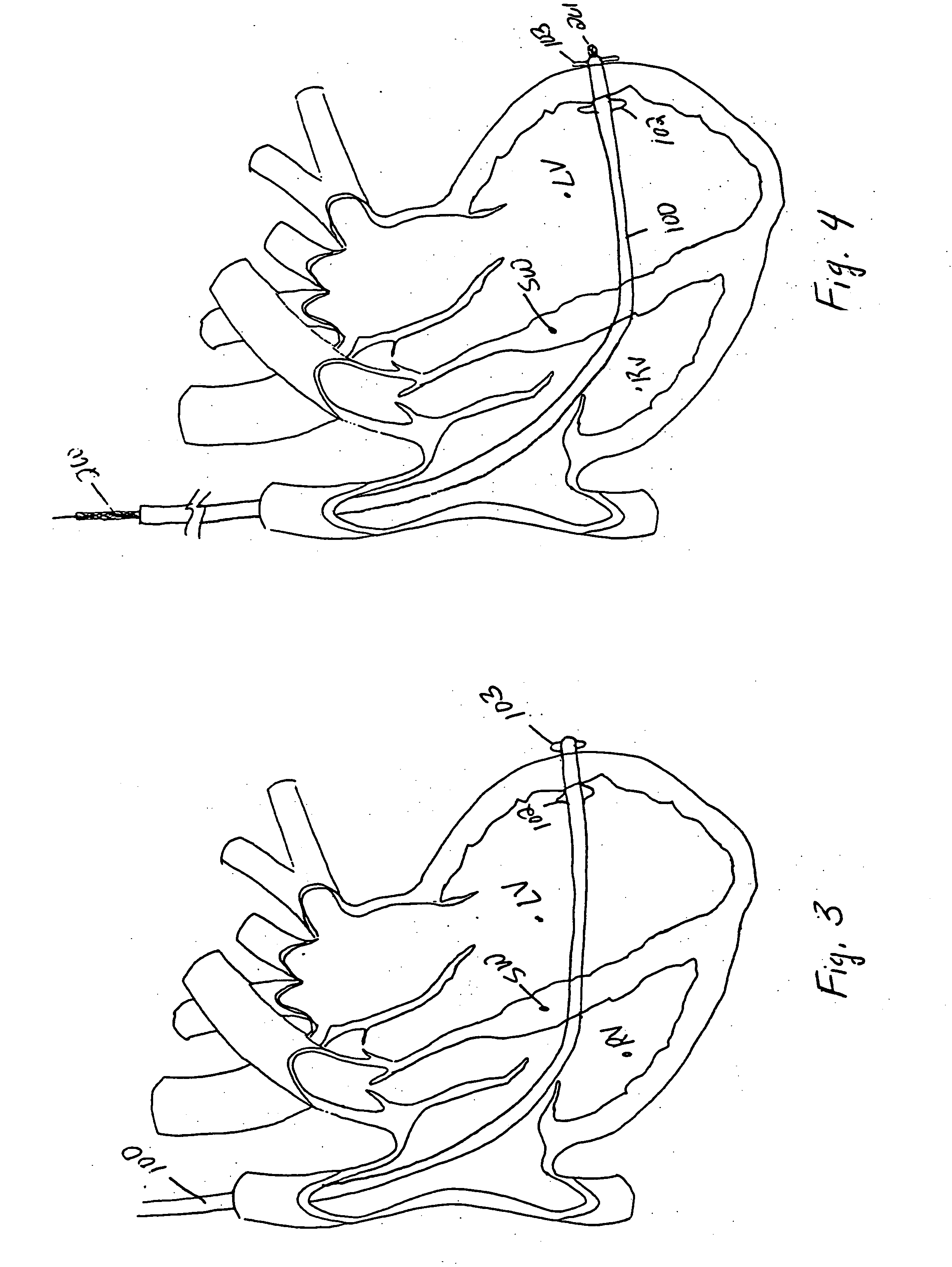
[0058] The various aspects of the invention to be discussed herein generally pertain to devices and methods for treating heart conditions, including, for example, dilatation, valve incompetencies, including mitral valve leakage, and other similar heart failure conditions. Each device of the present invention preferably operates passively in that, once placed in the heart, it does not require an active stimulus, either mechanical, electrical, or otherwise, to function. Implanting one or more of these devices alters the shape or geometry of the heart, both locally and globally, and thereby increases the heart's efficiency. That is, the heart experiences an increased pumping efficiency through an alteration in its shape or geometry and concomitant reduction in stress on the heart walls. In addition, the devices of the present invention may operate to assist in the apposition of heart valve leaflets to improve valve function.
[0059] The inventive devices and related methods offer numero...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com