Patents
Literature
539 results about "Myocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes with distinct properties: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the oesophagus and stomach.
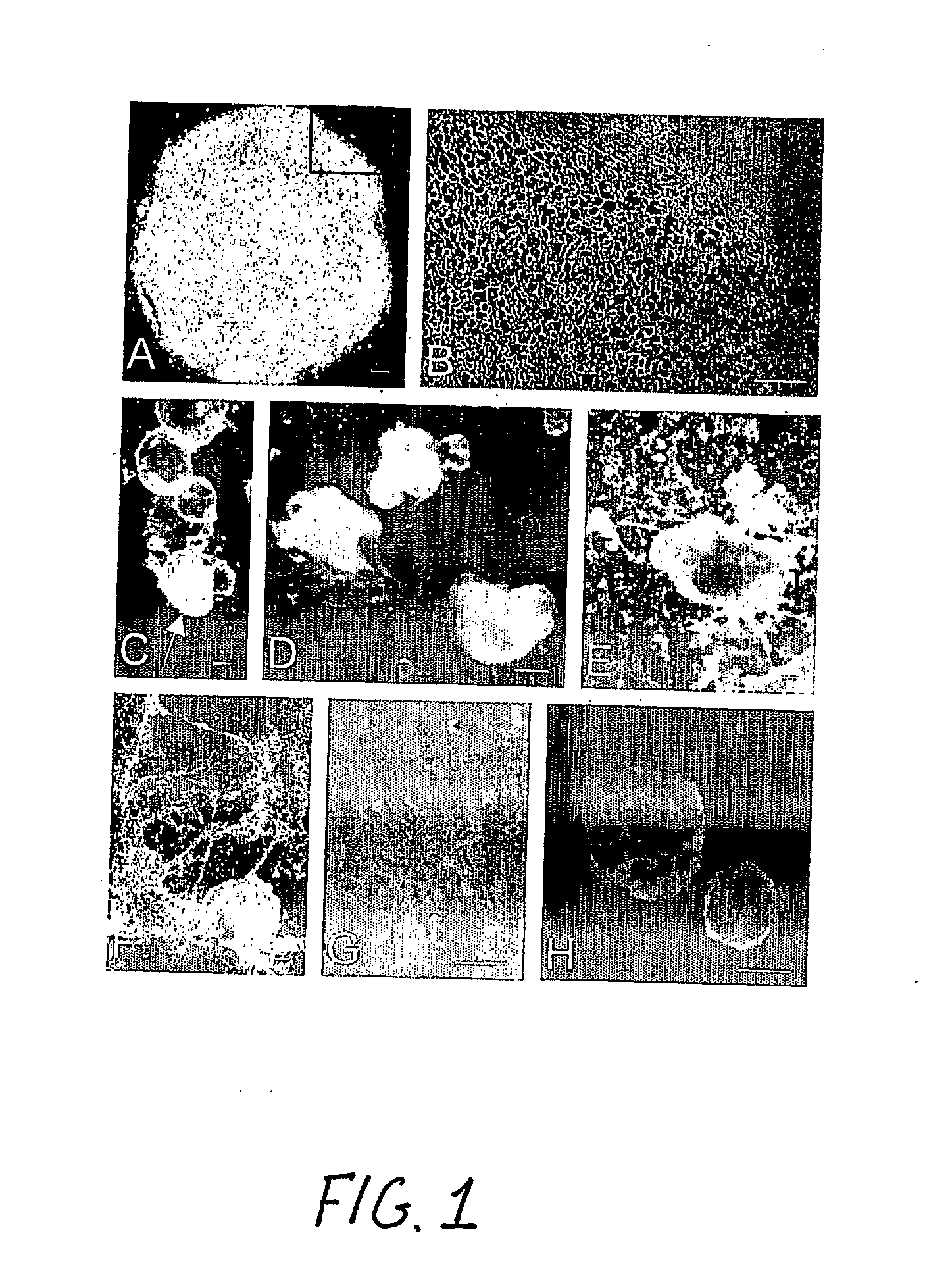
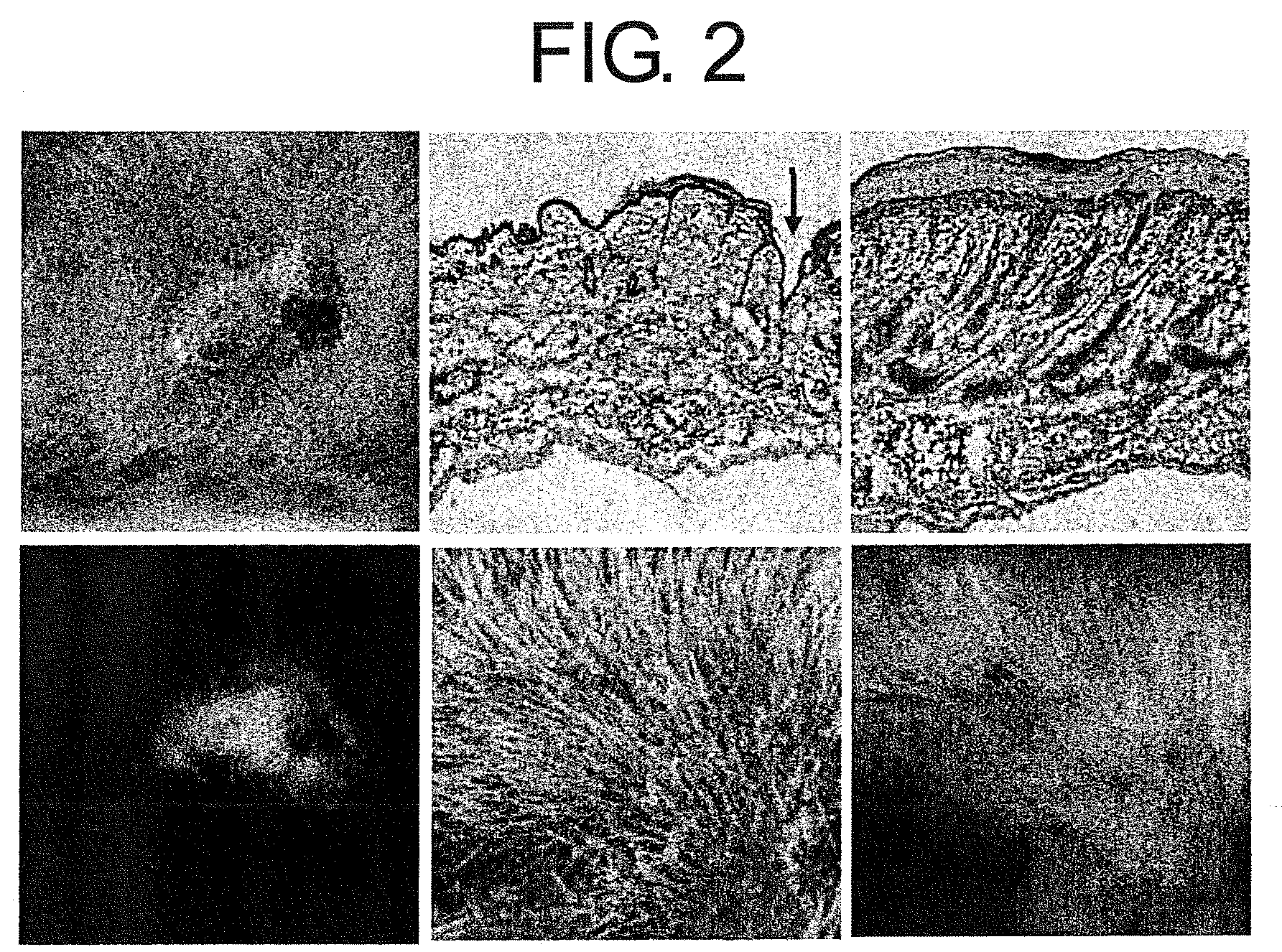
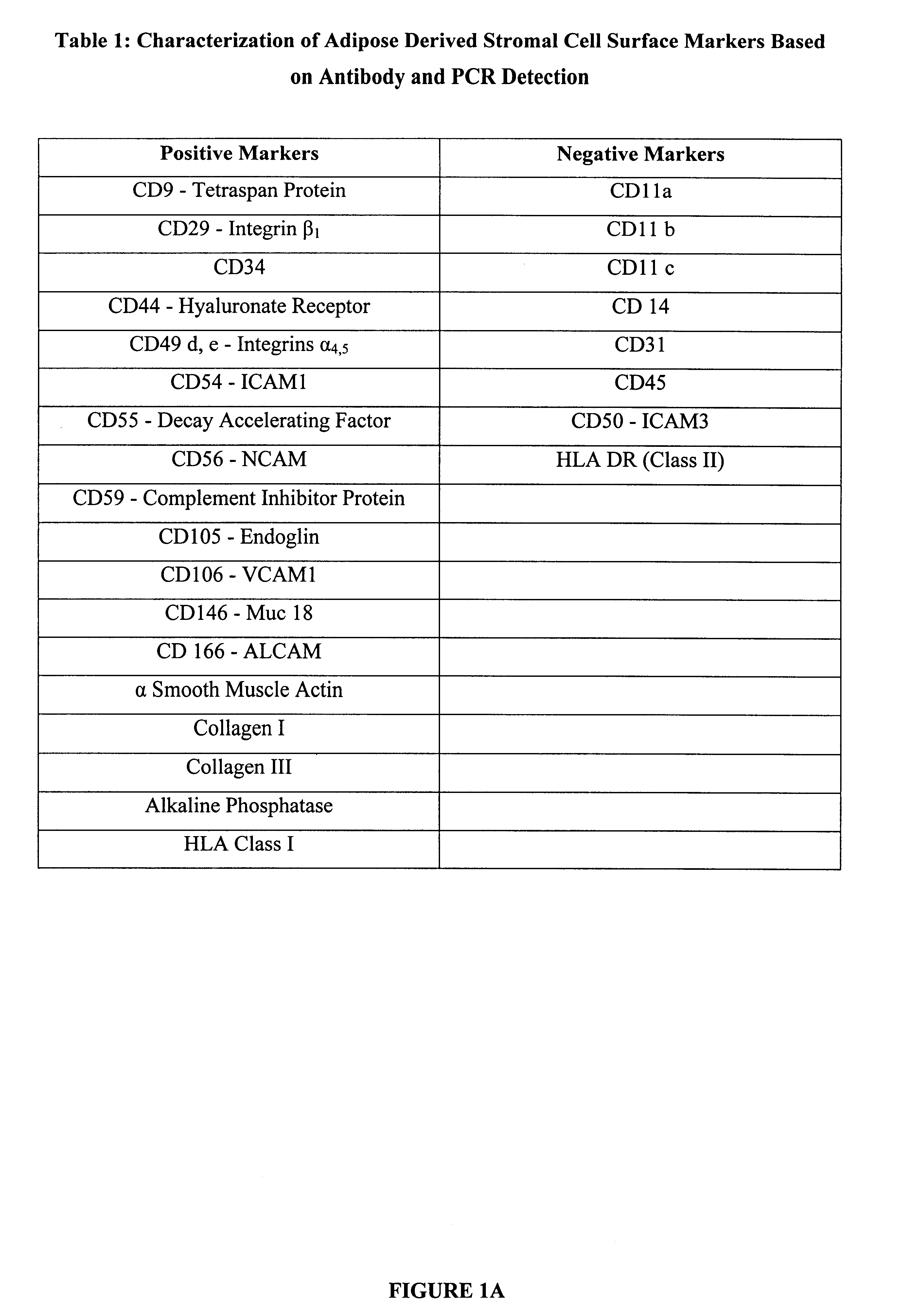
Multiple mesodermal lineage differentiation potentials for adipose tissue-derived stromal cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS6555374B1Enhance and inhibit differentiationIncrease differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementMammal material medical ingredientsGerm layerSmooth muscle
The invention relates to methods and compositions for the differentiation of stromal cells from adipose tissue into hematopoietic supporting stromal cells and myocytes of both the skeletal and smooth muscle type. The cells produced by the methods are useful in providing a source of fully differentiated and functional cells for research, transplantation and development of tissue engineering products for the treatment of human diseases and traumatic tissue injury repair.
Owner:COGNATE BIOSERVICES
Muscle-specific expression vectors
The invention is directed to novel combinations of muscle-specific enhancers and promoter elements useful for achieving persistent expression in the muscle or myocyctes. The muscle-specific promoter elements are derived from a muscle creatine kinase promoter, a troponin I promoter, a skeletal alpha-actin promoter, or a desmin promoter. The muscle-specific enhancer elements are derived from either troponin I internal regulatory elements, muscle creatine kinase enhancers, or desmin enhancers.
Owner:SOUZA DAVID +1
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor mediated gene transfer into muscle cells
InactiveUS20120122801A1Organic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryGlycoside formationMannose 6-phosphate receptor
The invention relates to glycoside-compound conjugates for use in antisense strategies and / or gene therapy. The conjugates comprise a glycoside linked to a compound, in which the glycoside is a ligand capable of binding to a mannose-6-phosphate receptor of a muscle cell. For example the cells are muscle cells of a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patient and the conjugate comprises an antisense oligonucleotide which causes ex on skipping and induces or restores the synthesis of dystrophin or variants thereof.
Owner:PROSENSA THERAPEUTICS
Platform for engineered implantable tissues and organs and methods of making the same
Disclosed are engineered tissues and organs comprising one or more muscle cell-containing layers, the engineered tissue or organ consisting essentially of cellular material, provided that the engineered tissue or organ is implantable in a vertebrate subject and not a vascular tube.
Owner:ORGANOVO
Treatment of cardiac tissue following myocardial infarction utilizing high intensity focused ultrasound
InactiveUS20050165298A1Ultrasound therapyDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac cycleInvasive treatments
A noninvasive or minimally invasive treatment of infarct areas of the heart with High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) emitted without respect to the timing or phase of the cardiac cycle, intended to remodel cardiac tissue by inducing angiogenesis and / or the formation of myocytes to improve cardiac function.
Owner:SONORHYTHM
Multipotent stem cells derived from placenta tissue and cellular therapeutic agents comprising the same
InactiveUS20070243172A1Negative immunological responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsGerm layerDisease
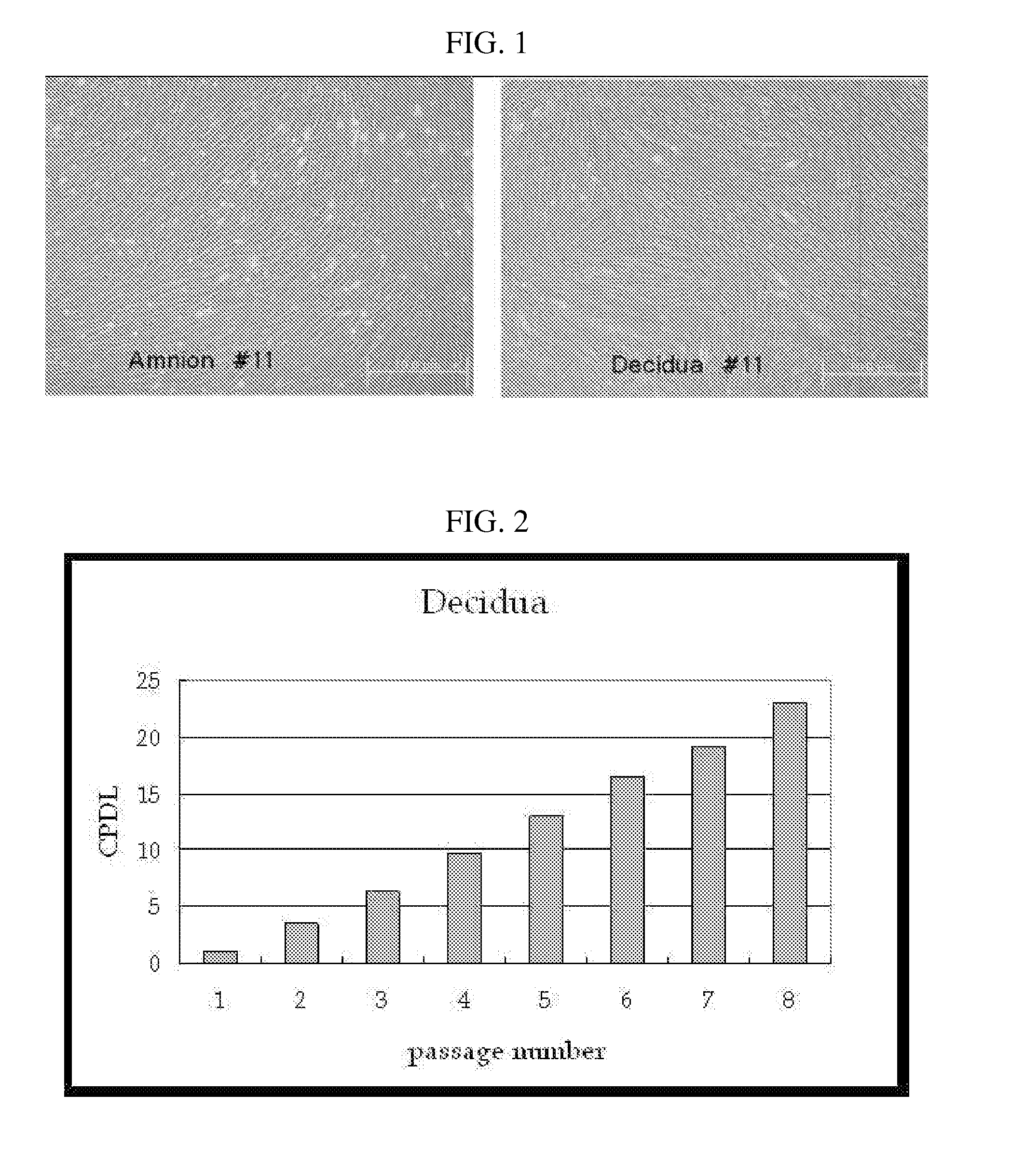
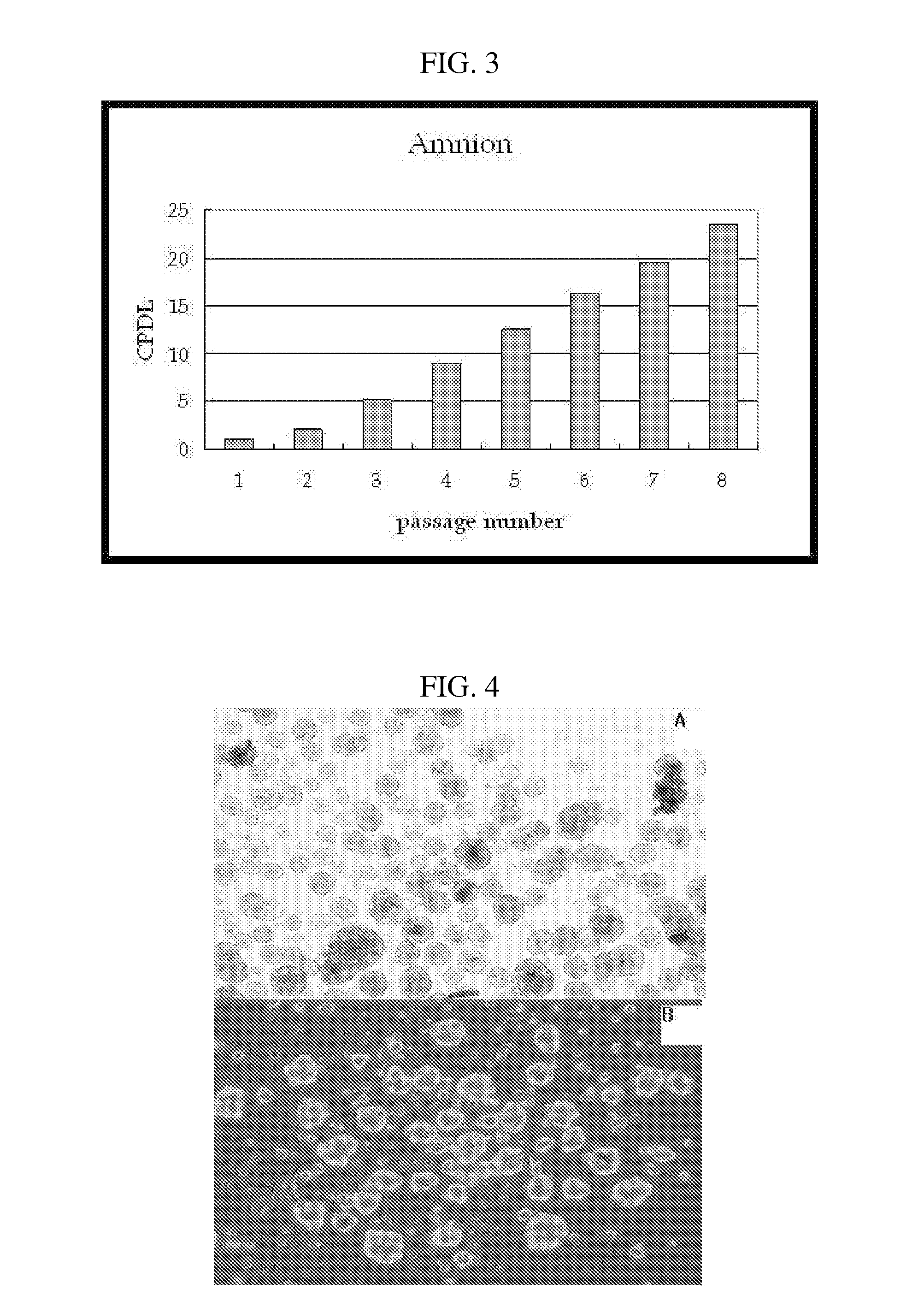
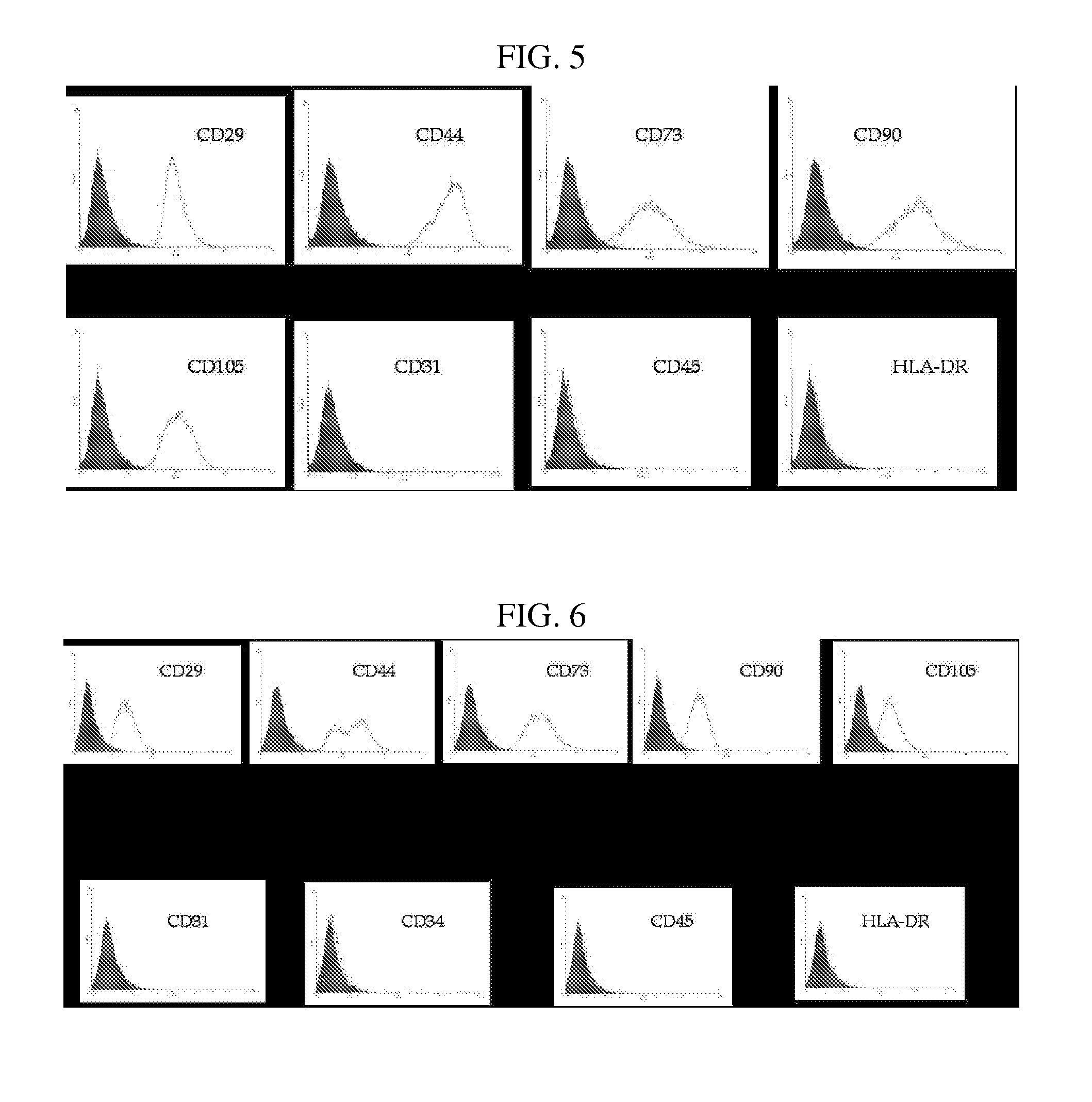
The present invention relates to placenta tissue-derived multipotent stem cells and cell therapeutic agents containing the same. More specifically, to a method for producing placenta stem cells having the following characteristics, the method comprising culturing amnion, chorion, decidua or placenta tissue in a medium containing collagenase and bFGF and collecting the cultured cells: (a) showing a positive immunological response to CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105, and showing a negative immunological response to CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-DR; (b) showing a positive immunological response to Oct4 and SSEA4; (c) growing attached to plastic, showing a round-shaped or spindle-shaped morphology, and forming spheres in an SFM medium so as to be able to be maintained in an undifferentiated state for a long period of time; and (d) having the ability to differentiate into mesoderm-, endoderm- and ectoderm-derived cells. Also the present invention relates to placenta stem cells obtained using the production method. The inventive multipotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, osteogenic cells, nerve cells, satellite cells, fat cells, cartilage-forming cells, osteogenic cells, or insuline-secreting pancreatic β-cells, and thus are effective for the treatment of muscular diseases, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, nervous diseases, diabetes and the like, and are useful for the formation of breast tissue.
Owner:RNL BIO
Engineered comestible meat
ActiveUS20130029008A1Increased formationArtificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingMyocyteBiology
Provided are engineered meat products formed as a plurality of at least partially fused layers, wherein each layer comprises at least partially fused multicellular bodies comprising non-human myocytes and wherein the engineered meat is comestible. Also provided are multicellular bodies comprising a plurality of non-human myocytes that are adhered and / or cohered to one another; wherein the multicellular bodies are arranged adjacently on a nutrient-permeable support substrate and maintained in culture to allow the multicellular bodies to at least partially fuse to form a substantially planar layer for use in formation of engineered meat. Further described herein are methods of forming engineered meat utilizing said layers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor mediated gene transfer into muscle cells
InactiveUS20110110960A1Organic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryDystrophinMannose 6-phosphate receptor
The invention relates to glycoside-compound conjugates for use in antisense strategies and / or gene therapy. The conjugates comprise a glycoside linked to a compound, in which the glycoside is a ligand capable of binding to a mannose-6-phosphate receptor of a muscle cell. For example the cells are muscle cells of a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patient and the conjugate comprises an antisense oligonucleotide which causes exon skipping and induces or restores the synthesis of dystrophin or variants thereof.
Owner:PROSENSA
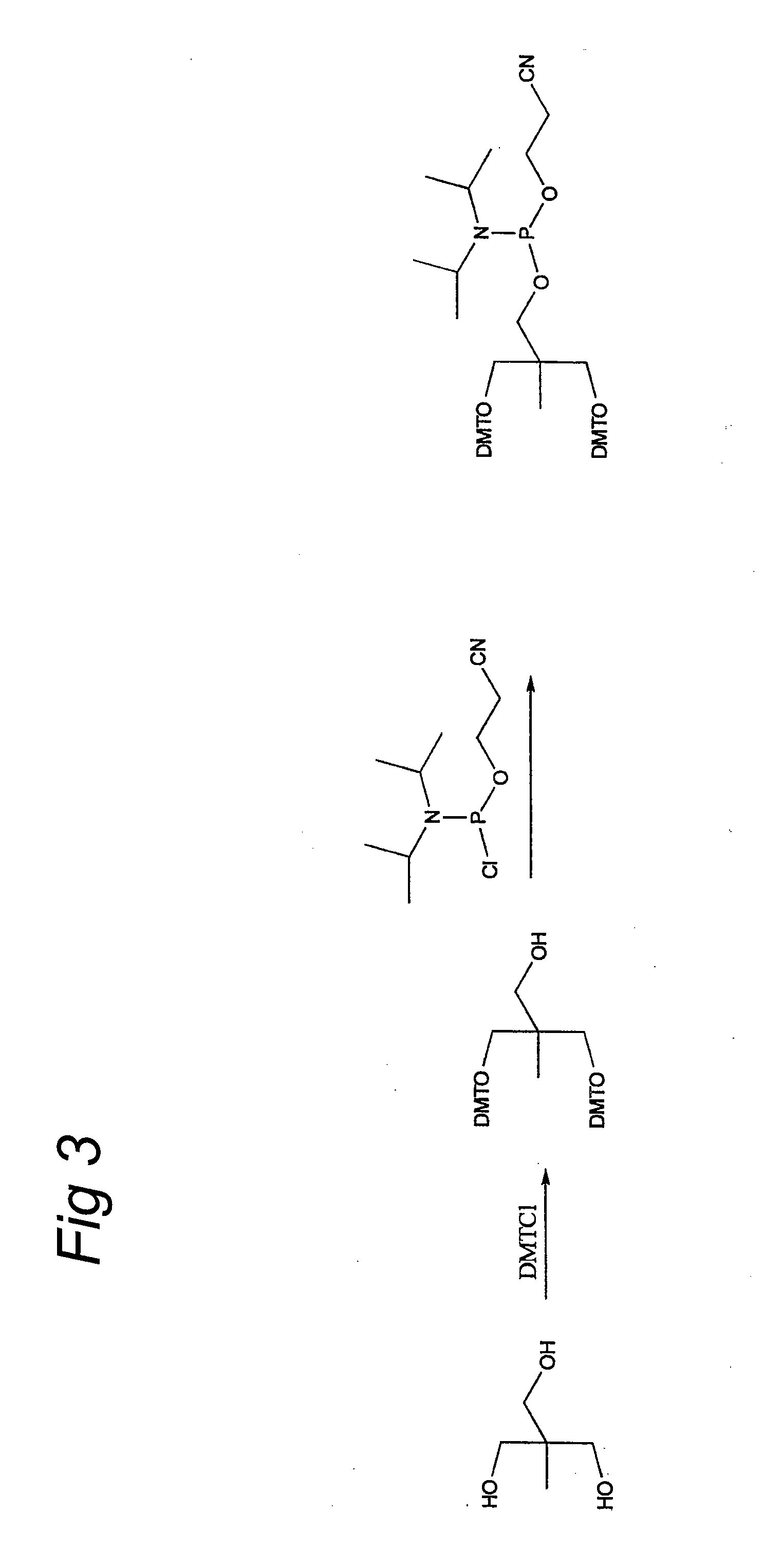
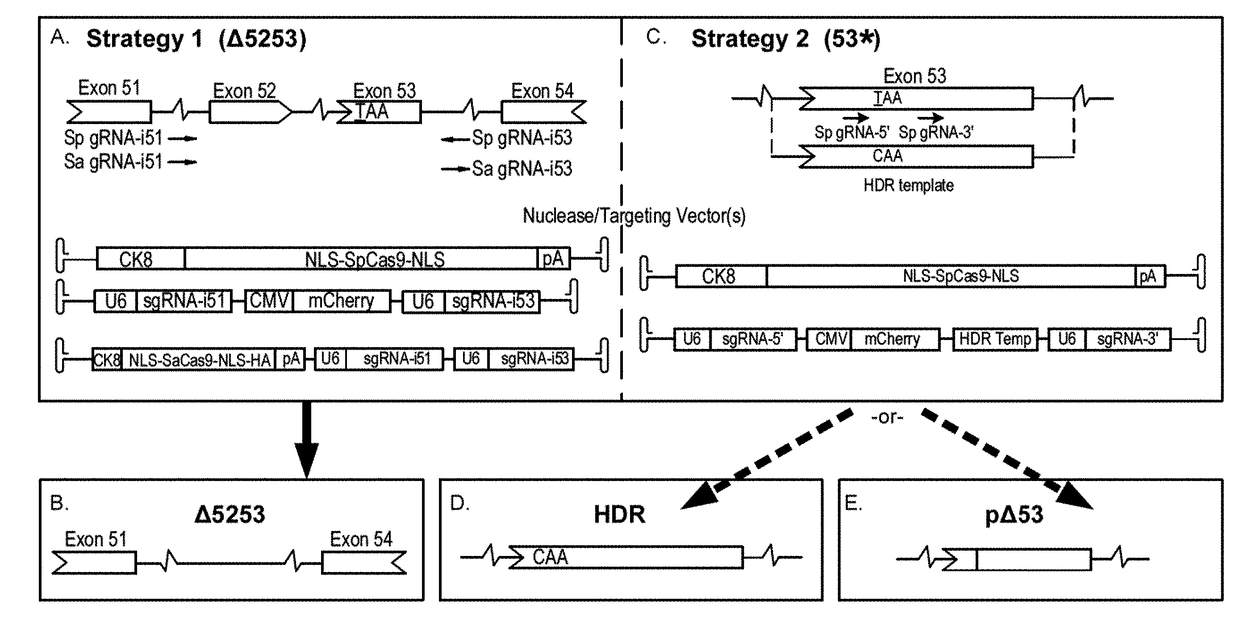
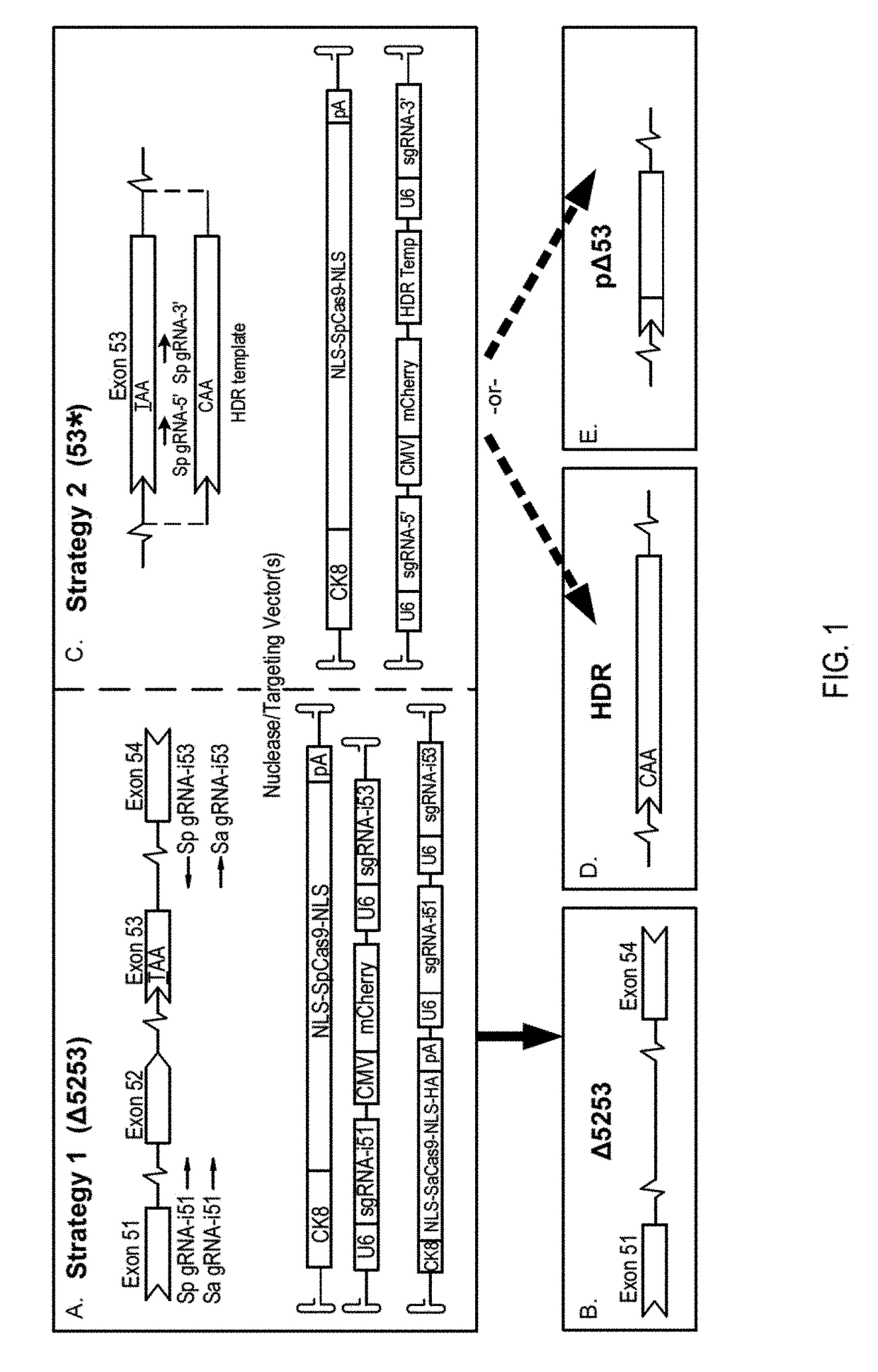
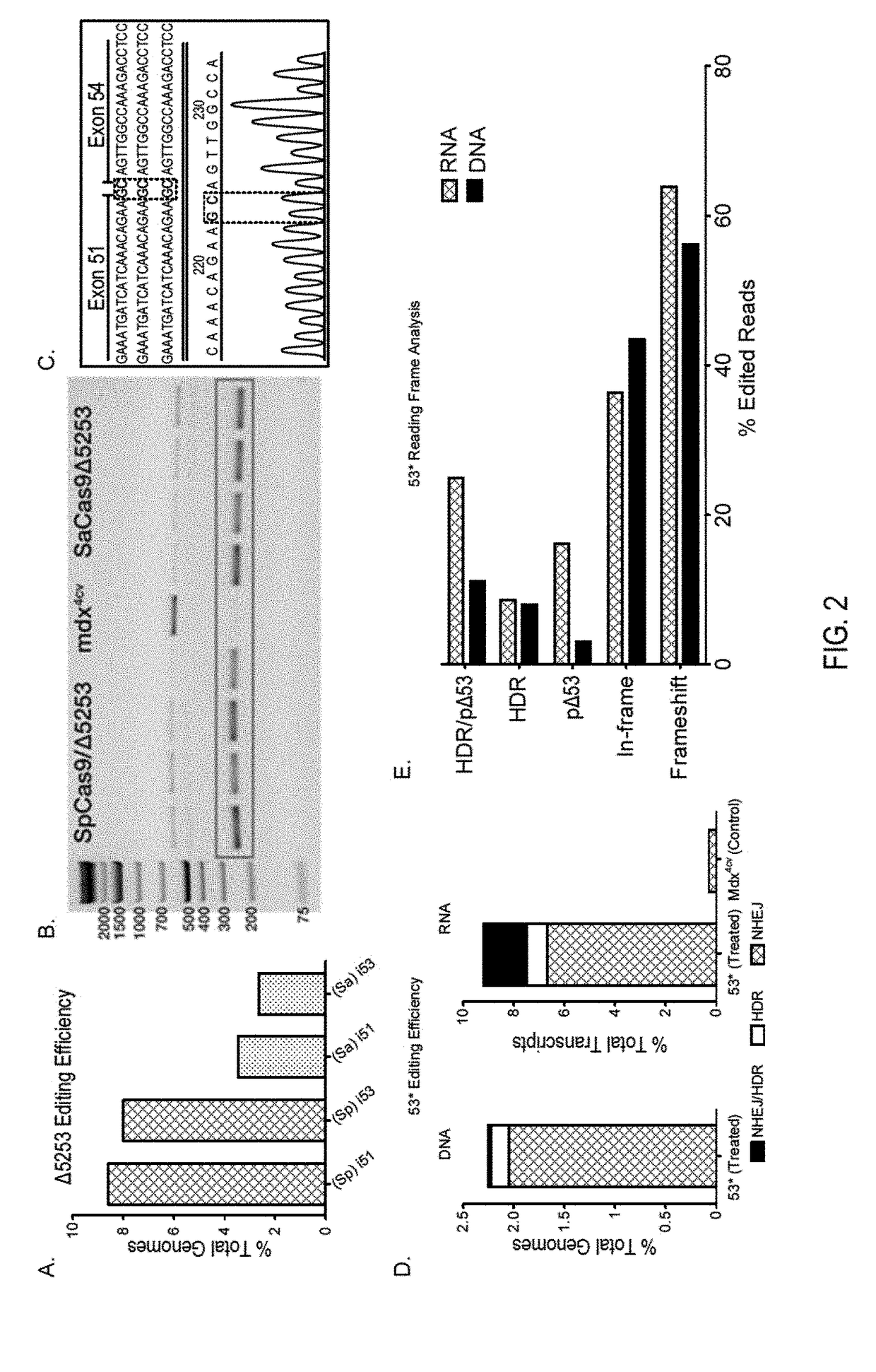
Muscle-specific crispr/cas9 editing of genes
Pharmaceutical compositions including a muscle-specific nuclease cassette, one or more guide RNA cassettes, and a delivery system for delivery of the muscle-specific nuclease cassette and the one or more gRNA cassettes are provided. The pharmaceutical composition may also include a mutation-corrected DNA template including a modification to be made in a target nucleic acid sequence. Methods for treating a subject having a muscular or neuromuscular disorder are also provided. The methods may include administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition. Methods of modifying or editing the sequence of a target nucleic acid sequence in a muscle cell are also provided. The methods may include contacting or transducing the muscle cell with a muscle-specific nuclease cassette and one or more gRNA cassettes.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Engineered comestible meat
Provided are engineered meat products formed as a plurality of at least partially fused layers, wherein each layer comprises at least partially fused multicellular bodies comprising non-human myocytes and wherein the engineered meat is comestible. Also provided are multicellular bodies comprising a plurality of non-human myocytes that are adhered and / or cohered to one another; wherein the multicellular bodies are arranged adjacently on a nutrient-permeable support substrate and maintained in culture to allow the multicellular bodies to at least partially fuse to form a substantially planar layer for use in formation of engineered meat. Further described herein are methods of forming engineered meat utilizing said layers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Engineered comestible meat
Provided are engineered meat products formed as a plurality of at least partially fused layers, wherein each layer comprises at least partially fused multicellular bodies comprising non-human myocytes and wherein the engineered meat is comestible. Also provided are multicellular bodies comprising a plurality of non-human myocytes that are adhered and / or cohered to one another; wherein the multicellular bodies are arranged adjacently on a nutrient-permeable support substrate and maintained in culture to allow the multicellular bodies to at least partially fuse to form a substantially planar layer for use in formation of engineered meat. Further described herein are methods of forming engineered meat utilizing said layers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Device for proactive modulation of cardiac strain patterns
ActiveUS20050004420A1Maintain strainReduces apoptosis in the myocardiumHeart valvesIntravenous devicesCardiac muscleApoptosis
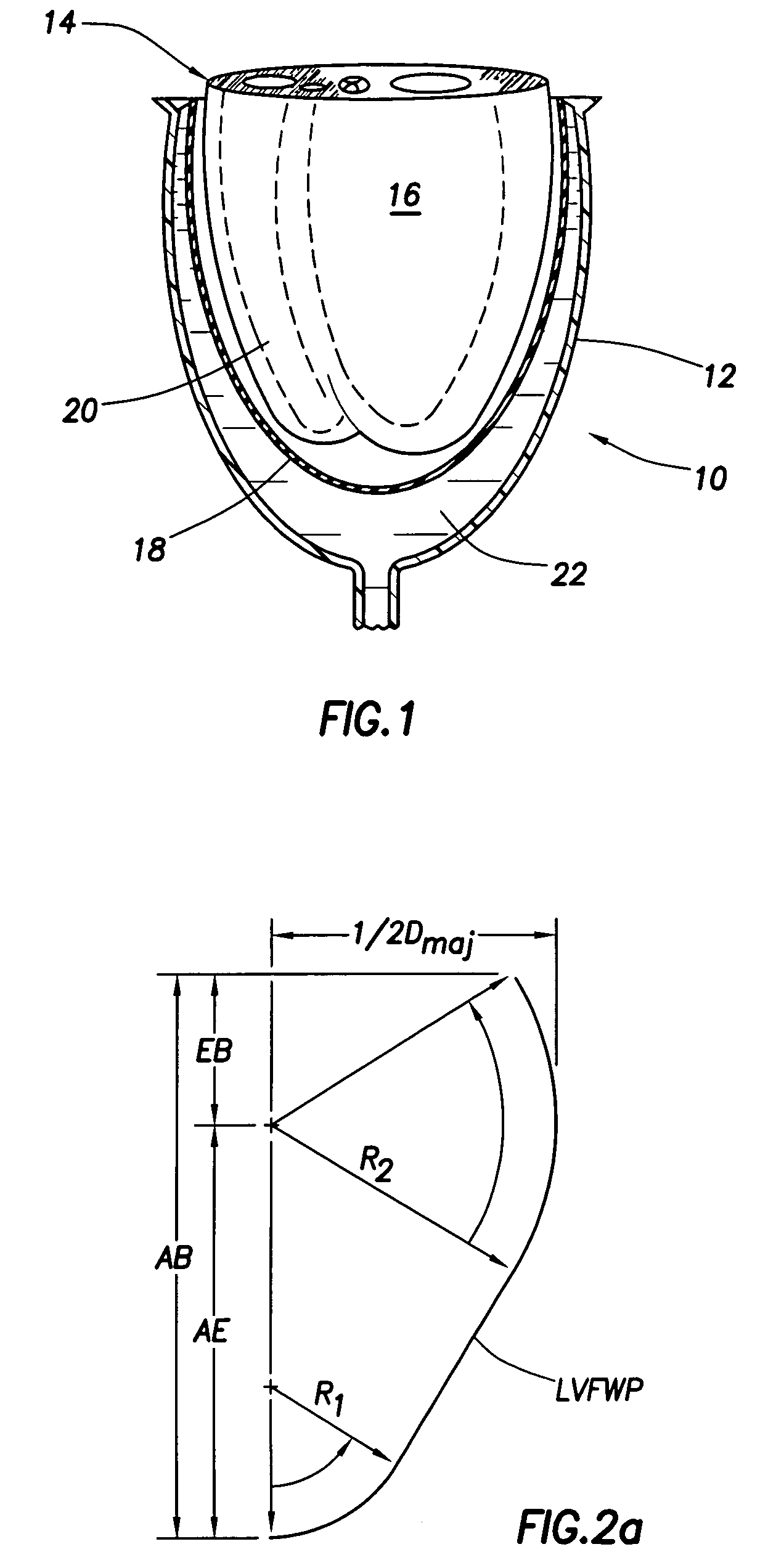
A direct cardiac assist device which may aid in ventricular recovery. The device proactively modulates cardiac strain pattern to produce a contraction strain pattern that induces beneficial growth and remodeling of the myocardium or prevents or reduces apoptosis of the myocytes. The device may include an outer shell. membrane, or mesh and an inner membrane. The space between the outer member and the membrane may be filled with fluid that is pressurized during contraction. The device prescribes a beneficial strain pattern during heart contraction. This strain pattern does not invert the curvatures or grossly alter the curvatures of the heart and may assist in myocyte regrowth and healing of the failing heart.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS20070161107A1Improve compatibilityPromote differentiationArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCardiac muscleCo culturing
A method for inducing cardiomyocyte differentiation of a hES cell, the method comprising co-culturing the hES cell with a cell excreting at least one cardiomyocyte differentiation inducing factor or with an extracellular medium therefrom, under conditions that induce differentiation, cells and cell populations so produced, and uses of the cells.
Owner:MUMMERY CHRISTINE LINDSAY +2
Compositions and methods for treatment of lymphatic and venous vessel arterialization
InactiveUS20060025338A1Promote healingReduce edemaOrganic active ingredientsVirusesSmooth muscleLymphatic vessel
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions that may be used in disrupting the association of smooth muscle cells with lymphatic endothelial cells and in correcting the valvular dysfunction in veins and lymphatic vessels. Such compositions are useful for therapeutic and prophylactic treatment of impaired lymphatic and venous function, particularly for the treatment of lymphedema distichiasis or chronic venous insufficiency.
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
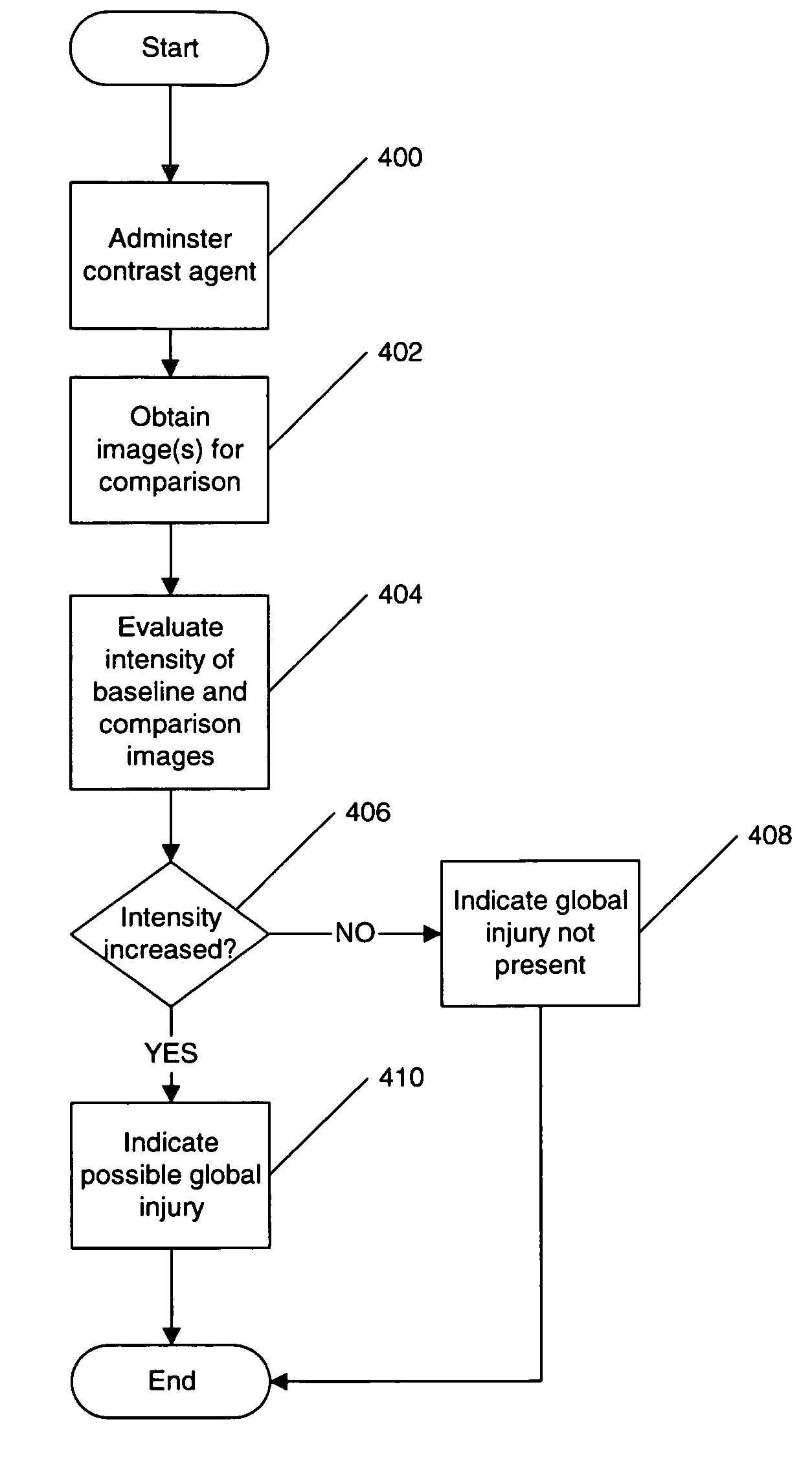
Non-invasive imaging for determination of global tissue characteristics
Evaluating tissue characteristics including identification of injured tissue or alteration of the ratios of native tissue components such as shifting the amounts of normal myocytes and fibrotic tissue in the heart, identifying increases in the amount of extracellular components or fluid (like edema or extracellular matrix proteins), or detecting infiltration of tumor cells or mediators of inflammation into the tissue of interest in a patient, such as a human being, is provided by obtaining a first image of tissue including a region of interest from a first acquisition, for example, after administration of a contrast agent to the patient, and obtaining a second image of the tissue including the region of interest during a second, subsequent acquisition, for example, after administration of a contrast agent to the patient. The subsequent acquisition may be obtained after a period of time to determine if injury has occurred during that period of time. The region of interest may include heart, blood, muscle, brain, nerve, skeletal, skeletal muscle, liver, kidney, lung, pancreas, endocrine, gastrointestinal and / or genitourinary tissue. A global characteristic of the region of interest of the first image and of the second image is determined to allow a comparison of the global characteristic of the first image and the second image to determine a potential for a change in global tissue characteristics. Such a comparison may include comparison of mean, average characteristics, histogram shape, such as skew and kurtosis, or distribution of intensities within the histogram.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Cellular transplantation for heart regeneration
InactiveUS20050244384A1Improved integration and survivalHighly integratedBiocideGenetically modified cellsProgenitorDisease
Myoblast cells obtained by culturing, particularly from satellite cells or other progenitor cells, are transplanted into tissue such as diseased heart tissue to form healthy repair tissue and reverse disease. This technique can be carried out in various ways and preferably includes a cellular integration factor to assist cellular survival, integration and longevity into the treated organ. Angiogenesis factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor are particularly preferred and may be transgenically expressed by the transplanted cell. Other factors that may be used to augment the procedure include migratory and scaffolding molecules. The methods and materials are particularly useful in combination with an automated cell processor and an automated catheter delivery system. The materials and methods for their use may be applied to the prophylaxis and therapy of damaged hearts, using cells originally obtained from the patient, another human, or another animal.
Owner:LAW
Two-stage culture protocol for isolating mesenchymal stem cells from amniotic fluid
ActiveUS7101710B2Encourage illegal terminationRaise the possibilityArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAmniotic fluid cellAmniotic fluid
A method of harvesting mesenchymal stem cells from human amniotic fluid uses a two-stage culture protocol comprising culturing human amniocytes and then culturing mesenchymal stem cells. For culturing human amniocytes, primary amniocyte cultures are set up using routine or standard culture protocol in a cytogenetic laboratory. Non-adherent human amniotic fluids cells in the supernatant medium are collected. For culturing mesenchymal stem cells (“MSC”), the non-adherent cells are centrifuged and then plated with an alpha-modified Minimum Essential Medium supplemented with fetal bovine serum. Incubate with humidified CO2 for MSC growth. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (“RT-PCR”) and immunocytochemical analyses reveal that Oct-4 mRNA and OCT-4 protein expression is detectable in the cultured amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells (“AFMSCs”). Under differentiation culture conditions, the AFMSCs can be induced to develop into multi-lineage cells, such as adipocytes, osteocytes, neuronal cells, etc.
Owner:U NEURON BIOMEDICAL INC
Inducing culture medium for inducing fibroblast to trans-differentiate into cardiac muscle cells and application of inducing culture medium
ActiveCN105861428ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsFibroblastCells fibroblast
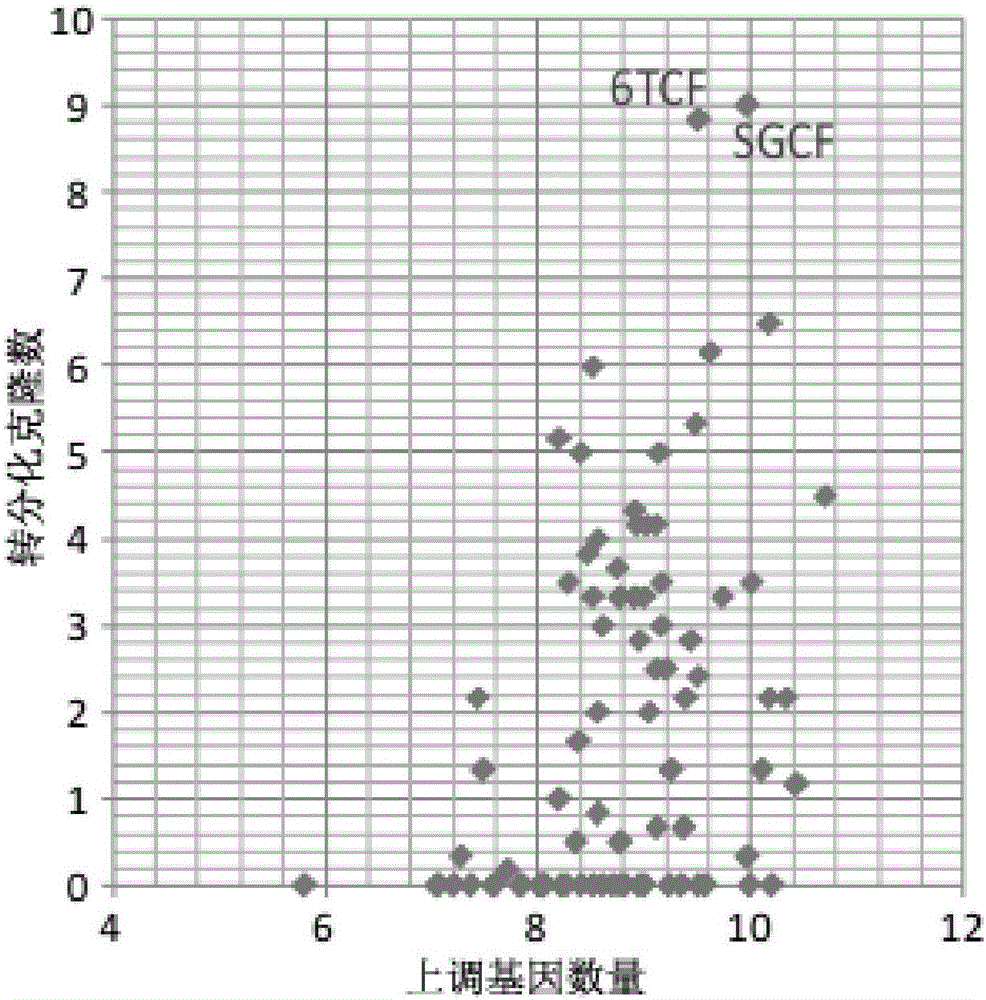
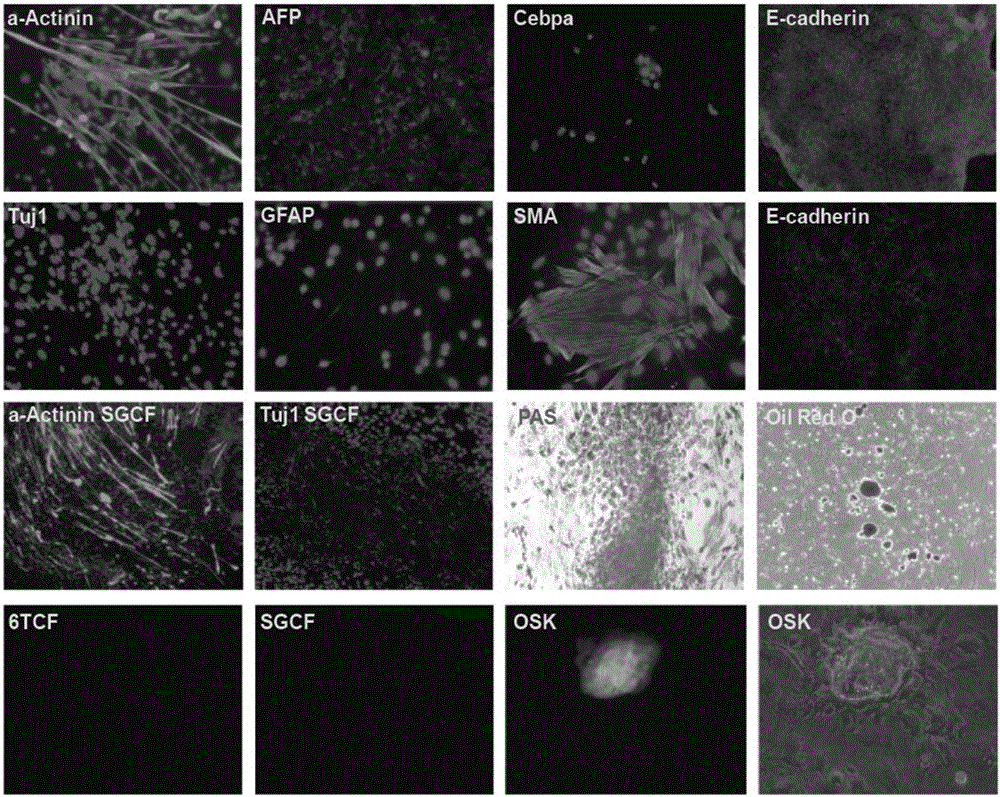
The invention discloses an inducing culture medium for inducing fibroblast to trans-differentiate into cardiac muscle cells, a method and an application of the inducing culture medium. The inducing culture medium comprises a basic culture medium and an inducing small molecular assembly which is 6TCFOW or SCFOV, wherein 6 is E61541, T is tranylcypromine, C is CHIR99021, F is forskolin, O is Dorsomorphin, W is IWR-I, S is SB431542, and V is valproic acid. The inducing culture medium can trans-differentiate the fibroblast into the cardiac muscle cells which have normal cardiac muscle cell specific molecular tags and a normal cardiac muscle function, so that a new way is provided for solving the cell source problem of the regenerative medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dedifferentiation of adult mammalian cardiomyocytes into cardiac stem cells
InactiveUS20100093089A1Raise the ratioUnknown materialsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSurface markerMammal
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Integrated device for ischemic treatment
InactiveUS20090287166A1Stable tractionLow profileGuide needlesBalloon catheterReperfusion injuryKidney
A system and method in accordance with the present invention provides a infusion catheter that is flexible, has such a smooth traction and a low profile to minimize break up of the obstruction when crossing it, can access distal vasculature quickly, is easy to use and readily to be implemented in the conventional PCI. Another object is to provide a method that can be performed within a short period of time and employs the catheter described herein to infuse a therapeutic agent distally to the obstruction before it is removed as a means of reducing reperfusion injury, protecting distal vasculature and microcirculation, preserving myocytes, reducing infarct size and ischemic damages in the heart, brain, lung, liver, kidney and limb. Another object is to provide complementary feature options to the infusion catheter and the aspiration catheter to improve the speed and quality of the vessel clearance.
Owner:CNATEK
Pharmaceuticals That Promote Functional Regeneration of Damaged Tissues
InactiveUS20090202500A1Promote functional tissue regenerationPromote tissue regenerationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDamages tissueInjury brain
The present inventors revealed the following for the first time in the world:1) a large amount of bone marrow-derived cells are mobilized to grafted skin;2) the mobilized bone marrow-derived cells are differentiated into any of dermal fibroblasts, adipocytes, muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, and epidermal keratinocytes in the grafted skin, and the mobilized bone marrow derived cells include bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells;3) the factors which mobilize bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells from peripheral blood to the grafted skin are HMGB1, HMGB2, and HMGB3 released from the necrosed tissue of recipient skin;4) purified HMGB1, HMGB2, and HMGB3 promote the migration of mesenchymal stem cells isolated and cultured from bone marrow;5) activators containing HMGB1 which allows the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can be conveniently purified from several organ extracts including skin, brain, and heart;6) activators which allow the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can be conveniently extracted from cultured cells; and7) a heparin-column purified fraction of skin extract mobilizes a large amount of bone marrow-derived cells in case of brain injury.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Mesenchymal stem cell and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20110111499A1Efficiently and in large quantity producingEffectively lead to differentiationBiocideMuscular disorderMesenchymal stem cellMyocyte
The present invention provides a method for producing a mesenchymal stem cell having an ability to differentiate into a myoblast by culturing a pluripotent stem cell derived from a human or animal, including: i) preparing the pluripotent stem cell that has been cryopreserved, ii) sub-culturing the prepared pluripotent stem cell in an undifferentiated state for a prescribed number of times, iii) culturing the subcultured pluripotent stem cell under conditions that enable induction of differentiation into an adipocyte in vitro, and iv) separating and collecting a CD105-positive cell during the culturing process.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Cultured cartilage/bone cells/tissue, method of generating same and uses thereof
A method of generating cultured chondrocytes / endochondral bone cells is provided. The method comprising isolating chondrocytes from mandibular condyle tissue, and culturing the isolated chondrocytes. A method of isolating chondrocytes from mandibular condyle tissue is further provided. The method comprises isolating mandibular condyle tissue from a mammal and treating the mandibular condyle tissue so as to selectively remove fibroblast-like cells and / or myocytes therefrom, the modified mandibular condyle tissue including chondrocytes, and selectively collecting the chondrocytes from the modified mandibular condyle tissue.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Interventional medical device
InactiveCN102526861AReduce restenosis rateRepair damageStentsBalloon catheterBalloon dilatation catheterSmooth muscle
The invention discloses an interventional medial device comprising a balloon dilatation catheter body. A balloon on the balloon dilatation catheter body consists of a straightness section and conical sections positioned at two ends of the straightness section, wherein a medical coating is coated on the surface of the straightness section of the balloon and consists of medicaments and a medicine delivery promoting agent. When the balloon is used for dilating the narrow blood vessel, the medicament in the medical coating can be released rapidly, so that the injury of the endothelium of the blood vessel can be repaired, the hyperplasia of smooth muscle cells can be inhibited, the restenosis rate of the blood vessel can be reduced, and the endothelialization dysfunction possibly caused by the long-term continuous contact between the medical coating and the blood vessel wall can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT MEDICAL (GROUP) CO LTD
Device for proactive modulation of cardiac strain patterns
ActiveUS7445593B2Reduces apoptosis in the myocardiumPromote growthHeart valvesIntravenous devicesApoptosisCardiac muscle
A direct cardiac assist device which may aid in ventricular recovery. The device proactively modulates cardiac strain pattern to produce a contraction strain pattern that induces beneficial growth and remodeling of the myocardium or prevents or reduces apoptosis of the myocytes. The device may include an outer shell. membrane, or mesh and an inner membrane. The space between the outer member and the membrane may be filled with fluid that is pressurized during contraction. The device prescribes a beneficial strain pattern during heart contraction. This strain pattern does not invert the curvatures or grossly alter the curvatures of the heart and may assist in myocyte regrowth and healing of the failing heart.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
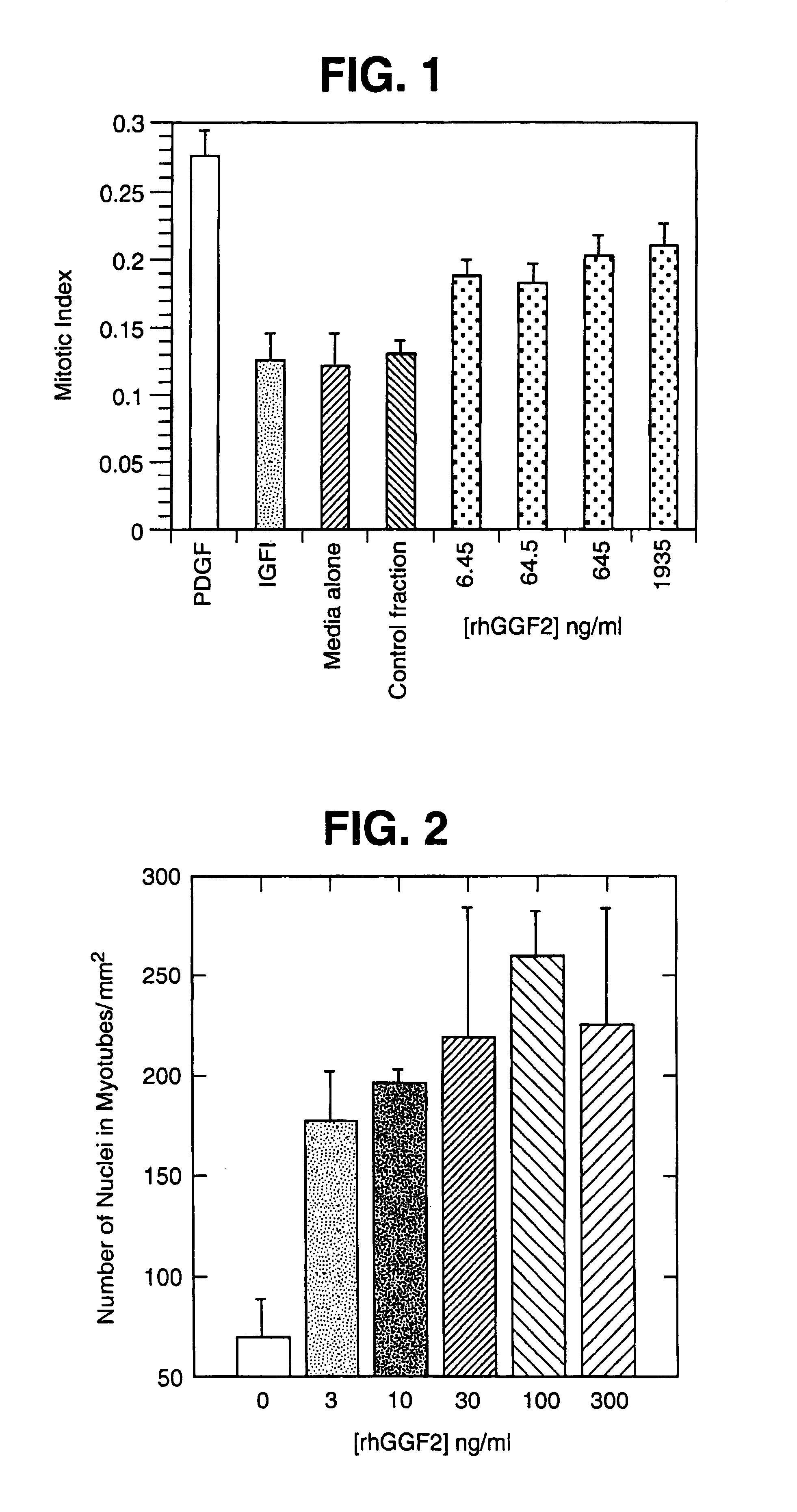
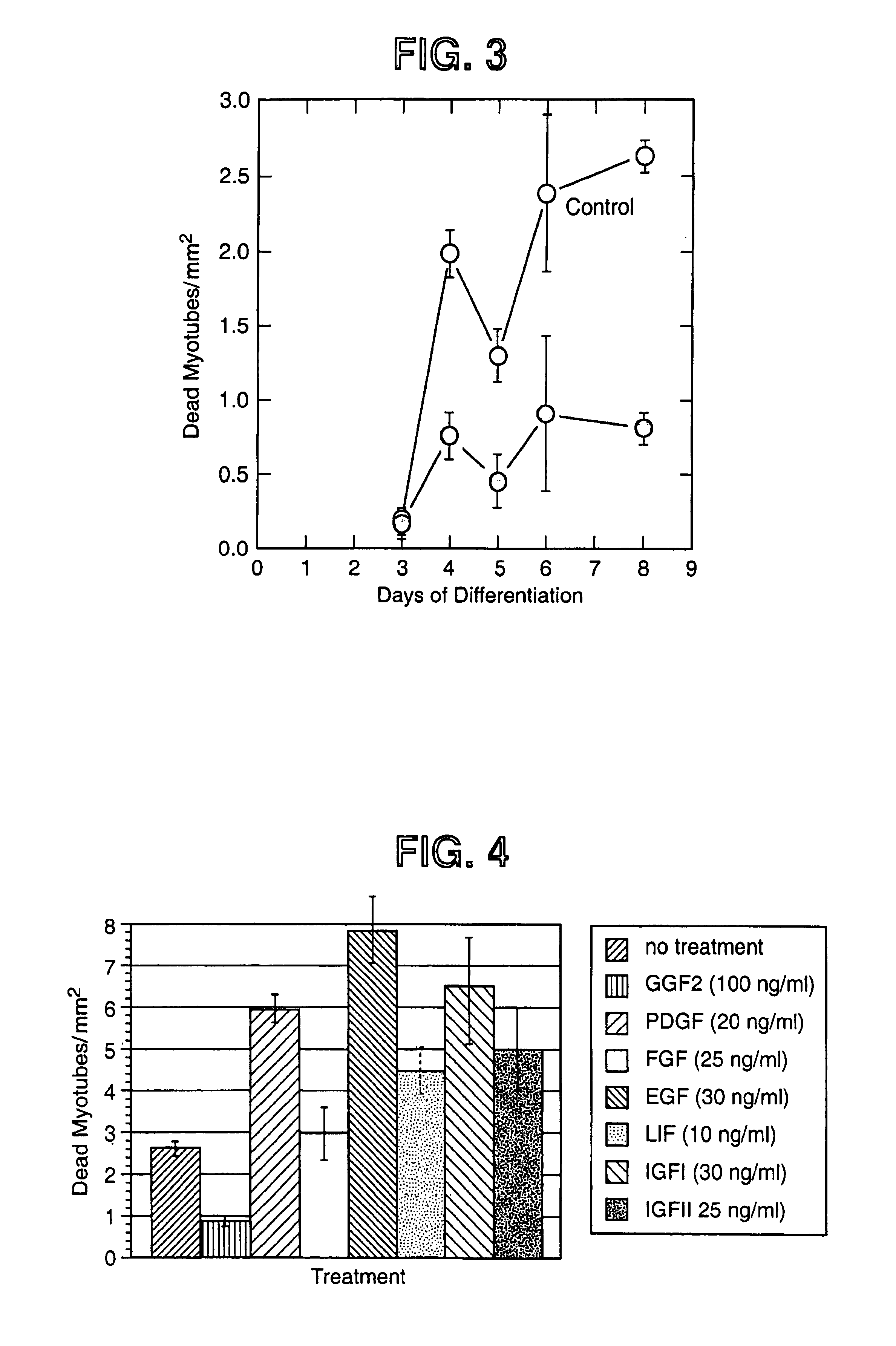
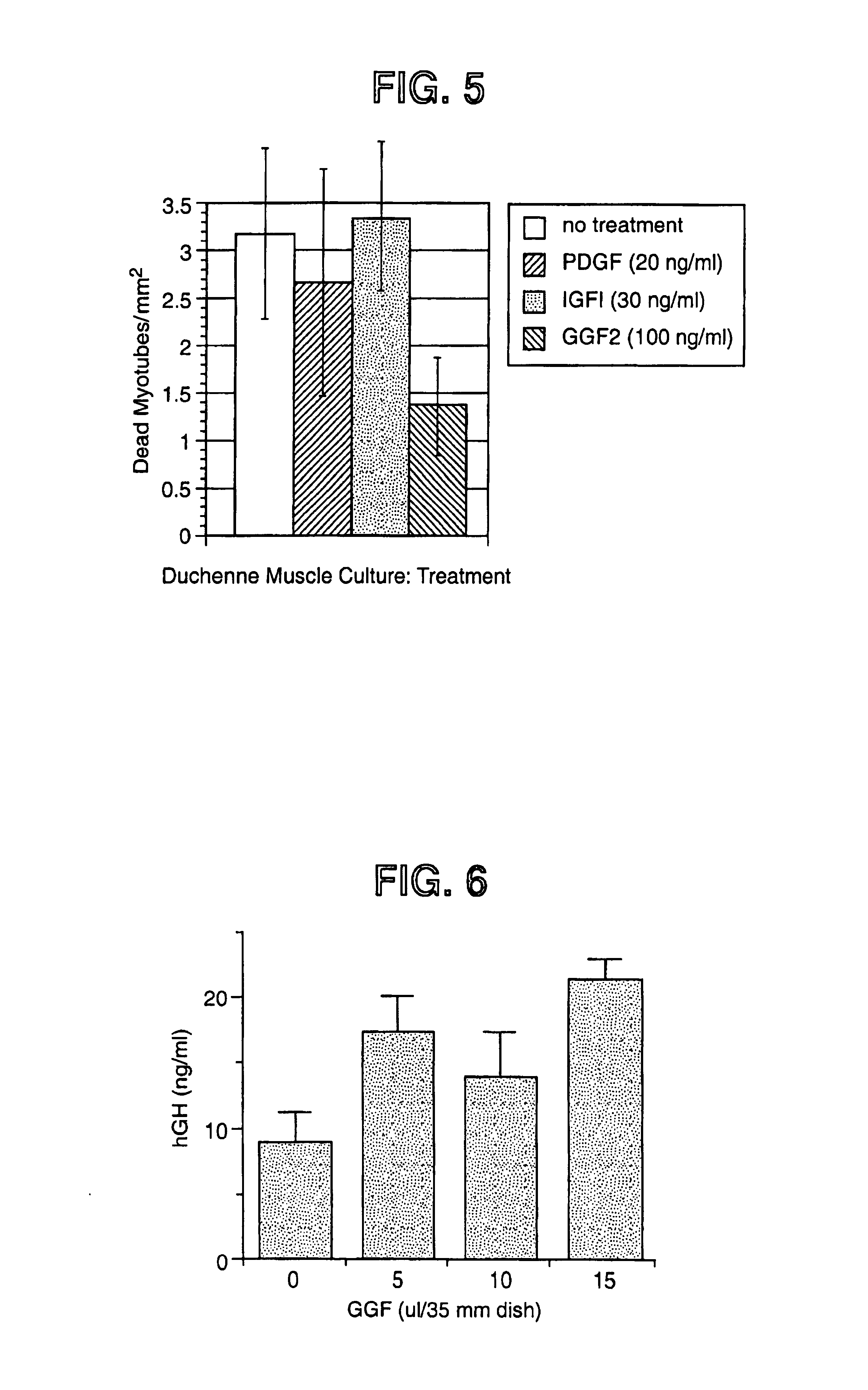
Methods of increasing myotube formation or survival or muscle cell mitogenesis differentiation or survival using neuregulin GGF III
ActiveUS7115554B1Increase in satellite cell activationIncrease in activation of cellNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscle tissueNeurulation
The invention relates to methods of treating diseases and disorders of the muscle tissues in a vertebrate by the administration of compounds which bind the p185erbB2 receptor. These compounds are found to cause increased differentiation and survival of cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscle.
Owner:ACORDA THERAPEUTICS INC
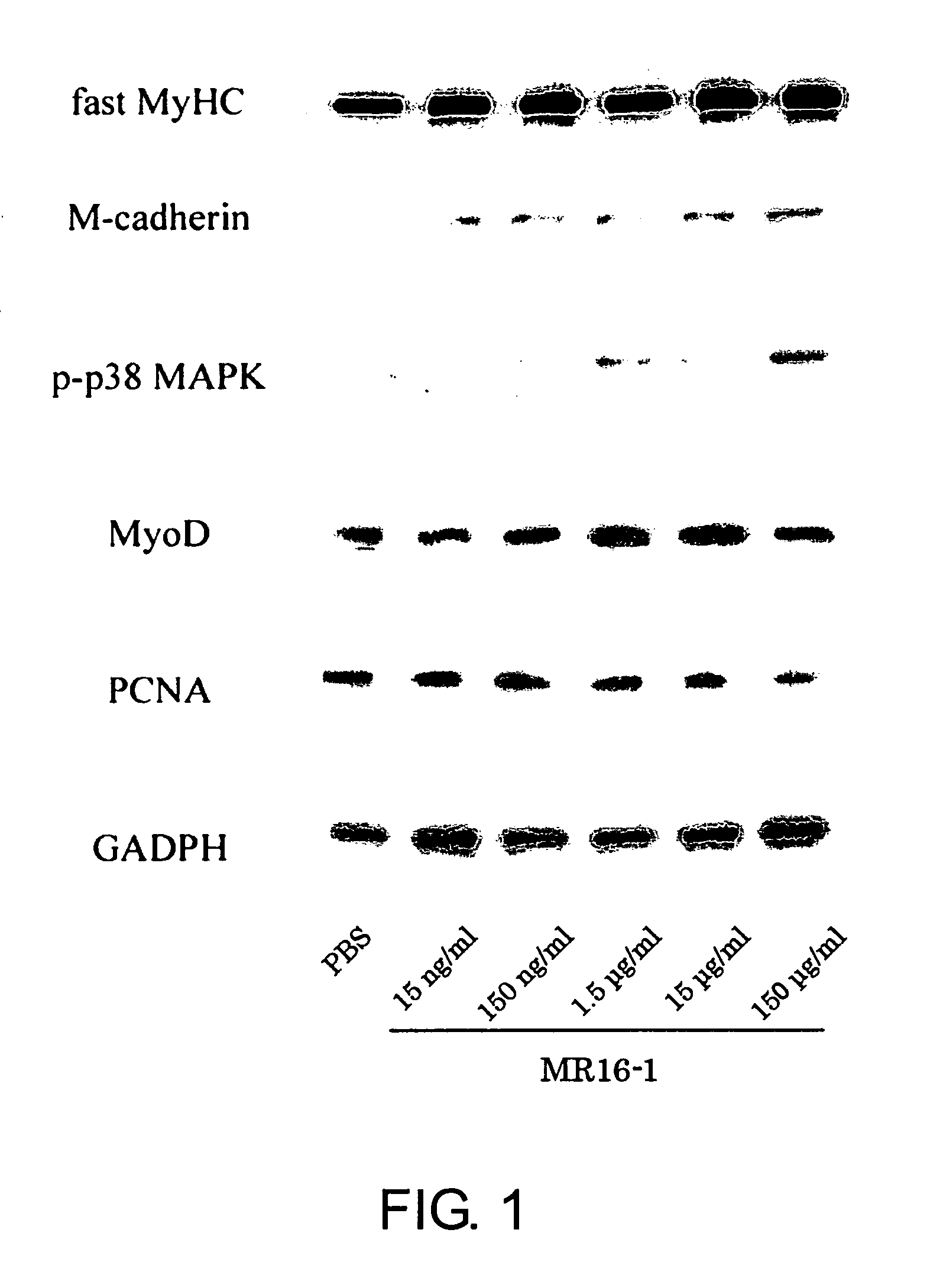
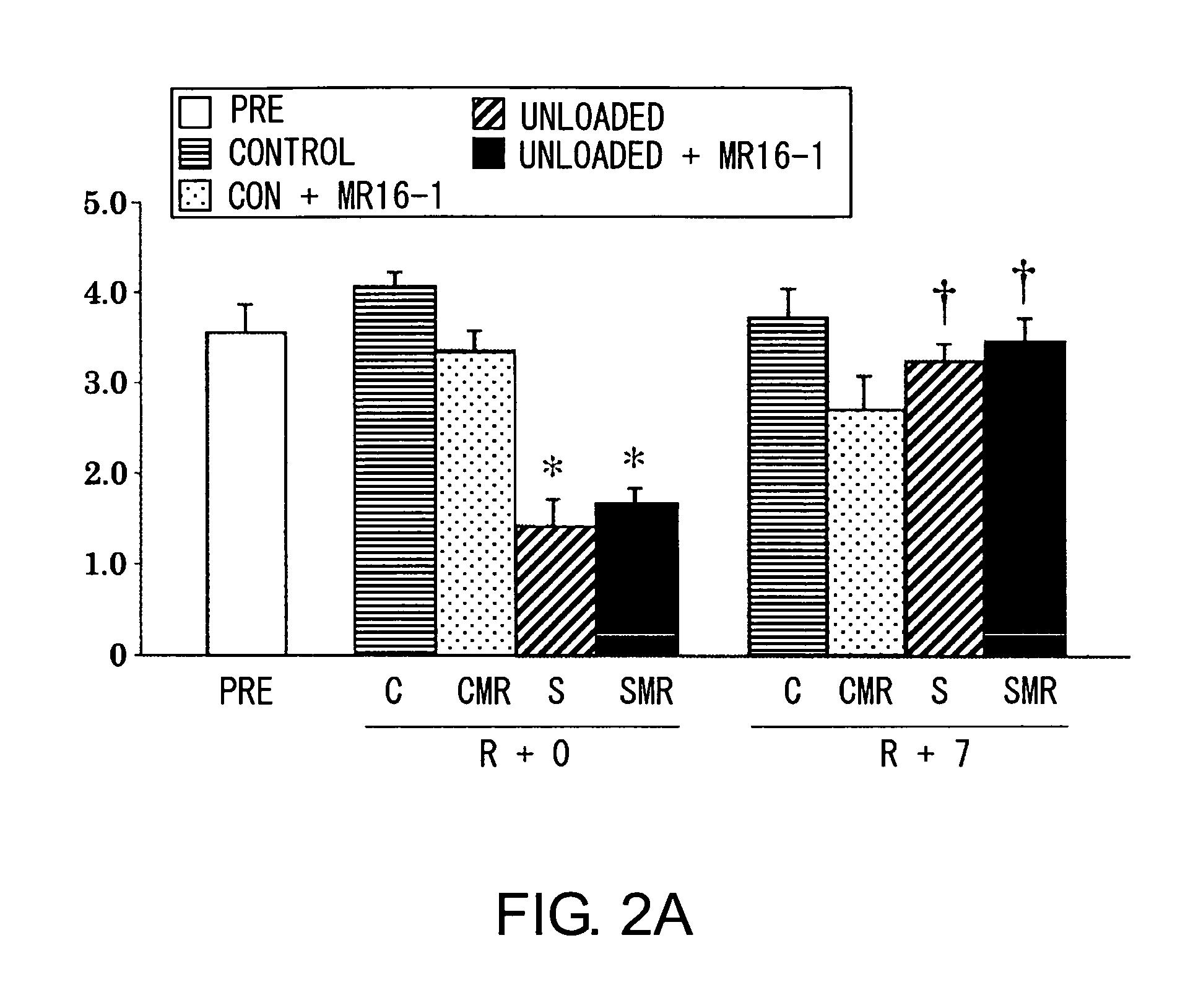
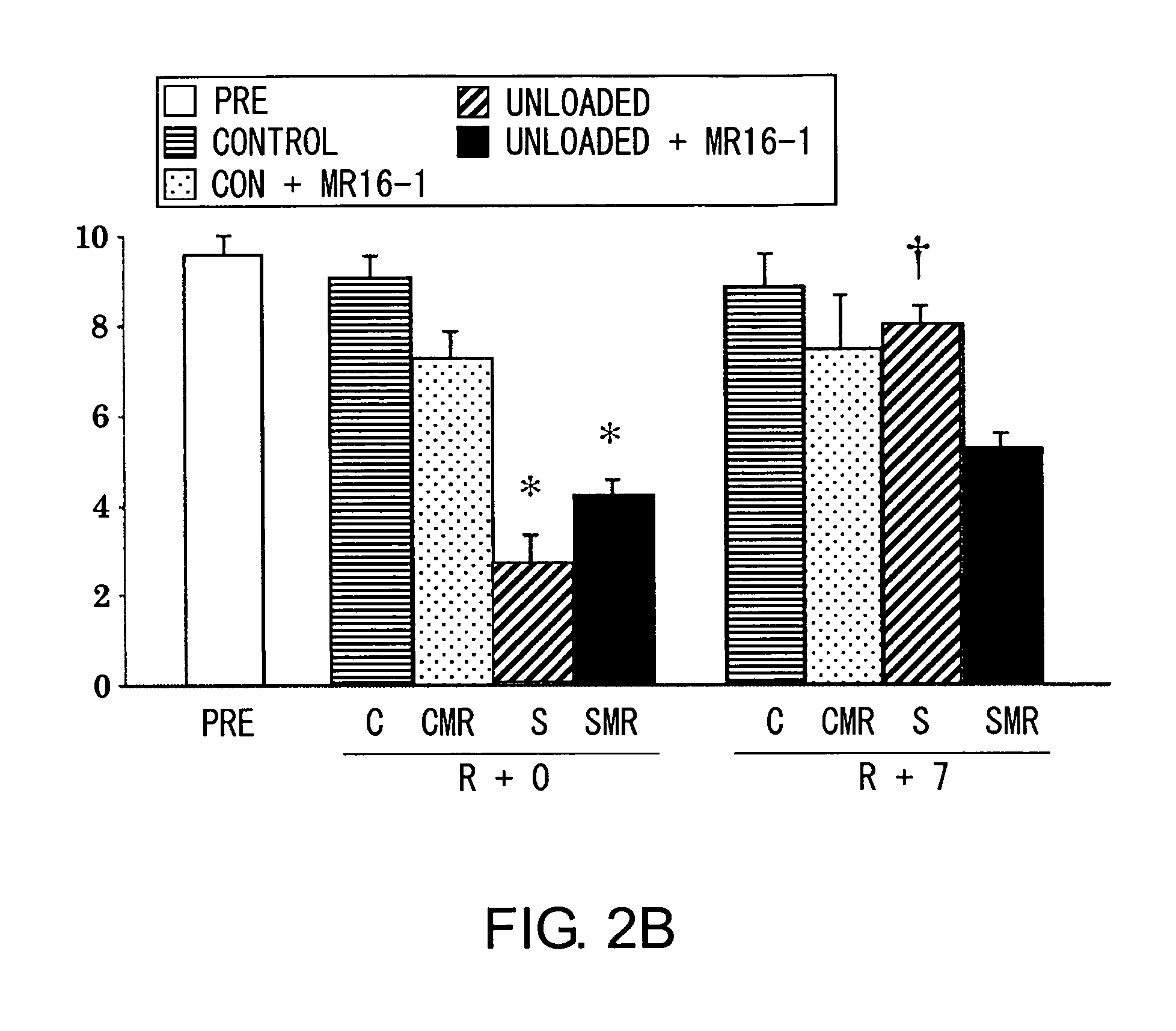
Method for promoting muscle regeneration by administering an antibody to the IL-6 receptor
ActiveUS9260516B2Promote adhesion and proliferation and differentiationPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsMyocyteCell growth
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Simulation system of cardiac function, simulation method of cardiac function, simulation program of cardiac function, and composite material sheet
ActiveUS20100318326A1Simple designImprove impaired cardiac functionMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesFiberCardiac feature
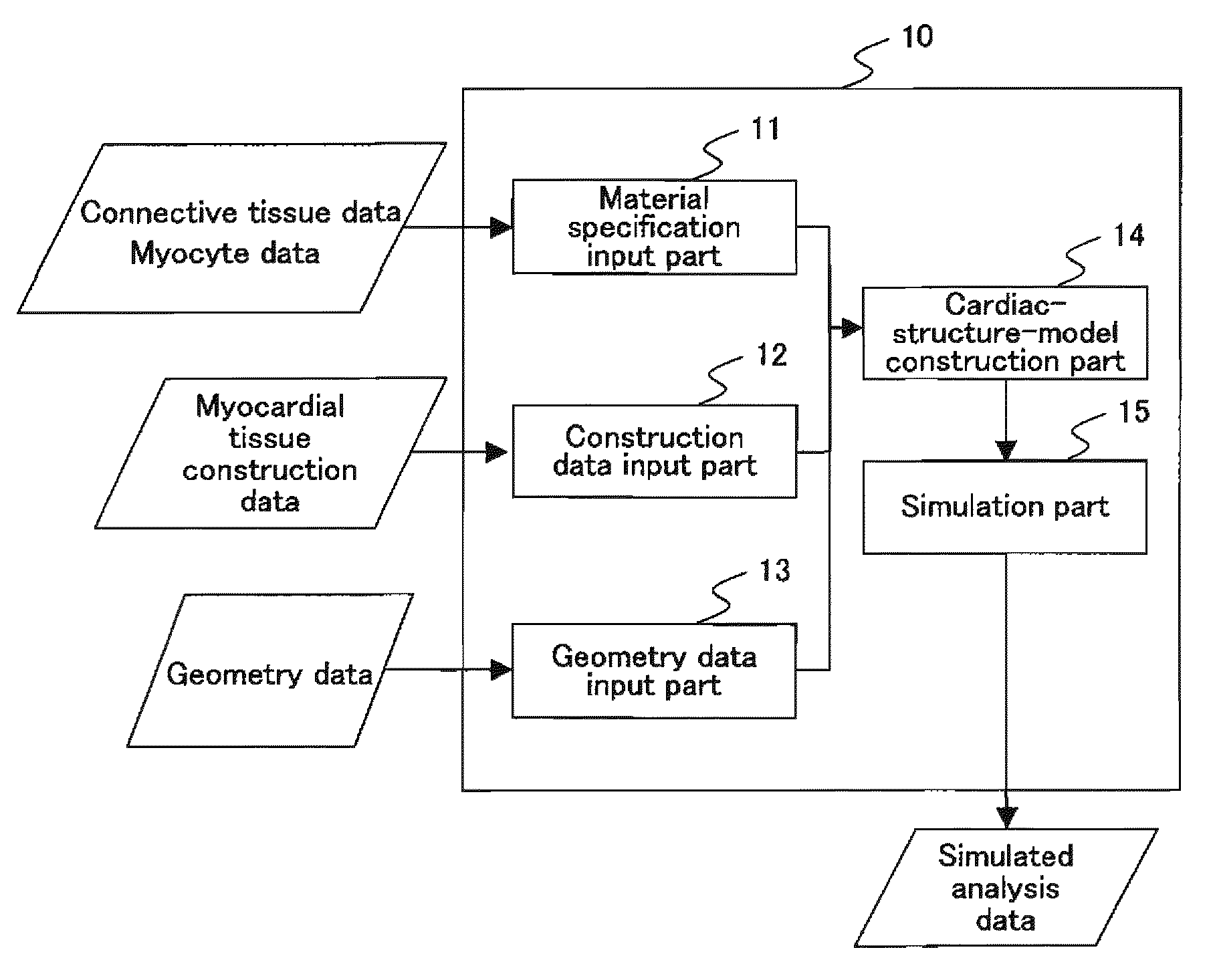
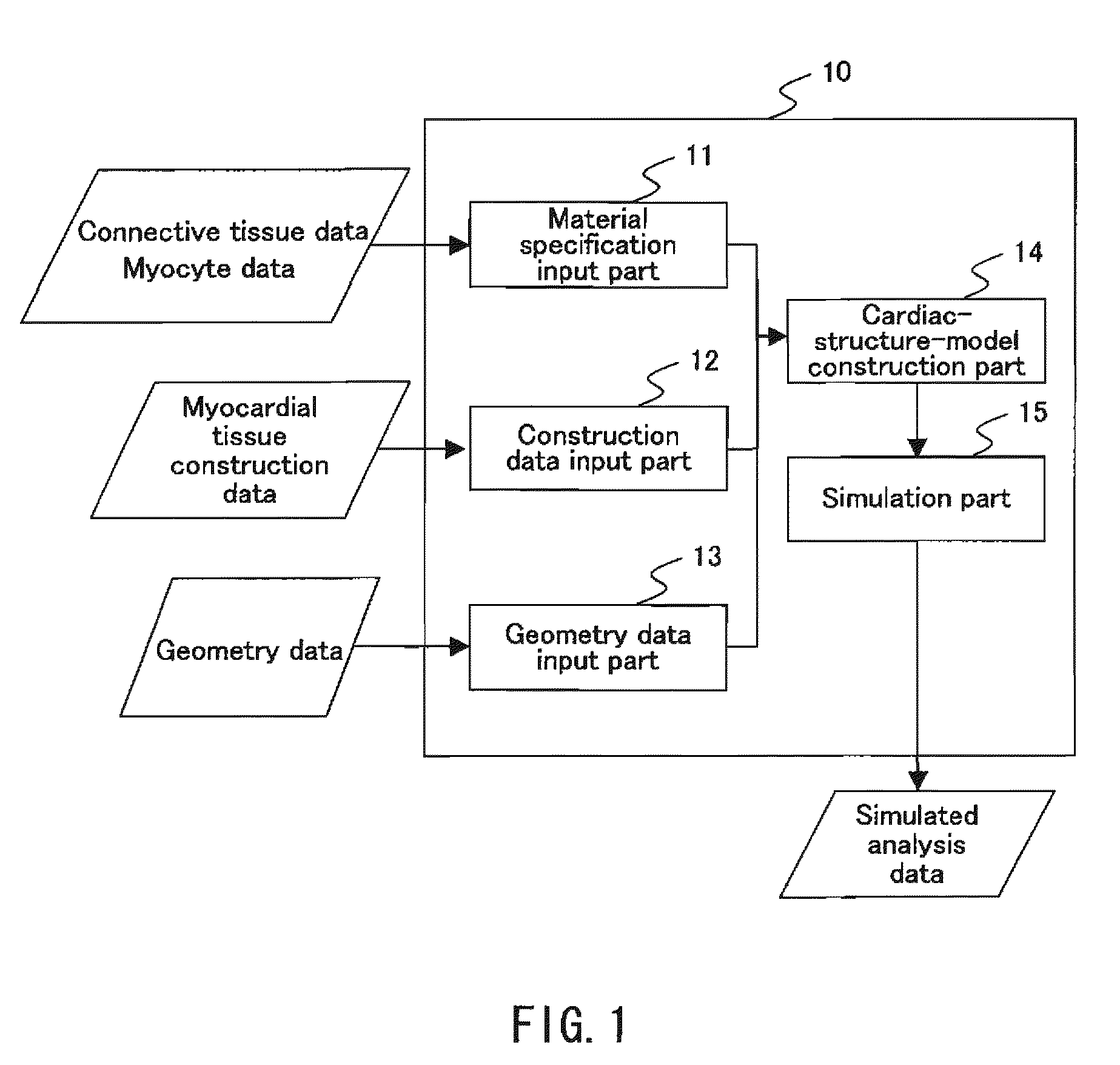
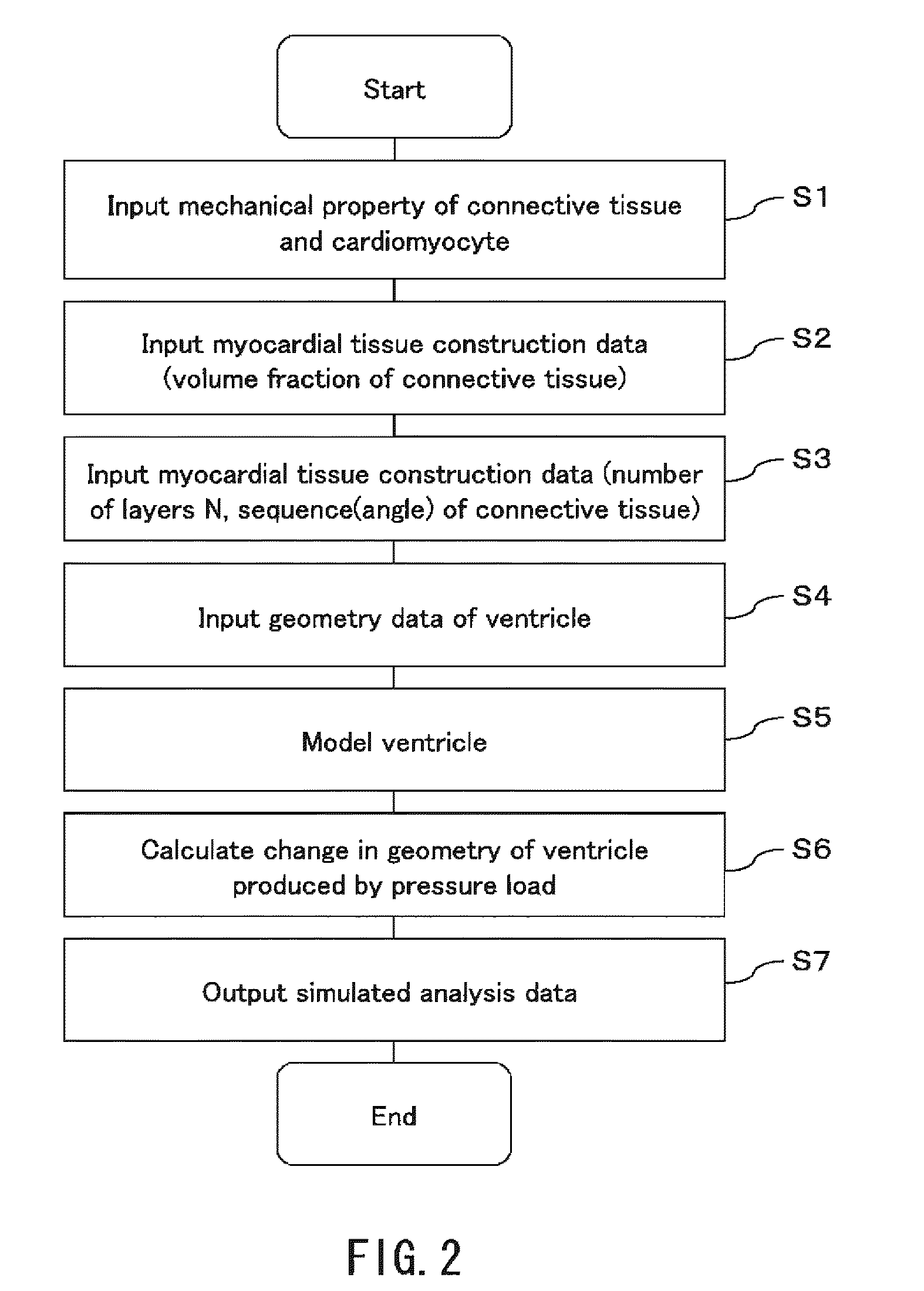
To provide a simulation system of cardiac function utilizing a cardiac structure model which is generated based on an appropriate composite material view representing the myocardial tissue. A simulation system of cardiac function to predict a change in cardiac geometry using a cardiac structure model contains a material specification input part 11 to determine both connective tissue data and myocyte data, a geometry data input part 13 to input geometry data of three-dimensional geometry of a heart, and a cardiac-structure-model construction part 14 wherein a cardiac structure model assumes assembly of finite elements based on continuum data of three-dimensional geometry defined by geometry data and made of composite material containing matrix and reinforcement fiber, and possesses mechanical properties of reinforcement fiber reflecting mechanical properties of connective tissue data and mechanical properties of matrix reflecting mechanical properties of myocyte data. The simulation system also contains a simulation part 15 which predicts a change of geometry of the cardiac structure model produced by pressure load utilizing finite element method with computation.
Owner:YAMAMOTO SHOJI
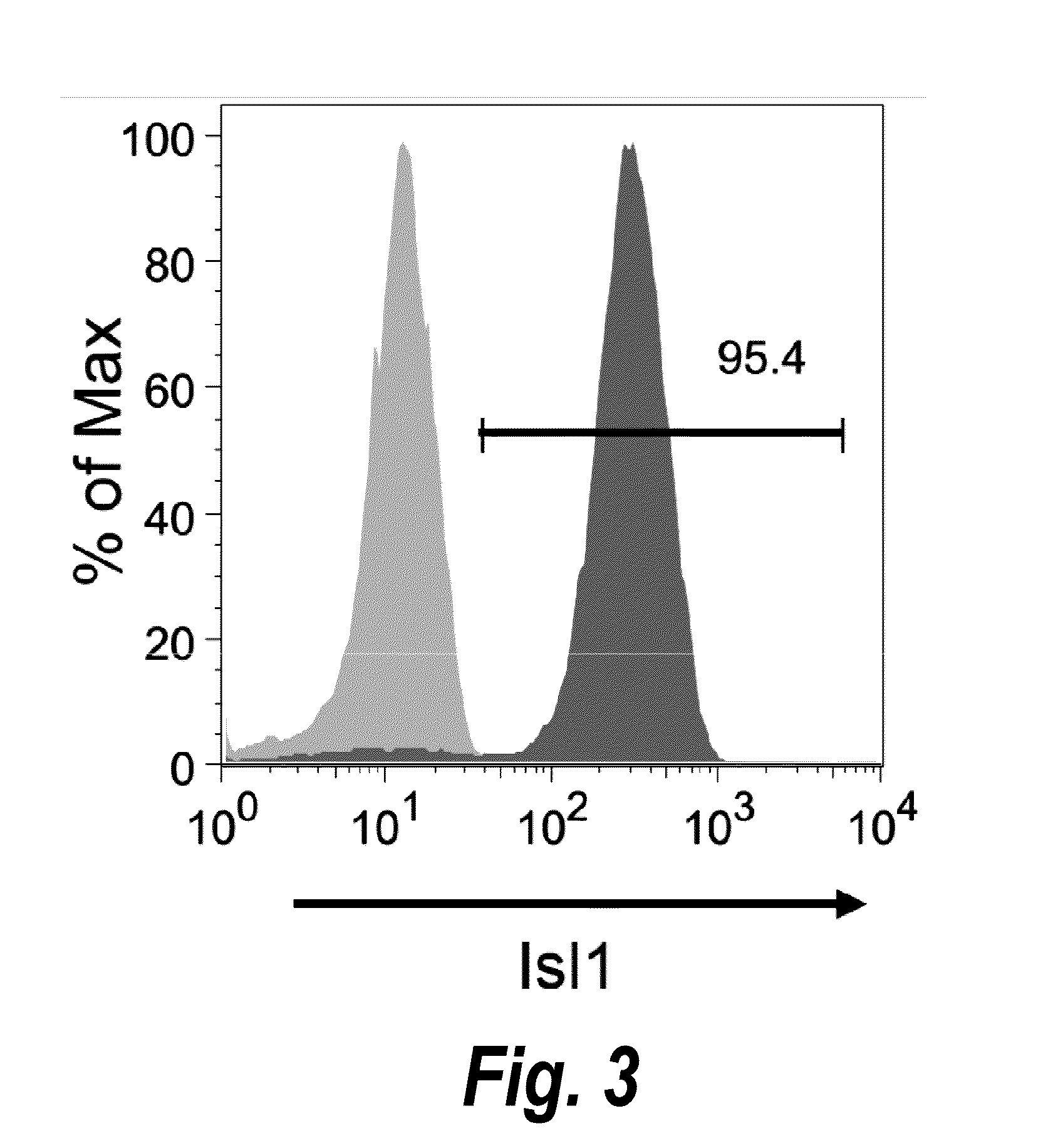
Use of lifr or fgfr3 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveUS20160108363A1Easy and rapid isolationFunction increaseBiocideArtificial cell constructsSurface markerProgenitor
The present invention provides LIFR and FGFR3 as cell surface markers for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells, in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Thus, the invention provides human ventricular progenitor (HVP) cells. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of Islet 1+ LIFR+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / LIFR+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
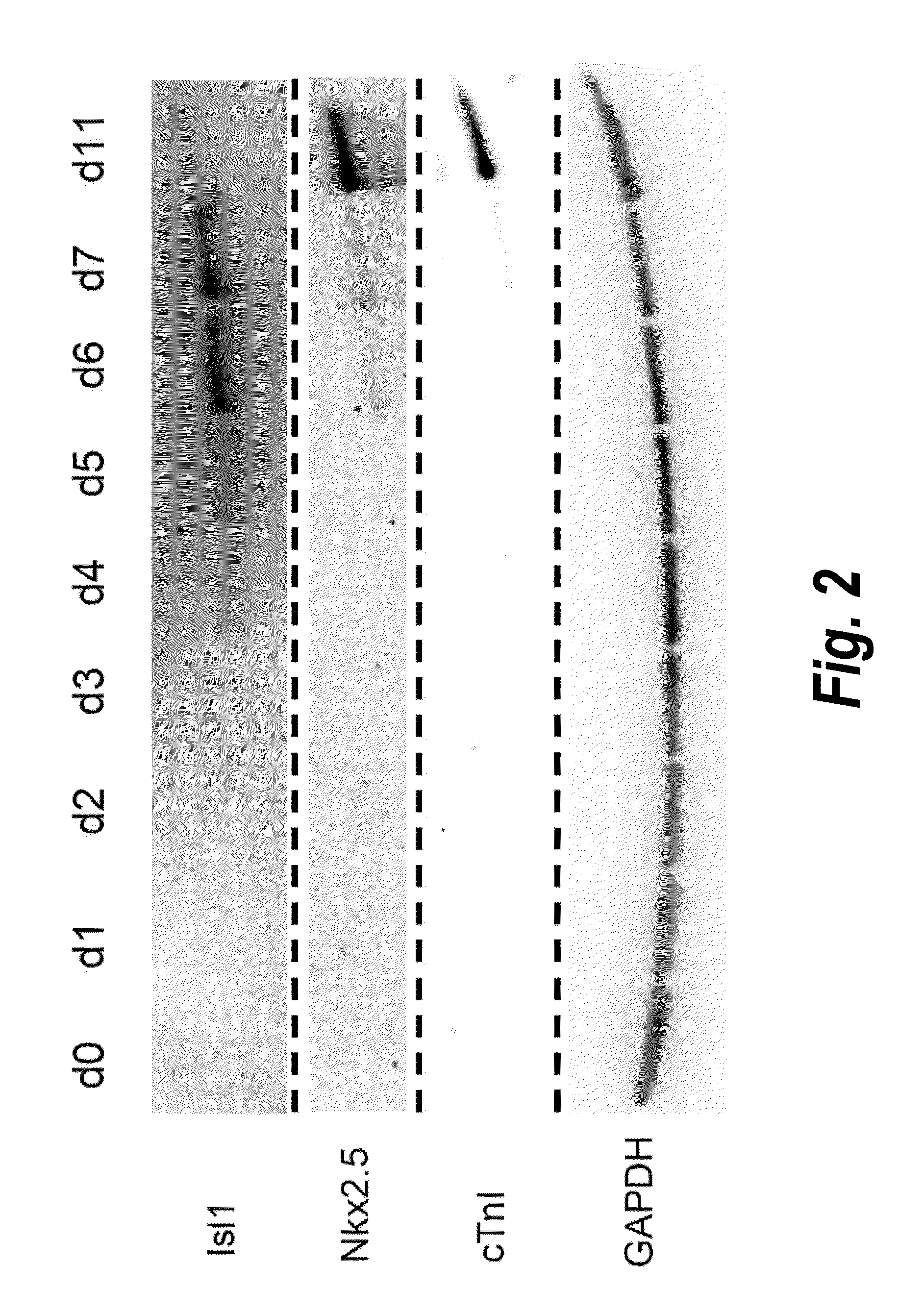
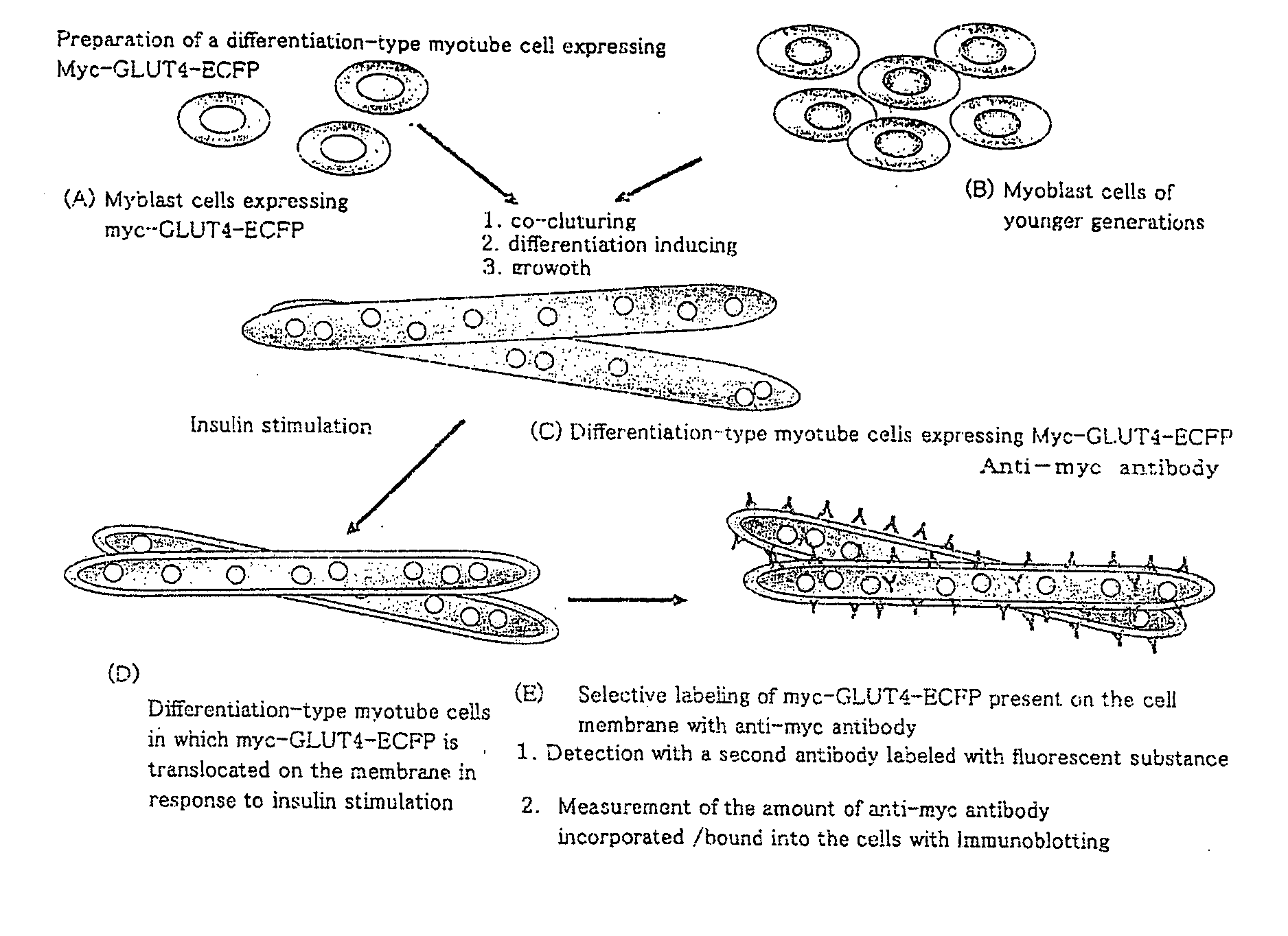
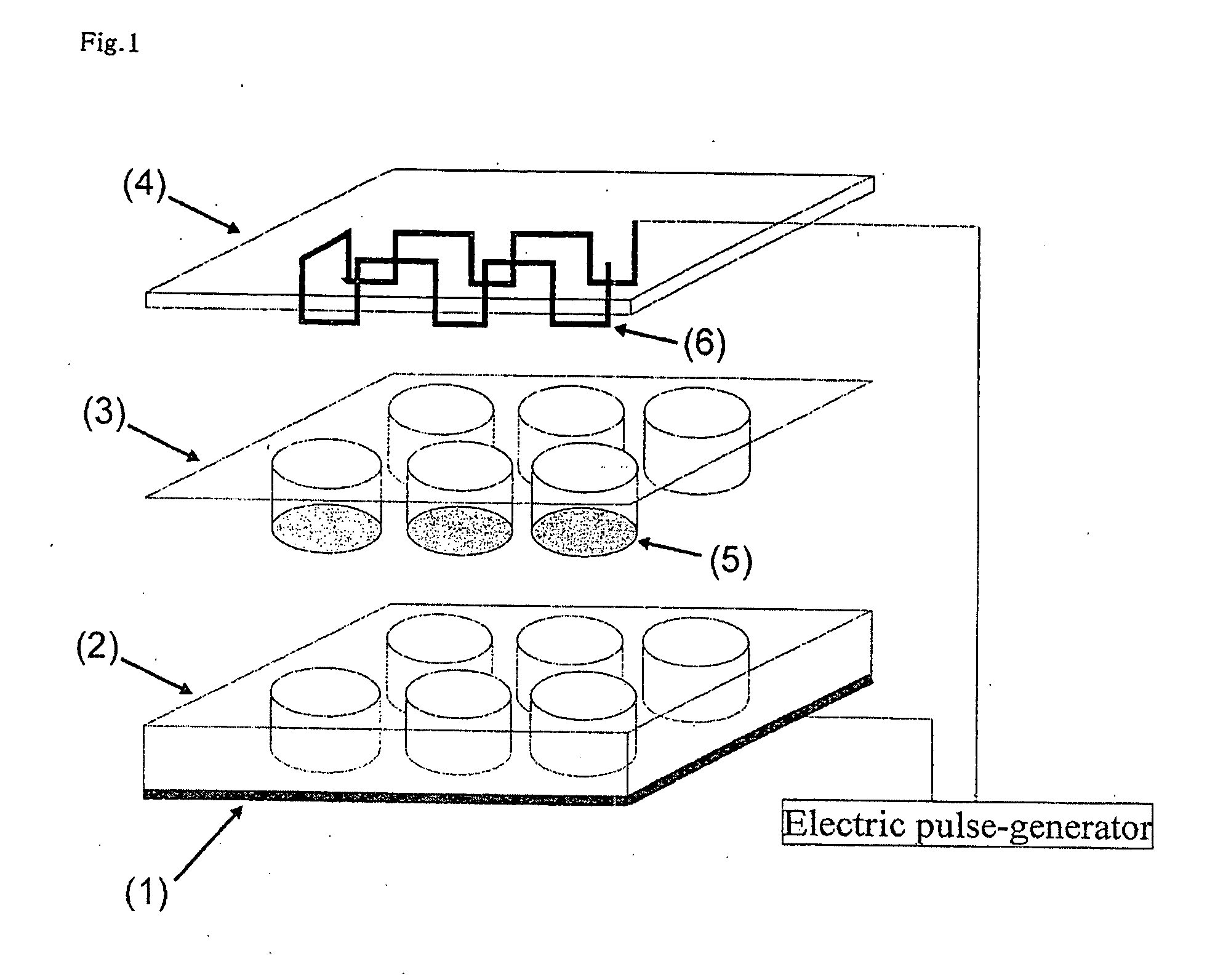
Cultured muscle cells with high metabolic activity and method for production of the cultured muscle cells
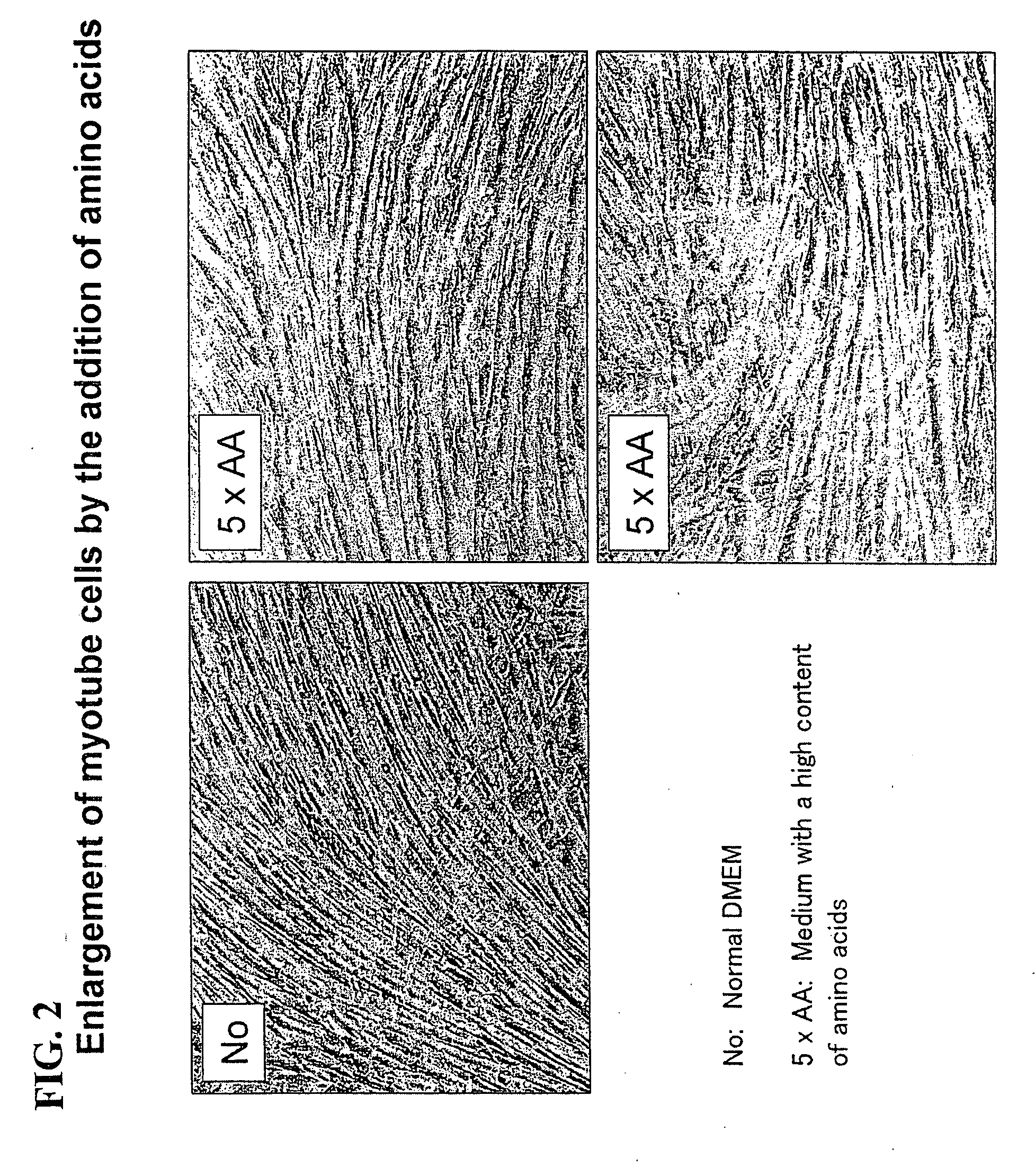
InactiveUS20080299086A1Improve glucose metabolismSimple structureBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMyogenic cellInsulin dependent
The object of the present invention is to provide a method of preparing excellent cultured muscle cells having high metabolic capacity and insulin responsiveness, and further provide a method for the measurement of sensitive metabolic capacity using the cells. Moreover, its purpose is to provide a culture system / culture apparatus that can smoothly translocate such highly advanced cultured muscle cells intact to activity evaluation systems of a number of drugs. Moreover, the object of the present invention is to provide cultured muscle cells that are very suitable for measurement of the membrane-translocation activity of GLUT4 in an extraneous stimulus-dependent manner such as insulin, etc., and to provide a method for the measurement of the membrane-translocation activity of GLUT4 using the cells. The present invention is a method of preparing myotube cells, comprising a step (1) of culturing myoblast cells, a step (2) of differentiation-inducing the myotube cells into the myoblast cells in a culture medium with a high content of amino acids, and a step (3) of applying an electric pulse to the differentiation-induced myotube cells, and a method for the measurement of insulin-dependent sugar uptake using the myotube cells prepared by said method, and relates to the method for the measurement, comprising applying insulin stimulation by culturing the cells in a culture medium containing insulin, culturing the cells in the culture medium further supplemented with sugar, and measuring the sugar uptake. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a differentiation-type culture myotube cell constitutively expressing a recombinant GLUT4 having a labeled substance at its extra-cellular site, which is prepared by co-culturing wild-type myoblast cells and recombinant myoblast cells constitutively expressing said recombinant GLUT4, and a method for the measurement of membrane-translocation activity of the recombinant GLUT4 using the cells, and particularly a method for the measurement of insulin-dependent sugar uptake activity.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com