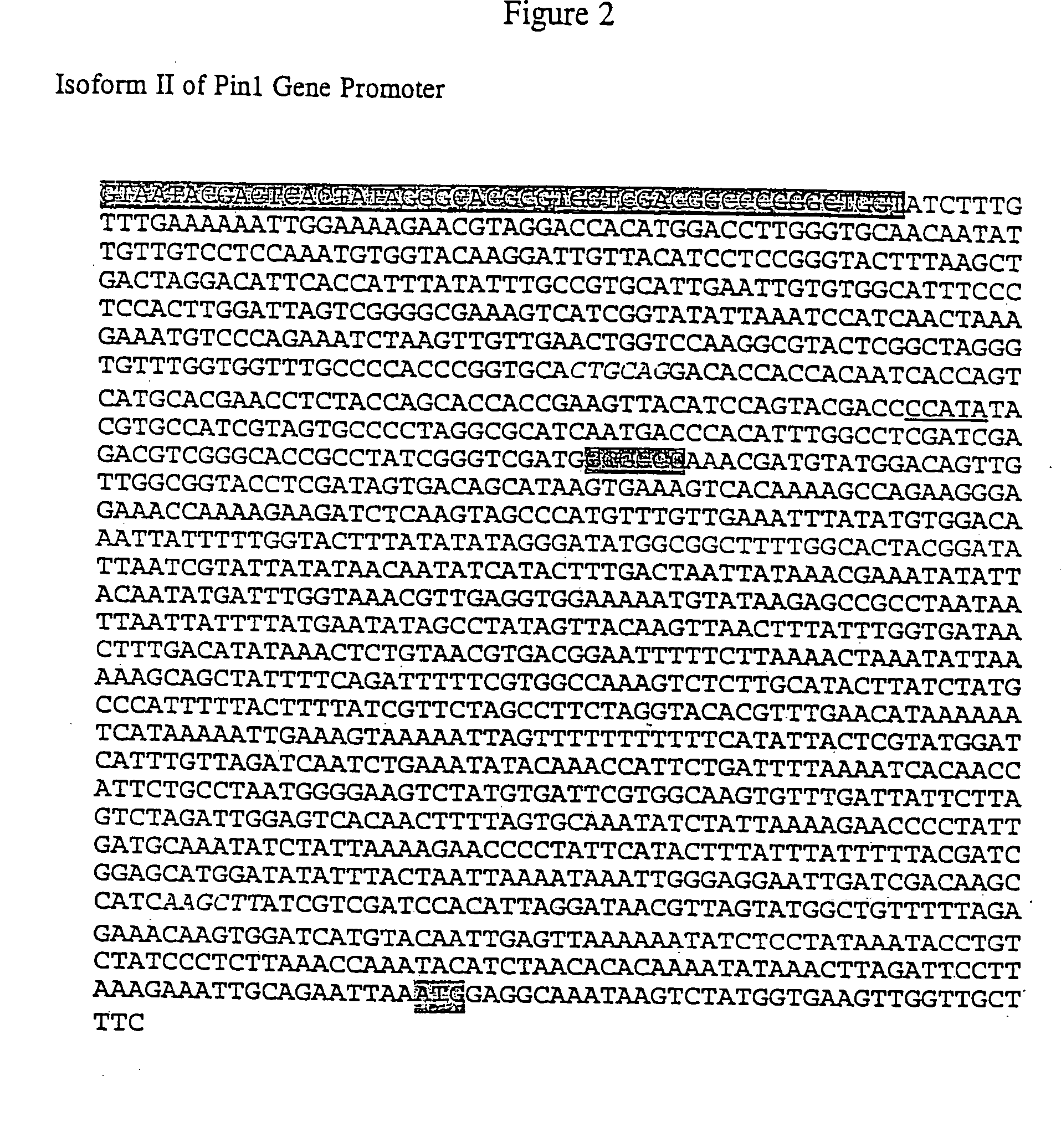Patents
Literature
33 results about "Enhancer Elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
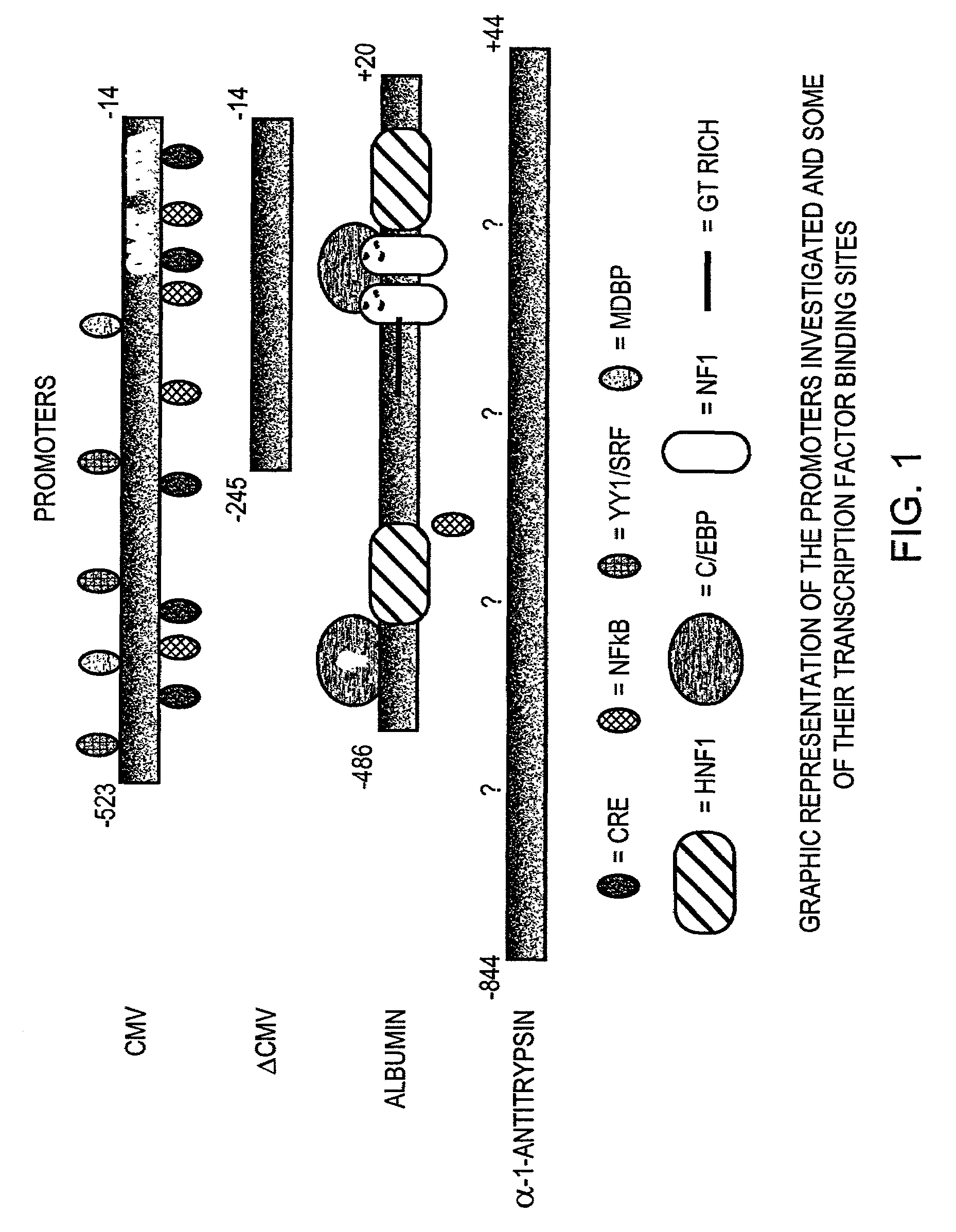
In genetics, an enhancer is a short (50–1500 bp) region of DNA that can be bound by proteins to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These ... Enhancer+Elements,Genetic at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) TFSEARCH;
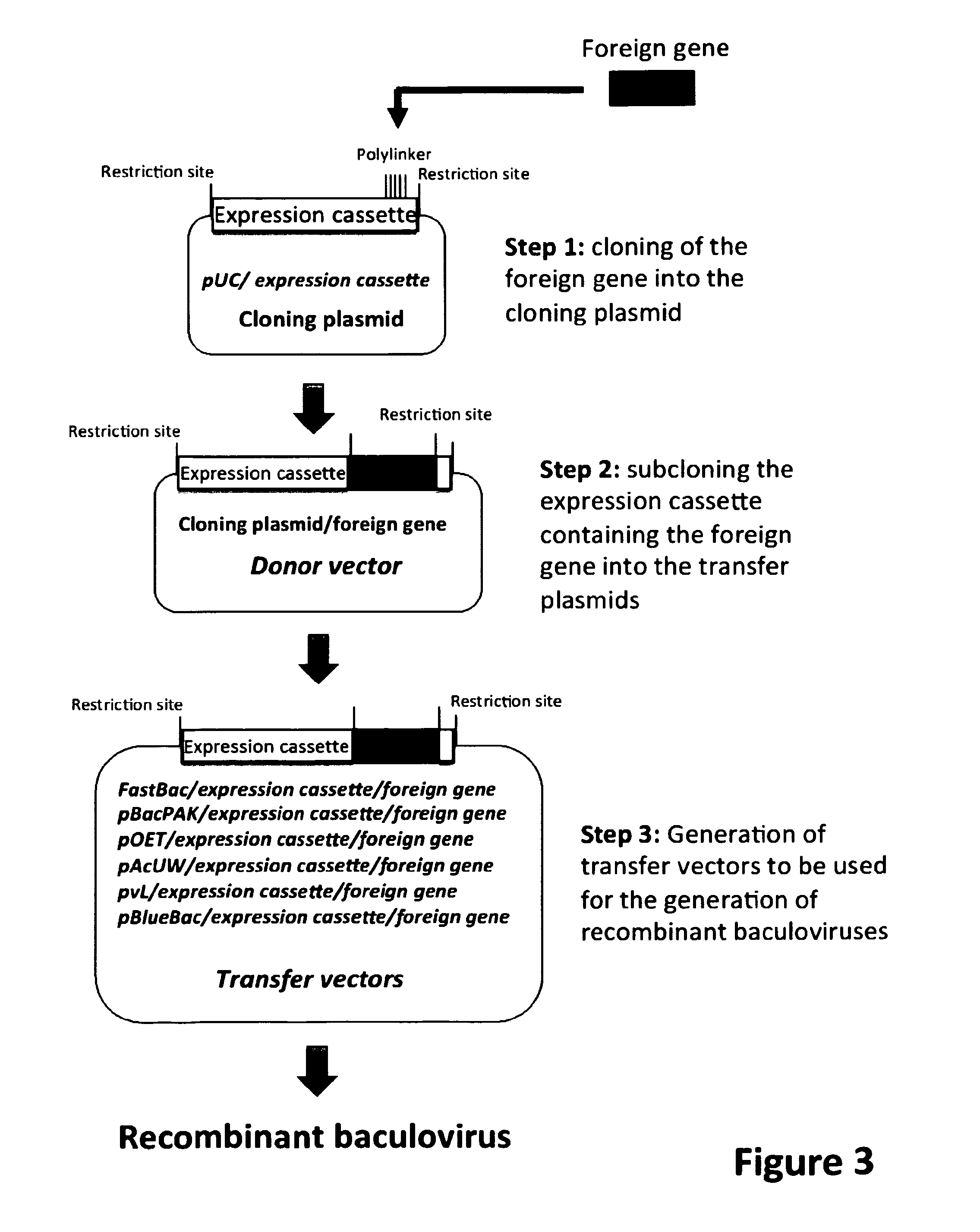
Muscle-specific expression vectors
The invention is directed to novel combinations of muscle-specific enhancers and promoter elements useful for achieving persistent expression in the muscle or myocyctes. The muscle-specific promoter elements are derived from a muscle creatine kinase promoter, a troponin I promoter, a skeletal alpha-actin promoter, or a desmin promoter. The muscle-specific enhancer elements are derived from either troponin I internal regulatory elements, muscle creatine kinase enhancers, or desmin enhancers.
Owner:SOUZA DAVID +1
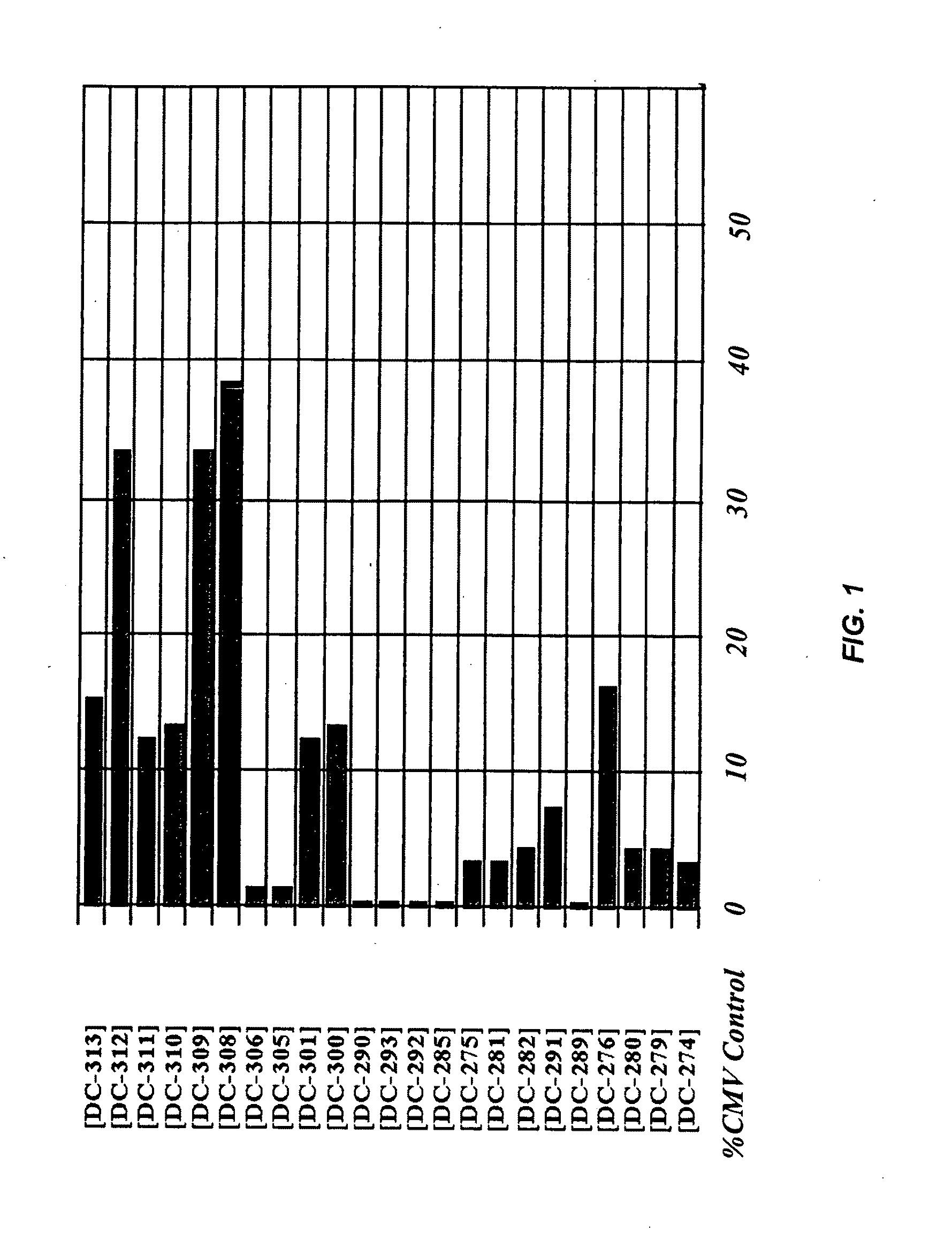
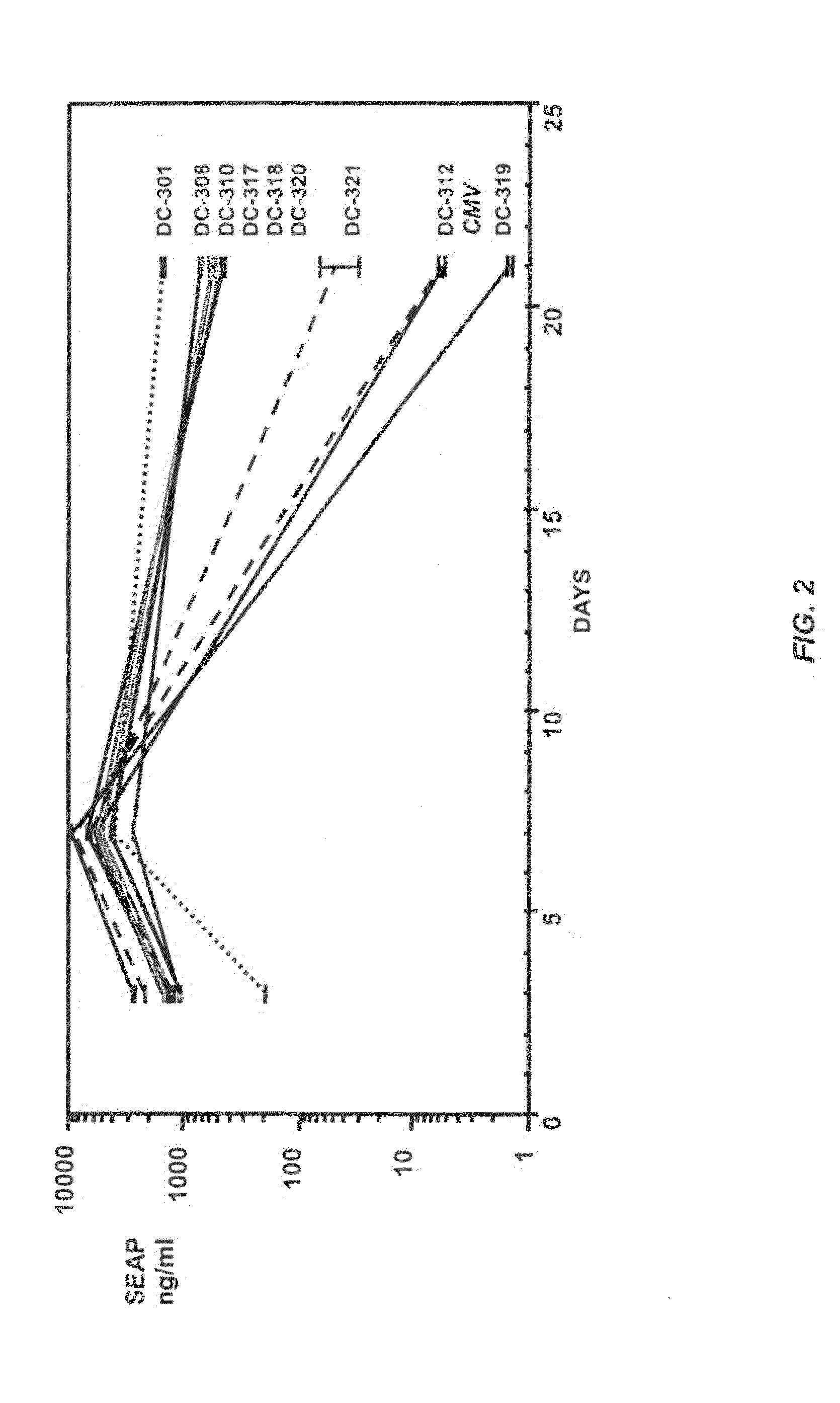
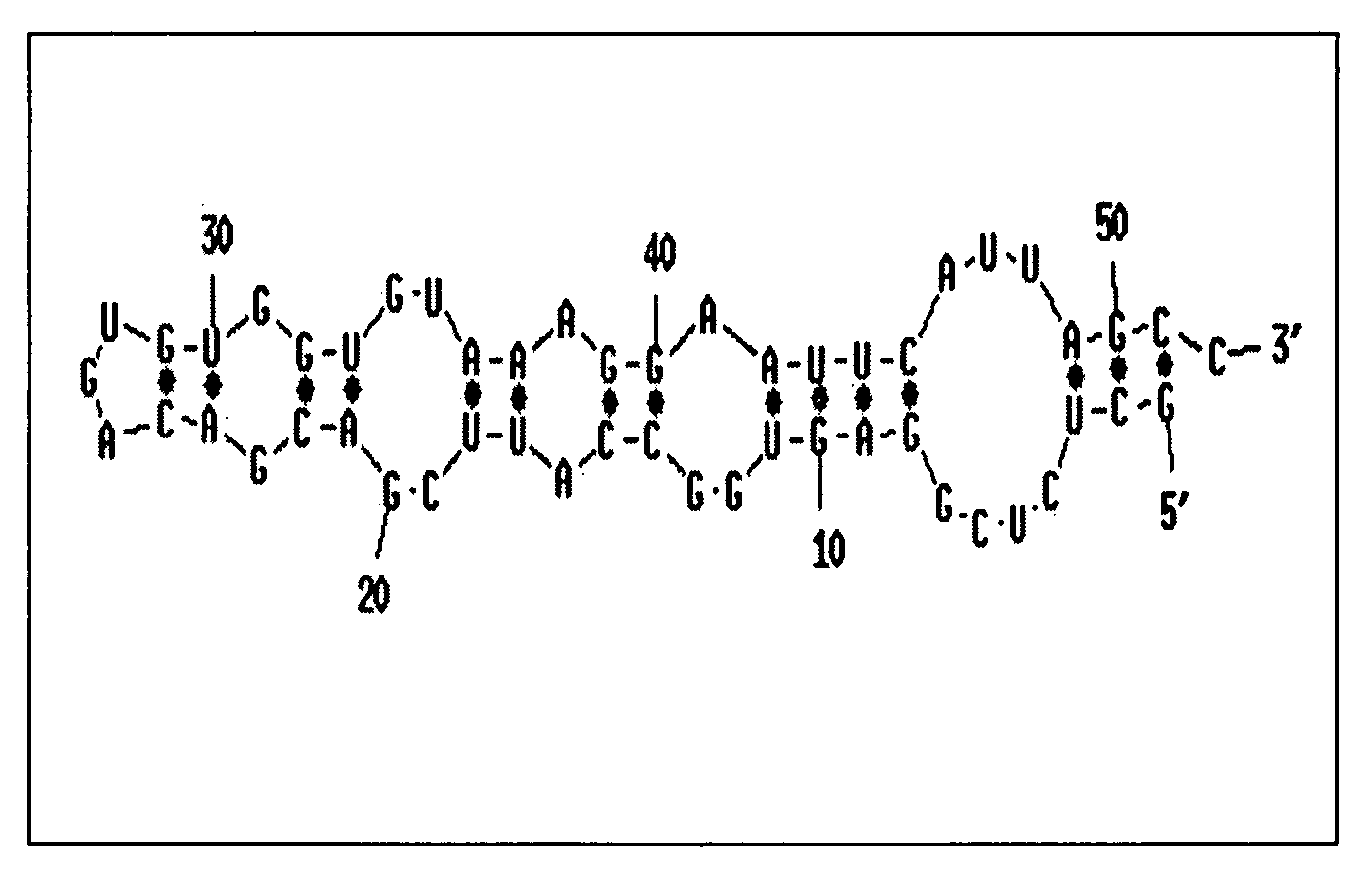
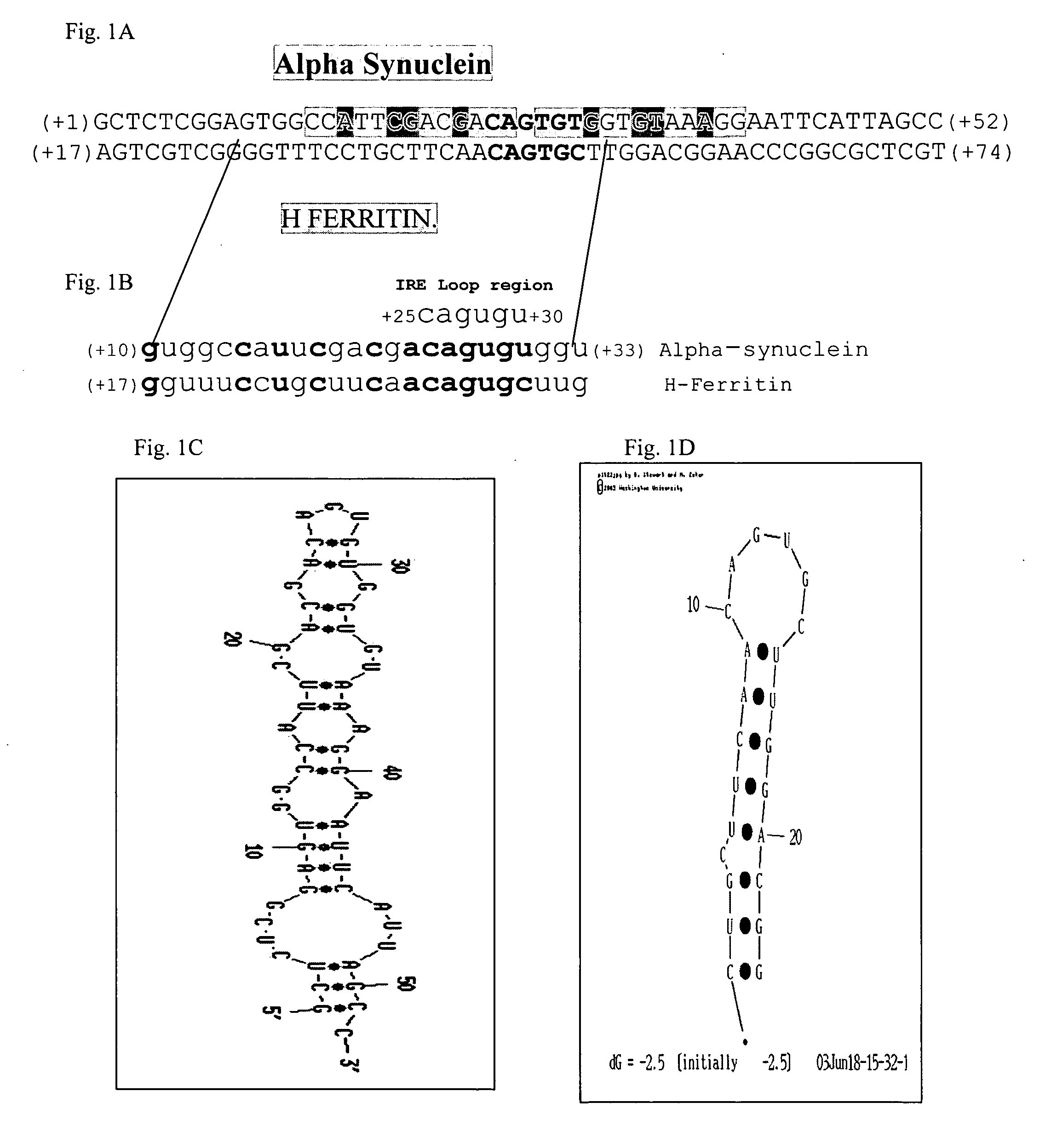
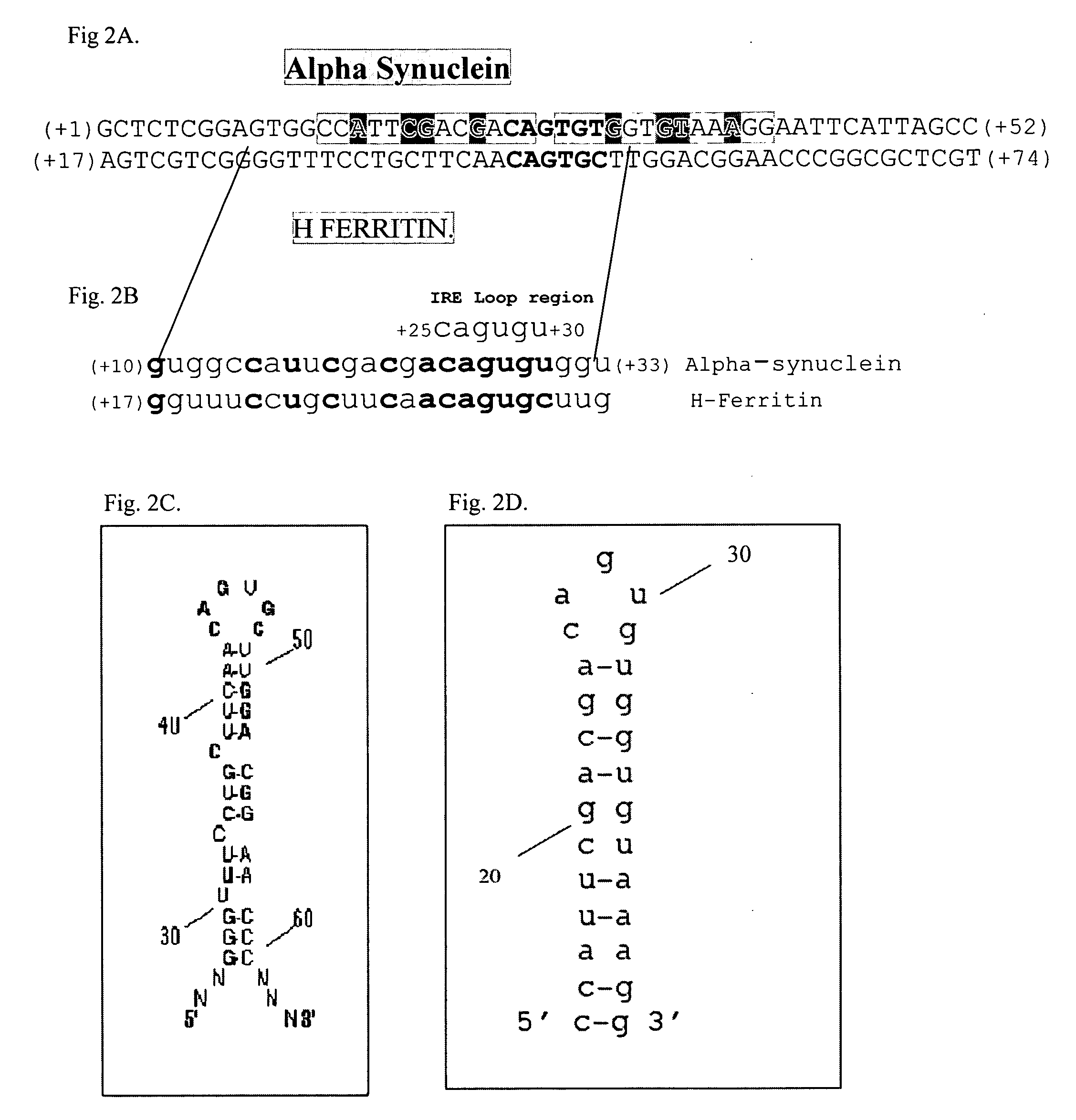
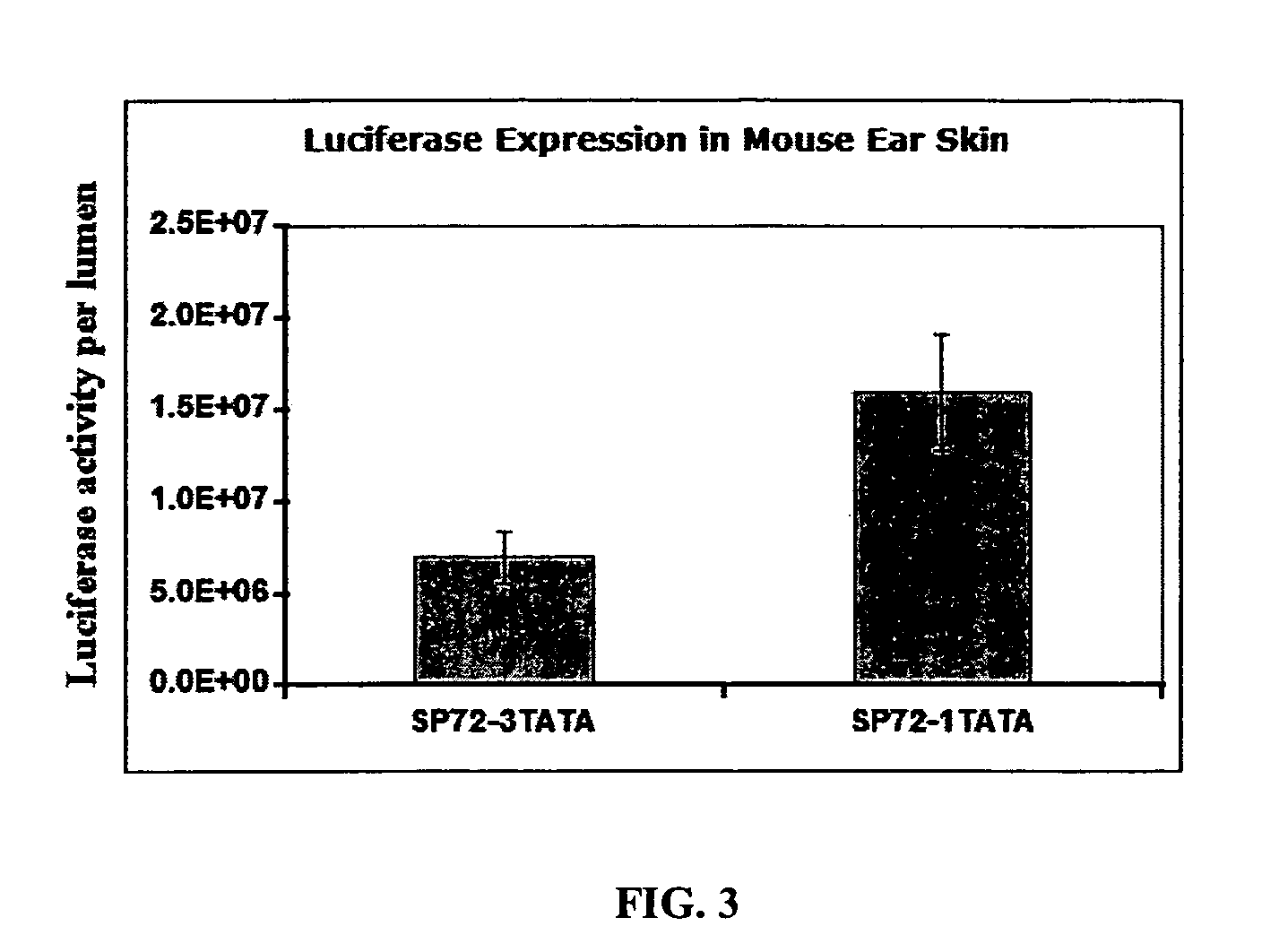
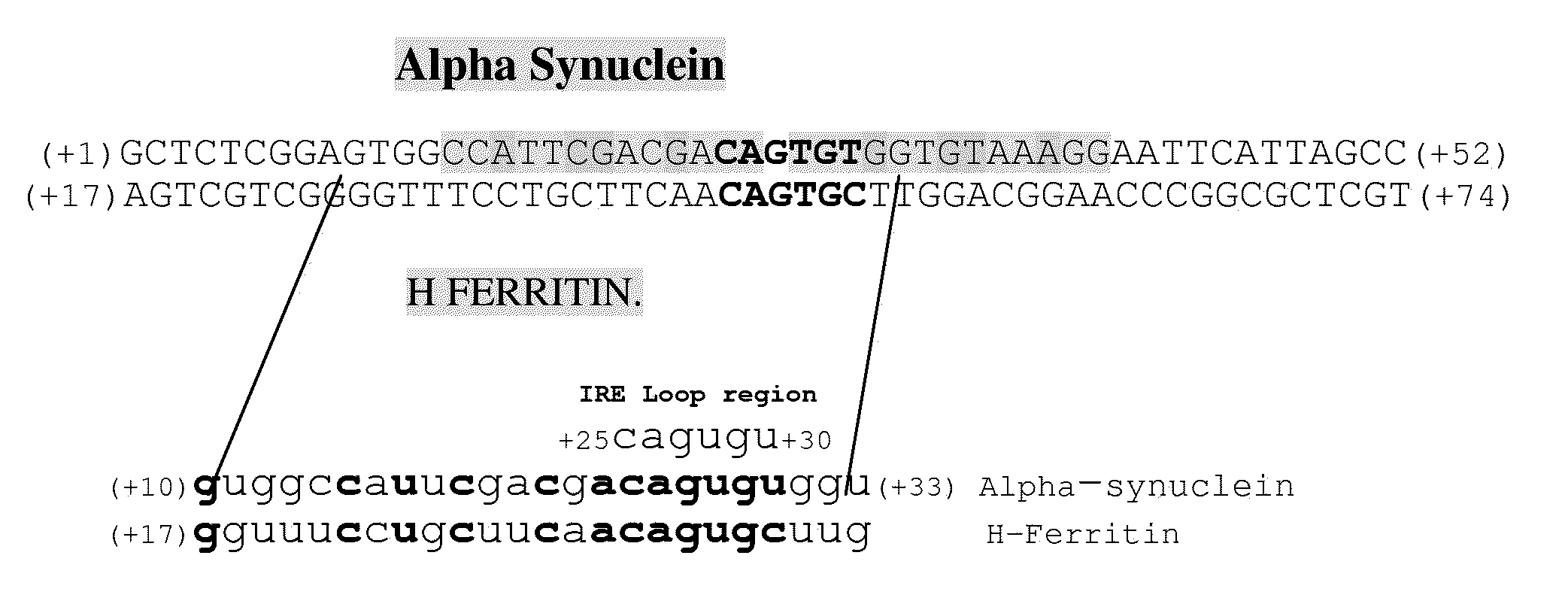
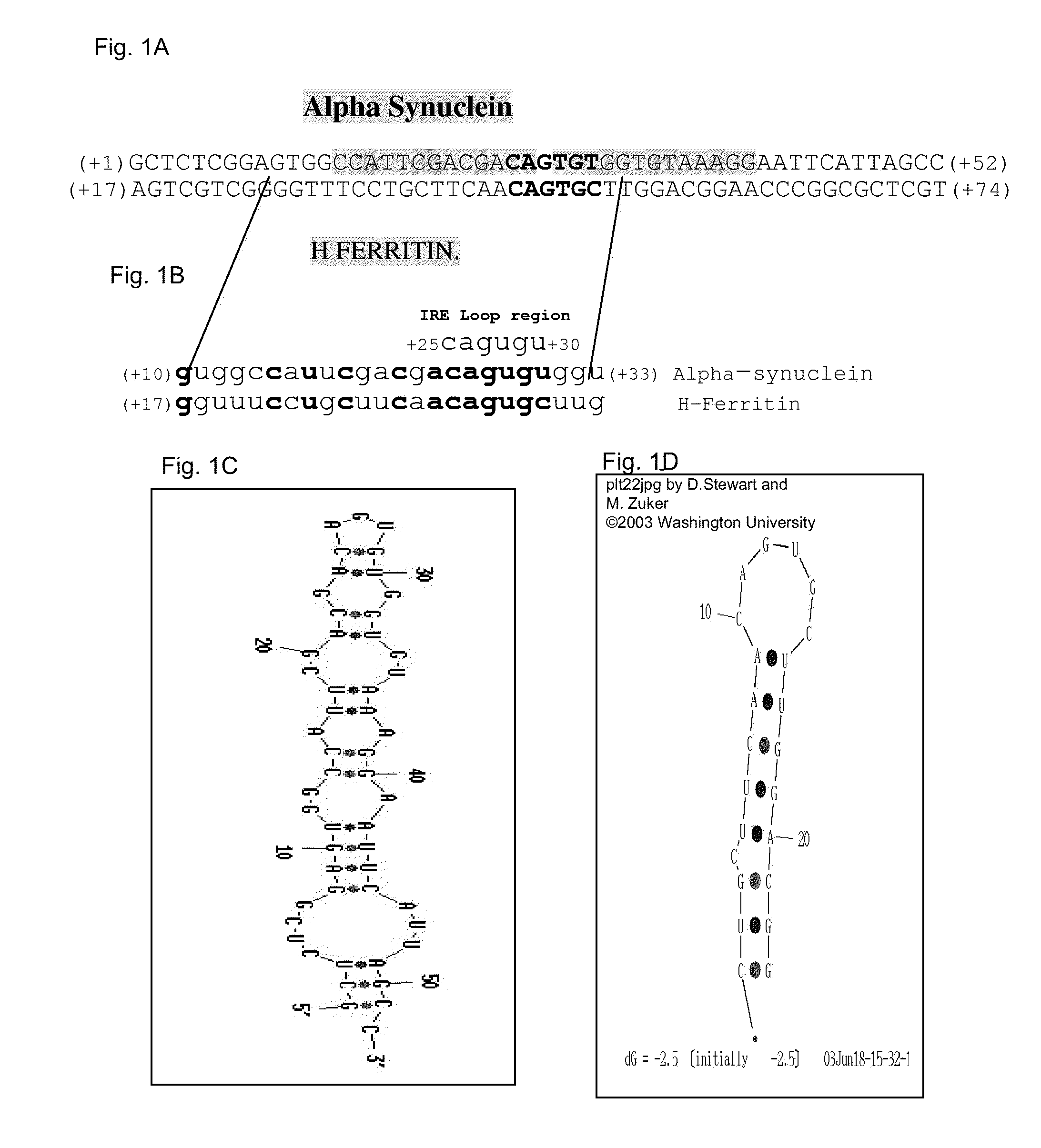
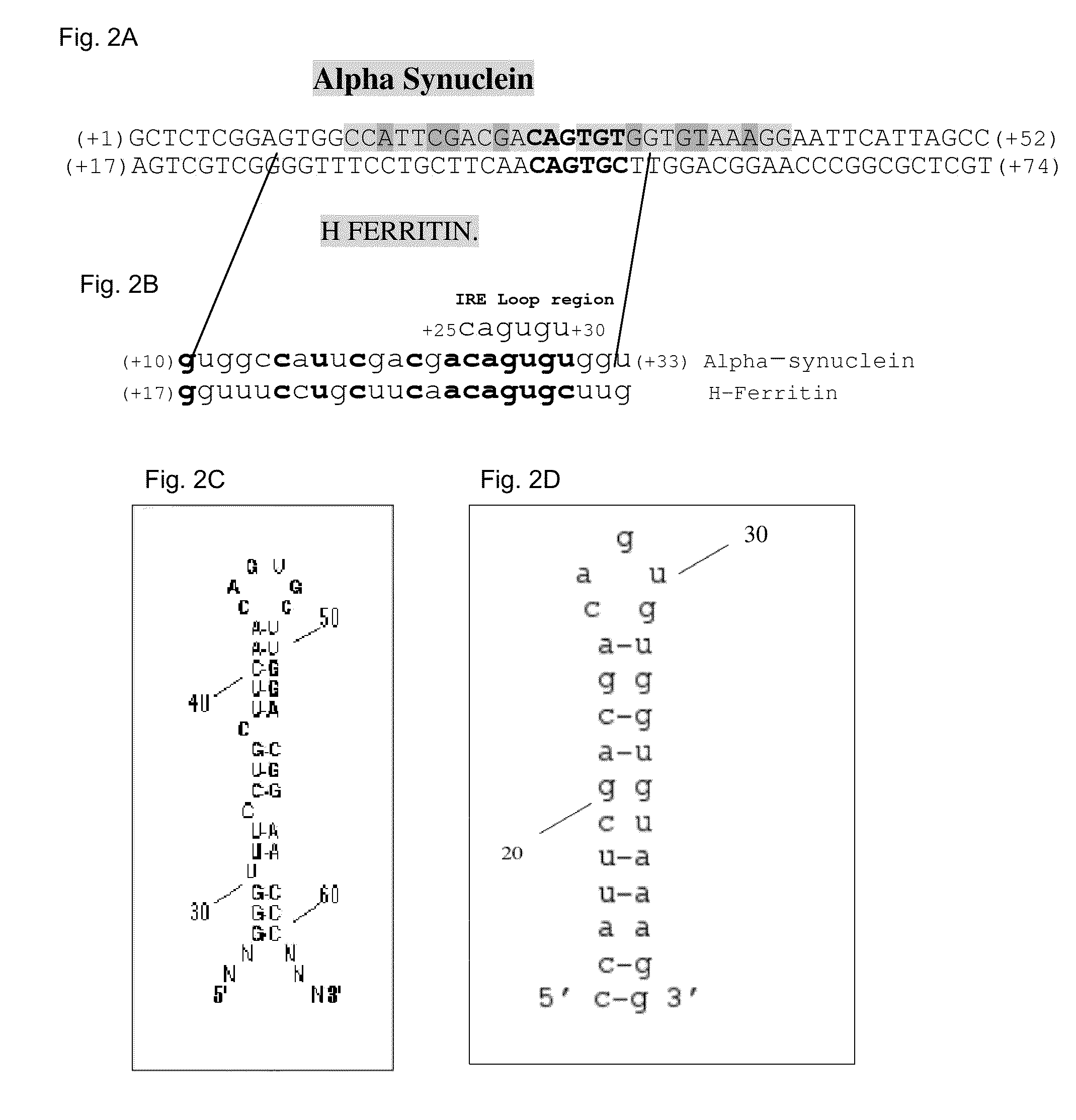
Translation enhancer elements of genes encoding human Tau protein and human alpha-synuclein protein
InactiveUS20080003570A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNeuro-degenerative diseaseEnhancer Elements
The invention relates to translation enhancer elements that enhance translation of the gene encoding the human microtubule-associated tau protein and nucleic acid molecules that enhance translation of the gene encoding the human α-synuclein protein. The translation enhancer elements of the invention are useful in compositions and methods for identifying compounds for the prevention and / or treatment of neurodegenerative disease. The invention also includes in some aspects, vectors that include a translation enhancer element of the invention. The invention also includes the use of enhancer element containing vectors in methods to produce recombinant protein and in assays to identify compounds that modulate expression of tau protein or α-synuclein protein.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Enhancer elements for increased translation in plant plastids
InactiveUS6271444B1Improve translationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesHigh level expressionBinding site
Provided are methods for increasing the production of protein in a plant cell by transforming plastids of plant cells with a construct comprising a promoter functional in a plant plastid, a ribosome binding site, DNA sequence of interest and a transcription termination region, and growing plant cells comprising the transformed plastids under conditions wherein the DNA encoding sequence is transcribed in the plastid. Also provided are methods for increasing protein production by fusing a coding sequence to a gene of interest to a secondary protein for cleavage or targetting of the protein of interest within the plastid, whereby high levels of expression of protein is achieved.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
Crustacean Expression Vector
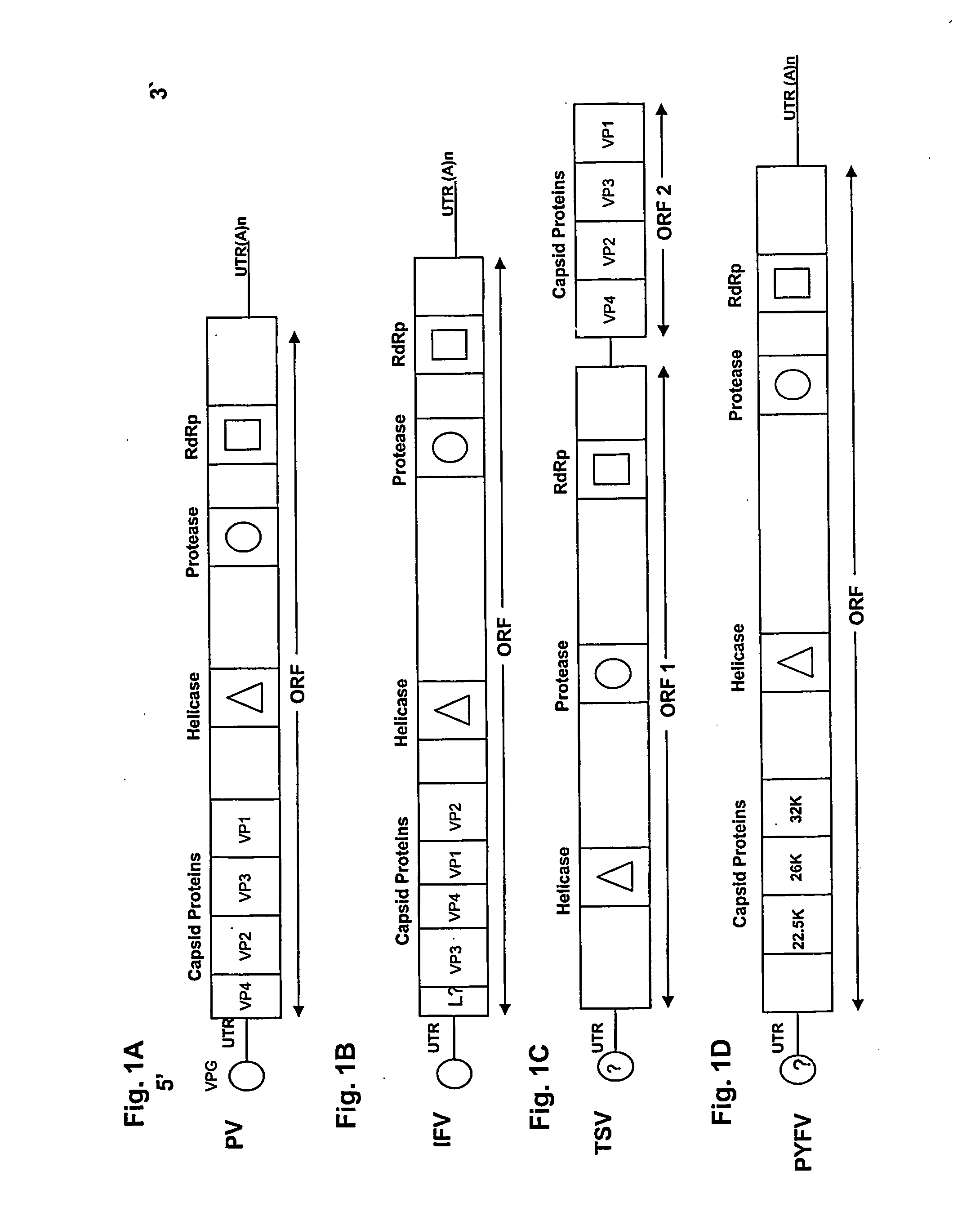
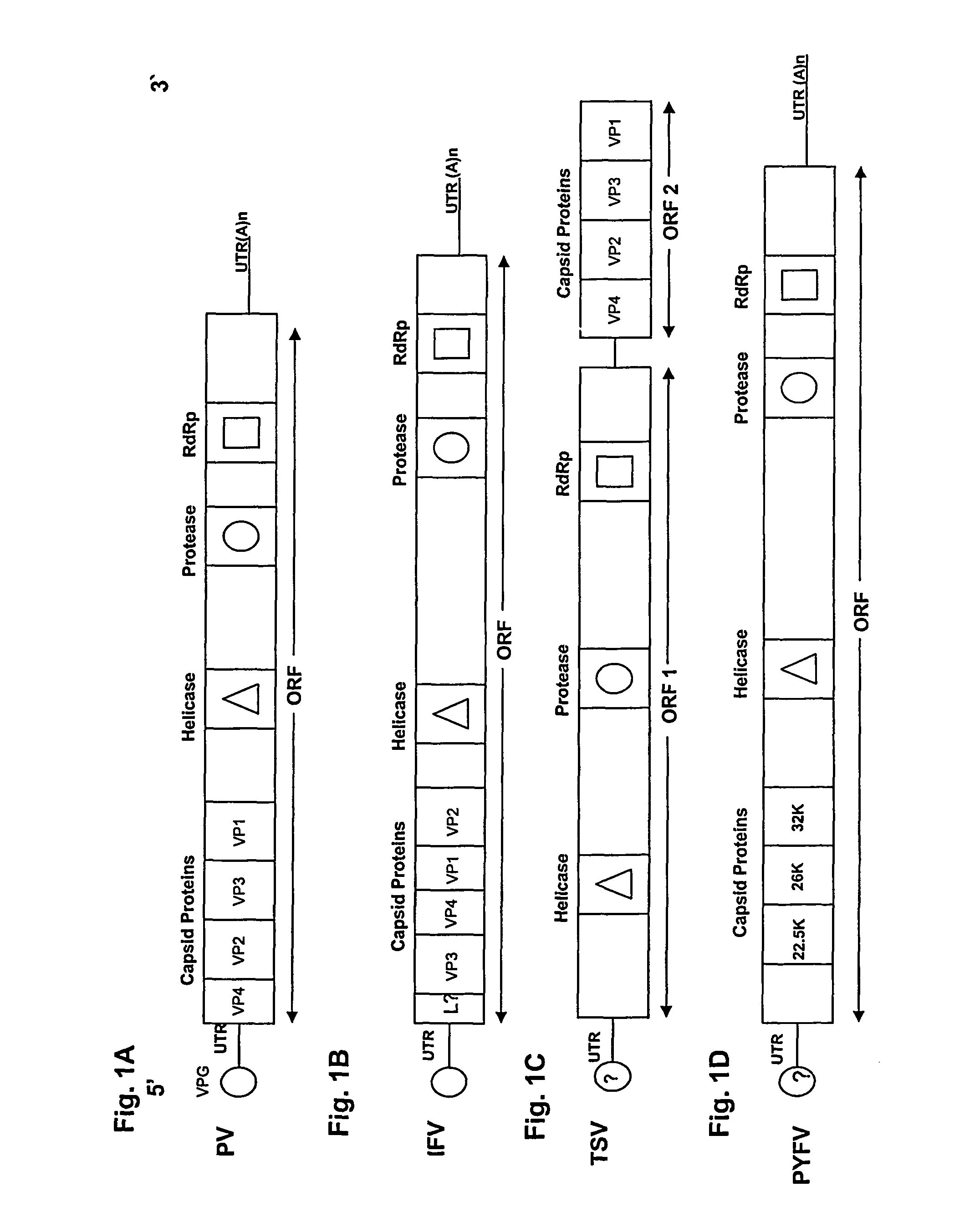
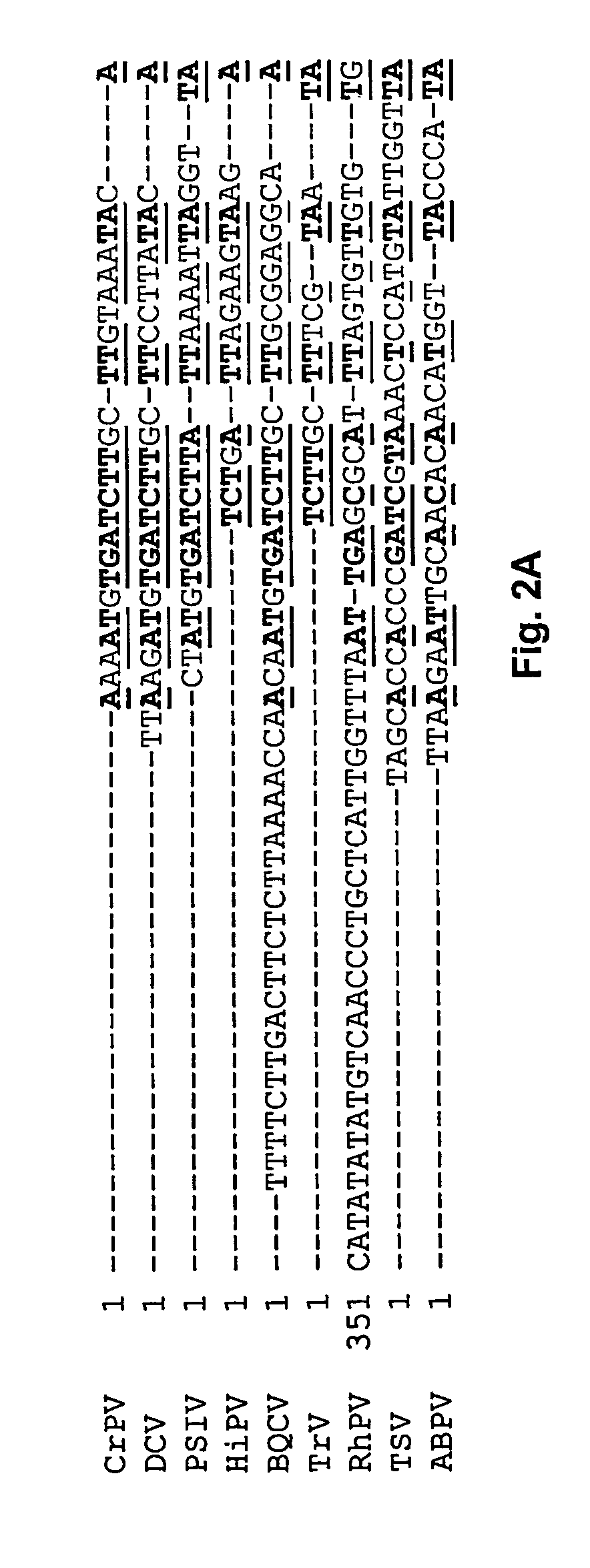
Methods and constructs for genetic manipulation of one or more of shrimp, shellfish, mollusks, and fish are disclosed. The nucleic acid construct includes a promoter and an internal ribosome entry site of an insect picomavirus, such as a cricket paralysis-like picomavirus. One or more open reading frames can be operably associated with one or both of the promoter and the internal ribosome entry site, and one or more proteins or protein subunits can be expressed upon introduction of the construct into a host cell, such as into a shrimp. Method for producing immortalized crustacean cell lines using enhancer elements derived from shrimp and / or shrimp viruses are also described.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Lipids and lipid assemblies comprising transfection enhancer elements
InactiveUS20080145413A1Promote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticLipid formationCell membrane
This disclosure describes structural elements that enhance fusogenicity of lipids and lipid assemblies (e.g. liposomes) with biological membranes, in particular cell membranes, and use of such structures. The elements are pH sensitive in terms of charge and hydrophilicity and undergo a polar—apolar transition when exposed to low pH.
Owner:MARINA BIOTECH INC
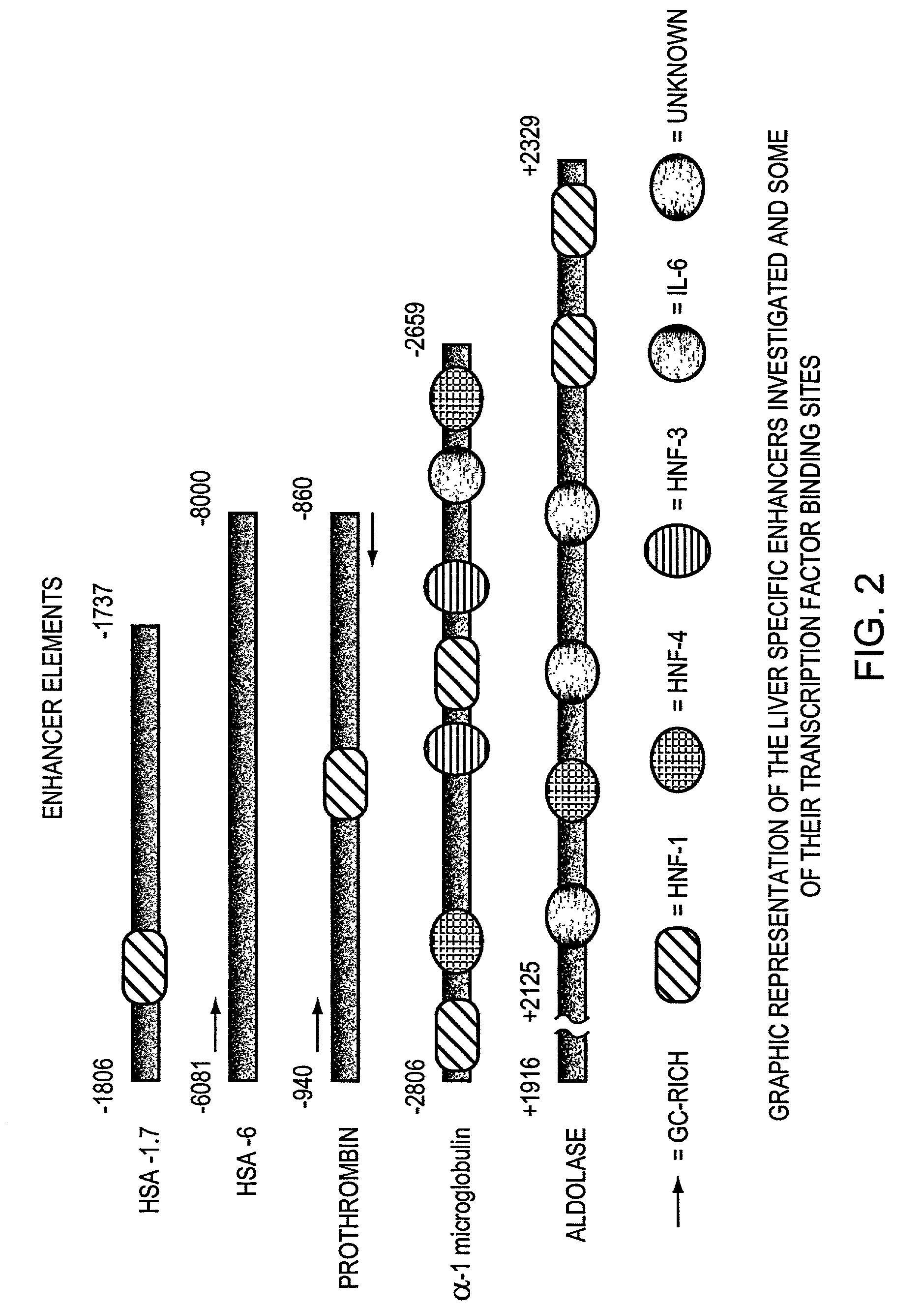
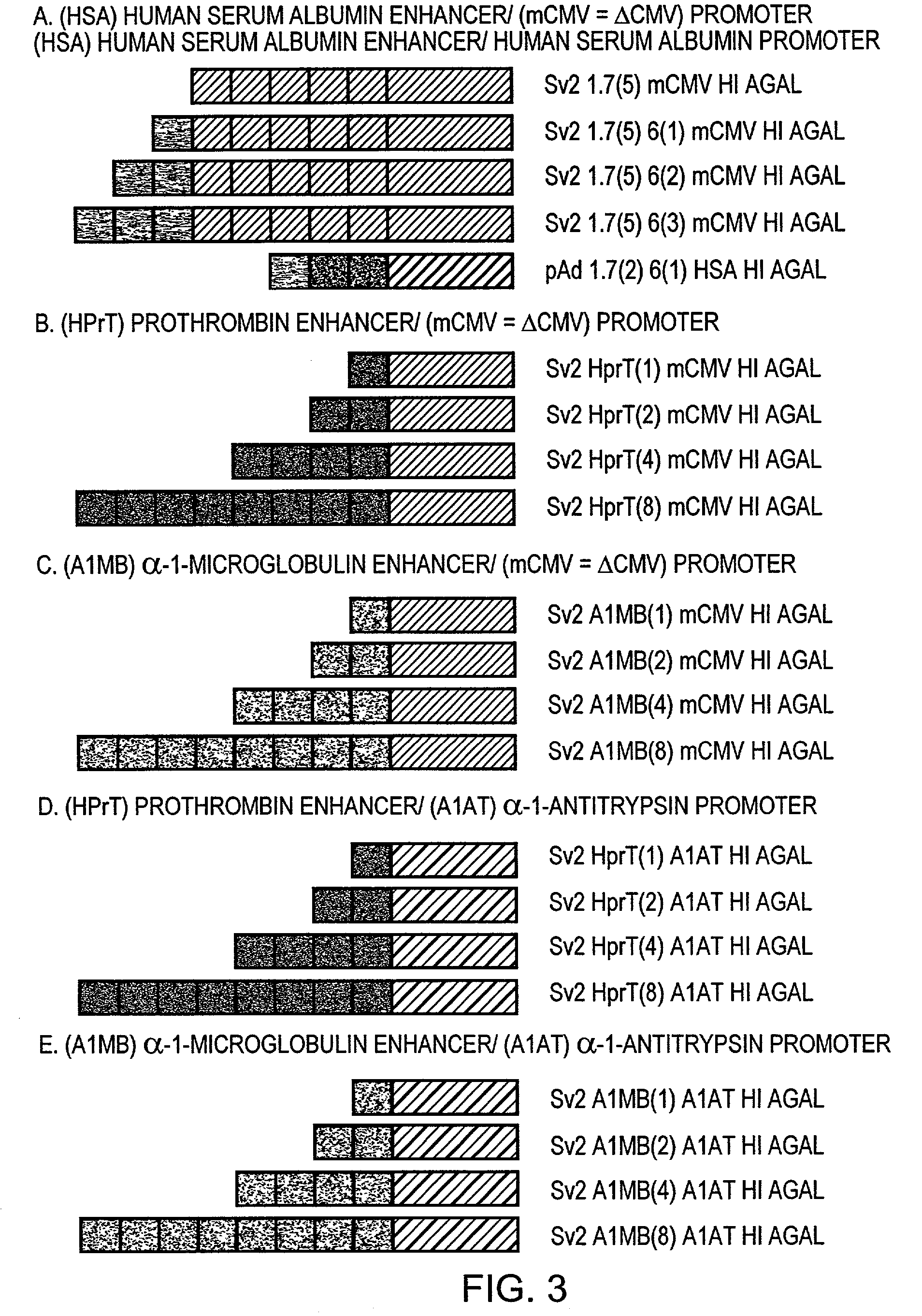
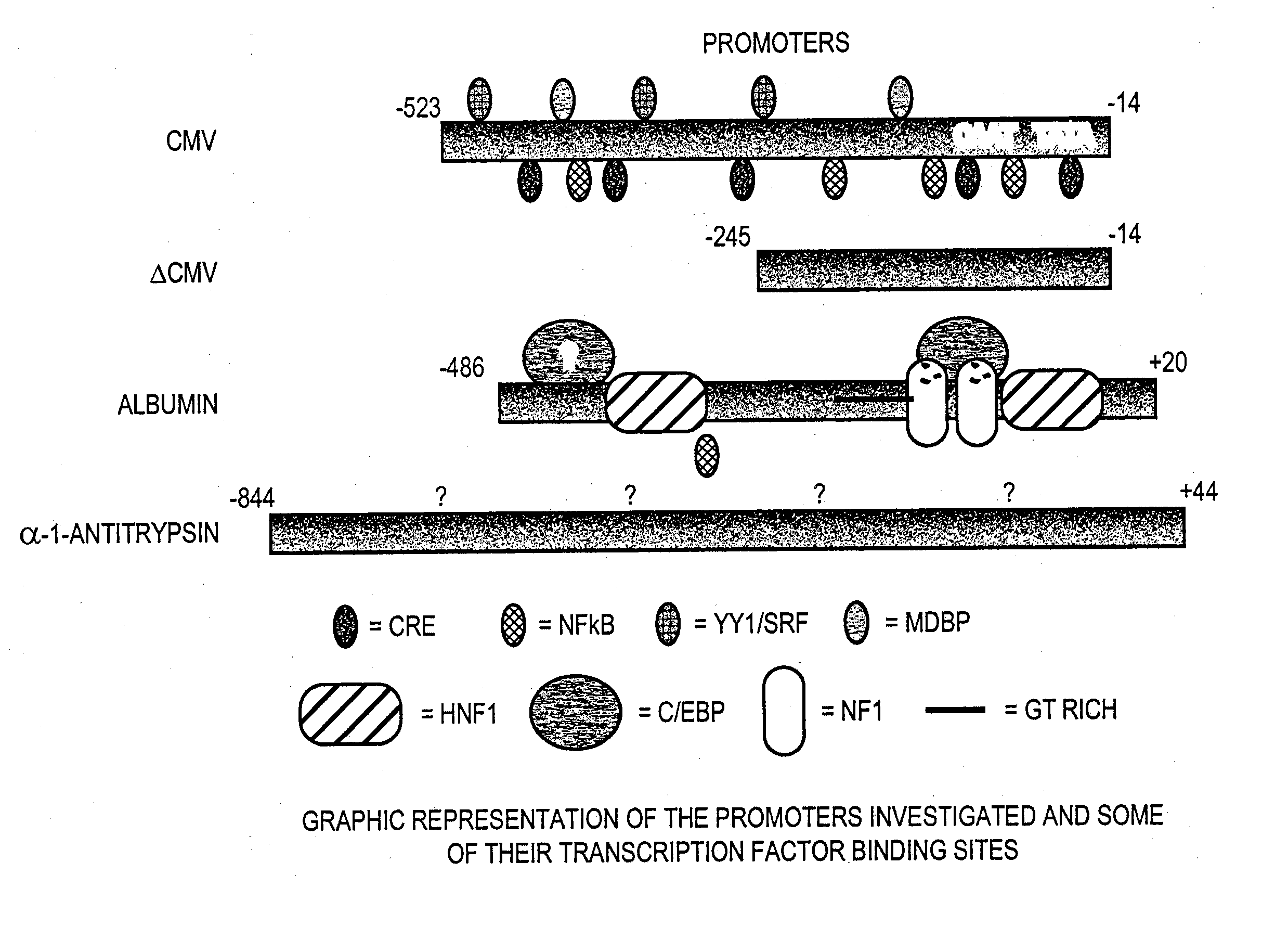
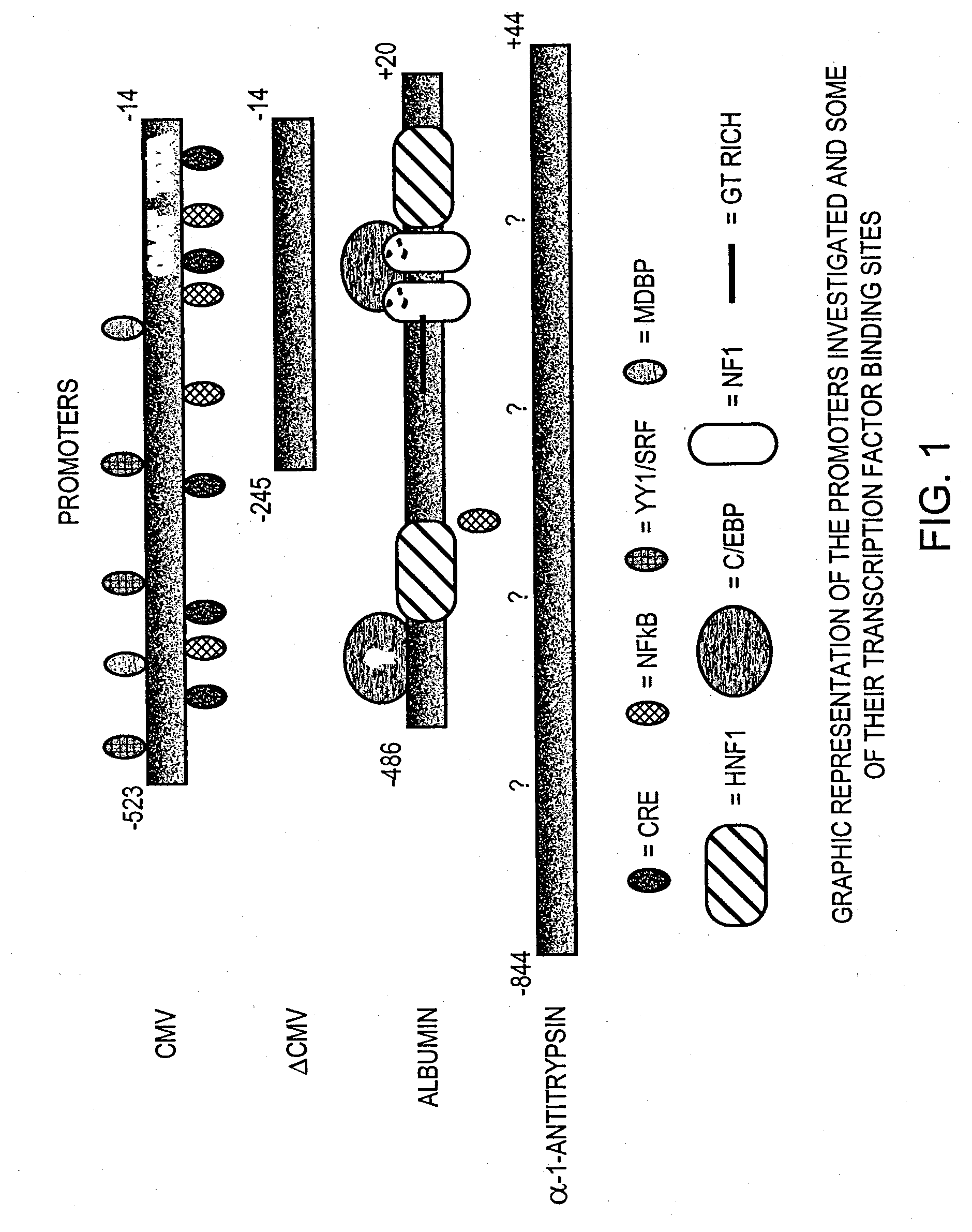
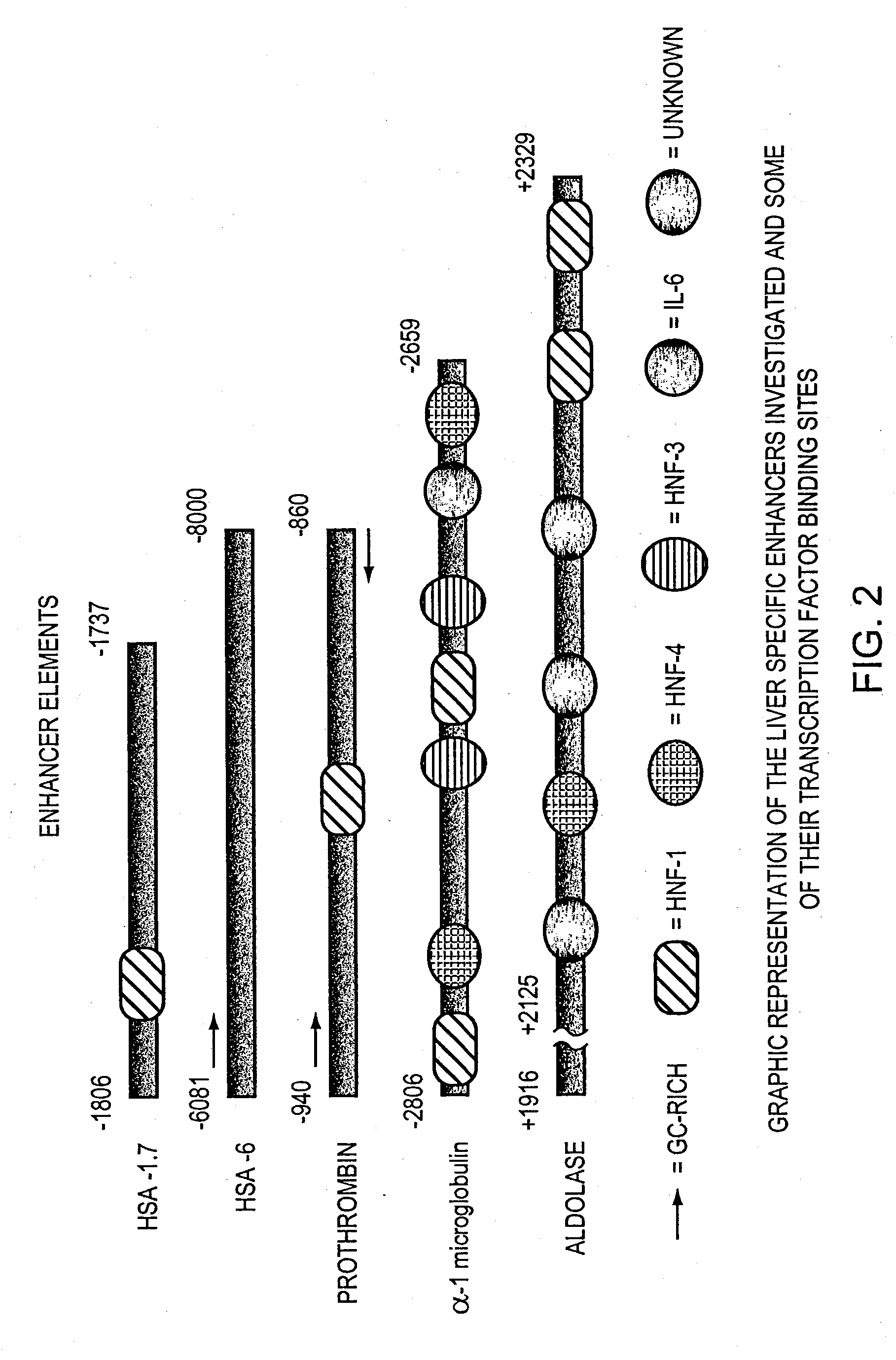
Regulatory elements for delivery to the liver
The invention is directed to novel combinations of liver specific enhancers and promoter elements for achieving persistent transgene expression in the liver. The liver specific enhancer elements may be derived from either the human serum albumin, prothrombin, α-1microglobulin or aldolase genes in single copies or in multimerized form linked to elements derived from the cytomegalovirus intermediate early (CMV), α-1-antitrypsin or albumin promoters. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, an adenoviral vector comprising a liver specific enhancer / promoter combination operably linked to a transgene is administered to recipient cells. In other embodiments of the invention, adeno-associated viral vectors, retroviral vectors, lentiviral vectors or a plasmid comprising the liver specific enhancer / promoter combination linked to a transgene is administered to recipient cells. Also within the scope of the invention are promoter elements derived from the human prothrombin gene and the β-fibrinogen gene.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method for improving transgenic insect cell expression exogenous gene level
InactiveCN101270366AAchieve continuous expressionHigh biosecurityVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsHigh level expressionGenetically modified insect
The invention discloses a method for improving expression of extraneous genes by insect transgene cells. In the method, active promoter controlled neomycin resistance gene expression cassettes, enhancer elements and extraneous gene expression cassettes inside the cells of insects are cloned into a vector with reporter genes based on transposon piggyBAC factors; subsequently, the vector is mixed with subsidiary plasmids expressing transposase to transfect insect cell lines; transgene insect cells are acquired through sectionalized screening of G418. Engineering cells expressing extraneous genes at high level are acquired by cell clone technology in combination practical examination of expression level of extraneous genes. With the method, transgene insect cells can express extraneous genes at high level continuously; the expression products are free of rhabdoviruses with good bio-safety, and are processed perfectly as well as natural.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
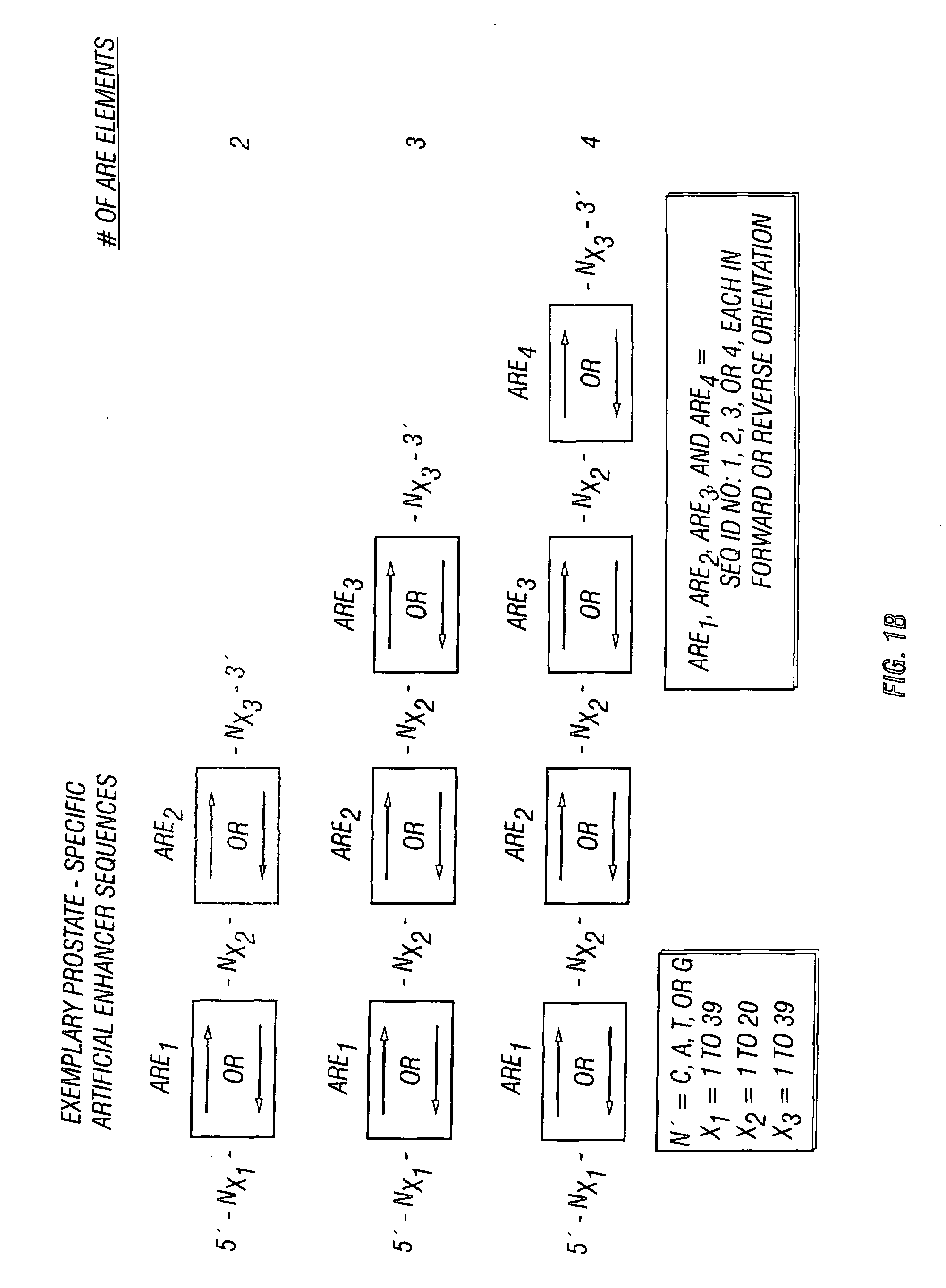
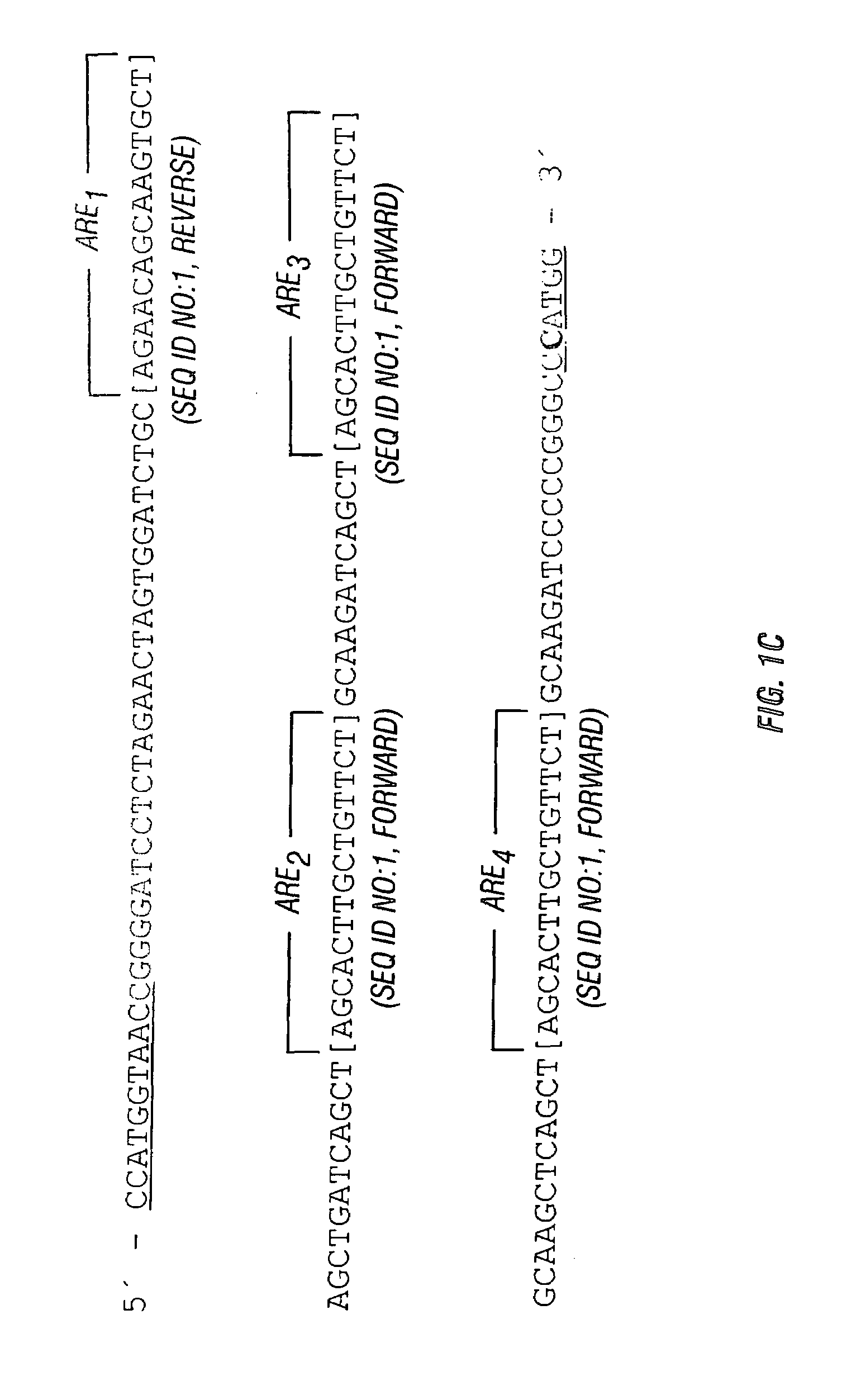
Chimeric transcriptional regulatory element compositions and methods for increasing prostate-targeted gene expression
InactiveUS7267978B1High expressionPromoting transcriptionVectorsGenetic material ingredientsHeterologousDisease
Disclosed are compositions and methods for achieving successful treatment of disorders of the human prostate. In preferred embodiments, methods and compositions are provided that improve the specificity and safety of gene delivery vectors, and improve the prostate-specificity and activity of genetic constructs targeted for prostate-specific expression. Also disclosed are methods utilizing a variety of therapeutic genes, including those encoding tumor-specific therapeutics, e.g., TRAIL, tumor suppressors, cytotoxins, and the like, for the treatment of proliferative disorders of the prostate, and in particular, prostatic hyperplasia, prostate cancer and prostatic tumors. In preferred embodiments genetic constructs are disclosed comprising one or more prostate-specific chimeric enhancer elements in combination with one or more wildtype core enhancer elements and a prostate-specific proximal promoter that increase expression of selected heterologous genes operably positioned under their control.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
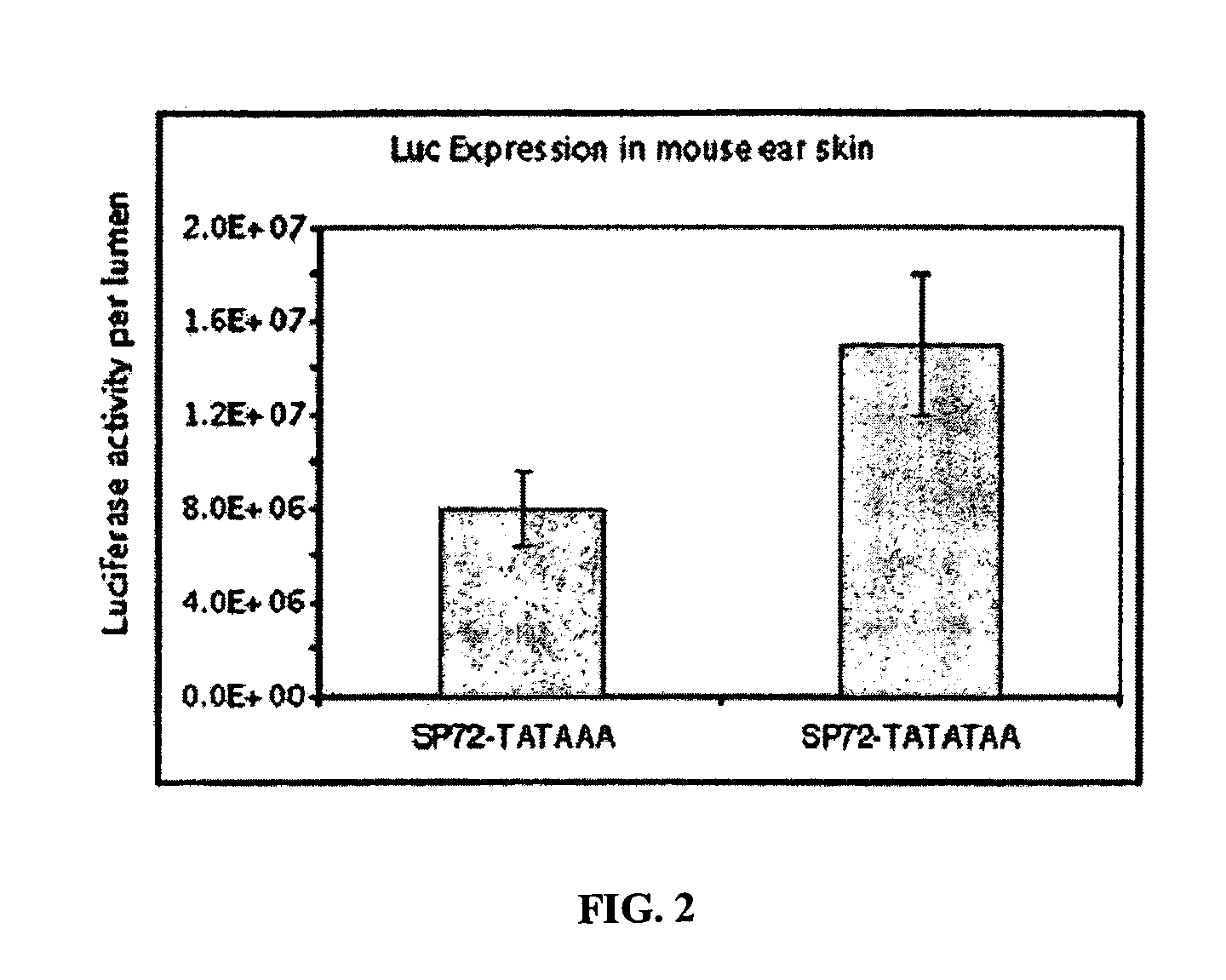
Rationally designed and chemically synthesized promoter for genetic vaccine and gene therapy
ActiveUS7312202B2High activityEnhance immune responseBiocideGenetic material ingredientsChemical synthesisIntramuscular injection
The present invention relates to chemically synthesized promoters that circumvent the disadvantages of the universal CMV promoter / enhancer elements. The promoter may be used in a variety of applications, particularly in genetic immunization. The chemically synthesized promoter overcomes the common problems of the CMV promoter element such as: low transgene expression levels, transient expression, and the large amount of plasmid DNA needed for intramuscular injection in subjects.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Translation Enhancer Elements Of Genes Encoding Human Tau Protein and Human Alpha-Synuclein Protein
The invention relates to translation enhancer elements that enhance translation of the gene encoding the human microtubule-associated tau protein and nucleic acid molecules that enhance translation of the gene encoding the human α-synuclein protein. The translation enhancer elements of the invention are useful in compositions and methods for identifying compounds for the prevention and / or treatment of neurodegenerative disease. The invention also includes in some aspects, vectors that include a translation enhancer element of the invention. The invention also includes the use of enhancer element containing vectors in methods to produce recombinant protein and in assays to identify compounds that modulate expression of tau protein or α-synuclein protein.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Aberrant Myc/TIP60 interactions as a target for anti-cancer therapeutics
InactiveUS20050186604A1Enhance transforming potentialSpeed upMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsStructural proteinEnhancer Elements
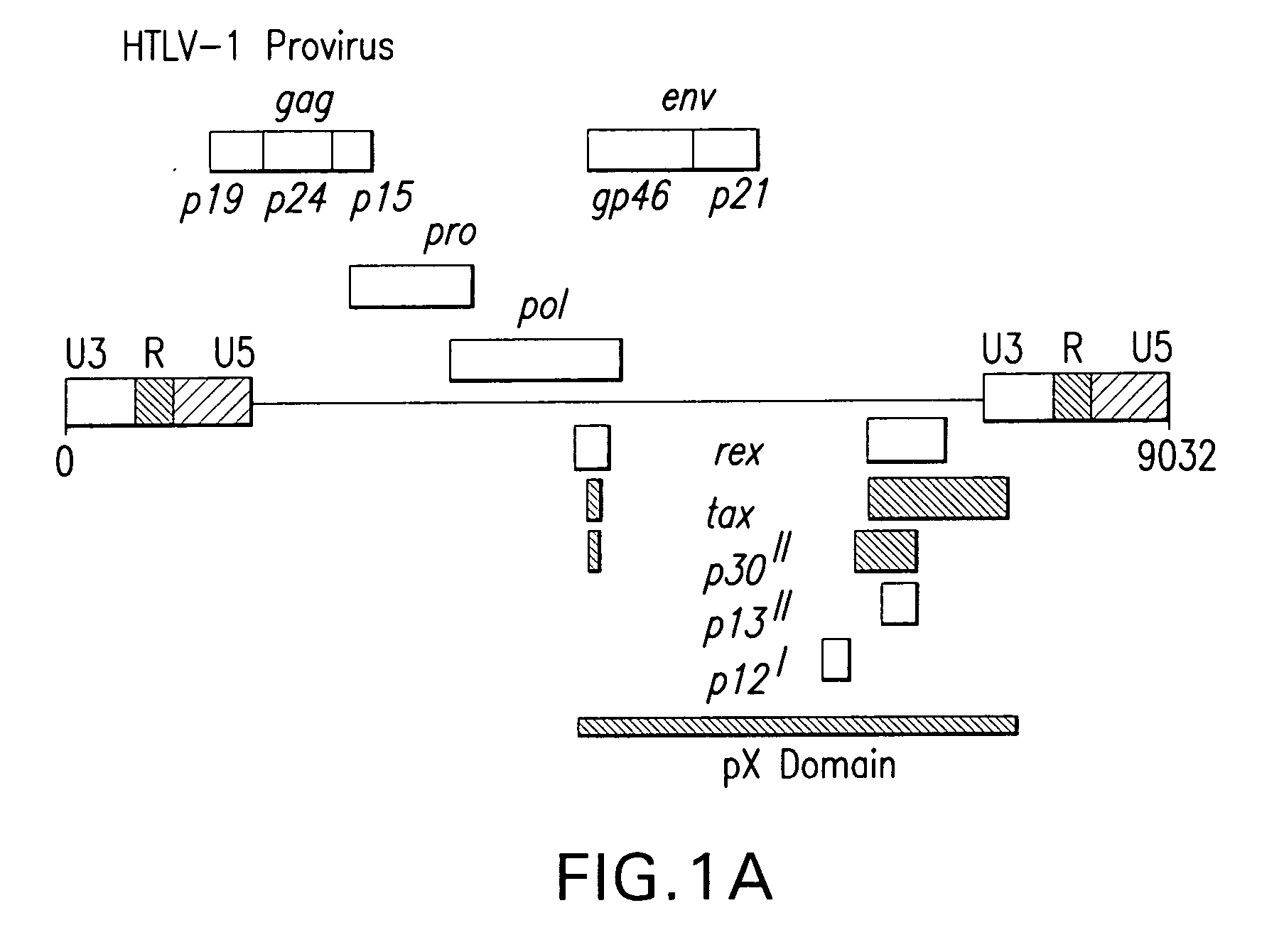
Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1) infects and transforms CD4+ lymphocytes and causes Adult T-cell Leukemia / Lymphoma (ATLL), an aggressive, often fatal, lymphoproliferative disease. A conserved HTLV-1 3+ regulatory domain, pX, encodes at least five non-structural proteins, including the alternative splice-variant p30II. HTLV-1 p30II may enhance the transforming activity of Myc and transcriptionally activate the human cyclin D2 promoter, dependent upon its conserved Myc-responsive enhancer elements, associated with markedly increased S-phase entry and multi-nucleation. Enhancement of Myc transforming activity by HTLV-1 p30II may be dependent upon the transcriptional coactivators, TRRAP / p4346-8 and TIP60, require TIP60 histone acetyltransferase activity, and strongly correlate with interactions between HTLV-1 p30II and Myc-TIP60 complexes in HTLV-1-infected ATLL patient-derived lymphocytes. Thus, p30II may function as a novel retroviral modulator of Myc-transforming interactions that may prominently contribute to adult T-cell leukemogenesis. Thus, the present invention provides methods and compositions for screening and identifying agents that interfere with transformation.
Owner:SOUTHERN METHODIST UNIVERSITY
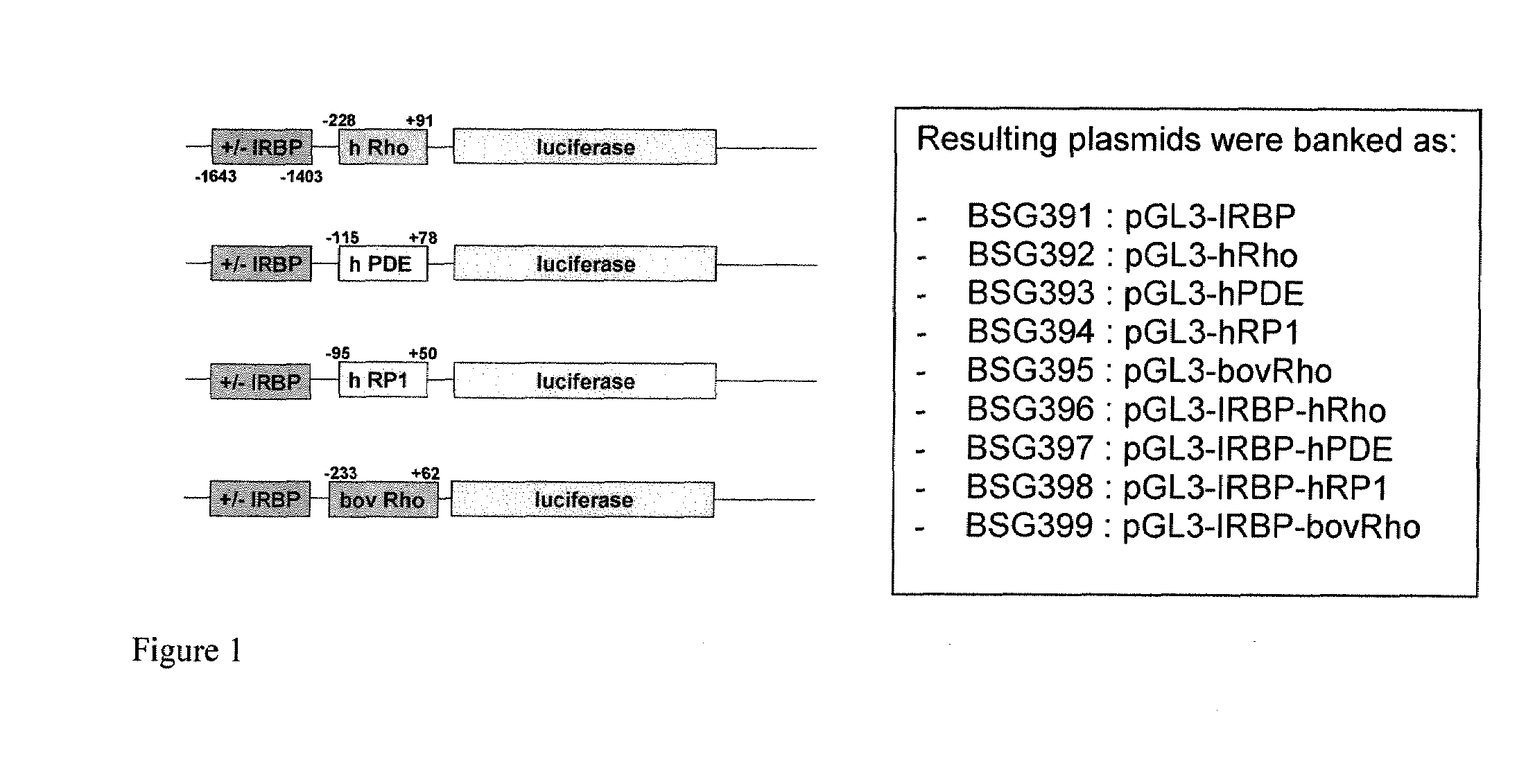
Promoter construct
A polynucleotide comprising a β subunit cGMP-phosphodiesterase promoter operably linked to one or more enhancer elements.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
Regulatory elements for delivery to the liver
The invention is directed to novel combinations of liver specific enhancers and promoter elements for achieving persistent transgene expression in the liver. The liver specific enhancer elements may be derived from either the human serum albumin, prothrombin, α-1microglobulin or aldolase genes in single copies or in multimerized from linked to elements derived from the cytomegalovirus intermediate early (CMV), α-1-antitrypsin or albumin promoters. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, an adenoviral vector comprising a liver specific enhancer / promoter combination operably linked to a transgene is administered to recipient cells. In other embodiments of the invention, adeno-associated viral vectors, retroviral vectors, lentiviral vectors or a plasmid comprising the liver specific enhancer / promoter combination linked to a transgene is administered to recipient cells. Also within the scope of the invention are promoter elements derived from the human prothrombin gene and the β-fibrinogen gene.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
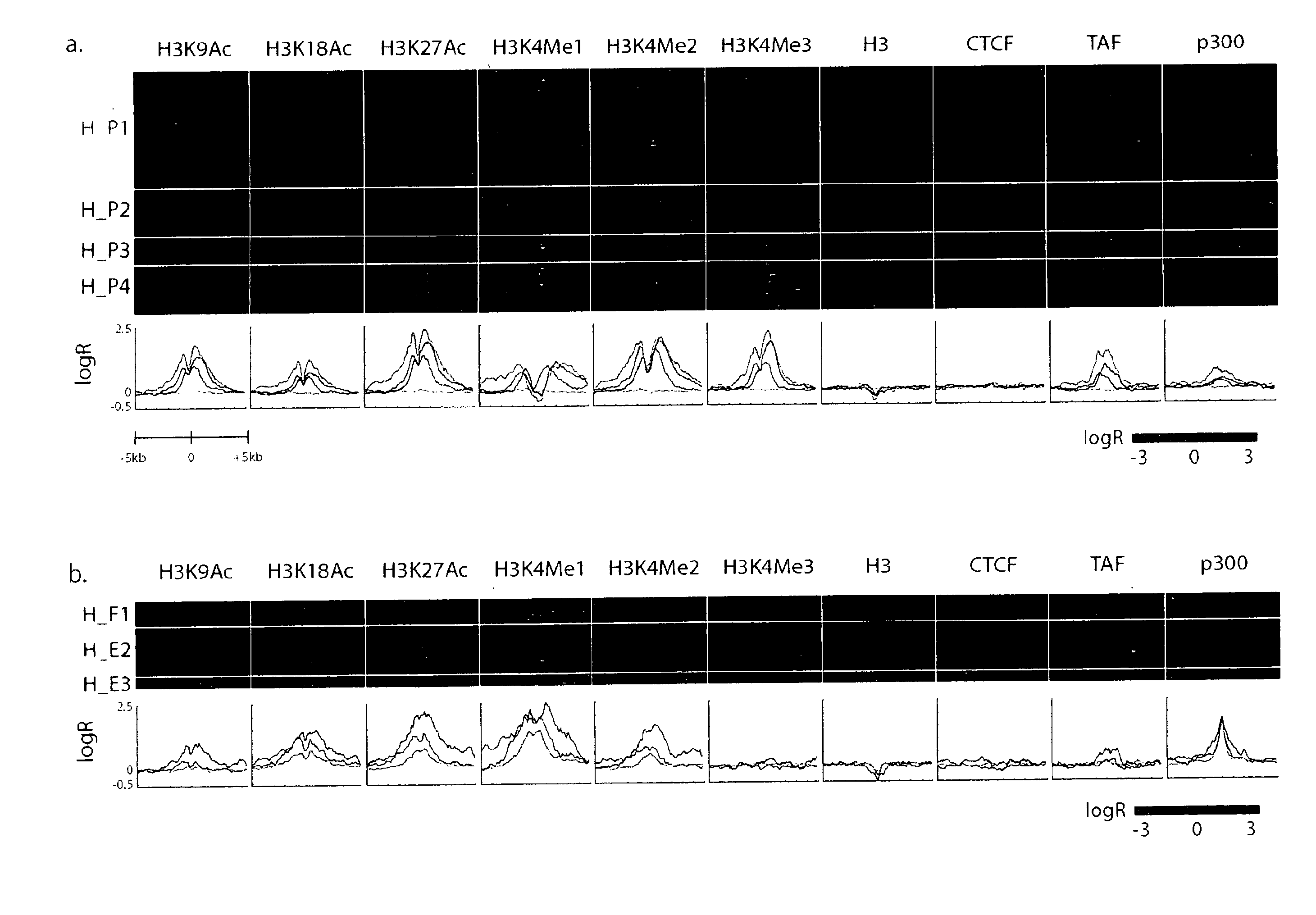
Enhancer signatures in the prognosis and diagnosis of cancers and other disorders
InactiveUS20100256008A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell type specificEnhancer Elements
It has been discovered that enhancer signatures distinguish enhancer elements from other regulatory elements and that the characteristic enhancer signatures vary in a cell-type specific manner. These discoveries provide the basis for novel methods of predicting, diagnosing and monitoring of diseases, particularly cancer.
Owner:REN BING +3
Novel peptides for use in transfection
InactiveUS20110200624A1NanomedicineSaccharide peptide ingredientsComplementarity determining regionIn vivo
Novel peptides derived from antibody complementarity determining regions (CDRs) that enhance delivery of macromolecules into cells, particularly when used in combination with cationic lipids, are provided. The peptides can be combined with cationic lipids, and compositions of cationic lipids associated with enhancer elements, to provide reagents that can complex with macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins and peptides and permit introduction of these macromolecules into a variety of cells and tissues in vitro or in vivo with greatly enhanced efficiency compared to other lipid-based reagents. Methods for delivering macromolecules into target cells and tissues using the lipids and enhancer elements are provided.
Owner:MOLECULAR TRANSFER
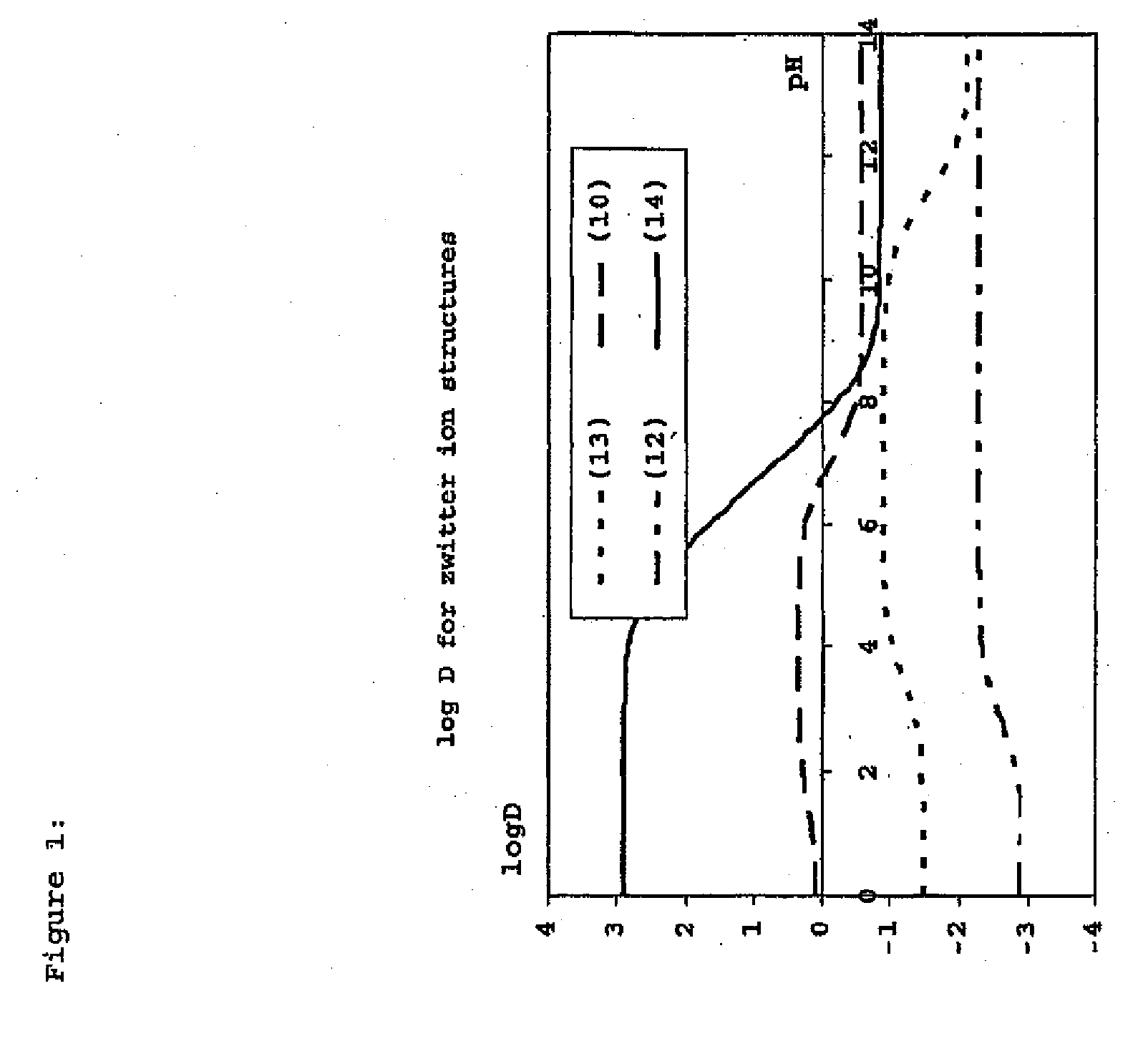
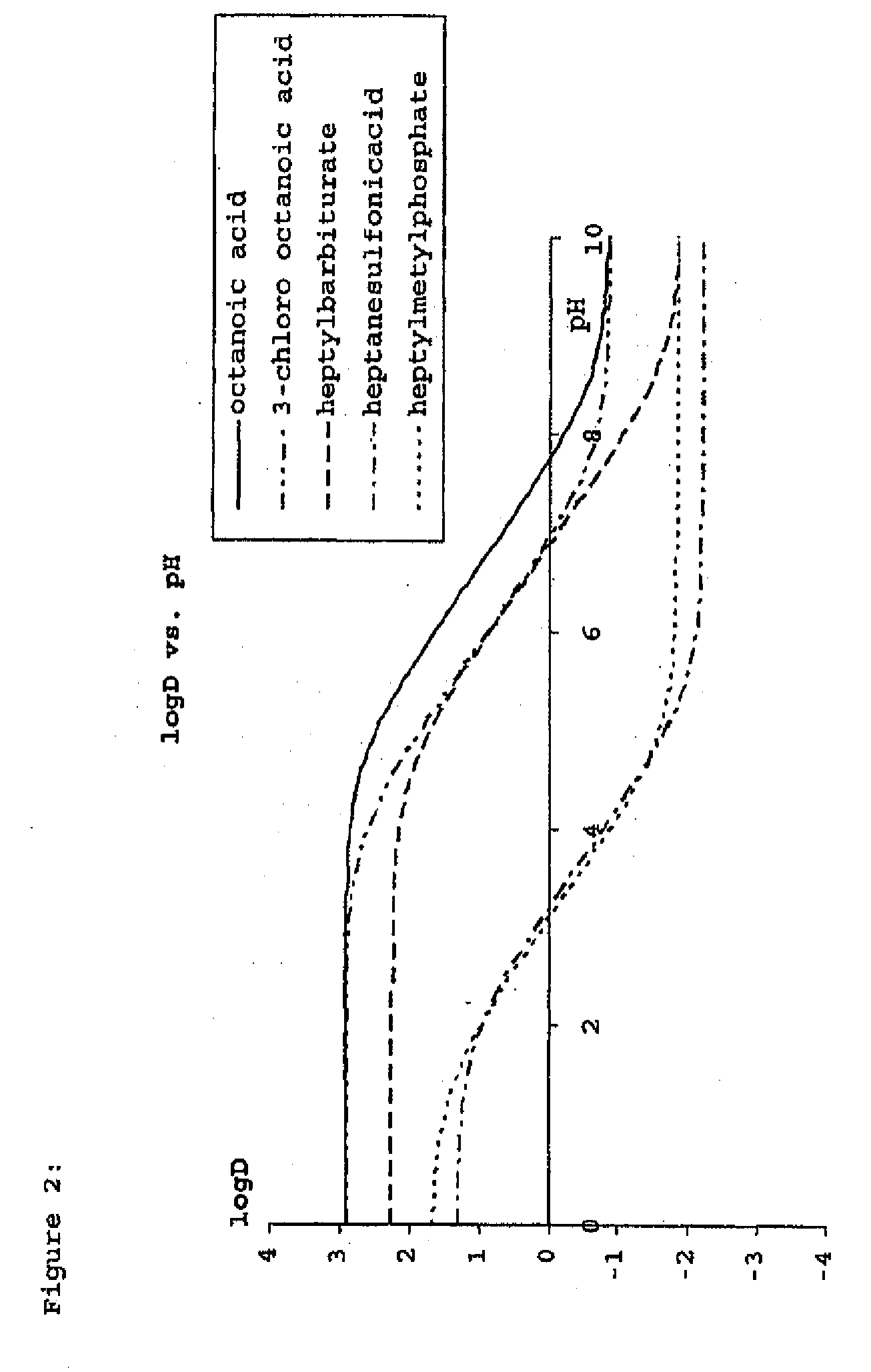
Construction and use of transfection enhancer elements
InactiveUS20130011916A1Improved cell penetrationEnhance cellular uptakePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsCrystallographyEnhancer Elements
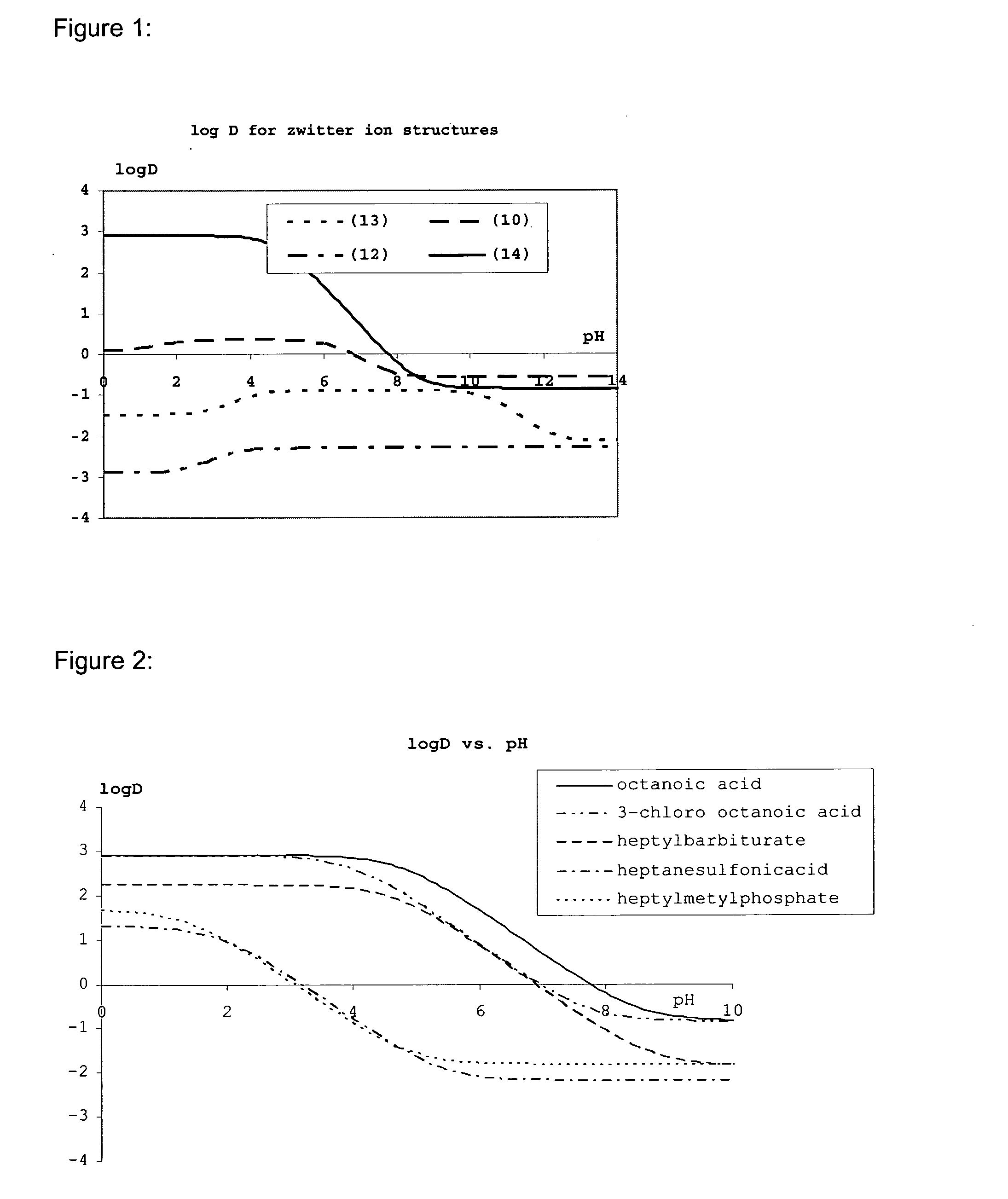
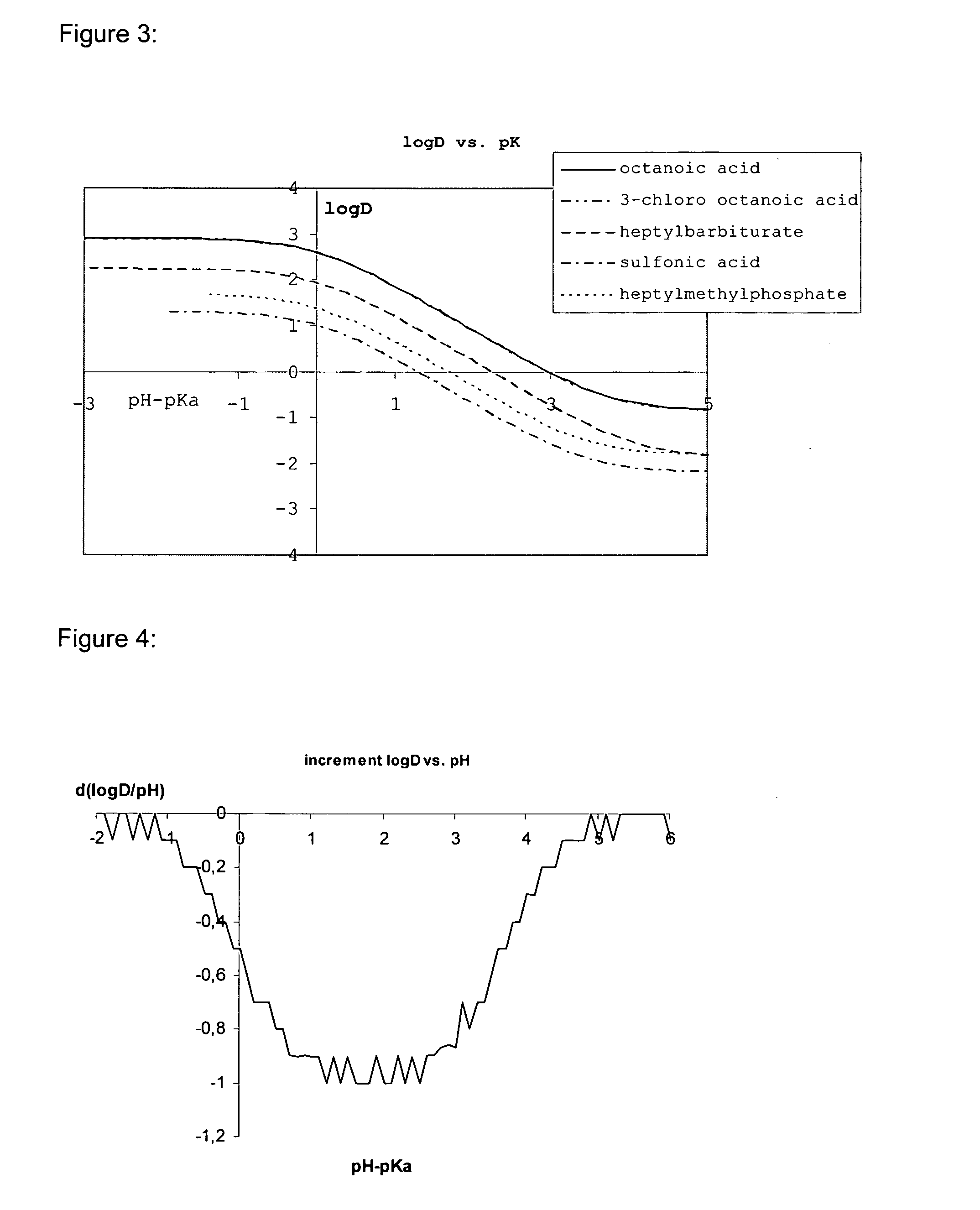
Nucleic acids comprising a nucleic acid moiety and two or more transfection enhancer elements (TEE's) according to the general formula (I): Hydrophobic moiety—pH-responsive hydrophilic moiety, wherein said pH sensitive hydrophilic moiety of said TEE is independently a weak acid having a pka of between 4 and 6.5 or is a zwitterionic structure comprising a combination of acidic groups with weak basis having a pKa of between 4.5 and 7.
Owner:LIPOCALYX
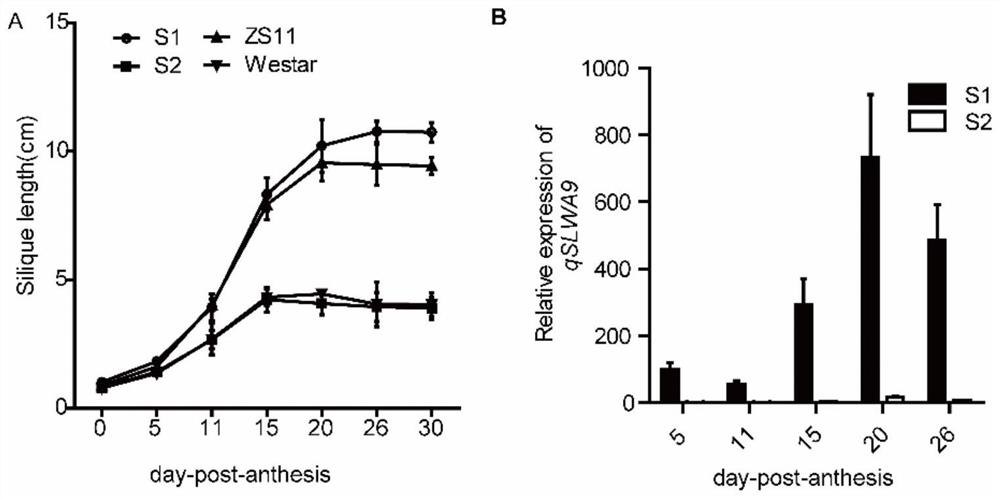
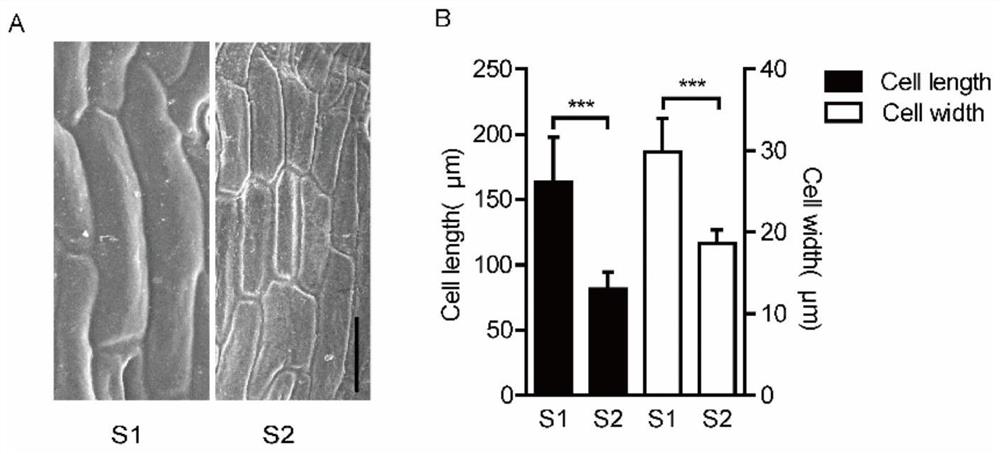
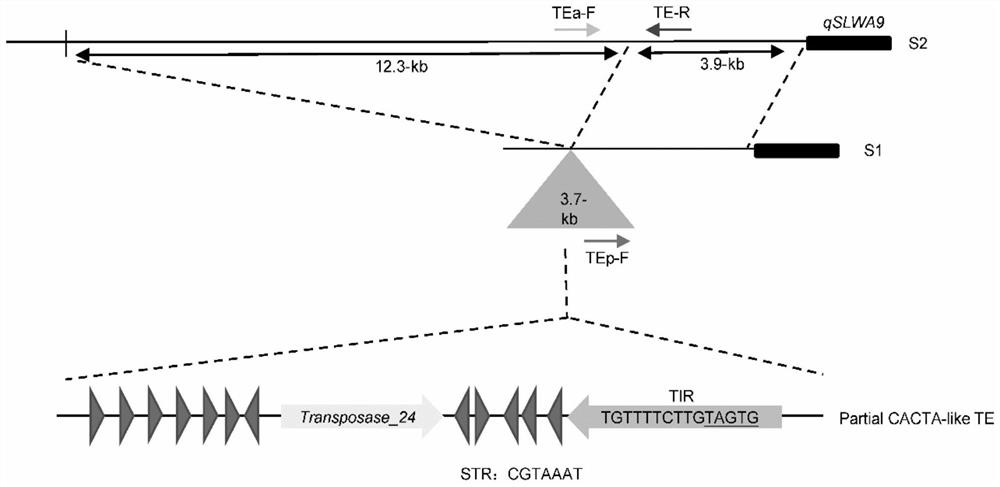
Identification of enhanced gene expression sequence in cabbage type rape and application thereof
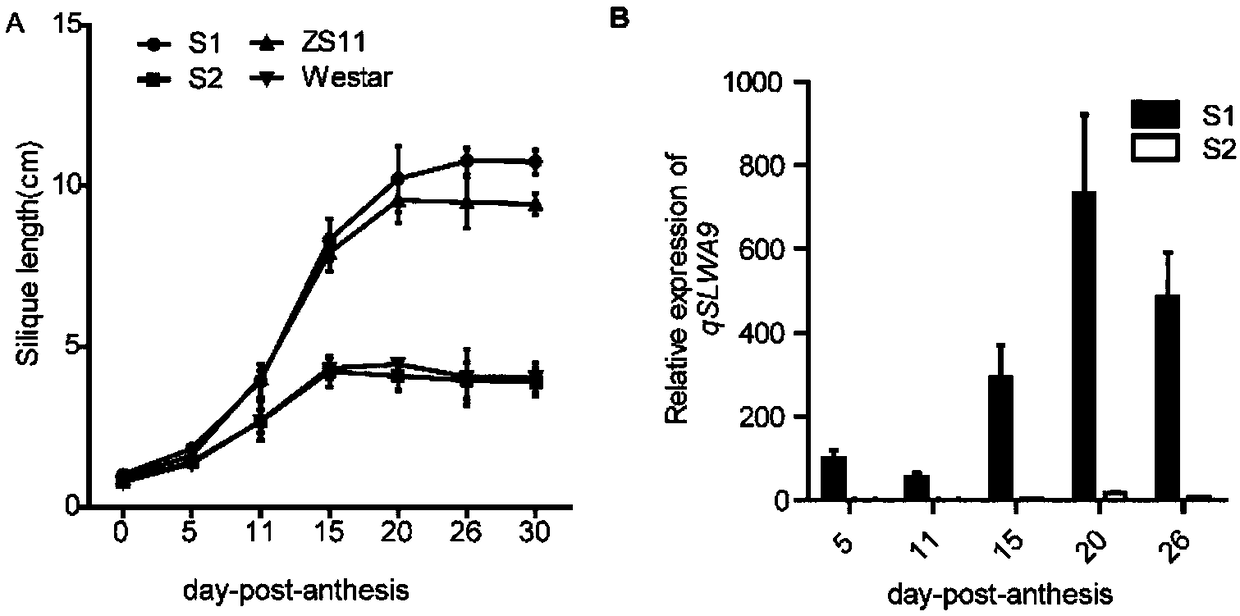
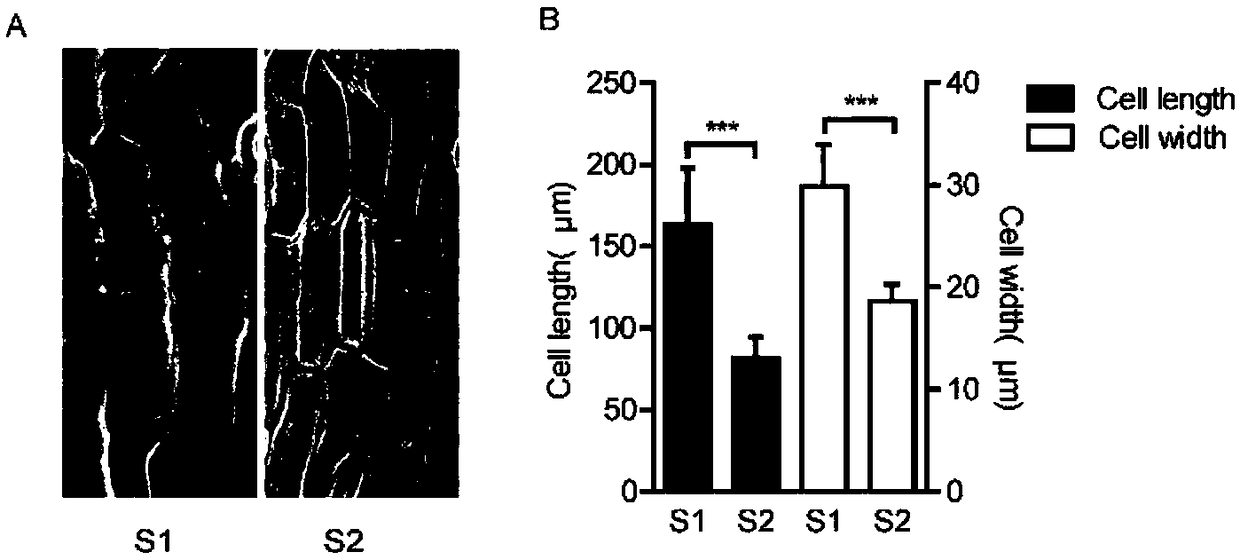
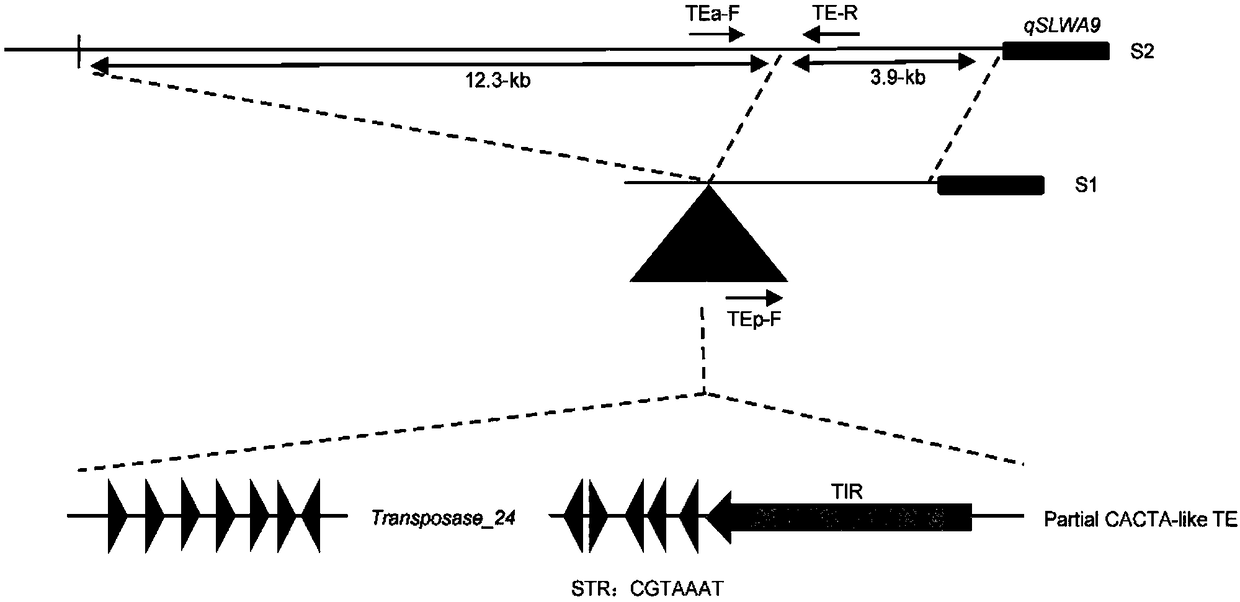
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to identification of an enhanced gene expression sequence in a cabbage type rape and application thereof. A 3.7-kb DNA fragment in an upstream regulatory region of a qSLWA9 gene of the cabbage type rape is identified, the nucleotide sequence thereof is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, belongs to incomplete CACTA-like (CACTA-like) transposons, has enhancer function, and can enhance gene expression levels. The combination of markers with the presence of enhancers is developed. Genotype analysis of 245 cabbage type rape materials is conducted, pod length and grain weight phenotype is combined, and the identification of the enhanced gene expression sequence in the cabbage type rape shows that the presenceor absence of the CACTA-like transposons is closely related to phenotype. Further validation shows that the CACTA-like transposons fragment contains enhancer elements, can enhance gene expression inall tissues. The CACTA-like transposons and markers of the invention can be used for improvement of yield-related traits in the cabbage type rape.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
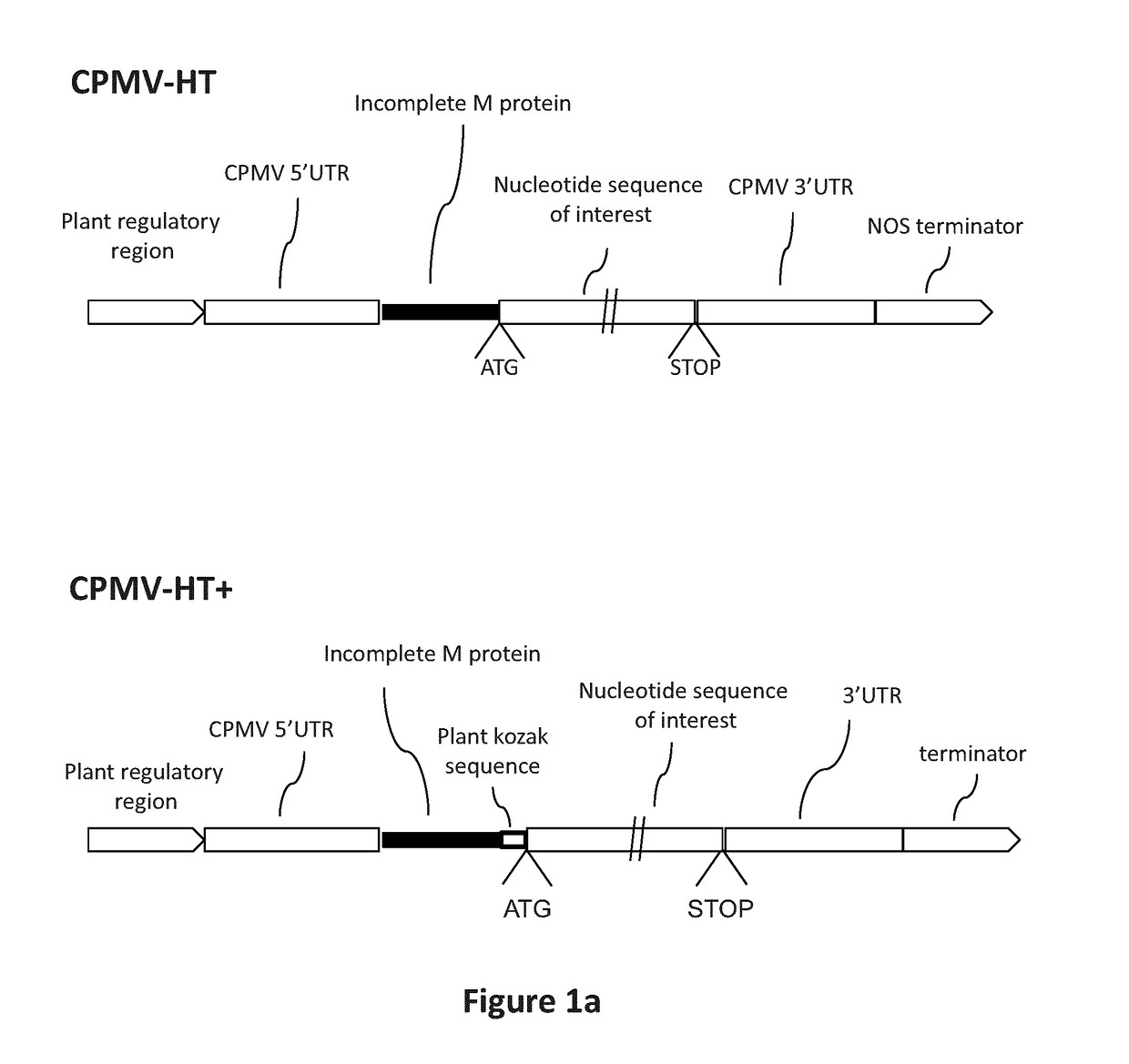
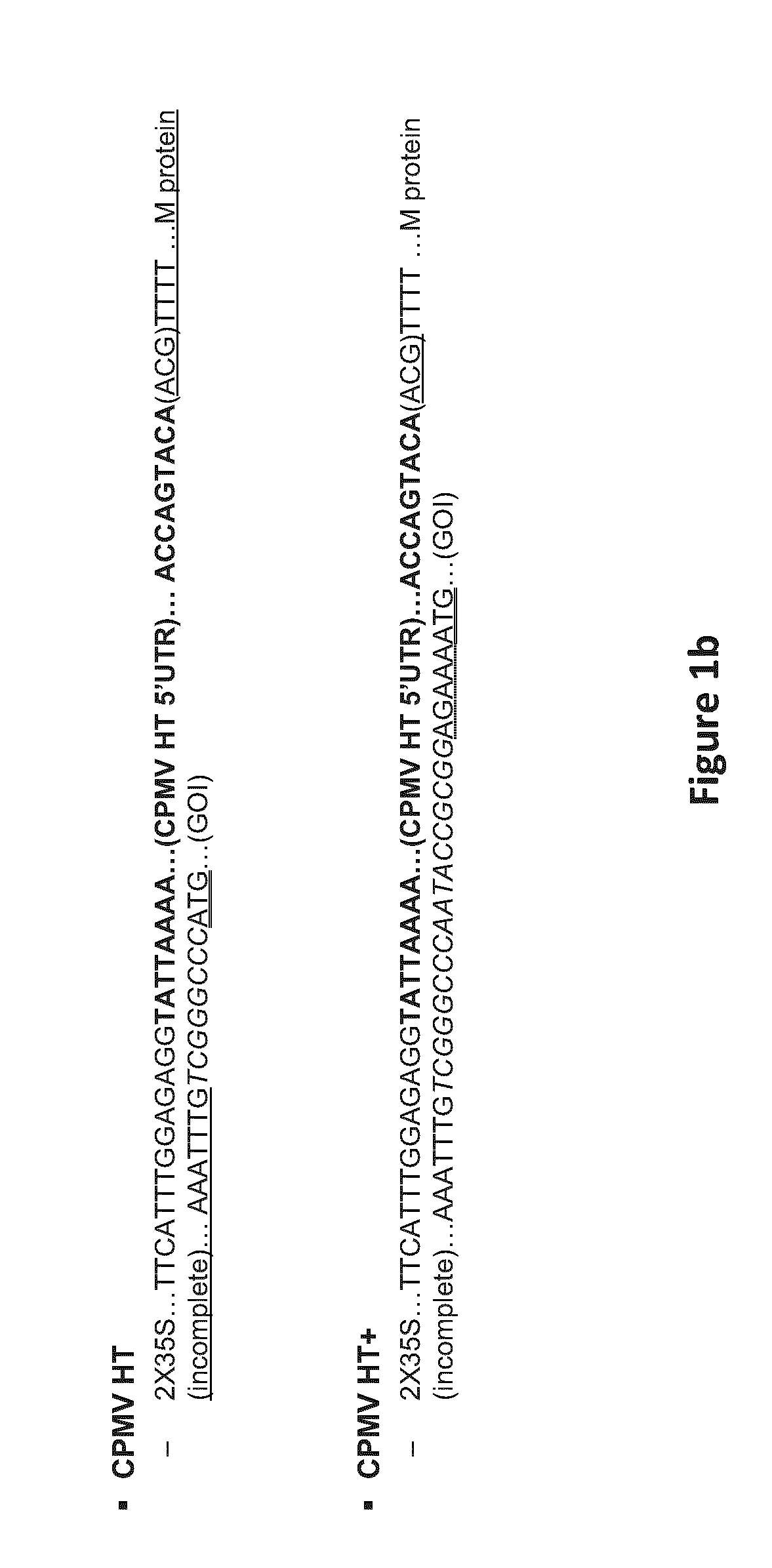
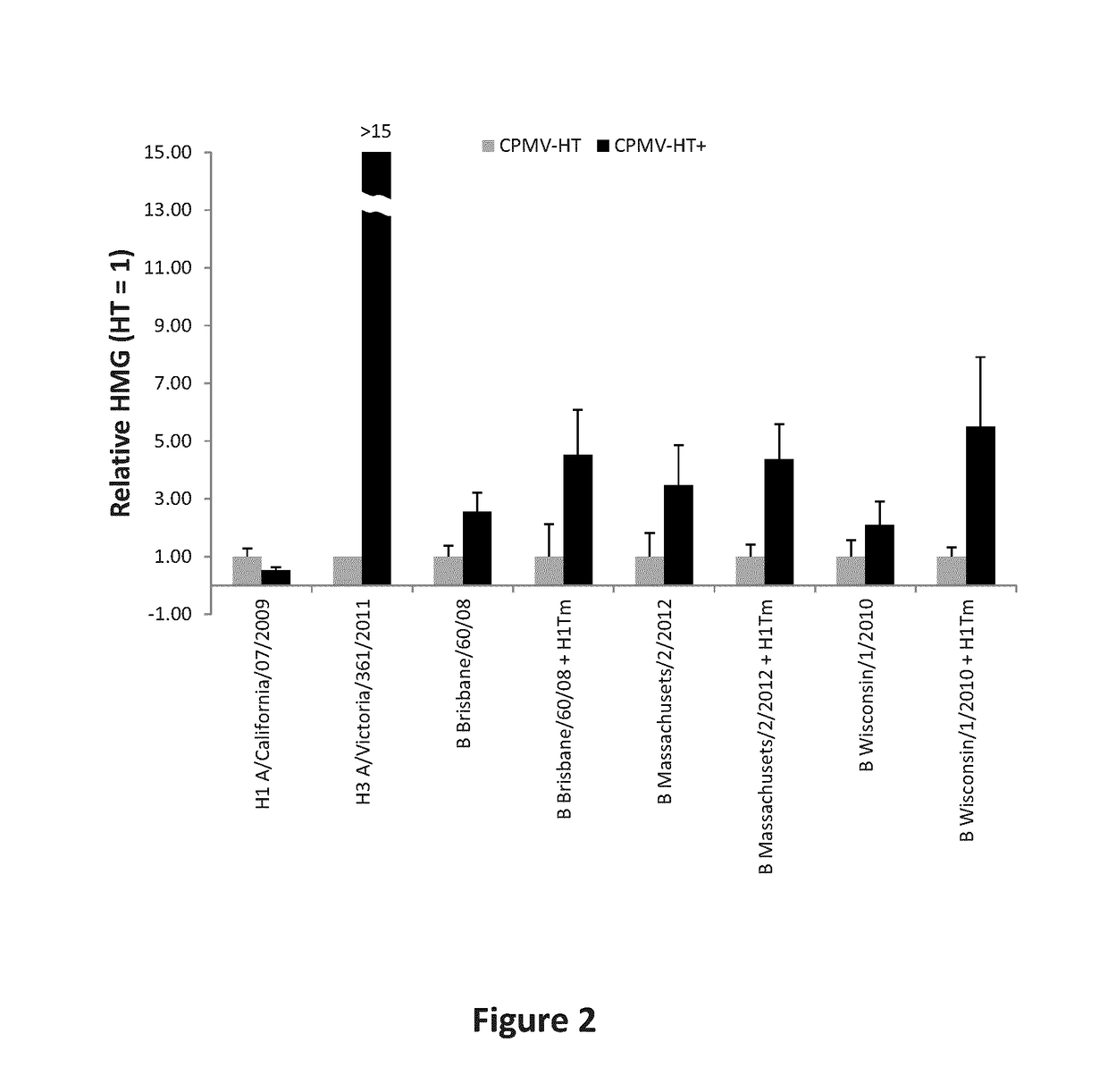
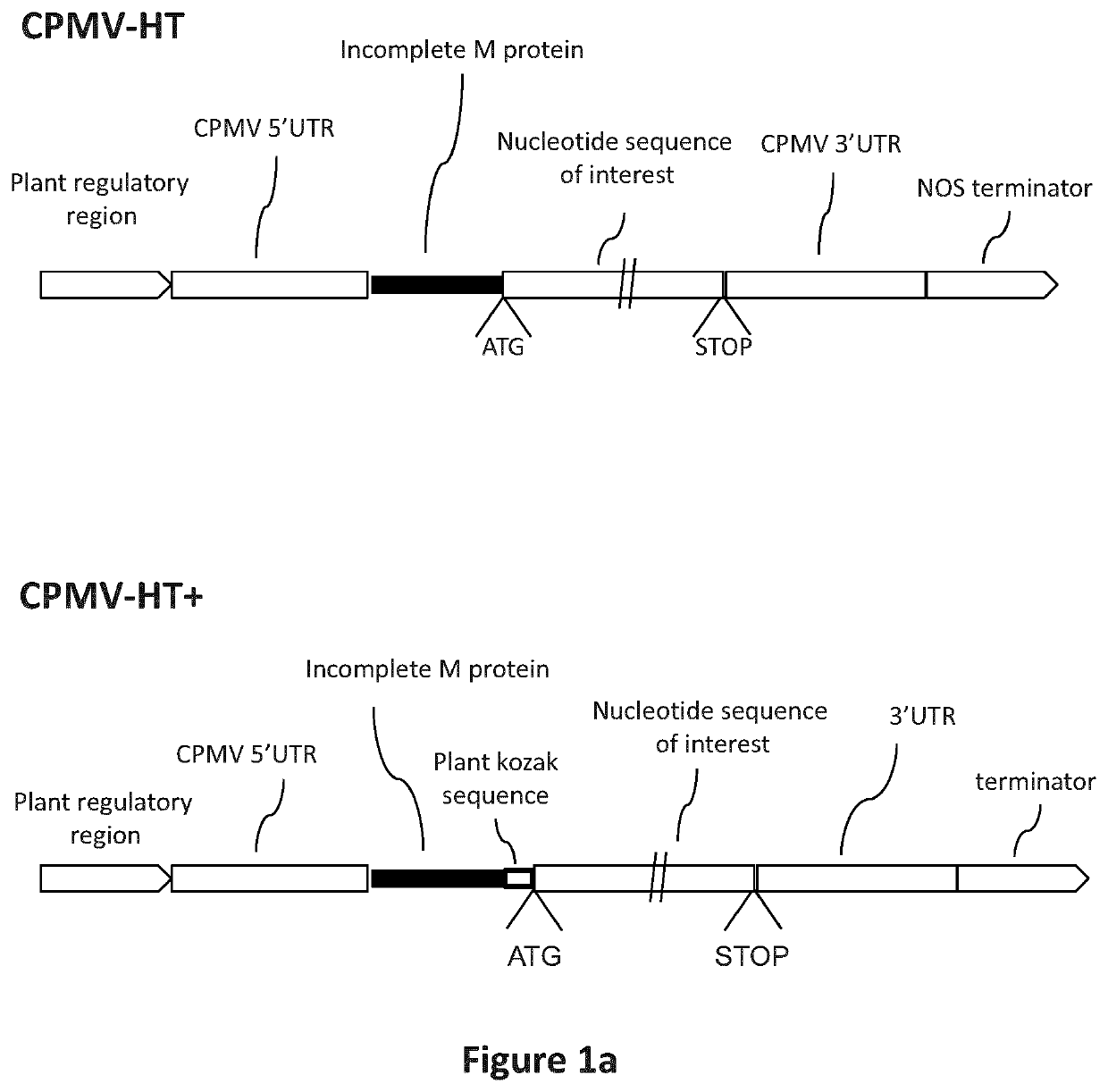
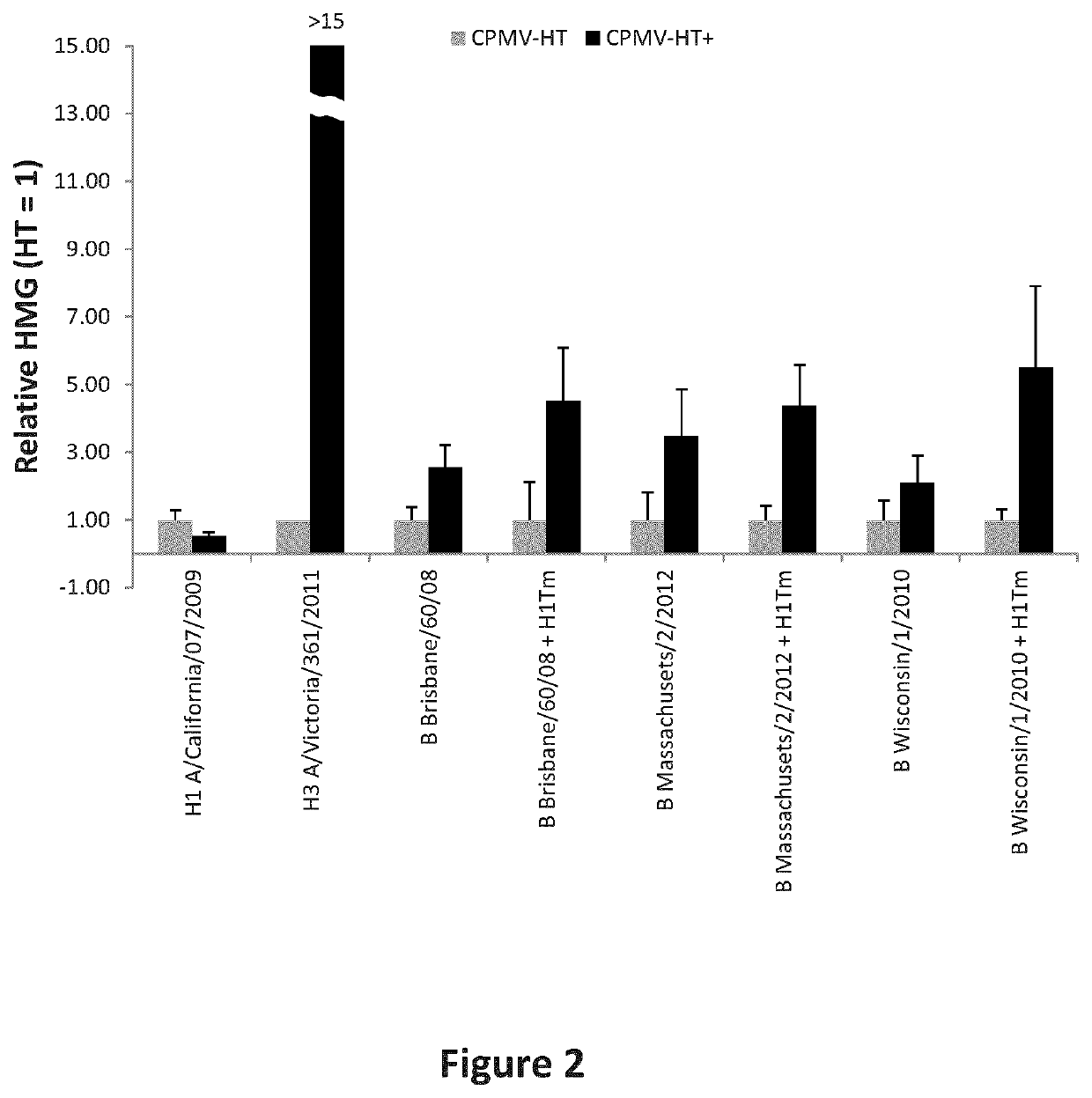
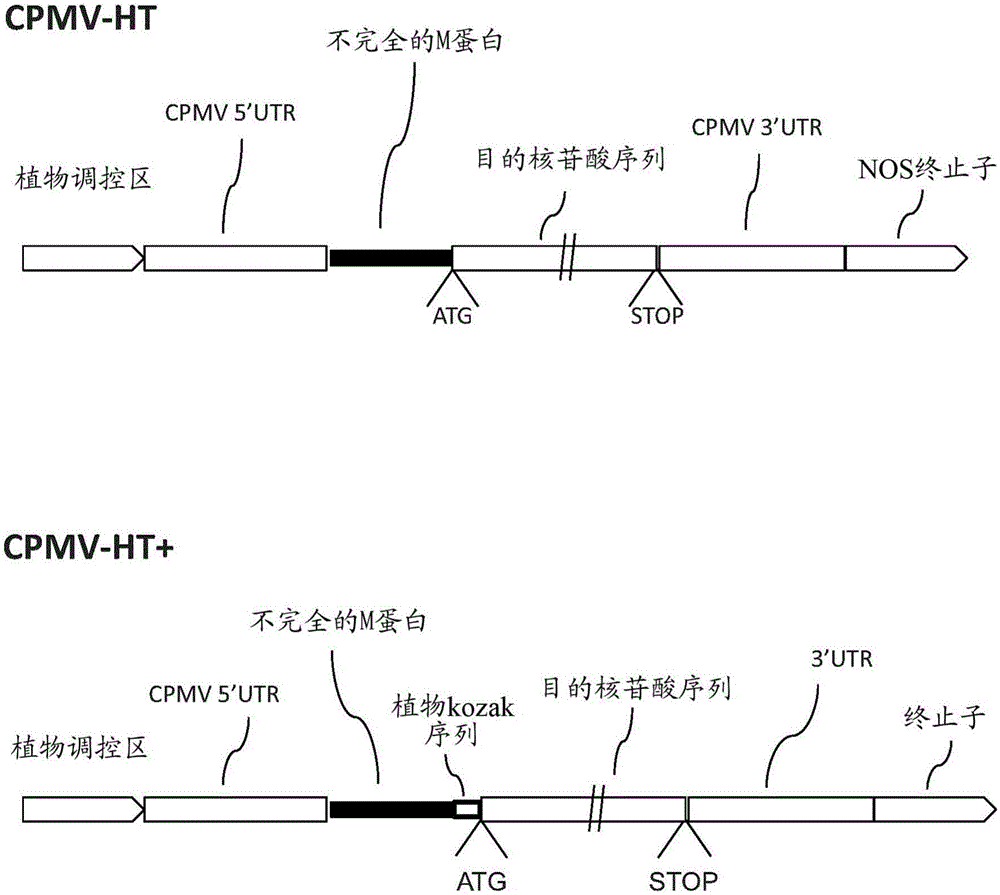
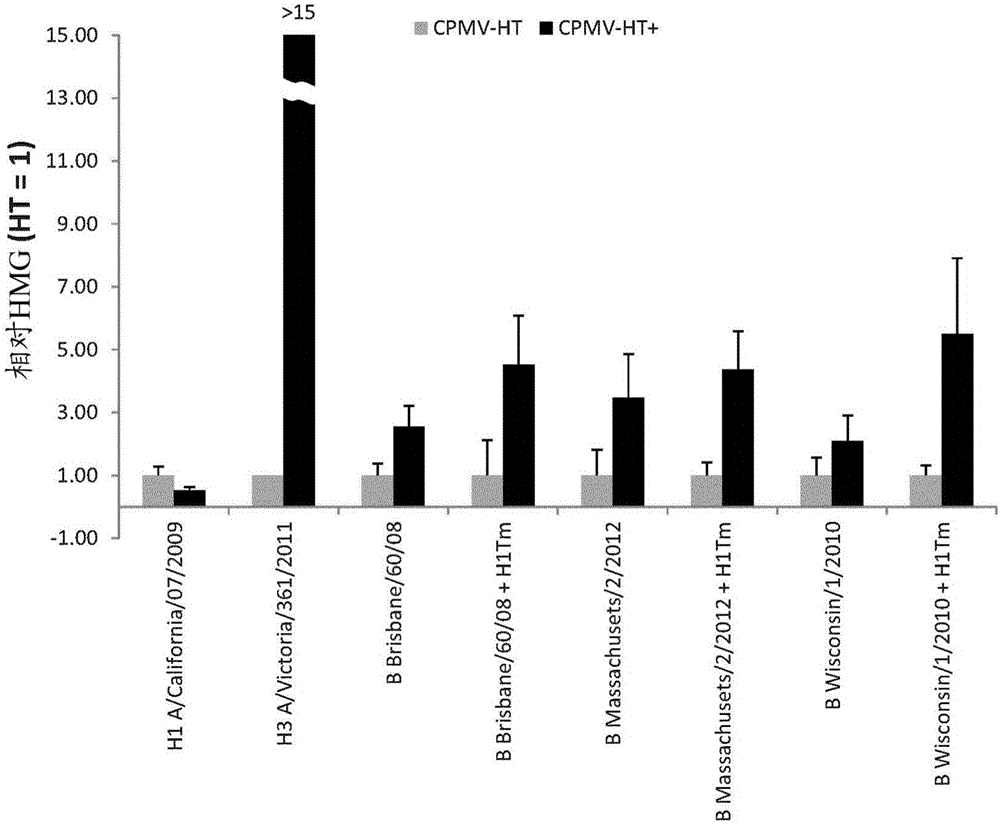
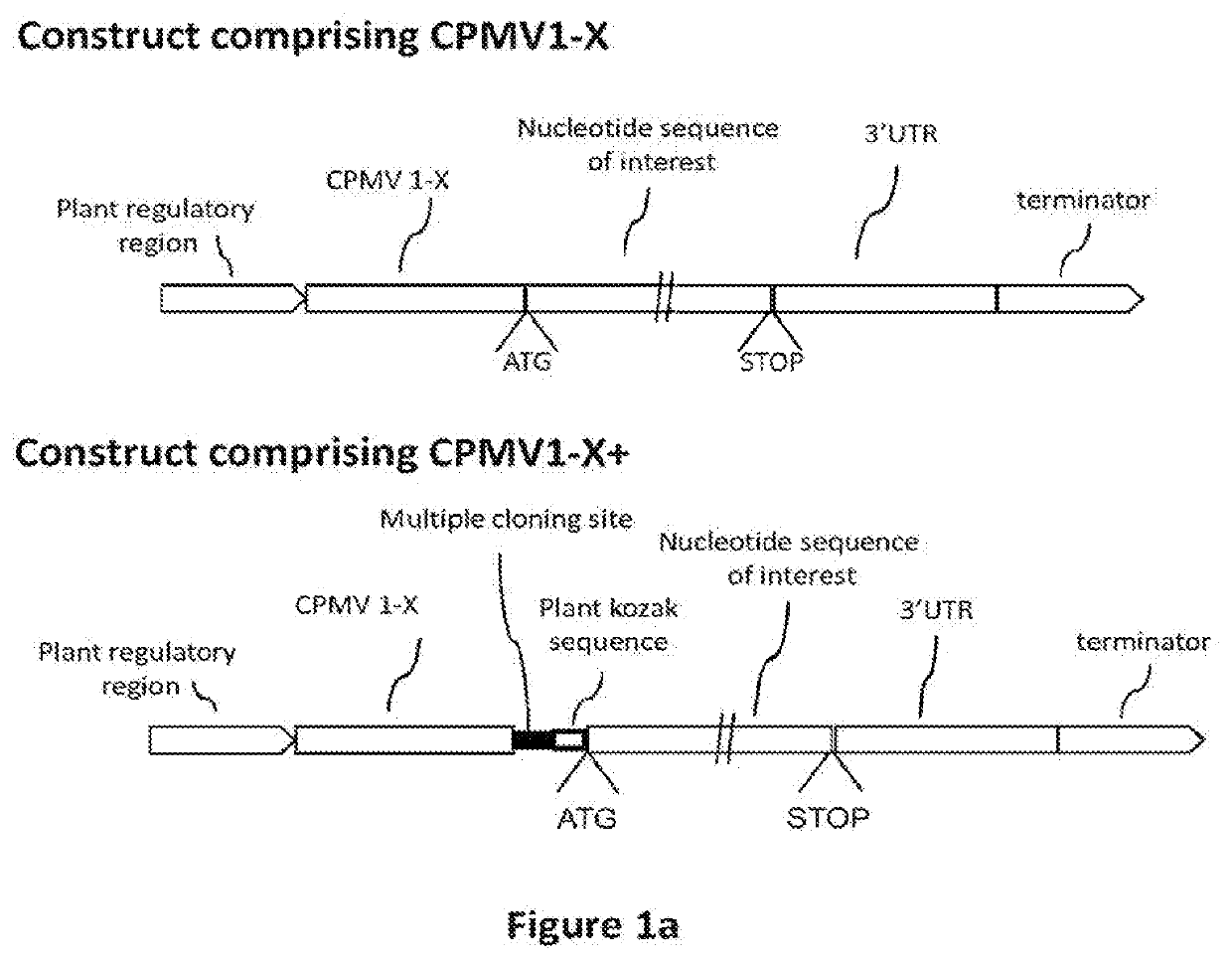
Modified CPMV Enhancer Elements
ActiveUS20180119158A1Prone to infectionHigh yieldSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesNucleotideGenetics
An expression enhancer comprising, in series, a CPMV 5′UTR nucleotide sequence comprising nucleotides 1-160 of SEQ ID NO:1, or comprising a nucleotide sequence comprising from about with 80% to 100% sequence similarity with SEQ ID NO:1, and a stuffer fragment is provided. The stuffer fragment comprises a nucleotide sequence encoding an incomplete M protein and one or more kozak sequence active in a plant. Plants and plant matter comprising the expression enhancer and methods using the expression enhancer are also described.
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
Modified CPMV enhancer elements
An expression enhancer comprising, in series, a CPMV 5′UTR nucleotide sequence comprising nucleotides 1-160 of SEQ ID NO:1, or comprising a nucleotide sequence comprising from about with 80% to 100% sequence similarity with SEQ ID NO:1, and a stuffer fragment is provided. The stuffer fragment comprises a nucleotide sequence encoding an incomplete M protein and one or more kozak sequence active in a plant. Plants and plant matter comprising the expression enhancer and methods using the expression enhancer are also described.
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
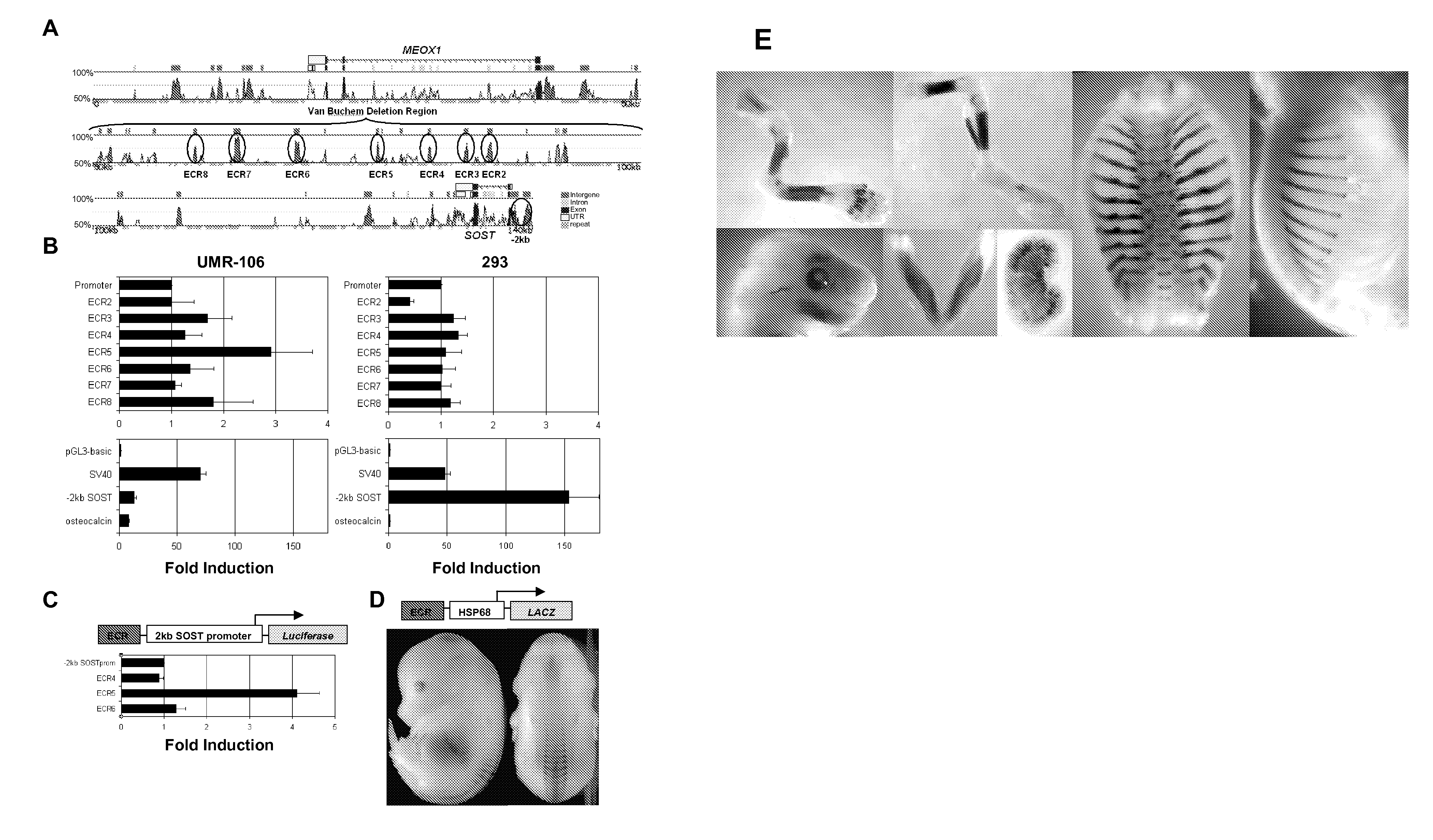
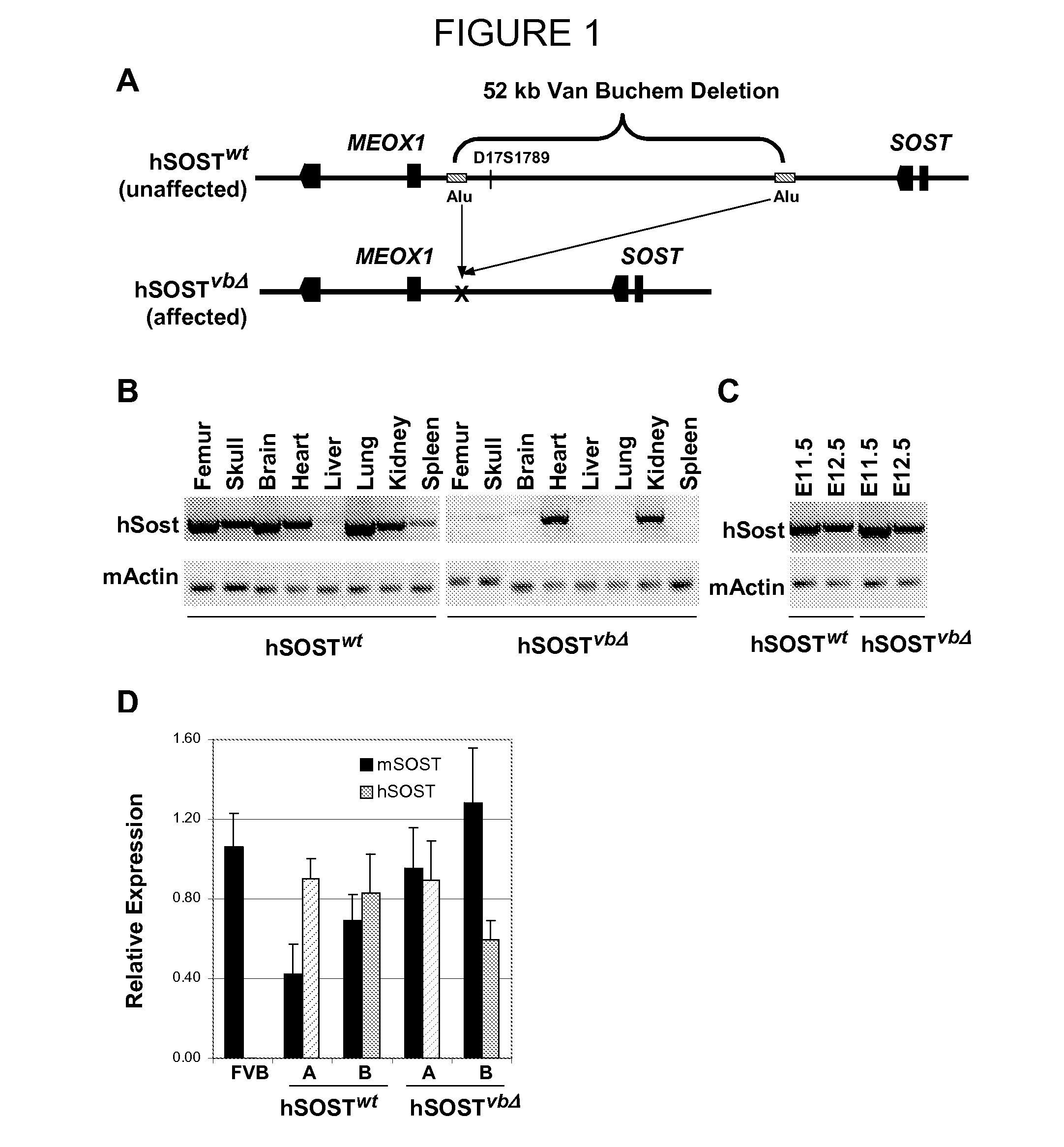
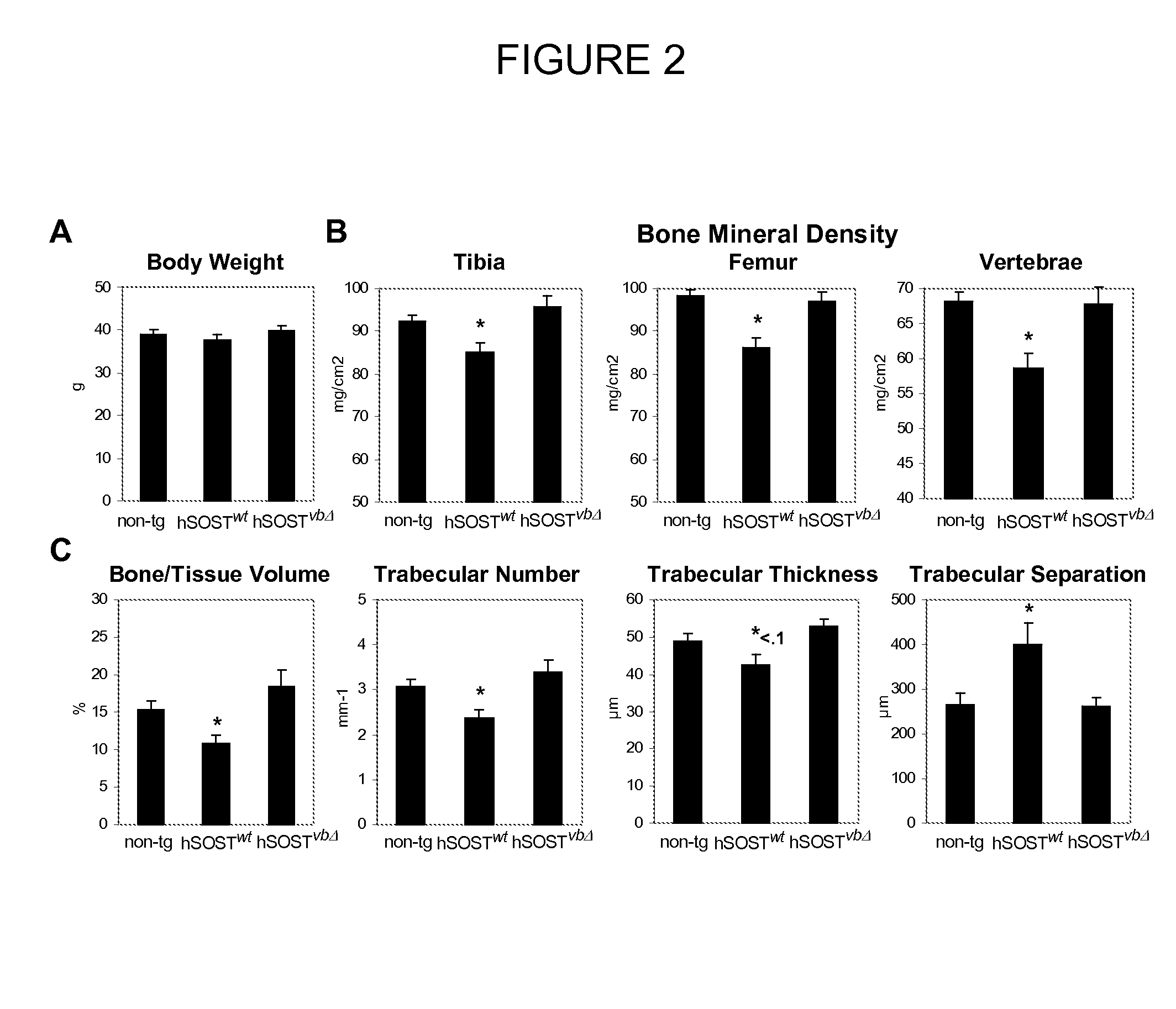
Compositions and methods for altering bone density and bone patterning
InactiveUS20090017008A1High in mineralsUtility in treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic acid vectorDiseaseBone density
By exploiting cross-species sequence comparisons with in vitro and in vivo enhancer assays we were able to identify enhancer elements that drives human SOST expression in the adult mouse skeleton, and discovered a novel function for sclerostin during limb development. The enhancer elements and reagents described in the present invention facilitate the methods for development of products and methods to increase the mineral content of bone, which can consequently be utilized to treat a wide variety of bone related conditions, including, osteopenia, osteoporosis, fractures and other disorders in which low bone mineral density are the main cause of the disease as well as sclerosteosis, Van Buchem disease and other related disorders of the skeleton. Furthermore, the present invention provides enhancer elements and reagents useful for bone pattering and growth, limb development, and the formation of individual bones
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Crustacean expression vector
Methods and constructs for genetic manipulation of one or more of shrimp, shellfish, mollusks, and fish are disclosed. The nucleic acid construct includes a promoter and an internal ribosome entry site of an insect picomavirus, such as a cricket paralysis-like picomavirus. One or more open reading frames can be operably associated with one or both of the promoter and the internal ribosome entry site, and one or more proteins or protein subunits can be expressed upon introduction of the construct into a host cell, such as into a shrimp. Method for producing immortalized crustacean cell lines using enhancer elements derived from shrimp and / or shrimp viruses are also described.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Baculoviral DNA elements for the expression of recombinant proteins in a host insect
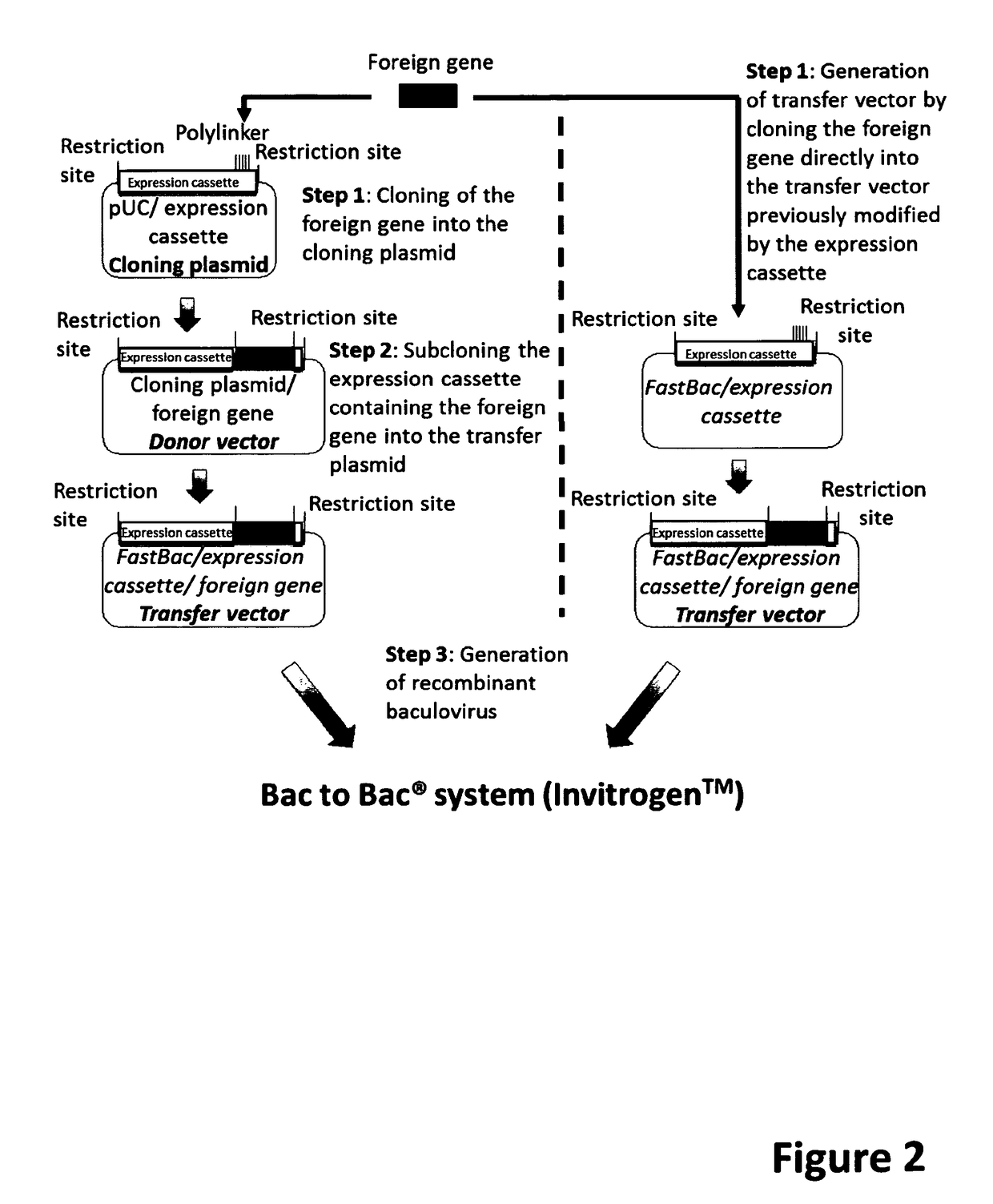
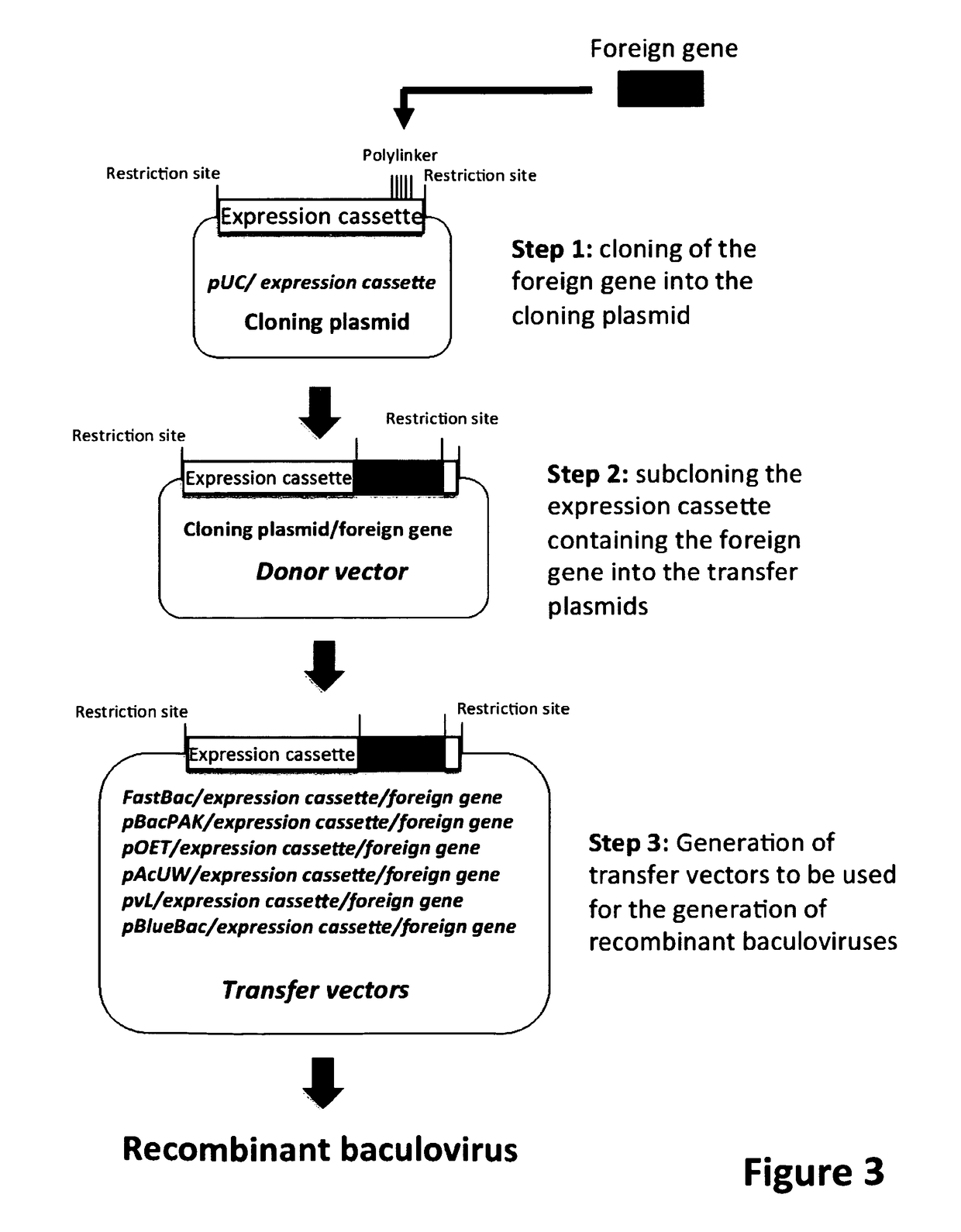
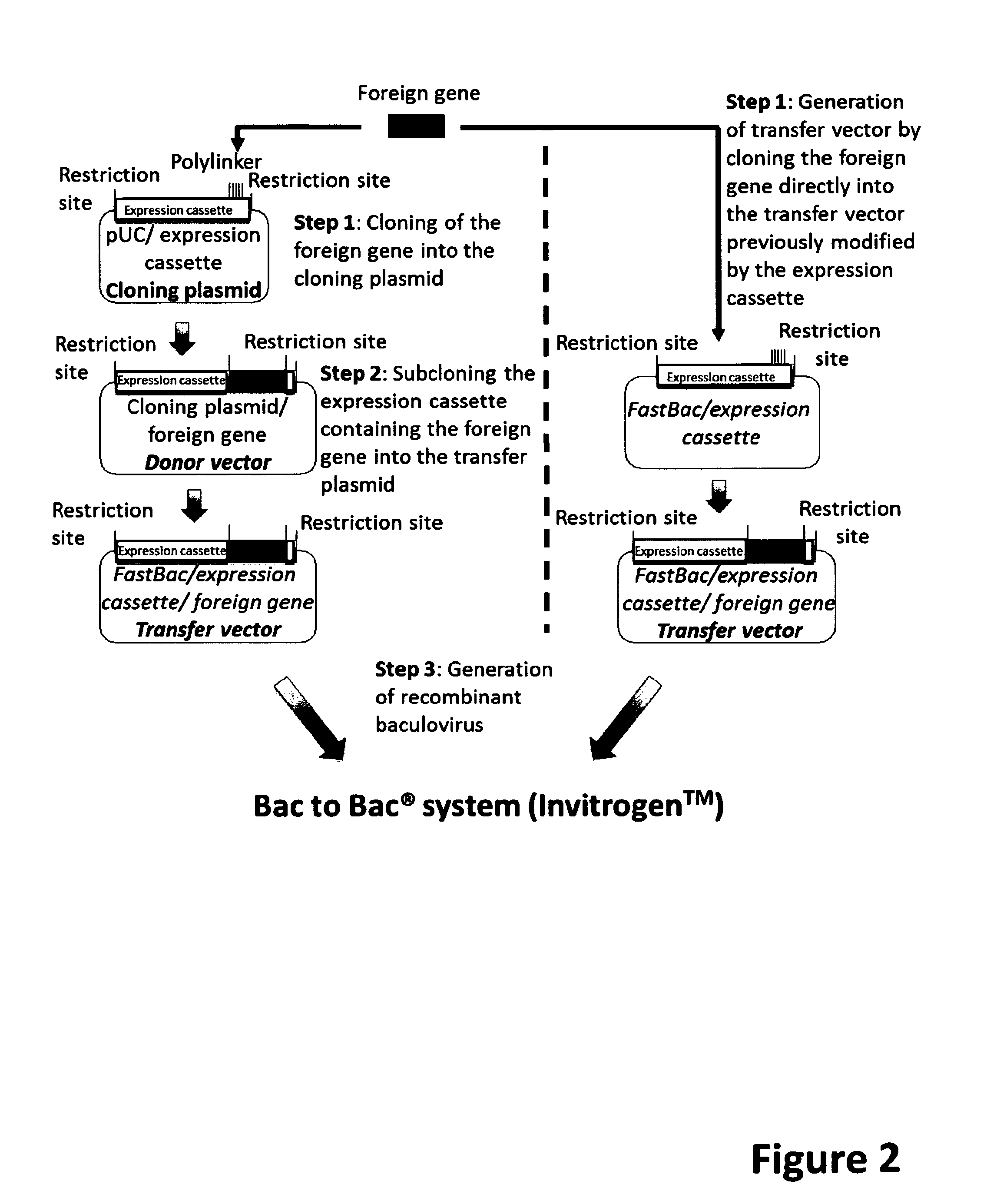
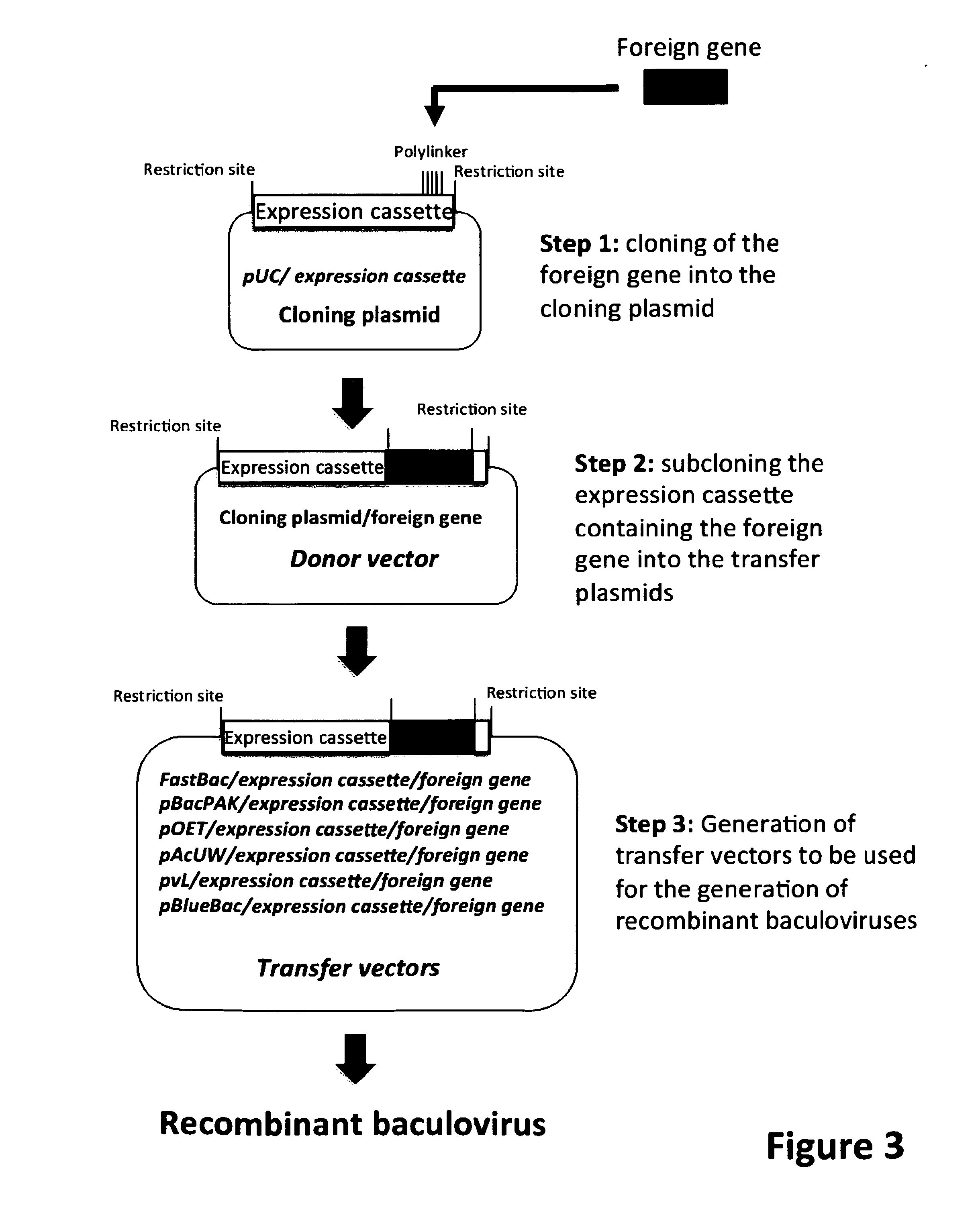
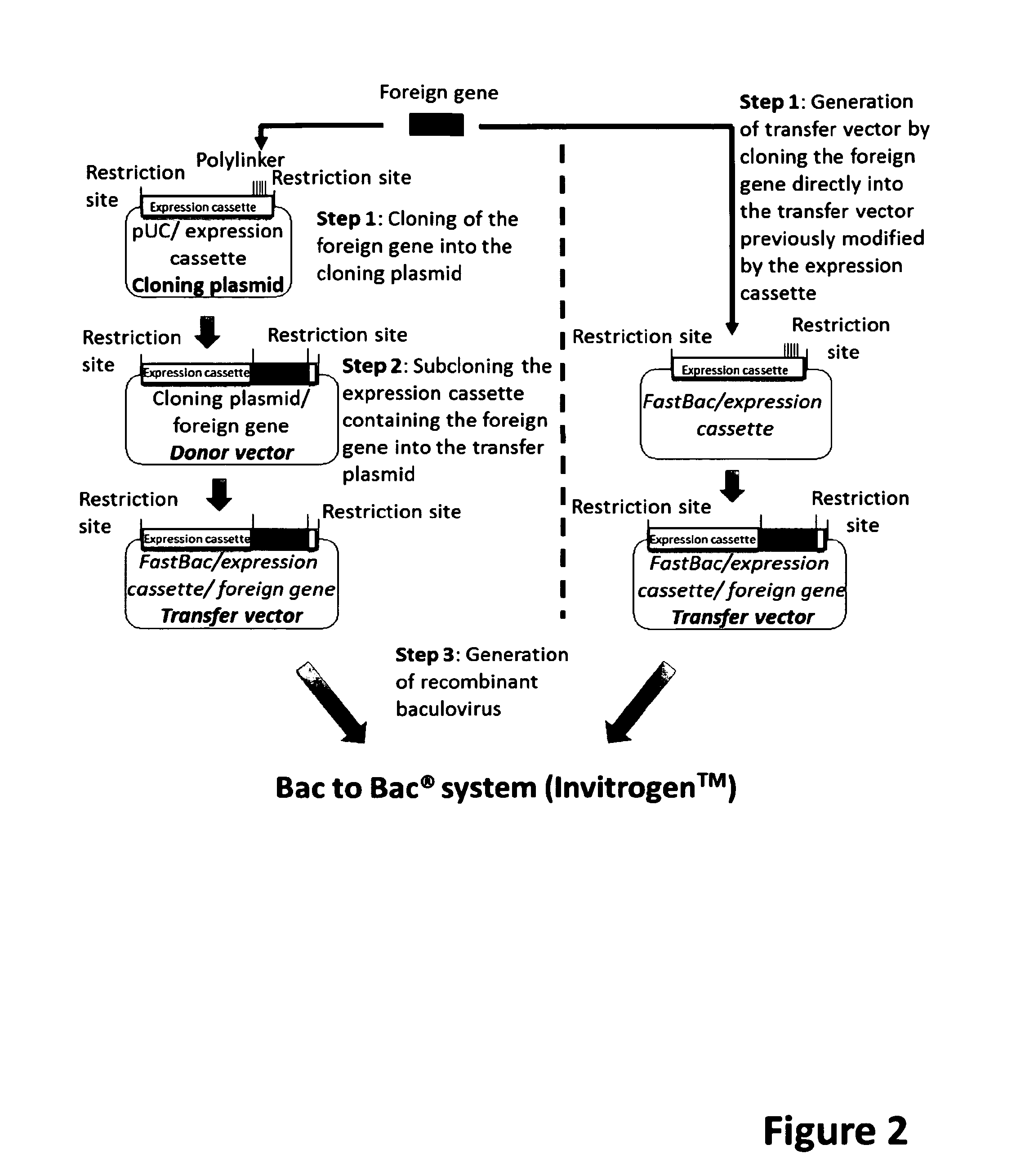
ActiveUS9701983B2Maximum productivityImprove survival rateBiocideVectorsADAMTS ProteinsEnhancer Elements
Reagents and methods are provided that allow for an improved expression of a recombinant protein in an insect, More specifically, the introduction of recombinant DNA elements into an insect larva allows for the increased expression of a recombinant protein, an improvement of the correct folding of said protein and an increase in the survival rate after infection of the insect These recombinant DNA elements can be introduced, for example, into insect larvae via a recombinant baculovirus, which has incorporated said elements. The recombinant DNA elements include nucleic acids encoding transcriptional regulators, such as IE-0 and IE-1, transcriptional, enhancer elements, such as the homologous region (hr) and promoters.
Owner:ALTERNATIVE GENE EXPRESSION
Baculoviral DNA elements for the expression of recombinant proteins in a host insect
ActiveUS20150240260A1High expressionMaximum productivityVectorsFermentationADAMTS ProteinsEnhancer Elements
Reagents and methods are provided that allow for an improved expression of a recombinant protein in an insect, More specifically, the introduction of recombinant DNA elements into an insect larva allows for the increased expression of a recombinant protein, an improvement of the correct folding of said protein and an increase in the survival rate after infection of the insect These recombinant DNA elements can be introduced, for example, into insect larvae via a recombinant baculovirus, which has incorporated said elements. The recombinant DNA elements include nucleic acids encoding transcriptional regulators, such as IE-0 and IE-1, transcriptional, enhancer elements, such as the homologous region (hr) and promoters.
Owner:ALTERNATIVE GENE EXPRESSION
Modified CPMV enhancer elements
An expression enhancer comprising, in series, a CPMV 5'UTR nucleotide sequence comprising nucleotides 1-160 of SEQ ID NO:1, or comprising a nucleotide sequence comprising from about 80% to 100% sequence similarity with SEQ ID NO:1, and a stuffer fragment is provided. The stuffer fragment comprises a nucleotide sequence encoding an incomplete M protein and one or more kozak sequence active in a plant. Plants and plant matter comprising the expression enhancer and methods using the expression enhancer are also described.
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
Construction and use of transfection enhancer elements
InactiveUS20100022621A1Improved cell penetrationPromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCrystallographyEnhancer Elements
Nucleic acids comprising a nucleic acid moiety and two or more transfection enhancer elements (TEE's) according to the general formula (I): Hydrophobic moiety—pH-responsive hydrophilic moiety, wherein said pH sensitive hydrophilic moiety of said TEE is independently a weak acid having a pka of between 4 and 6.5 or is a zwitterionic structure comprising a combination of acidic groups with weak basis having a pKa of between 4.5 and 7.
Owner:LIPOCALYX
CPMV Enhancer Elements
PendingUS20200283784A1Prone to infectionHigh yieldInactivation/attenuationAntiviralsZ-nucleotideGenetics
An expression enhancer comprising a CPMV 5′UTR nucleotide sequence consisting of X nucleotides (CMPVX), where X=160, 155, 150, or 114 of SEQ ID NO:1, or consisting of a nucleotide sequence comprising from about 80% to 100% sequence similarity with CMPVX, where X=160, 155, 150, or 114 of SEQ ID NO:1 SEQ ID NO:1 is provided. The expression enhancer may further comprise a stuffer sequence fused to the 3′ end of the 5′UTR nucleotide sequence (CMPVX+, where X=160, 155, 150, or 114 of SEQ ID NO:1). The stuffer sequence may comprise one or more plant kozak sequences. Plants comprising the expression enhancer and methods using the expression enhancer are also described
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
Baculoviral DNA elements for the expression of recombinant proteins in a host cell
ActiveUS20150353898A1High expressionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesCellular viabilityEnhancer Elements
Reagents and methods are provided that allow for an improved expression of a recombinant protein. More specifically, the introduction of recombinant DNA elements into a host cell allows for the increased expression of a recombinant protein, an improvement of the correct folding of said protein and an increase in cell viability and proliferation of the host cell, These recombinant DNA elements can be introduced into host cells, for example, via a recombinant baculovirus, which has incorporated said elements. The recombinant DNA elements include nucleic acids encoding transcriptional regulators, such as IE-0 and IE-1, transcriptional enhancer elements, such as the homologous region (hr) and promoters.
Owner:ALTERNATIVE GENE EXPRESSION
Identification and Application of an Enhanced Gene Expression Sequence in Brassica napus
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and specifically relates to the identification and application of an enhanced gene expression sequence in Brassica napus. The present invention identifies a 3.7-kb DNA fragment in the upstream regulatory region of Brassica napus qSLWA9 gene, its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the sequence belongs to an incomplete CACTA-like (CACTA-like) transgenic region. Transposons have the function of enhancers, which can enhance the expression level of genes. A combination of markers related to the presence of enhancers was developed, and genotype analysis was performed on 245 Brassica napus materials. Combining the silique length and grain weight phenotypes, it was found that the presence or absence of CACTA-like transposons was closely related to the phenotype. Further validation revealed that CACTA-like transposon fragments contain enhancer elements that enhance gene expression in various tissues. The CACTA-like transposon and the marker of the invention can be used to improve the yield-related traits of Brassica napus.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
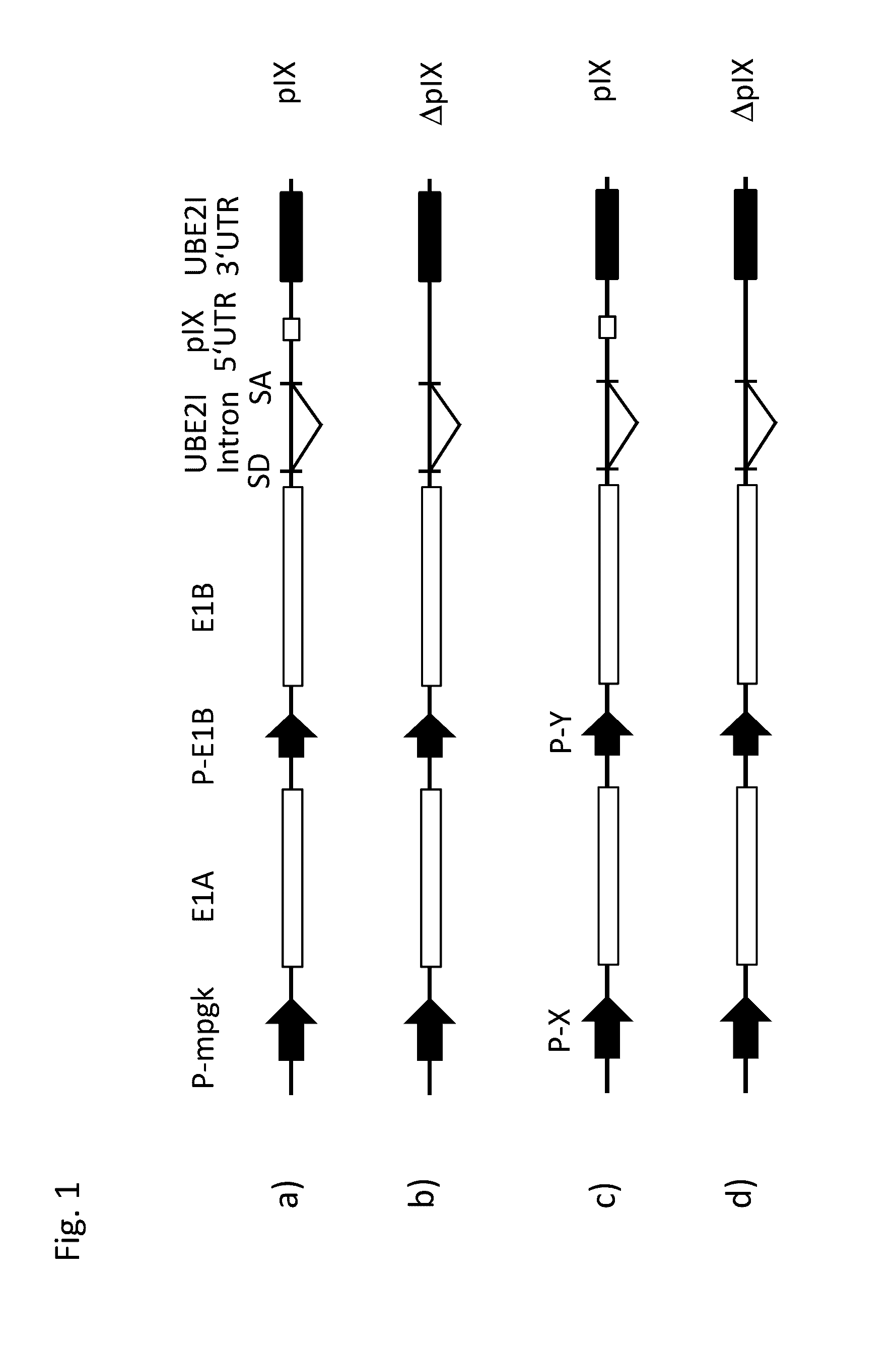
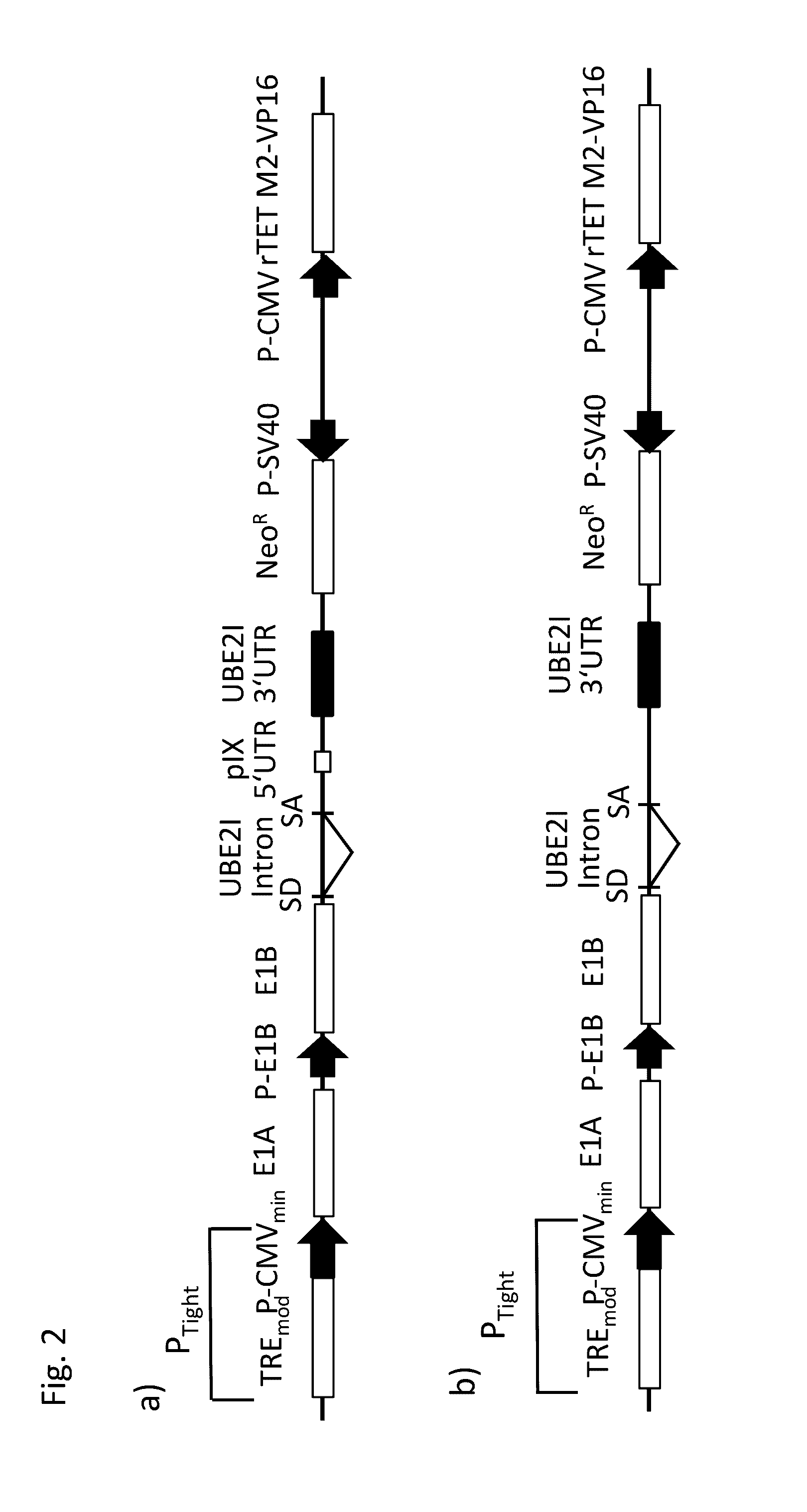
Nucleic acid construct and use of the same
The present invention is related to a nucleic acid construct comprisingan expression unit for the expression of E1B, wherein the expression unit comprises a promoter, a nucleotide sequence coding for E1B, and a 3′UTR, wherein the promoter is operatively linked to the nucleotide sequence coding for E1B, wherein the 3′UTR comprises 30 or less than 30 Exonic Enhancer Elements (ESEs), preferably 20 or less than 20 Exonic Enhancer Elements (ESEs), and wherein the 3′ UTR is a non-viral 3′ UTR.
Owner:KOCHANEK STEFAN
Gene promoters isolated from potato and use thereof
InactiveUS20050005324A1High level gene expression and flexible control of such expressionIncrease gene expressionSugar derivativesTransferasesBiotechnologySolanum tuberosum
There are disclosed novel pin1 gene promoter isoforms and amt gene promoter isoforms. The promoters and their functional elements may be used independently or in combination with one or more enhancer elements to increase or otherwise manipulate gene expression. The promoters disclosed may be used in Controlled Environment Agriculture for heterologous protein production. Also disclosed are methods for using the promoter and promoter elements of the instant invention, as well as vectors and transgenic plants comprising the same.
Owner:DAI ZIYU +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com