Patents
Literature
33 results about "Genetically modified insect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
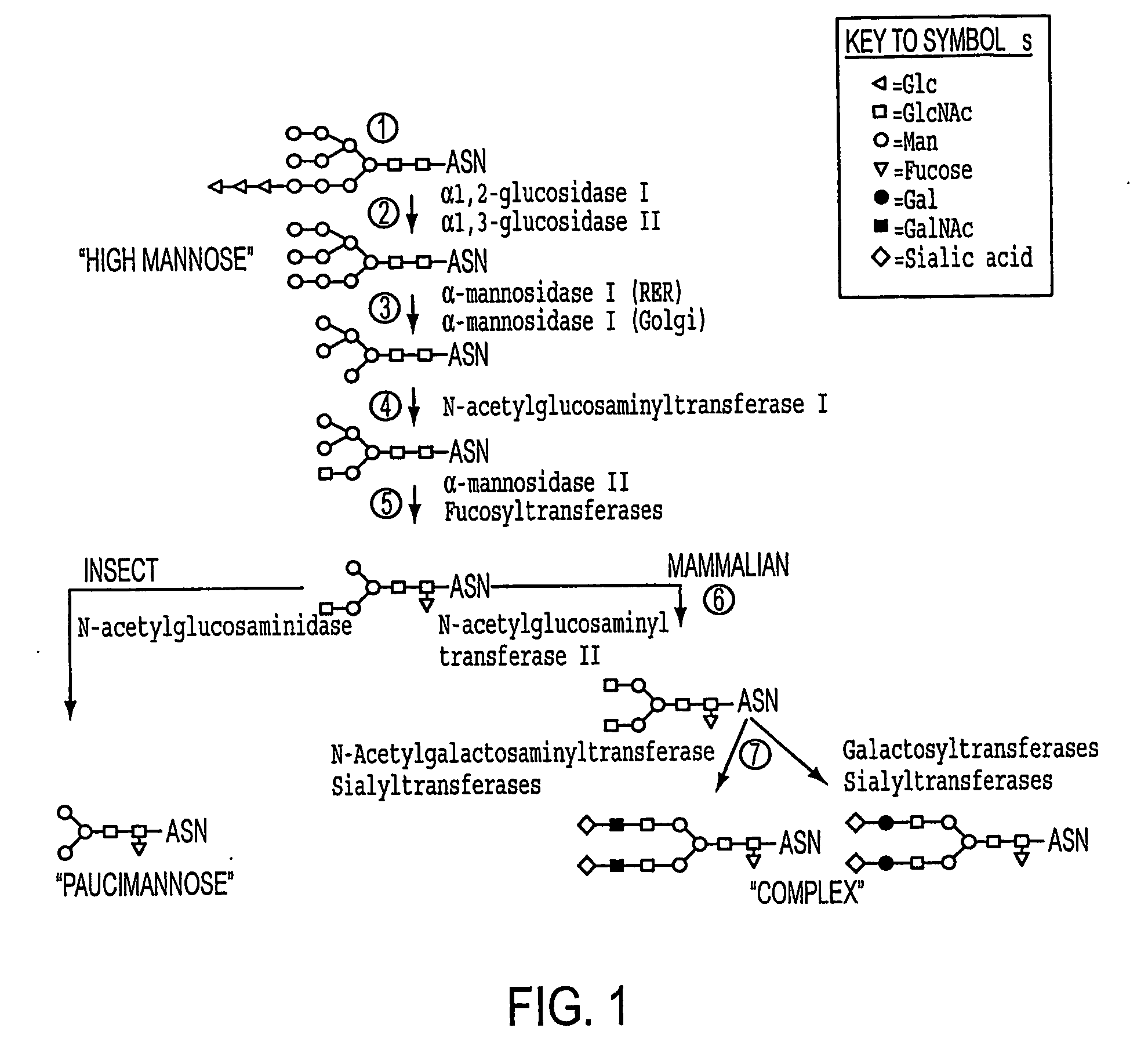
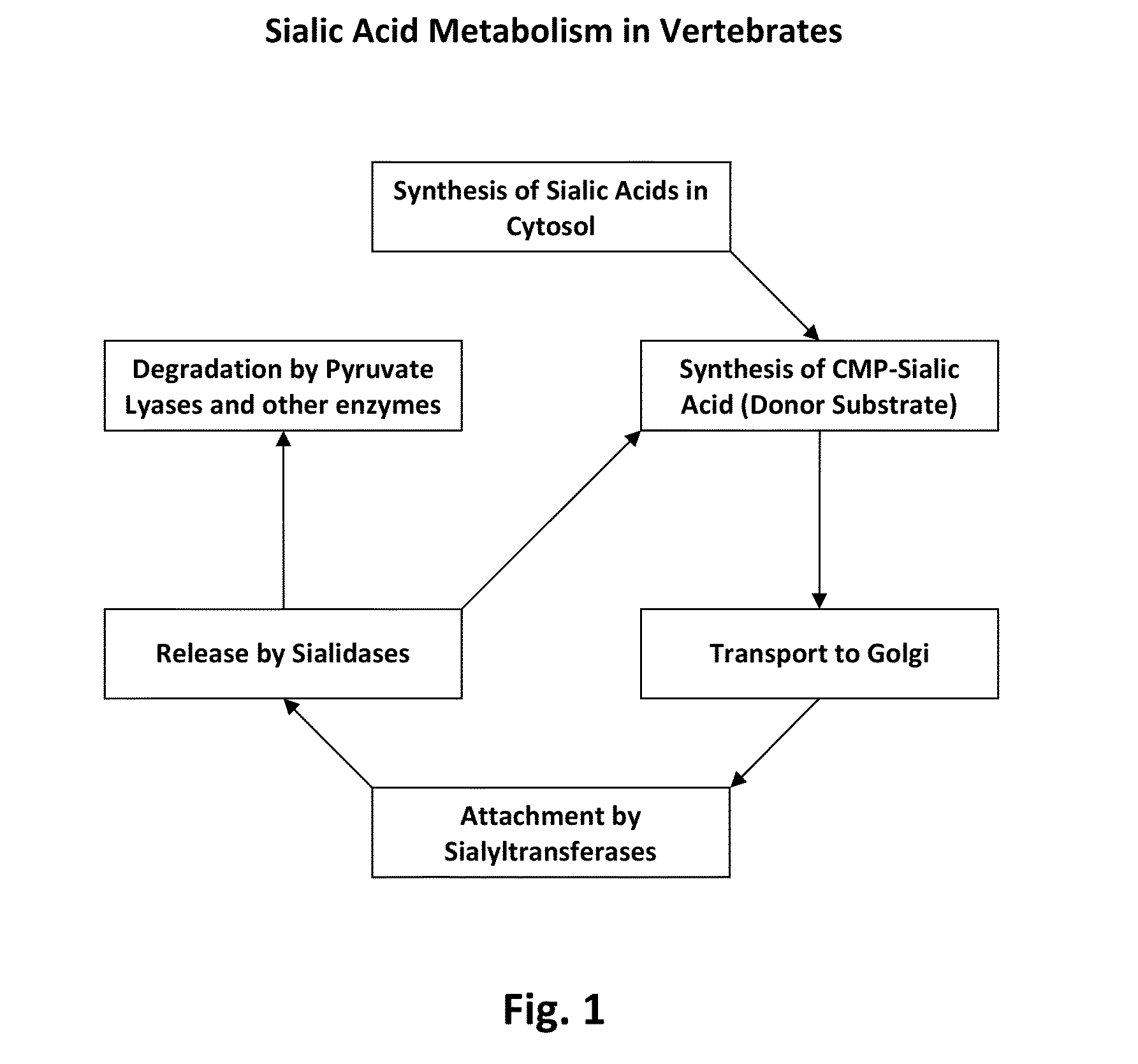
A genetically modified (GM) insect is an insect that has been genetically modified, either through mutagenesis, or more precise processes of transgenesis, or cisgenesis. Motivations for using GM insects include biological research purposes and genetic pest management. Genetic pest management capitalizes on recent advances in biotechnology and the growing repertoire of sequenced genomes in order to control pest populations, including insects. Insect genomes can be found in genetic databases such as NCBI, and databases more specific to insects such as FlyBase, VectorBase, and BeetleBase. There is an ongoing initiative started in 2011 to sequence the genomes of 5,000 insects and other arthropods called the i5k. Some Lepidoptera (e.g. monarch butterflies and silkworms) have been genetically modified in nature by the wasp bracovirus.
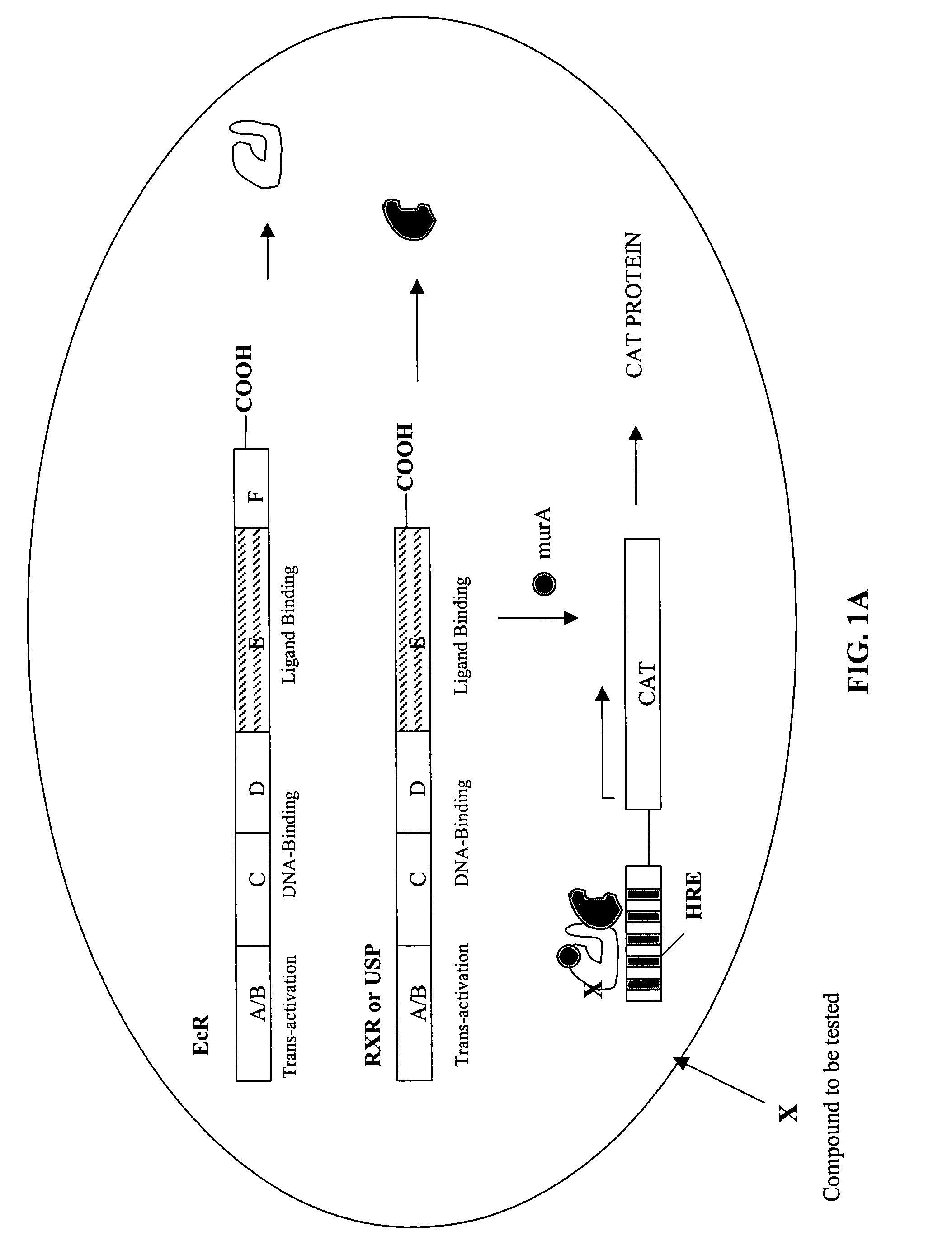
Compounds that act to modulate insect growth and methods and systems for identifying such compounds
InactiveUS20050049230A1Improve performanceSmall impactOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGenetically modified insectGene
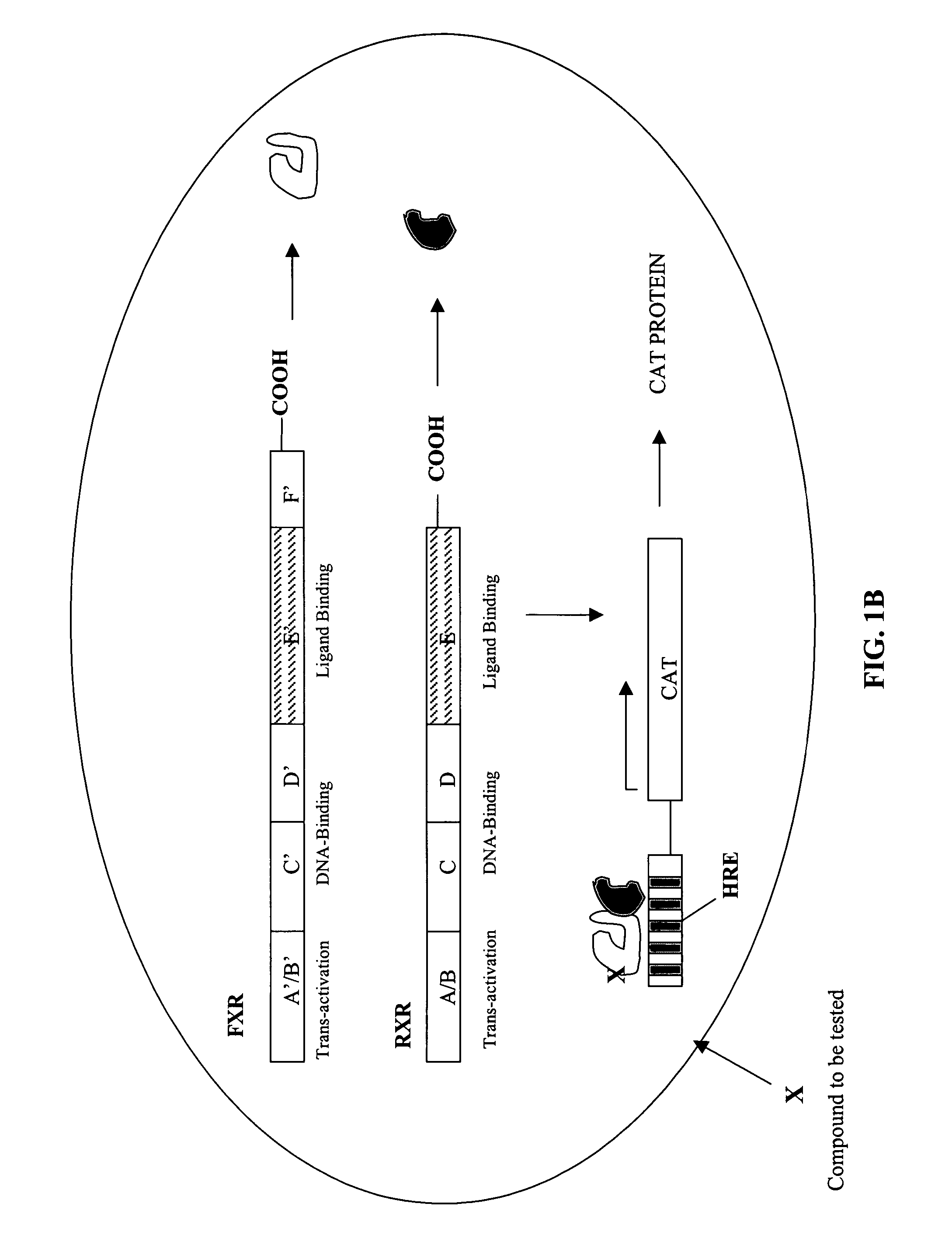
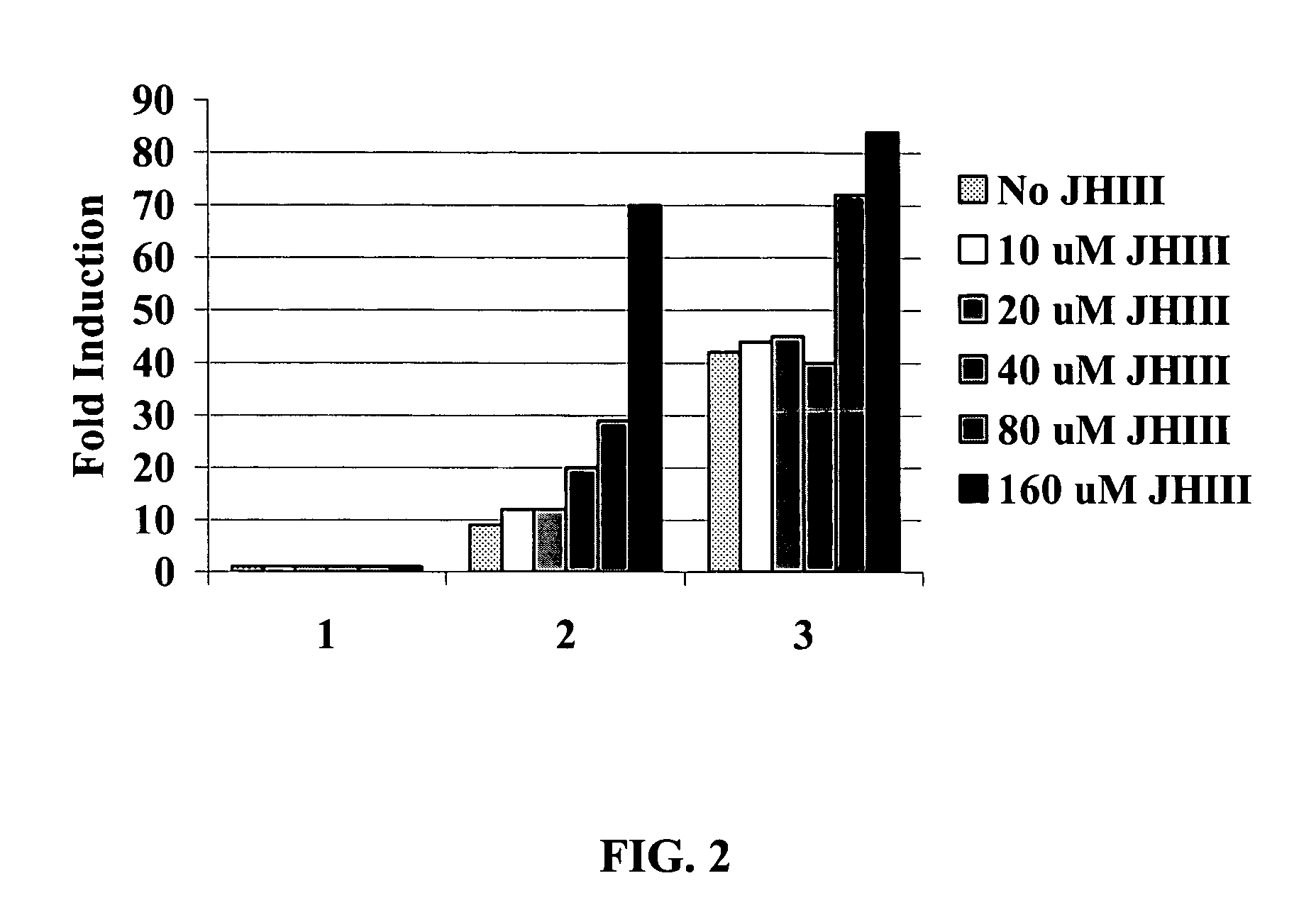
Disclosed are methods and systems for screening for compounds that act to modulate insect growth. Bioassays including cell culture and / or transgenic insects engineered with various components of the ecdysoid receptor (EcR) and / or the farsenoid-X receptor (RXR) systems to identify compounds that act as insecticides and / or hormone receptor activators are described. Also described are compounds, and compositions, identified as being putative insecticides based upon their ability to activate EcR and / or FXR mediated transcription.
Owner:UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT GREENSBORO THE
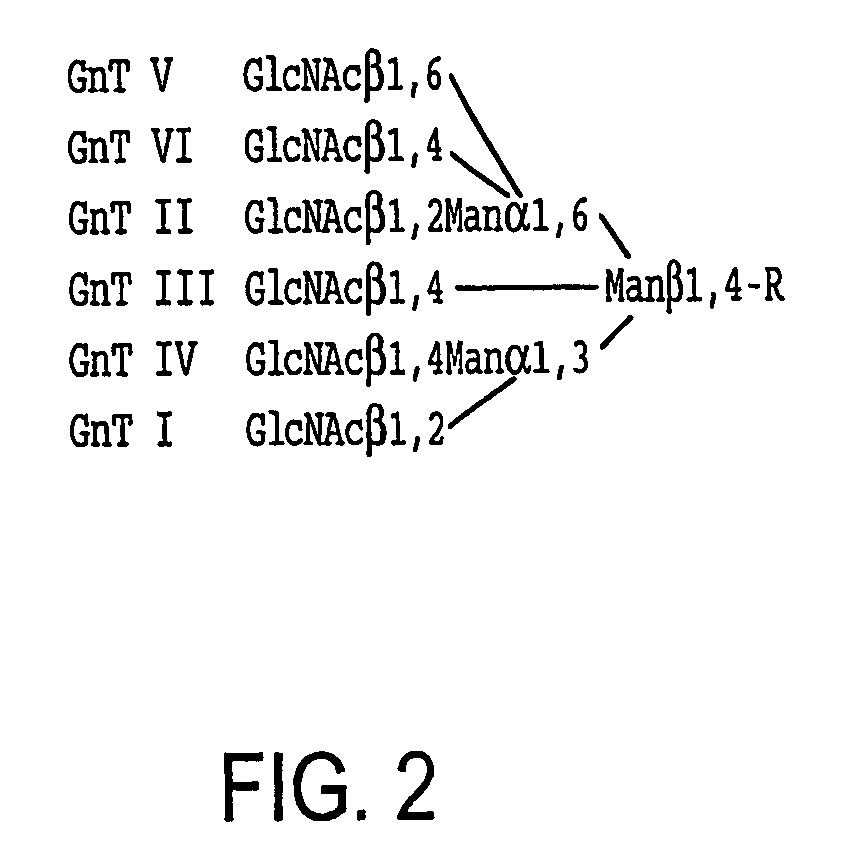
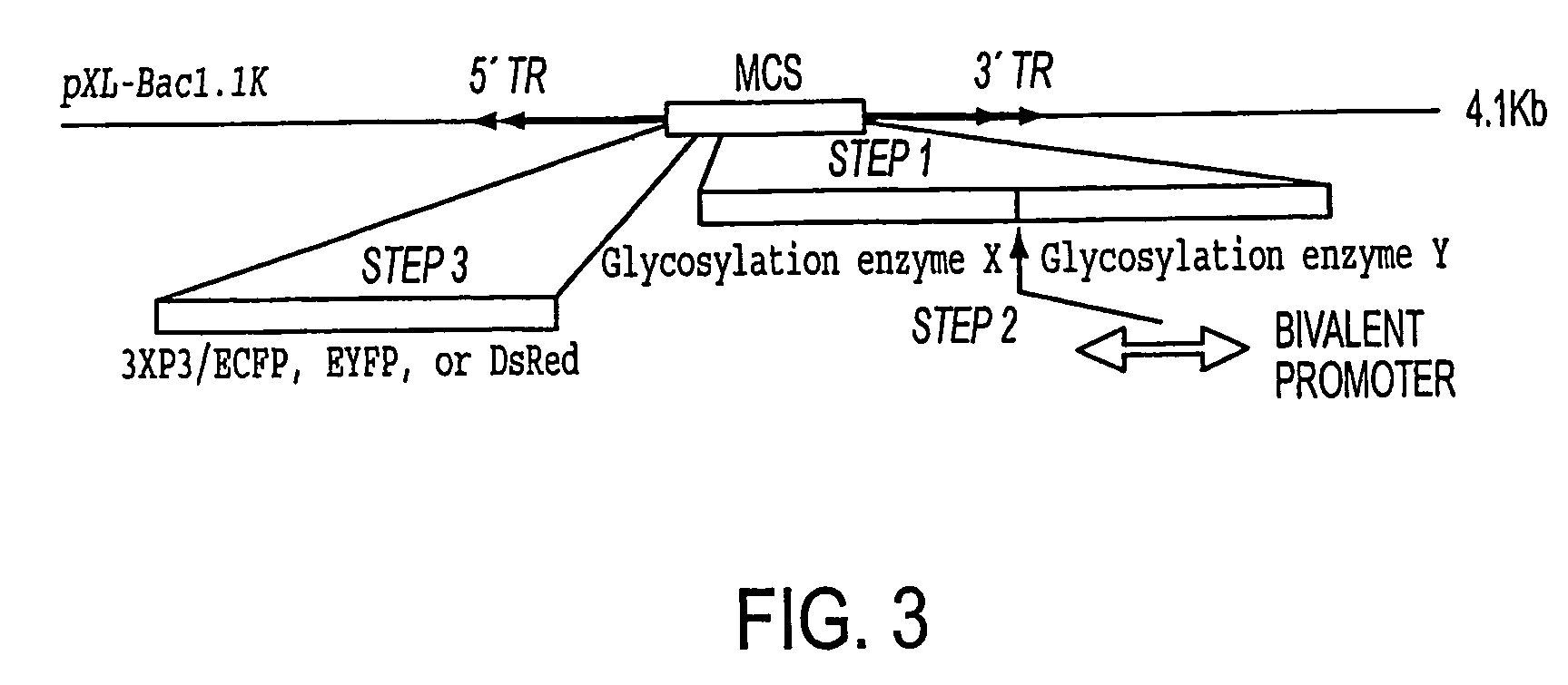
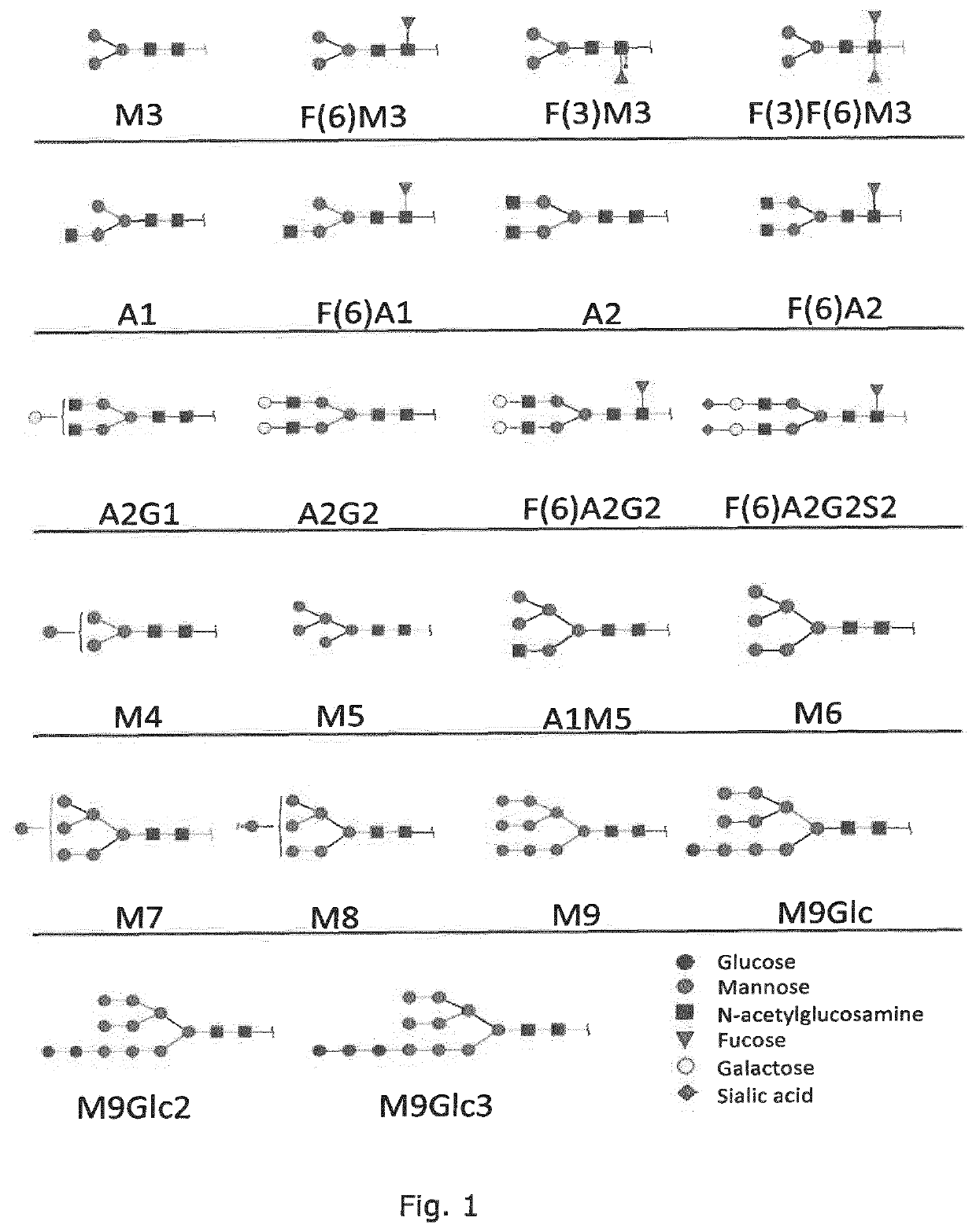
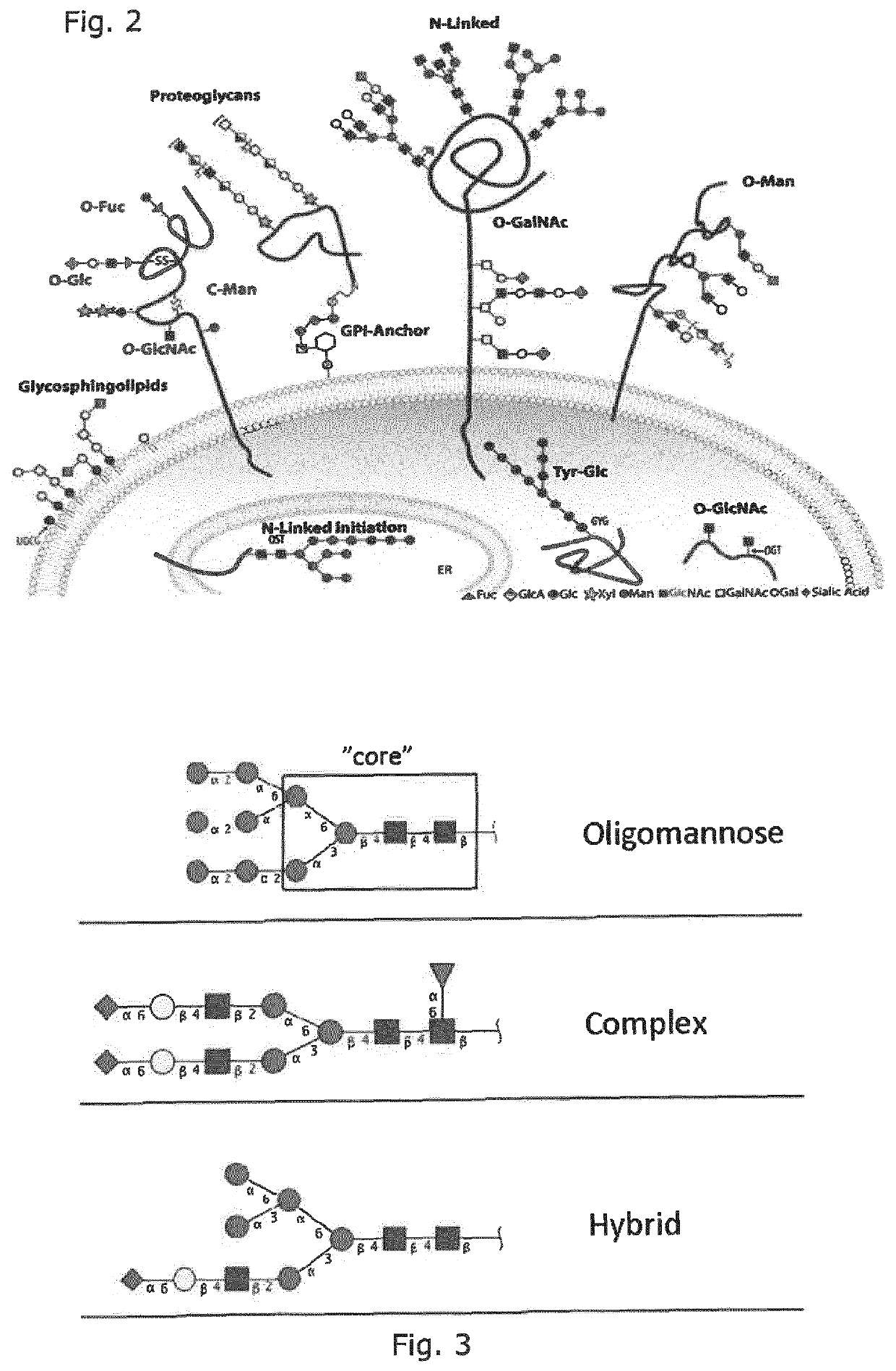
Production of human glycosylated proteins in transgenic insects
This invention relates, e.g., to transgenic insects, or progeny thereof, whose cells contain at least one genomically integrated, expressible, nucleic acid encoding two or more of a set of Nglycosylation enzymes that can glycosylate a heterologous protein with a mammalianized (e.g., humanized) glycosylation pattern. The glycosylation genes are preferably expressed in the insect cells in catalytic amounts. Also described are methods to use such a transgenic insect to produce heterologous, mammalianized polypeptides of interest.
Owner:CHESAPEAKE PERL
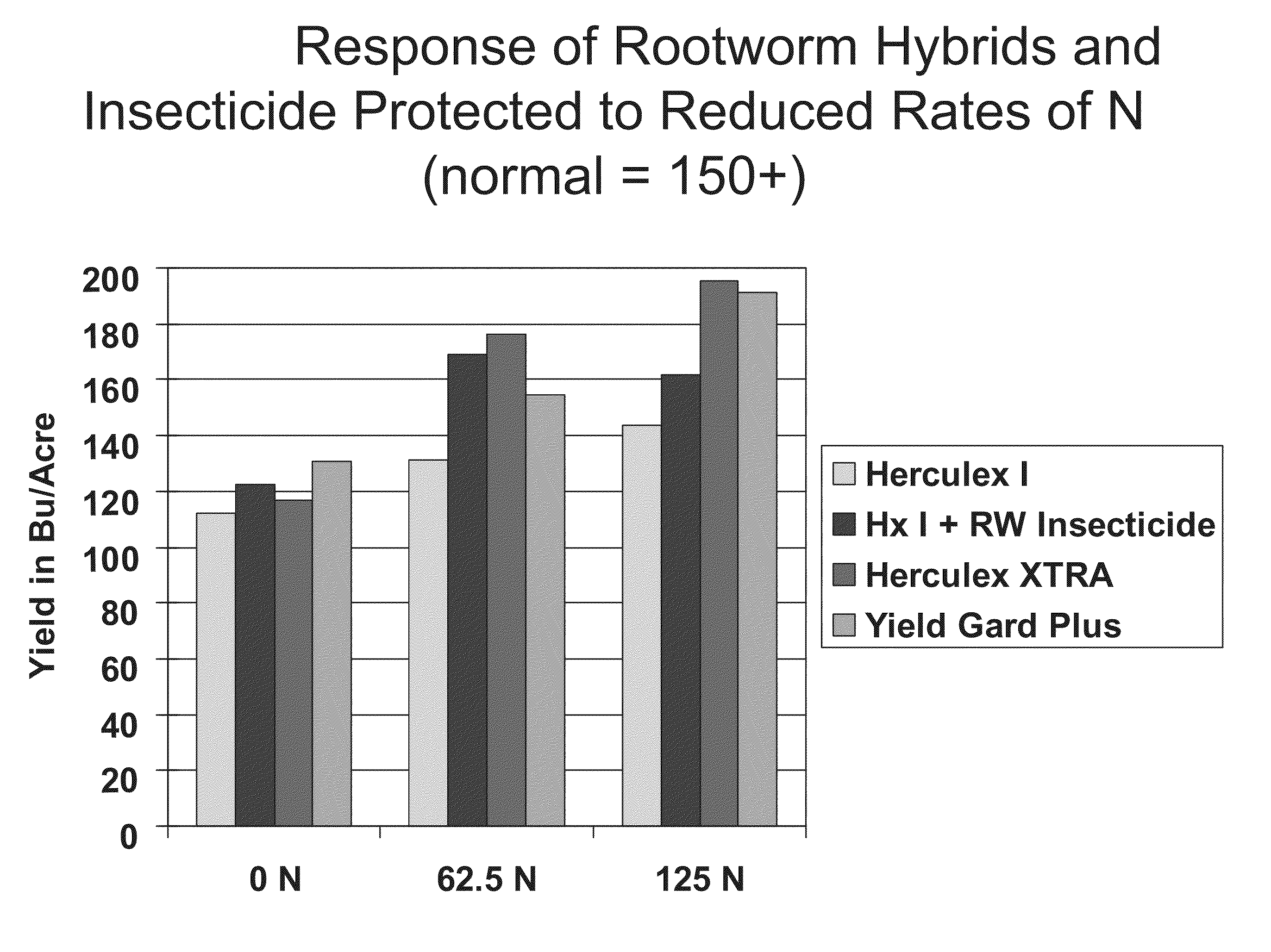
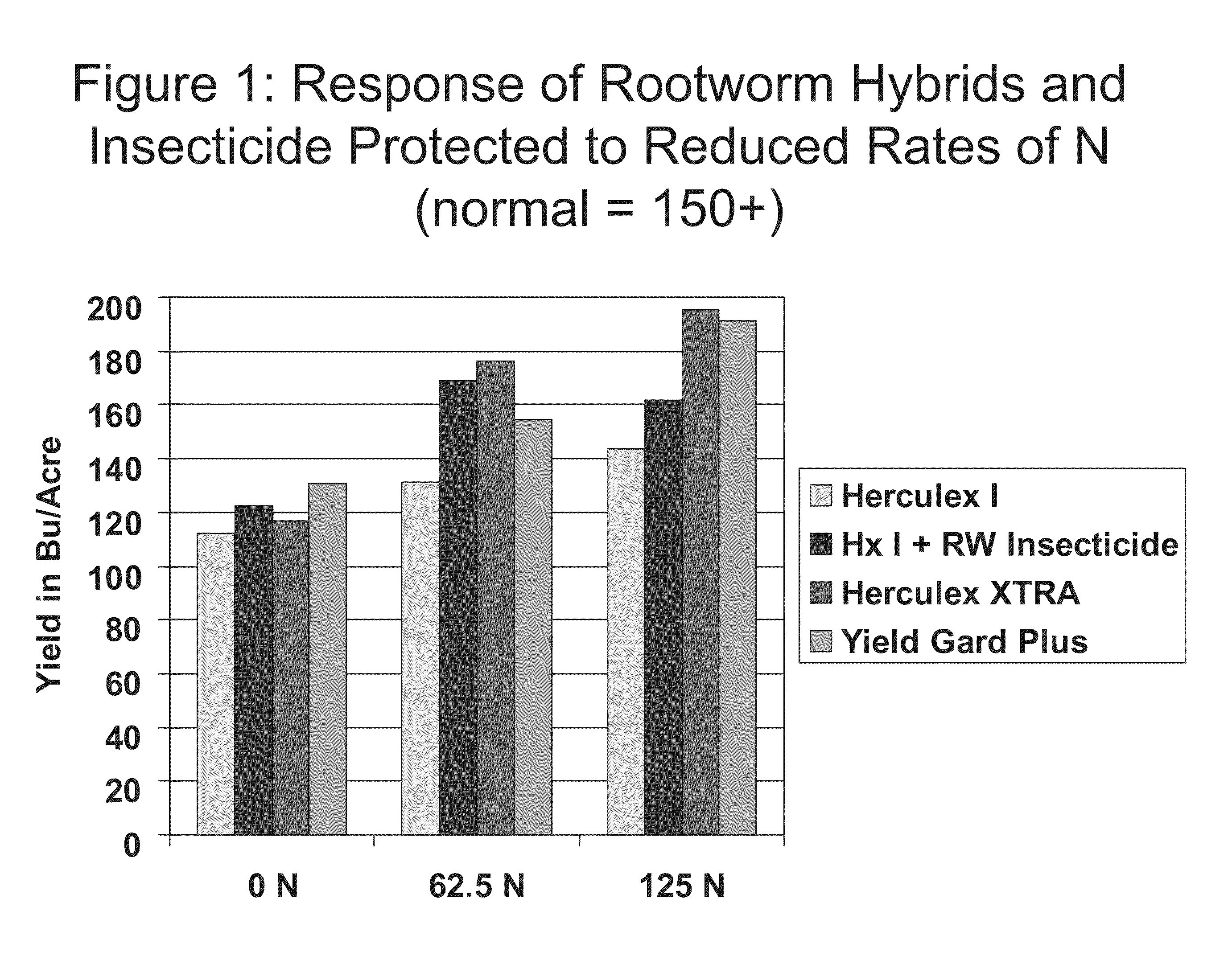
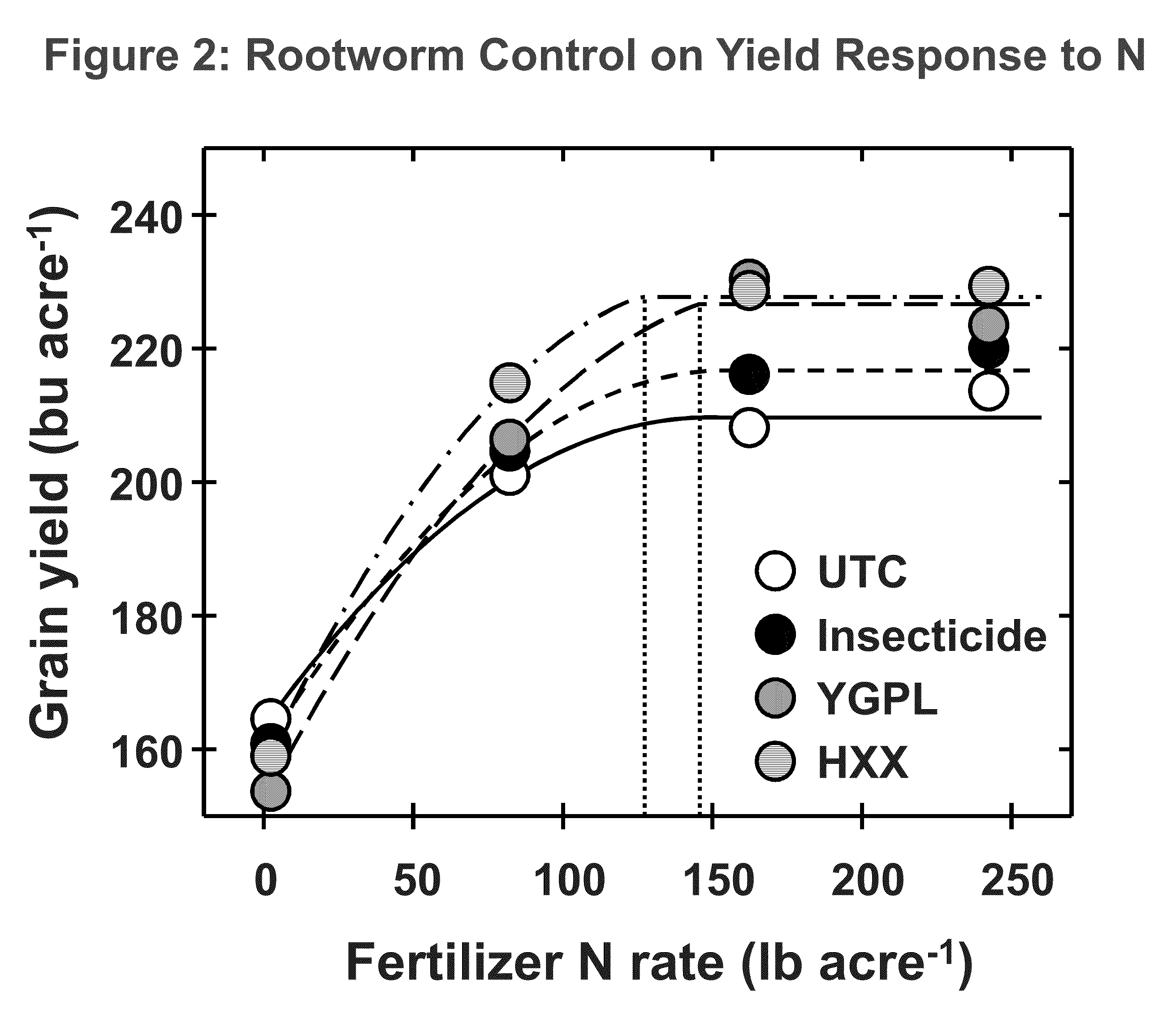
Corn with transgenic insect protection traits utilized in combination with drought tolerance and/or reduced inputs particularly fertilizer
InactiveUS20090300980A1Effective absorptionClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsGenetically modified insectPotassium
The subject invention relates in part to the use of insect-protected corn to modify fertility recommendations for given yield targets on any transgenic corn type. The insect-protected plants are unexpectedly more effective at assimilating not only nitrogen but also less valuable nutrients such as phosphorous, potassium and micronutrients such as zinc. The subject invention also relates to the discovery that transgenic corn plants with insect protection traits exhibit drought tolerance. For example, the protected plants are also much more effective at extracting moisture and are therefore more drought resistant and require less supplemental irrigation to produce the same yields as unprotected plants.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
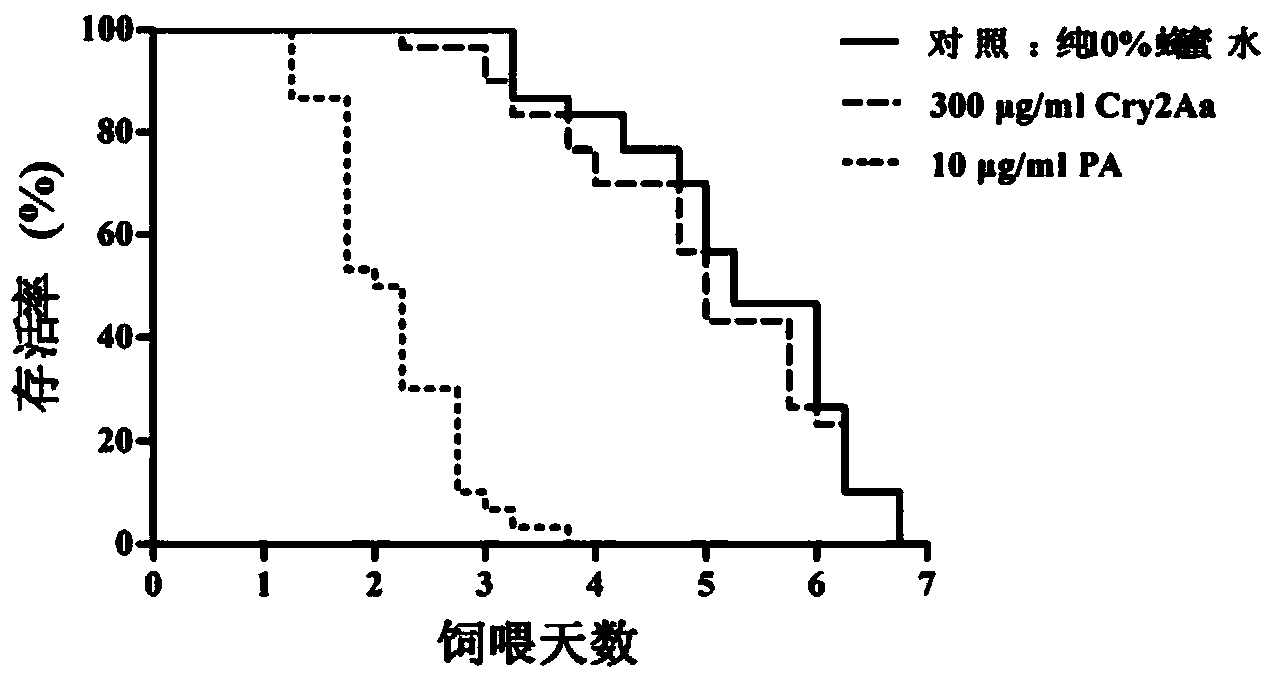
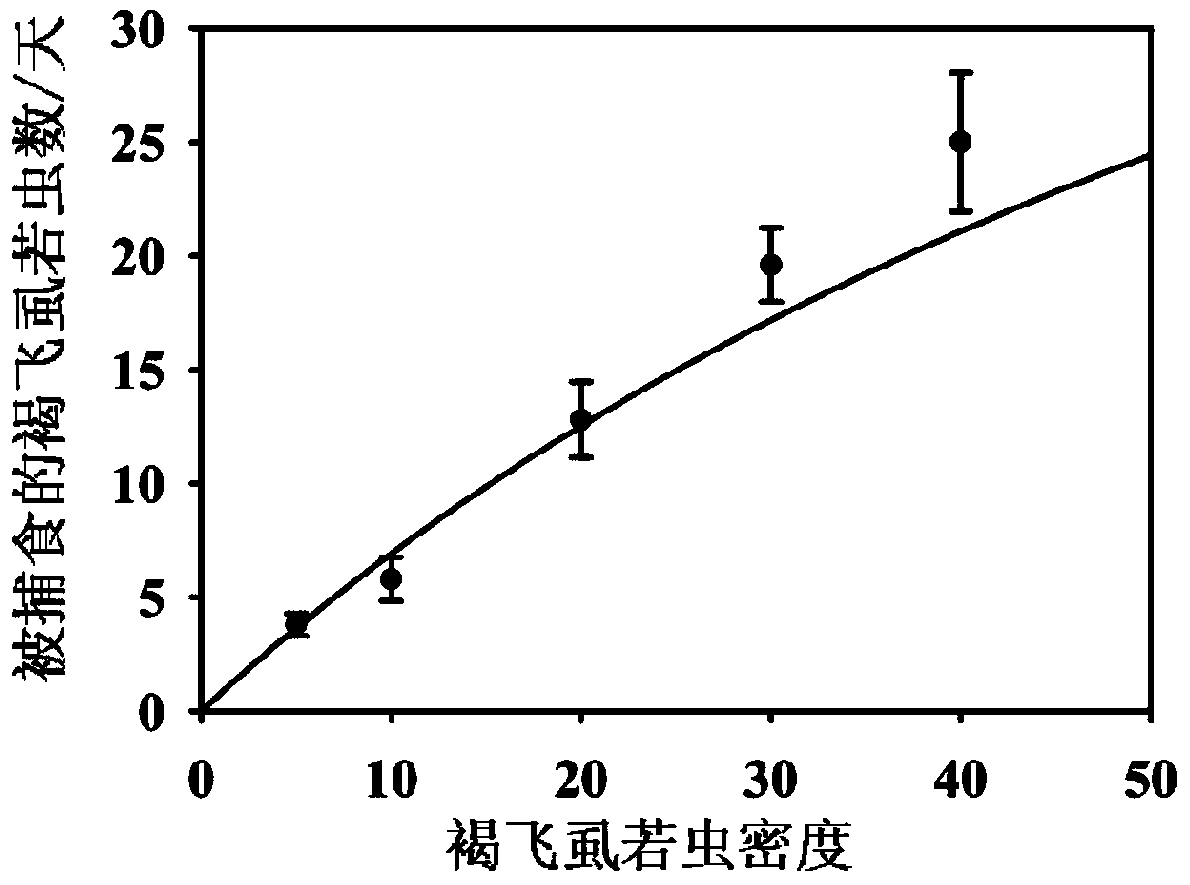
Evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to parasite anagrus nilaparvatae
The invention relates to an evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to parasite anagrus nilaparvatae. The evaluation method includes three parts of Tier-1 toxicity determination test, wherein the potential toxicity of Bt proteins expressed by Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on non-target organism anagrus nilaparvatae is evaluated; successive generation three-level nutrition test, wherein the influence of the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on the safety of the anagrus nilaparvatae through parasitic mediators is evaluated according to the food chain of rice-delphacidae-anagrus nilaparvatae; a protein transfer rule, wherein the way and degree that the anagrus nilaparvatae is exposed in the Bt proteins expressed by the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice are identified through an ELISA detection means; finally, the ecological consequences generated by genetically modified crop cultivation on non-target organisms are evaluated synthetically according to the data of the three parts. The evaluation method is systematic and scientific, and has great significance for the research of the influence of genetically modified crops on the non-target organisms and ecological safety of genetically modified crop cultivation.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Maize event DP-004114-3 and methods for detection thereof
The invention provides DNA compositions that relate to transgenic insect resistant maize plants. Also provided are assays for detecting the presence of the maize DP-004114-3 event based on the DNA sequence of the recombinant construct inserted into the maize genome and the DNA sequences flanking the insertion site. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
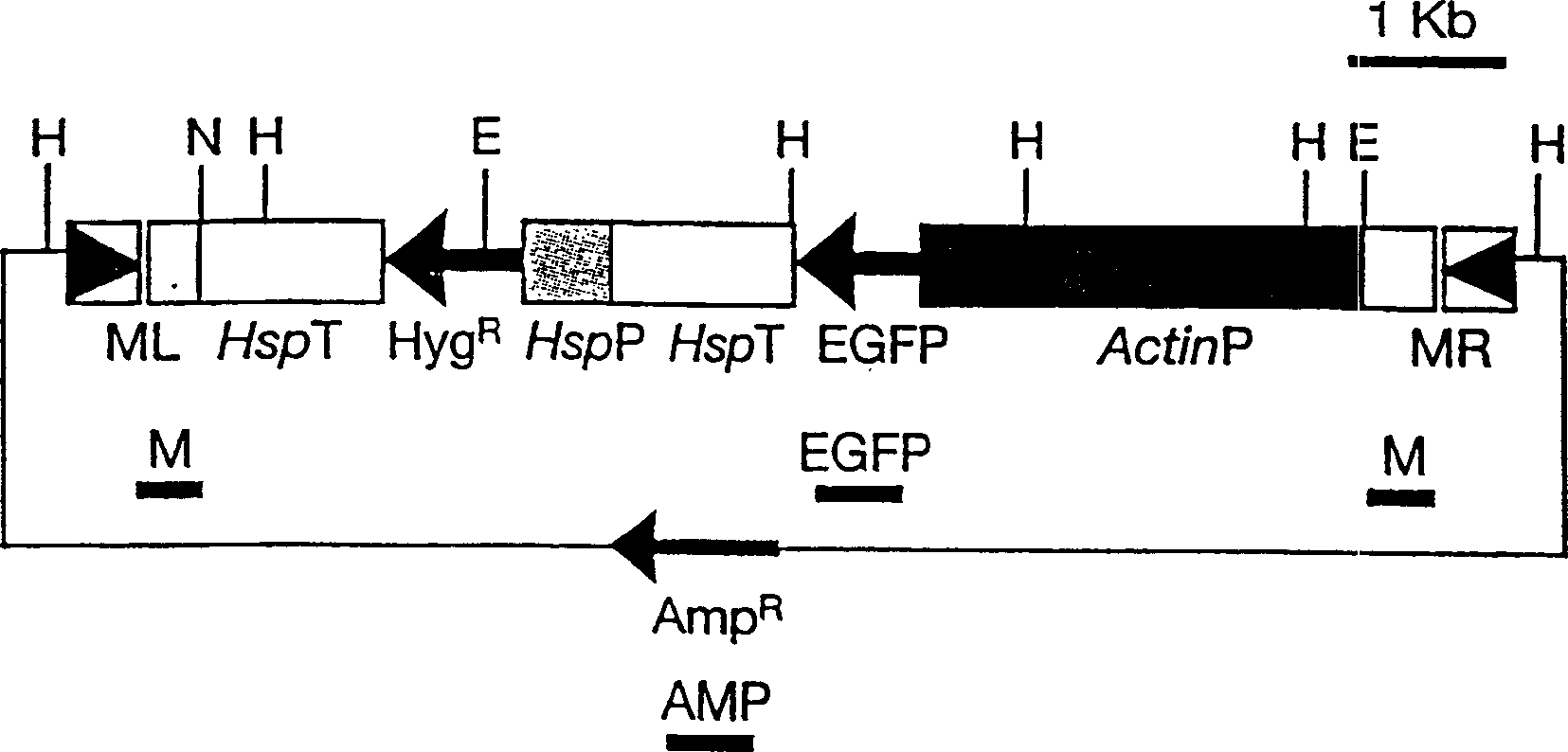
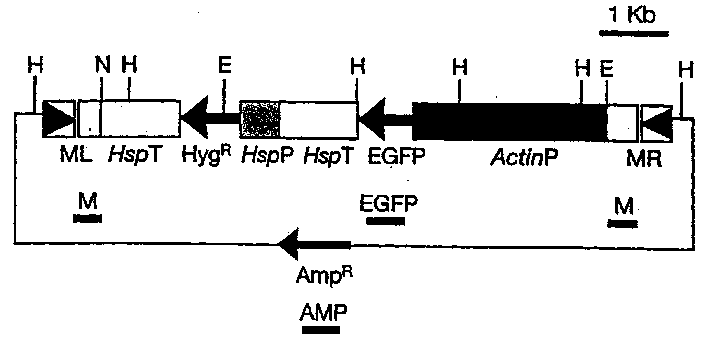
Method for improving transgenic insect cell expression exogenous gene level
InactiveCN101270366AAchieve continuous expressionHigh biosecurityVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsHigh level expressionGenetically modified insect
The invention discloses a method for improving expression of extraneous genes by insect transgene cells. In the method, active promoter controlled neomycin resistance gene expression cassettes, enhancer elements and extraneous gene expression cassettes inside the cells of insects are cloned into a vector with reporter genes based on transposon piggyBAC factors; subsequently, the vector is mixed with subsidiary plasmids expressing transposase to transfect insect cell lines; transgene insect cells are acquired through sectionalized screening of G418. Engineering cells expressing extraneous genes at high level are acquired by cell clone technology in combination practical examination of expression level of extraneous genes. With the method, transgene insect cells can express extraneous genes at high level continuously; the expression products are free of rhabdoviruses with good bio-safety, and are processed perfectly as well as natural.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Insect cell line for production of recombinant glycoproteins with sulfated complex n-glycans
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
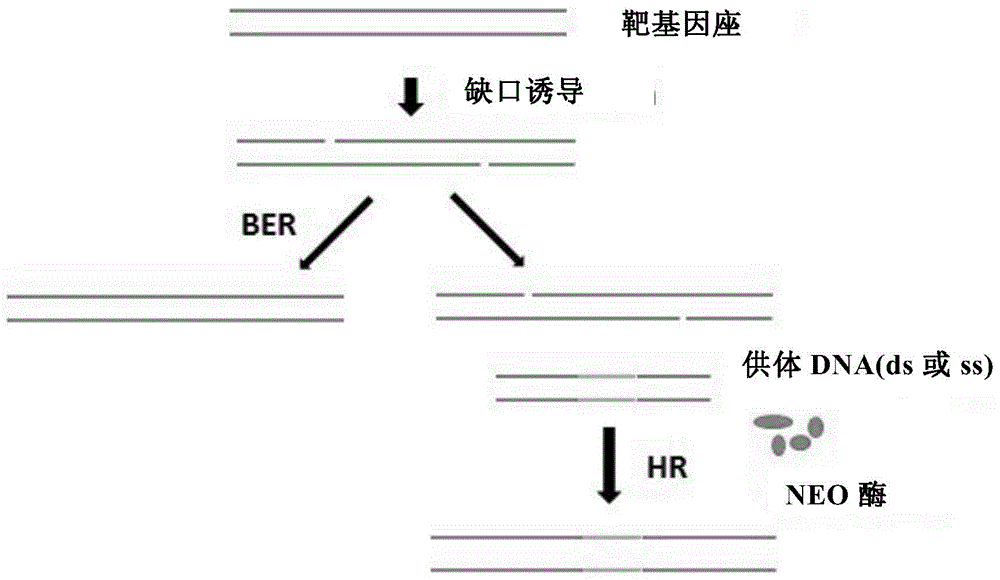
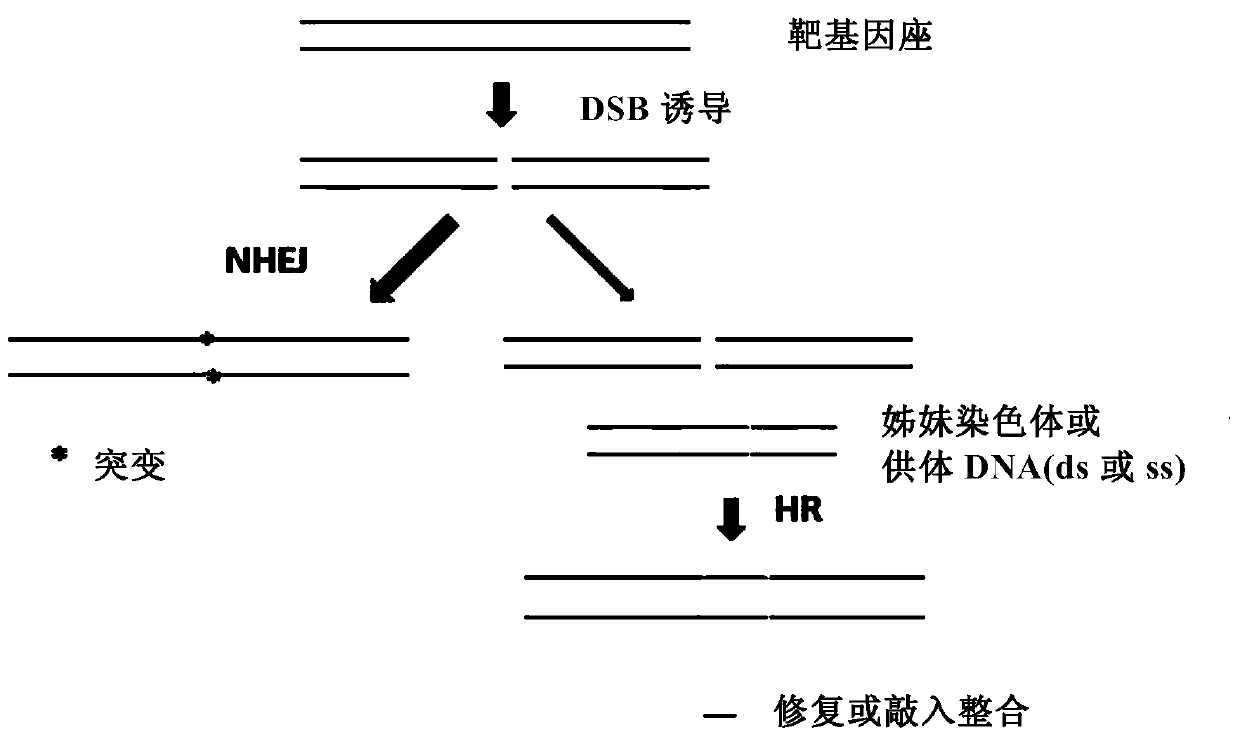
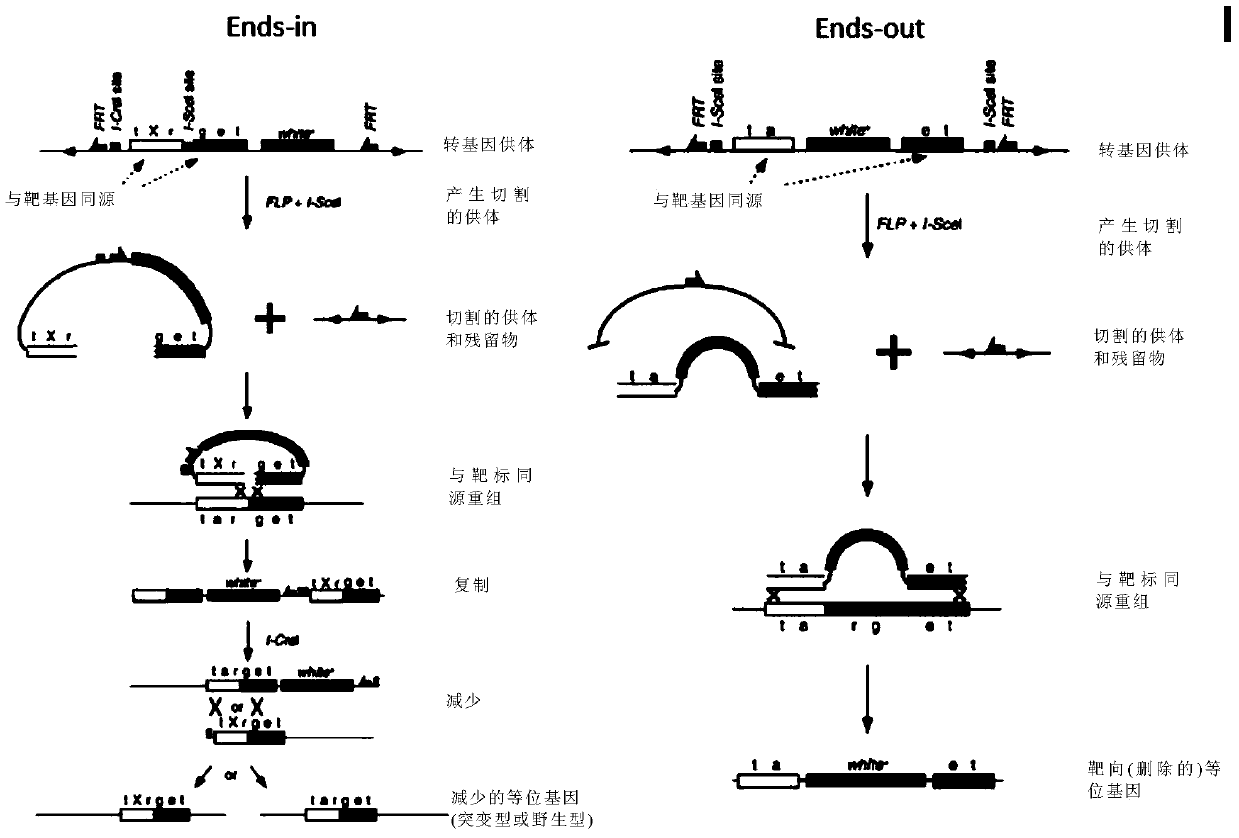
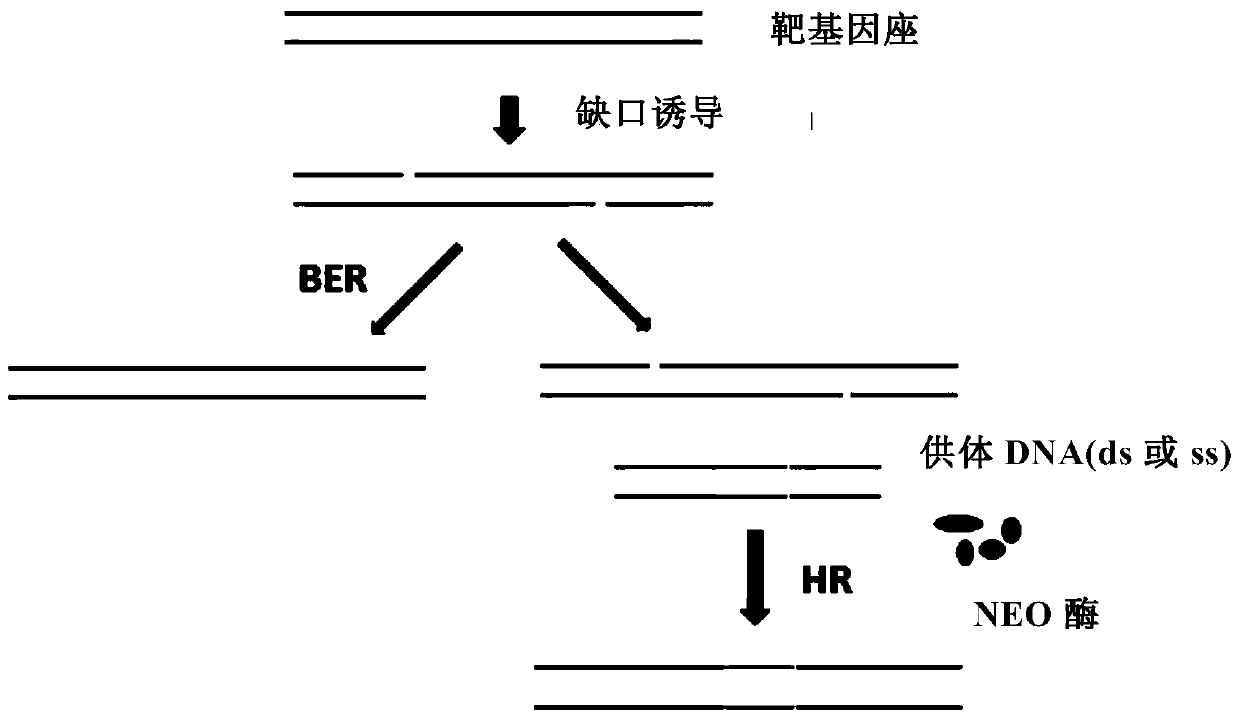
Insect targeted gene knock-in composition, use method and application thereof
ActiveCN105315352AImprove the efficiency of homologous recombinationDepsipeptidesGenetic engineeringNucleotideGenetically modified insect
The invention provides a composition used in insect targeted gene knock-in, which includes a single nickase or an encoding polynucleotide thereof; a recombinant factor or an encoding polynucleotide thereof; and optionally, a donor DNA of an exogenous gene. The invention also provides a corresponding gene knock-in method and a method for preparing transgenic insects. The composition and the method in the invention can achieve high-effective homologous recombination integration in insect cells and meanwhile can avoid the defects in gene knock-in technologies in the prior art. The composition also can stably and high-effectively achieve homologous recombination integration of a fragment being more than 10 kb in length in the insect cells, so that the composition can be used for transferring a genetic selection marker into the insect cells, preferably a visible genetic selection marker, which is convenient to determine strains of transgenic insects.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
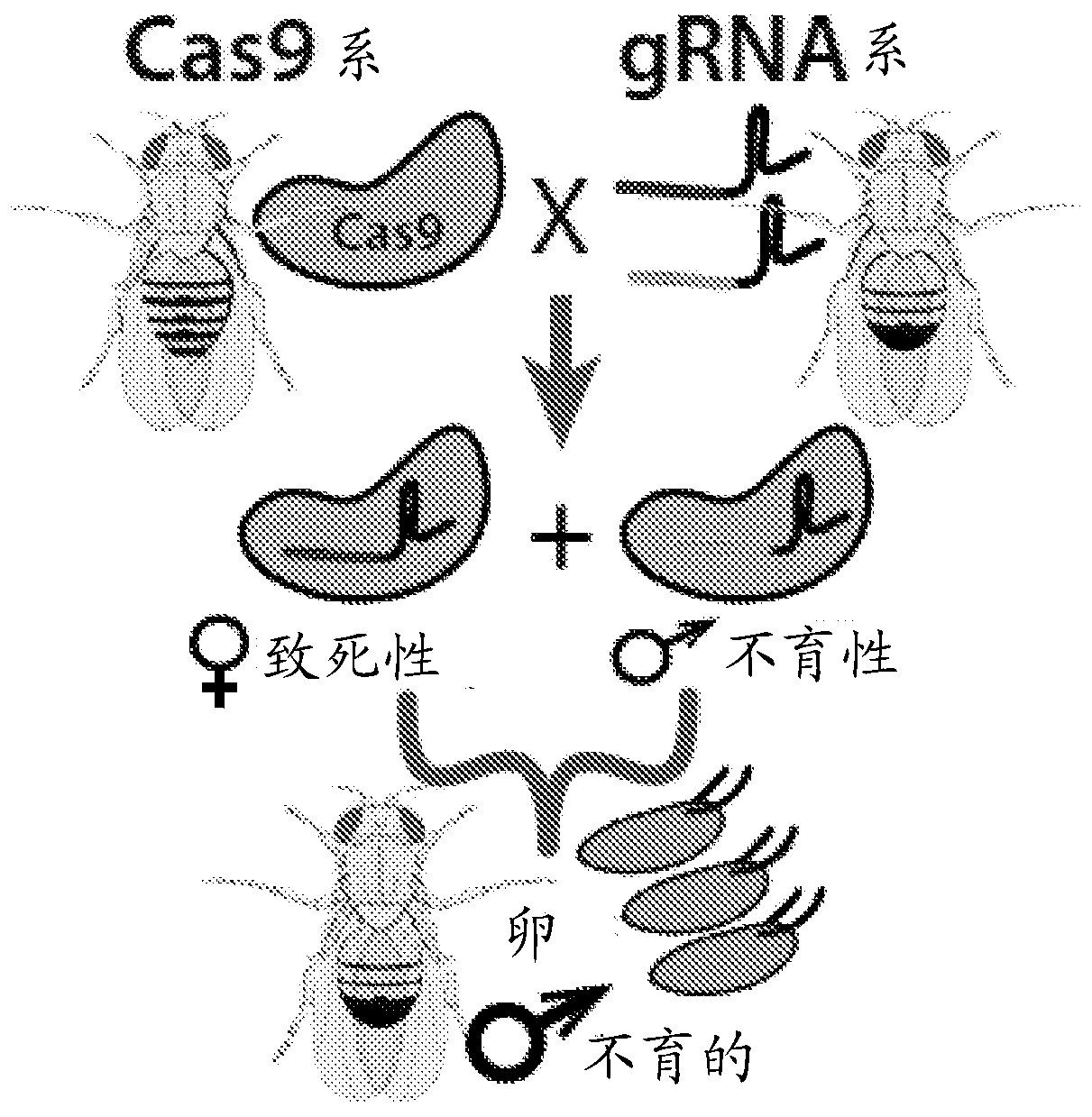
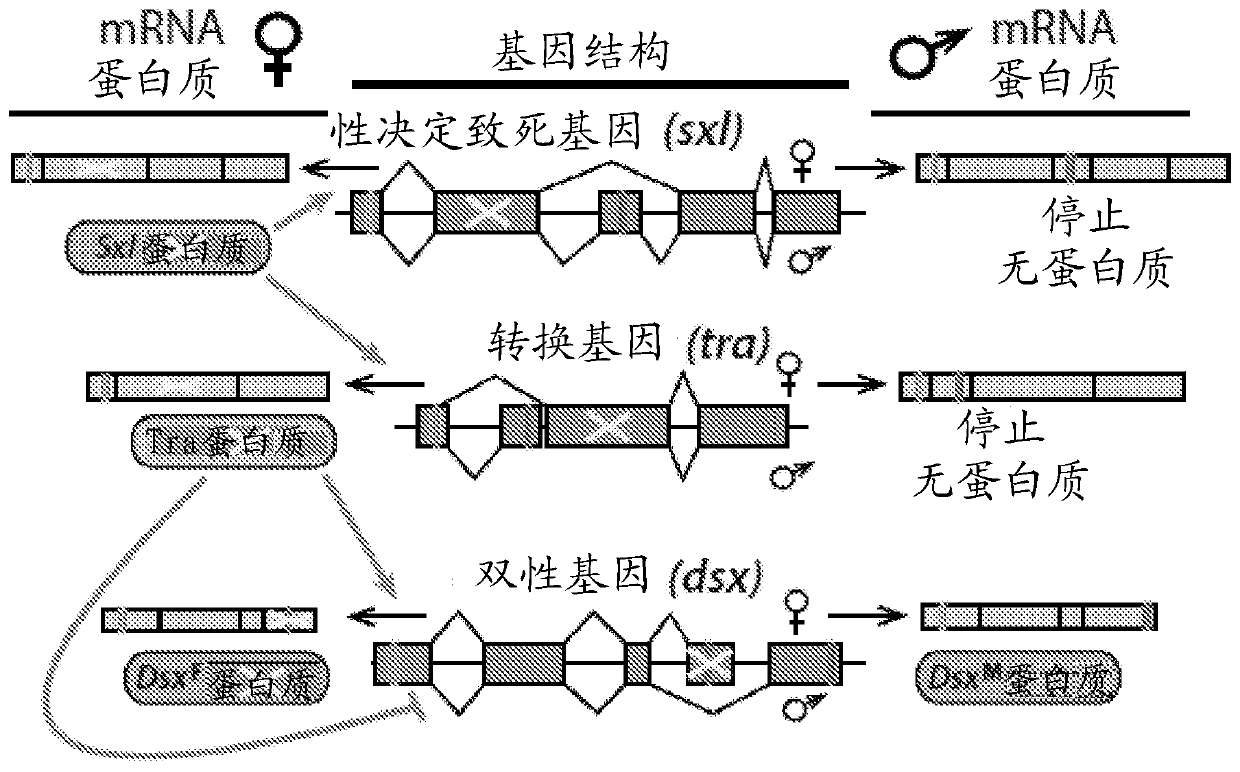
Endonuclease sexing and sterilization in insects
Methods of the disclosed precision guided sterile insect technique (pgSIT) include methods for directing male sexing in a genetically modified insect and methods of producing a progeny of geneticallymodified sterile male insect egg. These methods include integrating at least one nucleic acid sequence into a genome of a first insect, the at least one nucleic acid sequence having at least one firstguide polynucleotide targeting a female-essential genomic sequence that is required for female-specific viability, introducing an endonuclease into a second insect, and genetically crossing the firstinsect and the second insect thereby producing progeny expressing the endonuclease and the at least one nucleic acid sequence. For male sterility a second guide polynucleotide targets a male sterility genomic sequence that is required for male-specific sterility.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Visuble self-sucking extrinsic gene induction of insect egg
InactiveCN1644702AGenetic stabilityStable expressionOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified insectTransgene
Visual self-sucking method for inducing external gene into insect eggs is carried out by: under telescope, coating solution with external genes on insect eggs, pricking eggs to make external gene into eggs, making external genes combined with insect's gene to form transgenic insects. It makes technicians to do researches on transgenic insects with cheap instrument.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Transgenic insect cell line for high-yield baculovirus, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102807969AMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesGenetically modified insectOvary cell
The invention provides a transgenic insect cell line for high-yield baculovirus, and a preparation method and the application thereof. The name of the transgenic insect cell line is IOZCAS-Spex IX and the preservation number of the cell line is CGMCC No.4506. The preparation method of the transgenic insect cell line comprises the steps as follows: spodoptera exigua ovary cells are cultured; humantelomerase reverse transcriptase genes are transformed into known expression vectors to obtain recombinant vectors; the recombinant vectors are introduced into the spodoptera exigua ovary cells; and the spodoptera exigua ovary cells are enabled to express human telomerase reverse transcriptase, so as to obtain the transgenic insect cell line. The transgenic insect cell line is applied to the production of the baculovirus.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to predator hylyphantes graminicola
The invention relates to an evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to predator hylyphantes graminicola. The evaluation method is composed of a three-level nutrition test part, a protein transfer rule part, a predation function reaction part and a population density and population dynamics comparison part. The influence of Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on the hylyphantes graminicola is evaluated through the food chain of the hylyphantes graminicola; the way and degree that the hylyphantes graminicola is exposed in Bt proteins are identified through an ELISA detection means; the influence of the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on a non-target organism predation function is evaluated; the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice and non-genetically-modified parent are compared, and the influence on the hylyphantes graminicola population is evaluated; finally, the ecological consequences generated by genetically modified crop cultivation on non-target organisms are evaluated synthetically according to the data of the four parts. The evaluation method is systematic and scientific, and has great significance for the research of the influence of genetically modified crops on the non-target organisms and ecological safety of the genetically modified crop cultivation.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Transgenic insect
InactiveCN1409766APeptide/protein ingredientsMicroinjection basedGenetically modified insectTransposable element
A method for the genetic modification of an insect embryo, comprises first treating an insect egg under conditions which prevent or delay the hardening of the insect egg chorion, and then injecting a transposable element into the egg to permit integration of the element into the genome of the embryo. The method permits modifications to be made to mosquitoes, which may prevent transmission of a host parasite.
Owner:IMPLYX
Compounds that act to modulate insect growth and methods and systems for identifying such compounds
InactiveUS7790377B2Improve performanceSmall impactBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGenetically modified insectReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Owner:UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT GREENSBORO THE
Safety evaluation method of transgenic insect-resistant rice against parasitic natural enemy Oryza spp.
The invention relates to an evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to parasite anagrus nilaparvatae. The evaluation method includes three parts of Tier-1 toxicity determination test, wherein the potential toxicity of Bt proteins expressed by Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on non-target organism anagrus nilaparvatae is evaluated; successive generation three-level nutrition test, wherein the influence of the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on the safety of the anagrus nilaparvatae through parasitic mediators is evaluated according to the food chain of rice-delphacidae-anagrus nilaparvatae; a protein transfer rule, wherein the way and degree that the anagrus nilaparvatae is exposed in the Bt proteins expressed by the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice are identified through an ELISA detection means; finally, the ecological consequences generated by genetically modified crop cultivation on non-target organisms are evaluated synthetically according to the data of the three parts. The evaluation method is systematic and scientific, and has great significance for the research of the influence of genetically modified crops on the non-target organisms and ecological safety of genetically modified crop cultivation.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Transgenic fat body cell line of high-yield baculovirus and preparation method as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102807968AMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesBiotechnologyGenetically modified insect
The invention provides a transgenic fat body cell line of high-yield baculovirus and a preparation method as well as application thereof. The cell line which is named as IOZCAS-Spex X has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 4505; and the preparation method of the transgenic fat body cell line comprises following steps of: culturing asparagus caterpillar fat body cells; transforming genes containing human telomerase reverse transeriptase into a known expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector; leading the recombinant expression vector into the asparagus caterpillar fat body cells; and enabling the asparagus caterpillar fat body cells to express human telomerase reverse transeriptase so as to obtain the transgenic fat body cell line. In addition, the invention discloses application of the transgenic fat body cell line to production of baculovirus.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
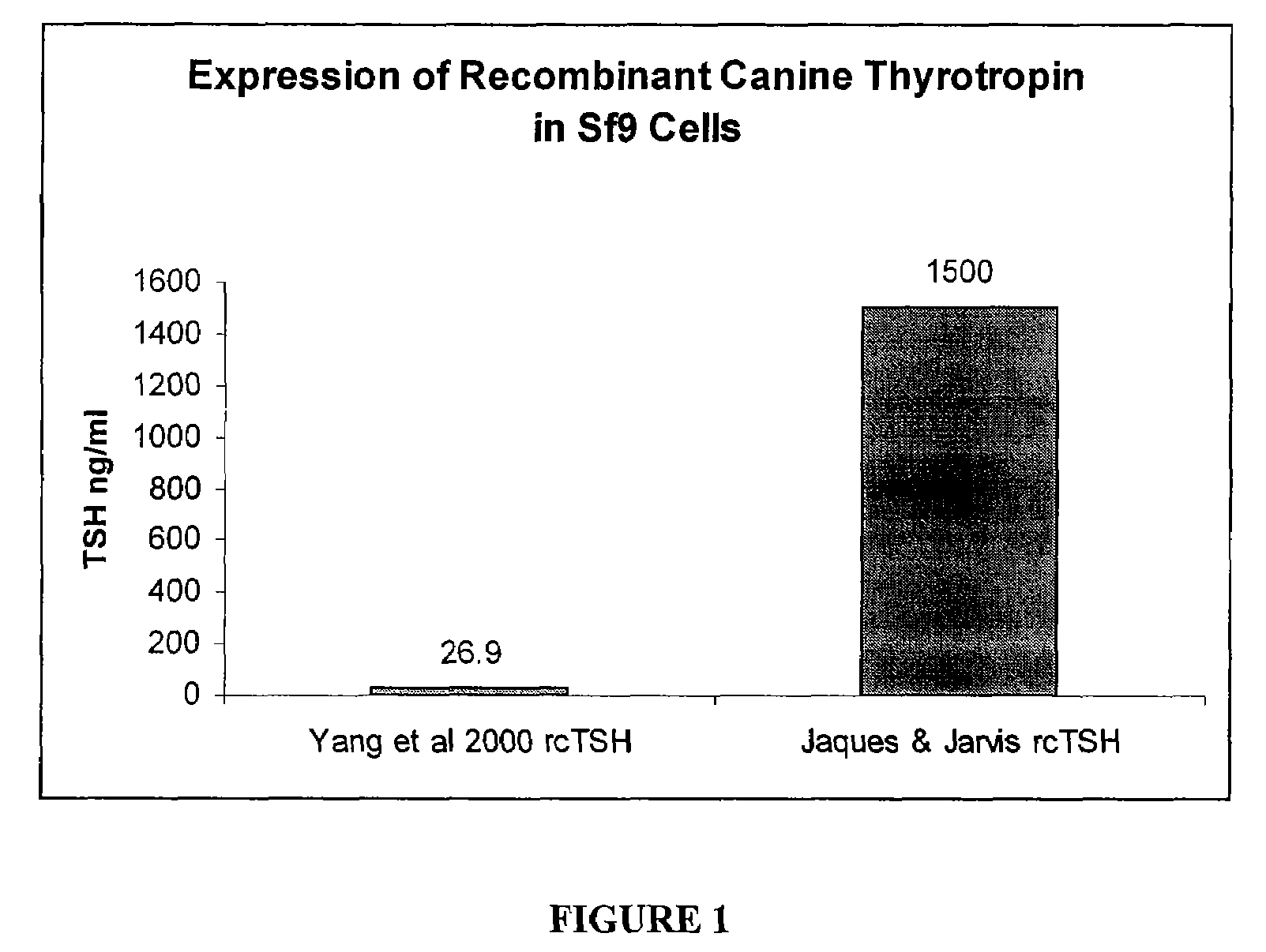
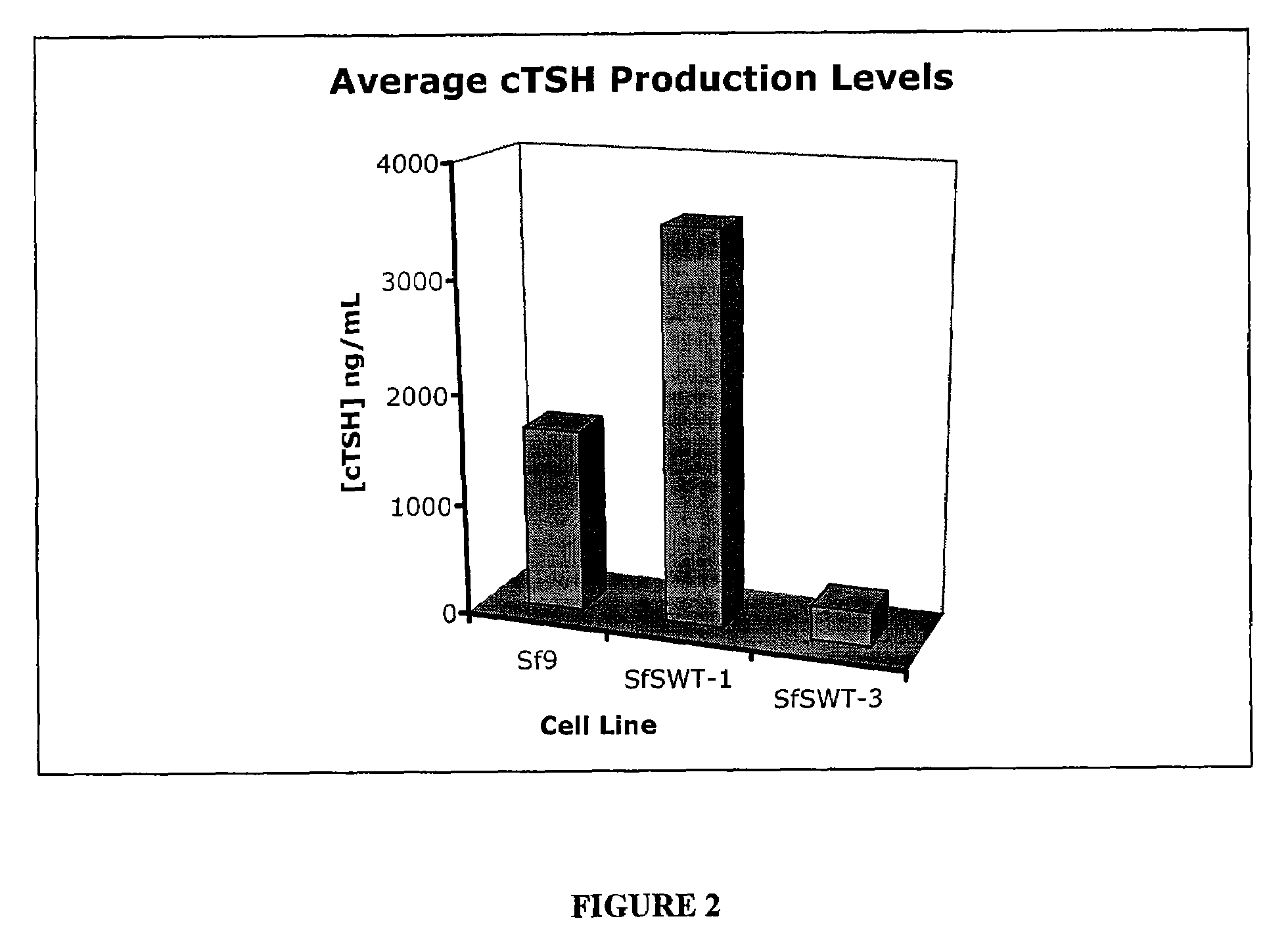
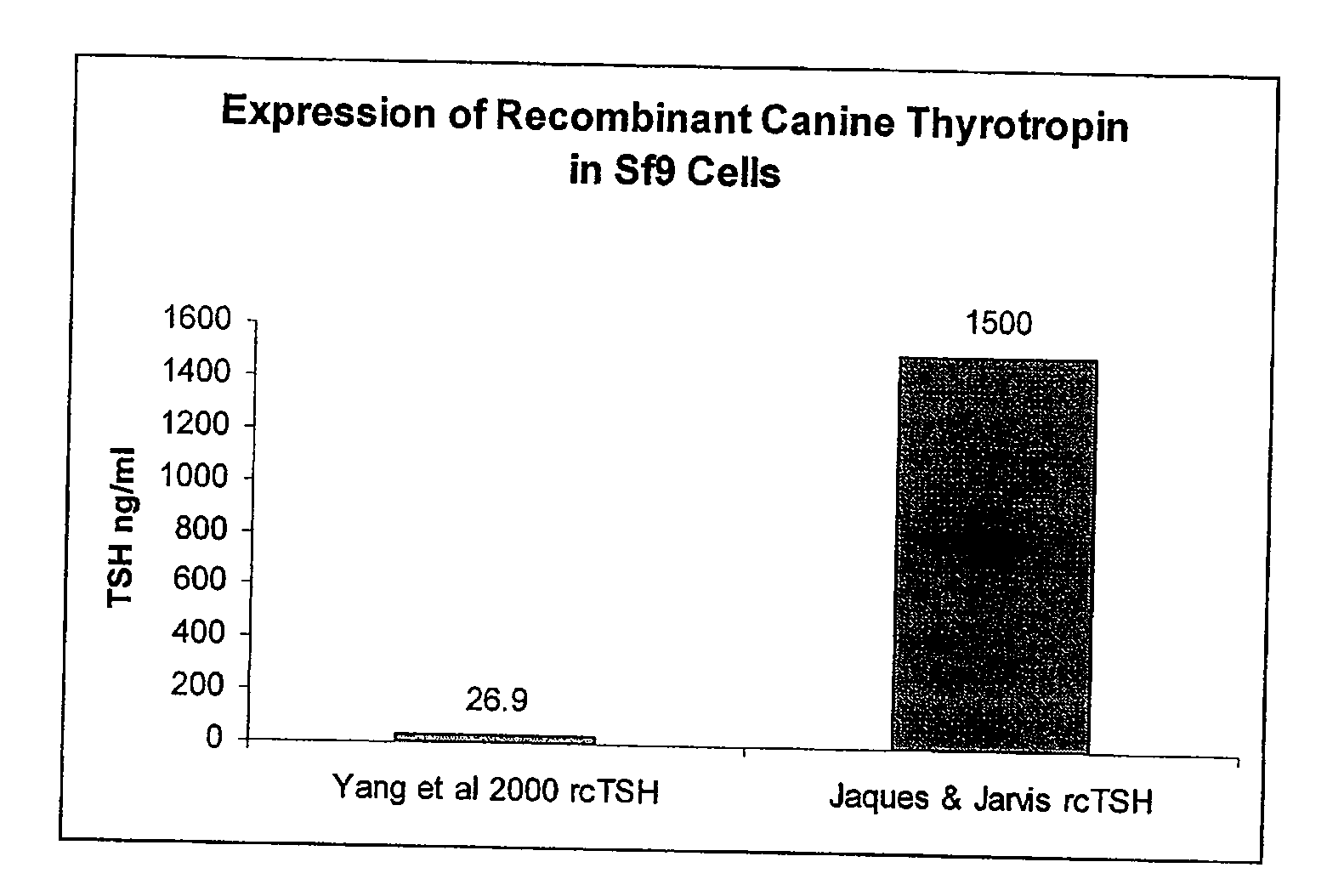
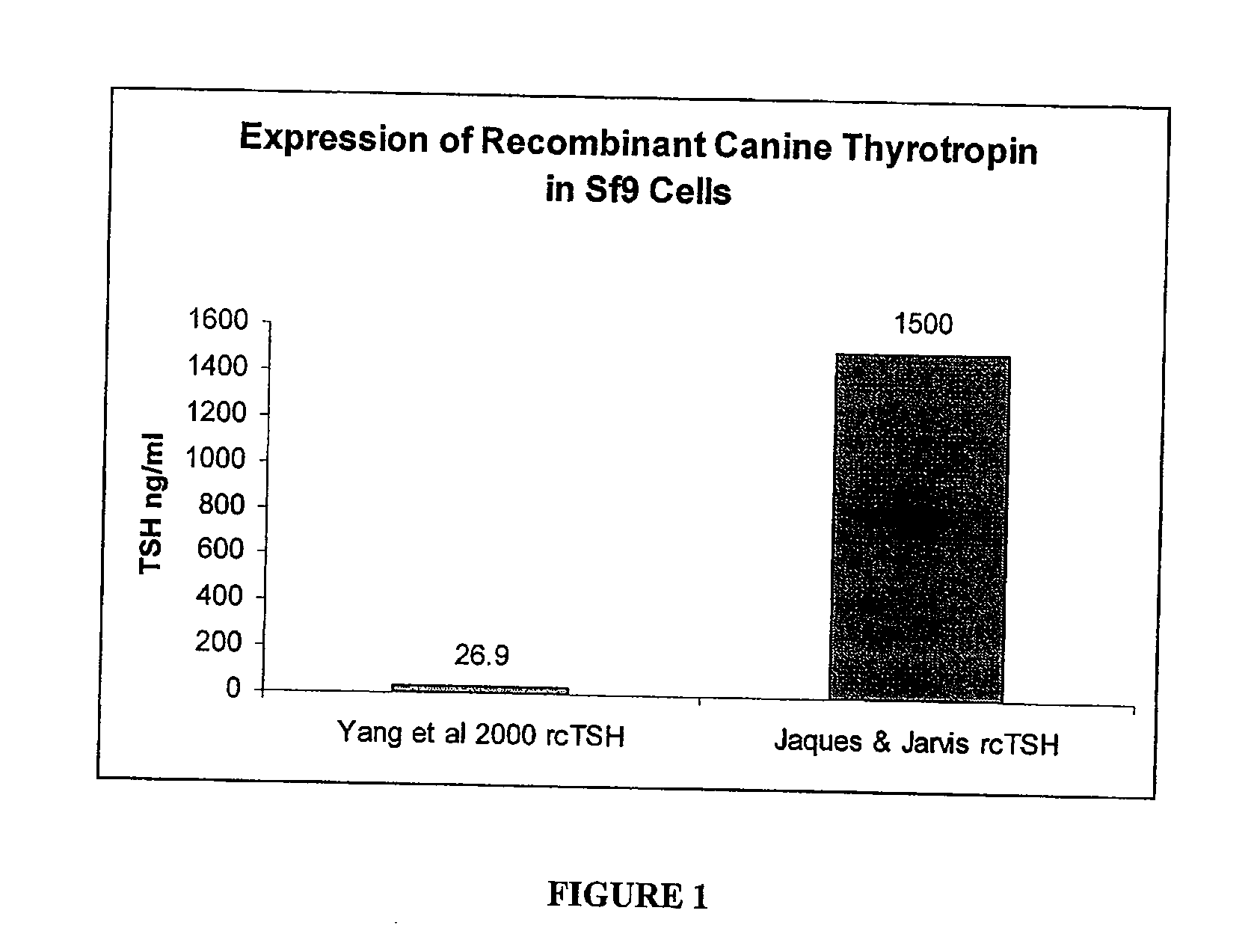
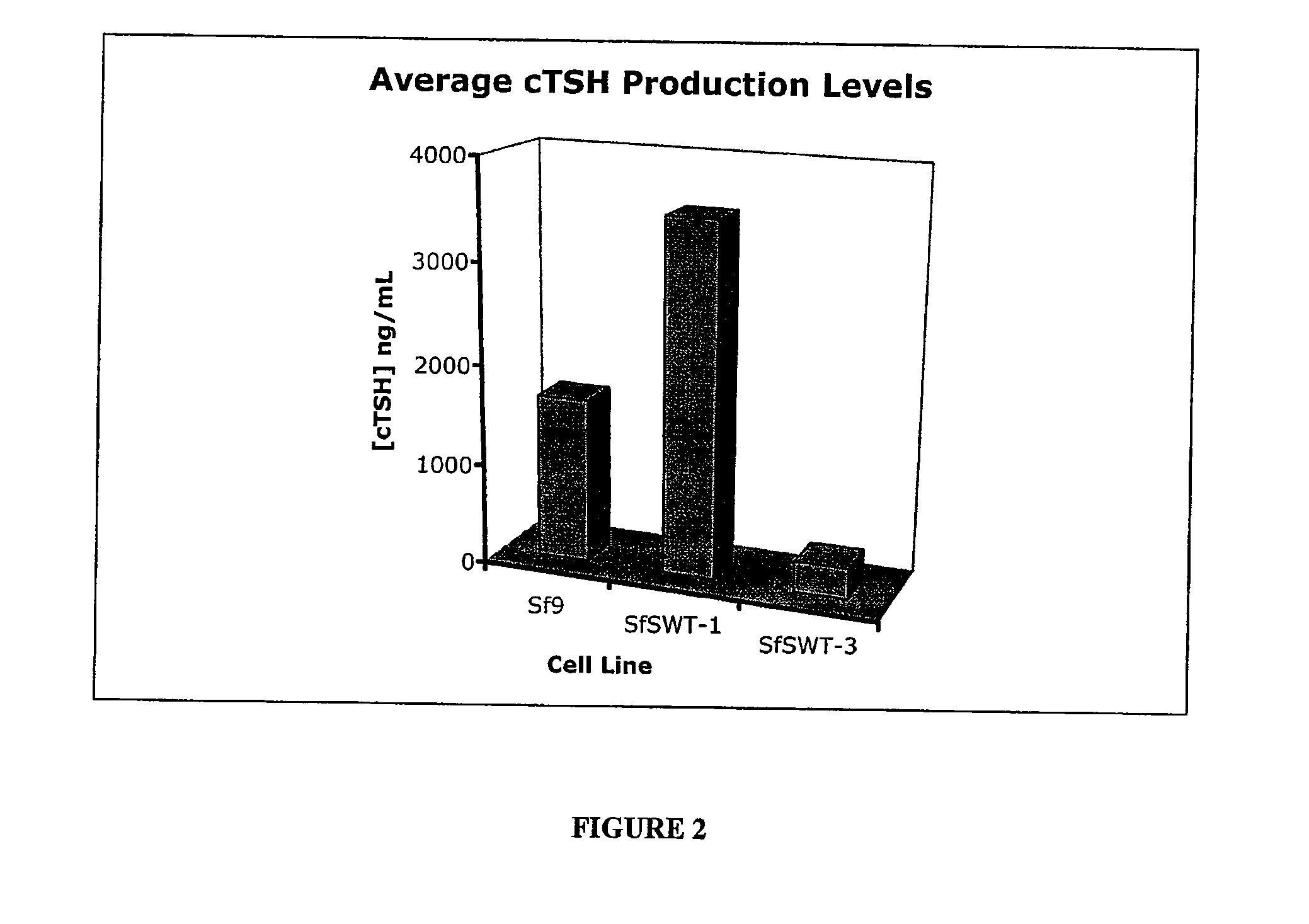
Recombinant canine thyroid stimulating hormone and methods of production and use thereof
The invention includes a nucleic acid having a sequence at least 98% homologous to SEQ ID NO: 1, which encodes the α subunit of canine thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). The invention also includes a nucleic acid having a sequence at least 98% homologous to SEQ ID NO: 2, which encodes the β subunit of canine TSH. The invention also includes a method of producing an recombinant canine thyroid stimulating hormone (rcTSH) subunit by expressing a nucleic acid having a sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 and a nucleic acid having a sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 in a transgenic insect cell modified to sialylate proteins and producing a sialylated rcTSH subunit. The insect cell may be a lepidopteran cell. The rcTSH may be used for diagnosis and treatment. It may be used to diagnose canine hypothyroidism.
Owner:JAQUES JOHN SCOTT T +1
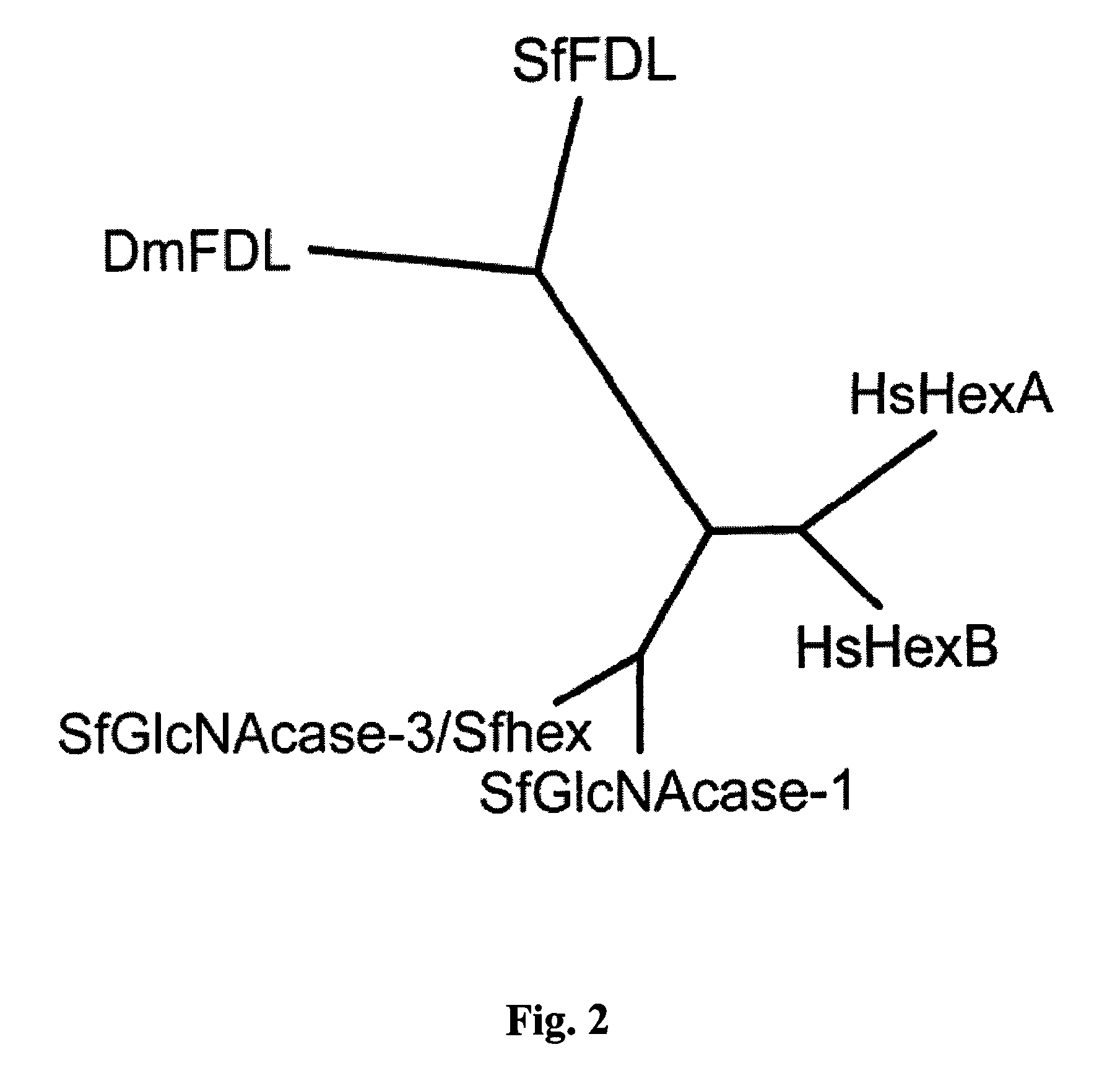
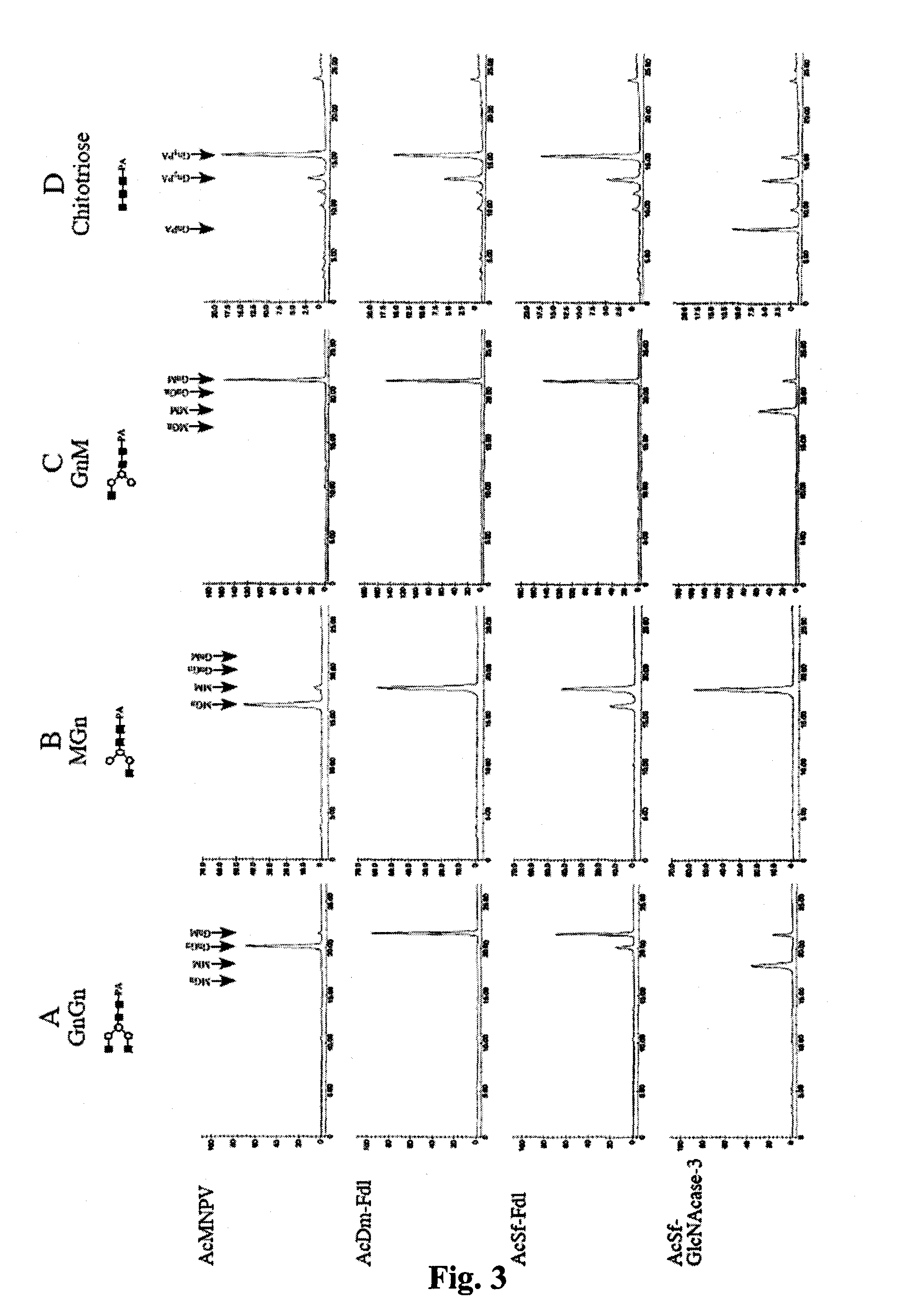
Lepidopteran insect n-acetylglucosaminidase genes and their use in glycoengineering
ActiveUS20100279415A1Solve bulkyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesN acetylglucosaminidaseGenetically modified insect
A transgenic insect cell line for production of elevated levels of recombinant glycoproteins comprising mammalian-like N-glycans is provided. Also disclosed are nucleic acid sequences encoding β-N-acetylglucosaminidases.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Insect ammunition vectors and methods of use to identify pesticide targets
InactiveUS20050229265A1Genetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified insectTransposable element
The present invention provides methods for identifying pesticide targets and pesticidal agents using transposable elements in insects and insect cells lines. The invention provides engineered transposable elements for use in identification of pesticide targets. The invention further provides a biological array, a collection of transgenic insect lines or insect cell lines, the genome of each containing at least one transposable element that mutates one of the insect's genes, such that the complete collection contains a mutation in essentially every gene in the insect's genome.
Owner:EXELIXIS INC
Visuble self-sucking extrinsic gene induction of insect egg
InactiveCN1268754CGenetic stabilityStable expressionOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified insectTransgene
Visual self-sucking method for inducing external gene into insect eggs is carried out by: under telescope, coating solution with external genes on insect eggs, pricking eggs to make external gene into eggs, making external genes combined with insect's gene to form transgenic insects. It makes technicians to do researches on transgenic insects with cheap instrument.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Safety evaluation method of transgenic insect-resistant rice against predatory natural enemy Auranthus praecox
The invention relates to an evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to predator hylyphantes graminicola. The evaluation method is composed of a three-level nutrition test part, a protein transfer rule part, a predation function reaction part and a population density and population dynamics comparison part. The influence of Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on the hylyphantes graminicola is evaluated through the food chain of the hylyphantes graminicola; the way and degree that the hylyphantes graminicola is exposed in Bt proteins are identified through an ELISA detection means; the influence of the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on a non-target organism predation function is evaluated; the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice and non-genetically-modified parent are compared, and the influence on the hylyphantes graminicola population is evaluated; finally, the ecological consequences generated by genetically modified crop cultivation on non-target organisms are evaluated synthetically according to the data of the four parts. The evaluation method is systematic and scientific, and has great significance for the research of the influence of genetically modified crops on the non-target organisms and ecological safety of the genetically modified crop cultivation.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Transgenic insect cell line for high-yield baculovirus, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102807969BMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesGenetically modified insectOvary cell
The invention provides a transgenic insect cell line for high-yield baculovirus, and a preparation method and the application thereof. The name of the transgenic insect cell line is IOZCAS-Spex IX and the preservation number of the cell line is CGMCC No.4506. The preparation method of the transgenic insect cell line comprises the steps as follows: spodoptera exigua ovary cells are cultured; human telomerase reverse transcriptase genes are transformed into known expression vectors to obtain recombinant vectors; the recombinant vectors are introduced into the spodoptera exigua ovary cells; and the spodoptera exigua ovary cells are enabled to express human telomerase reverse transcriptase, so as to obtain the transgenic insect cell line. The transgenic insect cell line is applied to the production of the baculovirus.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production of protein with humanized n-glycosylation in insect cells
PendingUS20220112535A1Reduce and even abolish immunogenicityReduce or even abolish immunogenicity against the antigensInvertebrate cellsEnzymesGenetically modified insectGene Modification
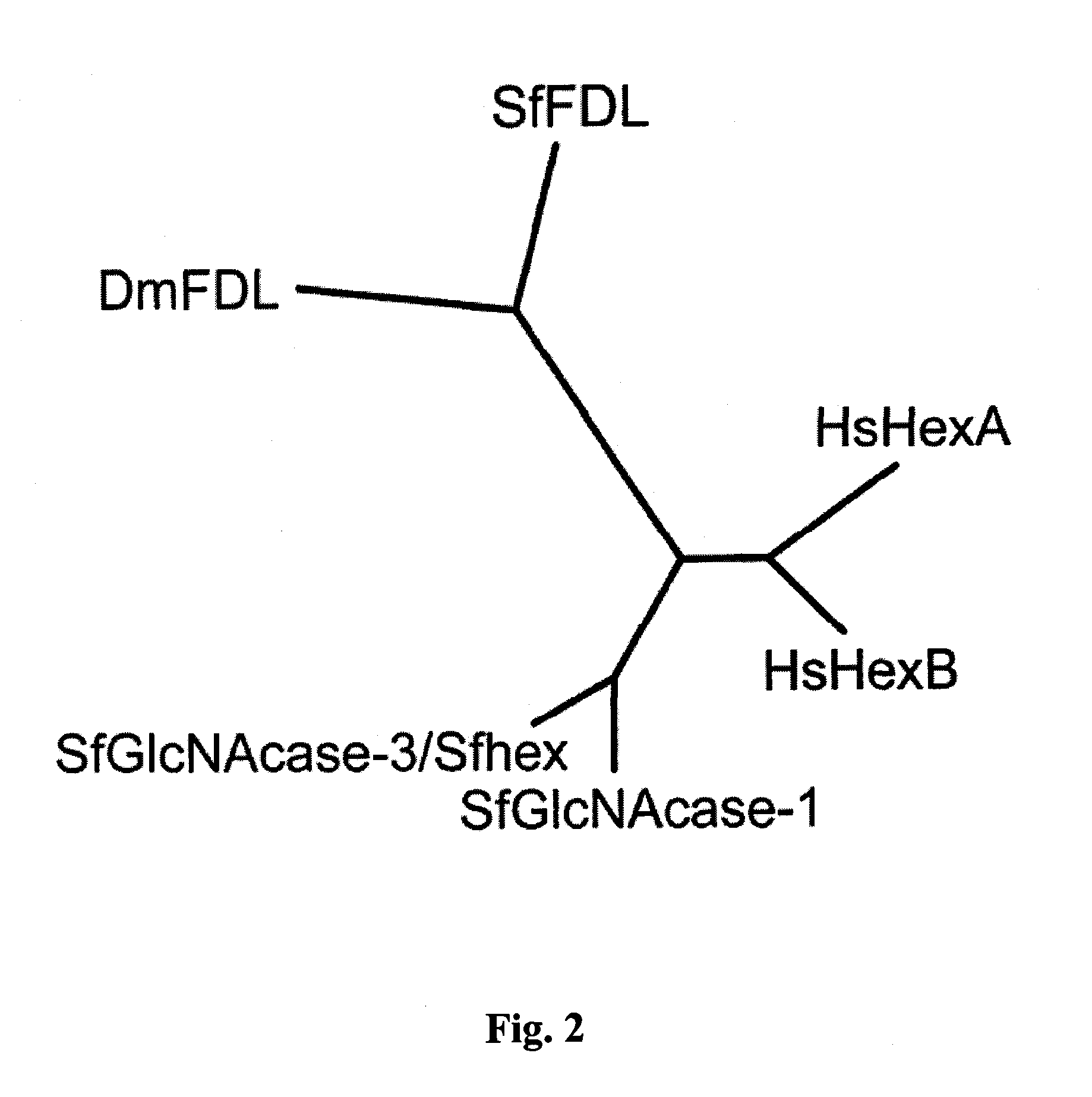
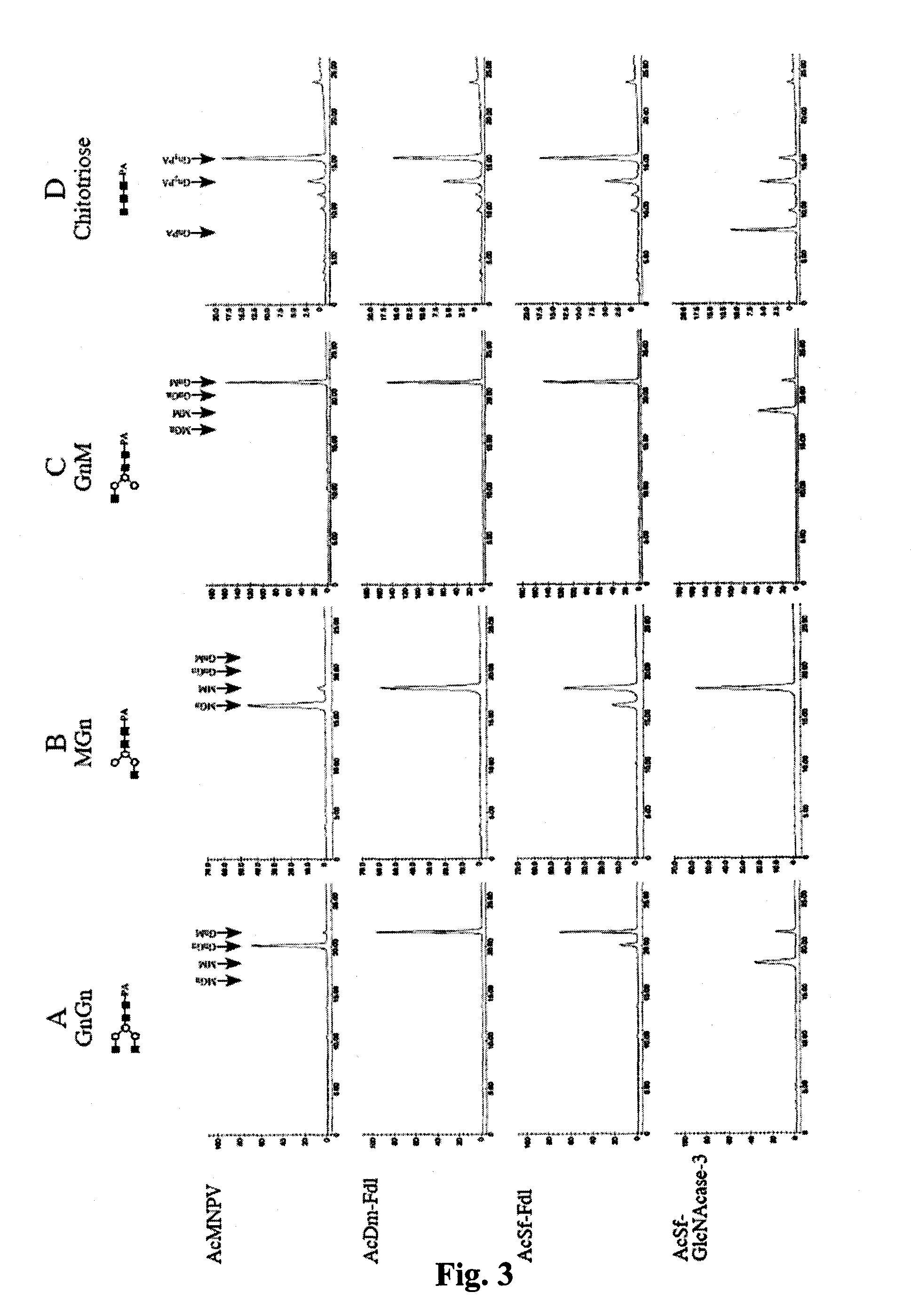
The present disclosure provides genetically modified insect cells that can produce glycosylated expression products having a human-like glycosylation pattern. In particular, the cells comprise disruption of the fdl and / or FucT6 genes. Also provided is expression systems and methods for recombinant protein production.
Owner:EXPRES2ION BIOTECHNOLOGIES APS
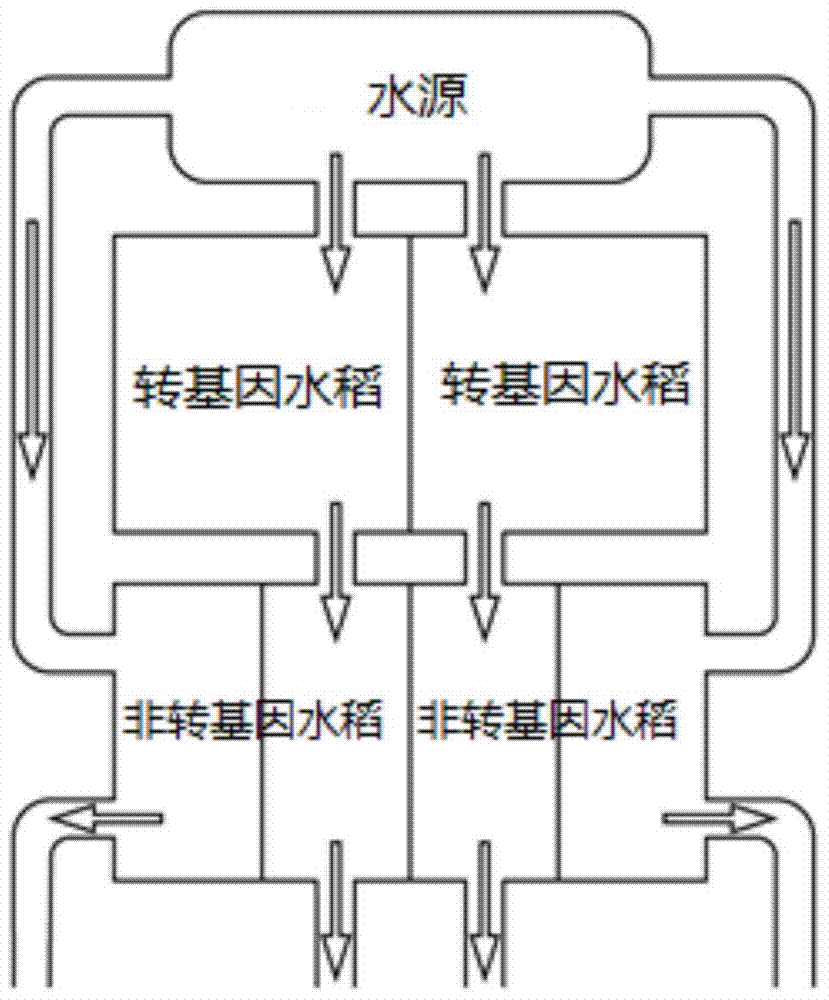
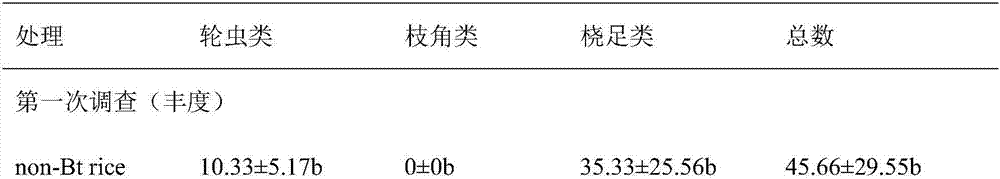
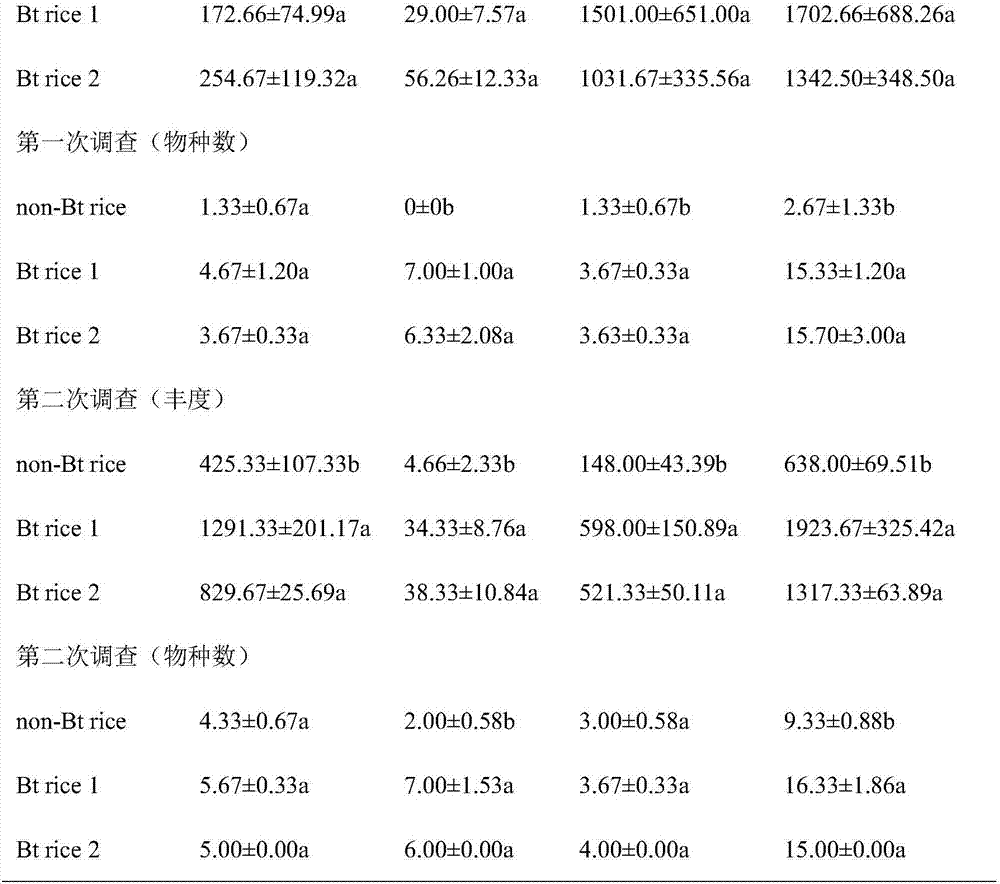
A method for evaluating the safety of the aquatic environment of transgenic insect-resistant rice
ActiveCN104982241BMonitor concentrationMonitor spreadHorticulture methodsGenetically modified insectOrganism
The invention provides a method for evaluating the safety of aquatic environment for genetically modified insect resistant rice. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging and managing genetically modified paddies and non-genetically modified paddies; determining foreign protein in water layers and silt of the paddies, which comprises pretreating samples and extracting and determining the foreign protein; separating plankton in the water layers of the paddies, which comprises collecting water samples and precipitating and separating the plankton; determining the kind and the abundance of the plankton in the water layers of the paddies, which comprises identifying living bodies and counting the number; and planting the genetically modified insect resistant rice and evaluating the safety of the plankton, performing statistical analysis on the kind, the number and the occurrence period of the plankton by using analysis software so as to obtain parameters of a diversity index, a uniformity index and the like, and comparing the parameters with those of conventional paddies so as to evaluate the safety of the aquatic environment for the genetically modified 53 insect resistant rice. The method disclosed by the invention has practical application value for systematically assessing the safety of the aquatic environment for the genetically modified insect resistant rice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Transgenic fat body cell line of high-yield baculovirus and preparation method as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102807968BMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesBiotechnologyGenetically modified insect
The invention provides a transgenic fat body cell line of high-yield baculovirus and a preparation method as well as application thereof. The cell line which is named as IOZCAS-Spex X has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 4505; and the preparation method of the transgenic fat body cell line comprises following steps of: culturing asparagus caterpillar fat body cells; transforming genes containing human telomerase reverse transeriptase into a known expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector; leading the recombinant expression vector into the asparagus caterpillar fat body cells; and enabling the asparagus caterpillar fat body cells to express human telomerase reverse transeriptase so as to obtain the transgenic fat body cell line. In addition, the invention discloses application of the transgenic fat body cell line to production of baculovirus.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Insect site-directed gene knock-in composition and method and application thereof
ActiveCN105315352BImprove the efficiency of homologous recombinationDepsipeptidesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetically modified insect
The invention provides a composition used in insect targeted gene knock-in, which includes a single nickase or an encoding polynucleotide thereof; a recombinant factor or an encoding polynucleotide thereof; and optionally, a donor DNA of an exogenous gene. The invention also provides a corresponding gene knock-in method and a method for preparing transgenic insects. The composition and the method in the invention can achieve high-effective homologous recombination integration in insect cells and meanwhile can avoid the defects in gene knock-in technologies in the prior art. The composition also can stably and high-effectively achieve homologous recombination integration of a fragment being more than 10 kb in length in the insect cells, so that the composition can be used for transferring a genetic selection marker into the insect cells, preferably a visible genetic selection marker, which is convenient to determine strains of transgenic insects.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
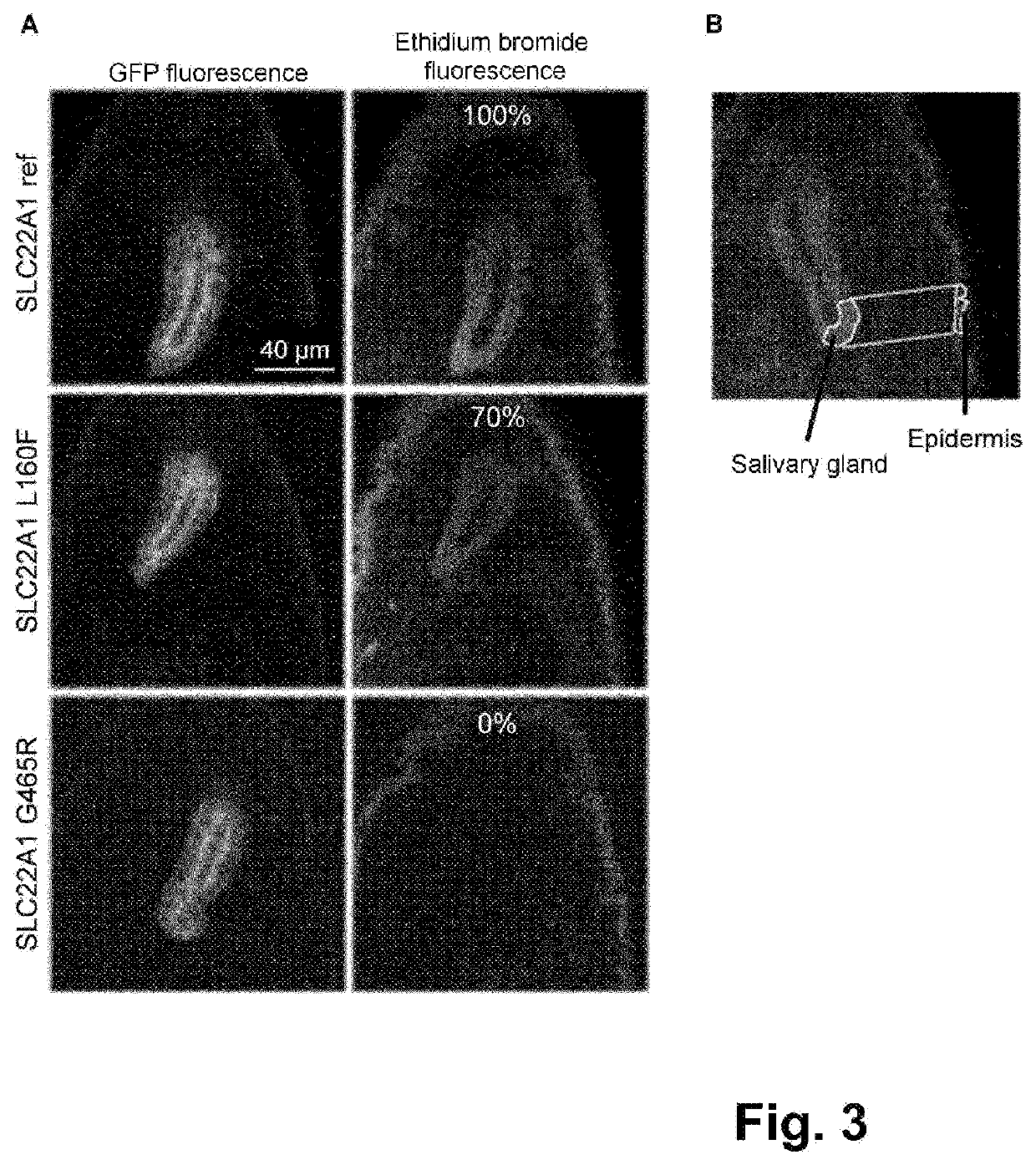
Transgenic Insect and Use of Same in Methods for Testing Natural or Synthetic Substances
InactiveUS20200260700A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAnimal husbandryBiotechnologyMembrane Transporters
A transgenic insect includes a genome which has at least one first exogenic DNA sequence, which is coded for a human membrane transporter protein. The expression of the first exogenic DNA sequence leads to a functional human membrane transporter protein in the transgenic insect.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH FUR MEDIZINISCHE FORSCHUNG MBH +1
Lepidopteran insect N-acetylglucosaminidase genes and their use in glycoengineering
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
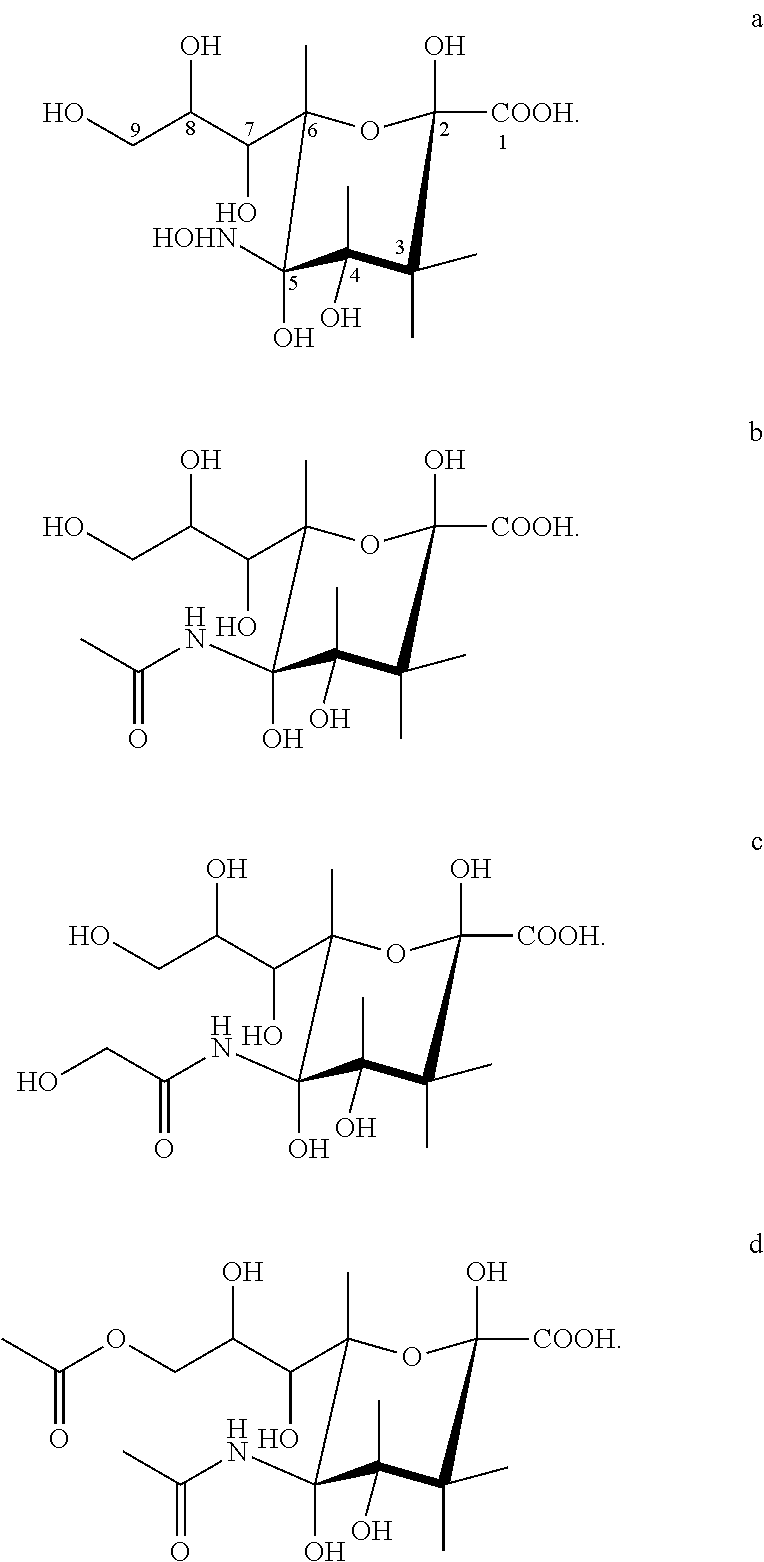
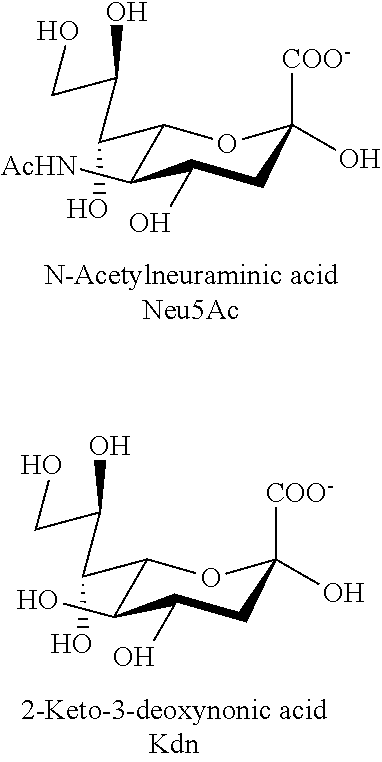
Transgenic insect cells comprising a bacterial glcnac-6-p 2prime-epimerase
The present invention relates to methods of facilitating the expression of recombinant polypeptides from cells, extracellular fluids, extracellular fibers, or any combination thereof, obtained from transgenic insect cells and larvae comprising a bacterial GlcNAc-6-P 2′-epimerase (GNPE), which is capable of converting N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcNAc-6-P) to N-acetyl-D-mannosamine-6-phosphate (ManNAc-6-P). The invention relates to methods to promote efficient glycoconjugate sialylation, by providing simpler ways to produce large intracellular pools of sialic acid precursors. The invention is also directed to nucleic acids, vectors, and cells comprising nucleic acids encoding polypeptides involved in the synthesis of sialic acid precursors, and cells in combination with nucleic acids encoding glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferases, to facilitate the production of humanized recombinant glycoproteins. The engineered cells can be used to produce glycosylated proteins lepidopteran insects and cultured cell lines derived from Spodoptera frugiperda, Trichoplusia ni, and silkworms, such as Bombyx mori, particularly those that can be infected by baculovirus expression vectors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Recombinant canine thyroid stimulating hormone and methods of production and use thereof
The invention includes a nucleic acid having a sequence at least 98% homologous to SEQ ID NO: 1, which encodes the α subunit of canine thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). The invention also includes a nucleic acid having a sequence at least 98% homologous to SEQ ID NO: 2, which encodes the β subunit of canine TSH. The invention also includes a method of producing a recombinant canine thyroid stimulating hormone (rcTSH) subunit by expressing a nucleic acid having a sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 and a nucleic acid having a sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 in a transgenic insect cell modified to sialylate proteins and producing a sialylated rcTSH subunit. The insect cell may be a lepidopteran cell. The rcTSH may be used for diagnosis and treatment. It may be used to diagnose canine hypothyroidism.
Owner:JAQUES JOHN SCOTT T +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com