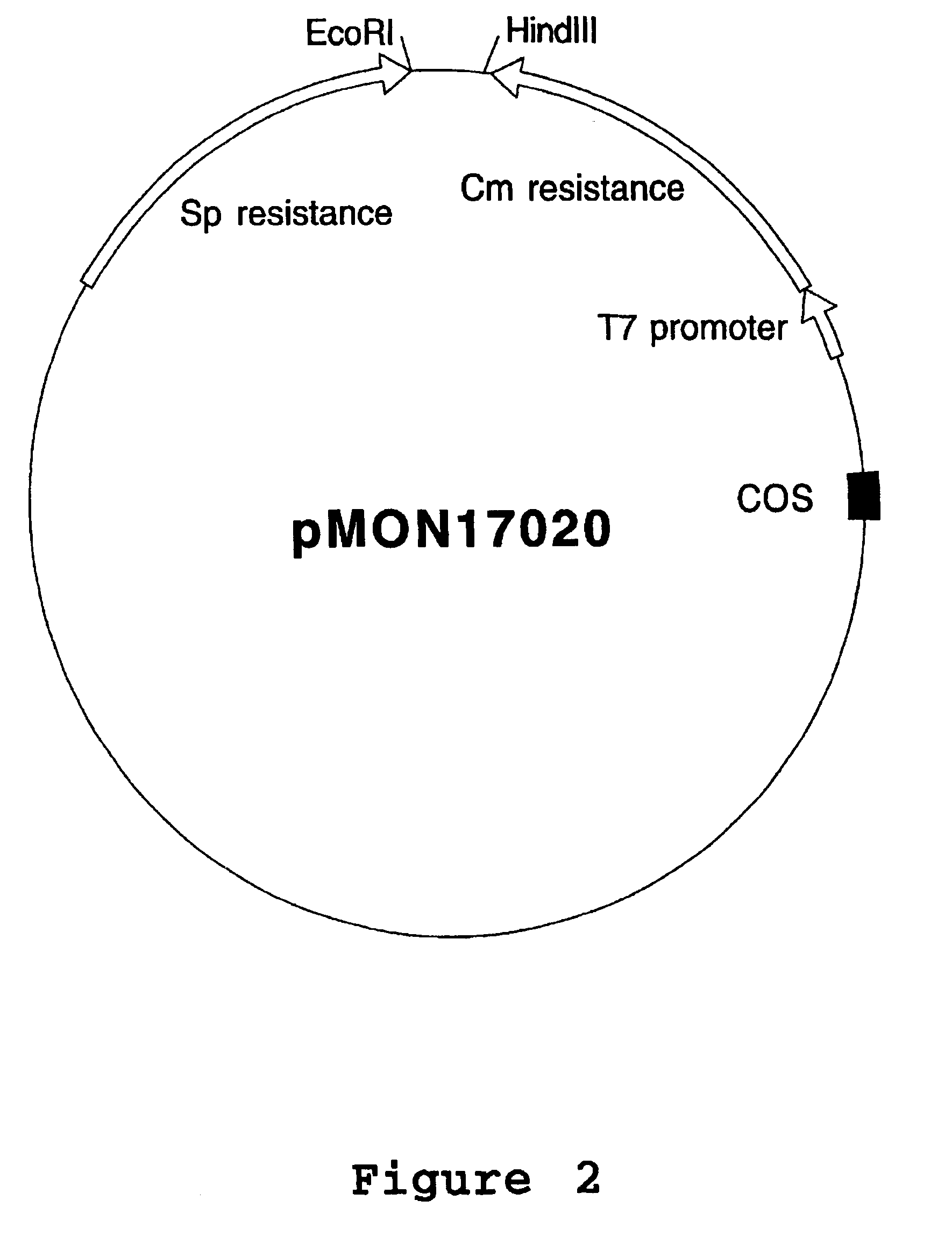
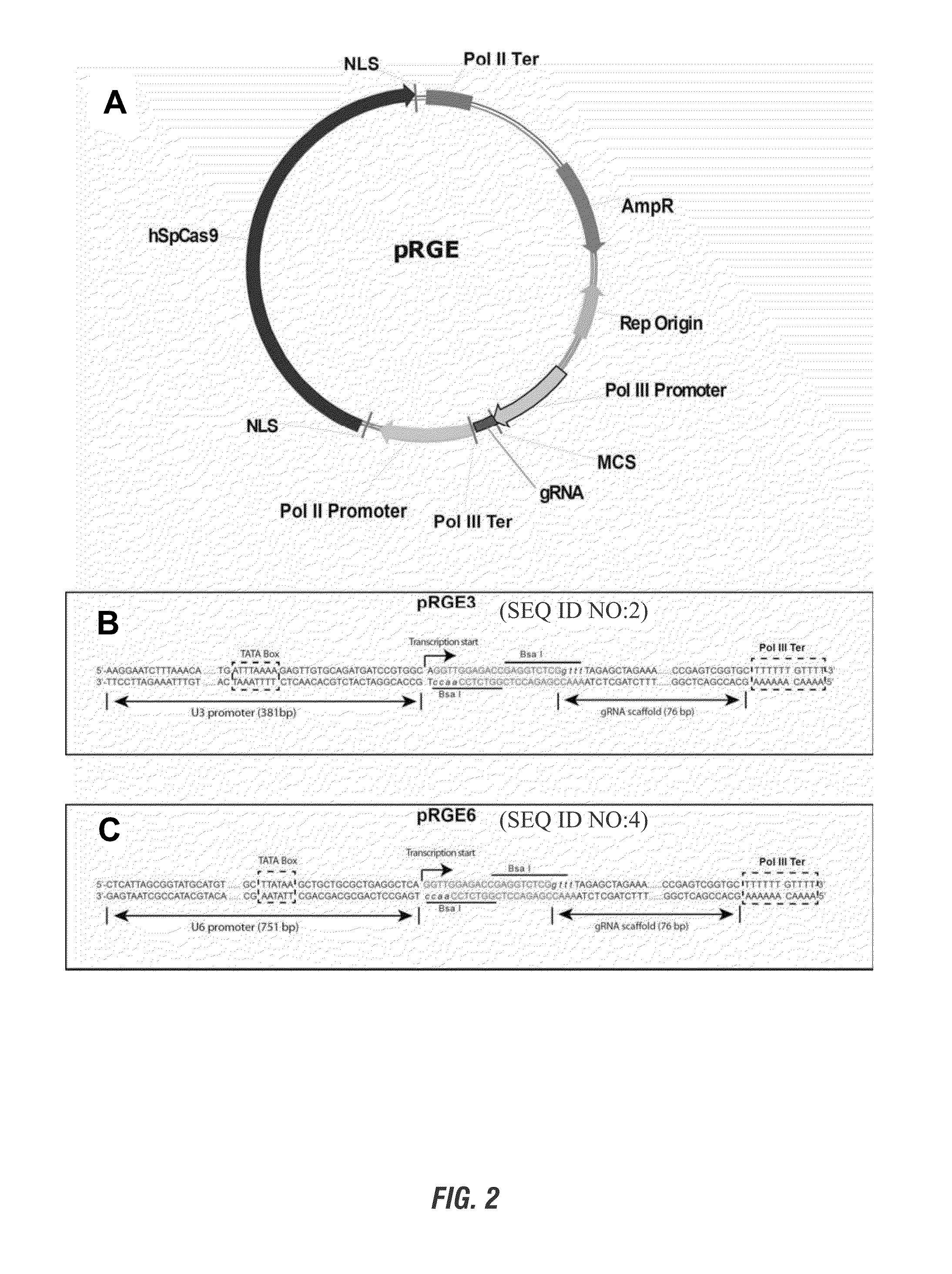
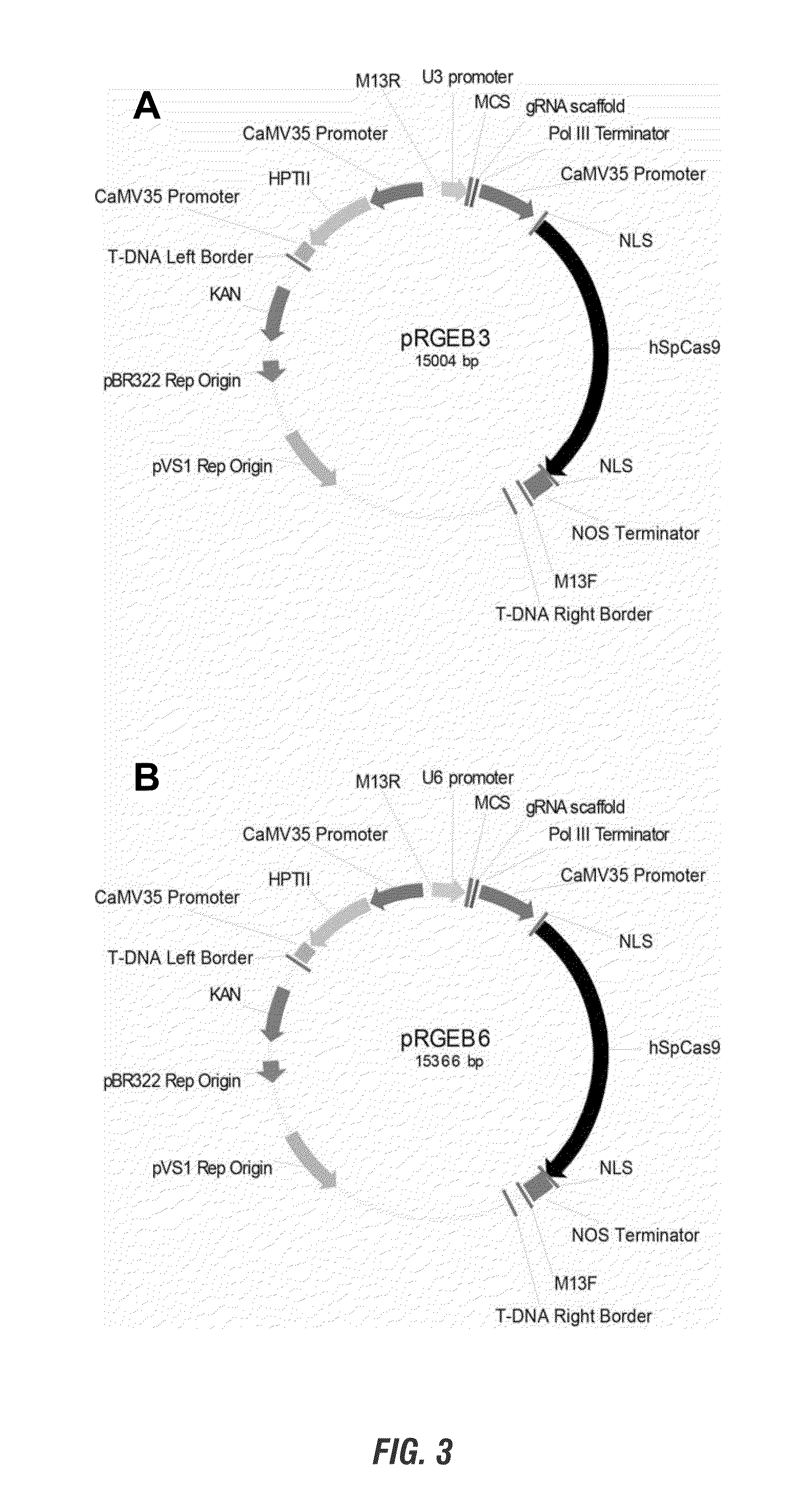
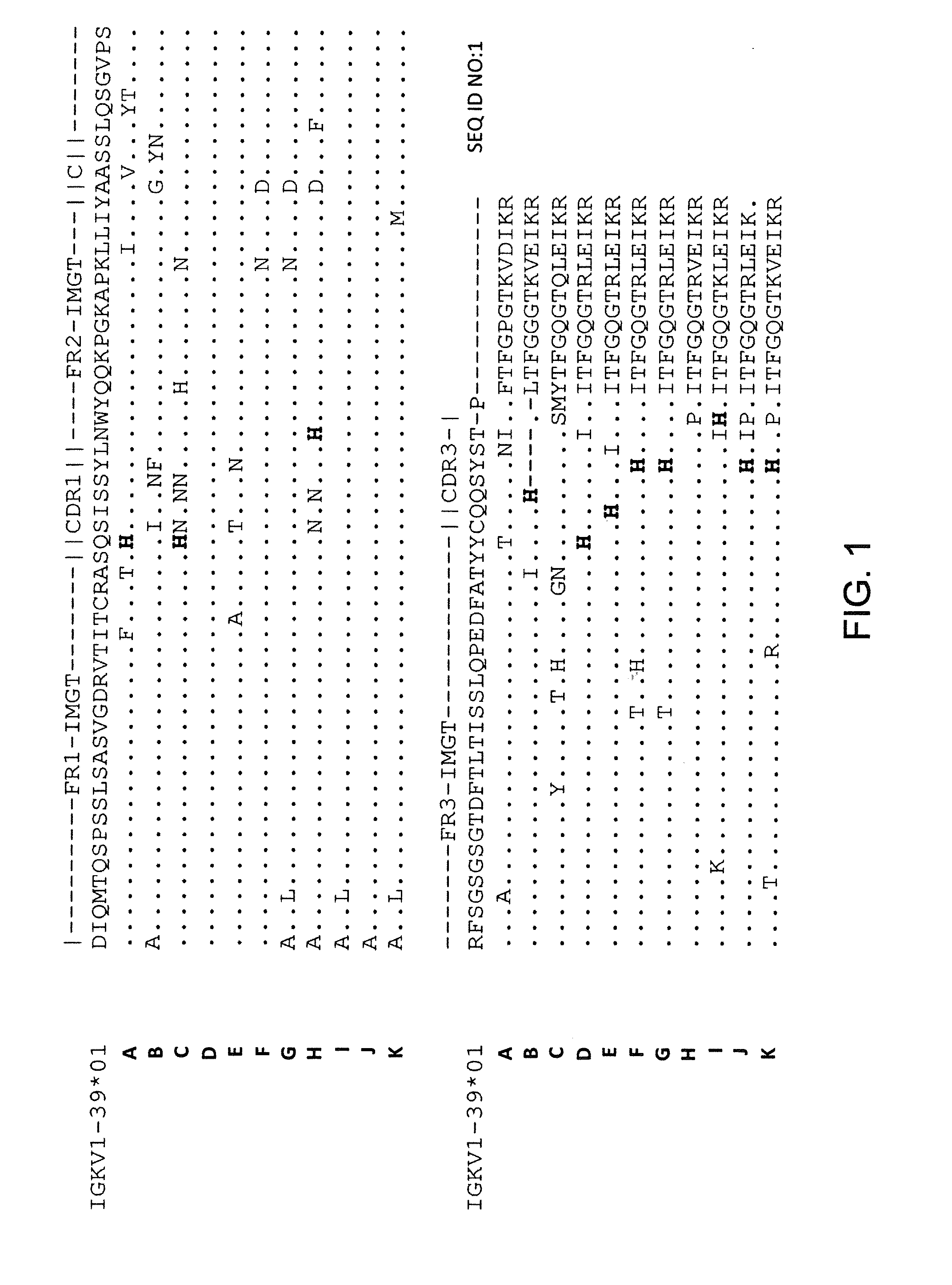
Patents
Literature
342 results about "Genetically modified crops" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. In most cases, the aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. Examples in food crops include resistance to certain pests, diseases, environmental conditions, reduction of spoilage, resistance to chemical treatments (e.g. resistance to a herbicide), or improving the nutrient profile of the crop. Examples in non-food crops include production of pharmaceutical agents, biofuels, and other industrially useful goods, as well as for bioremediation.
Method of controlling weeds in transgenic crops
The invention relates to a method for the control of weeds at a crop locus, said method comprising the application of an effective amount of: (a) a glyphosate herbicide which is glyphosate or a derivative thereof; and (b) at least one HPPD-inhibiting herbicide; wherein the crop is tolerant to glyphosate and optionally the HPPD-inhibiting herbicide.
Owner:BAYER SAS
Glyphosate-tolerant 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthases
InactiveUSRE39247E1Reduce amount of overproductionGlyphosate toleranceSugar derivativesTransferasesPhosphateGenetically modified crops
Genes encoding Class II EPSPS enzymes are disclosed. The genes are useful in producing transformed bacteria and plants which are tolerant to glyphosate herbicide. Class II EPSPS genes share little homology with known, Class I EPSPS genes, and do not hybridize to probes from Class I EPSPS's. The Class II EPSPS enzymes are characterized by being more kinetically efficient than Class I EPSPS's in the presence of glyphosate. Plants transformed with Class II EPSPS genes are also disclosed as well as a method for selectively controlling weeds in a planted transgenic crop field.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Gene targeting and genetic modification of plants via rna-guided genome editing
InactiveUS20150067922A1Improve stateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenome editingGenetically modified crops
The present invention provides compositions and methods for specific gene targeting and precise editing of DNA sequences in plant genomes using the CRISPR (cluster regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) associated nuclease. Non-transgenic, genetically modified crops can be produced using these compositions and methods.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
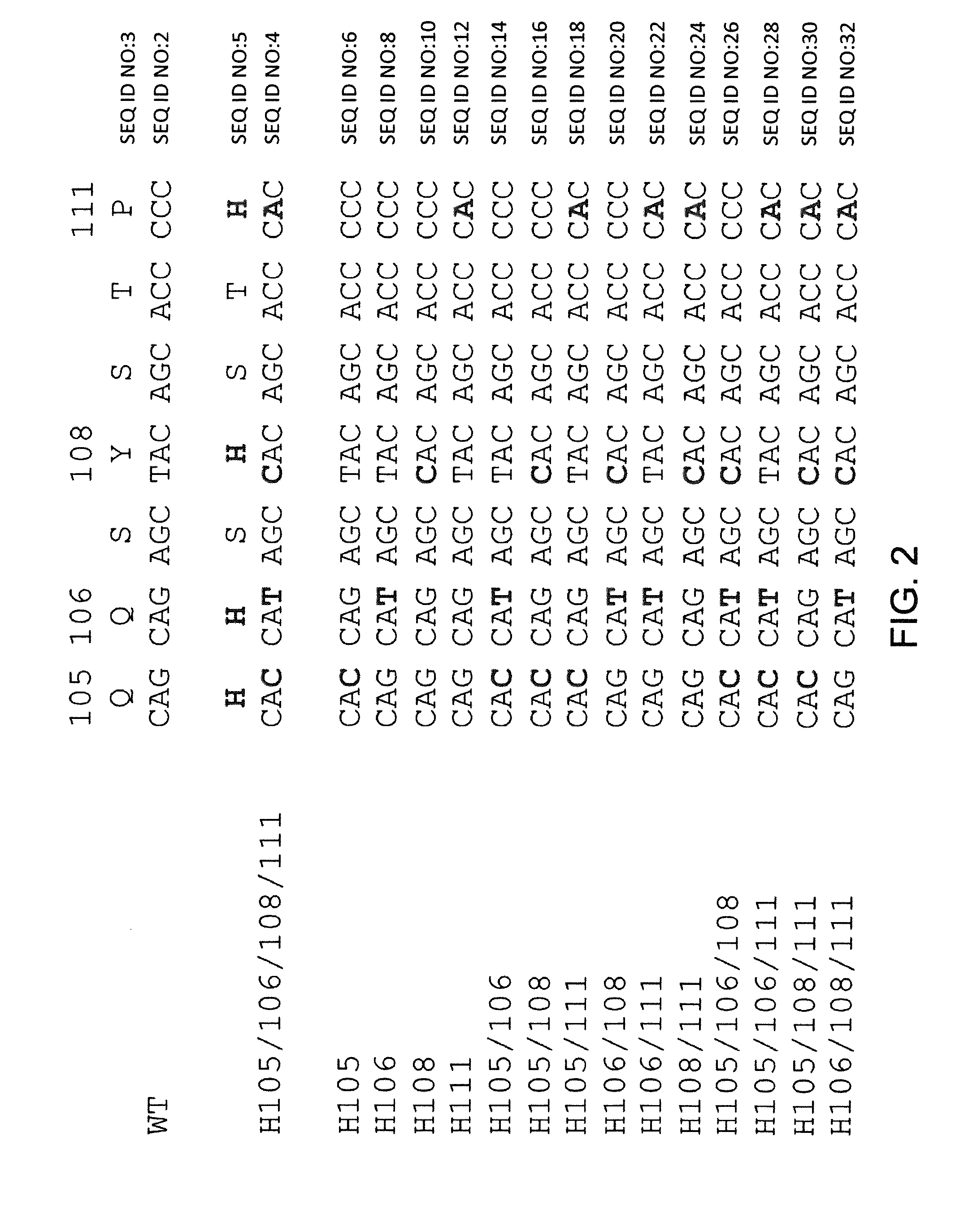
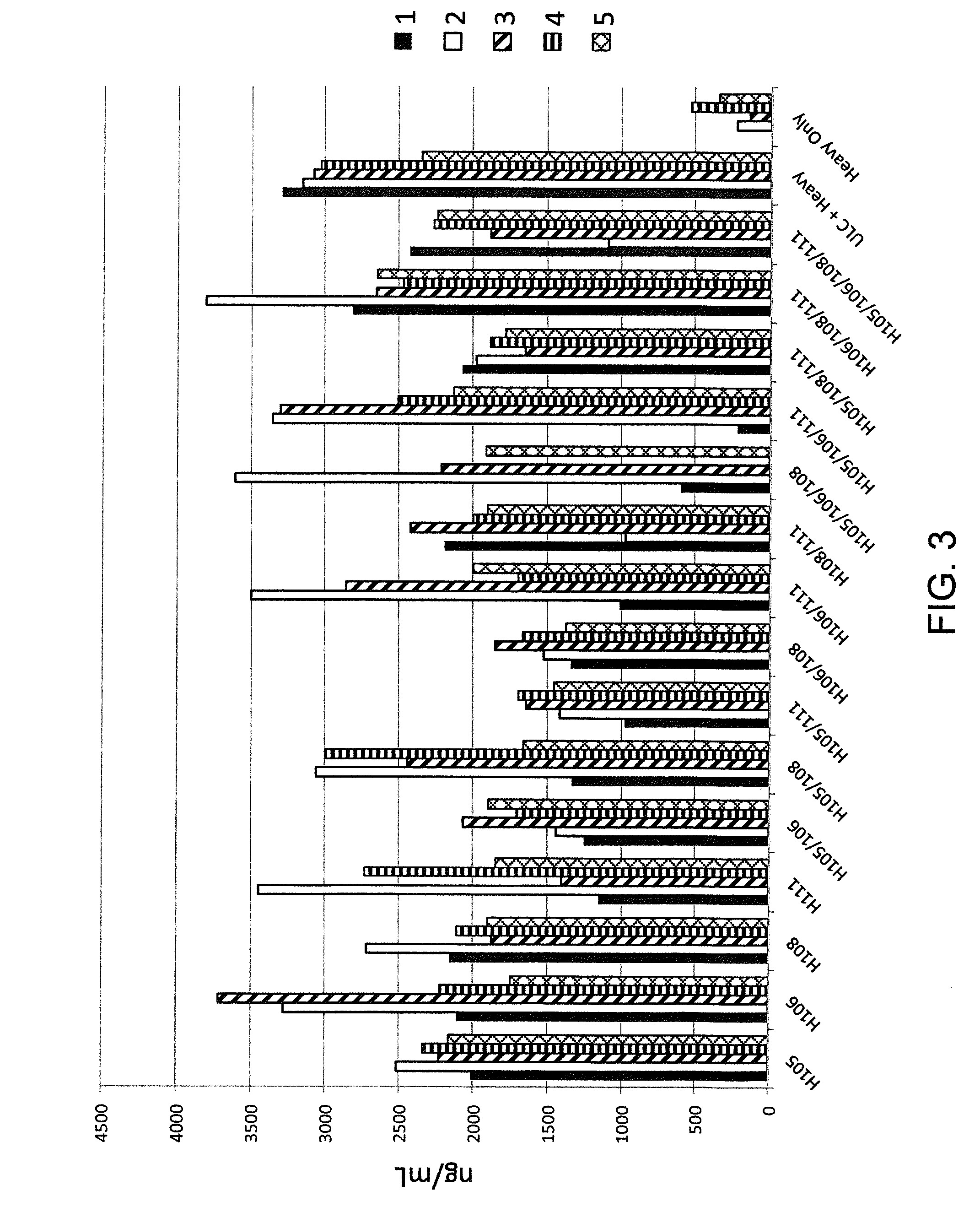
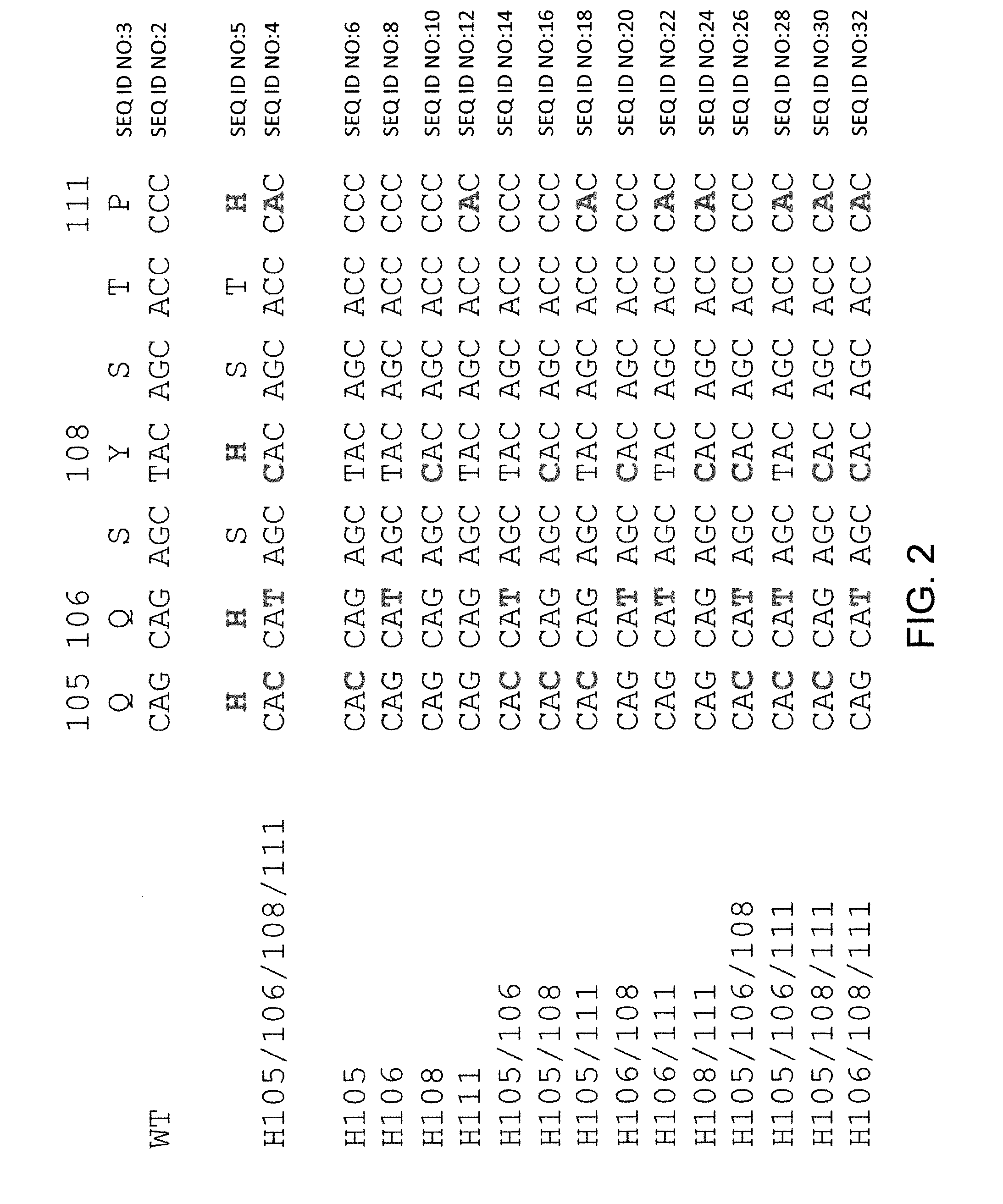
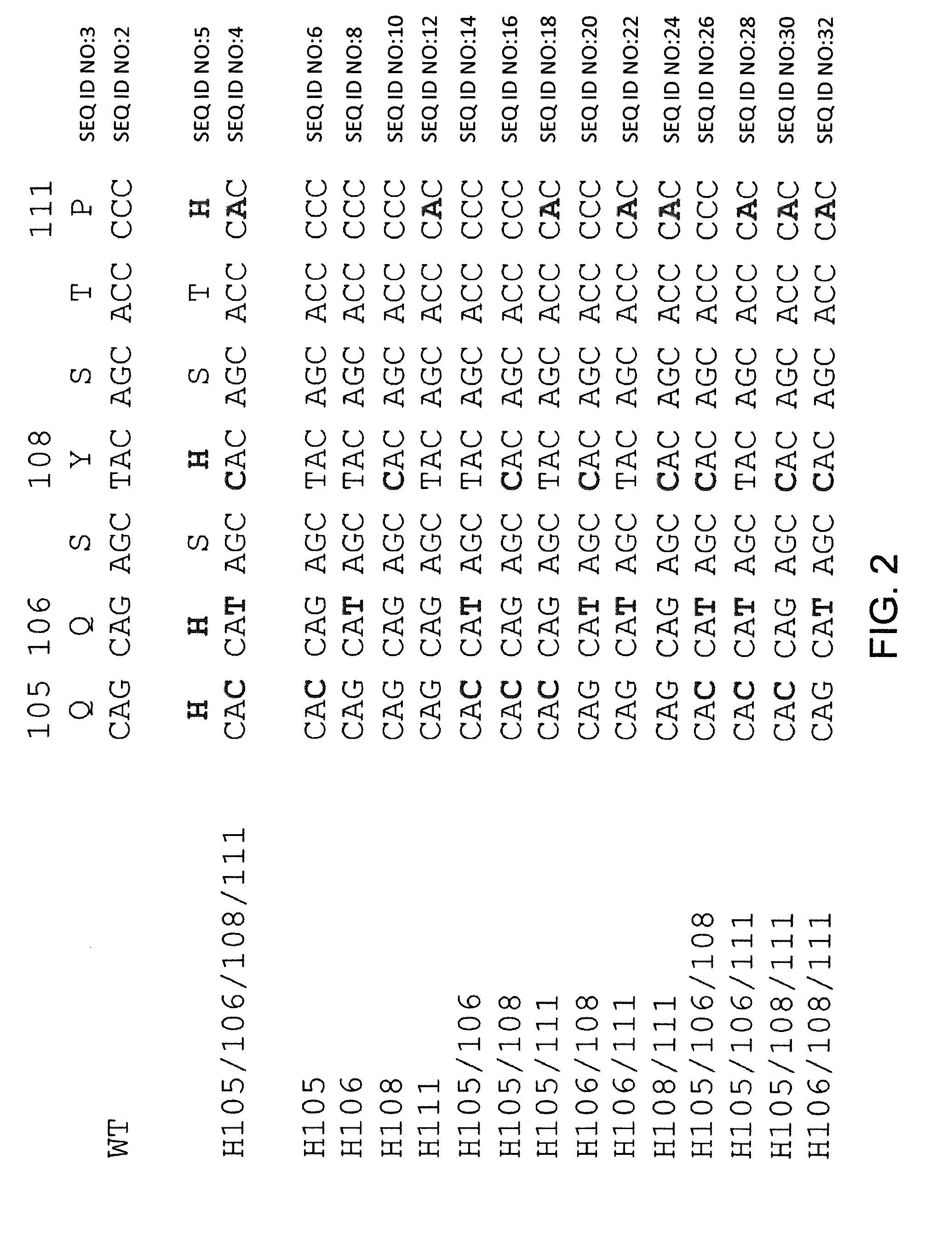
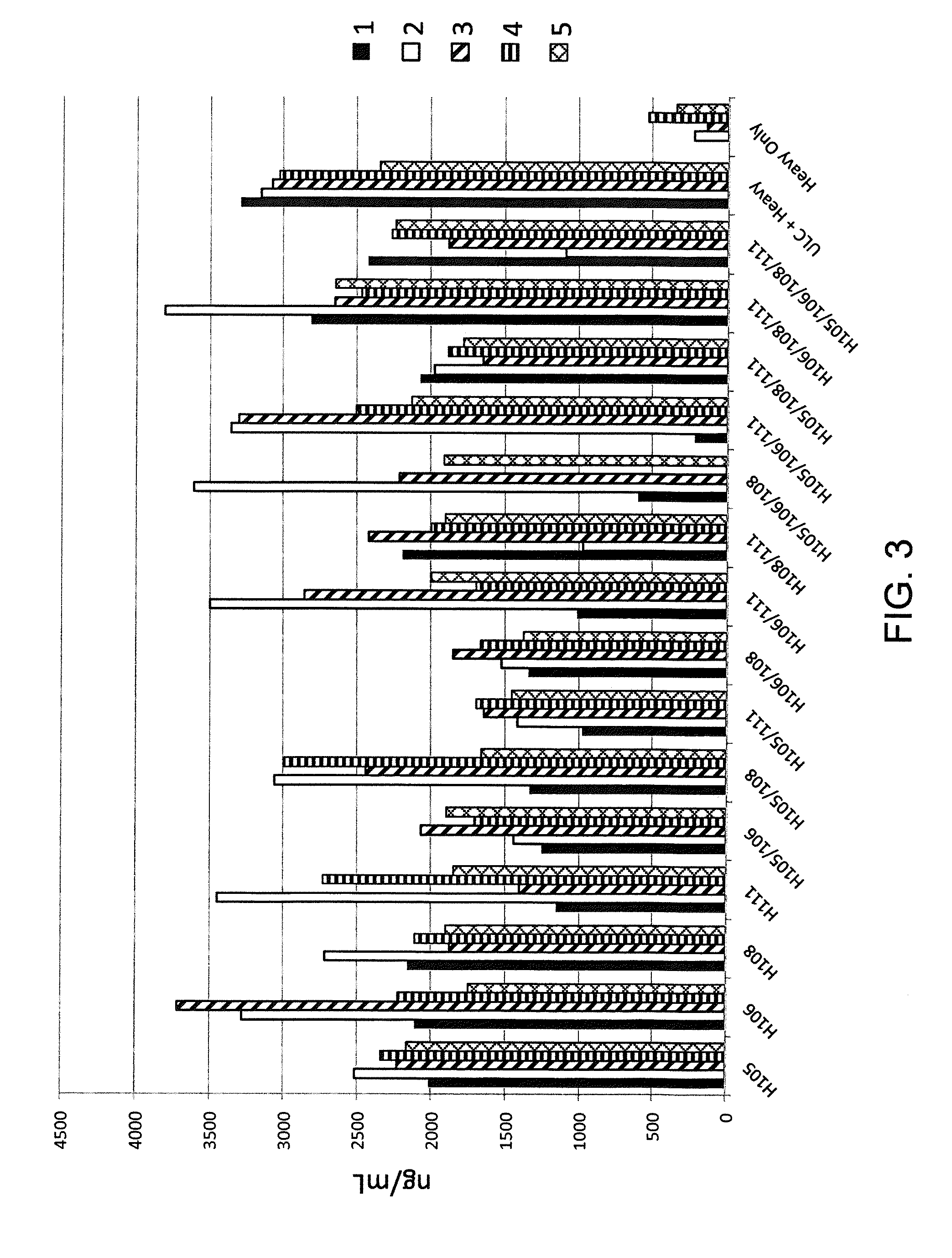
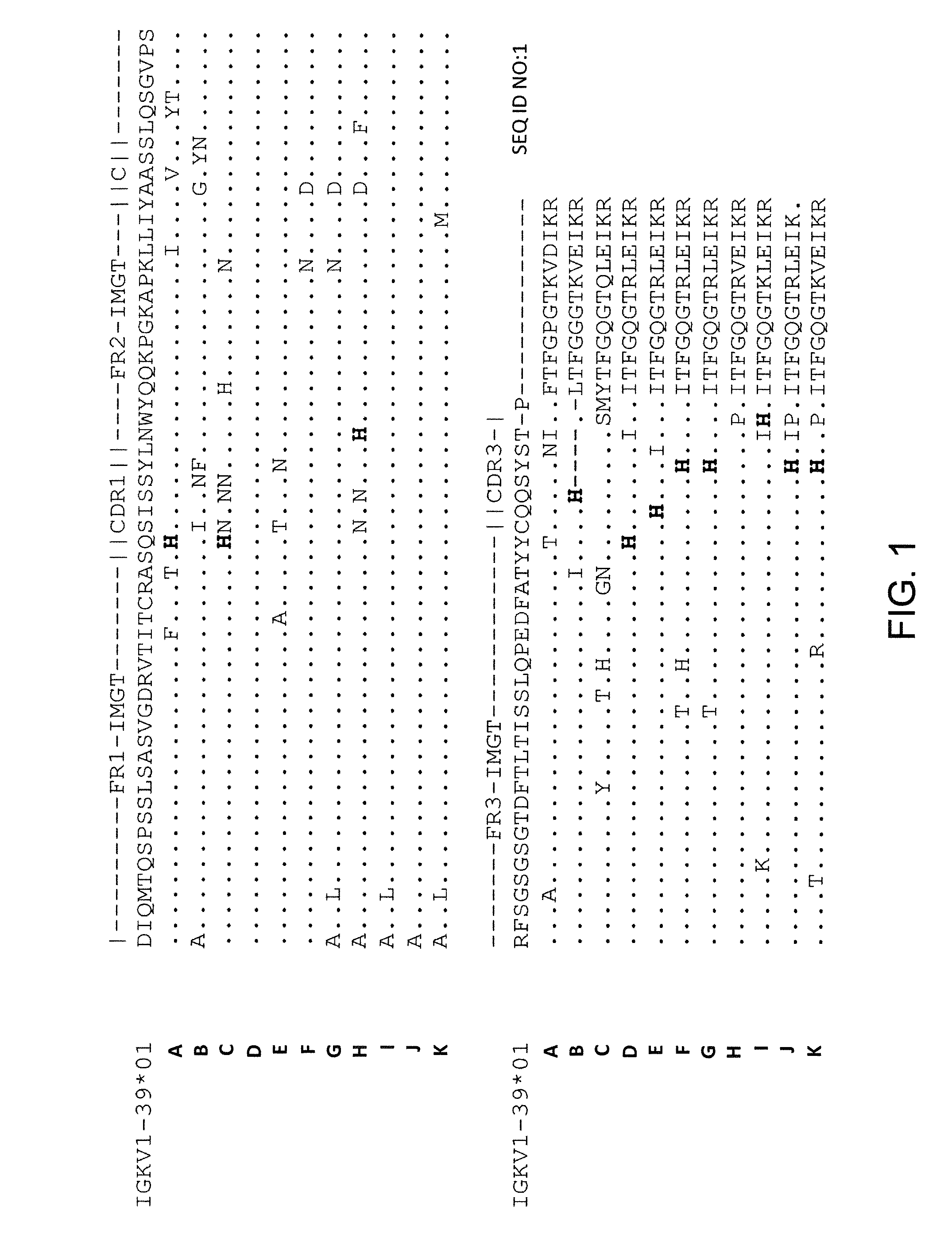
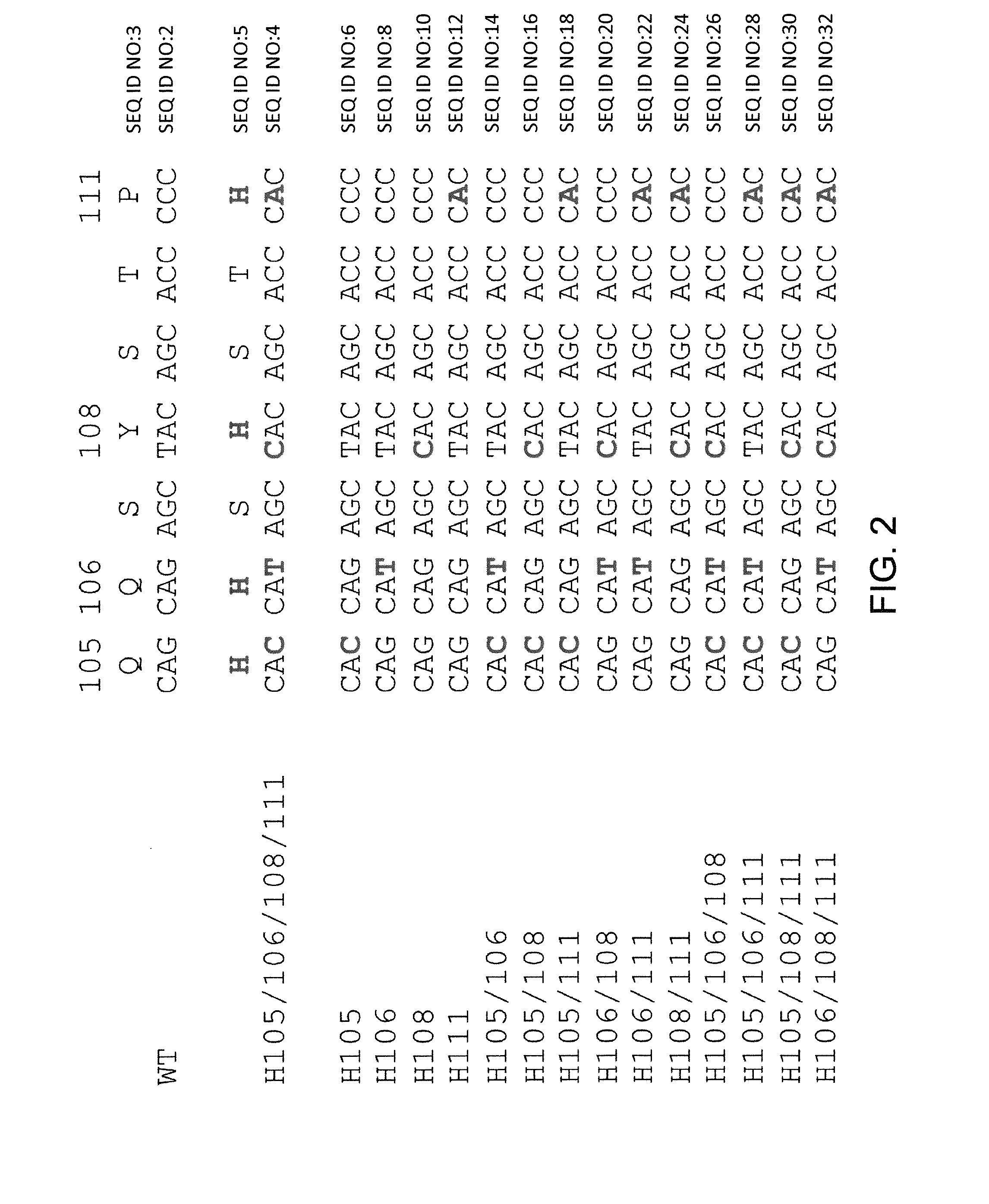
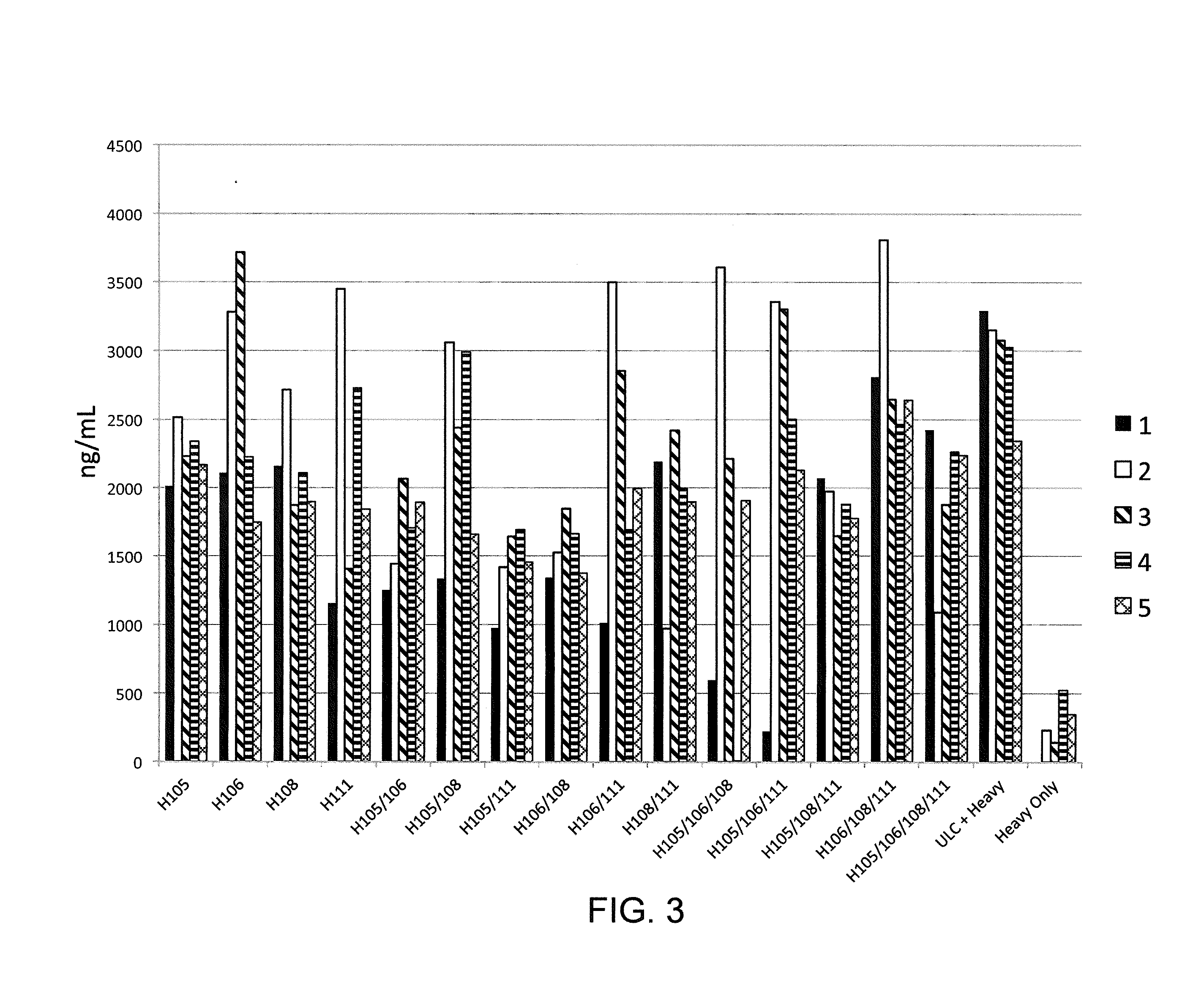
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
InactiveUS20140013456A1Reduce the binding forceNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsNucleotideGenetically modified crops
A genetically modified non-human animal is provided, wherein the non-human animal expresses an antibody repertoire capable of pH dependent binding to antigens upon immunization. A genetically modified non-human animal is provided that expresses human immunoglobulin light chain variable domains derived from a limited repertoire of human immunoglobulin light chain variable gene segments that comprise histidine modifications in their germline sequence. Methods of making non-human animals that express antibodies comprising histidine residues encoded by histidine codons introduced into immunoglobulin light chain nucleotide sequences are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
ActiveUS20130247234A1Reduce the binding forceImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsHuman animalVariable domain
A genetically modified non-human animal is provided, wherein the non-human animal expresses an antibody repertoire capable of pH dependent binding to antigens upon immunization. A genetically modified non-human animal is provided that expresses a single light chain variable domain derived from a single rearranged light chain variable region gene in the germline of the non-human animal, wherein the single rearranged light chain variable region gene comprises a substitution of at least one non-histidine encoding codon with a histidine encoding codon. Methods of making non-human animals that express antibodies comprising a histidine-containing universal light chain are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Zoophobous fusion protein and use thereof
ActiveCN1818067ABroad insecticidal spectrumHigh insecticidal rateFermentationHybrid peptidesOpen reading frameNucleotide
The invention opened an antiworm fusion gene which includes the nucleotides sequence with encoding the BT crystalline toxin and the Vip3 toxin from 5'-3'. The two sequences are in the same open reading frame. The BT crystalline toxin is the whole long or the active toxin without C end. The invention also opened the use of the fusion gene in the antiworm plants.
Owner:沈志成
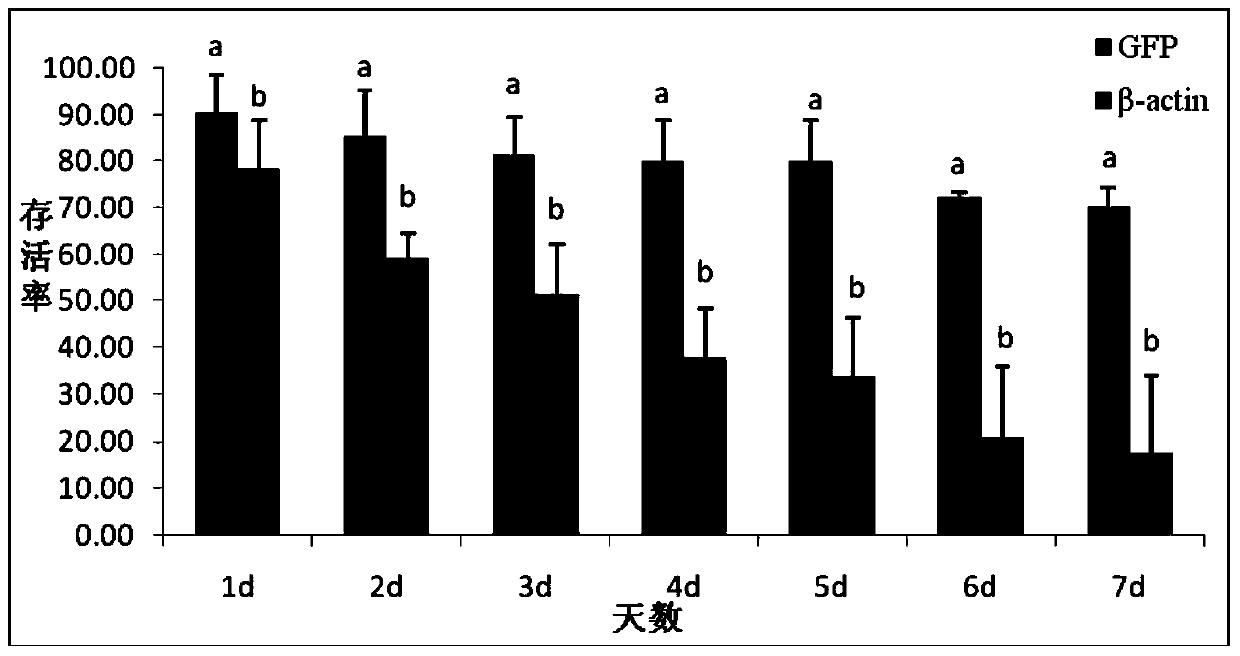
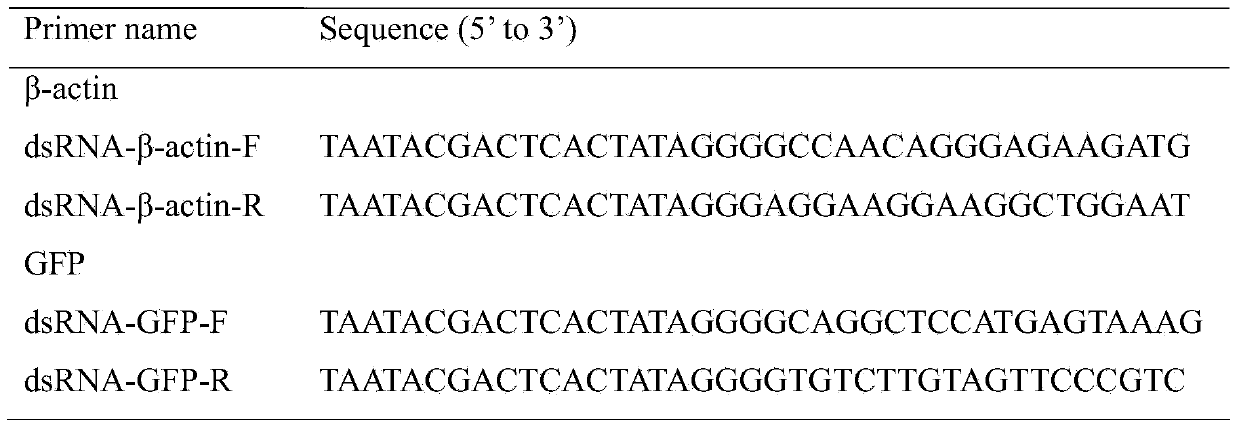
Method for determining influence of exogenous dsRNA on toxicity of ladybugs
ActiveCN107858405ASimple methodImprove effectivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementSaccharumSucrose solution
The invention discloses a method for determining influence of exogenous dsRNA on toxicity of ladybugs. The method comprises the following specific steps: uniformly mixing the exogenous dsRNA into a sucrose solution, directly feeding the ladybugs for 2-3 days and then feeding with pea aphids; then detecting and analyzing the expression changes of target genes in the ladybugs, and observing the biological changes of the ladybugs so as to evaluate the toxicity of the exogenous dsRNA to the ladybugs, wherein the ladybugs include harmonia axyridis, coccinella septempunctata or henosepilachna pusillanima. By the method, direct influence of the exogenous dsRNA on the toxicity of the harmonia axyridis, the coccinella septempunctata or the henosepilachna pusillanima or other ladybugs can be effectively determined; in addition, the method is simple, feasible and high in effectiveness and sensitivity, and has a great significance and an application prospect in study on functions of related genesas well as environmental risk assessment on related RNAi transgenic crops.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Antibody immunoreactive with a 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase
InactiveUS7183110B2Reduce amount of overproductionGlyphosate toleranceMicroorganismsTransferasesGlyphosateGenetically modified crops
Genes encoding Class II EPSPS enzymes are disclosed. The genes are useful in producing transformed bacteria and plants which are tolerant to glyphosate herbicide. Class II EPSPS genes share little homology with known, Class I EPSPS genes, and do not hybridize to probes from Class I EPSPS's. The Class II EPSPS enzymes are characterized by being more kinetically efficient than Class I EPSPS's in the presence of glyphosate. Plants transformed with Class II EPSPS genes are also disclosed as well as a method for selectively controlling weeds in a planted transgenic crop field.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
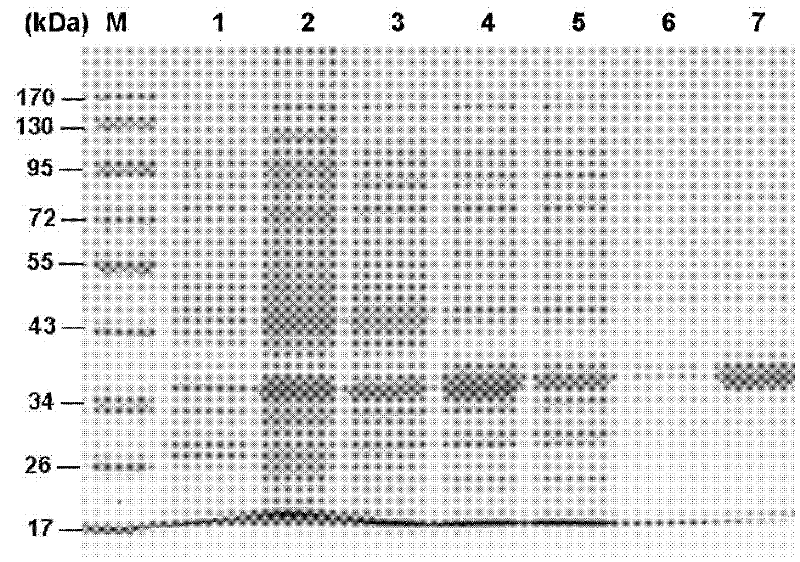
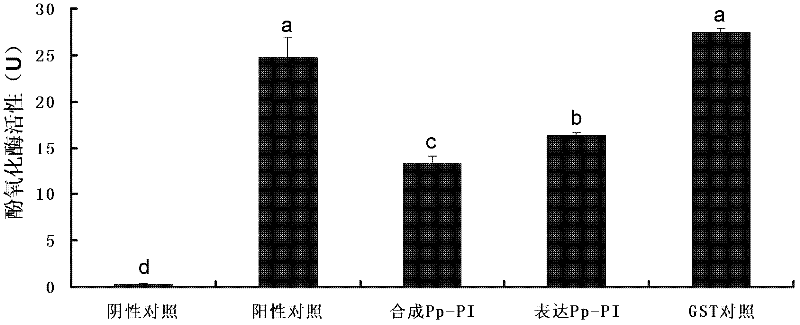
Serine protease inhibitor pp-pi polypeptide from chrysalis chrysalis chrysalis venom and its application
ActiveCN102260348AMicroorganism based processesRecombinant DNA-technologySerine Protease InhibitorsSymbiotic bacteria
The invention discloses a Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor Pp-PI polypeptide which has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. At the same time, the invention also discloses a gene for encoding the Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor Pp-PI polypeptide. The gene has a nucleotide sequence from the 126th nucleotide to the 290th nucleotide in SEQ ID NO: 1; or the gene has at least 70% homology with the nucleotide sequence from the 126th nucleotide to the 290th nucleotide in SEQ ID NO: 1; or the gene has a nucleotide sequence which can hybridize with the nucleotide sequence from the 126th nucleotide to the 290th nucleotide in SEQ ID NO: 1 at 40-55 DEG C. The Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor Pp-PI polypeptide can be used to prepare a Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor for genetically modifying crops or altering plant symbiotic bacteria.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Injection method for realizing RNA interference on Apolygus lucorum and application of same in gene screening
The invention relates to an injection method for realizing RNA interference on Apolygus lucorum and application of the same in gene screening, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The injection method for realizing RNA interference on Apolygus lucorum is characterized in that the outmost side of an intersegmental membrane of metastethidium and an abdomen is the position for injection of dsRNA. An RNAi platform used for researching gene functions of Apolygus lucorum is established for the first time; an injection method is creatively used to determine an optimal injection position for RNAi of Apolygus lucorum and an optimal injection volume at a specific dsRNA concentration, and changes of the phenotype of Apolygus lucorum after injection is detected and recorded. The method provides a novel technological means and a novel technological platform for screening of novel pest-resistant genes and novel gene resources for development of anti-Apolygus lucorum transgenic crops, thereby realizing development of an economic, effective, environment-friendly and novel method for controlling of harm of Apolygus lucorum.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Safety evaluation method of transgene insect-resistant rice on predative natural enemy cyrtorhinus lividipennis
The invention relates to a safety evaluation method of transgene insect-resistant rice on predative natural enemy cyrtorhinus lividipennis. The safety evaluation method includes the five parts including Tier-1 toxicity testing, three-level nutrition testing, protein transferring rules, predation function reaction and population density and population dynamic comparison. The potential toxicity of Bt protein expressed by Bt transgene insect-resistant rice on the cyrtorhinus lividipennis are respectively evaluated by the five parts; influences of the Bt transgene insect-resistant rice on the cyrtorhinus lividipennis on prey media are evaluated; paths and degrees for the cyrtorhinus lividipennis to be exposed in Bt protein are evaluated; influences of the Bt transgene insect-resistant rice on the cyrtorhinus lividipennis population are evaluated. Finally generated ecological effects of transgenic crop planting on non-target organisms are comprehensively evaluated according to data in the five parts. The safety evaluation method is systematic and scientific, and is of great significance on perfecting influence studying of transgenic crops on the non-target organisms and determining the ecological safety of transgenic crop planting.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Pest and glyphosate resistant expression vector, and plasmid and application thereof
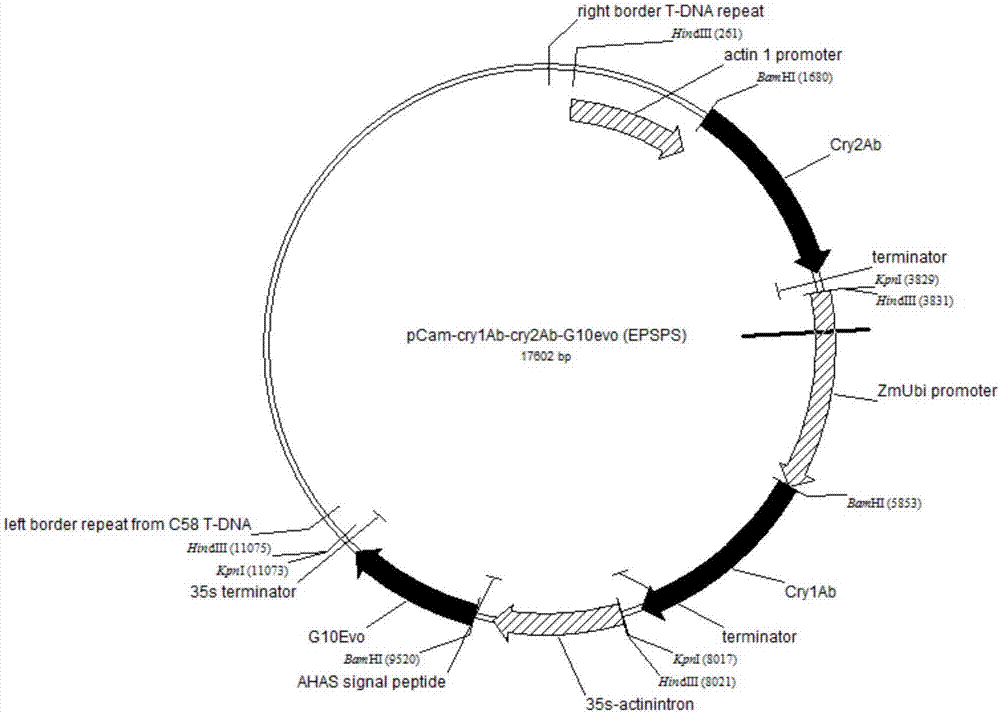
ActiveCN106916844ALower resistanceExpand insecticidal spectrumPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceOrder Lepidoptera
The invention discloses a pest and glyphosate resistant expression vector, and a plasmid and an application thereof. The expression vector contains a pest-resistant gene cry1Ab, a pest-resistant gene cry2Ab and a glyphosate-resistant gene G10evo. The vector simultaneously expresses Cry1Ab, Cry2Ab and G10evo proteins, and transgenic crops obtained by transferring crops with the vector can simultaneously resist cotton bollworms, beet armyworms, corn borers, striped rice borer and other main lepidoptera pests of rice, corn and cotton, so the insecticidal spectrum is widened, the pest resistance is effectively delayed, the transgenic crops have glyphosate resistance, the transgenic crops with composite properties accord with the current development direction of transgenic crops, and demands of large-scale agricultural production are met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for acquiring transgenic gramineae farm crop capable of being selectively eliminated
InactiveCN101205537AAvoid spreadingAvoid mixingClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionAntisense RNASulfonylurea
The invention provides an acquisition method for transgenic gramineous crops capable of being selectively perished, comprising the following steps: when target genes are expressed, expression of genes participating in herbicide detoxification in the transgenic gramineous crops is inhibited by utilization of antisense RNA or RNAi means, and the transgenic gramineous crops capable of being selectively perished are obtained. The invention mainly has the advantages that: the transgenic gramineous crops acquired by utilization of the method can be selectively perished by Bentazon or sulphuryl carbamide herbicide as required, thereby transmission of the transgenic gramineous crops and interfusion to non-transgenic gramineous crops are prevented, and the method has great significance in transgenic crop research later on.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
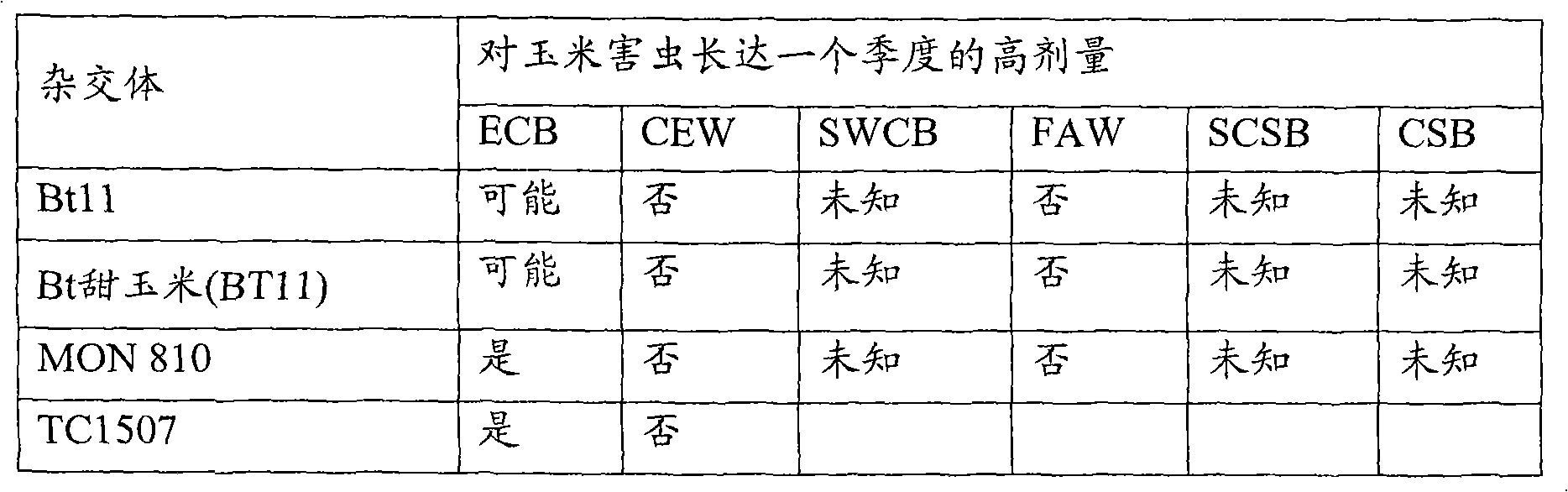
Method of Reducing Insect Resistant Pests in Transgenic Crops
The present invention discloses Resistance Management (RM) practices that are critical to safeguarding Bacillus thuringiensis as a natural resource and to sustaining genetically modified crops that express Bt toxins for managing ECB and WCRW. The methods involve blending seed transformed with a nucleic acid encoding a different pesticidal protein, where both proteins target the same pest, but use different modes of pesticidal action. The seed can be also treated with pesticidal agents.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to parasite anagrus nilaparvatae
The invention relates to an evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to parasite anagrus nilaparvatae. The evaluation method includes three parts of Tier-1 toxicity determination test, wherein the potential toxicity of Bt proteins expressed by Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on non-target organism anagrus nilaparvatae is evaluated; successive generation three-level nutrition test, wherein the influence of the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on the safety of the anagrus nilaparvatae through parasitic mediators is evaluated according to the food chain of rice-delphacidae-anagrus nilaparvatae; a protein transfer rule, wherein the way and degree that the anagrus nilaparvatae is exposed in the Bt proteins expressed by the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice are identified through an ELISA detection means; finally, the ecological consequences generated by genetically modified crop cultivation on non-target organisms are evaluated synthetically according to the data of the three parts. The evaluation method is systematic and scientific, and has great significance for the research of the influence of genetically modified crops on the non-target organisms and ecological safety of genetically modified crop cultivation.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
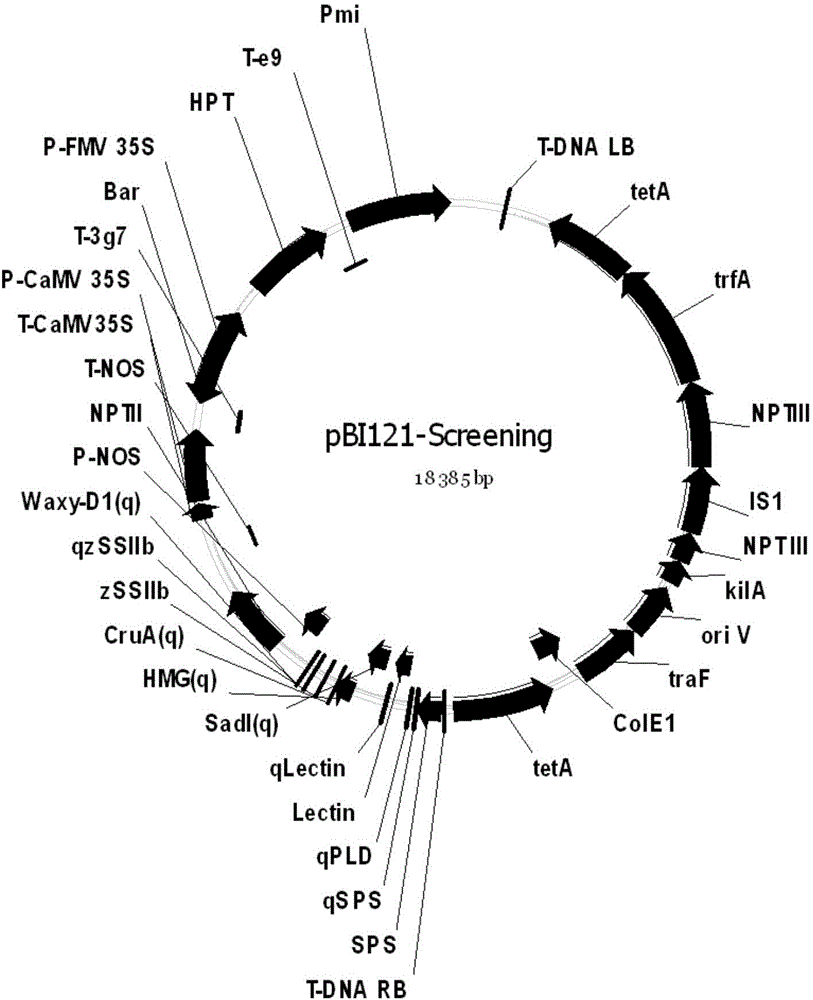
Positive plasmid molecule pBI121-Screening and application thereof
InactiveCN104651511AAvoid the problem of setting up multiple positive controlsReduce labor costsMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceGenetics
The invention discloses a positive plasmid molecule pBI121-Screening and application thereof and relates to the technical field of safety supervision and screening detection of transgenic crops in the transgenic safety field. The base sequence of the pBI121-Screening is as shown in SEQ NO.1. serving as both a positive contrast and a quality control sample, pBI121-Screening disclosed by the invention can be respectively used in general PCR and real-time fluorescence PCR screening detection of transgenic components of six transgenic crop samples, namely paddy rice, rapes, soybeans, corns, cotton and wheat. The pBI121-Screening disclosed by the invention can be used for solving the technical problem that the lack of a positive contrast or a standard sample in the screening detection of the transgenic crops, and prevents the problem that a plurality of positive contrasts are arranged for a plurality of detection targets in the screening detection, thus reducing the labor cost and economic cost for preparing the plurality of positive contrasts.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Hybridoma cell strains and monoclonal antibodies generated by same and application of hybridoma cell strain and monoclonal antibody in detecting G2-EPSPS protein
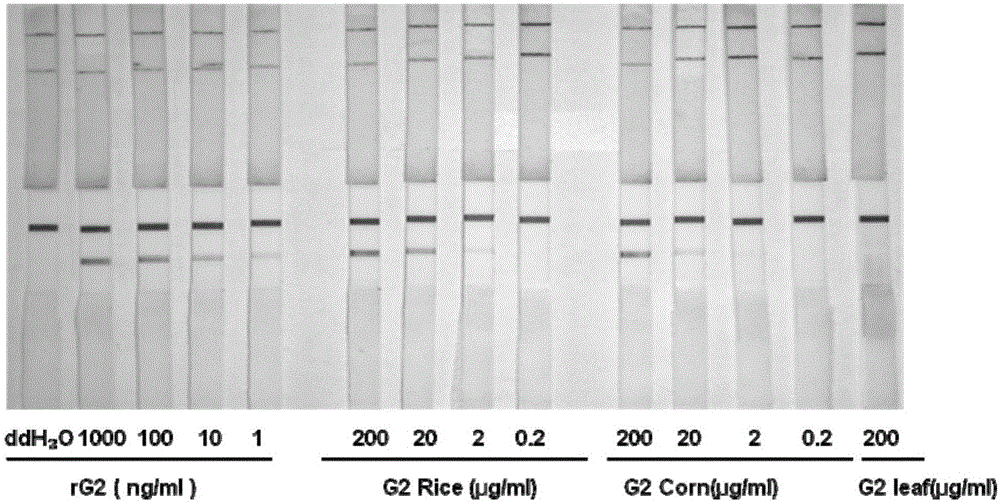
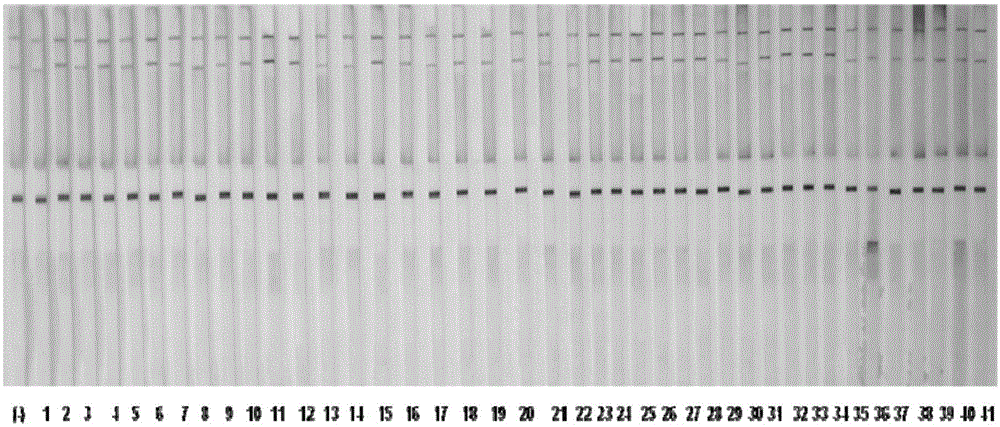
ActiveCN105154409ANo cross-reactivityIncreased sensitivityMicroorganism based processesTissue cultureTrue positive rateMicrobiology
The invention provides a pair of hybridoma cell strains. The hybridoma cell strains comprise the first hybridoma cell strain and the second hybridoma cell strain which are stored independently. The preservation number of the first hybridoma cell strain is CGMCC NO.10495. The preservation number of the second hybridoma cell strain is CGMCC NO.10494. The invention further provides a pair of paired monoclonal antibodies excreted by the two hybridoma cell strains, an application of the paired monoclonal antibodies in detecting G2-EPSPS protein and immuno gold staining test paper. According to the technical scheme, the sensitivity of 1 ng / mL can be obtained through detection of the immuno gold staining test paper on G2-EPSPS protein, no cross reaction is carried out on CP4-EPSPS protein, no cross reaction is carried out on 27 non-GMO crops and 14 G2-EPSPS transgenic crops with different sources, and high sensitivity and specificity are achieved.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Resistance management strategies
InactiveCN101568641AImprove toleranceIncrease resistanceBiocideClimate change adaptationMode of actionResistance development
Insect refuge strategies are described for the management of insect resistance development. The present invention relates generally to the control of pests that cause damage to crop plants, and in particular to corn plants, by their feeding activities directed to root damage, and more particularly to the control of such plant pests by exposing target pests to seeds or mixtures of seeds having multiple different modes of action. The first one or more transgenes and the second one or more transgenes are each, respectively, insecticidal to the same target insect but have different modes of action, and bind either semi-competitively or non-competitively to different binding sites in the target pest. In addition, the treatment of such seed with a chemical or peptide-associated pesticide prior to planting the seed is also disclosed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
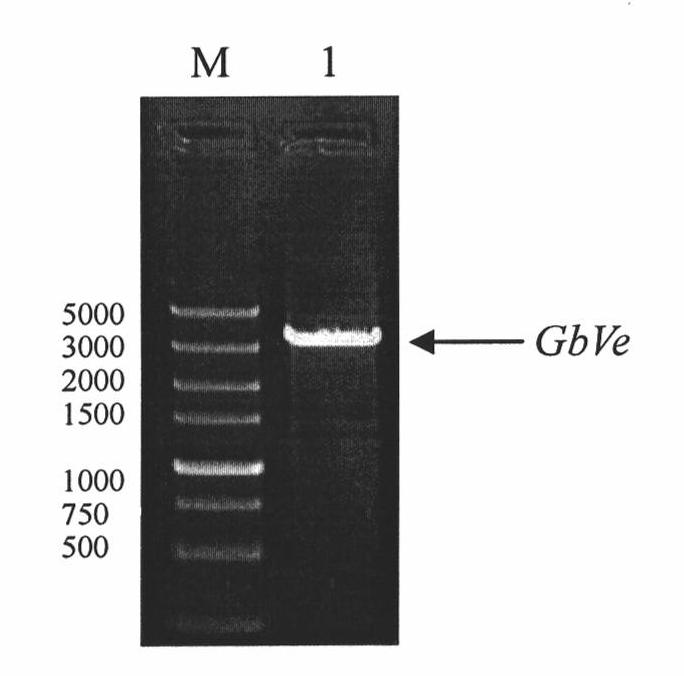
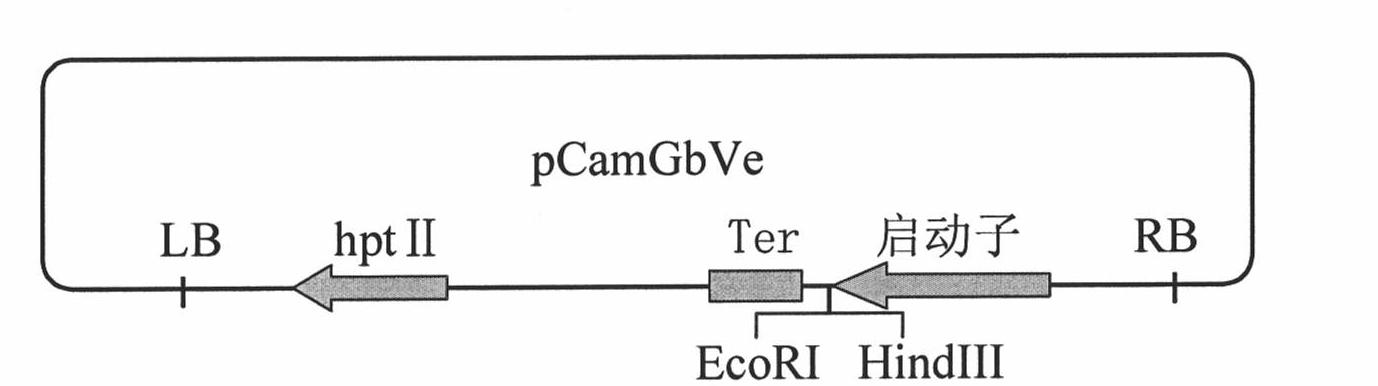
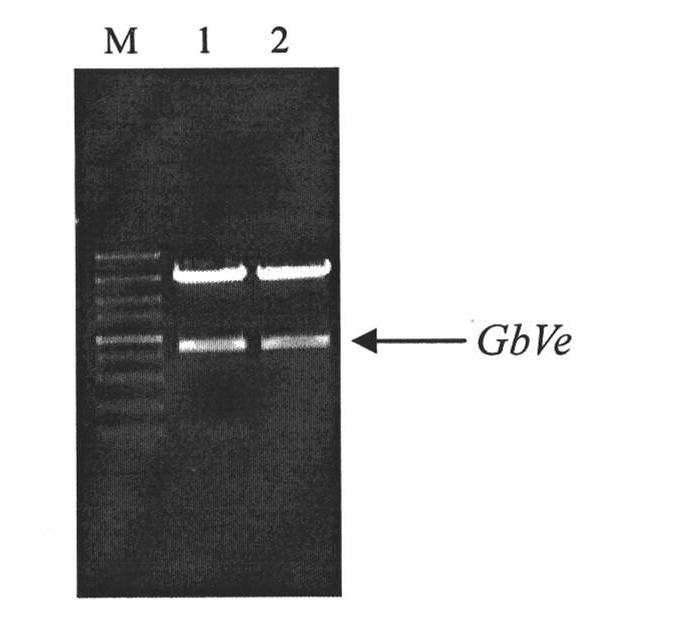
Cotton GbVe gene, protein coded thereby and use thereof in vegetable verticillium wilt resistance
InactiveCN101928338AVerticillium wilt resistance increasedHelps reveal molecular mechanismsFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention relates to cotton GbVe gene and a protein coded thereby. In the invention, a Ve gene associated with verticillium wilt resistance is obtained by cloning in a gossypium barbadense variety having high verticillium wilt resistance; a 5'-terminal GbVe gene fragment and a 3'-terminal GbVe gene fragment, which are obtained by amplification, are spliced; a primer capable of amplifying the full-length GbVe gene is designed and synthesized according to a gene sequence; the sequence of the full-length GbVe gene is obtained by the conventional colony sequencing method according to an RT-PCR technique; and the nucleotide sequence of the full-length GbVe gene is represented by SEQ ID No.1. In the invention; a new and important candidate gen is provided for vegetable verticillium wilt resistant gene project; and the obtained full-length GbVe gene and a vegetable expression vector constructed by the full-length GbVe gene lay a foundation for further transforming important crops for improving the verticillium wilt resistance of transgenic crops and have great economic benefits and application values.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
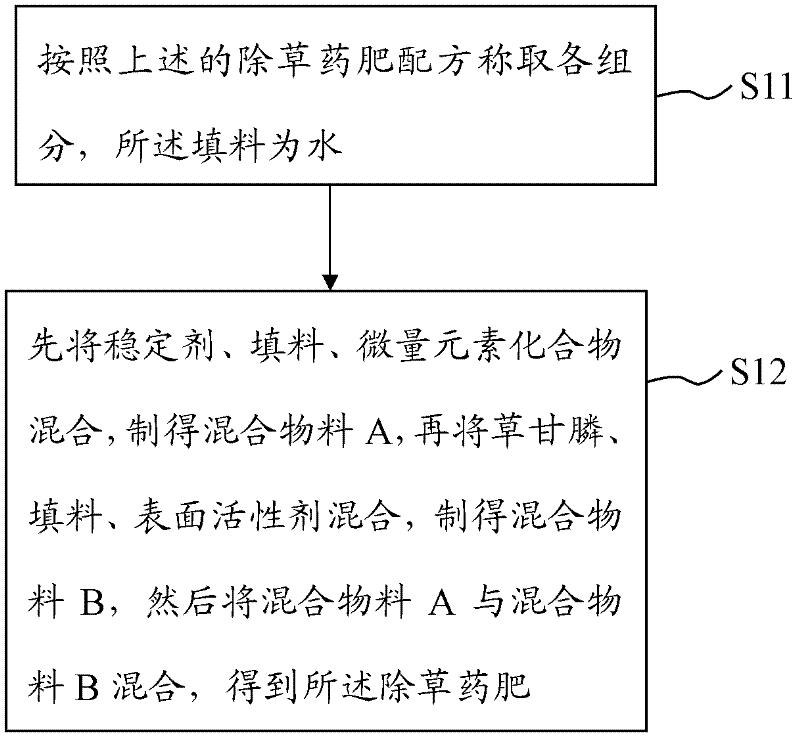
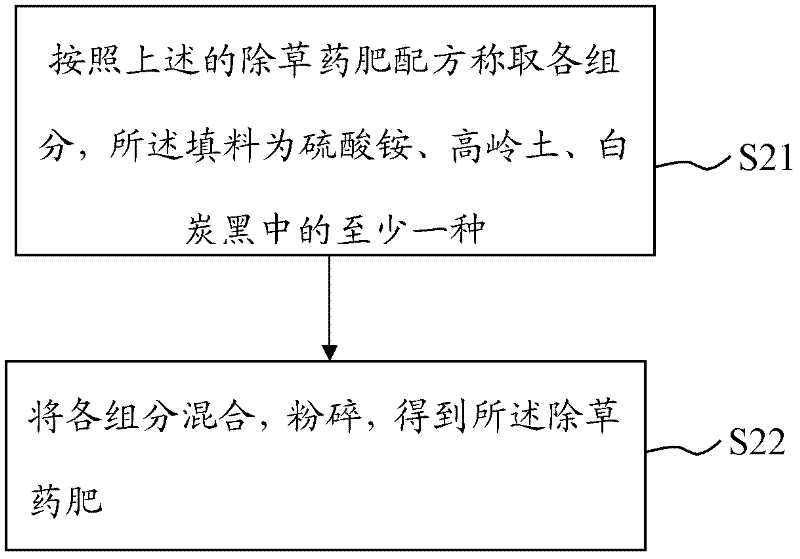
Herbicide-containing fertilizer and preparation method and use thereof
The invention provides a herbicide-containing fertilizer and a preparation method and use thereof. The herbicide-containing fertilizer, based on 100 percent of total mass, consists of the following formula components in percentage by weight: 15 to 40 percent of glyphosate, 0.4 to 8 percent of trace element compound, 5 to 15 percent of surfactant, 0.5 to 20 percent of stabilizer and the balance of filler. In the herbicide-containing fertilizer provided by the embodiment of the invention, because the glyphosate, trace element component and the like are mixed reasonably, the soil fertility, resistance in crops (particularly glyphosate resistant transgenic corps) and crop yield are all increased, and the crop yield is improved by up to 30 percent; and the herbicide effectively lowers the labor intensity and manual cost of agricultural production. In addition, the herbicide-containing fertilizer is produced by mixing by group or mixing by crushing, so the dispersion uniformity of the components is improved effectively, the preparation method is simple in process and low in energy consumption and the production cost is lowered; and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHAANXI BIAOZHENG CROP SCIENCE CO LTD
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Protein chip kit and method for detecting transgenic crops
InactiveCN101914156AImprove accuracyImprove stabilityImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against plantsPhytaseProtein insertion
The invention discloses a protein chip for detecting transgenic products. The protein chip is a film which is arranged on the plane of a plane type supporting carrier and coated with a modified material; and protein antibody probes for detecting transgenic agricultural products are arranged on the surface of the film in a lattice mode and comprise 1) a Bt cry1Ac / Ab monoclonal antibody, 2) a Bt cry1Ah monoclonal antibody, 3) a phytase PHY monoclonal antibody, 4) a glyphosate-tolerant G2-EPSPS polyclonal antibody and 5) a salt-tolerant IrrE polyclonal antibody. The invention further provides a chip kit for detecting transgenic crops and performing result judgment simply and rapidly based on antigen antibody reaction, which belongs to the field of inspection and quarantine. The protein chip kit has the advantages of: 1) high speed, wherein the detection time is only 1.5 to 2 hours; 2) specificity, wherein protein antigens and antibodies are specifically combined and each antibody performs a point system process repeatedly for three times, so that the result correctness is greatly improved; 3) high flux, wherein the protein chip kit can detect the proteins of five kinds of commercial transgenic components at the same time; and 4) stability, wherein the results of the repeated tests show that the stability of the method is high.
Owner:PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA BEIJING ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
Method for detecting number of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in wheat rhizosphere soil based on real-time fluorescence quantification PCR
InactiveCN106011256AStable and repeatable resultsStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiFluorescence
The invention provides a method for detecting the number of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in wheat rhizosphere soil based on real-time fluorescence quantification PCR. The method includes the steps that firstly, sample total DNA of wheat rhizosphere soil is extracted and serves as a template of PCR amplification; then, amplification is conducted with SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No. 2 as primers, and specific fragments of 129 bp are obtained; after bond and conversion are conducted, qPCR amplification is conducted. By means of the method, arbuscular mycorrhiza is authenticated, absolute quantification can be conducted on the arbuscular mycorrhiza accurately, the copy number of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in all periods of duration of transgenic wheat is obtained, and in the growth and development stages of wheat, the arbuscular mycorrhiza copy number tends to be gradually increased as a whole. The rapid, convenient and precise authentication method is built, a theoretical and test basis is provided for subsequent tests, great significance is provided for further evaluation of safety of transgenic crops, and compared with an existing method, the method is high in sensitivity, high in specificity, good in repeatability, convenient to operate and visual in result.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
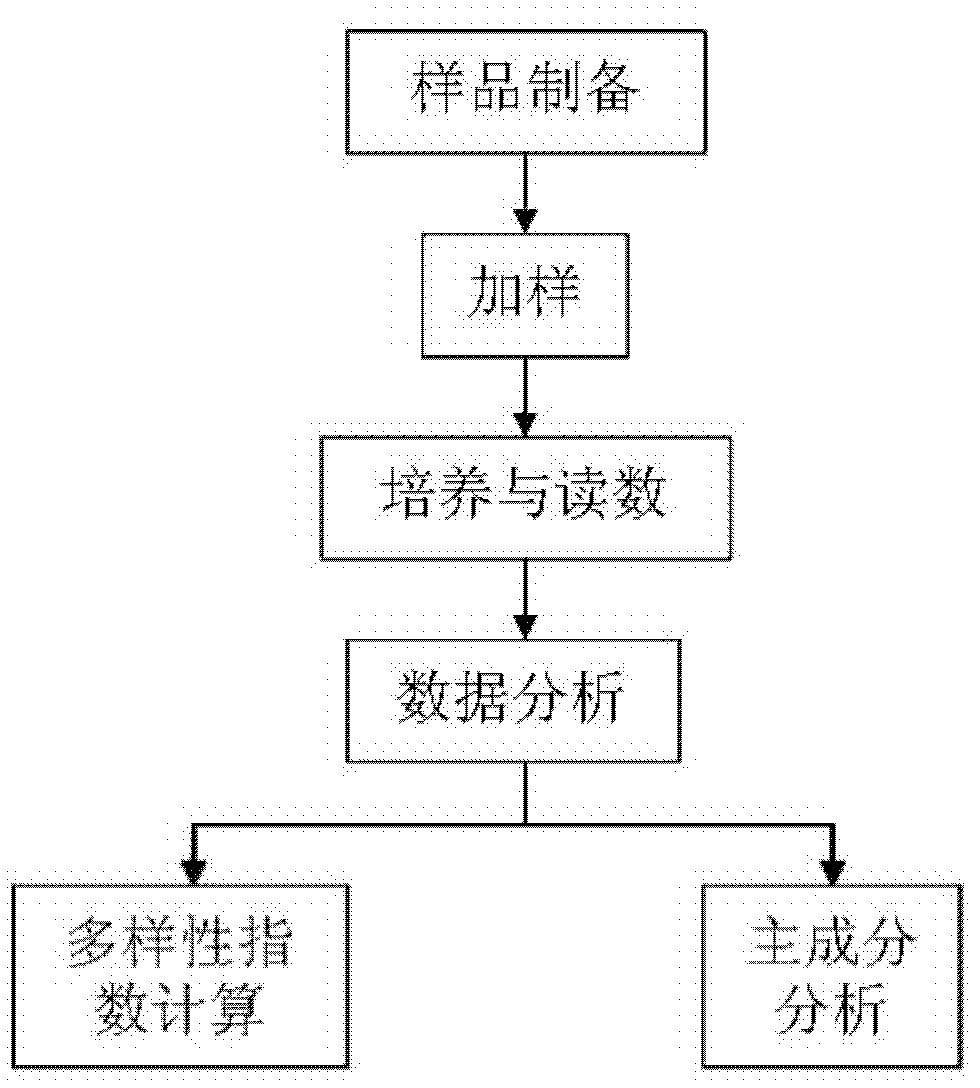
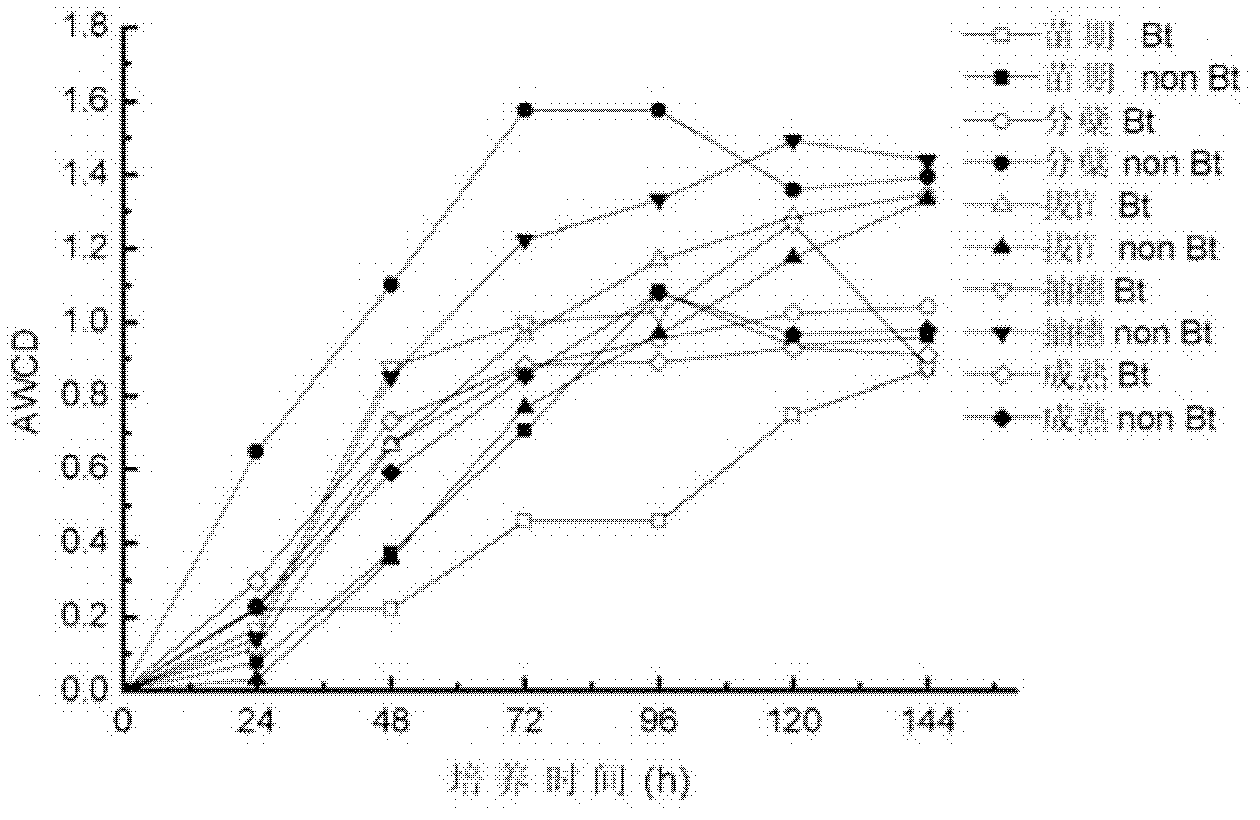
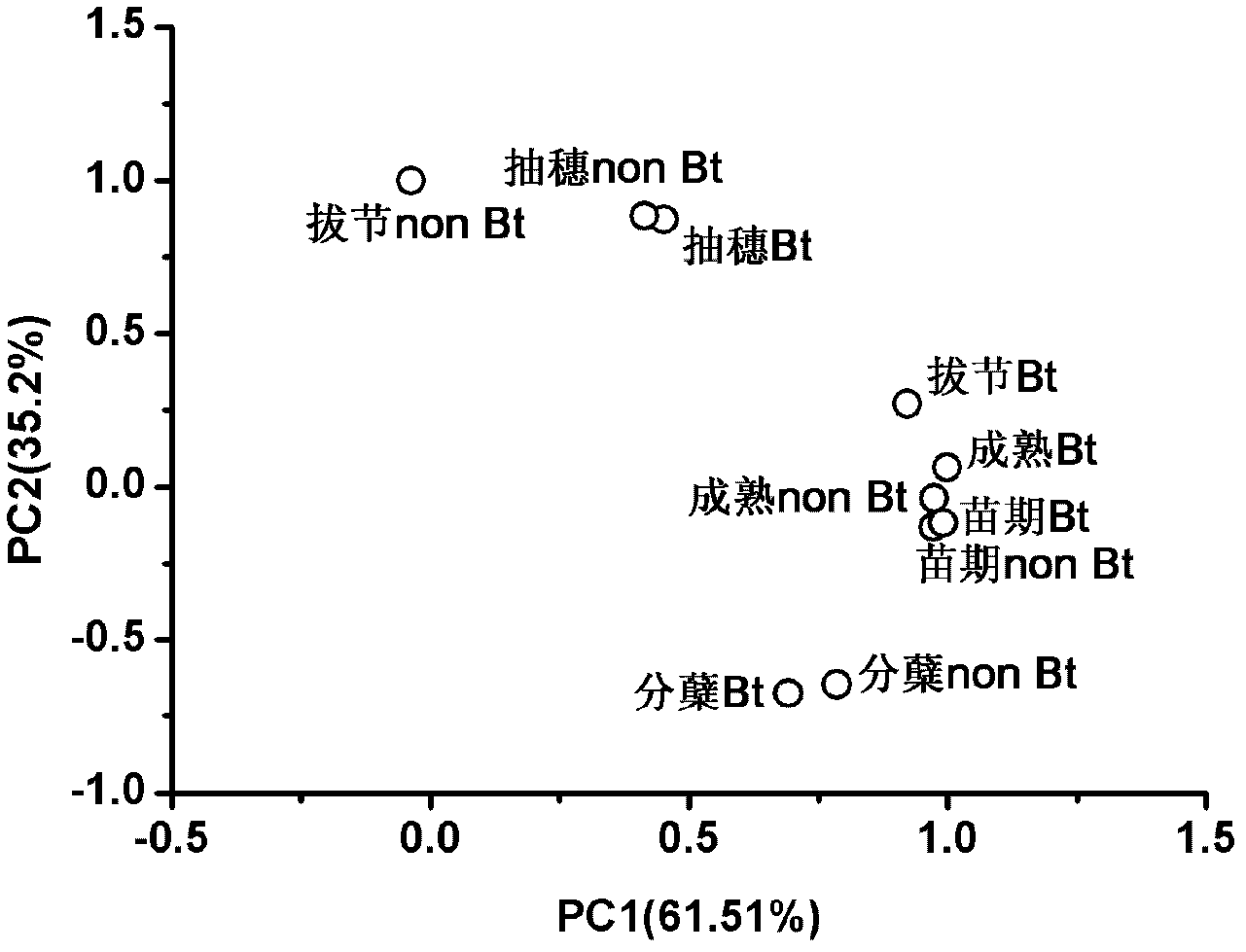
Biolog ECO micro-plate technique applied to soil microecological safety evaluation for genetically modified (GM) crops
InactiveCN102251016ASimple methodFast wayMicrobiological testing/measurementDiversity indexMicroorganism
The invention discloses a Biolog ECO micro-plate technique applied to soil microecological safety evaluation for genetically modified (GM) crops. The Biolog ECO micro-plate technique comprises the following steps: (1) collecting rhizosphere soil samples of the GM crops and non-GM parent crops during different childbearing periods; (2) performing Biolog ECO experiments; (3) calculating average well color development (AWCD) and diversity indexes; and (4) performing principal component analysis (PCA). The Biolog ECO micro-plate technique can be used for evaluating the influence of the GM crops on functions of rhizosphere soil microbial communities so as to evaluate the potential security risk of the GM crops for a rhizosphere soil microecosystem.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Non-destructive imaging of crop plants
The present disclosure relates to methods for non-destructively assessing yield and / or stress tolerance in crop plants through the use of high-energy particle based imaging and analysis including X rays. Also provided are methods to non-destructively assess transgenic crop plants for the effects of a transgene on yield and / or on stress tolerance.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
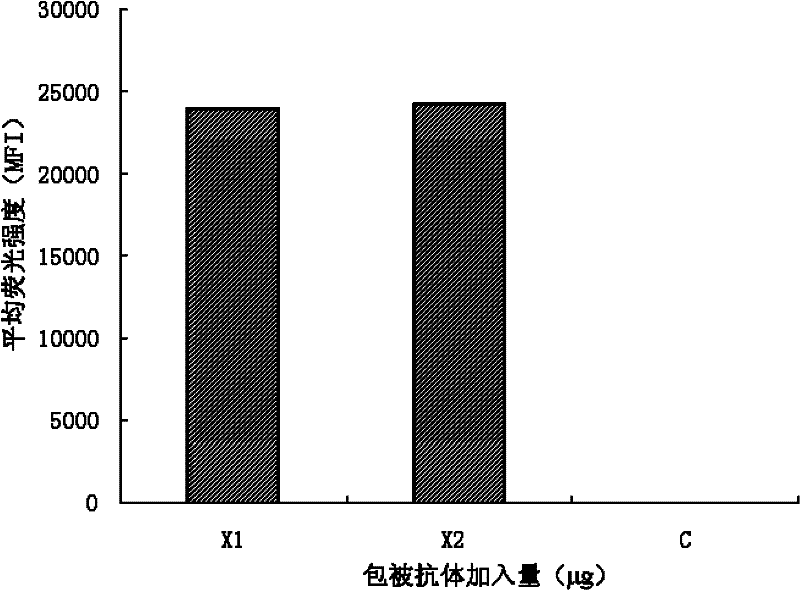
A liquid chip for detecting bt cry1 Ac protein and its application
The invention discloses a liquid phase chip for detecting Bt cry1 Ac protein and its application. The liquid phase chip provided by the present invention includes fluorescent microspheres coated with anti-Bt cry1 Ac monoclonal antibodies, biotinylated monoclonal antibodies against different antigenic epitopes of Bt cry1 Ac, and streptavidin phycoerythrin. The present invention also provides using the liquid phase chip to detect whether the plant is a transgenic Bt cry1 Ac plant. The present invention utilizes a monoclonal antibody against Bt cry1 Ac and adopts a double antibody sandwich method to establish a liquid phase chip detection method for Btcry1 Ac protein in transgenic crops (GMO). Good repeatability.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
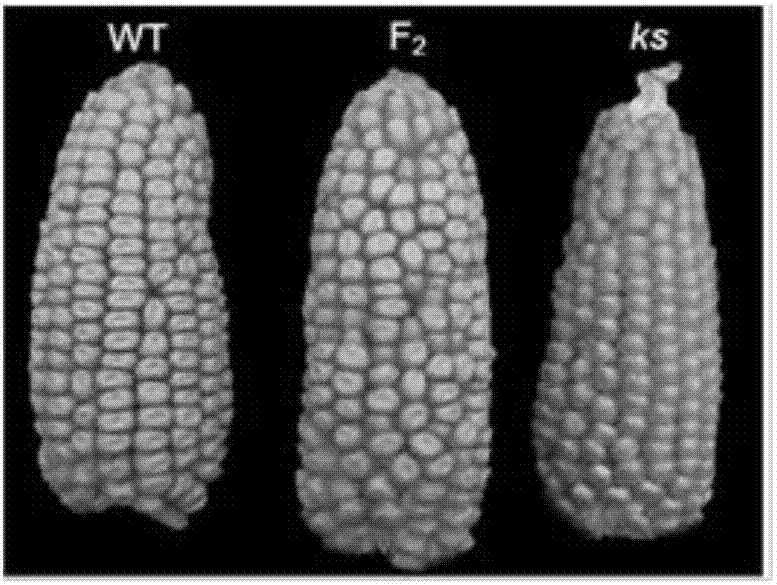
Maize kernel size mutant ks and its application
InactiveCN107501400AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAgricultural scienceGene cluster
The invention specifically relates to a maize kernel size mutant ks deleted of a maize hexose transport protein gene (ZmSWEET4) and its application. According to a technical scheme in the invention, a coding gene is cloned from the maize mutant ks, and verification results show that the coding gene can regulate and control the maize kernel filling process so as to influence kernel sizes. Experiments of overexpression of the gene cluster in common maize are carried out; and the kernel output of overexpressed transgenic plants is obviously higher than the kernel output of a control group, and transgenic crops with higher output than the output of wild plants can be obtained. The gene obtained in the invention provides a theoretic basis and gene source for cultivation of new crop varieties and plays an important role in genetic improved breeding of germplasm resources of maize.
Owner:MAIZE RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Insecticidal protein as well as coded gene and application of insecticidal protein
ActiveCN104311648AImprove insecticidal effectBiocideDepsipeptidesOrder LepidopteraGenetically modified crops
The invention relates to an insecticidal protein Cry1m7, which is 1) a protein composed of an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1, or 2) a protein which is obtained by substituting, deleting or inserting one or more amino acid sequences in the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and has an equivalent activity. The invention further provides a coded gene, an expression vector and an engineering bacterium of the insecticidal protein, an application of the protein to insecticides and an application of the coded gene of the protein to plant conversion. The invention provides the high-toxicity insecticidal protein Cry1m7 and the coded gene thereof; and the insecticidal protein provided by the invention can be used for killing Asiatic corn borers and other lepidoptera pests to improve the insecticidal capability of genetically modified crops.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com