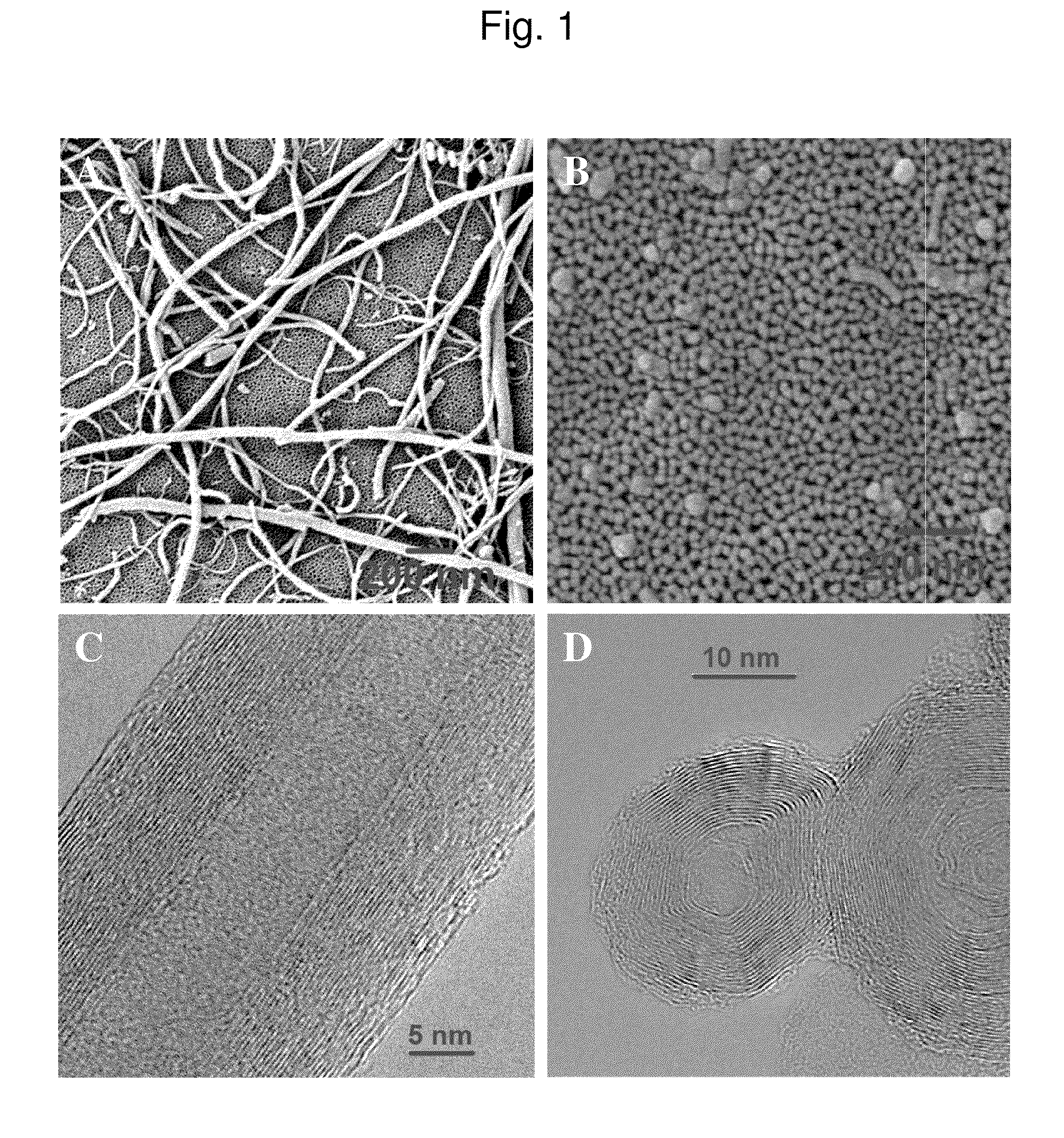
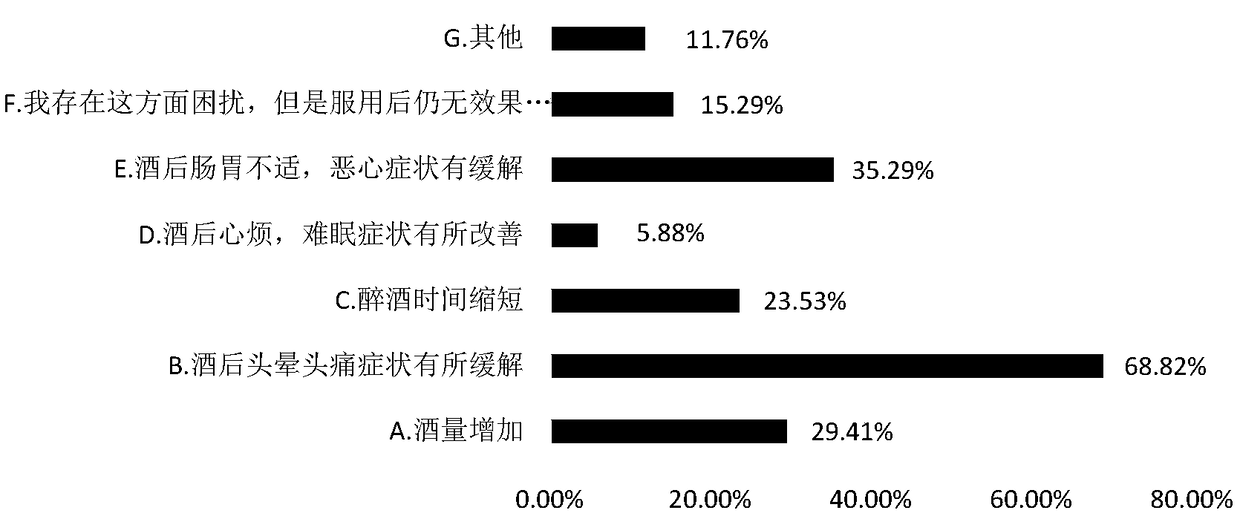
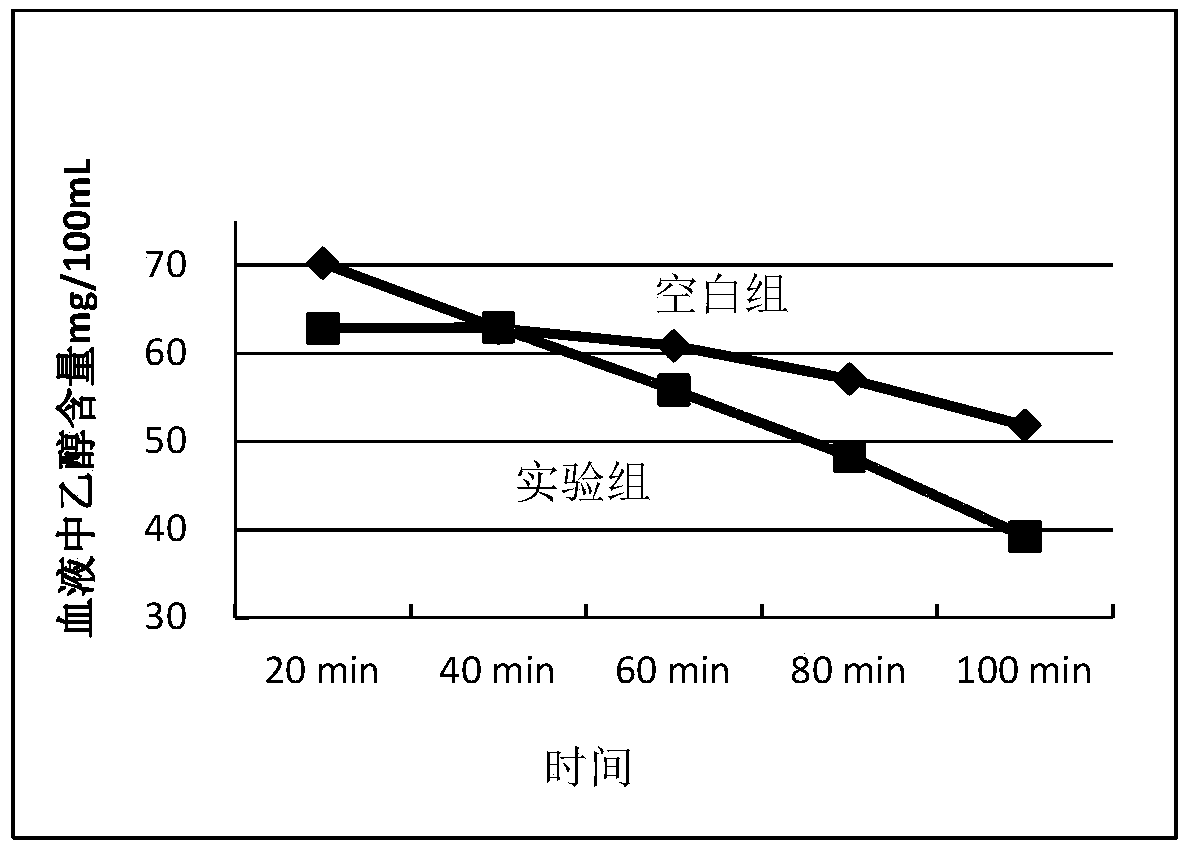
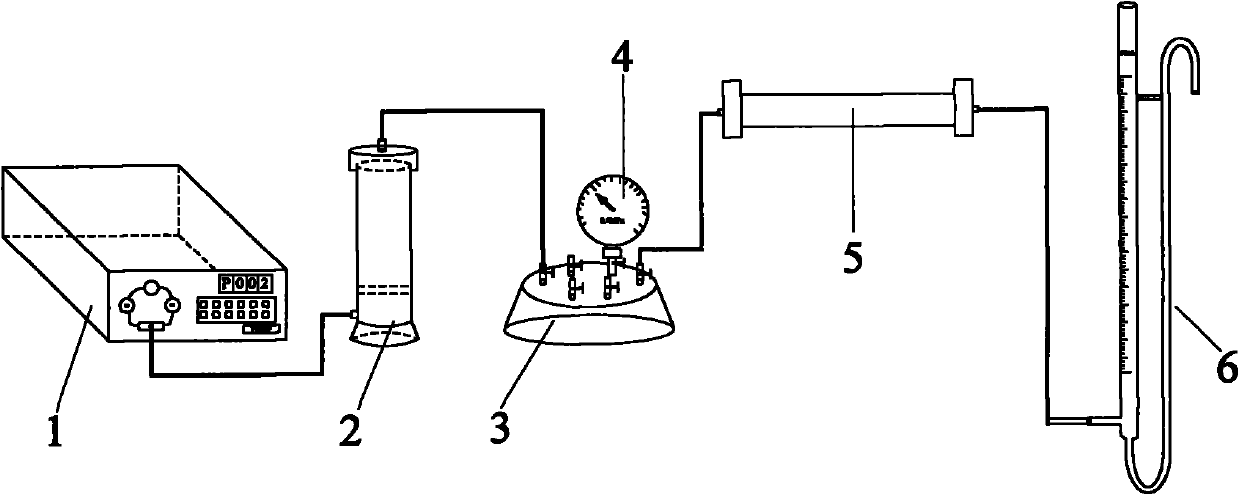
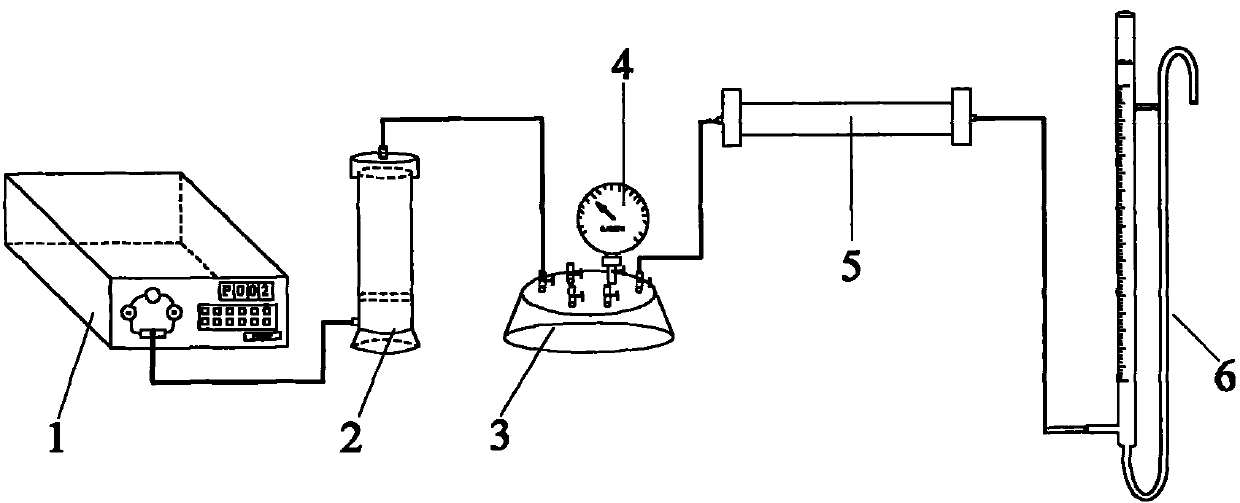
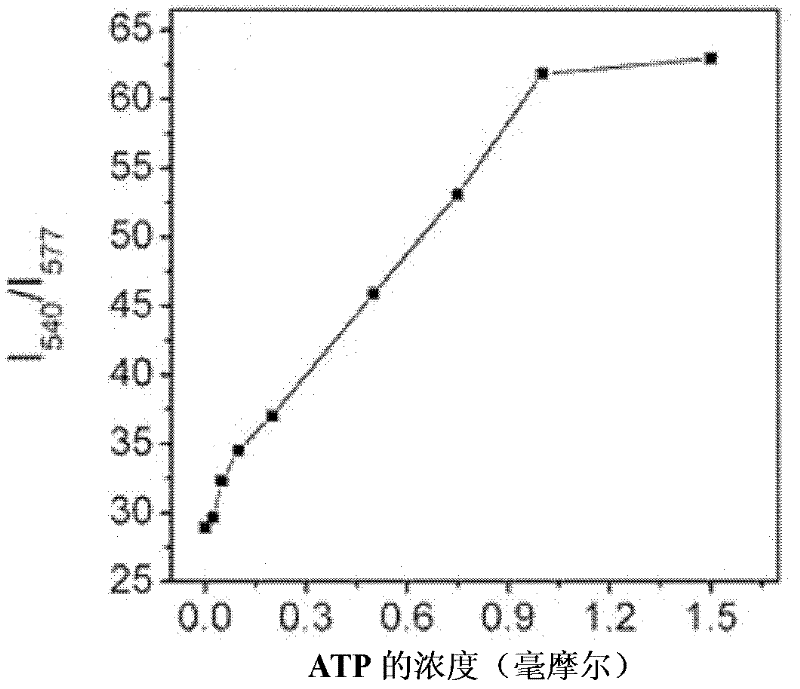
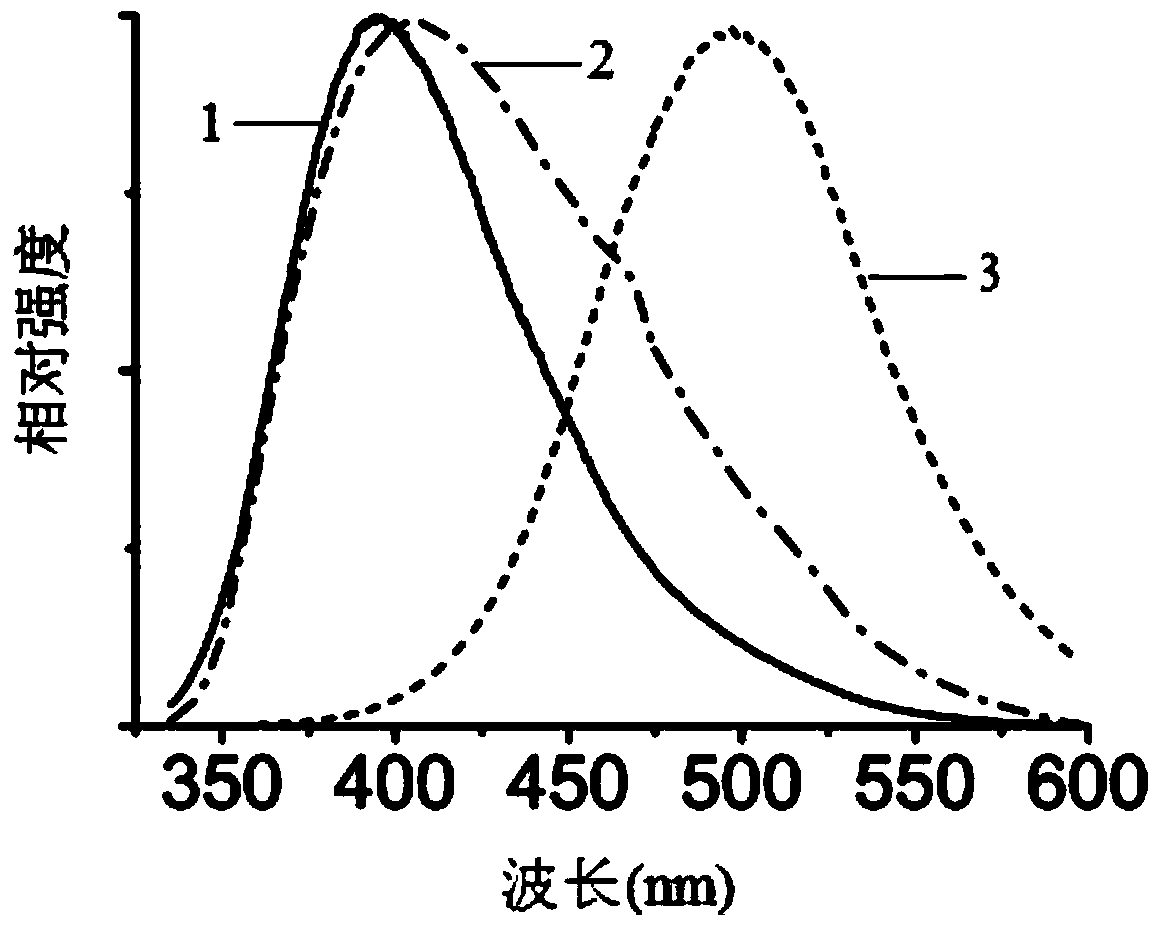
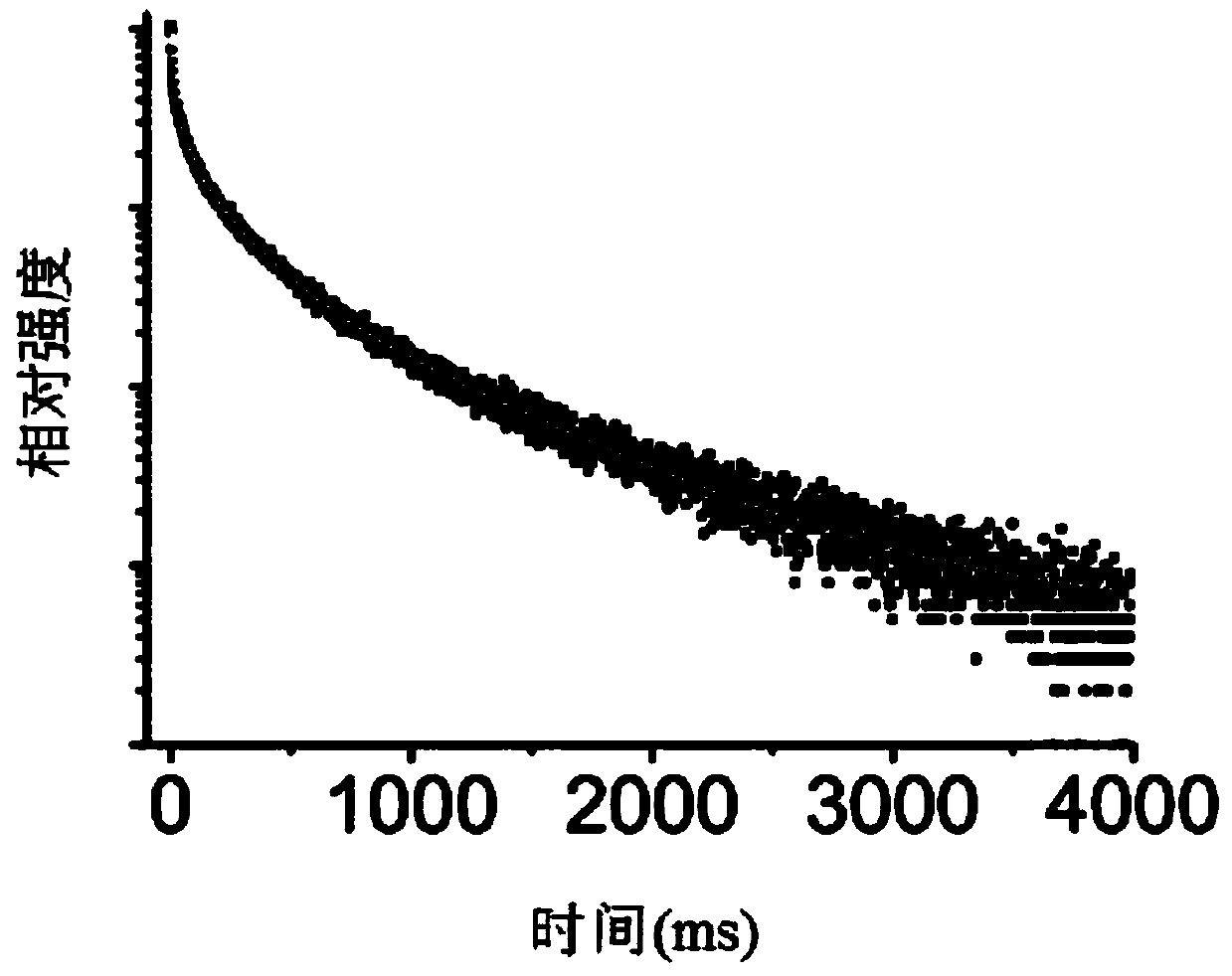
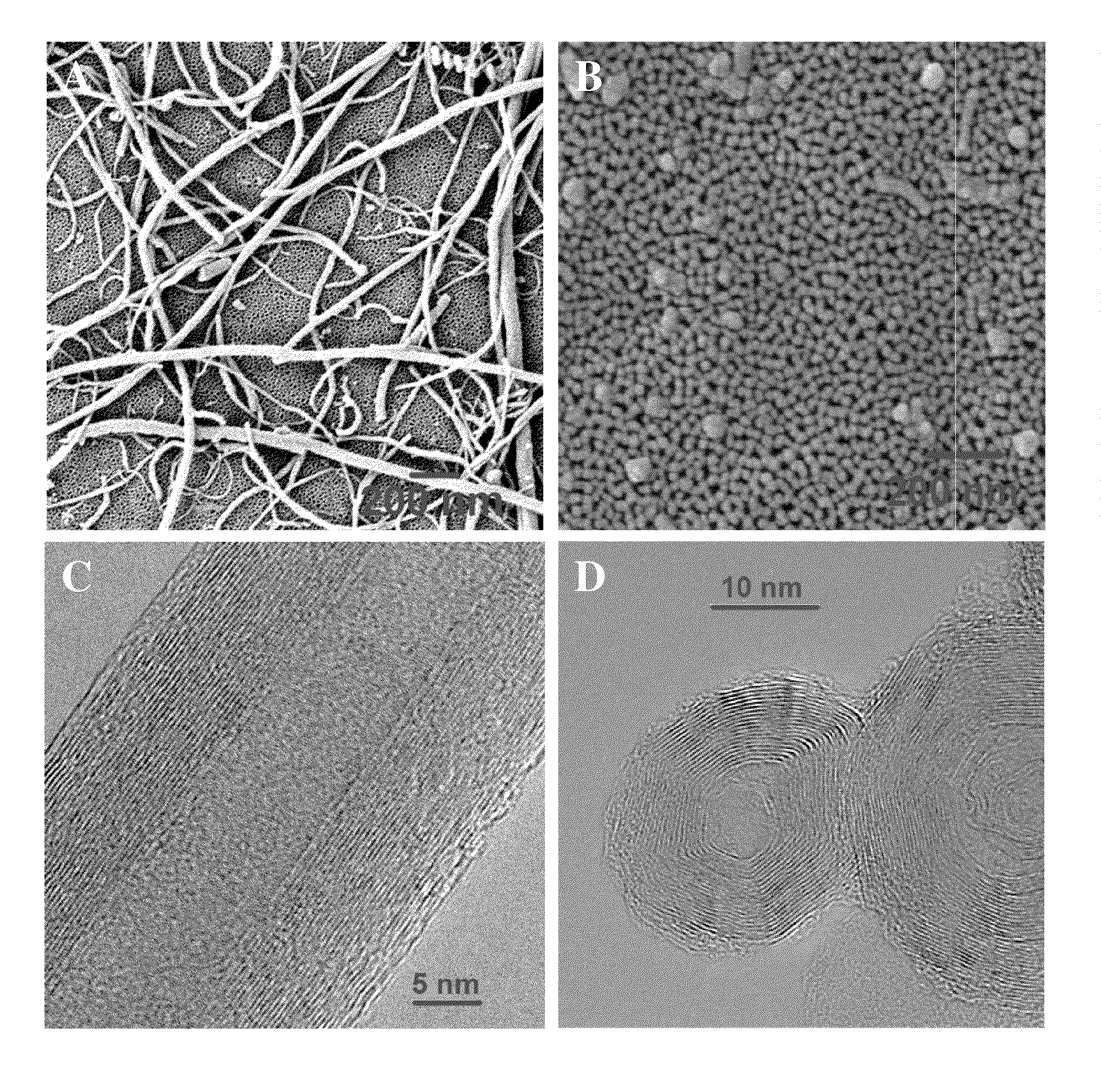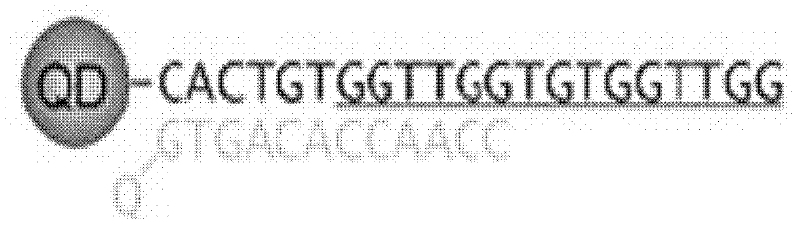Patents
Literature
79 results about "Potential toxicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Human Toxicity Potential (HTP) is a quantita tive toxic equivalency potential (TEP) that has been introduced previously to express the potential harm of a unit of chemical released into the environment. HTP includes both inherent toxicity and generic source-to-dose relationships for pollutant emissions.
Neuroceutical for improving memory and cognitive abilities
Owner:SUMMERS WILLIAM K
Method and apparatus for inactivating contaminants in blood products
InactiveUS6190608B1Structure is often disruptedAvoid disruptionOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesPotential toxicityWhole blood product
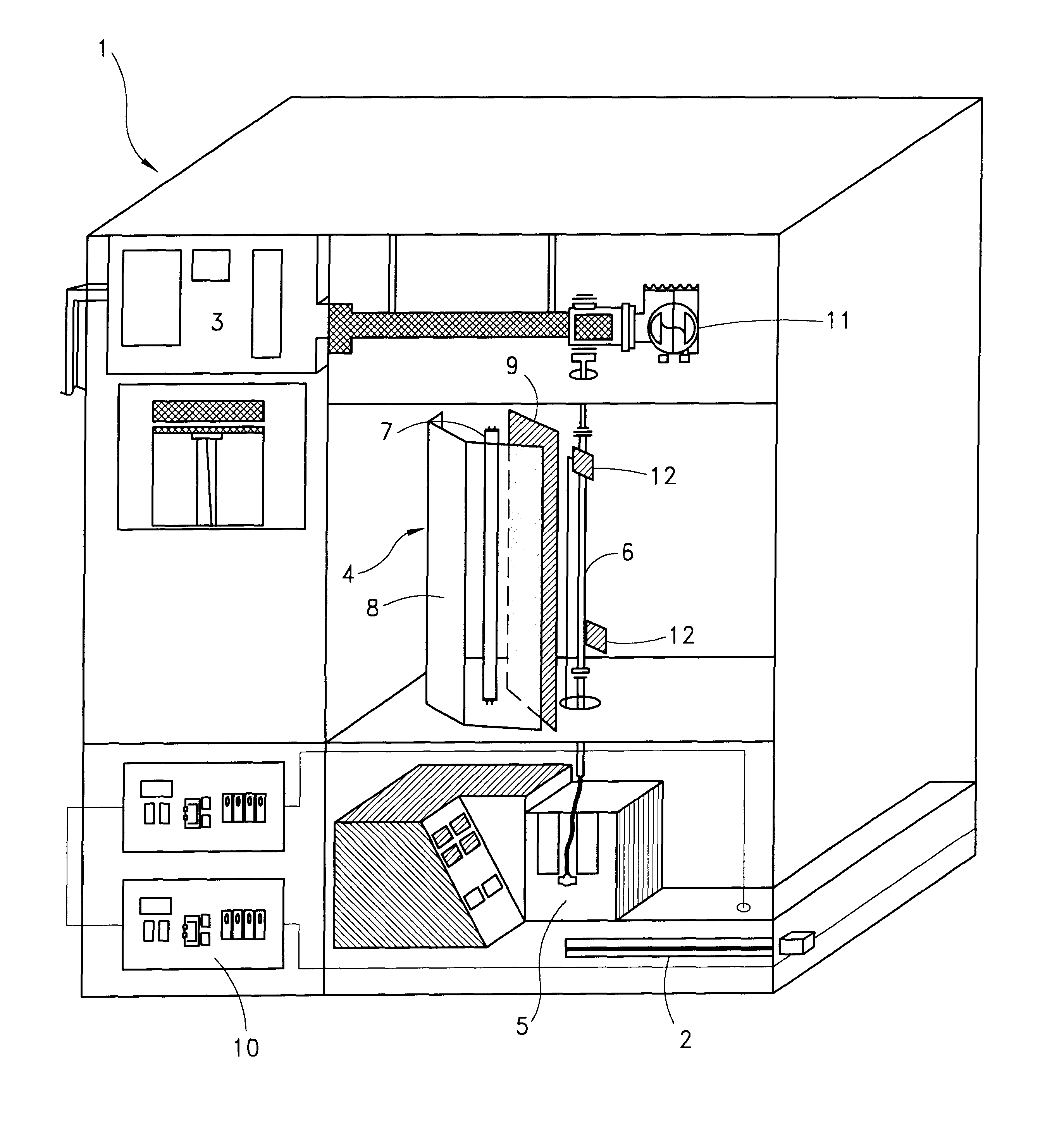
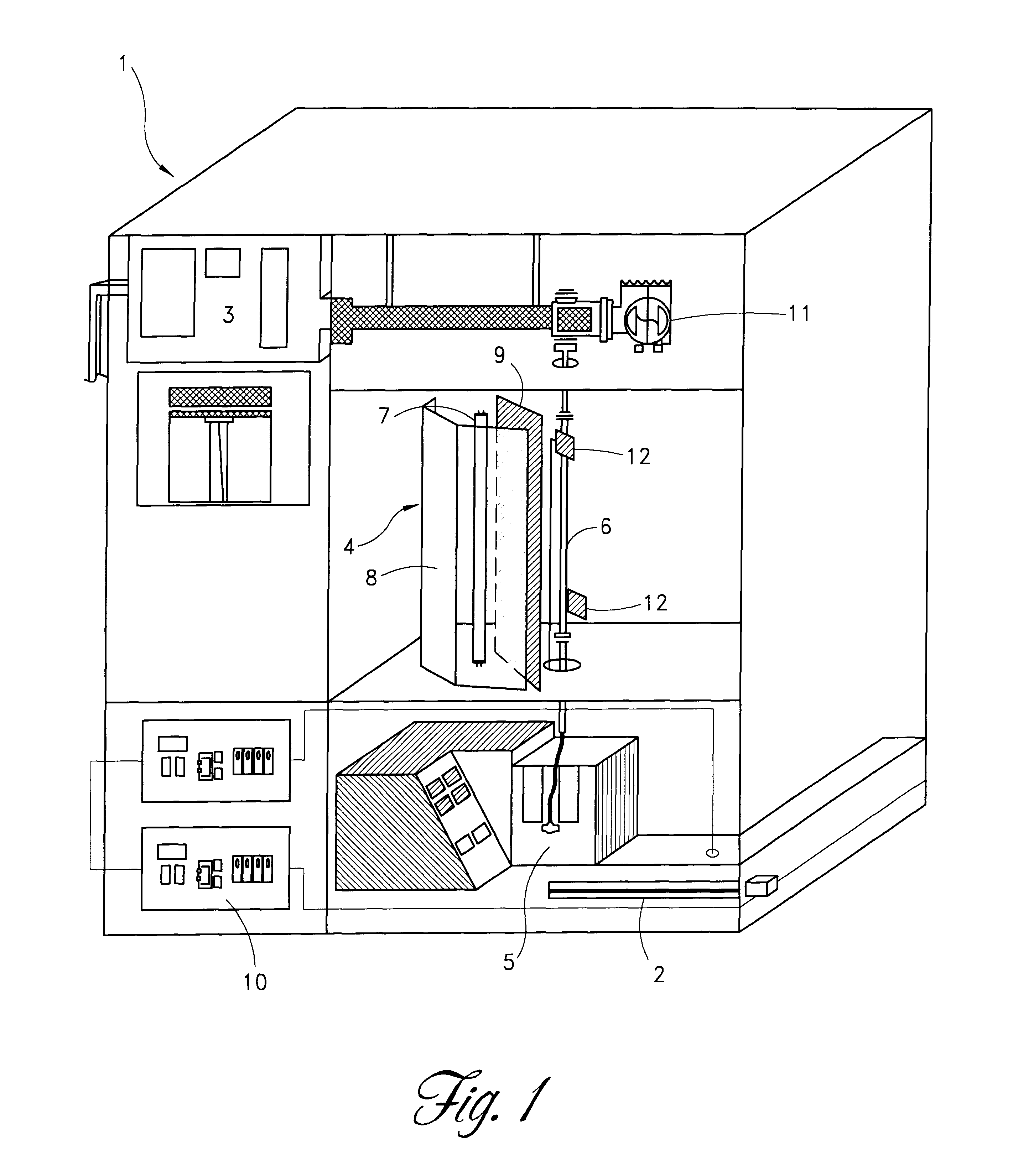
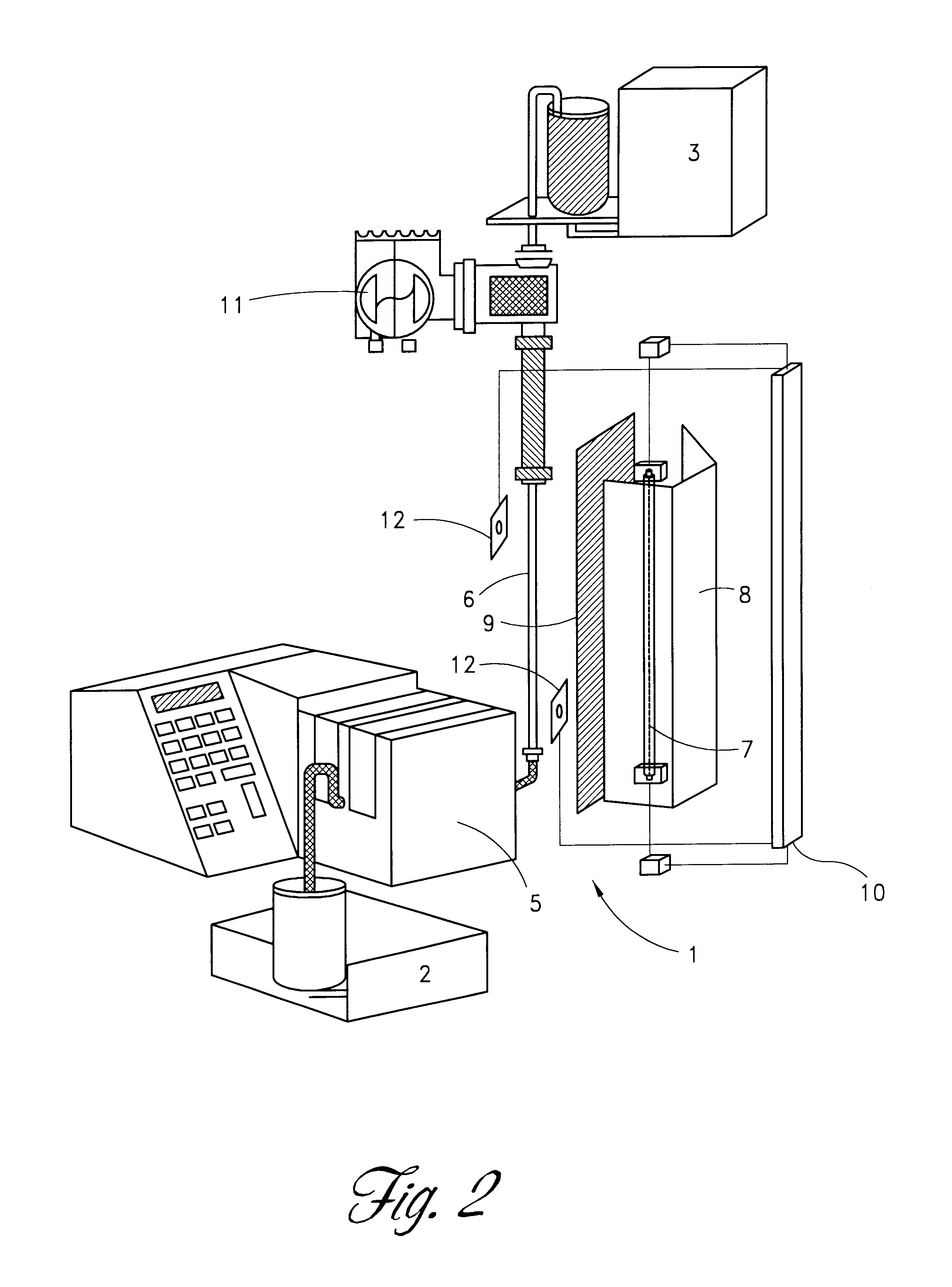
A method and apparatus for inactivating contaminants, particularly nonenveloped viruses, in blood products without the need for quenchers in the blood products. The blood product is flowed through a flow meter at a controlled flow rate and subjected to type C ultraviolet radiation, where the irradiation dose received by the blood product is less than 640 joules / m2. The blood product does not contain quenchers when being irradiated, and the blood product retains more than 85% of its Factor VIII activity after being subjected to the radiation. The produced blood product is free of viruses and quenchers, avoiding potential toxicity due to the quenchers. The apparatus includes a source of UVC light, a quartz tube containing the blood product while it is exposed to the UVC light, a flow meter for controlling the flow rate of the blood product to be treated, and a pump. The UV light preferably emits light at 254 nm.
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM BIOTECH GMBH
Application of carbon nanodots as water-soluble ratiometric fluorescent probe
ActiveCN102942175ARealize detectionOvercome costsMaterial nanotechnologyNano-carbonPotential toxicityFluorescence spectrometry
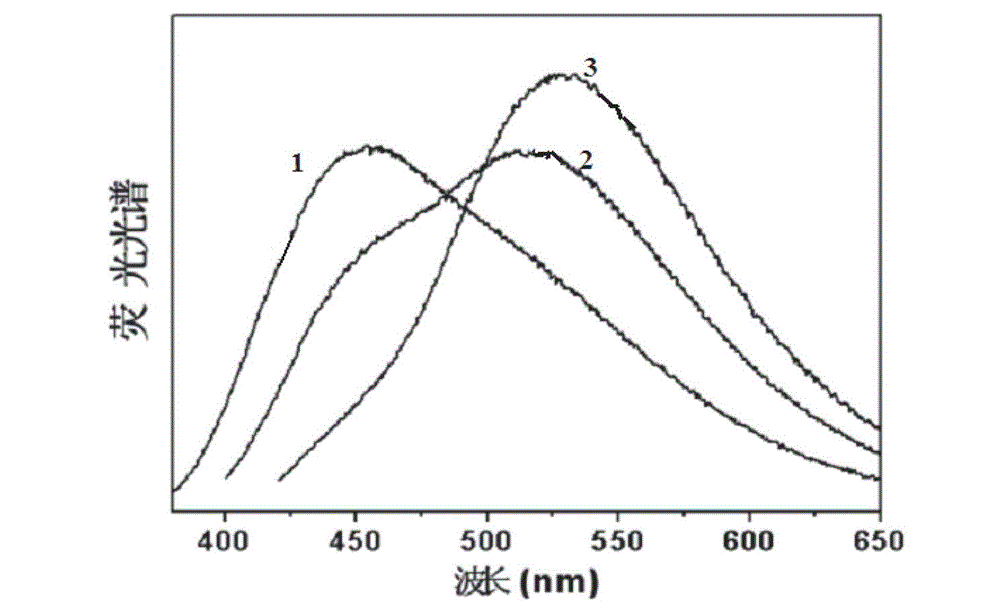
The invention discloses an application of carbon nanodots as a water-soluble ratiometric fluorescent probe and solves the problems that the existing ratiometric fluorescent probes are high in preparation cost, poor in luminescent stability and provided with potential toxicity. According to the application, the carbon nanodots are dissolved in a solution to be measured, an excitation wavelength is fixed at 360-400nm,the solution to be measured dissolved with the carbon nanodots is subjected to fluorescence spectrum detection at a fixed temperature, intensities of a blue maximum fluorescence-emission peak and a green maximum fluorescence-emission peak are measured, the ratios of the blue maximum fluorescence-emission peak intensity and the green maximum fluorescence-emission peak intensity are calculated, so that the detection of the objective to be measured is achieved. The application has the advantages of being low in cost, good in luminescent stability, non-toxic, high in sensitivity and capable of achieving detection for temperature, pH of water solution, ethanol concentration in ethanol water and Fe3+ concentration in Fe3+-containing neutral water solution simply, accurately and quickly.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of induced pluripotent stem cells to generate adoptive cell therapy products
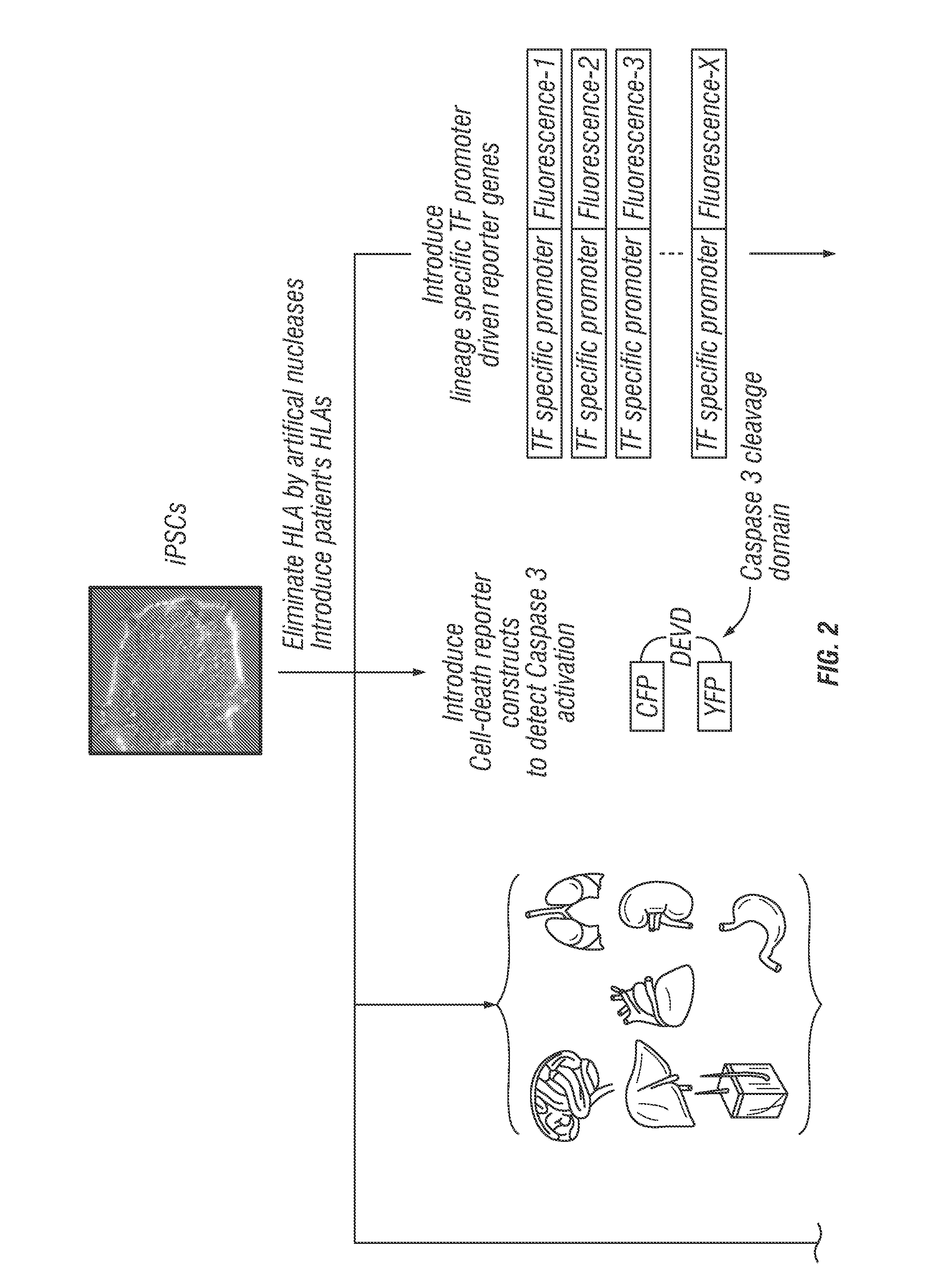
The application of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to generate adoptive cell therapy products and usage of iPSCs for screening potential toxicity of immune receptors are described herein. In some aspects, iPSCs and cells differentiated therefrom are provide which do not express a HLA gene (e.g., HLA-A).
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Safety evaluation method of transgene insect-resistant rice on predative natural enemy cyrtorhinus lividipennis
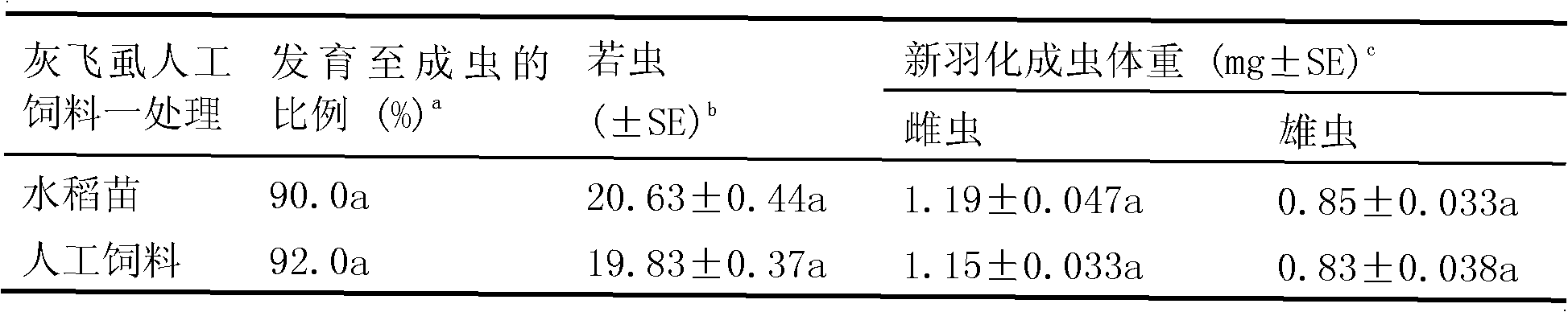
The invention relates to a safety evaluation method of transgene insect-resistant rice on predative natural enemy cyrtorhinus lividipennis. The safety evaluation method includes the five parts including Tier-1 toxicity testing, three-level nutrition testing, protein transferring rules, predation function reaction and population density and population dynamic comparison. The potential toxicity of Bt protein expressed by Bt transgene insect-resistant rice on the cyrtorhinus lividipennis are respectively evaluated by the five parts; influences of the Bt transgene insect-resistant rice on the cyrtorhinus lividipennis on prey media are evaluated; paths and degrees for the cyrtorhinus lividipennis to be exposed in Bt protein are evaluated; influences of the Bt transgene insect-resistant rice on the cyrtorhinus lividipennis population are evaluated. Finally generated ecological effects of transgenic crop planting on non-target organisms are comprehensively evaluated according to data in the five parts. The safety evaluation method is systematic and scientific, and is of great significance on perfecting influence studying of transgenic crops on the non-target organisms and determining the ecological safety of transgenic crop planting.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Nutritional supplement with functions of oxidation resistance and fatigue resistance
ActiveCN102150861AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove fatigue resistanceFood preparationPotential toxicityGrape seed
The invention relates to a nutritional supplement with functions of oxidation resistance and fatigue resistance, which is prepared from active ingredients and auxiliary materials such as multiple vitamins, mineral substances, siberian ginseng extracts, astragalus mongholicus extracts, medlar extracts, grape seed extracts and the like. The active ingredients in the supplement have a special proportion; the nutritional supplement can achieve the same effects of oxidation resistance and fatigue resistance by using a dose of traditional Chinese medical extracts smaller than the conventional dose;and the nutritional supplement has the characteristics of low potential toxicity, low production cost, obvious treatment effect and low price, thereby being suitable for long-time use.
Owner:辽宁亿邦制药有限公司
Anti-alcohol liver-protecting composition and anti-alcohol liver-protecting preparations comprising composition
InactiveCN109007808AHas anti-cancer propertiesShort stayHydrolysed protein ingredientsDigestive systemPotential toxicityAlcohol
The invention discloses an anti-alcohol liver-protecting composition and anti-alcohol liver-protecting preparations comprising the composition, and relates to the technical field of food preparations.The anti-alcohol liver-protecting composition comprises 10-55 parts of corn oligopeptide, 2-20 parts of turmeric, 2-20 parts of kudzuvine root extract, 5-20 parts of raisin tree seed extract, and 0.5-23 parts of broccoli seed water extract. The invention also provides a preparation method of tablet-type, solid beverage-type and drink-type anti-alcohol liver-protecting preparations. The anti-alcohol liver-protecting preparations of the invention solve the problems that anti-alcohol liver-protecting products in the prior art have poor anti-alcohol effect, some traditional Chinese medicine ingredients have potential toxicity, and the product stability in actual production is difficult to ensure. The preparation method is simple and convenient.
Owner:宝健(北京)生物技术有限公司
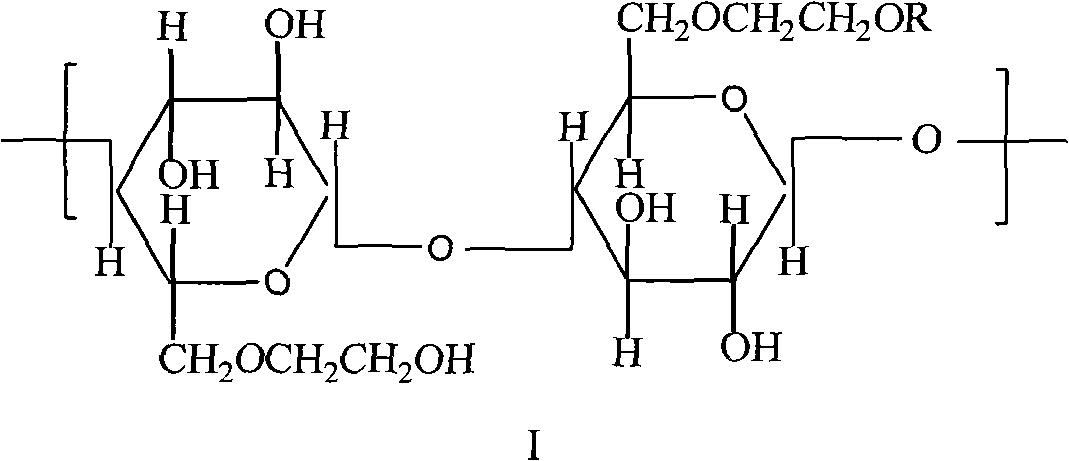
Hydrophobically associating hydroxyethylcellulose oil displacement agent
ActiveCN102140337AStrong stickinessIncrease stickinessFluid removalDrilling compositionPotential toxicityPolymer science
The invention relates to a hydrophobically associating hydroxyethylcellulose oil displacement agent. The hydrophobically associating hydroxyethylcellulose has the constitutional unit shown in the formula I. In the formula I, R is -C12H25, -C14H29 or -C16H33. The hydrophobically associating hydroxyethylcellulose is used to prepare 2000-8000mg / L of solution and the solution is injected in formationor core so as to increase the oil recovery. In the oil displacement agent, the modified natural polymer-hydrophobically associating hydroxyethylcellulose is used to replace the refractory polyacrylamide oil displacement agent with potential toxicity.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to parasite anagrus nilaparvatae
The invention relates to an evaluation method of safety of genetically modified insect resistant rice relative to parasite anagrus nilaparvatae. The evaluation method includes three parts of Tier-1 toxicity determination test, wherein the potential toxicity of Bt proteins expressed by Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on non-target organism anagrus nilaparvatae is evaluated; successive generation three-level nutrition test, wherein the influence of the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice on the safety of the anagrus nilaparvatae through parasitic mediators is evaluated according to the food chain of rice-delphacidae-anagrus nilaparvatae; a protein transfer rule, wherein the way and degree that the anagrus nilaparvatae is exposed in the Bt proteins expressed by the Bt-gene modified insect resistant rice are identified through an ELISA detection means; finally, the ecological consequences generated by genetically modified crop cultivation on non-target organisms are evaluated synthetically according to the data of the three parts. The evaluation method is systematic and scientific, and has great significance for the research of the influence of genetically modified crops on the non-target organisms and ecological safety of genetically modified crop cultivation.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Toxicology and Cellular Effect of Manufactured Nanomaterials
ActiveUS20090269279A1Low toxicityElimination of nanotoxicityPowder deliveryMicrobiological testing/measurementPotential toxicityInducer Cells
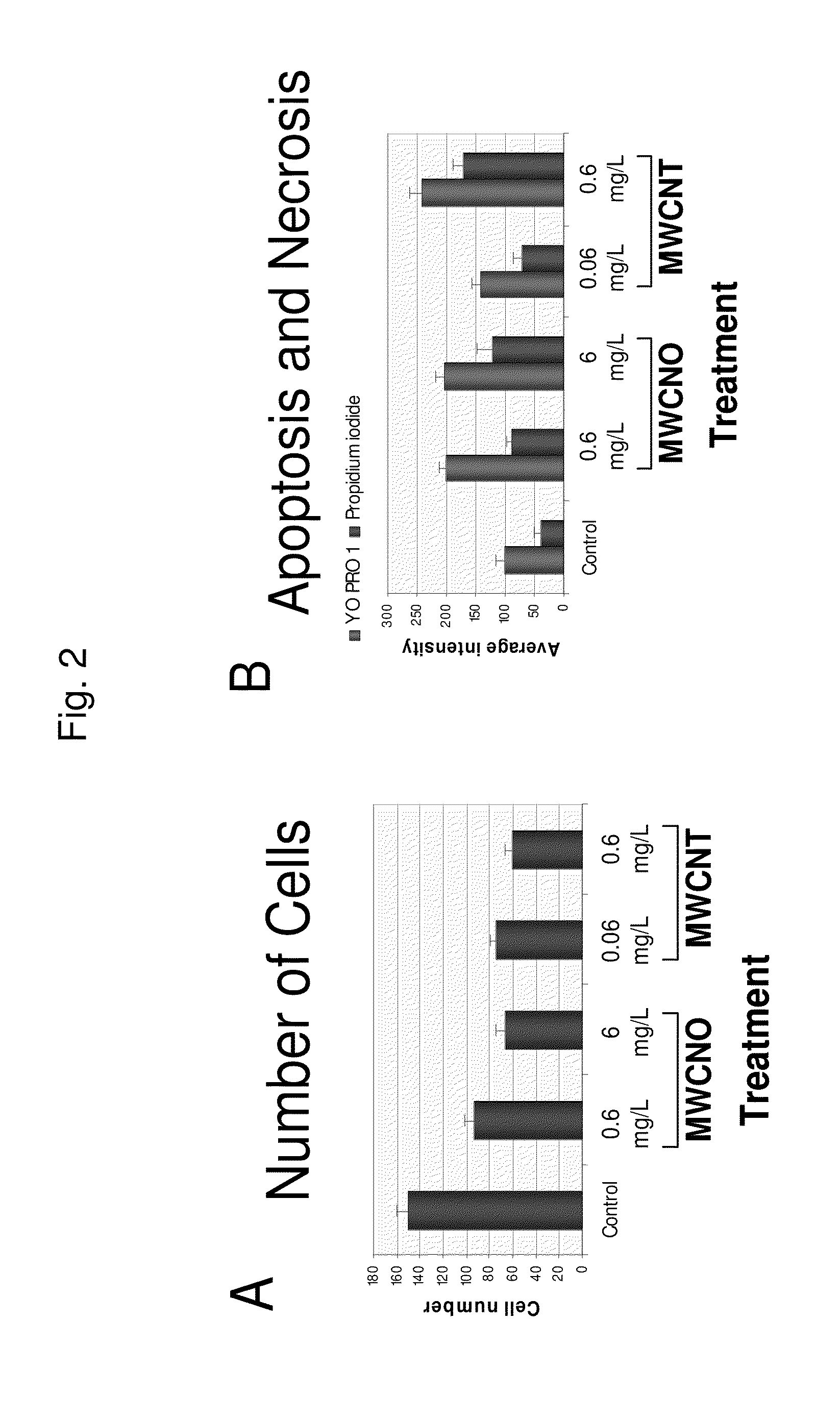
The increasing use of nanotechnology in consumer products and medical applications underlies the importance of understanding its potential toxic effects to people and the environment. Herein are described methods and assays to predict and evaluate the cellular effects of nanomaterial exposure. Exposing cells to nanomaterials at cytotoxic doses induces cell cycle arrest and increases apoptosis / necrosis, activates genes involved in cellular transport, metabolism, cell cycle regulation, and stress response. Certain nanomaterials induce genes indicative of a strong immune and inflammatory response within skin fibroblasts. Furthermore, the described multiwall carbon nanoonions (MWCNOs) can be used as a therapeutic in the treatment of cancer due to its cytotoxicity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fluorescent bioprobes for upconversion nanoparticle-labeled aptamers
InactiveCN102260745AAvoid damageAvoid autofluorescenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPotential toxicityA-DNA
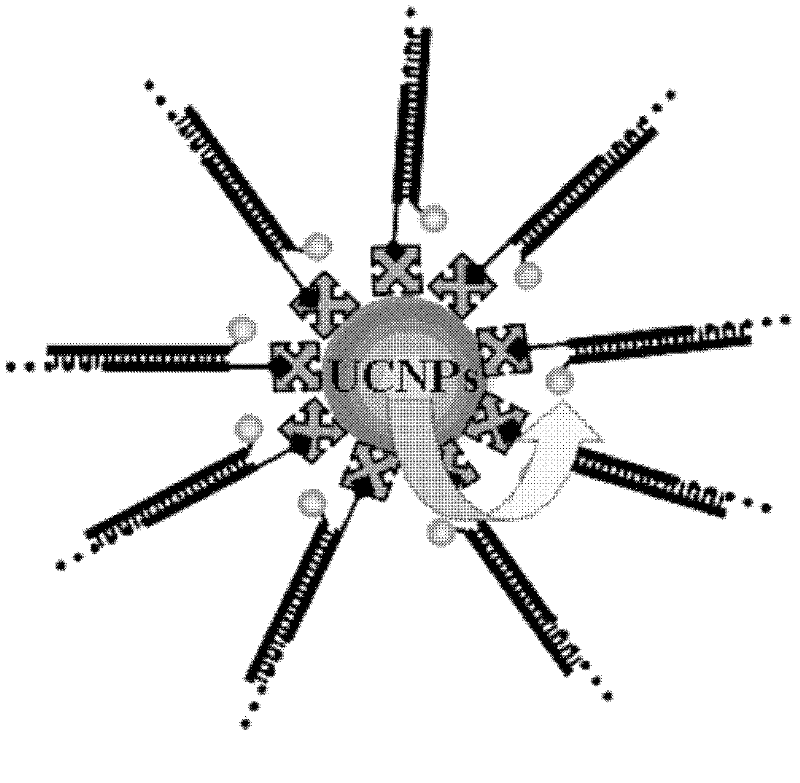
The invention relates to a fluorescent bioprobe for upconverting nanoparticle-labeled aptamers, which belongs to the technical field of biomolecular detection. In order to overcome the technical problems of existing QDs-labeled aptamer biological probes, including damage to the nucleic acid of the organism where the target molecule is located, high background signal of QDs, potential toxicity, "blinking" effect and chemical instability, provide A fluorescent bioprobe for up-conversion nanoparticle-labeled aptamers, including aptamers labeled with up-conversion nanoparticles as fluorescent donors, and DNA strands complementary to the aptamers, which are connected with fluorescent The donor undergoes a FRET effect as the fluorescent acceptor dye molecule. The fluorescent donors used in the present invention are UCNPs, which have the advantages of low background signal, non-toxicity, no "blinking" effect and strong chemical stability.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pure-organic long-afterglow composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103694994ARich in carbon-oxygen bondsGood biocompatibilityLuminescent compositionsPotential toxicityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a pure-organic long-afterglow composite material and a preparation method thereof, belongs to the technical field of luminescent materials and is used for solving the problems that the preparation process of a long-afterglow luminescent material is complex, potential toxicity exists in the preparation process, and preparation raw materials are scarce in the prior art. The preparation method comprises the following steps of pyrolyzing ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid disodium for 2-4 hours at 200-400 DEG C in inert atmosphere so as to obtain black fluffy solids, carrying out ultrasonic dissolving on the black fluffy solids, carrying out centrifuging to remove black precipitates, taking an upper-layer tan clear solution as a water solution of carbon nanodots, finally adequately mixing the water solution of the carbon nanodots with a polyvinyl alcohol water solution, and drying to obtain the pure-organic long-afterglow composite material. The pure-organic long-afterglow composite material has the advantages that the afterglow decay time can reach multiple seconds, and the material is non-toxic, is good in biocompatibility and can be applied to the field of biological medicines.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clean sterile high-barrier medical rubber plug and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a clean sterile high-barrier medical rubber plug and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a medical rubber plug which is free of potential toxicity on medicines and human tissues and has bacteria restraining and sterilizing performance and high barrier performance and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of medical rubber accessories. The preparation method for the clean sterile high-barrier medical rubber plug comprises the following steps: performing processes such as mixing medical raw rubber, natural aloe extract powder, medical-level sheet micro nano filler, processing auxiliaries and a radiation sensitizer in proportion, performing mould base pressing and molding, radiation vulcanizing, trimming, and drying, thereby preparing the medical rubber plug. The sterile high-barrier medical rubber plug is simple in formula system, adopts normal-temperature radiation vulcanization, is free of high-temperature decomposition products and free of potential toxicity on medicines and human tissues, and can be used for medical rubber accessories such as a medical injector rubber piston and a medical rubber plug which directly contact with the medicines.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
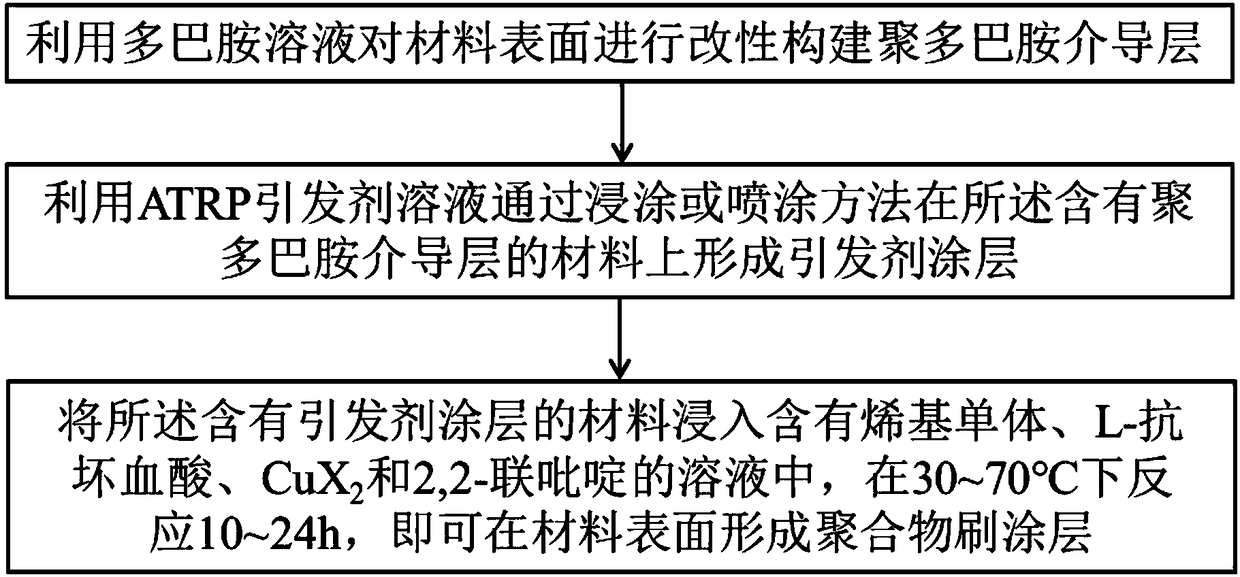
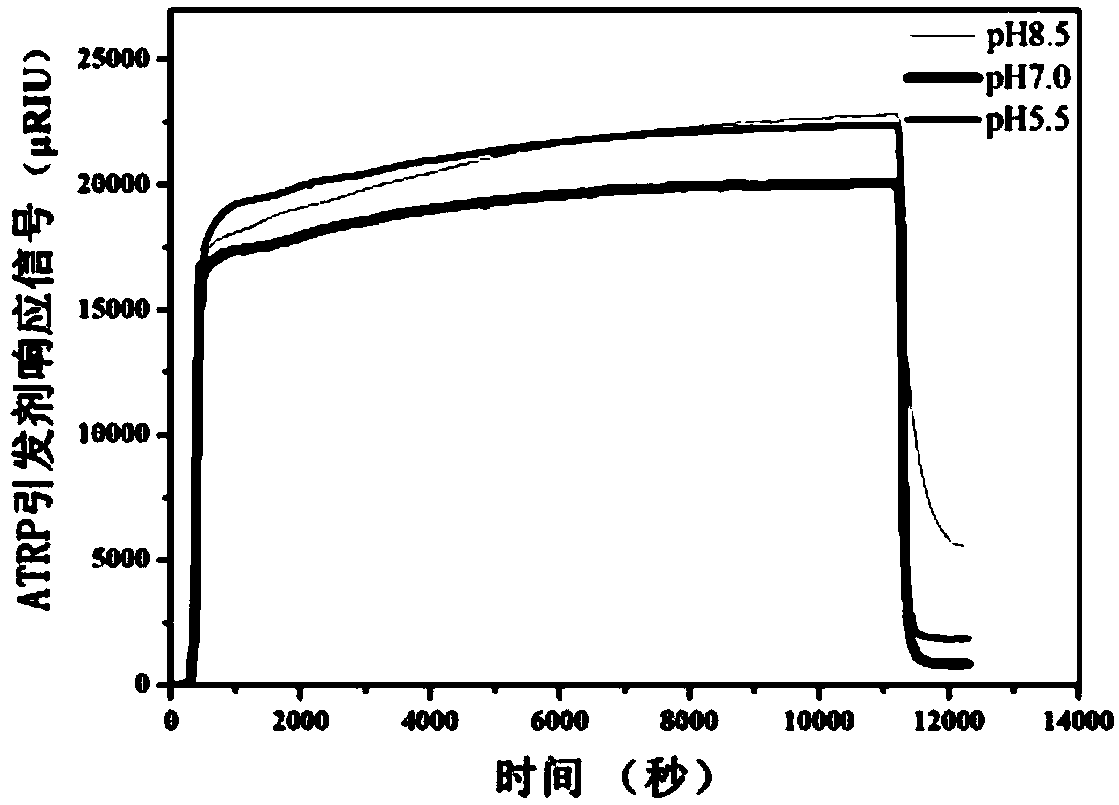
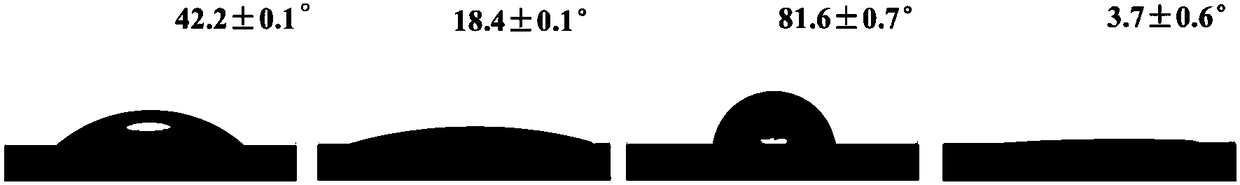
Method for constructing polymer brush on surface of material
InactiveCN108529895AImprove hydrophobicityLower surface free energyCoatingsPotential toxicityAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention provides a method for constructing a polymer brush on the surface of a material. The method comprises the following steps: modifying the surface of the material with a dopamine solutionto construct a polydopamine-mediated layer; forming an initiator coating on the material containing the polydopamine-mediated layer by using an atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) initiator solution by means of dip coating or spraying; dipping the material containing the initiator coating into a solution containing an ethylenic monomer, L-ascorbic acid, CuX2 and 2,2-bipyridyl, and carryingout a reaction for 10-24h at 30-70 DEG C so as to form a polymer brush coating on the surface of the material. The method for constructing the polymer brush on the surface of the material can be performed under the air condition, and omits the step of oxygen removal; the copper salt consumption of the method is very little and is only several parts per ten thousands of the traditional ATRP, so that the problem that the traditional ATRP product has potential toxicity can be solved; furthermore, the method can be used for forming the polymer brush on the surface of any material, and is simple,convenient and high in universality.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
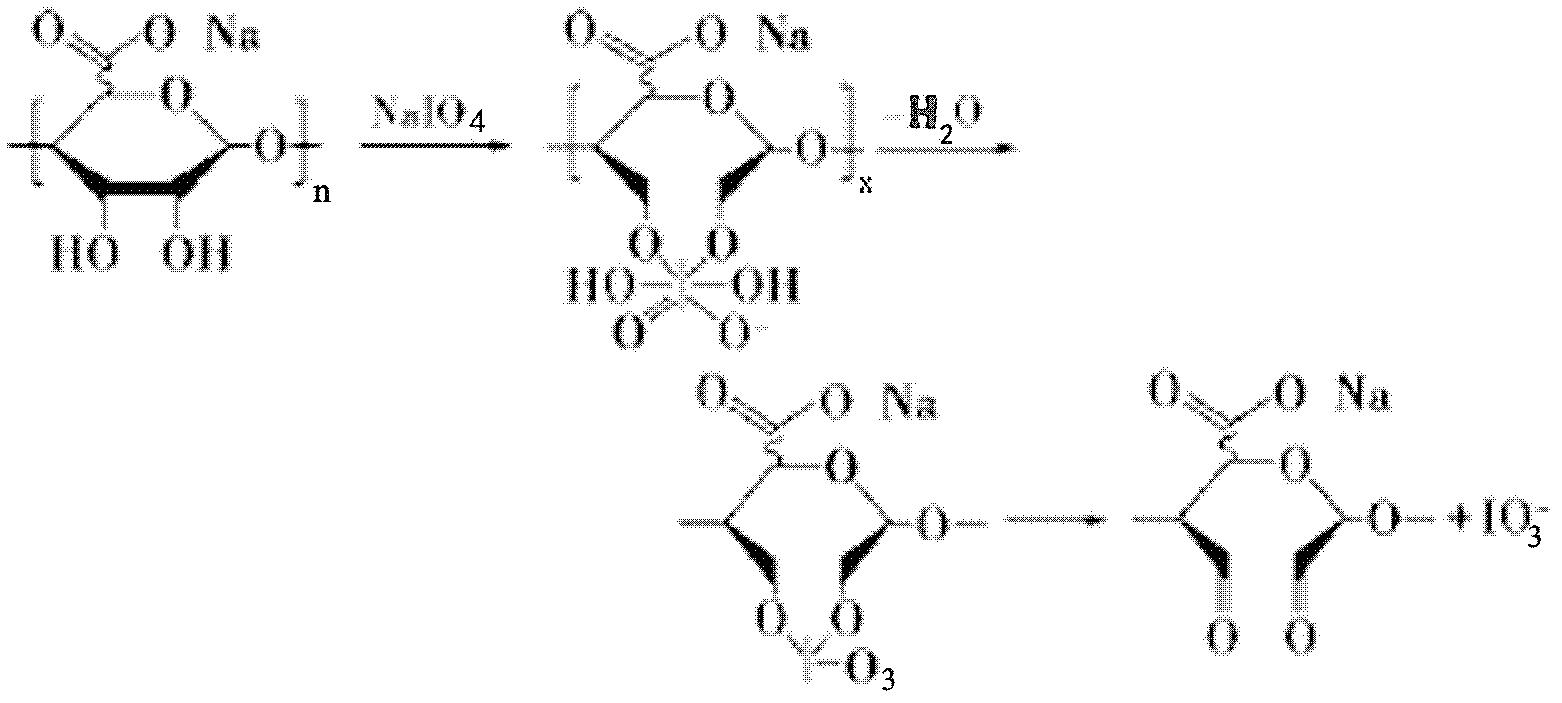
End-point fixing preparation method for multi-aldehyde alginic acid coating
InactiveCN102617880AImprove bindingGood spatial conformationPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPotential toxicityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses an end-point fixing preparation method for a multi-aldehyde alginic acid coating. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, polymer material is soaked into sulfuric acid solution of potassium permanganate for acidizing treatment; then the material subjected to acidizing treatment is placed into polyethylene imine solution so as to obtain an amination decorated surface after reaction; periodic acid or sodium periodate is used for oxidation treatment to sodium alginate, aldehyde group is exposed at the tail end of the segment of alginic acid, and multi-aldehyde sodium alginate is obtained; the liquid reactant of the multi-aldehyde sodium alginate is prepared, the material on the amination decorated surface is placed into the liquid reactant, and the multi-aldehyde alginic acid coating is obtained through an end-point fixing method. The preparation method provided by the invention overcomes the defects of bad biocompatibility, poor anticoagulant activity,potential toxicity and the like in common polymer material.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY THIRD CENT HOSPITAL
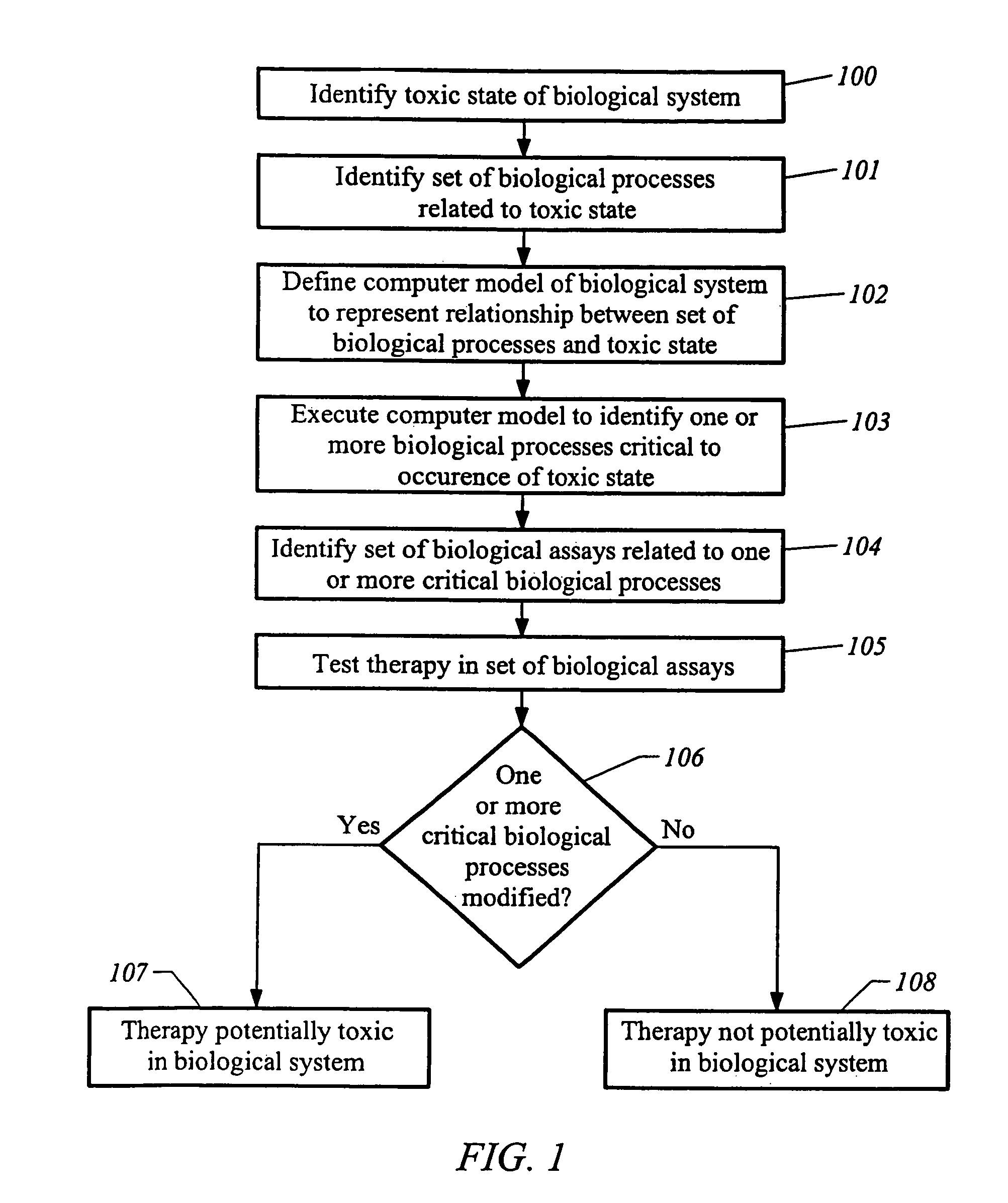
Predictive toxicology for biological systems
InactiveUS7853406B2Chemical property predictionBiological testingPotential toxicityOrganismal Process
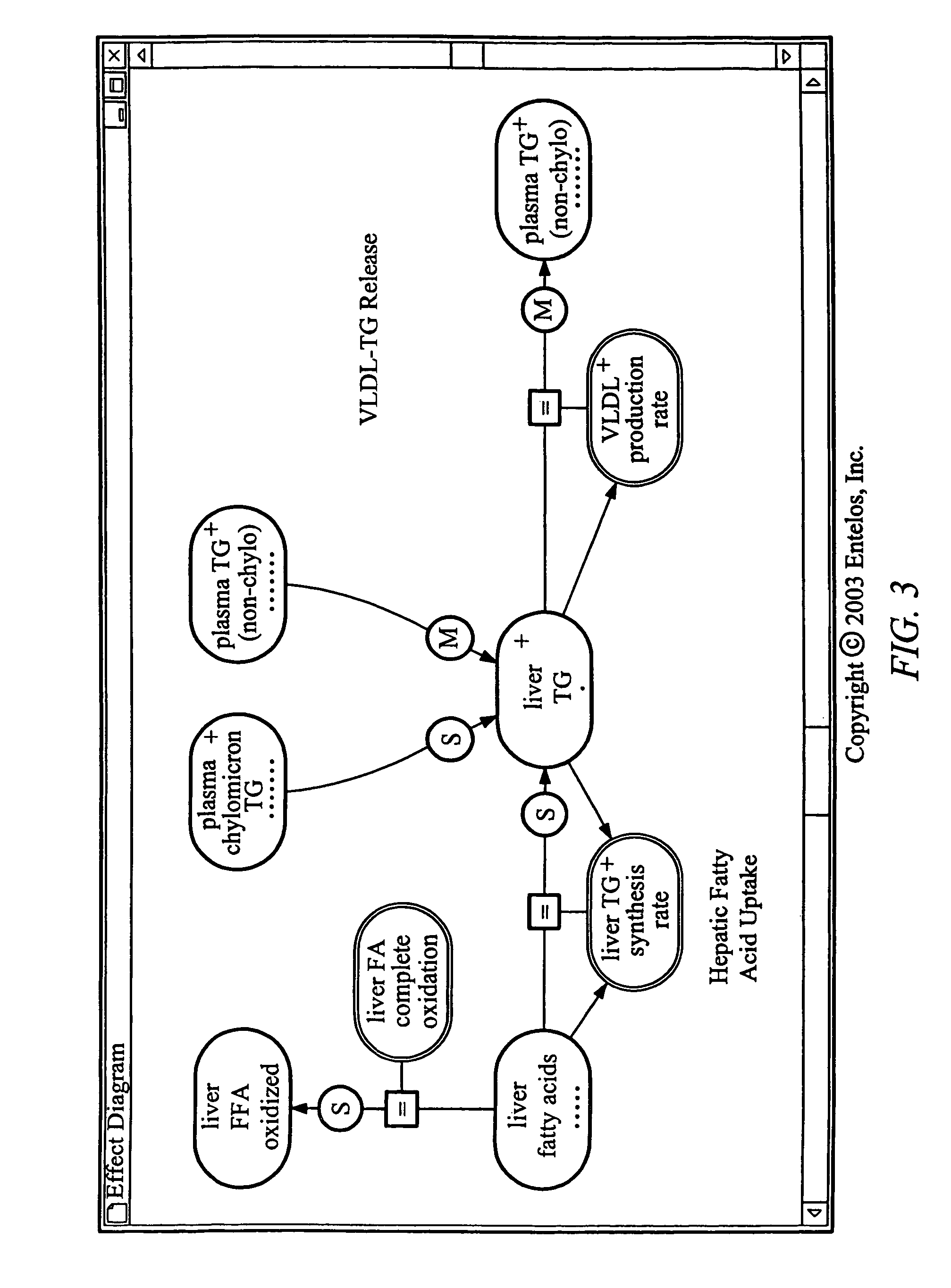
Methods and apparatus to identify a potential toxicity of a therapy in a biological system are described. In one embodiment, a method uses a computer model that represents a set of biological processes of the biological system. The method includes executing the computer model to identify a first set of biological processes contributing to the occurrence of a toxic state of the biological system. The method also includes identifying a set of biological assays based on the first set of biological processes and testing the therapy in the set of biological assays to identify a second set of biological processes modified by the therapy. The method further includes identifying the potential toxicity of the therapy based on the second set of biological processes.
Owner:ENTELOS HLDG
Safety evaluation method of transferring Bt gene insect-resistant paddy for predator paederus fuscipes
InactiveCN104322452ASimple and fast operationLow costBiological testingAnimal husbandryThree levelPotential toxicity
The invention relates to a safety evaluation method of transferring Bt gene insect-resistant paddy for predator paederus fuscipes. The method comprises three parts which are three-level nutrition test, protein transfer rule and Tier-1 toxicity determination test, wherein each part evaluates the influence on the paederus fuscipes by the transferring Bt gene insect-resistant paddy through prey mediation, the approach and degree of the paederus fuscipes exposed to Bt protein, and the potential toxicity of the Bt protein expressed by the transferring Bt gene insect-resistant paddy to the paederus fuscipes, and finally ecological results to non-target organism by the transferring Bt gene insect-resistant paddy are comprehensively evaluated according to data on the three aspects. The evaluation method is systematic and scientific, and has important significance on perfecting the research on the influence of transferring Bt gene crop on non-target organisms and confirming the ecological safety of transferring Bt gene crop planting.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
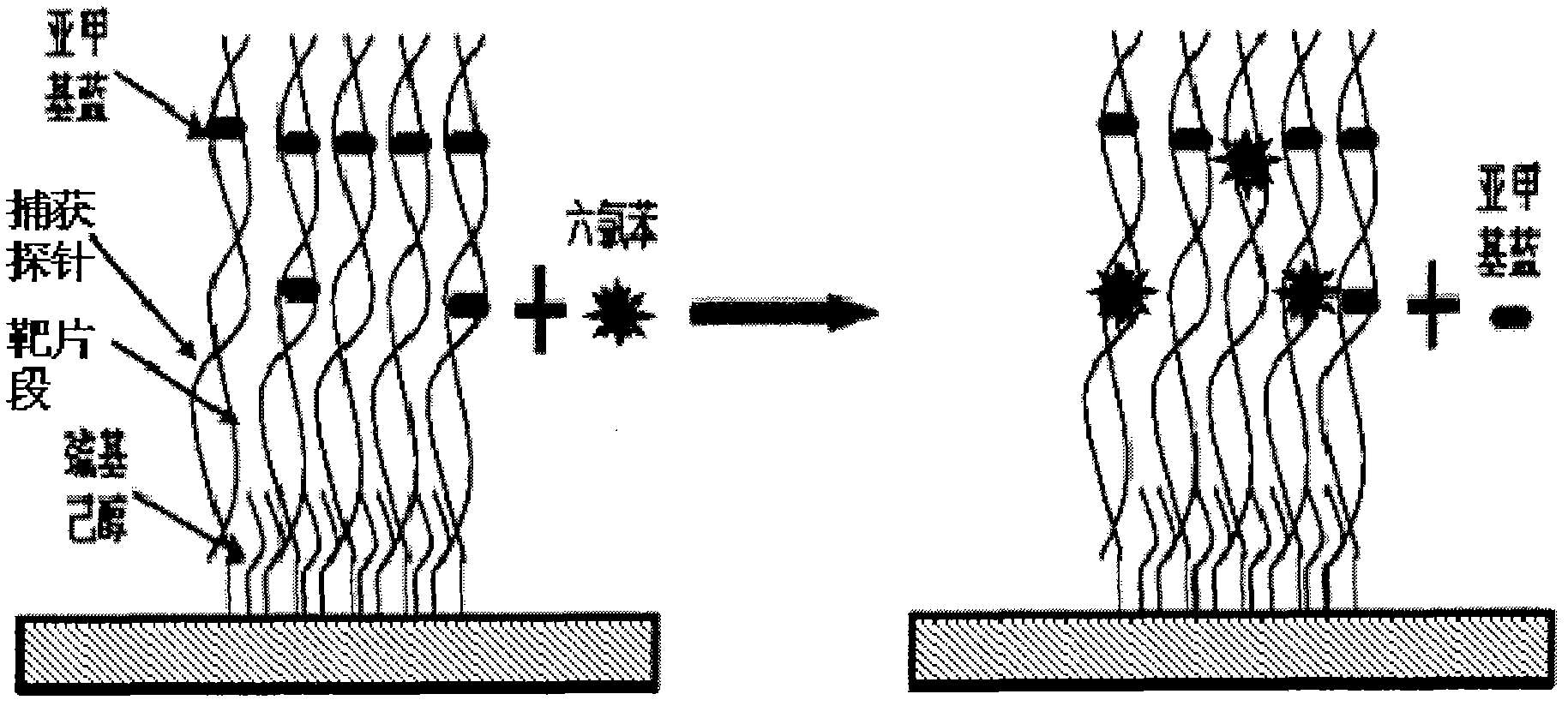
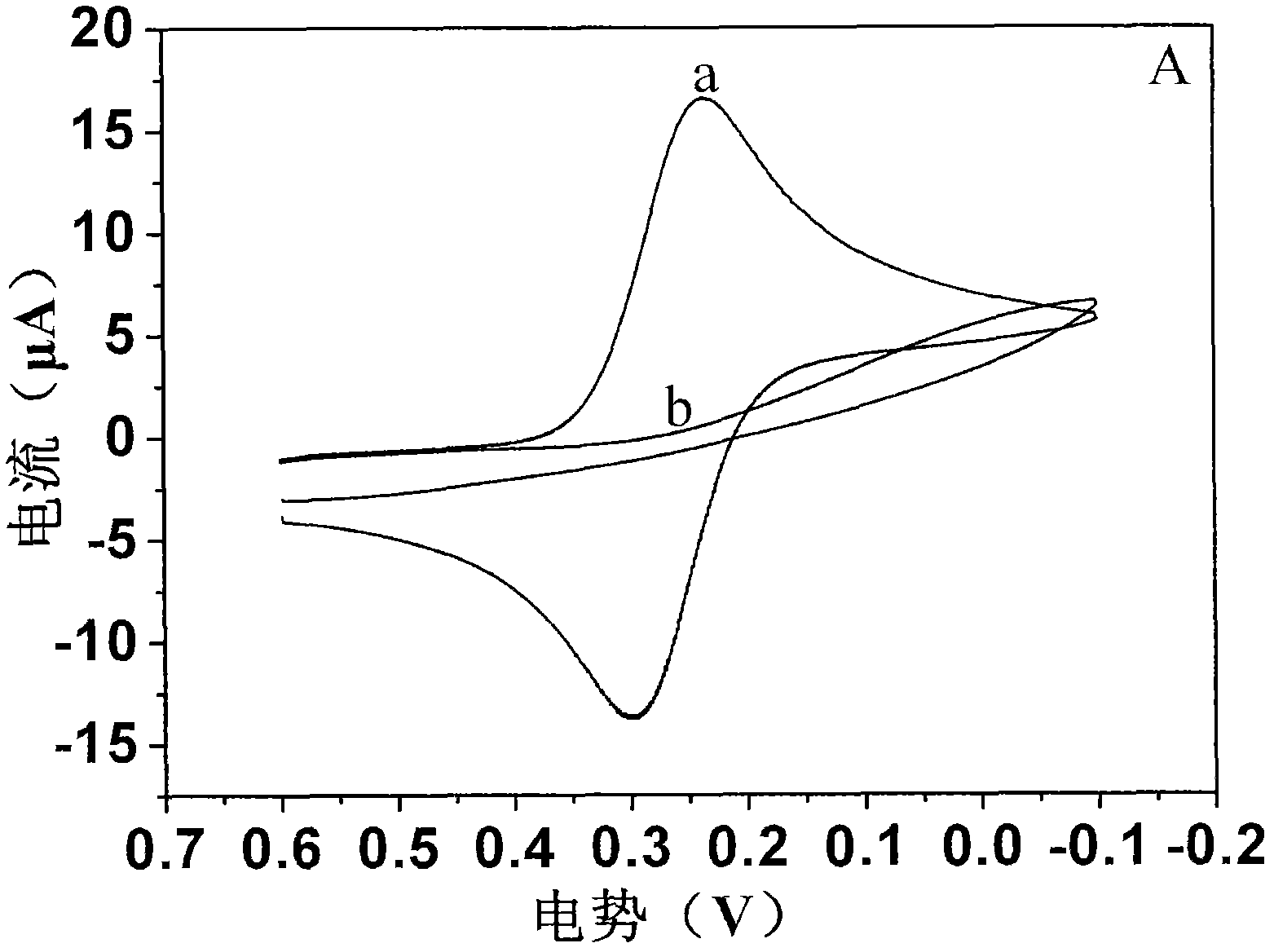
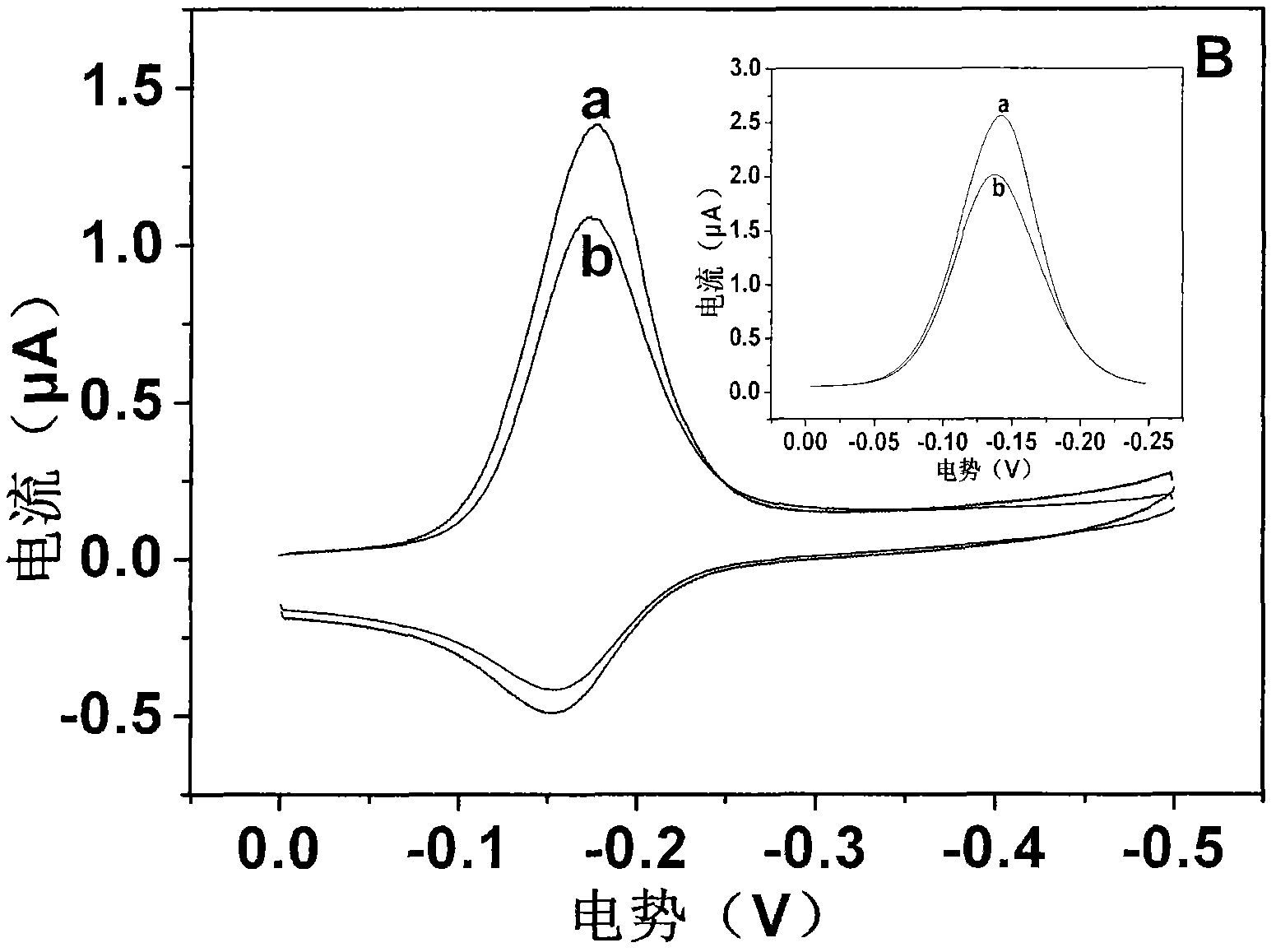
Electrochemical method employing DNA as probe to detect environmental pollutant
ActiveCN102375021AImprove stabilityReliable test resultsMaterial electrochemical variablesPotential toxicitySignalling molecules
An electrochemical method employing DNA as a probe to detect environmental pollutants. A biosensor detector comprises a working electrode, an auxiliary electrode, a reference electrode, a detection cell and an electrochemical working station. The working electrode is modified with nucleic acid probes on a surface thereof, and a genotoxicity compound in an environment sample is detected in a buffer system. When a detection result is positive, a signal of the sensor is changed obviously. Compared with an existing biosensor, the method has main advantages of: 1. high sensitivity; combination of an electrical active molecule and nucleic acid probes to increase a response current; 2. miniature and cheap apparatus and equipment, large detection flux, simple sample pre-treatment, and suitabilityfor on spot rapid screening detection. The method can not only carry out screening detection on a known genotoxicity compound but also evaluate potential toxicity effect of a newly synthesized compound; and the method can screen whether an actual sample contains a genotoxicity compound.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
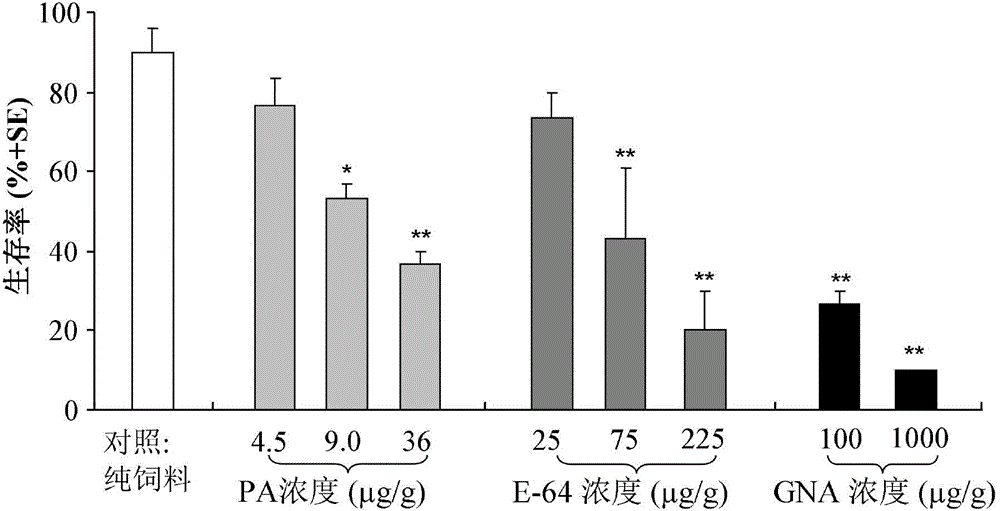
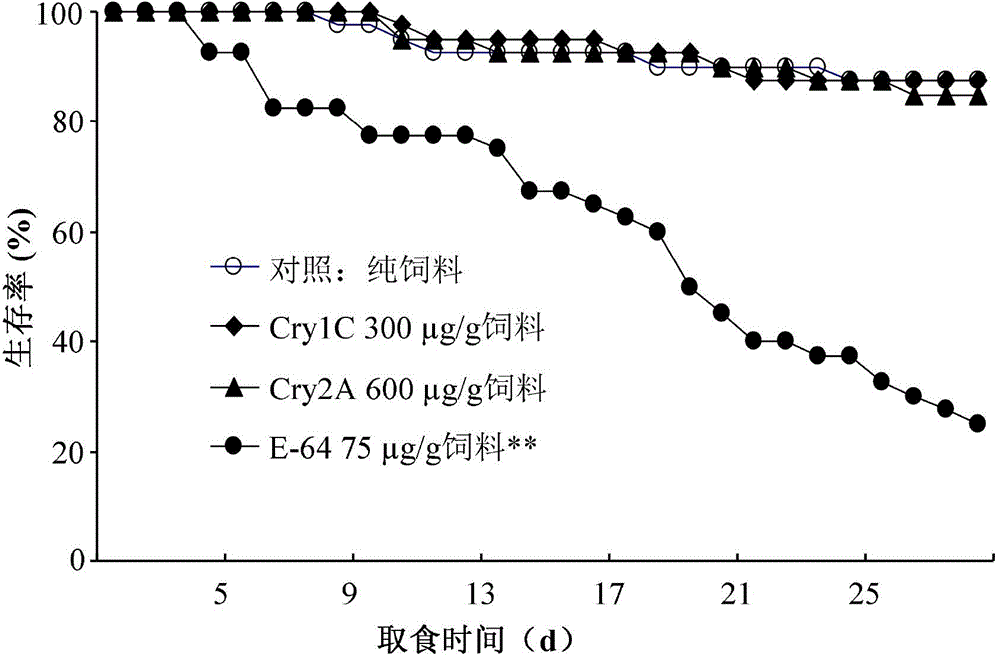
Method for determining potential toxicity influence of insecticidal compounds on Laodelphax striatellus
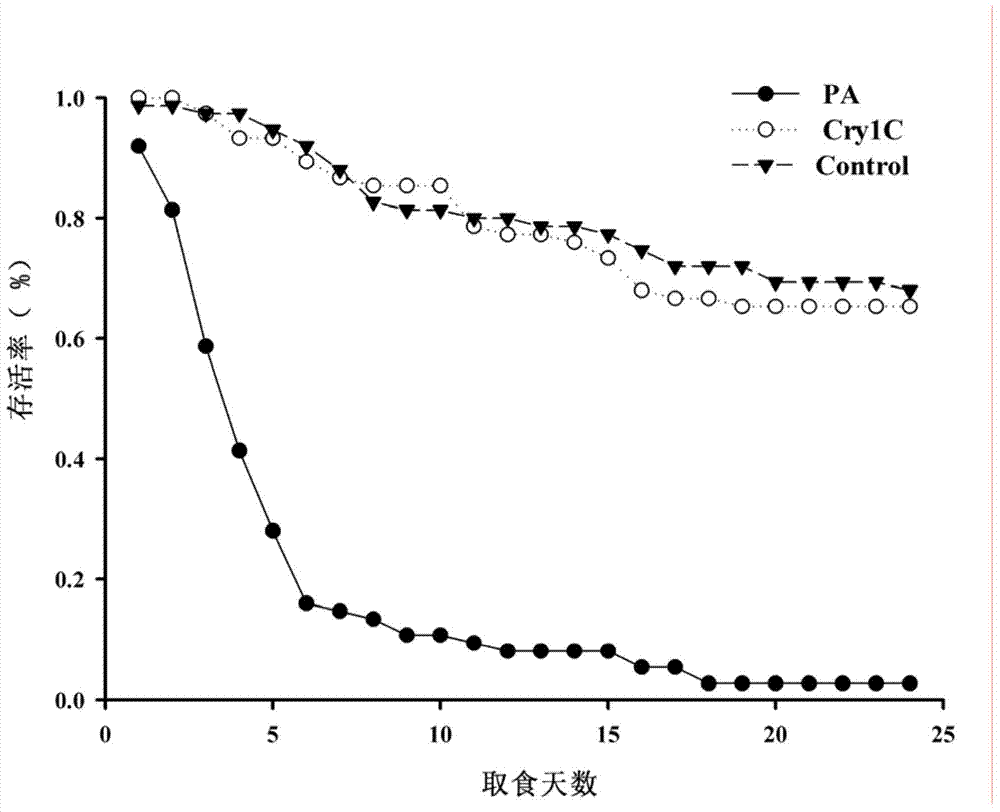
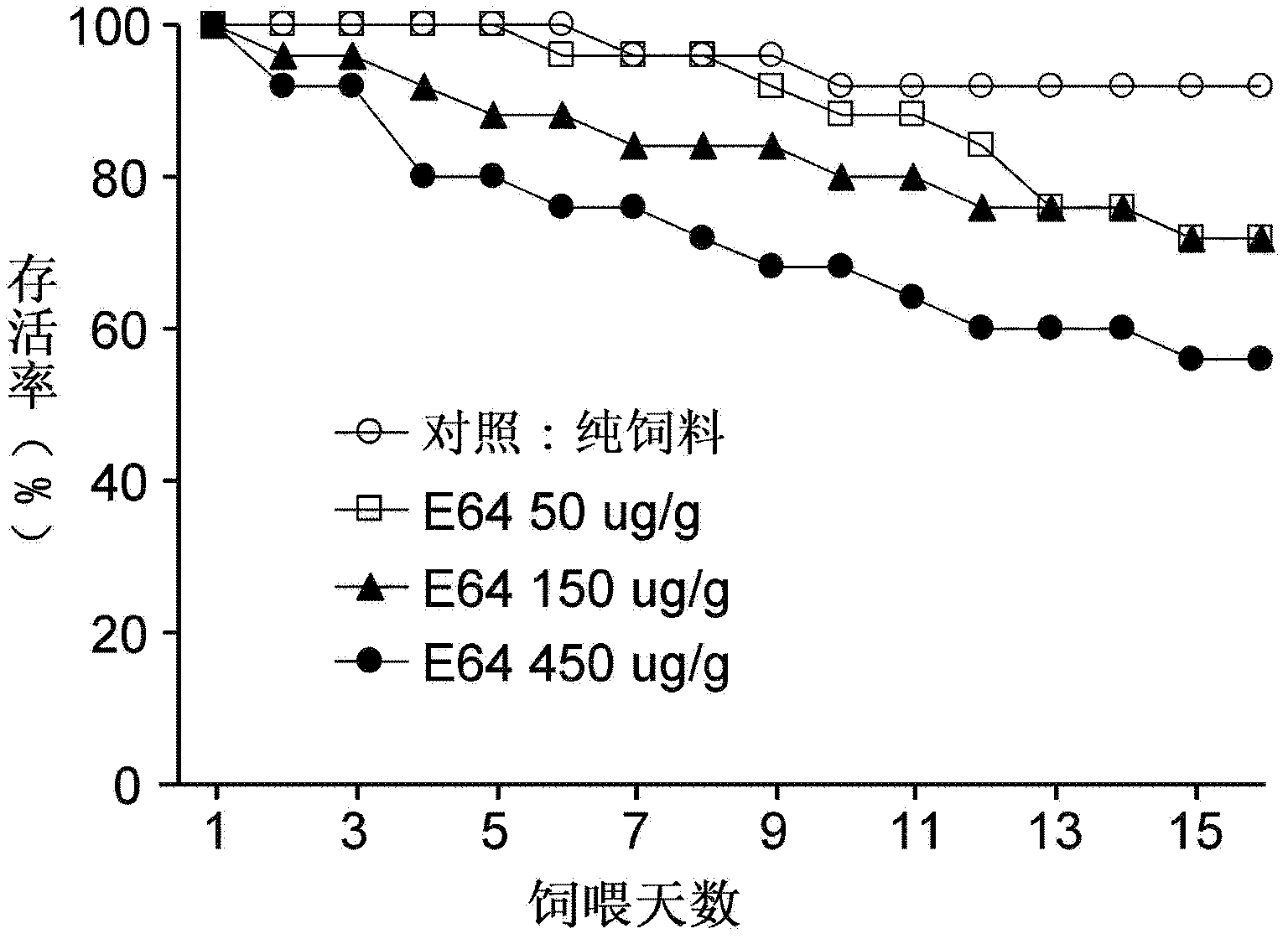
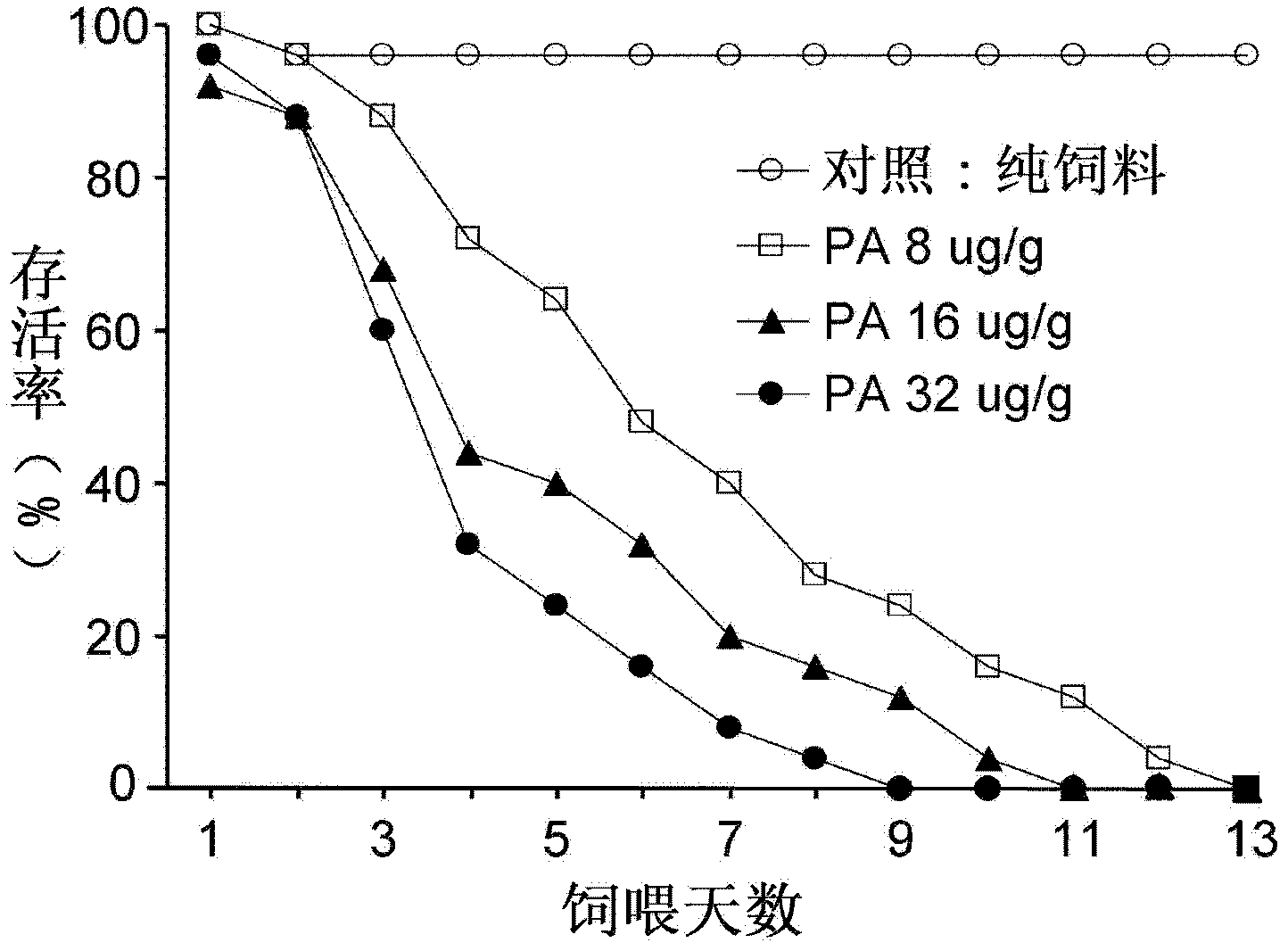
InactiveCN102608307AToxicity manifestsHigh sensitivityBiological testingPotential toxicityExperimental research
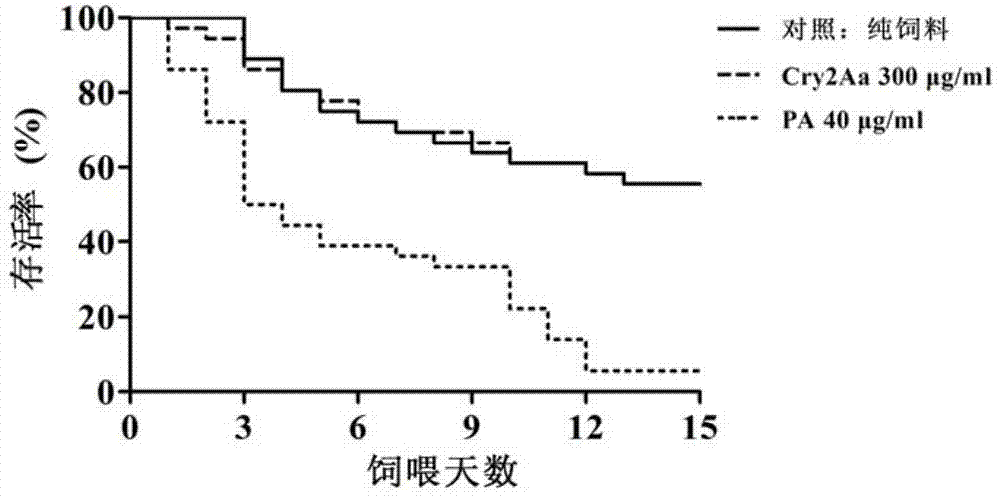
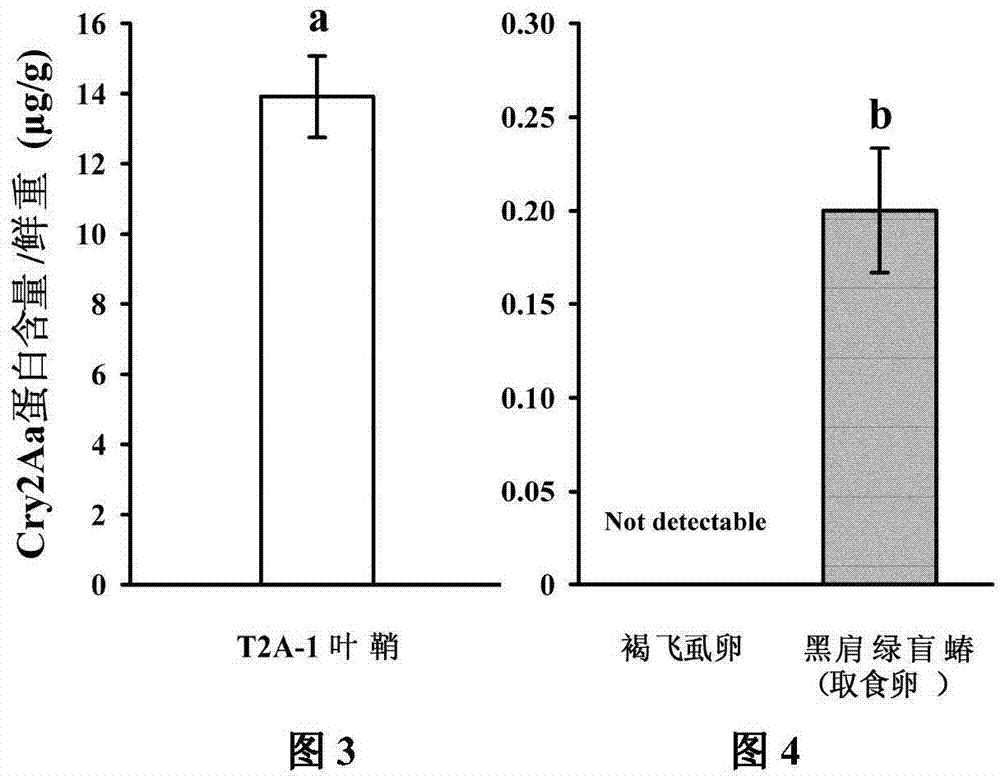
The invention provides a method for determining influence of insecticidal compounds on potential toxicity of Laodelphax striatellus, which includes: determining artificial feed effective to a determination system of toxicity on Laodelphax striatellus; developing a technique and a method for adding different organic or inorganic insecticidal compounds into the artificial feed; screening positive comparative compounds (protease inhibitor E-64 or inorganic compound, PA (potassium dihydrogen arsenate)) suitable for the determination system; providing suitable toxicity influence evaluation indexes for Laodelphax striatellus by experimental research; using E-64 and PA as modal compounds; verifying effectiveness and sensitiveness of the built method of toxicity determination for Laodelphax striatellus by dose-reaction bioassay; and finally building the systematic and sensitive method for determining potential toxicity influence of insecticidal compounds on Laodelphax striatellus. The method can be used for evaluating potential toxicity of exogenous insecticidal protein expressed in insect-resistant transgenic crops on Laodelphax striatellus and screening novel insecticidal protein genes resistant to Laodelphax striatellus, and can also be used for determining potential influence of different insecticides on Laodelphax striatellus.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
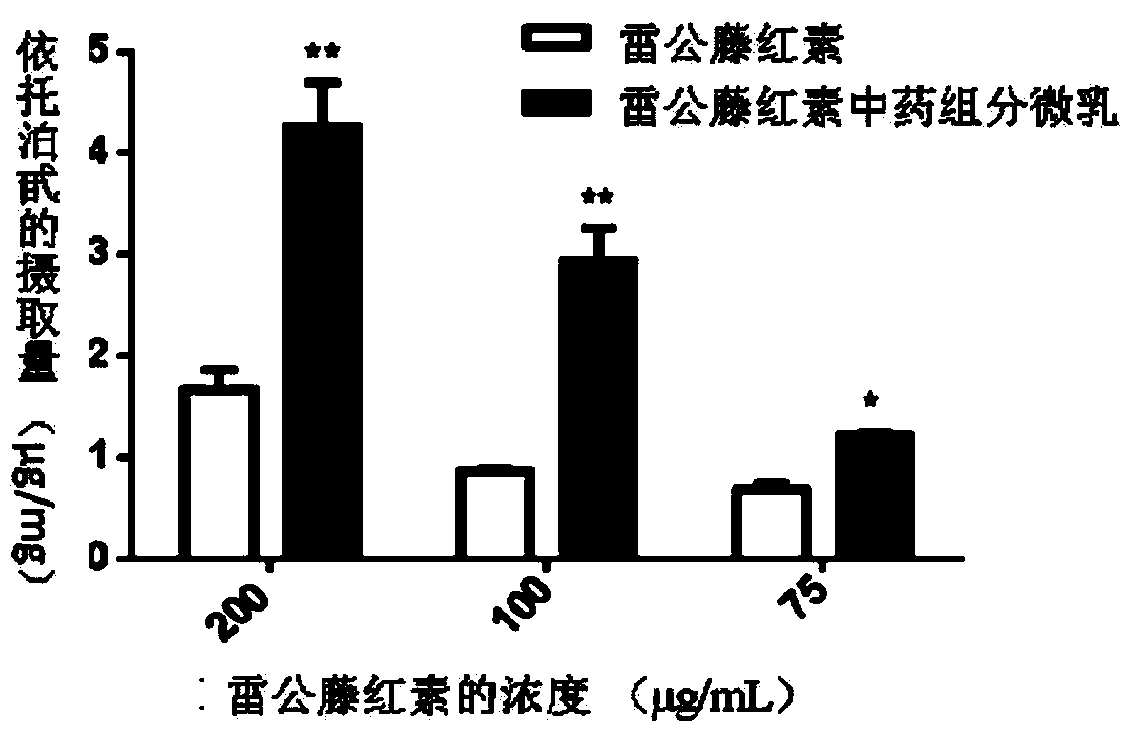
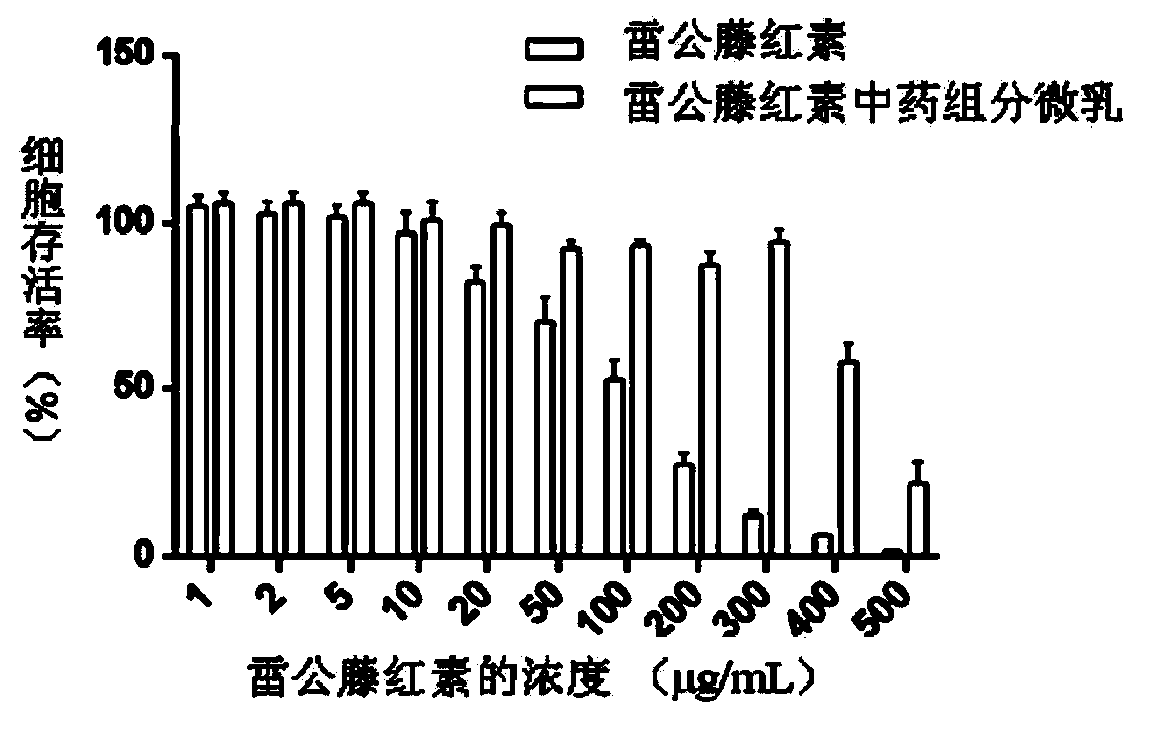
Traditional Chinese medicine component micro emulsion nano delivery system as well as preparation method and application thereof in preparing pharmaceutical preparation
ActiveCN103932984ALow toxicityHigh drug loadingOrganic active ingredientsNanomedicinePotential toxicityIn vivo
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine component micro emulsion nano delivery system as well as a preparation method and an application thereof in preparing a pharmaceutical preparation. The system consists of oil components, saponin components and insoluble components of traditional Chinese medicines, and is characterized by further comprising a co-emulsifier and water, wherein the weight ratio of the oil components to the saponin components to the insoluble components to the co-emulsifier to water is 40:(20-40):(1-4):(10-20):(80-200). The micro emulsion constructed by active components of traditional Chinese medicines can be used for solubilizing the insoluble components on one hand to control drug release and further form a nanoscale emulsion in water; on the other hand, by virtue of in vivo absorptive characteristics of the nano emulsion, the oral absorptive availability of the traditional Chinese medicine components is remarkably enhanced. The drug loading capacity can be greatly improved, and the potential toxicity in vivo can be reduced. Saponins and oils are combined to further have the synergic antitumor effect.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Aerobic active marine bacteria and preparation method of decolorizing flocculant of aerobic active marine bacteria
ActiveCN107460144AGood decolorization effectHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMalachite green
The invention discloses aerobic active marine bacteria and a preparation method of a decolorizing flocculant of the aerobic active marine bacteria. The aerobic active marine bacteria is formed by performing isolation and screening on mud disgorged by ruditapes philippinarum bred in a sea farm in a Zhujiajian, Zhoushan, Zhejiang in China, and is authenticated to be pseudoalteromonas ((i) Pseudoalteromonas ( / i)sp.). The decolorizing flocculant has the beneficial effects that the formed adecolorizing flocculant has good decoloration effect, and the flocculation rate of the decolorizing flocculant to kaolin reaches greater than 90 percent; the decolorizing flocculant has high activity for performing decoloration on high-concentration waste water, and the flocculation rate of the decolorizing flocculant to methylene blue, malachite green and crystal violet reaches greater than 92 percent, 99 percent and 98 percent; the decolorizing flocculant does not have potential toxicity for organisms, and is green and healthy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
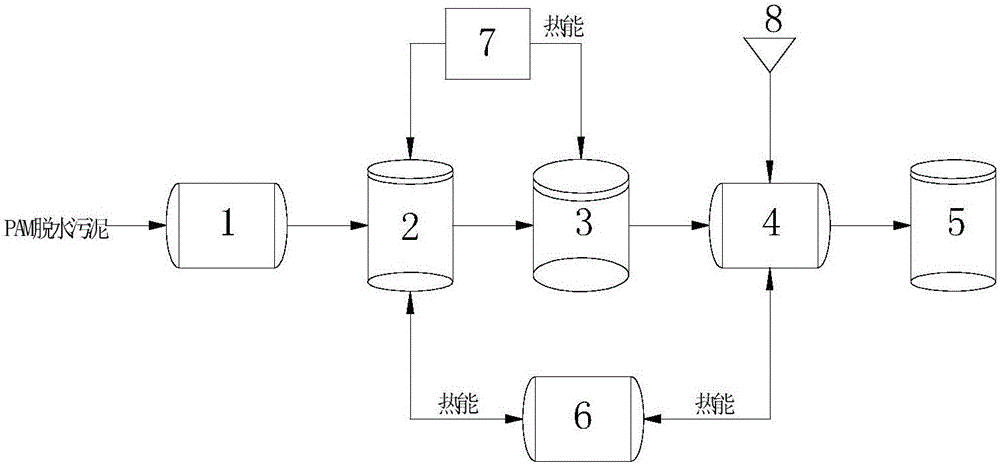
System and method for promoting hydrolysis of PAM (polyacrylamide) in dewatered sludge and simultaneously producing short-chain fatty acids
ActiveCN105948448AIncrease hydrolysis rateRealize resource processingWaste based fuelBiological sludge treatmentPotential toxicityZoogloea
The existing PAM (polyacrylamide) dewatered sludge has poor digestion efficiency due to oversize flocs in the anaerobic digestion process, thereby inhibiting the high-molecular organic matrix in the sludge from leaching, prolonging the retention time of the sludge, and providing possibility for degradation of PAM into the monomer acrylamide. The invention provides a recycling harmless system and method for promoting hydrolysis of residual PAM in dewatered sludge and simultaneously producing short-chain fatty acids, belonging to the field of sludge treatment and disposition. The method comprises the following steps: PAM dewatered sludge is subjected to pyrohydrolysis treatment to promote PAM flocs in dewatered sludge to dissociate; alkaline conditioning is carried out to sufficiently destroy the pyrohydrolysis sludge zoogloea floc structure; and the sludge is sent into an anaerobic fermentation tank to produce short-chain fatty acids. The method enhances the PAM hydrolysis rate, lowers the PAM potential toxicity, and implements recycling harmless utilization of PAM dewatered sludge.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
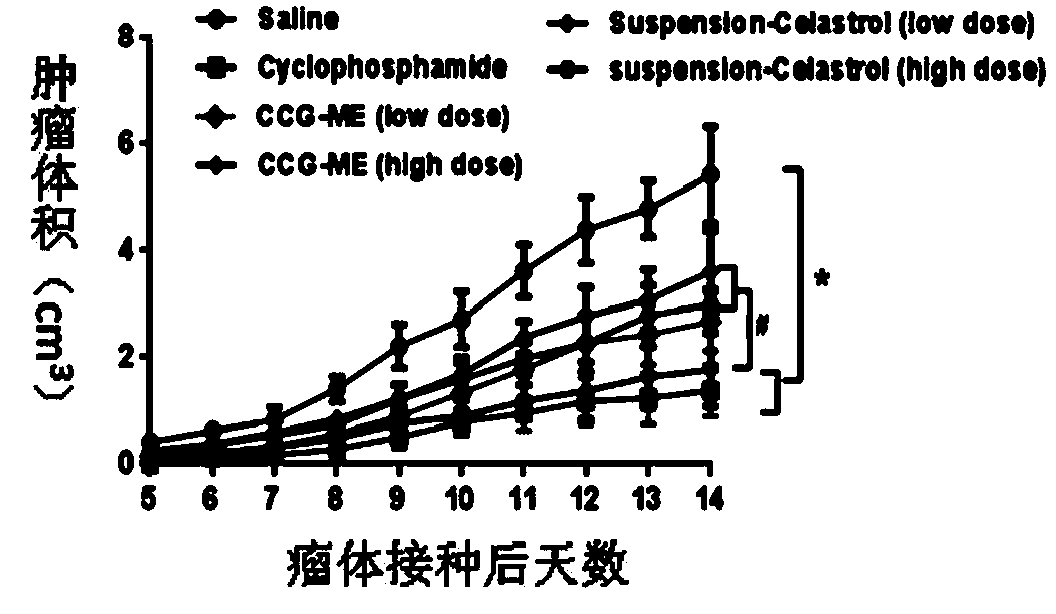
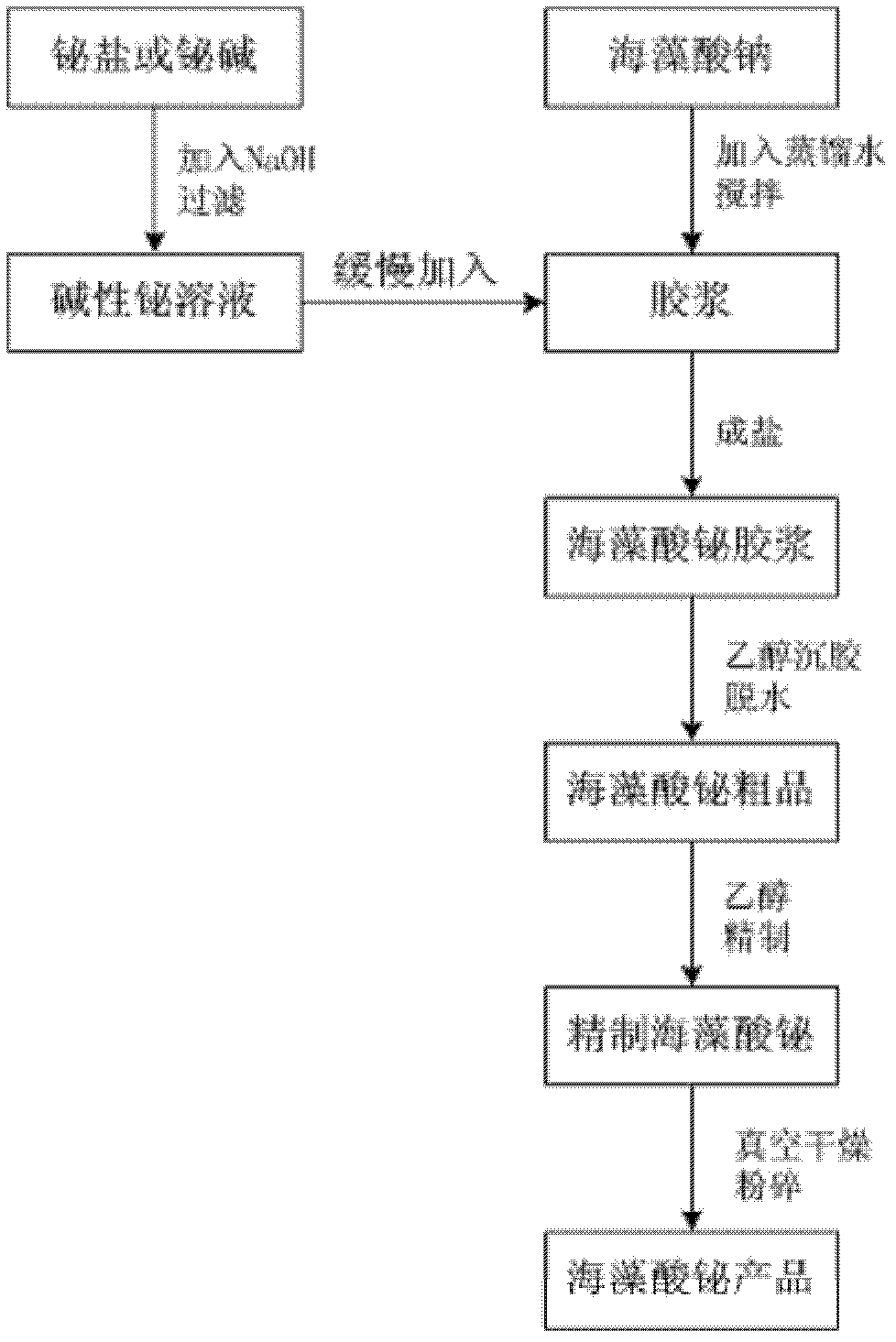
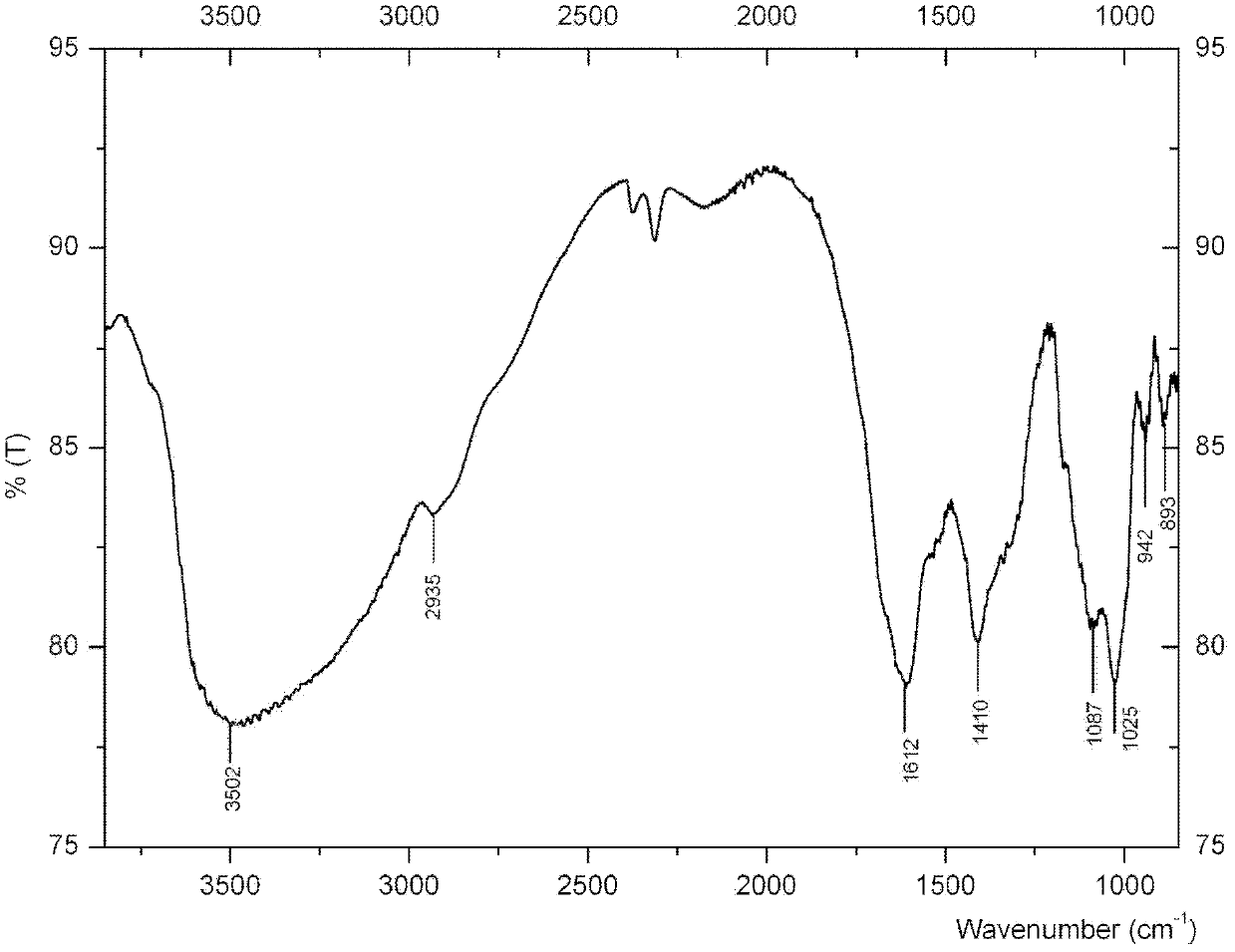
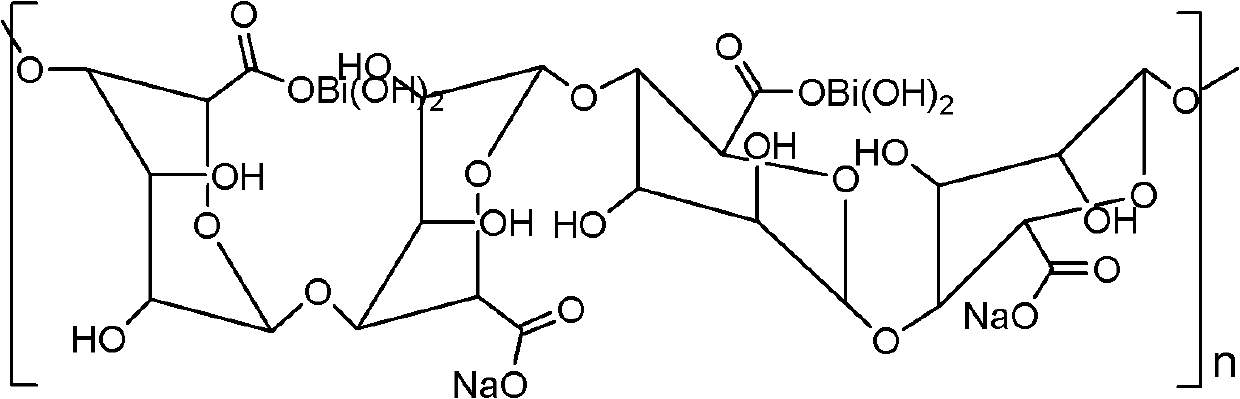
Bismuth alginate and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102558383APromote wound healingGood development valueAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPotential toxicityEthanol precipitation
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A test method for detecting the potential toxic influence of stomach poisoning insecticide compounds on folsomia candida
InactiveCN105075991ARapid detection of potential toxic effectsSimple methodAnimal husbandryPotential toxicityPositive control
The invention provides a test method for detecting the potential toxic influence of stomach poisoning insecticide compounds on folsomia candida. The method is characterized in that an insecticide or transgenic insecticidal protein is added into yeast powder (feed) uniformly and the mixture is directly delivered to folsomia candida; yeast mixed with a protease inhibitor with a concentration of 75 micrograms E-64 / g is used for positive control treatment and feed without any insecticide compounds is used for negative control treatment; potential toxicity of the tested insecticide compounds on spring tails is assessed by comparing the important life parameters such as the survival rate, the head breadth, the body length and the egg laying amount of folsomia candida of the treatment group and the control groups. By using the method, the biological reaction of folsomia candida to potassium arsenate [PA], E-64 and galanthus nivalis agglutinin (GNA) with different concentrations can be tested. It is shown that the different life parameters of folsomia candida show an obvious dose-effect relationship along with the change of the concentrations of PA, E-64 and GNA, so that the effectiveness and the sensitivity of the method are testified.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods and compositions for the stabilization of biologic material
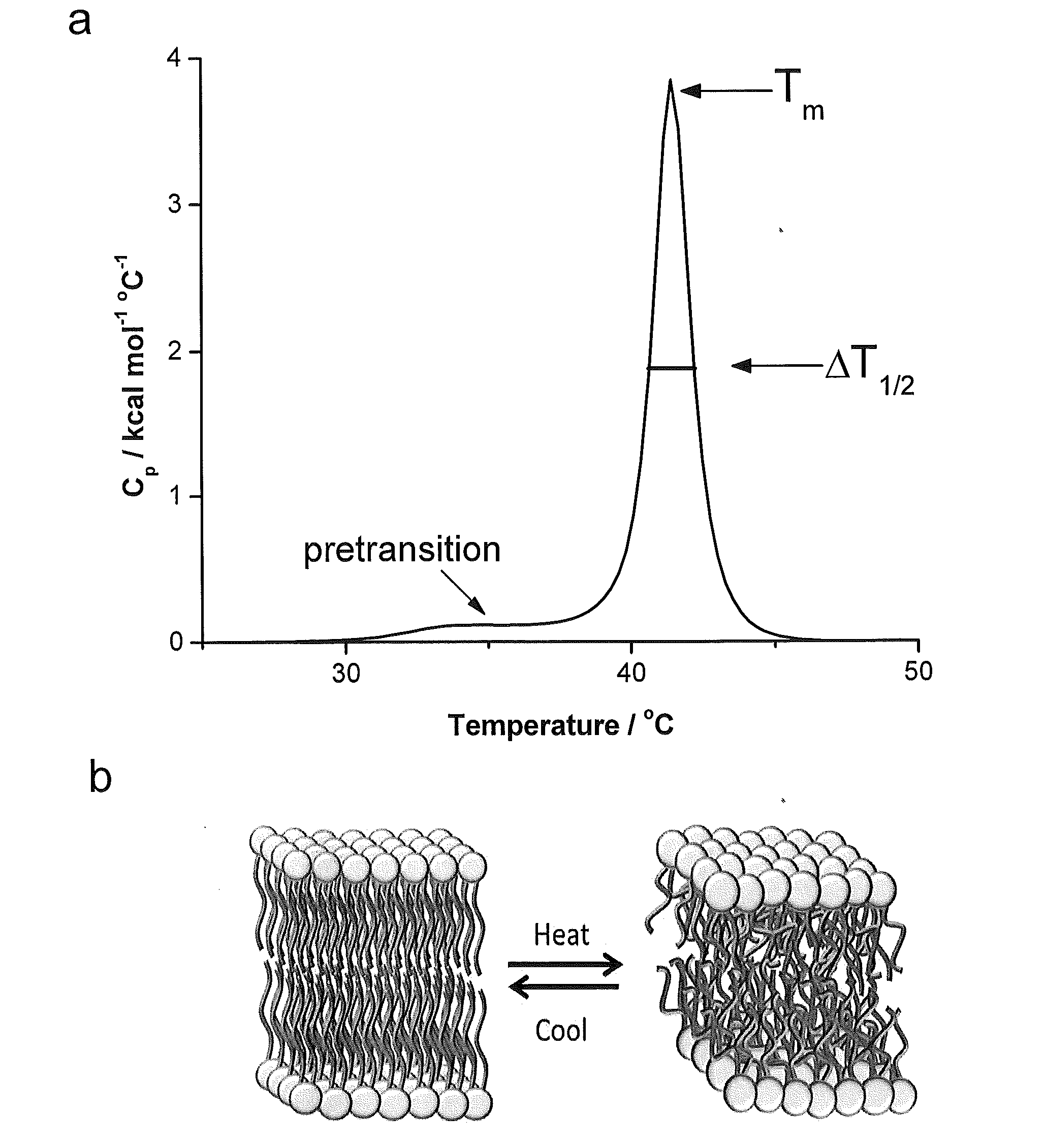
InactiveUS20130089912A1Nervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsPotential toxicityBiological materials
A method of screening an organic salt for potential toxicity if used as a stabilizing agent for live cells or viruses, the method comprising: (a) providing a composition of unilamellar vesicles; then (b) contacting an organic salt to the unilamellar vesicles; and then (c) detecting a change in at least one thermal parameter of the unilamellar vesicles caused by the organic salt at said known concentration. A change in the at least one thermal parameter indicates the organic salt is potentially toxic for use as a stabilizing agent for live cells or viruses. Compositions of organic salts identified by such methods, along with methods of using the same in stabilizing live cells or viruses, are also described.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Bacterial exopolysaccharide-based drinking water heavy metal adsorbent
ActiveCN107523515AImprove adsorption capacityImprove qualityBacteriaWater contaminantsPotential toxicitySorbent
The invention discloses a bacterial exopolysaccharide-based drinking water heavy metal adsorbent, which is prepared from exopolysaccharides produced by a marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. GHS18 strain with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 12913, agar and starch, wherein the mass ratio of the agar to the starch is (1 to 2) : (2 to 1). The beneficial effects are as follows: the prepared adsorbent can adsorb various heavy metal such as cadmium, lead and copper in drinking water, has the advantages of high adsorption efficiency and stable performance, and overcomes the defects of potential toxicity of inorganic polymeric adsorbents and synthetic organic polymeric adsorbents to organisms, thus ultimately achieving non-polluting emission. When being used, the adsorbent just needs to be put into the drinking water, the use is convenient, and drinking water quality is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Extraction method for material with antioxidant activity in peony leaves and method for preparing material into powder
InactiveCN108219023AAddress potential toxicityAddressing the problem of carcinogenesisSocial benefitsPotential toxicity
The invention discloses an extraction method for a material with antioxidant activity in peony leaves and a method for preparing material into powder, which comprise the following steps: firstly, thematerial with antioxidant activity is extracted from peony leaves, the extracted material with antioxidant activity is then purified, and finally, powder is prepared from the purified material. The extraction method for the material with antioxidant activity in peony leaves and the method for preparing powder which are disclosed by the invention solve the problem that antioxidants synthesized by the prior art have potential toxicity and carcinogenic effect; the methods are easy to operate, and has good repeatability; by applying the methods disclosed by the invention, a natural, highly effectively and low-toxicity antioxidant can be obtained, moreover, the comprehensive utilization of oil peony resource is also increased, and certain social benefit is generated.
Owner:XIAN MEDICAL UNIV
A strain of Pseudoalteromonas marina, and Pseudoalteromonas marina decolorization flocculant preparation method
ActiveCN107805614AReduce manufacturing costEasy to separateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPotential toxicityCulture fluid
The invention discloses a strain of Pseudoalteromonas marina, and a Pseudoalteromonas marina decolorization flocculant preparation method, wherein the is Pseudoalteromonas marina separated and screened from the mud discharged by Ruditapes philippinarum bred in the marine farm of Zhujiajian, Zhoushan, Zhejiang, China, and the identifying results show that the strain is Pseudoalteromonas sp.. The preparation method comprises: seed liquid culture, liquid culture medium preparation, expansion fermentation culture, and flocculant preparation. According to the present invention, the carbon source inthe culture medium is replaced with the hydrolysis liquid obtained through the crop waste hydrolysis with the inorganic acid, such that the cost is saved; the sandy soil is used as the carrier, and the bacteria are adhered to the carrier, such that the effective components of the flocculant can be simply and completely separated from the culture liquid; and the prepared decolorization flocculanthas advantages of less consumption, high decoloration rate, large floc forming, quick settling, stable performance, good decolorization flocculation effect, no potential toxicity to organisms, healthand environmental protection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Nutritional agent with noise induced hearing loss resistance
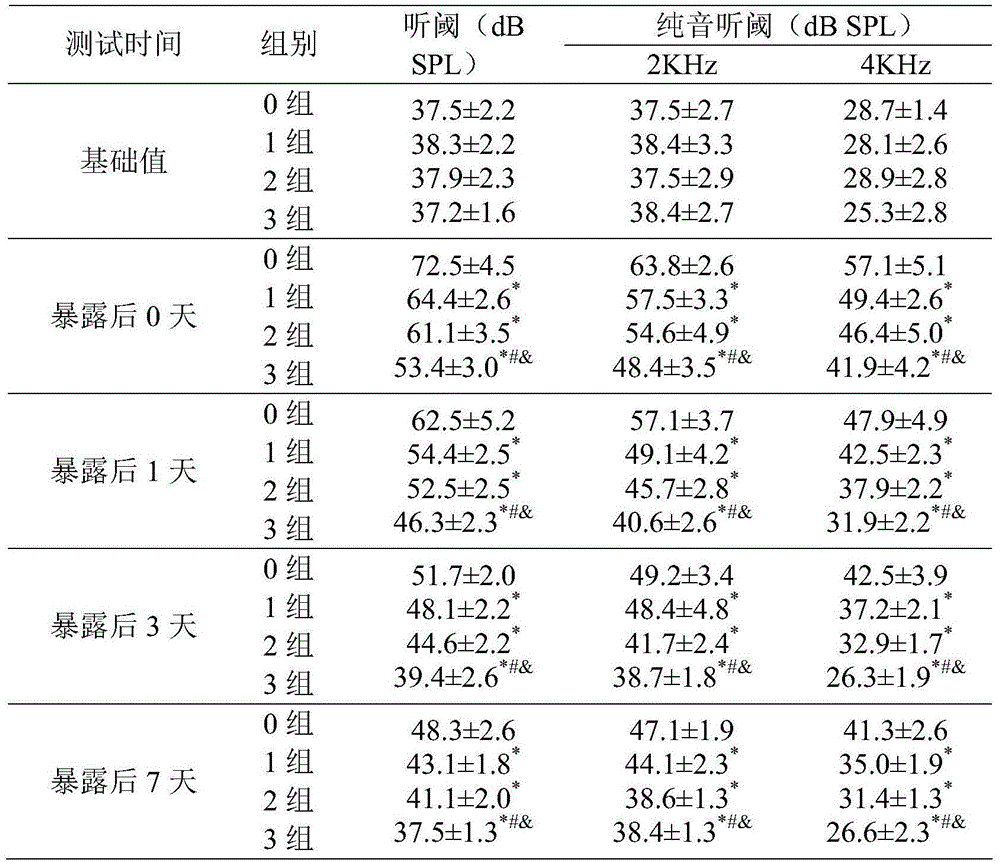
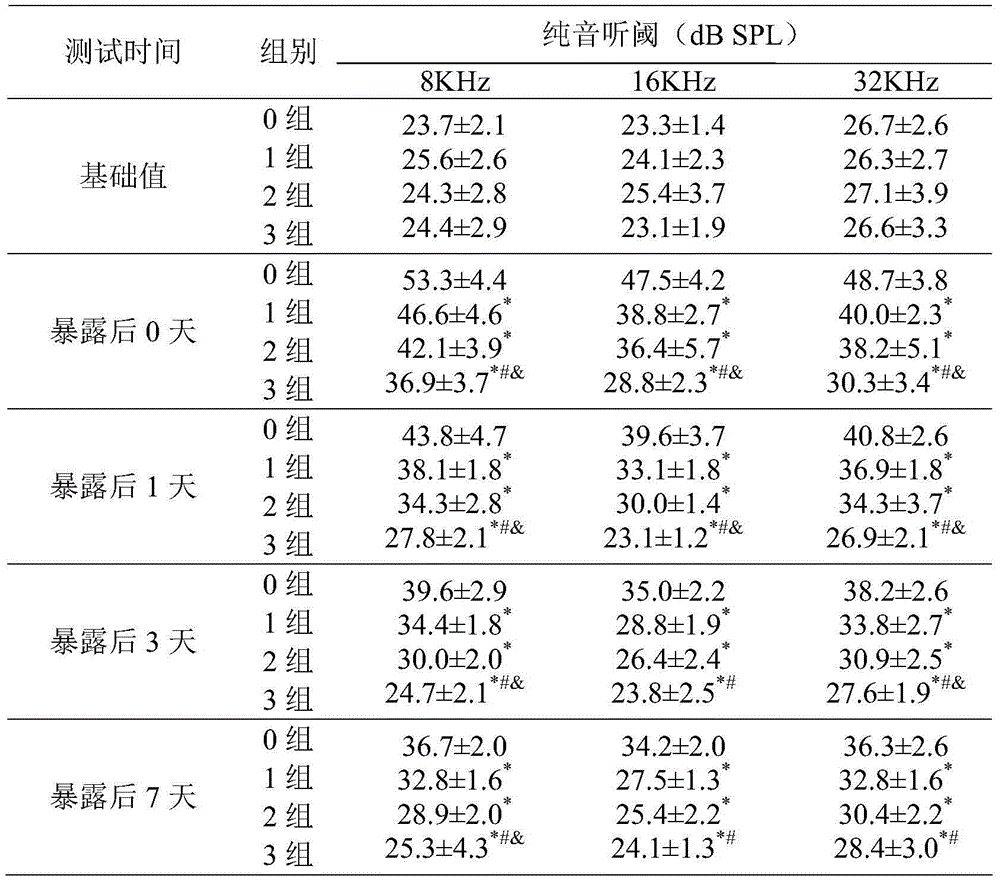
ActiveCN104664407AGood noise immunity hearing lossPromote aerobic metabolismFood preparationPotential toxicityData display
The invention discloses a nutritional agent with noise reduced hearing loss resistance. The nutritional agent is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 600-1000 parts of N-acetyl-L-cysteine, 1-4 parts of vitamin A, 1-5 parts of vitamin B1, 1-5 parts of vitamin B2, 1-10 parts of vitamin B6, 0.01-0.05 part of vitamin B12, 60-1000 parts of vitamin C, 15-300 parts of vitamin E which is based on alpha-totaxin, 50-400 parts of magnesium and 79-3175 parts of food acceptable accessories. Experiment data displays that the nutritional agent has remarkable effect of preventing and controlling the noise induced hearing loss. The nutritional agent can be used for enhancing the anti-oxidation ability of the organism and lightening the exitotoxicity damage, has the characteristics of being remarkable in curative effect, low in potential toxicity and low in cost, and is suitable for the noise reduced hearing loss protection and daily nutrient supplementation of people who live and work in the environment with continuous exposed high-intensity noise.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Polypeptide for preparing hydrogel and hydrogel made from polypeptide
ActiveCN105669832AAchieve degradationAvoid harmPeptidesCell culture supports/coatingPotential toxicityUltraviolet lights
The invention provides a polypeptide for preparing hydrogel. The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is SEQ ID NO: 1. The polypeptide is used for preparing the hydrogel. The prepared hydrogel can be used for producing cell culture holders. The polypeptide has the advantages that enzymes of organisms are catalyzed under physiological conditions to form the hydrogel, and accordingly, damage of external chemical agents, ultraviolet light and the like to tissues is avoided; the biological enzymes can be degraded, the hydrogel is degraded by endogenous substances in the organisms, and accordingly, potential toxicity and immunogenicity risks caused by introduction of exogenous chemical agents are avoided; the polypeptide is an ideal tissue engineering material and is significant to human life health.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com