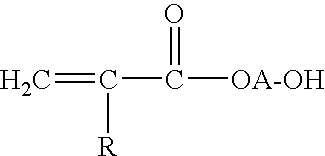
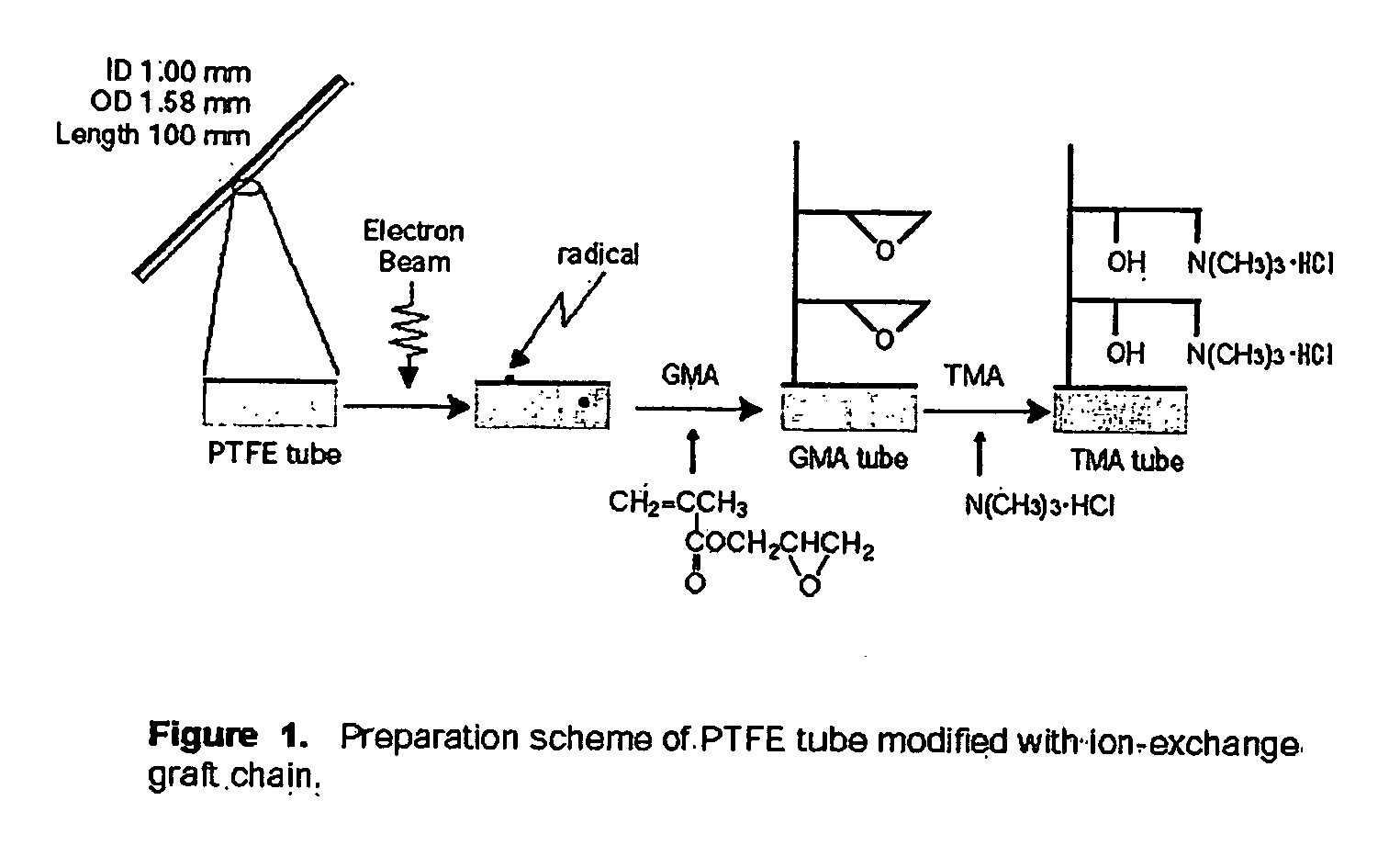
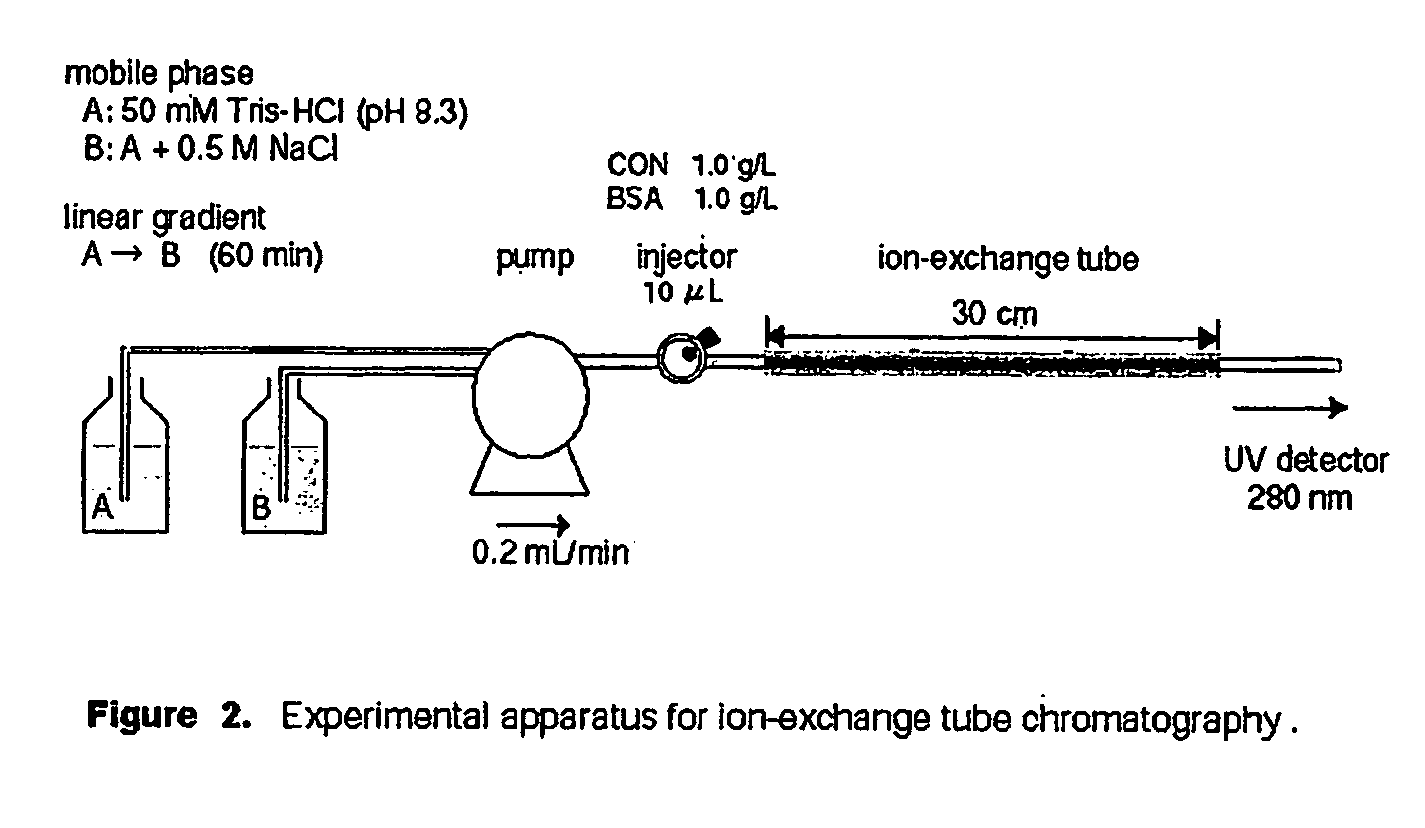
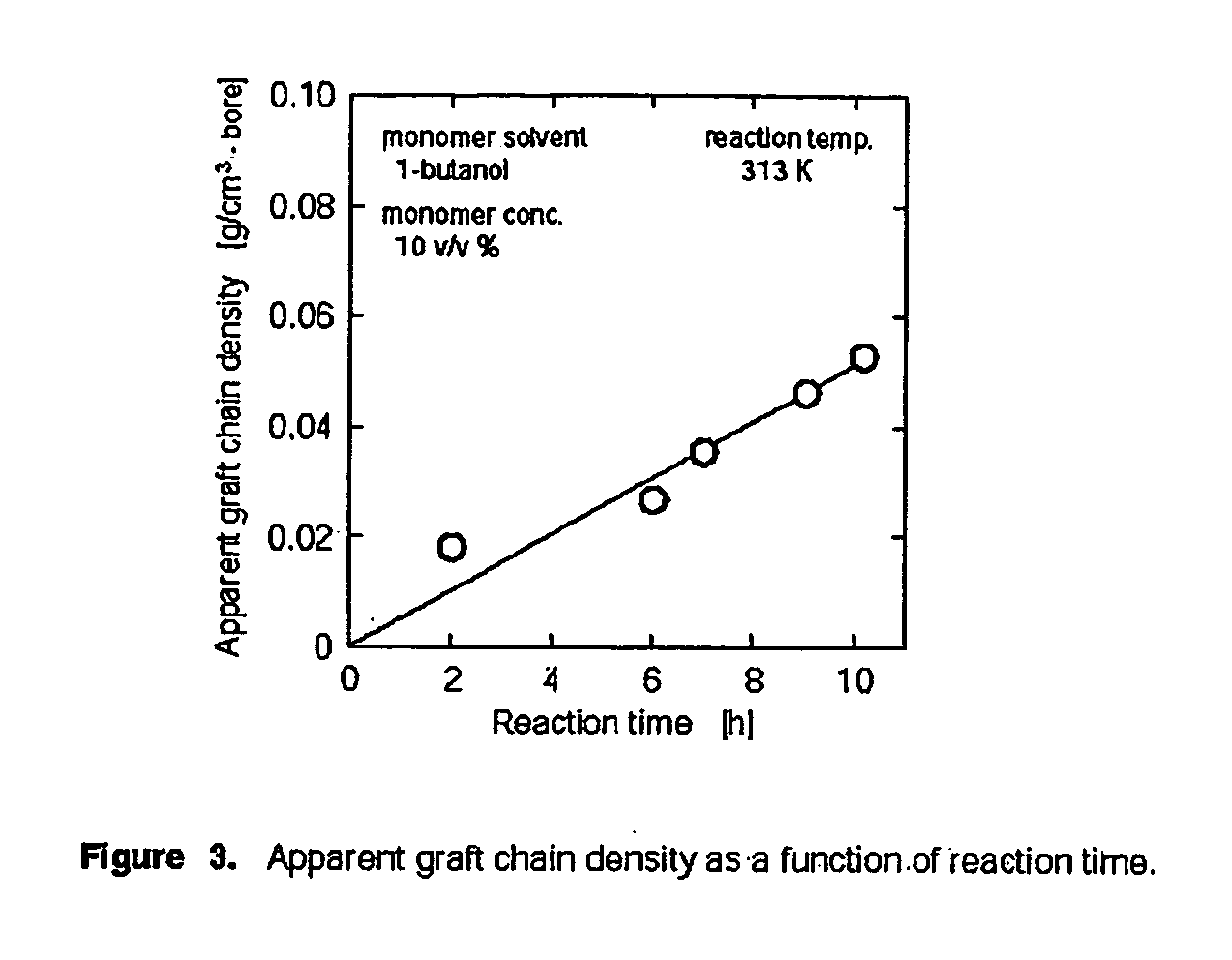
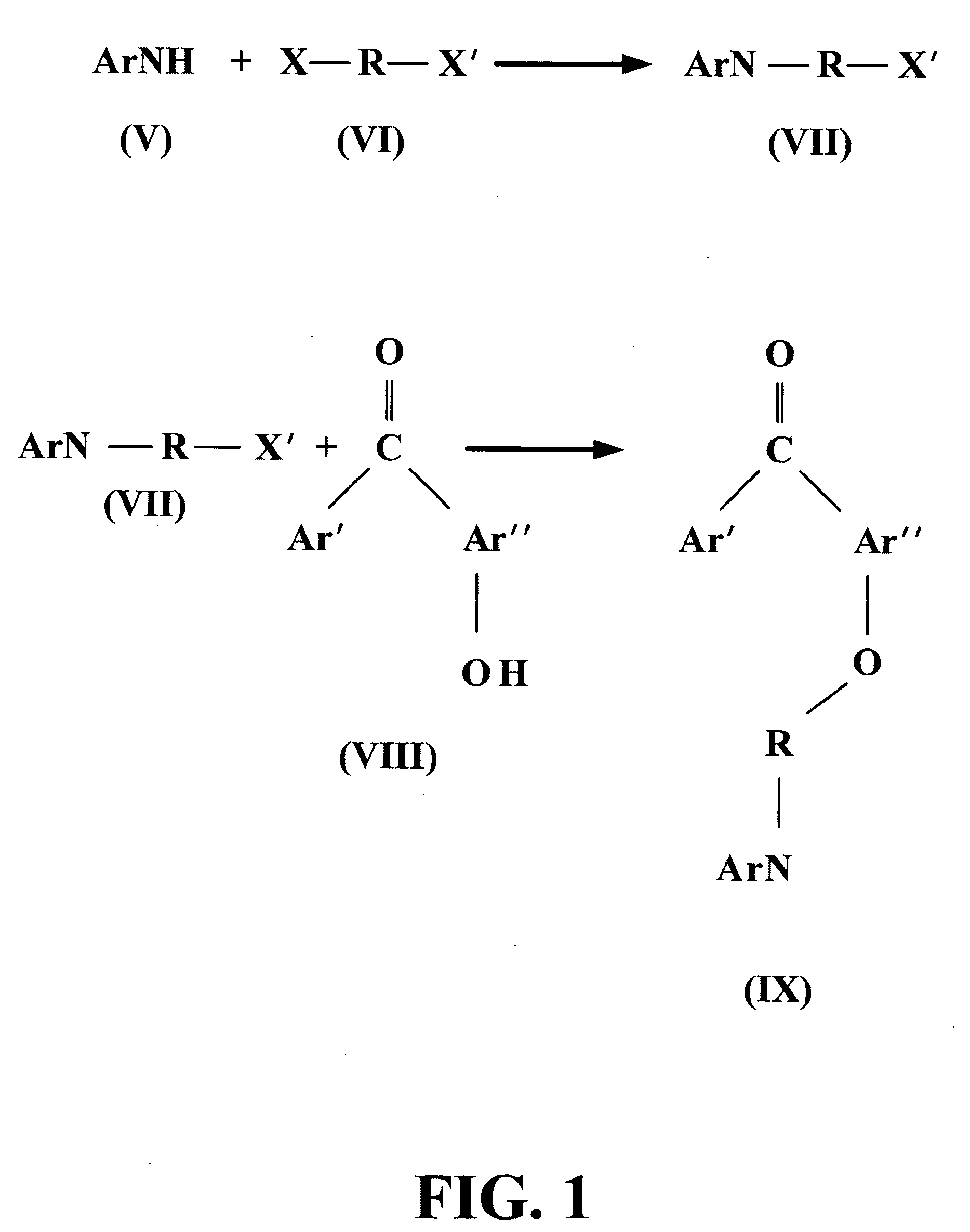
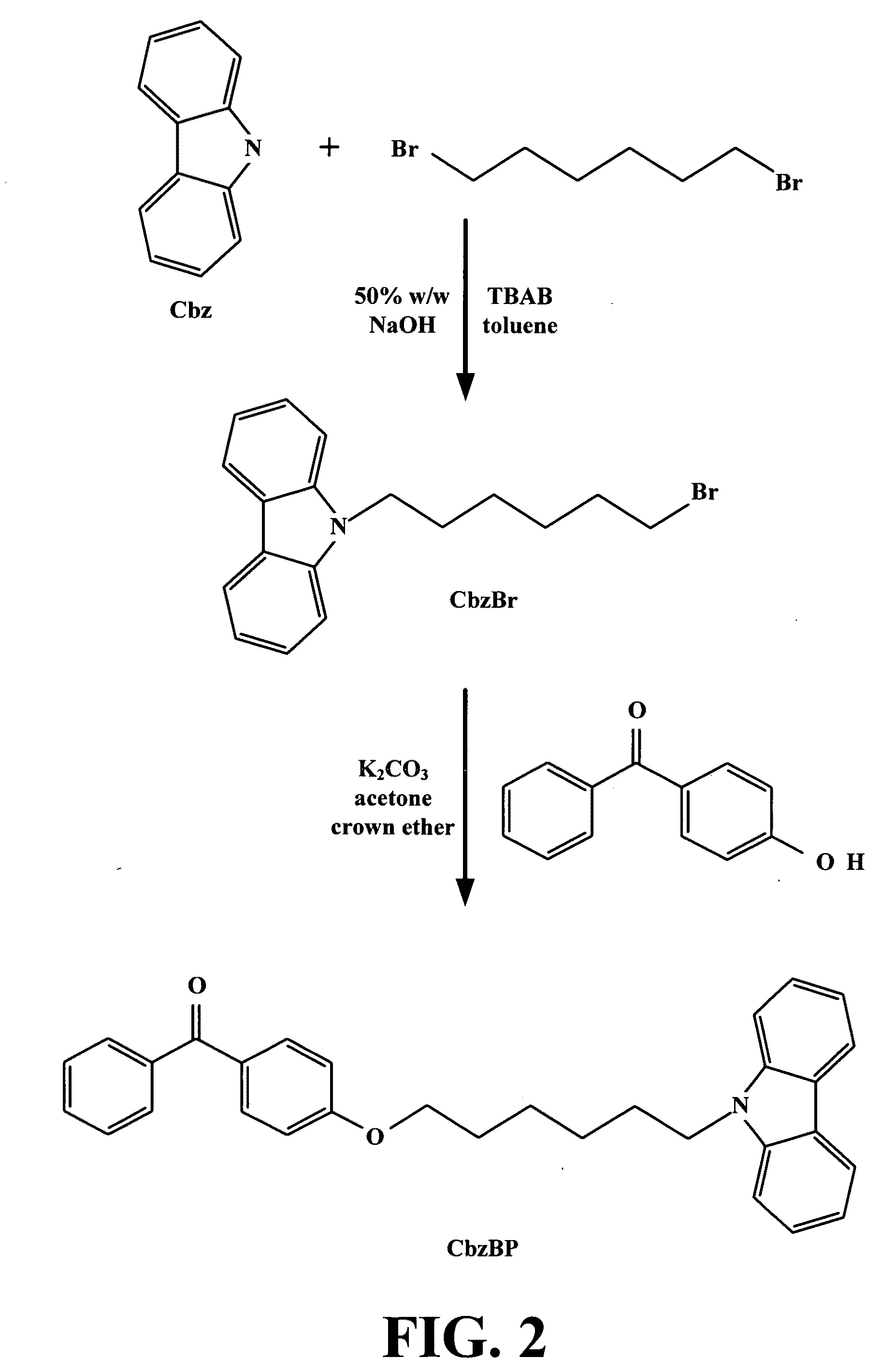
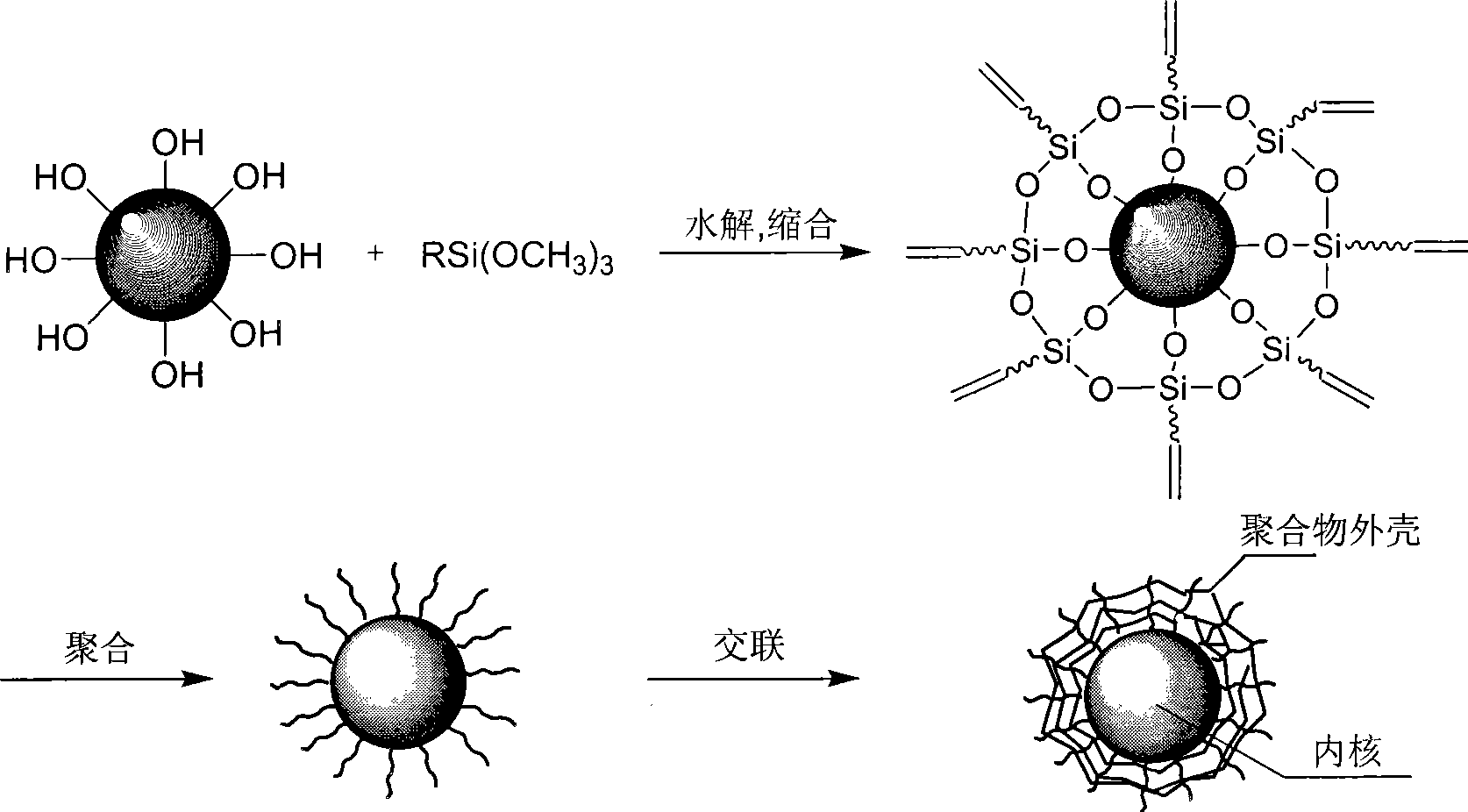
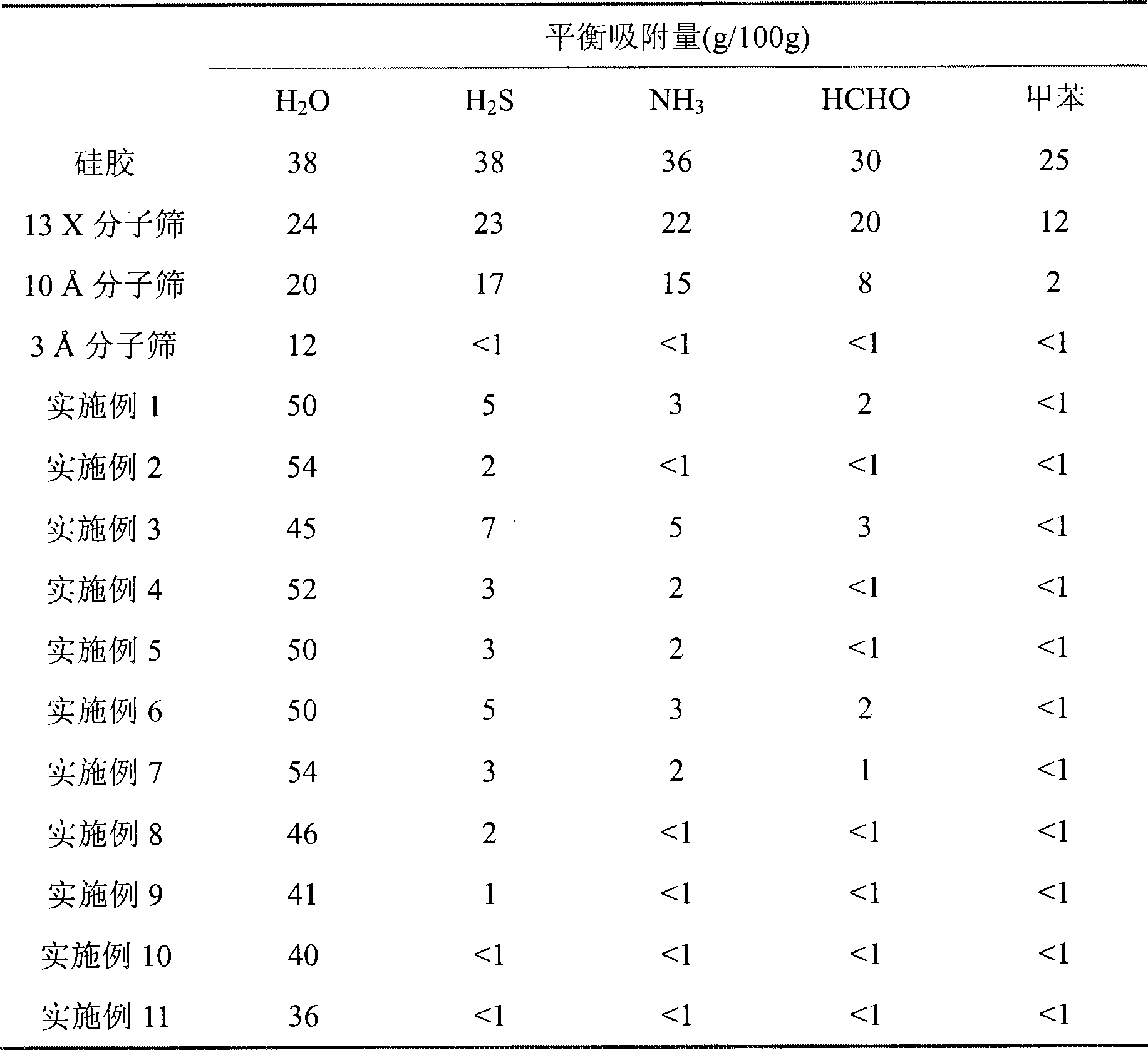
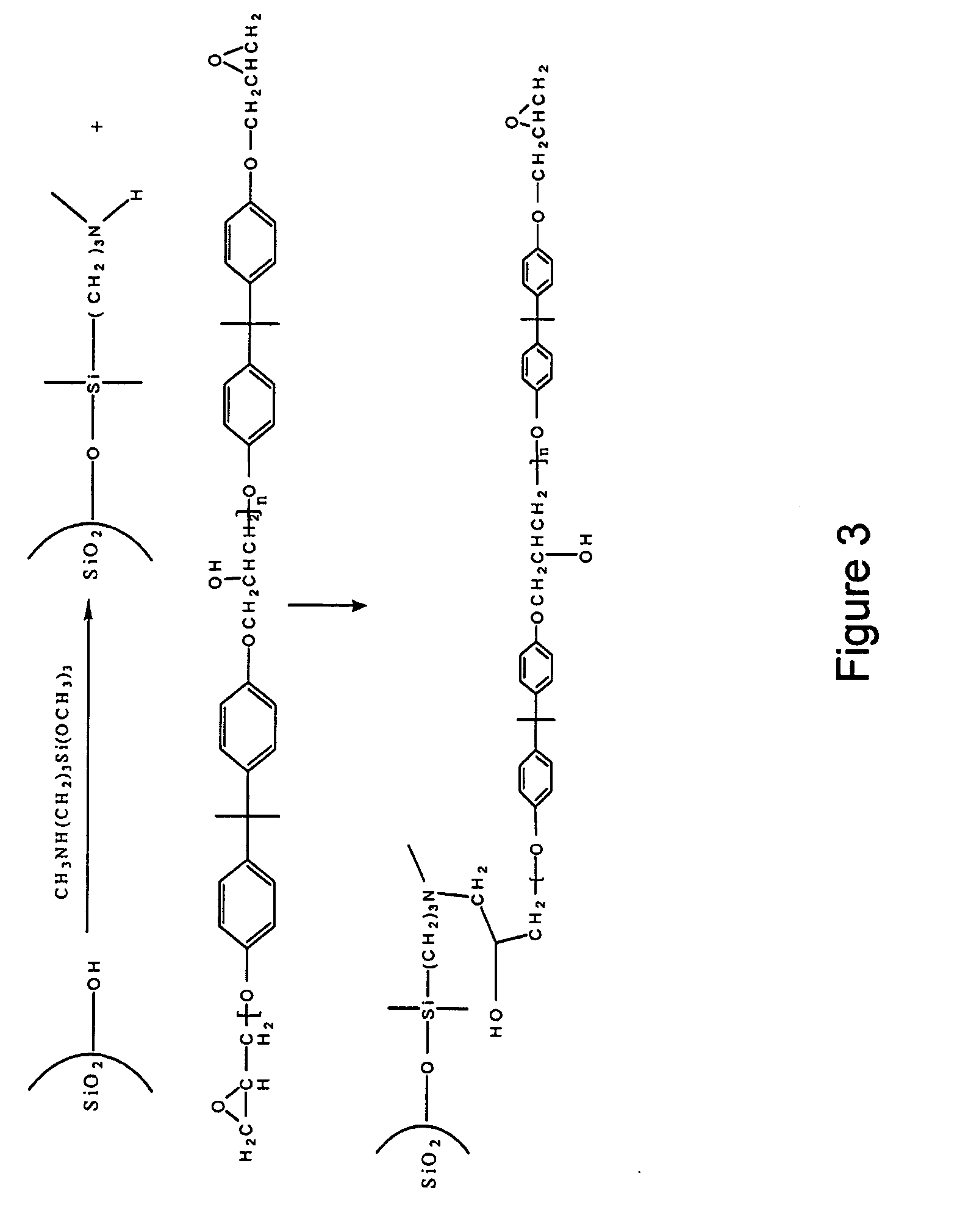
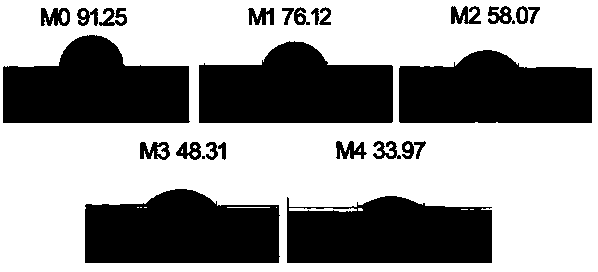
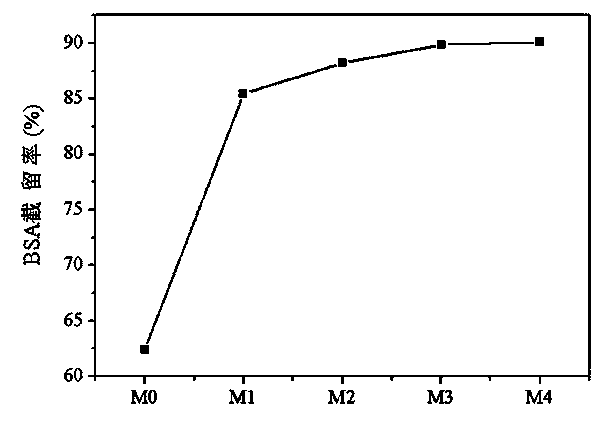
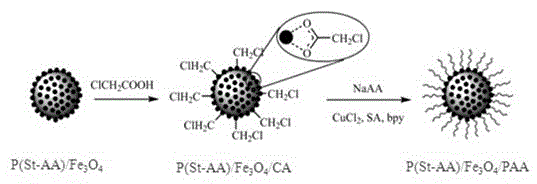
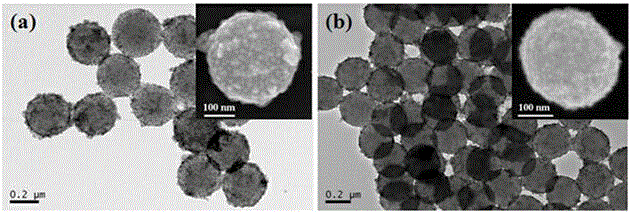
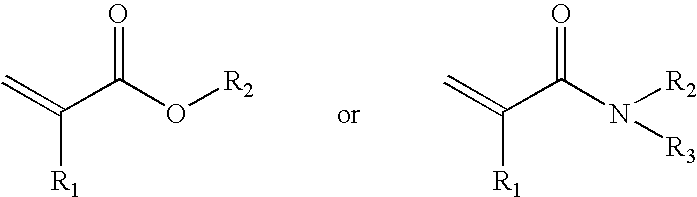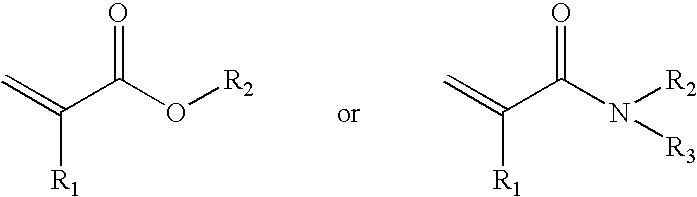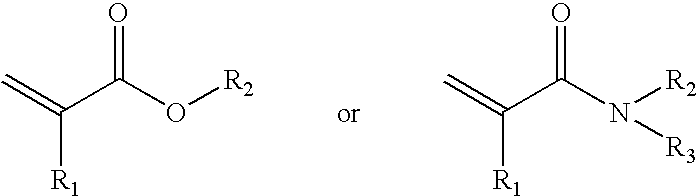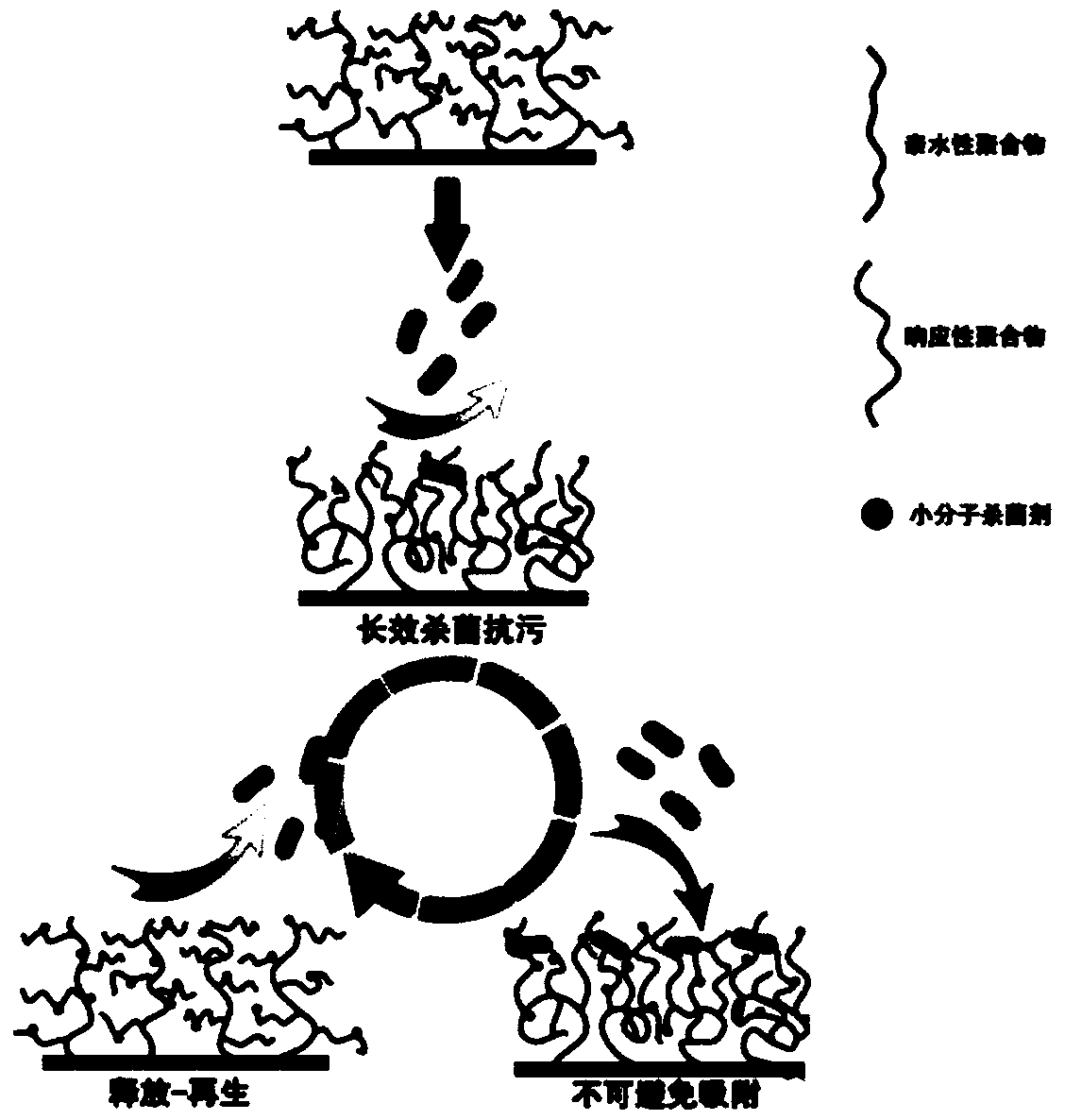Patents
Literature
349 results about "Polymer brush" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
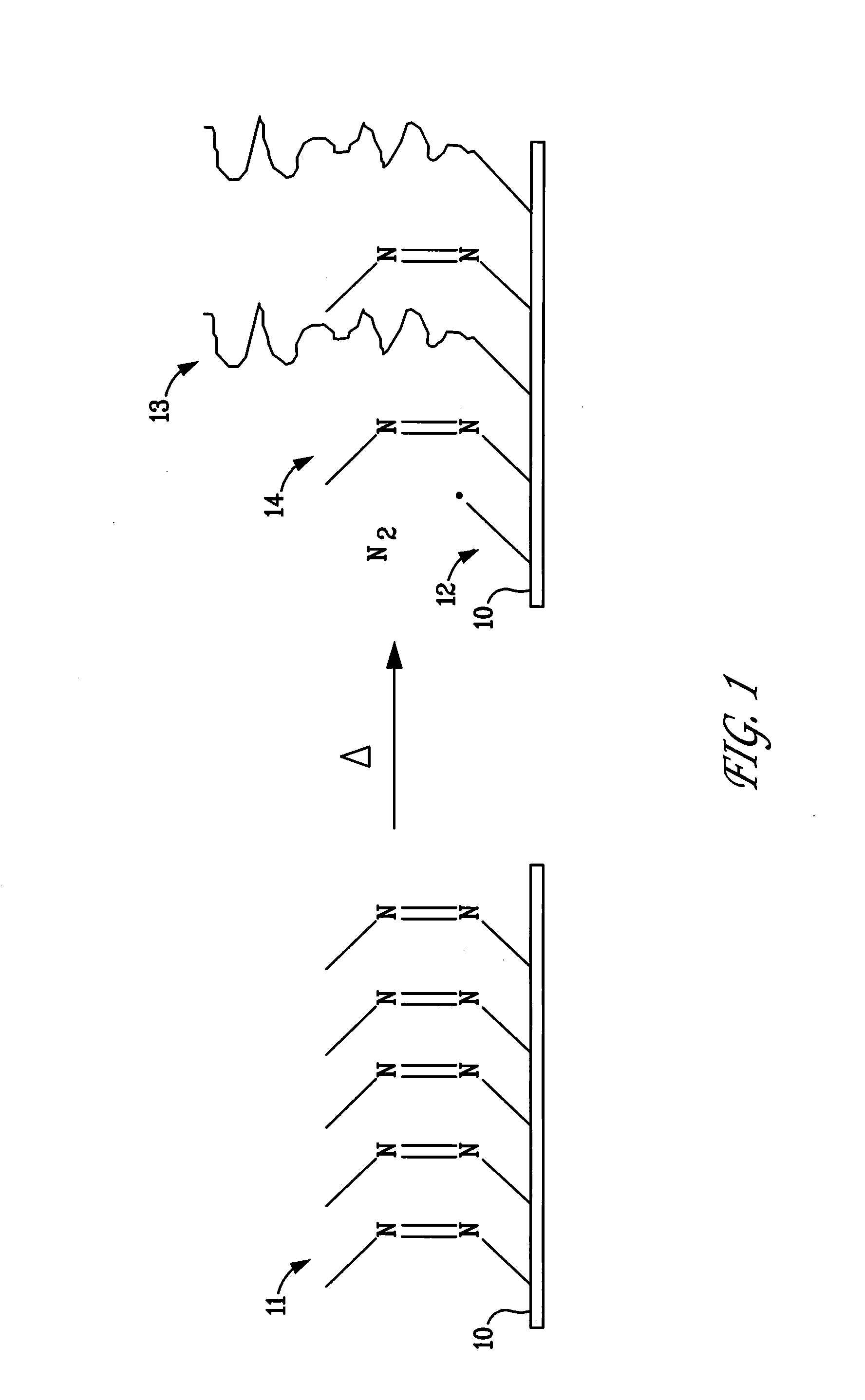
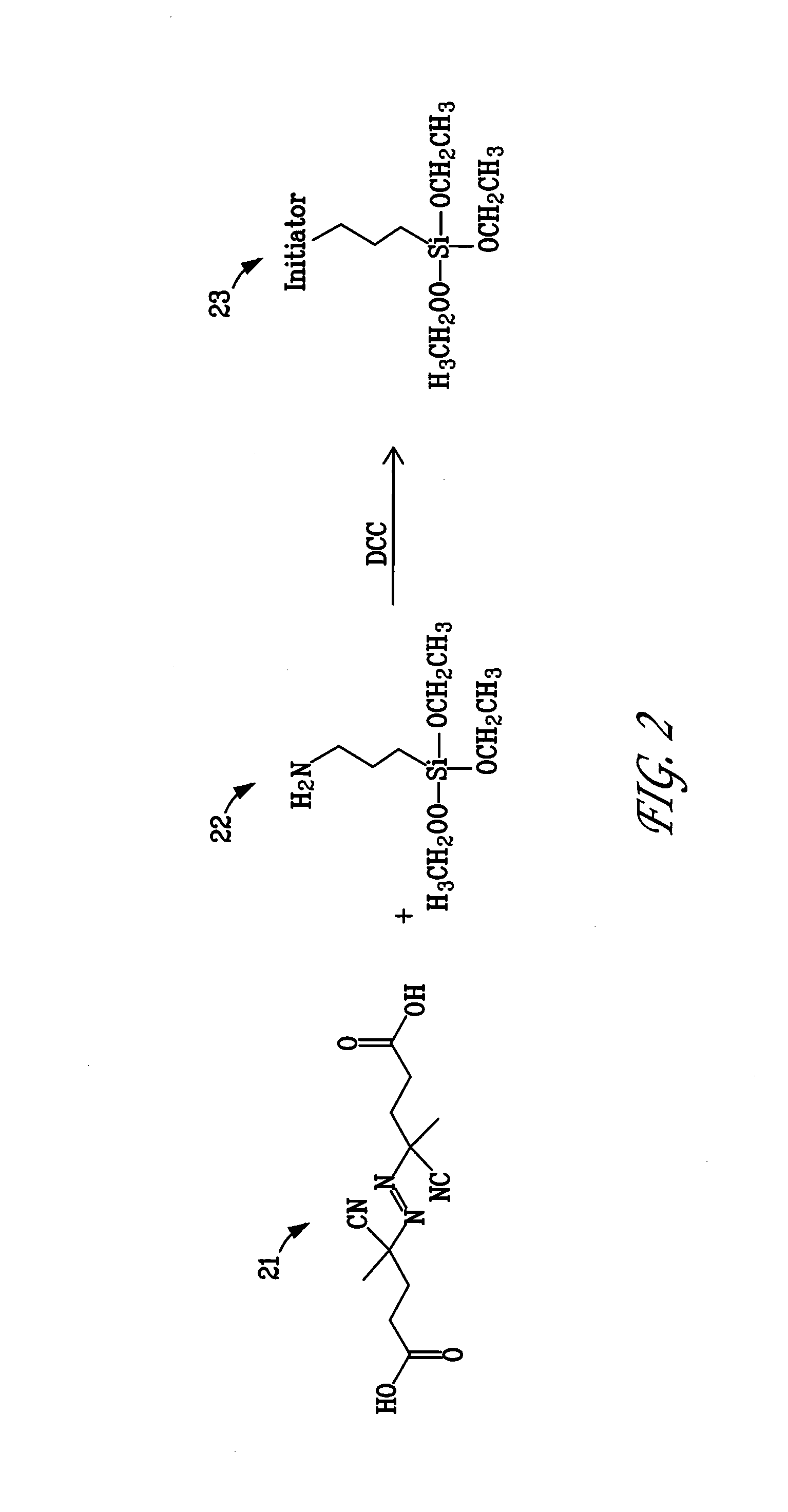
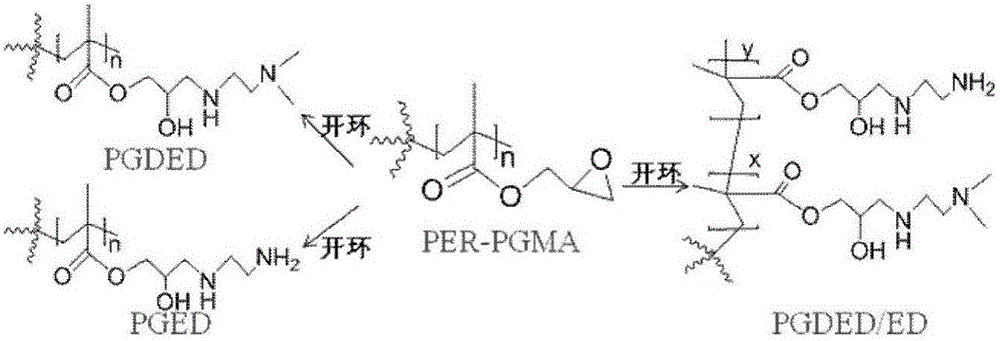
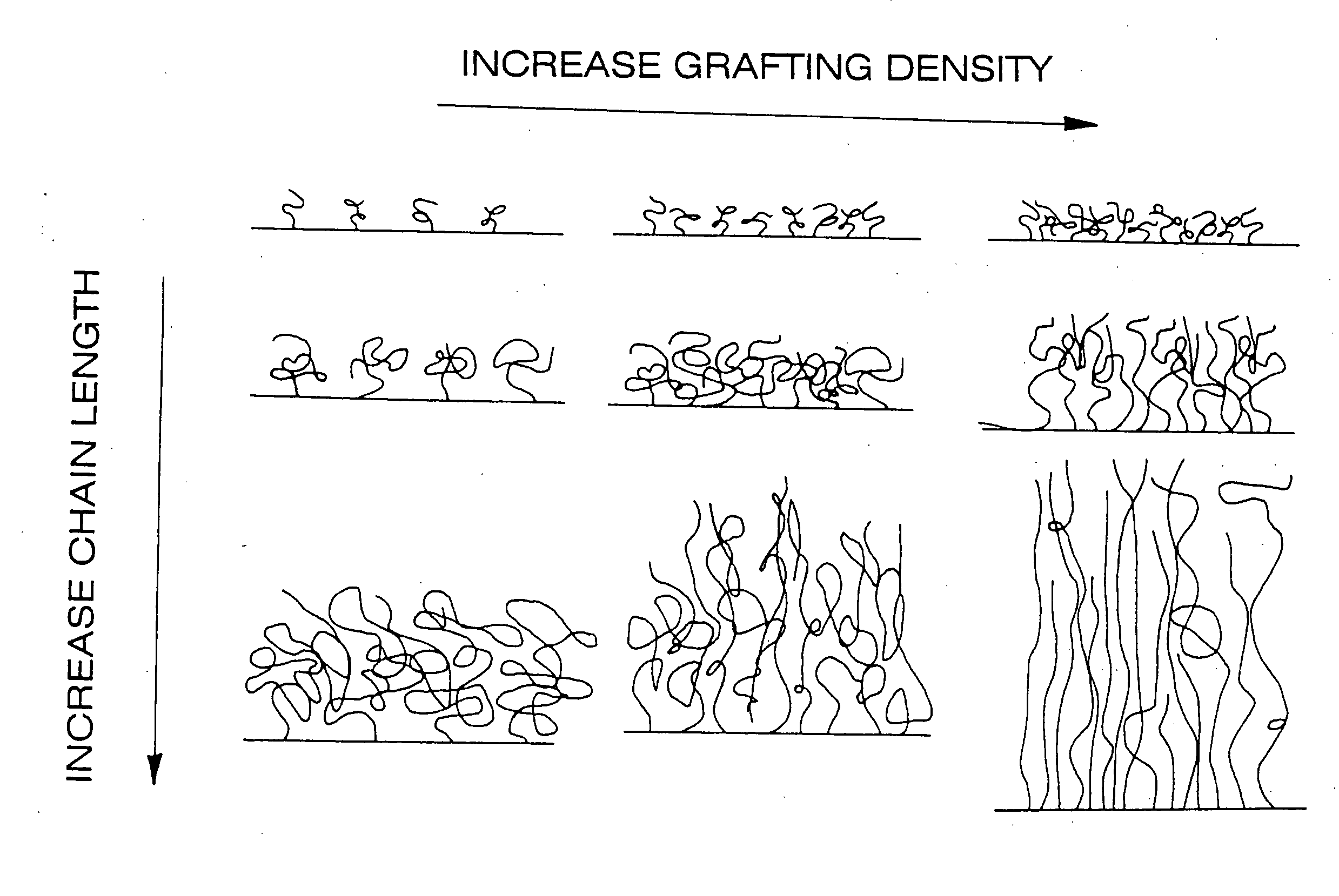
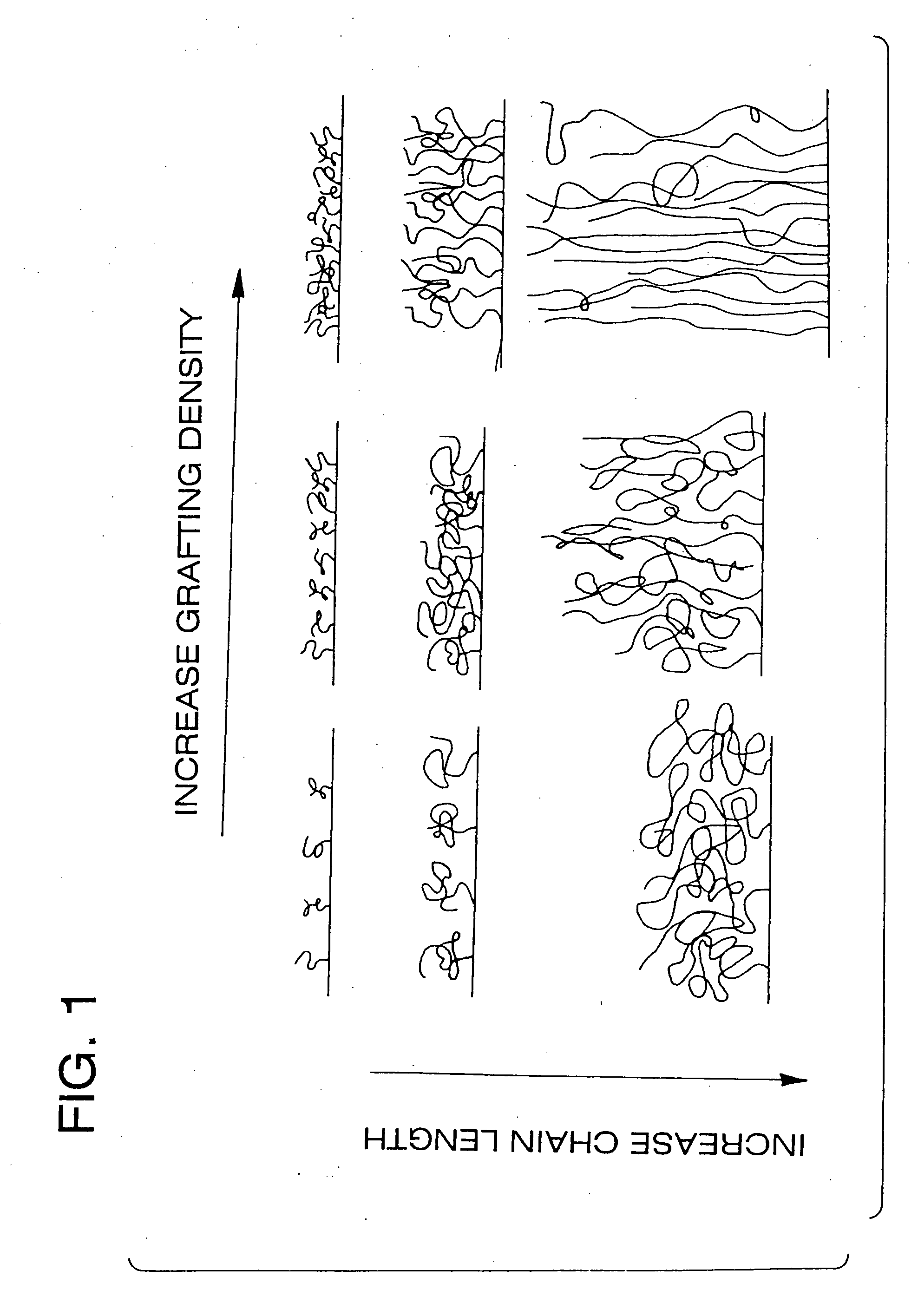
A polymer brush is the name given to a surface coating consisting of polymers tethered to a surface. The brush may be either in a solvated state, where the tethered polymer layer consists of polymer and solvent, or in a melt state, where the tethered chains completely fill up the space available. These polymer layers can be tethered to flat substrates such as silicon wafers, or highly curved substrates such as nanoparticles. Also, polymers can be tethered in high density to another single polymer chain, although this arrangement is normally named a bottle brush. Additionally, there is a separate class of polyelectrolyte brushes, when the polymer chains themselves carry an electrostatic charge.
Polymers, supersoft elastomers and methods for preparing the same
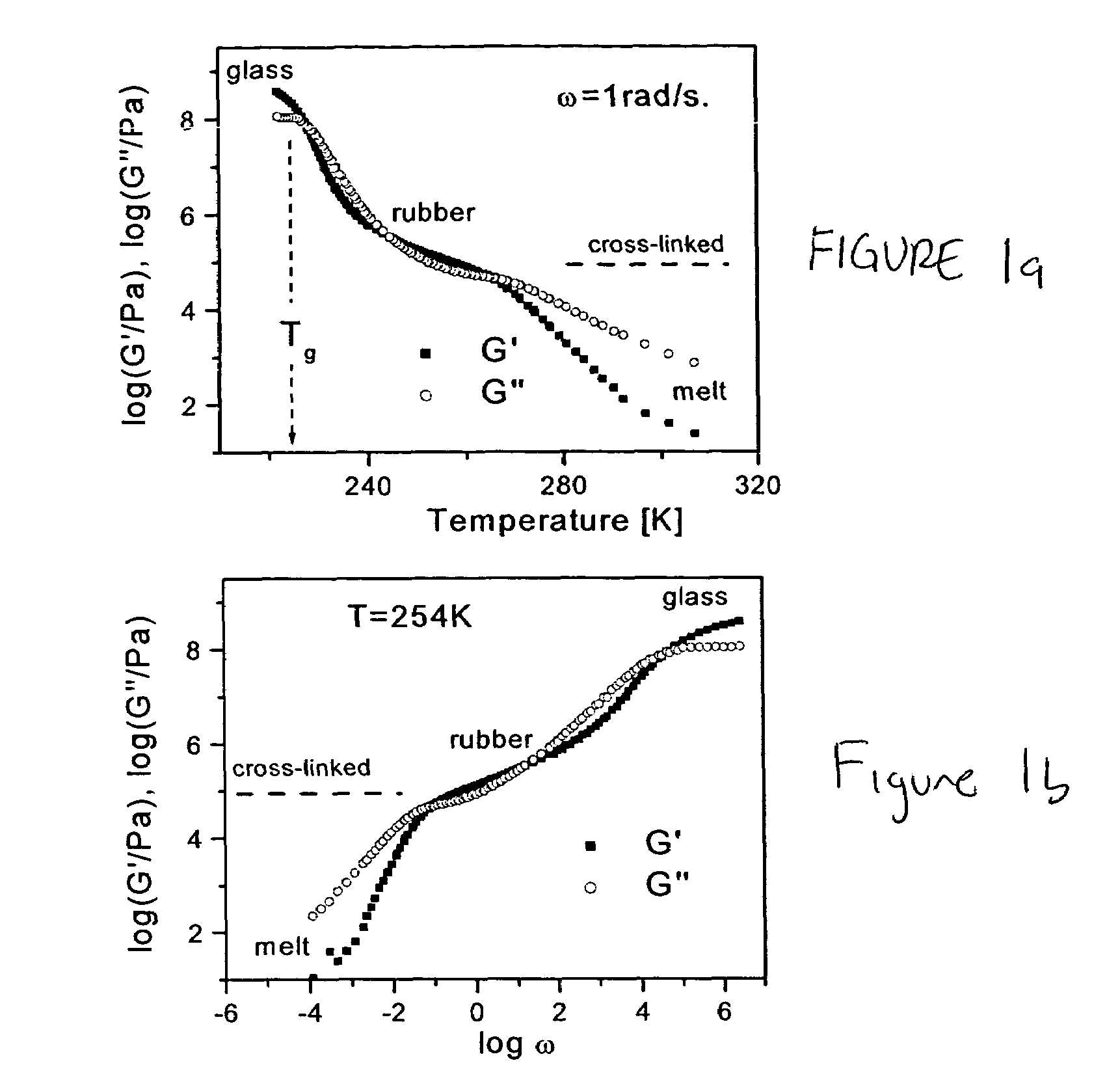
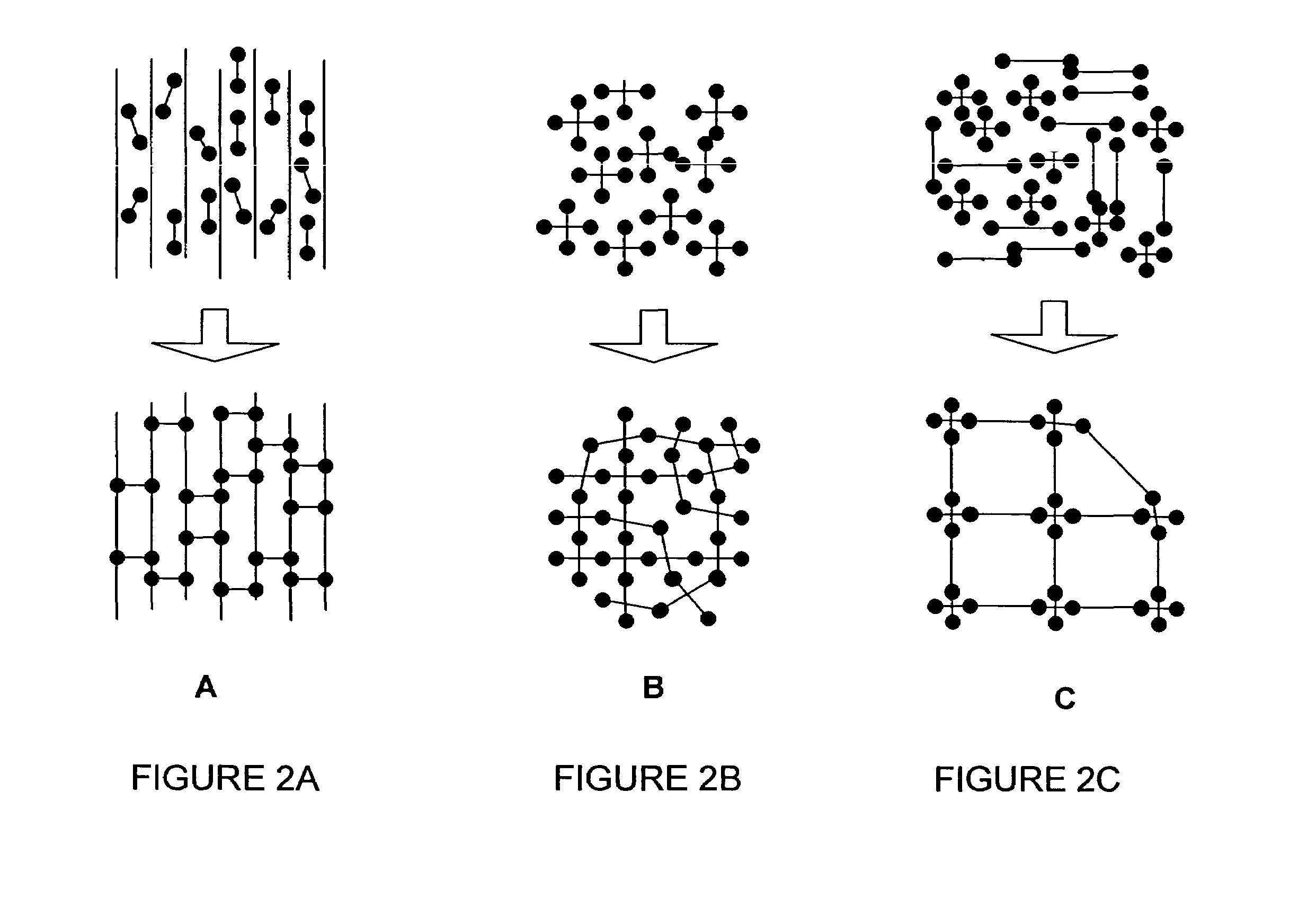
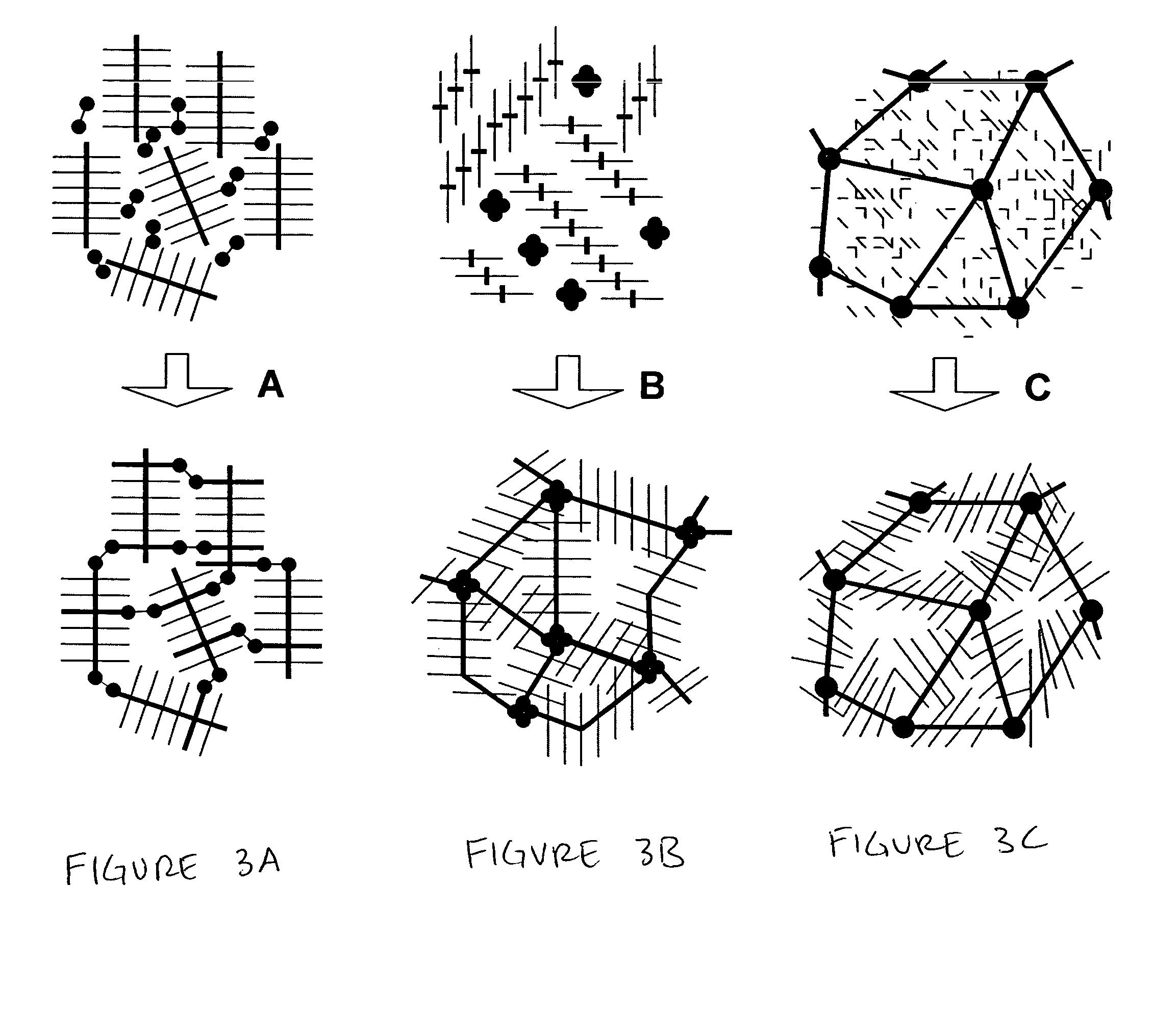
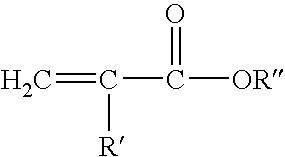
Embodiments of the present invention include a material comprising a polymer having a modulus of elasticity less than 105 Pa and a material comprising a polymer having a modulus of elasticity of less than 5×104 Pa. Embodiments also include a material comprising a polymeric network and a multiplicity of side chains attached to the polymeric network. The multiplicity of side chains may have an average molecular weight below the critical molecular weight for entanglements. In certain embodiments it may be advantageous for the side branches to have a glass transition temperature below the use temperature of the material. The polymer network may comprise at least two monomers so that the polymer network is a copolymer. Embodiments of the present invention also include methods of forming a polymer network. Such as, for example, a method of preparing a polymer network comprising cross-linking a polymer, wherein the polymer comprises a multiplicity of side chains. The polymer may be at least one of a polymer brush, a polymer comb, and a nanocomposite material. An additional embodiment may include polymerizing macromonomers in the presence of a crosslinking agent. This embodiment may result in the forming a polymer network, wherein the polymer network comprises a multiplicity of branches attached to the polymer network, wherein the macromonomers may have a molecular weight less than the critical molecular weight for entanglements. Another embodiment of the method of forming a polymer network may comprising polymerizing monomers directly from a crosslinked polymer network. This method may result in forming a branched polymer network, wherein the polymer network comprises a multiplicity of branches attached to the polymer network.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
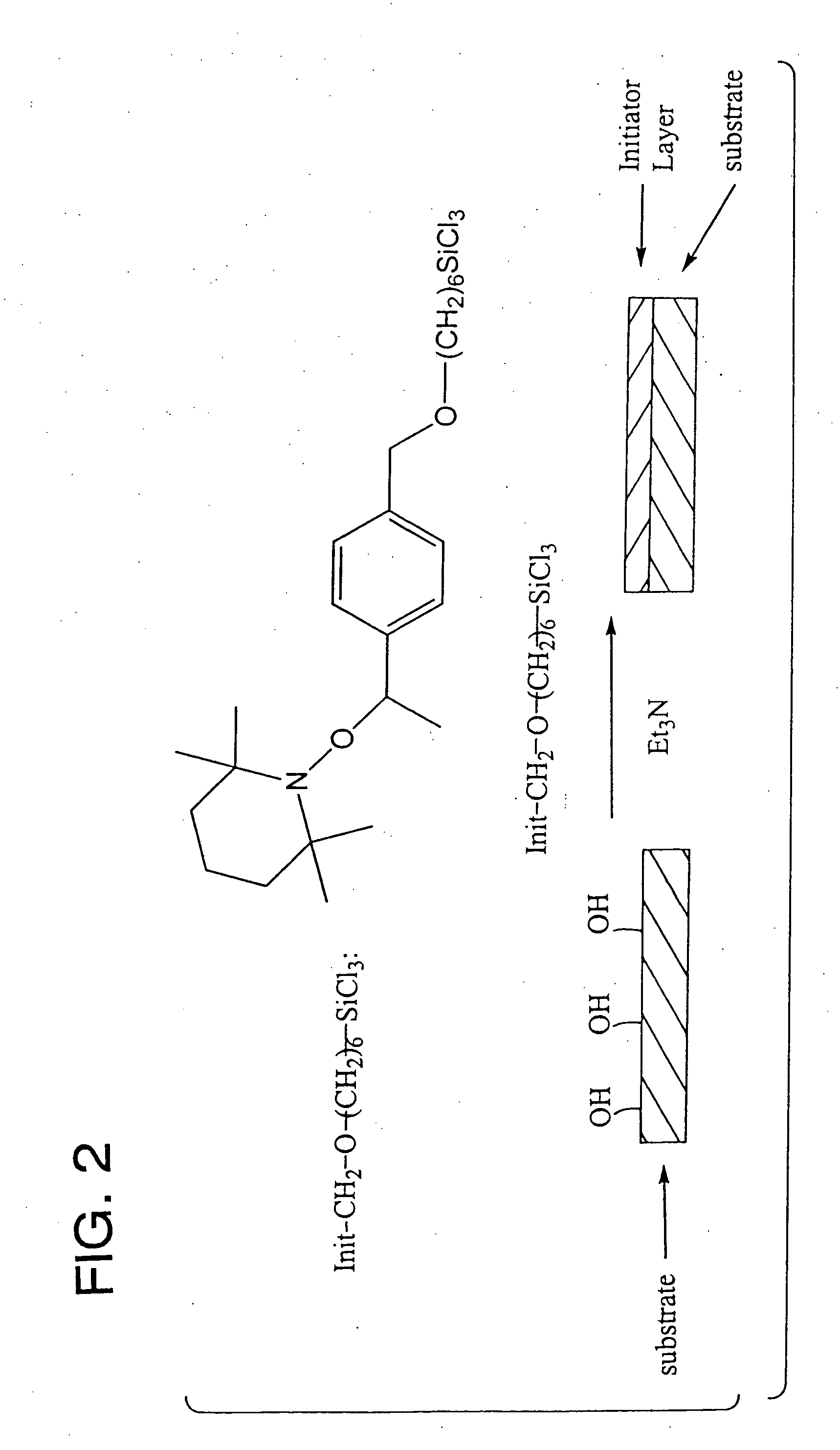
Method of Modifying Materials Surfaces
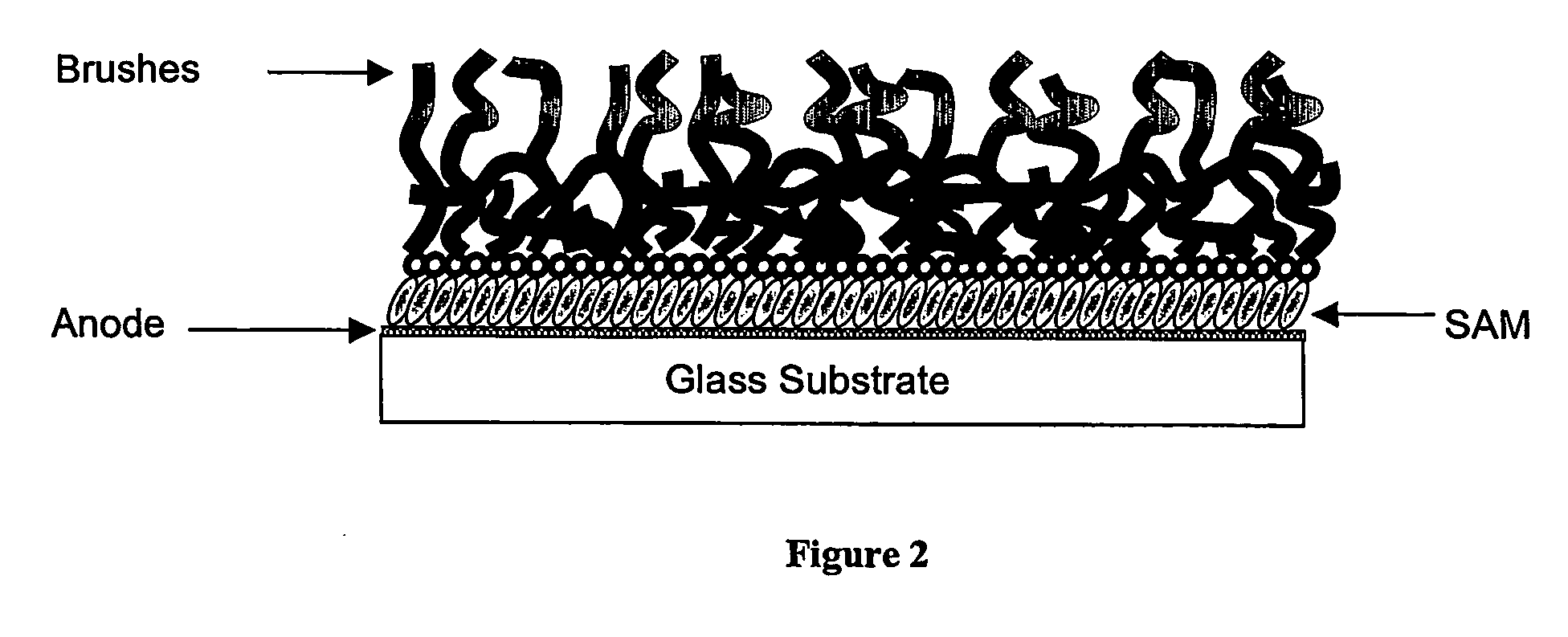
The present invention relates to “grafting to” methods of modifying materials surfaces with high-density polymer brushes. A method of the present invention comprises contacting in succession or simultaneously an activated material surface, a solution of a polymeric material having a polymeric backbone with pendant reactive moieties, and a melt of brush-forming terminally-functionalized polymer chains, in order to allow a covalent bonding reaction to occur between surface and polymers, wherein upon completion of the reaction, the polymeric material forms a layer between the material surface and the brush polymer chains.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Functionalized materials and methods of using same
InactiveUS20060040280A1Reduce concentrationPrevent disengagementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCompound (substance)Hydrolysis
Owner:LEE WILLIAM +1
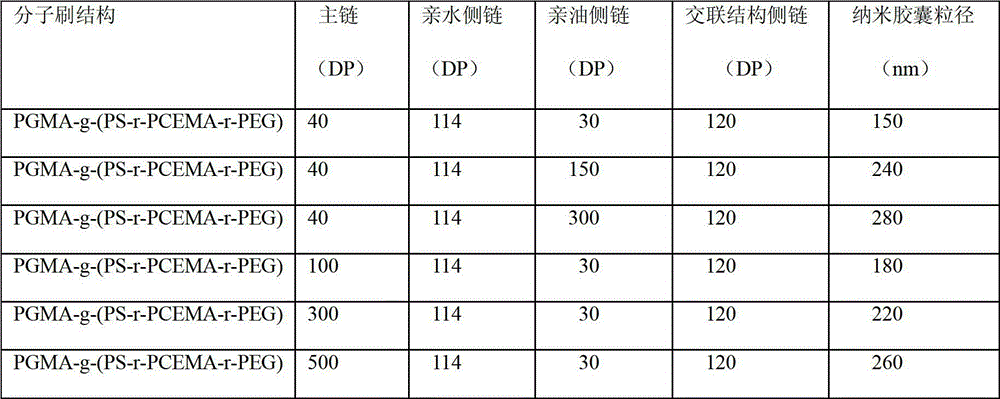
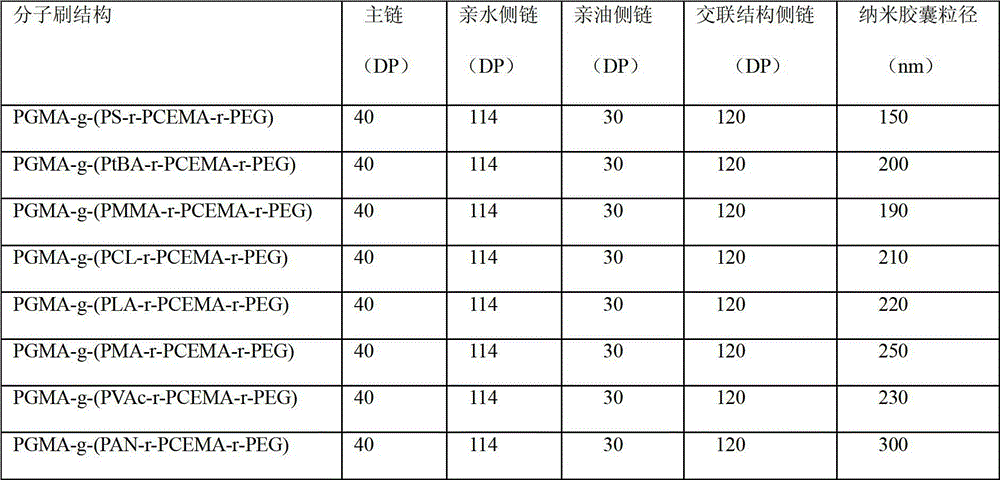
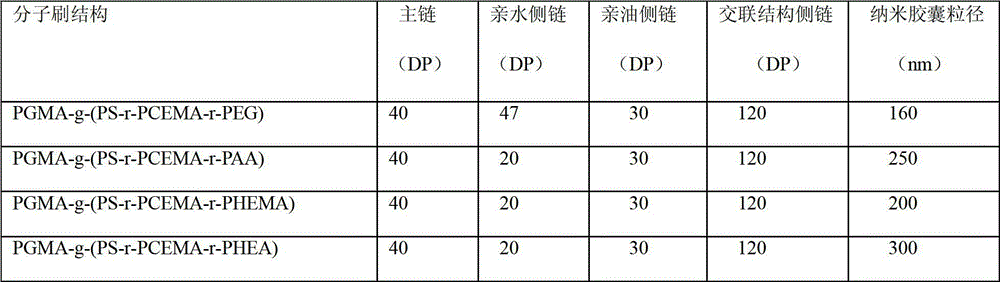
Amphiphilic ternary polymer brush and nano capsule
ActiveCN102911370AEasy to adjust and control the sizeThe particle size is easy to adjust and controllableMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationPolymer scienceSide chain
The invention discloses an amphiphilic ternary polymer brush and a nano capsule. The amphiphilic ternary polymer brush has the following general formula, wherein A is polymer main chain, B is lipophilic polymer side chain, C is photo-crosslinked polymer side chain, D is hydrophilic polymer side chain, and the side chains B, C and D are randomly grafted onto the main chain A; and the nano capsule is prepared through dispersing the amphiphilic ternary polymer brush into an oil-water two-phase system, and then performing light crosslinking reaction or reaction initiated by light. The amphiphilic ternary polymer brush solves the difficulty that the particle size of the capsule can not be adjusted and controlled effectively by using the conventional segmented copolymers, and the size of the prepared photo-crosslinked nano capsule is easily adjusted and controlled; the nano capsule prepared by the emulsion self-assembly method is simple in operation and easy to use in large-scale preparation; the prepared hollow nano capsule is large in casting quantity; the photo-crosslinked nano capsule provided by the invention is stable, and according to the light crosslinking method, nontoxicity and safety are reliazed, and the environmental protection is realized. The amphiphilic ternary polymer brush has the following general formula: A-g-(B-r-C-r-D).
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
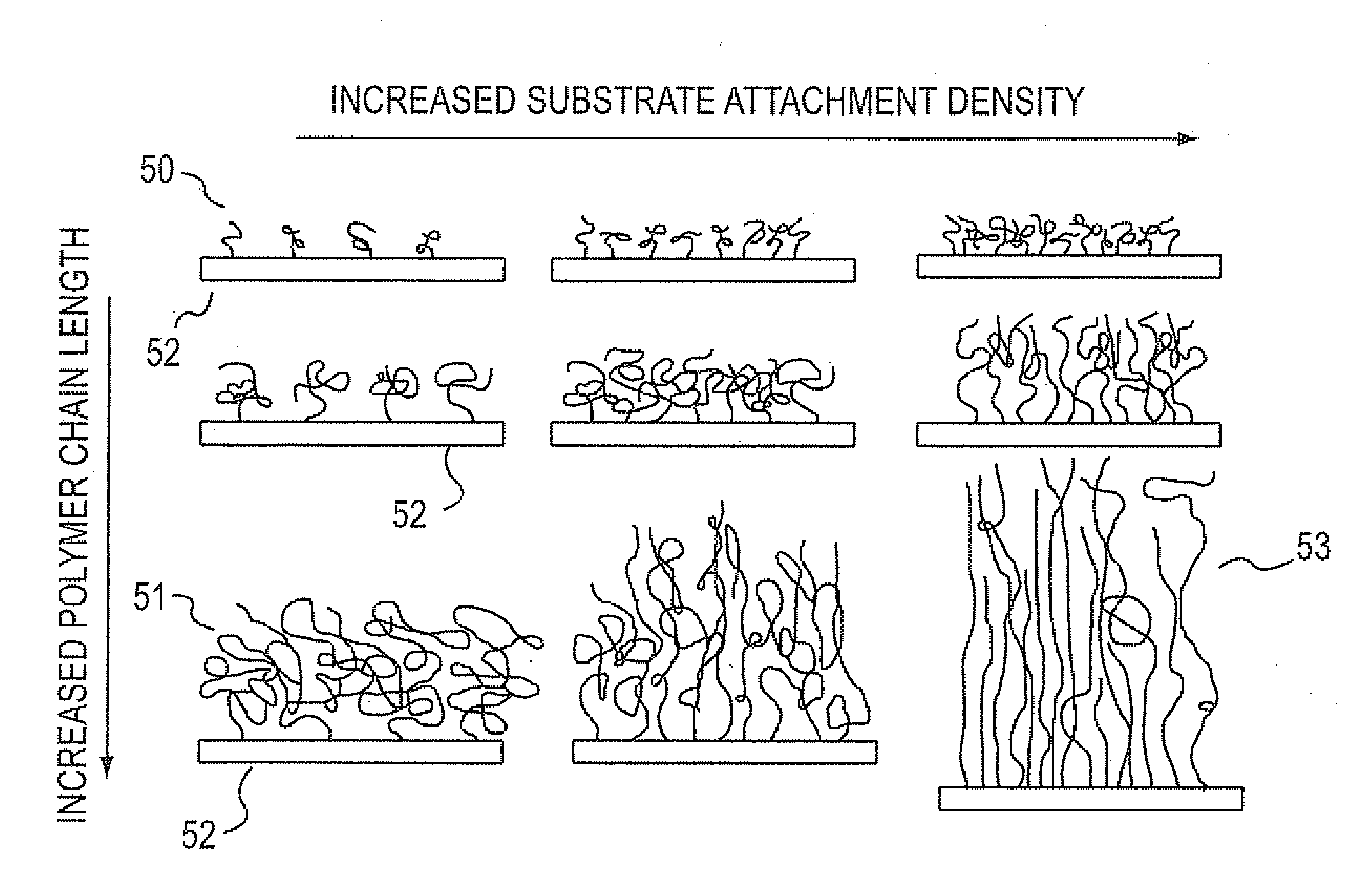
Polymer Brushes
InactiveUS20080262128A1Easy to transportReduces phonon scatteringPrinted circuit aspectsConductive materialPolymer scienceChain length
Polymer brushes (50) in a resin that create phonon pathways therein The polymer brushes themselves comprise structured polymer hairs having a density of 0.8 to 1.0 g / cc, a chain length of 1 to 1000 nm, and a thermal conductivity of 0.5 to 5.0 W / mK. The polymer brushes are 10-25% by volume of the resin, and the polymer hairs can orient surrounding resin molecules to the polymer hairs alignment (55).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Cosmetic Applicator Assembly
InactiveUS20090276973A1Efficient executionImprove gripBrush bodiesBristleBristleInjection molding process
A cosmetic applicator assembly, which includes a polymeric brush and a twisted wire brush. Specifically, the polymeric brush comprises an elongated polymeric core and multiple polymeric tines protruding from the elongated polymeric core. The elongated polymeric core comprises a first polymeric material of a first tensile modulus, while at least some of the polymeric tines comprise a second polymeric material of a second tensile modulus that is smaller than the first tensile modulus. The twisted wire brush comprises a metal wire core and multiple bristles protruding from the metal wire core. The elongated polymeric core of the polymeric brush is complementarily engaged with at least a portion of the metal wire core of the twisted wire brush to form the cosmetic applicator assembly. The polymeric brush of the present invention is preferably formed by a bi-injection molding process.
Owner:ELC MANAGEMENT LLC
Method for sidewall spacer line doubling using polymer brush material as a sacrificial layer
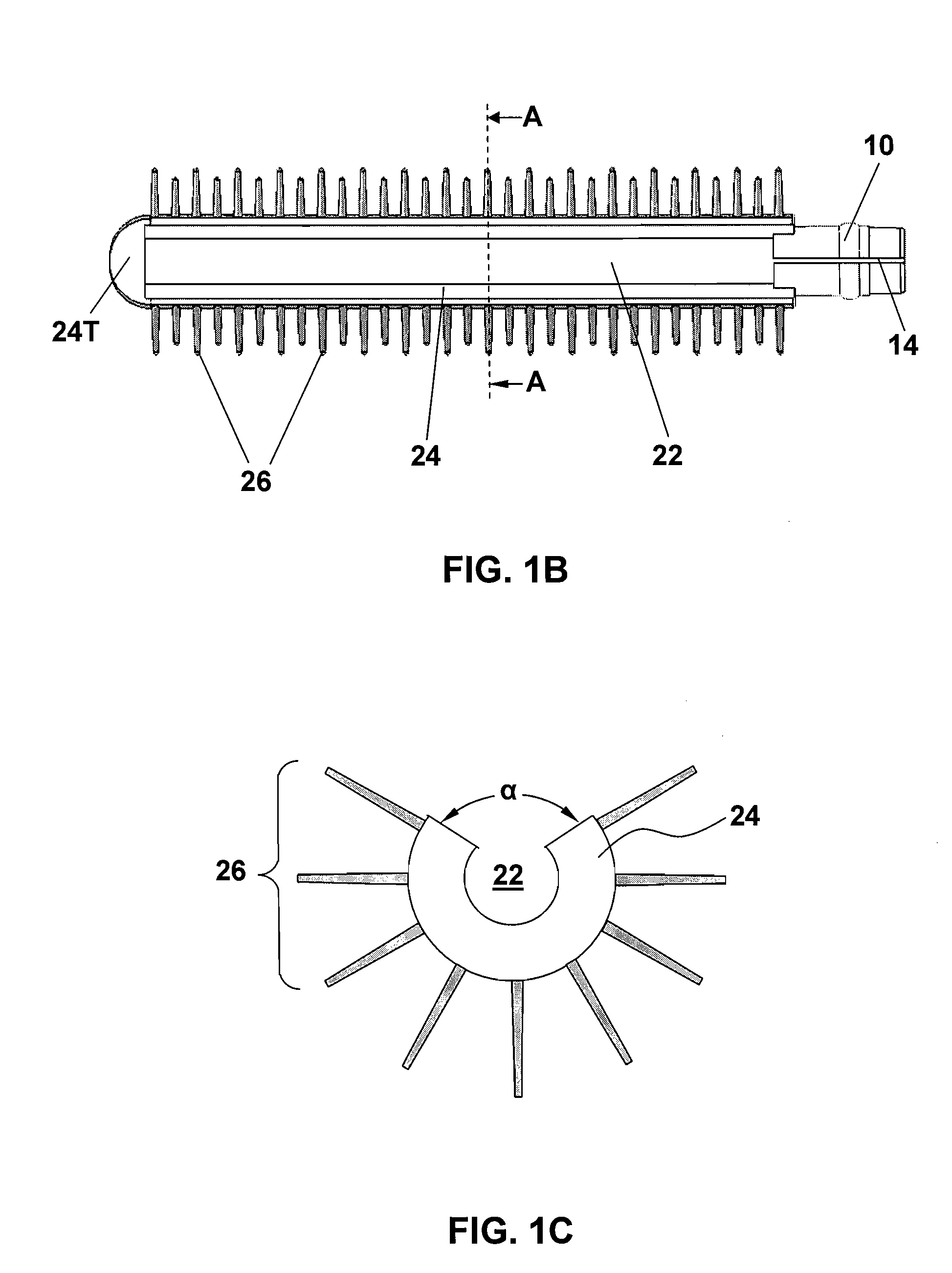
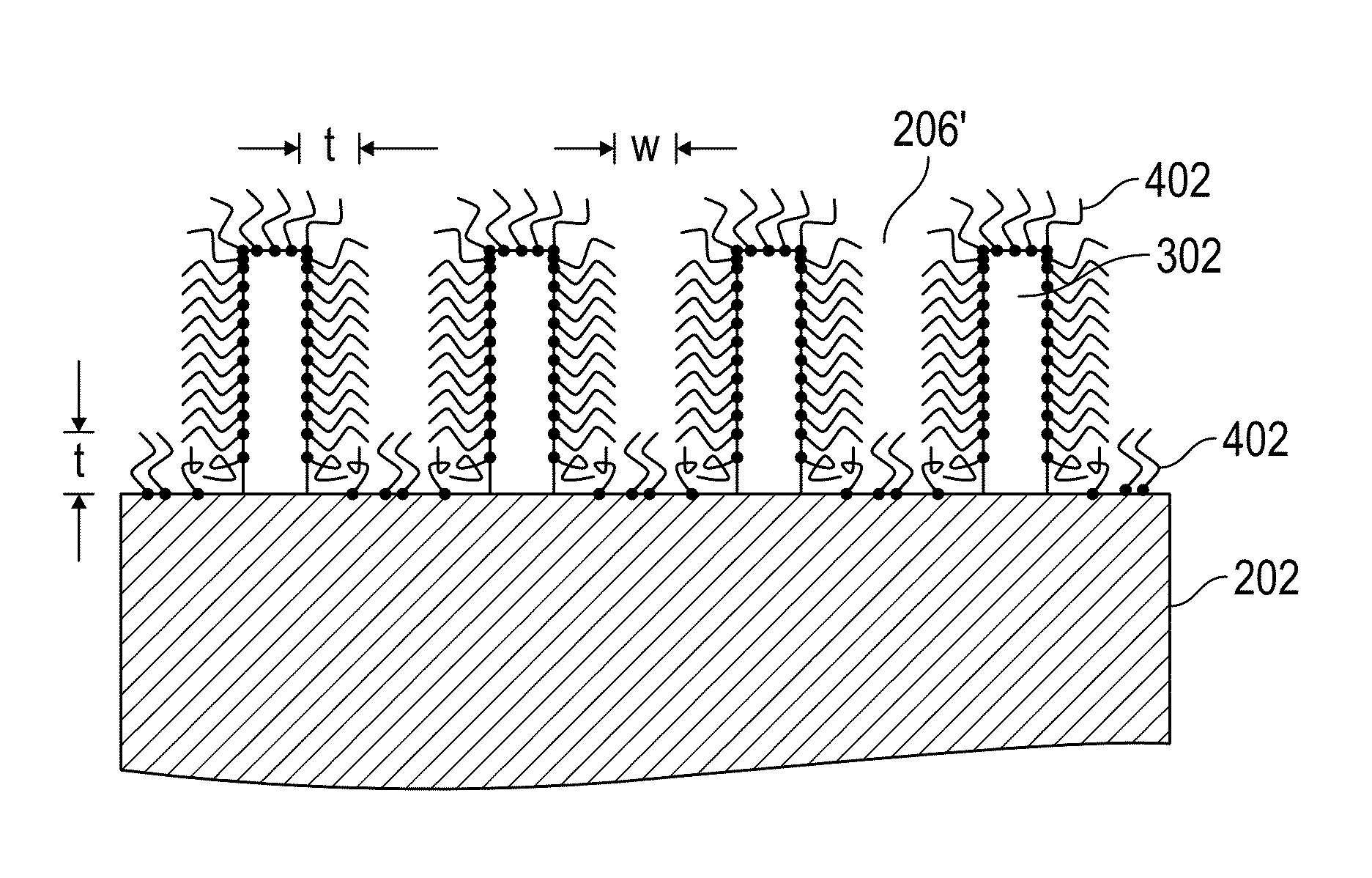
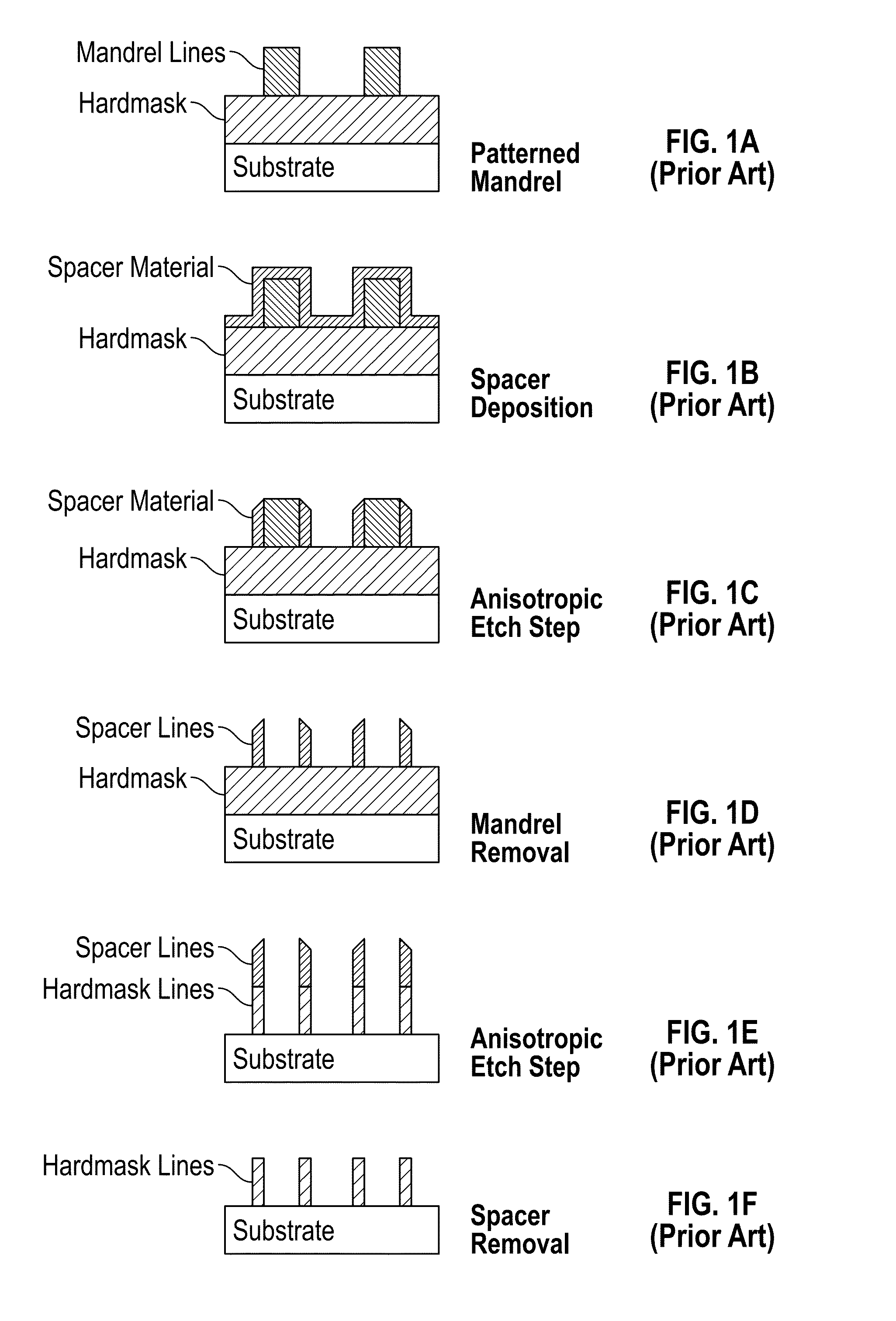
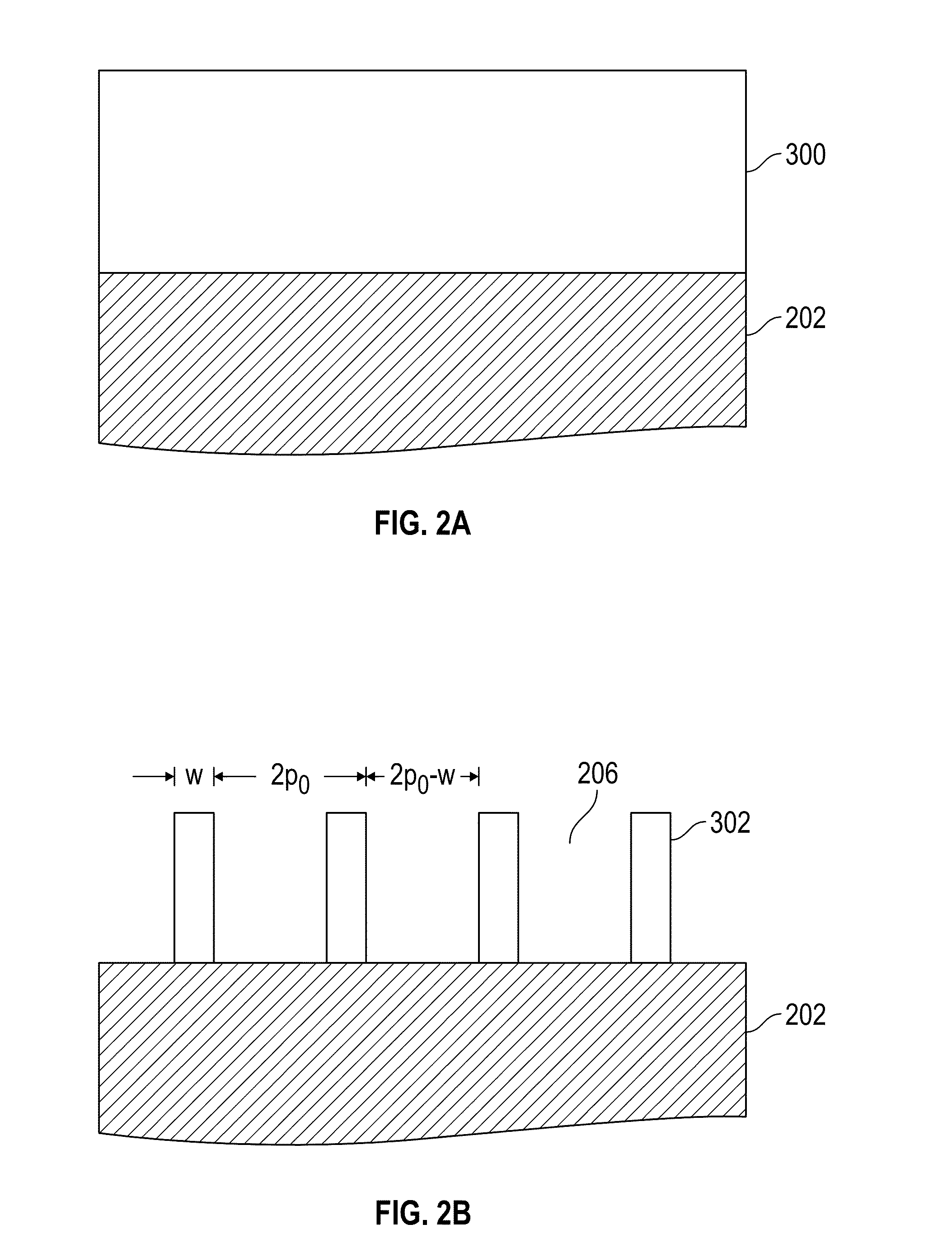
A method for sidewall spacer line doubling uses sacrificial sidewall spacers. A mandrel layer is deposited on a substrate and patterned into mandrel stripes with a pitch double that of the desired final line pitch. A functionalized polymer is deposited over the mandrel stripes and into the gaps between the stripes. The functionalized polymer has a functional group that reacts with the surface of the mandrel stripes when heated to graft a monolayer of polymer brush material onto the sidewalls of the mandrel stripes. A layer of etch mask material is deposited into the gaps between the polymer brush sidewall spacers to form interpolated stripes between the mandrel stripes. The polymer brush sidewall spacers are removed, leaving on the substrate a pattern of mandrel stripes and interpolated stripes with a pitch equal to the desired final line pitch. The stripes function as a mask to etch the substrate.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Macromolecular arrays on polymeric brushes and methods for preparing the same
InactiveUS6994964B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorosityCrystallography
Polymeric brush substrates and methods for their preparation are provided. Methods are also provided for preparing macromolecular arrays on such polymeric brush substrates. Using polymeric brush substrates allows control over functional site density as well as wettability and porosity of the substrate. These polymeric brushes are useful in solid-phase synthesis of arrays of peptides, polynucleotides or small organic molecules.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
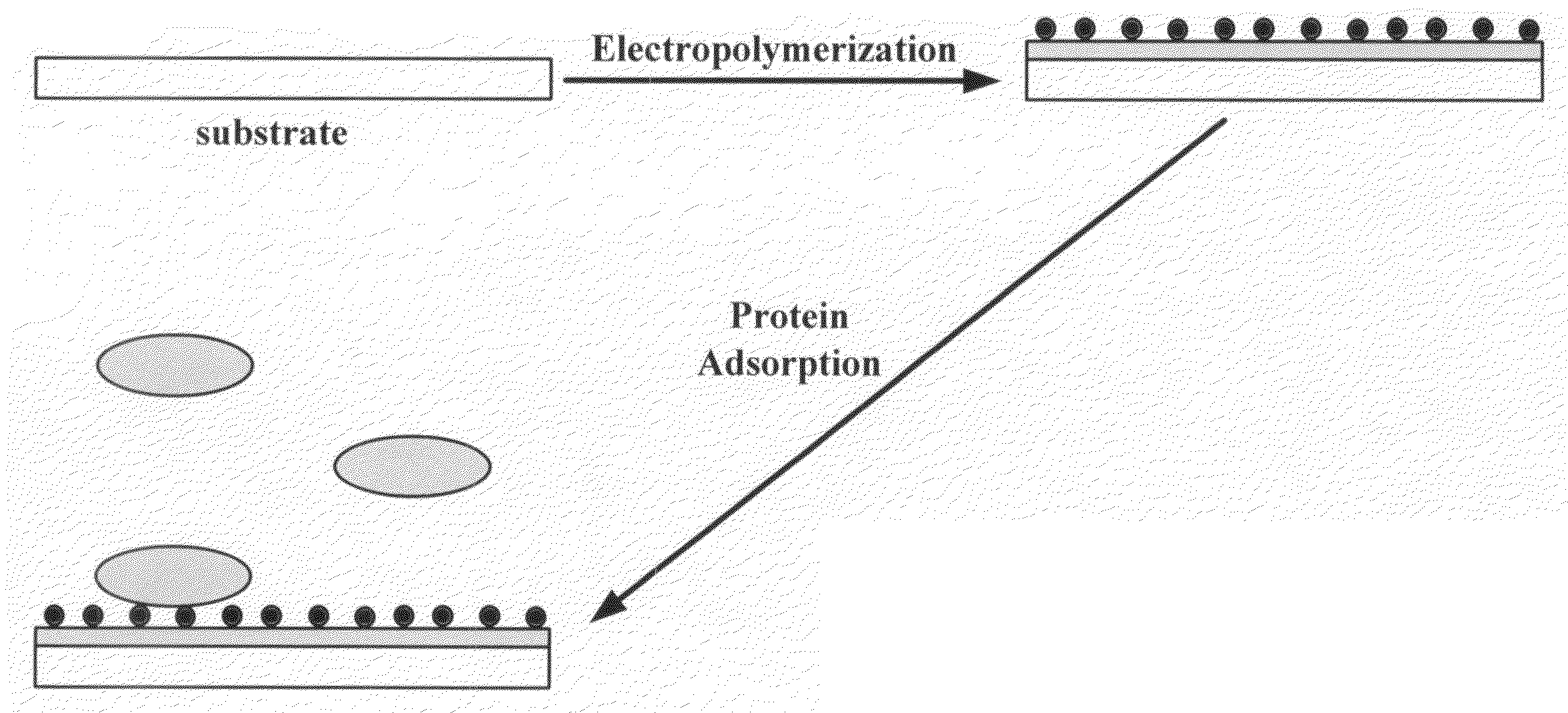
Methods for preparing polymer coatings by electrochemical grafting of polymer brushes, compositions prepared thereby and compositions for preparing the coatings
InactiveUS20090236229A1Surface reaction electrolytic coatingElectrolytic organic material coatingPolymer sciencePolymer coatings
New methods for the grafting of complex polymer coatings onto conducting surfaces, new grafting compositions and new substrates with grafted coating of the grafting compositions are disclosed. The method offers a new and convenient approach for the preparation of polymer coatings by electrochemically grafting and reactive crosslinking, and / or graft polymerizing.
Owner:ADVINCULA RIGOBERTO
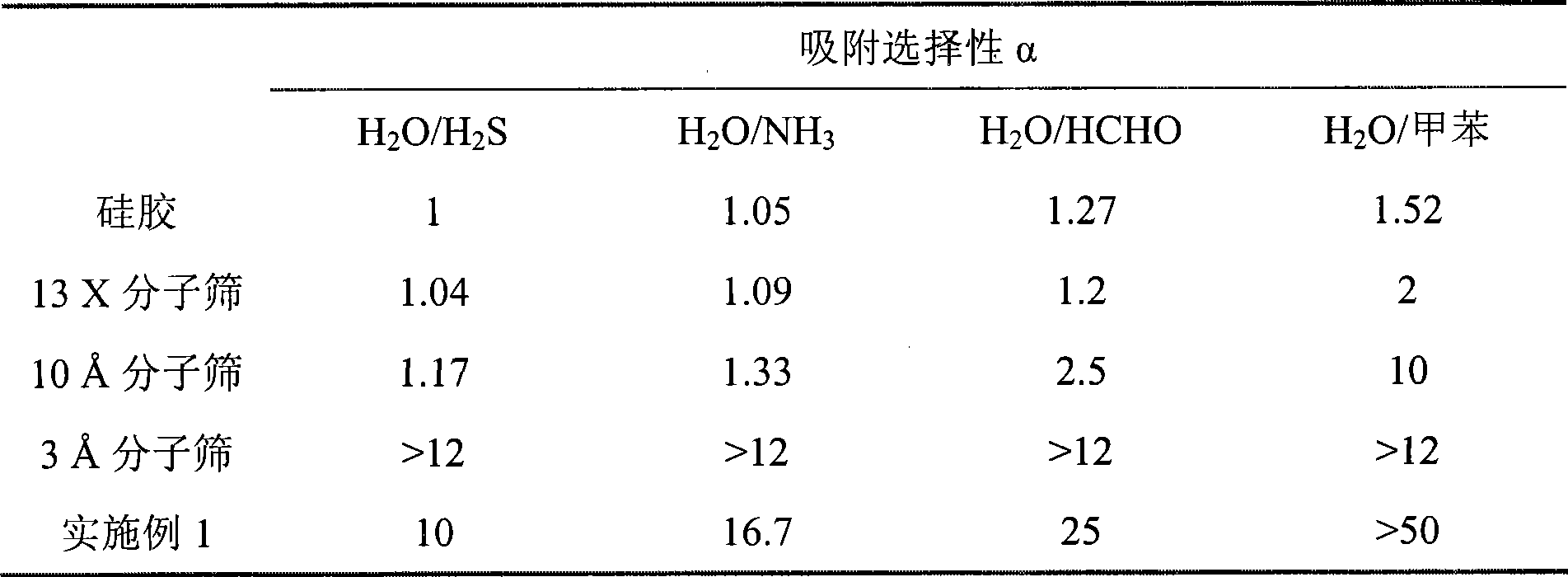
High selectivity hygroscopic agent with shell and core structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101381437AHigh selectivityHigh moisture absorptionOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationMoistureAcrylic monomers
The invention discloses a high selectivity moisture absorber with a shell-core structure and a method for preparing the same. The moisture absorber is an organic-inorganic composite adsorbent which takes an inorganic porous material the surface of which contains a hydroxyl group as an inner core and a hydrophilic polymer ultra-thin film as a shell, wherein by the condensation and polymerization reactions, the shell is grafted with a hydrophilic polymer brush on the surface of the inner core; and further by the cross linking, the hydrophilic polymer ultra-thin film shell is formed. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, the inorganic porous material the surface of which contains the hydroxyl group is subjected to activating treatment and then subjected to hydrolytic condensation with a silane coupler to form an inorganic porous material containing vinyl; and the inorganic porous material containing the vinyl is subjected to free radical polymerization reaction with an acrylic monomer and then is subjected to cross linking reaction with a diamine compound so as to obtain the high selectivity moisture absorber with the shell-core structure. Compared with prior art, the moisture absorber has the advantages of high selectivity, large hygroscopic capacity, simple preparation process, low cost and easy control of selectivity, and can meet the requirements of different application occasions.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
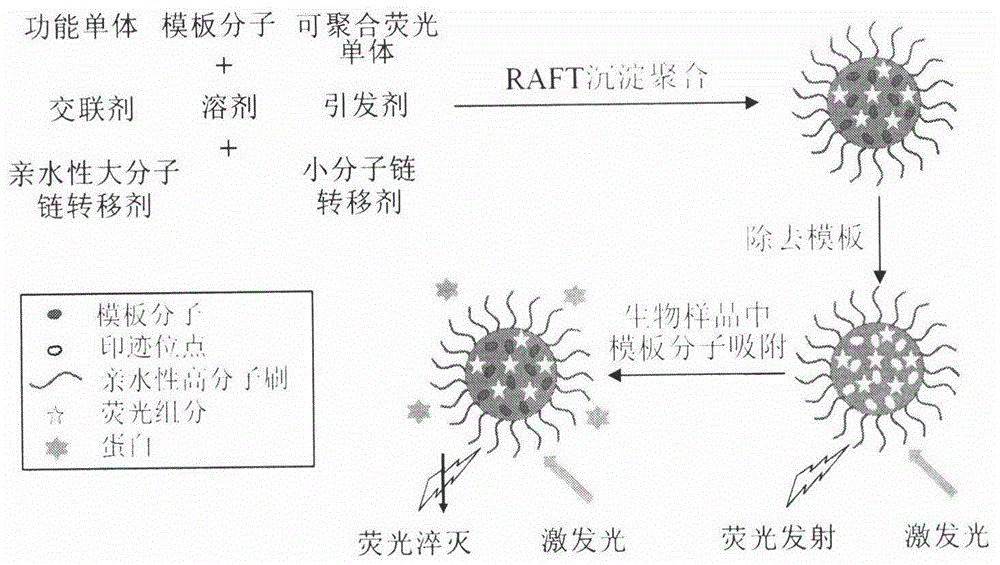
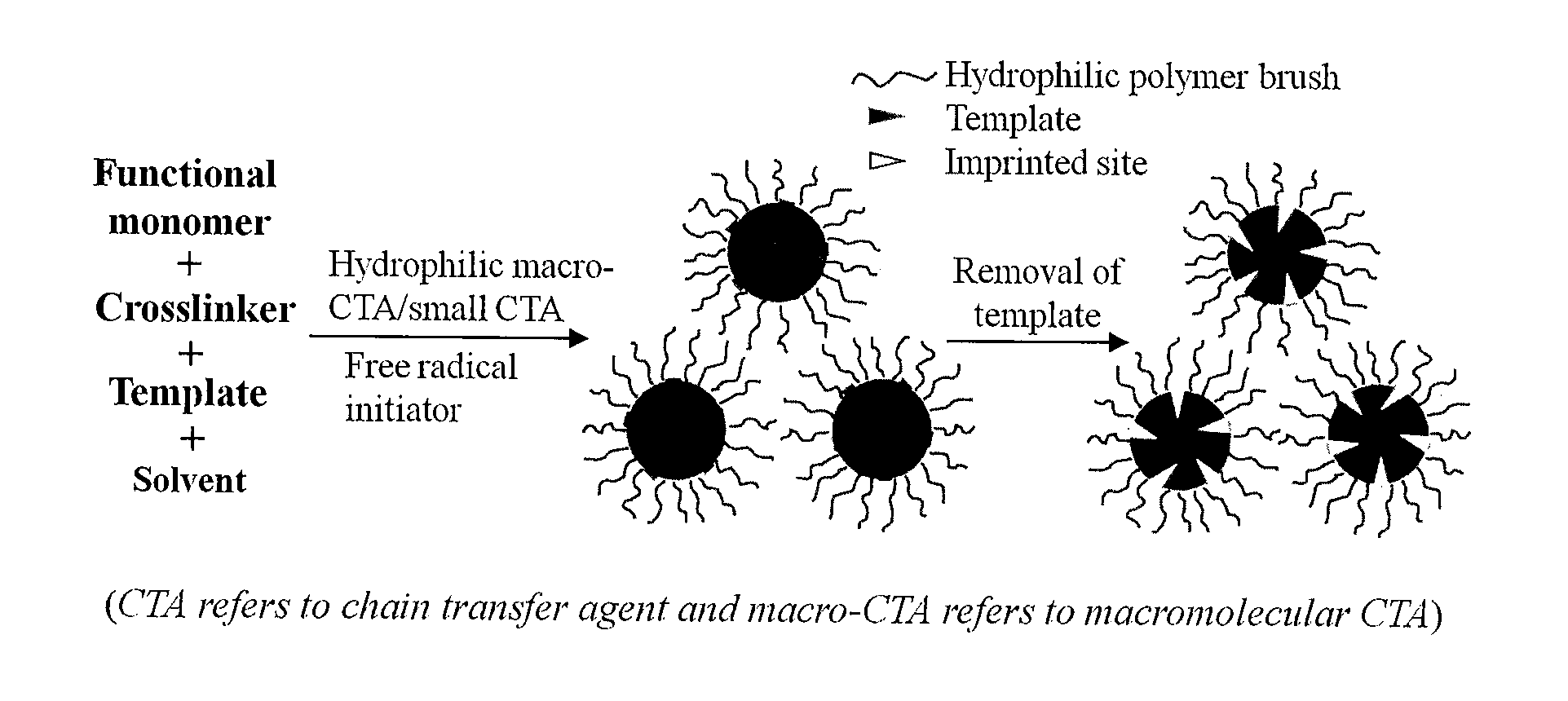
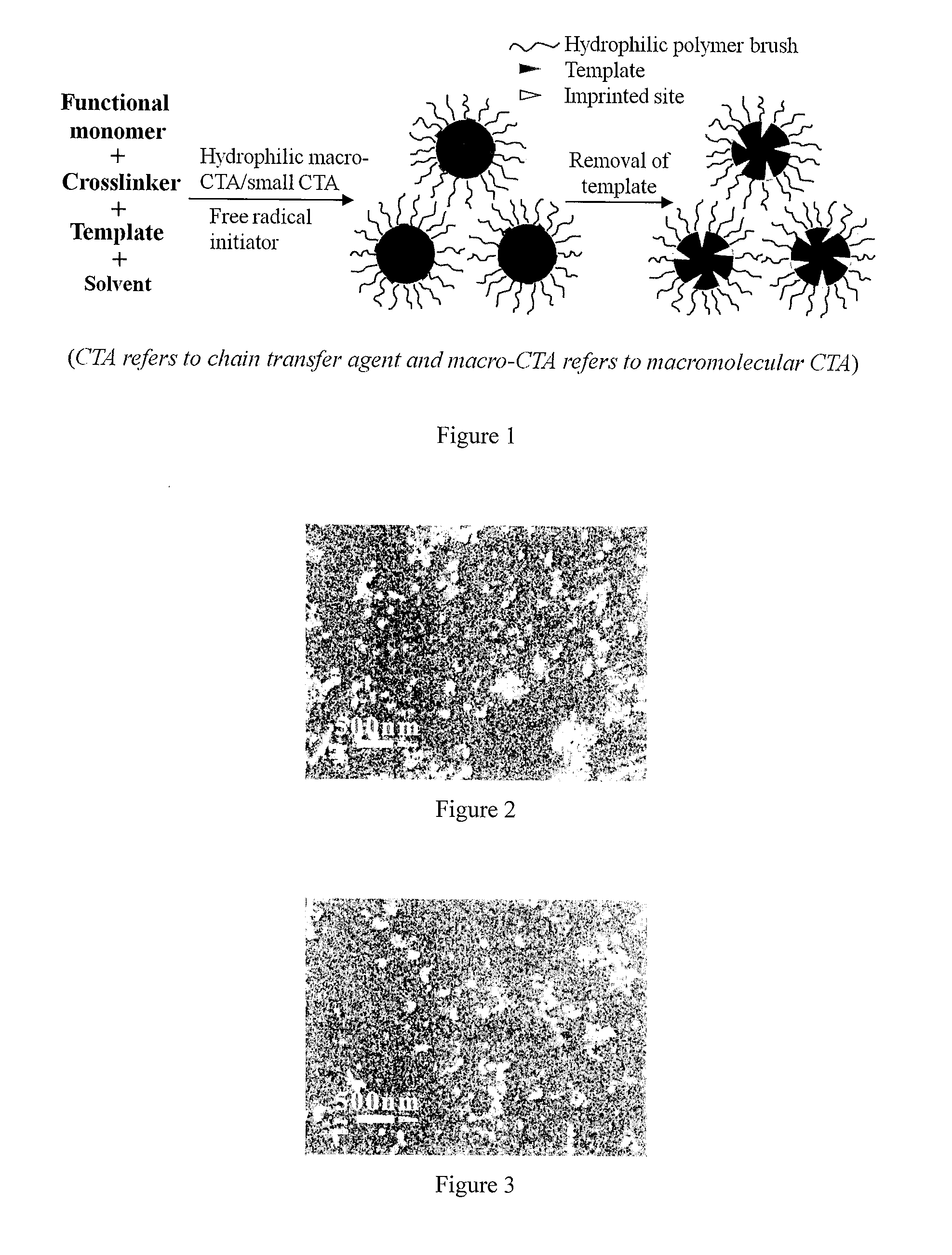
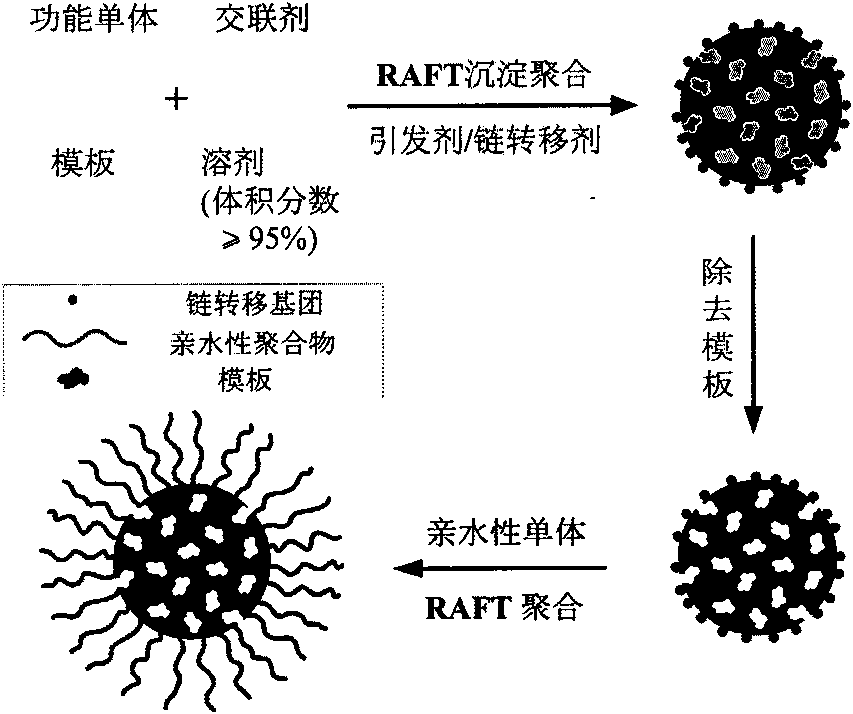
Molecularly imprinted polymer sensing material suitable for biological samples and preparation method of sensing material
The invention relates to a molecularly imprinted polymer photochemical sensing micro / nanoparticle capable of rapidly and quantitatively detecting an organic small molecule in a biological sample and a preparation method of the micro / nanoparticle. The molecularly imprinted polymer micro / nanoparticle has a cross-linking degree of 50% or more and a particle size of 0.01-5 micrometers, and the molecularly imprinted polymer micro / nanoparticle is grafted with a hydrophilic polymer brush on the surface and has a fluorescent property. The molecularly imprinted polymer micro / nanoparticle is synthesized in one step by the use of a hydrophilic macromolecule chain transfer agent induced reversible addition-cleavage chain transfer (RAFT) precipitation polymerization technique in the presence of polymerizable fluorophores. The molecularly imprinted polymer photochemical sensing micro / nanoparticle has the advantages of simple synthesis method, wide application range, pure product and the like, and has broad application prospects in the fields of food safety, environmental monitoring, clinical diagnosis and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
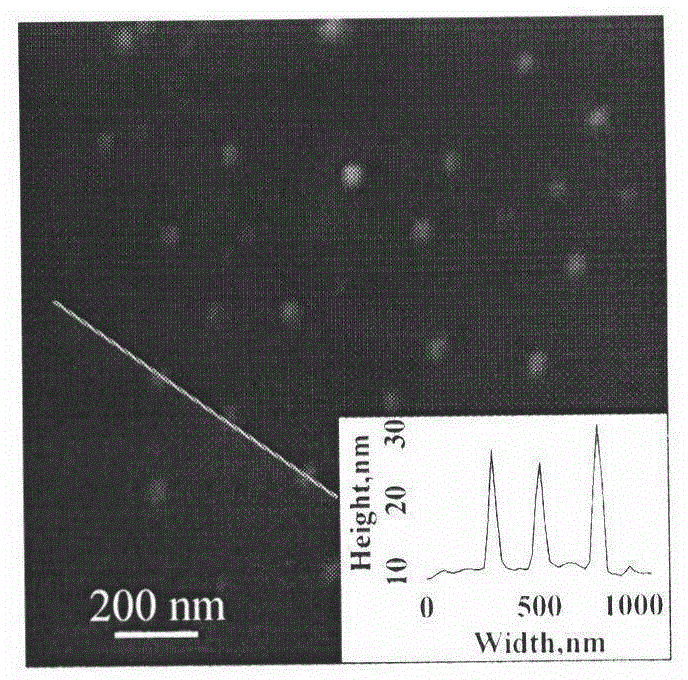
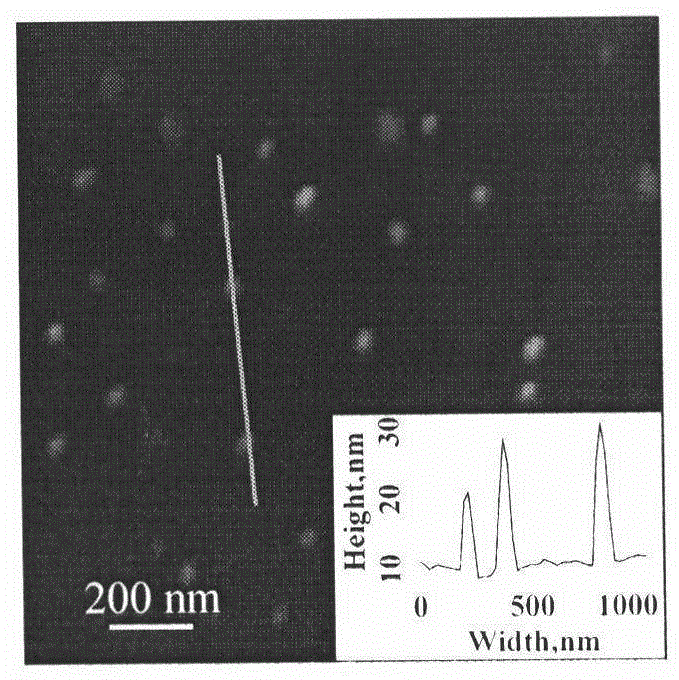
Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles compatible with biological samples and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20150299366A1Biological material analysisSynthetic resin layered productsOne-pot synthesisMolecularly imprinted polymer
This invention provides molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles compatible with biological samples, and in particular pure biological samples and a preparation method thereof. Said molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles have a crosslinking degree exceeding 50%, a particle diameter of 10 to 500 nm, hydrophilic polymer brushes on its surfaces and can be prepared by introducing appropriate hydrophilic macromolecular chain transfer agents into reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) precipitation polymerization systems through the one-pot synthesis. The preparation method is simple, features a broad range of application and yields a pure product. The obtained hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles have prospects for a wide range of application in biological sample analysis, medical clinical immune analysis, food and environmental monitoring, biomimetic sensors, etc.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
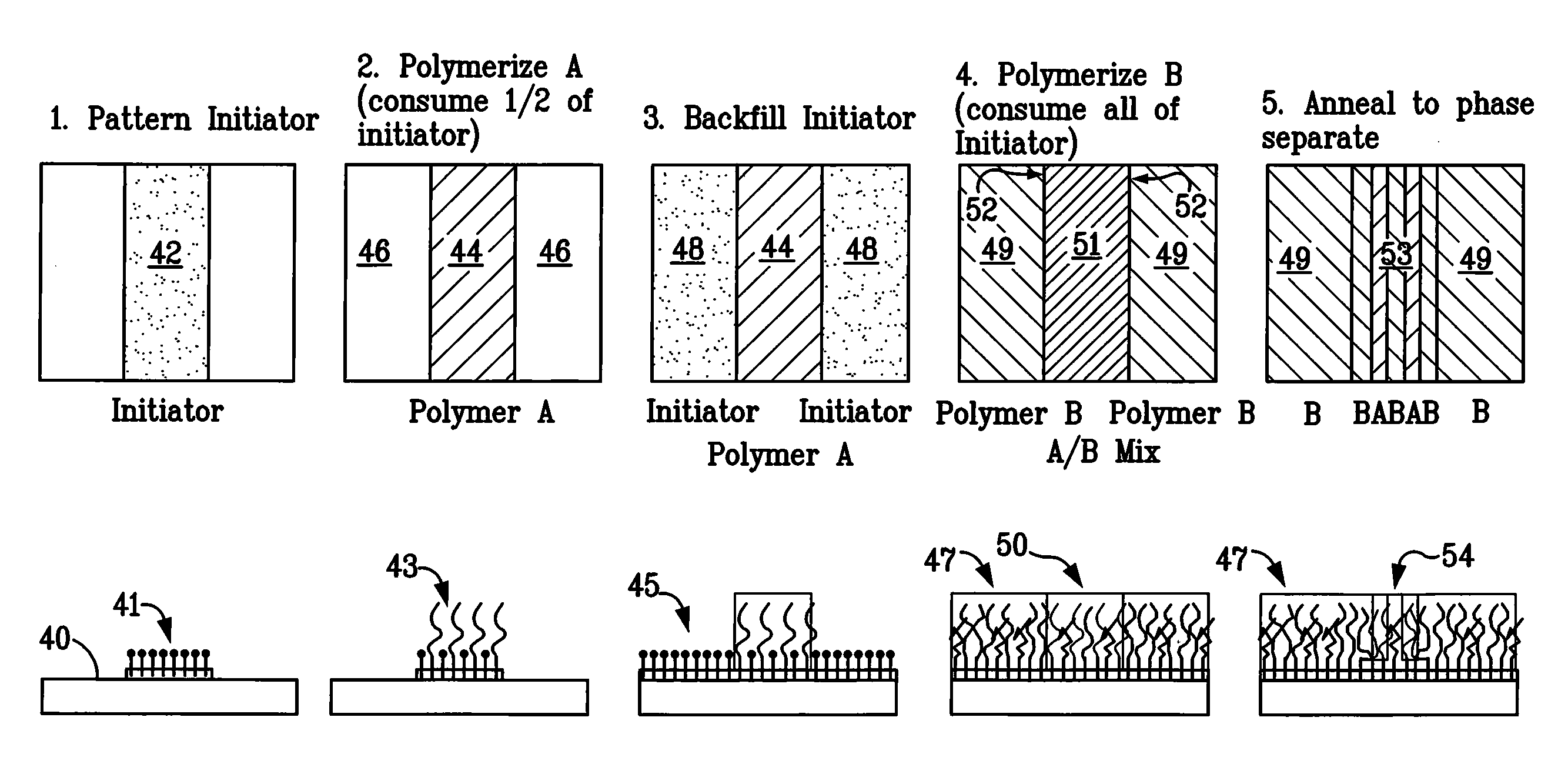
Nanopatterns by phase separation of patterned mixed polymer monolayers
Micron-size and sub-micron-size patterns on a substrate can direct the self-assembly of surface-bonded mixed polymer brushes to create nanoscale patterns in the phase-separated mixed polymer brush. The larger scale features, or patterns, can be defined by a variety of lithographic techniques, as well as other physical and chemical processes including but not limited to etching, grinding, and polishing. The polymer brushes preferably comprise vinyl polymers, such as polystyrene and poly(methyl methacrylate).
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
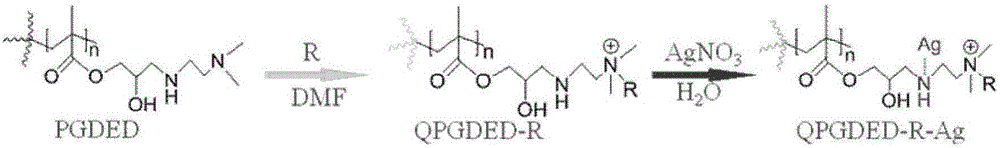
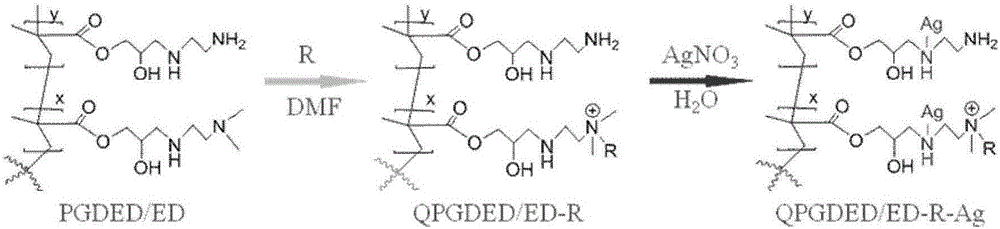
Preparation method of quaternary ammonium salt polymer antibacterial agent and silver-loaded compound antibacterial agent thereof on basis of ATRP method
InactiveCN105801734AControllable silver ion contentMolecular weight controllableAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesPolymer scienceInitiation point
The invention discloses a preparation method of a quaternary ammonium salt polymer antibacterial agent and a silver-loaded compound antibacterial agent thereof on the basis of an ATRP method. According to the method, various monomers are grafted onto initiation points of an initiator through atom transfer radical active polymerization, a high molecular polymer is obtained, ring-opening reacting is conducted on the high molecular polymer, and an antibacterial agent polymer framework material can be obtained; different modifications are conducted on the antibacterial agent polymer framework material, and a quaternary ammonium salt polymer antibacterial agent, a silver-loaded-quaternary ammonium salt polymer compound antibacterial agent and a silver-loaded polymer antibacterial agent are obtained respectively. The obtained antibacterial agents are low in antibacterial concentration and obvious in sterilizing effect and can be used for modifications of the surfaces of glass sheets, polystyrene and the like by combining the adsorption property of dopamine to form a surface antibacterial polymer brush. The antibacterial effect of the antibacterial agents is obvious, and high commercial potential is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Surface-hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102059104AOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMicrosphereSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a surface-hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere has the crosslinking degree of over 60 percent and a grain size of 1 to 5mu m. The surface of the microsphere is provided with a hydrophilic polymer brush, and the microsphere has excellent molecular recognition performance on template molecules in a pure aqueous solution system. The microspheres are synthesized by a two-step process in reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) controlled free radical polymerization technology. The invention has the advantages of simple synthesis method, wide application range, pure products and the like. The prepared molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere has a wide application prospect in the fields of chromatographic stationary phases, biological sample analysis, medically clinical immunoassay, food and environment monitoring, mimic enzyme catalysis, bionic sensors and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Polyethylene artificial joint capable of improving biocompatibility and tribological property and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102078227AGood biocompatibilityBiodescriptiveJoint implantsArtificial jointsBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a polyethylene artificial joint capable of improving biocompatibility and tribological property and a preparation method thereof. The polyethylene artificial joint comprises a joint head and a superhigh molecular weight polyethylene cotyle, wherein a bionic polymer brush layer is grafted on the surface of the superhigh molecular weight polyethylene cotyle rubbed with the joint head; and the bionic polymer brush layer is a brush-shaped structure formed by connecting a super-lubricant and hydrophilic polymer chain on the surface of polyethylene. The high-biocompatibility polymer brush layer is grafted on the surface of the artificial joint polyethylene by simulating a brush-shaped structure and a lubricating antifriction function of a natural joint cartilage epilimmion synovial cavity, so that the biocompatibility and the tribological property of the artificial joint are obviously improved, and tissue reaction and aseptic loosening are relieved; and the polymer brush molecular chain is chemically bonded on the surface of the superhigh molecular weight polyethylene firmly by an ultraviolet grafting technique. The artificial joint prepared by the method has high wettability and biocompatibility on the friction surface and low friction coefficient, and can relive aseptic loosening and prolong service life.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polymers, supersoft elastomers and methods for preparing the same
Embodiments of the present invention include a material comprising a polymer having a modulus of elasticity less than 10<5 >Pa and a material comprising a polymer having a modulus of elasticity of less than 5x10<4 >Pa. Embodiments also include a material comprising a polymeric network and a multiplicity of side chains attached to the polymeric network. The multiplicity of side chains may have an average molecular weight below the critical molecular weight for entanglements. In certain embodiments it may be advantageous for the side branches to have a glass transition temperature below the use temperature of the material. The polymer network may comprise at least two monomers so that the polymer network is a copolymer. Embodiments of the present invention also include methods of forming a polymer network. Such as, for example, a method of preparing a polymer network comprising cross-linking a polymer, wherein the polymer comprises a multiplicity of side chains. The polymer may be at least one of a polymer brush, a polymer comb, and a nanocomposite material. An additional embodiment may include polymerizing macromonomers in the presence of a crosslinking agent. This embodiment may result in the forming a polymer network, wherein the polymer network comprises a multiplicity of branches attached to the polymer network, wherein the macromonomers may have a molecular weight less than the critical molecular weight for entanglements. Another embodiment of the method of forming a polymer network may comprising polymerizing monomers directly from a crosslinked polymer network. This method may result in forming a branched polymer network, wherein the polymer network comprises a multiplicity of branches attached to the polymer network.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
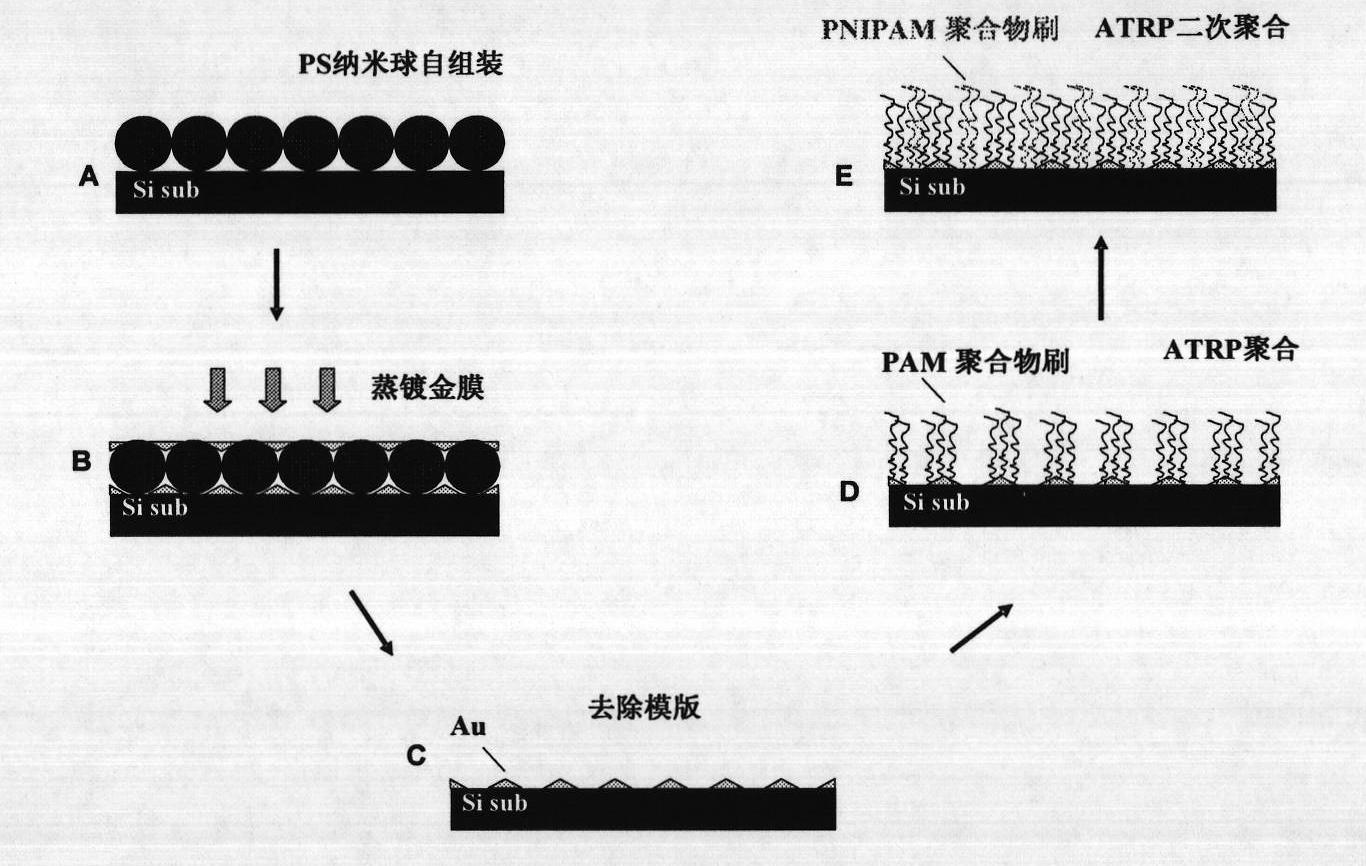
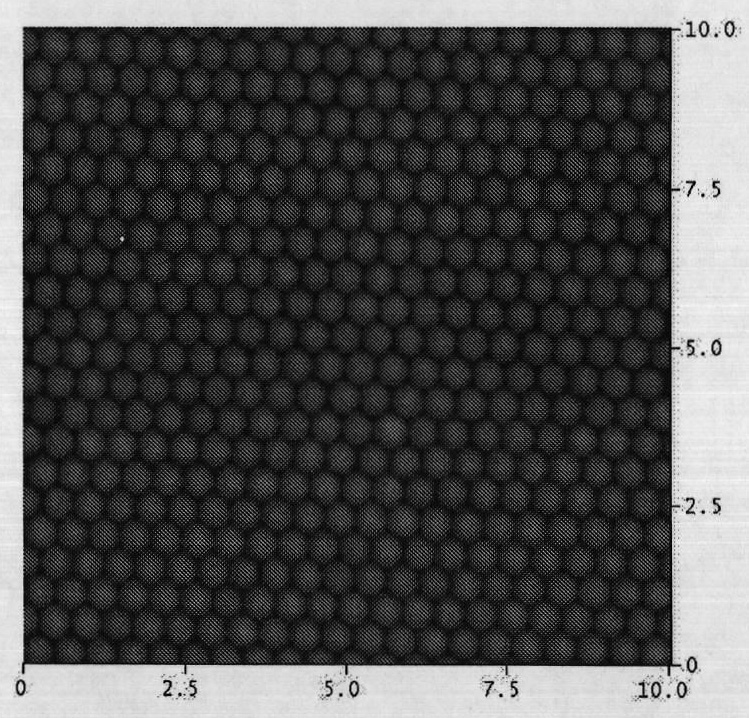
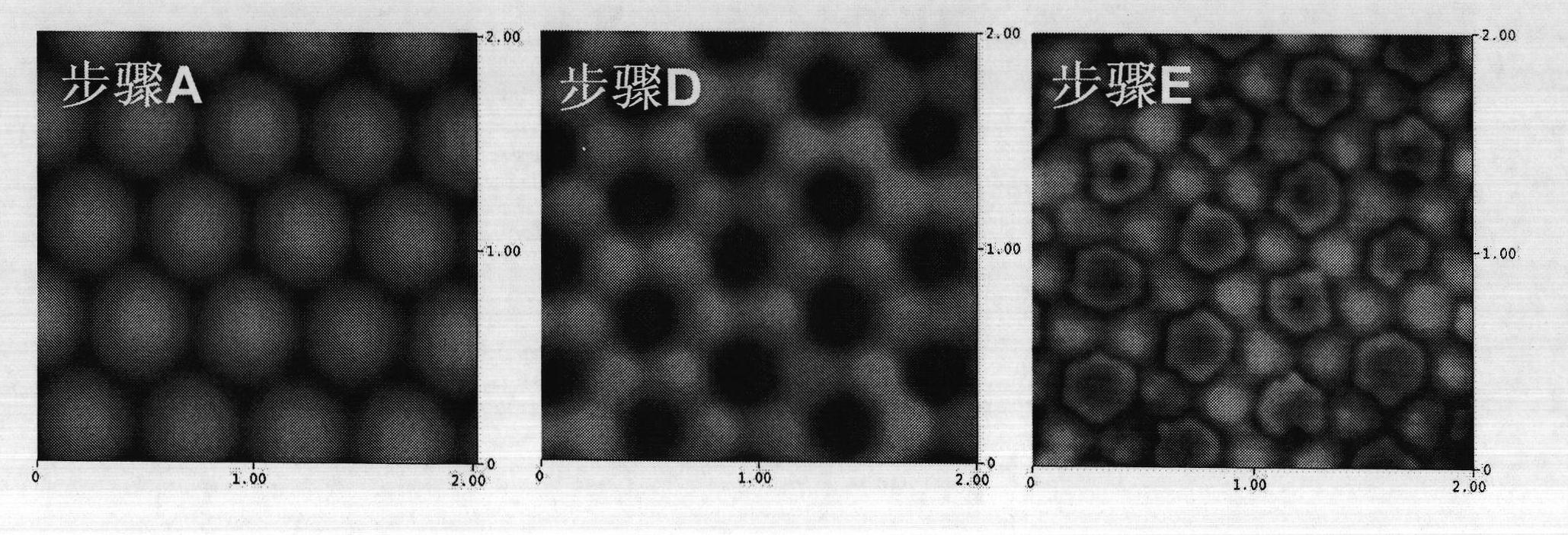
Method for preparing nanometer patterning bipolymer brush
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nanometer patterning bipolymer brush. The method for preparing a nanometer patterning bipolymer brush combines a nanosphere etching print method and a surface controlled polymerization method together. Polystyrene nanospheres are assembled on a substrate to obtain a hexagonal heaped sphere array pattern which is used as a mask for carrying out surface gold spraying, after small spheres are removed, a regular nanopore array pattern of which the surface component consists of gold and silicon, and surface polymerization is respectively initiated on the gold and the silicon twice to obtain the nano-scale bipolymer brush. The method is simple and efficient, the size of the pattern can be conveniently regulated by using the small spheres with different diameters, and a functional patterning polymer brush can be prepared with the method.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Surface modification method, surface-modified elastic body, gasket for injector, injector, and tire
ActiveUS20130274367A1Imparting slidabilityPiston ringsBraking action transmissionElastomerPolymer science
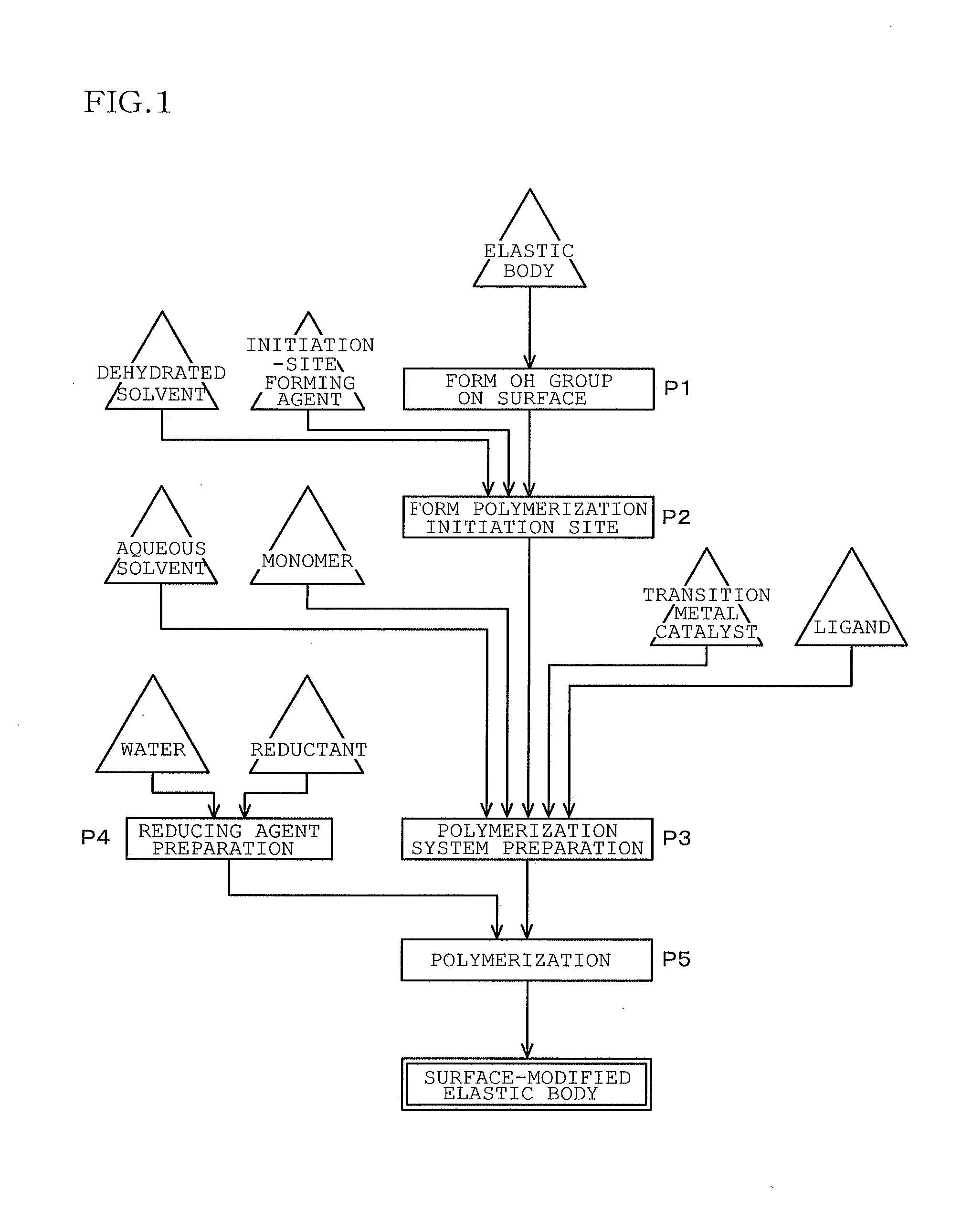
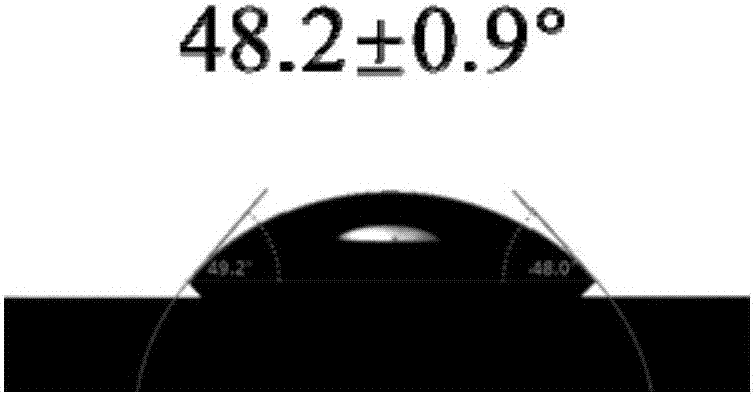
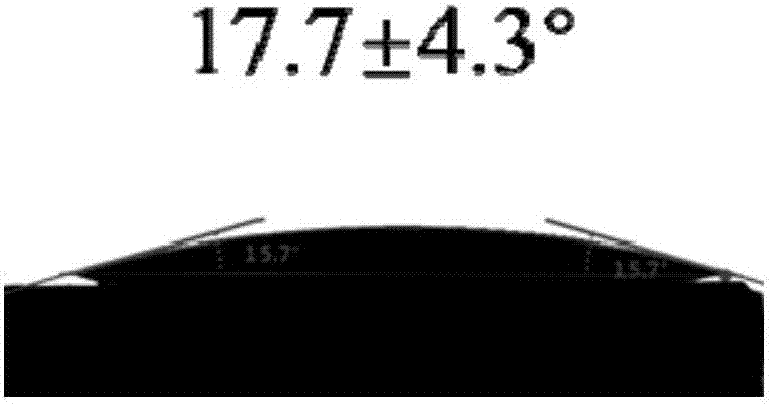
Provided are: surface modification method for imparting slidability to surface of elastic body such as vulcanized rubber or thermoplastic elastomer without using expensive self-lubricating resin; surface-modified elastic body with polymer brush formed on its surface; and gasket for injector and injector formed of surface-modified elastic body. The surface modification method applies to surface of thermoplastic elastomer or vulcanized rubber. The surface modification method comprises the step of forming hydroxyl group on surface of to-be-modified object such as rubber so that water contact angle of the surface becomes 8 to 50 degrees smaller than original water contact angle in unmodified condition, the step of forming polymerization initiation site by subjecting the hydroxyl group to action of secondary or tertiary organic halide, and the step of growing polymer brush on the surface of to-be-modified object by subjecting monomer to radical polymerization at the polymerization initiation site acting as a point of initiation.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD +1
Polymer-brush modified fillers for composites
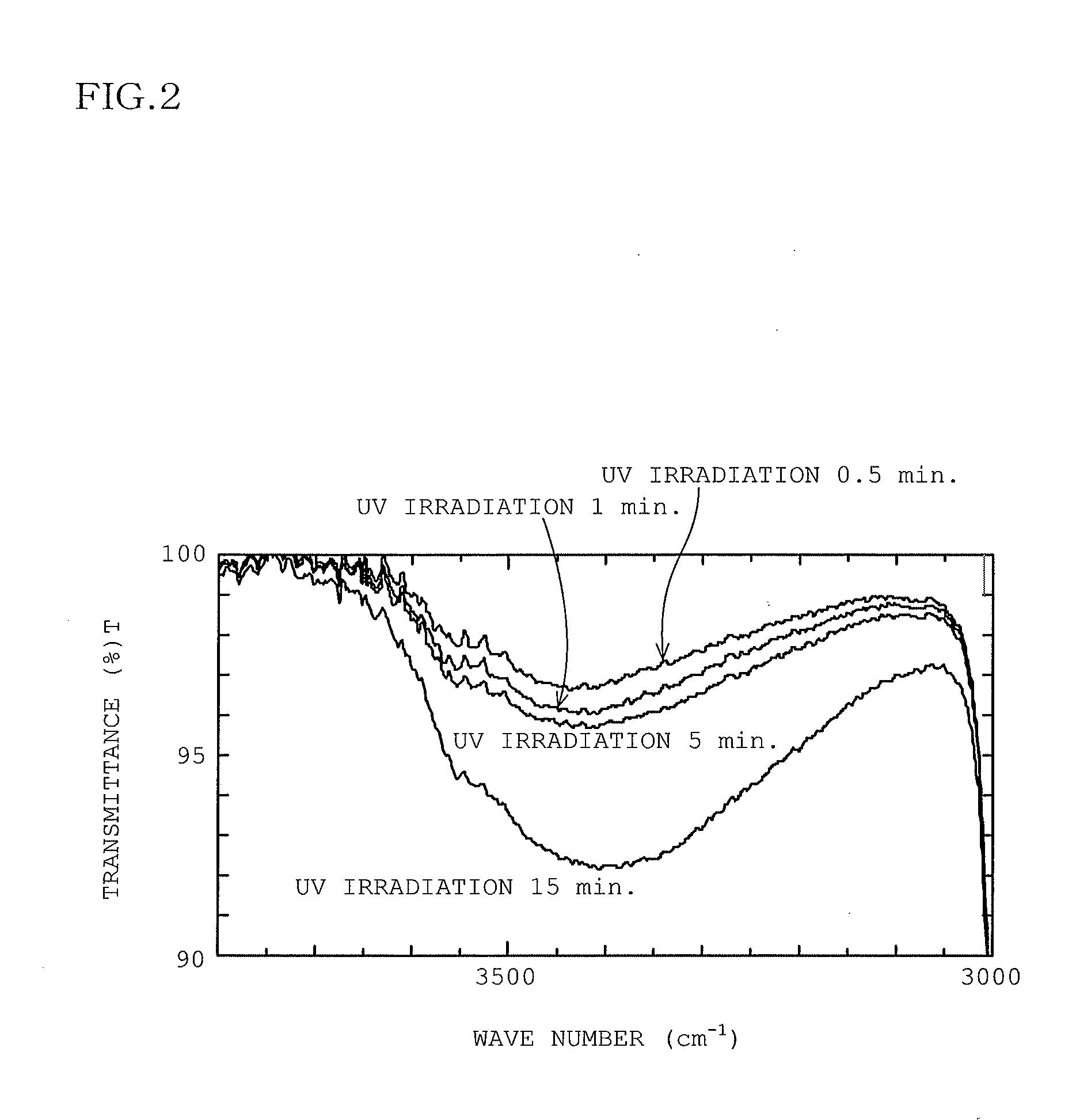
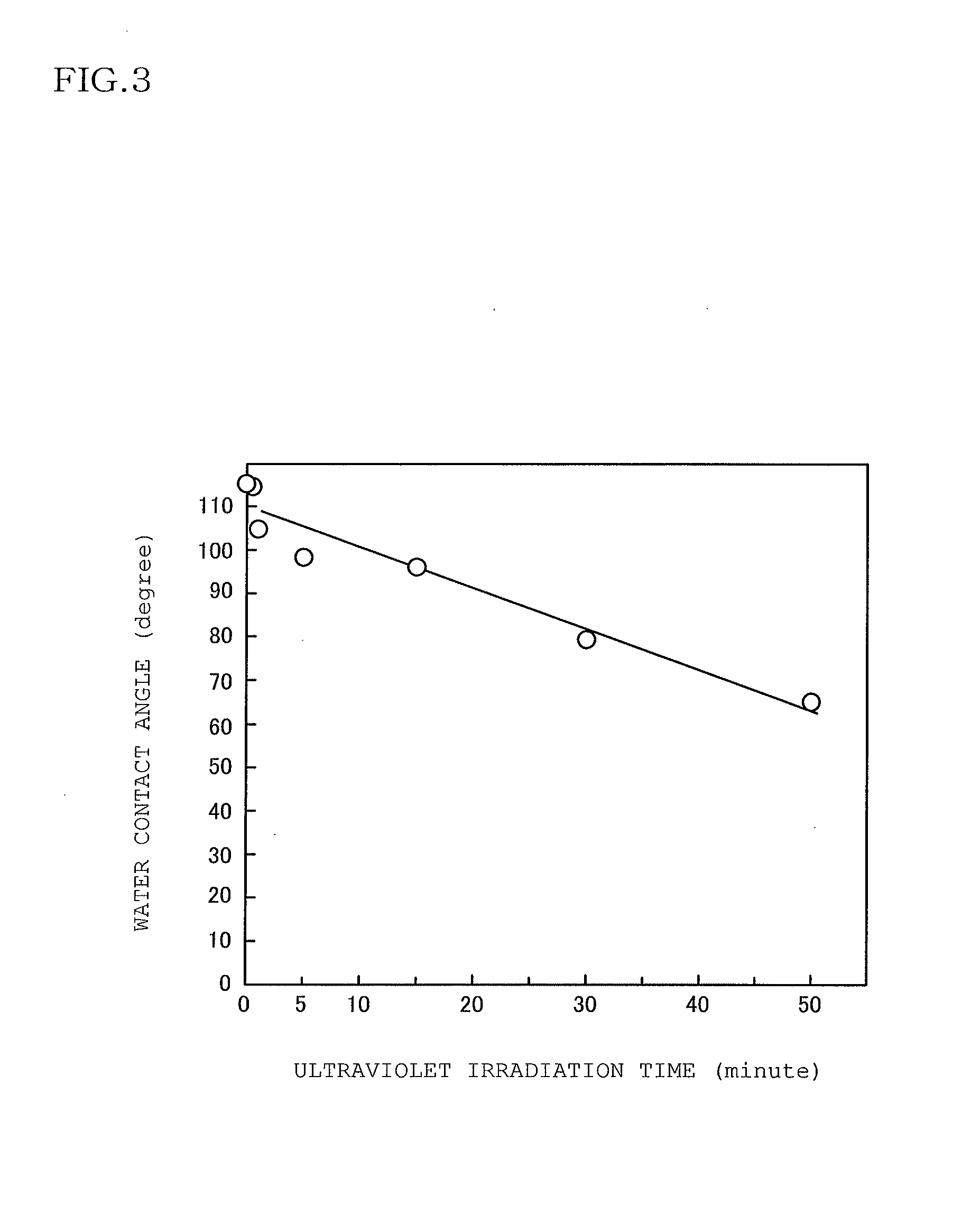
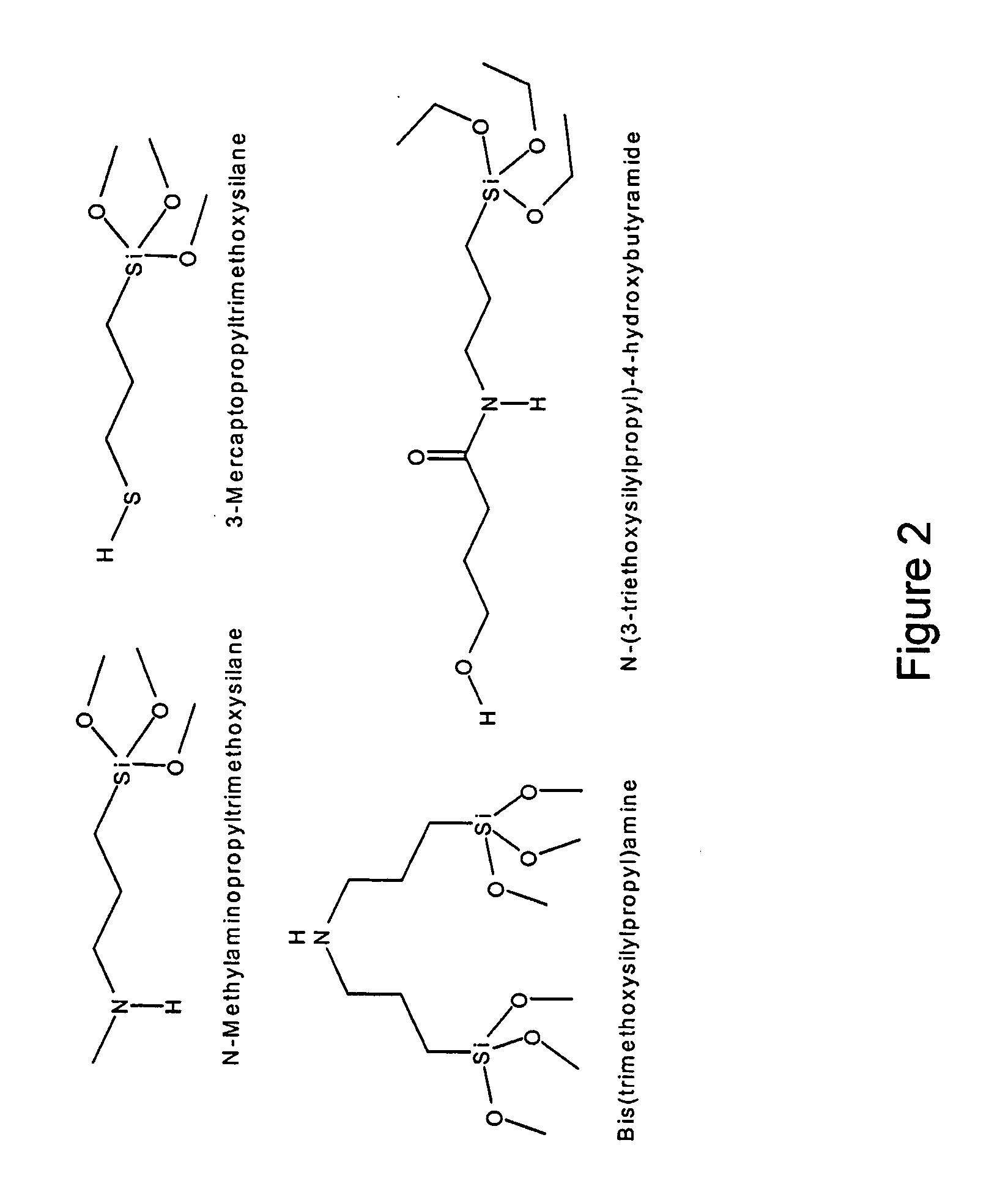
The present invention relates to polymer-brush modified fillers and methods, compositions and processes of modification of fillers and more particularly fillers useful in dental materials and other compositions that exhibit higher mechanical strength, longer hydrolytic stability, lower polymerization stress and improved wear and abrasion resistance. The present invention provides a method for making a polymer-brush modified filler comprising: providing a filler material; silanizing the filler material with a silane; and reacting the silanized filler with a telechelic oligomer. The present invention further provides a method of preparing a shaped dental prosthetic device for use in a human mouth comprising: dispensing a mixture having at least one monomer and a polymer brush modified filler; shaping the mixture; and photopolymerizing the mixture.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Preparation method of hydrophilic magnetic halloysite surface molecularly-imprinted nano composite material
InactiveCN103509161AUniform sizeEvenly distributedOther chemical processesWater contaminantsHalloysitePolymer science
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hydrophilic magnetic halloysite surface molecularly-imprinted nano composite material and belongs to the technical field of preparation of an environment functional material. Magnetic halloysite is synthesized by an impregnation method and a high temperature reducing method, and magnetic nano particles have a uniform size and are uniformly distributed; an initiator is grafted to the surface of the magnetic halloysite by the surface amination and amidation reaction and a molecularly-imprinted polymerization layer grafted to the surface of the magnetic halloysite is controlled in the nanoscale by surface atom transfer radical polymerization; due to existence of a tail-end ATRP (atom transfer radical polymerization) active group, the hydrophilic magnetic halloysite surface molecularly-imprinted nano composite material is successfully grafted with a hydrophilic polymer brush, is successfully applied to high-efficiency selective removal and rapid magnetic separation of sulfamethazine in the water environment and has excellent regenerability.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for preparing antibacterial surface on medical material surface
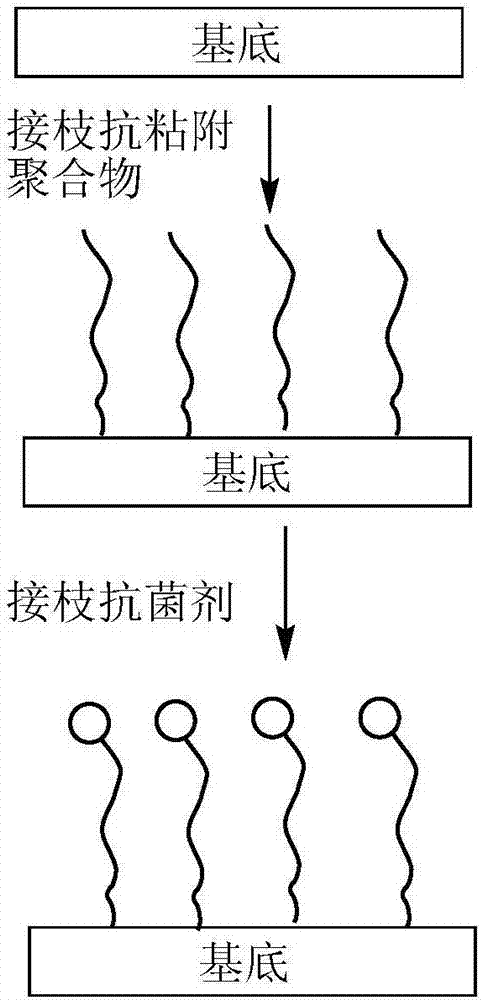
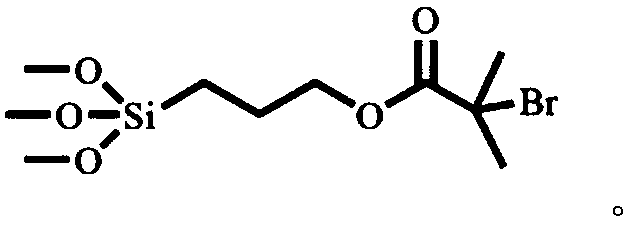
ActiveCN106902396AReduce adverse effectsAvoid Performance InterferenceSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSilanesBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for preparing antibacterial surface on medical material surface. The method comprises the following steps: (1) conducting chemical grafting of amino silane after performing oxygen plasma pretreatment to the medical material surface and then reacting the medical material of the amino silane grafted surface with an acyl compound; (2) placing the medical material of an initiator modified surface into an anti-adhesion water solution for graft polymerization reaction; (3) placing the medical material of an anti-adhesion polymer brush-modified surface into an azide compound-containing dimethylformamide solution; and (4) placing the medical material of the azide surface into an antibacterial agent click solution for click reaction, to obtain anti-adhesion polymer surface and antibacterial agent-comodified antibacterial surface. According to the method, the mutual interference of the anti-ahdesion capability and sterilization capability can be avoided, the antibacterial surface has excellent long-acting antibacterial performance, the adverse effect of the sterilized surface on blood and somatic cells can be reduced, and the biocompatibility is excellent.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
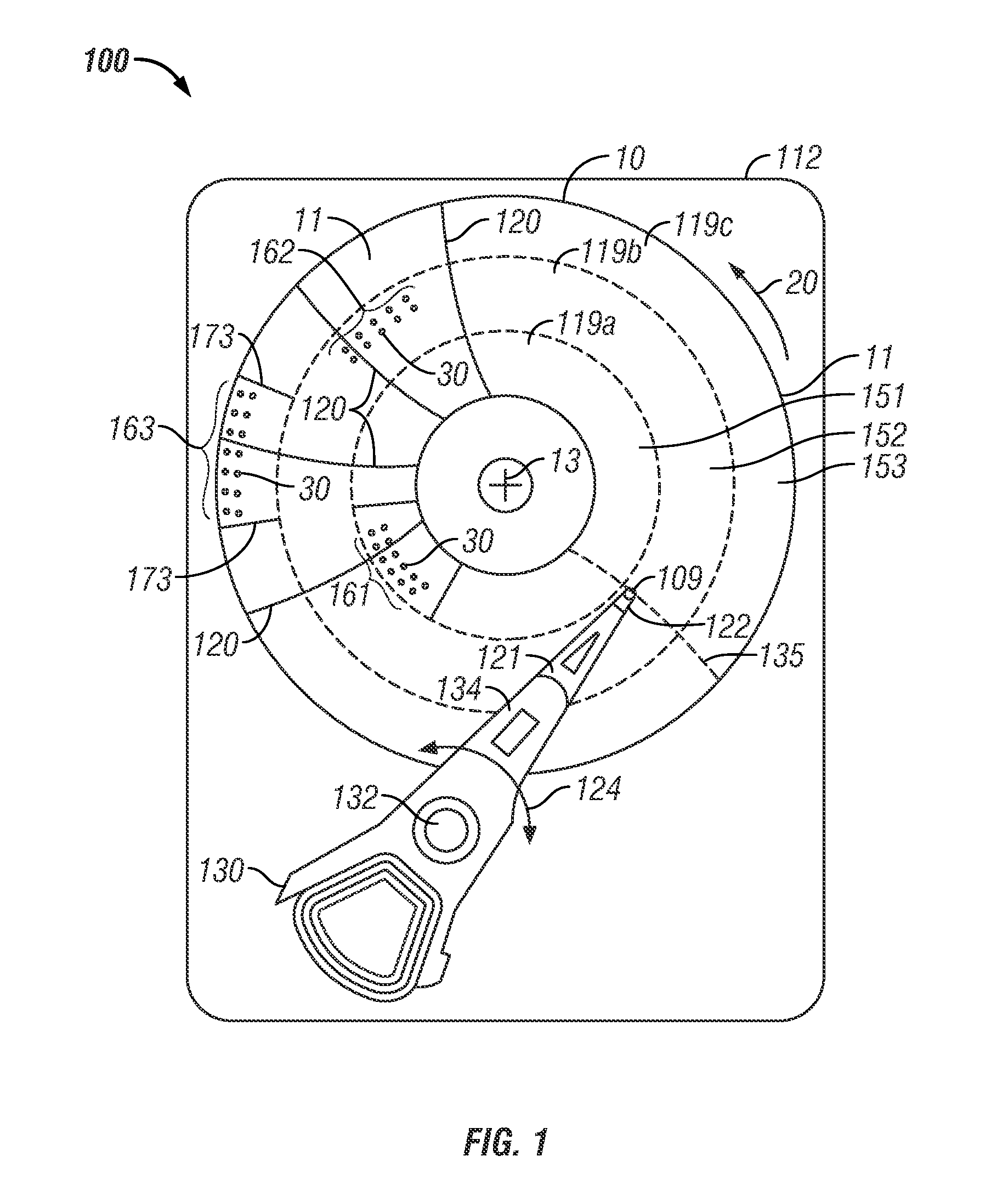
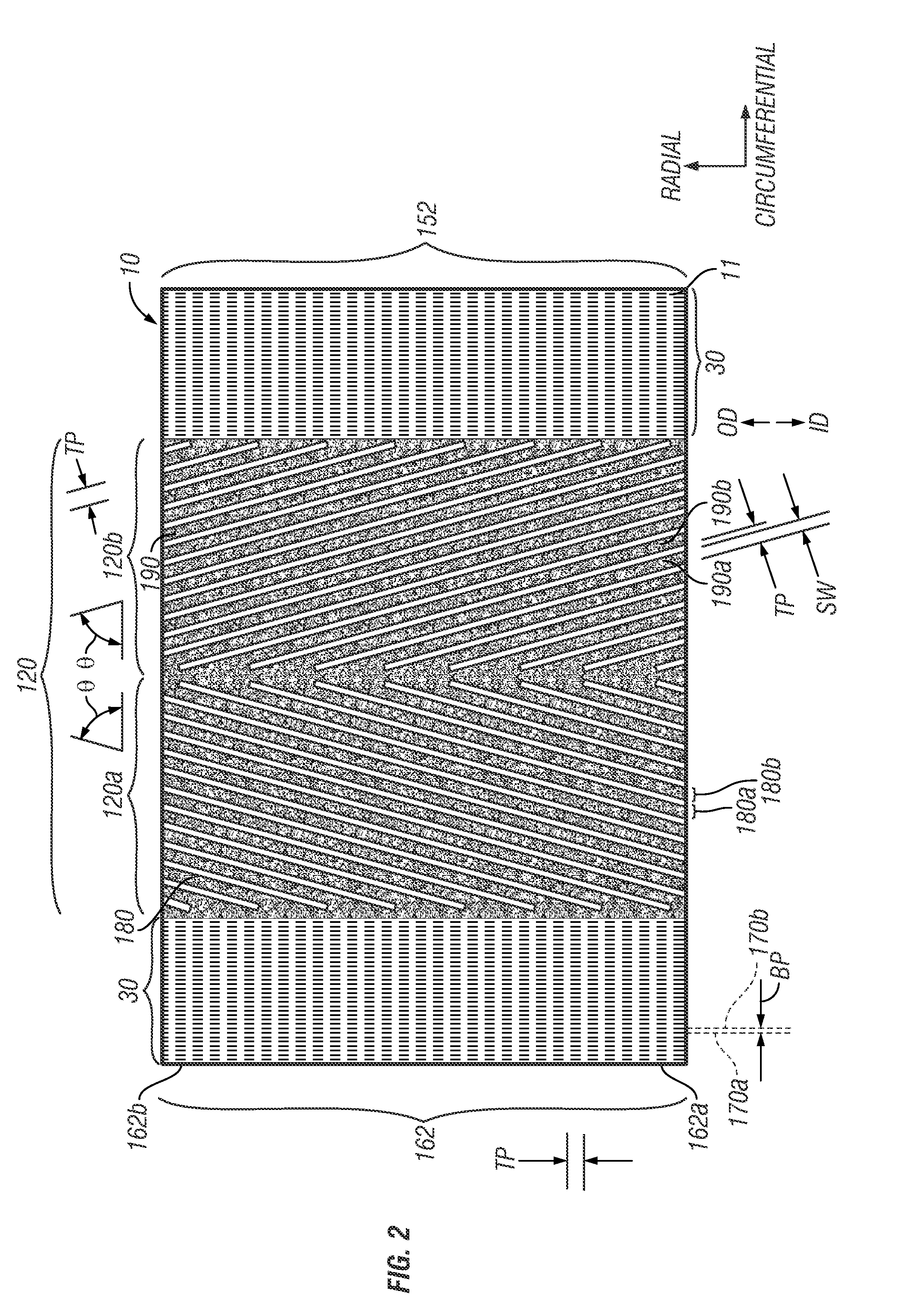
Method using block copolymers for making a master mold for nanoimprinting patterned magnetic recording disks with chevron servo patterns
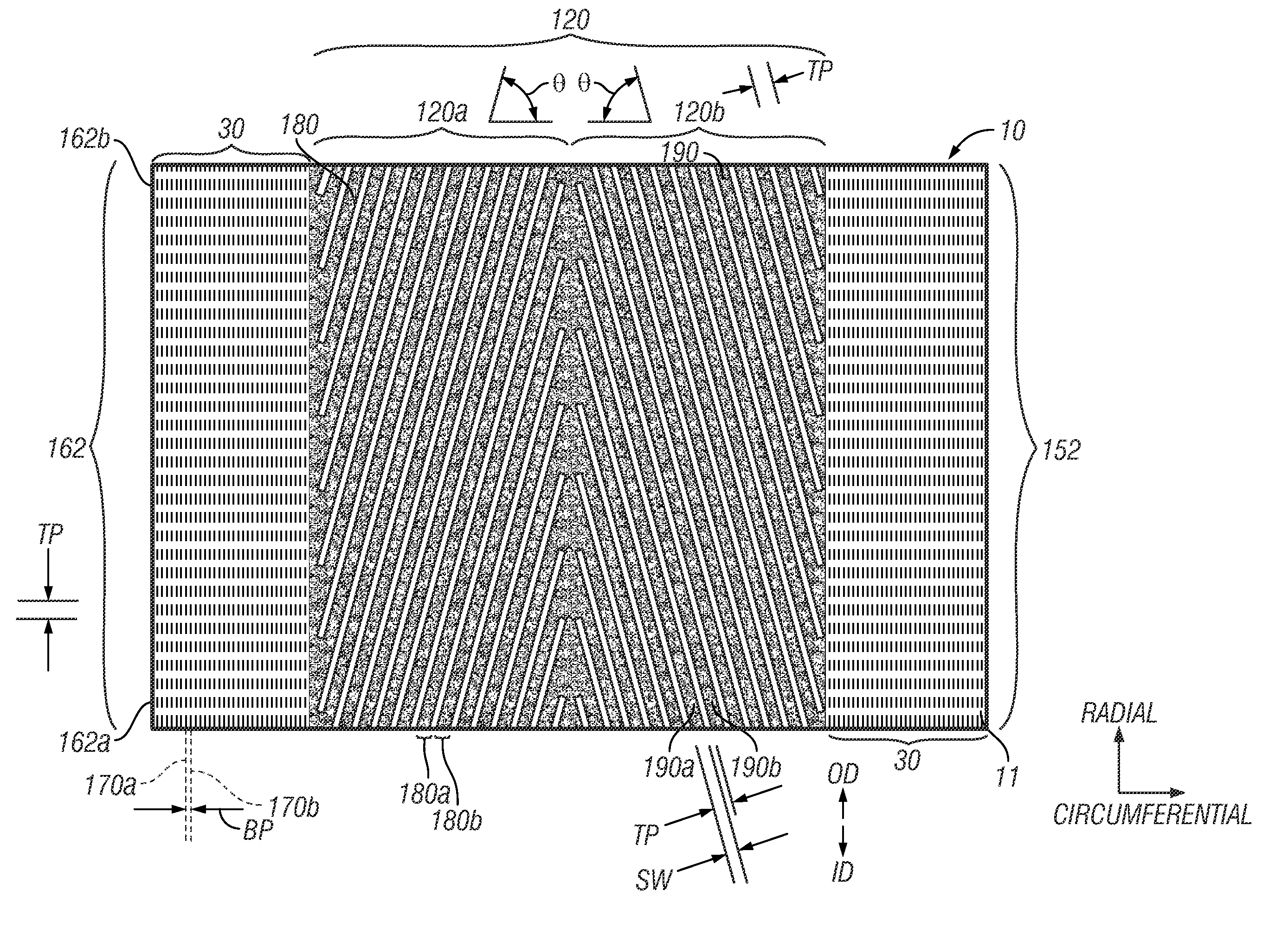
ActiveUS20120217220A1Reduce defectsReduced defective areaDecorative surface effectsNanoinformaticsDirected self assemblyMaterials science
A method for making a master mold used to nanoimprint patterned magnetic recording disks that have chevron servo patterns with minimal defects uses directed self-assembly of block copolymers. A pattern of chemically modified polymer brush material is formed on the master mold substrate. The pattern includes sets of slanted stripes and interface strips between the sets of slanted stripes. A block copolymer material is deposited on the pattern, which results in directed self-assembly of the block copolymer as lamellae perpendicular to the substrate that are formed into alternating slanted stripes of alternating first and second components of the block copolymer. This component also forms on the interface strips, but as a lamella parallel to the substrate. One of the components is then removed, leaving the remaining component as a grid that acts as a mask for etching the substrate to form the master mold. The disks nanoimprinted by the master mold have reduced defective areas in the transition regions of the chevron servo patterns.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
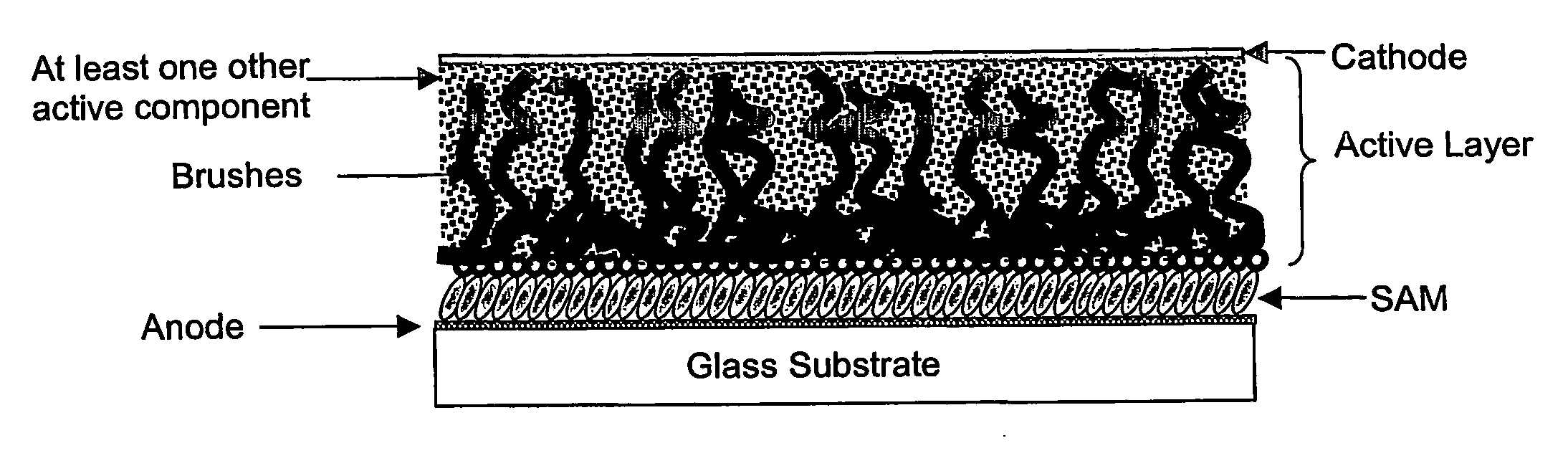
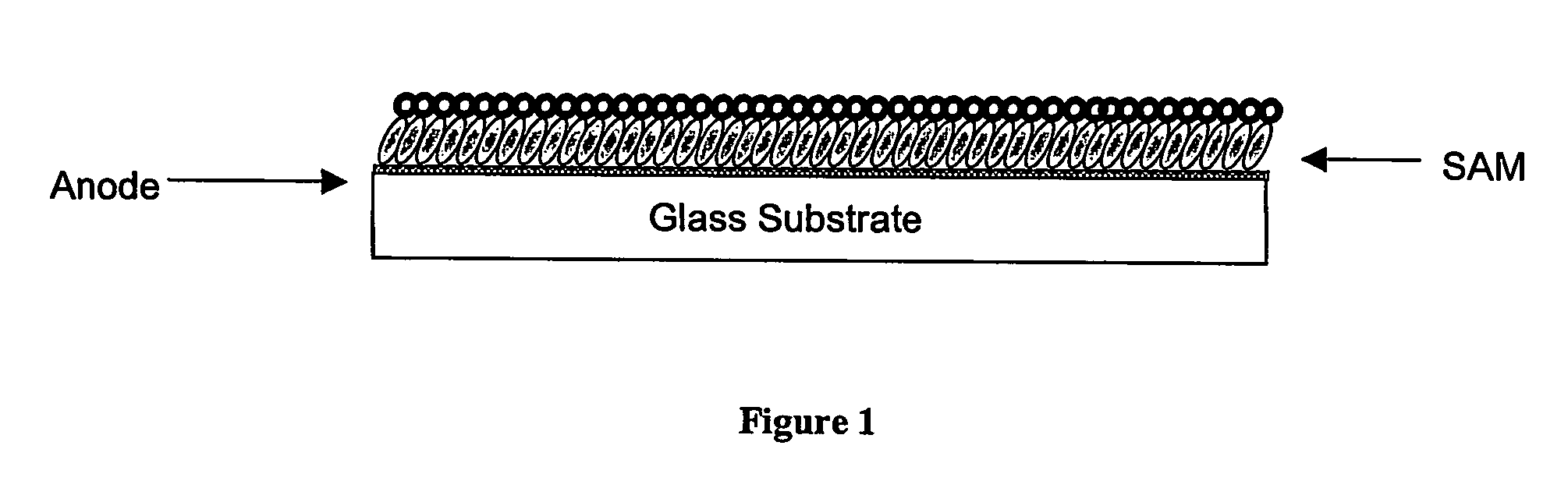
Organic electronic devices incorporating semiconducting polymer brushes
InactiveUS20070169814A1Improve device characteristicsHigh charge transport performanceMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor materialsPolymer chemistry
An organic electronic device comprises at least two electrodes and a semiconducting layer comprising a mixture of at least one hole-transporting semiconducting material and at least one electron-transporting semiconducting material, wherein at least one of said semiconducting materials is in the form of semiconducting polymer brushes which are attached to the surface of at least one of said electrodes and are in contact with at least one of said other semiconducting materials. Also provided is an organic electronic device comprising at least two electrodes and a semiconducting layer comprising at least one hole-transporting or electron-transporting semiconducting material, wherein said at least one semiconducting material is in the form of semiconducting polymer brushes which are attached to the surface of at least one of said electrodes. Processes for the manufacture of said devices are also provided.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE UNIV TECH SERVICES LTD
Preparation method of antimicrobial polymer brush with triple functions of anti-fouling, sterilization and release
The invention discloses a preparation method of an antimicrobial polymer brush with triple functions of anti-fouling, sterilization and release. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) an active free radical initiator is grafted onto the surface of a backing material; 2) the backing material grafted with the initiator is polymerized with a stimulus-responsive monomer for obtaininga responsive polymer brush; 3) the responsive polymer brush is polymerized with a hydrophilic monomer for obtaining a hydrophilic responsive polymer brush; and 4) the hydrophilic responsive polymer brush is grafted with a trichloromethane antimicrobial agent or loaded with silver nanoparticles for obtaining the antimicrobial polymer brush. The polymer brush obtained with the method provided by the invention has the triple functions of anti-fouling, sterilization and release, and the antimicrobial surface is endowed with multiple functions of long-term anti-fouling, high-efficiency sterilization and bacteria release, thereby greatly expanding the application field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Antibacterial polyvinylidene fluoride membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104190274AClean thoroughlyAchieve pollutionSemi-permeable membranesSilver ionMaterials science
The invention provides an antibacterial polyvinylidene fluoride membrane and a preparation method thereof. Polyvinylidene fluoride, silver ions and zwitterionic monomers are used as main raw materials to prepare a silver nanometer particle / zwitterionic polymer brush grafted polyvinylidene fluoride membrane. According to the invention, the technology is simple, the operation is easy, costly instruments are not needed, the antibacterial polyvinylidene fluoride membrane is easy to popularize, the prepared antibacterial polyvinylidene fluoride membrane has favorable temperature response performance and self-cleaning performance, and the antibacterial polyvinylidene fluoride membrane has a potential wide application value in the fields of intelligent parts, water treatment, biochemical engineering and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Polymer-brush-modified magnetic composite microsphere as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a polymer-brush-modified magnetic composite microsphere as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The polymer-brush-modified magnetic composite microsphere comprises a polymer core, a super-paramagnetic nanoparticle shell and a polymer brush in sequence from inside to outside, wherein the polymer brush is directly grafted onto the super-paramagnetic nanoparticle shell through atom transfer radical polymerization by using a carboxyl-containing water-soluble unsaturated monomer. By grafting the polymer brush onto a magnetic nanoparticle surface, the specific surface area and the protein binding site of the microsphere can be increased greatly, and the probability of the contact of a protein with a material is increased. Moreover, a specific functional group can be further grafted onto the polymer brush conveniently, so that the specific binding ability of the microsphere with a separation object is improved, and the aim of finer separation is fulfilled. The preparation method is simple, and is convenient to promote and apply; and the stability, operability and environmental friendliness of a reaction system are improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
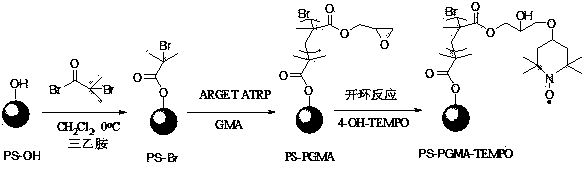
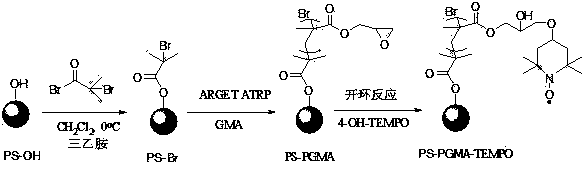
Preparation method and application of free nitroxide radical polymer brush polymerization inhibitor
ActiveCN104211863APerformance is not affectedAvoid self-polymerizationOrganic chemistryFatty acid esterificationEpoxyPolymer science
The invention relates to a preparation method of a free nitroxide radical polymer brush polymerization inhibitor, and application of the free nitroxide radical polymer brush polymerization inhibitor in synthesis of epoxy soybean oil acrylic ester. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, grafting a polyglycidyl methacrylate polymer brush on the surfaces of cross-linked polystyrene microspheres by using an electron transfer regenerated catalyst atom transfer free radical polymerization technique, and secondly, bonding tetramethyl piperidine free nitroxide radical onto the polyglycidyl methacrylate polymer brush, thereby obtaining the free nitroxide radical polymer brush. The application comprises: taking the free nitroxide radical polymer brush as a main polymerization inhibitor and a small molecule polymerization inhibitor as a polymerization inhibitor aid, thereby forming a composite polymerization inhibition system for preparing epoxy soybean oil acrylic ester. The composite polymerization inhibition system not only has a high-efficiency polymerization inhibition function in the epoxy soybean oil acrylic ester preparation, but also is easy in recycling the main polymerization inhibitor, namely the free nitroxide radical polymer brush, so that the free nitroxide radical polymer brush can be recycled, and a product can be prevented from self-polymerization when being preserved when a small amount of the polymerization inhibitor is retained in the system.
Owner:廊坊市安次区调河头振达生物技术推广中心
Polymer brushes for immobilizing molecules to a surface and having water-soluble or water-dispersible segments therein and probes bonded thereto
InactiveUS20050158879A1Eliminate the effects ofHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWater dispersibleSynthesis methods
Sensors for determining the presence and concentration of bio-molecules in a biological sample are provided in the form of polymer brushes, which comprise a substrate having a surface that is modified with a water-dispersible or water-soluble polymer segment having functional groups that bind probes. The method of synthesis of such sensors preferably includes use of controlled free radical polymerization techniques, and in particular the use of an iniferter initiator, which allows for controlled architecture polymers to modify the surface of the substrate. In this manner functional groups in the polymer chain are removed from the surface, which allows for solution chemistry to be more realistically reproduced with the benefits of a solid bound probe.
Owner:FREESLATE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com