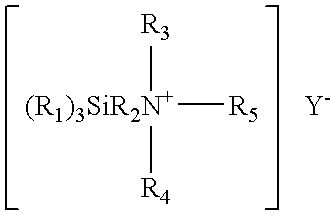Patents
Literature
176 results about "Antimicrobial surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An antimicrobial surface contains an antimicrobial agent that inhibits the ability of microorganisms to grow on the surface of a material. Such surfaces are becoming more widely investigated for possible use in various settings including clinics, industry, and even the home. The most common and most important use of antimicrobial coatings has been in the healthcare setting for sterilization of medical devices to prevent hospital associated infections, which have accounted for almost 100,000 deaths in the United States. In addition to medical devices, linens and clothing can provide a suitable environment for many bacteria, fungi, and viruses to grow when in contact with the human body which allows for the transmission of infectious disease.
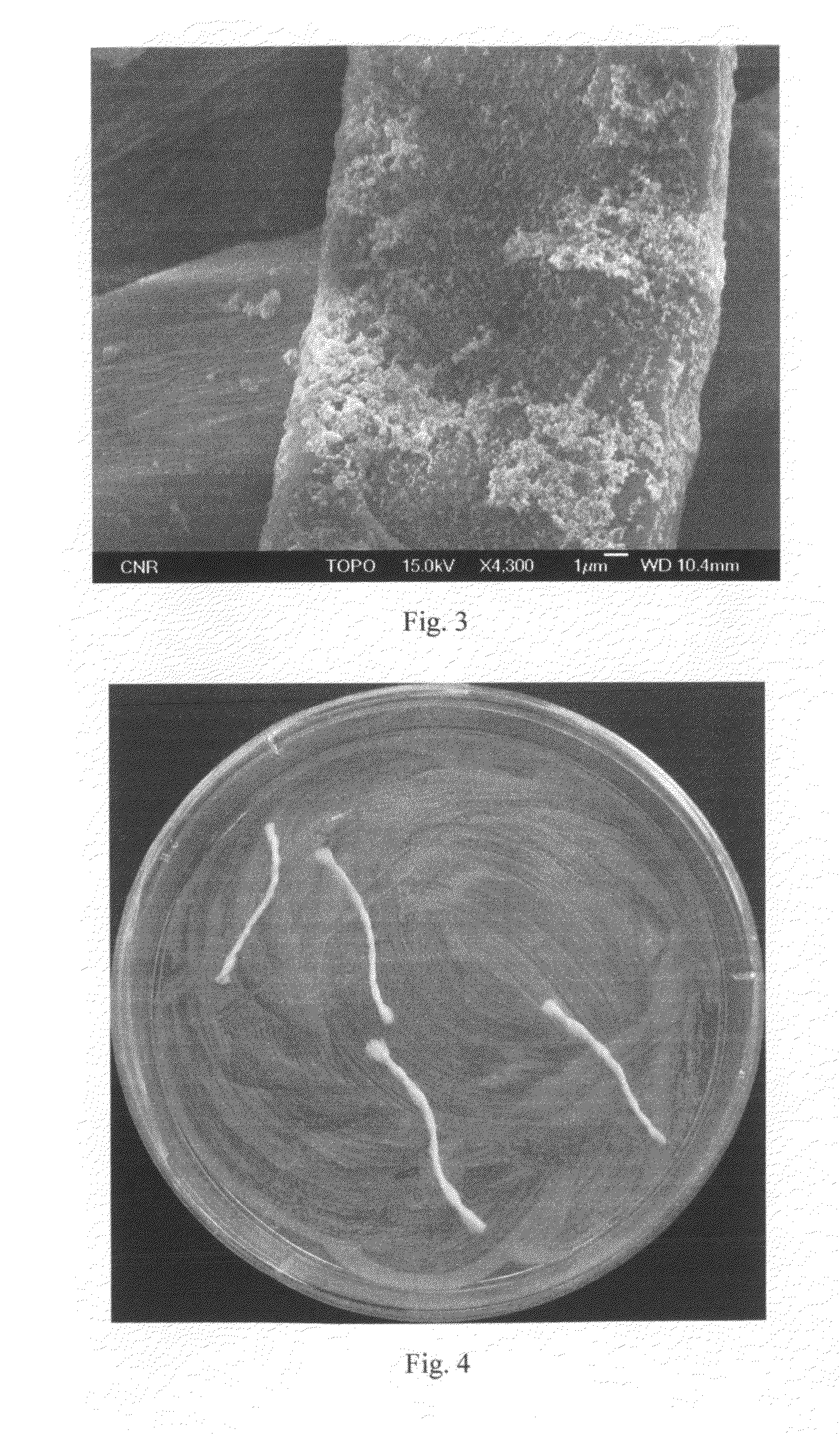
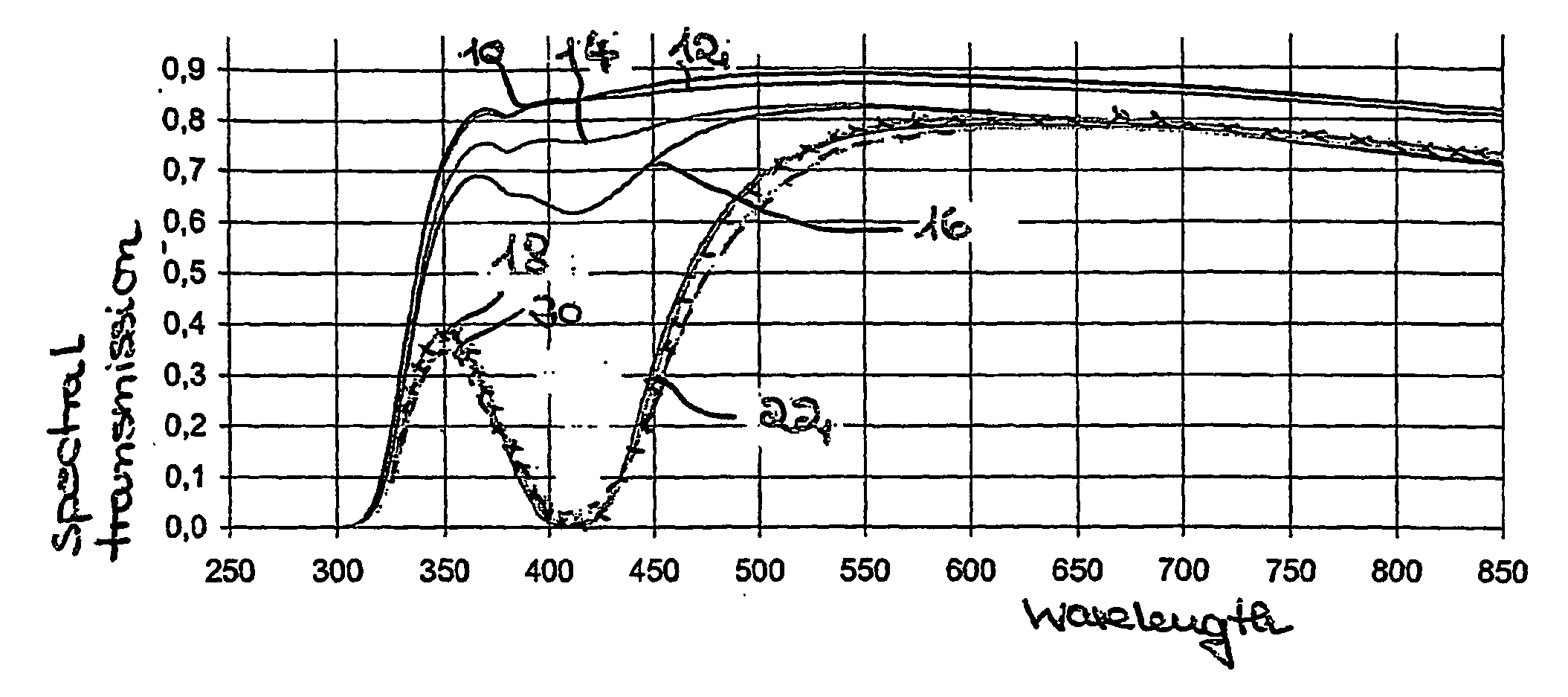
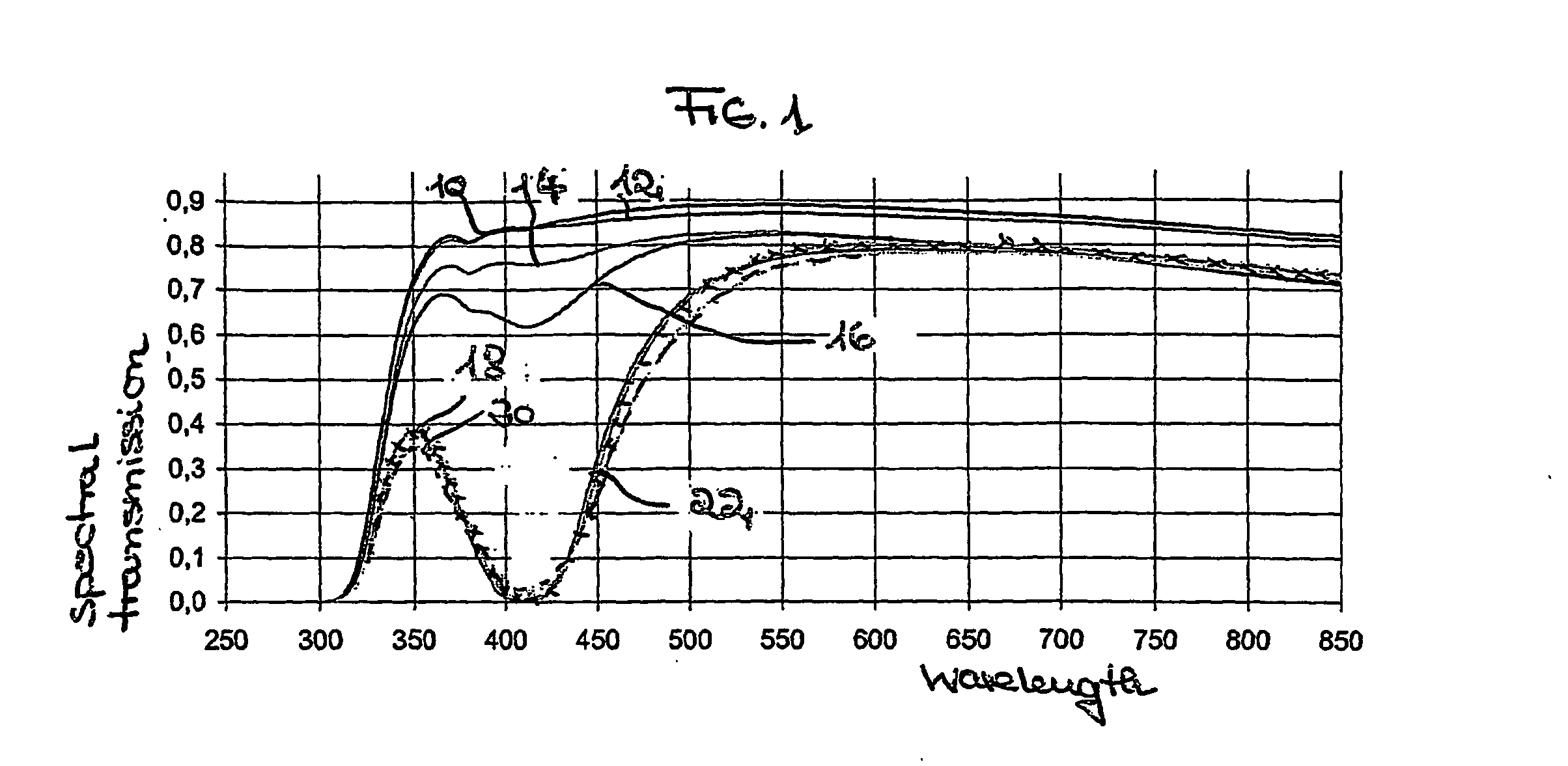
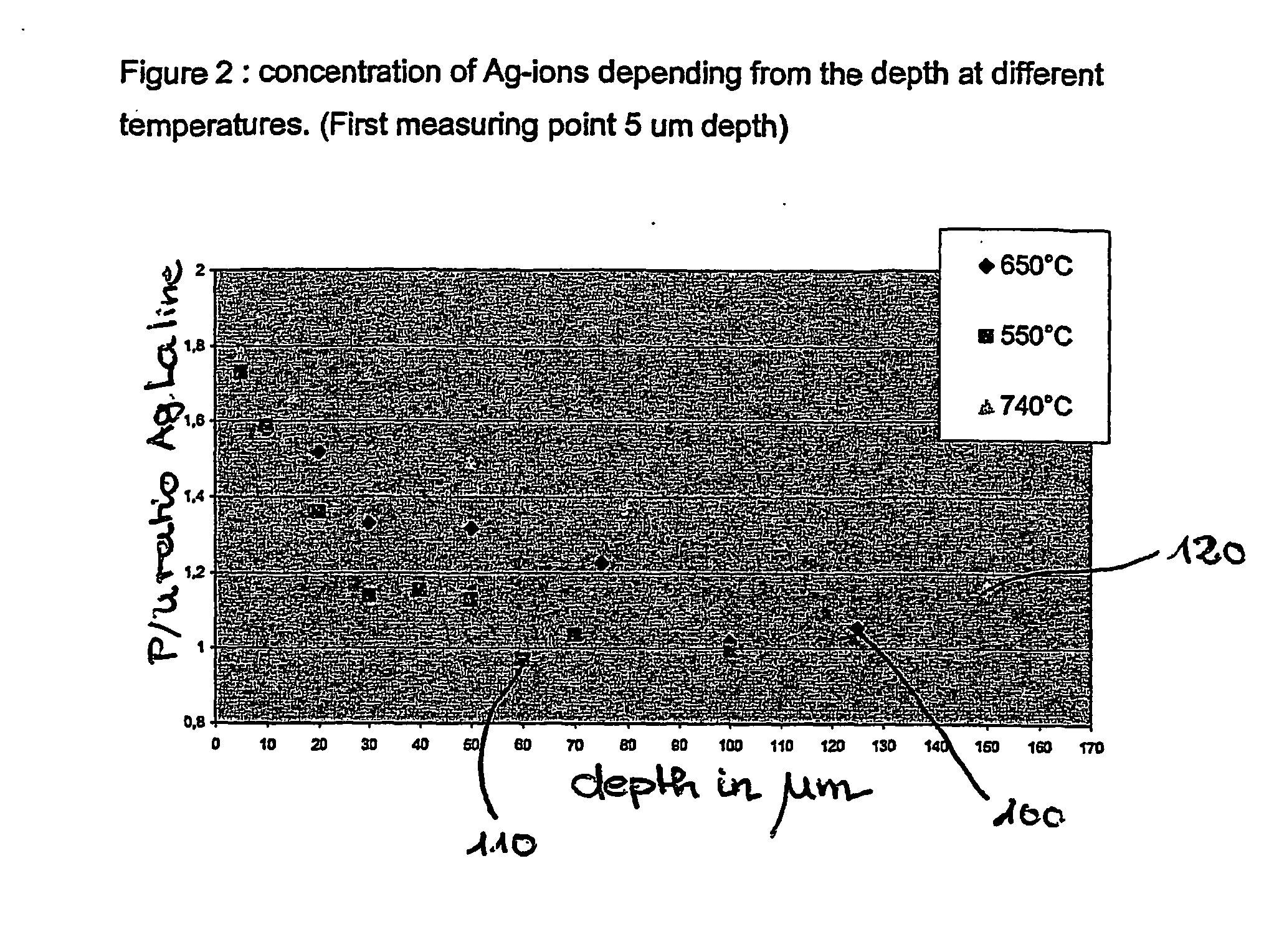
Antimicrobial glass and glass ceramic surfaces and their production
InactiveUS20070172661A1Long term efficacyBiocidePretreated surfacesAntimicrobial surfaceGlass-ceramic
The application relates to an article having a antimicrobial surface with a metal ion concentration, especially a Ag-concentration in a depth of about 0 um to about 2 um of the article measured from the surface higher than 0,6 wt %, preferably 0,8 weight-%, most preferably 1 weight-%.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Methods and compositions for antimicrobial surfaces
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for treating solid surfaces having antimicrobial and biocidal properties. Such surfaces are capable of controlling or killing a broad spectrum of biological agents, including viruses, bacteria and other microbial agents in solids, liquids or gases that subsequently contact the treated surface.
Owner:SISHIELD TECH
Surface sanitizer
A non-toxic antimicrobial surface sanitizer composition comprising a water-miscible alcohol, water, a weak acid and a multivalent cation (e.g., metal ion or metal compound). The composition may also include one or more of an emollient, oxidative agent, humectant, lubricant, plant-derived alkene, antimicrobial component or plant-derived essential oil. These compositions can be formulated as solutions for sanitizing hard surfaces such as countertops and floors, or as solutions / gels for application to animal skin.
Owner:FITCHMUN MARK I
Actively sterile surfaces
InactiveUS6080490AImprove responseImprove antibacterial propertiesSurgeryCatheterGalvanic cellAntimicrobial surface
An actively antimicrobial surface for a substrate and for use in a biologically dynamic environment, such as for treating and preventing microbial infections, including a film consisting of at least an antimicrobial element and another electrochemically nobler element and which forms multitudinous galvanic cells with electrolyte-containing biological fluids, such as body fluids from wounds, etc., for releasing the antimicrobial element at the surface.
Owner:NUCRYST PHARMA
Laser based metal deposition (LBMD) of antimicrobials to implant surfaces
InactiveUS20070287027A1Improved bearing propertyImprove propertiesFinger jointsDental implantsWear resistantBearing surface
A method is provided for depositing a hard wear resistant surface onto a porous or non-porous base material of a medical implant. The wear resistant surface of the medical implant device may be formed by a Laser Based Metal Deposition (LBMD) method such as Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). The wear resistant surface may include a blend of multiple different biocompatible materials. Further, functionally graded layers of biocompatible materials may be used to form the wear resistant surface. Usage of a porous material for the base may promote bone ingrowth to allow the implant to fuse strongly with the bone of a host patient. The hard wear resistant surface provides device longevity, particularly when applied to bearing surfaces such as artificial joint bearing surfaces or a dental implant bearing surfaces. An antimicrobial material such as silver may be deposited in combination with a metal to form an antimicrobial surface deposit.
Owner:MEDICINELODGE
Process for production of actively sterile surfaces
InactiveUS6365220B1Improve responseImprove antibacterial propertiesBiocideVacuum evaporation coatingGalvanic cellAntimicrobial surface
A process for production of an actively antimicrobial surface for a substrate and for use in a biologically dynamic environment, such as for treating and preventing microbial infections, including a film consisting of at least an antimicrobial element and another electrochemically nobler element and which forms multitudinous galvanic cells with electrolyte-containing biological fluids, such as body fluids from wounds, etc., for releasing the antimicrobial element at the surface.
Owner:NUCRYST PHARMA
Generation of antimicrobial surfaces using dendrimer biocides
A silane-QAC-dendritic polymer biocide surface treatment for bath, screen or spray-on application. The silane-QAC-dendritic polymer biocide generally comprises a hyperbranched polymer modified to include functionalized quaternary ammonium for biocidal activity, and further modified to include a functionalized silane moiety to covalently attach the polymer biocide to a variety of substrates through hydrolysis. The hyperbranched polymer may be any one from among a group consisting of dendrimers, dendritic polymers, and hyperbranched polymers, and the functionalized silane moiety may be Siloxane (—Si(OR)3). The resulting surface treatment combines the demonstrated high potency of quaternary ammonium compound dendrimers and hyperbranched polymers with the well-established coupling chemistry of silane functional groups. Upon hydrolysis, the silane groups will covalently attach to functional groups such as amines and hydroxyl groups. This provides an effective biocidal surface treatment for any substrates having exposed hydroxyl, amine or other suitable reactive groups.
Owner:LAMBA KOHLI NINA M
Method of attaching drug compounds to non-reactive polymer surfaces
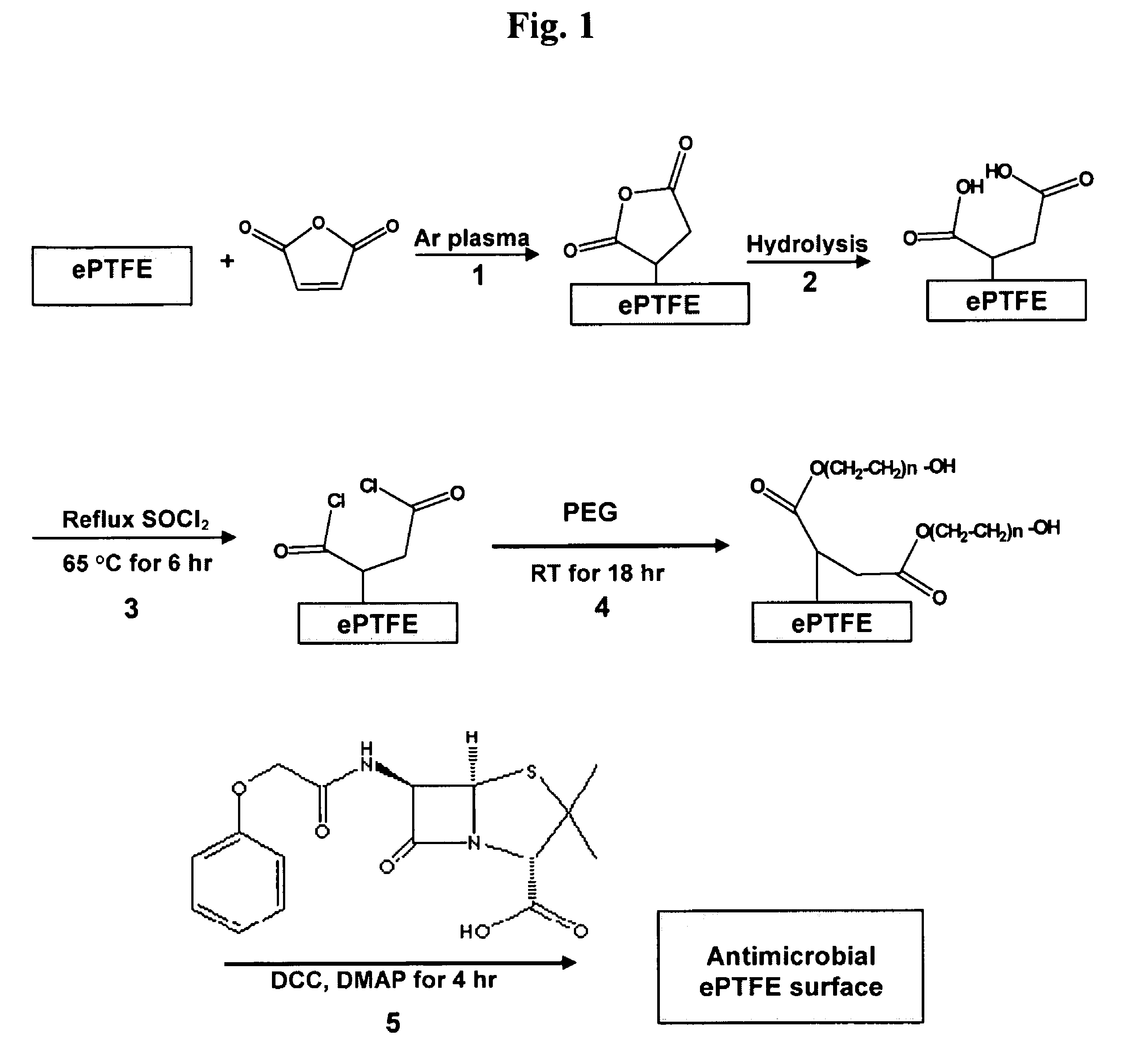
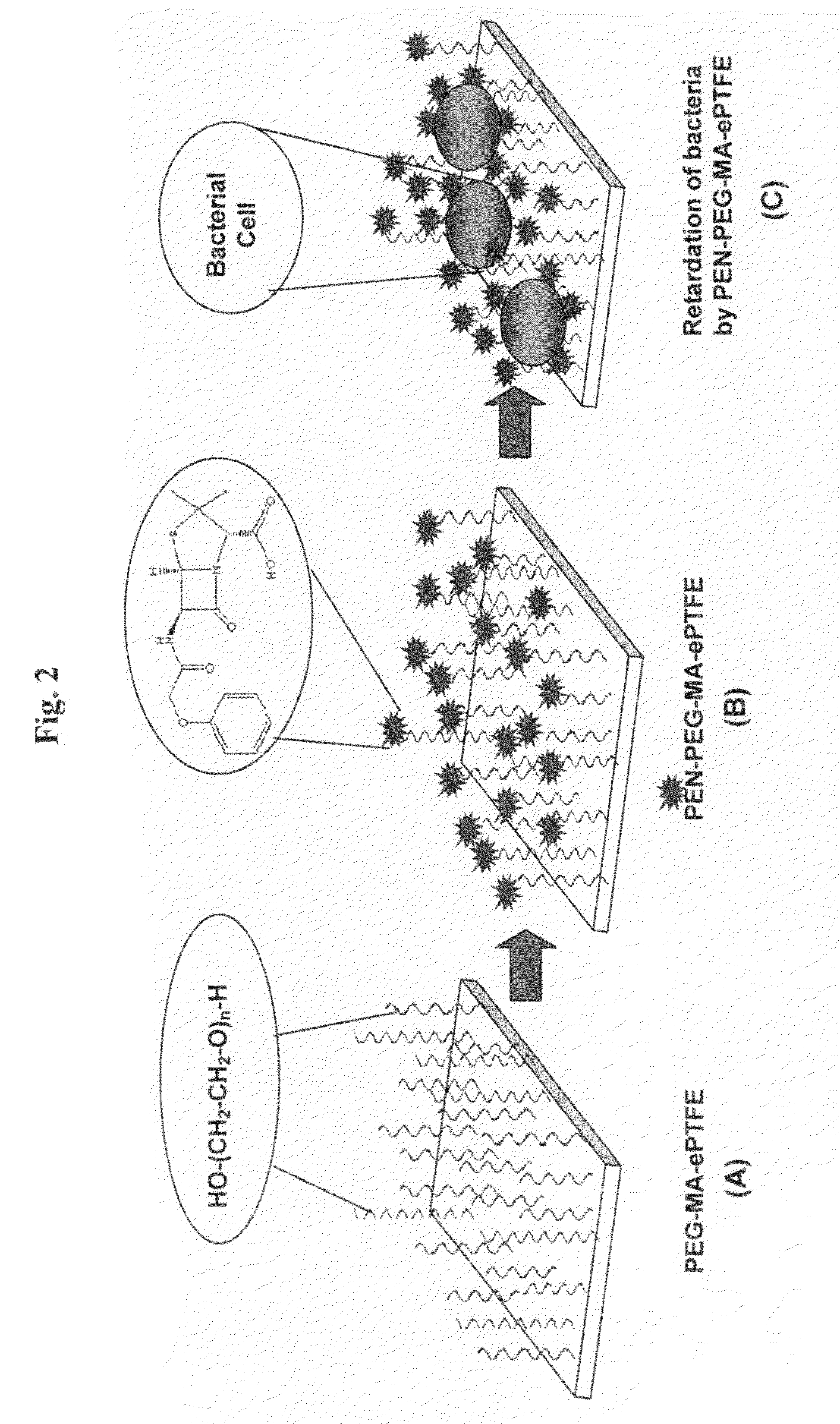
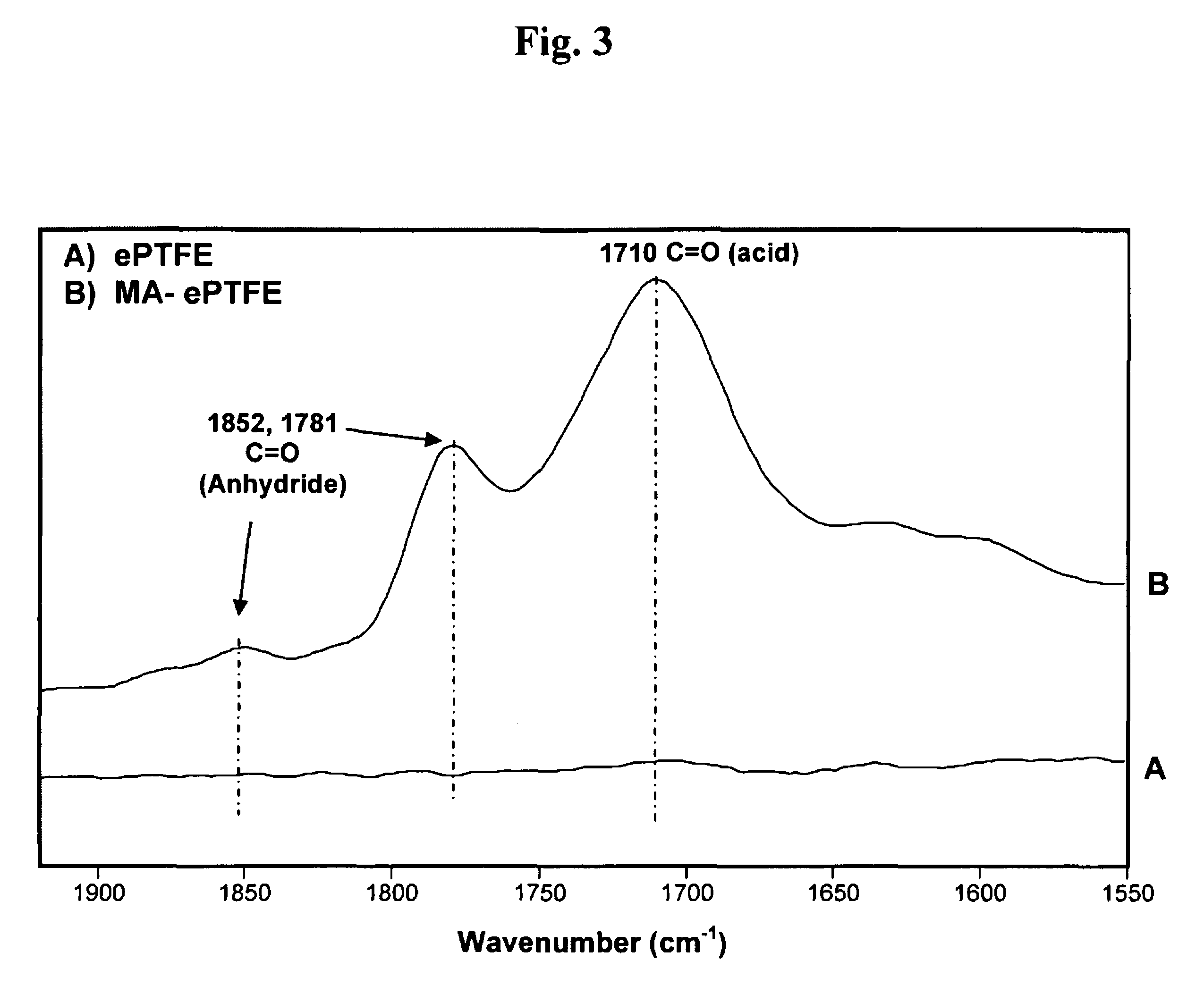
Polymers are disclosed that are chemically modified to retard bacterial growth. Such modified polymers (e.g. ePTFE and polypropylene) are produced by first creating acid groups on the polymer surface through reactions with an anhydride. The acid groups are then linked to polyethylene glycol (PEG) through esterification or other reactions such as amidation. Preferably, at least two different molecular weight PEG species are employed. The antimicrobial surface is completed by linking antibiotics (e.g. β-lactam antibiotics) to the PEG extensions. One preferred embodiment of such a modified polymer is produced using ePTFE, maleic anhydride (MA), and penicillin (PEN) to yield PEN-PEG-MA-ePTFE, which inhibits gram-positive bacteria. The PEG spacer is critical for PEN function in this context, since PEN-ePTFE is ineffective against bacterial growth. Another preferred embodiment incorporates ampicillin (AMP) and a heterobifunctional PEG, HOOC—(CH2—CH2—O)n—NH2, to yield AMP-PEG-MA-ePTFE. This latter example inhibits both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
Owner:SOUTHERN MISSISSIPPI THE UNIV OF
Antimicrobial Lining for Gas Cylinders and Coupling Components
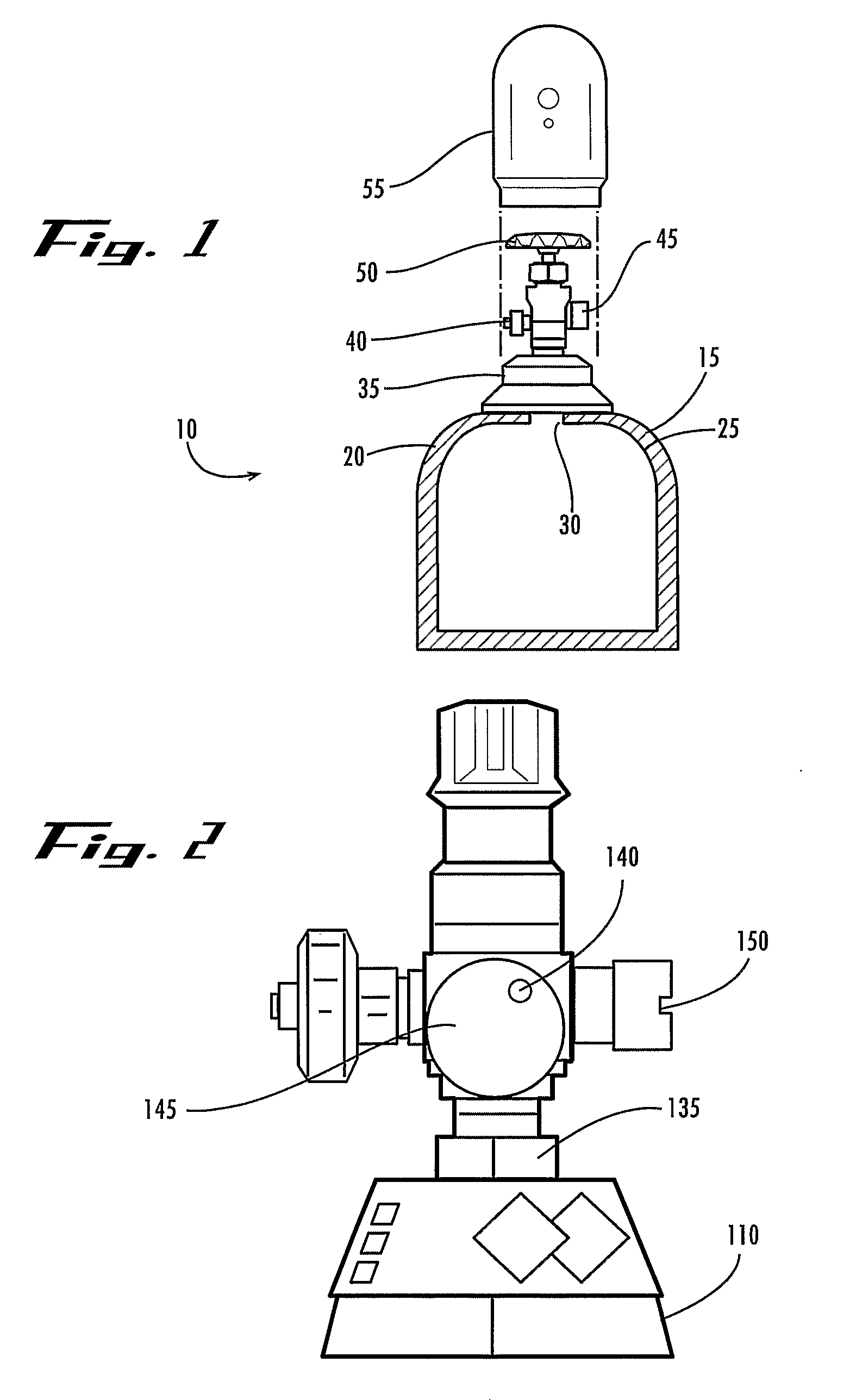
This invention relates to the field of gas-containing storage vessels, and more specifically to the provision for antimicrobial surfaces within such vessels and in the connecting hardware associated with various applications of such vessels, so that microbial colonization of the interior of such vessels may be eliminated or retarded. This antimicrobial feature may result in improved safety in the use of such vessels, with reduced risk of the transmission of infection to a user. The invention further includes methods to provide gas-containing storage vessels with antimicrobial surfaces, so that microbial colonization of the interior of such vessels may be eliminated or retarded.
Owner:BOC GRP INC
Antimicrobial introducer and needle
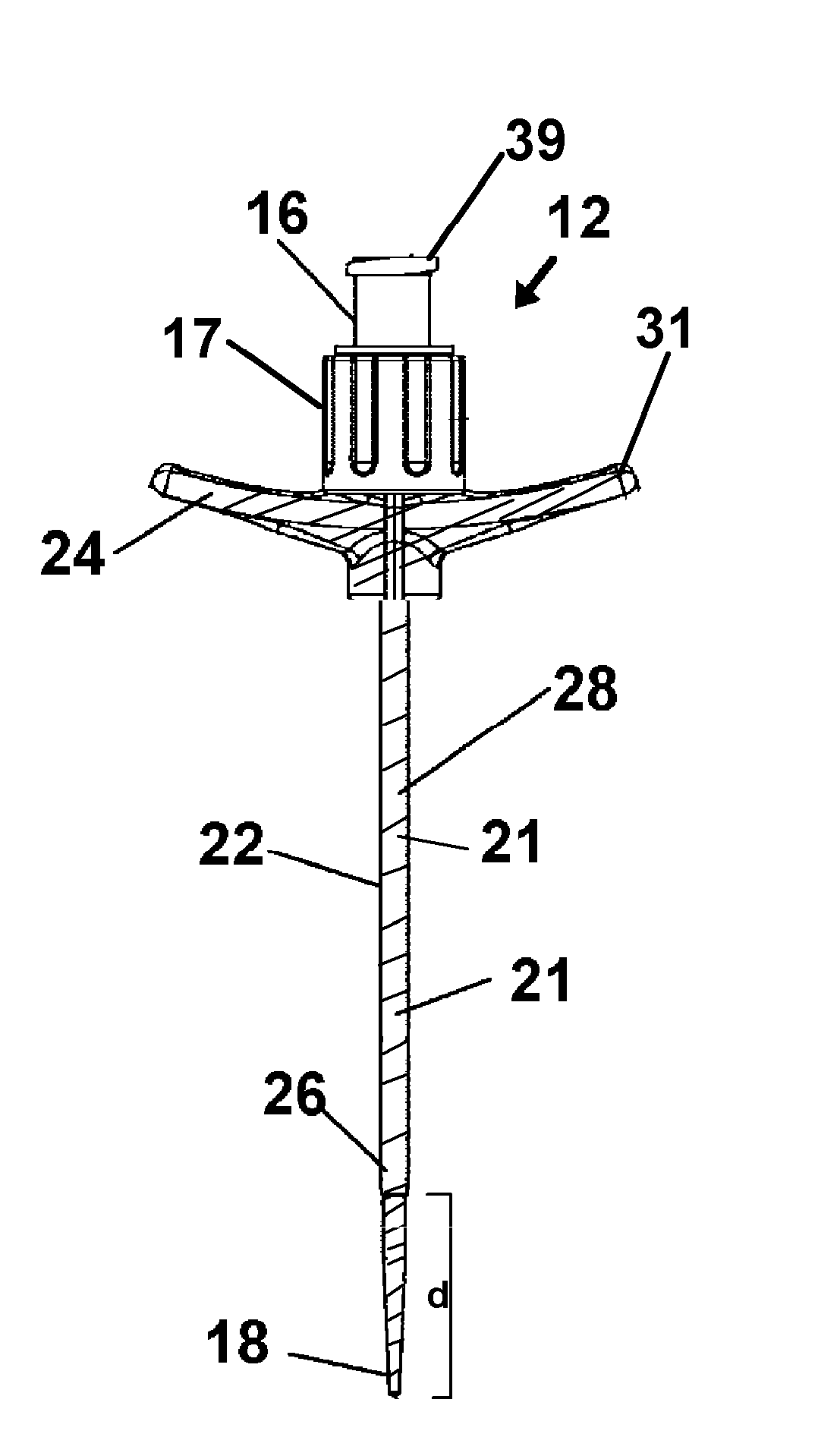
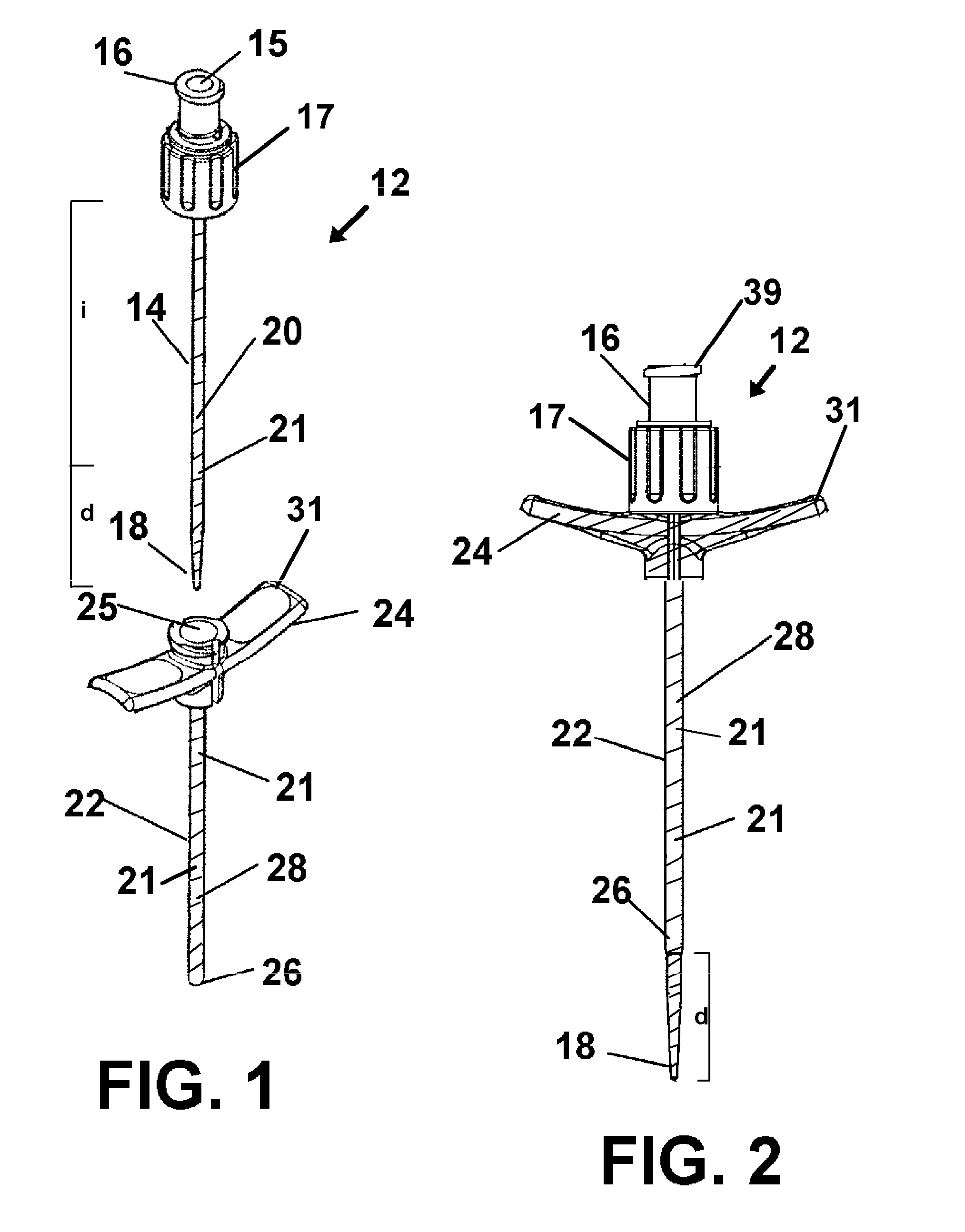
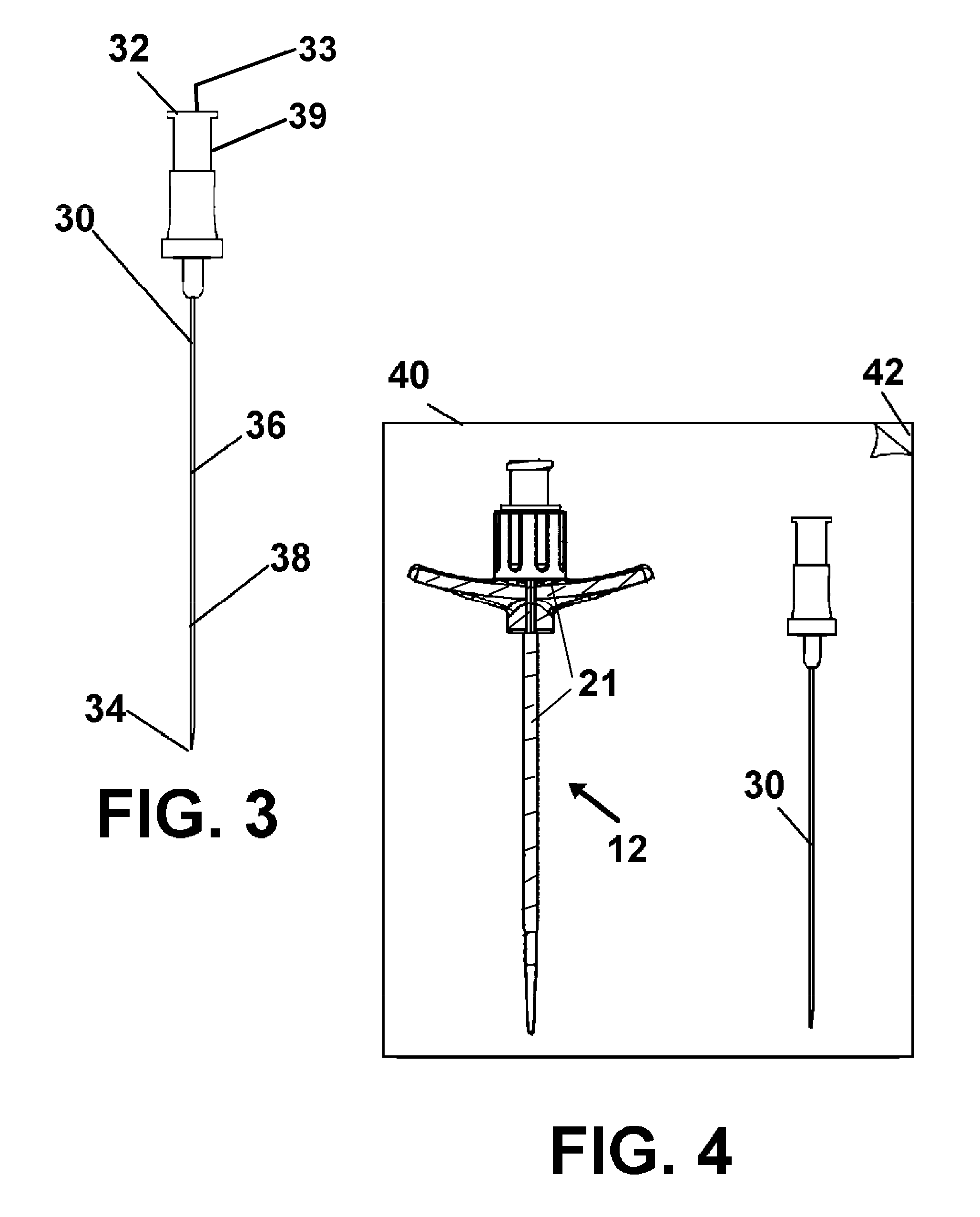
A device for threading a conduit into a communication with a vein or artery beneath the skin of a patient, during insertion of components such as a PICC line is provided. Surfaces of a hollow needle, dilator, and sheath included in kit, and which are anticipated to contact the skin of a patient during the procedure are provided with an antimicrobial surface area formed thereon. The surface area so positioned prevents bacteria and other pathogens from occupying the contacting surfaces and thereby being communicated into the tissue below the patient's skin.
Owner:PFM MEDICAL
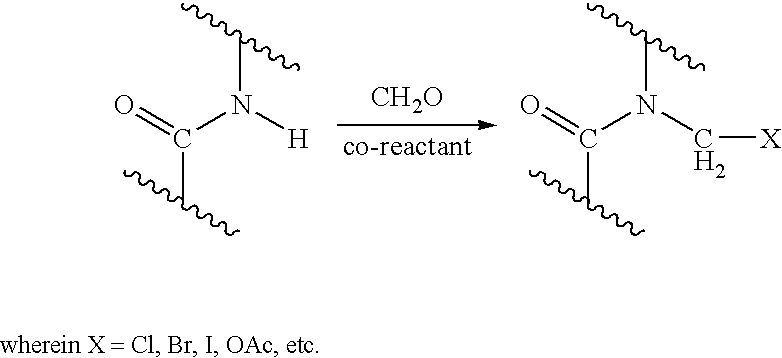
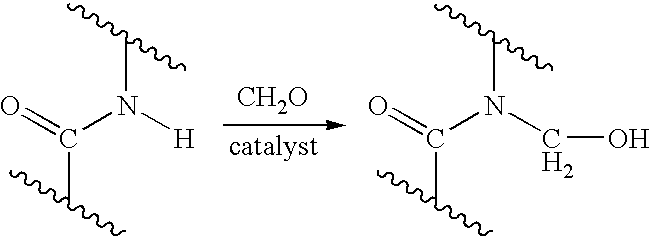
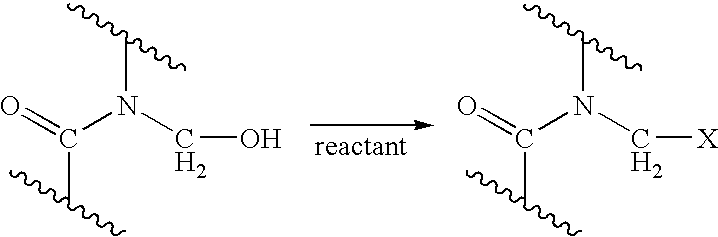
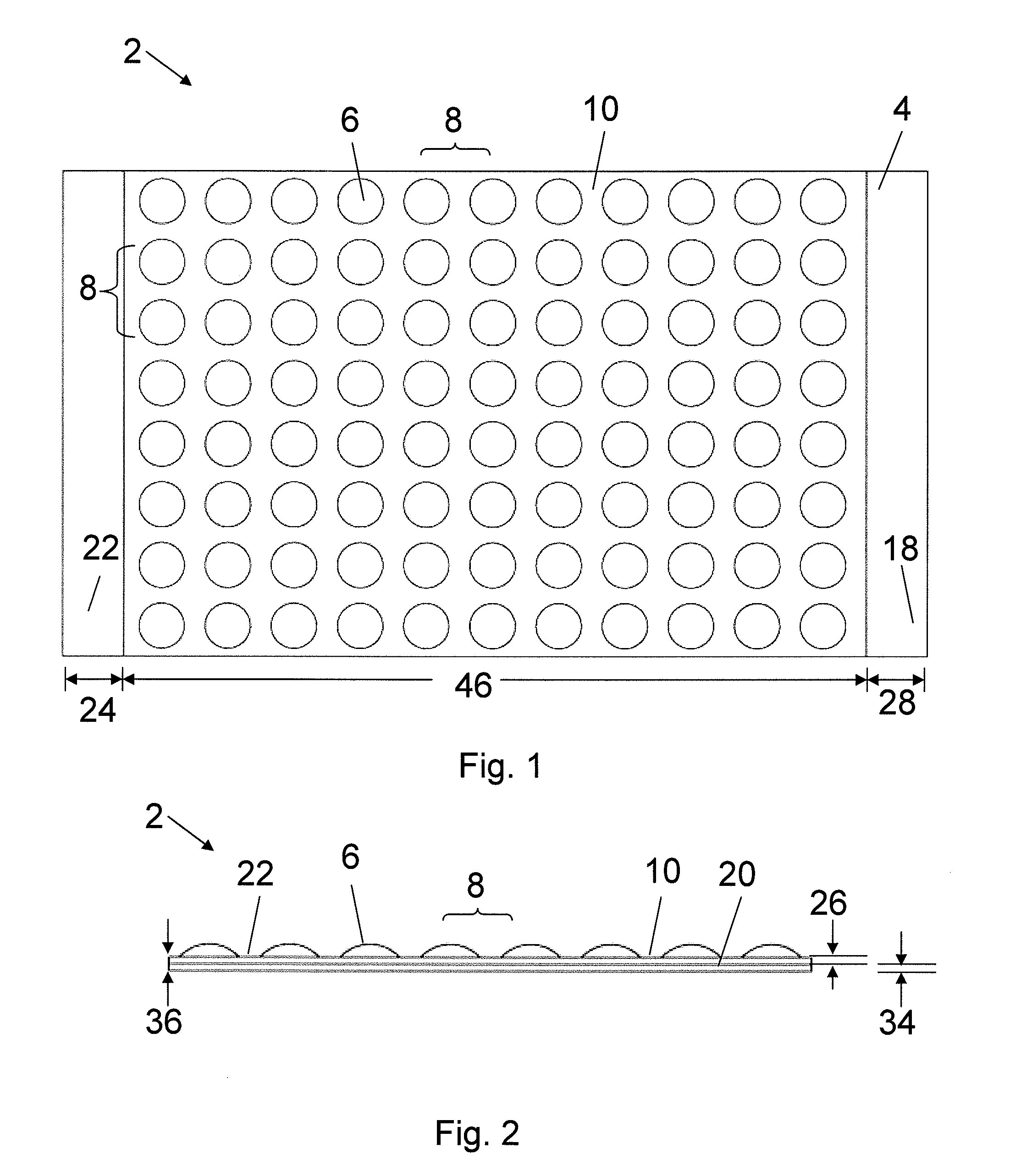
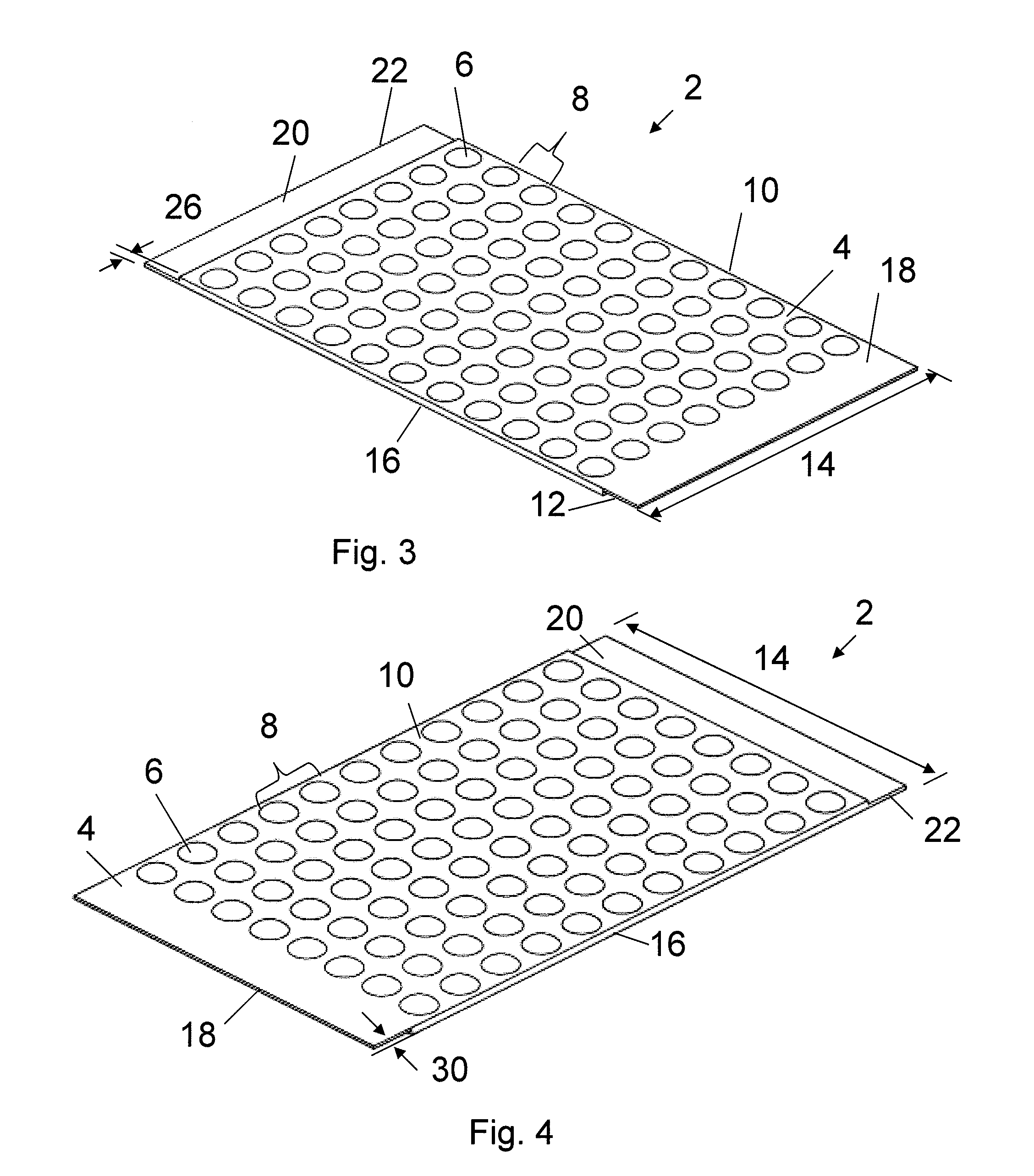
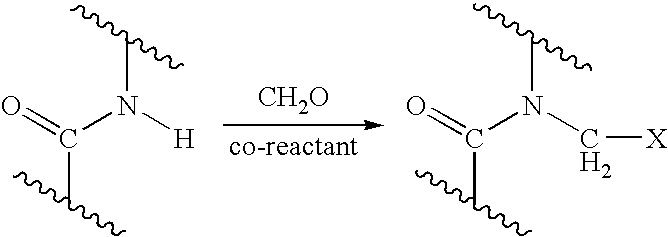
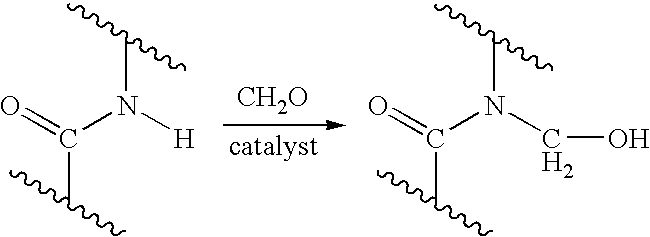
Process for providing antimicrobial surfaces
Processes for providing durable antimicrobial surfaces are disclosed that comprise treating a polymer substrate surface with formaldehyde followed by treatment with an antimicrobial peptide. Further embodiments include articles, including medical devices, characterized by a durable antimicrobial surface provided by the processes of the invention.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Medical devices having antimicrobial properties
Microbial growth on the surface of a valve of a voice prosthesis and optionally the cartridge or ring supporting the valve, is inhibited by providing antimicrobial activity at a level sufficient to retard growth of a microbial film by dispersing an inorganic antimicrobial agent such as silver oxide or an organic antimicrobial agent such as triclosan or butyl paraben dispersed in a medical grade silicone elastomer. The valve, ring or cartridge is in contact with body fluids containing microorganisms and nutrients therefor. The antimicrobial surface can interfere with or inhibit the growth of a biofilm, bacterial layer or a yeast layer. The body of the prosthesis may also contain an antimicrobial surface as long as it is non-toxic to the tissue it contacts.
Owner:FREUDENBERG MEDICAL
Chemical vapor deposition of antimicrobial polymer coatings
InactiveUS20060228966A1Improve effectivenessReduce morbidityLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsGas phaseAntimicrobial surface
One aspect of the present invention is directed to antimicrobial surfaces comprised of hydrocarbon polymers with significant hydrophobic character which also contain an amino group with a pKa greater than or equal to about 8. In certain embodiments initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) is used to coat a surface with an antimicrobial polymer.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Antimicrobial melamine resin and products
An antimicrobial melamine resin includes an antimicrobial agent incorporated therein. The melamine resin is useful for making melamine-based decorative laminate articles having a tough, mar-resistant antimicrobial surface and for molded melamine articles exhibiting antimicrobial properties.
Owner:MICROBAN PROD CO INC
Polymers containing quaternized nitrogen
The invention provides polymers, methods of preparing polymers, and compositions that include polymers, wherein said polymers include a plurality of two-carbon repeating units in a polymer chain, wherein one or more of the two-carbon repeating units of the polymer chain have tertiary amine or pyridine-containing substituents; and at least about 10% of the nitrogen atoms of the tertiary amine or pyridine-containing substituents are quaternized with alkyl groups or with an alkyl group that contains one or more ethylene glycol groups. The alkyl or ethoxylated alkyl groups can also be at least partially fluorinated. The polymers can be used to provide antimicrobial surfaces and antifouling coatings.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Antimicrobial electret web
InactiveUS20110290119A1Deactivate antimicrobial efficacyElectrostatic chargeCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentMedicineAntimicrobial surface
Antimicrobial electret material are described. In some embodiments, the materials comprise a unitary web comprising an antimicrobial surface treatment and having certain properties. In other embodiments, an antimicrobial electret material is described comprising an electret web comprising an antimicrobial surface treatment wherein the surface treatment comprises a sparingly soluble silver-containing compound, a photosensitive antimicrobial agent that forms reactive oxygen species, a biguanide compound, or a combination thereof.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Antimicrobial colloidal silver and gold products and method of making same
Gelatinous foam, coated paper, fabric, and polymer materials combined with the Colloidal Silver or Gold additive to formulate products with antimicrobial surfaces. Some embodiments of the present invention can include gelatinous materials selected from a group consisting of thermosetting polymer, Styrene-Ethylene-Butadiene-Styrene polymer (SEBS), Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE), and Polyurethane (PU) gelatin with and without a raised geometry on an outer surface and in any shape. The various embodiments include coated polymer sheets, polymer trays, bamboo and / or cotton towels and fabric, polymer foam, or polymer mats containing nano-silver or nano-gold in an scheduled and organized manner (with input / requests from the customer) to create permanent or semi-permanent anti-microbial surfaces.
Owner:ECO PROD GROUP
Process for providing antimicrobial surfaces
Processes for providing durable antimicrobial surfaces are disclosed that comprise treating a polymer substrate surface with formaldehyde followed by treatment with an antimicrobial peptide. Further embodiments include articles, including medical devices, characterized by a durable antimicrobial surface provided by the processes of the invention.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Silver coated nylon fibers and associated methods of manufacture and use
InactiveUS20100166832A1Heat dissipationWear safeBiocideInorganic active ingredientsYarnAntimicrobial surface
Silver coated nylon fibers are disclosed that can be used to make fabrics that are silver coated on one side of the fabric. Silver coated nylon fabrics provide an antimicrobial surface which remains on the surface and retains its antimicrobial characteristic until destroyed. The methods of adherence of the silver to the nylon fabric may be performed in a number of ways. The creation of a single fabric with one side silver coated and the other side being dyed or left natural is encompassed within this invention. In addition there can be more than two yarns creating the fabric such as the use of spandex to provide a more elastic garment.
Owner:BRAND SOLUTION
Laser Based Metal Deposition LBMD of Antimicrobials to Implant Surfaces
InactiveUS20110208304A1Minimize adverse effectsHigh hardnessFinger jointsDental implantsWear resistantBone ingrowth
A method is provided for depositing a hard wear resistant surface onto a porous or non-porous base material of a medical implant. The wear resistant surface of the medical implant device may be formed by a Laser Based Metal Deposition (LBMD) method such as Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). The wear resistant surface may include a blend of multiple different biocompatible materials. Further, functionally graded layers of biocompatible materials may be used to form the wear resistant surface. Usage of a porous material for the base may promote bone ingrowth to allow the implant to fuse strongly with the bone of a host patient. The hard wear resistant surface provides device longevity, particularly when applied to bearing surfaces such as artificial joint bearing surfaces or a dental implant bearing surfaces. An antimicrobial material such as silver may be deposited in combination with a metal to form an antimicrobial surface deposit.
Owner:MEDICINELODGE
Method for preparing antibacterial surface on medical material surface
ActiveCN106902396AReduce adverse effectsAvoid Performance InterferenceSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSilanesBiocompatibility Testing
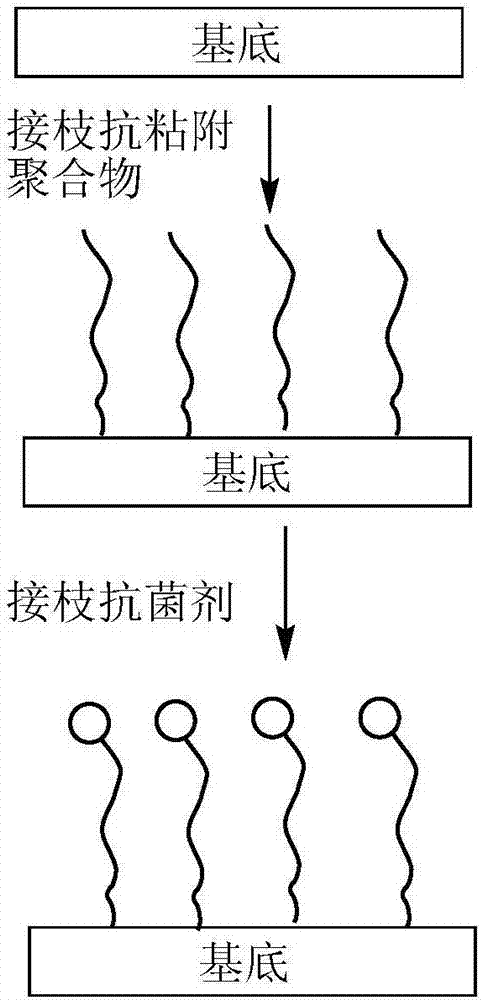
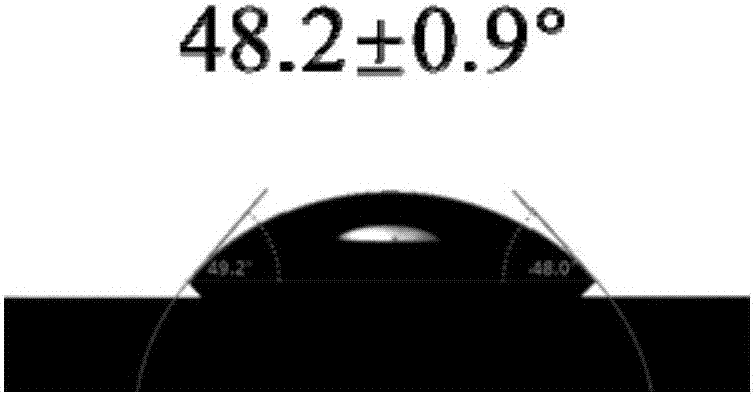
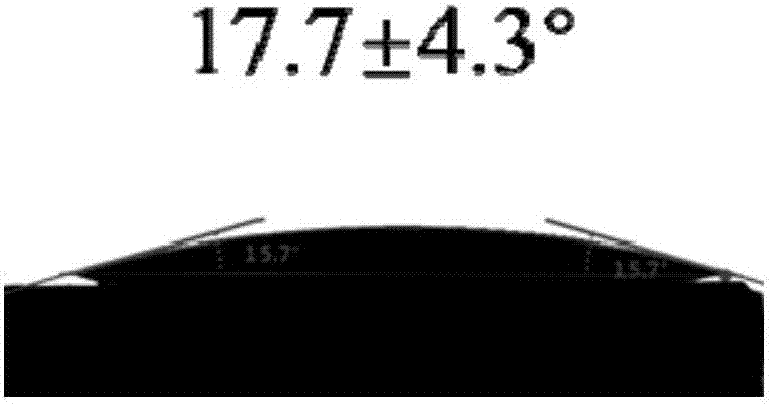
The invention discloses a method for preparing antibacterial surface on medical material surface. The method comprises the following steps: (1) conducting chemical grafting of amino silane after performing oxygen plasma pretreatment to the medical material surface and then reacting the medical material of the amino silane grafted surface with an acyl compound; (2) placing the medical material of an initiator modified surface into an anti-adhesion water solution for graft polymerization reaction; (3) placing the medical material of an anti-adhesion polymer brush-modified surface into an azide compound-containing dimethylformamide solution; and (4) placing the medical material of the azide surface into an antibacterial agent click solution for click reaction, to obtain anti-adhesion polymer surface and antibacterial agent-comodified antibacterial surface. According to the method, the mutual interference of the anti-ahdesion capability and sterilization capability can be avoided, the antibacterial surface has excellent long-acting antibacterial performance, the adverse effect of the sterilized surface on blood and somatic cells can be reduced, and the biocompatibility is excellent.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method and substance for obtaining surfaces with antimicrobial properties
InactiveUS20030035750A1Reduce the possibilityInhibit microbial growthBiocideLavatory sanitoryDispensarySinglet oxygen
The present invention involves the use of photosensitizers to provide antibacterial surfaces on consumer and industrial items. This approach avoids the used of chemicals and solutions that may be toxic. The inventions also avoids the use of chemical compositions that might form degradation products which may be unacceptable to healthy persons or irritating to persons who may have allergies or are otherwise sensitized. According to the invention, photosensitizers with specific properties and specific design features are selected to make practical use of photosensitizers in the consumer and industrial market place. It is important to select a photosensitizer with an activation spectrum that is matched to the environmental conditions under which the surface to be protected is required to exhibit its antimicrobial properties. This means that the illumination energy and intensity levels expected need to yield enough singlet oxygen to destroy the targeted microbes. It is also possible to select photosensitizers that are activated only by wavelengths prominently present in certain illumination lamps, such as those lamps commonly present in a laboratories, medical offices, pharmacies and food service areas, thereby making the surfaces antimicrobial only on demand when the illumination lamps are turned on.
Owner:BIOLITEC UNTERNEHMENSBETEILLIGUNGS II AG
Preparation method of antimicrobial polymer brush with triple functions of anti-fouling, sterilization and release
The invention discloses a preparation method of an antimicrobial polymer brush with triple functions of anti-fouling, sterilization and release. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) an active free radical initiator is grafted onto the surface of a backing material; 2) the backing material grafted with the initiator is polymerized with a stimulus-responsive monomer for obtaininga responsive polymer brush; 3) the responsive polymer brush is polymerized with a hydrophilic monomer for obtaining a hydrophilic responsive polymer brush; and 4) the hydrophilic responsive polymer brush is grafted with a trichloromethane antimicrobial agent or loaded with silver nanoparticles for obtaining the antimicrobial polymer brush. The polymer brush obtained with the method provided by the invention has the triple functions of anti-fouling, sterilization and release, and the antimicrobial surface is endowed with multiple functions of long-term anti-fouling, high-efficiency sterilization and bacteria release, thereby greatly expanding the application field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Antibacterial Surface Treatments Based on Silver Cluster Deposition
InactiveUS20090130181A1High antibacterial activityIncrease surface areaAntibacterial agentsBiocideAlcoholSynthetic materials
Process to obtain antibacterial surfaces by silver deposition in the form of firmly bonded small particles and to the antibacterial substances obtained by aforementioned treatments. Silver deposition is obtained by surface impregnation of natural or synthetic material in an alcoholic solution with silver salt and, later, by their exposure to UV-rays until metal silver clusters form as a result of silver ions reduction on the material surface. The invention relates to the obtained antibacterial substances.The simple preparation of the antibacterial material makes the whole process easier both for required time and for costs: the needed devices are just a UV lamp and an Ultrasound bath.
Owner:POLLINI MAURO +3
Antimicrobial surface preparation and method for producing the same
The claimed invention involves a novel preparation comprising a dispersion of wax and silver particles that is effective for reducing bacteria on surfaces. The surface preparation according to the present invention comprises particles of silver dispersed in wax. A method for making the surface preparation according to the present invention includes combining a supply of wax with a supply of silver particles.
Owner:CLIMAX ENGINEERED MATERIALS
Modified Anti-microbial surfaces, devices and methods
Methods for making modified surfaces and in particular, surfaces that may be lubricious and may be further treated to be anti-microbial are disclosed. Devices comprising modified surfaces prepared by the methods are also disclosed. An exemplary method comprises incubating a photo-initiator-coated substrate in an aqueous monomer solution that is capable of free radical polymerization, exposing the incubating substrate to ultraviolet (UV) light creating a modified surface on the substrate. An anti-microbial agent may be added to the modified surface.
Owner:COVALON TECH LTD
Coatings, coated surfaces, and methods for production thereof
InactiveUS20150099095A1Reduce depthBiocideLiquid surface applicatorsCoated surfaceAntimicrobial surface
A substrate having an antimicrobial surface. The texture of the surface which has exposed metal e.g., copper or copper alloy contributes to the antimicrobial properties. Cavities or depressions in the surface can be coated or partially coated with an organic polymer, and the polymer can contain antimicrobial agents. Methods of preparing a coated surface, and uses are described.
Owner:AEREUS TECH
Silver coated nylon fibers and associated methods of manufacture and use
InactiveUS20120129418A1High strengthEliminating and reducing and ameliorating any odorInorganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAntimicrobial surfaceSilver coating
Silver coated nylon woven and non-woven fibers are disclosed that can be used to make fabrics, bags, and pads that are silver coated on one side of the fabric, bag, and / or pad. Silver coated nylon fabrics, bags, and pads provide an antimicrobial surface which remains on the surface and retains its antimicrobial characteristic until destroyed. The silver coating can be used as a way to eliminate, reduce and / or ameliorate odors emanating from the bacteria. The methods of adherence of the silver to the nylon may be performed in a number of ways. The pads may be further associated with protective gear that can be used by professions and athletes that use protective gear.
Owner:BRAND SOLUTIONS
Laser based metal deposition (LBMD) of antimicrobials to implant surfaces
InactiveUS7951412B2Minimize adverse effectsHigh hardnessDental implantsFinger jointsWear resistantBone ingrowth
Owner:MEDICINELODGE
Antimicrobial surface treatment
ActiveUS20130052342A1Inhibit microbial growthGrowth inhibitionFireproof paintsBiocideMicroorganismPhosphate
A surface treatment powder comprising (a) about 50 wt. % or more of a percarbonate, perphosphate, persulfate, peroxide or perborate salt; (b) about 0.2-10 wt. % of a chlorinated isocyanurate salt; and (c) a bleach activator, and method of using same to inhibit the growth of a microorganism on a surface.
Owner:DEVERE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com