Patents
Literature
10792 results about "Adverse effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
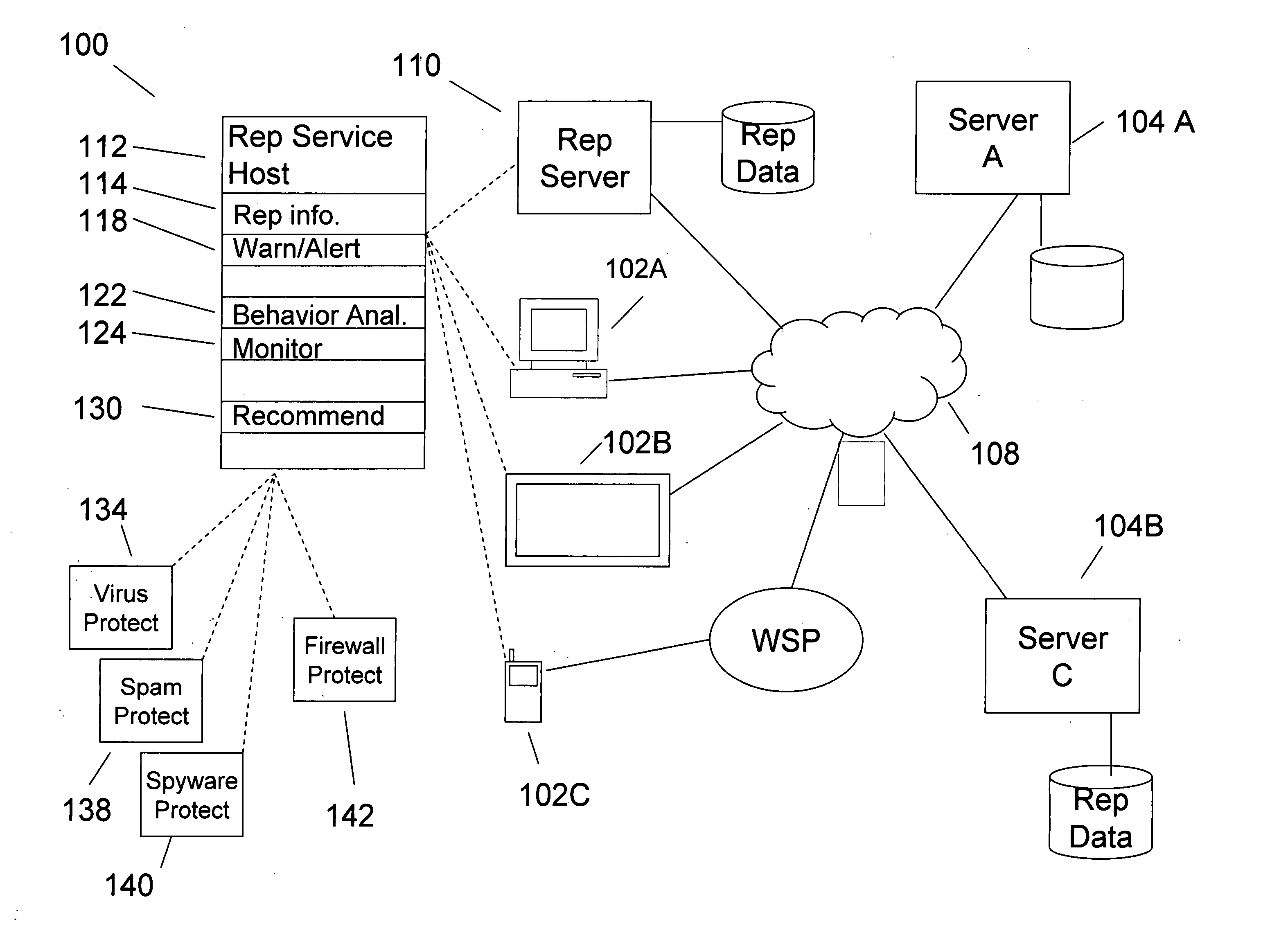
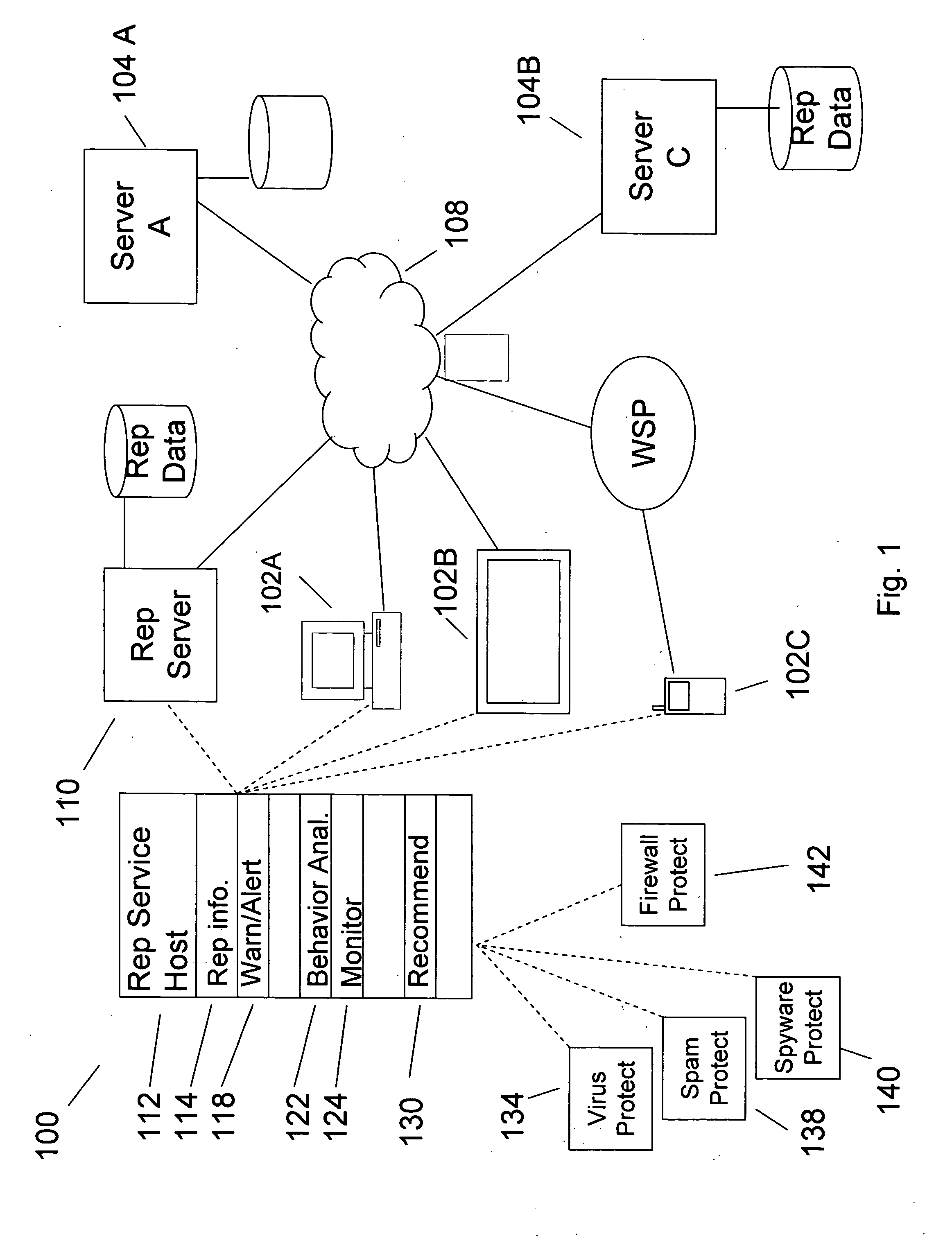
Reputation of an entity associated with a content item
InactiveUS20060253584A1Mitigate potential adverse effectDigital computer detailsTransmissionAdverse effectInformation retrieval
Owner:MCAFEE INC
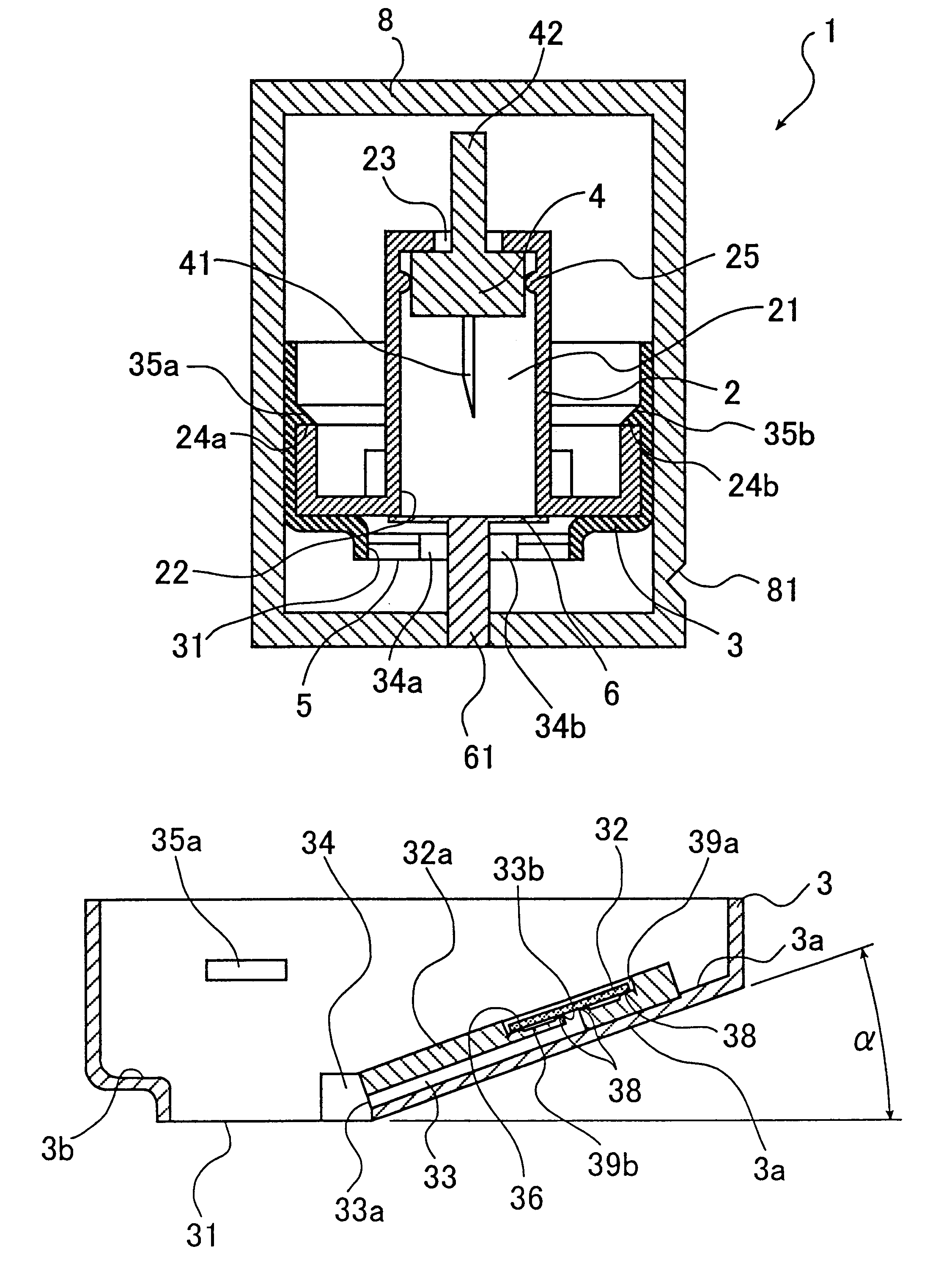
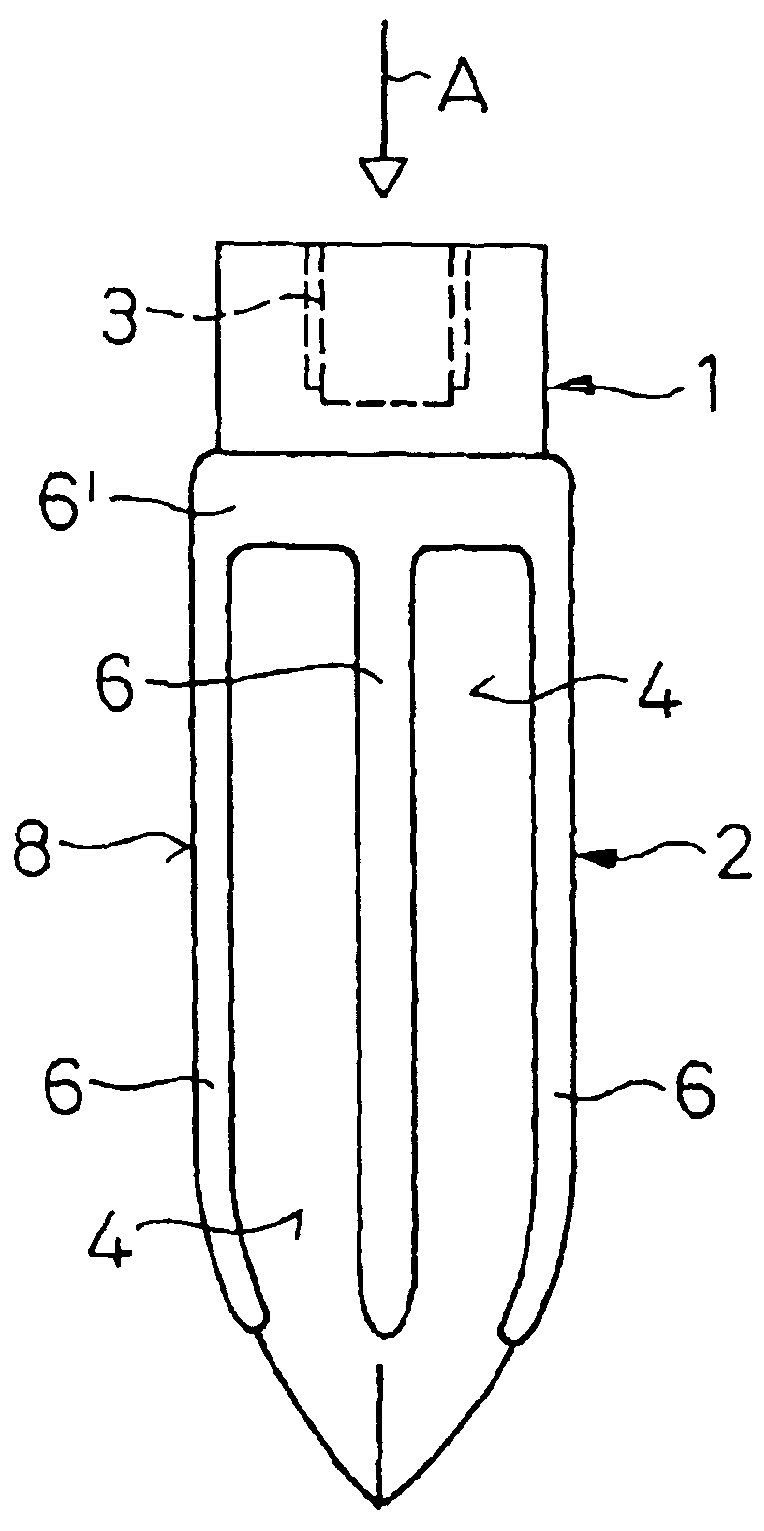
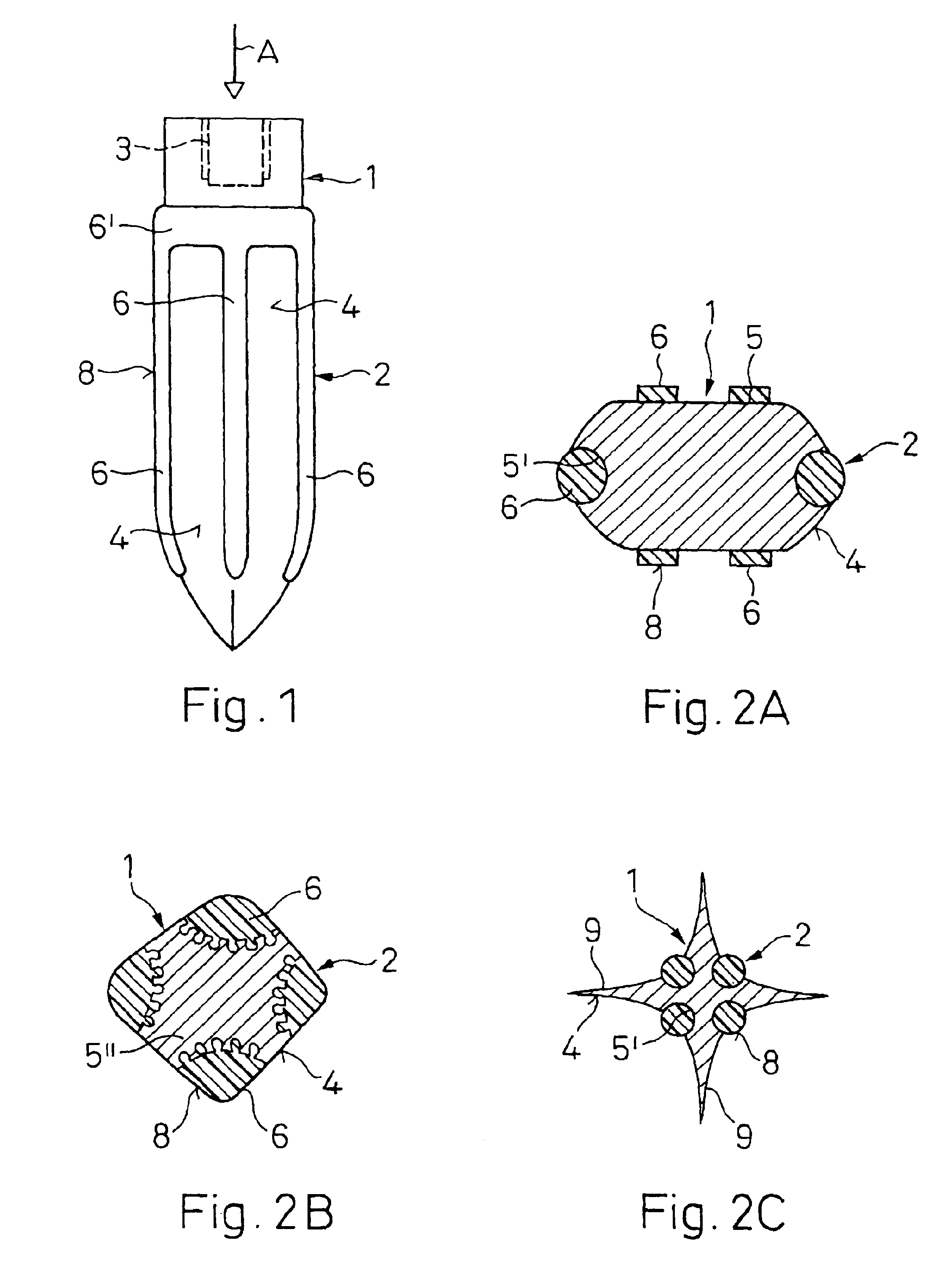
Assembly having lancet and means for collecting and detecting body fluid
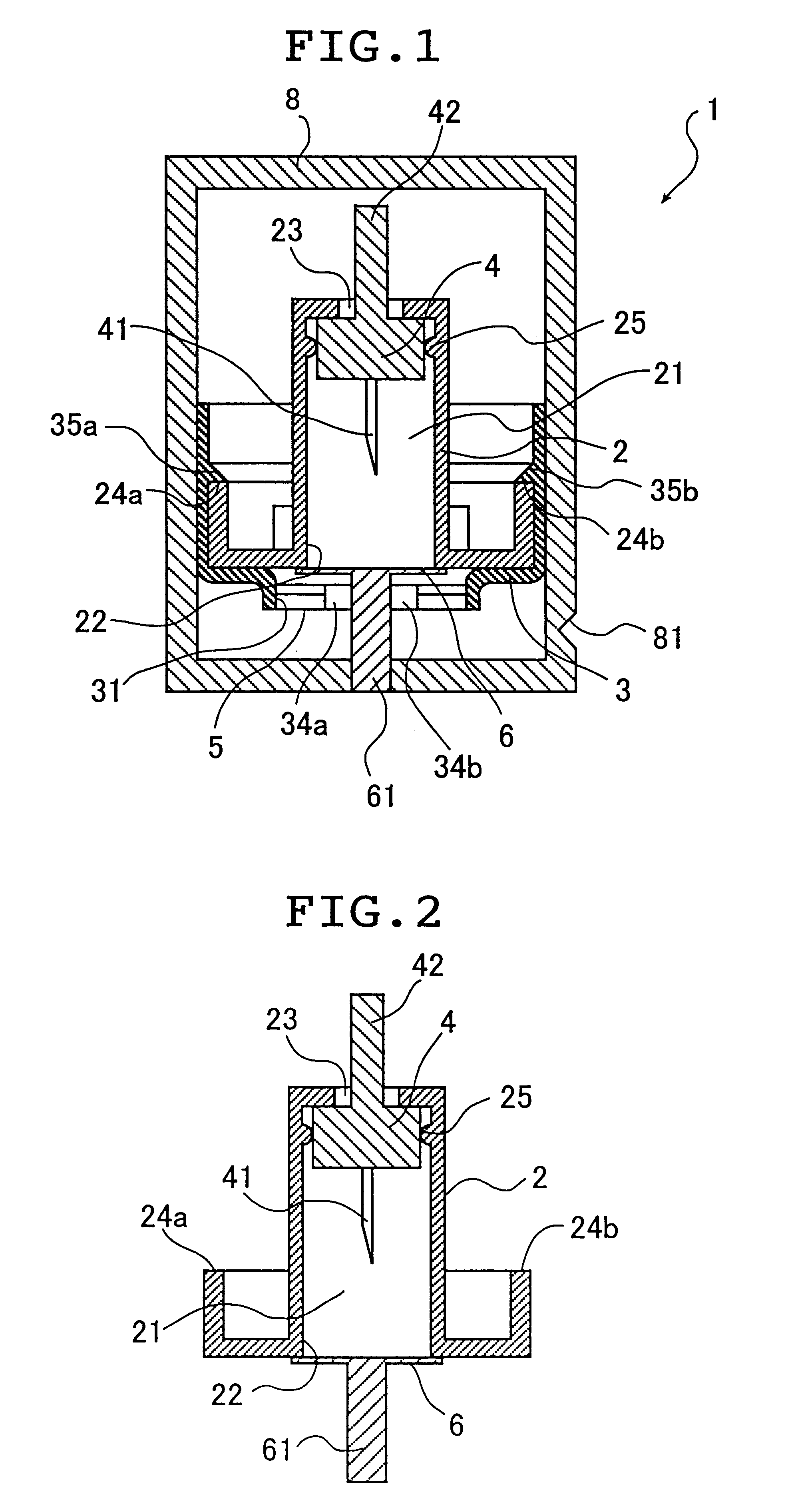
An assembly to be detachably mounted on a body fluid monitoring system is provided. The assembly has a lancet and a device for collecting and detecting a body fluid. The lancet has a puncture needle. In this assembly, the puncture needle is maintained in sterilized conditions until its use, and the sterilization can be conducted with no adverse effects on the detection device. A readily sterilizable lancet unit and a body fluid-collecting and detecting unit adapted for use in such an assembly as well as a body fluid-monitoring system including such an assembly are also provided. The assembly comprises a first housing having a sleeve which movably accommodates the lancet in its interior, and a second housing having the body fluid detection device. The first housing and the second housing share an opening. The lancet is sterilized before the assembly. The body fluid-collecting and detecting section has a body fluid guide on the periphery of the inlet.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Network based multiple sensor and control device with temperature sensing and control
InactiveUS20050043907A1Minimize adverse effectsPartial latencyThermometer detailsElectric devicesMultiple sensorControl equipment
A multifunction sensor device which provides various transducer functions including means for performing temperature sensing, humidity sensing, ambient light sensing, motion detection, thermostat functions, switching functions, load switching and dimming functions, displaying actual and set temperature values, displaying time of day values and a means to put the device in an on, off or auto mode. The device has utility in environments such as that found in offices, schools, homes, industrial plants or any other type of automated facility in which sensors are utilized for energy monitoring and control, end user convenience or artificial or natural cooling, heating and HVAC control. The device can be used as a switch or dimmer, sensor or thermostat as well as to adjust and control all natural and artificial lighting, temperature and humidity devices. Key elements of the invention include overcoming the difficulty of mounting diverse sensors or transducers within the same device or housing; permitting these various sensors to exist in a single package that can be mounted to a wall in a substantially flush manner; and eliminating the requirement of an air flow channel in the device, thus minimizing any adverse effects on the motion detecting element or sensor as well as providing built in partial hysteresis. The device may include additional transducers or sensors and is constructed such that the temperature and humidity sensors are neither exposed to the flow of air in a room or area nor in an airflow channel whereby a chimney effect may occur. The device can transmit and receive real time data, relative data and actual discrete data in addition to switching and controlling loads locally or remotely. An embodiment utilizing airflow channels to direct air over the temperature and humidity sensors is also disclosed.
Owner:ECKEL DAVID P +2
Vagal nerve stimulation techniques for treatment of epileptic seizures
InactiveUS6920357B2ElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringImplantable ElectrodesCardiac pacemaker electrode
The present invention uses electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve to treat epilepsy with minimized or no effect on the heart. Treatment is carried out by an implantable signal generator, one or more implantable electrodes for electrically stimulating a predetermined stimulation site of the vagus nerve, and a sensor for sensing characteristics of the heart such as heart rate. The heart rate information from the sensor can be used to determine whether the vagus nerve stimulation is adversely affecting the heart. Once threshold parameters are met, the vagus nerve stimulation may be stopped or adjusted. In an alternative embodiment, the invention may include a modified pacemaker to maintain the heart in desired conditions during the vagus nerve stimulation. In yet another embodiment, the invention may be simply a modified pacemaker having circuitry that determines whether a vagus nerve is being stimulated. In the event that the vagus nerve is being stimulated, the modified pacemaker may control the heart to maintain it within desired conditions during the vagus nerve stimulation.
Owner:OSORIO IVAN +1
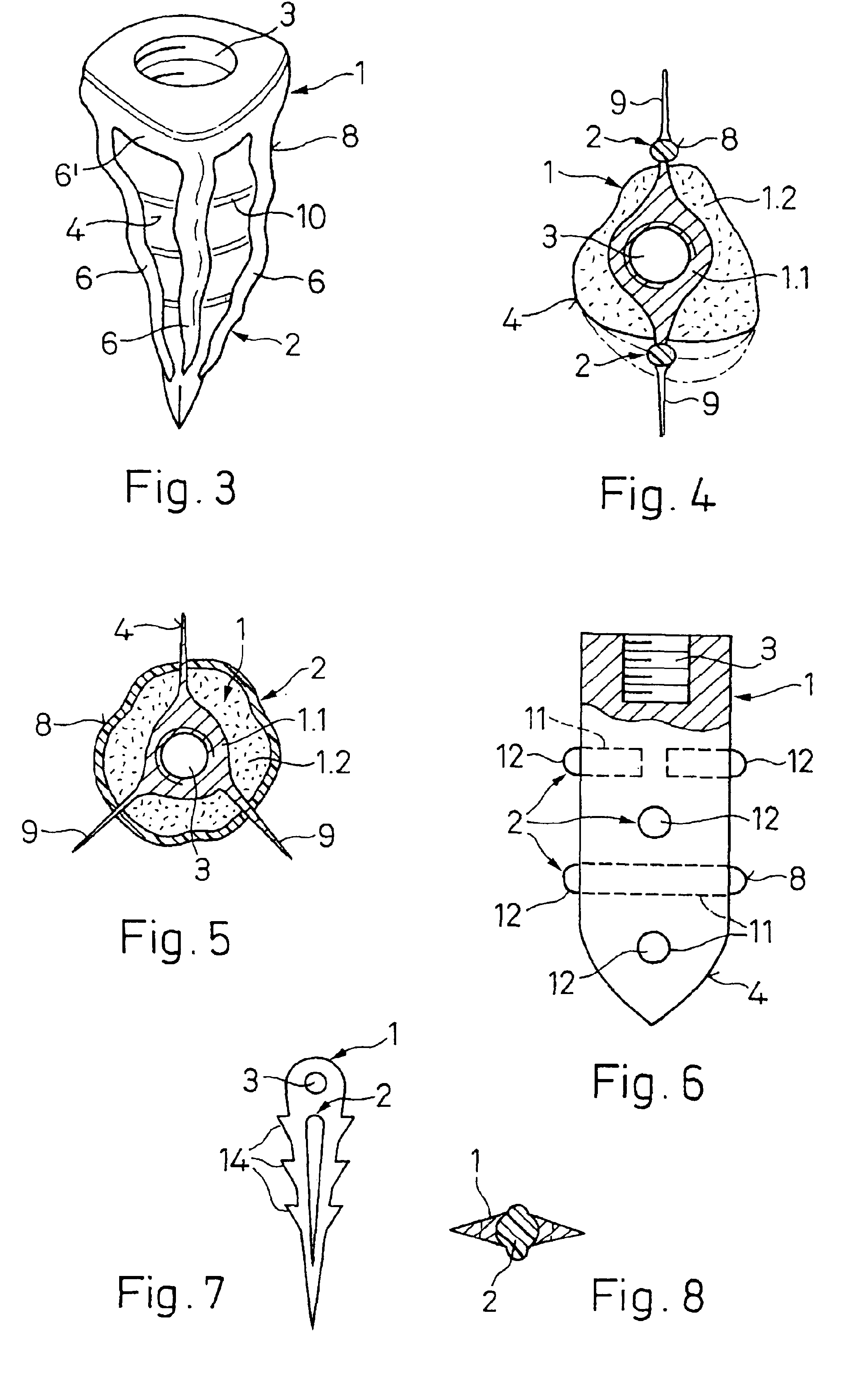
Implant to be implanted in bone tissue or in bone tissue supplemented with bone substitute material
InactiveUS6921264B2High softening temperatureLow softening temperatureDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBone tissueGrowth promoting
An implant (1) to be implanted in bone tissue, e.g. a dental implant or an implant for an orthopedic application, comprises surface regions (4) of a first type which have e.g. osseo-integrative, inflammation-inhibiting, infection-combating and / or growth-promoting properties, and surface regions (8) of a second type which consist of a material being liquefiable by mechanical oscillation. The implant is positioned in an opening of e.g. a jawbone and then mechanical oscillations, e.g. ultrasound is applied to it while it is pressed against the bone. The liquefiable material is such liquefied at least partly and is pressed into unevennesses and pores of the surrounding bone tissue where after resolidification it forms a positive-fit connection between the implant and the bone tissue. The surface regions of the two types are arranged and dimensioned such that, during implantation, the liquefied material does not flow or flows only to a clinically irrelevant degree over the surface regions of the first type such enabling the biologically integrative properties of these surface regions to start acting directly after implantation. The implant achieves with the help of the named positive fit a very good (primary) stability, i.e. it can be loaded immediately after implantation. By this, negative effects of non-loading are prevented and relative movements between implant and bone tissue are reduced to physiological measures and therefore have an osseo-integration promoting effect.
Owner:WOODWELDING
Accessory mounting device for a traffic light assembly
InactiveUS7137605B1Good adhesionInterference minimizationCandle holdersLighting support devicesEngineeringAdverse effect
An accessory mounting device is used with a traffic light assembly. The accessory mounting device fits over the top of a mounting pole for a traffic light assembly; due to an enlarged, gripping, lower portion with a mounting cylinder on the top thereof forming the accessory mounting device. The accessory mounting device of this invention supports a desired accessory on a traffic light assembly in a secure fashion, with minimal adverse effect on the traffic light assembly.
Owner:GUERTLER JAMES J
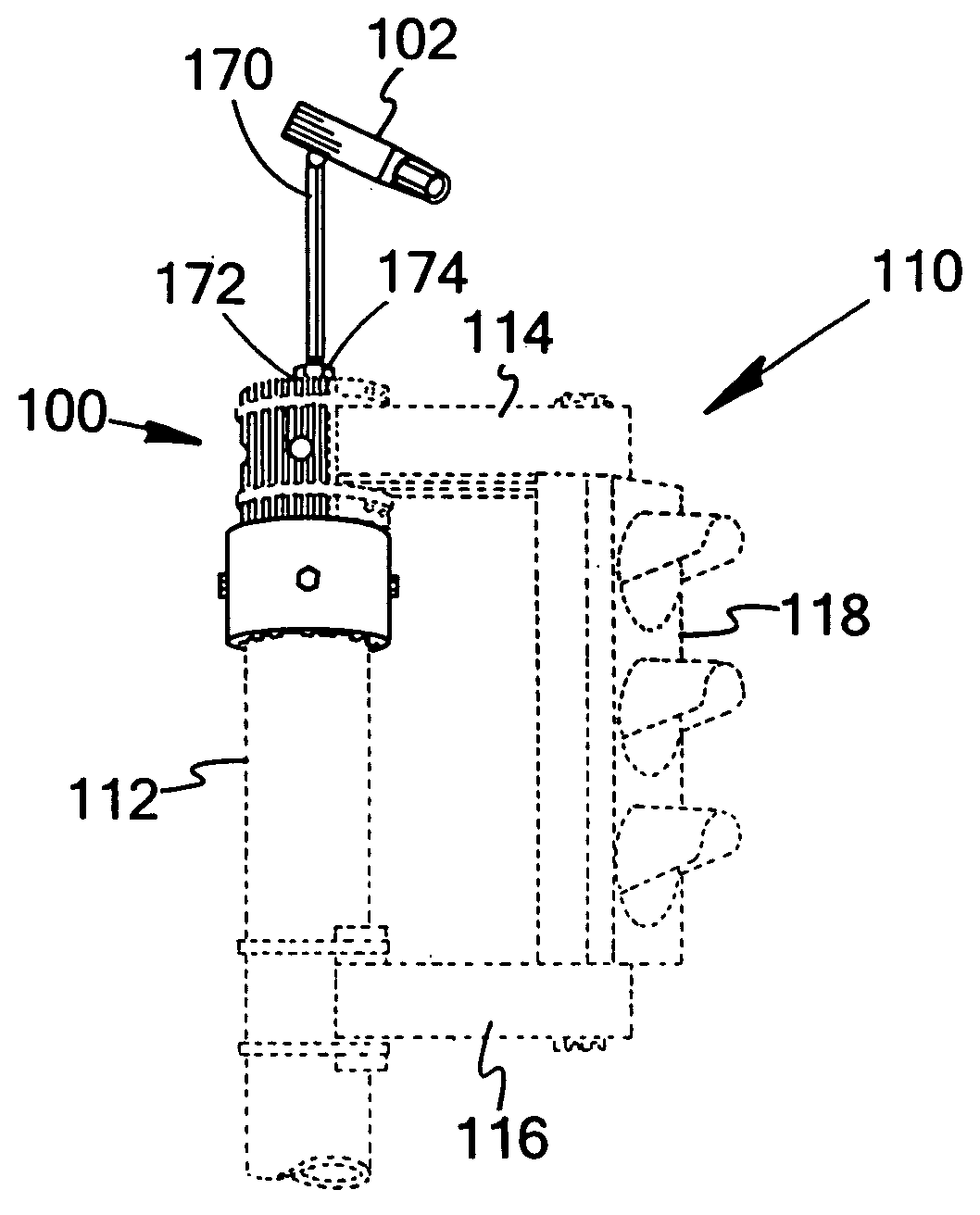
Configuration management and retrieval system for proton beam therapy system
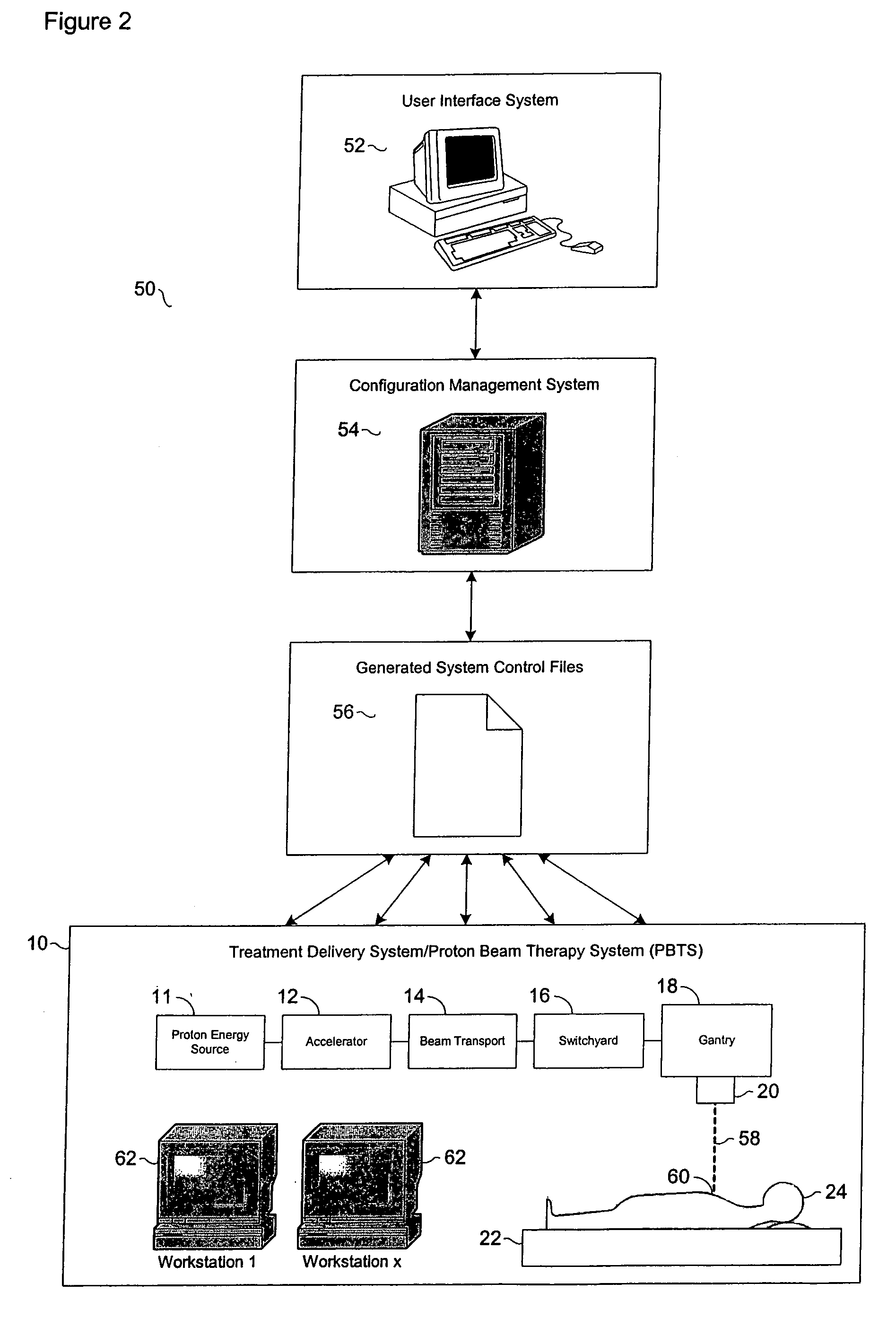
InactiveUS7084410B2Reduce generationEasy accessNuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsOperation modeSingle point of failure
In a complex, multi-processor software controlled system, such as proton beam therapy system (PBTS), it may be important to provide treatment configurable parameters that are easily modified by an authorized user to prepare the software controlled systems for various modes of operation. This particular invention relates to a configuration management system for the PBTS that utilizes a database to maintain data and configuration parameters and also to generate and distribute system control files that can be used by the PBTS for treatment delivery. The use of system control files reduces the adverse effects of single point failures in the database by allowing the PBTS to function independently from the database. The PBTS accesses the data, parameters, and control settings from the database through the system control files, which insures that the data and configuration parameters are accessible when and if single point failures occur with respect to the database.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Nonwoven composite containing an apertured elastic film
ActiveUS7803244B2Lamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringBond formation
An elastic nonwoven composite that contains an elastic film laminated to one or more nonwoven web materials is provided. The composite is formed by passing the film through a nip to bond the film to the nonwoven web material(s). Concurrent with bond formation, apertures are also formed in the elastic film. The apertures are of a size sufficient to provide a desired level of texture, softness, hand feel, and / or aesthetic appeal to the composite without having a significant adverse effect on its elastic properties. Aperture and bond formation are accomplished in the present invention by selectively controlling certain parameters of the lamination process, such as film content, bonding pattern, degree of film tension, bonding conditions, etc.
Owner:KIMBERLY CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Oral dosage form comprising a therapeutic agent and an adverse-effect agent
InactiveUS20030044458A1Reduce eliminateReduce and eliminate pharmacological effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderOral medicationTherapeutic effect
The present invention provides an oral dosage form comprising a first composition and a second composition. The first composition comprises an effective amount of a therapeutic agent and the second composition comprises an effective amount of an adverse-effect agent. The adverse-effect agent is covered with a coating that is substantially insoluble in the gastrointestinal tract. In one embodiment, the adverse-effect agent is coated with an outer base-soluble layer and an inner acid-soluble layer. The therapeutic agent can be uncoated or can be coated with a coating having an outer acid-soluble layer and an inner base-soluble layer. The dosage form discourages administration of the therapeutic agent by other than oral administration.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
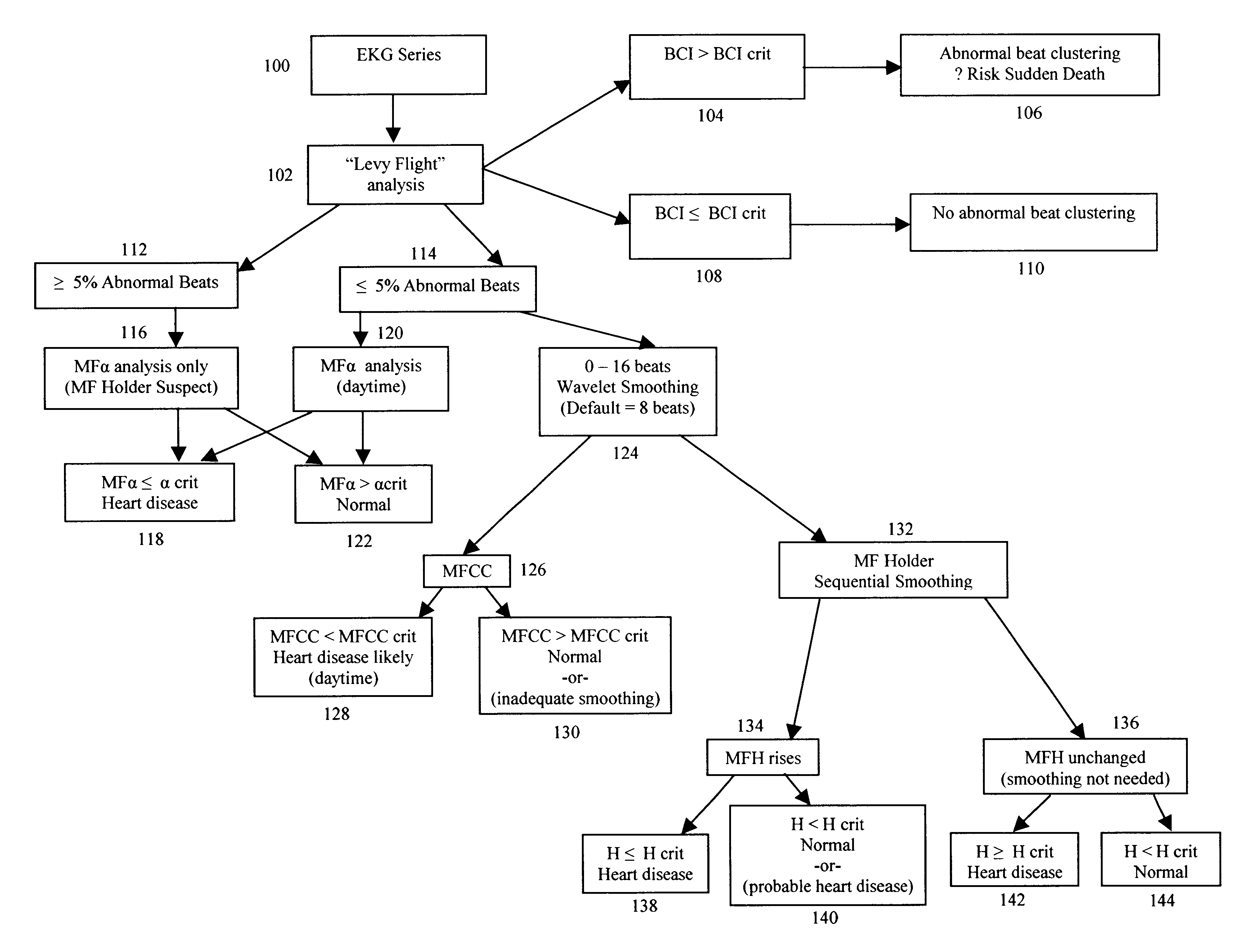
Method for diagnosing heart disease, predicting sudden death, and analyzing treatment response using multifractal analysis
InactiveUS6993377B2Reducing minimum sizeIncreased analytic detailMedical simulationMedical report generationTest batterySudden death
A method of analyzing electrocardiogram (EKG) data for use in the diagnosis of heart disease, prognosis of cardiac conditions, and the monitoring of heart disease therapies is disclosed. The method utilizes a wavelet-based multifractal analysis with one or more of (1) a discrete wavelet smoothing step to remove the effects of abnormal beats; (2) “Levy flight” analysis to detect the frequency of abnormal beats known to adversely affect the multifractal (MF) analysis; and (3) MF alpha analysis, a multifractal extension of monofractal short term (ST) alpha analysis. The invention further comprises an EKG test battery comprising Levy flight anomalous beat / beat cluster screening, followed by (ST) MF alpha analysis and MF Holder analysis (when validated by the Levy flight analysis). The wavelet smoothing step can also be used to classify human EKGs by observing the effect of sequential smoothing on the MF Holder coefficient. Alternative choices to the wavelet smoothing approach to removal of abnormal beat effects include probability distribution function analysis to determine the MF Holder coefficient directly, abnormal beat ridge skeleton removal to remove the offending beats based on a direct multifractal spectrum calculation, and the calculation of various types of entropy coefficients for the EKG time series.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Parasympathetic pacing therapy during and following a medical procedure, clinical trauma or pathology
ActiveUS20060206155A1Increase parasympathetic toneReduced responseSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsParasympathetic ganglionPathology diagnosis
A treatment method is provided, including identifying a subject as one who is selected to undergo an interventional medical procedure, and, in response to the identifying, reducing a likelihood of a potential adverse effect of the procedure by applying an electrical current to a parasympathetic site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a jugular vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, a parasympathetic ganglion of the subject, and a parasympathetic nerve of the subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Oral dosage form comprising a therapeutic agent and an adverse-effect agent
The present invention provides an oral dosage form comprising a first composition and a second composition. The first composition comprises an effective amount of a therapeutic agent and the second composition comprises an effective amount of an adverse-effect agent. The adverse-effect agent is covered with a coating that is substantially insoluble in the gastrointestinal tract. In one embodiment, the adverse-effect agent is coated with an outer base-soluble layer and an inner acid-soluble layer. The therapeutic agent can be uncoated or can be coated with a coating having an outer acid-soluble layer and an inner base-soluble layer. The dosage form discourages administration of the therapeutic agent by other than oral administration.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
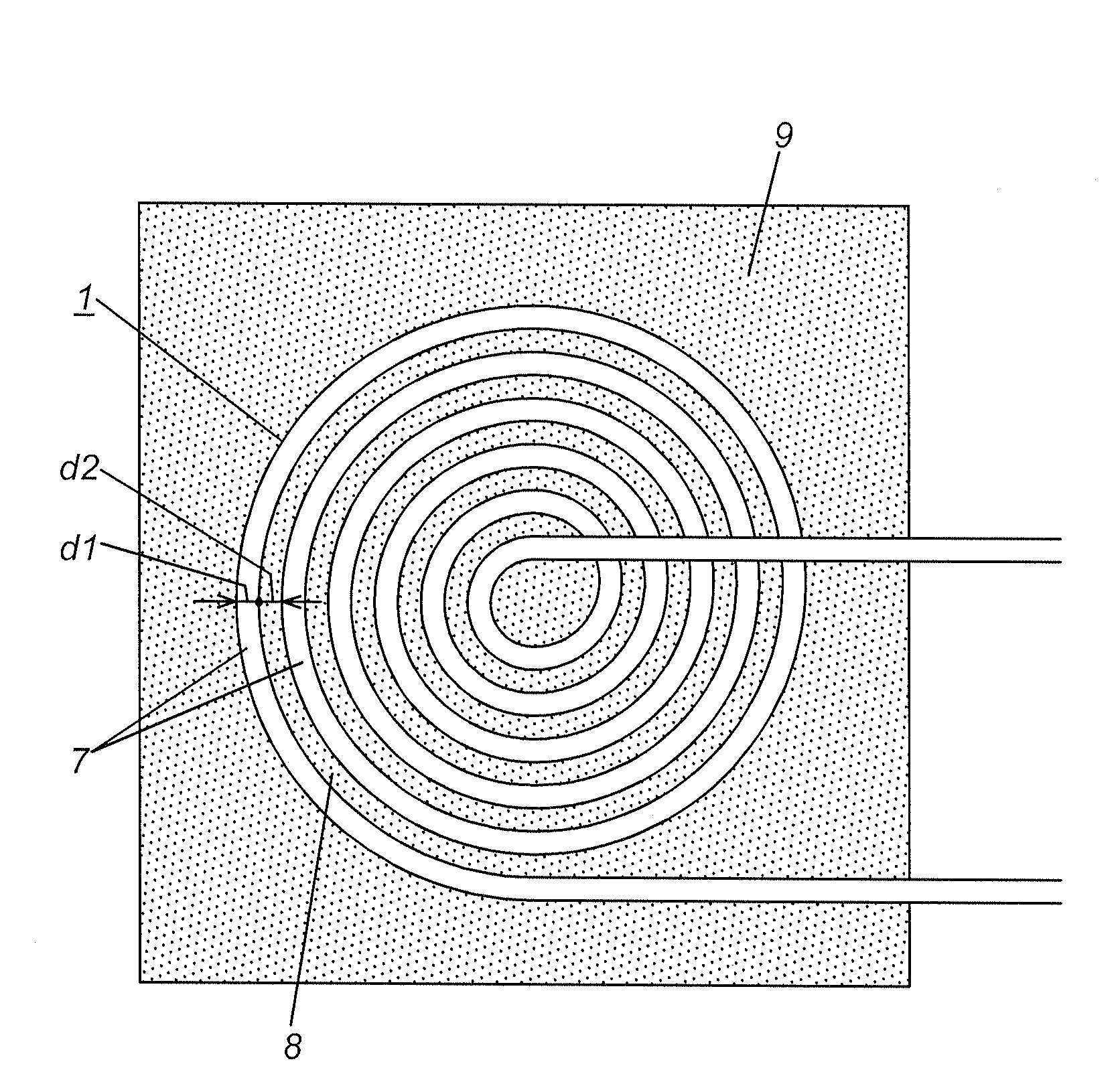
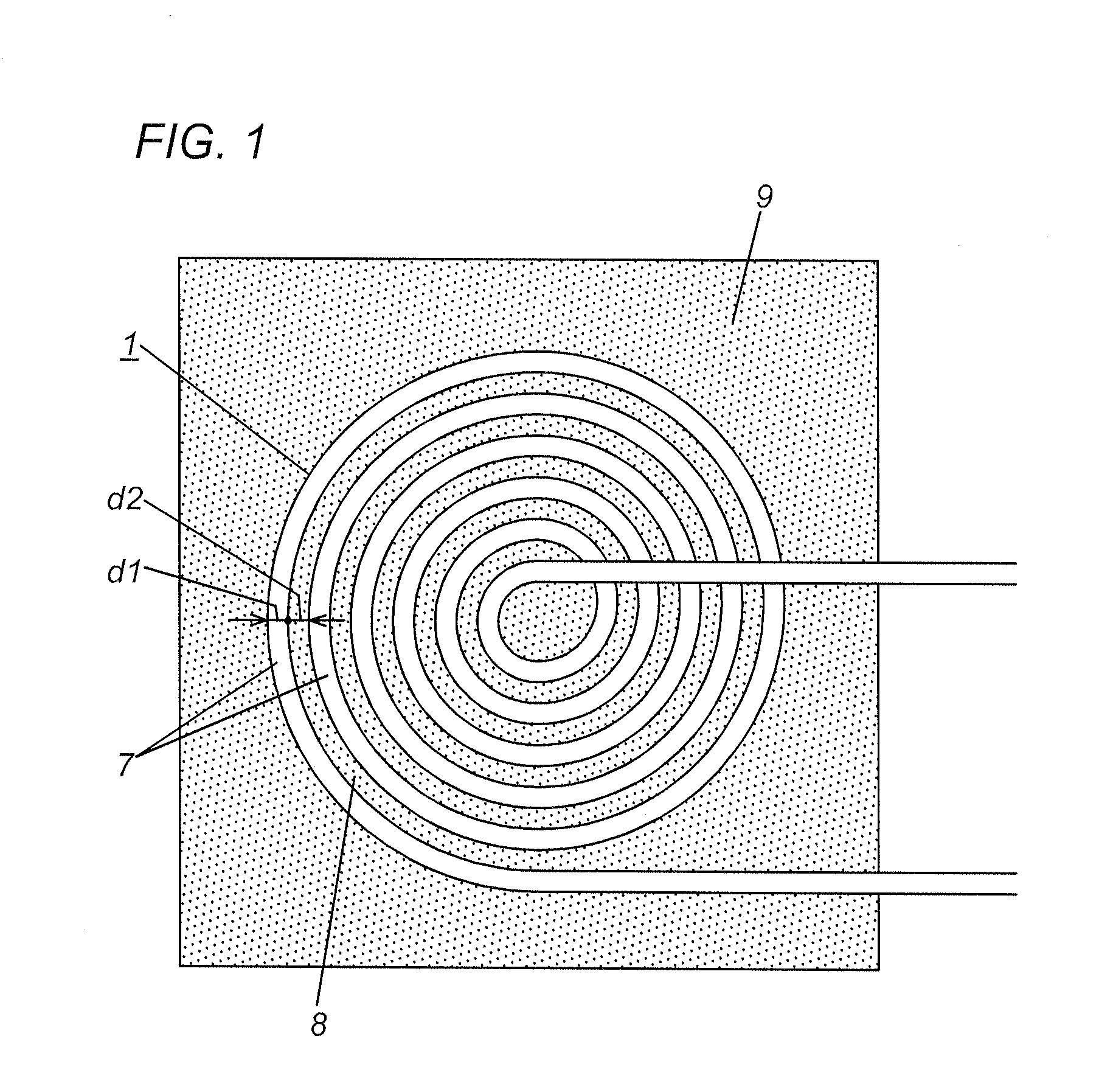
Planar coil and contactless electric power transmission device using the same
InactiveUS20100277004A1Avoid it happening againImprove productivityBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionEddy current
This invention has an object to a planar coil, a contactless electric power transmission device using the same. This planar coil is configured to suppress an eddy current developed between adjacent turns of wire for minimizing adverse effects on ambient electrical appliances resulting from heat generation. The planar coil 1 in the present invention is formed of spiral shaped wire 7 coated with thinned insulative film, in which adjacent turns of the wire 7 are spaced in radial direction at such a predetermined interval to suppress an eddy current. This planar coil 1 is preferably employed as a power transmission coil or power receiving coil.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
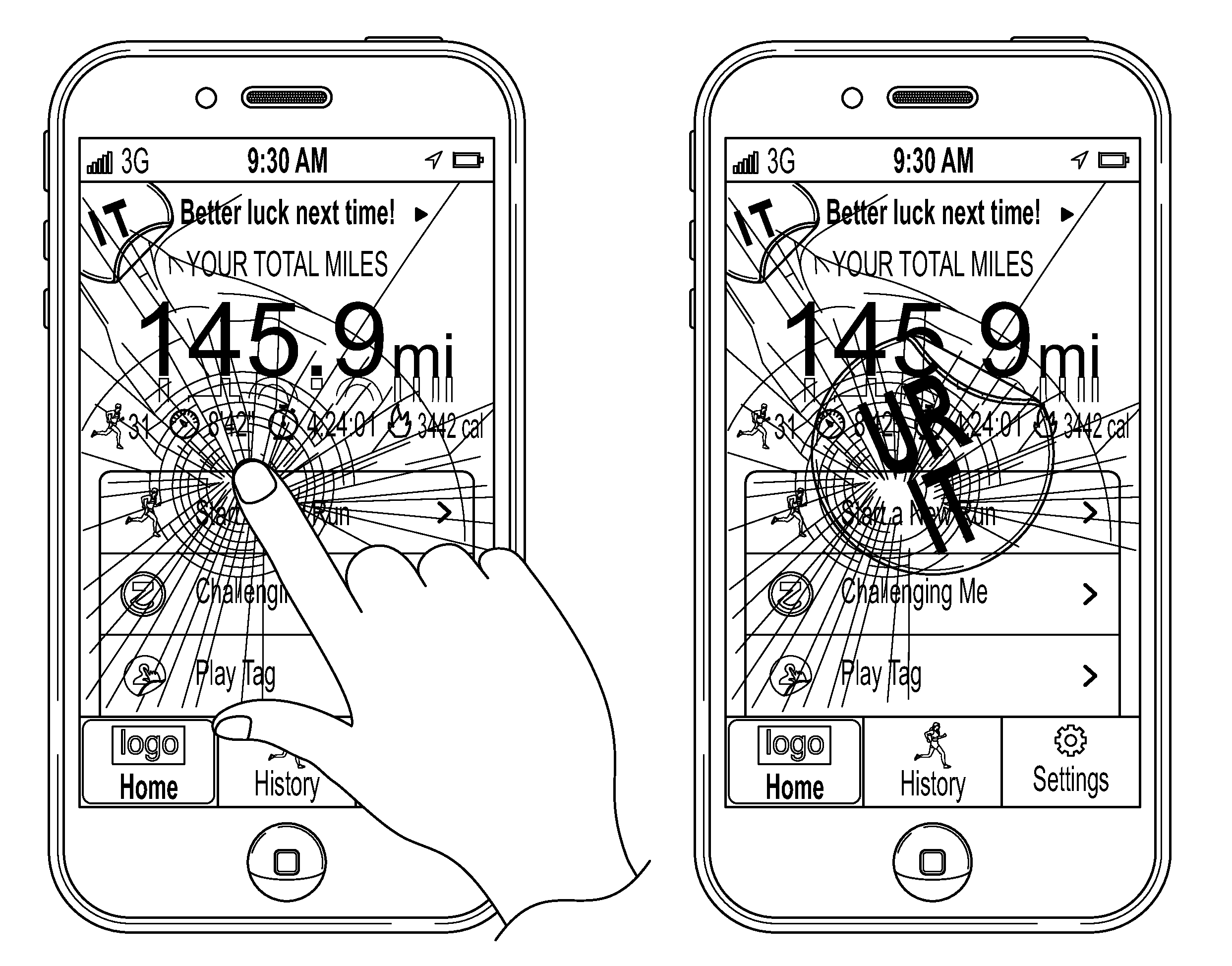
Methods and systems for encouraging athletic activity
ActiveUS8597093B2Physical therapies and activitiesComputer-assisted treatment prescription/deliveryMovement activityHuman–computer interaction
Individuals may be encouraged to perform athletic activity based on punishments or adverse effects that may be applied if the individual loses an athletic activity competition. For example, a user's device may be adversely affected by visual or functional effects configured to obscure or obstruct one or more functions of the user's device. The punishment or adverse effect might not be removed or deactivated until a user has completed a new competition without losing. In some arrangements, the user may be required to win in order to have the adverse effect removed.
Owner:NIKE INC
Methods and Systems for Encouraging Athletic Activity
ActiveUS20120290109A1Physical therapies and activitiesComputer-assisted treatment prescription/deliveryMovement activityHuman–computer interaction
Individuals may be encouraged to perform athletic activity based on punishments or adverse effects that may be applied if the individual loses an athletic activity competition. For example, a user's device may be adversely affected by visual or functional effects configured to obscure or obstruct one or more functions of the user's device. The punishment or adverse effect might not be removed or deactivated until a user has completed a new competition without losing. In some arrangements, the user may be required to win in order to have the adverse effect removed.
Owner:NIKE INC
Movement disorder stimulation with neural block
InactiveUS20050070970A1Ameliorate disorderReduce adverse effectsInternal electrodesExternal electrodesBlocking nerveSignal on
A method and apparatus for treating patients suffering from involuntary movement disorders (including epilepsy) by stimulating a selected cranial nerve of the patient with an electrical signal applied to induce a signal at brain by applying an electrical signal at the nerve to ameliorate the disorder and by applying a neural conduction block at the nerve selected to at least partially block nerve impulses on said nerve at a blocking site and reduce adverse effects of said signal on an organ.
Owner:RESHAPE LIFESCIENCES INC
Distributed agent based model for security monitoring and response
ActiveUS20140237599A1Quick checkHigh and uniform level of securityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionCountermeasureAgent-based model
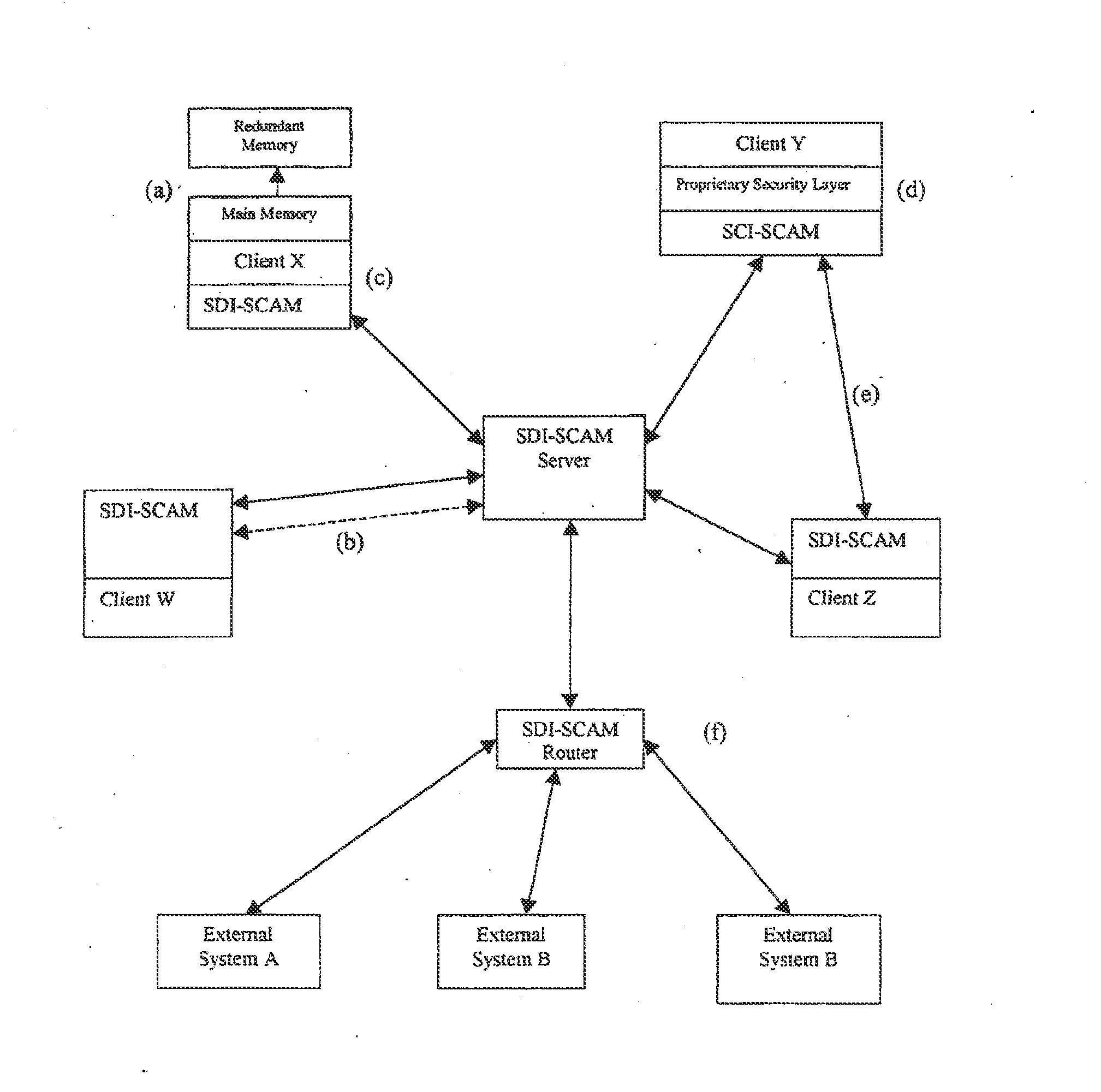
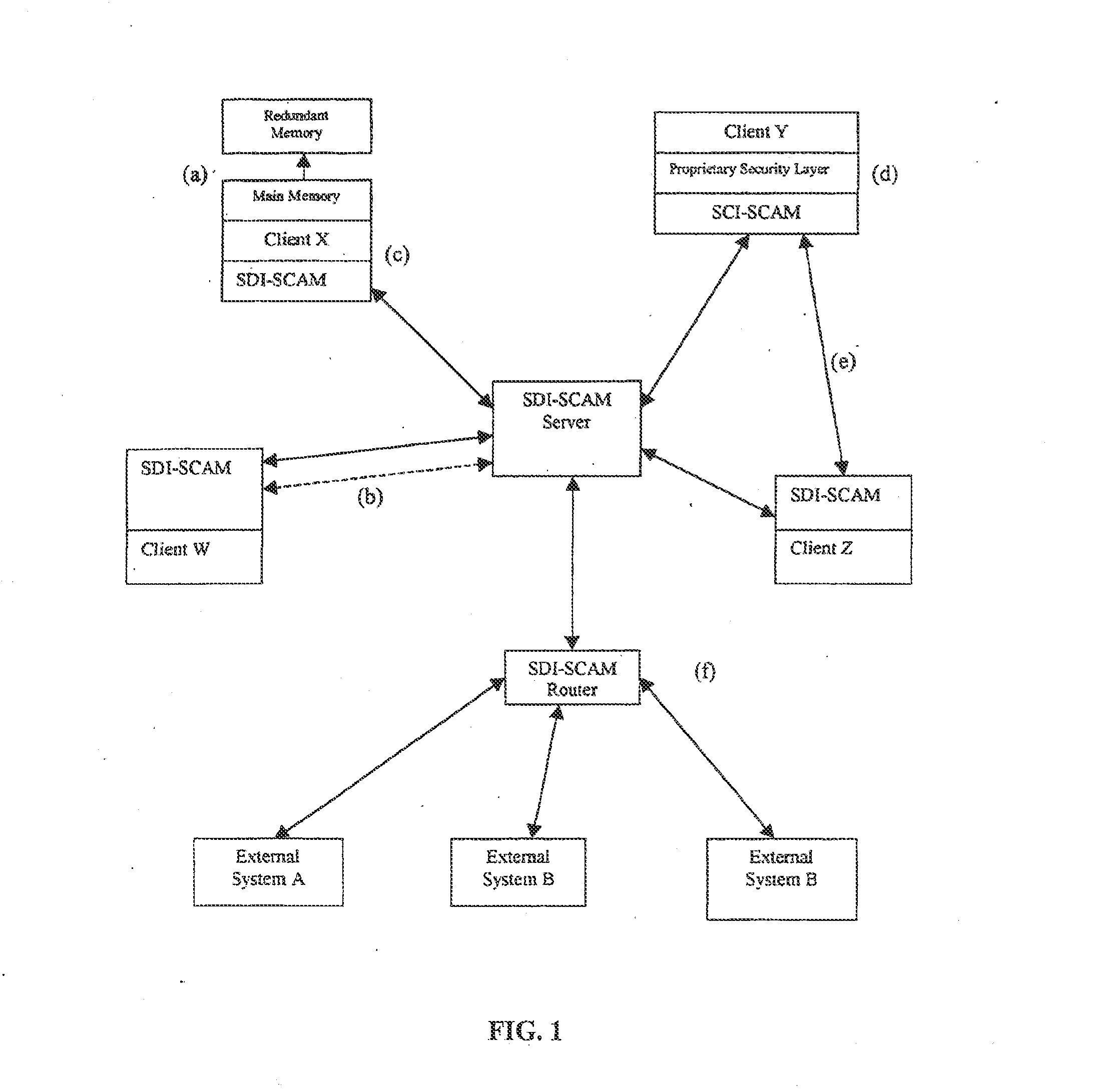
An architecture is provided for a widely distributed security system (SDI-SCAM) that protects computers at individual client locations, but which constantly pools and analyzes information gathered from machines across a network in order to quickly detect patterns consistent with intrusion or attack, singular or coordinated. When a novel method of attack has been detected, the system distributes warnings and potential countermeasures to each individual machine on the network. Such a warning may potentially include a probability distribution of the likelihood of an intrusion or attack as well as the relative probabilistic likelihood that such potential intrusion possesses certain characteristics or typologies or even strategic objectives in order to best recommend and / or distribute to each machine the most befitting countermeasure(s) given all presently known particular data and associated predicted probabilistic information regarding the prospective intrusion or attack. If any systems are adversely affected, methods for repairing the damage are shared and redistributed throughout the network.
Owner:INVENTSHIP LLC
Stable aqueous surfactant compositions
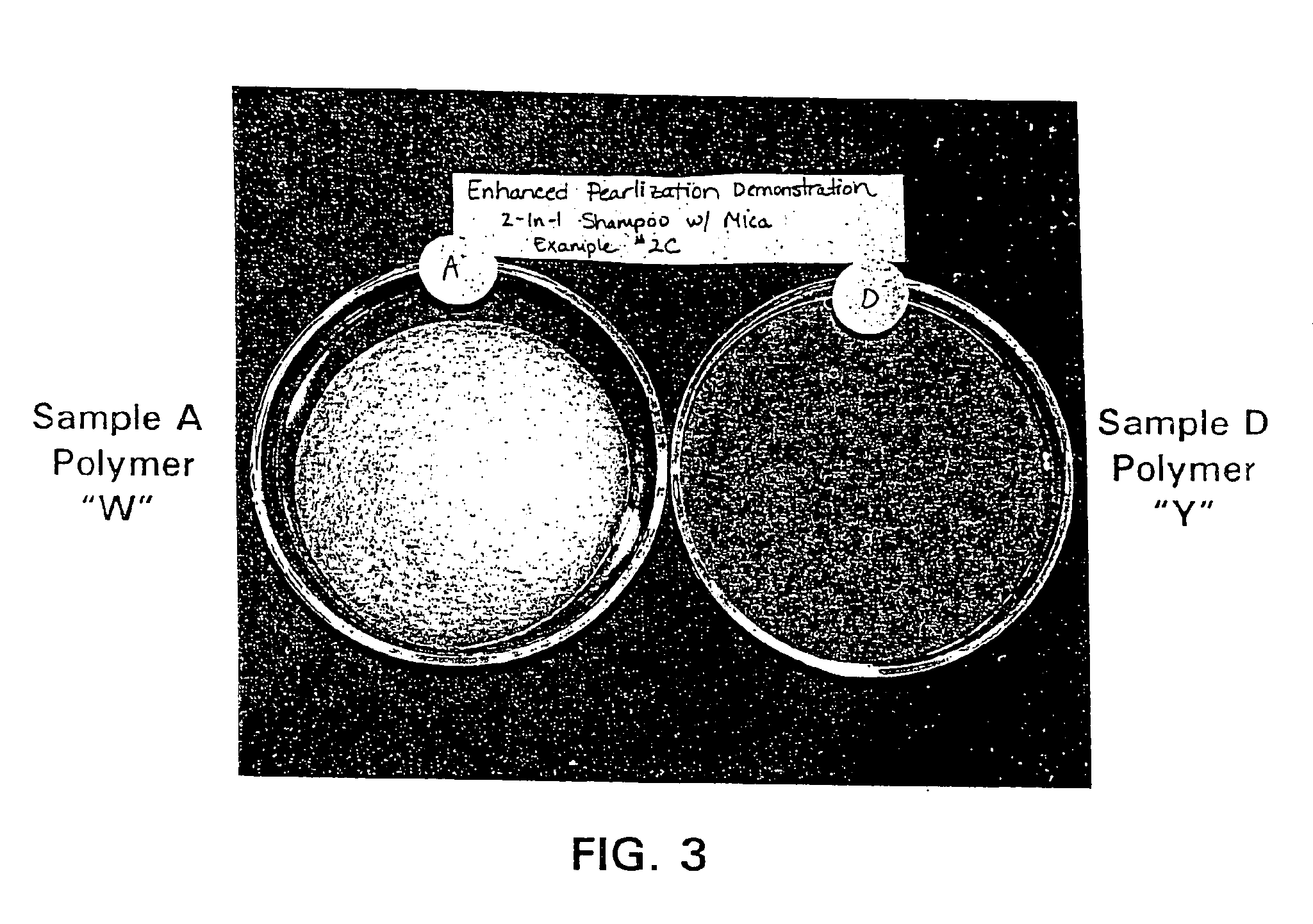
InactiveUS6897253B2Enhanced pearlescent appearanceLow compositionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideHair dyesAcid substances
A stable, aqueous composition containing a substantially crosslinked alkali-swellable acrylate copolymer rheology modifier, a surfactant, an alkaline material, and various compounds therein, as for example substantially insoluble materials requiring suspension or stabilization, such as a silicone, an oily material, or a pearlescent material. Additionally, this invention also relates to the formation of a rheologically and phase stable cationic hair dye composition. The invention further relates to the incorporation of an acidic material after the addition of an alkaline material to reduce the pH of the composition without negatively impacting the viscosity of the composition.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for optimizing GPS-based position location in presence of time varying frequency error
InactiveUS6903684B1Easy to measurePrecise positioningBeacon systems using radio wavesRadio transmissionContinuous measurementDoppler measurements
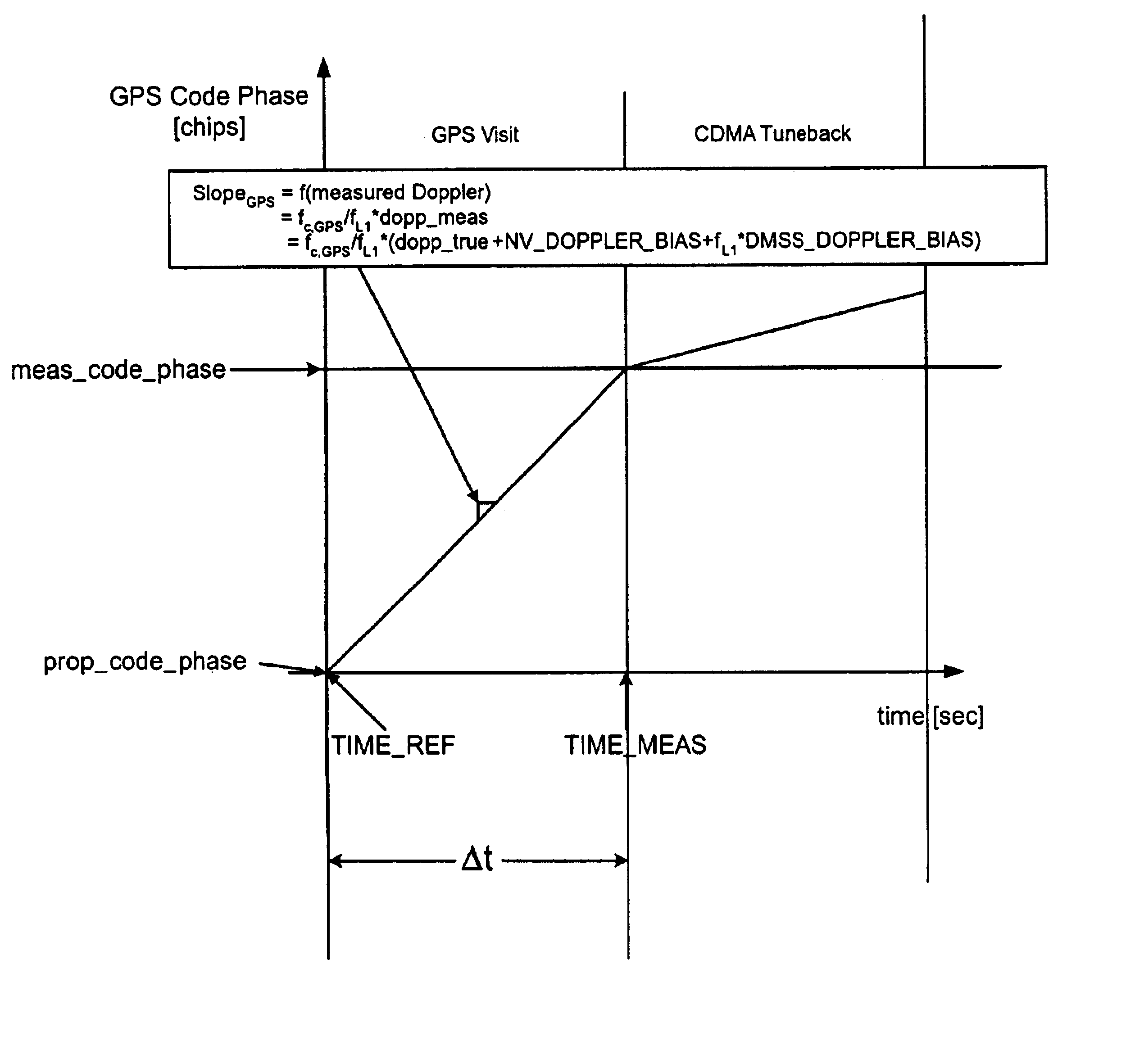
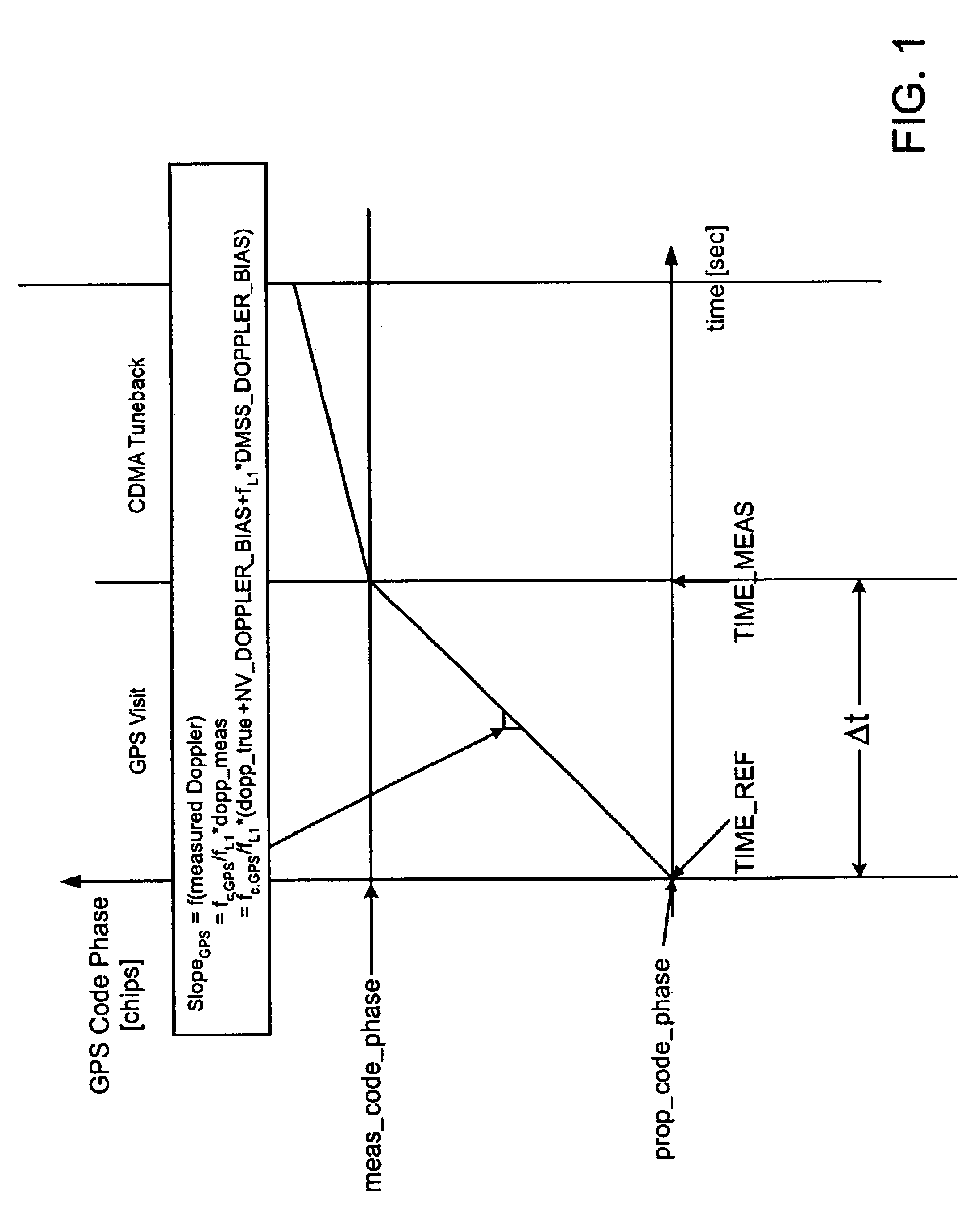
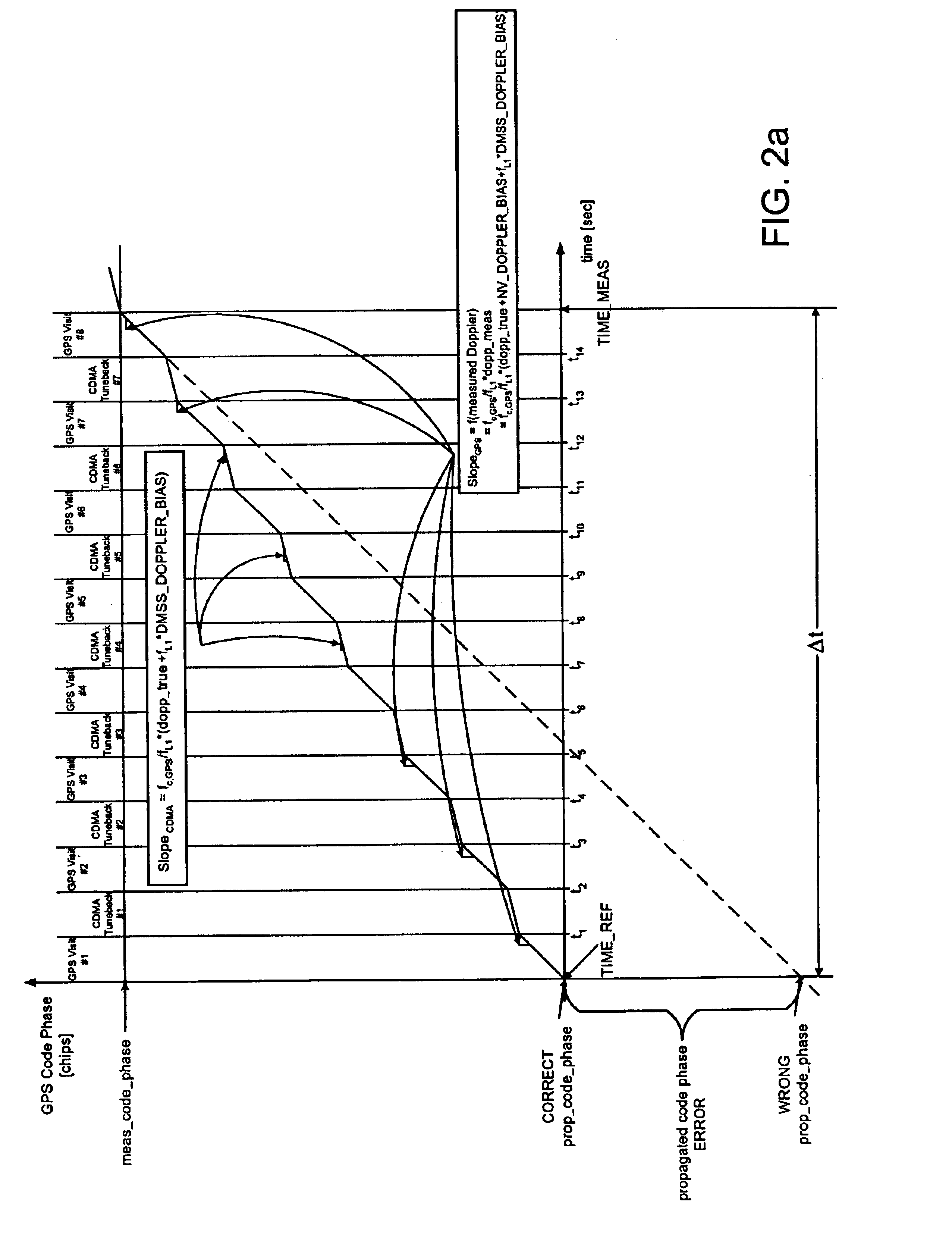
Position determination accuracy of a wireless communication device may be negatively affected by a large unaccounted GPS doppler bias, which in turn may affect GPS doppler estimations and GPS doppler measurements conducted by the wireless communication device. The quality of GPS doppler measurements is very important for position location, because poor quality GPS doppler measurements may prevent the wireless communication device from acquiring satellites in the most sensitive modes with narrow frequency ranges, which results in reduced GPS pseudorange measurement yield. Large unaccounted GPS doppler bias also adversely affects position accuracy because of the adverse effect on the GPS code phase measurements time propagation to common time prior to their use in position location calculation. The same is true in the case of unaccounted CDMA code doppler, through the adverse effect on the AFLT code phase measurements time propagation to common time prior to their use in a position location engine. This effect is the biggest concern in the case of large search windows. Therefore, the present disclosure provides a method of optimizing GPS based position location in the presence of time-varying frequency error, including the steps of continuously measuring and / or calculating resulting GPS doppler bias and CDMA code doppler bias and then minimizing their adverse effects with regard to position location determination by re-centering GPS doppler search windows based on the GPS doppler bias value, as well as using GPS doppler bias and CDMA code doppler bias value to properly propagate GPS pseudorange and AFLT pilot phase measurements, respectively, to common time prior to their use in a position location engine.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
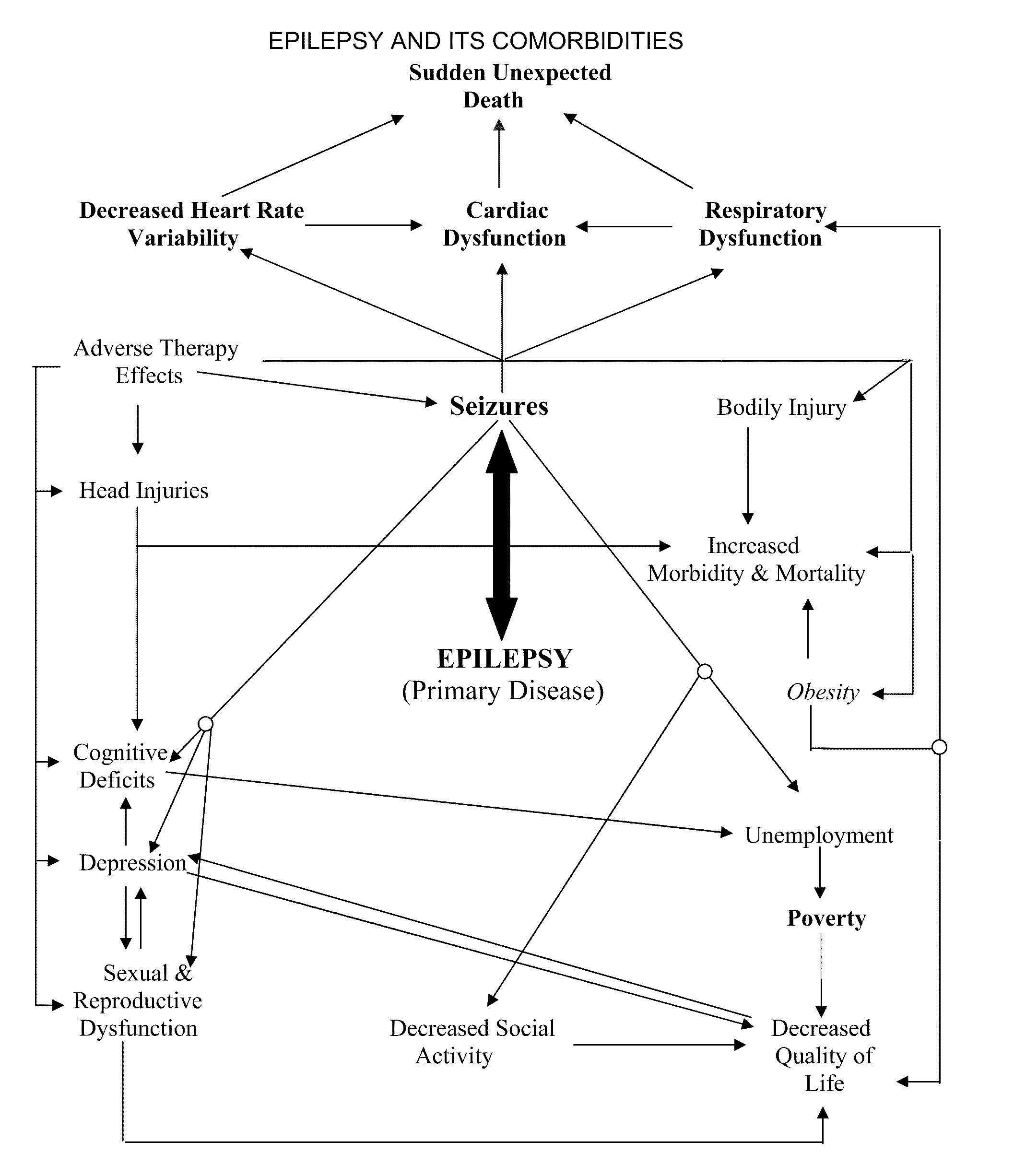
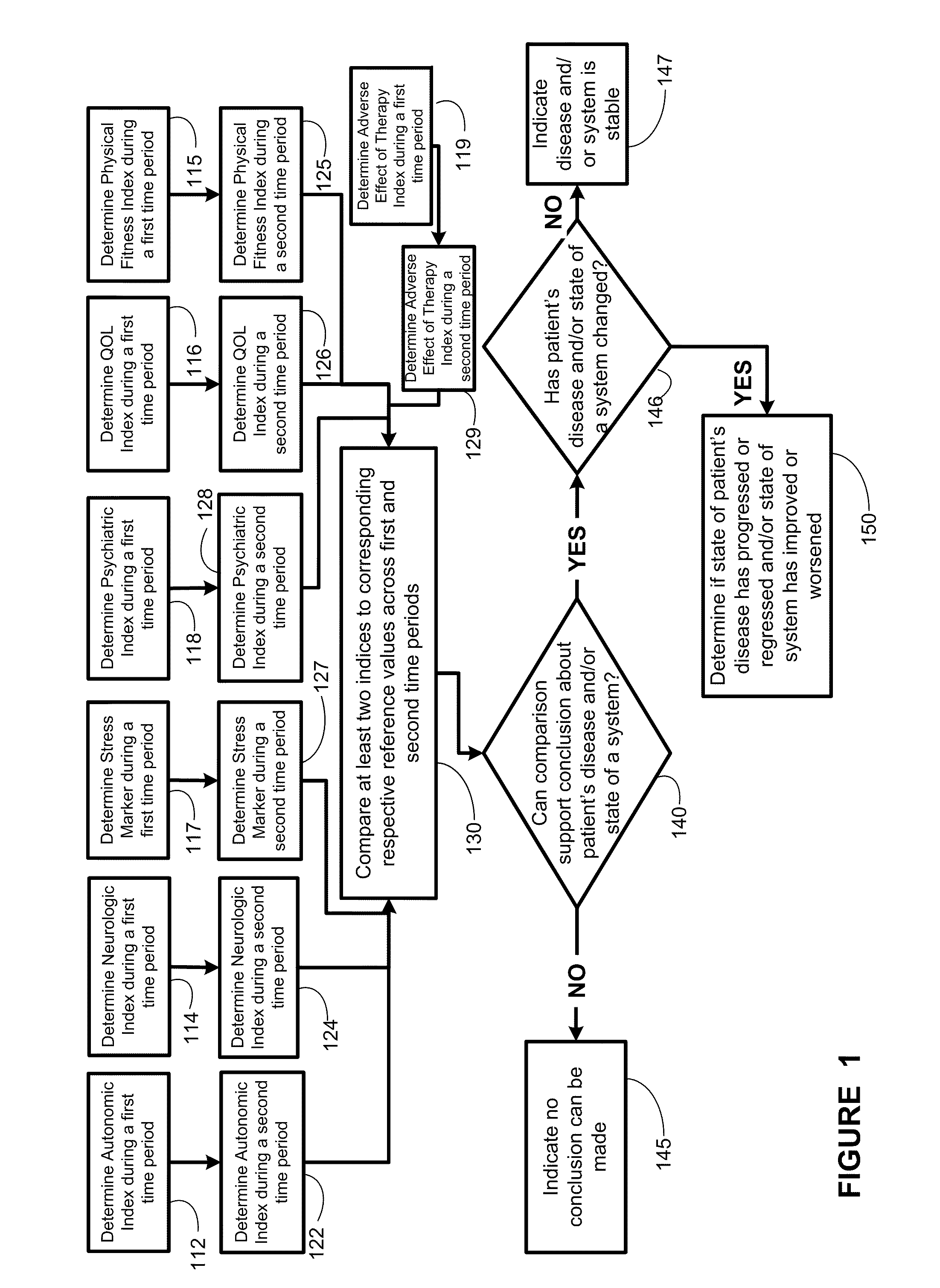
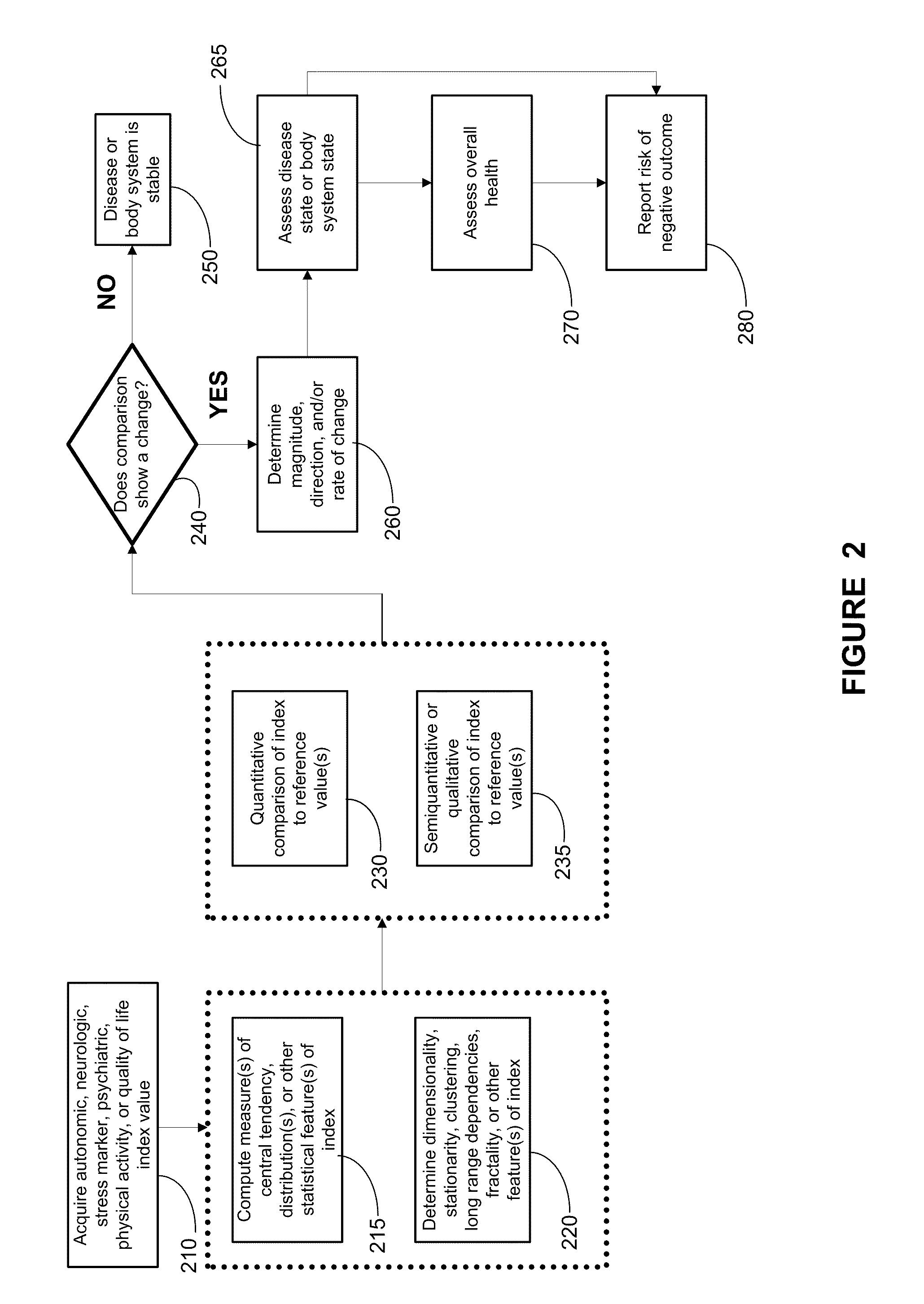
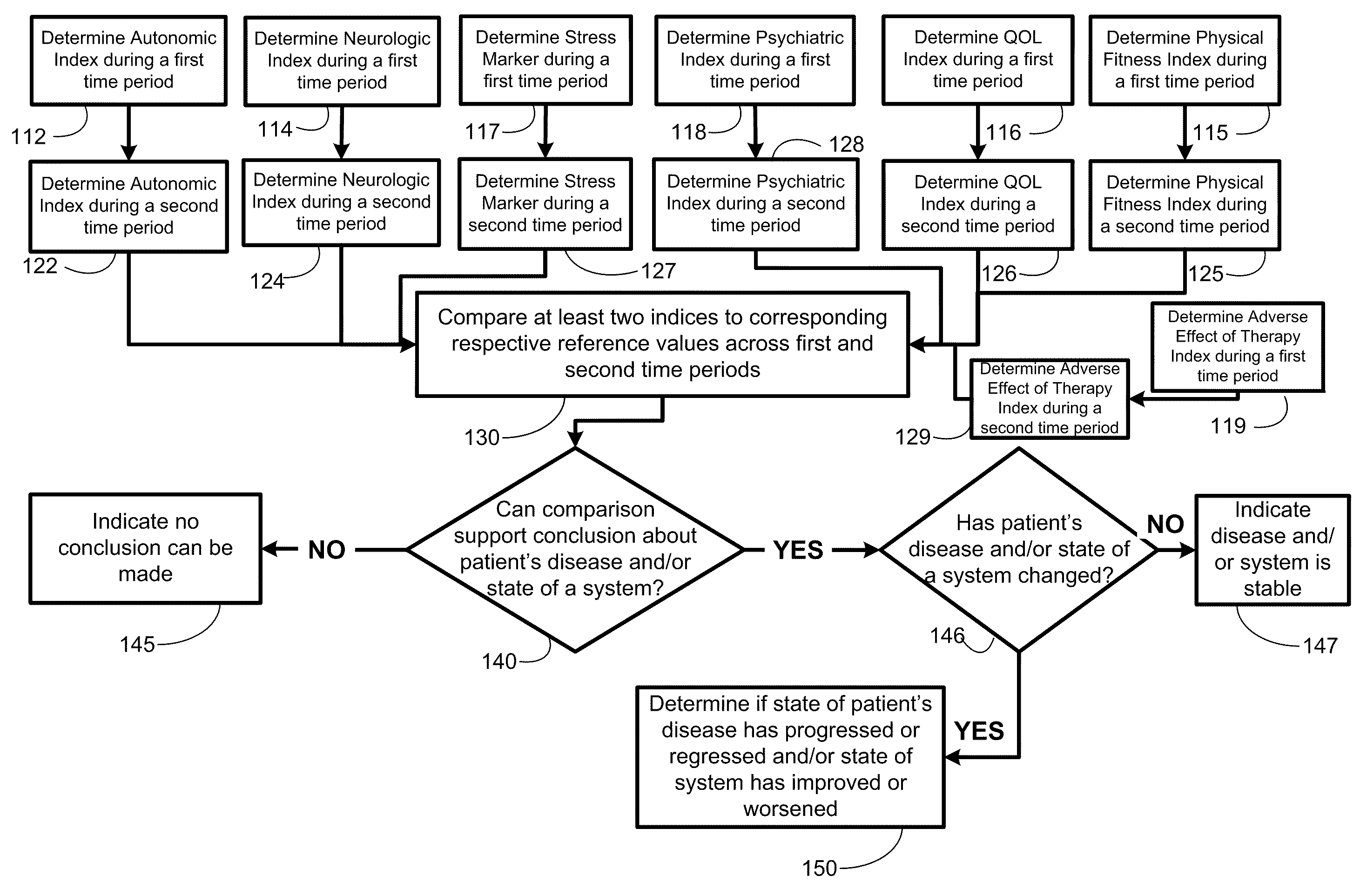
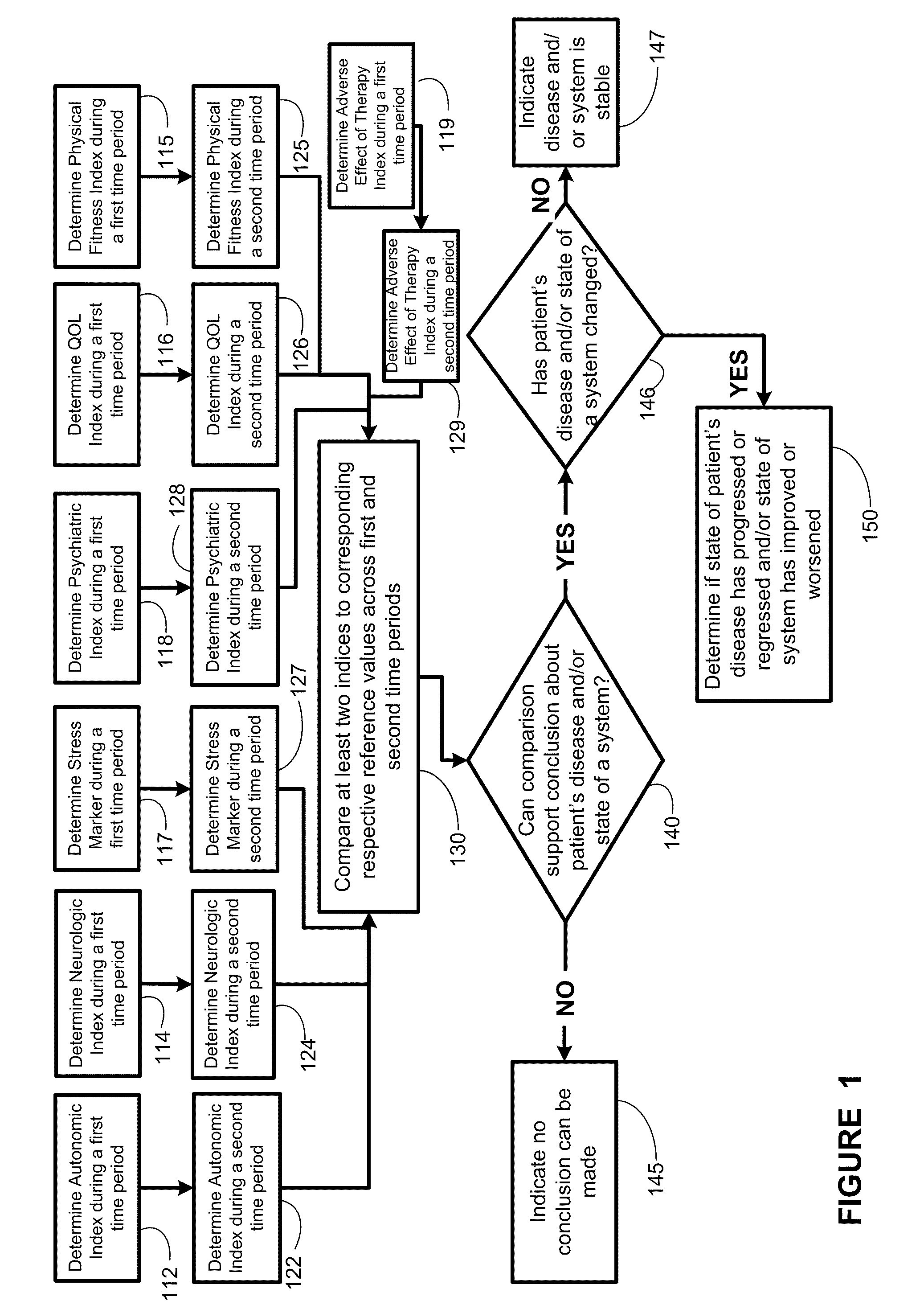
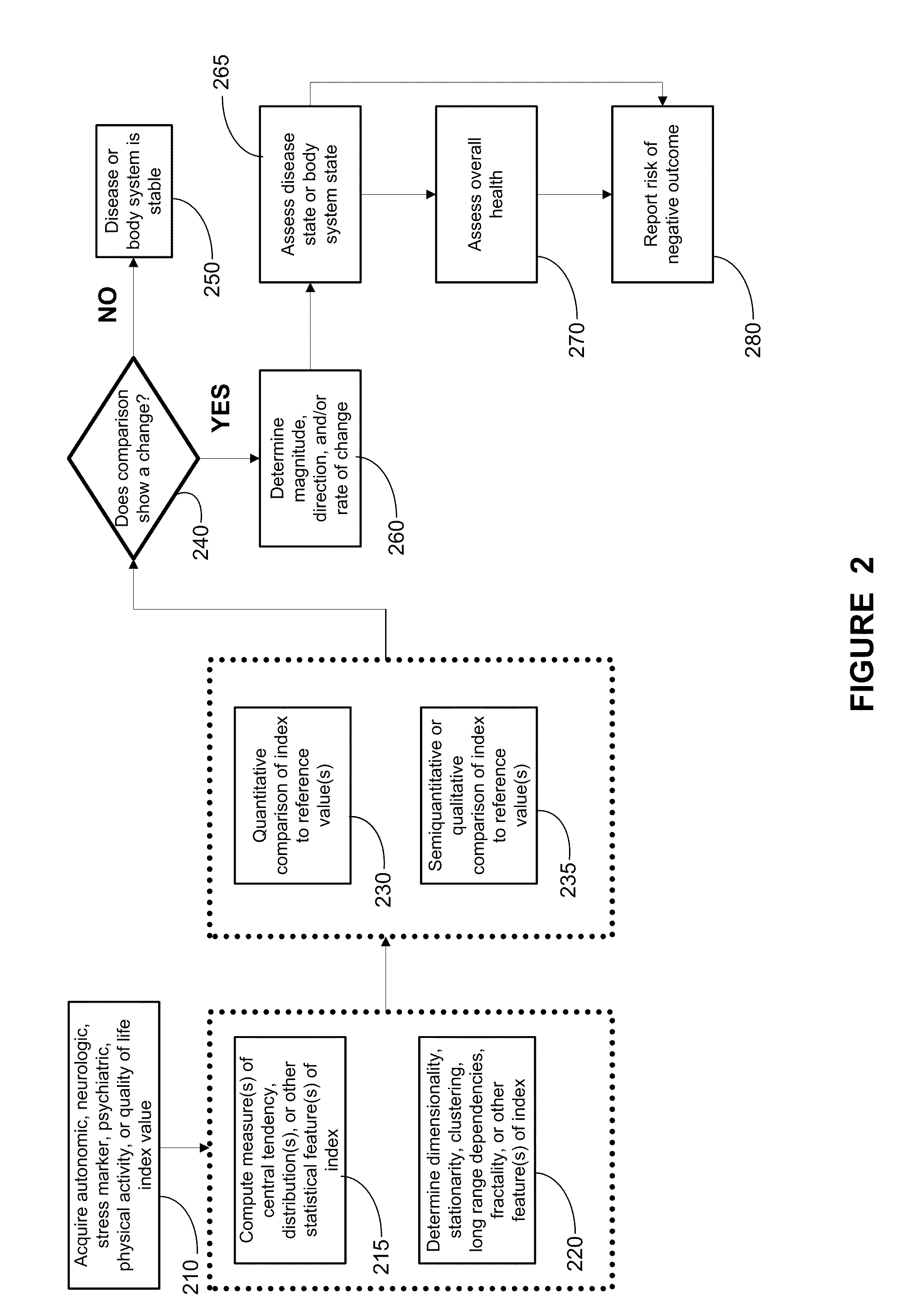
Systems approach to disease state and health assessment
Methods, systems, and apparatus for assessing a state of an epilepsy disease or a comorbidity thereof are provided. The methods comprise receiving at least one autonomic index, neurologic index, stress marker index, psychiatric index, endocrine index, adverse effect of therapy index, physical fitness index, or quality of life index of a patient; comparing the at least one index to at least one reference value; and assessing a state of an epilepsy disease or a body system of the patient based on the comparison. A computer readable program storage device encoded with instructions that, when executed by a computer, perform the method described above is also provided. A medical device system capable of implementing the method described above is also provided.
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
Device transferring method, and device arraying method and image display unit fabricating method using the same
InactiveUS6872635B2Efficiently and accurately transferringEfficiently re-arrayDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesIrradiationMaterials science
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
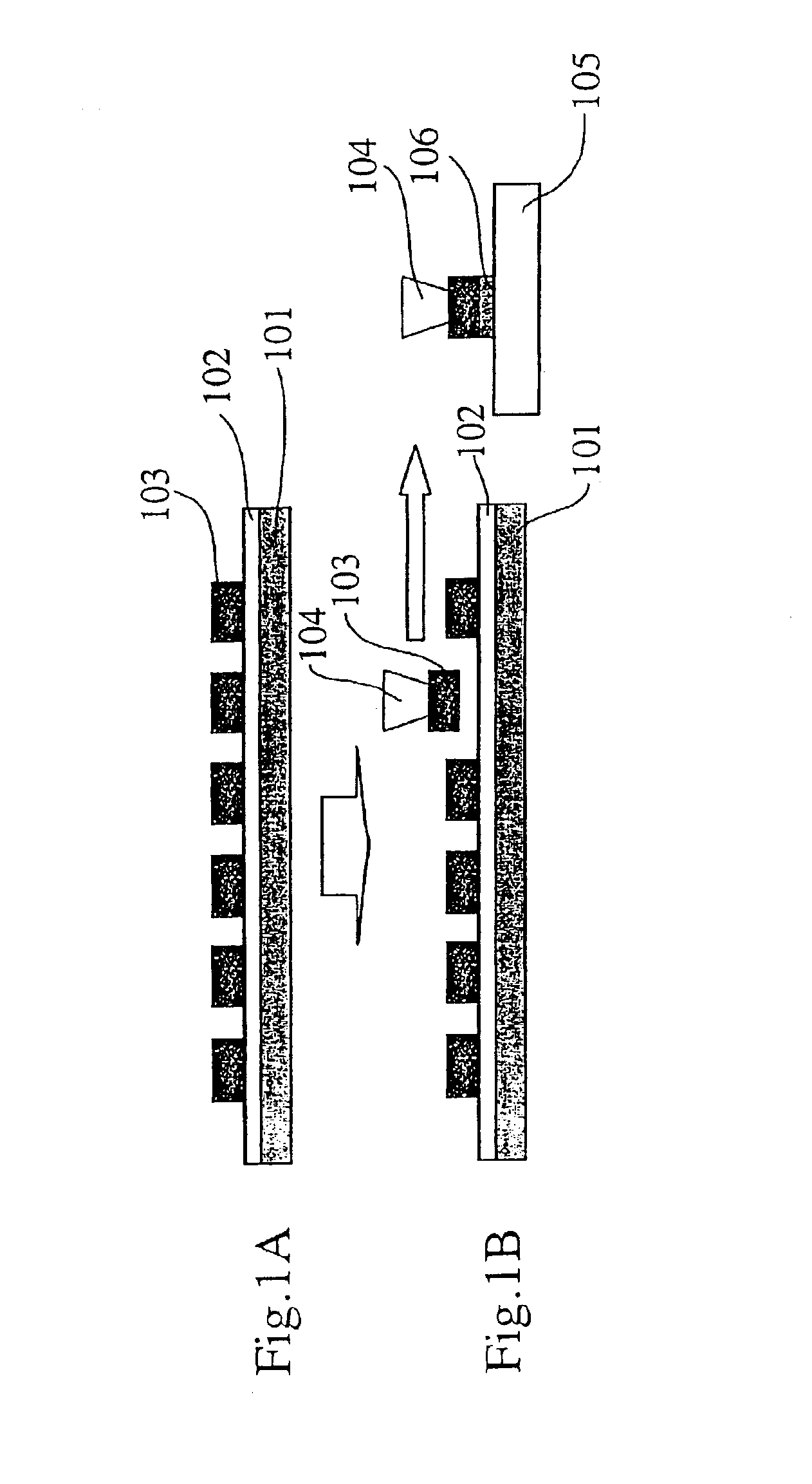
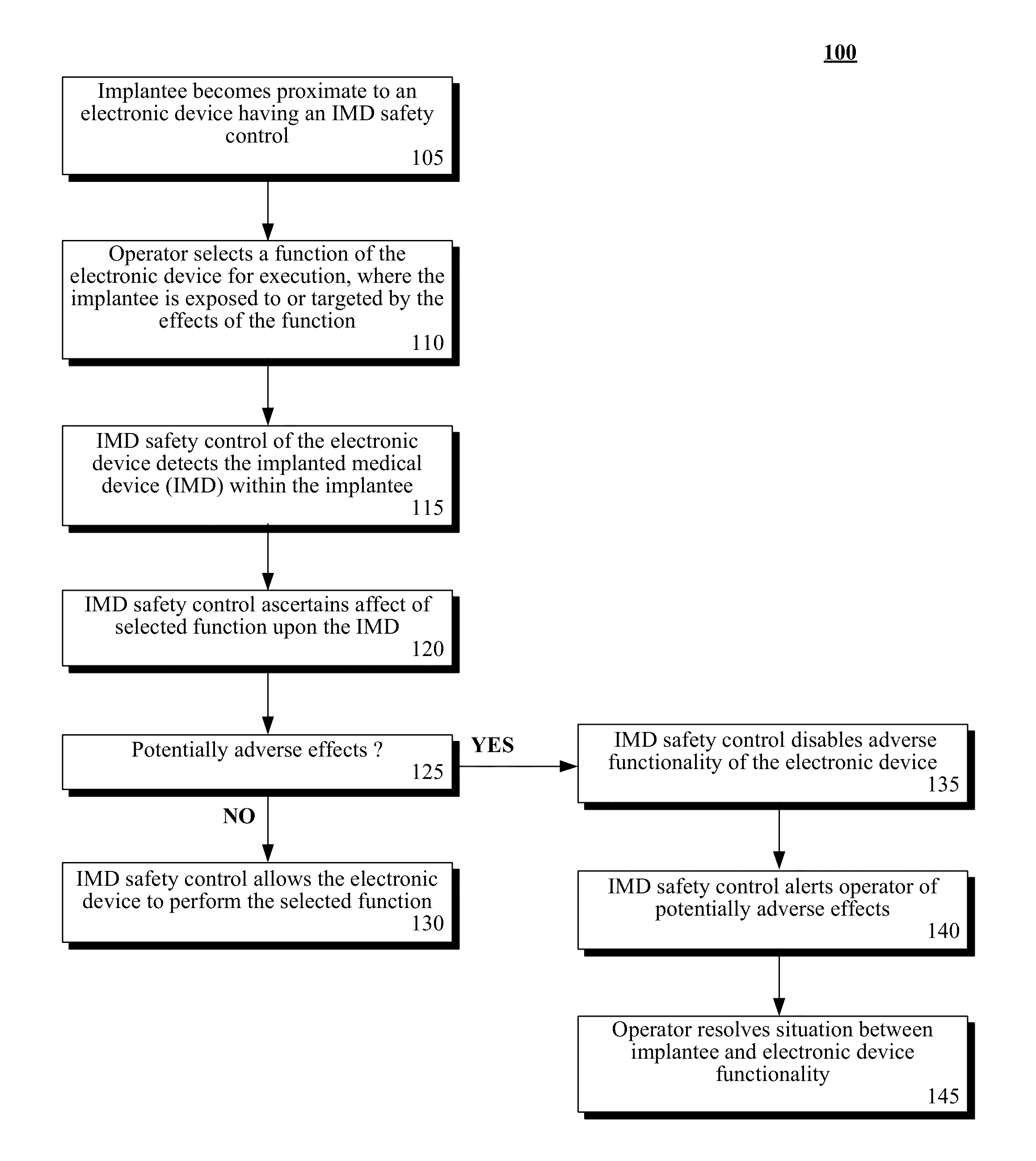
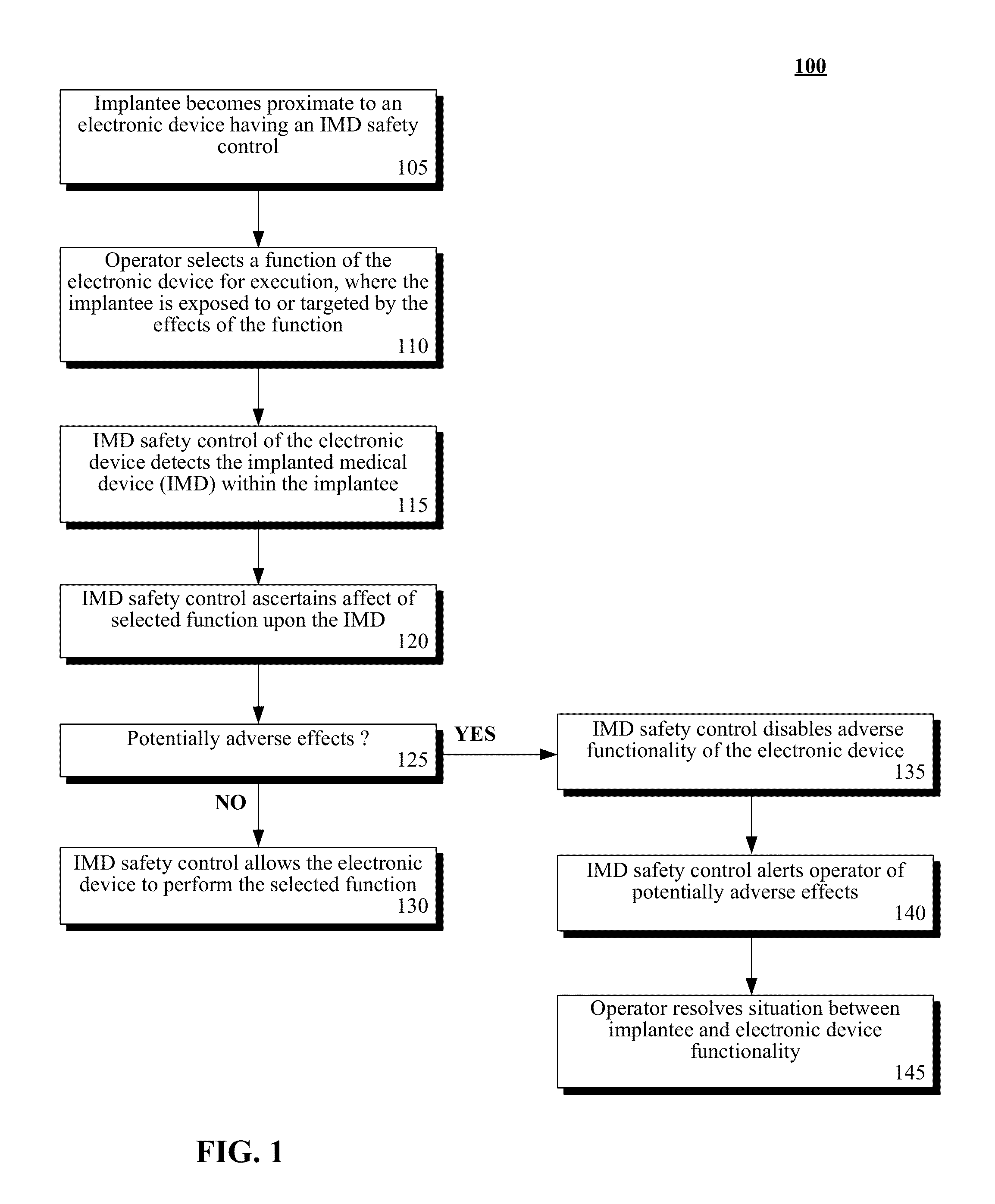
Safety feature to disable an electronic device when a wireless implantable medical device (IMD) is proximate
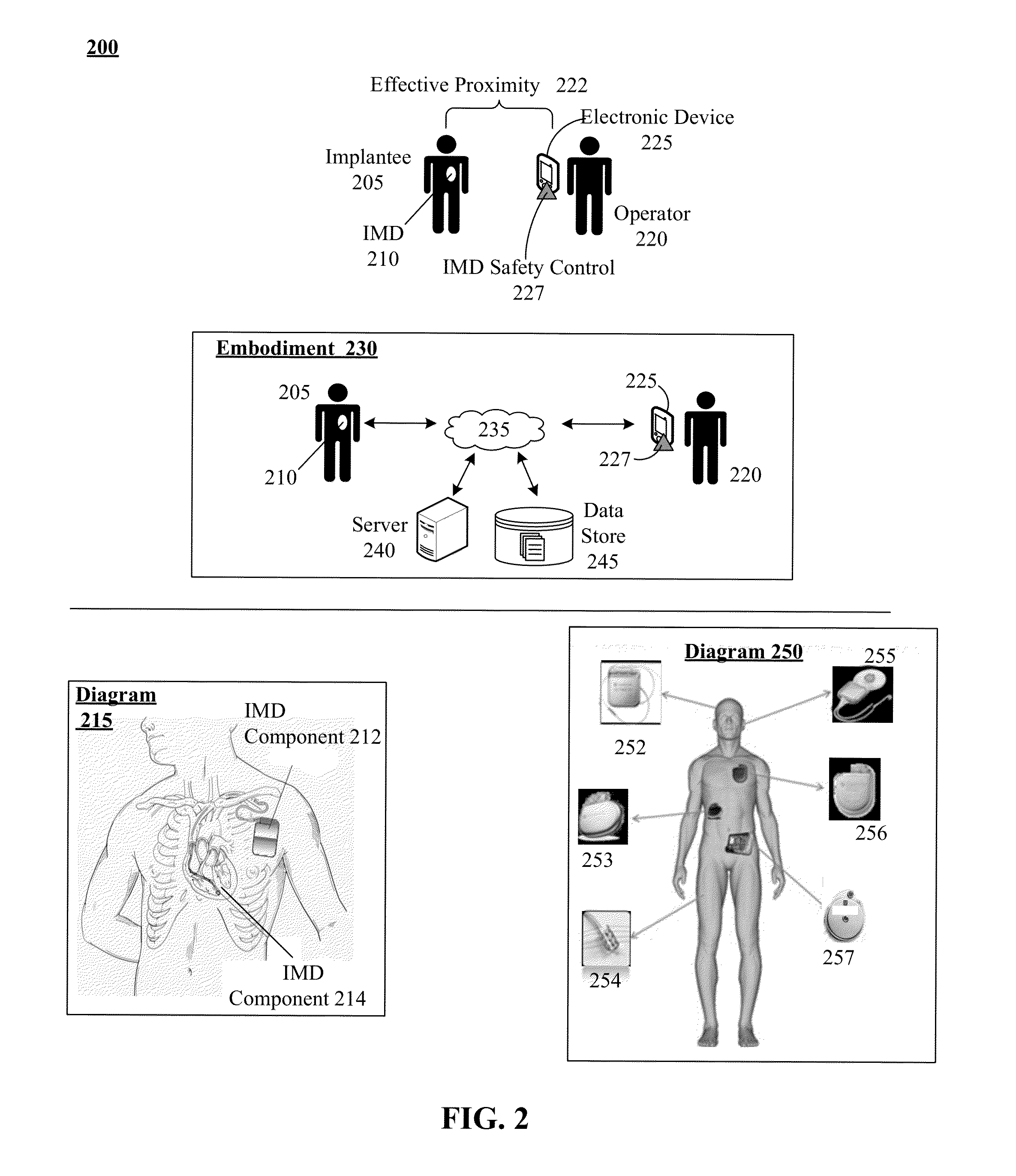
InactiveUS8761717B1Improve performanceInterfere with their operationElectrotherapyTelephonic communicationProximateImage resolution
An implanted medical device can be detected within an effective proximity of an electronic device by an IMD safety control module coupled with the electronic device, in response to the performance of a function by the electronic device. Performance of the function by the electronic device can be known to have the potential to cause adverse effects to operation of and / or a treatment provided by the implanted medical device within the effective proximity. The implanted medical device can be an active implanted medical device having wireless communication capabilities. Performance of the function by the electronic device can be disabled. Resolution from an operator of the electronic device can be requested. Upon receipt of the resolution, performance of the function by the electronic device can be enabled.
Owner:BUCHHEIT BRIAN K
System and method for reducing excitability of dorsal root fiber by introducing stochastic background noise
ActiveUS20110009923A1Reduce adverse effectsReduce excitabilityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationBackground noiseAdverse effect
A method and neurostimulator for providing therapy to a patient is provided. In one technique, electrical background energy is conveyed to a first tissue region of the patient in accordance with stochastic parameter, thereby modulating the excitability of the first tissue region, and electrical stimulation energy is conveyed to the first tissue region when its excitability is modulated. In one example, the stimulation energy may be conveyed to a second tissue region of the patient, thereby therapeutically stimulating the second tissue region. In this case, the excitability of the first tissue region is decreased, thereby reducing any adverse effect that the conveyed stimulation energy has on the first tissue region. As another example, the conveyed stimulation energy stimulates the first tissue region, in which case, the excitability of the first tissue region may be increased, thereby enhancing the stimulation of the first tissue region by the conveyed stimulation energy.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Systems approach to comorbidity assessment
Methods, systems, and apparatus for assessing a state of a comorbidity associated with a primary disease are provided. The methods comprise receiving at least one autonomic index, neurologic index, stress marker index, psychiatric index, endocrine index, adverse effect of therapy index, physical fitness index, or quality of life index of a patient; comparing the at least one index to at least one reference value; and assessing a state of a body system of the patient that is a site of the comorbidity, based on the comparison. A computer readable program storage device encoded with instructions that, when executed by a computer, perform the method described above is also provided. A medical device system capable of implementing the method described above is also provided.
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
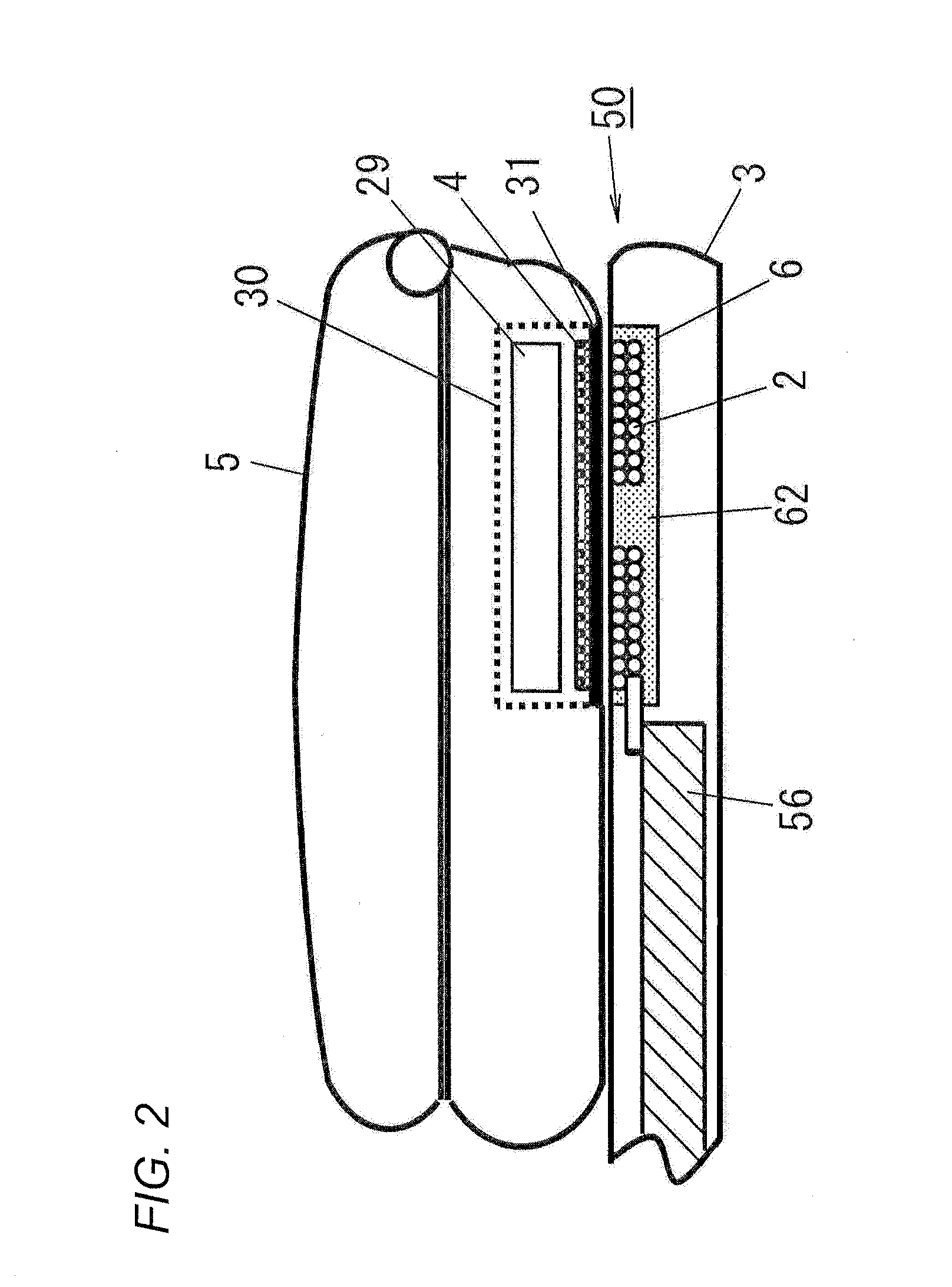
Pulse oximetry sensor and technique for using the same on a distal region of a patient's digit
ActiveUS20060224058A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOxygen Saturation MeasurementDistal portion
A sensor may be placed on a distal portion of a patient's finger or toe to obtain pulse oximetry measurements. The distal portion of a digit contains few if any large vascular structures that could adversely affect pulse oximetry measurements, but the distal portion does contain microvasculature that carries arterial blood that facilitates pulse oximetry measurements. The sensor may include an emitter and a detector that are spaced apart by an appropriate distance so that they may be located on the distal portion of a patient's digit during pulse oximetry measurements.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Drospirenone for hormone replacement therapy
InactiveUS20020132801A1Dissolve fastImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDrospirenoneBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Drospirenone for Hormone Replacement Therapy A pharmaceutical composition comprising as a first active ingredient an estrogen, such as estradiol or estradiol valerate, in sufficient amounts to treat disorders and symptoms associated with deficient endogenous levels of estrogen in women, and as a second active ingredient 6beta,7beta; 15beta; 16beta-dimethylene-3-oxo-17alpha-preg-4-ene-21,17-carbolactone (drospirenone, DRSP) in sufficient amounts to protect the endometrium from the adverse effects of estrogen is useful for, amongst others, treating peri-menopausal, menopausal and post-menopausal women. This composition may be used for hormone replacement therapy and may be administered as a multi-phased pharmaceutical preparation. This combination therapy may comprise continuous, sequential or interrupted administration, or combinations thereof, of DRSP and estrogen, each optionally in micronized form.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Droplet-based cell culture and cell assays using digital microfluidics
ActiveUS20090203063A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssay3D cell culture
We introduce a new method for implementing cell-based assays and long-term cell culture. The method is based on digital microfluidics (DMF) which is used to actuate nanoliter droplets of reagents and cells on a planar array of electrodes. DMF method is sutable for assaying and culturing both cells in suspension and cells grown on surface (adherent cells). This method is advantageous for cell culture and assays due to the automated manipulation of multiple reagents in addition to reduced reagent use and analysis time. No adverse effects of actuation by DMF were observed in assays for cell viability, proliferation, and biochemistry. These results suggest that DMF has great potential as a simple yet versatile analytical tool for implementing cell-based assays and cell culture on the microscale.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
Sensing system and method for motion-controlled foot unit
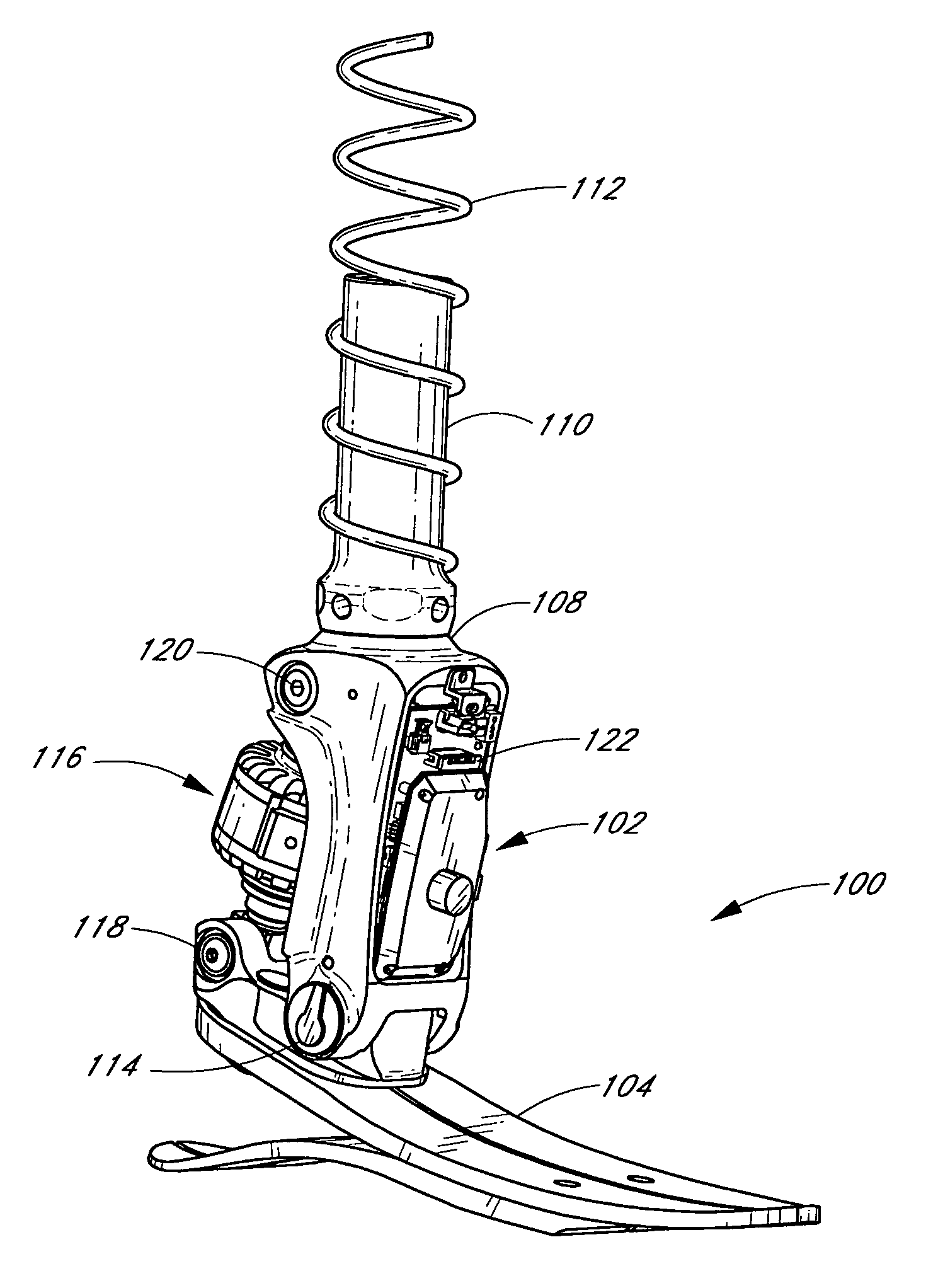
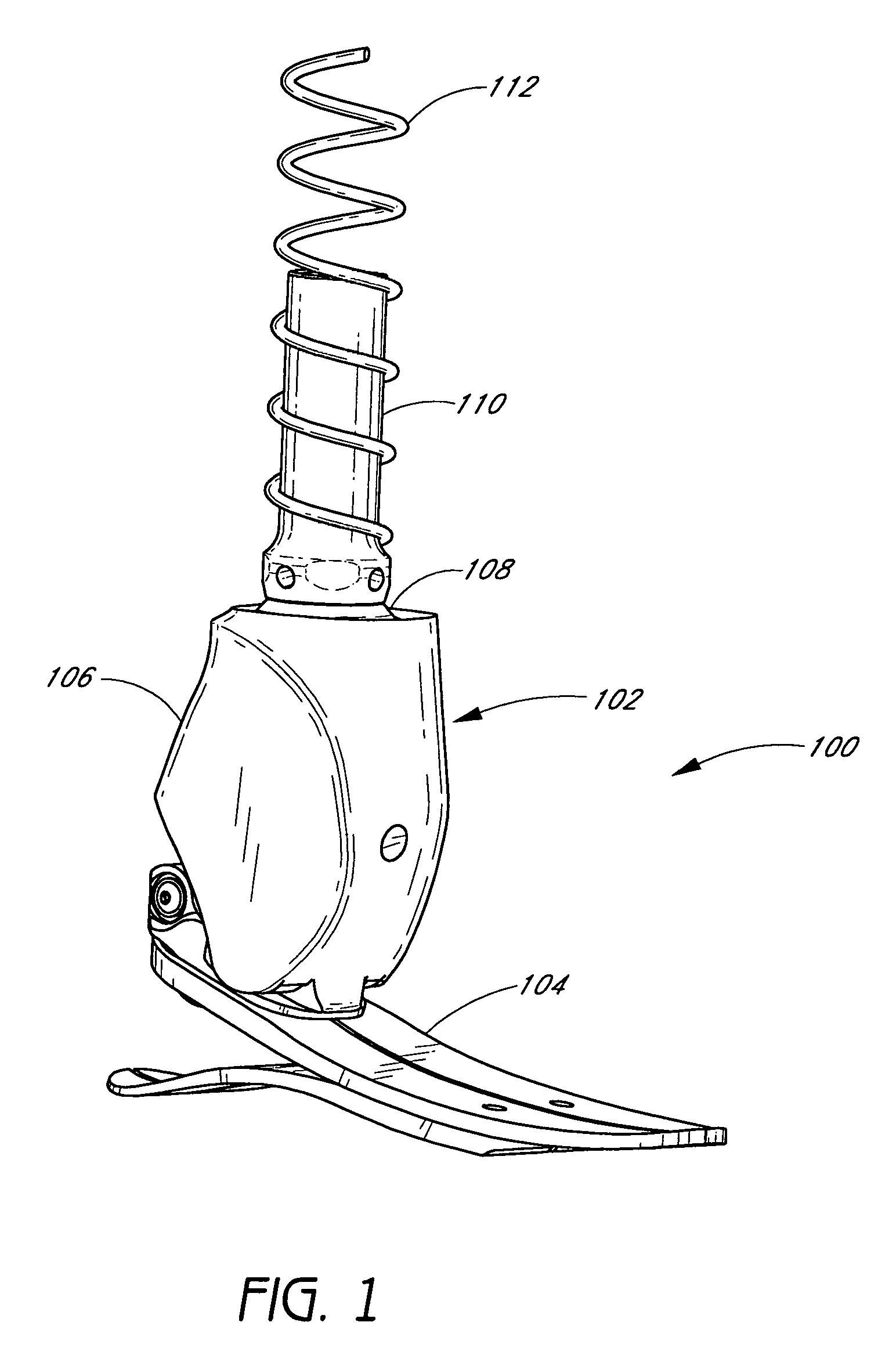
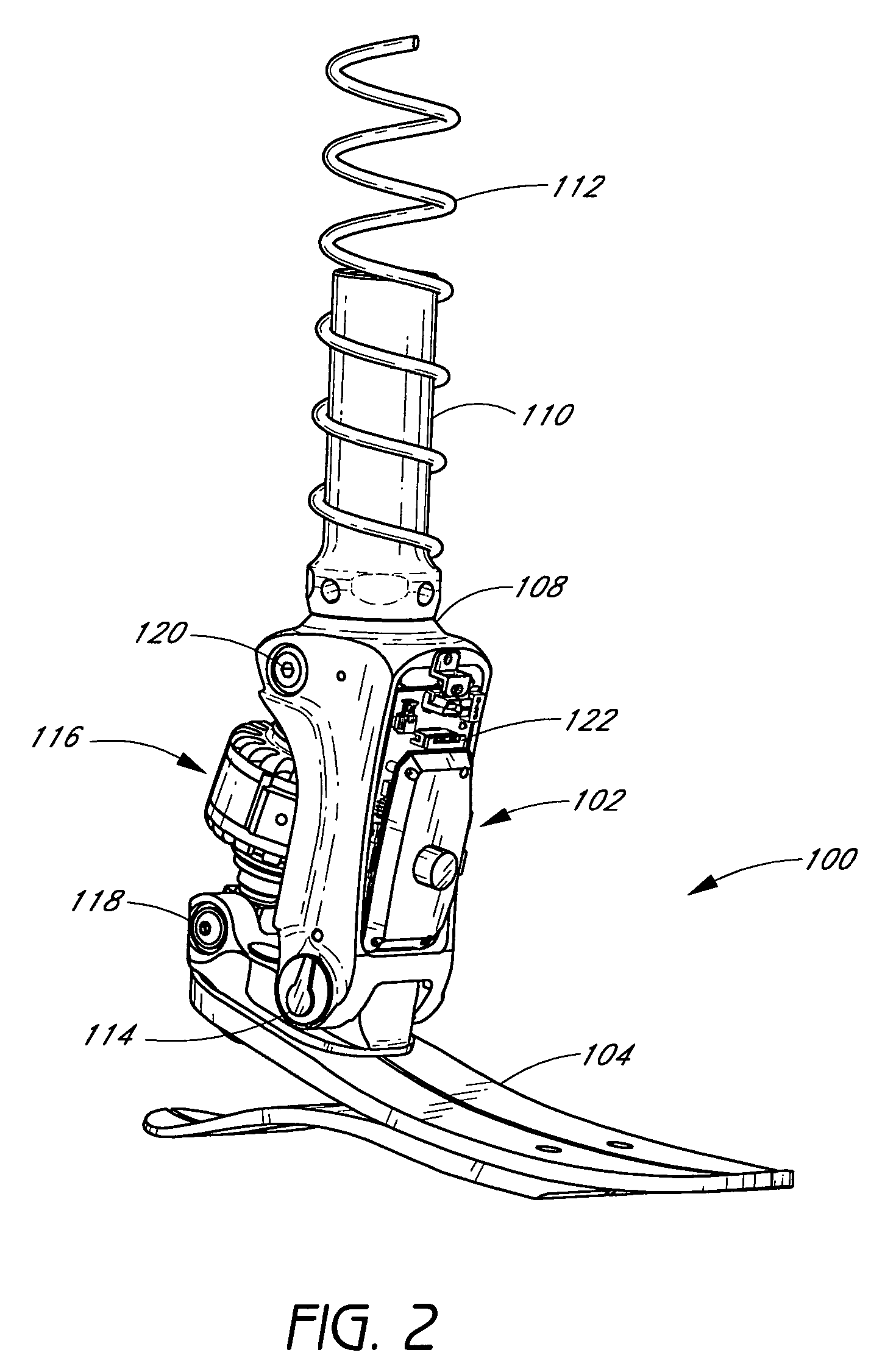
ActiveUS7531006B2Enhanced couplingNon-surgical orthopedic devicesArtificial legsAxial forceEngineering
A system and method for sensing movement of a device associated with a limb. In one example, a prosthetic or orthotic system includes a sensor assembly configured to measure movement of a component of the system in a single direction while substantially isolating negative effects of forces and / or loads in other directions. For instance, the sensor assembly may be advantageously coupled to a pivot assembly configured to substantially mimic a natural ankle joint. The sensor assembly may monitor rotation of a foot unit about an axis of a pivot pin of the pivot assembly and disregard other movements and / or forces. For example, the sensor assembly may include a potentiometer that detects rotation of an associated elongated bellow portion about the axis, wherein the bellow portion includes a plurality of ridges configured to substantially eliminate effects of radial and / or axial forces.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Material storage and dispensing packages and methods
InactiveUS20090212071A1Solve the lack of spaceInhibit productionPower operated devicesShock-sensitive articlesEngineeringParticle generation
Packages and methods for storage and dispensing of materials, e.g., high purity liquid reagents and chemical mechanical polishing compositions used in the manufacture of microelectronic device products, including containment structures and methods adapted for pressure-dispensing of high-purity liquids. Liner packaging of liquid or liquid-containing media is described, in which zero or near-zero head space conformations are employed to minimize adverse effects of particle generation, formation of bubbles and degradation of contained material.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Pharmaceutical formulations of potassium ATP channel openers and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060051418A1Enhanced drug releaseReduces food uptakeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPotassium channel openerPotassium
Provided are immediate or prolonged administration of certain potassium ATP (KATP) channel openers to a subject to achieve novel pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic, therapeutic, physiological, metabolic and compositional outcomes in the treatment of diseases or conditions involving KATP channels. Also provided are pharmaceutical formulations, methods of administration and dosing of KATP channel openers that achieve these outcomes and reduce the incidence of adverse effects in treated individuals. Further provided are method of co-administering KATP channel openers with other drugs to treat diseases of humans and animals.
Owner:ESSENTIALIS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com