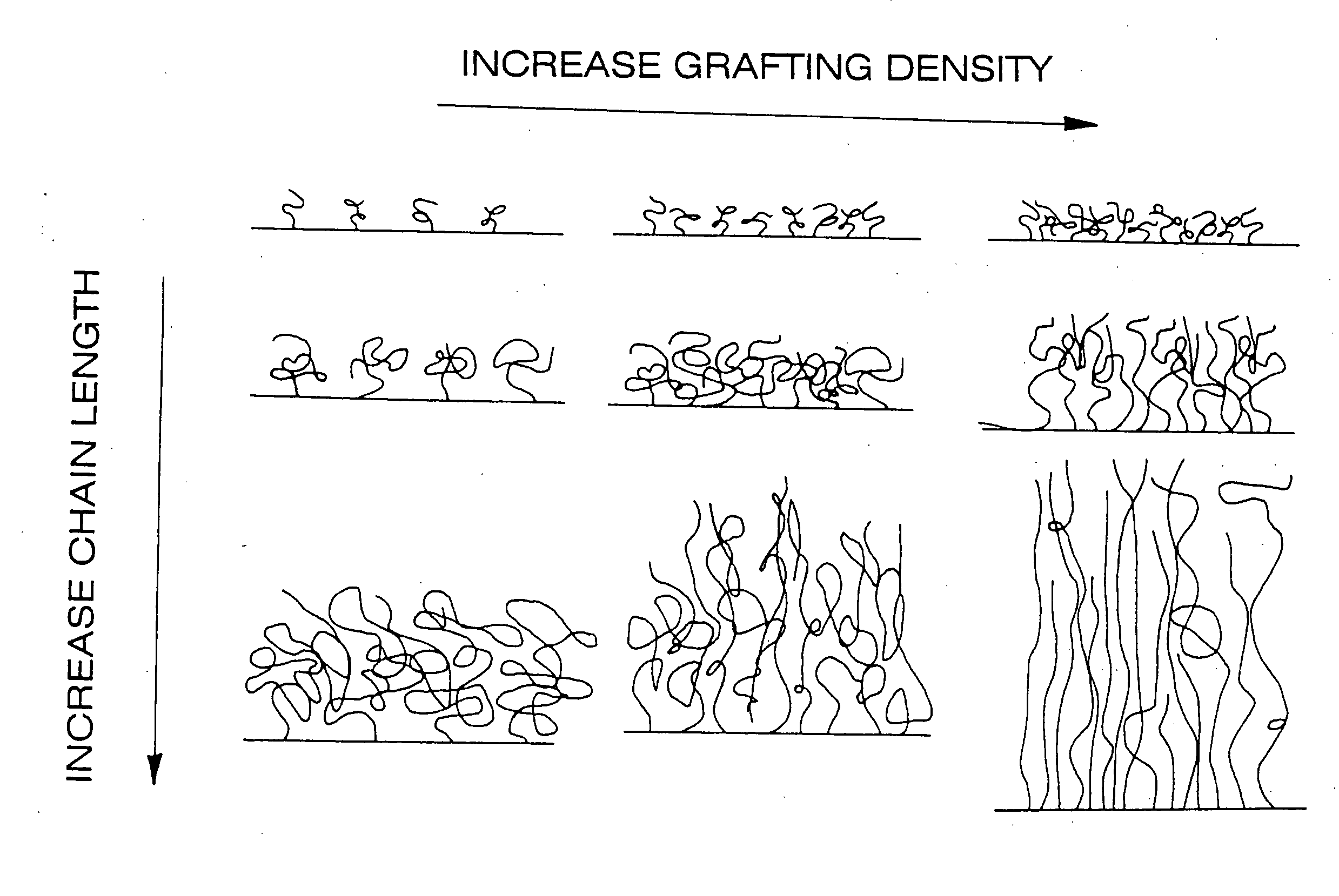
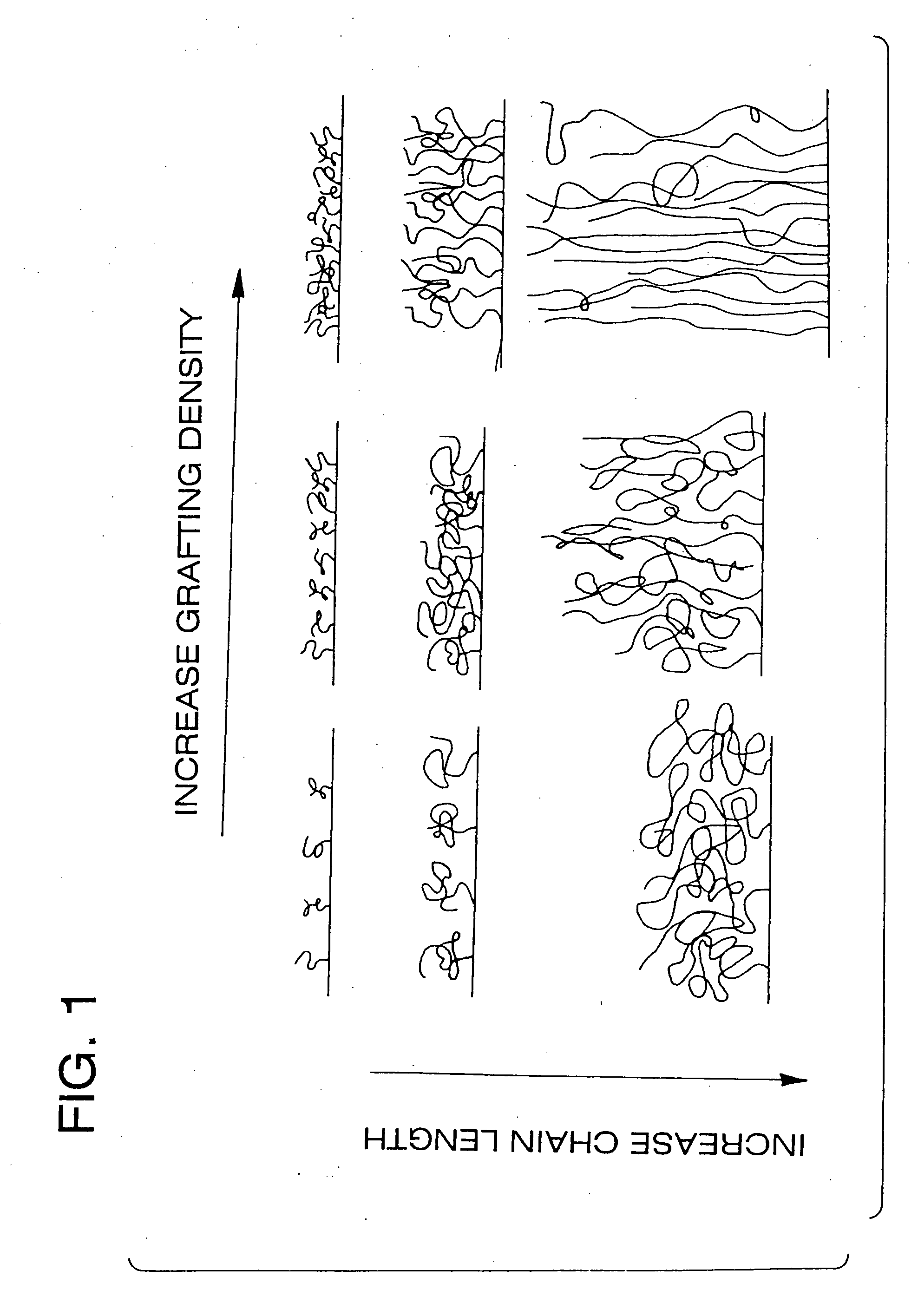
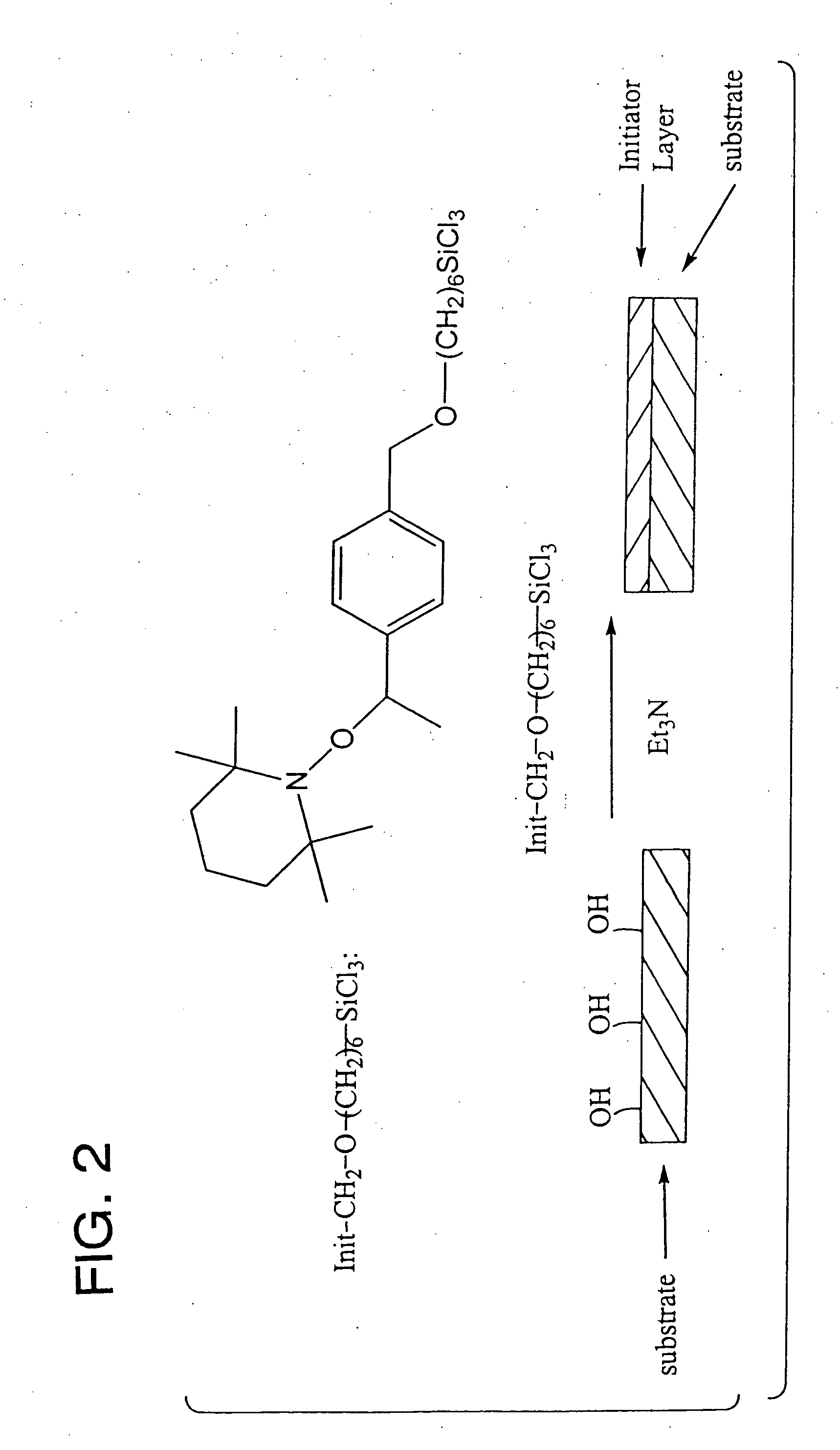
Polymer brushes for immobilizing molecules to a surface and having water-soluble or water-dispersible segments therein and probes bonded thereto
a technology of polymer brushes and probes, which is applied in the field of polymer brushes, can solve the problems of affecting the accessibility of biological molecules, difficult to attach probe molecules to surfaces, and impede so as to optimize the accessibility of probes of a given size or type, the effect of optimizing the attachment of probe molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0185] The following example illustrates one approach for the preparation of a monomer suitable for use in the present invention for polymer brush preparation.
I. Synthesis of N-Methyl,N-(2-hydroxyethyl)acrylamide
A. Synthesis of N-Methyl,N-2-(1-Trimethylsiloxy)ethylacrylamide
[0186]
[0187] An ovendried 4 L three-necked flask equipped with an overhead mechanical stirrer, a 250 mL dropping funnel and an adapter to an argon line was charged under an atmosphere of argon with 113 g (1.5 mol, 121 mL) 2-(methylamino)ethanol (1), commercially available from Sigma-Aldrich, 1500 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, and 334 g (460 mL, 3.3 mol) of triethylamine. The solution was chilled to ca. 0° C. (icebath) and 171 g (1.58 mol, 200 mL) of chlorotrimethylsilane (TMSCl) were added dropwise. Upon completion of the exothermic reaction (ca. 1 h), the reaction mixture is cooled again to ca. 0° C. (icebath) and acryloyl chloride (2) (136 g, 1.5 mol, 122 mL) were added dropwise and the reaction mixture w...
example 2
[0202] This example describes the preparation of a surface-bound copolymer having a target molecular weight of 50,000 daltons and 10 mol % of N-methyl-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-acrylamide and 90 mol % N,N-dimethylacrylamide. Three fused silica wafers and one silicon wafer were used in this experiment. It was assumed that each surface contained hydroxyl functionalities typically in the picomole per square inch range. In order to add an initiator-control ageht adduct to each surface hydroxyl functionality, 5×10−4 mol of the trichlorosilyl-substituted initiator-control agent adduct was used per 2×3 in. wafer. Thus, the surface in this example is considered to have a fraction of chain initiator to the total number of reactive sites on the substrate surface of about 1.
[0203] Unbound initiator-control agent adduct (1.9 g) was dissolved in 291 mL of N,N-dimethylacrylamide, 37.9 g of N-methyl-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)acrylamide, 32 mg of α-hydridonitroxide, and 30 mL of water. The reaction vessel was se...
example 3
[0204] This example describes the preparation of a surface-bound copolymer brush having a target molecular weight of 50,000 daltons and 25 mol % incorporation of N-methyl-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)acrylamide.
[0205] Substantially following Example 2, three fused silica wafers and one silicon wafer were modified with the trichlorosilyl-substituted initiator / control agent adduct to provide a fraction of chain initiator to the total number of surface functionalities of about 1. 1.9 g of unbound initiator-control agent adduct was dissolved in 232 mL of N,N-dimethylacrylamide, 90.8 g of N-methyl-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)acrylamide, 32 mg of α-hydridonitroxide, and 30 mL of water. The reaction vessel was sealed under argon and heated at 130° C. for 48 h. After the polymerization reaction, the wafers were placed in a DMF bath and heated at 50° C. for 12 h to remove non-covalently attached polymer that was then analyzed by SEC, as described above. After washing with water and acetone, the wafers were air ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electric charge | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com