Patents
Literature
657results about How to "Suppression of short channel effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
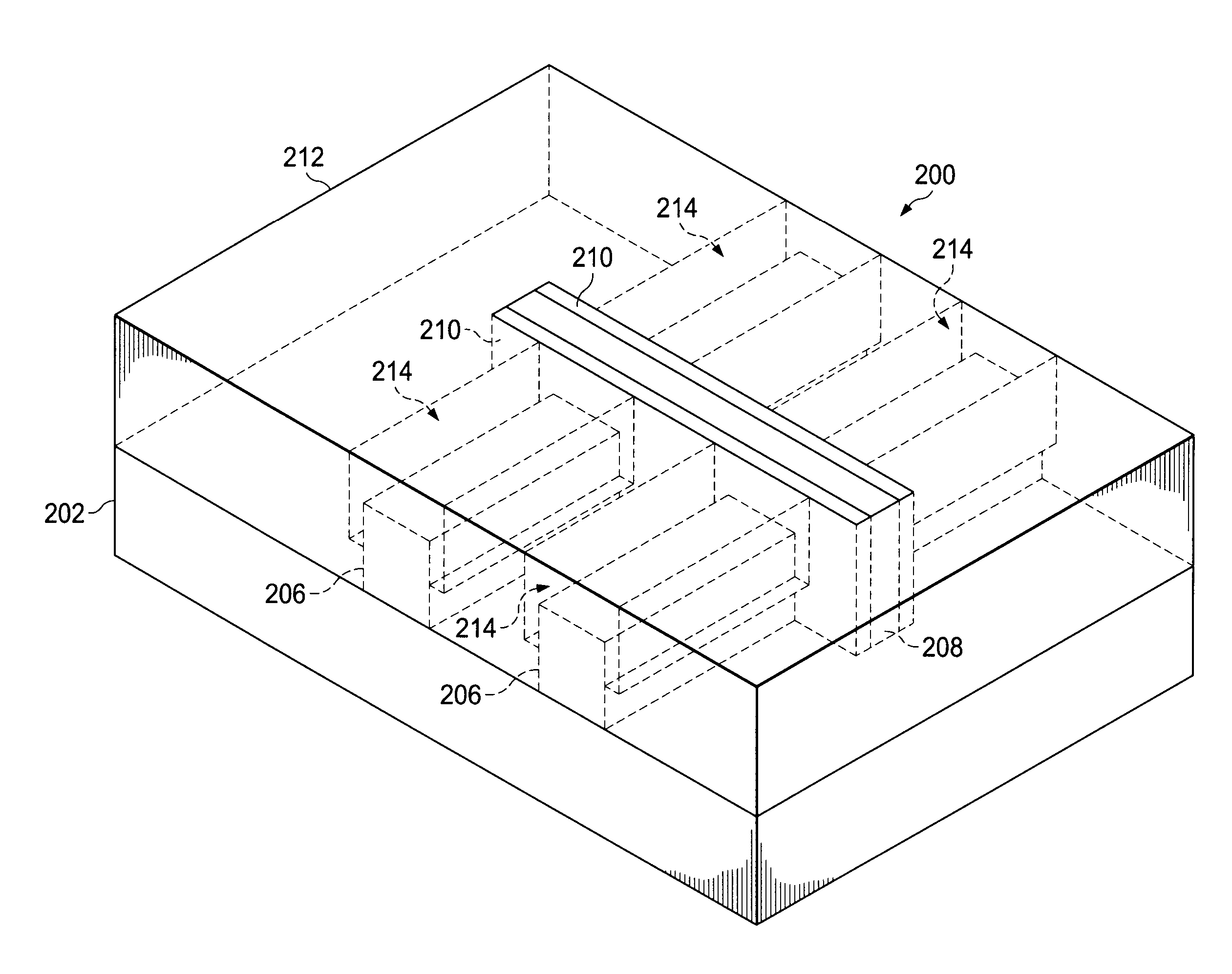
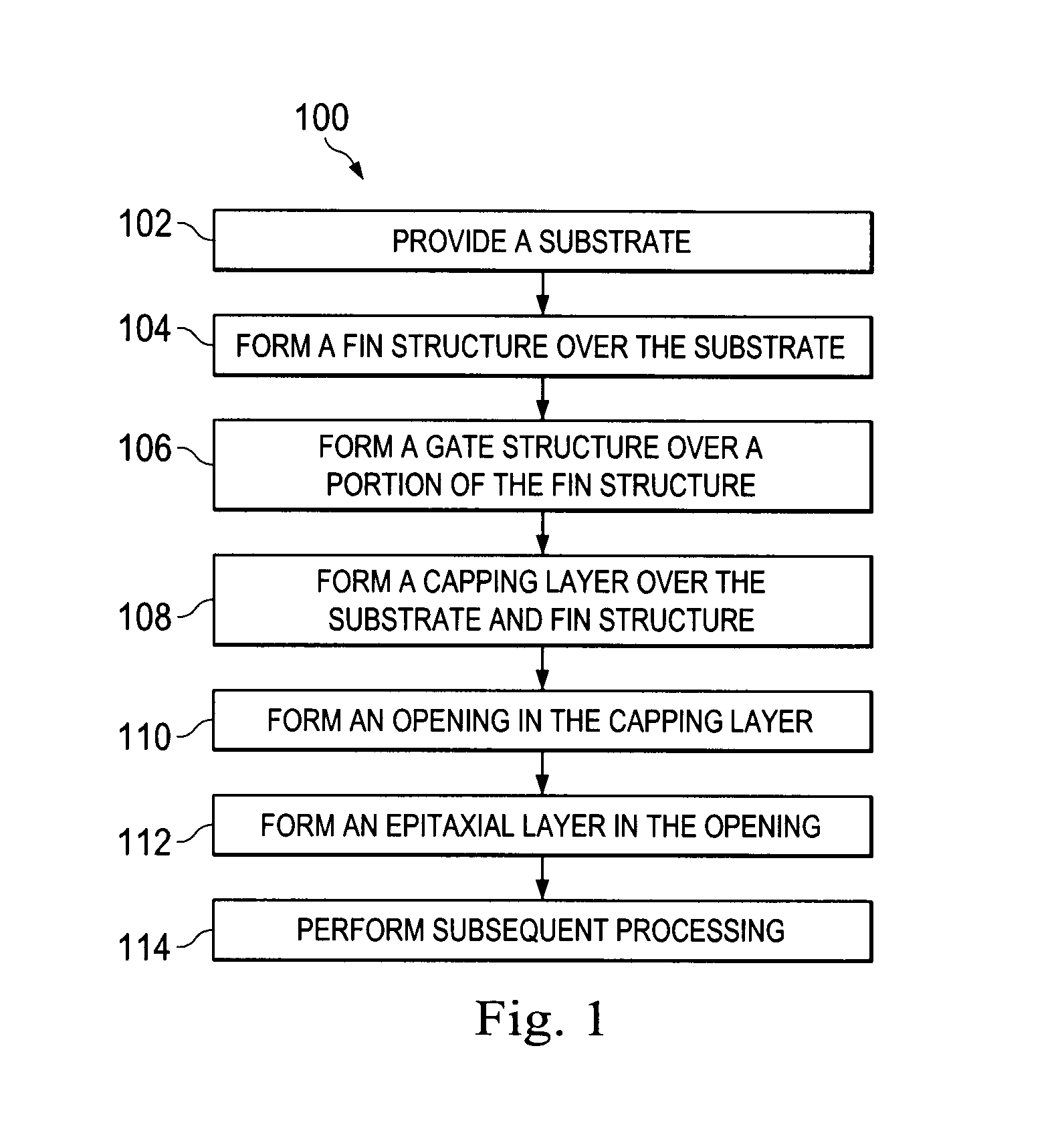
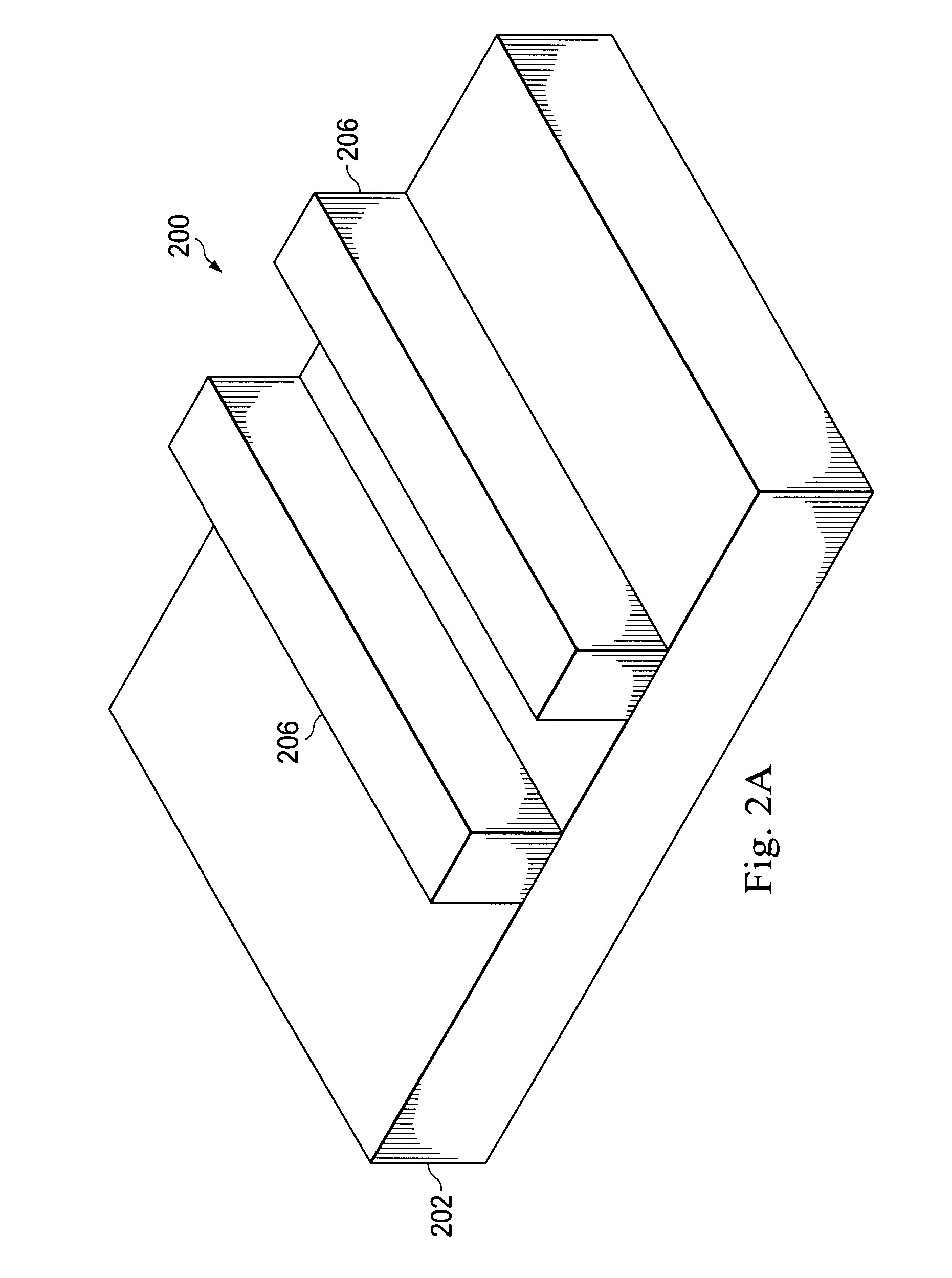
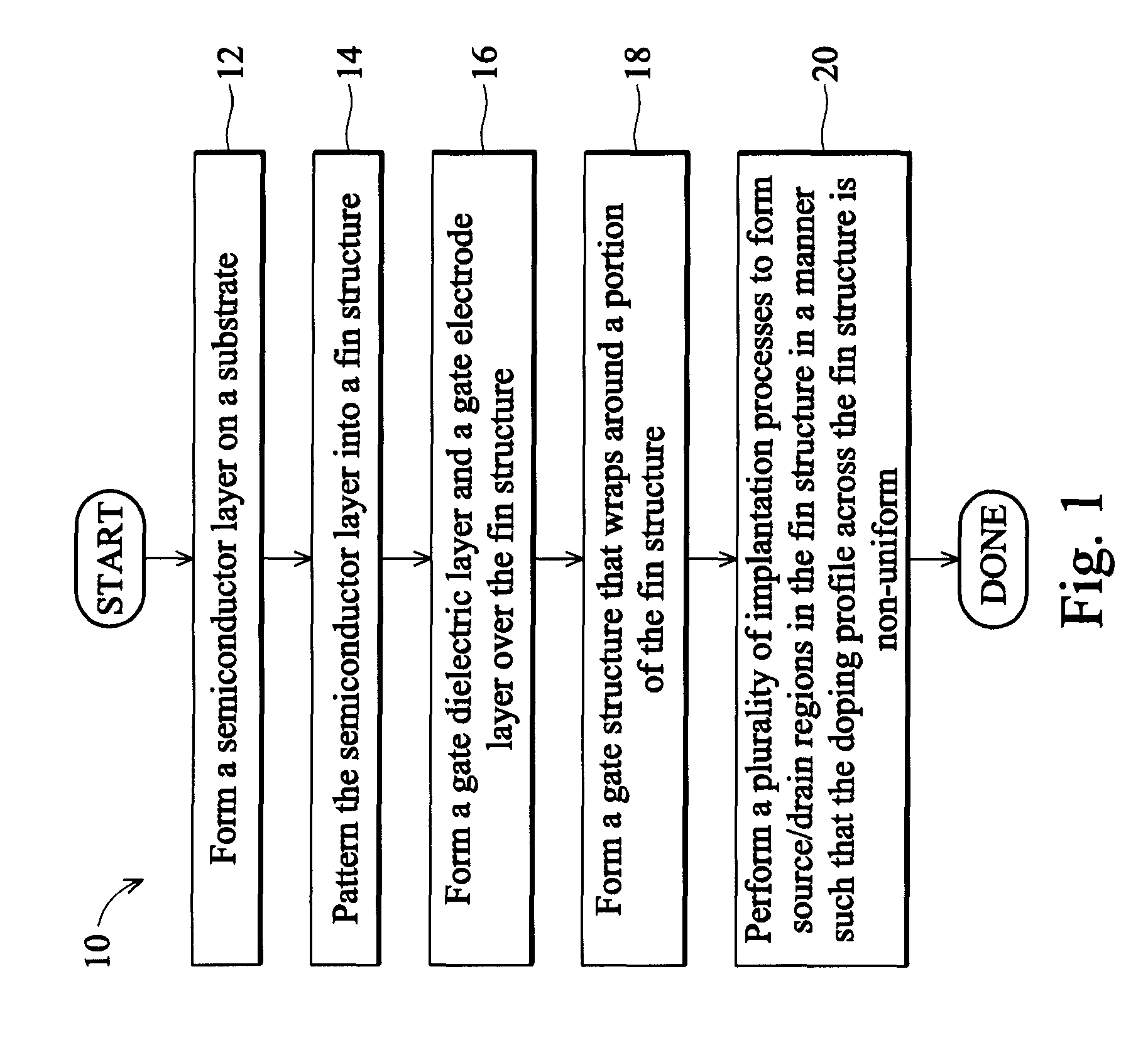
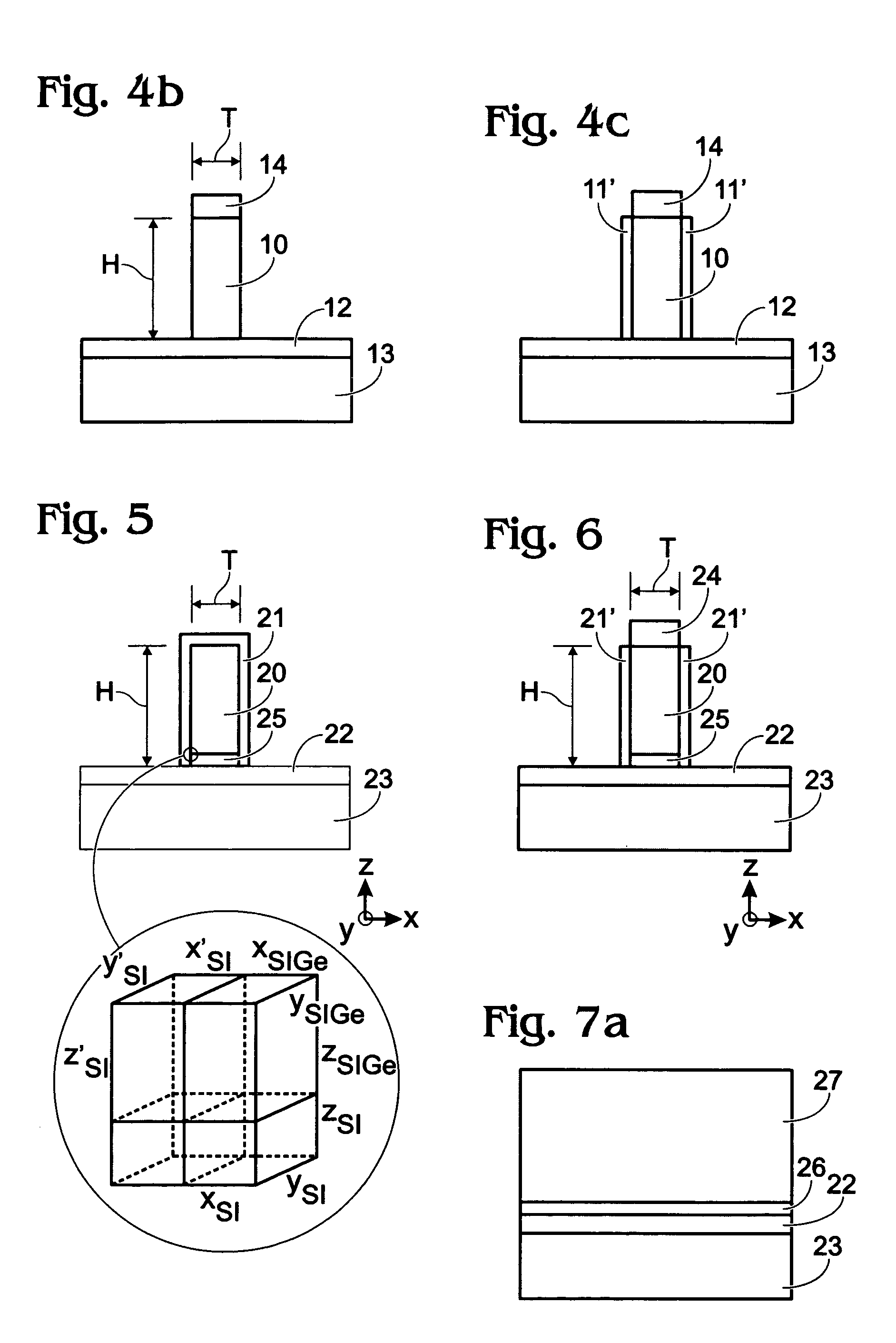
Method for fabricating a FinFET device
ActiveUS8652894B2Improve device densityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
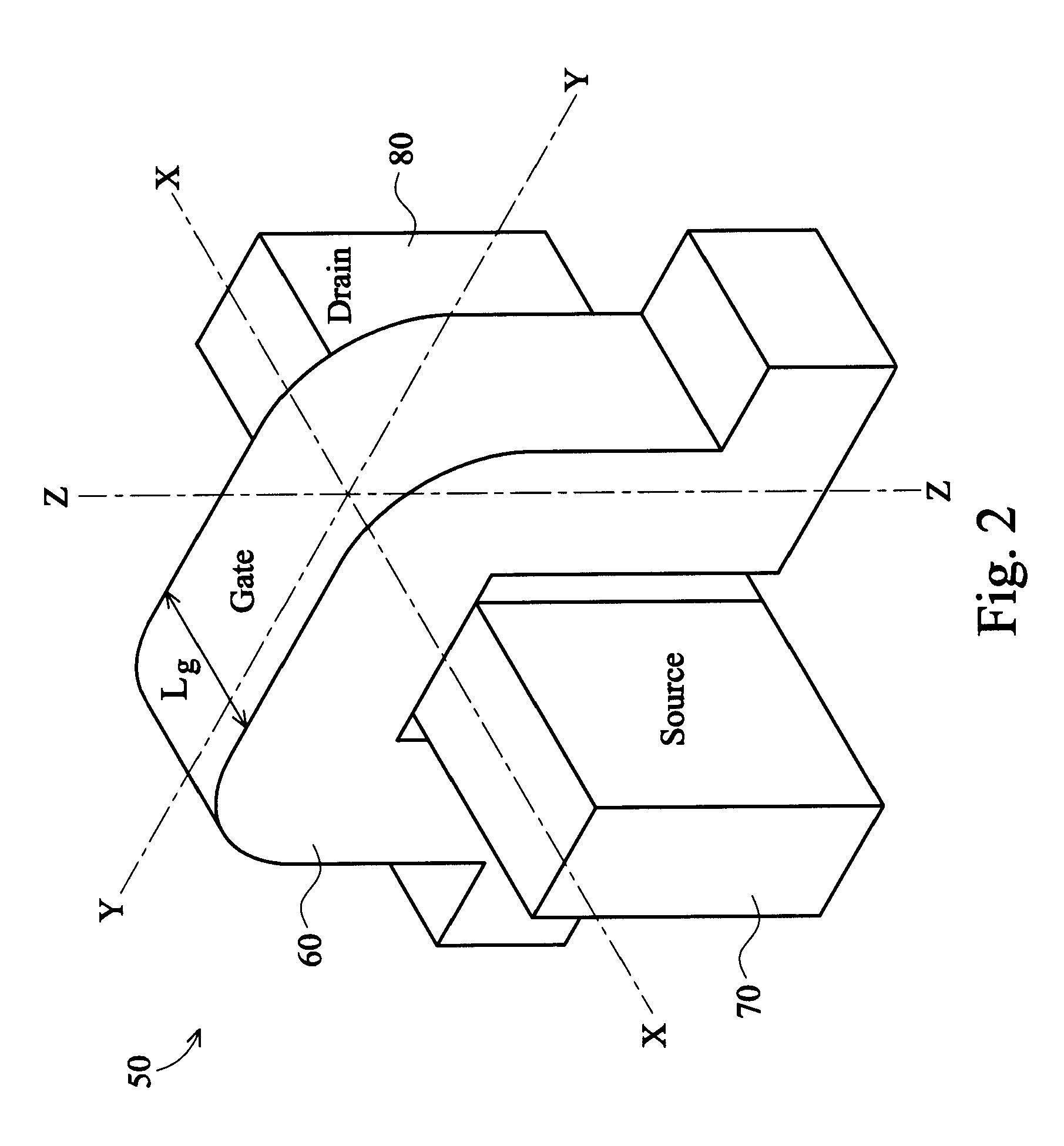
Non-uniform channel junction-less transistor
ActiveUS8487378B2Easy to controlImprove device densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSemiconductor
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Strained silicon fin structure
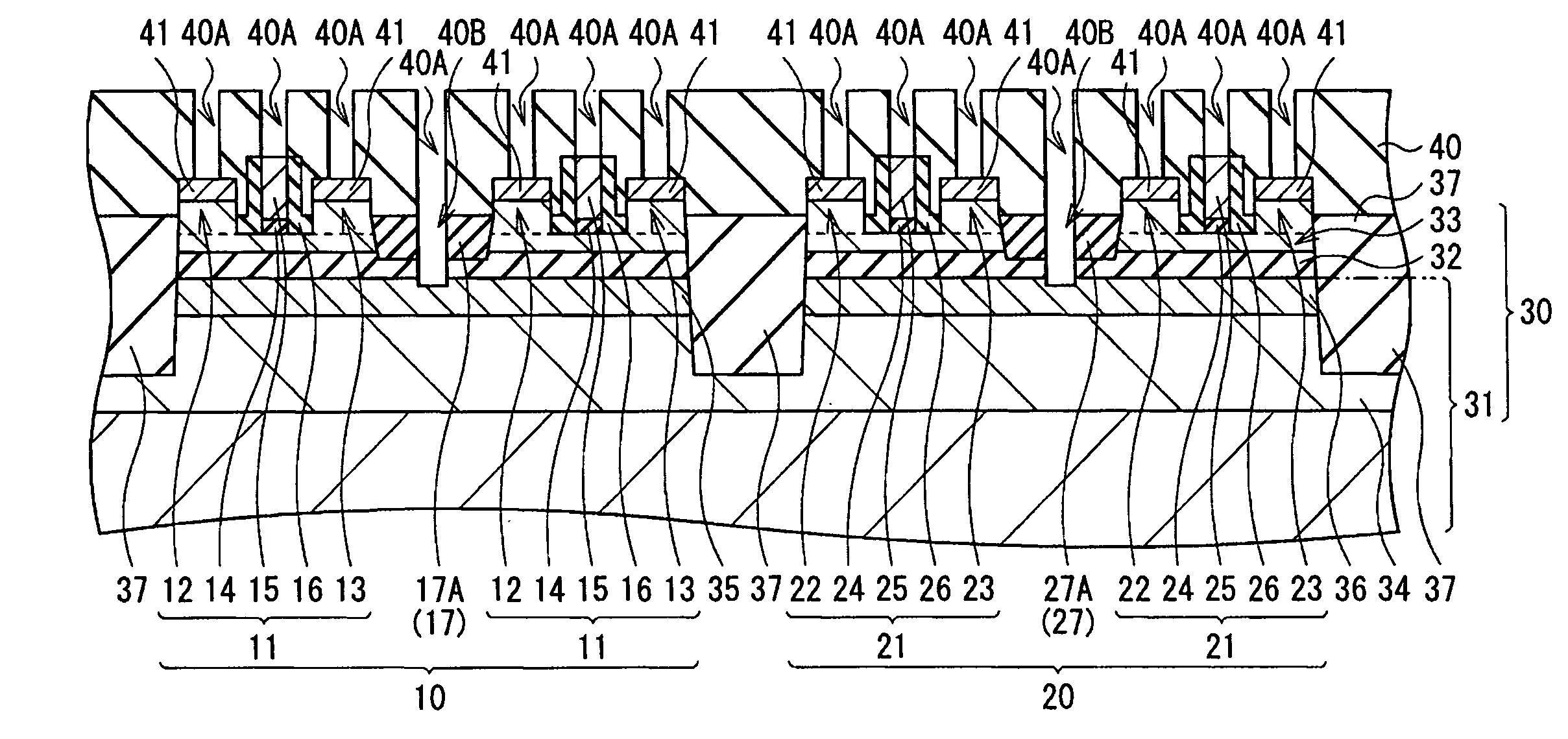
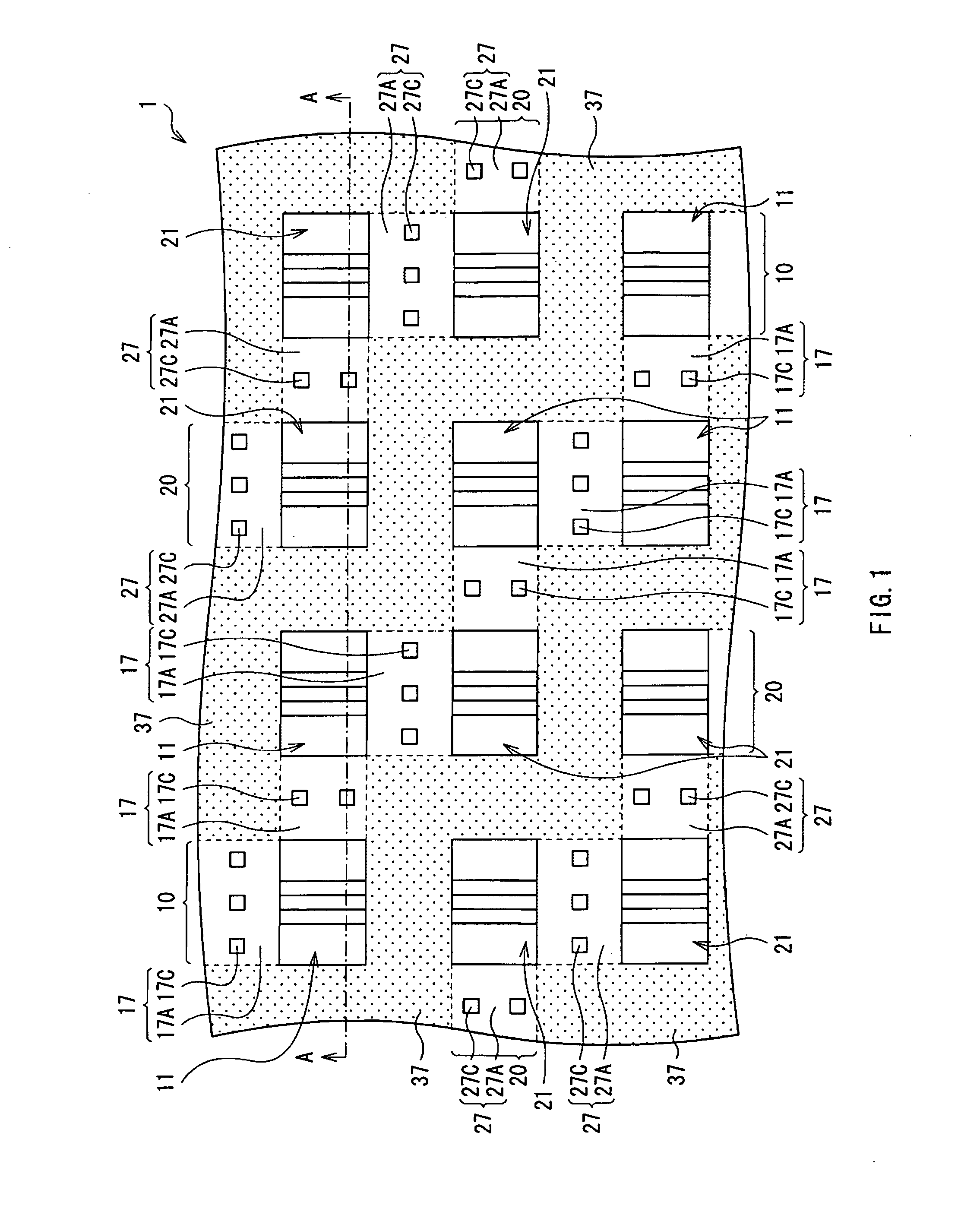
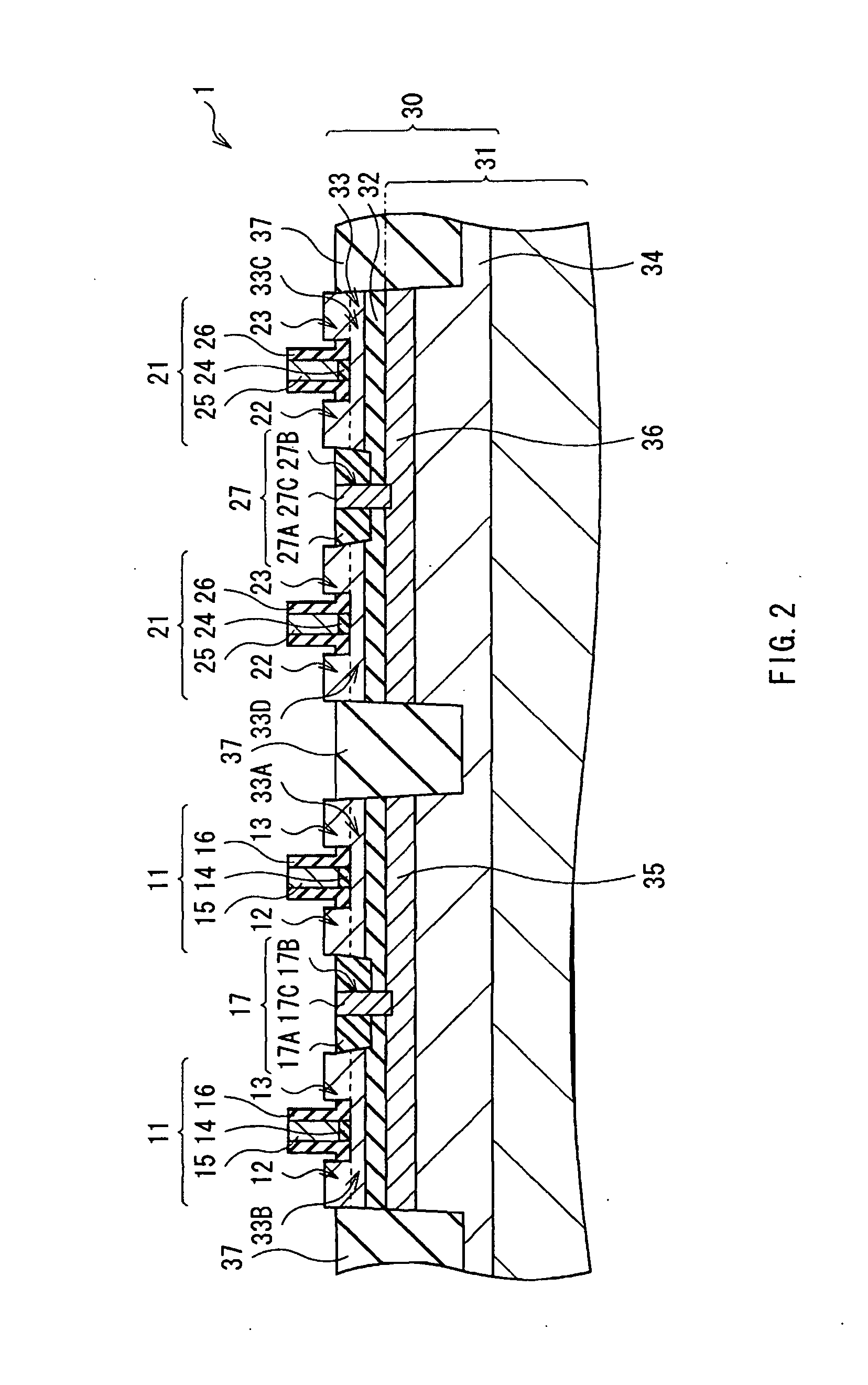
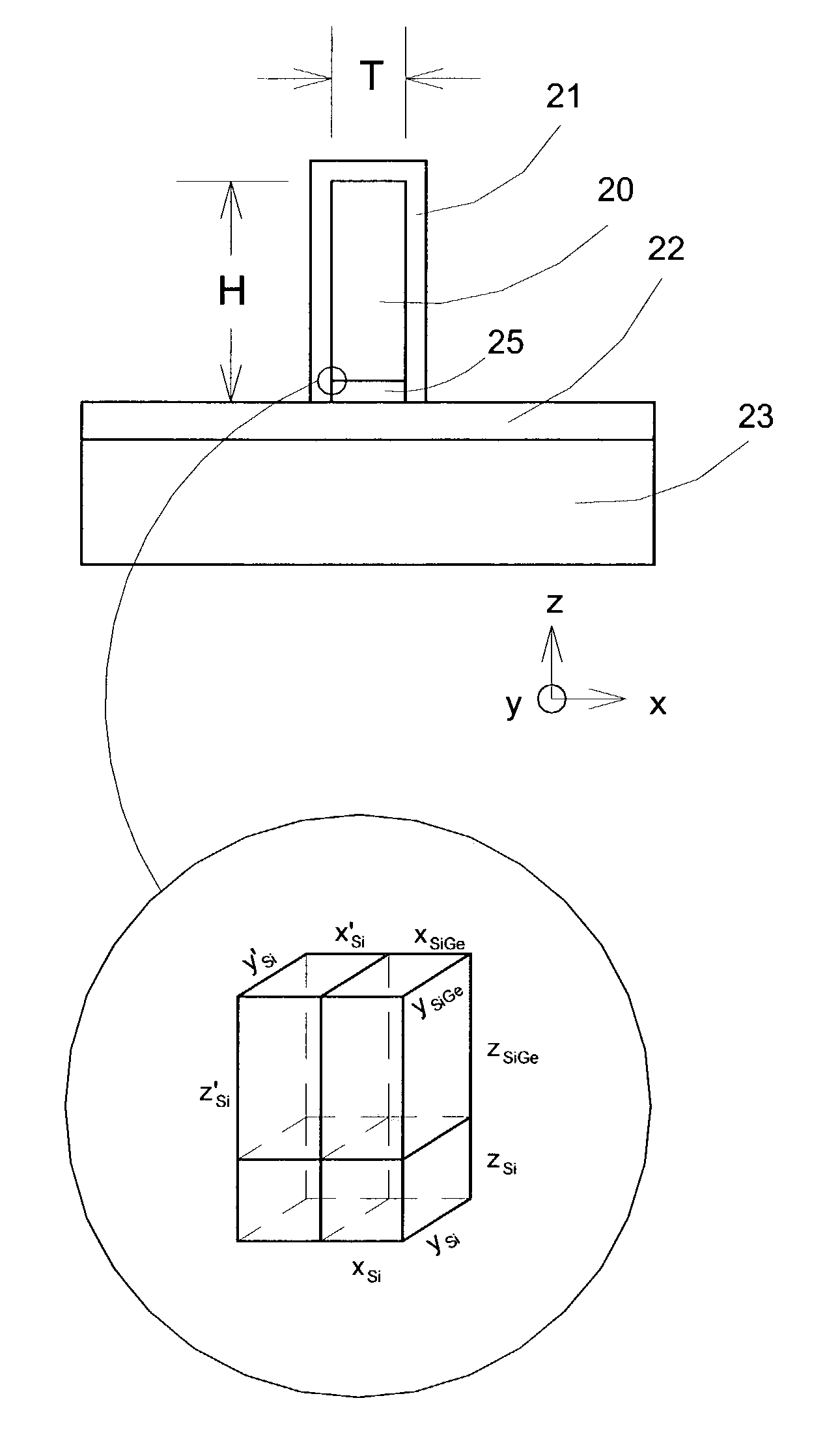
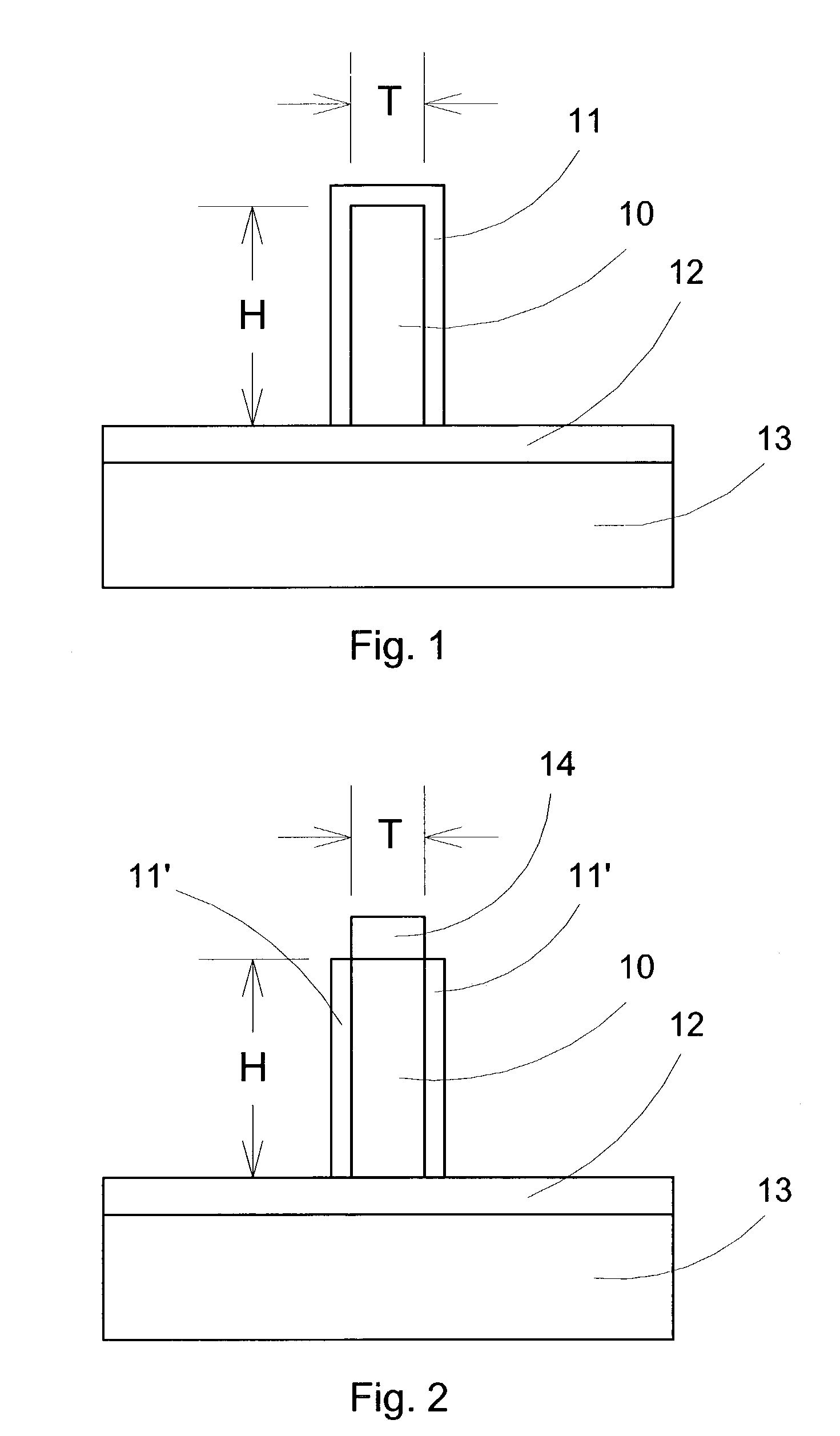
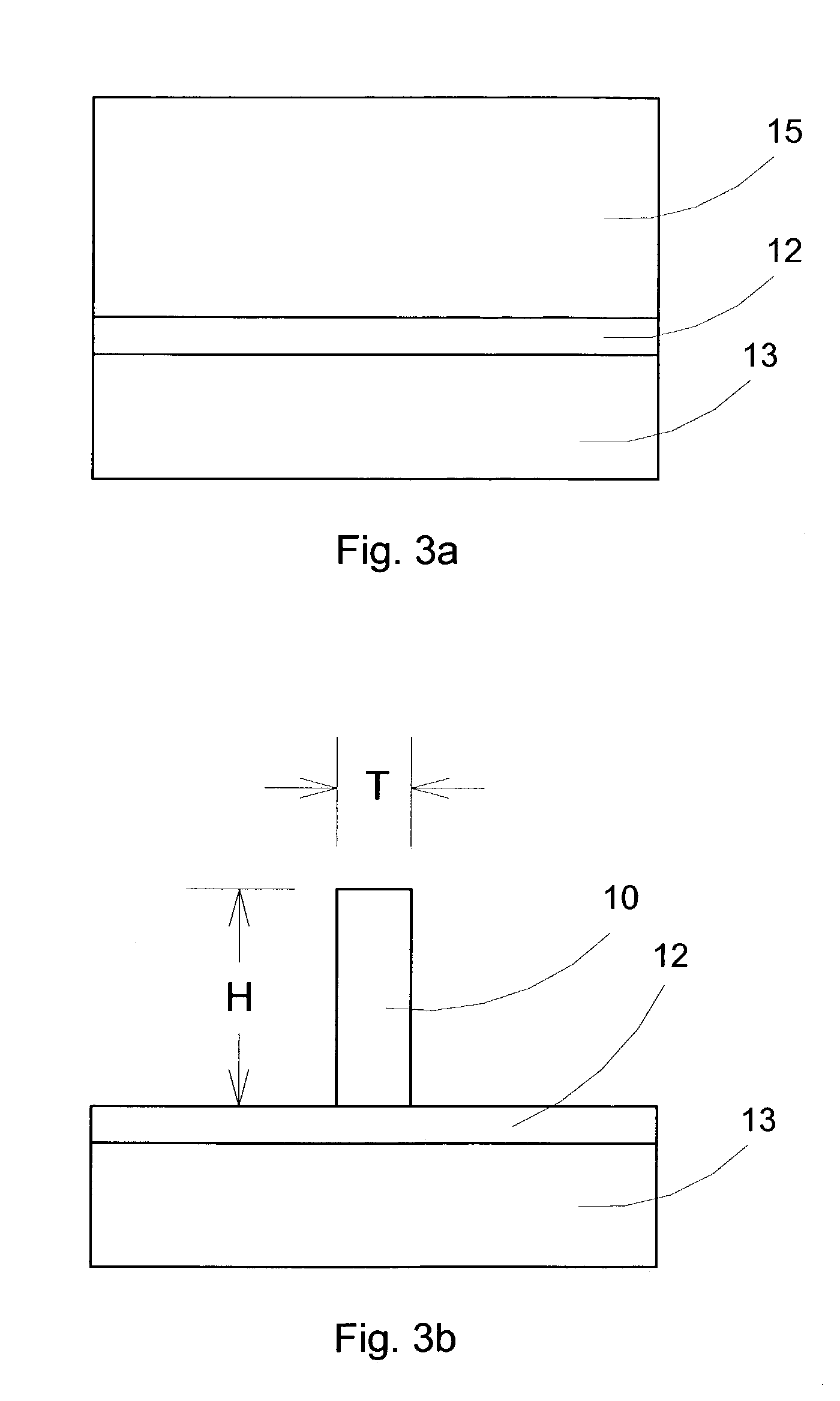
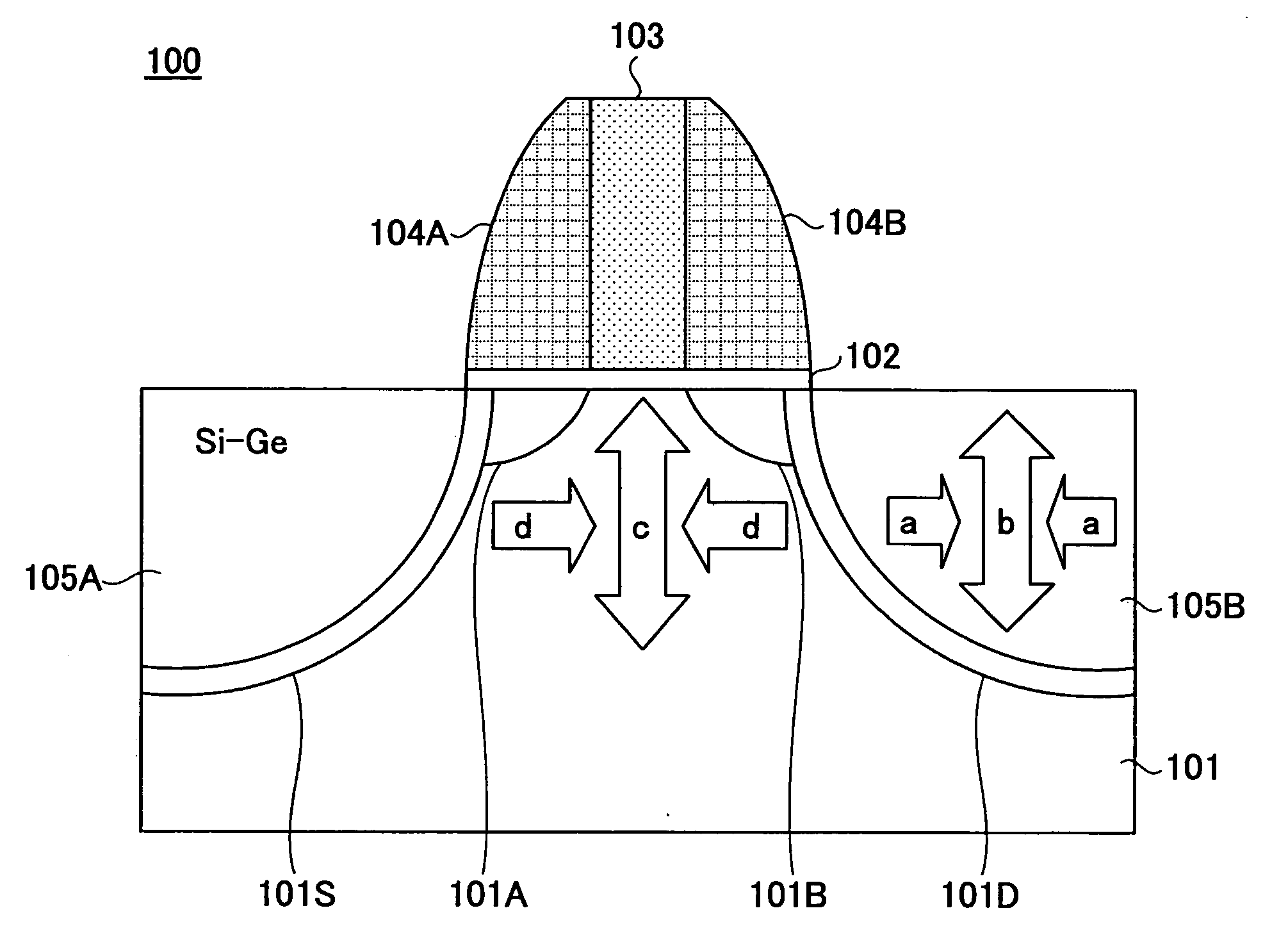
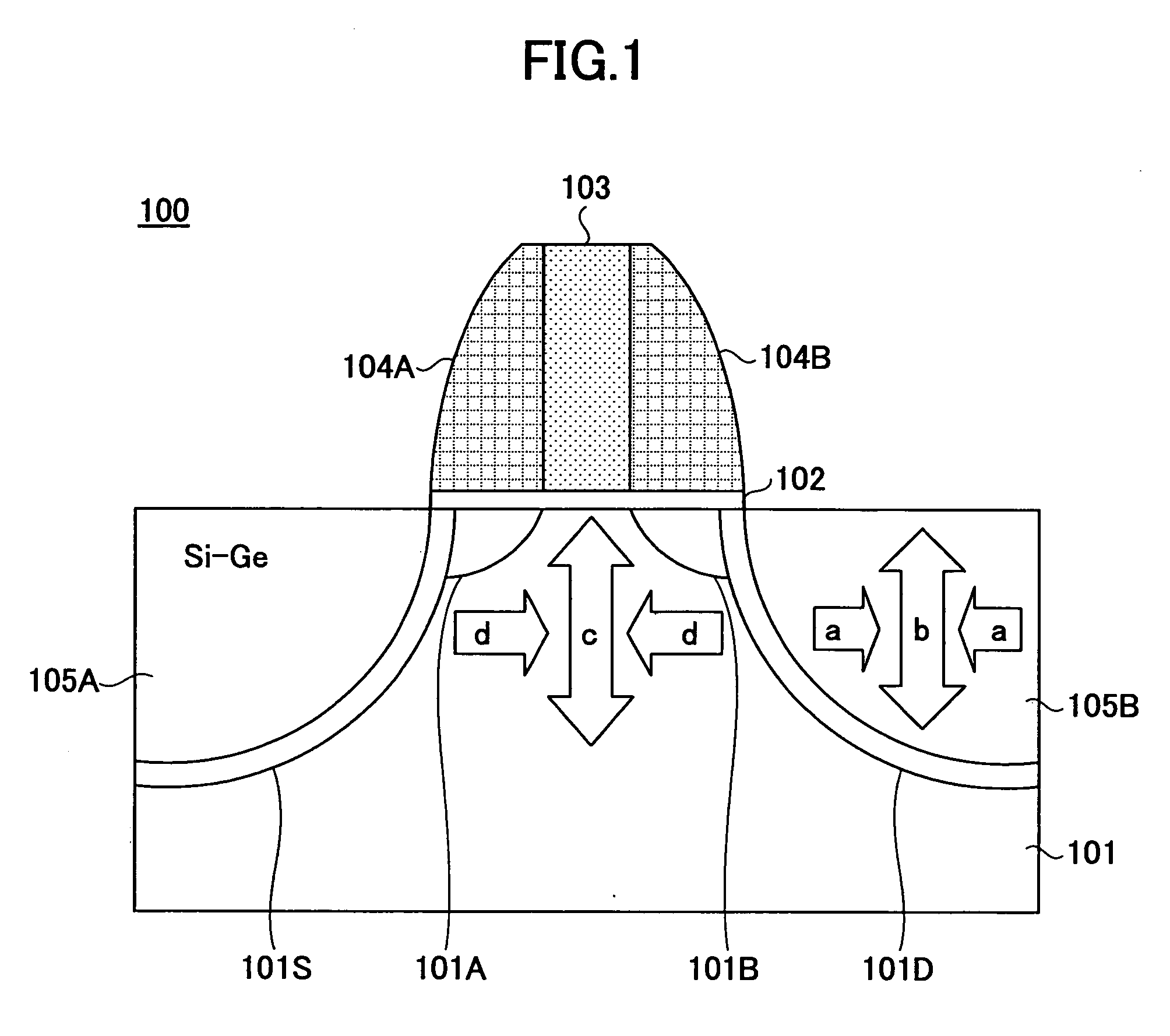
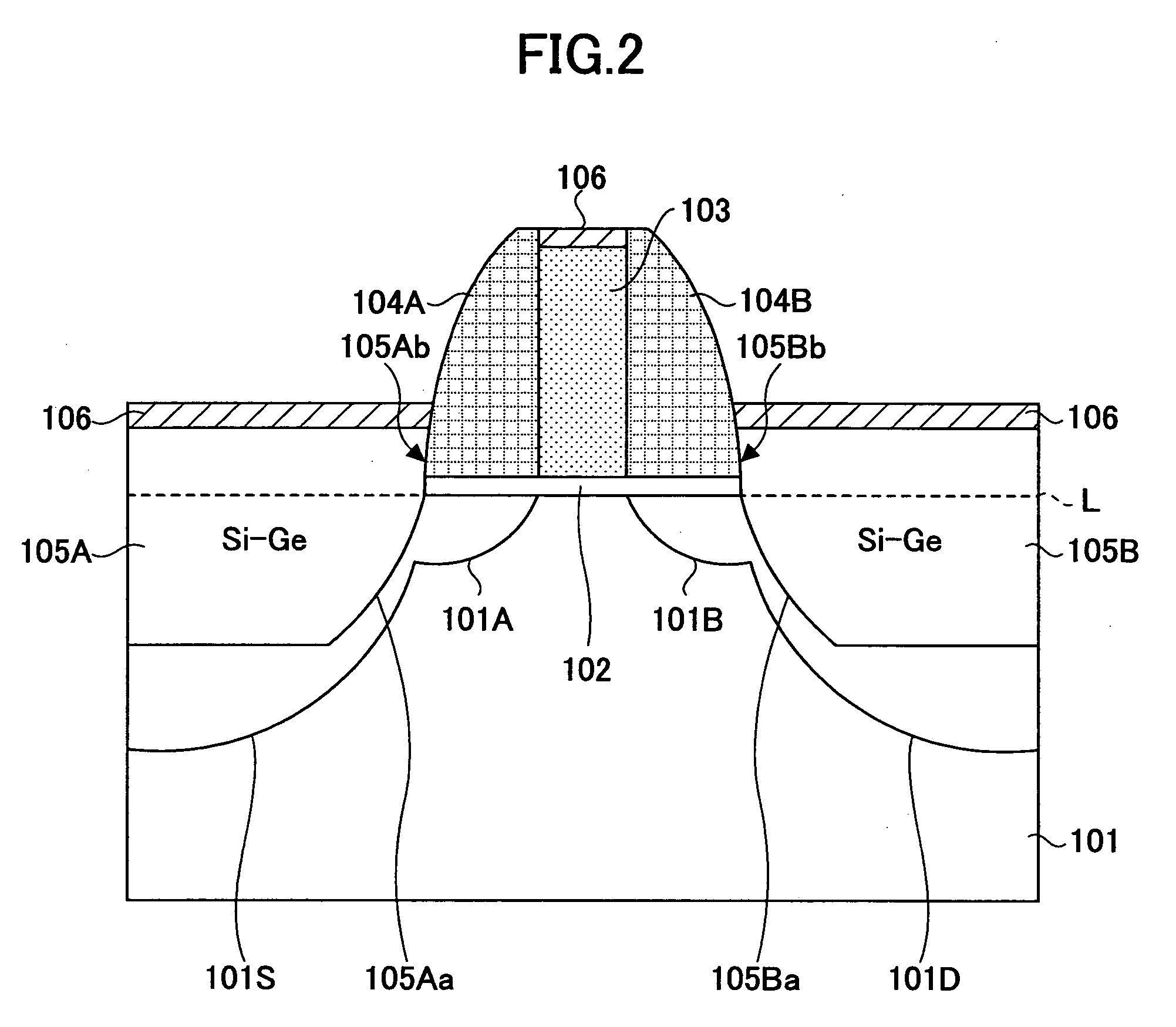
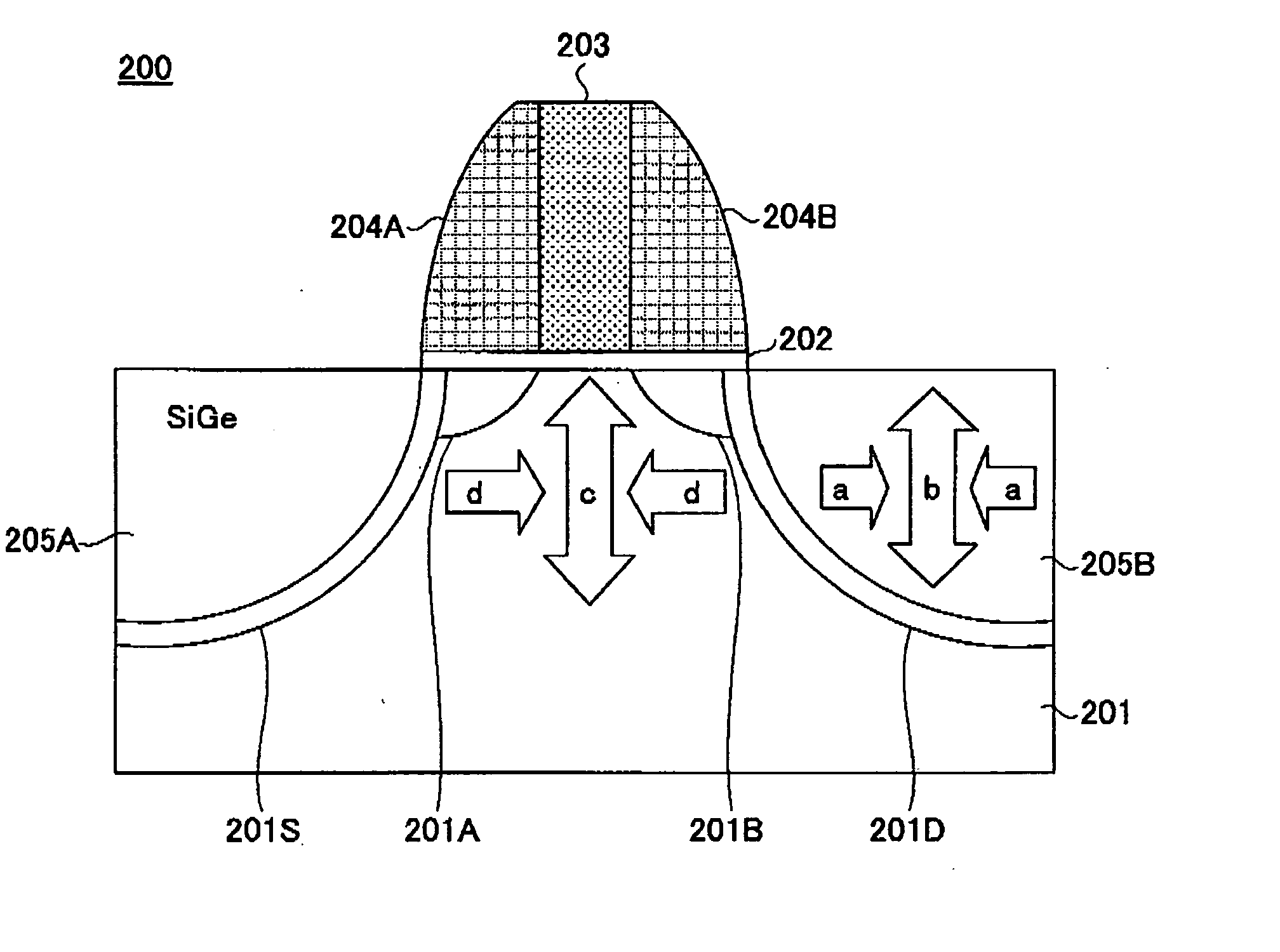
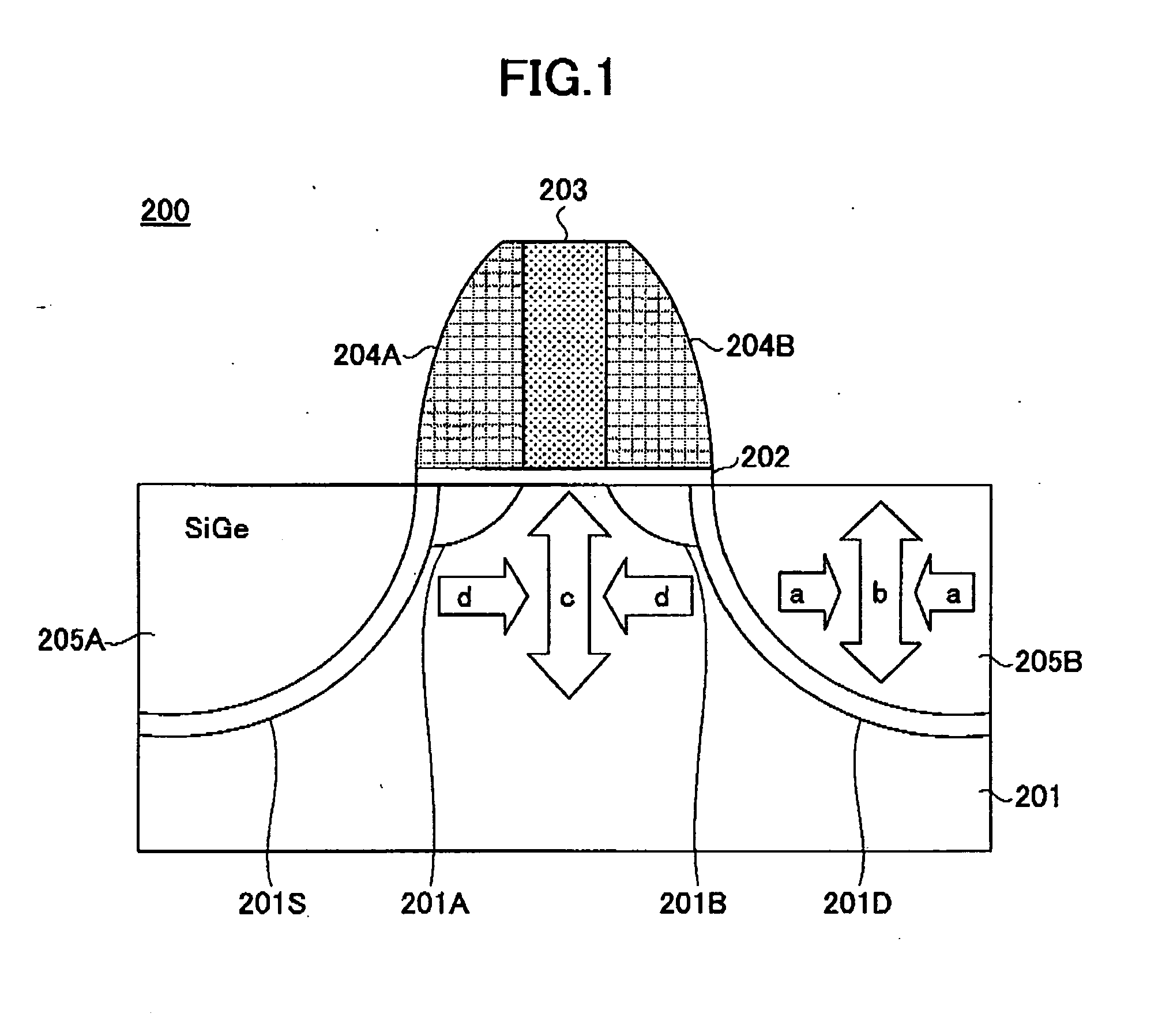
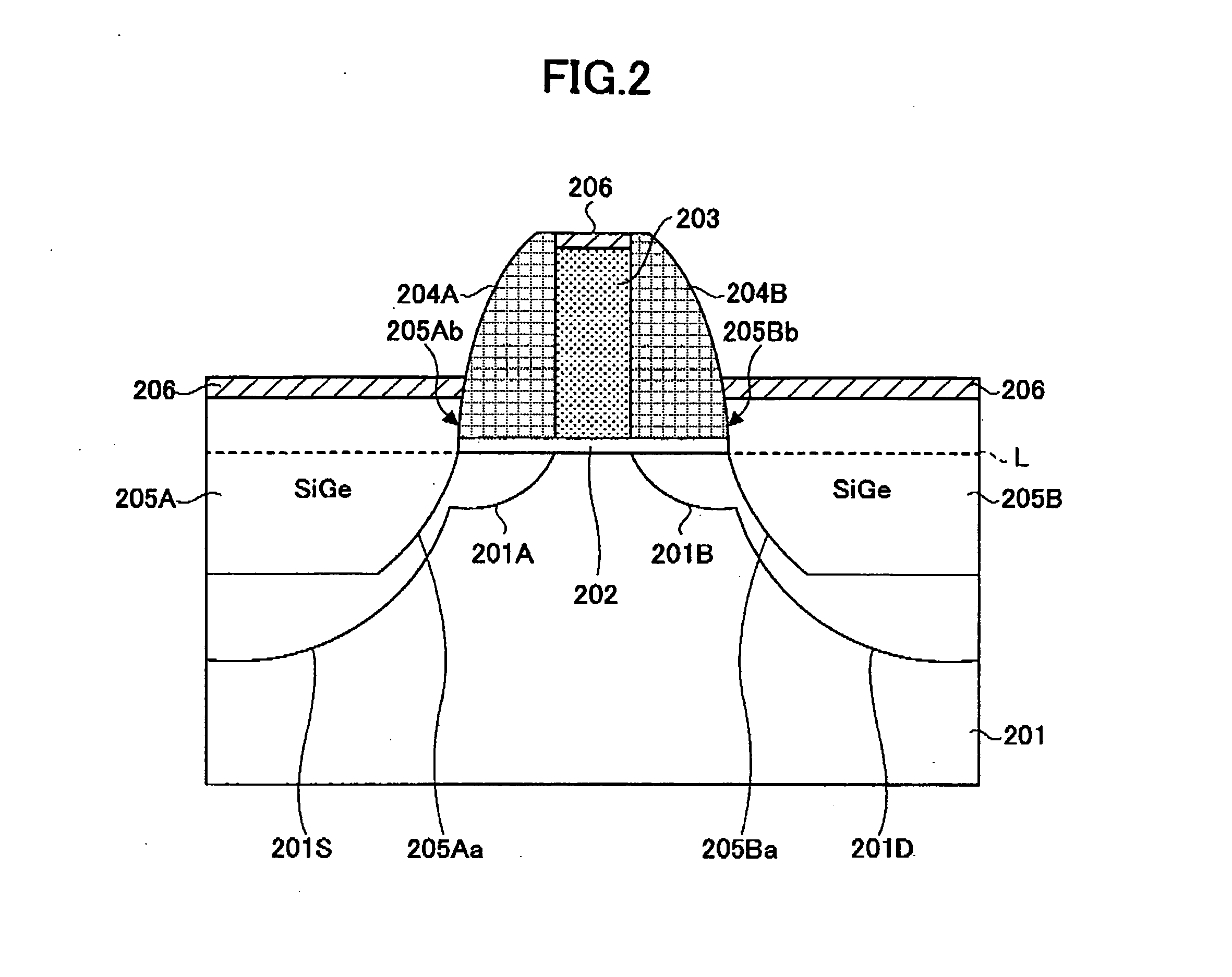
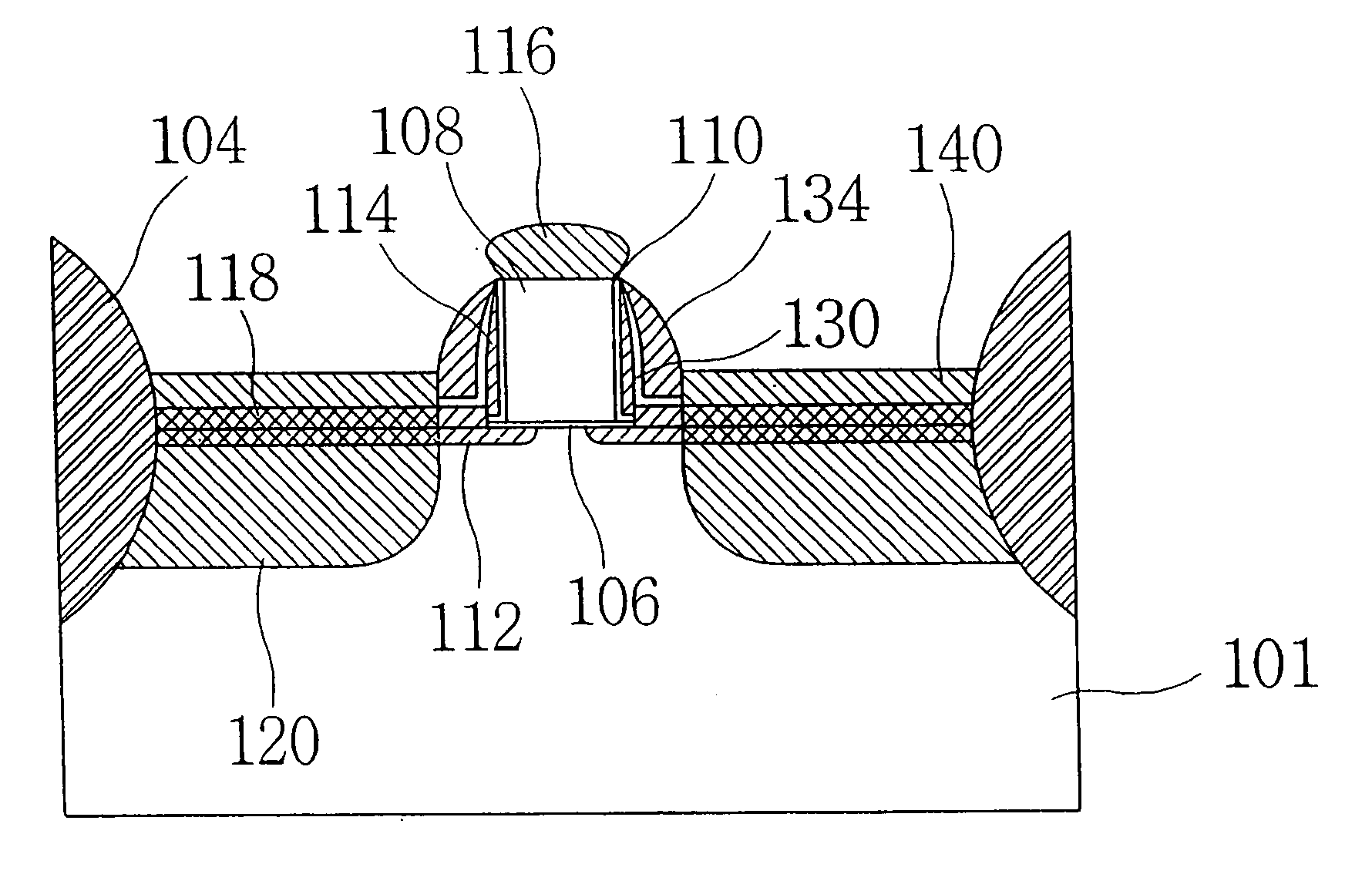
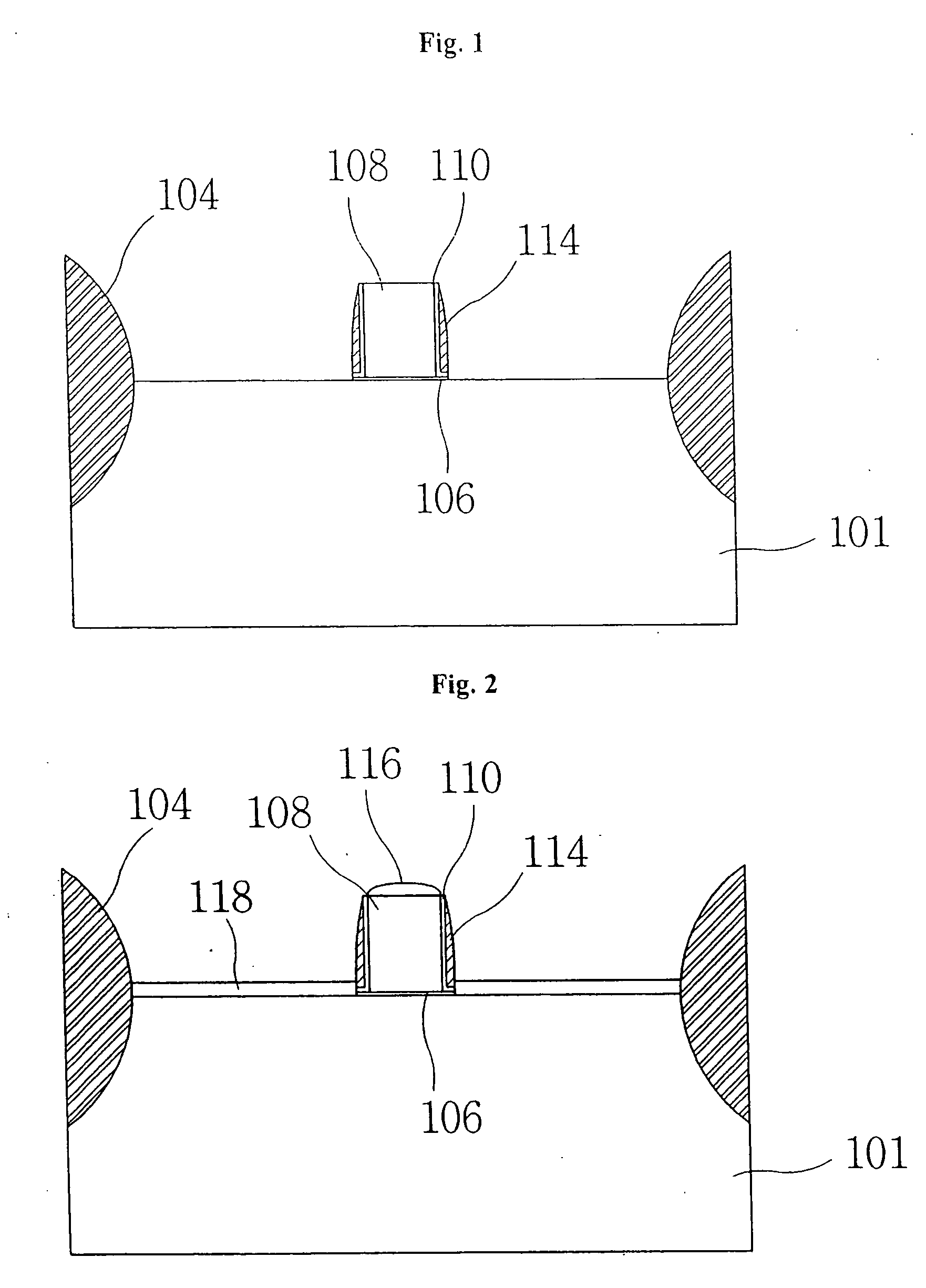
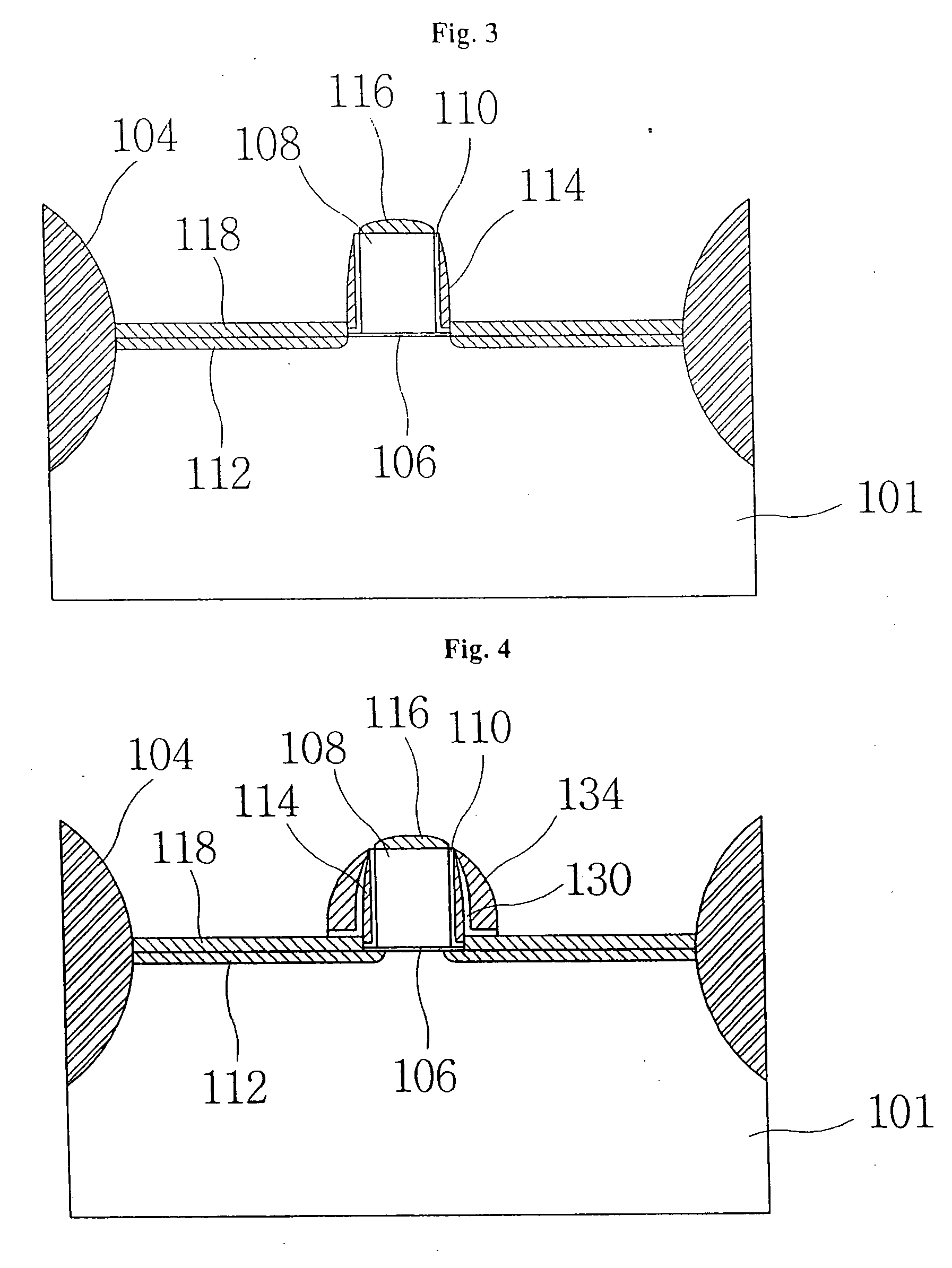
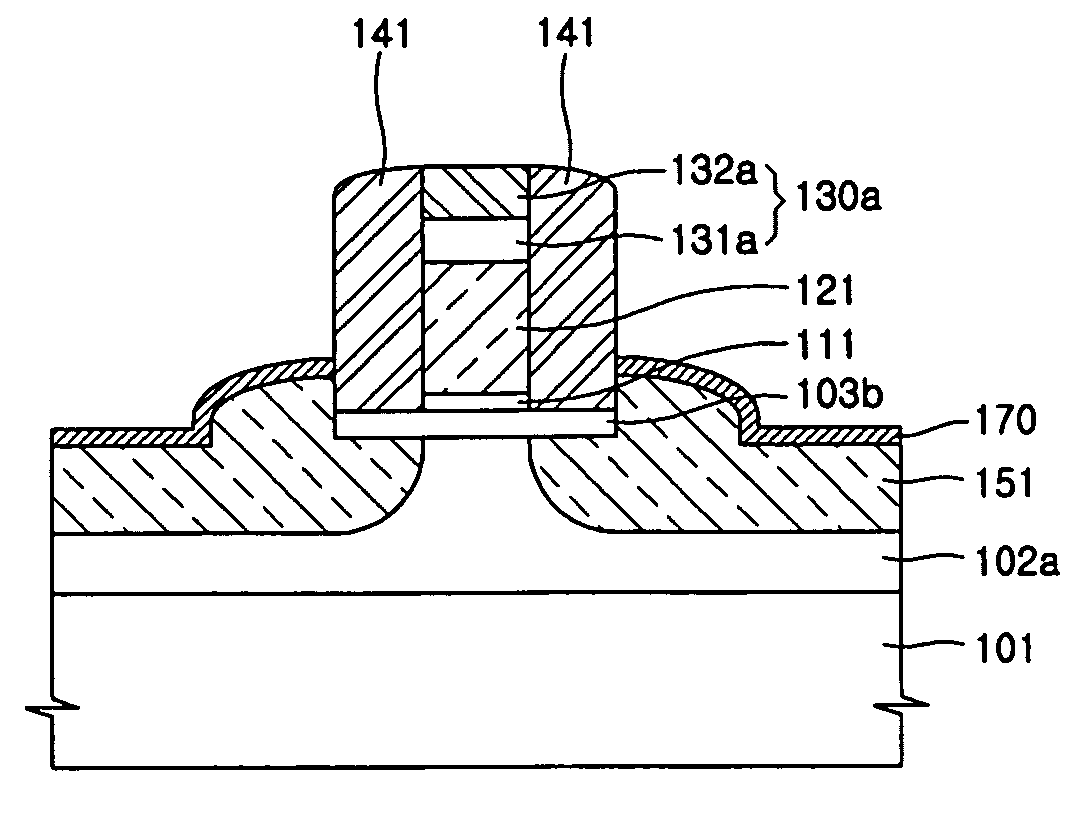
InactiveUS20060113522A1Suppression of short channel effectsIncrease currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentLattice mismatch
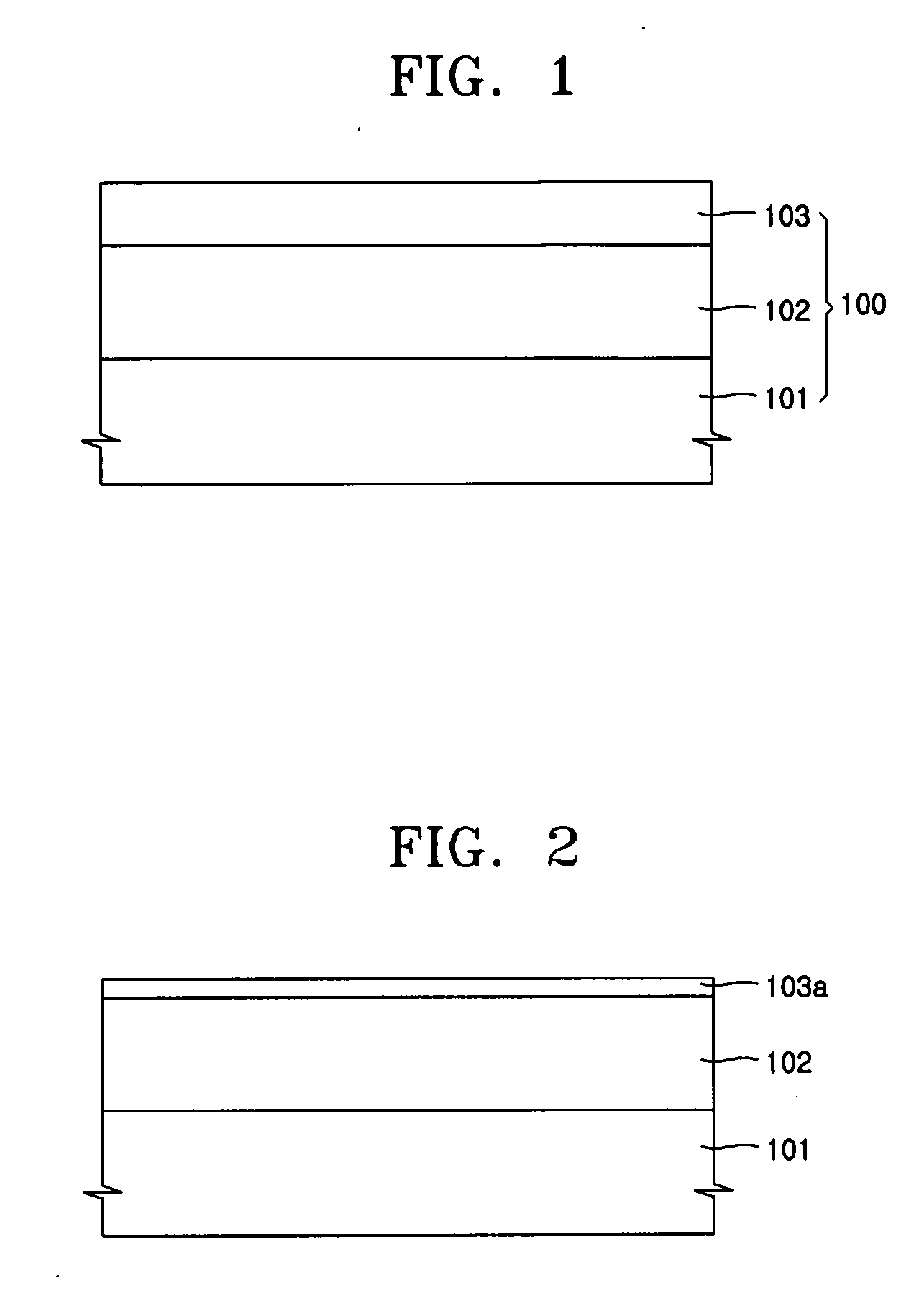
Disclosing is a strained silicon finFET device having a strained silicon fin channel in a double gate finFET structure. The disclosed finFET device is a double gate MOSFET consisting of a silicon fin channel controlled by a self-aligned double gate for suppressing short channel effect and enhancing drive current. The silicon fin channel of the disclosed finFET device is a strained silicon fin channel, comprising a strained silicon layer deposited on a seed fin having different lattice constant, for example, a silicon layer deposited on a silicon germanium seed fin, or a carbon doped silicon layer deposited on a silicon seed fin. The lattice mismatch between the silicon layer and the seed fin generates the strained silicon fin channel in the disclosed finFET device to improve hole and electron mobility enhancement, in addition to short channel effect reduction characteristic inherently in a finFET device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
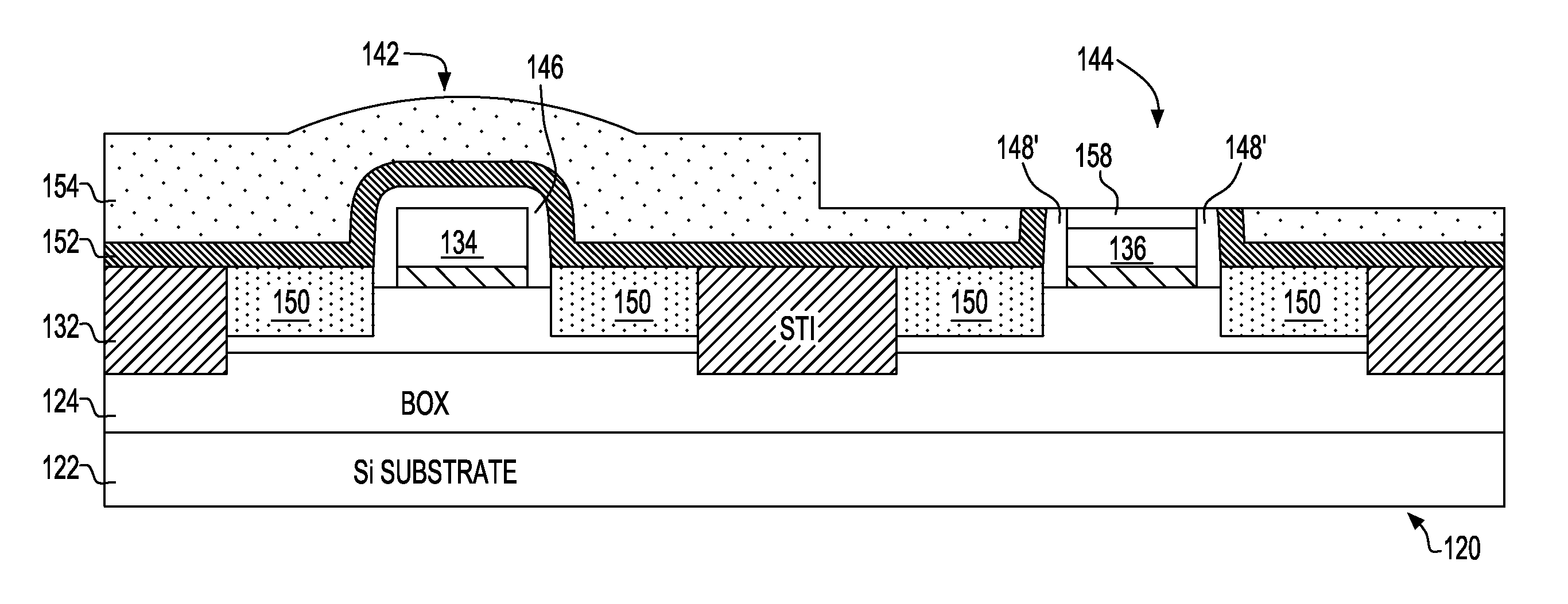
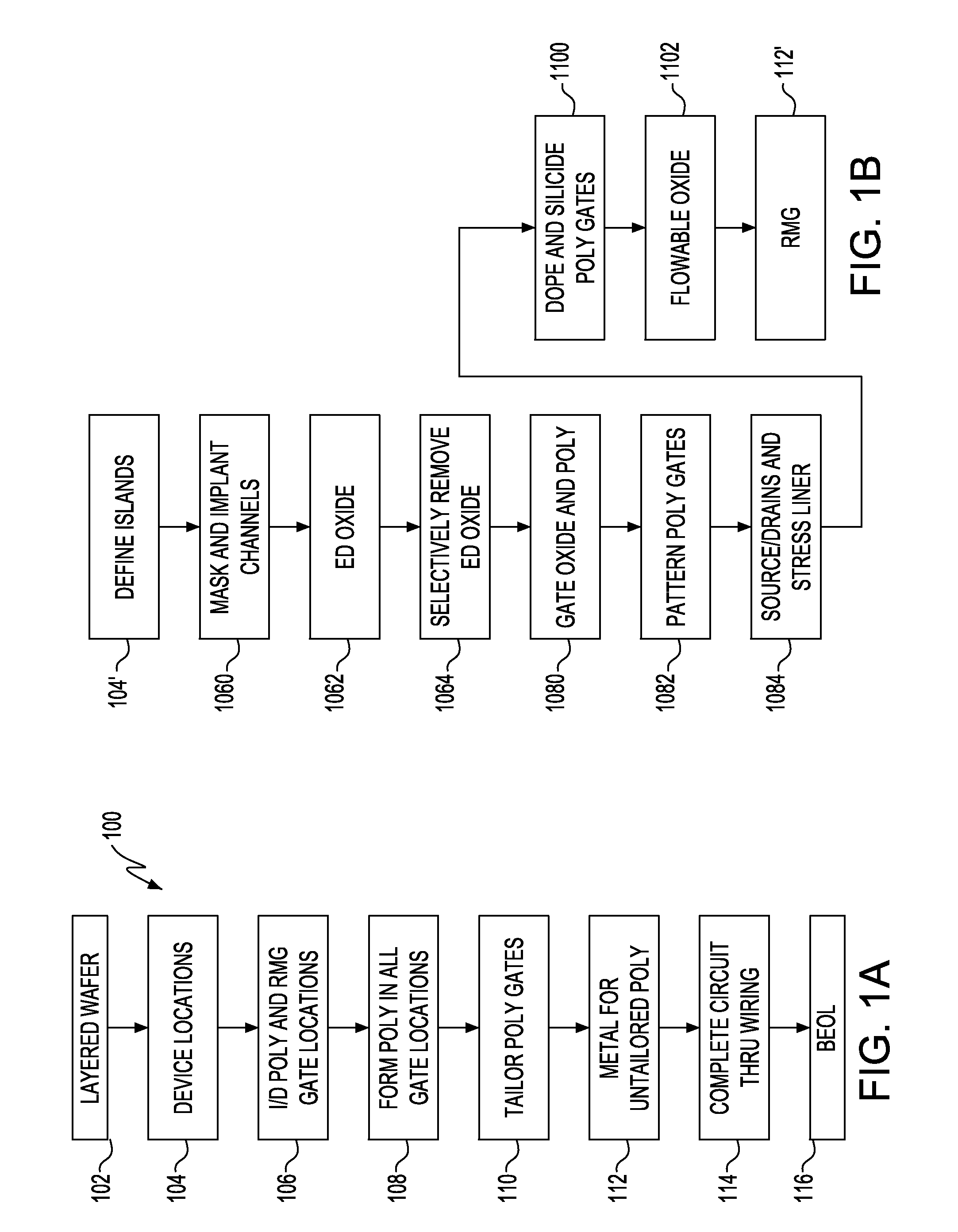
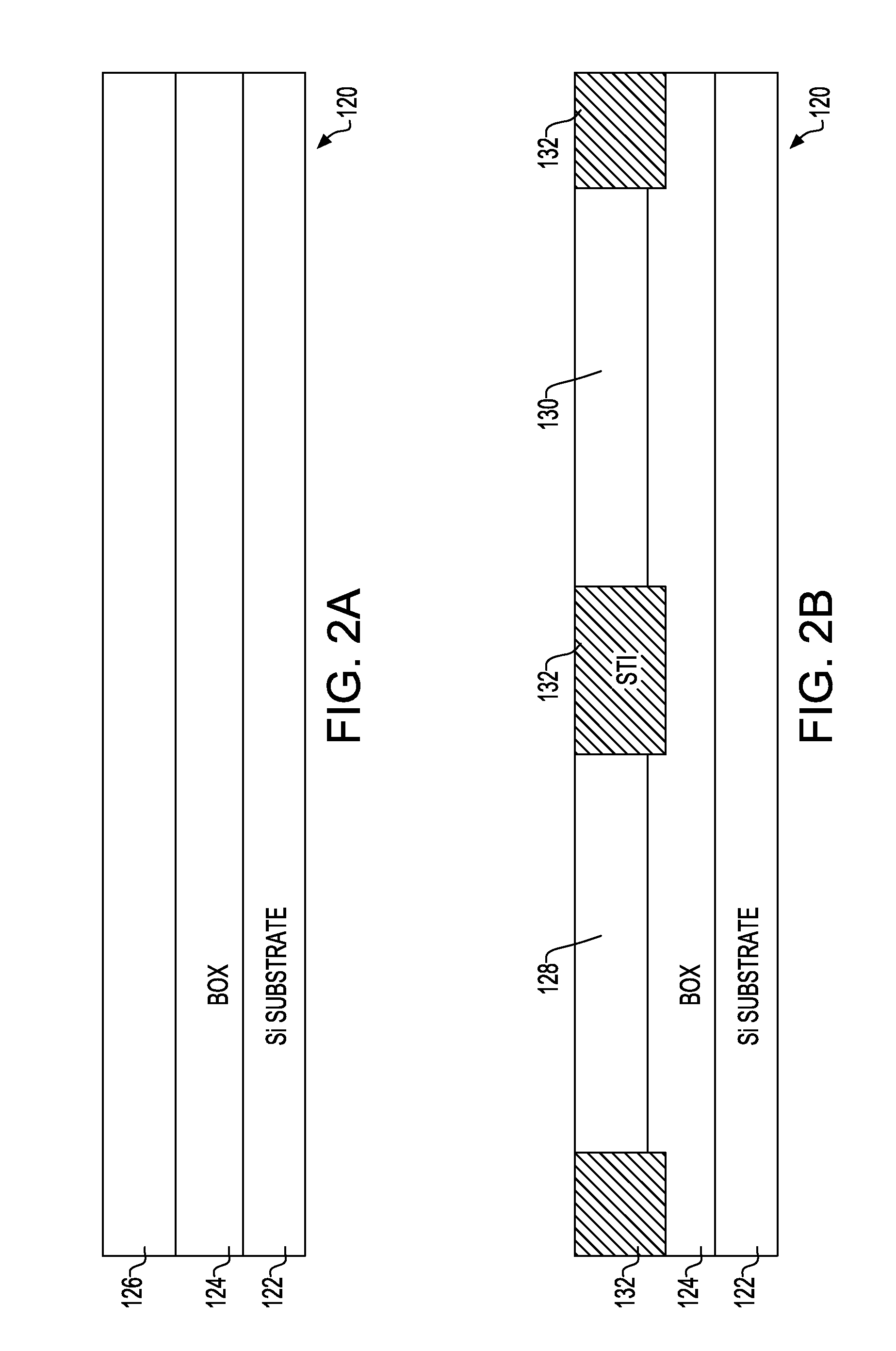
Integrated Circuit (IC) Chip Having Both Metal and Silicon Gate Field Effect Transistors (FETs) and Method of Manufacture
InactiveUS20120292664A1Suppression of short channel effectsWithout impairing performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsField-effect transistorPolysilicon gate
Field Effect Transistors (FETs), Integrated Circuit (IC) chips including the FETs, and a method of forming the FETs on ICs. FET locations are defined on a layered semiconductor wafer, preferably a Silicon On Insulator (SOI) wafer. One or more FET locations are defined as silicon gate locations and remaining as Replacement Metal Gate (RMG) FET locations with at least one of each on the IC. Polysilicon gates are formed in all FET locations. Gates in silicon gate locations are tailored, e.g., doped and silicided. Remaining polysilicon gates are replaced with metal in RMG FET locations. FETs are connected together into circuits with RMG FETs being connected to silicon gate FETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor device
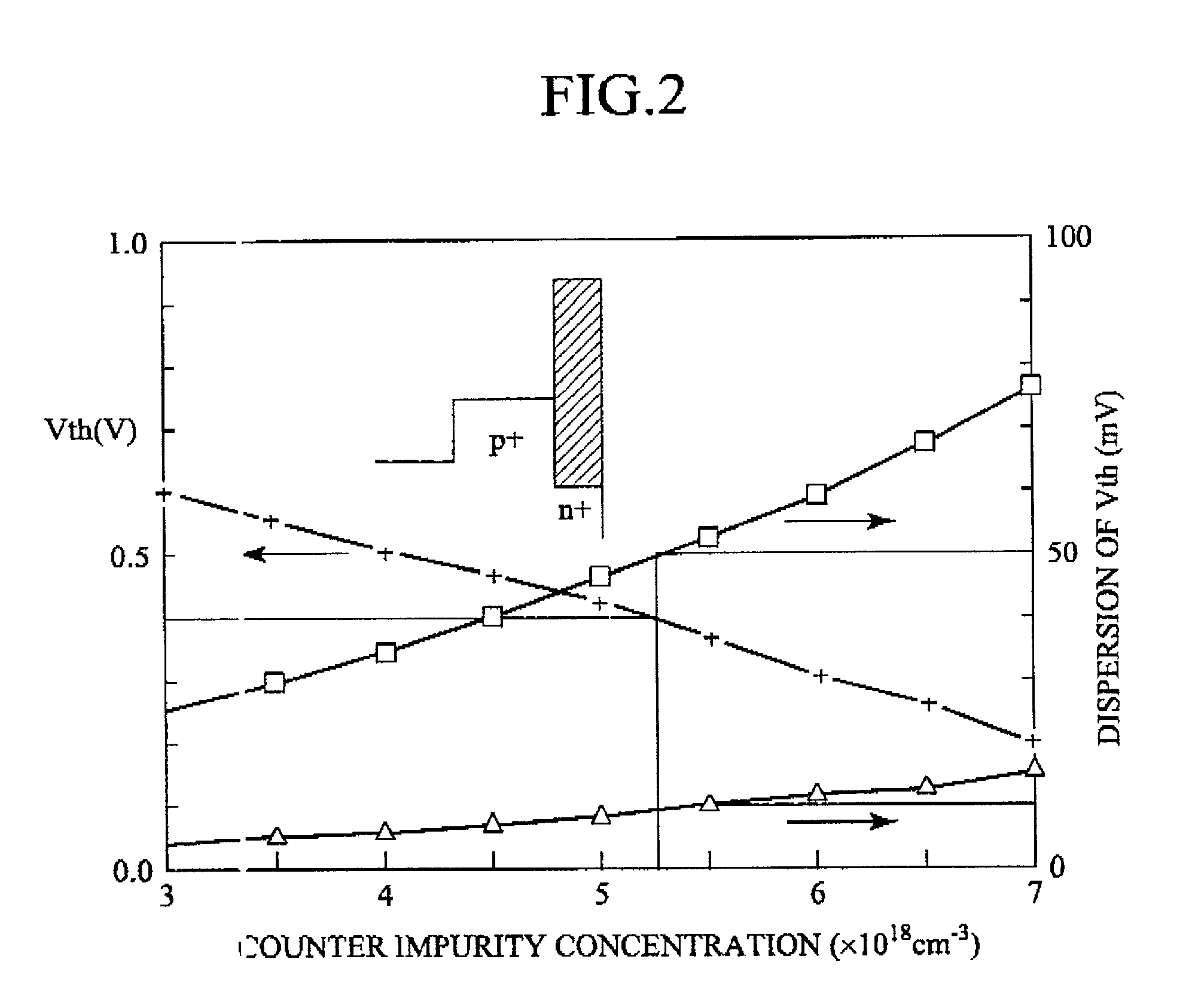
ActiveUS20100200919A1Suppression of short channel effectsSpeed up the flowTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor packageImpurity
The invention provides a semiconductor device capable of suppressing a short channel effect and fluctuation in a threshold. The semiconductor device includes: a plurality of first transistors formed in a first region in a semiconductor layer in a multilayer substrate having, on a semiconductor substrate, an insulating layer and the semiconductor layer in order from the semiconductor substrate; a plurality of second transistors formed in a second region in the semiconductor layer; a first impurity layer formed in a region opposed to the first region in the semiconductor substrate; a second impurity layer formed in a region opposed to the second region in the semiconductor substrate; and a first isolation part that isolates the first and second regions from each other and electrically isolates the first and second impurity layers from each other to a degree that at least current flowing between the first and second impurity layers is interrupted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Strained silicon finFET device
ActiveUS7045401B2Short effectEnhance carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon dopedElectron mobility
Disclosing is a strained silicon finFET device having a strained silicon fin channel in a double gate finFET structure. The disclosed finFET device is a double gate MOSFET consisting of a silicon fin channel controlled by a self-aligned double gate for suppressing short channel effect and enhancing drive current. The silicon fin channel of the disclosed finFET device is a strained silicon fin channel, comprising a strained silicon layer deposited on a seed fin having different lattice constant, for example, a silicon layer deposited on a silicon germanium seed fin, or a carbon doped silicon layer deposited on a silicon seed fin. The lattice mismatch between the silicon layer and the seed fin generates the strained silicon fin channel in the disclosed finFET device to improve hole and electron mobility enhancement, in addition to short channel effect reduction characteristic inherently in a finFET device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Mosfet and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130099315A1Adjustment of threshold voltageRaise the threshold voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETWafering
The present disclosure discloses a MOSFET and a method for manufacturing the same, wherein the MOSFET comprises: an SOI wafer which comprises a semiconductor substrate, a buried insulating layer, and a semiconductor layer, the buried insulating layer being on the semiconductor substrate, and the semiconductor layer being on the buried insulating layer; a gate stack on the semiconductor layer; a source region and a drain region, which are in the semiconductor layer and on opposite sides of the gate stack; and a channel region, which is in the semiconductor layer and sandwiched by the source region and the drain region, wherein the MOSFET further comprises a back gate, the back gate being located in the semiconductor substrate and having a first doped region in a lower portion of the back gate and a second doped region in an upper portion of the back gate. The MOSFET can adjust the threshold voltage by changing the doping type and doping concentration of the anti-doped region.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110127522A1High on-off ratioHigh puritySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsElectron donor
Objects are to provide a semiconductor device for high power application in which a novel semiconductor material having high productivity is used and to provide a semiconductor device having a novel structure in which a novel semiconductor material is used. The present invention is a vertical transistor and a vertical diode each of which has a stacked body of an oxide semiconductor in which a first oxide semiconductor film having crystallinity and a second oxide semiconductor film having crystallinity are stacked. An impurity serving as an electron donor (donor) which is contained in the stacked body of an oxide semiconductor is removed in a step of crystal growth; therefore, the stacked body of an oxide semiconductor is highly purified and is an intrinsic semiconductor or a substantially intrinsic semiconductor whose carrier density is low. The stacked body of an oxide semiconductor has a wider band gap than a silicon semiconductor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Low threshold voltage semiconductor device
InactiveUS7078776B2Easy to changeSuppression of short channel effectsTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor package
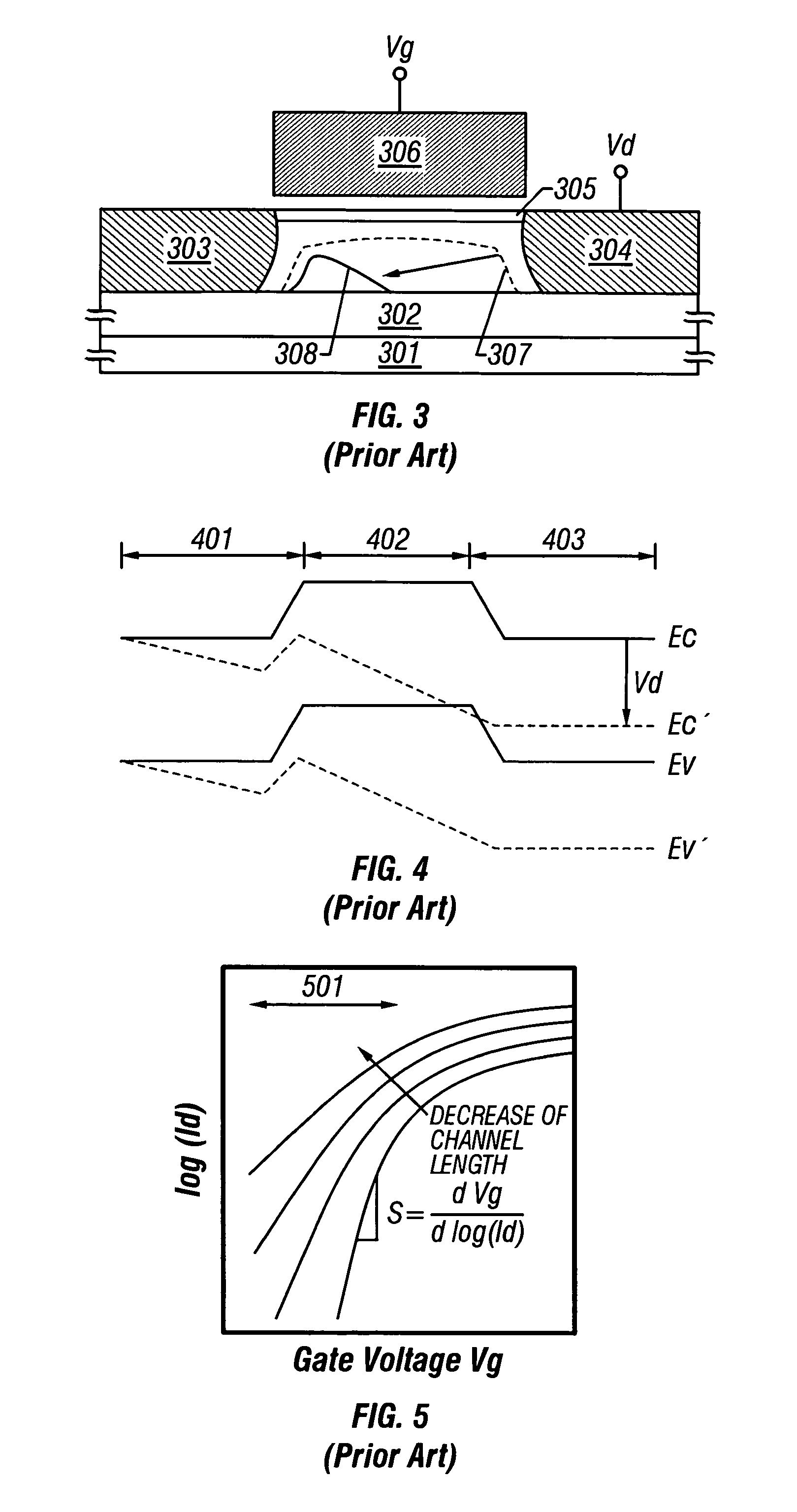
A semiconductor device has a first semiconductor region formed in a semiconductor substrate and having a first conductivity type due to first-conductivity-type active impurities contained in the first semiconductor region, and a second semiconductor region formed between the first semiconductor region and the surface of the semiconductor substrate and having a second conductivity type due to second-conductivity-type active impurities contained in the second semiconductor region. The second semiconductor region contains first-conductivity-type active impurities, whose concentration is zero or smaller than a quarter of a concentration of the second-conductivity-type active impurities contained in the second semiconductor region. An insulating film and a conductor are formed on the second semiconductor region. Third and fourth semiconductor regions of the second conductivity type are formed at the semiconductor surface in contact with the side faces of the second semiconductor region. This semiconductor device is capable of suppressing net impurity concentration variations as well as threshold voltage variations to be caused by a short channel effect or manufacturing variations.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Mos transistor for reducing short-channel effects and its production
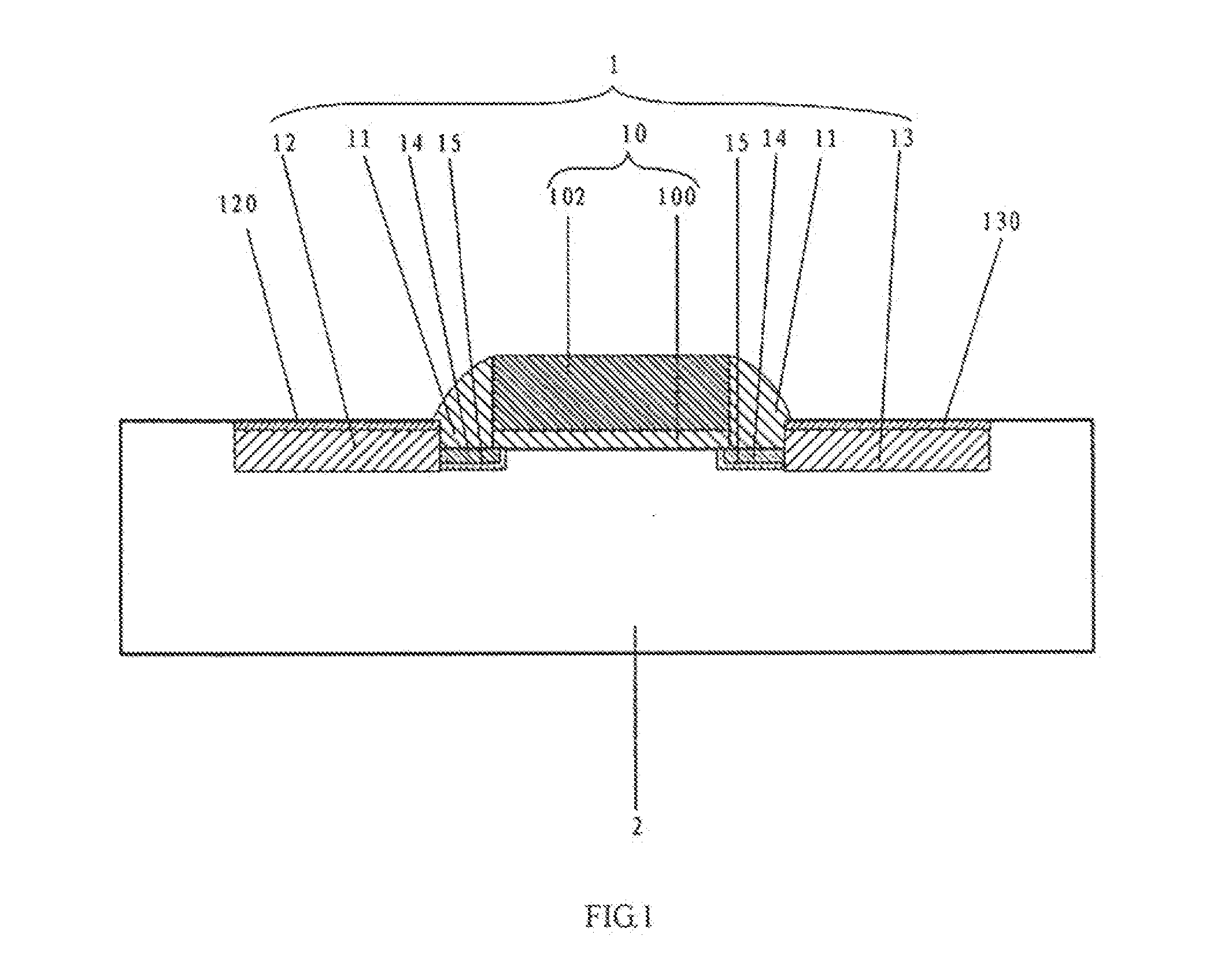
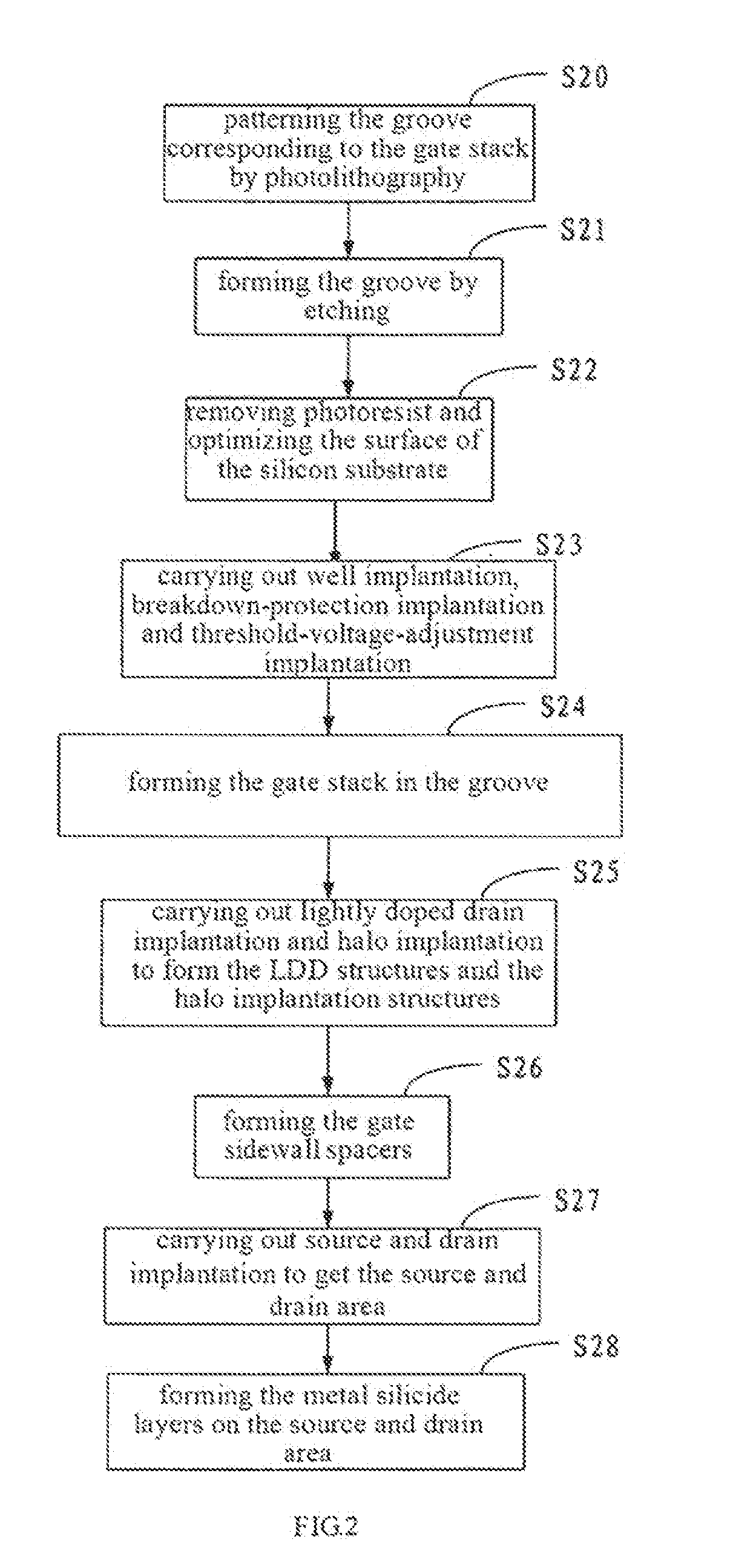
ActiveUS20110059588A1Suppression of short channel effectsReduce impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMetal silicideGate stack
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
Integrated circuit device and method of producing the same
InactiveUS7084507B2Good resistanceImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsElectric fieldCarbon nanotube
An integrated circuit device having vias having good resistance to migration causing the breaking of a wiring line, or an integrated circuit device having a wiring structure that is fined by breaking the limit of lithography technique is provided. The former device comprises a plurality of elements fabricated on a semiconductor substrate, wiring lines for making the elements and the integrated circuit device function, and vias for interconnecting wiring lines in separate layers, the via being formed of one or more cylindrical structures made up of carbon atoms. The latter device comprises a plurality of elements fabricated on a semiconductor substrate and wiring members for making the elements and the integrated circuit device function, at least part of the wiring members being formed of one or more cylindrical structures made up of carbon atoms. The latter device is preferably manufactured by a method comprising using a CVD process for the formation of the cylindrical structures, while applying a direct current electric field so as to grow the cylindrical structures in one direction, or applying an alternating current electric field so as to grow the cylindrical structures in two directions. A semiconductor device using a carbon nanotube and a method of forming a pattern using a carbon nanotube as a mask are also disclosed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method of fabricating a double gate MOSFET device
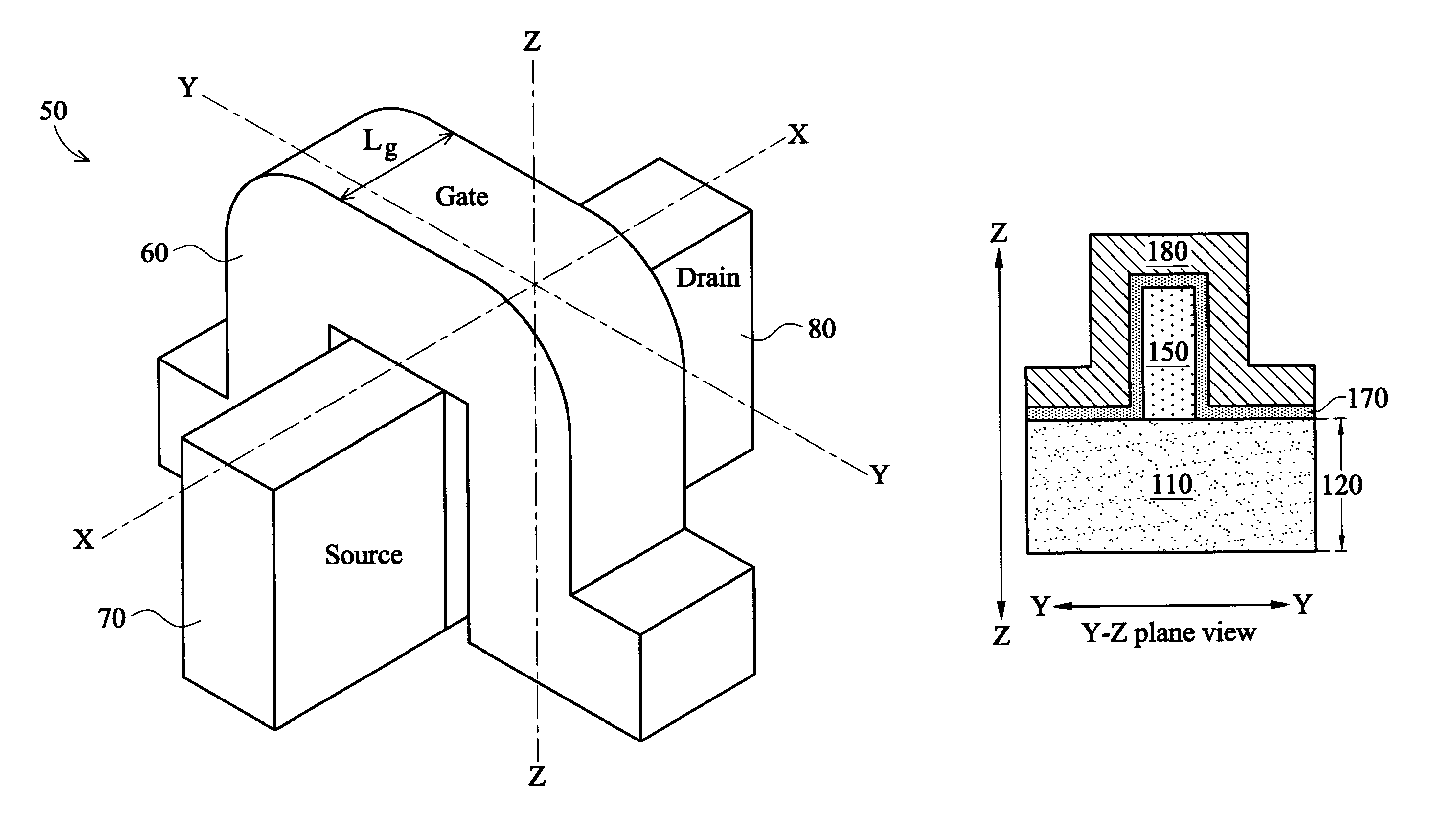
ActiveUS6855588B1Excellent short channel behaviorBetter gate controlTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentDouble gate
A method of fabricating a double gate MOSFET device is provided. The present invention overetches a silicon layer overlying a buried oxide layer using a hard mask of cap oxide on the silicon layer as an etching mask. As a result, source, drain and channel regions are formed extending from the buried oxide layer, and a pair of recesses are formed under the channel regions in the buried oxide layer. The channel is a fin structure with a top surface and two opposing parallelly sidewalls. The bottom recess is formed under each opposing sidewall of the fin structure. A conductive gate layer is formed straddling the fin structures. The topography of the conductive gate layer significantly deviates from the conventional plainer profile due to the bottom recess structures under the channel regions, and a more uniformly distributed doped conductive gate layer can be obtained. Hence, the depletion effect of the conductive polysilicon gate while operating the device can be suppressed and the device drive-on currents can be further enhanced.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and production method thereof
ActiveUS20060289856A1Suppression of short channel effectsHigh carrier mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesShort-channel effectEngineering
A method of fabricating a semiconductor device is disclosed that is able to suppress a short channel effect and improve carrier mobility. In the method, trenches are formed in a silicon substrate corresponding to a source region and a drain region. When epitaxially growing p-type semiconductor mixed crystal layers to fill up the trenches, the surfaces of the trenches are demarcated by facets, and extended portions of the semiconductor mixed crystal layers are formed between bottom surfaces of second side wall insulating films and a surface of the silicon substrate, and extended portion are in contact with a source extension region and a drain extension region.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Technique to mitigate short channel effects with vertical gate transistor with different gate materials
InactiveUS20050145959A1Reduce negative impactImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
A process of forming a transistor with three vertical gate electrodes including a high-k gate dielectric and the resulting transistor. By forming such a transistor it is possible to maintain an acceptable aspect ratio as MOSFET structures are scaled down to sub-micron sizes. The transistor gate electrodes can be formed of different materials so that the workfunctions of the three electrodes can be tailored. The three electrodes are positioned over a single channel and operate as a single gate having outer and inner gate regions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Technique to mitigate short channel effects with vertical gate transistor with different gate materials
InactiveUS20020130378A1Improve performanceSuppression of short channel effectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReverse short-channel effectScale down
This invention relates to a process of forming a transistor with three vertical gate electrodes and the resulting transistor. By forming such a transistor it is possible to maintain an acceptable aspect ratio as MOSFET structures are scaled down to sub-micron sizes. The transistor gate electrodes can be formed of different materials so that the workfunctions of the three electrodes can be tailored. The three electrodes are positioned over a single channel and operate as a single gate having outer and inner gate regions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor device having SOI structure and manufacturing method thereof
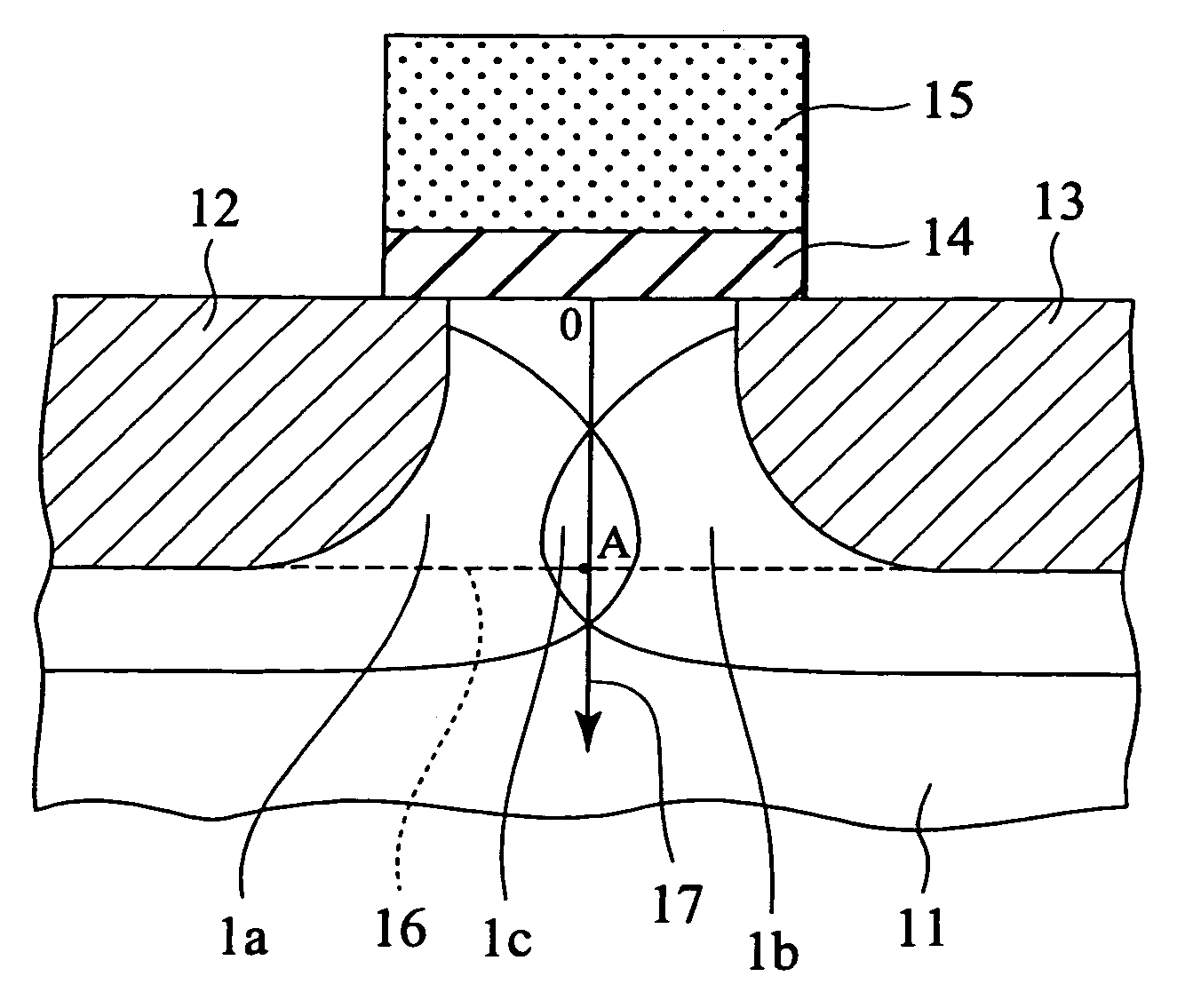
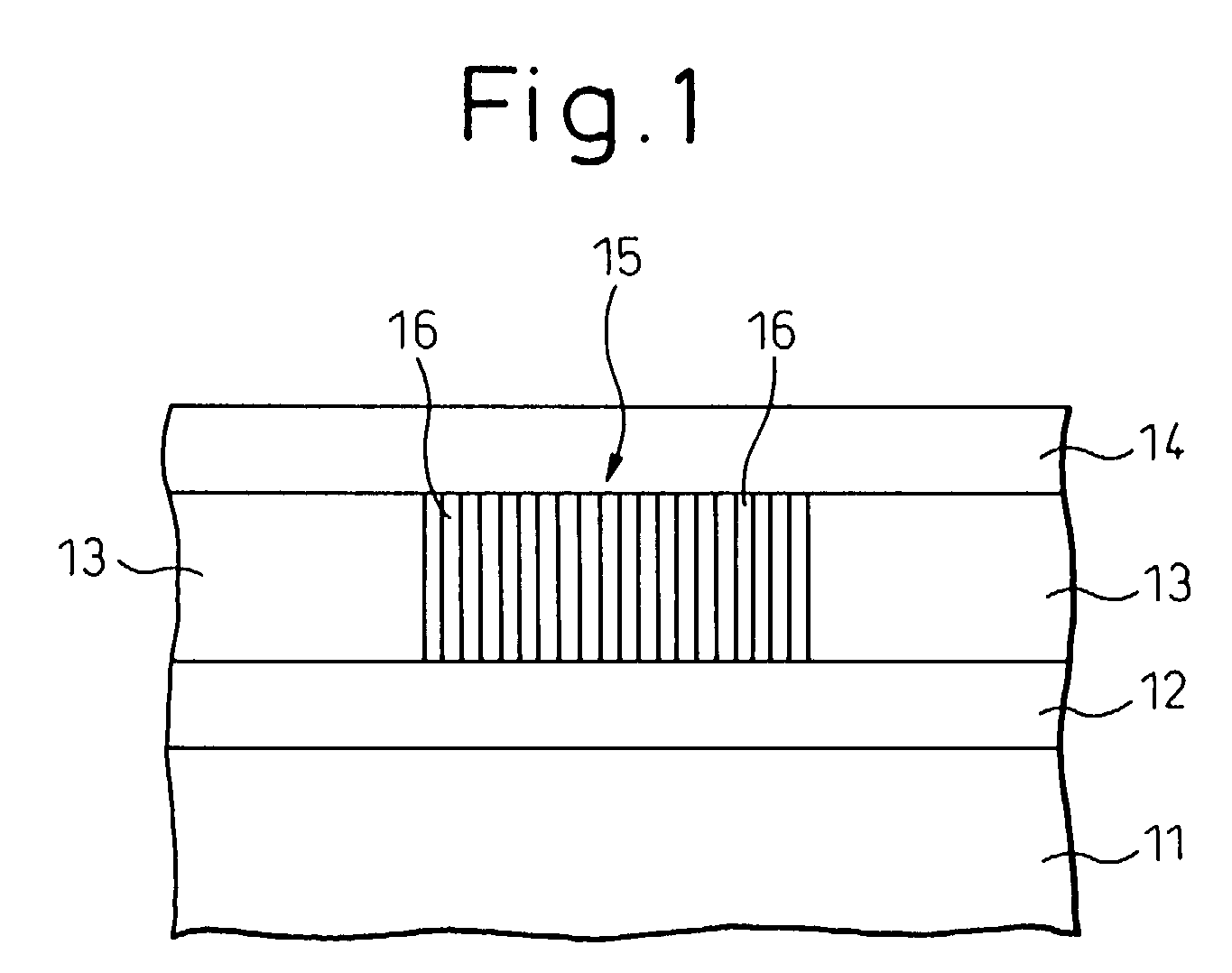
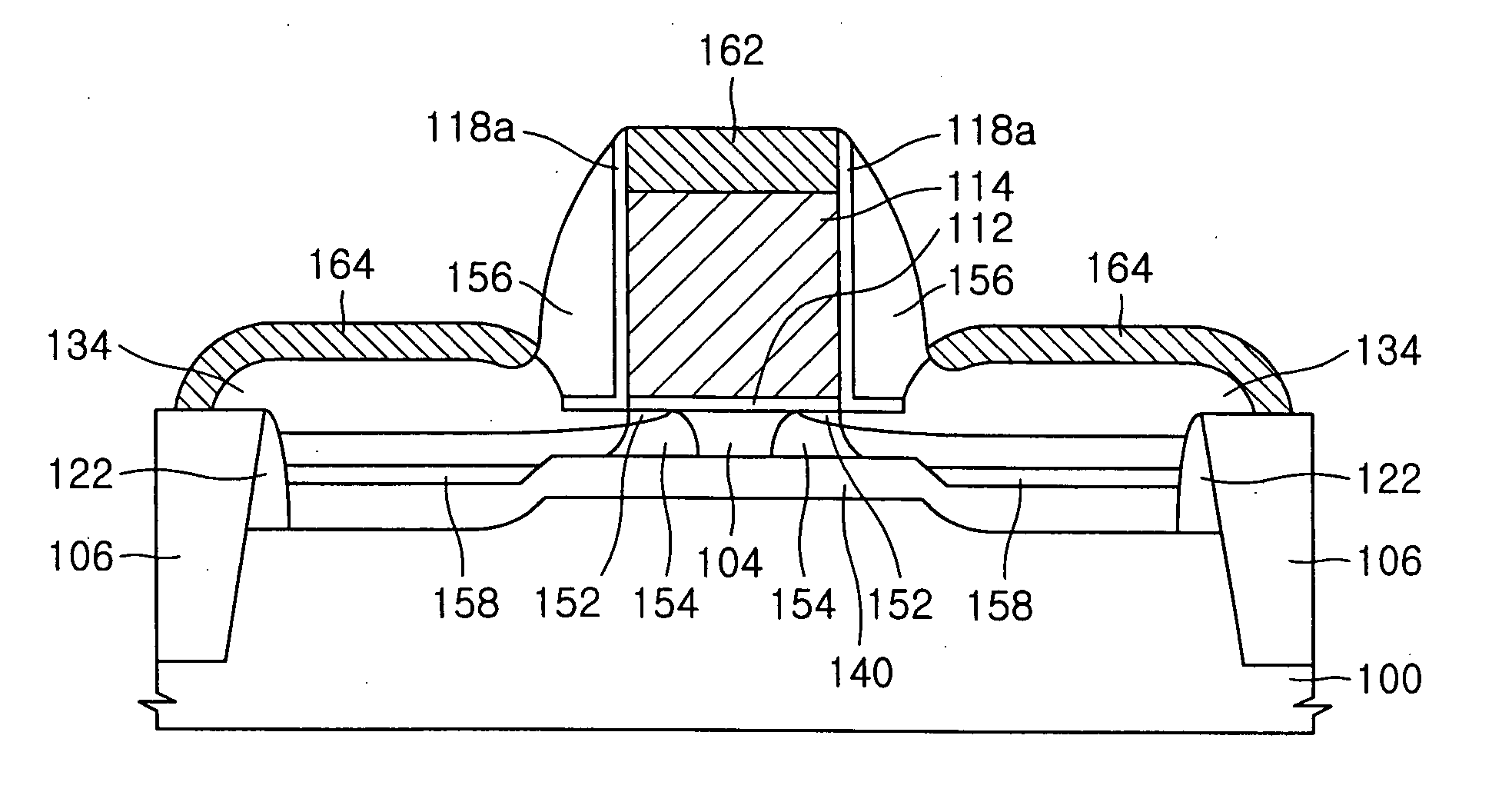
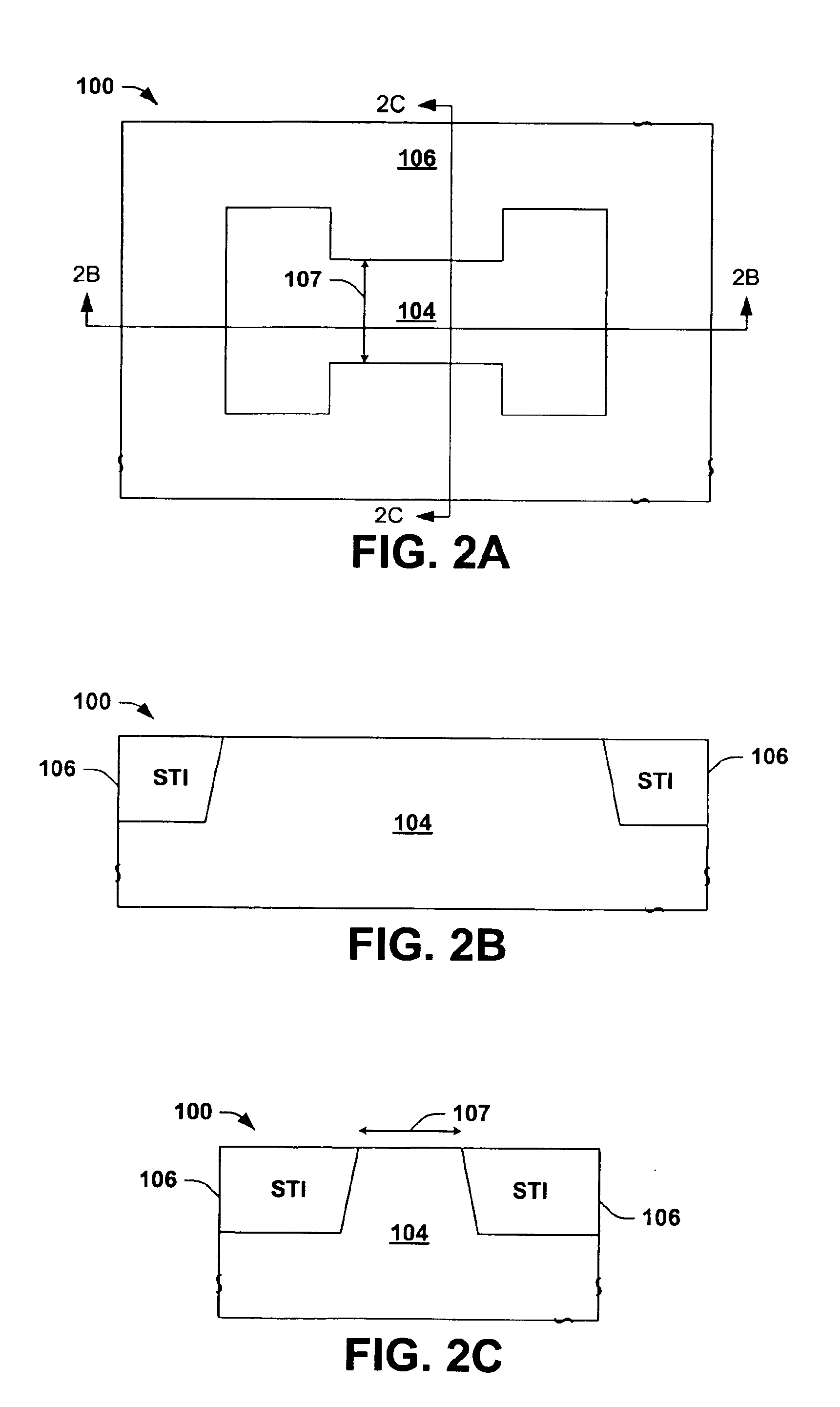
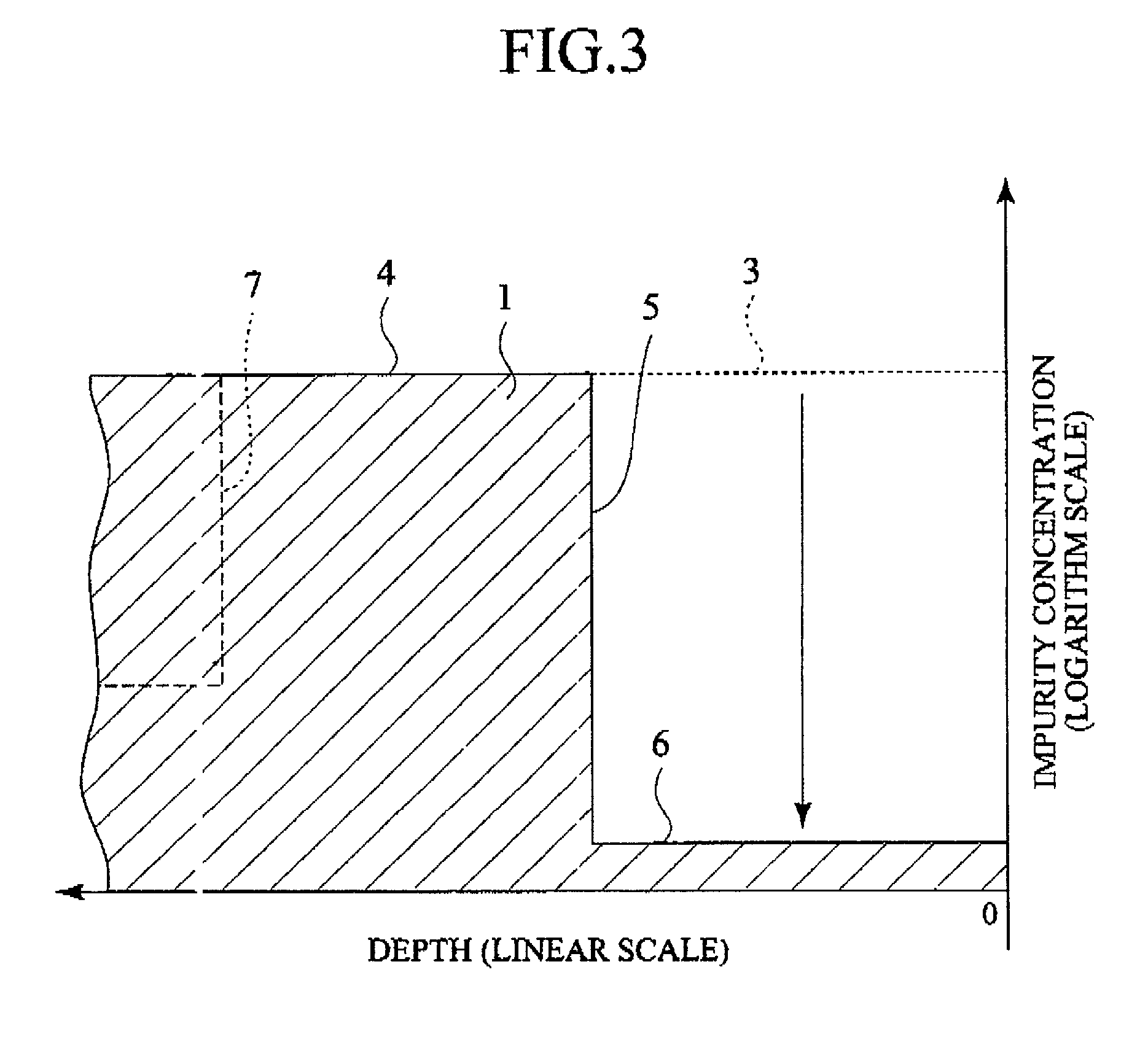
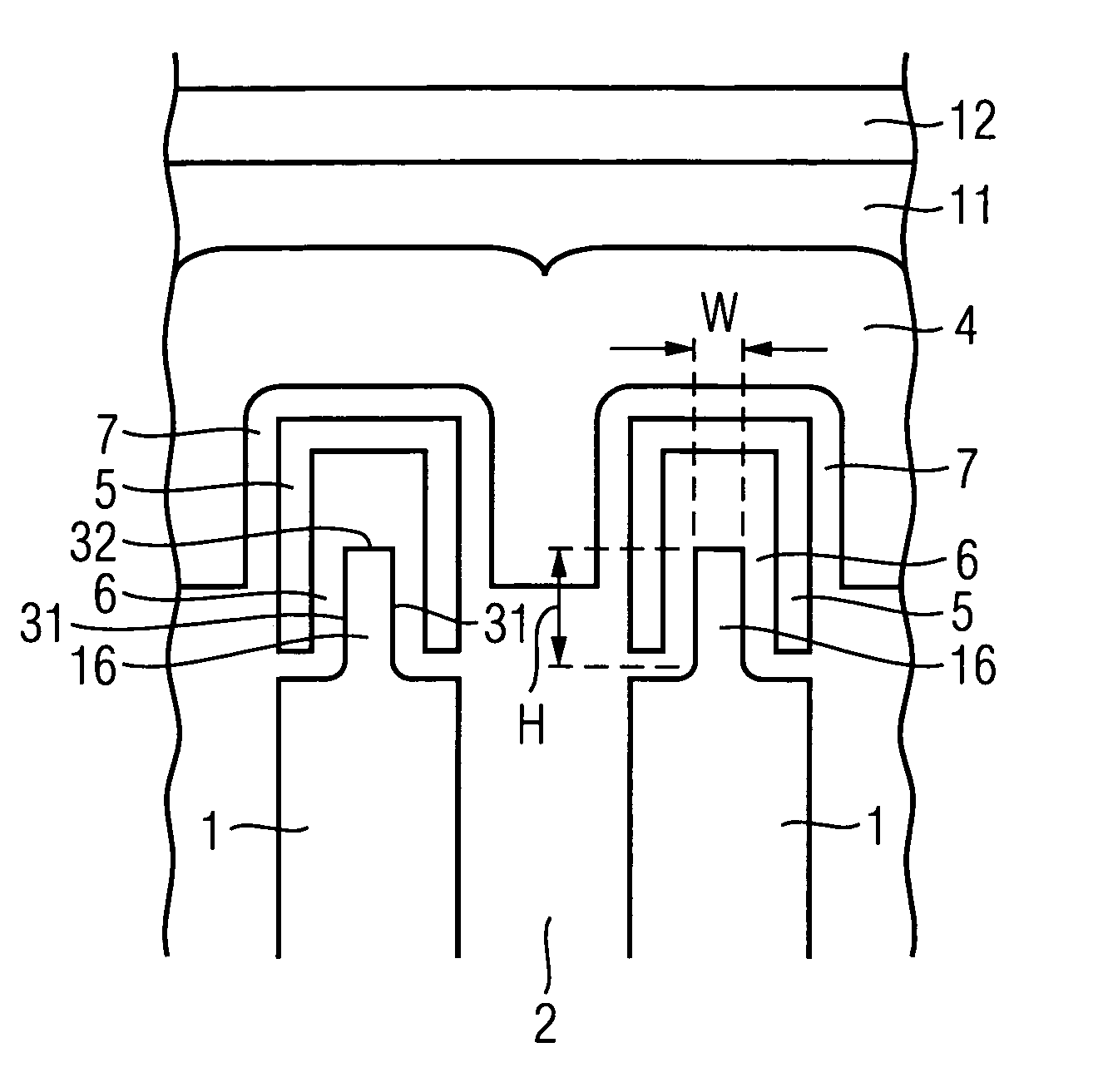
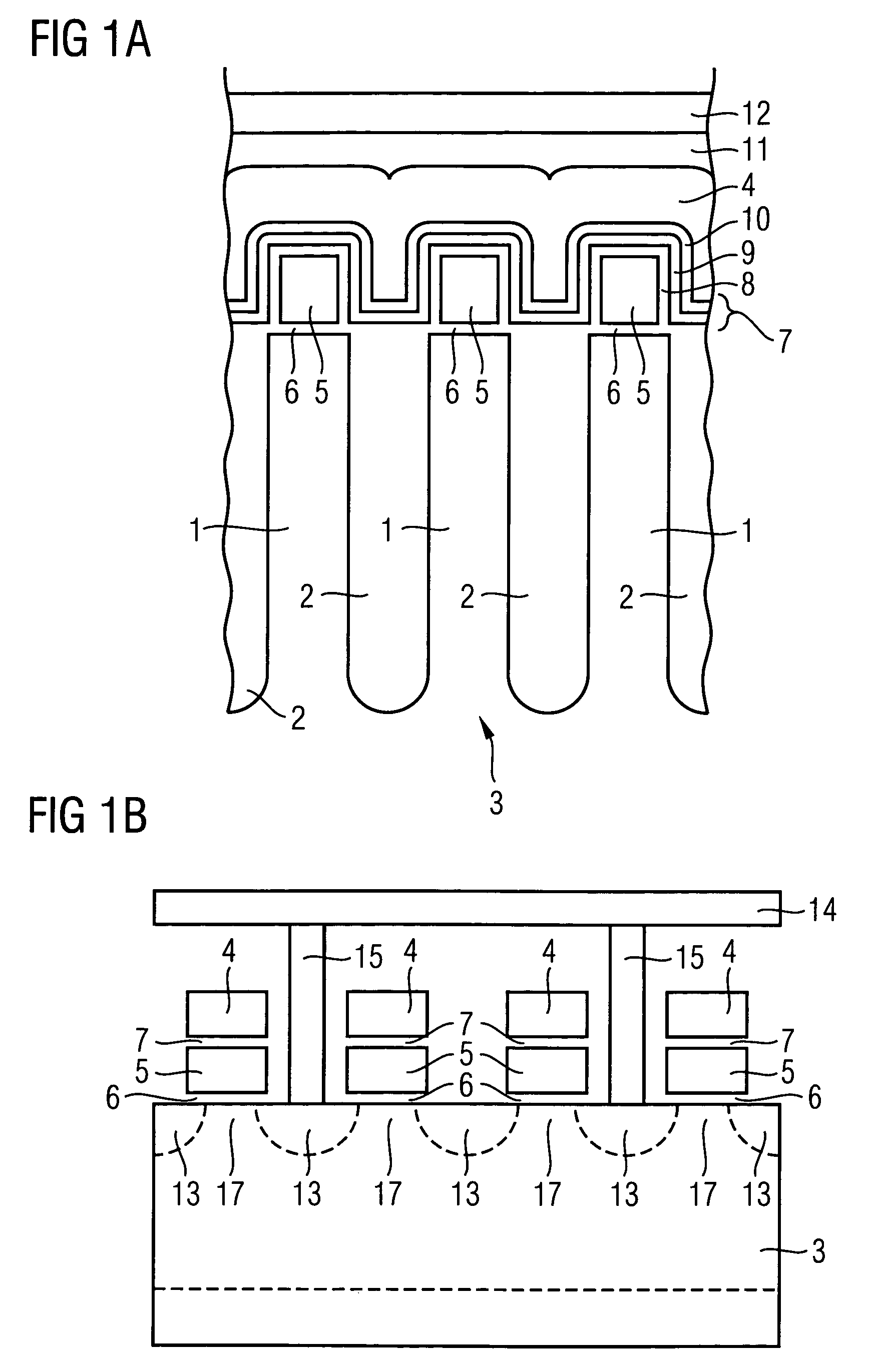
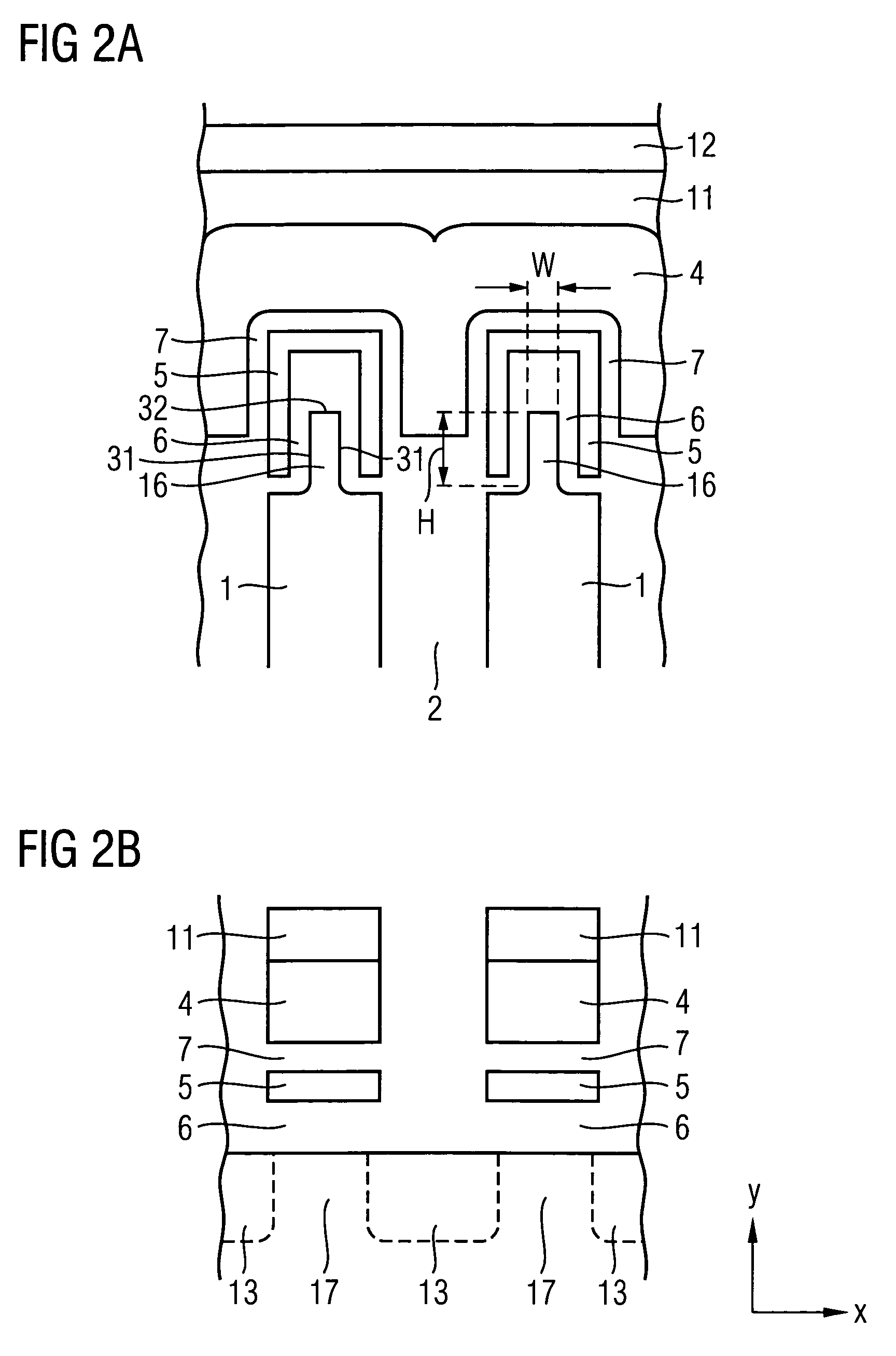
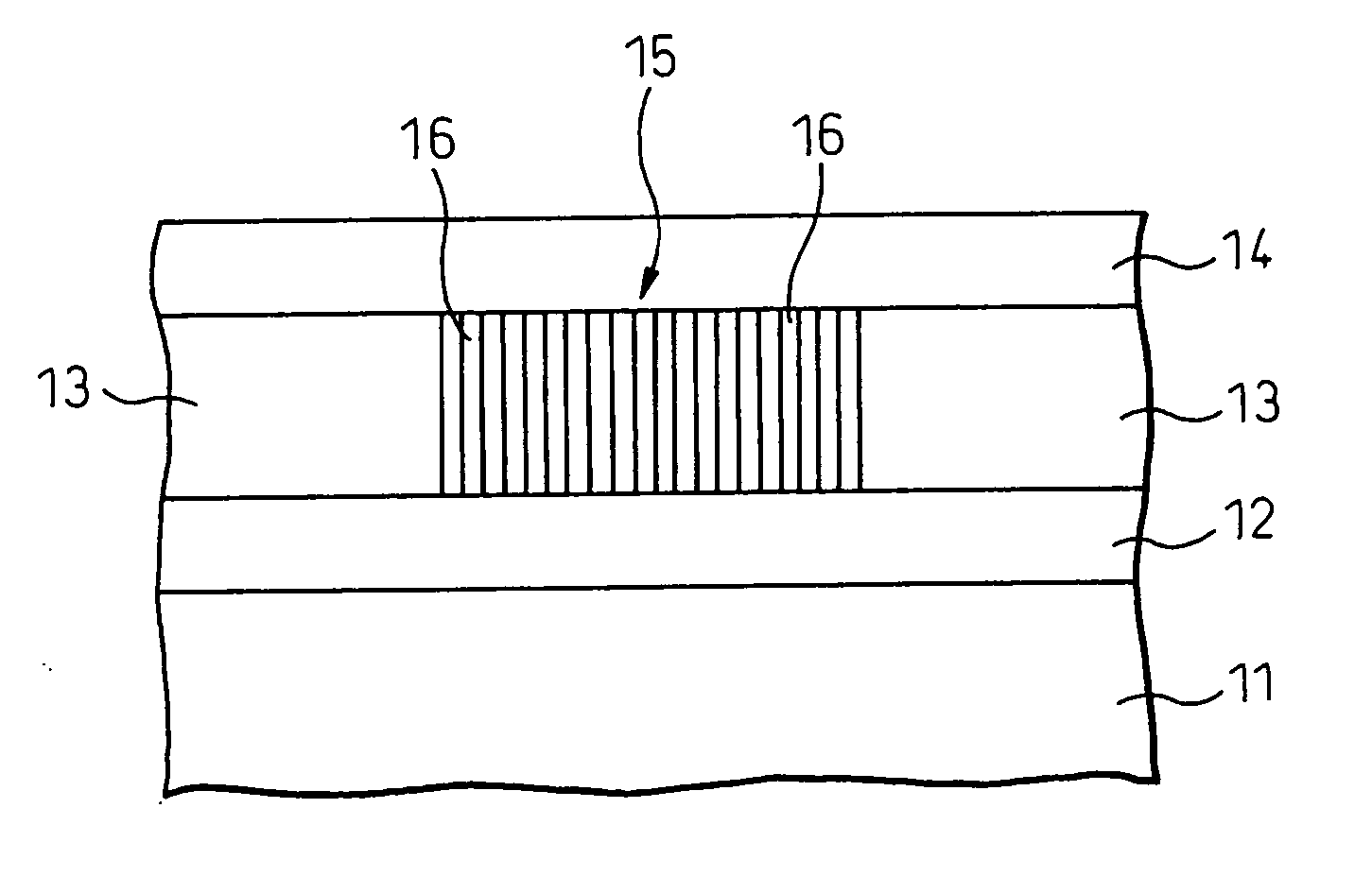
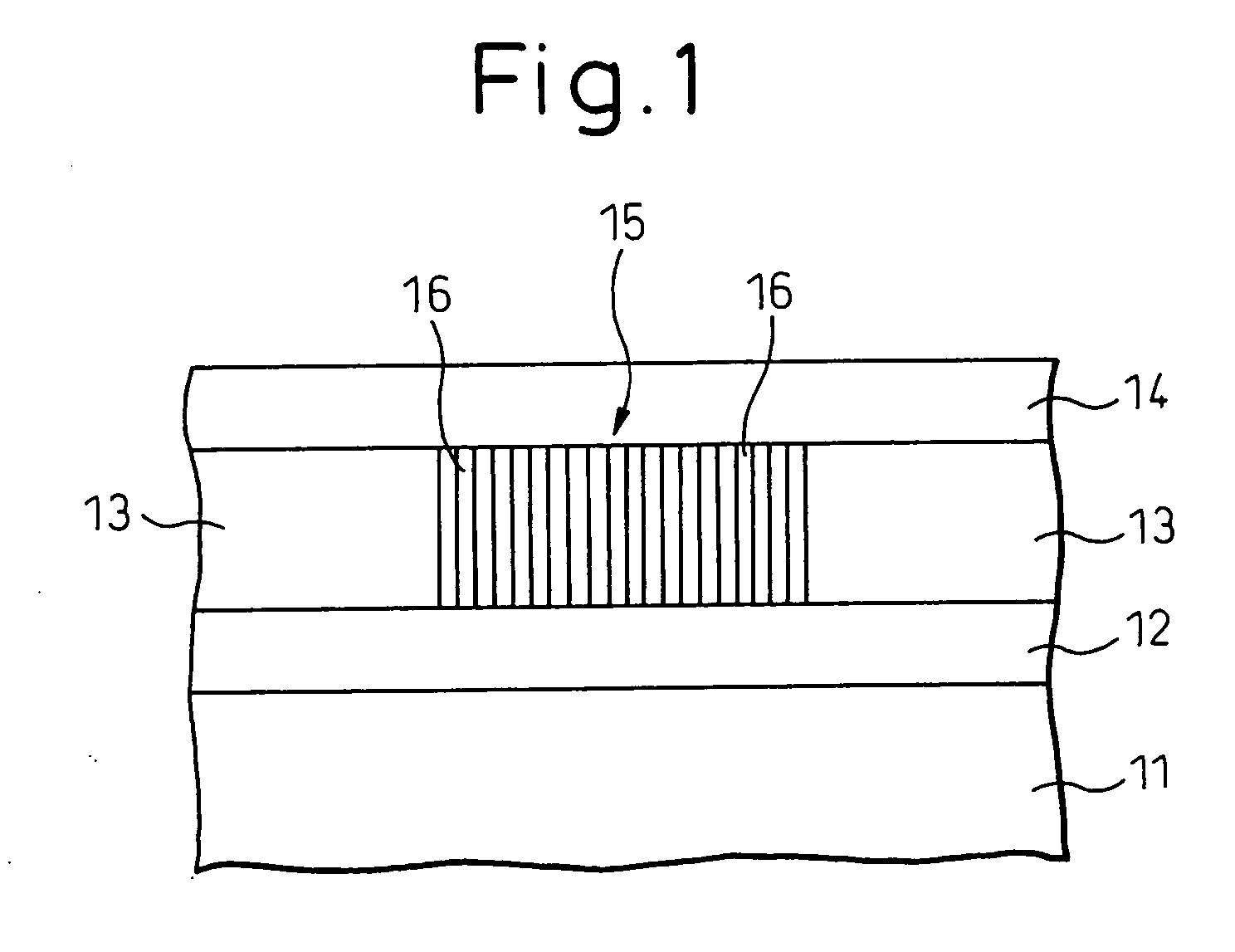
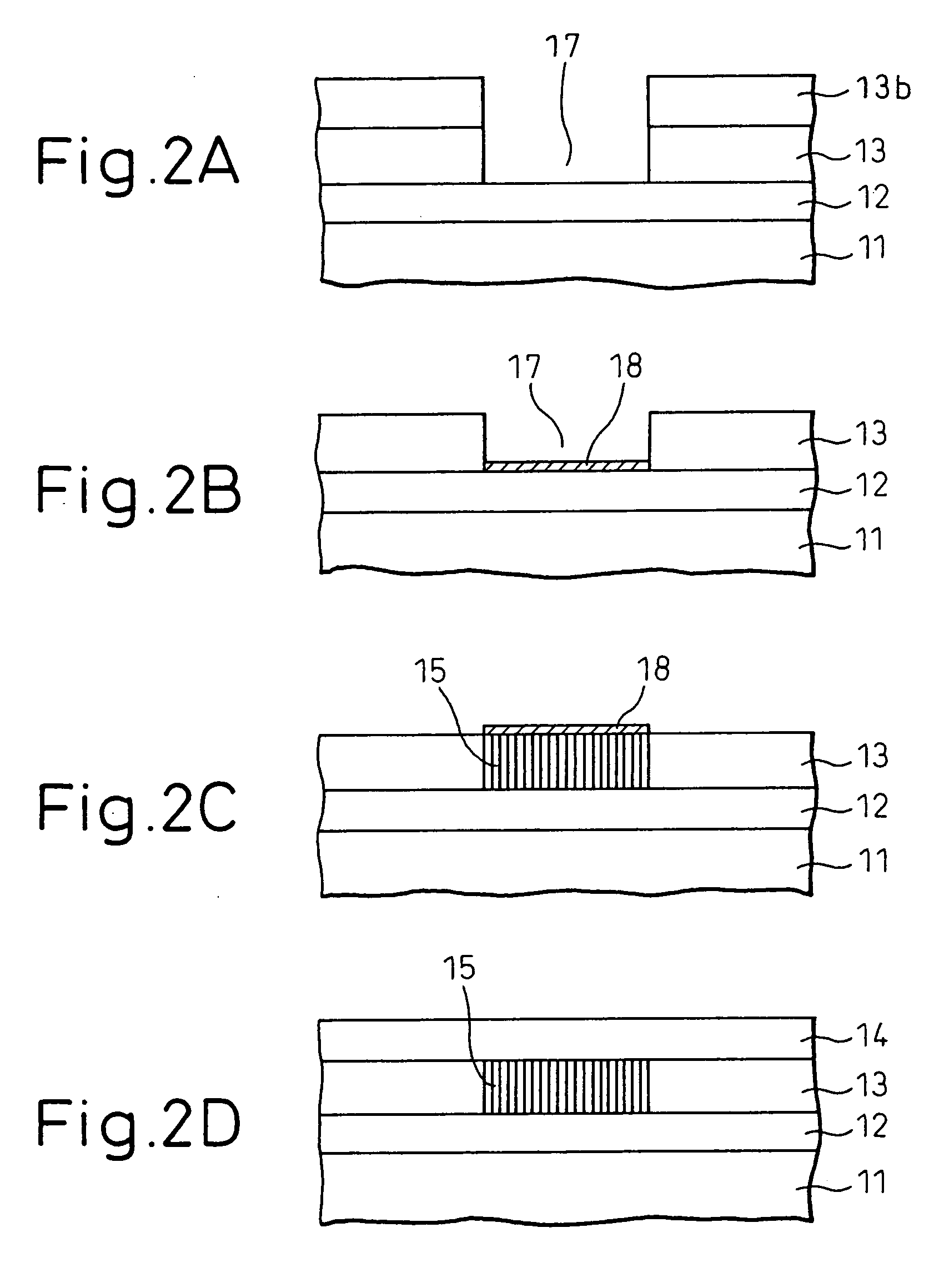
InactiveUS7339235B1Suppression of short channel effectsEffectively suppress a depletion layerTransistorIndividual molecule manipulationEngineeringSemiconductor
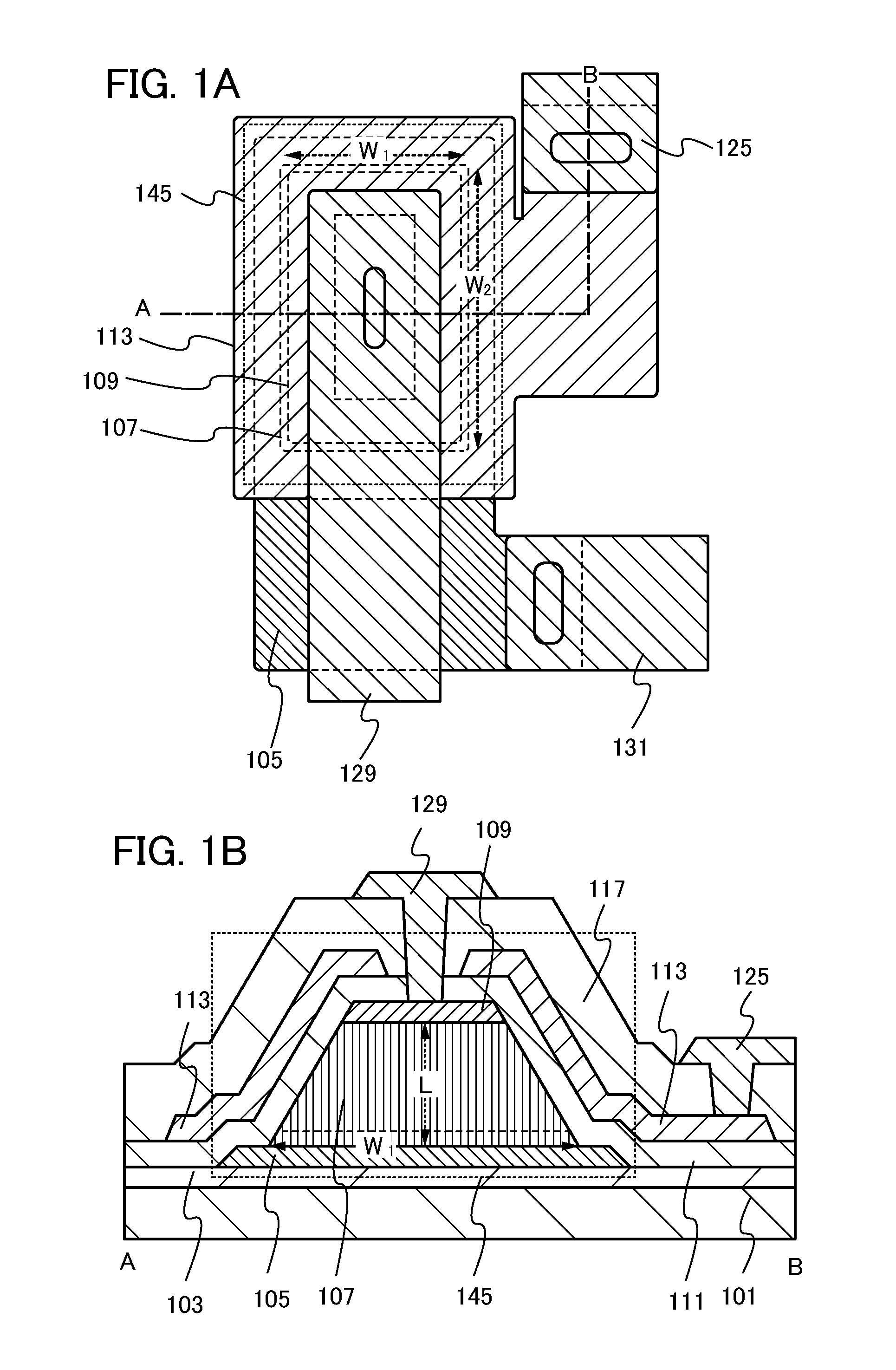
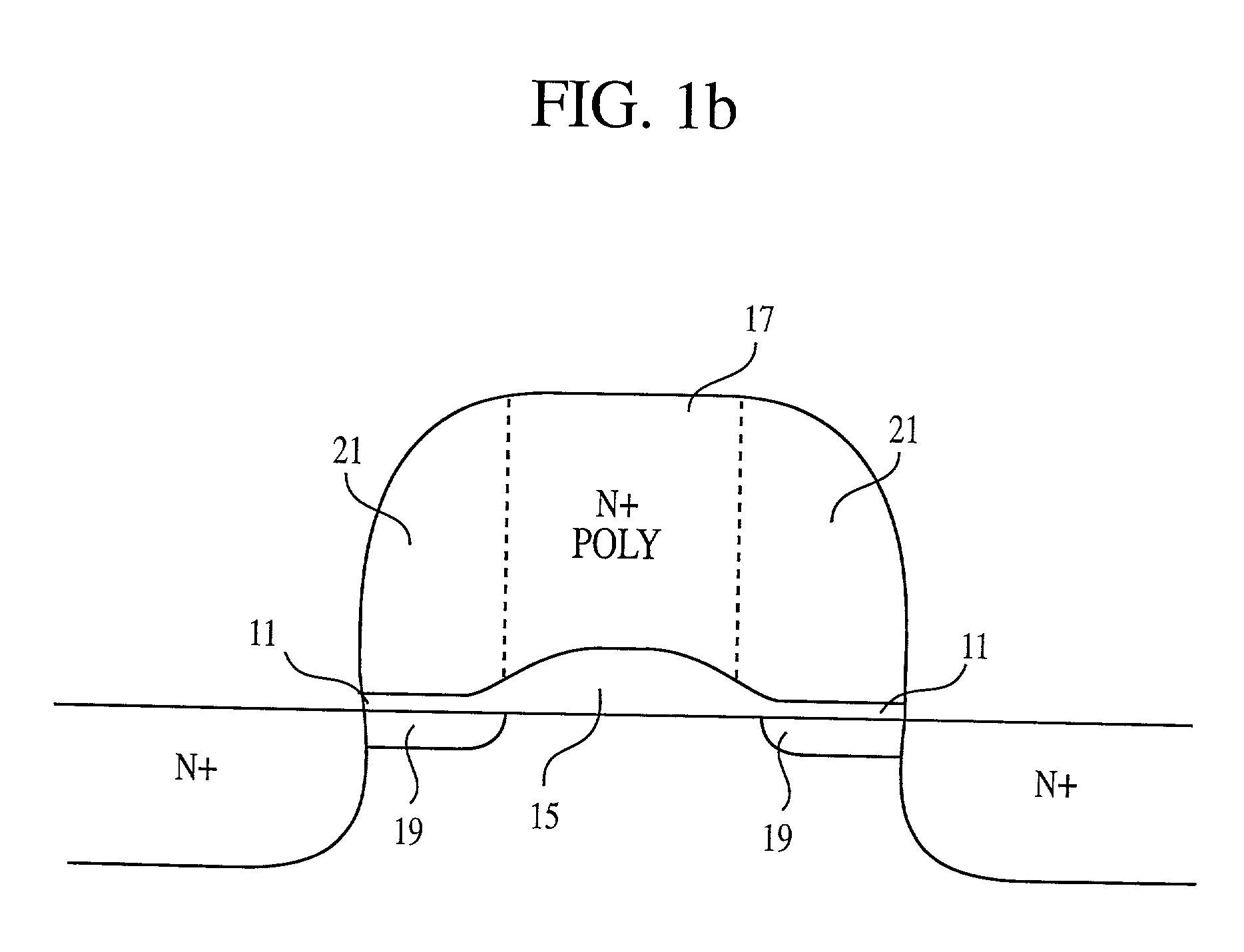
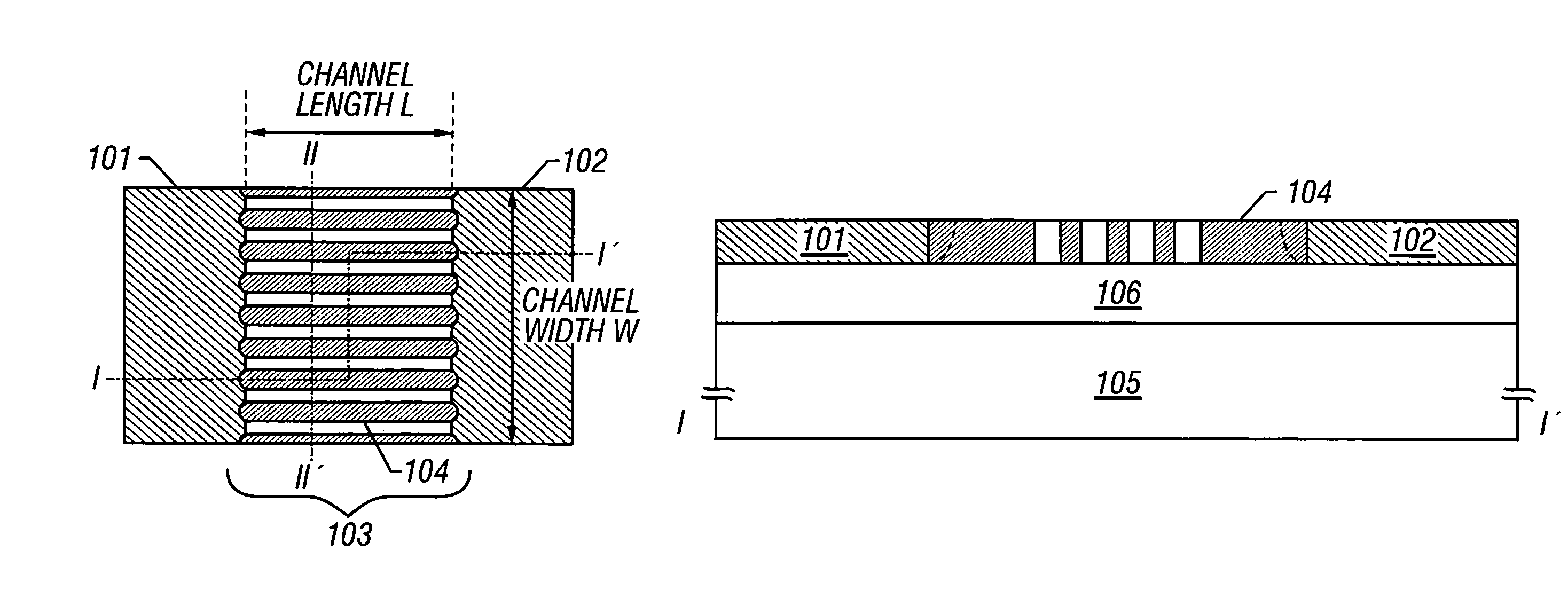
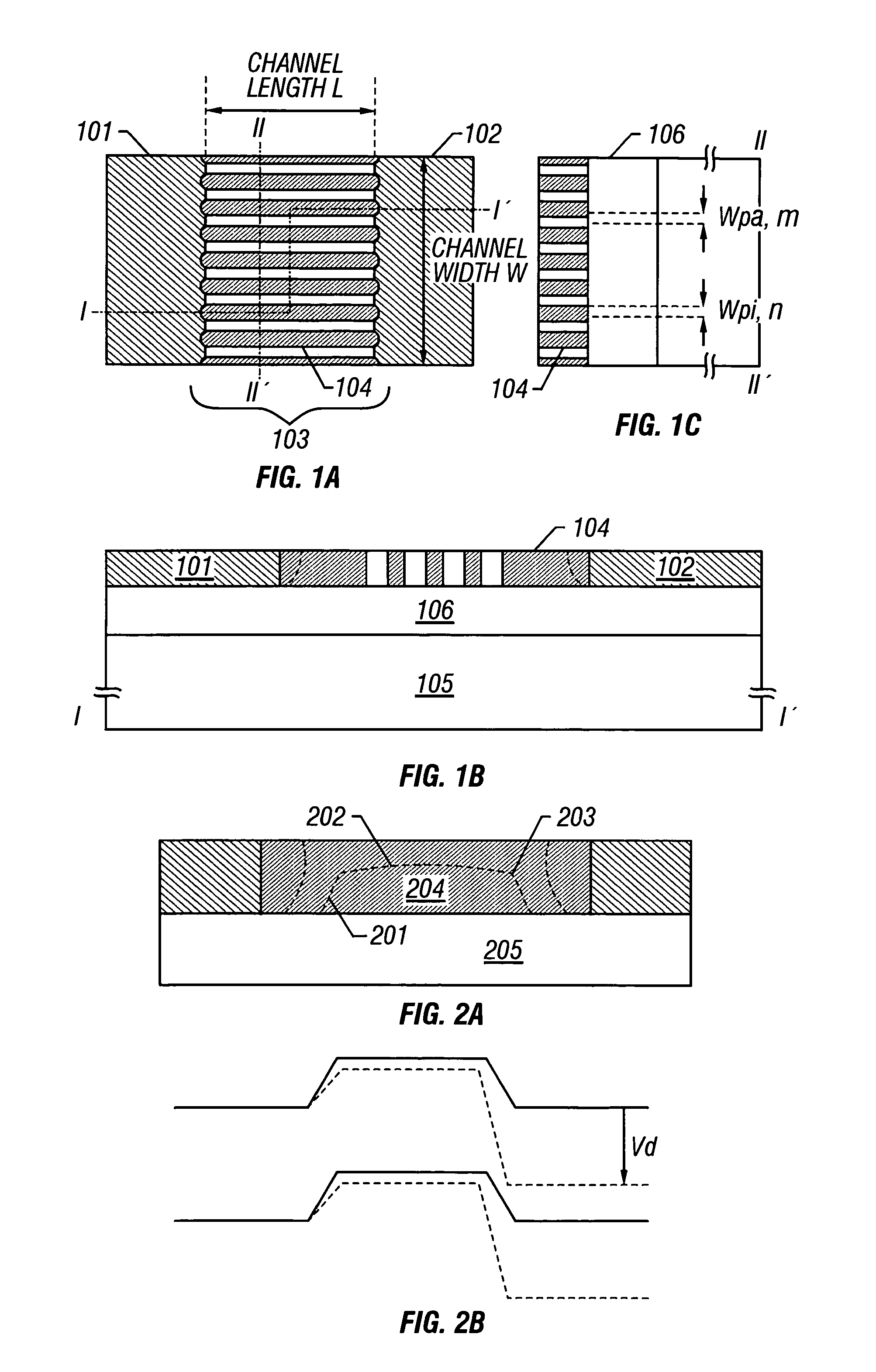
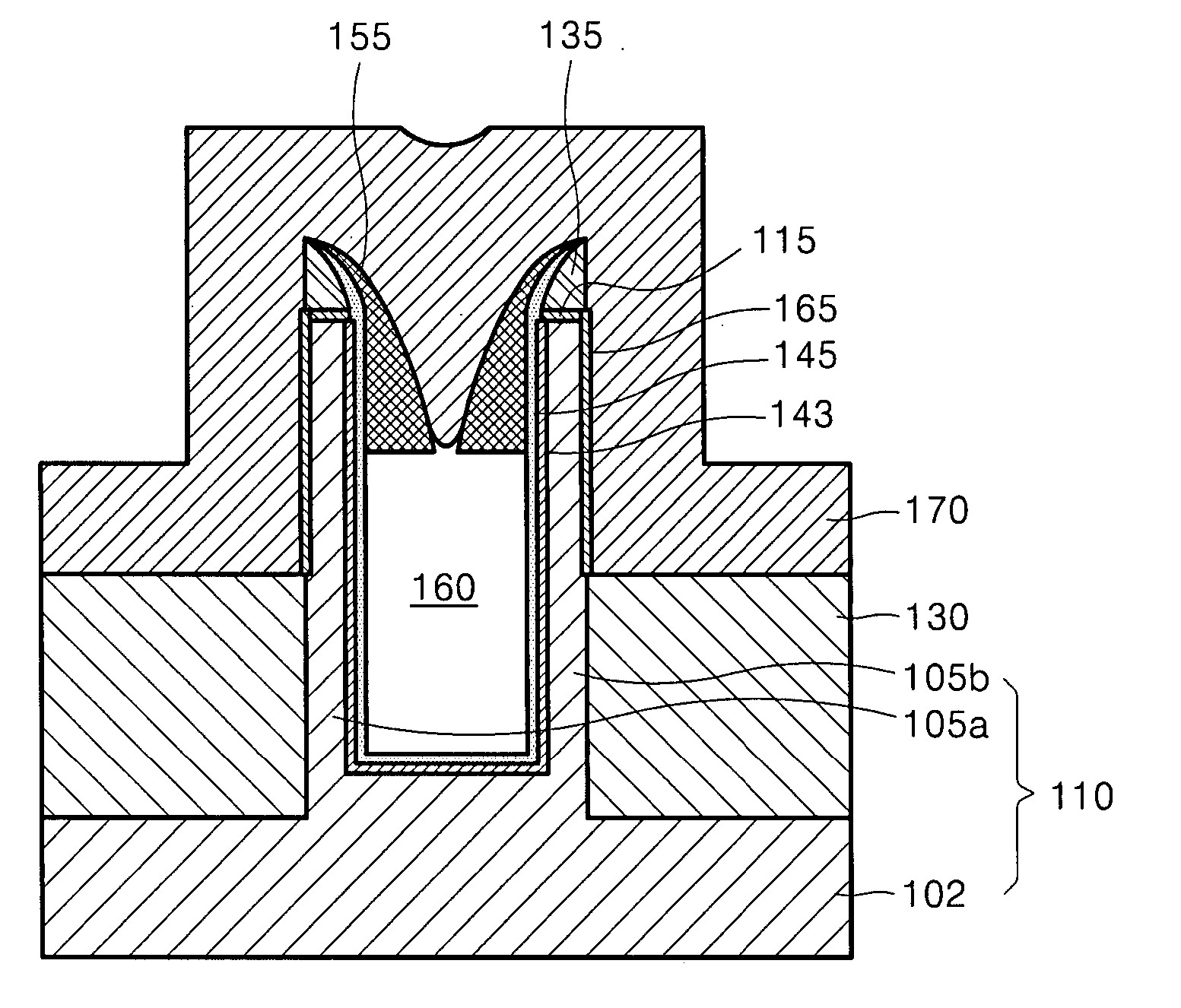
A fine semiconductor device having a short channel length while suppressing a short channel effect. Linearly patterned or dot-patterned impurity regions 104 are formed in a channel forming region 103 so as to be generally parallel with the channel direction. The impurity regions 104 are effective in suppressing the short channel effects. More specifically, the impurity regions 104 suppress expansion of a drain-side depletion layer, so that the punch-through phenomenon can be prevented. Further, the impurity regions cause a narrow channel effect, so that reduction in threshold voltage can be lessened.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and production method thereof
ActiveUS20070012913A1Avoid layeringSuppression of short channel effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialCharge carrier mobility
A method of fabricating a semiconductor device is disclosed that is able to suppress a short channel effect and improve carrier mobility. In the method, trenches are formed in a silicon substrate corresponding to a source region and a drain region. When epitaxially growing p-type semiconductor mixed crystal layers to fill up the trenches, the surfaces of the trenches are demarcated by facets, and extended portions of the semiconductor mixed crystal layers are formed between bottom surfaces of second side wall insulating films and a surface of the silicon substrate, and extended portion are in contact with a source extension region and a drain extension region.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20050285193A1Efficient solutionHigh carrier mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A semiconductor device and related method of manufacture are disclosed. The semiconductor device comprises a gate electrode formed on a semiconductor substrate, an active region containing spaces formed below the gate electrode, a channel region formed between the gate electrode and the spaces, and source and drain regions formed on opposite sides of the gate electrode within the active region. The spaces are formed by etching a semiconductor layer formed below the gate electrode in the active region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multiple-gate MOSFET device with lithography independent silicon body thickness and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS6946377B2Avoidance and mitigationSuppression of short channel effectsTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETLithographic artist
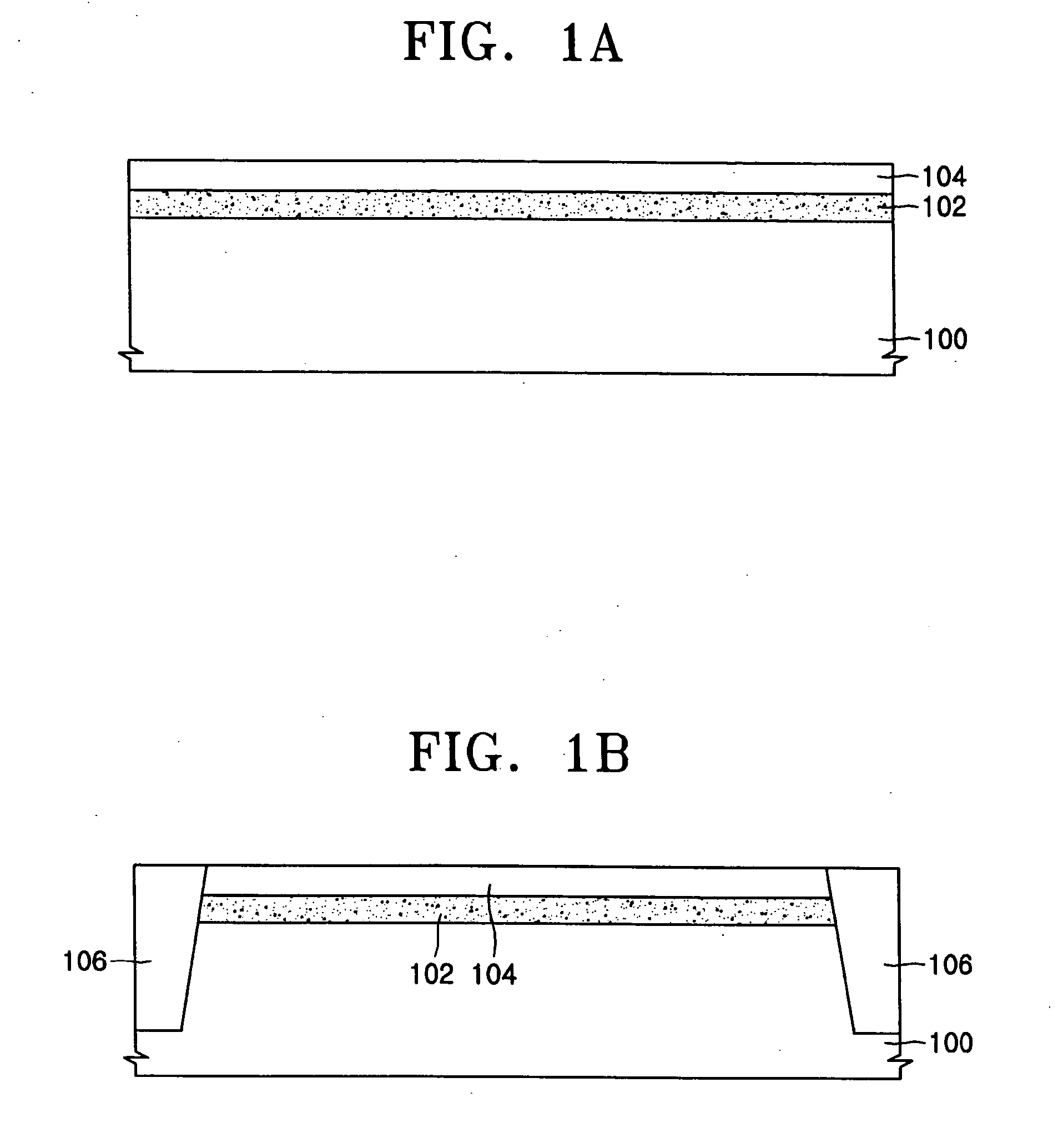
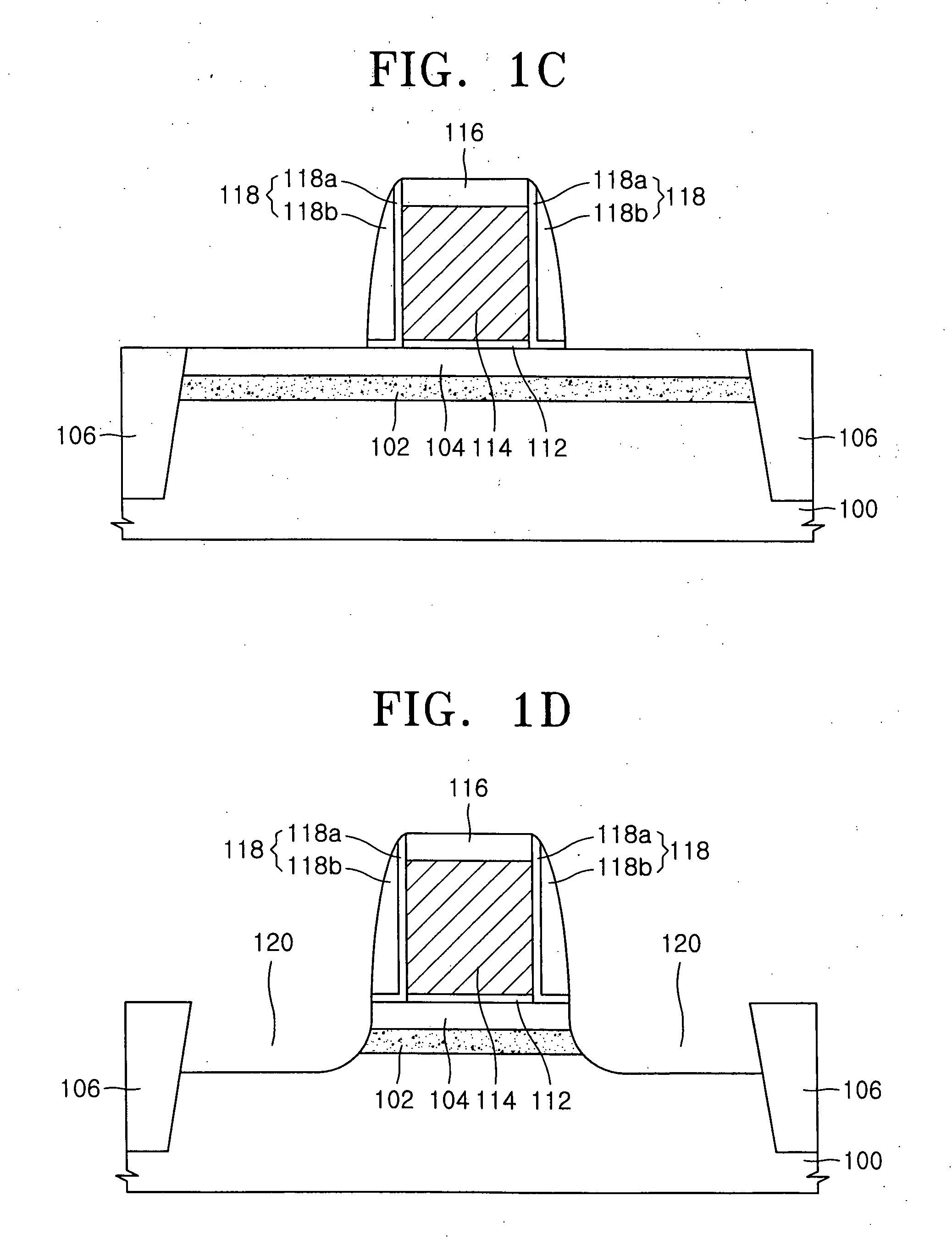
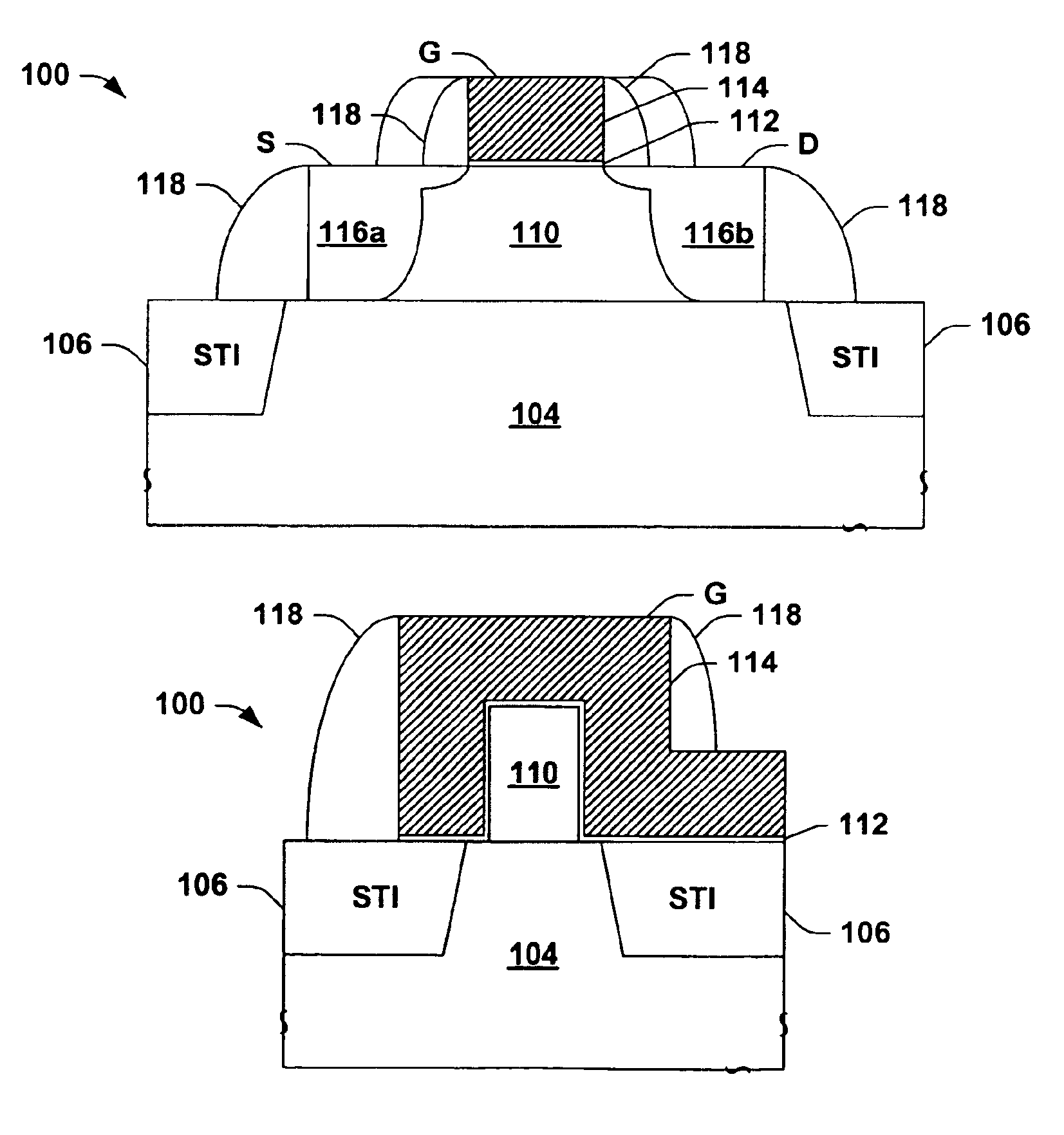
Multi-gate MOS transistors and fabrication methods are described, in which the transistor semiconductor body thickness or width is lithography independent, allowing scaled triple and quad-gate devices having semiconductor bodies smaller than a lateral gate length dimension. A form structure is provided over a semiconductor wafer starting structure, and spacers are formed along one or more sidewalls of an opening in the form structure. A semiconductor material is deposited in the opening by epitaxial growth or other deposition process, and the form structure and the spacer are removed. A gate structure is then formed along the top and sides of a central portion of the formed semiconductor body. The spacer may be L-shaped, providing an undercut or recess at the bottom of the semiconductor body sidewall, and the gate may be formed in the undercut area to allow fabrication of more than three gates.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090032849A1Increase currentReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor device
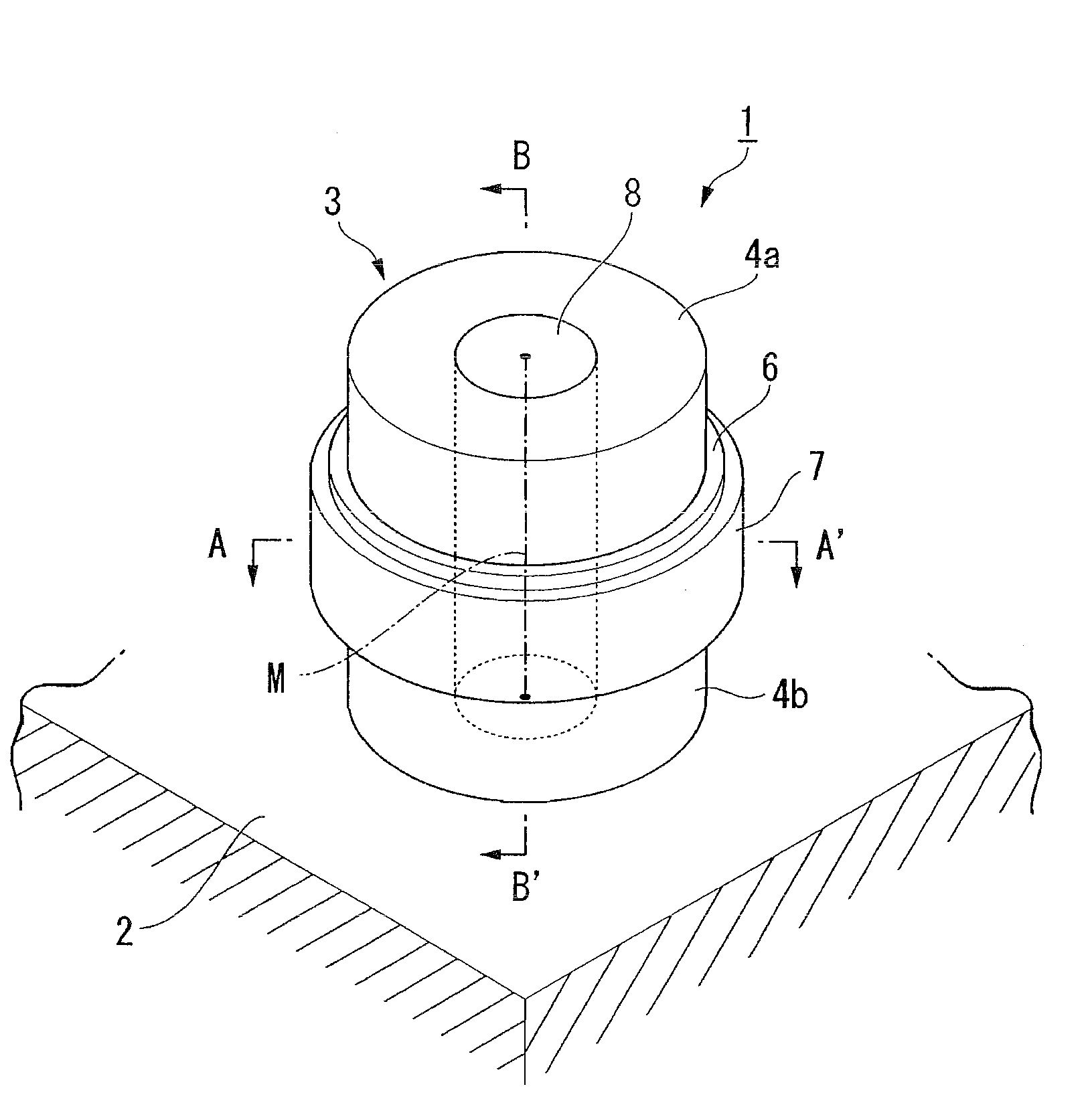
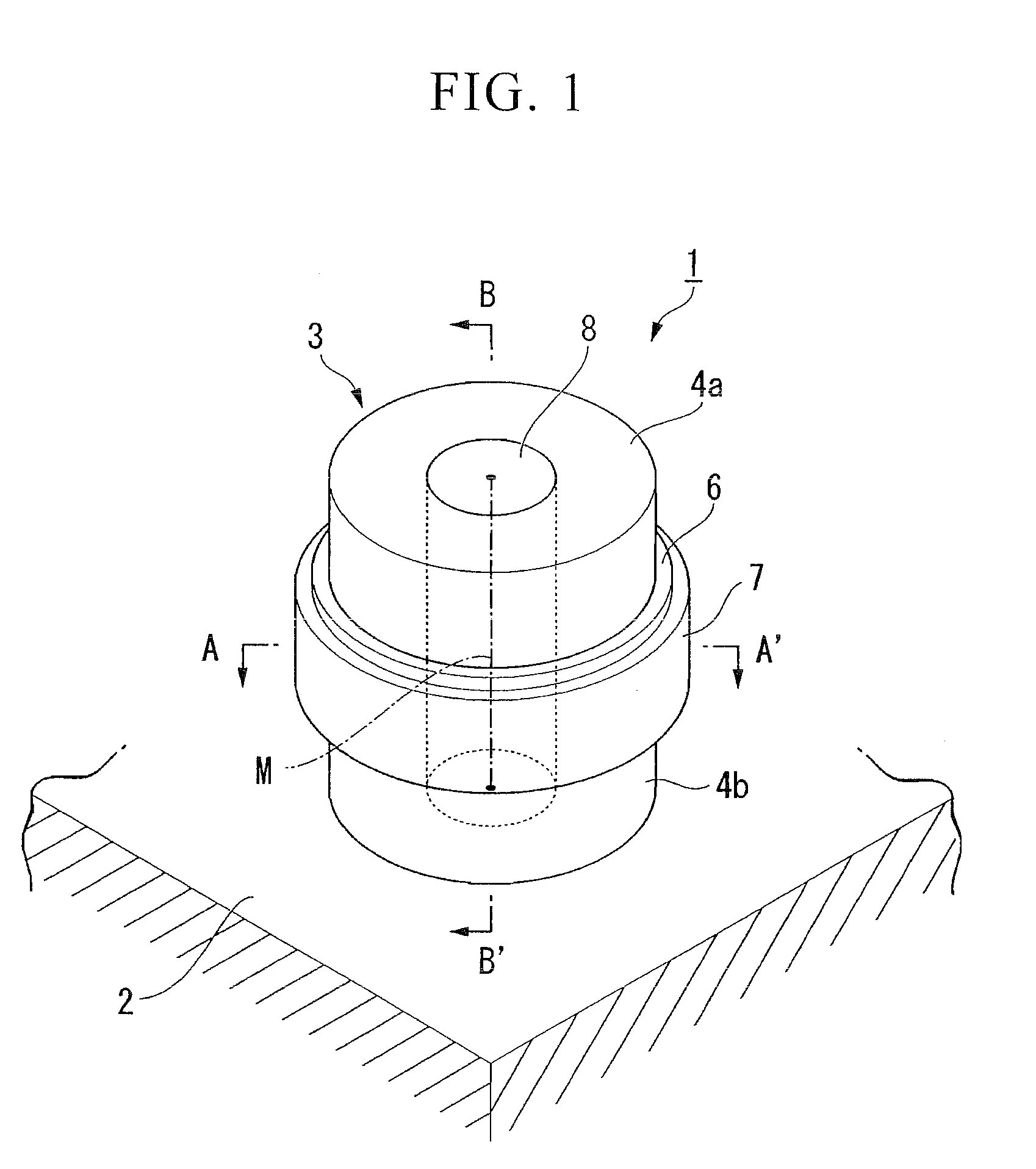
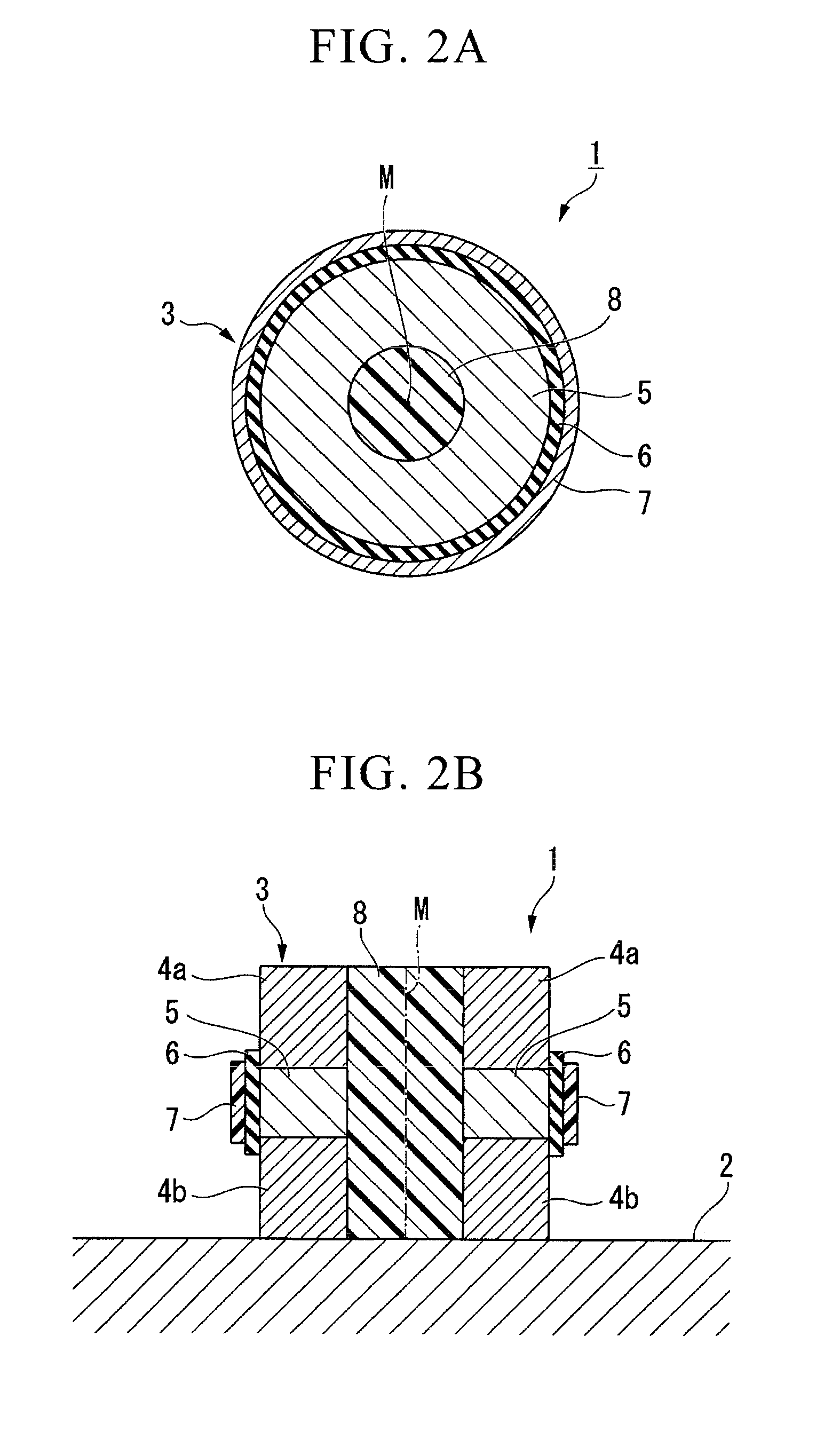
A semiconductor device includes a cylindrical main pillar that is formed on a substrate and of which a central axis is perpendicular to the surface of the substrate, source and drain diffused layers that are formed in a concentric shape centered on the central axis at upper and lower portions of the main pillar and made from a first-conduction-type material, a body layer that is formed at an intermediate portion of the main pillar sandwiched between the source and drain diffused layers and made from the first-conduction-type material, and a front gate electrode that is formed on a lateral face of the main pillar while placing a gate insulating film therebetween. Moreover, a back gate electrode made from a second-conduction-type material is formed in a pillar shape penetrating from an upper portion to a lower portion on an inner side of the main pillar.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
Semiconductor device having a pair of fins and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080111199A1Read operationSuppression of short channel effectsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEngineering
Example embodiments relate to a semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same. A semiconductor device according to example embodiments may have reduced disturbances during reading operations and a reduced short channel effect. The semiconductor device may include a semiconductor substrate having a body and a pair of fins protruding from the body. Inner spacer insulating layers may be formed on an upper portion of an inner sidewall of the pair of fins so as to reduce the entrance to the region between the pair of fins. A gate electrode may cover a portion of the external sidewalls of the pair of fins and may extend across the inner spacer insulating layers so as to define a void between the pair of fins. Gate insulating layers may be interposed between the gate electrode and the pair of fins.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20010009292A1Minimizes heat treatmentSteep impurity concentration profileTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorManufacturing variation
A semiconductor device has a first semiconductor region formed in a semiconductor substrate and having a first conductivity type due to first-conductivity-type active impurities contained in the first semiconductor region, and a second semiconductor region formed between the first semiconductor region and the surface of the semiconductor substrate and having a second conductivity type due to second-conductivity-type active impurities contained in the second semiconductor region. The second semiconductor region contains first-conductivity-type active impurities whose concentration is zero or smaller than a quarter of a concentration of the second-conductivity-type active impurities contained in the second semiconductor region. An insulating film and a conductor are formed on the second semiconductor region. Third and fourth semiconductor regions of the second conductivity type are formed at the semiconductor surface in contact with the side faces of the second semiconductor region. This semiconductor device is capable of suppressing net impurity concentration variations as well as threshold voltage variations to be caused by a short channel effect or manufacturing variations.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Fabrication of silicon nano wires and gate-all-around MOS devices
InactiveUS20070298551A1Quality improvementEnhance the quantum effectNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETCapacitance
The invention relates to methods for manufacturing semiconductor devices. Processes are disclosed for implementing suspended single crystal silicon nano wires (NWs) using a combination of anisotropic and isotropic etches and spacer creation for sidewall protection. The core dimensions of the NWs are adjustable with the integration sequences: they can be triangular, rectangular, quasi-circular, or an alternative polygonal shape. Depending on the length of the NWs, going from the sub-micron to millimeter range, the NWs may utilize support from anchors to the side, during certain processing steps. By changing the lithographic dimensions of the anchors compared to the NWs, the anchors may be reduced or eliminated during processing. The method covers, among other things, the integration of Gate-All-Around NW (GAA-NW) MOSFETs on a bulk semiconductor. The GAA structure may consist of a silicon core fabricated as specified in the invention, surrounded by any usable gate dielectric, and finally by a gate material, such as polysilicon or metal. The source and drain of the GAA-NW may be connected to the bulk semiconductor to avoid self heating of the device over a wide range of operating conditions. The GAA-NW MOS capacitor can also be used for the integration of a Gate-All-Around optical phase modulator (GAA modulator). The working principle for the optical modulator is modulation of the refractive index by free carrier accumulation or inversion in a MOS capacitive structure, which changes the phase of the propagating light.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Methods of fabricating a dielectric plug in MOSFETs to suppress short-channel effects
InactiveUS20050035408A1Increasing source-drain junction capacitanceEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBulk negative resistance effect devicesDielectricShort-channel effect
The invention provides a technique to fabricate a dielectric plug in a MOSFET. The dielectric plug is fabricated by forming an oxide layer over exposed source and drain regions in the substrate including a gate electrode stack. The formed oxide layer in the source and drain regions are then substantially removed to expose the substrate in the source and drain regions and to leave a portion of the oxide layer under the gate electrode stack to form the dielectric plug and a channel region between the source and drain regions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
MOS transistor with elevated source/drain structure
ActiveUS20060163558A1Prevent degradationReduce sheet resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorEpitaxy
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ultra thin film SOI MOSFET having recessed source/drain structure and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20060131648A1Reduce resistanceTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesGate stackField-effect transistor
There are provided an ultra thin film silicon on insulator (SOI) metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) having a recessed source / drain structure, and a method of fabricating the same. The ultra thin film SOI MOS transistor includes a semiconductor substrate; a buried insulating layer disposed on the semiconductor substrate, and formed recessed except for a center portion thereof; an ultra thin film single crystalline silicon layer pattern disposed on the recessed buried insulating layer; a gate stack disposed on the ultra thin film single crystalline silicon layer pattern, and including a gate insulating layer pattern and a gate conductive layer pattern, which are sequentially stacked; a gate spacer layer disposed on sidewalls of the gate stack; and a recessed source / drain region disposed on the recessed buried insulating layer, and formed to overlap a bottom surface portion of the ultra thin film single crystalline silicon layer pattern, which does not overlap the center portion of the recessed buried insulating layer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Schottky barrier quantum well resonant tunneling transistor
InactiveUS20100102298A1High speedReduce series resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesQuantum wellSchottky barrier
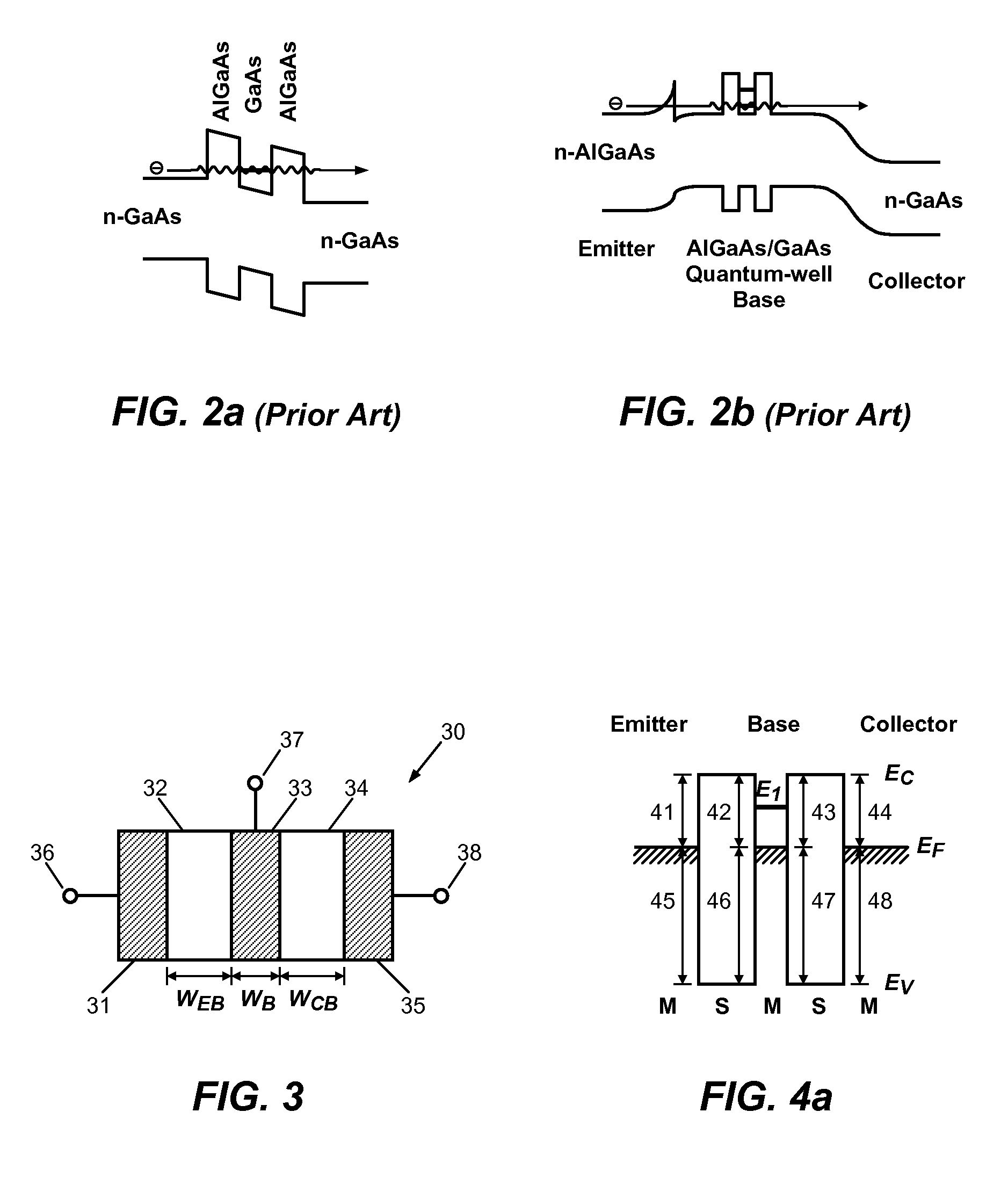
A semiconductor transistor device includes one or more conductive base regions, a first semiconductor barrier region, a second semiconductor barrier region, a conductive emitter region, and a conductive collector region. The first semiconductor barrier region or the second semiconductor barrier region has a dimension smaller than 100 Å. A first Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the first semiconductor barrier region and the one or more conductive base regions. A second Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the second semiconductor barrier region and the one or more conductive base regions. A third Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the conductive emitter region and the first semiconductor barrier region. A fourth Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the conductive collector region and the second semiconductor barrier region.
Owner:WU KOUCHENG
FinFET device with reduced DIBL
ActiveUS7009250B1Reduce resistanceSuppression of floating body effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBorophosphosilicate glassEngineering
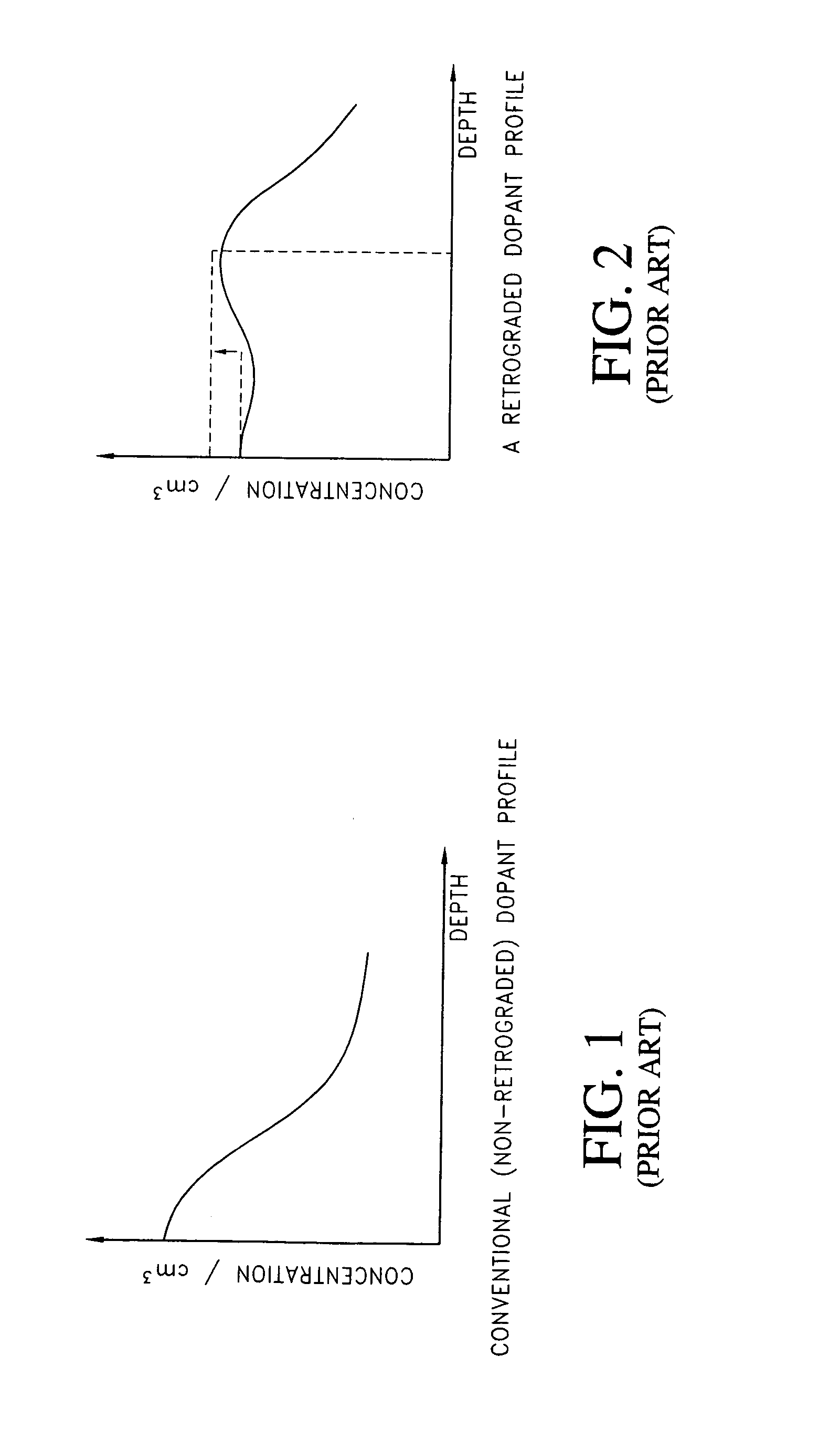
FinFET devices formed with a Silicon On Insulator (SOI) technology with reduced Drain Induced Barrier Lowering (DIBL) characteristics and methods for producing the same. The methods involve dopant implants into the insulator layer, thereby creating borophosphosilicate glass (BPSG) diffusion sources within the insulation layer underlying the active regions of the SOI wafer. Backend high temperature processing steps induce diffusion of the dopants contained in the diffusion source into the active regions, thereby forming a retrograde dopant profile extending towards the channel region. The method can be selectively applied to selected portions of a wafer to tailor device characteristics, such as for memory cells.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Flash memory cell, flash memory device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7087950B2High density integrationReducing parasitic coupling noiseTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric layerSilicon
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com