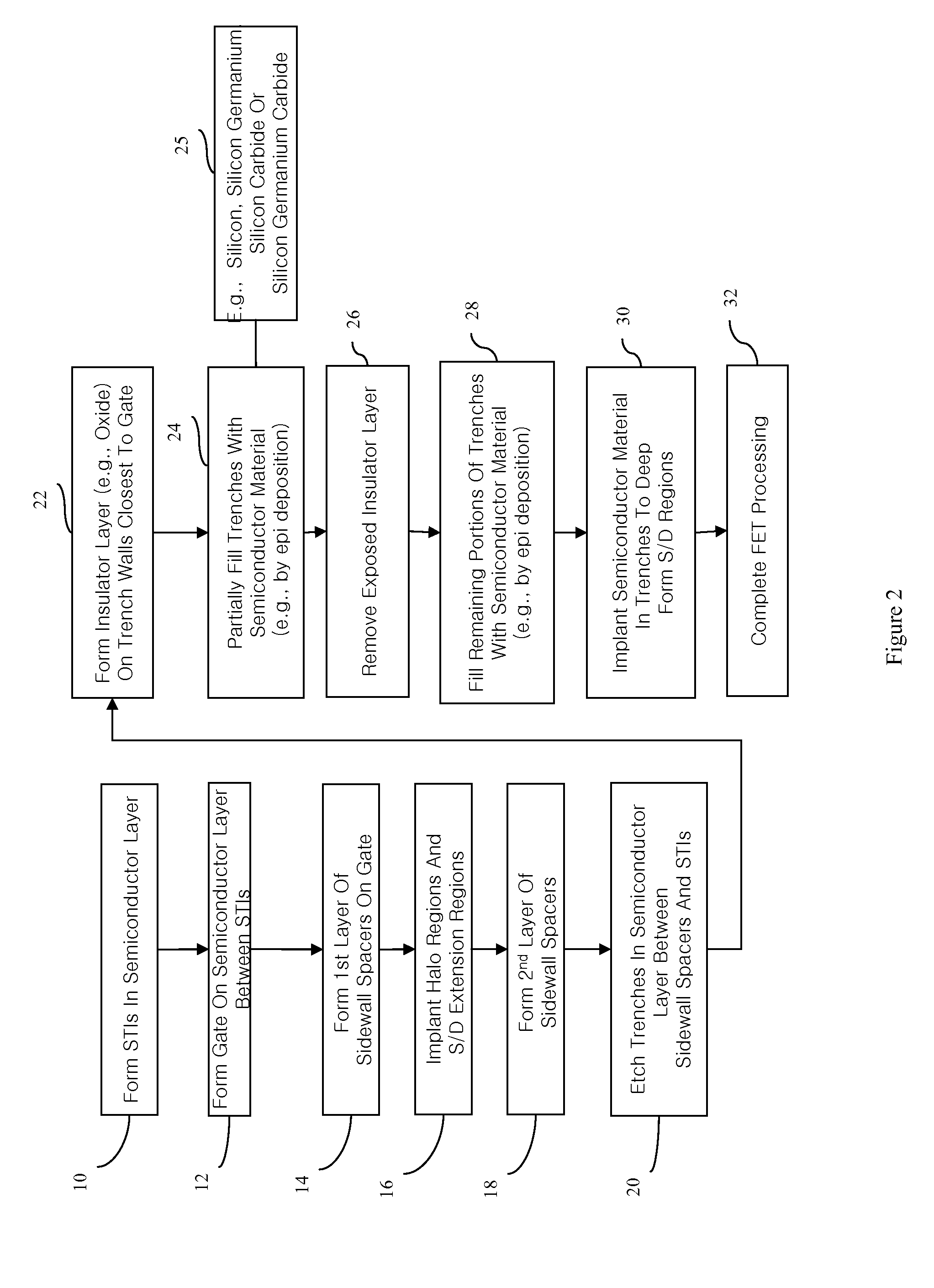
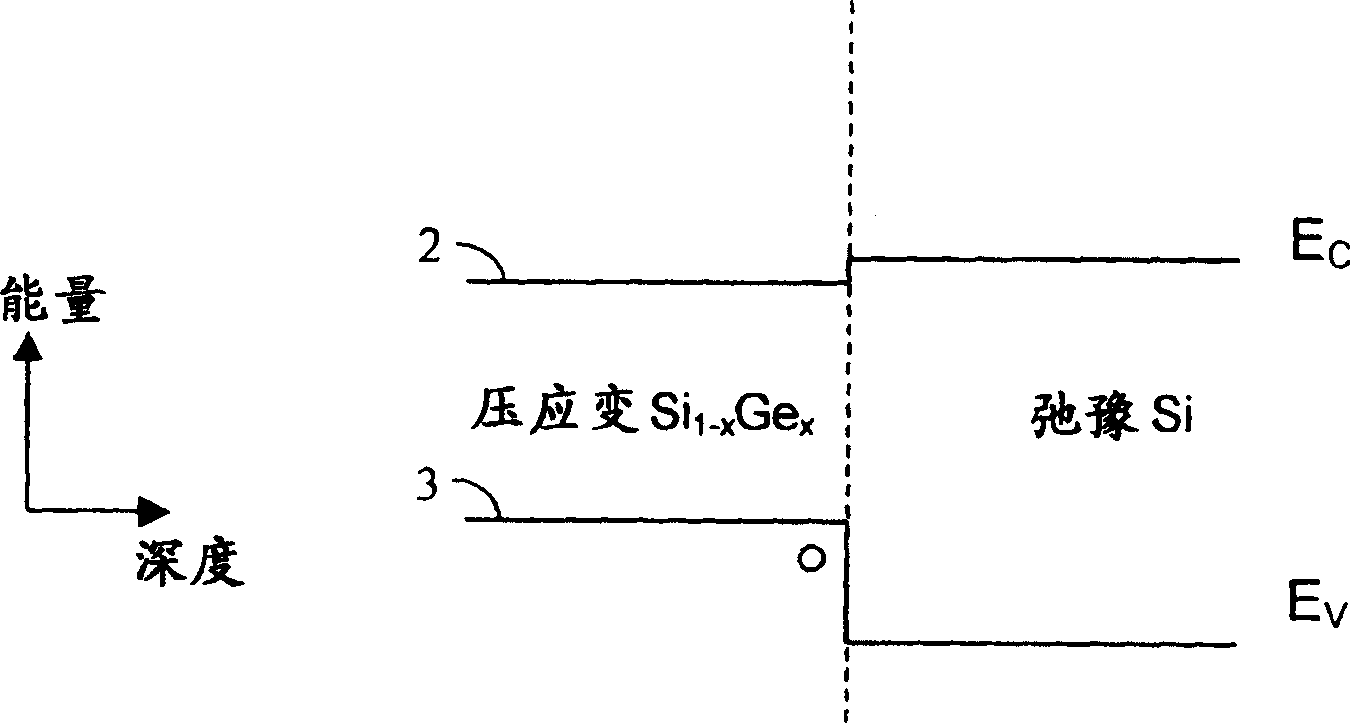
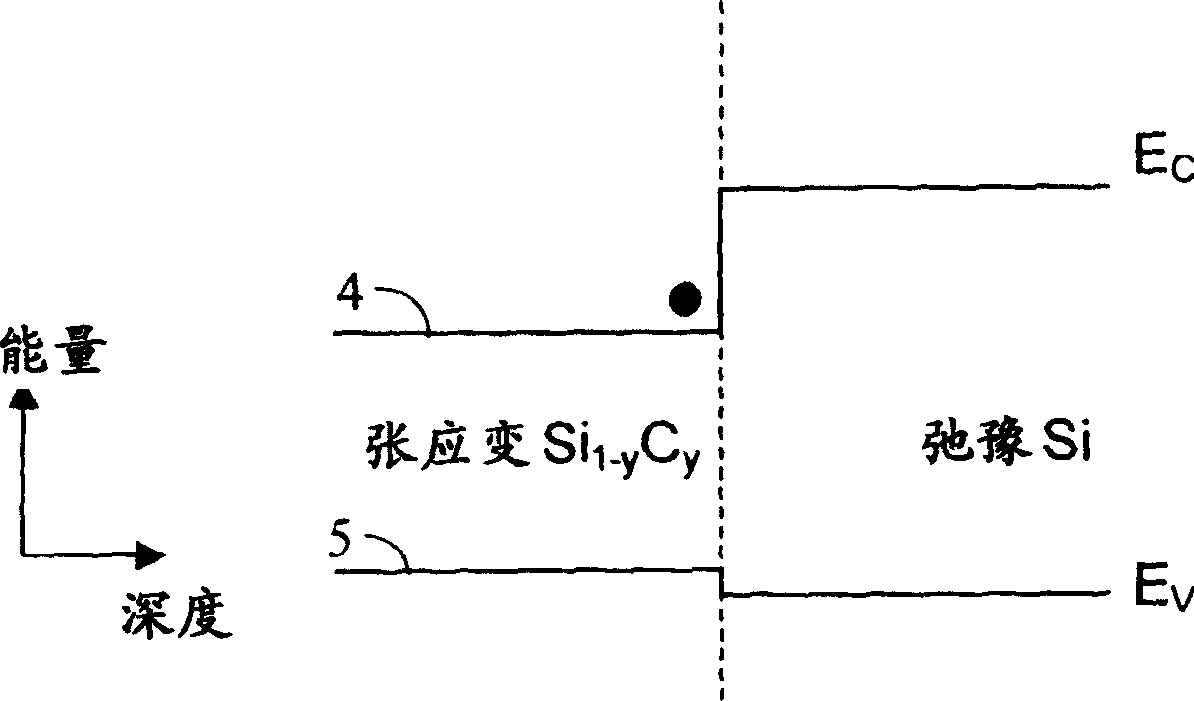
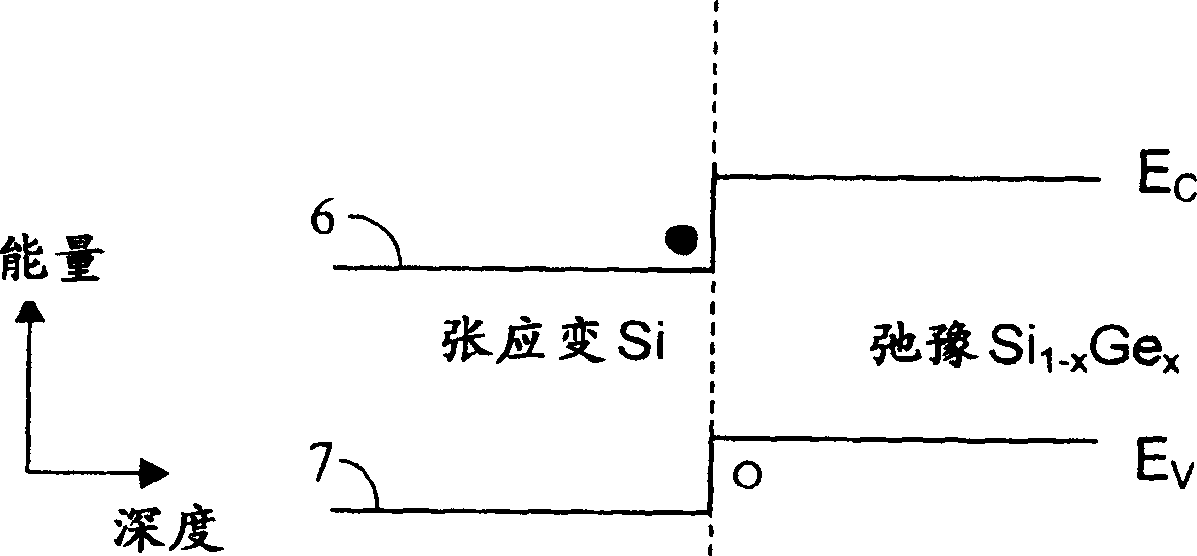
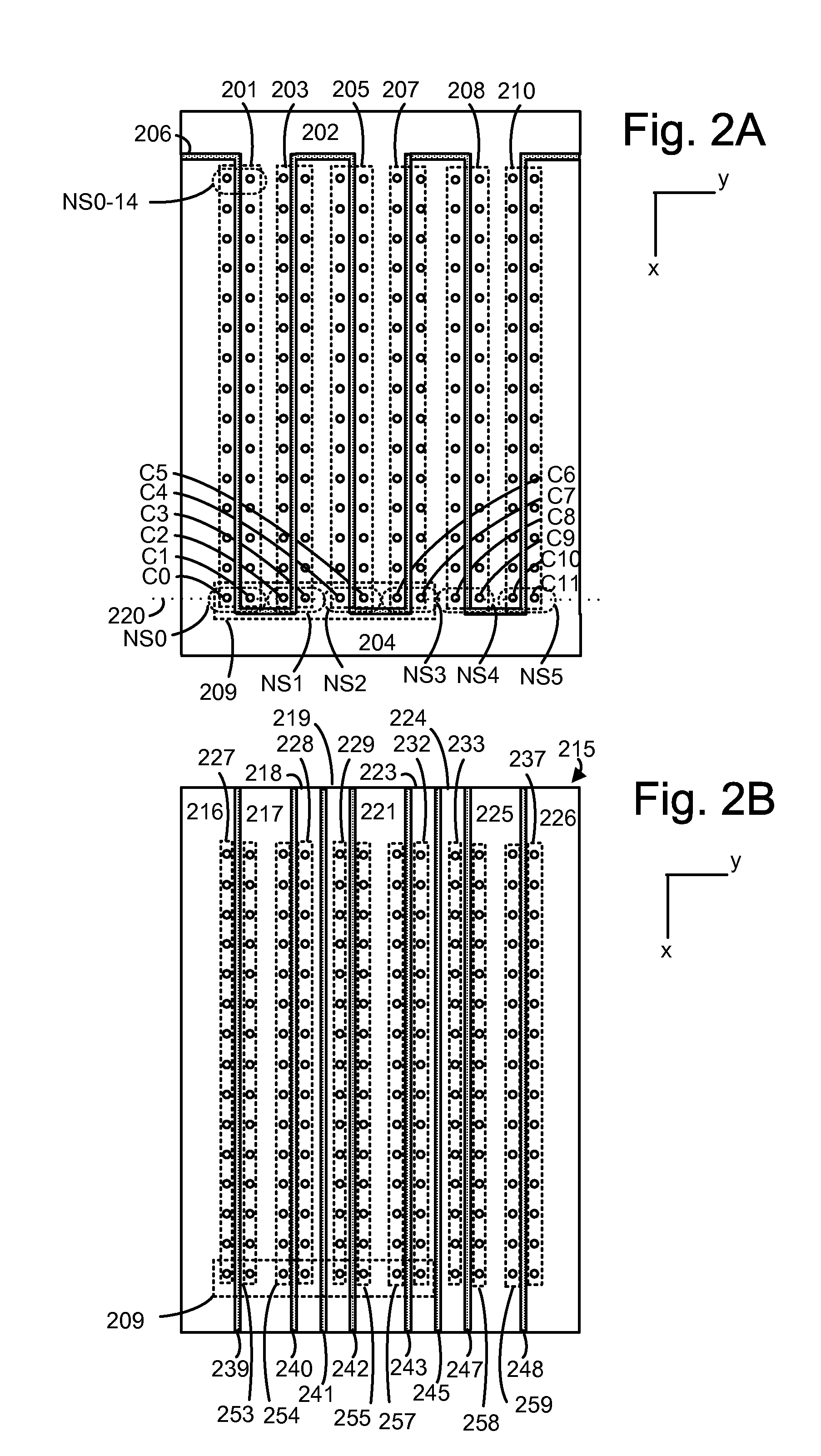
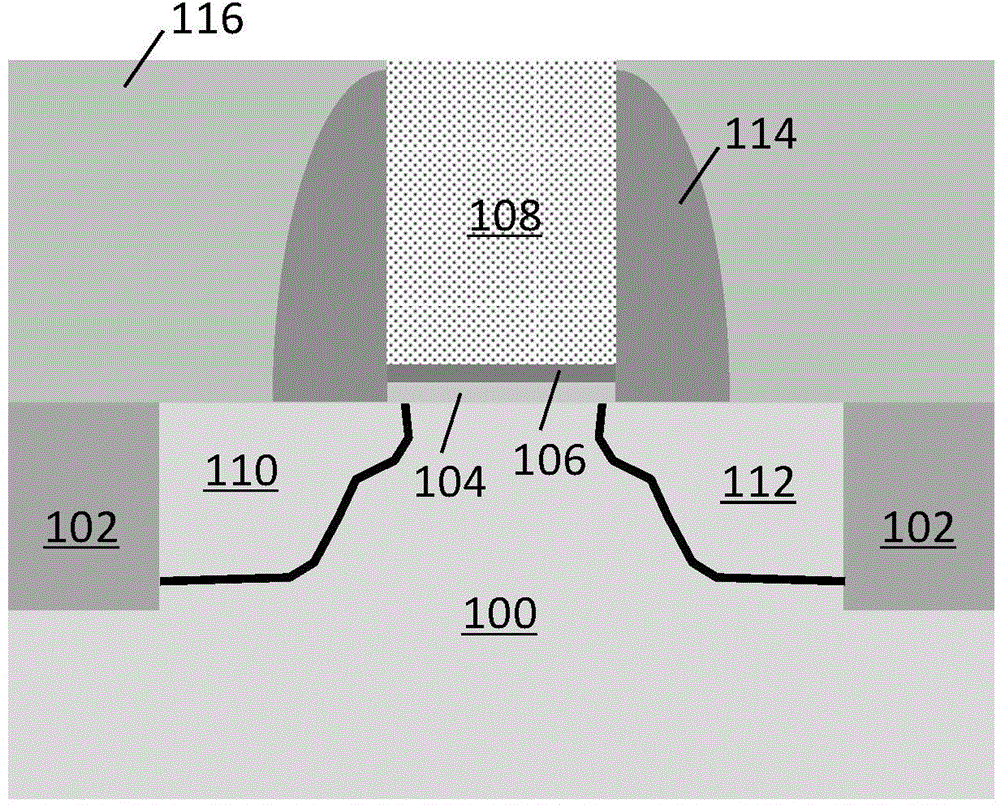
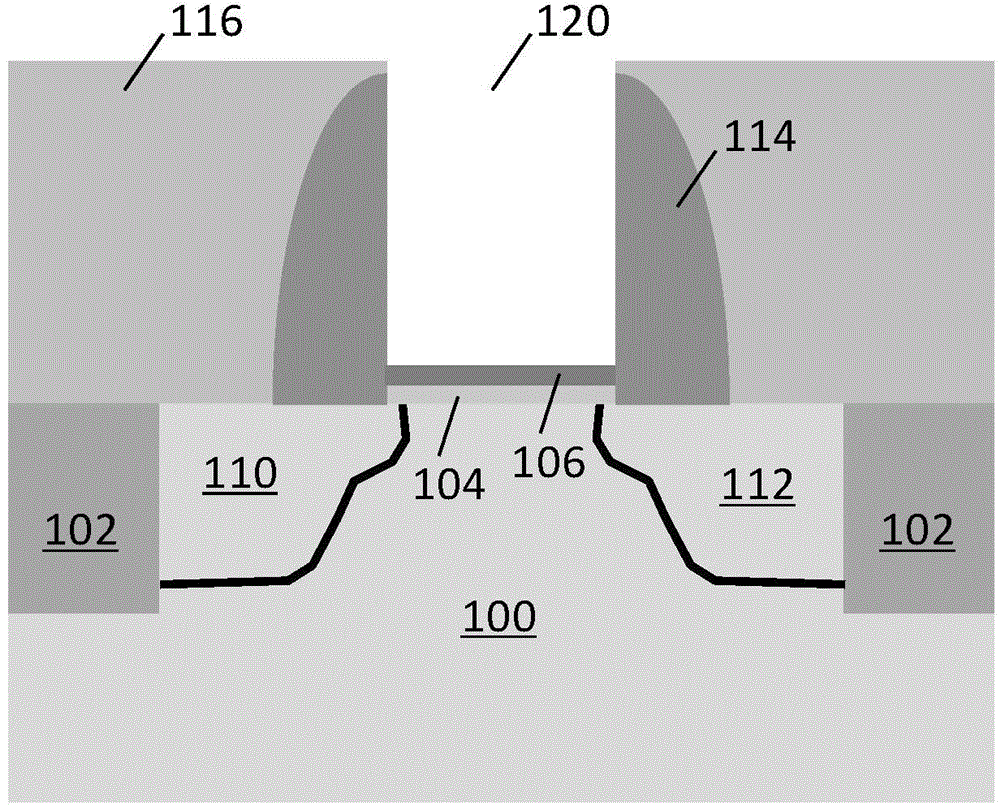
Patents
Literature
68 results about "Drain-induced barrier lowering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
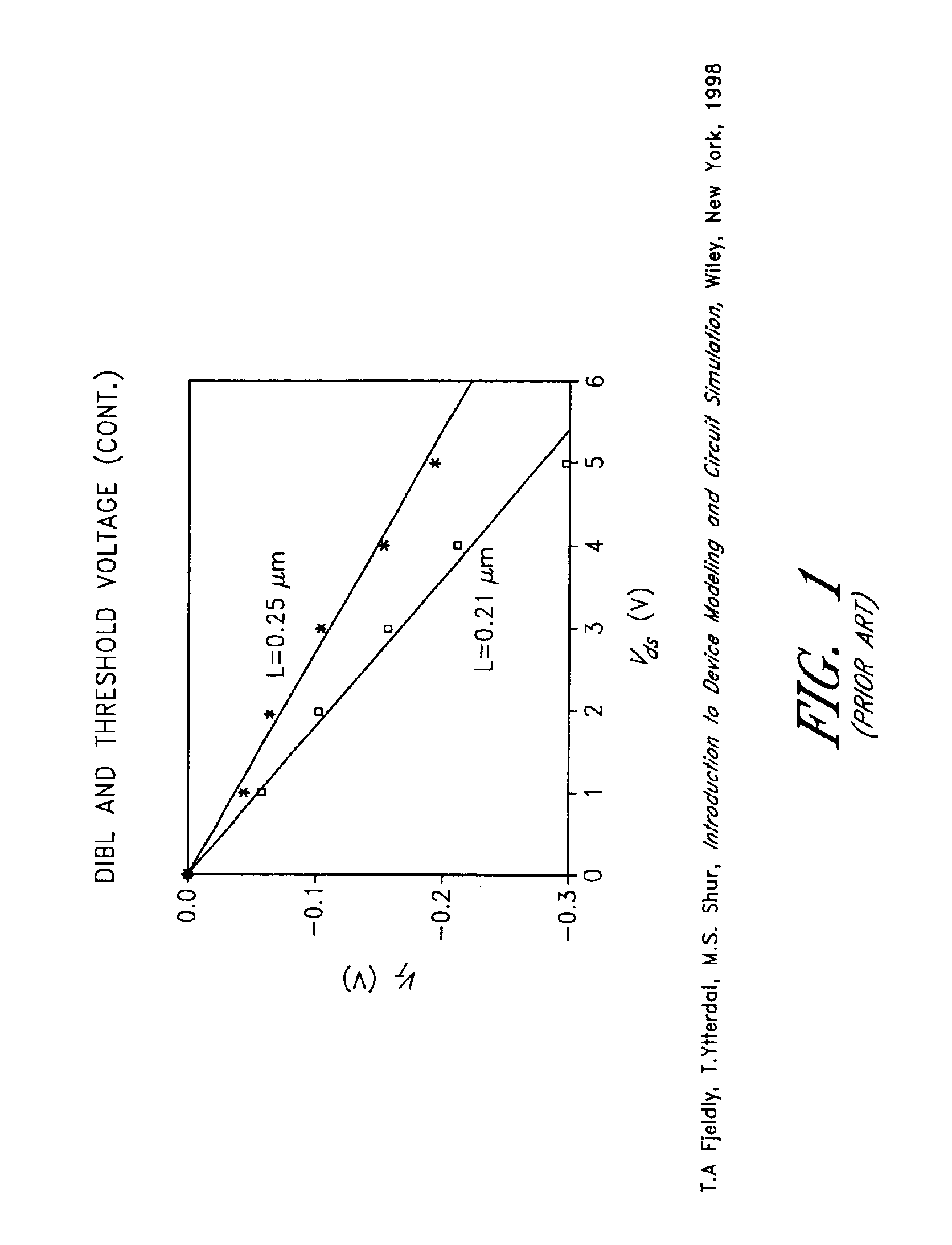
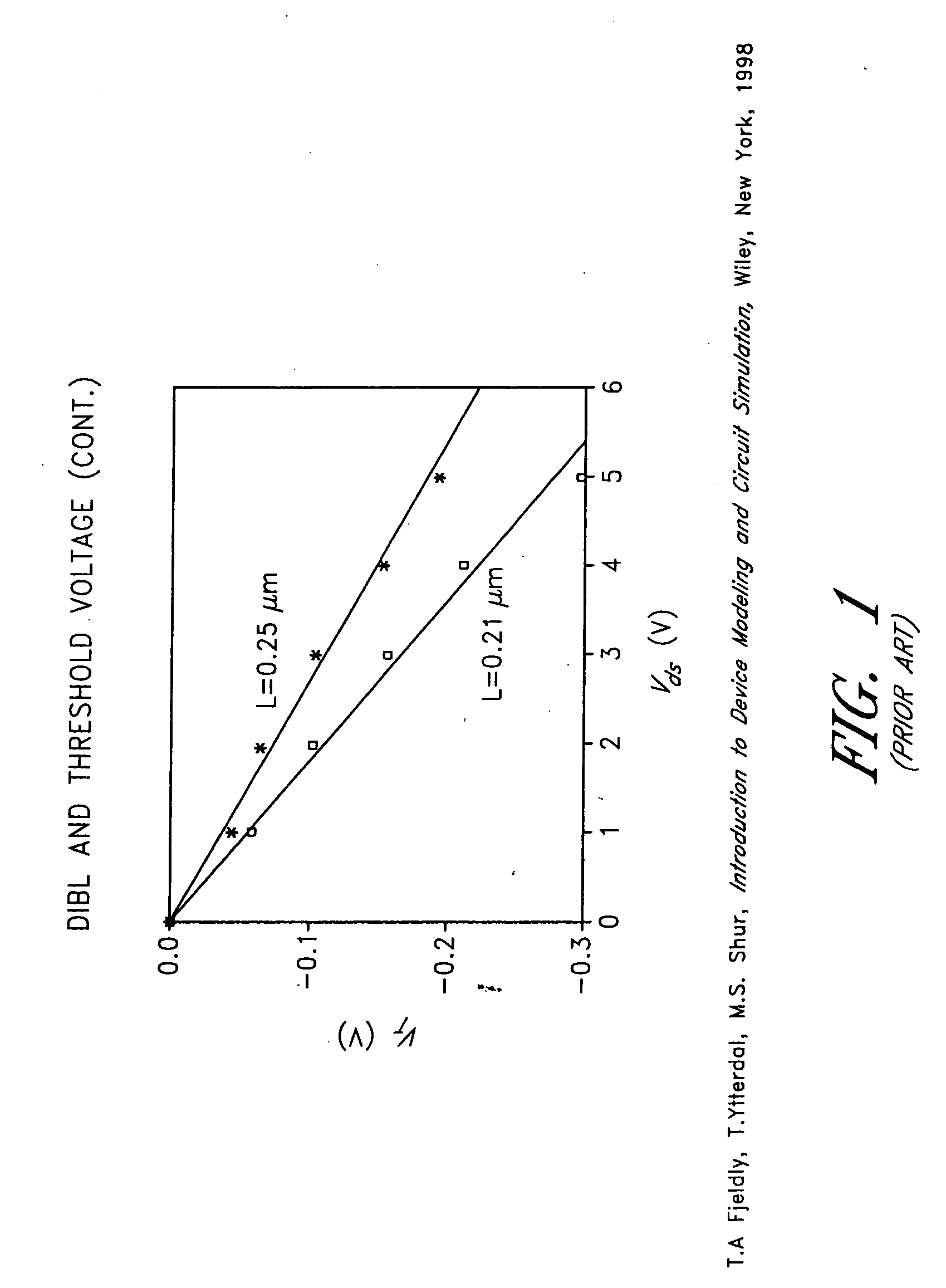
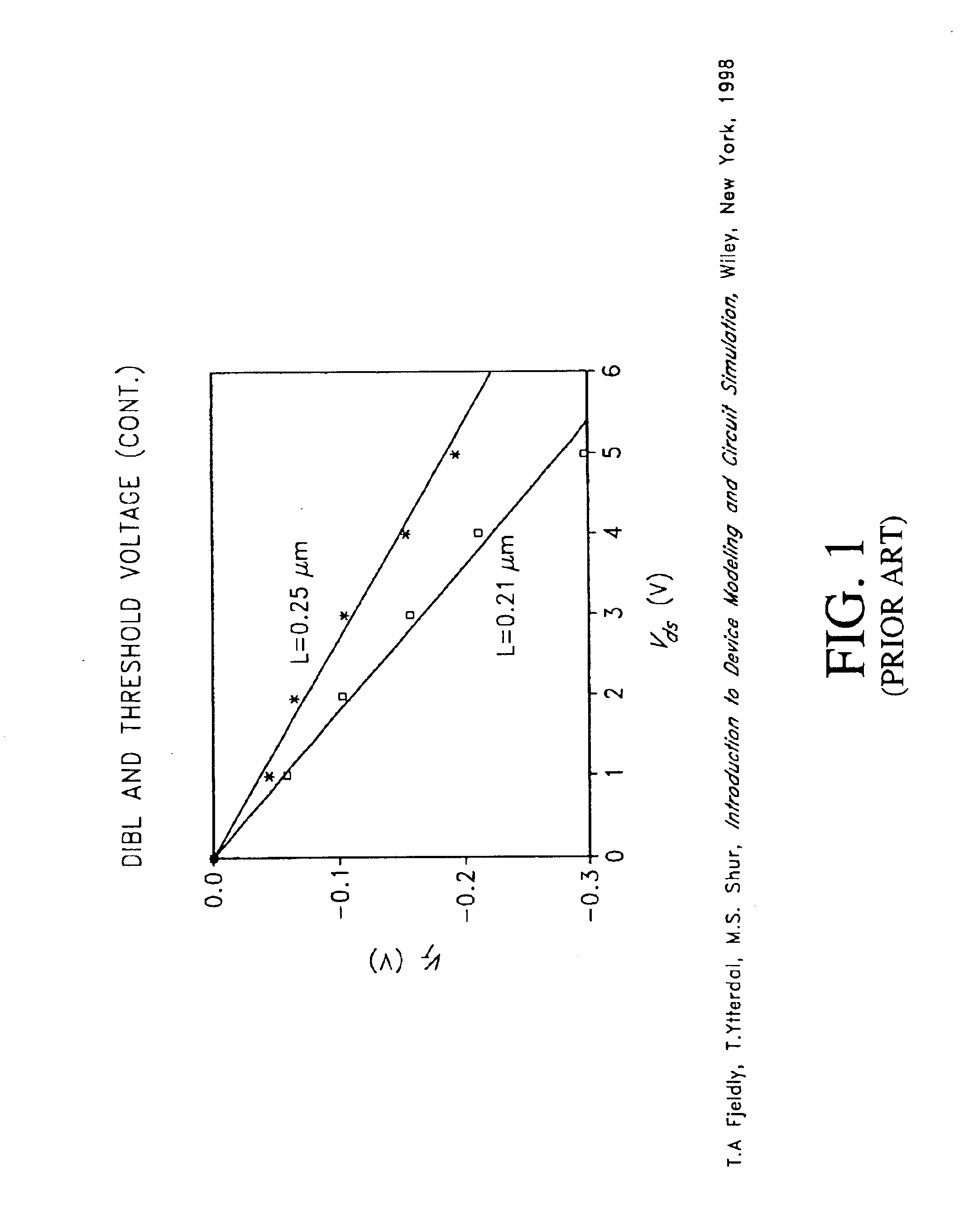
Drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL) is a short-channel effect in MOSFETs referring originally to a reduction of threshold voltage of the transistor at higher drain voltages. In a classic planar field-effect transistor with a long channel, the bottleneck in channel formation occurs far enough from the drain contact that it is electrostatically shielded from the drain by the combination of the substrate and gate, and so classically the threshold voltage was independent of drain voltage.
Low leakage heterojunction vertical transistors and high performance devices thereof
InactiveUS6943407B2Superb performanceSuperb scalabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesReverse short-channel effectHeterojunction
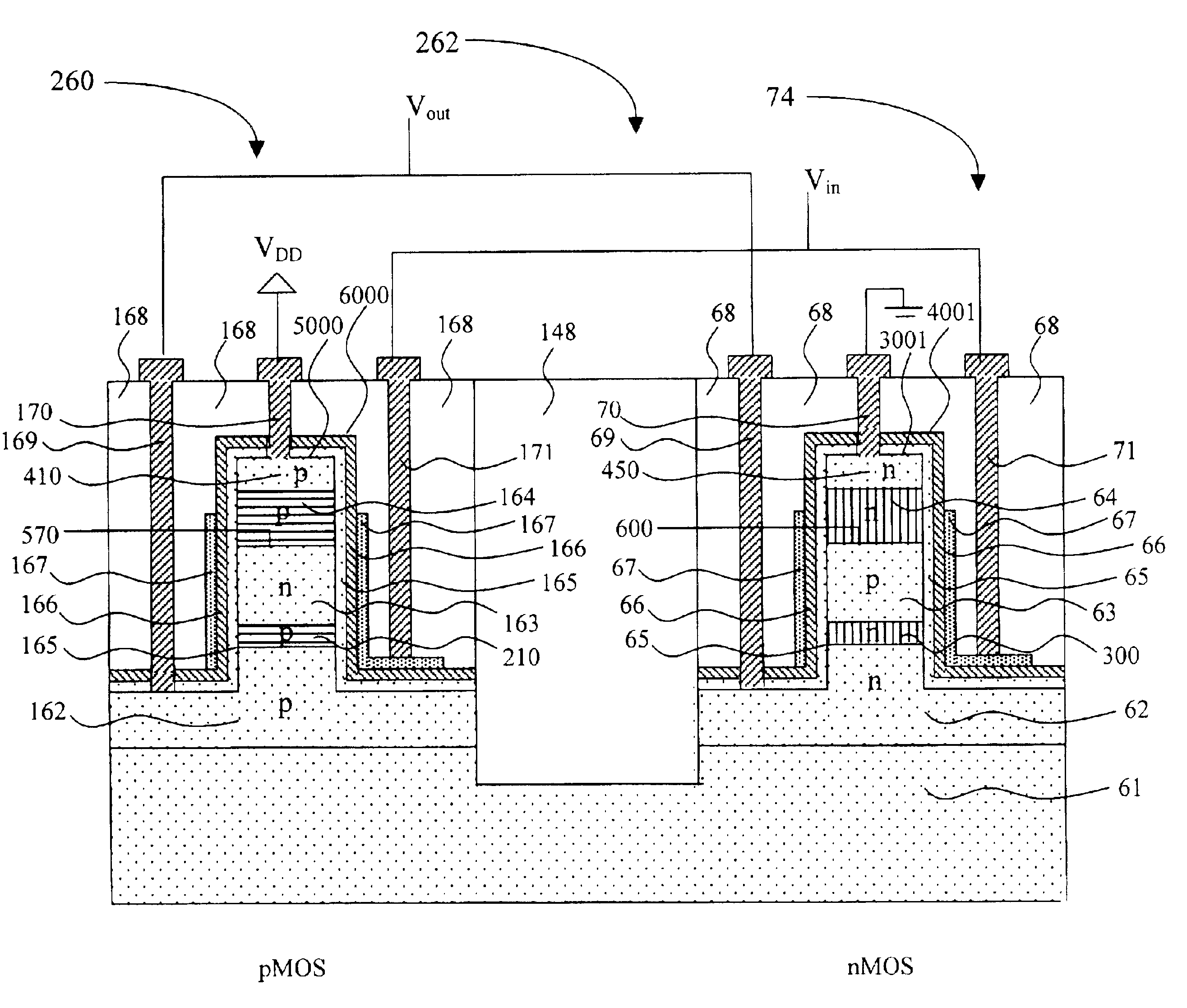
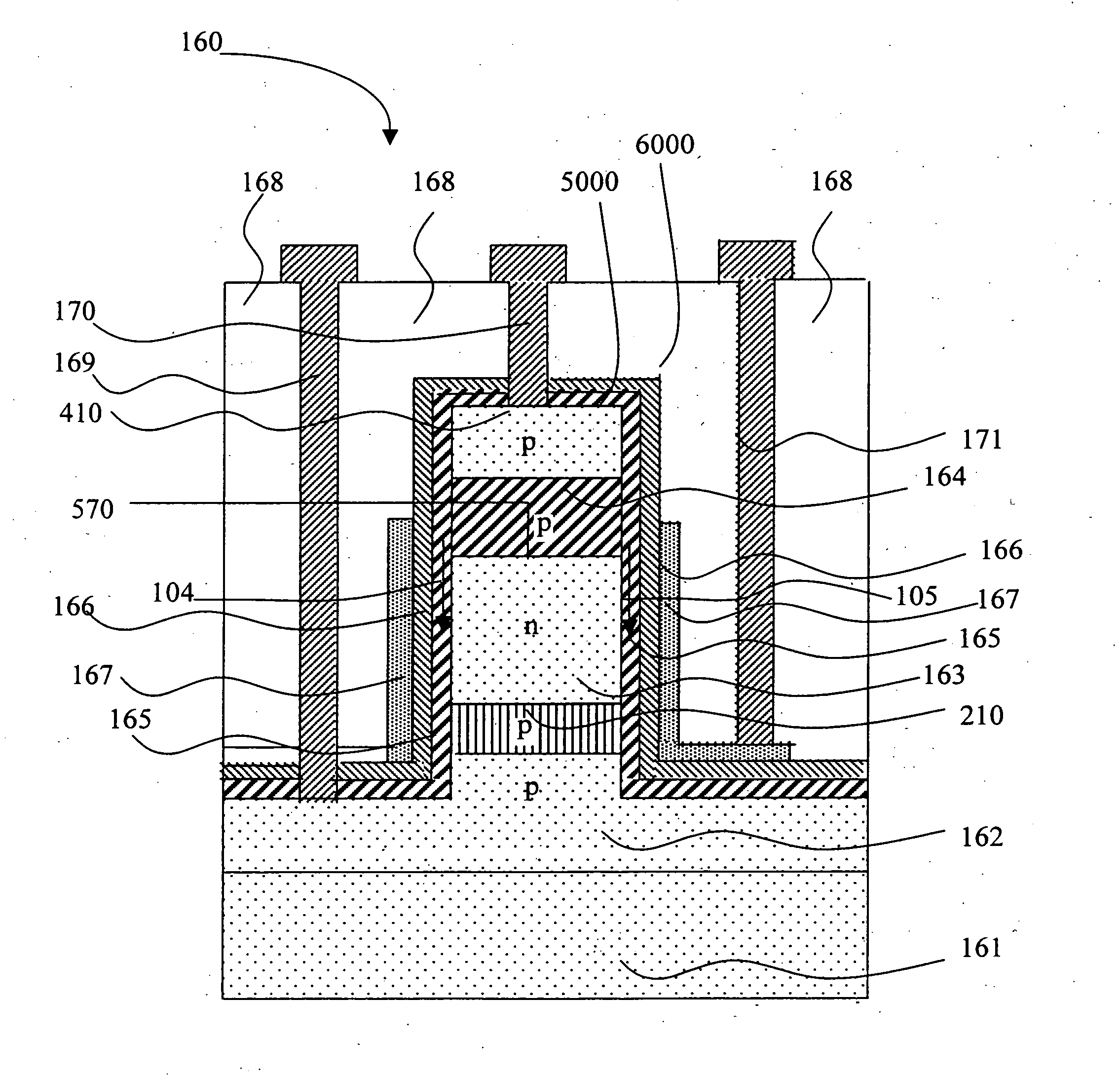
A method for forming and the structure of a vertical channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry are described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a sidewall of a vertical single crystal semiconductor structure wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect the body region and wherein the drain region contains a carbon doped region to prevent the diffusion of dopants (i.e., B and P) into the body. The invention reduces the problem of short channel effects such as drain induced barrier lowering and the leakage current from the source to drain regions via the hetero-junction and while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials. The problem of scalability of the gate length below 100 nm is overcome by the heterojunction between the source and body regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Low leakage heterojunction vertical transistors and high performance devices thereof
InactiveUS20070148939A1Superb performanceSuperb scalabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
A method for forming and the structure of a vertical channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry are described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a sidewall of a vertical single crystal semiconductor structure wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect the body region and wherein the drain region contains a carbon doped region to prevent the diffusion of dopants (i.e., B and P) into the body. The invention reduces the problem of short channel effects such as drain induced barrier lowering and the leakage current from the source to drain regions via the hetero-junction and while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials. The problem of scalability of the gate length below 100 nm is overcome by the heterojunction between the source and body regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
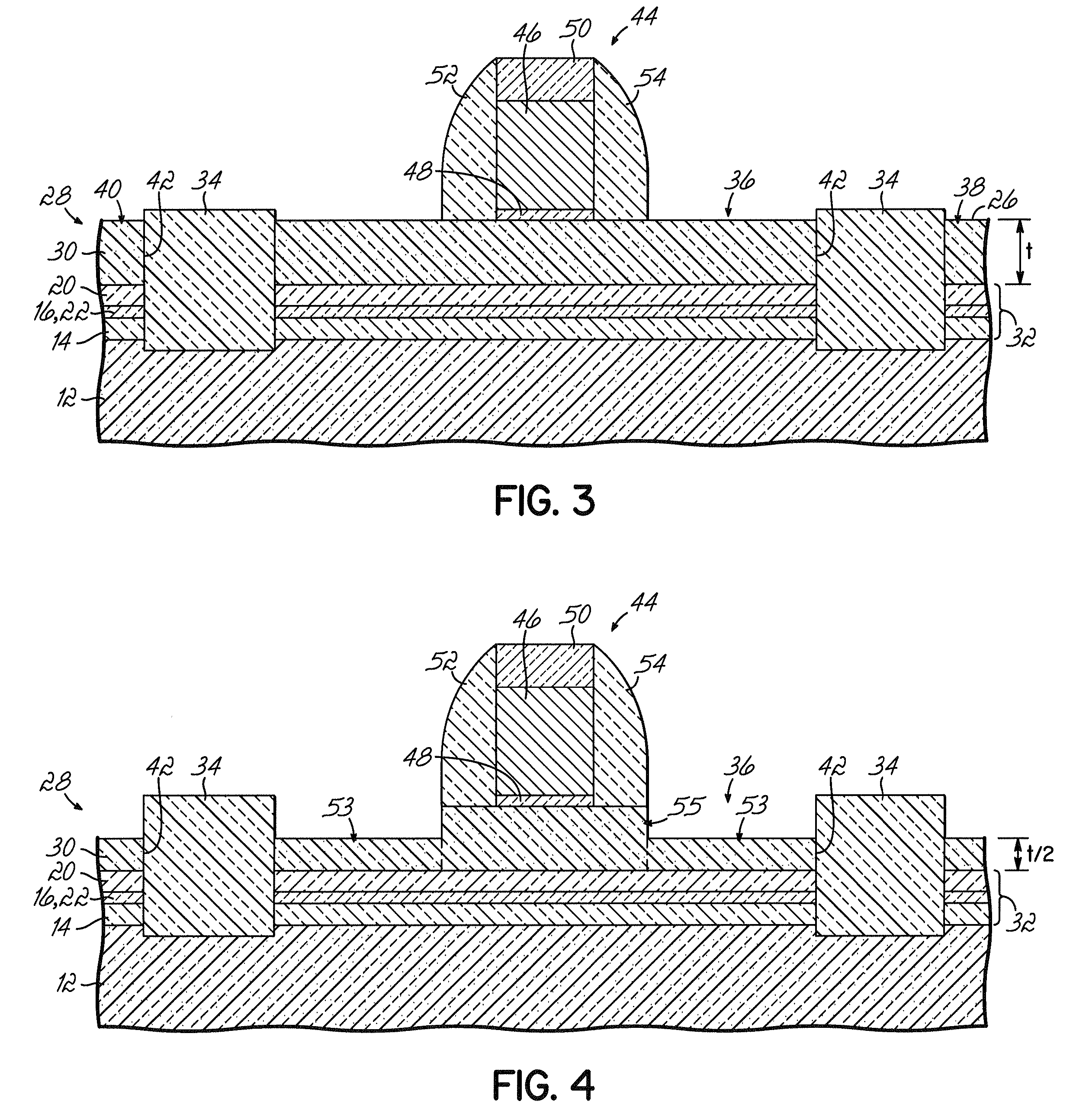
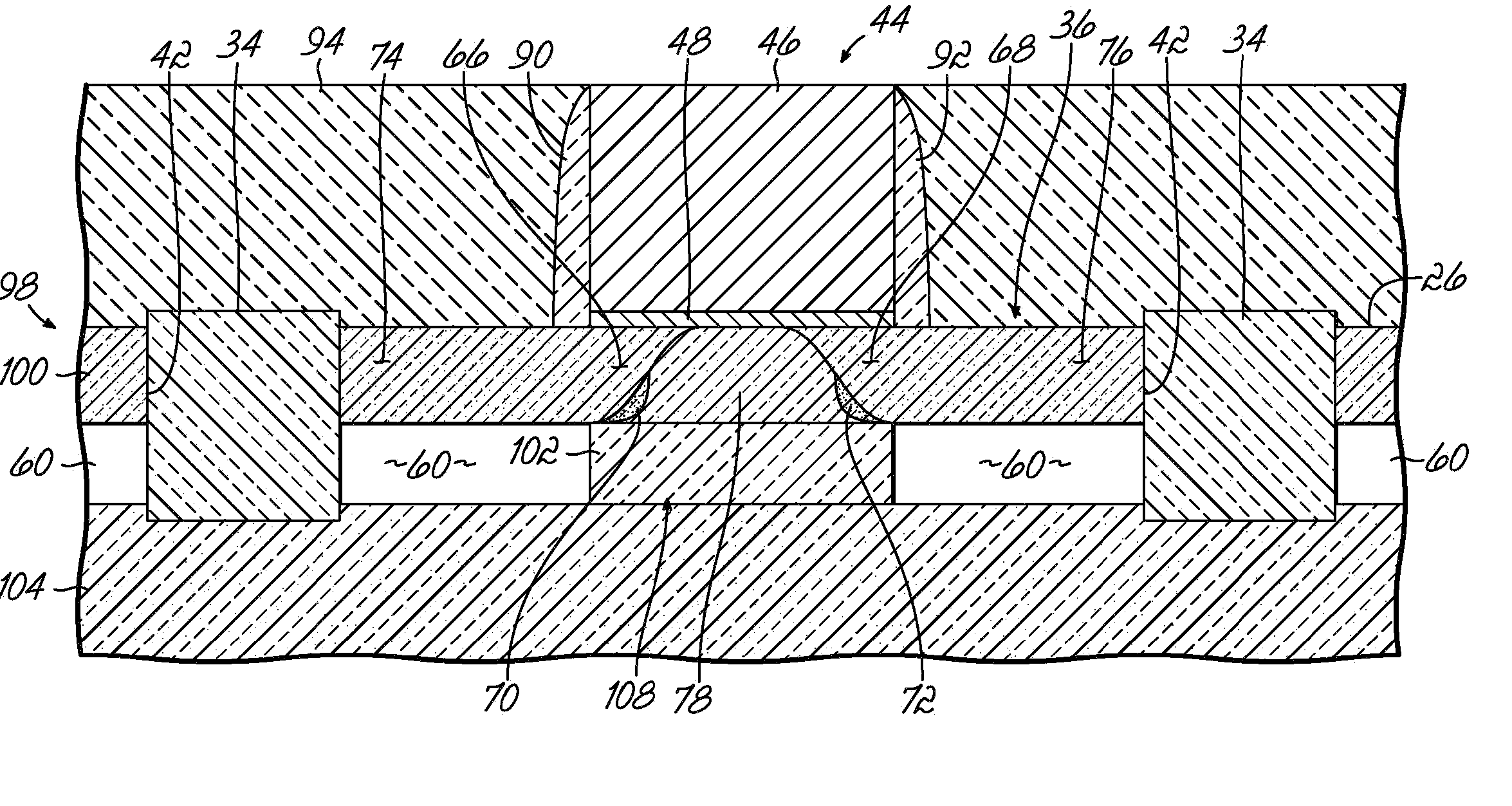
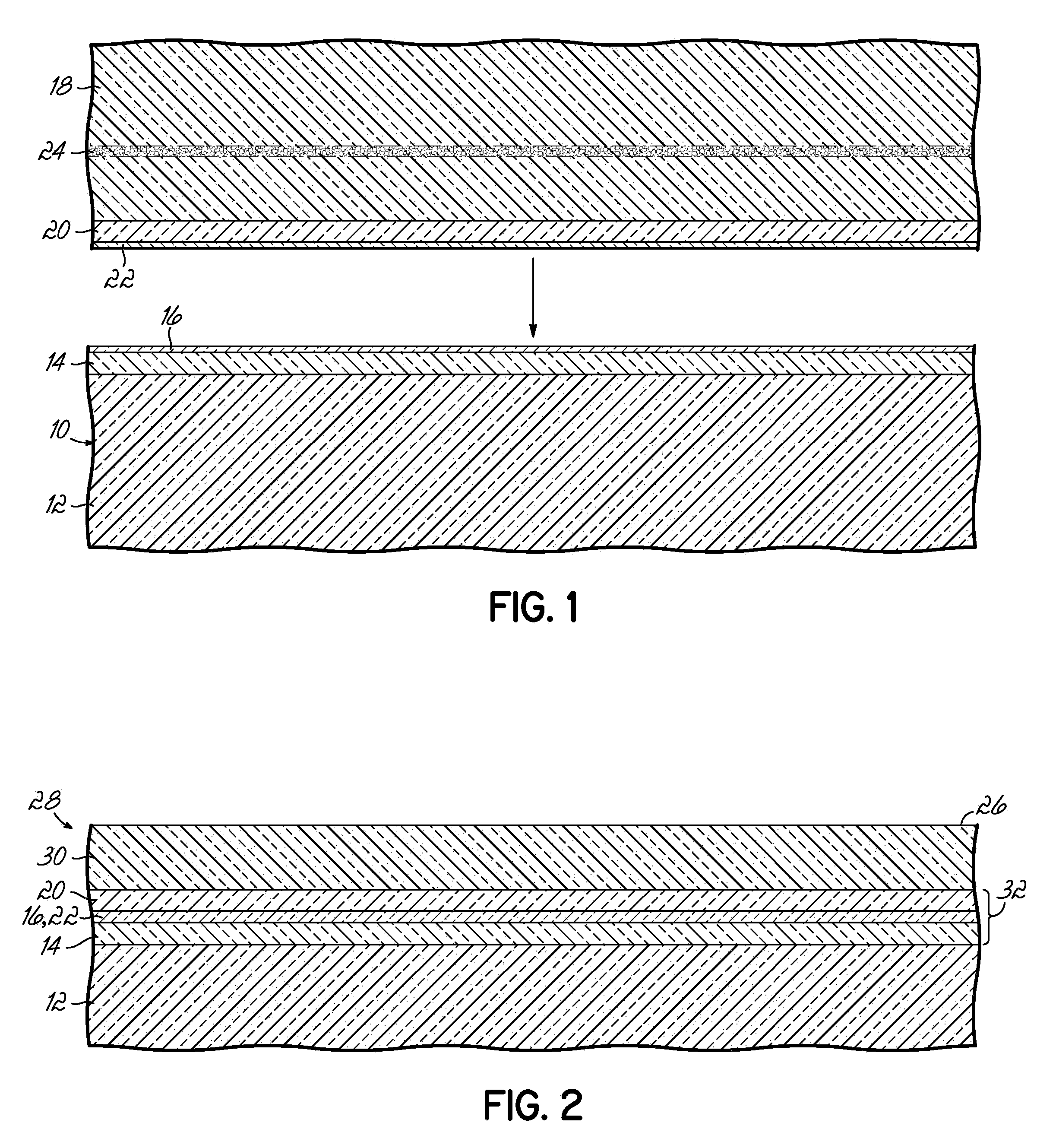
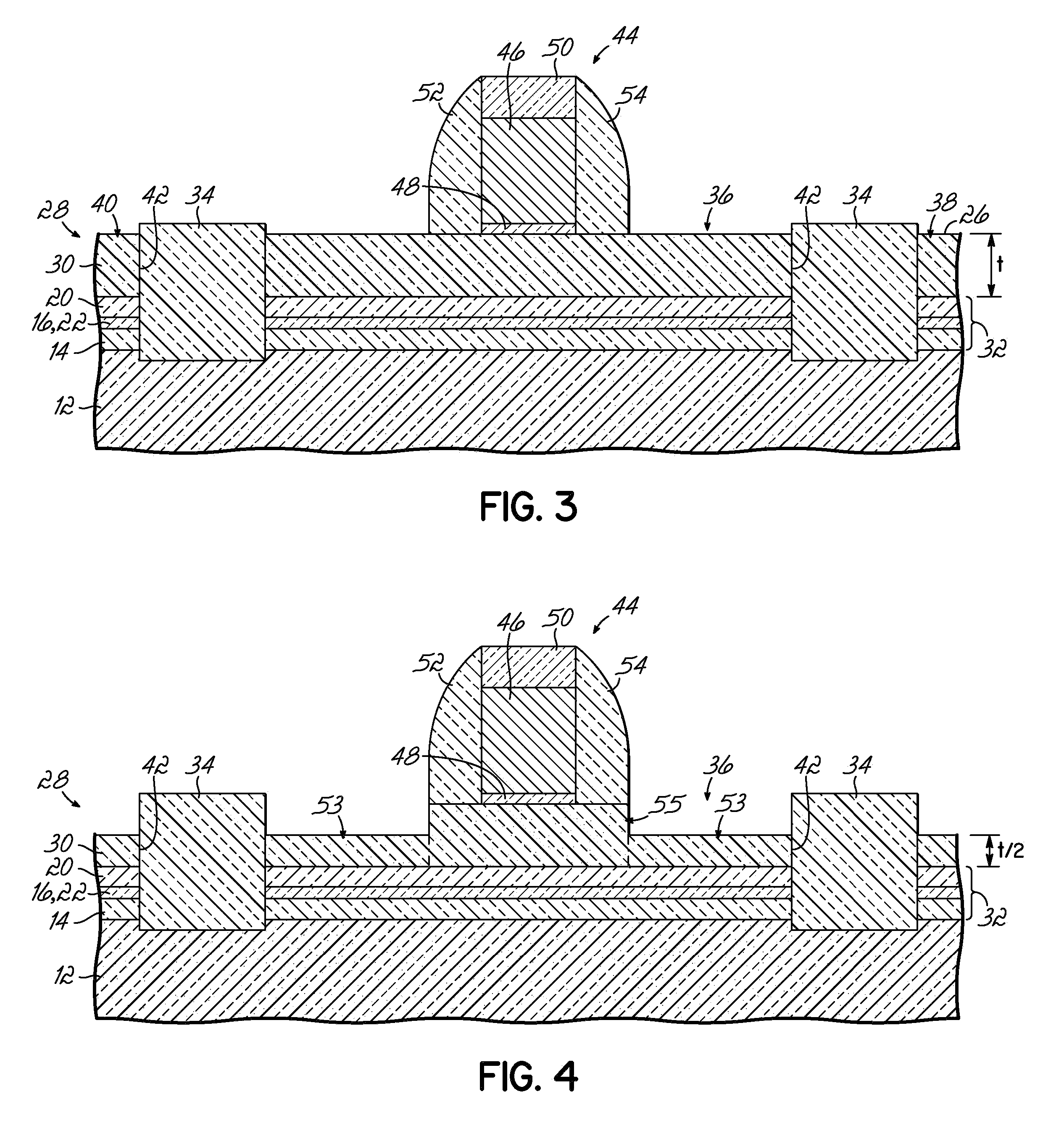
Semiconductor device structures with reduced junction capacitance and drain induced barrier lowering and methods for fabricating such device structures and for fabricating a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate
InactiveUS20070246752A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceSemiconductor structure
Semiconductor device structures with reduced junction capacitance and drain induced barrier lowering, methods for fabricating such device structures, and methods for forming a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate. The semiconductor structure comprises a semiconductor layer and a dielectric layer disposed between the semiconductor layer and the substrate. The dielectric layer includes a first dielectric region with a first dielectric constant and a second dielectric region with a second dielectric constant that is greater than the first dielectric constant. In one embodiment, the dielectric constant of the first dielectric region may be less than about 3.9 and the dielectric constant of the second dielectric region may be greater than about ten (10). The semiconductor-on-insulator substrate comprises a semiconductor layer separated from a bulk layer by an insulator layer of a high-dielectric constant material. The fabrication methods comprise modifying a region of the dielectric layer to have a lower dielectric constant.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Design Structures Incorporating Semiconductor Device Structures with Reduced Junction Capacitance and Drain Induced Barrier Lowering
InactiveUS20080034335A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStatic storageCapacitanceDevice material
Design structure embodied in a machine readable medium for designing, manufacturing, or testing a design. The design structure includes semiconductor device structures characterized by reduced junction capacitance and drain induced barrier lowering. The semiconductor device structure of the design structure includes a semiconductor layer and a dielectric layer disposed between the semiconductor layer and the substrate. The dielectric layer includes a first dielectric region with a first dielectric constant and a second dielectric region with a second dielectric constant that is greater than the first dielectric constant.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
SOI CMOS device with reduced DIBL
ActiveUS6872640B1Prevent penetrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi cmosDopant
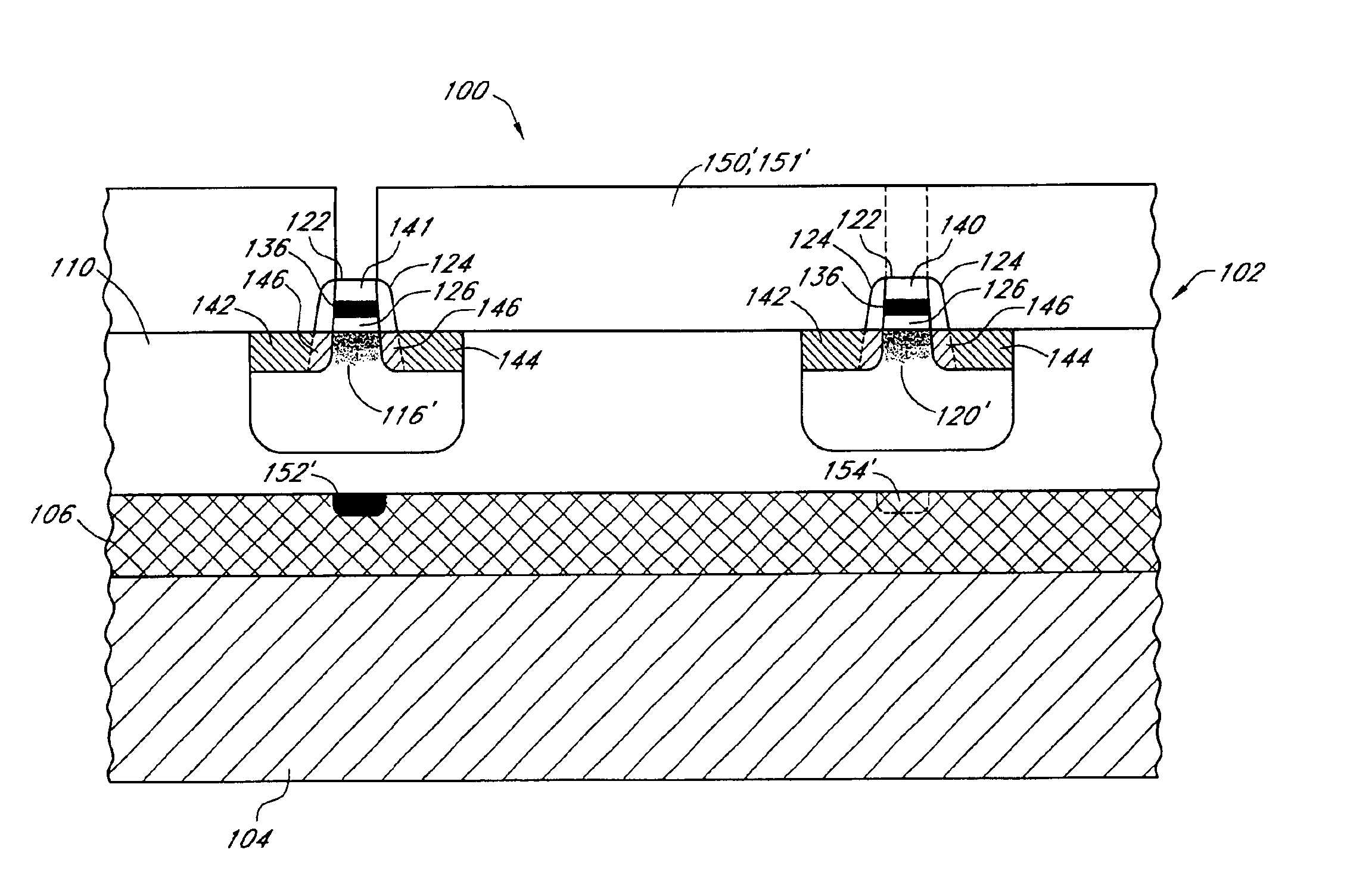
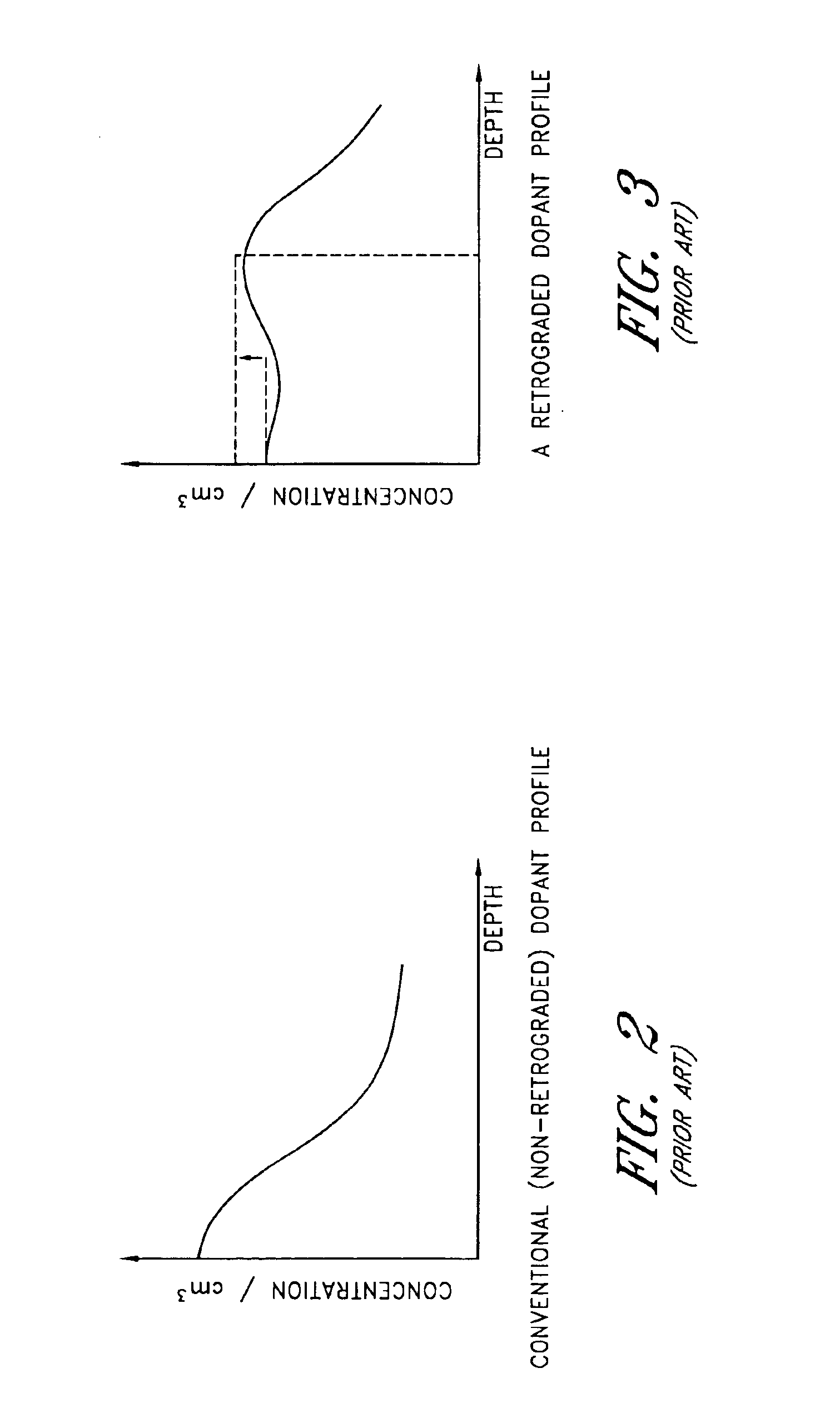
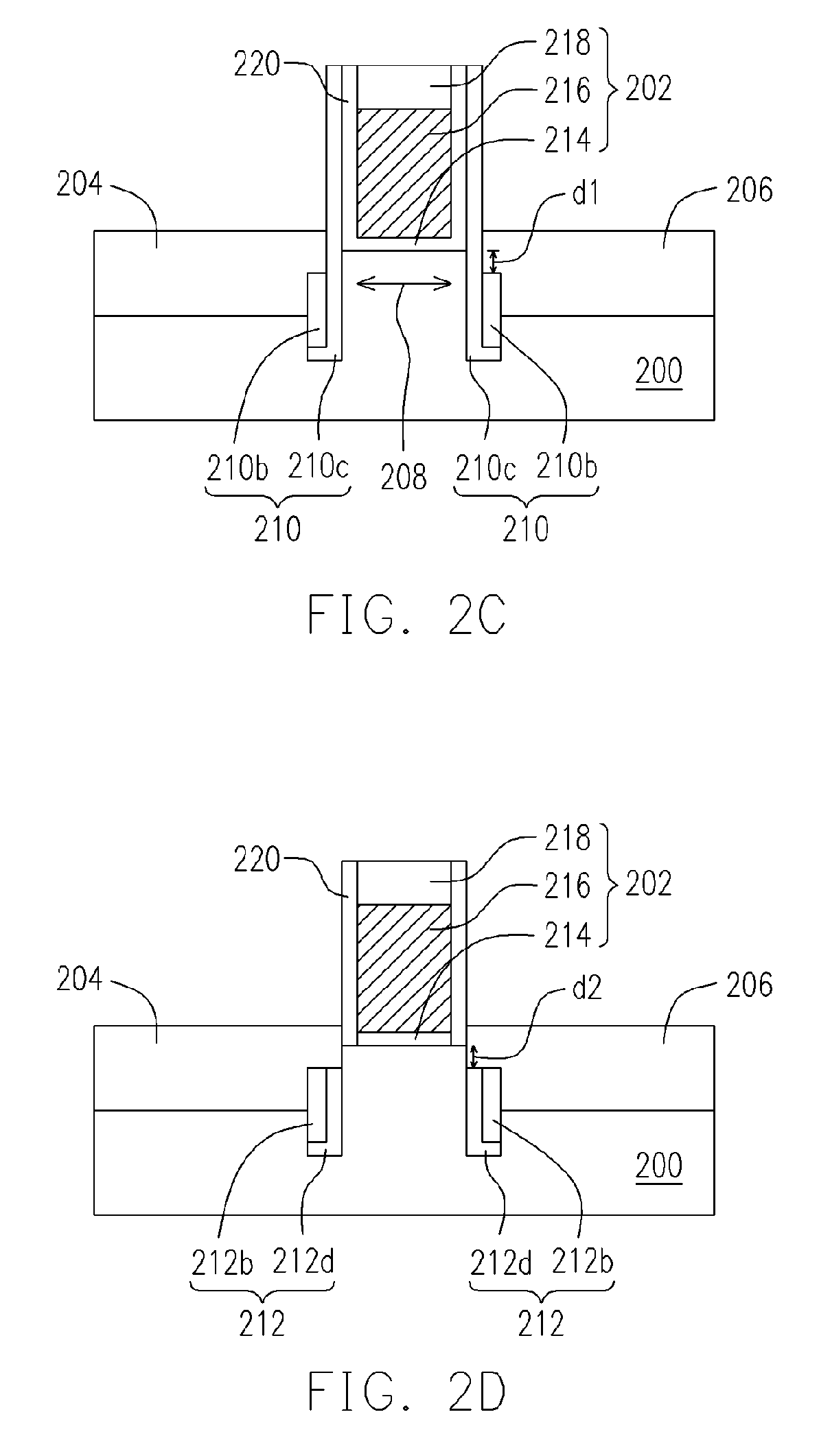
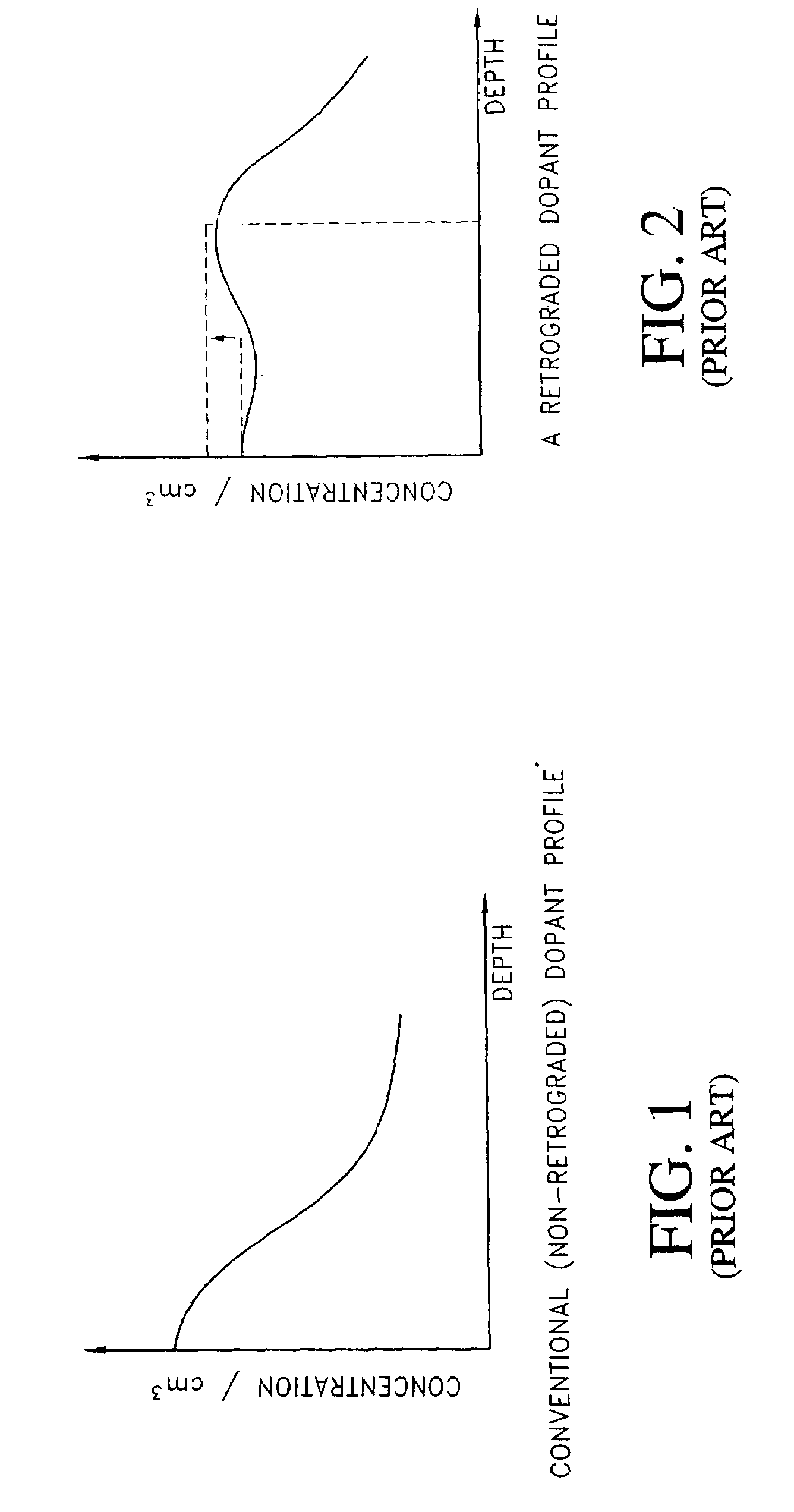
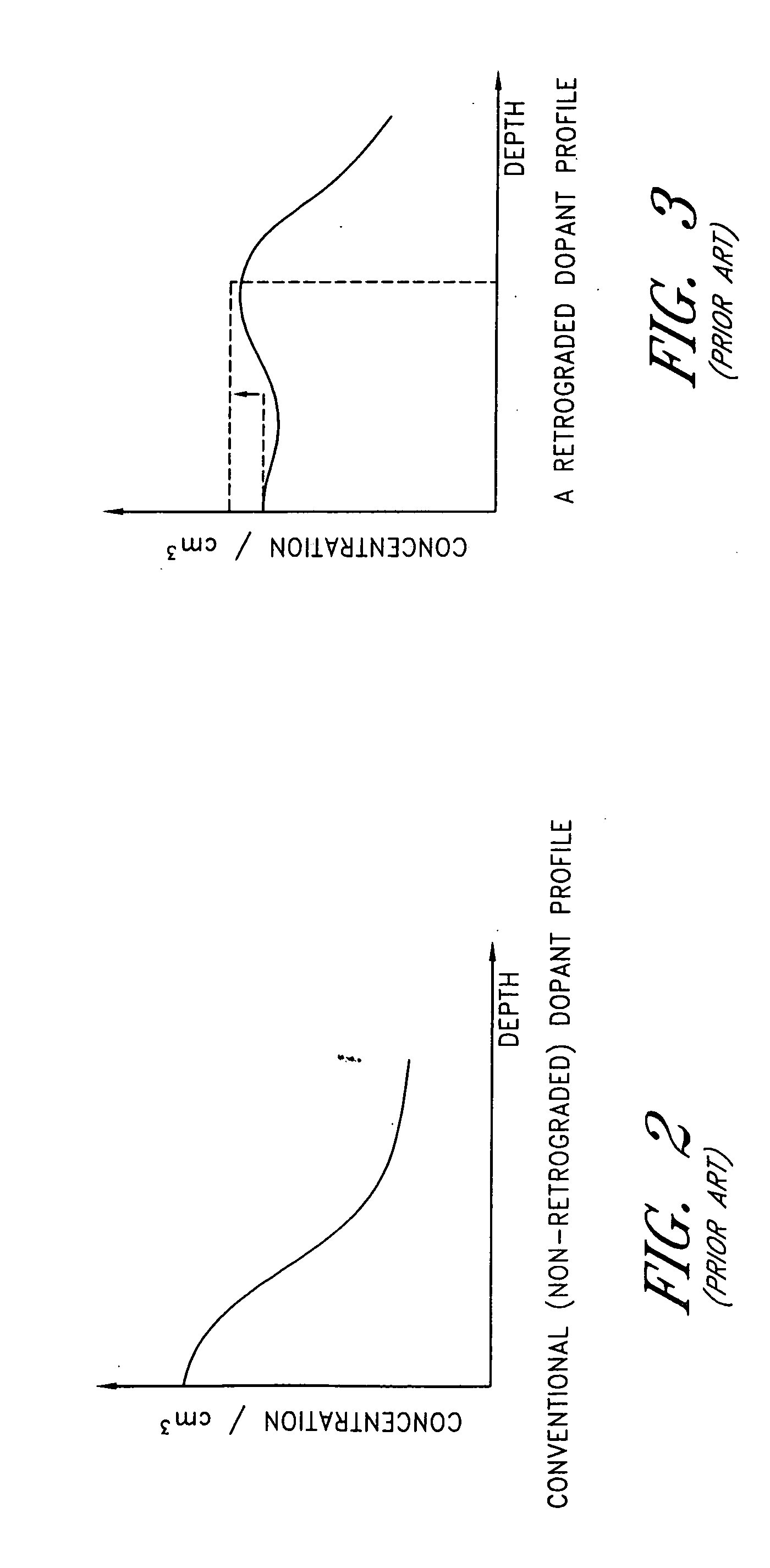
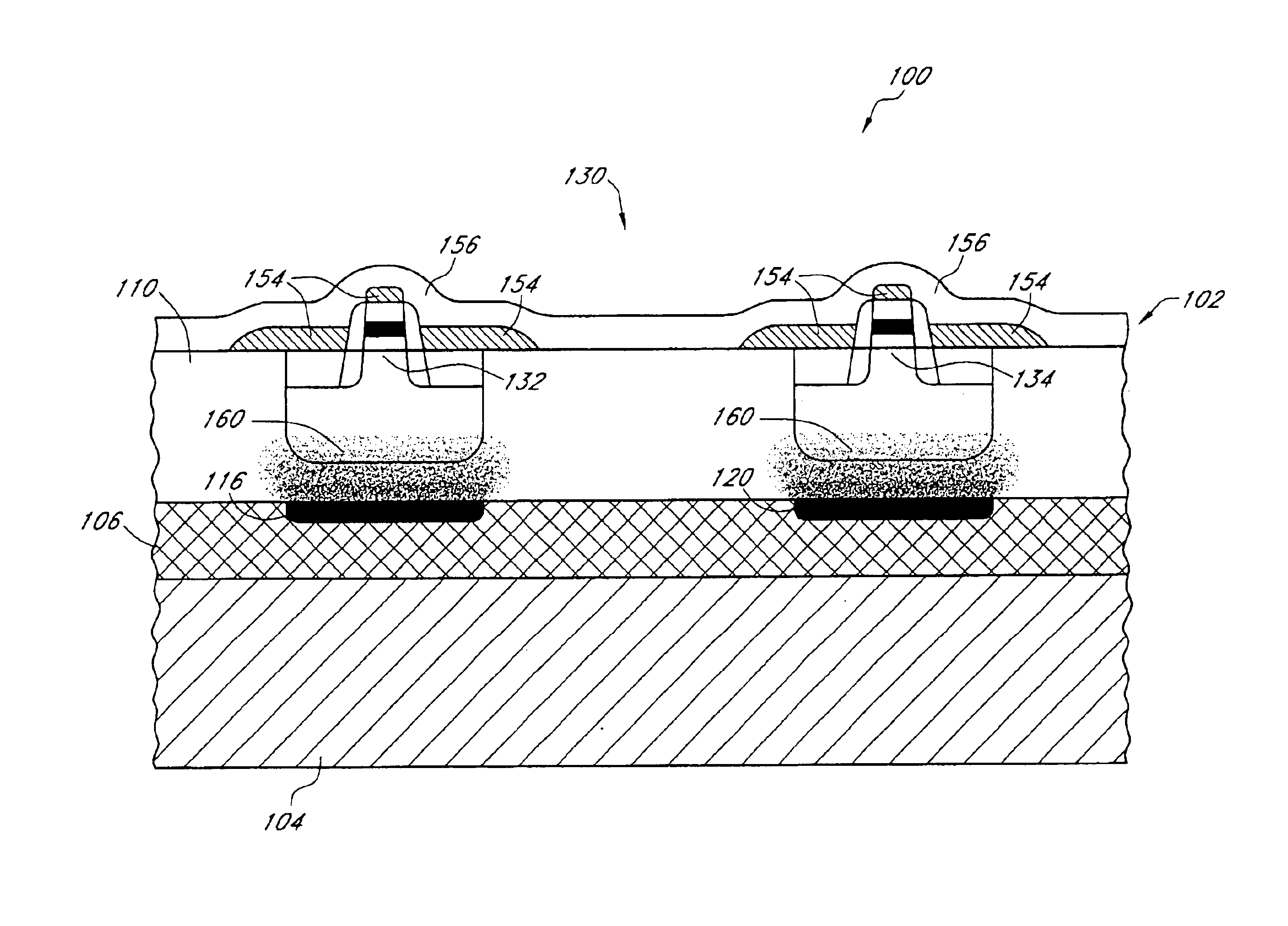
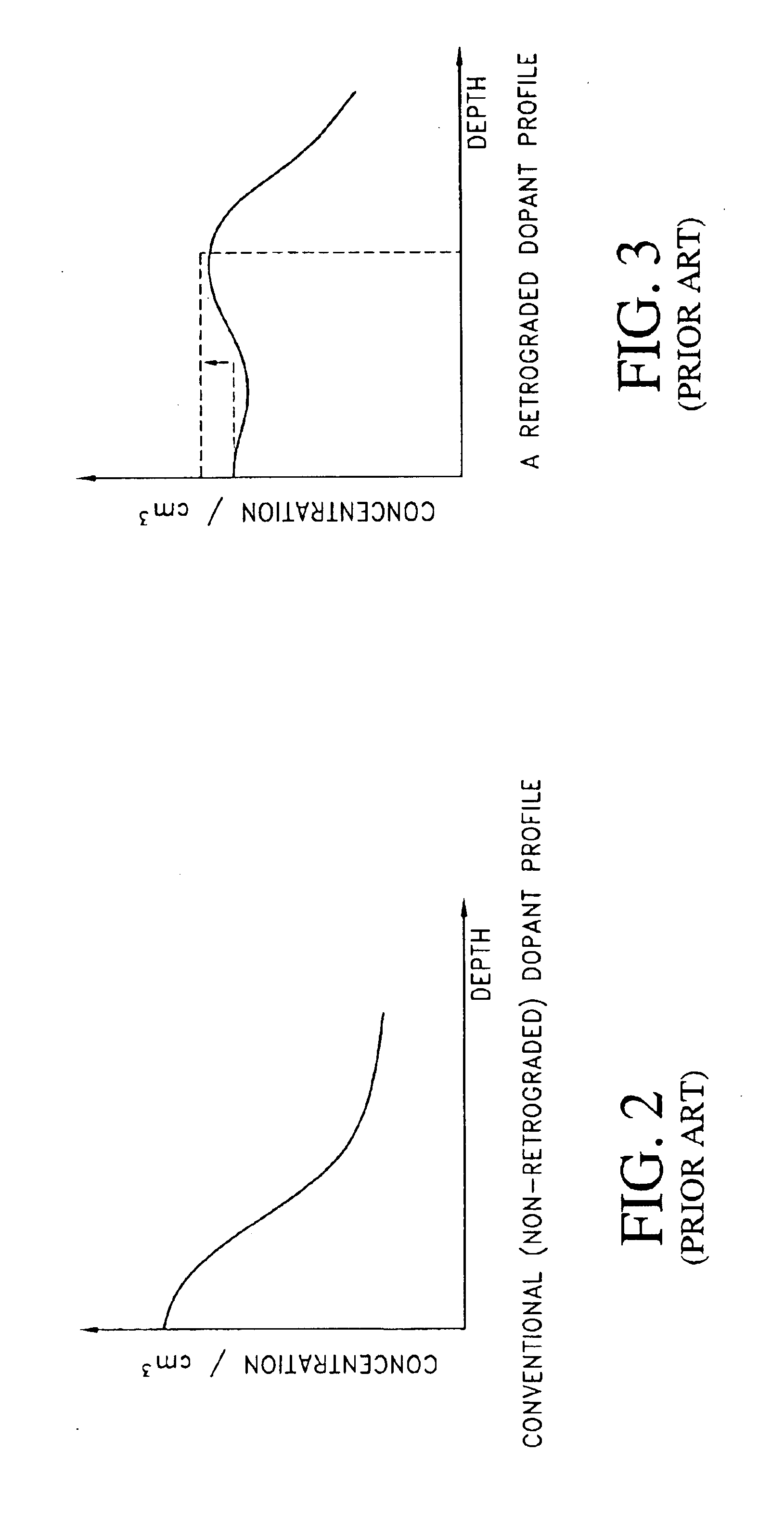
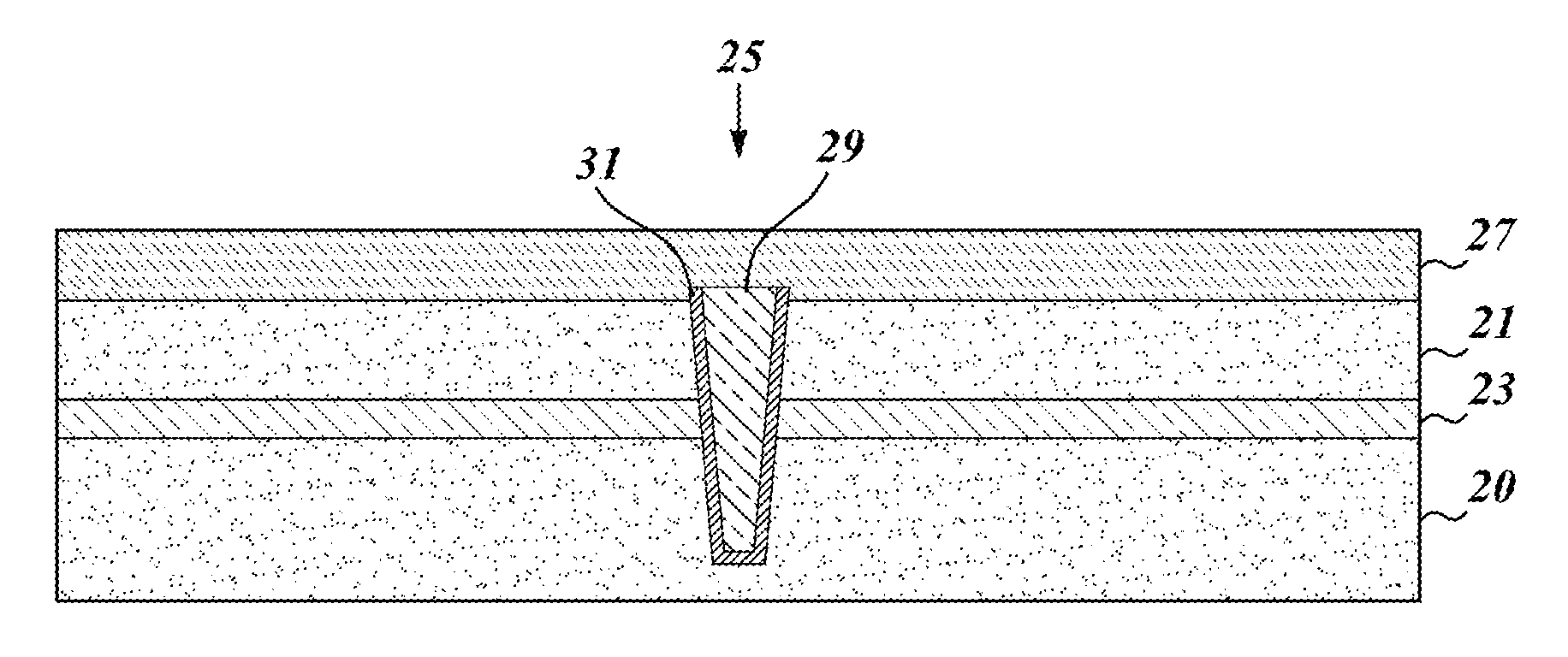
CMOS devices formed with a Silicon On Insulator (SOI) technology with reduced Drain Induced Barrier Lowering (DIBL) characteristics and a method for producing the same. The method involves a high energy, high dose implant through openings in a masking layer and through channel regions of the p- and n-wells, into the insulator layer, thereby creating a borophosphosilicate glass (BPSG) diffusion source within the insulation layer underlying the gate regions of the SOI wafer substantially between the source and drain. Backend high temperature processing steps induce diffusion of the dopants contained in the diffusion source into the p- and n-wells, thereby forming asymmetric retrograde dopant profiles in the channel under the gate. The method can be selectively applied to selected portions of a wafer to tailor device characteristics, such as for memory cells.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Structures incorporating semiconductor device structures with reduced junction capacitance and drain induced barrier lowering
InactiveUS7984408B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStatic storageCapacitanceElectricity
Design structure embodied in a machine readable medium for designing, manufacturing, or testing a design. The design structure includes semiconductor device structures characterized by reduced junction capacitance and drain induced barrier lowering. The semiconductor device structure of the design structure includes a semiconductor layer and a dielectric layer disposed between the semiconductor layer and the substrate. The dielectric layer includes a first dielectric region with a first dielectric constant and a second dielectric region with a second dielectric constant that is greater than the first dielectric constant.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semicondutor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20070012994A1Electric fieldSuppression of short channel effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCondensed matter physicsSemiconductor
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
FinFET device with reduced DIBL
ActiveUS7235468B1Suppression of short channel effectsReduce resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantInsulation layer
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Curved fractional CMOS bandgap reference
InactiveUS6841982B2Voltage is accurateArea minimizationElectric variable regulationEngineeringDigital control
A high shunt regulator provides precise voltage over process, temperature, power supply, and foundries. The HV level is settable by a digital control bits such as fuse bits. A filter network filters out the ripple noise and charge transient. A tracking capacitor divider network speeds up response time. A fractional band gap reference provides fractional bandgap voltage and current, and operates at low power supply and has superior power supply rejection. It is unsusceptible to substrate hot carrier effect. It exposes very little to drain induced barrier lowering effect. The bandgap core has better than conventional transient response and stability. One embodiment has adjustable level control. Complementary TC (temperature coefficient) trimming allows efficient realization of zero temperature coefficients of current and voltage. Higher order curvature correction of voltage and current is integrated. Replica bias for the control loop is presented. A Binary and Approximation Complementary TC search trimming is described. A zero TC fractional voltage less than the theoretical bandgap voltage (<<−1.2. Volt) is realizable. The bandgap core has a filtering mechanism to reject high frequency noise. A low power startup circuit powers up the band gap. The band gap also has variable impedance.
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
Drain induced barrier lowering with Anti-punch-through implant
ActiveUS20130161639A1Reduce leakage currentReduce counterdopingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesIntegrated circuitTransistor
An integrated circuit containing an MOS transistor with epitaxial source and drain regions may be formed by implanting a retrograde anti-punch-through layer prior to etching the source drain regions for epitaxial replacement. The anti-punch-through layer is disposed between stressor tips of the epitaxial source and drain regions, and does not substantially extend into the epitaxial source and drain regions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Structure and method to improve short channel effects in metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors
InactiveUS20080121985A1Suppression of short channel effectsCapacitance minimizedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceCMOS
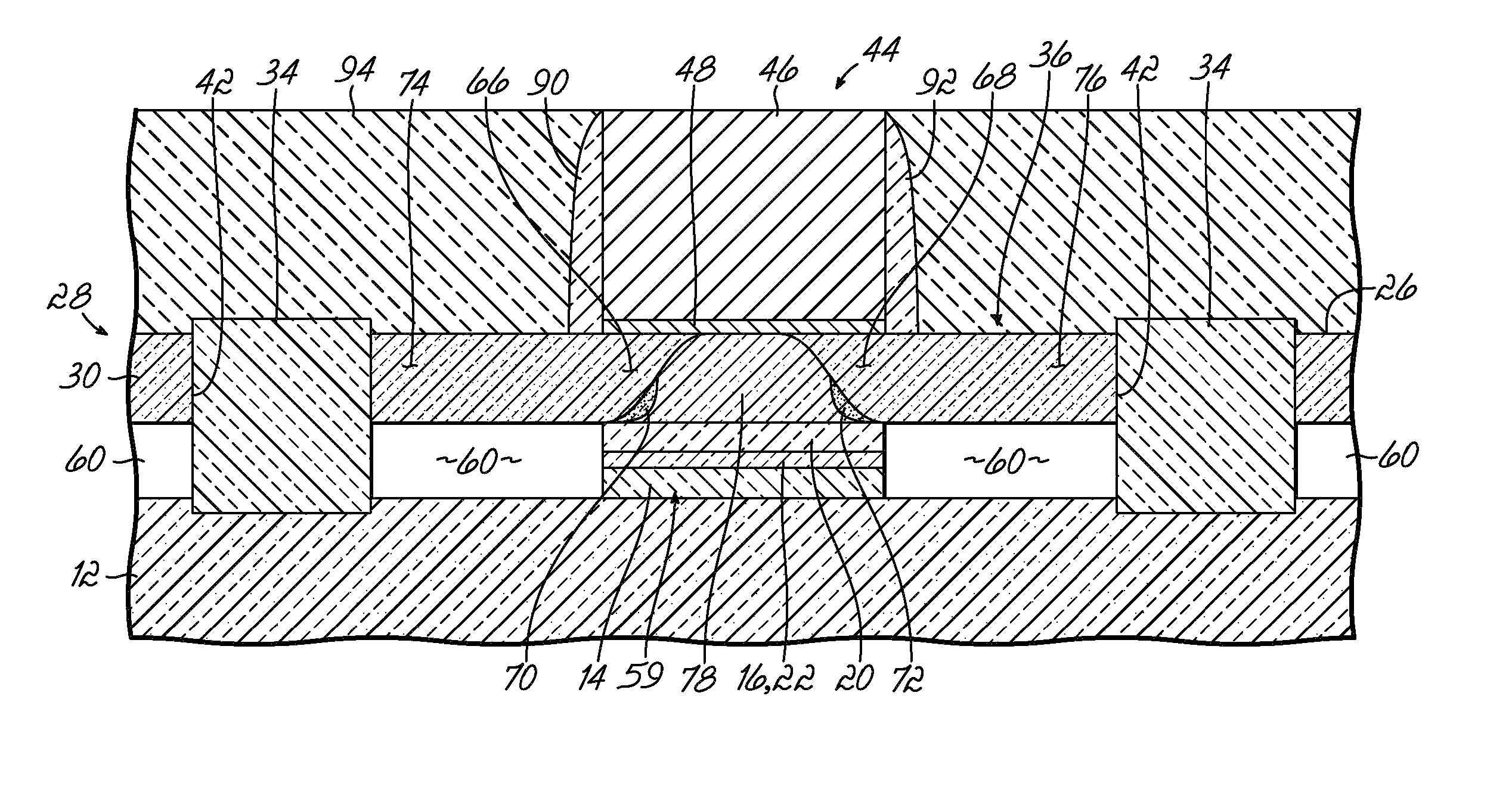
Disclosed are embodiments of improved MOSFET and CMOS structures that provides for increased control over short channel effects. Also disclosed are embodiments of associated methods of forming these structures. The embodiments suppress short channel effects by incorporating buried isolation regions into a transistor below source / drain extension regions and between deep source / drain regions and the channel region and, particularly, between deep source / drain regions and the halo regions. Buried isolation regions between the deep source / drain regions and the channel region minimize drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL) as well as punch through. Additionally, because the deep source / drain regions and halo regions are separated by the buried isolation regions, side-wall junction capacitance and junction leakage are also minimized.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Low leakage heterojunction vertical transistors and high performance devices thereof
InactiveCN1574253ALow power applicationsLower the barrierTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
A method for forming and the structure of a vertical channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry are described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a sidewall of a vertical single crystal semiconductor structure wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect the body region and wherein the drain region contains a carbon doped region to prevent the diffusion of dopants (i.e., B and P) into the body. The invention reduces the problem of short channel effects such as drain induced barrier lowering and the leakage current from the source to drain regions via the hetero-junction and while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials. The problem of scalability of the gate length below 100 nm is overcome by the heterojunction between the source and body regions.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of fabricating transistors and a transistor structure for improving short channel effect and drain induced barrier lowering
ActiveUS20110012197A1Improve short channel effectImproving drain induced barrier loweringTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSiliconShort-channel effect
A method of fabricating transistors includes: providing a substrate including an N-type well and P-type well; forming a first gate on the N-type well and a second gate on the P-type well, respectively; forming a third spacer on the first gate; forming an epitaxial layer in the substrate at two sides of the first gate; forming a fourth spacer on the second gate; forming a silicon cap layer covering the surface of the epitaxial layer and the surface of the substrate at two sides of the fourth spacer; and forming a first source / drain doping region and a second source / drain doping region at two sides of the first gate and the second gate respectively.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
SOI CMOS device with reduced DIBL
InactiveUS20050205931A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi cmosDopant
CMOS devices formed with a Silicon On Insulator (SOI) technology with reduced Drain Induced Barrier Lowering (DIBL) characteristics and a method for producing the same. The method involves a high energy, high dose implant through openings in a masking layer and through channel regions of the p- and n-wells, into the insulator layer, thereby creating a borophosphosilicate glass (BPSG) diffusion source within the insulation layer underlying the gate regions of the SOI wafer substantially between the source and drain. Backend, high temperature processing steps induce diffusion of the dopants contained in the diffusion source into the p- and n-wells, thereby forming asymmetric retrograde dopant profiles in the channel under the gate. The method can be selectively applied to selected portions of a wafer to tailor device characteristics, such as for memory cells.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Nano-wire field effect transistor
ActiveCN101740619AReduce off-state currentReduce static power consumptionSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricNanowire
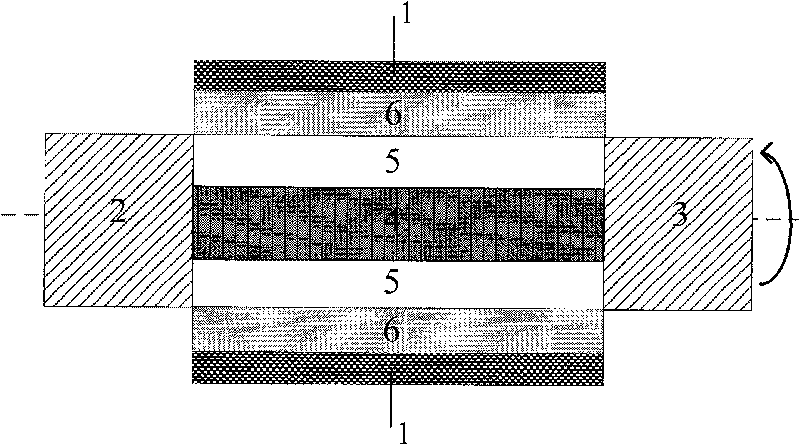
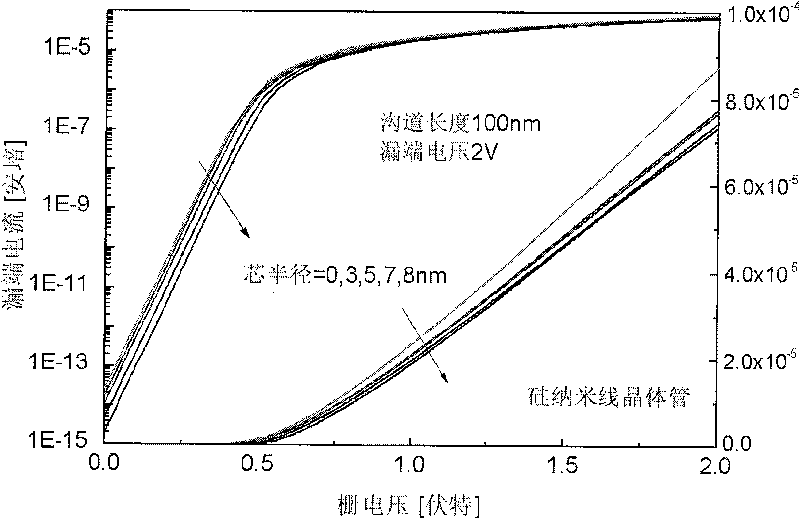
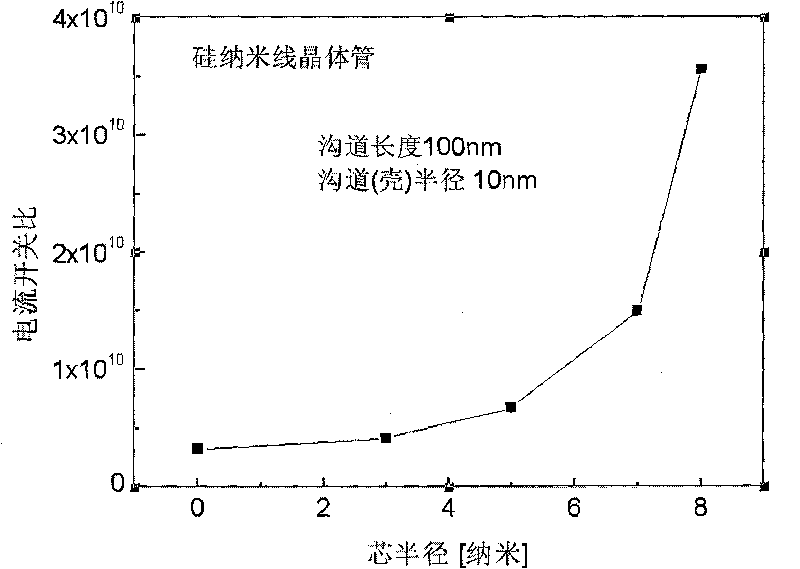
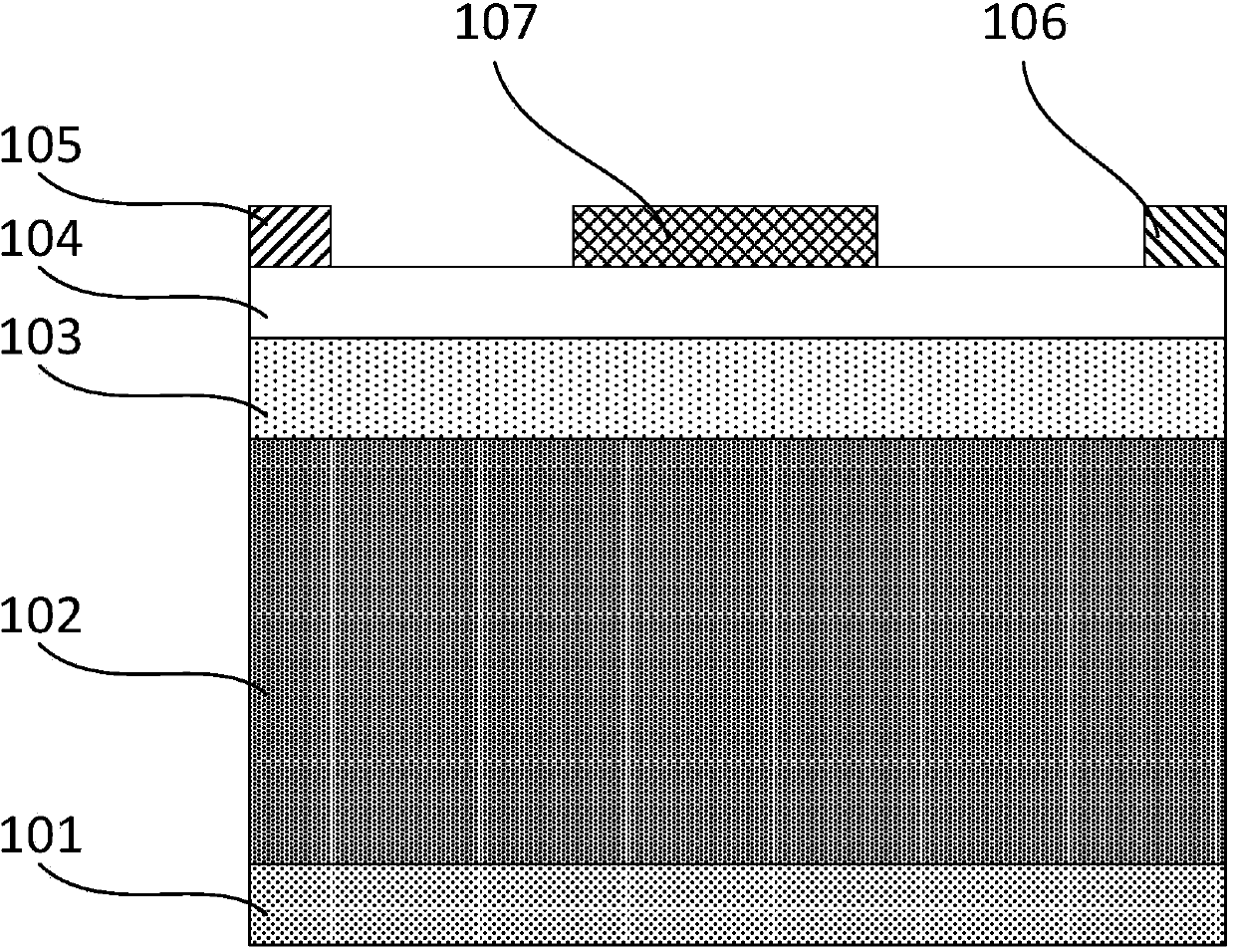
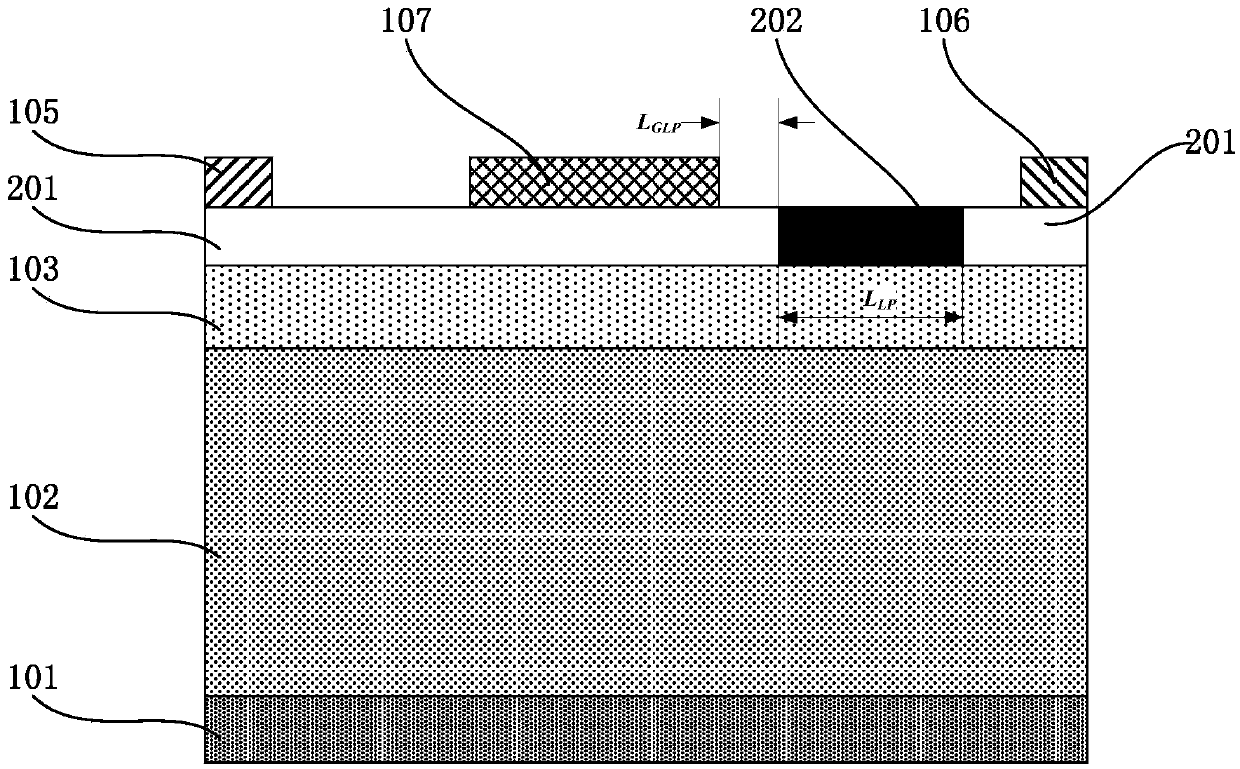
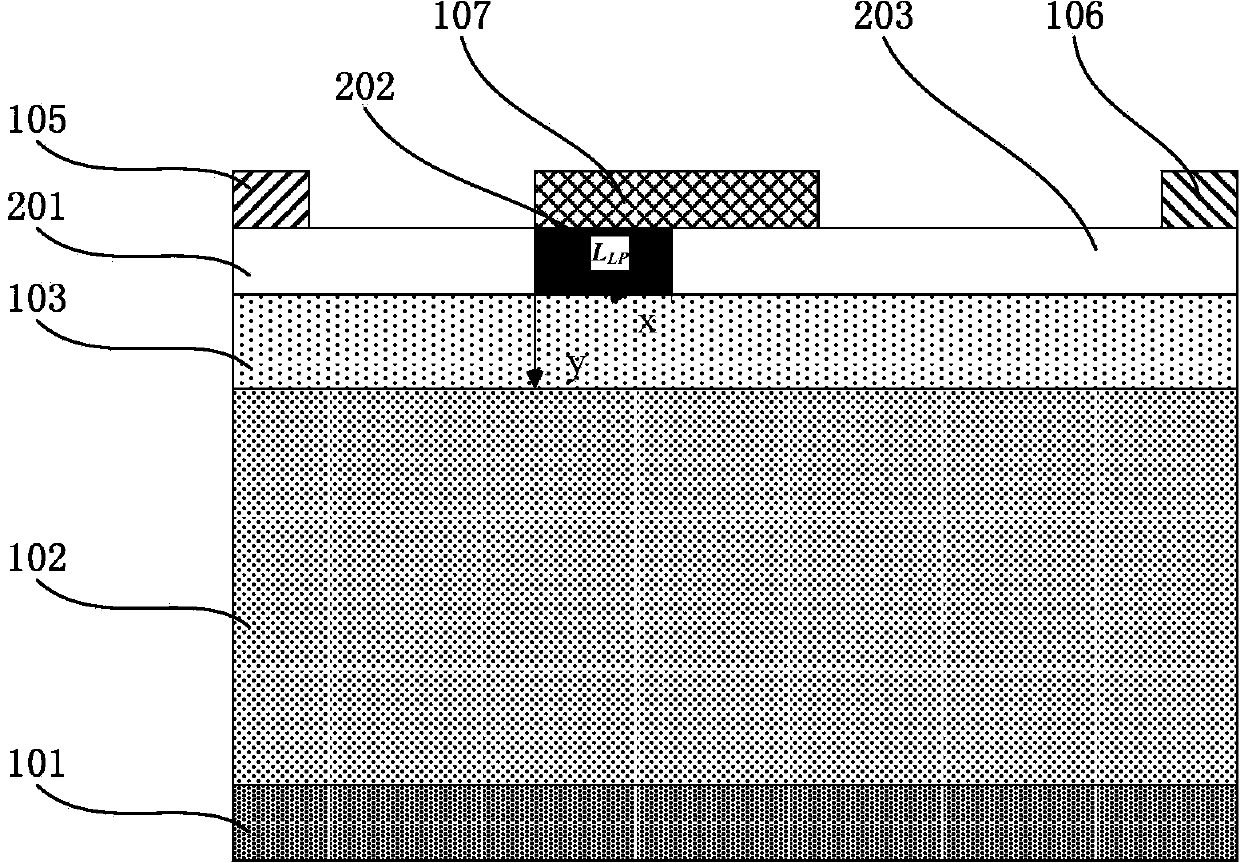
The invention discloses a nano-wire field effect transistor comprising a gate electrode, a source region, a drain region, a central region and a gate dielectric layer. The central region is in the core-shell structures which are coaxial; the gate dielectric layer fully surrounds the central region; the gate electrode fully surrounds the gate dielectric layer; the source region and the drain region are respectively arranged on two sides of the central region; the core structure of the central region is made from insulating material, and the shell structure of the central region is made from semiconductor material; the doping type and the doping concentration of the semiconductor material of the shell structure of the central region are adjustable; the lengths of both the core structure and the shell structure and the radii of both the core structure and the shell structure are adjustable; and the materials of the gate dielectric layer, the gate electrode, the source region and the drain region are adjustable. Due to the adoption of the insulating core structure, the off-current of the traditional nano-wire transistor can be reduced effectively, and the current on-off ratio of the devices can be increased. The threshold voltage shifting and the drain induced barrier lowering of the nano-wire field effect transistor are less affected by the short channel effect, and the size reducing performance of the nano-wire field effect transistor is more excellent.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
Gallium-nitride-based heterostructure field effect transistor with composite barrier layers
ActiveCN104201202ASuppression of short channel effectsImprove pressure resistanceSemiconductor devicesGallium nitrideDrift velocity
The invention discloses a gallium-nitride-based heterostructure field effect transistor with composite barrier layers. The composite barrier layers are formed by AlInGaN material with different polarization intensities. When the AlInGaN composite barrier layer with low polarization intensity is located at a grid drain terminal, the density of two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) of the channel below the barrier layer is smaller than that of the 2DEG at other positions of the channel drain terminal, an LDD structure is formed, and the electric field distribution of the channel is modulated to increase voltage endurance capability; when the AlInGaN composite barrier layer with low polarization intensity is located right below a grid, a below-grid gallium nitride (GaN) channel guide strip bottom is distributed in a stepped manner, the drift speed of a below-grid channel carrier is increased due to barrier descending, electric field peak is generated between AlInGaN composite barrier layer with two different elemental components, and more potential is distributed at the grid drain terminal instead of the whole grid to restrain drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL).
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
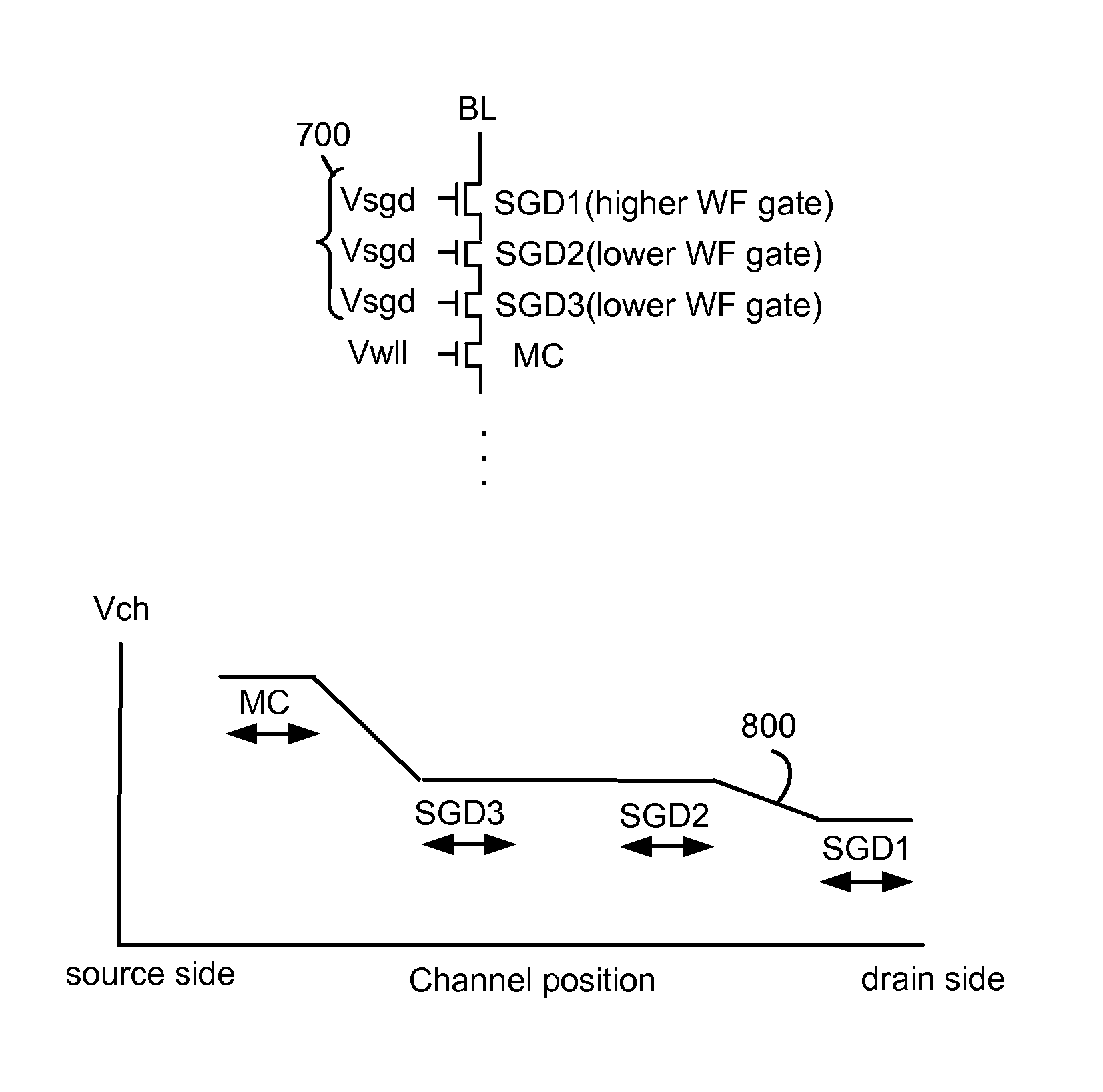
Adjusting control gate overdrive of select gate transistors during programming of non-volatile memory
In a 3D stacked non-volatile memory device, multiple smaller drain-end selected gate (SGD) transistors replace one larger SGD transistor. The SGD transistors have different control gate overdrive voltages so that, during a programming operation, a discontinuous channel potential is created in an inhibited NAND string. The SGD transistor closest to the bit line has a lower control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is lower, and the next SGD transistor has a higher control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is higher. The different control gate overdrive voltages can be provided by programming different threshold voltages, or by providing different control gates voltages, for the SGD transistors. Undesirable reductions in a Vsgd window due to drain-induced barrier lowering can be avoided.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method and structure for transistor with reduced drain-induced barrier lowering and on resistance
InactiveUS20140159052A1Improve methodSimple structureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStress inducedSemiconductor materials
Embodiments of the invention provide an improved method and structure for a transistor with reduced DIBL and RON. A sigma cavity is formed in a semiconductor substrate adjacent to a transistor. The sigma cavity is filled with an epitaxially grown semiconductor material that also serves as a stress-inducing region for the purposes of increasing carrier mobility. The epitaxially grown semiconductor material is doped with a reverse doping profile. A lightly doped region lines the interior of the sigma cavity, followed by an undoped region, followed by a heavily doped region. The shape of the lightly doped region is such that it is thicker adjacent to the channel, which reduces RON, and thinner below the channel, which reduces DIBL.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Adjusting Control Gate Overdrive Of Select Gate Transistors During Programming Of Non-Volatile Memory
In a 3D stacked non-volatile memory device, multiple smaller drain-end selected gate (SGD) transistors replace one larger SGD transistor. The SGD transistors have different control gate overdrive voltages so that, during a programming operation, a discontinuous channel potential is created in an inhibited NAND string. The SGD transistor closest to the bit line has a lower control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is lower, and the next SGD transistor has a higher control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is higher. The different control gate overdrive voltages can be provided by programming different threshold voltages, or by providing different control gates voltages, for the SGD transistors. Undesirable reductions in a Vsgd window due to drain-induced barrier lowering can be avoided.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Knot-free nanowire field effect transistor
InactiveCN102544073AImprove transconductance characteristicsHigh speedSemiconductor devicesNanowireLow voltage
The invention discloses a knot-free nanowire field effect transistor which comprises a channel, a source region and a drain region. The source region is arranged at one end of the channel, and the drain region is arranged at the other end of the channel; the outer surface of the channel is covered by a gate oxide layer which is covered by a grid electrode layer; and the grid electrode layer comprises a first grid electrode layer which is close to the source region and a second grid electrode layer which is close to the drain region. Compared with the prior art, the embodiment of the invention has the advantages that: by adopting a split gate structure, the speed of the charge carrier in the channel of the knot-free nanowire field effect transistor is increased, so the on-state current is increased, the off-state current of a device is reduced irrespective of the influence of the threshold voltage, the influence of the drain region on the device is screened, the drain induced barrier lowering effect is obviously weakened and the driving ability of the current is improved. Meanwhile, with the split gate, the transconductance feature of the knot-free nanowire field effect transistor under low voltage is obviously improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +1
SOI device with reduced drain induced barrier lowering
InactiveUS6905918B2Reduce resistanceEliminate the effects ofSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFloating body effectInsulation layer
A CMOS device formed with a Silicon On Insulator (SOI) technology with reduced Drain Induced Barrier Lowering (DIBL) characteristics and a method for producing the same. The method involves a high energy, high dose implant of boron and phosphorus through the p- and n-wells, into the insulator layer, thereby creating a borophosphosilicate glass (BPSG) structure within the insulation layer underlying the p- and n-wells of the SOI wafer. Backend high temperature processing steps induce diffusion of the boron and phosphorus contained in the BPSG into the p- and n-wells, thereby forming a retrograde dopant profile in the wells. The retrograde dopant profile reduces DIBL and also provides recombination centers adjacent the insulator layer and the active layer to thereby reduce floating body effects for the CMOS device.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
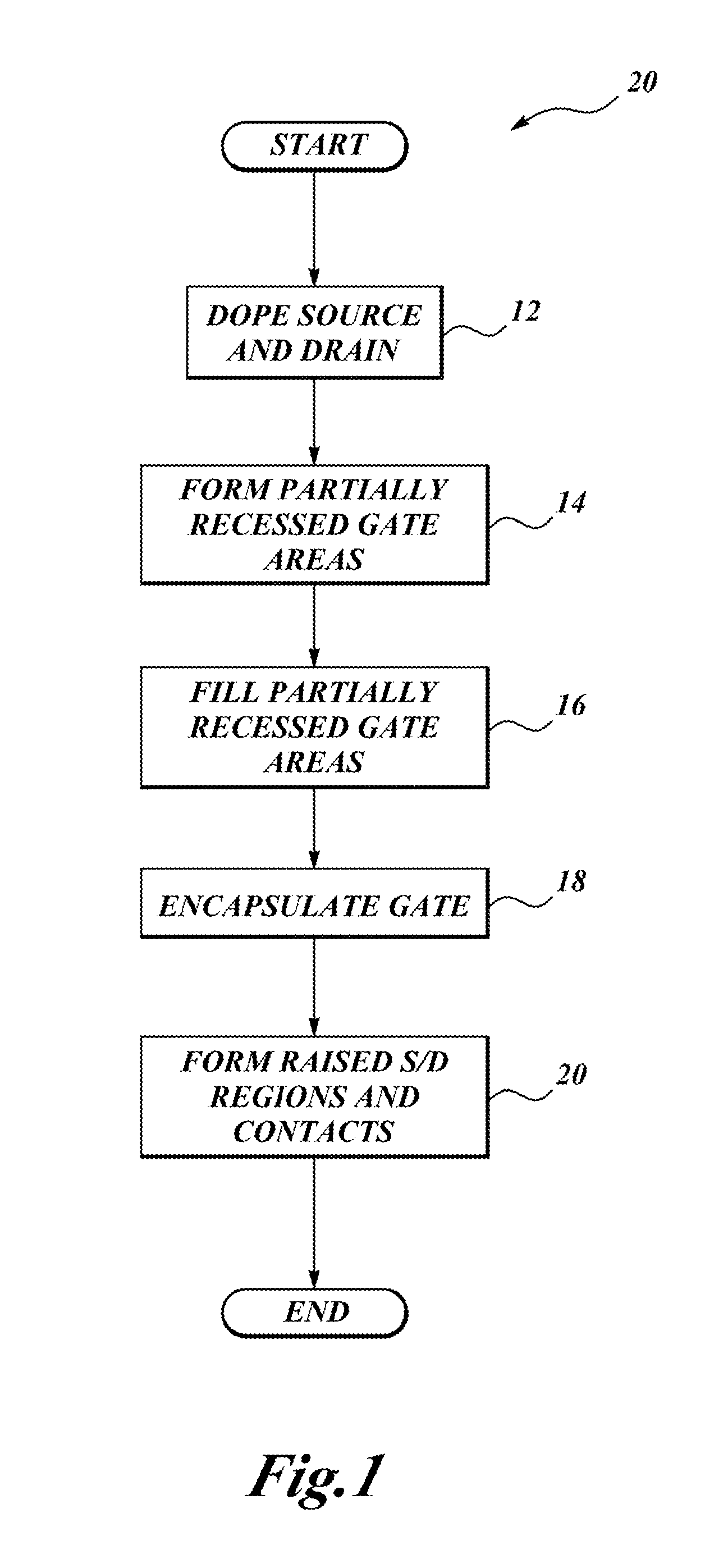
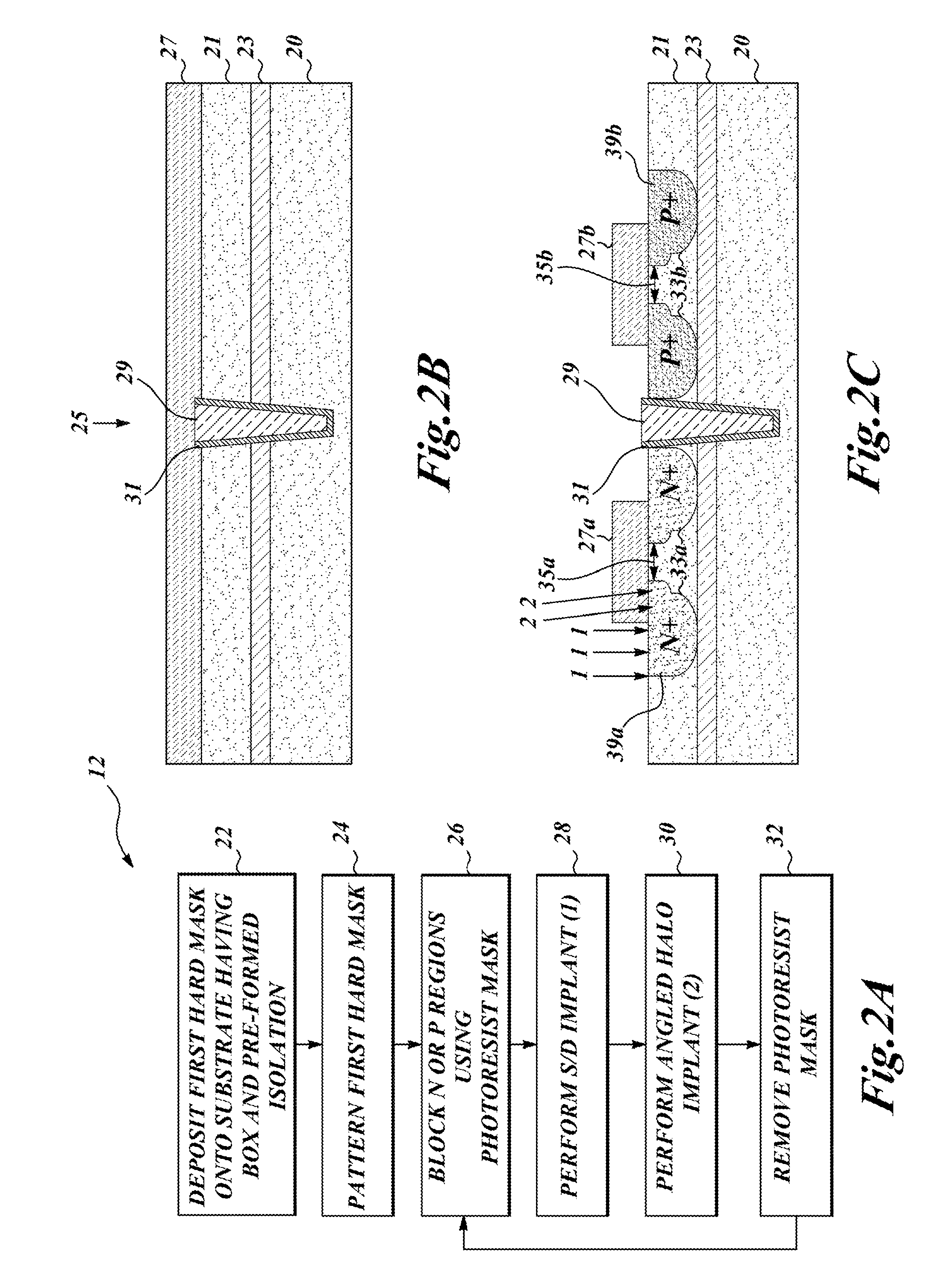
Silicon on insulator device with partially recessed gate
ActiveUS20150228777A1Enhanced transistor performanceSuppression of short channel effectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceDopant
Transistors having partially recessed gates are constructed on silicon-on-insulator (SOI) semiconductor wafers provided with a buried oxide layer (BOX), for example, FD-SOI and UTBB devices. An epitaxially grown channel region relaxes constraints on the design of doped source and drain profiles. Formation of a partially recessed gate and raised epitaxial source and drain regions allow further improvements in transistor performance and reduction of short channel effects such as drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL) and control of a characteristic subthreshold slope. Gate recess can be varied to place the channel at different depths relative to the dopant profile, assisted by advanced process control. The partially recessed gate has an associated high-k gate dielectric that is initially formed in contact with three sides of the gate. Subsequent removal of the high-k sidewalls and substitution of a lower-k silicon nitride encapsulant lowers capacitance between the gate and the source and drain regions.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
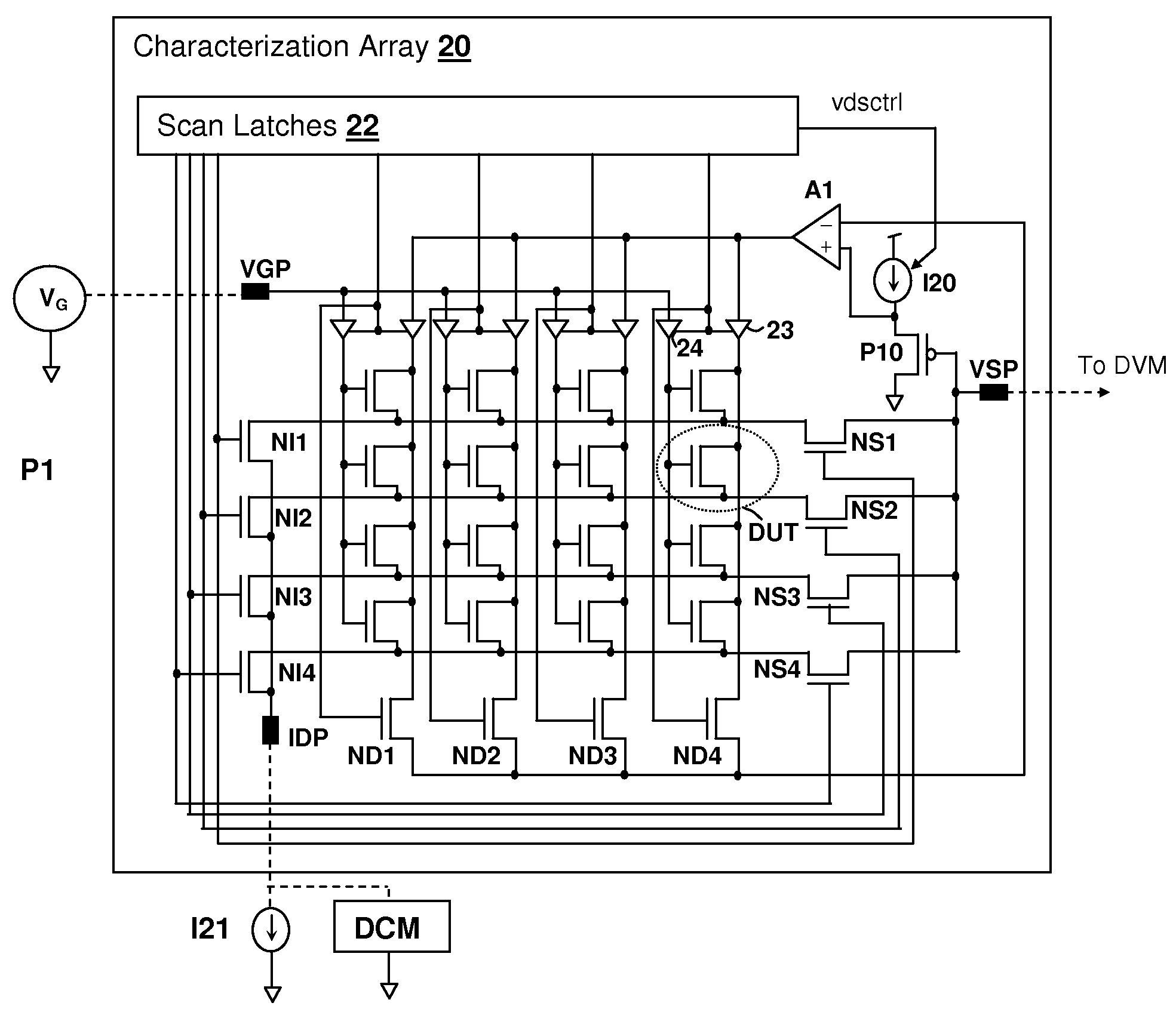
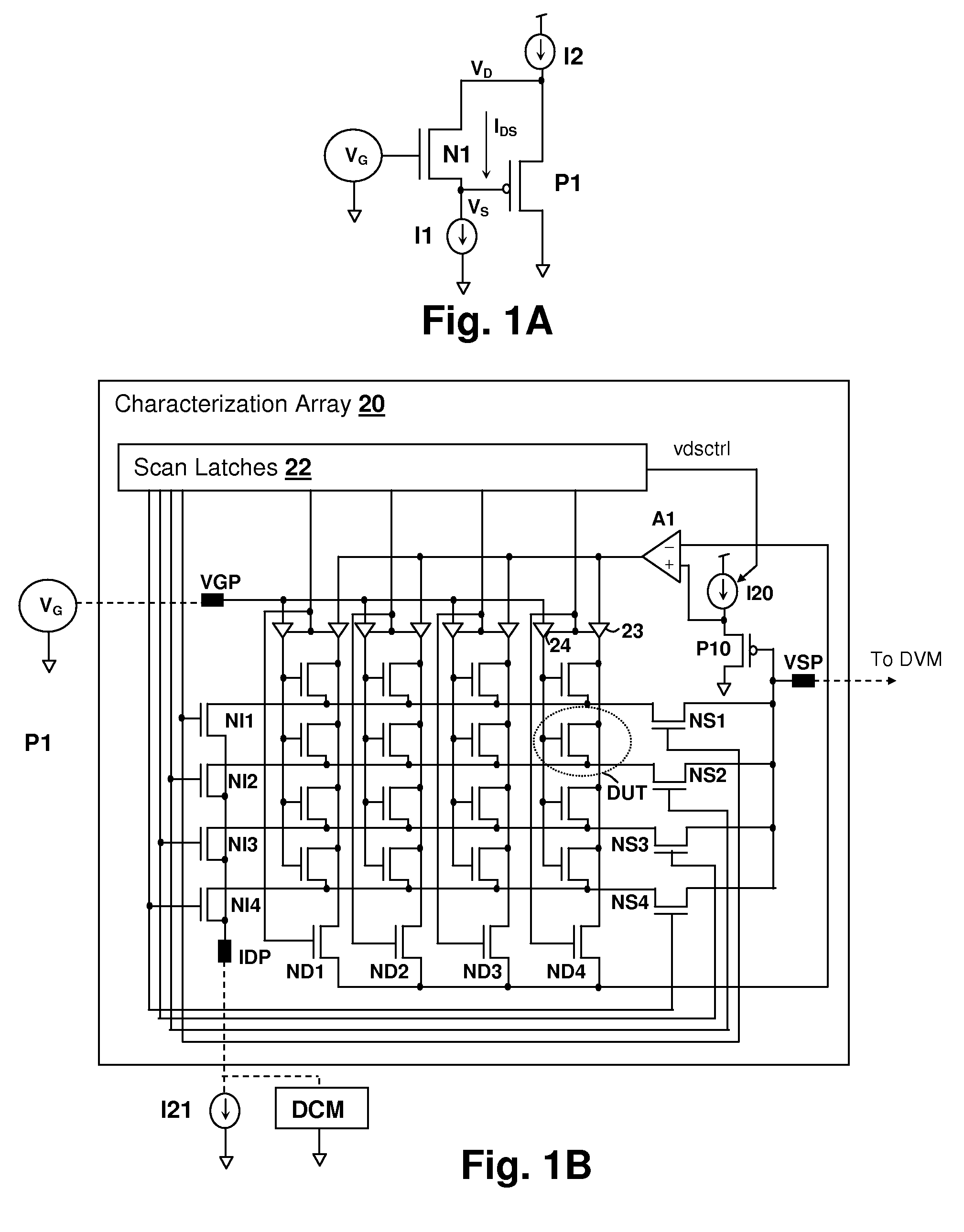
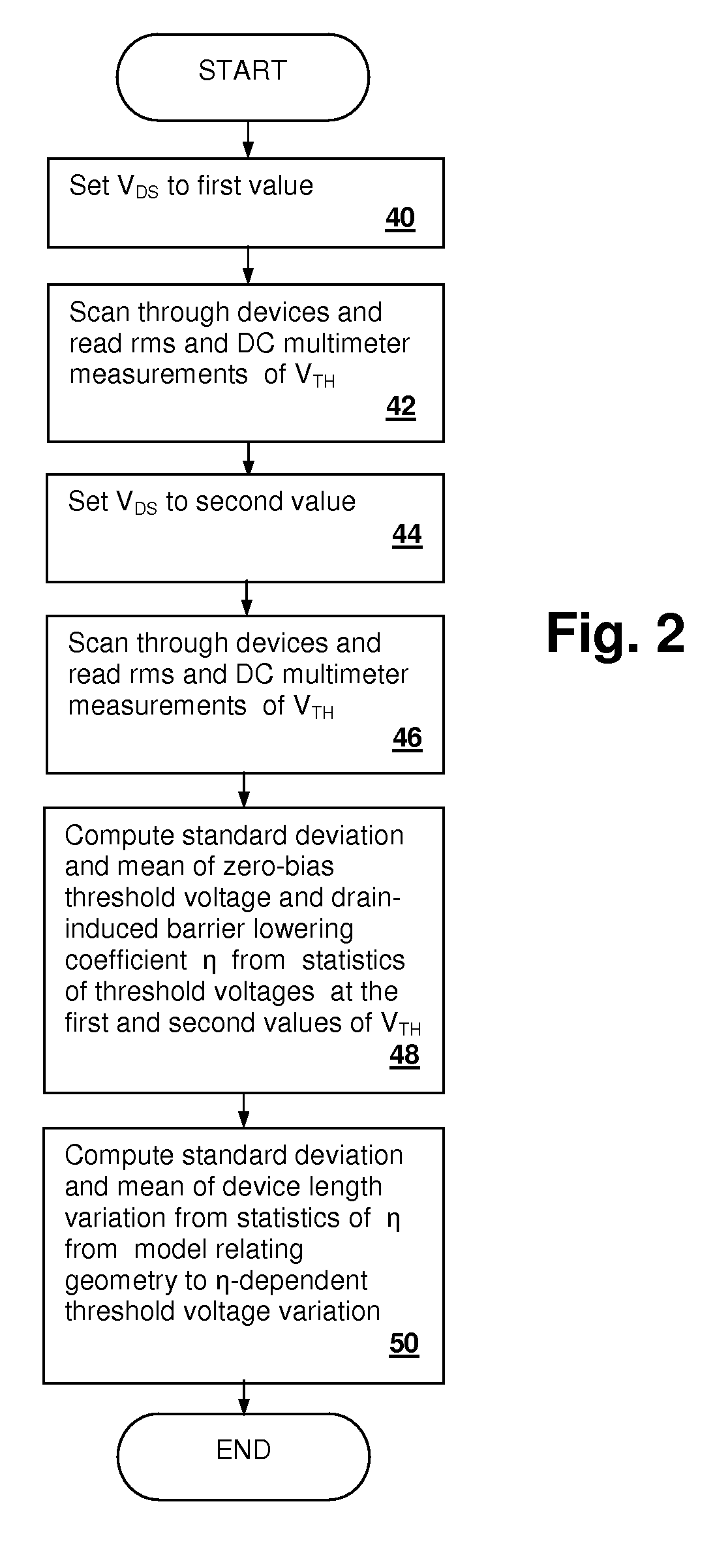
Method and system for isolating dopant fluctuation and device length variation from statistical measurements of threshold voltage
InactiveUS20090164155A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceDopantLength variation
A method and system for isolating dopant fluctuation and device length variation from statistical measurements of threshold voltage provides fast determination of process variation for devices in a characterization array. Statistics of threshold voltage are measured at two different values of drain-source voltage imposed on the devices in the characterization array. At least one moment of the a drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL) coefficient η, which is a measure of device length and zero-bias threshold voltage VTH0 are computed directly from the statistical moment values of the threshold variation. The standard deviation and mean of η and VTH0 can thereby be obtained having only a statistical description of the threshold voltage for the devices in the array at multiple drain-source voltages. The threshold voltage statistics can be obtained from a digital meter measurement (rms and DC average) of a waveform indicative of threshold voltage produced by sequentially selecting the array devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Preparation method of vertical silicon nanowire field effect transistor
ActiveCN102315129AReduce areaIncrease the areaNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntegrated circuit manufacturingManufacturing technology
The invention, which belongs to the super-large-scale integrated circuit manufacturing technology field, provides a preparation method of a vertical silicon nanowire field effect transistor with a small parasitic resistance. Compared to a traditional plane field effect transistor, by using the vertical silicon nanowire field effect transistor prepared in the invention, on one hand, a good abilityof restraining a short channel effect can be provided and leakage current and drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL) can be reduced because of a good gate control ability caused by a one-dimensional geometric structure of the vertical silicon nanowire field effect transistor; on the other hand, a device area can be further reduced and an integration level of an IC system can be raised.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
Silicided metal gate for multi-threshold voltage configuration
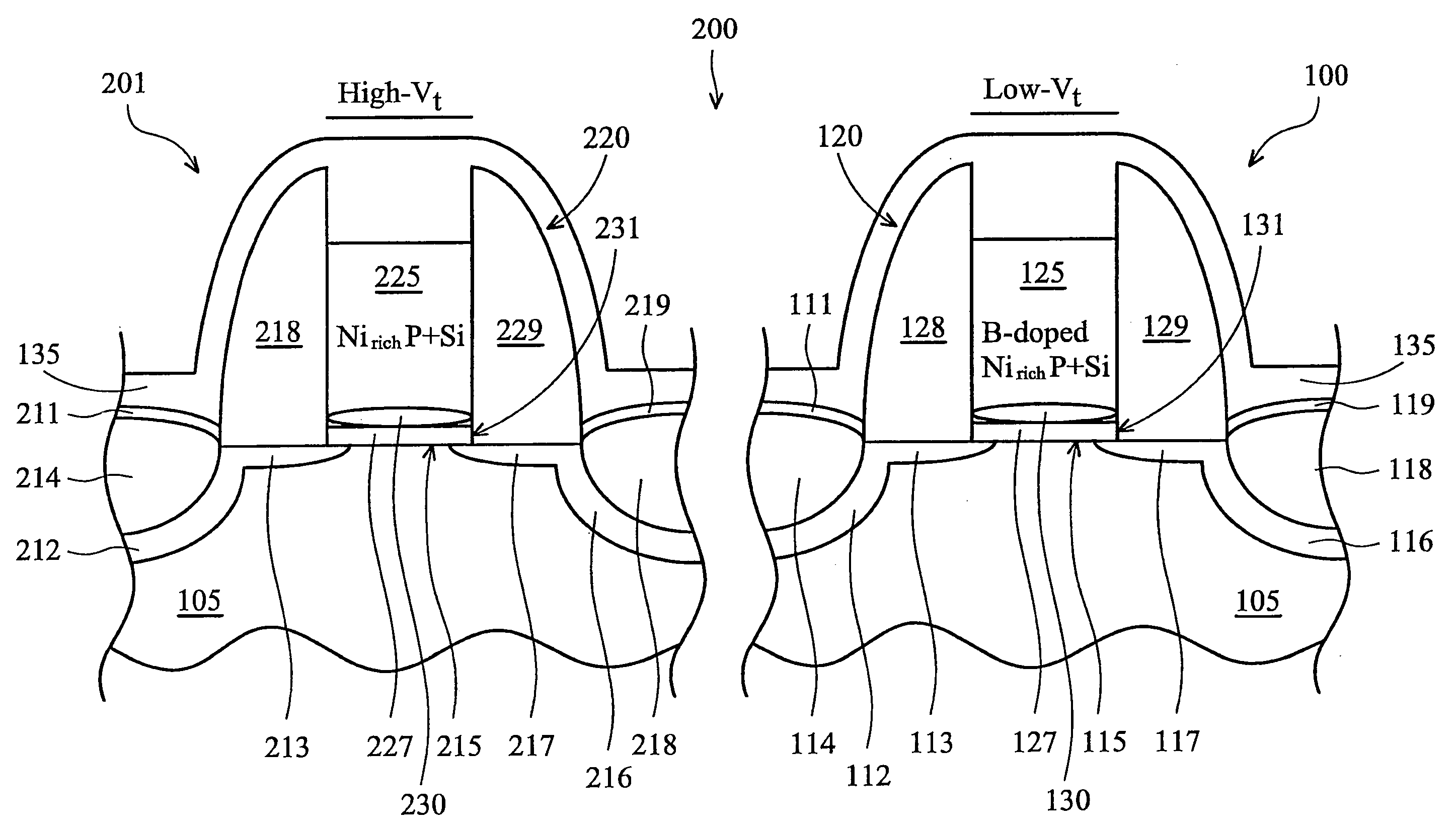
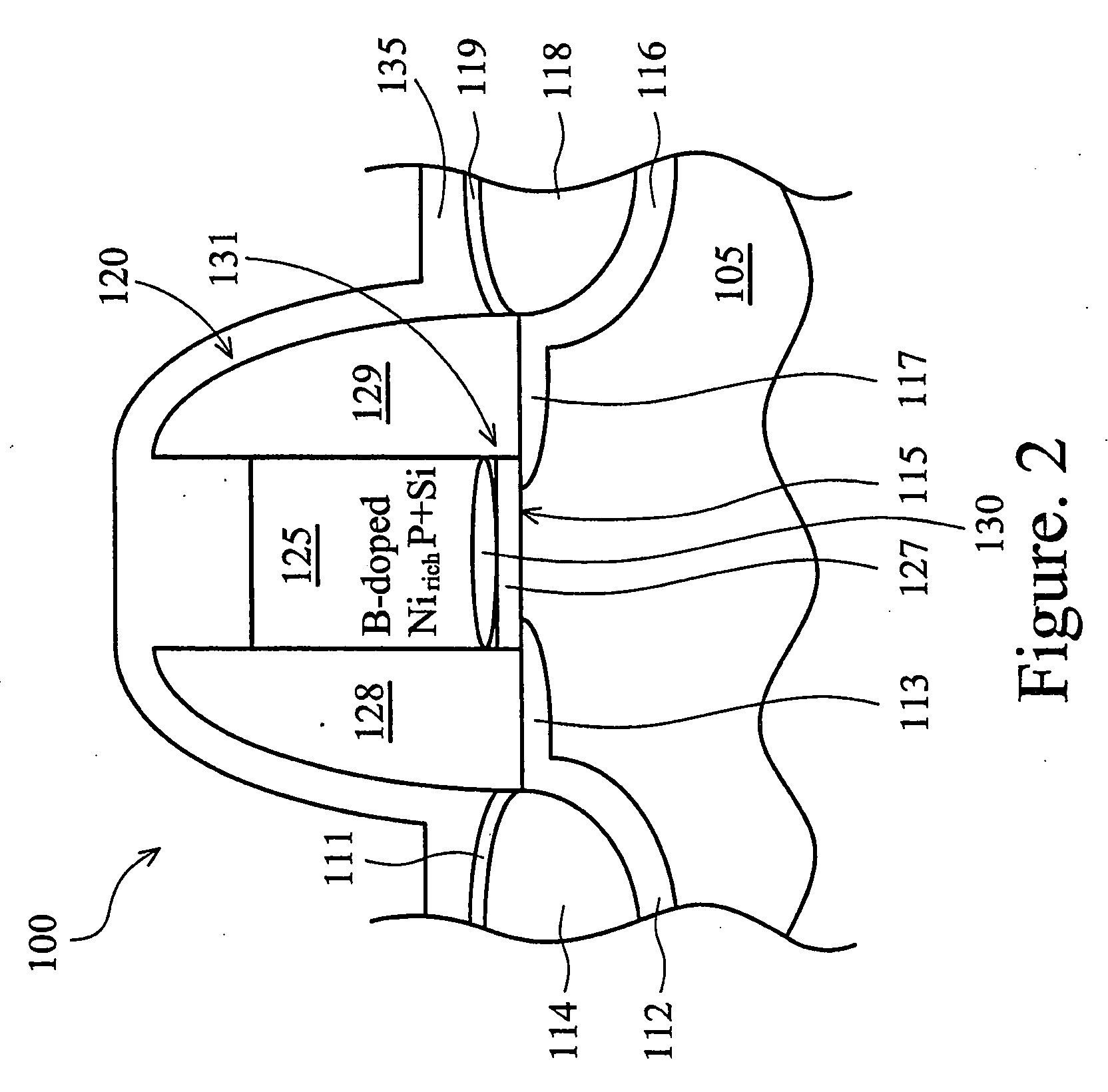
A PMOS (p-channel metal oxide semiconductor) device having at low voltage threshold MOSFET (MOS field effect transistor) with an improved work function and favorable DIBL (drain-induced barrier lowering) and SCE (short channel effect) characteristics, and a method for making such a device. The PMOS device includes a gate structure that is disposed on a substrate and includes a silicided gate electrode. The silicide is preferably nickel-rich and includes a peak platinum concentration at or near the interface between the gate electrode and a dielectric layer that separates the gate electrode from the substrate. The platinum peak region is produced by a multi-step rapid thermal annealing or similar process. The PMOS device may also include two such MOSFETs, one of which is boron-doped and one of which is not.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
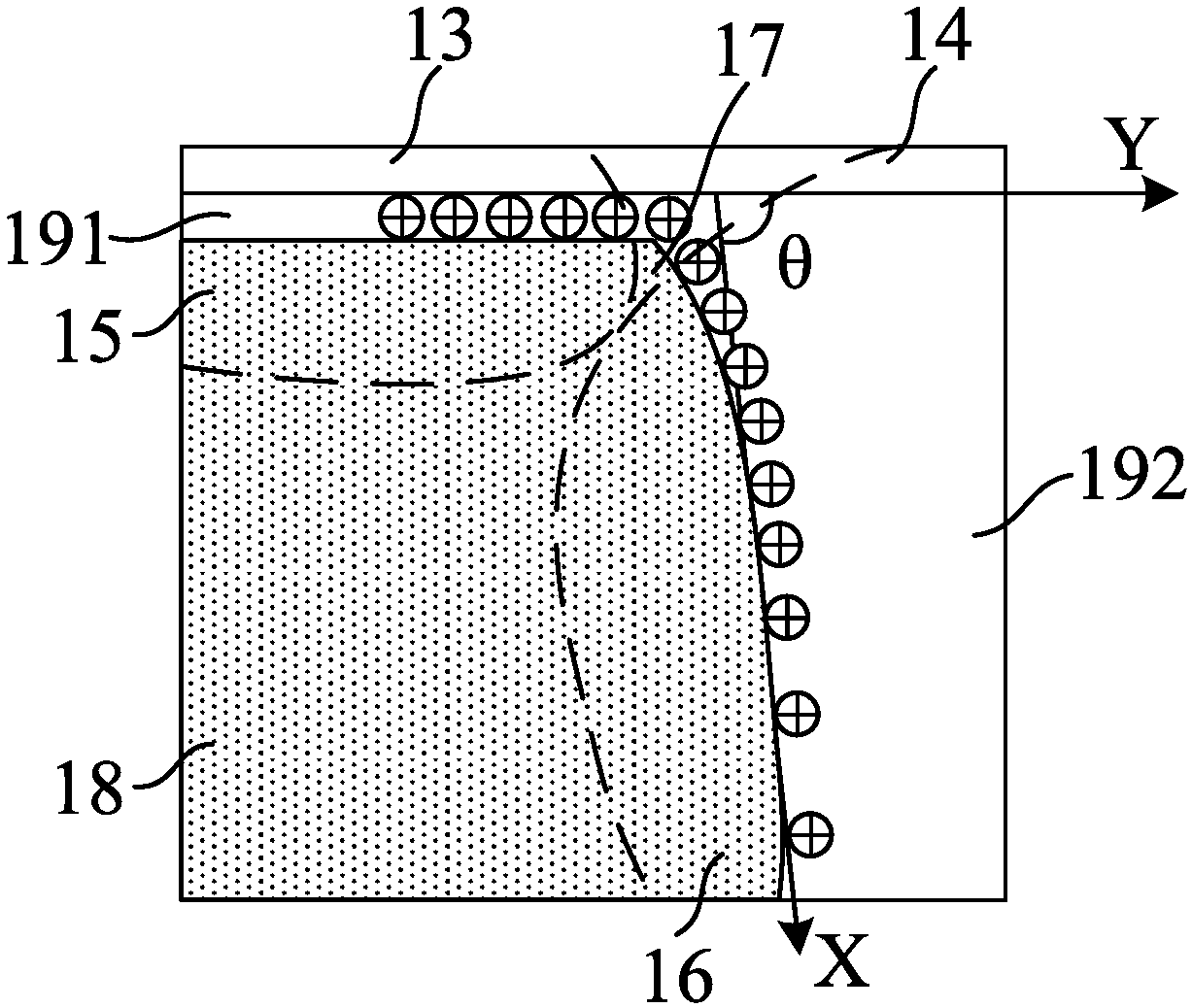
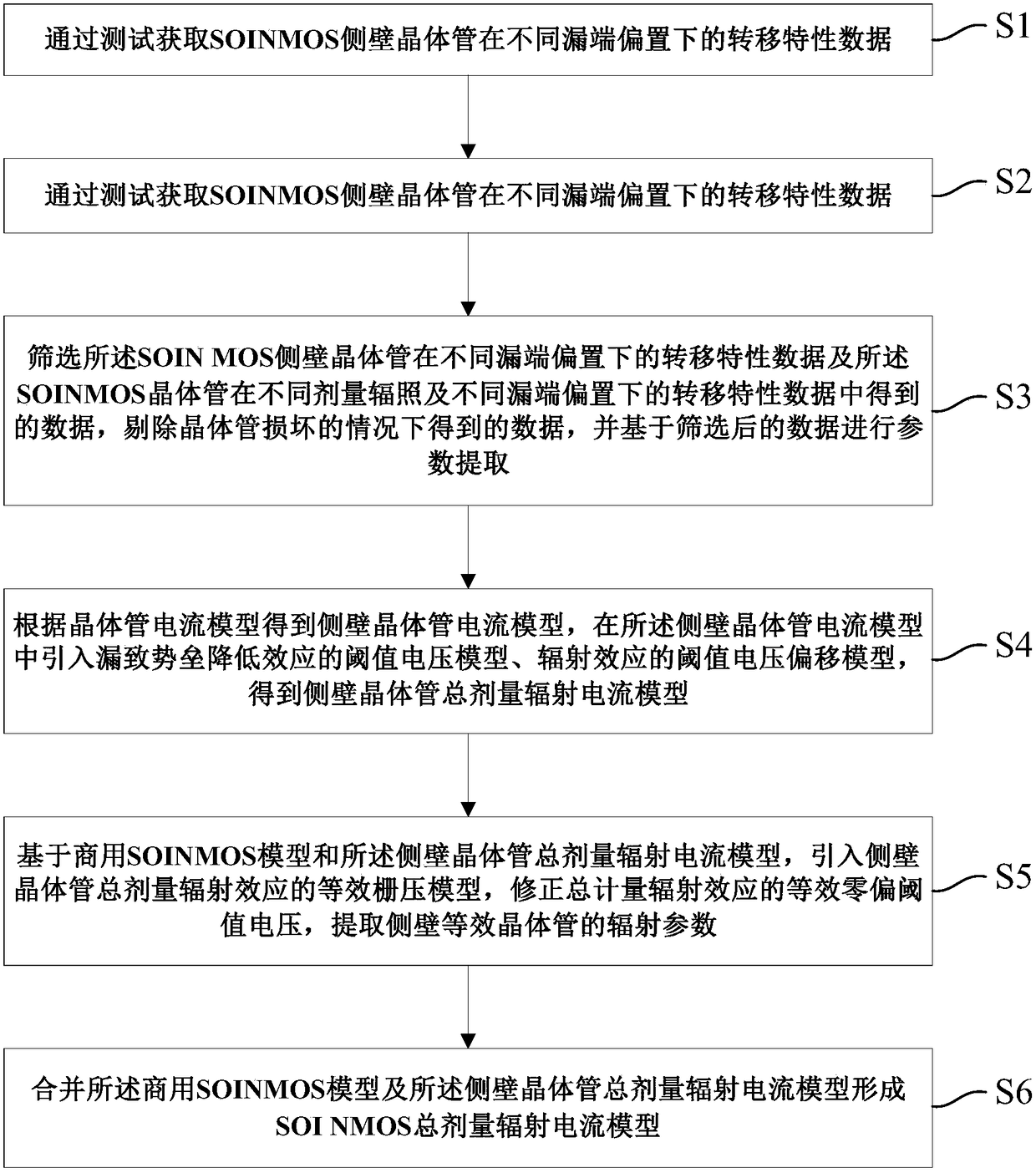
SOI NMOS total-dose radiation multi-offset point current model establishing method
ActiveCN108388721AShorten the development cycleLow costData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsGrid voltageElectrical current
The invention provides an SOI NMOS total-dose radiation multi-bias point current model establishing method. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining transfer characteristic data, under different drain terminal offsets, of an SOI NMOS side wall transistor and transfer characteristic data, under different doses of radiation and different drain terminal offsets, of the SOI NMOS side wall transistor through test; screening data and extracting parameters; importing a threshold voltage model of a drain-induced barrier lowering effect, a threshold voltage deviation model of a radiationeffect and an equivalent grid voltage model of a side wall transistor total-dose radiation effect into a side wall transistor current model; and forming an SOI NMOS total-dose radiation current model.The method is suitable for total-dose radiation simulation under different drain terminal offset voltages, is capable of fitting transfer characteristic curves, under different drain terminal offsets, of SOI NMOS when being influenced by the total-dose radiation effect more correctly, and is more suitable for total-dose radiation effect simulation of integrated circuits.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
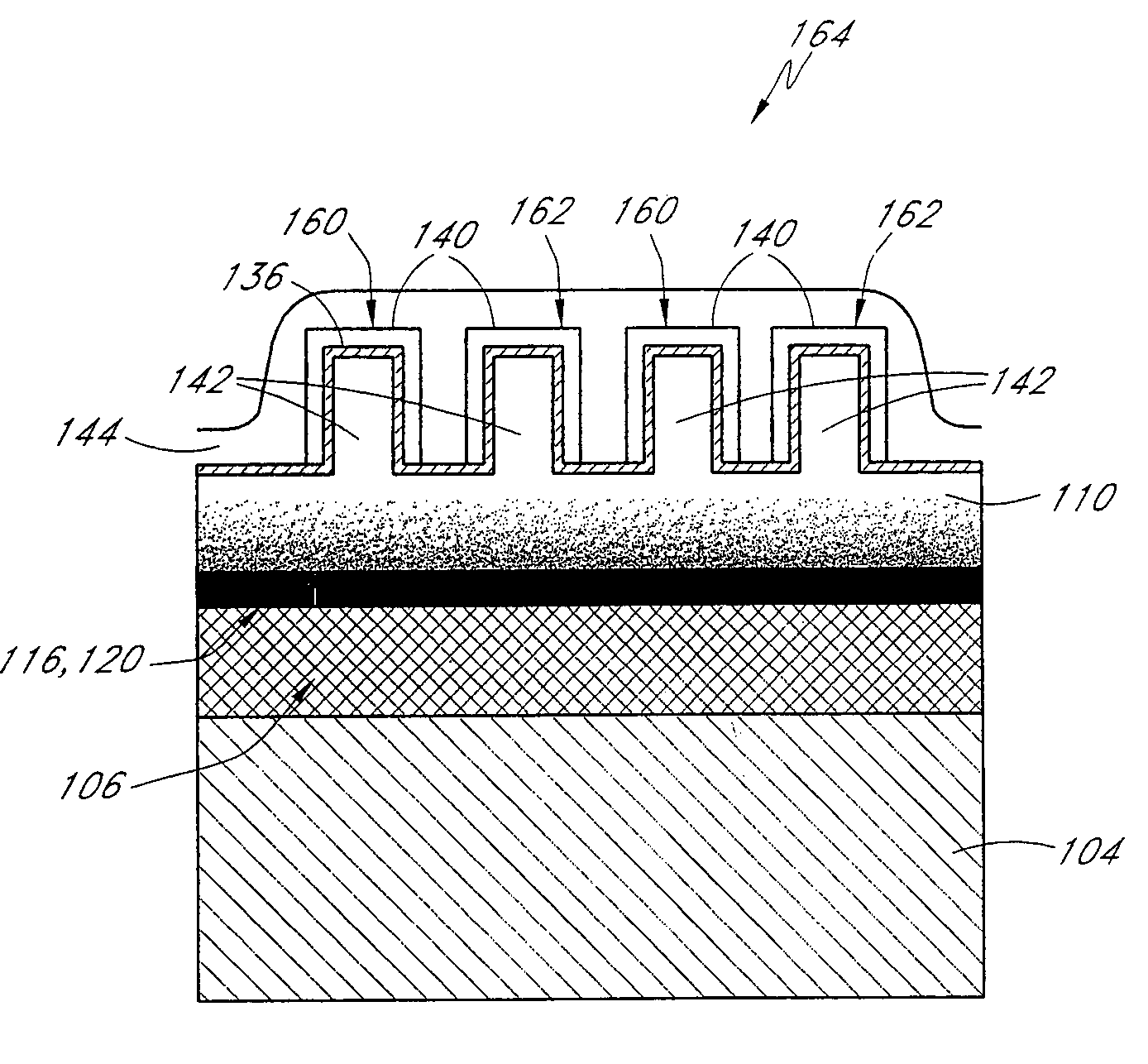
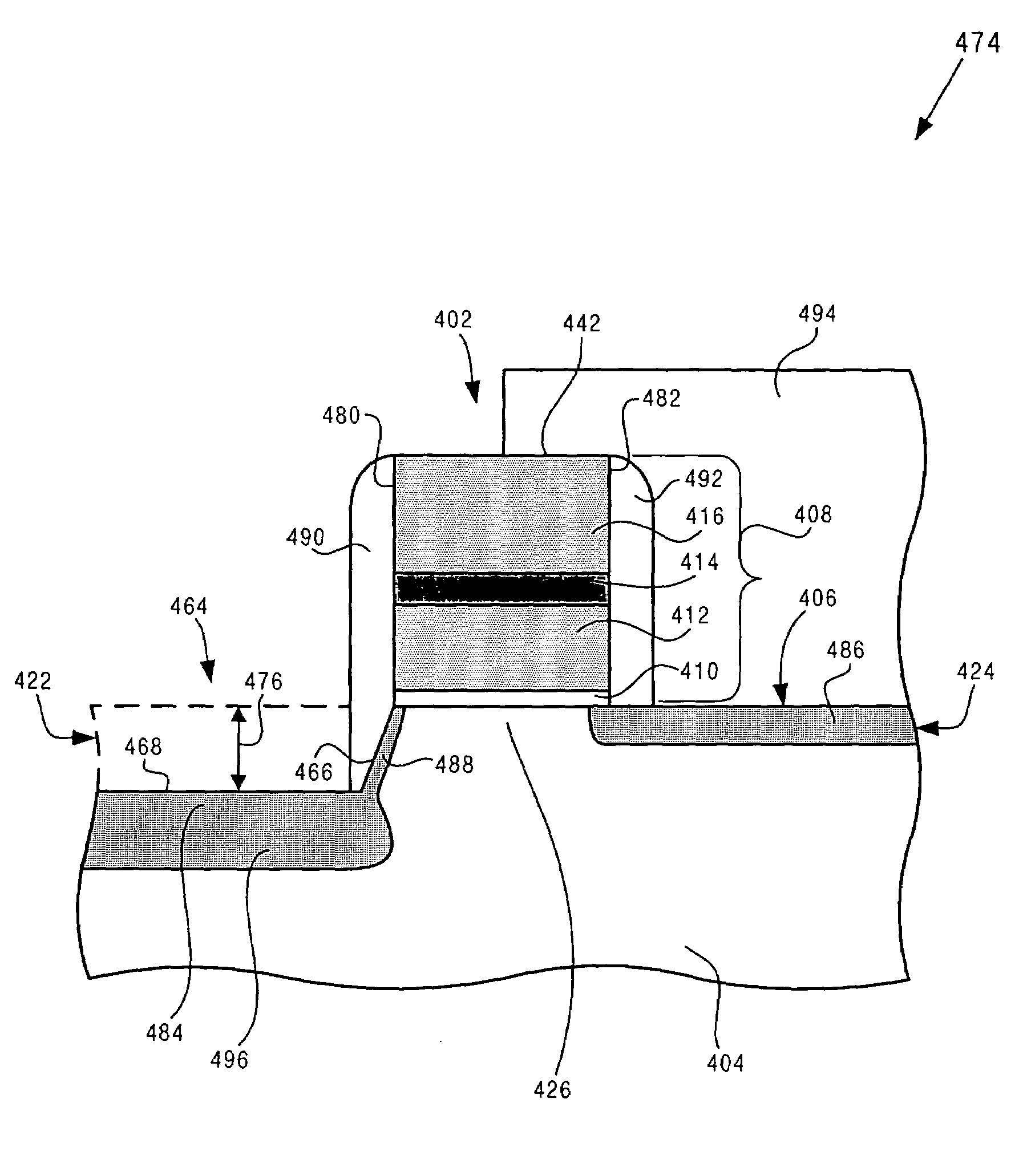
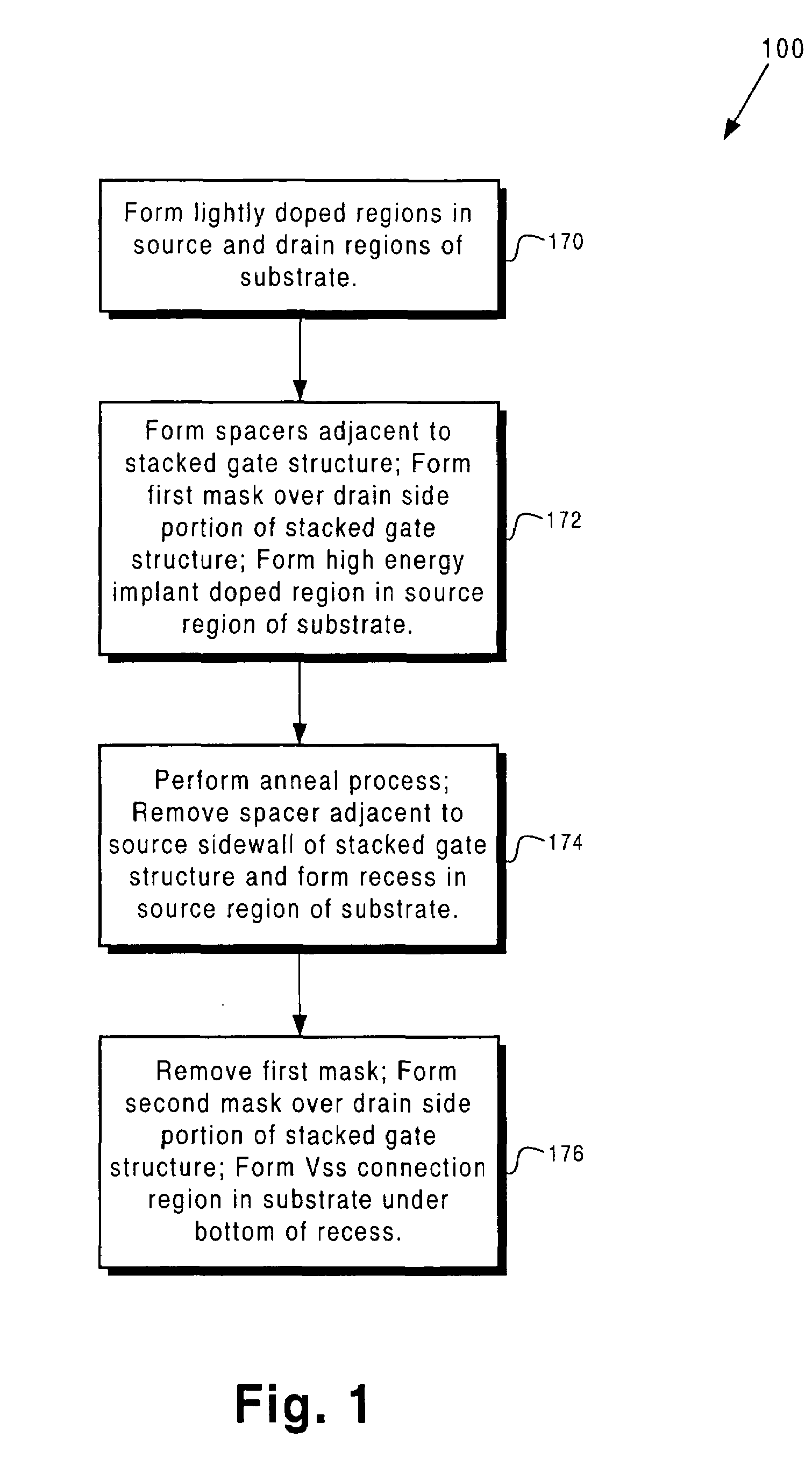
Memory cell with reduced DIBL and Vss resistance
ActiveUS7170130B2Reduced lateral straggle and diffusionReduction in drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL)TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energyEngineering
According to one exemplary embodiment, a method for fabricating a floating gate memory cell on substrate comprises a step of forming a spacer adjacent to a source sidewall of a stacked gate structure, where the stacked gate structure is situated over a channel region in substrate. The method further comprises forming a high energy implant doped region adjacent to the spacer in the source region of substrate. The method further comprises forming a recess in a source region of the substrate, where the recess has a sidewall, a bottom, and a depth, and where the sidewall of the recess is situated adjacent to a source of the floating gate memory cell. According to this exemplary embodiment, the spacer causes the source to have a reduced lateral straggle and diffusion in the channel region, which causes a reduction in drain induced barrier lowering (DIBL) in the floating gate memory cell.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Fabrication method of vertical silicon nanowire field effect transistor
ActiveUS20130011980A1Reduce leakage currentImprove gate control abilityNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceSilicon nanowires
The present invention discloses a fabrication method of a vertical silicon nanowire field effect transistor having a low parasitic resistance, which relates to a field of an ultra-large-integrated-circuit fabrication technology. As compared with a conventional planar field effect transistor, on one hand the vertical silicon nanowire field effect transistor fabricated by the present invention can provide a good ability for suppressing a short channel effect due to the excellent gate control ability caused by the one-dimensional structure, and reduce a leakage current and a drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL). On the other hand, an area of the transistor is further reduced and an integration degree of an IC system is increased.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Gallium nitride based high electron mobility transistor with composite metal gate
ActiveCN103474455AInhibition-lowering (DIBL) effectAvoid mechanical propertiesSemiconductor devicesIndiumGallium nitride
The invention relates to a gallium nitride based high electron mobility transistor with a composite metal gate. The gallium nitride based high electron mobility transistor comprises a substrate, a gallium nitride buffer layer, an aluminum nitride inserting layer, an aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer, and a source electrode, a drain electrode and a grid electrode on the aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer, wherein the source electrode and the drain electrode form ohmic contact with the aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer; the grid electrode and the aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer form Schottky contact; the grid electrode on the aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer is formed by connecting more than two metals with different work functions. Through the utilization of the influence of a step barrier shielding drain potential formed between the grid metals with different work functions on device channels, the Drain Induced Barrier Lowering (DIBL) effect is inhibited, and the SCEs (Short Channel Effects) of deep submicron gallium nitride based high electron mobility transistor are improved, thus the current gain cut-off frequency fT is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Semiconductor device and forming method of semiconductor device
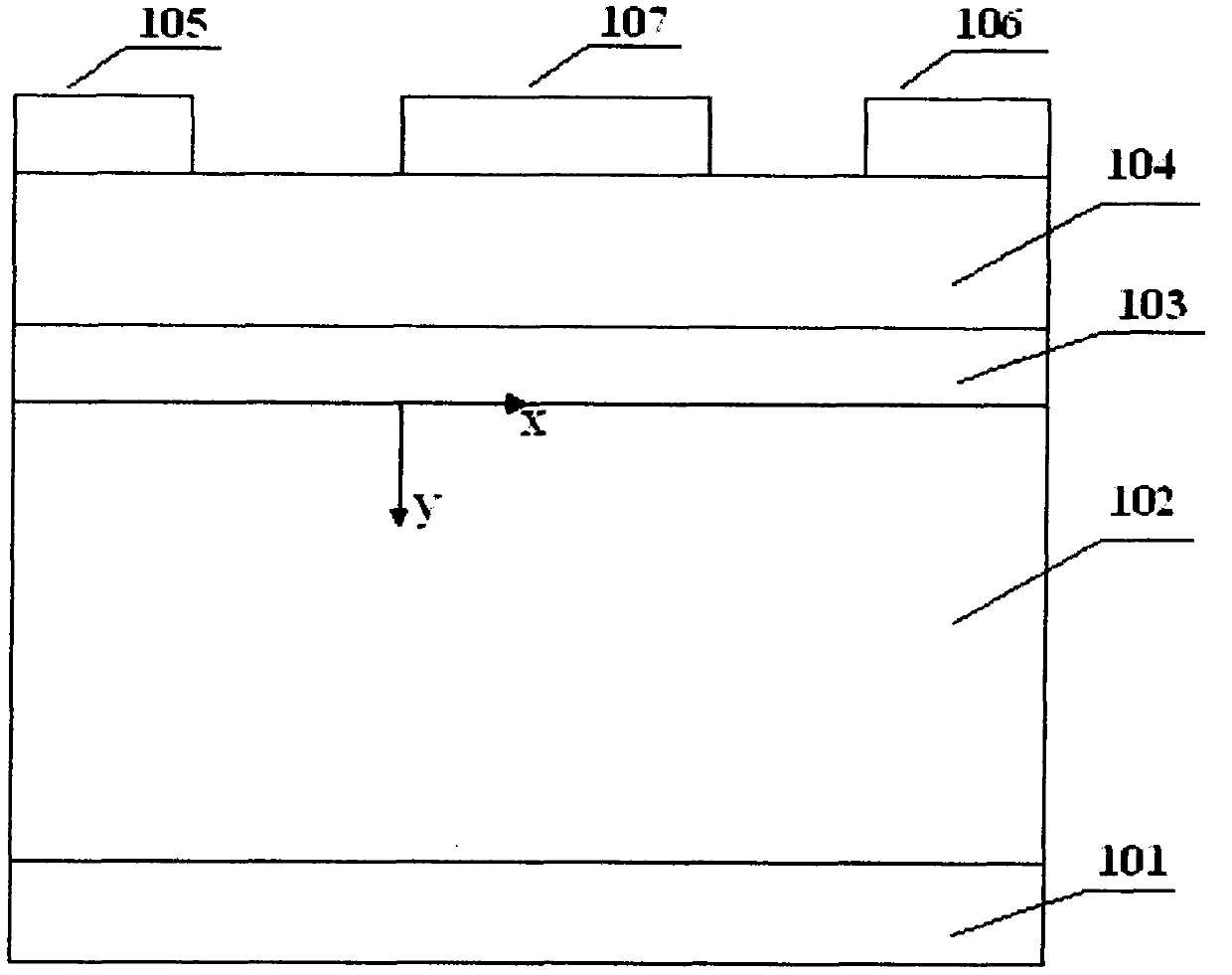
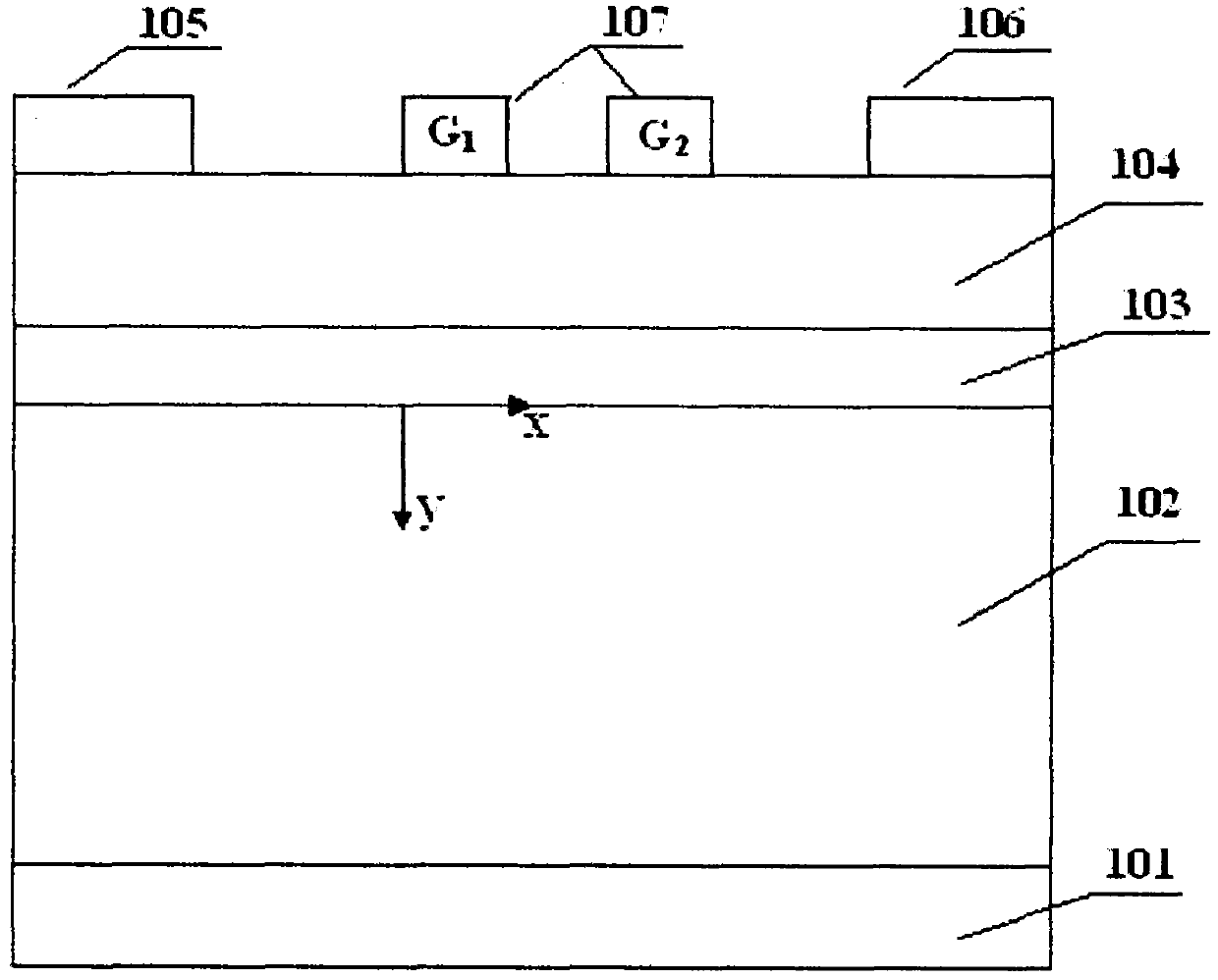
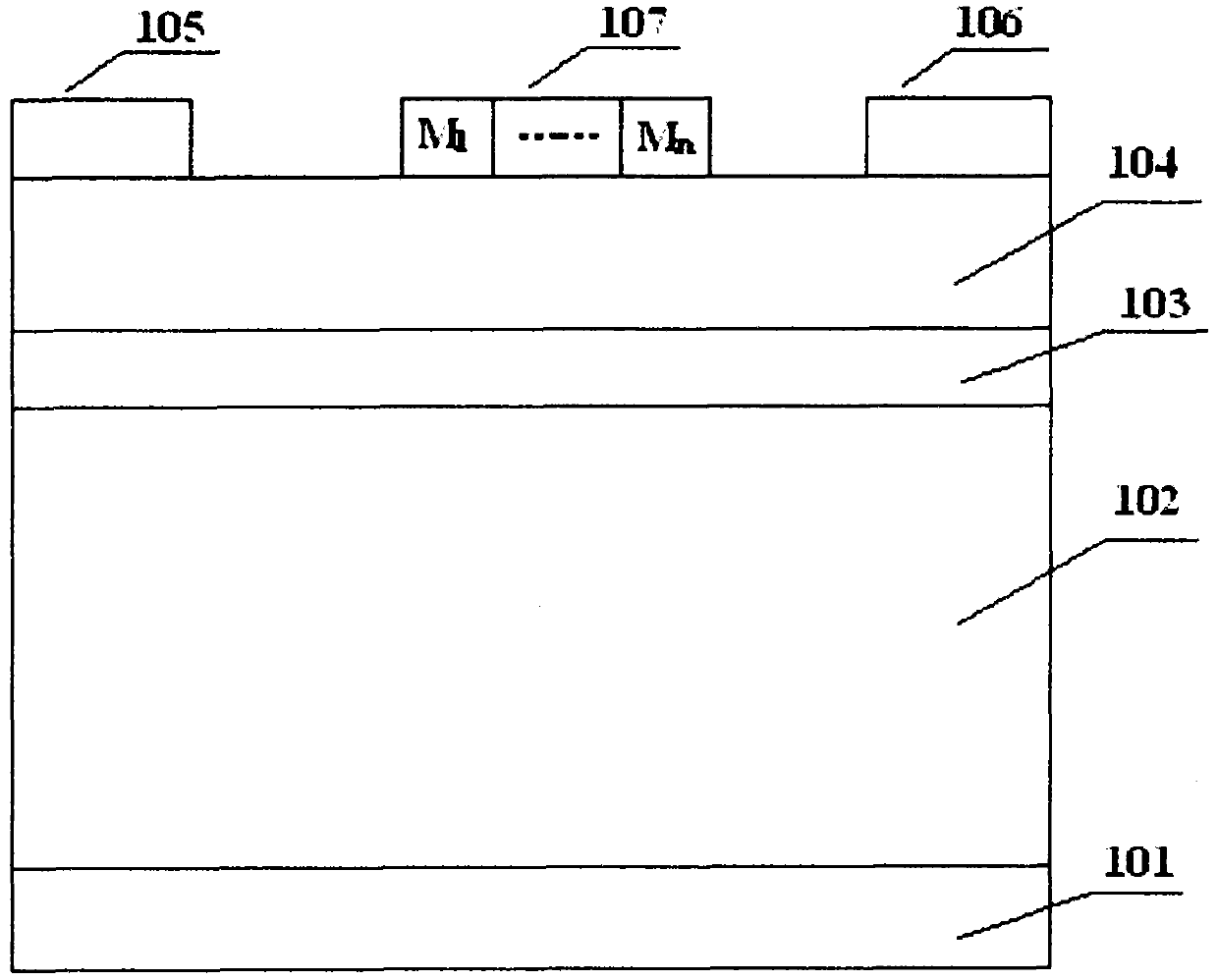
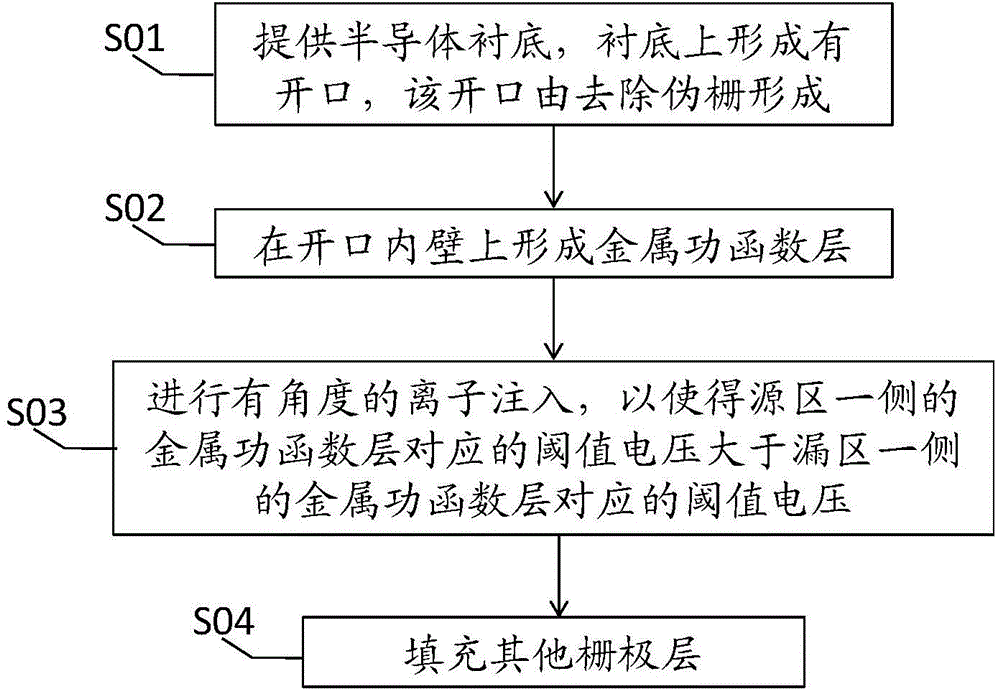
InactiveCN105870020AImprove performanceImprove shipping speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge carrierVoltage drop
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device. The method includes the following steps that: a semiconductor substrate is provided, an opening is formed in the substrate, and the opening is formed by removing a dummy gate; metal work function layers are formed at the internal wall of the opening; ion implantation of a certain angle is carried out, so that threshold voltage corresponding to a metal work function layer at one side of a source region is larger than threshold voltage corresponding to a metal work function layer at one side of a drain region; and other grid layers are filled. According to the manufacturing method of the invention, voltage drop of a channel region near a source end is increased, and voltage drop of a channel region near a drain end is decreased, and therefore, the electric field of the drain end can be decreased, and short-channel effects such as DIBL (drain induced barrier lowering) can be suppressed, and the electric field of the source end is increased, so that the transport speed of carriers can be improved, and the performance of the device can be improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com