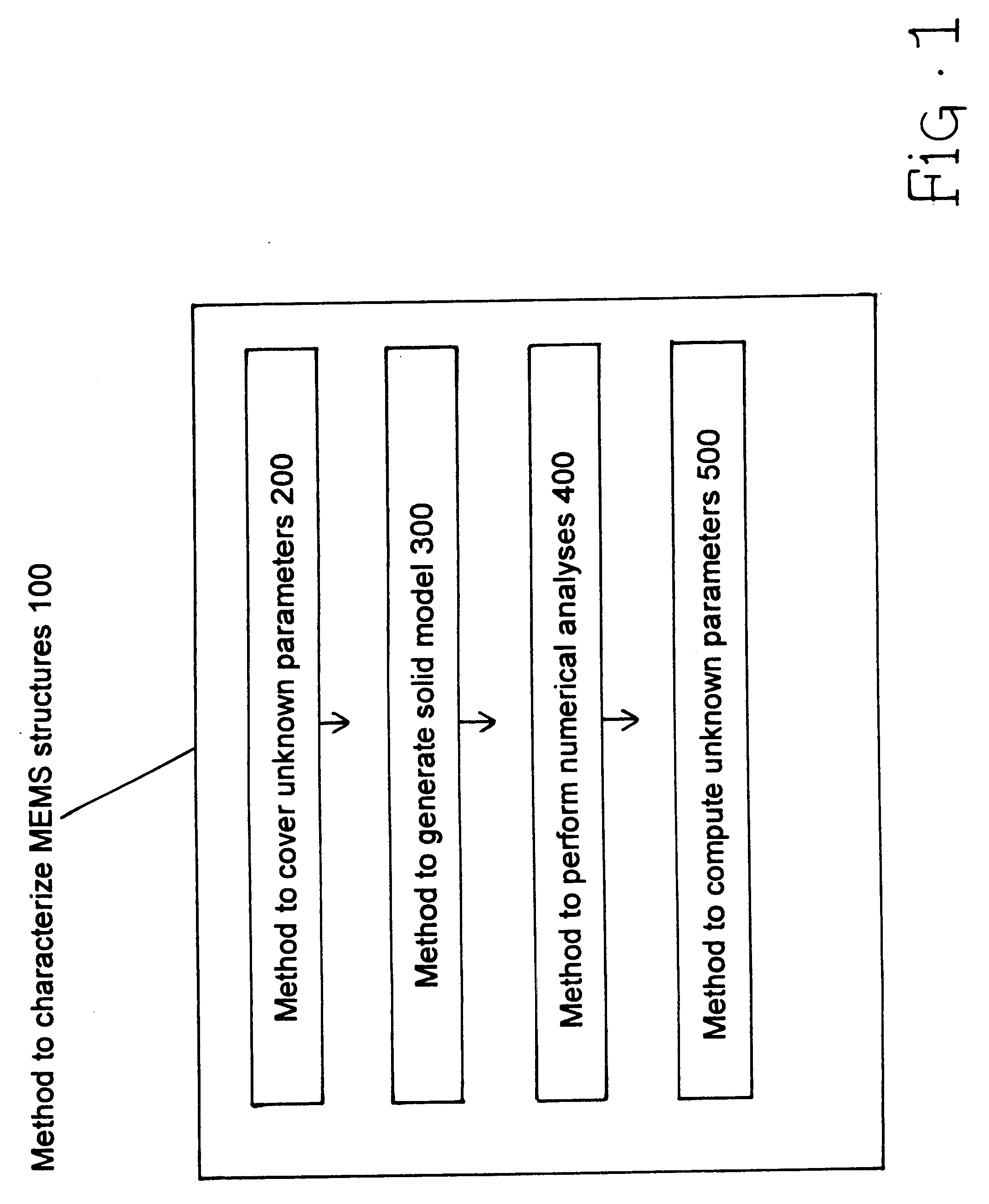
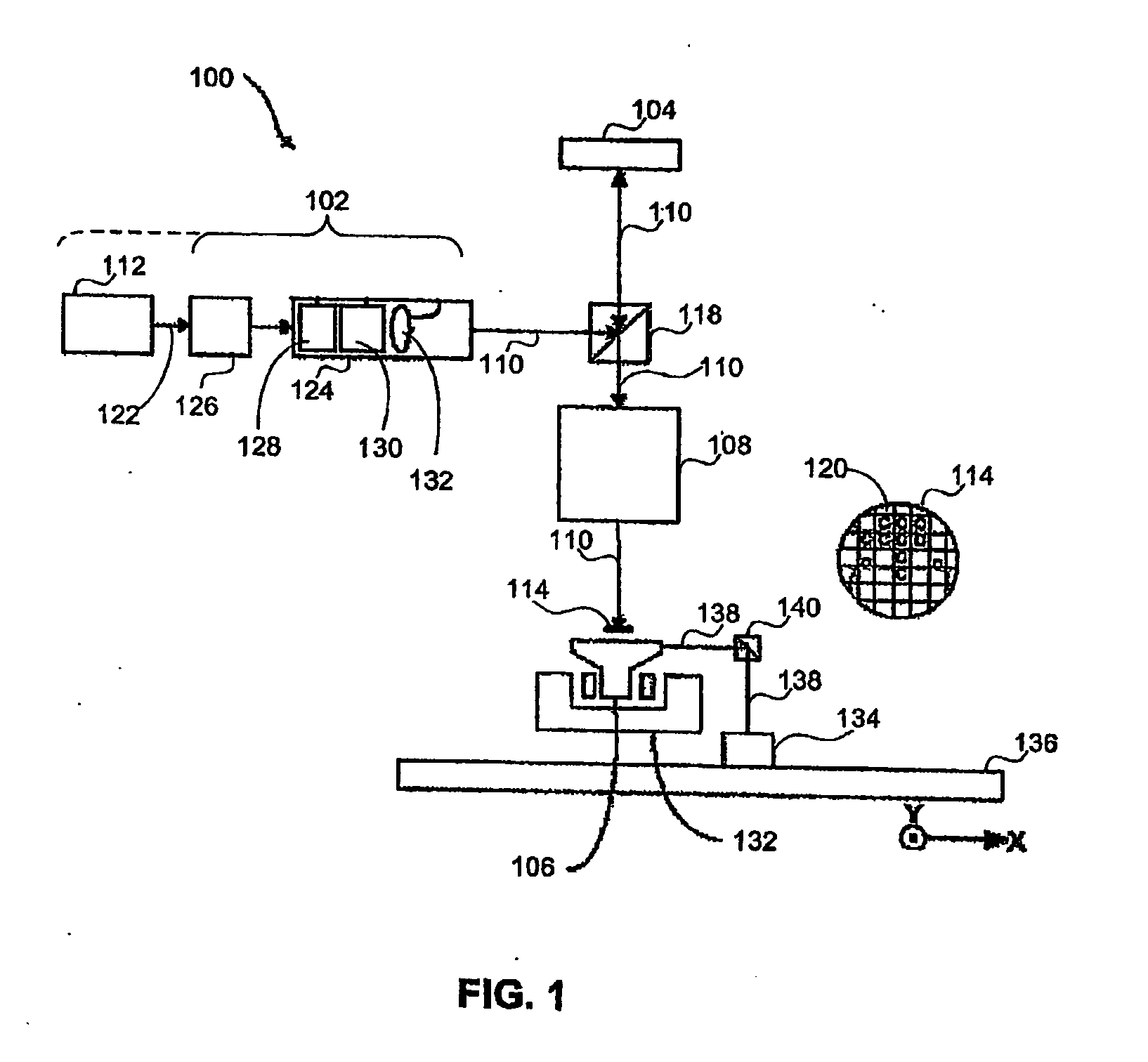
Patents
Literature
61 results about "Process variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process variation is the naturally occurring variation in the attributes of transistors (length, widths, oxide thickness) when integrated circuits are fabricated. The amount of process variation becomes particularly pronounced at smaller process nodes (<65 nm) as the variation becomes a larger percentage of the full length or width of the device and as feature sizes approach the fundamental dimensions such as the size of atoms and the wavelength of usable light for patterning lithography masks.
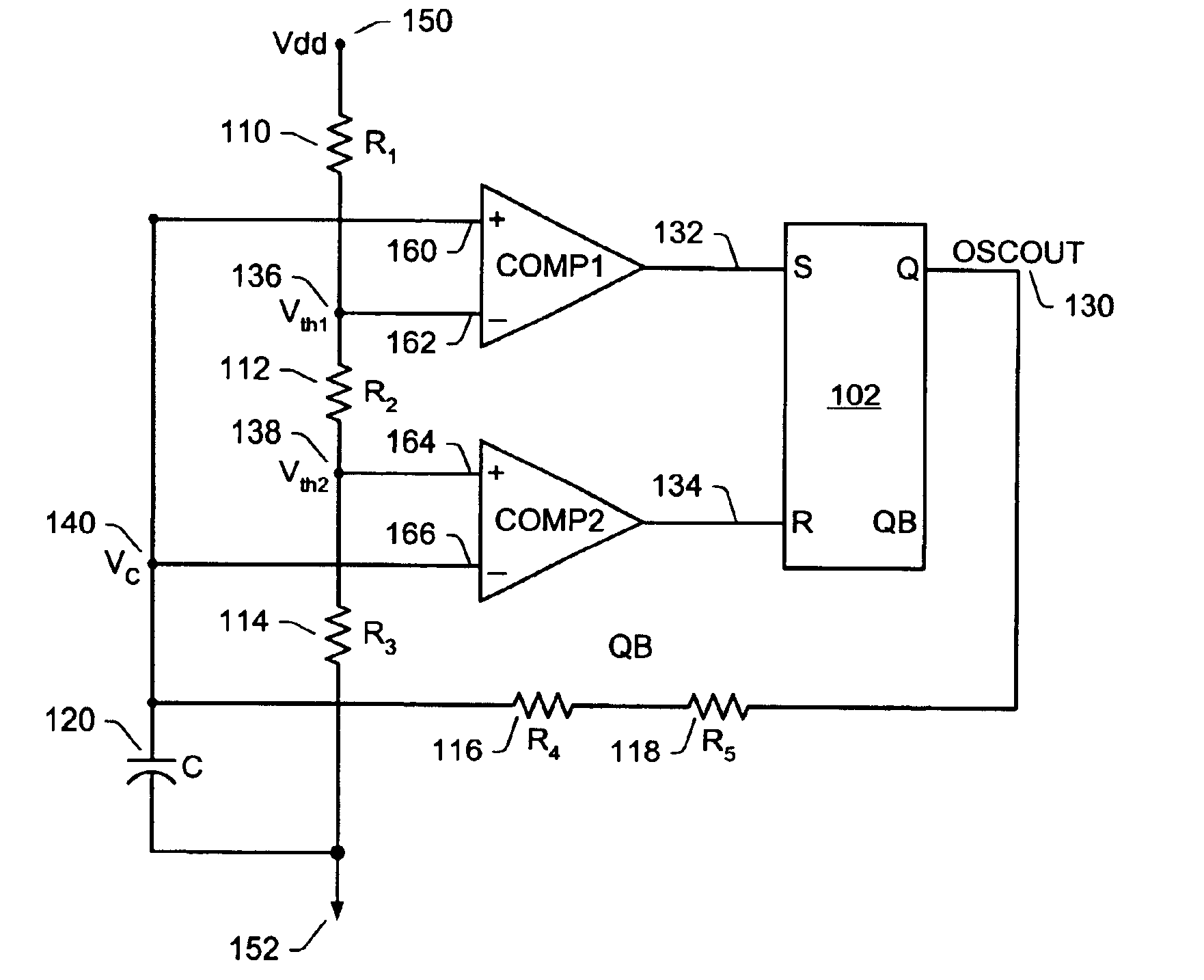
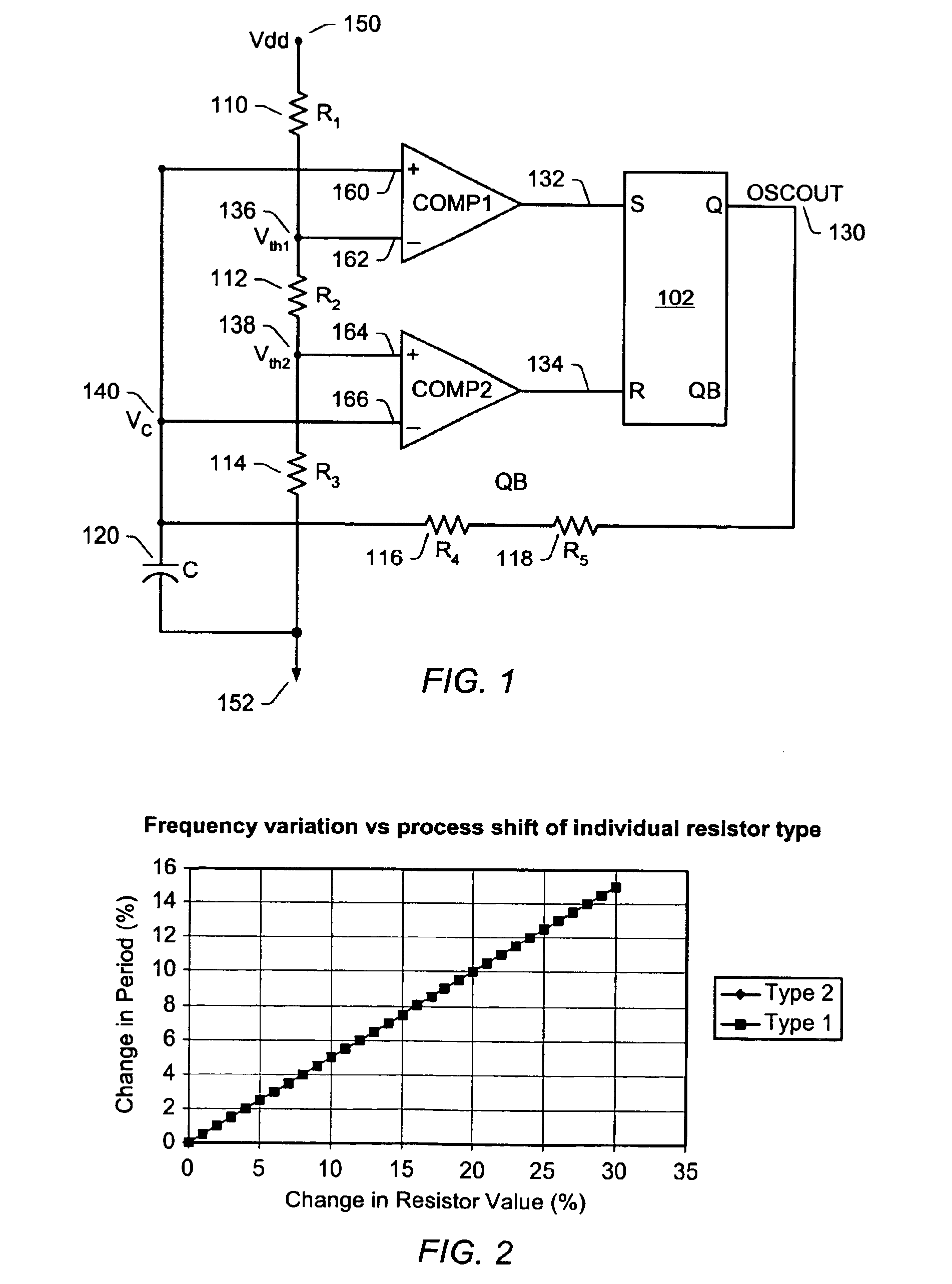
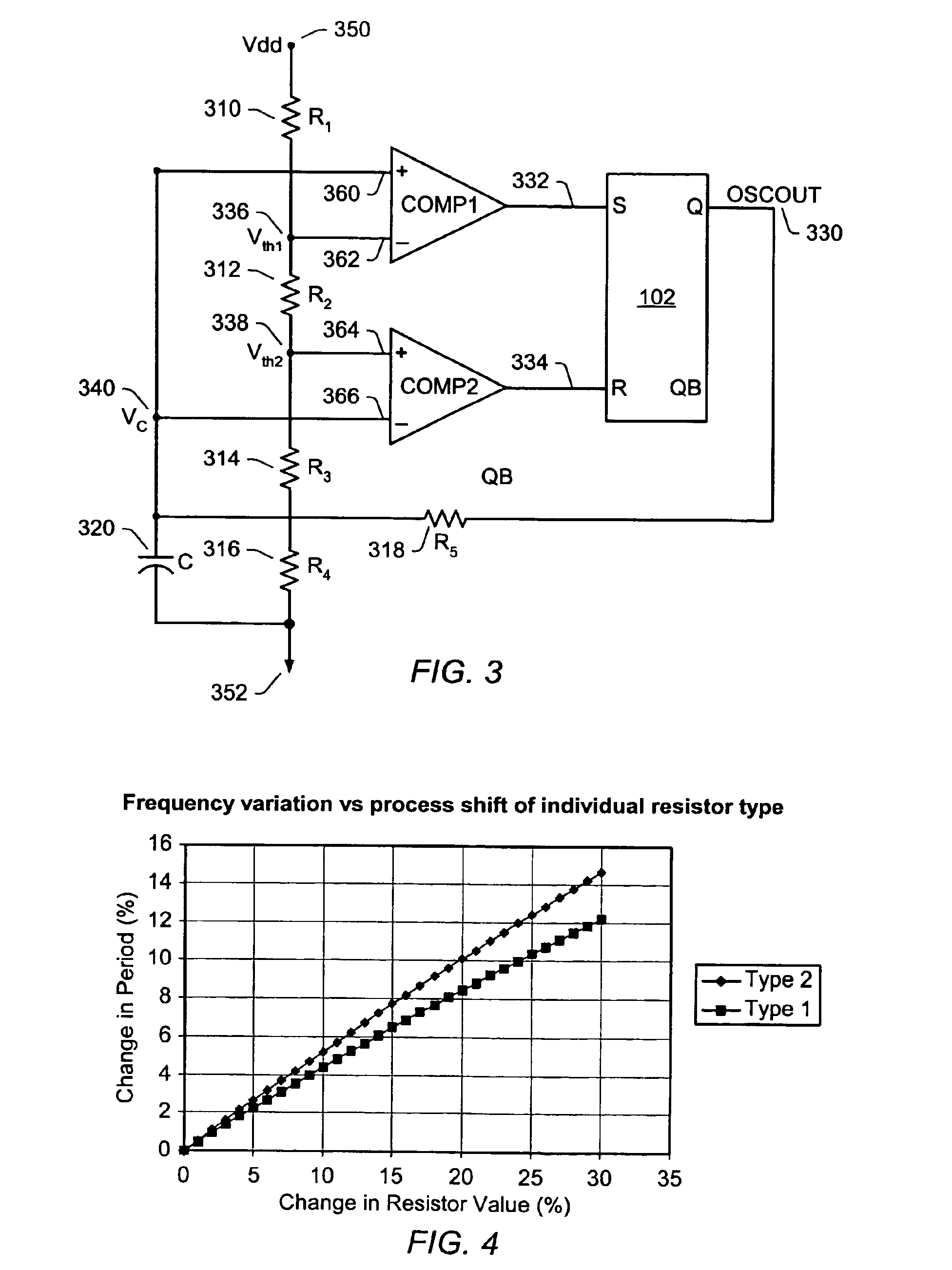
Integrated relaxation oscillator with improved sensitivity to component variation due to process-shift
ActiveUS6924709B2Improve performanceHigh sensitivityGenerator stabilizationElectric pulse generator circuitsDiffusionRC time constant
A system and method for designing an integrated relaxation oscillator that exhibits reduced change in the frequency of oscillation caused by process variation. Improved sensitivity to component variation due to process shift is achieved through using more than one structure type when implementing the resistors affecting the RC time constant and threshold (trip point) voltages of the oscillator. Structure types are related to the fabrication process and for a CMOS process include, but are not limited to n-diffusion, p-diffusion, n-well, p-well, pinched n-well, pinched p-well, poly-silicon and metal. Each structure type exhibits statistically independent process variations, allowing for application of Lyapunov's extension of the Central Limit Theorem for statistically uncorrelated events to desensitize the effect from different possible causes. Thus, improvement in the performance of the oscillator may be achieved with a reduced trim requirement and without using external precision resistors.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
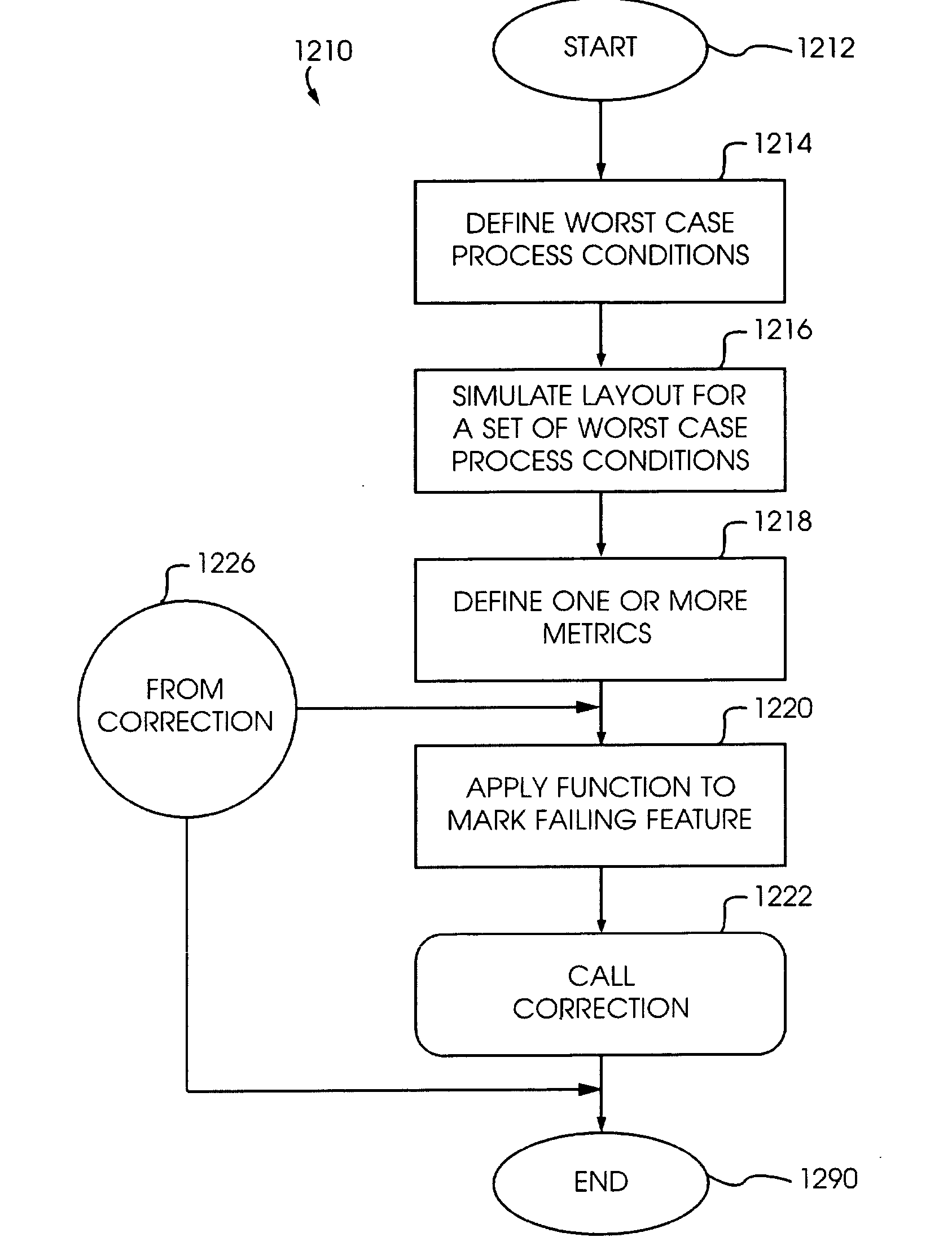
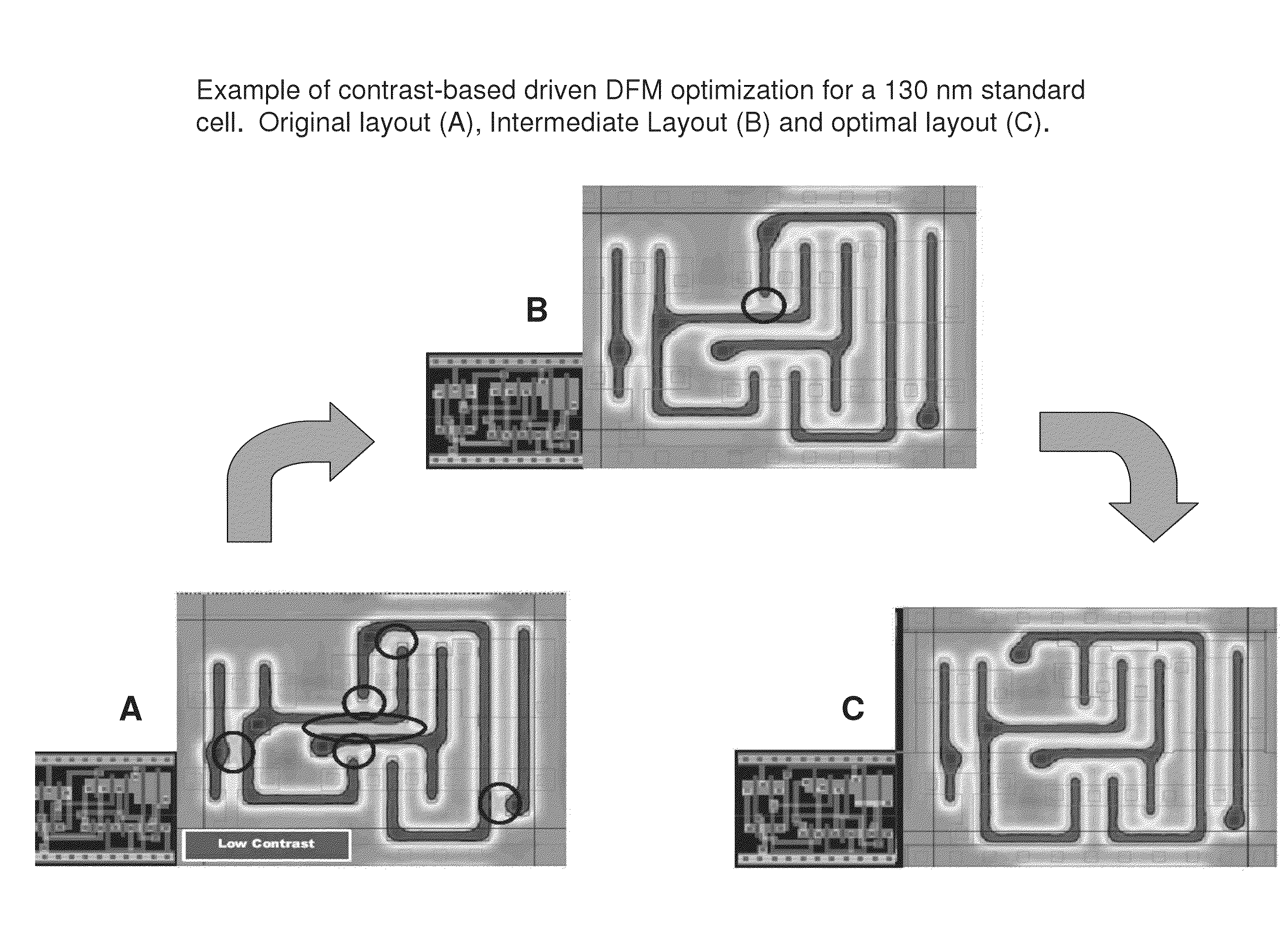
Optical lithography correction process
InactiveUS20060236271A1NanotechPhotomechanical apparatusElectrical and Electronics engineeringLithography
A apparatus and method for correcting a process critical layout includes characterizing the influence of individual ones of a set of worst case process variations on a simulated nano-circuit layout design and then correcting layout geometries in the simulated nano-circuit layout based on such characterizations.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
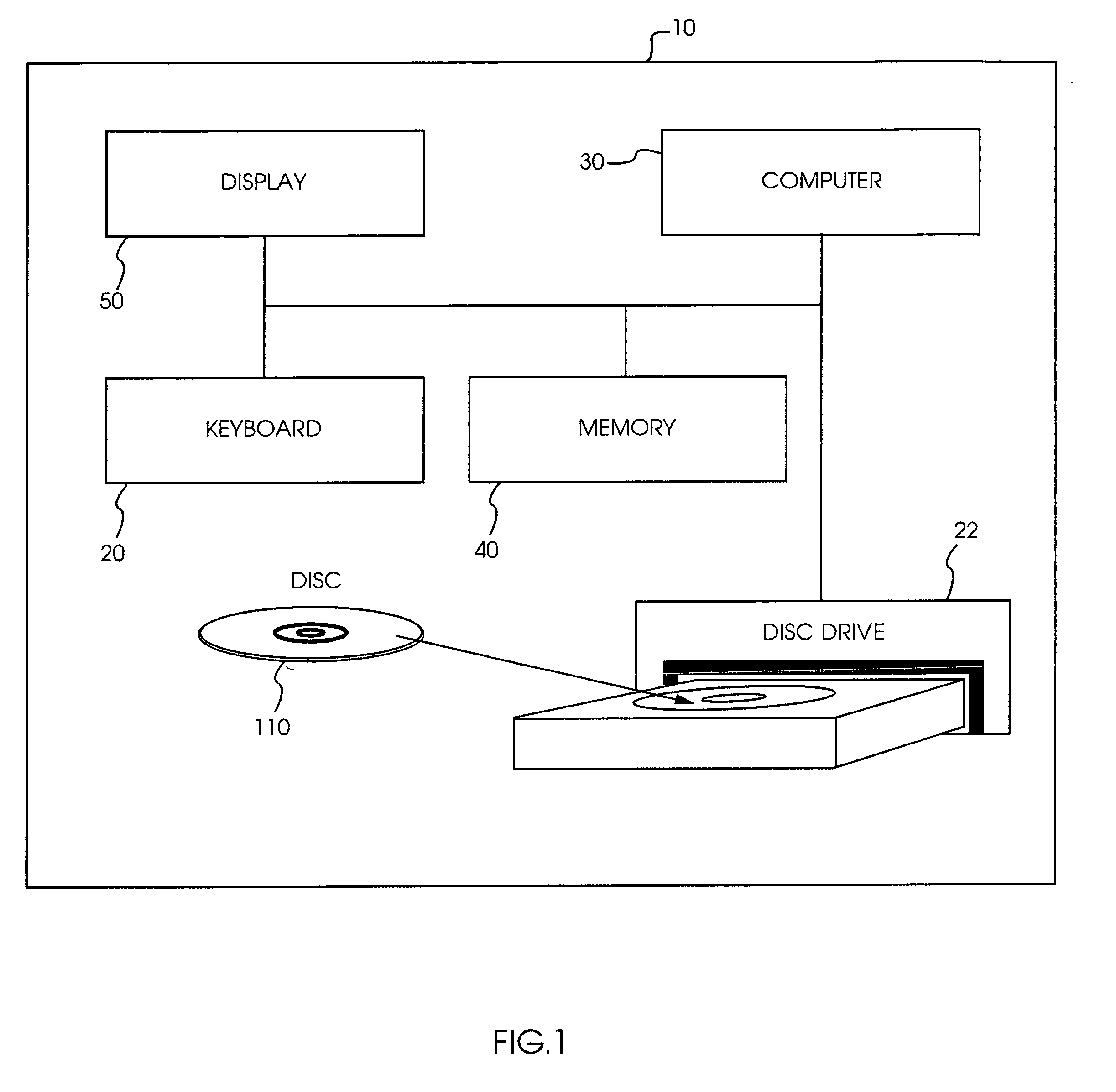
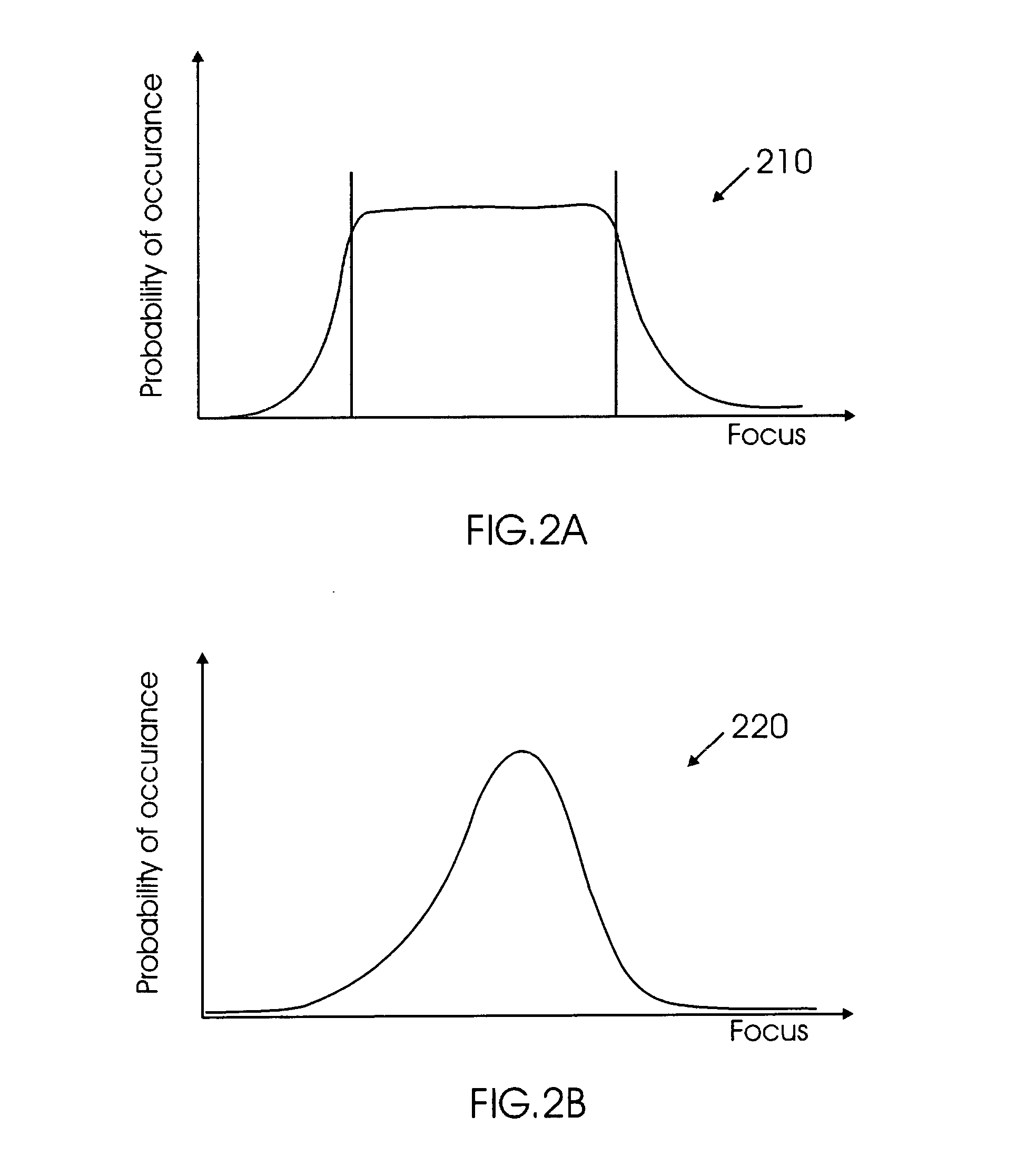
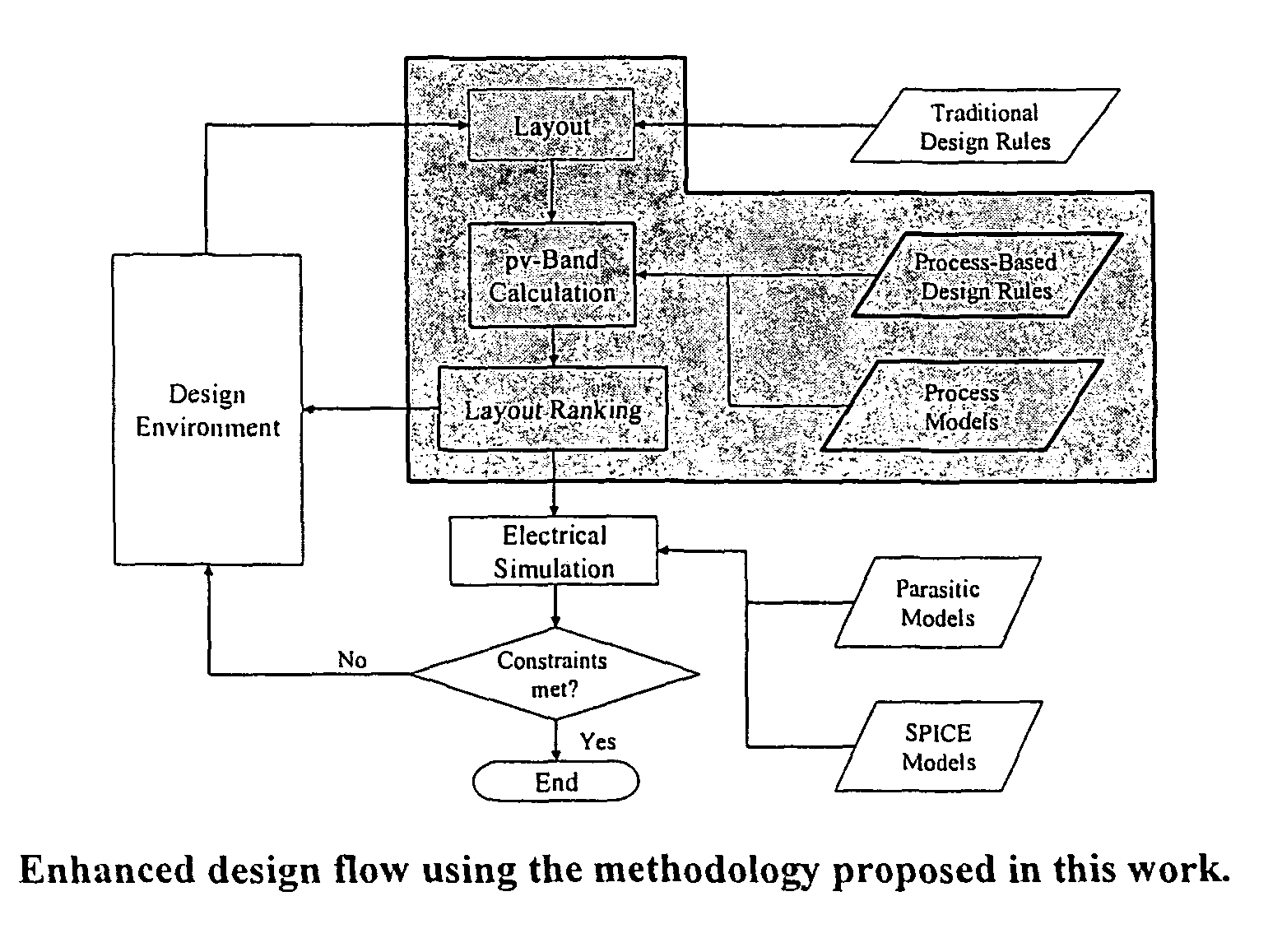
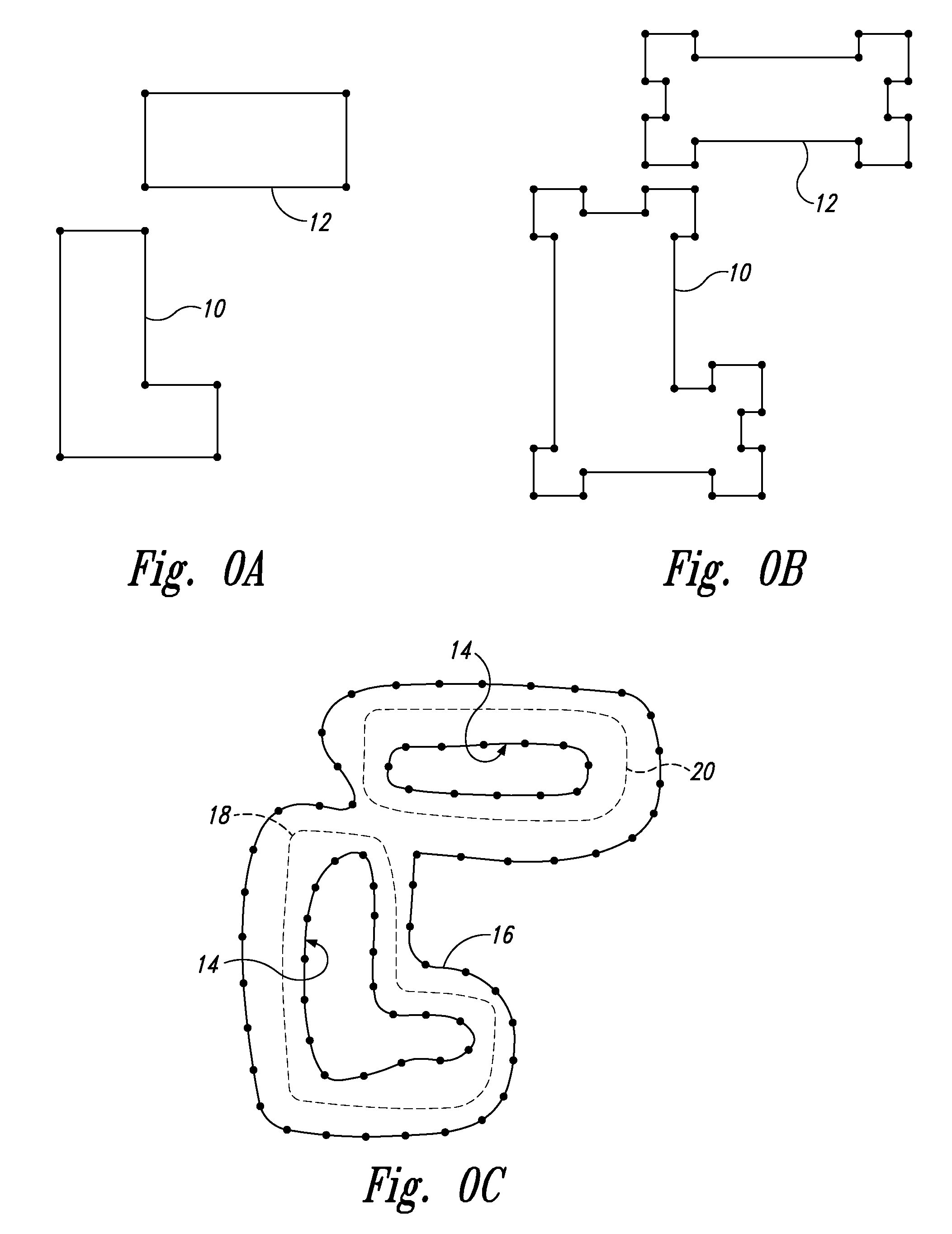
Integrated circuit layout design methodology with process variation bands
ActiveUS8799830B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareConstraint-based CADIntegrated circuit layoutProcess conditions
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
System and method for process variation monitor
InactiveUS6862491B2The result is accurate and reliableImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionEngineering
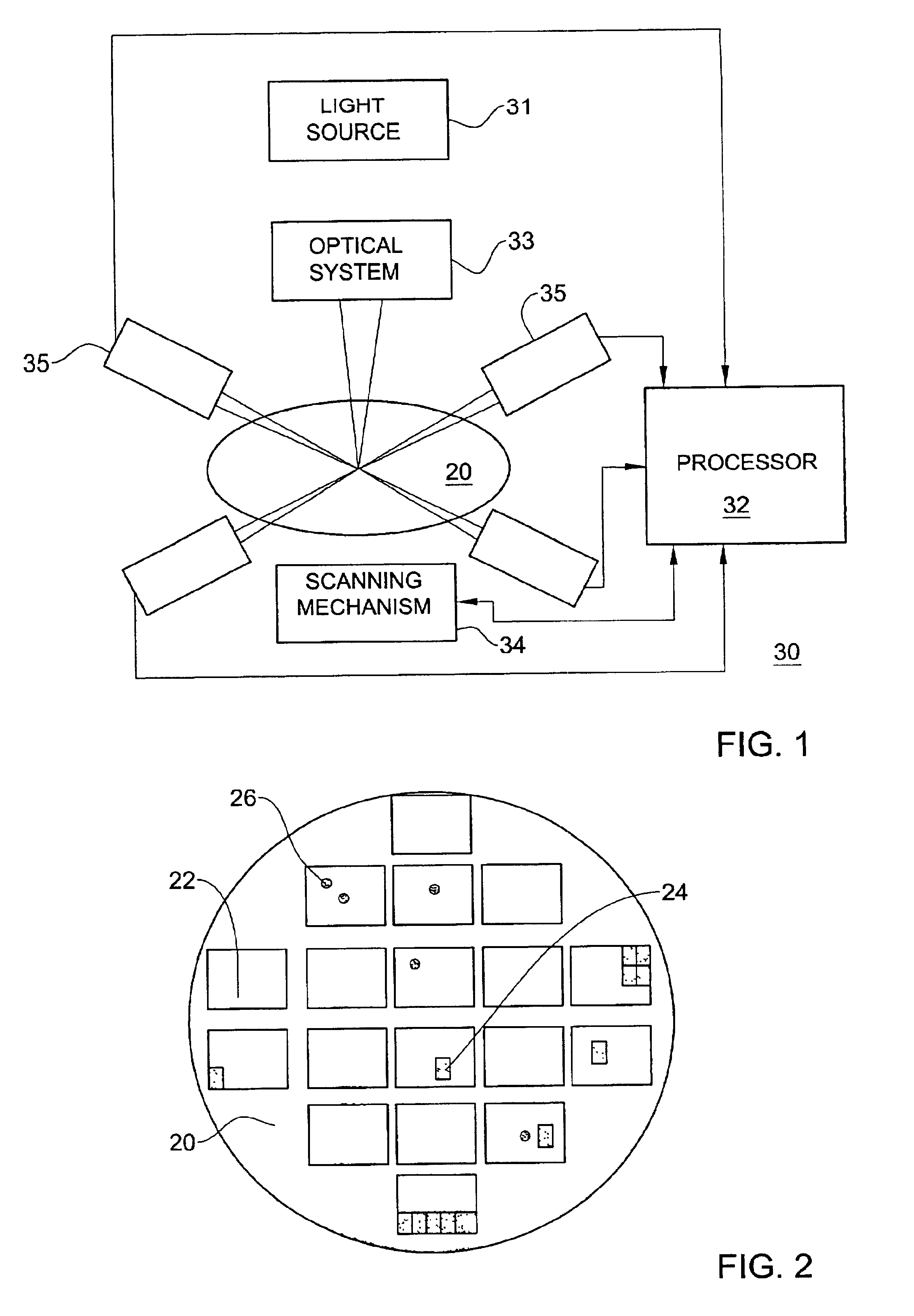
A method to extend the process monitoring capabilities of a semiconductor wafer optical inspection system so as to be able to detect low-resolution effects of process variations over the surface of a wafer at much higher sensitivity than heretofore possible. The method consists, in essence, of grouping sensed pixels by geometric blocks over the inspected surface and comparing each block with a corresponding one from another die on the same wafer, from another wafer or from a stored model image. In one embodiment of the invention, pixel values are compared directly and differences are thresholded at a considerably lower level than during a defects detection process. In another embodiment, there is calculated a signature for each block, based on the sensed light intensity values, and corresponding signatures are compared.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
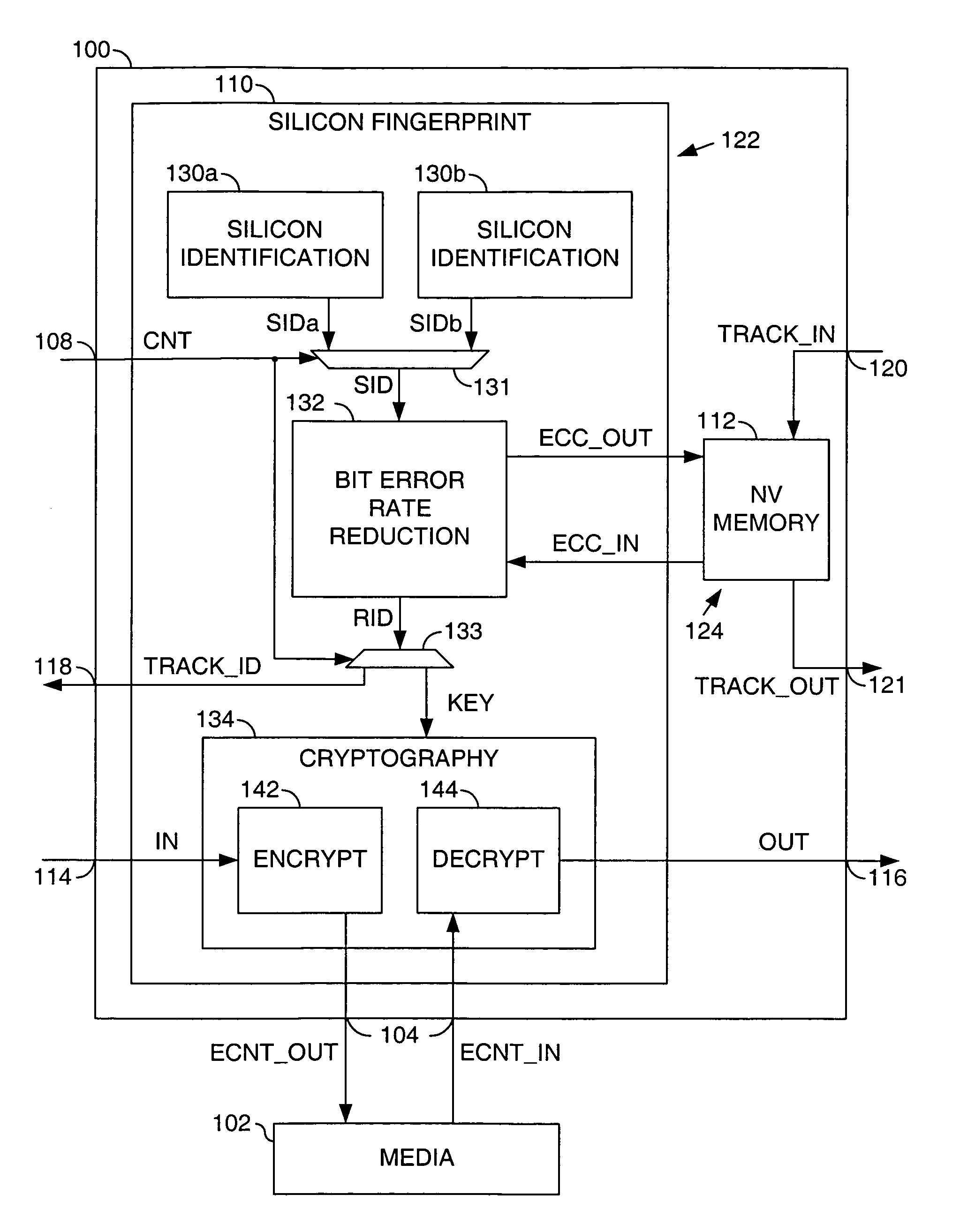
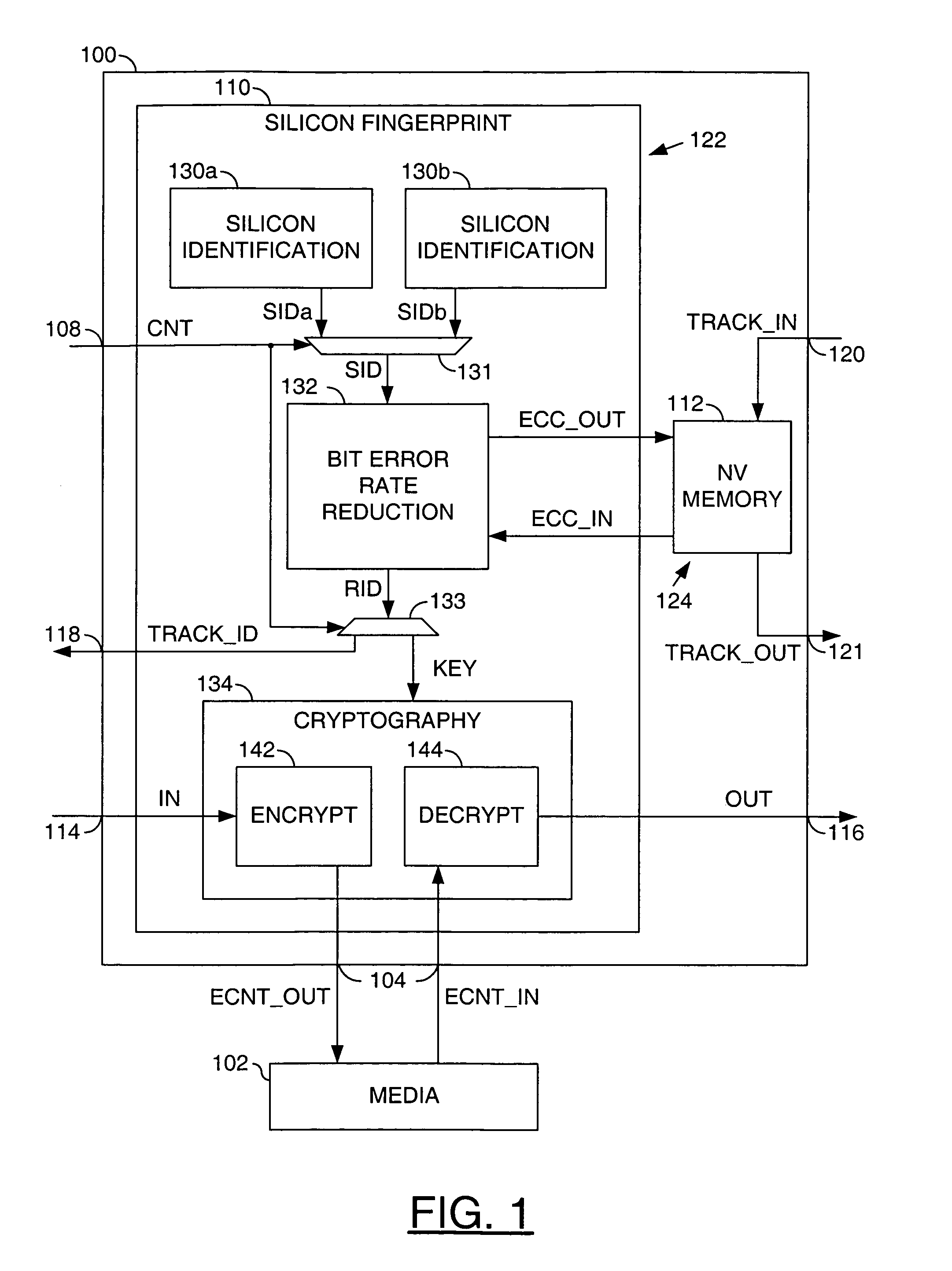
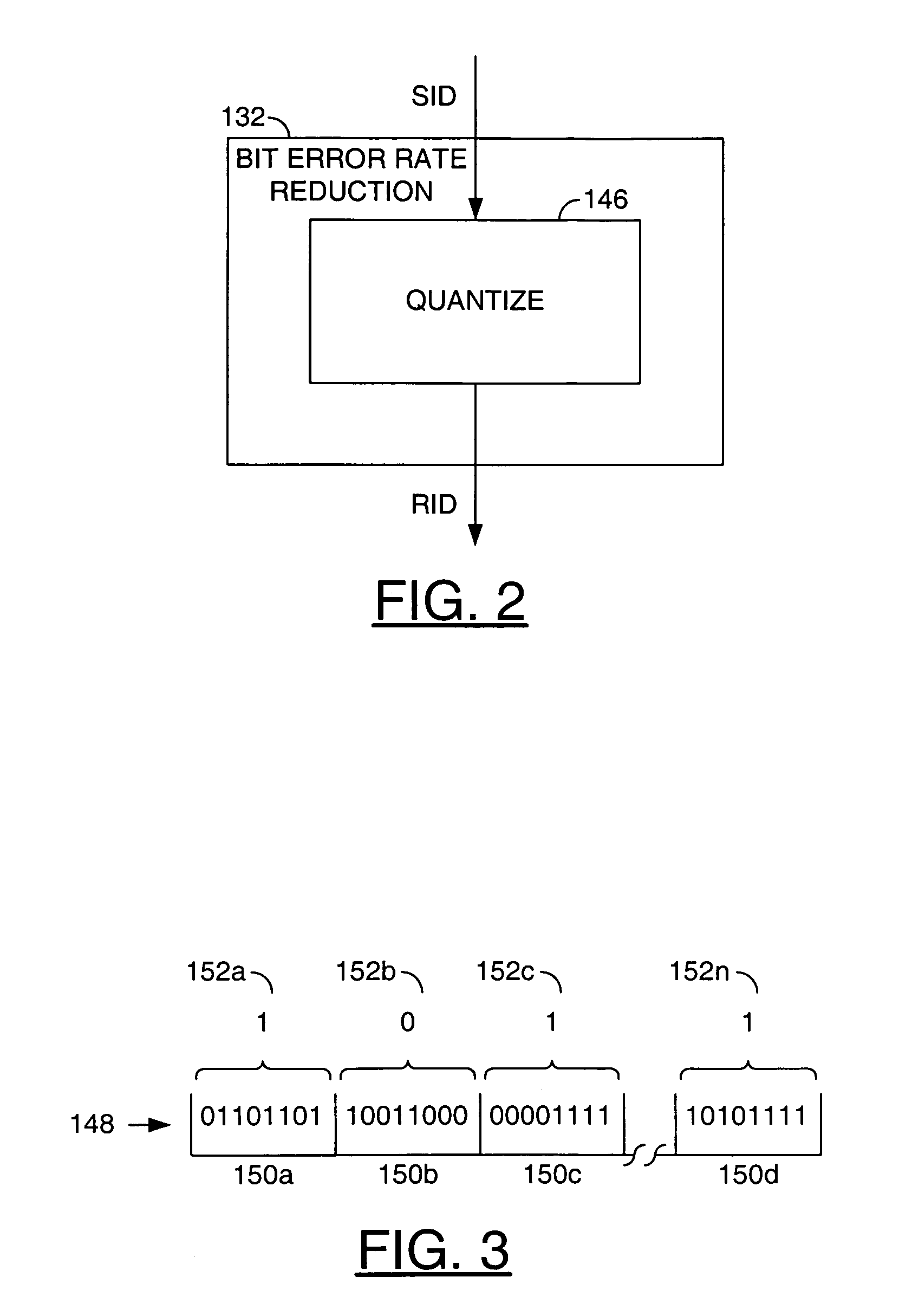
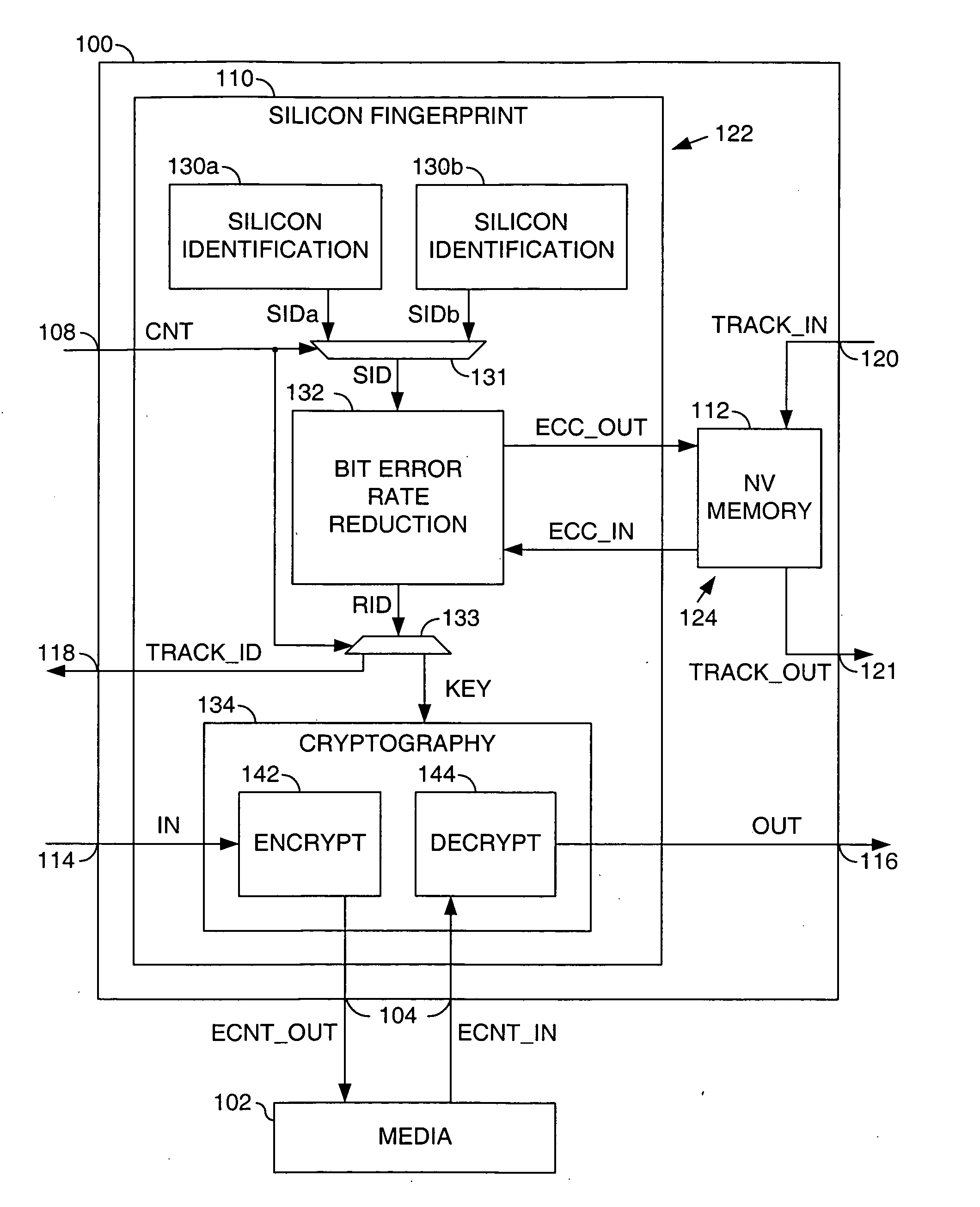
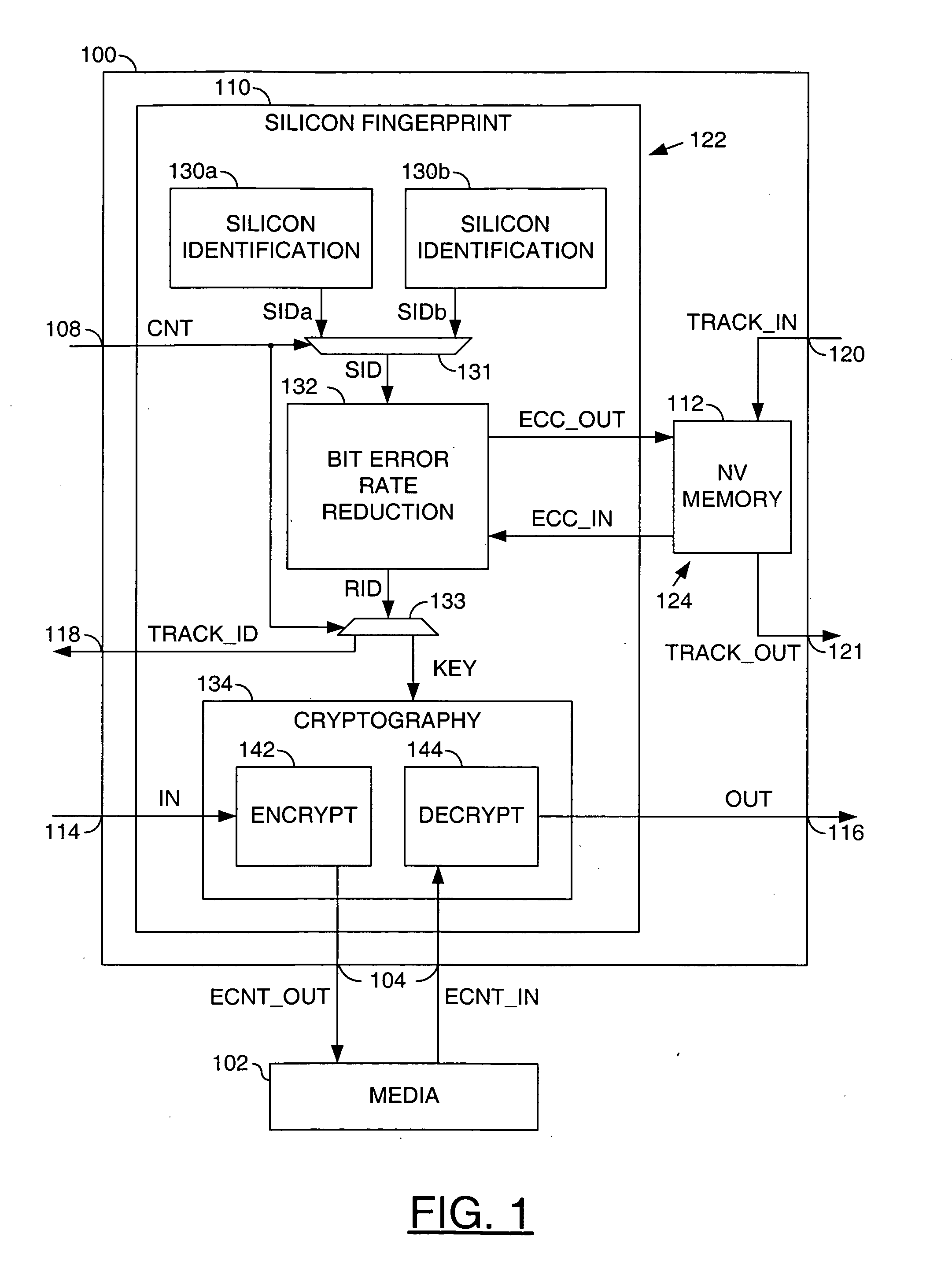
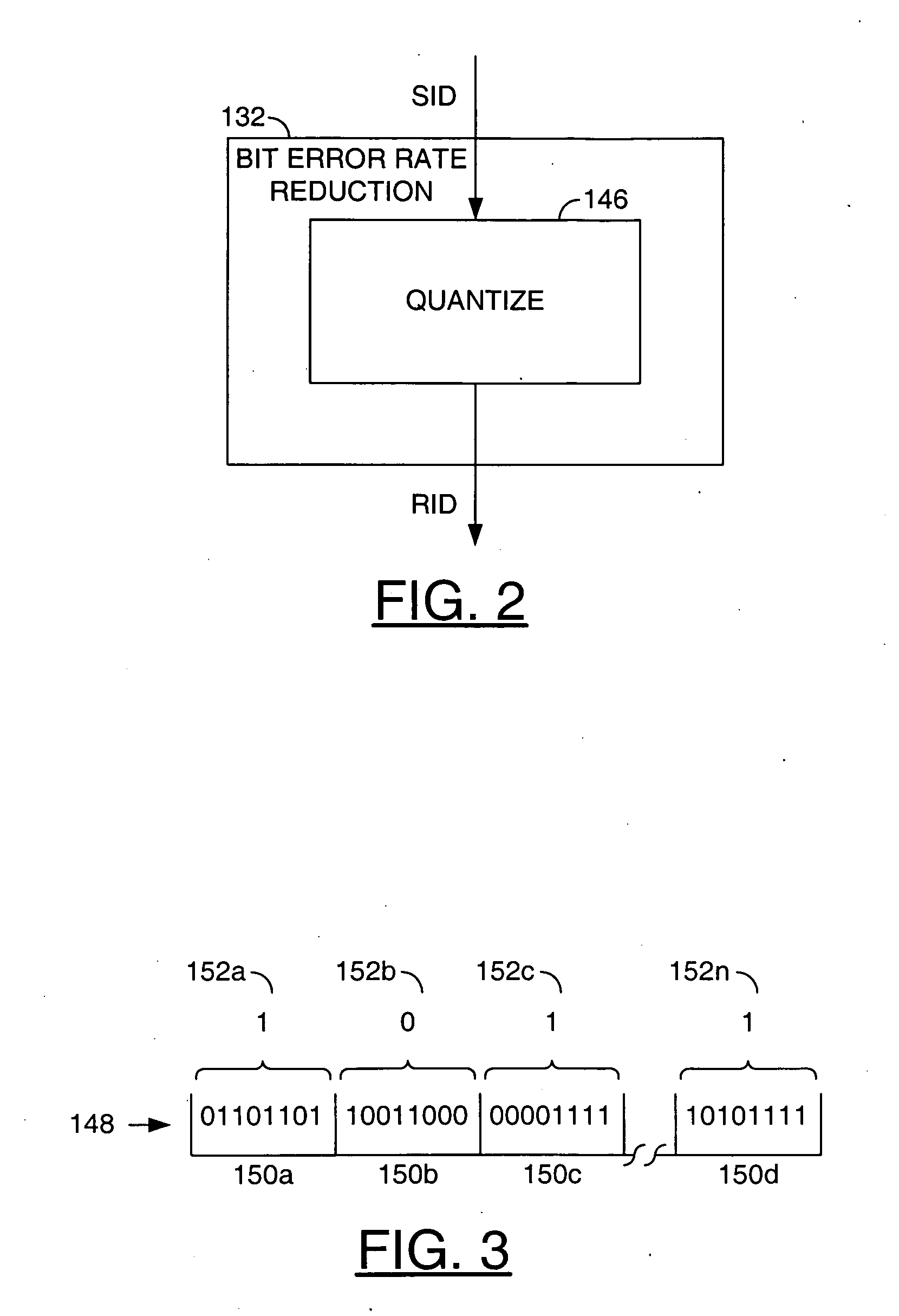
Security application using silicon fingerprint identification
InactiveUS7577850B2Reducing a bit error rate of the identification valueUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringAlgorithmSemiconductor
A method for using an identification value for a security application is disclosed. The method may include the steps of (A) generating the identification value based on a plurality of semiconductor fabrication process variations, (B) generating a key by reducing a bit error rate of the identification value, wherein the key may not be available external to the security application and (C) generating an output signal by one of (i) encoding and (ii) decoding an input signal in response to said key.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
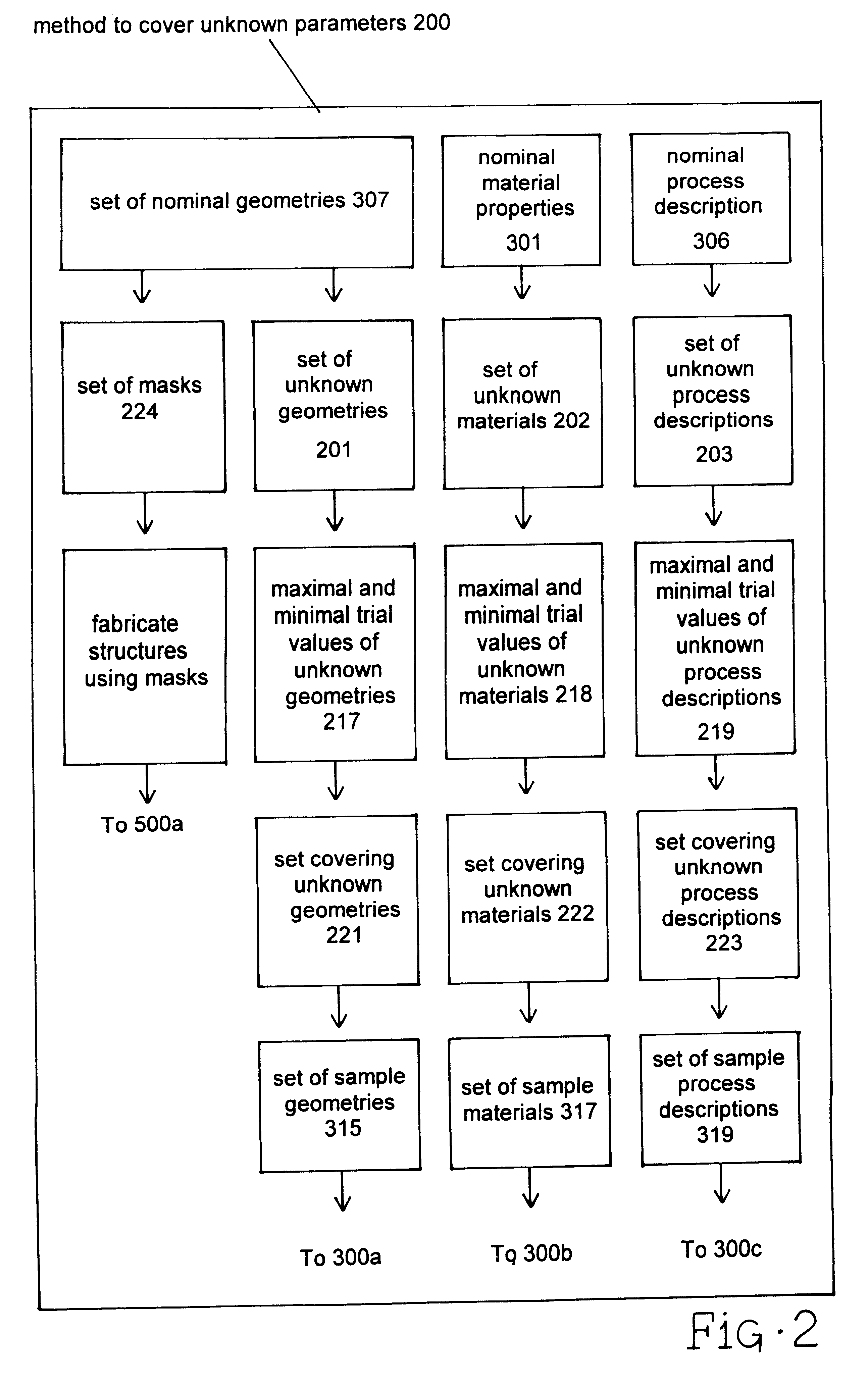
Characterization of microelectromechanical structures
Accurate characterization of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) geometry is critical for device design and simulation, for material property extraction, and for post-fabrication trimming. According to the present embodiment, a method for characterizing parameters describing MEMS structures resulting from the fabrication process or process variations is presented. According to the prefered embodiment, experimentally obtained natural frequencies are compared with numerical simulations to identify unknown values of structural parameters or parameter variations. Further, the prefered embodiment teaches how electrostatically-driven laterally resonant comb-drive MEMS test structures with prescribed changes in spring width are used to characterize systematic variations in process offsets and sidewall angles. The disclosed technique is both in-situ and non-destructive.
Owner:COVENTOR
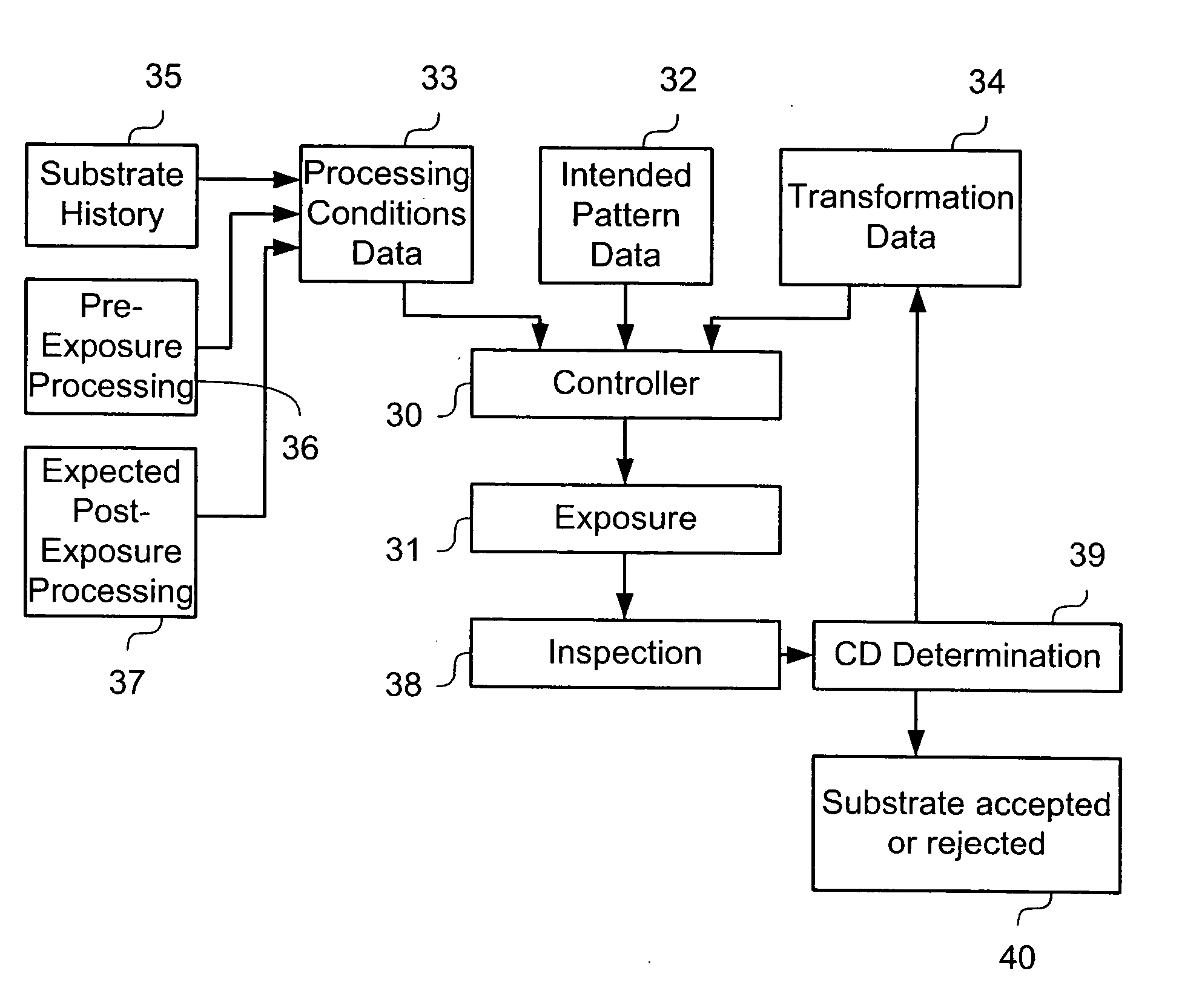
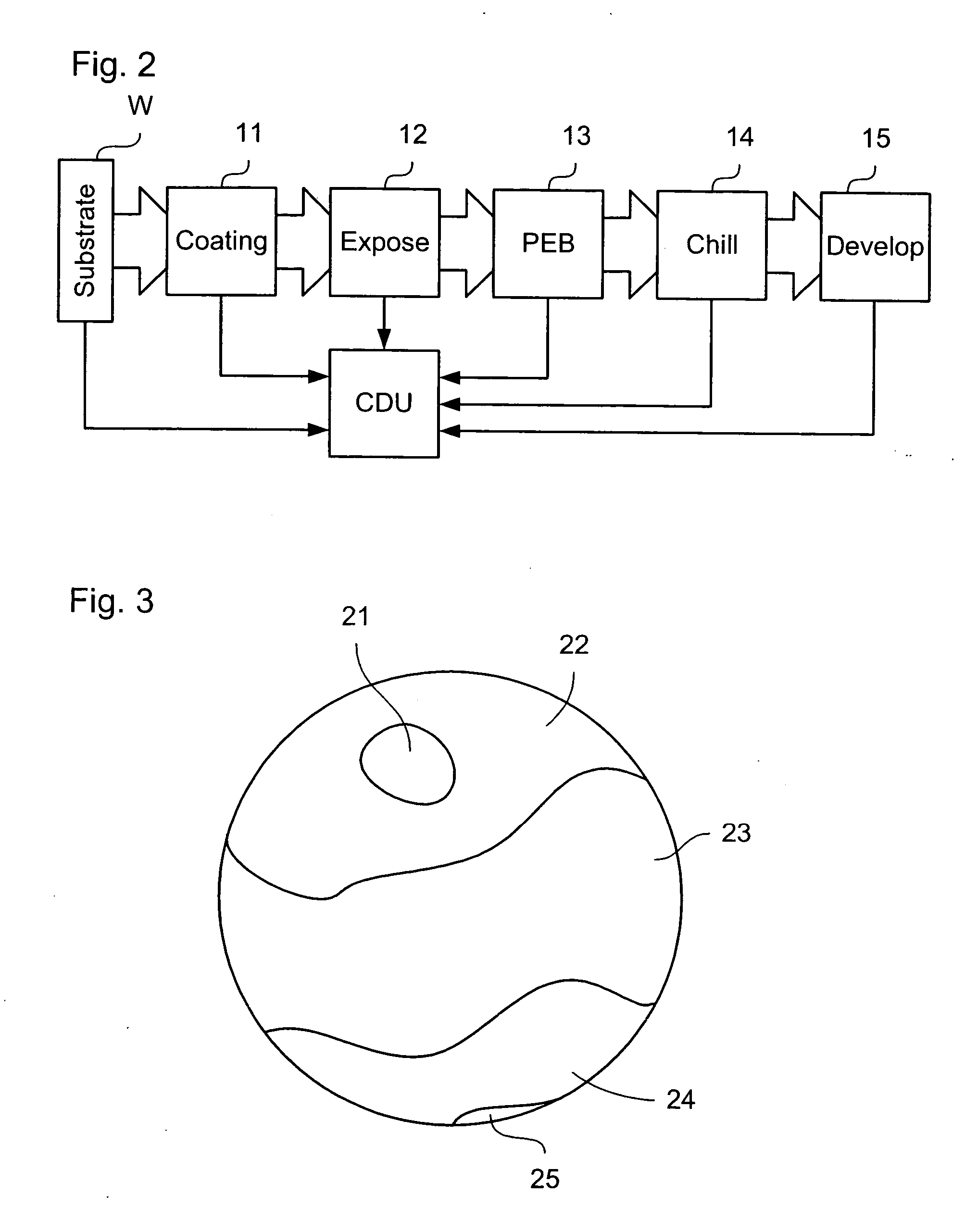
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060017903A1Improved CDUCDUPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingEngineeringCritical dimension
A lithographic apparatus is provided that uses an array of individually controllable elements to pattern the beam of radiation. The critical dimension uniformity of a substrate patterned using the apparatus is improved by adjusting the pattern data provided to the array of individually controllable elements to compensate for process variation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV +1
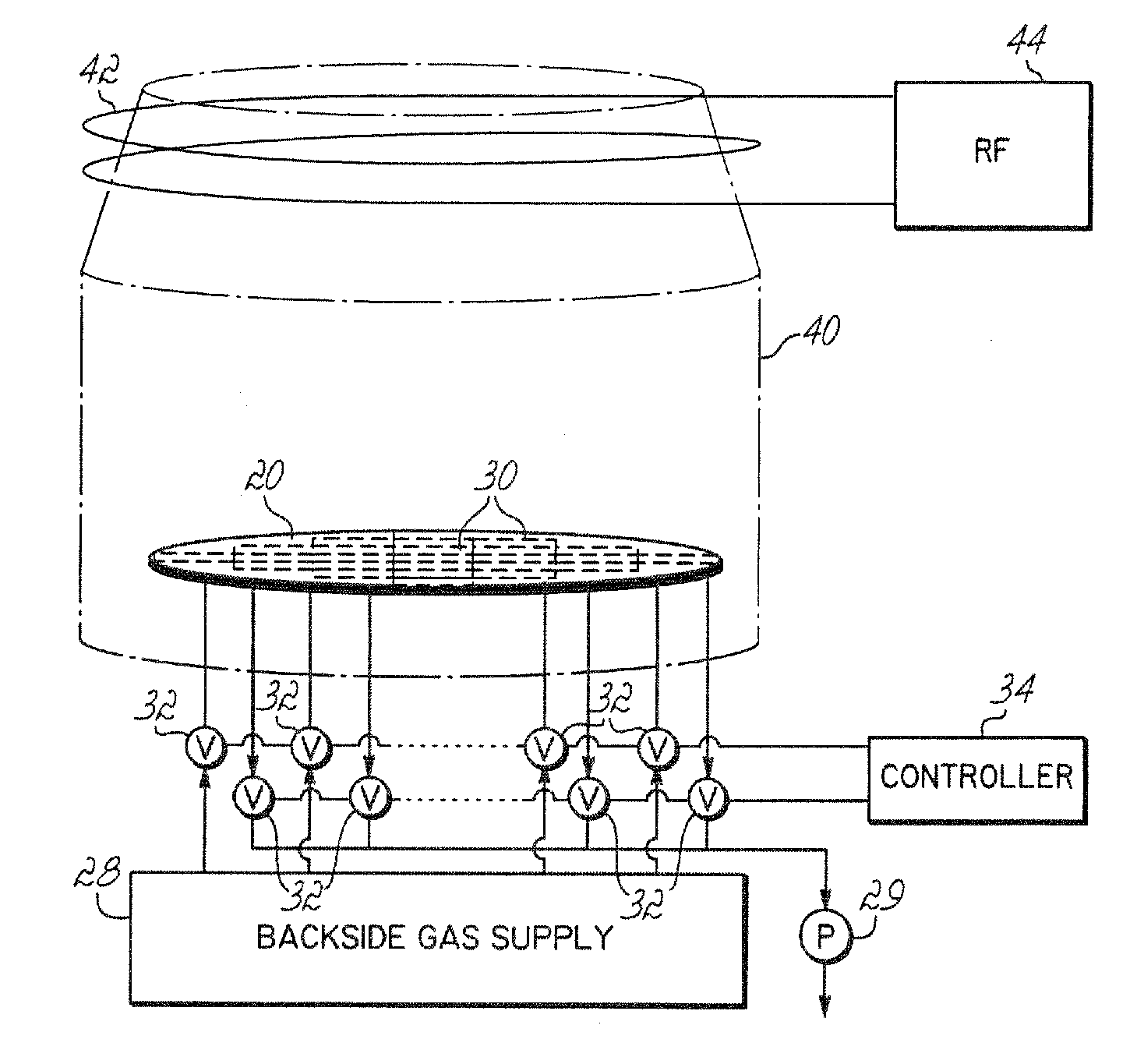
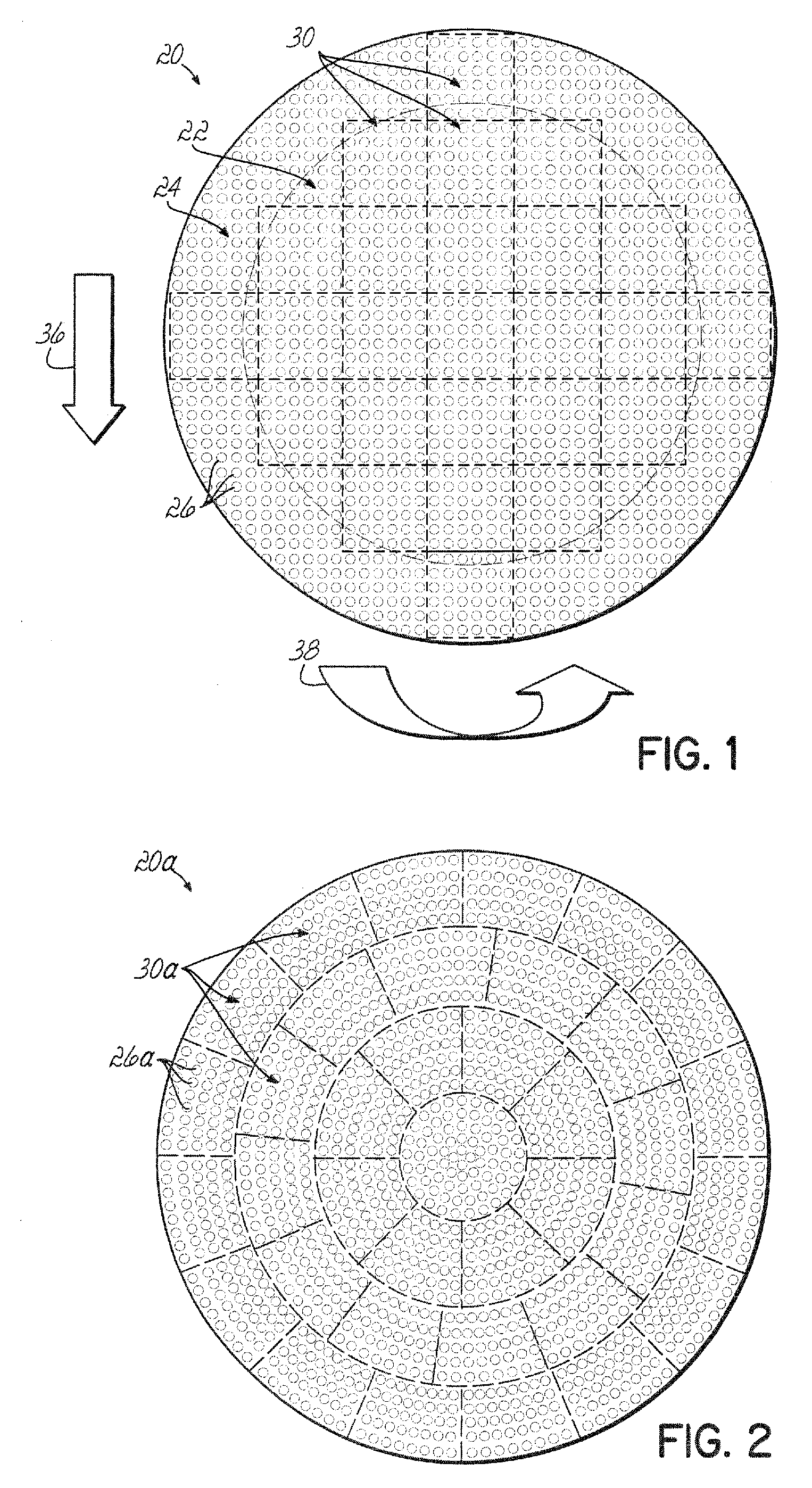
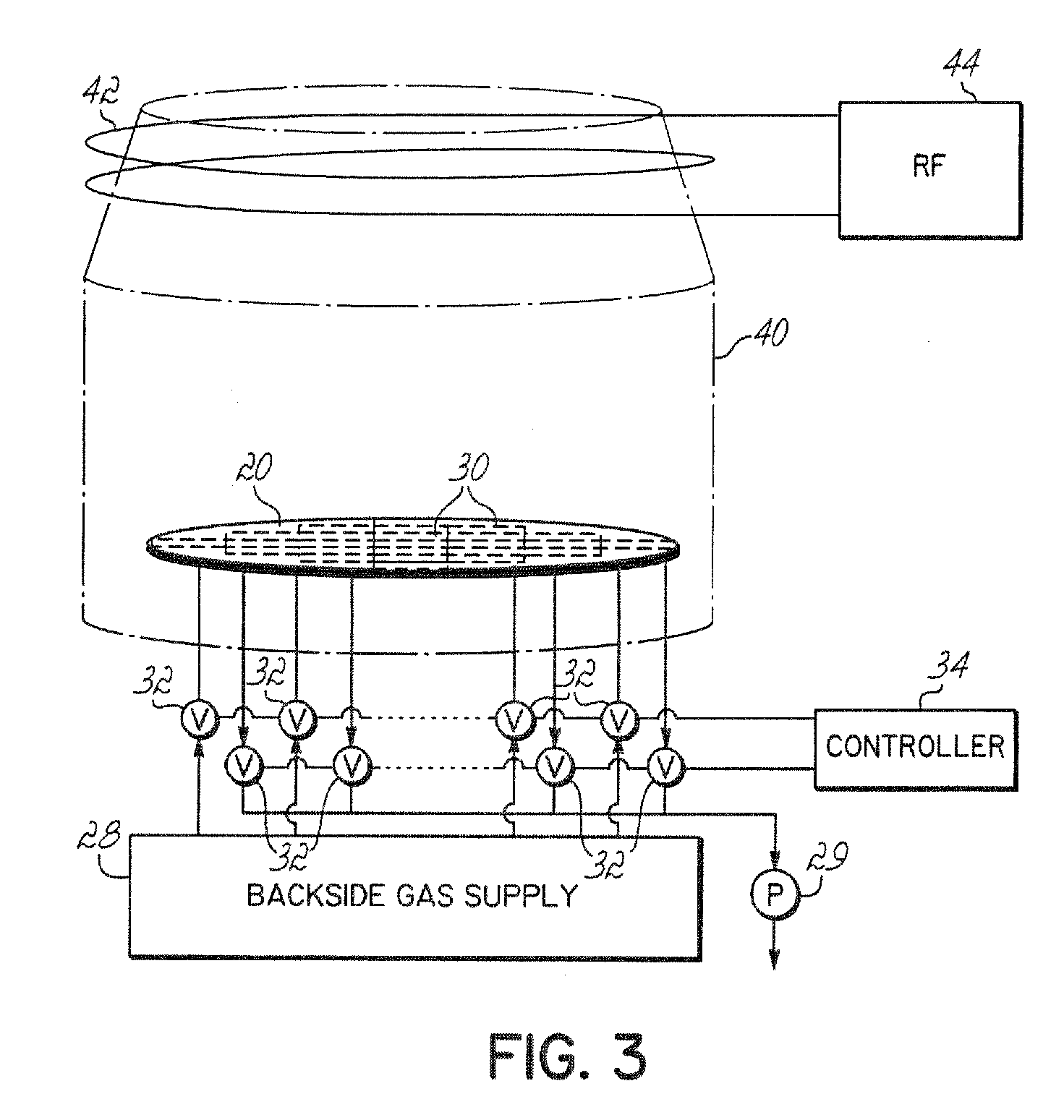
Dynamic temperature backside gas control for improved within-substrate process uniformity
ActiveUS20080227227A1Improve uniformityImprove process uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess engineeringHelium
A method and apparatus are provided to control the radial or non-radial temperature distribution across a substrate during processing to compensate for non-uniform effects, including radial and angular non-uniformities arising from system variations, or process variations, or both. The temperature is controlled, preferably dynamically, by flowing backside gas differently across different areas on a wafer supporting chuck to vary heat conduction across the wafer. Backside gas flow, of helium, for example, is dynamically varied across the chuck to control the uniformity of processing of the wafer. Ports in the support are grouped, and gas to or from the groups is separately controlled by different valves responsive to a controller that controls gas pressure in each of the areas to spatially and preferably dynamically control wafer temperature to compensate for system and process non-uniformities.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
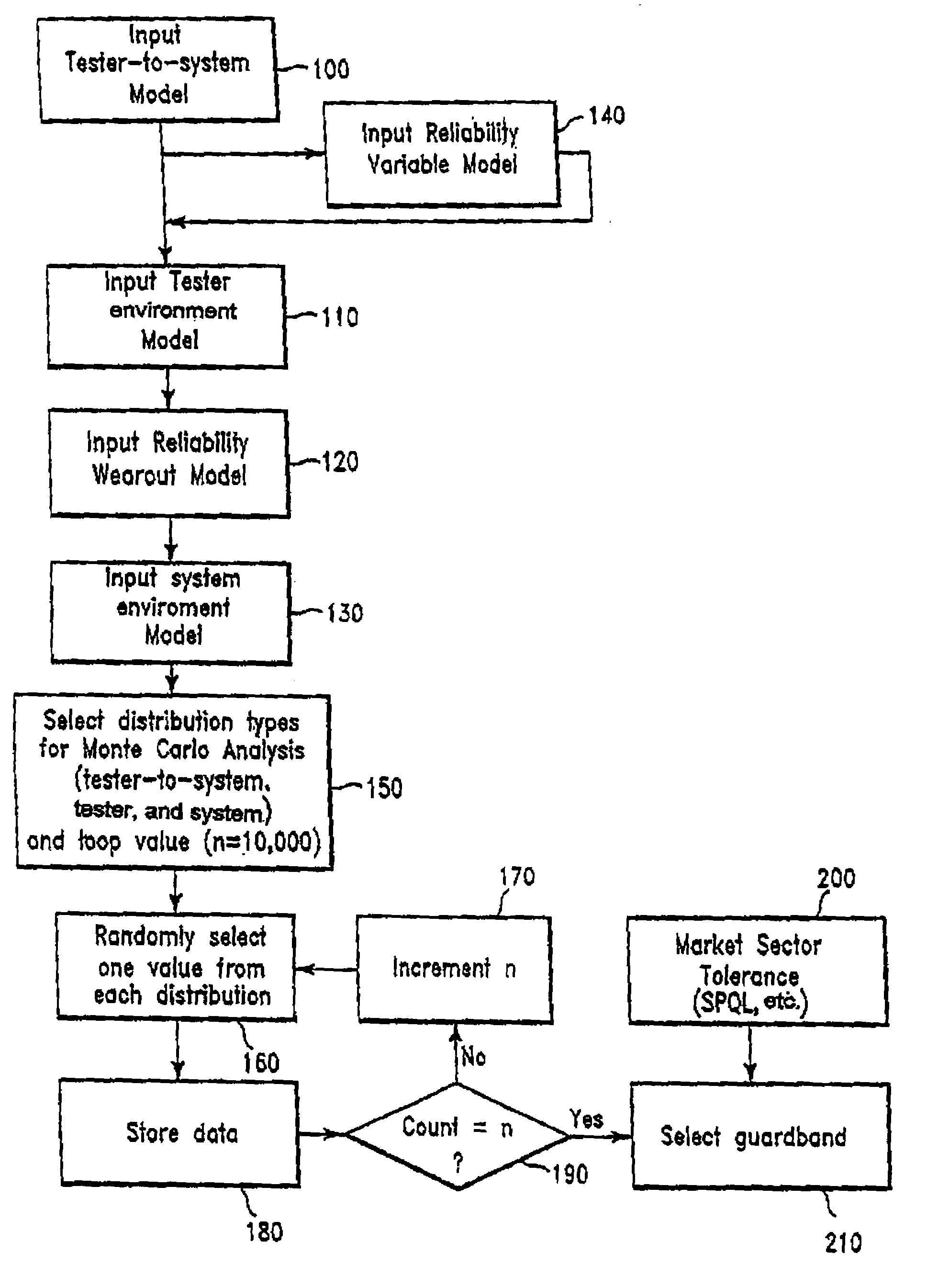
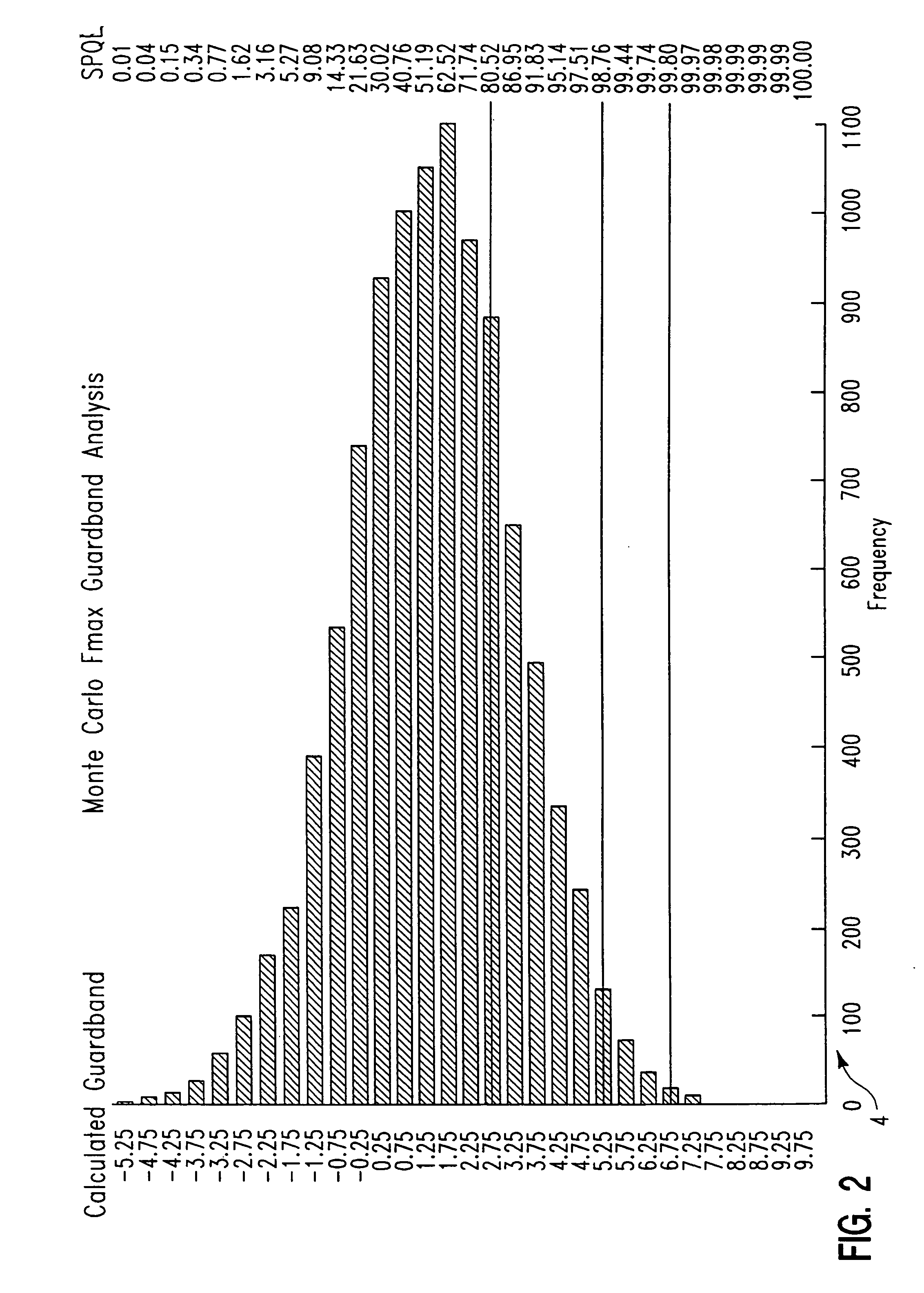
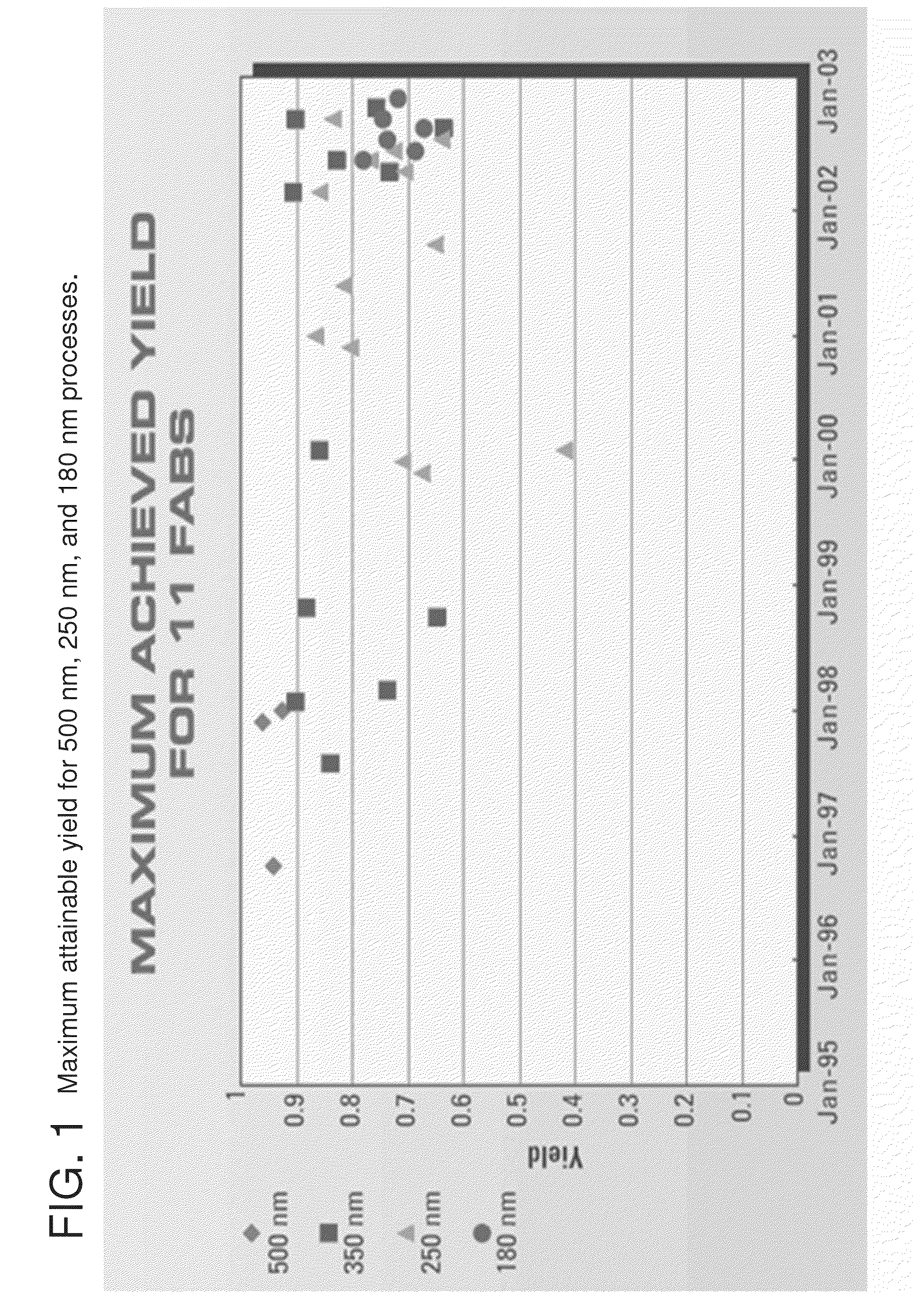
Statistical guardband methodology
InactiveUS6937965B1Reduction in yieldReduce frequencyTime indicationDigital data processing detailsEngineeringDependability
A method for creating a guardband that incorporates statistical models for test environment, system environment, tester-to-system offset and reliability into a model and then processes a final guardband by factoring manufacturing process variation and quality against yield loss.
Owner:IBM CORP
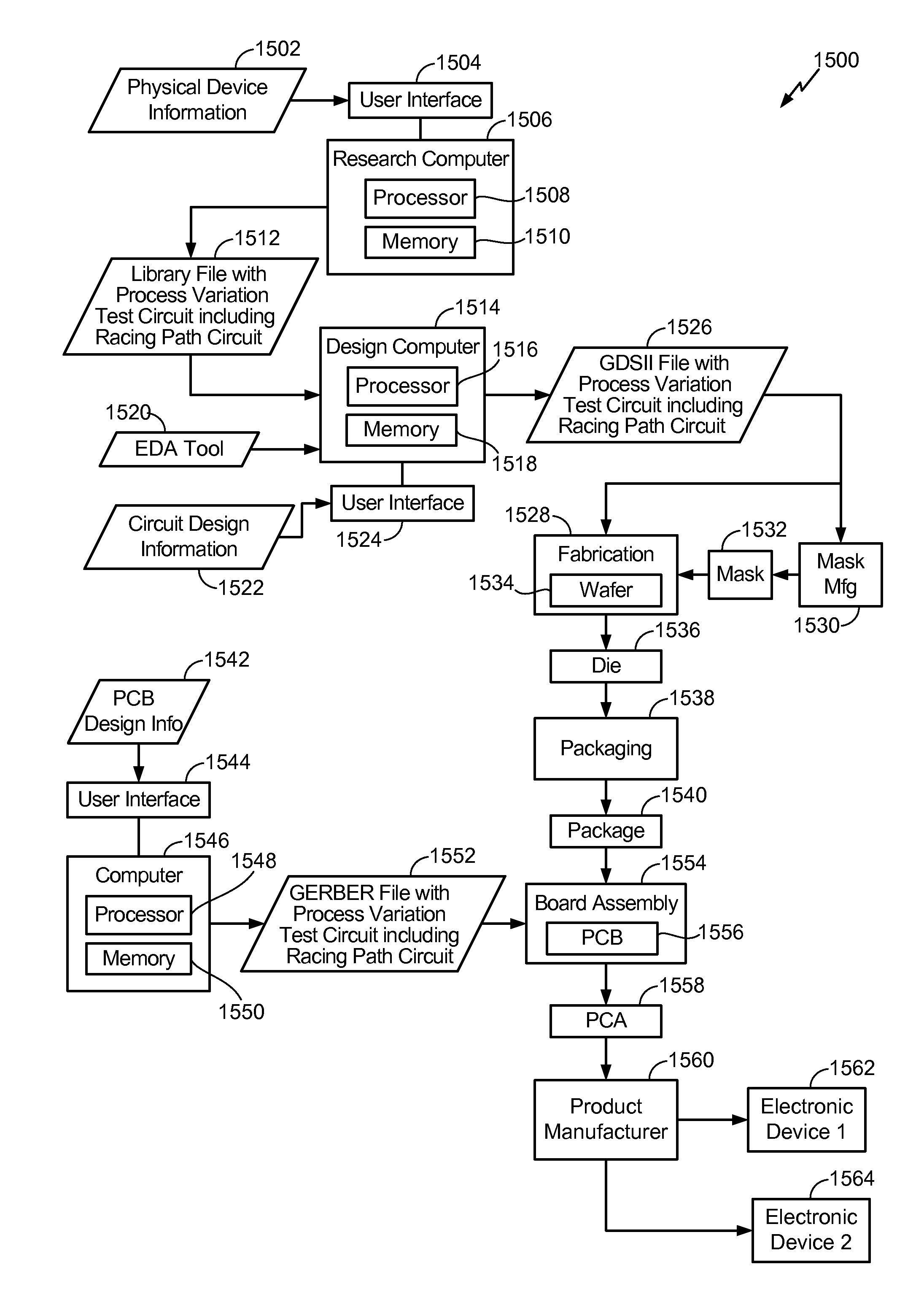
Method And Circuit To Generate Race Condition Test Data At Multiple Supply Voltages
InactiveUS20110245948A1Simple methodDigital data processing detailsMarginal checkingRace conditionSemiconductor
A method and circuit for characterizing a process variation of a semiconductor die is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, the method includes operating a circuit at multiple supply voltage levels to generate race condition testing data. The circuit is disposed on at least one die of a wafer and includes at least one racing path circuit having at least two paths. The method further includes collecting the race condition testing data and evaluating the collected race condition testing data. The race condition testing data is correlated to a process variation of the at least one die.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
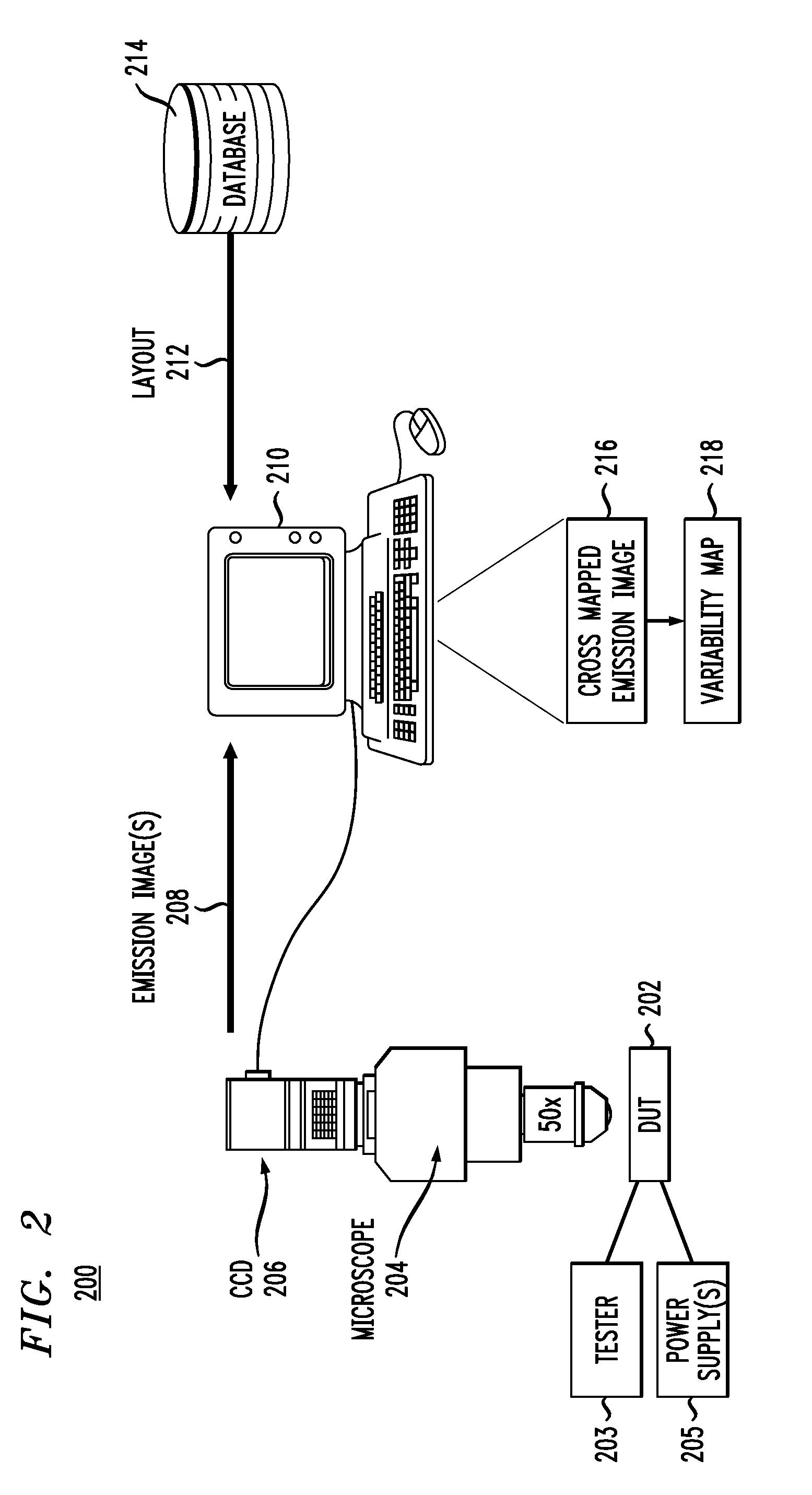
Constructing variability maps by correlating off-state leakage emission images to layout information
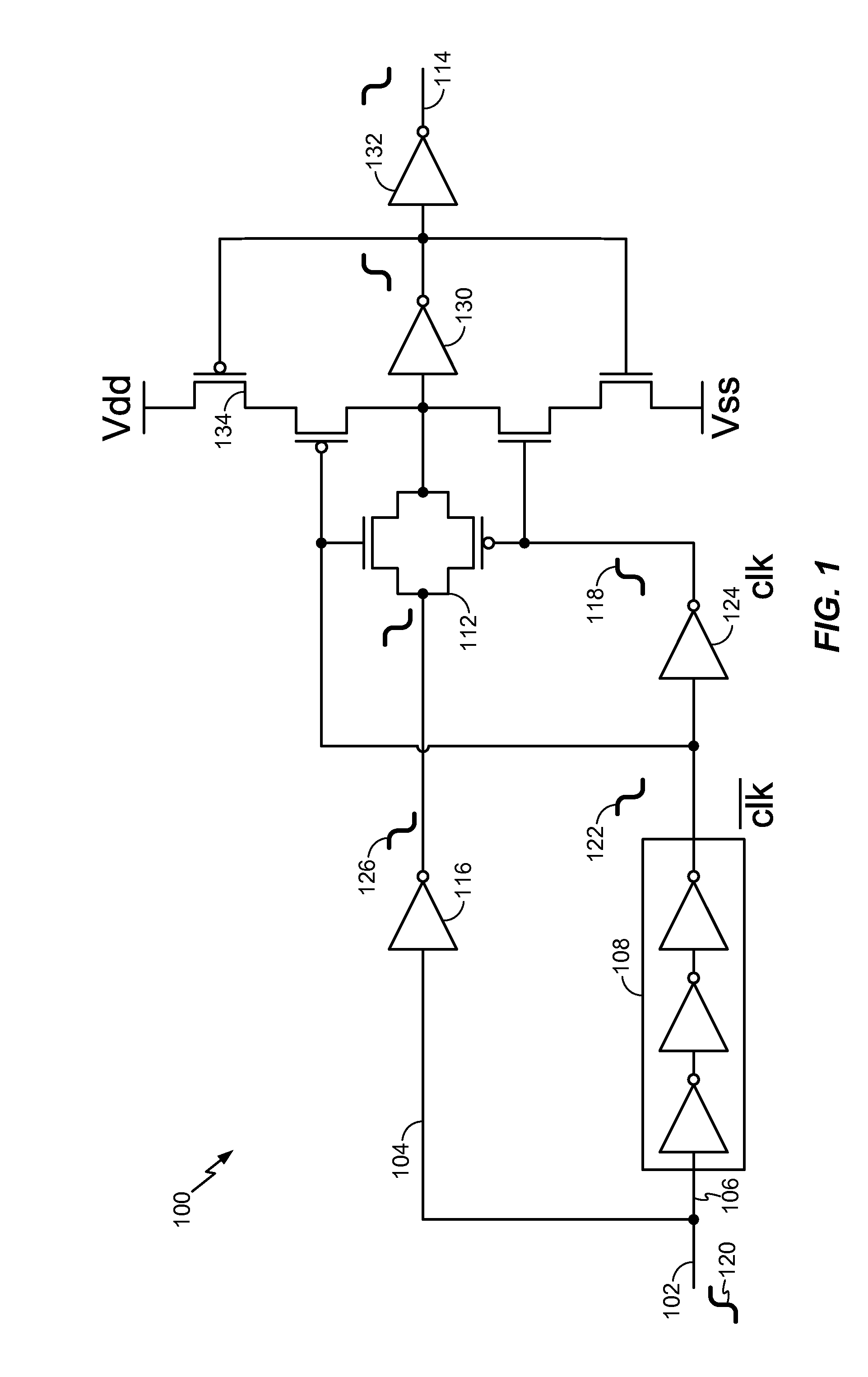
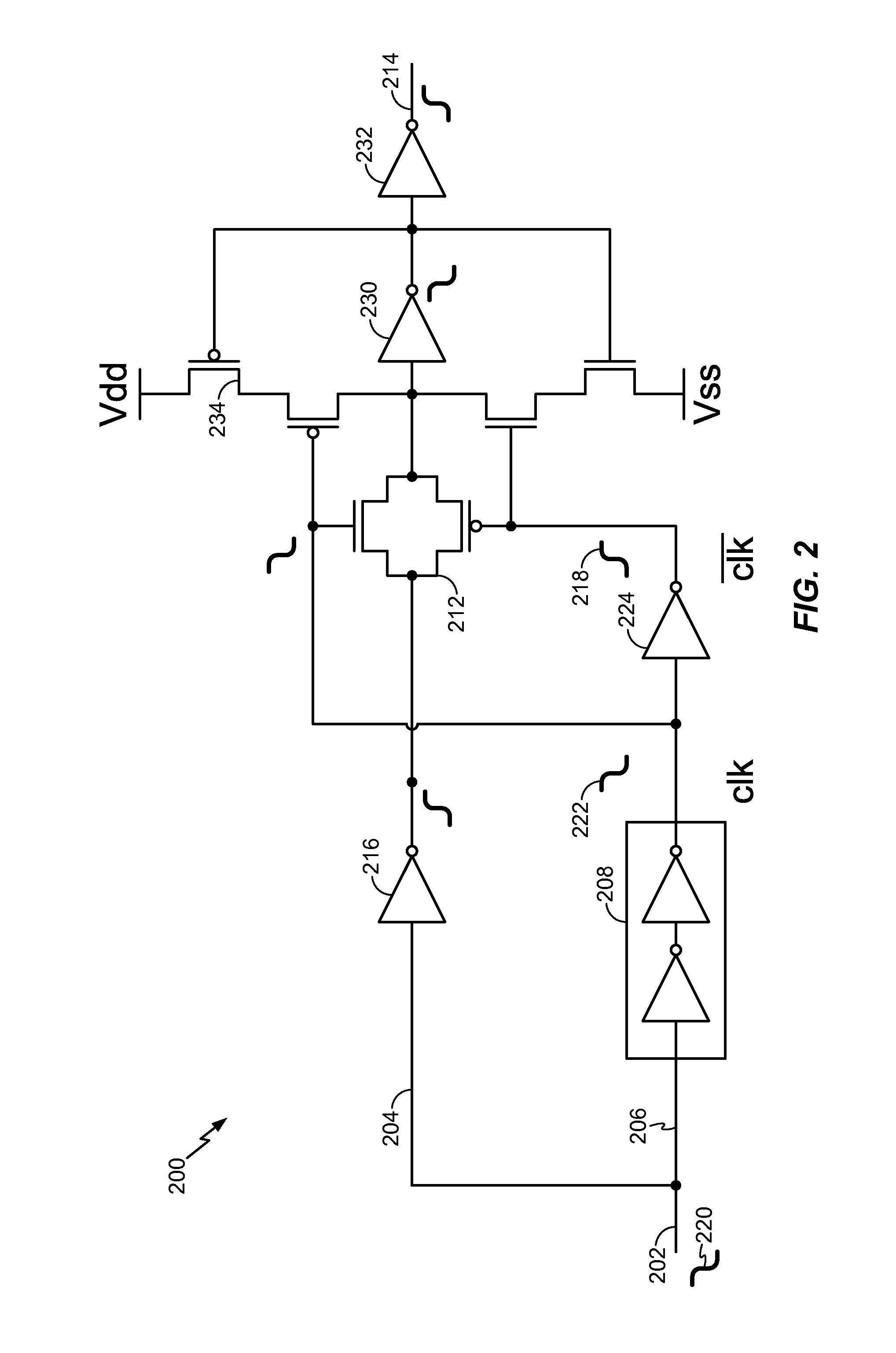
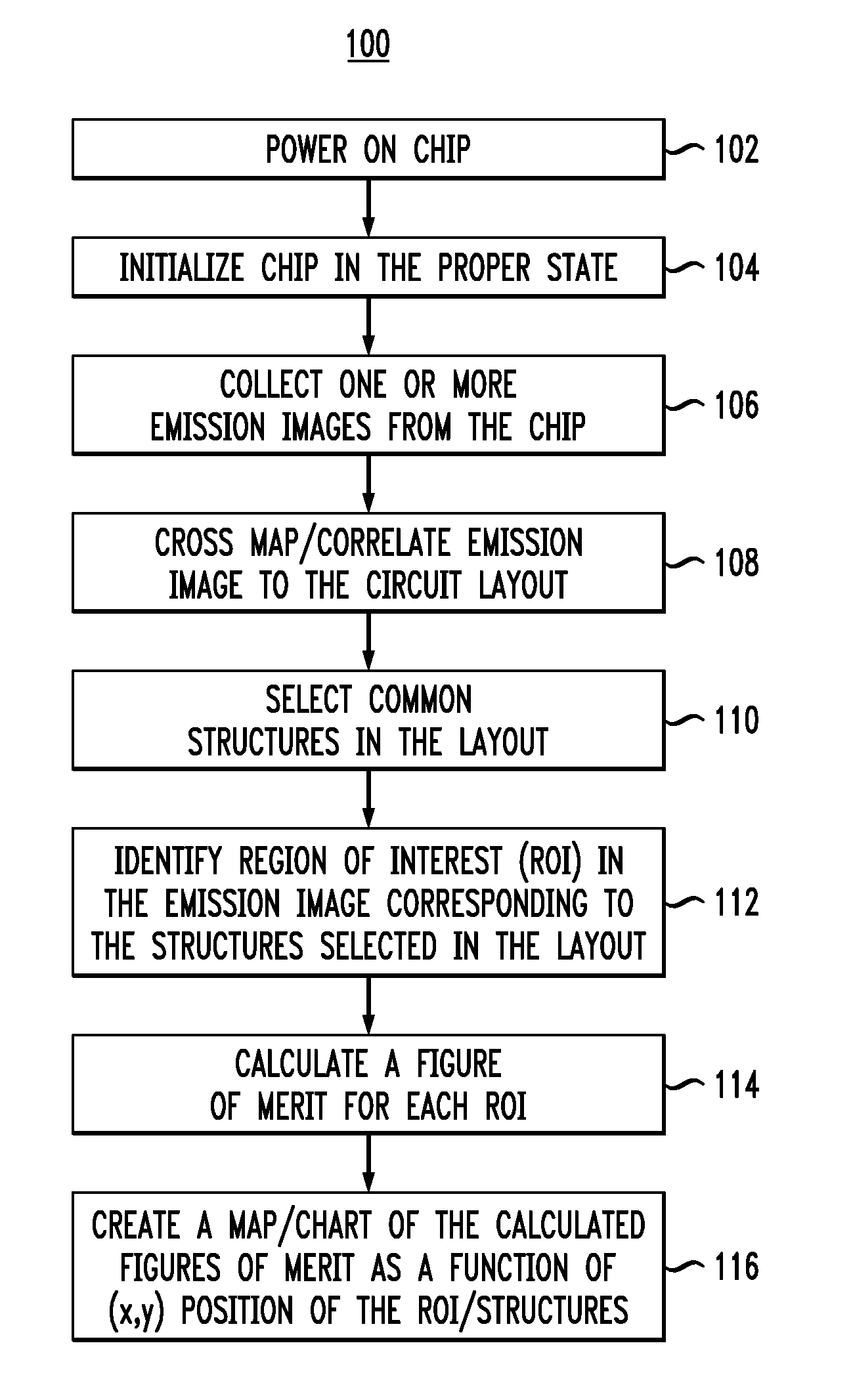
Improved techniques are disclosed for monitoring or sensing process variations in integrated circuit designs. Such techniques provide such improvements by constructing variability maps correlating leakage emission images to layout information. By way of example, a method for monitoring one or more manufacturing process variations associated with a device under test (e.g., integrated circuit) comprises the following steps. An emission image representing an energy emission associated with a leakage current of the device under test is obtained. The emission image is correlated with a layout of the device under test to form a cross emission image. Common structures on the cross emission image are selected and identified as regions of interest. One or more variability measures (e.g., figures of merit) are calculated based on the energy emissions associated with the regions of interest. A variability map is created based on the calculated variability measures, wherein the variability map is useable to monitor the one or more manufacturing process variations associated with the device under test.
Owner:IBM CORP
EEPROM reading device used for passive UHF RFID chip
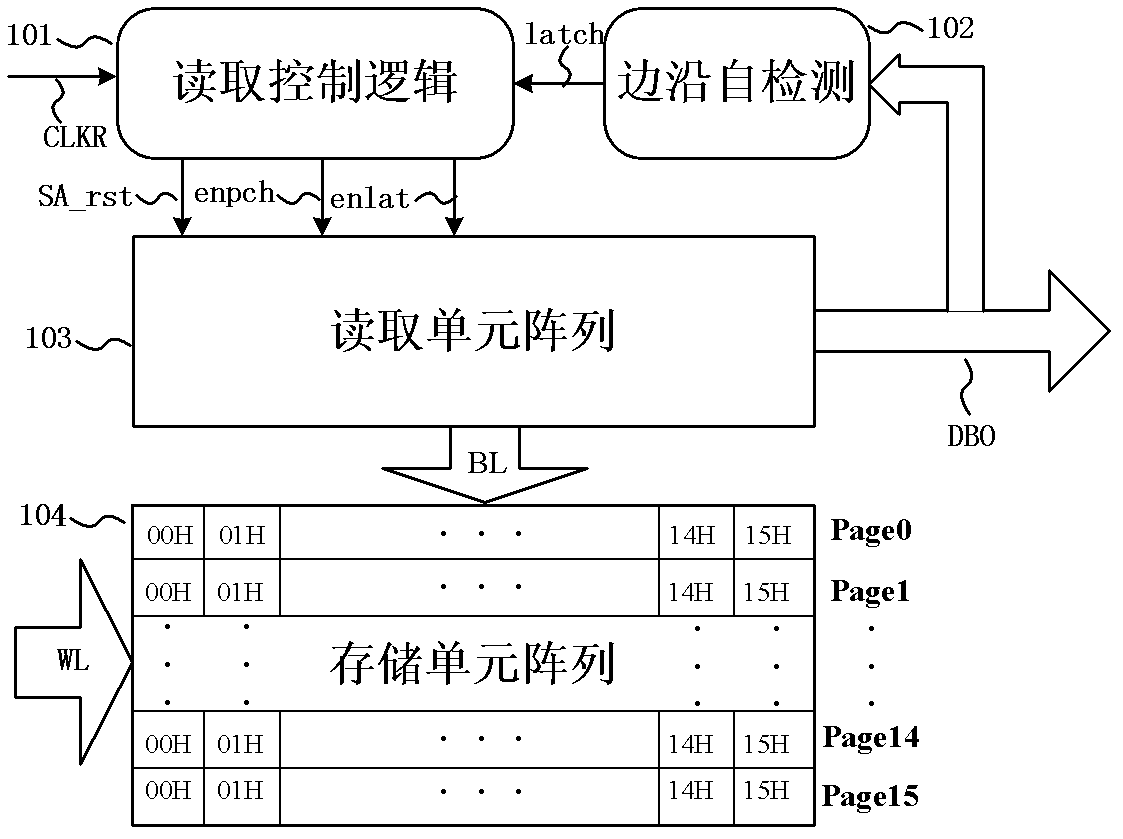
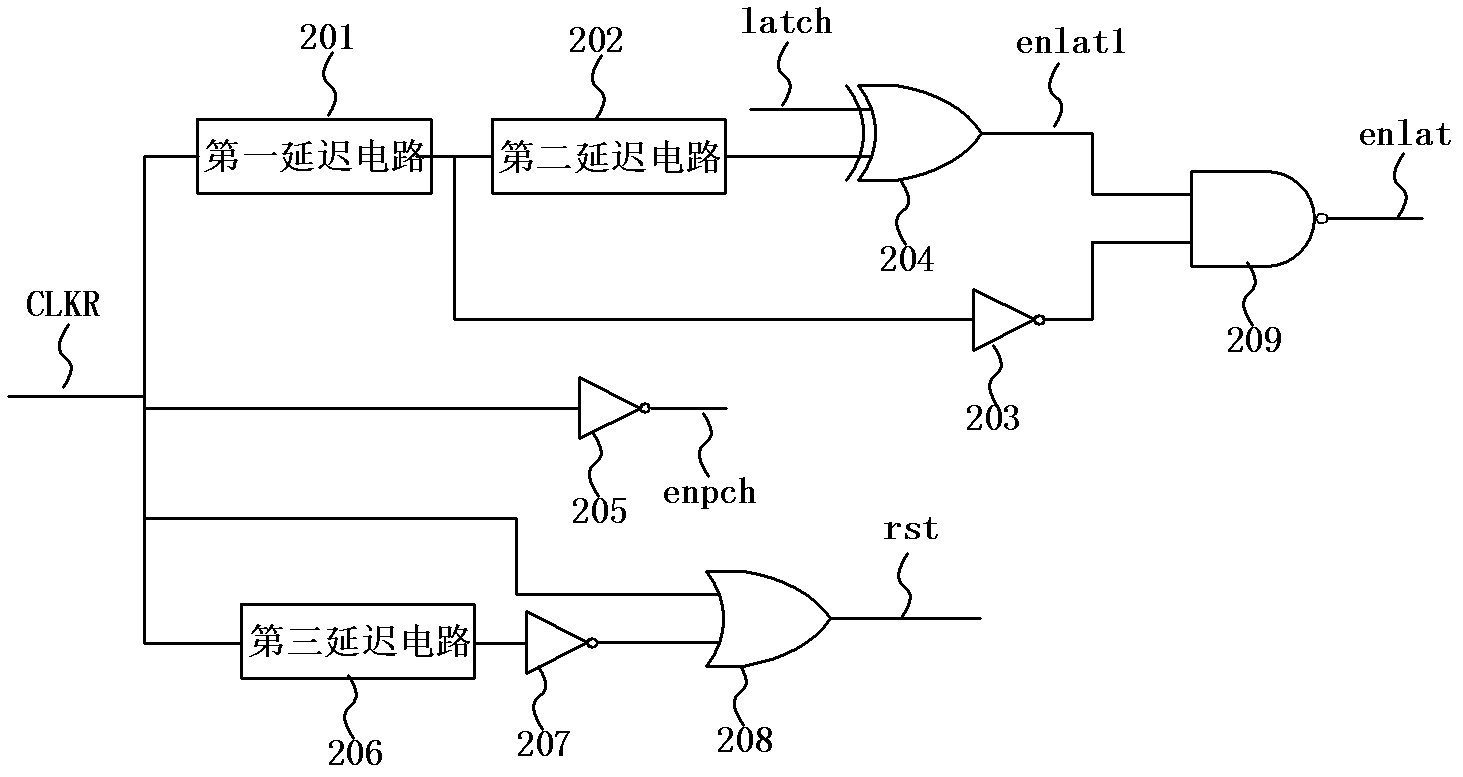
InactiveCN102354530AEliminate DC PathLower average power consumptionRead-only memoriesControl signalData signal
The invention discloses an EEPROM reading device used for a passive UHF RFID chip. The reading device is mainly used for solving problems in existing EEPROM reading devices of high peak and average power consumption, large process variation and floating-gate performance degradation. The reading device comprises: a reading controlling logic circuit, an edge self-detection circuit, a reading unit array, and a storing unit array. The storing unit array is connected to the reading unit array through bit lines (BL). Under the controlling of a reading clock signal CLKR, the reading controlling logic circuit generates a reset signal rst, a precharge signal enpch, and a latch signal enlat, and the signals are transmitted to the reading unit array. A data signals DBO is transmitted from the reading unit array to the edge self-detection circuit, and a controlling signal latch is generated. The signal is fed back to the reading controlling logic circuit. The reading device provided by the invention has advantages of low peak and average power consumption, process variation resistance and floating-gate performance degradation resistance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Integrated circuit layout design methodology with process variation bands
A system for analyzing IC layouts and designs by calculating variations of a number of objects to be created on a semiconductor wafer as a result of different process conditions. The variations are analyzed to determine individual feature failures or to rank layout designs by their susceptibility to process variations. In one embodiment, the variations are represented by PV-bands having an inner edge that defines the smallest area in which an object will always print and an outer edge that defines the largest area in which an object will print under some process conditions.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
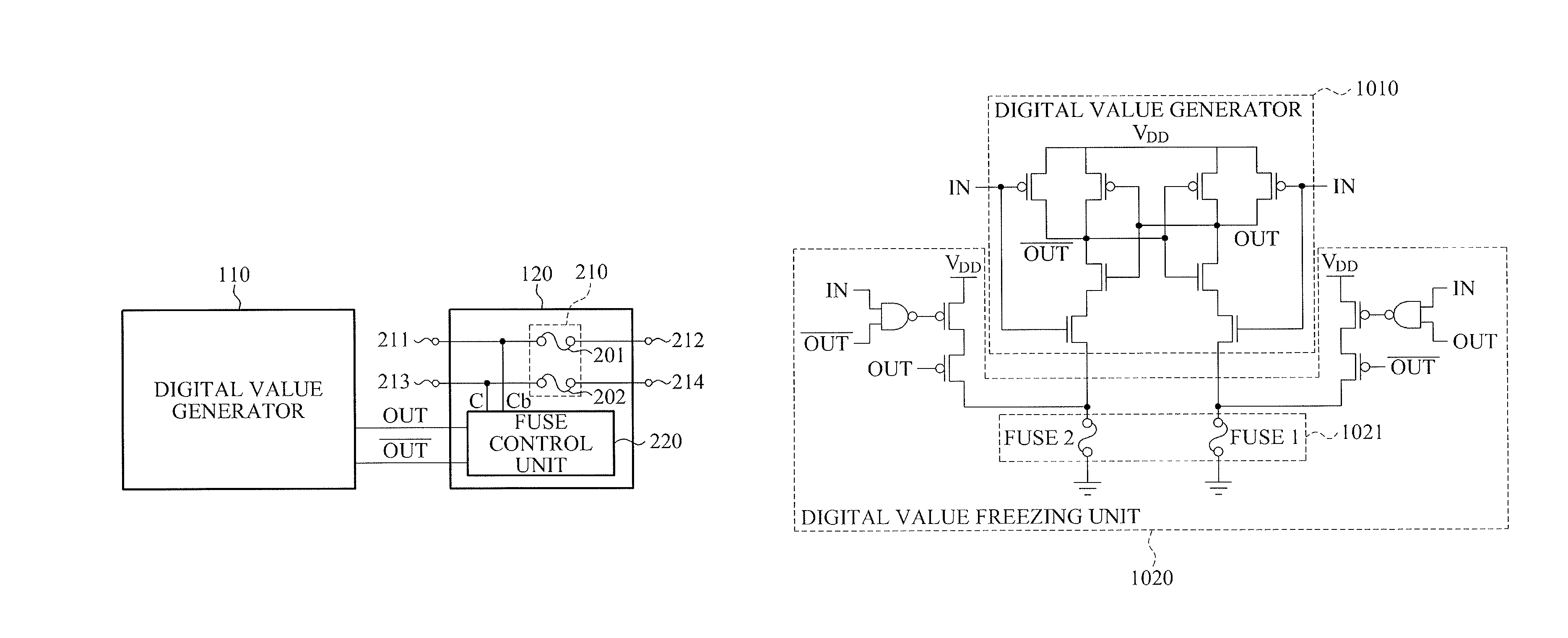
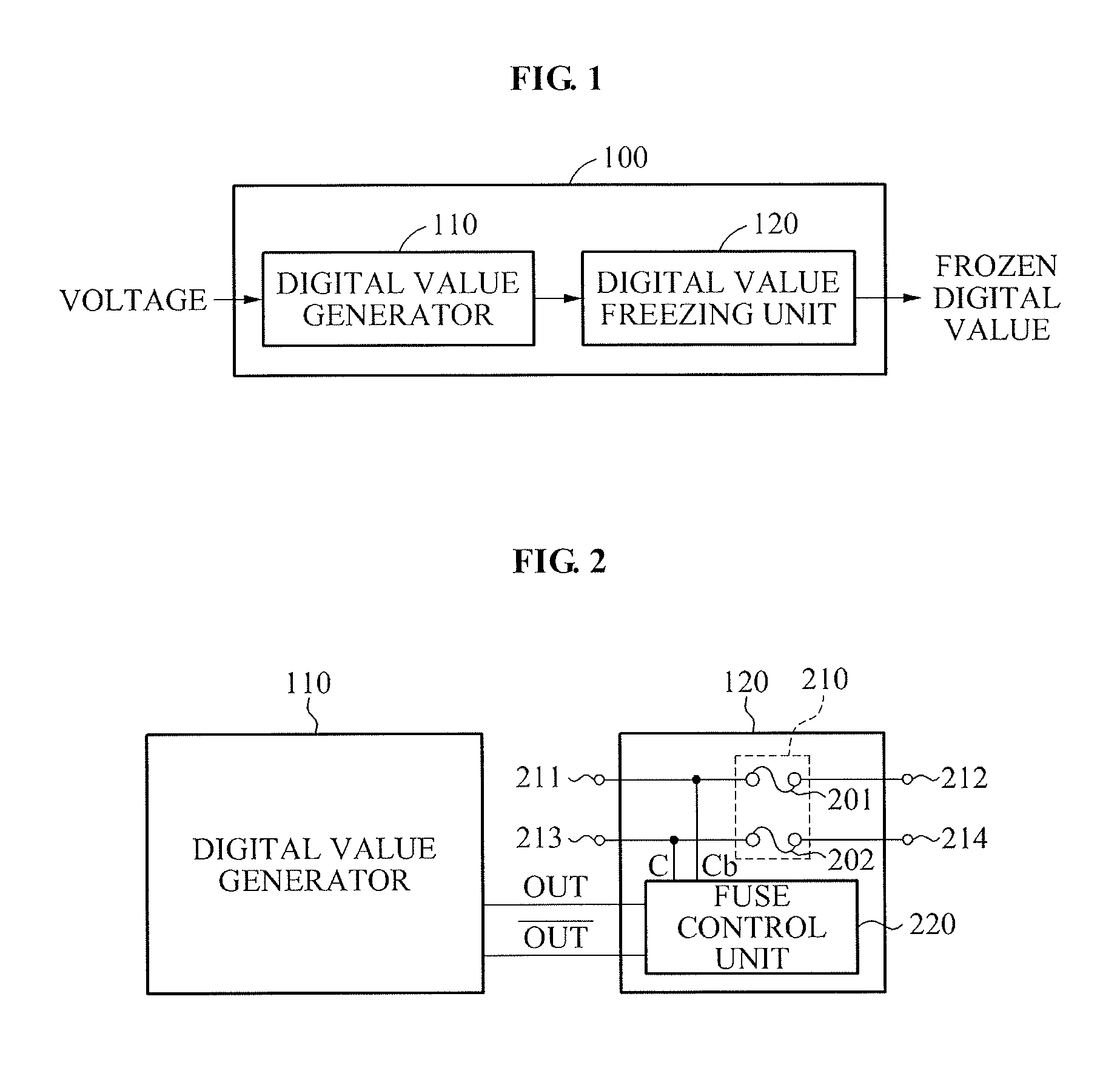
Apparatus and method for generating digital value
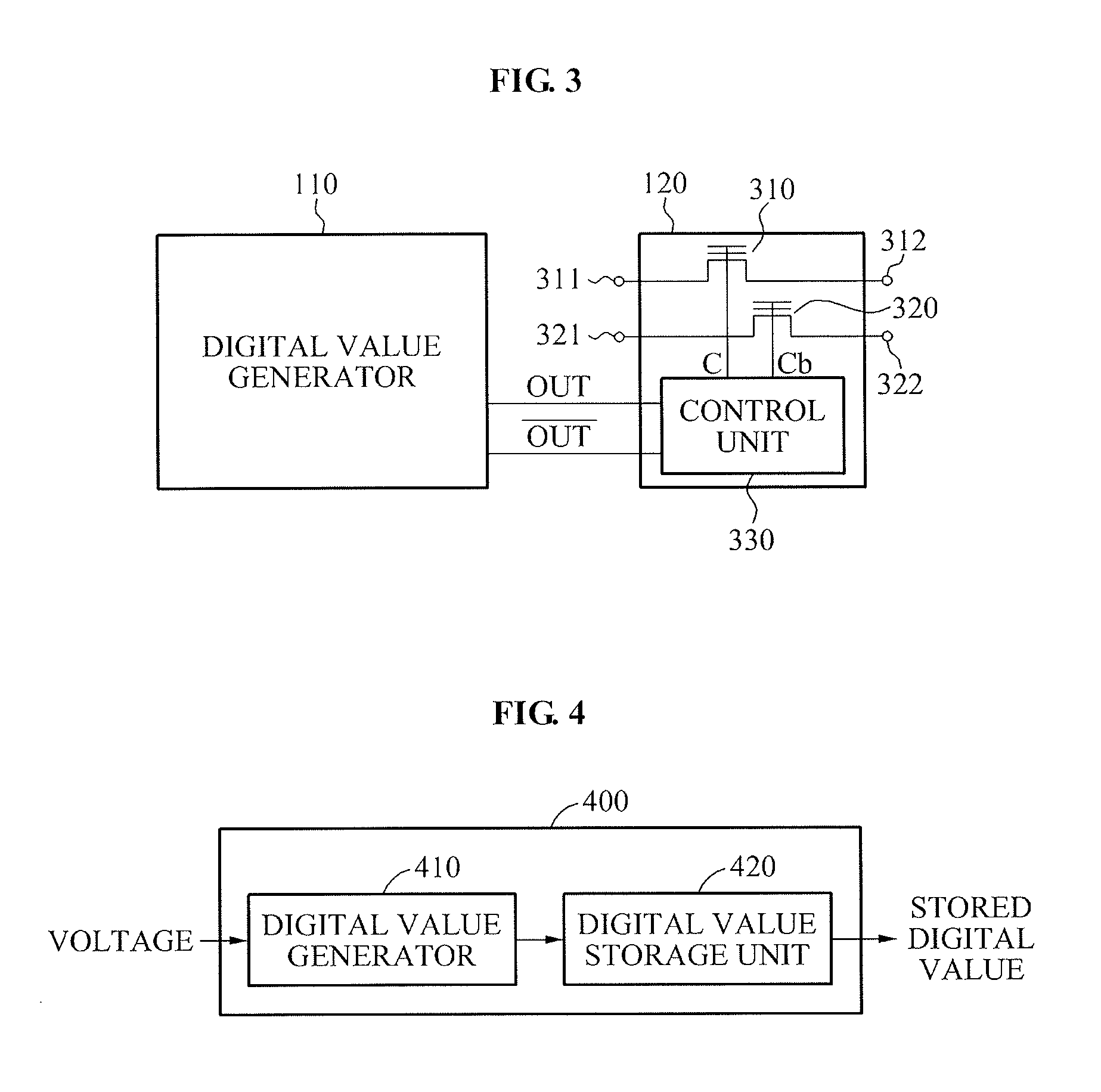
ActiveUS9105432B2Reliable valueSimple configurationKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsTheoretical computer scienceSemiconductor
Provided is an apparatus for generating a digital value that may generate a random digital value, and guarantee time invariance of the generated digital value. The apparatus may include a digital value generator to generate a random digital value using semiconductor process variation, and a digital value freezing unit that may be connected to the digital value generator and fixed to one of a first state and a second state based on the generated digital value, to freeze the digital value.
Owner:ICTK
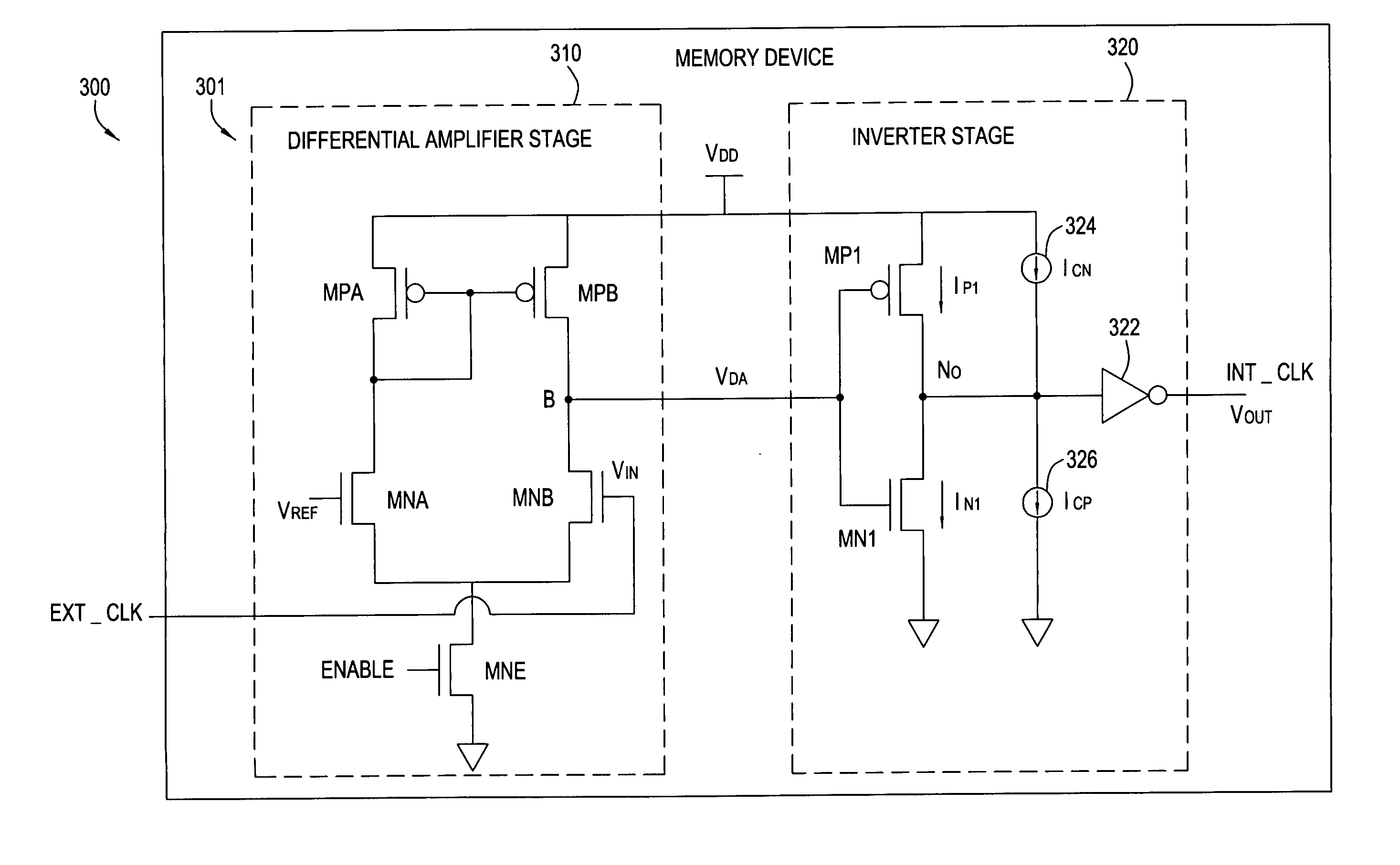
Low rise/fall skewed input buffer compensating process variation
InactiveUS20050104618A1Minimize skewElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorHemt circuitsInverter
Buffer circuits and techniques that reduce skew between rising and falling times of output data as process conditions vary are provided. One or more process-dependent current sources may be utilized to compensate for process variations by supplementing the current drive of transistors used to precharge (PMOS) or discharge (NMOS) an output node of a secondary (e.g., inverter) stage of the buffer circuit.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
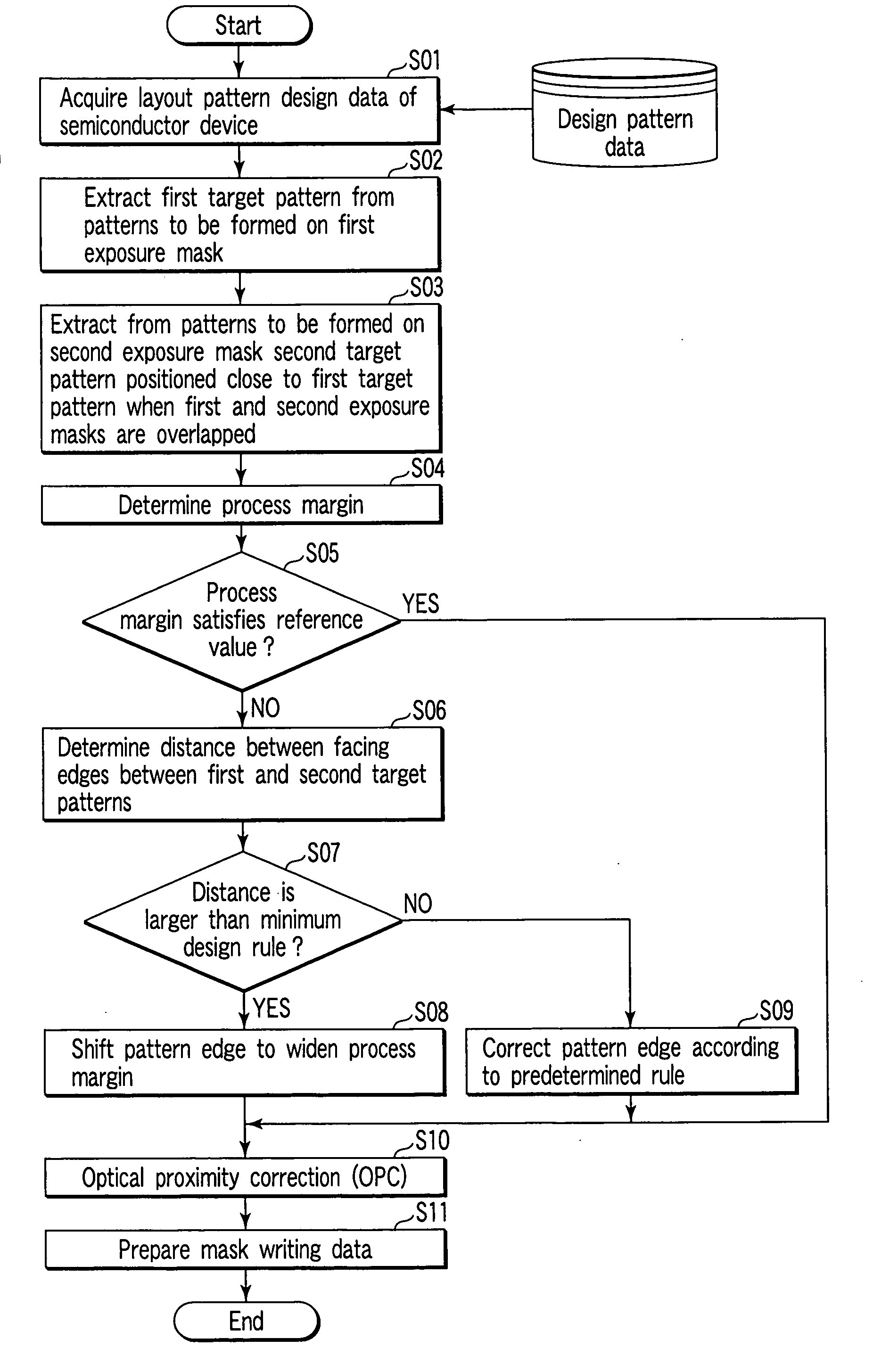
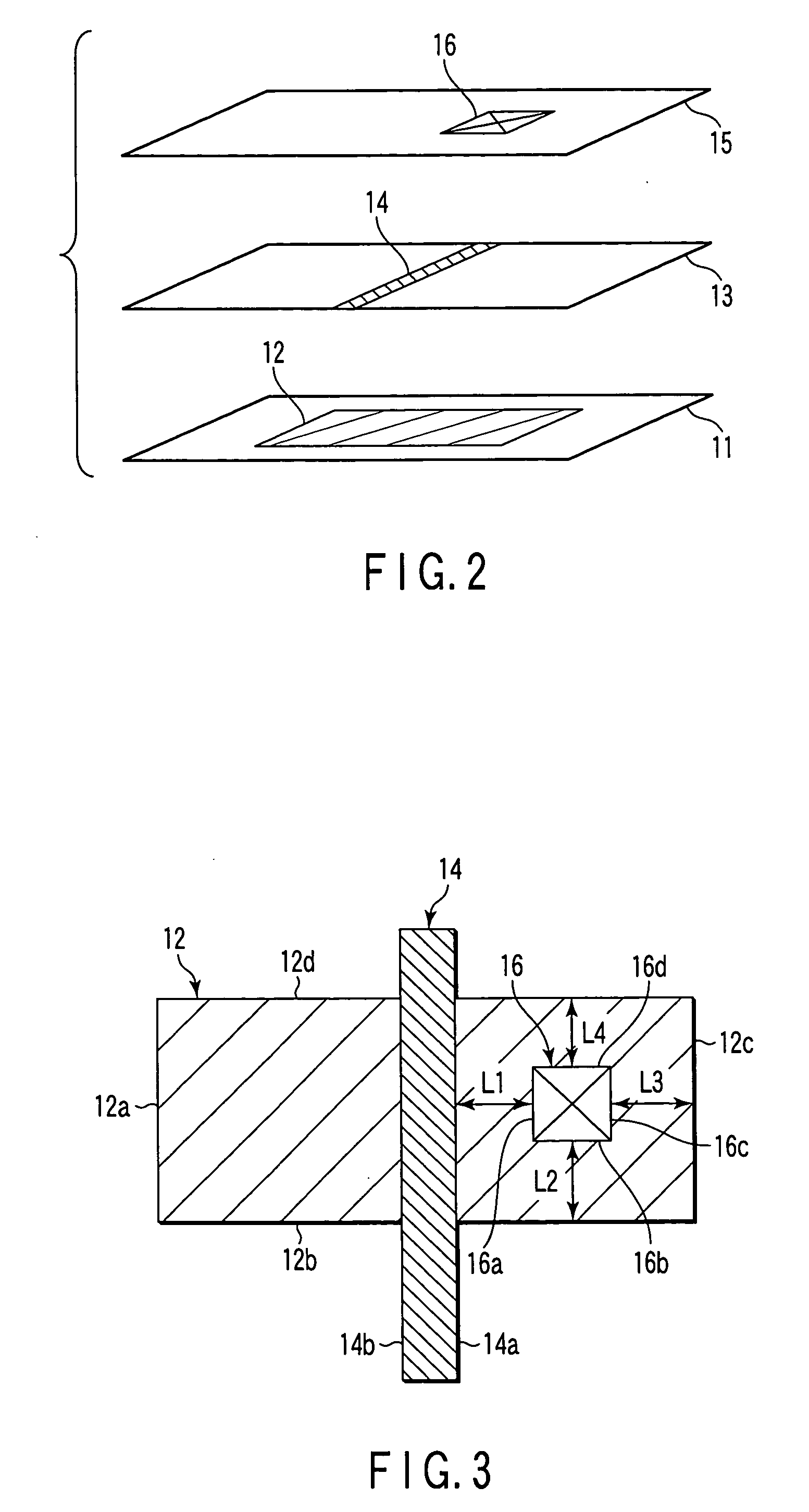
Pattern forming method and system, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20040259005A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEngineeringSemiconductor
A pattern forming method of forming a desired pattern on a semiconductor substrate is disclosed, which comprises extracting a first pattern of a layer, extracting a second pattern of one or more layers overlapped with the layer, the second pattern being arranged close to or overlapped with the first pattern, calculating a distance between the first and second patterns on a semiconductor substrate in consideration of a predetermined process variation, determining whether or not the distance between the first and second patterns satisfy an allowable margin given for the distance between the first and second patterns, and correcting, if the distance does not satisfy the allowable margin, at least one of the first and second patterns to satisfy the allowable margin.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
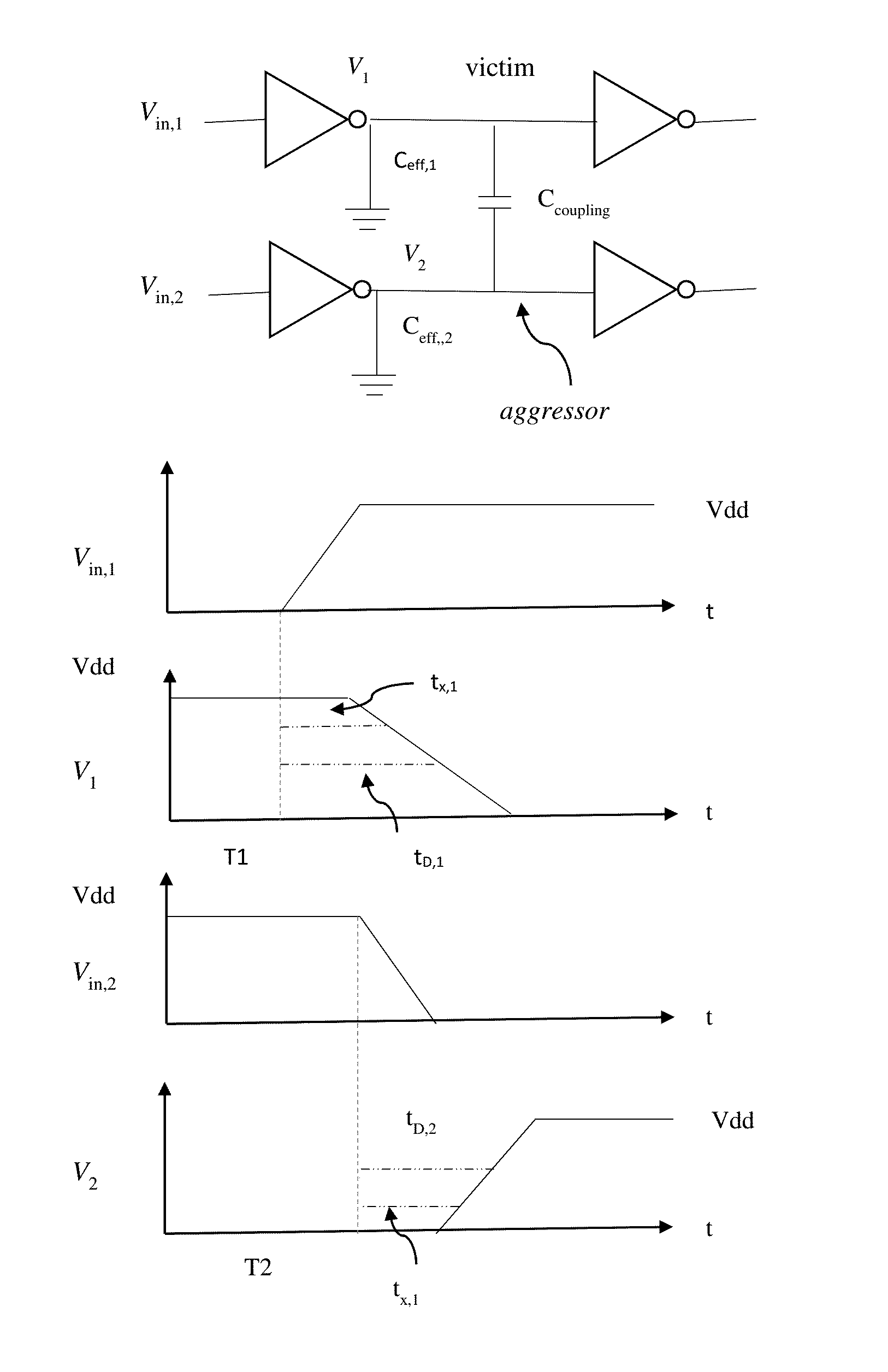
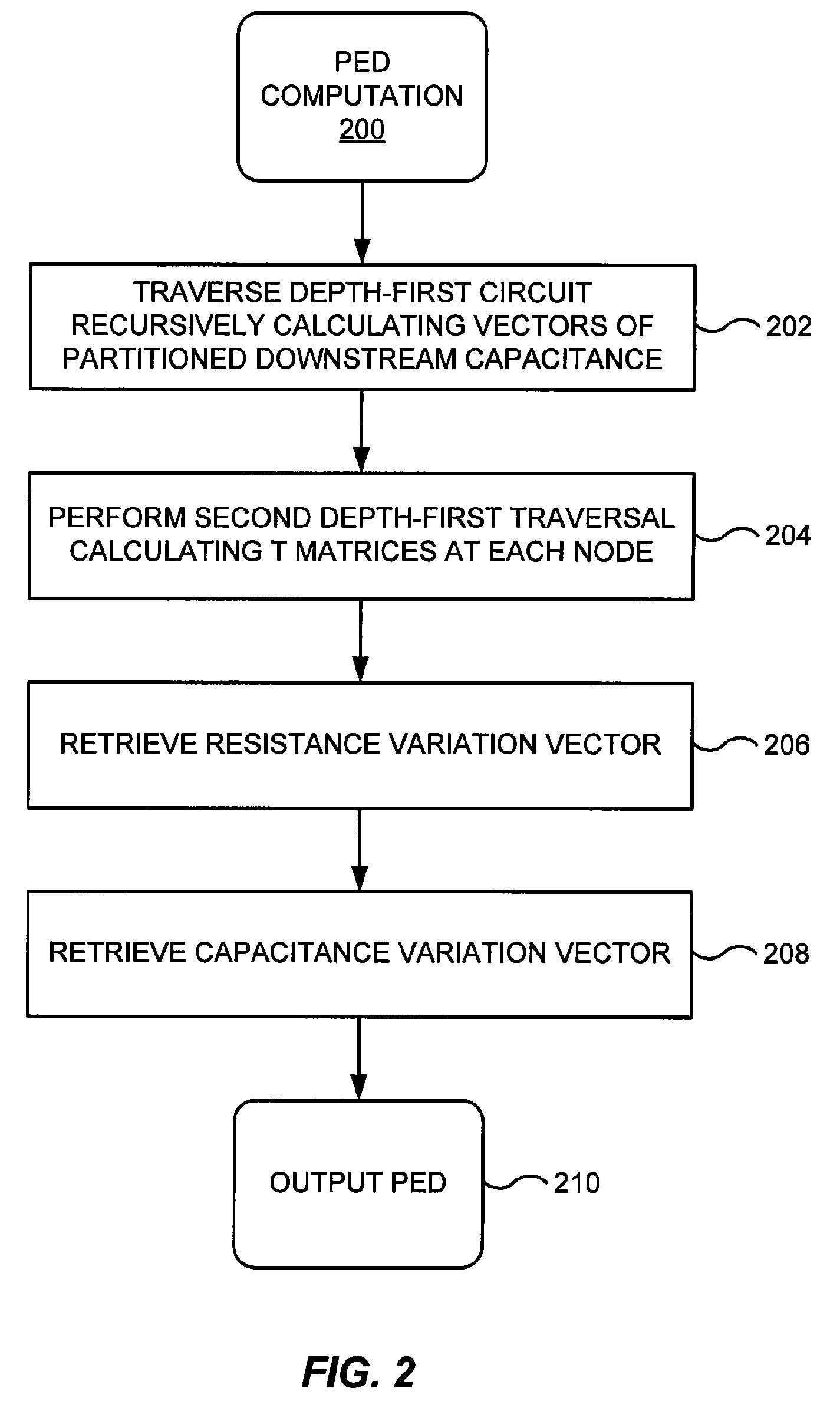
Ssta with non-gaussian variation to second order for multi-phase sequential circuit with interconnect effect
ActiveUS20150199462A1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEffective capacitanceCapacitance
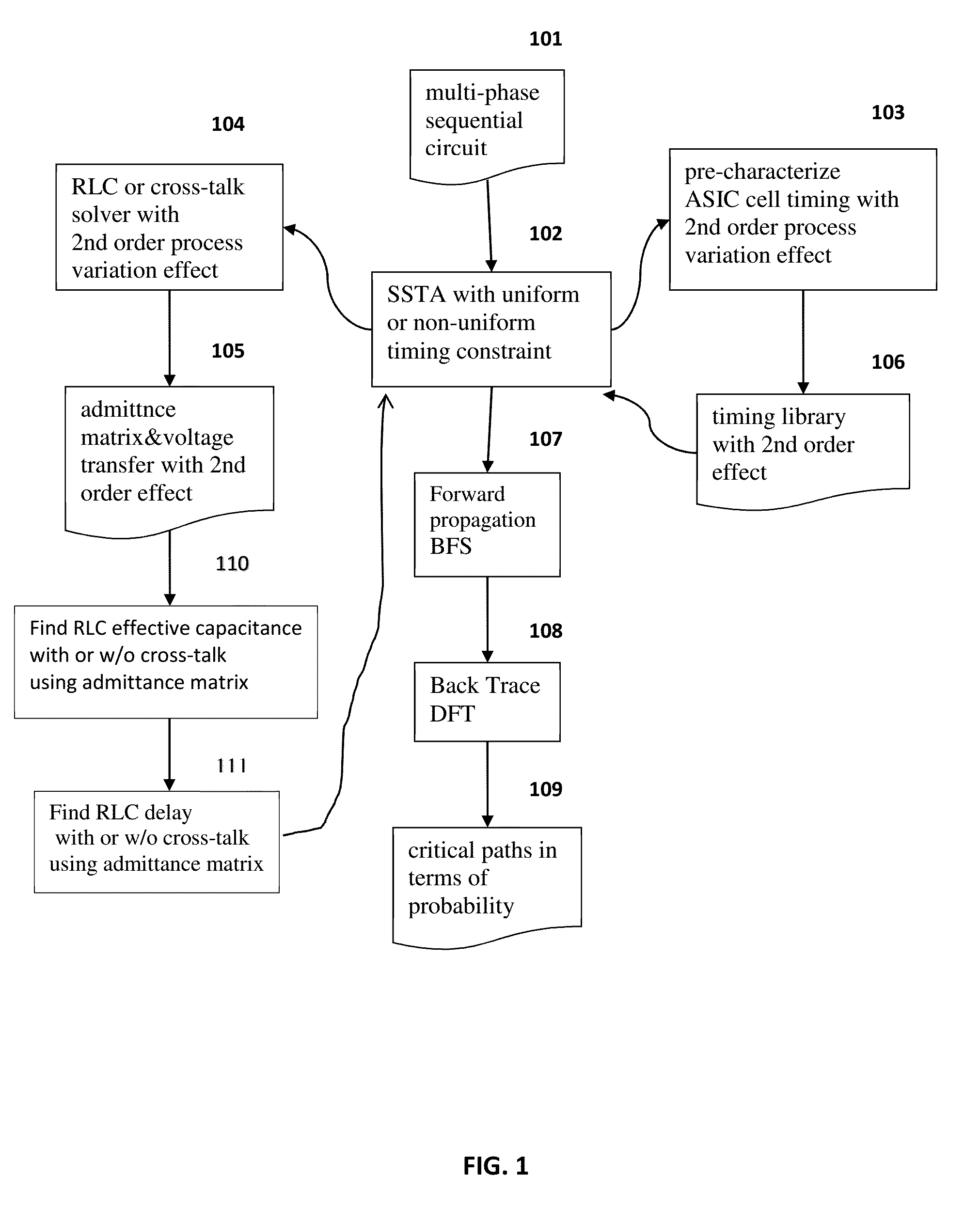
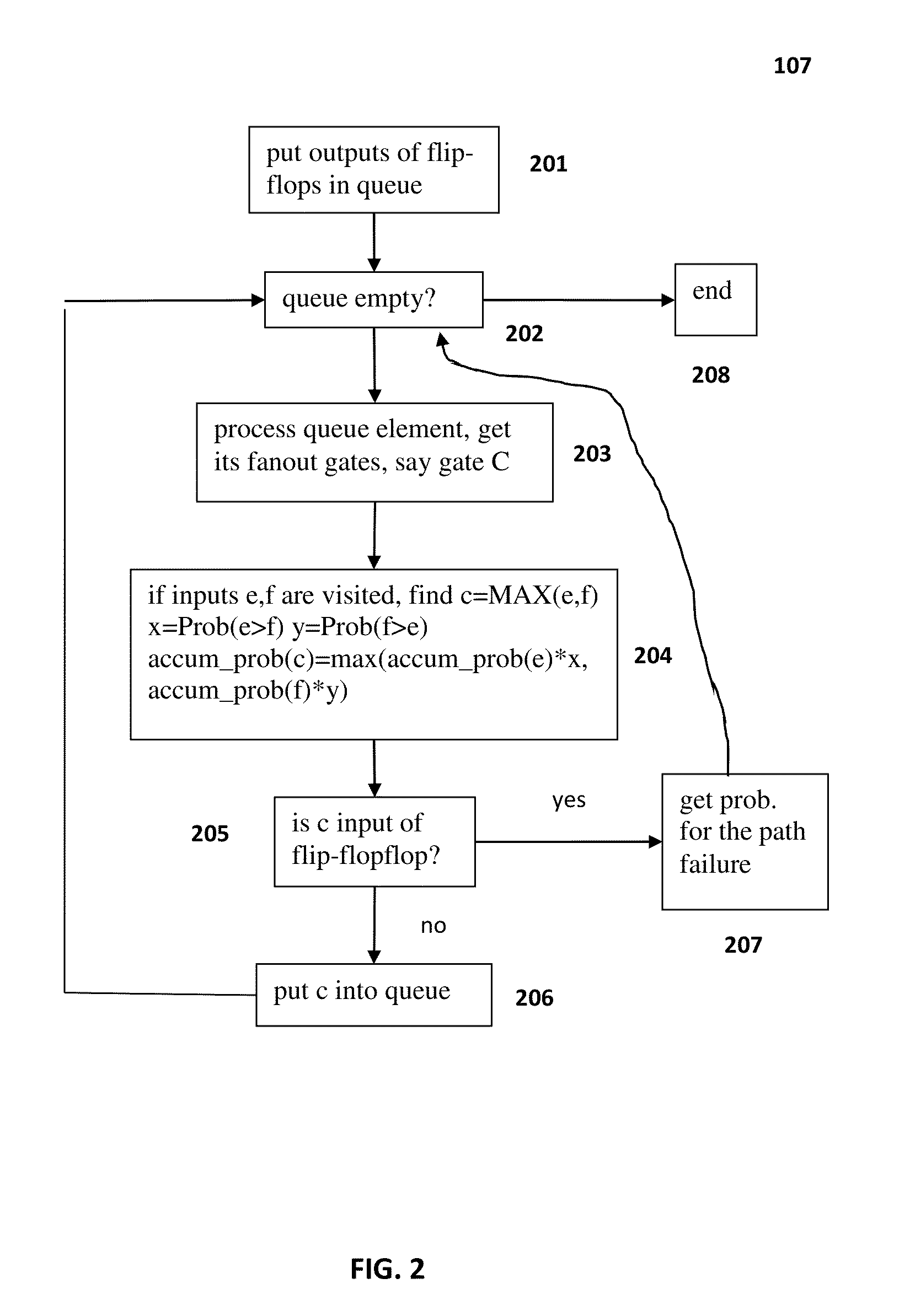
In the present invention the issue of SSTA in multi-phase sequential circuit with cross-talk in consideration of non-uniform timing constraint and process variations up to the 2nd order is proposed. Use forward breadth first search to calculate the accumulated probabilities at each node for clock phases and edge probability with respect to input and output clock phases, followed by backward depth first traversal to find all critical paths with their probabilities greater than user specified threshold. A method is proposed to pre-characterize the timing library including second order variations. For cross-talk, the poles and residues of admittance matrix and voltage transfer are carried out to 2nd order variations. Effective capacitances and waveforms at interconnect input or driver's immediate output are calculated to 2nd order variations. Delays at victim outputs are then calculated to 2nd order variations and fed back to SSTA, the probability of path occurrence can be calculated accurately.
Owner:SAGE SOFTWARE
Parametric timing analysis
ActiveUS7970590B1Accurate modelingIncrease productionComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designStatic timing analysisEngineering
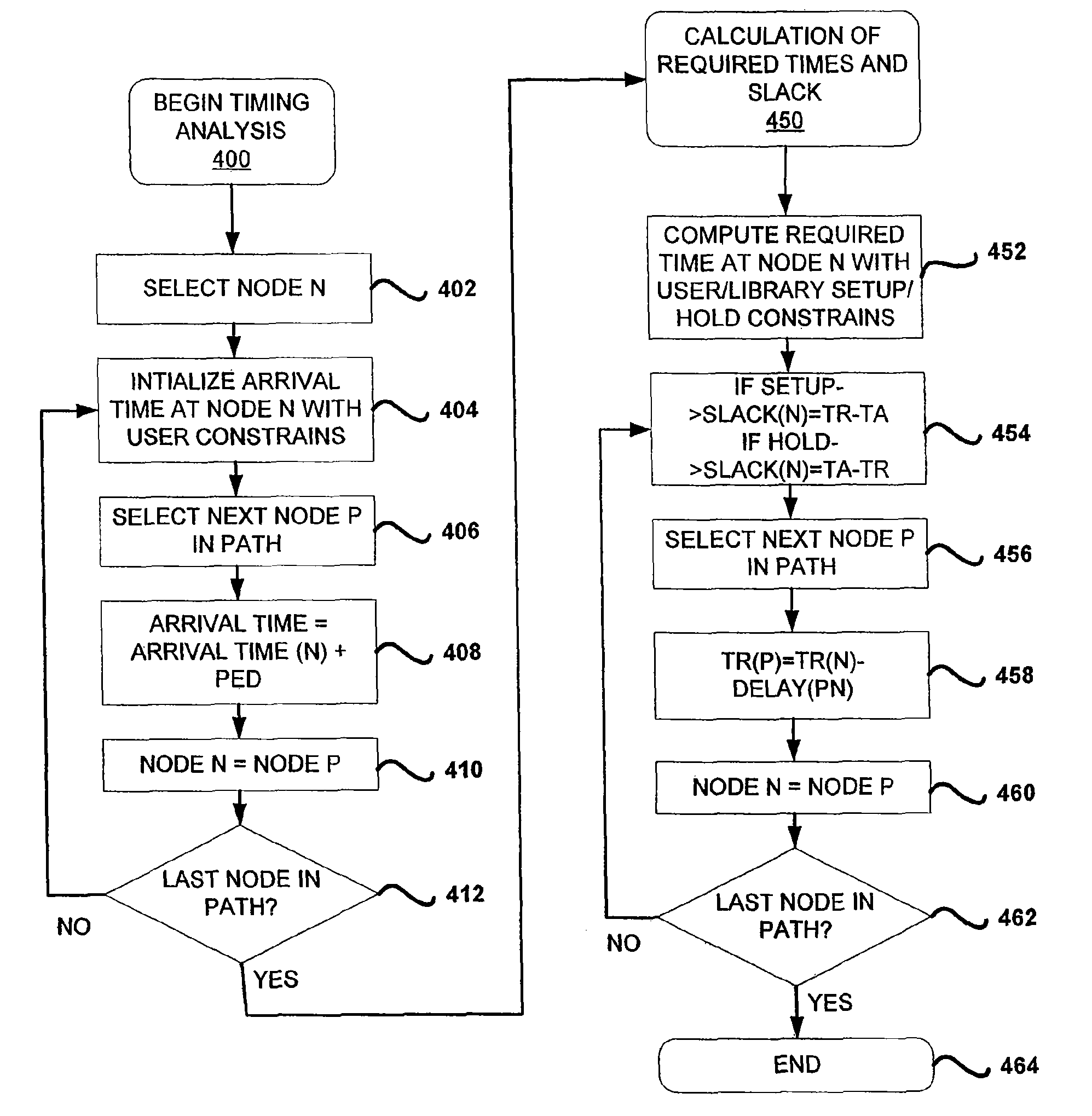
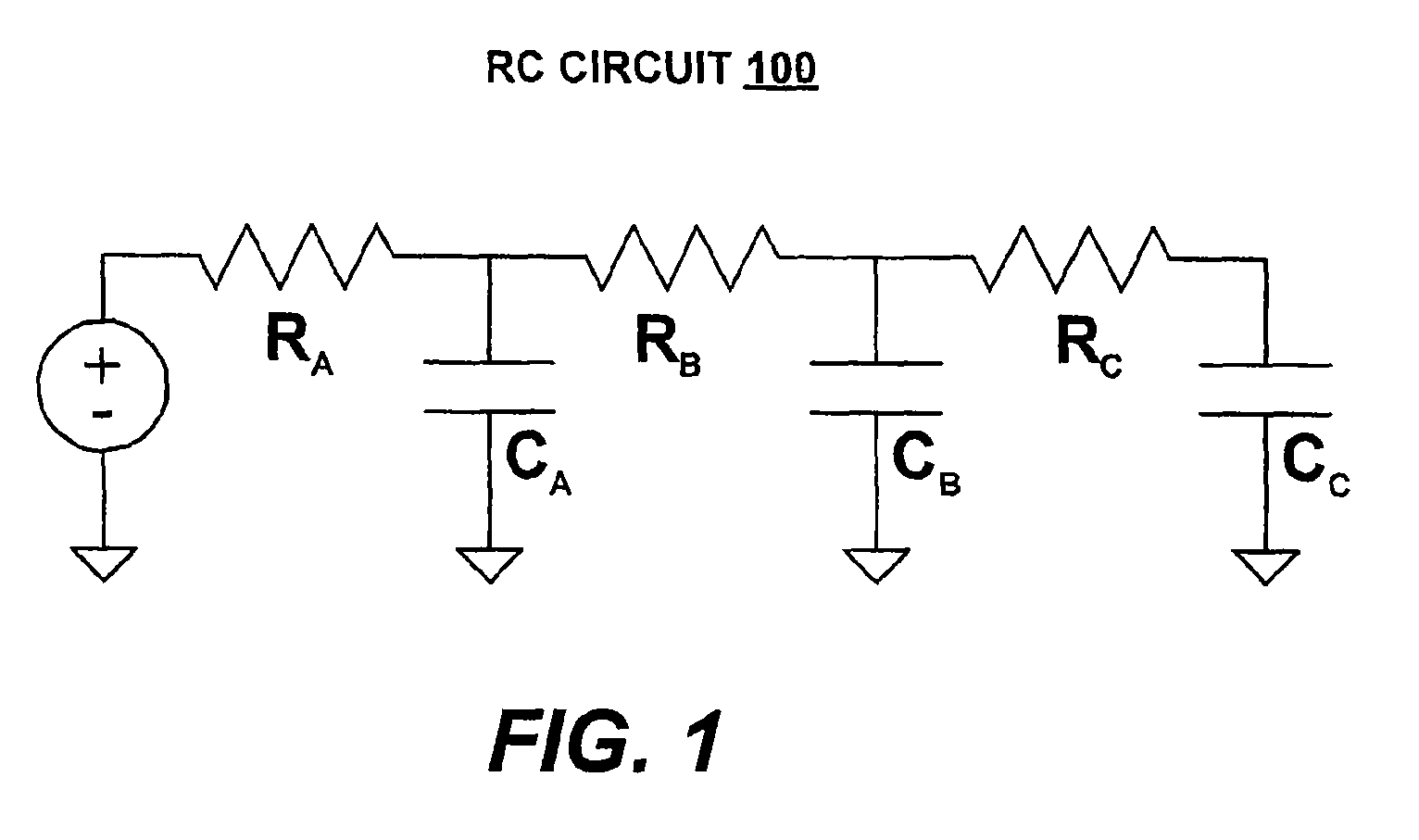
Electronic Design Automation tools are used to aid in the design and verification of integrated circuits. As part of the verification process, circuit designs are analyzed with respect to their timing performance. Timing analysis is susceptible to variation in circuit components due to fabrication process variation. Process variation is introduced as worst-case conditions or statistical probabilities. More accurate process variation is modeled by for timing sensitivity with Parametric Elmore Delay. Parametric Elmore Delay introduces effects on circuit components as parameters in the conventional Elmore Delay definition to model fabrication process variation in the timing analysis. Delay variance demonstrates sensitivities to process and design factors. Parametric timing analysis is used to anticipate fabrication yield and identify potential improvements in the design or fabrication process.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
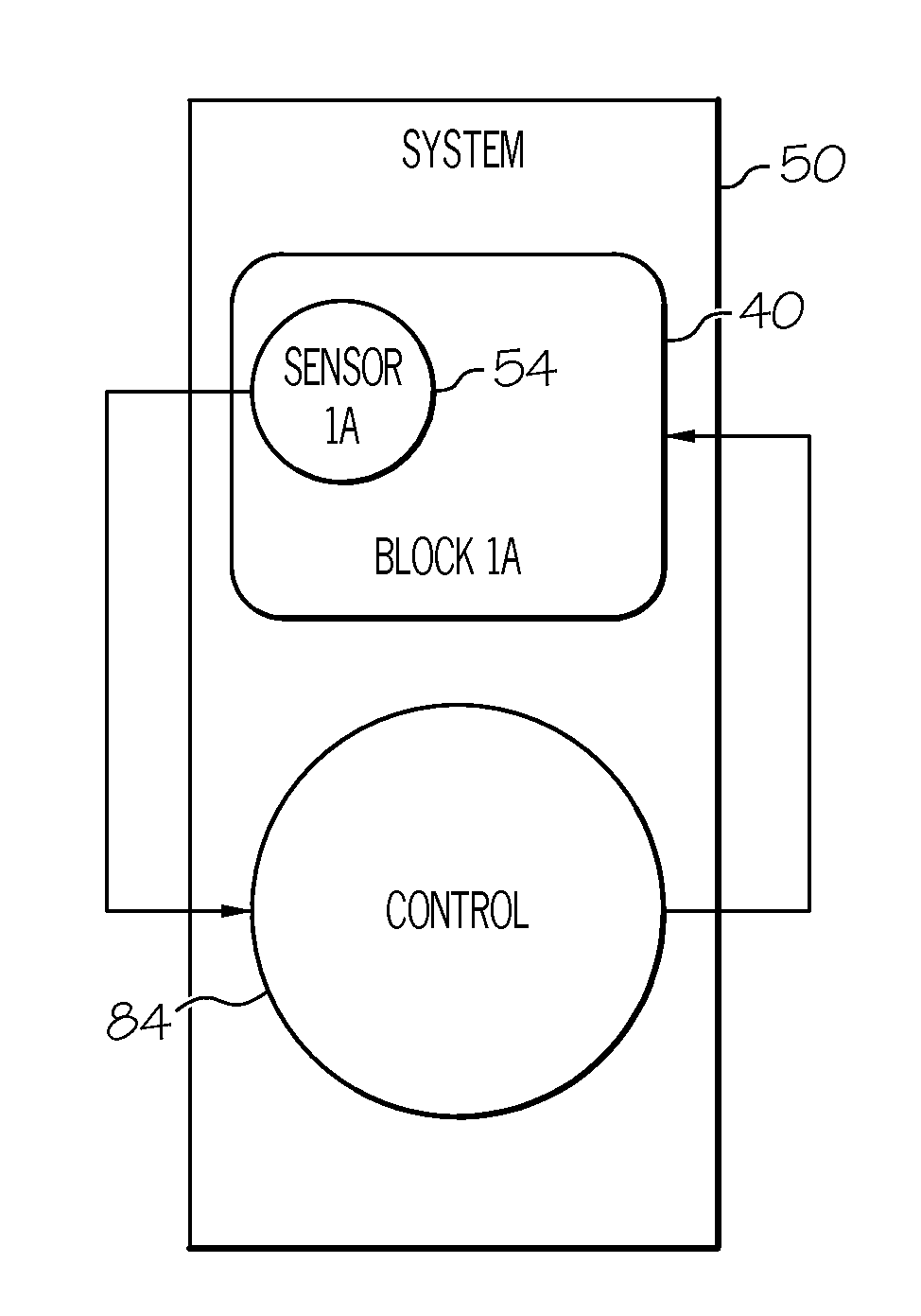
Semiconductor sensor reliability operation
ActiveUS20120153279A1Reduce semiconductor system degredationMaximum sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsModel selectionBehavioral modeling
Embodiments of the present invention provide a semiconductor sensor reliability system and method. Specifically, the present invention provides in-situ positioning of a reliability sensor (hereinafter sensors) within each functional block, as well as at critical locations, of a semiconductor system. The quantity and location of the sensors are optimized to have maximum sensitivity to known process variations. In general, the sensor models a behavior (e.g., aging process) of the location (e.g., functional block) in which it is positioned and comprises a plurality of stages connected as a network and a self-digitizer. Each sensor has a mode selection input for selecting a mode thereof and an operational trigger input for enabling the sensor to model the behavior. The model selection input and operation trigger enable the sensor to have an operational mode in which the plurality of sensors are subject to an aging process, as well as a measurement mode in which an age of the plurality of sensors is outputted. Based on the output, one or more functional blocks are modified by a control sensor component to reduce semiconductor system degredation in real-time.
Owner:SDEP CORP
Security application using silicon fingerprint identification
InactiveUS20060236123A1Reducing a bit error rate of the identification valueUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringSemiconductorSilicon
A method for using an identification value for a security application is disclosed. The method may include the steps of (A) generating the identification value based on a plurality of semiconductor fabrication process variations, (B) generating a key by reducing a bit error rate of the identification value, wherein the key may not be available external to the security application and (C) generating an output signal by one of (i) encoding and (ii) decoding an input signal in response to said key.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
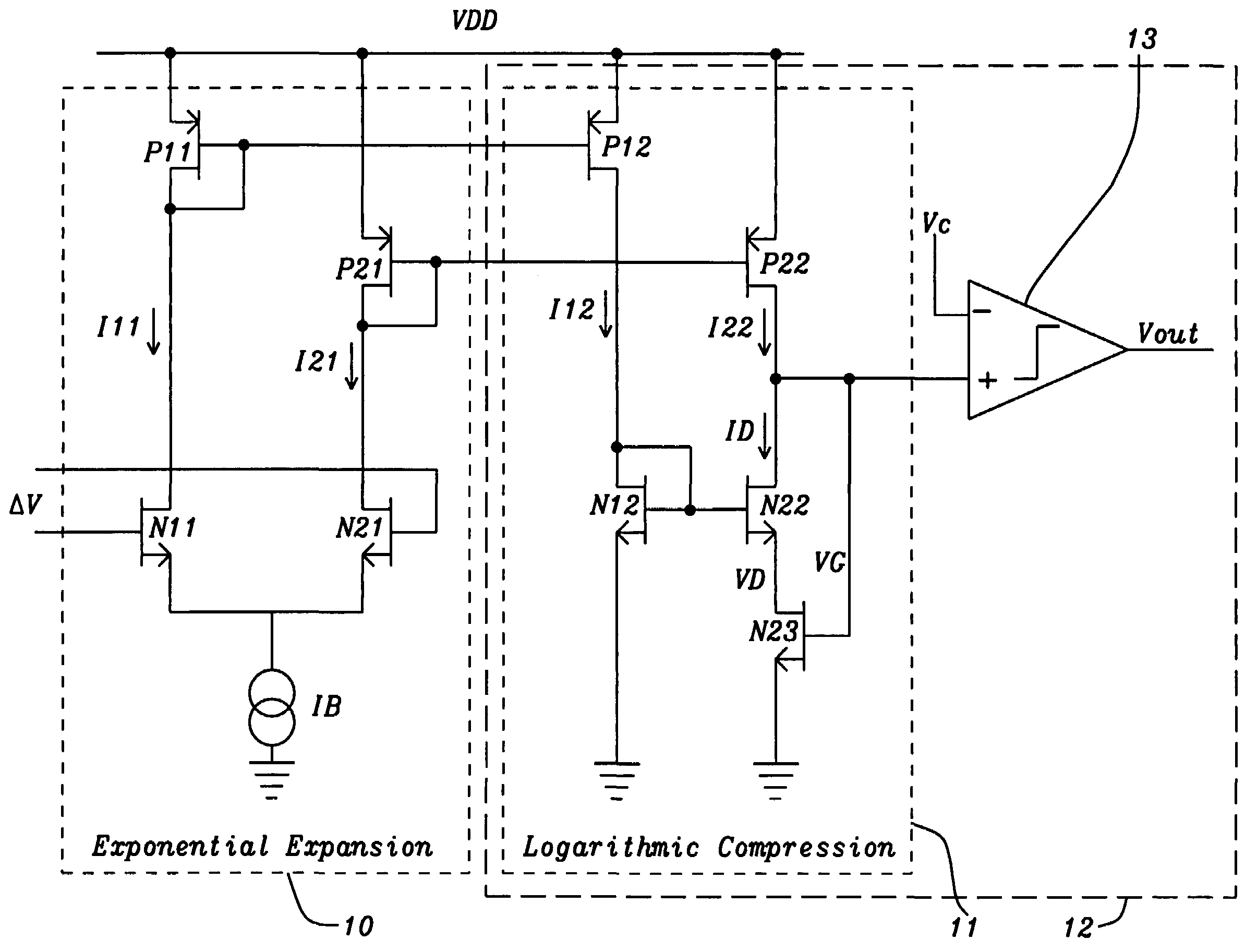
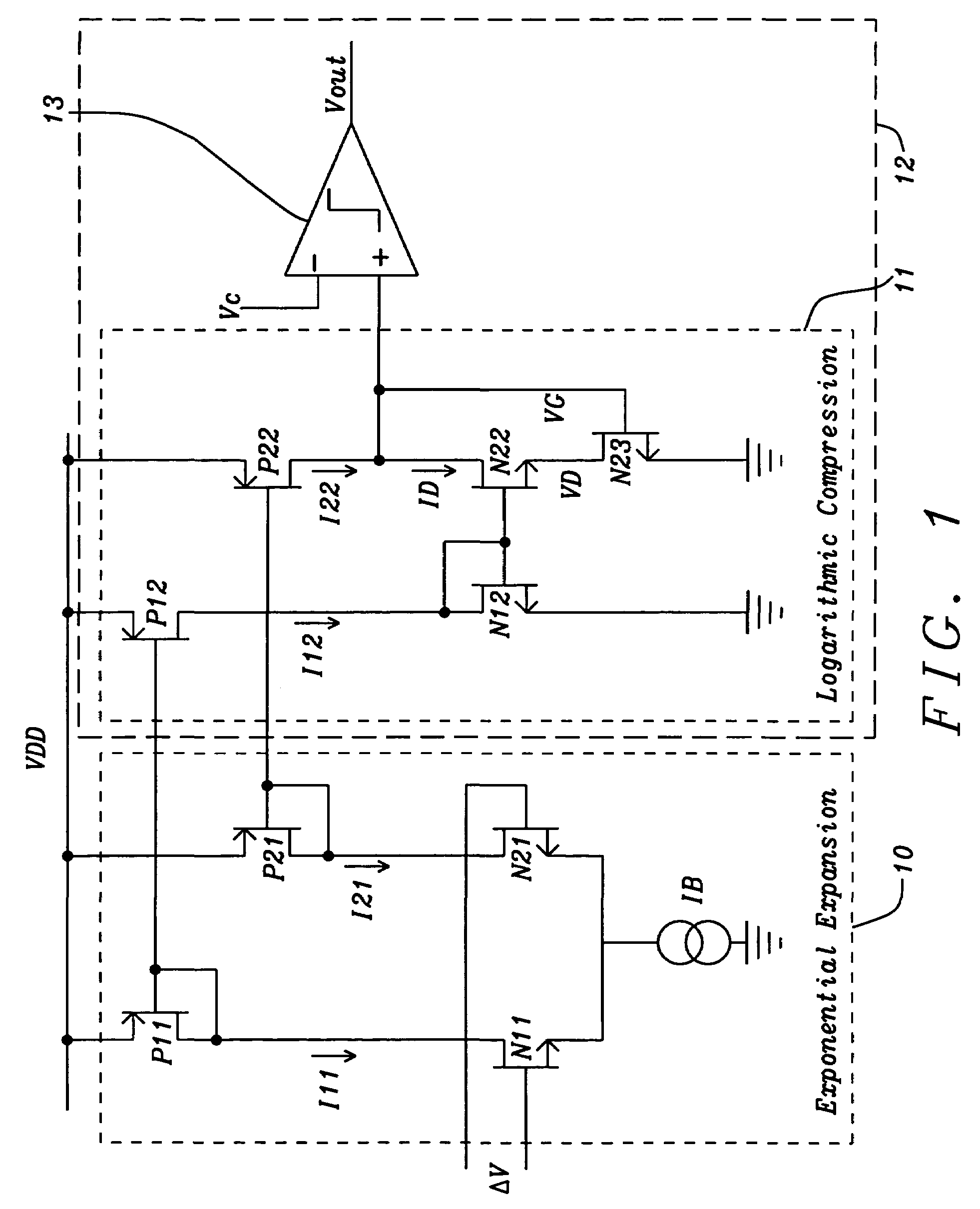
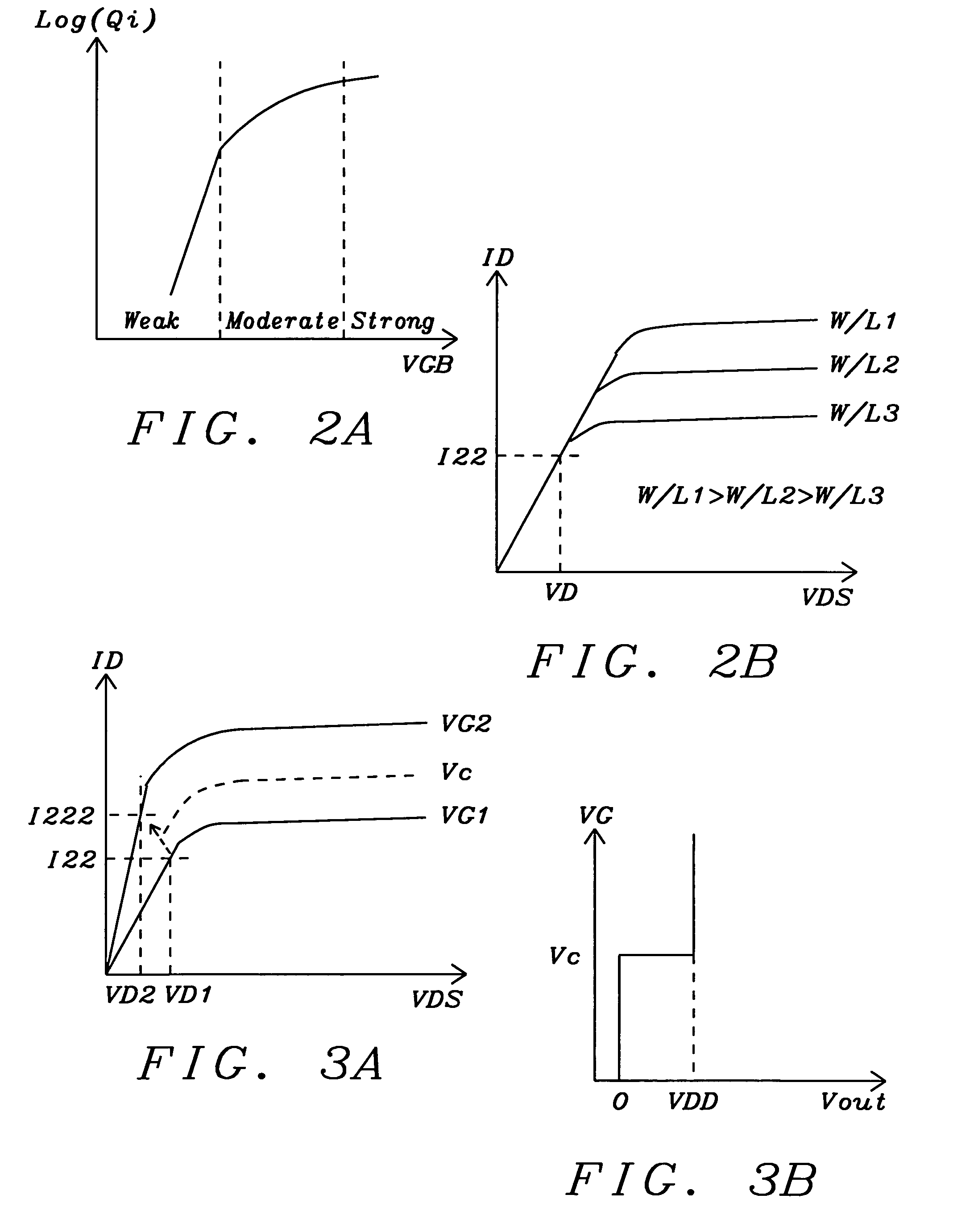
Class B amplifier with process variation independent deadband
A class B amplifier circuit produces a deadband that is independent of semiconductor process variations and creates a positive voltage when a differential input voltage is non-zero. A differential input amplifier couples differential currents representing the differential input voltage to a logarithmic compression circuit, which in turn creates an output voltage that is a function of the differential input voltage and is independent of semiconductor process variations. Transistor devices in the differential amplifier and the logarithmic compression circuit are biased in the non-saturated region of a transistor transfer curve in a weak inversion state. A combination of two comparator circuits compares the output voltage to a reference voltage to create a combined output voltage that is a positive when the input is non-zero.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Method and system for performing improved timing window analysis
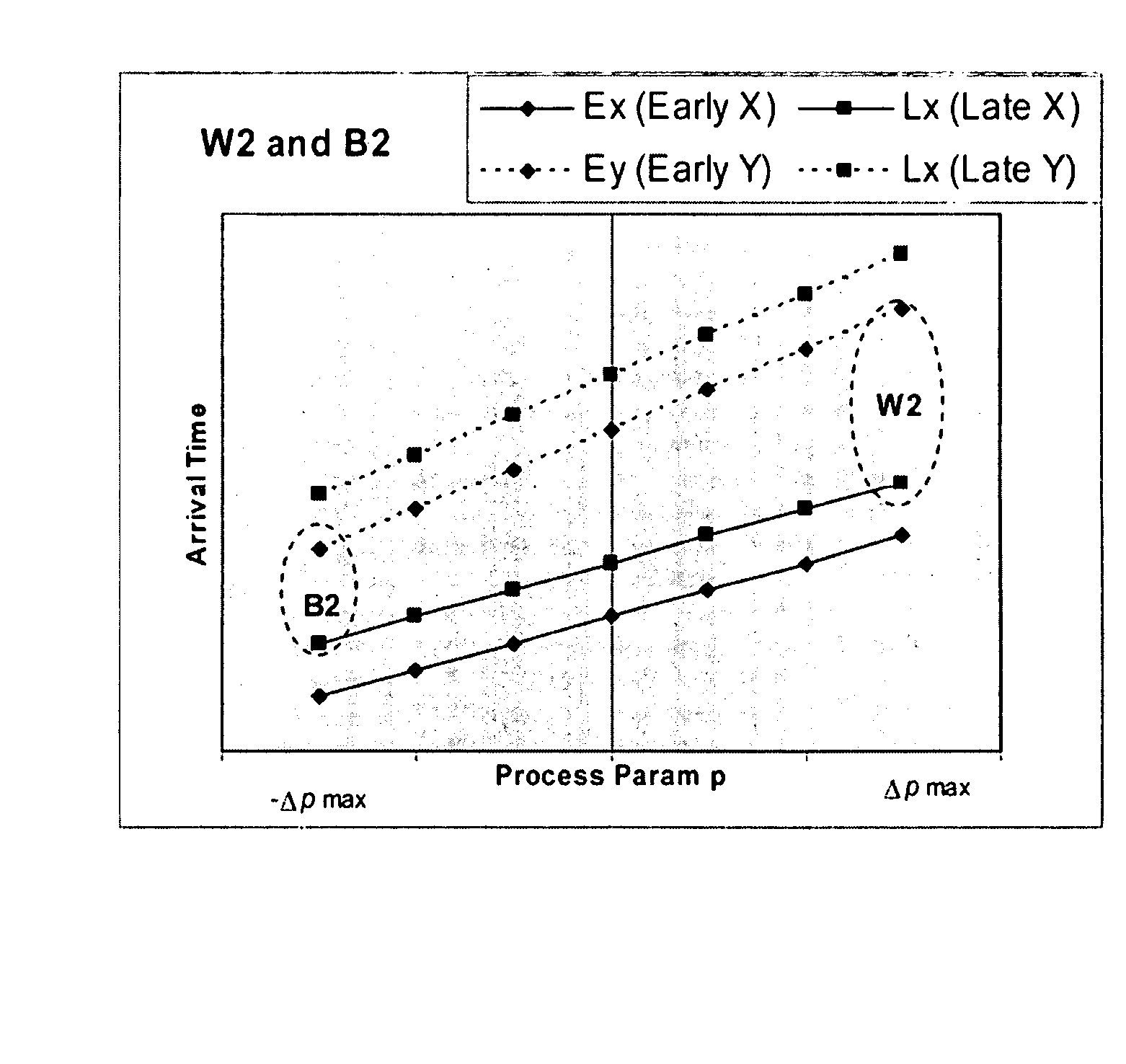
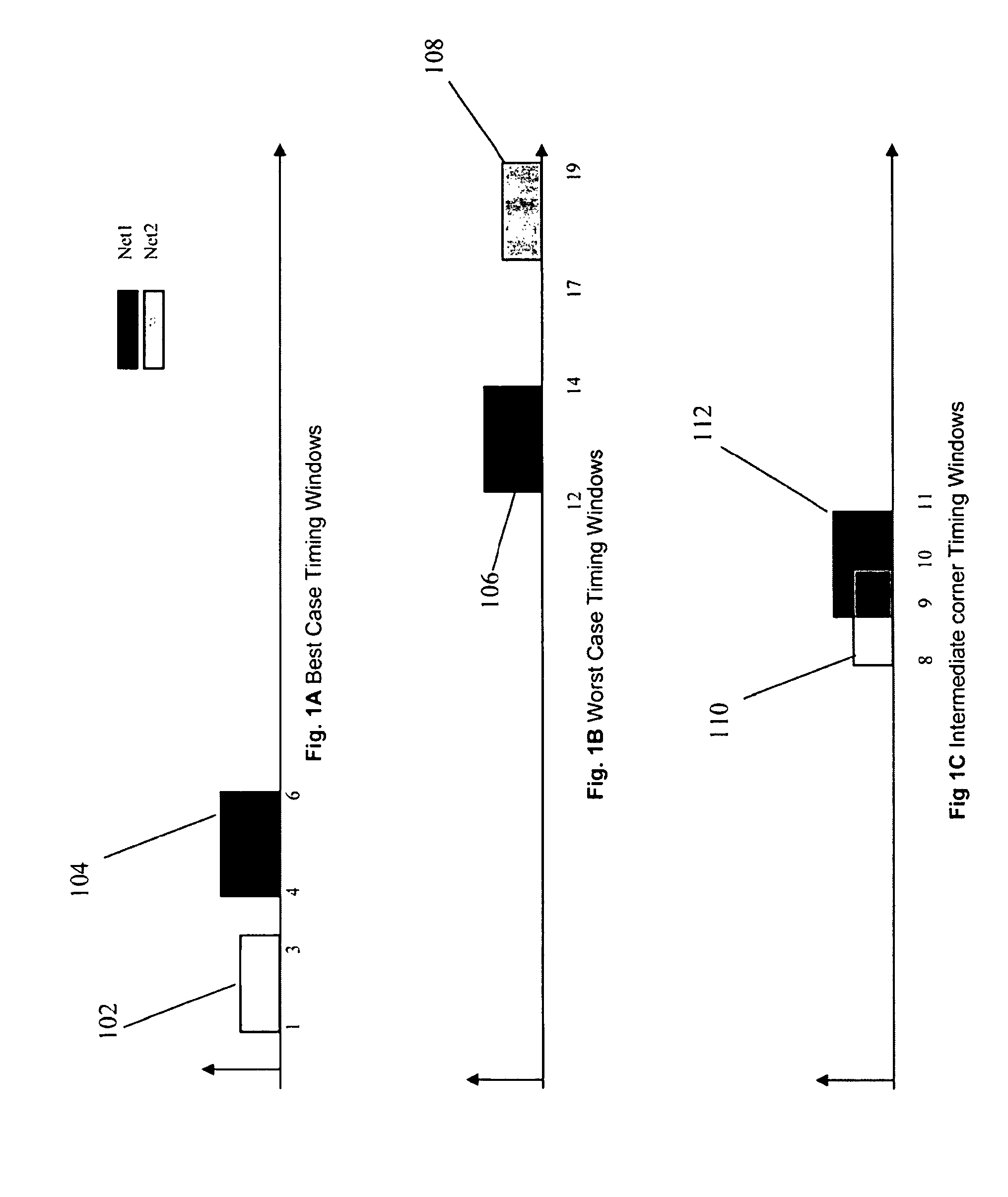
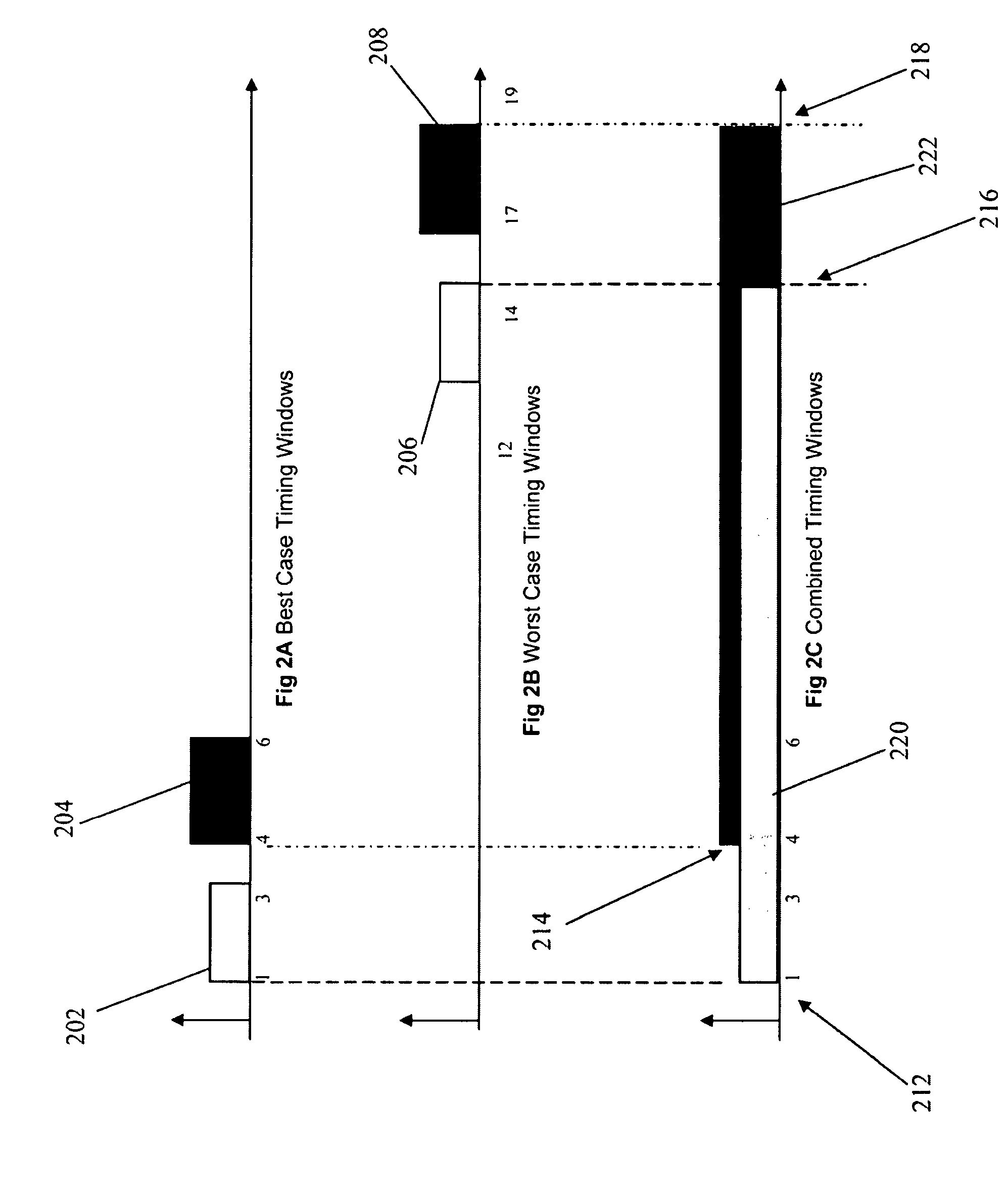
InactiveUS8086983B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCase analysisComputer program
A method, system, and computer program product are disclosed for performing crosstalk analysis using first-order parameterized analysis modeling. The approach can be used to factor in the effect of process variations within the definition of timing windows. This approach allows one to bypass the simplistic assumptions related to best-case / worst-case analysis using timing windows, and provide a realistic picture of the impact of timing windows on noise analysis. The timing windows can be viewed in terms of the individual process parameter. The process parameters could be real process parameters, or virtual / computed components based on the actual process parameters. The process parameters can be used to compute overlap of timing windows for performing noise analysis.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
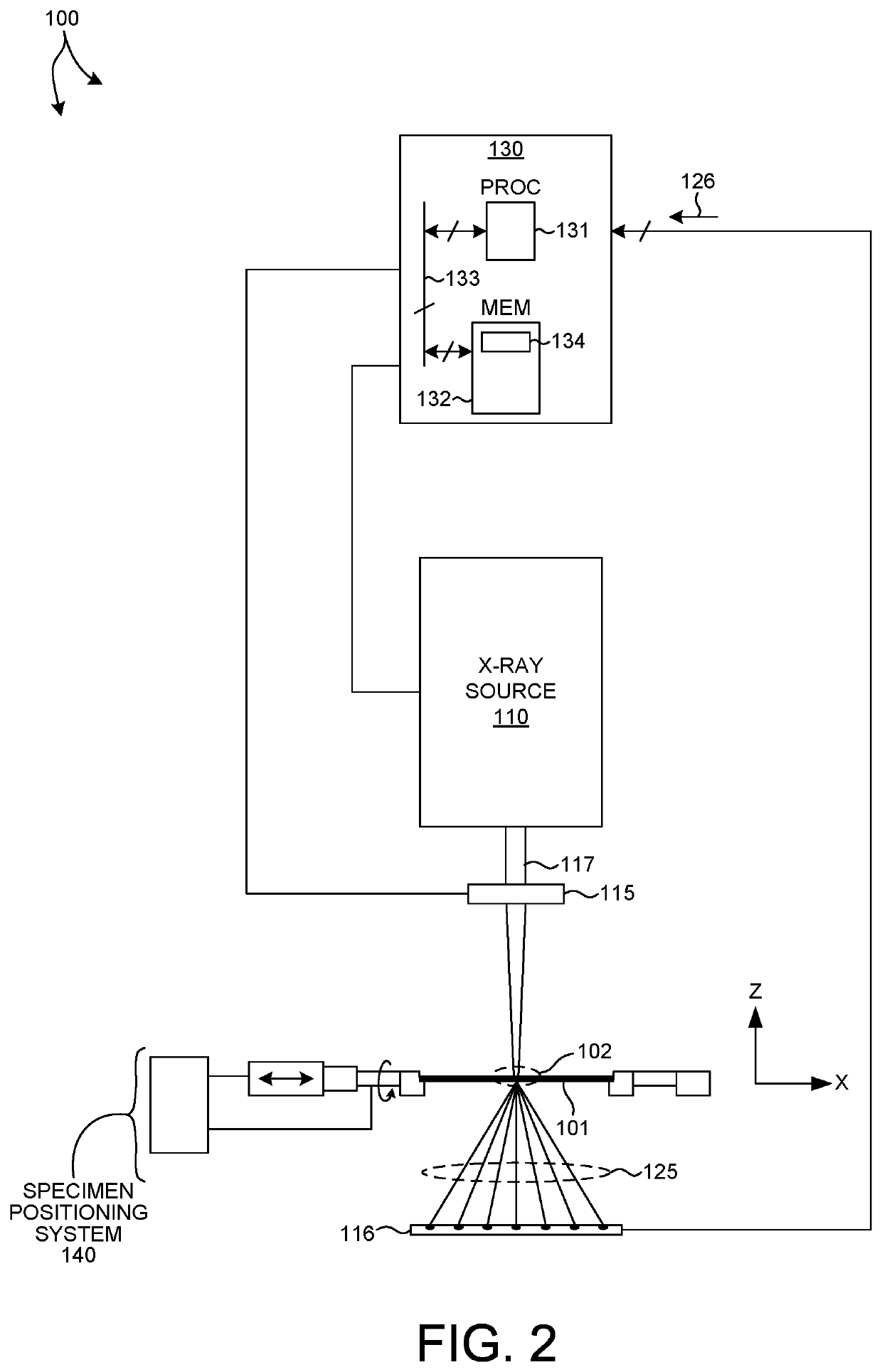
Device For In-Situ Fabrication Process Monitoring And Feedback Control Of An Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing Process
ActiveUS20200215810A1Maintain consistencyMaximize chanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationControl engineeringProcess engineering
A High Energy Beam Processing (HEBP) system provides feedback signal monitoring and feedback control for the improvement of process repeatability and three-dimensional (3D) printed part quality. Signals reflecting process parameters and the quality of the fabricated parts are analyzed by monitoring feedback signals from artifact sources with a process controller which adjusts process parameters. In this manner, fabricated parts are produced more accurately and consistently from powder feedstock by compensating for process variation in response to feedback signals.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP +1
System and method for wireless and dynamic intra-process measurement of integrated circuit parameters
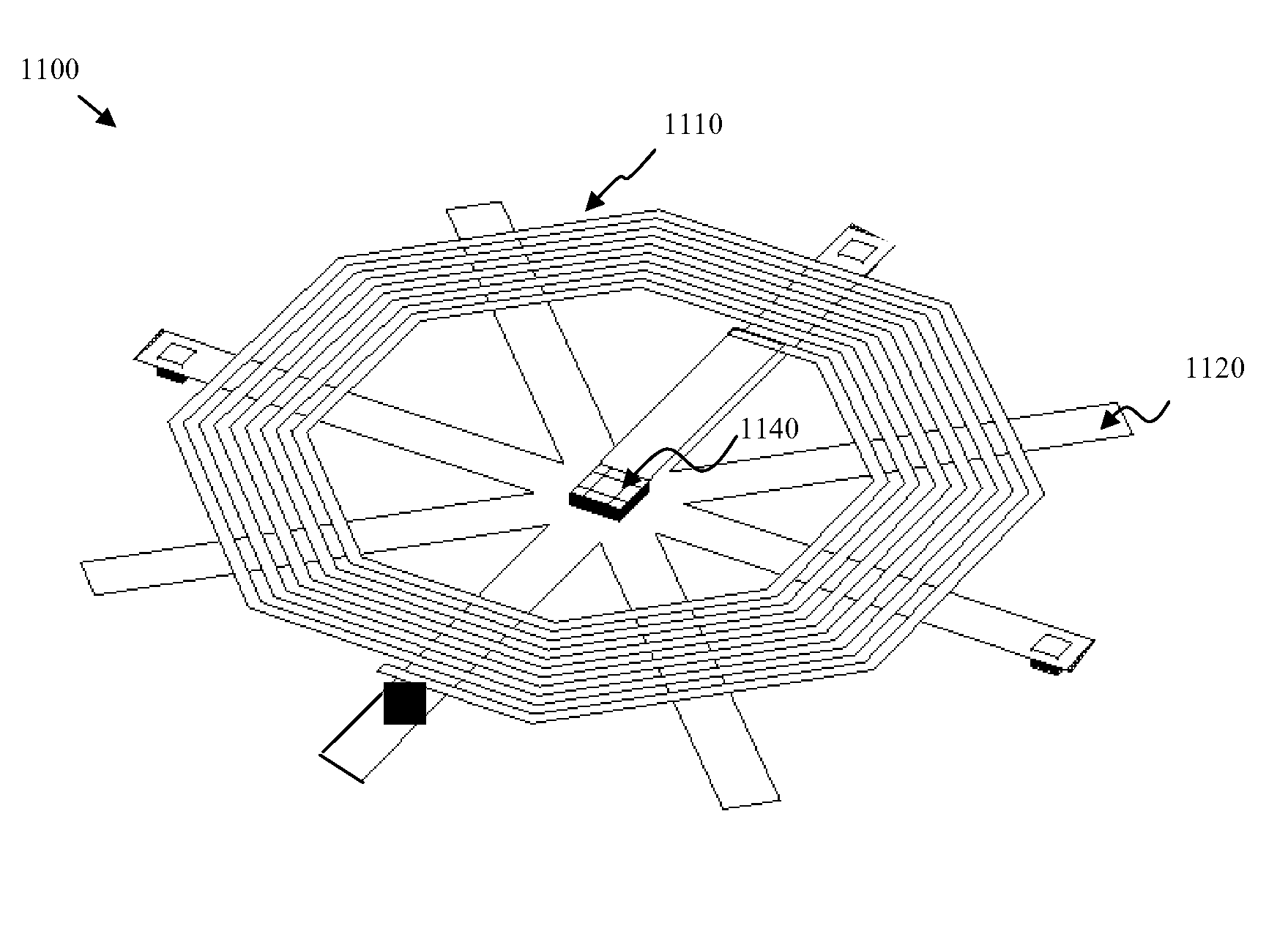
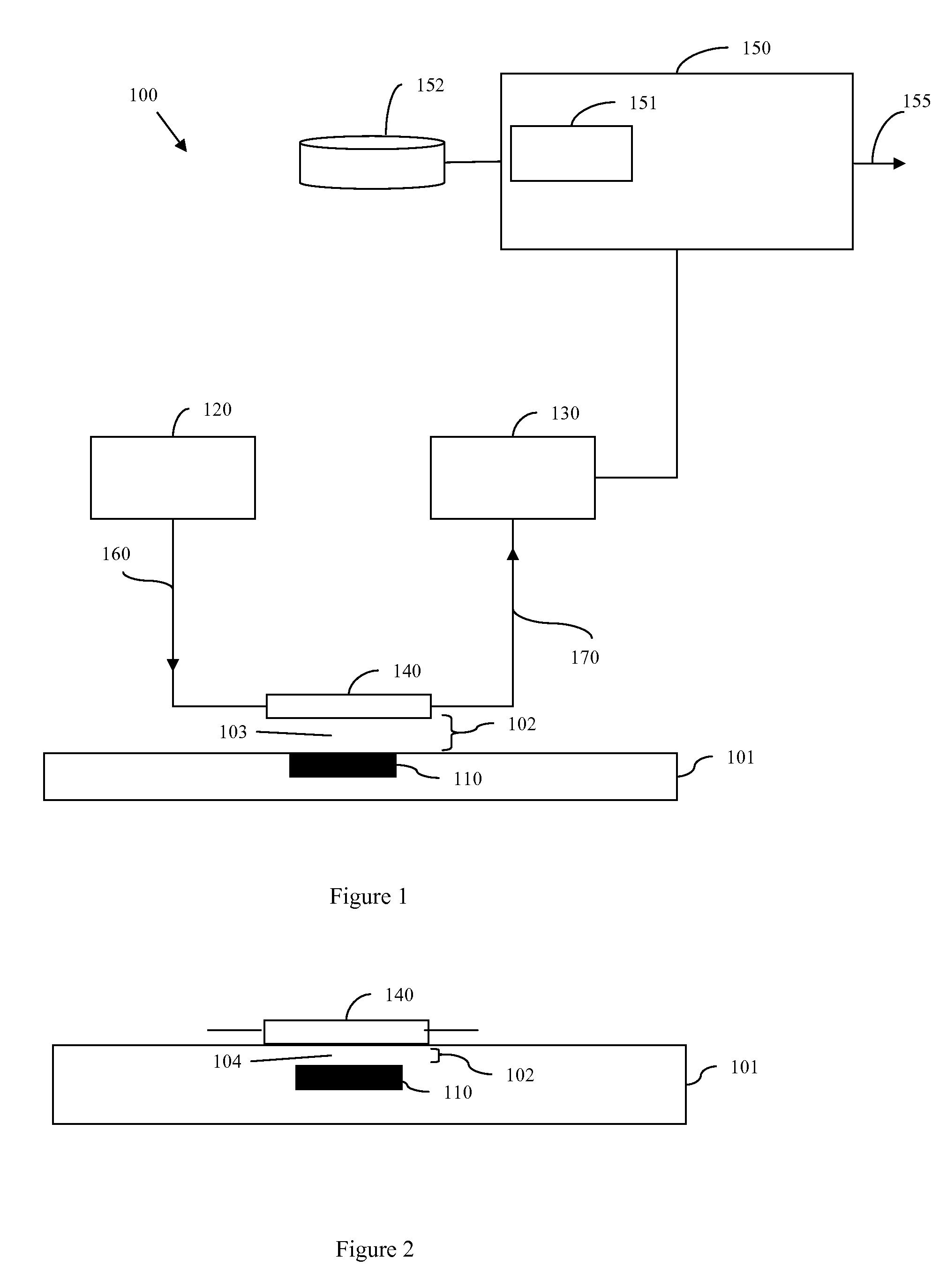
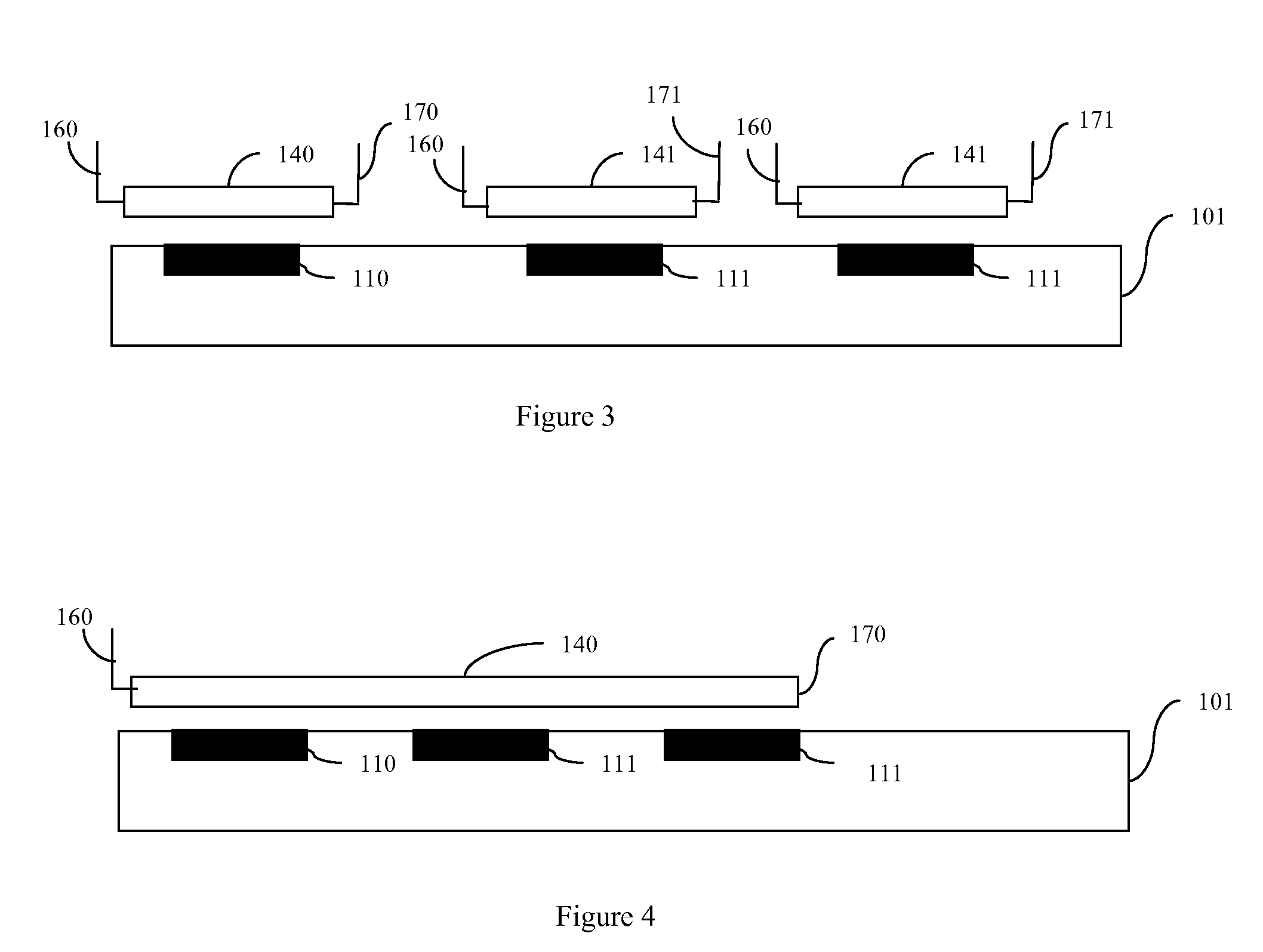
ActiveUS20090240452A1Accurately determinedSpectral/fourier analysisTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsInductorProcess measurement
Disclosed are embodiments of a system and a method that allow for wireless and dynamic intra-process (i.e., during and / or between process steps) measurements of integrated circuit parameters. The embodiments incorporate the use of a passive circuit, such as an inductor-capacitor-resistor (LCR) circuit resonator, that has a predetermined sensitivity to process variations in one or more physical or electrical integrated circuit parameters. The passive circuit can be wirelessly interrogated between and / or process steps. Then, the actual behavior exhibited by the passive circuit in response to the interrogation is compared to the expected behavior of an optimal circuit in the absence of process variations in order to determine the one or more parameters. Also disclosed is an embodiment of an exemplary passive circuit that can be used to implement the disclosed system and method embodiments.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
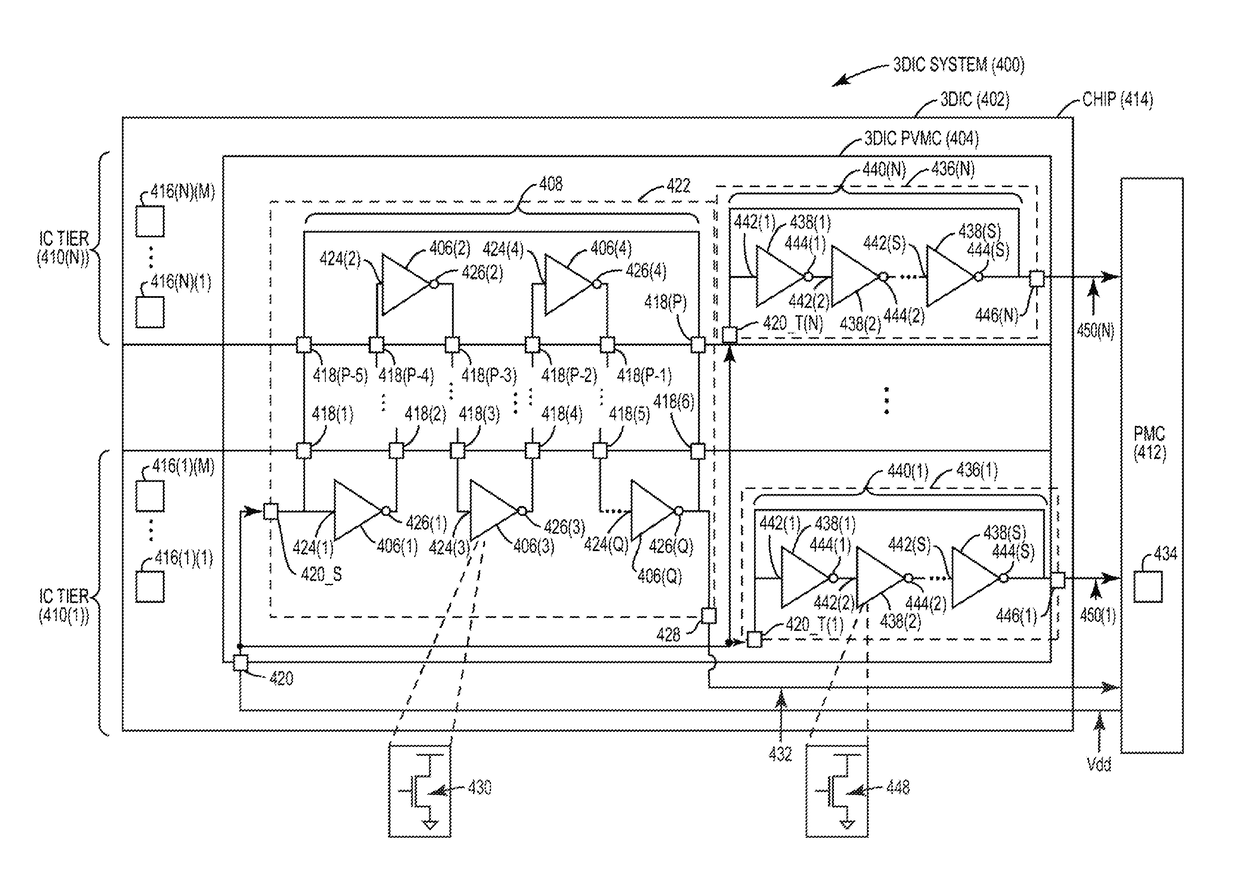
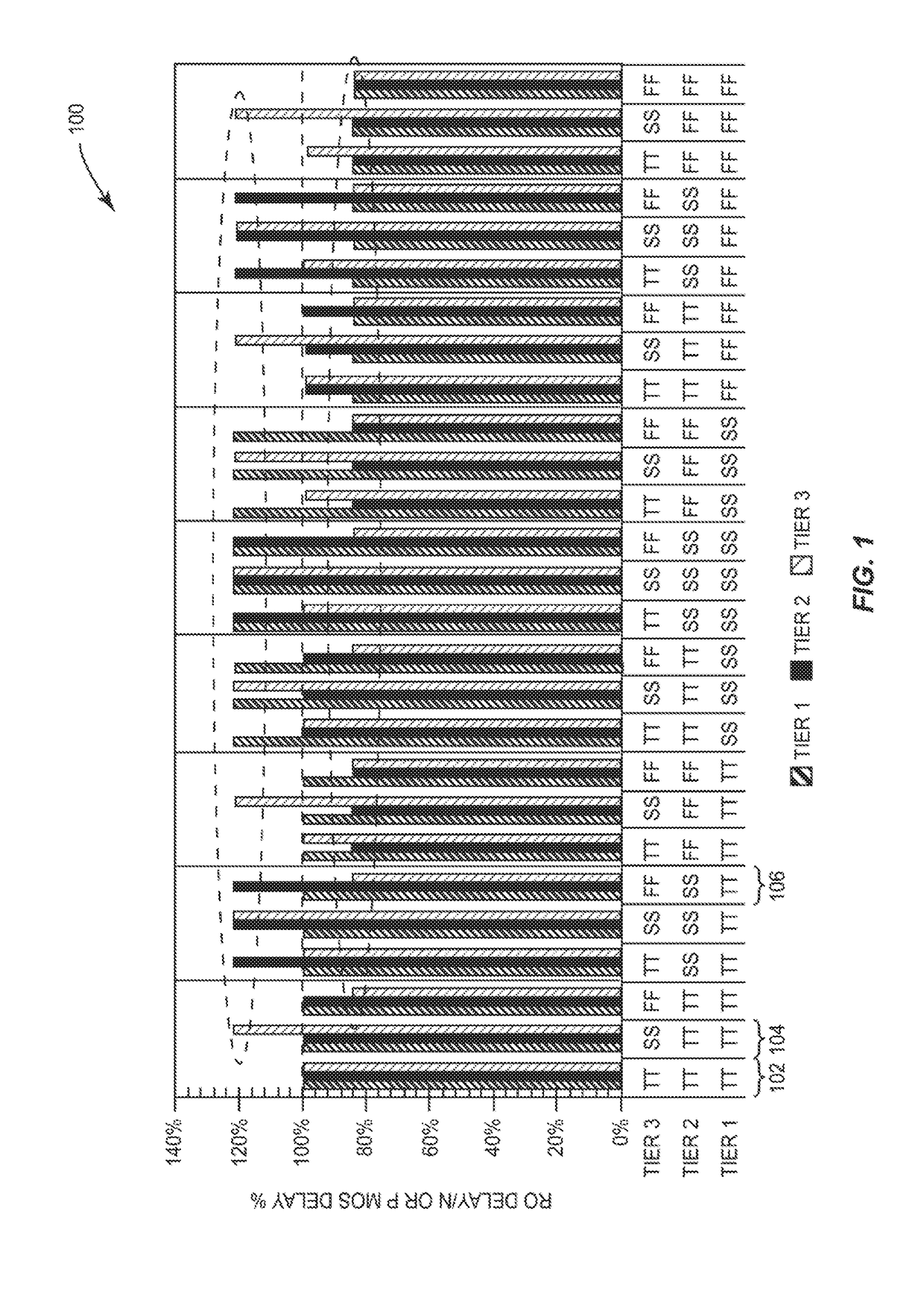
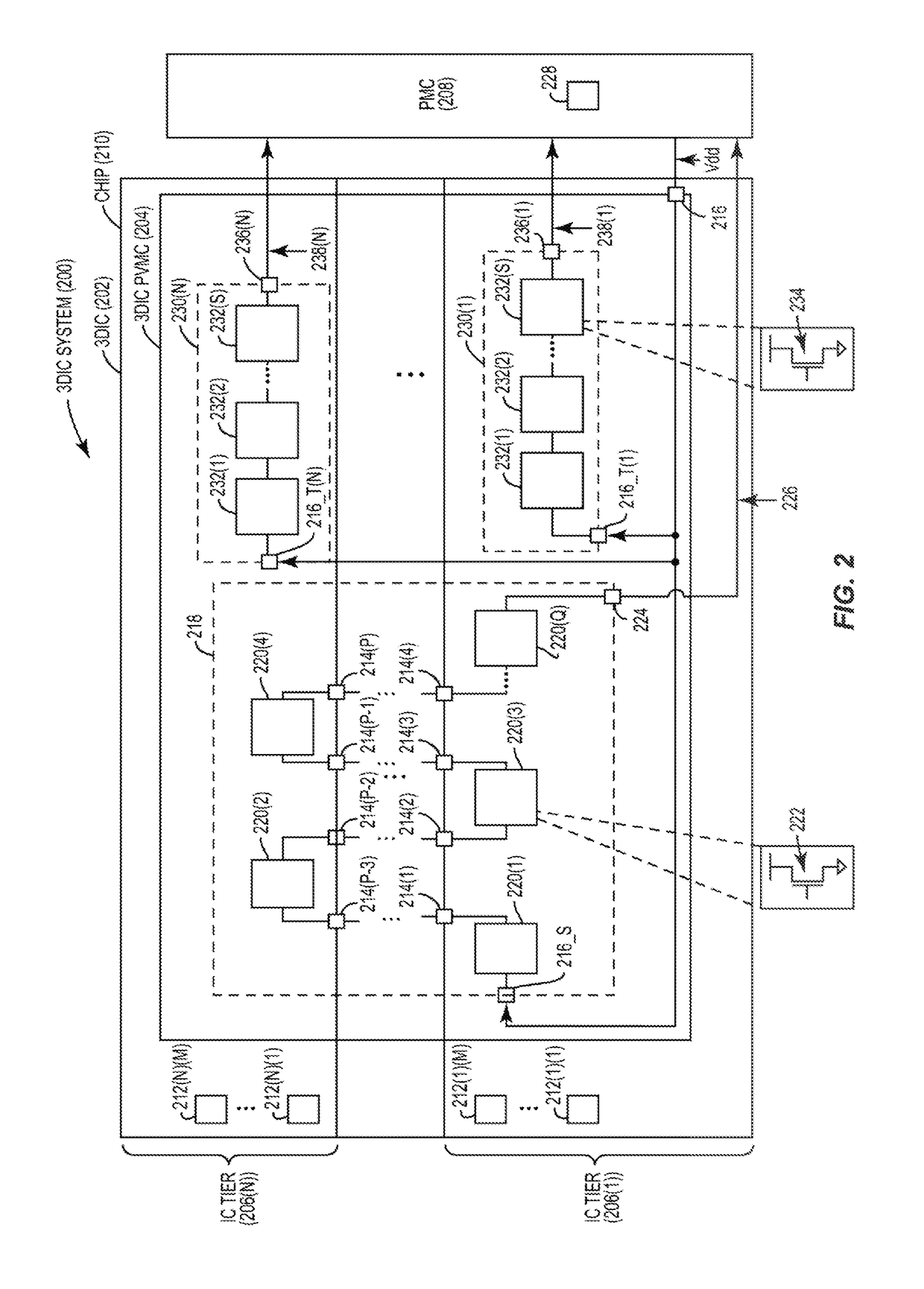
DYNAMICALLY CONTROLLING VOLTAGE PROVIDED TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL (3D) INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (ICs) (3DICs) TO ACCOUNT FOR PROCESS VARIATIONS MEASURED ACROSS INTERCONNECTED IC TIERS OF 3DICs
InactiveUS20180259581A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsProcess cornersHemt circuits
Dynamically controlling voltage provided to three-dimensional (3D) integrated circuits (ICs) (3DICs) to account for process variations measured across interconnected IC tiers of 3DICs are disclosed herein. In one aspect, a 3DIC process variation measurement circuit (PVMC) is provided to measure process variation. The 3DIC PVMC includes stacked logic PVMCs configured to measure process variations of devices across multiple IC tiers and process variations of vias that interconnect multiple IC tiers. The 3DIC PVMC may include IC tier logic PVMCs configured to measure process variations of devices on corresponding IC tiers. These measured process variations can be used to dynamically control supply voltage provided to the 3DIC such that operation of the 3DIC approaches a desired process corner. Adjusting supply voltage using the 3DIC PVMC takes into account interconnected properties of the 3DIC such that the supply voltage is adjusted to cause the 3DIC to operate in the desired process corner.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
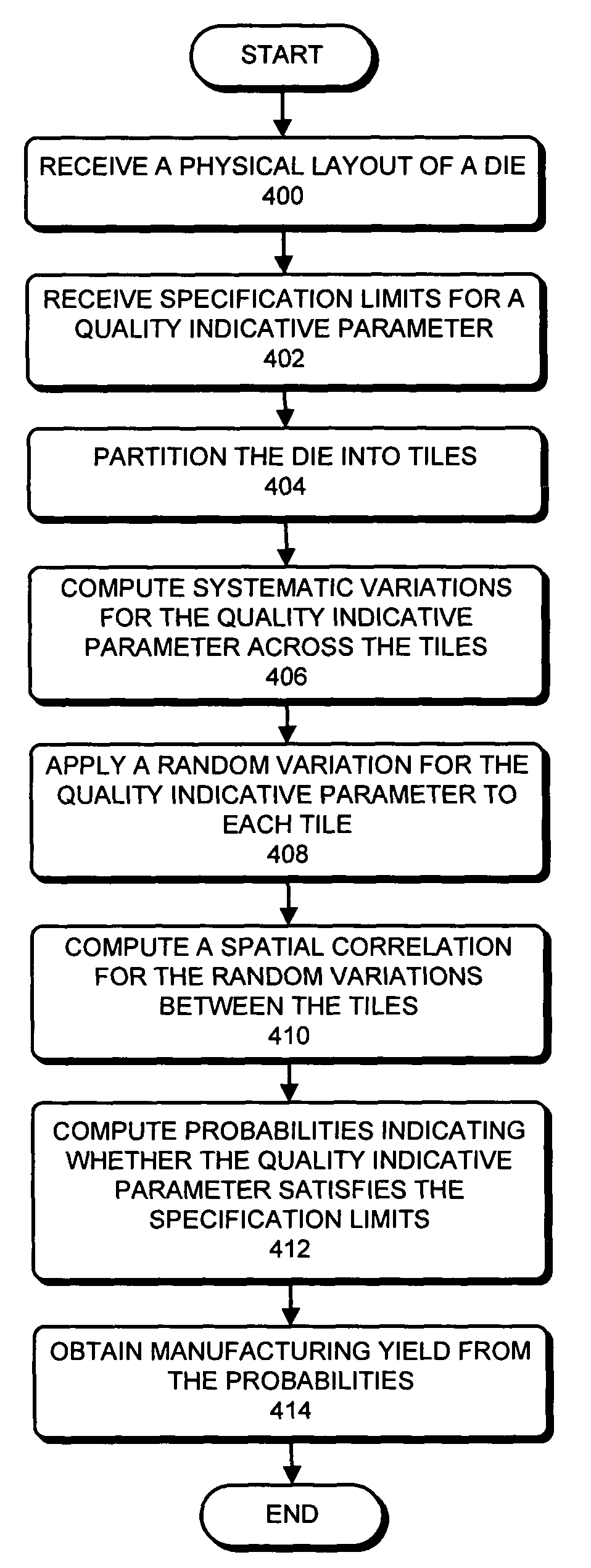
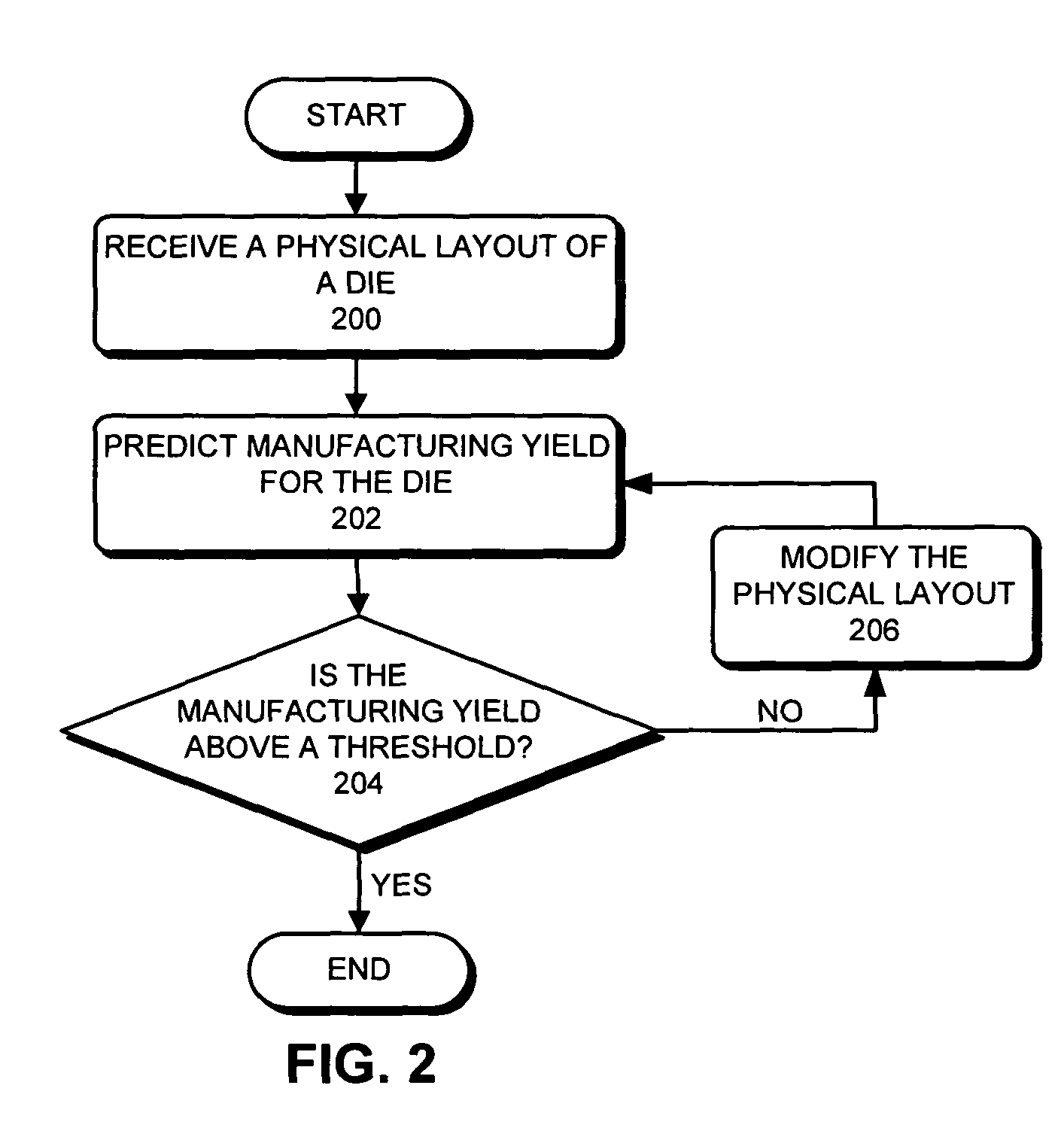
Predicting IC manufacturing yield by considering both systematic and random intra-die process variations
ActiveUS8000826B2Reduce complexityProgramme controlError detection/correctionSystematic variationDying processes
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that predicts manufacturing yield for a die within a semiconductor wafer. During operation, the system first receives a physical layout of the die. Next, the system partitions the die into an array of tiles. The system then computes systematic variations for a quality indicative value to describe a process parameter across the array of tiles based on the physical layout of the die. Next, the system applies a random variation for the quality indicative parameter to each tile in the array of tiles. Finally, the system obtains the manufacturing yield for the die based on both the systematic variations and the random variations.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
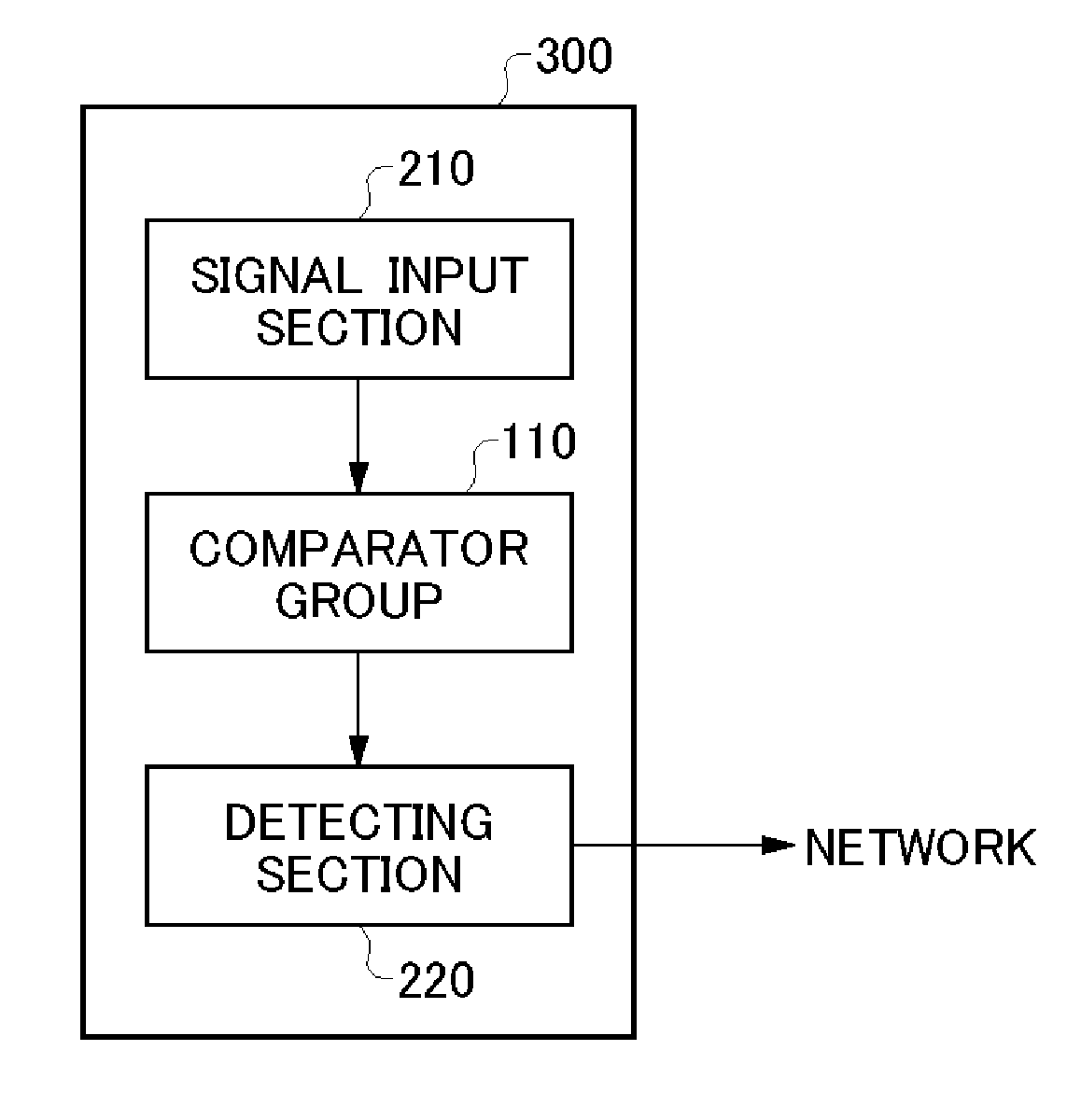
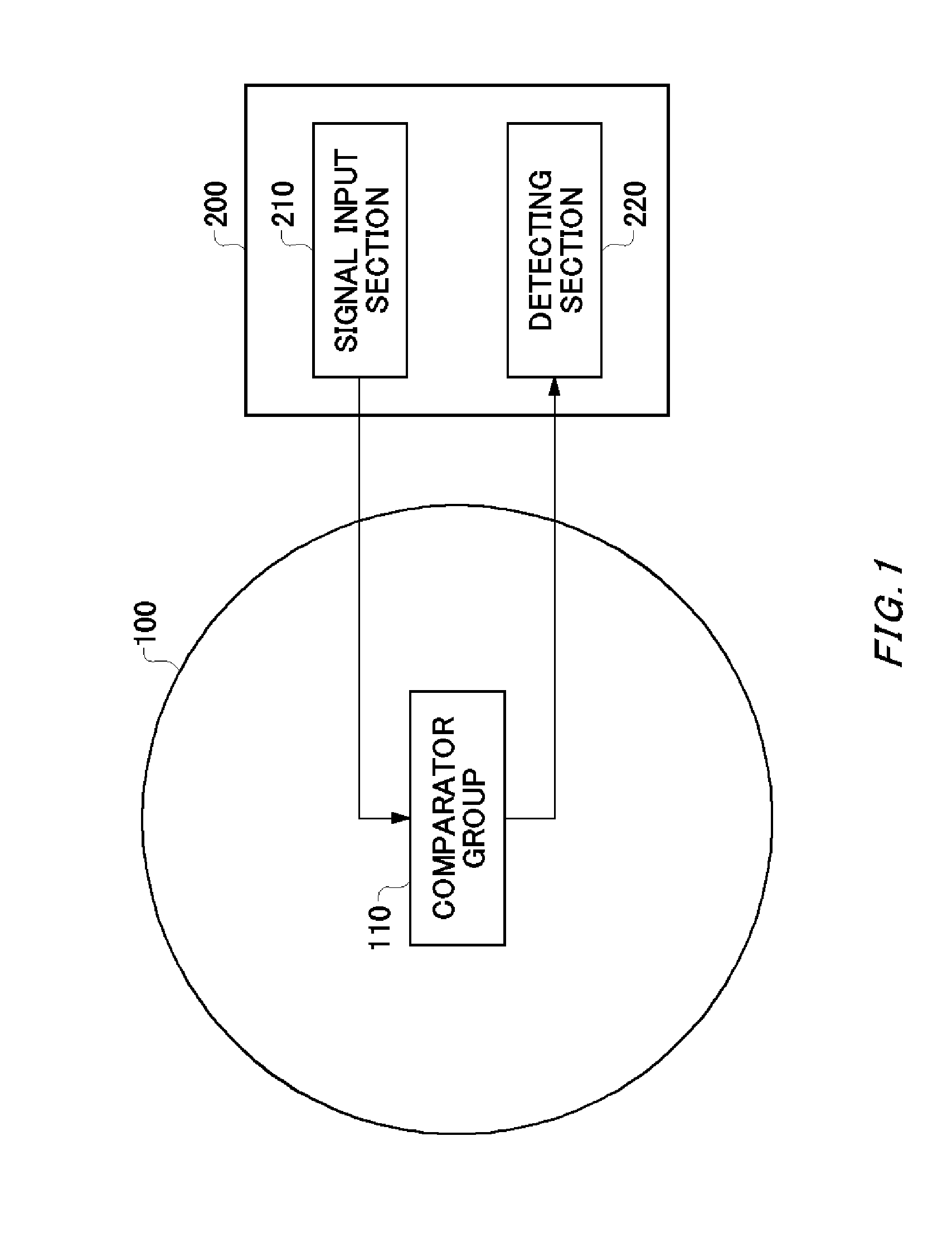
Detecting apparatus, wafer and electronic device
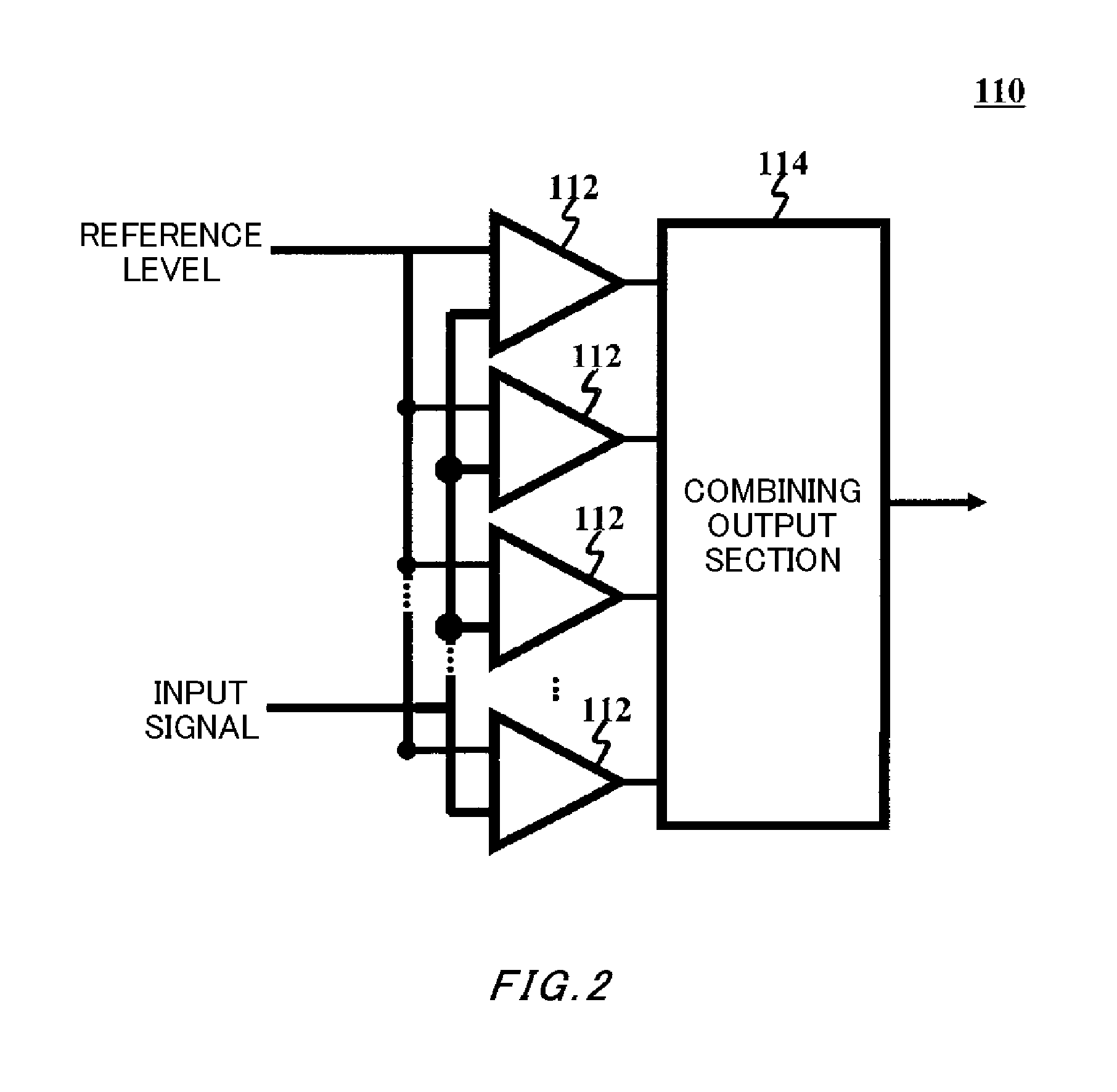
ActiveUS20140197846A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingEngineeringComparator
Provided is a detection apparatus that detects process variation in a plurality of comparators that each output a comparison result obtained by comparing a signal level of an input signal to a reference level, the detection apparatus comprising a signal input section that inputs the input signal and the reference level in common to the comparators, and sequentially changes the signal level of the input signal; and a detecting section that detects, for each signal level, a number of comparison results that indicate a predetermined result, from among the comparison results of the comparators, and detects the process variation based on a distribution of the number of comparison results that indicate the predetermined result.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
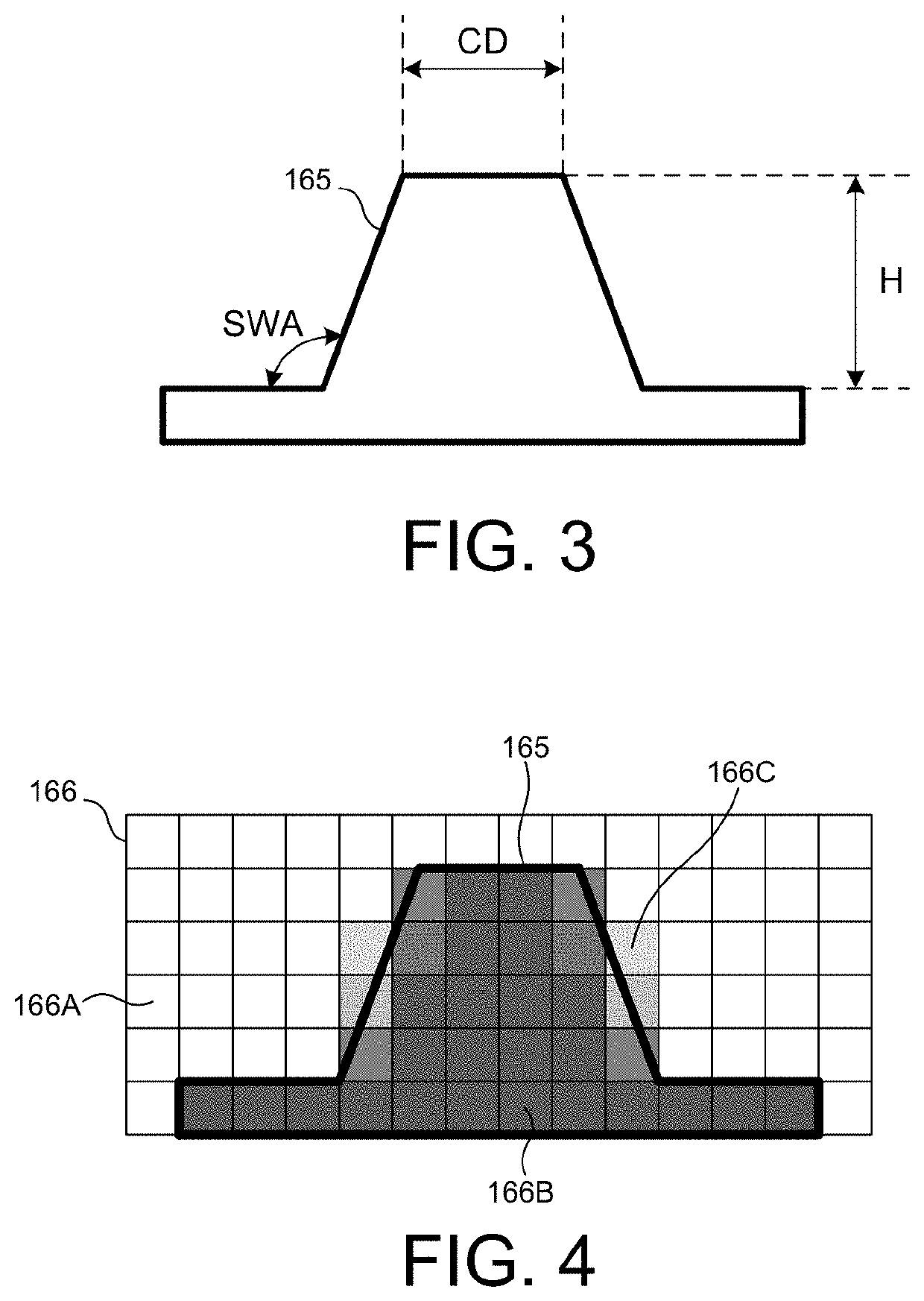
Removing process-variation-related inaccuracies from scatterometry measurements
ActiveUS9874527B2Scattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMeasurement variabilityEngineering
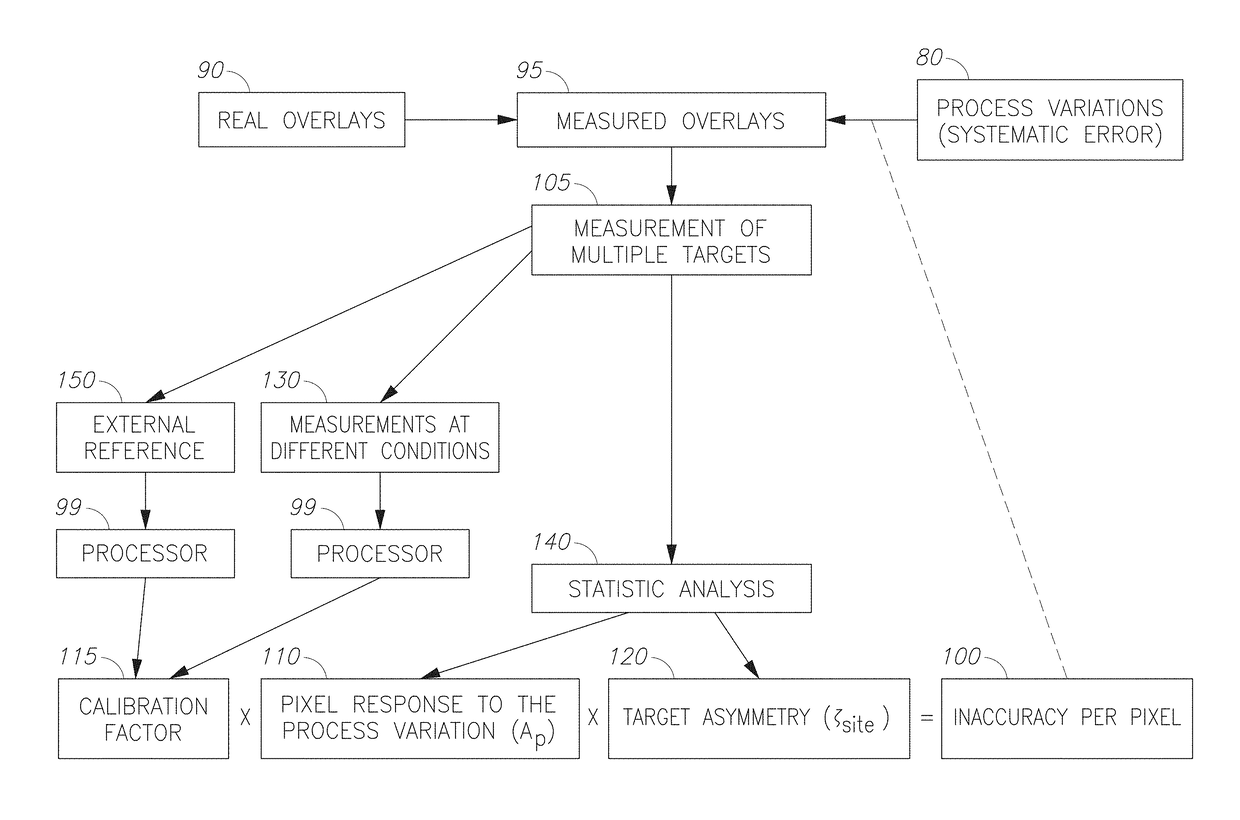
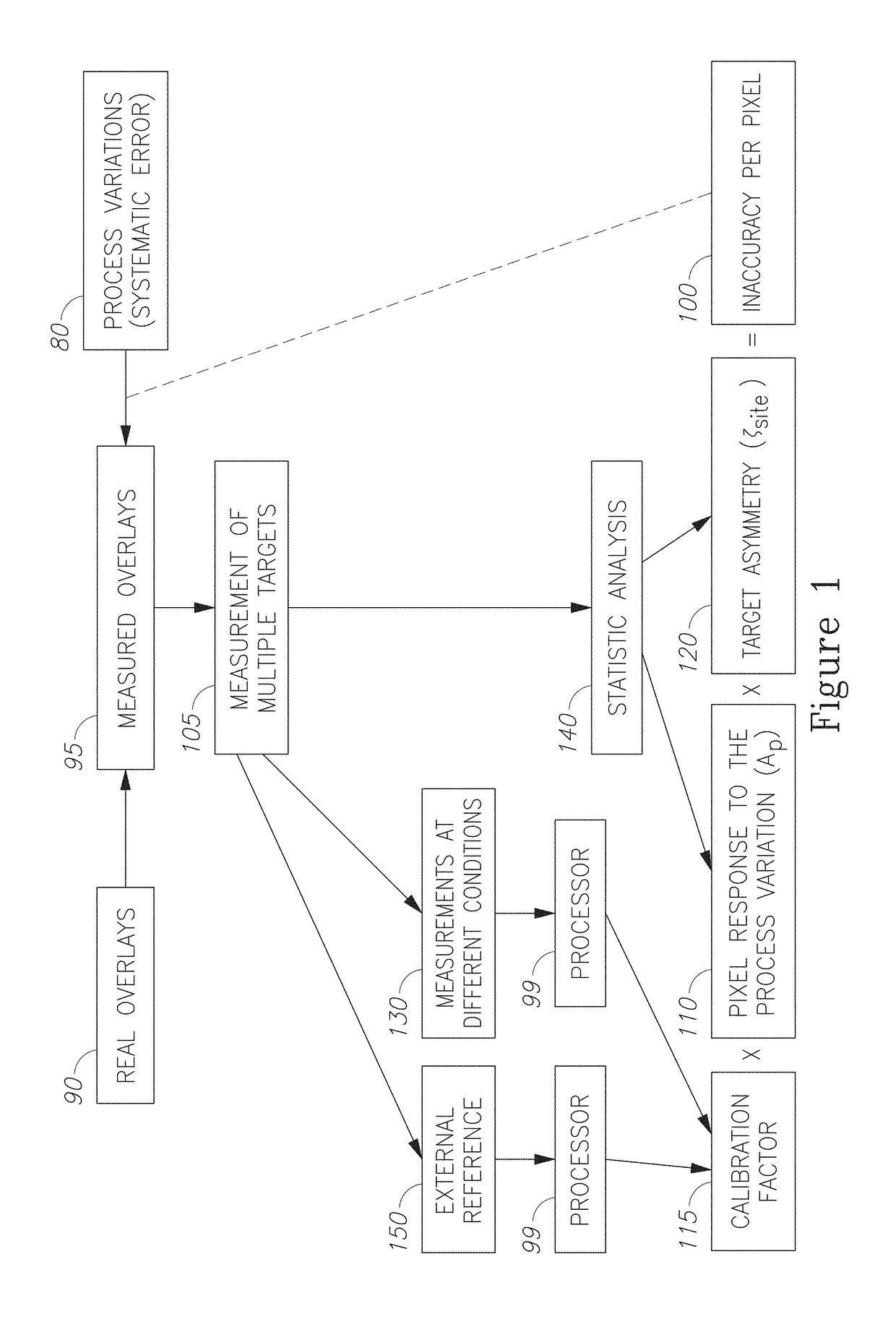
Metrology methods and respective software and module are provided, which identify and remove measurement inaccuracy which results from process variation leading to target asymmetries. The methods comprise identifying an inaccuracy contribution of process variation source(s) to a measured scatterometry signal (e.g., overlay) by measuring the signal across a range of measurement parameter(s) (e.g., wavelength, angle) and targets, and extracting a measurement variability over the range which is indicative of the inaccuracy contribution. The method may further assume certain functional dependencies of the resulting inaccuracy on the target asymmetry, estimate relative donations of different process variation sources and apply external calibration to further enhance the measurement accuracy.
Owner:KLA CORP
Tomography Based Semiconductor Measurements Using Simplified Models
ActiveUS20210166375A1Less computational effortData acquisition is reducedImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionReduced modelVoxel
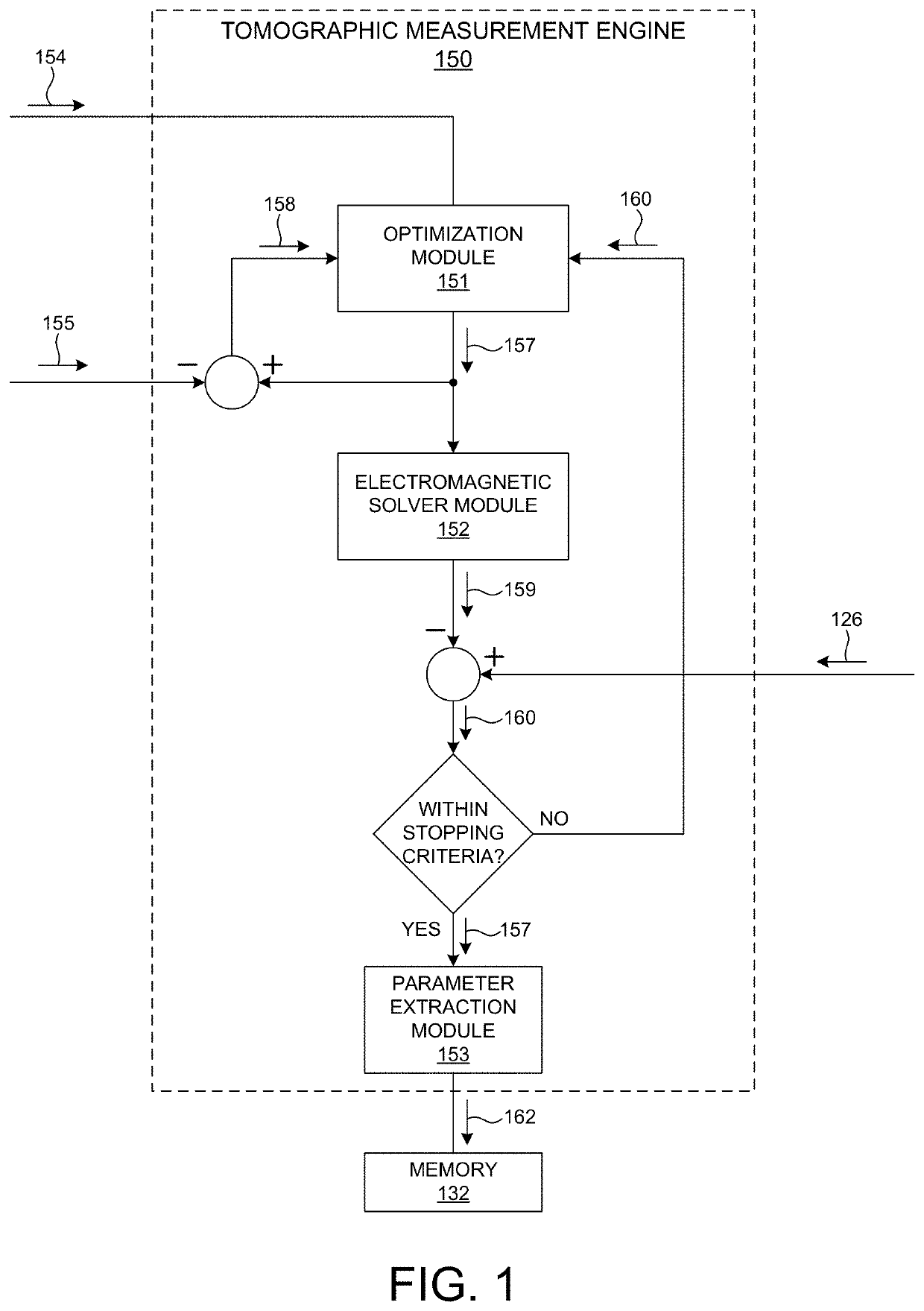
Methods and systems for improved regularization associated with tomographically resolved image based measurements of semiconductor structures are presented herein. The regularizations described herein are based on measurement data and parameterization of a constrained voxel model that captures known process variations. The constrained voxel model is determined based on simplified geometric models, process models, or both, characterizing the structure under measurement. A constrained voxel model has dramatically fewer degrees of freedom compared to an unconstrained voxel model. The value associated with each voxel of the constrained voxel model depends on a relatively small number of independent variables. Selection of the independent variables is informed by knowledge of the structure and the underlying fabrication process. Regularization based on a constrained voxel model enables faster convergence and a more accurate reconstruction of the measured structure with less computational effort. This enables semiconductor measurements with reduced data acquisition requirements, and reduced measurement time.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
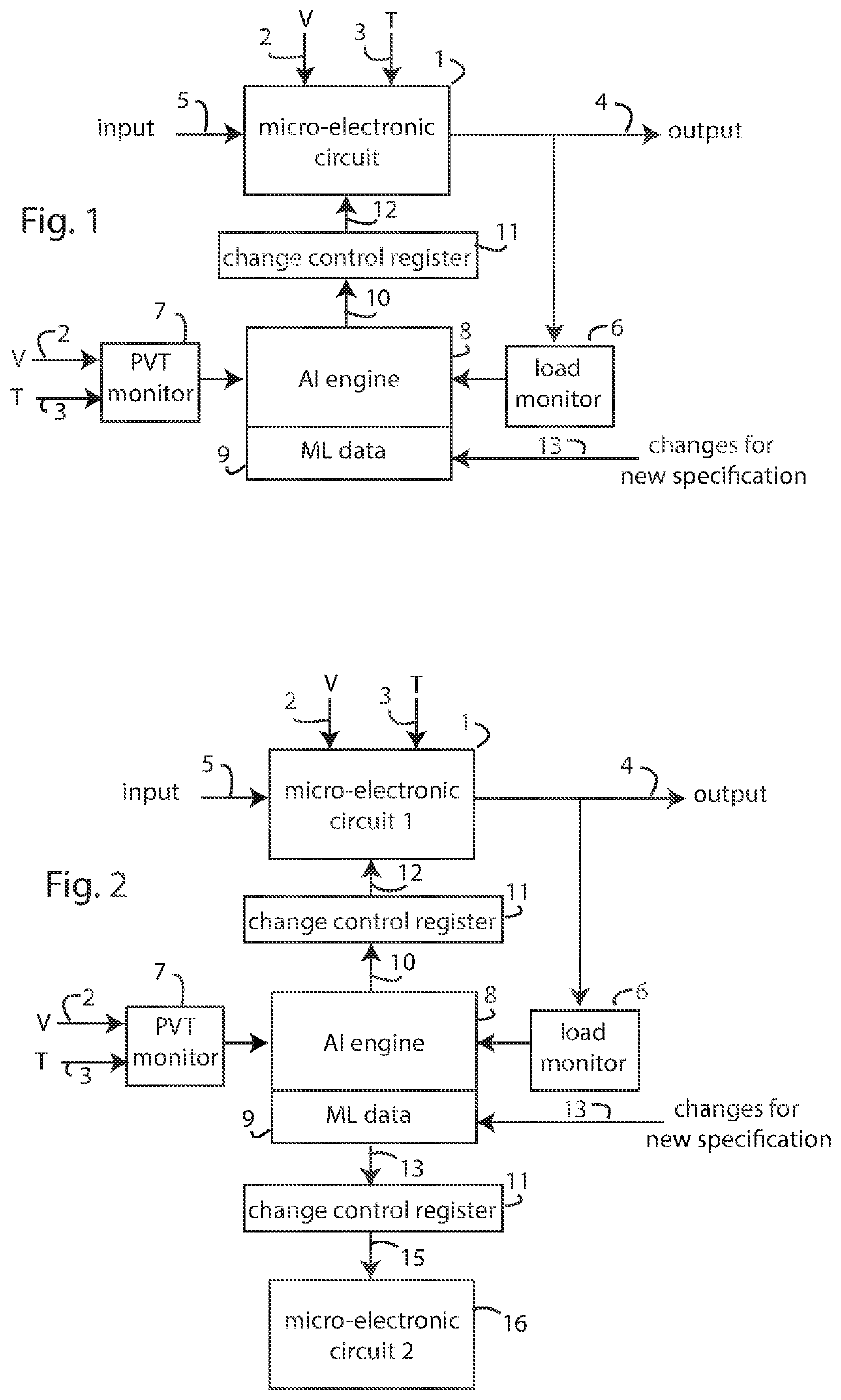
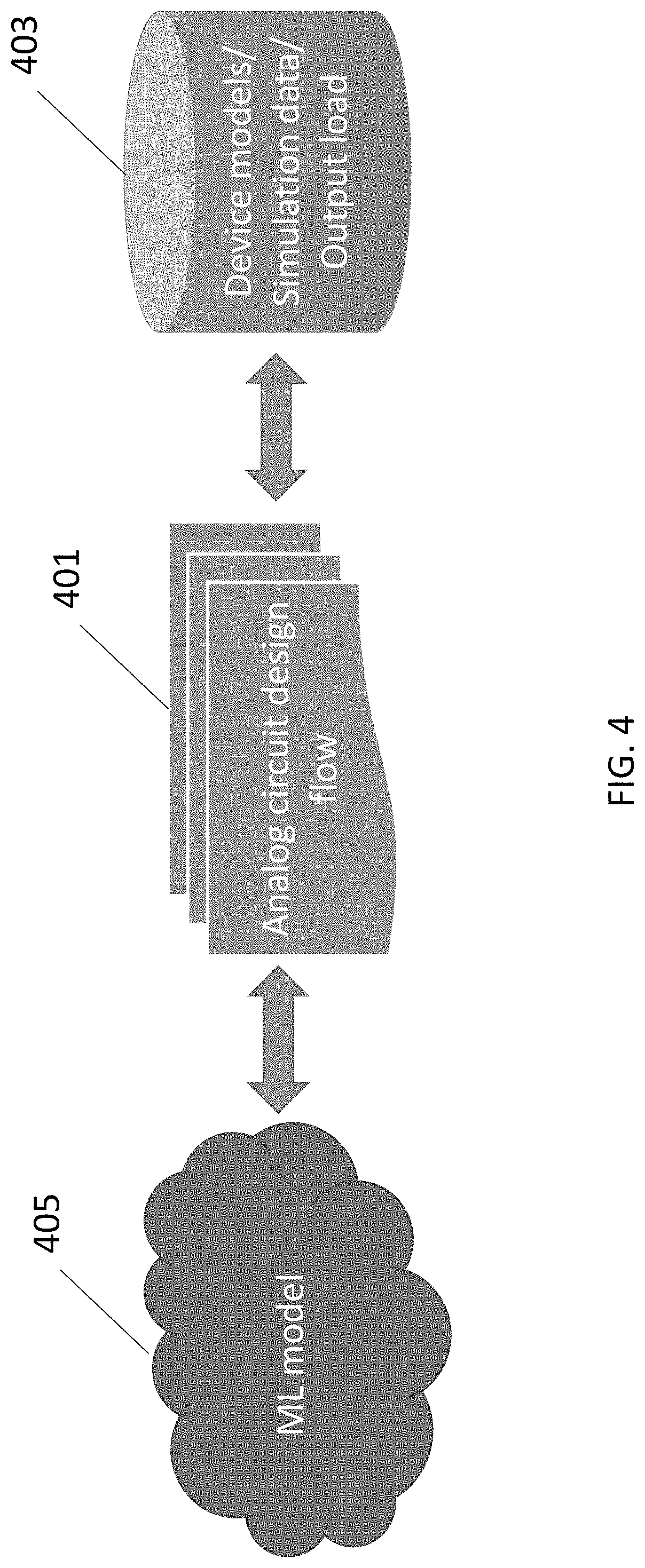
AI-driven self adapting microelectronic circuits
ActiveUS11416664B2Amortize overall impactReduce power consumptionPhysical realisationComputer aided designHemt circuitsNetwork model
The present description relates to a method based on artificial intelligence to implement a wide range of microelectronic circuits that can adapt by themselves to the usage conditions (e.g. loading changes), manufacturing variances or defects (e.g. process variations, device parameter mismatches, device model inaccuracies or changes, etc.), as well as environmental conditions (e.g. voltage, temperature, interference) in order to negate all or part of their effects on the circuit performance characteristics and achieve a very tight set of specifications over the wide range of conditions. Each microelectronic circuit is represented by a neural network model whose behavior is a function of the actual input signals, the usage and environmental conditions. An attached AI engine will infer from the model, the input signals, the usage conditions and the environmental conditions and create the adaptive changes required to modify the microelectronic circuit's behavior to negate all or part of their effects on the circuit performance characteristics and to achieve a very tight set of specifications.
Owner:ANALOG INTELLIGENT DESIGN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com