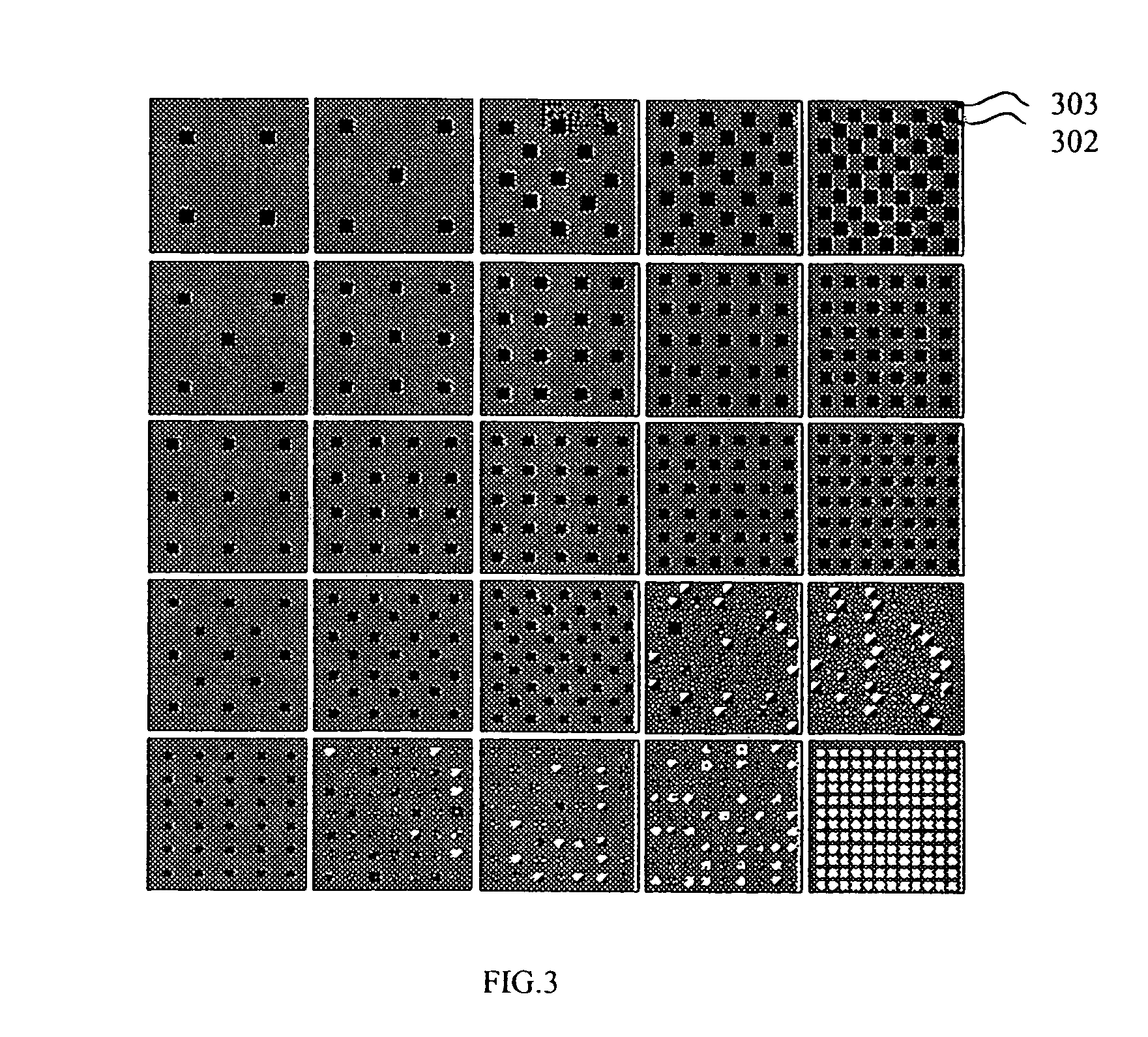
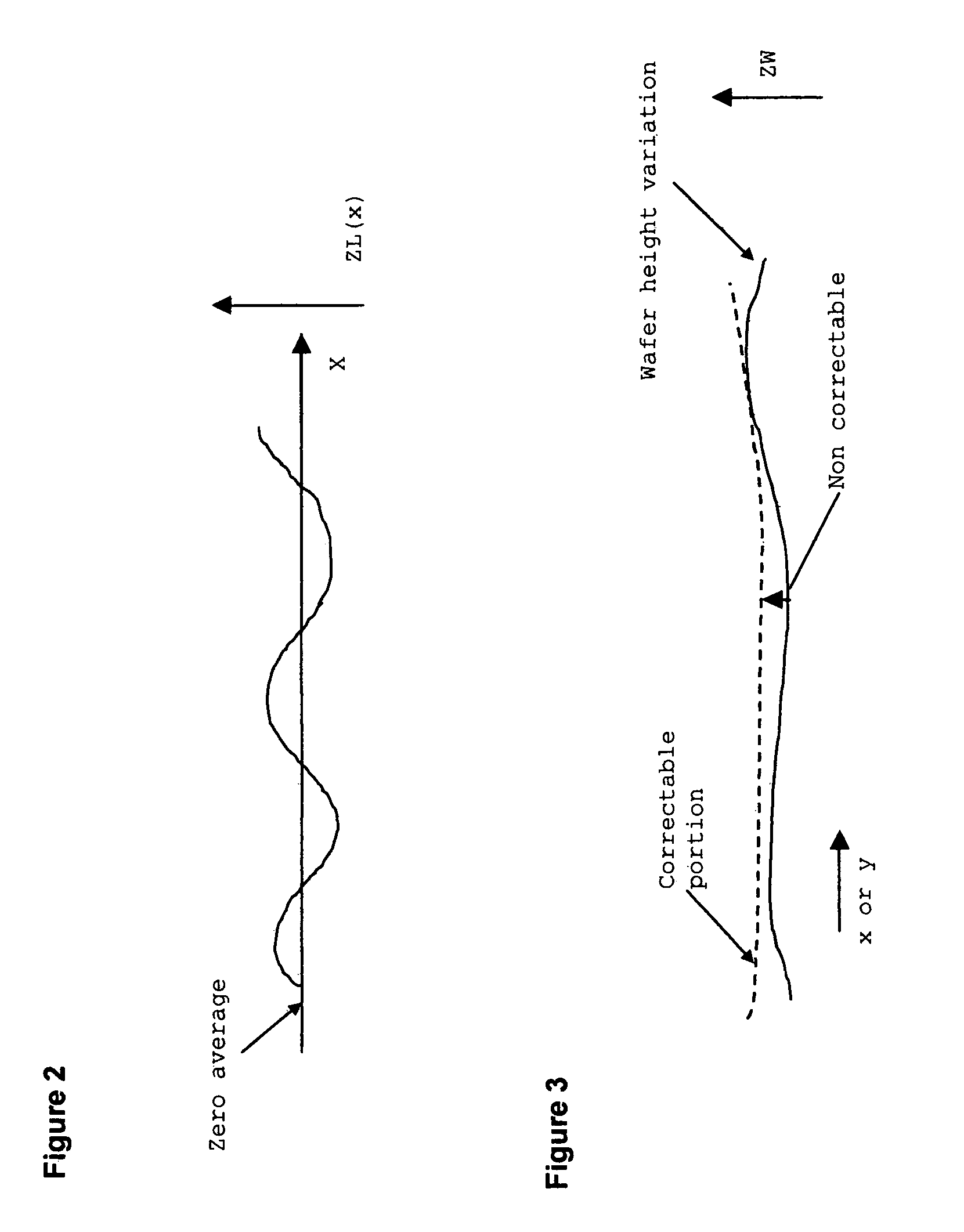
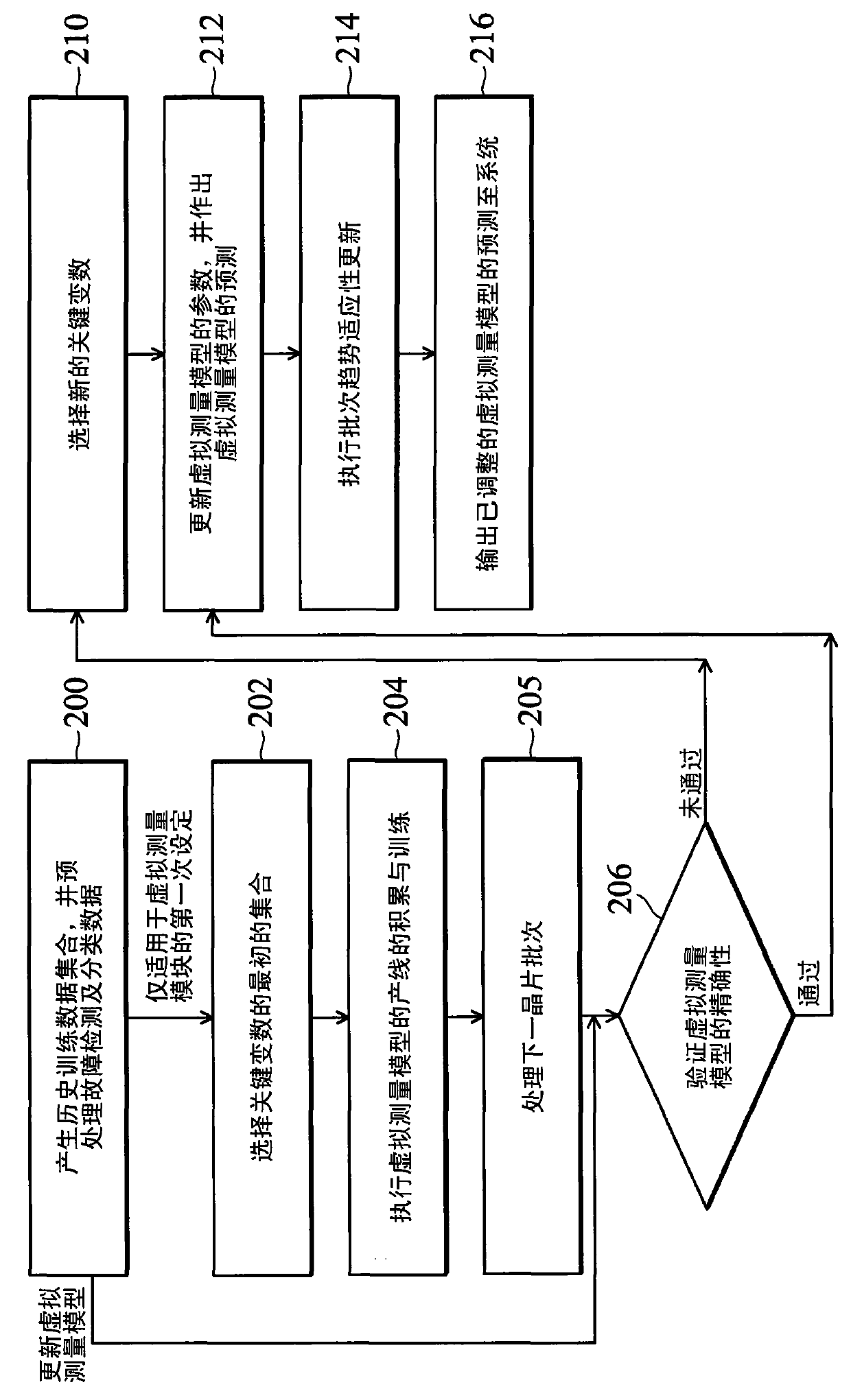
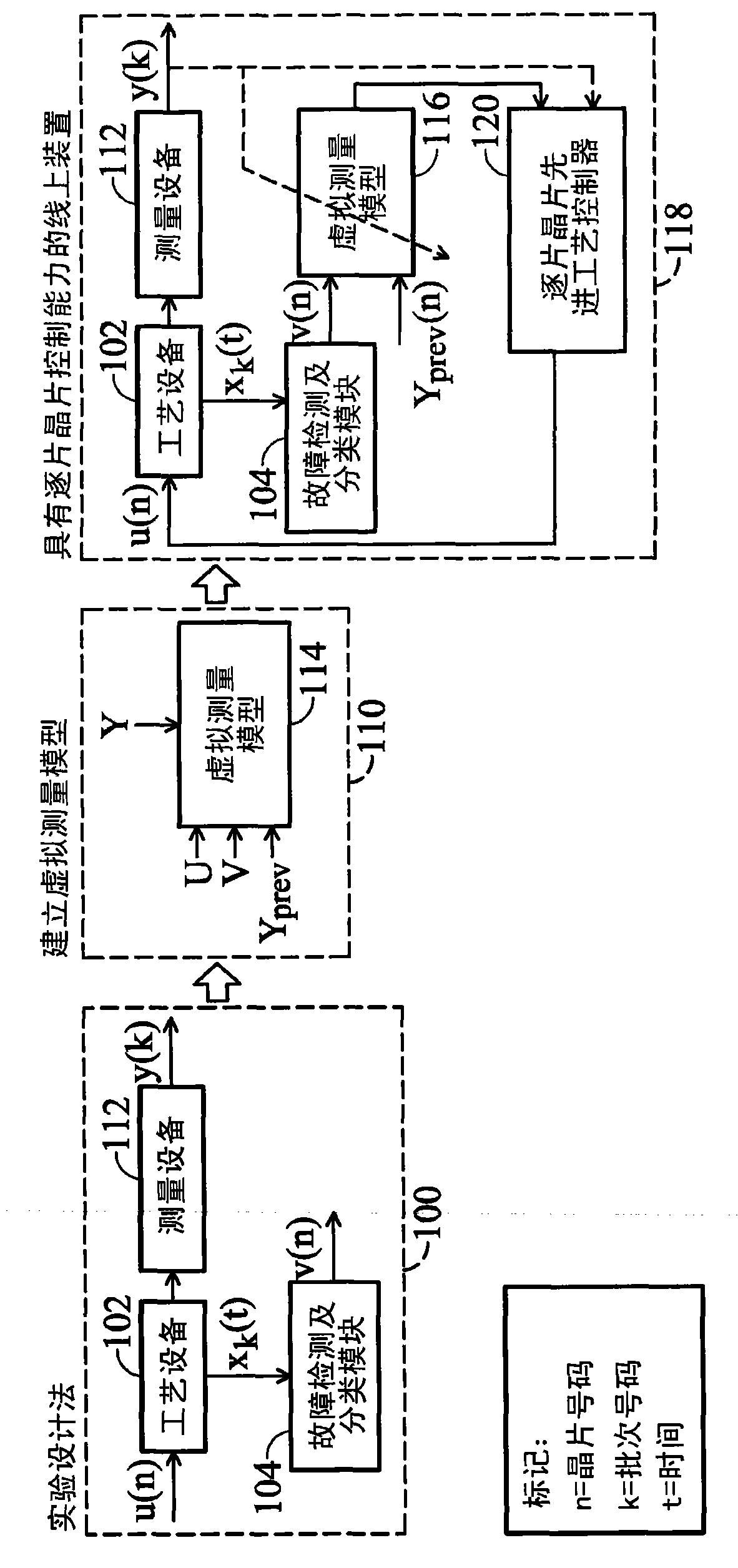
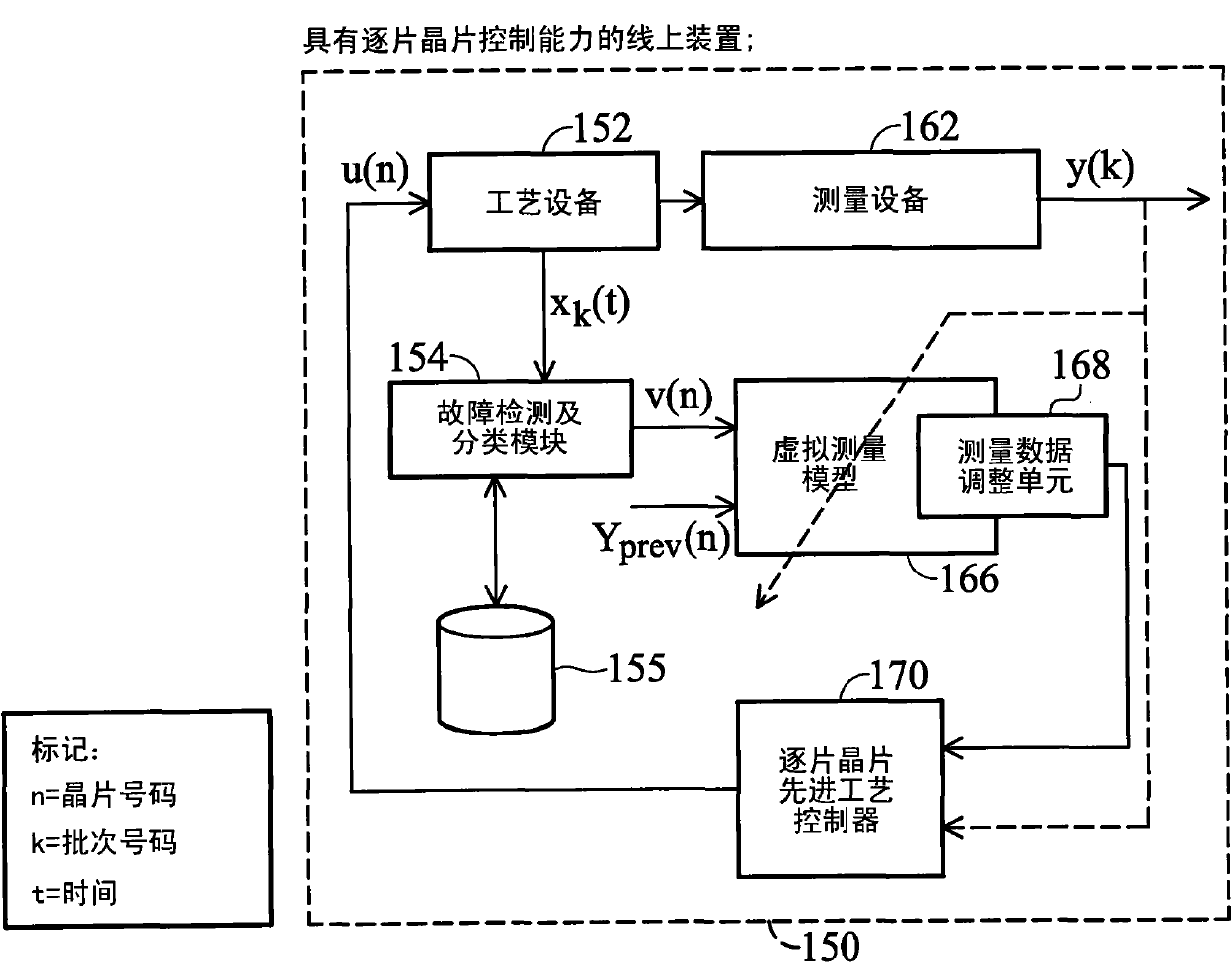
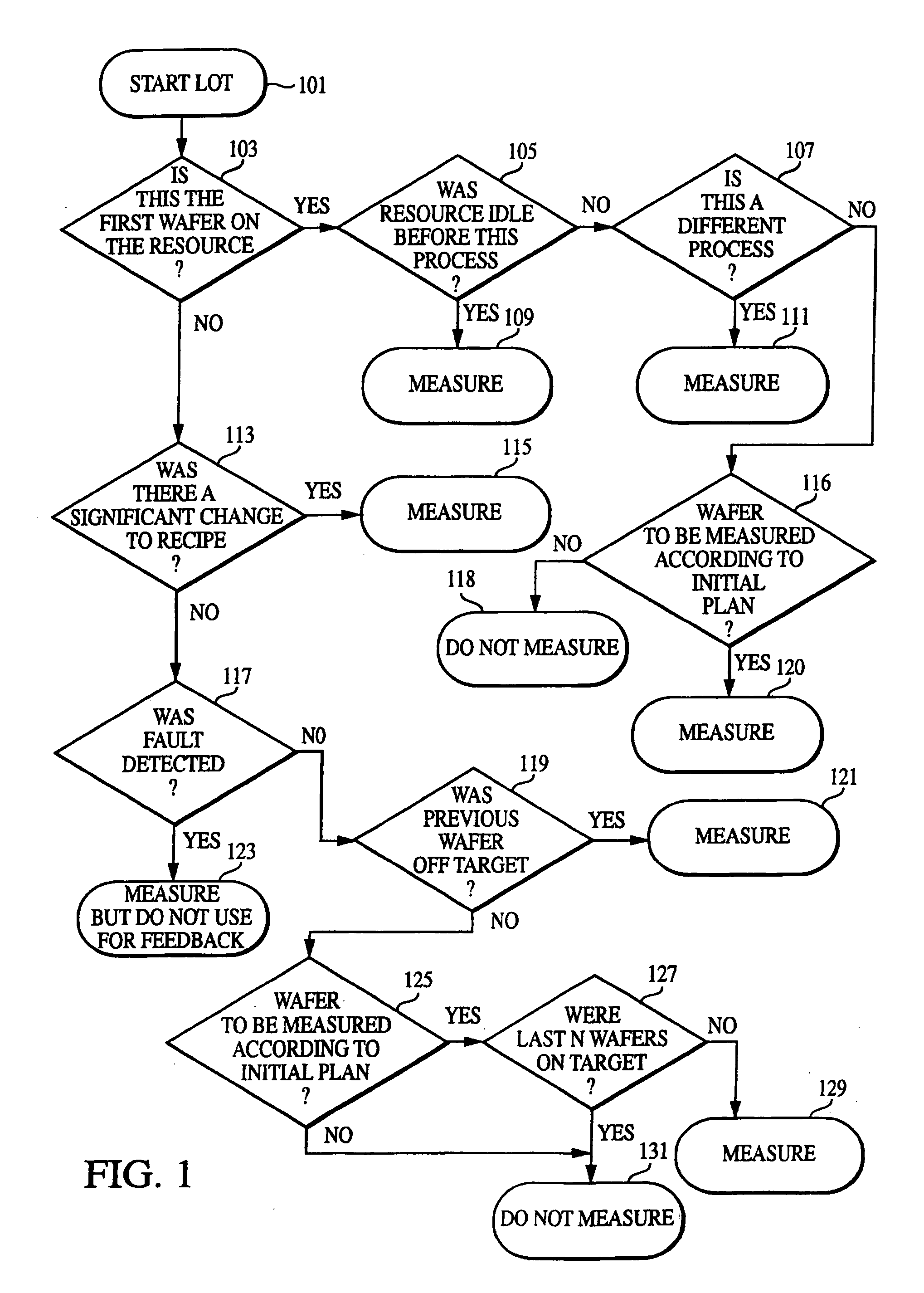
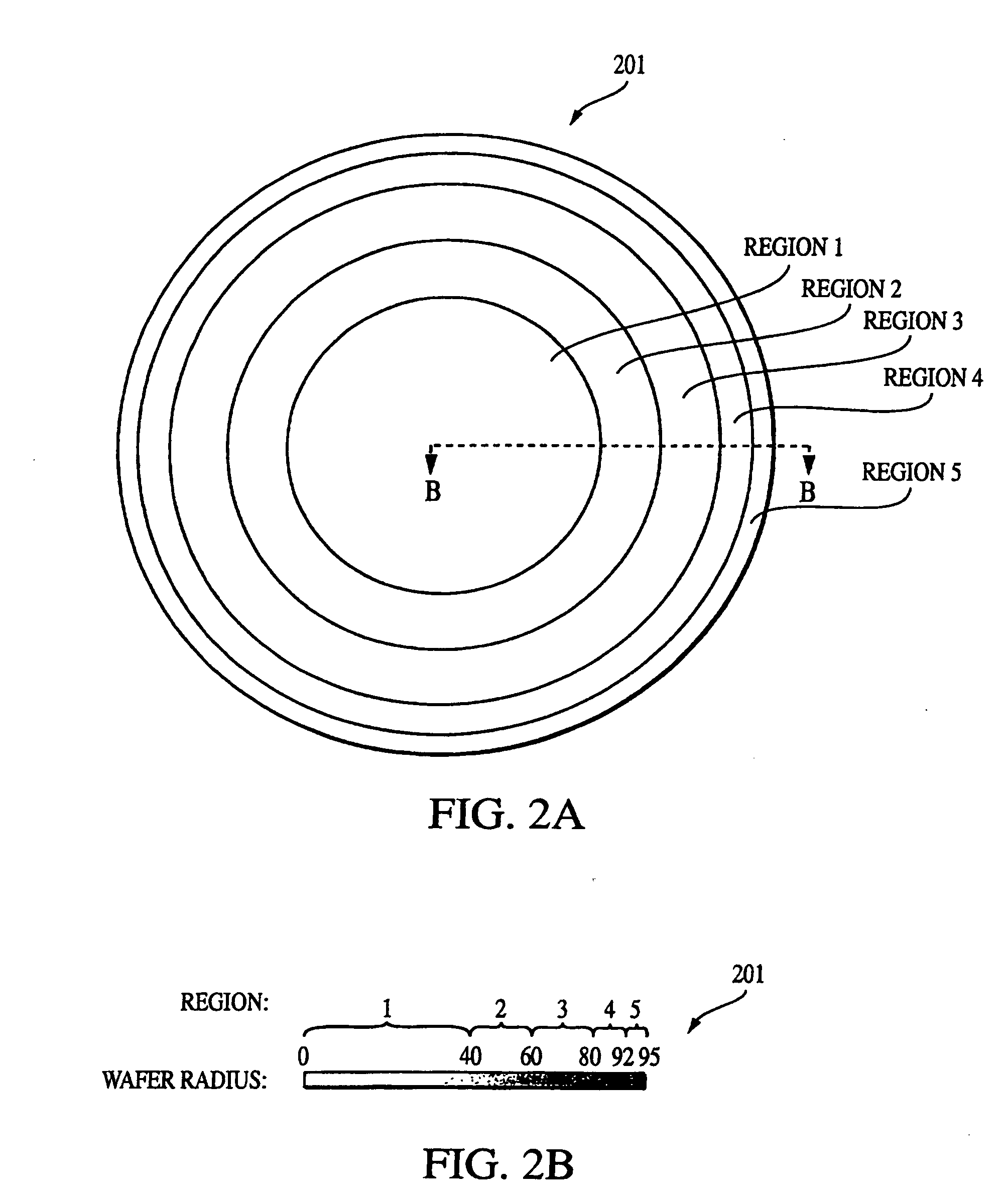
Patents
Literature
174 results about "Advanced process control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
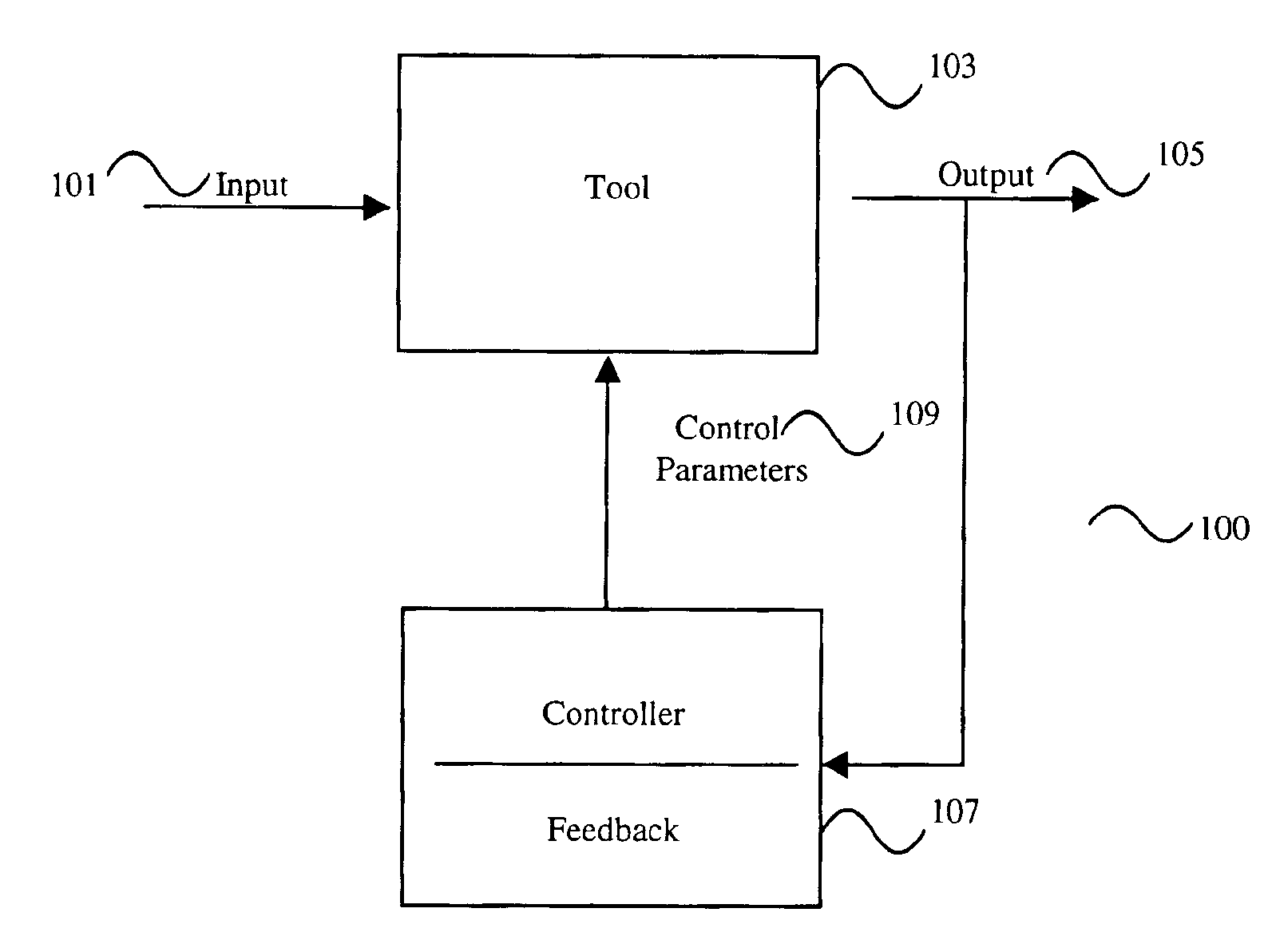
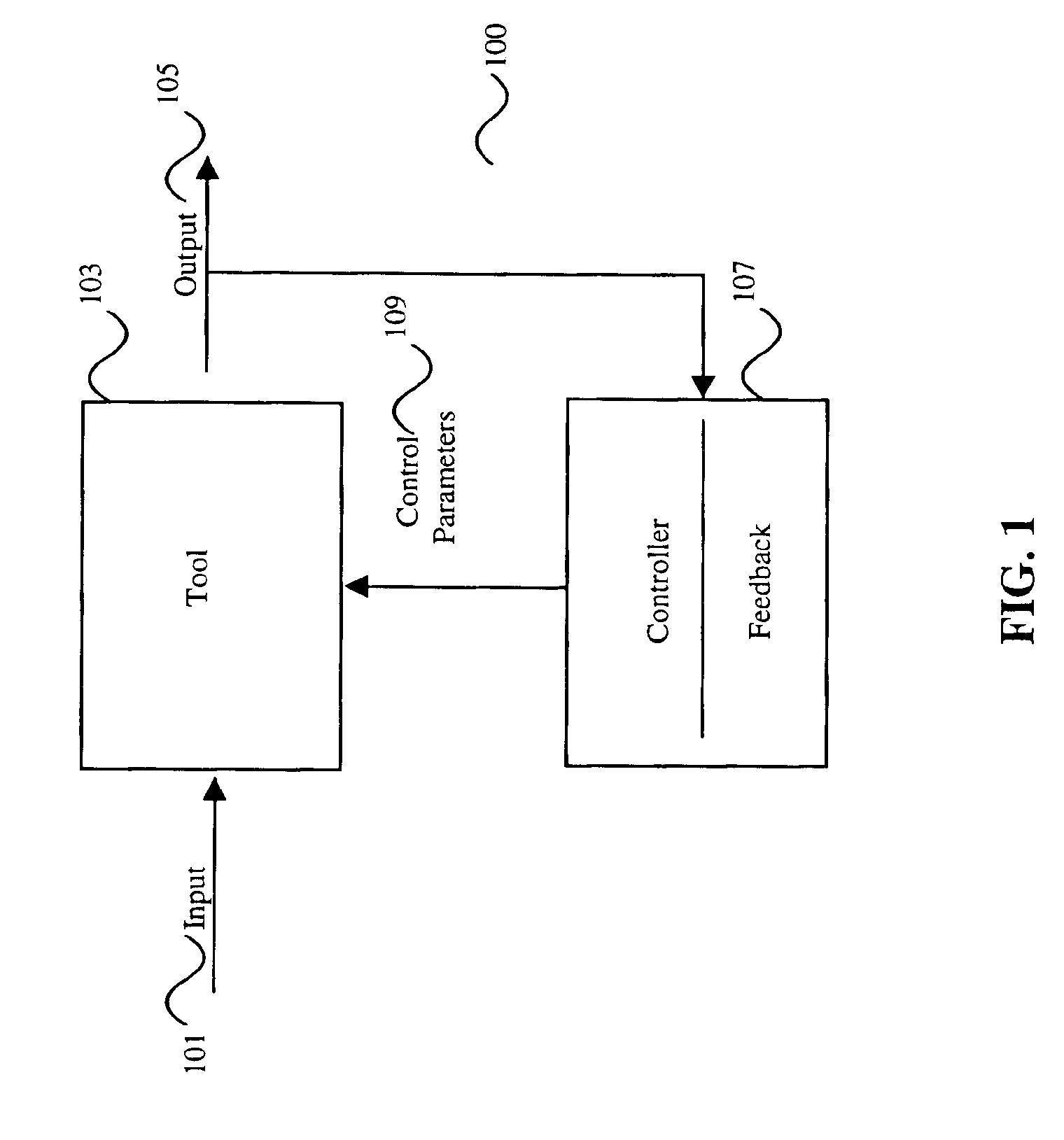
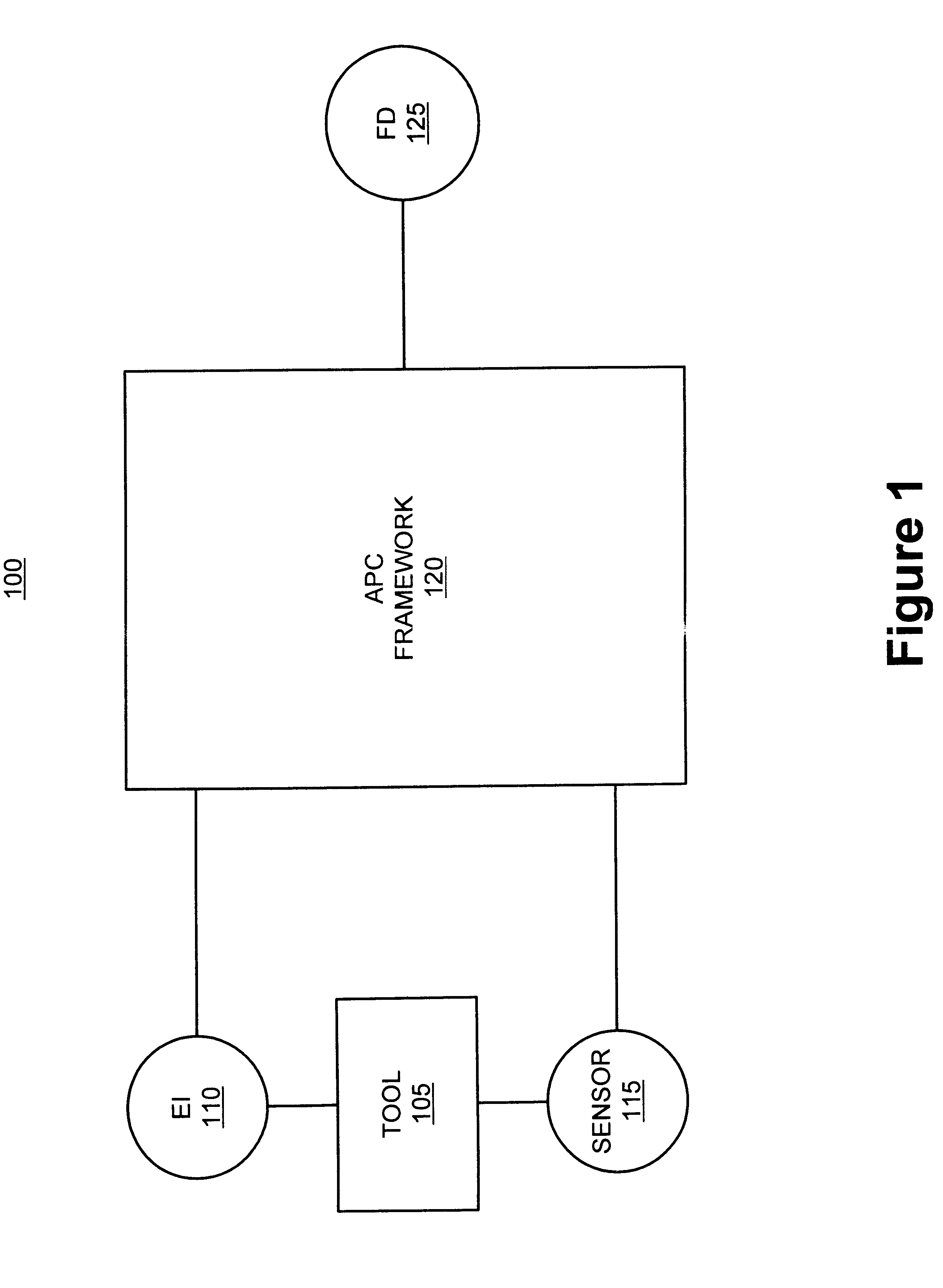
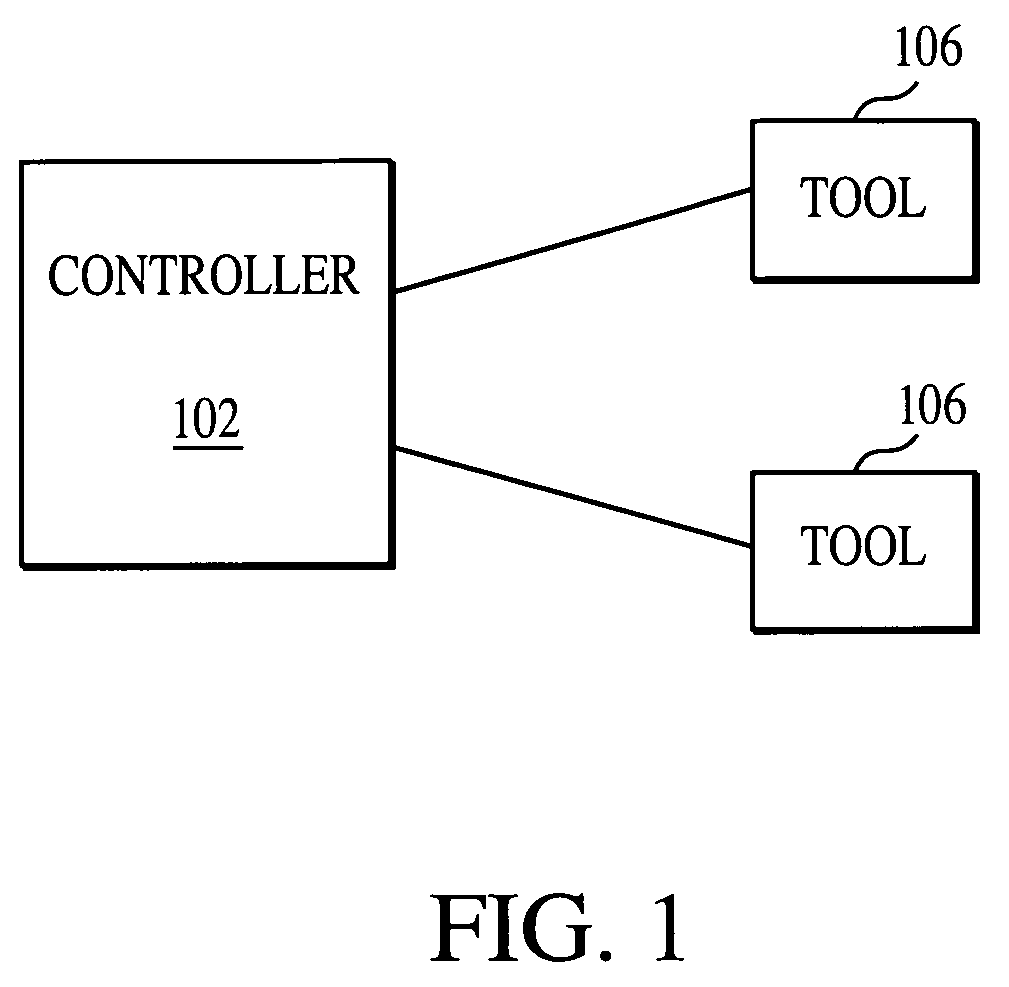
In control theory Advanced process control (APC) refers to a broad range of techniques and technologies implemented within industrial process control systems. Advanced process controls are usually deployed optionally and in addition to basic process controls. Basic process controls are designed and built with the process itself, to facilitate basic operation, control and automation requirements. Advanced process controls are typically added subsequently, often over the course of many years, to address particular performance or economic improvement opportunities in the process.
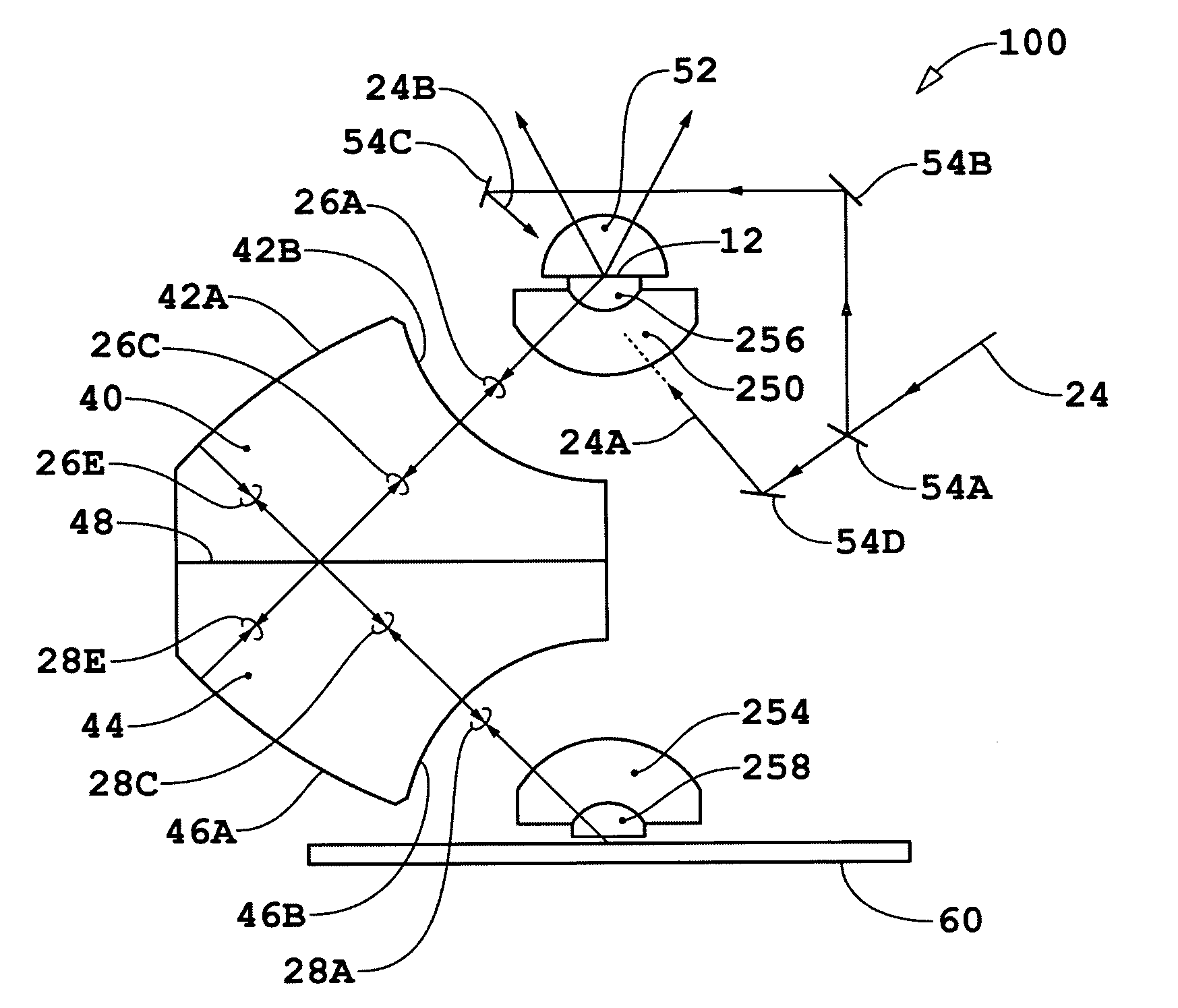
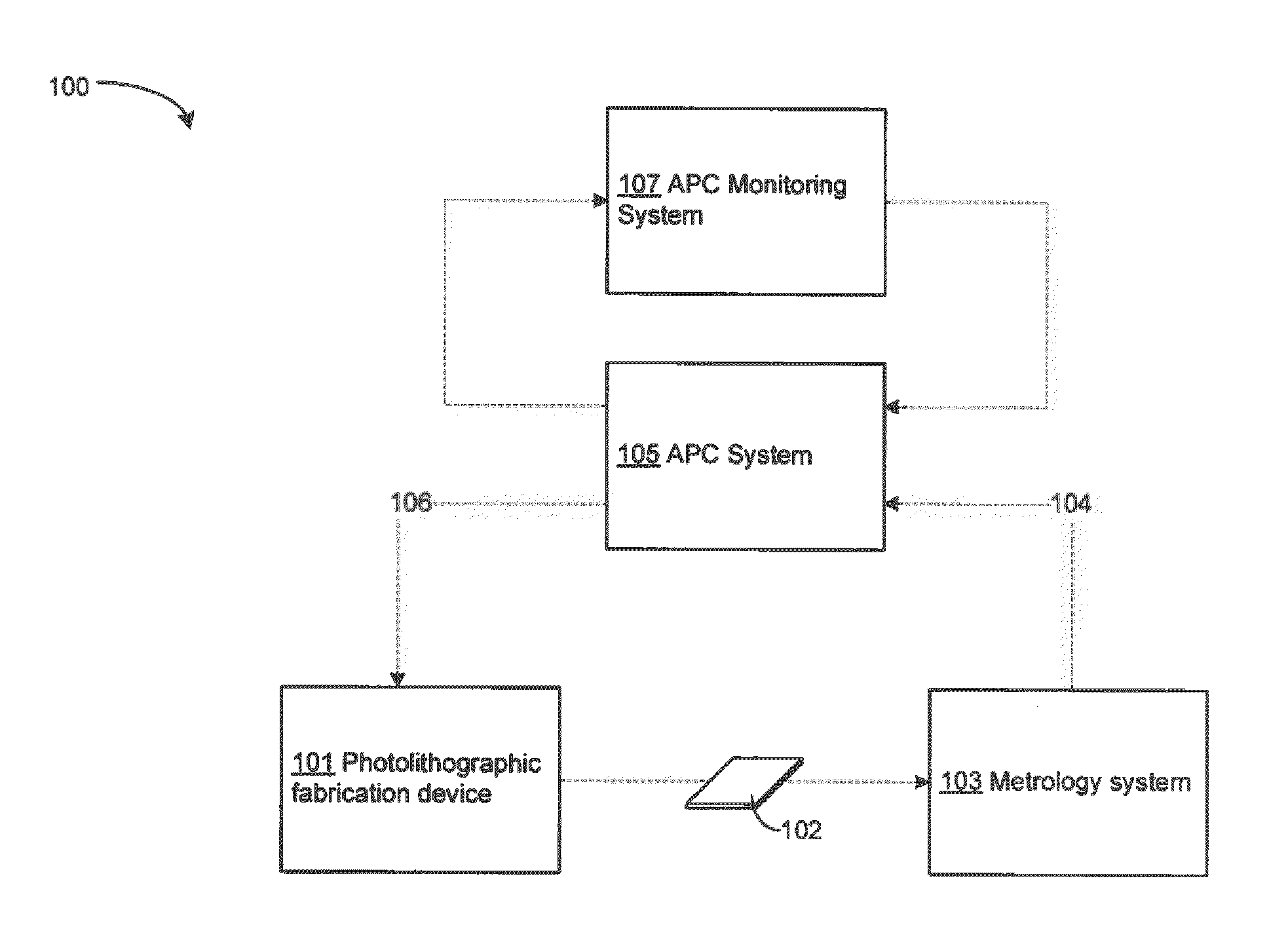
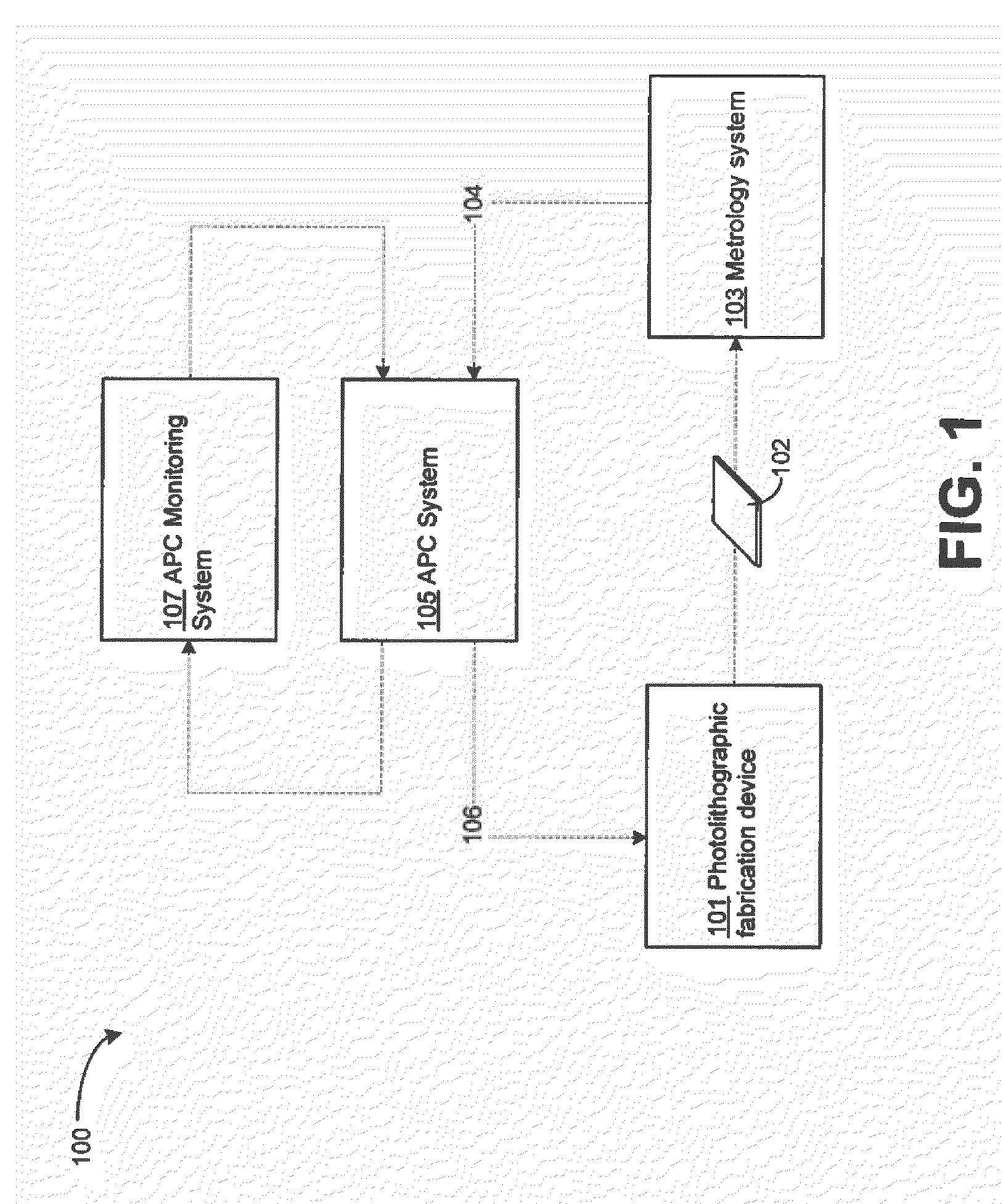
Method and apparatus for the monitoring and control of a semiconductor manufacturing process
InactiveUS7123980B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric testing/monitoringGraphicsWeb browser
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
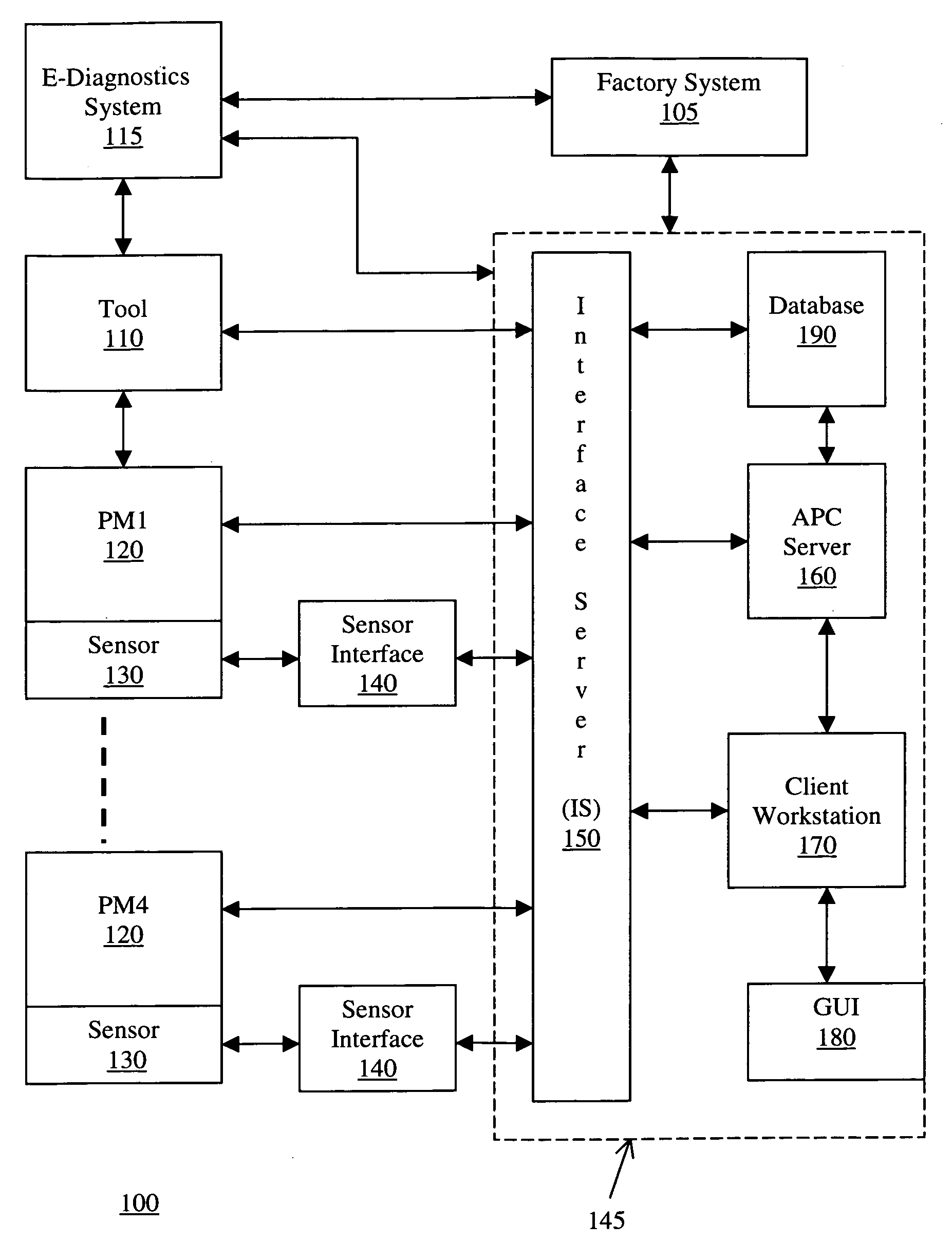
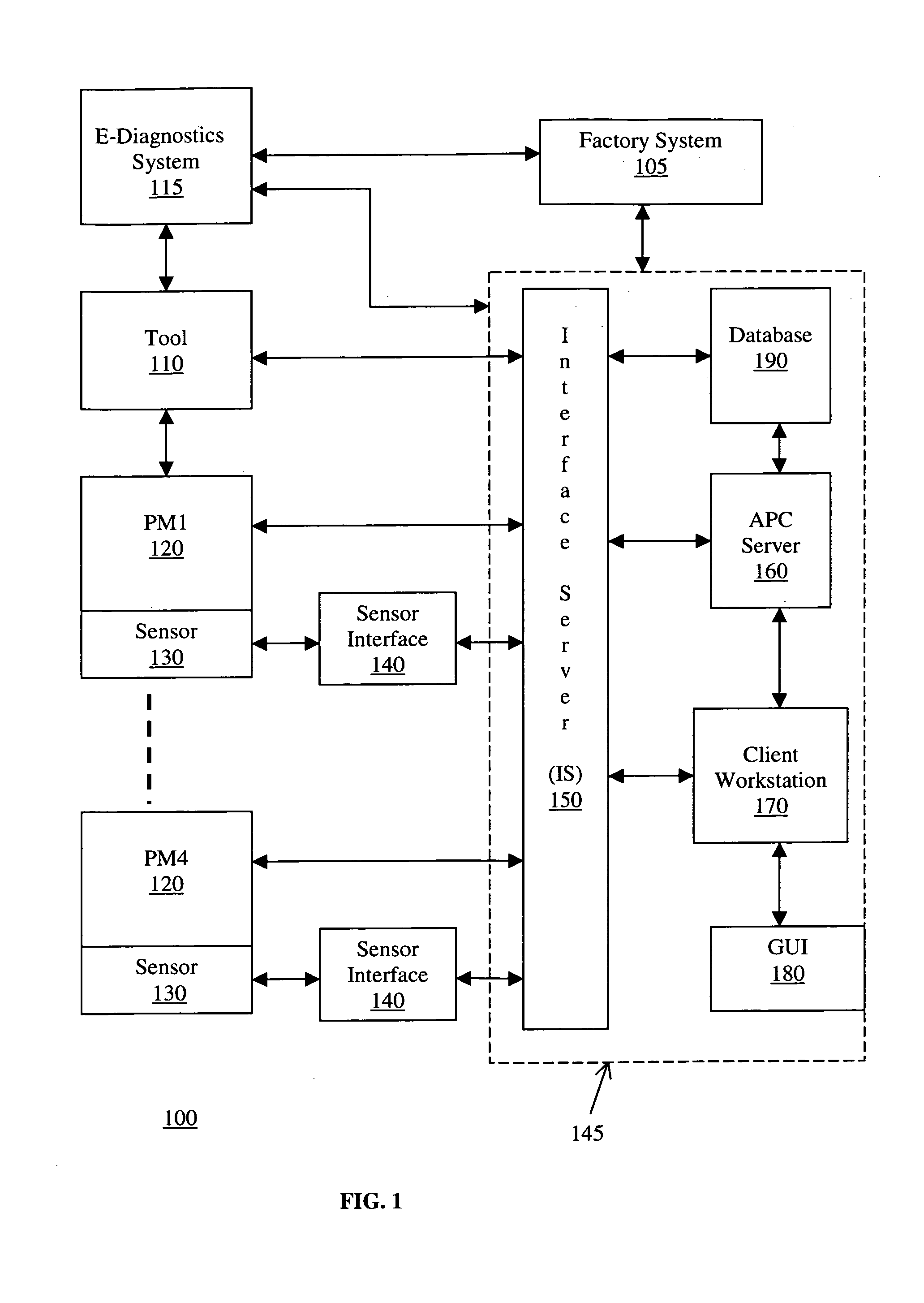
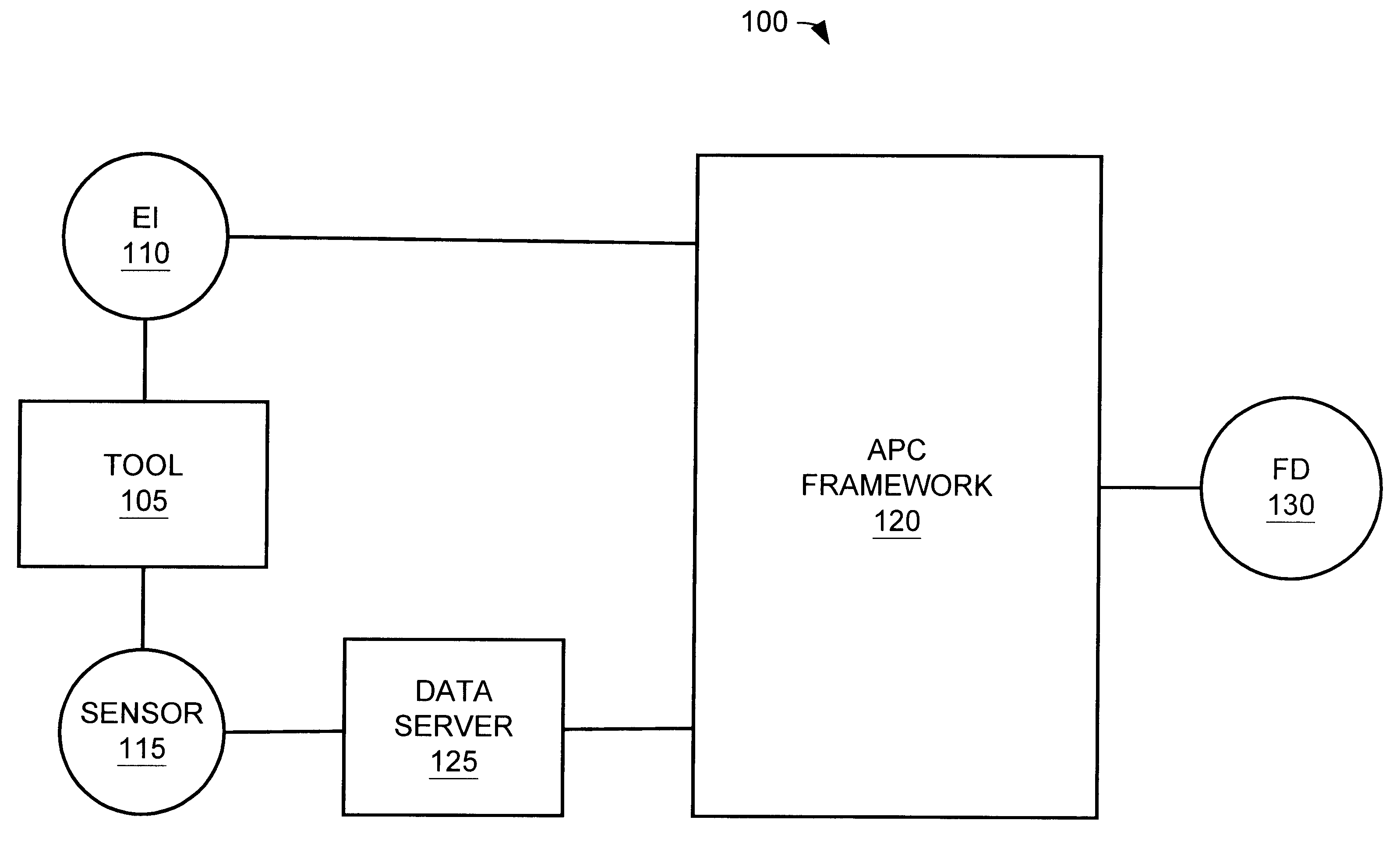
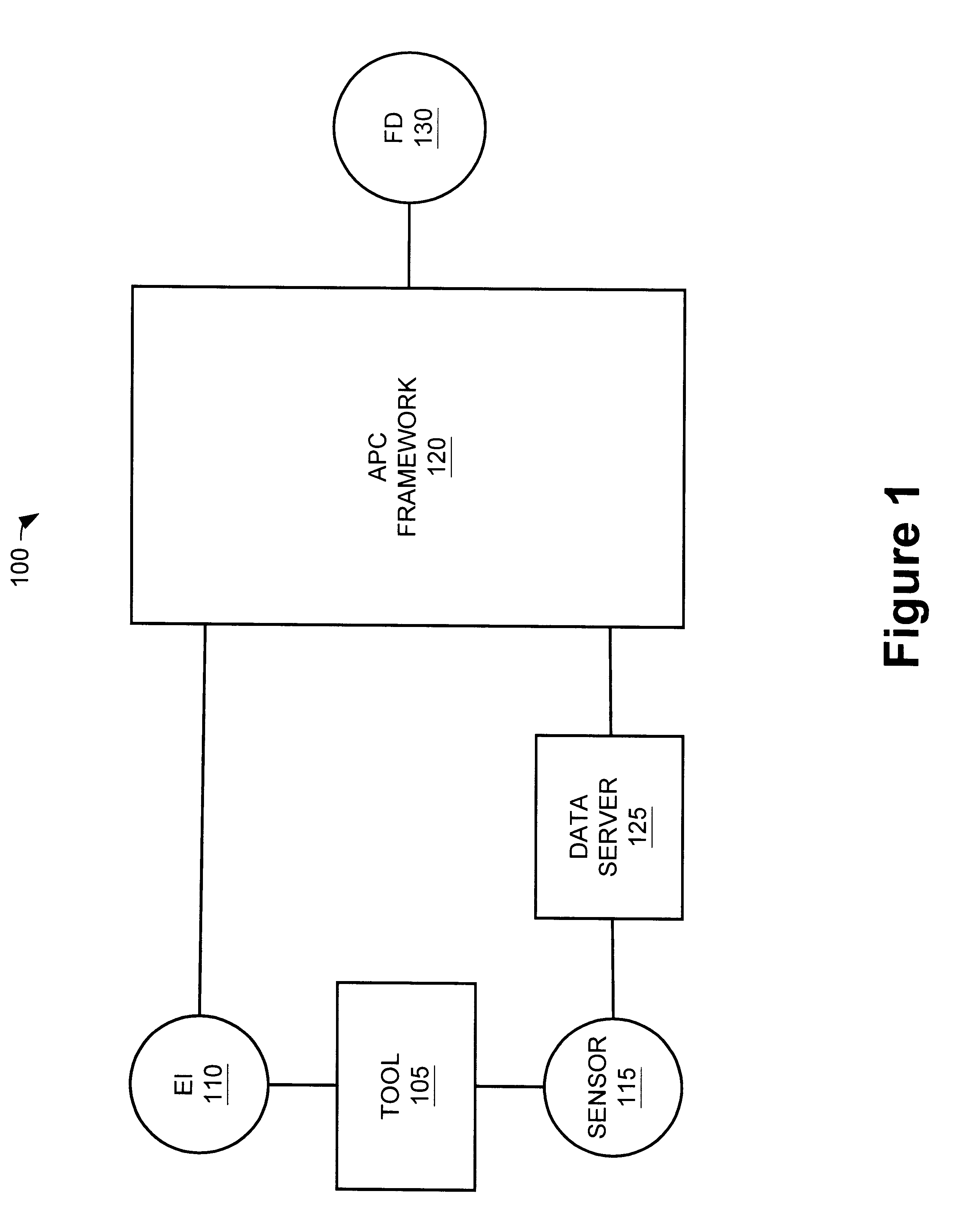
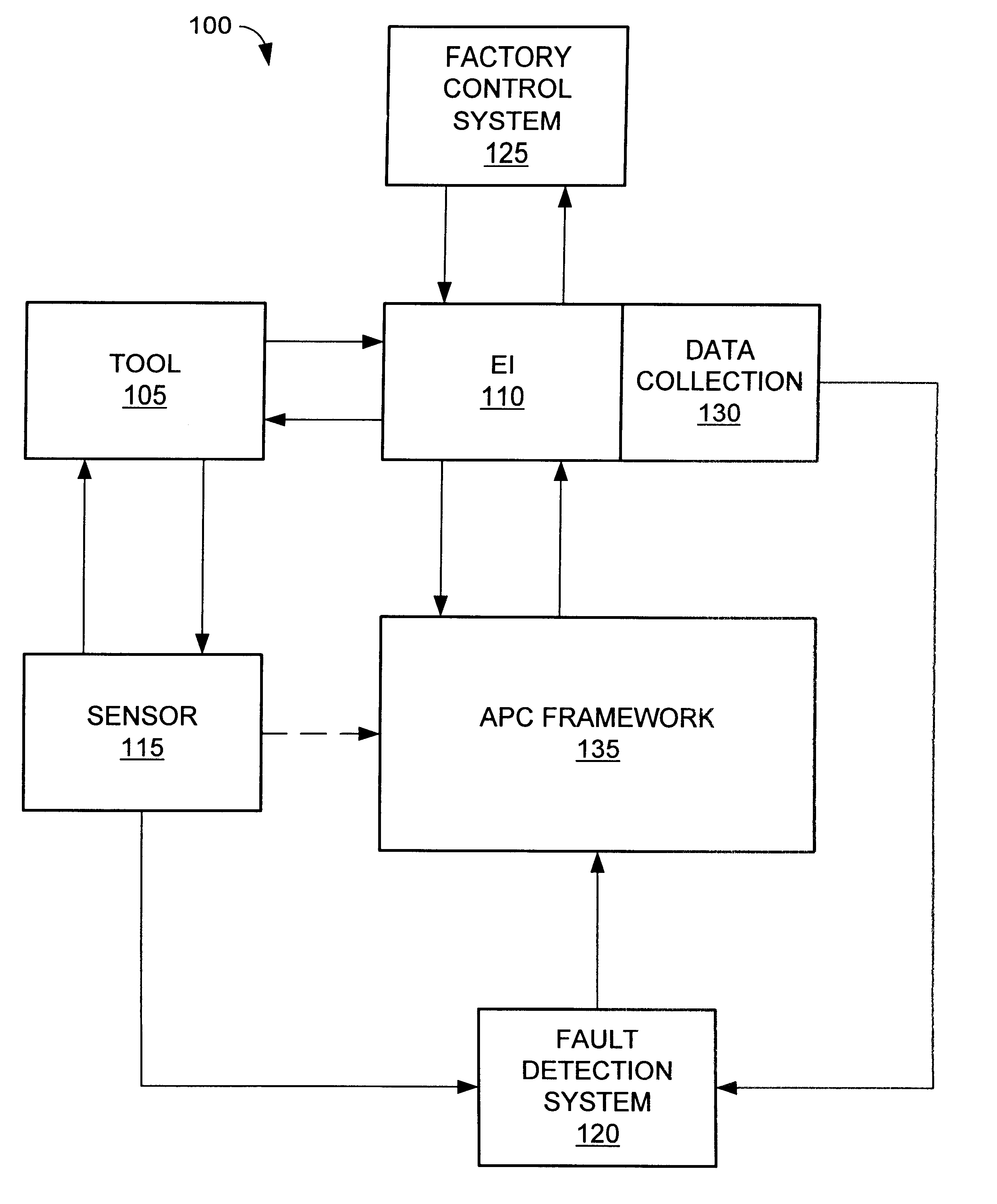
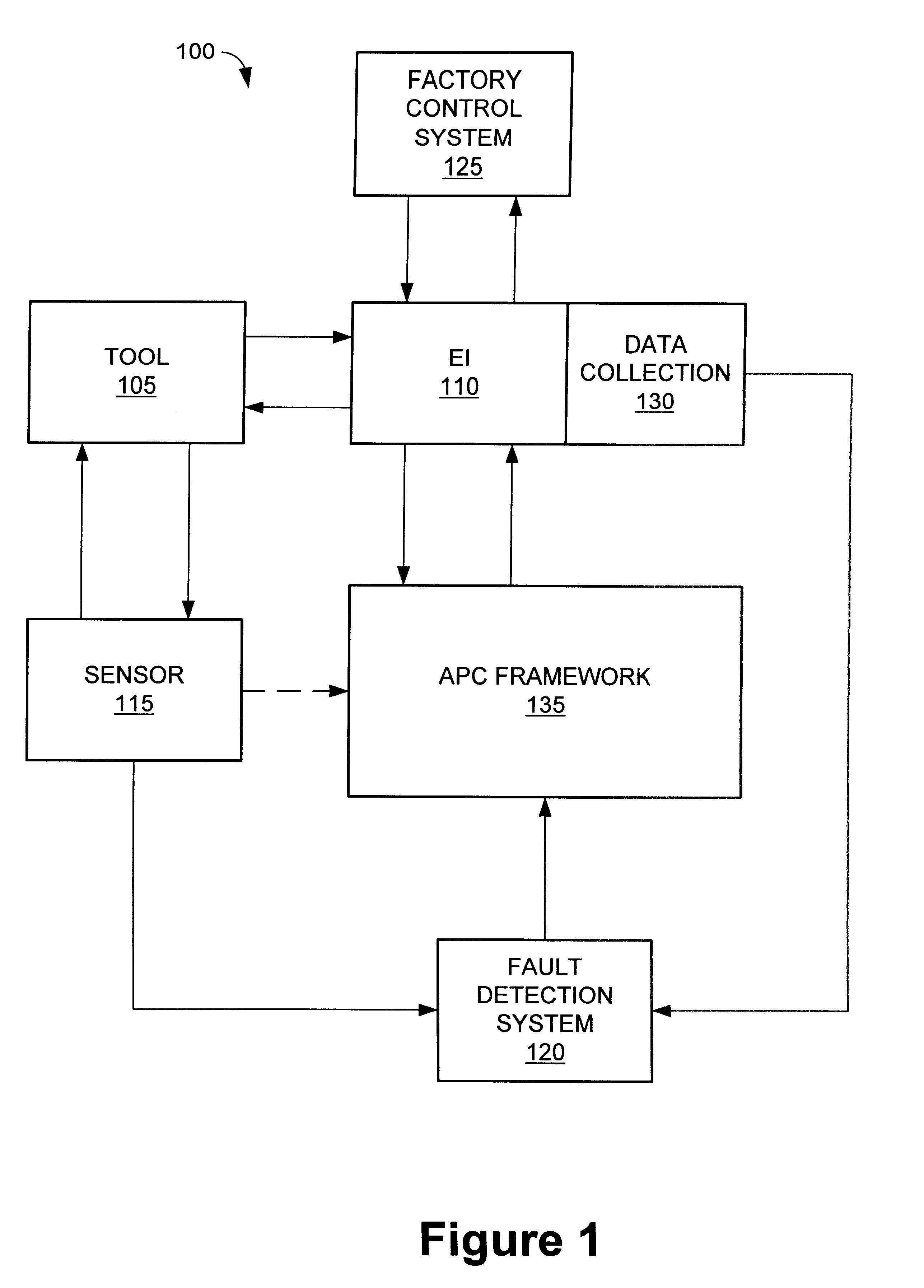
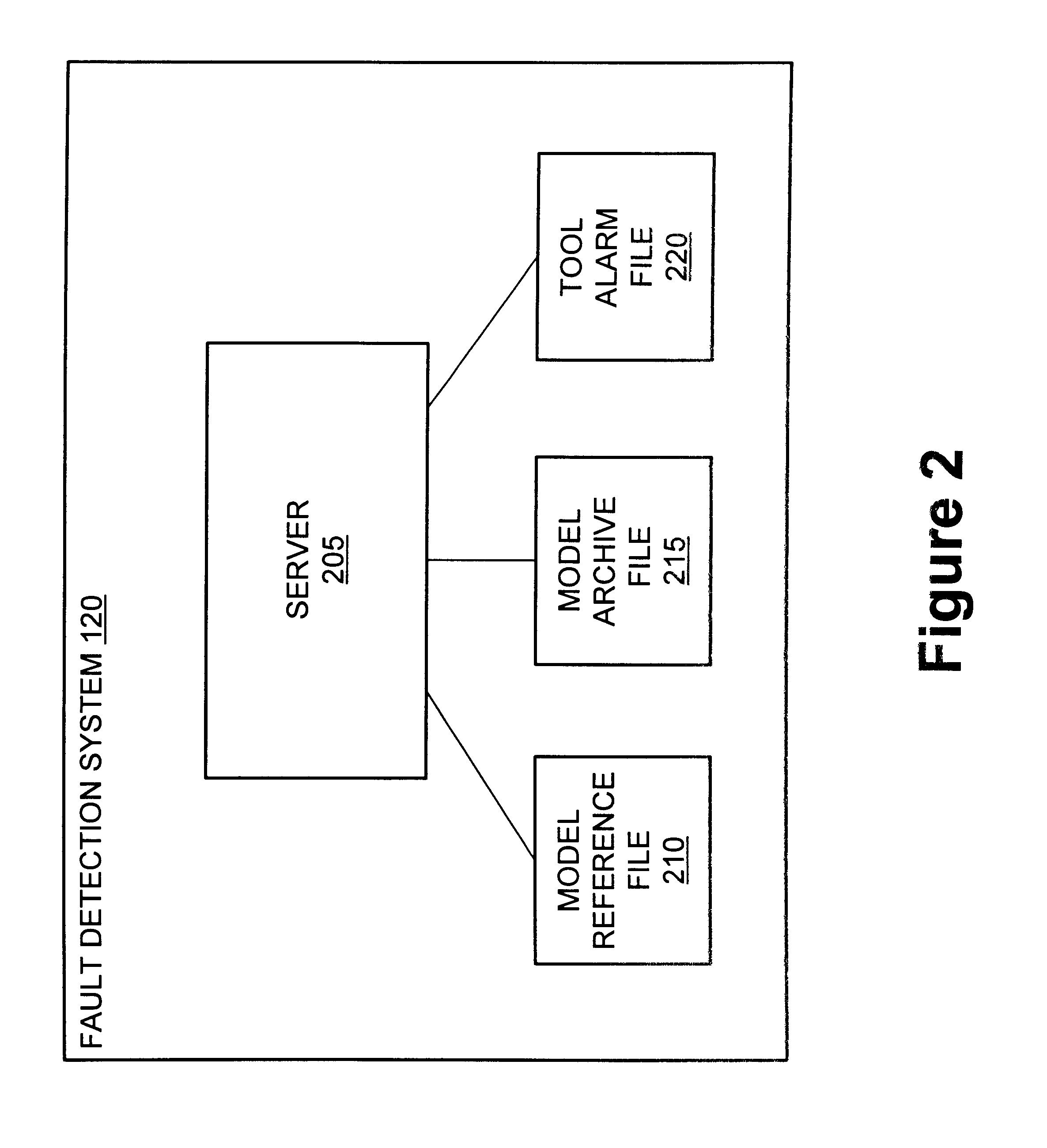
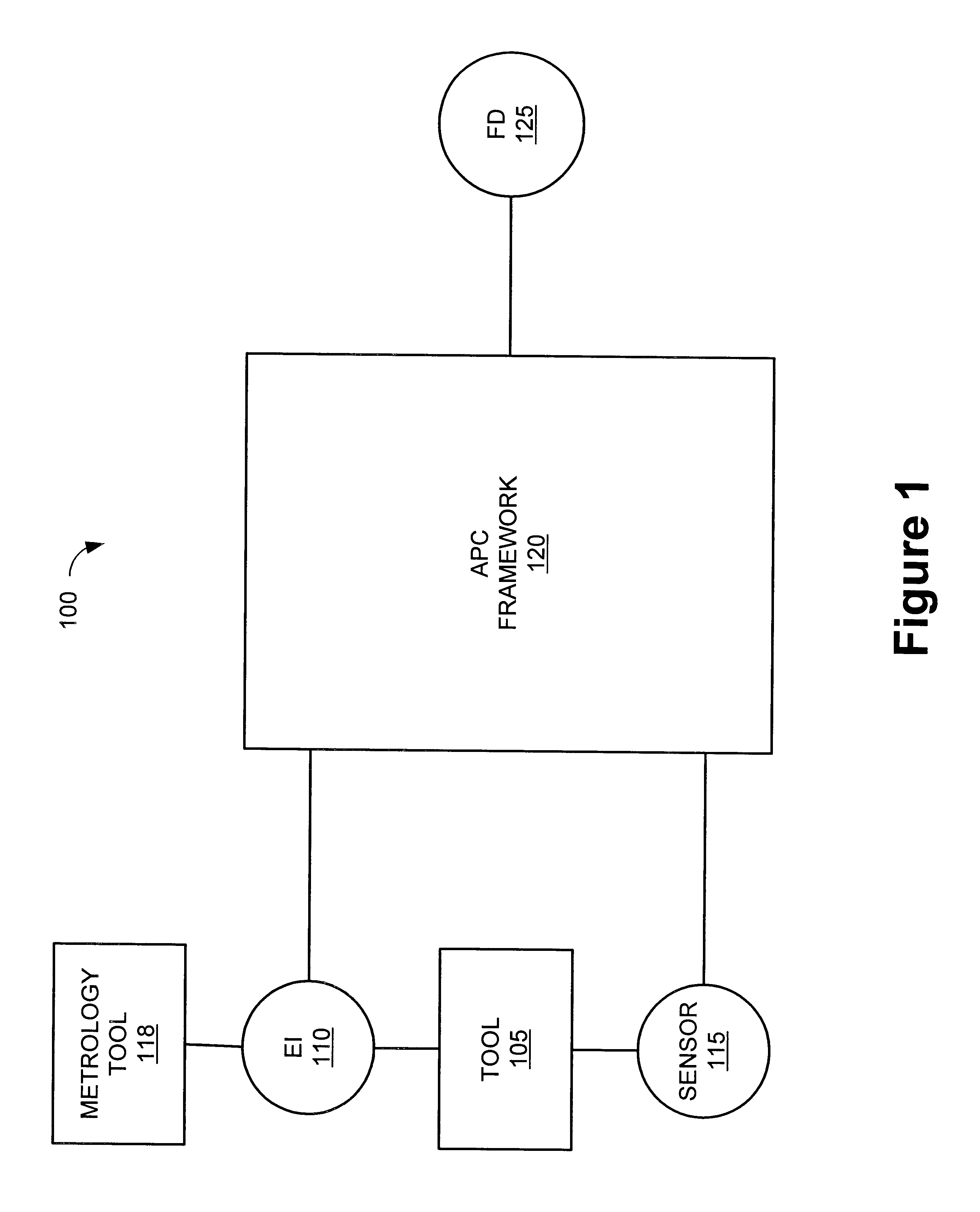
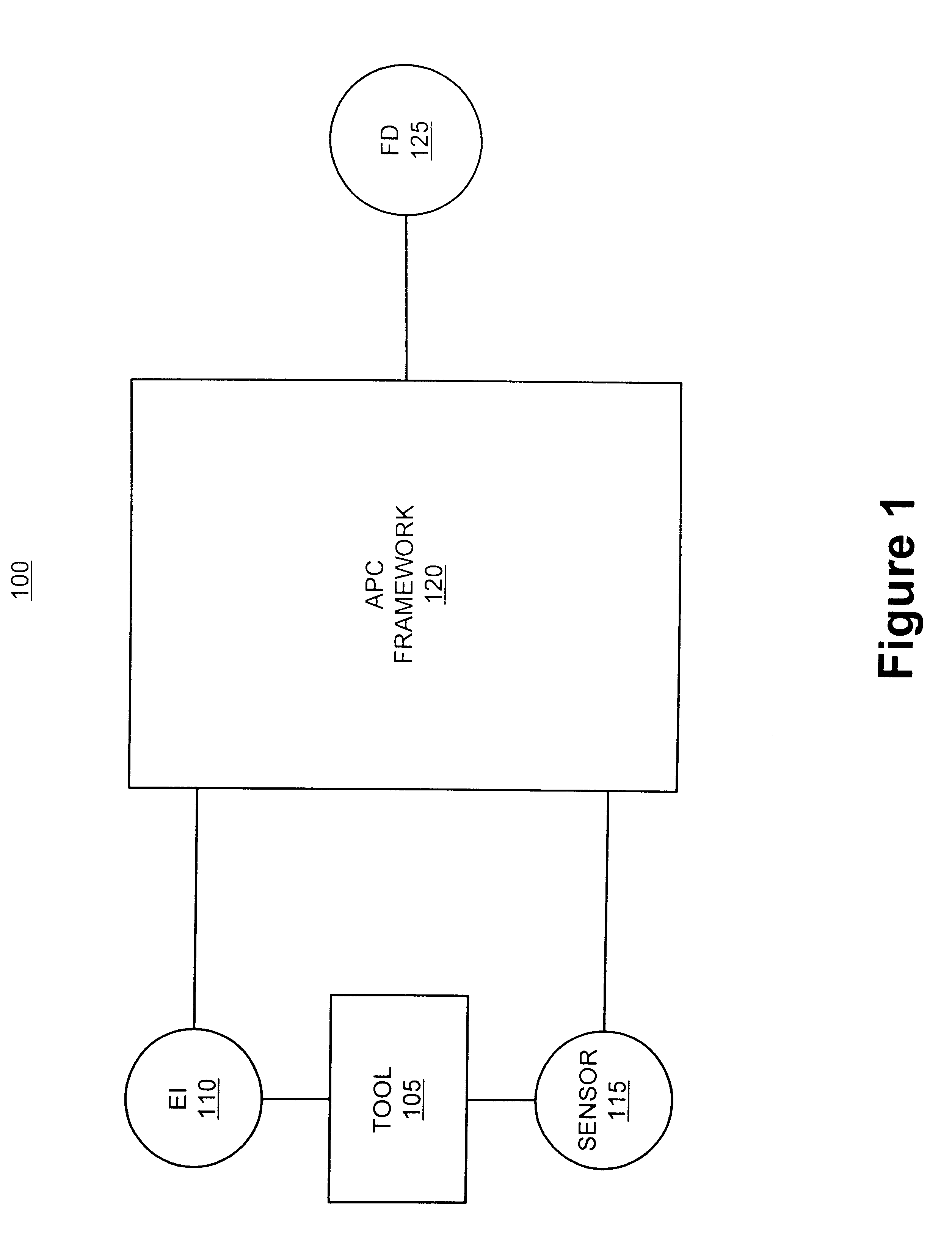
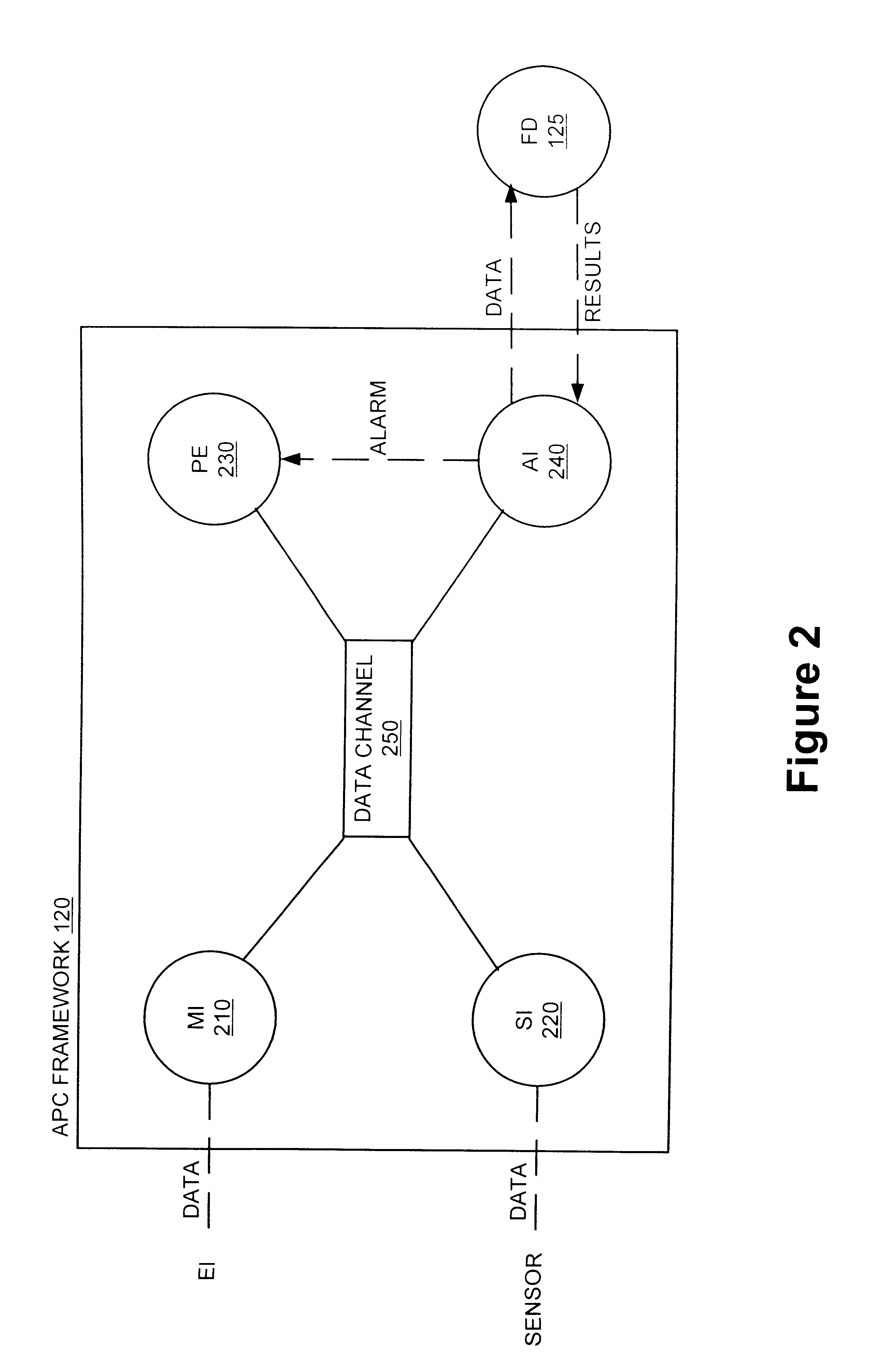
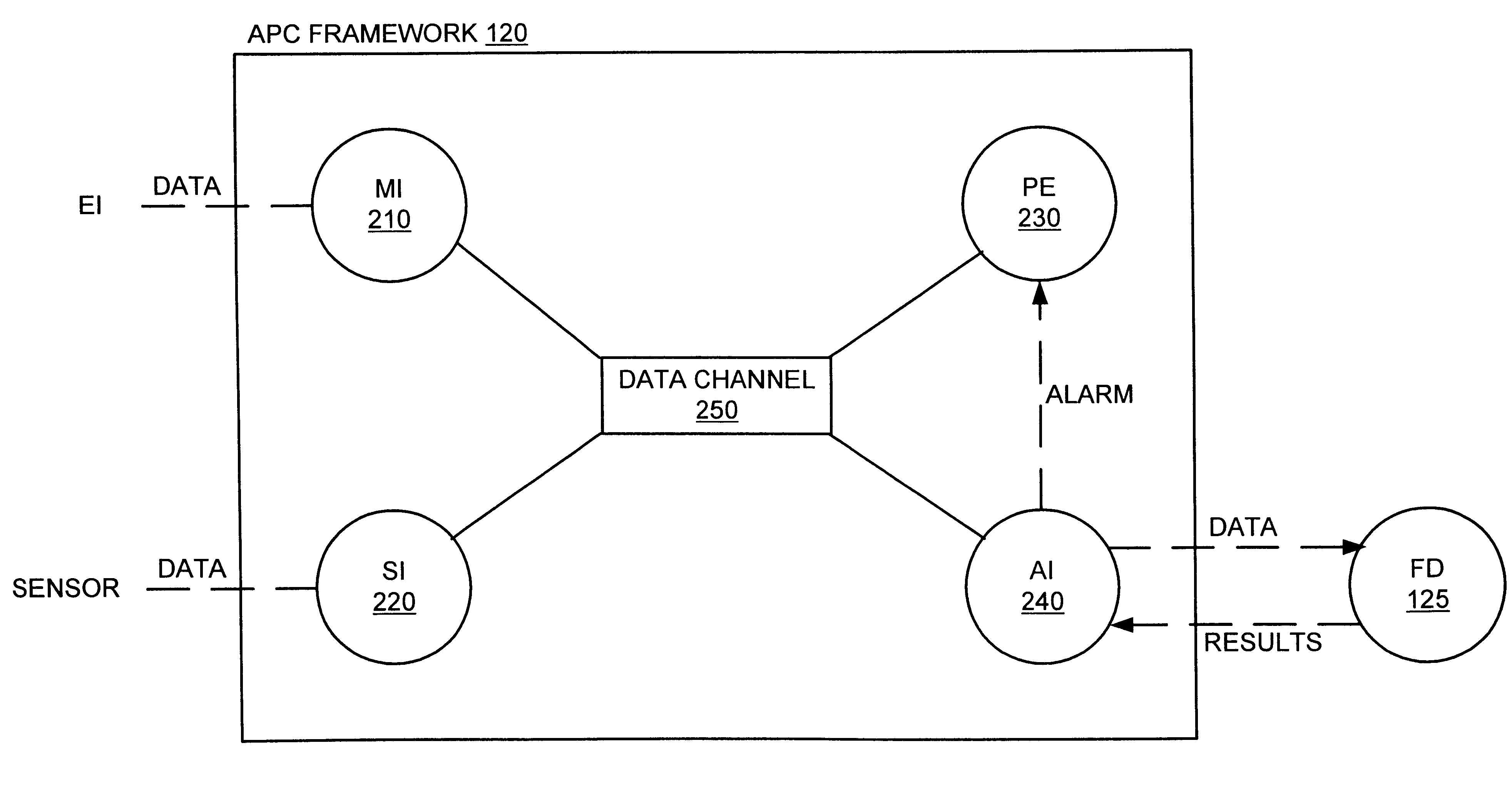
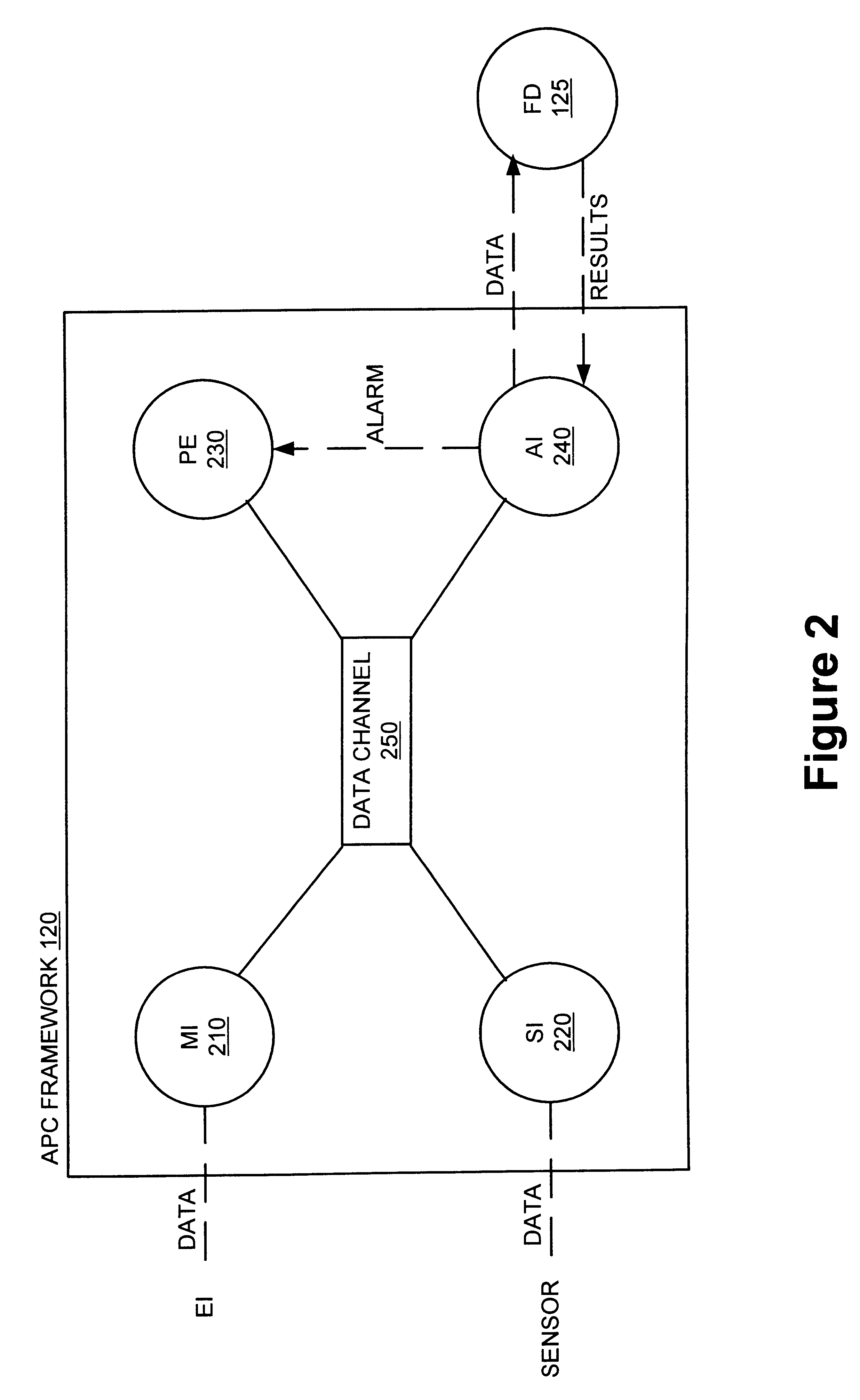
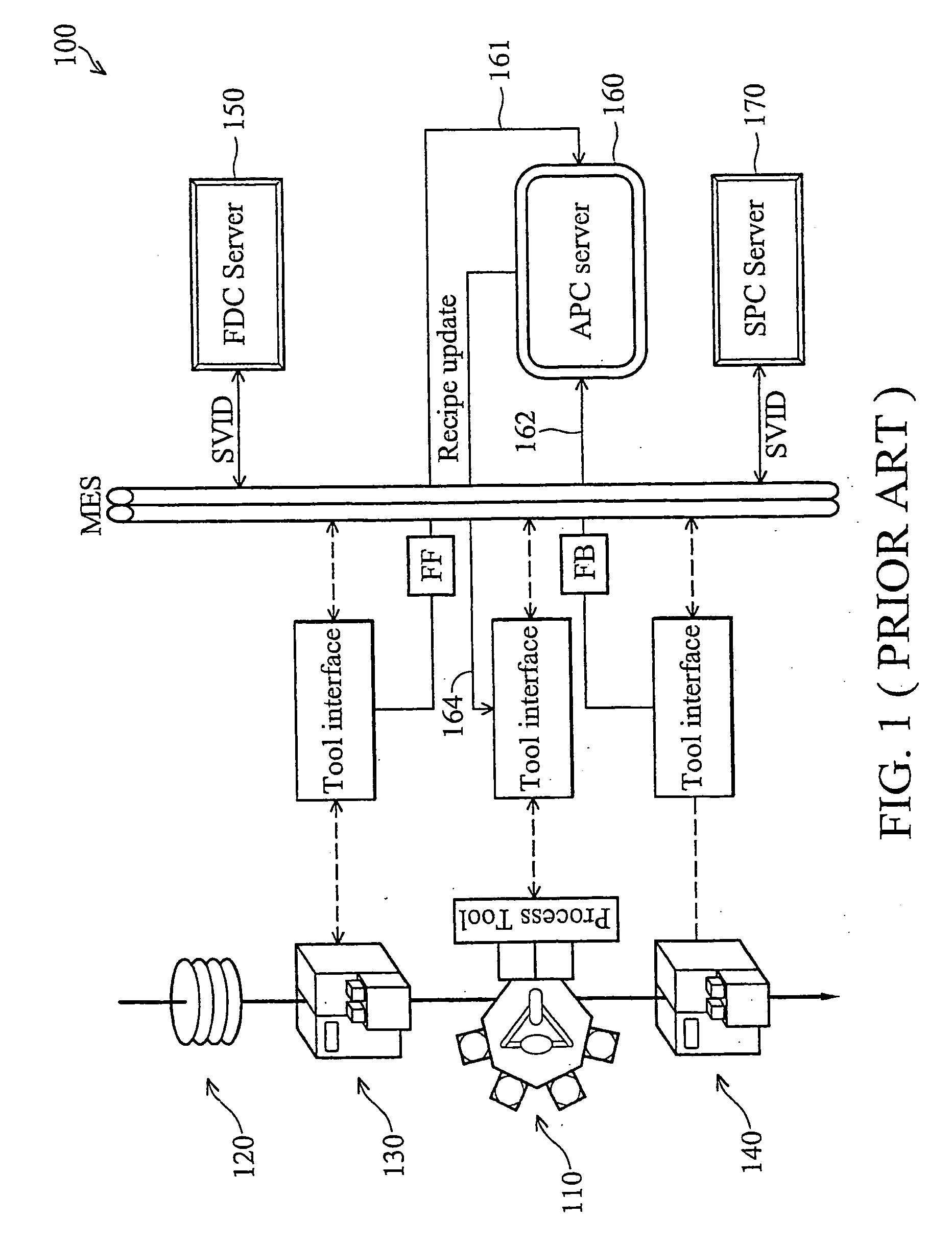
Method and apparatus for the integration of sensor data from a process tool in an advanced process control (APC) framework
InactiveUS6535783B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementError detection/correctionComputer scienceAdvanced process control
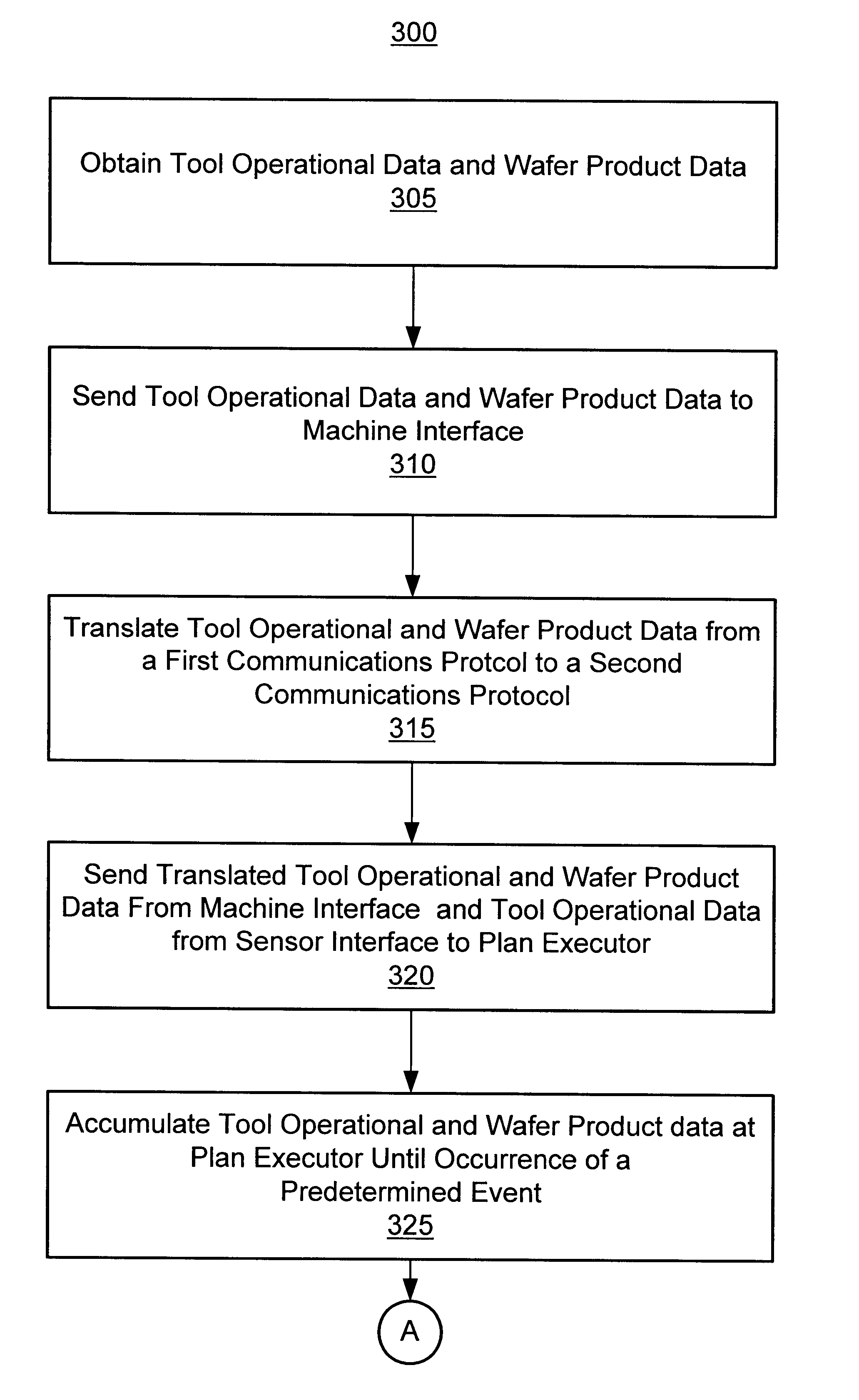
A method and apparatus for integrating tool sensor data in an Advanced Process Control (APC) application. A sensor receives operational state data of a processing tool related to the manufacture of a processing piece. The state data is sent from the sensor to a data server and accumulated therein. The data server processes the state data and forwards the data to an APC framework. The APC framework then forwards the state data to a fault detection unit. The fault detection unit determines if a fault condition exists with the processing tool based upon the state data. A predetermined action is performed on the processing tool in response to the presence of a fault condition. In accordance with one embodiment, the predetermined action is to shutdown the processing tool so as to prevent further production of faulty wafers.
Owner:FULLBRITE CAPITAL PARTNERS
Method for in-line monitoring of via/contact holes etch process based on test structures in semiconductor wafer manufacturing
InactiveUS7105436B2Reduce contactSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsImaging processingEngineering
Owner:HERMES MICROVISION TAIWAN +2
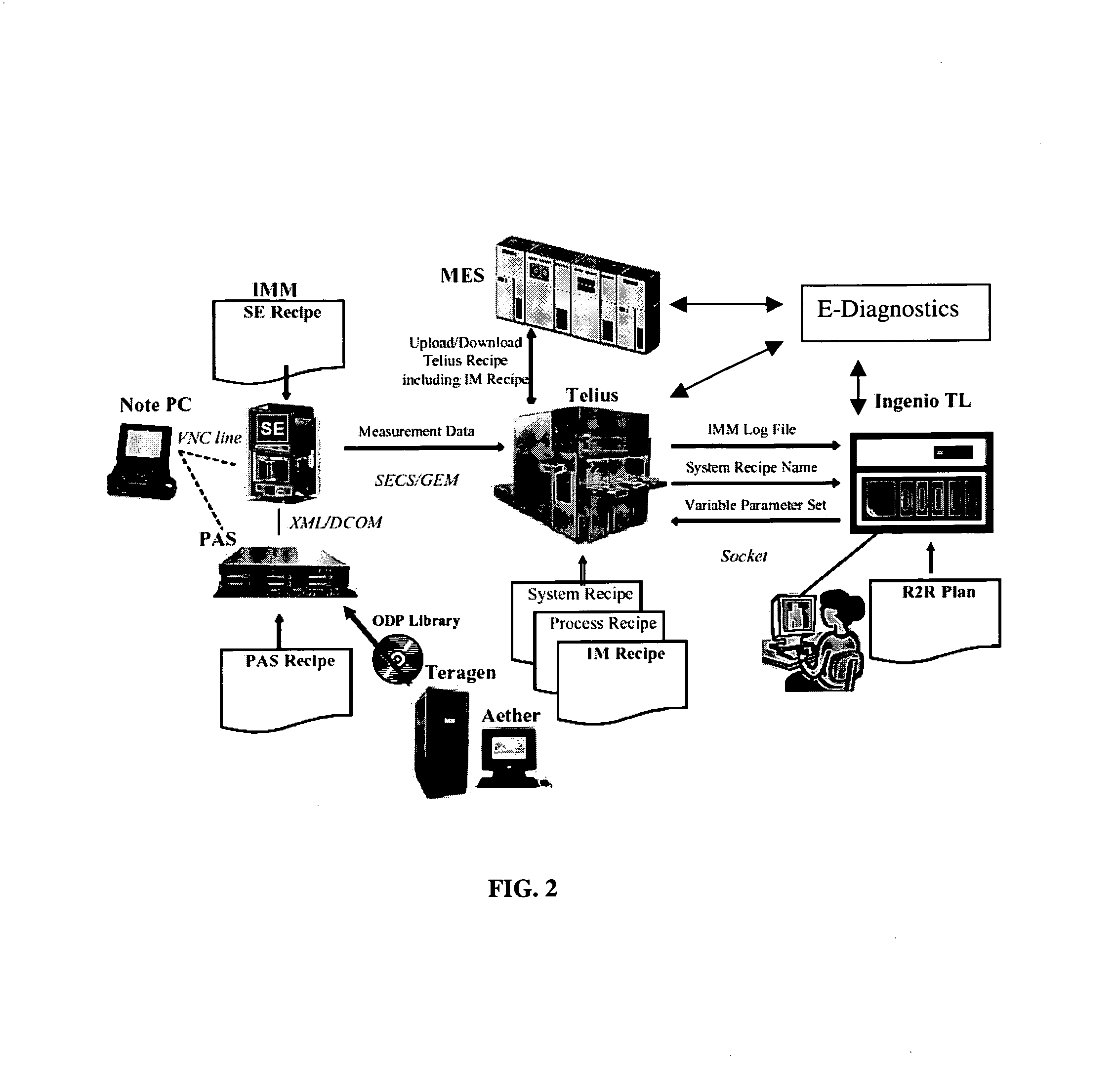
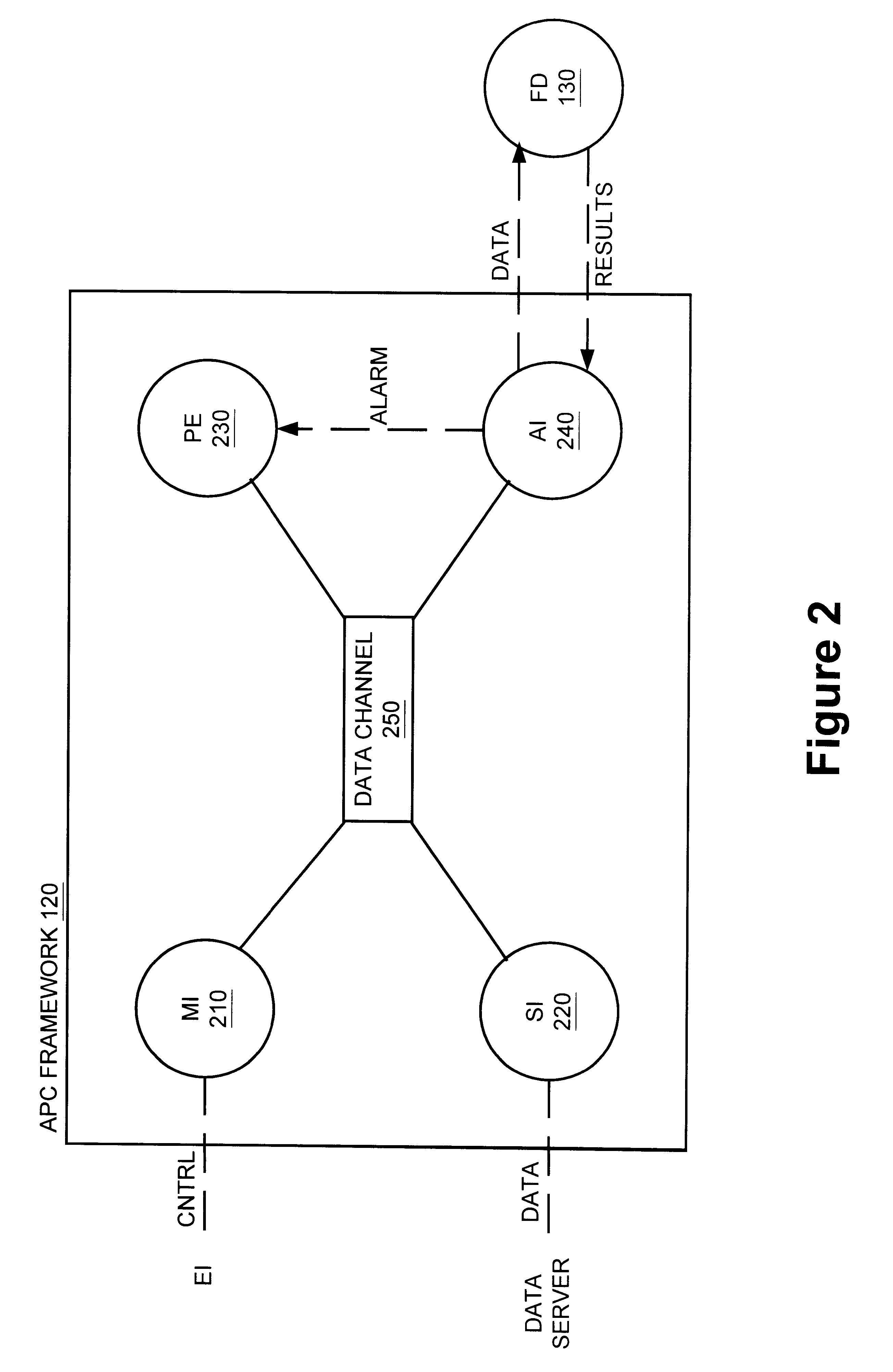
Method and apparatus for fault detection of a processing tool and control thereof using an advanced process control (APC) framework
InactiveUS6725402B1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionReliability engineeringAdvanced process control
A method and apparatus for providing fault detection in an Advanced Process Control (APC) framework. A first interface receives operational state data of a processing tool related to the manufacture of a processing piece. The state data is sent from the first interface to a fault detection unit. A fault detection unit determines if a fault condition exists with the processing tool based upon the state data. A predetermined action is performed on the processing tool in response to the presence of a fault condition. In accordance with one embodiment, the predetermined action is to shutdown the processing tool so as to prevent further production of faulty wafers.
Owner:OCEAN SEMICON LLC
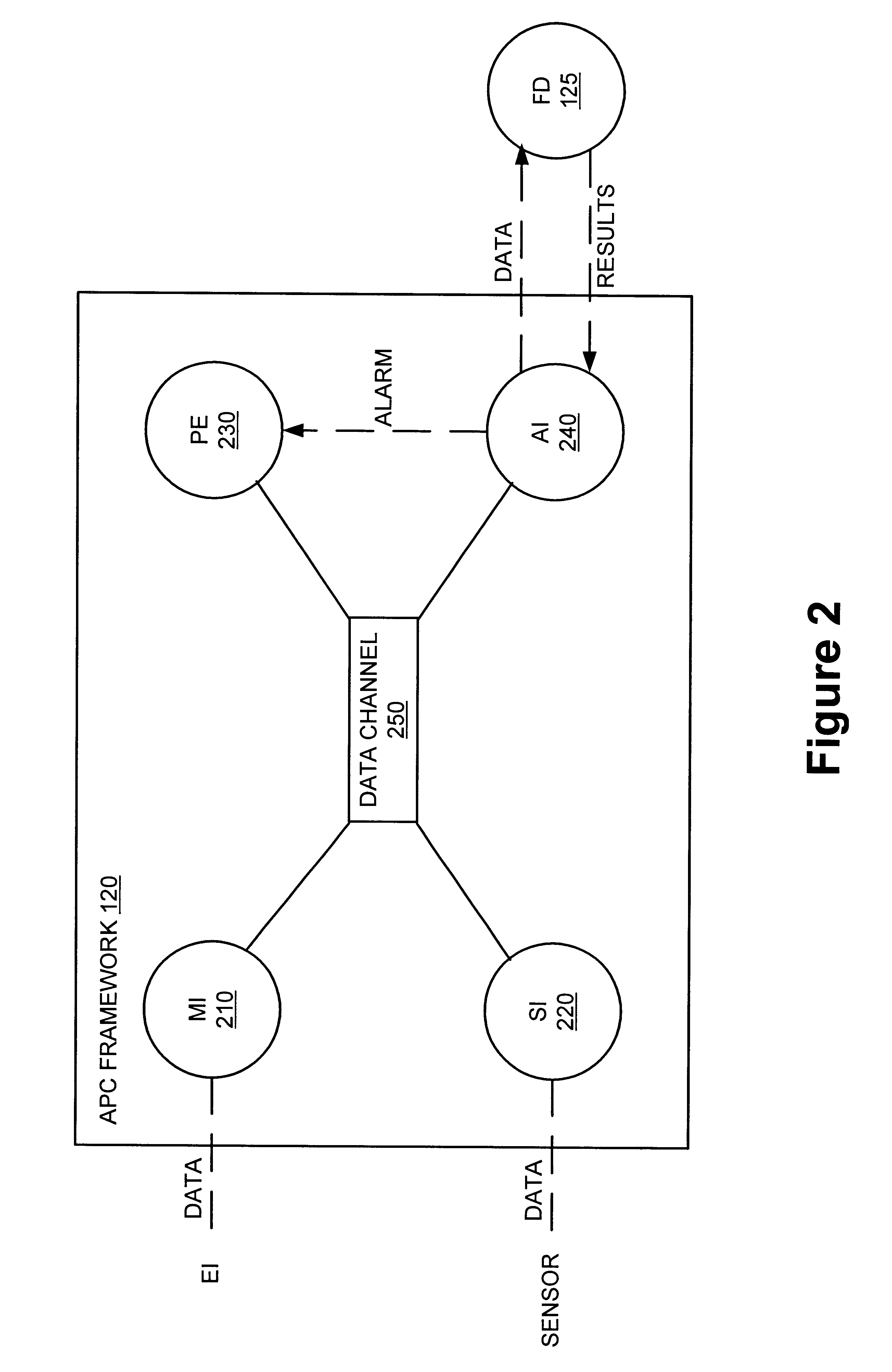
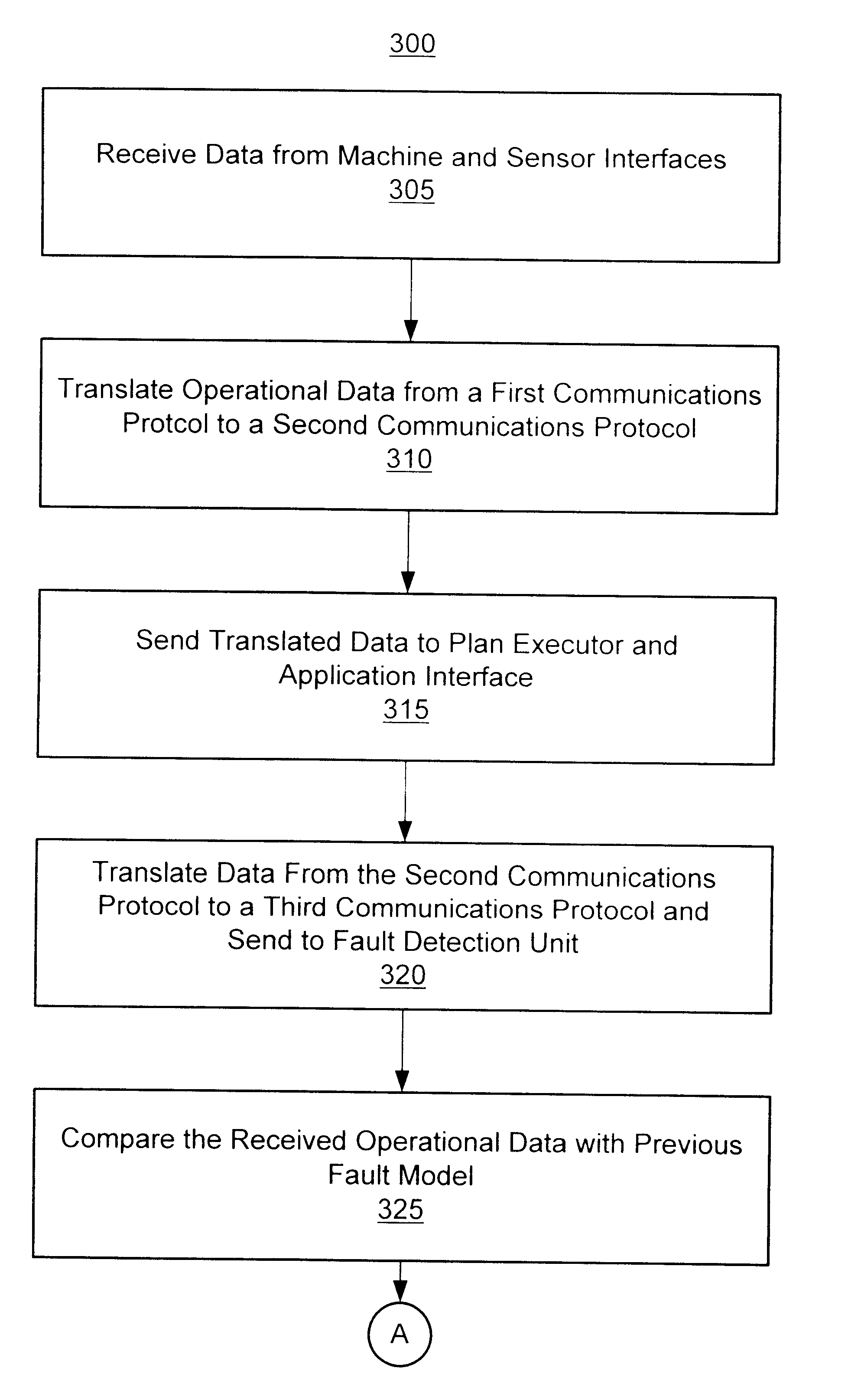
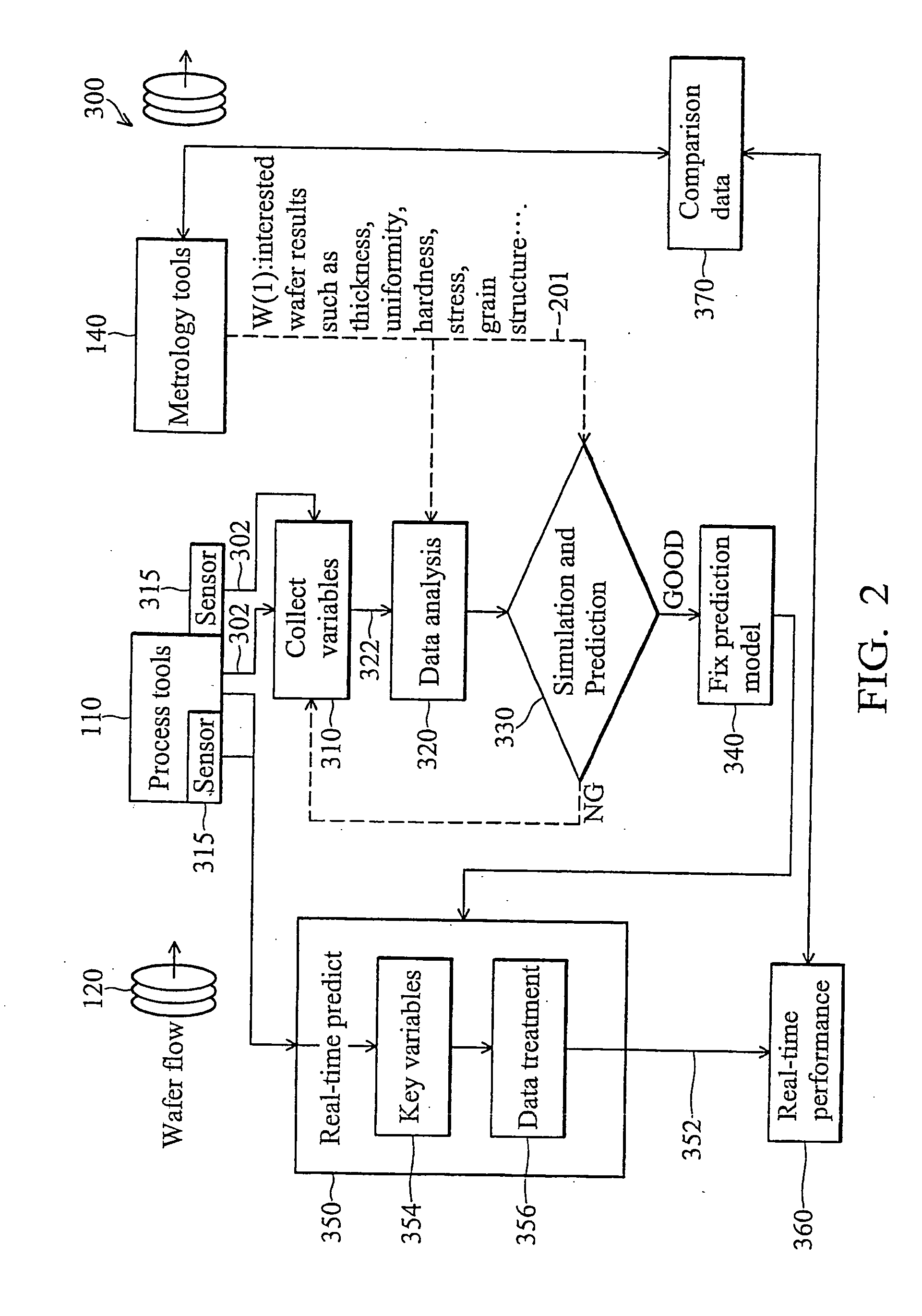
Method and apparatus for integration of real-time tool data and in-line metrology for fault detection in an advanced process control (APC) framework
A method and apparatus for providing near real-time fault detection in a manufacturing process is provided. The apparatus includes a processing tool adapted to manufacture a processing piece and an interface, coupled to the processing tool, for receiving operational data from the processing tool related to the manufacture of the processing piece, and product data defining characteristics of the processing piece. In one embodiment, the processing tool is in the form of semiconductor fabrication equipment and the processing piece is a silicon wafer. A fault detection unit is provided to determine if a fault condition exists with the processing tool from the operational data or with the processing piece from the product data. An Advanced Process Control (APC) framework is further provided to receive the operational and product data from the first interface, and to send the data to the fault detection unit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and apparatus for integrating near real-time fault detection in an APC framework
InactiveUS6556881B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesSiliconSemiconductor
A method and apparatus for providing near real-time fault detection in a manufacturing process is provided. The apparatus includes a processing tool adapted to manufacture a processing piece and an interface, coupled to the processing tool, for receiving operational data from the processing tool related to the manufacture of the processing piece. In one embodiment, the processing tool is in the form of semiconductor fabrication equipment and the processing piece is a silicon wafer. A fault detection unit is provided to determine if a fault condition exists with the processing tool. An Advanced Process Control (APC) framework is further provided to receive the operational data from the first interface, and to send the data to the fault detection unit as the data is received by the first interface.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method, system, and medium for handling misrepresentative metrology data within an advanced process control system
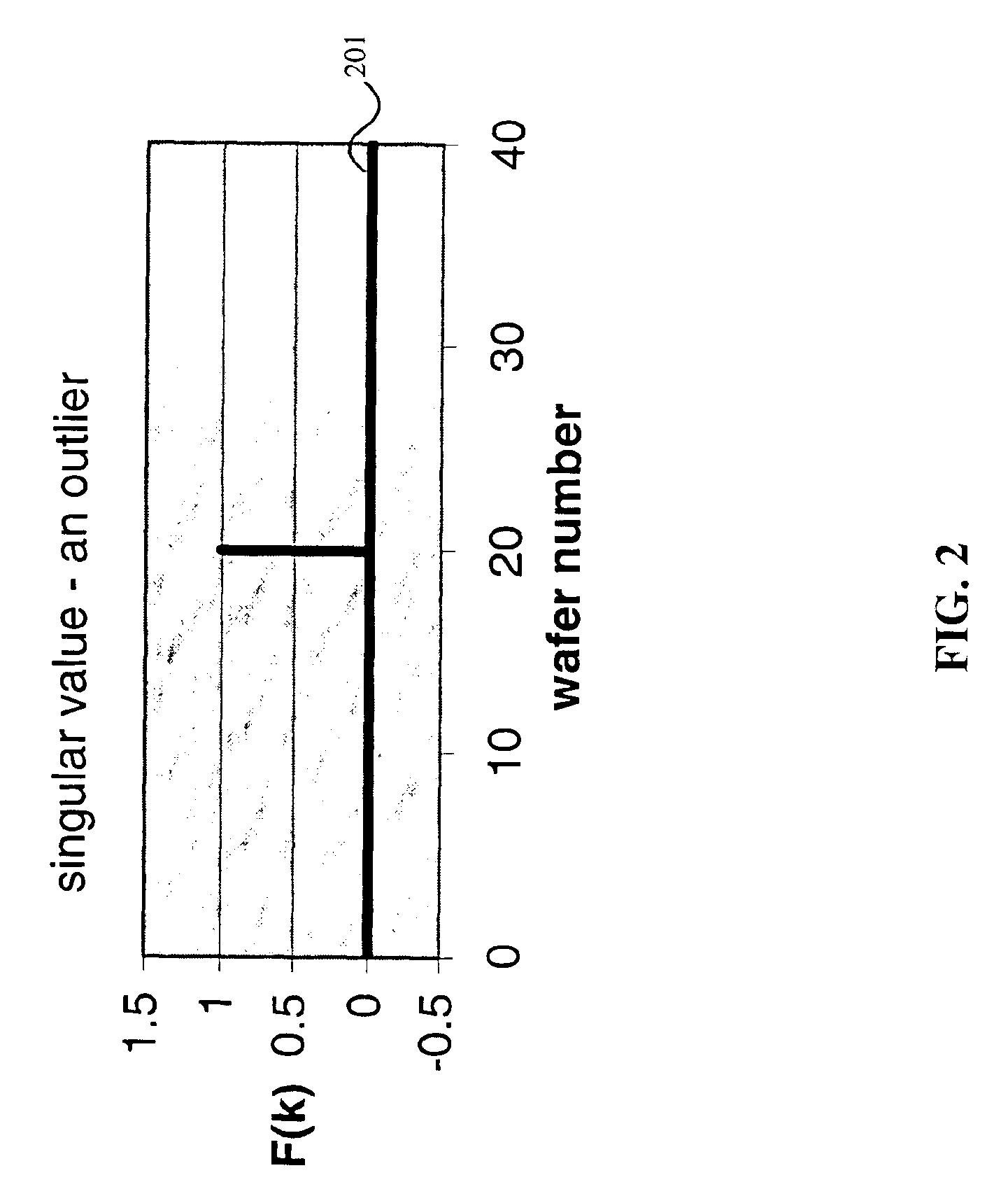
InactiveUS6999836B2Accurate measurementSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlMetrologyOutlier
A system, method and medium of controlling a semiconductor manufacturing tool using a feedback control mechanism. The feedback control mechanism includes features for receiving data points relating to an output of the tool. The data points include a current data point and at least one previous data point. The feedback control mechanism also includes features for determining whether the current data point is an erroneous outlier by comparing the current data point to a statistical representation of the at least one previous data point, and based on whether the at least one previous data point is an outlier. The feedback control mechanism further includes features for disregarding the current data point in calculating a feedback value of the feedback control mechanism if the current data point is determined as an erroneous outlier.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Method and apparatus for fault detection of a processing tool in an advanced process control (APC) framework
InactiveUS6546508B1Error detection/correctionTotal factory controlEngineeringReliability engineering
A method and apparatus for providing fault detection in an Advanced Process Control (APC) framework. A first interface receives operational state data of a processing tool related to the manufacture of a processing piece. The state data is sent from the first interface to a fault detection unit. A fault detection unit determines if a fault condition exists with the processing tool based upon the state data. A predetermined action is performed on the processing tool in response to the presence of a fault condition. In accordance with one embodiment, the predetermined action is to shutdown the processing tool so as to prevent further production of faulty wafers.
Owner:VANTAGE MICRO LLC
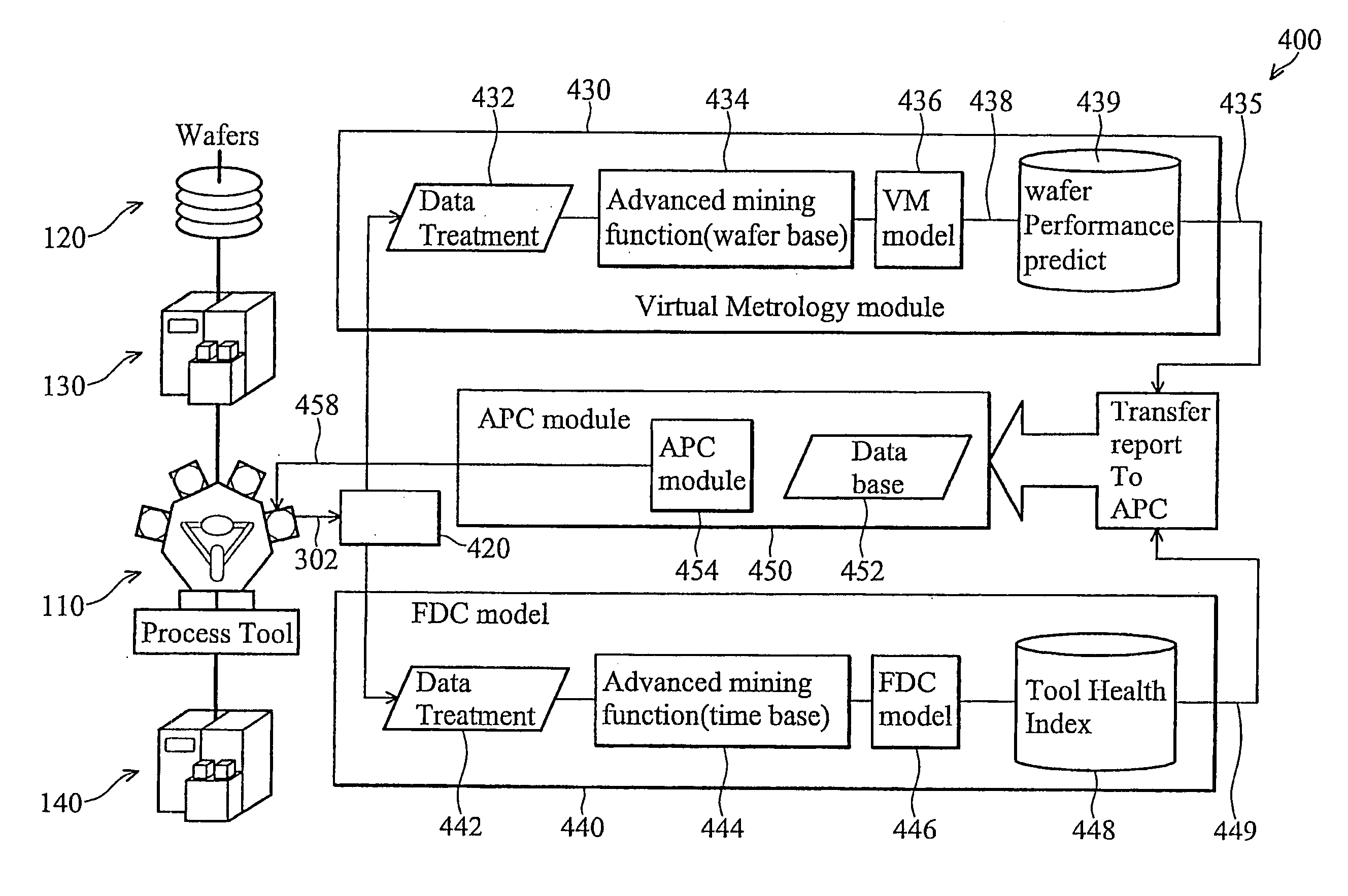
Novel method and apparatus for integrating fault detection and real-time virtual metrology in an advanced process control framework
InactiveUS20060129257A1Optimize preventative maintenance scheduleReduce the amount of controlProgramme controlTotal factory controlData acquisitionData system
A semiconductor manufacturing information framework to operate a processing tool includes a data acquisition system (DAS), a virtual metrology (VM) system, a fault detection and classification (FDC) system and an advanced process control (APC) system. The DAS is operable to receive data related to the processing of a workpiece by the processing tool or sensors coupled on tool. The VM system is operable to receive the data from the DAS and predict results of the workpiece processed by the processing tool or sensors. The VM system generates at least one first output indicative of the results. The FDC system is operable to receive the data and generate at least one second output indicative of an operating status of the processing tool. The APC system is operable to receive the at least one first or second outputs, and, in response, generate at least one third output to control the processing tool.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
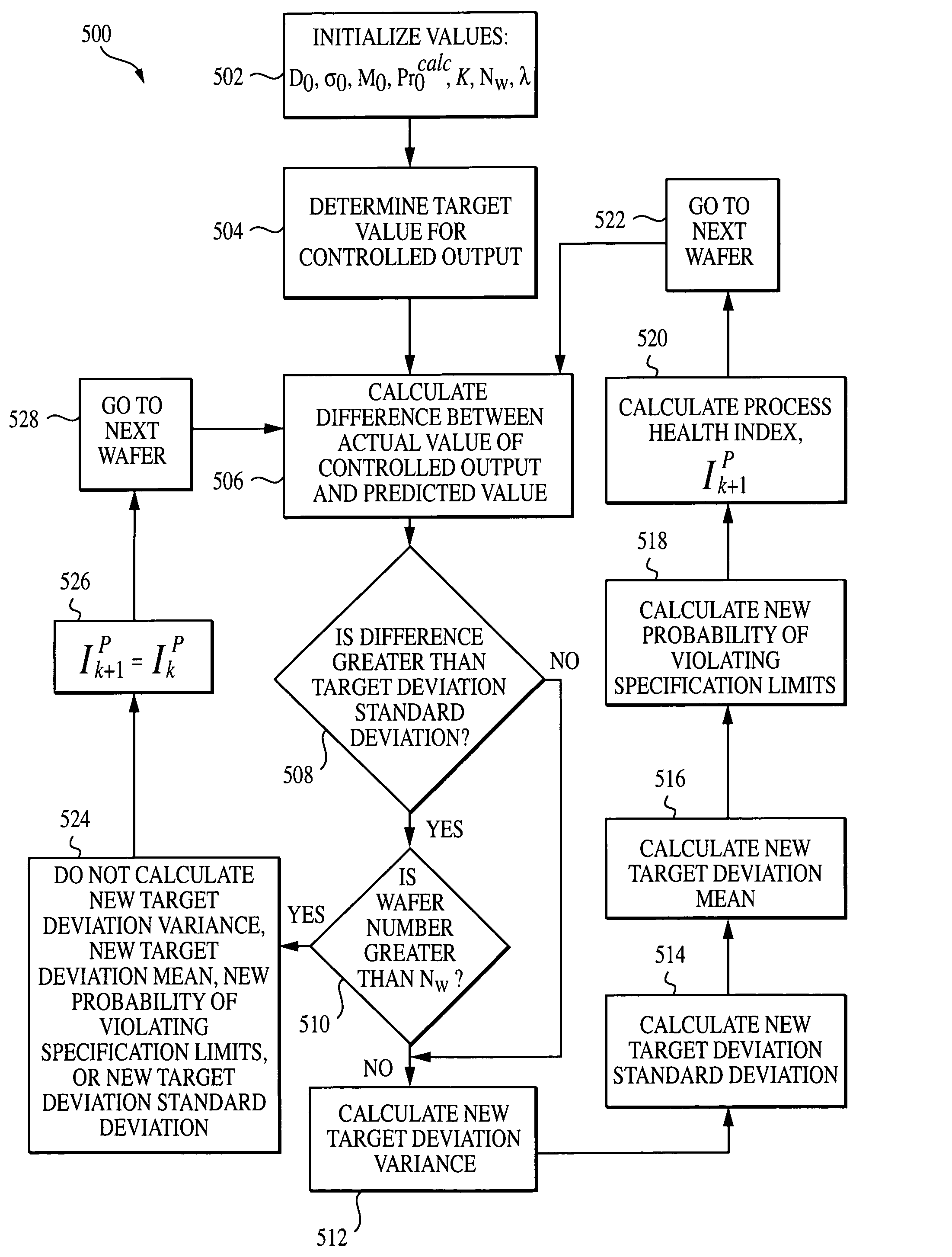
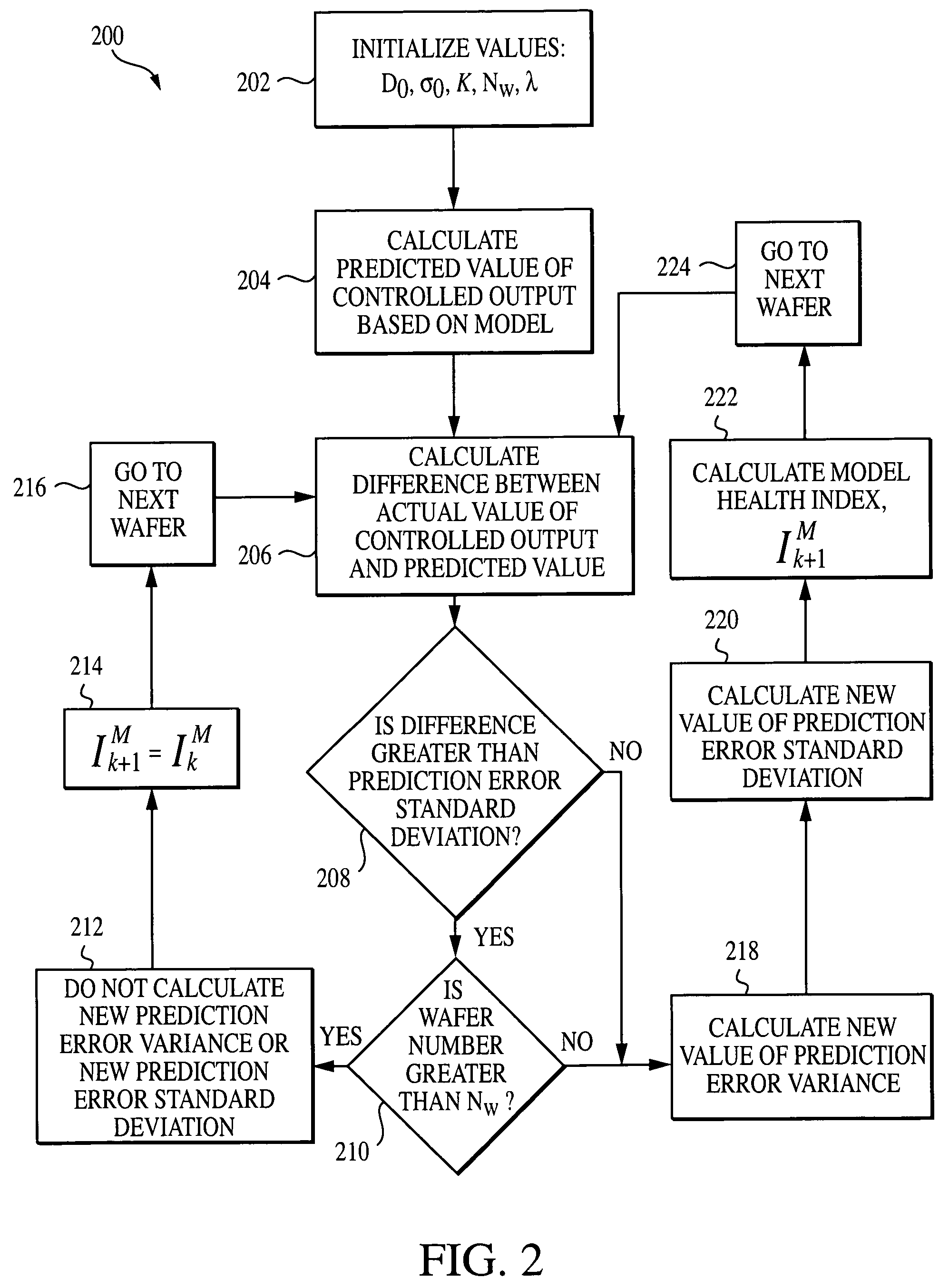
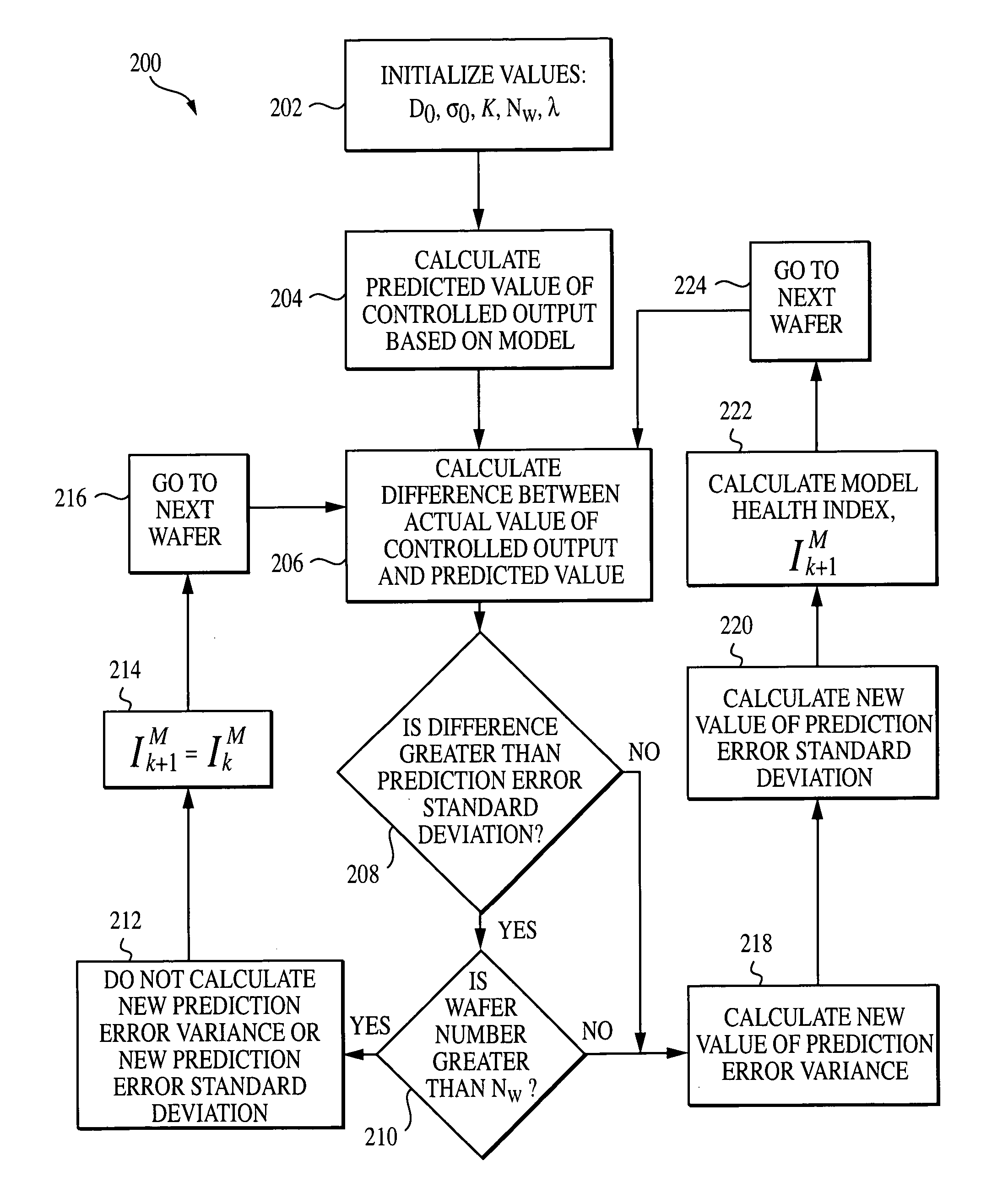
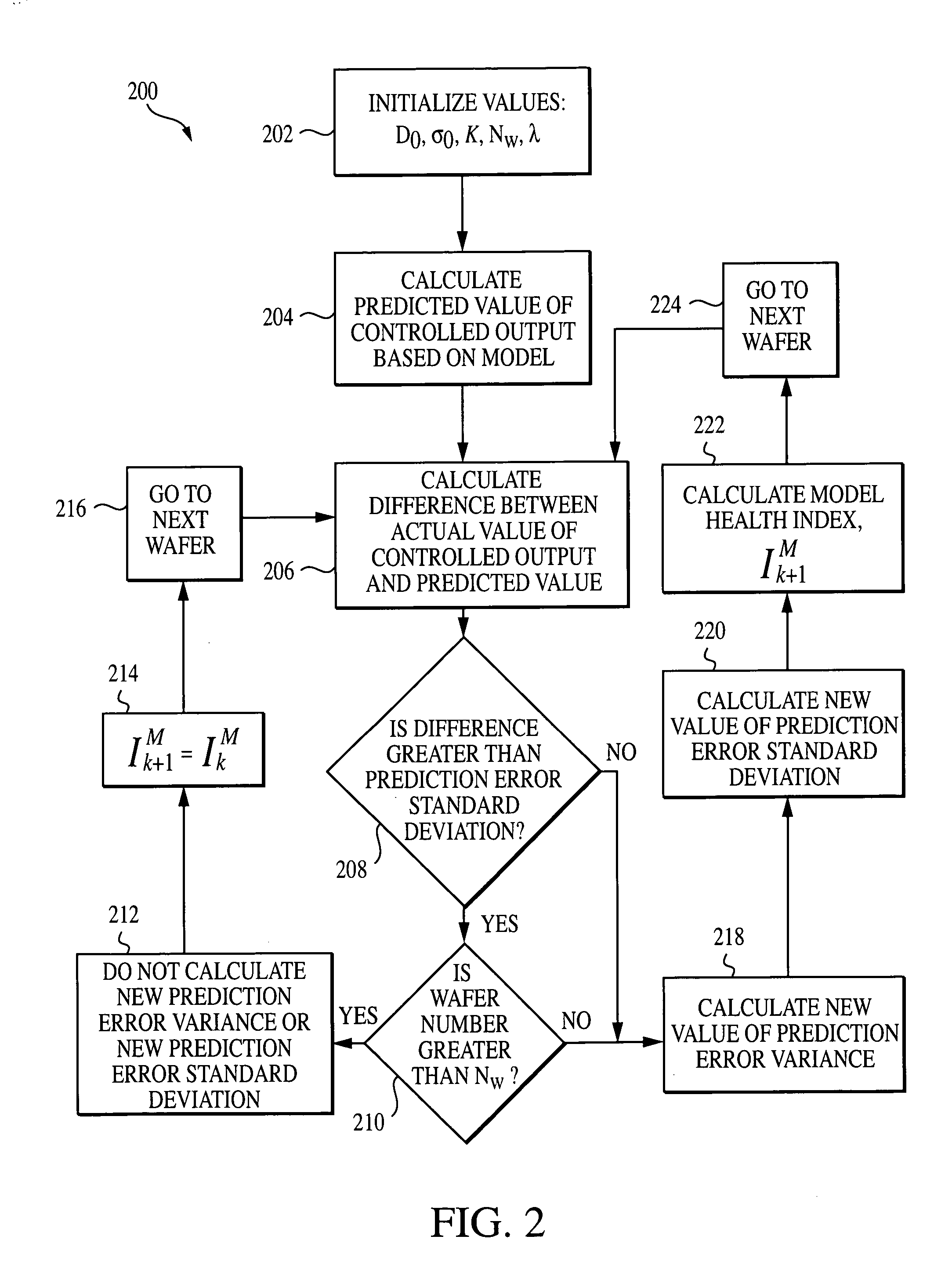
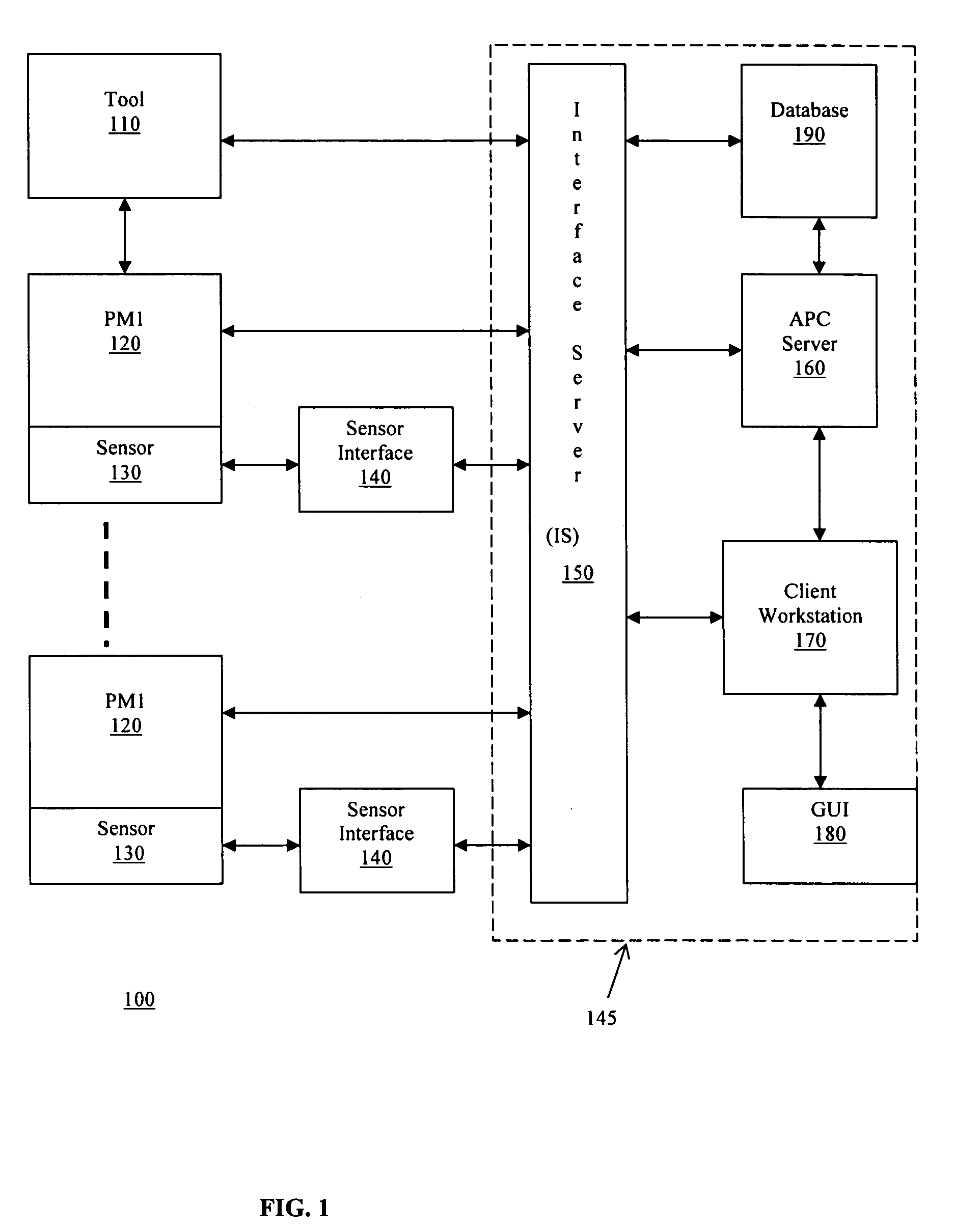
System, method, and medium for monitoring performance of an advanced process control system
InactiveUS7356377B2Monitor performanceElectric testing/monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsHealth indexComputation process
A method for monitoring performance of an advanced process control system for at least one process output includes calculating a variance of a prediction error for a processing performance and / or a probability for violating specification limits of the processing performance of the at least one process output. If the variance of the prediction error is calculated, the method also includes calculating a model health index. If the probability for violating specification limits is calculated, the method further includes calculating a process health index.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
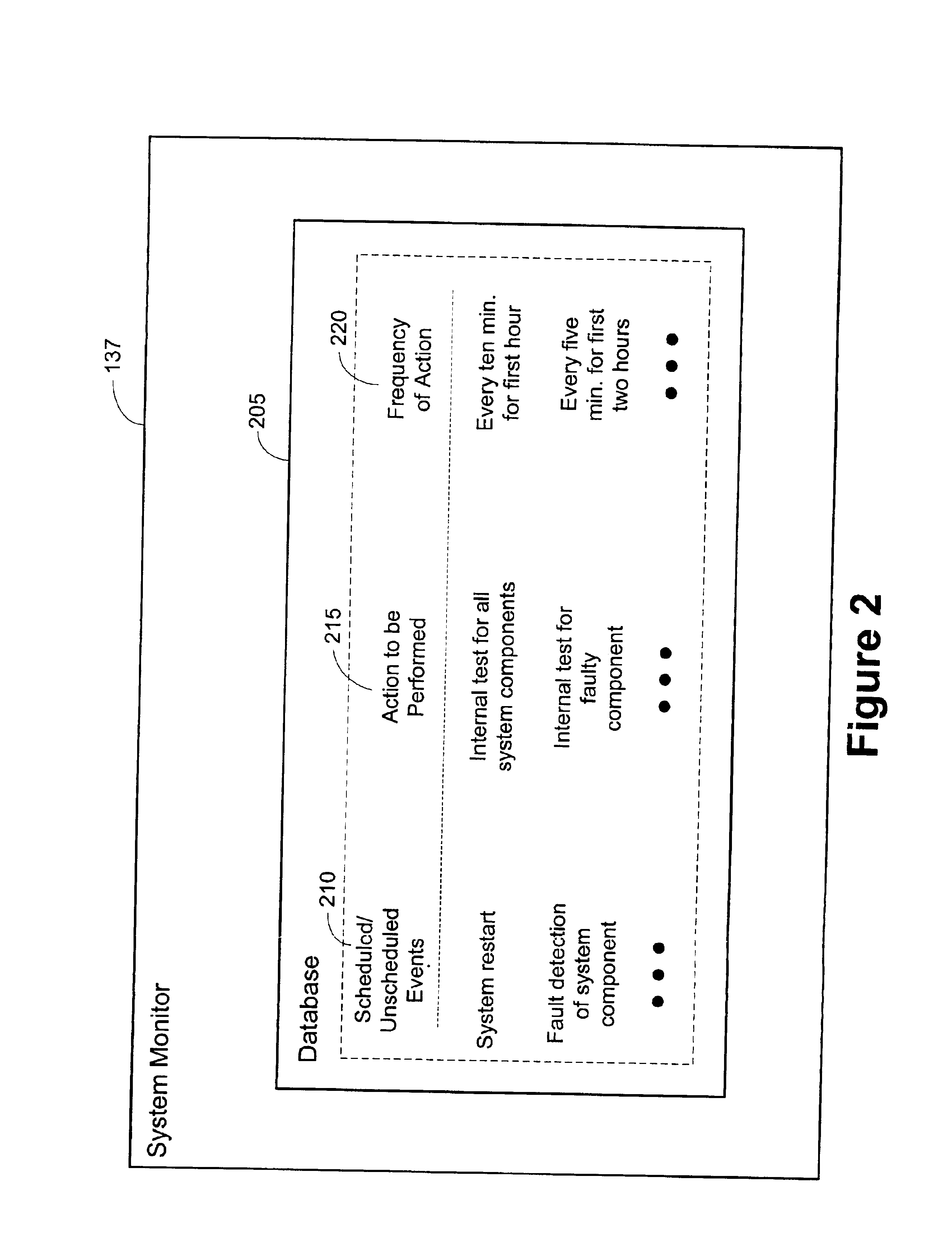
Method and apparatus for dynamically monitoring system components in an advanced process control (APC) framework
A method and system for monitoring a performance of at least one system component of a manufacturing system. At least one event that can occur within the system is defined. It is determined whether the at least one event has occurred within the system, and altering a frequency at which the at least one system component is monitored providing the at least one event has occurred within the system.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
System, method, and medium for monitoring performance of an advanced process control system
InactiveUS20050171626A1Monitor performanceElectric testing/monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsHealth indexComputation process
A method for monitoring performance of an advanced process control system for at least one process output includes calculating a variance of a prediction error for a processing performance and / or a probability for violating specification limits of the processing performance of the at least one process output. If the variance of the prediction error is calculated, the method also includes calculating a model health index. If the probability for violating specification limits is calculated, the method further includes calculating a process health index.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
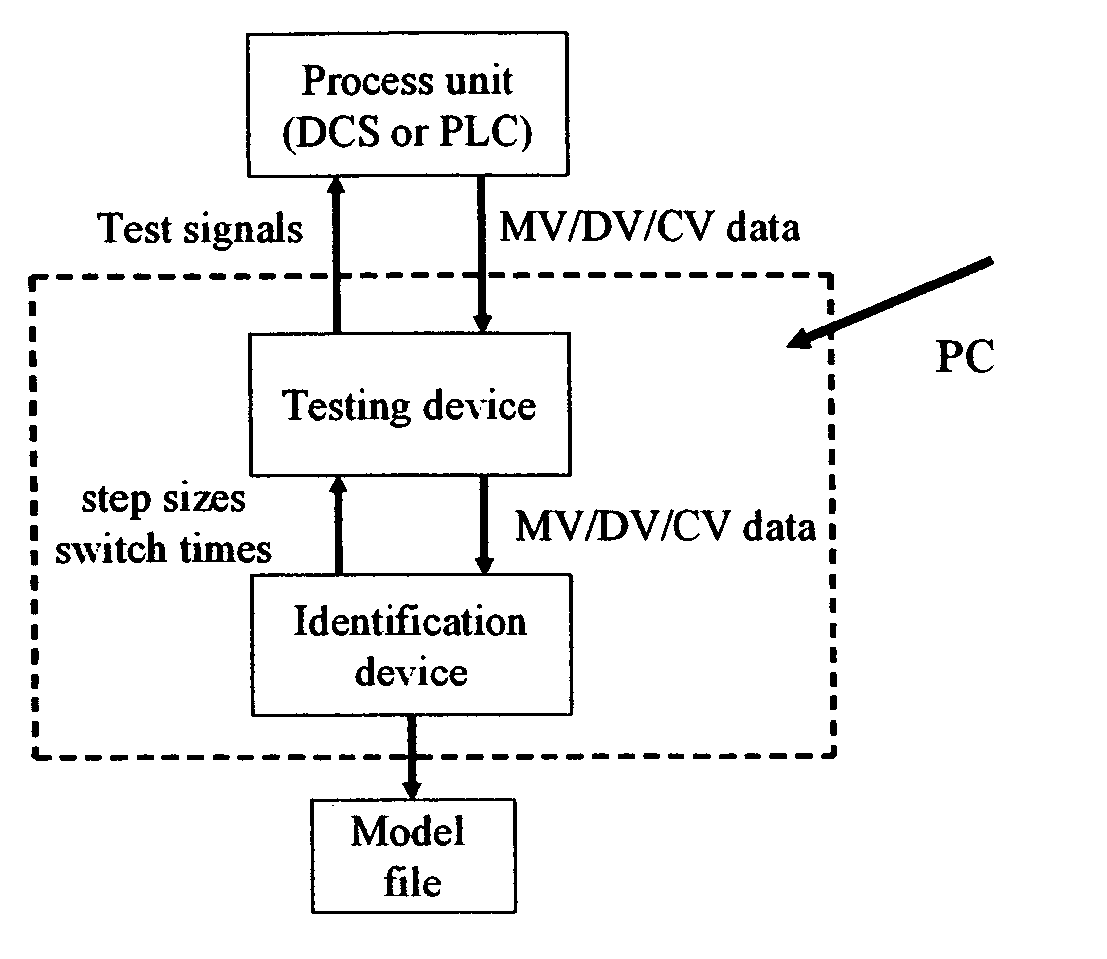
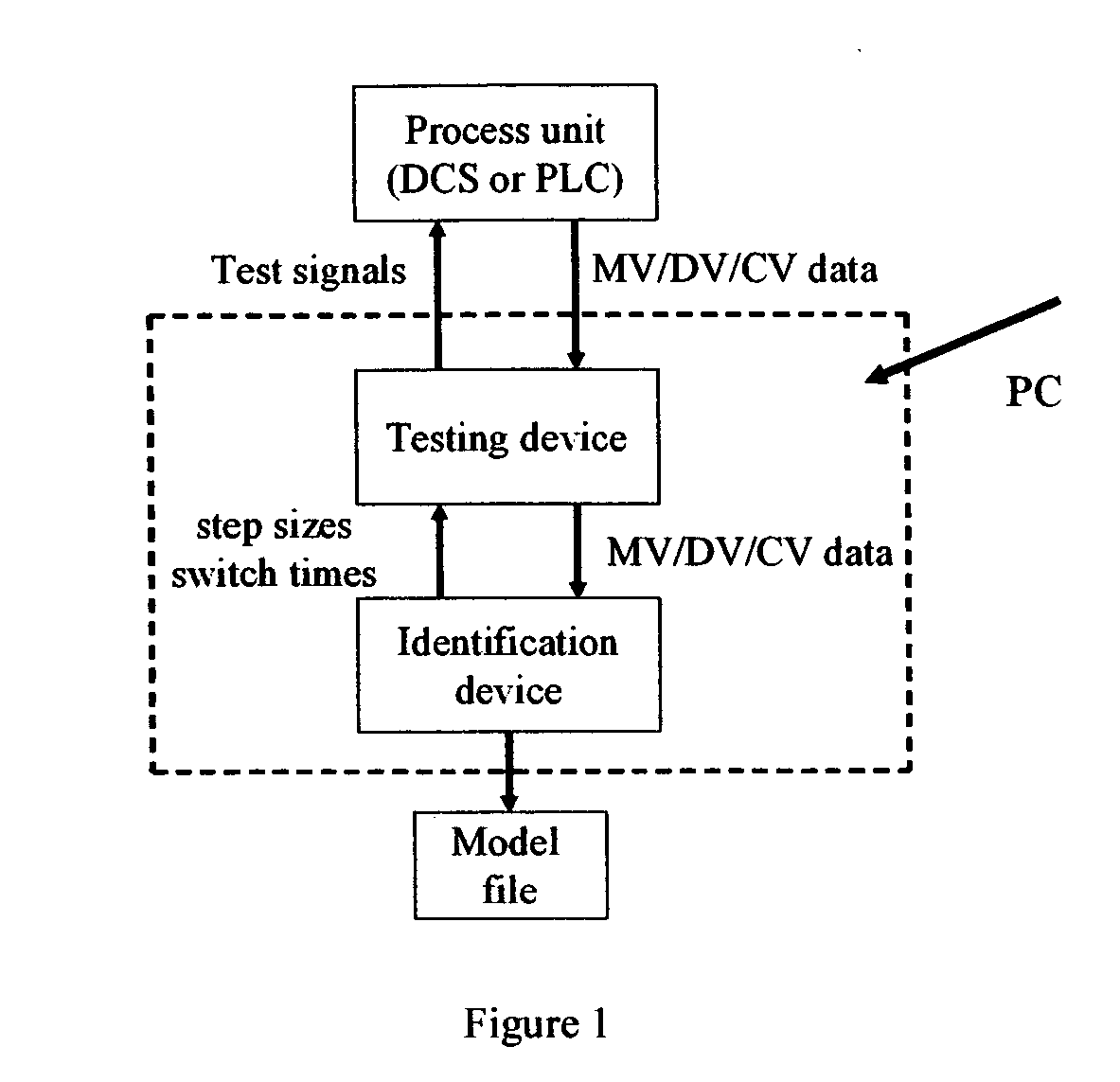
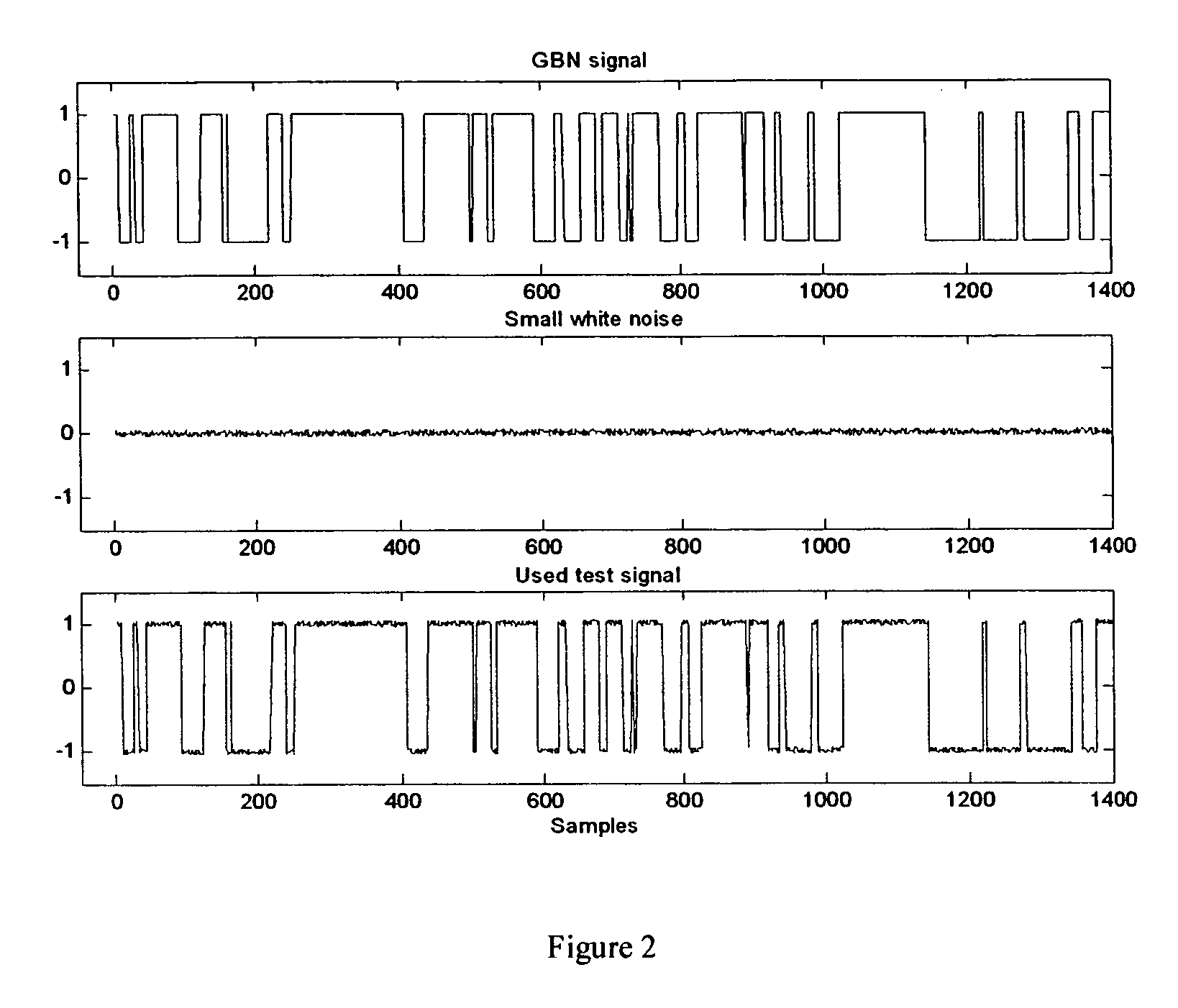
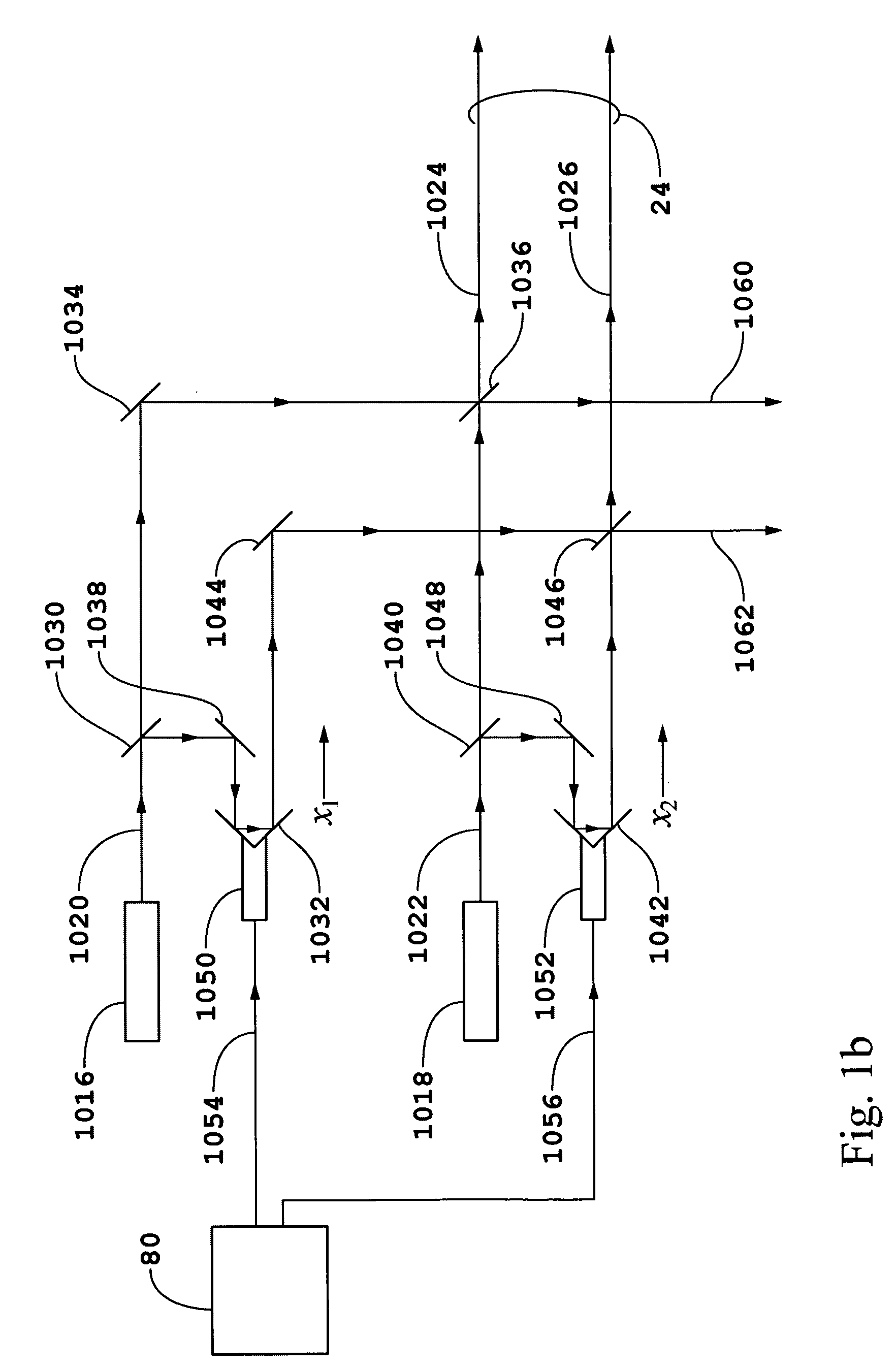
Computer method and apparatus for online process identification
InactiveUS20060111858A1Small sizeReduce stepsSimulator controlElectrical measurementsClosed loopPredictive controller
A computer method and apparatus of online automated model identification of multivariable processes is disclosed. The method and apparatus carries out automatically all the four basic steps of industrial process identification: 1) identification test signal design and generation, 2) identification plant test, 3) model identification and 4) model validation. During the automated plant test, process models will be automatically generated at a given time interval, for example, every hour, or on demand; the ongoing test can be automatically adjusted to meet the process constraints and to improve the data quality. Plant test can be in open loop operation, closed-loop operations or partly open loop and partly closed-loop. In a (partial) closed-loop plant test, any type of controller can be used which include proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers and any industrial model predictive controller (MPC). The obtained process models can be used as the model in advanced process controllers such as model predictive control (MPC) and linear robust control; they can also be used as inferential models or soft sensors in prediction product qualities. The apparatus can be used in new MPC controller commissioning as well as in MPC controller maintenance.
Owner:ZHU YUCAI
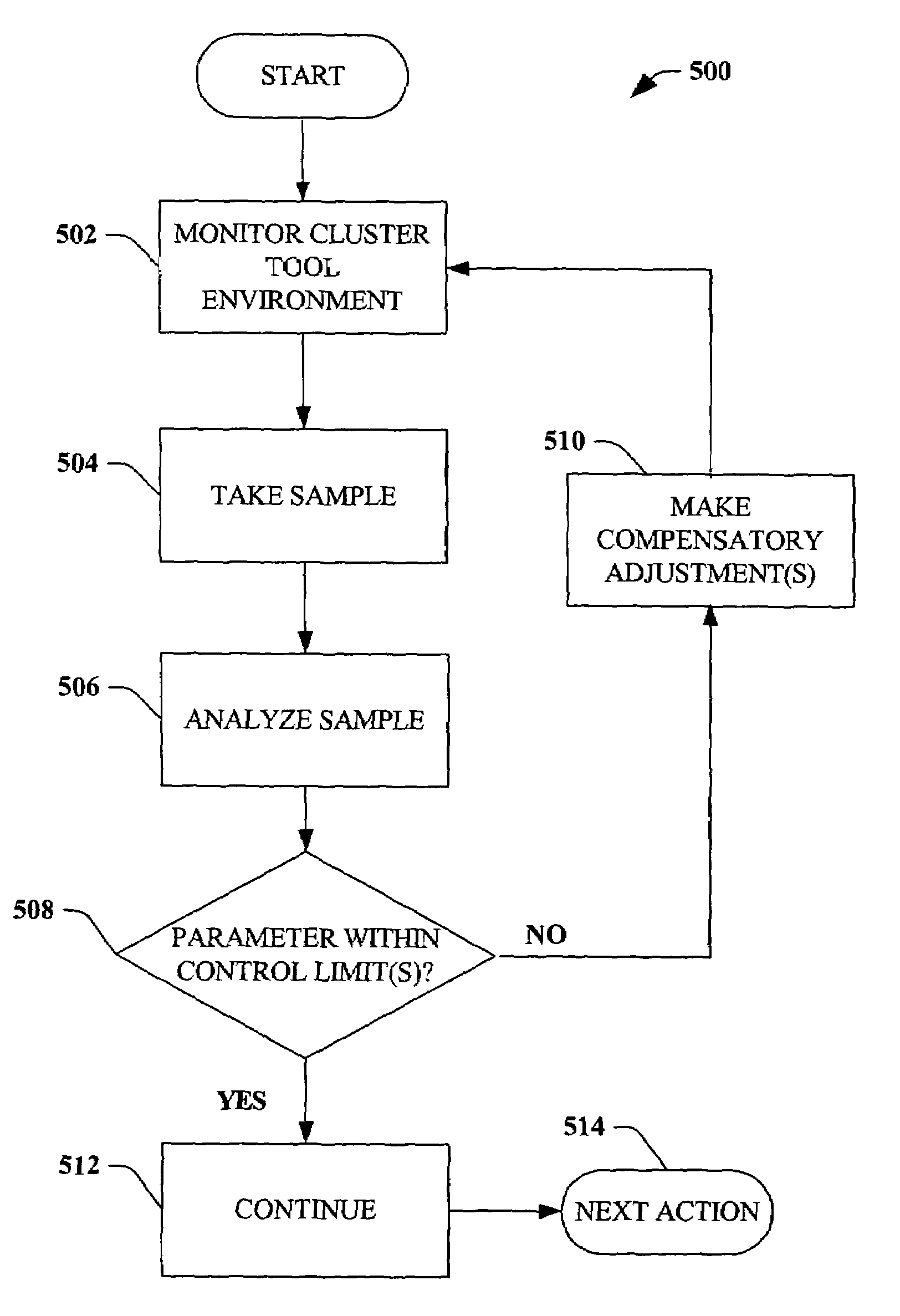
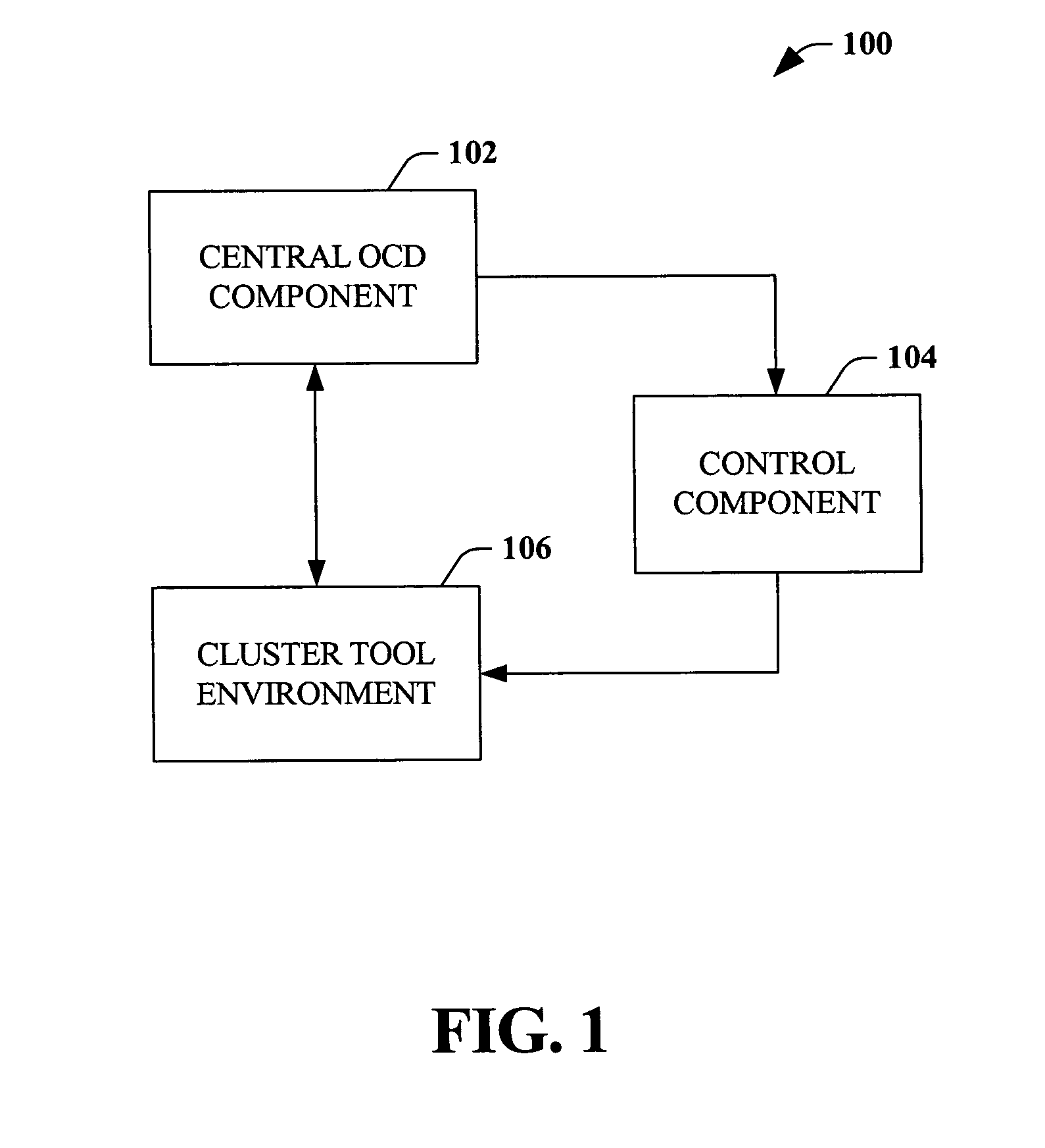
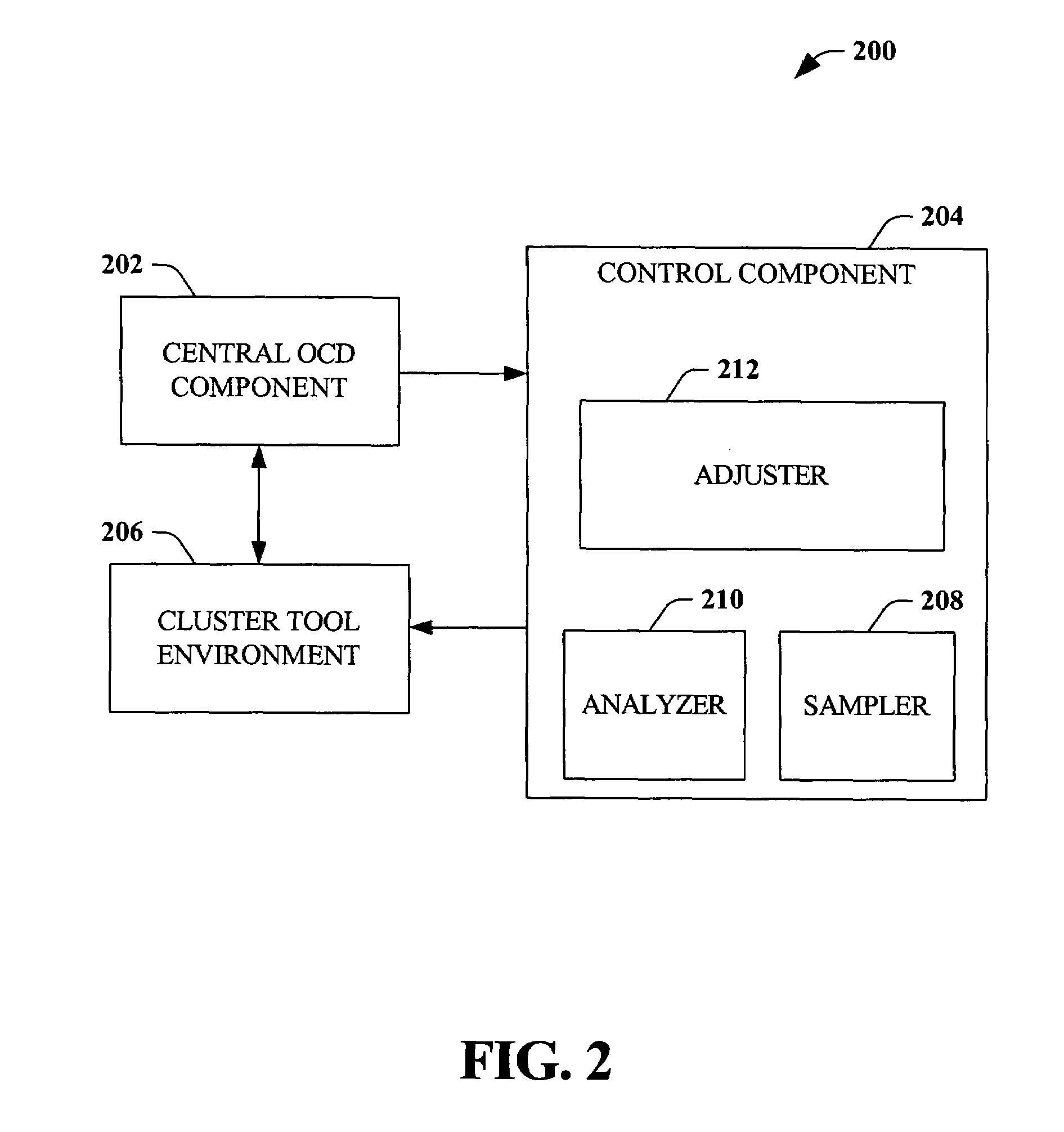
Scatterometry monitor in cluster process tool environment for advanced process control (APC)
ActiveUS7076320B1Strengthen process controlIncrease productivityFeeler-pin gaugesPhotomechanical apparatusControl limitsPlasma etcher
Systems and methods that improve process control in semiconductor manufacturing are disclosed. According to an aspect of the invention, conditions in a cluster tool environment and / or a wafer therein can be monitored in-situ via, for example, a scatterometry system, to determine whether parameters associated with wafer production are within control limits. A cluster tool environment can include, for example, a lithography track, a stepper, a plasma etcher, a cleaning tool, a chemical bath, etc. If an out-of-control condition is detected, either associated with a tool in the cluster tool environment or with the wafer itself, compensatory measures can be taken to correct the out-of-control condition. The invention can further employ feedback / feed-forward loop(s) to facilitate compensatory action in order to improve process control.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
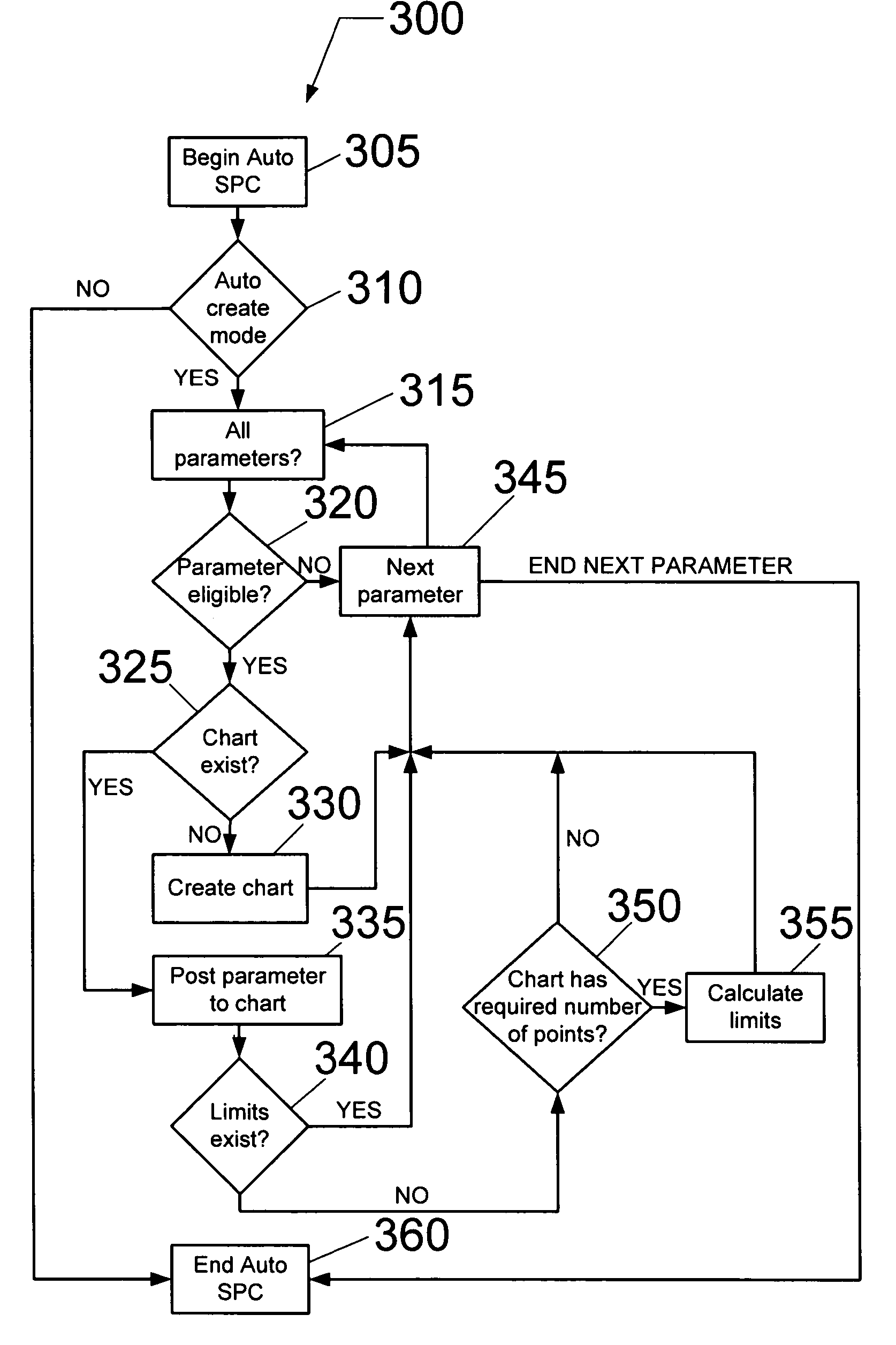
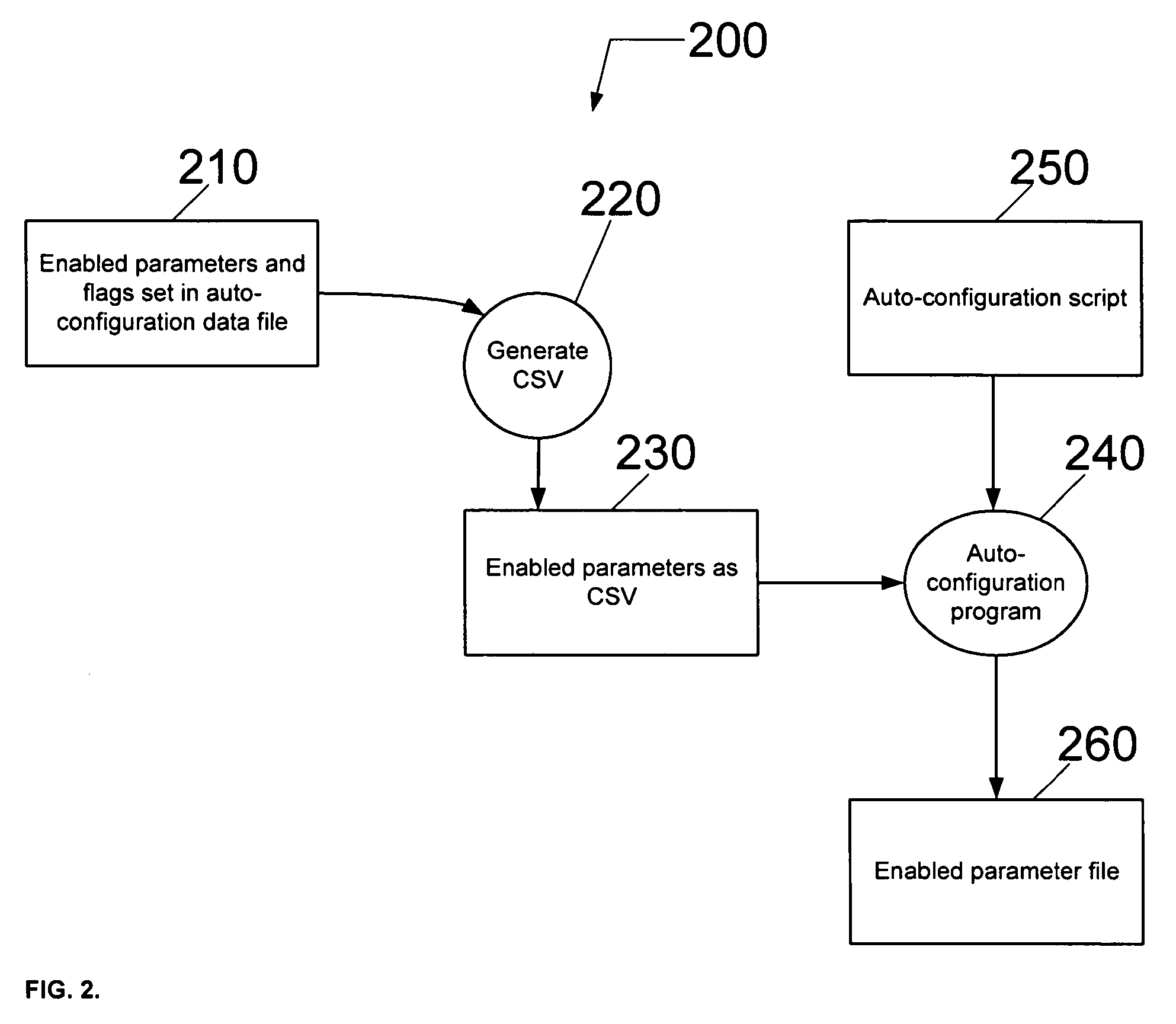
Method for automatic configuration of processing system
ActiveUS7213478B2Wave based measurement systemsCalibration apparatusAuto-configurationHandling system
A method of automatically configuring an Advanced Process Control (APC) system for a semiconductor manufacturing environment in which an auto-configuration script is generated for executing an auto-configuration program. The auto-configuration script activates default values for input to the auto-configuration program. The auto-configuration script is executed to generate an enabled parameter file output from the auto-configuration program. The enabled parameter file identifies parameters for statistical process control (SPC) chart generation.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
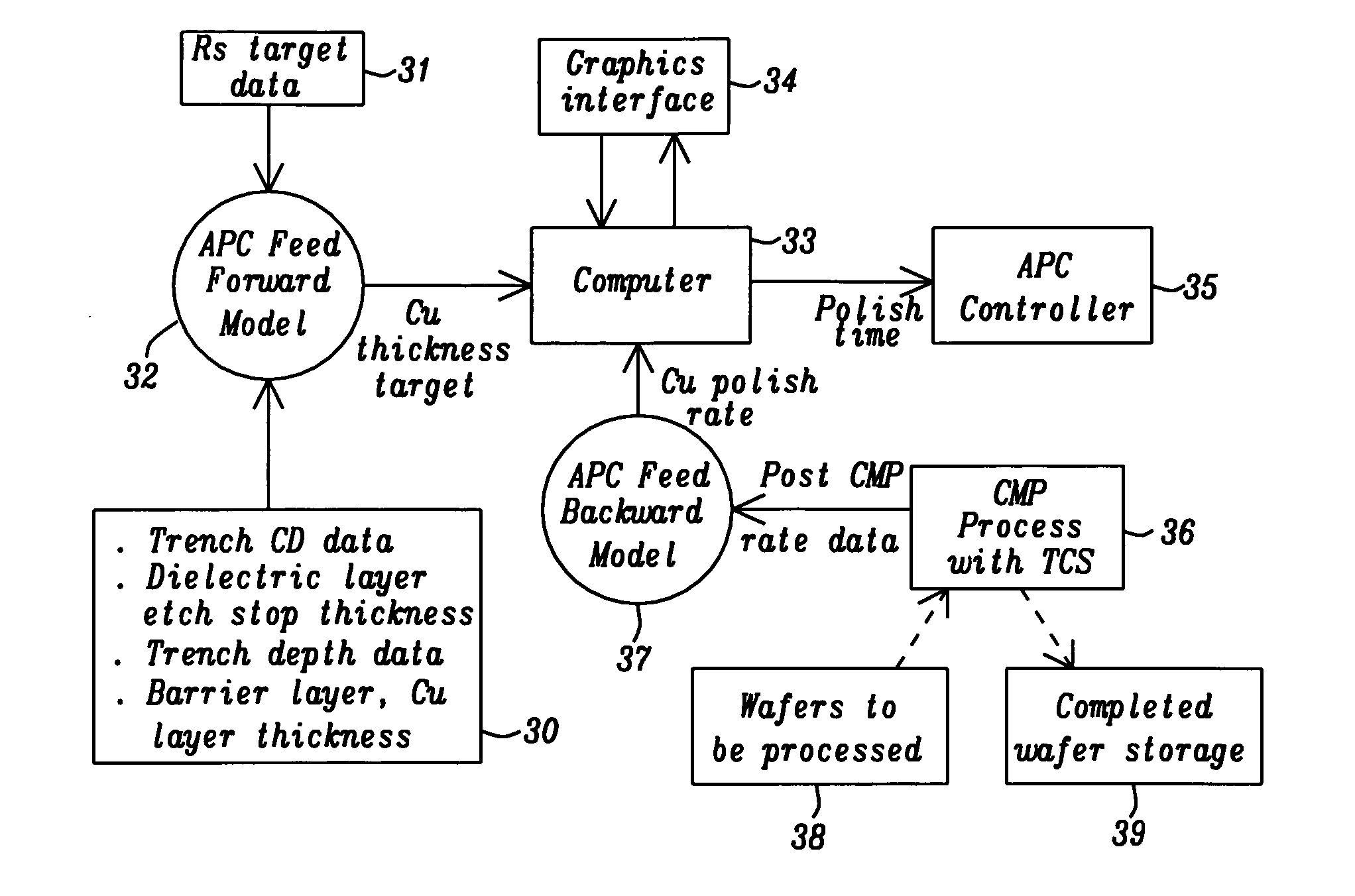
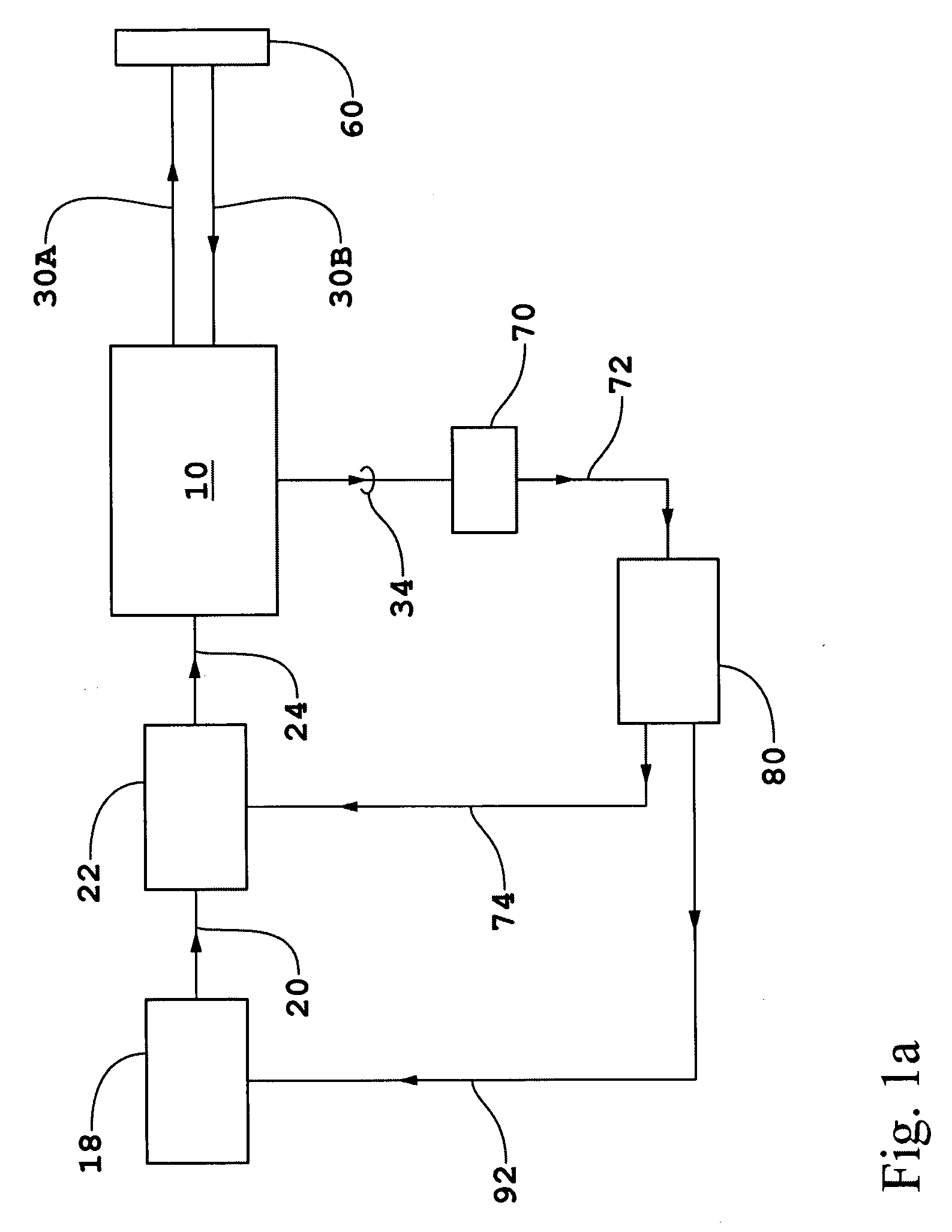
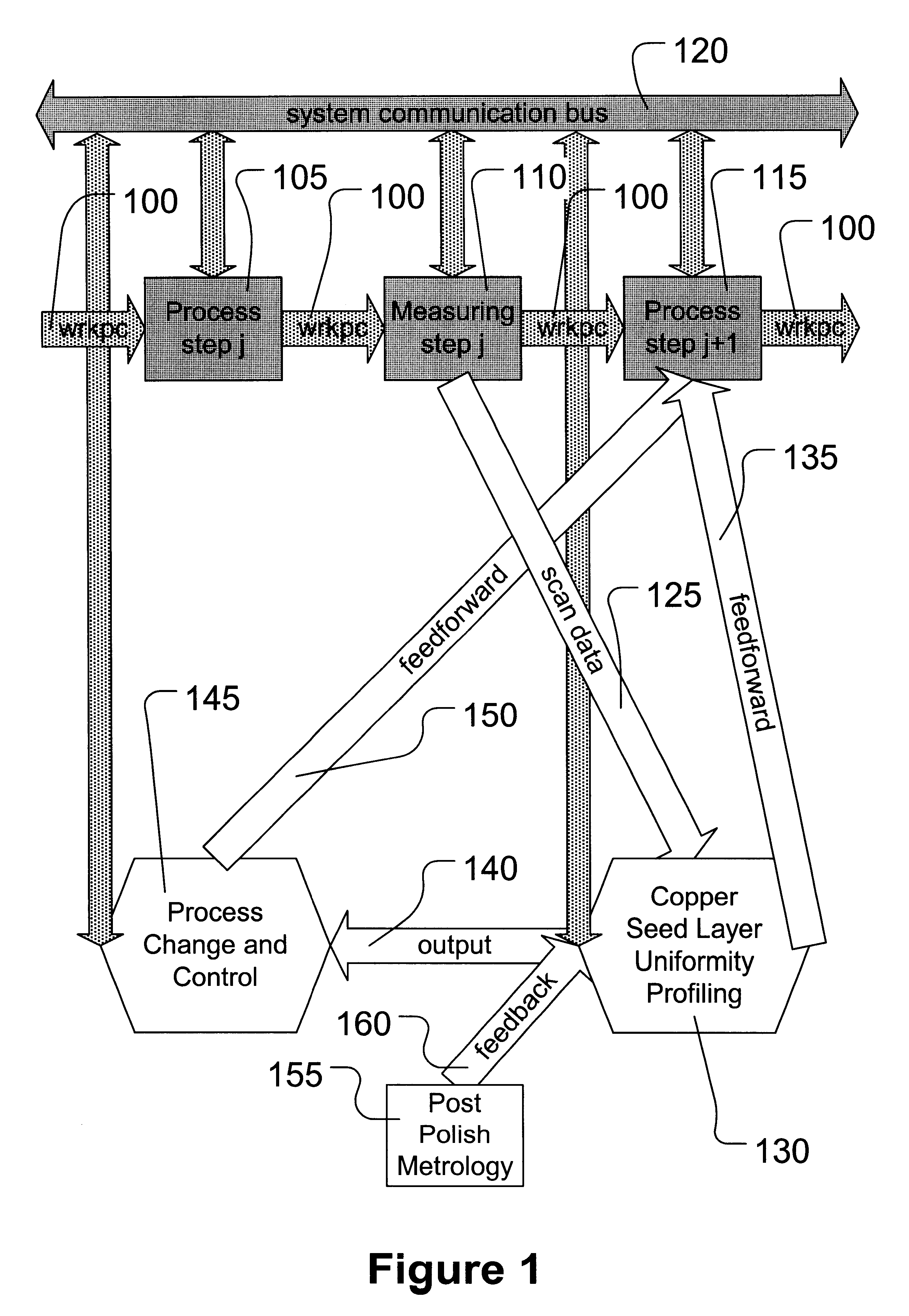
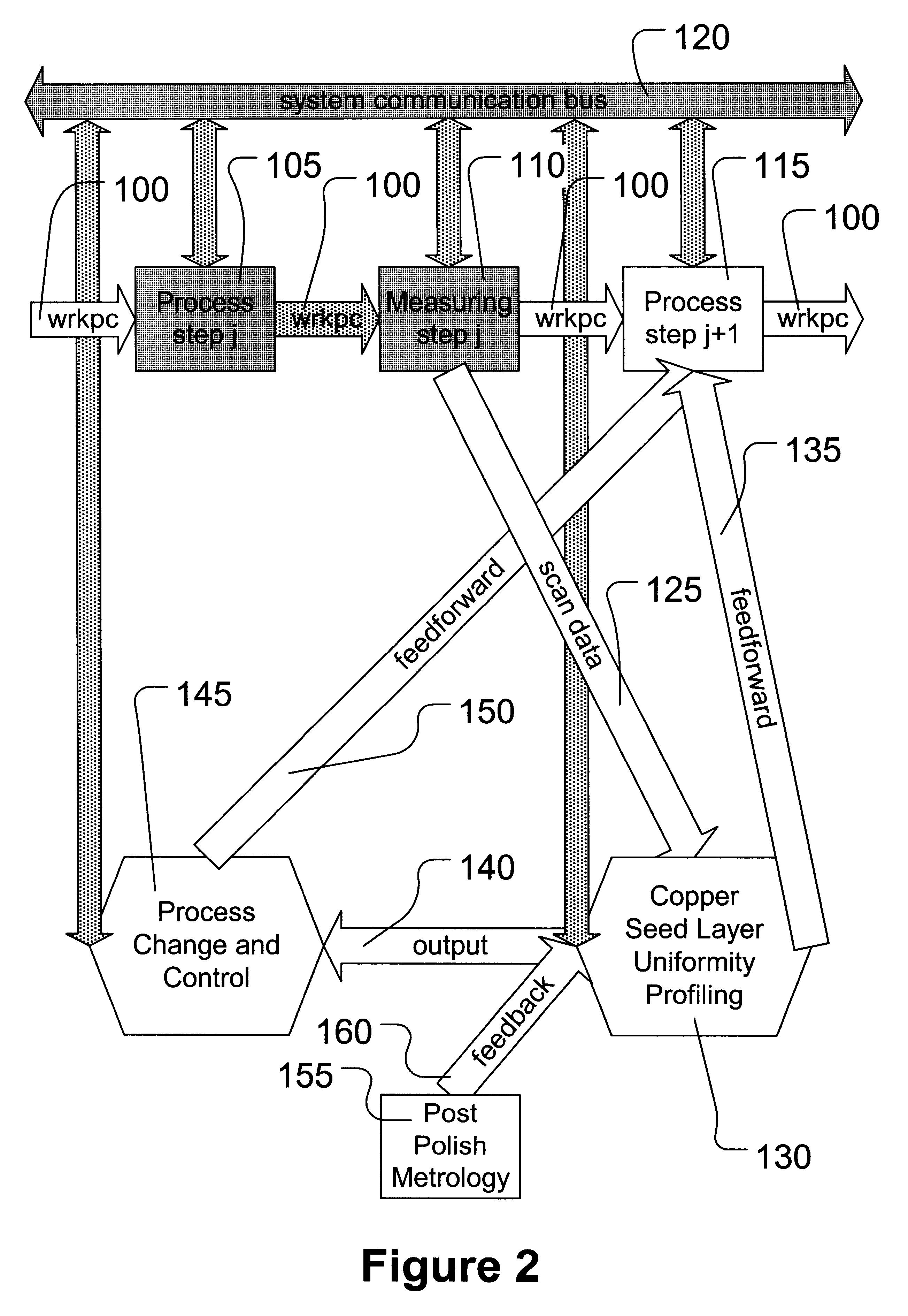
Advanced process control approach for Cu interconnect wiring sheet resistance control
InactiveUS20050112997A1Minimizes Cu sheet resistance (Rs) variationReduce variationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesElectrical resistance and conductanceMetrology
A wafer based APC method for controlling an oxide (Cu, or TaN) polish step is described and combines a feed forward model that compensates for incoming wafer variations with a feed backward model which compensates for CMP variations. The method is geared toward minimizing Rs 3σ variations. A Rs target value is inputted with metrology data from previous processes that affects the width and thickness of the copper layer. A copper thickness target and polish time for the first wafer is determined. Post CMP measurement data of the first wafer is used to modify the polish rate with a disturbance factor and an updated polish time is computed for subsequent wafers. The CMP recipe for each wafer is adjusted with metrology data and post CMP measurements. The APC method is successful in controlling copper Rs variations for the 90 nm technology node and is independent of copper pattern density.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
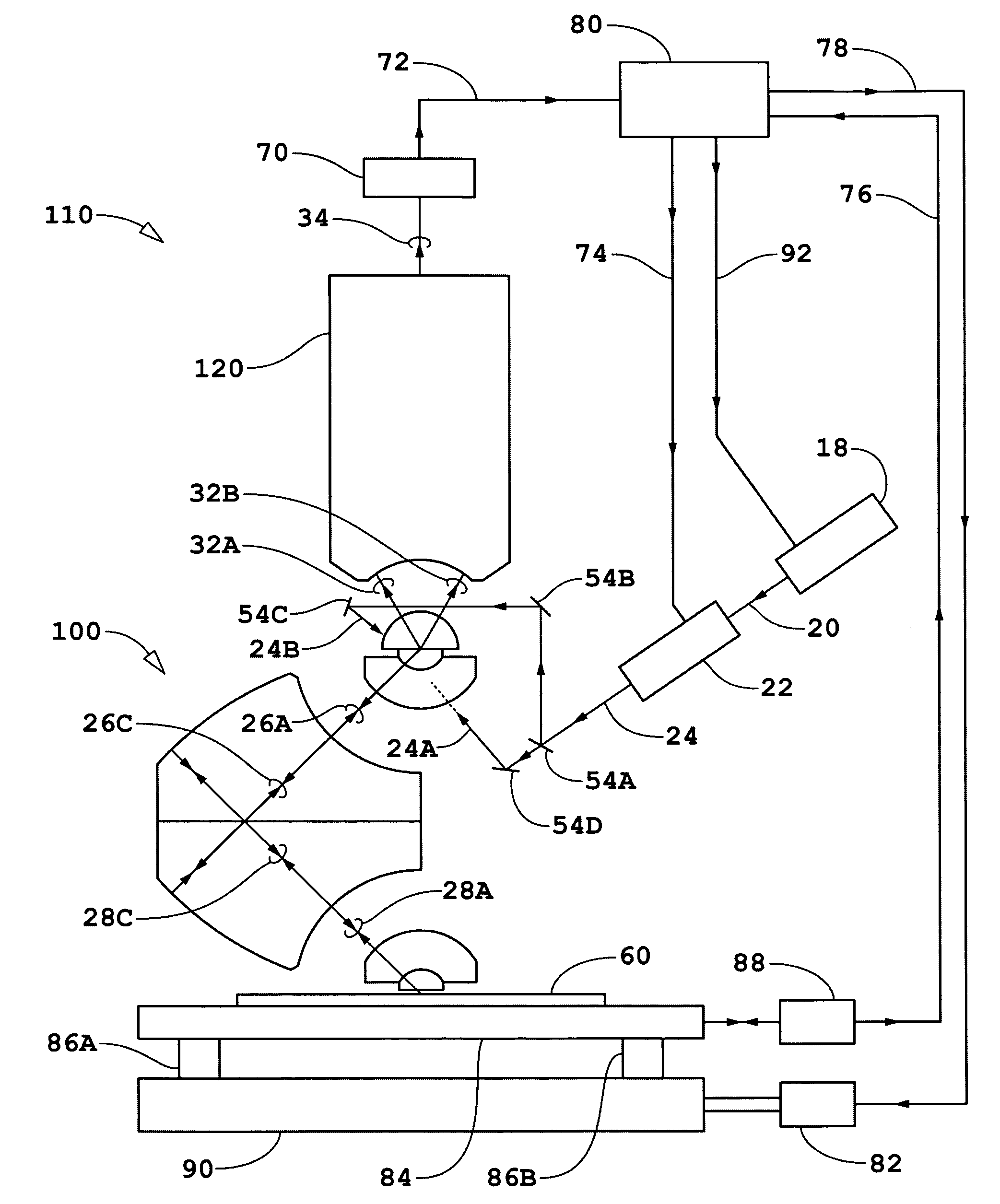
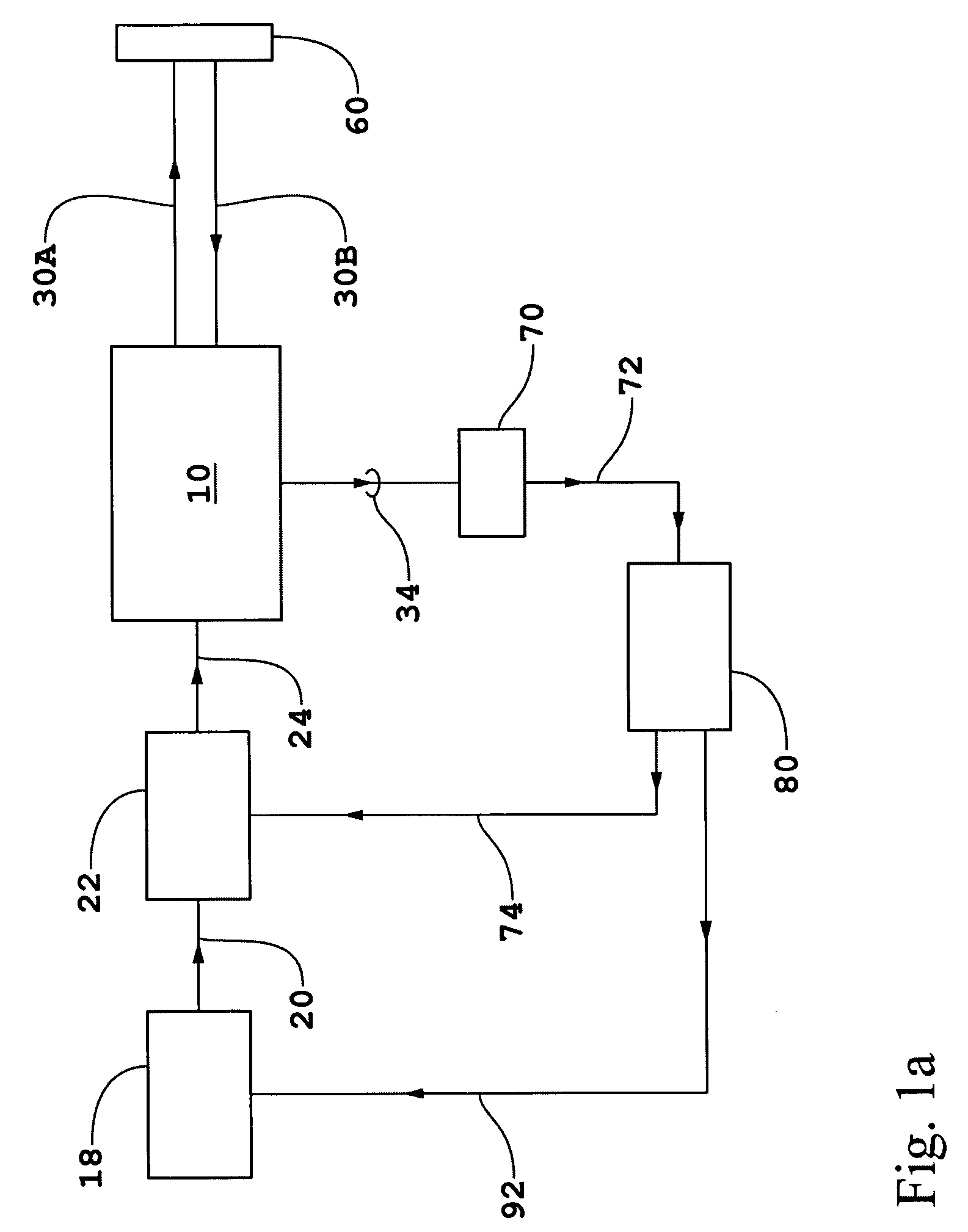
Apparatus and methods for overlay, alignment mark, and critical dimension metrologies based on optical interferometry
InactiveUS20050275848A1Degrading measurement sensitivityThe result is accurateInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansMetrologyInterferometric imaging
Methods and apparatus based on optical homodyne displacement interferometry, optical coherent-domain reflectometry (OCDR), and optical interferometric imaging are disclosed for overlay, alignment mark, and critical dimension (CD) metrologies that are applicable to microlithography applications and integrated circuit (IC) and mask fabrication and to the detection and location of defects in / on unpatterned and patterned wafers and masks. The metrologies may also be used in advanced process control (APC), in determination of wafer induced shifts (WIS), and in the determination of optical proximity corrections (OPC).
Owner:ZETETIC INST
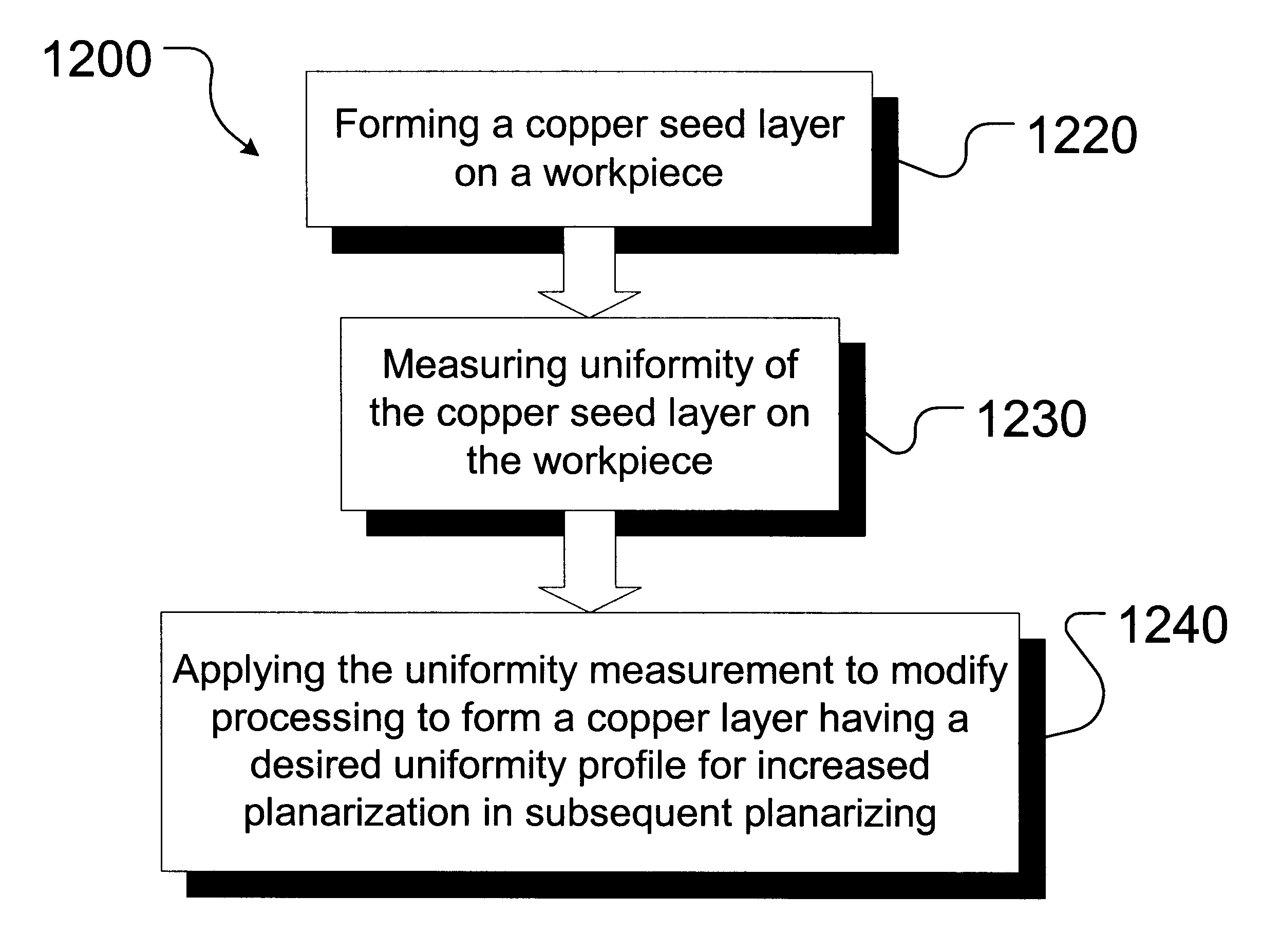
Advanced process control (APC) of copper thickness for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) optimization
InactiveUS6630360B2CellsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementCopperChemical-mechanical planarization
A method is provided that comprises forming a copper seed layer on a workpiece and measuring the uniformity of the copper seed layer on the workpiece. The method further comprises applying the uniformity measurement to modify processing to form a copper layer having a desired uniformity profile for increased planarization in subsequent planarizing.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Apparatus and methods for overlay, alignment mark, and critical dimension metrologies based on optical interferometry
InactiveUS7298496B2The result is accurateImprove accuracyInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansMetrologyInterferometric imaging
Methods and apparatus based on optical homodyne displacement interferometry, optical coherent-domain reflectometry (OCDR), and optical interferometric imaging are disclosed for overlay, alignment mark, and critical dimension (CD) metrologies that are applicable to microlithography applications and integrated circuit (IC) and mask fabrication and to the detection and location of defects in / on unpatterned and patterned wafers and masks. The metrologies may also be used in advanced process control (APC), in determination of wafer induced shifts (WIS), and in the determination of optical proximity corrections (OPC).
Owner:ZETETIC INST
Method of large scale process optimization and optimal planning based on real time dynamic simulation
ActiveUS20130317629A1Avoids costly step testingHigh precisionAdaptive controlProcess optimizationMulti unit
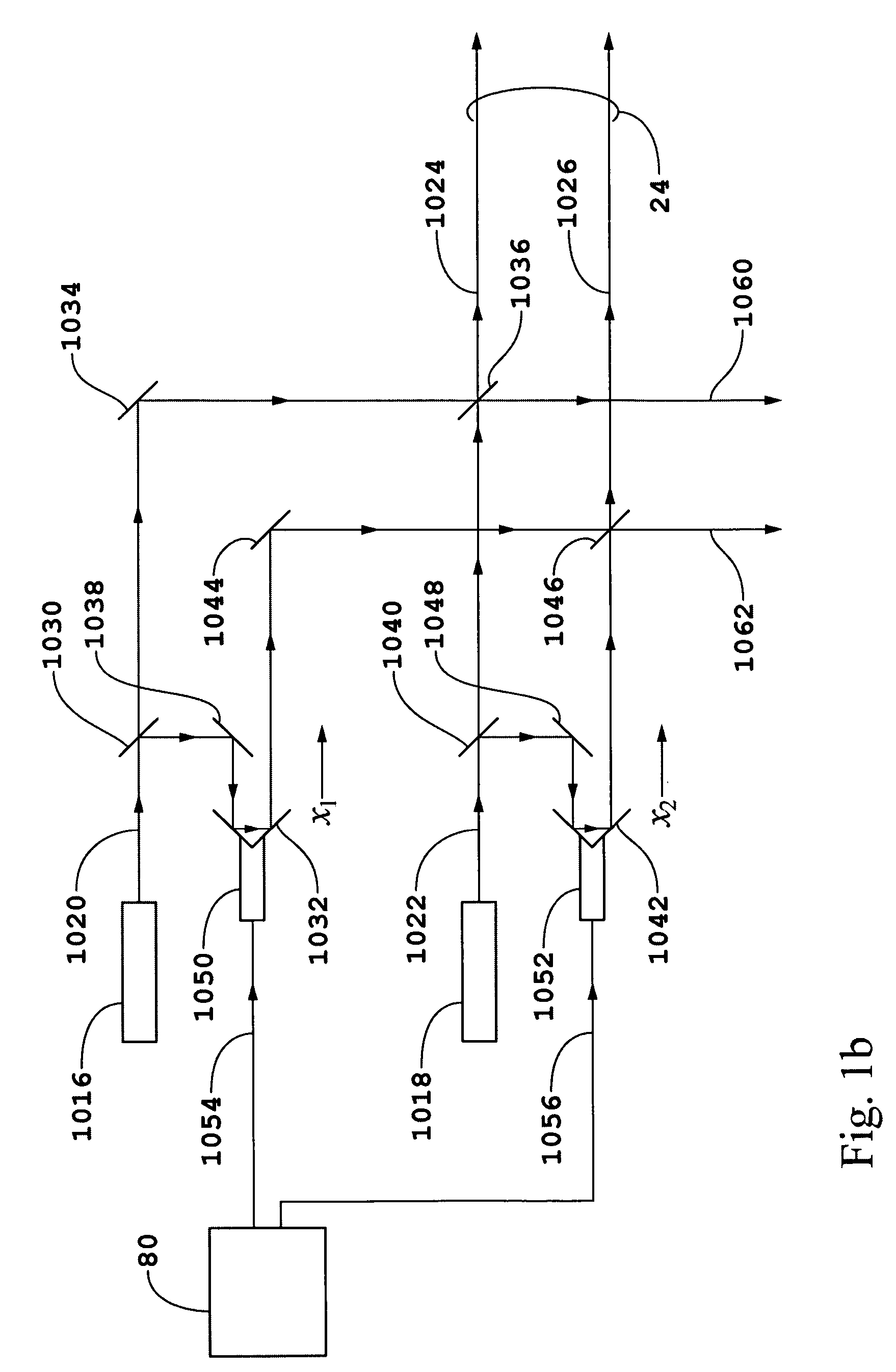
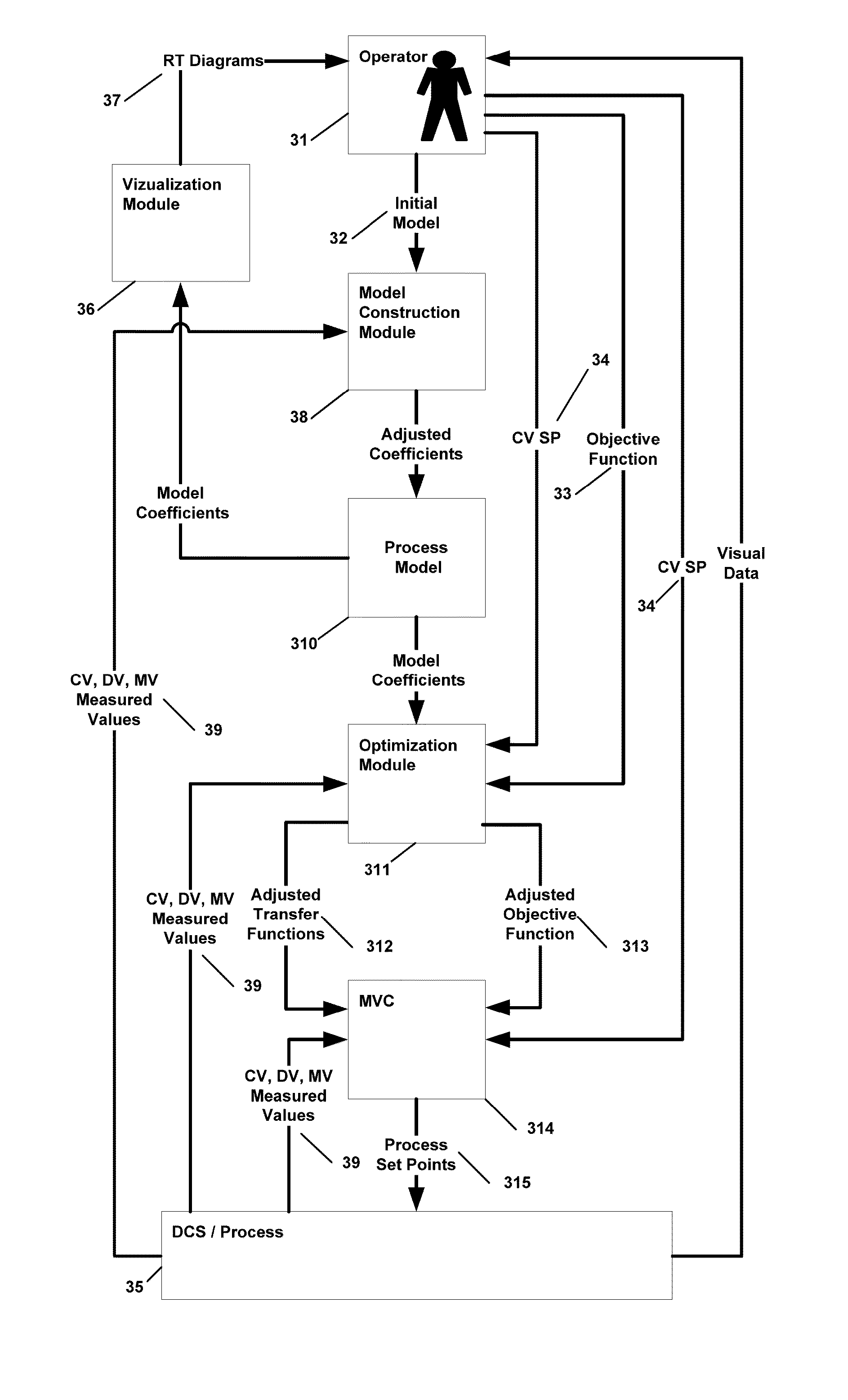
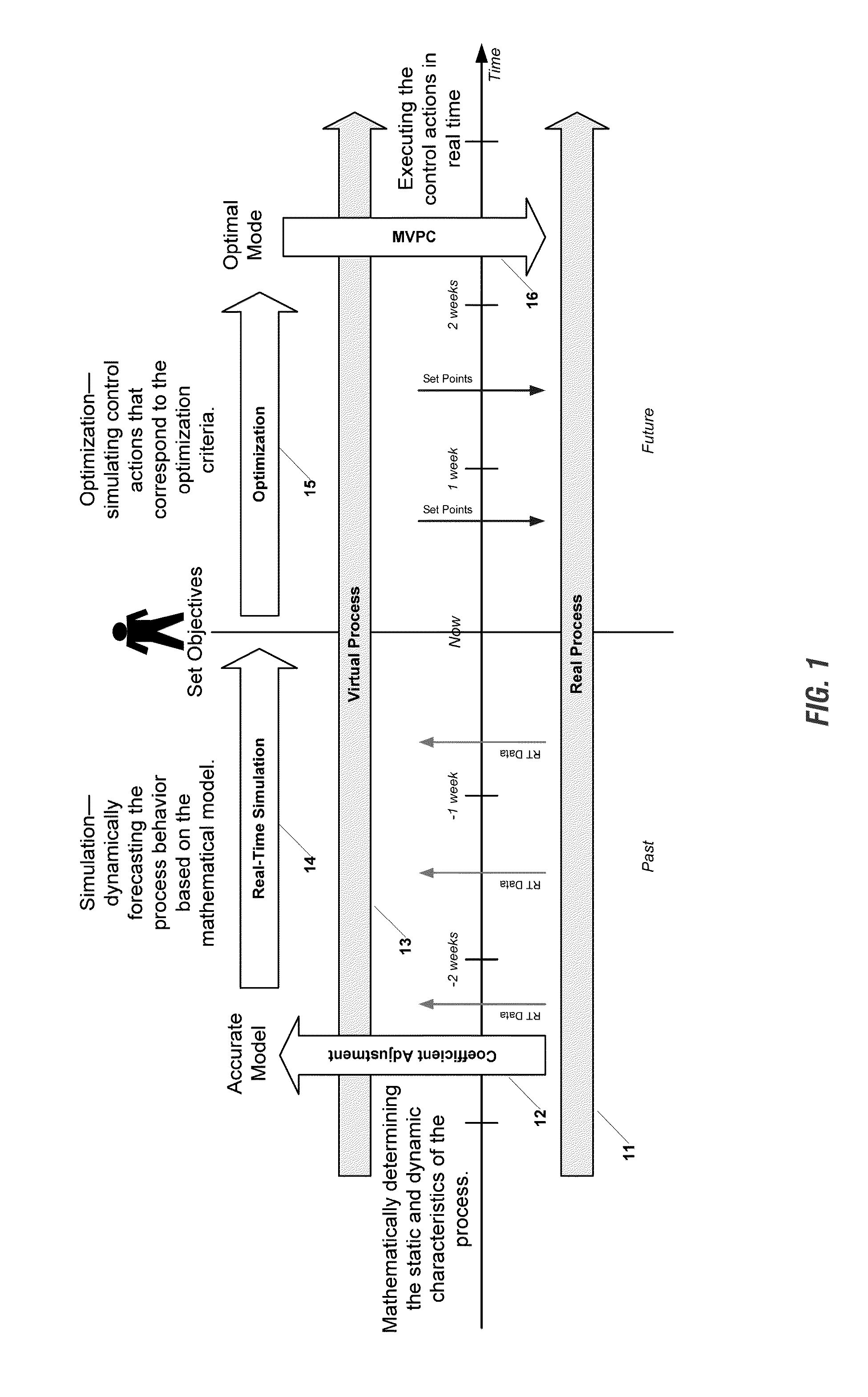
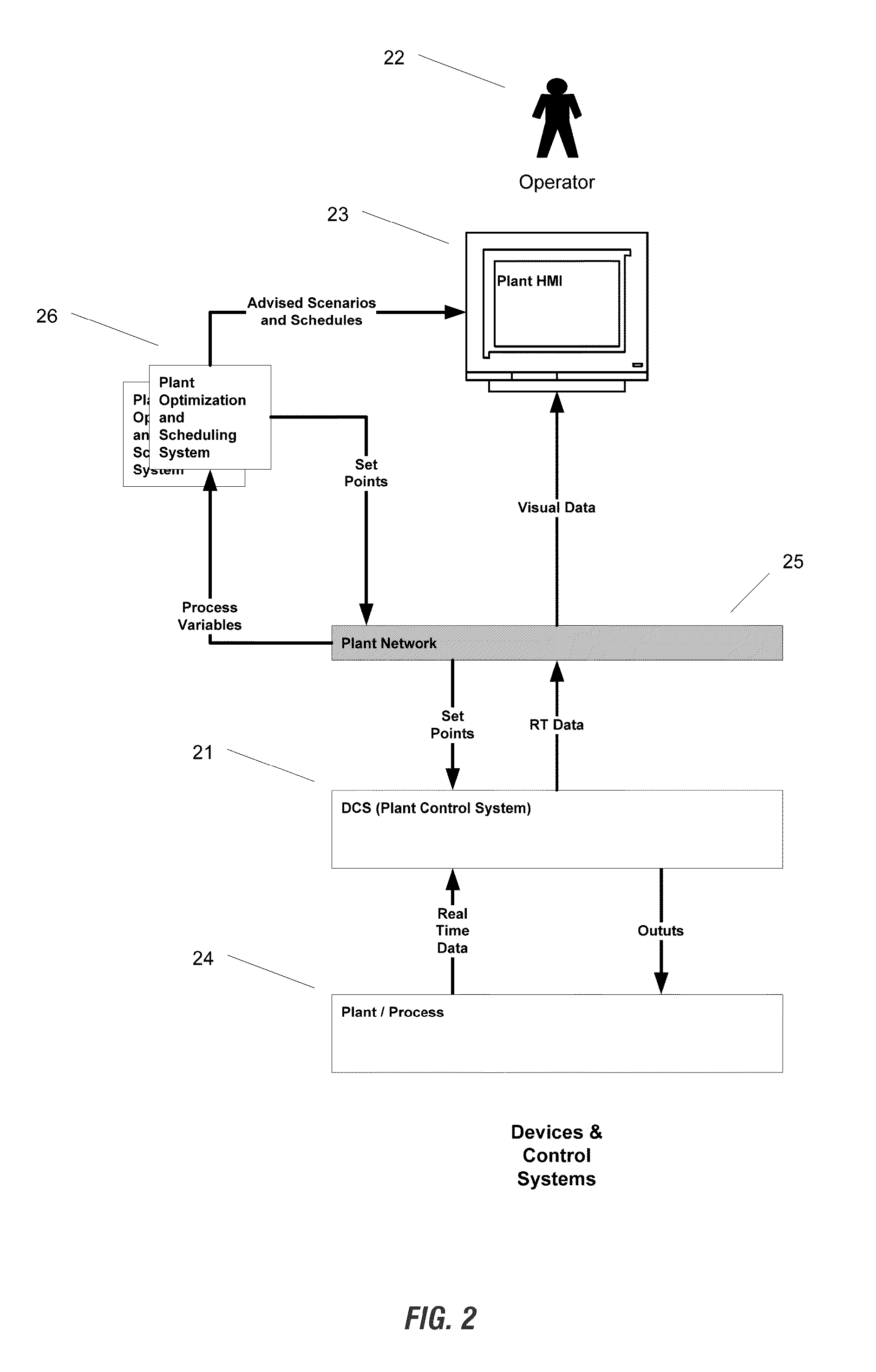
This invention provides a system and method of Advanced Process Control for optimal operation of multi-unit plants in large scale processing and power generation industries. The invention framework includes the following components: continuous real time dynamic process simulation, automatic coefficient adjustment of dynamic and static process models, automatic construction of transfer functions, determination of globally optimal operating point specific to current conditions, provision of additional optimal operating scenarios through a variety of unit combinations, and calculation of operational forecasts in accordance with planned production.
Owner:STATISTICS & CONTROL
Method and apparatus for fuzzy logic control enhancing advanced process control performance
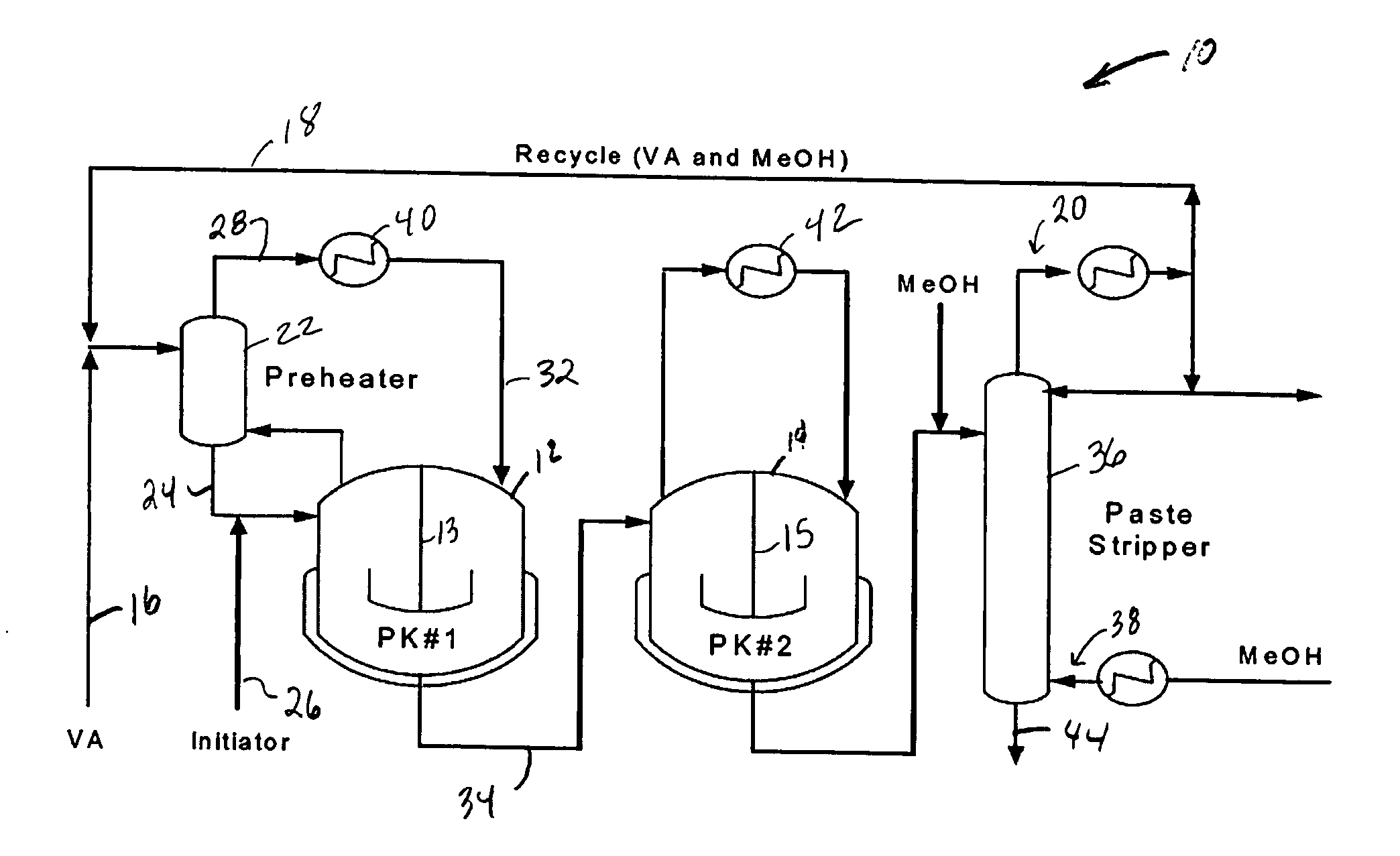
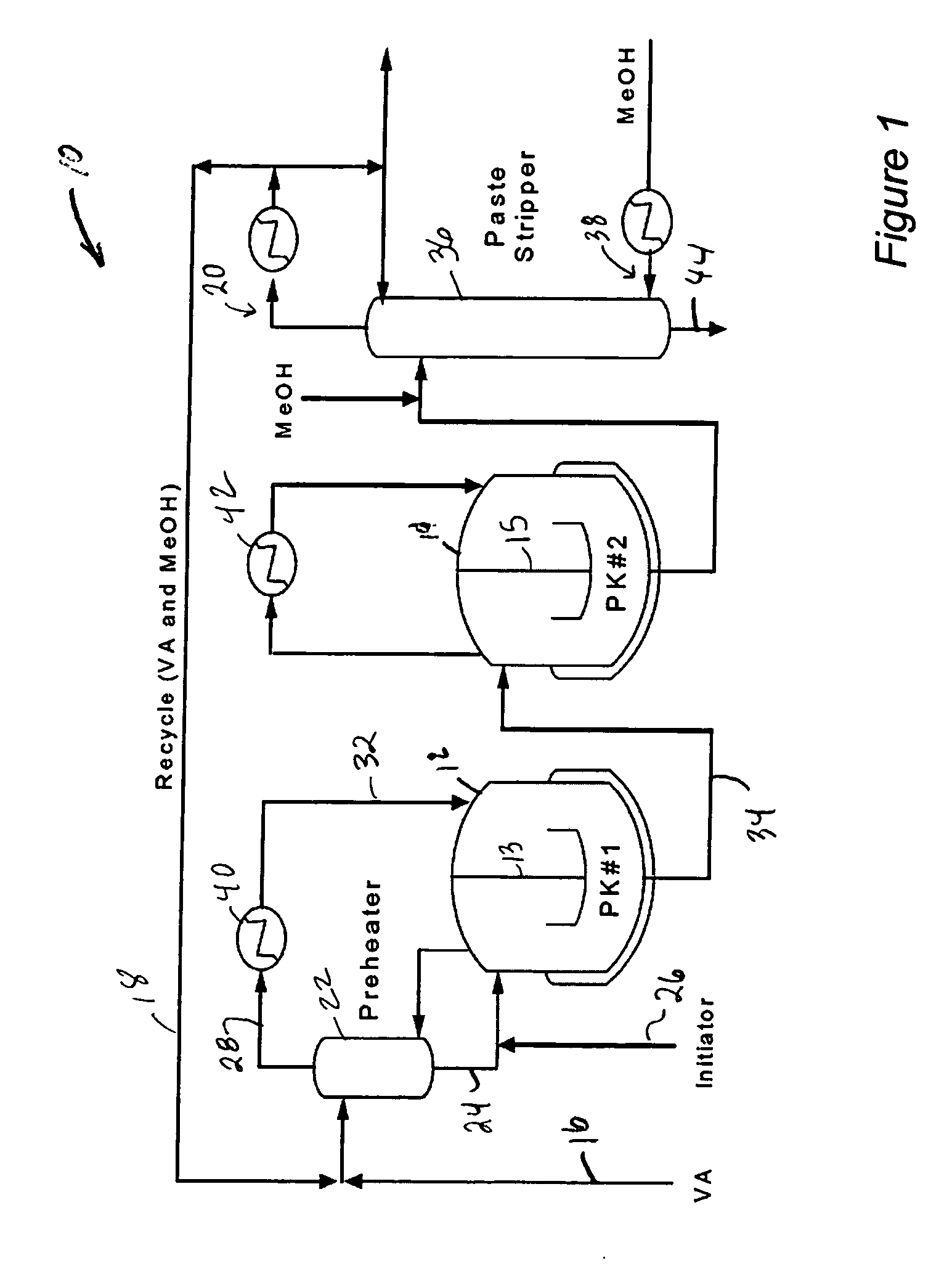
InactiveUS20070250214A1Process control/regulationSampled-variable control systemsFeedback controlPolymer
An apparatus and method for enhancing advanced process control (APC) performance based on fuzzy logic control (FLC) concept and methodology is described. The method and apparatus provide a systematic way to characterize / assess process operations (encompassing the manufacturing process, laboratory measurement systems, and control practices / results) automatically and then determine the best APC model update and feedback control strategies dynamically to cope with various control problems commonly observed in the polymer industry. Since the method is able to reach a single definite control output signal based upon vague, ambiguous, or imprecise input information, control issues that are difficult to quantify or model mathematically can now be addressed effectively and included as part of the APC control strategy. With the method, polymer manufactures can better use their existing off-line laboratory results for on-line APC controllers without resorting to costly on-line property measurements or inferential sensors.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
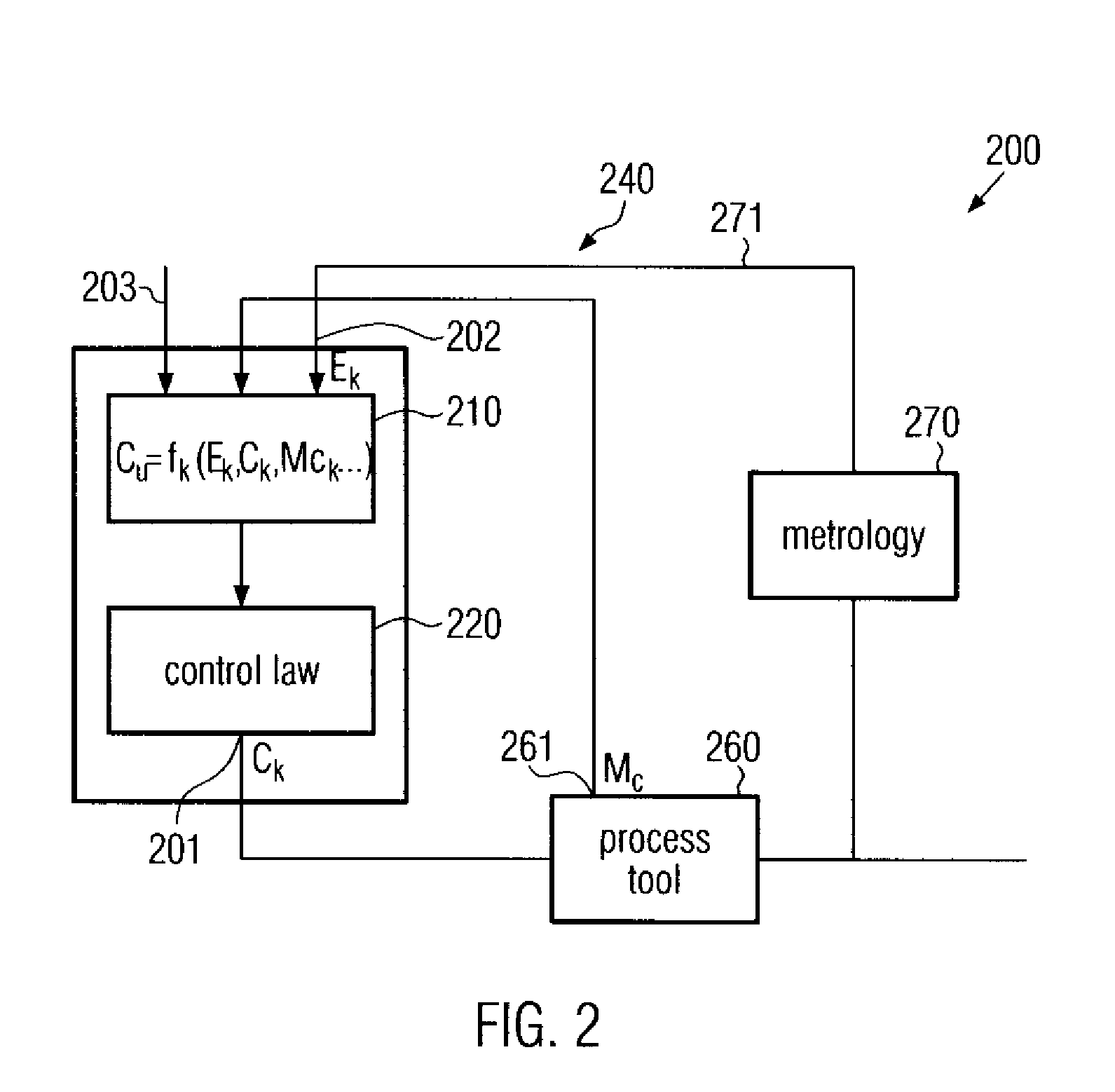
Method and system for advanced process control including tool dependent machine constants
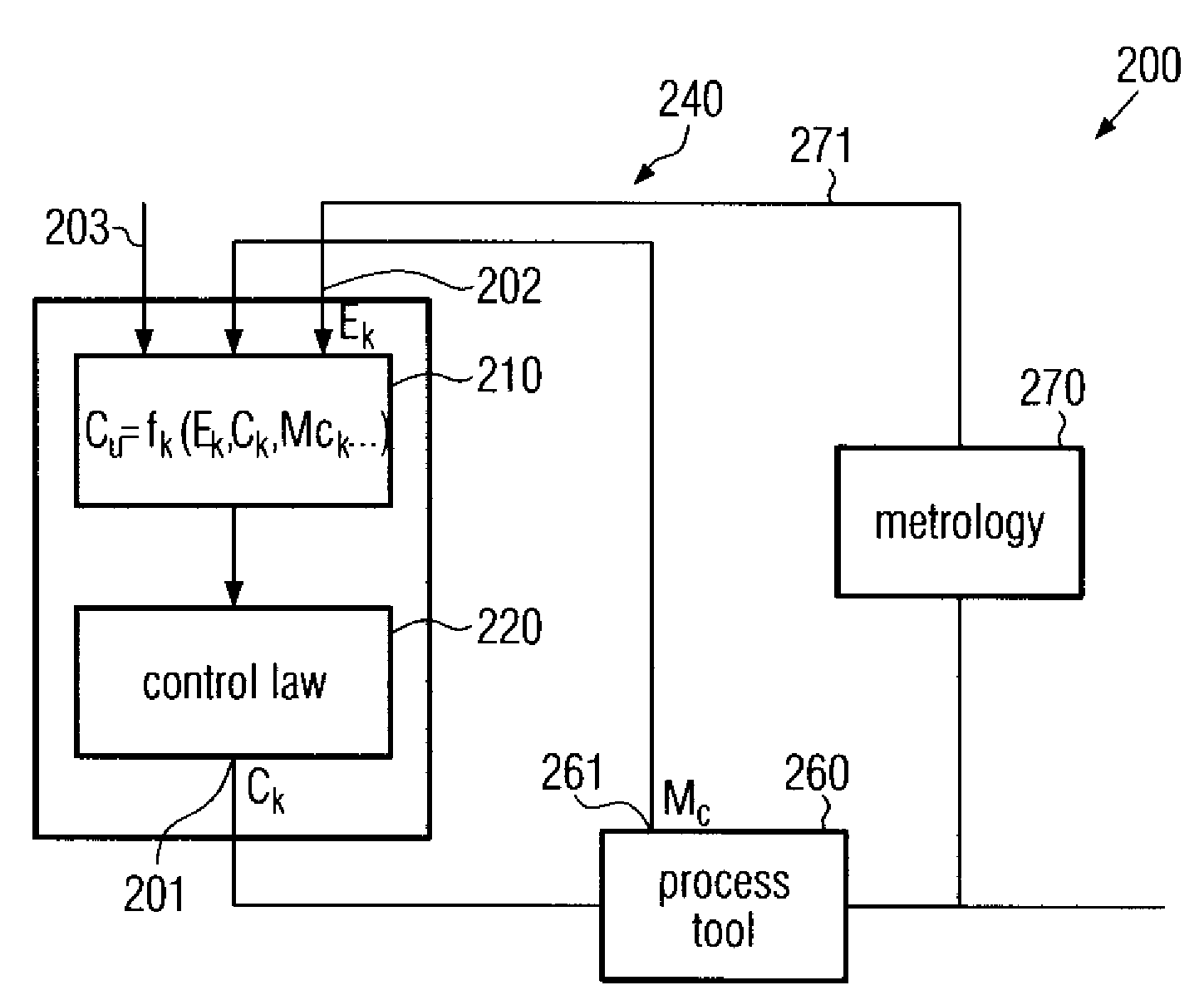
ActiveUS7403832B2Improve control efficiencyImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDecorative surface effectsControl theoryControl algorithm
A controller and a method of controlling a process tool is provided, in which machine constants used for calibrating manipulated variables of the control algorithm are explicitly introduced into the process model, thereby providing an enhanced controller behavior immediately after the introduction of new measurement values of the machine constants.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
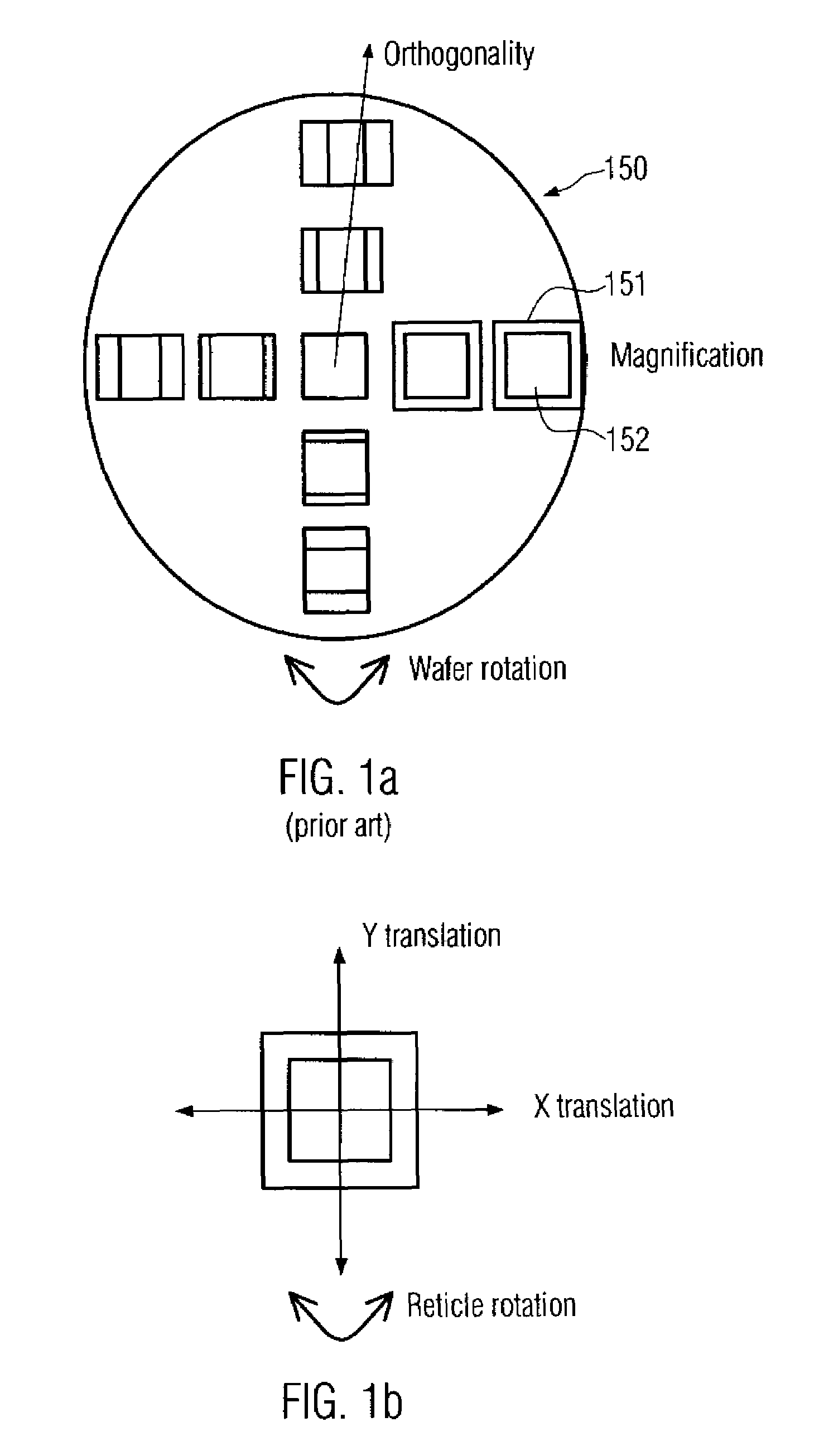
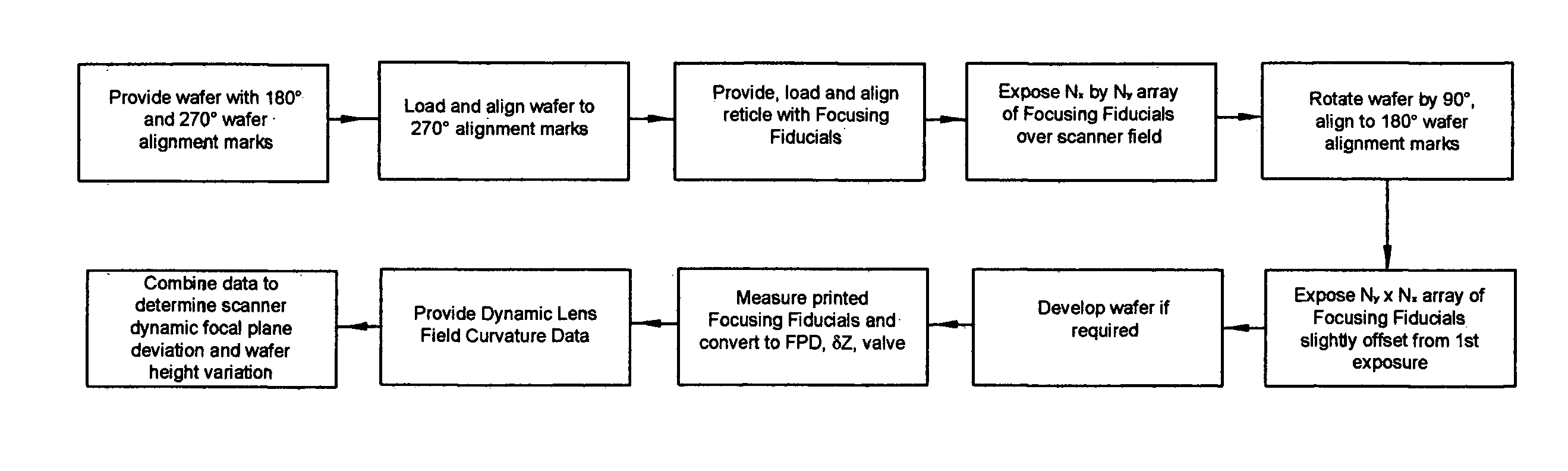
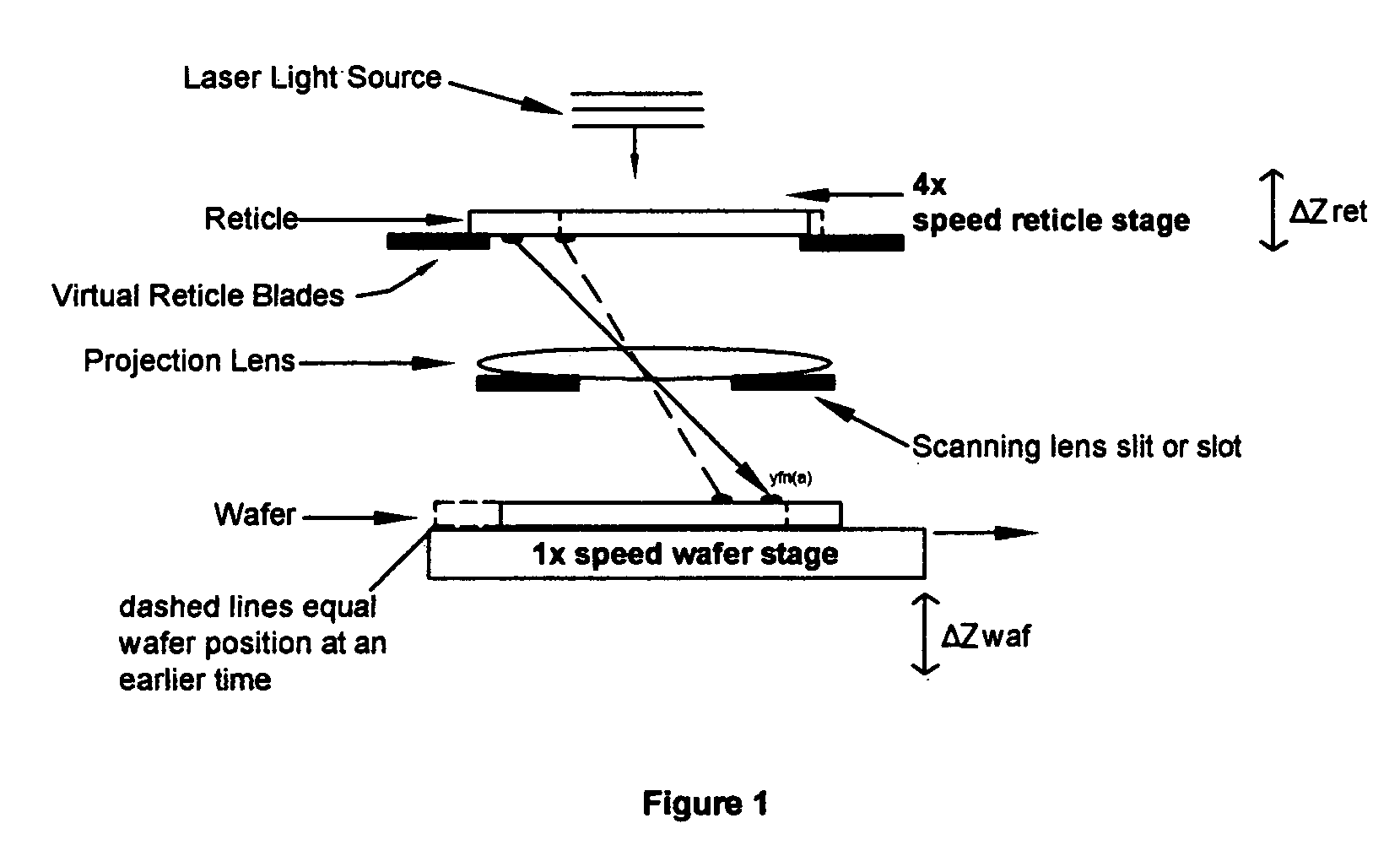
Apparatus and process for determination of dynamic scan field curvature
InactiveUS7126668B2Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistSilicon
Owner:LITEL INSTR
System and method for implementing a virtual metrology advanced process control platform
ActiveCN101908495ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess equipmentMetrology
System and method for implementing a Virtual Metrology ('VM') Advanced Process Control ('APC') platform are described. In one embodiment, the VM APC system comprises a process tool for processing a plurality of wafers, a metrology tool for measuring a sample wafer of the plurality of wafers and generating actual metrology data therefor, and a VM model for predicting metrology data for each of the plurality of wafers. The system also includes an APC controller for receiving the predicted metrology data and the actual metrology data and generating a process input of the process tool based on the received data. In the inventive VM APC system, process parameters after updating or modulating are not needed to perfrom individual measurement procedure, based on chip by chip control.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Process for determination of optimized exposure conditions for transverse distortion mapping
InactiveUS20050202328A1Eliminate the effects ofAccurately determineUsing optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMulti methodProjection lens
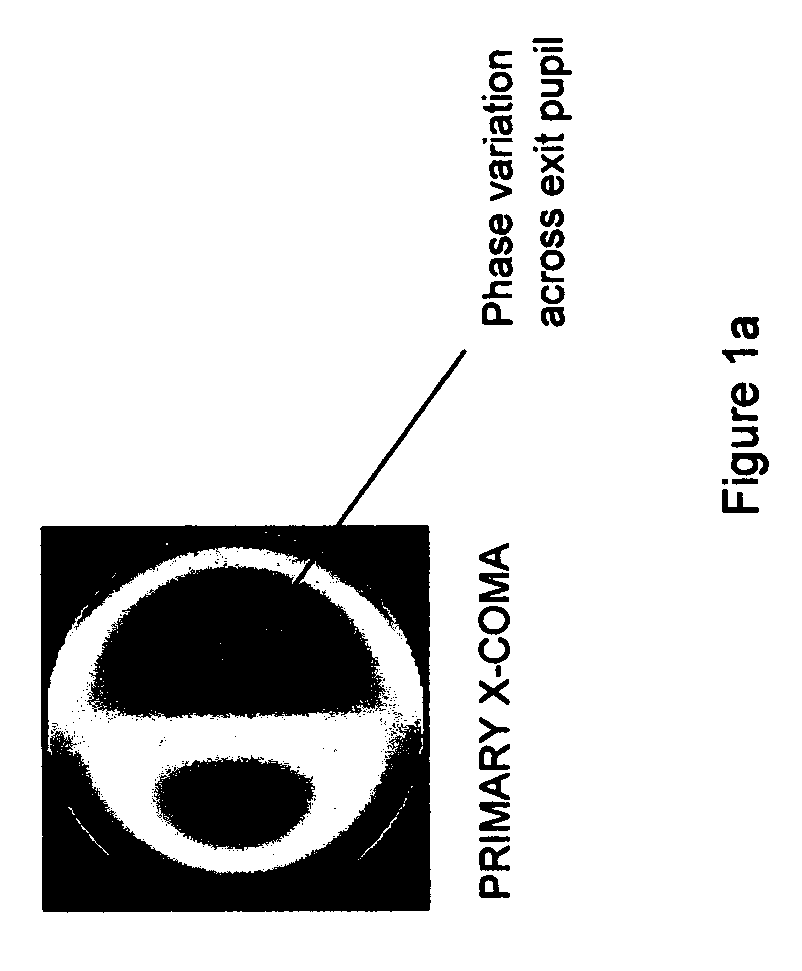
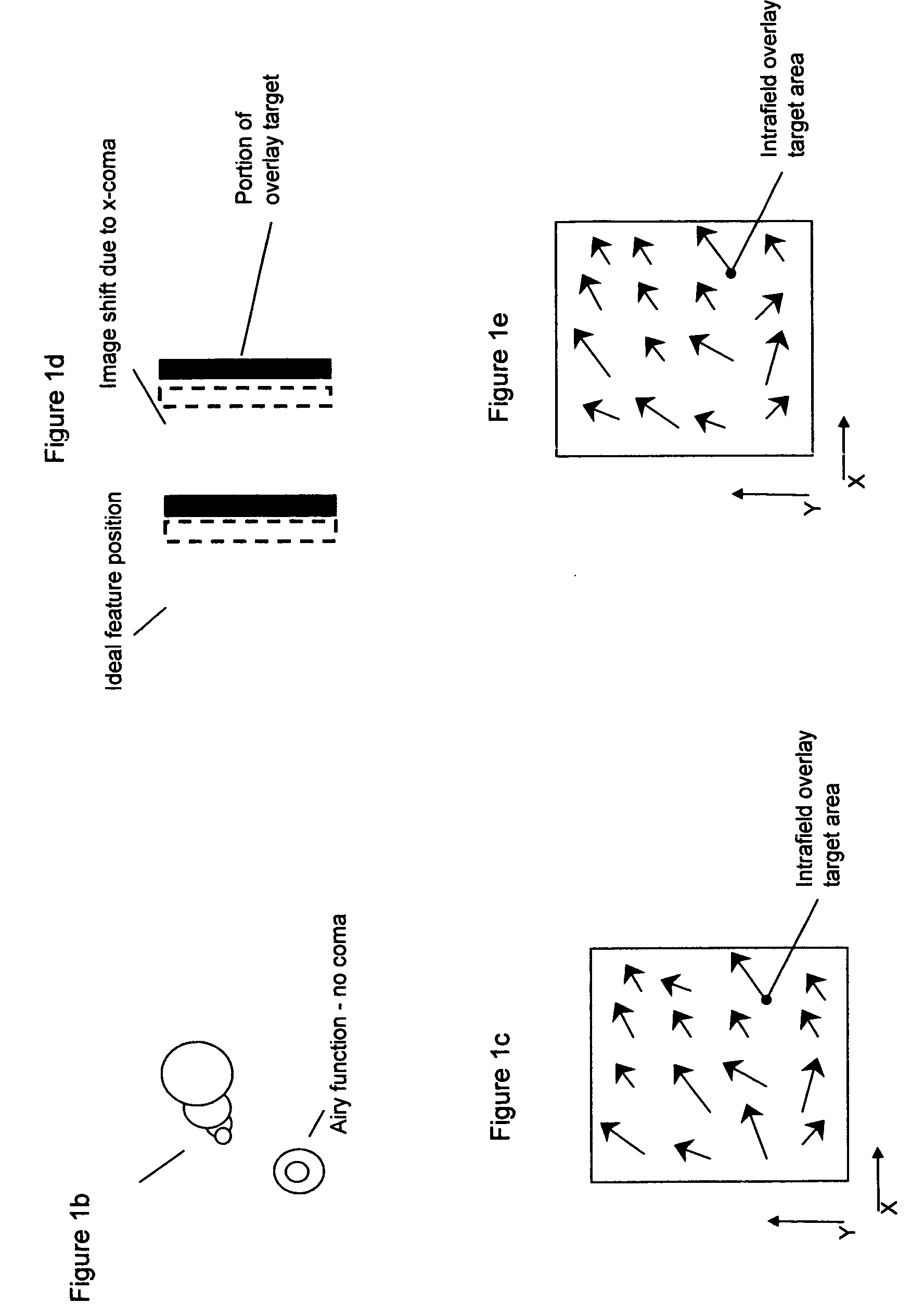
A process for providing illumination source conditions for the accurate determination Zernike tilt coefficients in the presence of coma is described. Large feature-shift coma sensitivity is simulated for a range of illumination conditions. The resulting source sensitivity data is modeled and a practical array of source shapes, each of which is optimized to eliminate the effects of transverse distortion due to third-order coma, is identified. The optimized set of source shapes can be used to more accurately determine Zernike terms a2 and a3 using a variety of methods. Knowledge of the lens distortion data in the absence of coma induced shifts can be entered into more traditional overlay regression routines to better identify systematic and random error. Additional applications of the above outlined procedure include: improved lithographic simulation using conventional optical modeling software and advanced process control in the form of feedback loops that automatically adjust the projection lens for optimum system performance.
Owner:LITEL INSTR
Dynamic metrology schemes and sampling schemes for advanced process control in semiconductor processing
InactiveUS20080133163A1Increase the number ofHigh frequencySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyProgram planning
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
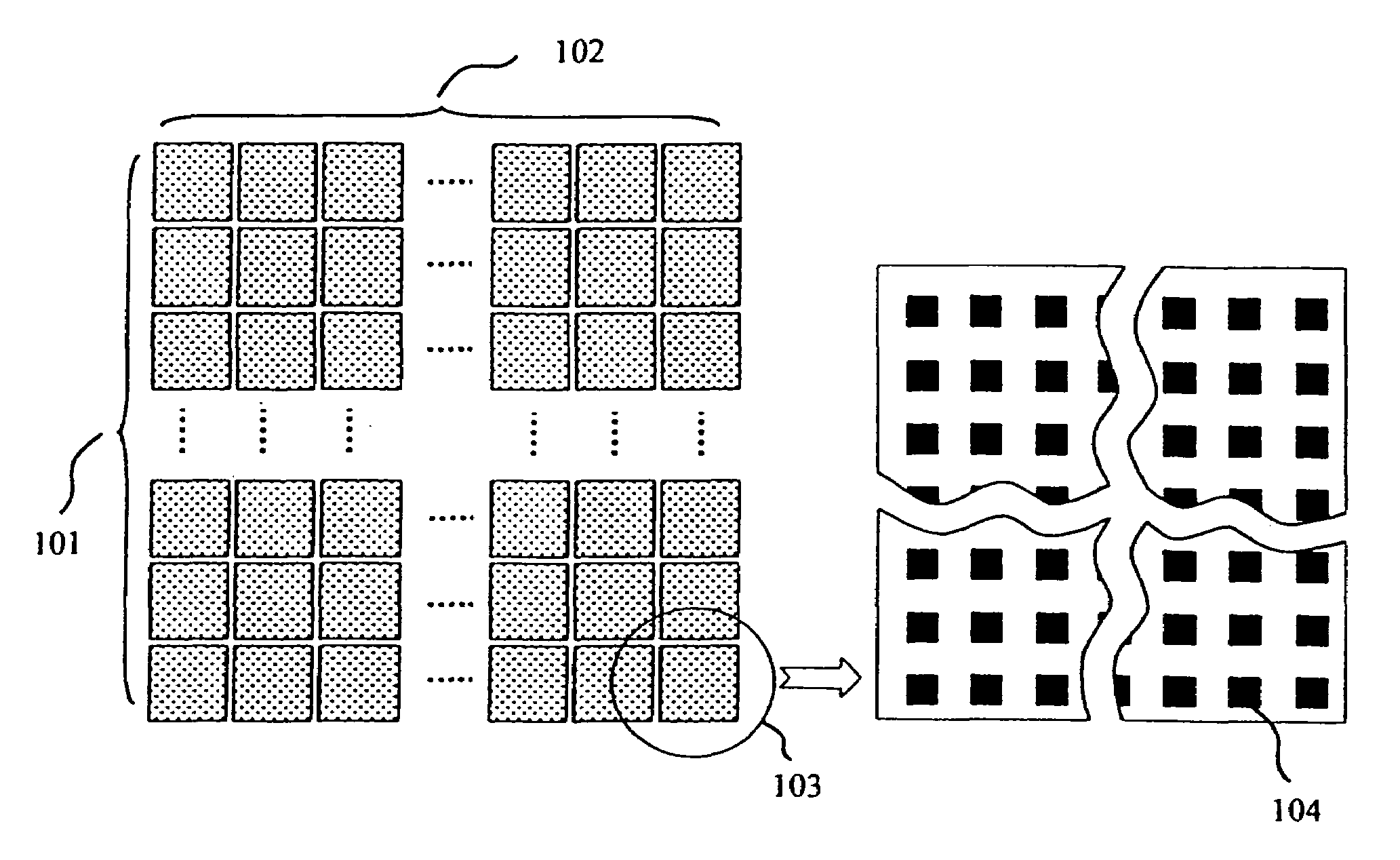
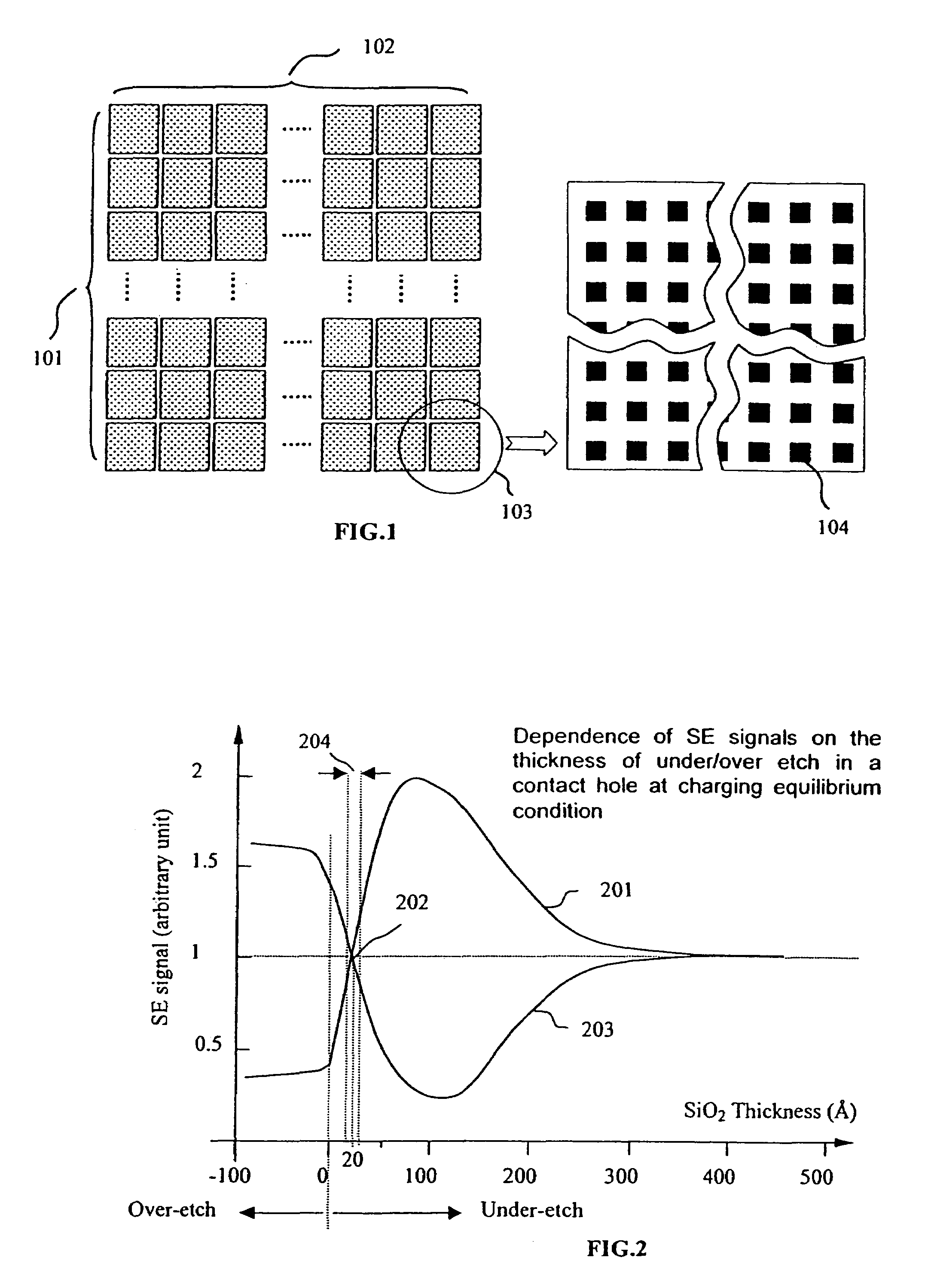
Method for in-line monitoring of via/contact holes etch process based on test structures in semiconductor wafer manufacturing
InactiveUS20050026310A1Contact hole can be reducedTime requiredSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsImaging processingEngineering
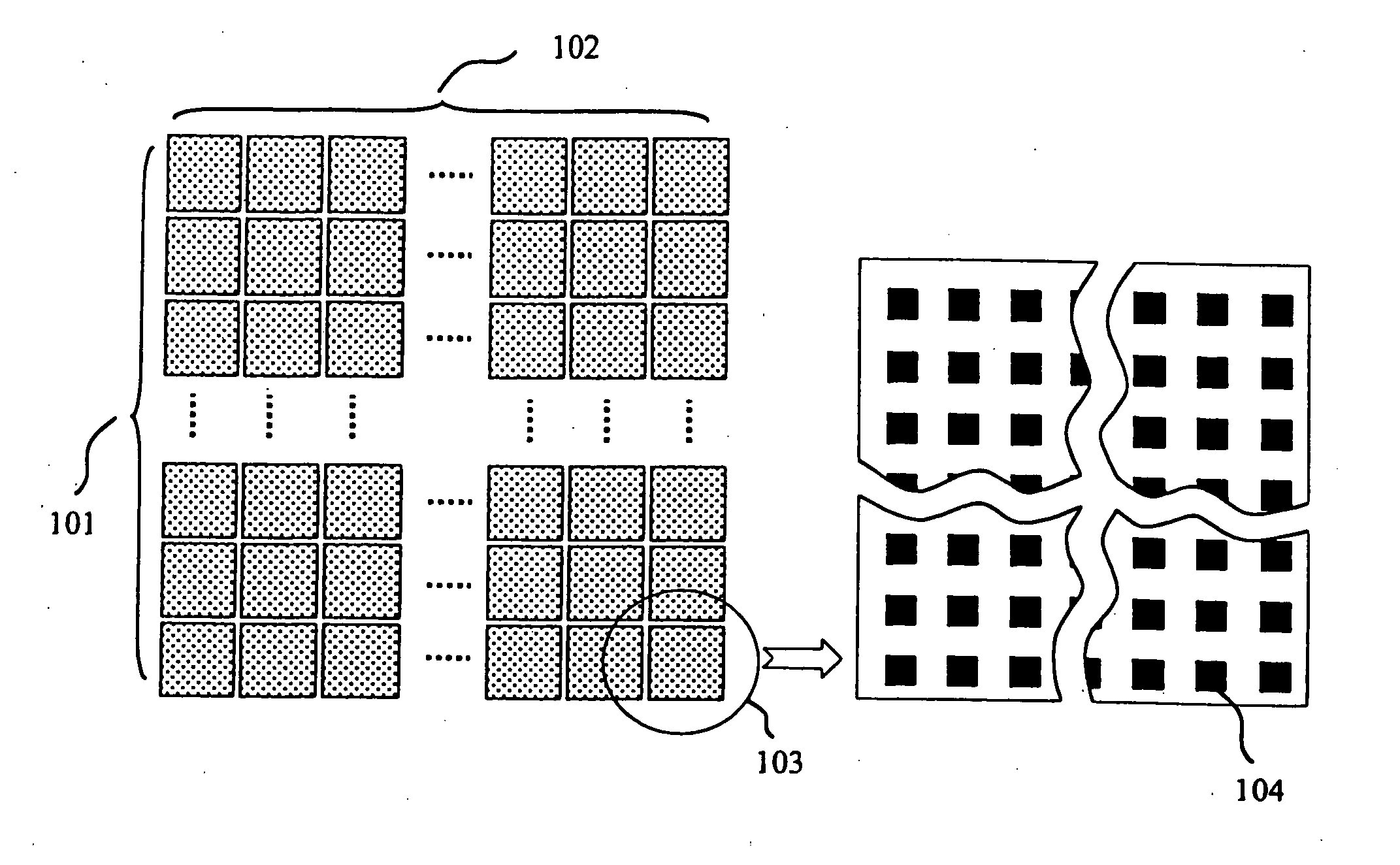
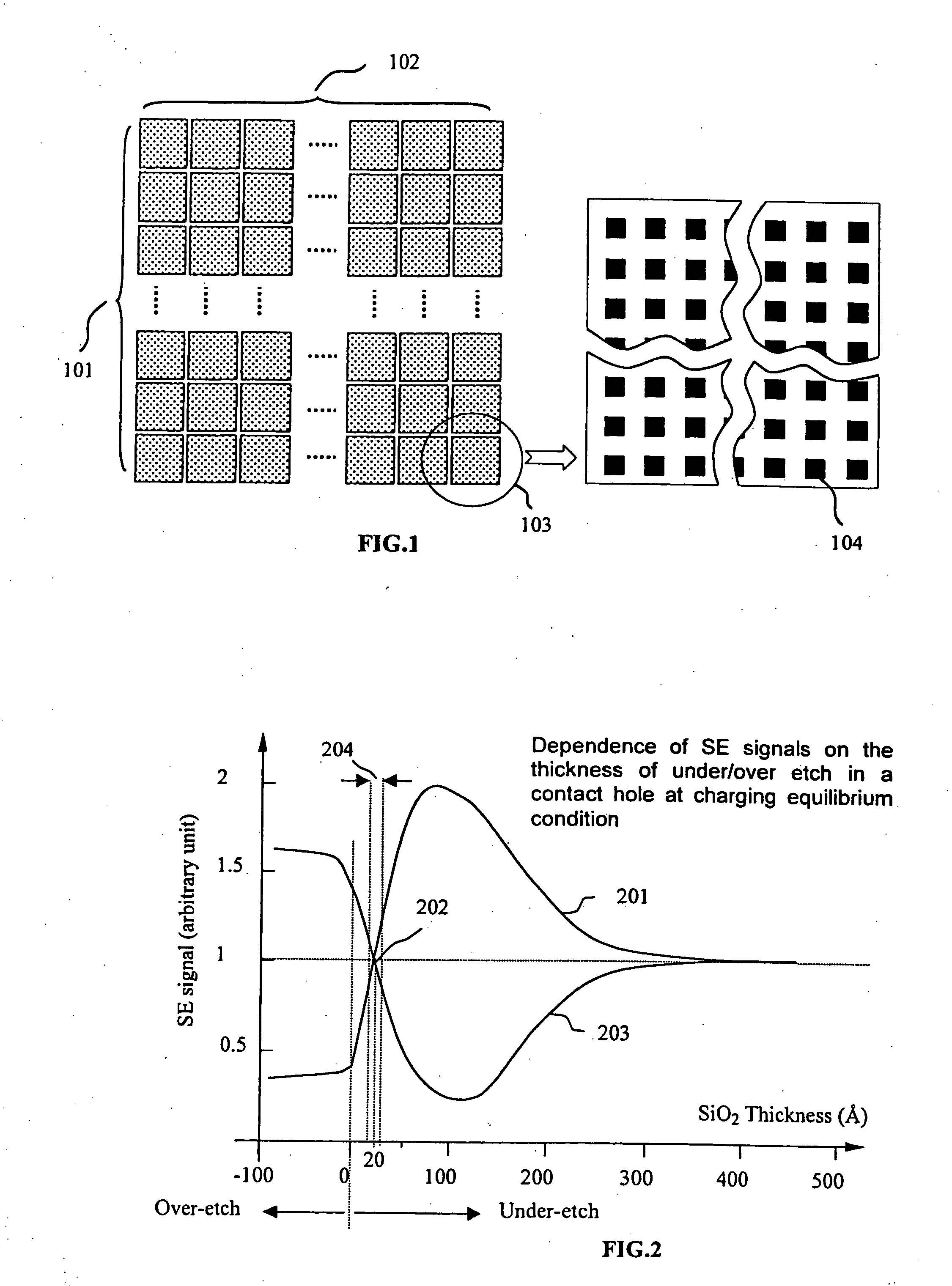
A method for in-line monitoring of via / contact etching process based on a test structure is described. The test structure is comprised of via / contact holes of different sizes and densities in a layout such that, for a certain process, the microloading or RIE lag induced non-uniform etch rate produce under-etch in some regions and over-etch in others. A scanning electron microscope is used to distinguish these etching differences in voltage contrast images. Image processing and simple calibration convert these voltage contrast images into a “fingerprint” image characterizing the etching process in terms of thickness over-etched or under-etched. Tolerance of shifting or deformation of this image can be set for validating the process uniformity. This image can also be used as a measure to monitor long-term process parameter shifting, as well as wafer-to-wafer or lot-to-lot variations. Advanced process control (APC) can be performed in-line with the guidance of this image so that potential electrical defects are avoided and process yield ramp accelerated.
Owner:HERMES MICROVISION TAIWAN +2
Advanced process control system and test method thereof
ActiveCN102540895AReduce testing costsReduce verification costsElectric testing/monitoringAdaptive controlTime errorProcess equipment
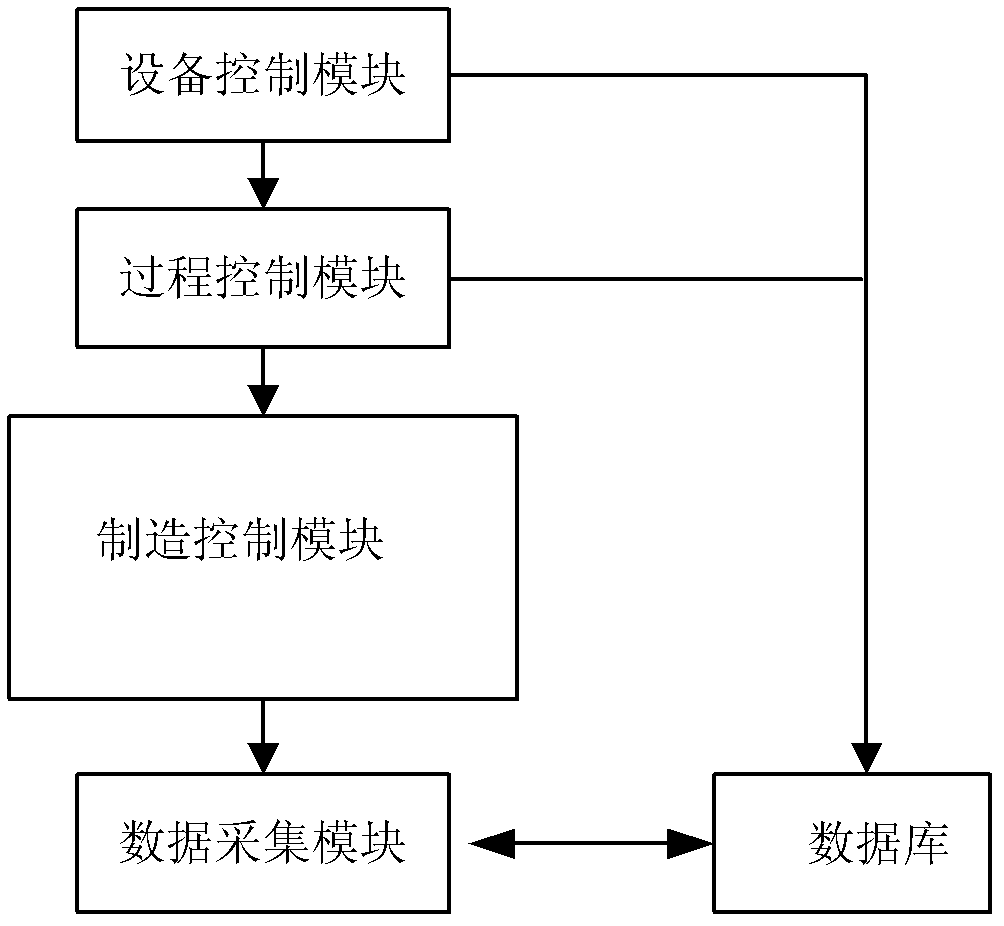
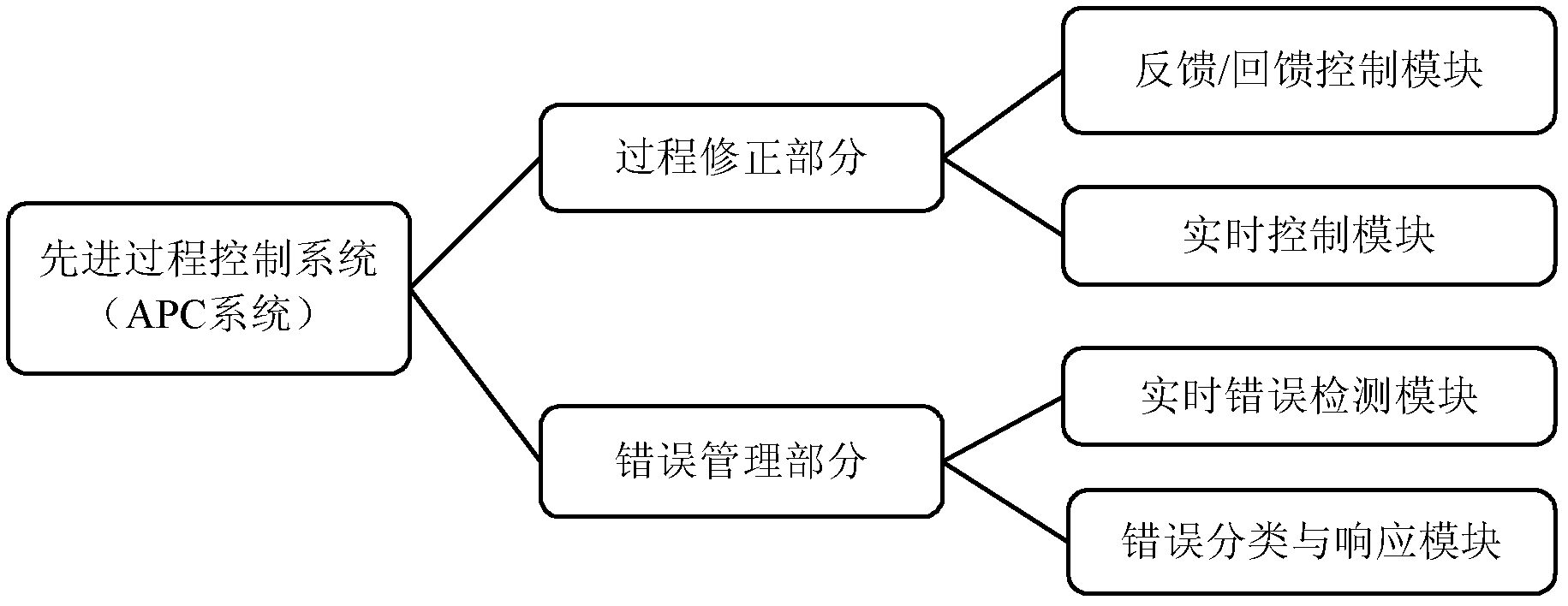
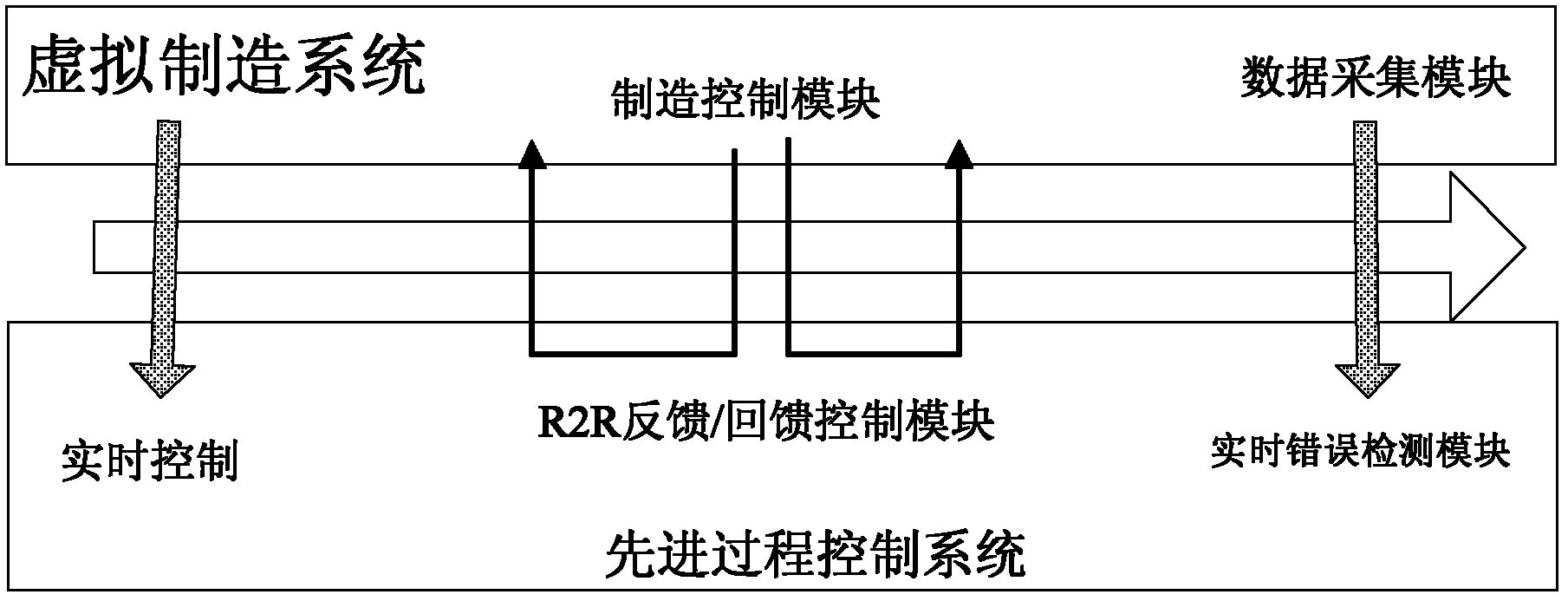
The invention discloses an advanced process control system and a test method of the advanced process control system. The advanced process control system is connected with a virtual manufacturing system and comprises a real-time error detection module, an error classifying and responding module and a feedback / feedback control module, wherein the real-time error detection module is used for acquiring performance parameters of a product in a virtual manufacturing process from a dada acquisition module of the virtual manufacturing system, comparing the performance parameters of the product with preset performance parameters of the product, and performing error detection on the performance parameters of the product in the virtual manufacturing process; the error classifying and responding module is used for classifying the detected errors and researching reasons for generating the errors; and the feedback / feedback control module is used for invoking a corresponding correcting model to correct technical / equipment parameters related to the errors so as to obtain the corrected technical / equipment parameters and sending the corrected technical / equipment parameters to a process control module of the virtual manufacturing system. The problems that much time is used and manufacturing equipment cannot work normally when the advanced process control system is embedded into an actual process line are solved, and the cost for test and verification of the advanced process control system is reduced.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
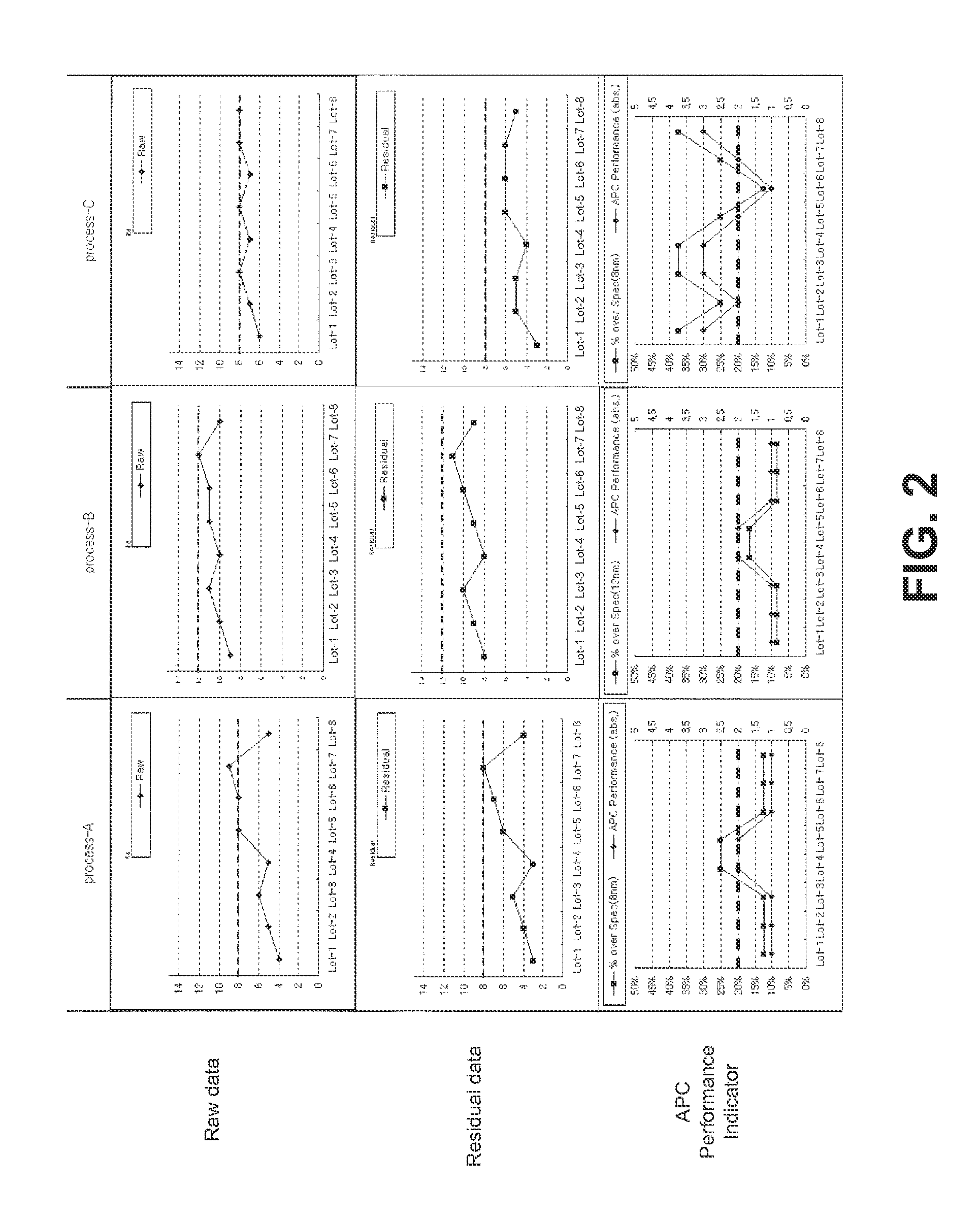
Advanced process control optimization
ActiveUS20120022679A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical apparatusDevice materialProcess engineering
A method for automatic process control (APC) performance monitoring may include, but is not limited to: computing one or more APC performance indicators for one or more production lots of semiconductor devices; and displaying a mapping of the one or more APC performance indicators to the one or more production lots of semiconductor devices.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
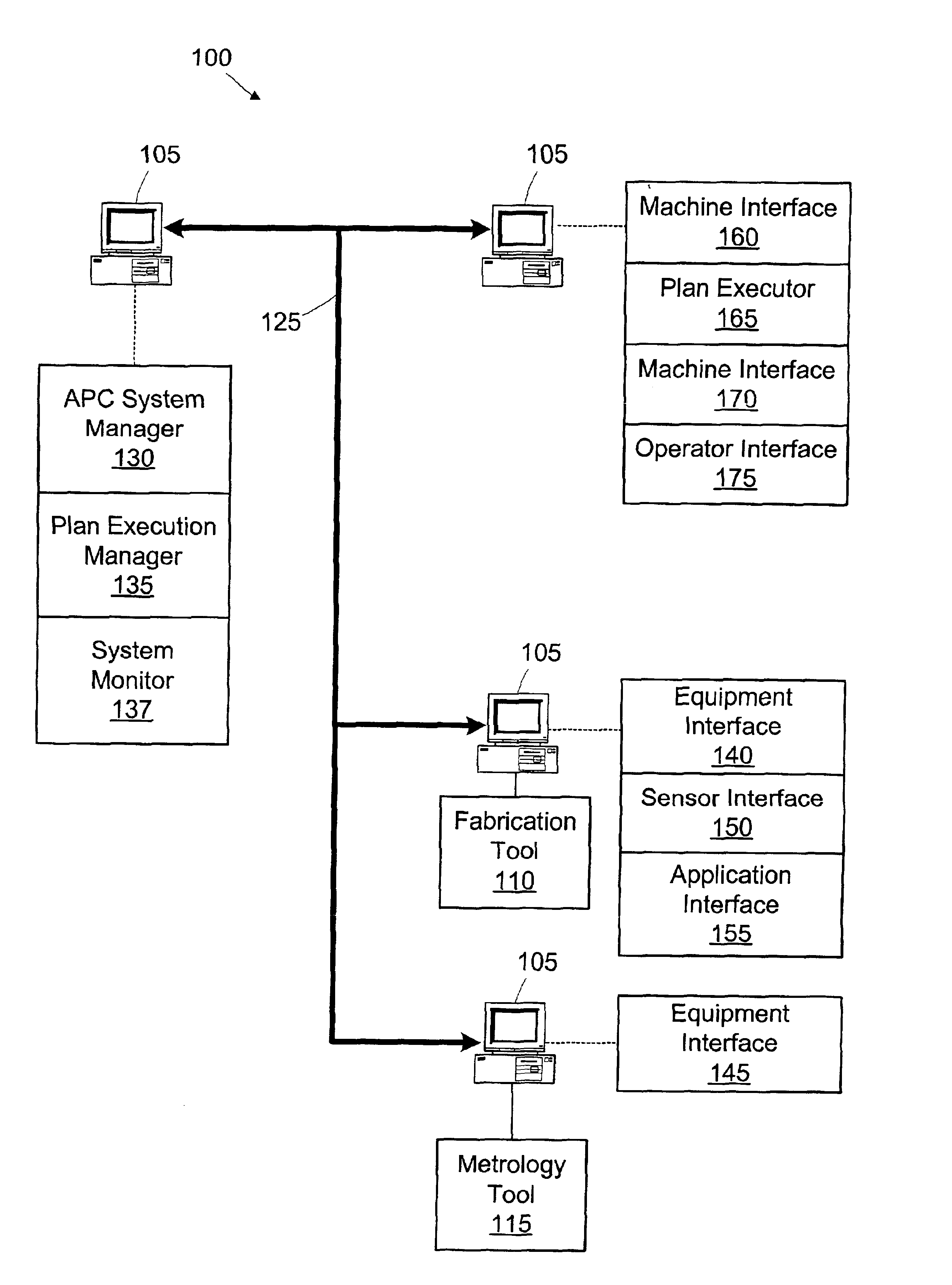
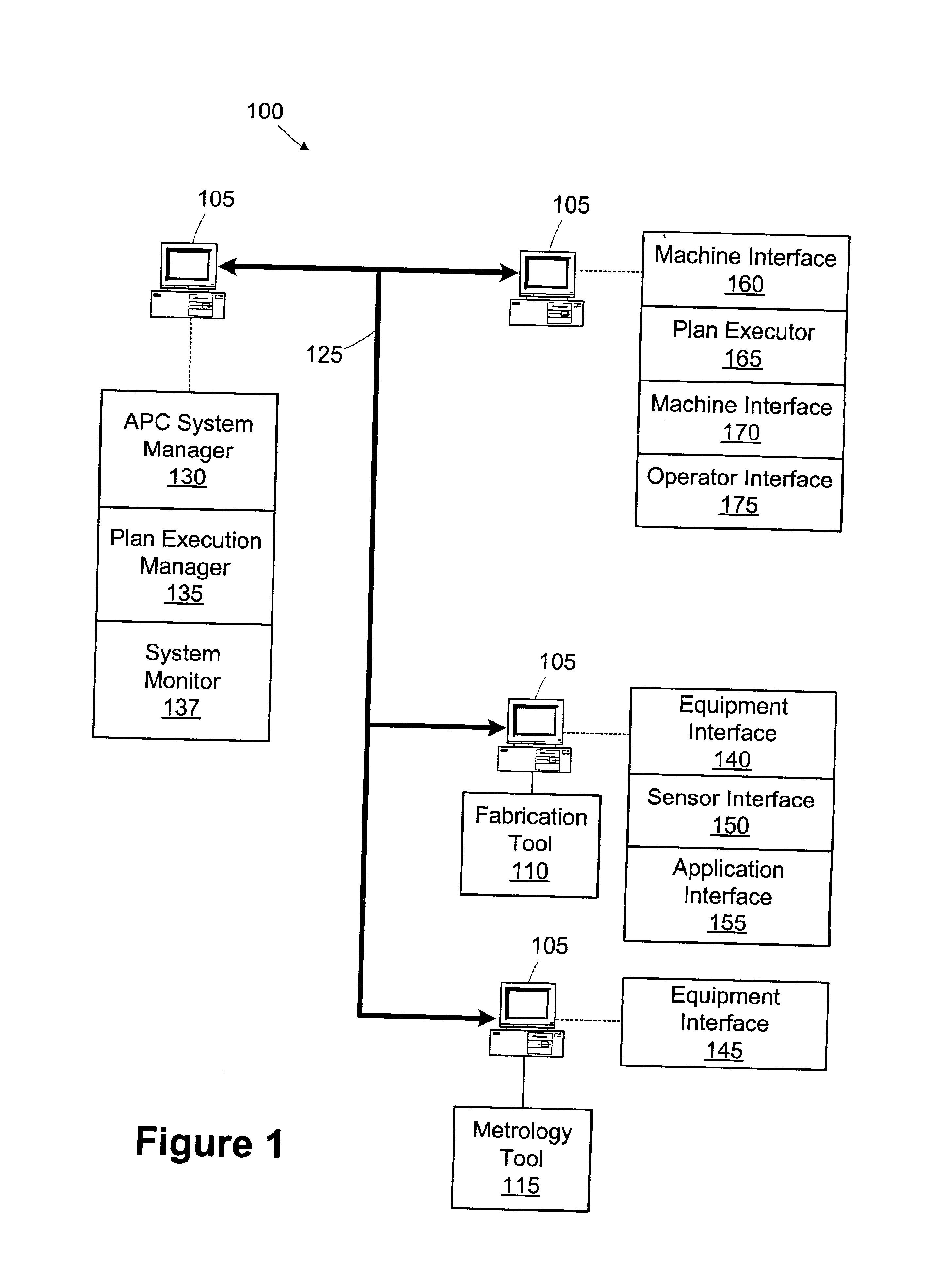
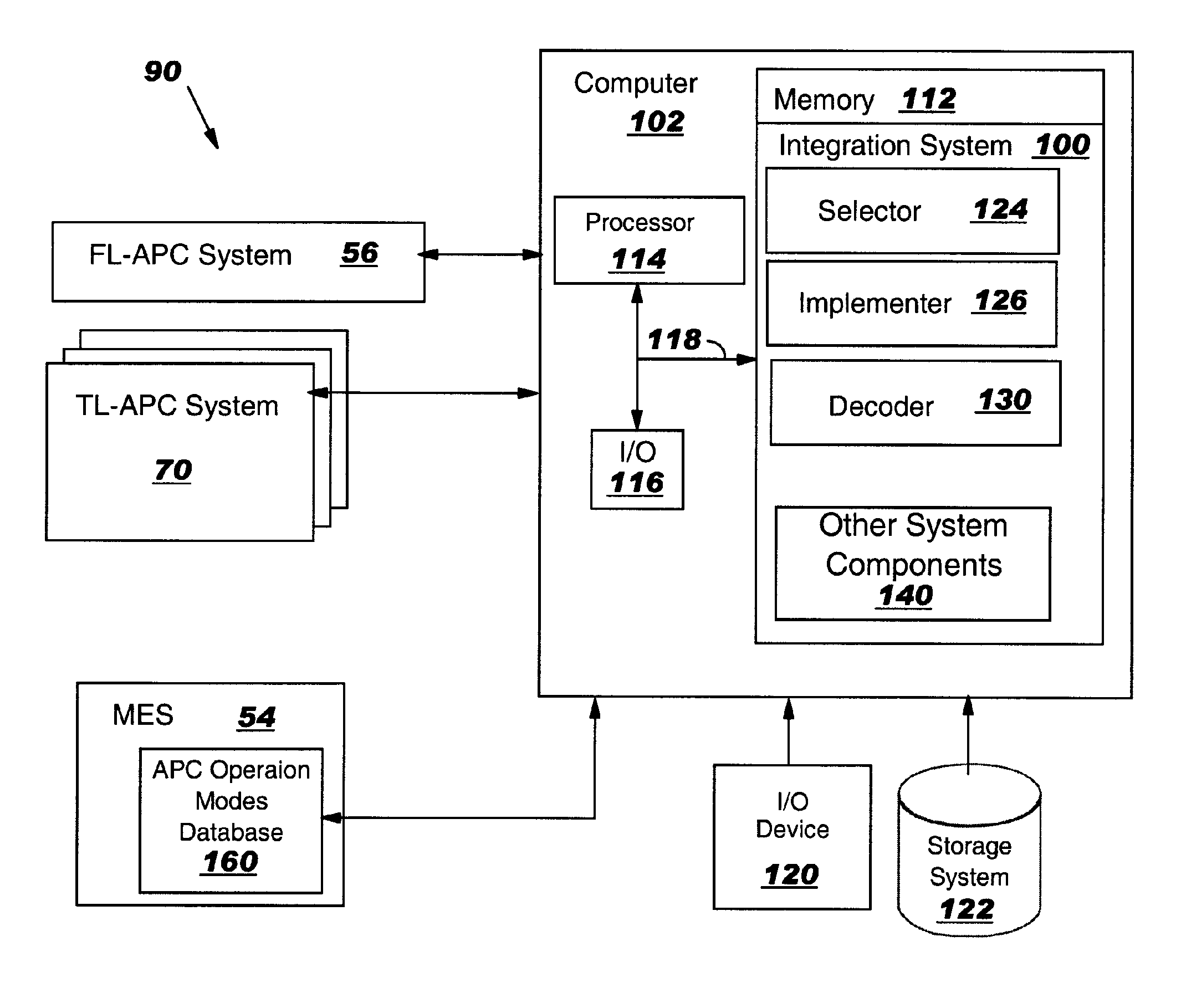
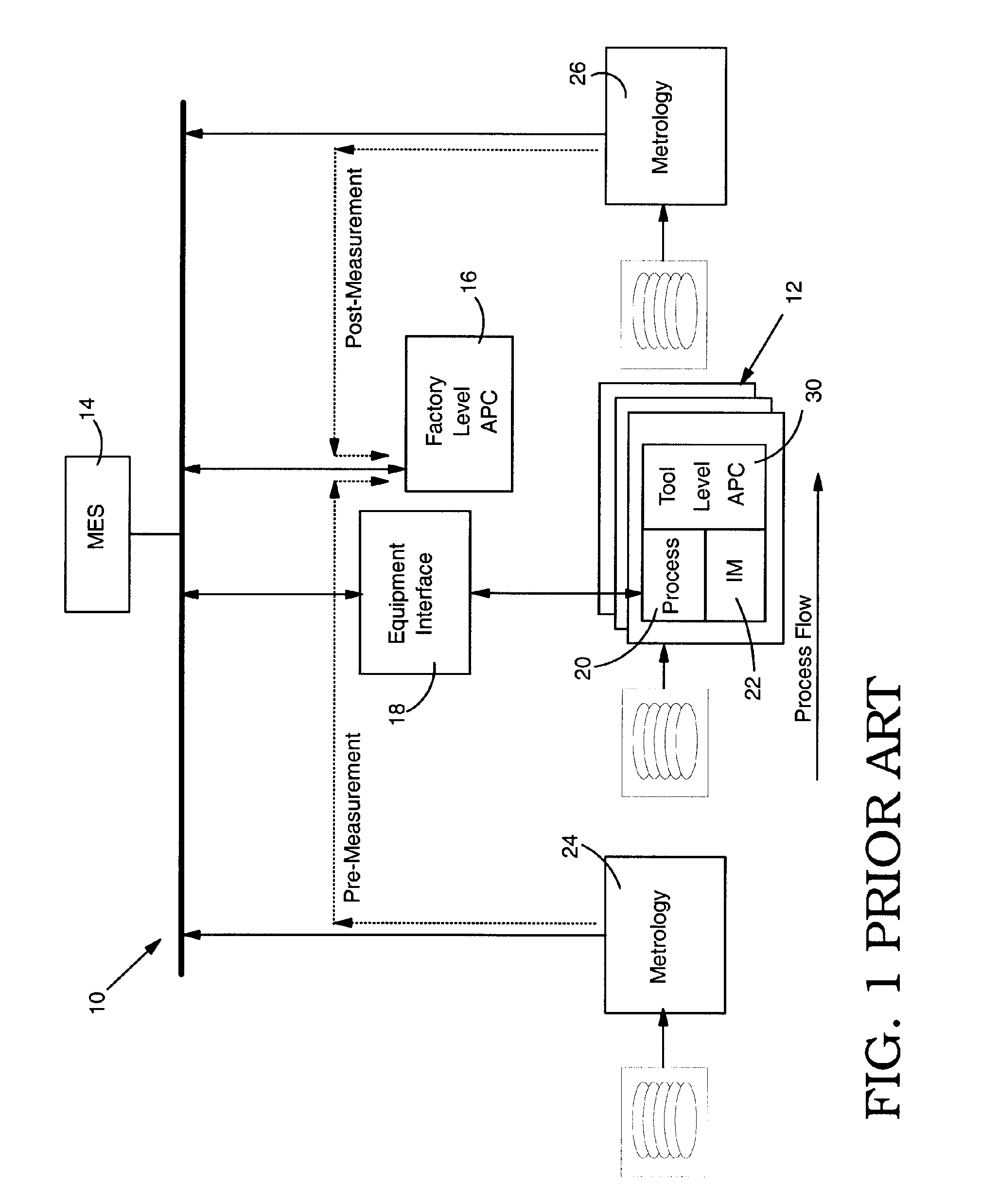
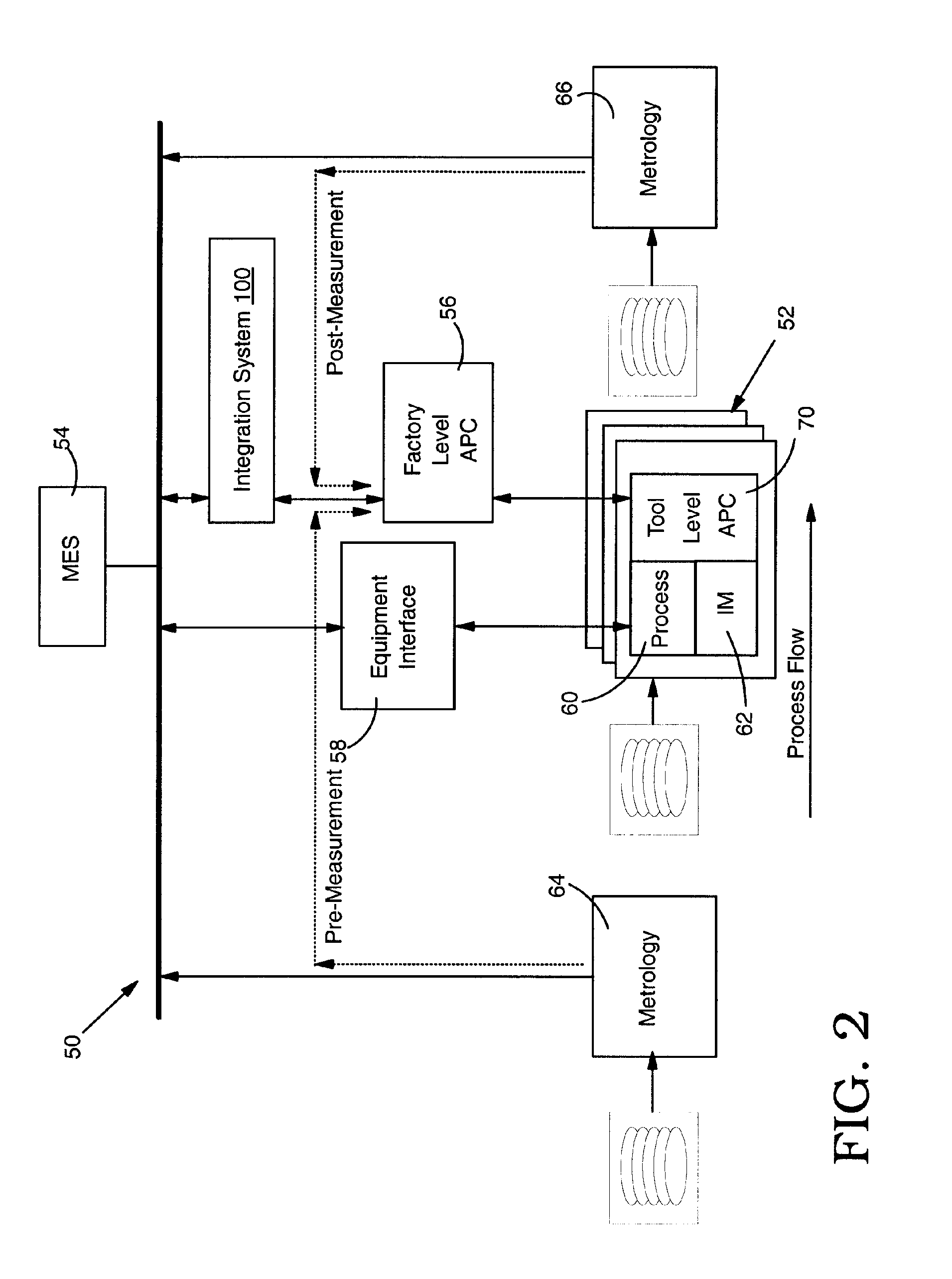
Integration of factory level and tool level advanced process control systems
ActiveUS7113845B1Improve rendering capabilitiesProgramme controlTotal factory controlSystem integrationOperation mode
Integration of factory level advanced process control (FL-APC) system and tool level advanced process control (TL-APC) system using selectable APC operation modes indicating different operational settings for the FL-APC system and at least one TL-APC system is disclosed. During operation, the FL-APC system controls operation of the TL-APC system. The invention allows a manufacturing execution system (MES) to have additional capability to run the process control functions at FL-APC system and / or TL-APC system, and allows integration of a variety of different tools with a TL-APC system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com