Patents
Literature
872results about "Vacuum gauge using ionisation effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
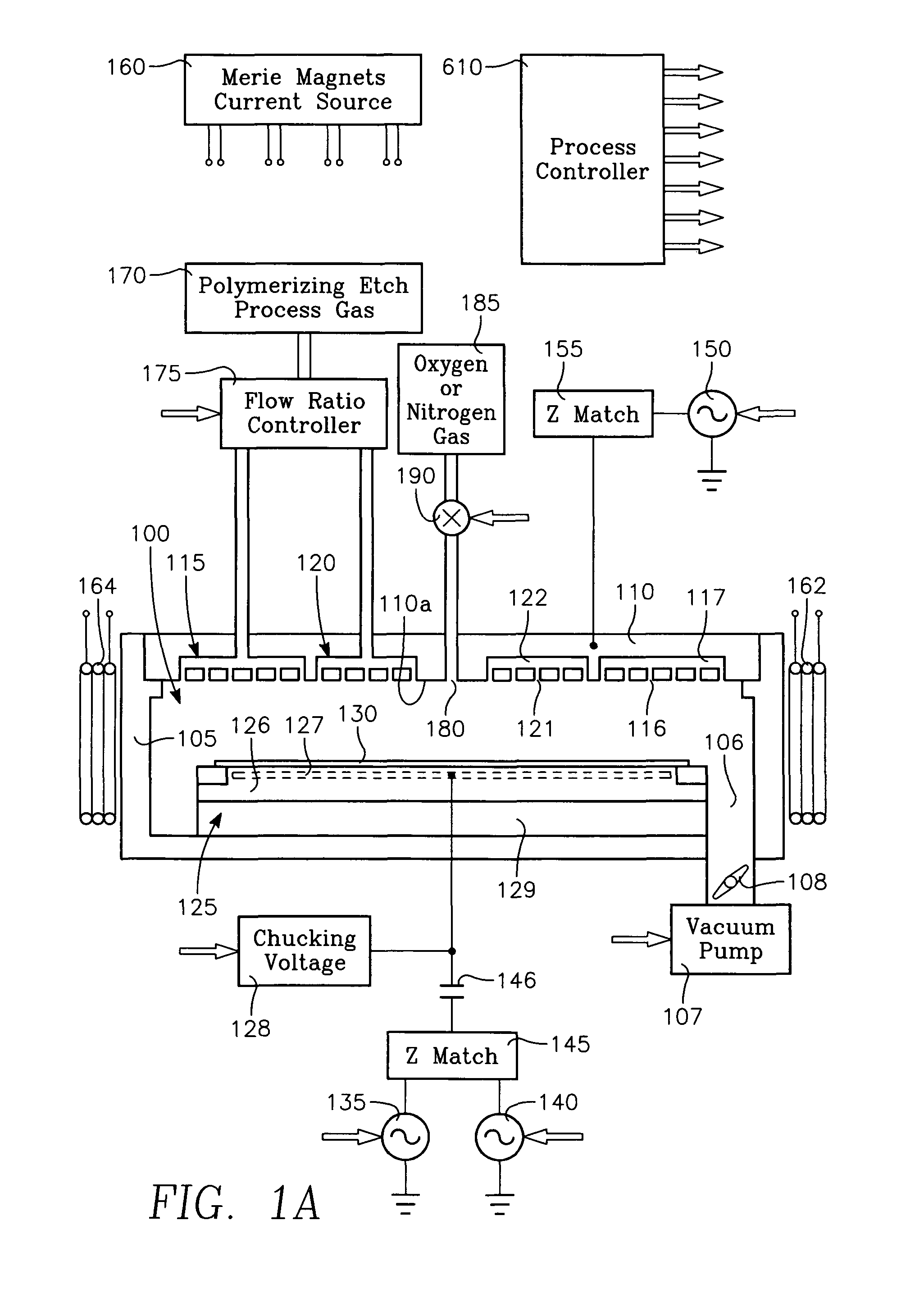
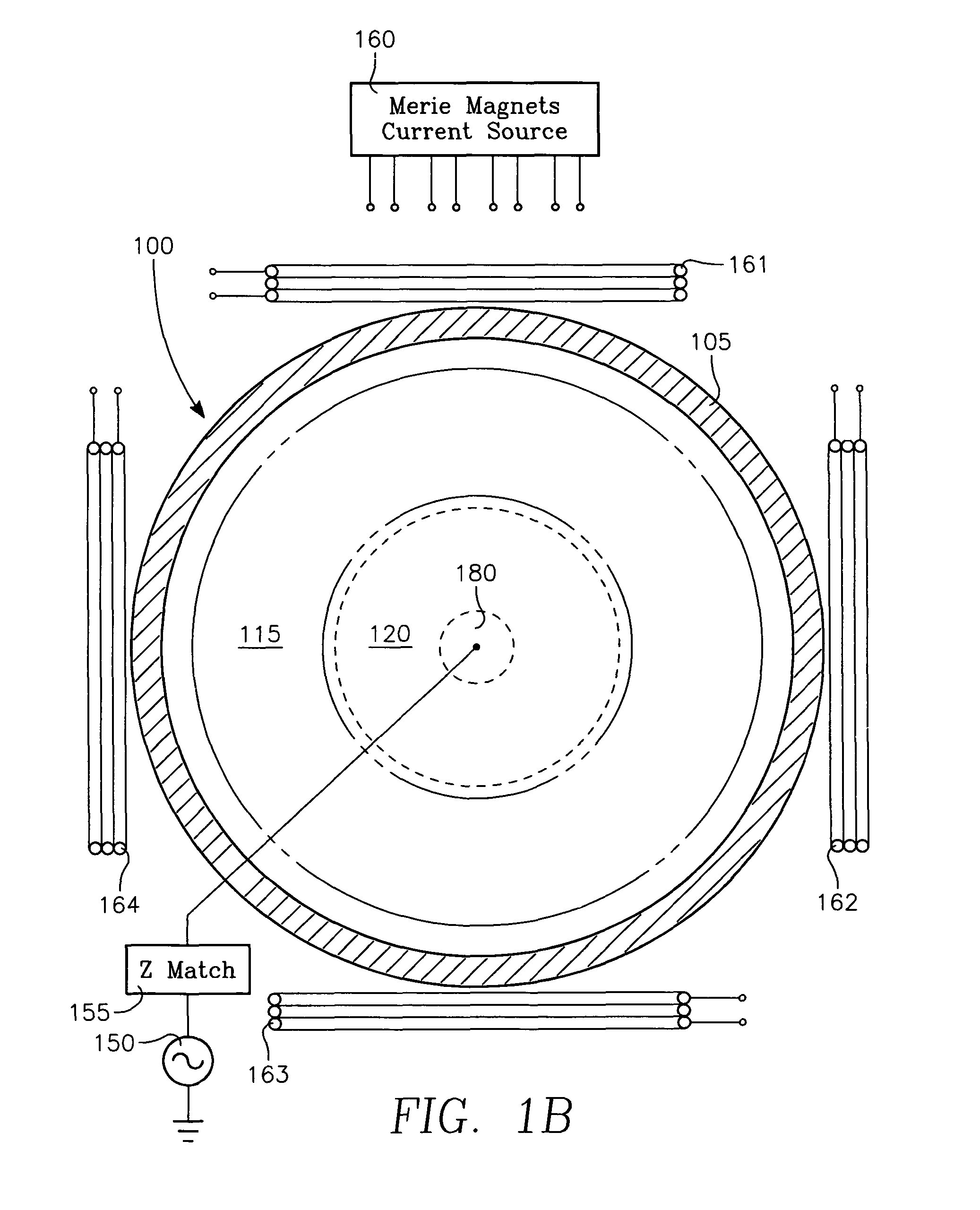
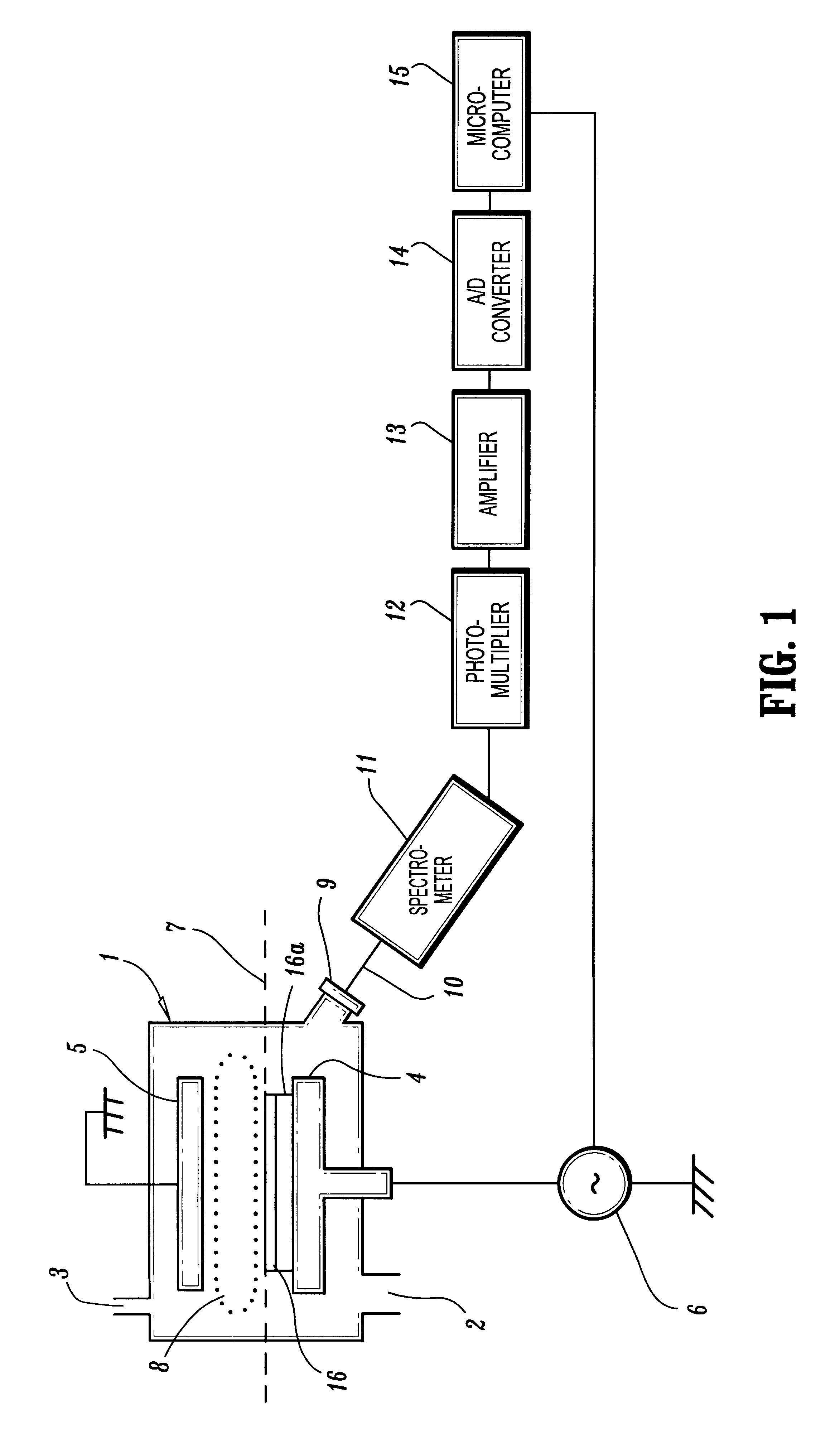
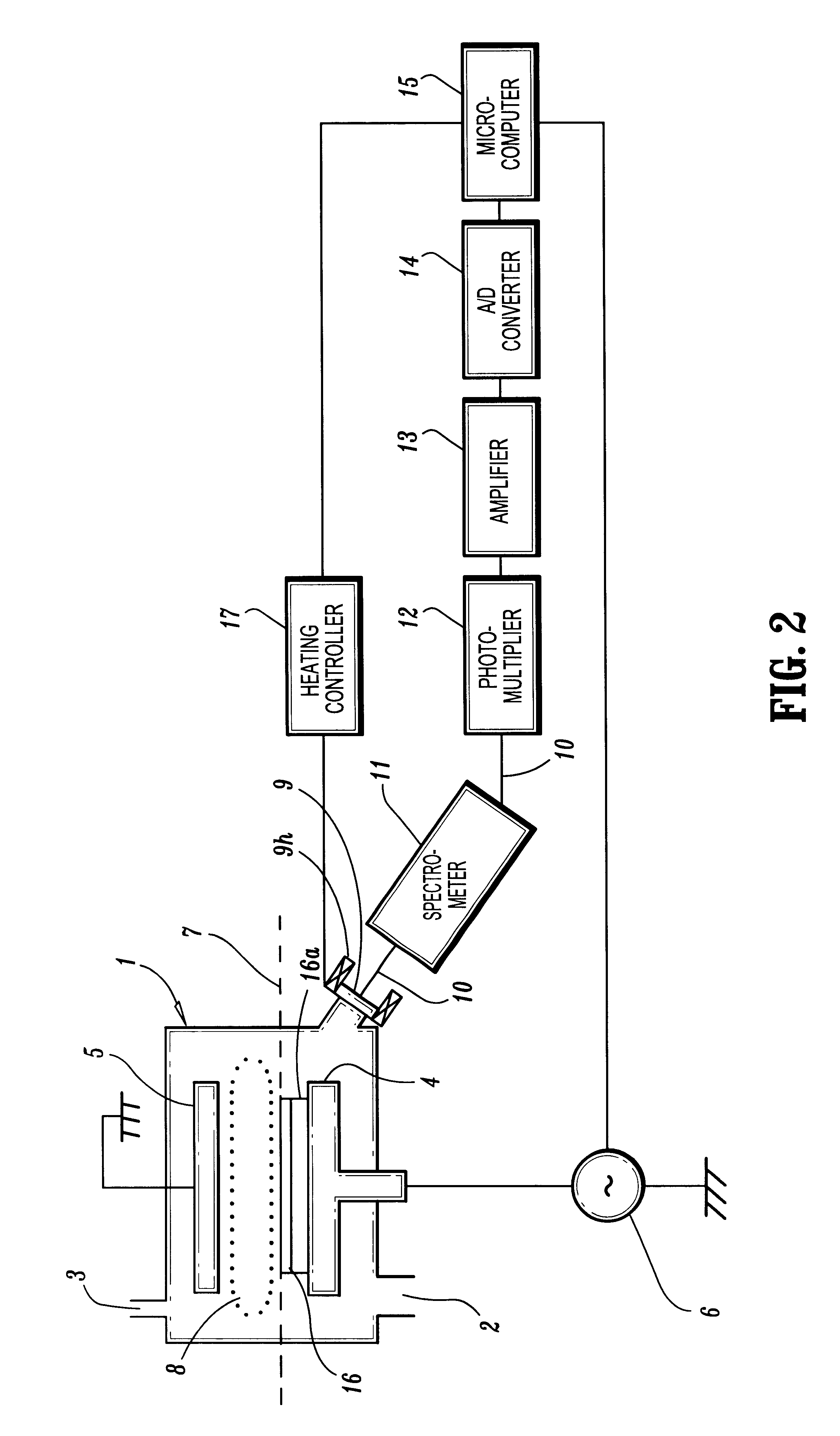
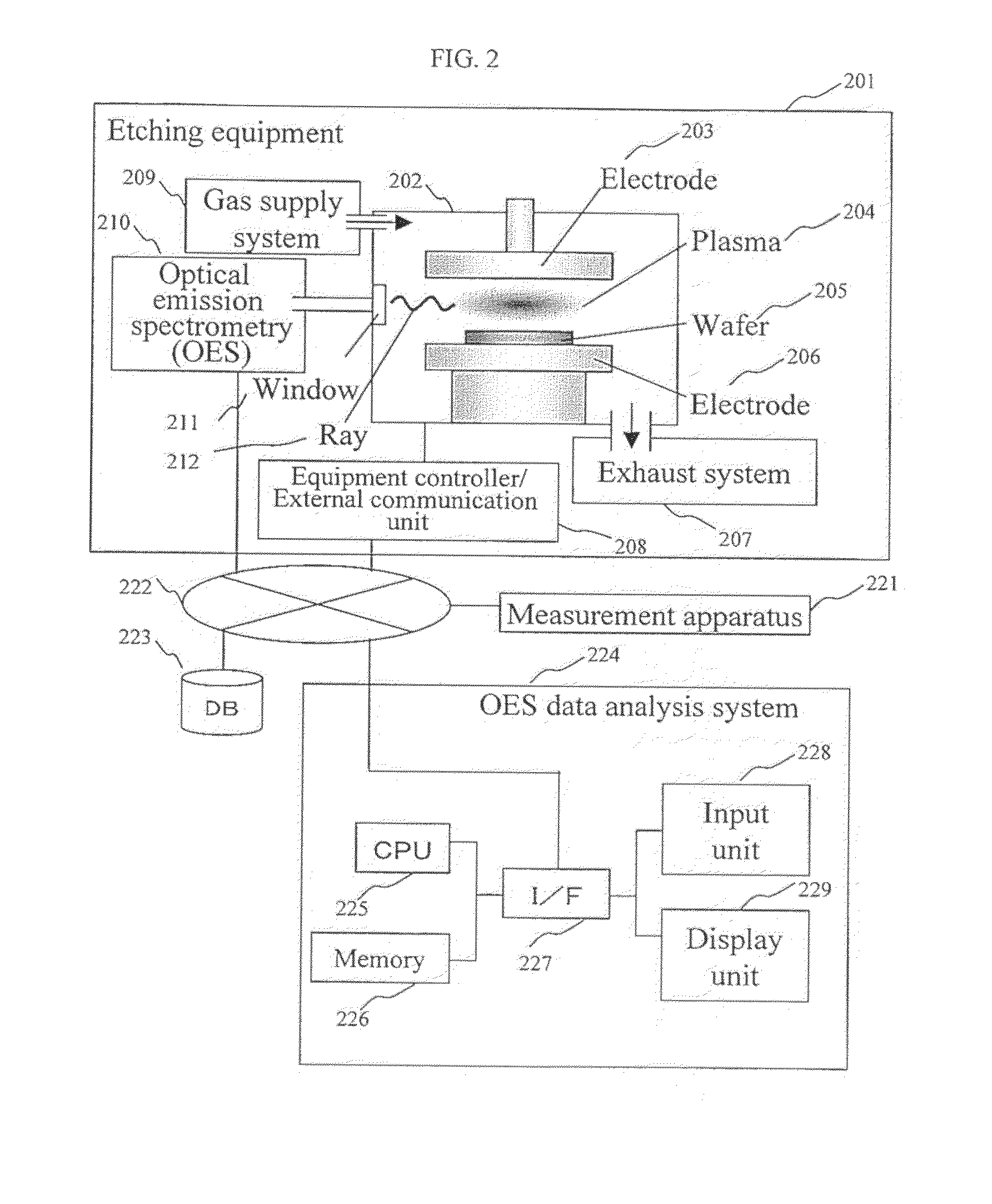
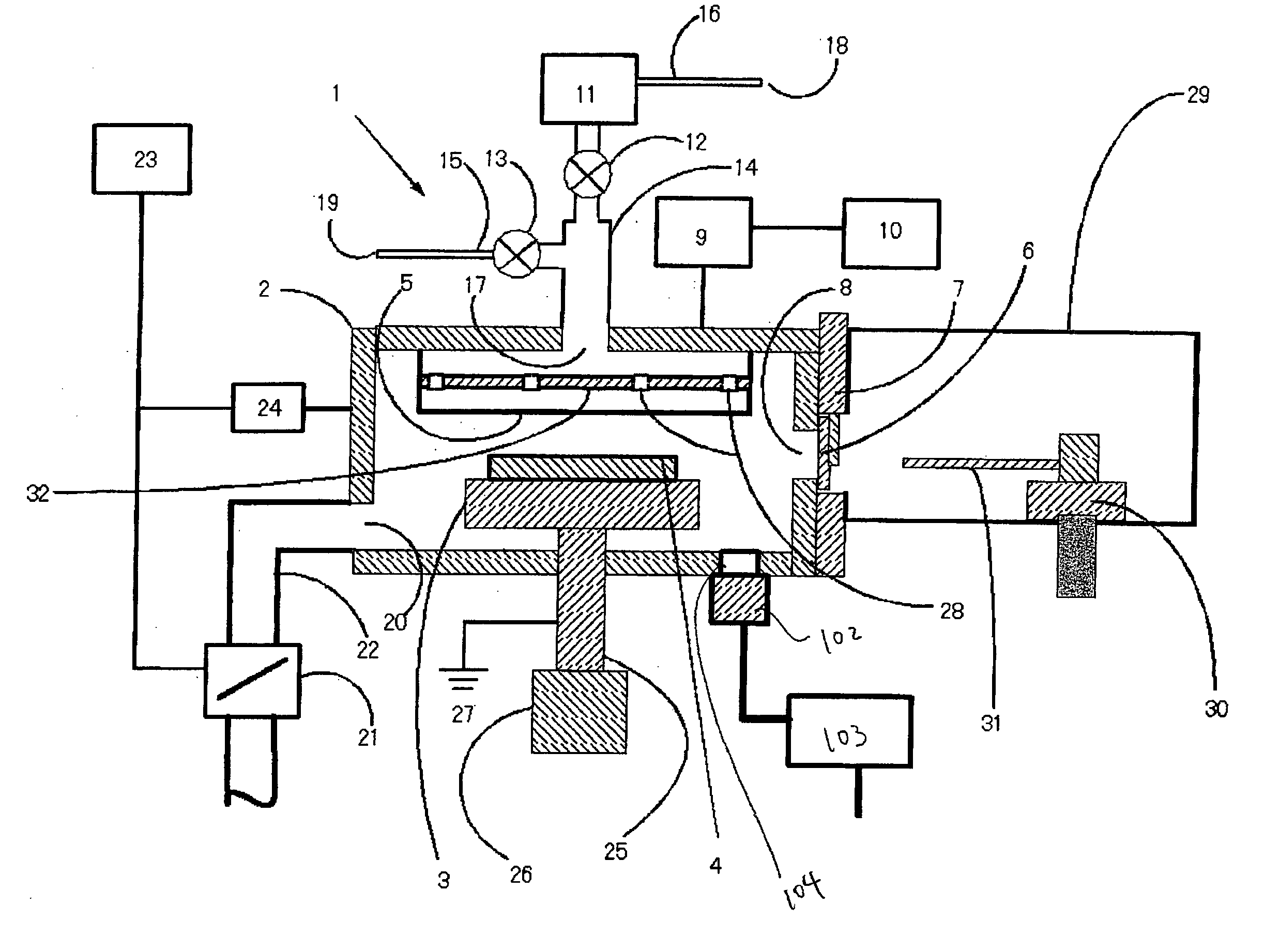
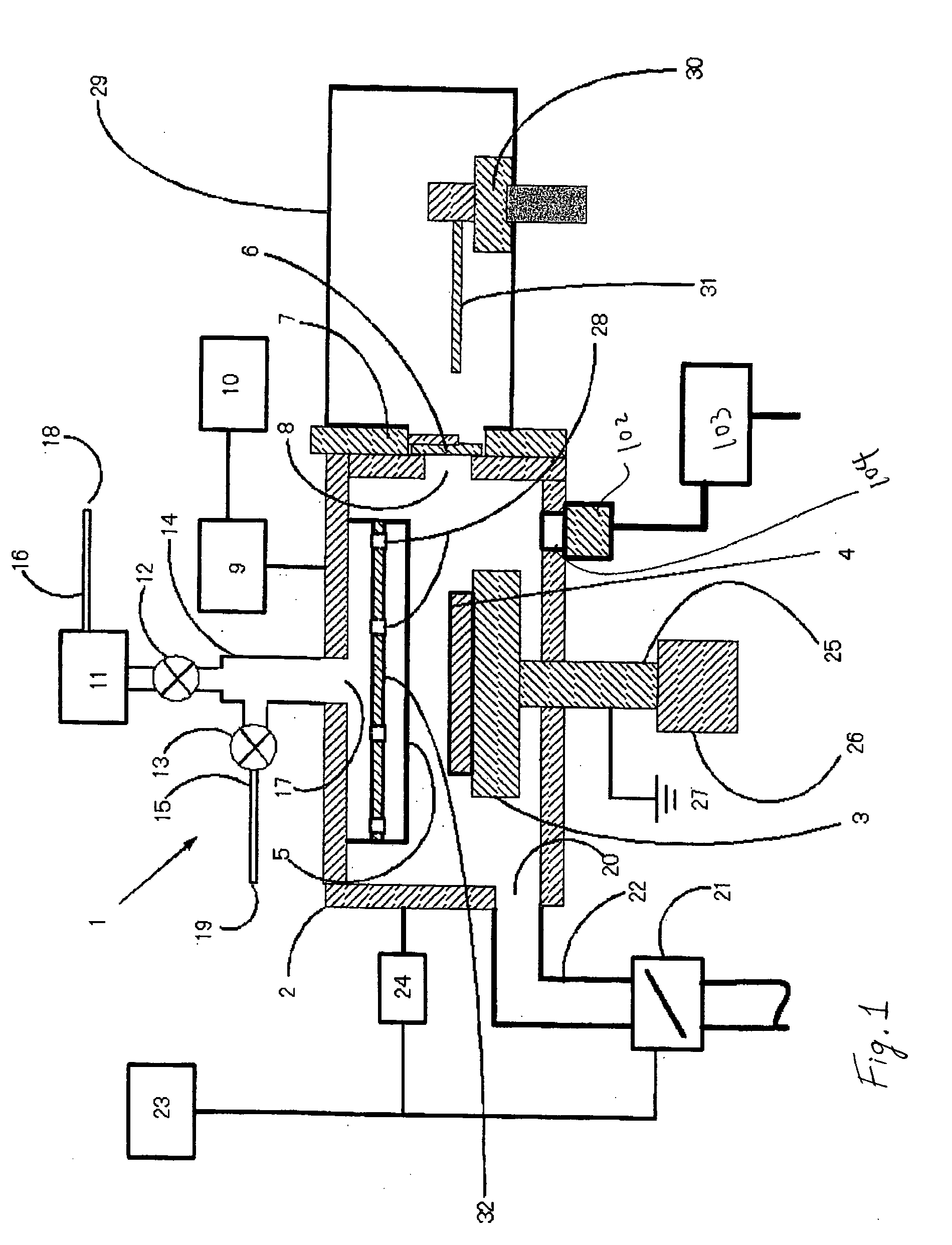
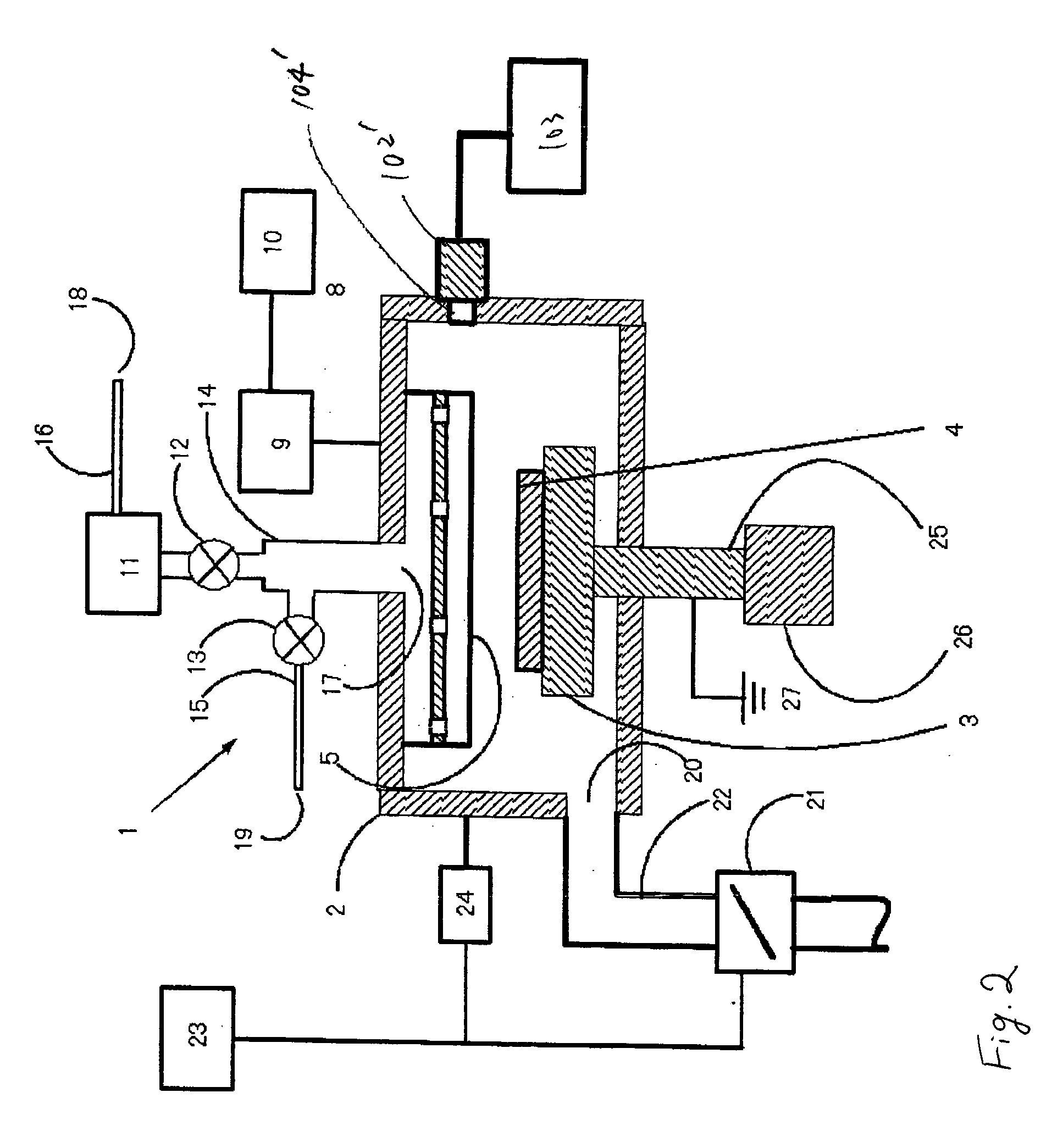
Plasma reactor apparatus with multiple gas injection zones having time-changing separate configurable gas compositions for each zone
ActiveUS8231799B2Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsGas compositionEngineering
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
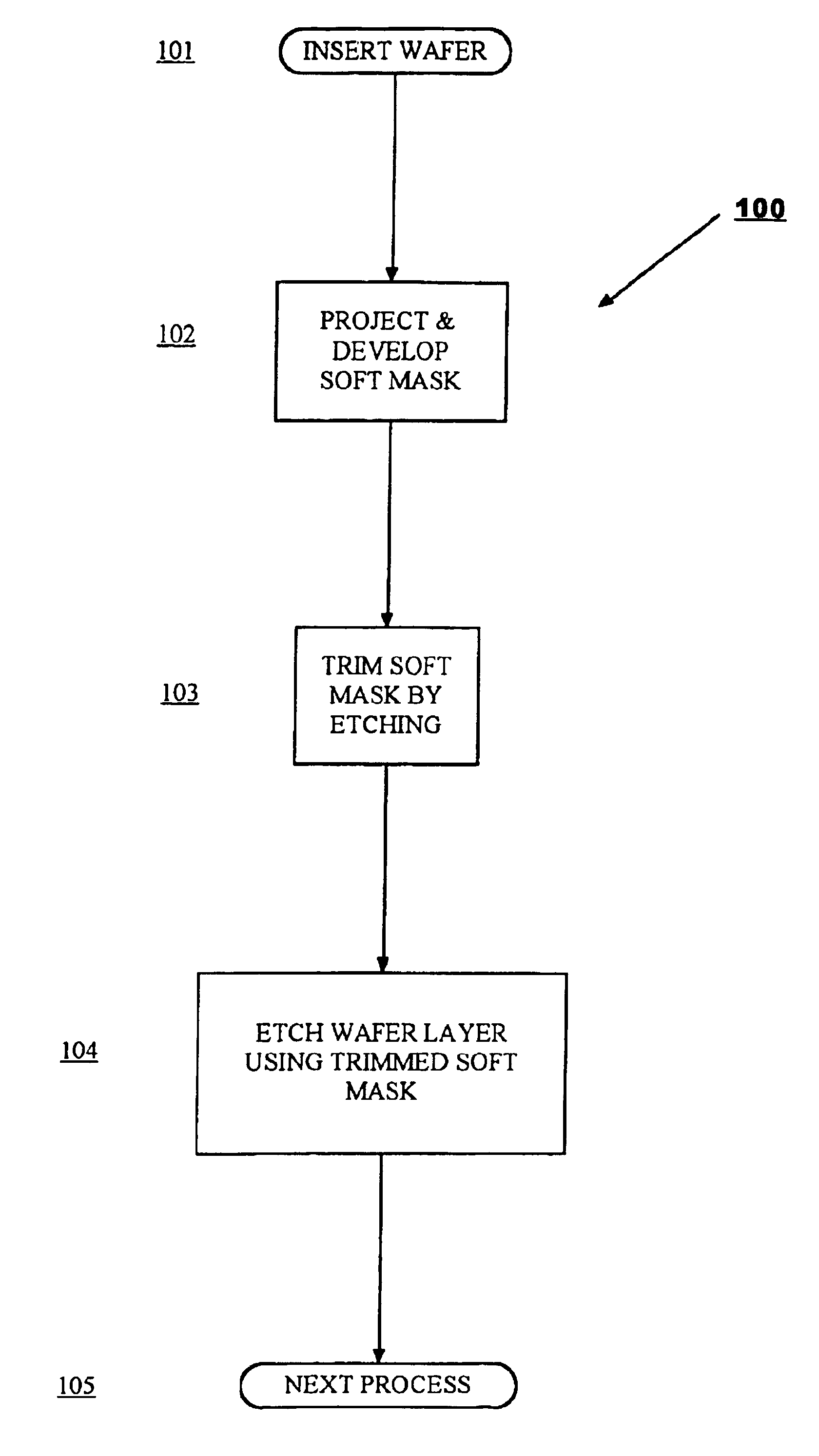
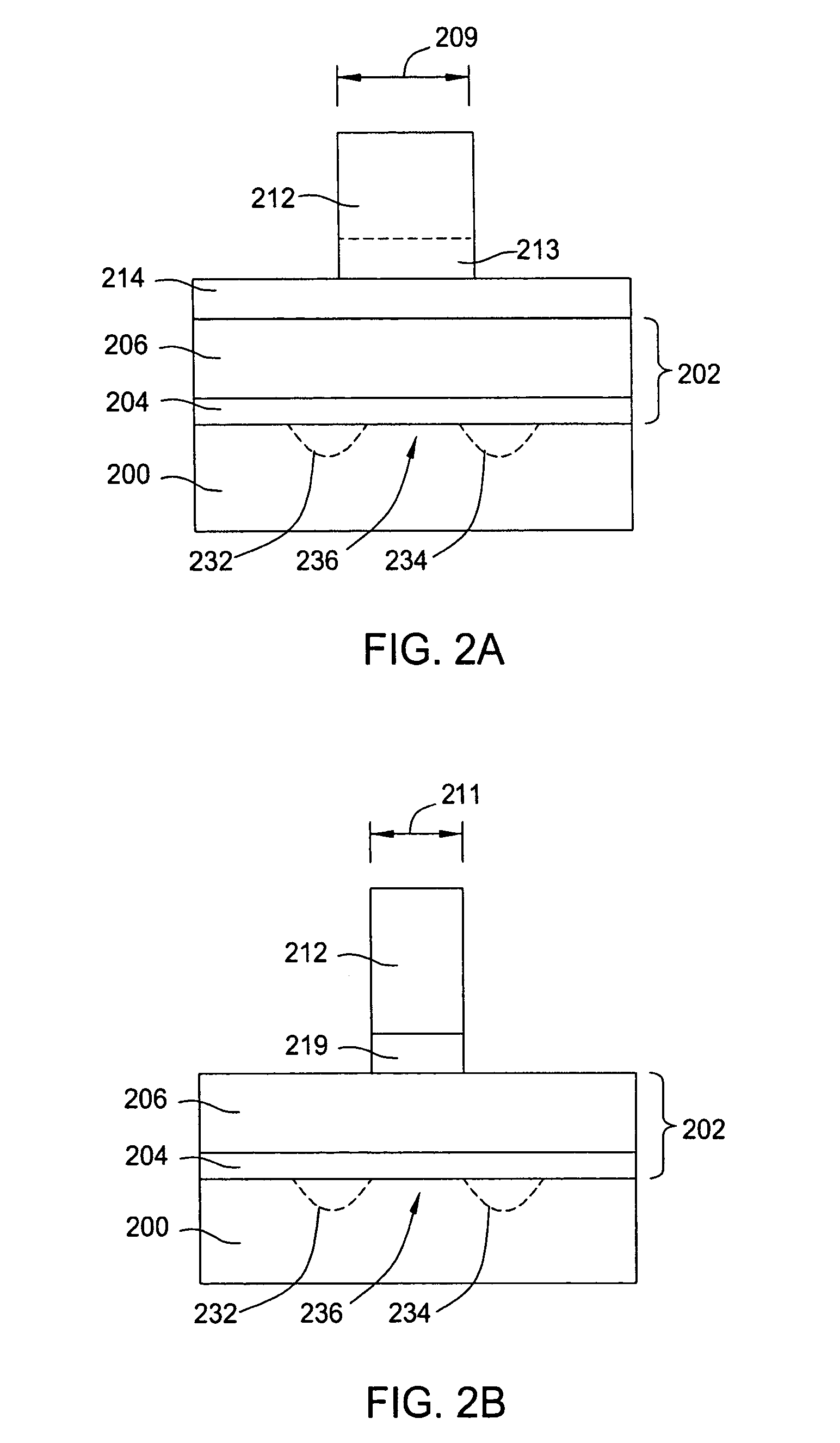
Gate linewidth tailoring and critical dimension control for sub-100 nm devices using plasma etching
InactiveUS6864041B2Tight tolerance variationMinimal variationVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsImage resolutionLine width
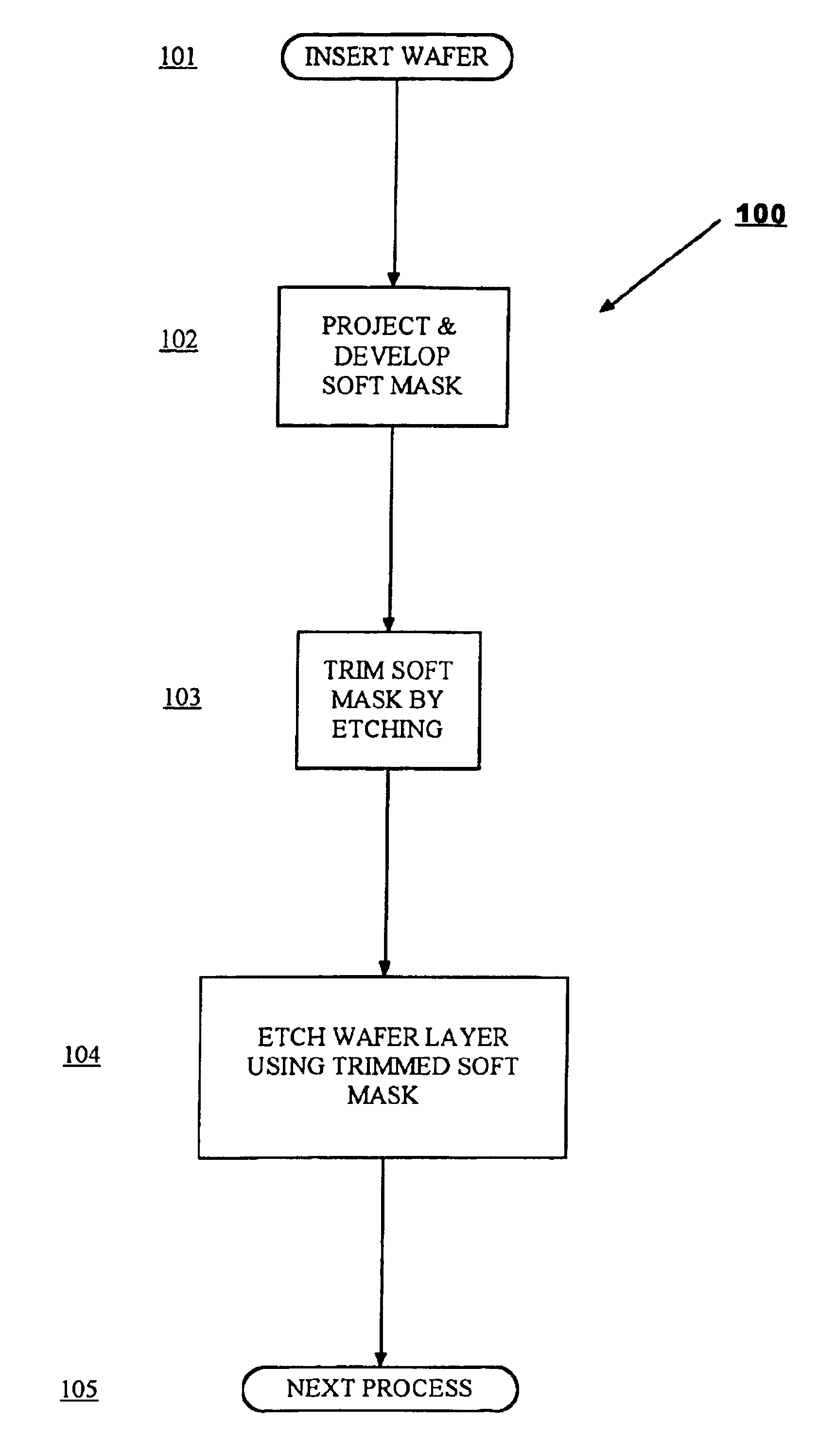
A method of fabricating an electronic chip on a wafer in which a first mask at a predetermined lower resolution is developed on the wafer and then etched under a first set of conditions for a predetermined period to achieve a mask that is below the resolution limit of current lithography. The etched mask is then used as a hard mask for etching material on a lower layer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Phase change based heating element system and method
InactiveUS20060226117A1Avoid overall overheatingVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsTemperature controlProcess engineering
A method of and apparatus for regulating carbon dioxide using a pre-injection assembly coupled to a processing chamber operating at a supercritical state is disclosed. The method and apparatus utilize a source for providing supercritical carbon dioxide to the pre-injection assembly and a temperature control element for maintaining the pre-injection region at a supercritical temperature and pressure.
Owner:SUPERCRITICAL SYSEMS
Substrate processing apparatus and substrate processing method
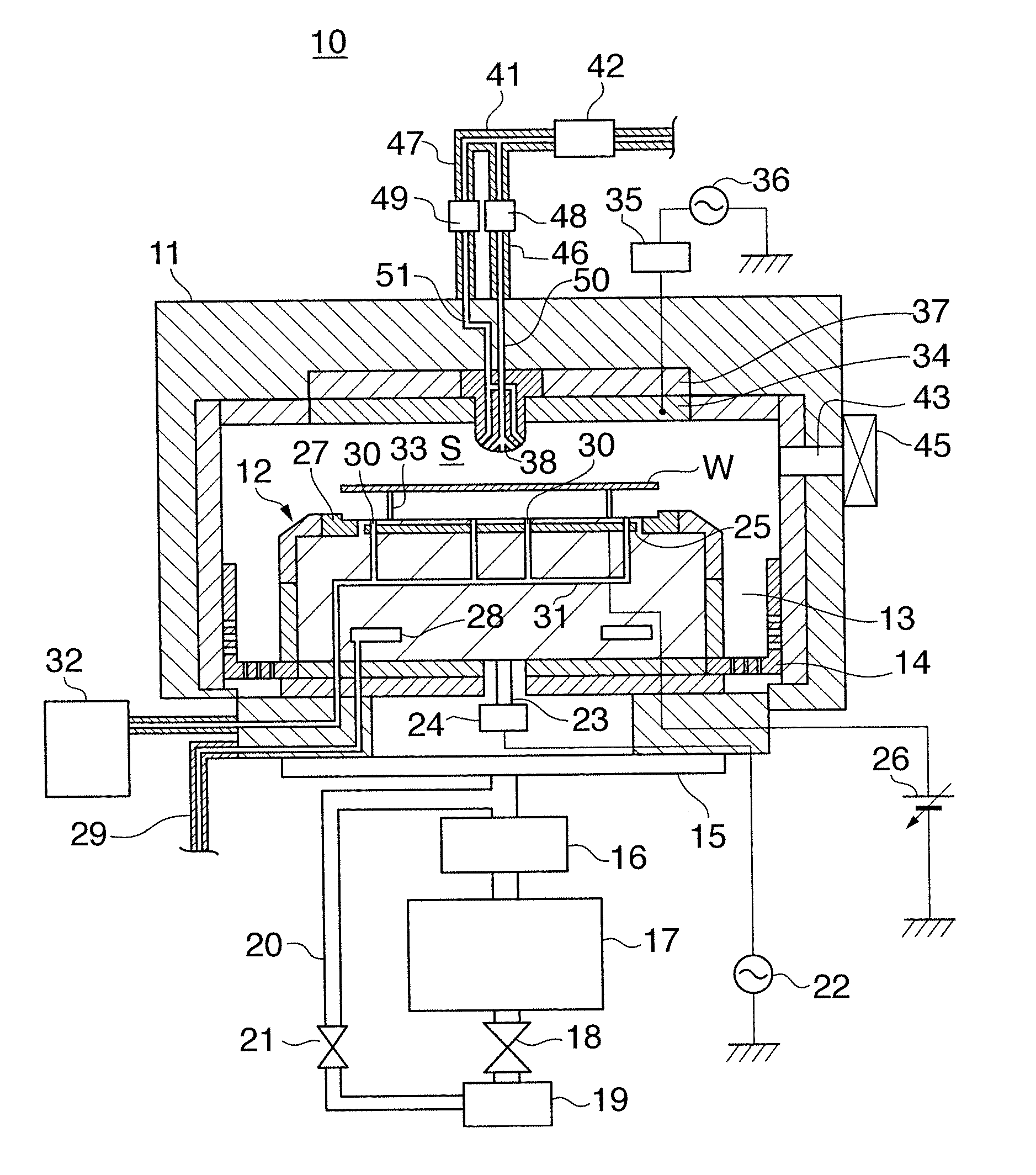
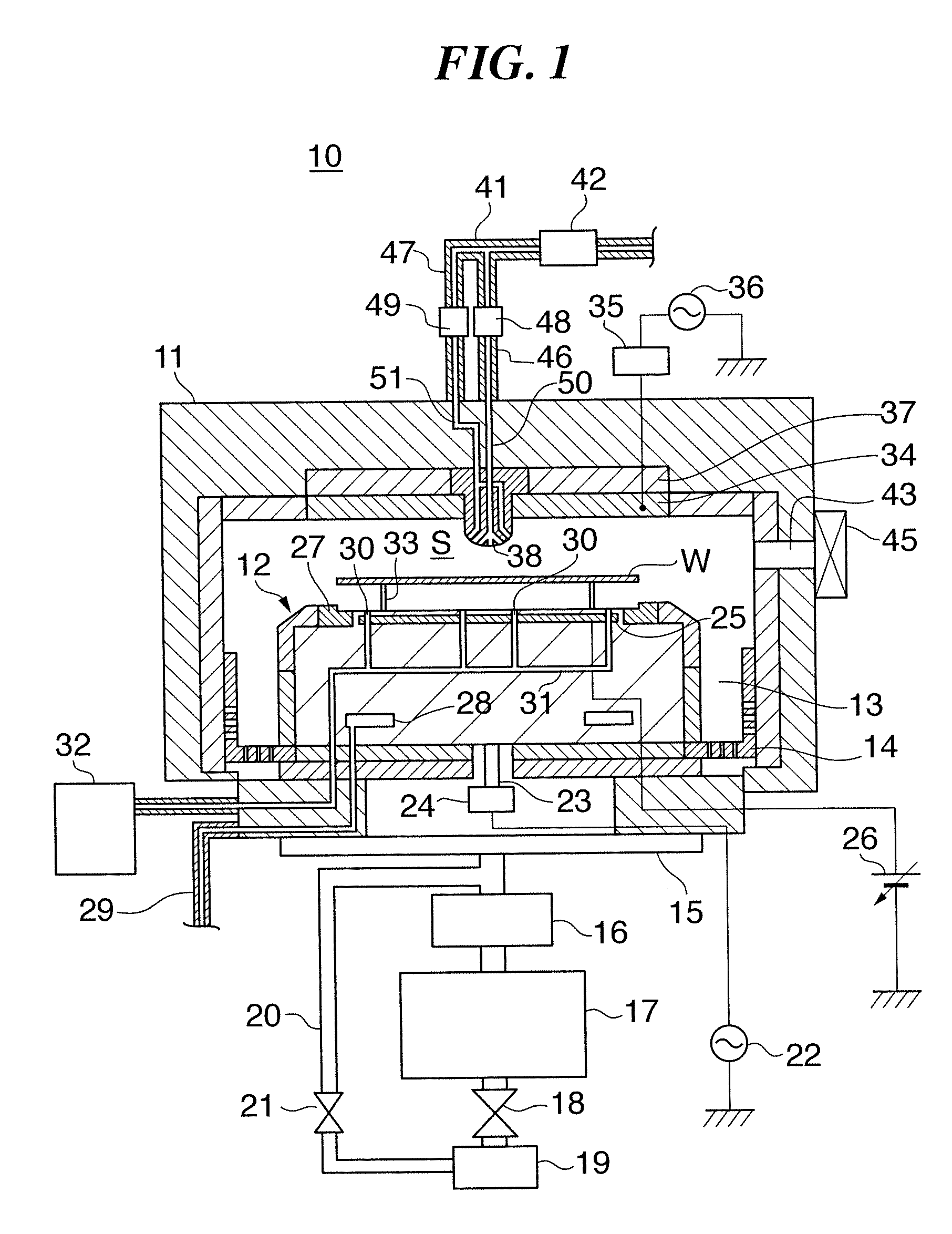
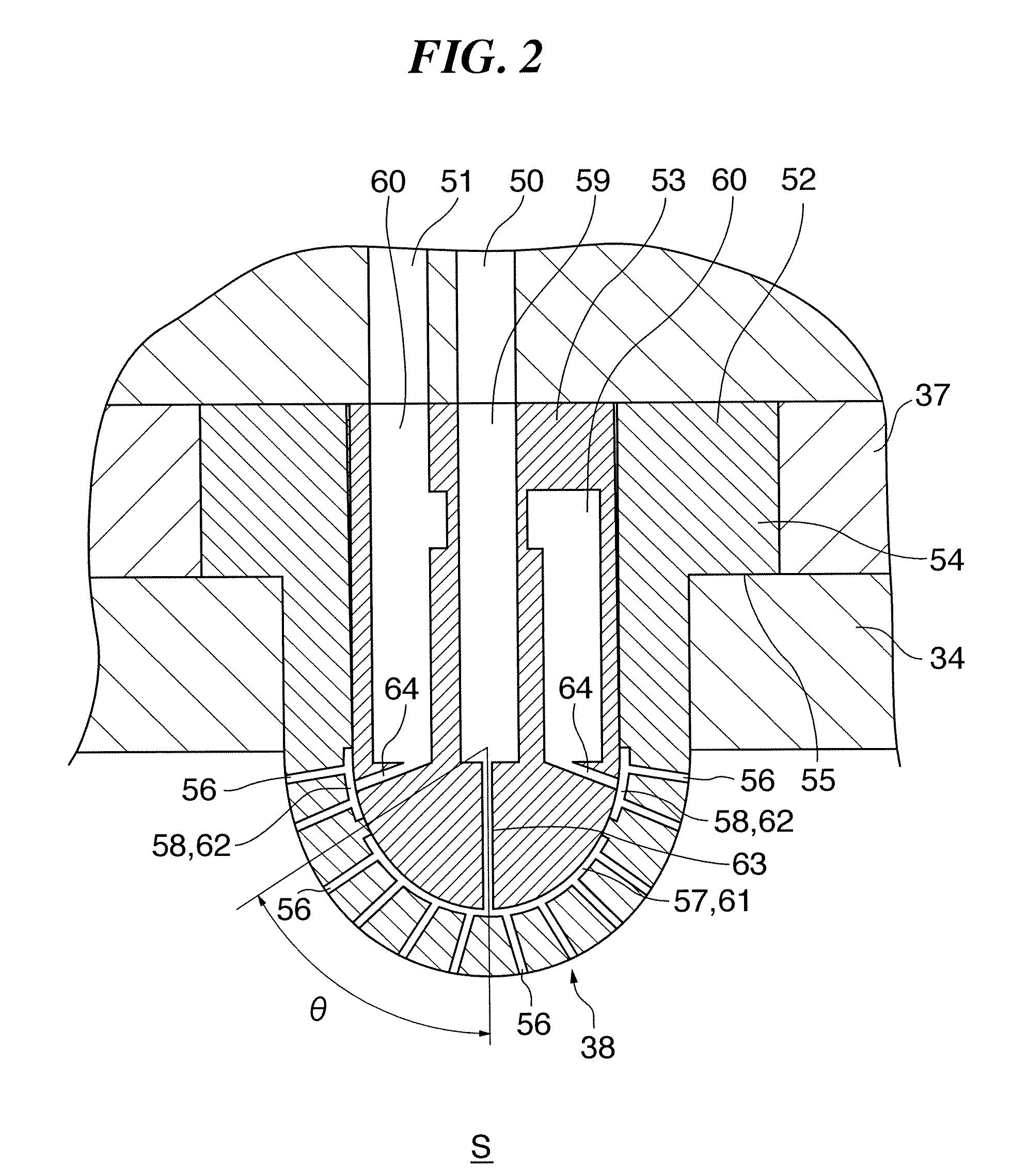
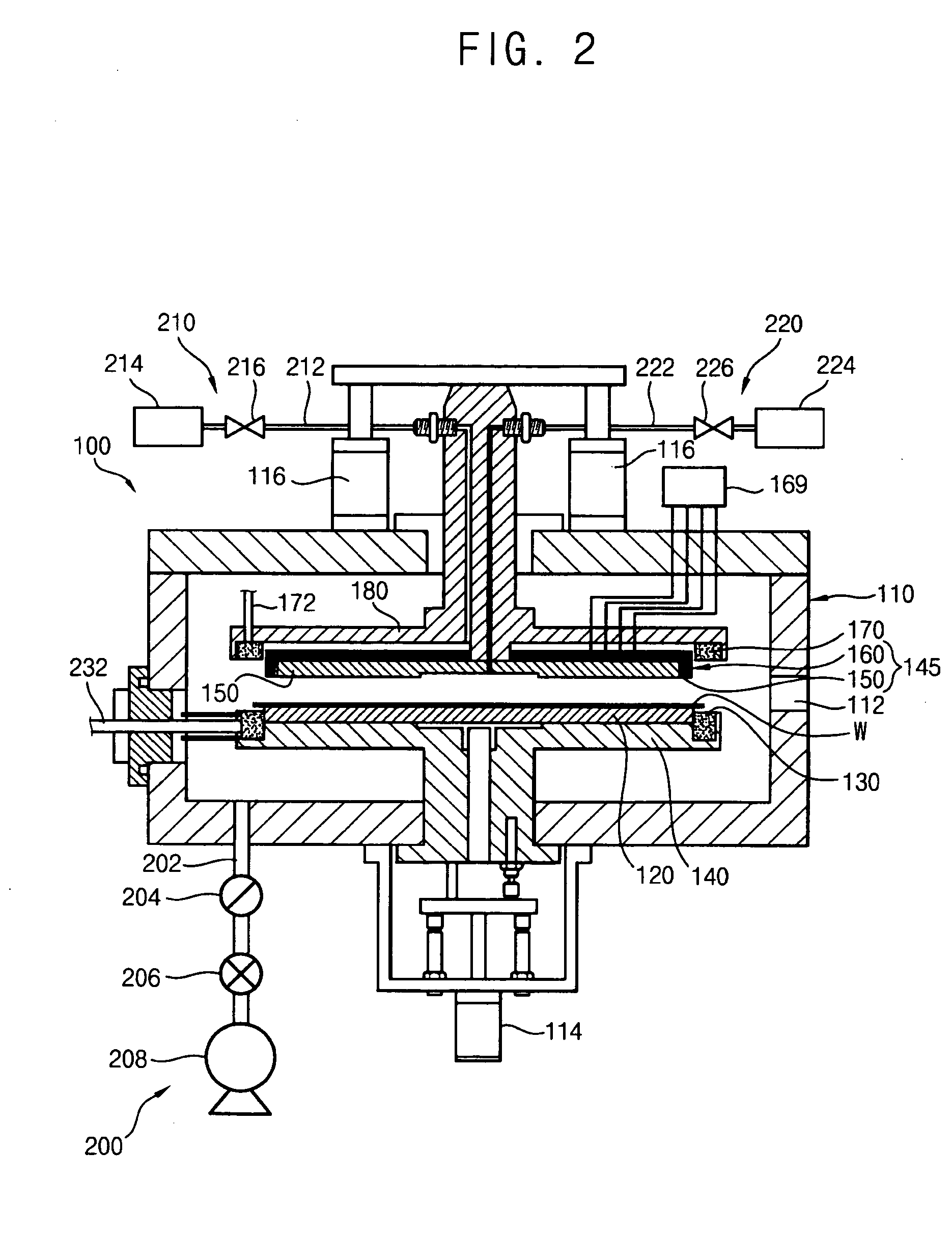
InactiveUS20070187363A1Easy maintenanceElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsEngineeringPlasma processing
A substrate processing apparatus that enables a state of plasma over a substrate to be maintained in a desired state easily. A plasma processing apparatus 10 that has therein a camber 11, a stage 12, and a processing gas introducing nozzle 38 carries out etching on a wafer W. The chamber 11 houses the wafer W. The stage 12 is disposed in the chamber 11 and the wafer W is mounted thereon. The processing gas introducing nozzle 38 is a projecting body that projects out into the chamber 11, and has therein a plurality of processing gas introducing holes 56 that open out in different directions to one another.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
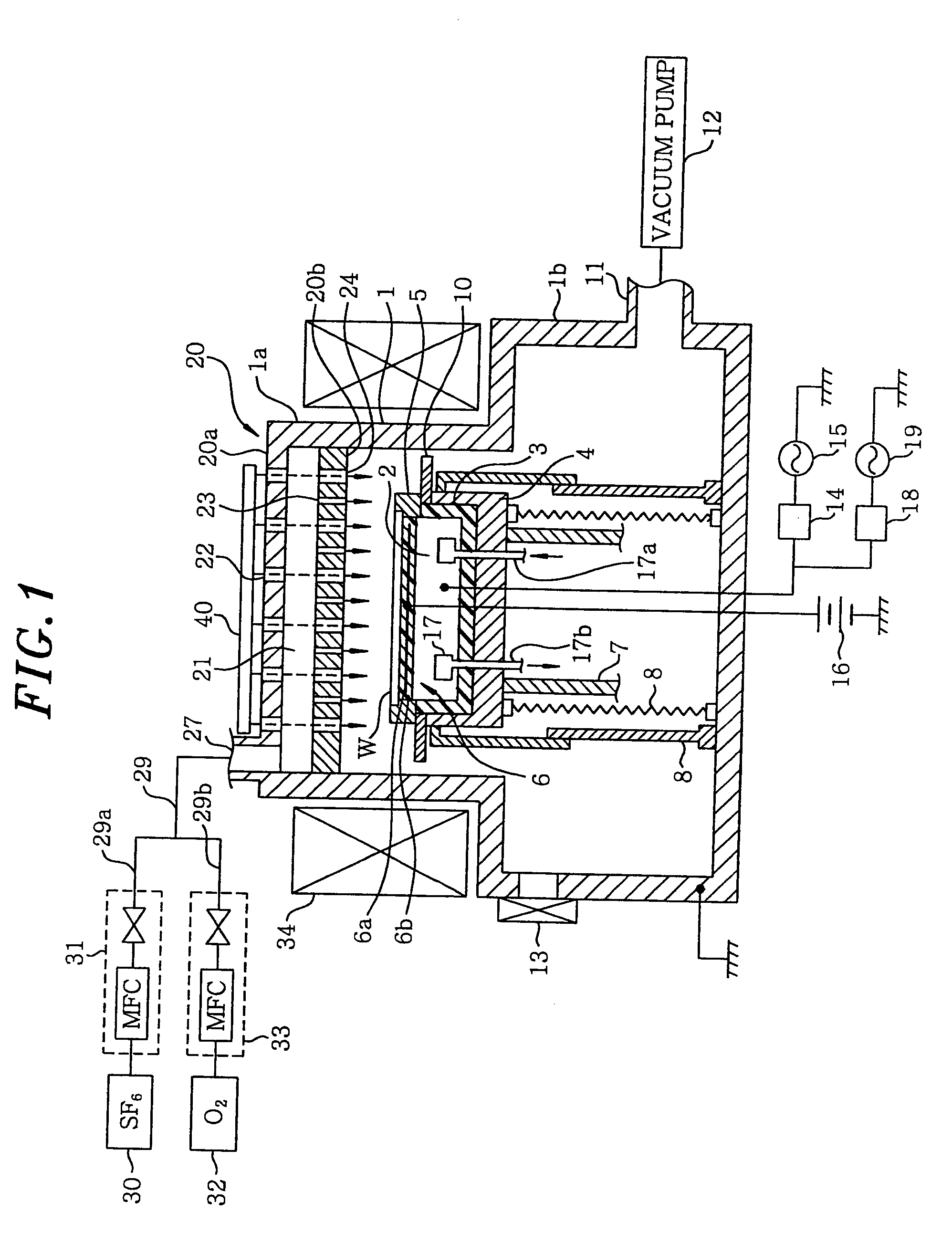
Plasma processing of tungsten using a gas mixture comprising a fluorinated gas and oxygen
InactiveUS6277763B1Good choiceElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsFluorinated gasesProduct gas
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plasma etching method and apparatus therefor
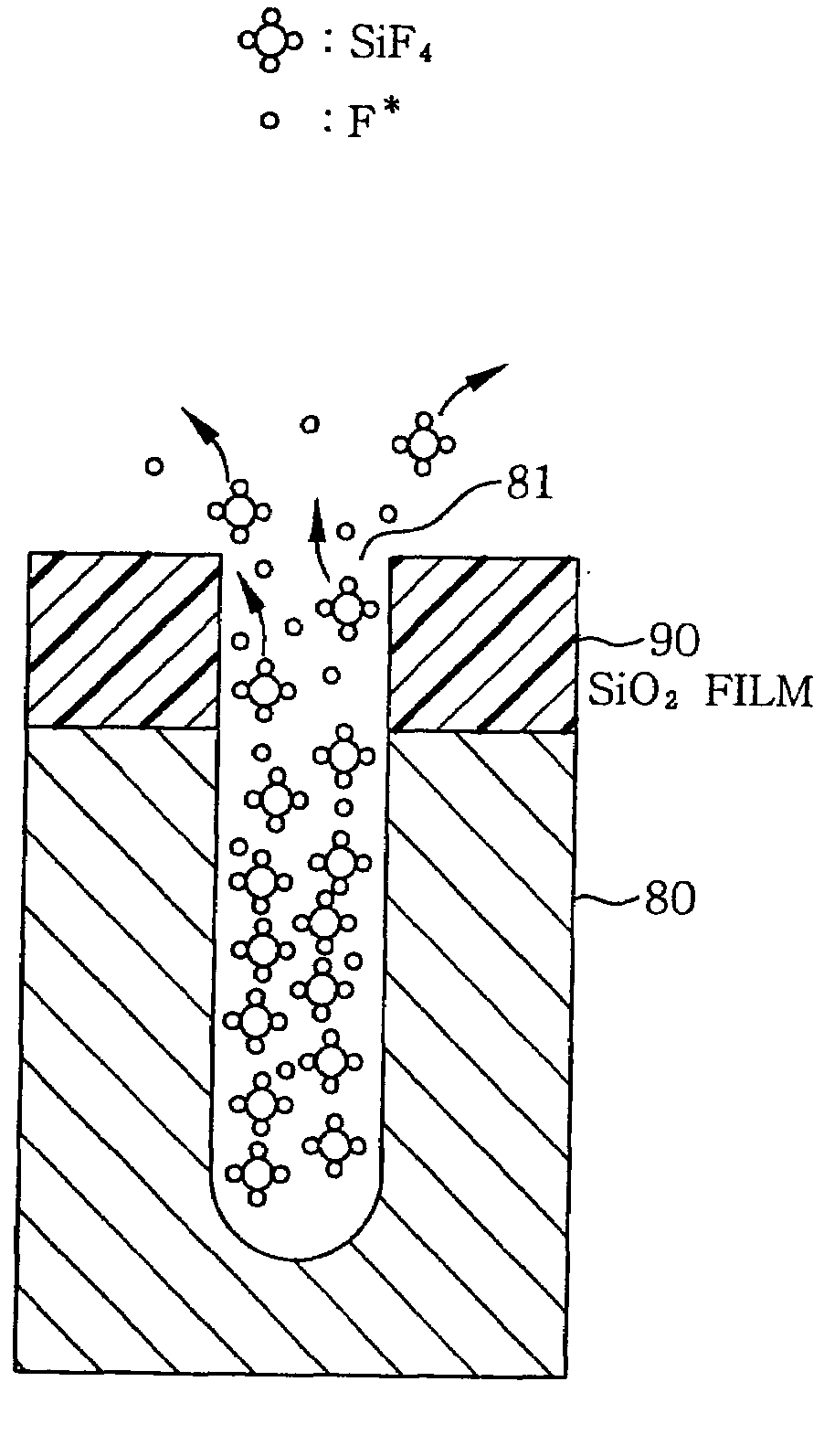
InactiveUS20090045167A1Increase chanceIncrease etch rateElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsPeak intensityFluorine containing
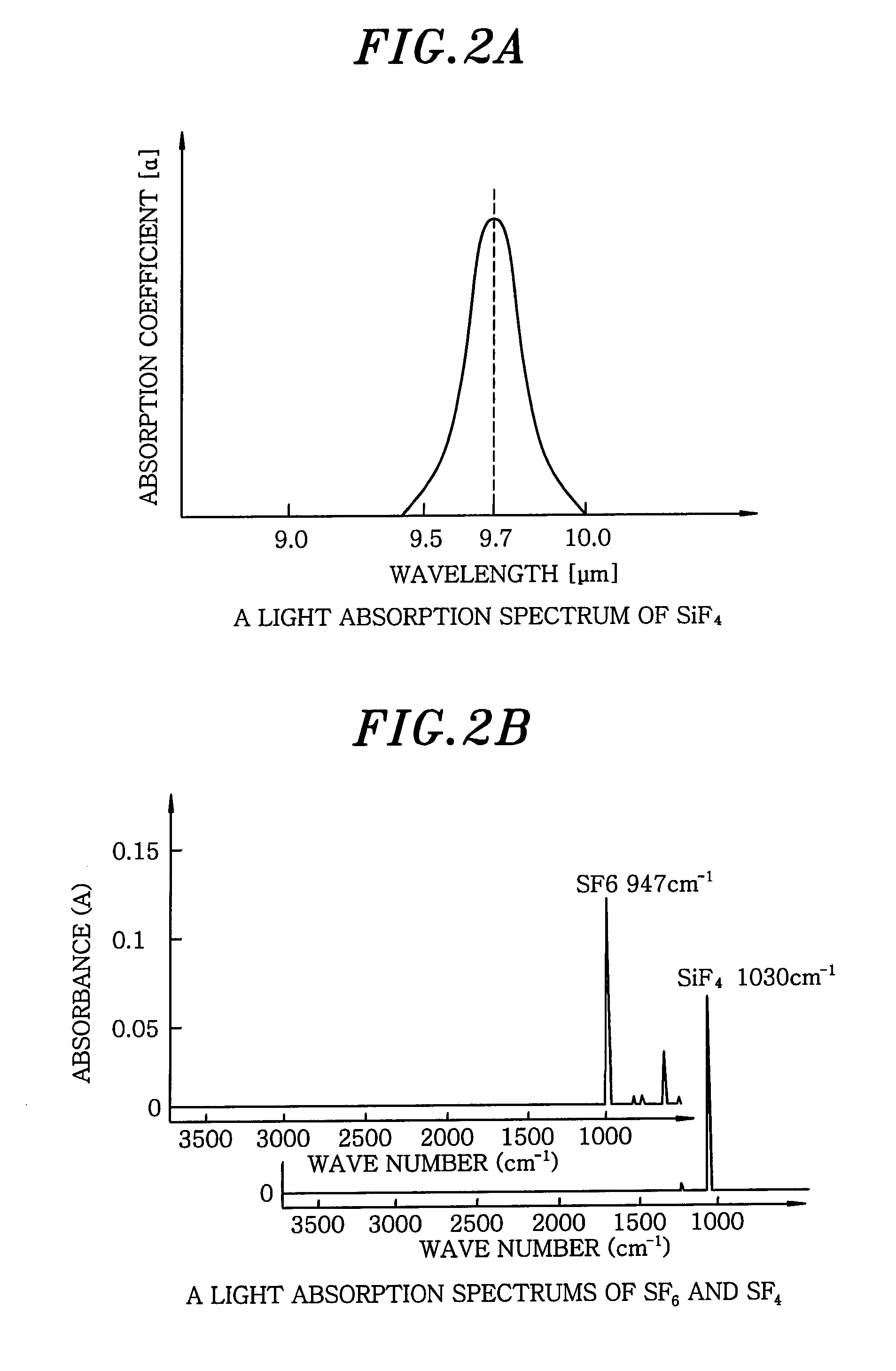
A fluorine-containing compound gas, e.g., SF6 gas, is converted into a plasma and a silicon portion of an object to be processed is etched by the plasma. At the same time, using a light source having a peak intensity of light in a wavelength range of light absorption of a reaction product, e.g., SiF4, for which, to be more precise, ranges from 9 μm to 10 μm, the light is irradiated onto a surface of an object to be processed from the light source. The SiF4 molecules absorb the light, become activated and gain kinetic energy to be used in gaining an easy escape from a hole. As a consequence, an amount (a partial pressure) of fluorine radicals (F*) used as an etchant is increased and an etching rate of a silicon is increased.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
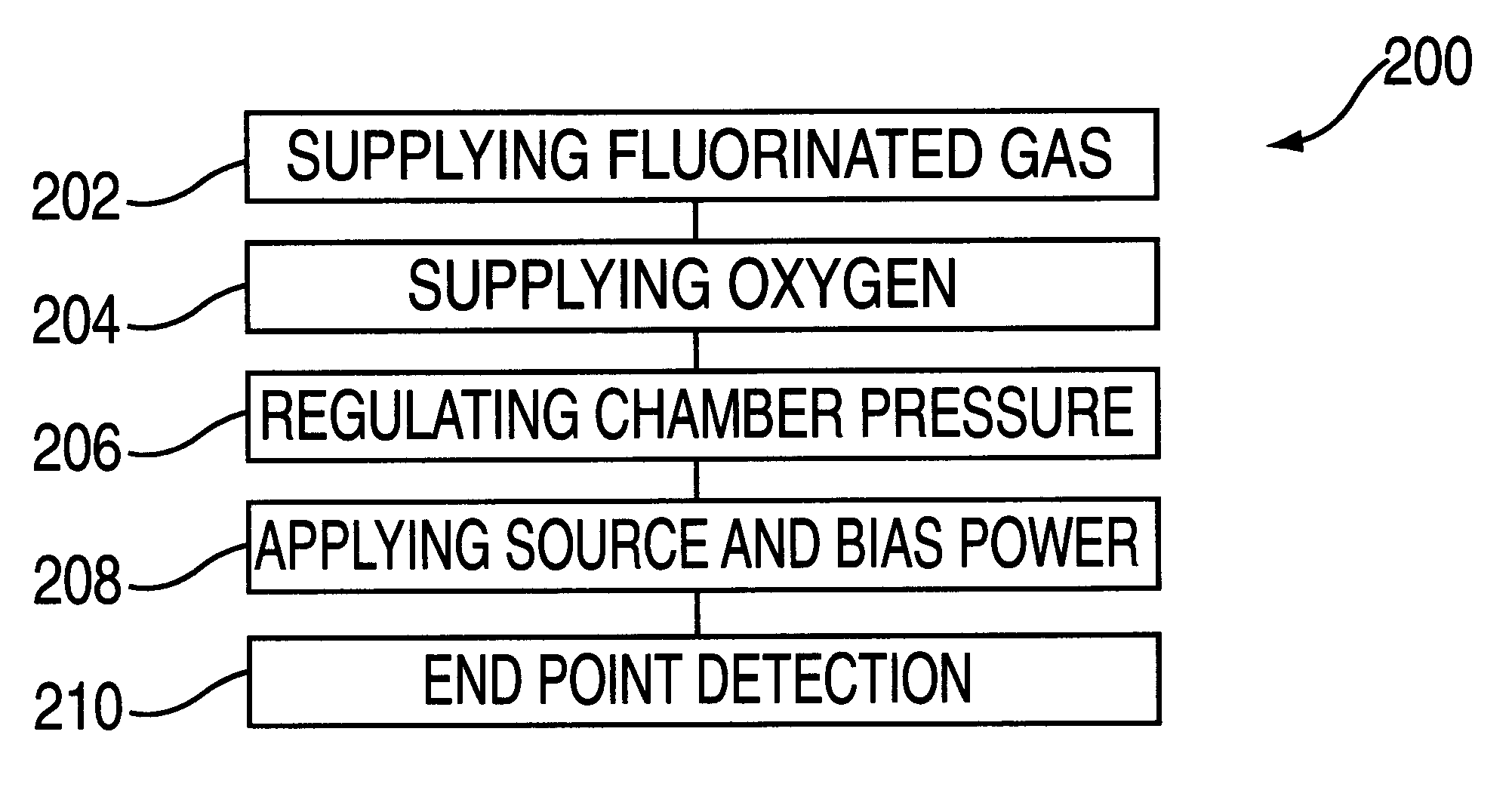
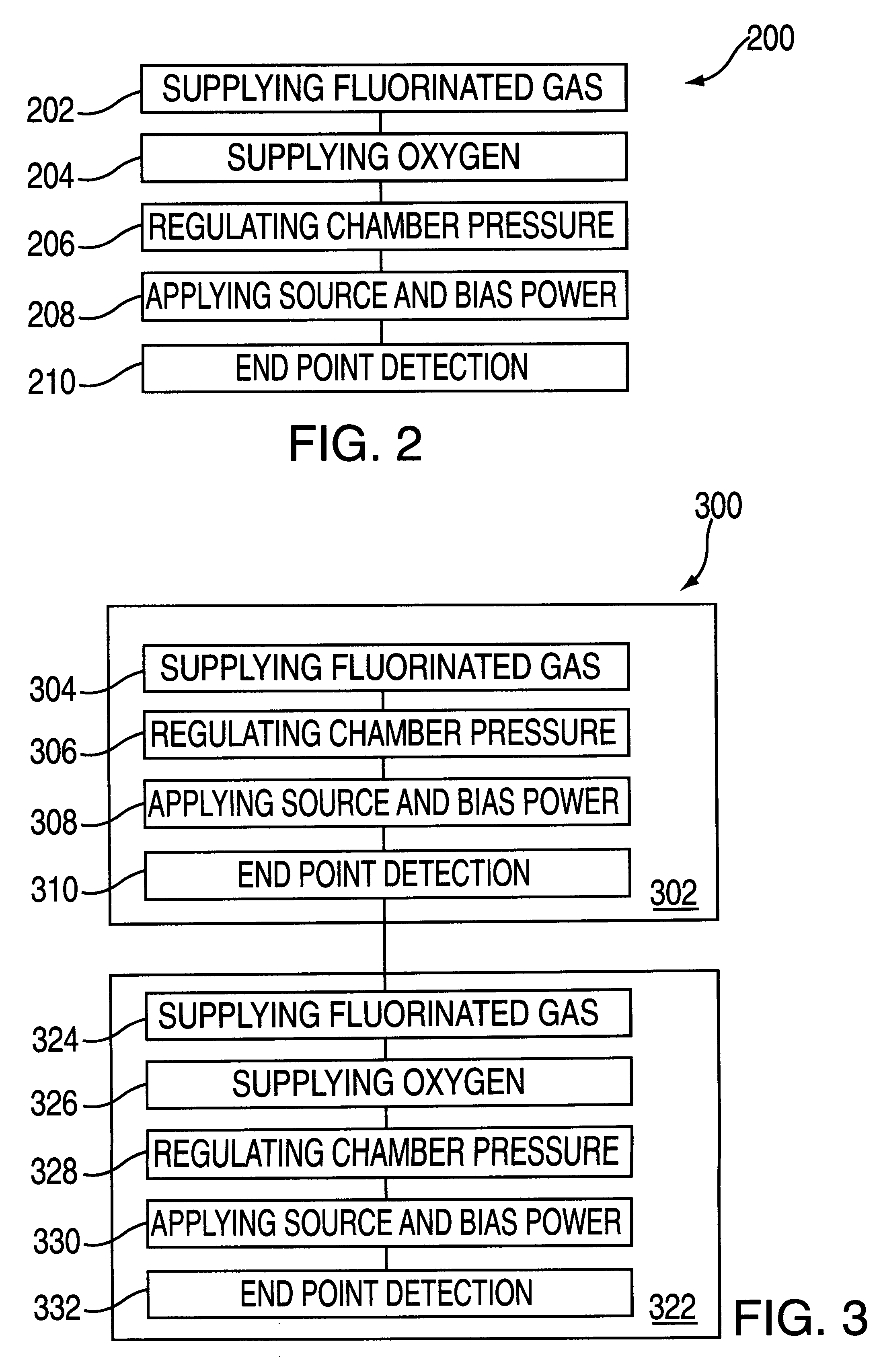
Methods of end point detection for substrate fabrication processes
InactiveUS20130193108A1Liquid surface applicatorsVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsEngineeringThroughput
Methods and substrate processing systems for analyzing an end point of a process are provided. By-products of the process are detected and monitored to determine the completion of various types of reaction processes within a substrate processing chamber. The methods provide real time process monitoring, thereby reducing the need to rigidly constrain other substrate processing parameters, increasing chamber cleaning efficiency, and / or increasing substrate processing throughput.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
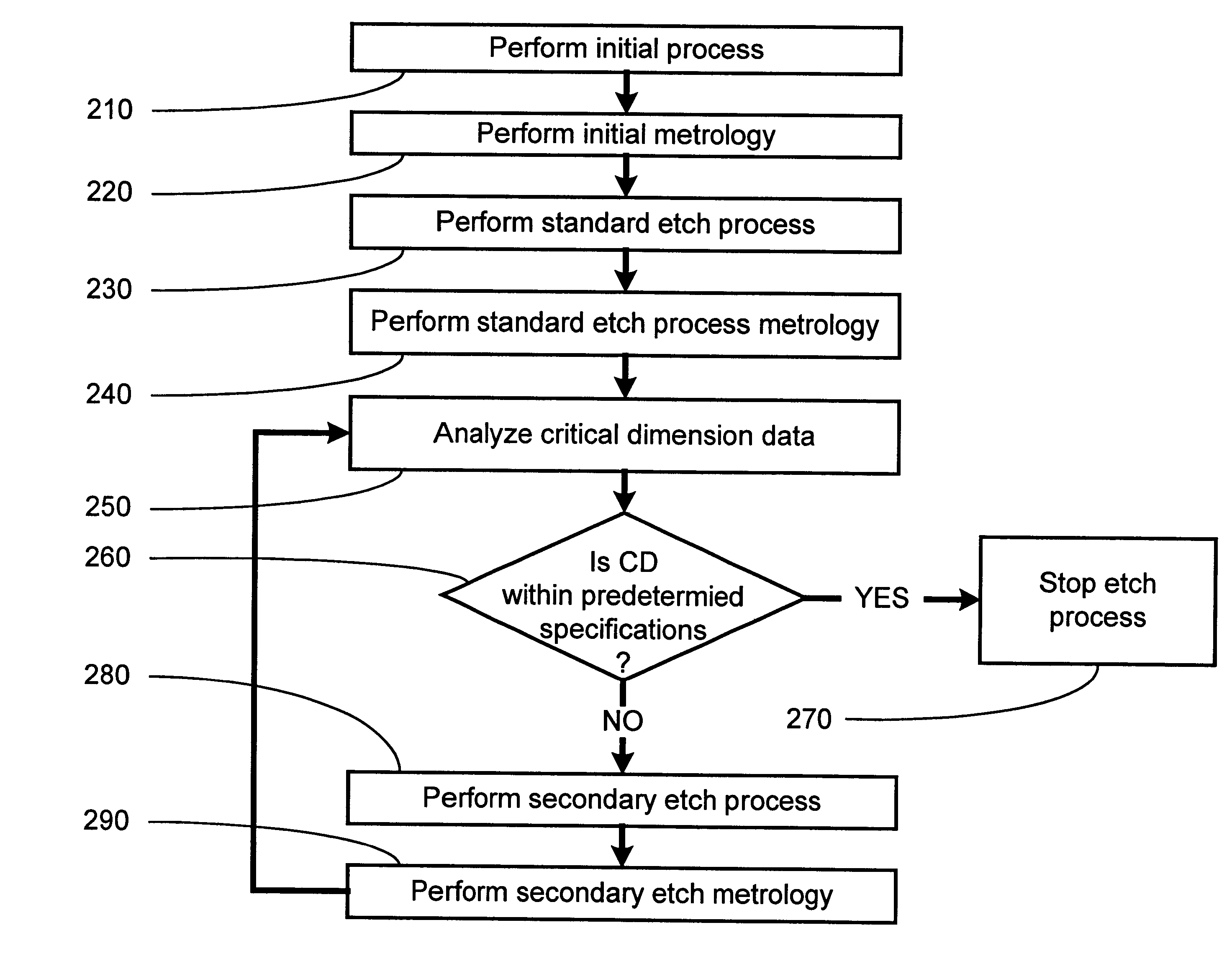
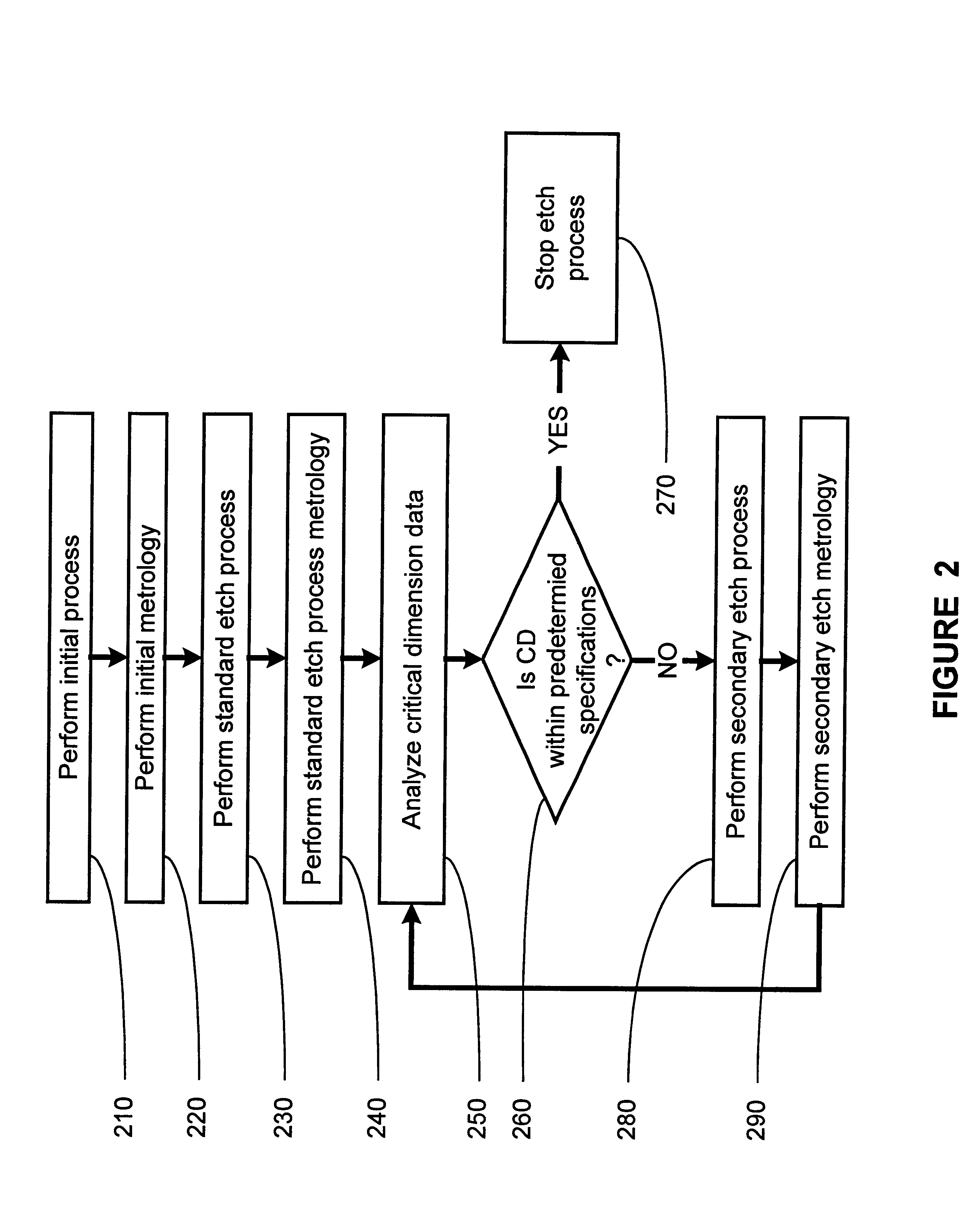
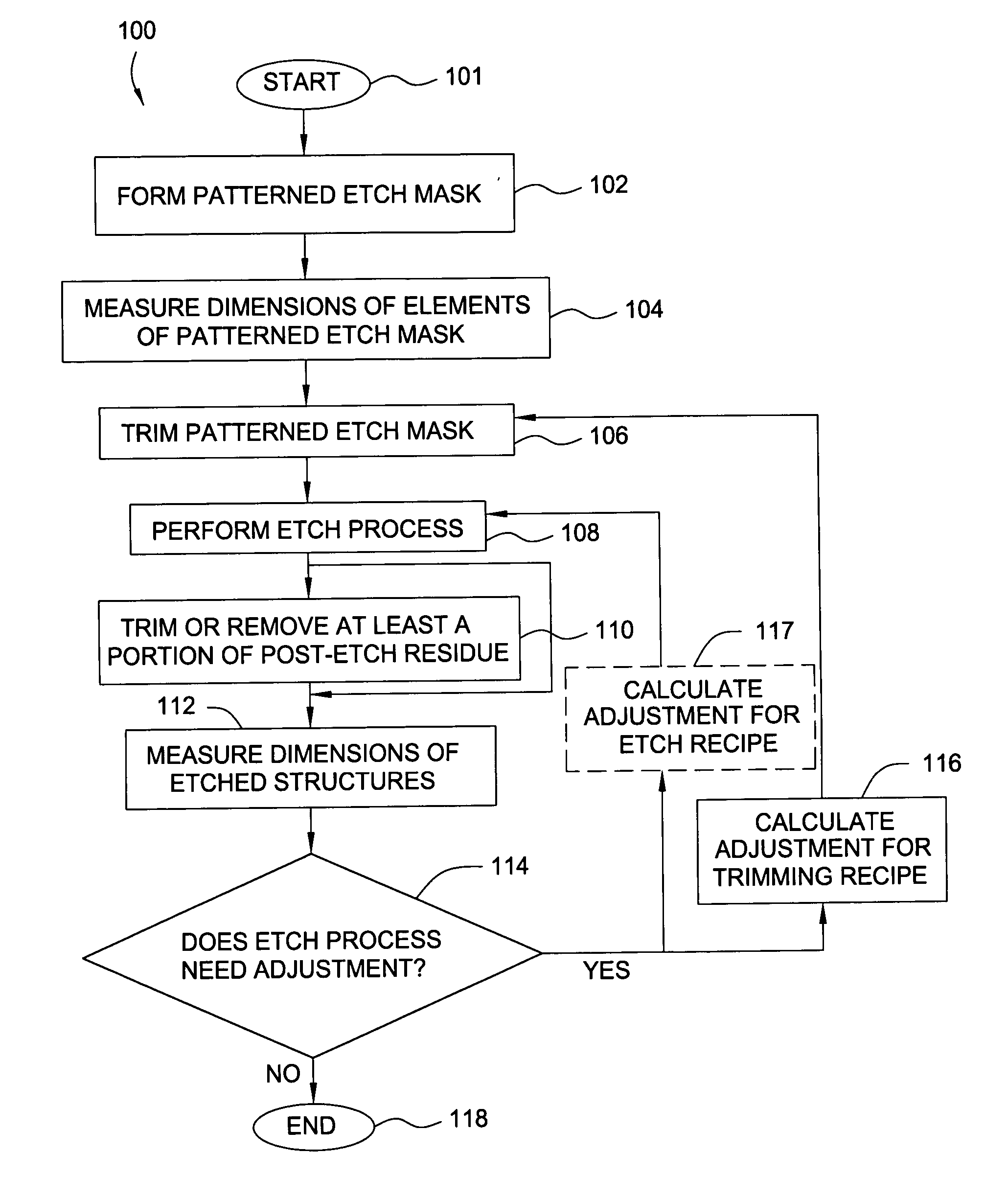
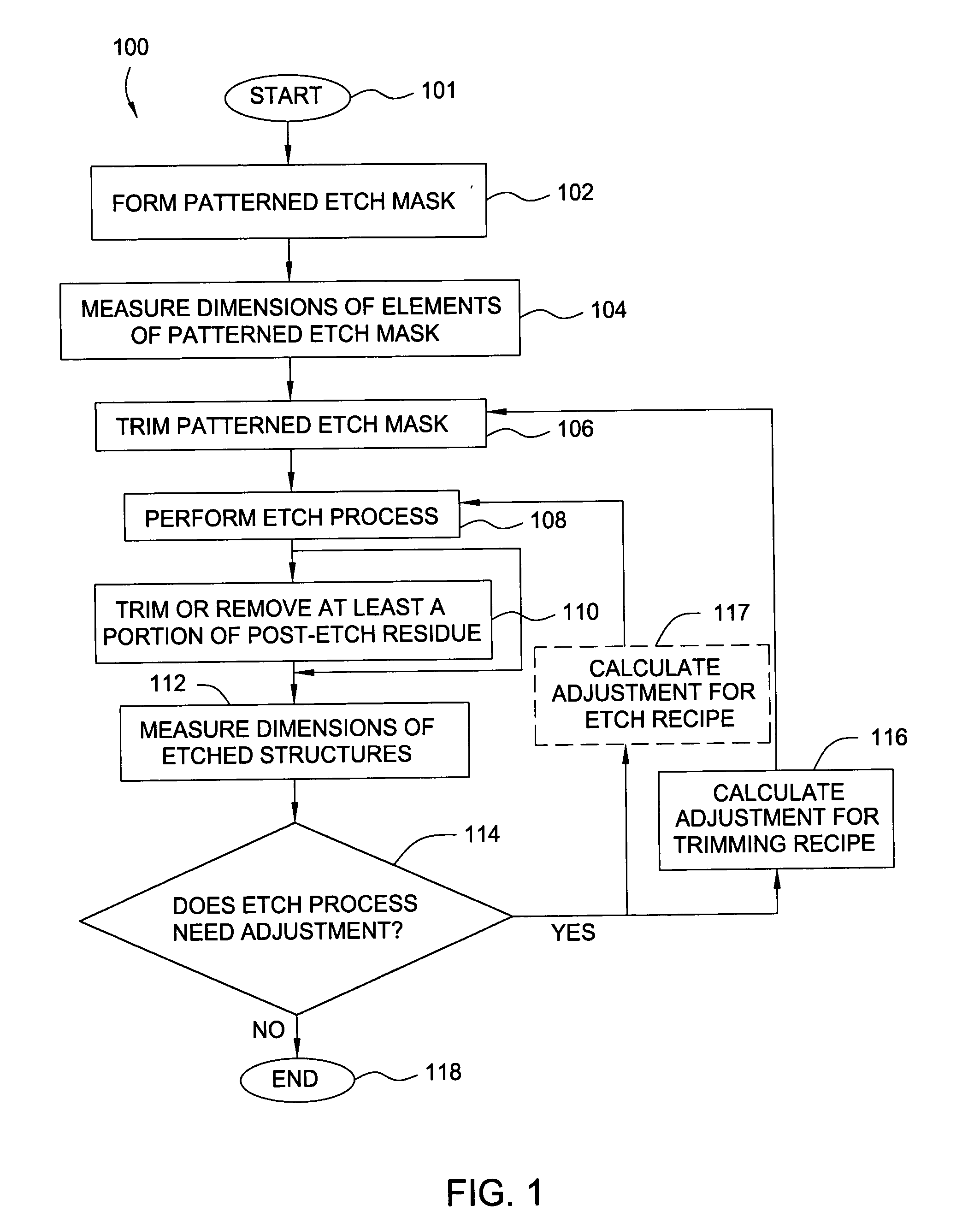
Method and apparatus for control of critical dimension using feedback etch control
InactiveUS6245581B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsEngineeringCritical dimension
The present invention provides for a method and an apparatus for controlling critical dimensions. At least one run of semiconductor devices is processed. A critical dimension measurement is performed upon at least one of the processed semiconductor device. An analysis of the critical dimension measurement is performed. A secondary process upon the semiconductor device in response to the critical dimension analysis is performed.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Plasma processing apparatus and a plasma processing method
InactiveUS20060157449A1Avoid volatilityElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsElectron temperatureCountermeasure
Owner:TAKAHASHI KAZUE +3
Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
ActiveUS20130119016A1The result is stableProgramme controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringActuator
A plasma processing apparatus includes a plasma processing chamber, a process monitor which monitors a condition in the plasma processing chamber, an actuator which controls a parameter constituting a plasma processing condition, N+1 correction amount calculating units which calculate a correction amount of a manipulated variable on the basis of a difference between a process monitor value monitored by the process monitor and a desired value of the process monitor and a correlation between the process monitor value and a manipulated variable, which is the parameter, the correlation having been acquired in advance, and N manipulated variable adding units that add a manipulated variable having a priority level next to an N-th manipulated variable. The N-th manipulated variable adding unit defines a correction amount calculated by the N+1-th correction amount calculating unit as the correction amount of an N+1-th manipulated variable.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method of setting thickness of dielectric and substrate processing apparatus having dielectric disposed in electrode
ActiveUS20110318935A1Avoid spendingElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDielectricSusceptor
Provided is a method of setting a thickness of a dielectric, which restrains the dielectric formed in an electrode from being consumed when etching a silicon dioxide film on a substrate by using plasma. In a substrate processing apparatus including an upper electrode facing a susceptor and the dielectric formed of silicon dioxide in the upper electrode, a silicon dioxide film formed on a wafer being etched by using plasma, an electric potential of the plasma facing the dielectric in a case where the dielectric is not formed in the upper electrode is estimated based on a bias power applied to the susceptor and an A / C ratio in a chamber, and the thickness of the dielectric is determined so that an electric potential of the plasma, which is obtained by multiplying the estimated electric potential of the plasma by a capacity reduction coefficient calculated when a capacity of the dielectric and a capacity of a sheath generated around a surface of the dielectric are combined, is 100 eV or less.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for controlling accuracy and repeatability of an etch process
InactiveUS20050085090A1Improve accuracyPoor repeatabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsEngineeringRepeatability
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to a method for etching in a processing platform (e.g. a cluster tool) wherein robust pre-etch and post-etch data may be obtained in-situ. The method includes the steps of obtaining pre-etched critical dimension (CD) measurements of a feature on a substrate, etching the feature; treating the etched substrate to reduce and / or remove sidewall polymers deposited on the feature during etching, and obtaining post-etched CD measurements. The CD measurements may be utilized to adjust the etch process to improved the accuracy and repeatability of device fabrication.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
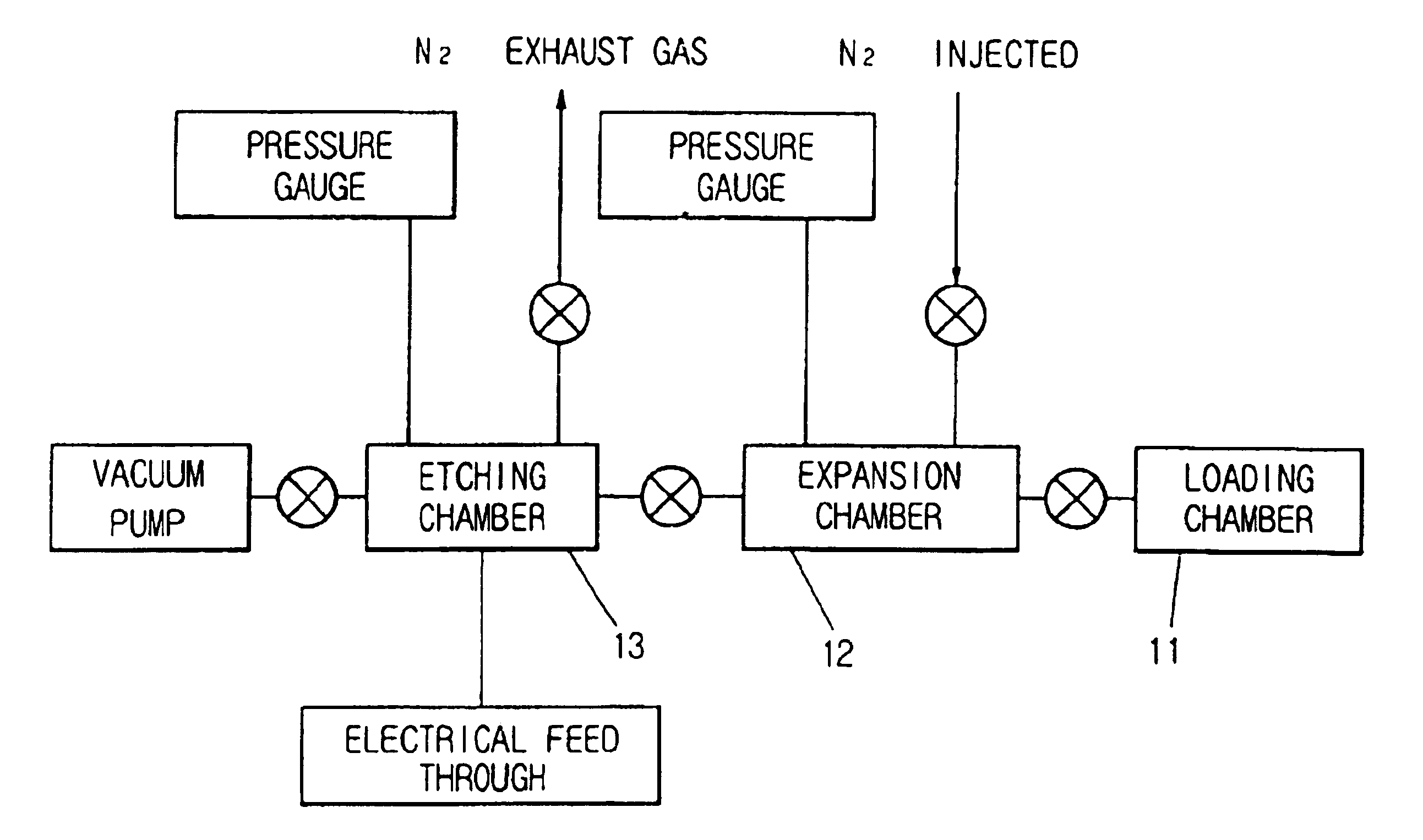
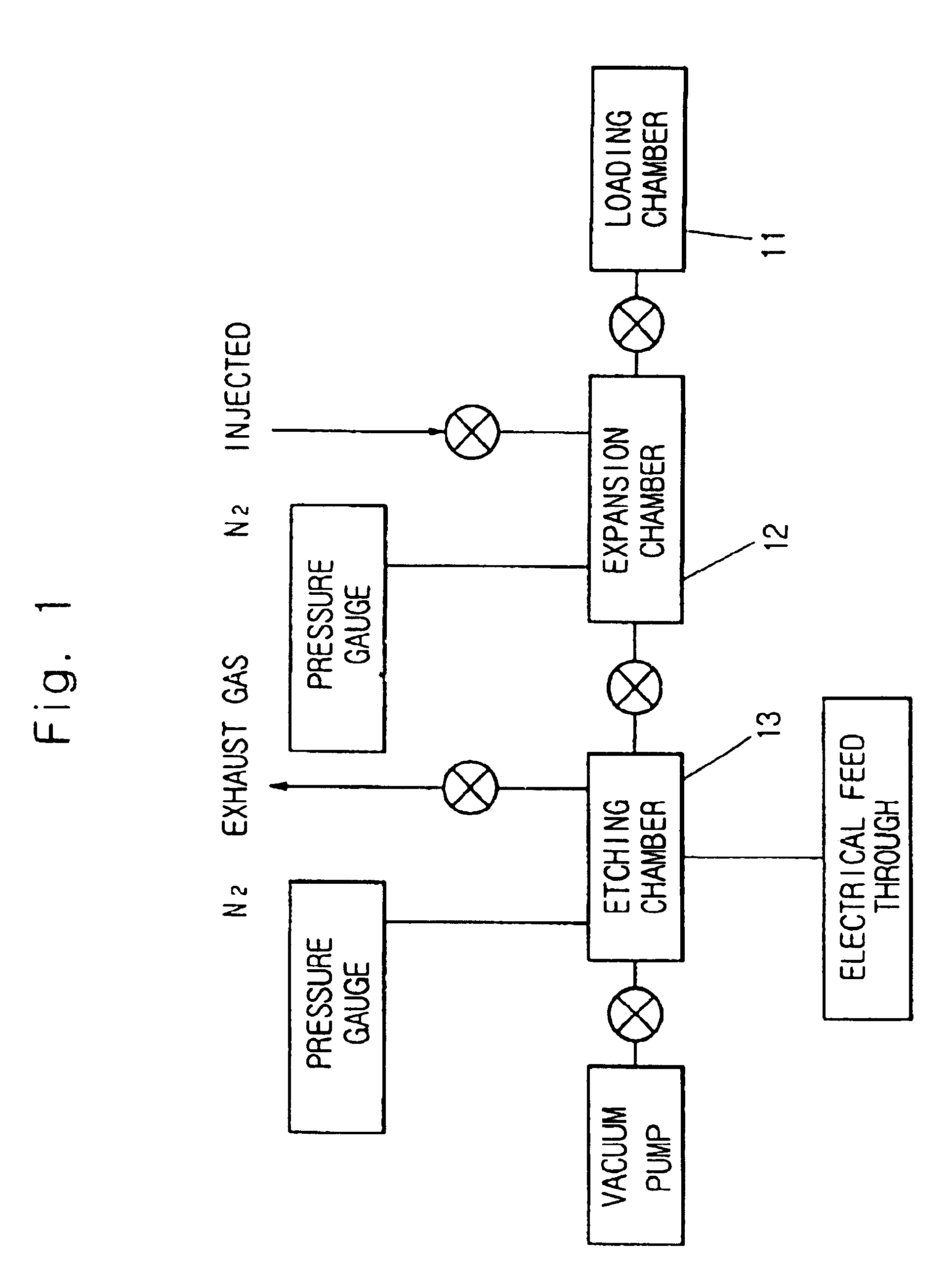
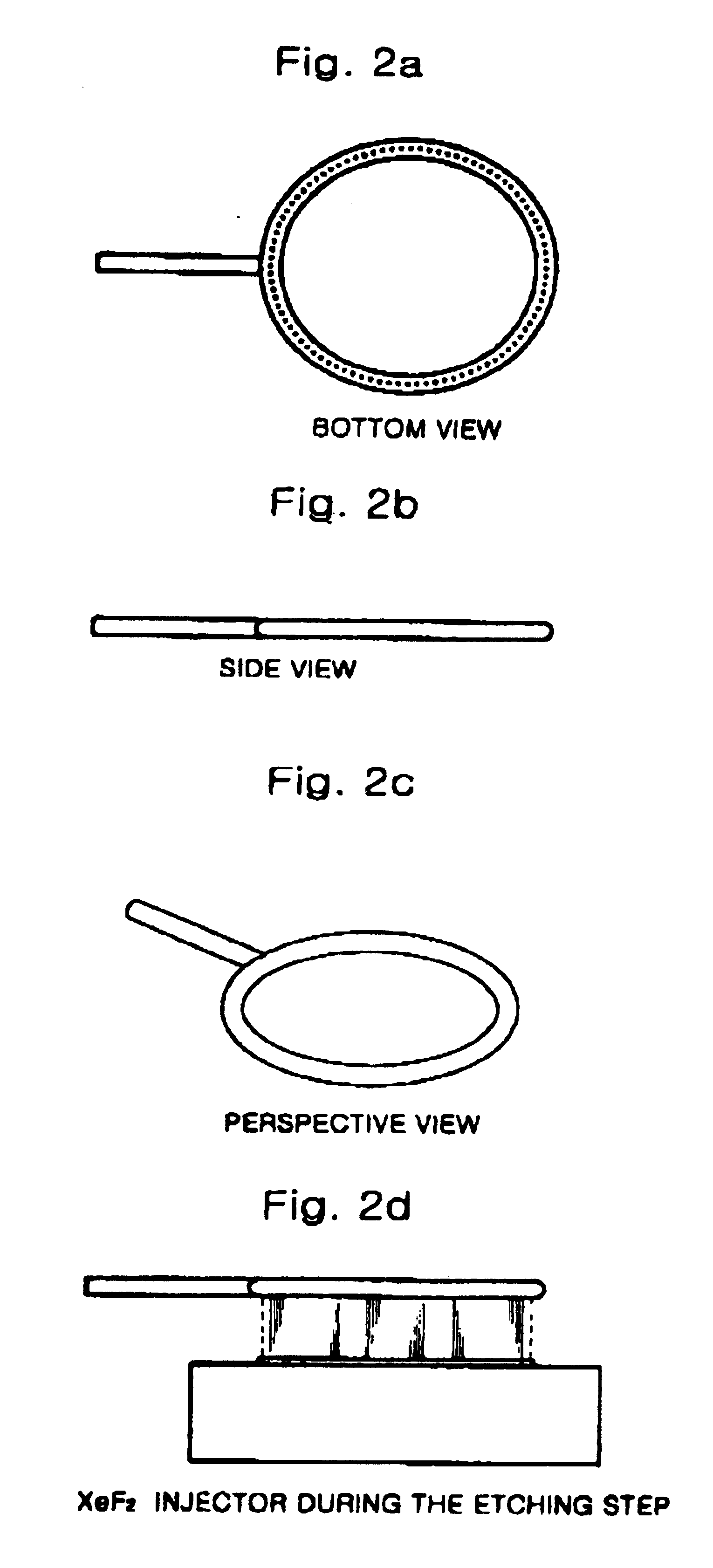
Silicon etching apparatus using XeF2
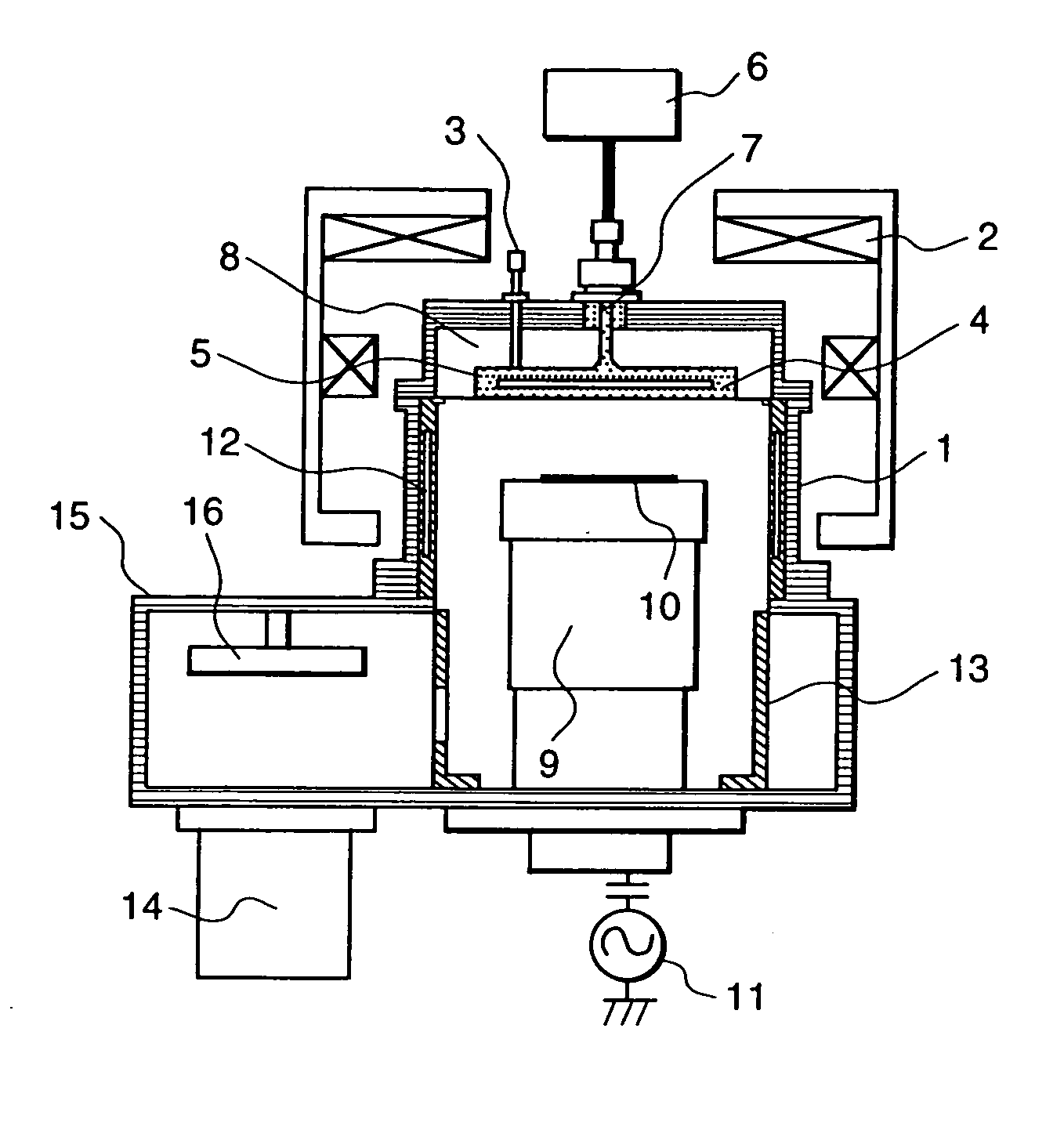
InactiveUS6736987B1Minimize damageUniform etchingVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsInternal pressureFeedback controller
The silicon etching apparatus using XeF2 includes: a basic structure composed of a loading chamber tot loading XeF2, an expansion chamber for collecting sublimated XeF2 gas, and an etching chamber for performing an etching process; and a means for injecting nitrogen prior to the etching process to eliminate air moisture in the apparatus and thus preventing the formation of HF. The silicon etching apparatus using XeF2 further includes: an injector having a predefined shape provided in the etching chamber for uniformly injecting the XeF2 gas downward on to surface of a wafer; a feedback controller for feedback controlling the internal pressure of the loading chamber in order to prevent sublimation of the residual XeF2 in the loading chamber; and a weight scale for measuring the weight of XeF2 in the loading chamber.
Owner:TECHBANK
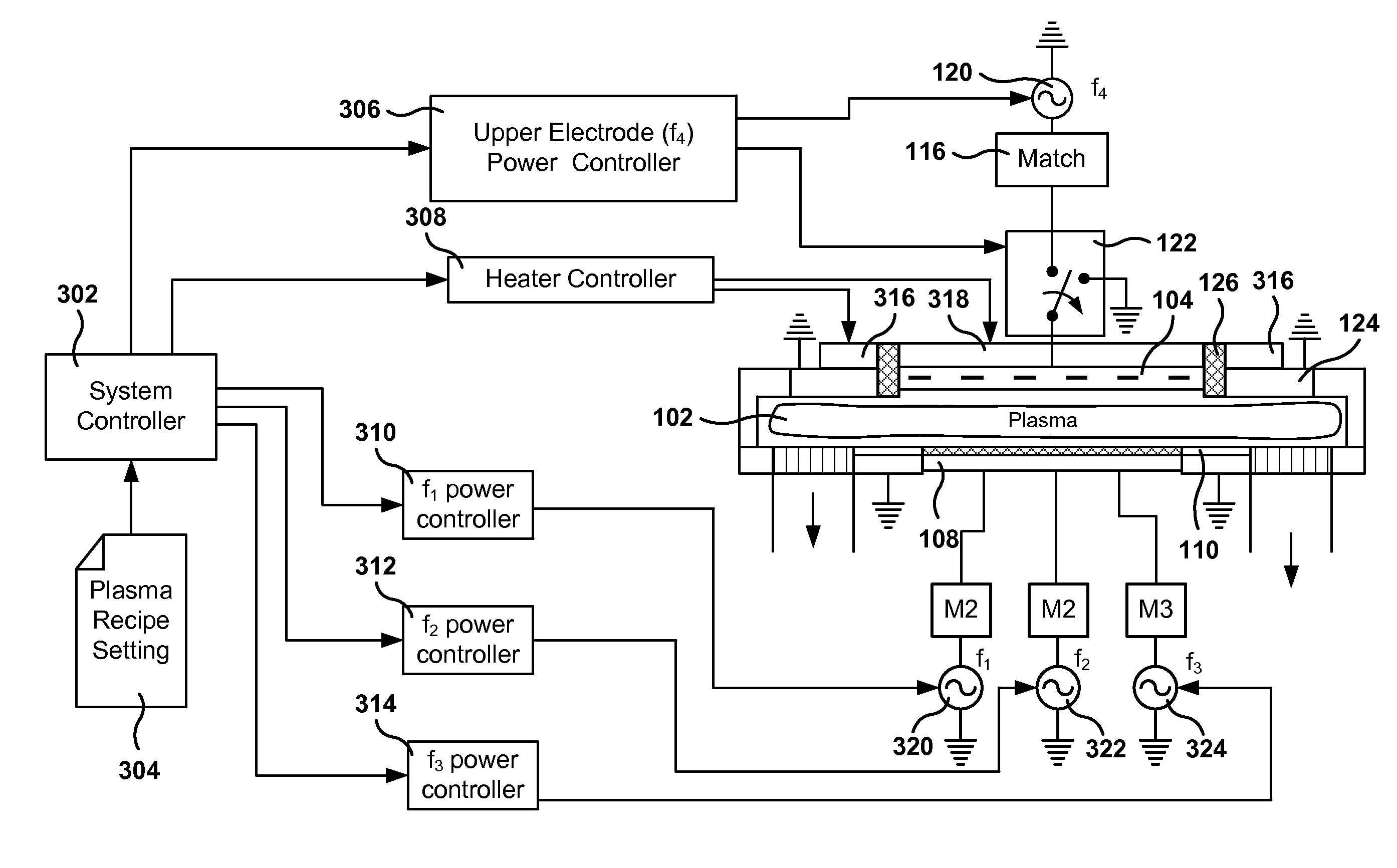
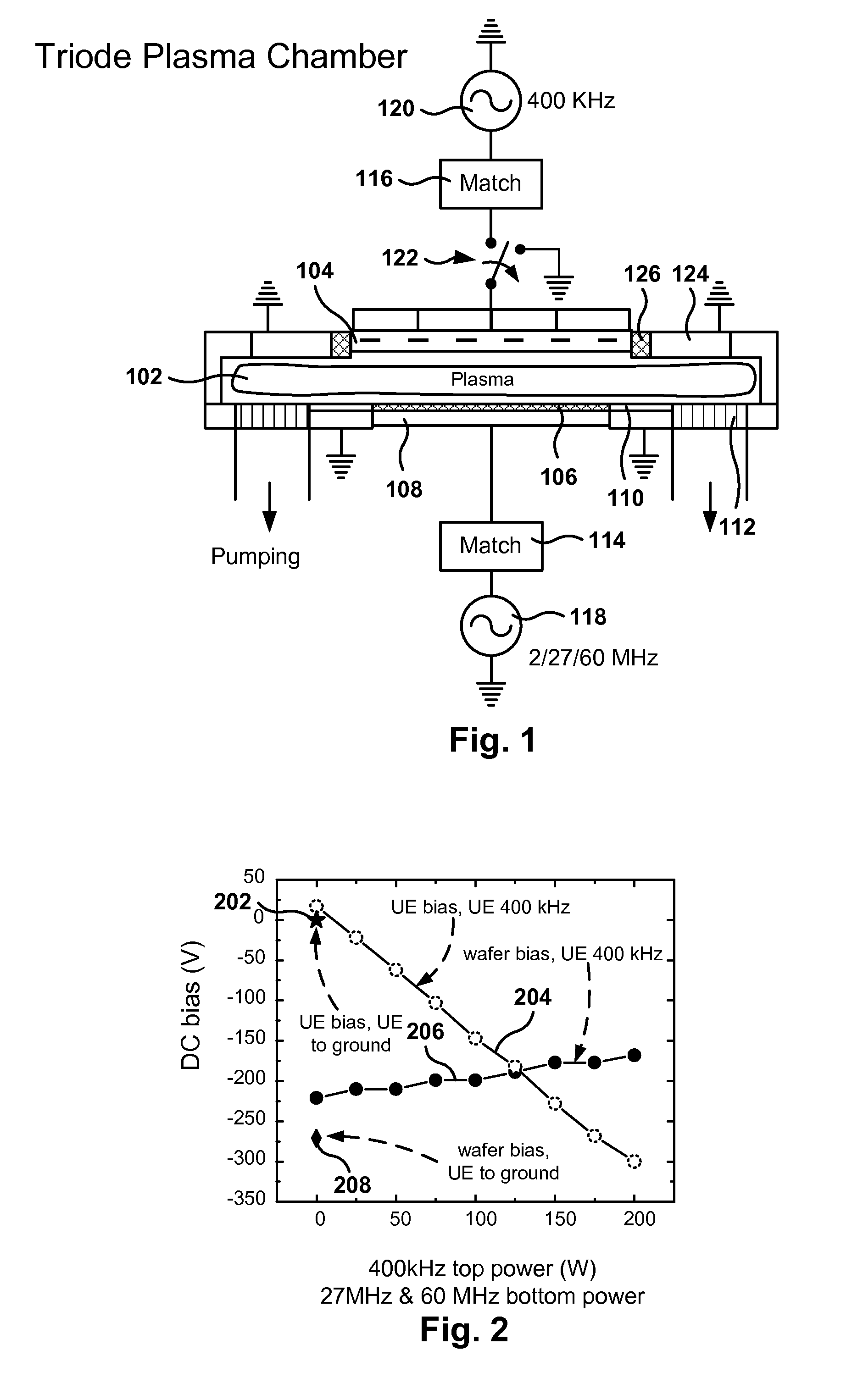
Triode reactor design with multiple radiofrequency powers
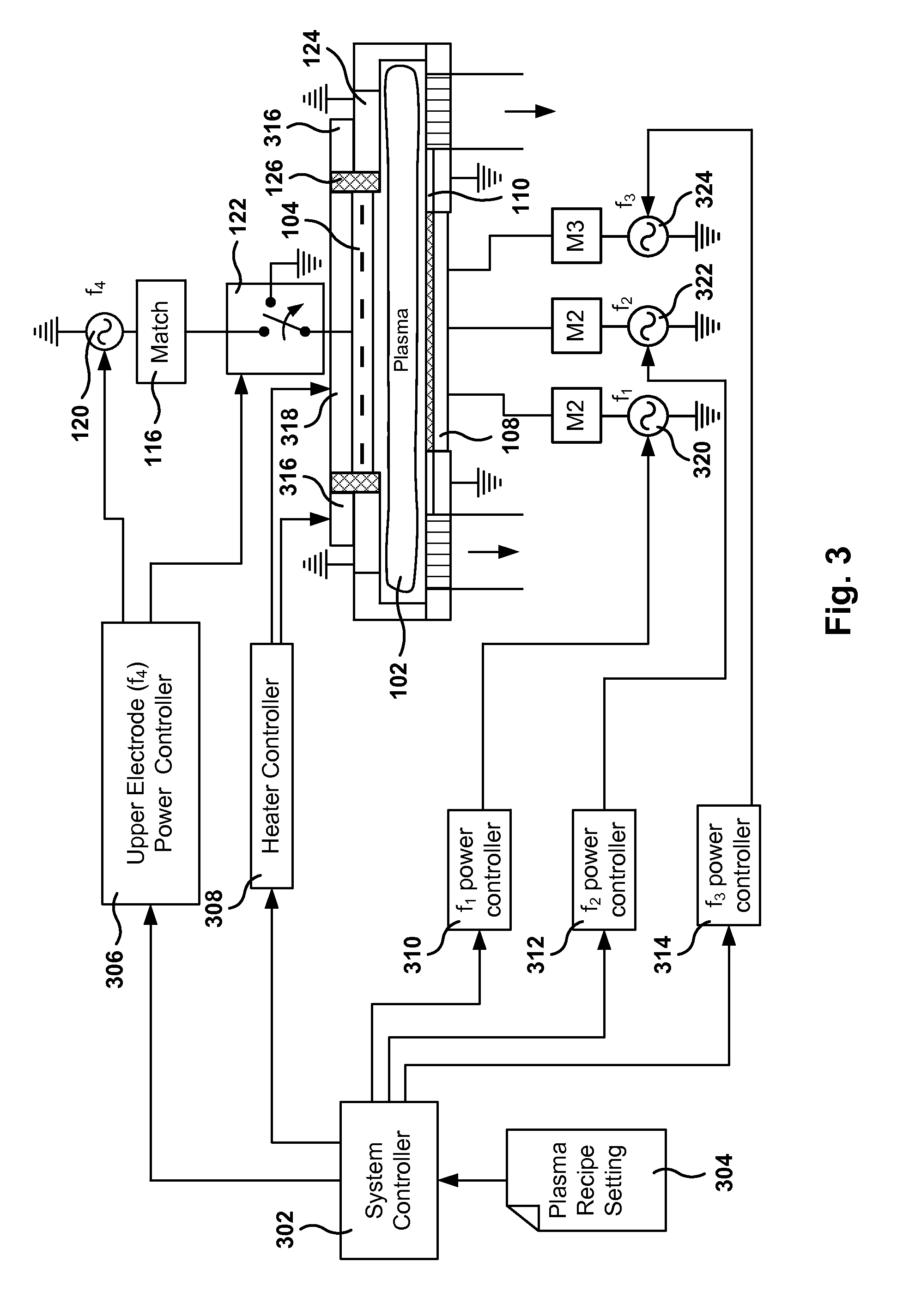
ActiveUS8652298B2Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsReactor designEngineering
Methods, systems, and computer programs are presented for semiconductor manufacturing are provided. One wafer processing apparatus includes: a top electrode; a bottom electrode; a first radio frequency (RF) power source; a second RF power source; a third RF power source; a fourth RF power source; and a switch. The first, second, and third power sources are coupled to the bottom electrode. Further, the switch is operable to be in one of a first position or a second position, where the first position causes the top electrode to be connected to ground, and the second position causes the top electrode to be connected to the fourth RF power source.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Processes for monitoring the levels of oxygen and/or nitrogen species in a substantially oxygen and nitrogen-free plasma ashing process
ActiveUS20070221620A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesOxygenAnalytical chemistry
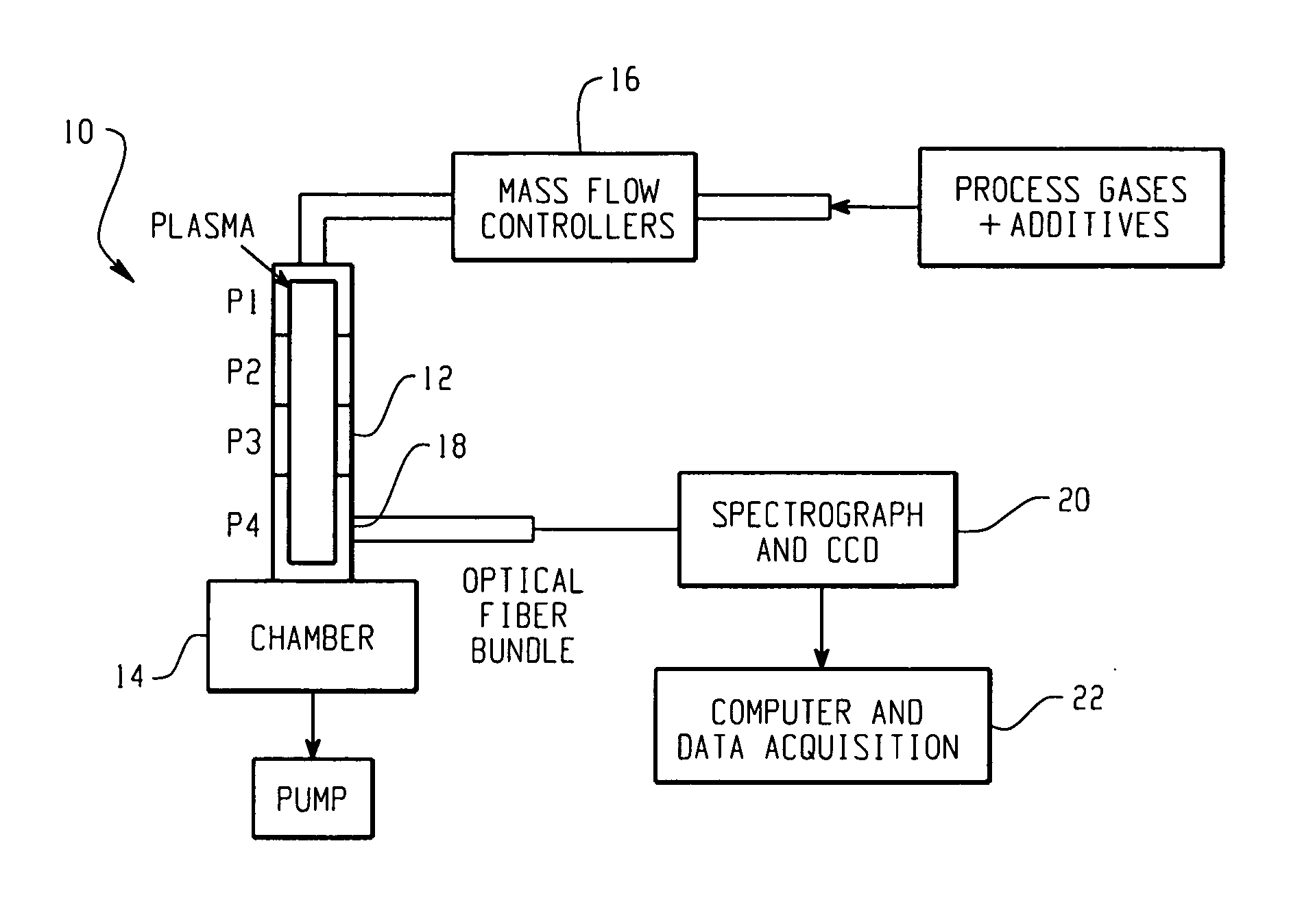
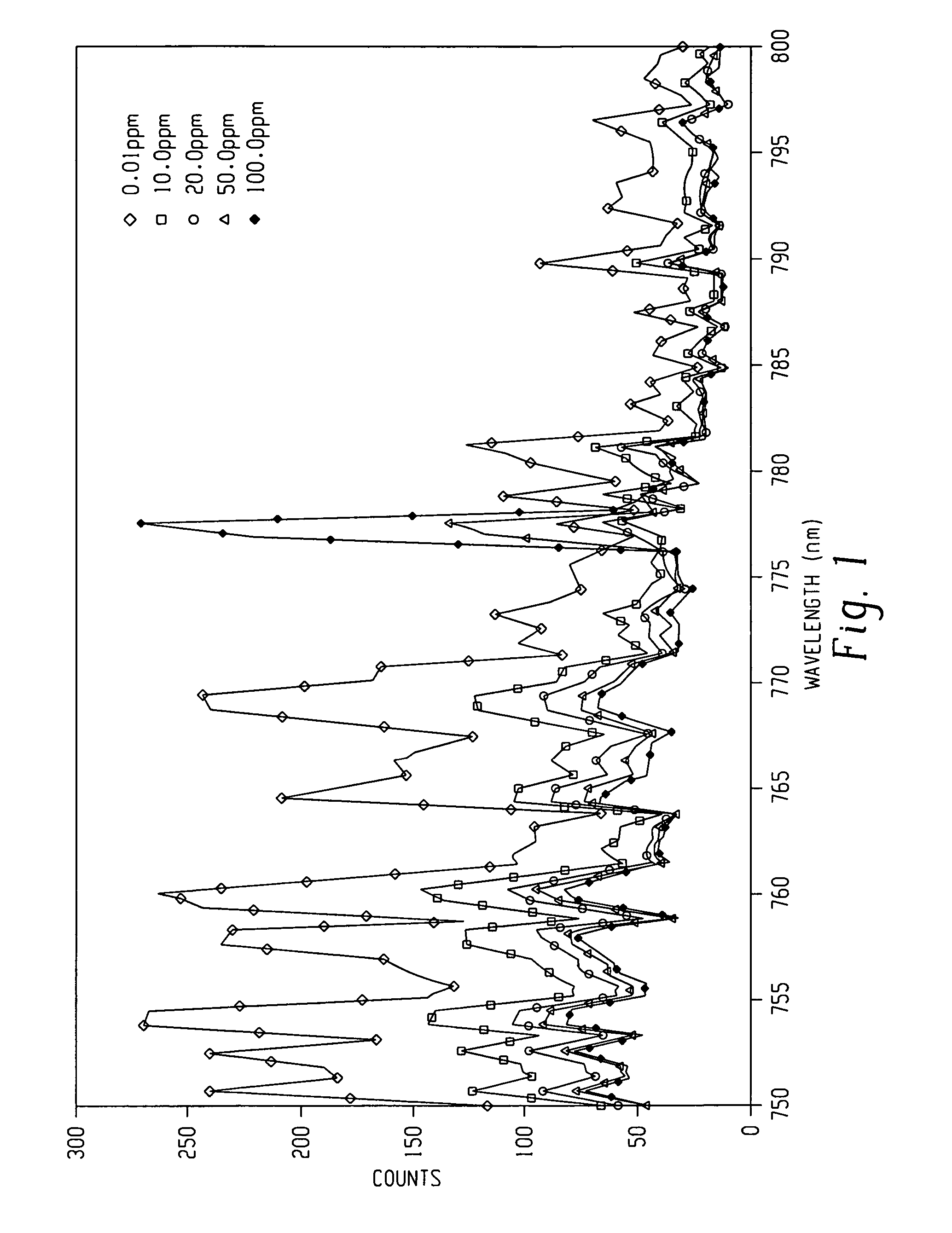
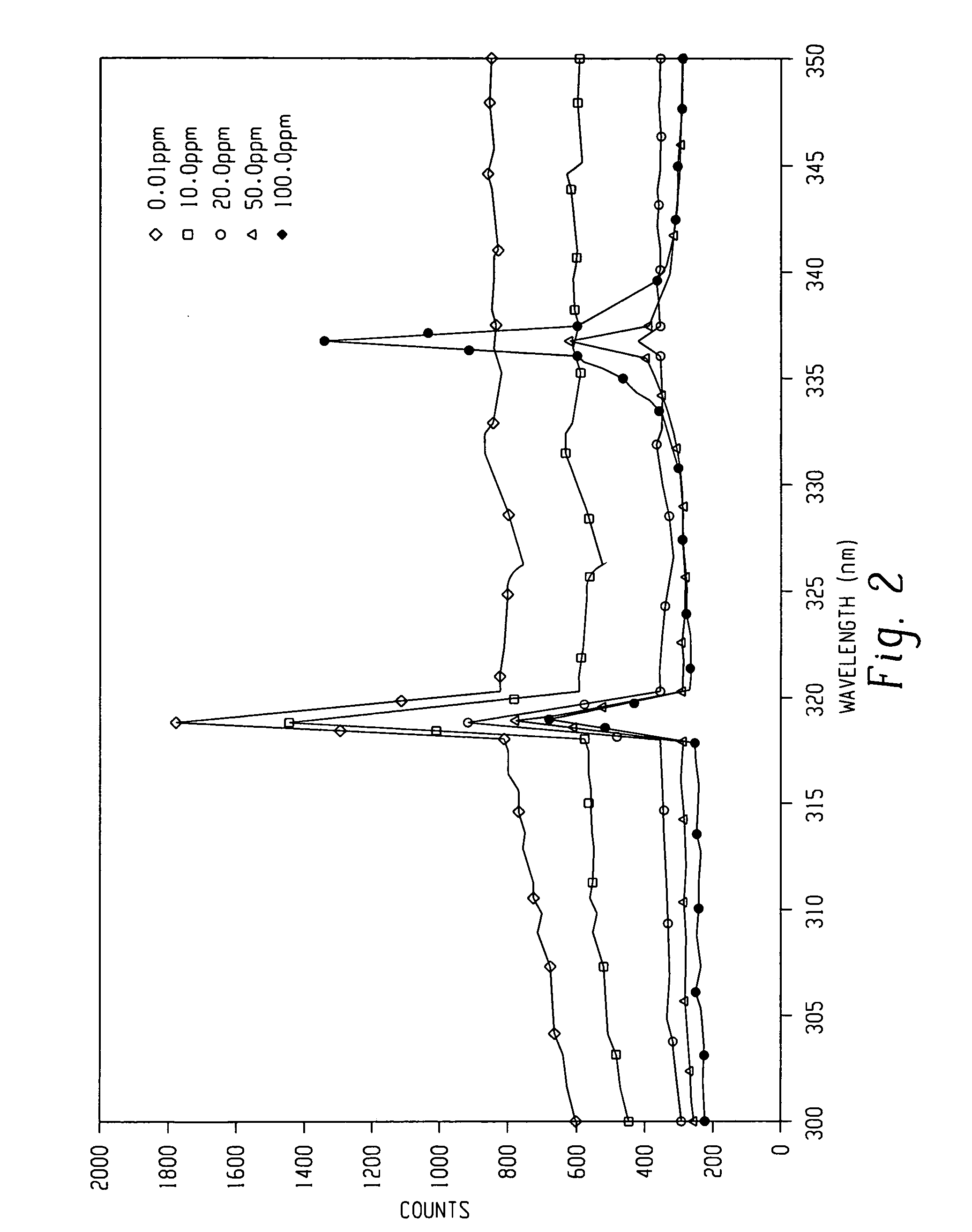
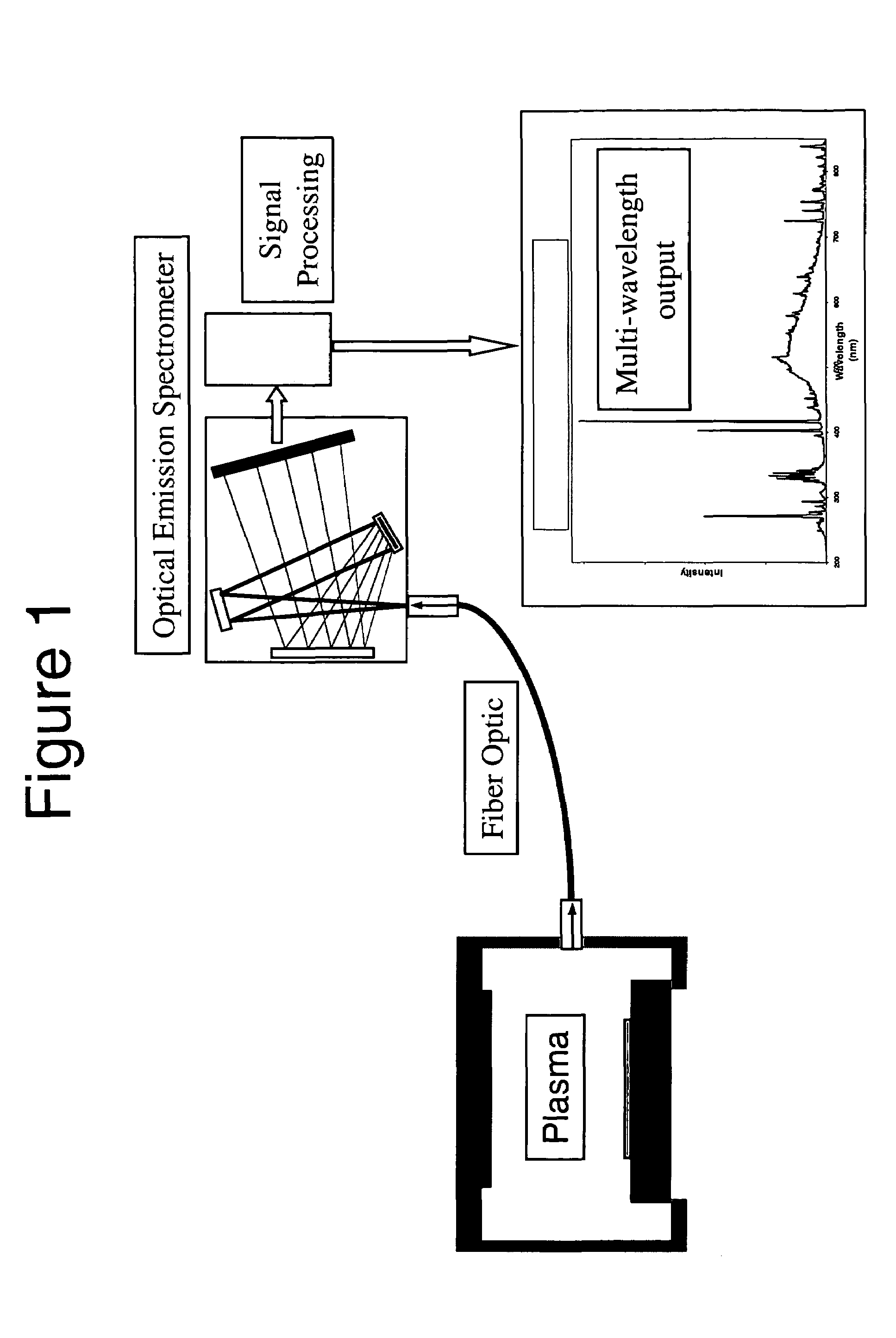
Processes for monitoring the levels of oxygen and / or nitrogen in a substantially oxygen and nitrogen-free plasma ashing process generally includes monitoring the plasma using optical emission. An effect produced by the low levels of oxygen and / or nitrogen species present on other species generally abundant in the plasma is monitored and correlated to amounts of oxygen and nitrogen present in the plasma. This so-called “effect detection” process monitors perturbations in the spectra specifically associated with species other than nitrogen and / or oxygen due to the presence of trace amounts of oxygen and / or nitrogen species and is used to quantitatively determine the amount of oxygen and / or nitrogen at a sensitivity on the order of 1 part per million and potentially 1 part per billion.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
HDP-CVD multistep gapfill process
InactiveUS7205240B2Reduce molecular weightReduced characteristicsCellsLiquid surface applicatorsChemistryInert gas
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Dry etching endpoint detection system
InactiveUS6207008B1Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsLuminous intensityComputational physics
A method and system for determining a dry etching endpoint, at which a dry etching process should be terminated. The dry etching process is carried out in a plasma etching system and comprises the steps of detecting an intensity of light emission generated in the dry etching process, the light emission being extracted through a window located on a side wall portion of a reaction chamber below a horizontal plane which is defined by a surface of a body to be etch treated. The detected intensity is compared to a predetermined threshold level.
Owner:RICOH KK
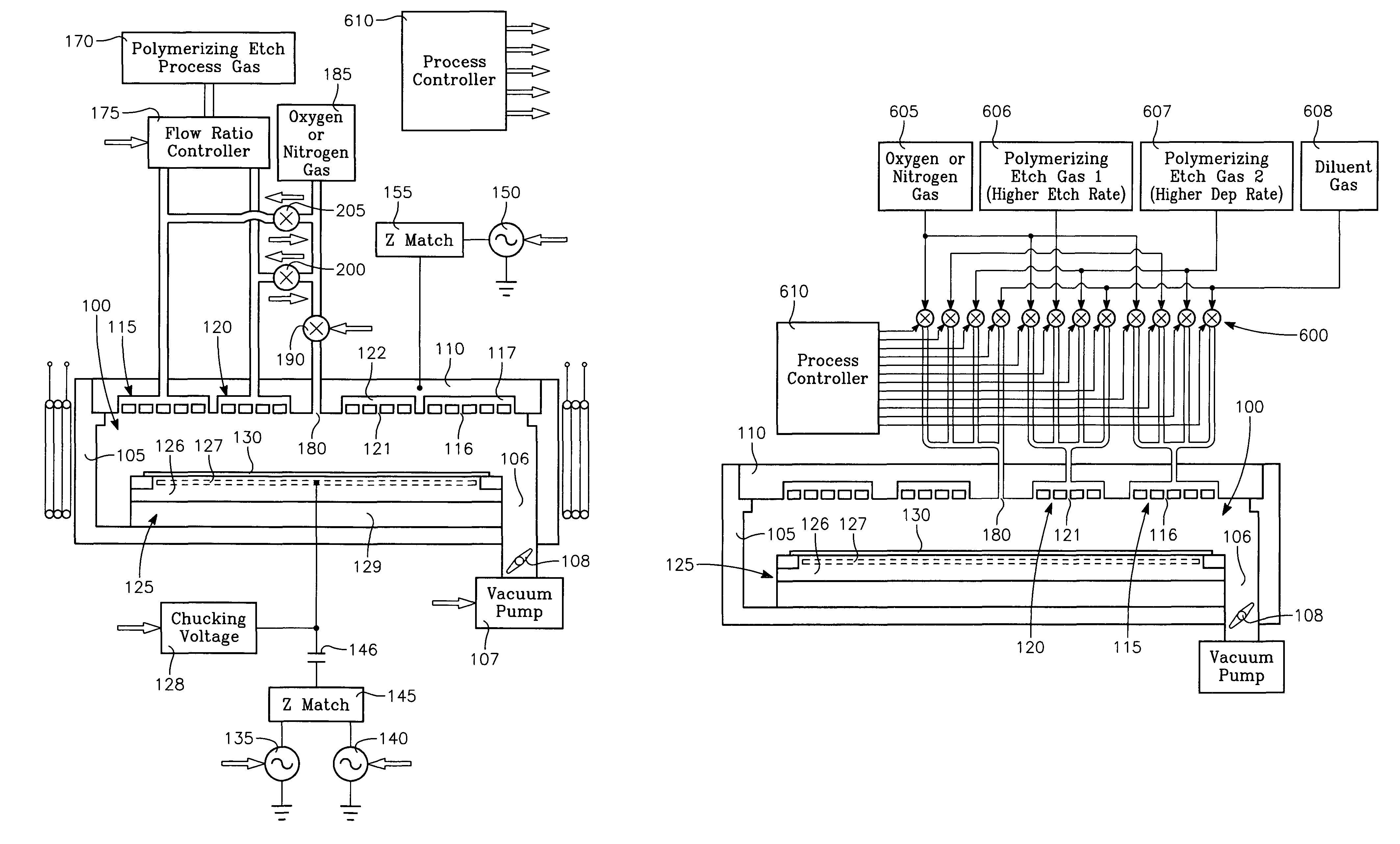
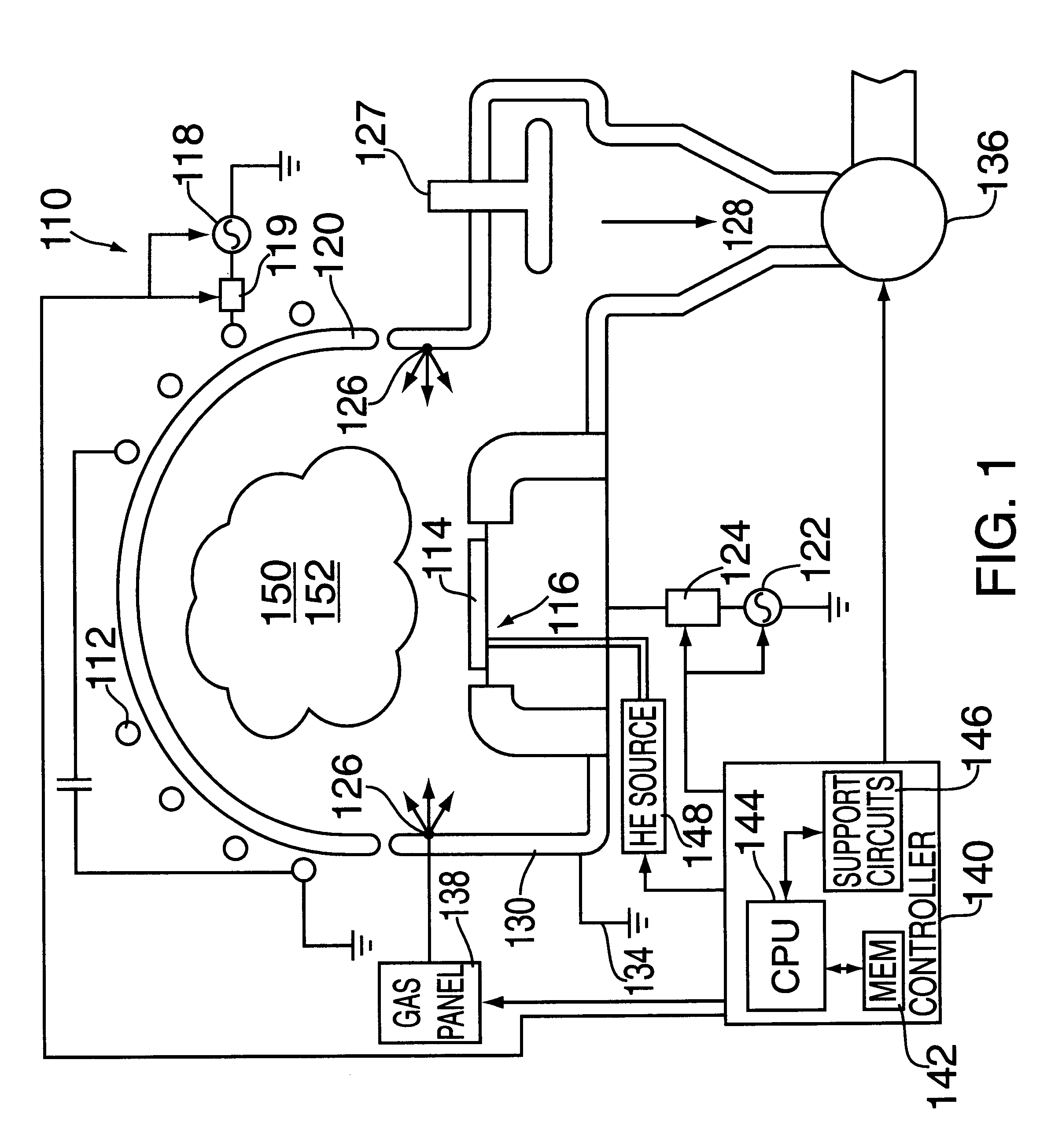
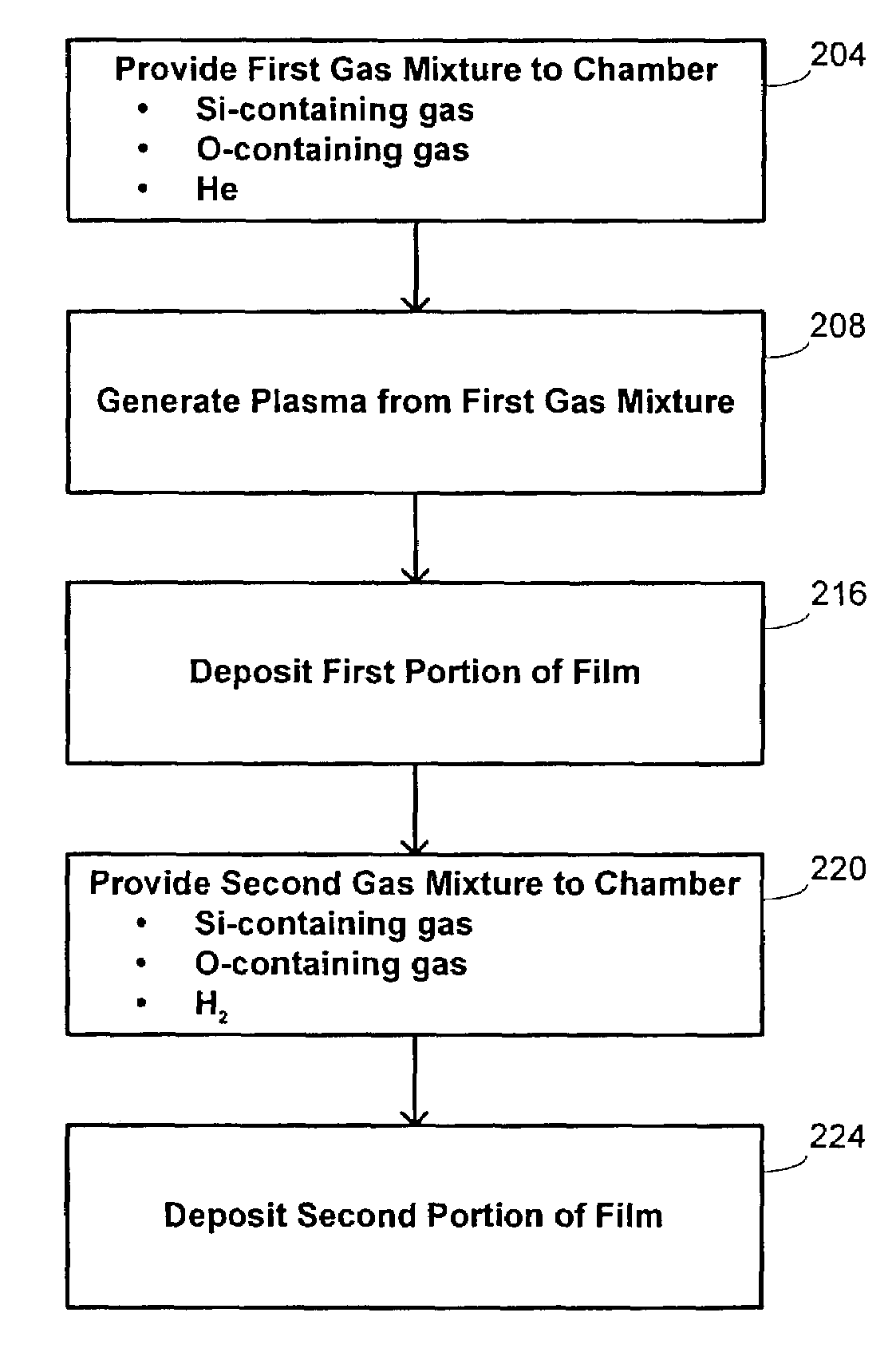
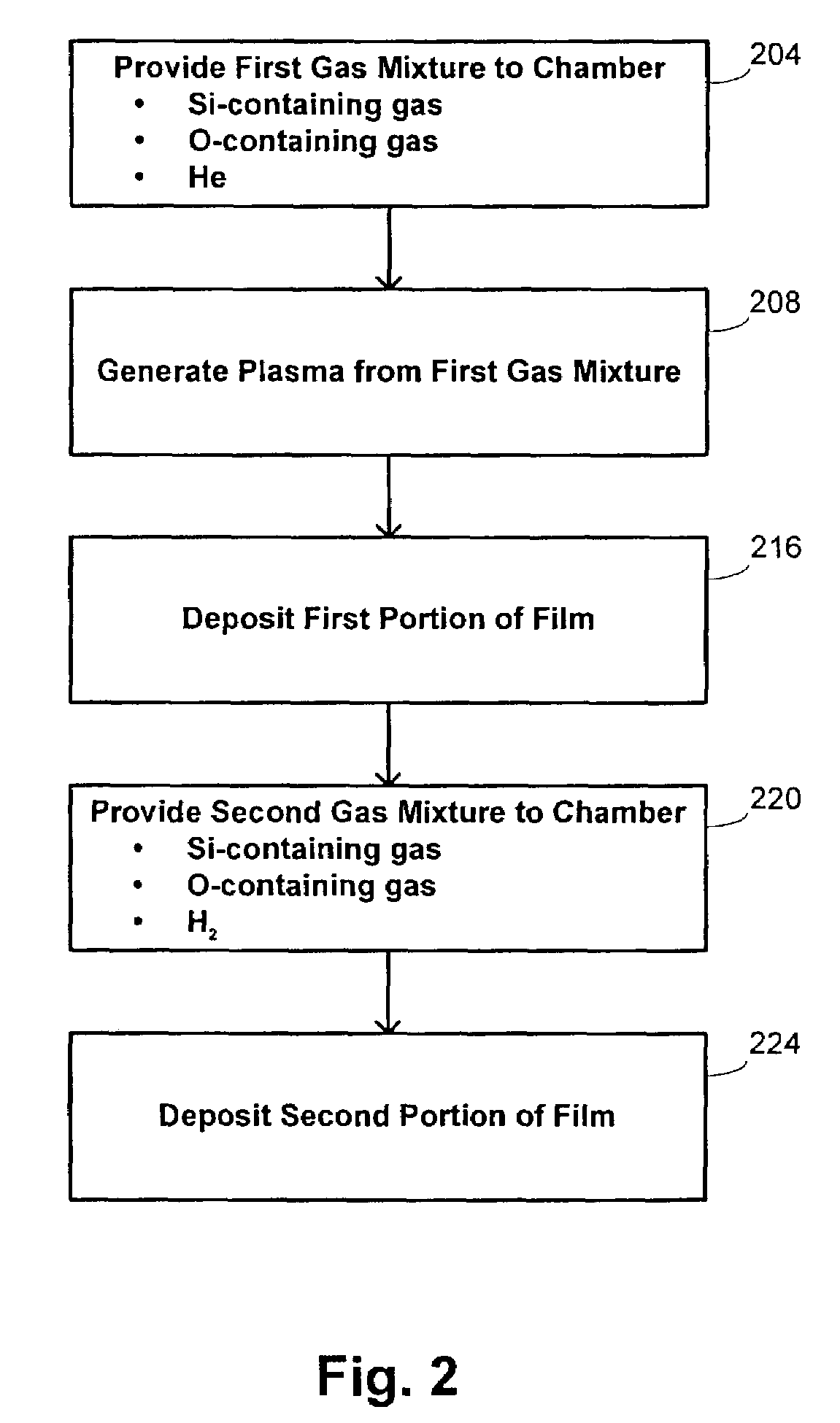
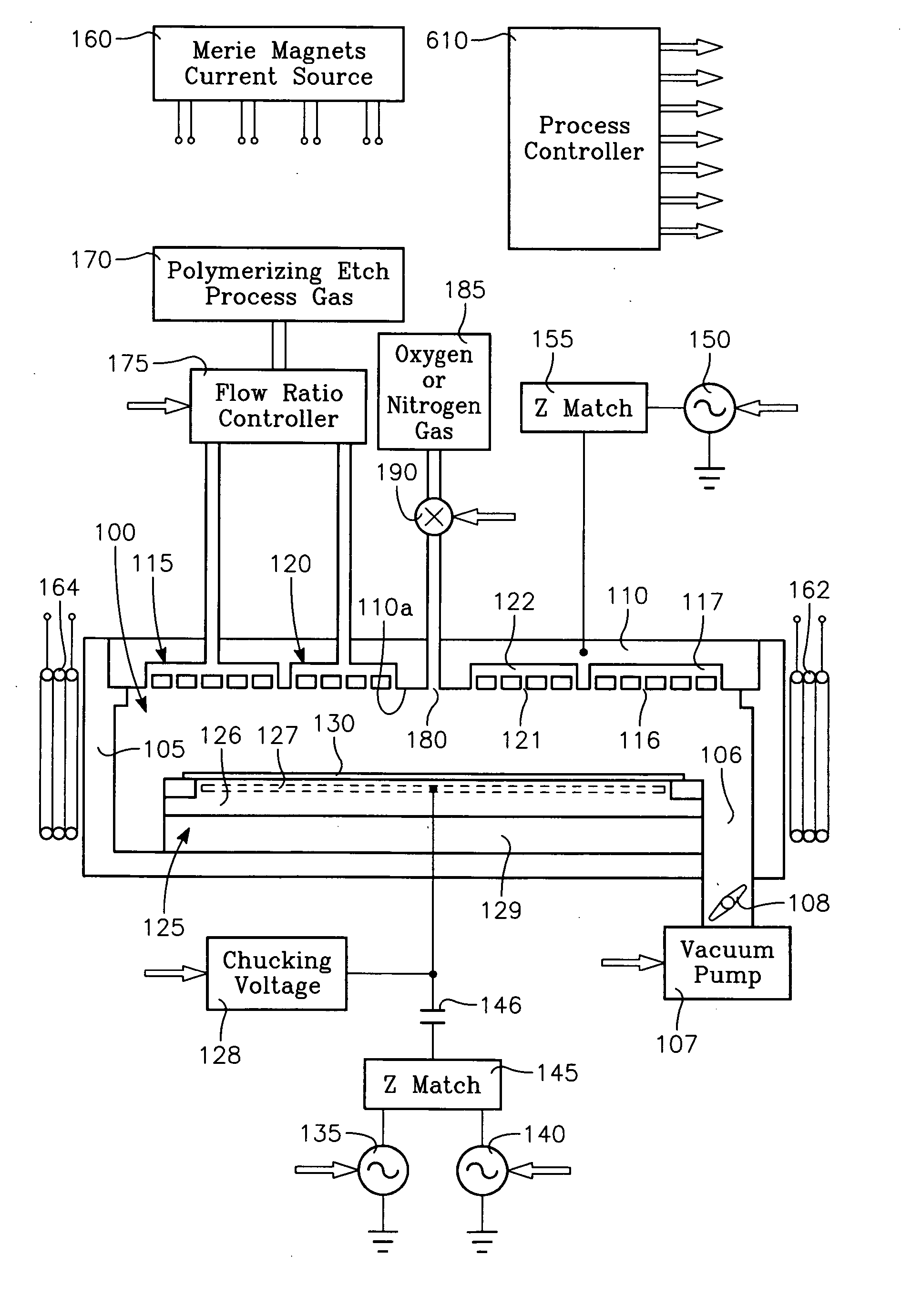
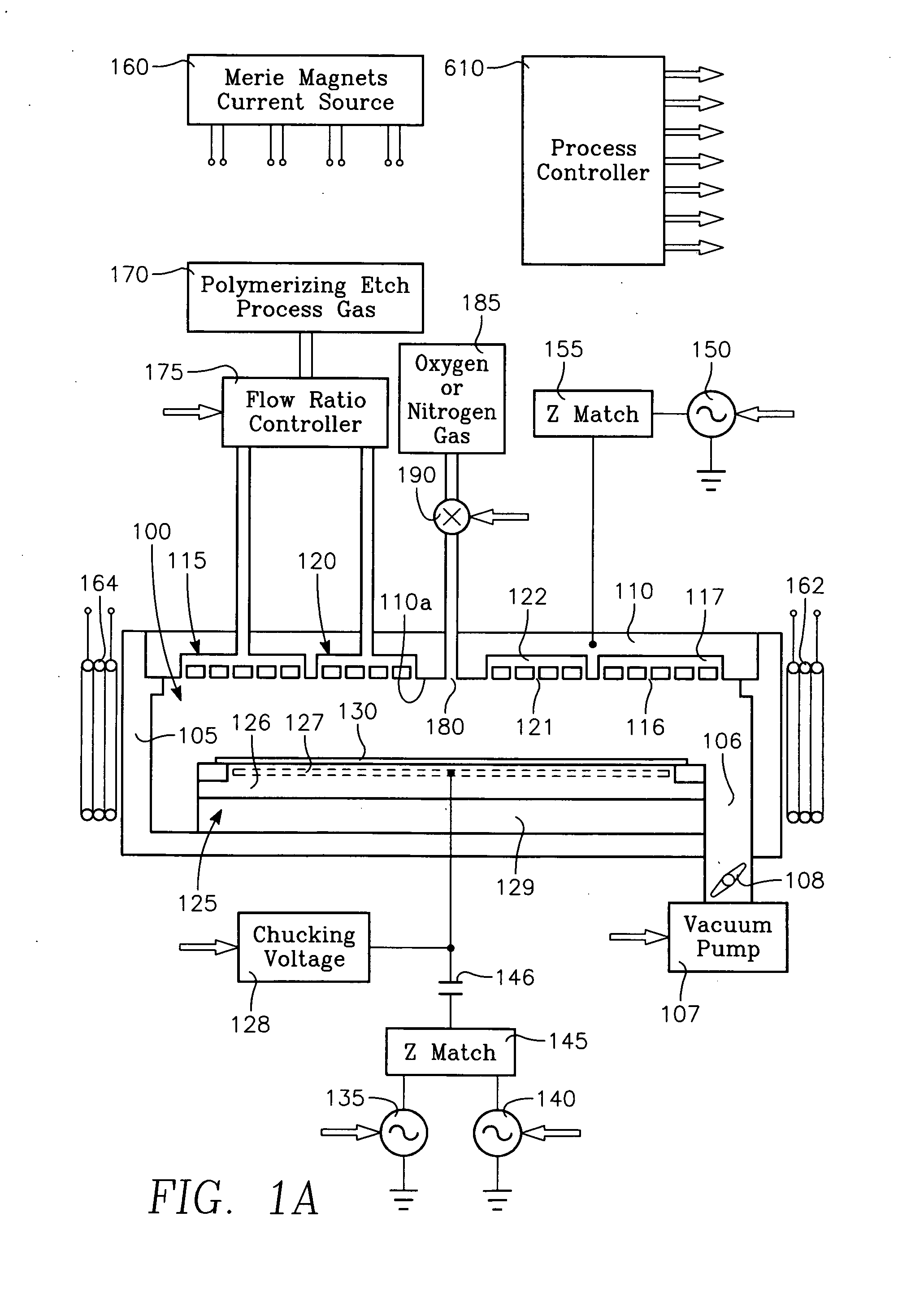
Plasma reactor apparatus with multiple gas injection zones having time-changing separate configurable gas compositions for each zone
ActiveUS20070251642A1Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsGas compositionOxygen
A plasma reactor for processing a workpiece such as a semiconductor wafer has a housing defining a process chamber, a workpiece support configured to support a workpiece within the chamber during processing and comprising a plasma bias power electrode. The reactor further includes plural gas sources containing different gas species, plural process gas inlets and an array of valves capable of coupling any of said plural gas sources to any of said plural process gas inlets. The reactor also includes a controller governing said array of valves and is programmed to change the flow rates of gases through said inlets over time. A ceiling plasma source power electrode of the reactor has plural gas injection zones coupled to the respective process gas inlets. In a preferred embodiment, the plural gas sources comprise supplies containing, respectively, fluorocarbon or fluorohydrocarbon species with respectively different ratios of carbon and fluorine chemistries. They further include an oxygen or nitrogen supply and a diluent gas supply. The controller is programmed to produce flow of different process gas species or mixtures thereof through different ones of said plural gas injection zones. The controller is further programmed to change over time the species content of the gases flowing through different ones of said plural gas injection zones.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
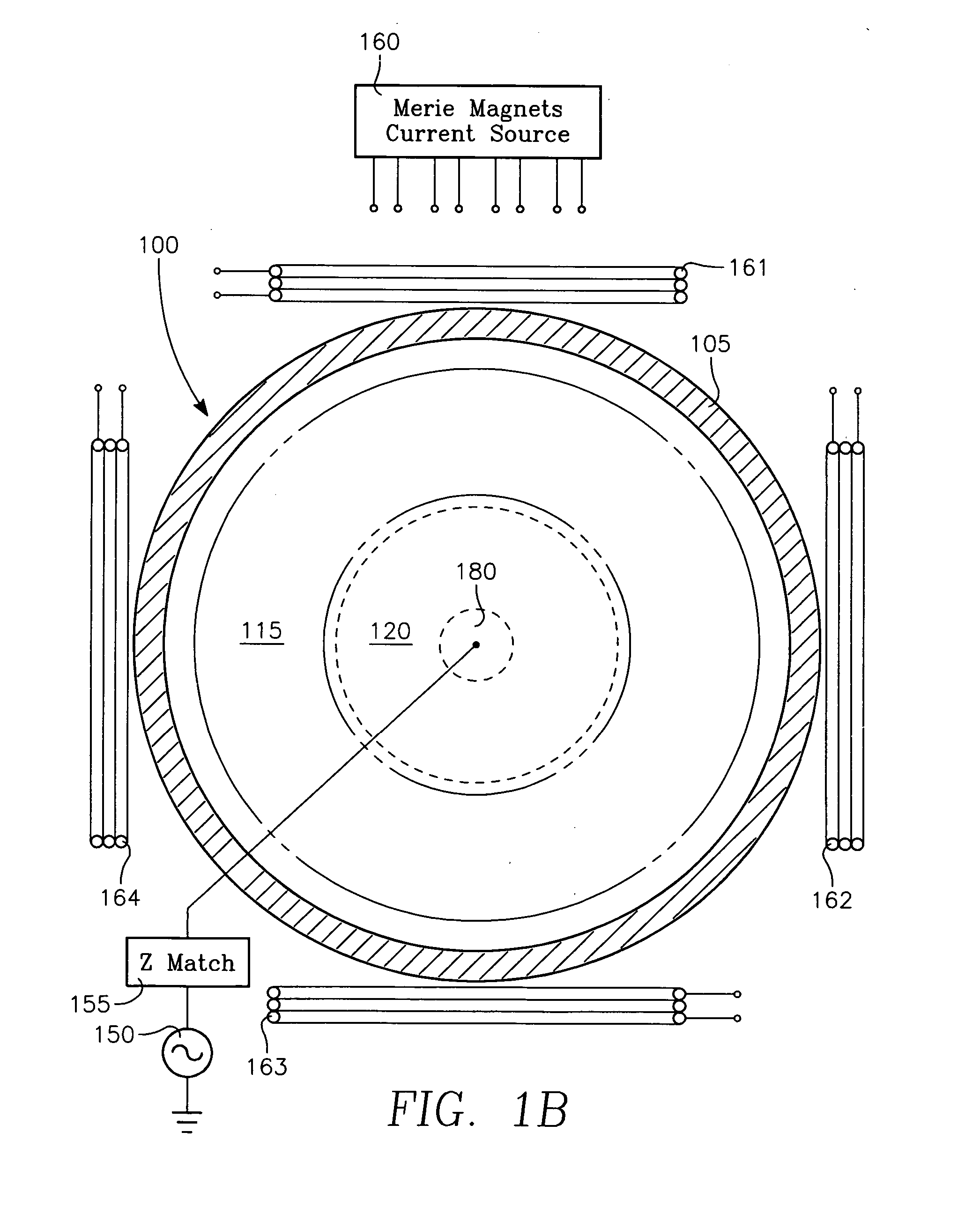
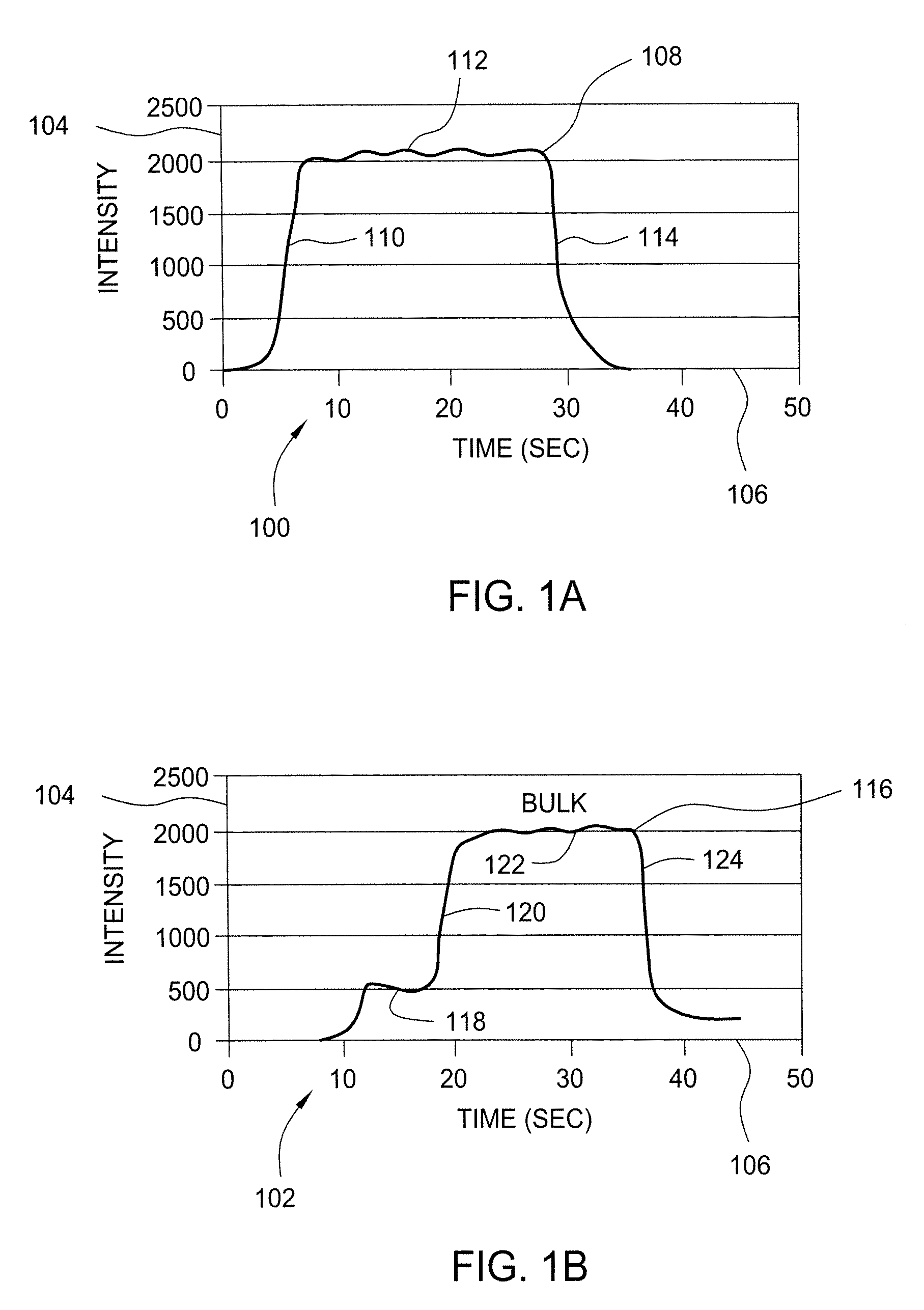
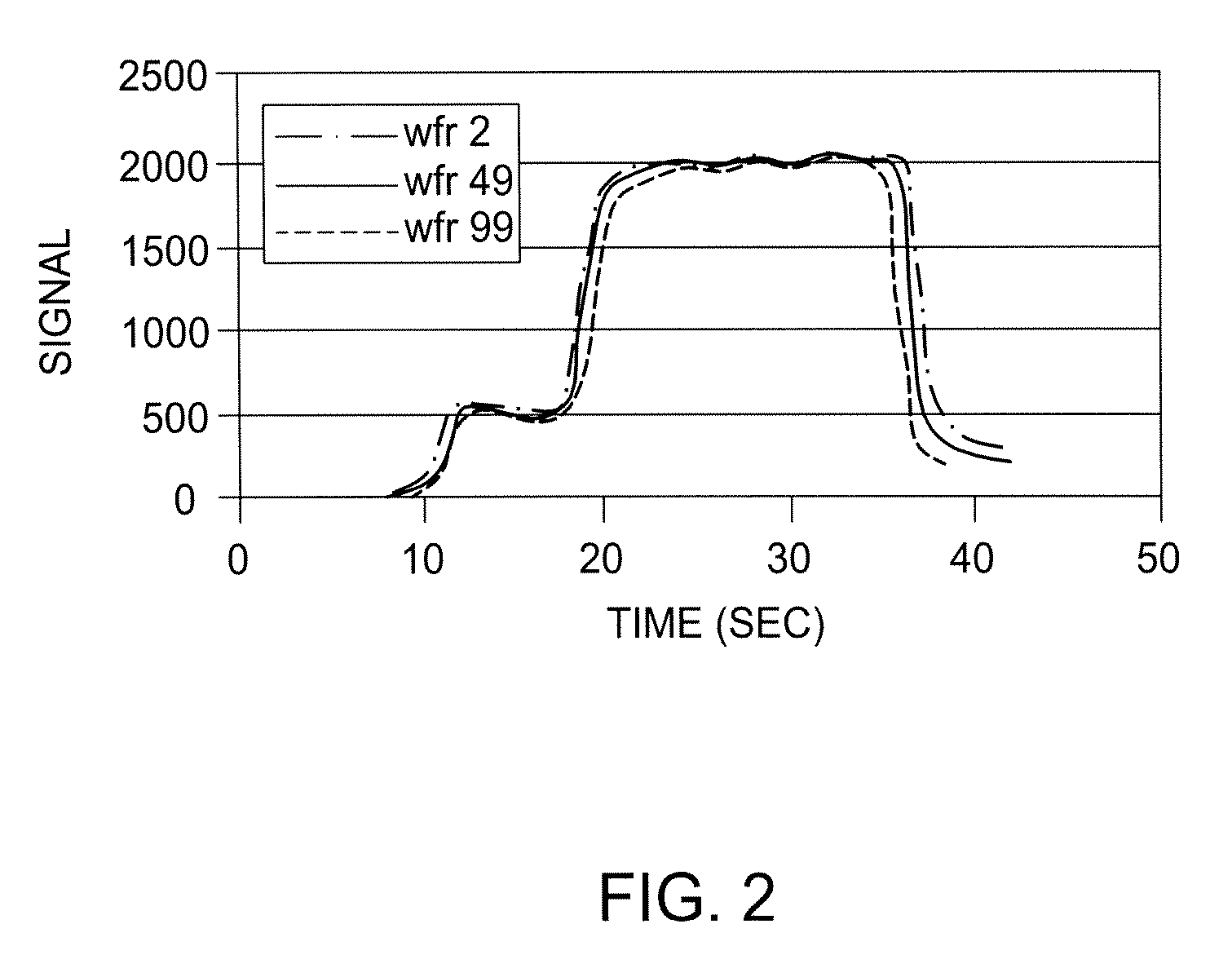
Method and apparatus for performing hydrogen optical emission endpoint detection for photoresist strip and residue removal
Methods for monitoring and detecting optical emissions while performing photoresist stripping and removal of residues from a substrate or a film stack on a substrate are provided herein. In one embodiment, a method is provided that includes positioning a substrate comprising a photoresist layer into a processing chamber; processing the photoresist layer using a multiple step plasma process; and monitoring the plasma for a hydrogen optical emission during the multiple step plasma process; wherein the multiple step plasma process includes removing a bulk of the photoresist layer using a bulk removal step; and switching to an overetch step in response to the monitored hydrogen optical emission.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
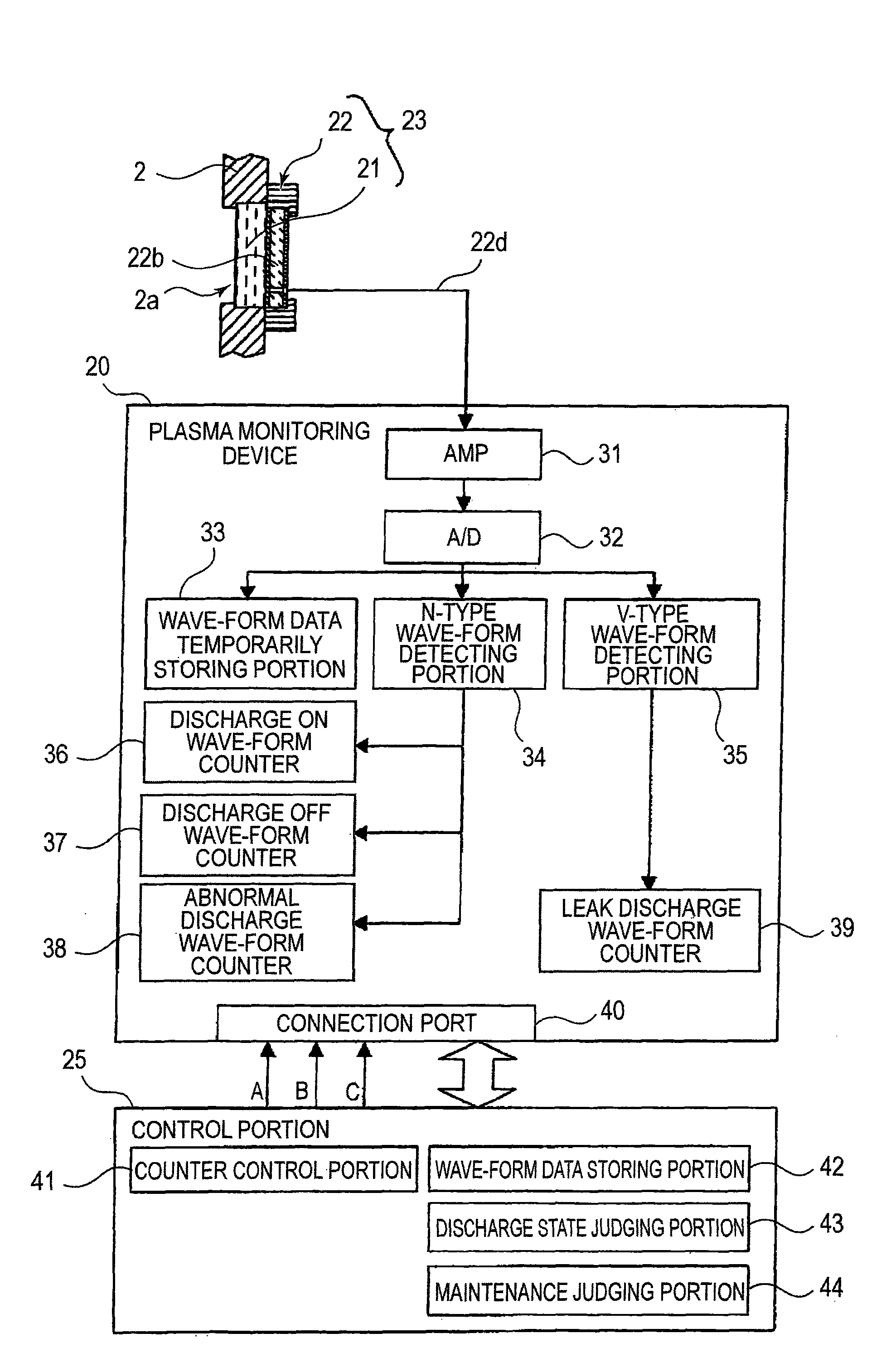
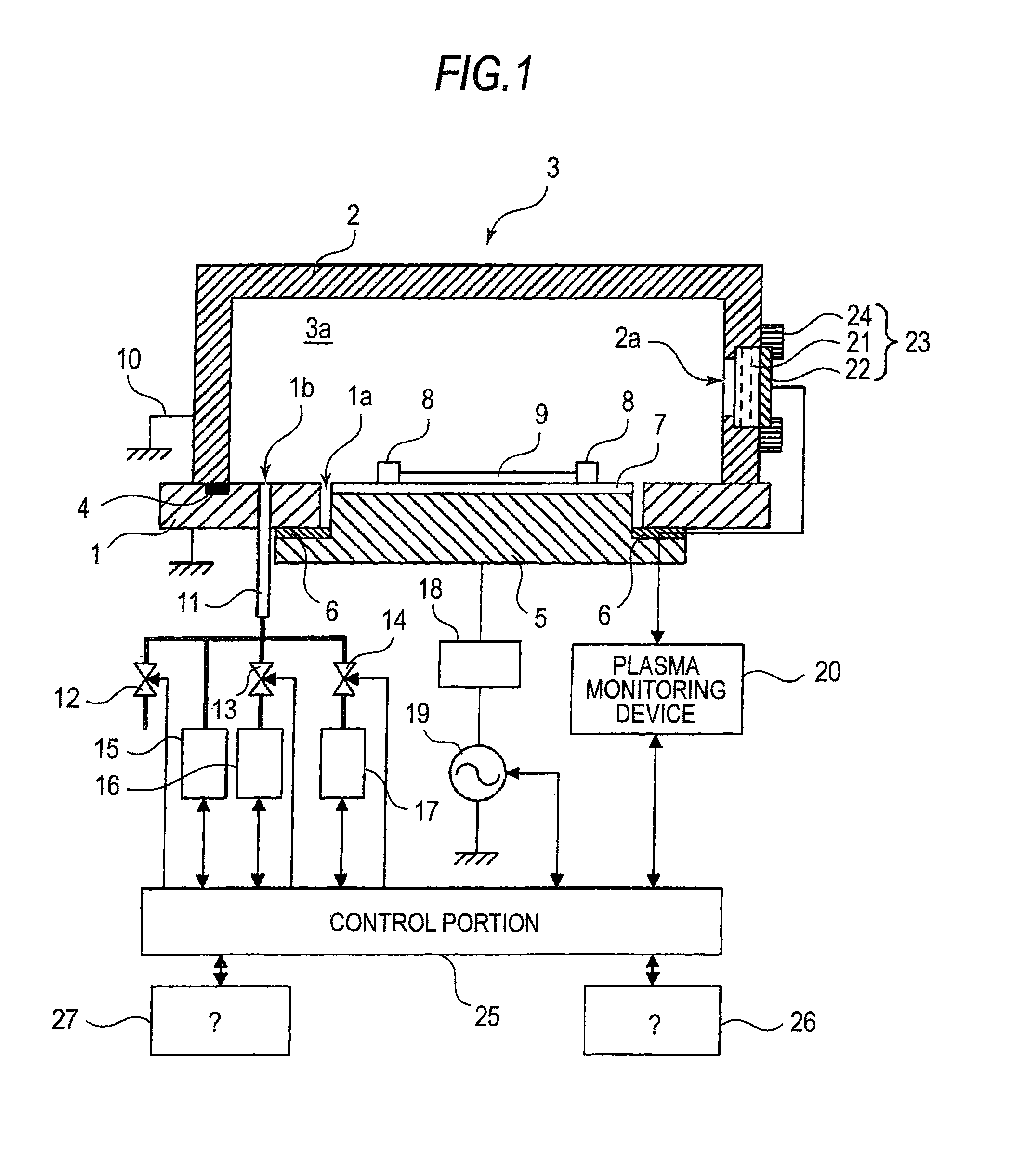
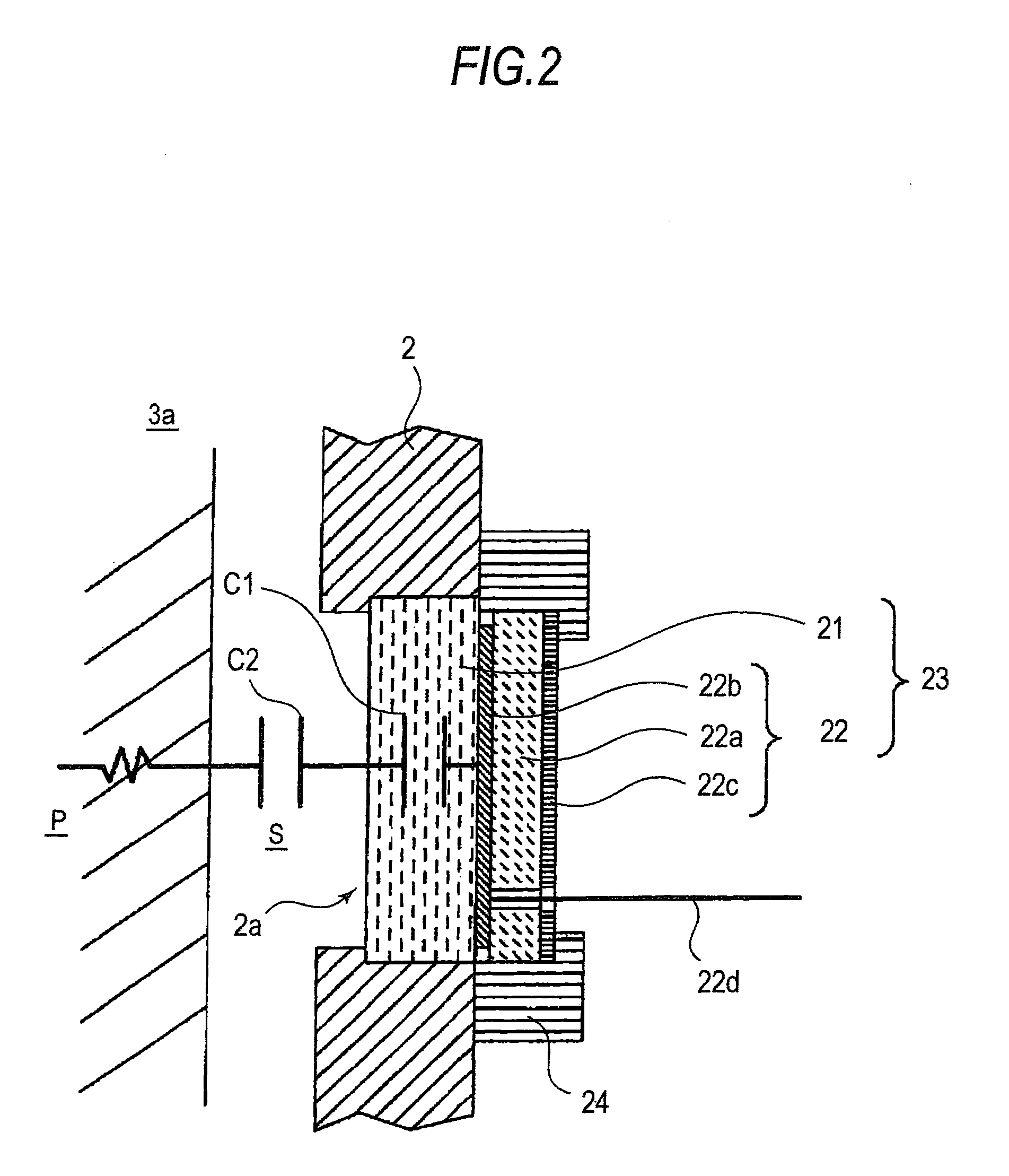
Plasma processing device and method of monitoring plasma discharge state in plasma processing device
ActiveUS8668836B2Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsElectricityElectric discharge
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
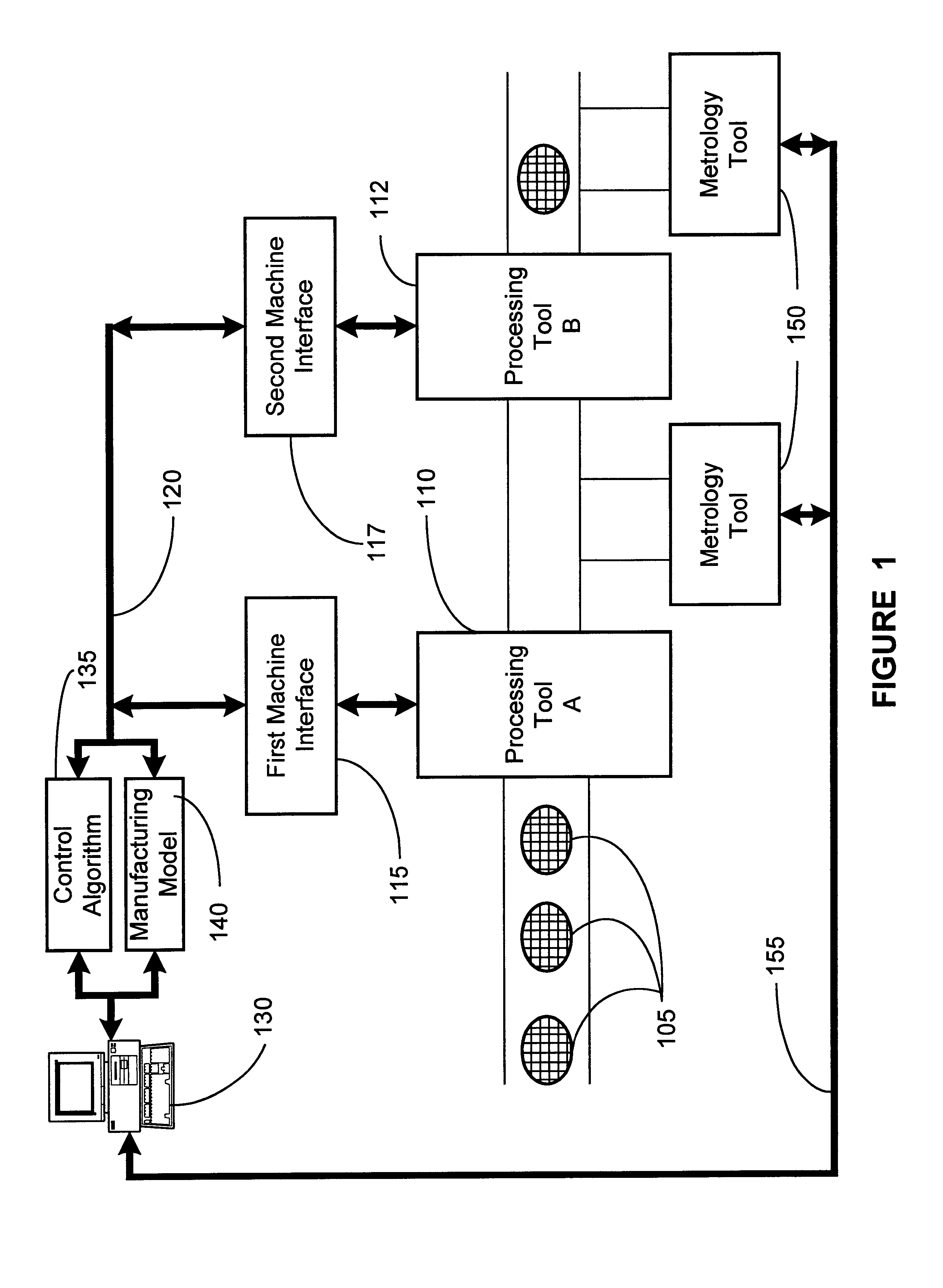
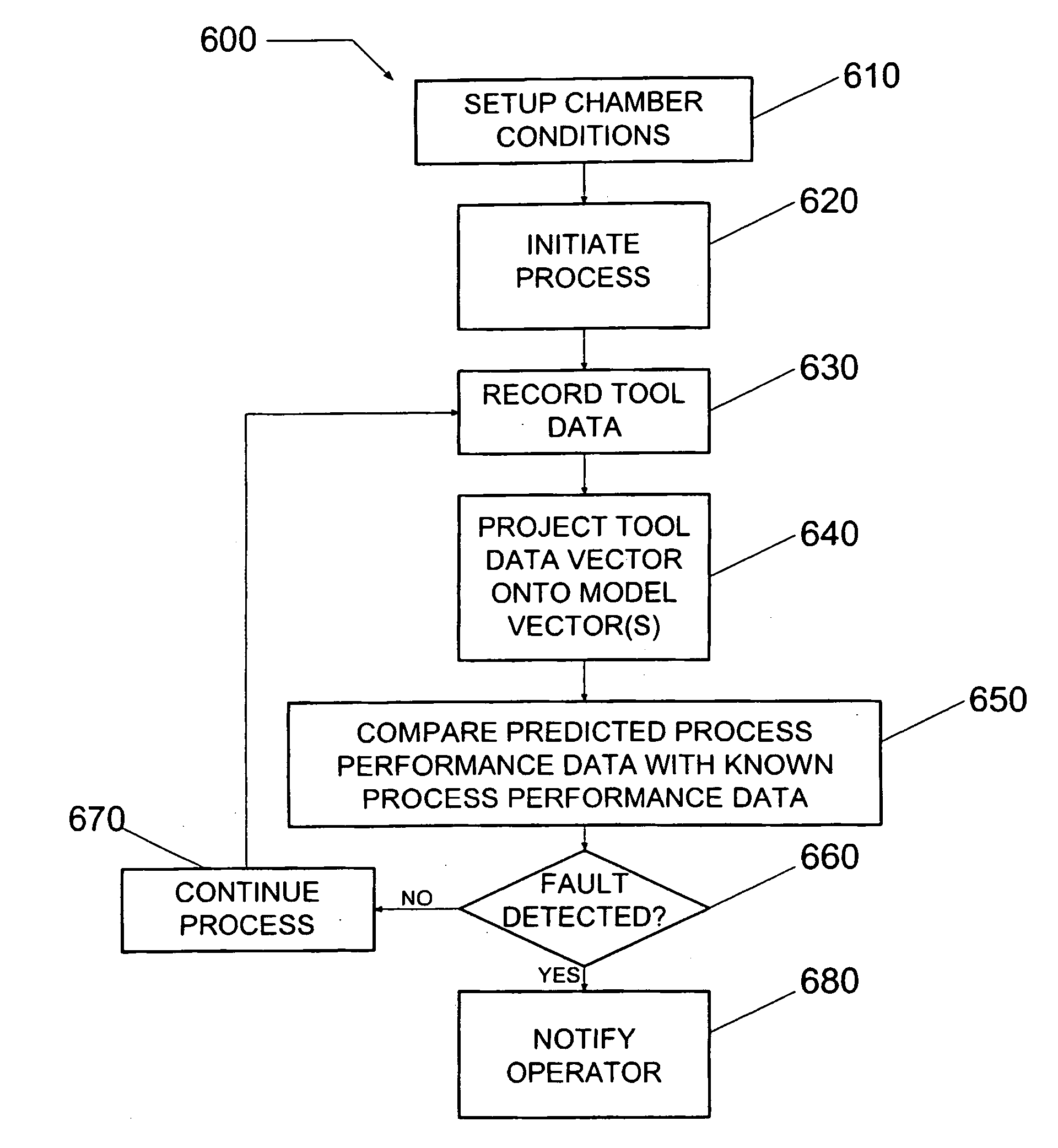
Method and system for predicting process performance using material processing tool and sensor data
InactiveUS20050252884A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesEngineeringMaterials processing
A material processing system including a process tool and a process performance prediction system. The performance prediction system includes sensors coupled to the tool to measure tool data and a controller coupled to the sensors to receive tool data, where the controller is configured to predict the process performance for the tool using the tool data. A method for detecting a fault in a material processing system using a process performance prediction model is also provided. The method includes preparing the tool, initiating a process in the tool, and recording tool data to form to a tool data matrix. The method also includes performing a matrix multiplication of the tool data matrix and a correlation matrix to form predicted process performance data, where the correlation matrix includes the performance prediction model, comparing the predicted data with target data, and determining a fault condition of the processing system from the comparing step.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Etching process state judgment method and system therefor
ActiveUS20090253222A1Impossible to accuratelyEmission spectroscopySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPeak valuePeak detection
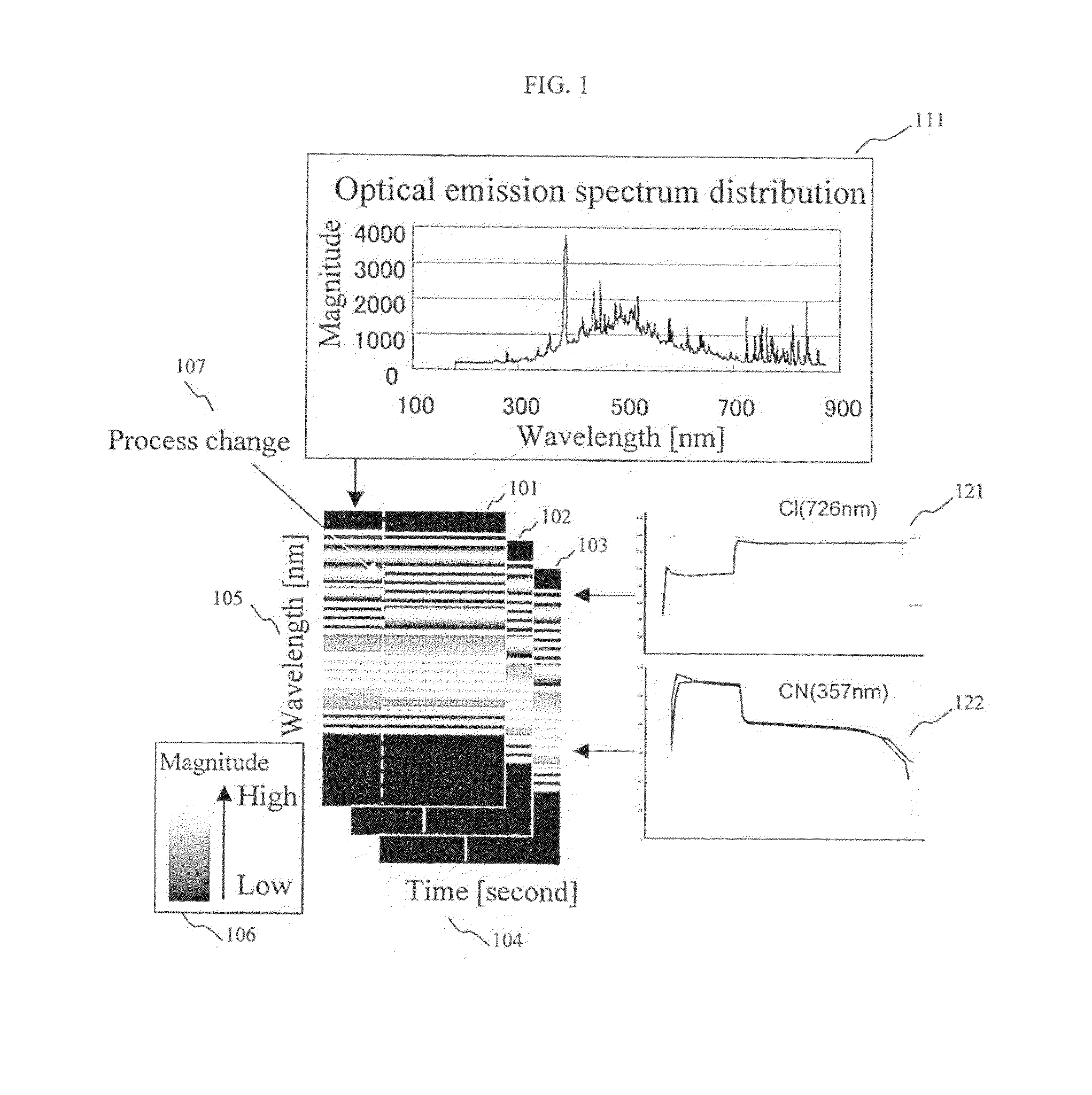
An etching process state judgment method comprising: a spectral data obtaining step, in which an optical emission spectrum distribution is obtained by monitoring optical emission during an etching process of a plurality of wafers; a peak detection step, in which peaks are detected from the optical emission spectrum distribution at a specific time point during the etching process, to obtain peak characteristics; a common peak identifying step, in which peaks common to the wafers are identified among the peaks detected in the peak detection step; and a state detection step, in which the characteristics are compared regarding the common peaks, to detect a state of each wafer in the etching process.A state (anomaly or normalcy) of an etching process is detected from optical emission spectrum distribution at the time of etching process, by a simple method without assuming substances.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method for in-line monitoring of via/contact holes etch process based on test structures in semiconductor wafer manufacturing
InactiveUS7105436B2Reduce contactSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsImaging processingEngineering
Owner:HERMES MICROVISION TAIWAN +2
Integration of photon emission microscope and focused ion beam
InactiveUS20060012385A1Vacuum gauge using ionisation effectsFault location by increasing destruction at faultPhoton emissionIon beam
An integrated FIB / PEM apparatus and method for performing failure analysis on integrated circuits. In-situ failure analysis is enabled by integrating Photon Emission Microscopy into a Focused Ion Beam system, thereby improving throughput and efficiency of Failure Analysis. An iterative method is described for identifying and localizing fault sites on the circuit.
Owner:DCG SYST
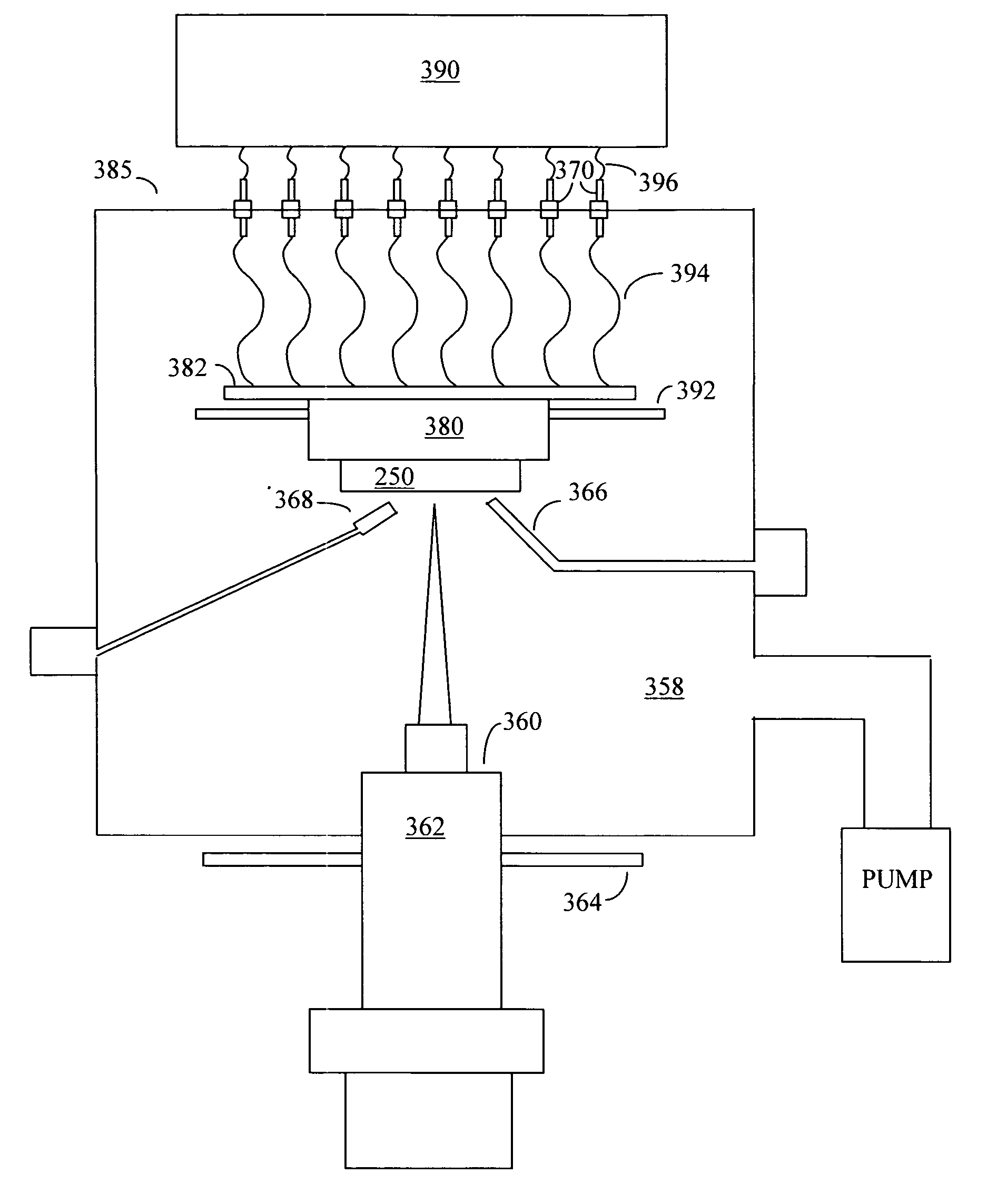
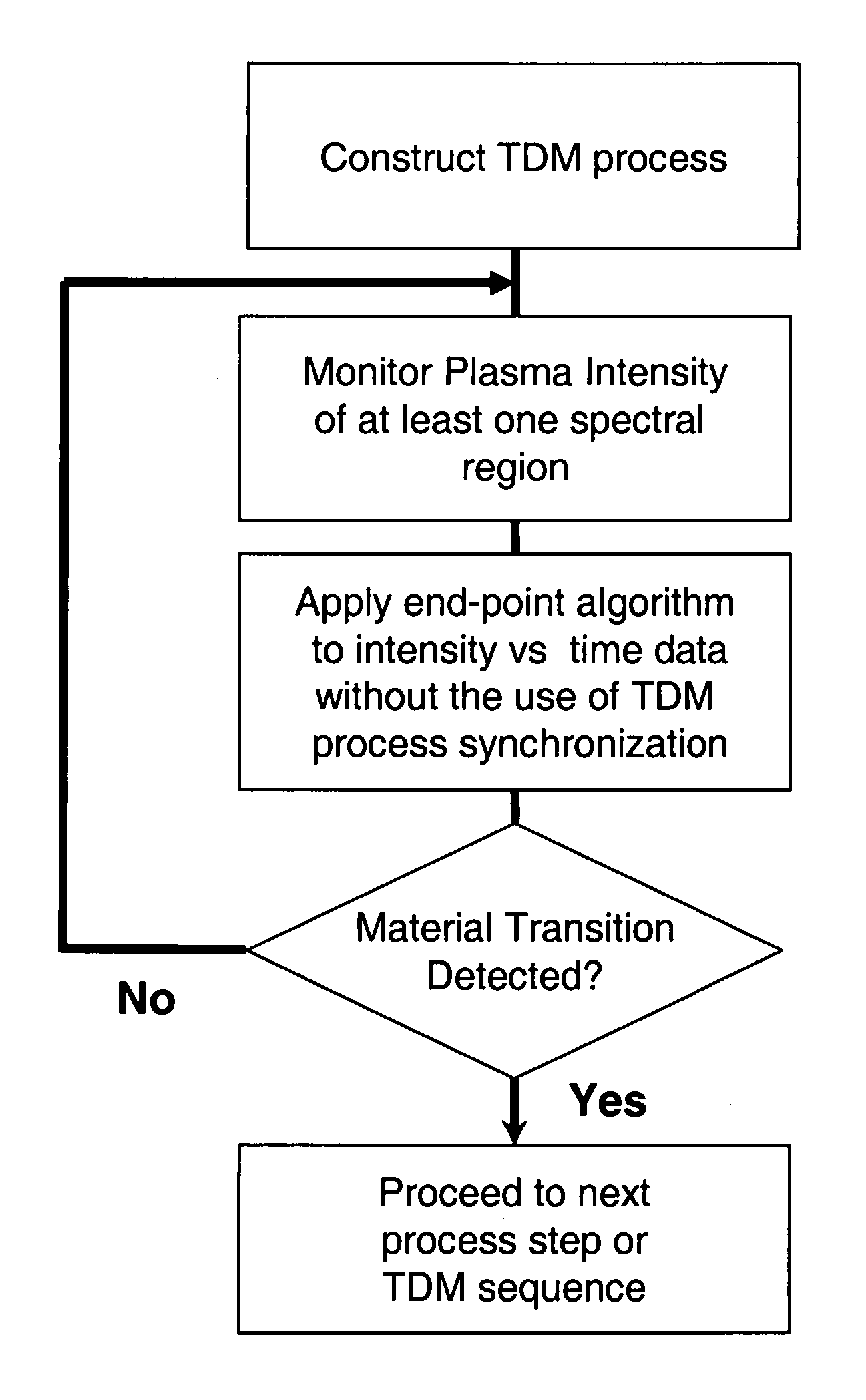
Envelope follower end point detection in time division multiplexed processes
ActiveUS7101805B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesOptical emission spectrometryPlasma chamber
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for establishing endpoint during an alternating cyclical etch process or time division multiplexed process. A substrate is placed within a plasma chamber and subjected to an alternating cyclical process having an etching step and a deposition step. A variation in plasma emission intensity is monitored using known optical emission spectrometry techniques. An amplitude information is extracted from a complex waveform of the plasma emission intensity using an envelope follower algorithm. The alternating cyclical process is discontinued when endpoint is reached at a time that is based on the monitoring step.
Owner:PLASMA THERM
Process using combined capacitively and inductively coupled plasma sources for controlling plasma ion radial distribution
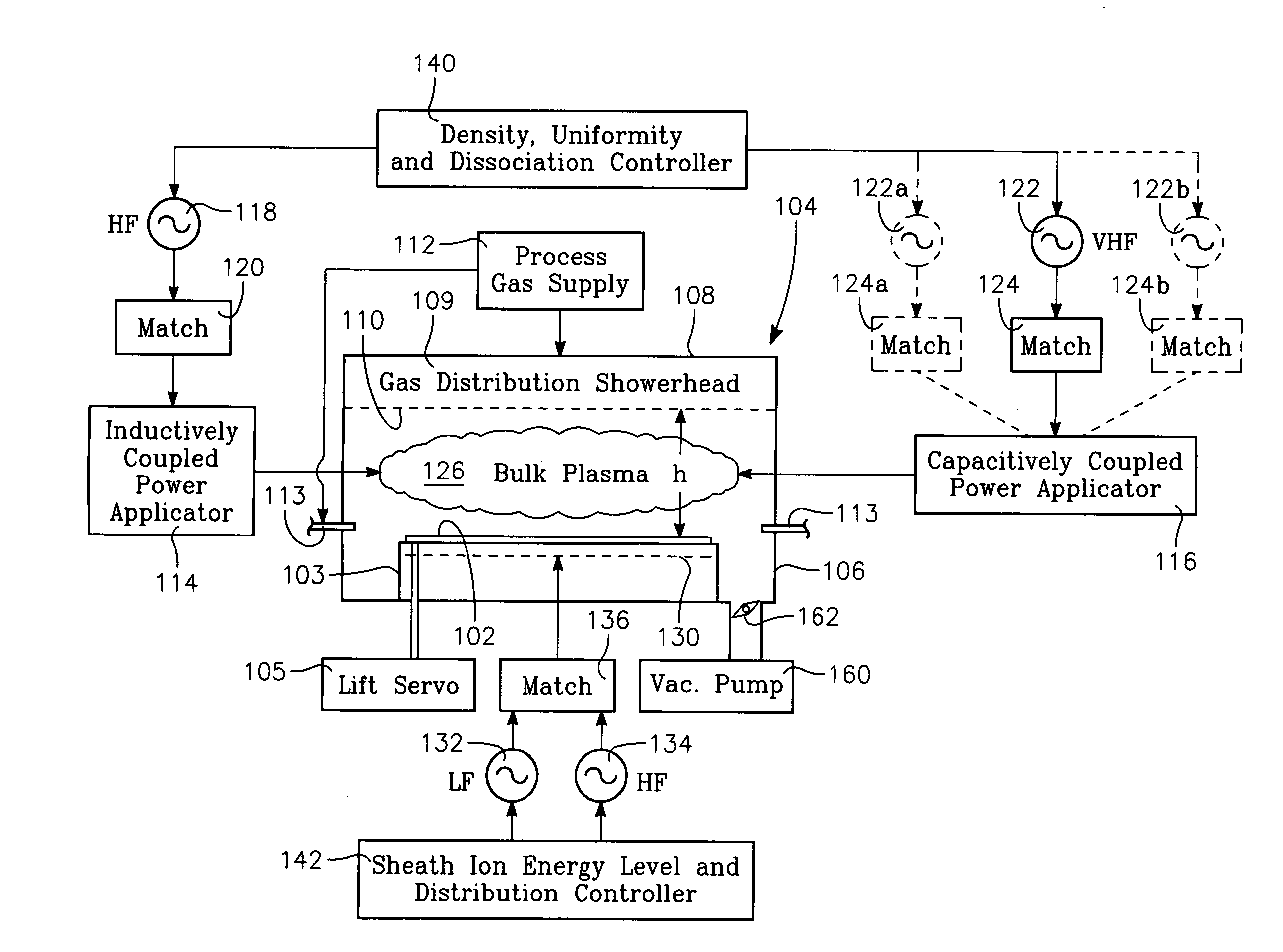
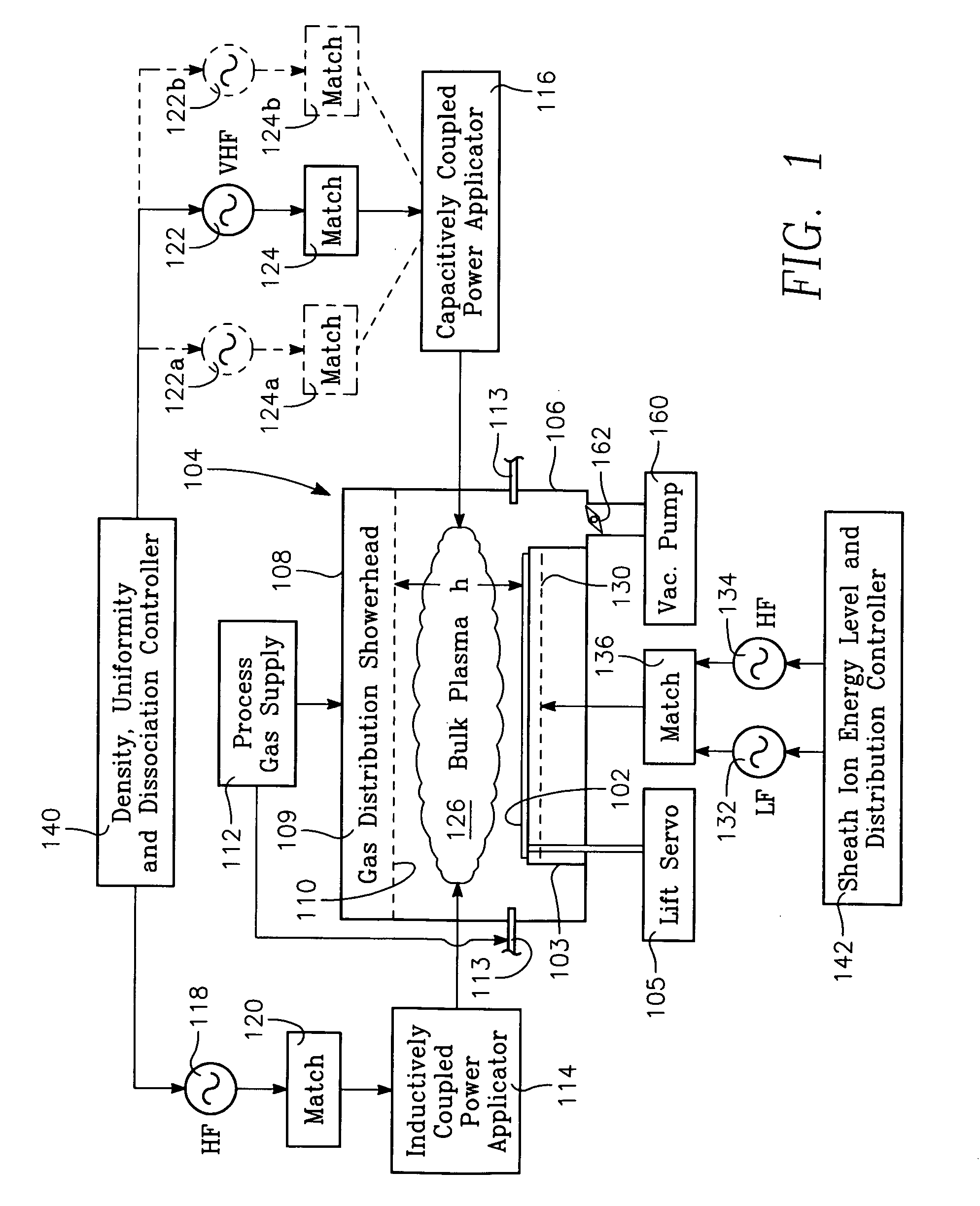
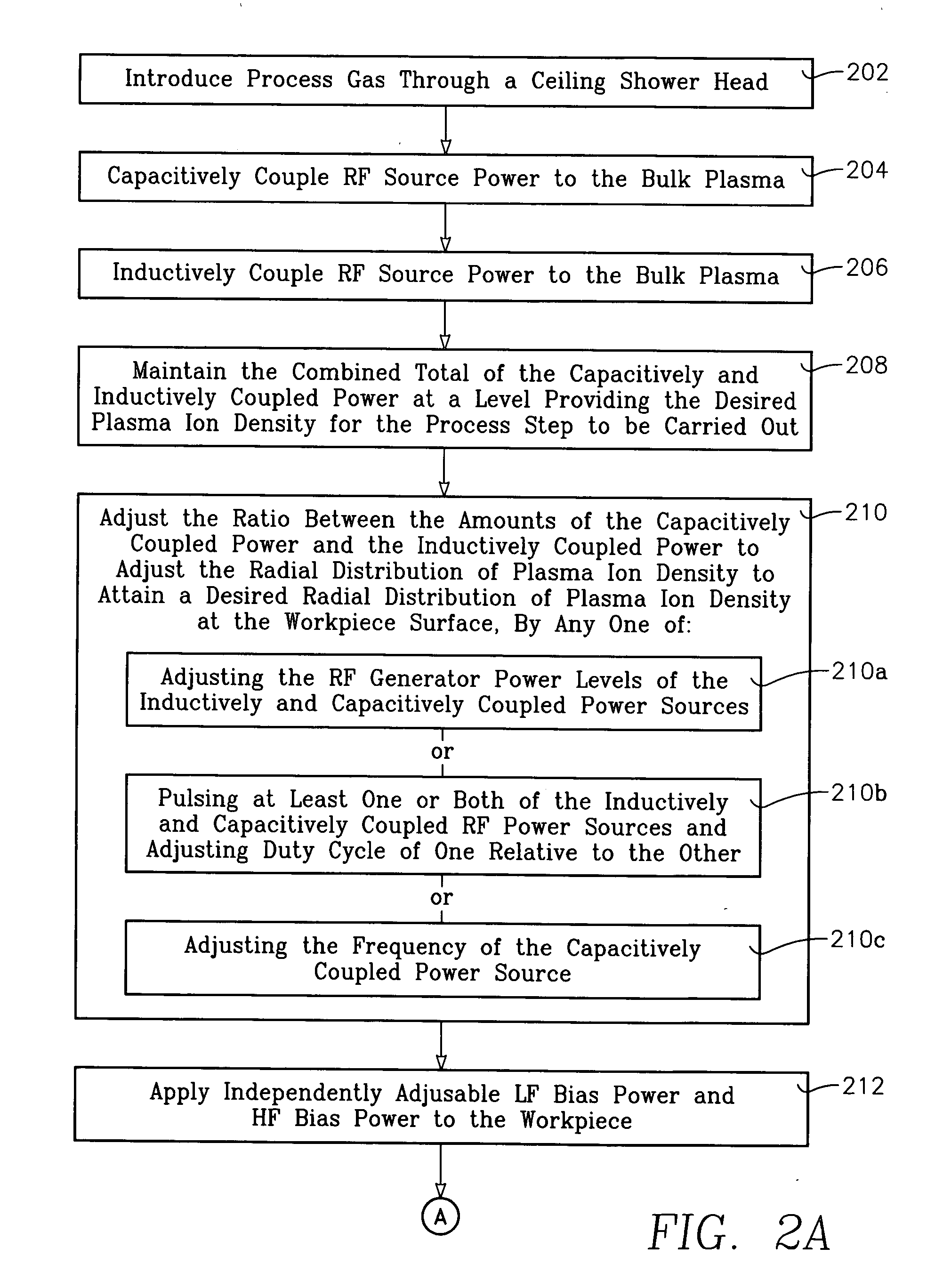
InactiveUS20070247074A1Increase ratingsIncrease ion densityElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsCapacitanceInductively coupled plasma
A method of processing a workpiece in the chamber of a plasma reactor includes introducing a process gas into the chamber, capacitively coupling VHF plasma source power into a process region of the chamber that overlies the wafer while inductively coupling RF plasma source power into the process region. A particular plasma ion density level is established by maintaining the total amount of plasma source power inductively and capacitively coupled into the process region at a level that provides the desired plasma ion density. The plasma ion density radial distribution in the process region is controlled by adjusting the ratio between the amounts of the (VHF) capacitively coupled power and the inductively coupled power while continuing to maintain the level of total plasma source power. The method can also include applying independently adjustable LF bias power and HF bias power to the workpiece and adjusting the average value and population distribution of ion energy at the surface of the workpiece by adjusting the proportion between the LF and HF bias powers. The VHF capacitively coupled power may be applied from the ceiling or from the wafer support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plasma cleaning method and plasma CVD method
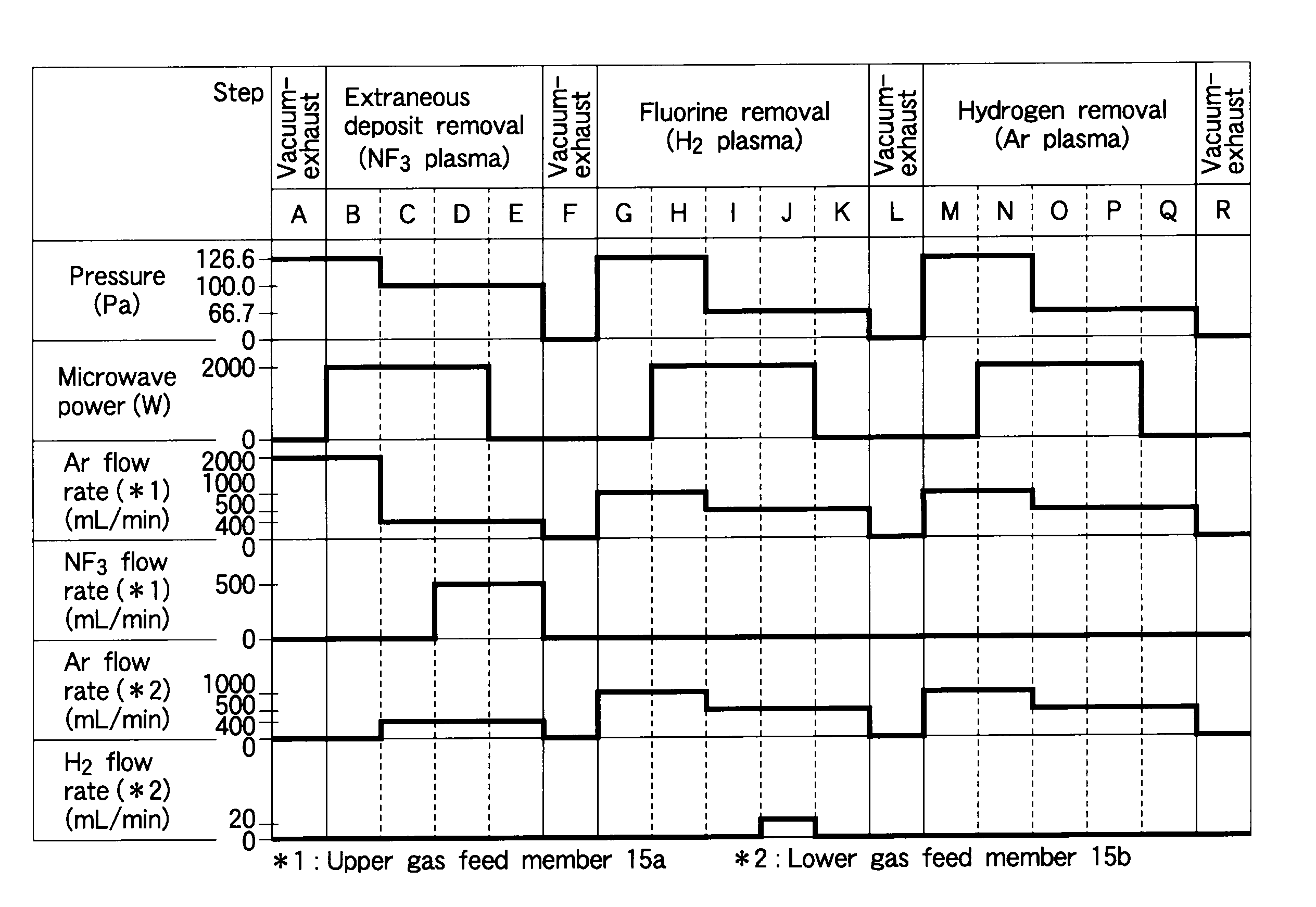
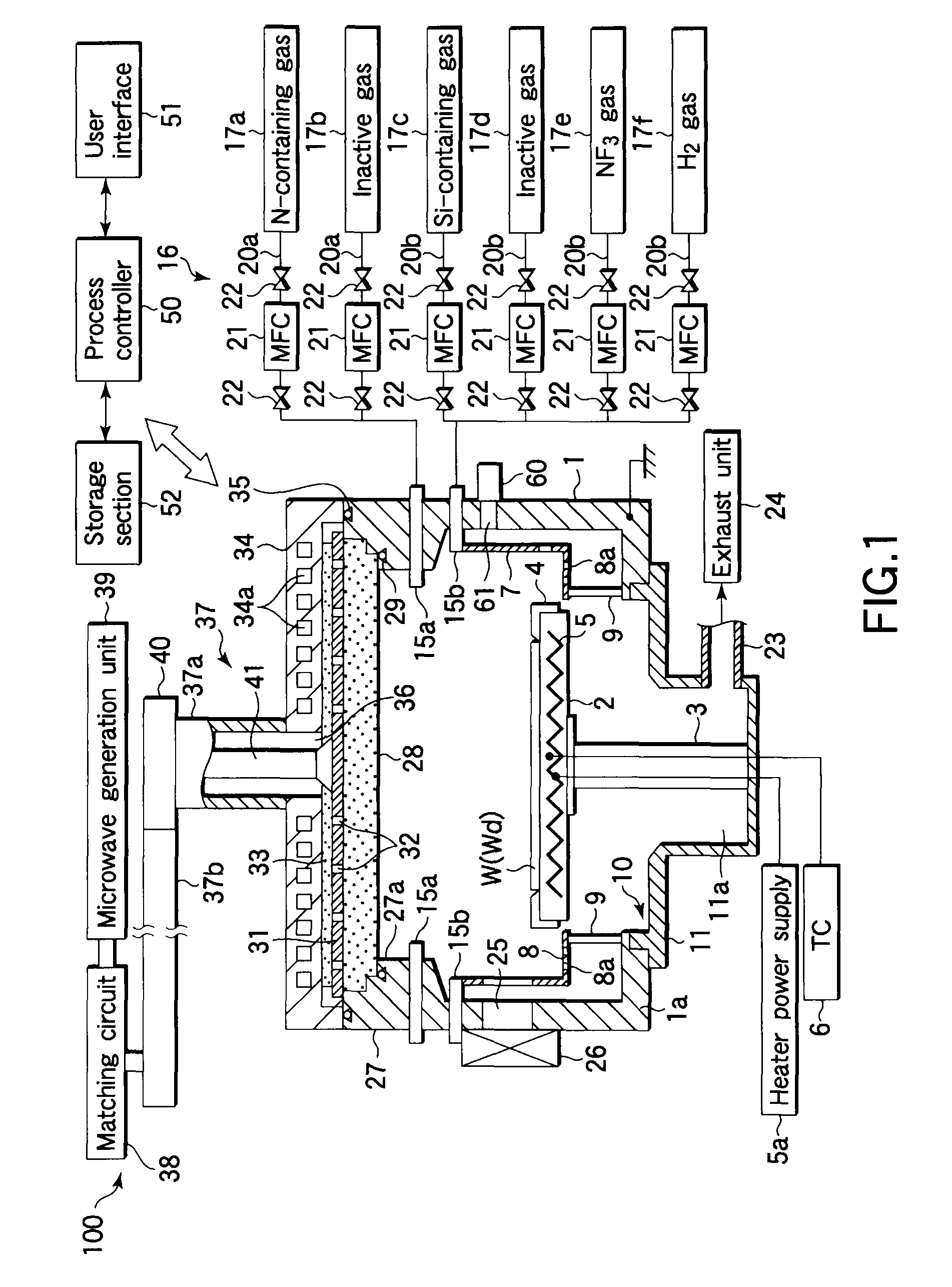
ActiveUS8366953B2Reliably decrease residual fluorineImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsHydrogenNoble gas
A plasma cleaning method is performed in a plasma CVD apparatus for depositing a silicon nitride film on a surface of a target substrate, and includes a stage (S1) of supplying a cleaning gas containing NF3 gas into a process container, thereby removing extraneous deposits formed on portions inside the process container; a stage (S2) of supplying a gas containing hydrogen gas into the process container and generating plasma thereof, thereby removing residual fluorine inside the process container; and a stage (S3) of supplying a gas containing a rare gas into the process container and generating plasma thereof, thereby removing residual hydrogen inside the process container.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Semiconductor-processing apparatus provided with self-cleaning device
InactiveUS20060228473A1Reliable completionImprove throughputLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsSemiconductorOptics
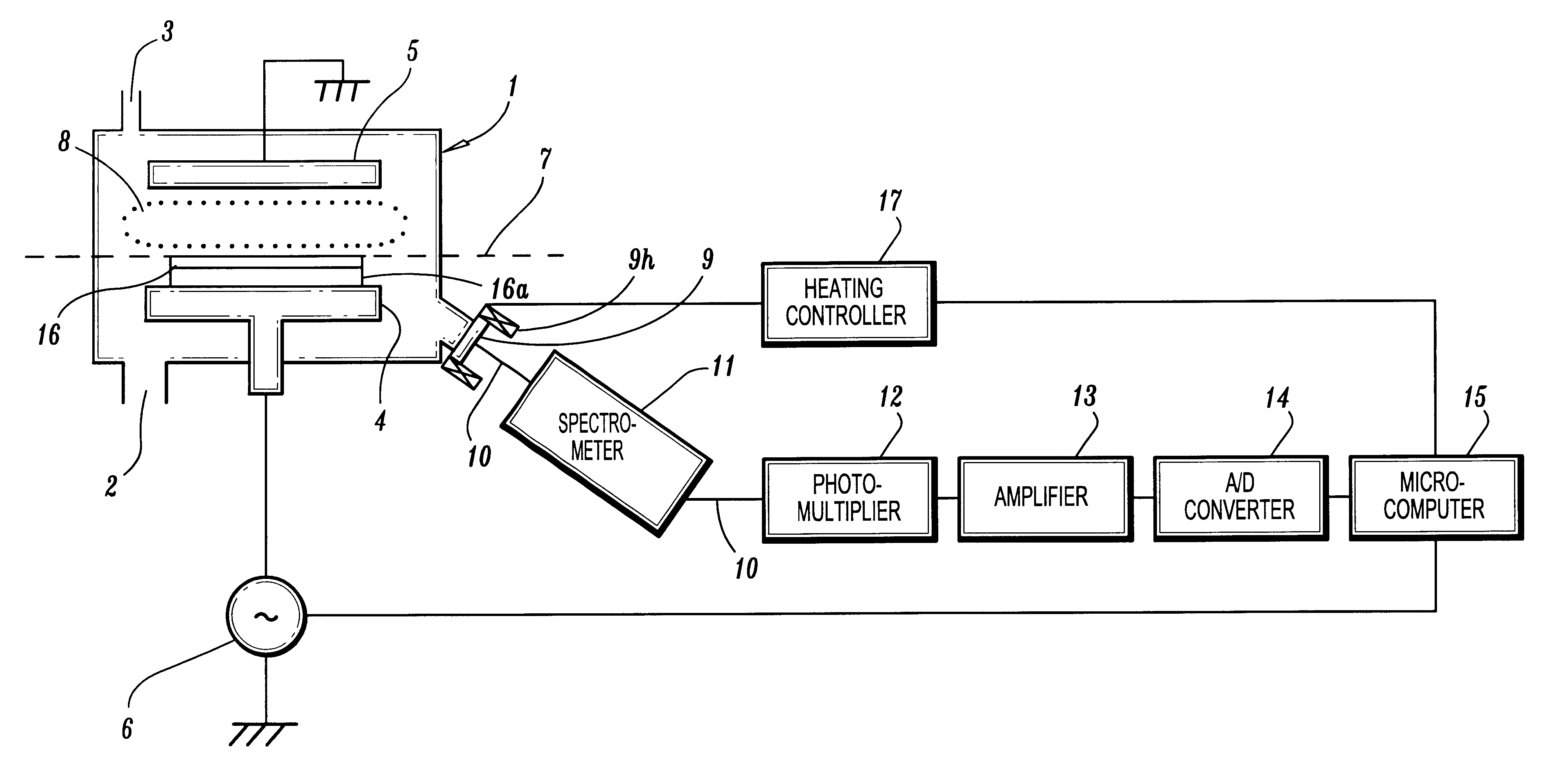
A CVD apparatus comprising an optical unit detecting the mass of contaminants adhering to an inner surface of a CVD reactor by irradiating an inner surface of the reactor with light having monochromaticity through an optical window provided on an inner wall of the reactor and receiving its reflected light is provided.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
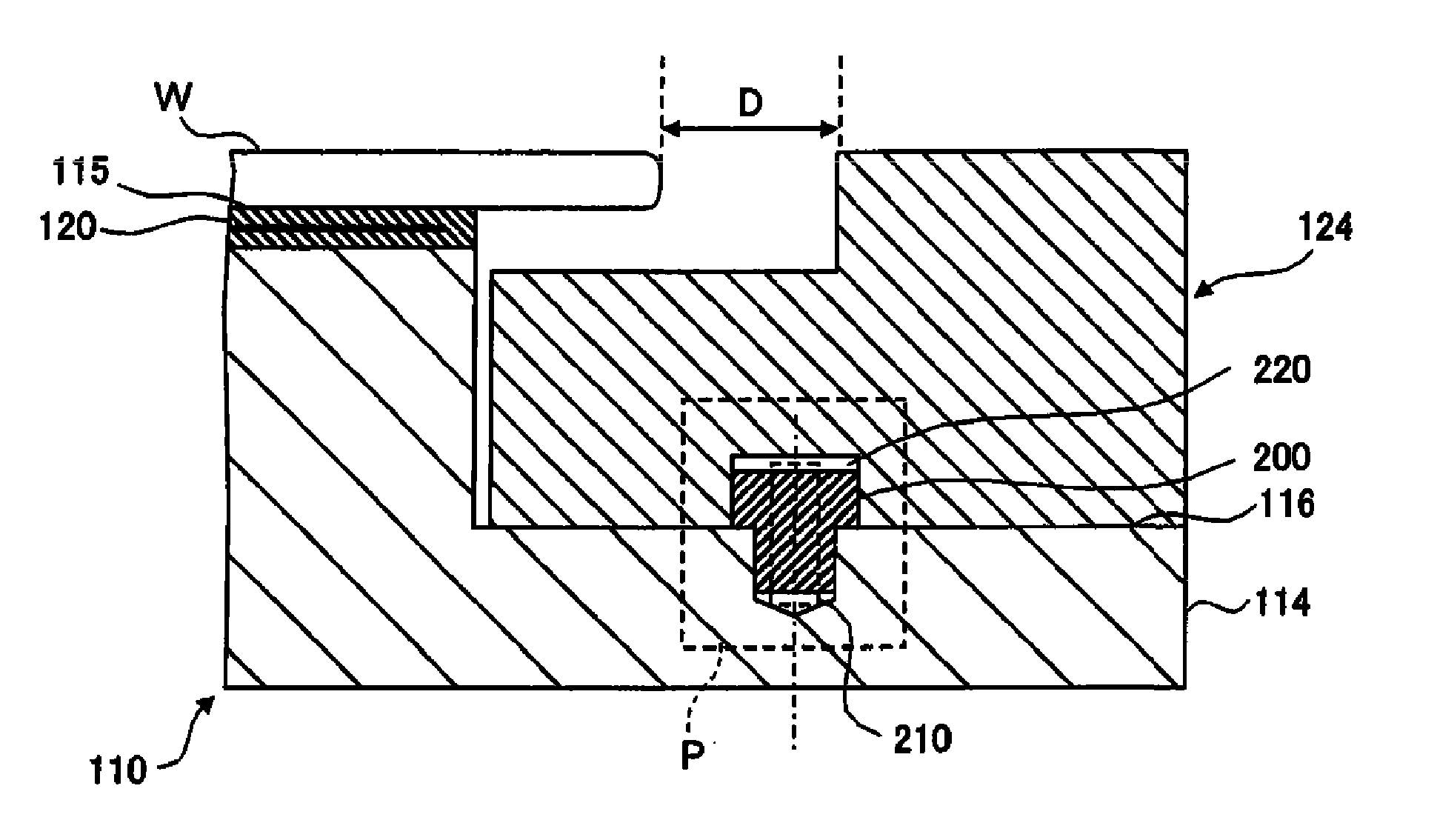
Substrate processing apparatus, positioning method and focus ring installation method
ActiveUS20110031111A1Precise positioningImprove insertion accuracyDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Positioning accuracy of a component in a substrate processing apparatus can be improved higher than a conventional case without increasing the insertion accuracy of positioning pins into positioning holes. Provided is a substrate processing apparatus including a mounting table 110 including a susceptor 114 having a substrate mounting surface 115 on which a wafer W is mounted and a focus ring mounting surface 116 on which a focus ring 124 is mounted; a plurality of positioning pins 200 made of a material expandable in a diametric direction by heating. Each positioning pin is inserted into a positioning hole (first reference hole) formed in the focus ring mounting surface of the susceptor and into a positioning hole (second reference hole) formed in the focus ring, and expanded in the diametric direction by heating and fitted into the positioning holes, thus allowing a position of the focus ring to be aligned.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Adjustable shielding plate for adjusting an etching area of a semiconductor wafer and related apparatus and methods
An apparatus for adjusting an etching area of a semiconductor wafer includes an adjustable shielding plate. The adjustable shielding plate includes a plurality of shielding members. Each of the plurality of shielding members are movable between a first position configured to shield a portion of a semiconductor wafer from an etching gas and a second position configured to expose an unshielded etching portion of the semiconductor wafer to the etching gas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Popular searches
Electrical testing Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Chemical vapor deposition coating Photosensitive material processing Originals for photomechanical treatment Photographic processes Photomechanical apparatus Semiconductor/solid-state device details Solid-state devices Surface treatment compositions
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com