Patents
Literature
267results about How to "Uniform etching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
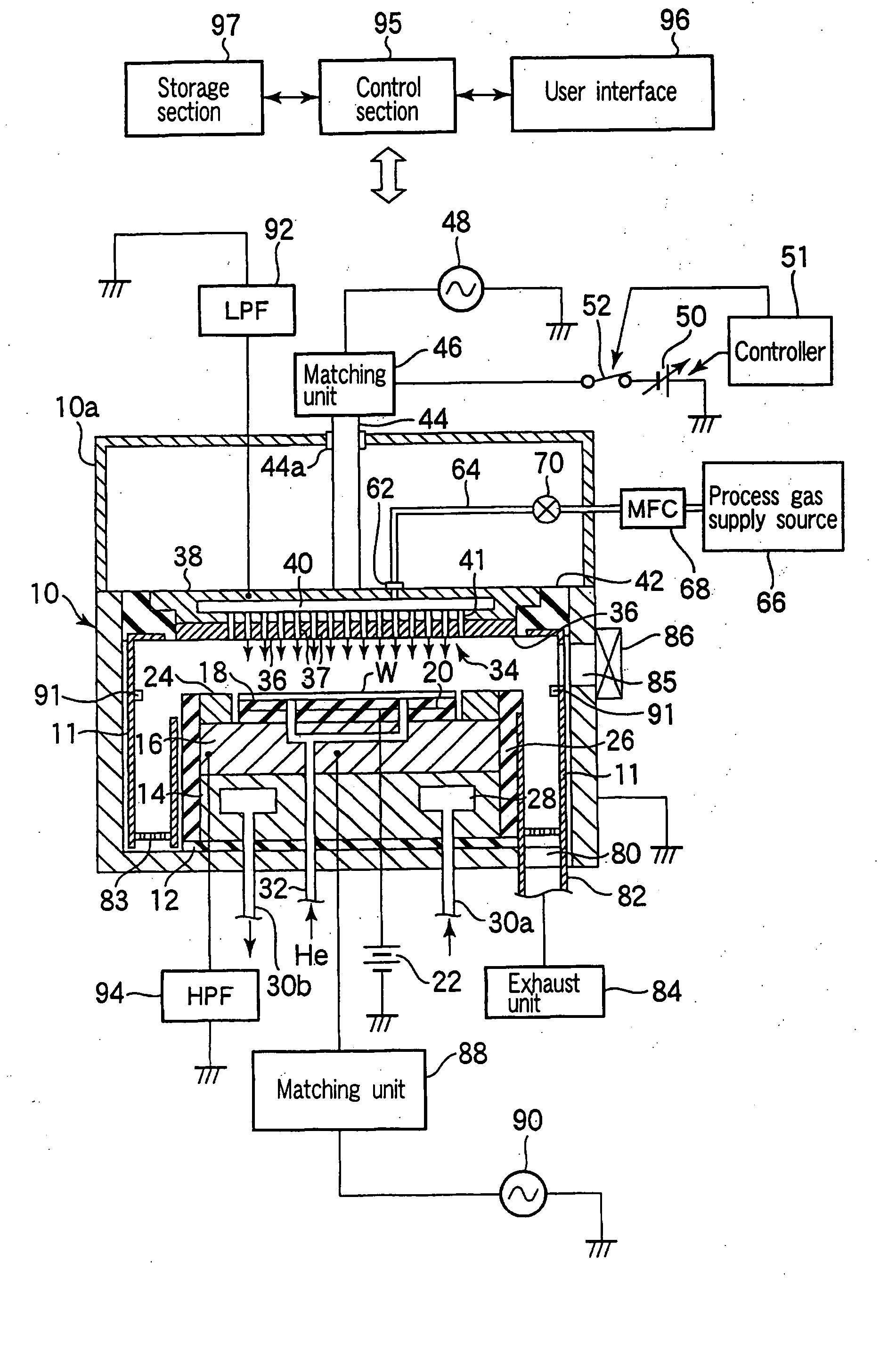
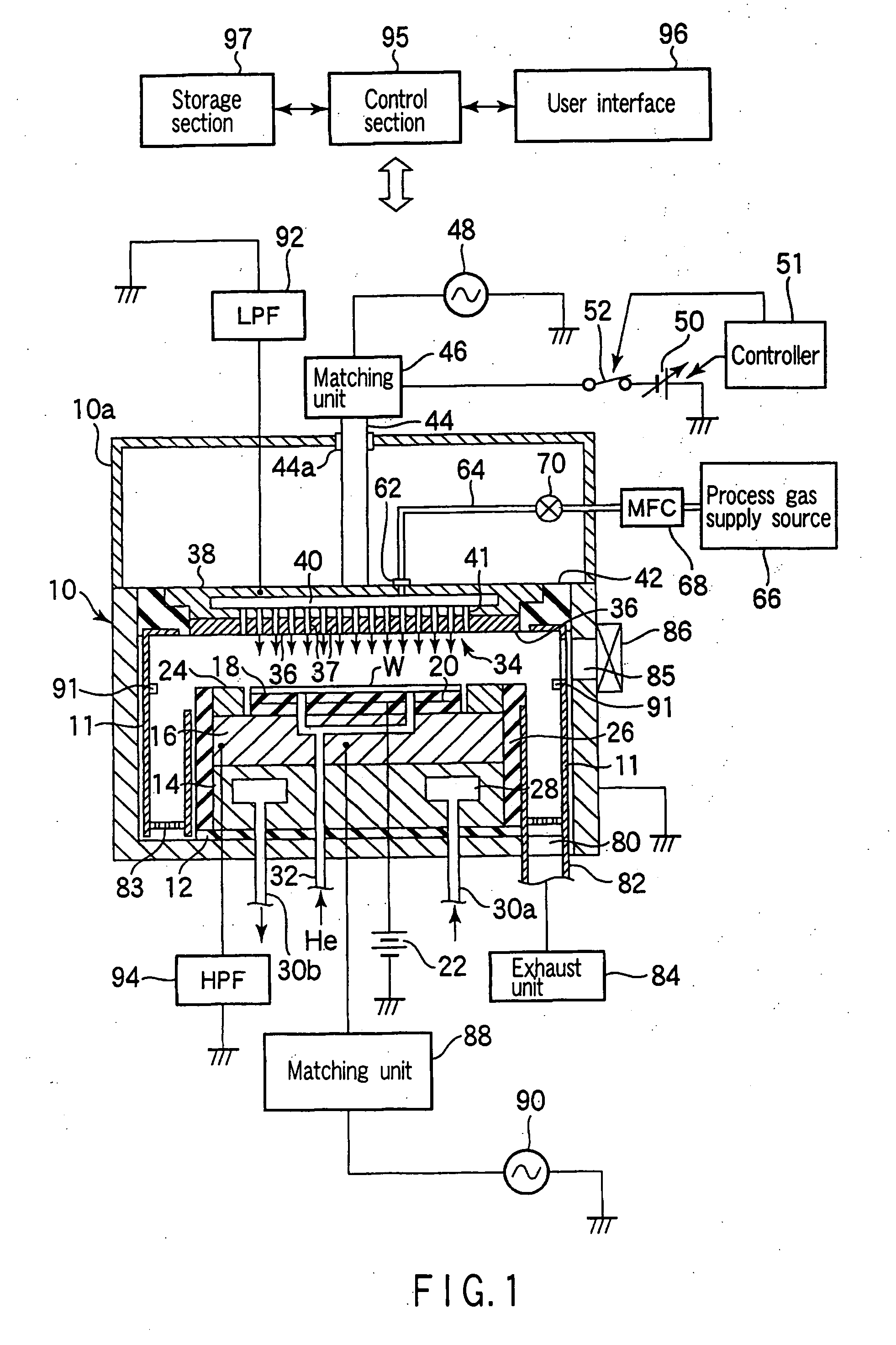
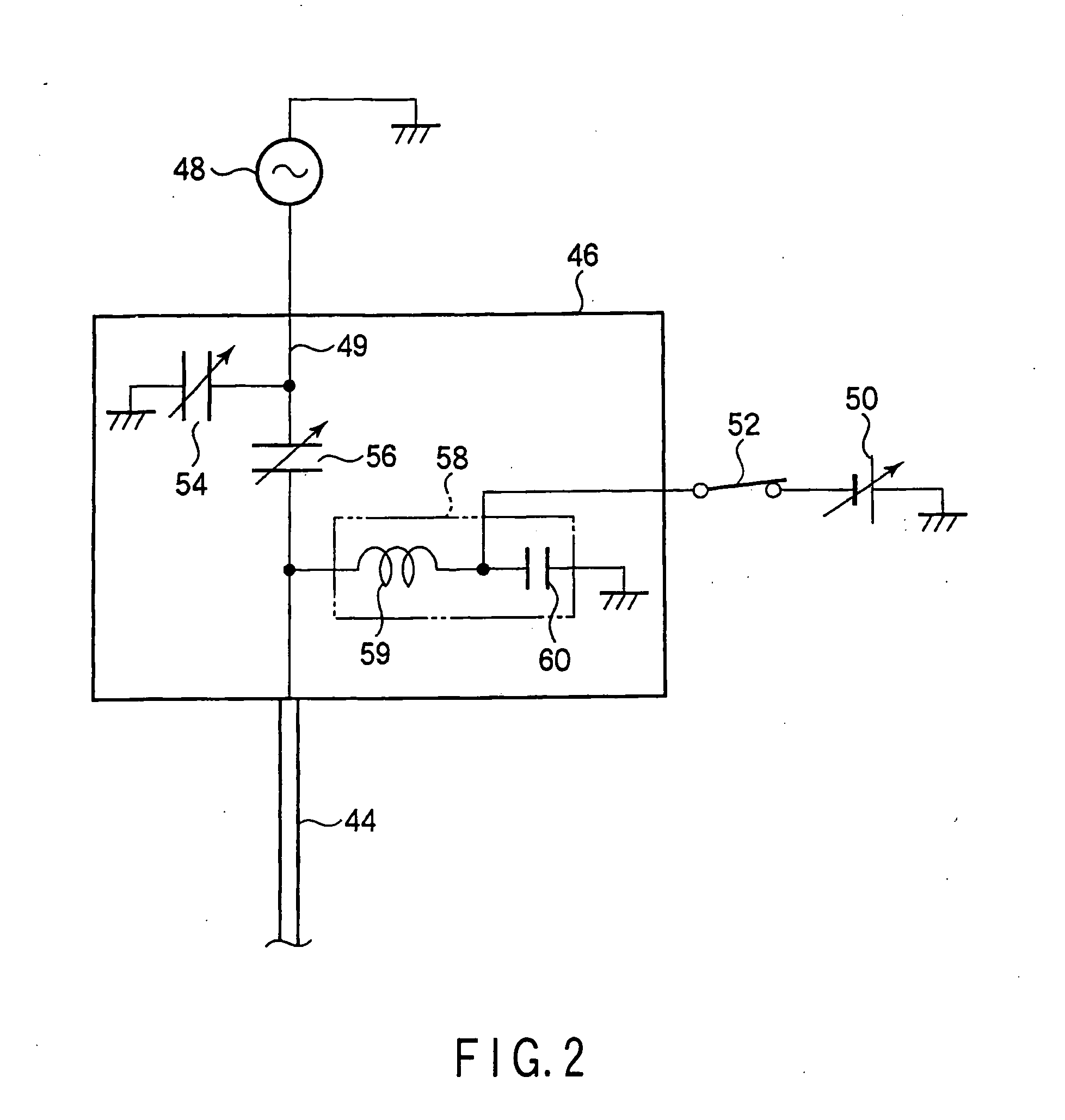
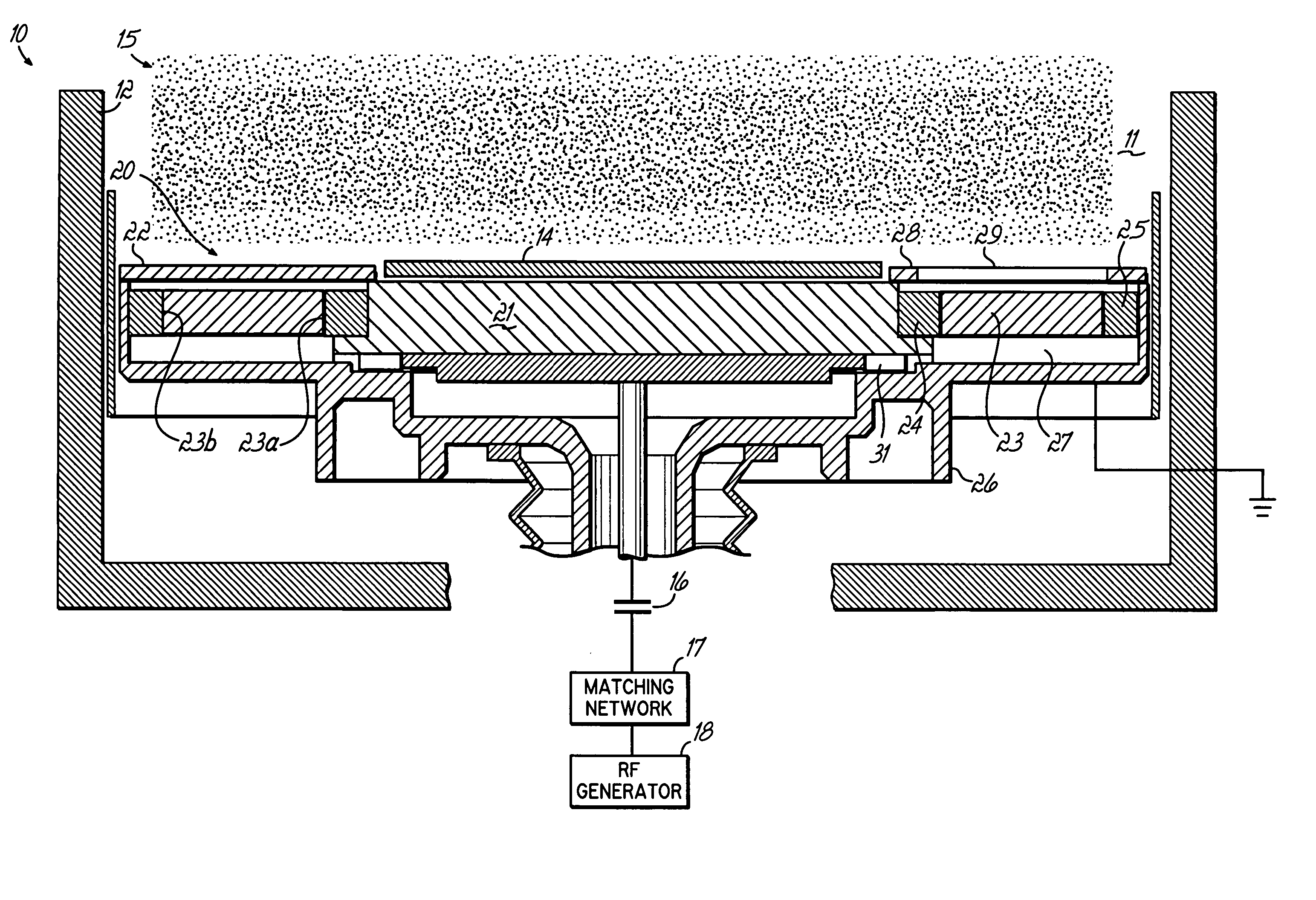
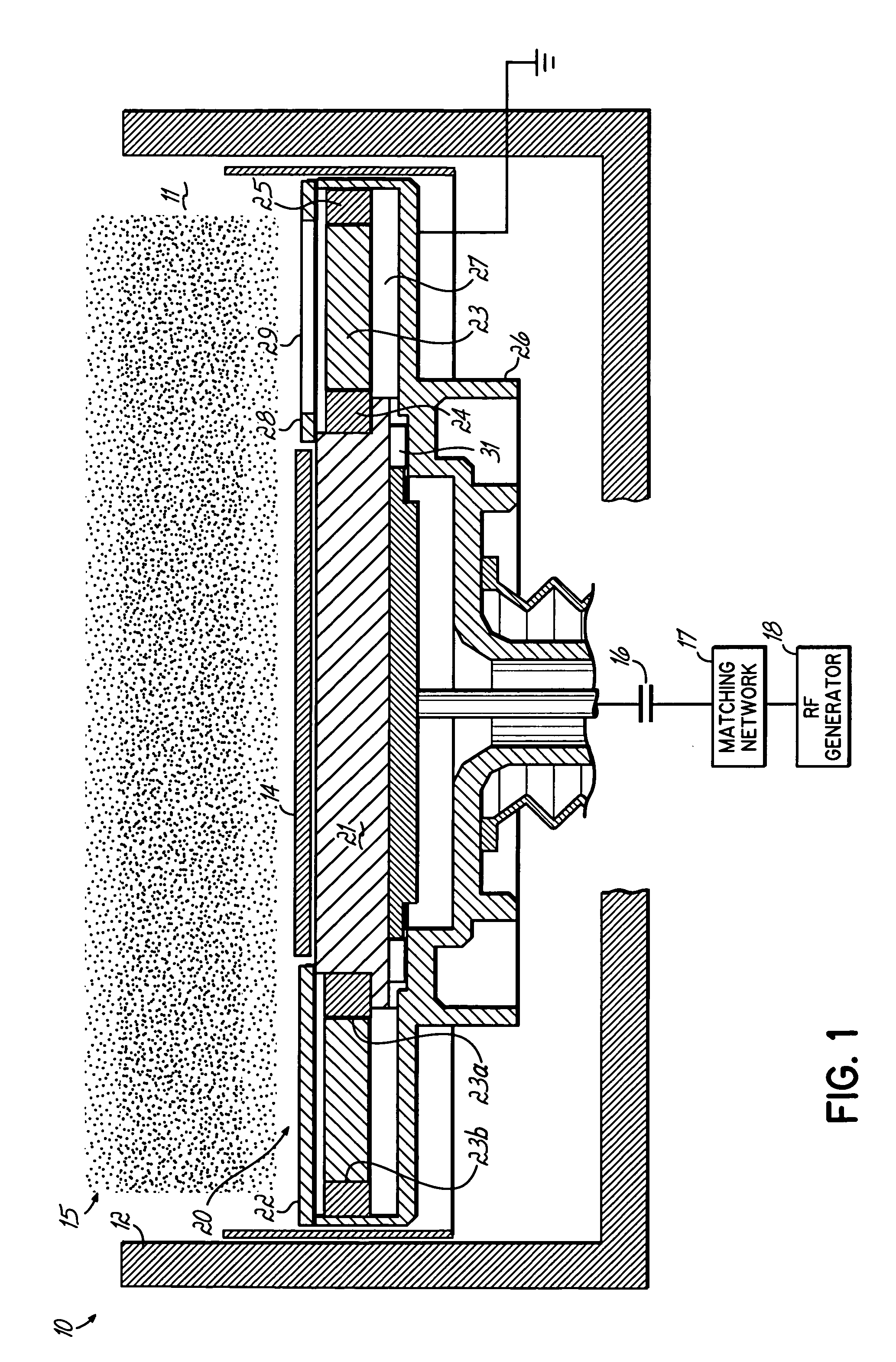
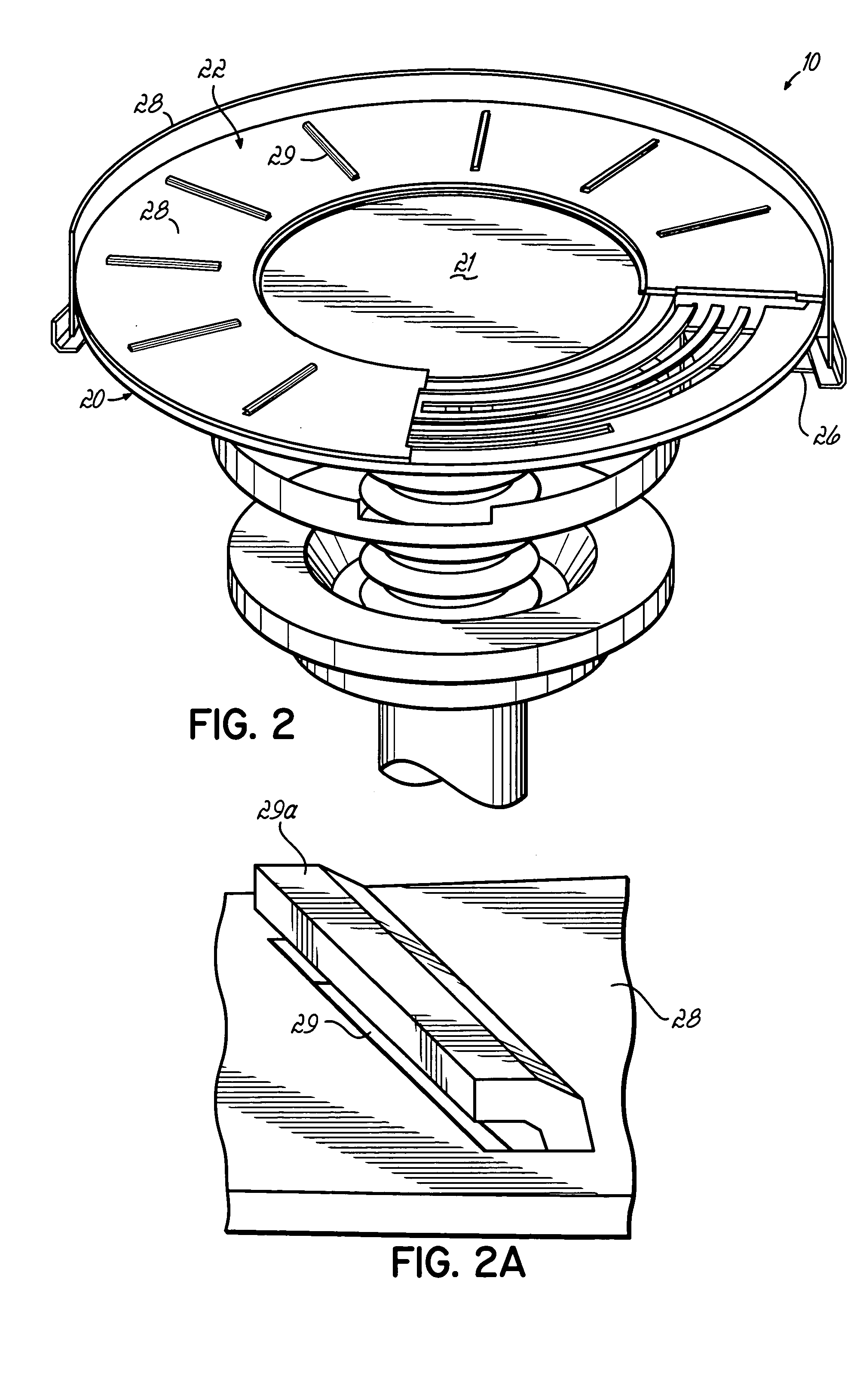
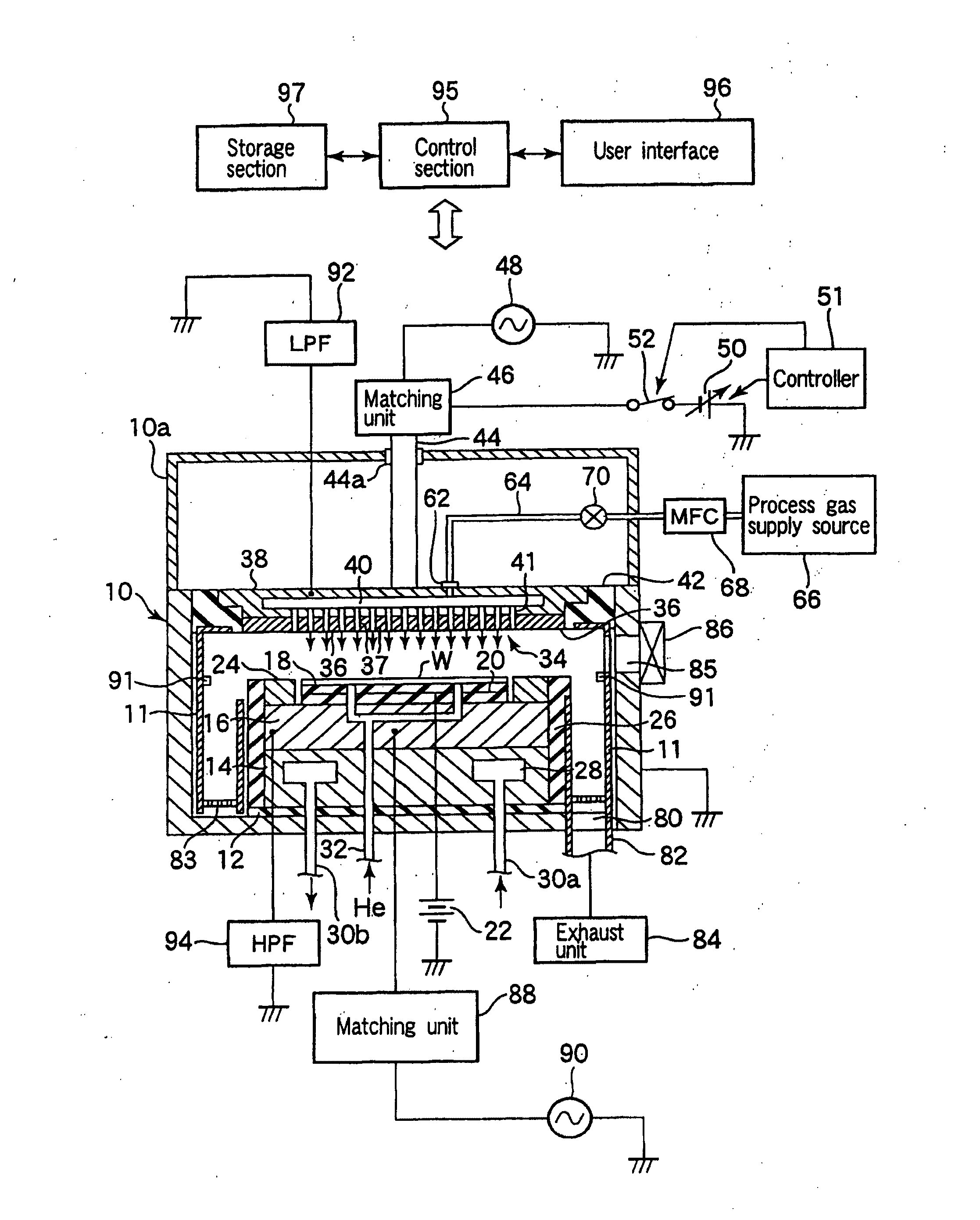
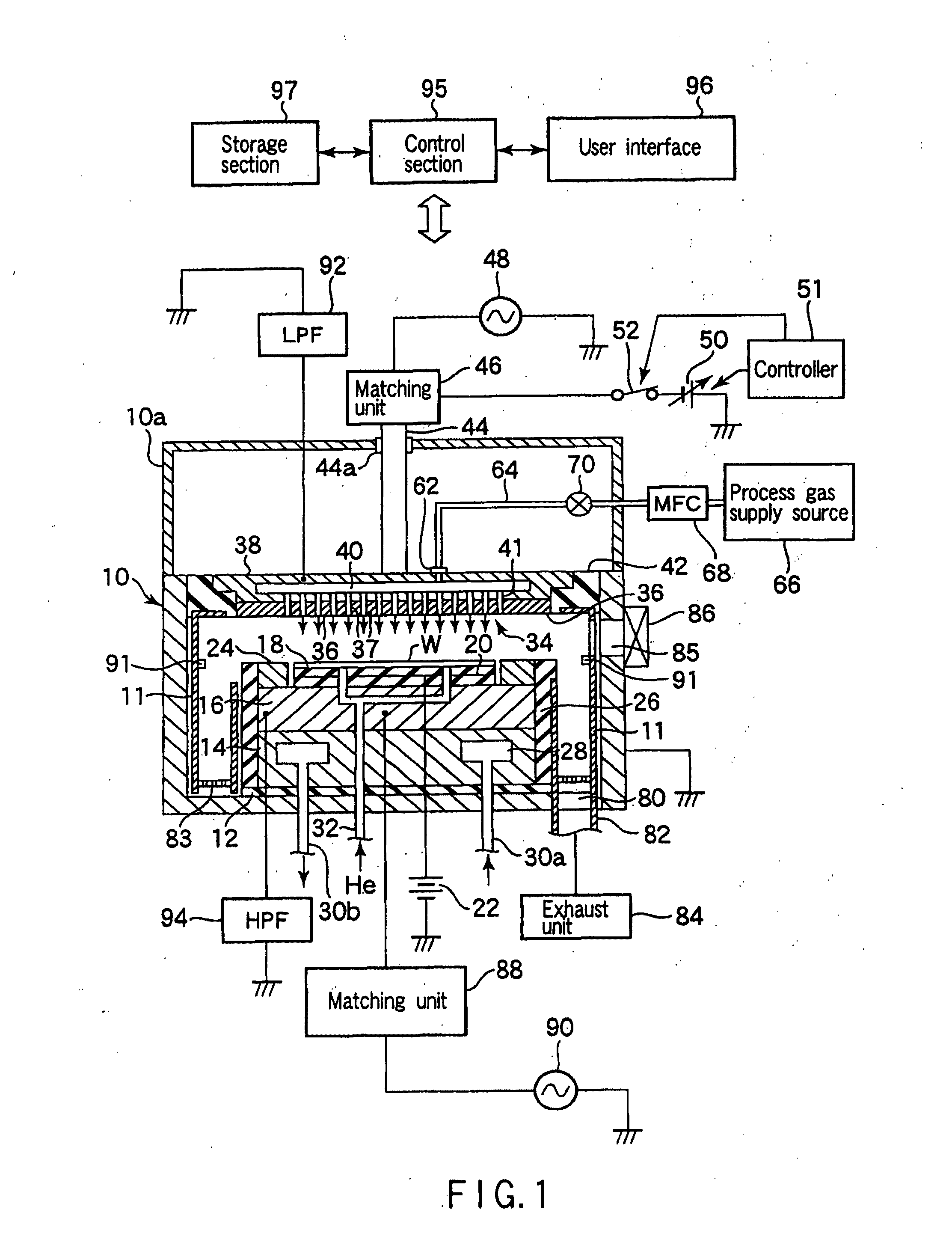
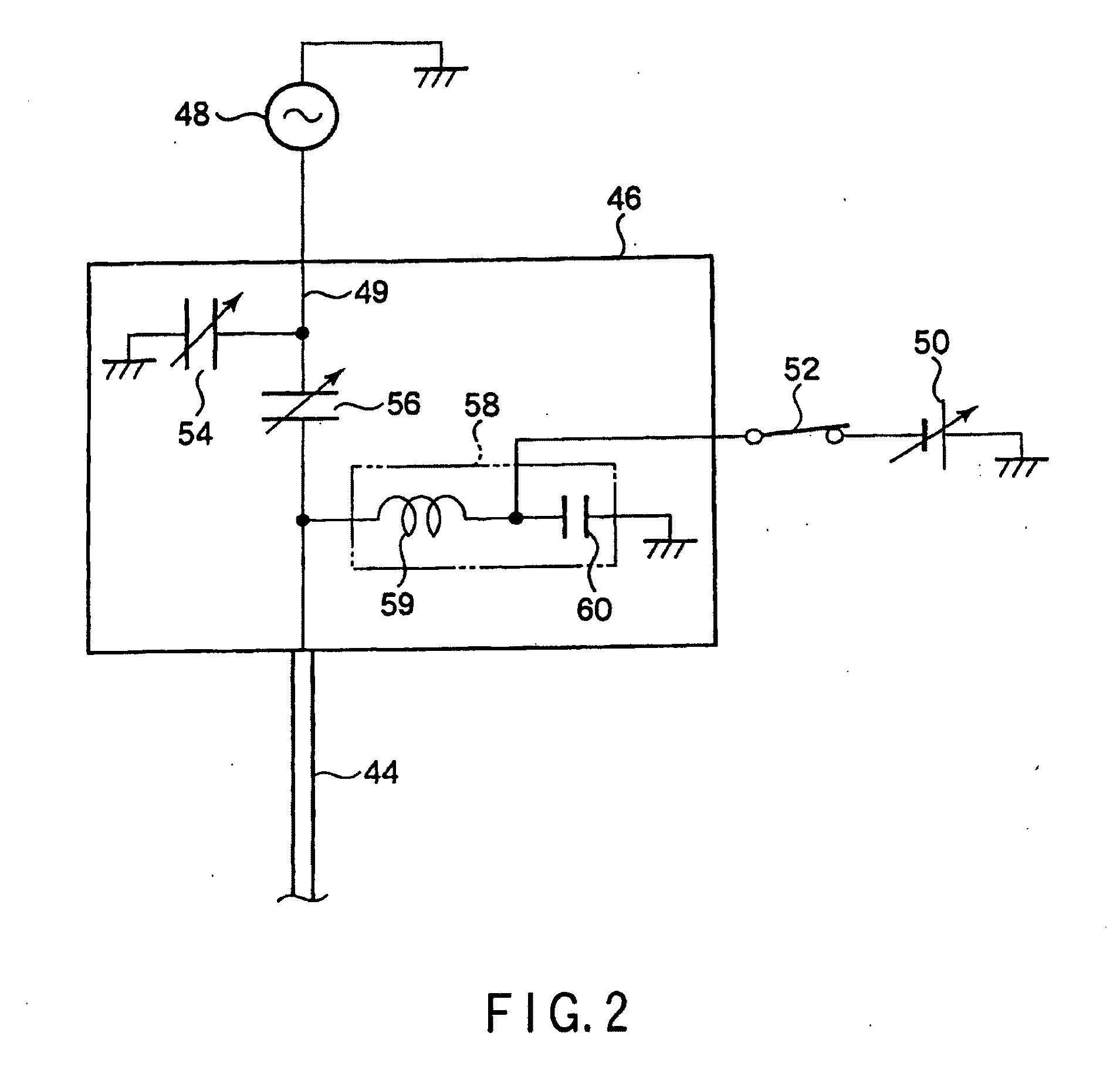
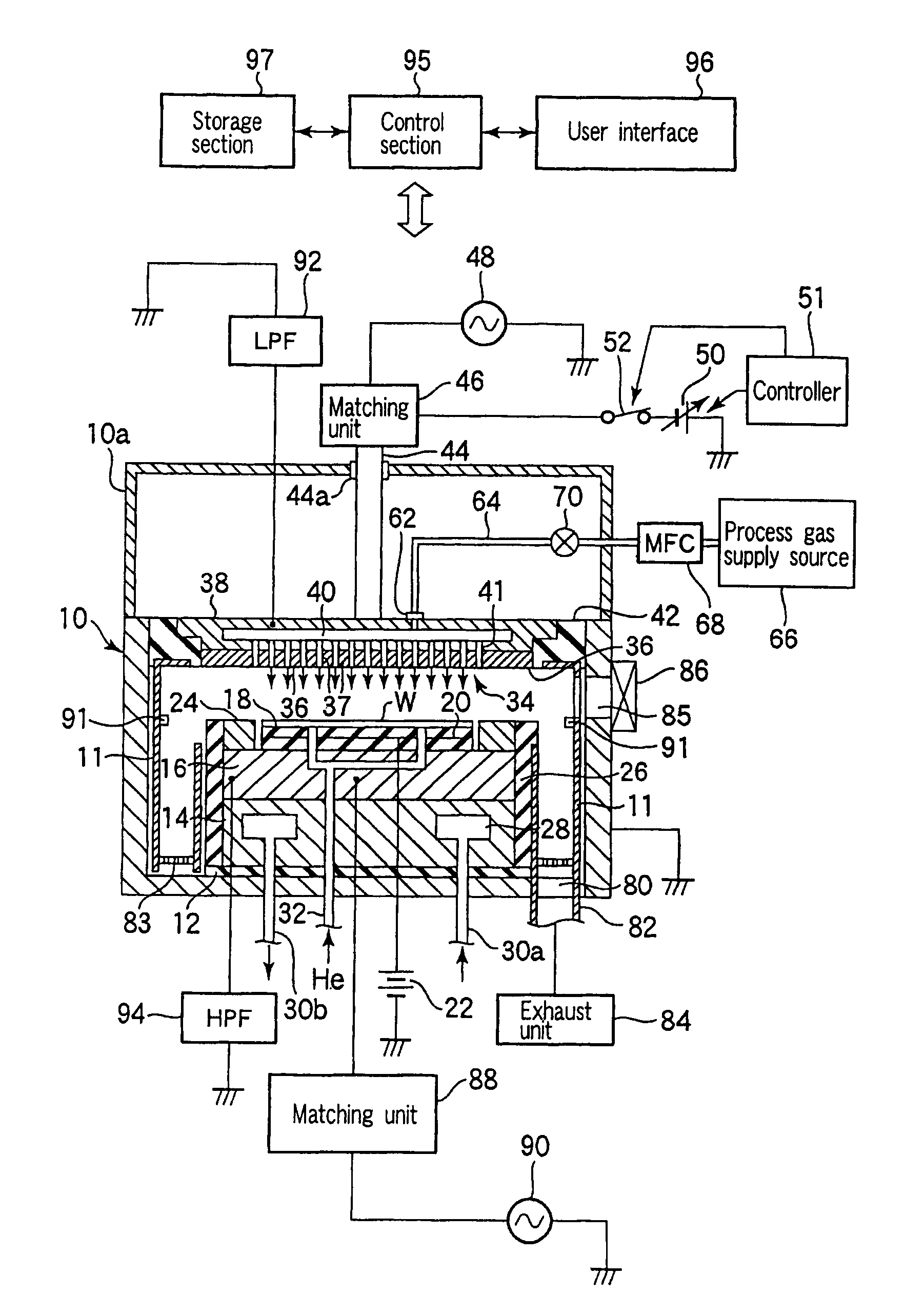
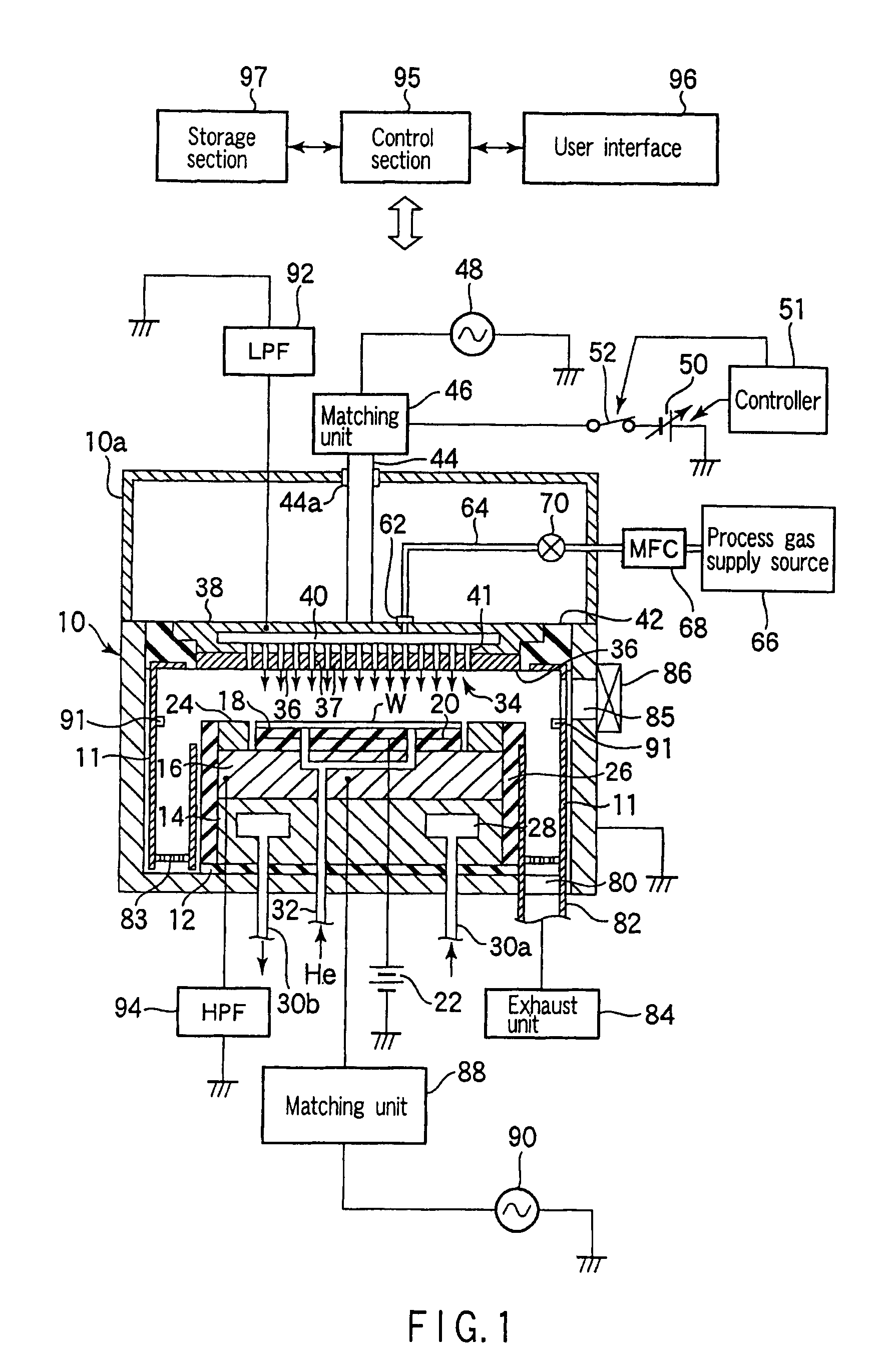
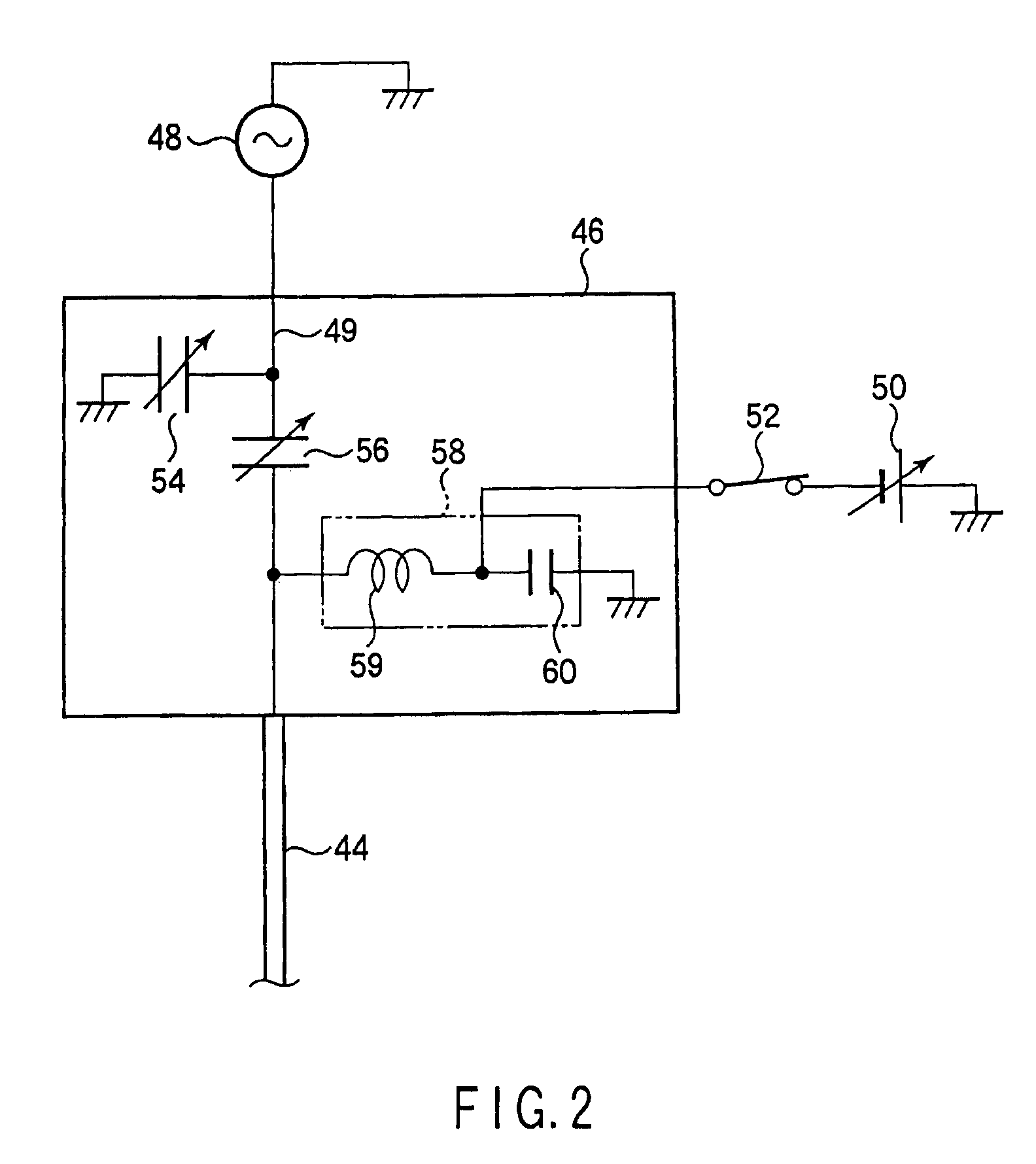
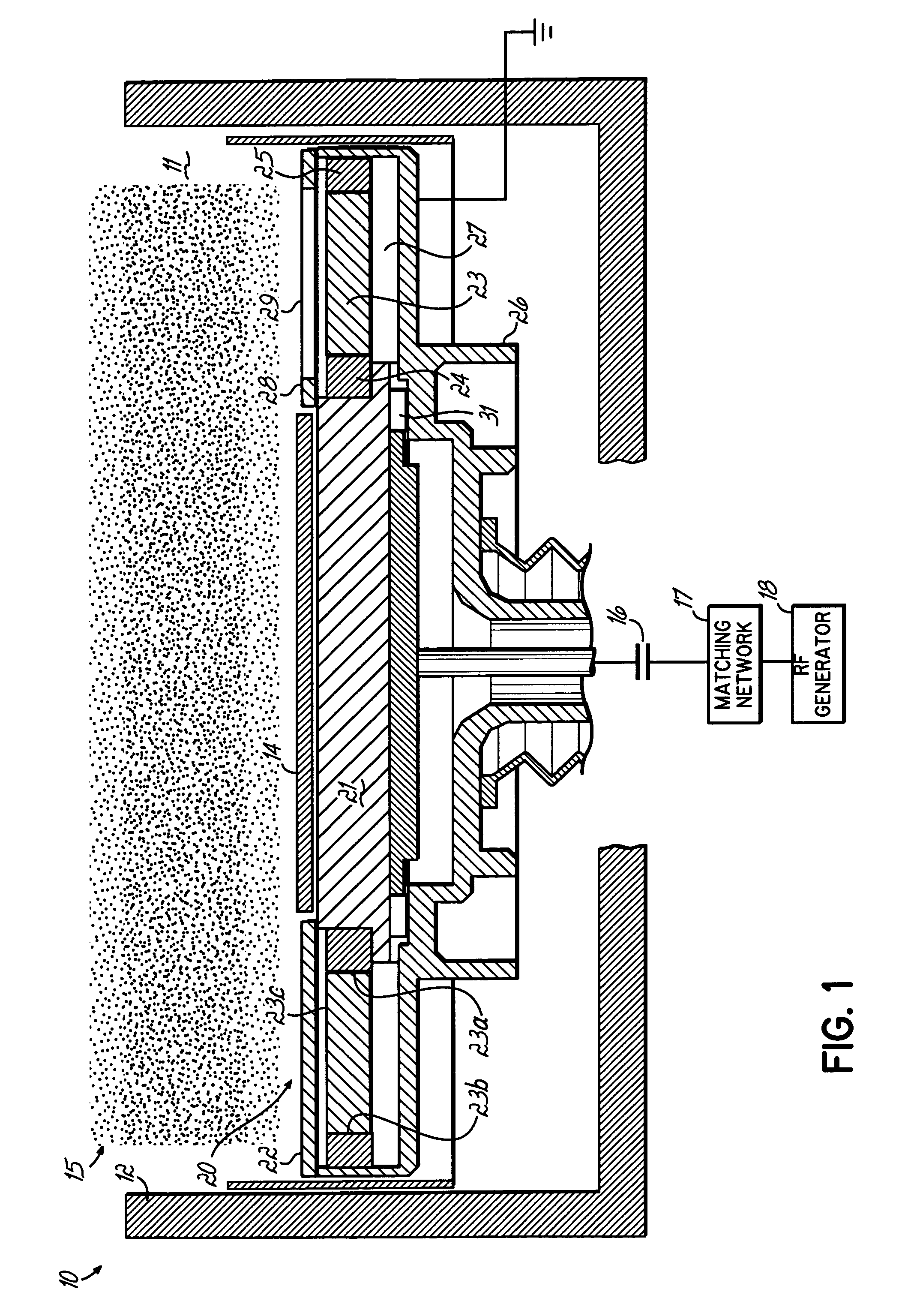
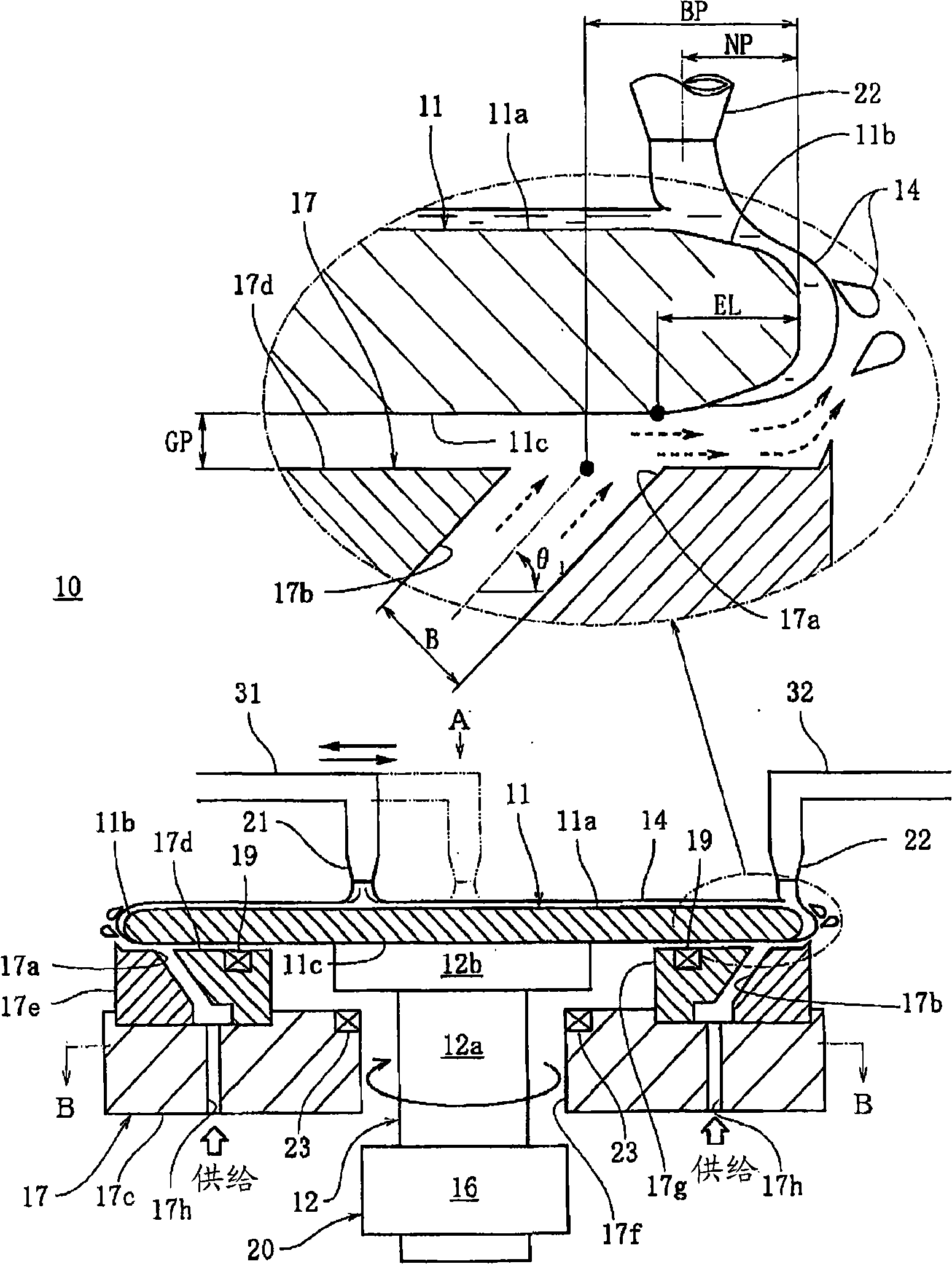
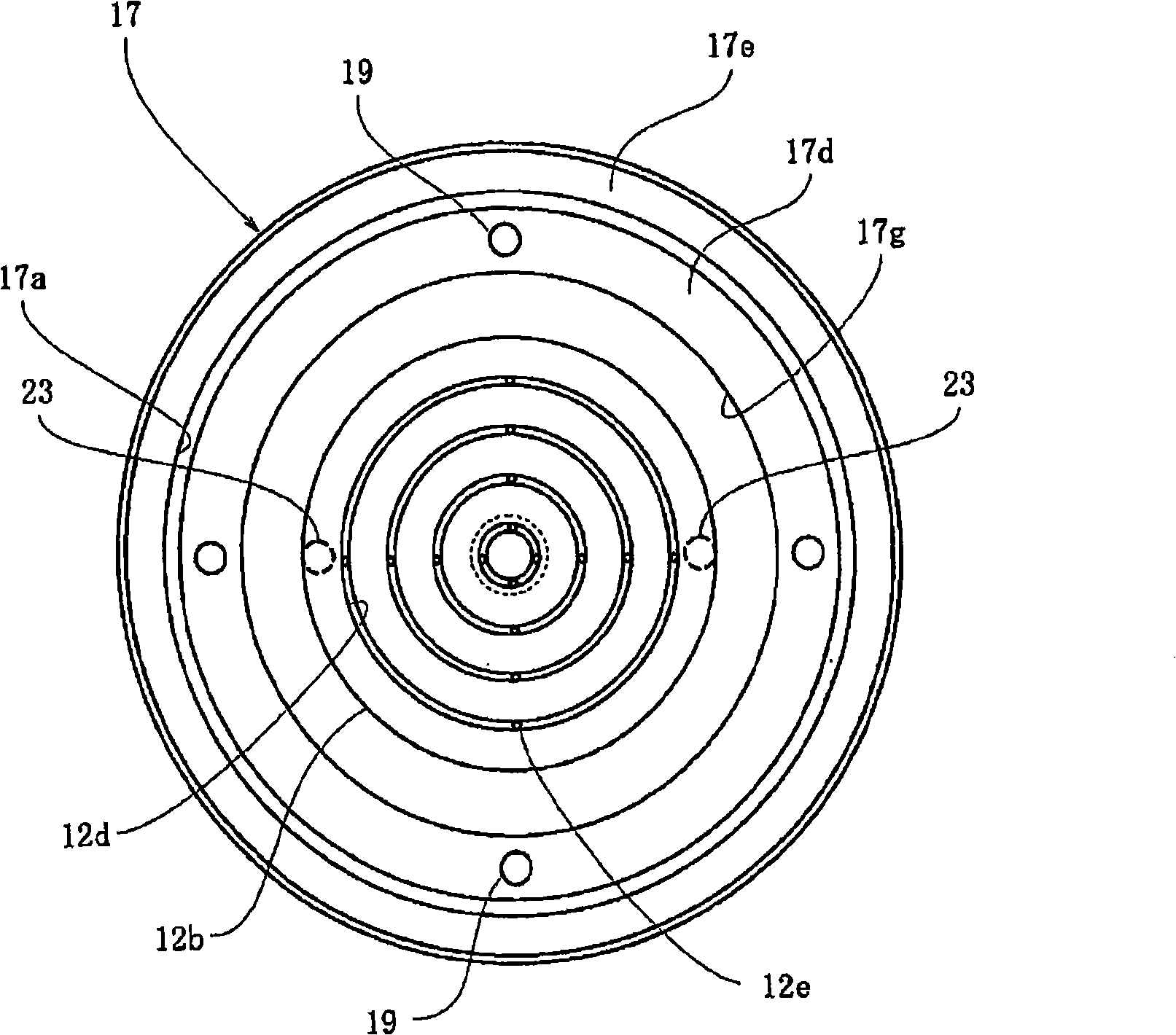
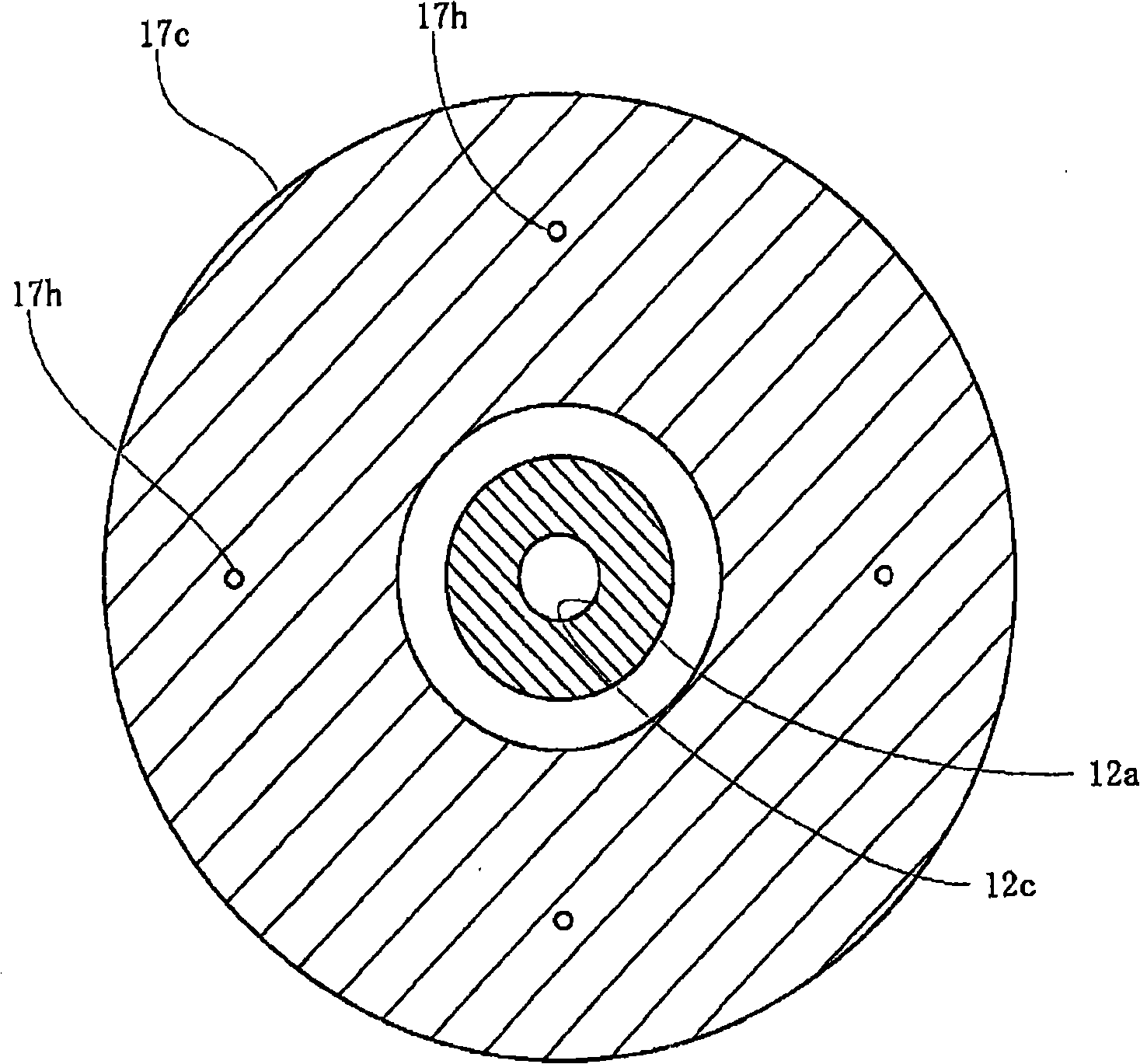
Plasma processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS7951262B2Improved resistance characteristicsIncrease chanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPlasma processing
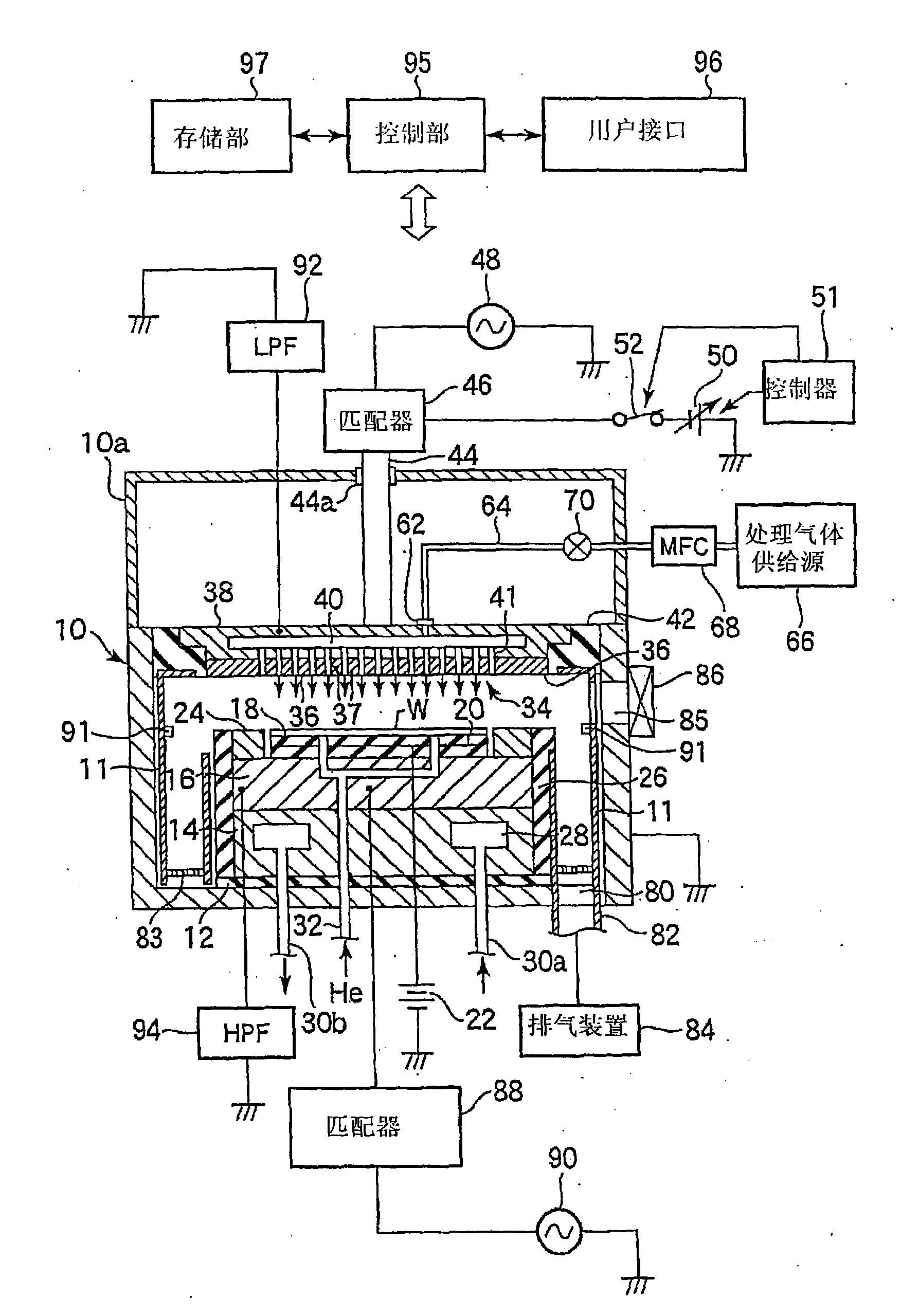
An apparatus includes an upper electrode and a lower electrode for supporting a wafer disposed opposite each other within a process chamber. A first RF power supply configured to apply a first RF power having a relatively higher frequency, and a second RF power supply configured to apply a second RF power having a relatively lower frequency is connected to the lower electrode. A variable DC power supply is connected to the upper electrode. A process gas is supplied into the process chamber to generate plasma of the process gas so as to perform plasma etching.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20060037701A1High selectivity etchHigh rateElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma processingPower flow
An apparatus includes an upper electrode and a lower electrode for supporting a wafer disposed opposite each other within a process chamber. A first RF power supply configured to apply a first RF power having a relatively higher frequency is connected to the upper electrode. A second RF power supply configured to apply a second RF power having a relatively lower frequency is connected to the lower electrode. A variable DC power supply is connected to the upper electrode. A process gas is supplied into the process chamber while any one of application voltage, application current, and application power from the variable DC power supply to the upper electrode is controlled, to generate plasma of the process gas so as to perform plasma etching.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
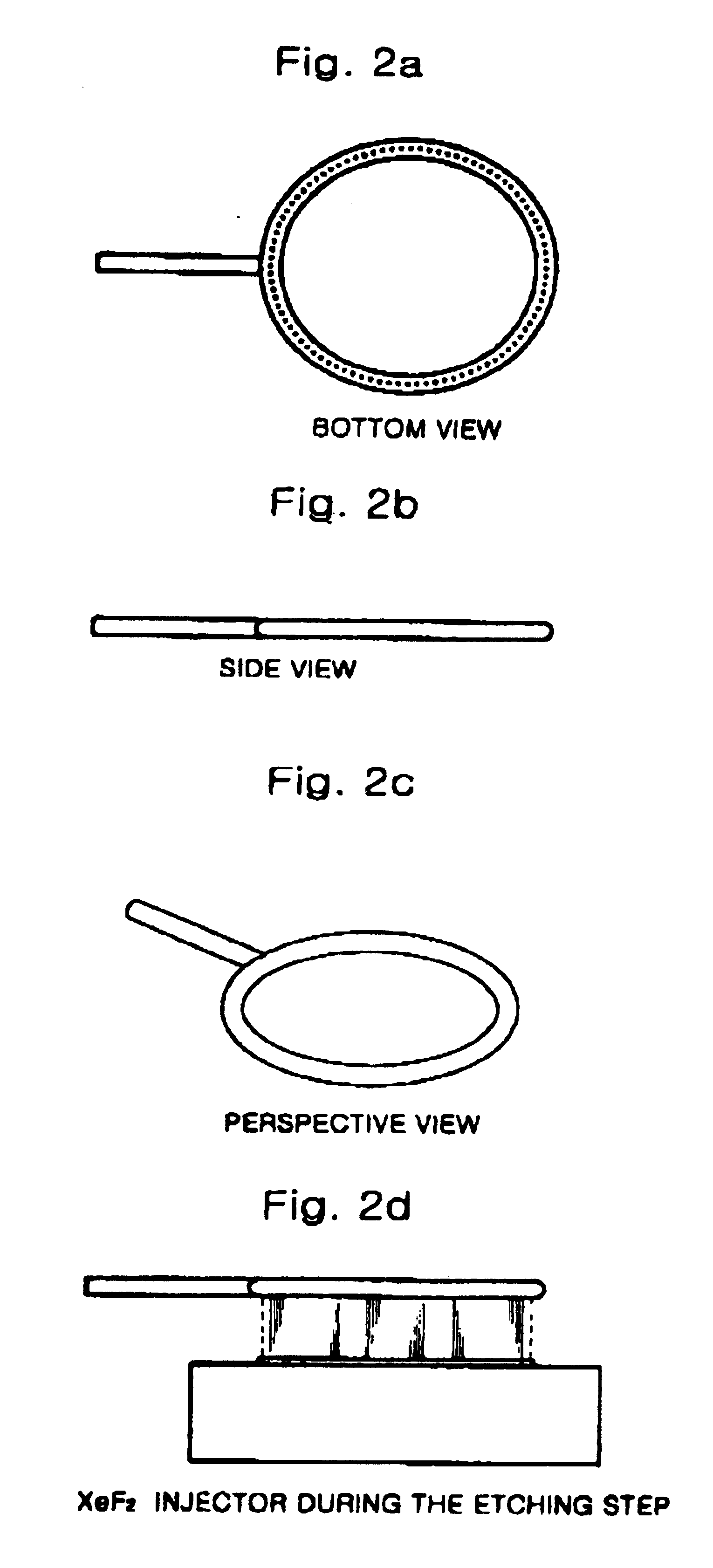
Silicon etching apparatus using XeF2
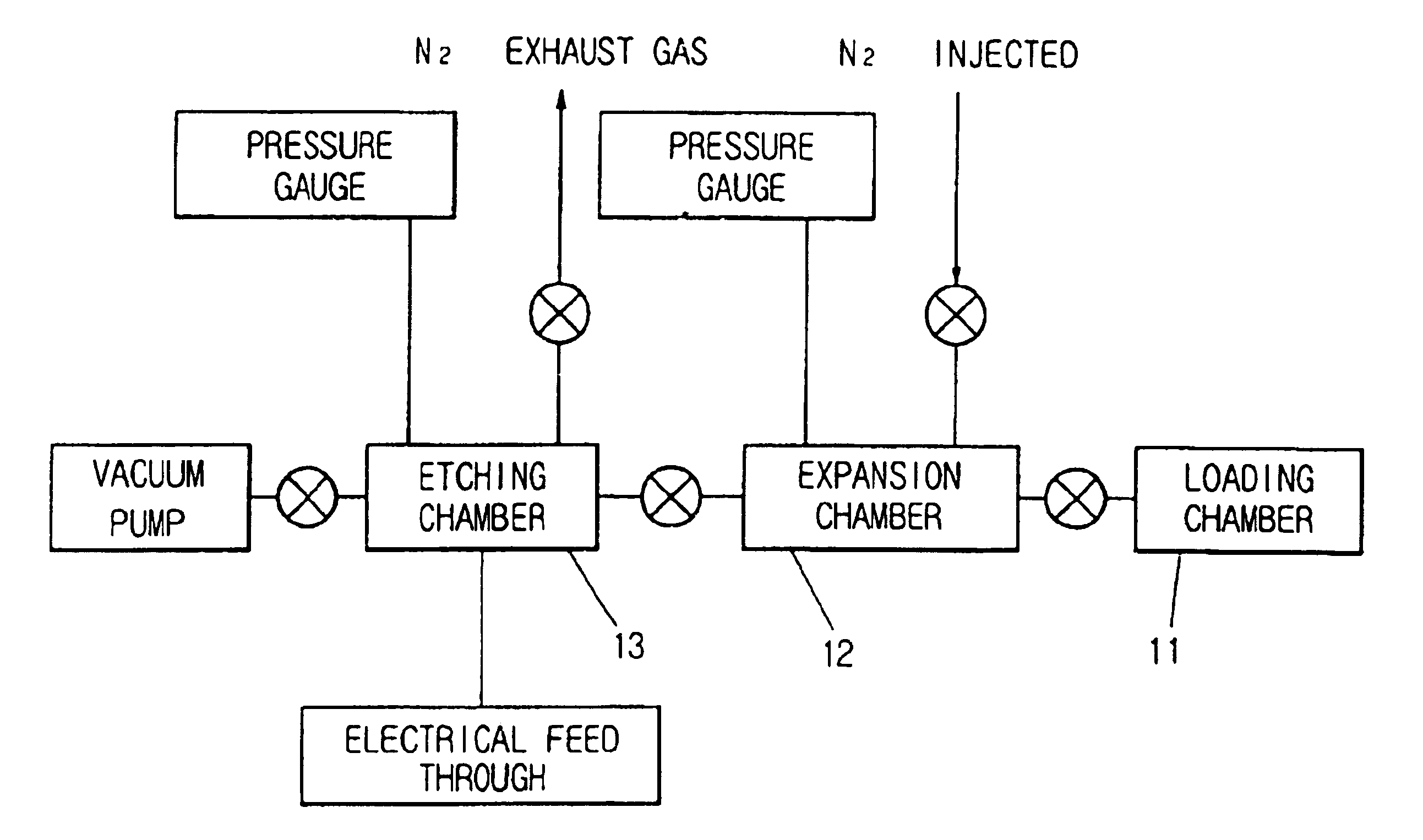
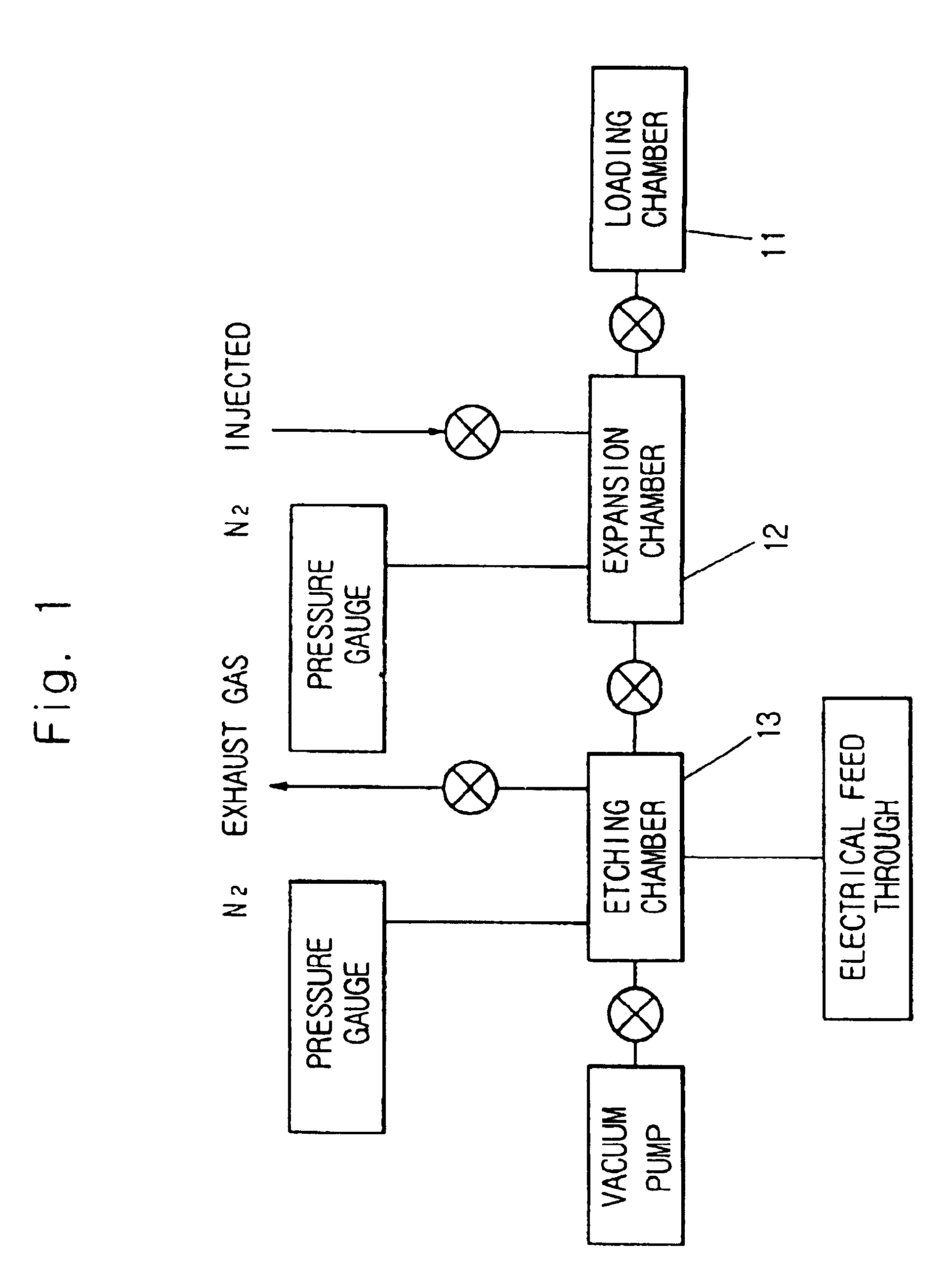
InactiveUS6736987B1Minimize damageUniform etchingVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsInternal pressureFeedback controller
The silicon etching apparatus using XeF2 includes: a basic structure composed of a loading chamber tot loading XeF2, an expansion chamber for collecting sublimated XeF2 gas, and an etching chamber for performing an etching process; and a means for injecting nitrogen prior to the etching process to eliminate air moisture in the apparatus and thus preventing the formation of HF. The silicon etching apparatus using XeF2 further includes: an injector having a predefined shape provided in the etching chamber for uniformly injecting the XeF2 gas downward on to surface of a wafer; a feedback controller for feedback controlling the internal pressure of the loading chamber in order to prevent sublimation of the residual XeF2 in the loading chamber; and a weight scale for measuring the weight of XeF2 in the loading chamber.
Owner:TECHBANK
Plasma processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20060066247A1Improved resistance characteristicsIncrease chanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDc voltagePlasma processing
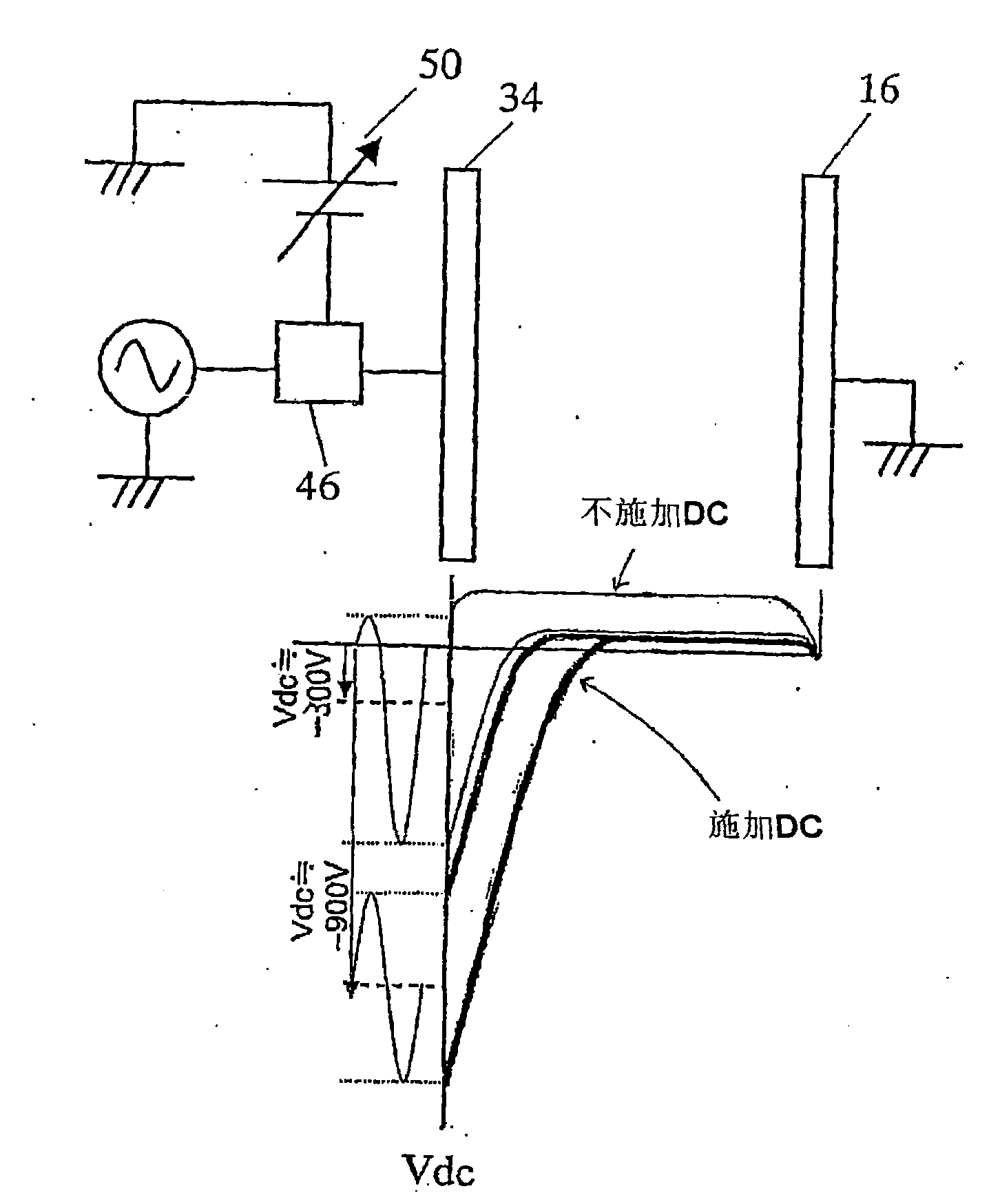
A plasma etching apparatus includes an upper electrode and a lower electrode, between which plasma of a process gas is generated to perform plasma etching on a wafer W. The apparatus further comprises a variable DC power supply to apply a DC voltage to the upper electrode, so as to cause the absolute value of a self-bias voltage on the surface thereof to be large enough to obtain a suitable sputtering effect on the surface, and to increase the plasma sheath length on the upper electrode side to generate predetermined pressed plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
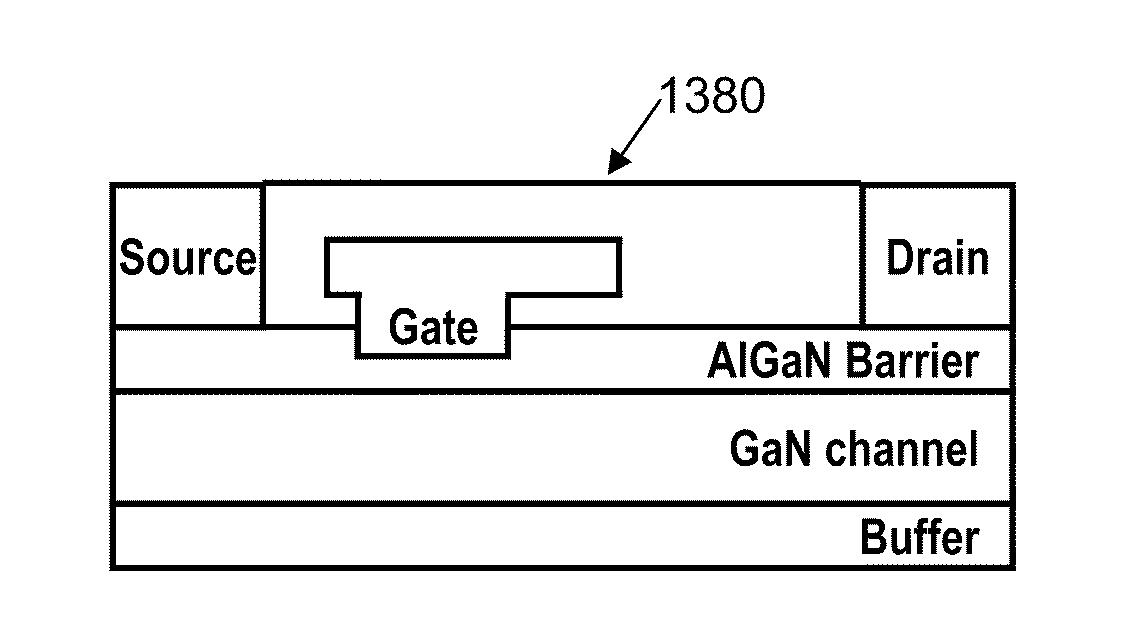
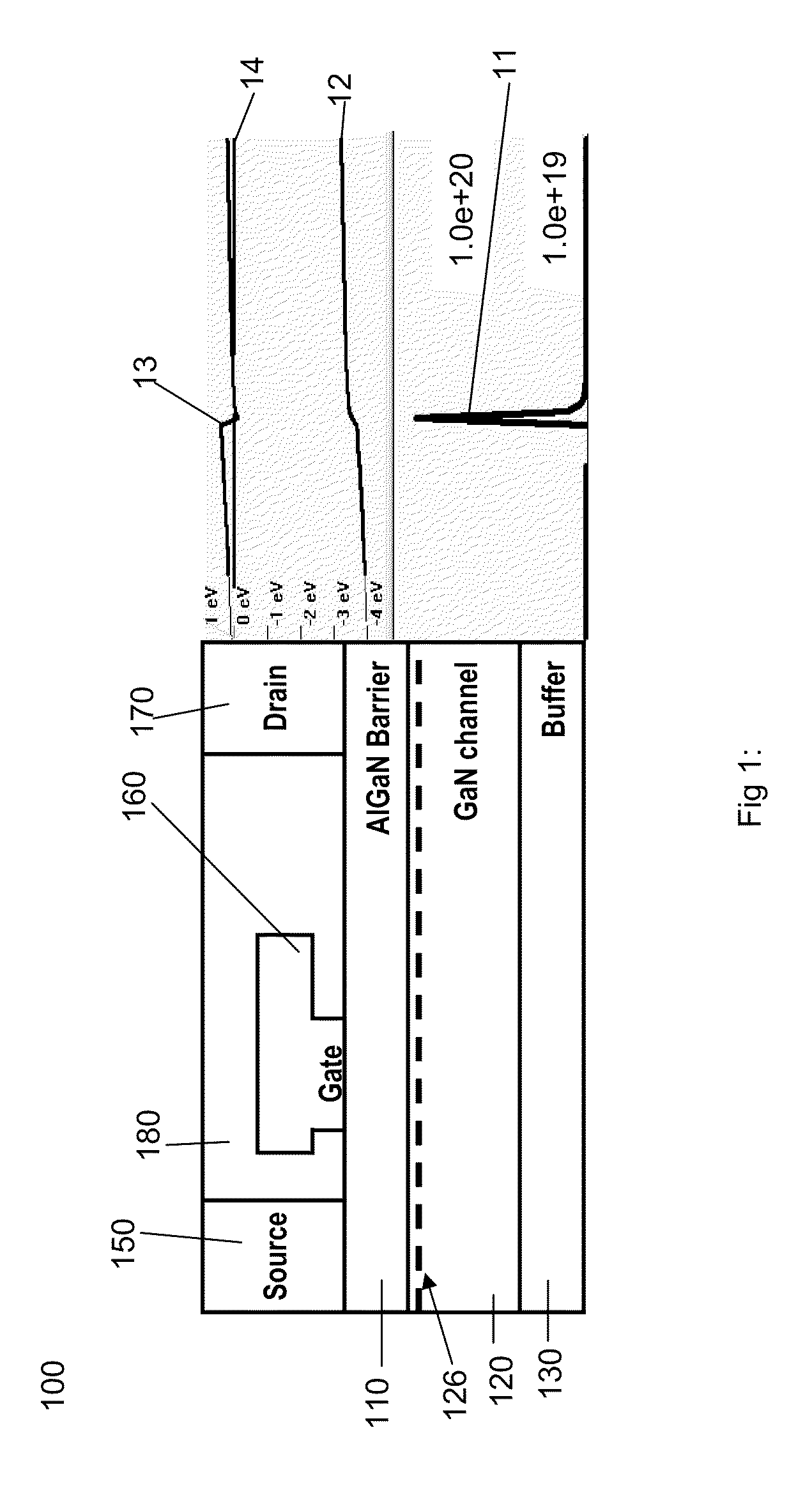
Two stage plasma etching method for enhancement mode GaN HFET
ActiveUS8124505B1Good control and uniformity of etchLess lattice damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPhysicsSelf limiting
A two stage plasma etching technique is described that allows the fabrication of an enhancement mode GaN HFET / HEMT. A gate recess area is formed in the Aluminum Gallium Nitride barrier layer of an GaN HFET / HEMT. The gate recess is formed by a two stage etching process. The first stage of the technique uses oxygen to oxidize the surface of the Aluminum Gallium Nitride barrier layer below the gate. Then the second stage uses Boron tricloride to remove the oxidized layer. The result is a self limiting etch process that uniformly thins the Aluminum Gallium Nitride layer below the HFET's gate region such that the two dimensional electron gas is not formed below the gate, thus creating an enhancement mode HFET.
Owner:HRL LAB
Integrated electrostatic inductive coupling for plasma processing
InactiveUS20050103444A1Highly effectiveLow costElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsCapacitancePlasma density
An integrated electrostatic inductively-coupled (i-ESIC) device is provided for plasma processing that may be used as a primary or secondary source for generating a plasma to prepare substrates for, and to process substrates by applying, dielectric and conductive coatings. The i-ESIC device is practical for processing advanced semiconductor devices and integrated circuits that require uniform and dense plasma. The invention may be embodied in an apparatus that contains a substrate support, typically including an electrostatic chuck, that controls ion energy by capacitively coupling RF power to the plasma and generating voltage bias on the wafer relative to the plasma potential. An integrated inductive coupling element is provided at the perimeter of the substrate support that increases plasma density at the perimeter of the wafer, compensating for the radial loss of charged particles toward chamber walls, to produce uniform plasma density above the processed wafer. An annular slotted shield protects the inductive coupling element from the plasma and provides conditions for effective inductive coupling of RF power into the plasma, such as eliminating capacitive coupling from the element to the plasma and unwanted sputtering of the element. The i-ESIC device has a capacitive coupling zone in its center where wafers are placed and an inductive coupling zone at the perimeter of the wafer coupled to a matching network and RF generator. Both zones together with plasma create a resonant circuit.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
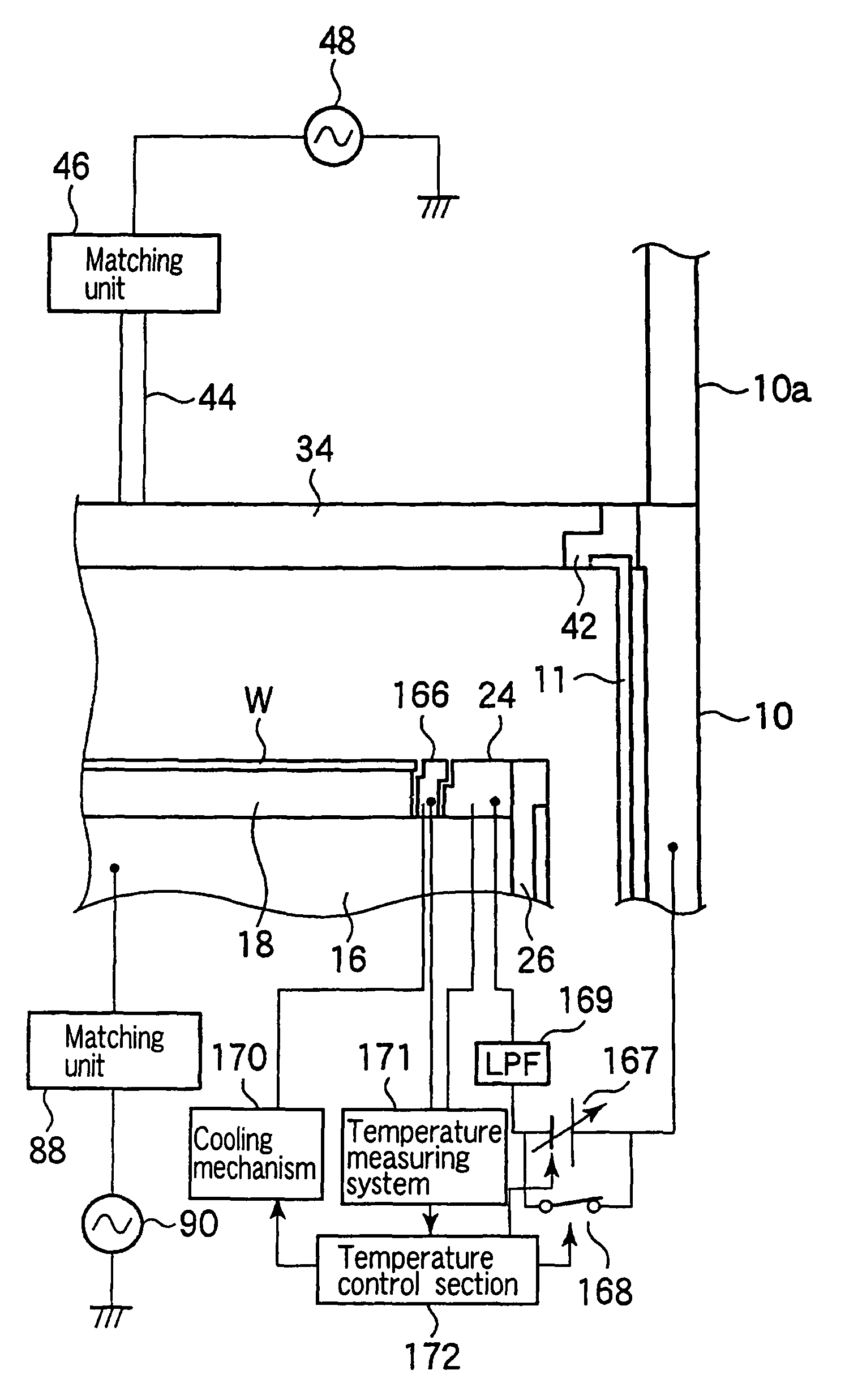
Plasma processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS7988816B2Improved resistance characteristicsIncrease chanceElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsNegative biasDc voltage
A plasma etching apparatus includes an upper electrode and a lower electrode, between which plasma of a process gas is generated to perform plasma etching on a wafer W. The apparatus further comprises a cooling ring disposed around the wafer, a correction ring disposed around the cooling ring, and a variable DC power supply directly connected to the correction ring, the DC voltage being preset to provide the correction ring with a negative bias, relative to ground potential, for attracting ions in the plasma and to increase temperature of the correction ring to compensate for a decrease in temperature of a space near the edge of the target substrate due to the cooling ring.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma processing apparatus and method
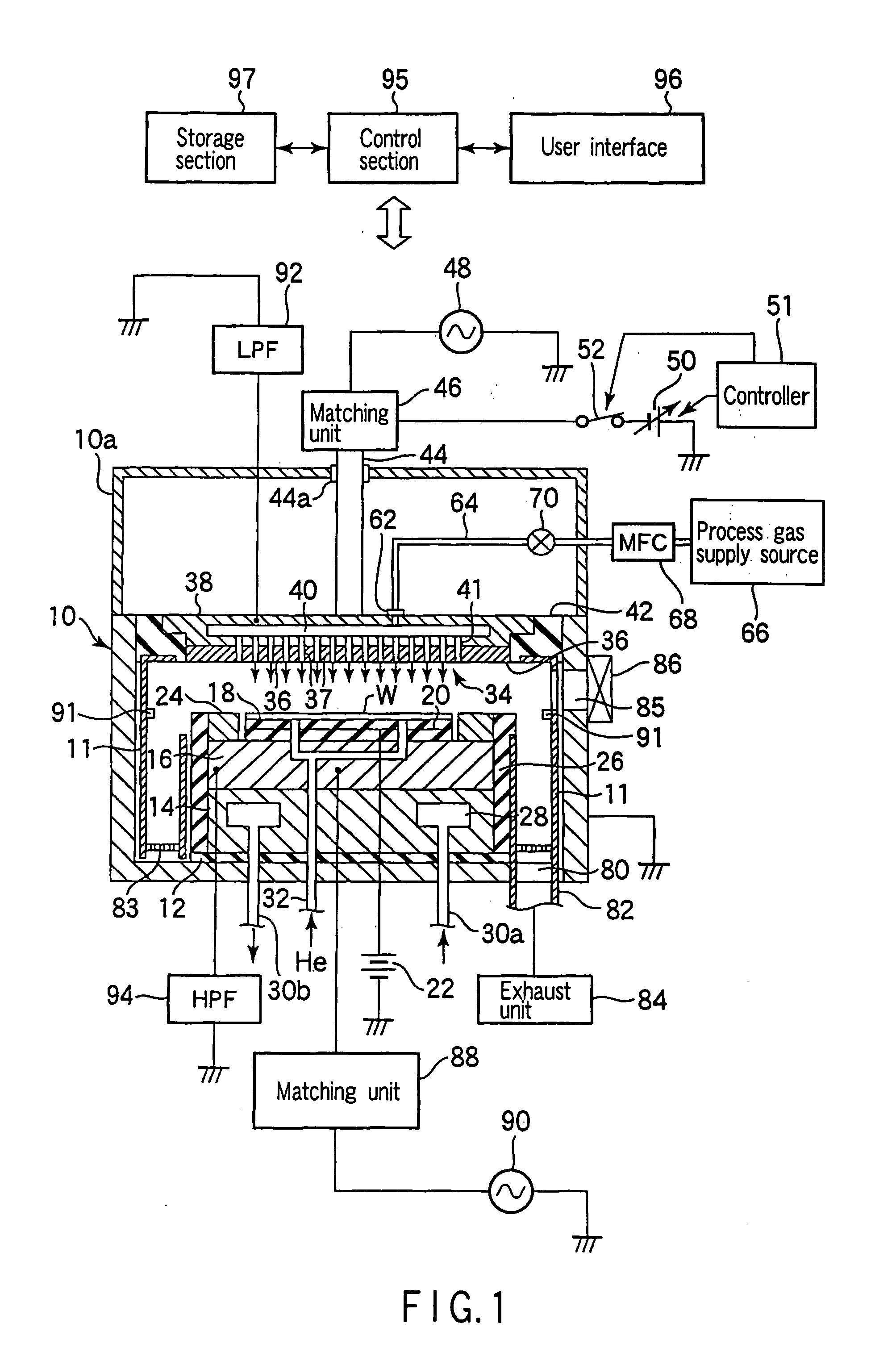
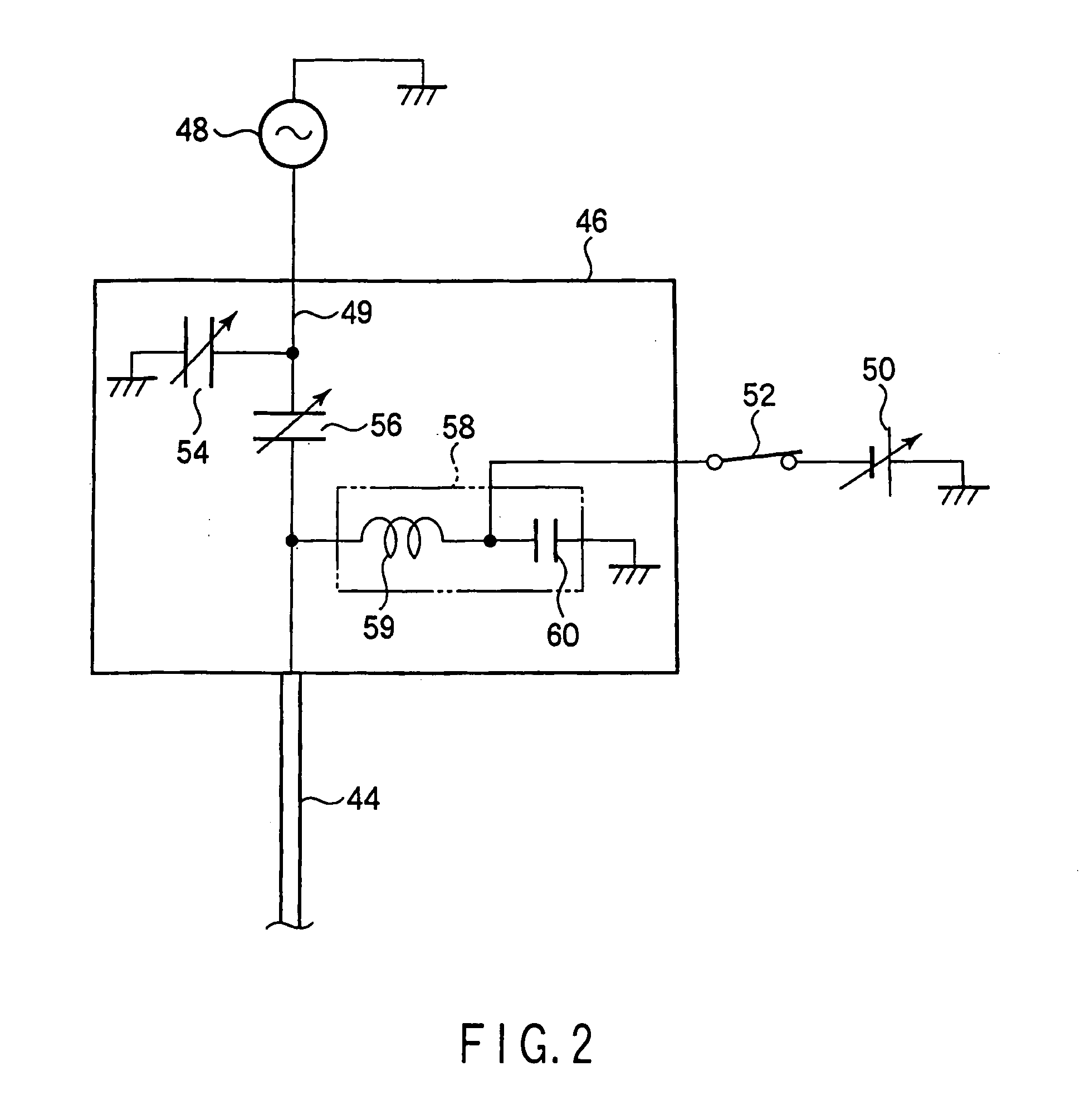
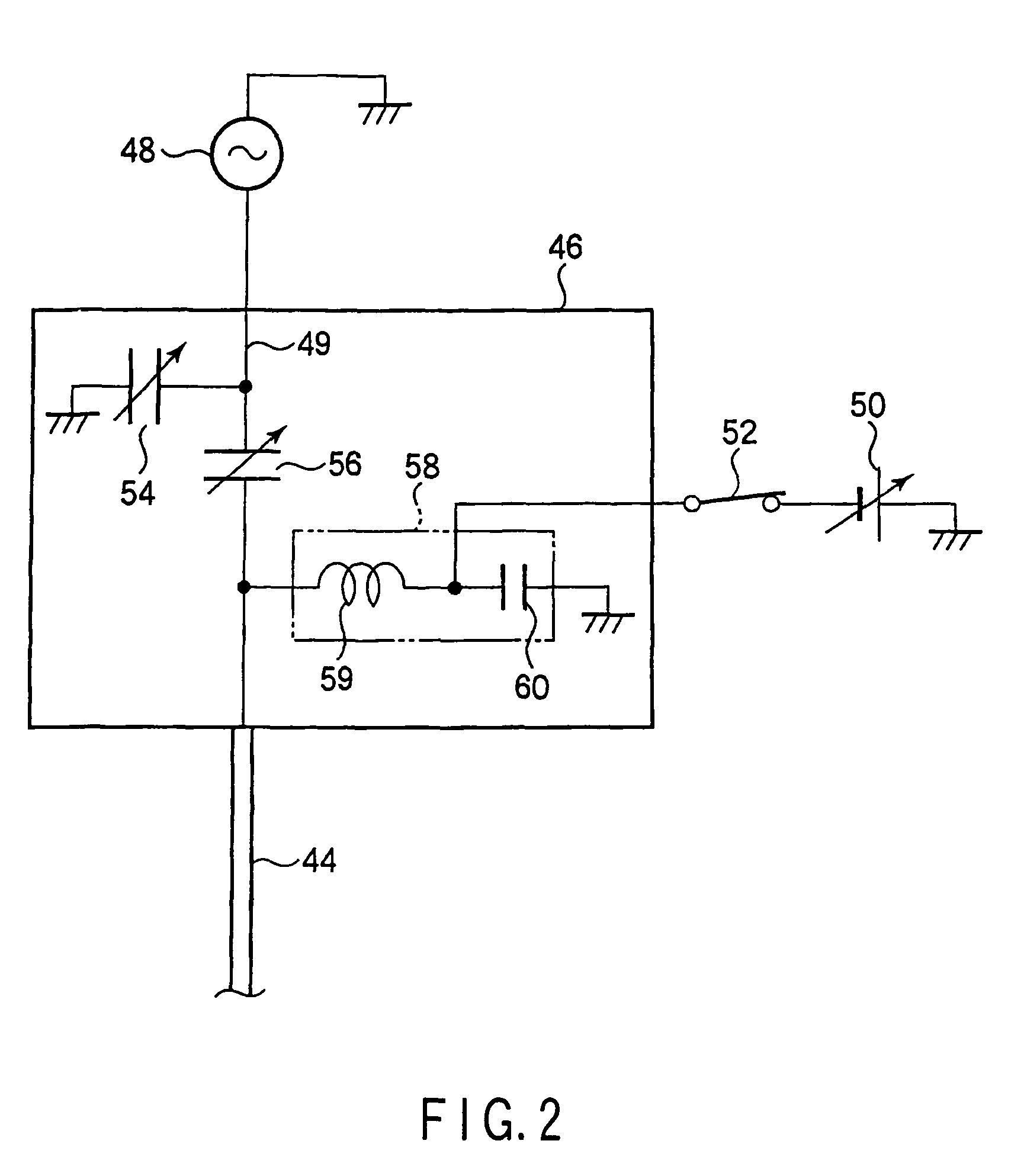
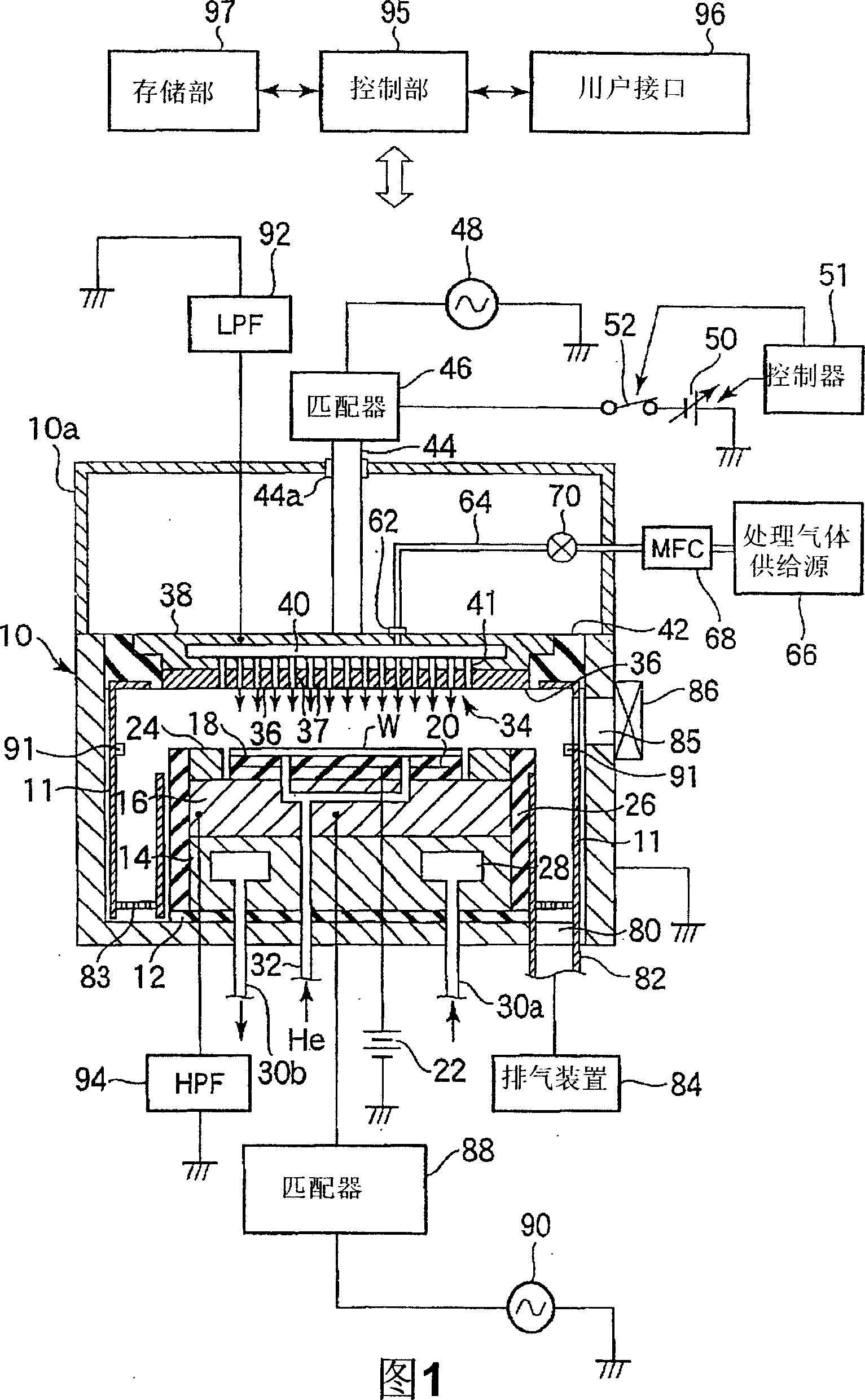
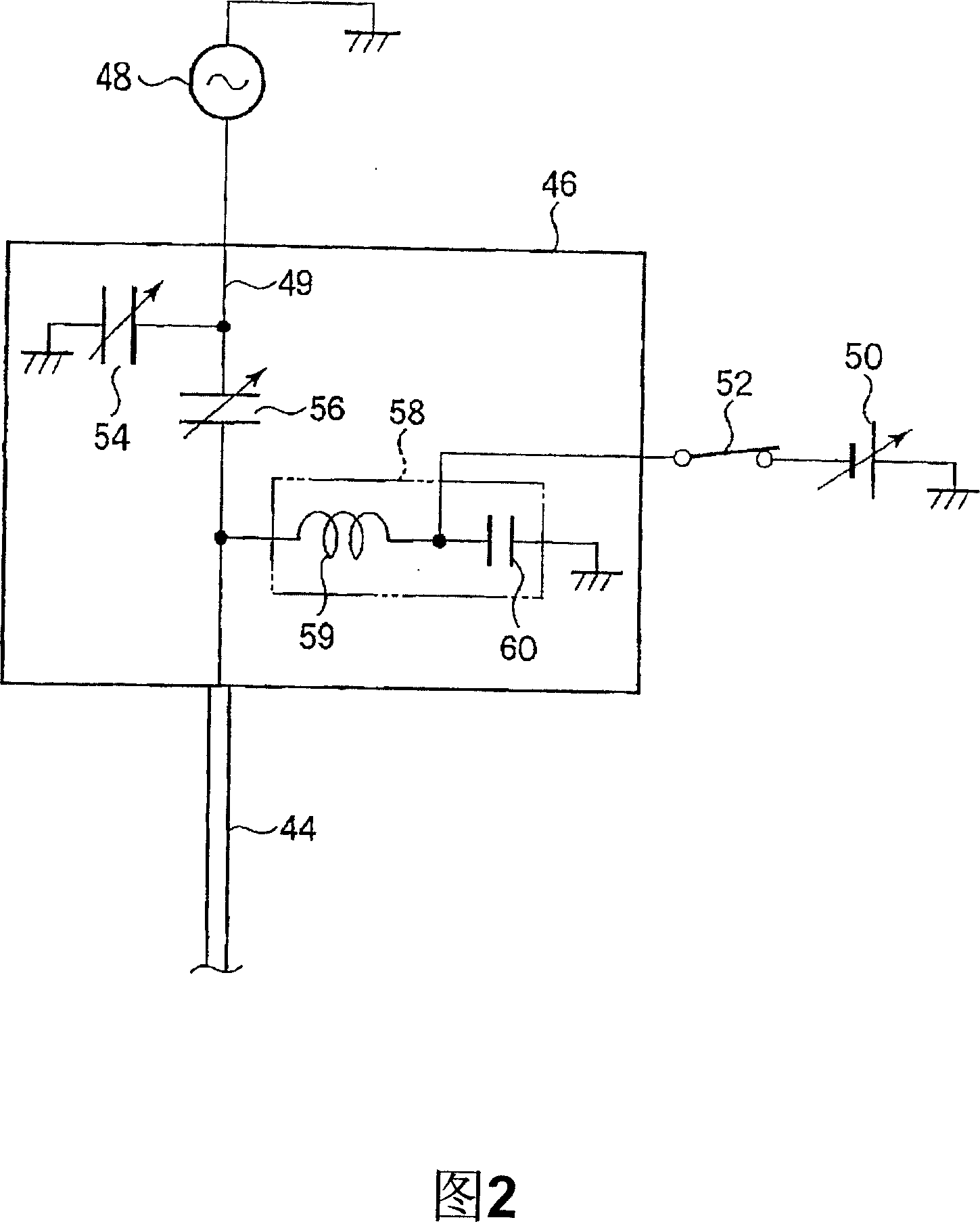
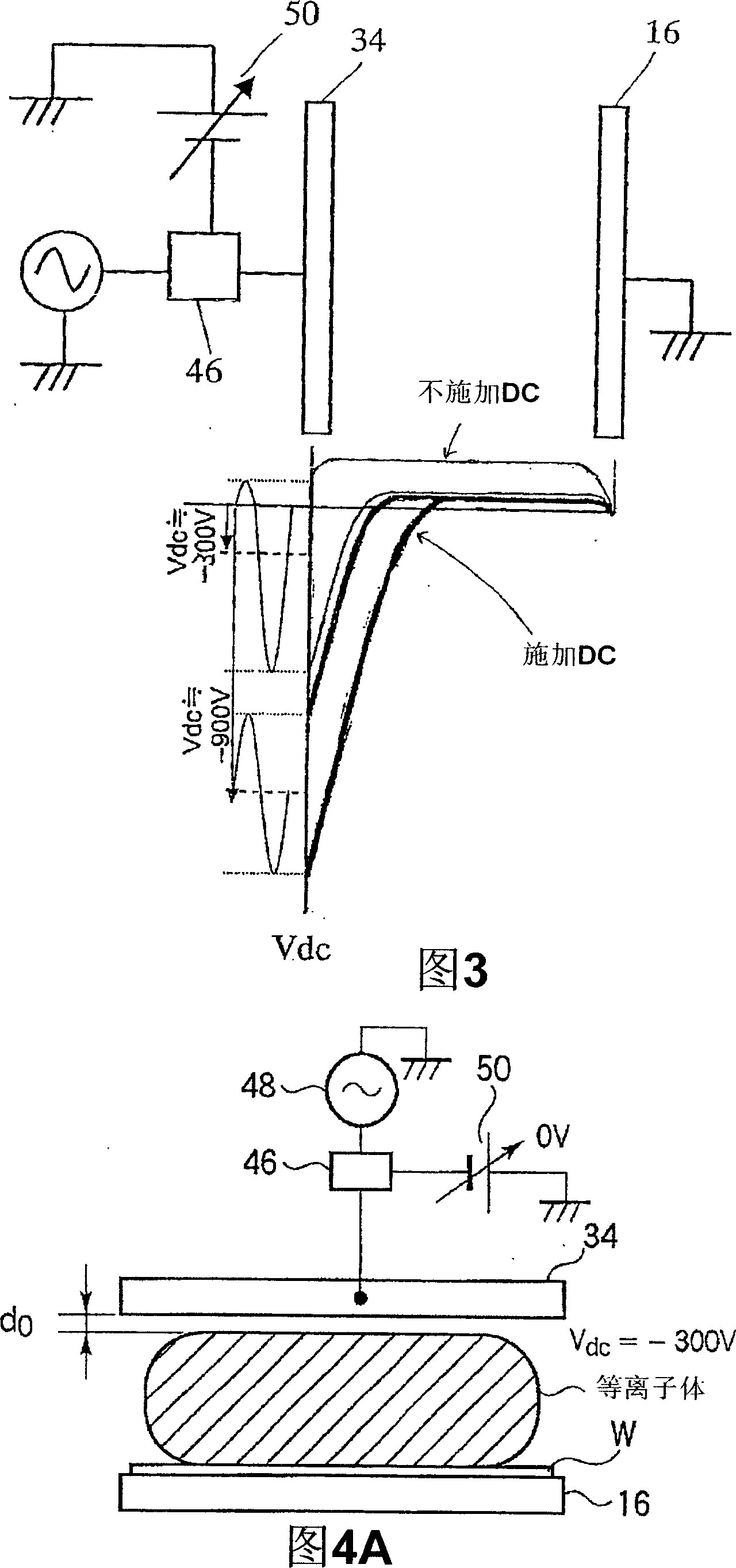
ActiveCN1973363AEliminate attachmentEtching high speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMiniaturizationDc voltage
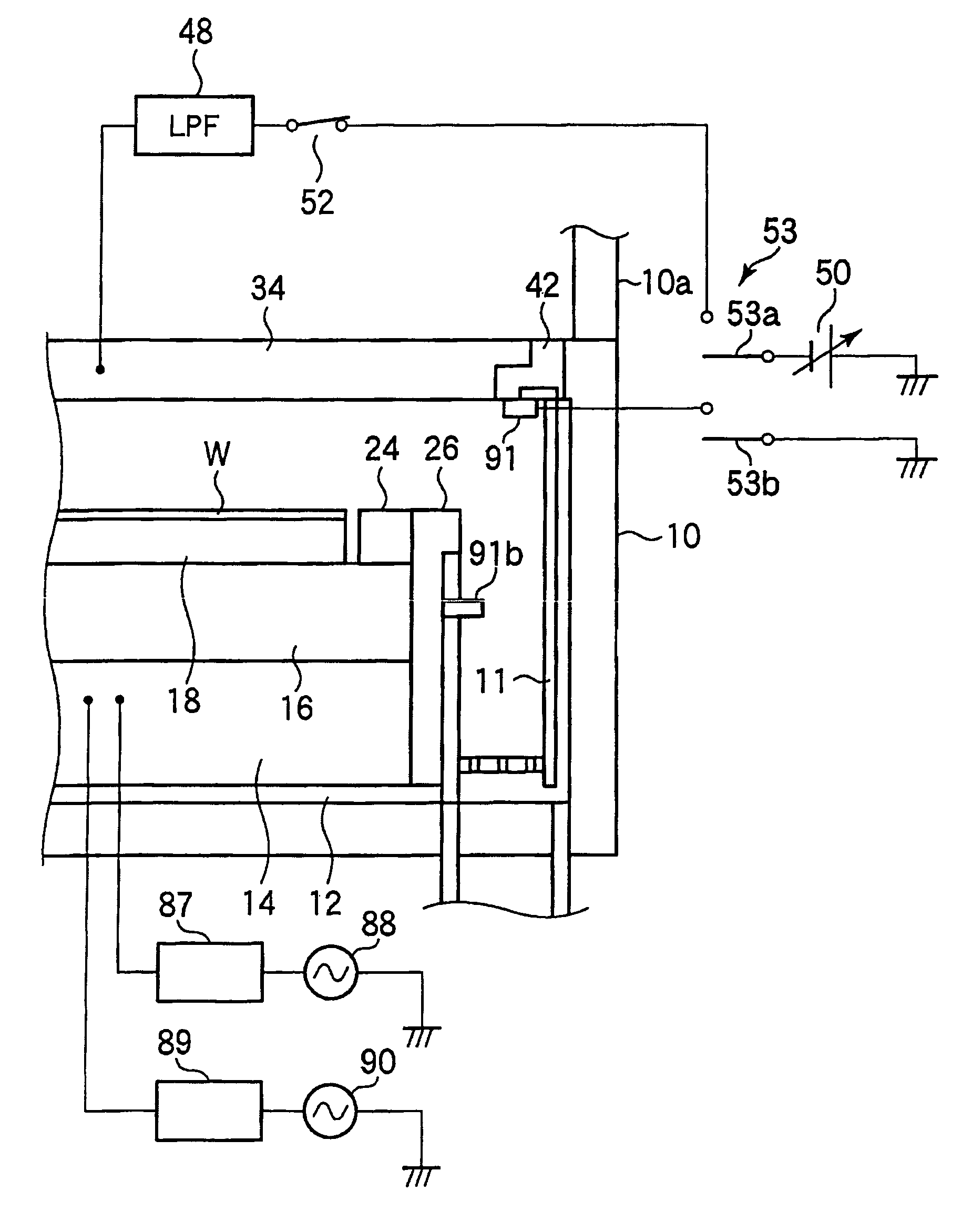
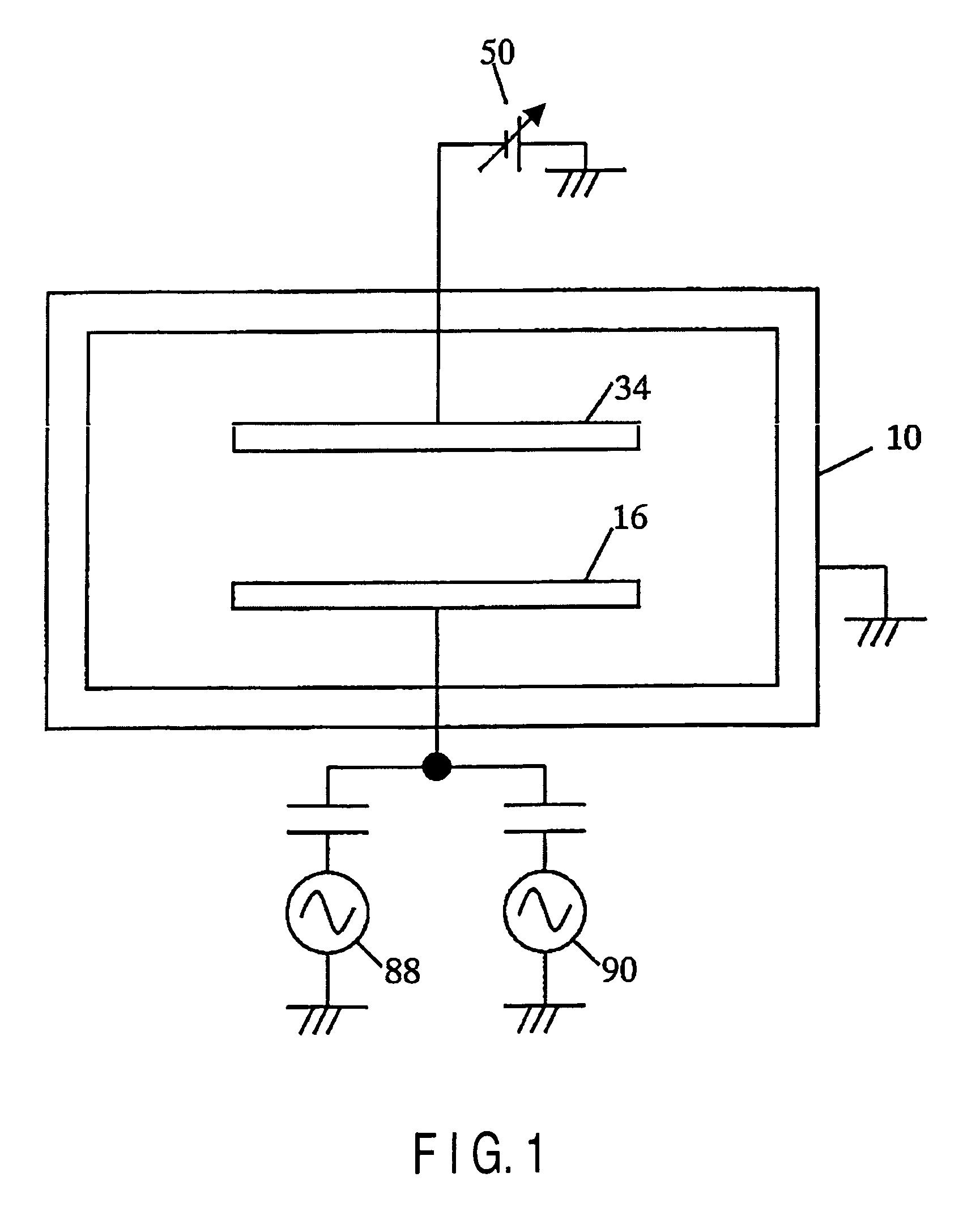
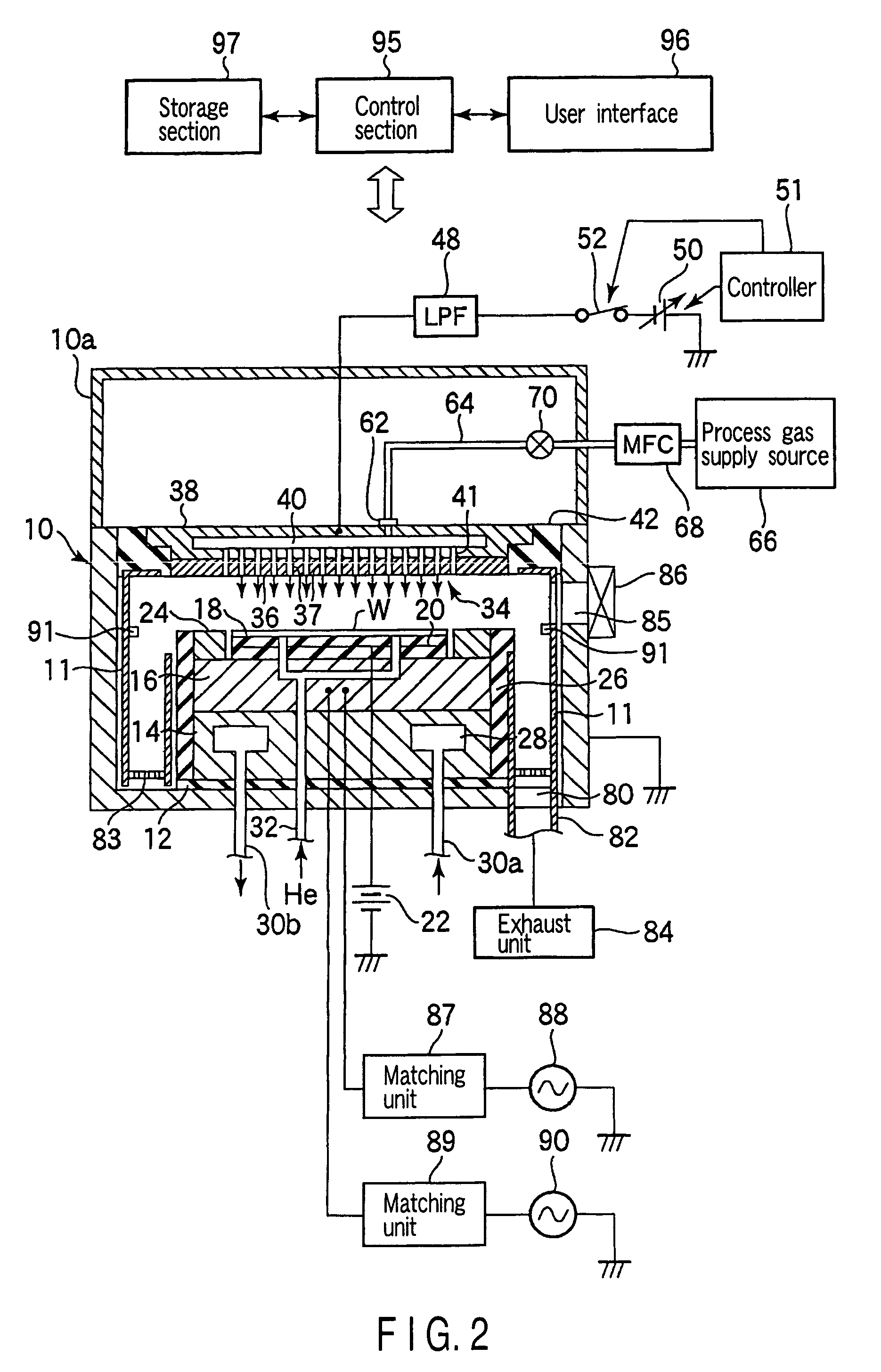
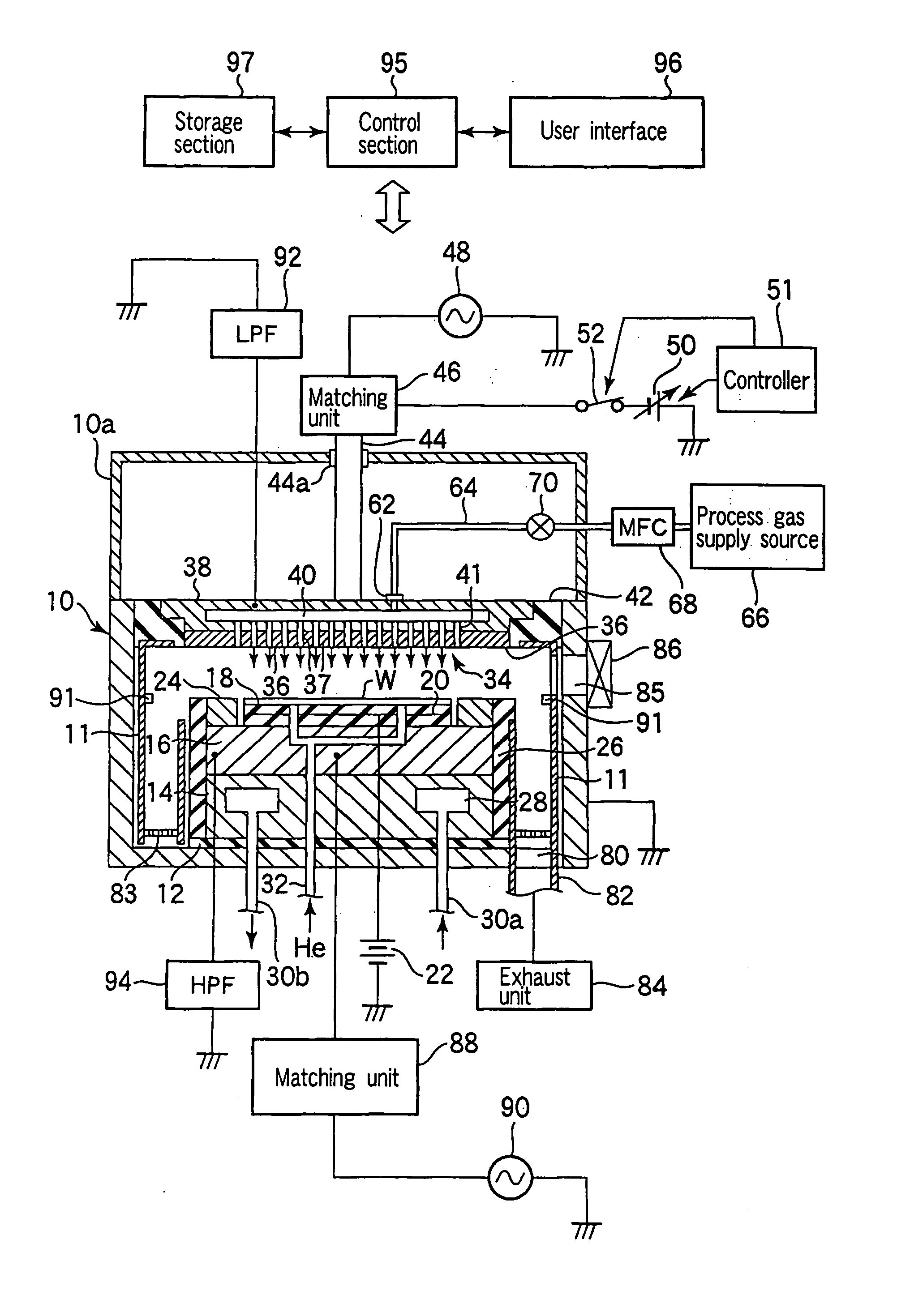
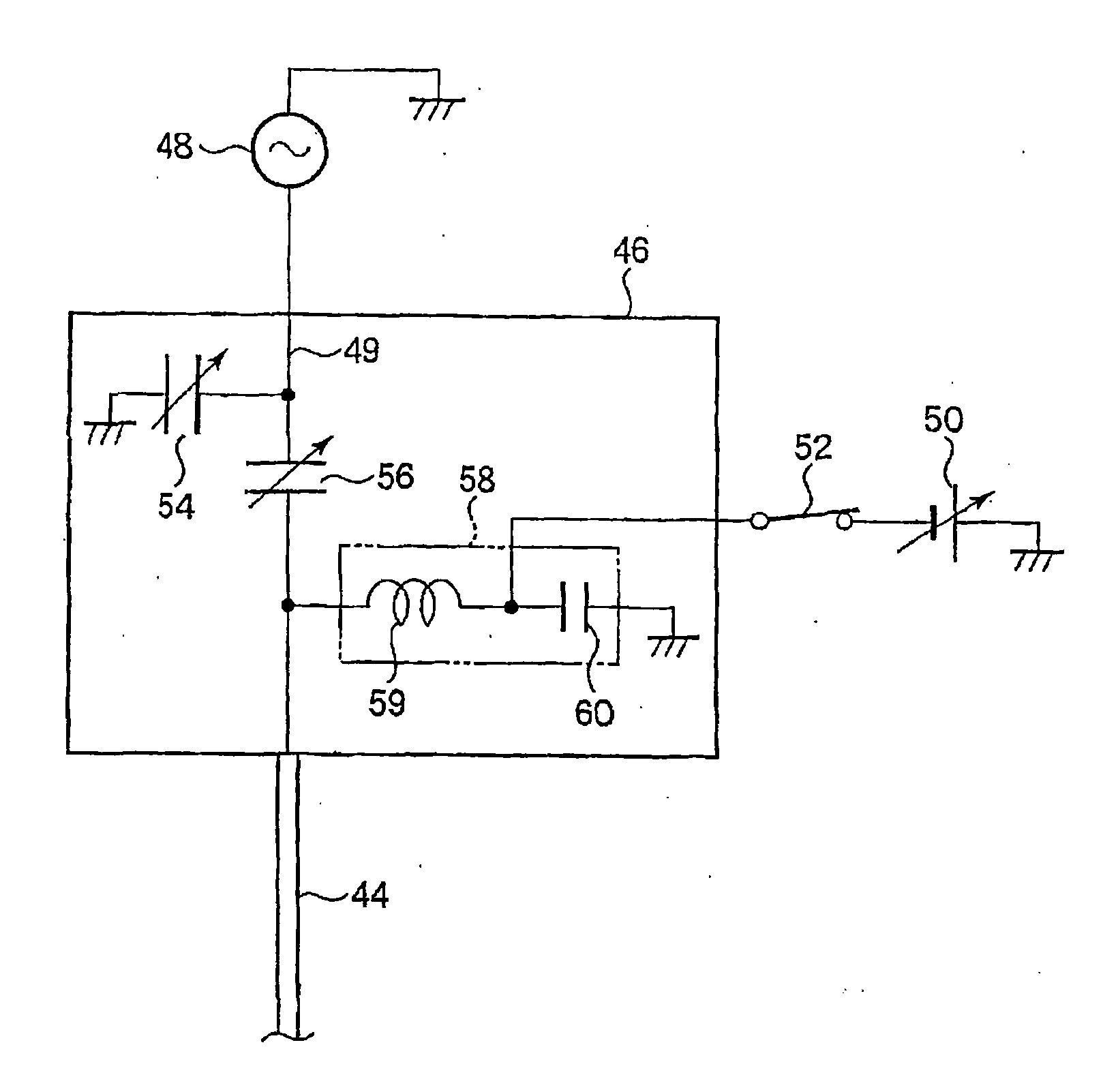
There is provided a plasma etching device for generating plasma as a processing gas between an upper electrode (34) and a lower electrode (16) and subjecting a wafer (W) to plasma etching. The upper electrode (34) includes a variable DC power source (50) for applying DC voltage so that the absolute value of the self bias voltage Vdc on the surface of the upper electrode (34) becomes large enough to obtain an appropriate sputter effect to the surface and the thickness of the plasma sheath on the upper electrode (34) becomes thick enough to form a desired miniaturization plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20110272097A1Improved resistance characteristicsIncrease chanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNegative biasDc voltage
A plasma etching apparatus includes an upper electrode and a lower electrode, between which plasma of a process gas is generated to perform plasma etching on a wafer W. The apparatus further comprises a cooling ring disposed around the wafer, a correction ring disposed around the cooling ring, and a variable DC power supply directly connected to the correction ring, the DC voltage being preset to provide the correction ring with a negative bias, relative to ground potential, for attracting ions in the plasma and to increase temperature of the correction ring to compensate for a decrease in temperature of a space near the edge of the target substrate due to the cooling ring.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Laser marking of raw aluminum anode foil to induce uniform patterning etching
InactiveUS7452473B1Improve distributionHigh strengthElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic capacitorsCapacitanceAluminum anode
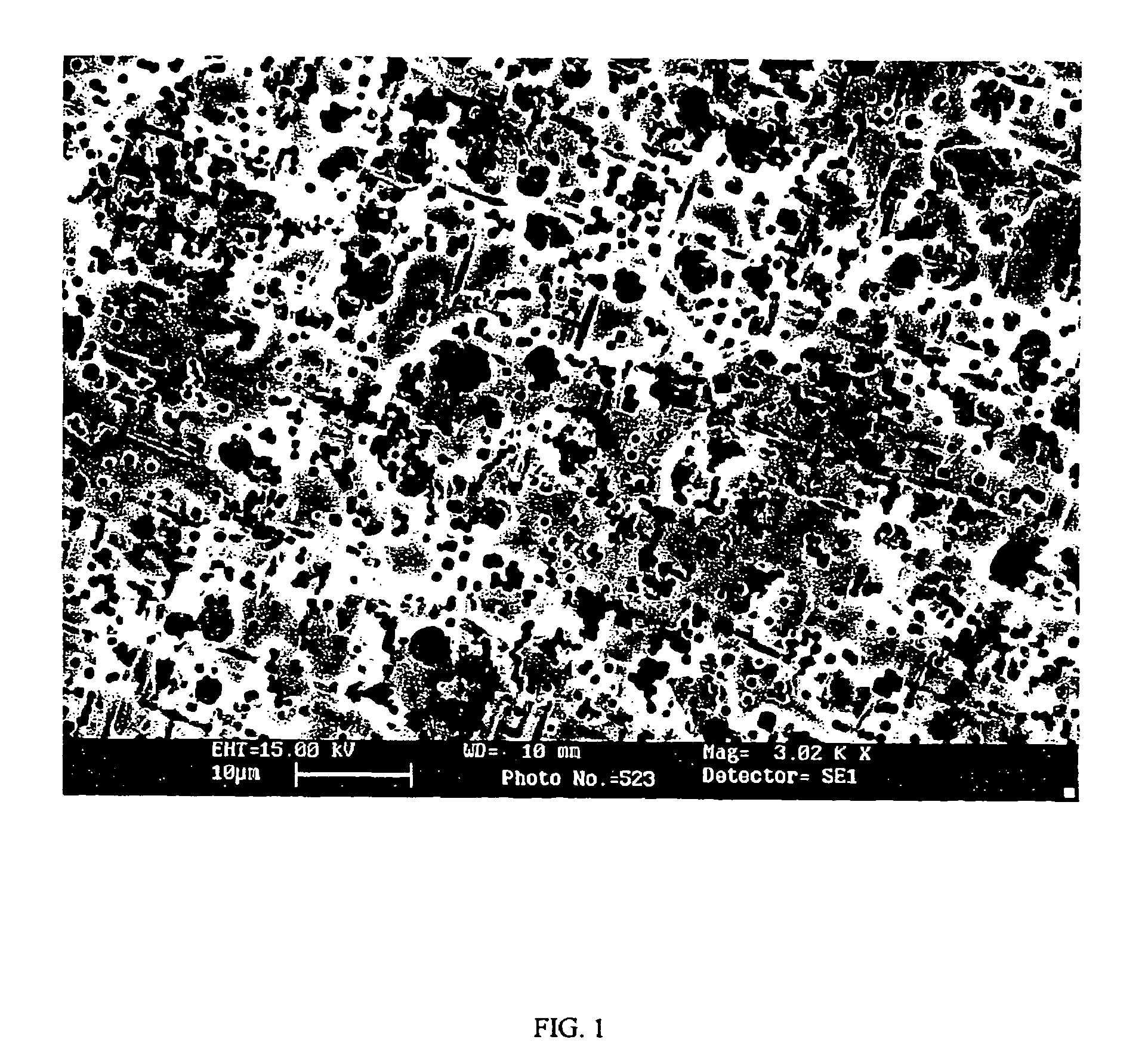
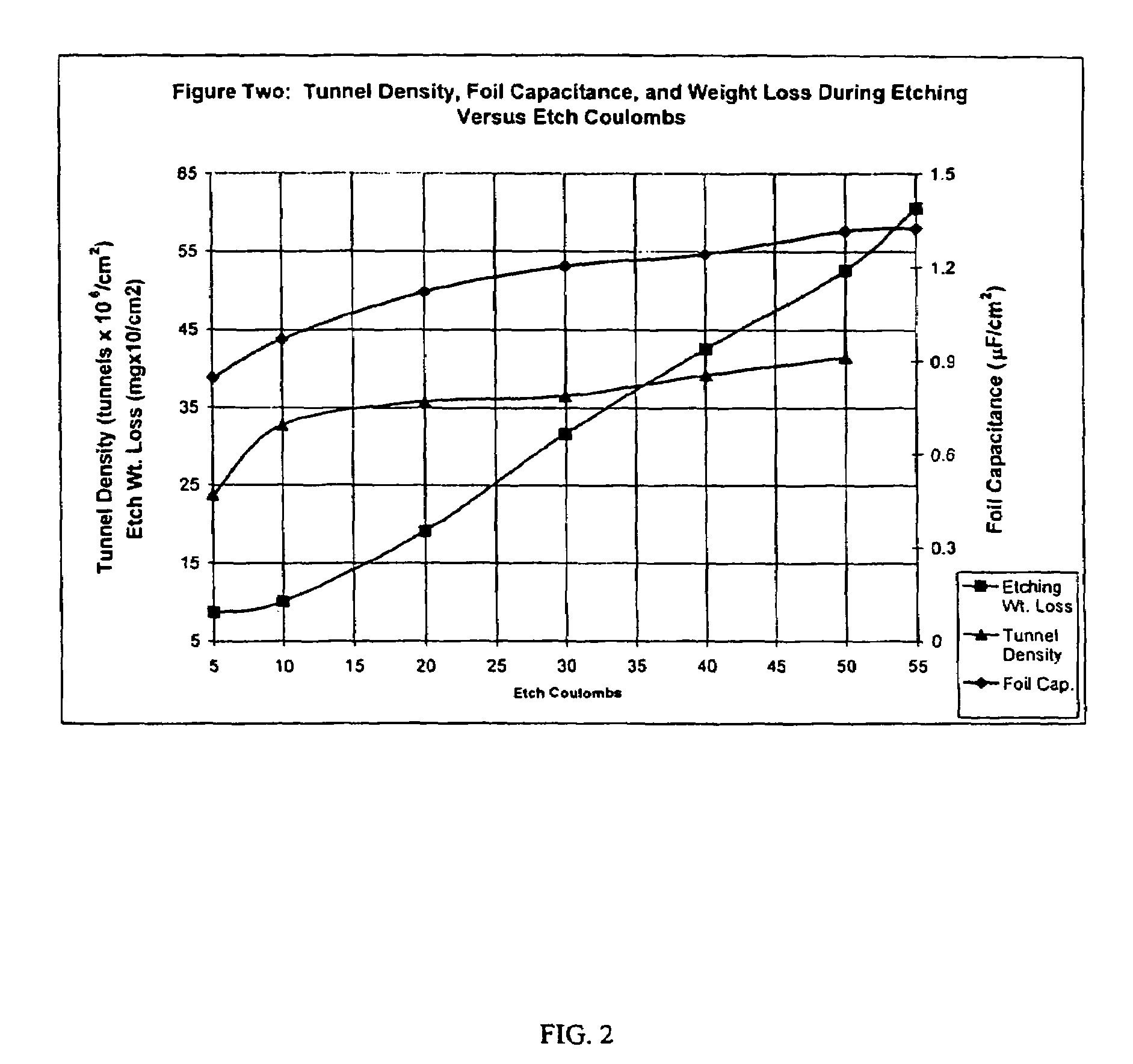
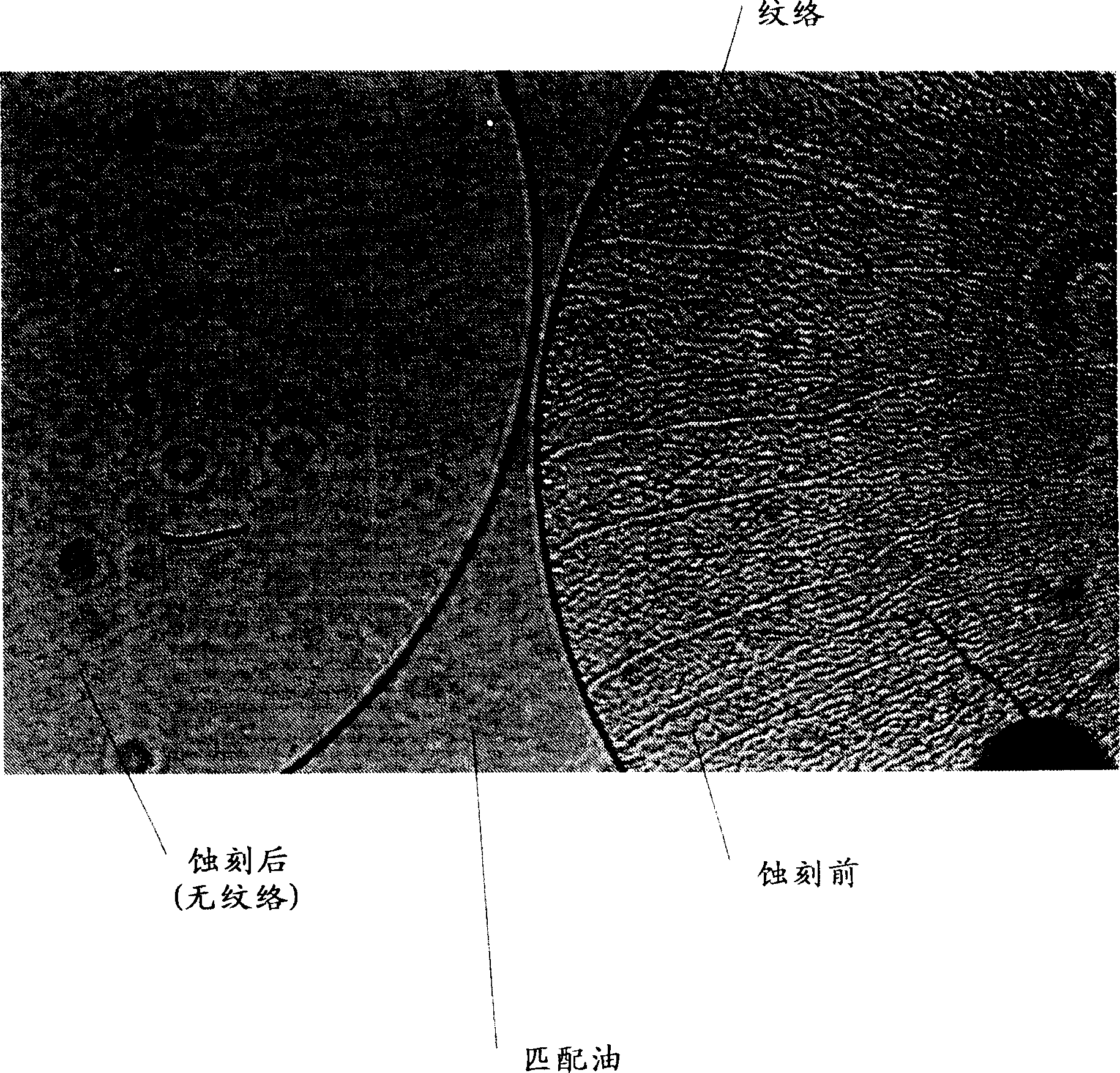
A method of producing a highly etched electrode for a capacitor from a foil is disclosed. The method comprises first applying a laser beam to the foil to form a plurality of marks on the foil surface and then etching the foil. Preferably, the laser marks facilitate etching of foil surface in areas near the marks and retard etching of foil surface inside the marks. After etching, the foil is further processed in a combination of optional steps such as forming and finishing steps. The laser marking of the foil allows for positional control of tunnel initiation, such that tunnel initiation density and the location of tunnel initiation is controlled. By controlling the position of tunnel initiation, foils are etched more uniformly and have optimum tunnel distributions, thus allows for the production of highly etched foils that maintain high strength and have high capacitance. The present invention further includes an electrolytic capacitor comprising etched aluminum anode foils, which have been prepared using the methods of the present invention.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Process for the production of precision press-molding preform and process for the production of optical element
InactiveCN1827541AIncrease production capacityImprove qualityGlass pressing apparatusLensSurface layerOptical glass
A process for producing a precision press-molding preform having a predetermined weight from a molten glass, wherein the molten glass is shaped into a glass gob and the above glass gob is etched to remove a surface layer of the glass gob to produce the precision press-molding preform formed of an optical glass having said weight, and further wherein said surface layer has a thickness of 0.5 mum or more.
Owner:HOYA CORP
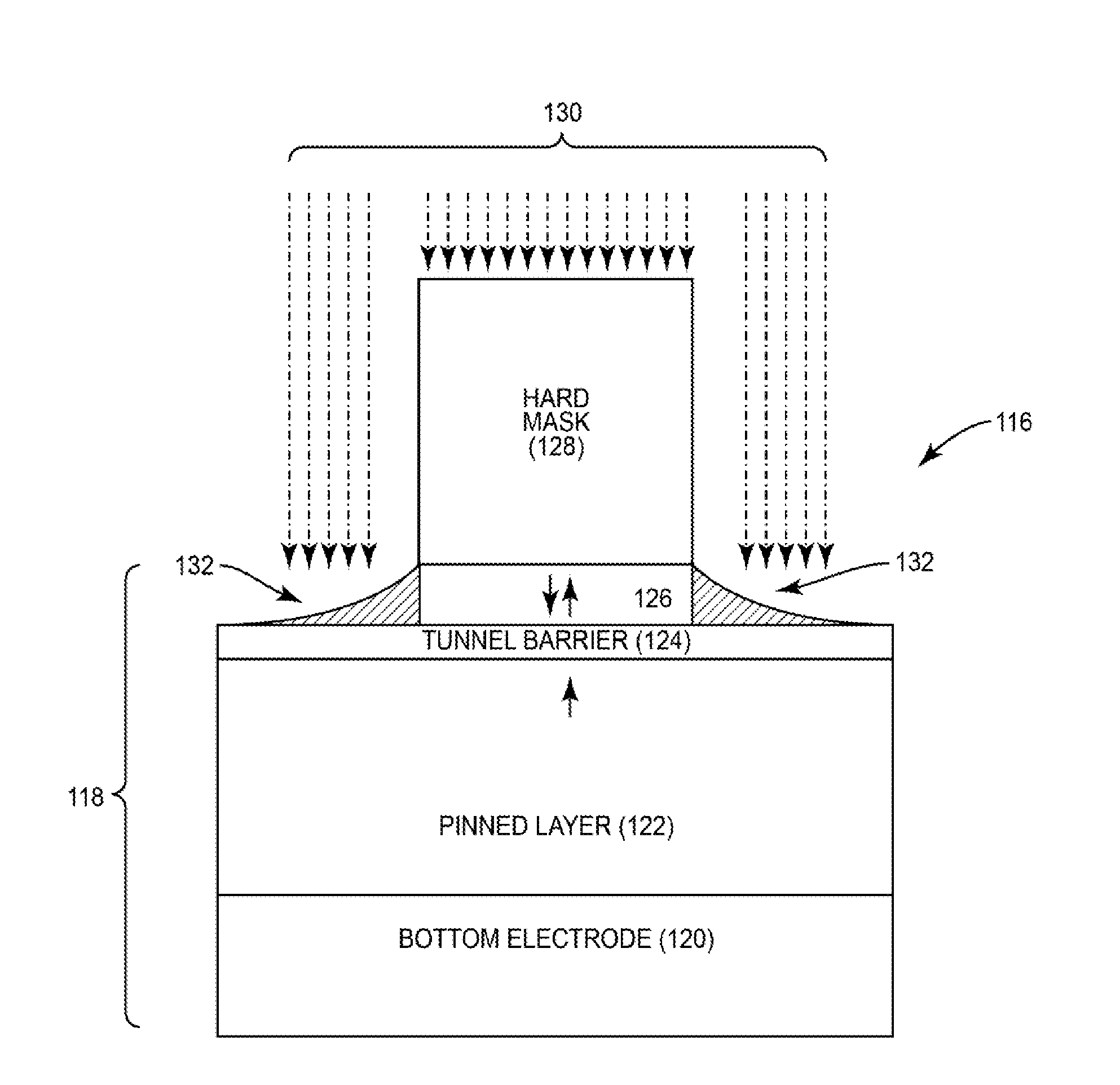
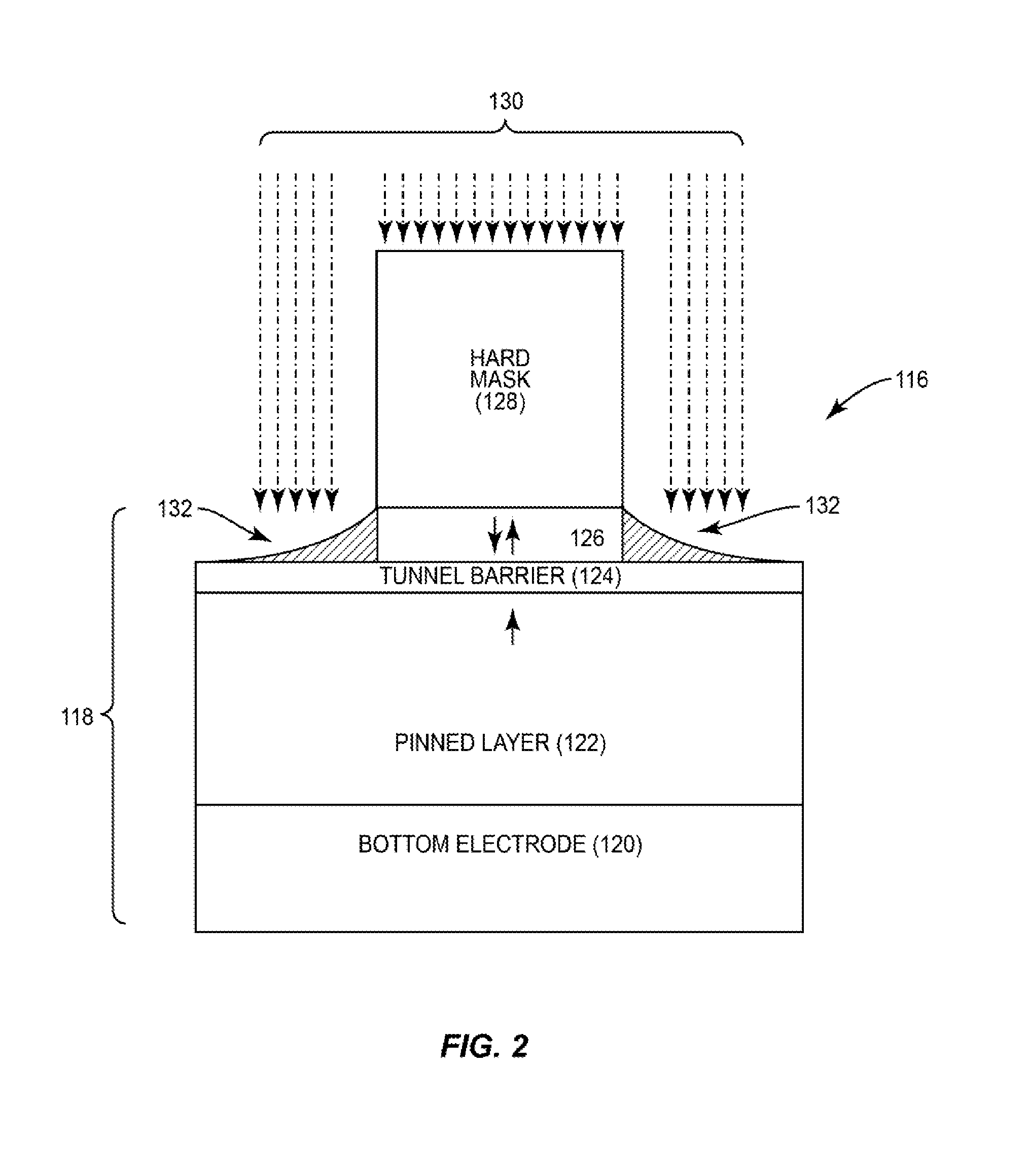
Shadow-effect compensated fabrication of magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) elements
InactiveUS20170047510A1Small sizeIncreasing write current operational marginMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesAngle of incidenceShadow effect
Shadow-effect compensated fabrication of magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) semiconductor elements is disclosed. Providing shadow-effect compensated fabrication of MTJ elements can provide reduced free layer sizing for enhanced MTJ operational margin. In certain aspects, to reduce size of a free layer during fabrication of an MTJ to provide enhanced write and retention symmetry, ion beam etching (IBE) fabrication process is employed to fabricate a free layer smaller than the pinned layer. To avoid asymmetrical footing being fabricated in free layer due to shadow-effect of neighboring MTJs, an ion beam directed at the MTJ is shadow-effect compensated. The angle of incidence of the ion beam directed at the MTJ is varied as the MTJ is rotated to be less steep when another MTJ is in directional line of the ion beam and the MTJ being fabricated. Thus, the free layer is etched more uniformly in the MTJ while avoiding increased etching damage.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
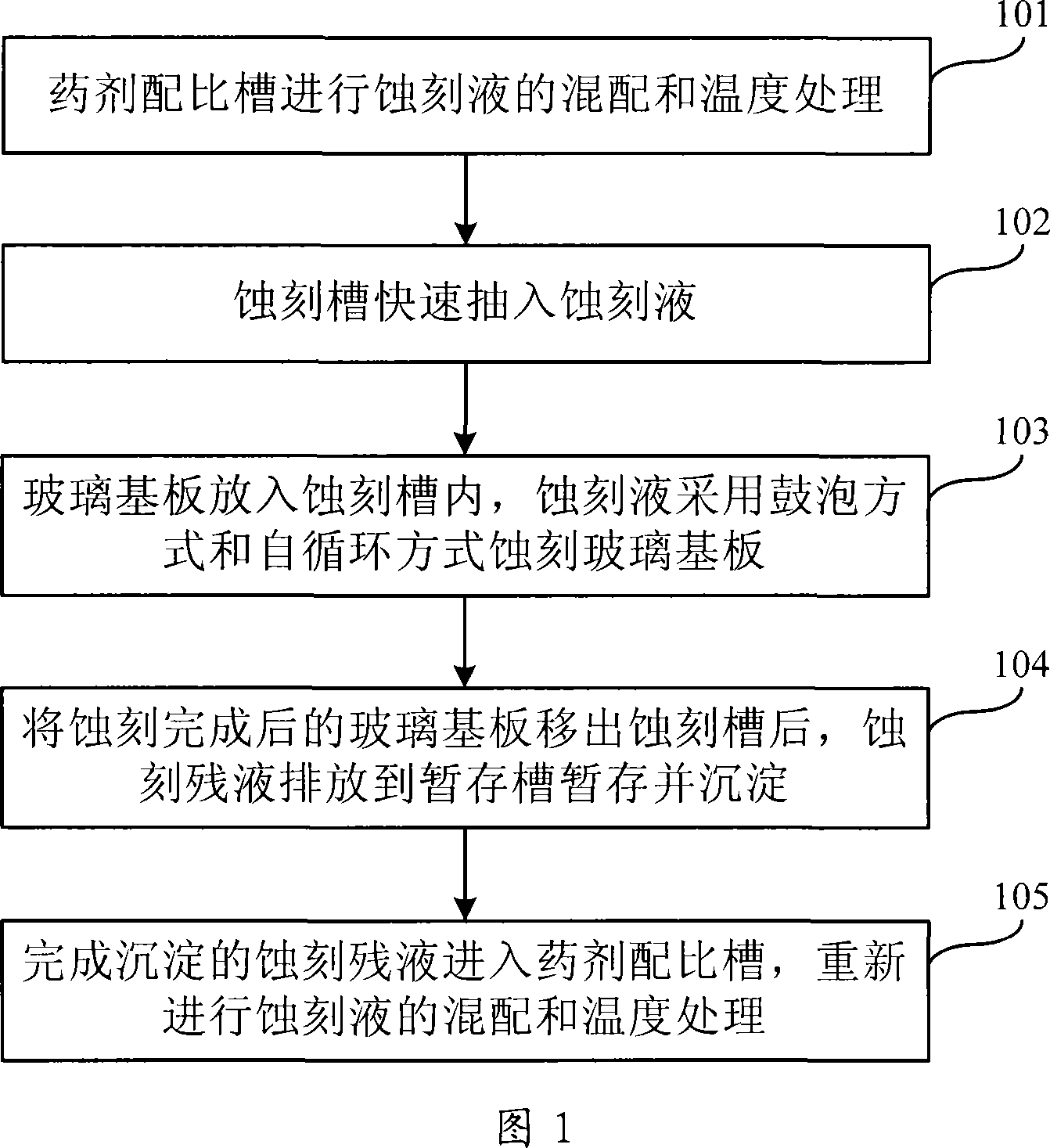
Attenuation method and device for flat glass substrate
ActiveCN101234853AUniform etchingTo achieve the purpose of mass productionFlat glassUltrasound attenuation
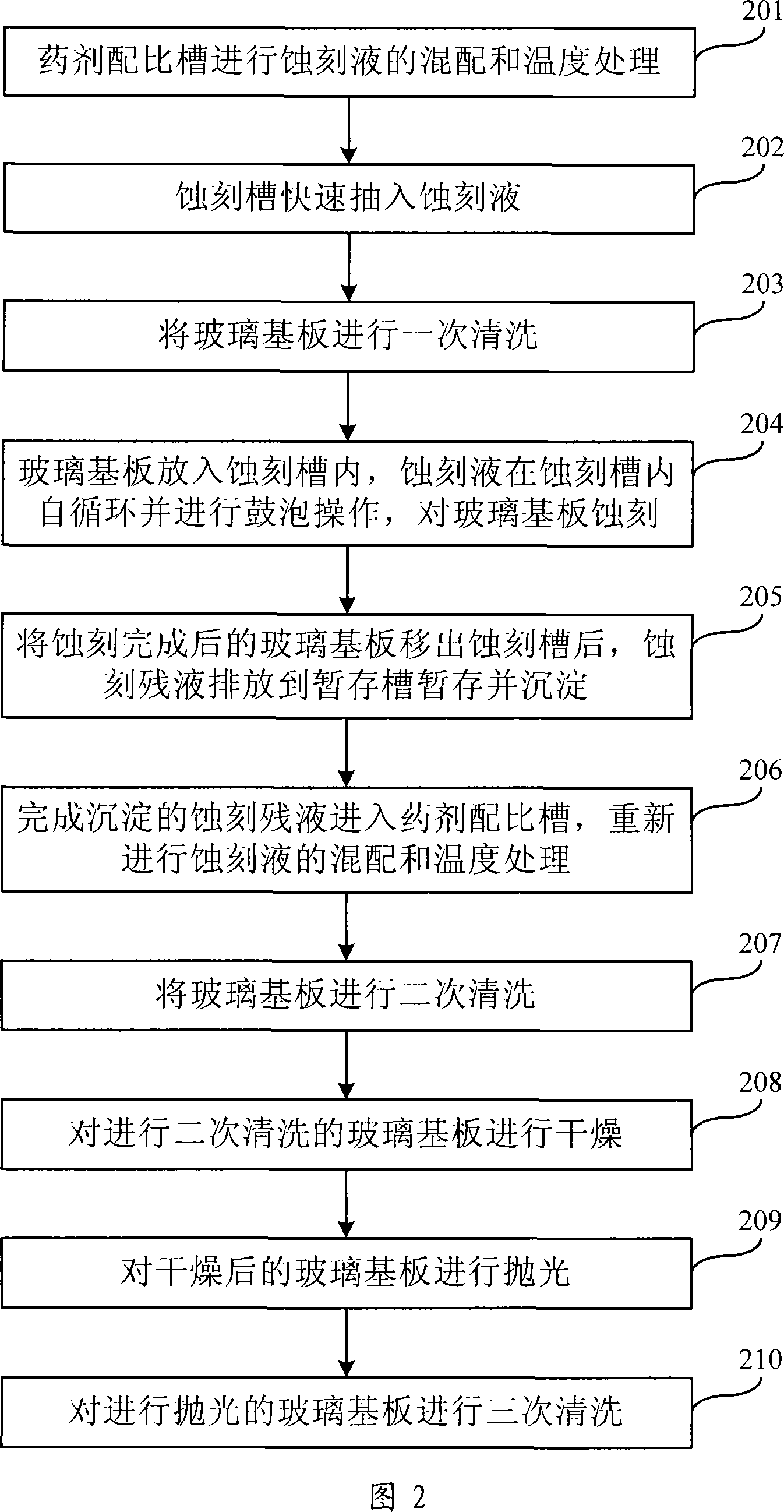
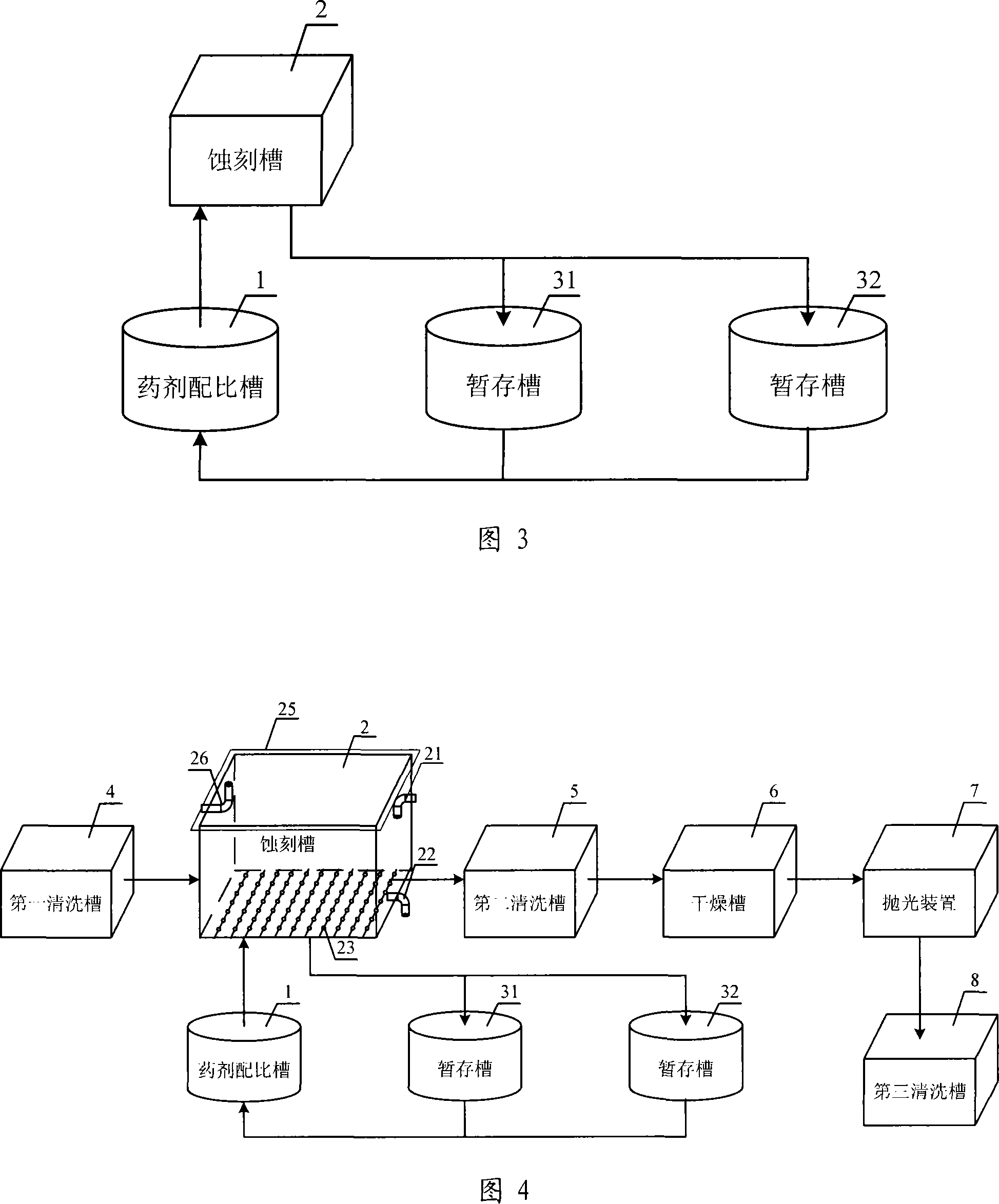
The invention relates to a method for thinning a flat glass substrate and a device thereof. First, etching liquor is mixed and processed of temperature treatment in a reagent preparation trough; the prepared etching liquor is quickly pumped into an etching trough. The glass substrate is placed into the etching trough and is etched by adopting a self-circulation way of bubbling and etching. After being etched, the glass substrate is taken out and the etching liquor is quickly poured into a temporary storage trough for a temporary storage and a precipitation. The etching liquor can be re-prepared and reused when the glass substrate is etched next time. The etched and thinned glass substrate is cleaned, dried and polished. The invention provides the method for thinning the flat glass substrate and a device thereof. By adopting the etching method of reagent circulation and bubbling, the aim of batch production can be received, thus supplying a thin glass substrate product and improving the good product rate and production quantity.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +2
Rotary cylindrical magnetron sputtering target
InactiveCN101285171AUniform etchingUniform etching is uniform, so the consumption of target materialVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhysicsGlow discharge
The invention provides a rotary cylindrical magnetic control sputtering target, which comprises a pole terminal, permanent magnets, hollow cylindrical target material and a mandrel, wherein, the permanent magnets are embedded into the pole terminal along the axial direction of the cylindrical target material; the permanent magnets are long permanent magnetic strips and short permanent magnetic strips; positioning slots which are used for arrangement of the long permanent magnetic strips and the short permanent magnetic strips are arranged on the pole terminal; the long permanent magnetic strips and the short permanent magnetic strips are respectively arranged in corresponding positioning slots; a multipath bar magnet is formed by alternate distribution of the long permanent magnetic strips and the short permanent magnetic strips along the circumferential direction of the pole terminal; the polarity of the long permanent magnetic strips and that of the short permanent magnetic strips are different; the polarization direction is perpendicular to a central axis of a sputtering cathode; and closed racetrack shaped magnetic force lines are formed by magnetic rings on both ends of the pole terminal and the long permanent magnetic strips and the short permanent magnetic strips. The rotary cylindrical magnetic control sputtering target realizes low air pressure, high density and uniformity of discharge plasma, guarantees formation of a closed electronic racetrack under the condition of glow discharge, makes sputtering perform stably, has good surface quality of membranous layers and compact membranous layers, and is uniform in the consumption of the target materials and high in the utilization rate of the target materials.
Owner:SUPERIOR COAT SUZHOUCO
Plasma processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20100126668A1Improved resistance characteristicsIncrease chanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectric power
An apparatus includes an upper electrode and a lower electrode for supporting a wafer disposed opposite each other within a process chamber. A first RF power supply configured to apply a first RF power having a relatively higher frequency is connected to the upper electrode. A second RF power supply configured to apply a second RF power having a relatively lower frequency is connected to the lower electrode. A variable DC power supply is connected to the upper electrode. A process gas is supplied into the process chamber while any one of application voltage, application current, and application power from the variable DC power supply to the upper electrode is controlled, to generate plasma of the process gas so as to perform plasma etching.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma processing apparatus and method
ActiveCN102157372AEliminate attachmentEtching high speedElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMiniaturizationDc voltage
There is provided a plasma etching device for generating plasma as a processing gas between an upper electrode (34) and a lower electrode (16) and subjecting a wafer (W) to plasma etching. The upper electrode (34) includes a variable DC power source (50) for applying DC voltage so that the absolute value of the self bias voltage Vdc on the surface of the upper electrode (34) becomes large enough to obtain an appropriate sputter effect to the surface and the thickness of the plasma sheath on the upper electrode (34) becomes thick enough to form a desired miniaturization plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
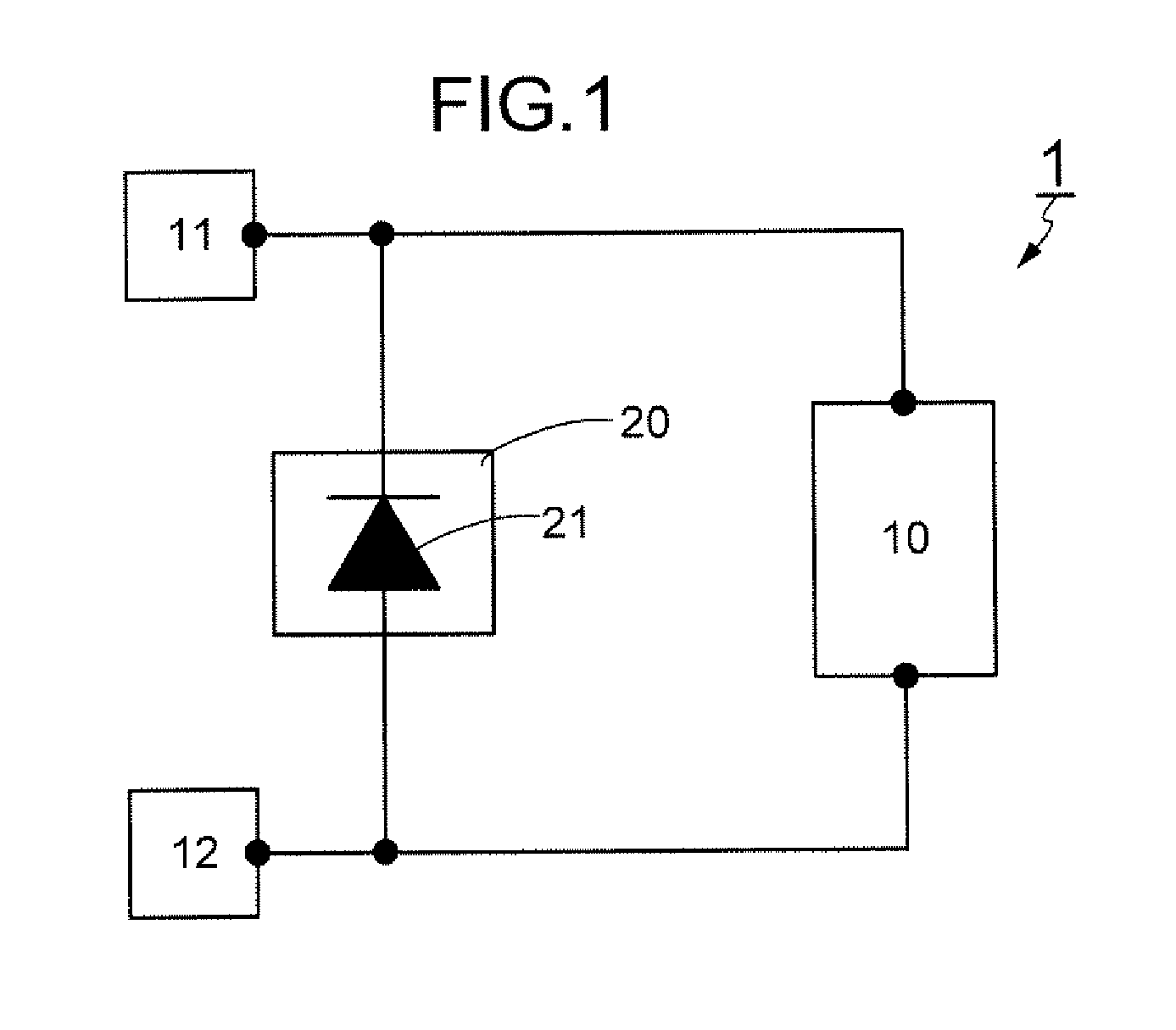
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100006848A1Wiring resistanceImprove protectionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
To improve the performance of a protection circuit including a diode formed using a semiconductor film. A protection circuit is inserted between two input / output terminals. The protection circuit includes a diode which is formed over an insulating surface and is formed using a semiconductor film. Contact holes for connecting an n-type impurity region and a p-type impurity region of the diode to a first conductive film in the protection circuit are distributed over the entire impurity regions. Further, contact holes for connecting the first conductive film and a second conductive film in the protection circuit are dispersively formed over the semiconductor film. By forming the contact holes in this manner wiring resistance between the diode and a terminal can be reduced and the entire semiconductor film of the diode can be effectively serve as a rectifier element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
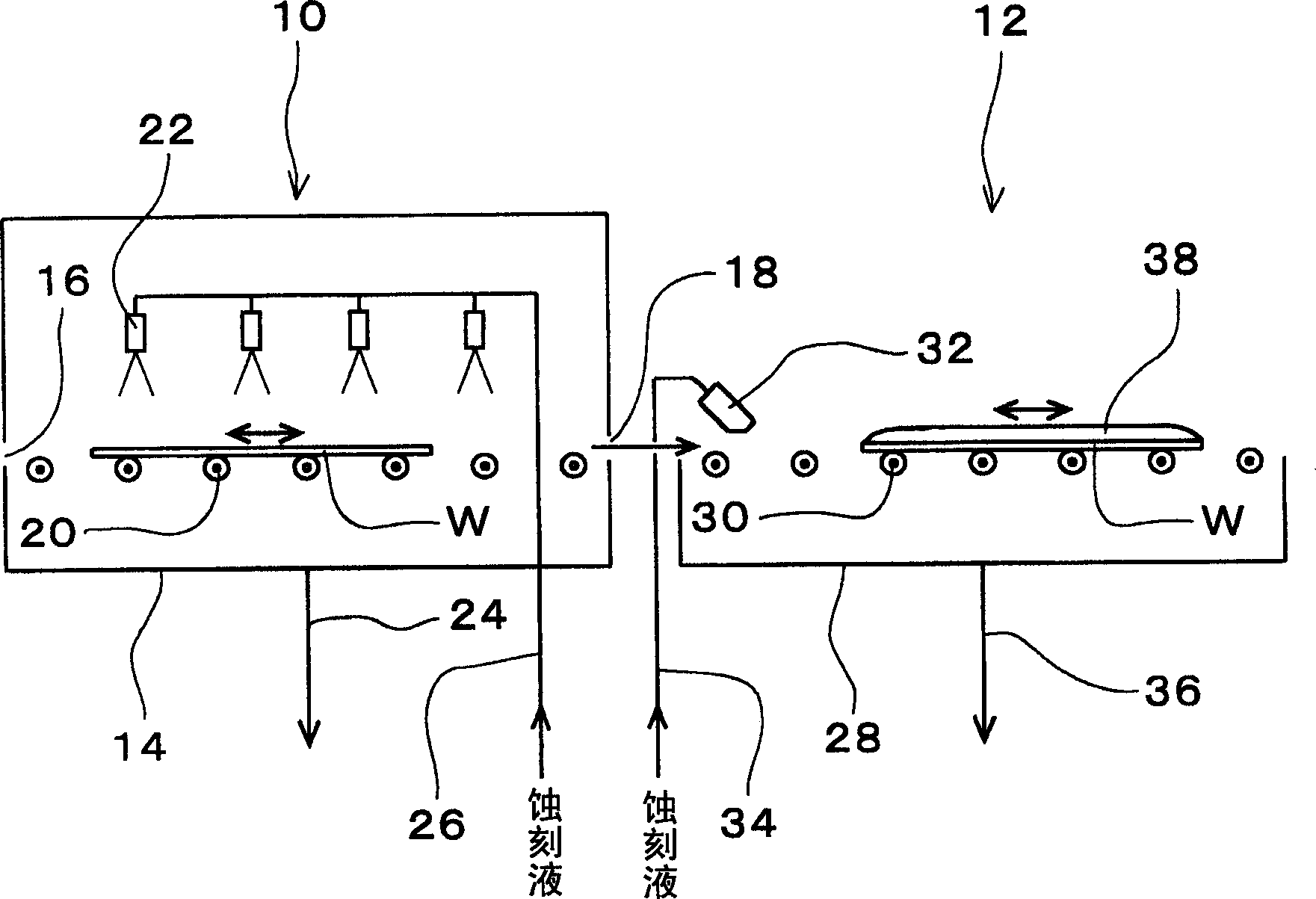
Substrate etching method and etching disposal device
InactiveCN1574251ATemperature does not dropUniform temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingEtchingEngineering
Provided is a device where treatment tanks are not required to be so enlarged for corresponding to the enlargement of a substrate, and the defect in etching does not occur as in the case where dipping treatment is performed. The device is provided with: a first treatment tank 14; conveyance rollers 20 arranged at the inside of the first treatment tank 14 and supportingly conveying a substrate W; spray nozzles 22 arranged at the upper part of a substrate conveyance path and jetting an etching liquid toward the surface of the substrate W; a second treatment tank 28 connected to the first treatment tank 14; conveyance rollers 30 arranged at the inside of the second treatment tank 28 and supportingly conveying the substrate W; and a discharge nozzle 32 feeding the etching liquid to the surface of the substrate W carried out from the inside of the first treatment tank 14 and carried into the second treatment tank 28 and applying the etching liquid to the whole of the surface of the substrate W.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
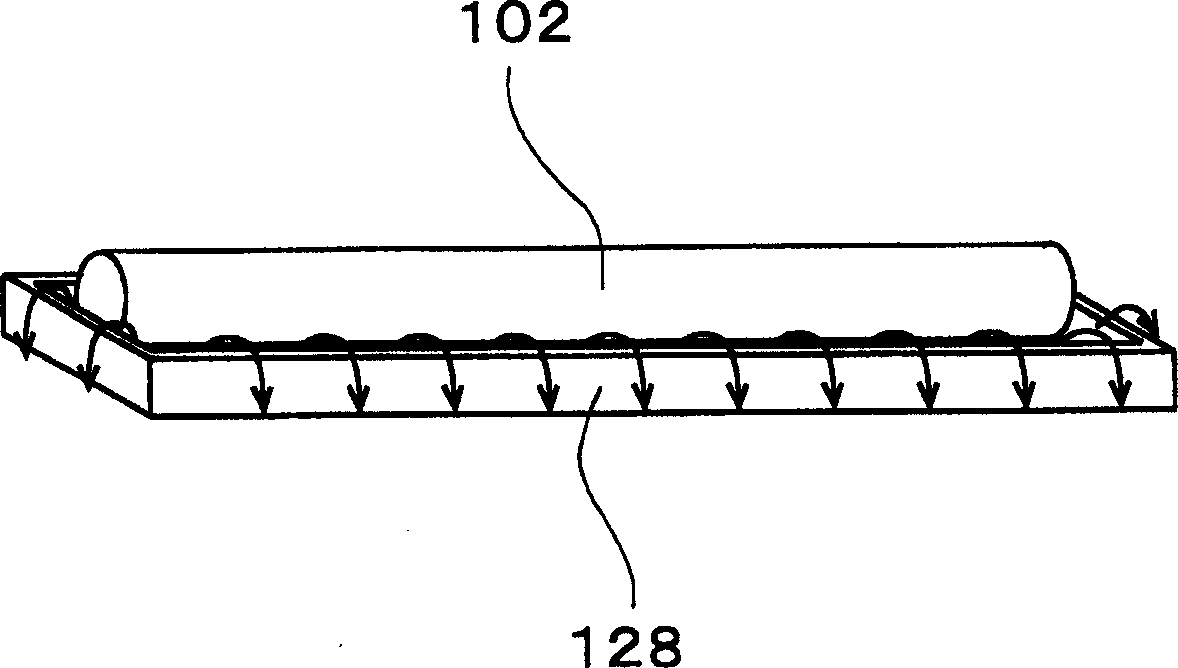
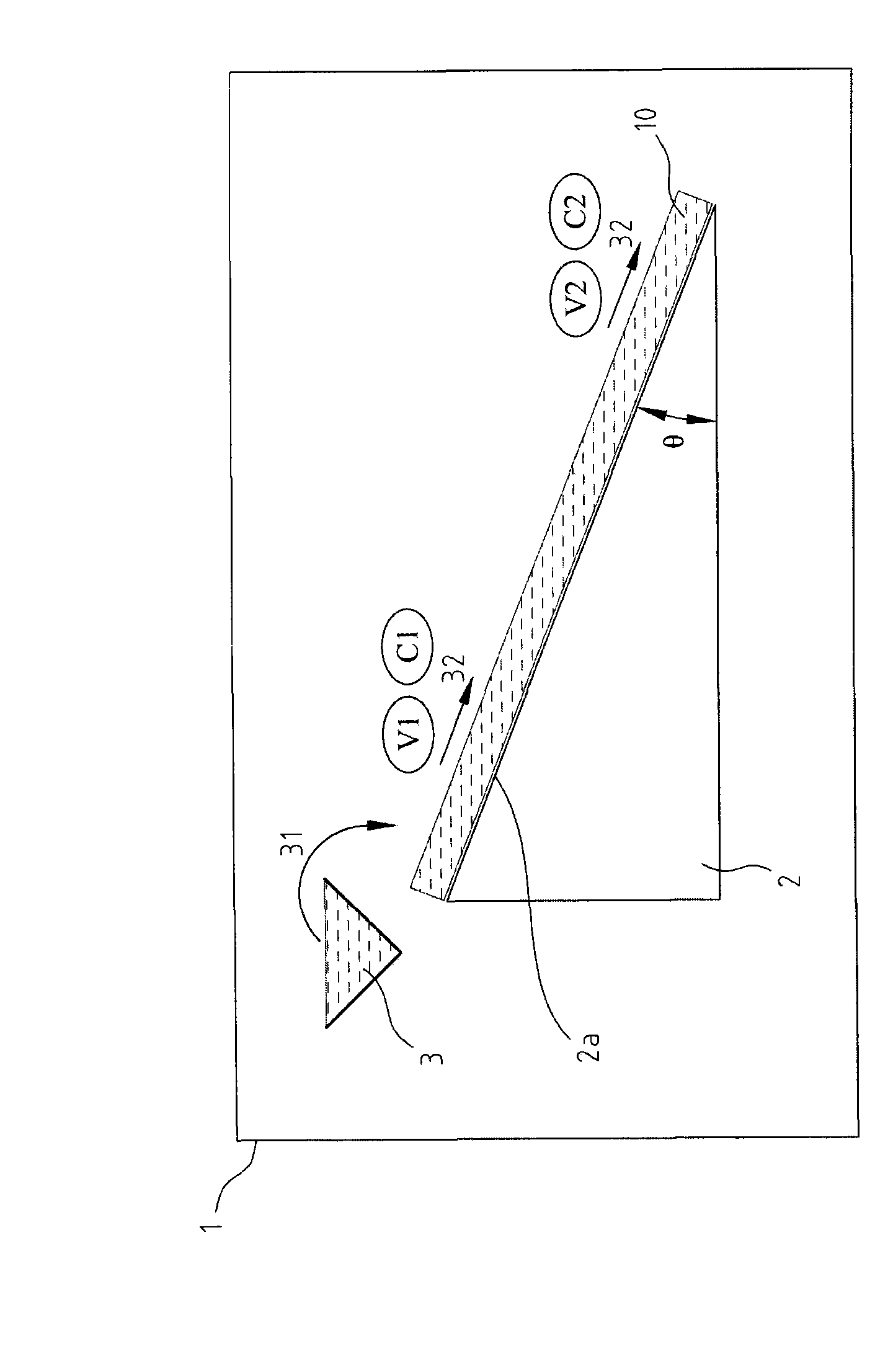
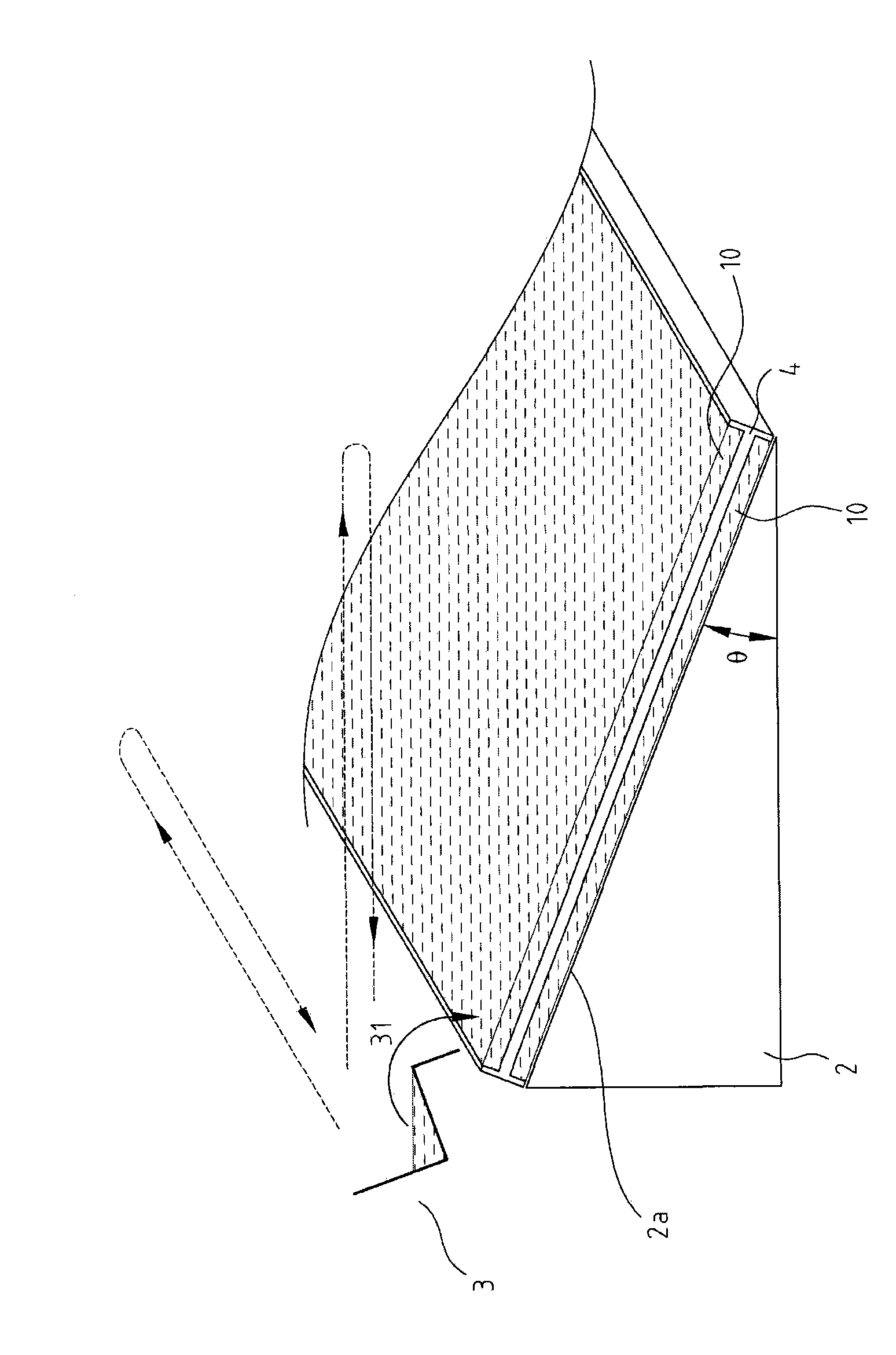
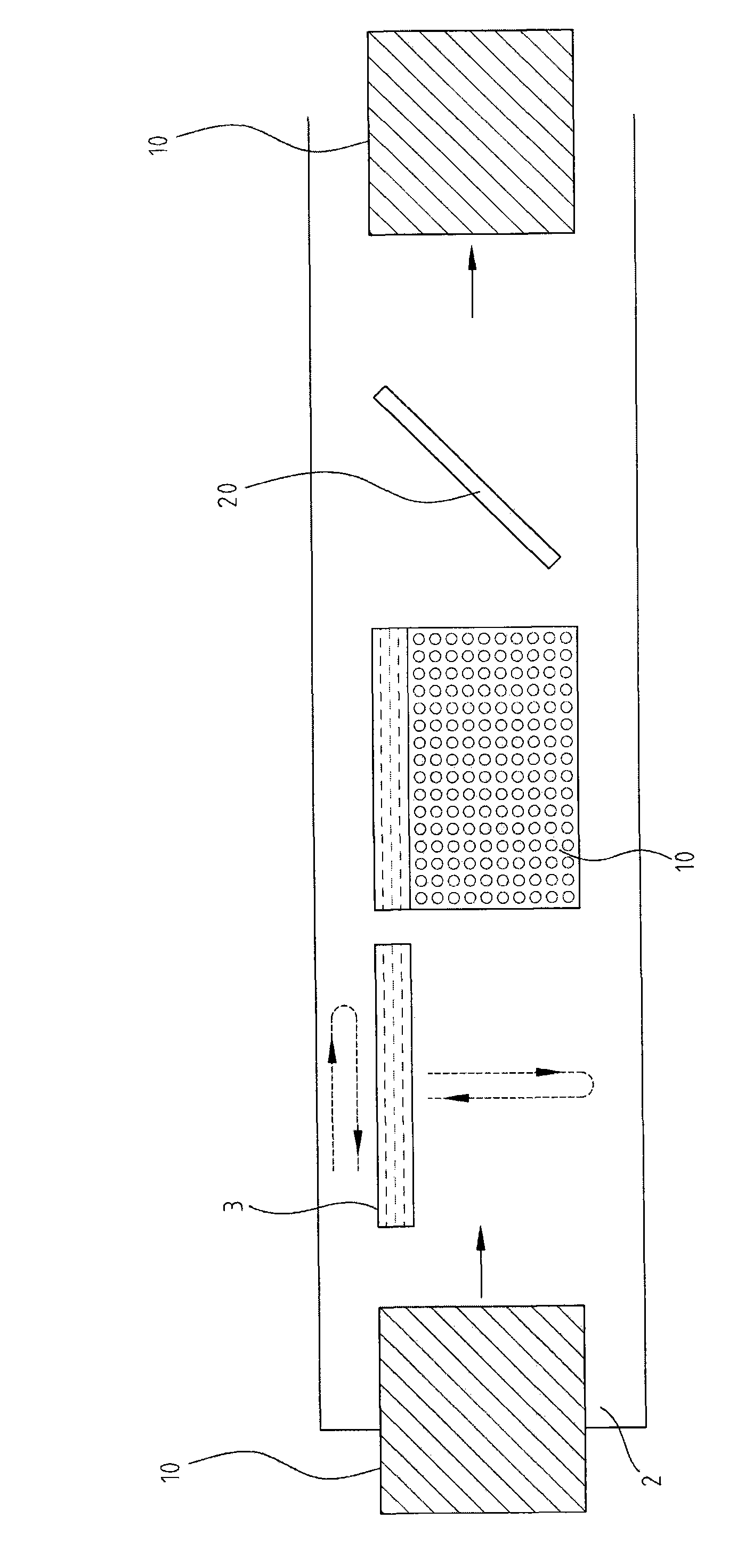
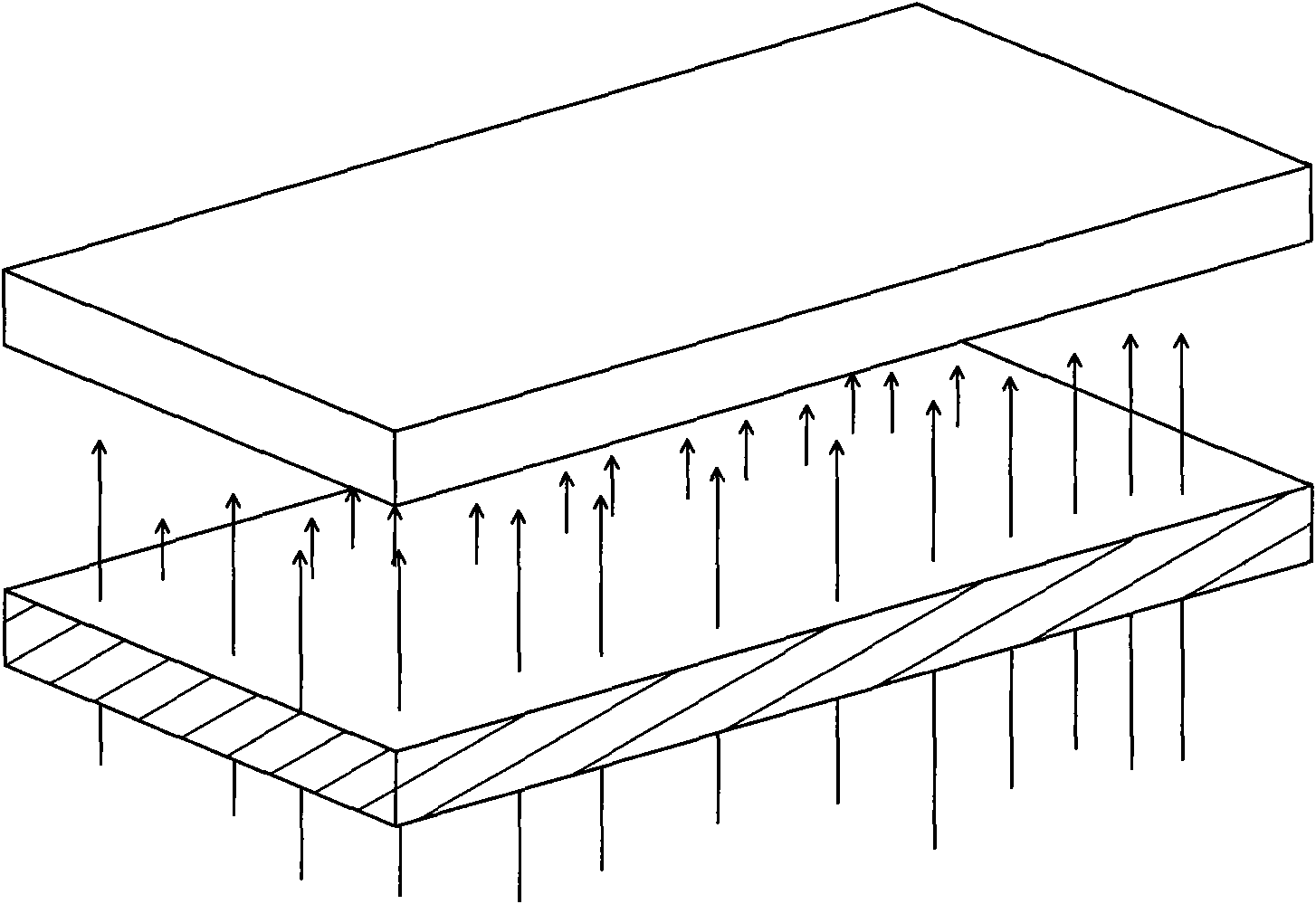
Device and method for etching optical glass
The invention discloses a device and a method for etching optical glass. When the glass of large size is etched and / or thinned, the device and the method are used for uniformly etching and / or thinning the optical glass in a driveline mode with inclination to reduce the stress of the optical glass and uniformly releasing an etching solution by adopting a scan-type waterfall layer sulfuric acid solution coating mode and a moving mode of scanning back and forth and / or left and right from the upside of the optical glass so as to uniformly etch and thin the optical glass. When the optical glass etching device of the invention is used for carrying out the optical glass etching method, because the optical glass is inclined, the limitation of the mechanical strength and the physical properties of the glass are reduced in conveying and transmission and the problems caused when the glass is vertically conveyed and transmitted are avoided; and due to the fact that the optical glass is coated with the sulfuric acid solution in a way of scanning type waterfall layer, the etching speed can be increased and the etching uniformity of the optical glass can be enhanced.
Owner:PHOTO JET INT
Thin-film transistor, manufacturing method thereof, array substrate and display device
The invention discloses a thin-film transistor, a manufacturing method thereof, an array substrate and a display device. The method includes the steps that a grid graph, a gate insulation layer thin film, an active layer thin film, an ohmic contact layer thin film, a first etching blocking module and a source drain metal layer thin film are sequentially formed on a substrate base plate, wherein the first etching blocking module and the source drain metal layer thin film are located in a channel region to be formed; the first etching blocking module shields the active layer thin film and the ohmic contact layer thin film corresponding to the channel region to be formed, and the graph containing source and drain is formed through wet etching; the graph containing an ohmic contact layer and an active layer is formed through a dry etching technology. According to the thin-film transistor, the manufacturing method thereof, the array substrate and the display device, on the basis that the first etching blocking module can protect the active layer thin film corresponding to the channel region to be formed, etching of the source metal layer and the drain metal layer is completed just through a wet etching technology, etching is even, and the problems that when the dry etching technology is adopted to etch the source metal layer and the drain metal layer, etching is uneven, the equipment loss is large, and the yield is low are solved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
ITO-Ag-ITO etching liquid for AMOLED
ActiveCN105463463AHigh viscosityReasonable concentration gradientSurface treatment compositionsPhosphoric acidDecomposition
The invention discloses ITO-Ag-ITO etching liquid for an AMOLED. The liquid comprises, by weight percentage, 3% to 10% of nitric acid, 10% to 25% of acetic acid, 30% to 60% of a mixture of phosphoric acid and soluble orthophosphate, 1% to 5% of an additive and the balance deionized water, wherein the additive comprises nitrate. The soluble orthophosphate is added so that the viscosity of the etching liquid can be properly increased, it is guaranteed that the etched surface has the reasonable reactant and product concentration gradient in the etching process, and compared with the prior art, the silver etching speed can be properly reduced, the even etching effect can be achieved, and the controllable electrode shape is obtained; and decomposition of the acetic acid, the nitric acid and nitrous acid in the etching process can be remarkably reduced, and environment-friendly production of the etching process can be achieved conveniently.
Owner:JIANGYIN JIANGHUA MICROELECTRONICS MATERIAL
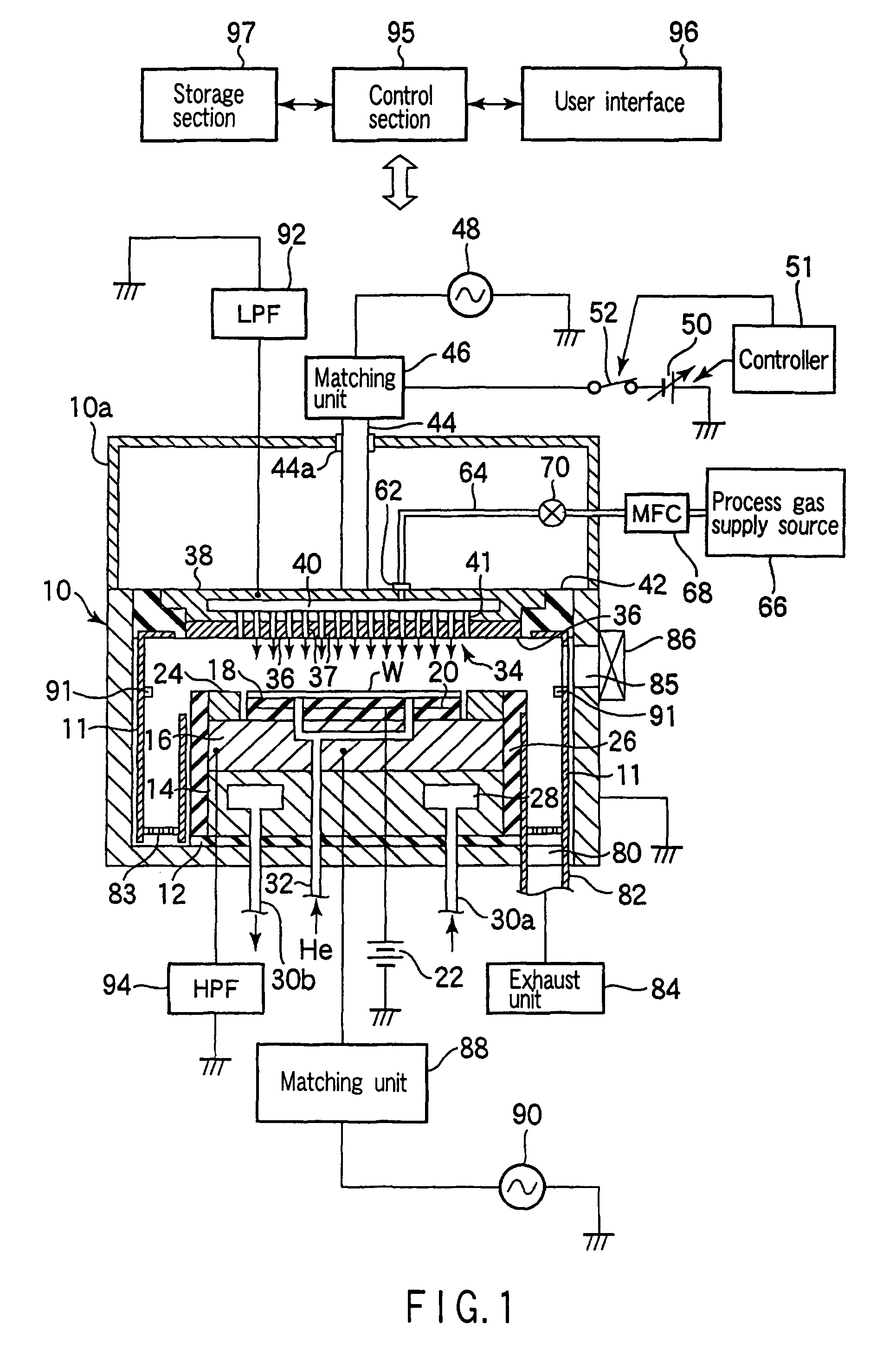
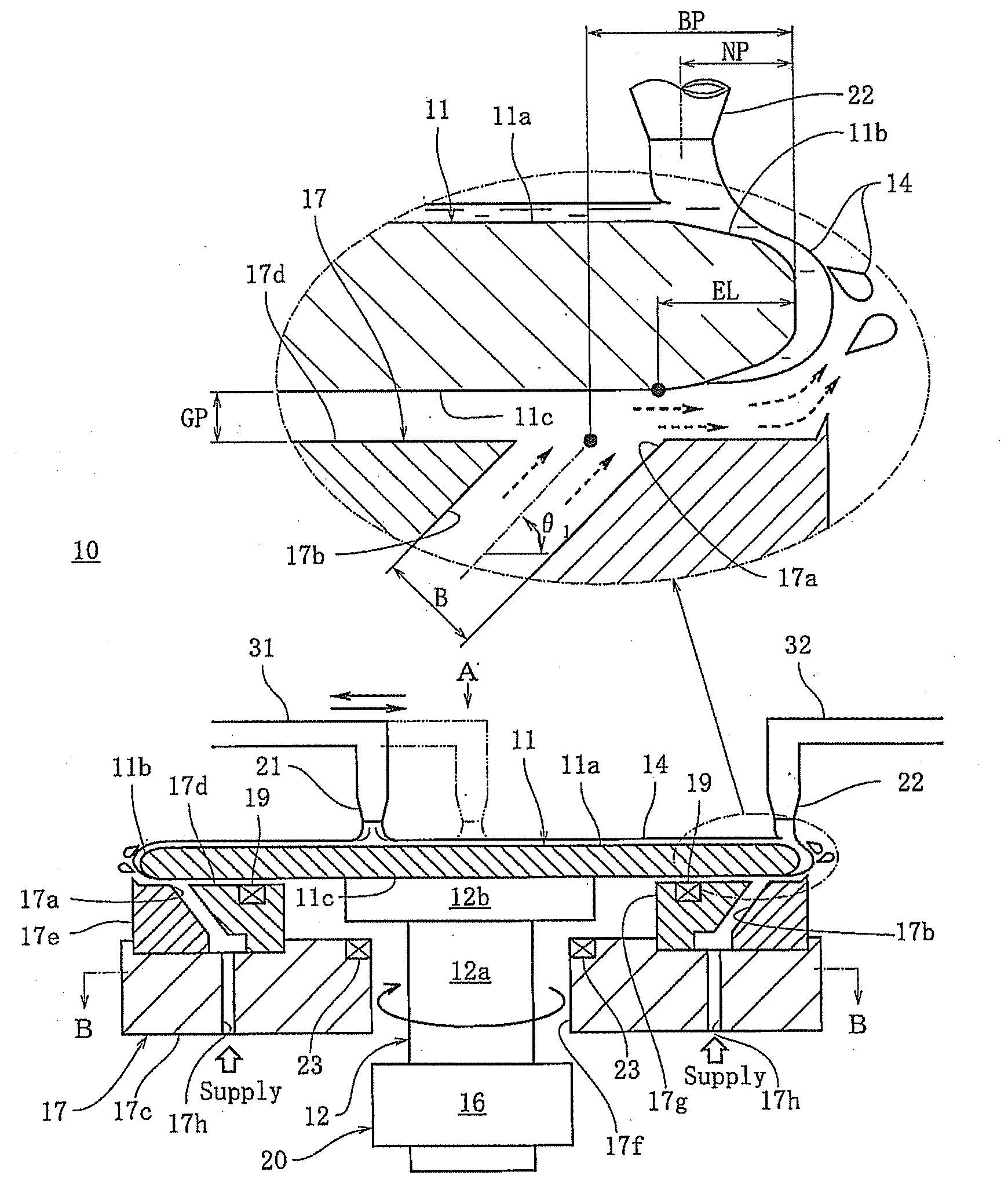
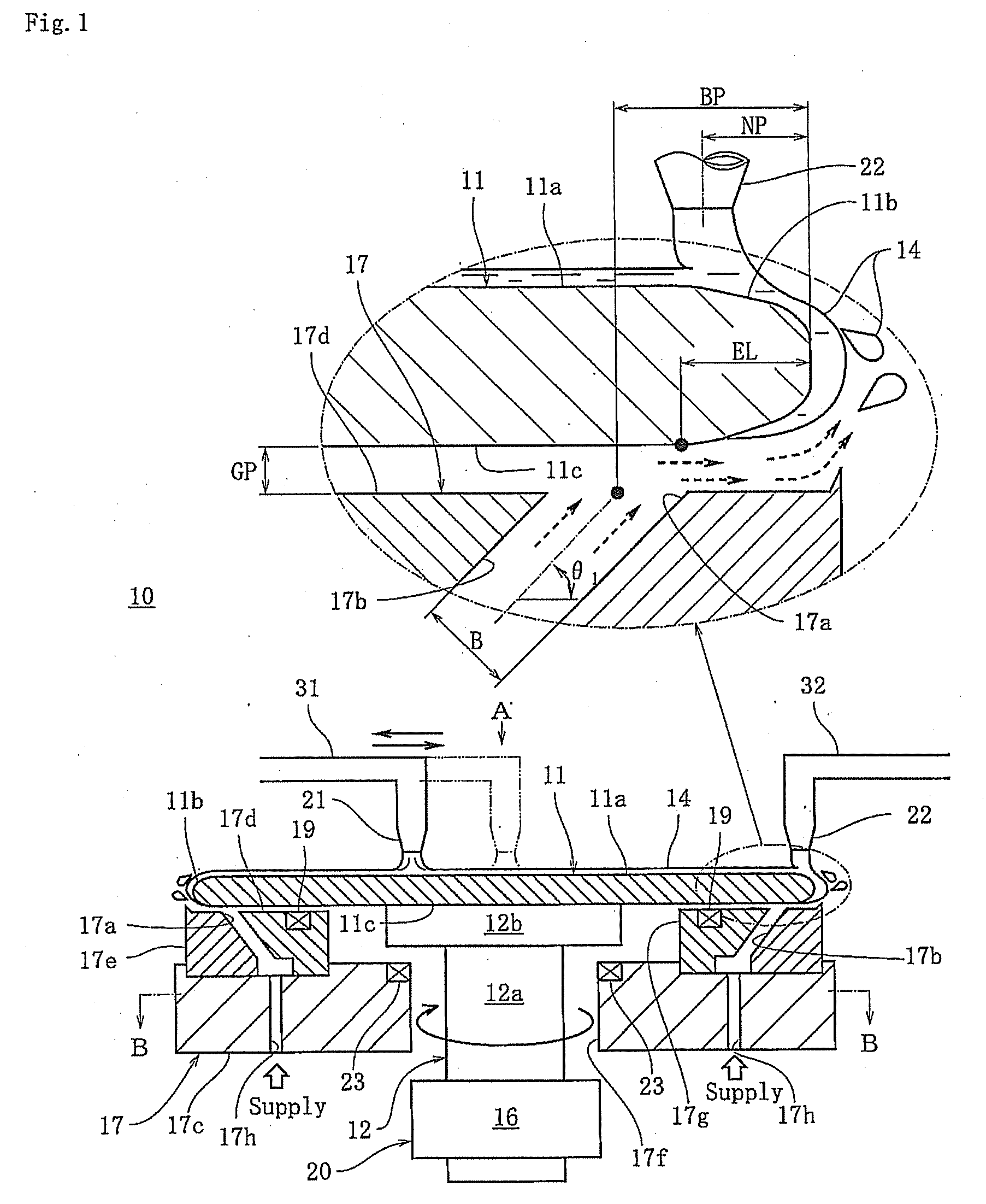
Plasma etching method and computer-readable storage medium
InactiveUS20070218681A1Increase etch rateFacilitated DiffusionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExecution controlElectric power
A plasma etching method for forming a trench on a substrate or on a film formed on the substrate, includes an substrate arranging step of arranging the substrate on which the trench is to be formed in a processing chamber having therein a first and a second electrode disposed to face each other vertically; a processing gas introducing step of introducing a processing gas for etching into the processing chamber; a plasma generating step of generating a plasma by applying a high frequency electric power to either of the first and the second electrode; and a DC voltage applying step of applying a DC voltage to said either of the electrodes. Further, a computer-readable storage medium stores therein a computer-executable control program, wherein, when the control program is being executed, a computer is made to control a plasma processing apparatus to perform the plasma etching method.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Etching method of single wafer
InactiveUS20070161247A1Suppressing local shape collapseAvoid flowDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringCentrifugal force
Local shape collapse of a wafer end portion is suppressed to the minimum level, and a wafer front surface as well as a wafer end portion is uniformly etched while preventing an etchant from flowing to a wafer rear surface. There is provided an etching method of a single wafer which supplies an etchant onto a wafer front surface in a state where a single wafer having flattened front and rear surfaces is held, and etches the wafer front surface and a front surface side end portion by using a centrifugal force generated by horizontally rotating the wafer. According to this method, the etchant is intermittently supplied onto the front surface of the wafer in twice or more, supply of the etchant is stopped after the etchant for one process is supplied, and the etchant for the next process is supplied after the supplied etchant flows off from the end portion of the wafer.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Integrated electrostatic inductive coupling for plasma processing
InactiveUS7426900B2Highly effectiveLow costElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsCapacitancePlasma density
An integrated electrostatic inductively-coupled (i-ESIC) device is provided for plasma processing that may be used as a primary or secondary source for generating a plasma to prepare substrates for, and to process substrates by applying, dielectric and conductive coatings. The i-ESIC device is practical for processing advanced semiconductor devices and integrated circuits that require uniform and dense plasma. The invention may be embodied in an apparatus that contains a substrate support, typically including an electrostatic chuck, that controls ion energy by capacitively coupling RF power to the plasma and generating voltage bias on the wafer relative to the plasma potential. An integrated inductive coupling element is provided at the perimeter of the substrate support that increases plasma density at the perimeter of the wafer, compensating for the radial loss of charged particles toward chamber walls, to produce uniform plasma density above the processed wafer. An annular slotted shield protects the inductive coupling element from the plasma and provides conditions for effective inductive coupling of RF power into the plasma, such as eliminating capacitive coupling from the element to the plasma and unwanted sputtering of the element. The i-ESIC device has a capacitive coupling zone in its center where wafers are placed and an inductive coupling zone at the perimeter of the wafer coupled to a matching network and RF generator. Both zones together with plasma create a resonant circuit.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
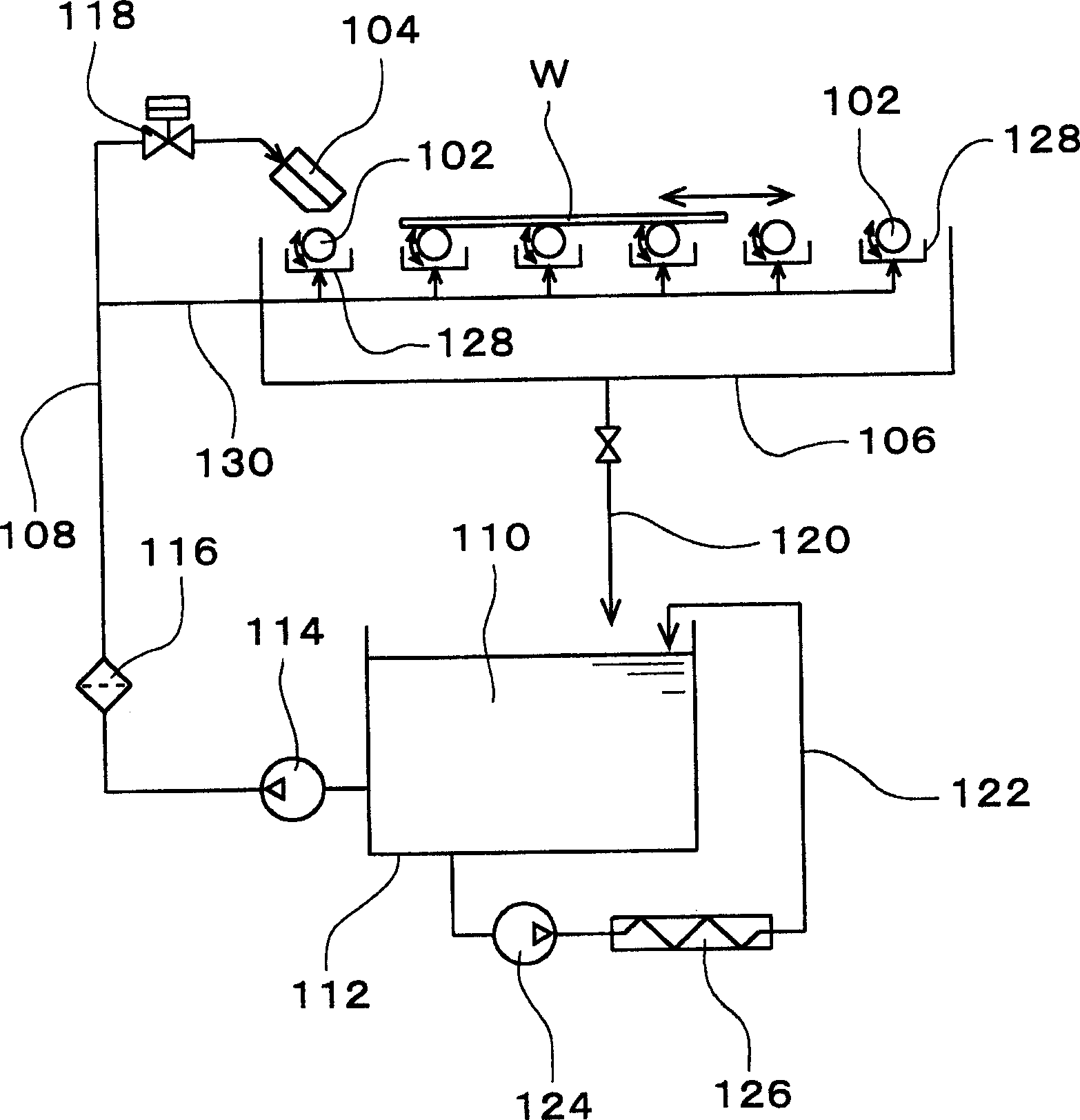
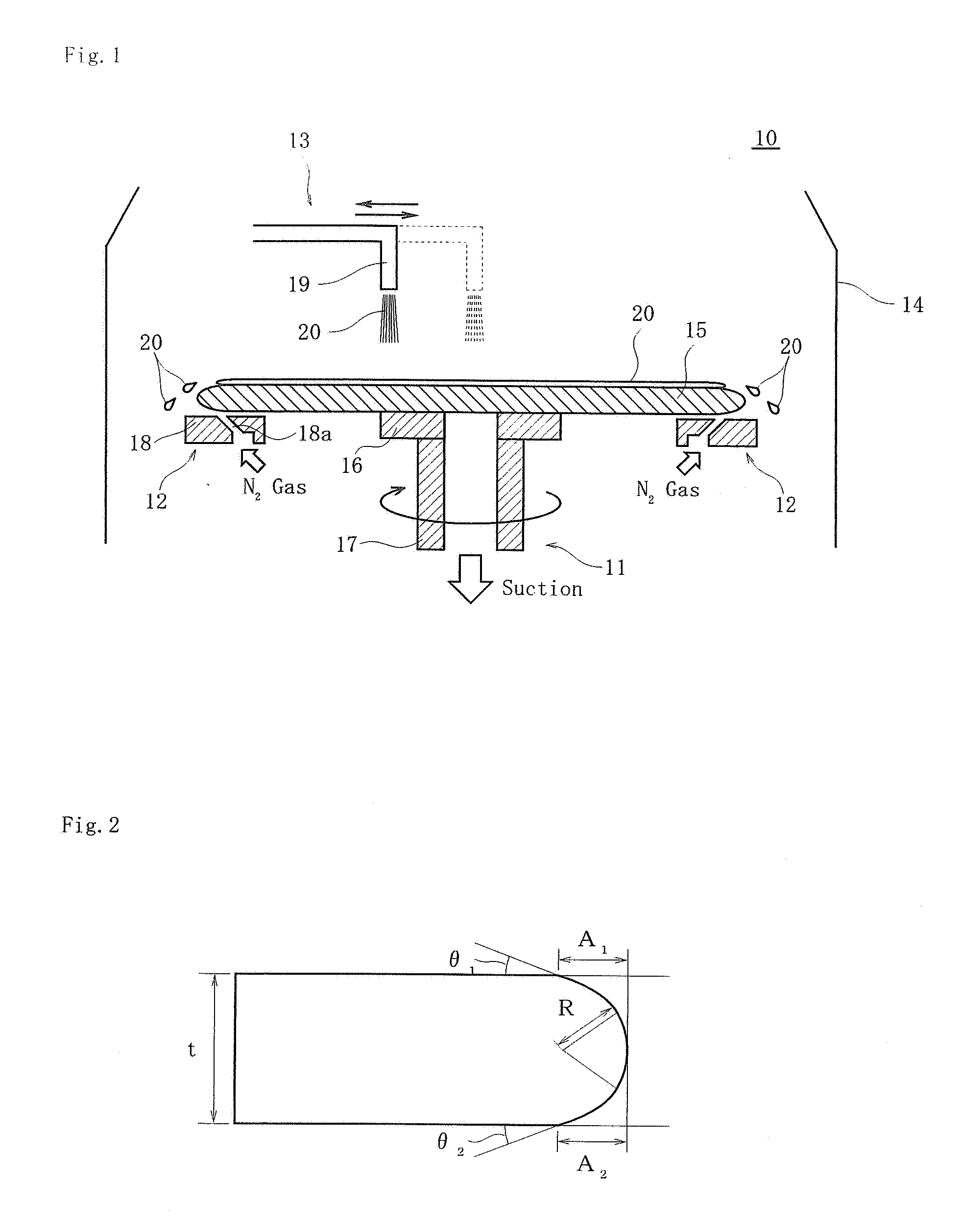
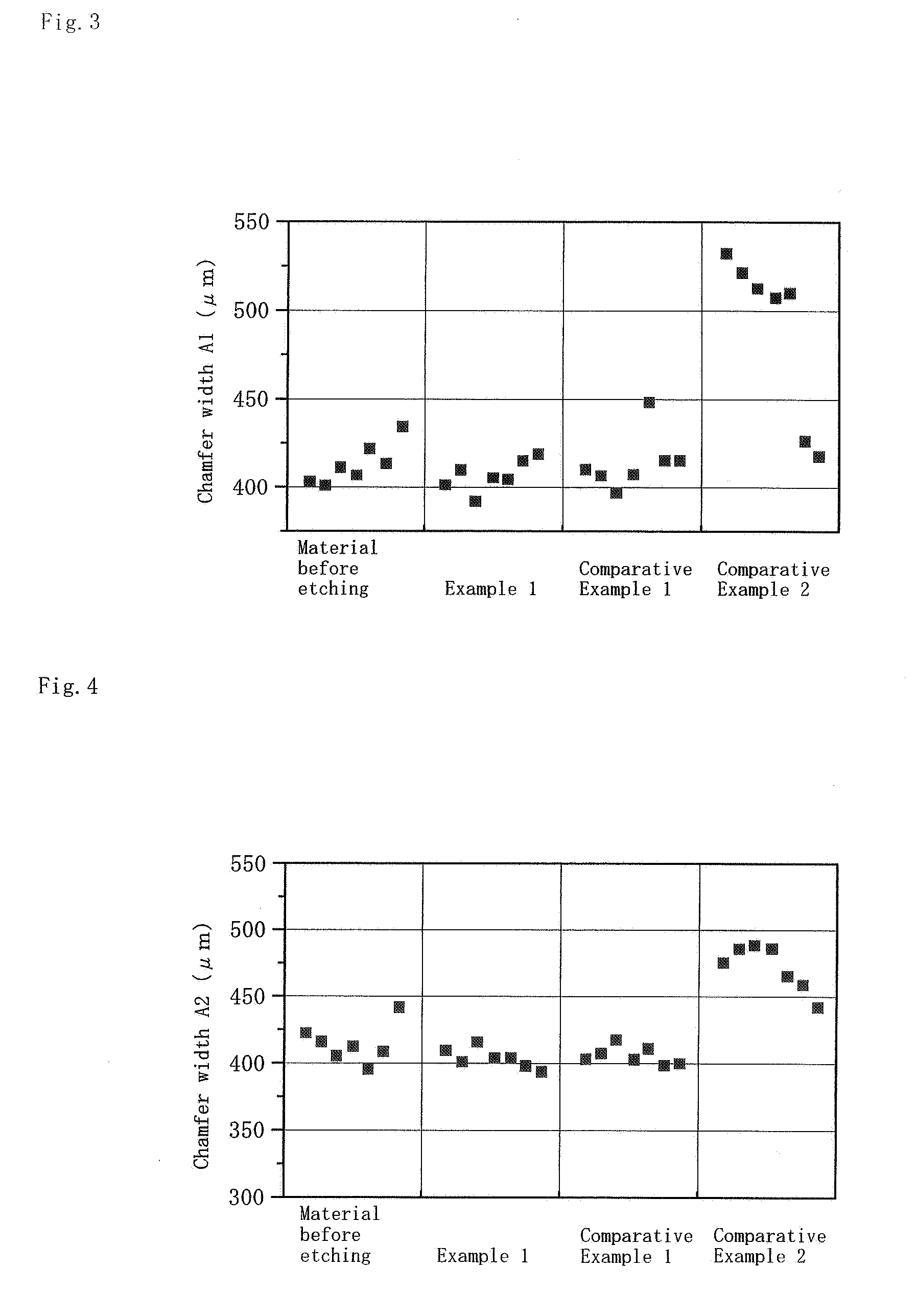
Single-Wafer Etching Method for Wafer and Etching Apparatus Thereof
InactiveUS20090181546A1Avoid flashUniform etchingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEdge surfaceEngineering
A single-wafer etching apparatus according to the present invention supplies an etchant to an upper surface of a wafer while rotating the wafer, thereby etching the upper surface of the wafer. Further, wafer elevating means moves up and down the wafer, and a lower surface blow mechanism which blows off the etchant flowing down on an edge surface of the wafer toward a radially outer side of the wafer by injection of a gas is fixed and provided without rotating together with the wafer. Furthermore, gap adjusting means controls the wafer elevating means based on detection outputs from gap detecting means for detecting a gap between the wafer and the lower surface blow mechanism, thereby adjusting the gap. The apparatus according to the present invention uniformly etches the edge portion without collapsing a chamfered shape of the edge portion of the wafer, and prevents a glitter from being produced on the edge surface of the wafer.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Rotary magnetron sputtering target
InactiveCN101285172AUniform etchingEven consumptionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhysicsSurface etching
The invention relates to a rotary magnetic control sputtering target, which comprises a pole terminal, permanent magnets and cylindrical target material, wherein, tree rows of permanent magnets are uniformly arranged in the pole terminal along the circumferential direction towards one side of a matrix within the range of 120 DEG; the permanent magnets comprise long permanent magnetic strips and short permanent magnetic strips; the short permanent magnetic strips are arranged in the middle position of the pole terminal; a long permanent magnetic strip is respectively arranged on both sides of the pole terminal; a shielding case is arranged on the circumference of the cylindrical target material and provided with sputtering openings on one sides of the permanent magnets facing to the matrix; the polarity of the long permanent magnetic strips and that of the short permanent magnetic strips are different; the polarization direction is perpendicular to a central axis of a sputtering cathode; and a closed racetrack shaped magnetic force line is formed by magnetic rings on both ends of the pole terminal and the long permanent magnetic strips and the short permanent magnetic strips. When the rotary magnetic control sputtering target is operated, the cylindrical target material is rotated at a constant speed and the surface etching of the target is uniform, thereby the consumption of the target material is uniform and the service life is long; the shielding case can effectively reduce sputtering precipitation of sputtering particles towards an anode and the wall of a vacuum cavity and satisfactorily guarantee stability of the sputtering process and the quality of a deposition film; the application prospect of the target is good.
Owner:SUPERIOR COAT SUZHOUCO
Laminated wafer and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101124657AUniform etchingReduce the number of stepsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringOxide
Disclosed is a method for manufacturing a bonded wafer which comprises a step for etching an oxide film in a terrace portion of the edge of a bonded wafer which is formed by bonding at least a base wafer and a bond wafer. This method for manufacturing a bonded wafer is characterized in that etching of the oxide film in the terrace portion is performed by spin etching while holding and rotating the bonded wafer. By this method, the oxide film formed in the terrace portion of the base wafer can be efficiently etched without etching the oxide film on the backside of the base wafer.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Sputter coating method
InactiveCN101565818AIncrease speedImprove crystal qualityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNon magneticElectric field
The invention discloses a sputter coating method, which adopts a magnetic field-assisted sputtering mode for coating, wherein a target and a substrate are arranged in parallel inside an electric field between two electrodes; the target is positioned on the surface of a cathode; the substrate is positioned on an anode; a plasma is formed between the target and the substrate; the target is bombarded by ions to generate sputtering; and sputtered target composition particles are deposited on the substrate to form a membrane. The sputter coating method is characterized in that: the target is positioned inside a magnetic field generated by a permanent magnet or an electromagnet or an electromagnetic coil, and the direction of the magnetic field is perpendicular to the surface of the target. The method can greatly improve the speed of sputter coating and the crystallization quality of the coating, integrally and uniformly etch the target, improve the utilization rate of the target to between 85 and 90 percent, and obtain higher sputtering speed and the same sputtering effect for both magnetic targets and nonmagnetic targets.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Etching method and apparatus for a single wafer
InactiveCN101276756AUniform etchingDoes not damage the chamfer shapeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEdge surfaceEngineering
A single-wafer etching apparatus according to the present invention supplies an etchant to an upper surface of a wafer while rotating the wafer, thereby etching the upper surface of the wafer. Further, wafer elevating means moves up and down the wafer, and a lower surface blow mechanism which blows off the etchant flowing down on an edge surface of the wafer toward a radially outer side of the wafer by injection of a gas is fixed and provided without rotating together with the wafer. Furthermore, gap adjusting means controls the wafer elevating means based on detection outputs from gap detecting means for detecting a gap between the wafer and the lower surface blow mechanism, thereby adjusting the gap. The apparatus according to the present invention uniformly etches the edge portion without collapsing a chamfered shape of the edge portion of the wafer, and prevents a glitter from being produced on the edge surface of the wafer.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Fabrication method of Ti movable device
InactiveCN101445218AHigh precisionUniform etchingDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingFilling materialsAspect ratio
The invention discloses a fabrication method of a Ti movable device. The fabrication method comprises the following steps: etching a Ti substrate by plasma etching technology to form a deep groove, and filling the deep groove; bonding the Ti substrate with another substrate; thinning the back of the Ti substrate by chemical corrosion and chemical mechanical polishing until the deep groove is exposed; removing the filler in the deep groove; and releasing the movable structure to obtain a Ti micro-device with the movable structure. The method can achieve high-accuracy and high-aspect-ratio 3D processing of Ti on a plurality kinds of substrates, and can be used for processing a plurality of MEMS devices. The entire process adopts micro-electronic processing method, and has the advantages of high accuracy and uniform etching. The fabricated device has the advantages of bright surface, smooth sidewall, flat surface and small stress.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com