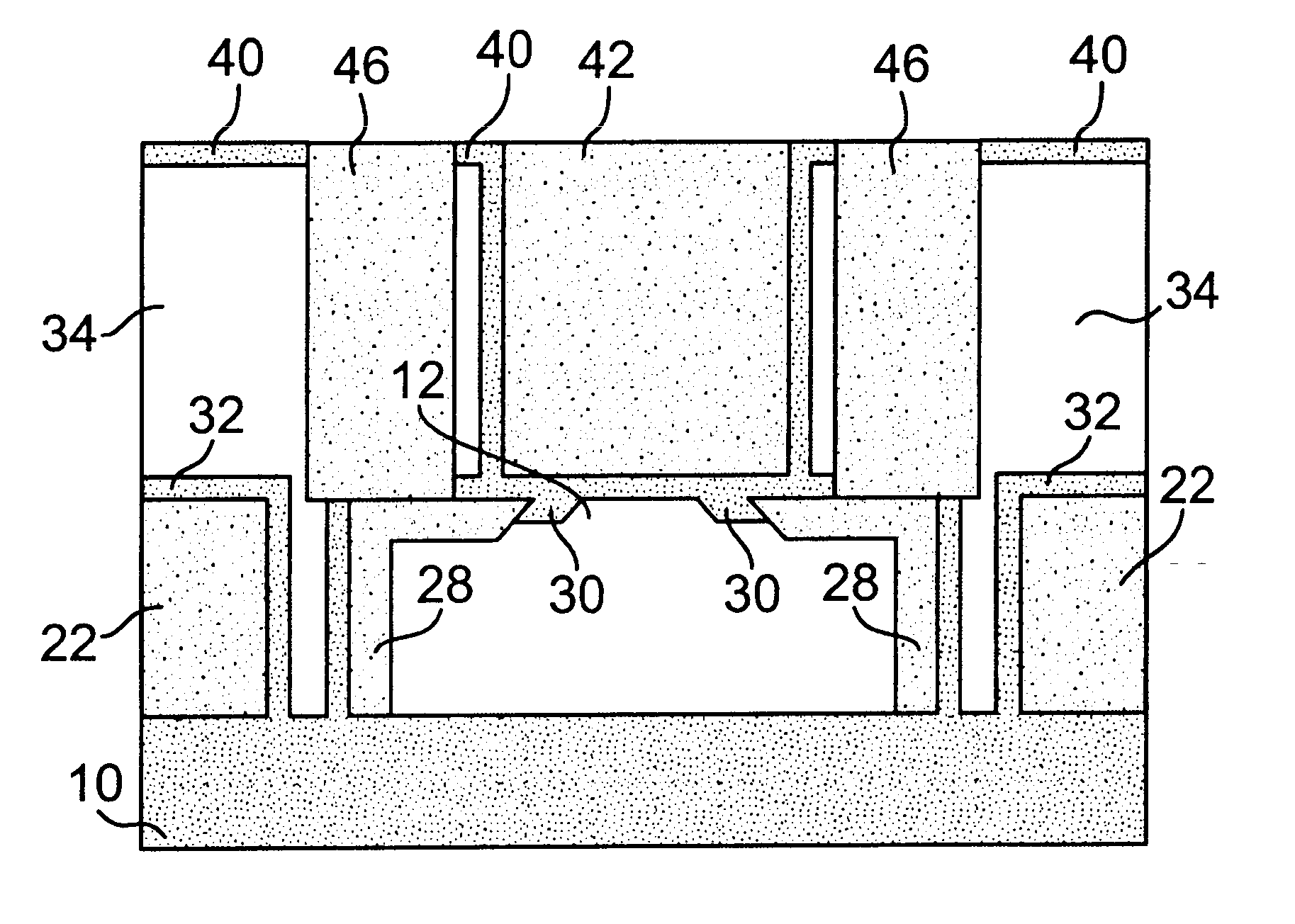
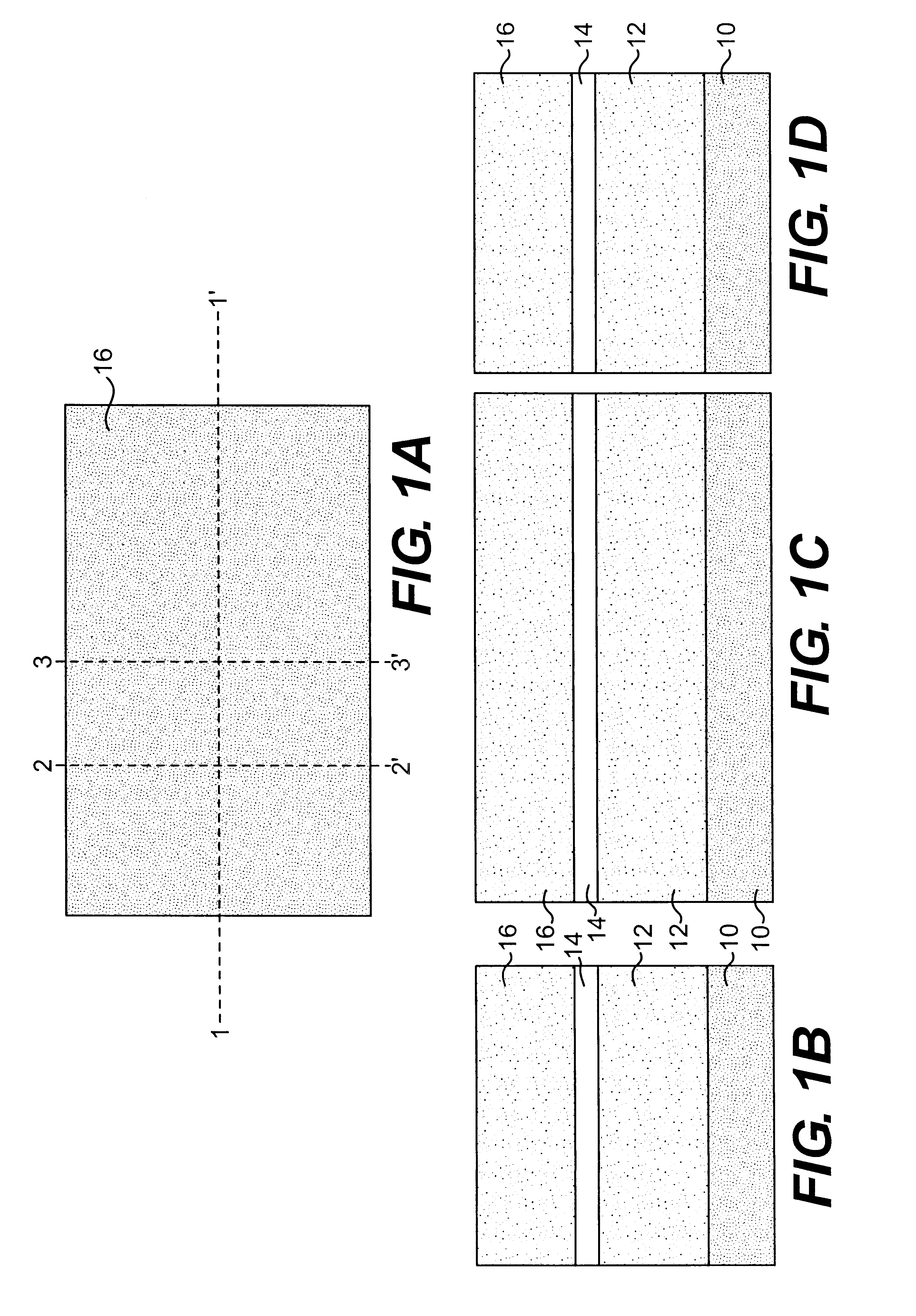
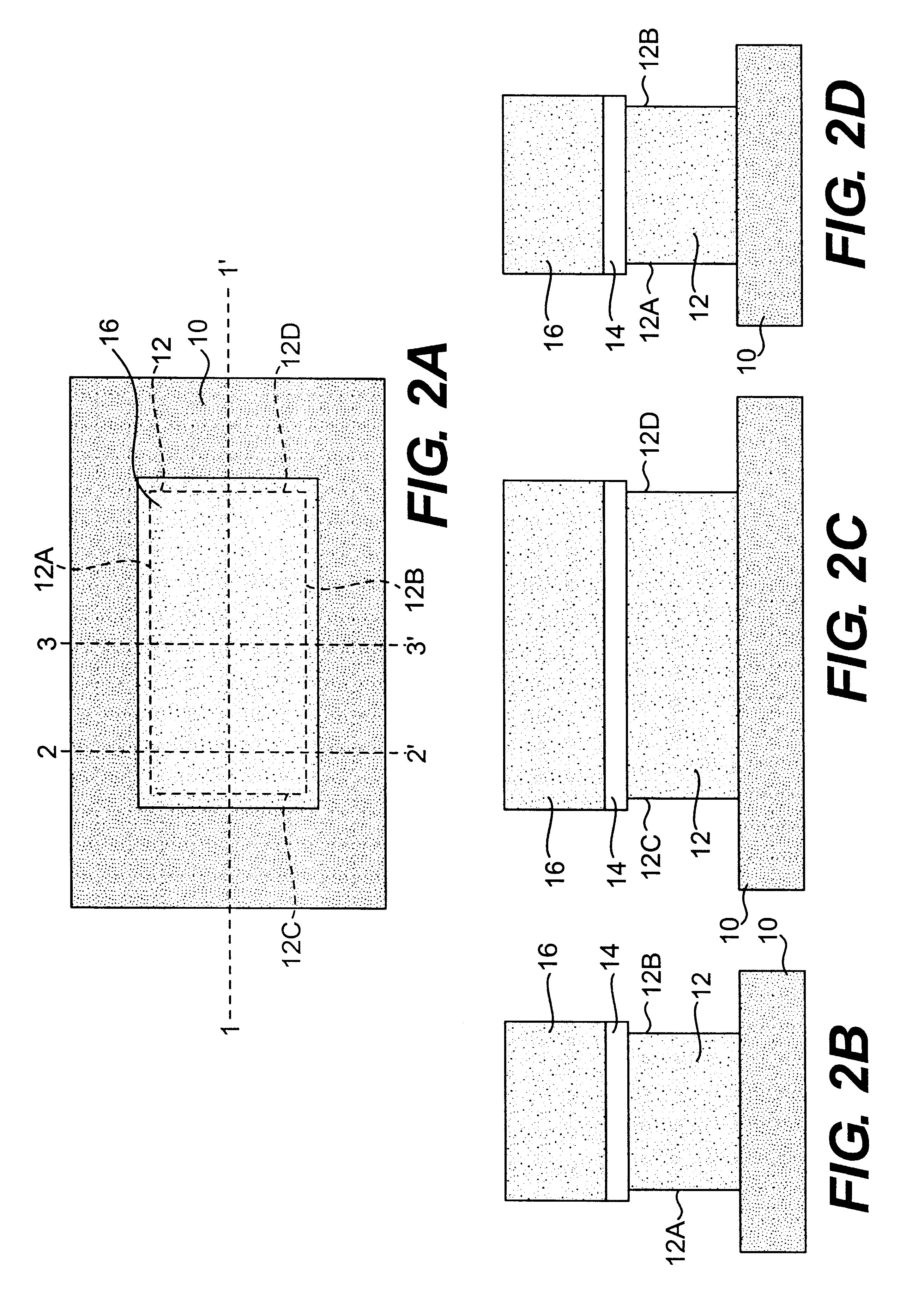
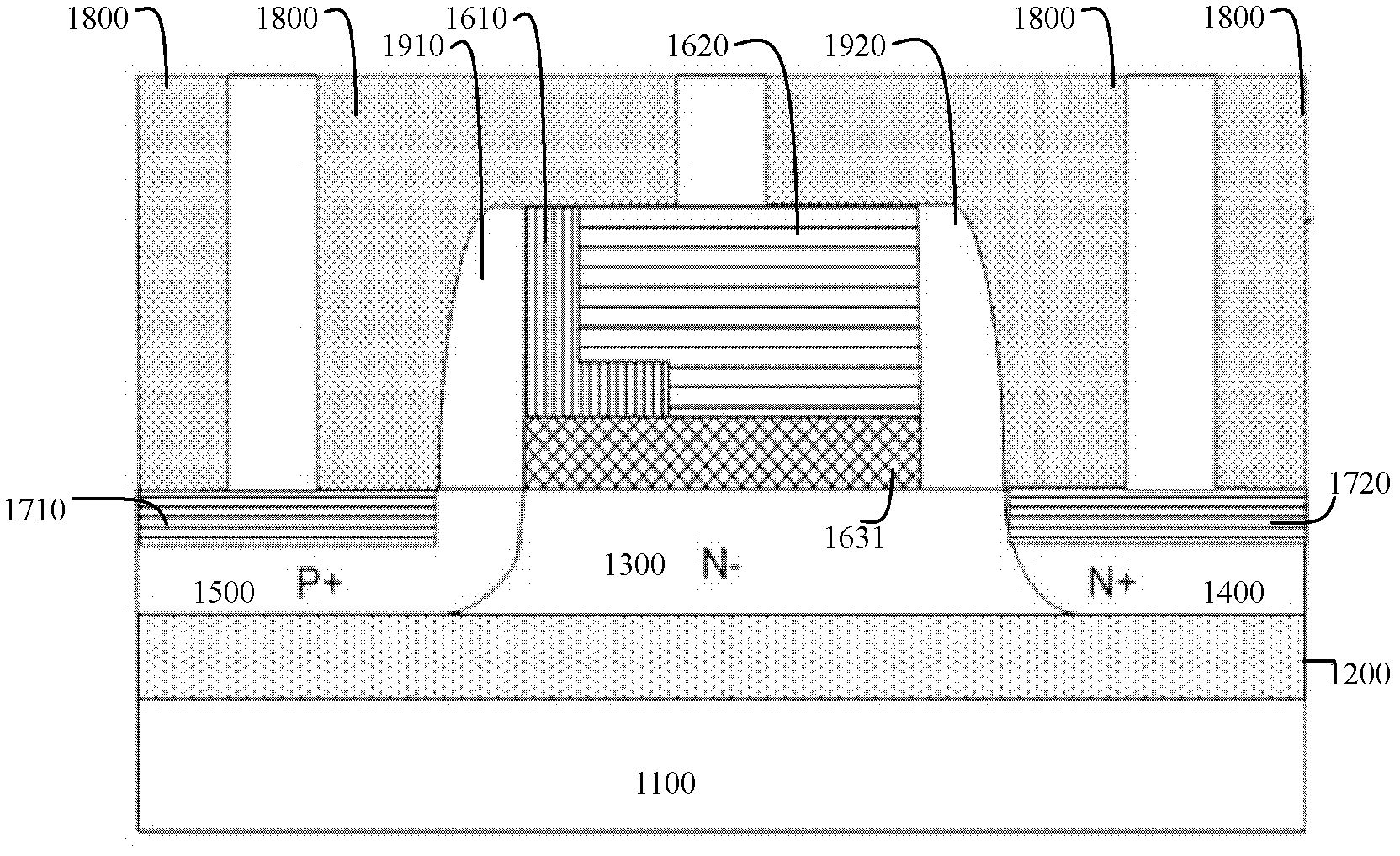
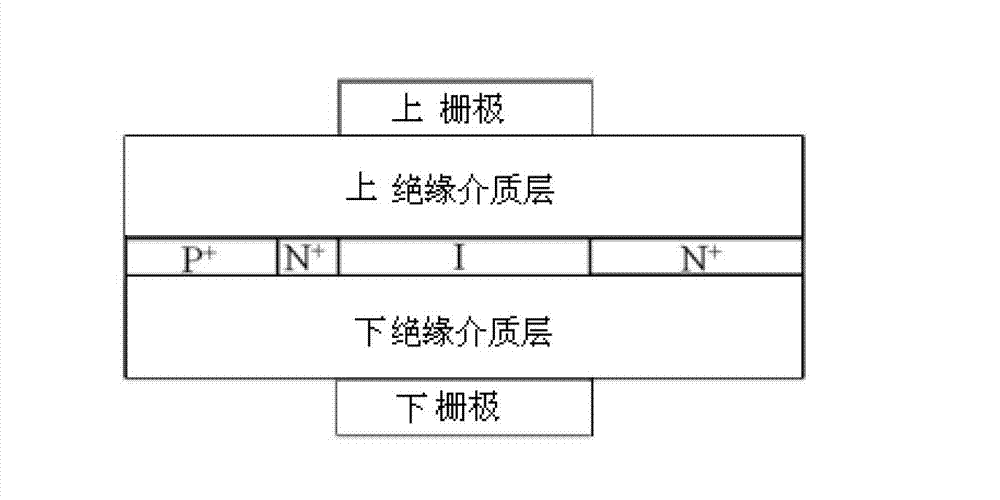
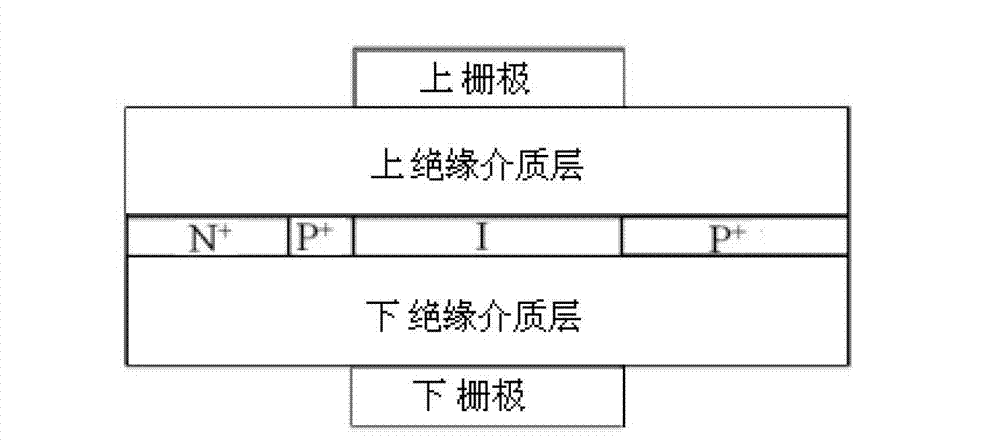
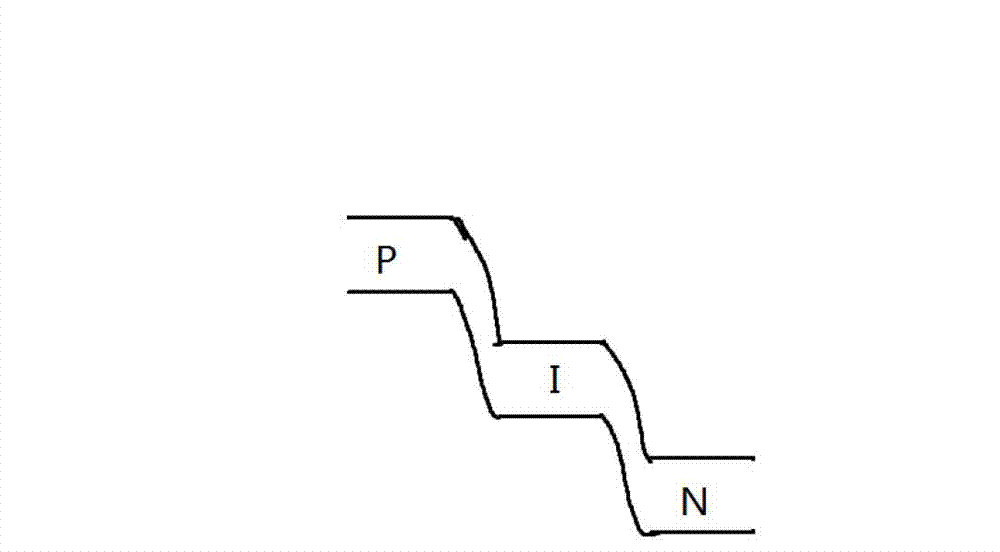
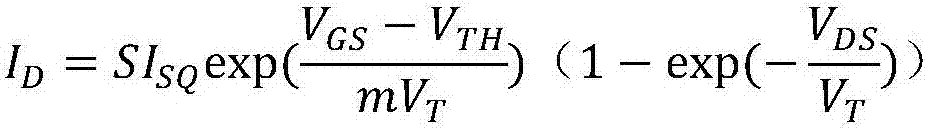Patents
Literature
156 results about "Subthreshold slope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
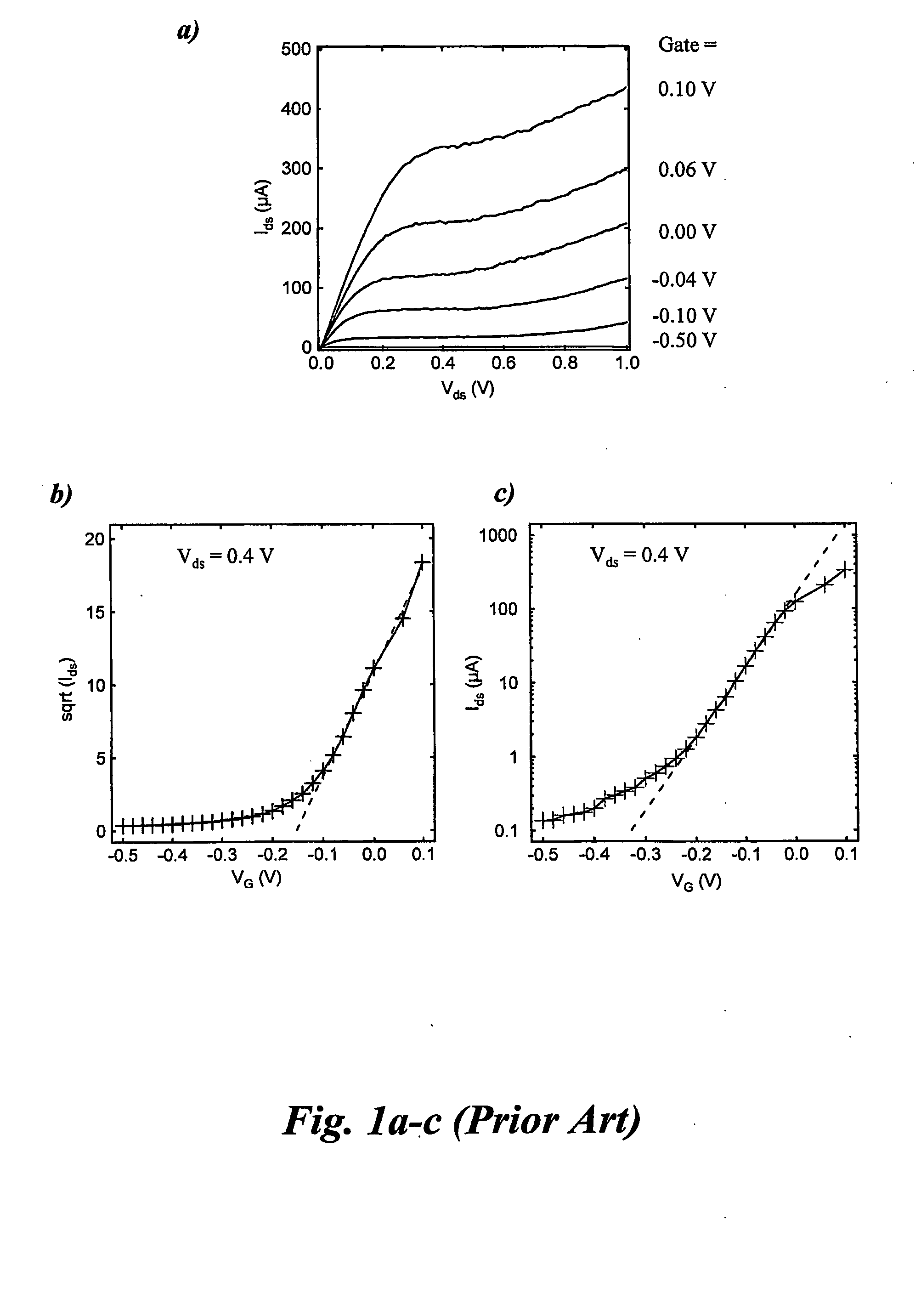
The subthreshold slope is a feature of a MOSFET's current–voltage characteristic. In the subthreshold region, the drain current behaviour – though being controlled by the gate terminal – is similar to the exponentially decreasing current of a forward biased diode. Therefore a plot of drain current versus gate voltage with drain, source, and bulk voltages fixed will exhibit approximately log linear behaviour in this MOSFET operating regime.
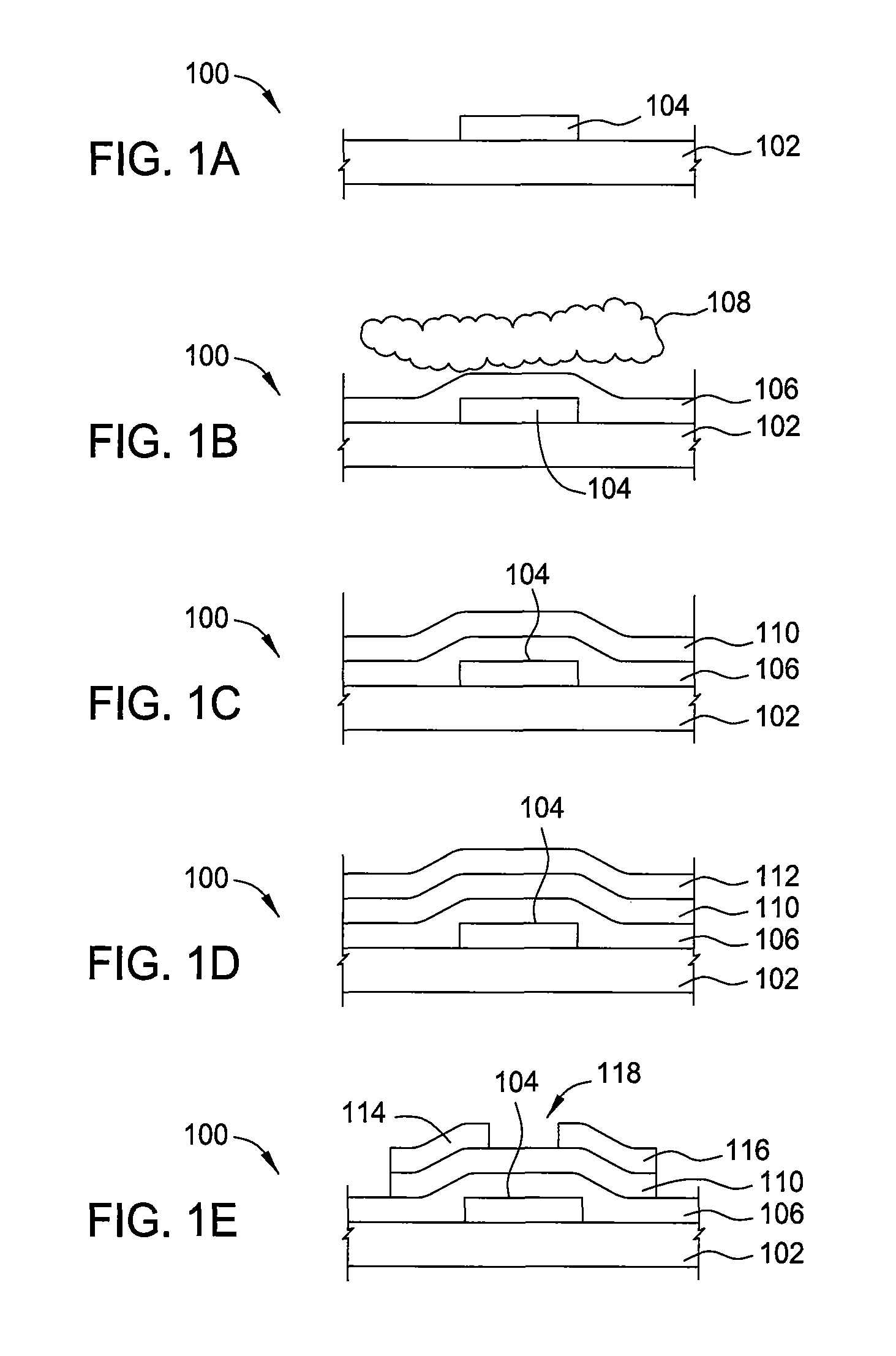
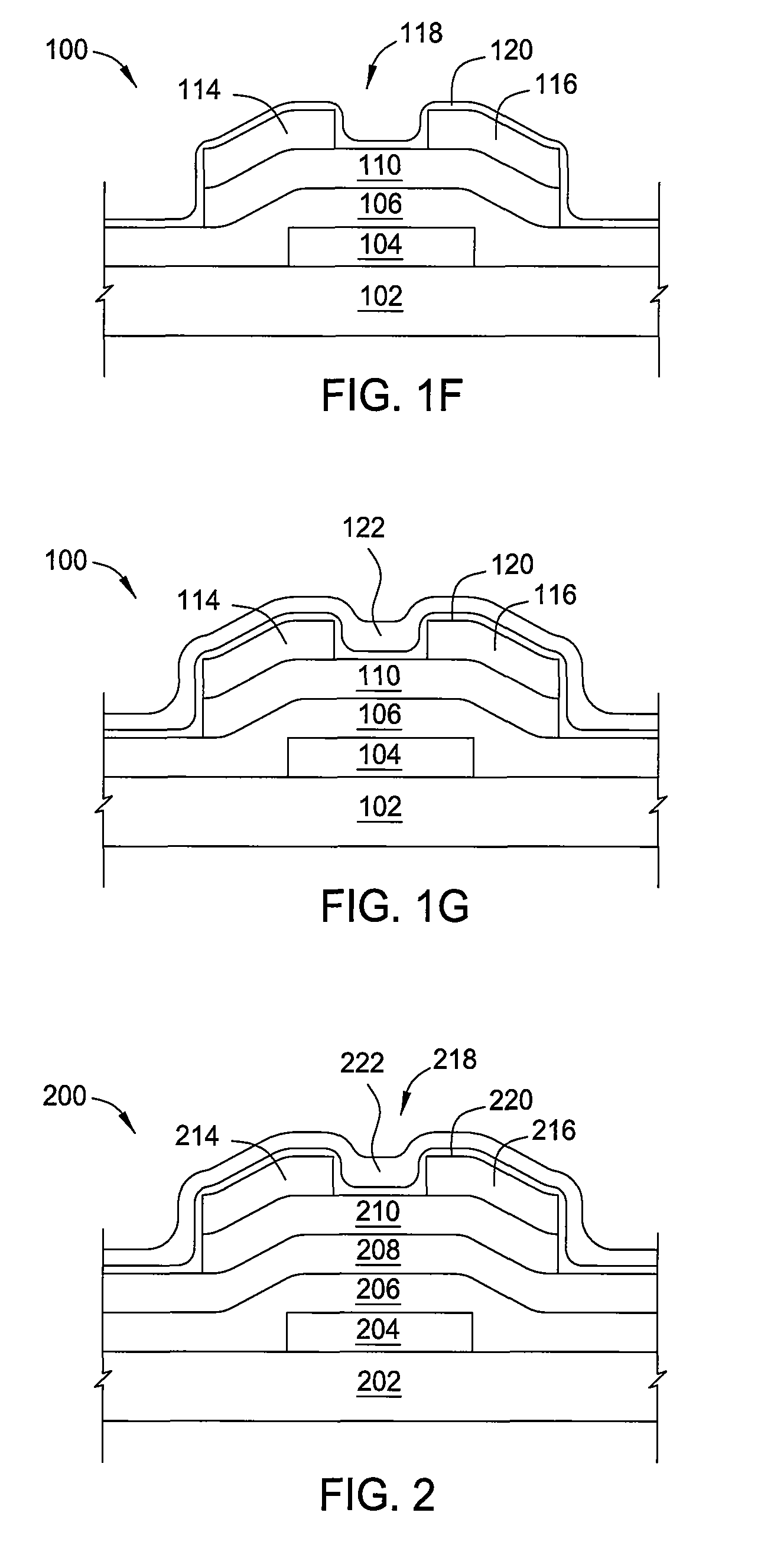
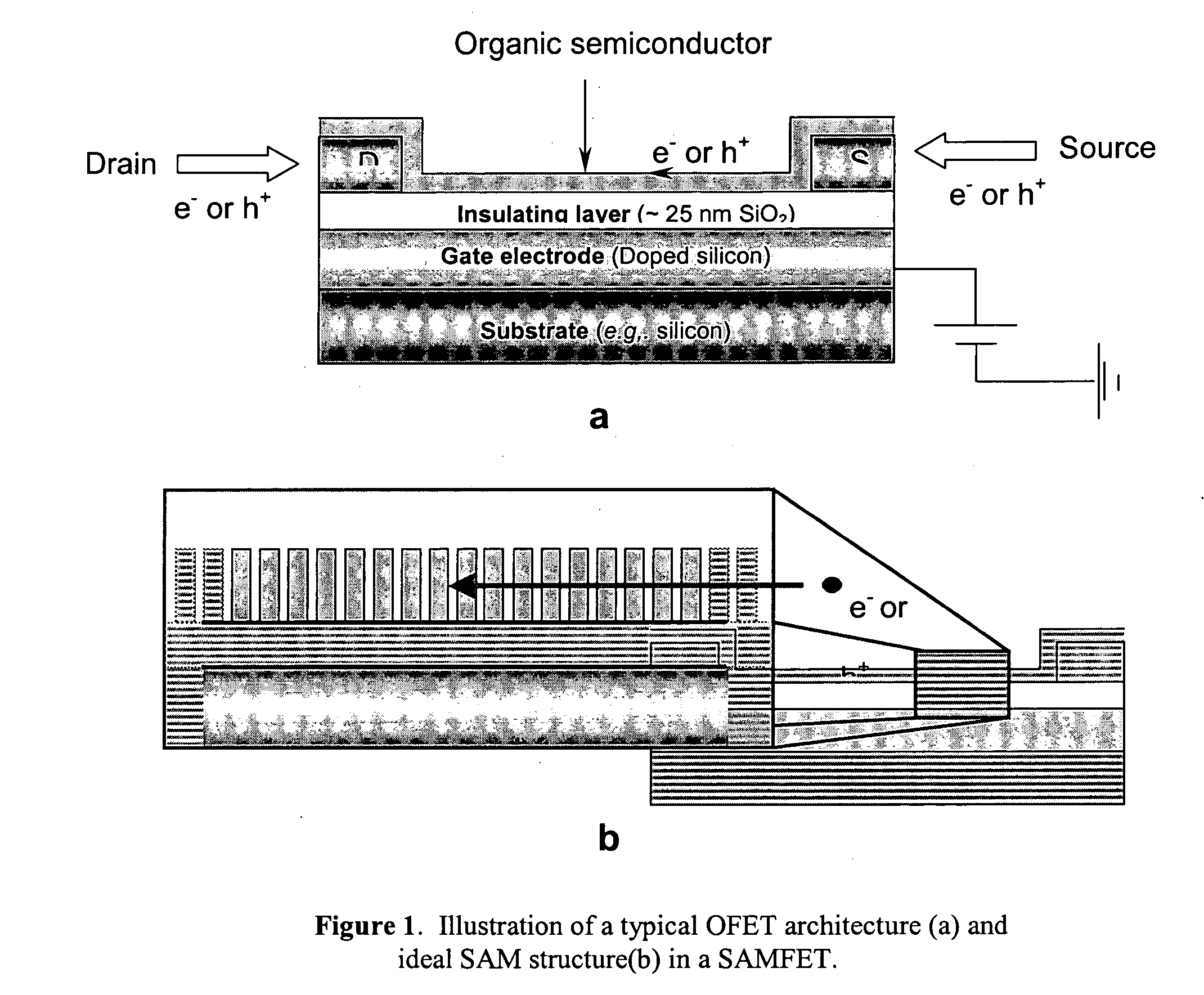
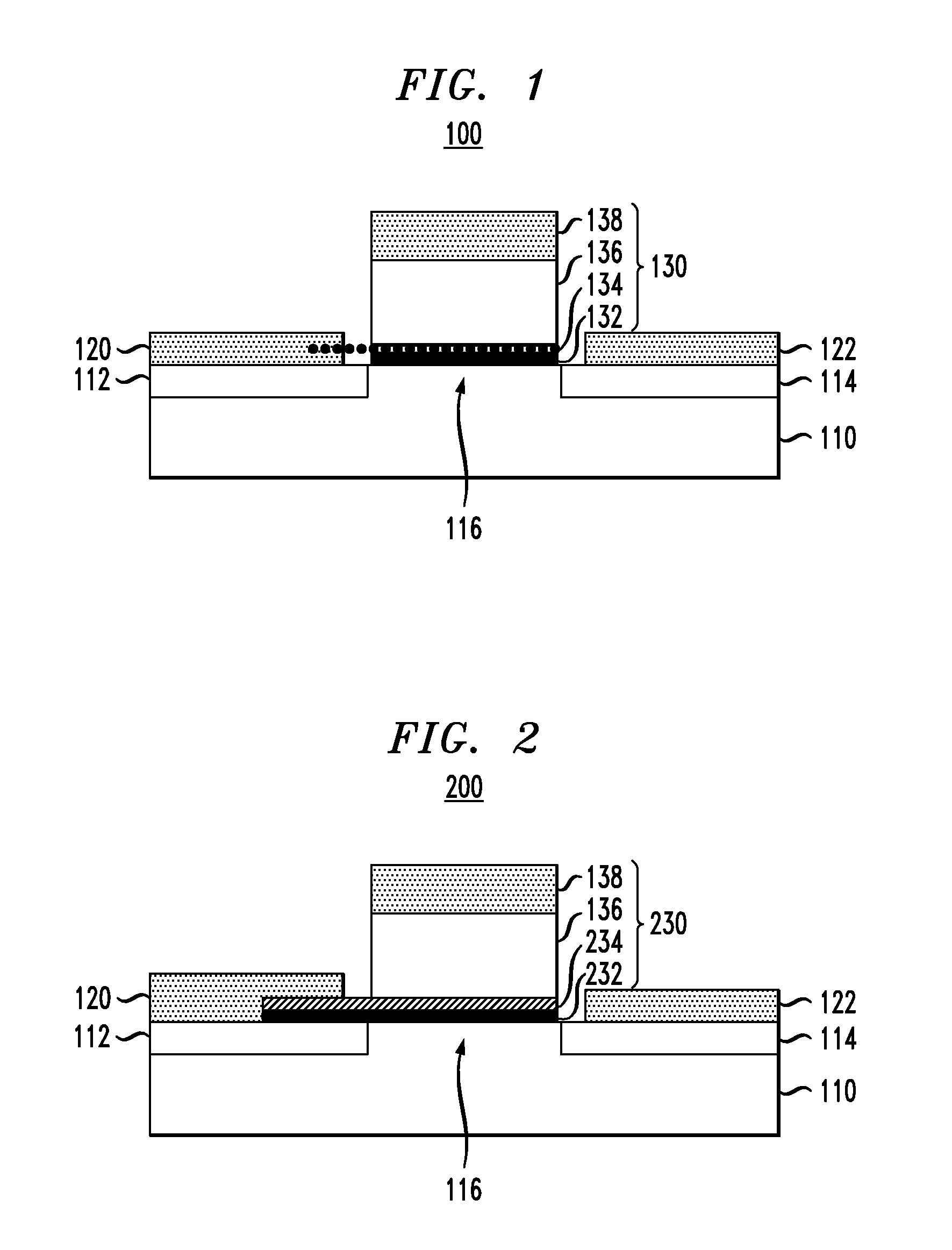
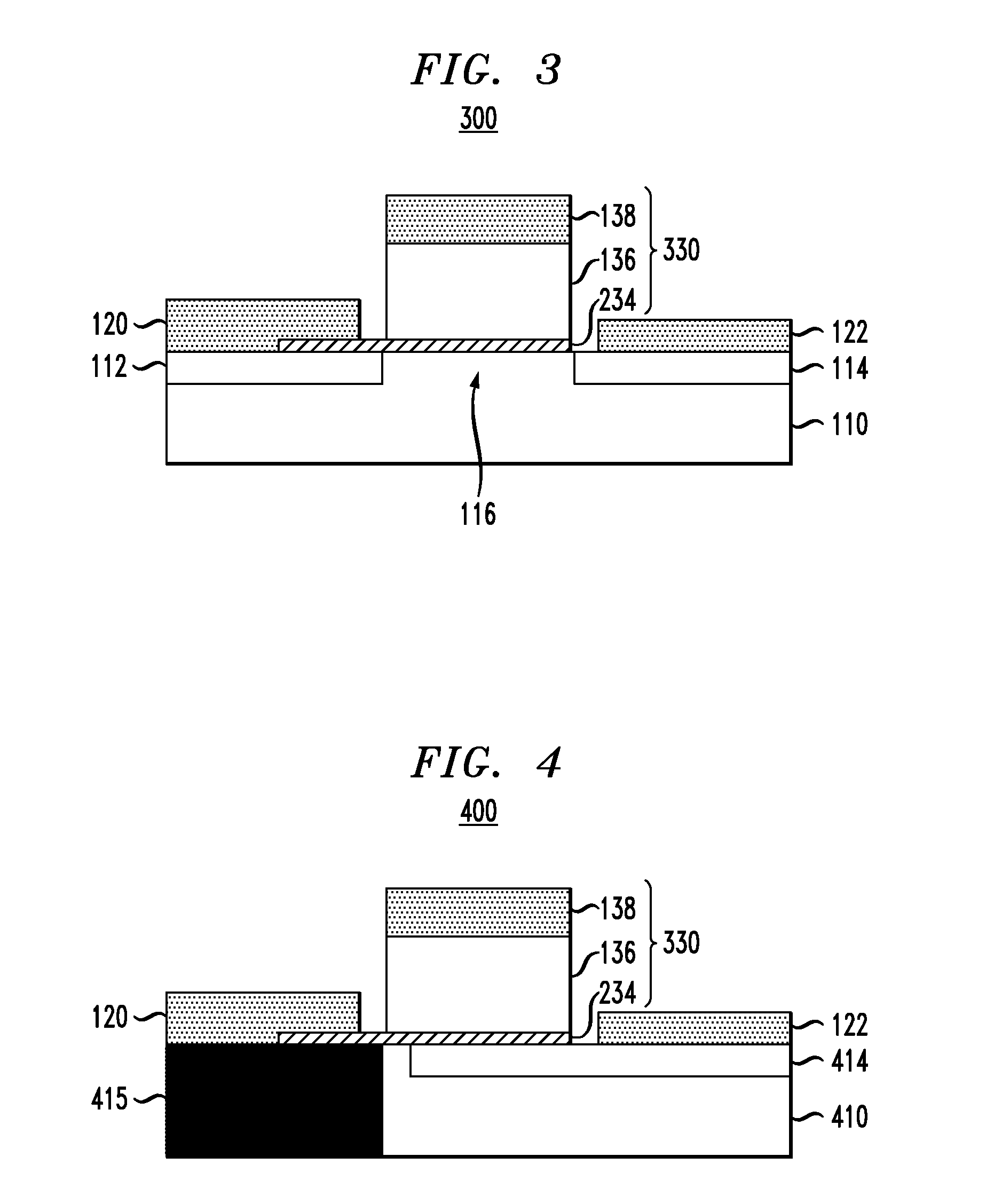
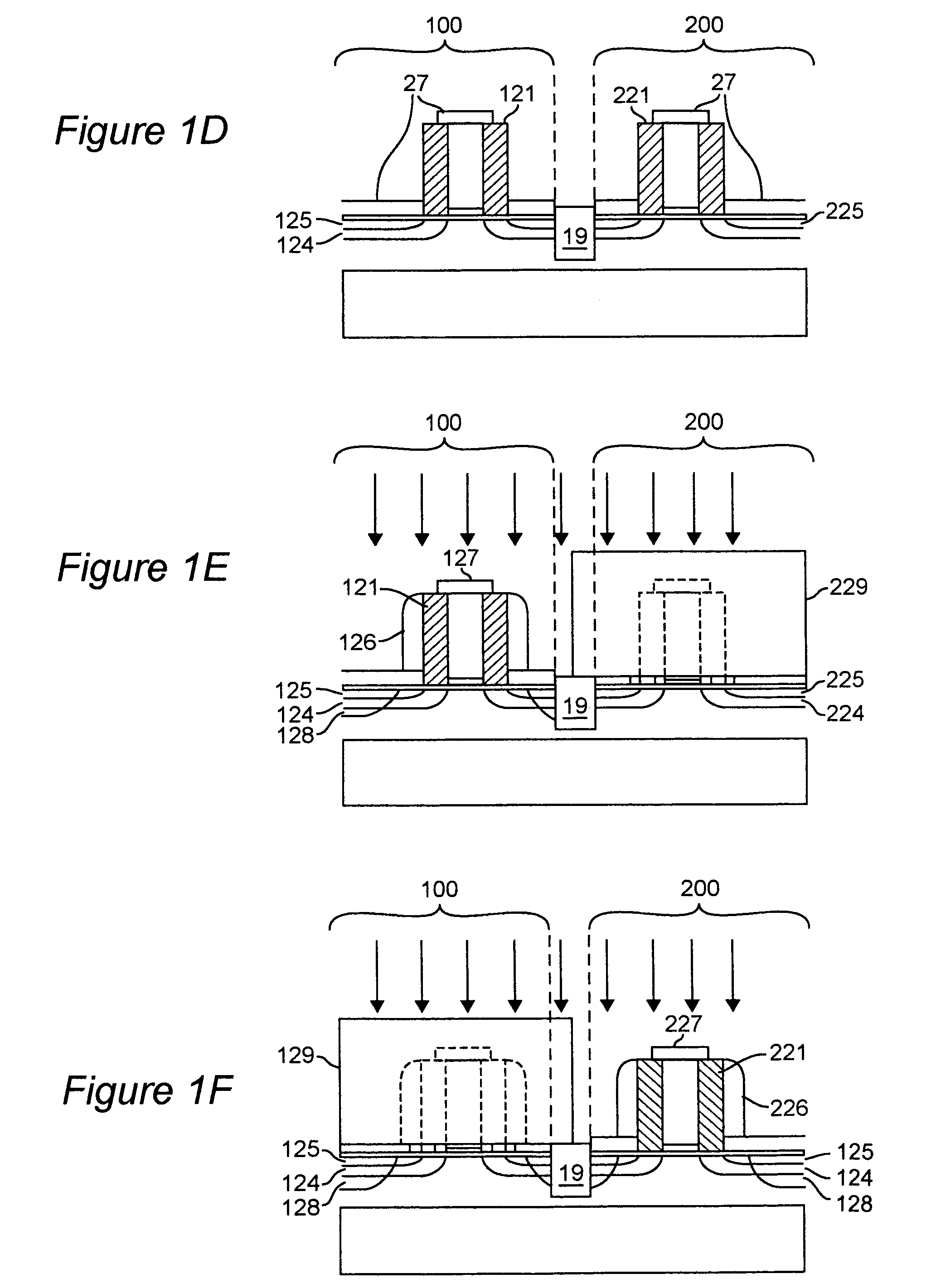
Thin-film field-effect transistor with organic semiconductor requiring low operating voltages
InactiveUS6344660B1Reduce thicknessImprove mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceFlat panel display
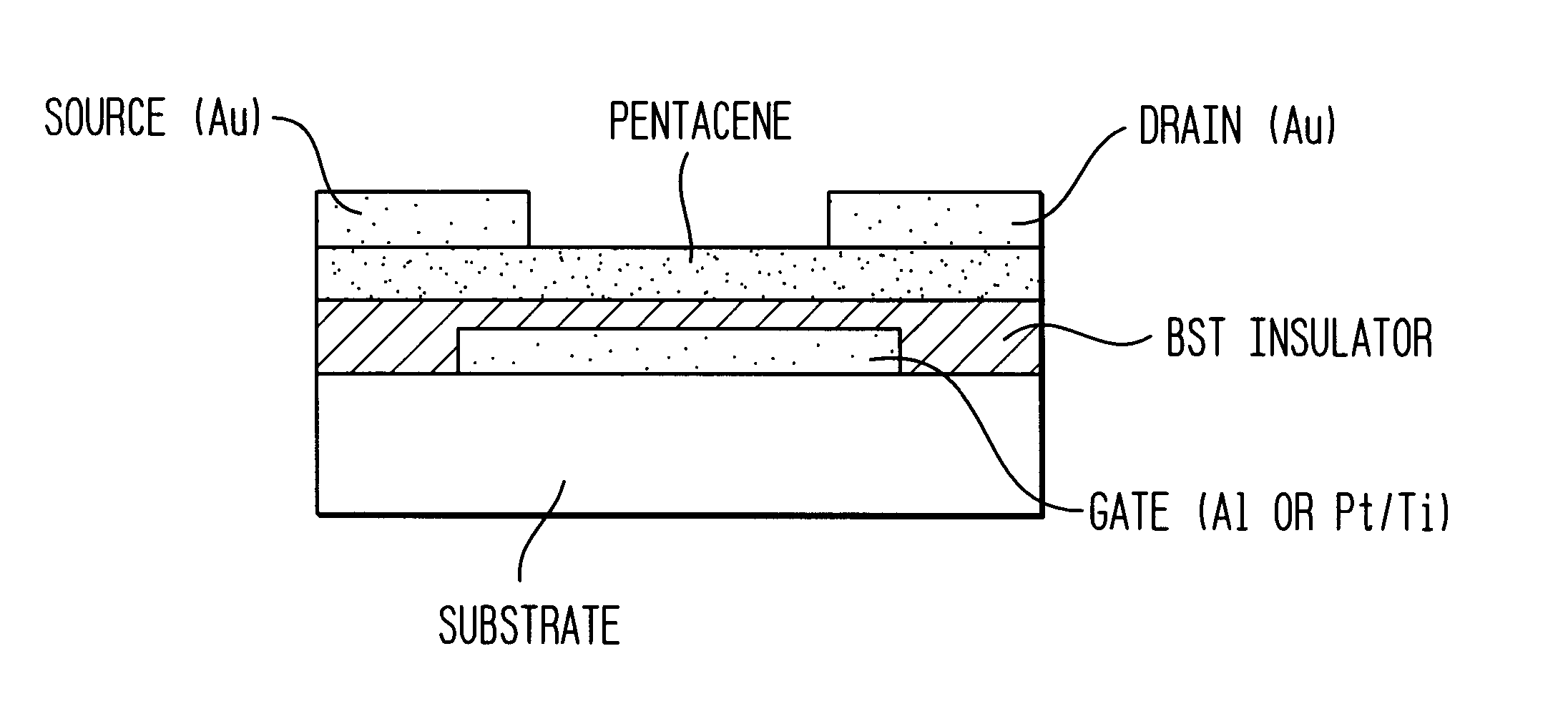
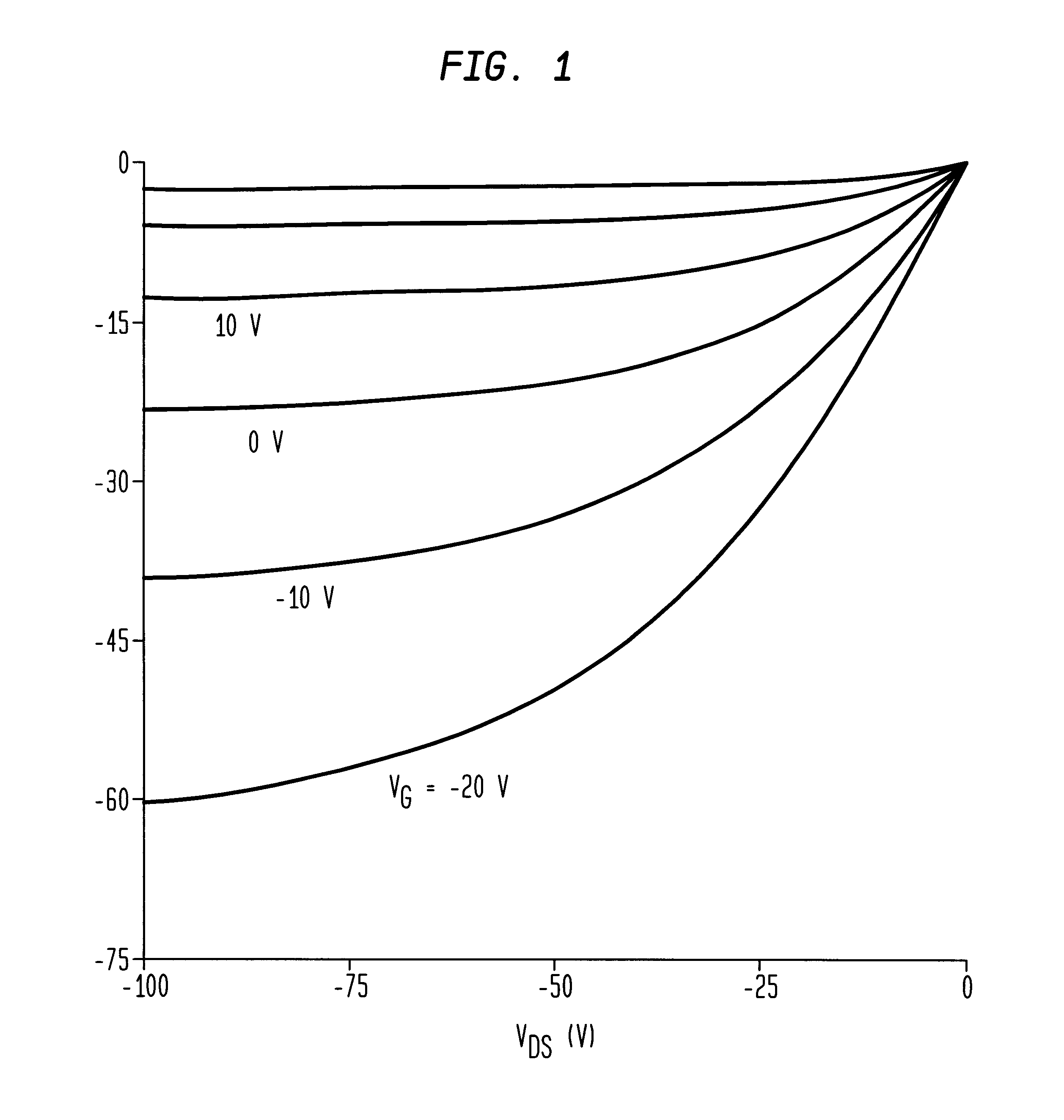
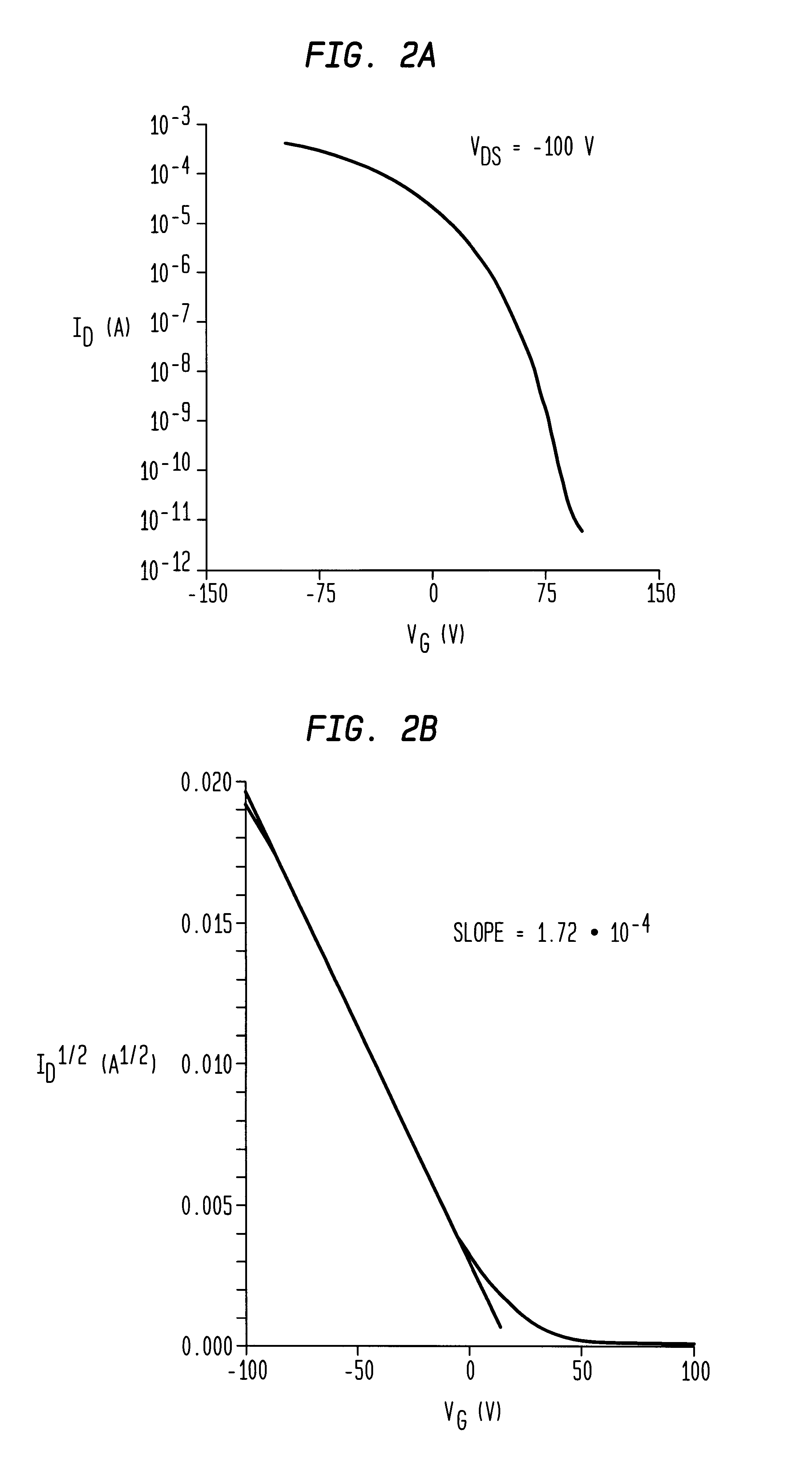
A thin film transistor (TFT) device structure based on an organic semiconductor material, that exhibits a high field effect mobility, high current modulation and a low sub-threshold slope at lower operating voltages than the current state of the art organic TFT devices. The structure comprises a suitable substrate disposed with he following sequence of features: a set of conducting gate electrodes covered with a high dielectric constant insulator, a layer of the organic semiconductor, sets of electrically conducting source and drain electrodes corresponding to each of the gate lines, and an optional passivation layer that can overcoat and protect the device structure. Use of high dielectric constant gate insulators exploits the unexpected gate voltage dependence of the organic semiconductor to achieve high field effect mobility levels at very low operating voltages. Judicious combinations of the choice of this insulator material and the means to integrate it into the TFT structure are taught that would enable easy fabrication on glass or plastic substrates and the use of such devices in flat panel display applications.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Capping layers for metal oxynitride TFTS
ActiveUS8012794B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHydrogenSub threshold
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
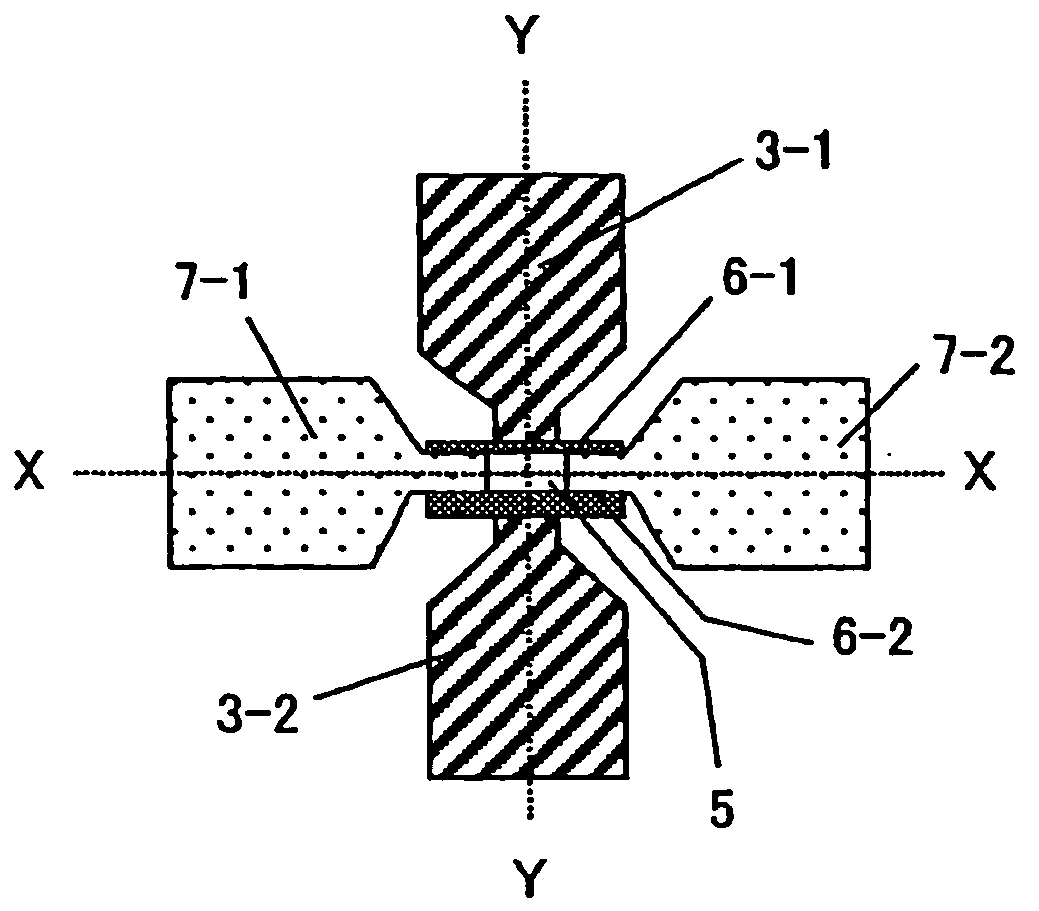
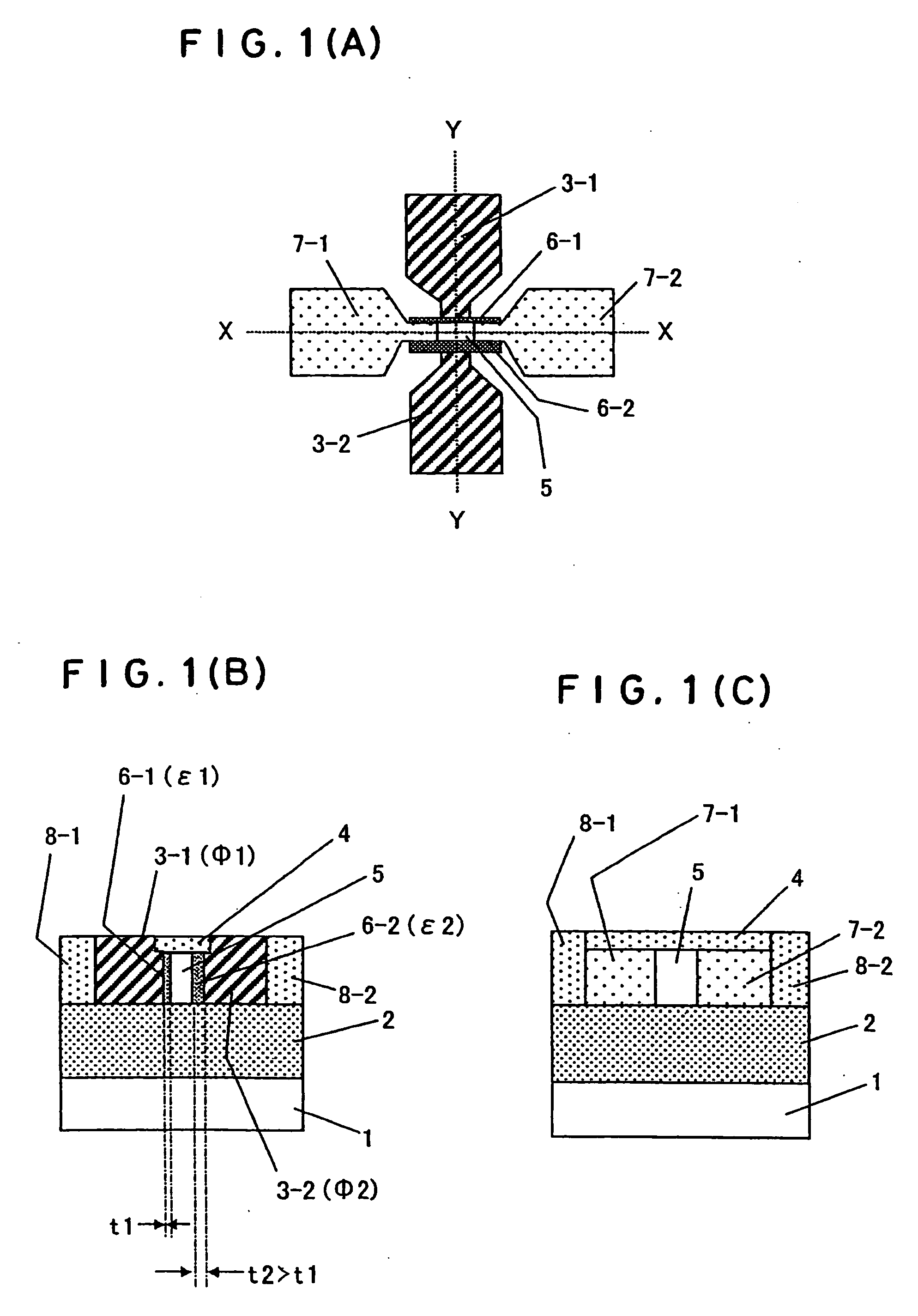
Dual-gate field effect transistor
InactiveUS20070029623A1Small thicknessHigh dielectric constantTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge carrierVertical channel
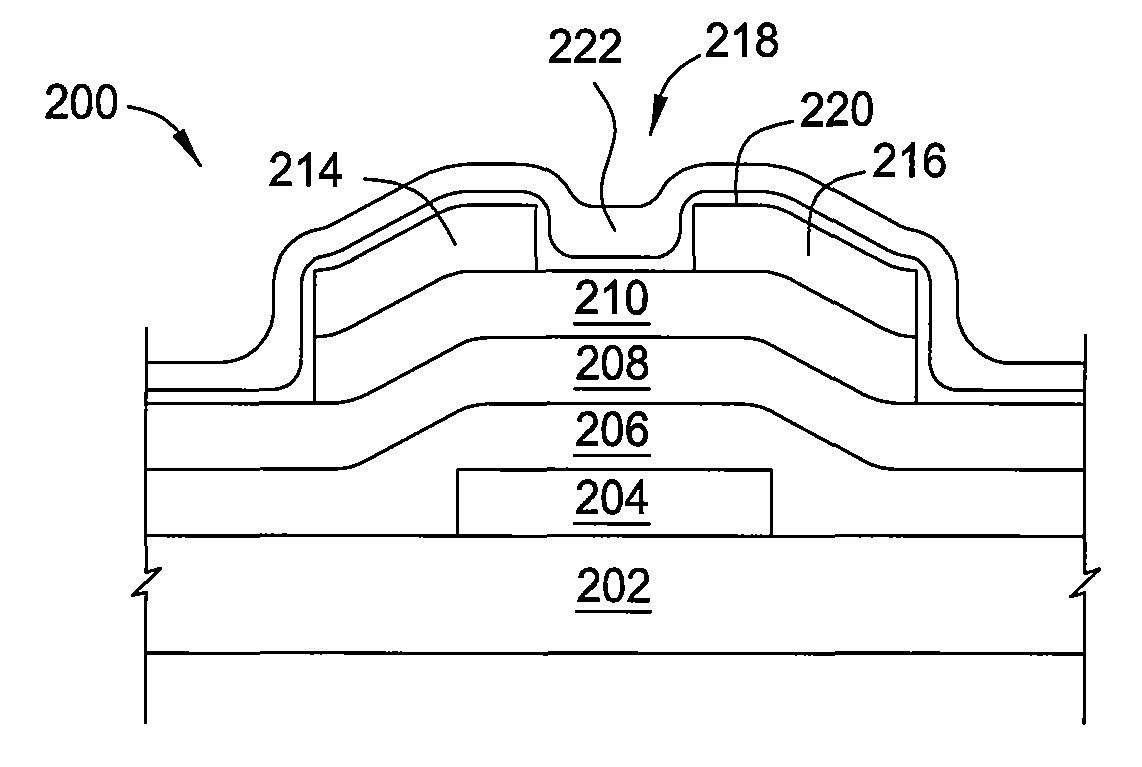
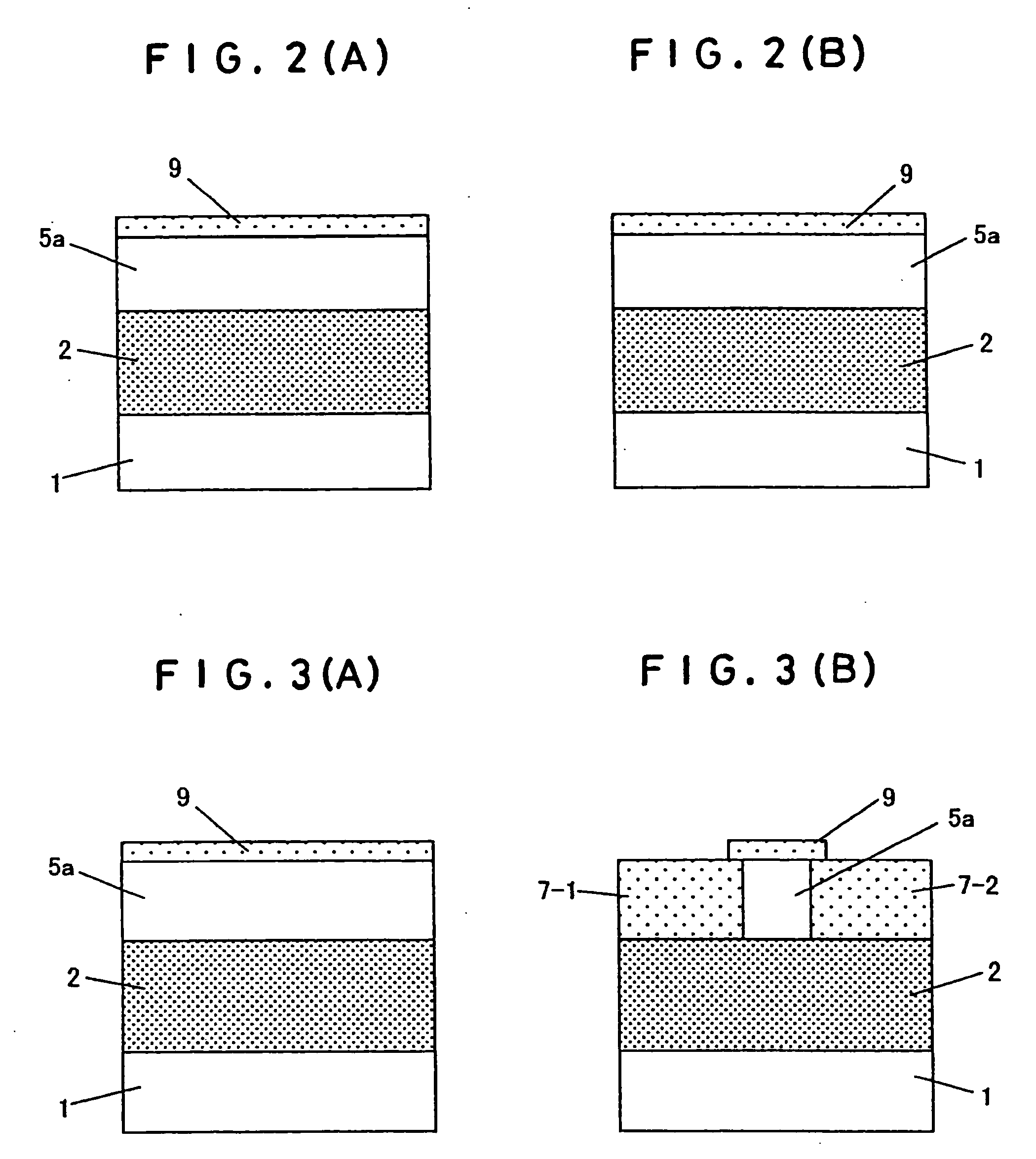
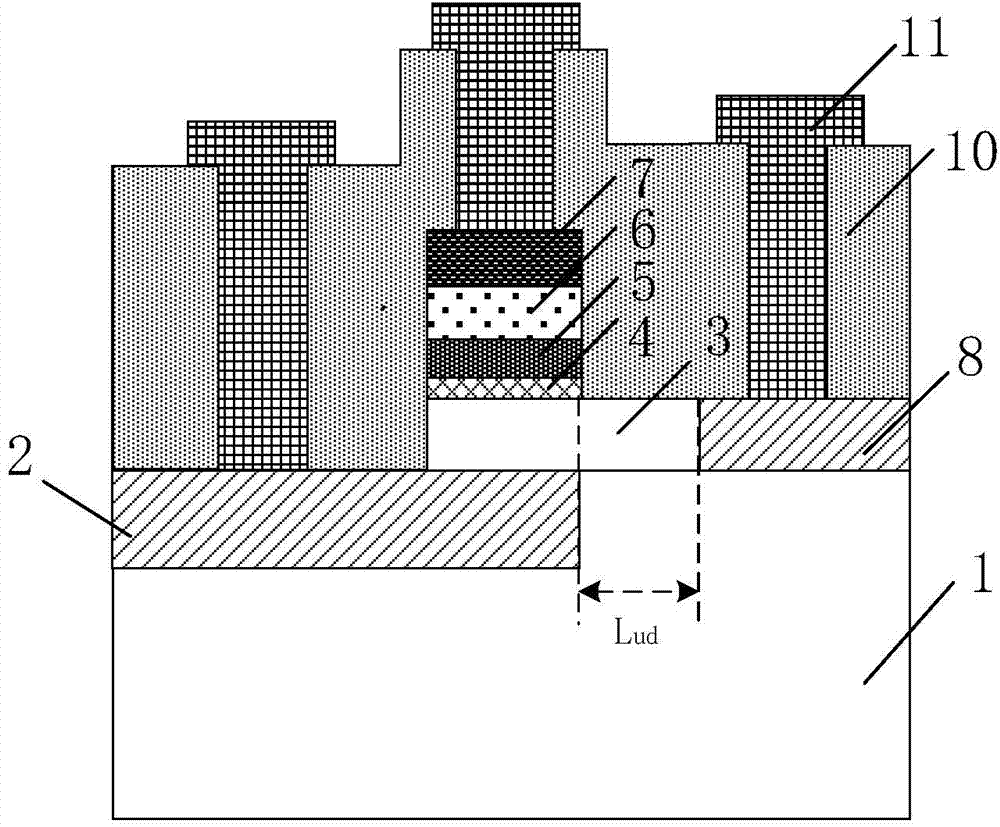
A dual-gate field effect transistor includes a substrate 1, a source 7-1, a drain 7-2, a vertical channel 5 provided between the source and the drain as rising from the substrate, a pair of gate insulation films 6-1 and 6-2 sandwiching the channel from a direction orthogonal to a carrier-running direction in the channel and a pair of gate electrodes 3-1 and 3-2 facing the vertical channel 5, respectively, via the pair of gate insulation films 6-1 and 6-2, wherein the pair of insulation films have different thicknesses t1 and t2. It is also possible that the pair of gate insulation films 6-1 and 6-2 have different permittivities ε1 and ε2 and that the pair of gate electrodes have different work functions Φ1 and Φ2. Thus, it is possible to set the threshold voltage of the dual-gate field effect transistor to a desired value when fabricating it. Furthermore, it is possible to avoid the problem of an increase in subthreshold slope that occurs in the prior art.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Formation of ordered thin films of organics on metal oxide surfaces
InactiveUS20050285101A1Total current dropEasy to fallMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsOrganic acidSub threshold
Owner:HANSON ERIC +5
Tunnelling field effect transistor based on work function of heterogeneous gate and forming method of tunnelling field effect transistor
ActiveCN102169900ASmall subthreshold slopeIncrease drive currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentGate dielectric
The invention provides a tunnelling field effect transistor based on a work function of a heterogeneous gate. The tunnelling field effect transistor comprises a substrate, a channel region, a source region, a drain region, a gate stack and side walls, wherein the channel region is formed in the substrate; the source region and the drain region are formed on two sides of the channel region; the drain region is in a first doping type; the source region is in a second doping type; the gate stack is formed on the channel region; the side walls are formed on the two sides of the gate stack; the gate stack comprises a first gate dielectric layer and at least comprises a first gate electrode and a second gate electrode; the first gate electrode and the second gate electrode are distributed alongdirection from the source region to the drain region and formed on the gate dielectric layer; and the first gate electrode and the second gate electrode have different work functions. In the embodiment of the invention, a lateral heterogeneous gate work function structure is introduced into the tunnelling field effect transistor, so that the distribution of energy bands of the channel region is modulated, the sub-threshold slope of the transistor is remarkably reduced, and a driving current is improved greatly at the same time.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
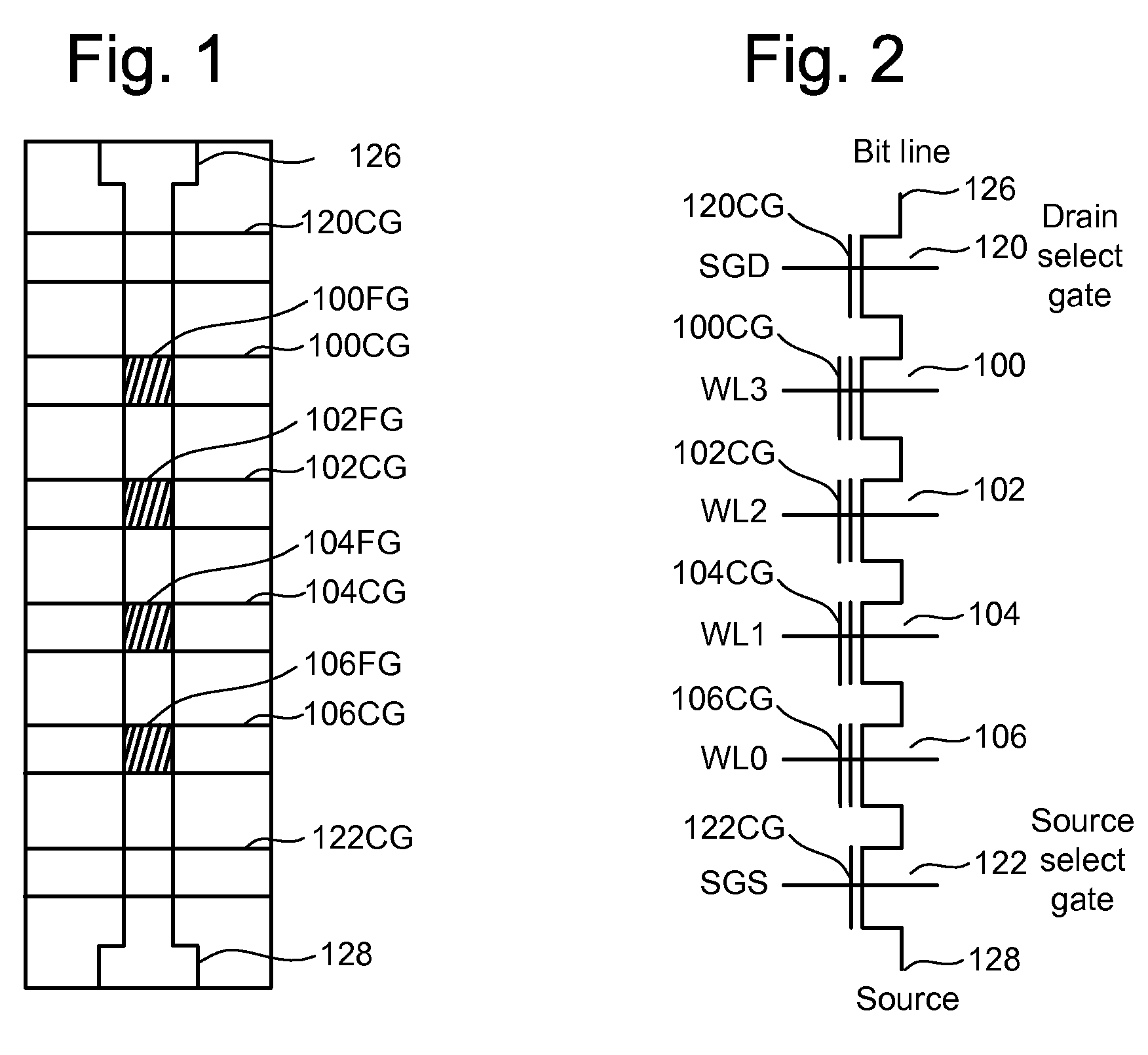
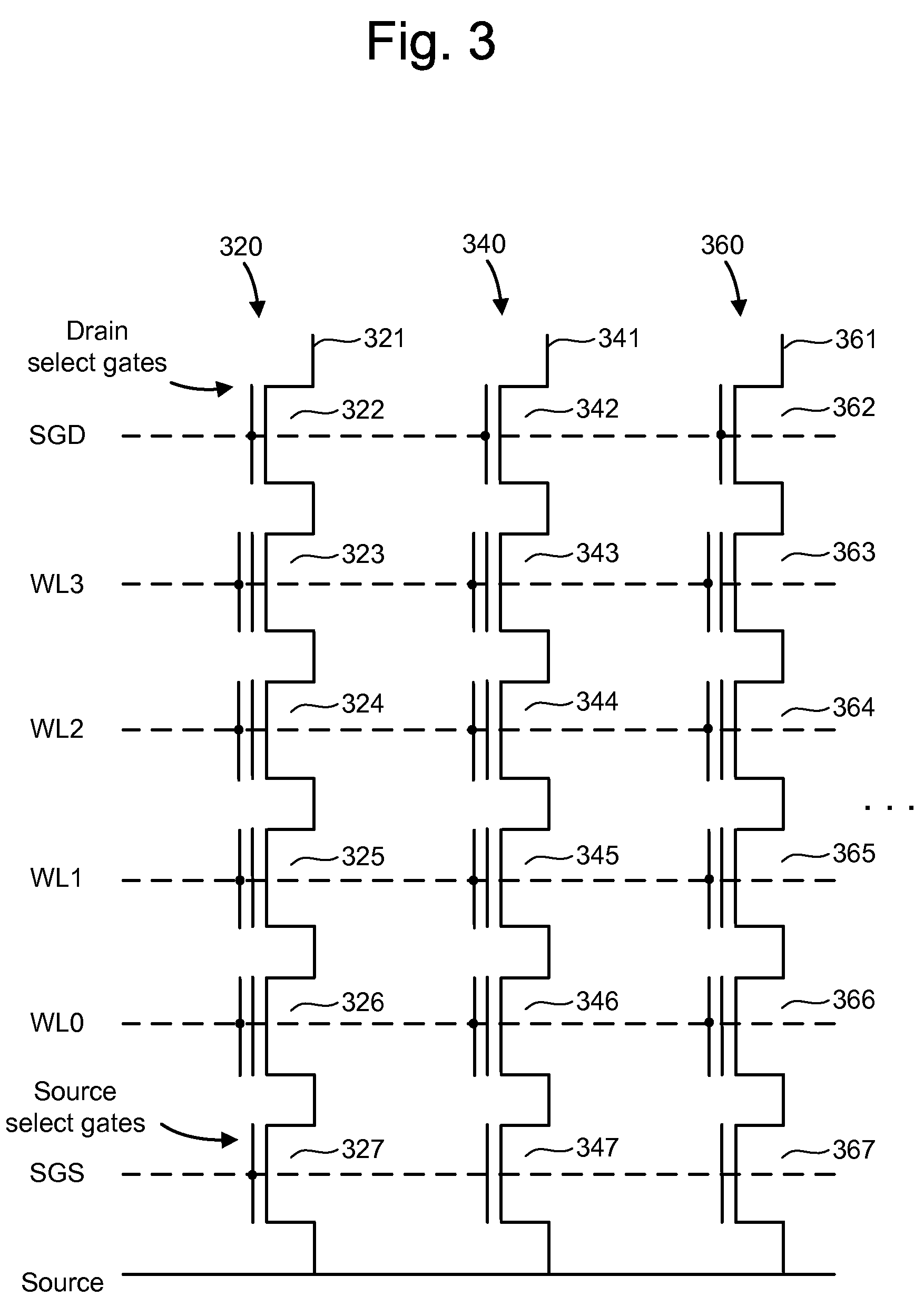
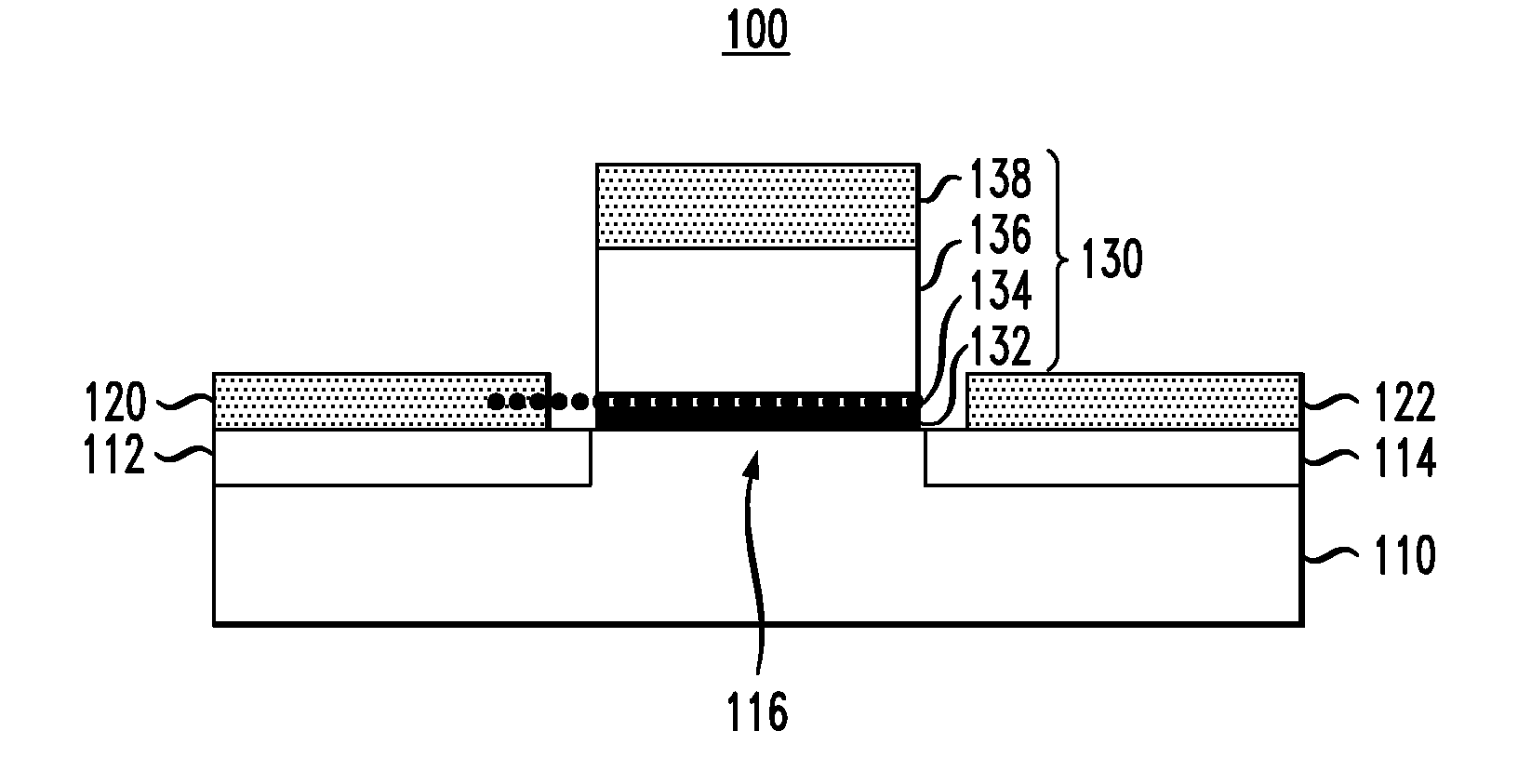
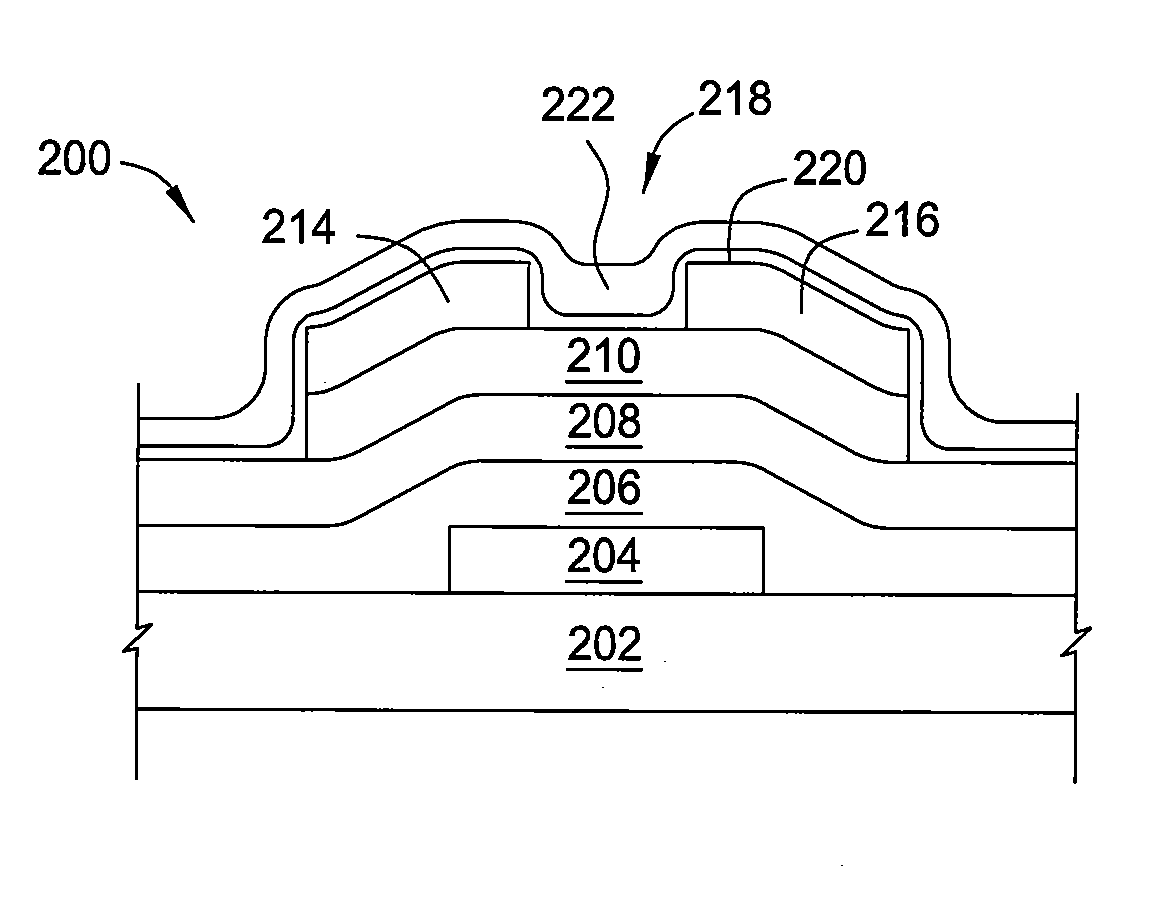
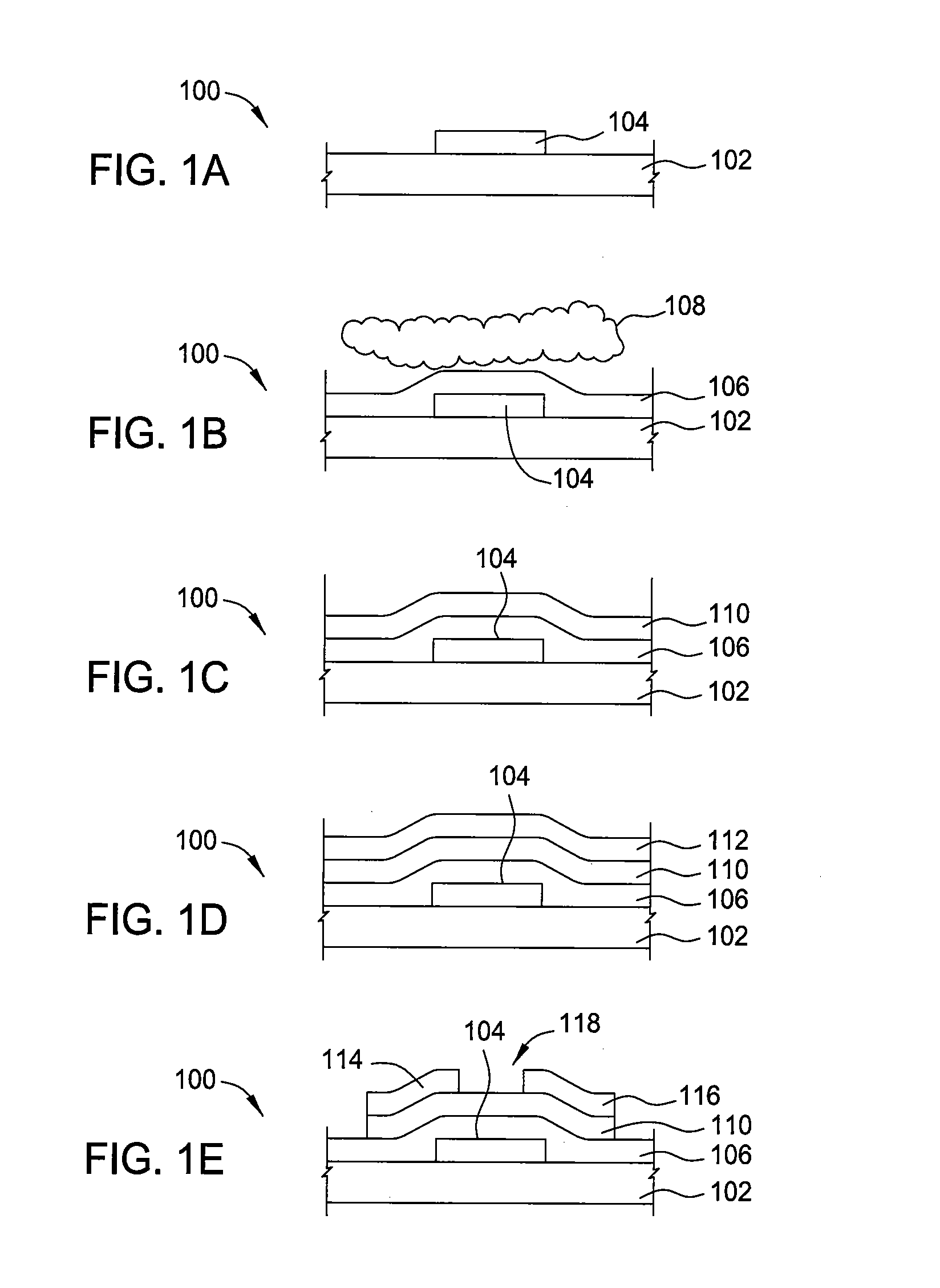
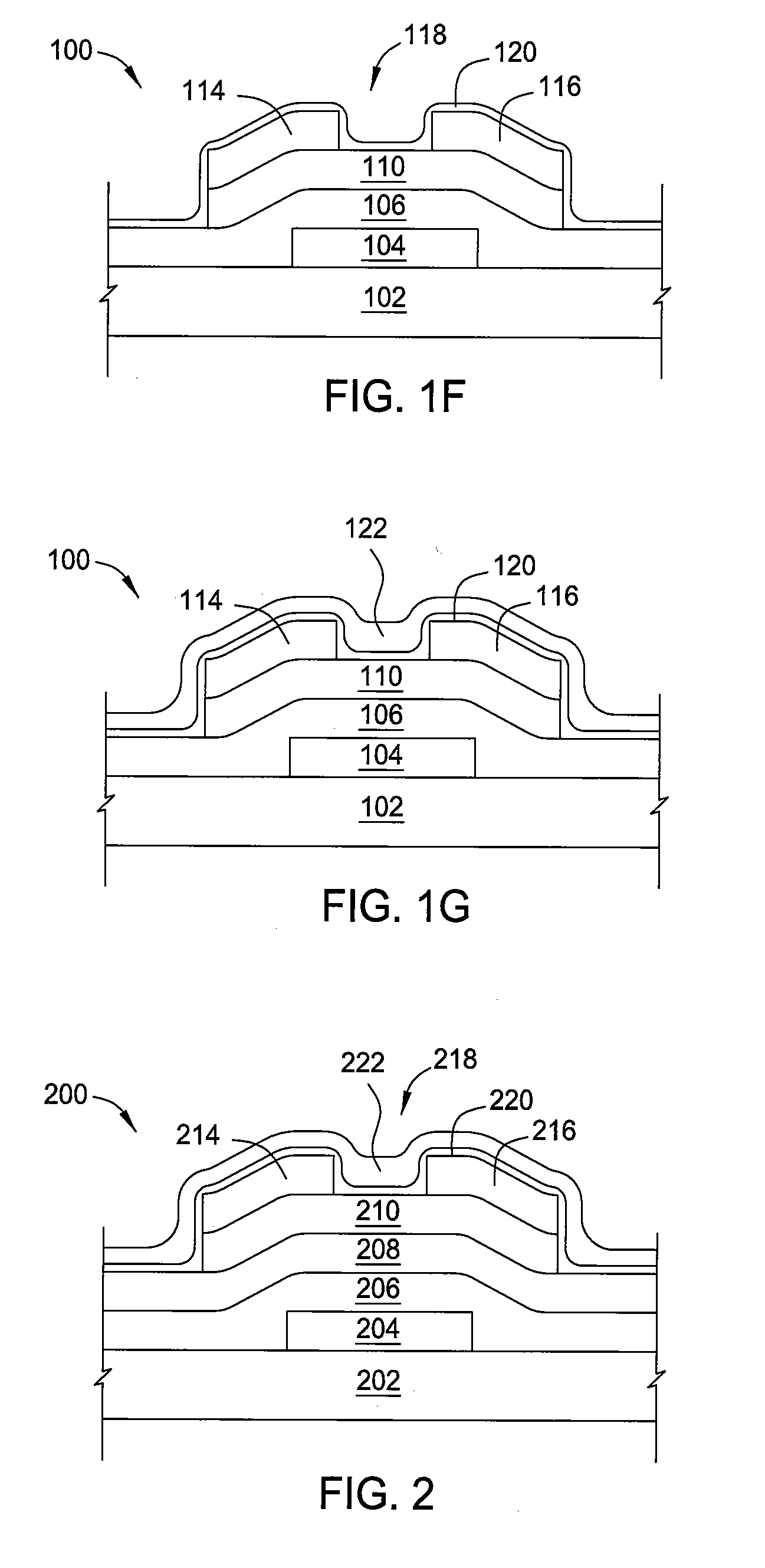
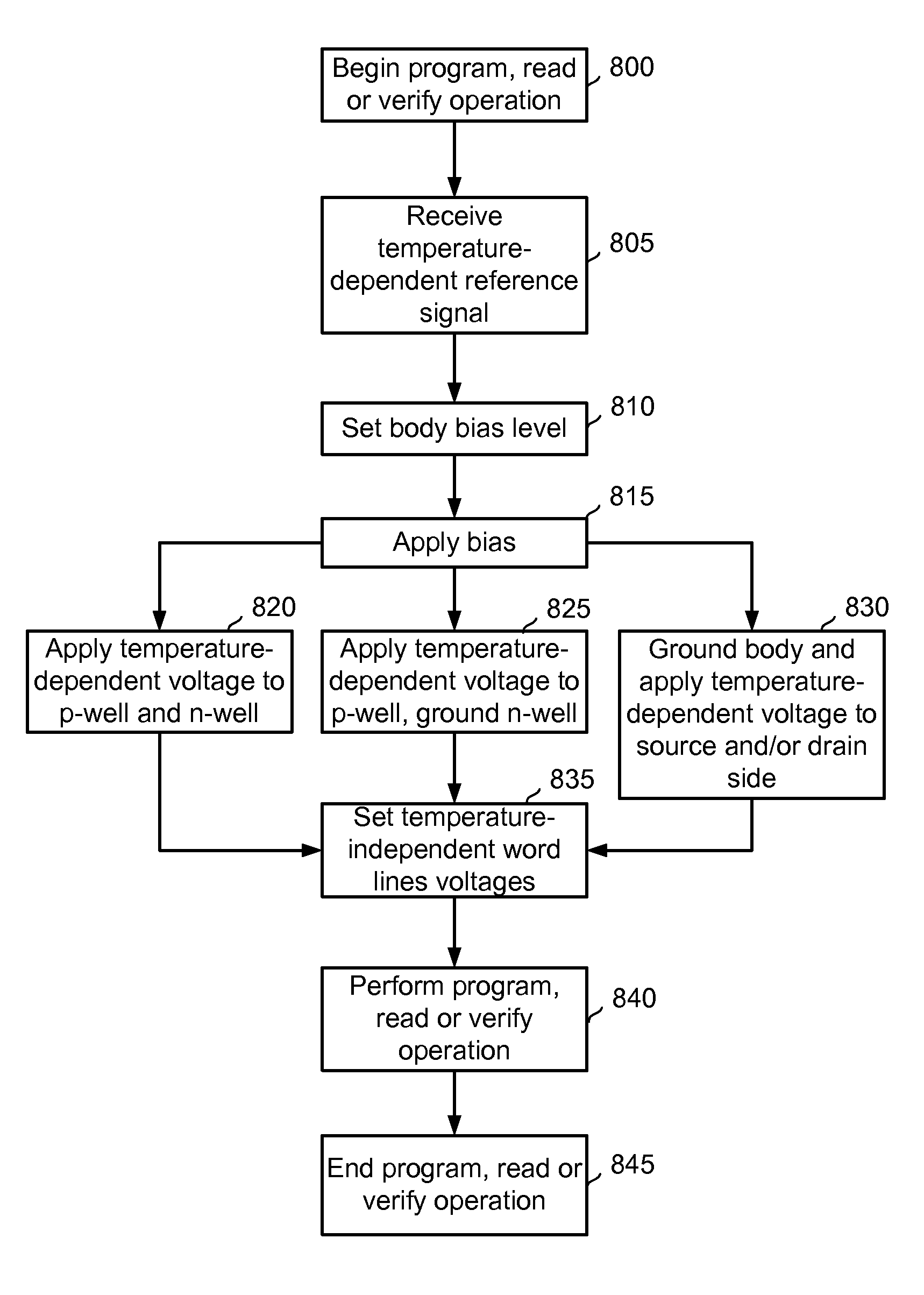
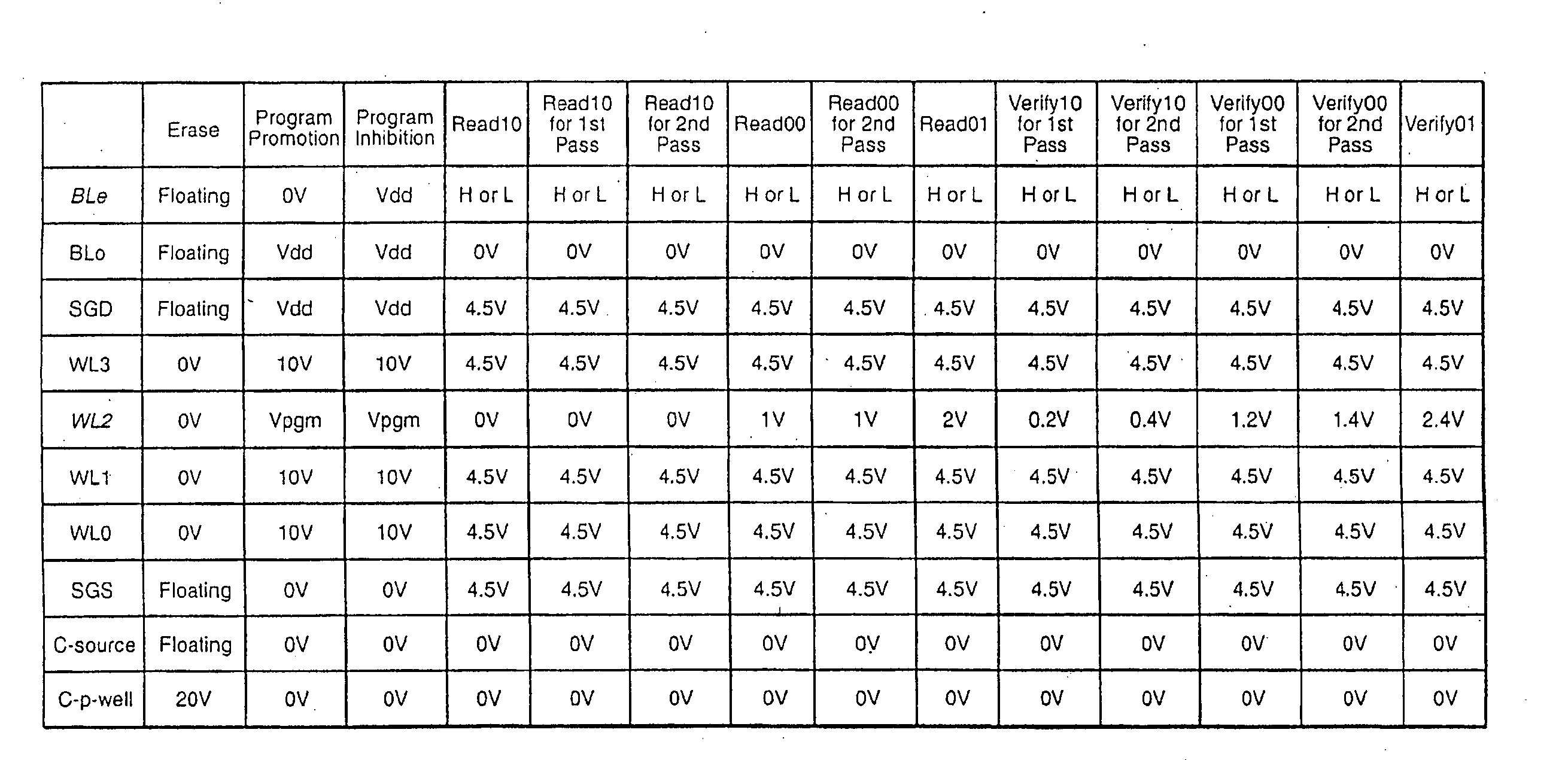
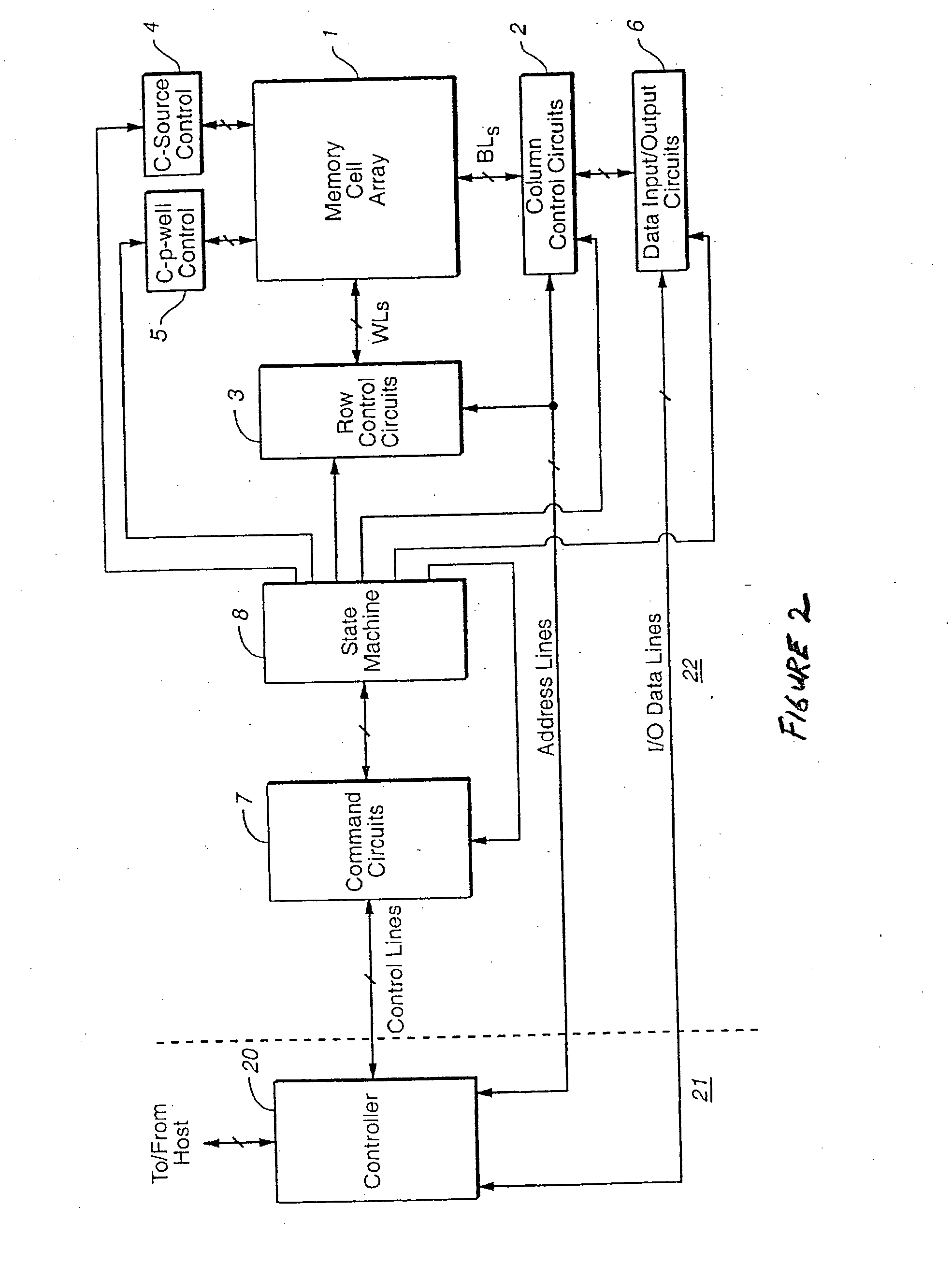
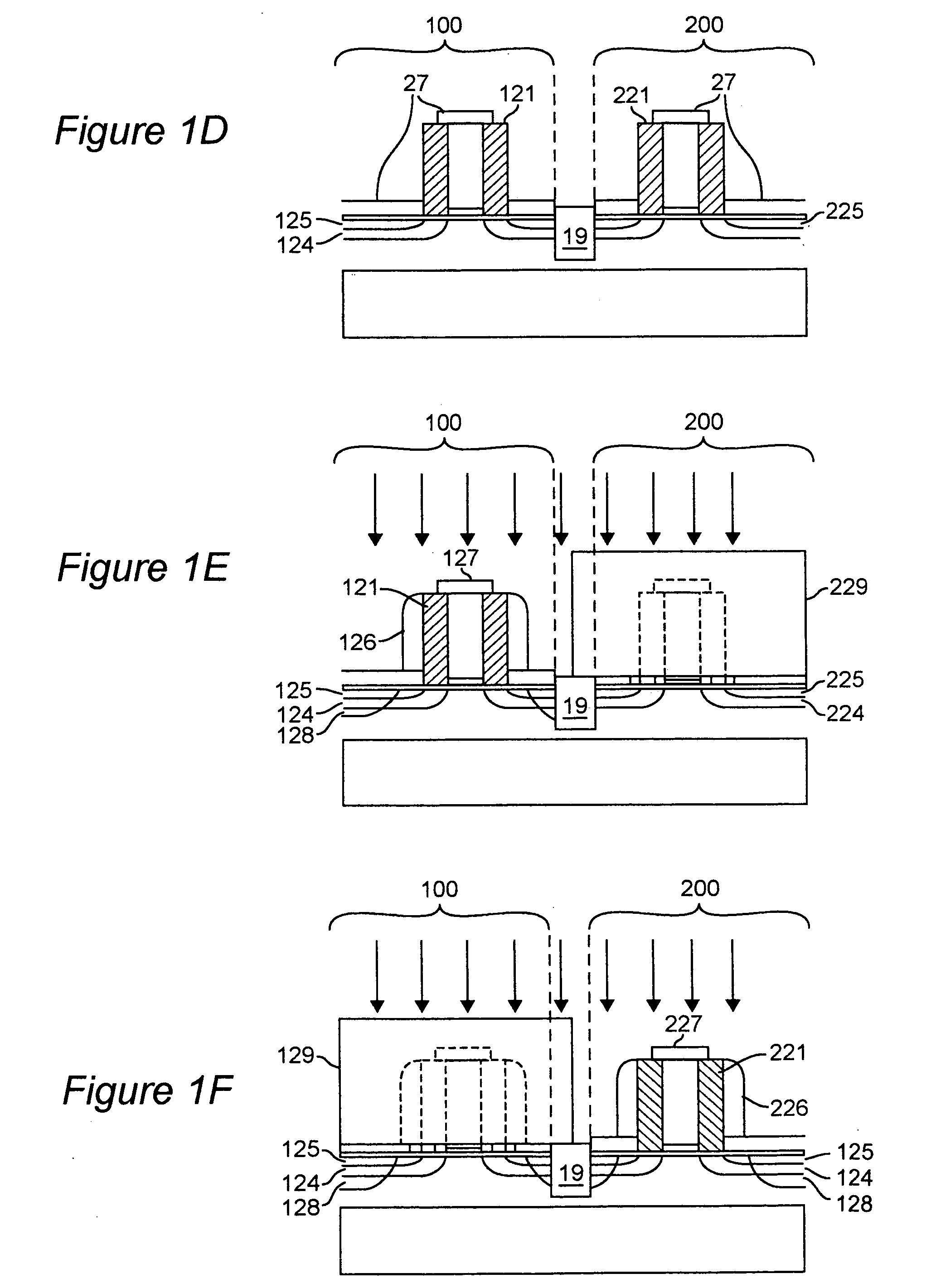
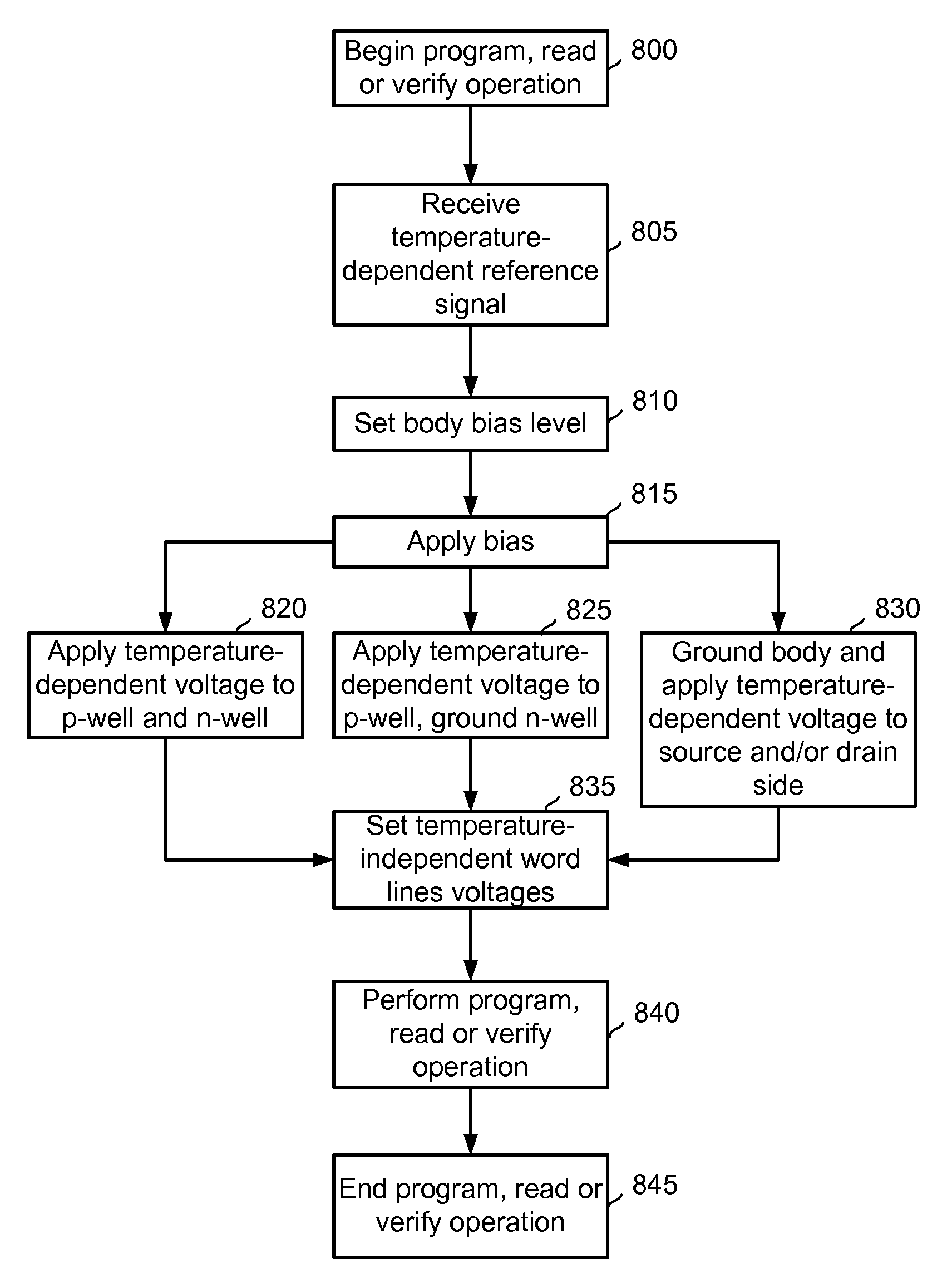
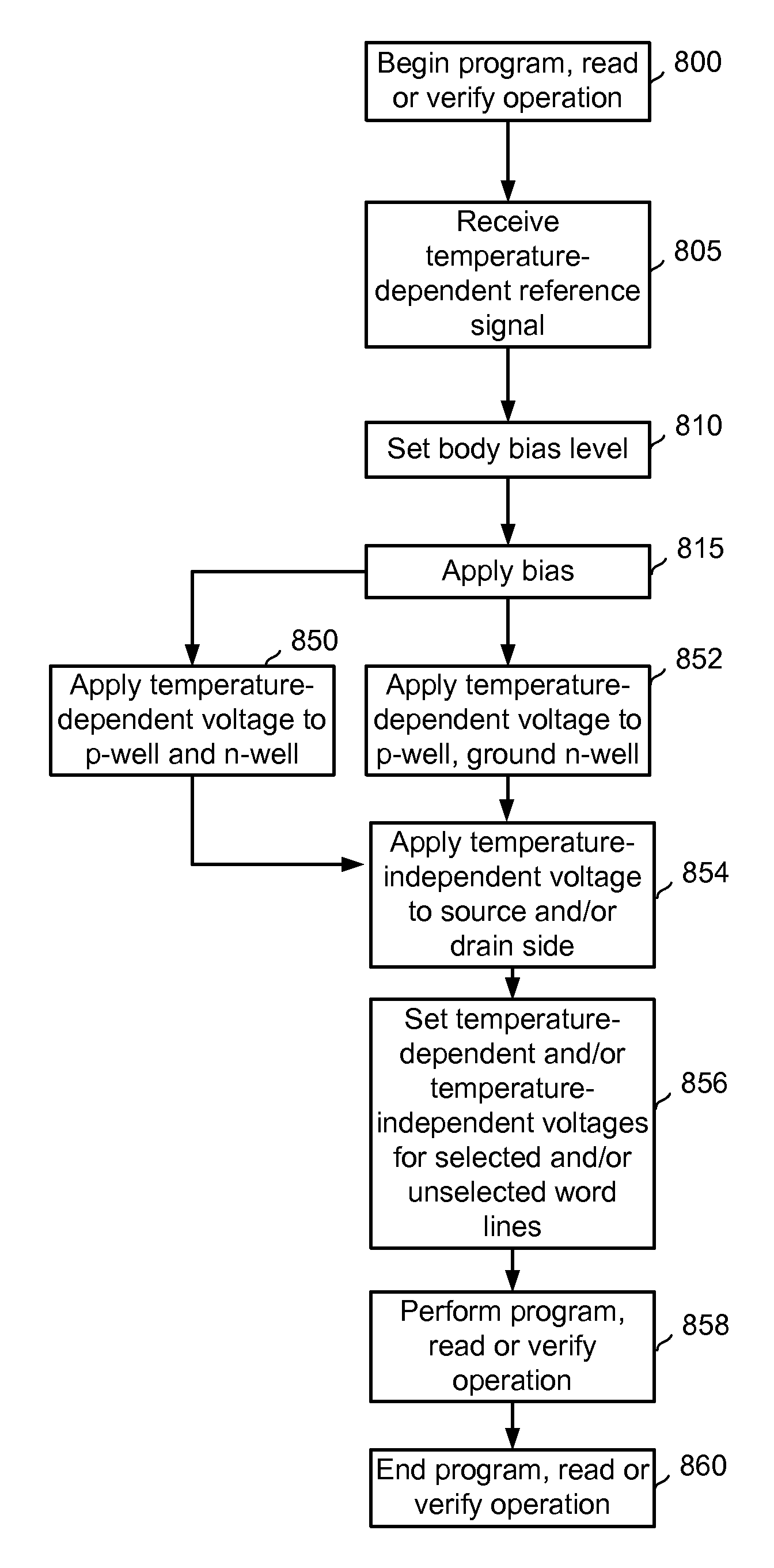
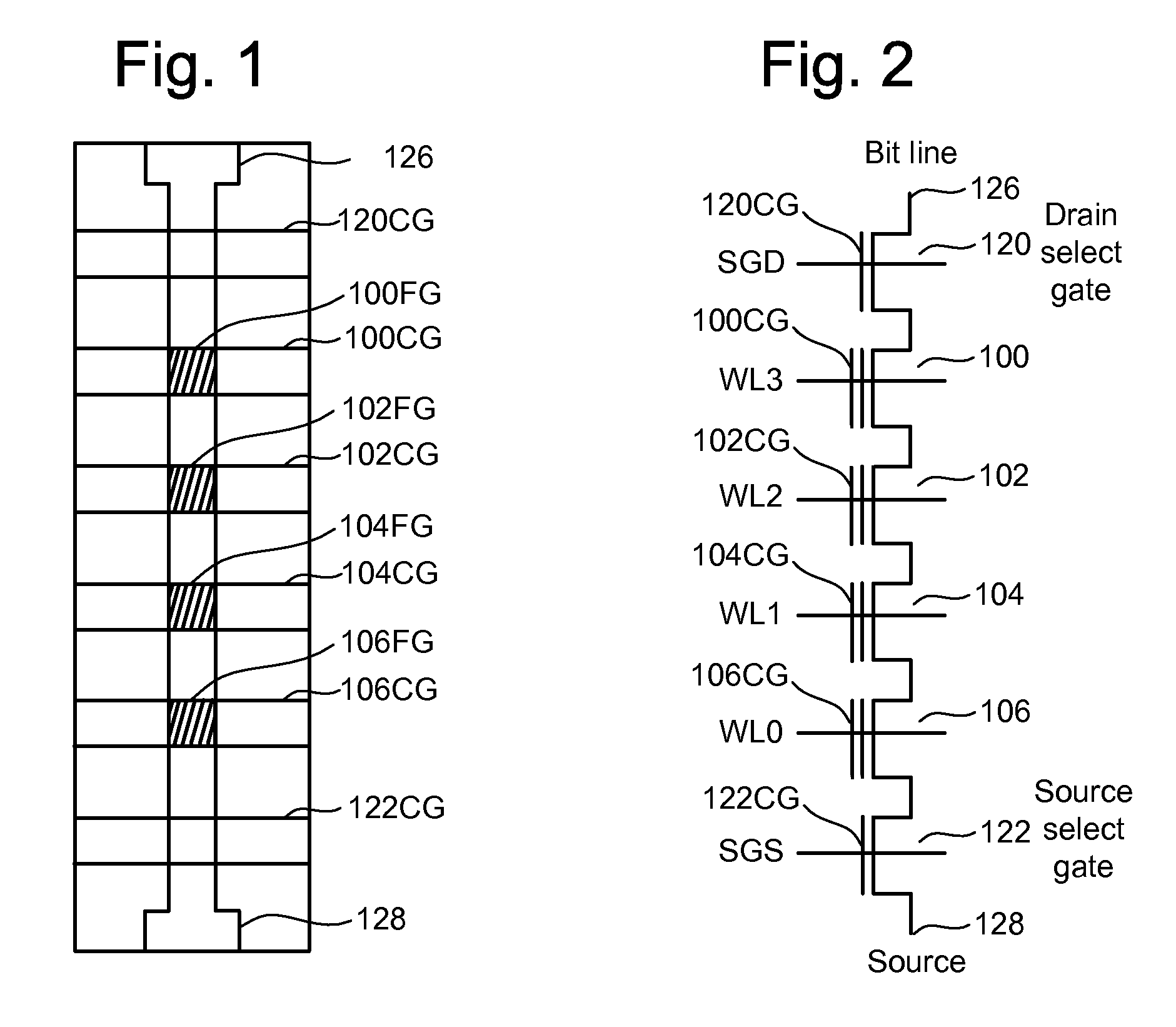
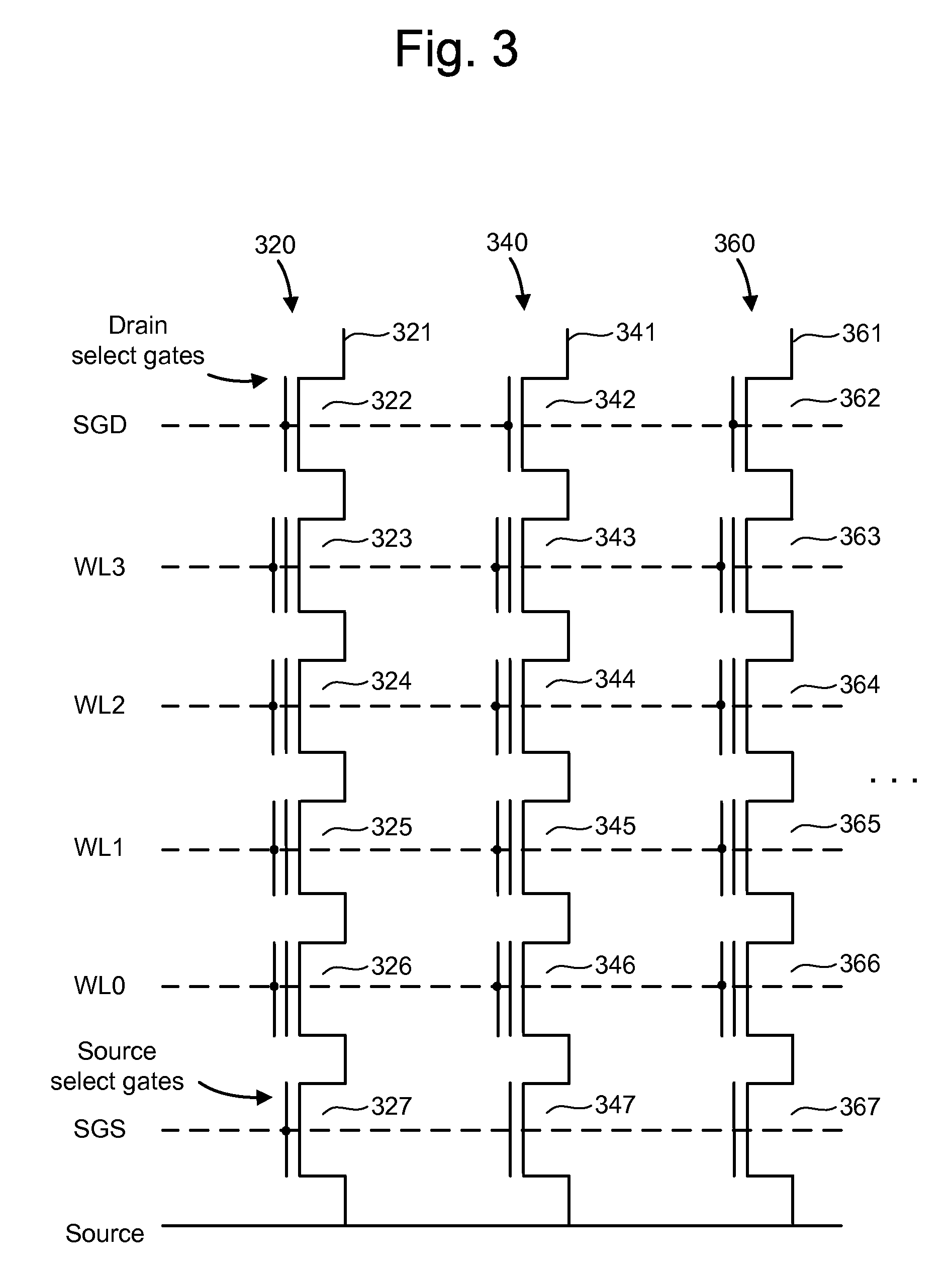
Biasing non-volatile storage to compensate for temperature variations
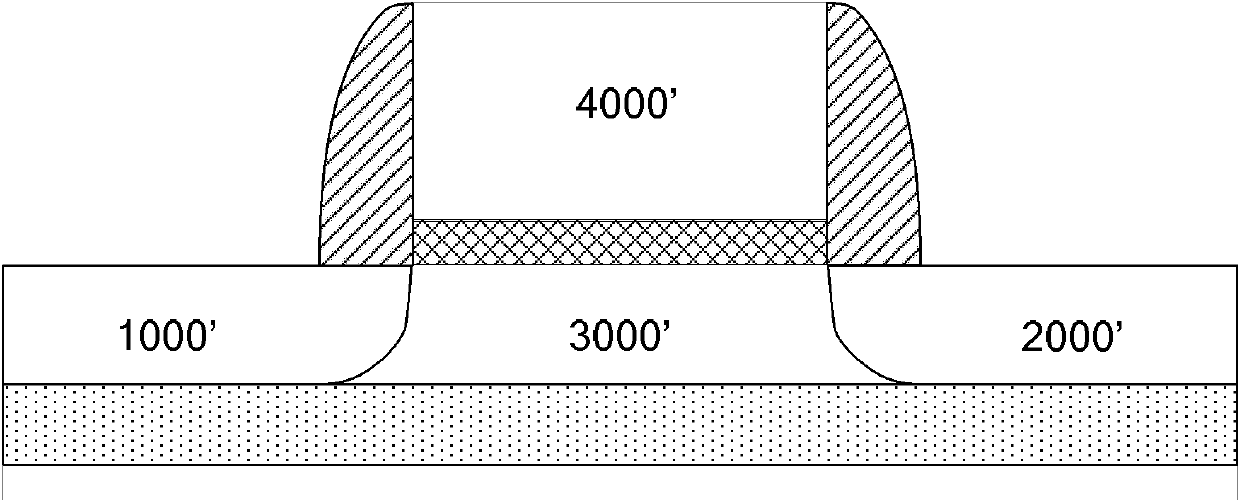
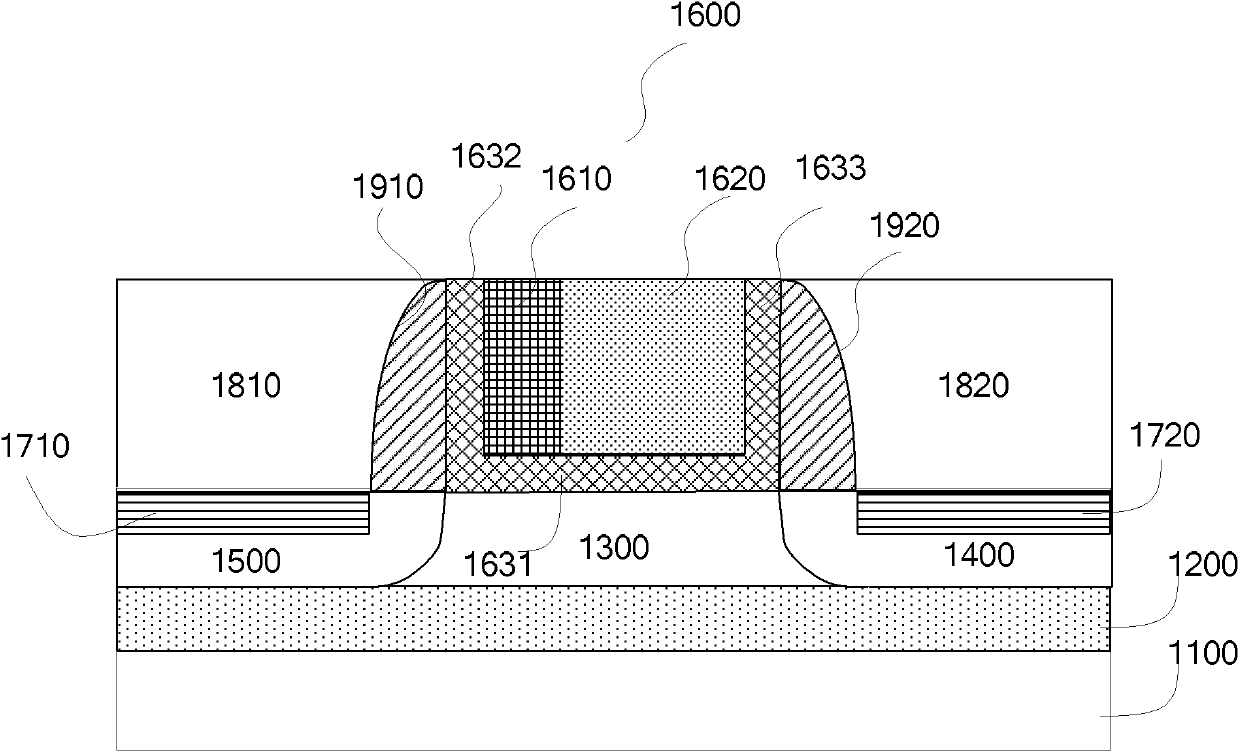
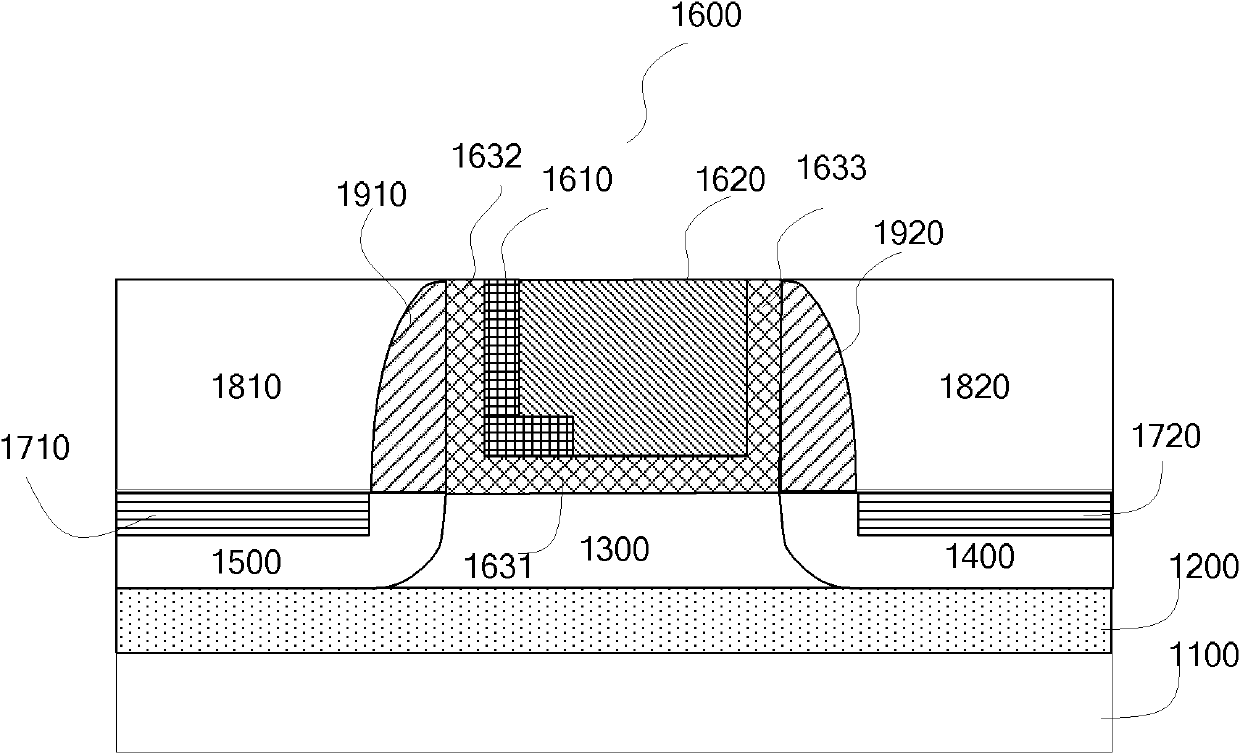
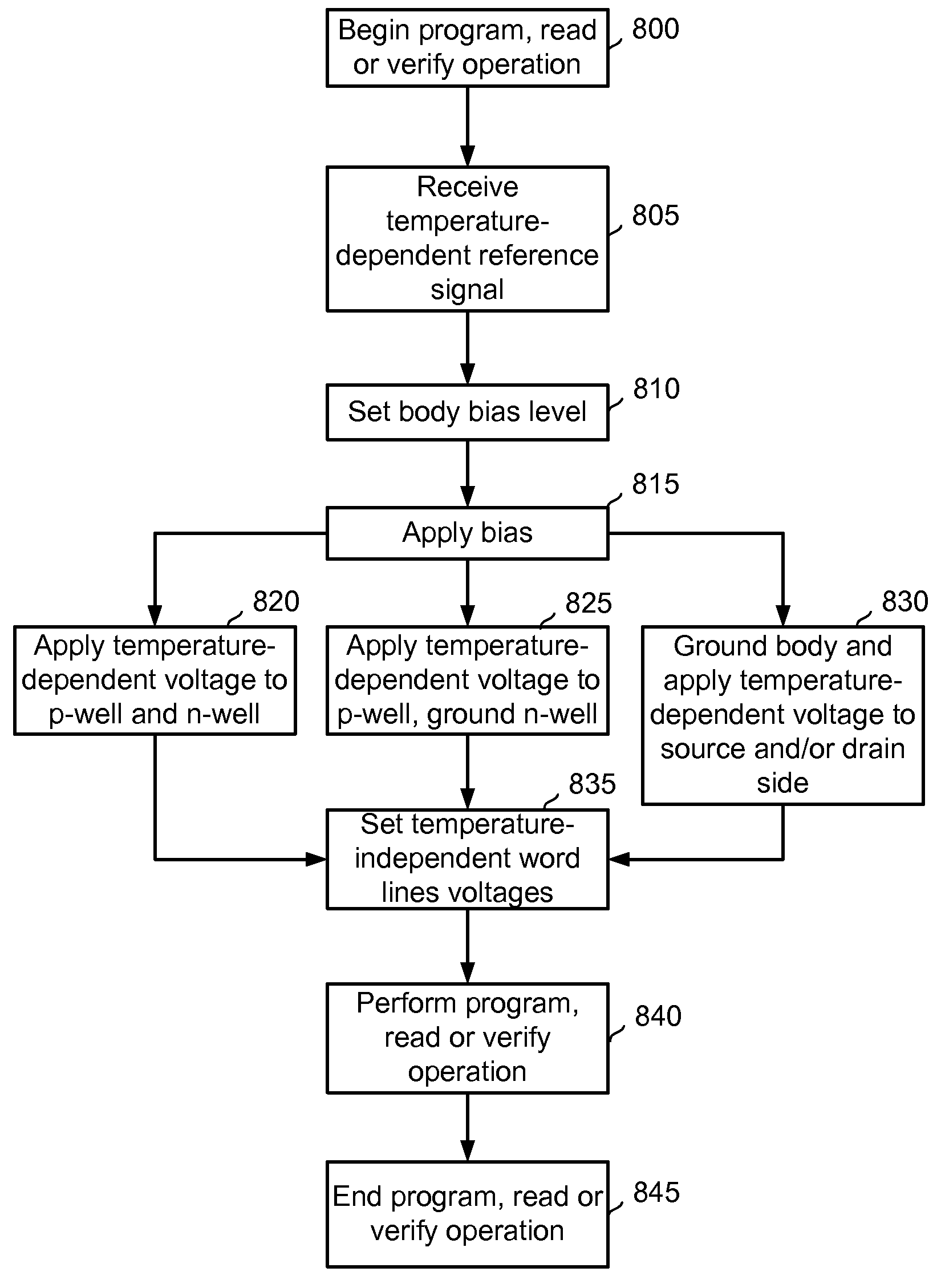
A body bias is applied to a non-volatile storage system to compensate for temperature-dependent variations in threshold voltage, sub-threshold slope, depletion layer width and / or 1 / f noise. A desired bias level is set based on a temperature-dependent reference signal. In one approach, a level of the biasing can decrease as temperature increases. The body bias can be applied by applying a voltage to a p-well and n-well of a substrate, applying a voltage to the p-well while grounding the n-well, or grounding the body and applying a voltage to the source and / or drain of a set of non-volatile storage elements. Further, temperature-independent and / or temperature-dependent voltages can be applied to selected and unselected word lines in the non-volatile storage system during program, read or verify operations. The temperature-dependent voltages can vary based on different temperature coefficients.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Ferroelectric semiconductor transistor devices having gate modulated conductive layer
ActiveUS20120292677A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSub thresholdWork function
Ferroelectric semiconductor switching devices are provided, including field effect transistor (FET) devices having gate stack structures formed with a ferroelectric layer disposed between a gate contact and a thin conductive layer (“quantum conductive layer”) . The gate contact and ferroelectric layer serve to modulate an effective work function of the thin conductive layer. The thin conductive layer with the modulated work function is coupled to a semiconductor channel layer to modulate current flow through the semiconductor and achieve a steep sub-threshold slope.
Owner:IBM CORP
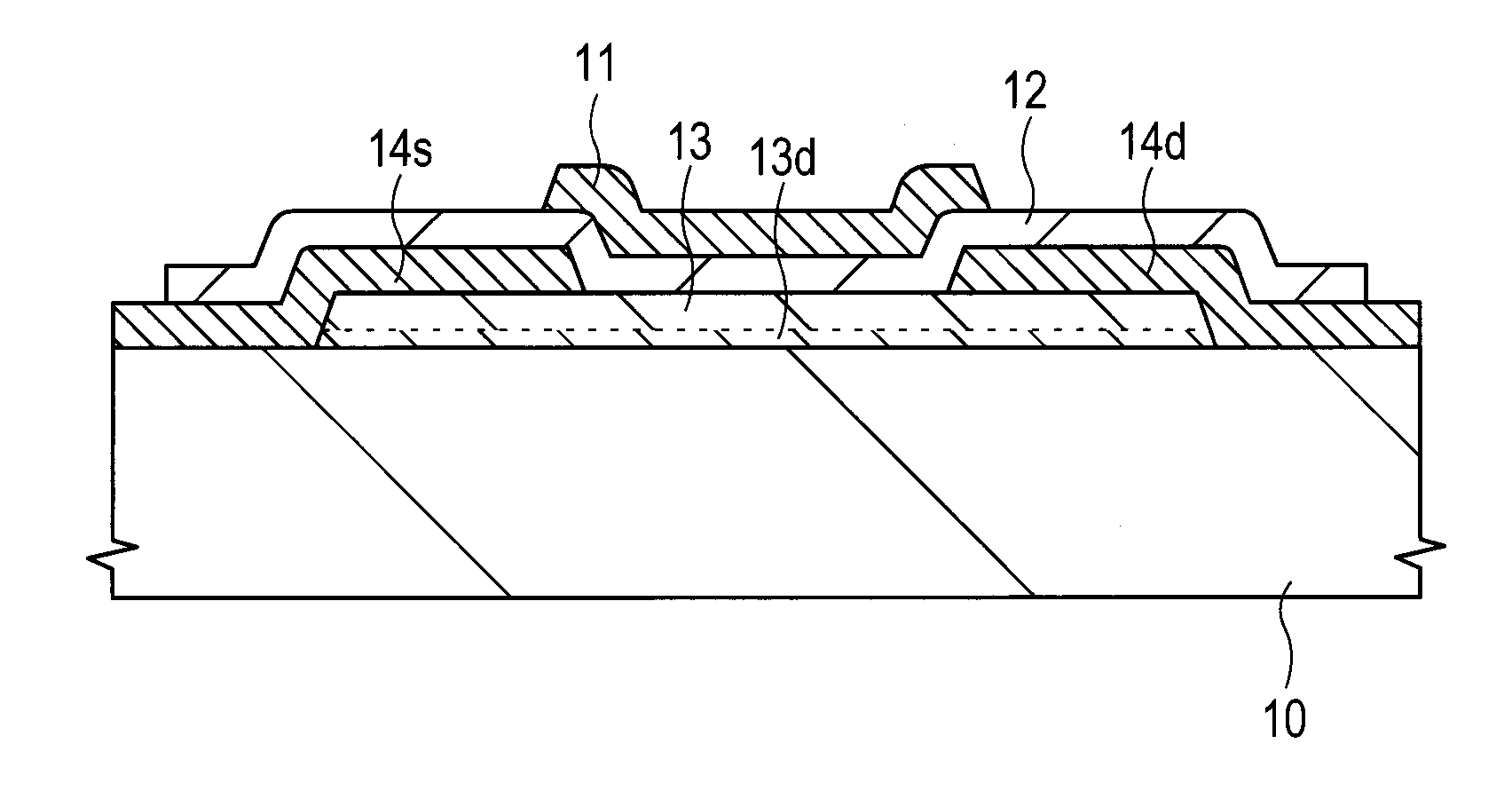
Semiconductor Device, RFID Tag Using the Same and Display Device
InactiveUS20130099229A1Increase the on-currentImprove mobilityTransistorHigh concentrationSub threshold
Disclosed is an oxide semiconductor layer (13) which forms a channel for a thin-film transistor and which includes at least In and oxygen and one or more types of elements from among Zn, Cd, Al, Ga, Si, Sn, Ce, and Ge. A high concentration region (13d) is disposed on one section of the oxide semiconductor layer (13), whereby said region has a maximum In concentration 30 at %; or higher than other regions on the oxide semiconductor layer (13). The film thickness of the oxide semiconductor layer (13) is 100 nm max., and the film thickness of the high concentration region (13d) is 20 nm max. or, preferably, 6 nm max. This enables a thin-film transistor with a sub-threshold slope of 100 mV / decade max., a high on-current, and a high field effect mobility to be achieved.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Capping Layers for Metal Oxynitride TFTS
ActiveUS20100001274A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringNitrogen gas
A capping layer may be deposited over the active channel of a thin film transistor (TFT) in order to protect the active channel from contamination. The capping layer may affect the performance of the TFT. If the capping layer contains too much hydrogen, nitrogen, or oxygen, the threshold voltage, sub threshold slope, and mobility of the TFT may be negatively impacted. By controlling the ratio of the flow rates of the nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen containing gases, the performance of the TFT may be optimized. Additionally, the power density, capping layer deposition pressure, and the temperature may also be controlled to optimize the TFT performance.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Non-volatile storage with bias for temperature compensation
ActiveUS20080158975A1Level of biasing decreaseLower Level RequirementsRead-only memoriesDigital storageSub thresholdTemperature coefficient
A non-volatile storage system in which a body bias is applied to a non-volatile storage system to compensate for temperature-dependent variations in threshold voltage, sub-threshold slope, depletion layer width and / or 1 / f noise. A desired bias level is set based on a temperature-dependent reference signal. In one approach, a level of the biasing can decrease as temperature increases. The body bias can be applied by applying a voltage to a p-well and n-well of a substrate, applying a voltage to the p-well while grounding the n-well, or grounding the body and applying a voltage to the source and / or drain of a set of non-volatile storage elements. Further, temperature-independent and / or temperature-dependent voltages can be applied to selected and unselected word lines in the non-volatile storage system during program, read or verify operations. The temperature-dependent voltages can vary based on different temperature coefficients.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Ultra-thin Si channel CMOS with improved series resistance
ActiveUS7018891B2Increase resistanceImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Thin silicon channel SOI devices provide the advantage of sharper sub-threshold slope, high mobility, and better short-channel effect control but exhibit a typical disadvantage of increased series resistance. This high series resistance is avoided by using a raised source-drain (RSD), and expanding the source drain on the pFET transistor in the CMOS pair using selective epitaxial Si growth which is decoupled between nFETs and pFETs. By doing so, the series resistance is improved, the extensions are implanted after RSD formation and thus not exposed to the high thermal budget of the RSD process while the pFET and nFET can achieve independent effective offsets.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Semiconductor Nanowire Transistor
ActiveUS20090321716A1Improve performanceReduce outputTransistorNanoinformaticsSemiconductor materialsNanowire
A nanowire wrap-gate transistor is realised in a semiconductor material with a band gap narrower than Si. The strain relaxation in the nanowires allows the transistor to be placed on a large variety of substrates and heterostructures to be incorporated in the device. Various types of heterostructures should be introduced in the transistor to reduce the output conductance via reduced impact ionization rate, increase the current on / off ratio, reduction of the sub-threshold slope, reduction of transistor contact resistance and improved thermal stability. The parasitic capacitances should be minimized by the use of semi-insulating substrates and the use of cross-bar geometry between the source and drain access regions. The transistor may find applications in digital high frequency and low power circuits as well as in analogue high frequency circuits.
Owner:QUNANO
Biosensor based on tunneling field effect transistor and preparation method of biosensor
InactiveCN103558280ASteep subthreshold slopeSensitiveMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGate dielectricOxygen
The invention provides a biosensor based on a tunneling field effect transistor and a preparation method of the biosensor. The preparation method of the biosensor at least comprises the steps of firstly, preparing a tunneling field effect transistor as a converter; and then carrying out activated modification on the surface of a channel in the tunneling field effect transistor by adopting a surface modification agent, wherein the step of preparing the tunneling field effect transistor specifically comprises the procedures of providing an SOI (Silicon On Insulator) substrate, wherein the SOI substrate comprises a top layer silicon, a buried oxygen layer and a bottom layer silicon; forming a gate dielectric layer on the surface of the top layer silicon; carrying out ion injection on the top layer silicon at two sides of the gate dielectric layer by adopting an ion injection process to form a source electrode and a leak electrode, defining the top layer silicon of the gate dielectric layer, which is not subjected to the ion injection, as a channel; and forming a back gate on the surface of the bottom layer silicon. The tunneling field effect transistor provided by the invention is abrupt in sub-threshold slope, and is sensitive in change of charges on the surface of the channel, thereby enabling the biosensor to be capable of detecting a biomolecule at high sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
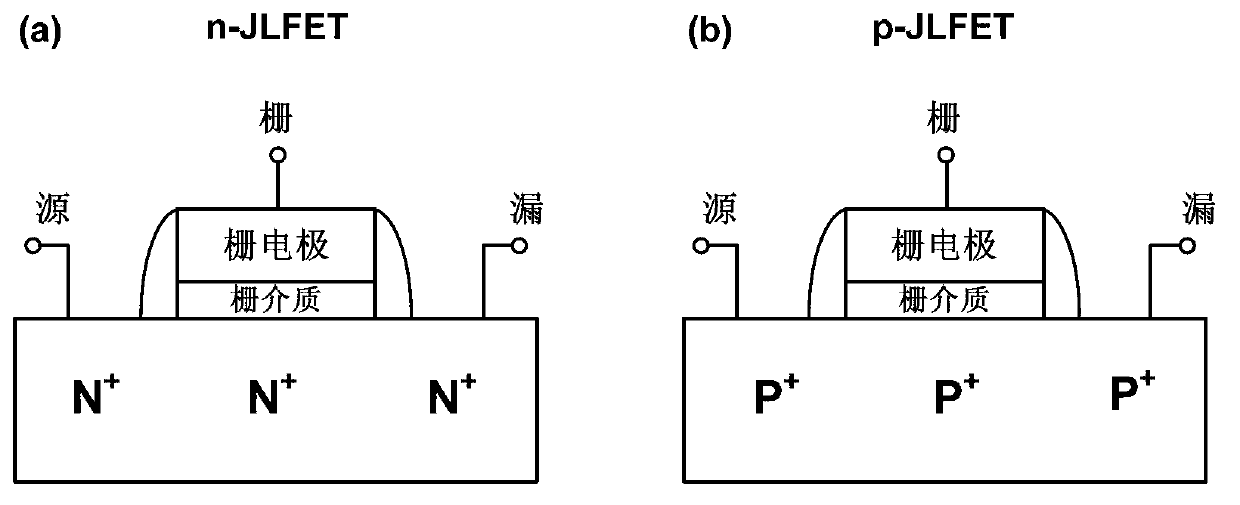
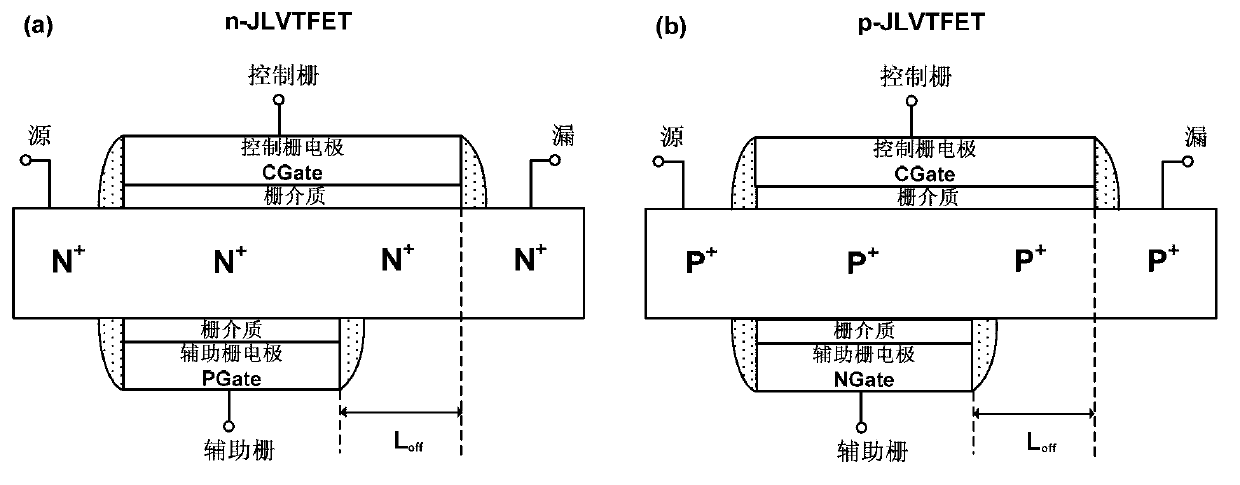
Junctionless lengthways tunneling field effect transistor
ActiveCN103280464ASmall sizeReduce processing difficultyTransistorSemiconductor materialsSwitched current
The invention provides a junctionless lengthways tunneling field effect transistor, comprising a source region, a drain region, a channel region, a control grid and an auxiliary grid, wherein the source region, the drain region and the channel region are formed into a whole and adopt the same doped semiconducting material; the doping concentration from the source region to a channel and the drain region is the same; the control grid and the auxiliary grid are respectively located on the two sides of the channel; at least a part of the control grid and a part of the auxiliary grid are opposite to each other; the control grid is used for controlling the breakover and closing of a device; and the auxiliary grid is used for making a semiconducting region under the auxiliary grid generate transoid. The junctionless lengthways tunneling field effect transistor has only one doping type, no PN junction is needed to be made, the process difficulty is reduced, the size reduction of the device is facilitated, a short channel effect is restrained, the switching current ratio is increased, off-state current leakage is further reduced through the distance region between the control grid and the auxiliary grid, the characteristics such as a subthreshold slope can be improved, the tunneling length is effectively reduced through controlling the thickness of a semiconductor film, and the tunneling current is increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
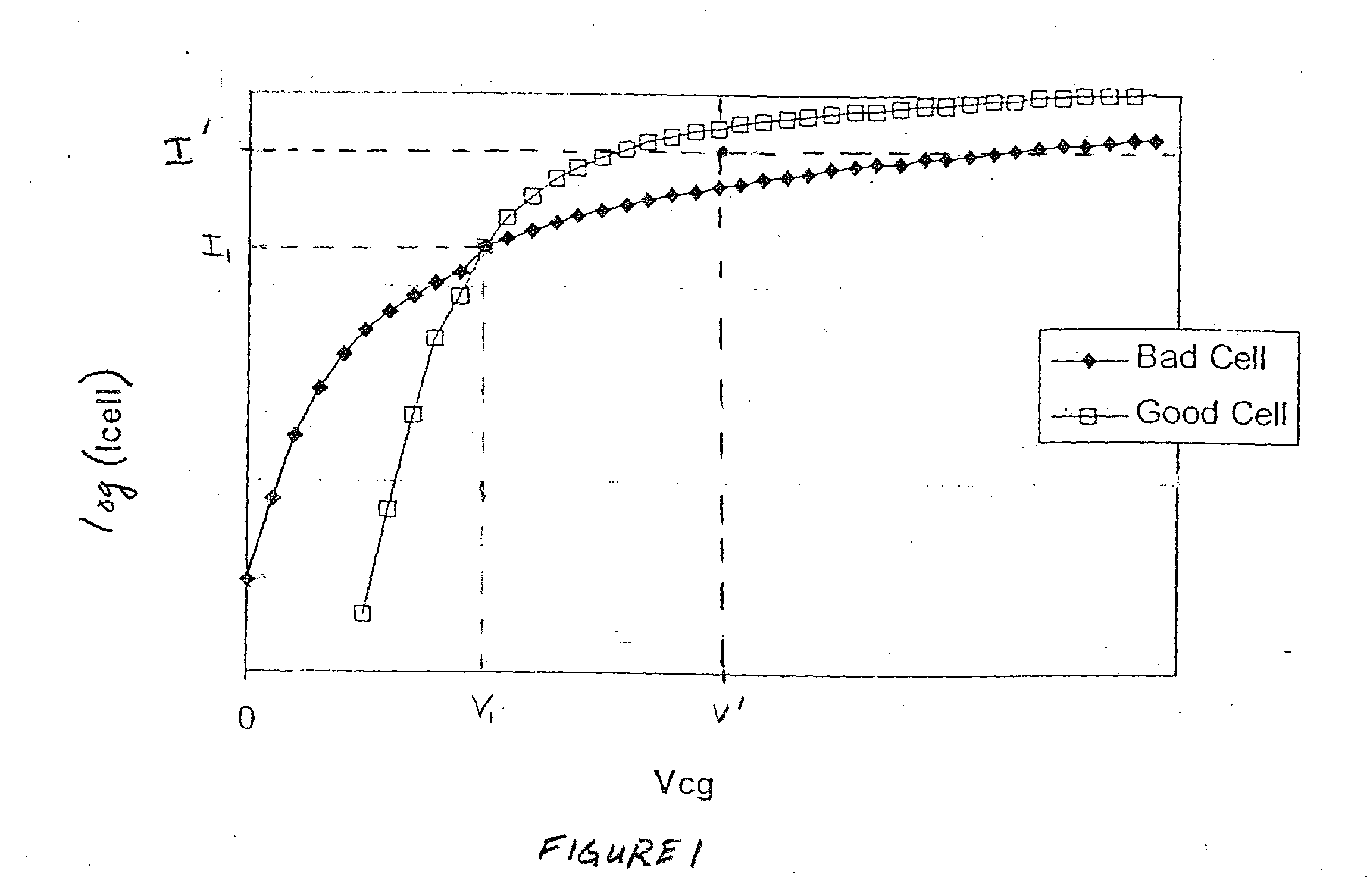
Methods for identifying non-volatile memory elements with poor subthreshold slope or weak transconductance
The present invention presents a number of methods for identifying cells with poor subthreshold slope and reduced transconductance. A first set of techniques focuses on the poor subthreshold behavior of degraded storage elements by cycling cells and then programming them to a state above the ground state and the reading them with a control gate voltage below the threshold voltage of this state to see if they still conduct. A second set of embodiments focuses on weak transconductance behavior by reading programmed cells with a control gate voltage well above the threshold voltage. A third set of embodiments alters the voltage levels at the source-drain regions of the storage elements. The current-voltage curve of a good storage element is relatively stable under this shift in bias conditions, while degraded elements exhibit a larger shift. The amount of shift can be used to differentiate the good elements from the bad.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC +1
Non-resistance type reference source
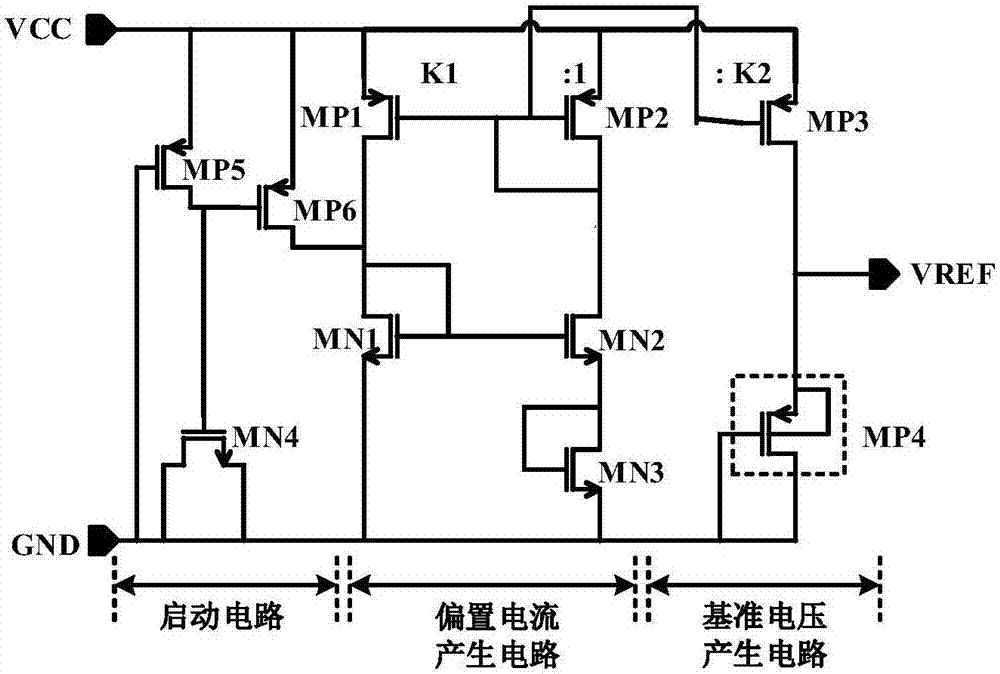
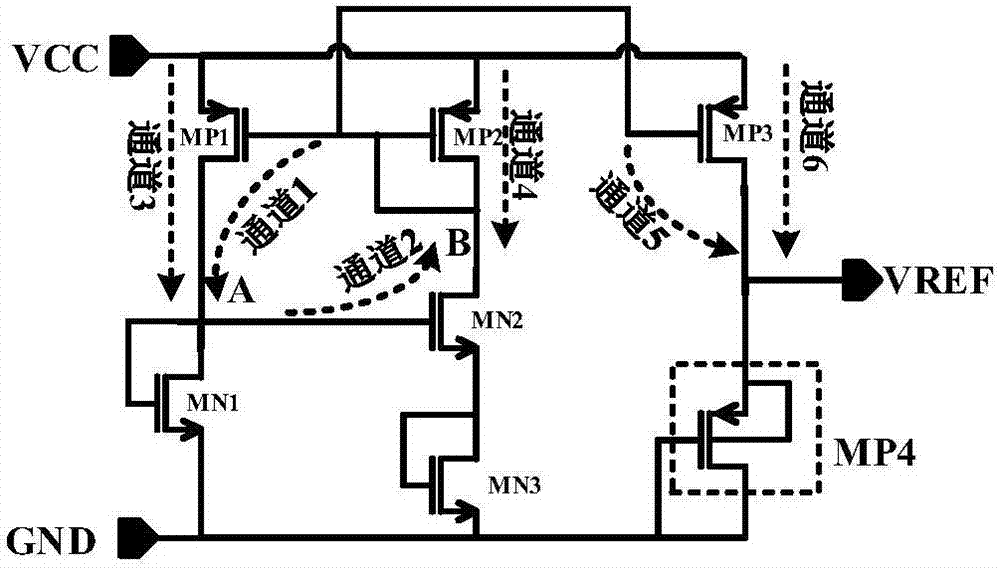
InactiveCN107256062AGood temperature characteristicsReduce power consumptionElectric variable regulationReference circuitPositive temperature
The invention discloses a non-resistance type reference source, and belongs to the technical field of power supply management. The non-resistance type reference source comprises a starting circuit, a reference voltage generation circuit and a bias current generation circuit, wherein when a power supply is constructed, the starting circuit makes the reference source disengaged from a zero state and then retreats after starting is completed; a PMOS pipe with large threshold voltage negative temperature coefficient and an NMOS pipe with small negative temperature coefficient are selected, the negative temperature voltage in reference voltage is obtained through the threshold voltage difference of the PMOS pipe and the NMOS pipe, the positive temperature voltage is determined according to the thermal voltage, the sub-threshold slope factor and the related width-to-length ratio of the MOS pipe, and then the reference voltage VREF with good temperature characteristics can be obtained; bias currents with positive temperature characteristics are generated through the NMOS pope working in a sub-region, and the positive temperature characteristics of the currents can be enhanced when temperature rises. On the basis of traditional threshold reference, reference circuit branches are reduced, so power consumption of a reference circuit is reduced, and the power supply rejection ratio of the reference voltage is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Semi-gate controlled source schottky barrier type tunneling field effect transistor
InactiveCN103500758AReduce processing difficultyReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor devicesGermanideGate voltage
The invention relates to a semi-gate controlled source schottky barrier type tunneling field effect transistor. On the premise of no requirements on the introduction of a material such as a compound semiconductor, silicon germanide and germanium with a smaller forbidden bandwidth into the generation of a tunneling part of a device, a source schottky barrier is formed between a metal source and intrinsic silicon, and a semi-gate is used for controlling the barrier width of the source schottky barrier and the energy band bending degree of the intrinsic silicon to control the switching of the device. An asymmetrical semi-gate structural design is adopted, so that gate-induced drain leakage current is remarkably reduced on the premise of keeping gate voltage well controlling the width of the schottky barrier and the energy band bending degree. The semi-gate controlled source schottky barrier type tunneling field effect transistor has the advantages of process simplicity, low cost, high sub-threshold slope, high breakover current, low reverse leakage current and the like, and is suitable to be popularized and used.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Biosensor based on silicon nanowire tunneling field effect transistor and manufacturing method of biosensor
ActiveCN103558279ASensitiveSensitive detectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOxygenIon implantation
The invention provides a biosensor based on a silicon nanowire tunneling field effect transistor and manufacturing method of the biosensor. The method comprises the following steps: step one, manufacturing a tunneling field effect transistor with a silicon nanowire channel as a converter; and step two, carrying out activated modification on the surface of the silicon nanowire channel by adopting a surface modifier; the specific step of preparing the silicon nanowire tunneling field effect transistor in the step one comprises the substeps: providing an SOI (silicon on insulator) substrate comprising a top silicon layer, an oxygen-burying layer and a bottom silicon layer; etching the top silicon layer to form the silicon nanowire channel, depositing a gate medium layer on the surface of the channel, performing ion injection on the top silicon layer by adopting an ion injection process, forming a source electrode and a drain electrode at two ends of the channel, and forming a back gate on the back of the bottom silicon. The tunneling field effect transistor based on the silicon nanowire has a steeper sub-threshold slope, and is more sensitive to the change of the surface charge of the channel, so that the biosensor is capable of detecting the biomolecules with high sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tunneling field effect transistor having heterogeneous grid work function and formation method thereof
ActiveCN102169901ASmall subthreshold slopeIncrease drive currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentEngineering
The invention provides a tunneling field effect transistor having heterogeneous grid work function, which comprises a substrate, a channel zone formed in the substrate, a source zone and a drain zone formed at two sides of the channel zone, and a grid stack, wherein the doping type of the source zone is opposite to that of the drain zone; the grid stack comprises a grid dielectric layer and further comprises a first grid electrode and a second grid electrode located on the grid dielectric layer and distributed along the direction from the source zone to the drain zone, and a first side wall and a second side wall located on the grid dielectric layer and respectively formed at a side of the first grid electrode and a side of the second grid electrode; and the first grid electrode and the second grid electrode have different work functions. In the embodiment of the invention, a structure of transverse heterogeneous grid work function is introduced to the tunneling field effect transistor, so the energy zone distribution of the channel zone is adjusted, the sub-threshold gradient of the transistor is substantially decreased, meanwhile, the driving current is greatly improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Junction-free transverse tunneling field effect transistor
ActiveCN103268889ASmall sizeReduce processing difficultySemiconductor devicesPower flowSwitched current
The invention provides a junction-free transverse tunneling field effect transistor which comprises a source region, a drain region, a channel region, a control grid and an auxiliary grid. The source region, the drain region and the channel region form a whole and are made of the same kind of doping type semiconductor materials. The doping density from the source region to a channel and the drain region is the same. The control grid and the auxiliary grid are placed on the same side of the channel, wherein the control grid is used for controlling switch-on and switch-off of a device, and the auxiliary grid is used for enabling transoid to happen to a semiconductor region below the auxiliary grid. The junction-free transverse tunneling field effect transistor is different from a traditional PN junction tunneling field effect transistor. According to the junction-free transverse tunneling field effect transistor, only one doping type is adopted, a PN junction does not need to be manufactured, and technology difficulty is lowered. The junction-free transverse tunneling field effect transistor is beneficial to diminishing the size of the device, restraining a short-channel effect, enlarging the switching current ratio, and improving the subthreshold slope.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for wrapped-gate MOSFET
A wrapped-gate transistor includes a substrate having an upper surface and first and second side surfaces opposing to each other. Source and drain regions are formed in the substrate with a channel region therebetween. The channel region extends from the first side surface to the second side surfaces of the substrate. A gate dielectric layer is formed on the substrate. A gate electrode is formed on the gate dielectric layer to cover the channel region from the upper surface and the first and second side surfaces with the gate dielectric therebetween. The substrate is a silicon island formed on an insulation layer of an SOI (silicon-on-insulator) substrate or on a conventional non-SOI substrate, and has four side surfaces including the first and second side surfaces. The source and drain regions are formed on the portions of the substrate adjoining the third and fourth side surfaces which are perpendicular to the first and second side surfaces. The wrapped-gate structure provides a better and quicker potential control within the channel area, which yields steep sub-threshold slope and low sensitivity to the "body-to-source" voltage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Heterogeneous gate tunneling transistor and forming method thereof
ActiveCN102629627AReduce controlReduce capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentCapacitance
The invention provides a structure of a heterogeneous gate tunneling transistor of an under-gate process and a forming method of the heterogeneous gate tunneling transistor. The heterogeneous gate tunneling transistor comprises a substrate, a channel region, a source region, a drain region and a gate stack, wherein the channel region is formed in the substrate; the source region and the drain region are arranged on the two sides of the channel region; the doping types of the source region and the drain region are reverse; the gate stack is formed on the channel region and comprises a gate dielectric layer, a first gate electrode, a second gate electrode, a first vacuum side wall and a second vacuum side wall; the first gate electrode and the second gate electrode are formed on the gate dielectric layer and have different work functions; and the first vacuum side wall and the second vacuum side wall are formed on the two sides of the first gate electrode and the second gate electrode. Since the vacuum side wall from the gate to the drain region is introduced, the control of the gate over the drain region is weakened, and the gate-drain capacitance is reduced; a certain distance which can be accurately controlled exists between the gate stack and the drain region of a device, so that a tunneling potential barrier path is increased, and a double-pole window is expanded; and the energy band distribution of the channel region is modulated by a work function structure of the transverse heterogeneous gate, so that the sub-threshold slope of a transistor is obviously reduced, the driving current is increased and the performance of the device is enhanced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ultra-thin Si channel CMOS with improved series resistance
ActiveUS20050127408A1Add series resistanceLow thermal budget processingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Thin silicon channel SOI devices provide the advantage of sharper sub-threshold slope, high mobility, and better short-channel effect control but exhibit a typical disadvantage of increased series resistance. This high series resistance is avoided by using a raised source-drain (RSD), and expanding the source drain on the pFET transistor in the CMOS pair using selective epitaxial Si growth which is decoupled between nFETs and pFETs. By doing so, the series resistance is improved, the extensions are implanted after RSD formation and thus not exposed to the high thermal budget of the RSD process while the pFET and nFET can achieve independent effective offsets.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Biasing non-volatile storage to compensate for temperature variations
A body bias is applied to a non-volatile storage system to compensate for temperature-dependent variations in threshold voltage, sub-threshold slope, depletion layer width and / or 1 / f noise. A desired bias level is set based on a temperature-dependent reference signal. In one approach, a level of the biasing can decrease as temperature increases. The body bias can be applied by applying a voltage to a p-well and n-well of a substrate, applying a voltage to the p-well while grounding the n-well, or grounding the body and applying a voltage to the source and / or drain of a set of non-volatile storage elements. Further, temperature-independent and / or temperature-dependent voltages can be applied to selected and unselected word lines in the non-volatile storage system during program, read or verify operations. The temperature-dependent voltages can vary based on different temperature coefficients.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
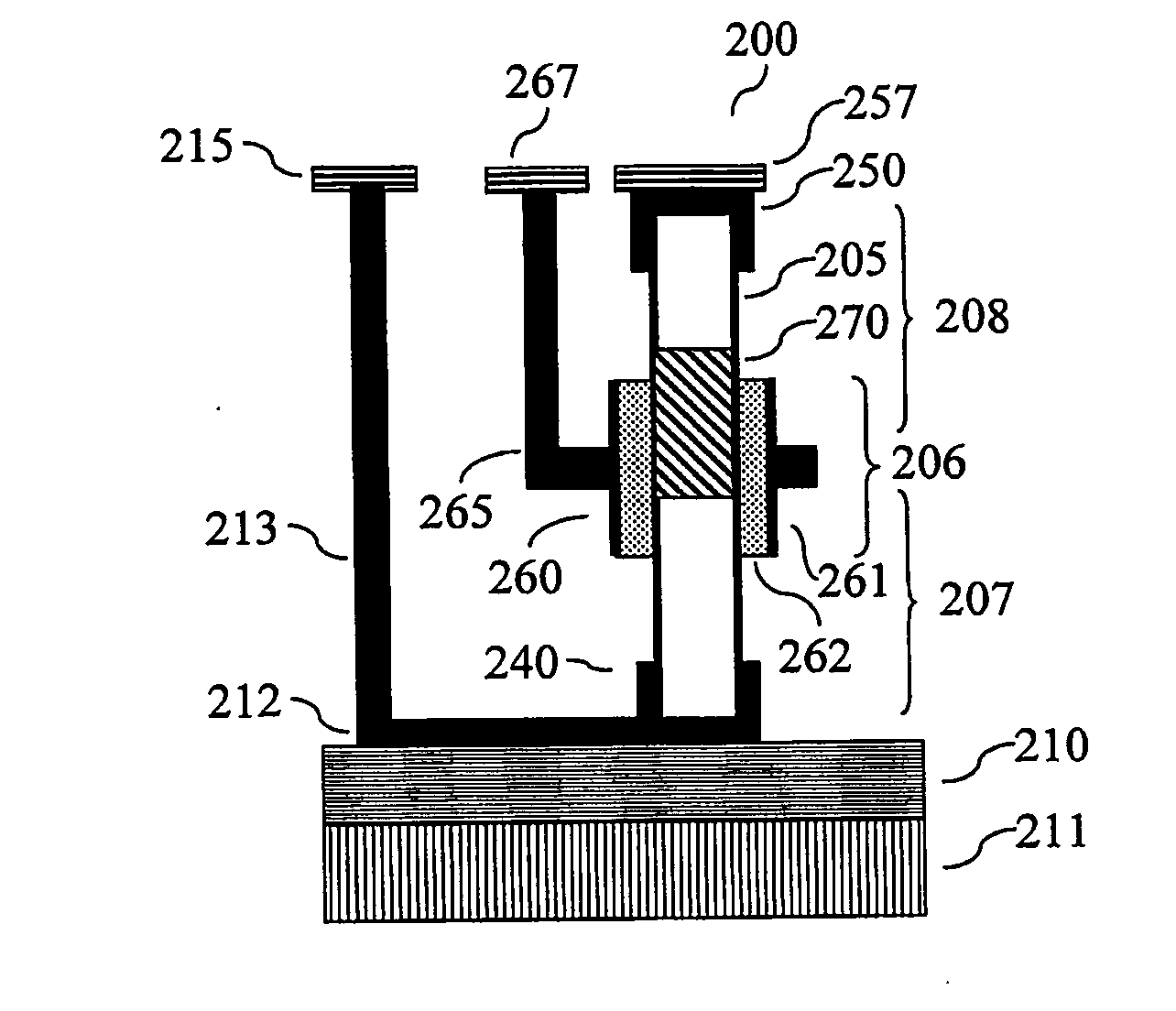
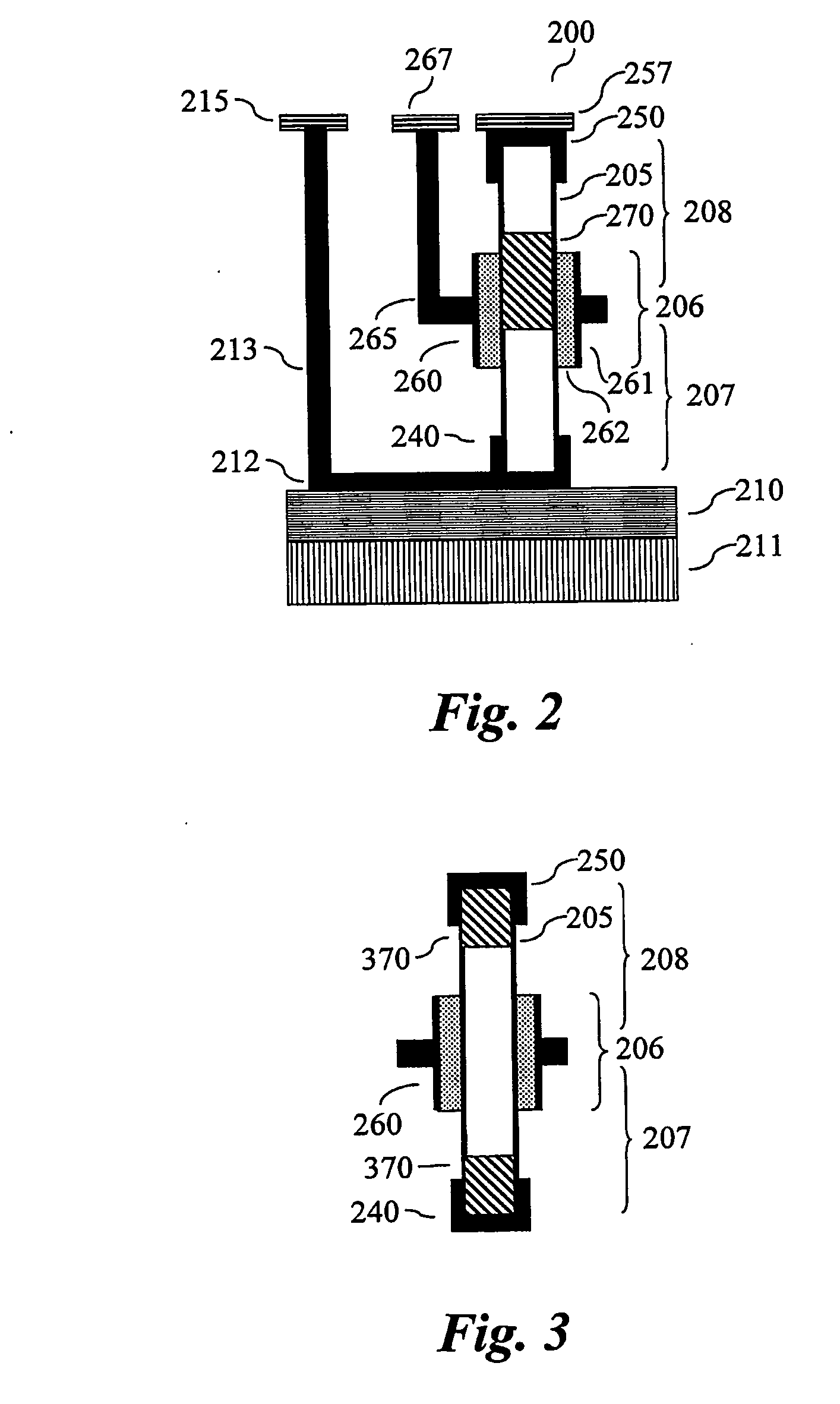
Two-dimensional electrostrictive field effect transistor (2d-efet)
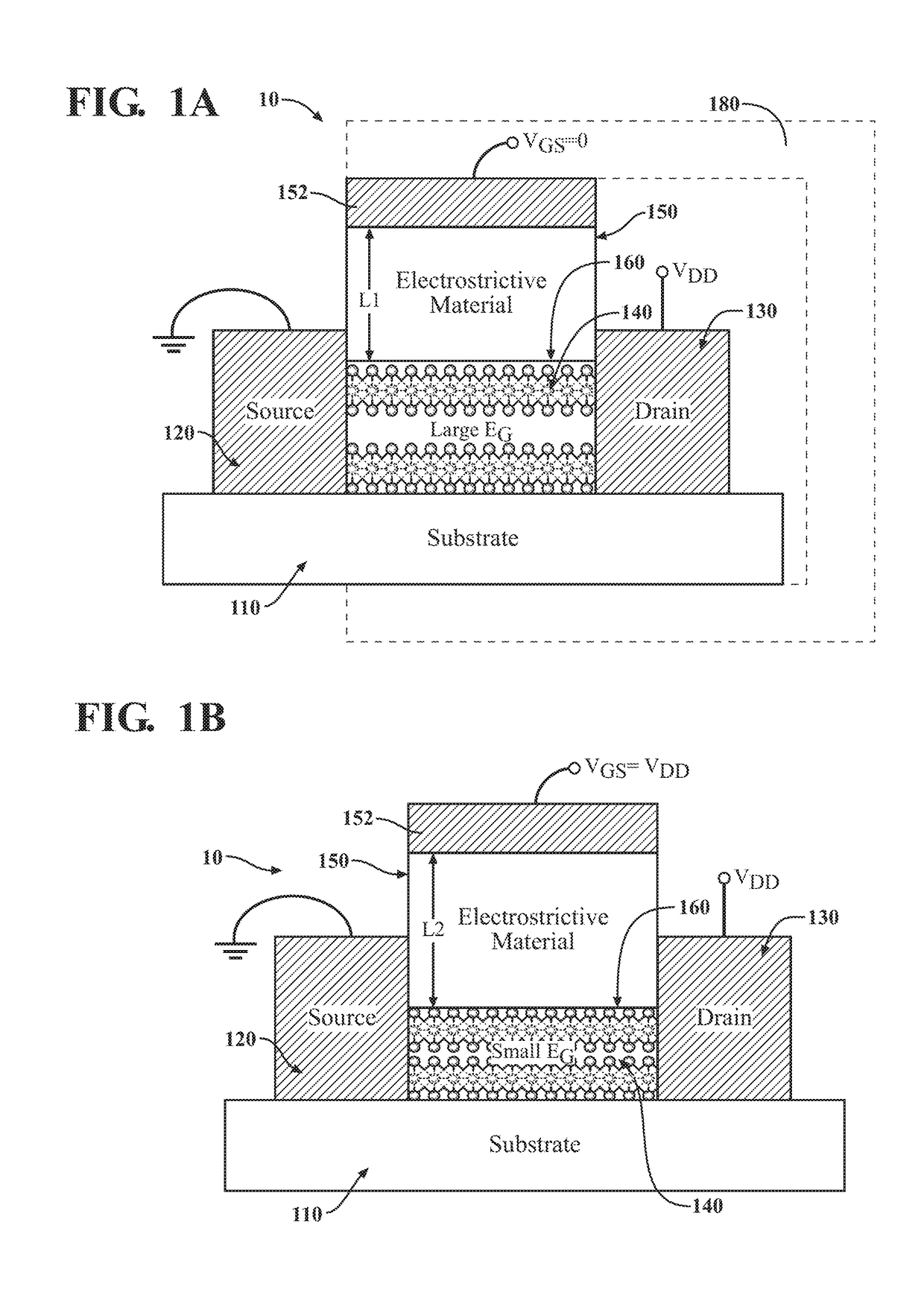
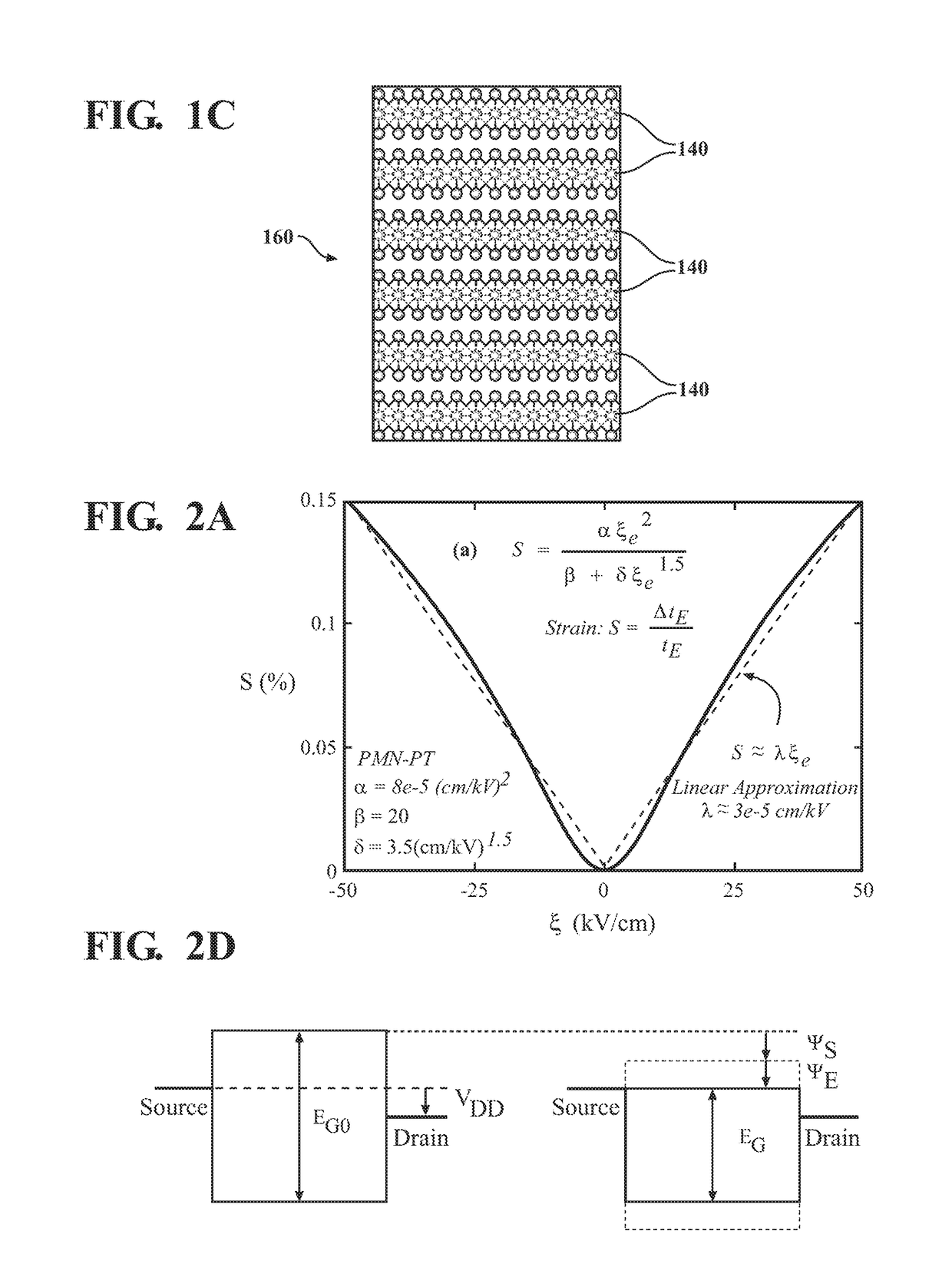
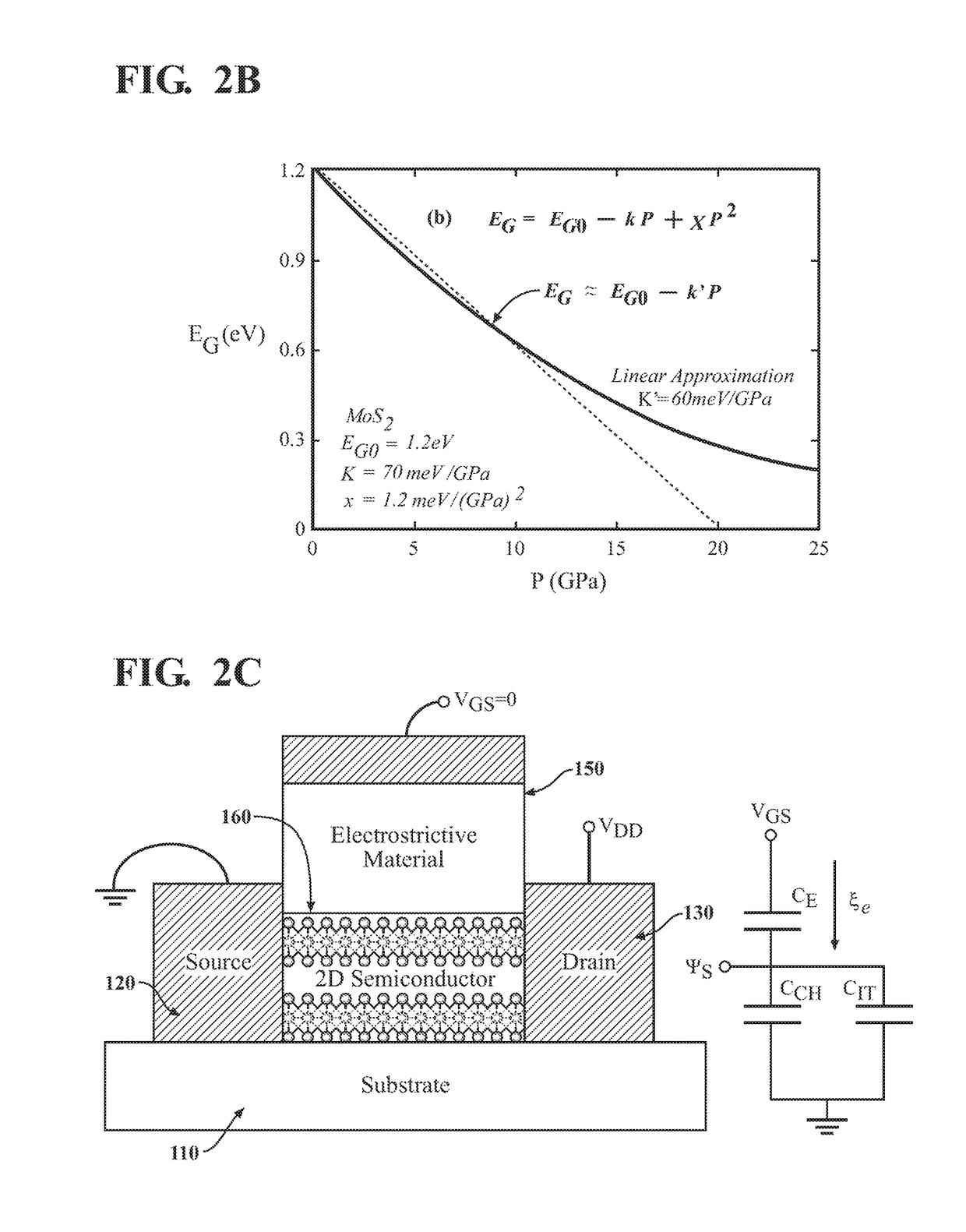
ActiveUS20180374962A1Bandgap decreaseHigh currentSemiconductor devicesCondensed matter physicsSubthreshold slope
A device and method for manufacturing a two-dimensional electrostrictive field effect transistor having a substrate, a source, a drain, and a channel disposed between the source and the drain. The channel is a two-dimensional layered material and a gate proximate the channel. The gate has a column of an electrostrictive or piezoelectric or ferroelectric material, wherein an electrical input to the gate produces an elongation of the column that applies a force or mechanical stress on the channel and reduces a bandgap of two-dimensional material such that the two-dimensional electrostrictive field effect transistor operates with a subthreshold slope that is less than 60 mV / decade.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Pixel structure of organic light emitting diode display and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110248245A1Fast switching rateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceEngineering
A pixel structure of an organic light emitting diode display includes a first transistor and a second transistor. The first transistor includes a first drain electrode and a first source electrode. When a voltage difference is provided between the first drain electrode and the first source electrode, the first transistor has a first subthreshold slope (SS). The second transistor includes a second drain electrode and a second source electrode. When the voltage difference is provided between the second drain electrode and the second source electrode, the second transistor has a second SS, and the second SS is larger than the first SS.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Resistive gate tunneling field effect transistor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104332500AGuaranteed repeated logic operationsIncrease the on-state currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesControl layerLow voltage
Disclosed is a resistive gate tunneling field effect transistor. The resistive gate tunneling field effect transistor comprises a control gate layer, a gate medium layer, a semiconductor substrate, a tunneling source area, a low-doped leakage area and a channel region. A control gate employs a gate stack structure and is successively composed of a bottom electrode layer, a volatile resistive material layer and a top electrode layer. The volatile resistive material layer is a material layer with a volatile resistive characteristic. The channel region is disposed above the tunneling source area and is partially overlapped with the tunneling source area in terms of position, a tunneling junction is formed at the interface of the channel region and the tunneling source area; the low-doped leakage area is disposed at the other side of the horizontal direction of the control gate and is spaced from the control gate by a horizontal interval; the low-doped leakage area and the tunneling source area are doped with impurities of different doping types; and the doping types of the semiconductor substrate and the channel region are consistent with that of the tunneling source area. The structure has large on-state currents and a steep subthreshold slope, and can satisfy the application demand of a low-voltage low-power logic device and a logic circuit when working under the condition of low bias.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Threshold voltage measuring method and system
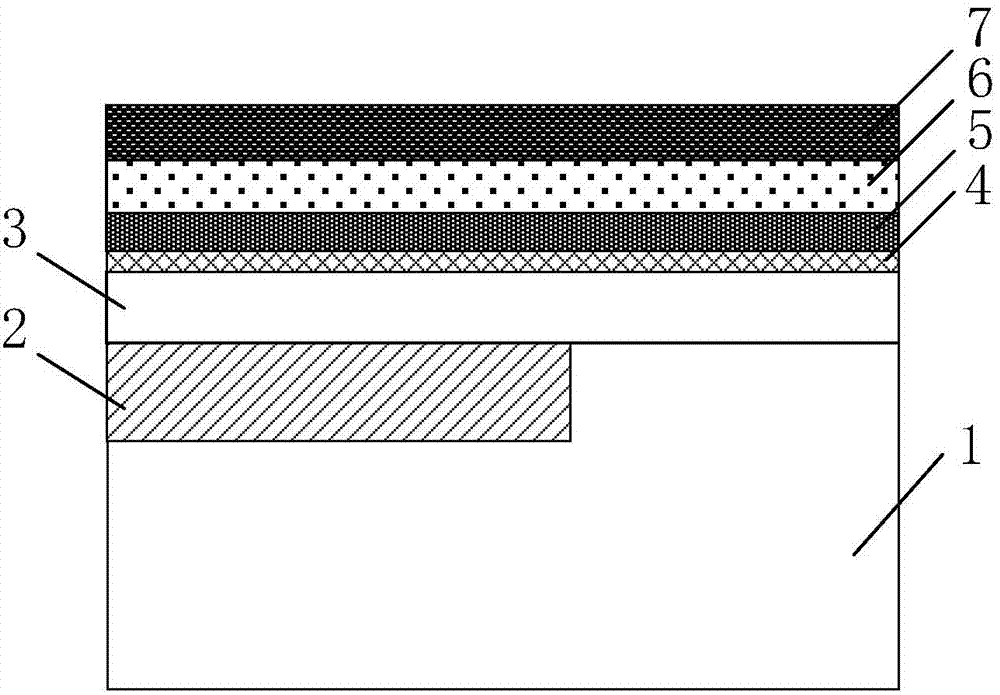
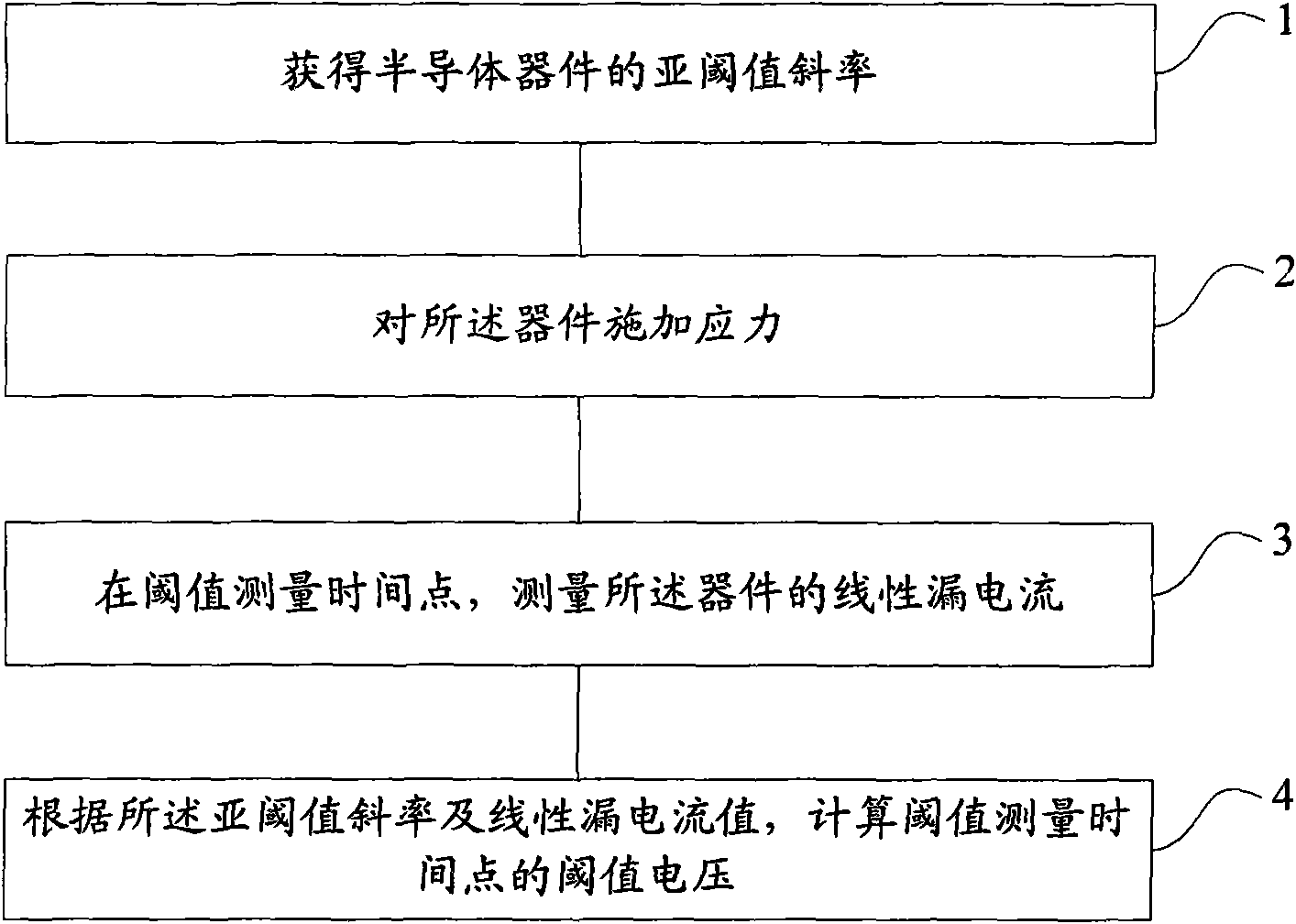
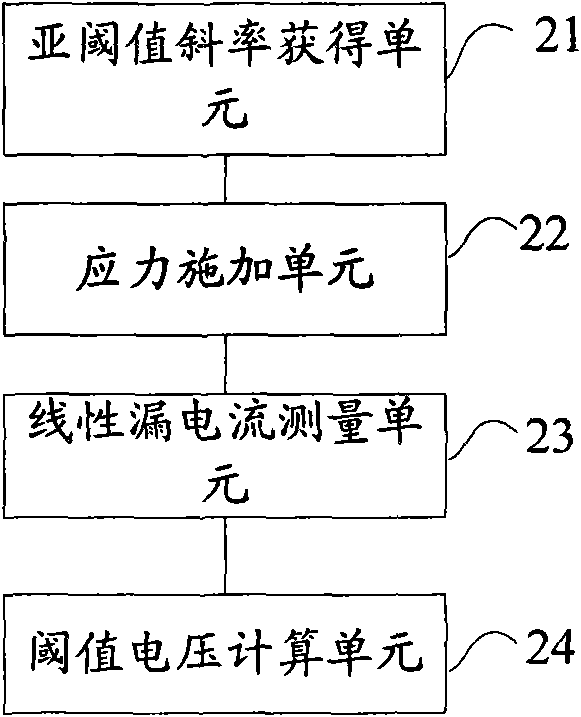
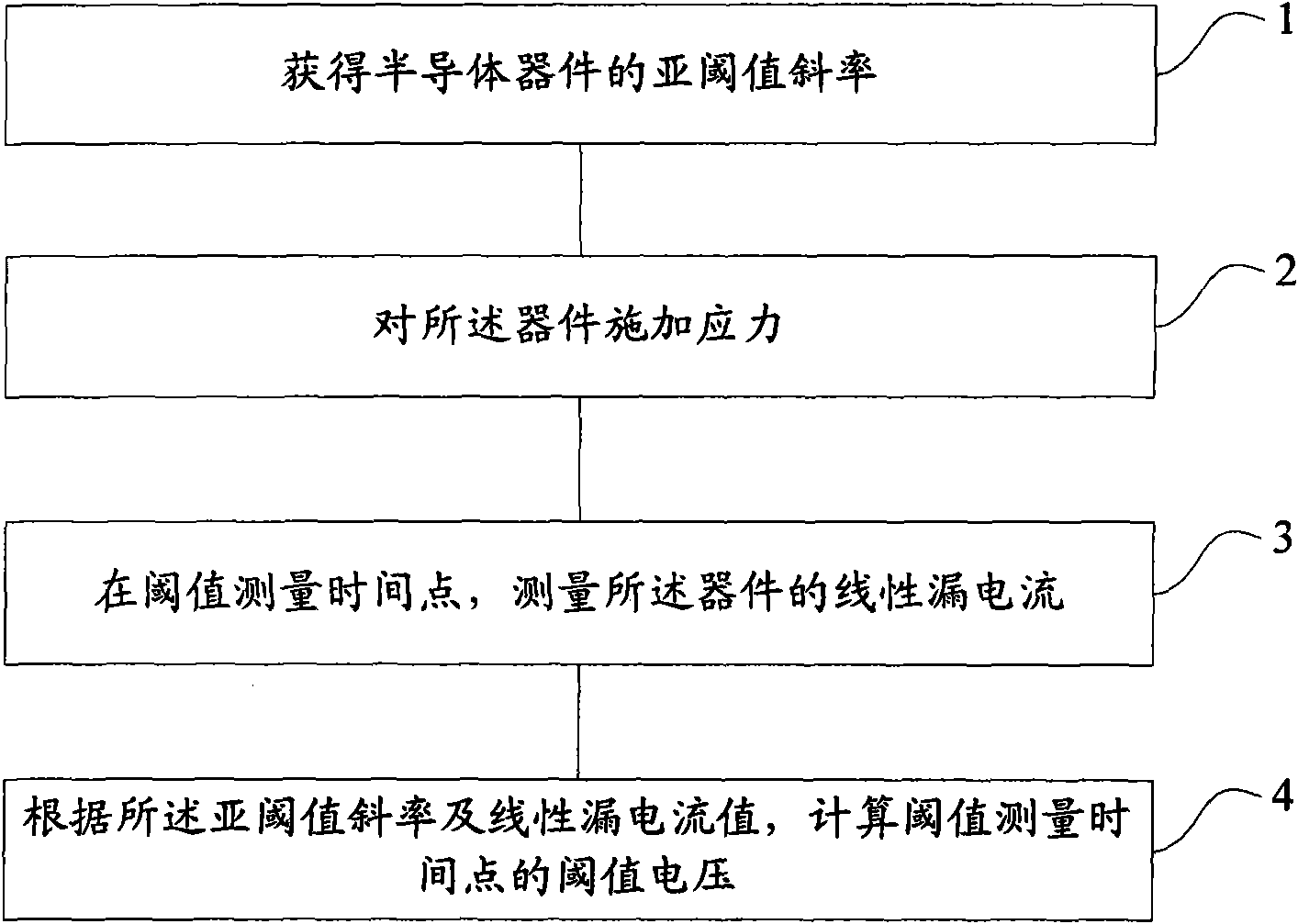
InactiveCN101825680AImprove accuracyShorten the timeIndividual semiconductor device testingDrain currentNegative-bias temperature instability
The invention provides a threshold voltage measuring method and a system, which are used for improving the accuracy of the measured threshold voltage and further improving the accuracy of a NBTI (Negative Bias Temperature Instability) test. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the subthreshold slope of a semiconductor device; applying the stress on the device; measuring the linear leakage current of the device at the threshold measuring time point; calculating the threshold voltage of the threshold measuring time point according to the subthreshold slope and the linear leakage current value, wherein the process of measuring the linear leakage current comprises the steps of removing the stress; connecting the test voltage to the device; and measuring the linear leakage current of the device under the test voltage.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Tunneling field effect transistor
InactiveCN102832256AImprove performanceIncrease the on-state currentTransistorSub thresholdCondensed matter physics
The invention relates to the technical field of field effect transistors and discloses a tunneling field effect transistor. The tunneling field effect transistor comprises a source region, a channel region and a drain region, wherein the source region and the drain region are respectively formed on the two sides of the channel region, and a contact region between the source region and the channel region is made of extrinsic materials and different from the doping type of the source region. According to the invention, the contact area between the source region and the channel region is doped differently from the source region, so that the device is relatively narrow in a tunneling layer from the source end to the channel in an ON state, and the ON-state current is increased. As the thickness of a tunneling layer from the source end to the drain end in an OFF state is not changed with the method, a relatively low OFF-state current can be kept, as a result, a higher switch ratio and a relatively low sub-threshold slope can be acquired with the method, so that a better device performance can be acquired.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Non-volatile storage with bias for temperature compensation
A non-volatile storage system in which a body bias is applied to a non-volatile storage system to compensate for temperature-dependent variations in threshold voltage, sub-threshold slope, depletion layer width and / or 1 / f noise. A desired bias level is set based on a temperature-dependent reference signal. In one approach, a level of the biasing can decrease as temperature increases. The body bias can be applied by applying a voltage to a p-well and n-well of a substrate, applying a voltage to the p-well while grounding the n-well, or grounding the body and applying a voltage to the source and / or drain of a set of non-volatile storage elements. Further, temperature-independent and / or temperature-dependent voltages can be applied to selected and unselected word lines in the non-volatile storage system during program, read or verify operations. The temperature-dependent voltages can vary based on different temperature coefficients.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com