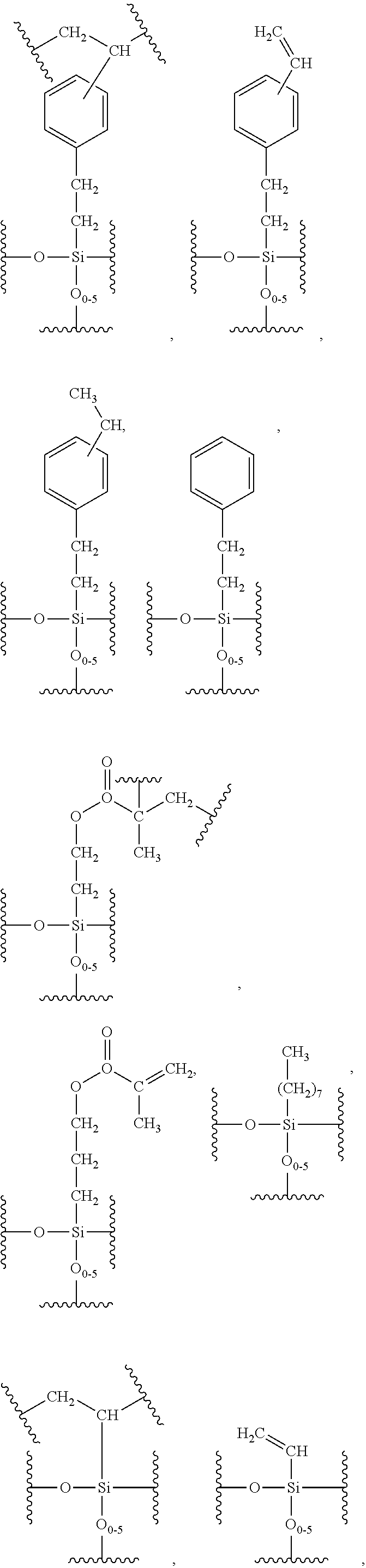
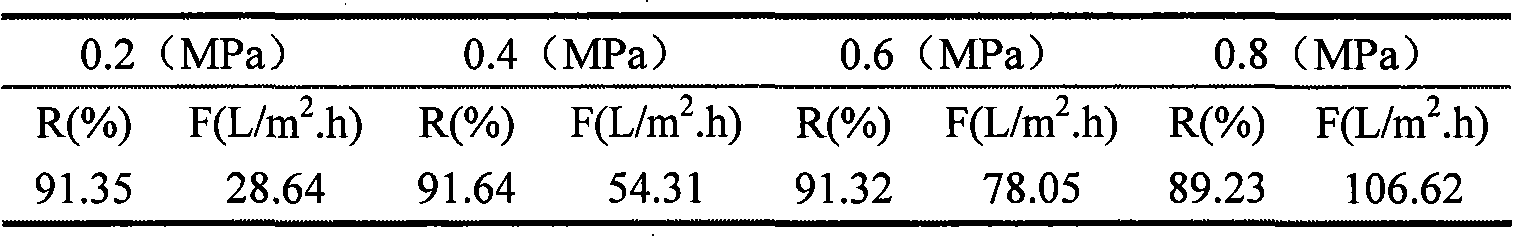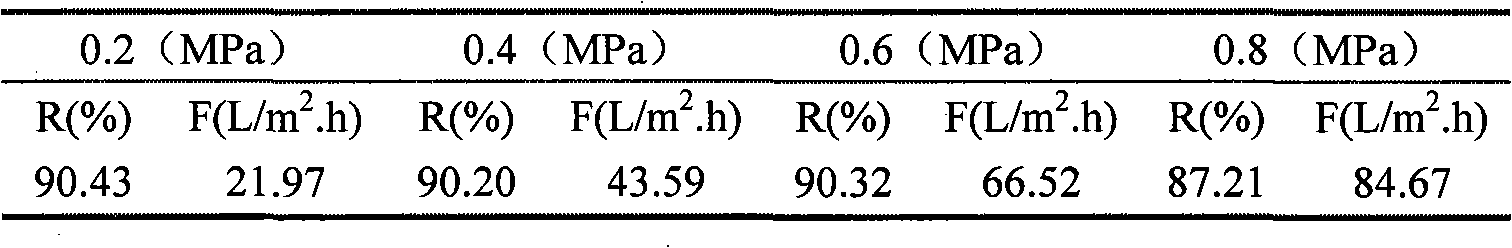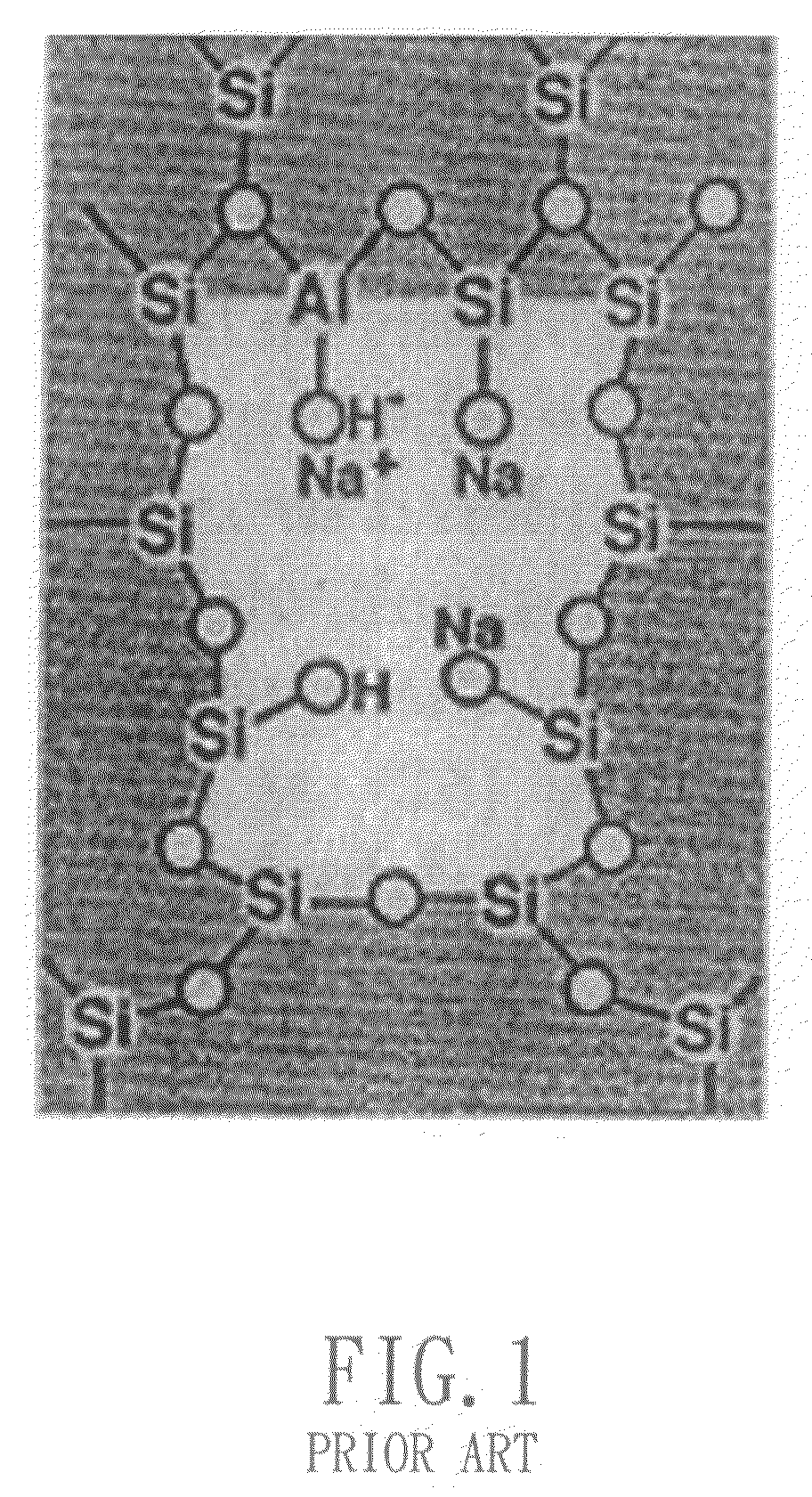Patents
Literature
299 results about "Surface charge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface charge is the electrical potential difference between the inner and outer surface of the dispersed phase in a colloid. There are many different processes which can lead to a surface being charged, including adsorption of ions, protonation/deprotonation, and the application of an external electric field. Surface charge causes a particle to emit an electric field, which causes particle repulsion and attraction, affecting many colloidal properties.
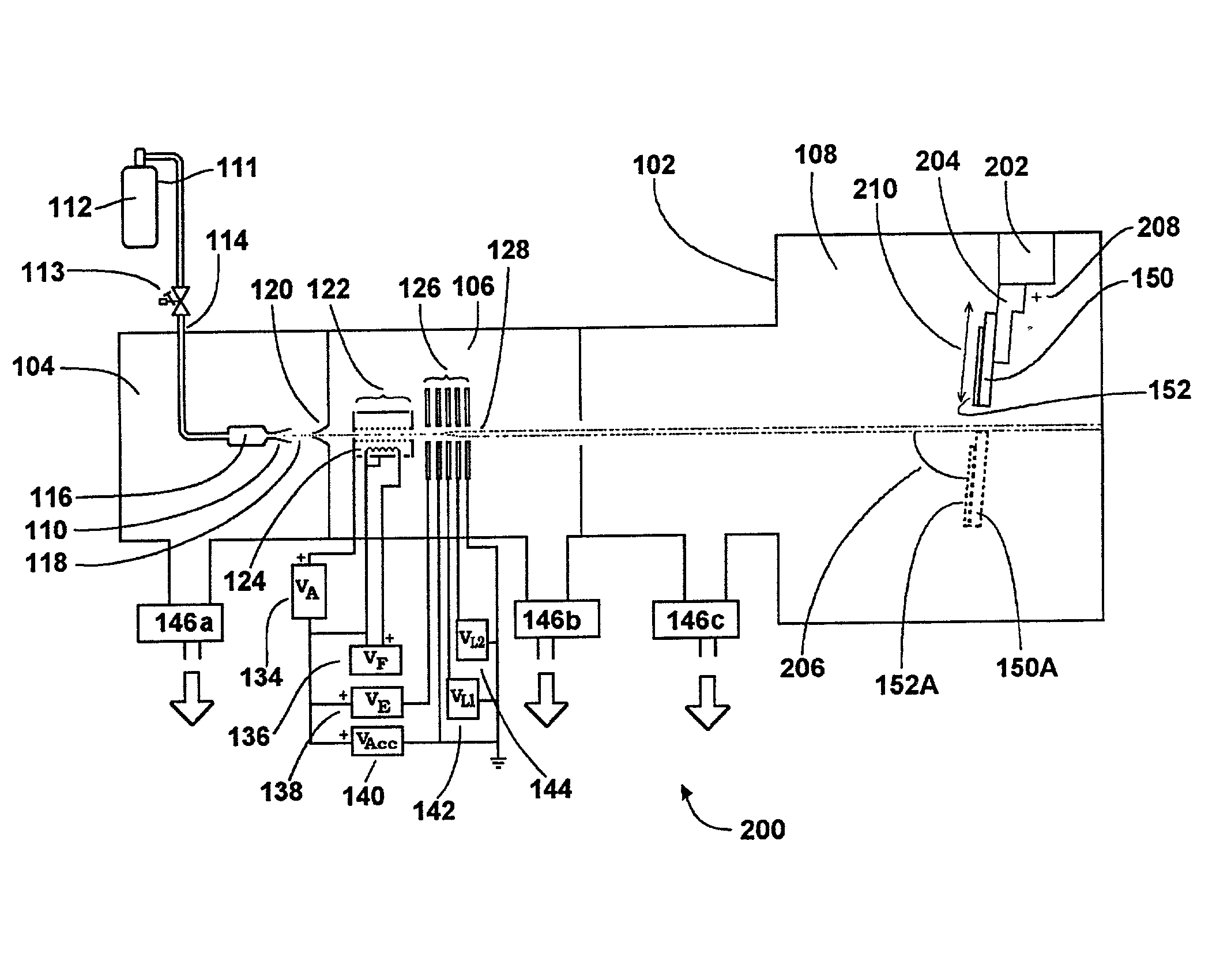
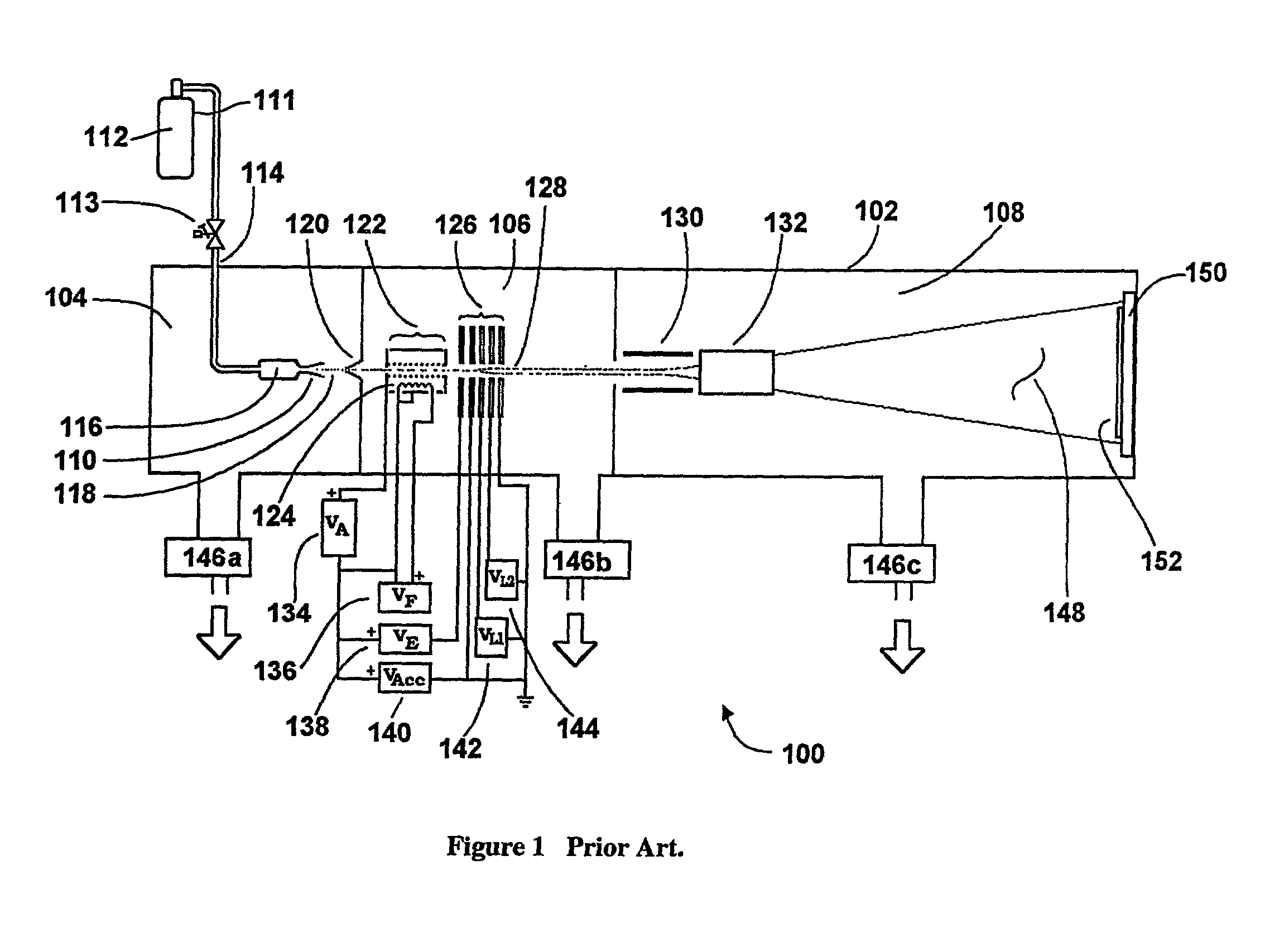
Charging control and dosimetry system for gas cluster ion beam
InactiveUS20020130275A1Reduce surface chargeImproved switchingElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingGas cluster ion beamCharge control
A method and apparatus for gas cluster ion beam (GCIB) processing uses X-Y scanning of the workpiece relative to the GCIB. A neutralizer reduces surface charging of the workpiece by the GCIB. A single Faraday cup sensor is used to measure the GCIB current for dosimetry and scanning control and also to measure and control the degree of surface charging that may be induced in the workpiece during processing.
Owner:TEL EPION
Method for preparing biomedical metal alloy material with multi-drug delivery system
InactiveUS20130164346A1Good biocompatibilityImprove adhesionInorganic non-active ingredientsSurgeryMetal alloyPharmaceutical drug
The present invention provides a method for preparing a biomedical metal alloy material with a multi-drug delivery system. A biomedical metal alloy material with a multi-drug delivery system according to the present invention is prepared by incorporating a therapeutic agent into a biodegradable material to prepare particles containing the therapeutic agent, treating the surface of the particles containing the therapeutic agent to have a charge opposite to the surface charge of a metal alloy material, and inducing an electrostatic interaction between the surface charges of the particles containing the therapeutic agent and the metal alloy material to immobilize the surface-treated particles containing the therapeutic agent on the surface of the metal alloy material.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Nanofludic field effect transistor based on surface charge modulated nanochannel
A field effect transistor device includes: a reservoir bifurcated by a membrane of three layers: two electrically insulating layers; and an electrically conductive gate between the two insulating layers. The gate has a surface charge polarity different from at least one of the insulating layers. A nanochannel runs through the membrane, connecting both parts of the reservoir. The device further includes: an ionic solution filling the reservoir and the nanochannel; a drain electrode; a source electrode; and voltages applied to the electrodes (a voltage between the source and drain electrodes and a voltage on the gate) for turning on an ionic current through the ionic channel wherein the voltage on the gate gates the transportation of ions through the ionic channel.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Process for preparing substrates with porous surface
InactiveUS20080277346A1Material nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsCoated surfacePolyelectrolyte
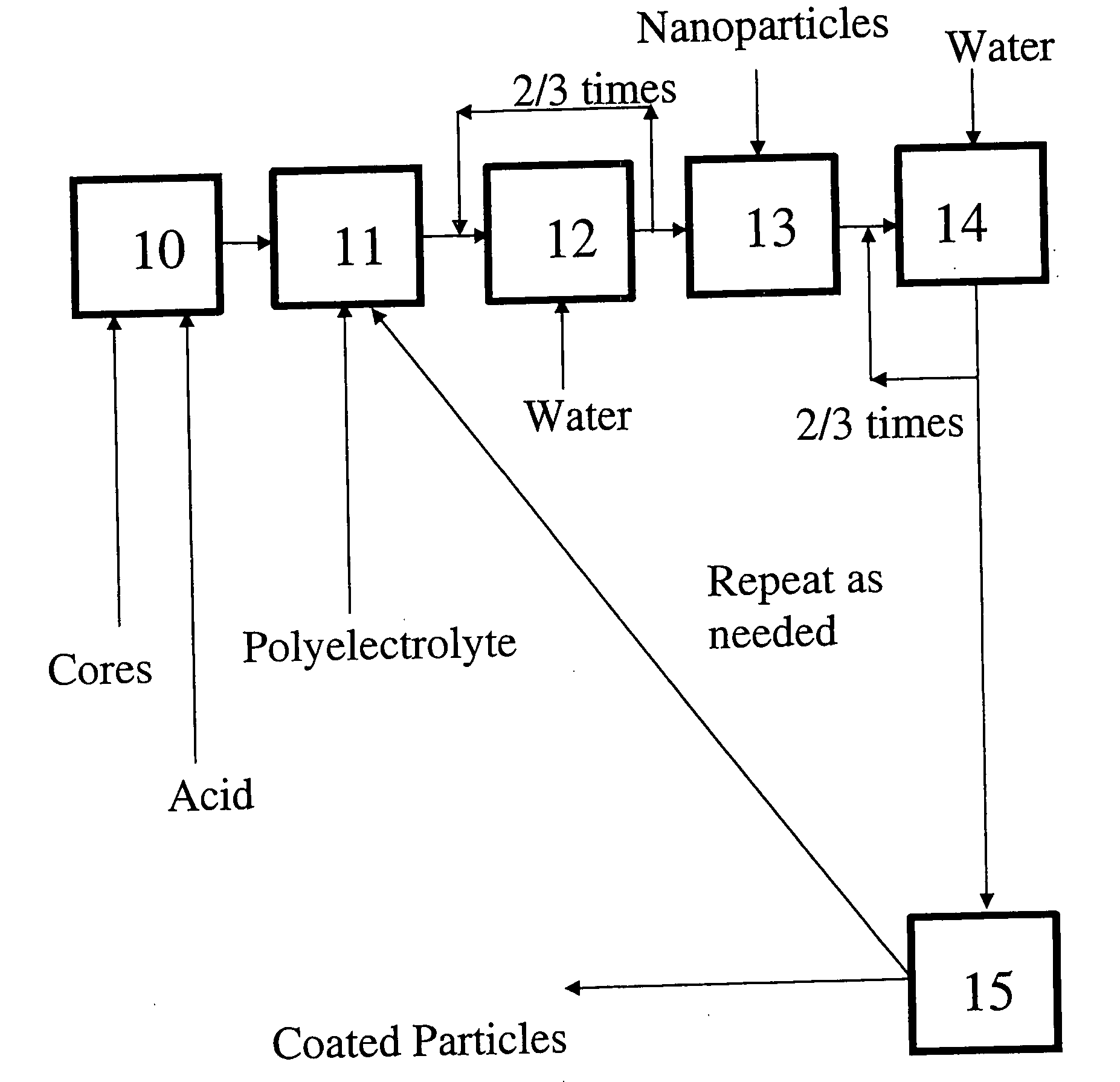
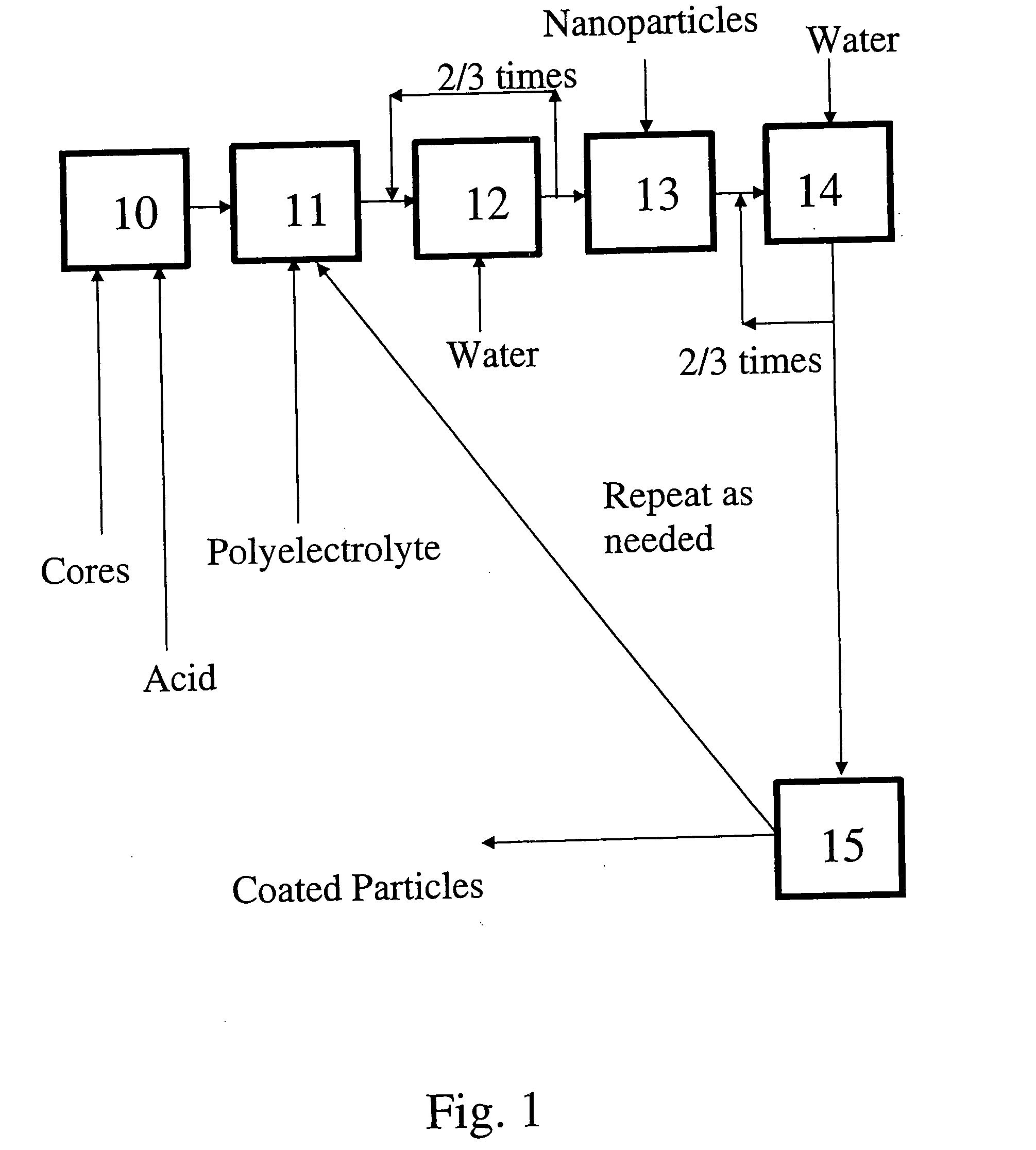
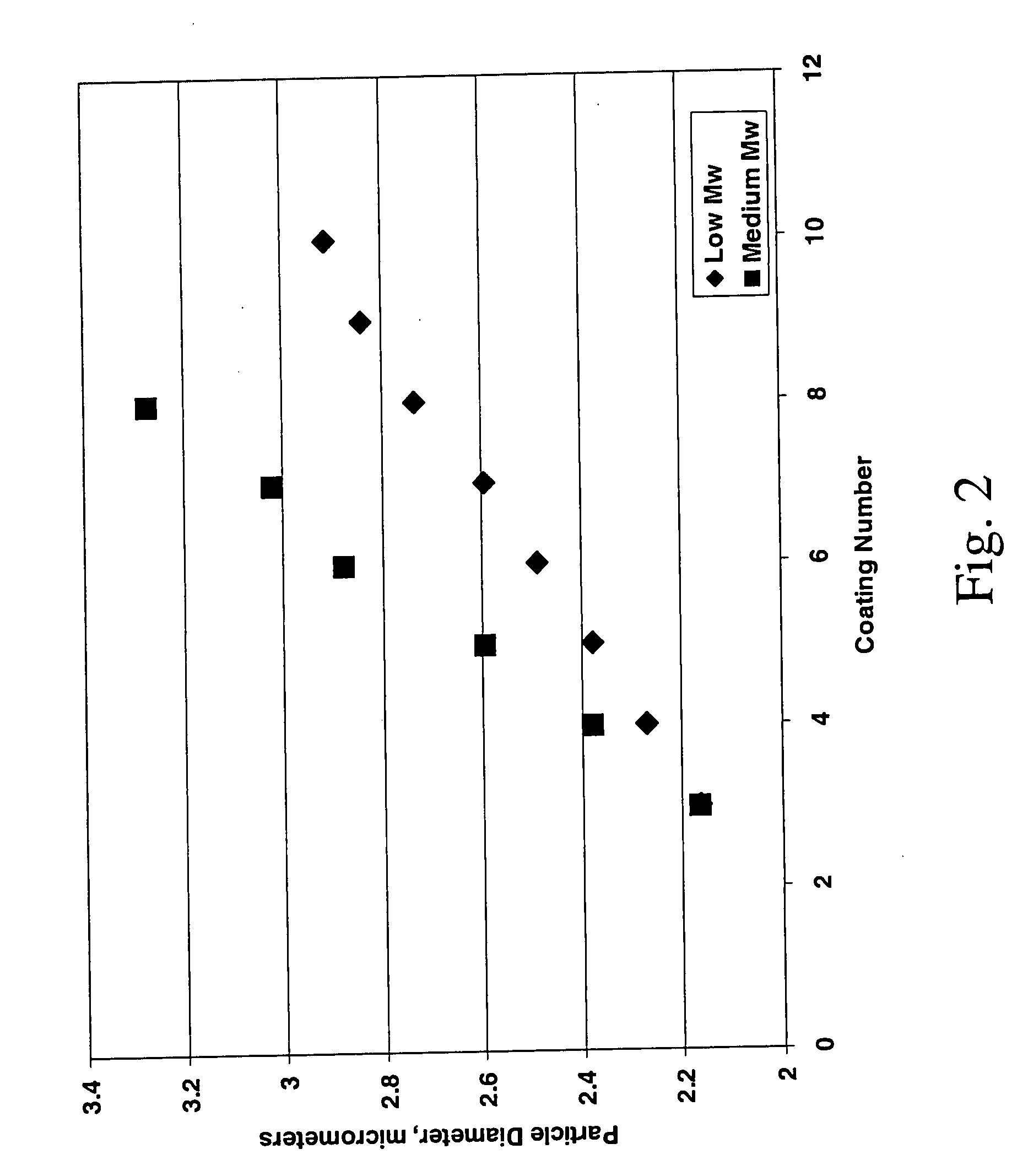
A process for preparing nanoparticle coated surfaces including the steps of electrostatically coating surfaces with polyelectrolyte by exposing the surface to a solution or suspension of polyelectrolyte, removing excess non-bound polyelectrolyte, then further coating the particles with a multi-layer of charged nanoparticles by exposing the polyelectrolyte-coated surface to a fluid dispersion including the charged nanoparticles. The process steps can optionally be repeated thereby adding further layers of polyelectrolyte followed by nanoparticles as many times as desired to produce a second and subsequent layers. The polyelectrolyte has an opposite surface charge to the charged nanoparticles and a molecular weight at the ionic strength of the fluid that is effective so that the first, second, and subsequent layers independently comprise a multiplicity of nanoparticle layers that are thicker than monolayers.
Owner:ADVANCED MATERIALS TECHNOLOGIES
Nanoparticle and surface-modified particulate coatings, coated balloons, and methods therefore
Devices, coatings, and methods therefore comprise a medical device for delivering nanoparticles of an active agent to a treatment site. A coating on the medical device comprises active agent nanoparticles, which delivers coating to the treatment site and releases active agent nanoparticles into the treatment site over at least one day. A coating may comprise a polymer, a surfactant, and the nanoparticles. The coating may be prepared by forming a nanoemulsion. A coating may comprise encapsulated active agent nanoparticles which comprise active agent nanoparticles encapsulated in a polymer. The coating may have a positive surface charge. The coating may deliver active agent nanoparticles into the treatment site over at least about one day. The coating may be formed of a surfactant and nanoparticles mixture. The active agent nanoparticles may be deposited on the medical device using electrostatic capture.
Owner:MICELL TECH INC
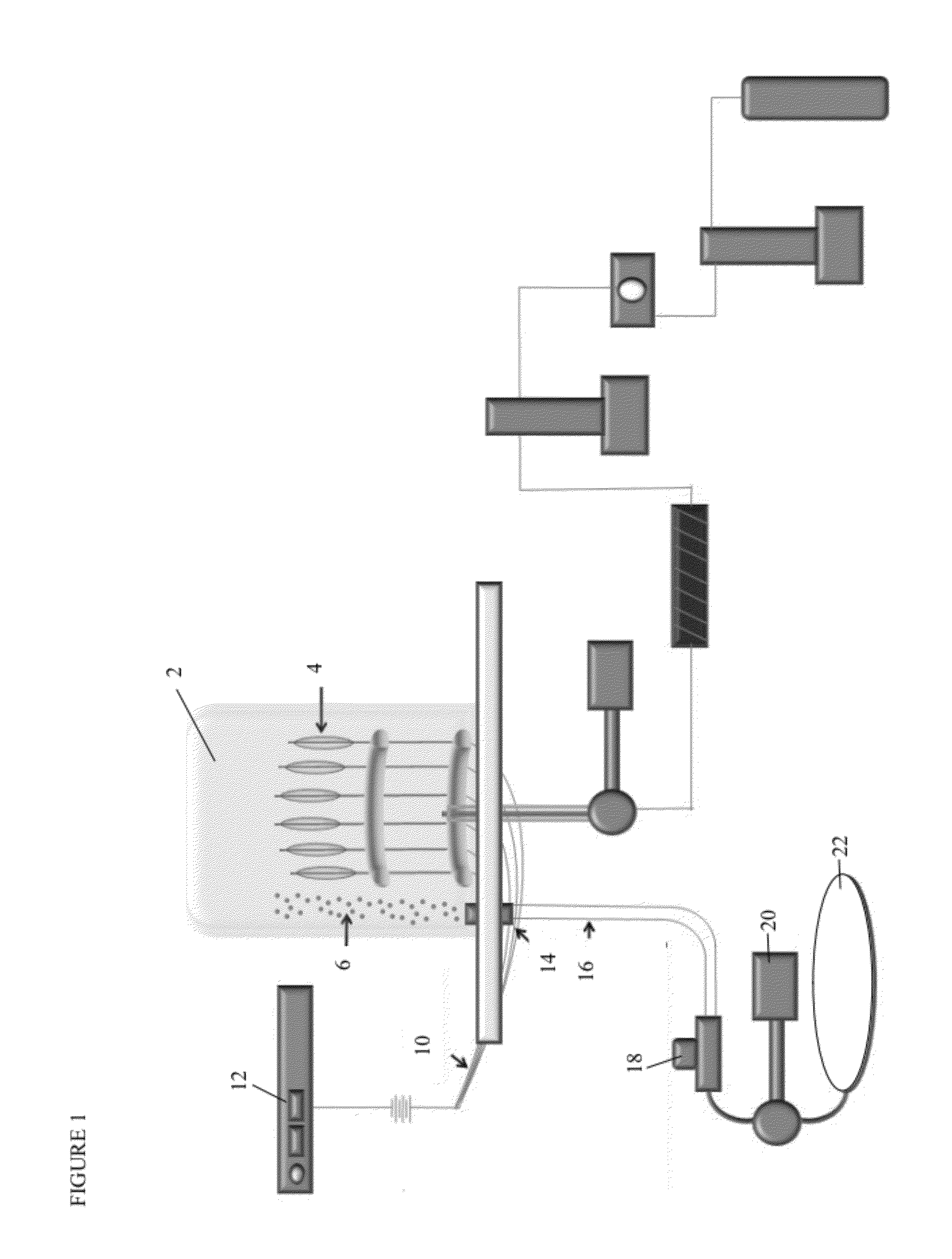
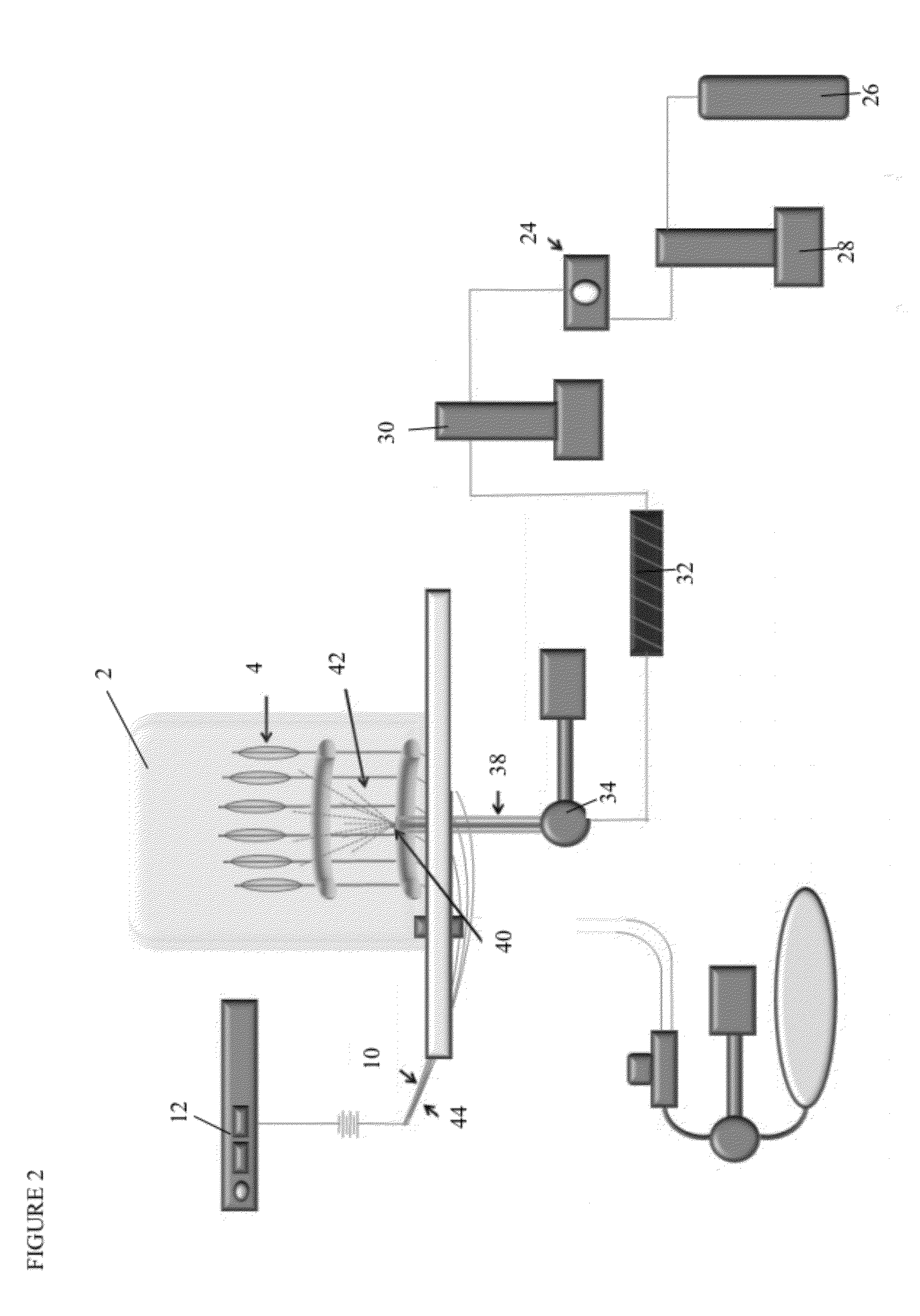
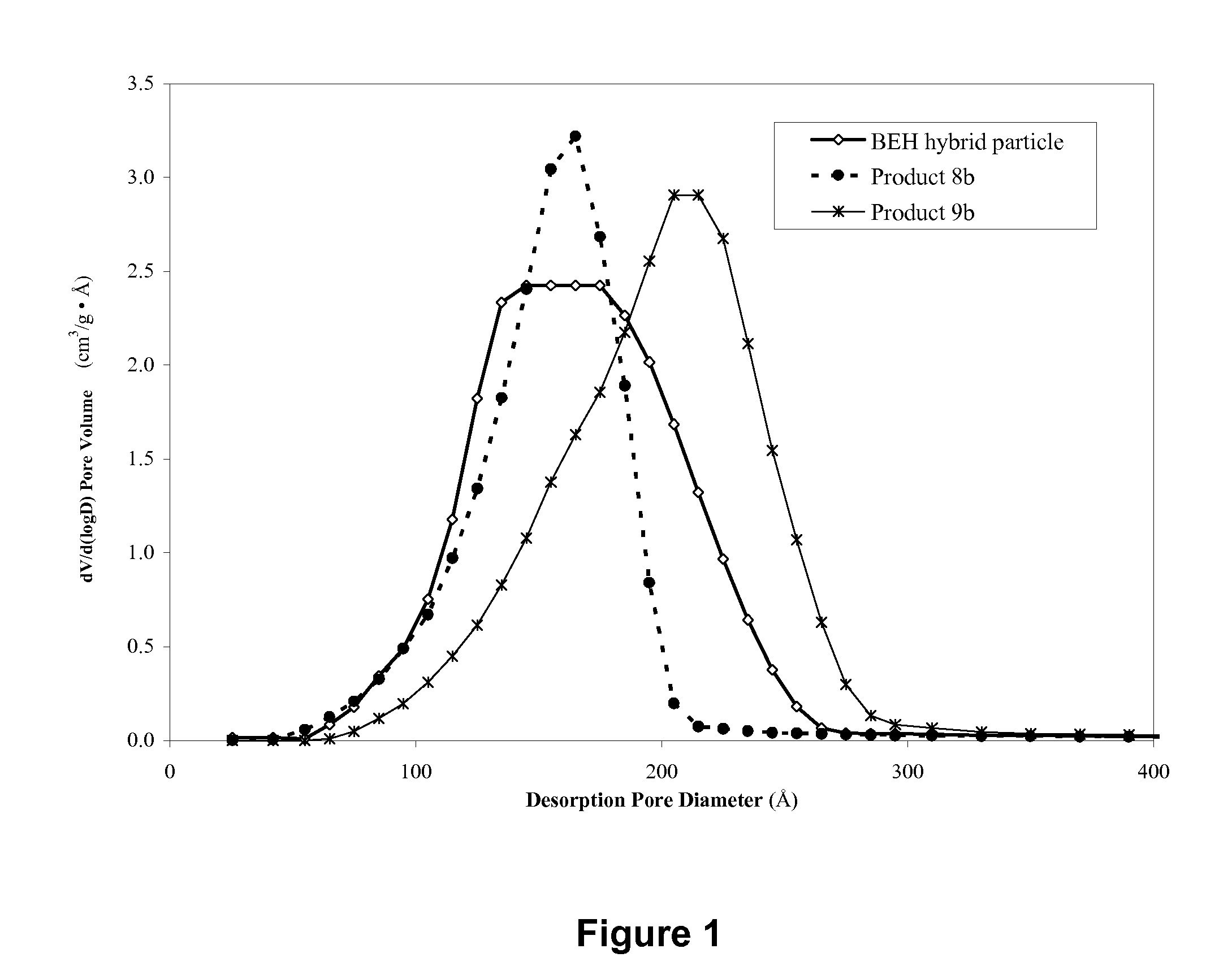
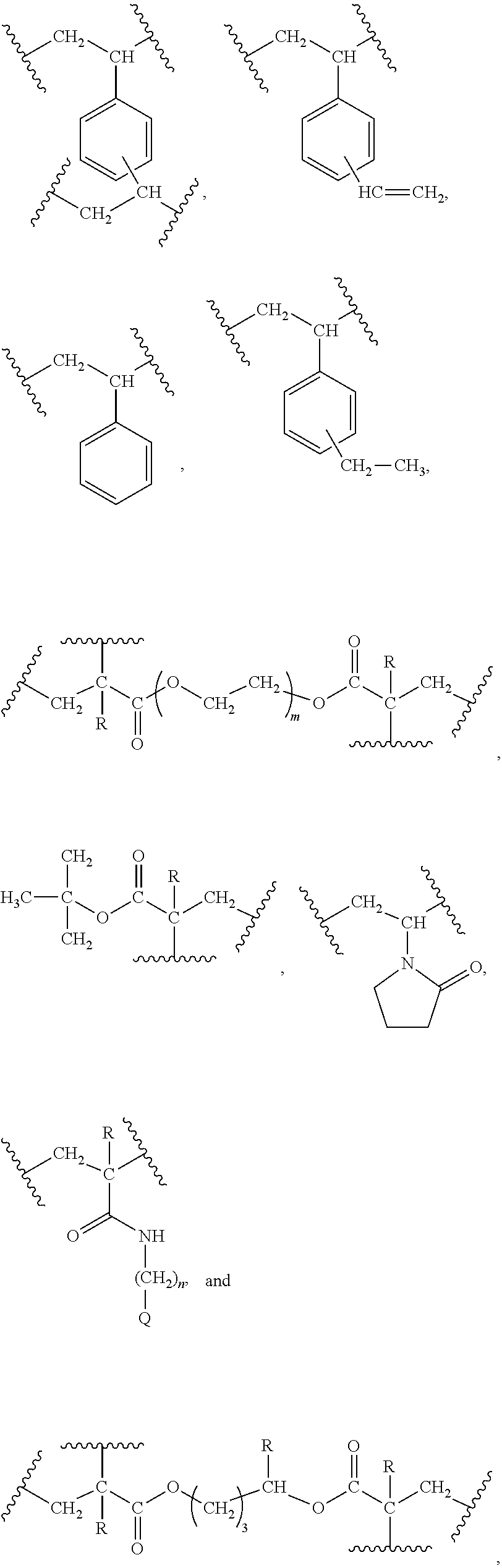
Hybrid inorganic/organic materials having novel surface modification; process for the preparation of inorganic/organic hybrid materials; and use of said particles for chromatographic separations
ActiveUS20120055860A1Enhancing oneMany of characteristicIon-exchange process apparatusSemi-permeable membranesChromatographic separationIon exchange
The present invention provides novel chromatographic materials, e.g., for chromatographic separations, processes for their preparation and separations devices containing the chromatographic materials. The preparation of the inorganic / organic hybrid materials of the invention wherein a surrounding material is condensed on a porous hybrid core material will allow for families of different hybrid packing materials to be prepared from a single core hybrid material. Differences in hydrophobicity, ion-exchange capacity, surface charge or silanol activity of the surrounding material may be used for unique chromatographic separations of small molecules, carbohydrates, antibodies, whole proteins, peptides, and / or DNA.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
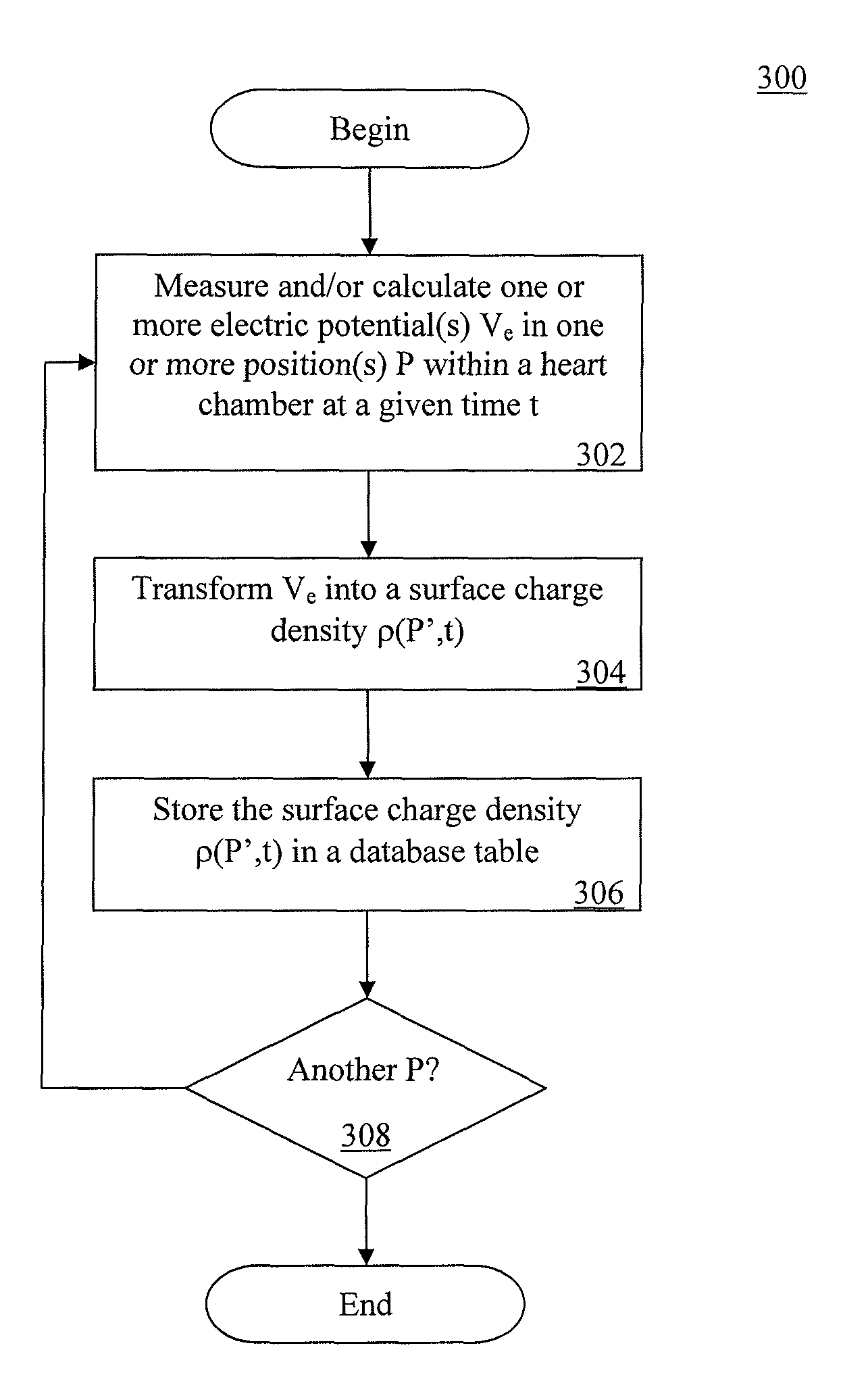
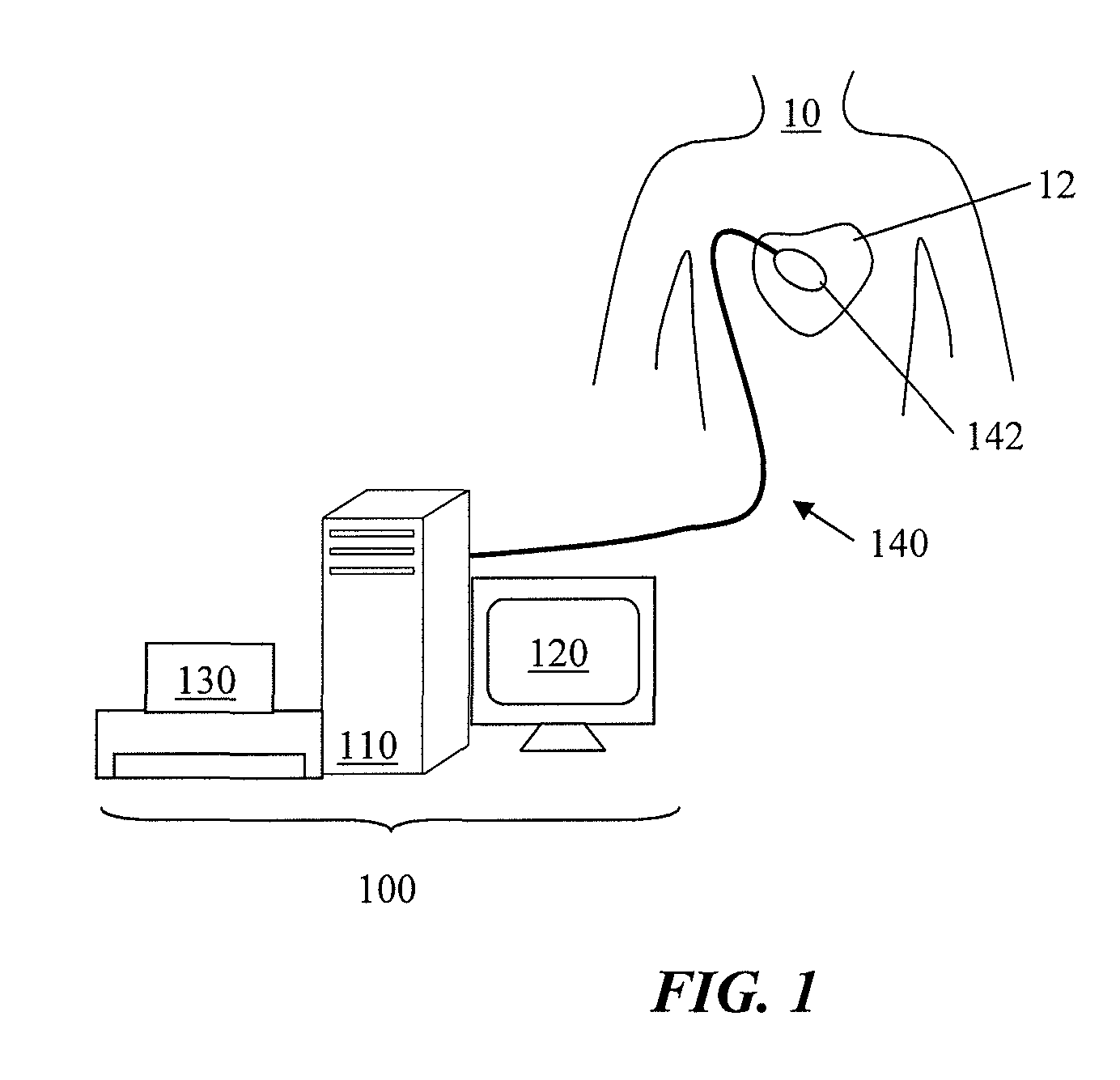
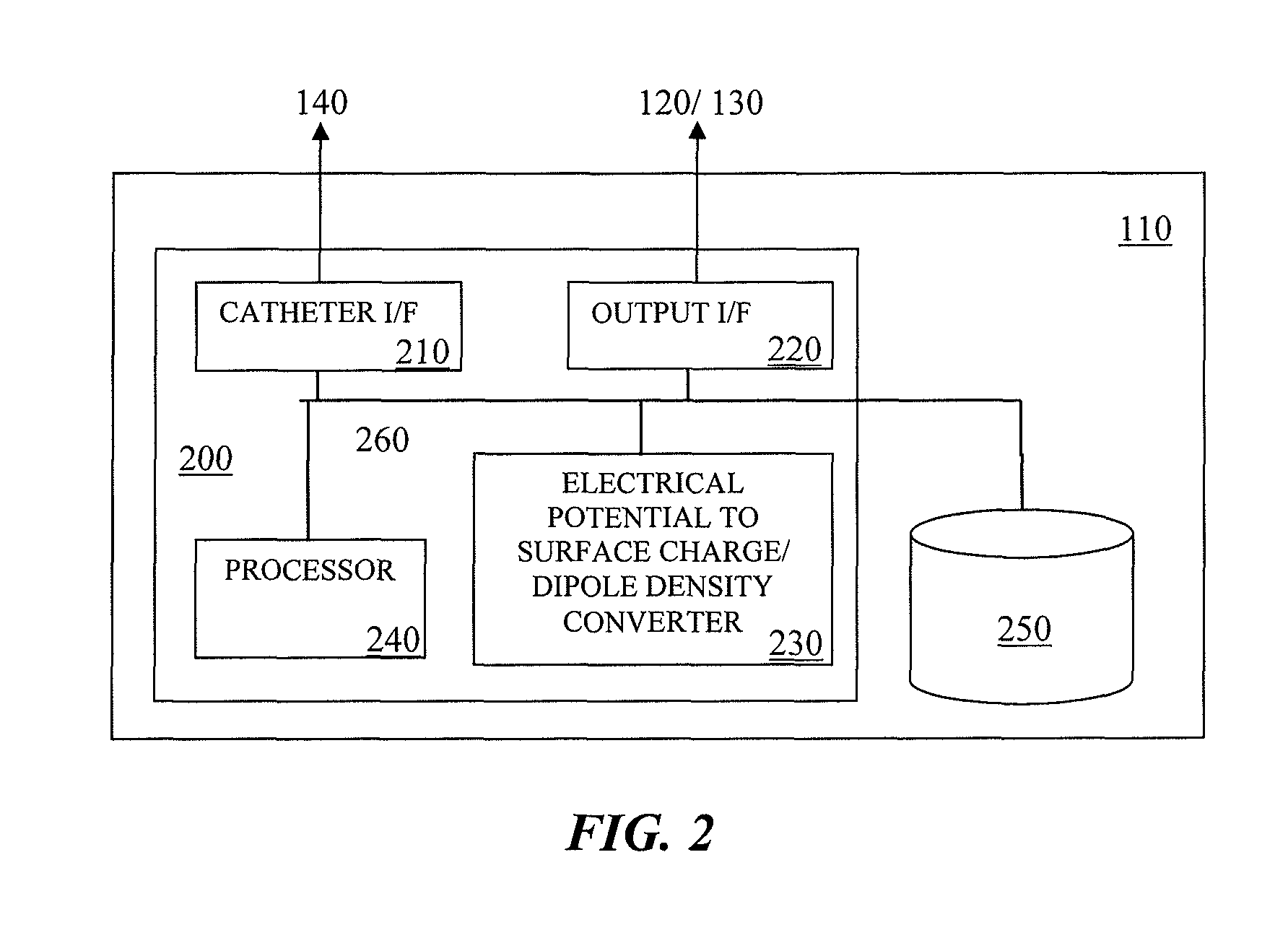
Method and device for determining and presenting surface charge and dipole densities on cardiac walls
The invention discloses a method, a system, a computer program and a device for determining the surface charge and / or dipole densities on heart walls. Using the foregoing, a table of dipole densities ν(P′, t) and / or a table of surface charge densities ρ(P′, t) of a given heart chamber can be generated.
Owner:SCHARF CHRISTOPH
Method and device for determining and presenting surface charge and dipole densities on cardiac walls
The invention discloses a method, a system, a computer program and a device for determining the surface charge and / or dipole densities on heart walls. Using the foregoing, a table of dipole densities ν(P′, t) and / or a table of surface charge densities ρ(P′, t) of a given heart chamber can be generated.
Owner:SCHARF CHRISTOPH
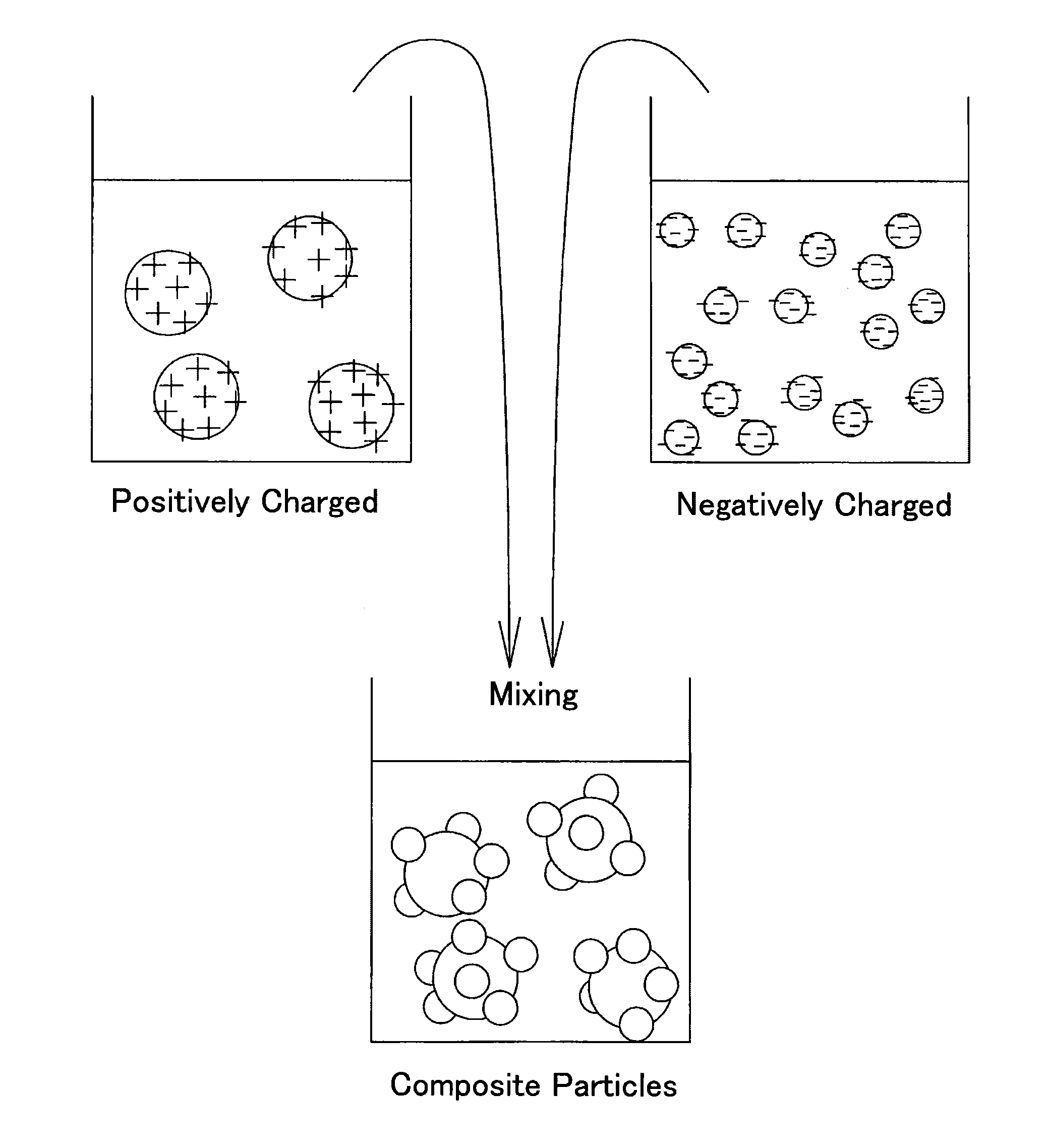
Device and process for producing composite particles
InactiveUS20150190840A1Simple processGuaranteed to workLiquid surface applicatorsGranulation in stationary drums/troughsPolymer electrolytesEngineering
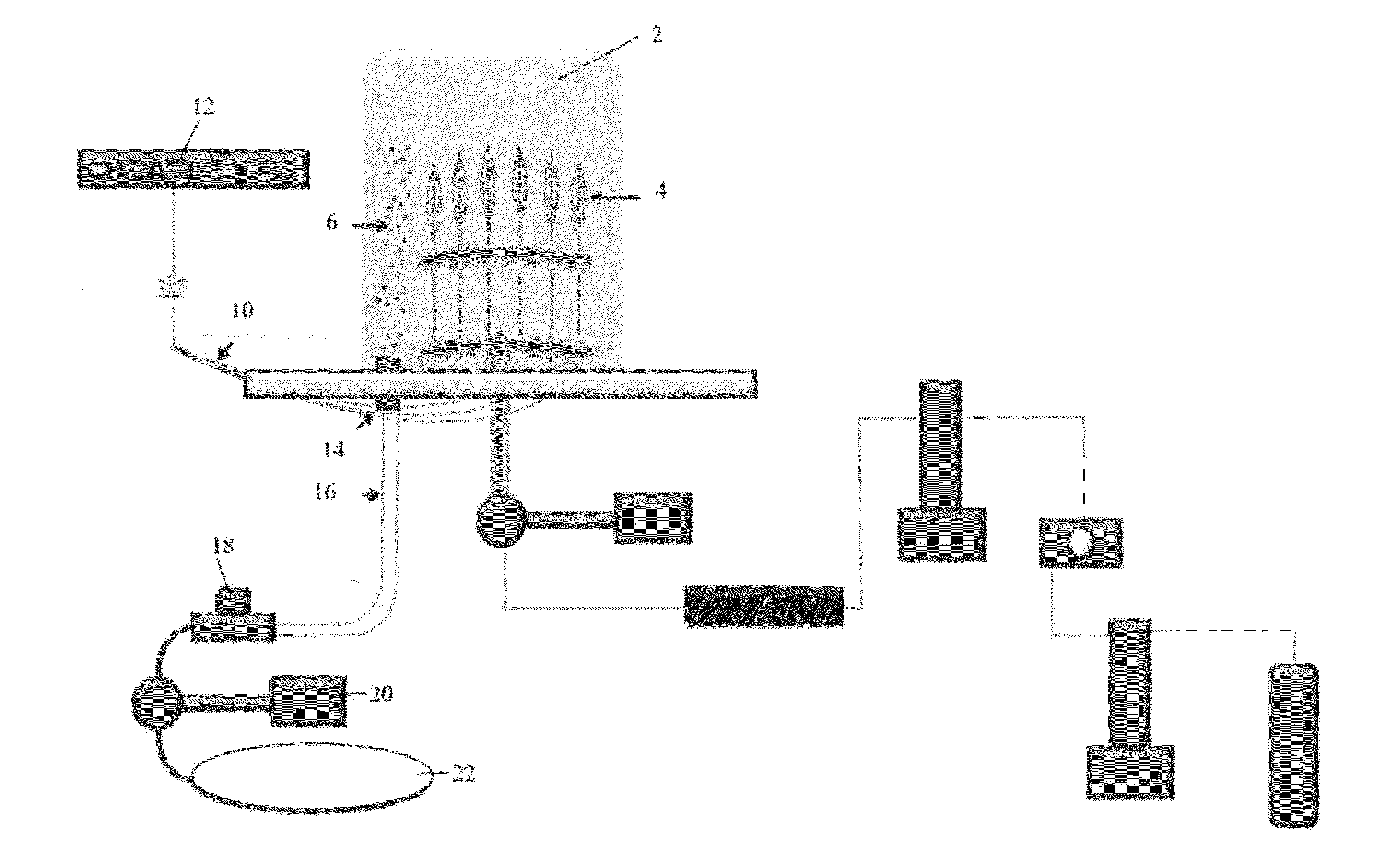
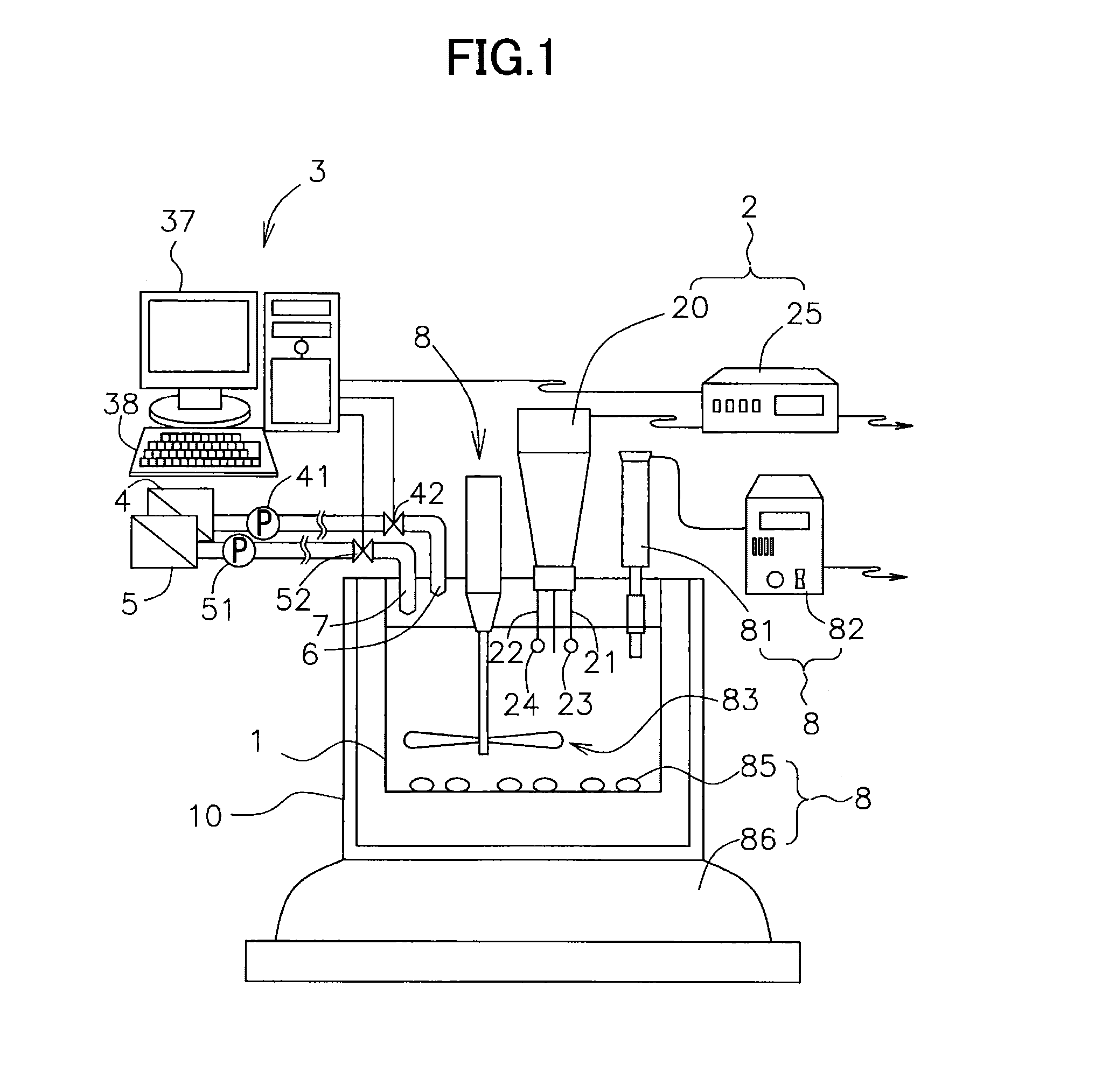
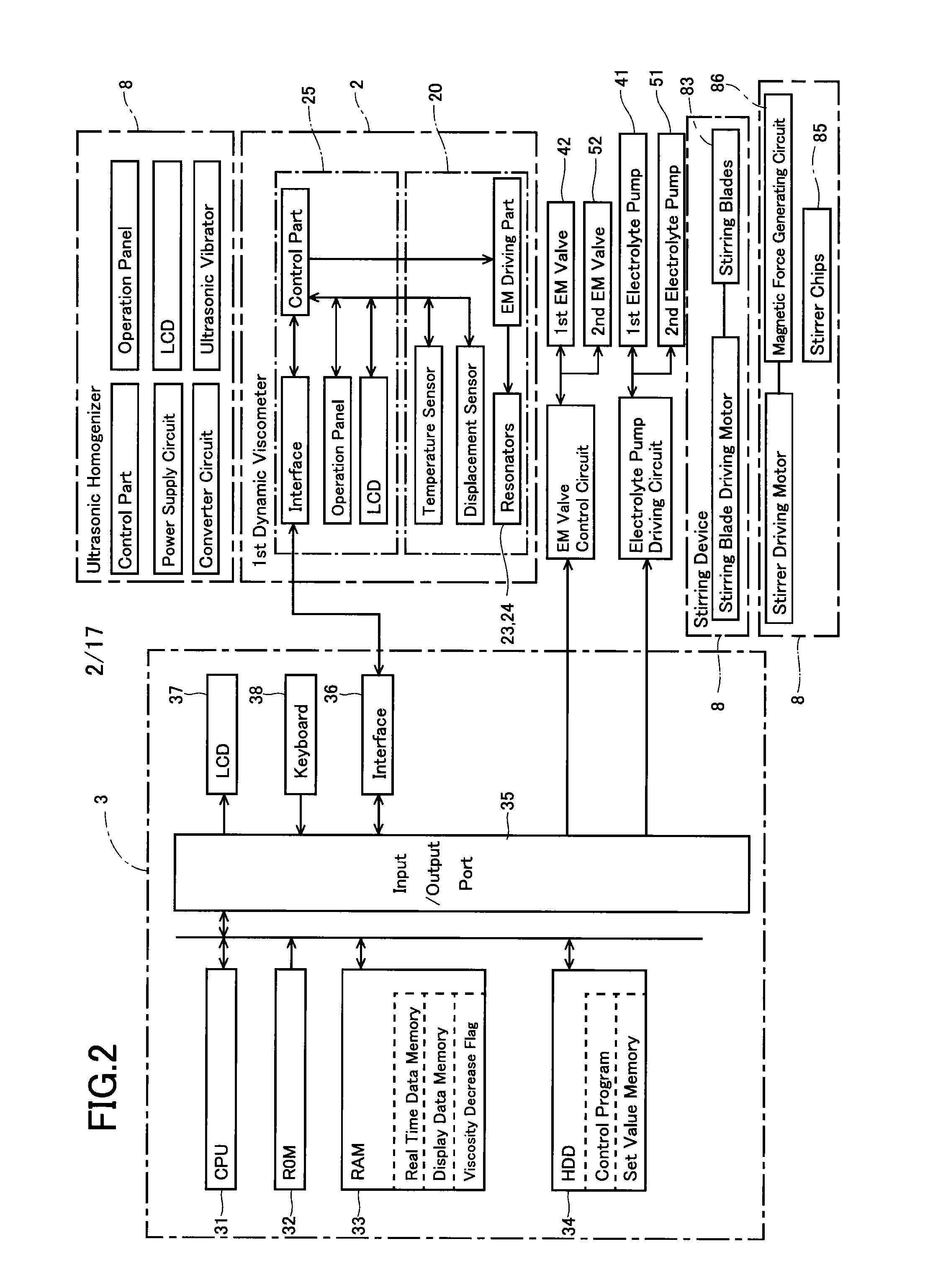
A device and process for producing composite particles capable of adding a control agent for controlling a surface charge of particles such as a polymer electrolyte without being in excess or short. The production device includes a reservoir tank holding liquid containing either a first group or a second group of particles; a dispersion state measuring mechanism measuring a dispersion state of the particles in the liquid held in the reservoir tank; a dispersion state storage storing the dispersion state measured by the dispersion state measuring mechanism when a control agent for controlling a surface charge of the particles contained in the liquid in the reservoir tank is added into the reservoir tank; and an information output outputting information indicating that the dispersion state of the particles in the liquid in the reservoir tank is a desired state, based on the dispersion state stored in the dispersion state storage.
Owner:TOYOHASHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Electrostatic impulse generator and direct current (DC) impulse generator
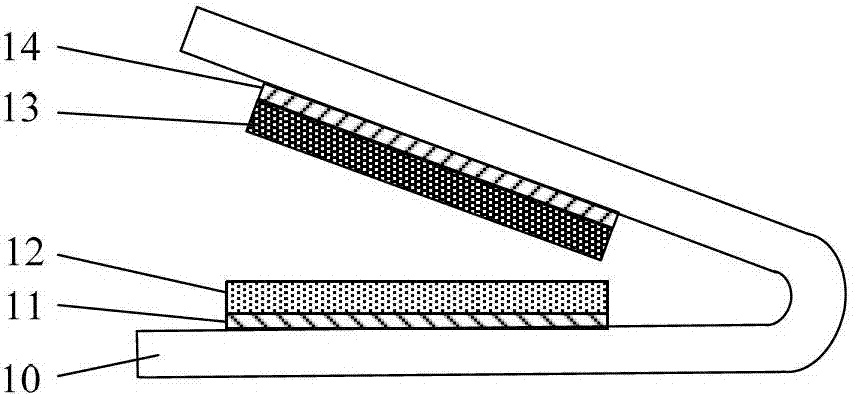
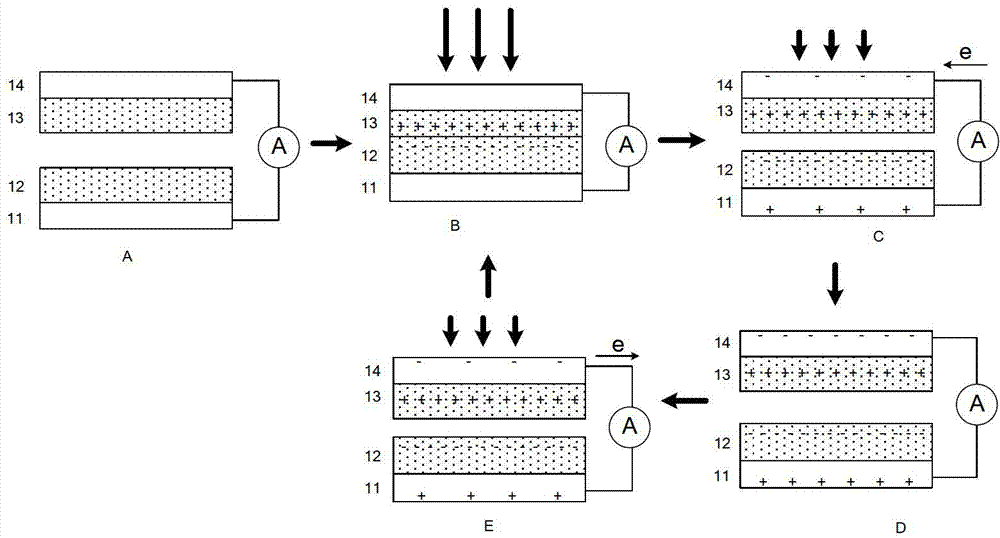
The invention provides an electrostatic impulse generator, which comprises a flexible base and power generation units, wherein any two adjacent layers of the base are mutually connected to form a V-shaped or U-shaped sunken structure, the power generation units are arranged in the sunken structures, the two layers on the inner surface of the V-shape or U-shape sunken structure respectively support a friction layer of the corresponding power generation unit, under the action of external force, the size of the opening of the V-shape or U-shape sunken structure of the flexible base is reduced to enable the two friction layers to be contacted with each other so as to generate surface charge transfer, when the external force disappears, the two friction layers of the power generation unit are separated from each other due to the rigidity of the flexible base, and pulse electrical signals are generated on electrode layers. Under the action of periodic external force, the two friction layers of the power generation unit are contacted with each other or separated from each other periodically by the drive of the flexible base, and the pulse electrical signals are generated between the two electrode layers of the power generation units.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
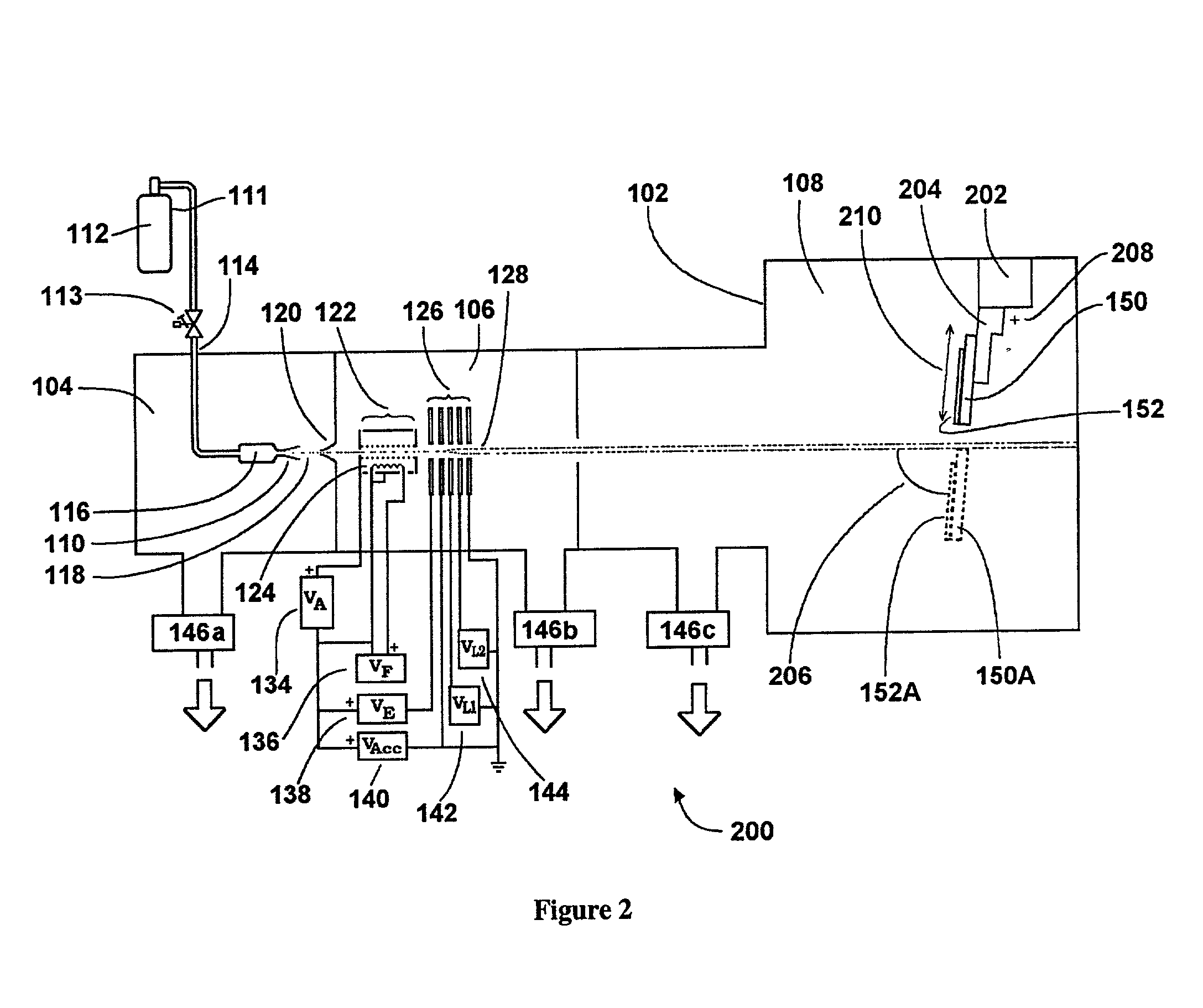
Electron beam apparatus
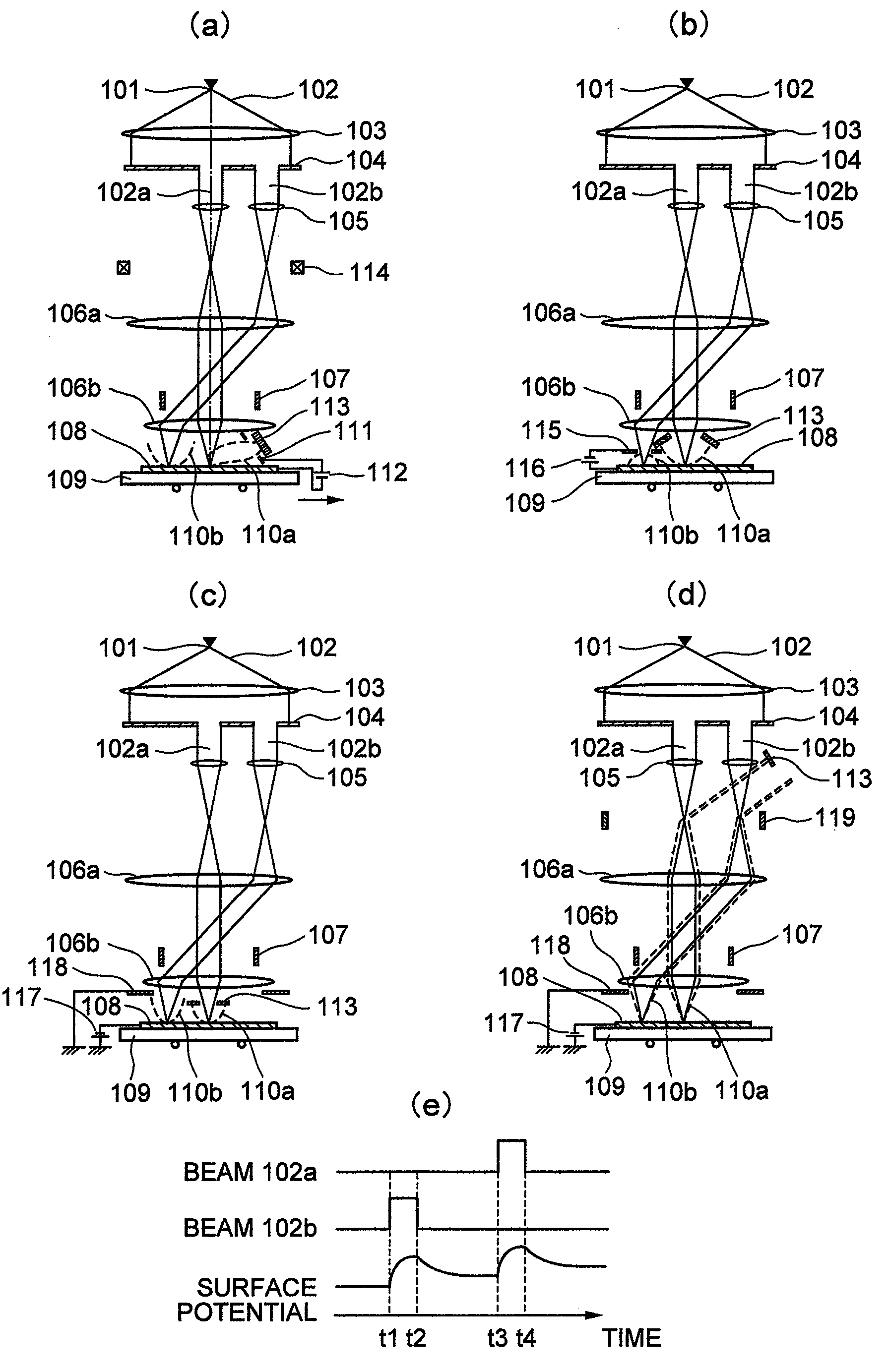
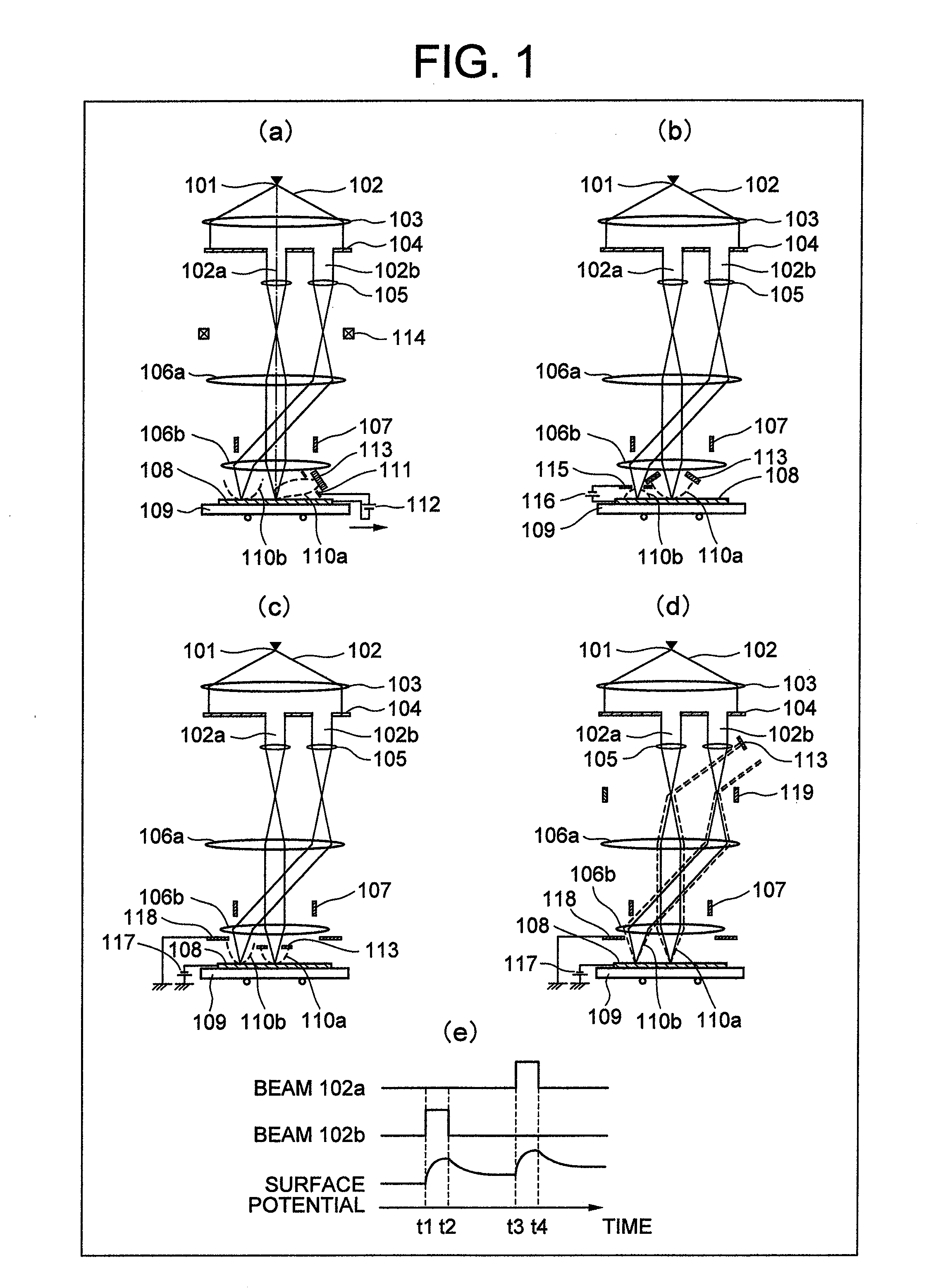
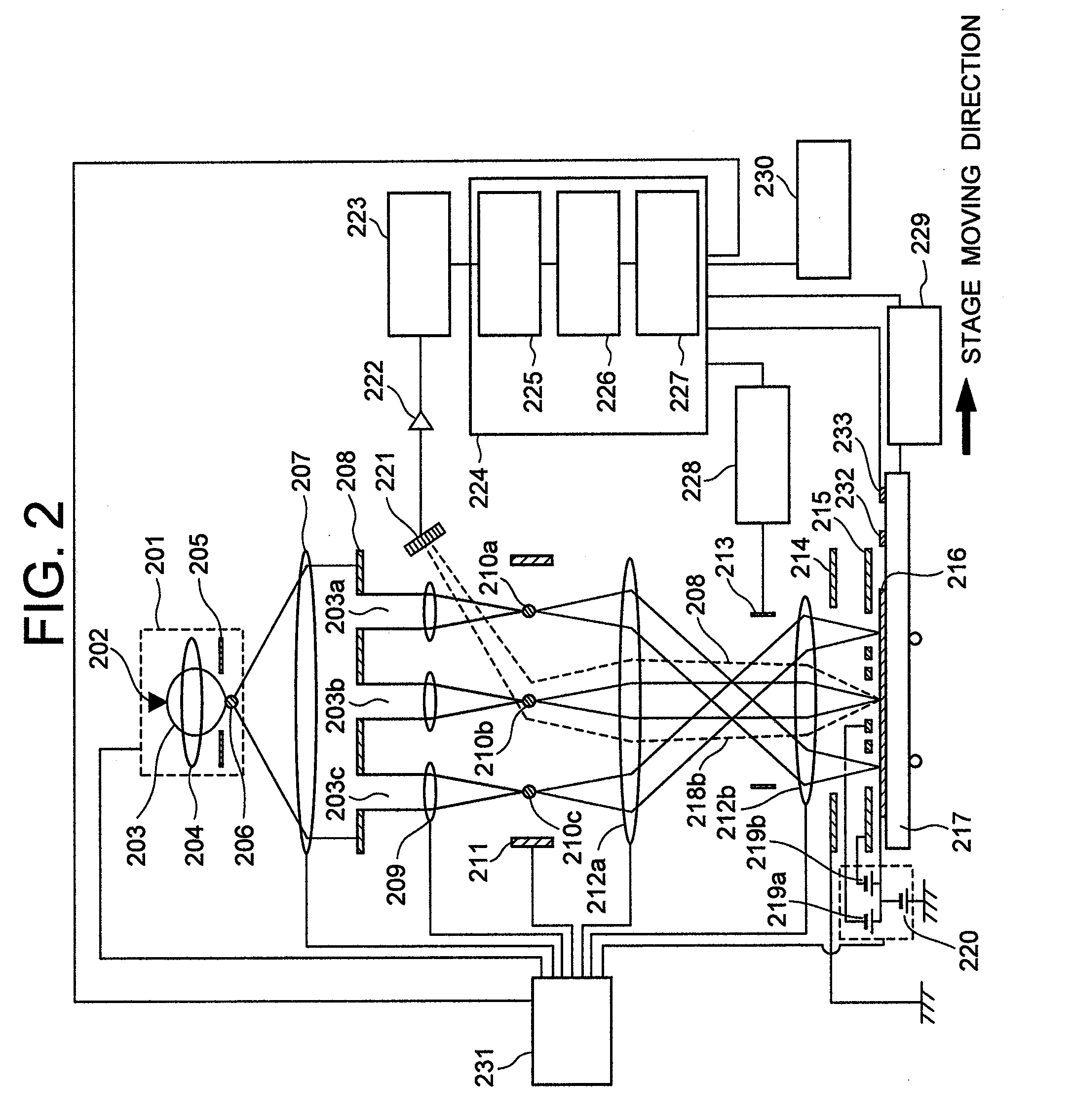
ActiveUS20100133433A1Improve throughputAchieve convergenceThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSingle electronLight beam
A plurality of primary beams are formed from a single electron source, the surface charge of a sample is controlled by at least one primary beam, and at the same time, the inspection of the sample is conducted using a primary beam other than this. Also, for an exposure area of the primary beam for surface charge control and an exposure area of the primary beam for the inspection, the surface electric field strength is set individually. Also, the current of the primary beam for surface charge control and the interval between the primary beam for surface charge control and the primary beam for inspection are controlled.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Dynamic self-assembled process for preparing low-pressure high-throughput charged nanofiltration membrane
InactiveCN101274222AImprove efficiencySimple methodSemi-permeable membranesFiltration membraneLow voltage
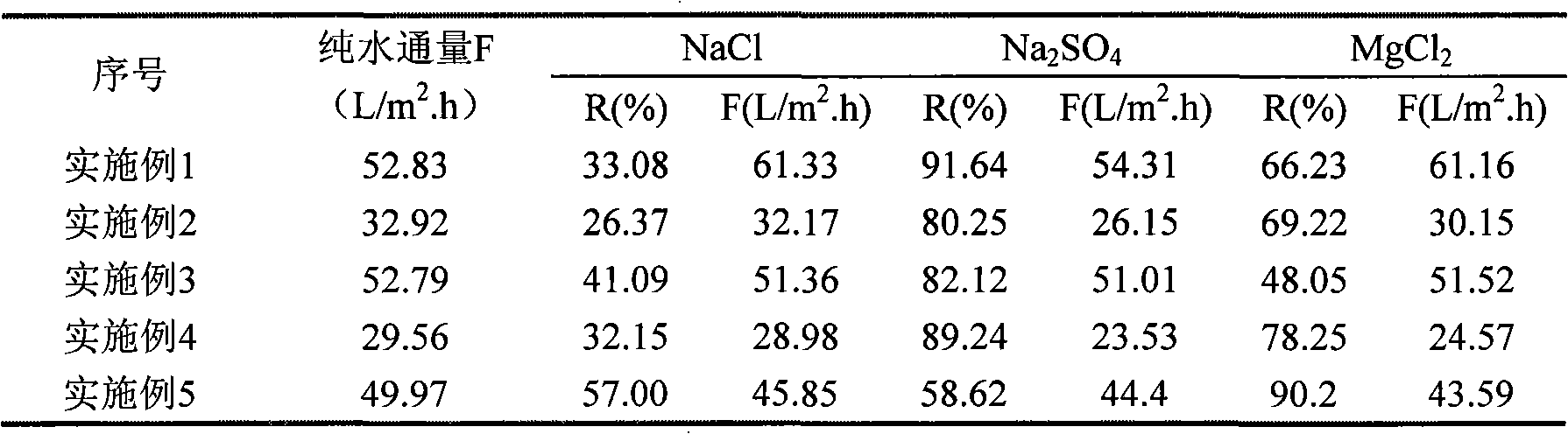
The invention discloses a method for preparing low-voltage high-flux charged nano-filtration membrane by dynamic self-assembly, which is characterized in that polymer ultra-filtration membrane is taken as a basic film; polycation electrolyte and polyanion electrolyte are alternatively and dynamically self-assembled on the surface of the basic film to gain a selective separation layer and to prepare the nano-filtration membrane of charged surface; wherein, the used ultra-filtration membrane molecular weight cutoff is less than 0.1 million; the ultra-filtration membrane material is surface-charged or modified-charged polymer. Nano-filtration membrane preparation by polyelectrolyte dynamic self-assembly has high efficiency, simple and convenient method and controllable assembly process and film structure; pure water solution is used in the whole preparation process, which is green and environmental protective; the applicable polyelectrolyte has a plurality of types; the separation films with different performances can be obtained by adjusting the types of the polyelectrolyte and the assembly conditions. Furthermore, the prepared nano-filtration membrane has low operation pressure, high removal rate on high valence inorganic salts and far greater flux than the current commercial nano-filtration membrane and the nano-filtration membrane preparation method has good application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods of surface modification for improving electrophoretic display performance
InactiveUS6870662B2Improve surface propertiesIncrease contrastSludge treatmentStatic indicating devicesImaging qualityDisplay device
The present invention is directed to methods for improving the performance of an electrophoretic display by modifying the display cell surface. More specifically, the methods are directed to modification of the microcup surface after the microcups are released from the mold. The microcups which have undergone any of the treatment methods of the invention show significant improvement in their surface properties, such as chemical functionality, surface roughness, surface tension, morphology, surface charge, surface reflectivity, surface conductivity and optical properties, particularly optical density in the visible light region. An electrophoretic display formed from the treated microcups has many advantages. For example, the display shows a higher contrast ratio, lower electro-optic response time, lower driving voltage, longer shelf life, higher imageincreasing bistability and higher threshold voltage. In addition, it exhibits an improved image quality by reducing undesirable scum formation or irreversible particle deposition on the microcup surface.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing bio-carrier by porous foam polymer modification
InactiveCN102786710AAdapt to fixityAdaptive performanceChemical industryDispersed particle separationCross-linkPolymer modified
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bio-carrier by porous foam polymer modification. The method is used for coating bonding modification of porous foam polymers. The method comprises the following steps of adding one or more cationized porous high-adsorptivity functional materials and one or more cationized polyhydric hydrophilic functional materials into coating modification slurry, mixing the coating modification slurry and a cationic acrylic acid emulsion, carrying out coating bonding of the mixture on one or more porous foam polymers, and carrying out cross-linking curing to obtain the modified bio-carrier having strong adsorbability, hydrophily, surface active functional group diversity, positive surface charges and strong biocompatibility. The method provided by the invention is not limited by structures, shapes, aperture sizes and physical properties of foam polymers and can be widely used for external coating modification of multiple carrier materials. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of convenient and simple operation, low investment and making cost, excellent carrier performances and long service life. The bio-carrier obtained by the method can be widely used in fields of fixed attachment of various microorganisms, and enhanced biological treatment.
Owner:纪群
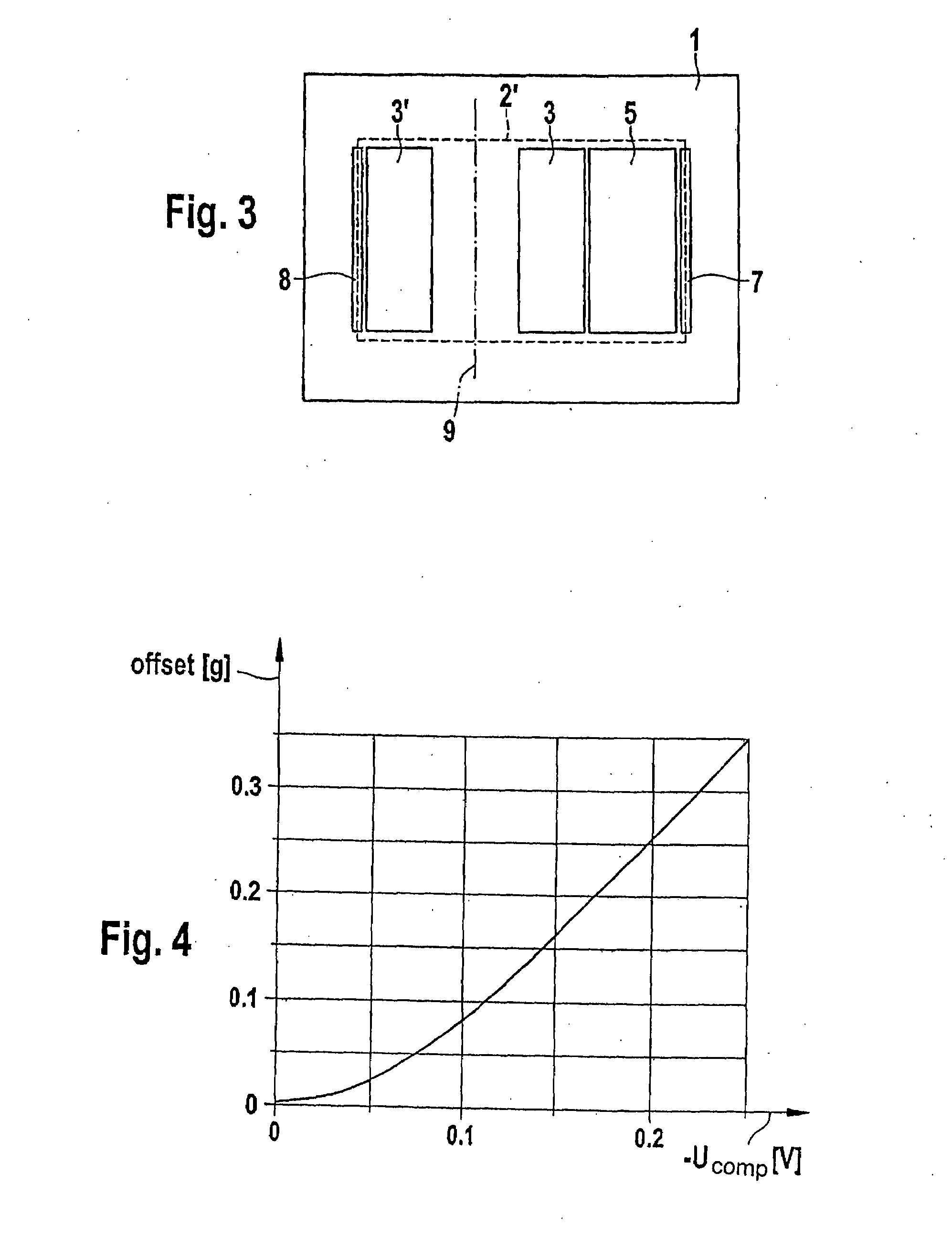
Micromechanical inertial sensor having reduced sensitivity to the influence of drifting surface charges, and method suited for operation thereof
A micromechanical inertial sensor having at least one seismic mass which may be deflected relative to a substrate, and at least one electrode surface which in terms of circuitry, together with at least portions of the seismic mass forms at least one capacitor having a capacitance which is dependent on the deflection of the seismic mass. At least one additional auxiliary electrode is included which is located outside the region which forms the capacitor and which may be set at a potential that deviates from the potential of the seismic mass.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
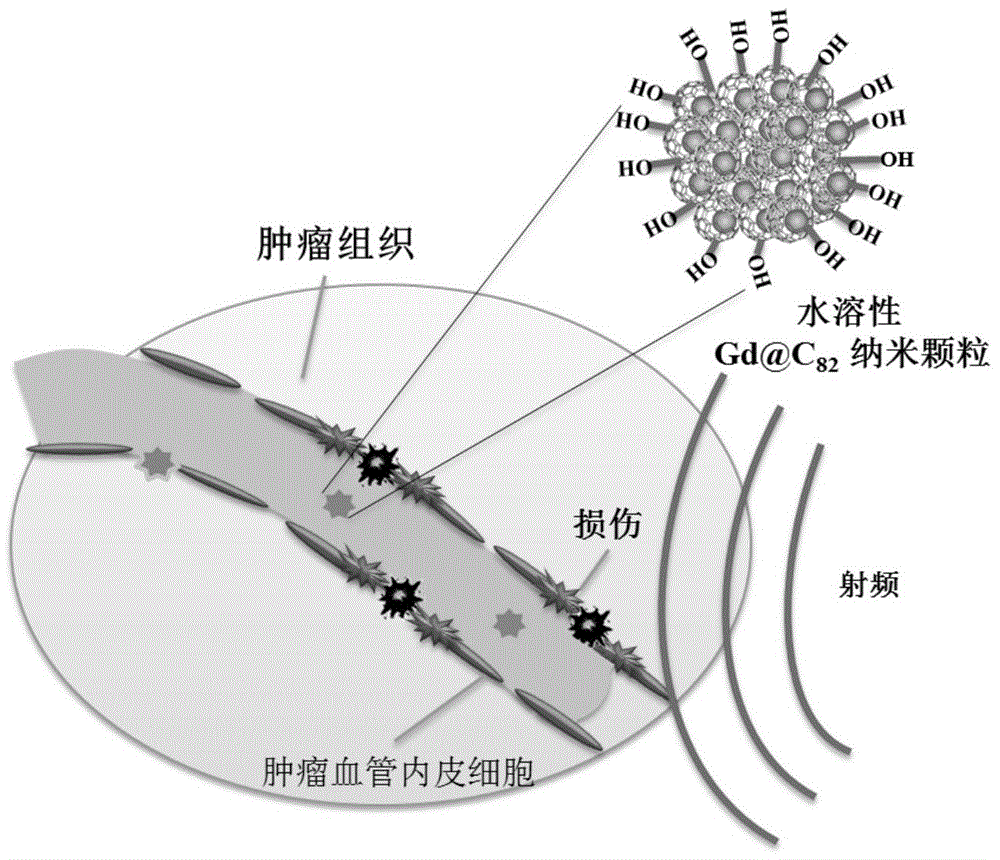
Application of metal fullerene monocrystal nanoparticles in preparation of specific tumor vascular disrupting agent
ActiveCN104127872AStrong specificityUnrestricted microenvironmentEnergy modified materialsAntineoplastic agentsTumor vesselSurface charges
The invention discloses an application of metal fullerene monocrystal nanoparticles in preparation of a tumor vascular disrupting agent. The monocrystal nanoparticles are water-soluble metal fullerene nanoparticles with the surface charged with negative electricity, and have the particle size range of 50-250 nm; the nanomaterial can absorb and convert outside world radiation energy into heat energy, and the volume is expanded sharply when a temperature reaches a phase transition point. During treatment, a tumor-carried living organism is injected and given with the metal fullerene monocrystal nanoparticles; the metal fullerene monocrystal nanoparticles reach a tumor part through blood circulation, and are stranded at tumor pores and defective parts; under the action of the outside world radiation energy, the metal fullerene monocrystal nanoparticles accumulate heat, the temperature rises, and the volume is expanded sharply when the temperature exceeds the phase transformation critical point, so that morphological structures or functions of tumor vascular endothelial cells are changed, and tumor vessels are interdicted so as to make the tumor cells starved to death.
Owner:赤峰福纳康生物技术有限公司 +1
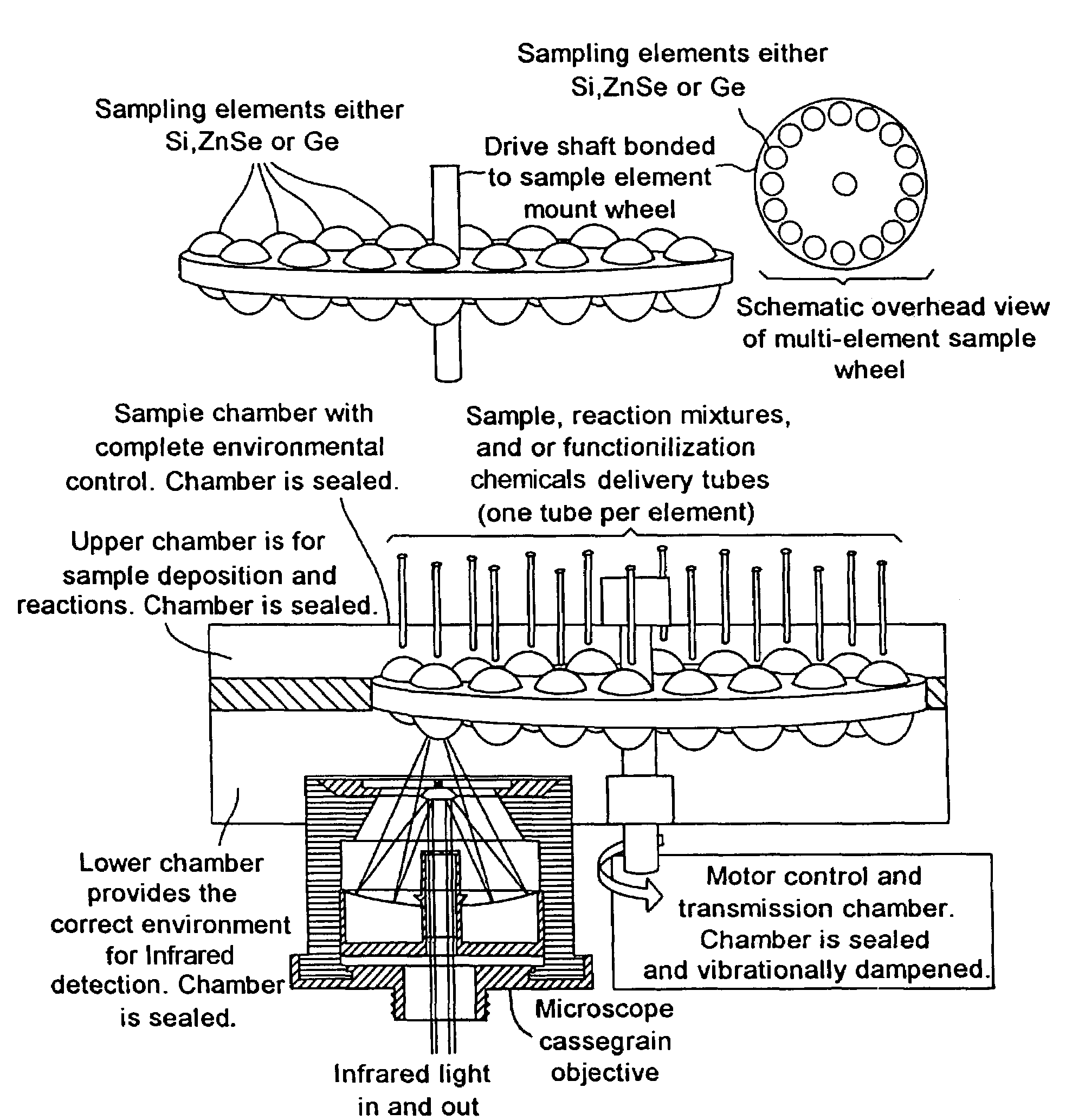
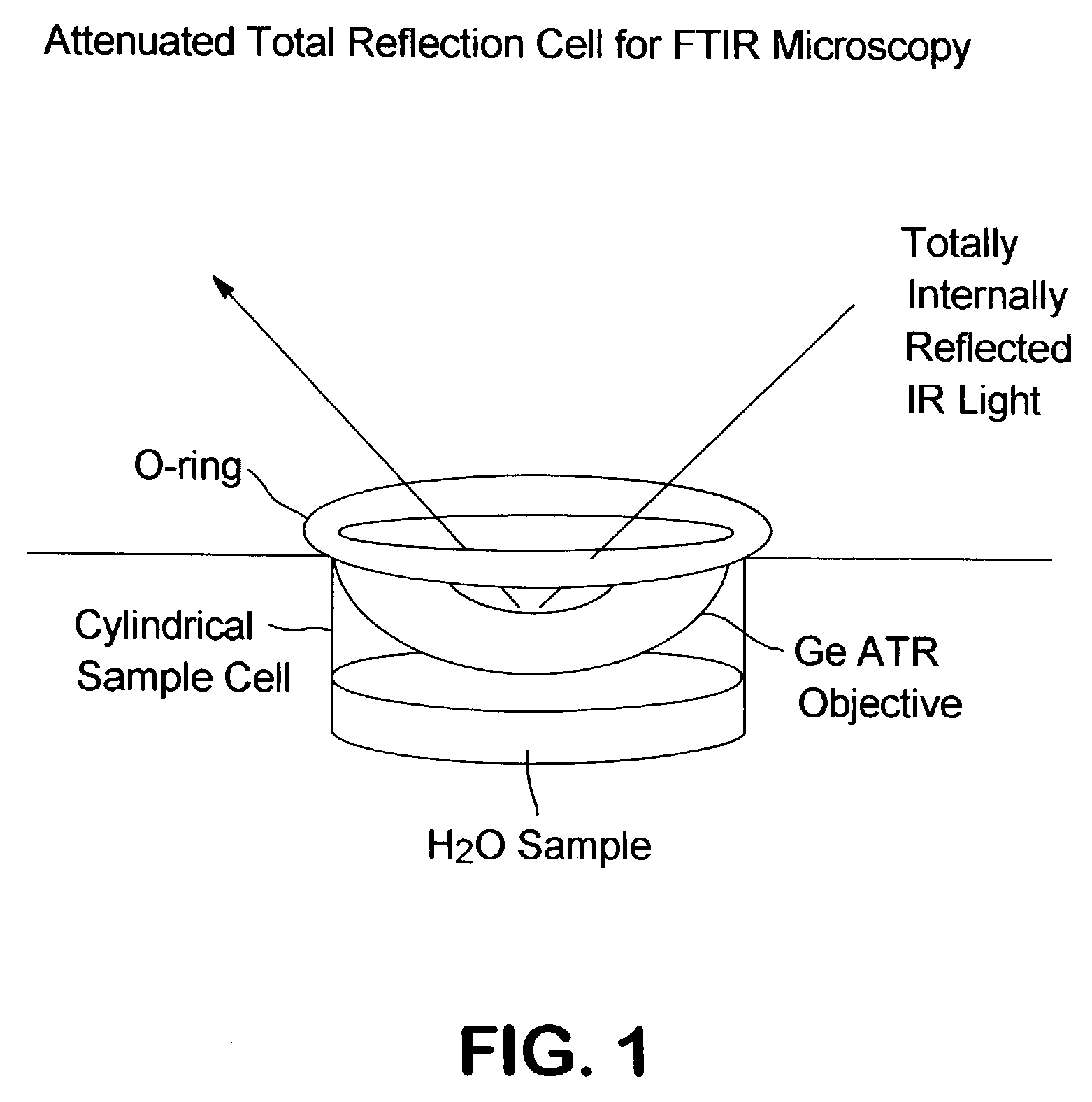
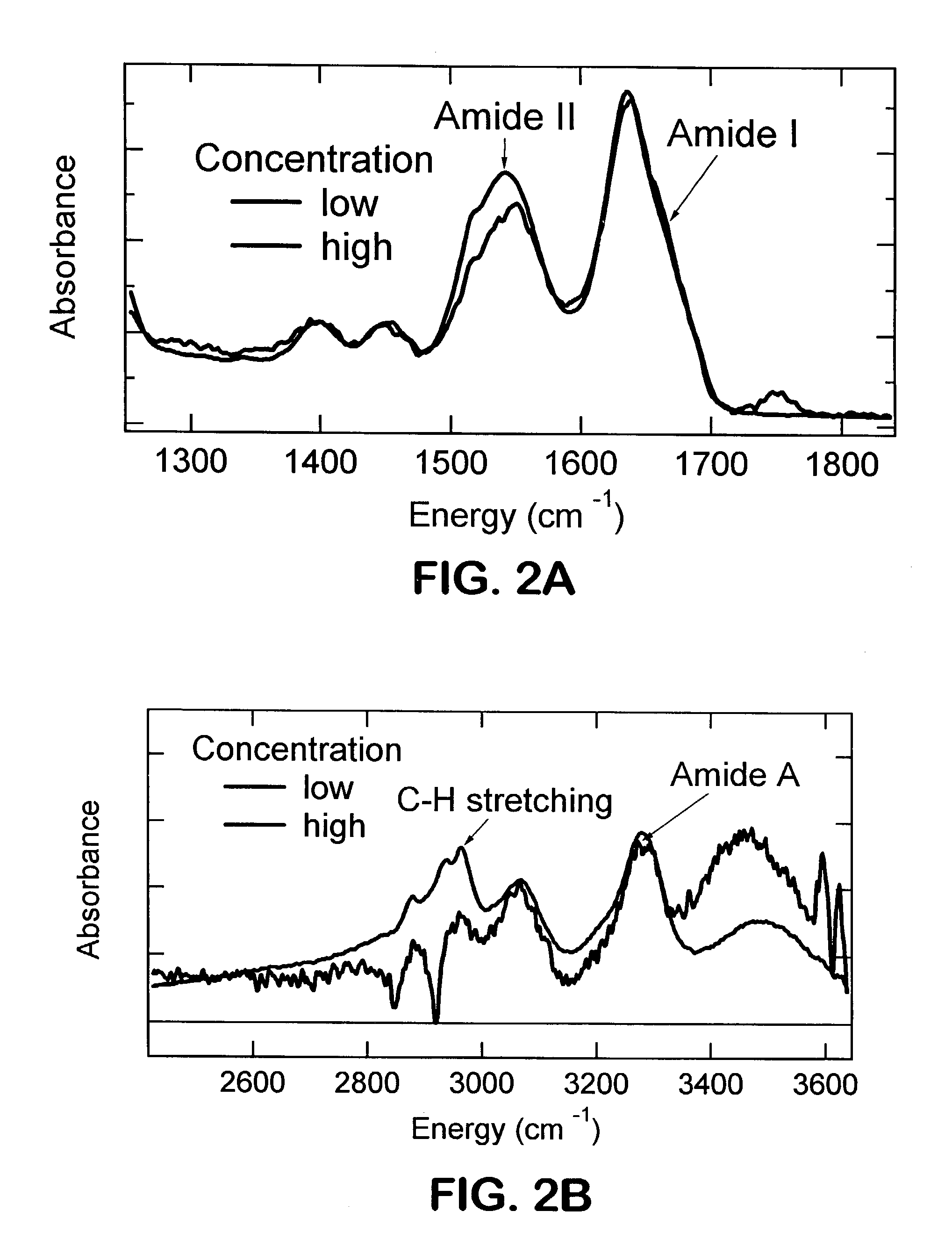
Single pass attenuated total reflection fourier transform infrared microscopy apparatus and method for identifying protein secondary structure, surface charge and binding affinity
InactiveUS7255835B2Facilitate acquisitionFacilitate dataBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReflectivityFourier transform
Apparatus and method for acquiring an infrared spectrum of a sample having or suspected to have an amide I band, an amide II band, an amide III band, an amide A band, an OH stretching region or a combination thereof. A representative method includes providing a sample; providing an internal reflecting element (IRE) with a functionalized tip; contacting the sample with the IRE to form a sample-IRE interface; directing a beam of infrared (IR) radiation through the IRE under conditions such that the IR radiation interacts with the sample-IRE interface once; recording a reflectance profile over a range of preselected frequencies, whereby an infrared spectrum of the of a sample having or suspected of having an amide I band, an amide II band, an amide III band, an amide A band, an OH stretching region or a combination thereof, disposed in an aqueous solution is acquired. Representative apparatus includes an internal reflecting element (IRE) comprising a reflection face located on the IRE at a region of intended contact between the IRE and a solublized sample; an infrared radiation source for supplying an evanescent wave of infrared radiation and directing the same from the outside of the IRE to the inside thereof so as to cause the infrared radiation to be incident on the reflection face, wherein the infrared radiation is reflected from the reflection face once; a sample cell; a functionalized tip comprising a surface-immobilized probe that partially or completely fills the volume exposed to the evanescent wave; and a detector for detecting the once-reflected infrared radiation.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Modified Biogenic Silica and Method for Purifying a Liquid
InactiveUS20090065435A1Improve filtering effectImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesSpecific water treatment objectivesParticulatesOil and grease
Biogenic silica is produced by combusting a biogenic source material such as rice hulls to give rich hull ash (RHA), and the combusted biogenic silica may be subsequently treated to improve the filtration or adsorption properties thereof e.g. by changing the surface charge, the surface tension, the surface area, the average pore size, the pore size distribution, particle size distribution, and / or the permeability thereof. Such biogenic silica is useful to remove a species, such as an impurity, from a fluid to purify the fluid and / or to recover the species therefrom. RHA may be used to remove species including organic, inorganic or microbial particulates, surfactants, metal ions, non-metallic anions, organic compounds, color bodies, odor-producing species, chlorinated compound, pigment, free fatty acids, phospholipids, peroxides, oil and / or grease different from the non-aqueous fluid, algae, bacteria, and combinations thereof.
Owner:POWELL INTPROP HLDG
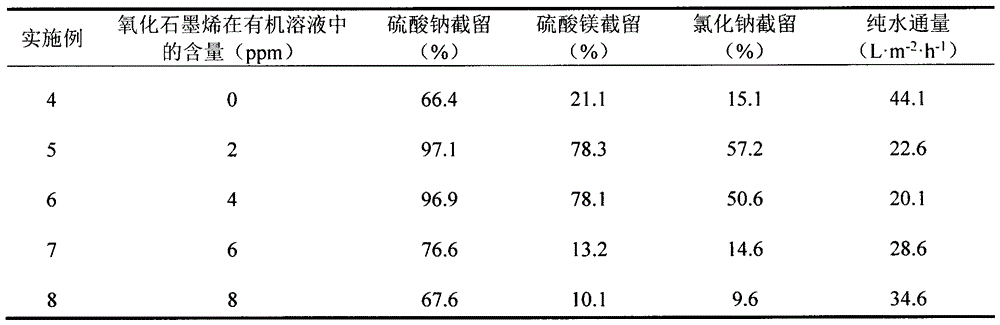
Oxidized graphene modified polyamide composite nano-filtration membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106076132AGood dispersionEasy to separateSemi-permeable membranesFiltration membranePolyamide
The invention relates to an oxidized graphene modified polyamide composite nano-filtration membrane. Water flux and salt interception of a traditional polyamide nano-filtration membrane can be simultaneously improved. The composite membrane takes an ultra-filtration membrane as a base membrane, oxidized graphene or modified oxidized graphene and co-solvents are added into oil-phase solution in the traditional interfacial polymerization preparation process of the polyamide composite membrane, and the composite membrane is prepared by interfacial polymerization. The oxidized graphene modified polyamide composite nano-filtration membrane has the remarkable advantages that an upper ultrathin polyamide layer and a lower ultrathin polyamide layer are formed on the composite nano-filtration membrane, an orderly arranged oxidized graphene or modified oxidized graphene sheet structure is clamped between the upper ultrathin polyamide layer and the lower ultrathin polyamide layer, a loose polyamide layer link is arranged between sheets, surface charge of the ultrathin polyamide layer and the oxidized graphene sheets gives the composite membrane a high salt interception rate, the ultrathin layer is thinner than a functional layer of the traditional polyamide nano-filtration membrane, membrane resistance is effectively reduced, and the water flux is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Microfluidic Liquid Stream Configuration System
A microfluidic liquid stream configuration system is provided including providing a substrate; forming a first co-planar electrode and a second co-planar electrode on the substrate; applying a dielectric layer, with a controlled surface energy, on the first co-planar electrode and the second co-planar electrode; forming an input reservoir on the first co-planar electrode and a second co-planar electrode; supplying a liquid in the input reservoir for analysis; and imposing an electric field, an electric field gradient, or a combination thereof on the liquid for respectively driving surface charge or dipole moments in the liquid for configuring a liquid stream.
Owner:ZYMERA
Device for preparing metal ultrafine powder and its method
The superfine metal powder preparing apparatus and method adopts double-layered composite atomizing nozzle and bipolar atomizing mode. The double-layered composite atomizing nozzle has one upper layer in traditional atomizing structure and one lower layer in Laval nozzle structure and has double-layered metal liquid tearing effect and ultrasonic metal liquid exciting effect. The present invention also adopts doped powder and vortex structure and thus has homogeneous mixing between solid and gas, vortex gas flow impulse and increased gas flow impact force on metal liquid for deep tearing of metal liquid and even small grains. In addition, present invention has increased electric field to make the falling metal powder produce surface charge effect to avoid agglomeration.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
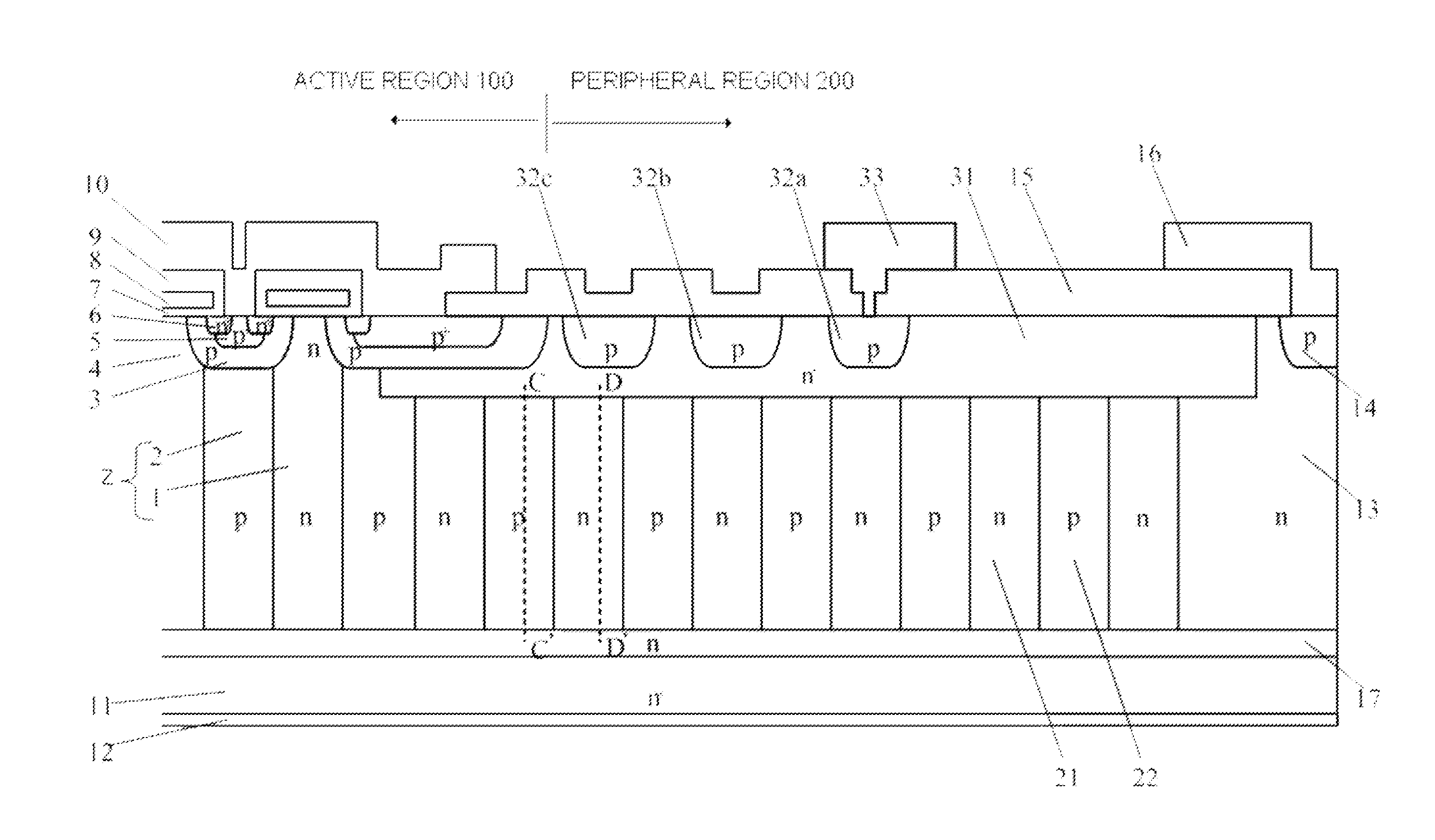
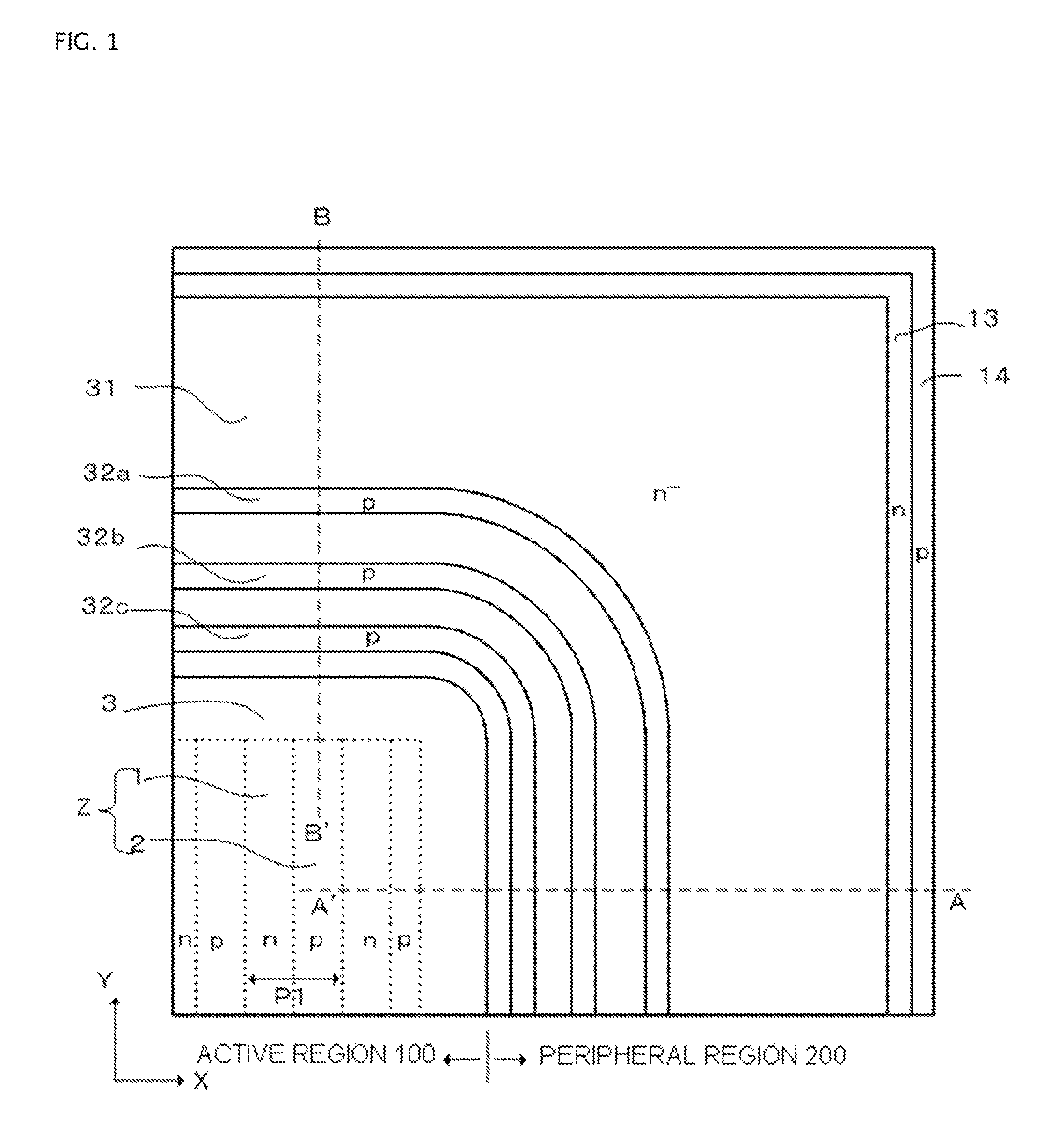
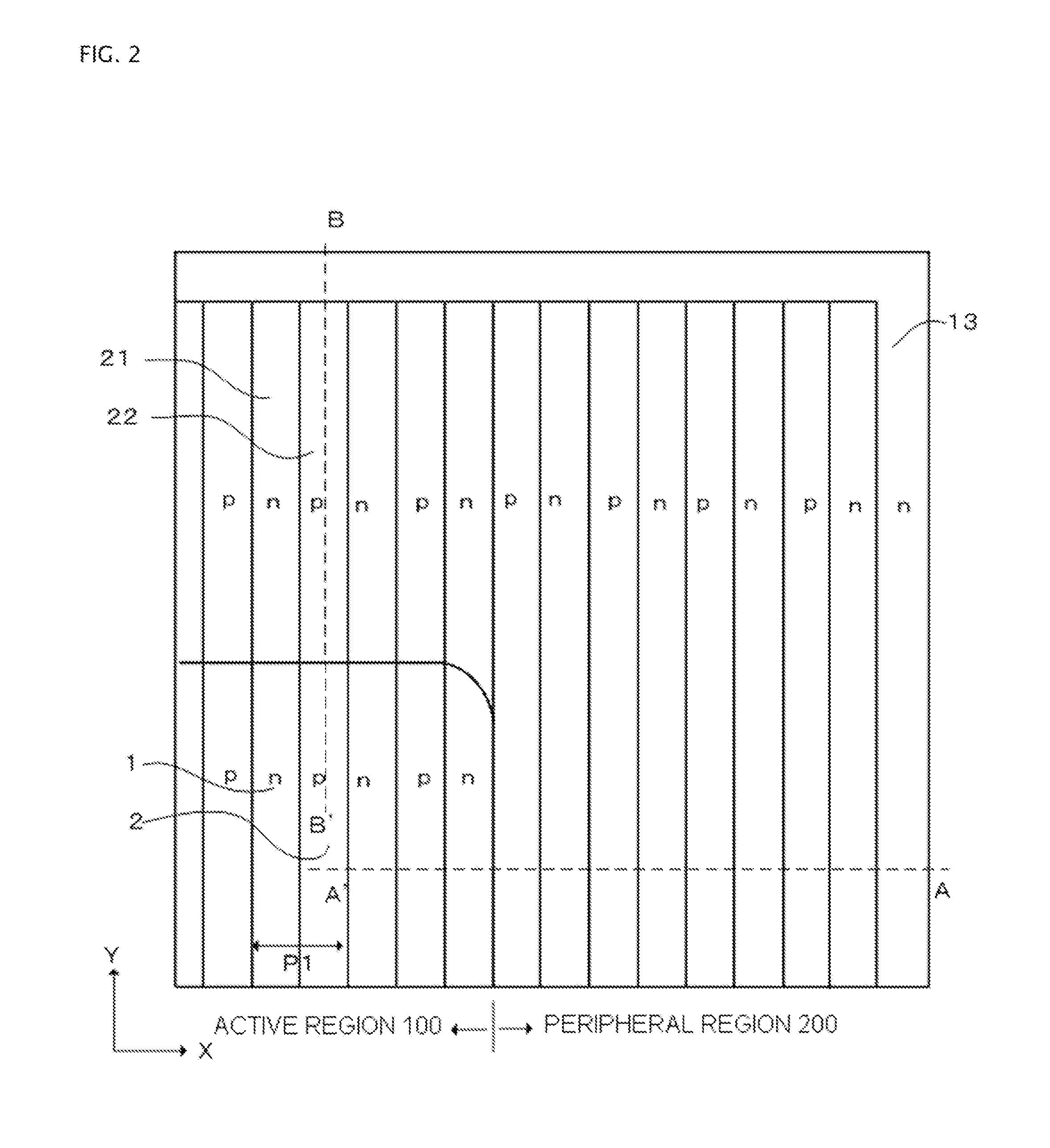
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120098064A1Improve batch productivityIncrease surface chargeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesProduction rateImpurity
A semiconductor device is disclosed wherein a peripheral region with a high breakdown voltage and high robustness against induced surface charge is manufactured using a process with high mass productivity. The device has n-type drift region and p-type partition region of layer-shape deposited in a vertical direction to one main surface of n-type semiconductor substrate with high impurity concentration form as drift layer, alternately adjacent parallel pn layers in a direction along one main surface. Active region through which current flows and peripheral region enclosing the active region include parallel pn layers. P-type partition region has impurity concentration distribution where concentration decreases from surface toward substrate side, n-type surface region disposed on parallel pn layers in peripheral region, p-type guard rings disposed separately from each other on n-type surface region, and field plate disposed on inner and outer circumferential sides of p-type guard rings, and electrically connected.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Sol-gel open tubular ODS columns with charged inner surface for capillary electrochromatography
InactiveUS6998040B2Sludge treatmentIon-exchanger regenerationElectricityCapillary electrochromatography
The present invention provides for a column for use in capillary electrochromatography including a tube, wherein the tube includes an inner surface having a positively or negatively charged, chemically-bonded stationary coating thereon. The present invention further provides for a method of making a column for use in capillary electrochromatography, including a tube, wherein the tube includes an inner surface having a positively or negatively charged chemically-bonded stationary coating thereon, wherein the steps include filling the column with a sol-gel solution, maintaining the sol-gel solution within the column, and forcing the sol-gel solution out of the column with an inert gas. Further, the present invention provides for a method of analytical separation with a column including an inner layer having a positively charged chemically-bonded stationary coating thereon that reverses the direction of electroosmotic flow in the column compared with a column without the positive surface charge. Additionally, the present invention provides for a method of using a column including an inner layer of positively charged chemically-bonded stationary coating thereon by introducing a sample into the column operating under reversed electroosmotic flow due to positively charged chemically-bonded stationary coating.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Deionization and desalination using electrostatic ion pumping
ActiveUS20070170060A1Promote sportsIncrease volumeMembranesElectrolysis componentsDesalinationElectric field
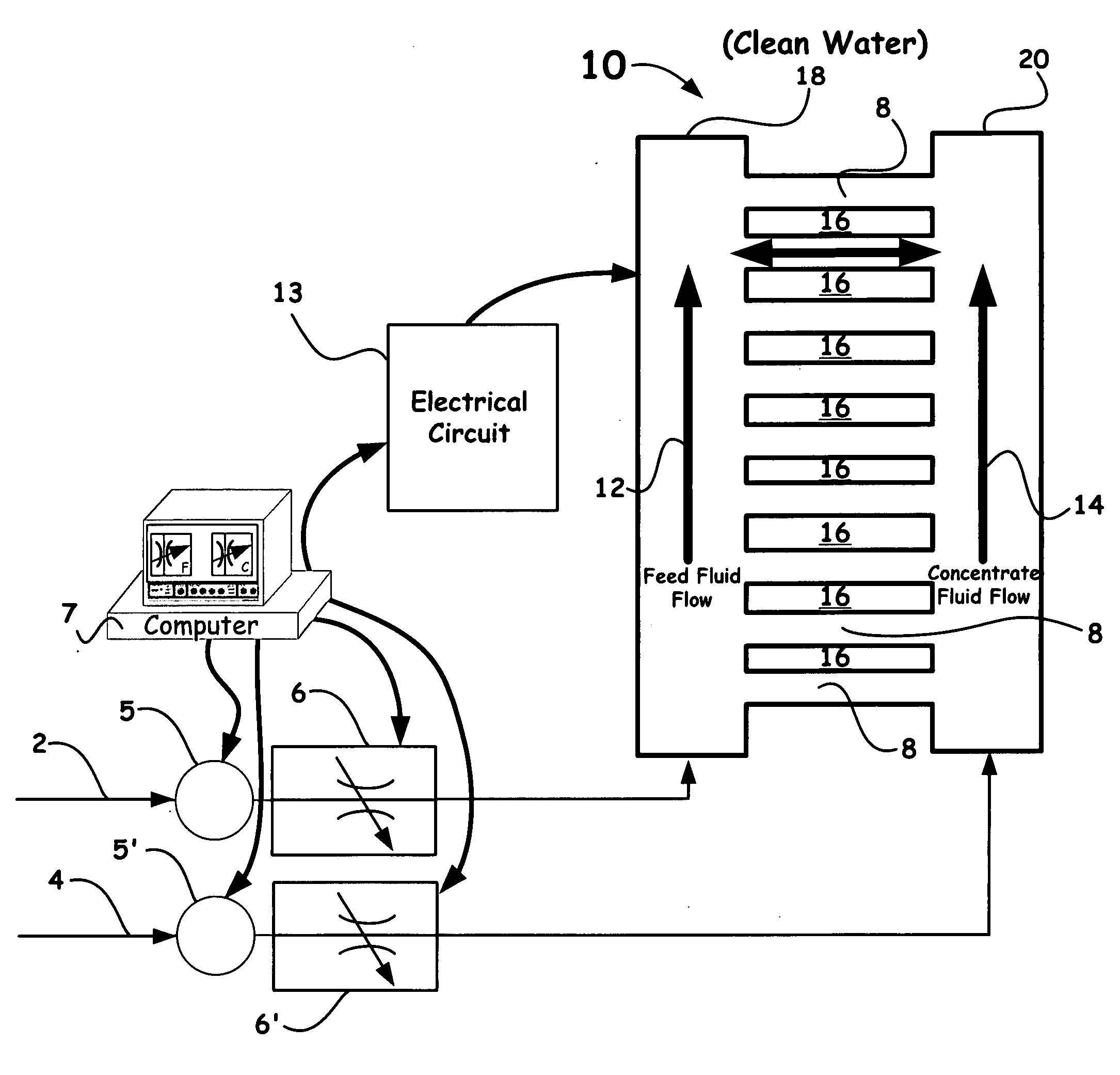
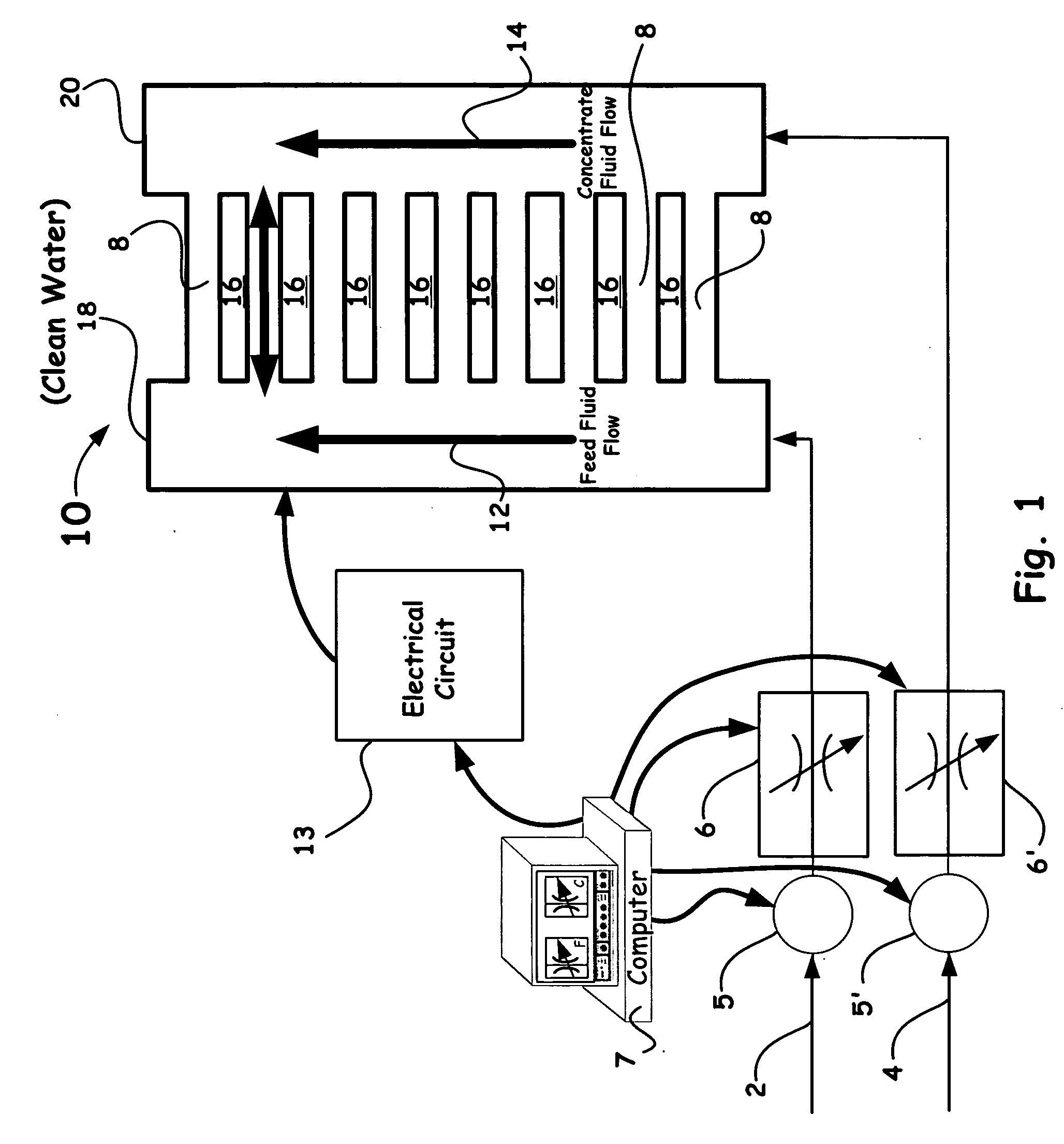
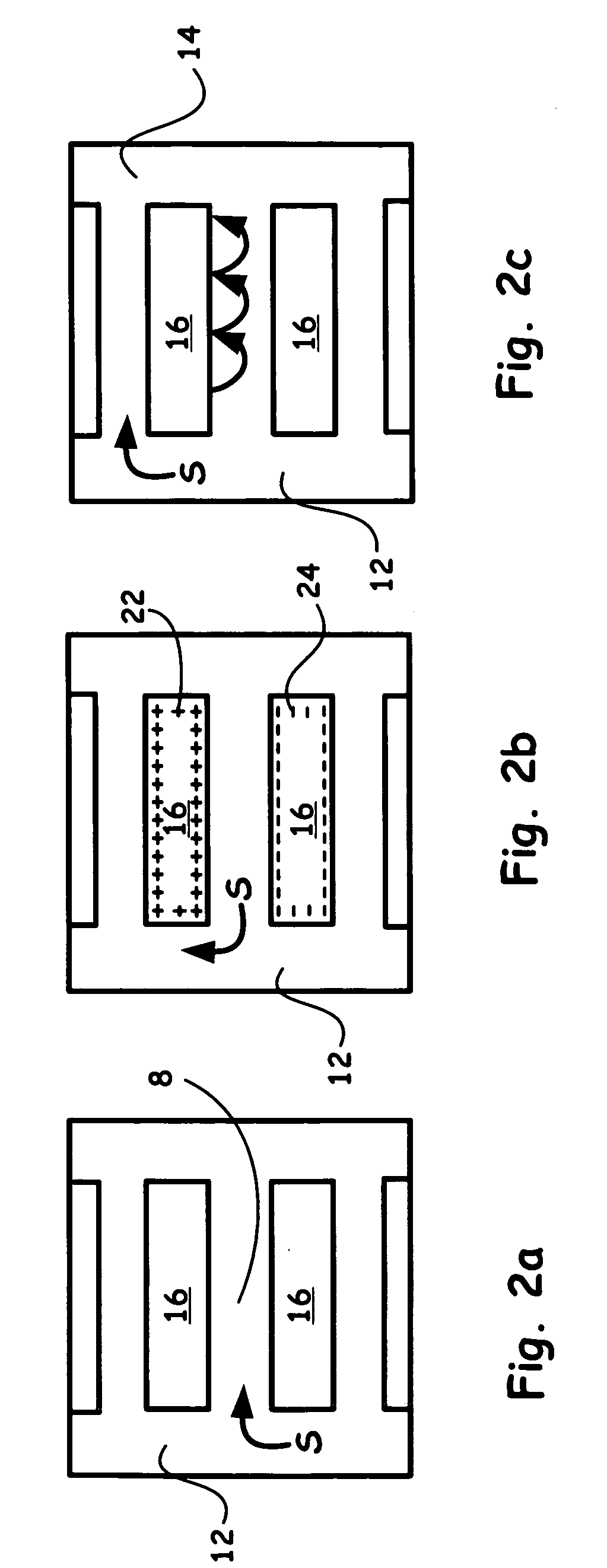
The present invention provides a new method and apparatus / system for purifying ionic solutions, such as, for example, desalinating water, using engineered charged surfaces to sorb ions from such solutions. Surface charge is applied externally, and is synchronized with oscillatory fluid movements between substantially parallel charged plates. Ions are held in place during fluid movement in one direction (because they are held in the electrical double layer), and released for transport during fluid movement in the opposite direction by removing the applied electric field. In this way the ions, such as salt, are “ratcheted” across the charged surface from the feed side to the concentrate side. The process itself is very simple and involves only pumps, charged surfaces, and manifolds for fluid collection.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
Theta-doped 4HSiC avalanche ultraviolet photoelectric detector and its production
The invention is concerned with delta-doped 4H-SiC ultraviolet avalanche photodetector and its production, involved with a kind of ultraviolet photodetector. Thedelta-doped 4H-SiC ultraviolet avalanche photodetector and production can enhance the capability of device, eliminate the restrict of quantum yield and respond time to avalanche device, control the thickness of elevated area, the concentration of surface charge and the length of absorbing area. The table-board owns n+ type of 4H-SiC under lay, and there is n+ type buffer layer, super-low-doped n- type layer, delta-doped n type layer, low-doped n- type layer and high-doped p+ type layer on the table-board one by one. The super-low-doped n- type layer, delta-doped n type layer, low-doped n- type layer form active layer. It has at least three table-boards, the lowest one sets on the n+ type buffer layer to isolation of device, the other table-boards set on active layer of device, while the surface of device owns compact Silica passivation film with p type and n type poles.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Biosensor based on tunneling field effect transistor and preparation method of biosensor
InactiveCN103558280ASteep subthreshold slopeSensitiveMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGate dielectricOxygen
The invention provides a biosensor based on a tunneling field effect transistor and a preparation method of the biosensor. The preparation method of the biosensor at least comprises the steps of firstly, preparing a tunneling field effect transistor as a converter; and then carrying out activated modification on the surface of a channel in the tunneling field effect transistor by adopting a surface modification agent, wherein the step of preparing the tunneling field effect transistor specifically comprises the procedures of providing an SOI (Silicon On Insulator) substrate, wherein the SOI substrate comprises a top layer silicon, a buried oxygen layer and a bottom layer silicon; forming a gate dielectric layer on the surface of the top layer silicon; carrying out ion injection on the top layer silicon at two sides of the gate dielectric layer by adopting an ion injection process to form a source electrode and a leak electrode, defining the top layer silicon of the gate dielectric layer, which is not subjected to the ion injection, as a channel; and forming a back gate on the surface of the bottom layer silicon. The tunneling field effect transistor provided by the invention is abrupt in sub-threshold slope, and is sensitive in change of charges on the surface of the channel, thereby enabling the biosensor to be capable of detecting a biomolecule at high sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Surface charge manipulation for improved fluid intake rates of absorbent composites
InactiveUS20050142965A1Improving fluid intake rateIncrease ratingsSynthetic resin layered productsAbsorbent padsFluid intakeFiber
This invention describes a novel means for improving fluid intake rates in disposable absorbent composites by altering the surface charge on the components of such composites through utilization of surface charge treatments (i.e., charge modifiers). The composite components contemplated for the invention may include, but are not limited to, conventional superabsorbent particles (SAP) and fluff fibers (fluff). The surface charge modifiers of the present invention are specifically selected to achieve an ionically (i.e., electrically) generated repulsive force between the individual composite components in the presence of an insulting fluid. This active repulsion between composite components creates a condition in the composite conducive to superabsorbent swelling and generation of void volume and flow channels, thus improving the fluid intake rate.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Chemical mechanical polishing slurry, its preparation method, and use for the same
InactiveUS20080096470A1Remove layerEfficient removalPigmenting treatmentPolishing machinesPotassium ionsSlurry
A chemical mechanical polishing slurry for polishing a copper layer without excessively or destructively polishing a barrier layer beneath the copper layer is disclosed and includes an acid, a surfactant, and a silica sol having silica polishing particles that are surface modified with a surface charge modifier and that have potassium ions attached thereto. A method for preparing the chemical mechanical polishing slurry and a chemical mechanical polishing method using the chemical mechanical polishing slurry are also disclosed.
Owner:EPOCH MATERIAL CO LTD
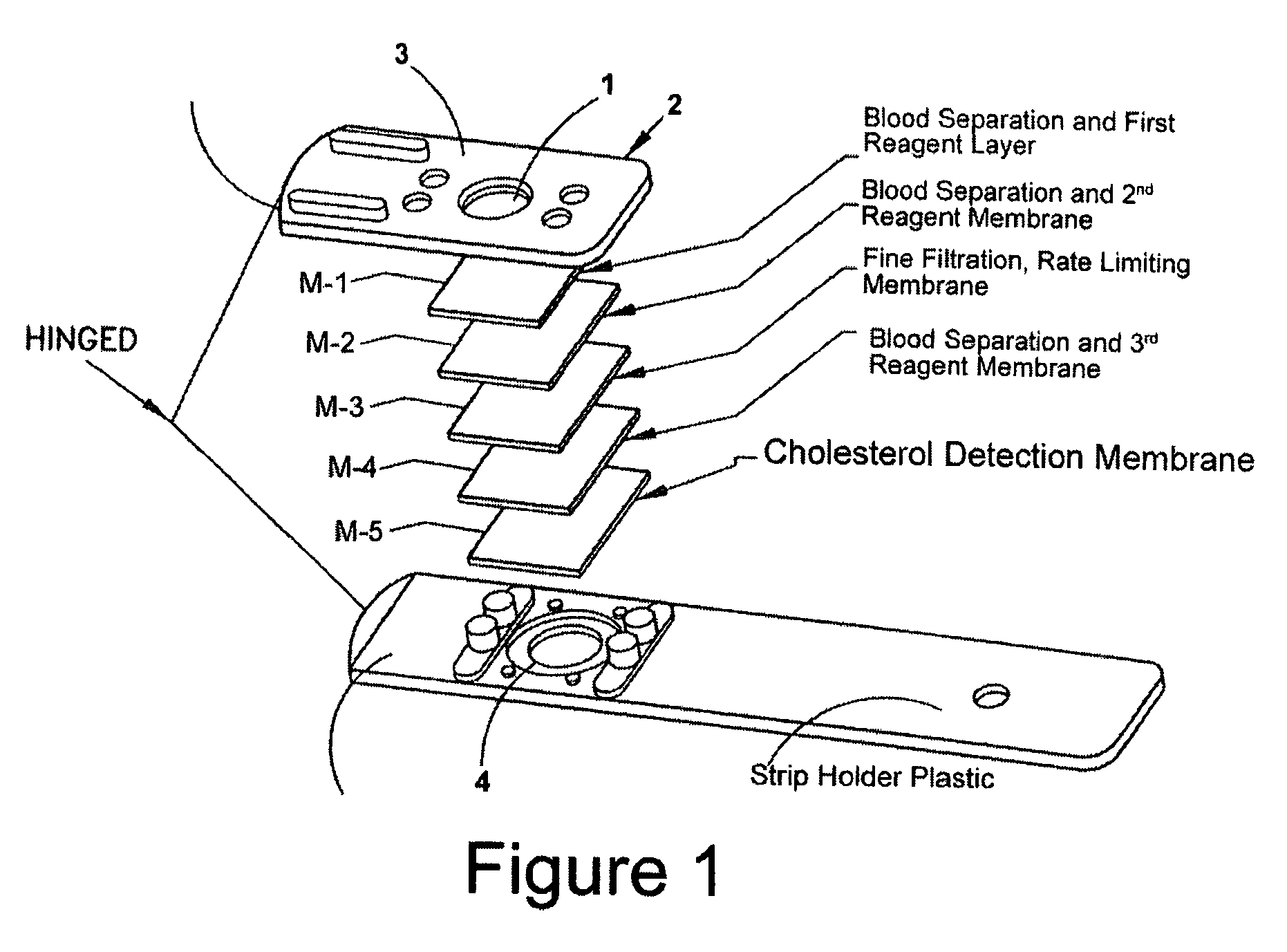
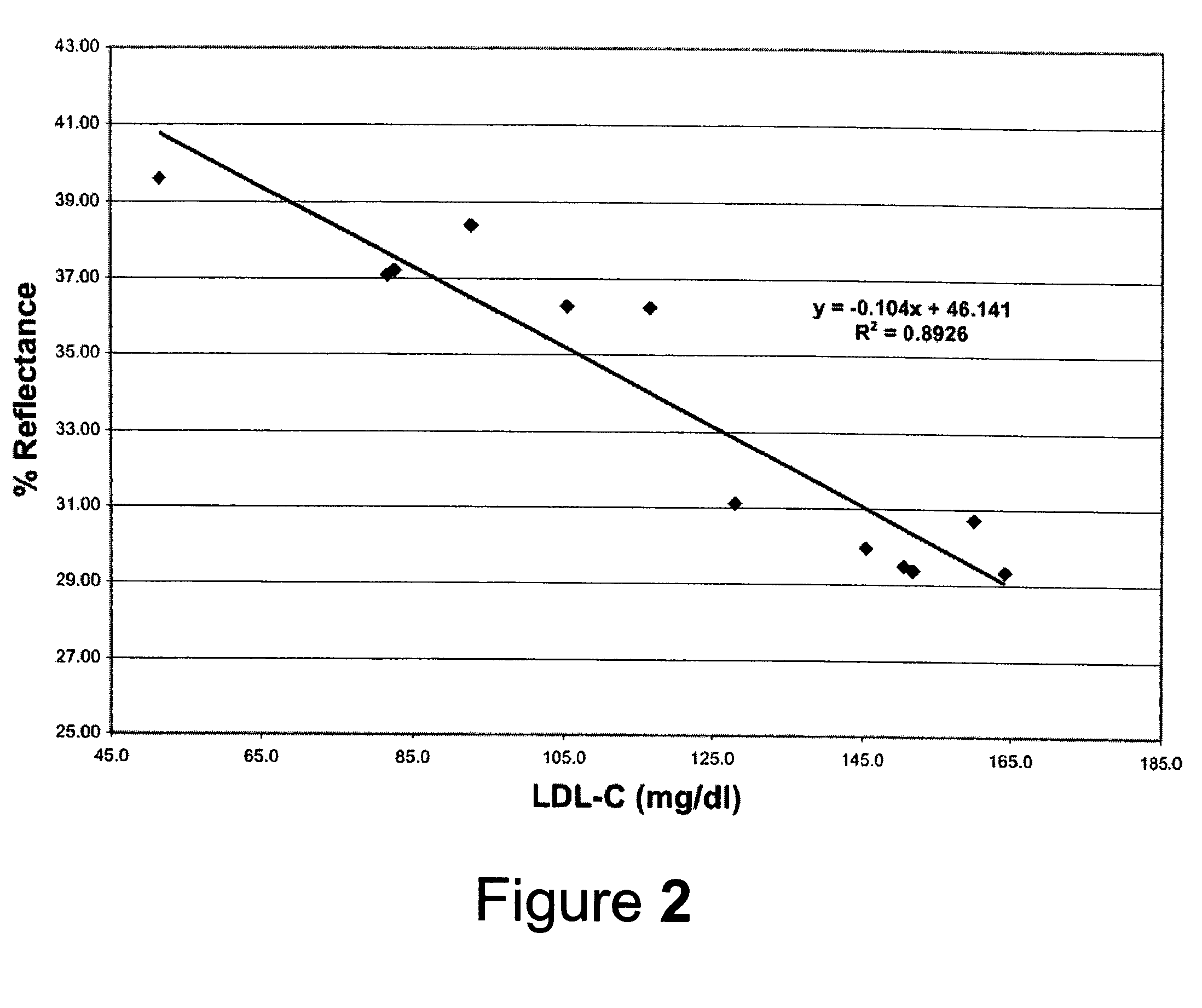
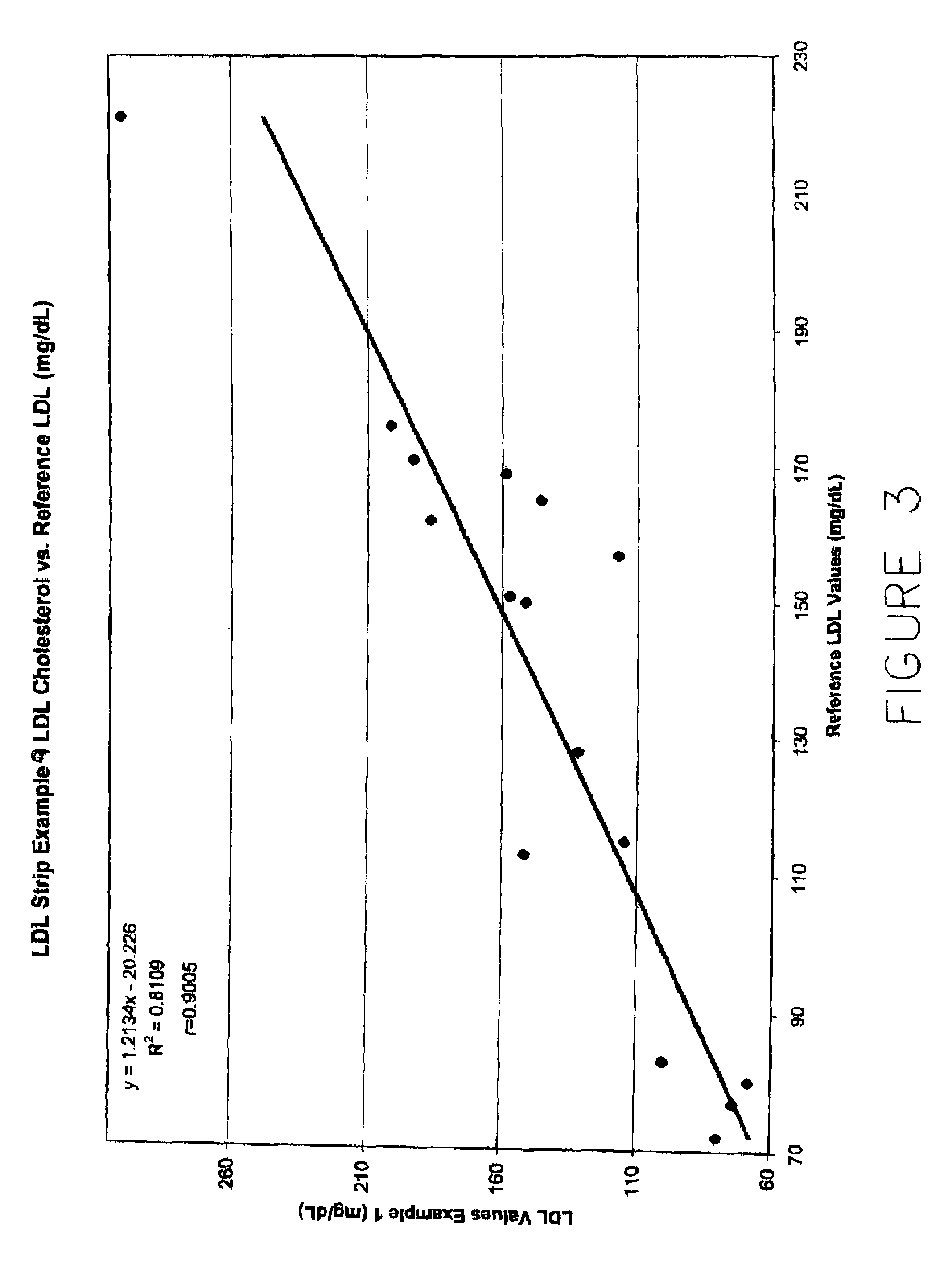
Direct measurement of chlolesterol from low density lipoprotein with test strip
ActiveUS7435577B2Improve solubilityReduce solubilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVery low-density lipoproteinRoom temperature
Cholesterol from Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL-C) is measured directly with a test strip at room temperature using a reagent that takes advantage of the varying surface charge density on LDLs and non-LDLs to selectively make LDL-C available for testing.
Owner:POLYMER TECH SYST
Method for preparing titanium dioxide composite material with fine silica flour
The invention discloses a method for preparing titanium white composite material with micro silicon powder, which belongs to the field of solid waste recycling. In the method, the titanium white composite material with a nuclear-shell structure is prepared by the following steps: activating the micro silicon powder, removing impurity, dispersing, regulating surface charges and cladding titanium dioxide on the surface. The mass ratio of the TiO2 in composite particles is 2 to 25 percent; the coverage rate of the composite particles is 70 to 95 percent; the particle diameter of the TiO2 crystal particle in the cladding layer of the composite particles is 5 to 35nm. The method is characterized by controllable particle structure and high surface coverage rate. Compared with sulfate process titanium dioxide, the titanium white composite material prepared by the method greatly saves the using amount of titanium liquid and reduces the discharging amount of wastes; besides, the method also has the advantages of simple technique, large handling capacity and little pollution, etc.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com