Patents
Literature
399 results about "Particle deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
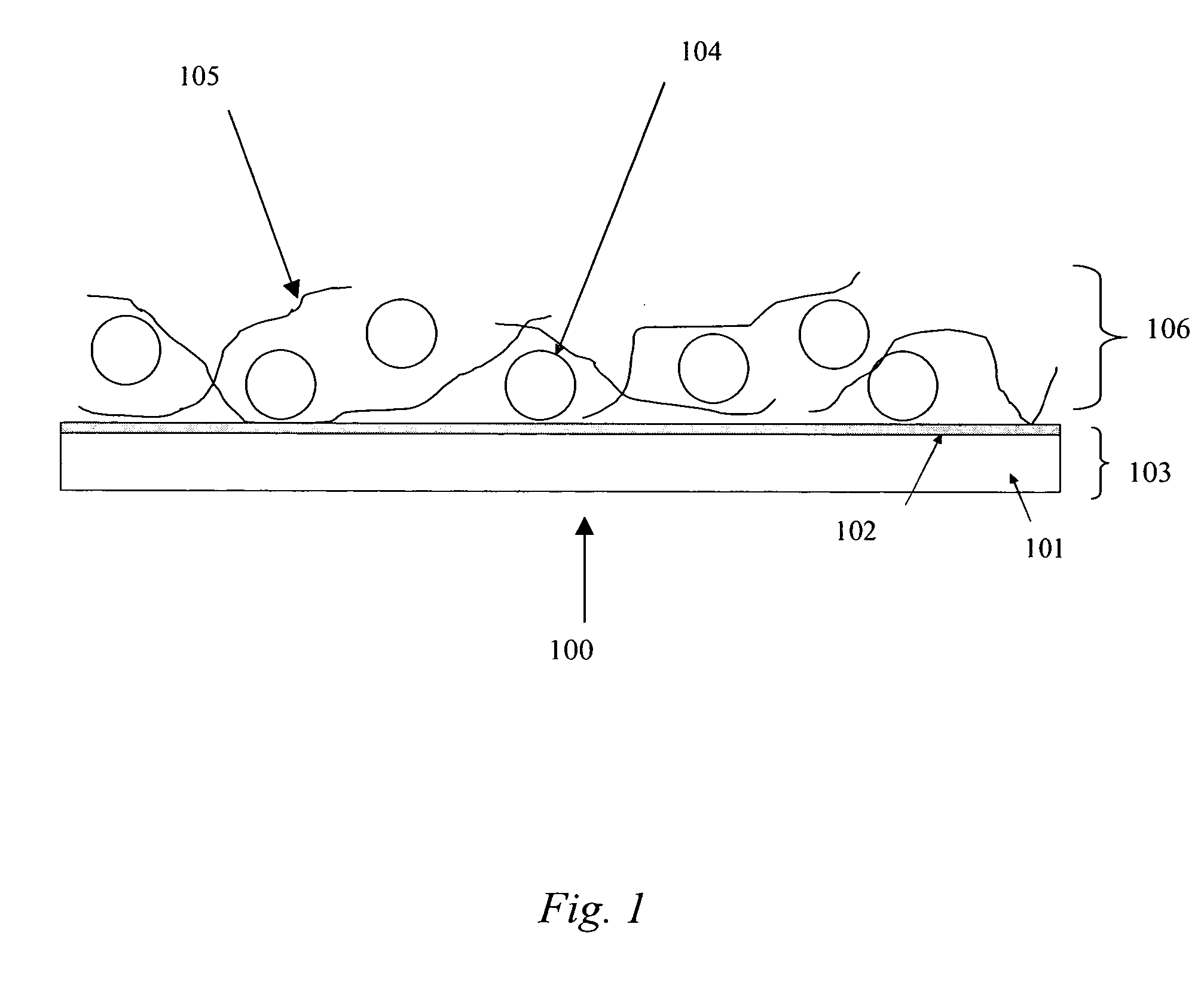
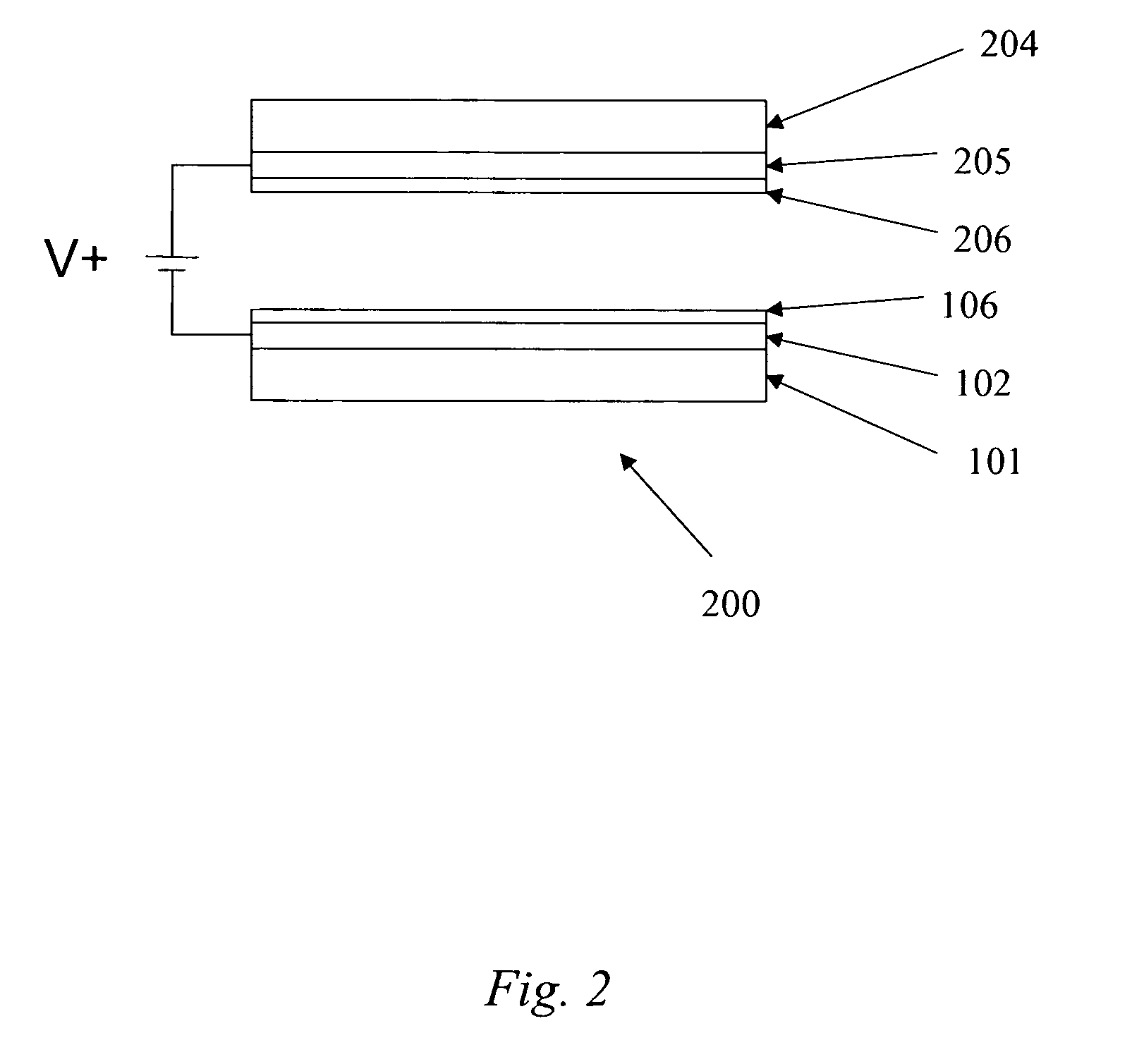
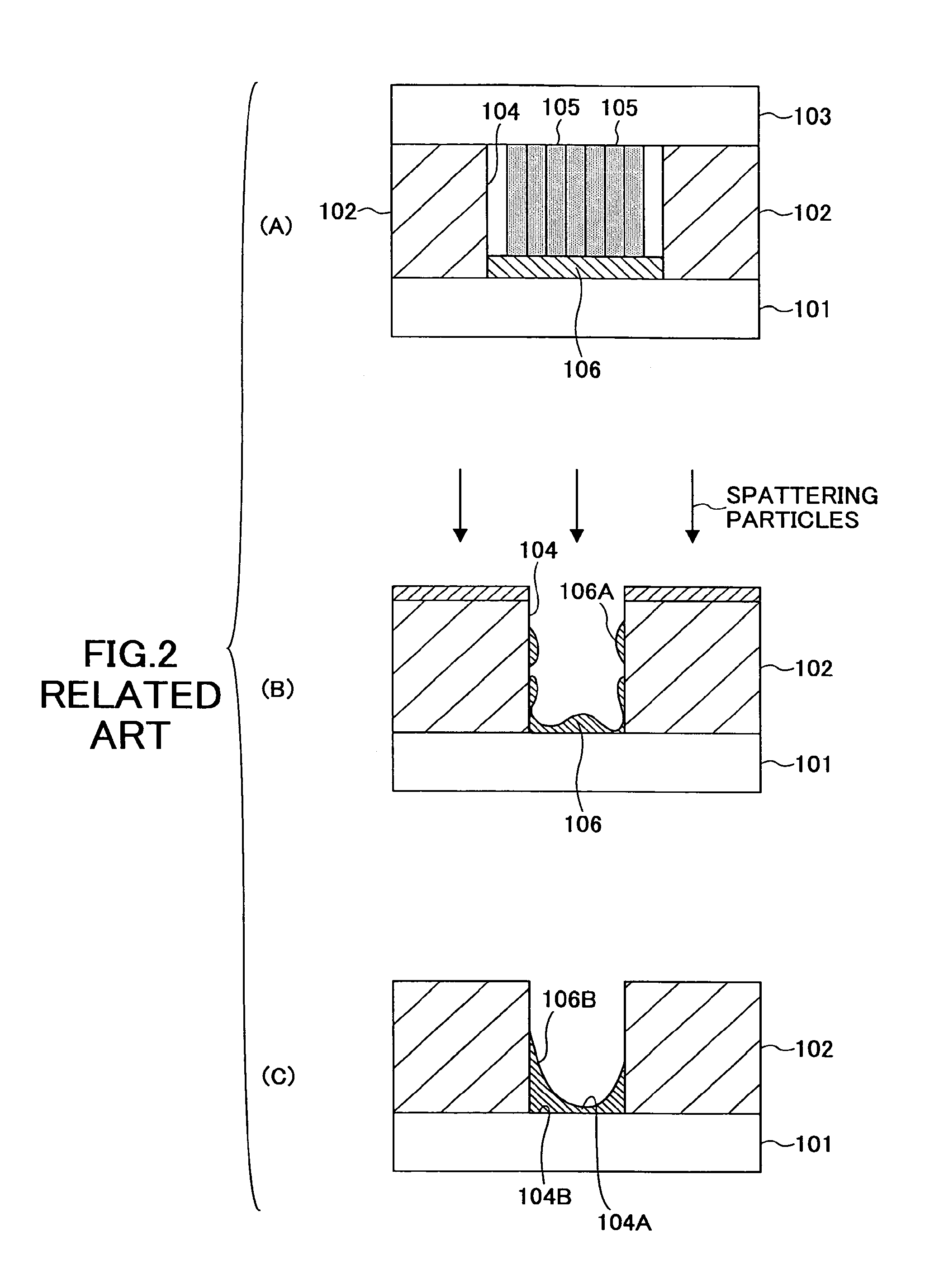
Particle deposition is the spontaneous attachment of particles to surfaces. The particles in question are normally colloidal particles, while the surfaces involved may be planar, curved, or may represent particles much larger in size than the depositing ones (e.g., sand grains). Deposition processes may be triggered by appropriate hydrodynamic flow conditions and favorable particle-surface interactions. Depositing particles may just form a monolayer which further inhibits additional particle deposition, and thereby one refers to surface blocking. Initially attached particles may also serve as seeds for further particle deposition, which leads to the formation of thicker particle deposits, and this process is termed as surface ripening or fouling. While deposition processes are normally irreversible, initially deposited particles may also detach. The latter process is known as particle release and is often triggered by the addition of appropriate chemicals or a modification in flow conditions.
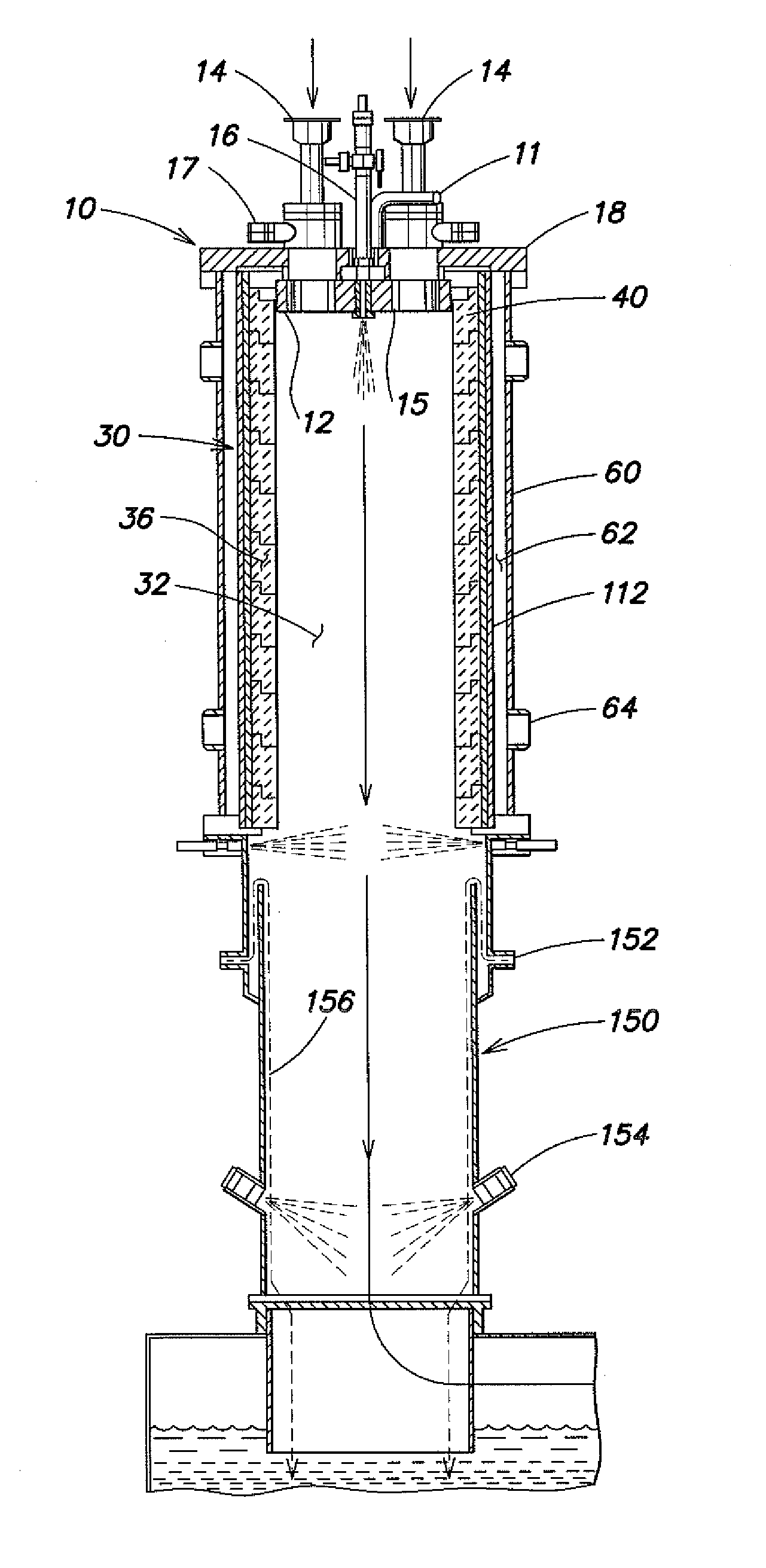
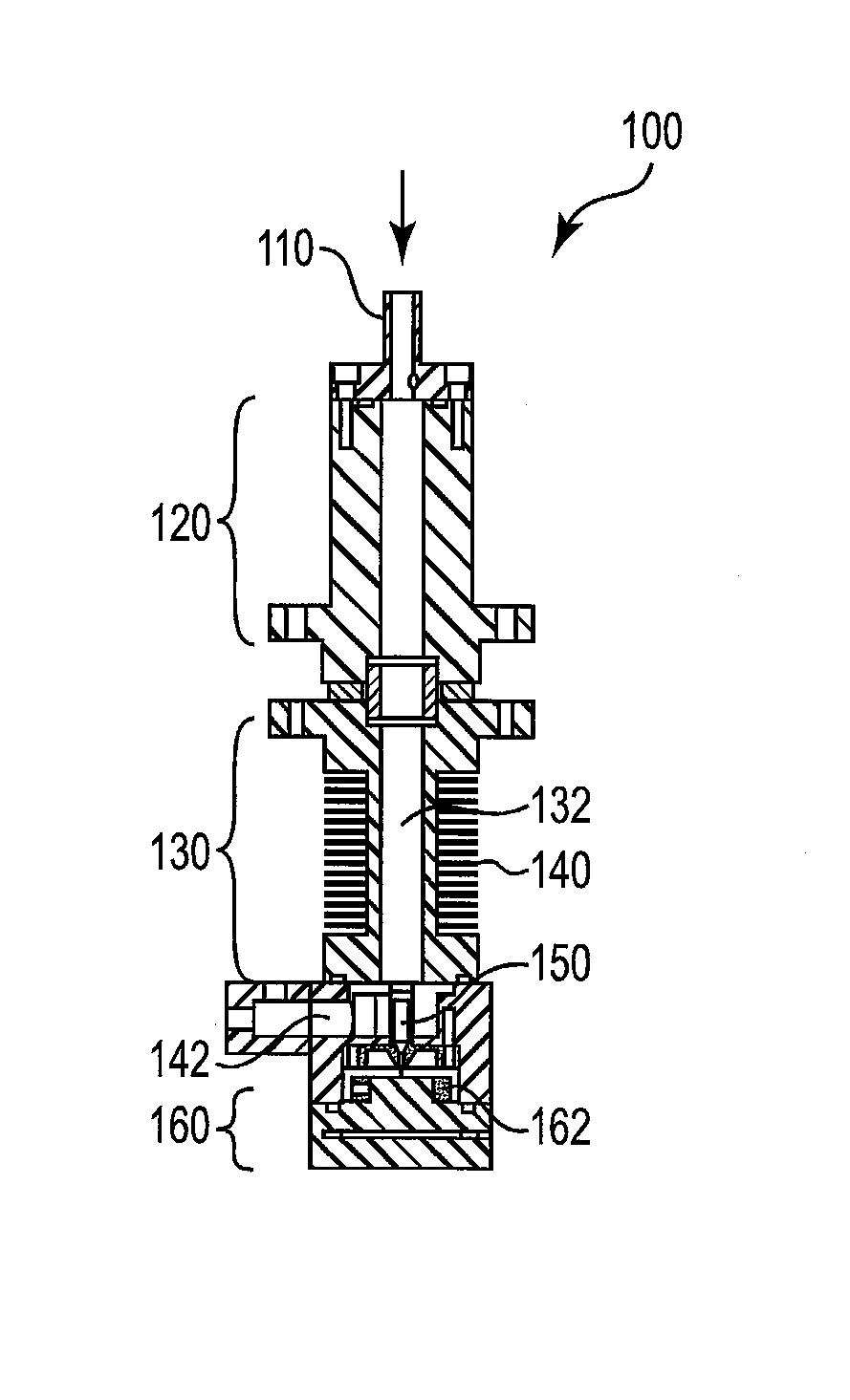
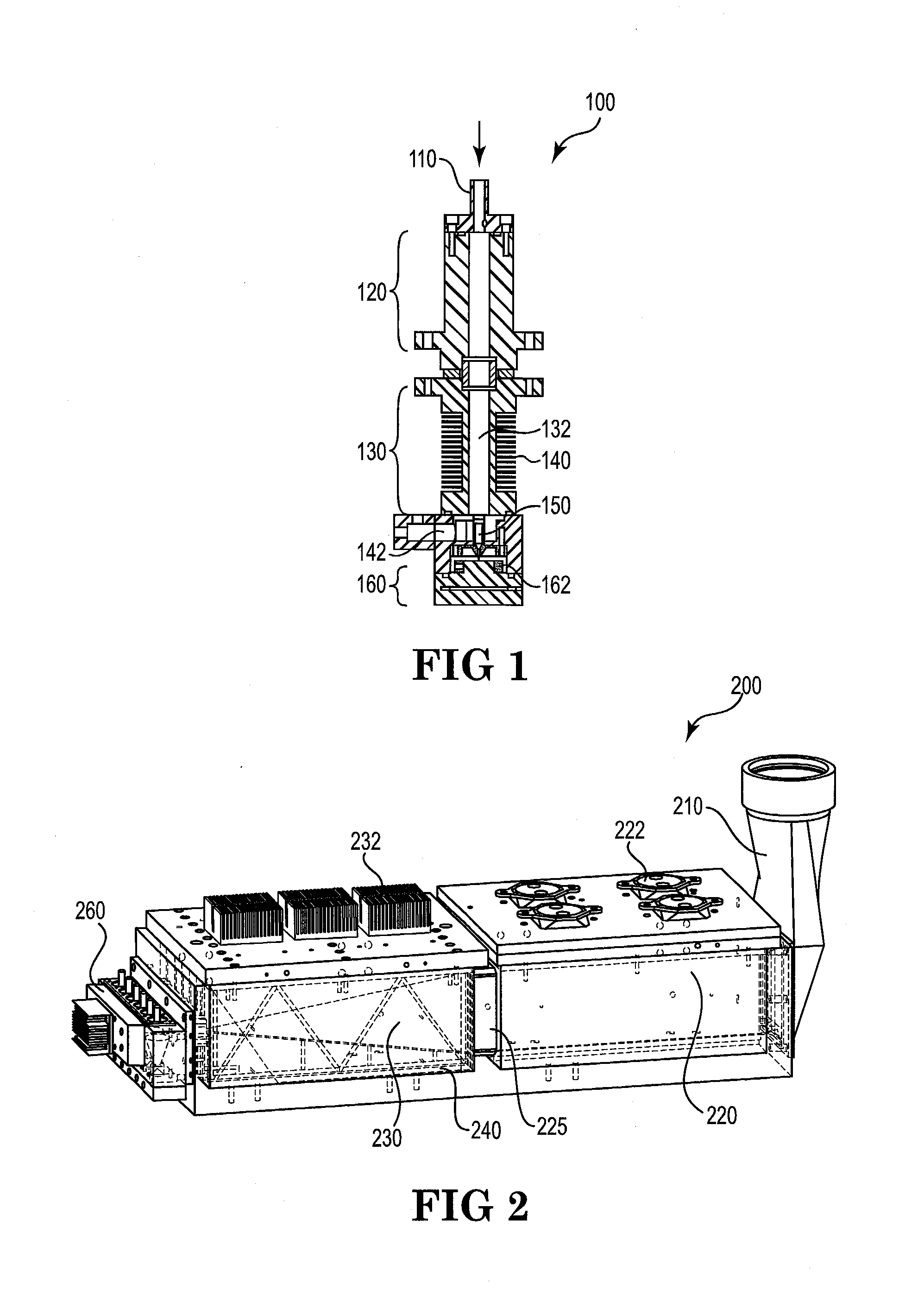
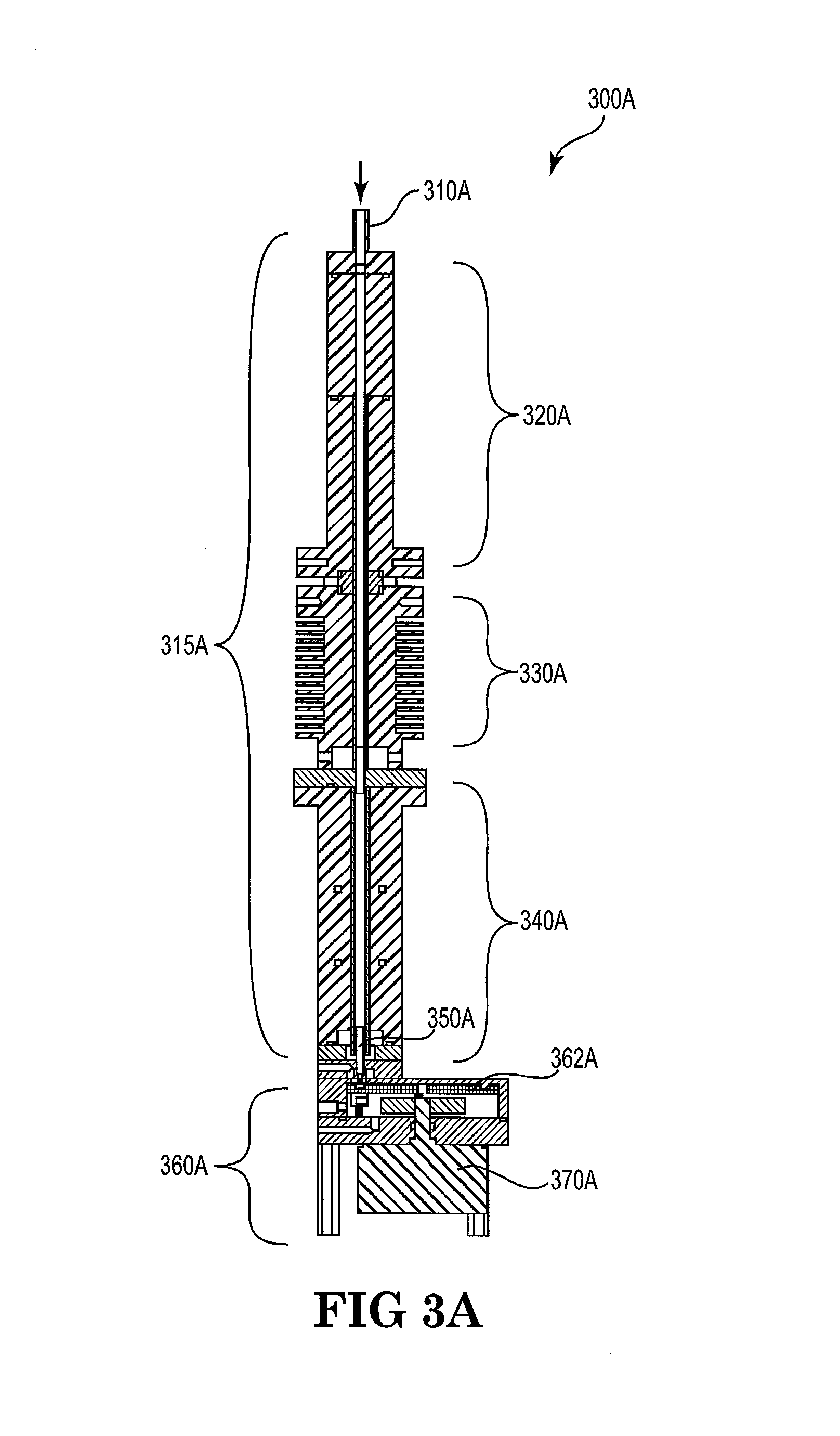
Method for multi-scale meshing of branching biological structures
InactiveUS20110093243A1Good specificationIncrease computing speedMedical simulationImage enhancementLocal pressureGrid partition
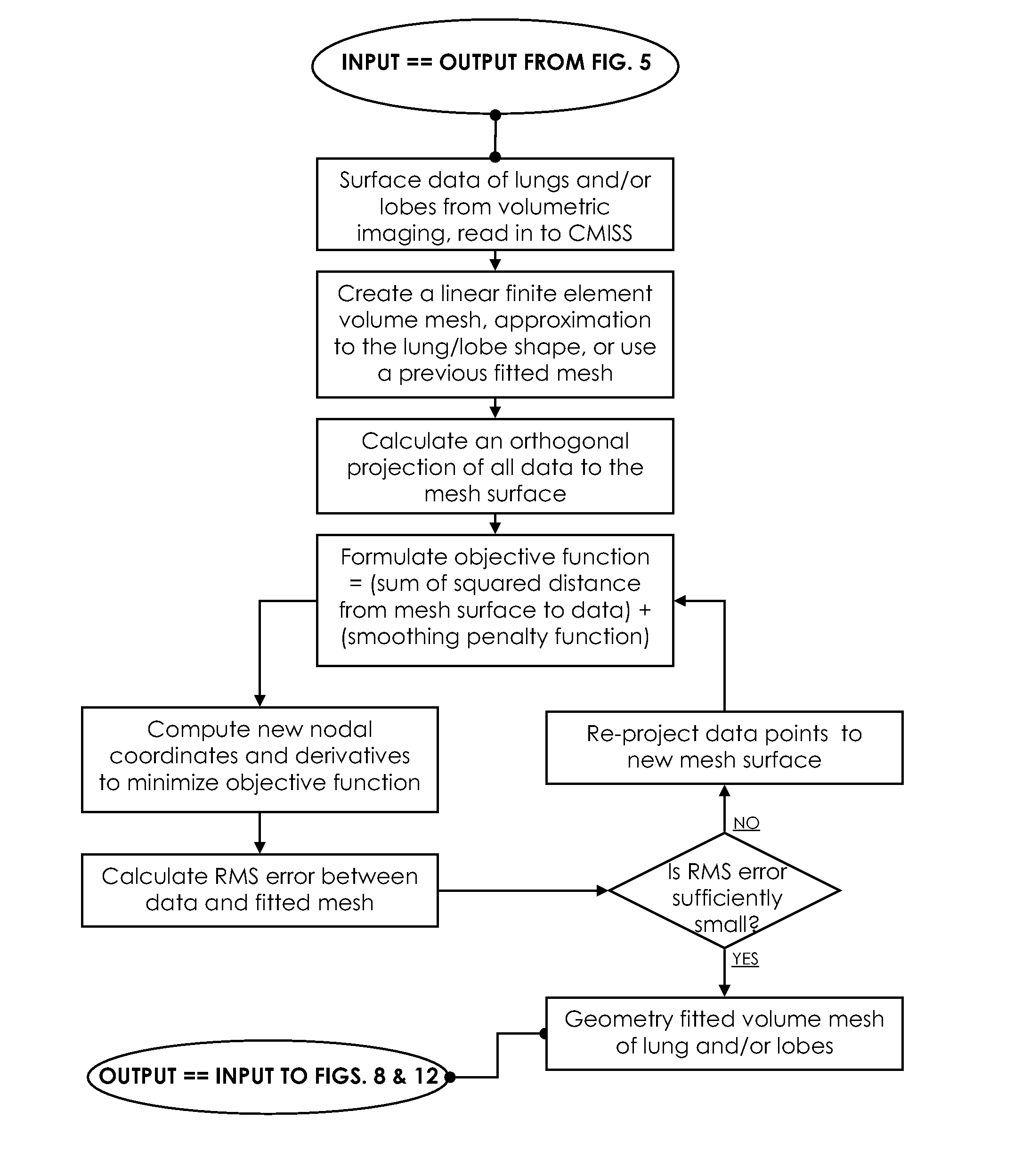
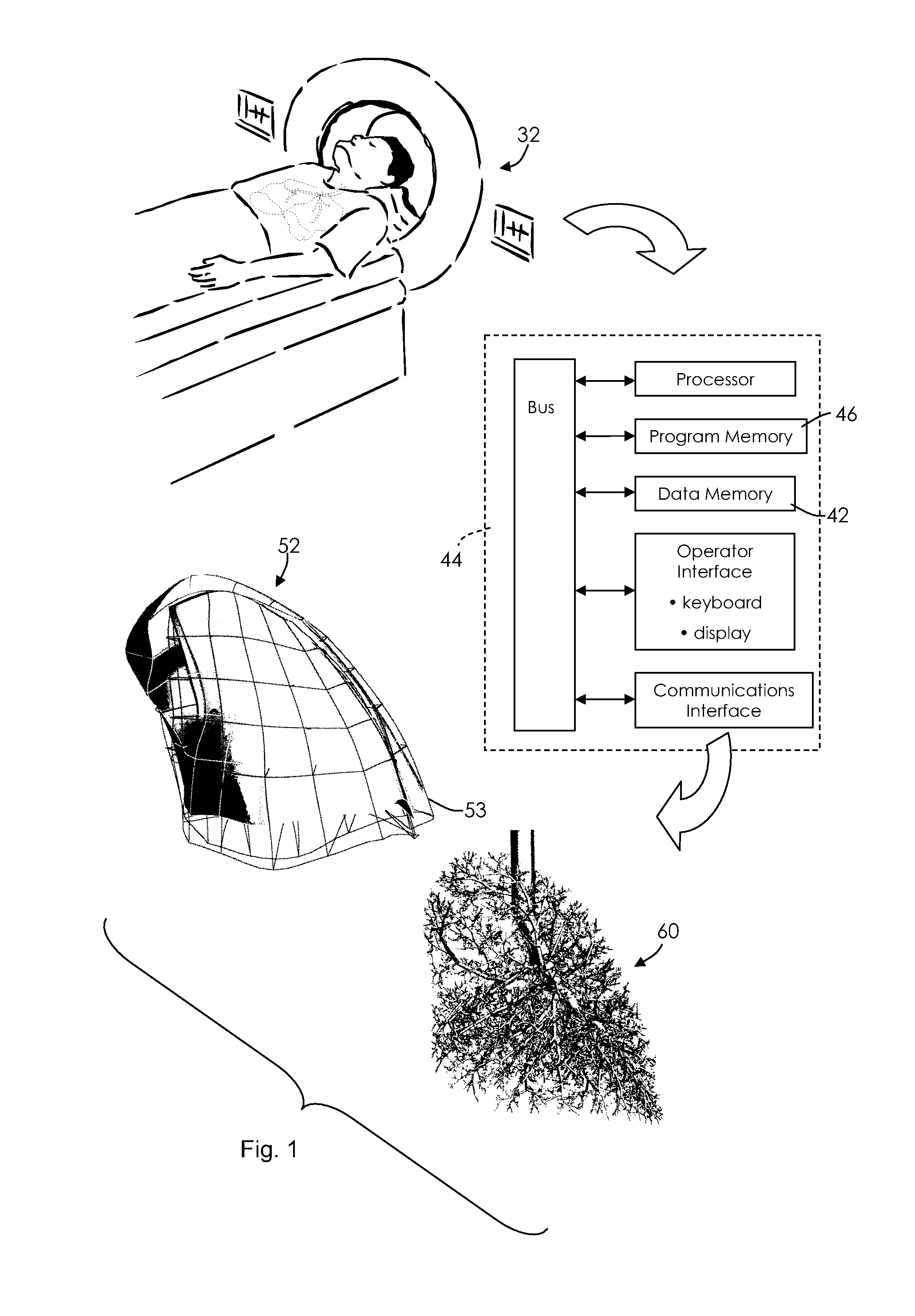
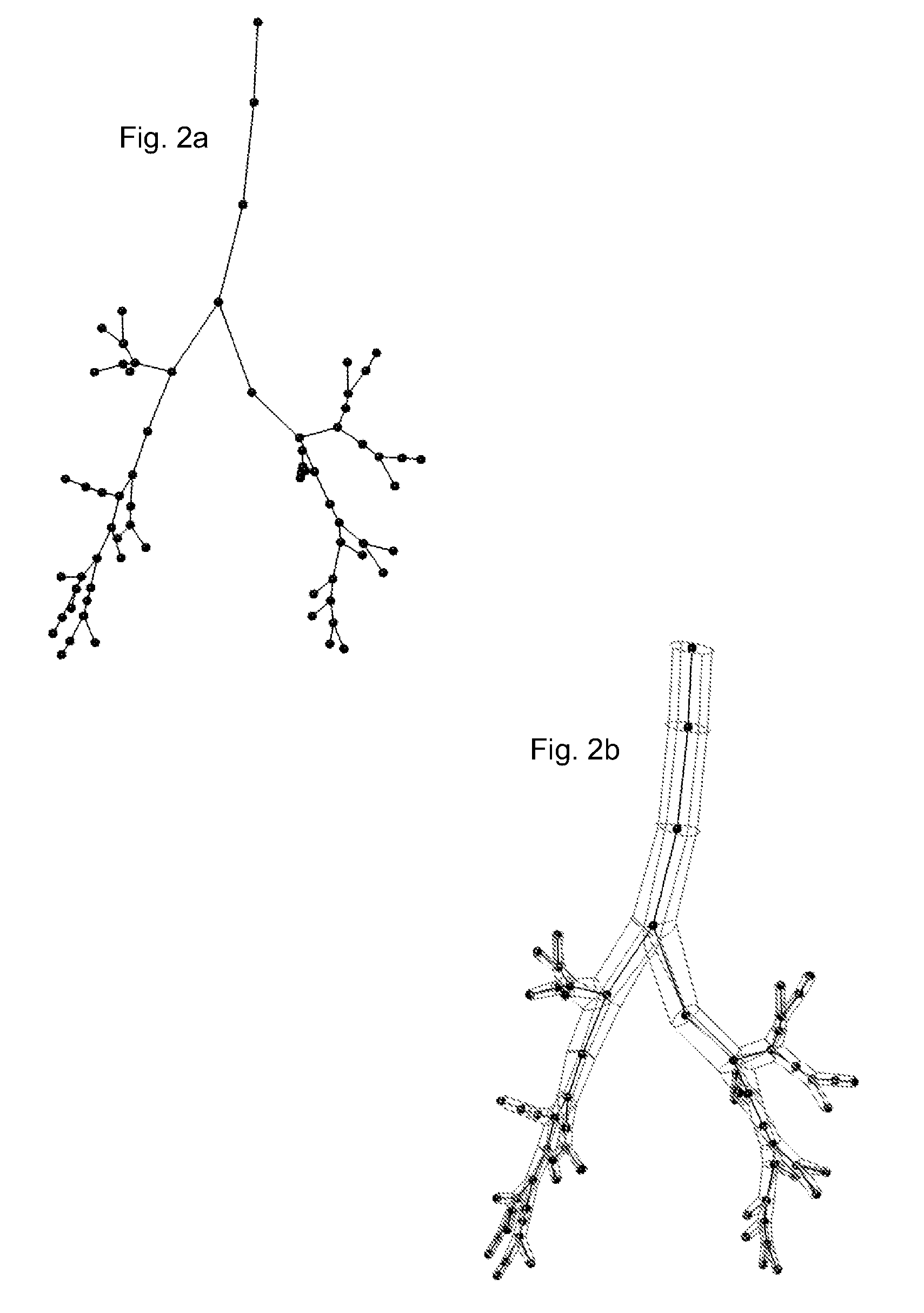
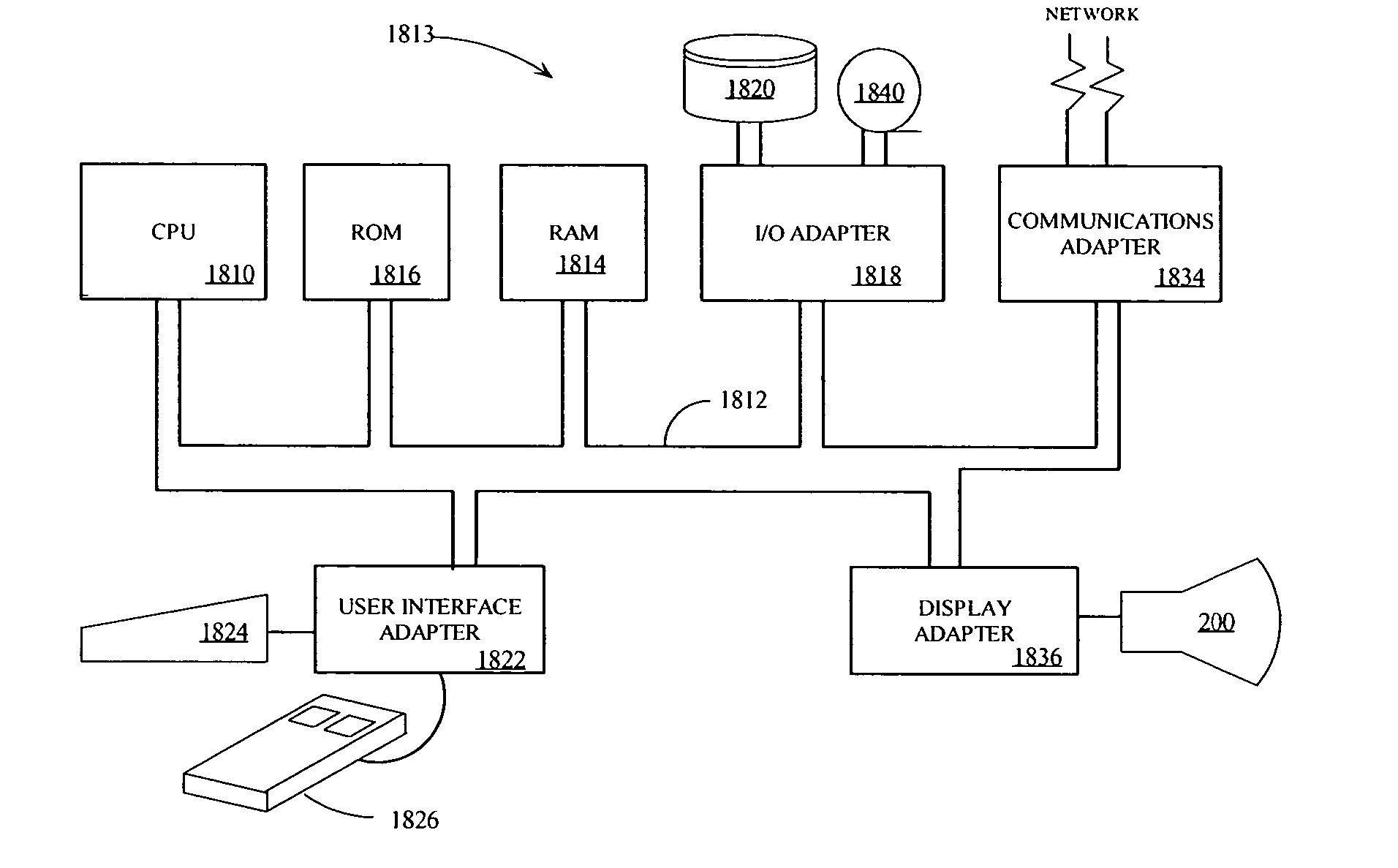
A structural and functional model for a lung or similar organ is virtually defined by encoding aspects of branching passageways. Larger passageways that are visible in medical images are surface mesh fitted to the anatomical surface geometry. Smaller distal passageways, beyond a given number of branch generations, are modeled by inference as linear passages with nominal diameters and branching characteristics, virtually filling the space within the outer envelope of the organ. The model encodes finite volumetric elements for elasticity and compliance in passageway walls, and for local pressure and flow conditions in passageway lumens during respiration. The modeling can assess organ performance, help to plan surgery or therapy, determine likely particle deposition, assess respiratory pharmaceutical dosing, and otherwise represent structural and functional organ parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Enhanced field emission from carbon nanotubes mixed with particles
InactiveUS20040070326A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsField emission deviceCarbon nanotube
The present invention is directed toward cathodes and cathode materials comprising carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and particles. The present invention is also directed toward field emission devices comprising a cathode of the present invention, as well as methods for making these cathodes. In some embodiments, the cathode of the present invention is used in a field emission display. The invention also comprises a method of depositing a layer of CNTs and particles onto a substrate to form a cathode of the present invention, as well as a method of controlling the density of CNTs used in this mixed layer in an effort to optimize the field emission properties of the resulting layer for field emission display applications.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Reactor design to reduce particle deposition during process abatement
InactiveUS20070274876A1Reduce accumulationReduce crackingCombination devicesBurnersCombustionDecomposition
The present invention relates to systems and methods for controlled combustion and decomposition of gaseous pollutants while reducing deposition of unwanted reaction products from within the treatment systems. The systems include a novel thermal reaction chamber design having stacked reticulated ceramic rings through which fluid, e.g., gases, may be directed to form a boundary layer along the interior wall of the thermal reaction chamber, thereby reducing particulate matter buildup thereon. The systems further include the introduction of fluids from the center pilot jet to alter the aerodynamics of the interior of the thermal reaction chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Nanoparticle and surface-modified particulate coatings, coated balloons, and methods therefore
Devices, coatings, and methods therefore comprise a medical device for delivering nanoparticles of an active agent to a treatment site. A coating on the medical device comprises active agent nanoparticles, which delivers coating to the treatment site and releases active agent nanoparticles into the treatment site over at least one day. A coating may comprise a polymer, a surfactant, and the nanoparticles. The coating may be prepared by forming a nanoemulsion. A coating may comprise encapsulated active agent nanoparticles which comprise active agent nanoparticles encapsulated in a polymer. The coating may have a positive surface charge. The coating may deliver active agent nanoparticles into the treatment site over at least about one day. The coating may be formed of a surfactant and nanoparticles mixture. The active agent nanoparticles may be deposited on the medical device using electrostatic capture.
Owner:MICELL TECH INC
Method for obtaining nanoparticles
ActiveUS20060222780A1High densityImprove conversion efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyMolten spray coatingNanoparticleNanometre
The method is intended for obtaining nanosize amorphous particles, which find use in various fields of science and technology; in particular, metallic nanostructures can be regarded as a promising material for creating new sensors and electronic and optoelectronic devices and for developing new types of highly selective solid catalysts. The method for obtaining nanoparticles includes the following stages: dispersion of a molten material; supply of the resulting liquid drops of this material into a plasma with parameters satisfying the aforementioned relationships, which is formed in an inert gas at a pressure of 10−4-10−1 Pa; cooling of liquid nanoparticles formed in the said plasma to their hardening; and deposition of the resulting solid nanoparticles onto a support.
Owner:GUREVICH +2
Coated and magnetic particles and applications thereof
InactiveUS20040115340A1Easy to controlImprove catalytic performanceNon-insulated conductorsVolume/mass flow measurementAlloyMaterials science
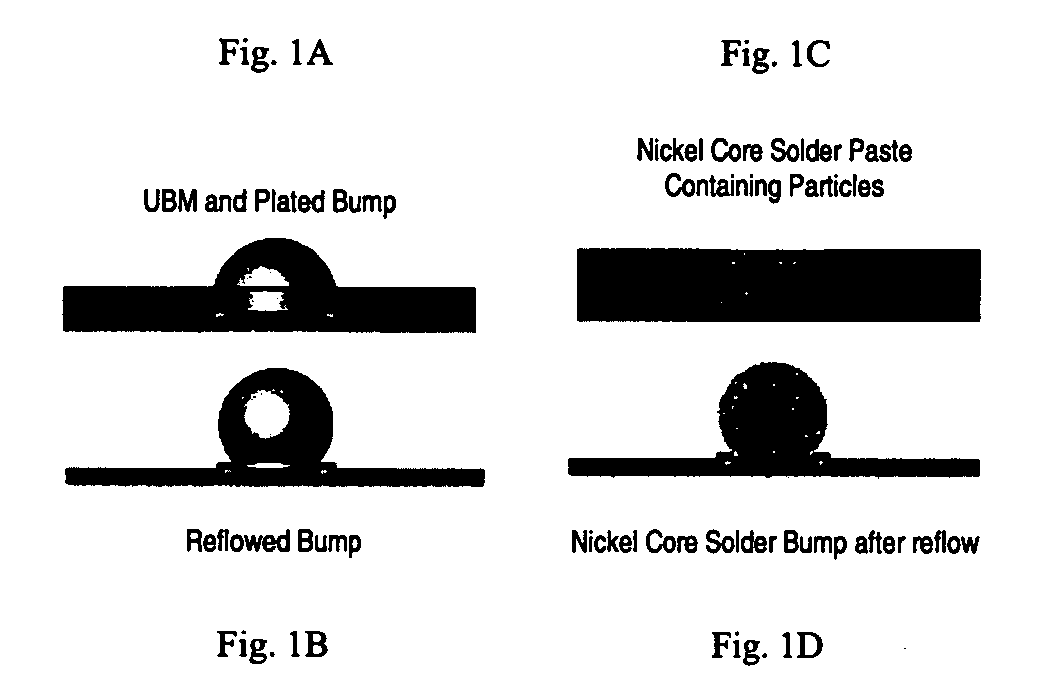
A method of using coated and / or magnetic particles to deposit structures including solder joints, bumps, vias, bond rings, and the like. The particles may be coated with a solderable material. For solder joints, after reflow the solder material may comprise unmelted particles in a matrix, thereby increasing the strength of the joint and decreasing the pitch of an array of joints. The particle and coating may form a higher melting point alloy, permitting multiple subsequent reflow steps. The particles and / or the coating may be magnetic. External magnetic fields may be applied during deposition to precisely control the particle loading and deposition location. Elements with incompatible electropotentials may thereby be electrodeposited in a single step. Using such fields permits the fill of high aspect ratio structures such as vias without requiring complete seed metallization of the structure. Also, a catalyst consisting of a magnetic particle coated with a catalytic material, optionally including an intermediate layer.
Owner:SURFECT TECH
FED cathode structure using electrophoretic deposition and method of fabrication
InactiveUS6902658B2High densityVolume/mass flow measurementNanoinformaticsField emission deviceElectrophoresis
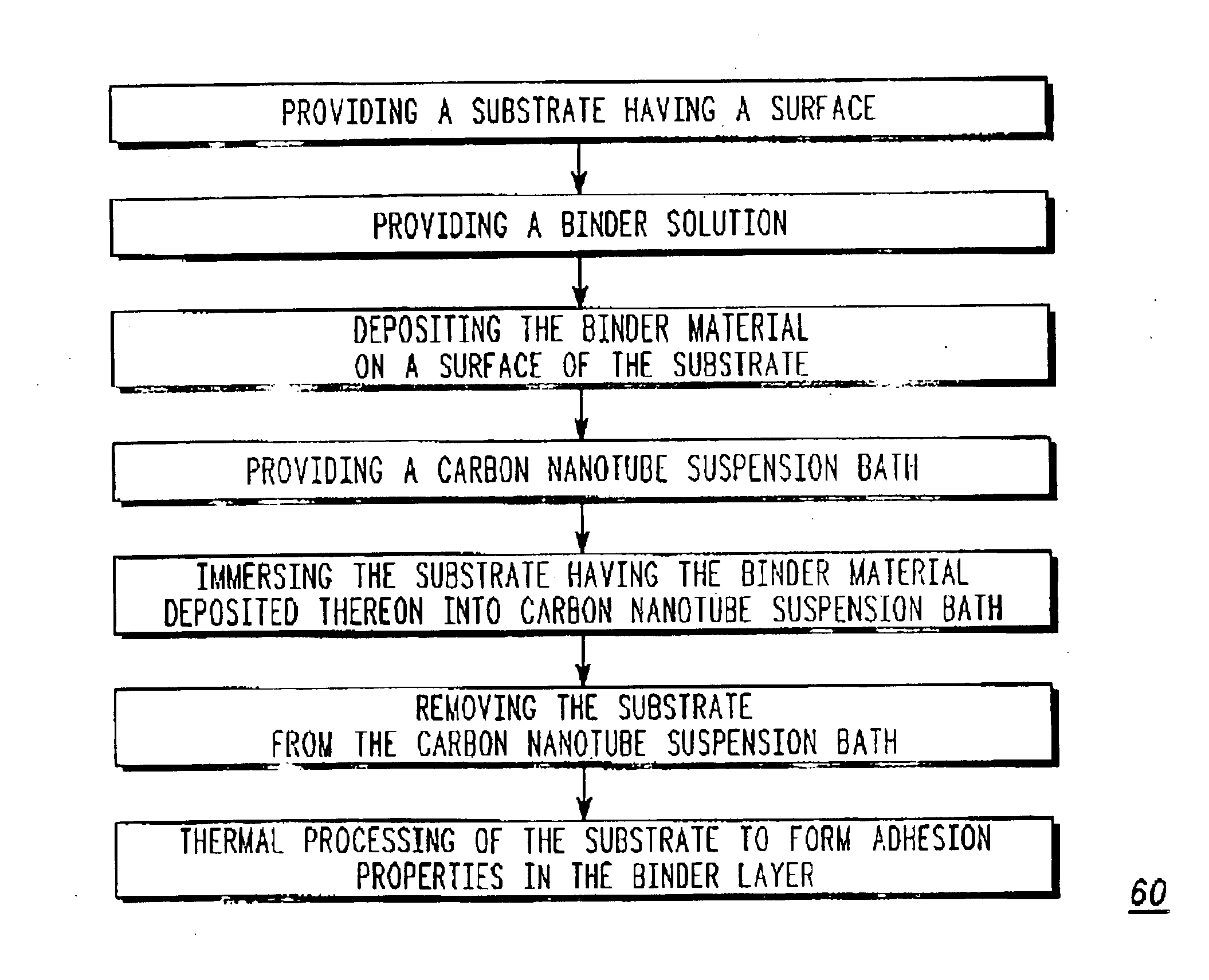
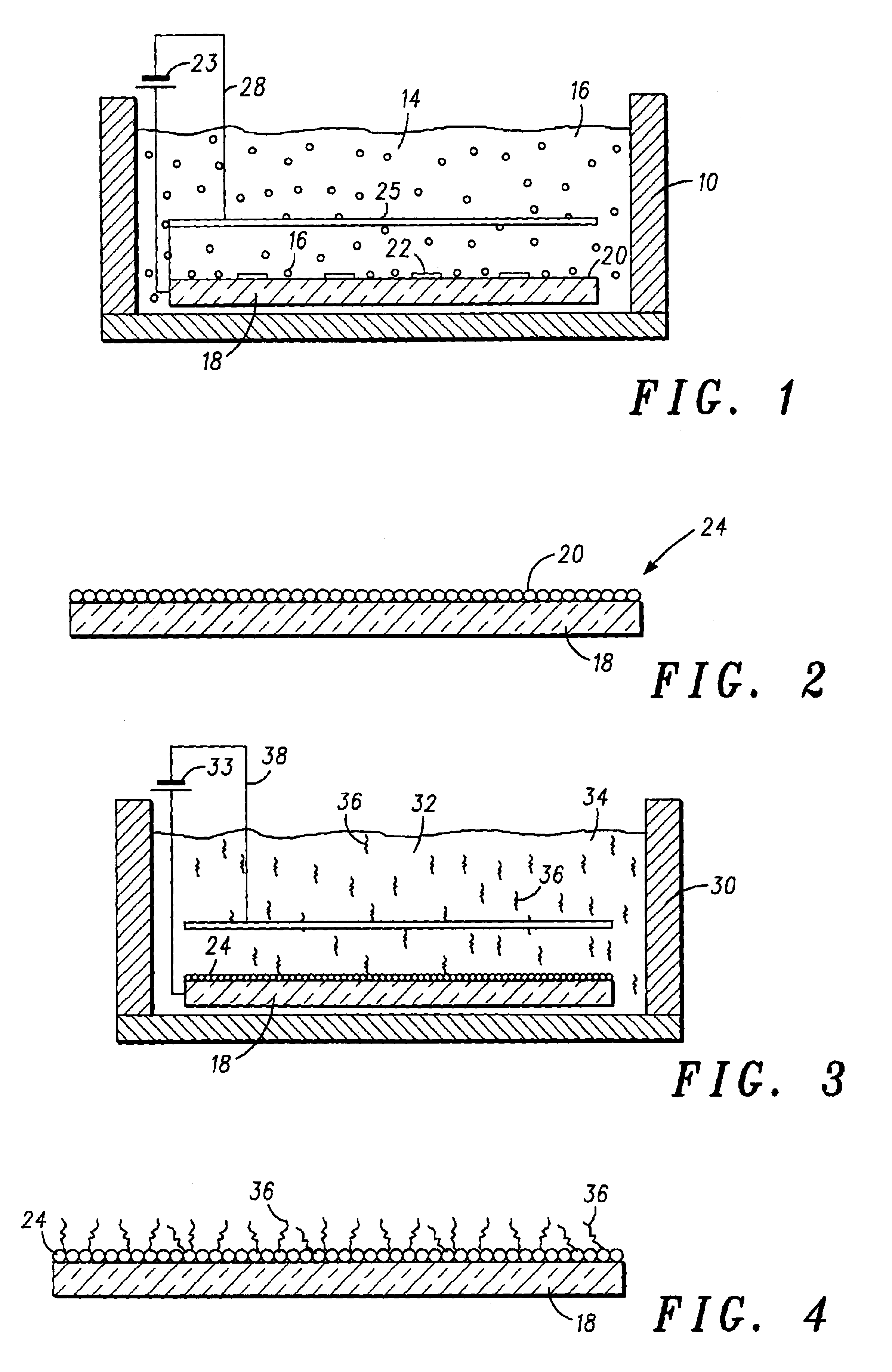
A method of fabricating a field emission device cathode using electrophoretic deposition of carbon nanotubes in which a separate step of depositing a binder material onto a substrate, is performed prior to carbon nanotube particle deposition. First, a binder layer is deposited on a substrate from a solution containing a binder material. The substrate having the binder material deposited thereon is then transferred into a carbon nanotube suspension bath allowing for coating of the carbon nanotube particles onto the substrate. Thermal processing of the coating transforms the binder layer properties which provides for the adhesion of the carbon nanotube particles to the binder material.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
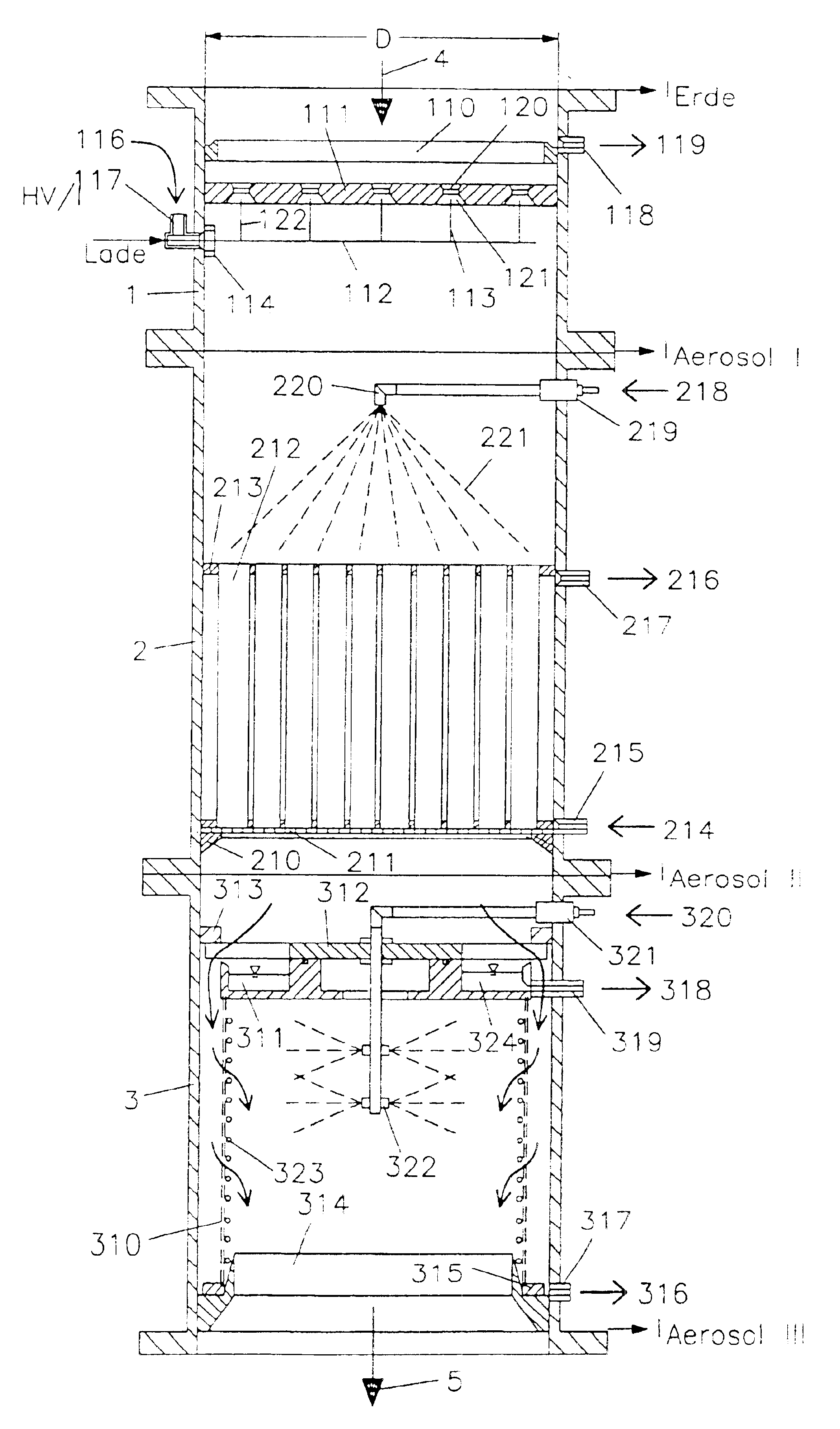
Electrostatic sampler and method
ActiveUS20070034025A1Improve performanceSmall particle captureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCollection systemHigh flux
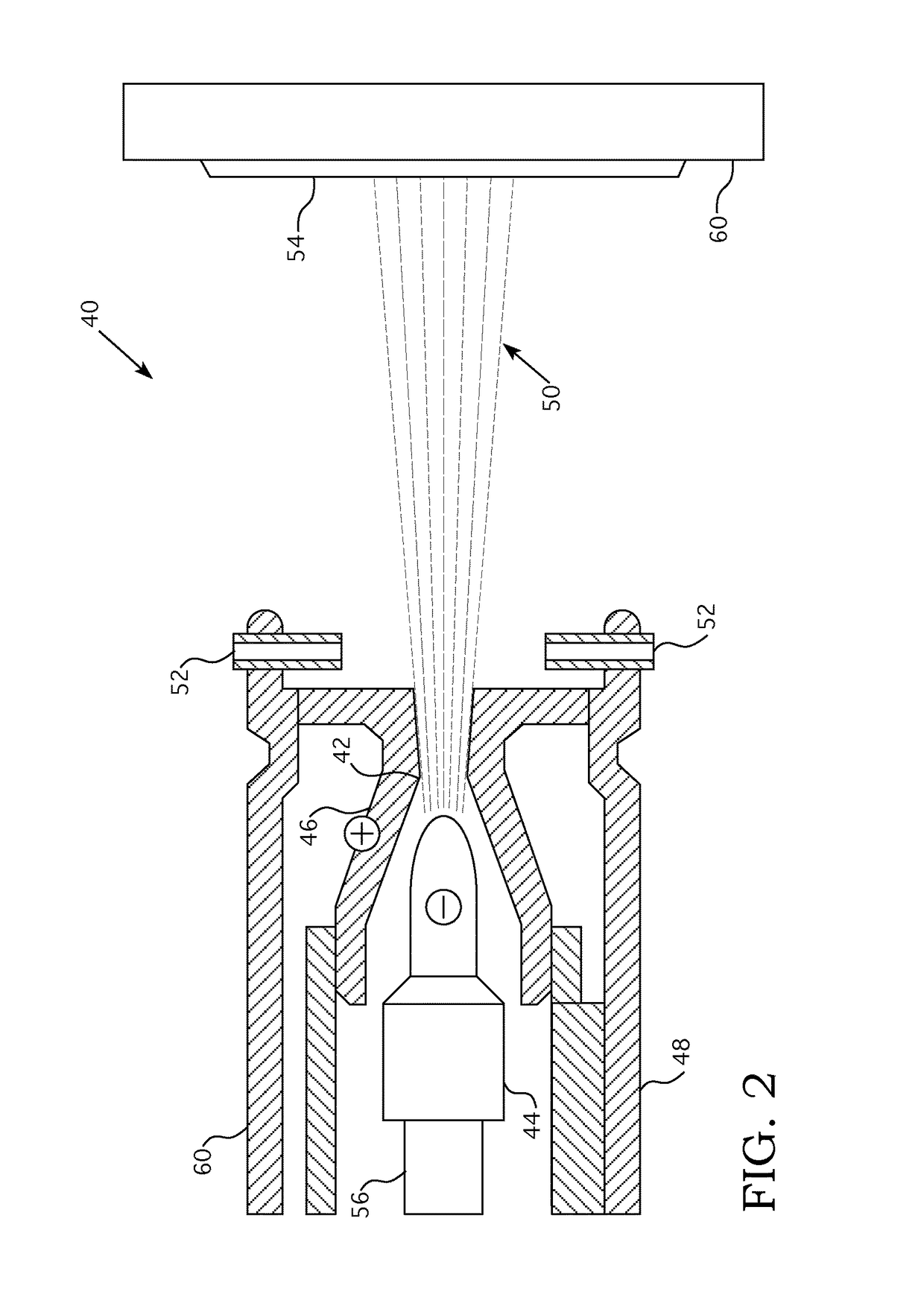
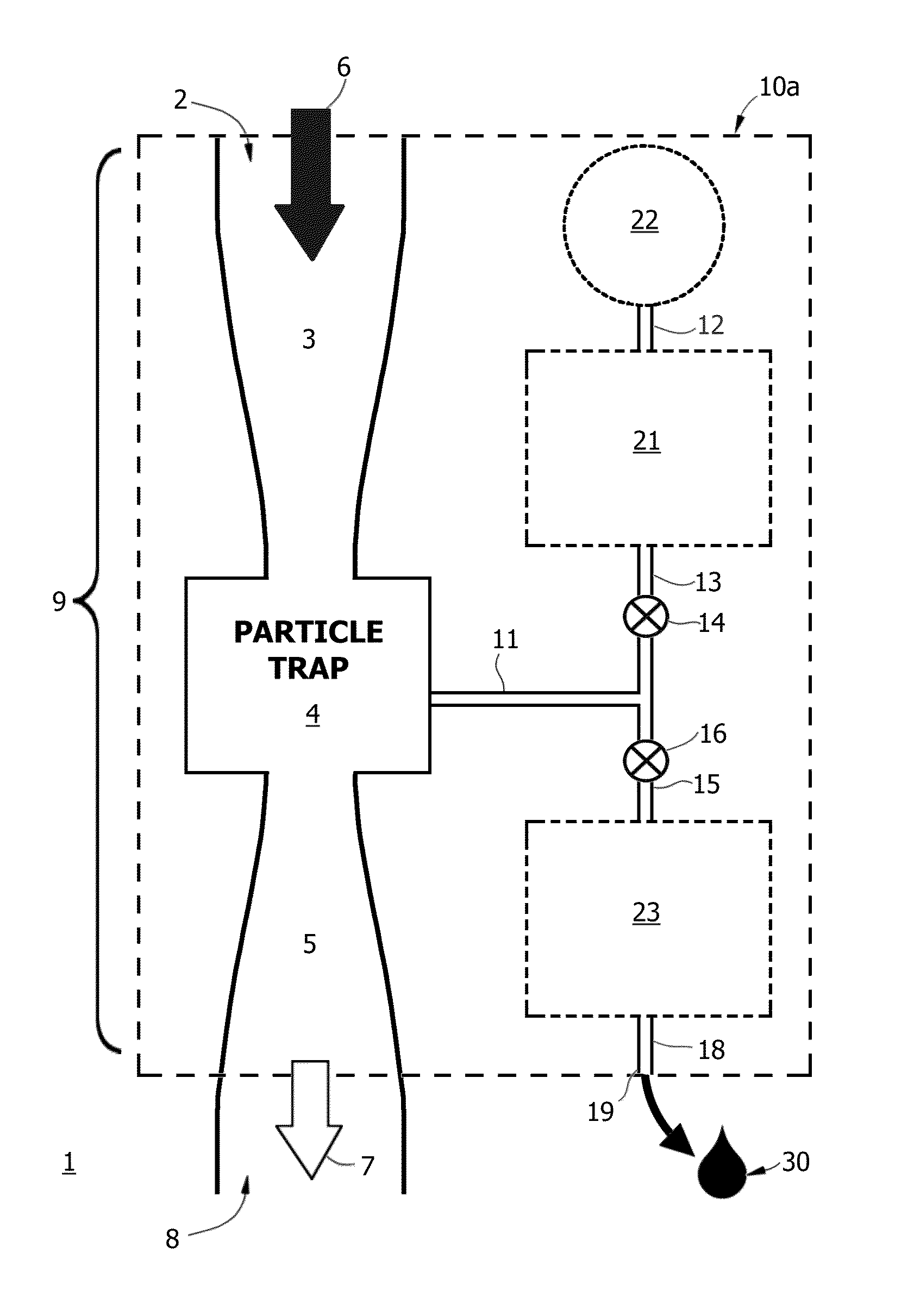
The present invention is an electrostatic collector for low cost, high throughput, high efficiency sampling and concentration of bioaerosols. The device is small enough to be portable and can be contained within or placed on the wall of a typical office or hospital building. The collector comprises one or more collector modules, each having an ionizing electrode, a conical outer electrode, a wet collection electrode, and a liquid collection system. Airflow through a collector module may be partially blocked to enhance the collection of smaller particles and the collection electrode may comprise multiple, programmable electrodes to focus particle deposition onto a smaller area. Particles are collected into a small volume of liquid to facilitate subsequent analysis by an attached analyzer or at a remote site.
Owner:CFD RES CORP
Method of growing semiconductor nanowires with uniform cross-sectional area using chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS20050266662A1Uniform cross-sectional areaUniform areaMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNanowireSemiconductor materials
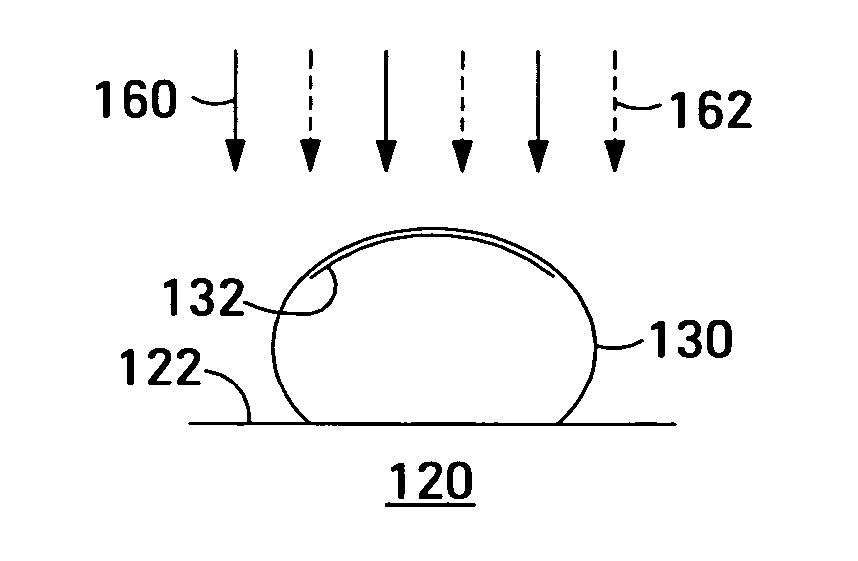
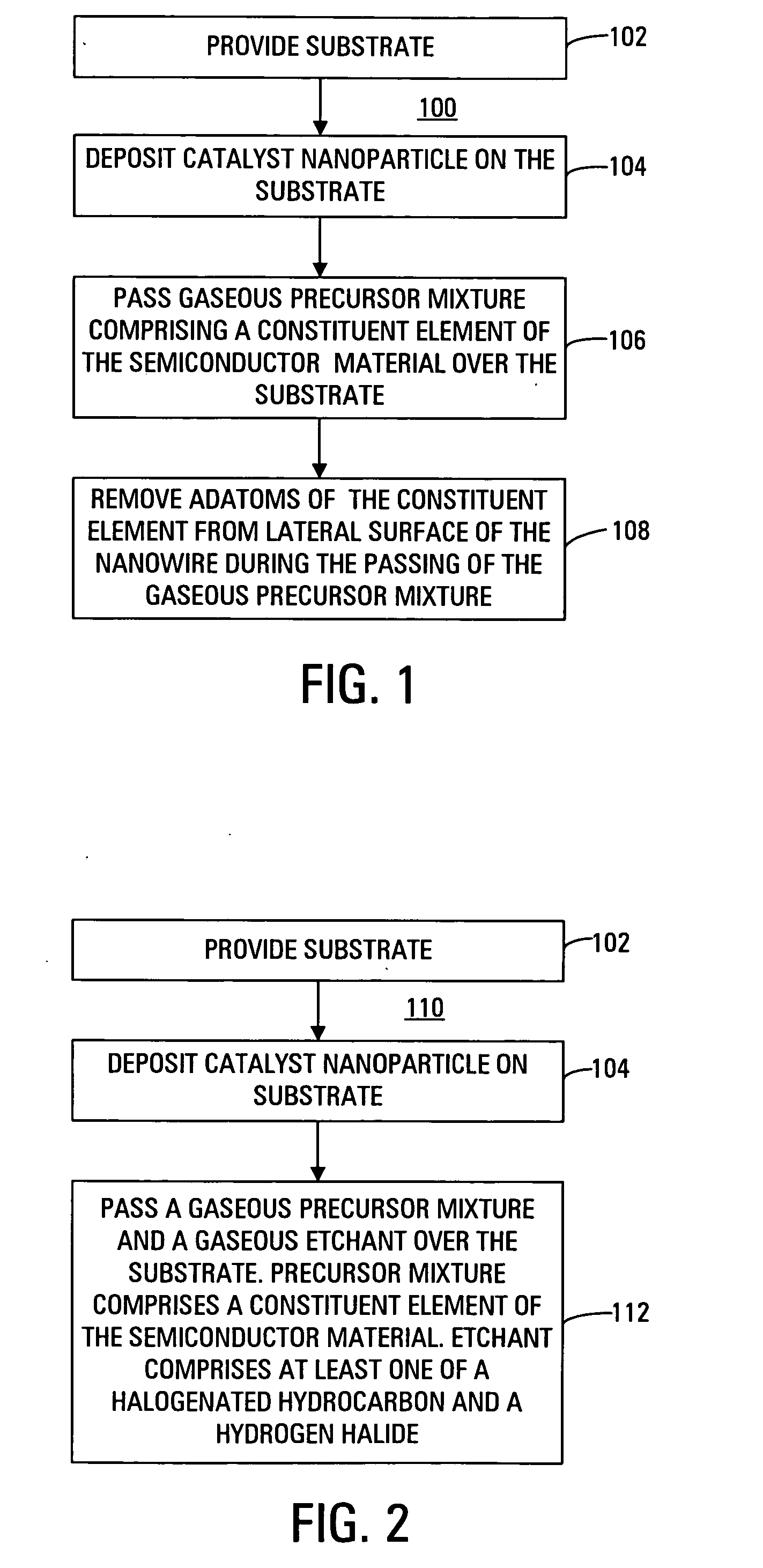
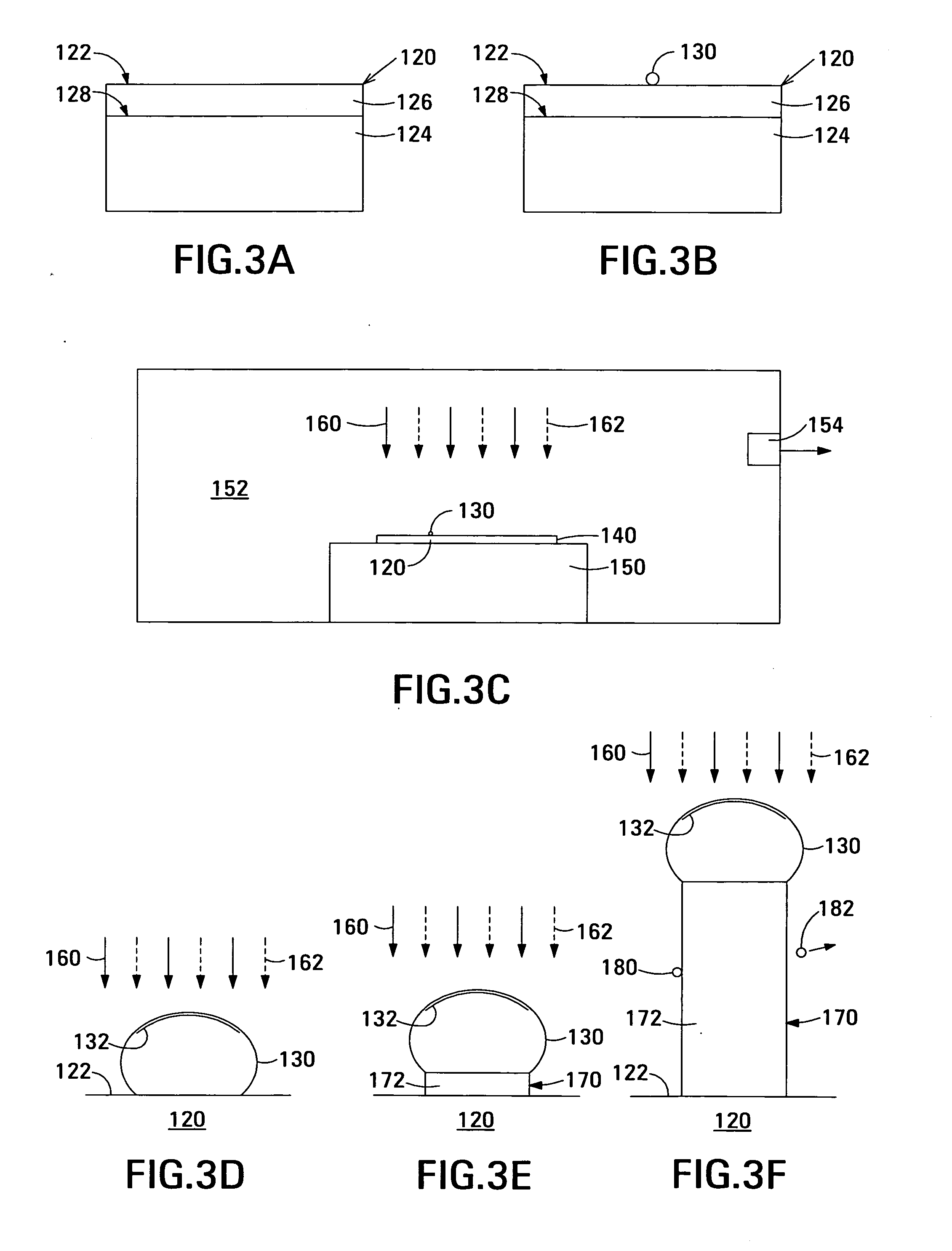
A nanowire of a semiconductor material and having a uniform cross-sectional area along its length is grown using a chemical vapor deposition process. In the method, a substrate is provided, a catalyst nanoparticle is deposited on the substrate, a gaseous precursor mixture comprising a constituent element of the semiconductor material is passed over the substrate, and adatoms of the constituent element are removed from a lateral surface of the nanowire during the passing of the precursor mixture. Removing the adatoms of the constituent element before such adatoms are incorporated into the nanowire prevents such adatoms from accumulating on the lateral surface of the nanowire and allows the nanowire to grow with a uniform cross-sectional area along its length.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Methods for producing films using supercritical fluid
A method for forming a continuous film on a substrate surface that involves depositing particles onto a substrate surface and contacting the particle-deposited substrate surface with a supercritical fluid under conditions sufficient for forming a continuous film from the deposited particles. The particles may have a mean particle size of less 1 micron. The method may be performed by providing a pressure vessel that can contain a compressible fluid. A particle-deposited substrate is provided in the pressure vessel and the compressible fluid is maintained at a supercritical or sub-critical state sufficient for forming a film from the deposited particles. The Tg of particles may be reduced by subjecting the particles to the methods detailed in the present disclosure.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Methods for producing films using supercritical fluid
A method for forming a continuous film on a substrate surface that involves depositing particles onto a substrate surface and contacting the particle-deposited substrate surface with a supercritical fluid under conditions sufficient for forming a continuous film from the deposited particles. The particles may have a mean particle size of less 1 micron. The method may be performed by providing a pressure vessel that can contain a compressible fluid. A particle-deposited substrate is provided in the pressure vessel and the compressible fluid is maintained at a supercritical or sub-critical state sufficient for forming a film from the deposited particles. The Tg of particles may be reduced by subjecting the particles to the methods detailed in the present disclosure.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
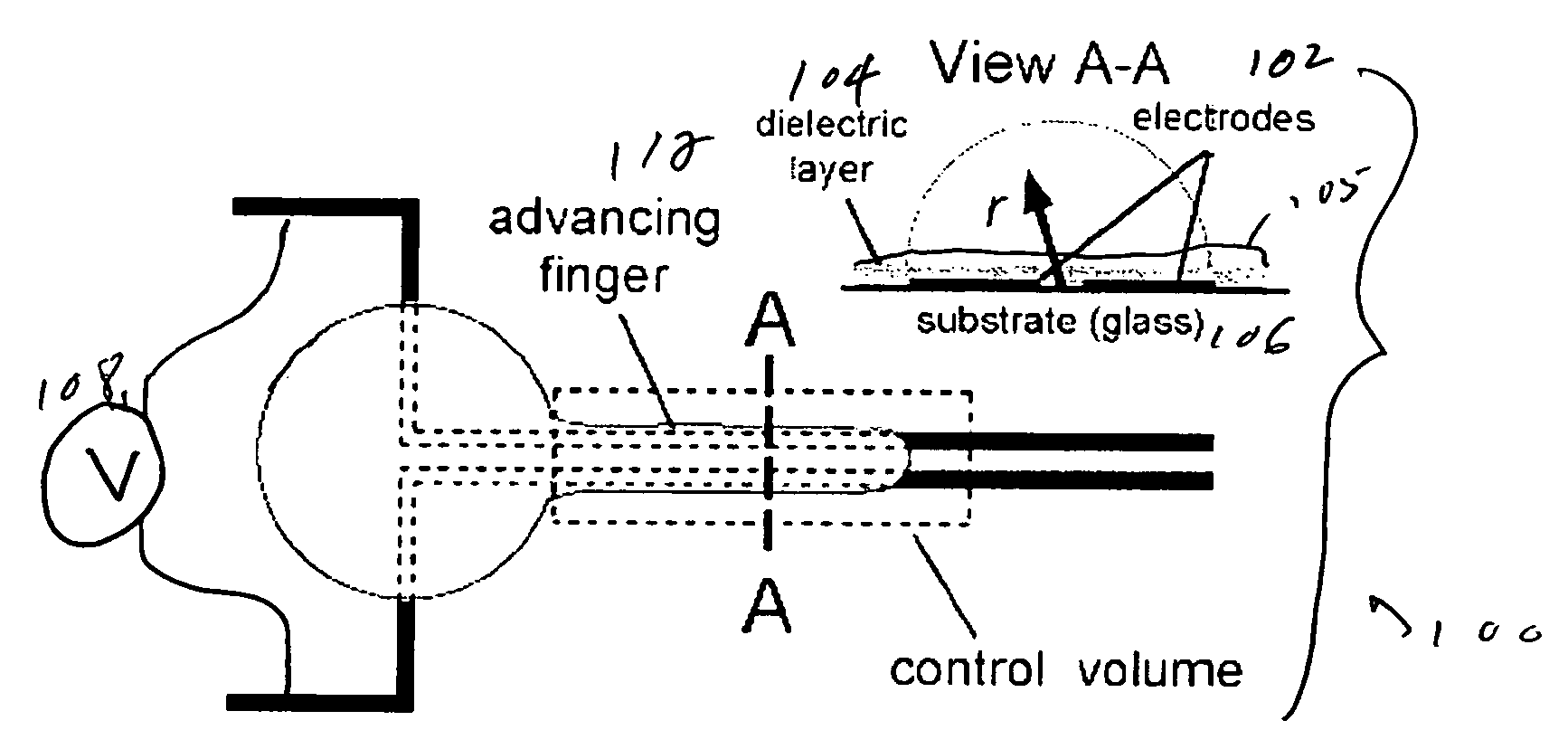
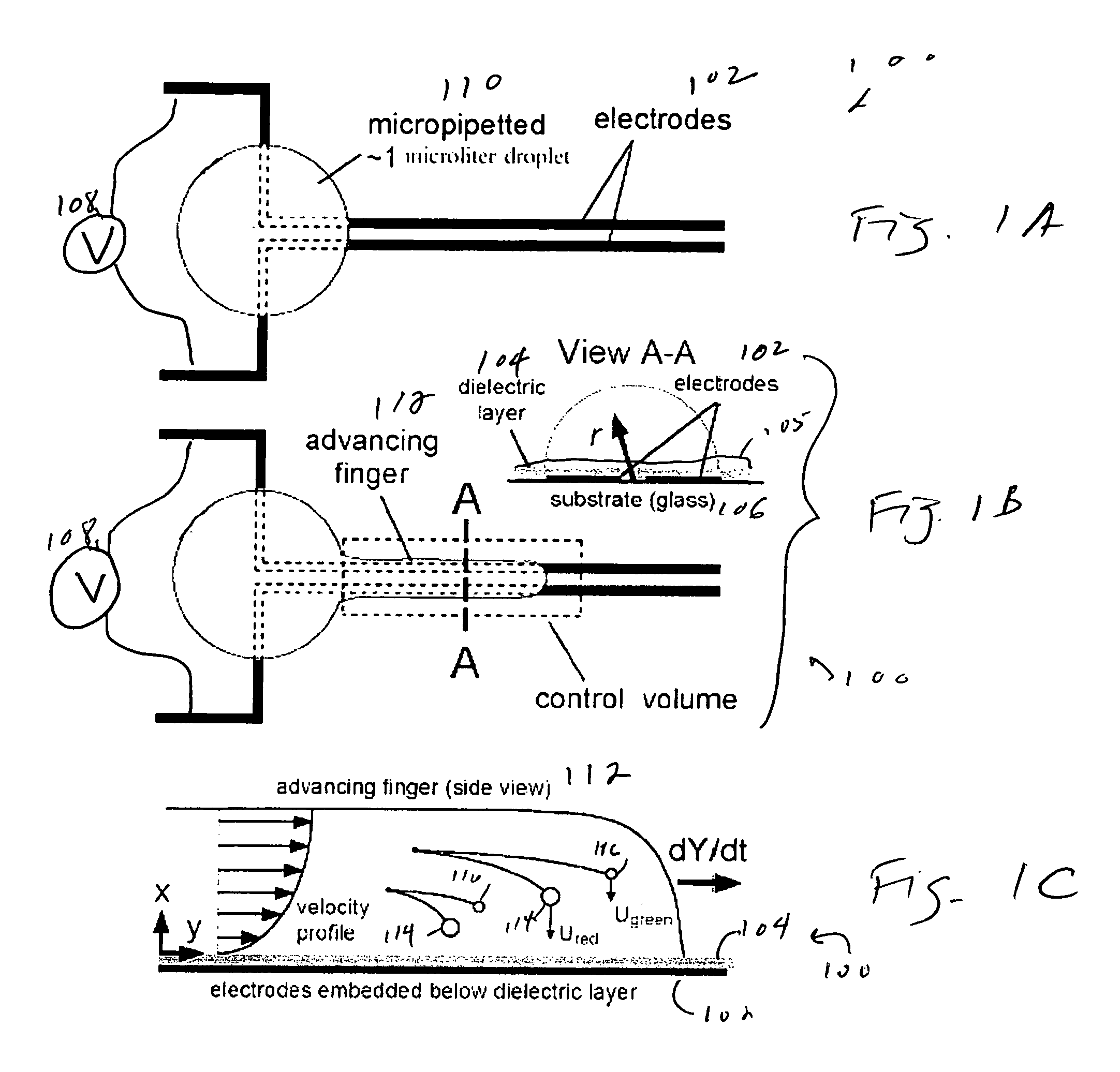
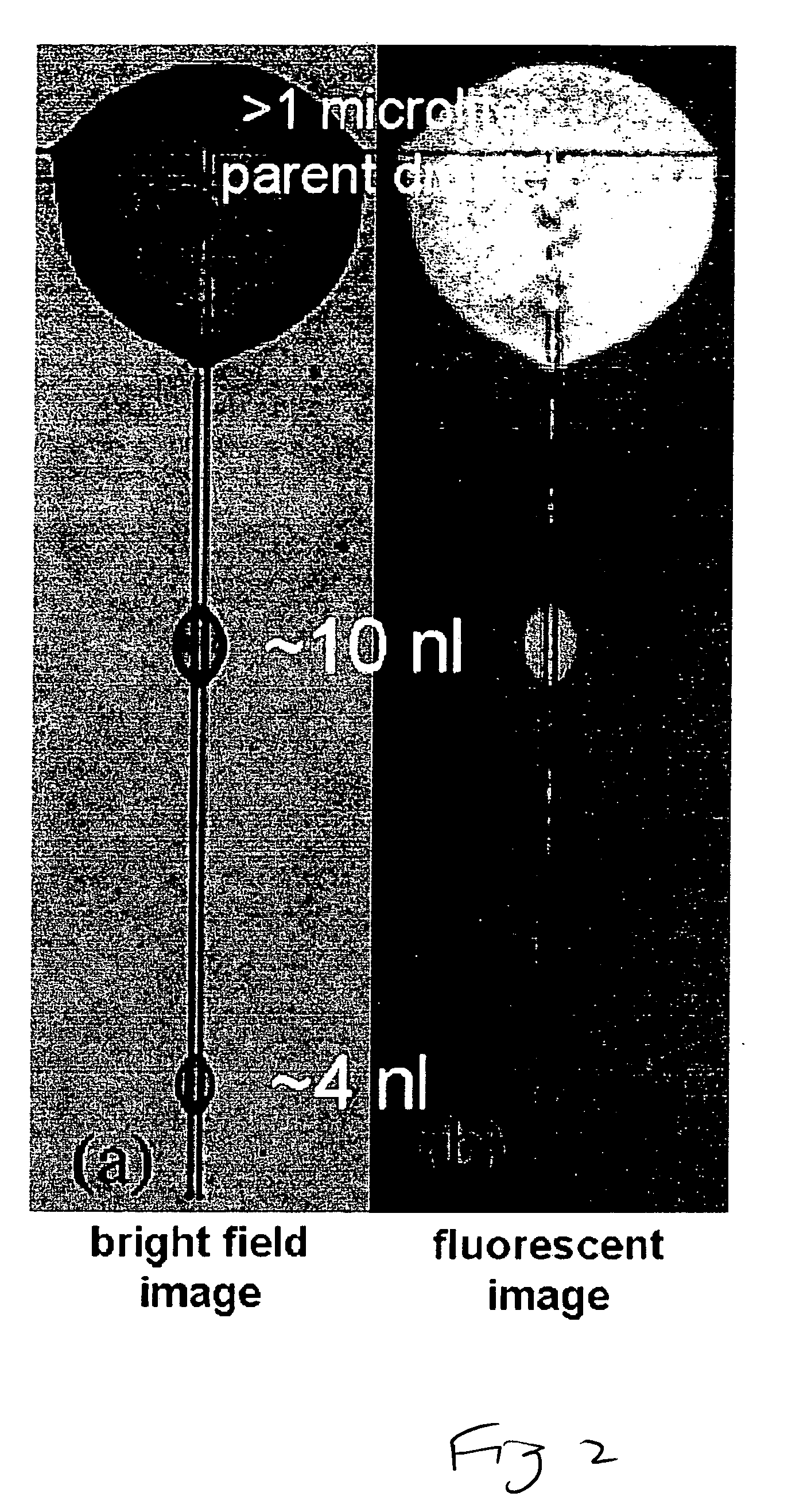
Rapid flow fractionation of particles combining liquid and particulate dielectrophoresis
Rapid, size-based, deposition of particles from liquid suspension is accomplished using a nonuniform electric field created by coplanar microelectrode strips patterned on an insulating substrate. The scheme uses the dielectrophoretic force both to distribute aqueous liquid containing particles and, simultaneously, to separate the particles. Size-based separation is found within nanoliter droplets formed along the structure after voltage removal. Bioparticles or macromolecules of similar size can also be separated based on subtle differences in dielectric property, by controlling the frequency of the AC current supplied to the electrodes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Reactor design to reduce particle deposition during process abatement
InactiveUS20060104879A1Reduce accumulationReduce reactor chamber crackingCombination devicesBurnersCombustionDecomposition
The present invention relates to systems and methods for controlled combustion and decomposition of gaseous pollutants while reducing deposition of unwanted reaction products from within the treatment systems. The systems include a novel thermal reaction chamber design having stacked reticulated ceramic rings through which fluid, e.g., gases, may be directed to form a boundary layer along the interior wall of the thermal reaction chamber, thereby reducing particulate matter buildup thereon. The systems further include the introduction of fluids from the center pilot jet to alter the aerodynamics of the interior of the thermal reaction chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
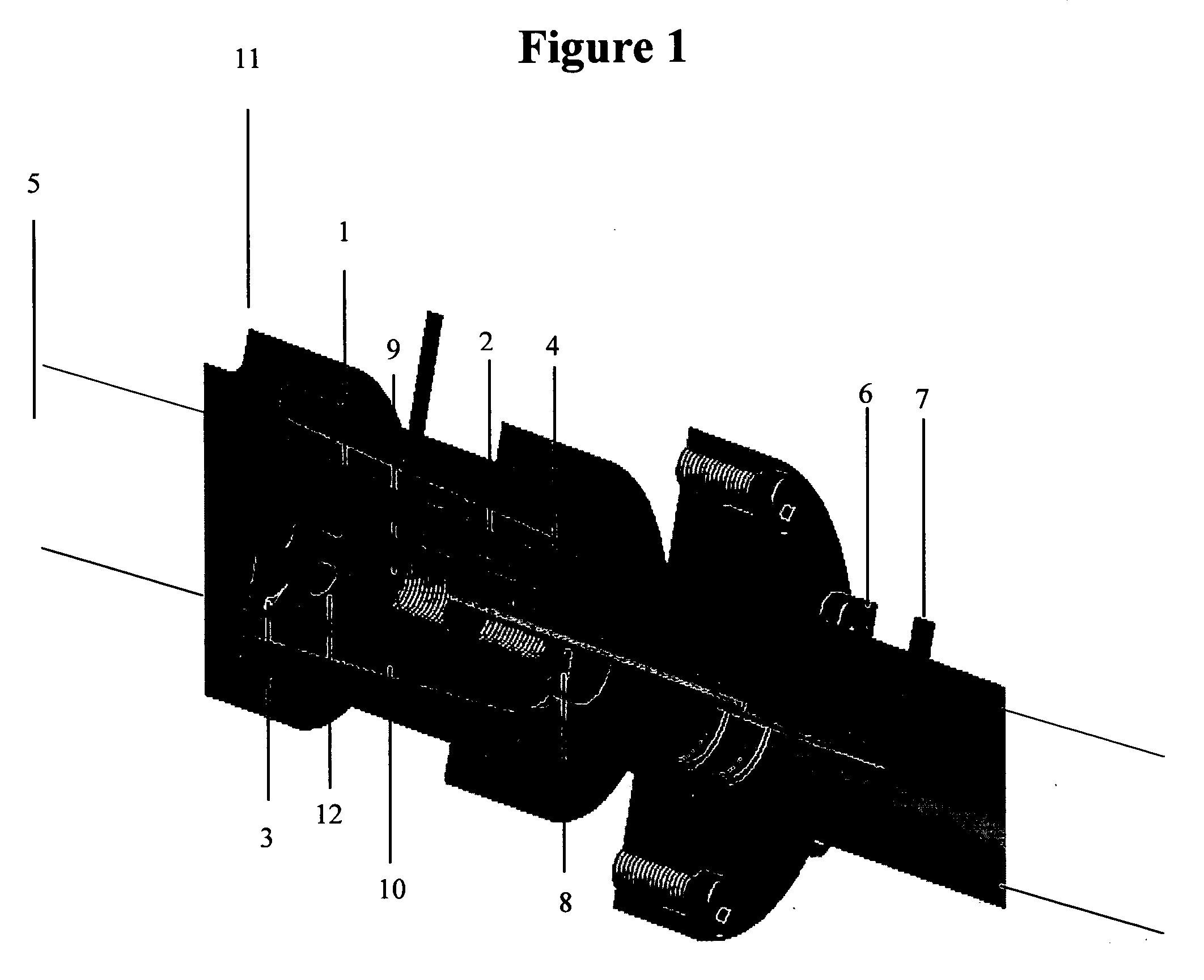
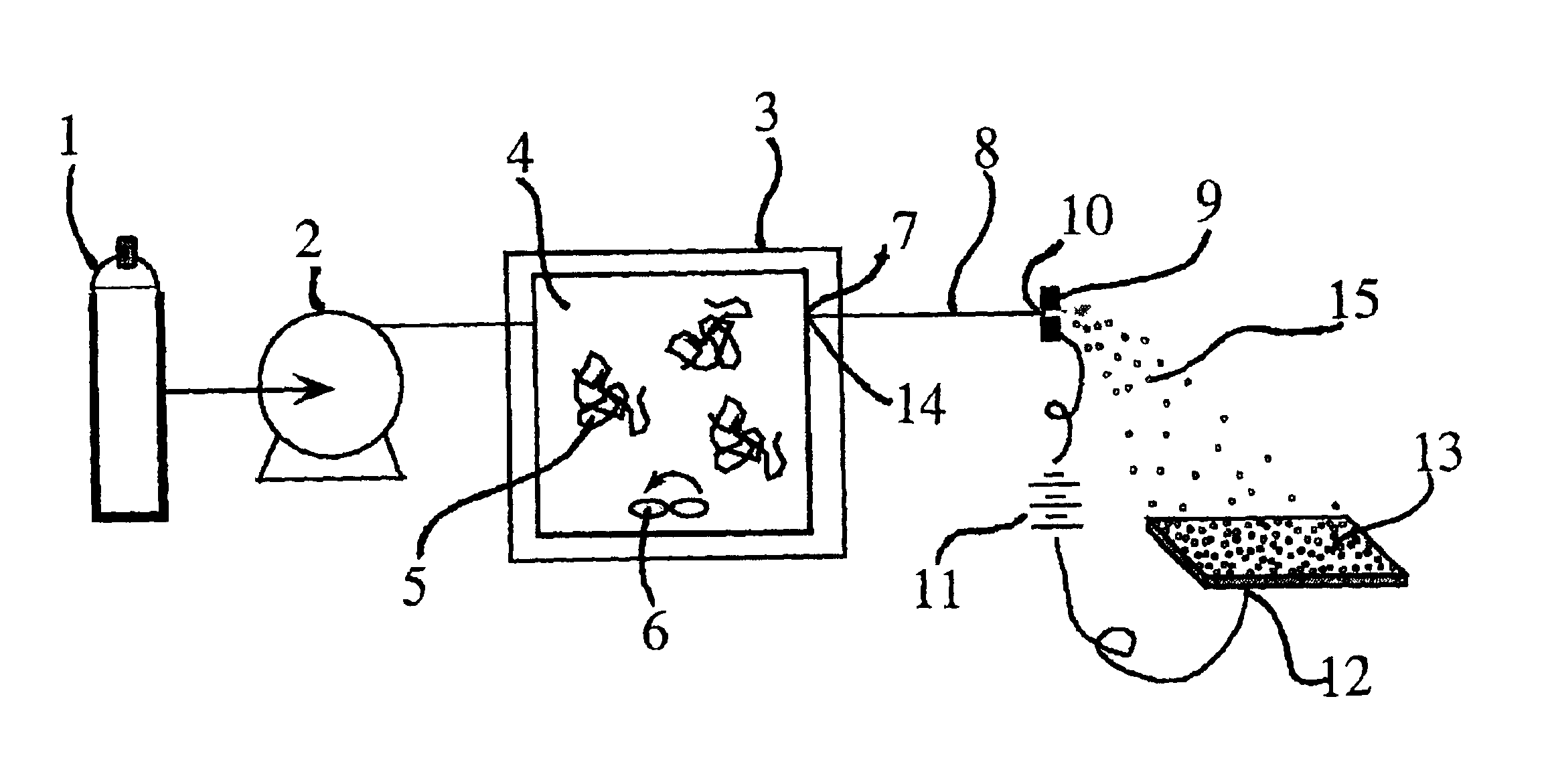
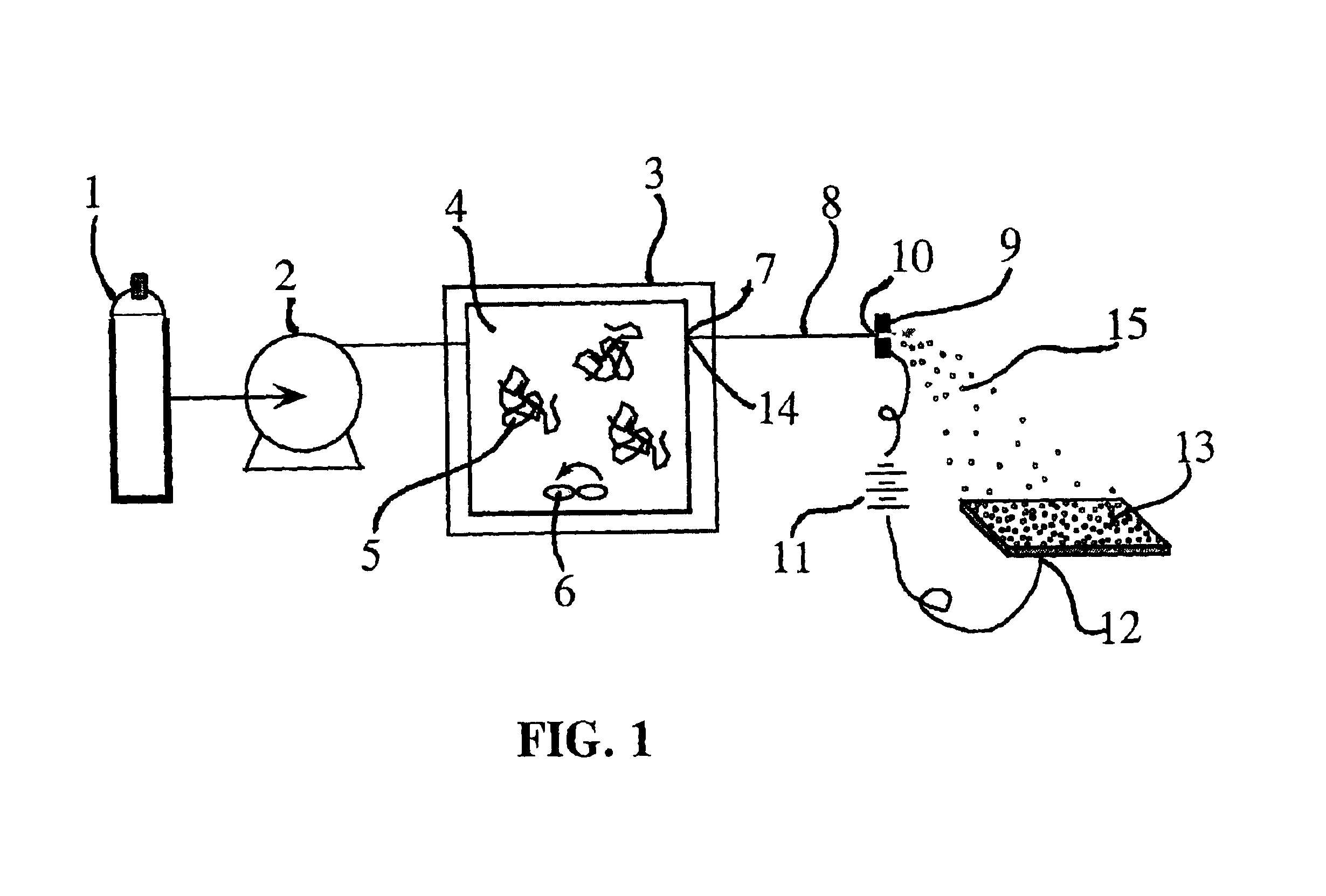
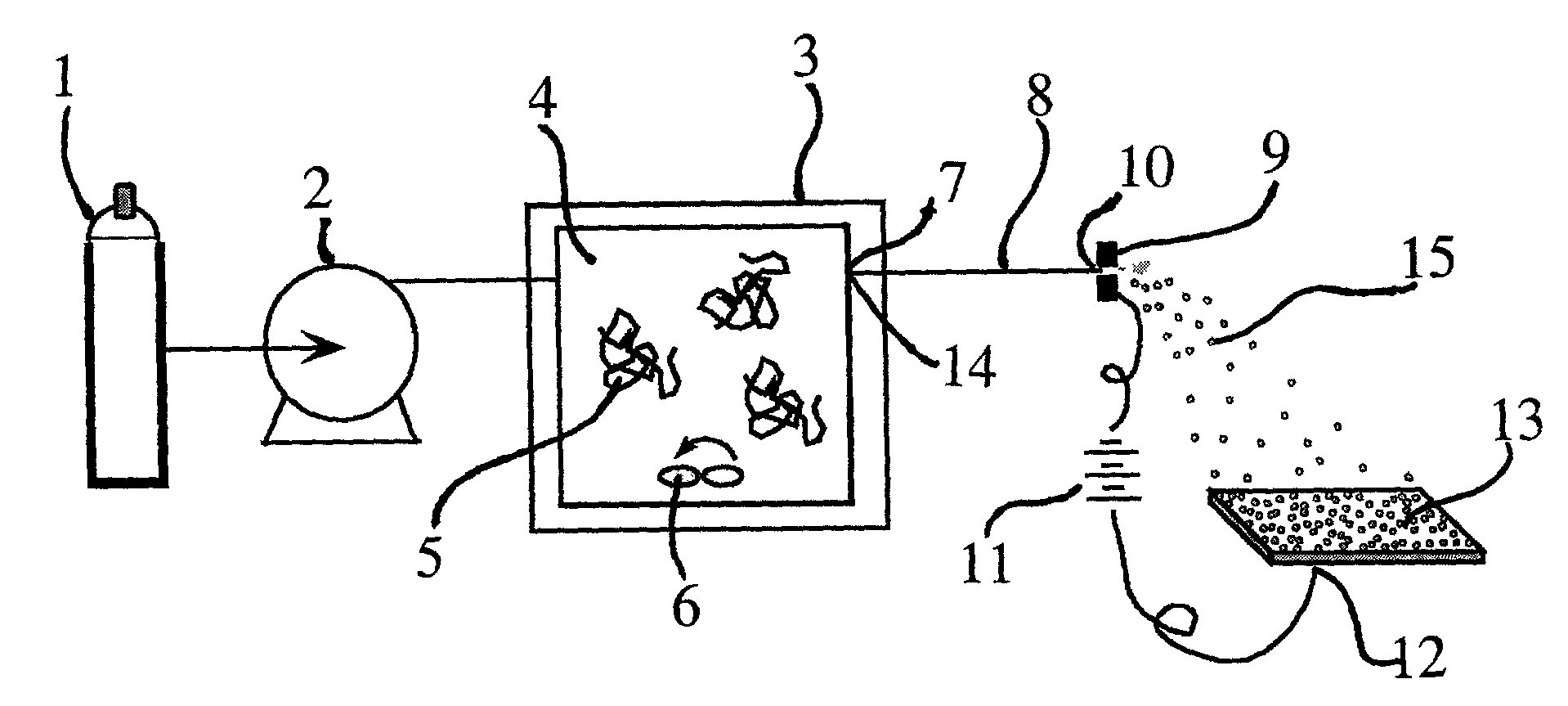
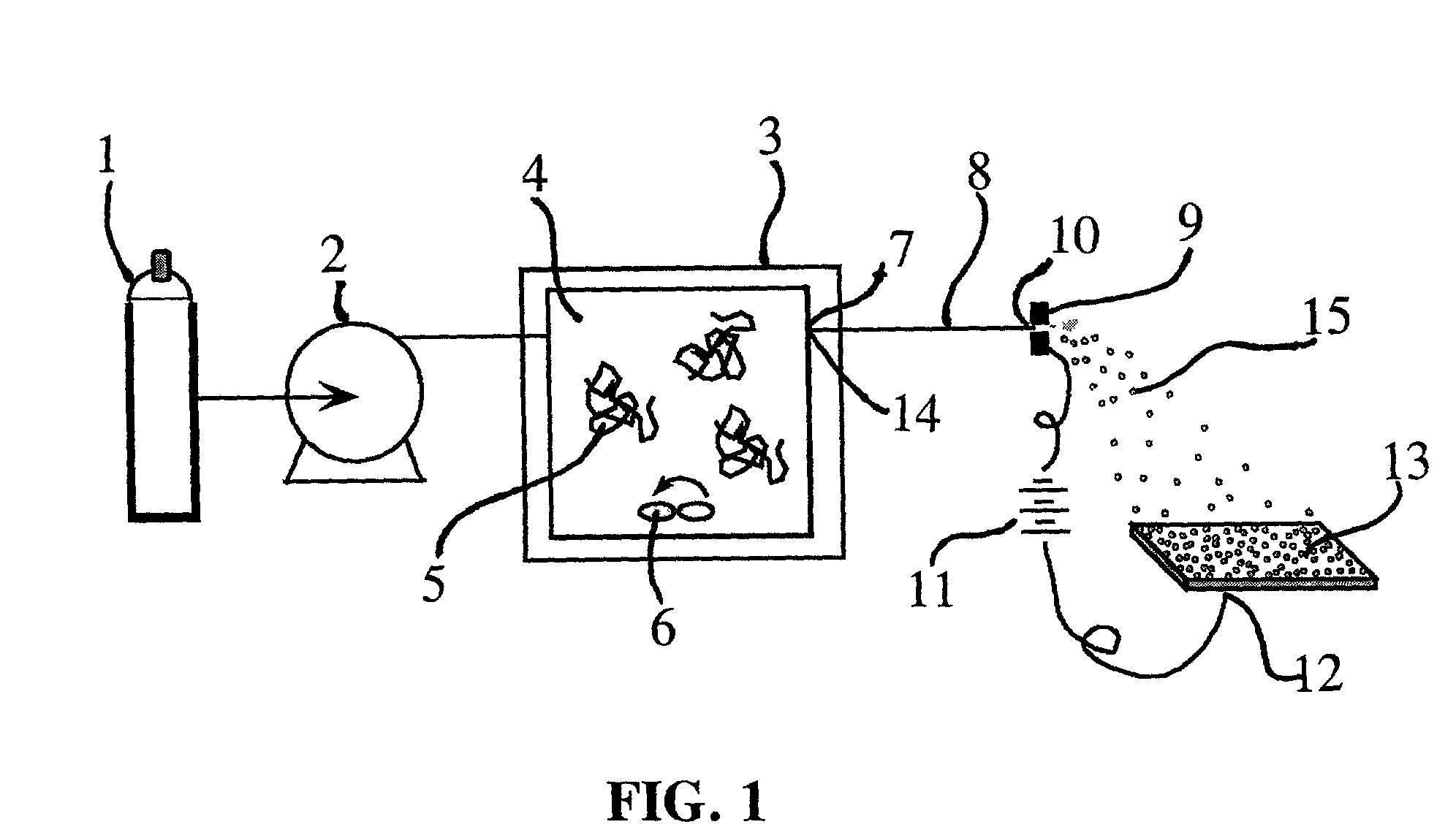
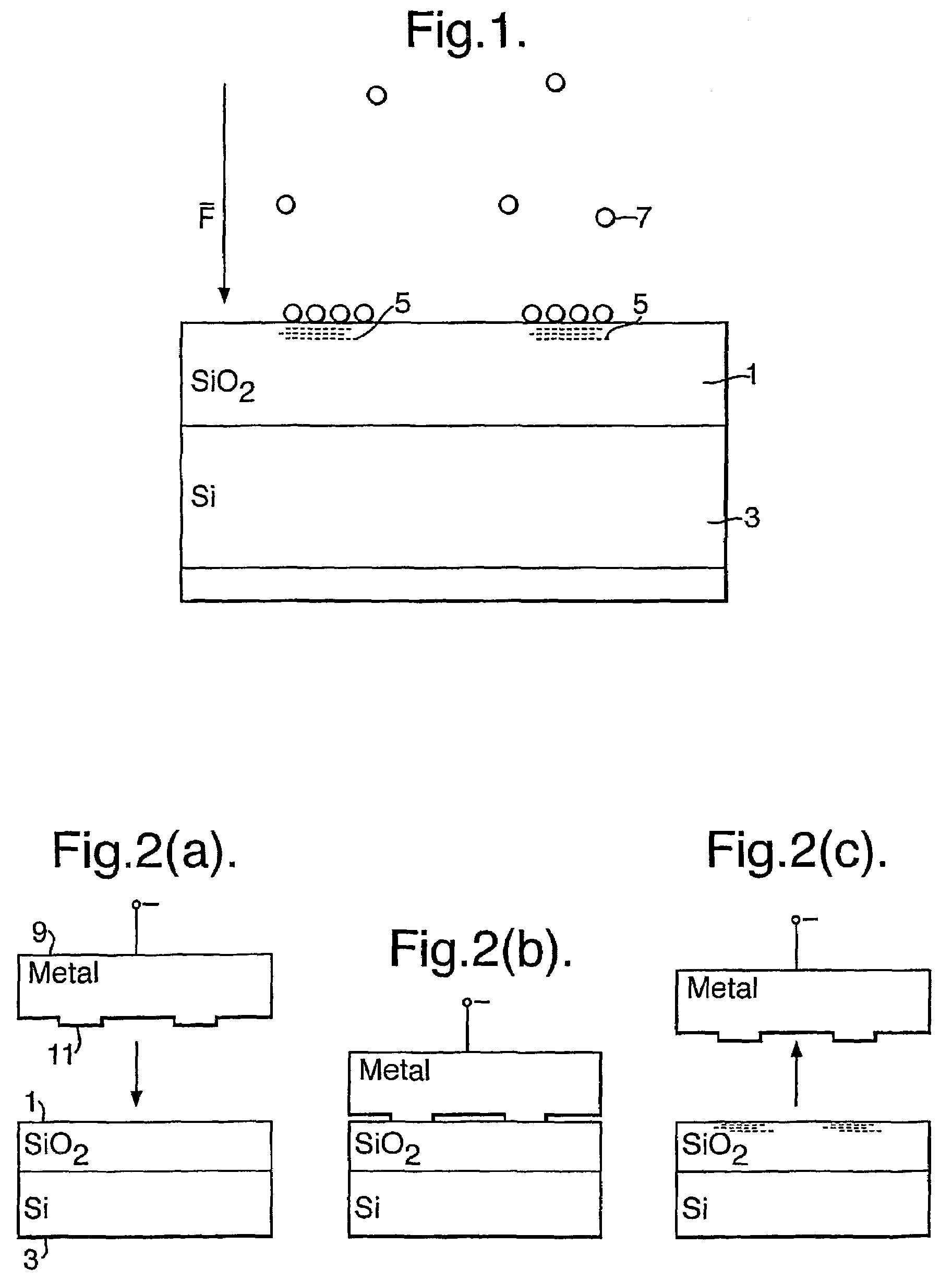
Particle deposition apparatus and methods for forming nanostructures
InactiveUS7223444B2Small geometric featureCarry-out quicklyLiquid surface applicatorsIndividual molecule manipulationNanoparticleFast methods
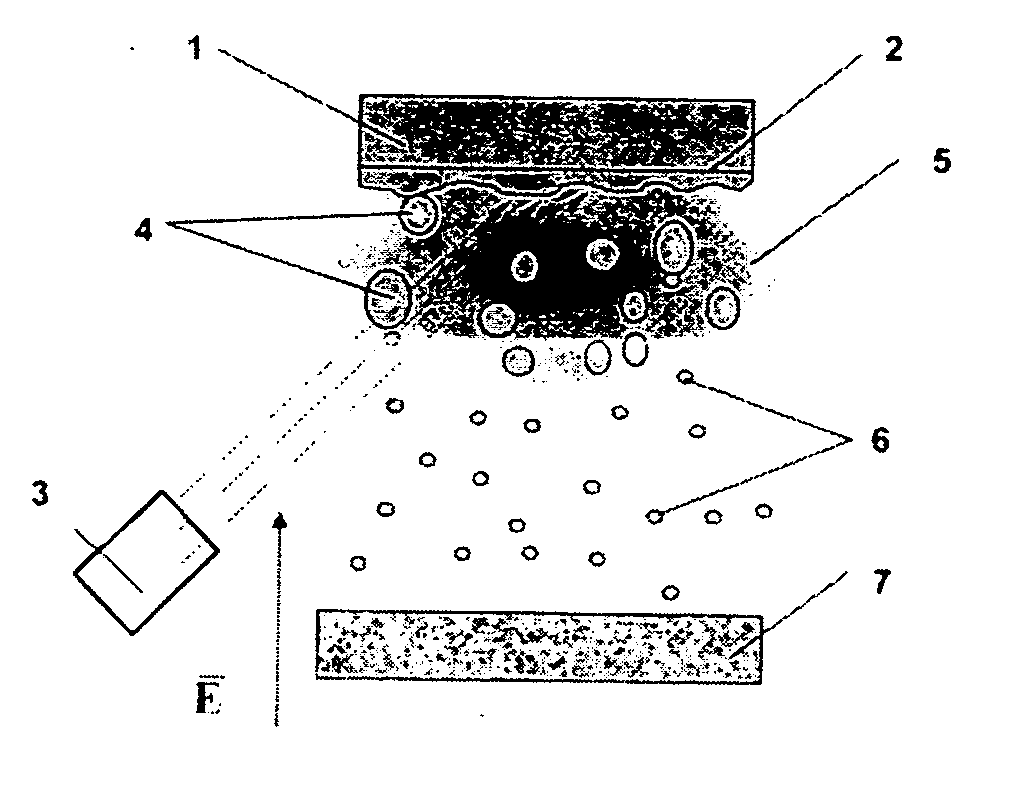
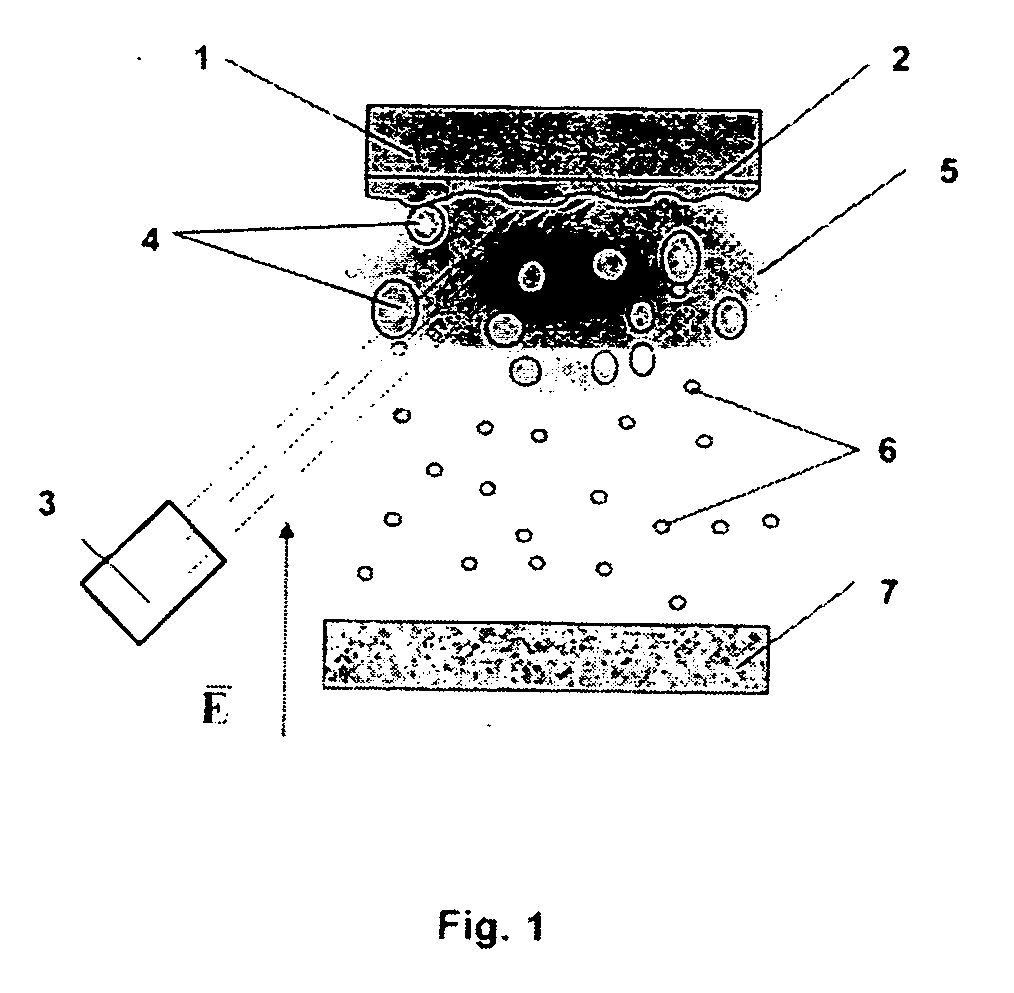
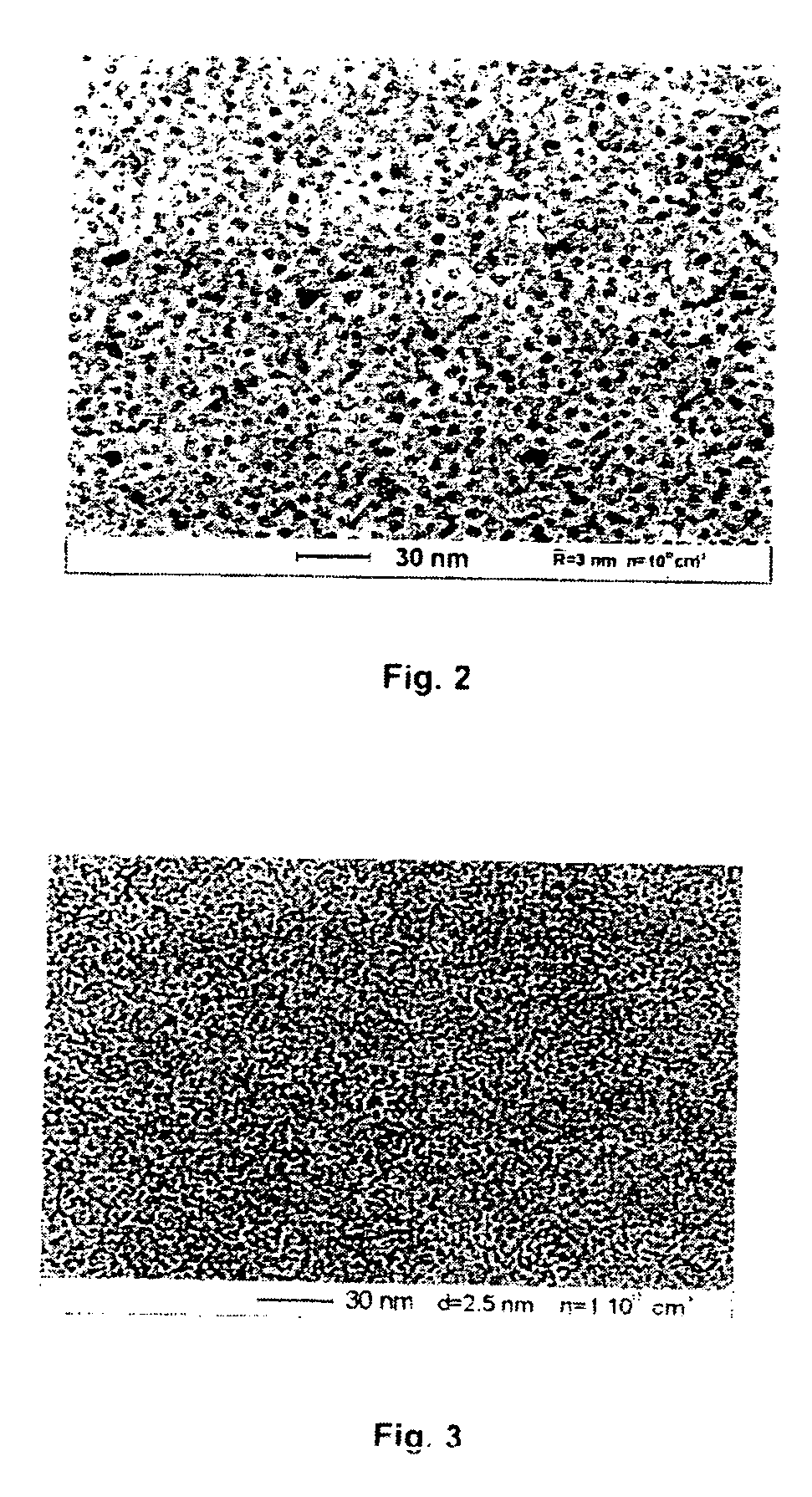
A fast method of creating nanostructures comprising the steps of forming one or more electrically-charged regions (5) of predetermined shape on a surface (1) of a first material, by contacting the regions with a stamp for transferring electric charge, and providing electrically charged nanoparticles (7) of a second material, and permitting the particles to flow in the vicinity of the regions, to be deposited on the regions.
Owner:QUNANO
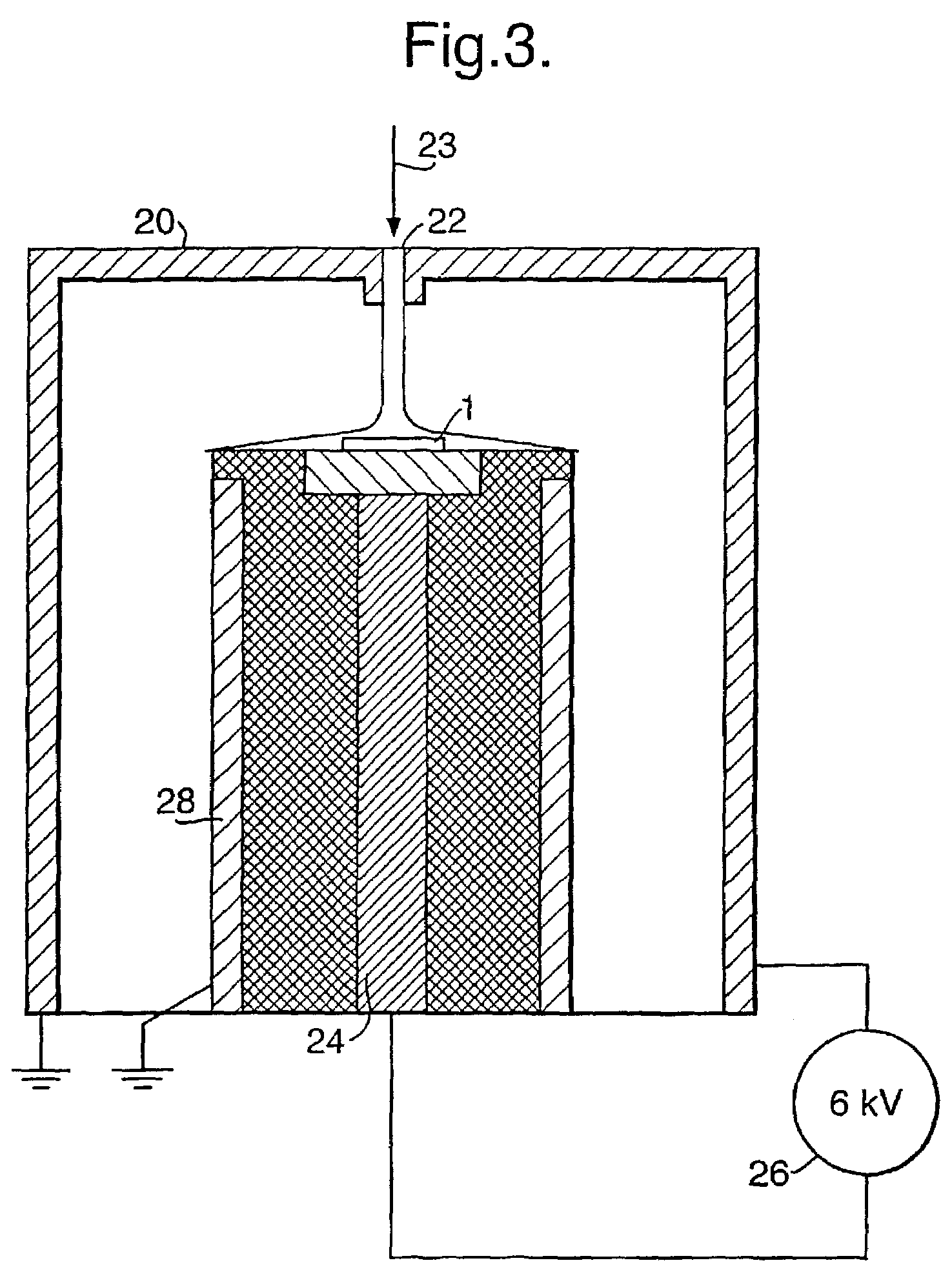
Apparatus for the electrostatic cleaning of gases and method for the operation thereof
InactiveUS6858064B2Improve efficiencyImprove heat transfer performanceElectrostatic separation housingDispersed particle filtrationProduct gasEngineering
In an apparatus for the purification of a gas which apparatus includes a three section conduit withan ionization and cleaning section in which particles contained in water-saturated air are ionized and then conducted through a chamber with grounded walls so that part of the particles are deposited on these walls,an additional cleaning section which includes grounded tubes past which the gas is conducted to remove additional charged particles anda filter section in which dry remaining fine particles are removed from the gas stream,the deposited particles are flushed from all three sections and the flushing water including the particles is cleaned and recycled.
Owner:KERNFORSCHUNGSZENTRUM KARLSRUHE GMBH
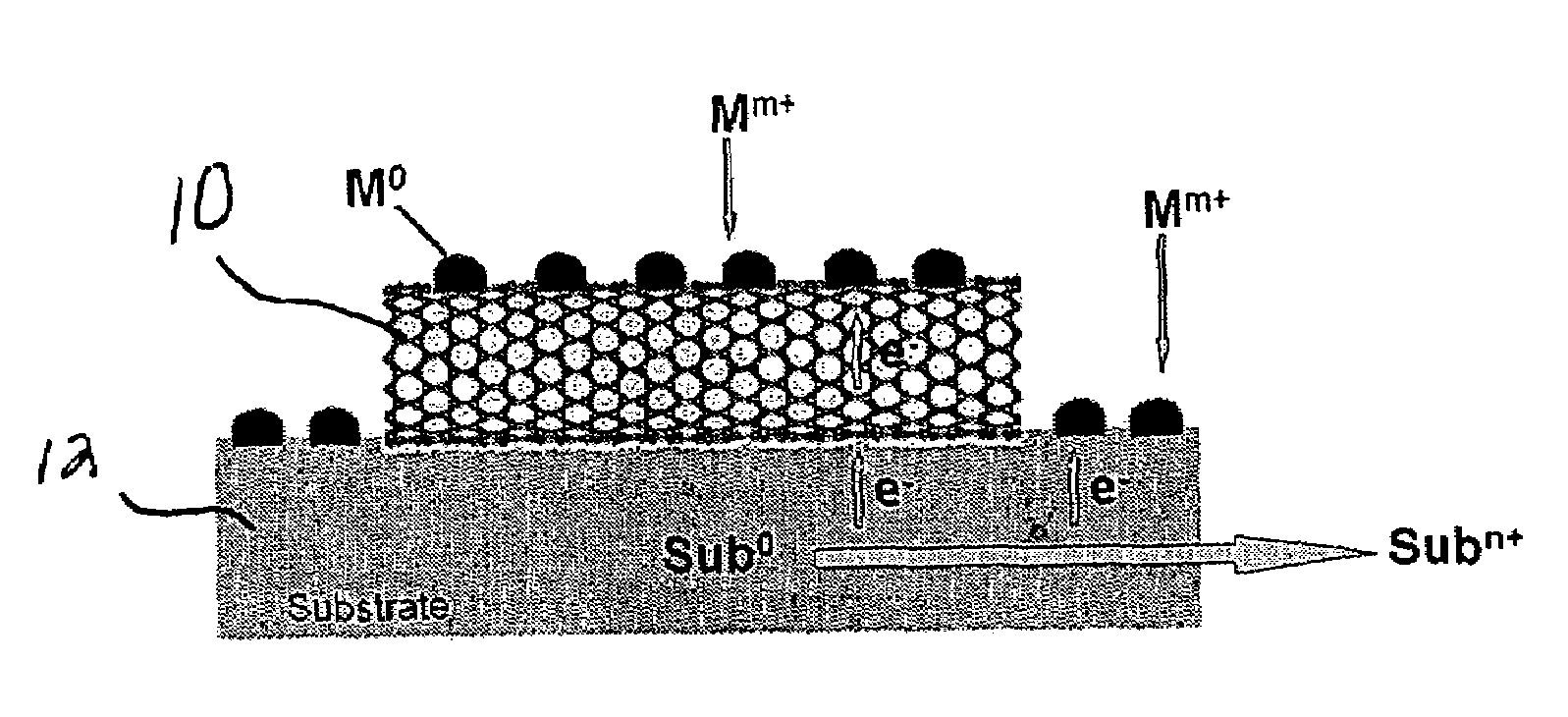
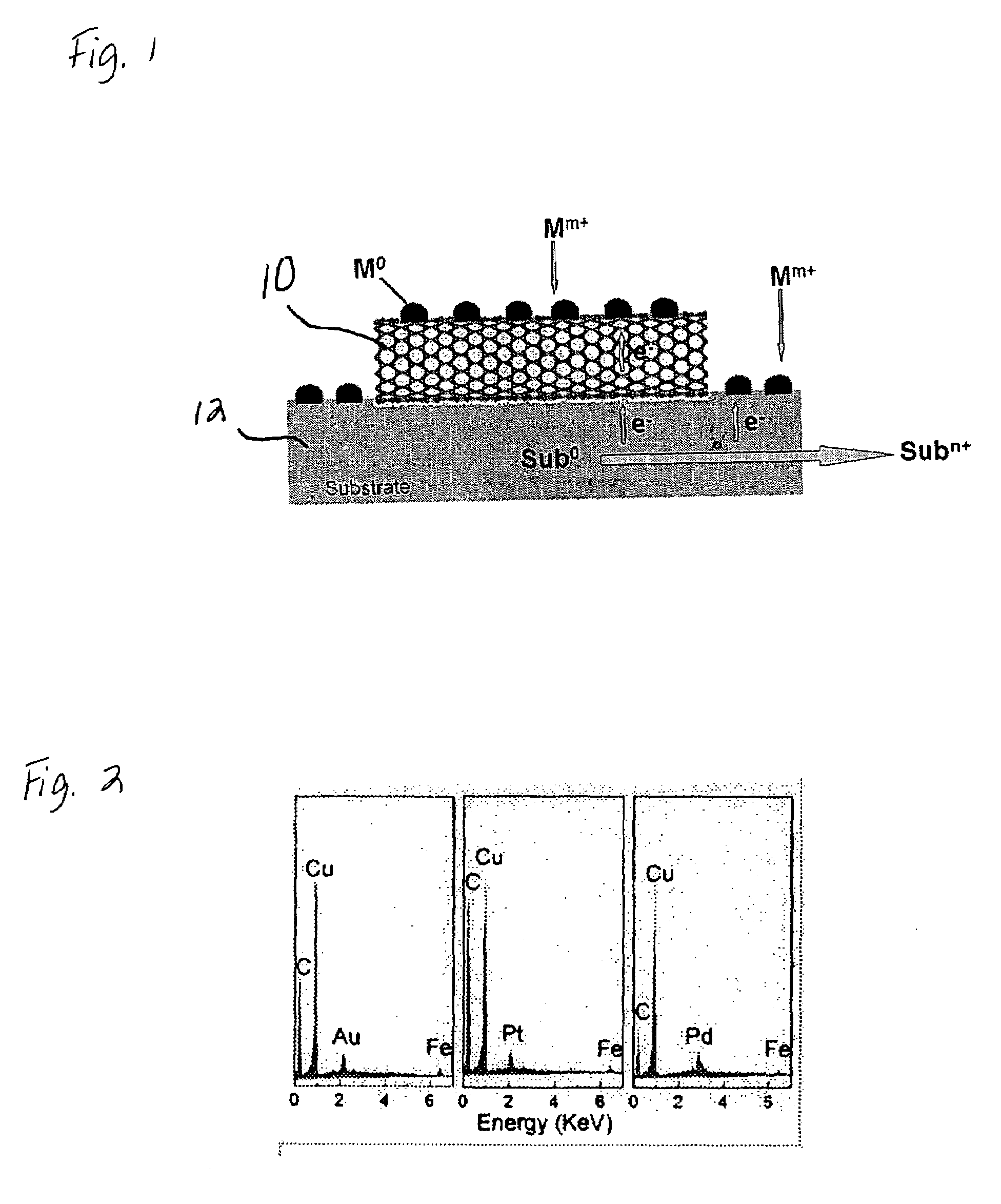
Substrate-enhanced electroless deposition (SEED) of metal nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes
An electroless deposition method of depositing metal nanoparticles onto conductive substrates such as carbon nanotubes is provided. The carbon nanotubes are provided on a support comprising a metal substrate and then immersed in an aqueous solution containing metal ions. The metal substrate metal has a redox potential which is lower than that of the metal ions in solution such that the metal ions are readily reduced into metal nanoparticles on the carbon nanotubes.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Method for applying solid edible particulates to an edible substrate
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Spray methods for coating nuclear fuel rods to add corrosion resistant barrier
InactiveUS20180025794A1Increase entropyPrevent and to mitigate diffusionMolten spray coatingOptical rangefindersHigh entropy alloysZirconium alloy
A method is described herein for coating the substrate of a component for use in a water cooled nuclear reactor to provide a barrier against corrosion. The method includes providing a zirconium alloy substrate; and coating the substrate with particles selected from the group consisting of metal oxides, metal nitrides, FeCrAl, FeCrAlY, and high entropy alloys. Depending on the metal alloy chosen for the coating material, a cold spray or a plasma arc spray process may be employed for depositing various particles onto the substrate. An interlayer of a different material, such as a Mo, Nb, Ta, or W transition metal or a high entropy alloy, may be positioned in between the Zr-alloy substrate and corrosion barrier layer.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP +1
Methods of surface modification for improving electrophoretic display performance
InactiveUS6870662B2Improve surface propertiesIncrease contrastSludge treatmentStatic indicating devicesImaging qualityDisplay device
The present invention is directed to methods for improving the performance of an electrophoretic display by modifying the display cell surface. More specifically, the methods are directed to modification of the microcup surface after the microcups are released from the mold. The microcups which have undergone any of the treatment methods of the invention show significant improvement in their surface properties, such as chemical functionality, surface roughness, surface tension, morphology, surface charge, surface reflectivity, surface conductivity and optical properties, particularly optical density in the visible light region. An electrophoretic display formed from the treated microcups has many advantages. For example, the display shows a higher contrast ratio, lower electro-optic response time, lower driving voltage, longer shelf life, higher imageincreasing bistability and higher threshold voltage. In addition, it exhibits an improved image quality by reducing undesirable scum formation or irreversible particle deposition on the microcup surface.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for making fused silica
ActiveUS20070130995A1High purityHigh OH concentration uniformityGlass furnace apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansBrickDeposition process
Disclosed are process and apparatus for making high purity fused silica glass materials. The process involves depositing soot particles onto an essentially planar deposition supporting surface and modulation of motion of the soot-generating device relative to the deposition supporting surface to result in a low local soot density variation. The apparatus is designed to implement the planar deposition process. The invention makes it possible to produce fused silica glass without the use of potentially contaminating refractory bricks.
Owner:CORNING INC
Apparatus and process for producing electrophoretic device
A system (apparatus and process) for producing an electrophoretic (display) device is provided for allowing production of such a device wherein charged phoretic particles in the dispersion liquid are easily and evenly distributed to respective cells (pixels) between two substrates of the device even in the case of a very small gap between the two substrates or the case of using a flexible substrate. The system includes a storage for a dispersion liquid containing the charged phoretic particles dispersed therein, a stirrer for stirring the dispersion liquid, a substrate-holder for holding the substrate in the dispersion liquid, and a voltage source for applying a voltage to the electrodes formed on the substrate thereby depositing the charged phoretic particles on the electrodes.
Owner:CANON KK
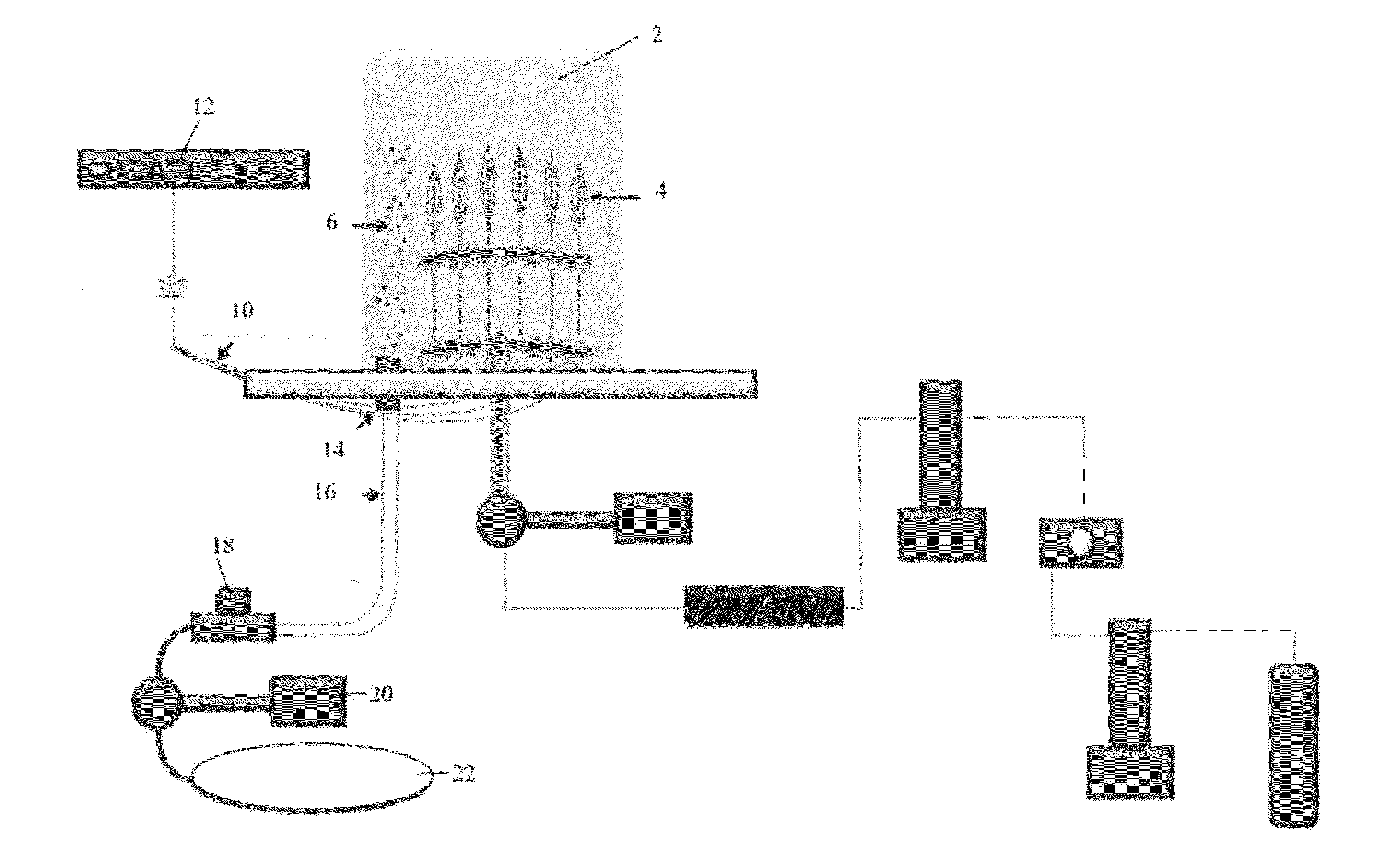
Aerosol Collection Apparatus and Methods
InactiveUS20130042893A1Large concentration factorImprove robustnessSamplingServomotor componentsAcoustic energyTransducer
The lifetime of aerosol monitoring, concentration and collection equipment is extended by acoustic cleaning of accreted particle deposits from internal surfaces where fouling occurs by application of acoustic energy to the particle accretion surface, optionally in combination with a liquid wash or sampling volume. In one application, acoustic cleaning or sampling of particle deposits for analysis is triggered by a signal indicating changes in gas flow associated with particle loading. In another application, electro-acoustic transducers may be used to prevent particle buildup without interruption of particle monitoring.
Owner:ENERTECHNIX
Hydrophobic surfaces with nanoparticles
InactiveUS7998554B2Fine surfaceSimple methodProjectorsRecord information storageNanoparticleWater contact
Hydrophobic surfaces with water contact angles greater than 120 degrees are created by the deposition of nano-particles. A process for the synthesis of suitable nano-particles is described as well as a process for the deposition of the particles.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Aerosol into liquid collector for depositing particles from a large volume of gas into a small volume of liquid
InactiveUS20060110818A1Fast processShort timeOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsParticle flowProduct gas
An aerosol-into-liquid collector (ALC) for collecting gas-borne particles from a large volume of gas such as air into a small volume of liquid is described. The ALC uses a linear quadrupole to concentrate particles flowing in a gas and to help direct these concentrated particles toward a small volume of collection liquid so that these particles tend to combine with a small volume of collection liquid that can then be drawn from the ACL for further analysis. The particles in the gas are typically given a charge that is opposite to that of the charge imparted to the volume of collection liquid so that electrostatic forces help draw particles from the flowing gas into the small volume of liquid. The linear quadrupole focuses toward it axis particles that have the charge, mass and mobility to be stable in the linear quadrupole.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
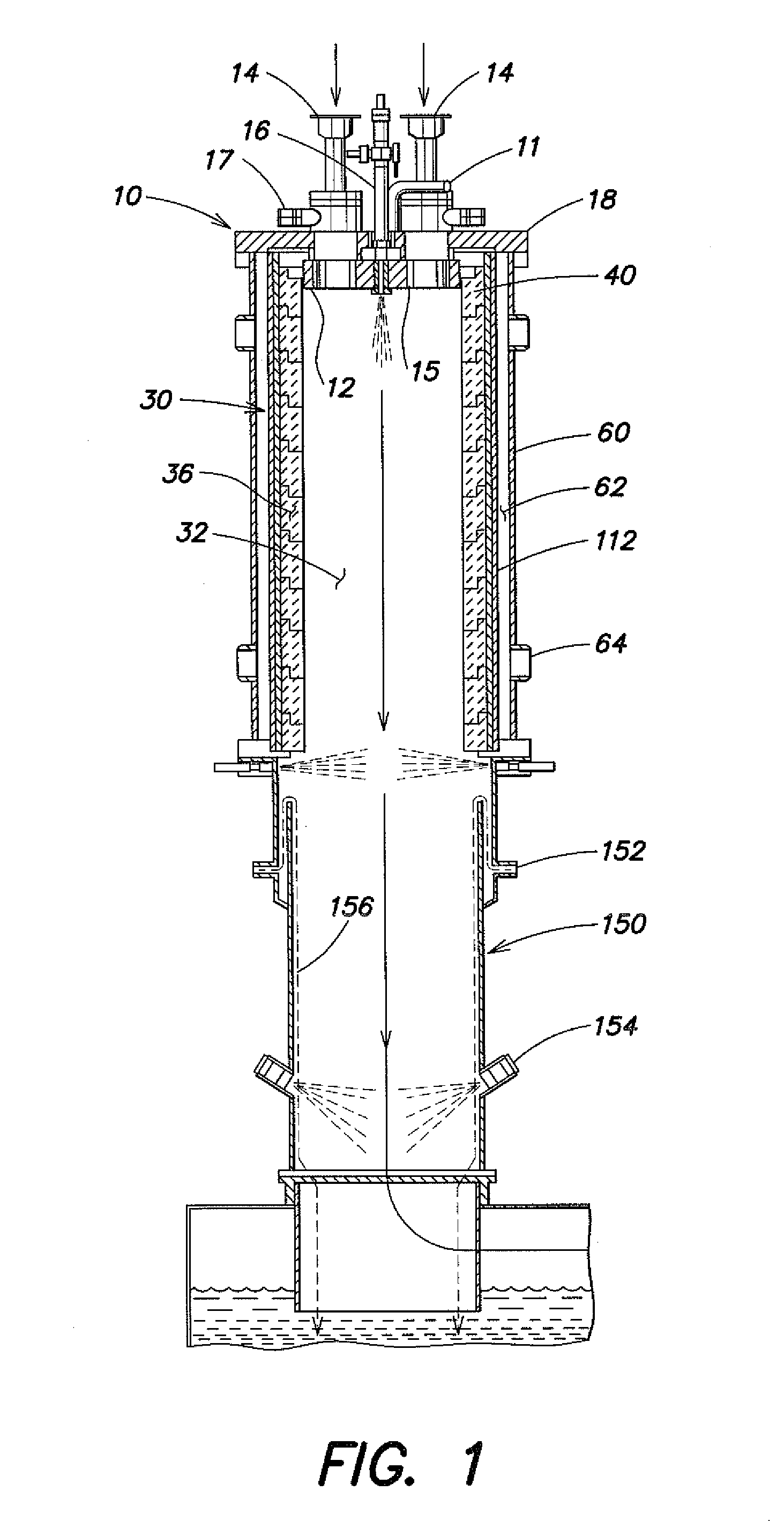
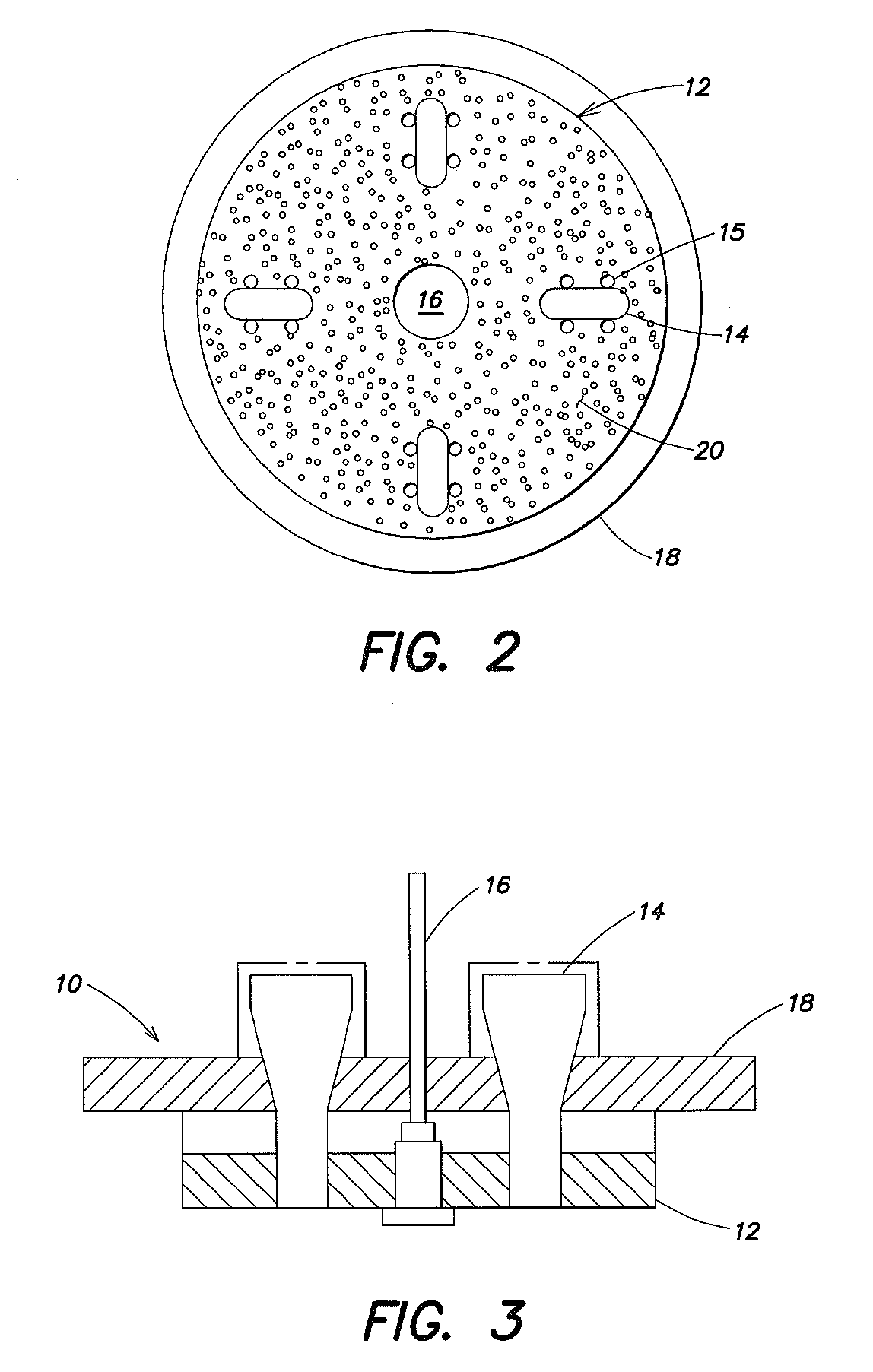
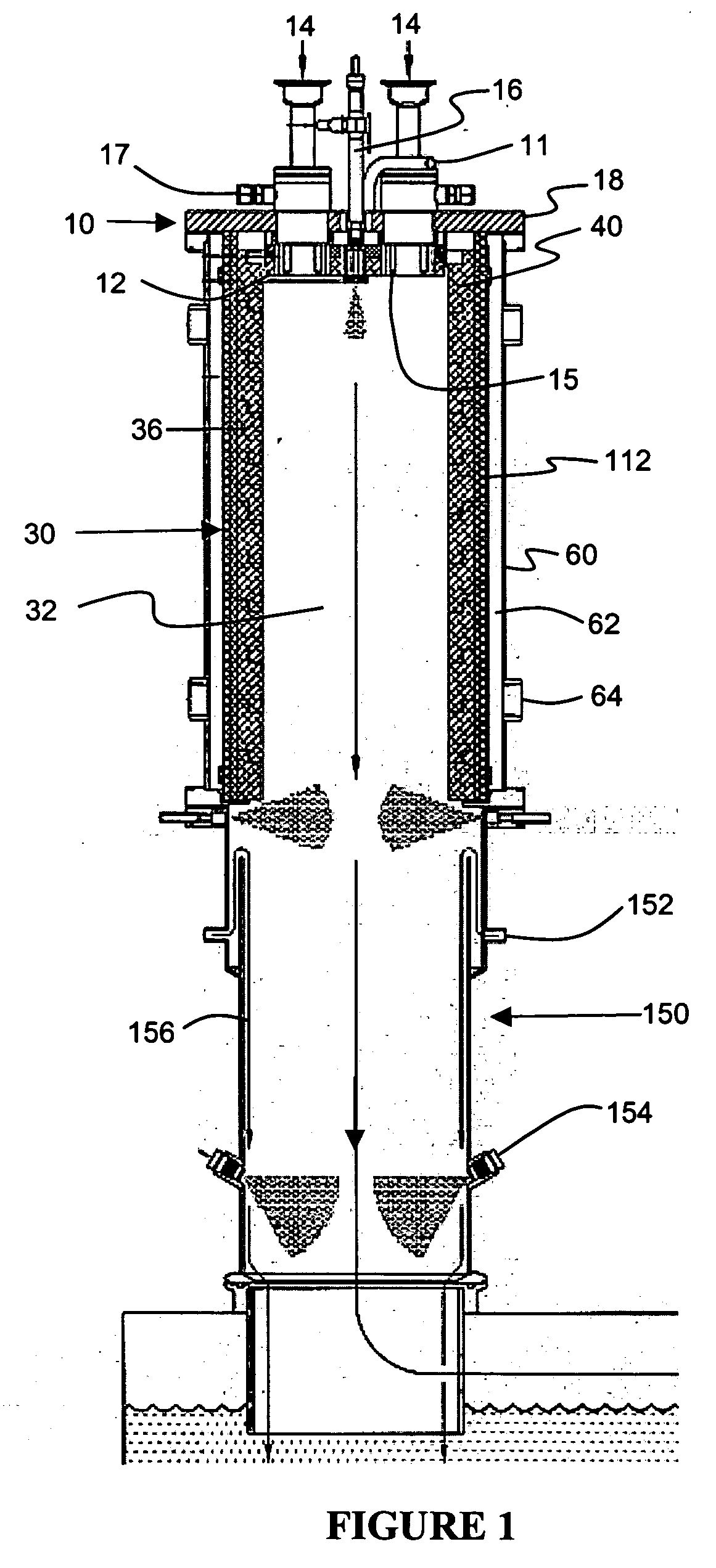
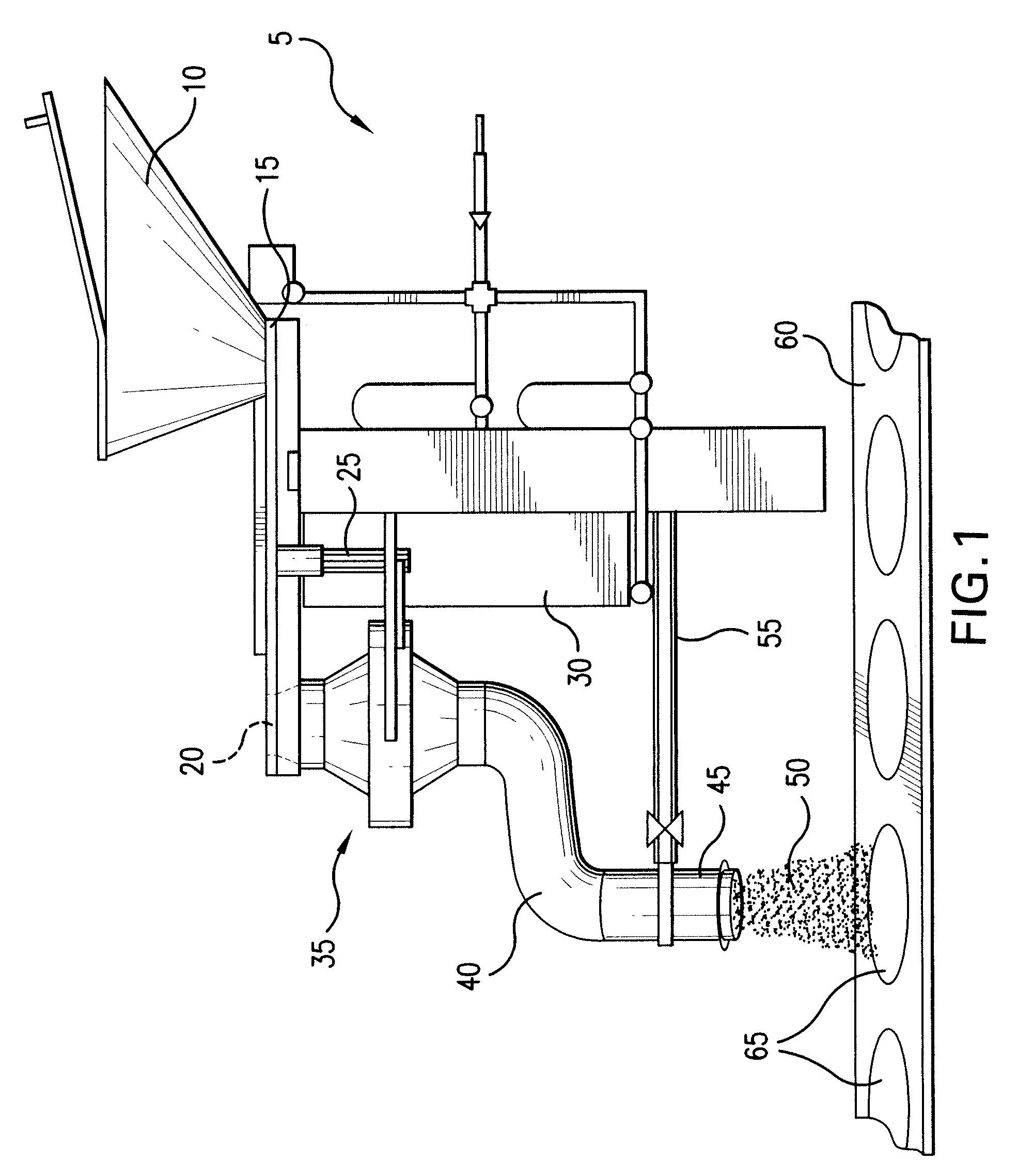
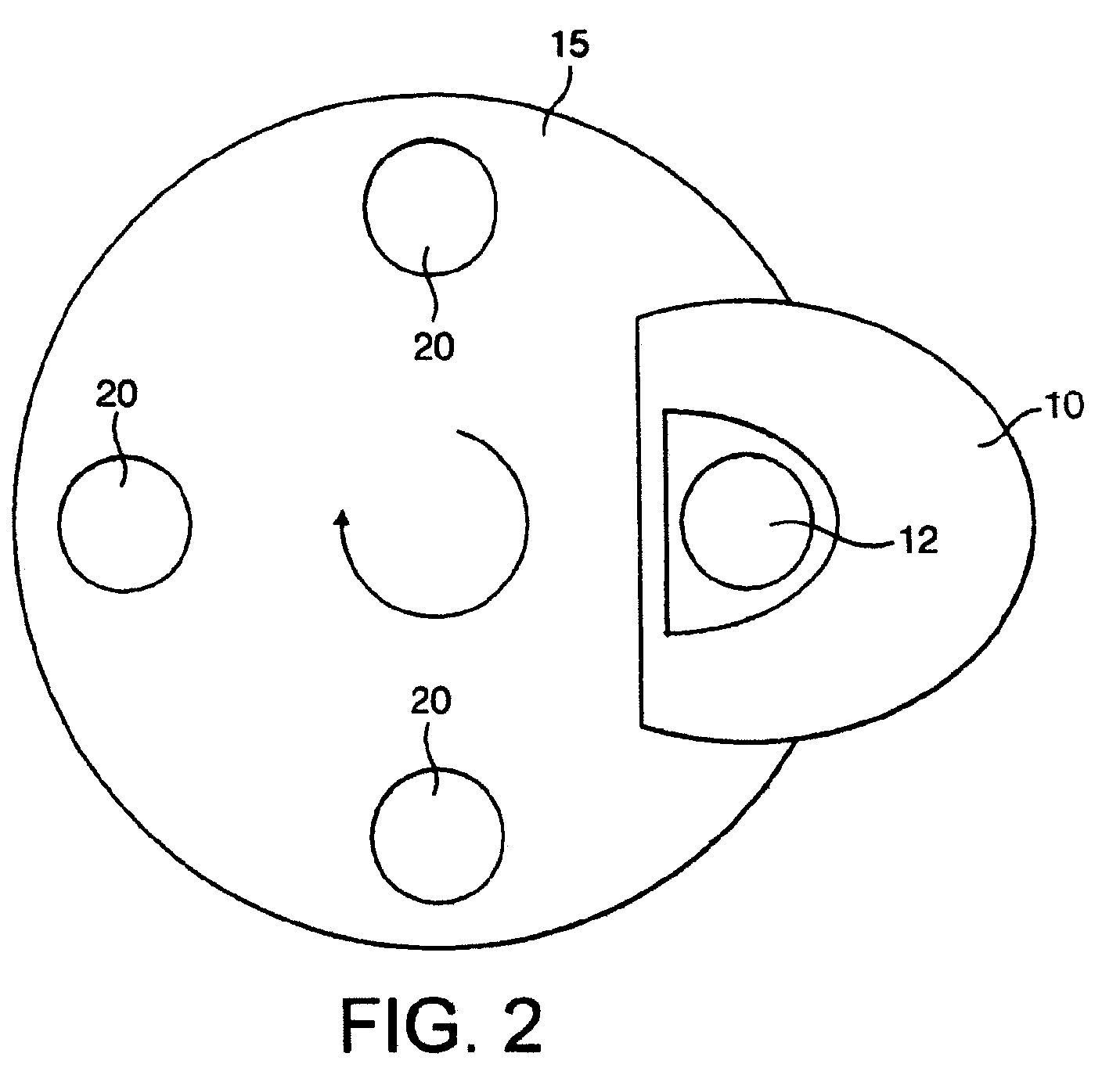
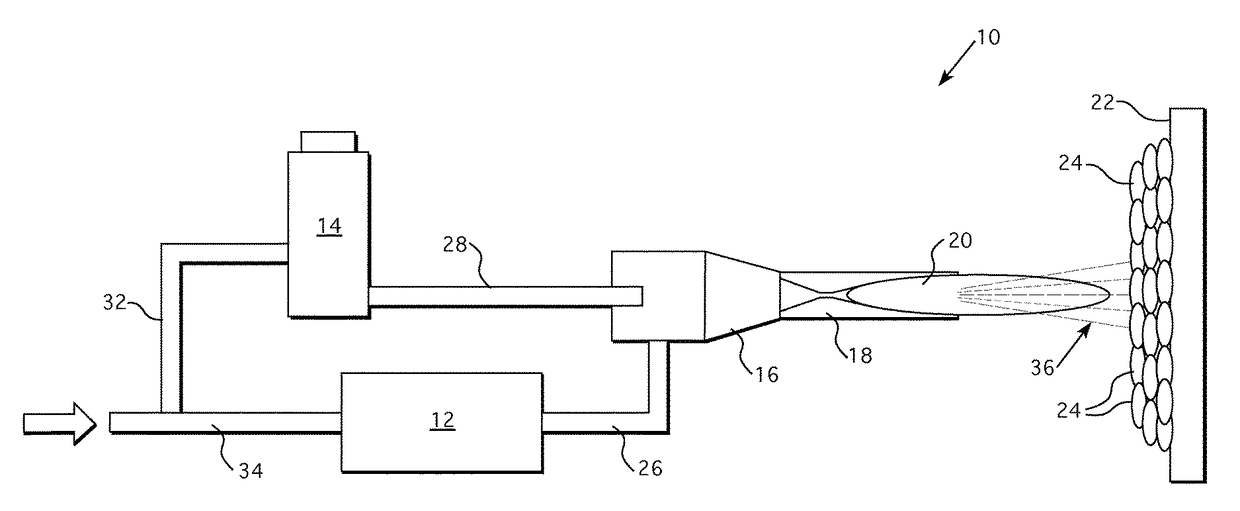
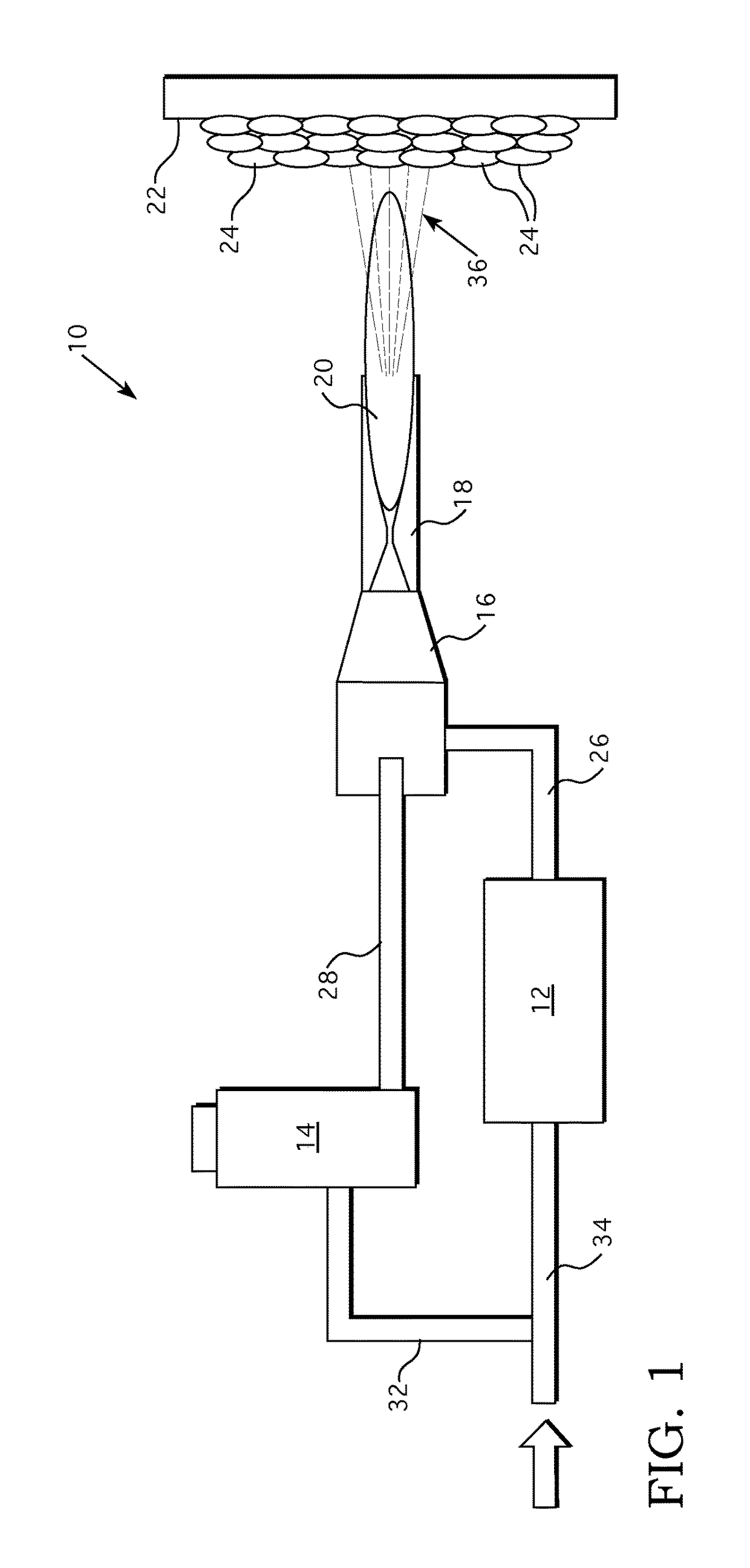
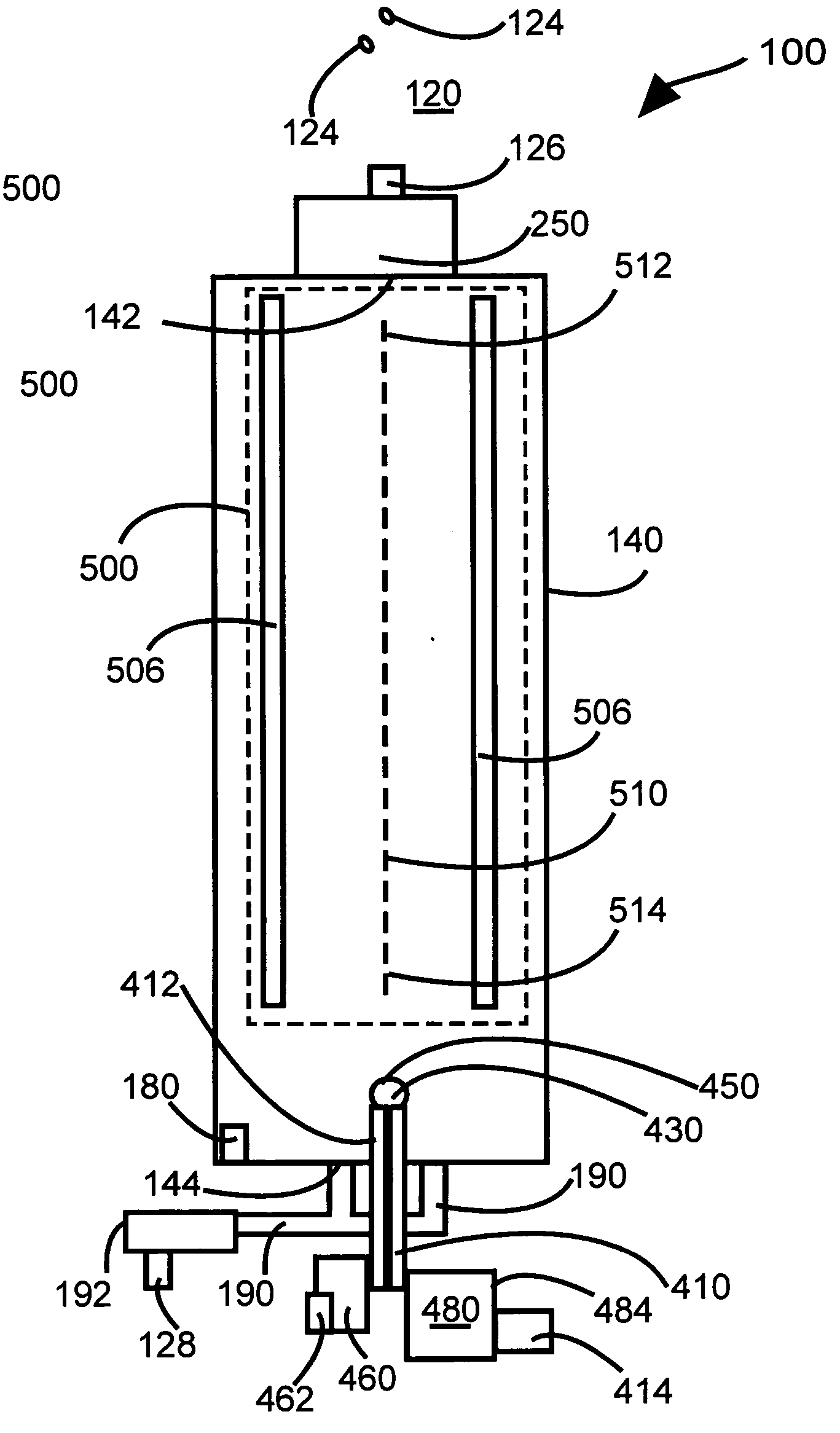
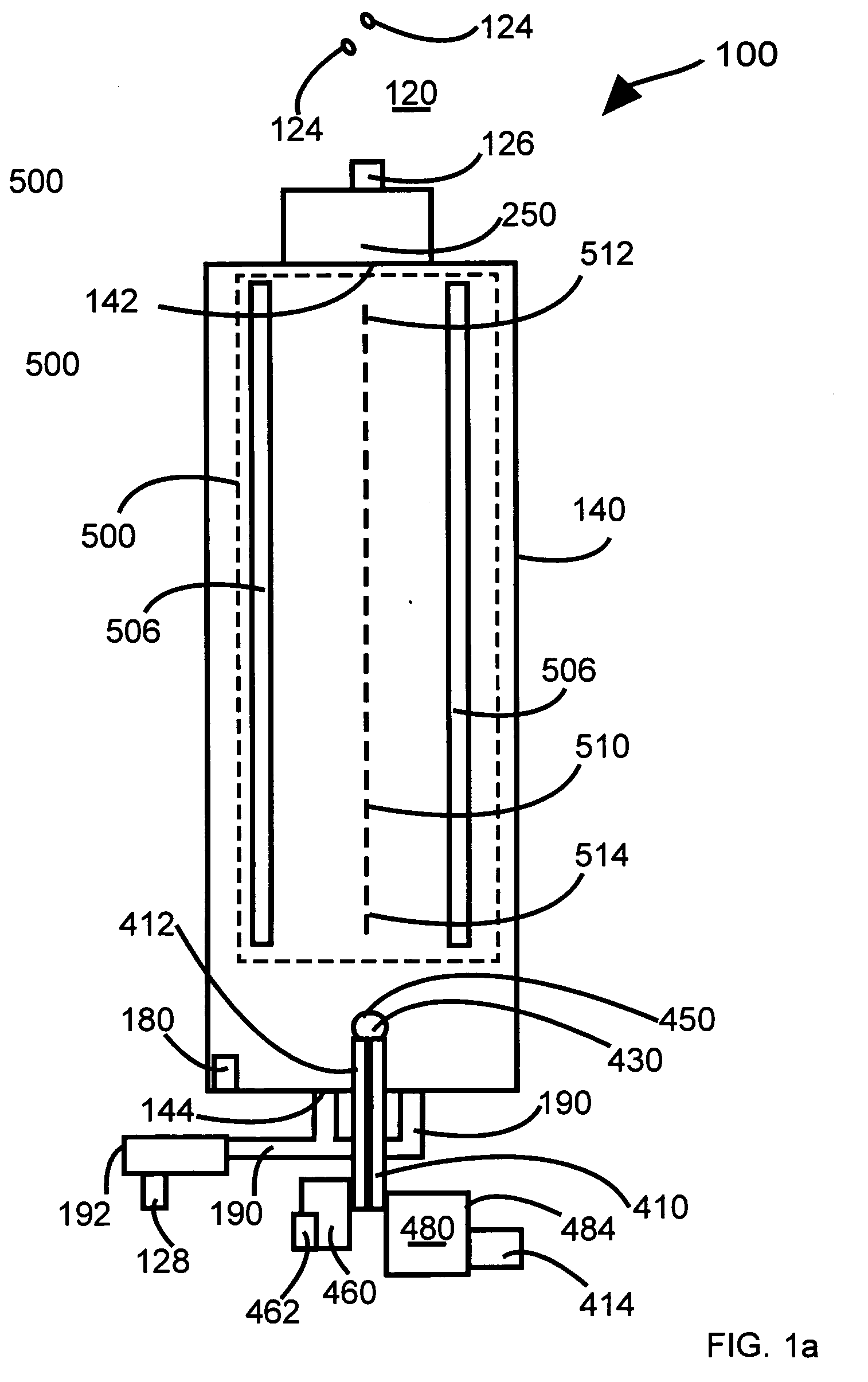
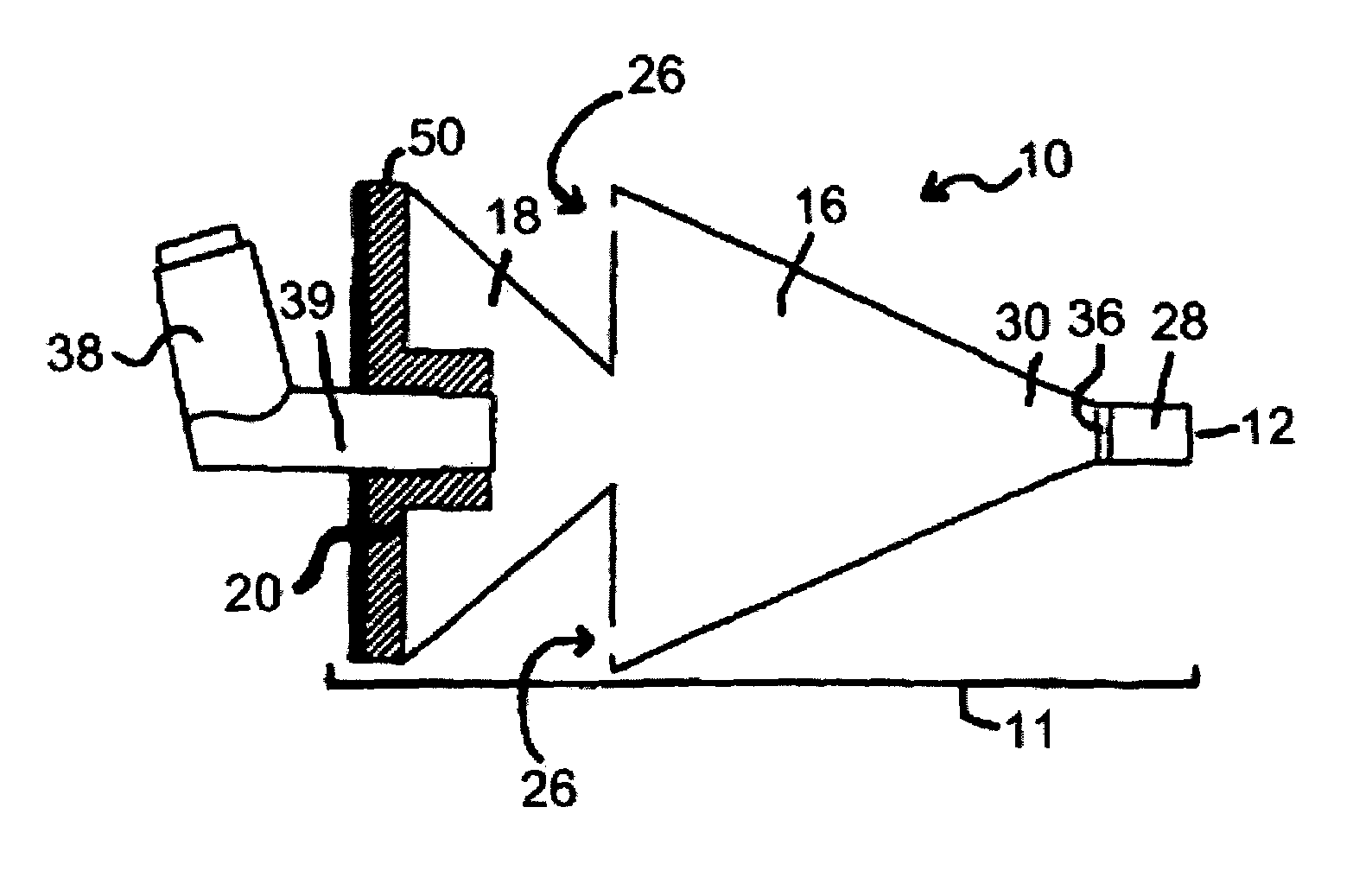
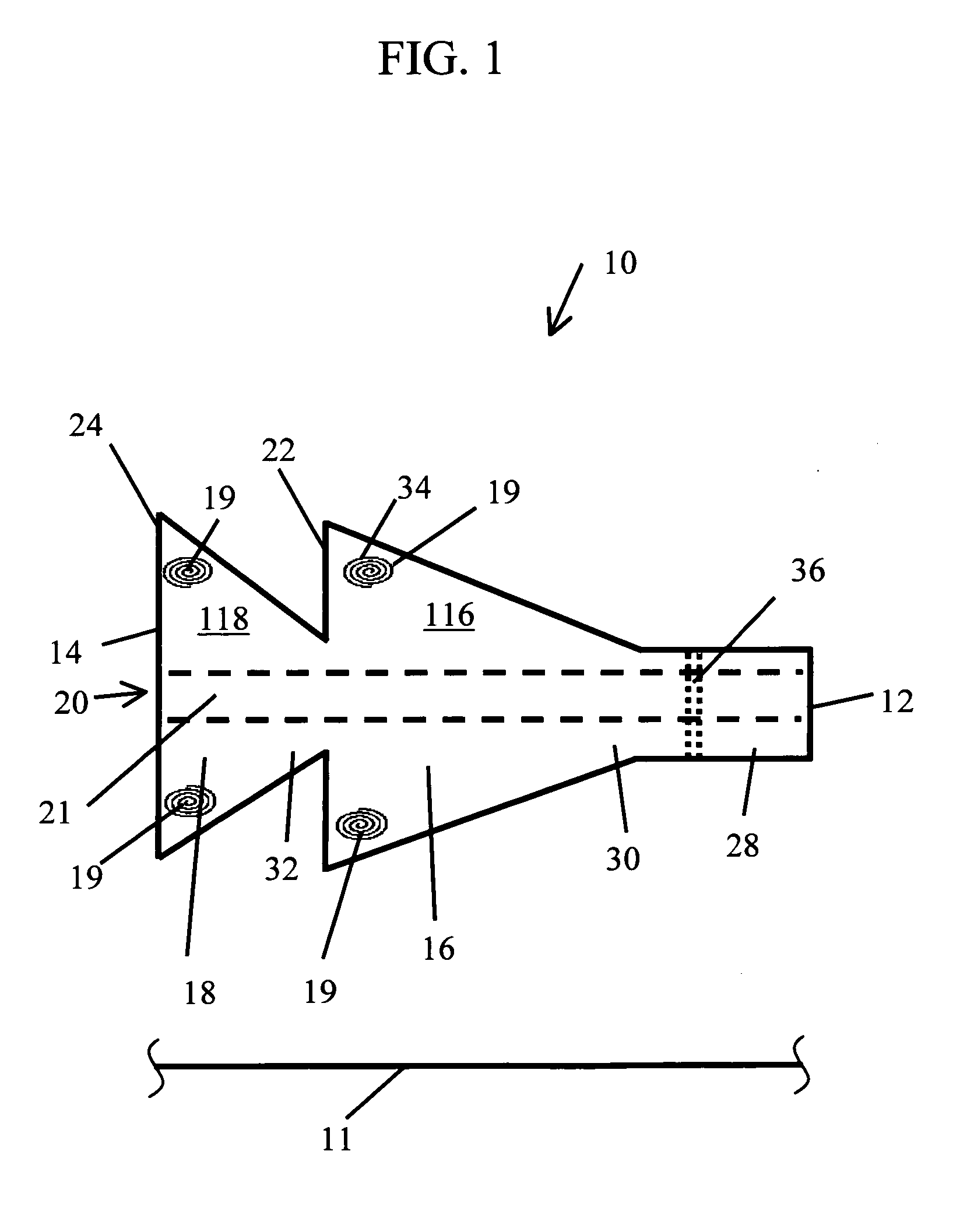
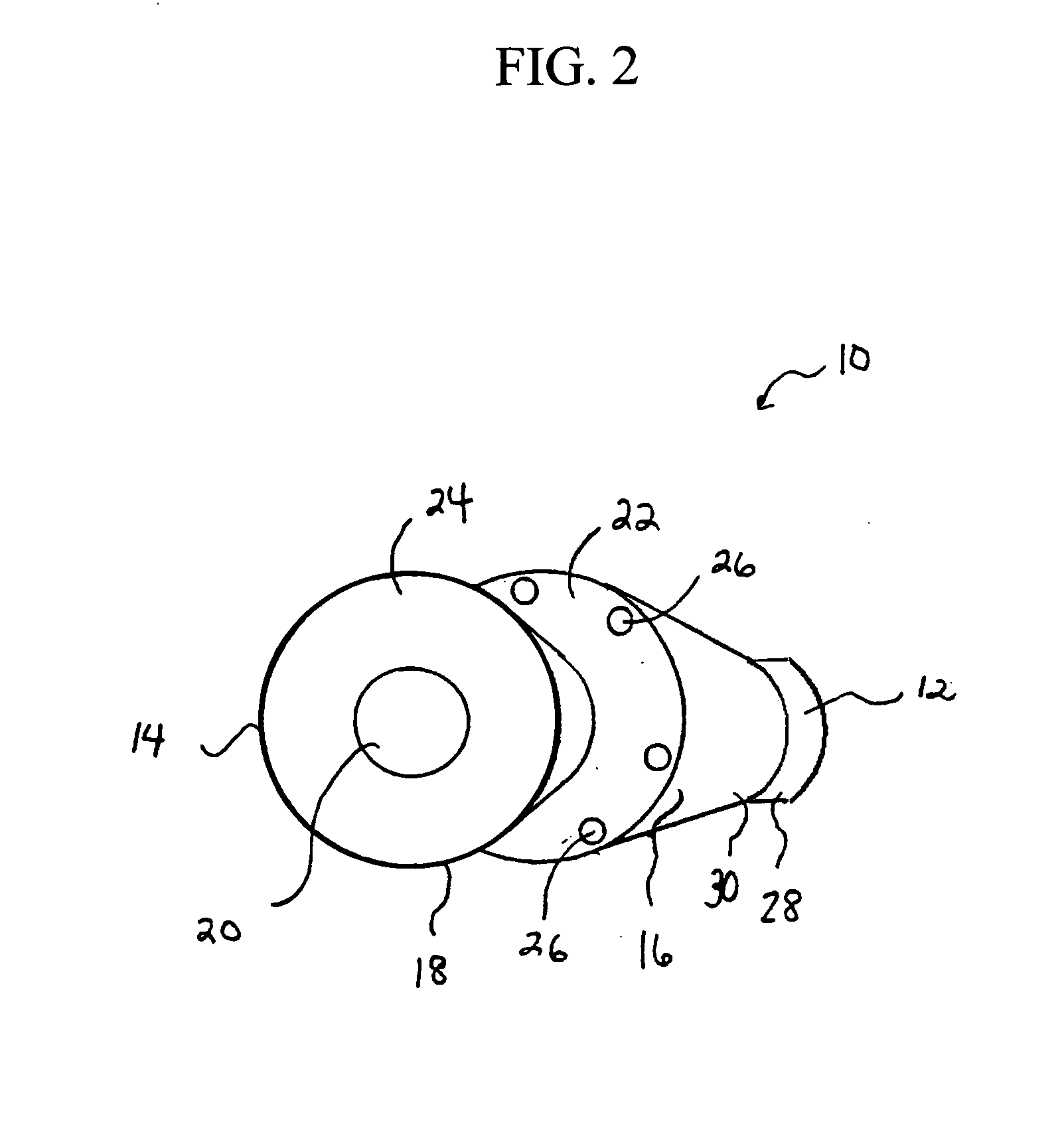
Spacer for delivery of medications from an inhaler to children and breathing impaired patients
ActiveUS7107987B2Minimize formationIncrease percentageRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsProximateCatheter
A spacer for delivering a medication spray from an inhaler includes a first conical body joined to a second conical body, forming a continuous spray conduit through first and second internal chambers of the respective first and second conical bodies. A mouthpiece is formed in the proximal end of the first conical body. A spray inlet for attachment to the inhaler is formed at the distal end of the second conical body. A plurality of air inlets are placed downstream of the medication inlet proximate to, or in, the large diameter distal end surface of the first conical body. Recirculation zones are created in the first and second chambers, to force the medication spray into a central airflow path through the spray conduit, minimizing particle deposition by contract with the walls of the spacer.
Owner:CFD RES CORP
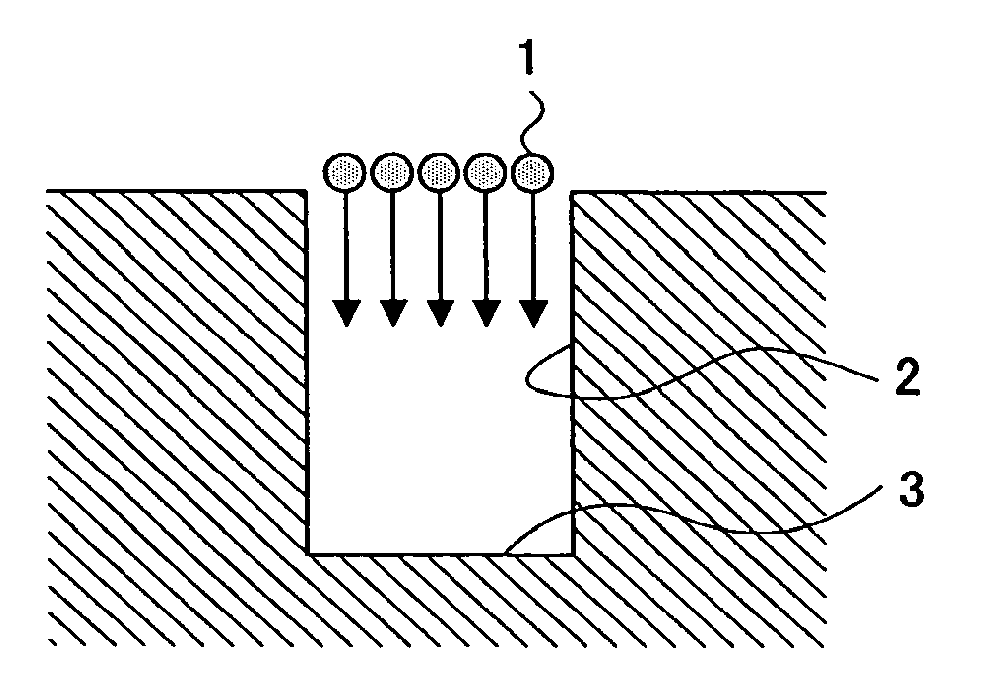
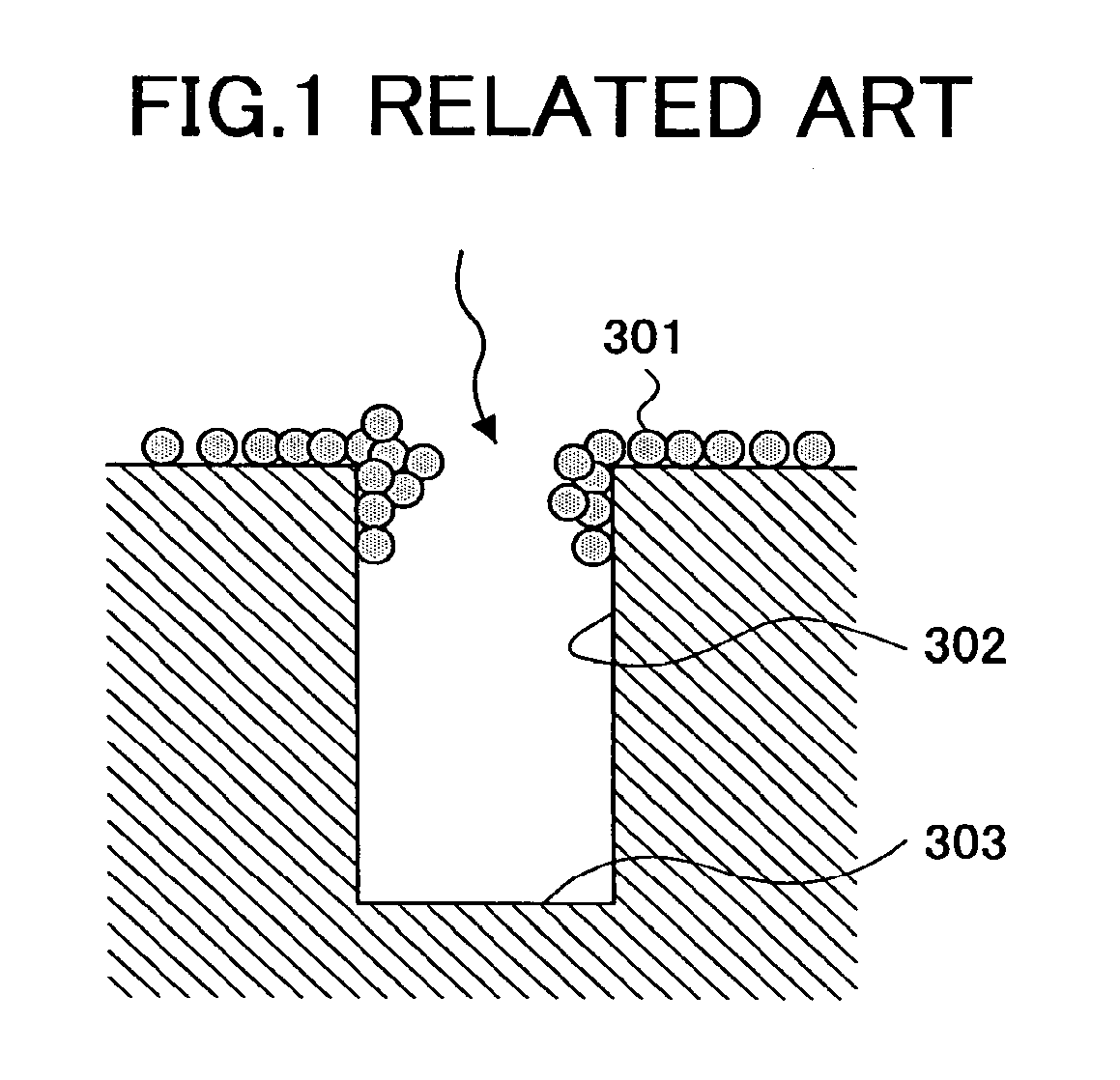
Deposition method and a deposition apparatus of fine particles, a forming method and a forming apparatus of carbon nanotubes, and a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method of the same
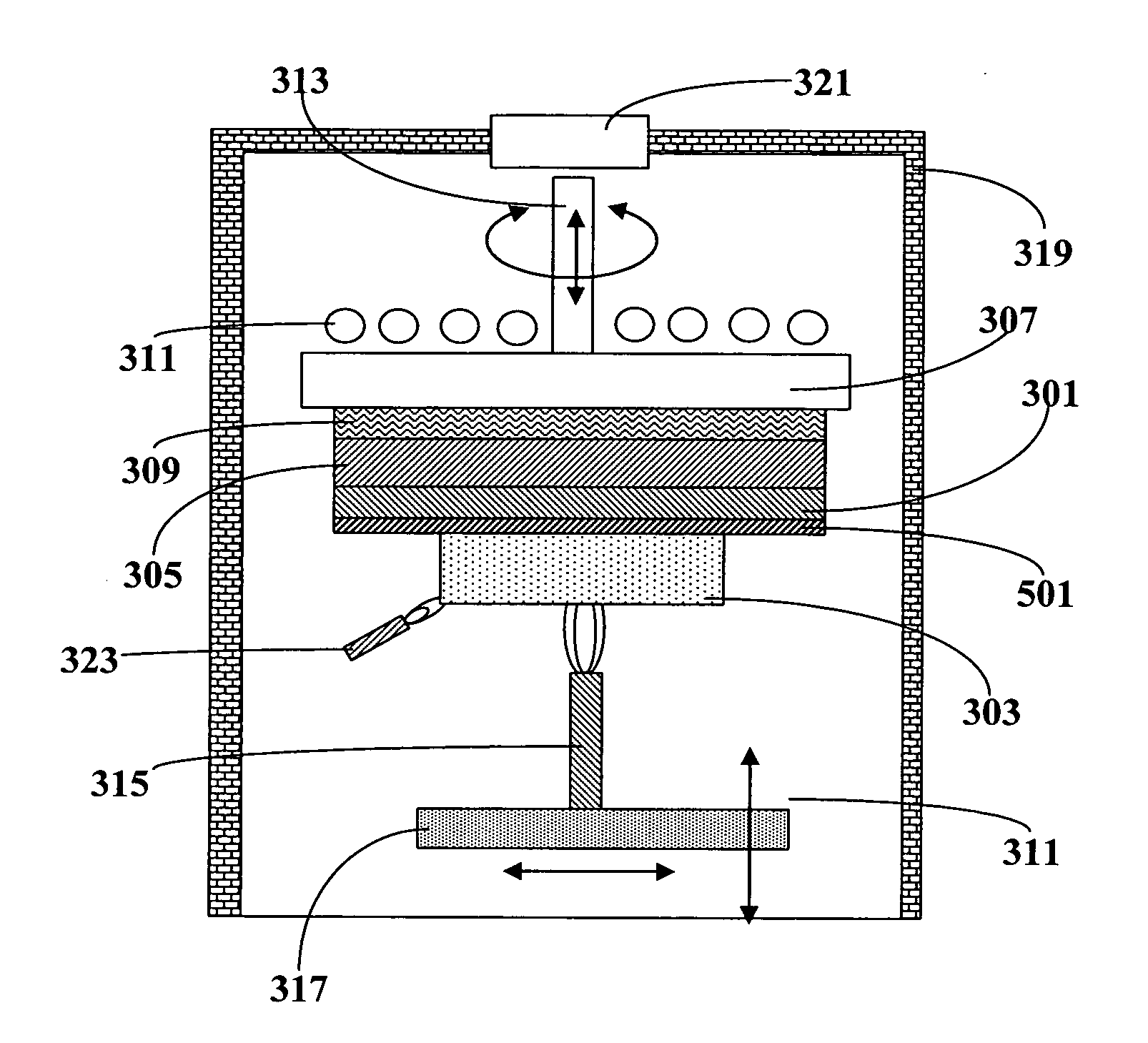
A deposition method of fine particles, includes the steps of irradiating a fine particle beam formed by size-classified fine particles to an irradiated subject under a vacuum state, and depositing the fine particles on a bottom part of a groove structure formed at the irradiated subject.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Methods to increase recovery of treatment fluid following stimulation of a subterranean formation comprising in situ fluorocarbon coated particles
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
System and method for the concentrated collection of airborne particles
ActiveUS20140060155A1Simplifying chain of custodyReducing data handlingWithdrawing sample devicesSolid surfaceAnalytical technique
A system and a method is described herein for the collection of small particles in a concentrated manner, whereby particles are deposited onto a solid surface or collected into a volume of liquid. The collected samples readily interface to any of a number of different elemental, chemical, or biological or other analysis techniques.
Owner:AEROSOL DYNAMICS INC +1
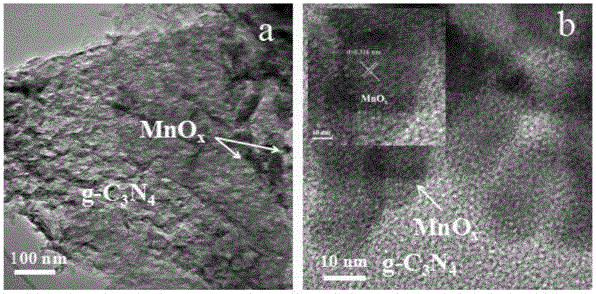
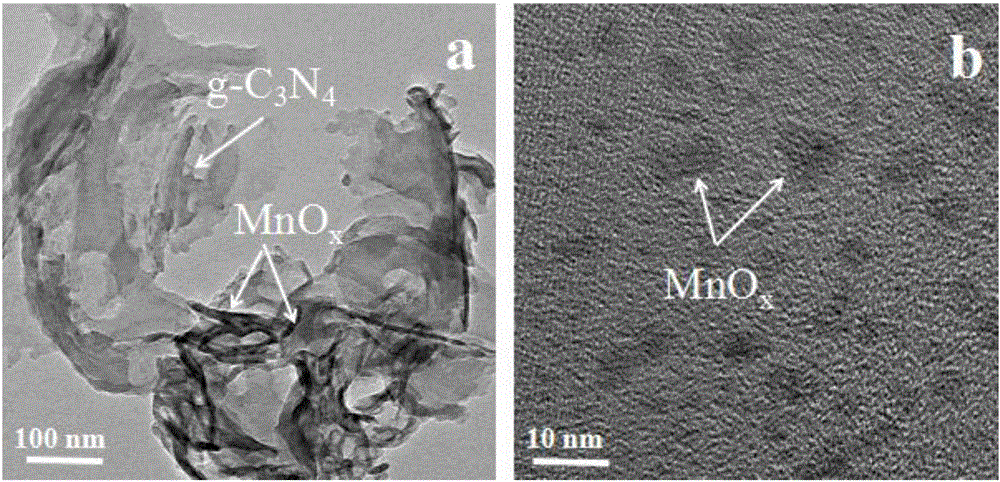
Manganese oxide-graphite phase carbon nitride composite photocatalytic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105817255AImprove thermal stabilityGood chemical stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsEnergy inputManganese oxideElectrochemistry
The invention relates to a manganese oxide-graphite phase carbon nitride composite photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof. The manganese oxide-graphite phase carbon nitride composite photocatalytic material is prepared by depositing manganese oxide nanoparticles on the surface of layered graphite phase carbon nitride, and the manganese element loading capacity of manganese oxide in the composite photocatalytic material is 0.3-1.2 mol%; manganese dioxide or trimanganese tetroxide or dimanganese trioxide or a mixed oxide of manganese dioxide, trimanganese tetroxide and dimanganese trioxide is adopted as manganese oxide. Manganese oxide in the composite photocatalytic material is uniformly loaded on graphite phase carbon nitride, the loading capacity is controllable, the good catalytic capacity is achieved, a manganese oxide cocatalyst is closely combined with graphite phase carbon nitride, therefore, the defects that a single photocatalyst is high in photoproduced electron hole pair composite ratio and low in photocatalytic efficiency are effectively overcome, the solar utilization efficiency is greatly improved, and the excellent catalytic activity is achieved when the composite photocatalytic material is used for photocatalytic hydrogen production. The composite photocatalytic material has the wide application prospect in the fields of photocatalysis, electrochemistry, energy, environments and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Plating structure and method for manufacturing electric material
InactiveUS20110012497A1Increase resistanceReduce contact resistanceIncadescent screens/filtersElectric discharge tubesTinningSilver plate
There is provided a plating structure obtained by heat-treating a silver-plated structure obtained by forming a tin-plated layer, an indium-plated layer, or a zinc-plated layer, having a thickness of 0.001 to 0.1 μm, on a surface of the silver-plated layer formed on a surface of a plating base. There is also provided a coating method for obtaining the plating structure which comprises the step of melting a particle deposit spottedly deposited at 2×10−6 to 8×10−6 g / cm2 such that the spot-deposited particles have gaps therebetween as viewed above and the particles each having an average diameter of 20 to 80 nm do not pile up in a direction perpendicular to the surface of the silver layer to obtain a film.
Owner:KYOWA ELECTRIC WIRE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com