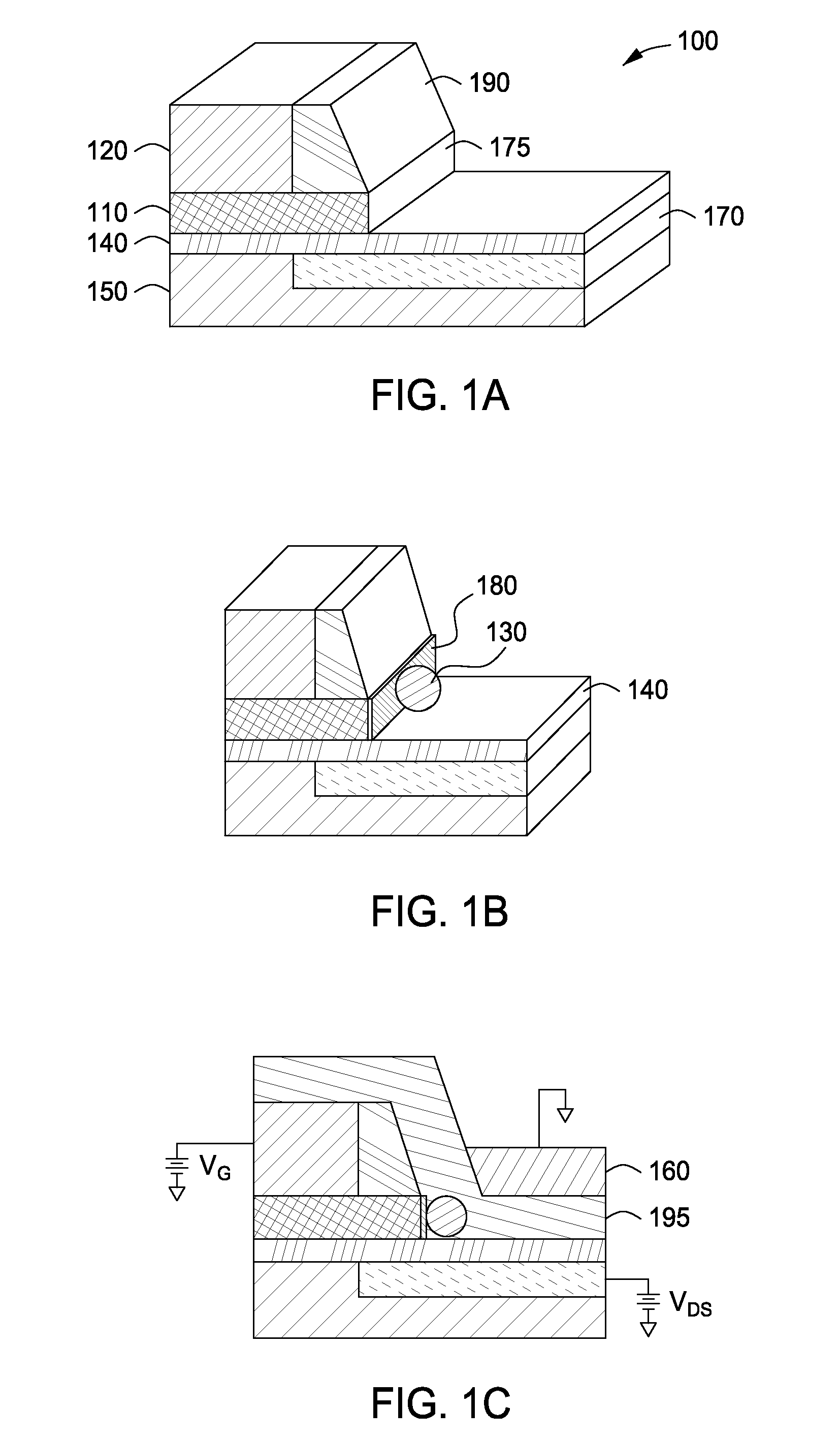
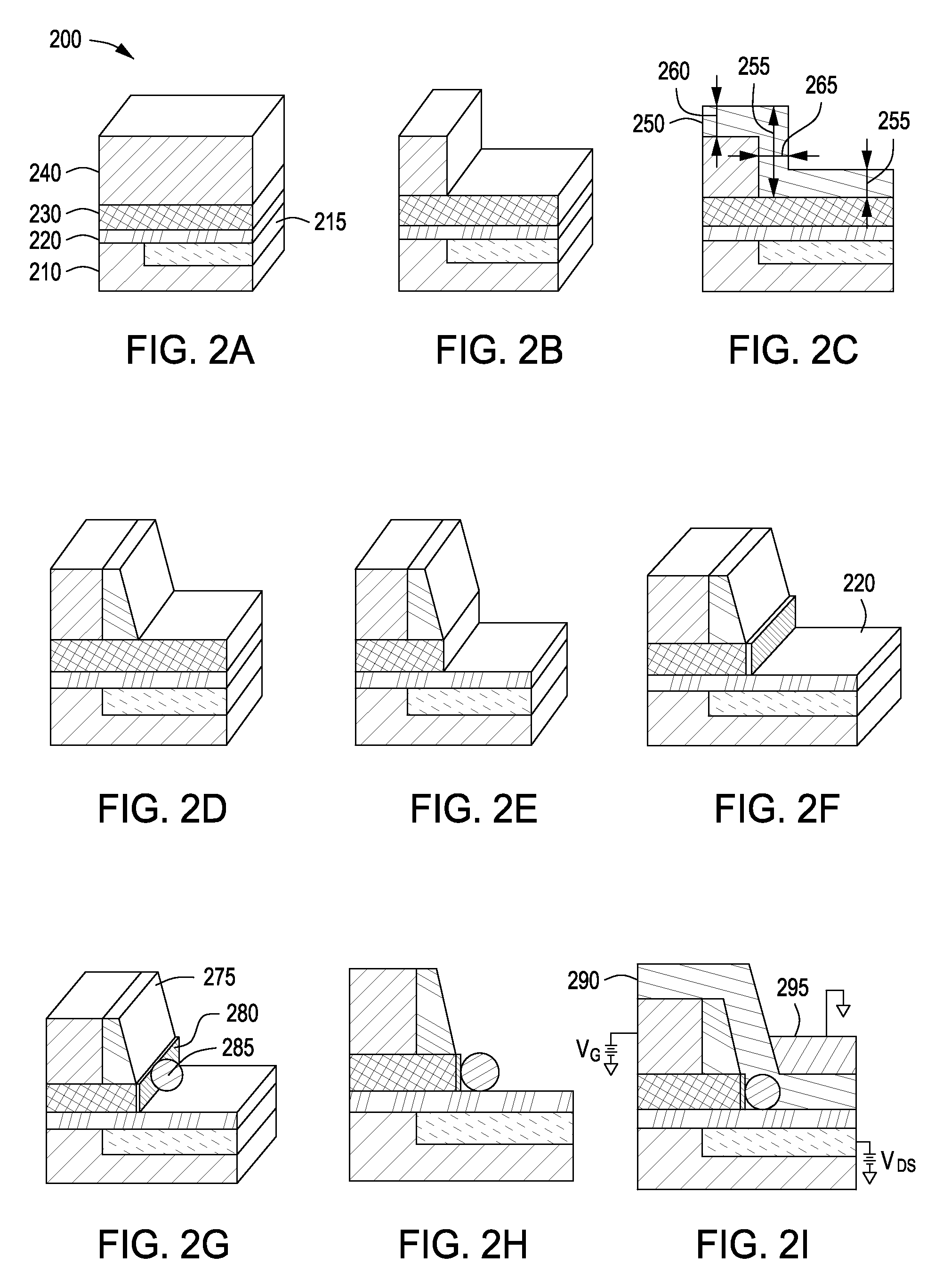
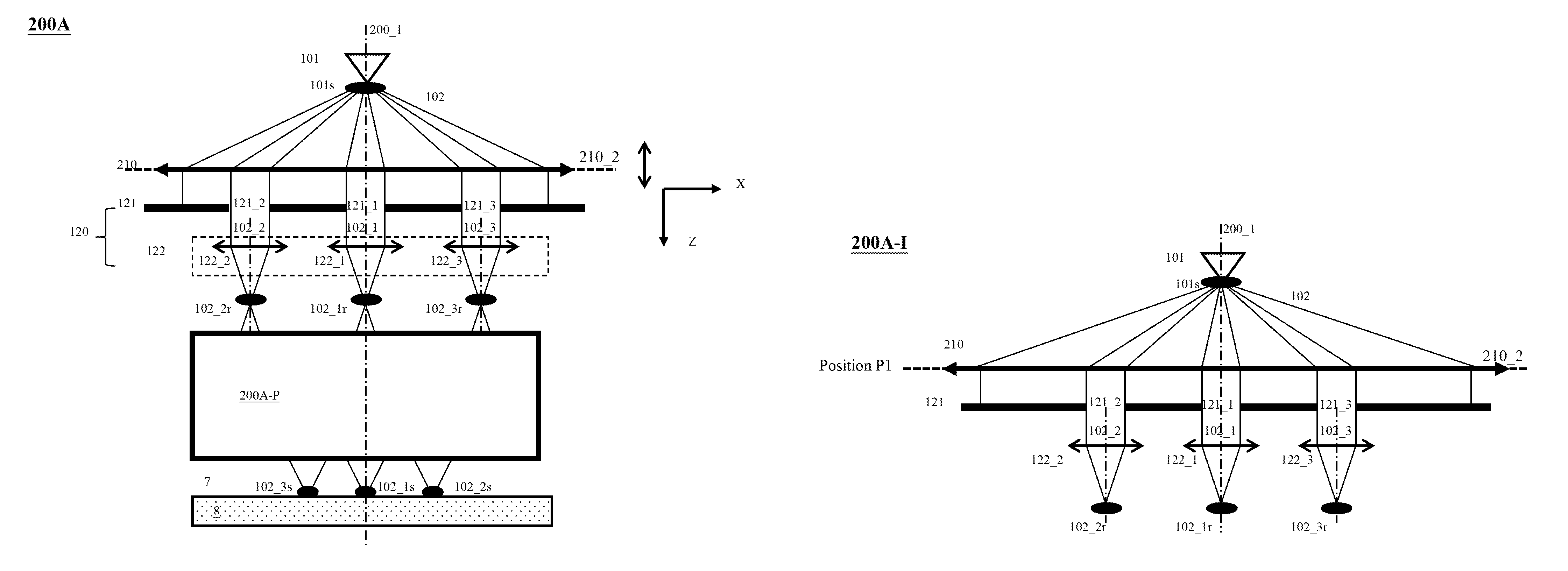
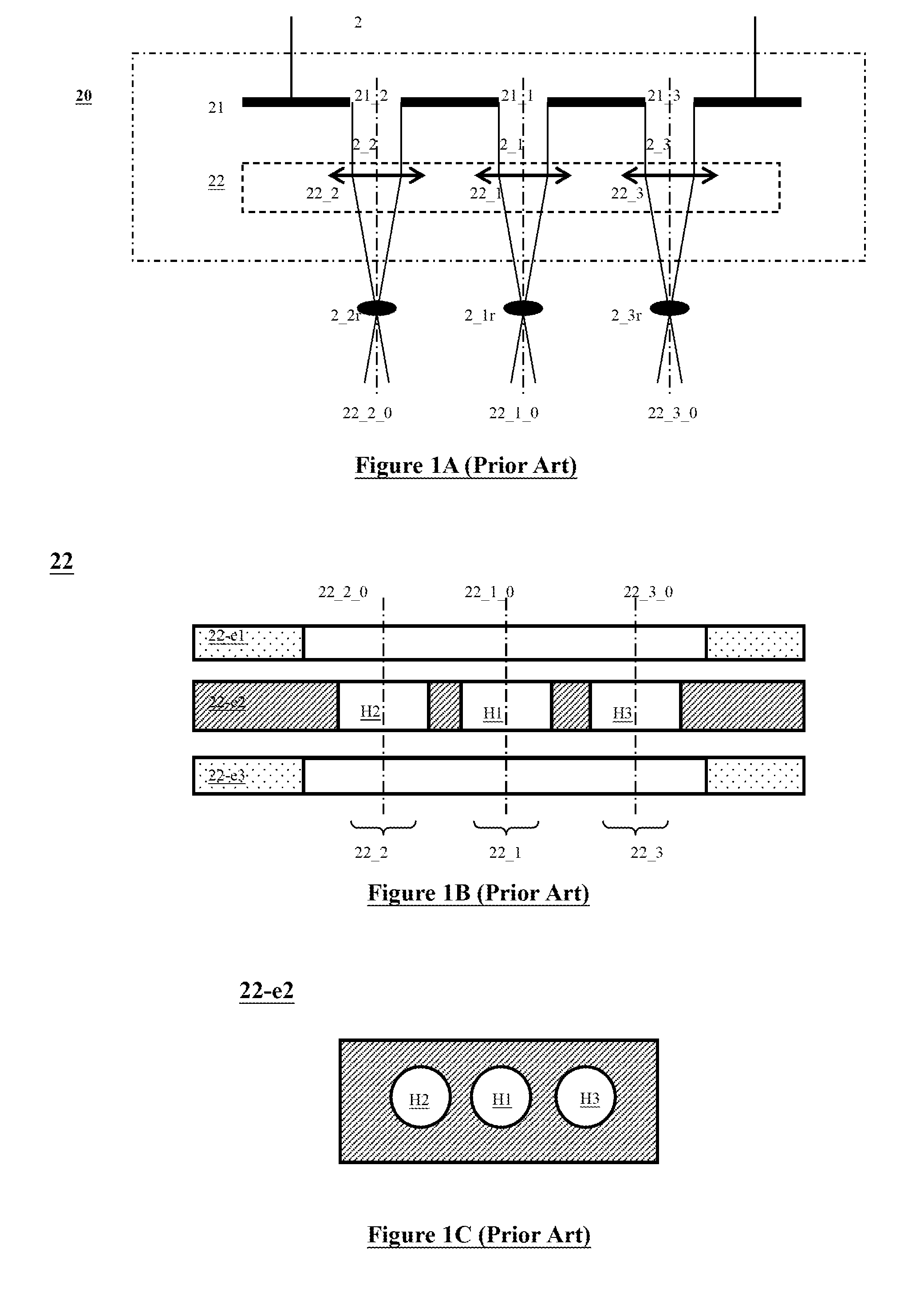
Patents
Literature
459 results about "Single electron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
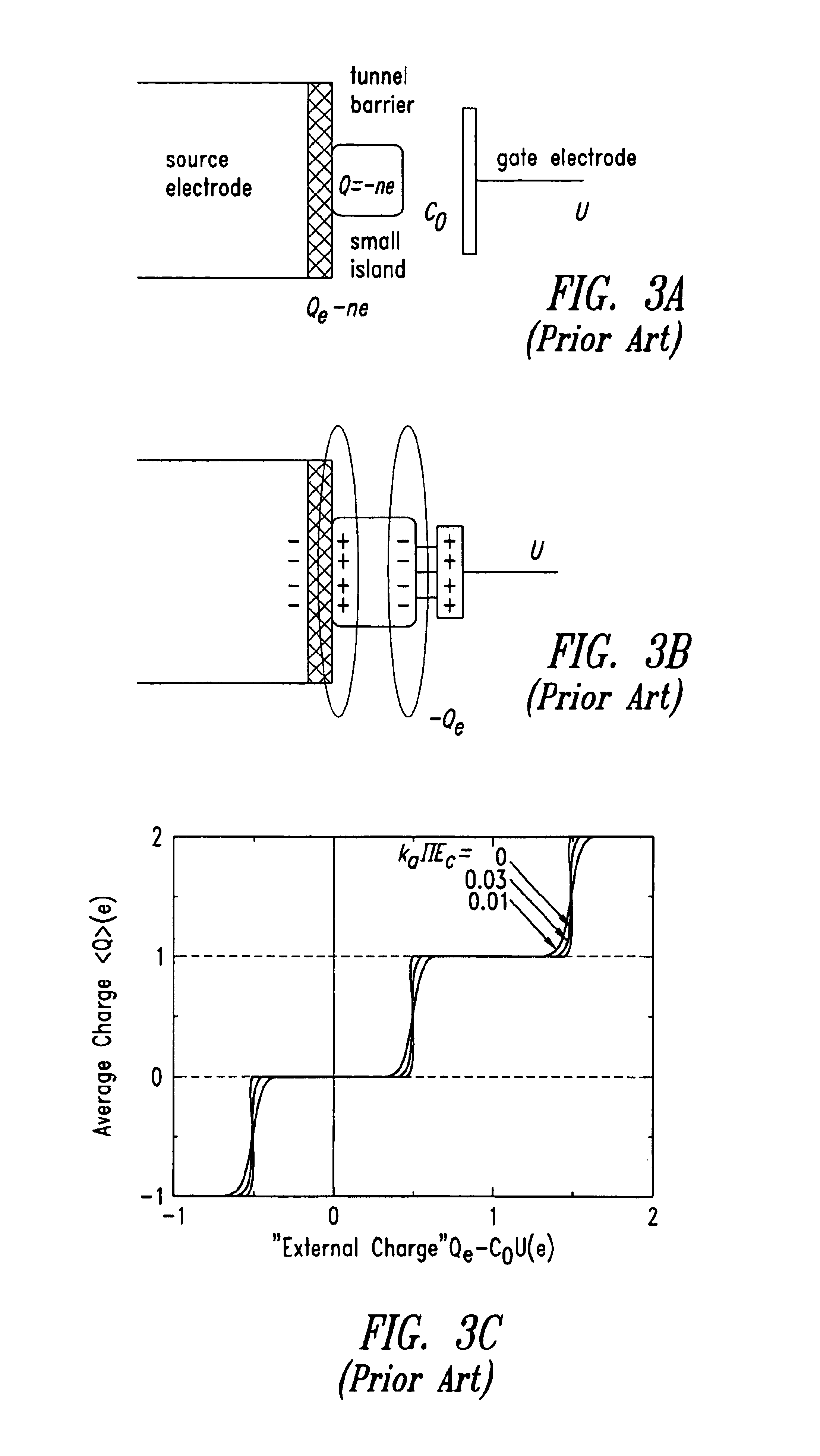
A single electron has a charge of 2.8×10 −15 Z . Using zeets and a fictitious unit of mass called the wiggle, w, the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron is 2.9×10 6 Z/w .
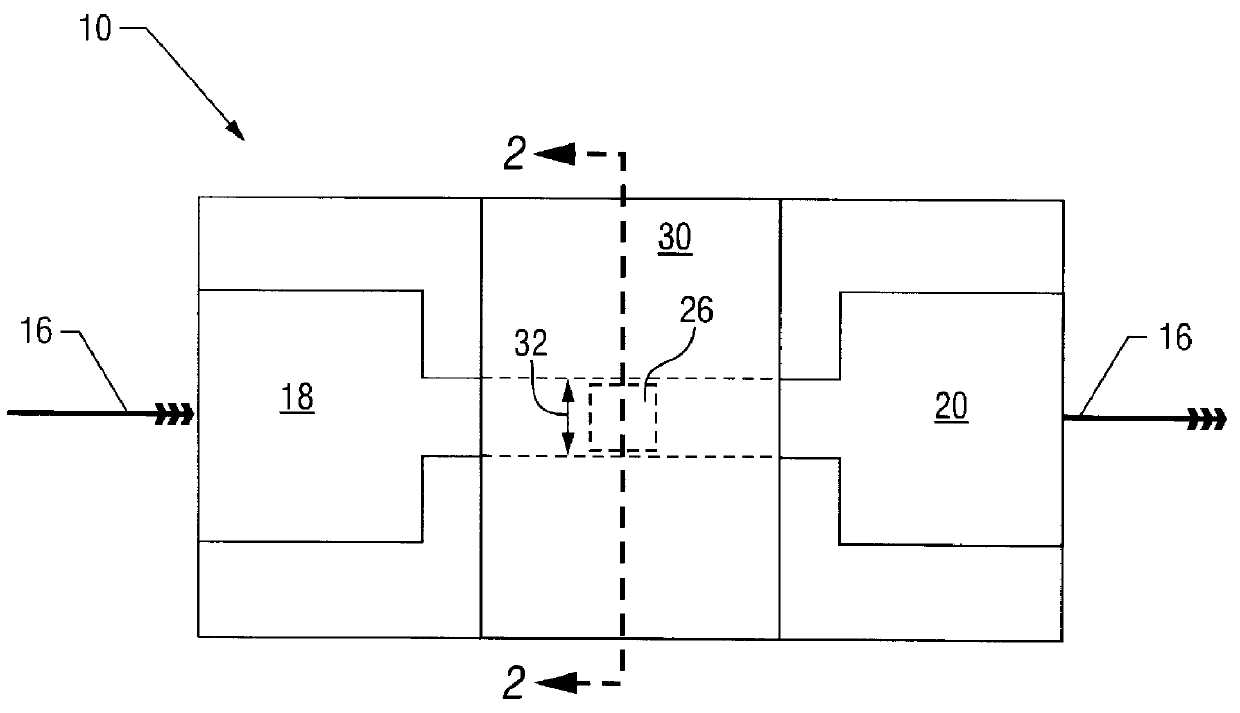
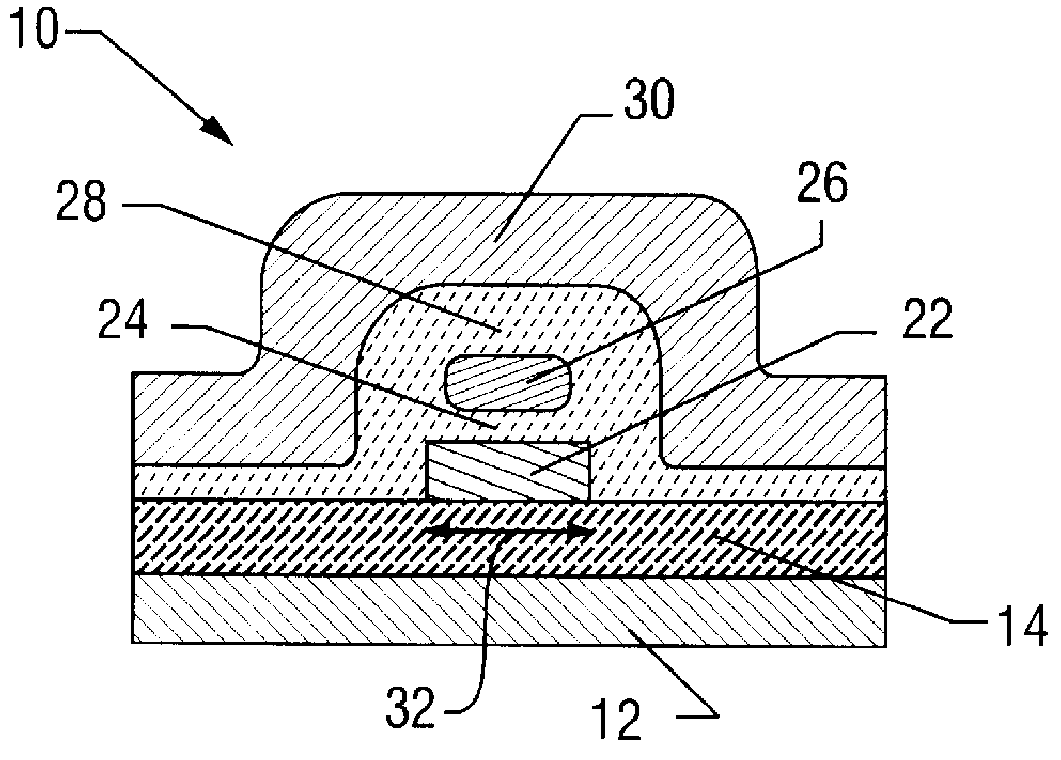
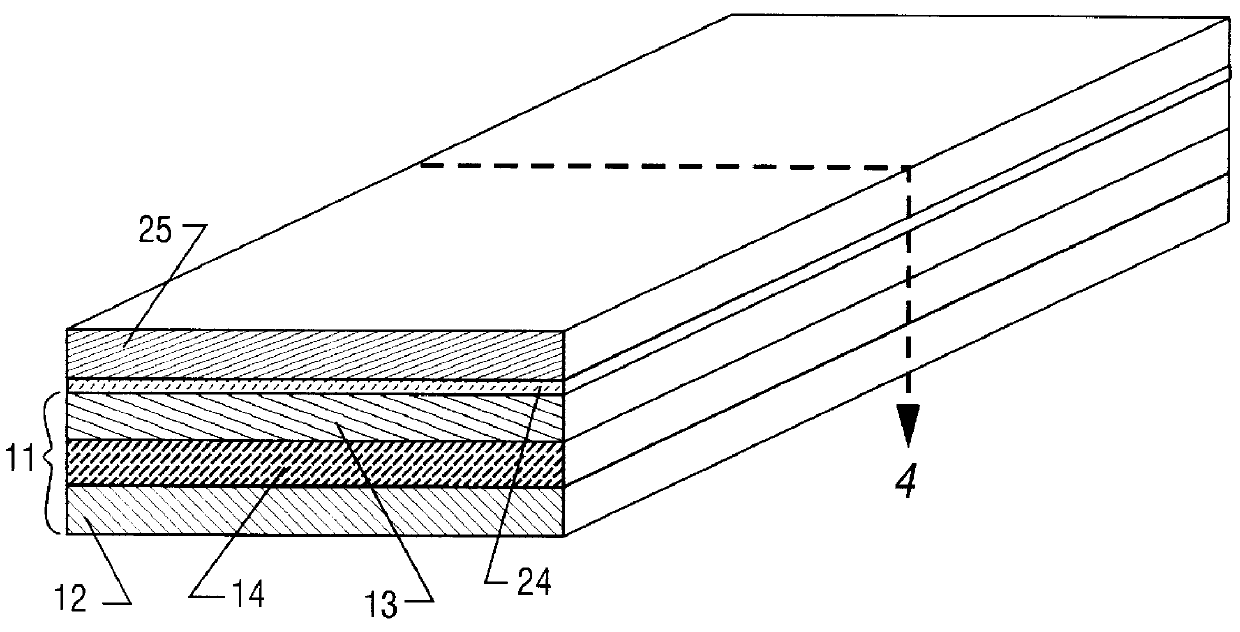
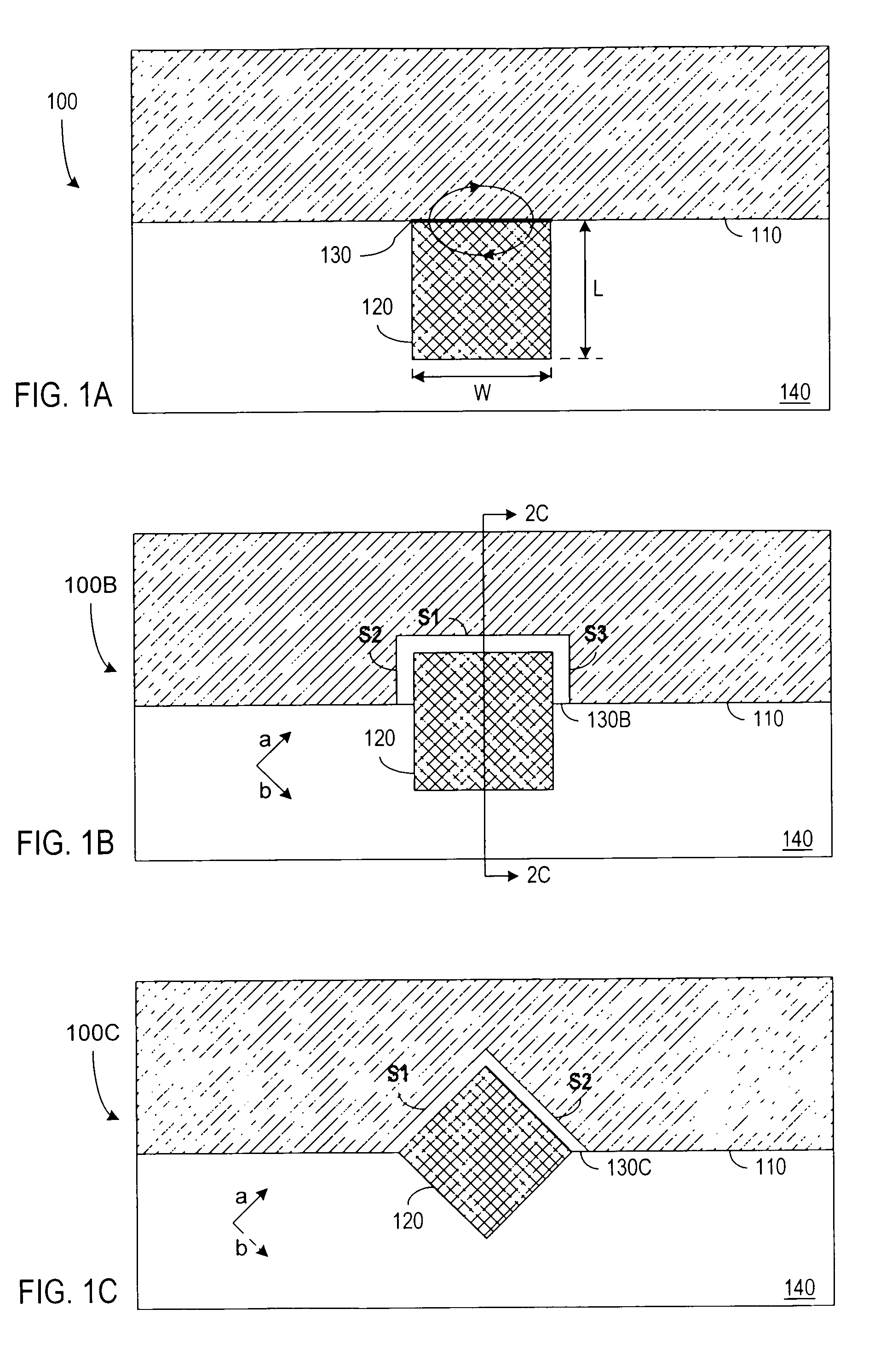
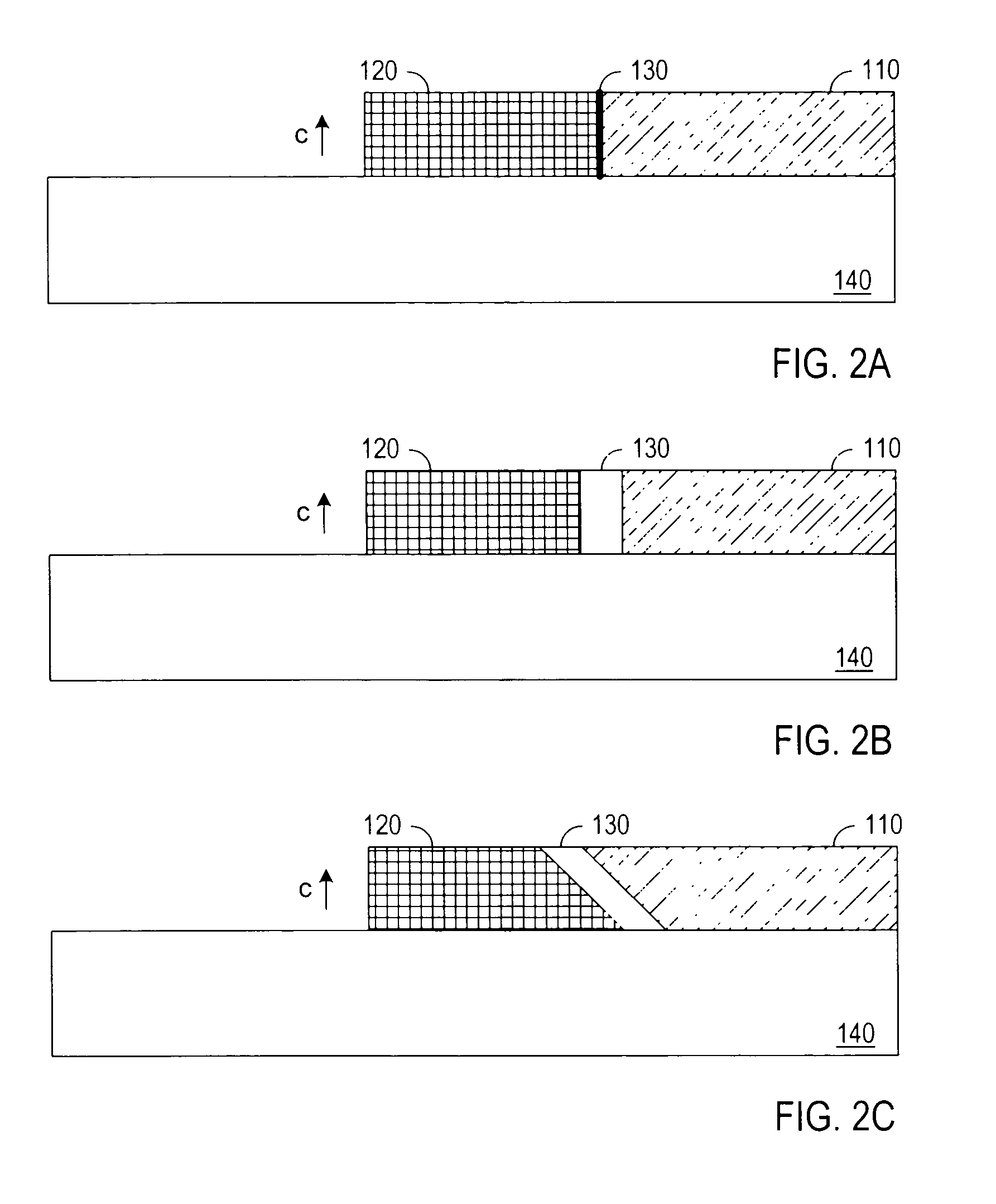
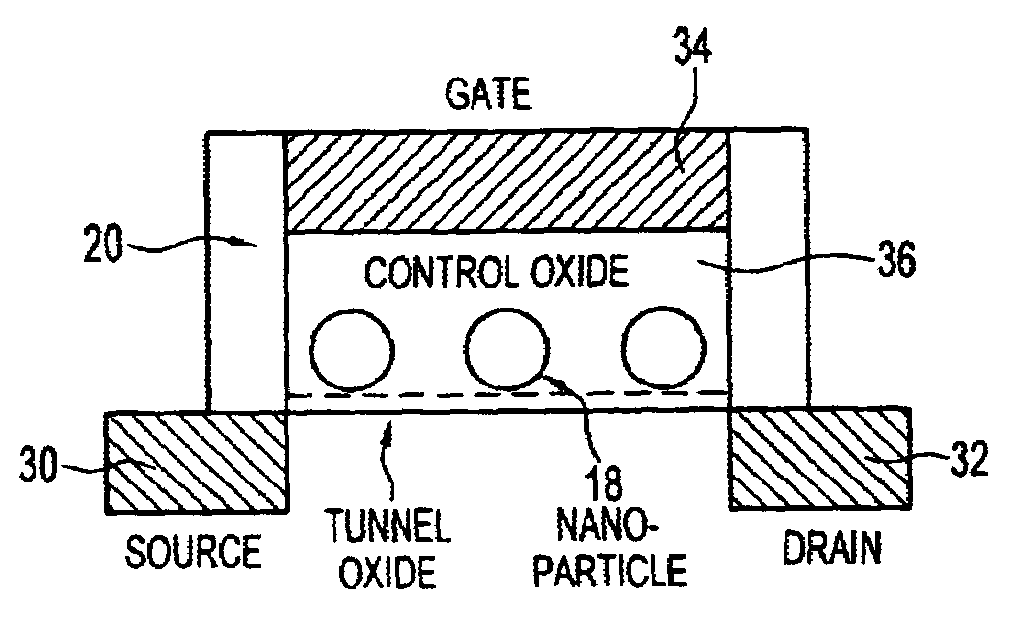
Single-electron floating-gate MOS memory
A Single Electron MOS Memory (SEMM), in which one bit of information is represented by storing only one electron, has been demonstrated at room temperature. The SEMM is a floating gate Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) transistor in silicon with a channel width (about 10 nanometers) which is smaller than the Debye screening length of a single electron stored on the floating gate, and a nanoscale polysilicon dot (about 7 nanometers by 7 nanometers by 2 nanometers) as the floating gate which is positioned between the channel and the control gate. An electron stored on the floating gate can screen the entire channel from the potential on the control gate, and lead to: (i) a discrete shift in the threshold voltage; (ii) a staircase relation between the charging voltage and the shift; and (iii) a self-limiting charging process. The structure and fabrication of the SEMM is well adapted to the manufacture of ultra large-scale integrated circuits.
Owner:MINNESOTA RGT UNIV OF A CORP OF MN
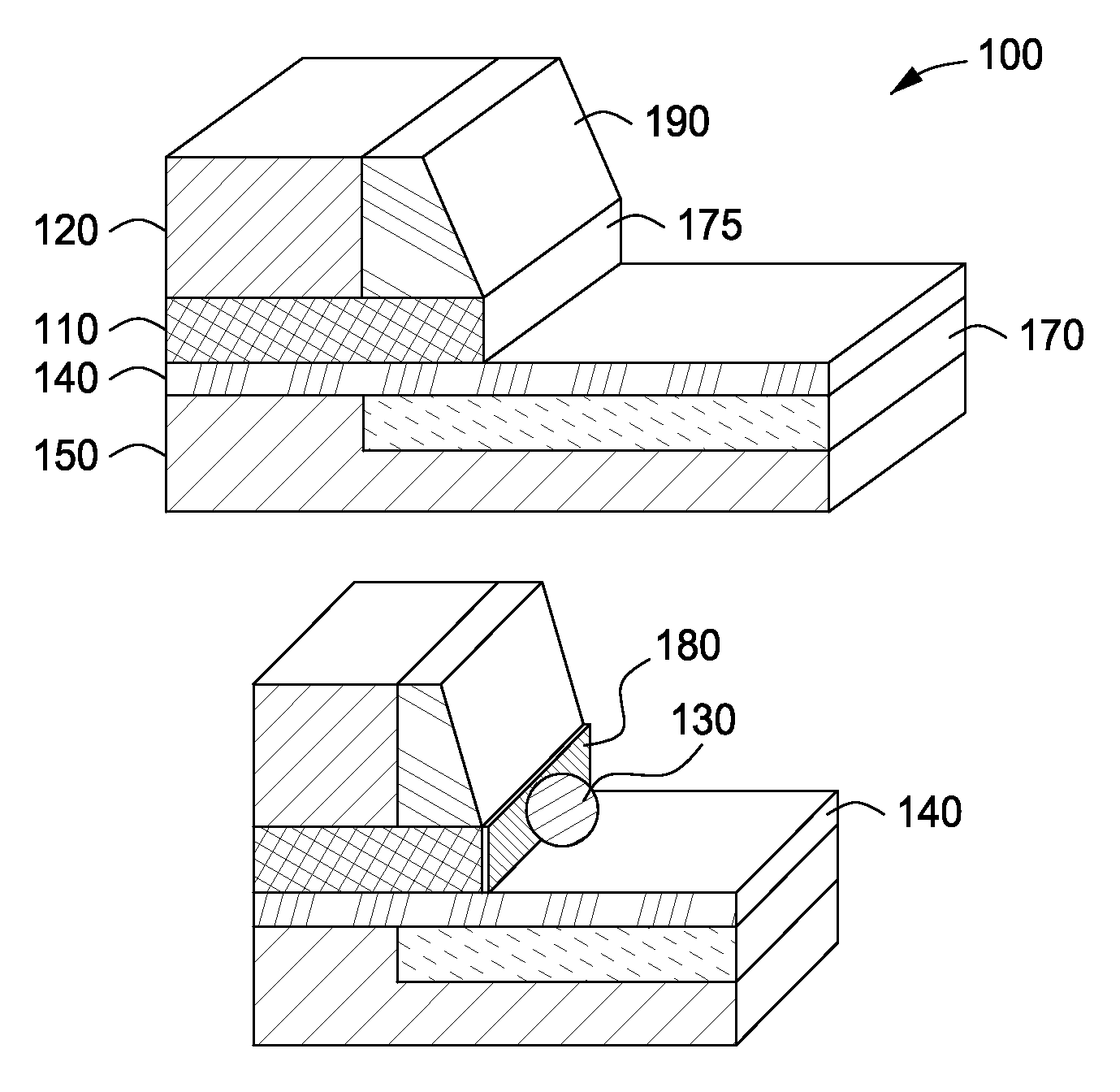
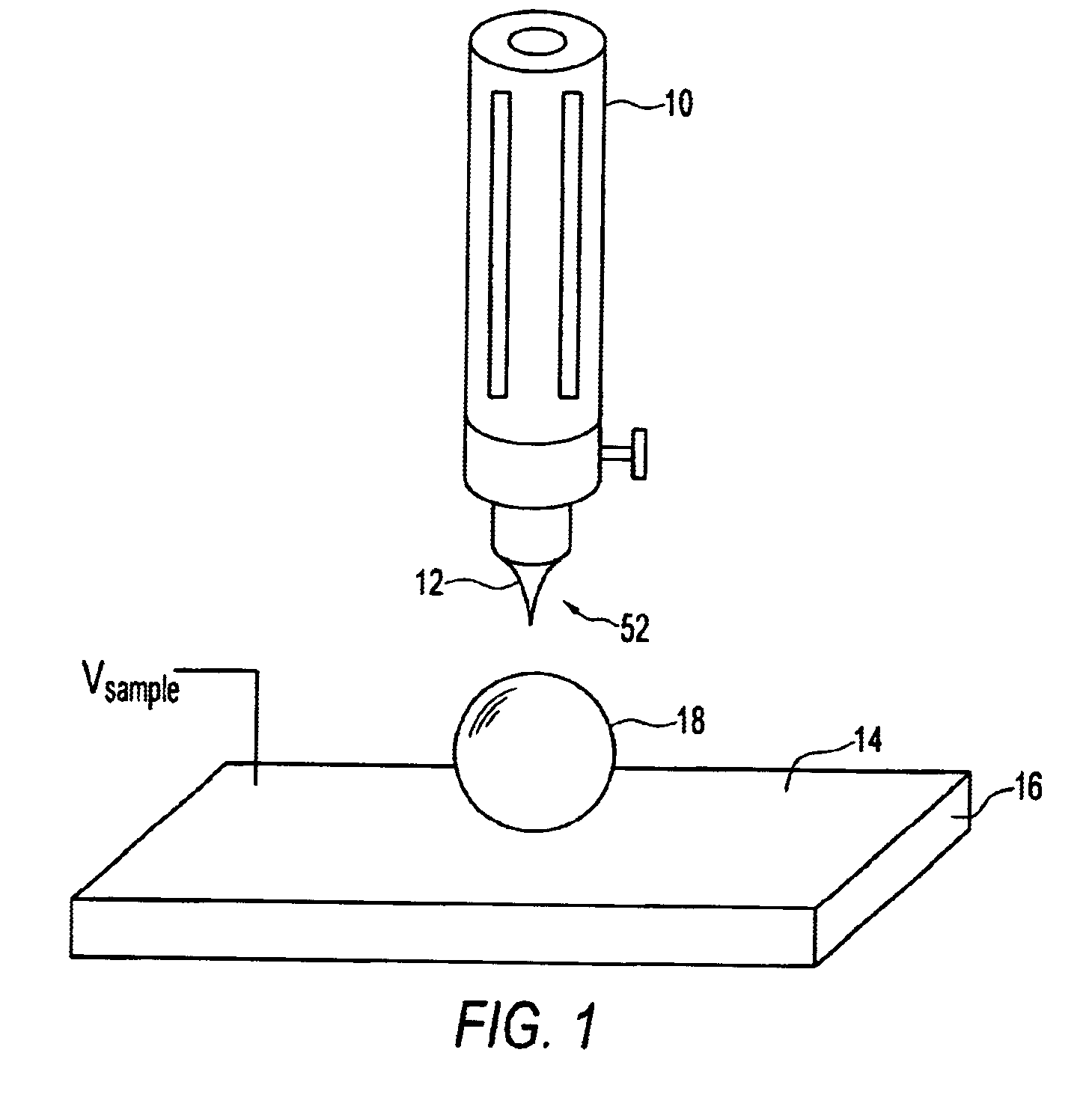
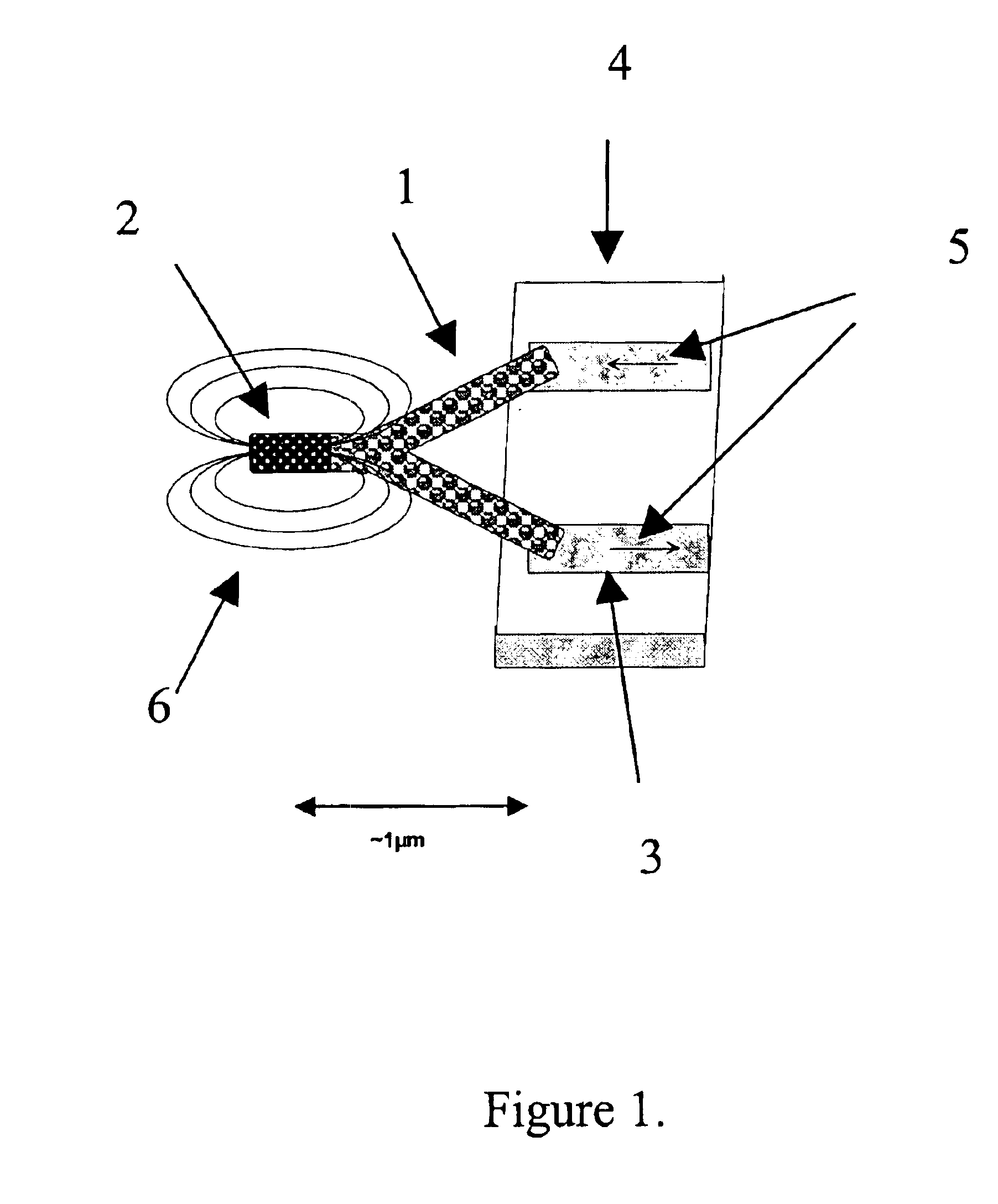
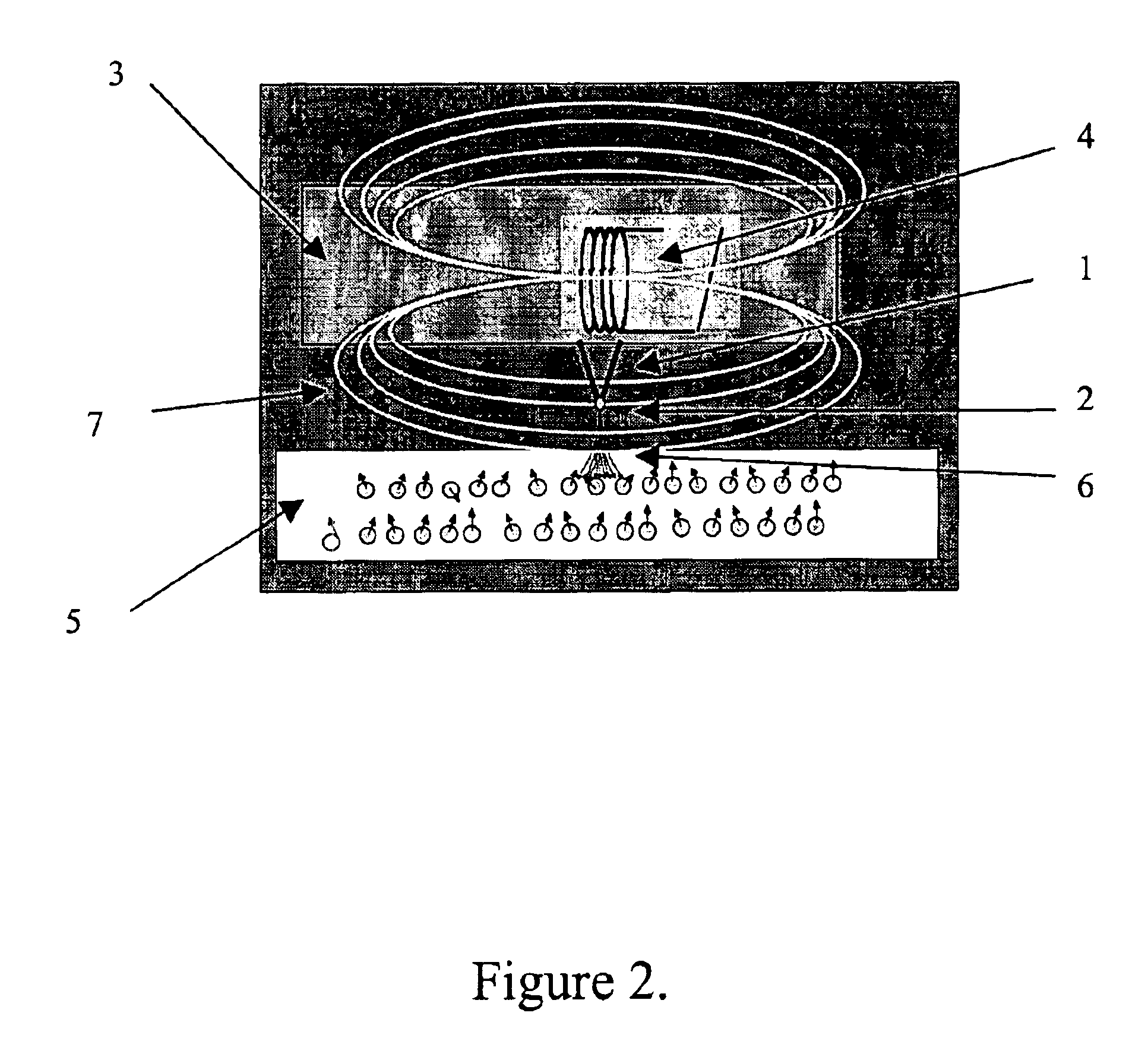
Positioning of nanoparticles and fabrication of single electron devices
InactiveUS7465953B1NanoinformaticsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSingle electronDevice form
The present invention includes single electron structures and devices comprising a substrate having an upper surface, one or more dielectric layers formed on the upper surface of the substrate and having at least one exposed portion, at least one monolayer of self-assembling molecules attracted to and in contact with the at least one exposed portion of only one of the one or more dielectric layers, one or more nanoparticles attracted to and in contact with the at least one monolayer, and at least one tunneling barrier in contact with the one or more nanoparticles. Typically, the single electron structure or device formed therefrom further comprise a drain, a gate and a source to provide single electron behavior, wherein there is a defined gap between source and drain and the one or more nanoparticles is positioned between the source and drain.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Apparatus of Plural Charged-Particle Beams
ActiveUS20170025241A1High resolutionImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesSingle electronElectron source
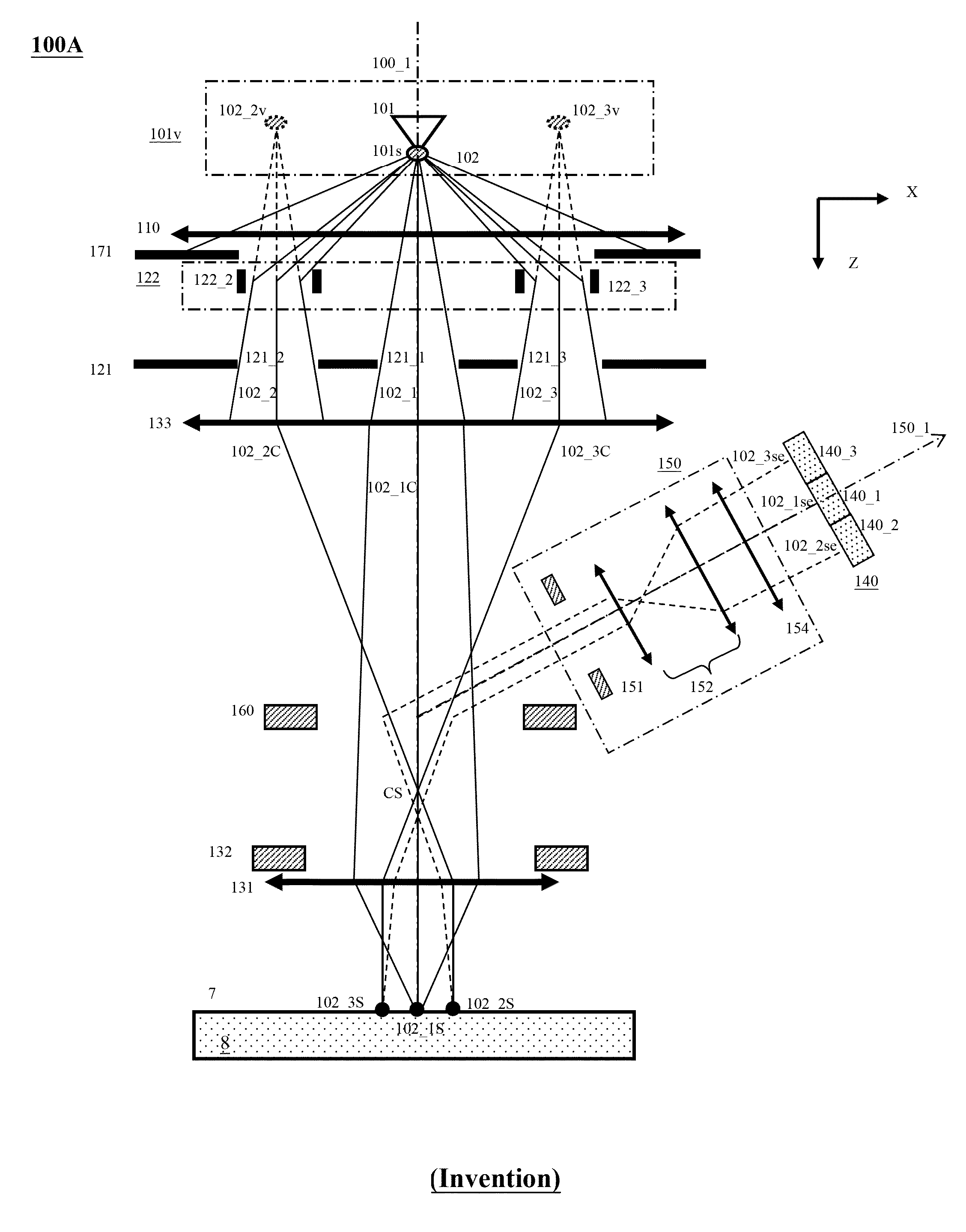
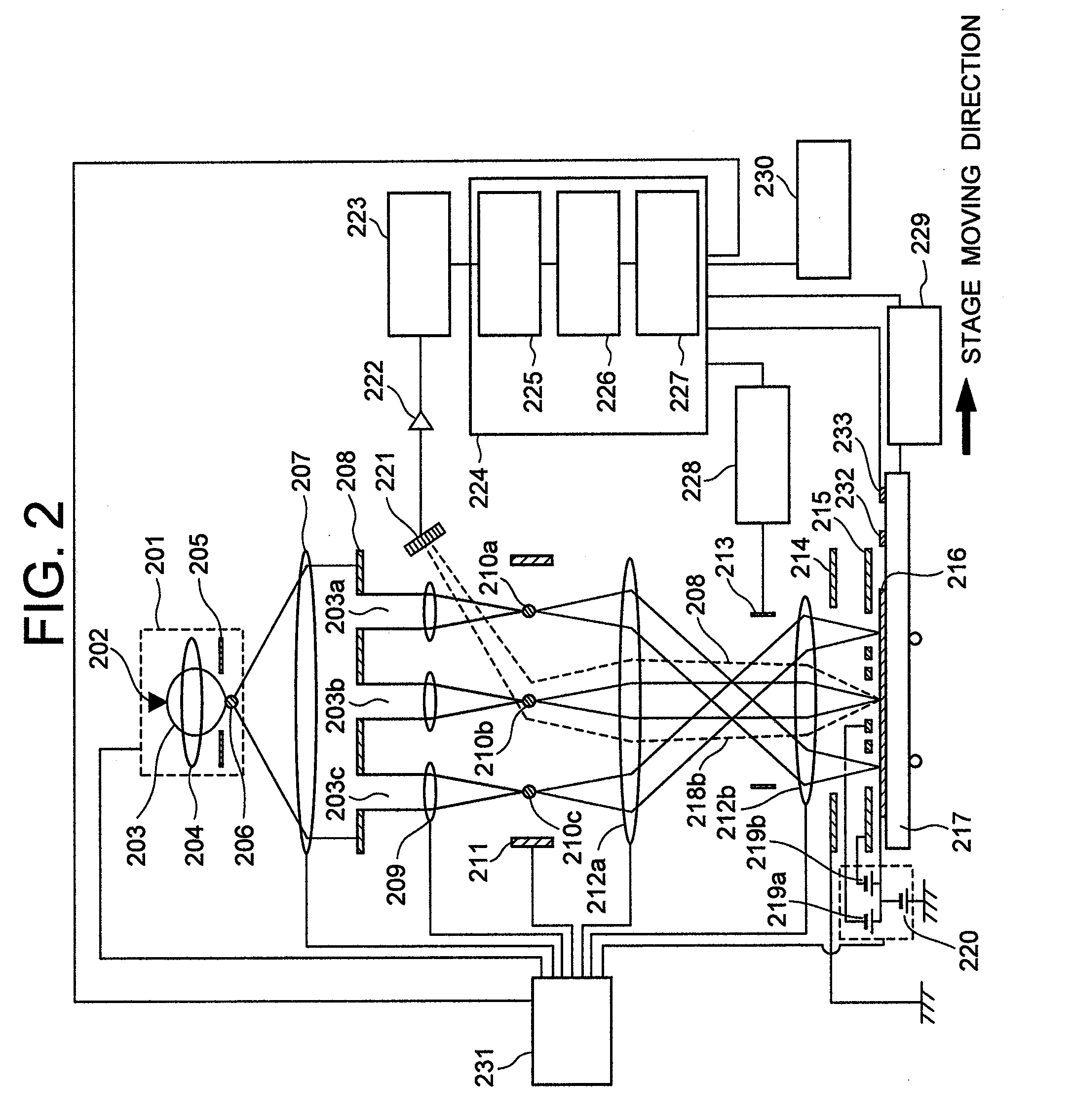
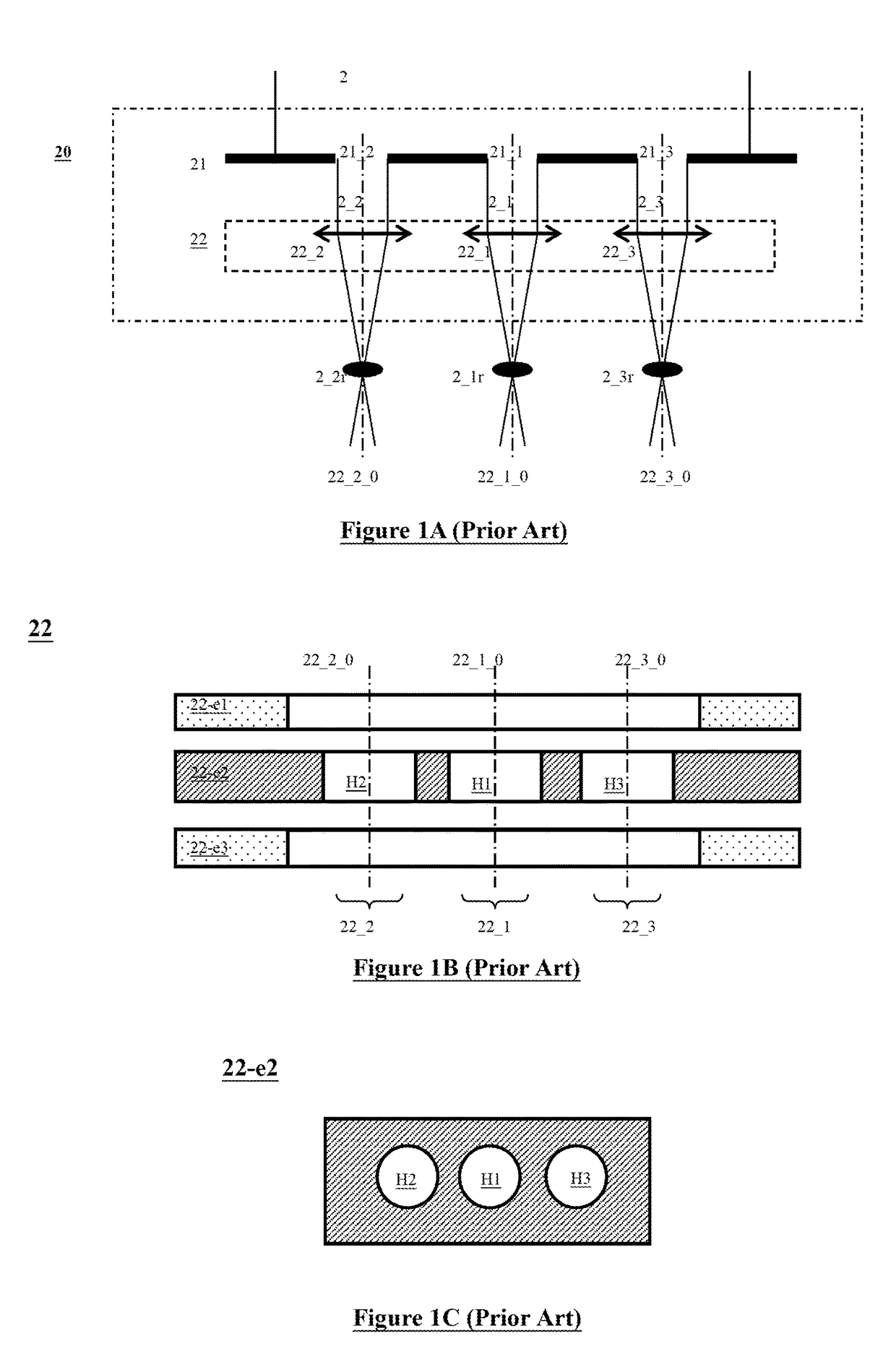
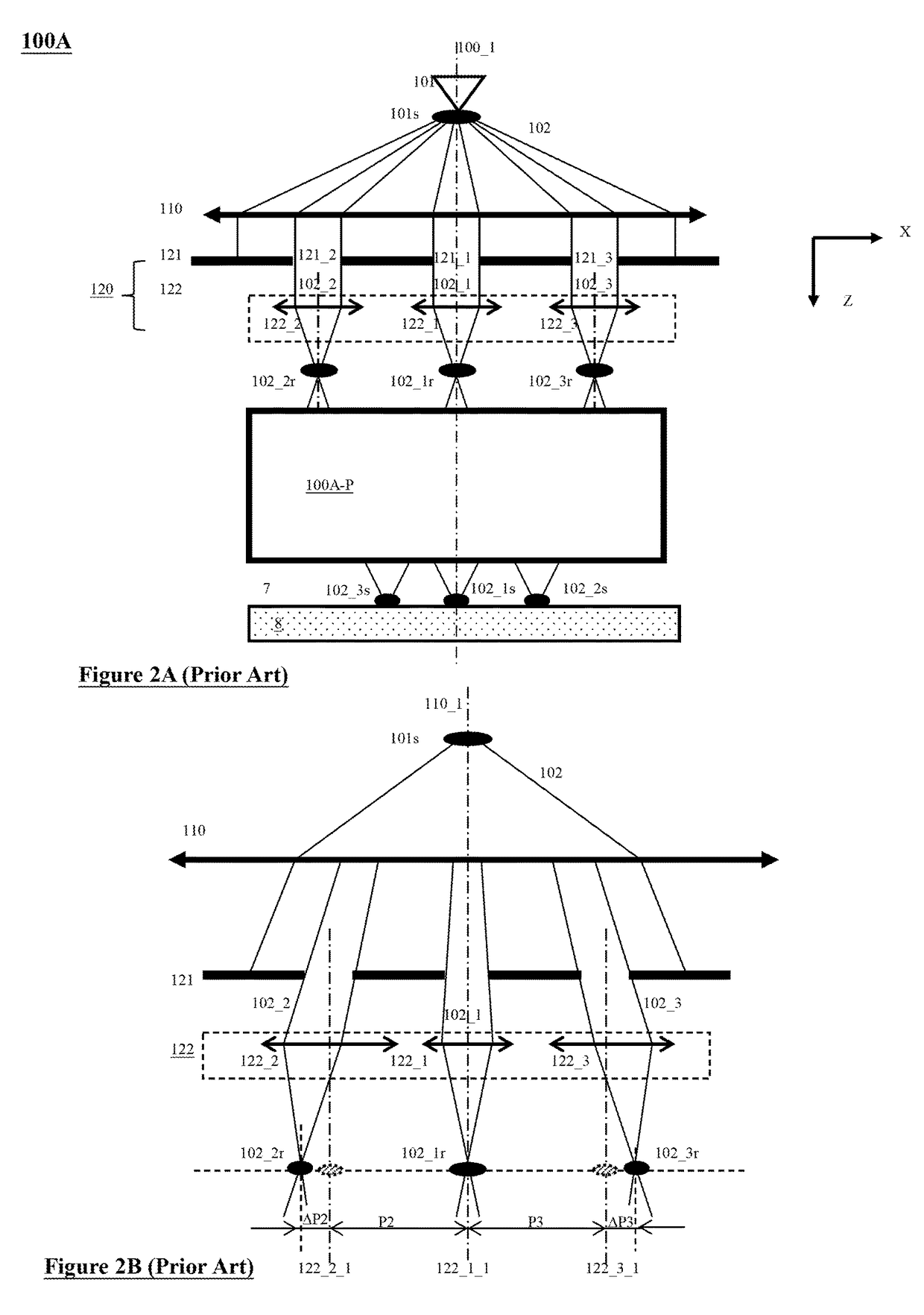
A multi-beam apparatus for observing a sample with high resolution and high throughput and in flexibly varying observing conditions is proposed. The apparatus uses a movable collimating lens to flexibly vary the currents of the plural probe spots without influencing the intervals thereof, a new source-conversion unit to form the plural images of the single electron source and compensate off-axis aberrations of the plural probe spots with respect to observing conditions, and a pre-beamlet-forming means to reduce the strong Coulomb effect due to the primary-electron beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method and apparatus for molecular analysis using nanoelectronic circuits
InactiveUS20060275778A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle electronNanoelectronic circuits
Devices and methods for detecting the constituent parts of biological polymers are disclosed. A molecular analysis device comprises a molecule sensor and a molecule guide. The molecule sensor comprises a single electron transistor including a first terminal, a second terminal, and a nanogap or at least one quantum dot positioned between the first terminal and the second terminal. A nitrogenous material disposed on the at least one quantum dot is configured for an interaction with an identifiable configuration of a molecule. The molecule sensor develops an electronic effect responsive to the interaction. The molecule guide is configured for guiding at least a portion of the molecule substantially near the molecule sensor to enable the interaction.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Apparatus of Plural Charged-Particle Beams
ActiveUS20160268096A1High resolutionImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesSingle electronElectron source
A multi-beam apparatus for observing a sample with high resolution and high throughput is proposed. In the apparatus, a source-conversion unit changes a single electron source into a virtual multi-source array, a primary projection imaging system projects the array to form plural probe spots on the sample, and a condenser lens adjusts the currents of the plural probe spots. In the source-conversion unit, the image-forming means is on the upstream of the beamlet-limit means, and thereby generating less scattered electrons. The image-forming means not only forms the virtual multi-source array, but also compensates the off-axis aberrations of the plurality of probe spots.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method and apparatus for detection of molecules using nanopores
InactiveUS20070178507A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle electronMolecular analysis
A molecular analysis device comprises a molecule sensor and a nanopore that passes through, partially through, or substantially near the molecule sensor. The molecule sensor may comprise a single electron transistor including a first terminal, a second terminal, and a nanogap or at least one quantum dot positioned between the first terminal and the second terminal. The molecular sensor may also comprise a nanowire that operably couples a first and a second terminal. A nitrogenous material that may be disposed on at least part of the molecule sensor is configured for a chemical interaction with an identifiable configuration of a molecule. The molecule sensor develops an electronic effect responsive to a molecule or responsive to a chemical interaction.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Single electron transistor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080246021A1Overcome problemsNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle electronNanowire
A single electron transistor includes source / drain layers disposed apart on a substrate, at least one nanowire channel connecting the source / drain layers, a plurality of oxide channel areas in the nanowire channel, the oxide channel areas insulating at least one portion of the nanowire channel, a quantum dot in the portion of the nanowire channel insulated by the plurality of oxide channel areas, and a gate electrode surrounding the quantum dot.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
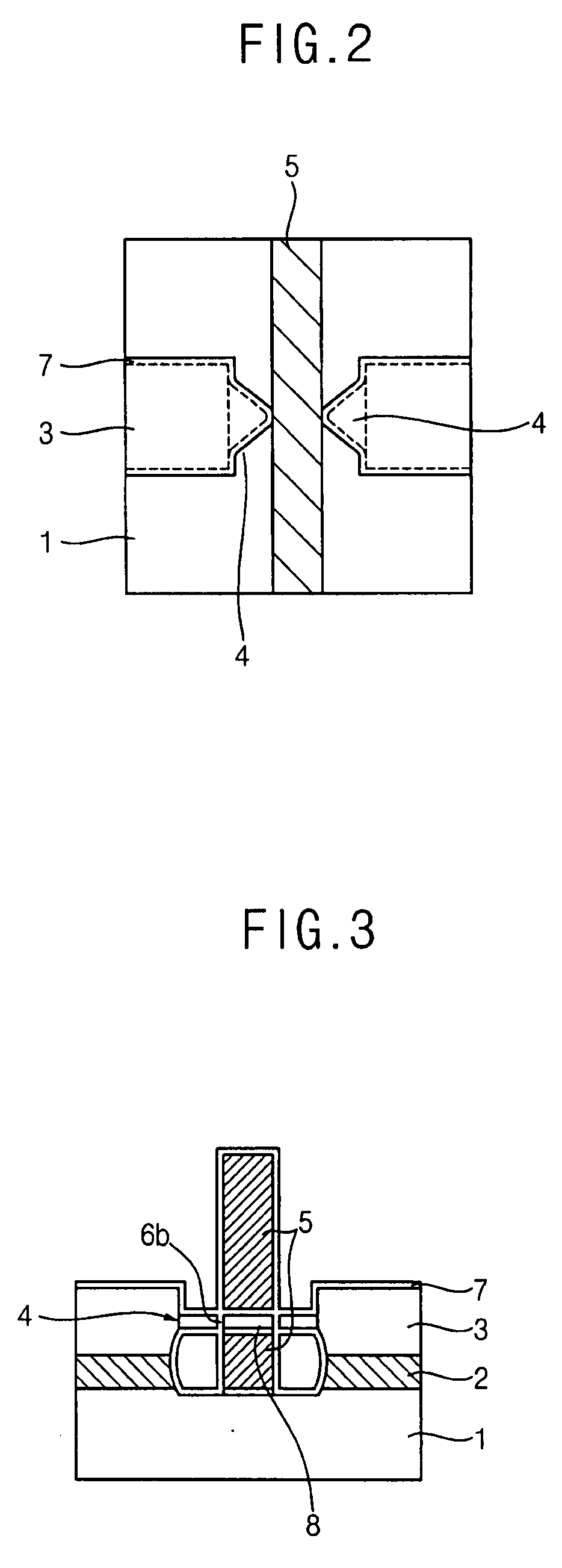
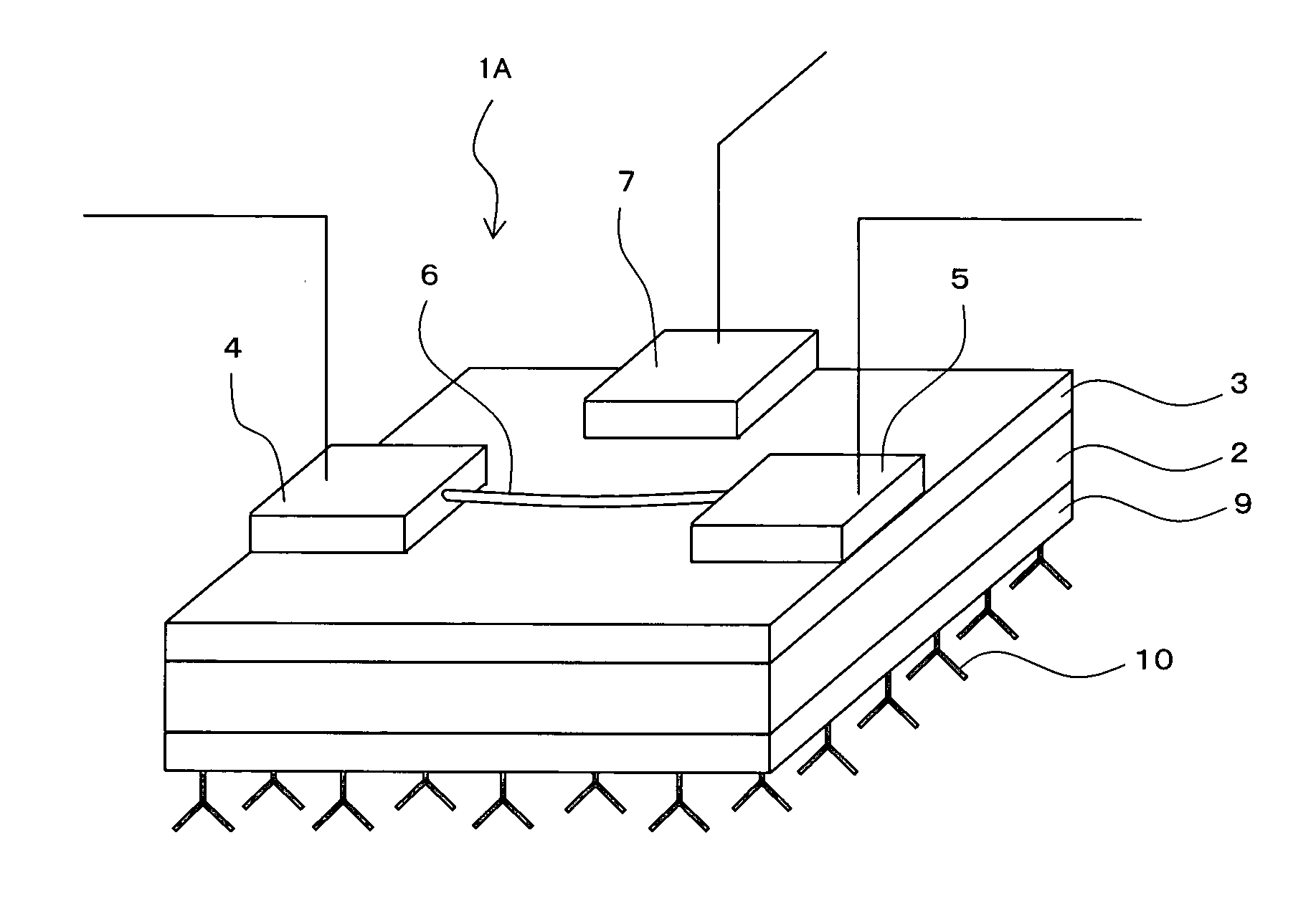
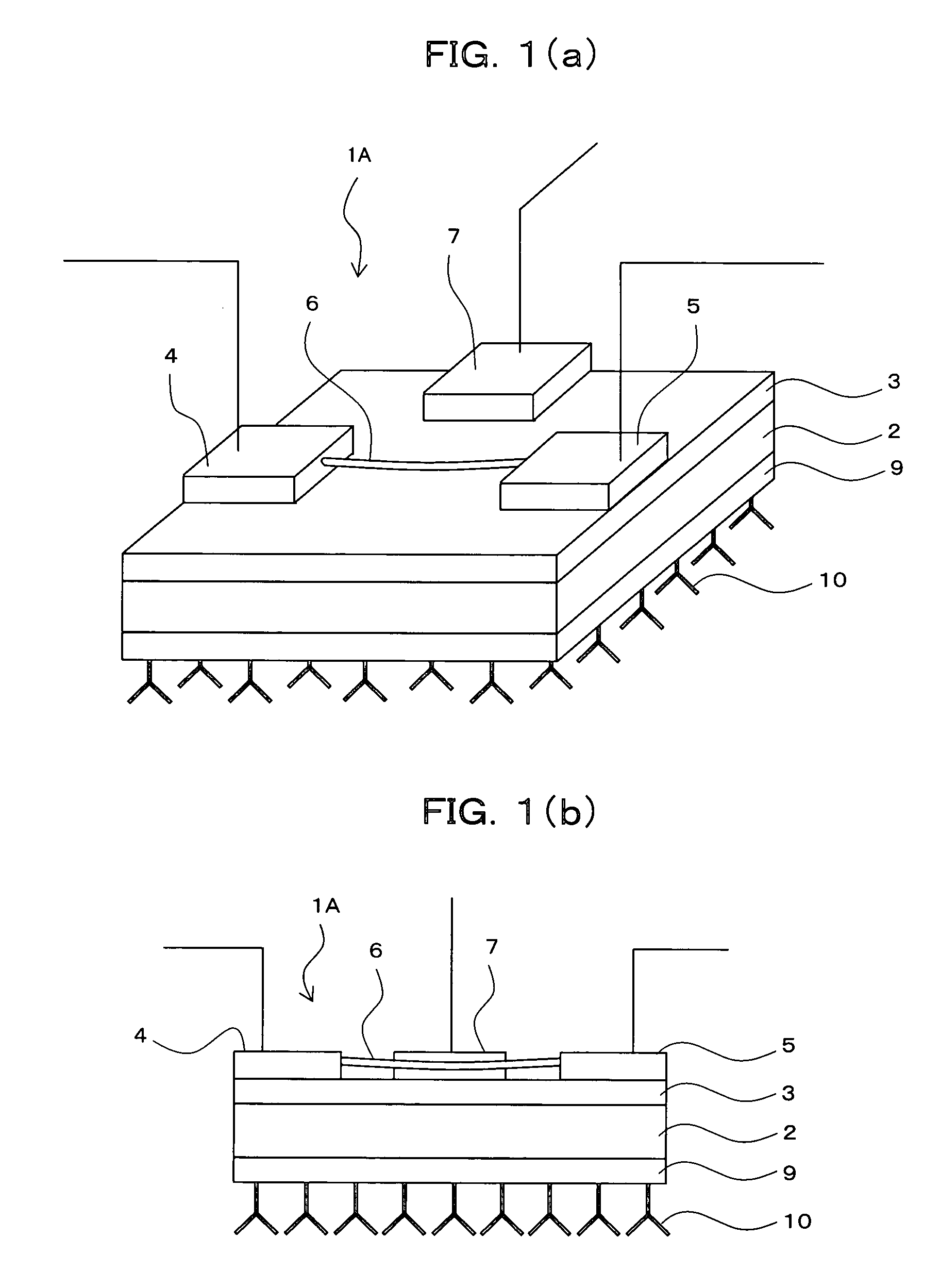
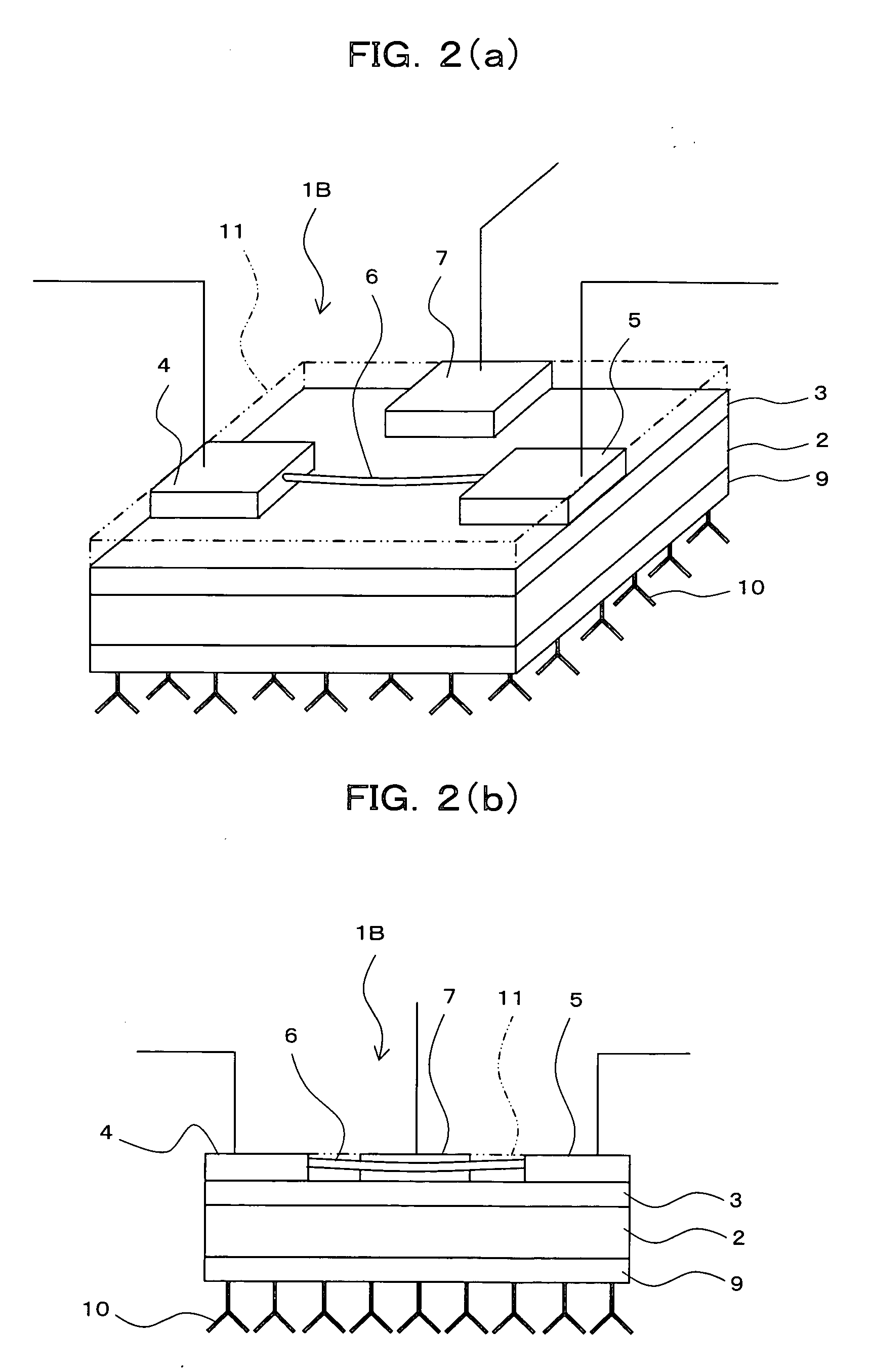
Field-effect transistor, single-electron transistor and sensor using the same
InactiveUS20070063304A1High detection sensitivityTransistorMaterial nanotechnologySingle electronField-effect transistor
A sensor capable of detecting detection targets that are necessary to be detected with high sensitivity is provided. It comprises a field-effect transistor 1A having a substrate 2, a source electrode 4 and a drain electrode 5 provided on said substrate 2, and a channel 6 forming a current path between said source electrode 4 and said drain electrode 5; wherein said field-effect transistor 1A comprises: an interaction-sensing gate 9 for immobilizing thereon a specific substance 10 that is capable of selectively interacting with the detection targets; and a gate 7 applied a voltage thereto so as to detect the interaction by the change of the characteristic of said field-effect transistor 1A.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Light-emitting element having nitride semiconductor multiquantum barrier, and process for production thereof
ActiveUS20130069034A1Improve blockageHigh barrier heightSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSingle electronLuminous intensity
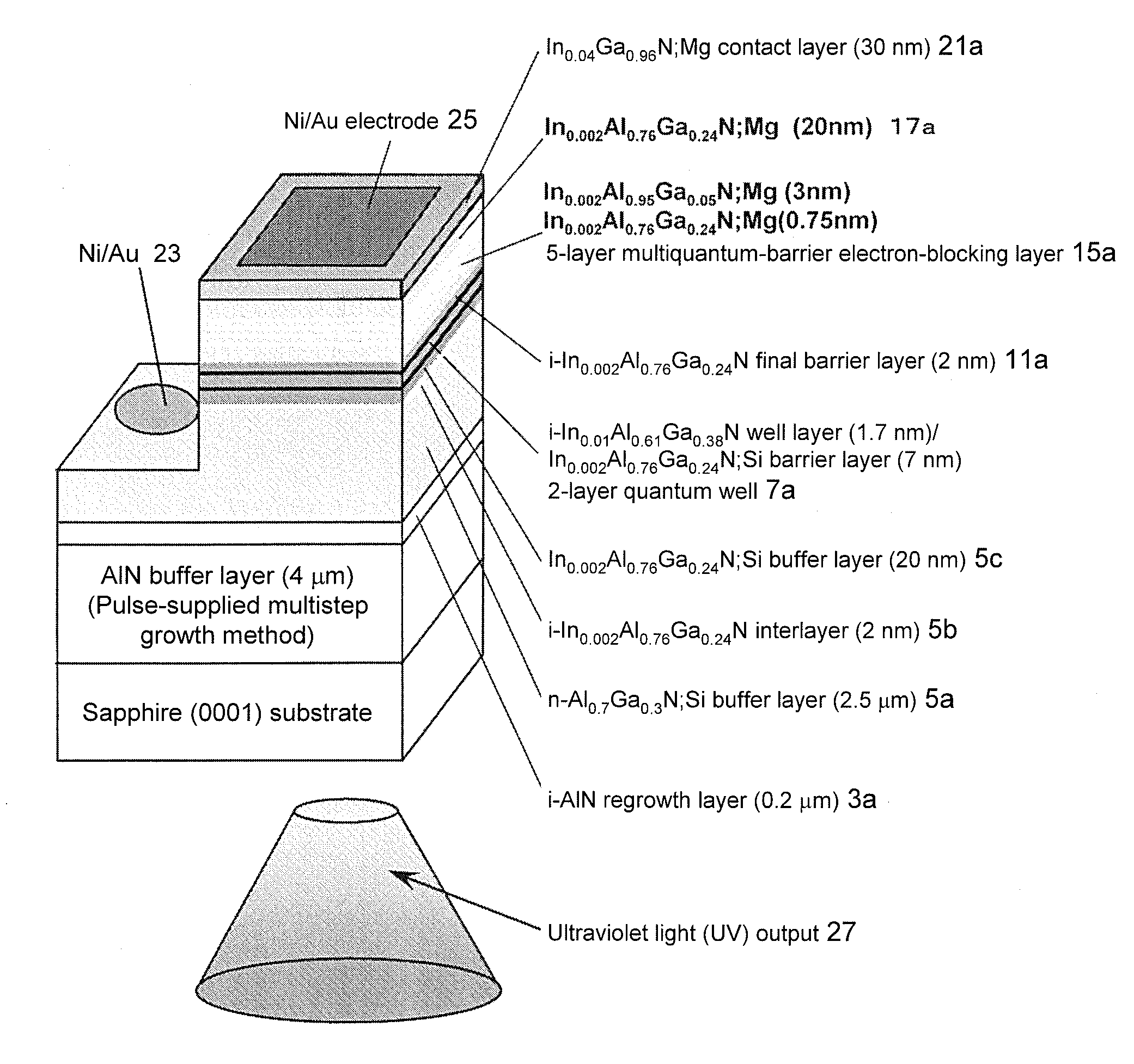
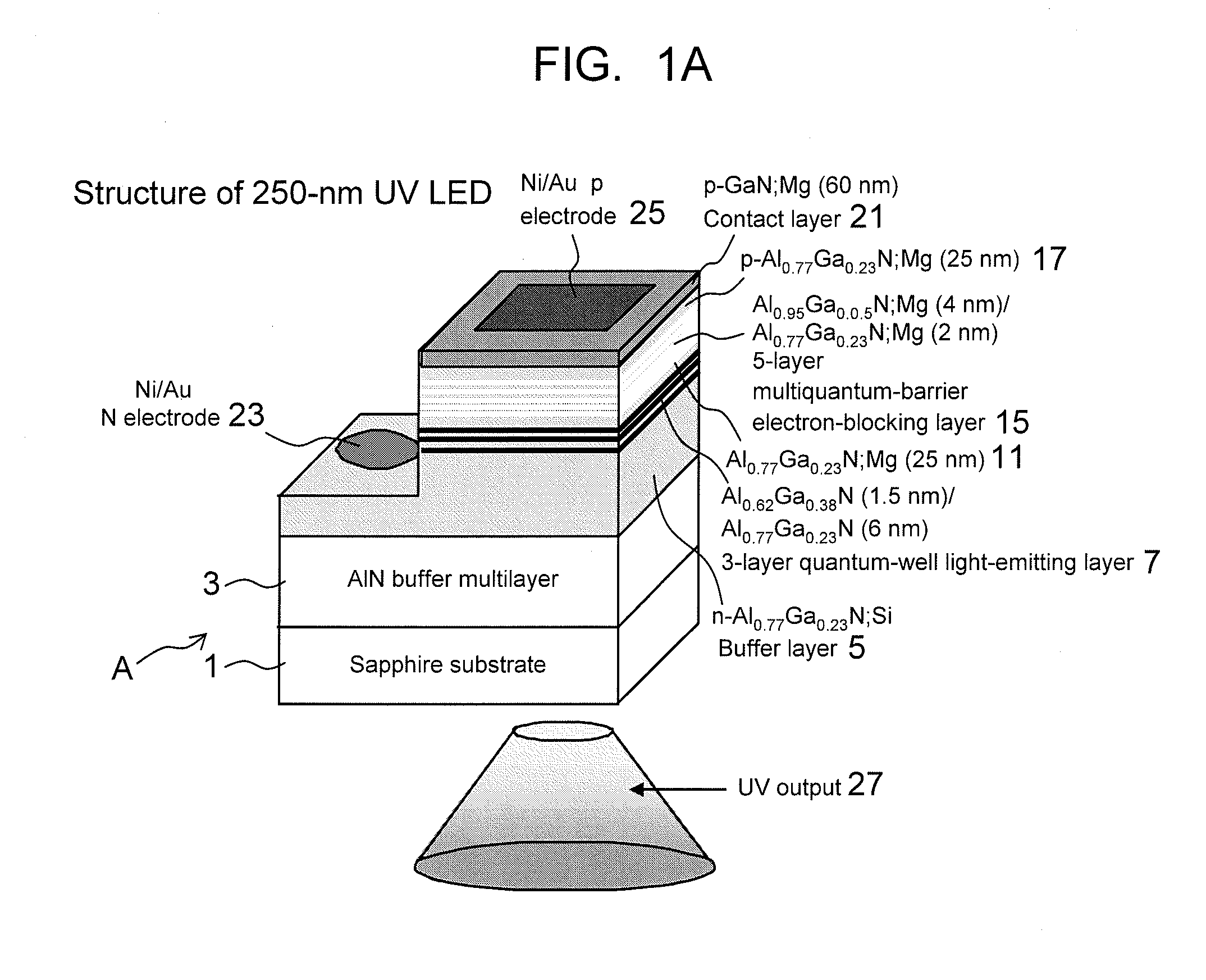
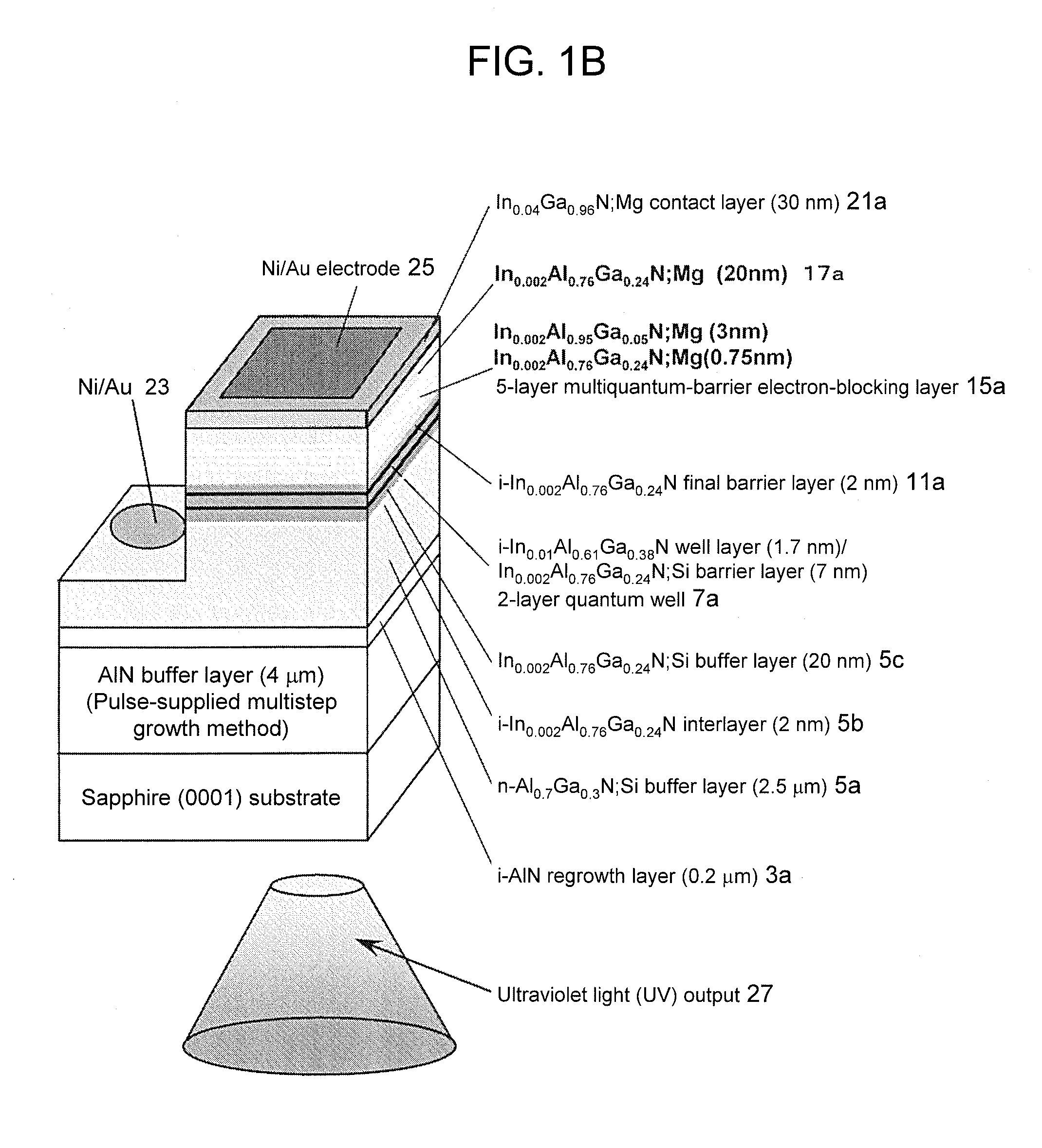
An Al0.95Ga0.05N:Mg (25 nm) single electron barrier can stop electrons having energy levels lower than the barrier height. Meanwhile, a 5-layer Al0.95Ga0.05N (4 nm) / Al0.77Ga0.23N (2 nm) MQB has quantum-mechanical effects so as to stop electrons having energy levels higher than the barrier height. Thus, electrons having energy levels higher than the barrier height can be blocked by making use of multiquantum MQB effects upon electrons. The present inventors found that the use of an MQB allows blocking of electrons having higher energy levels than those blocked using an SQB. In particular, for InAlGaN-based ultraviolet elements, AlGaN having the composition similar to that of AlN is used; however, it is difficult to realize a barrier having the barrier height exceeding that of AlN. Therefore, MQB effects are very important. Accordingly, it becomes possible to provide element technology for further improving deep UV light emission intensity using, as a light-emitting layer material, an AlGaInN-based material and, in particular, an AlGaN-based material.
Owner:RIKEN
Permanent readout superconducting qubit
InactiveUS7015499B1Quantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSingle electronCrystal orientation
A solid-state quantum computing structure includes a d-wave superconductor in sets of islands that clean Josephson junctions separate from a first superconducting bank. The d-wave superconductor causes the ground state for the supercurrent at each junction to be doubly degenerate, with two supercurrent ground states having distinct magnetic moments. These quantum states of the supercurrents at the junctions create qubits for quantum computing. The quantum states can be uniformly initialized from the bank, and the crystal orientations of the islands relative to the bank influence the initial quantum state and tunneling probabilities between the ground states. A second bank, which a Josephson junction separates from the first bank, can be coupled to the islands through single electron transistors for selectably initializing one or more of the supercurrents in a different quantum state. Single electron transistors can also be used between the islands to control entanglements while the quantum states evolve. After the quantum states have evolved to complete a calculation, grounding the islands, for example, through yet another set of single electron transistors, fixes the junctions in states having definite magnetic moments and facilitates measurement of the supercurrent when determining a result of the quantum computing.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Solid state charge qubit device
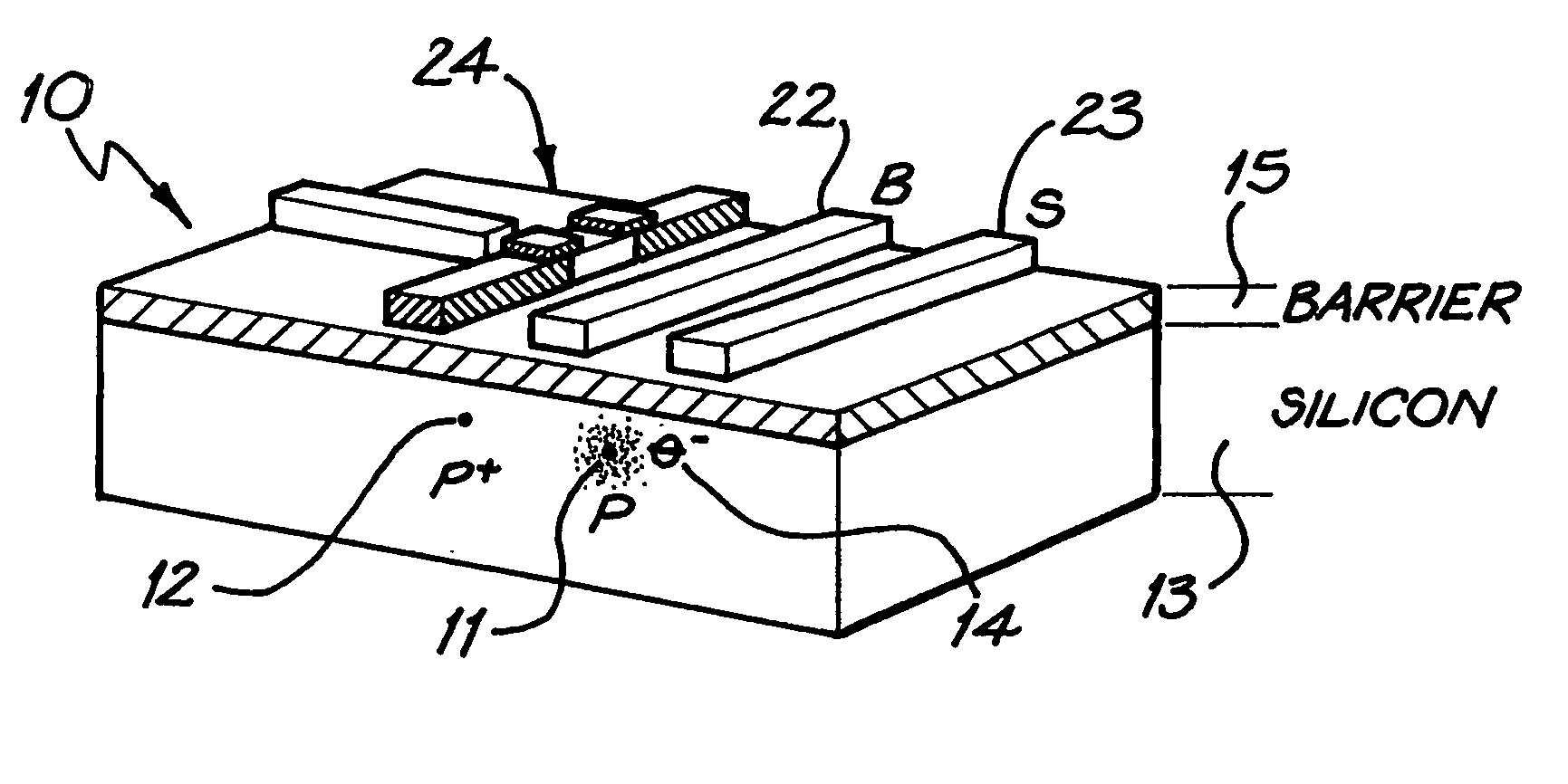
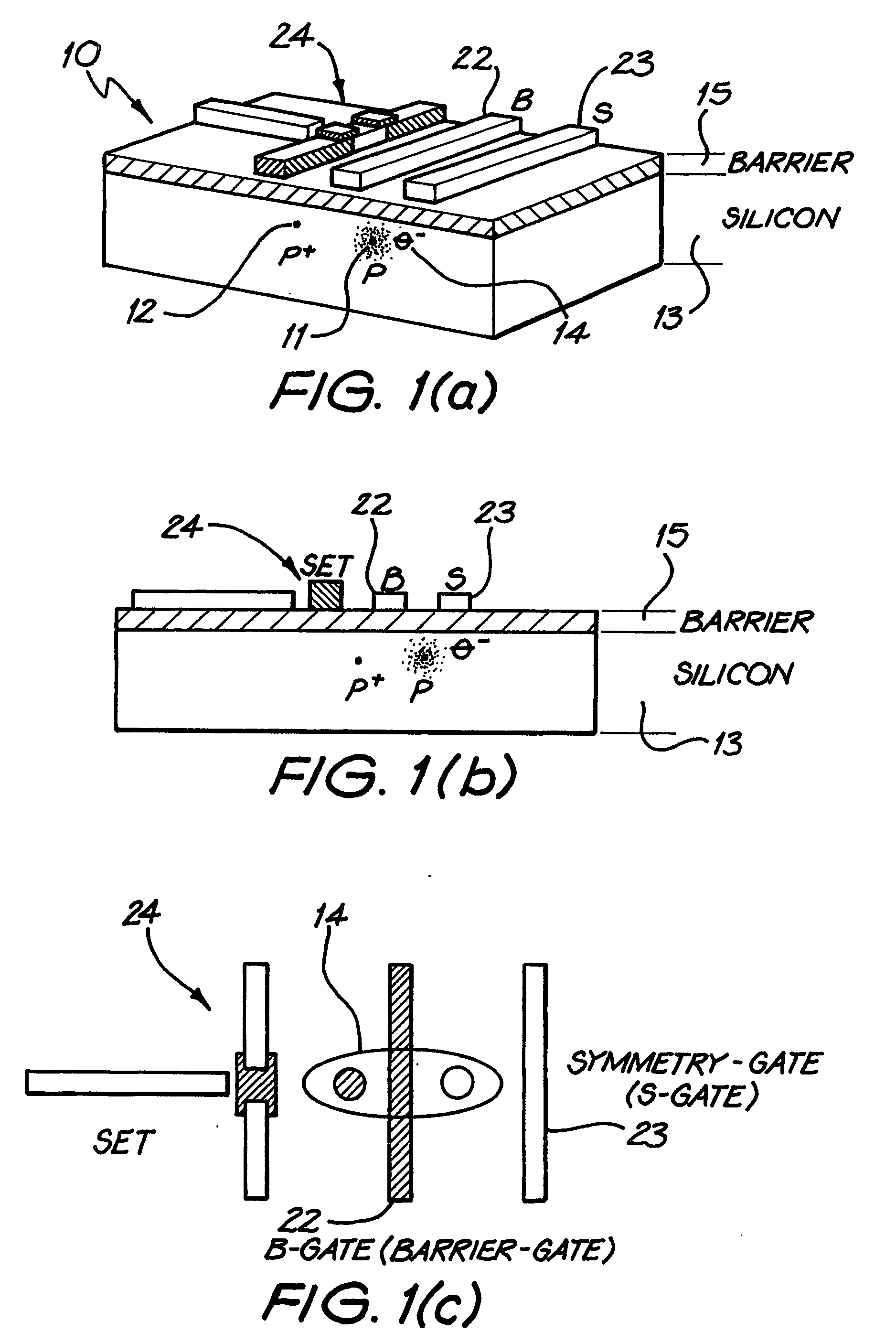
ActiveUS20060151775A1Minimize couplingNanofabrication considerably easierQuantum computersNanoinformaticsPhosphorous acidDouble-well potential
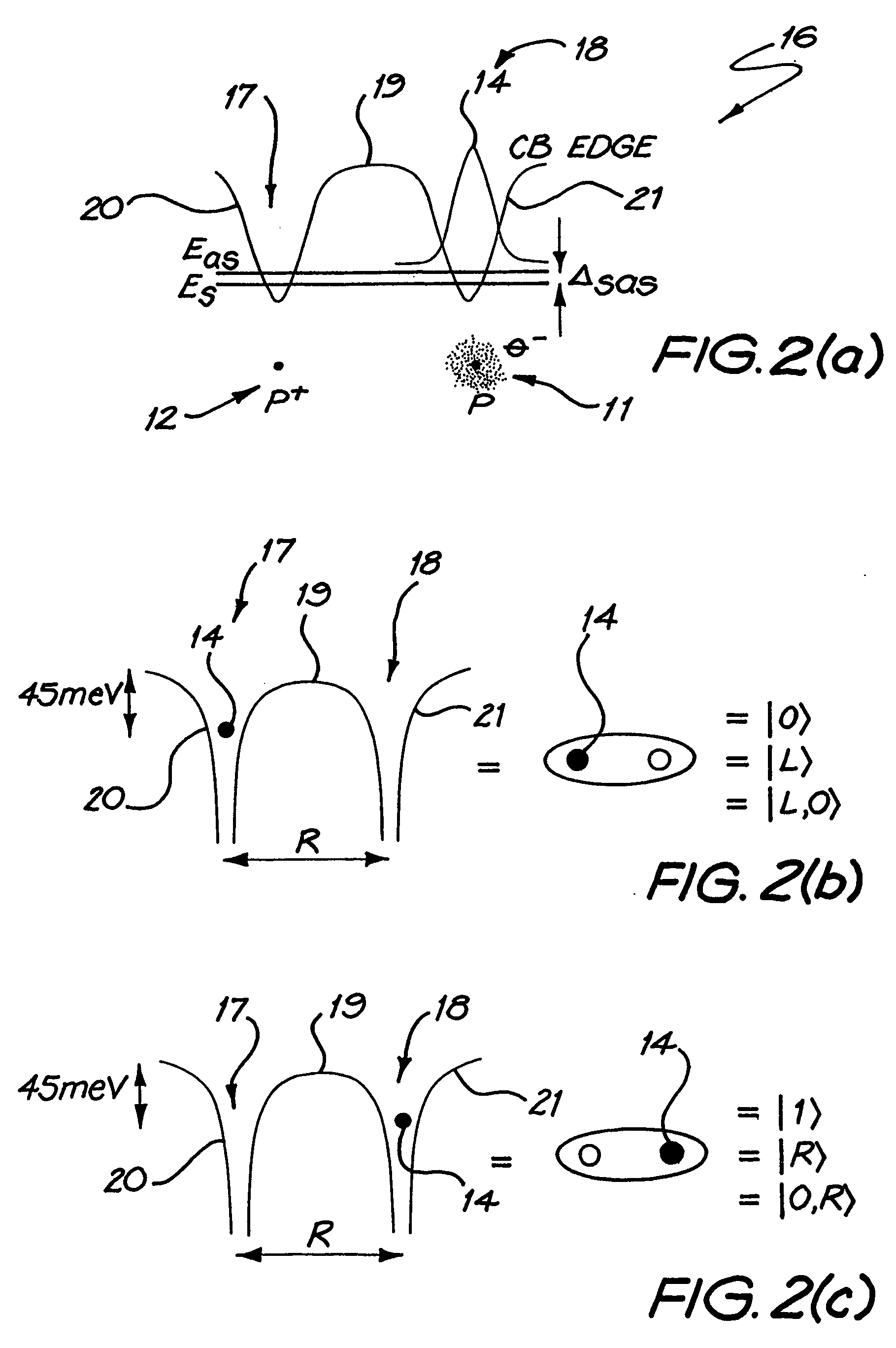
Ionisation of one of a pair of dopant atoms (11, 12) in a substrate (13) creates a double well potential, and a charge qubit is realised by the location of one or more electrons or holes (14) within this potential. The dopant atoms may comprise phosphorous atoms, located in a silicon substrate. A solid state quantum computer may be formed using a plurality of pairs of dopant atoms (11, 12), corresponding gate electrodes (22, 23), and read-out devices comprising single electron transistors (24).
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
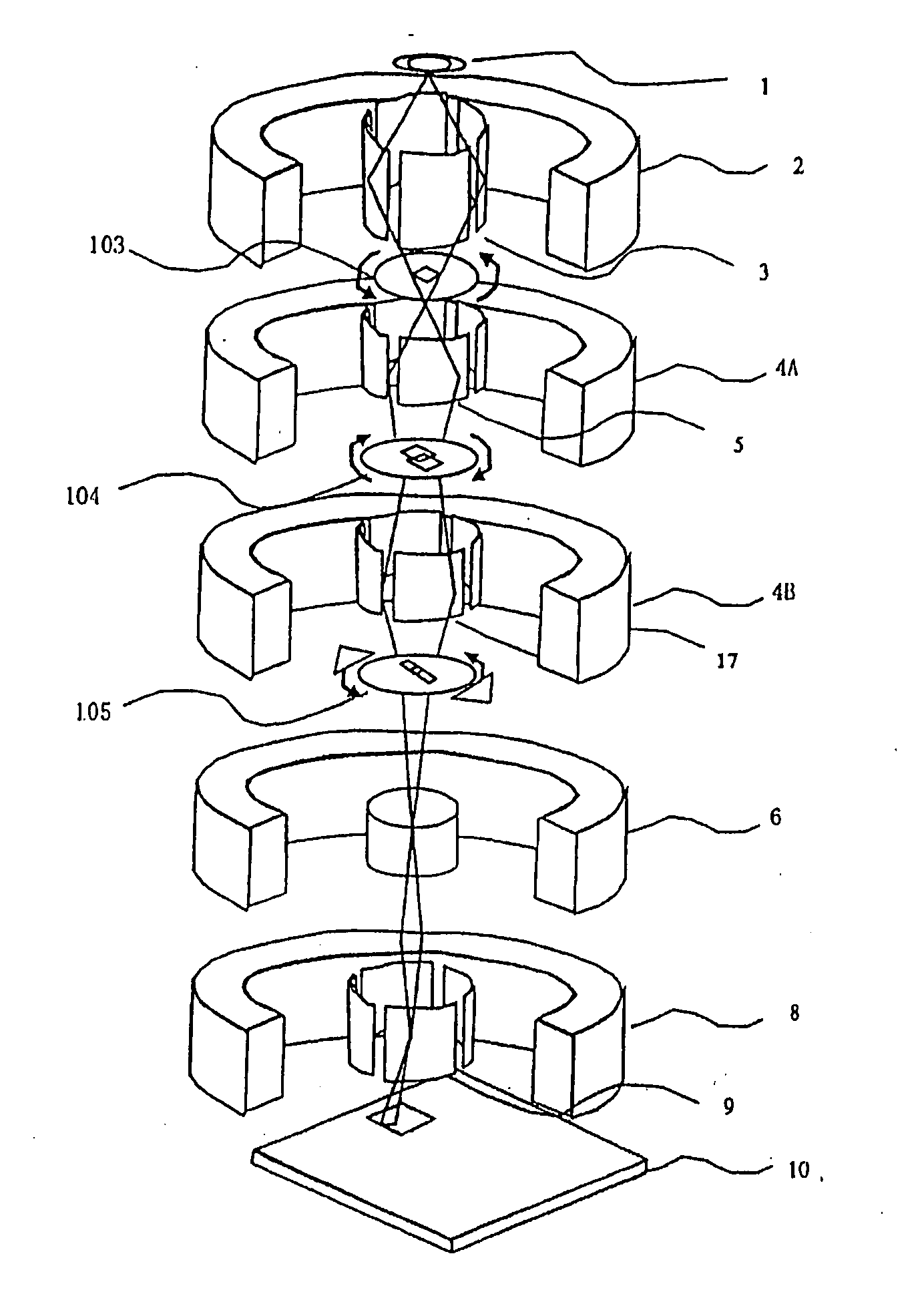
Electron beam apparatus
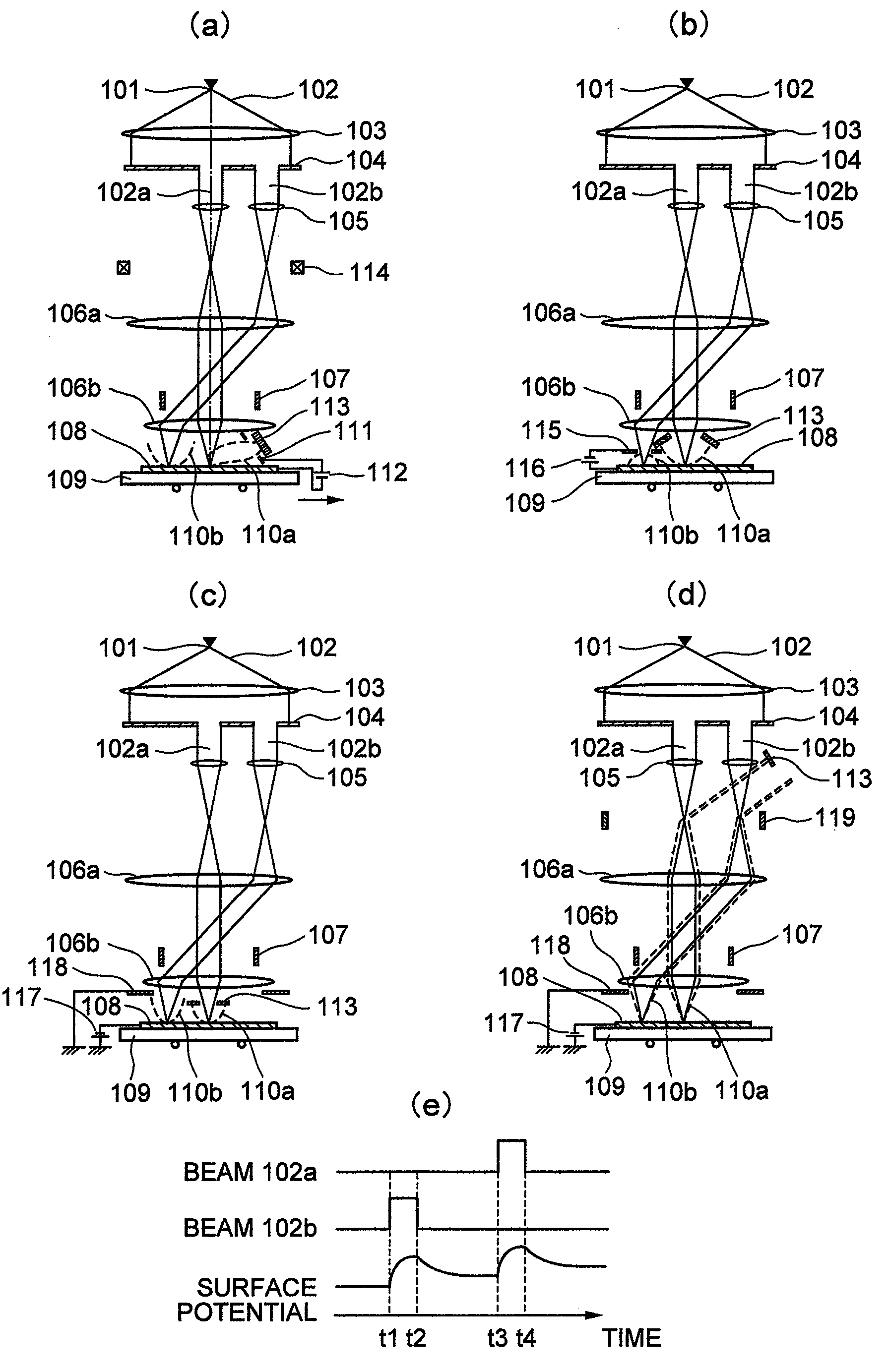
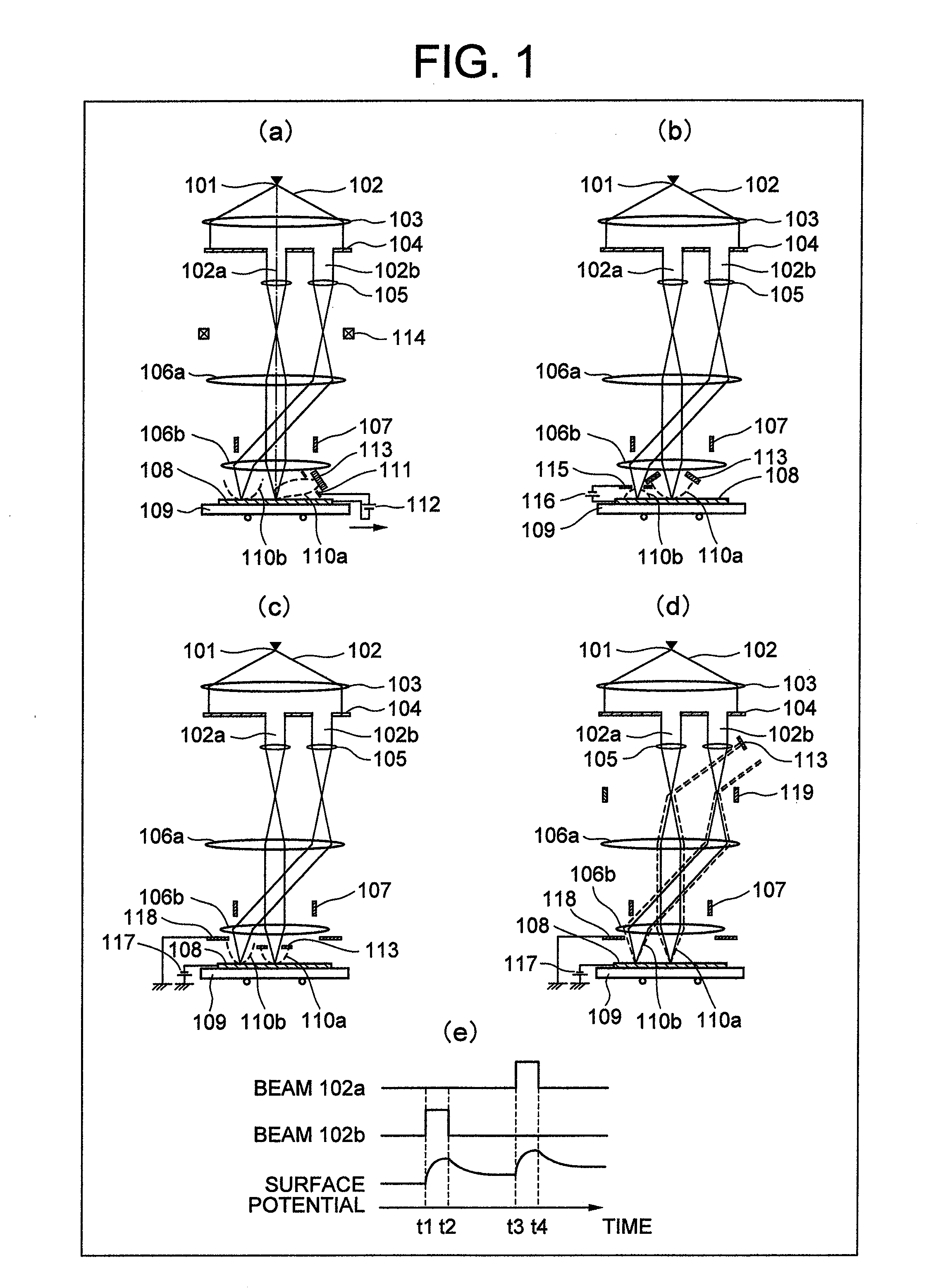
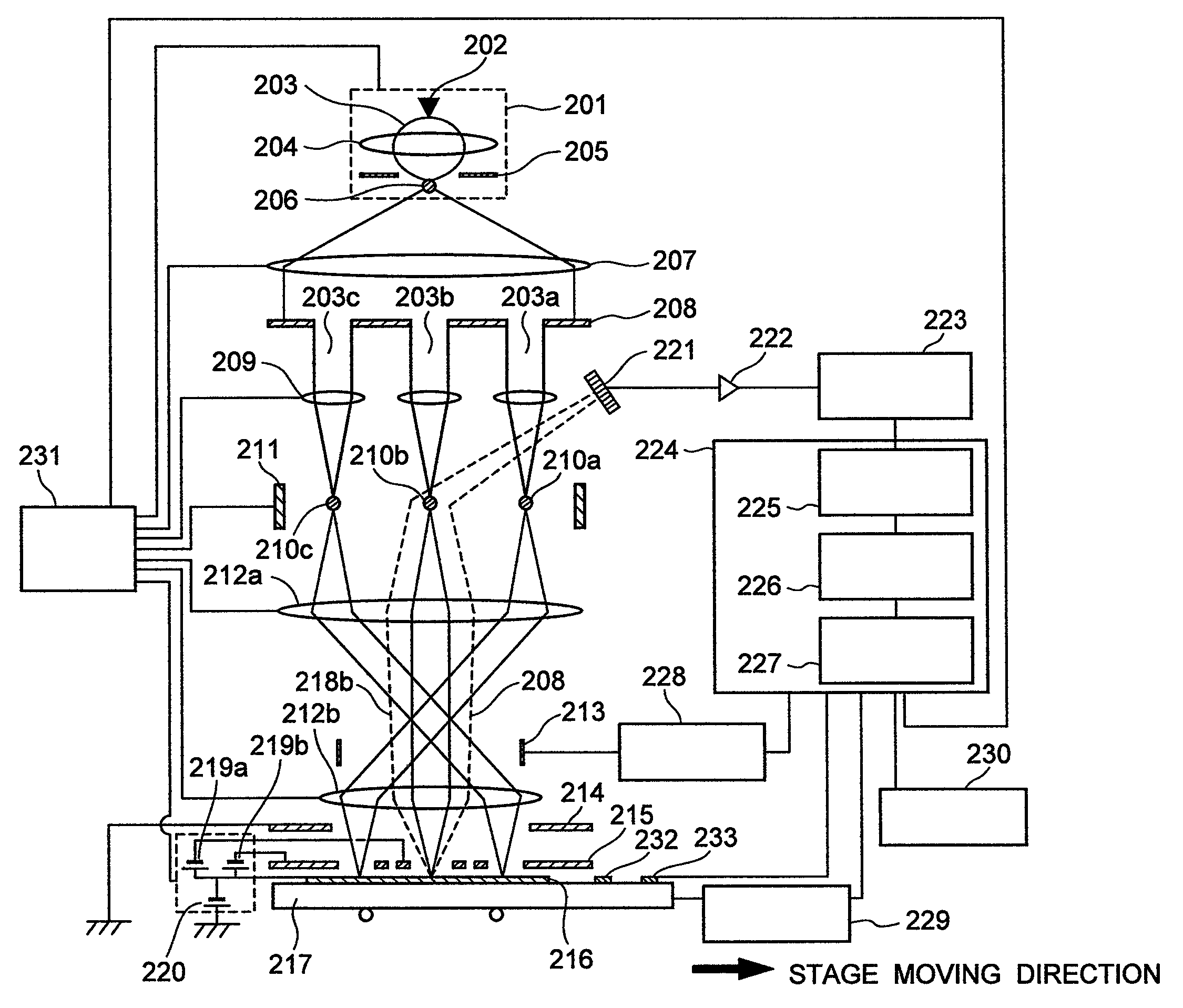
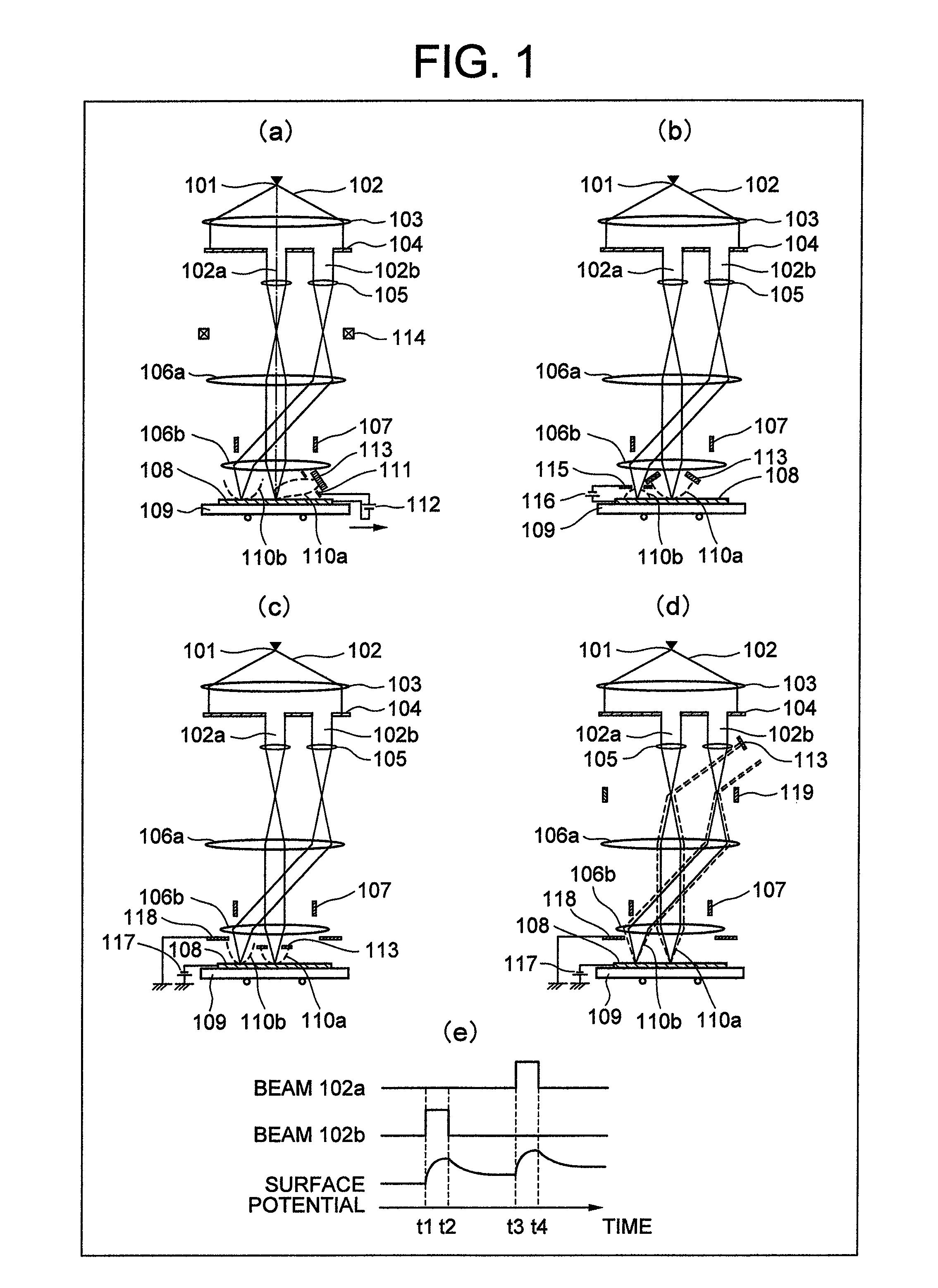
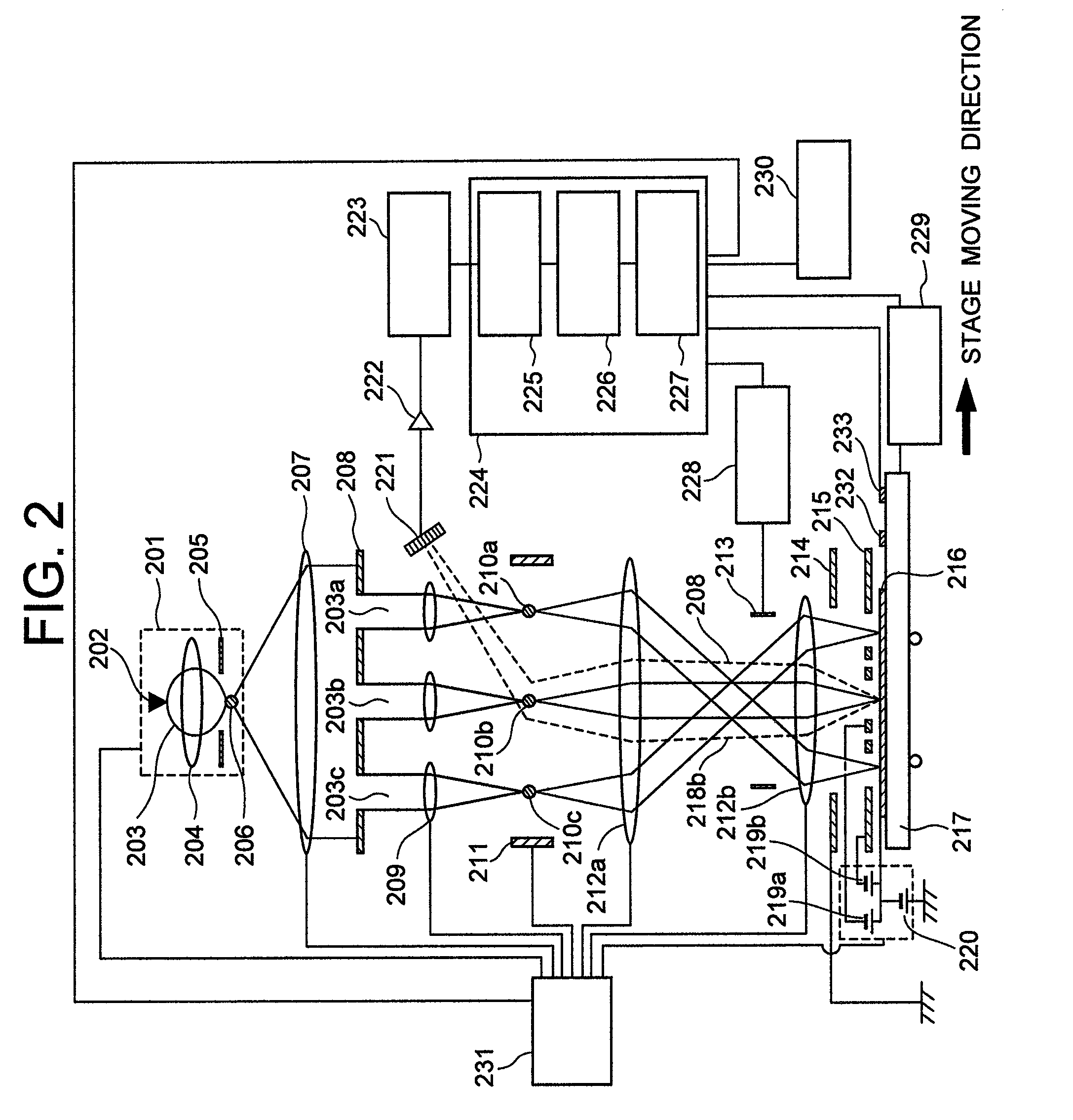
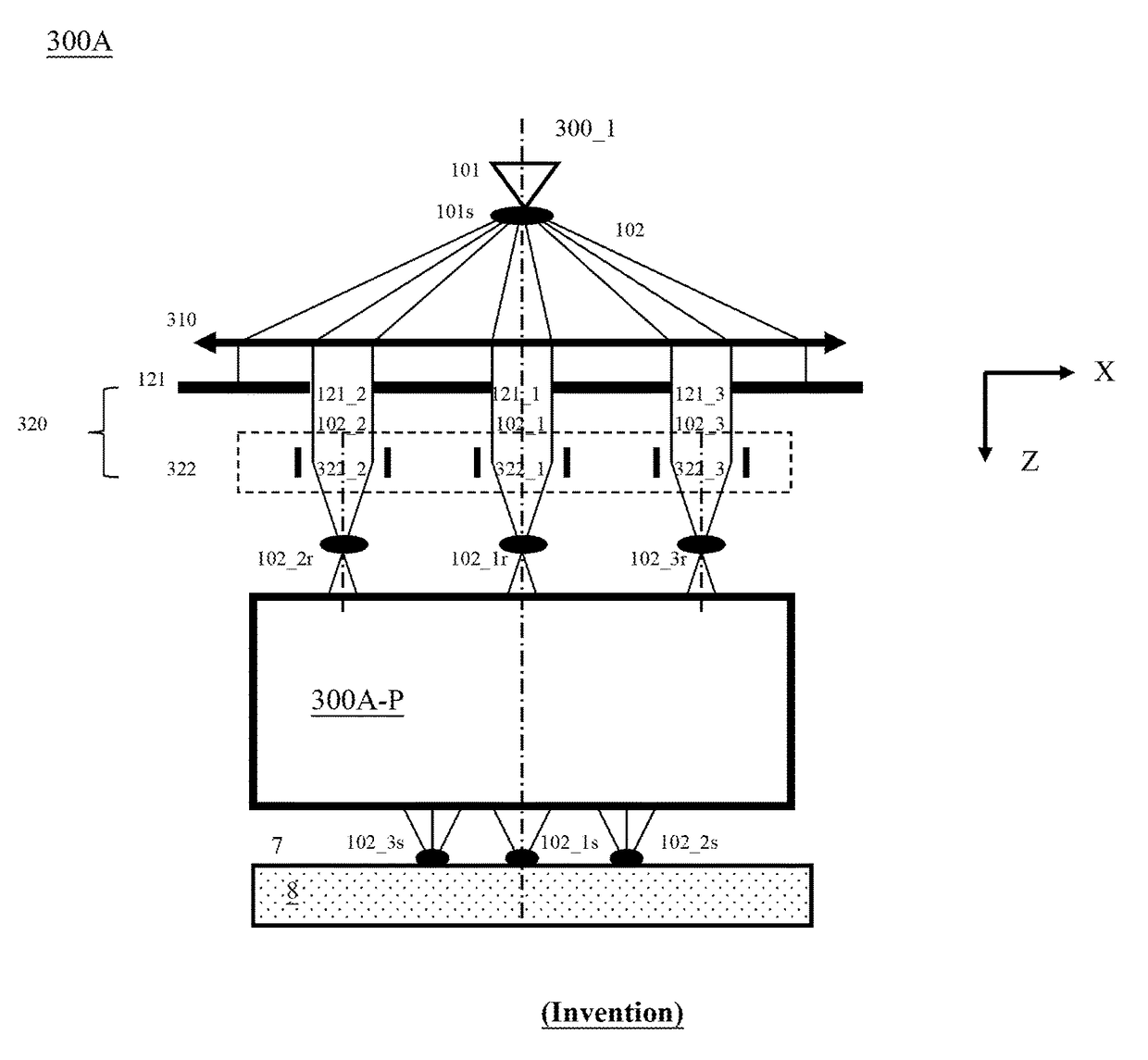
ActiveUS20100133433A1Improve throughputAchieve convergenceThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSingle electronLight beam
A plurality of primary beams are formed from a single electron source, the surface charge of a sample is controlled by at least one primary beam, and at the same time, the inspection of the sample is conducted using a primary beam other than this. Also, for an exposure area of the primary beam for surface charge control and an exposure area of the primary beam for the inspection, the surface electric field strength is set individually. Also, the current of the primary beam for surface charge control and the interval between the primary beam for surface charge control and the primary beam for inspection are controlled.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Silicon nanoparticle field effect transistor and transistor memory device
A silicon nanoparticle transistor and transistor memory device. The transistor of the invention has silicon nanoparticles, dimensioned on the order of 1 nm, in a gate area of a field effect transistor. The resulting transistor is a transistor in which single electron flow controls operation of the transistor. Room temperature operation is possible with the novel transistor structure by radiation assistance, with radiation being directed toward the silicon nanoparticles to create necessary holes in the quantum structure for the flow of an electron. The transistor of the invention also forms the basis for a memory device. The device is a flash memory device which will store electrical charge instead of magnetic effects.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Variable shaped electron beam lithography system and method for manufacturing substrate
InactiveUS20080054196A1Reduce drawing timeDrawn preciselyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesSingle electronOptical axis
This VSB lithography system includes a first, second and third aperture for forming a single electron beam in each of the rectangular opening portion that are provided, and draws a figure pattern using the single electron beam formed by passing the beam through the first, second and third aperture in sequence. Each of the first, second and third aperture has a mechanism for rotationally driving the aperture around an optical axis up to an arbitrary angle from 0 to 360°. Further, in the third aperture, a mechanism for varying the opening slit width of the rectangular opening portion is provided.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Apparatus of plural charged-particle beams
ActiveUS9607805B2Reduce impactPrevent deviationElectric discharge tubesSingle electronElectron source
One modified source-conversion unit and one method to reduce the Coulomb Effect in a multi-beam apparatus are proposed. In the modified source-conversion unit, the aberration-compensation function is carried out after the image-forming function has changed each beamlet to be on-axis locally, and therefore avoids undesired aberrations due to the beamlet tilting / shifting. A Coulomb-effect-reduction means with plural Coulomb-effect-reduction openings is placed close to the single electron source of the apparatus and therefore the electrons not in use can be cut off as early as possible.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Terahertz light source chip and manufacturing method thereof, terahertz light source device and manufacturing method thereof, and terahertz light source module and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104466617AAvoid frequencyAvoid temperatureSolid masersSemiconductor devicesGratingWorking temperature
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Electron beam apparatus
ActiveUS7880143B2High inspection and measurement throughputFast convergenceThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersSingle electronElectron source
A plurality of primary beams are formed from a single electron source, the surface charge of a sample is controlled by at least one primary beam, and at the same time, the inspection of the sample is conducted using a primary beam other than this. Also, for an exposure area of the primary beam for surface charge control and an exposure area of the primary beam for the inspection, the surface electric field strength is set individually. Also, the current of the primary beam for surface charge control and the interval between the primary beam for surface charge control and the primary beam for inspection are controlled.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Nanoscale heterojunctions and methods of making and using thereof
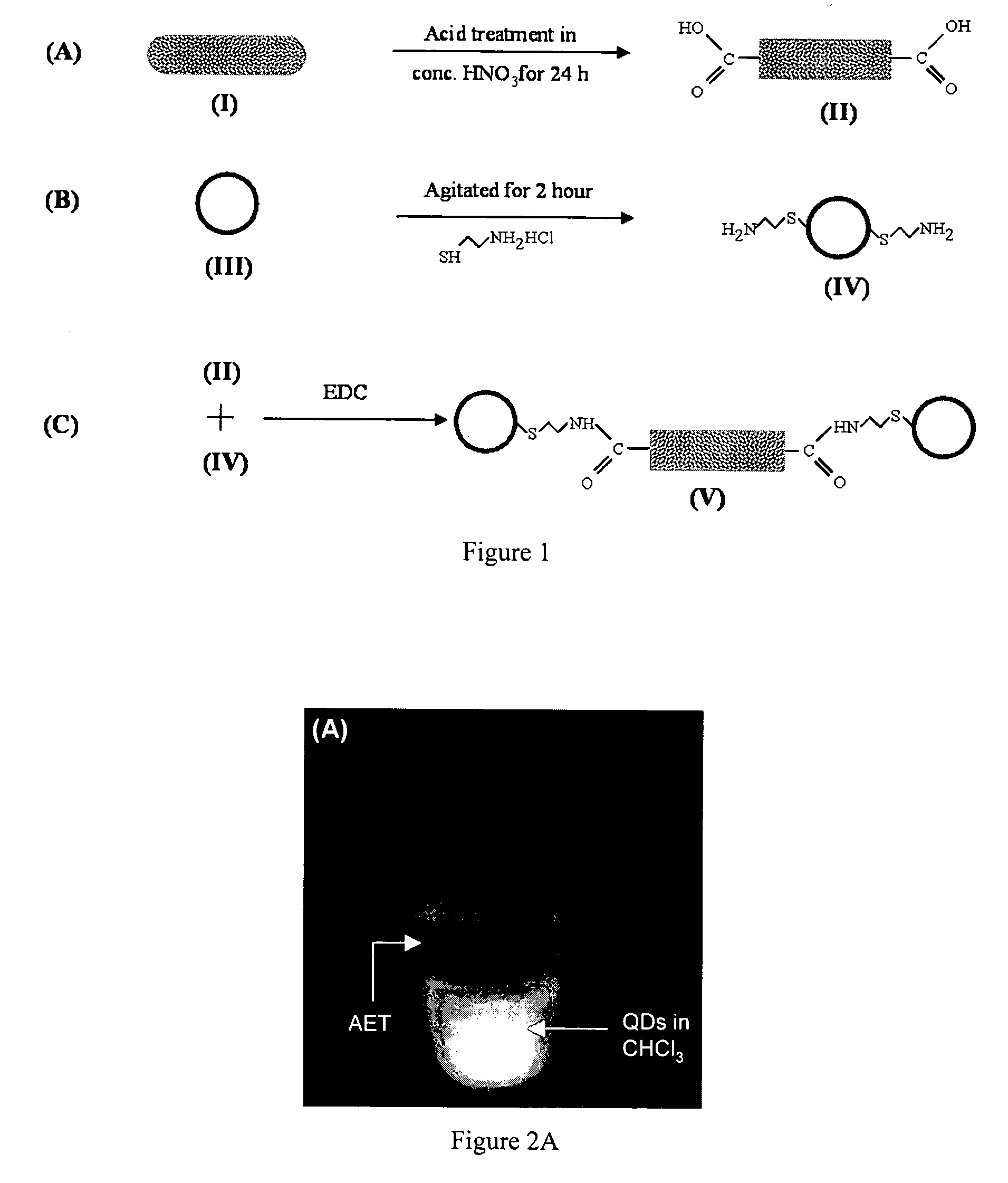
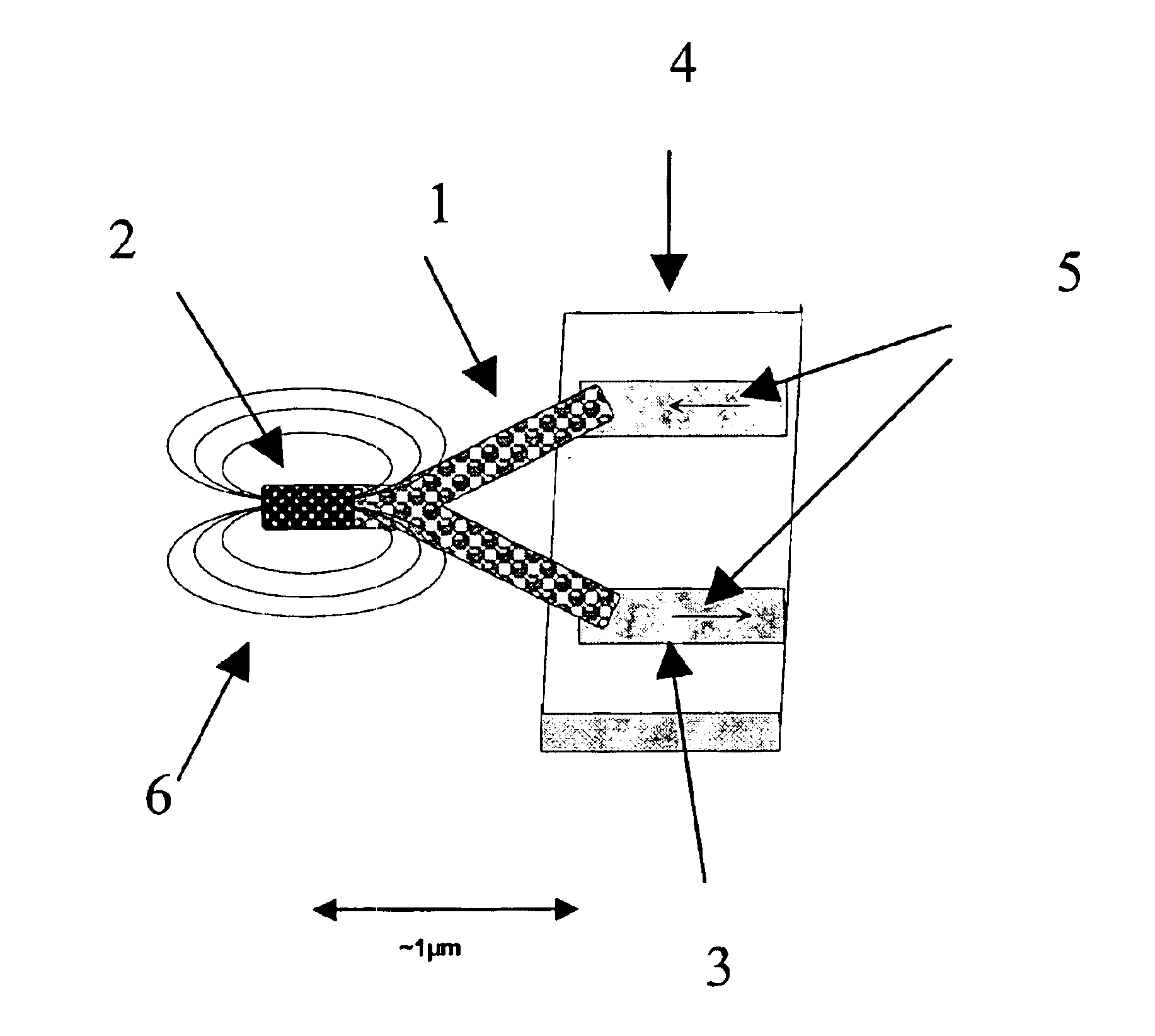
Disclosed herein are nanoscale heterojunctions and methods of making and using thereof. The heterojunctions comprise at least one carbon nanotube with at least one nanostructure such as a quantum dot connected, immobilized, attached, or affixed thereto. The carbon nanotubes may be single walled, multi-walled, or a combination of both. The nanostructure is preferably a quantum dot such as a ZnS capped CdSe core. The carbon nanotube heterojunctions may be employed in various nanoscale electronics and optoelectronic devices and multilayered systems including light emitting diodes, single electron transistors, spintronic devices, field emission flat panel displays, vacuum microelectronic sources, biosensors, random access memories, spin valves, and the like.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Single electron transistor manufacturing method by electro-migration of metallic nanoclusters
ActiveUS7067341B2Material nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationSingle electronRoom temperature
A method manufactures a single electron transistor device by electro-migration of nanocluster wherein said nanoclusters are metallically passivated and forced to assembly over a lithographic patterned substrate under control of a non homogeneous electric field at room temperature. A controlled migration and the desired location of the metallic passivated nanoclusters are based on a dielectrophoretic process.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
System and method for evaluation using electron beam and manufacture of devices
InactiveUS20060060790A1Extended service lifeEliminate the effects ofMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesMagnifying glassElectron gun
An electron beam apparatus having a longer life time of cathode, and allowing a plurality of electron beams to be arranged adequately around an optical axis and five or more electron beams to be formed from a single electron gun. The electron beams emitted from a cathode made of ZrO / W (tungsten zirconium oxide) or a cathode made of carbide of transition metal to the off-optical axis directions may be converged on a sample to scan it. The apparatus includes a plate for reducing a vacuum conductance defined between the electron gun chamber side and the sample side, and apertures are formed through the plate at locations offset from the optical axis allowing for the passage of the electron beams. In order to evaluate a pattern on the sample, the electron beam emitted from the electron gun is incident to the sample surface via an objective lens. The objective lens is composed of a flat electrode having an aperture centered on the optical axis and placed in parallel with the sample surface and an electromagnetic lens including a gap formed in a side facing to the sample. Further, in order to inspect a mask, spacing among a plurality of electron beams after having passed through the mask are extended by a magnifying lens and thus widely spaced electron beams are then converted into optical signal in a scintillator.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Data storage nanostructures
InactiveUS20070206488A1Wide rangeNanoinformaticsMechanical record carriersSingle electronEngineering
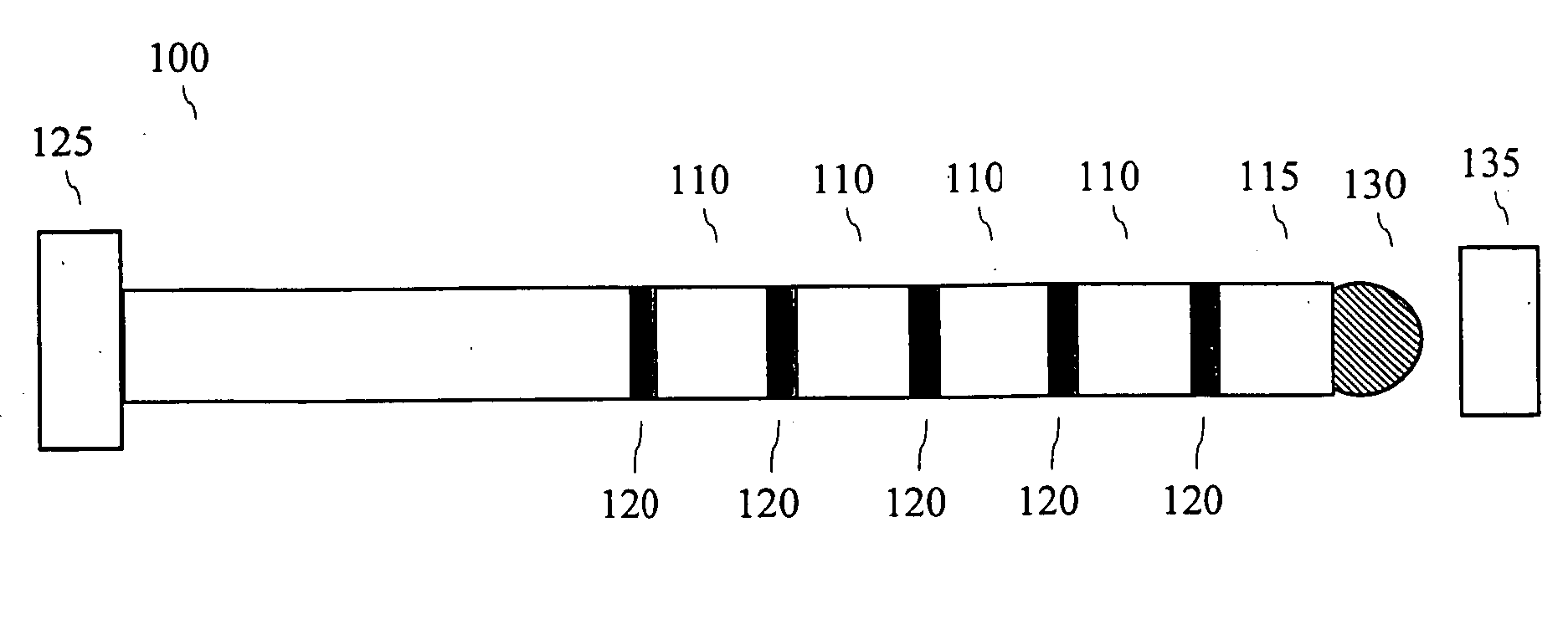
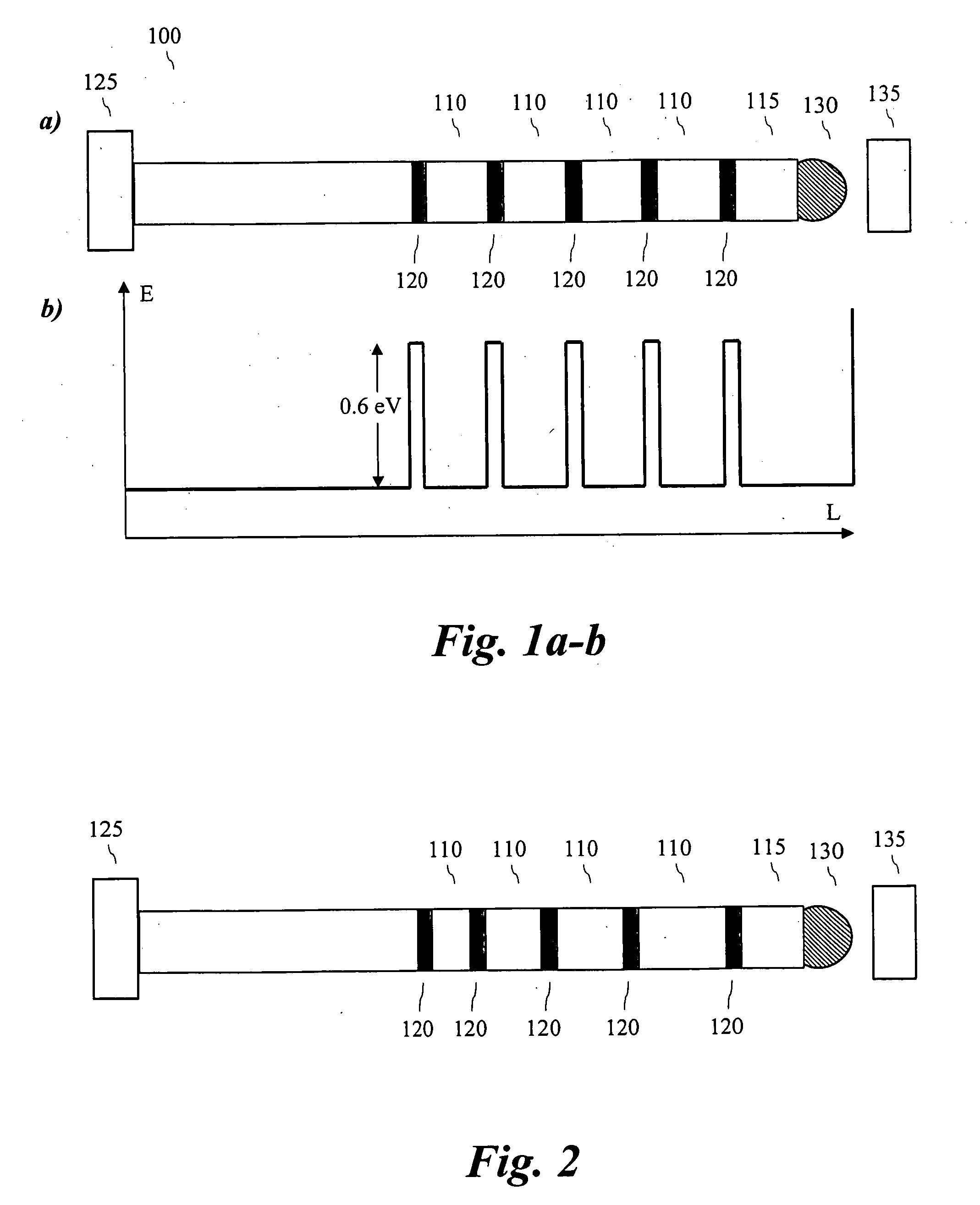
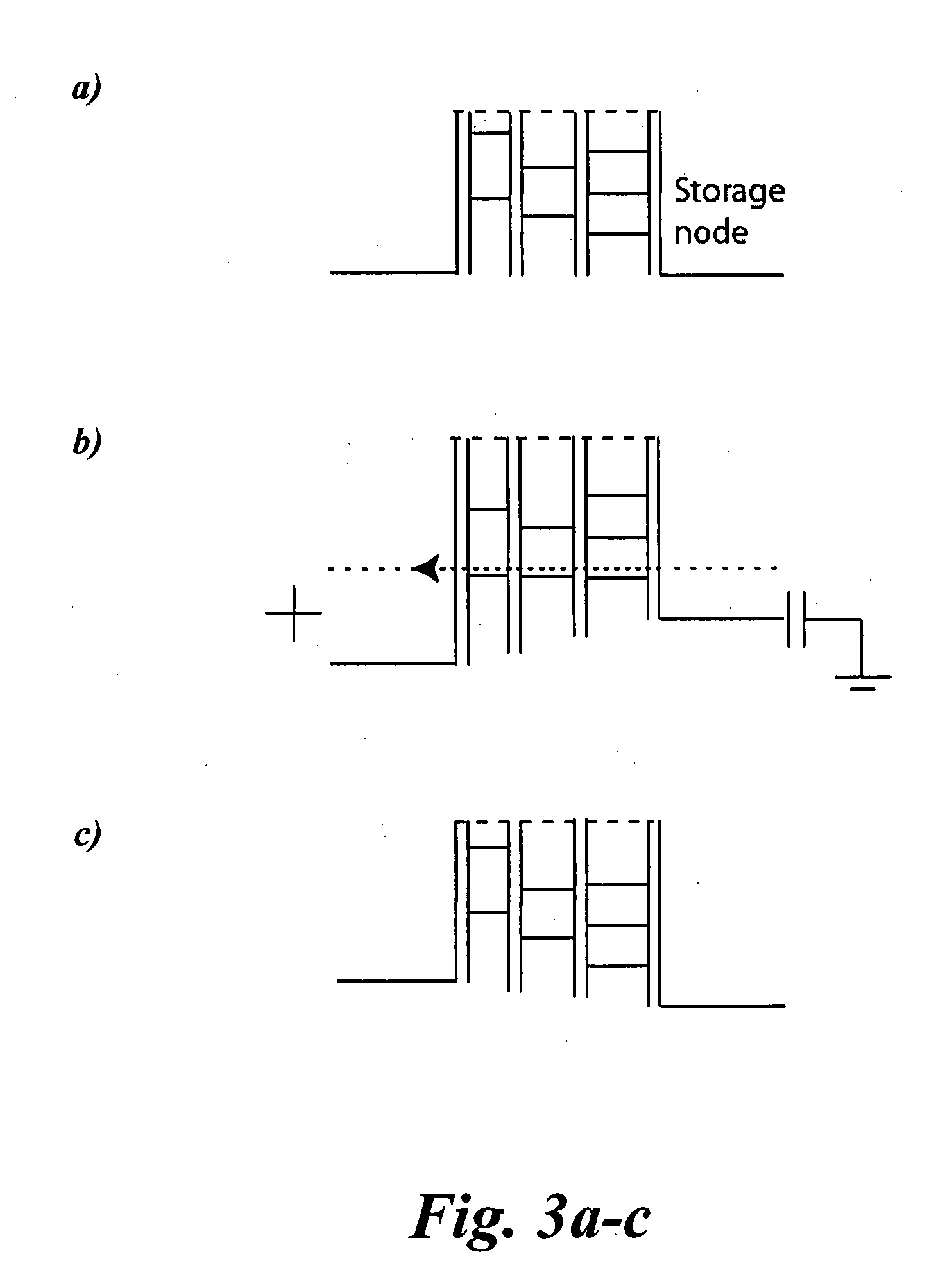
The present invention relates to a device for data storage. In particular the invention relates to a single electron memory device utilizing multiple tunnel junctions, and arrays or matrixes of such devices. The data storage device according to the invention comprises at least one nanowhisker adapted to store a charge. Each of the nanowhiskers comprises a sequence of axial segments of materials of different band gaps, arranged to provide a sequence of conductive islands separated by tunnel barriers and a storage island arranged at one end of the conductive island / tunnel barrier sequence, whereby to provide a data storage capability. The number of conductive islands should preferably be between five and ten.
Owner:QUNANO
Nanotube cantilever probes for nanoscale magnetic microscopy
InactiveUS6887365B2Eliminate needRaise the ratioNanomagnetismMagnetic field measurement using permanent magnetsScanning electron microscopeMicroscopic scale
The present invention provides an MFM or MRFM analytical device comprising a micro-dimensional probe that is capable of detecting single proton and single electron spin. Furthermore, it provides an MFM or MRFM device comprising a micro-dimensional probe, that is capable of detecting magnetic structures of size of order one nanometer. In particular, the present invention provides a micro-dimensional probe for an MFM or MRFM device that comprises a CNT cantilever that comprises a nanoscale ferromagnetic material. The CNT cantilever can be attached to an electrode as a component of a microscopic probe which is coupled with an electrical circuit as a component of a device for nanoscale MFM or MRFM micro-dimensional probes. The device comprising the probe and electrical circuit can be incorporated into an existing scanning probe microscope (SPM) apparatus having accommodation for electrical readout.
Owner:BOSTON COLLEGE
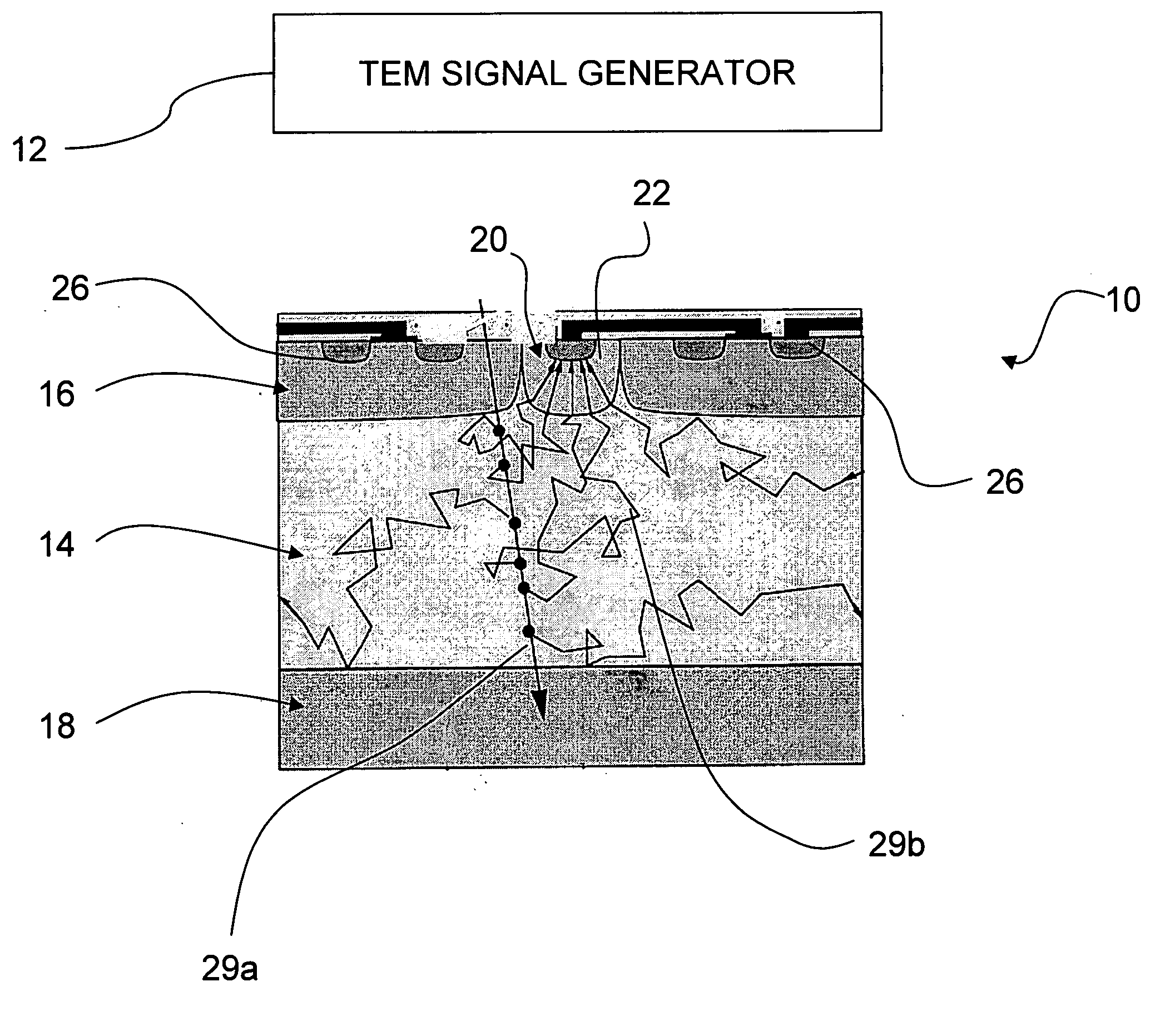
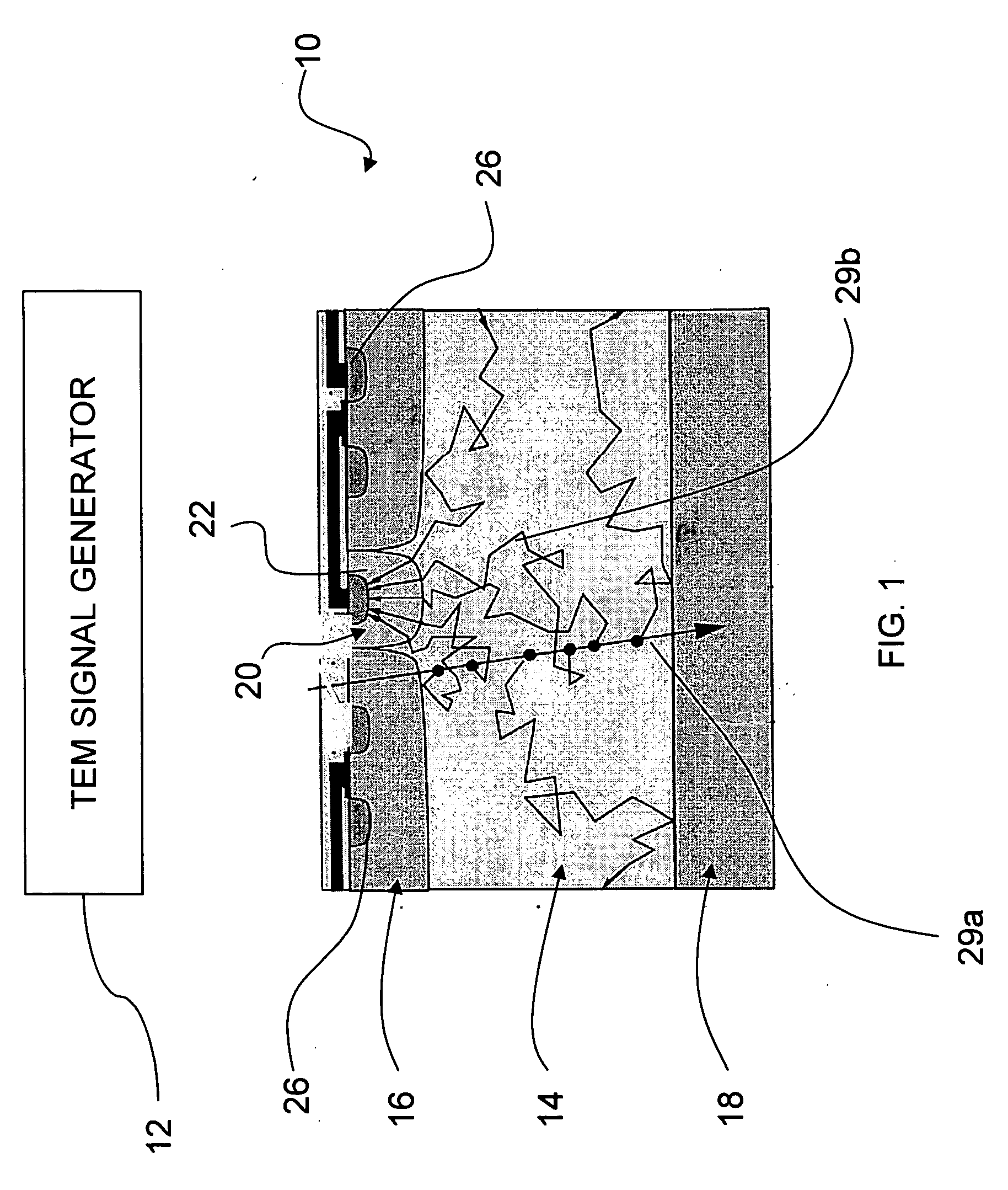
Direct collection transmission electron microscopy
InactiveUS20060169901A1Fast readoutEasy data collectionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSingle electronPhotodiode
A preferred method for transmission electron microscopy includes a step of generating a microscopy signal. The microscopy signal is then detected with an active pixel detector that includes a plurality of pixels. Each of the pixels includes at least one photodiode. Each pixel integrates an incident signal over a collection time period. Using a massibel parallel on chip analog to digital conversion, very fast read out times can be achieved, e.g., many frames per second. In a preferred embodiment, the read out time permits there to be a single electron event recorded per pixel, indicating either a single electron or the lack thereof. This permits simple accumulation of the pixel counts for each pixel in read-out and storage electronics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
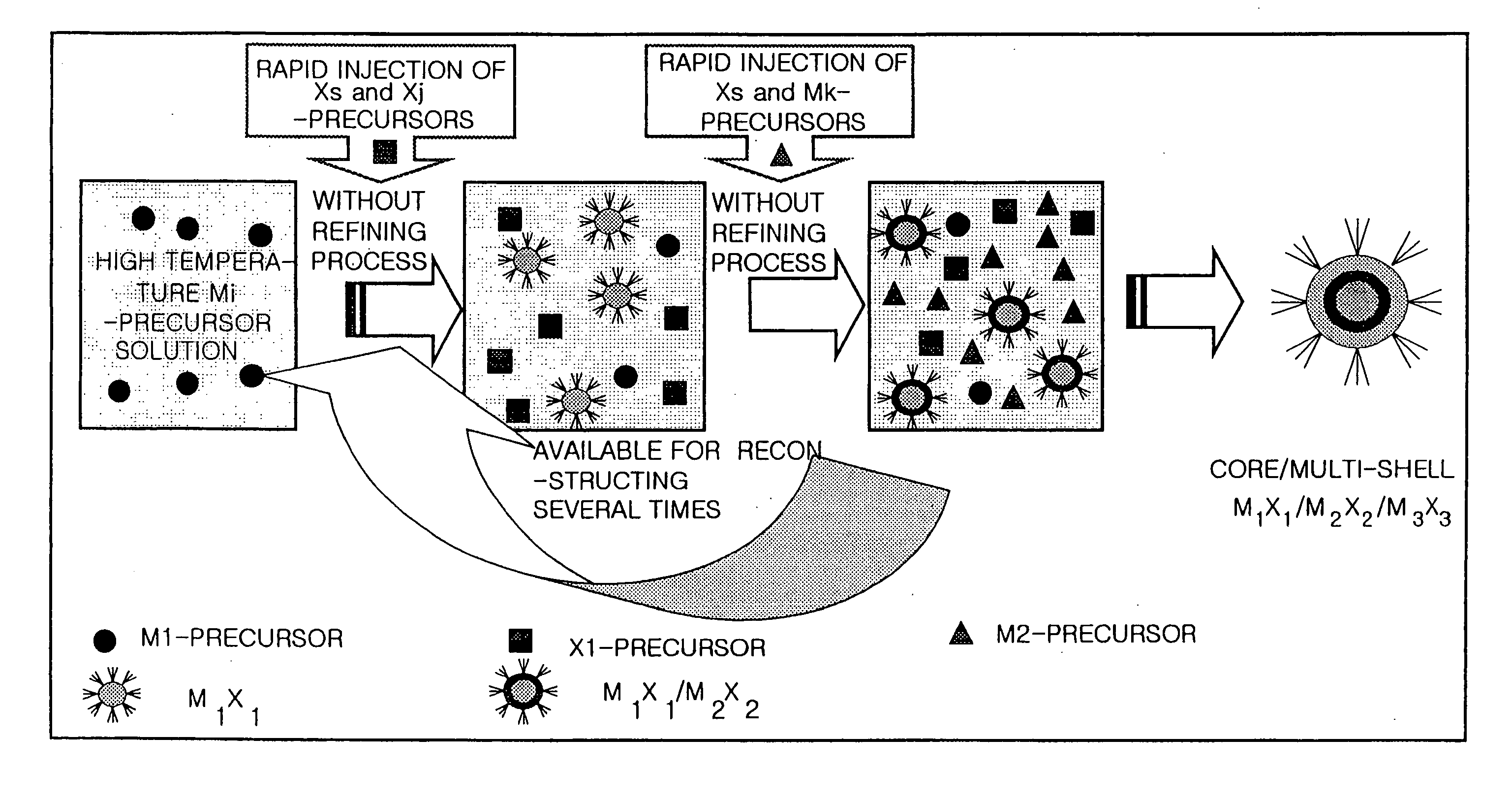
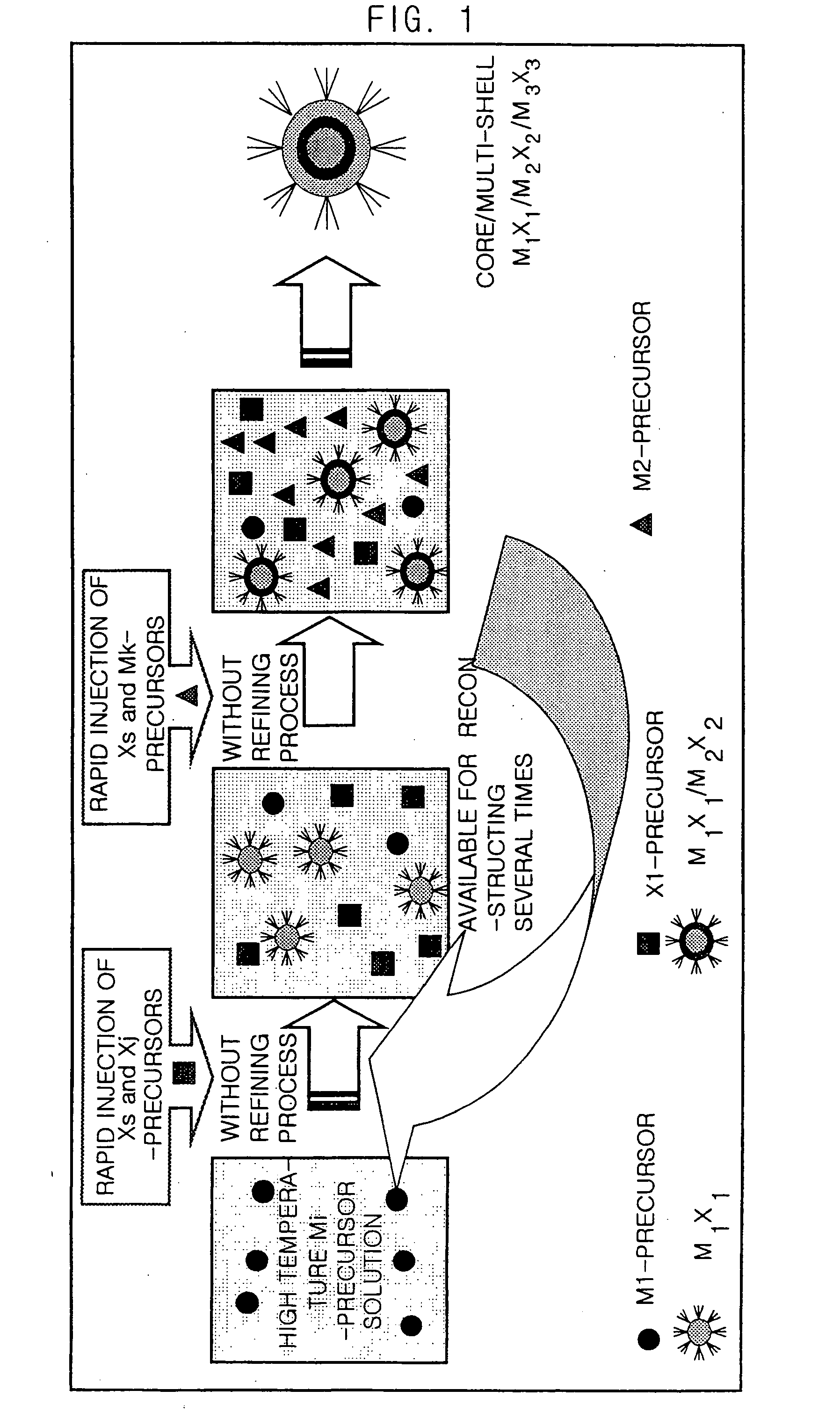
Method for Synthesizing Semiconductor Quantom Dots
InactiveUS20070295266A1Solve low luminous efficiencyStable in viewMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsSolar cellLuminescence
The present invention relates to a method for synthesizing high luminescence semiconductor quantum dots with a core-shell structure in a short time in large quantity. Using the method of synthesizing the quantum dots in accordance with the present invention, a large quantity of quantum dots can be economically synthesized in a rapid time without an explosion. And, the present invention can be applied to the fields employing various luminous materials since the luminous semiconductor quantum dots synthesized by the present invention has a high luminous efficiency and they can emit a light at various wavelengths in the whole range of a visible ray. And also, the present invention can be applied to a light emission device, a single electron transistor, a solar cell photo-sensitizer material and a bio-labelling tag since it is excellently stable.
Owner:NANOSQUARE CO LTD
Control and readout of electron or hole spin
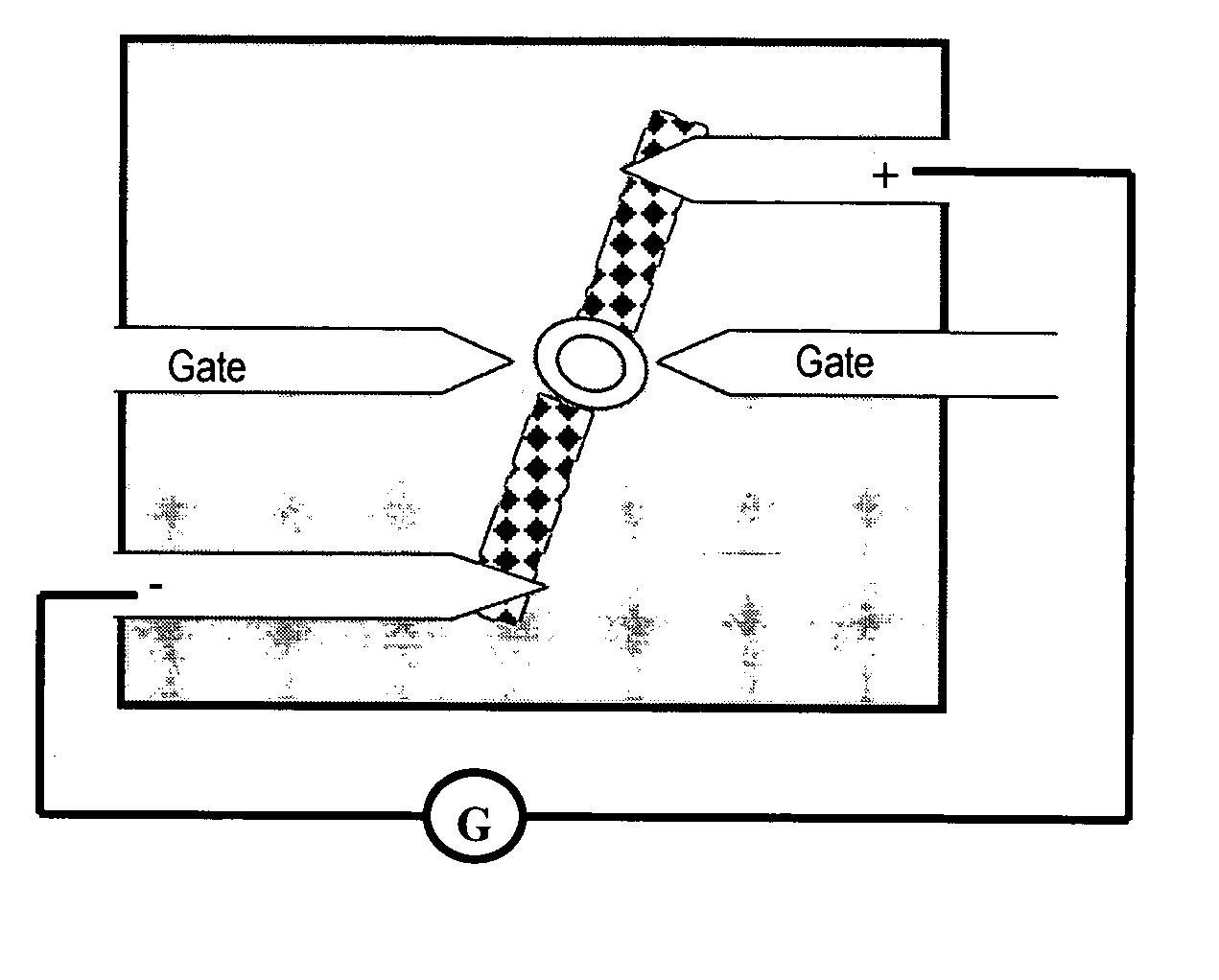
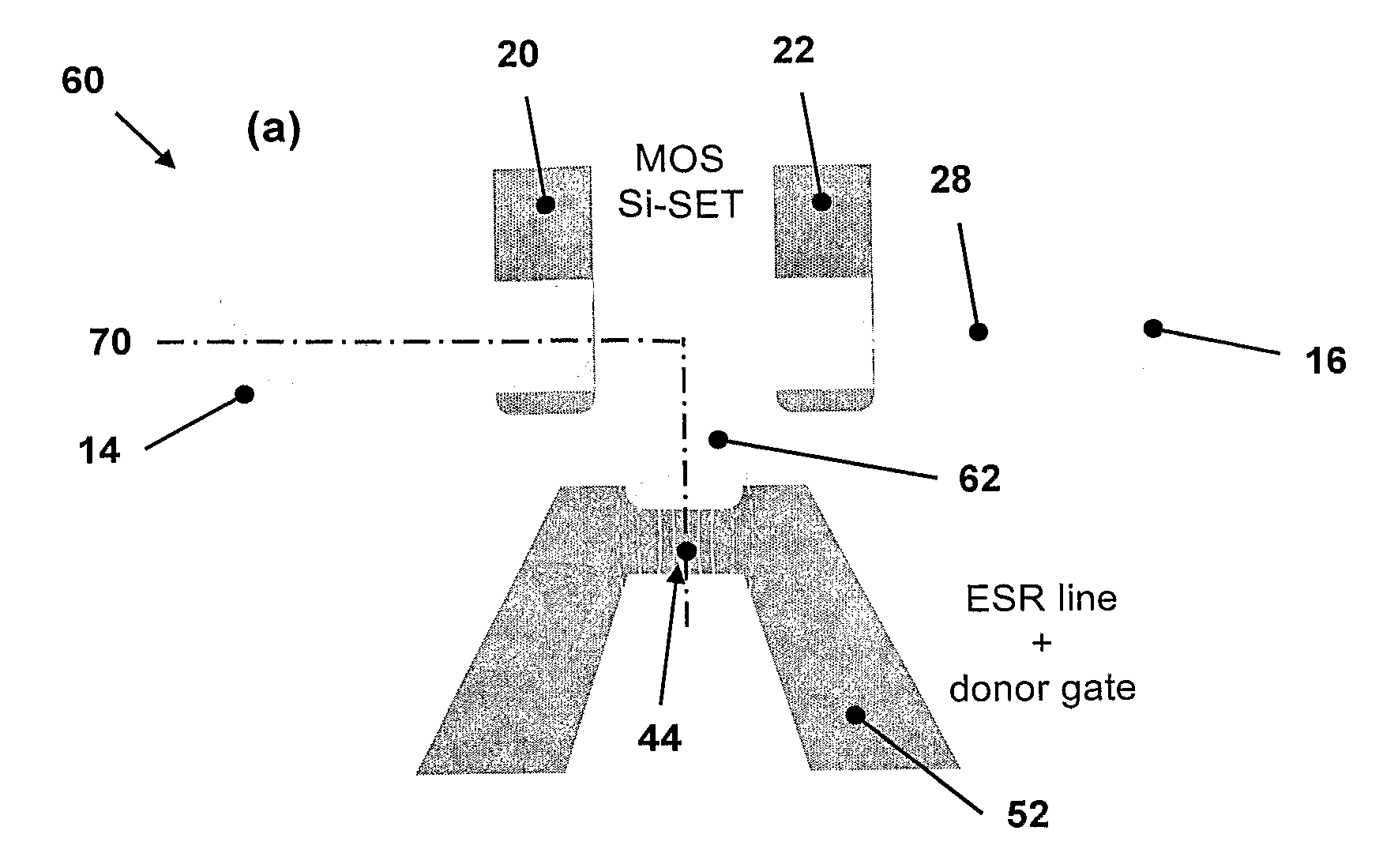
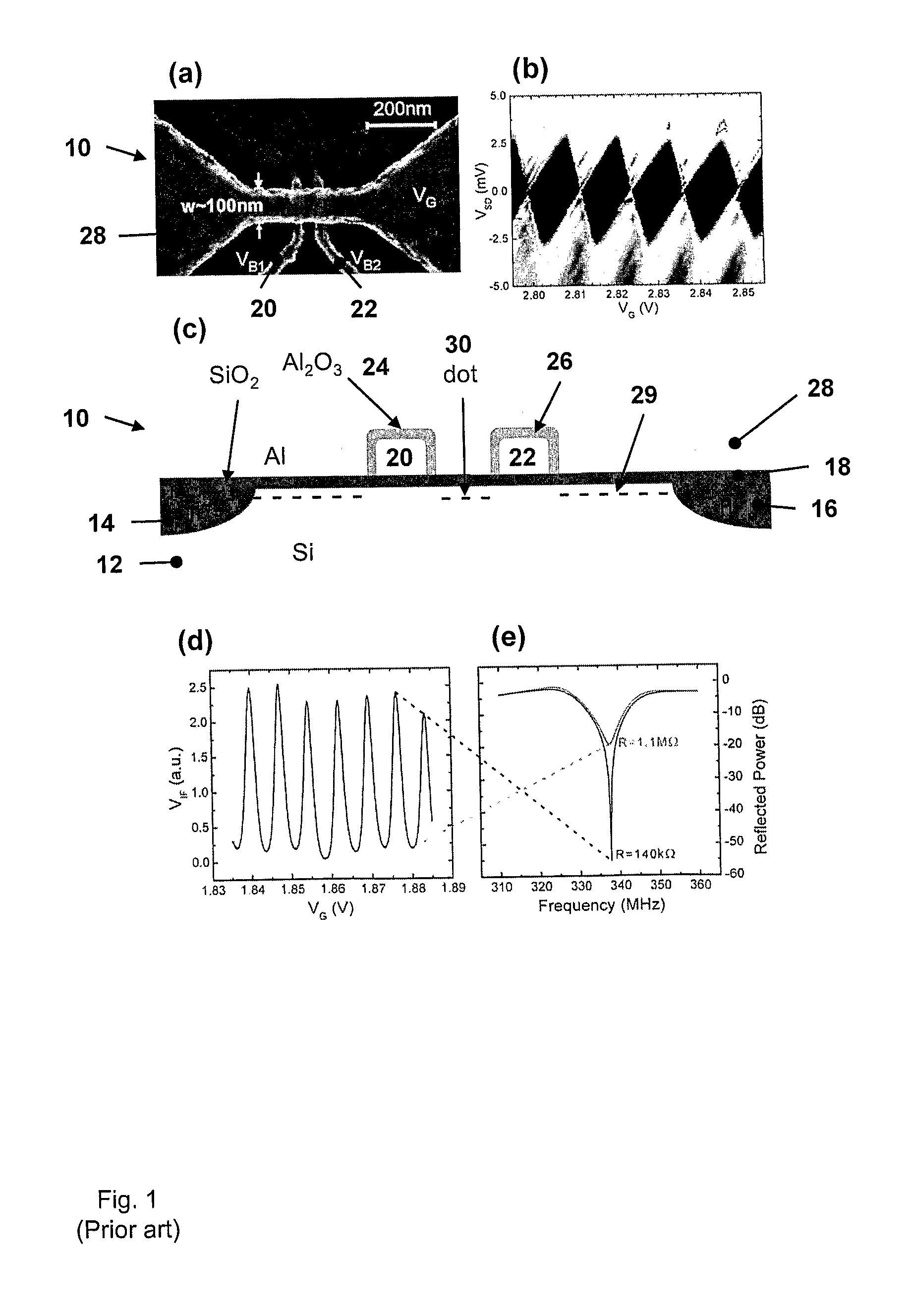
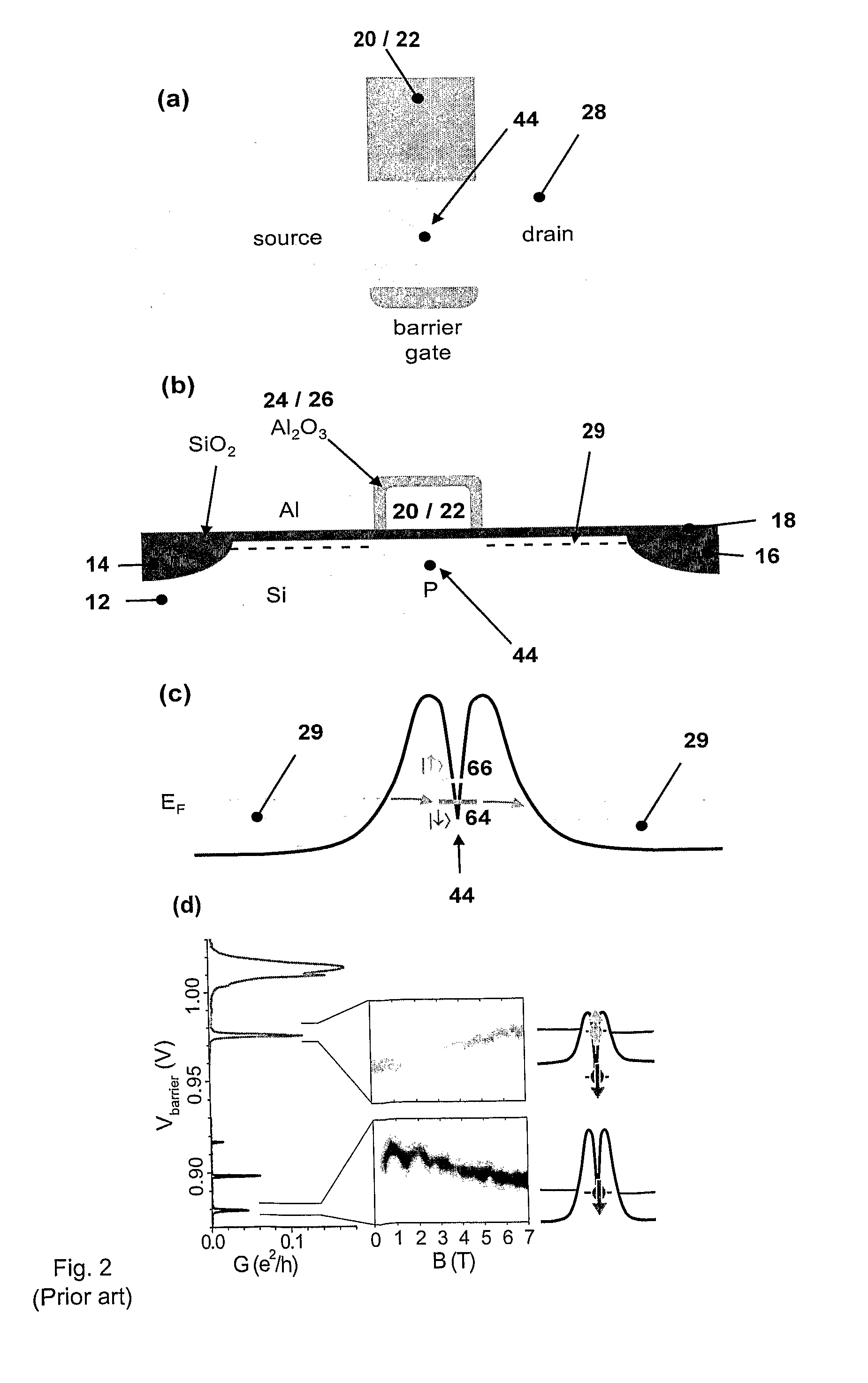
This invention concerns an electronic device for the control and readout of the electron or hole spin of a single dopant in silicon. The device comprises a silicon substrate in which there are one or more ohmic contact regions. An insulating region on top of the substrate. First and second barrier gates spaced apart to isolate a small region of charges to form an island of a Single Electron Transistor (SET). A third gate over-lying both the first and second barrier gates, but insulated from them, the third gate being able to generate a gate-induced charge layer (GICL) in the ESR line substrate beneath it. A fourth gate in close proximity to a single dopant donor gate atom, the dopant atom being encapsulated in the substrate outside the region of the GICL but close enough to allow spin-dependent charge tunnelling between the dopant atom and the SET island under the control of gate potentials, mainly the fourth gate. In use either the third or fourth gate also serve as an Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) line to control the spin of the single electron or hole of the dopant atom. In a further aspect it concerns a method for using the device.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
Apparatus of plural charged-particle beams
ActiveUS9922799B2High resolutionImprove throughputElectric discharge tubesThroughputCharged particle beam
A multi-beam apparatus for observing a sample with high resolution and high throughput and in flexibly varying observing conditions is proposed. The apparatus uses a movable collimating lens to flexibly vary the currents of the plural probe spots without influencing the intervals thereof, a new source-conversion unit to form the plural images of the single electron source and compensate off-axis aberrations of the plural probe spots with respect to observing conditions, and a pre-beamlet-forming means to reduce the strong Coulomb effect due to the primary-electron beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Quantum bit with a multi-terminal junction and loop with a phase shift
A solid-state quantum computing qubit includes a multi-terminal junction coupled to a superconducting loop where the superconducting loop introduces a phase shift to the superconducting order parameter. The ground state of the supercurrent in the superconducting loop and multi-terminal junction is doubly degenerate, with two supercurrent ground states having distinct magnetic moments. These quantum states of the supercurrents in the superconducting loop create qubits for quantum computing. The quantum states can be initialized by applying transport currents to the external leads. Arbitrary single qubit operations may be performed by varying the transport current and / or an externally applied magnetic field. Read-out may be performed using direct measurement of the magnetic moment of the qubit state, or alternatively, radio-frequency single electron transistor electrometers can be used as read-out devices when determining a result of the quantum computing. Further, qubits as described above can form arrays of qubits for performing controlled quantum computing calculations. In one example, an array of qubits can be utilized as a random number generator.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
External cathode ion source
An ion source is disclosed for use in fabrication of semiconductors. The ion source includes an electron emitter that includes a cathode mounted external to the ionization chamber for use in fabrication of semiconductors. In accordance with an important aspect of the invention, the electron emitter is employed without a corresponding anode or electron optics. As such, the distance between the cathode and the ionization chamber can be shortened to enable the ion source to be operated in an arc discharge mode or generate a plasma. Alternatively, the ion source can be operated in a dual mode with a single electron emitter by selectively varying the distance between the cathode and the ionization chamber.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
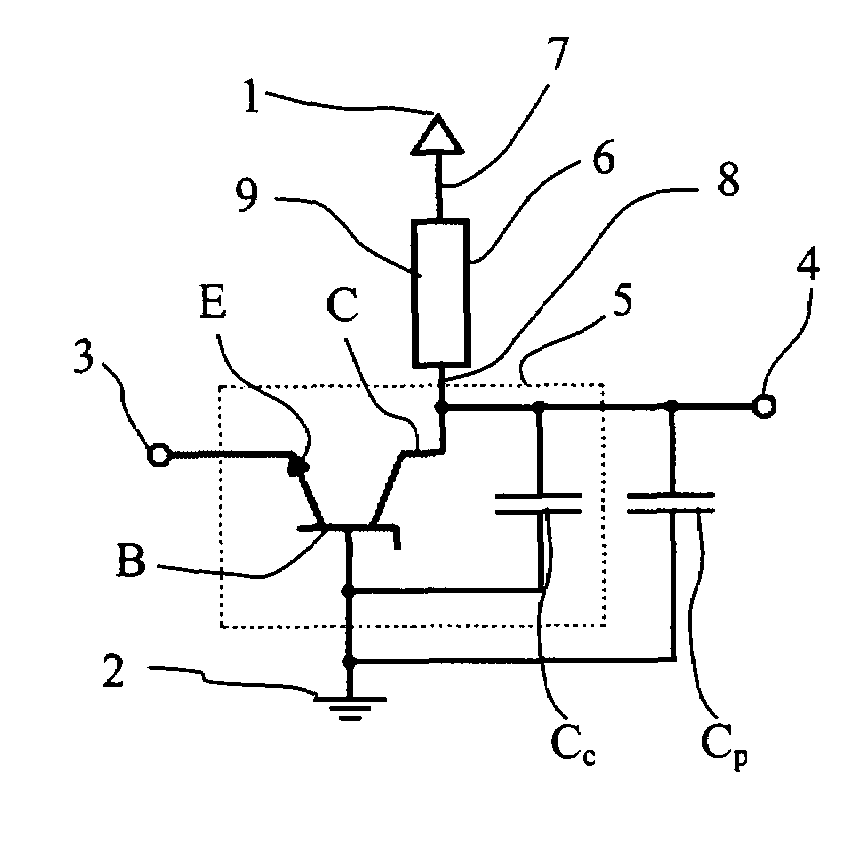
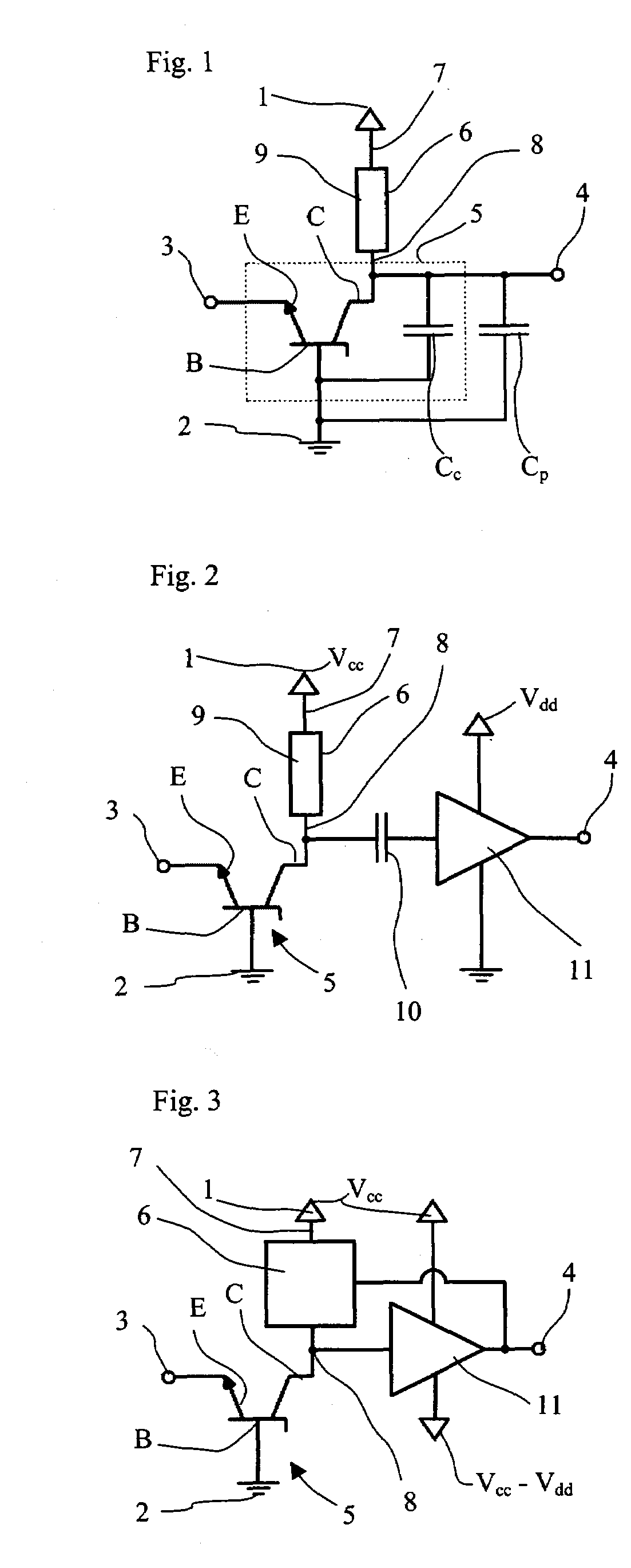
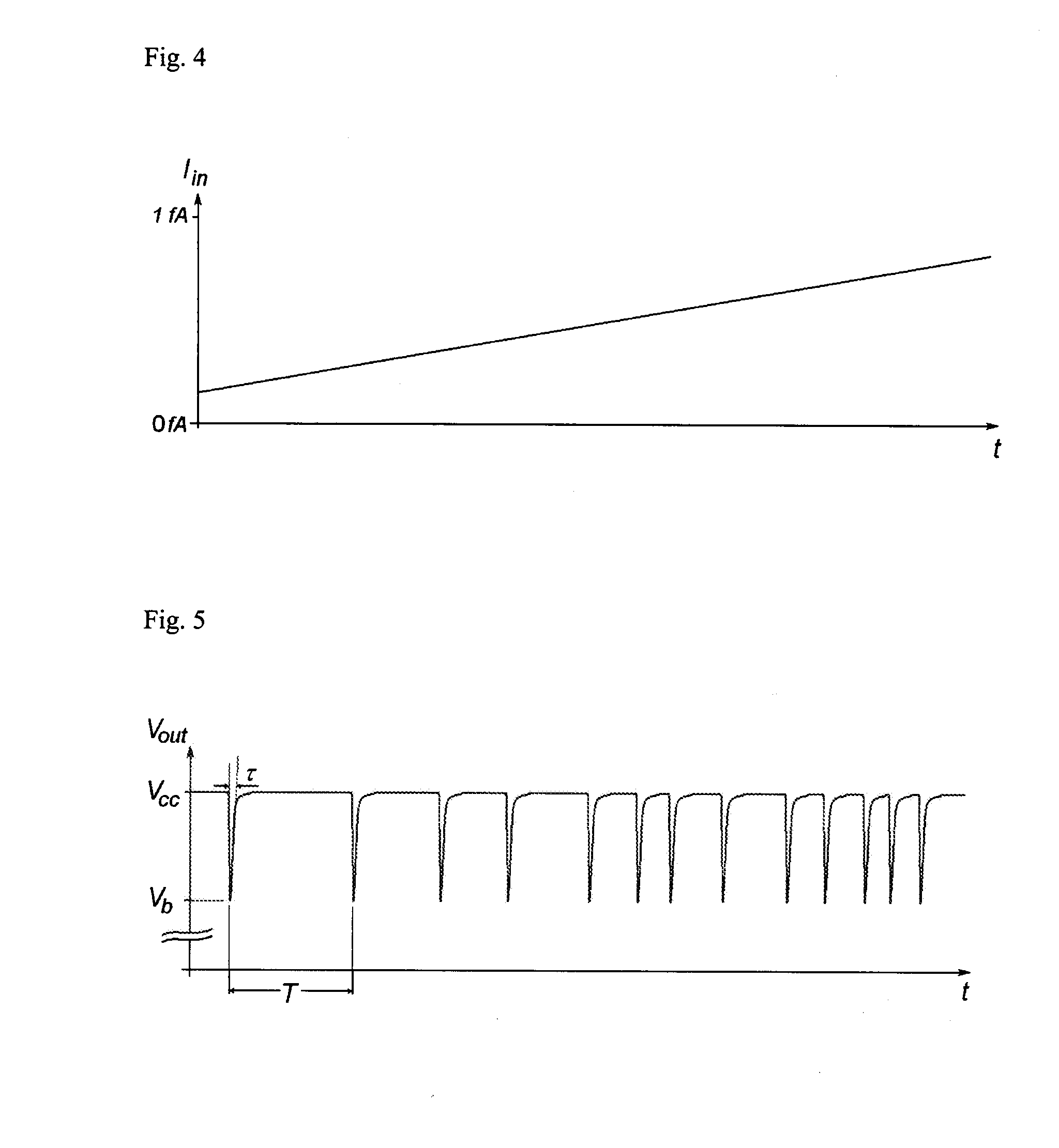
Semiconductor Device For Measuring Ultra Small Electrical Currents And Small Voltages
InactiveUS20100013458A1Reduce bias voltageIncrease kinetic energyElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingSingle electronLow voltage
A semiconductor device for measuring ultra low currents down to the level of single electrons or low voltages comprises a first and a second voltage supply terminal, an input terminal for receiving an electrical current or being supplied with a voltage to be measured, a bipolar transistor having a base, an emitter and a collector, wherein a first PN junction is formed between the base and the collector and a second PN junction is formed between the base and the emitter, wherein the emitter is coupled to the input terminal and the base is coupled to the second voltage supply terminal, and wherein the first PN junction is designed for reverse biased operation as an avalanche diode, and a quenching and recharging circuit having a first terminal coupled to the first voltage supply terminal and a second terminal coupled to the collector of the bipolar transistors, the quenching and recharging circuit permitting operation of the first PN junction reverse biased above the breakdown voltage of the first PN junction.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Sensor for Detection of Single Molecules
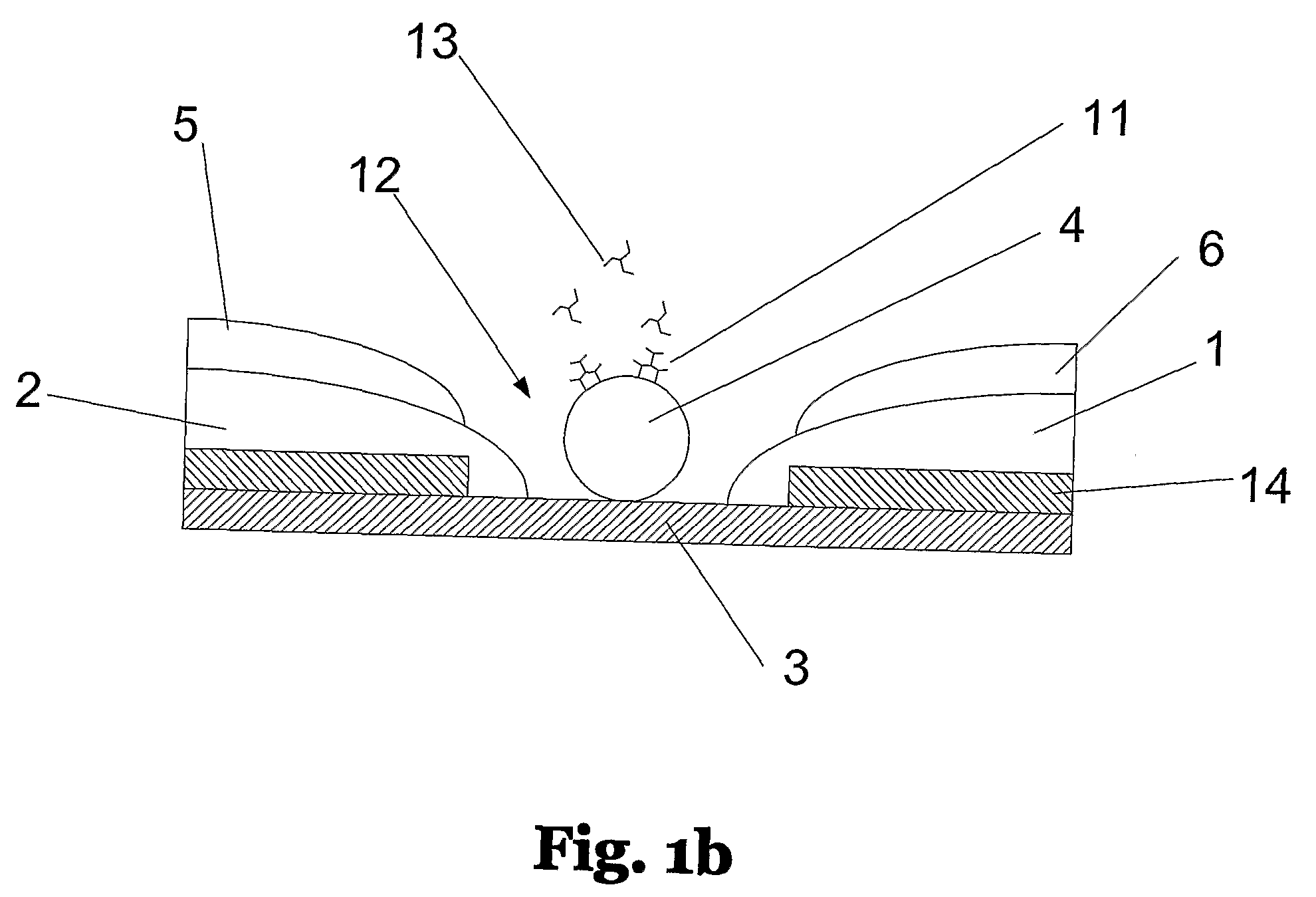
InactiveUS20080149479A1High sensitivityReduce distortion problemsImmobilised enzymesMaterial nanotechnologySingle electronNano manufacturing
A single electron transistor device for sensing at least one particle, includes at least two electrodes positioned with a gap formed between the electrodes and an activation object positioned in the gap with an insulating layer between the activation object and each electrode. The activation object which is able to transfer electrons is arranged with at least one binding structure bonded to it for receiving the at least one particle. The electrodes are formed with an inter distance of less than 50 nm and the electrodes are connectable directly or indirectly to a signal acquisition system. The sensing device is arranged to allow a tunnelling current proportional to the presence of the at least one particle in the binding structure, to flow through the activation object. A method, and system using a single electron transistor device fabricated with micro / nano fabrication methods are also disclosed.
Owner:MIDORION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com