Patents
Literature
196 results about "Molecular sensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A molecular sensor or chemosensor is a molecular structure (organic or inorganic complexes) that is used for sensing of an analyte to produce a detectable change or a signal. The action of a chemosensor, relies on an interaction occurring at the molecular level, usually involves the continuous monitoring of the activity of a chemical species in a given matrix such as solution, air, blood, tissue, waste effluents, drinking water, etc. The application of chemosensors is referred to as chemosensing, which is a form of molecular recognition. All chemosensors are designed to contain a signalling moiety and a recognition moiety, that is connected either directly to each other or through a some kind of connector or a spacer. The signalling is often optically based electromagnetic radiation, giving rise to changes in either (or both) the ultraviolet and visible absorption or the emission properties of the sensors. Chemosensors may also be electrochemically based. Small molecule sensors are related to chemosensors. These are traditionally, however, considered as being structurally simple molecules and reflect the need to form chelating molecules for complexing ions in analytical chemistry. Chemosensors are synthetic analogues of biosensors, but such sensors incorporate biological receptor such as antibodies, aptamers or large biopolymers.
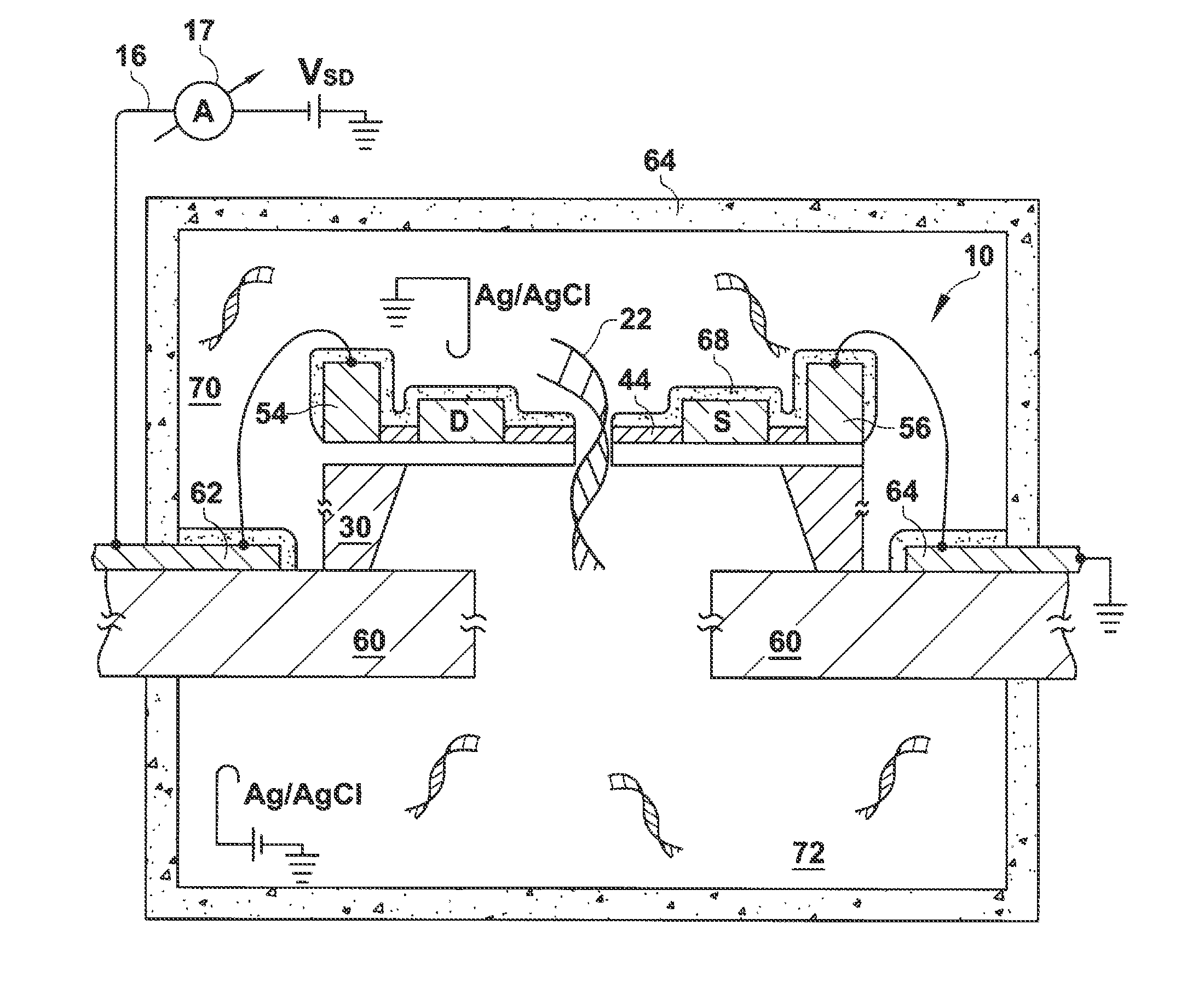
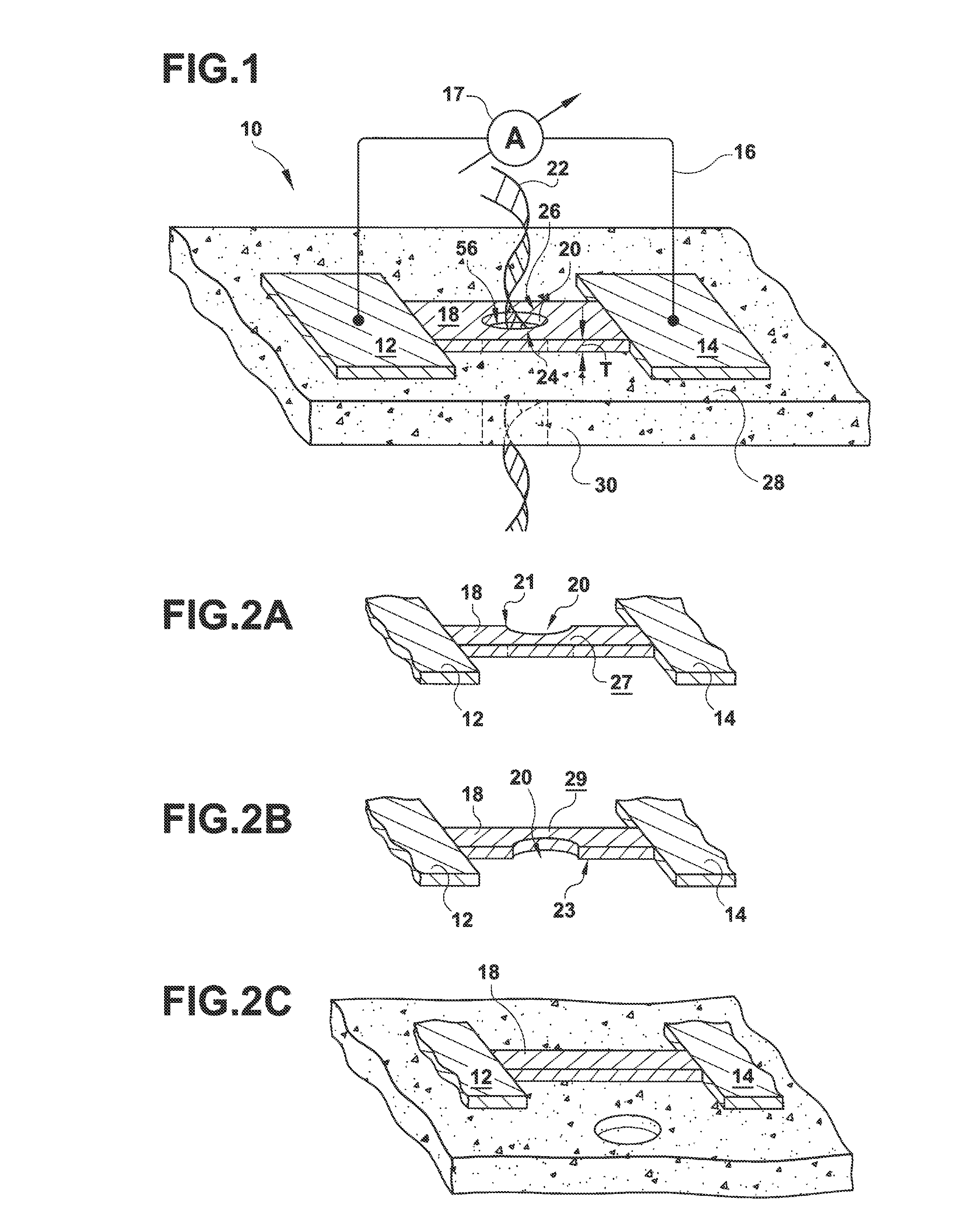
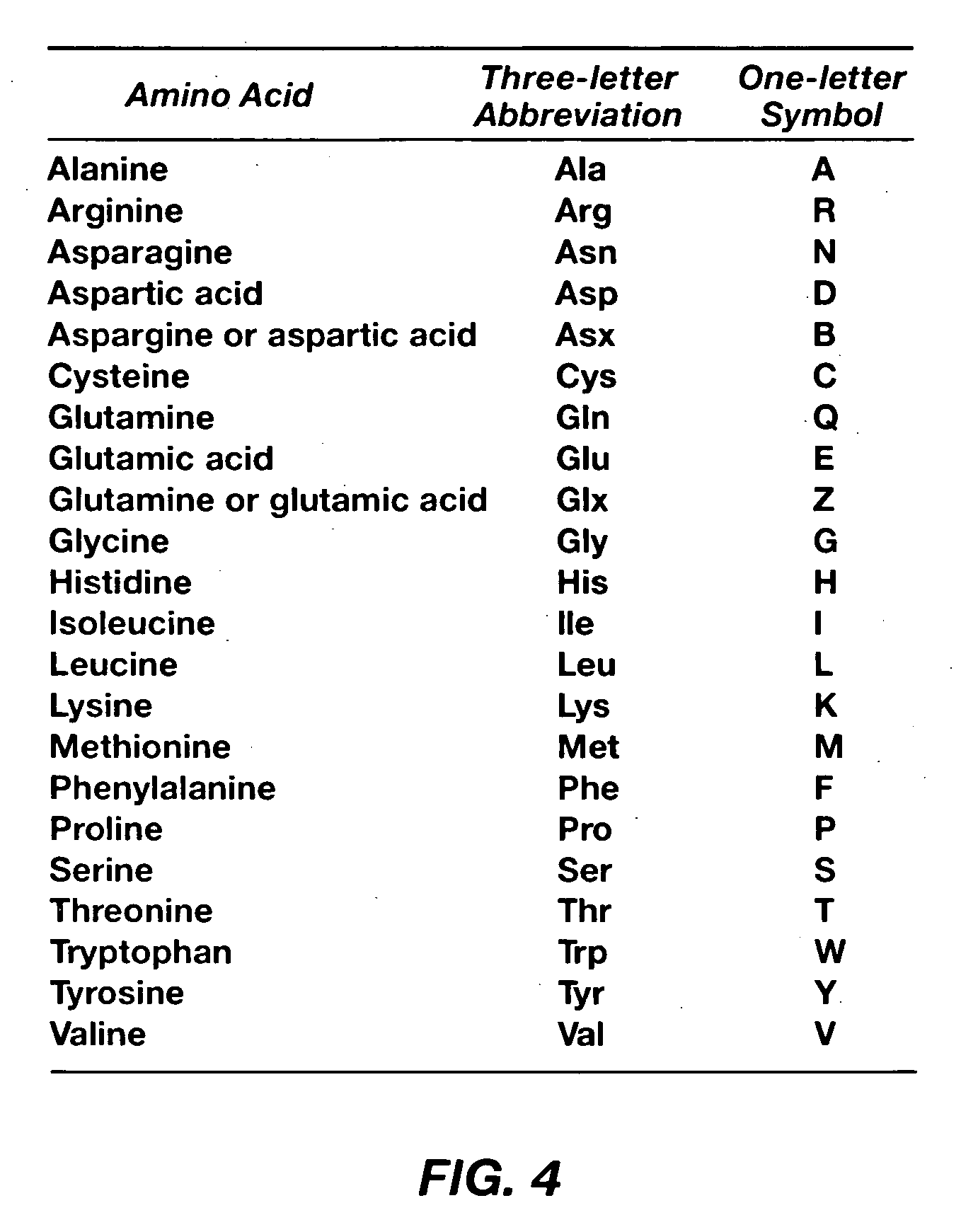
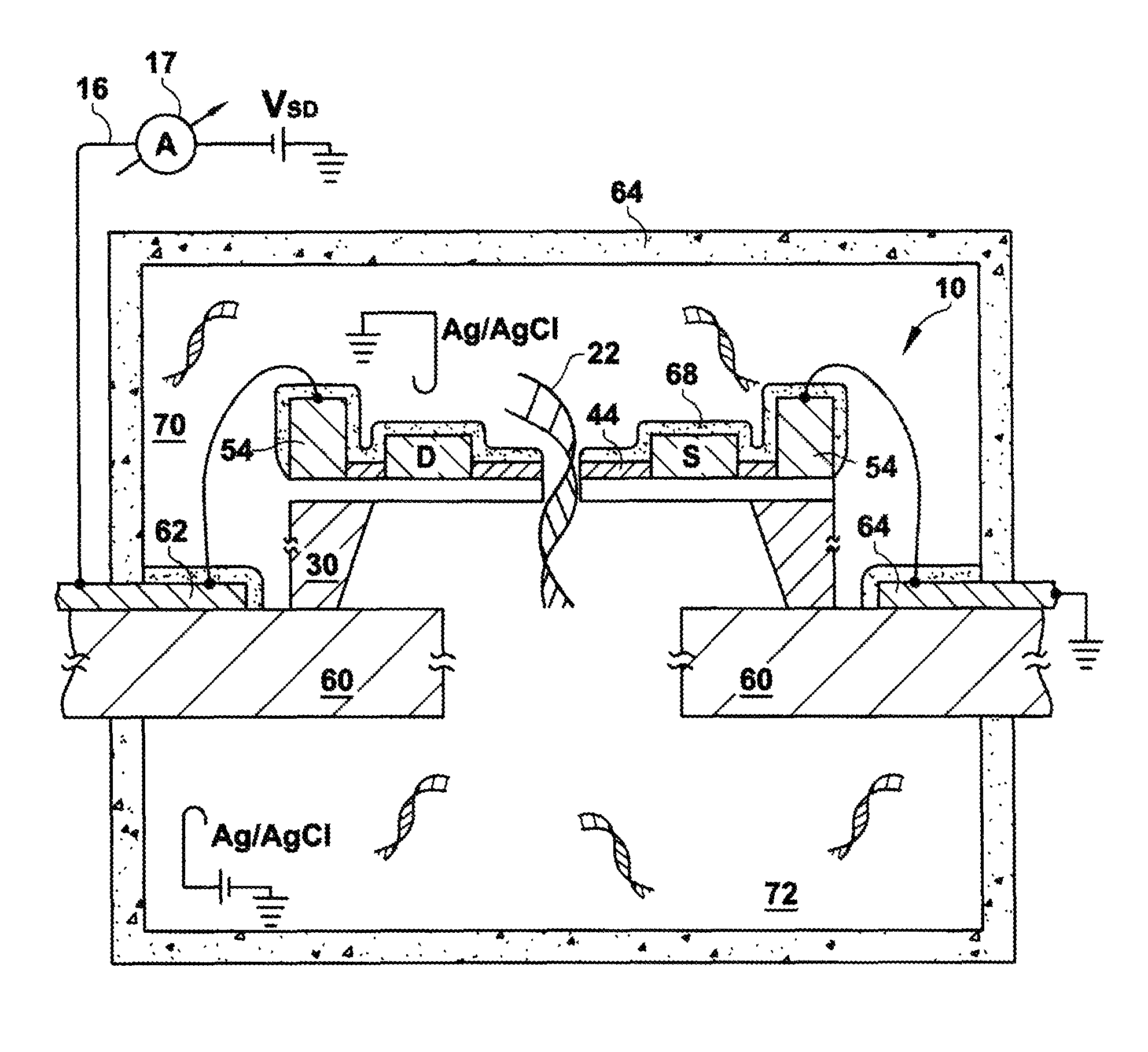
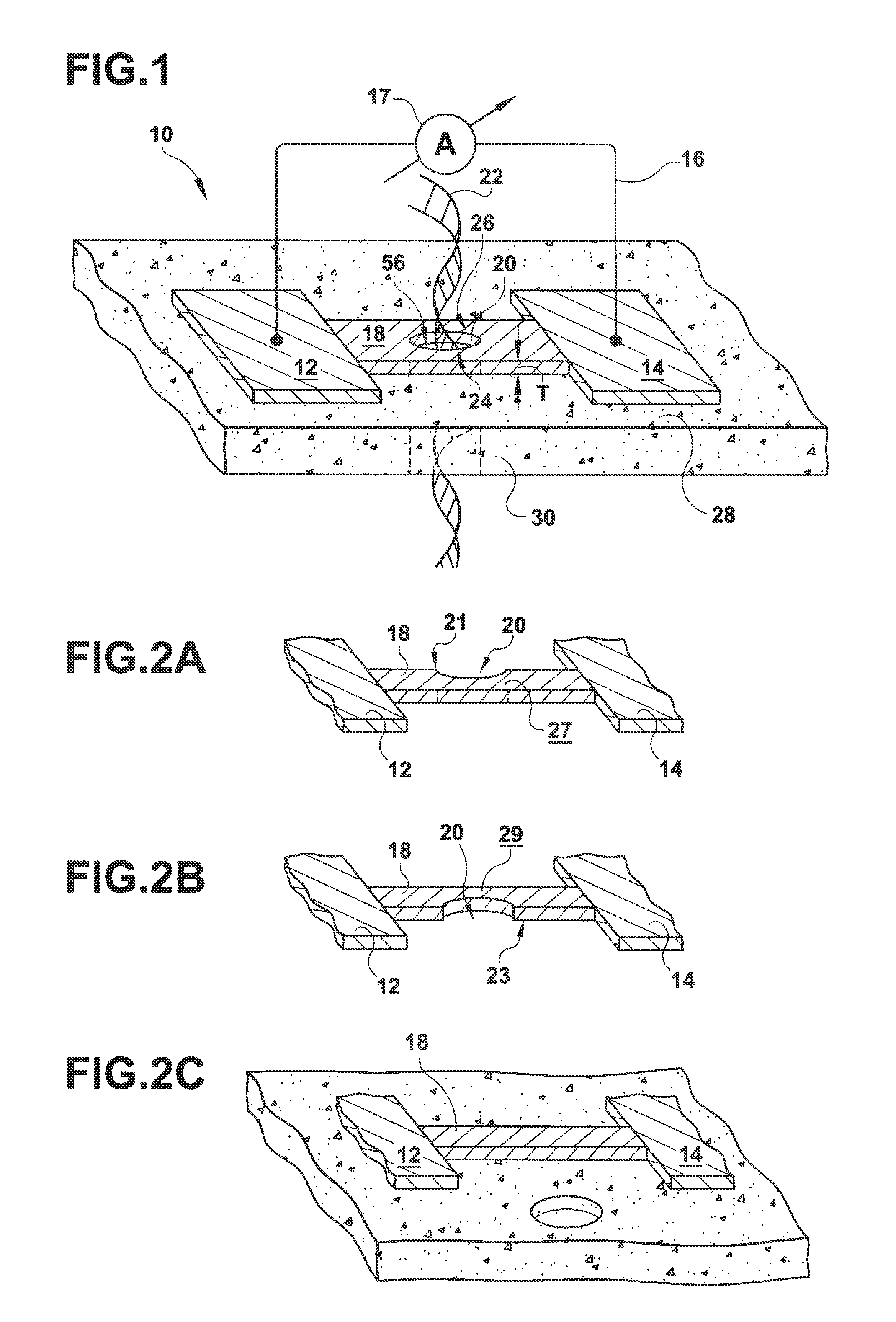
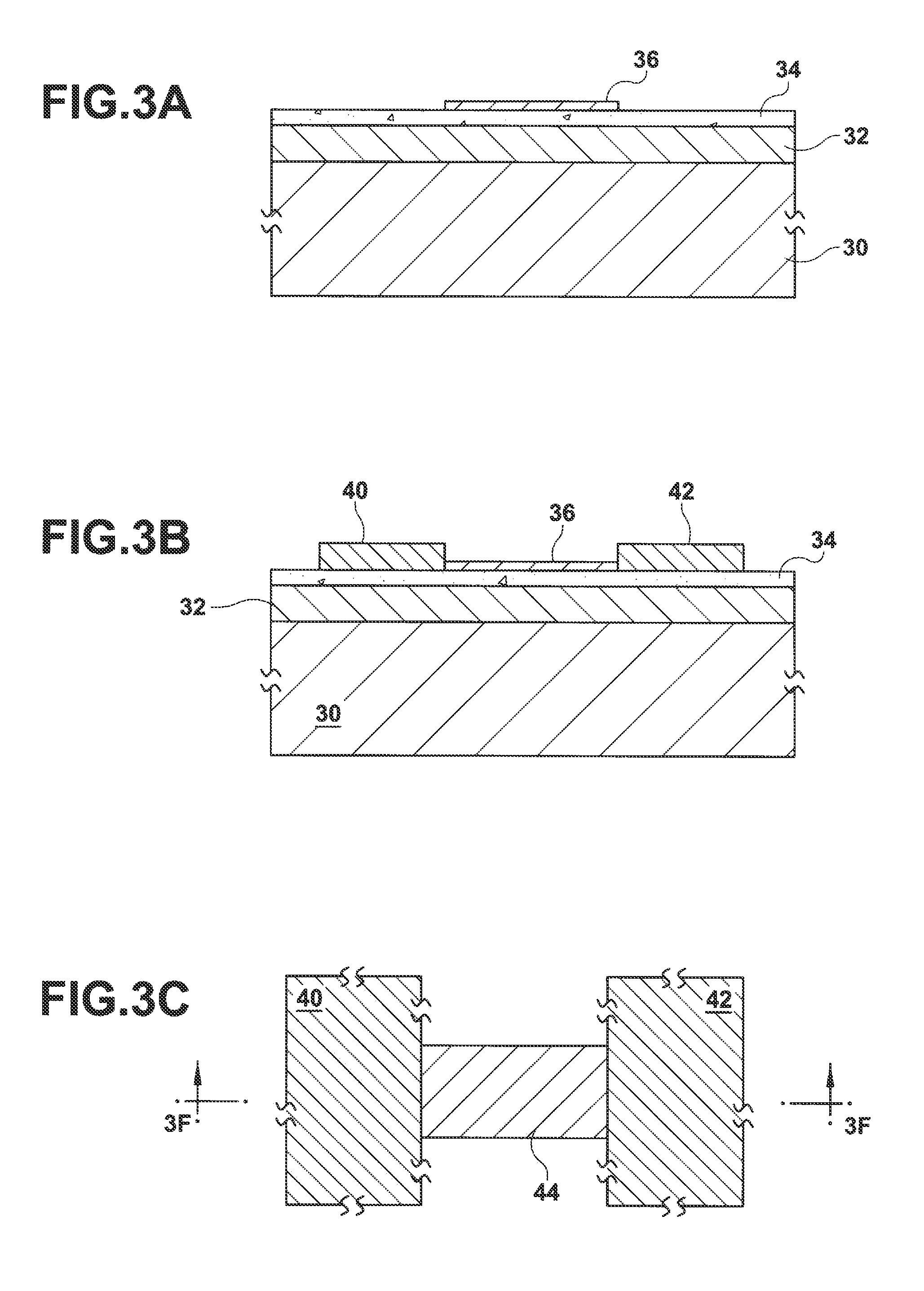
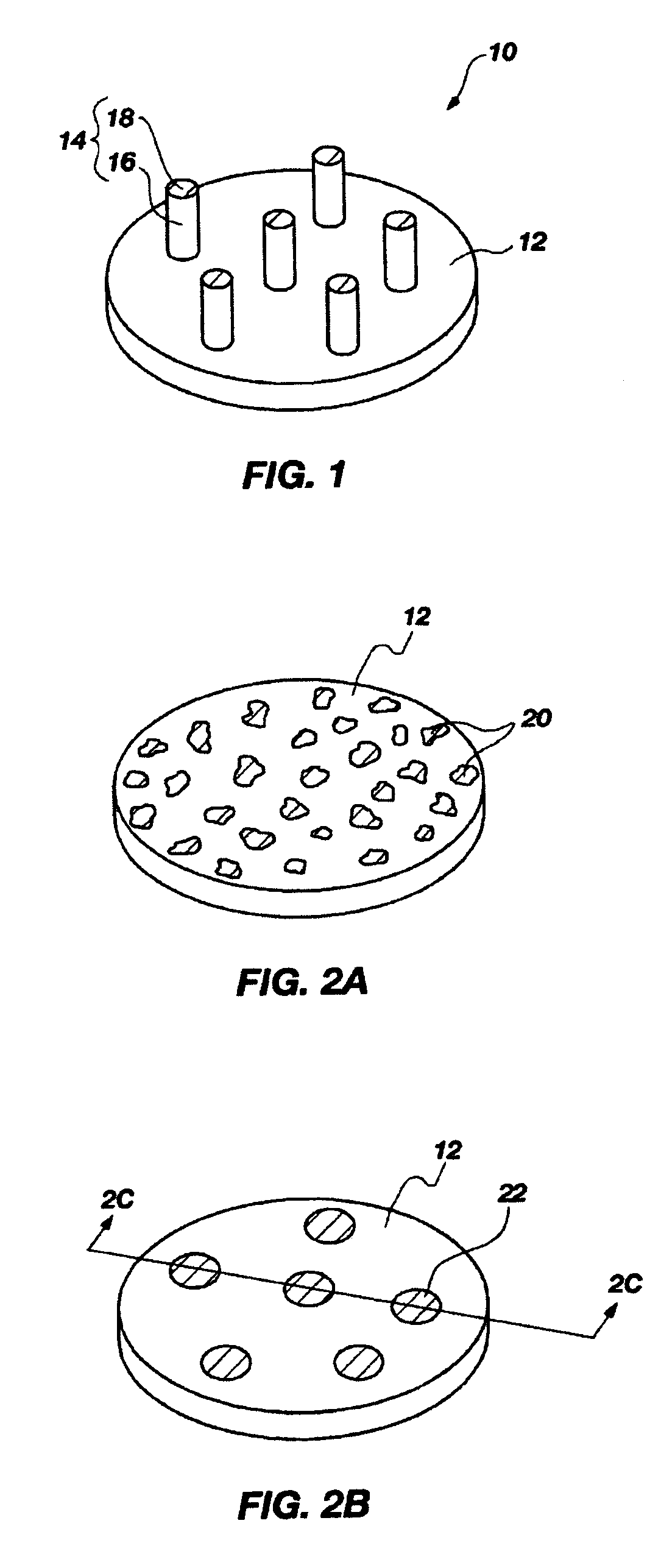
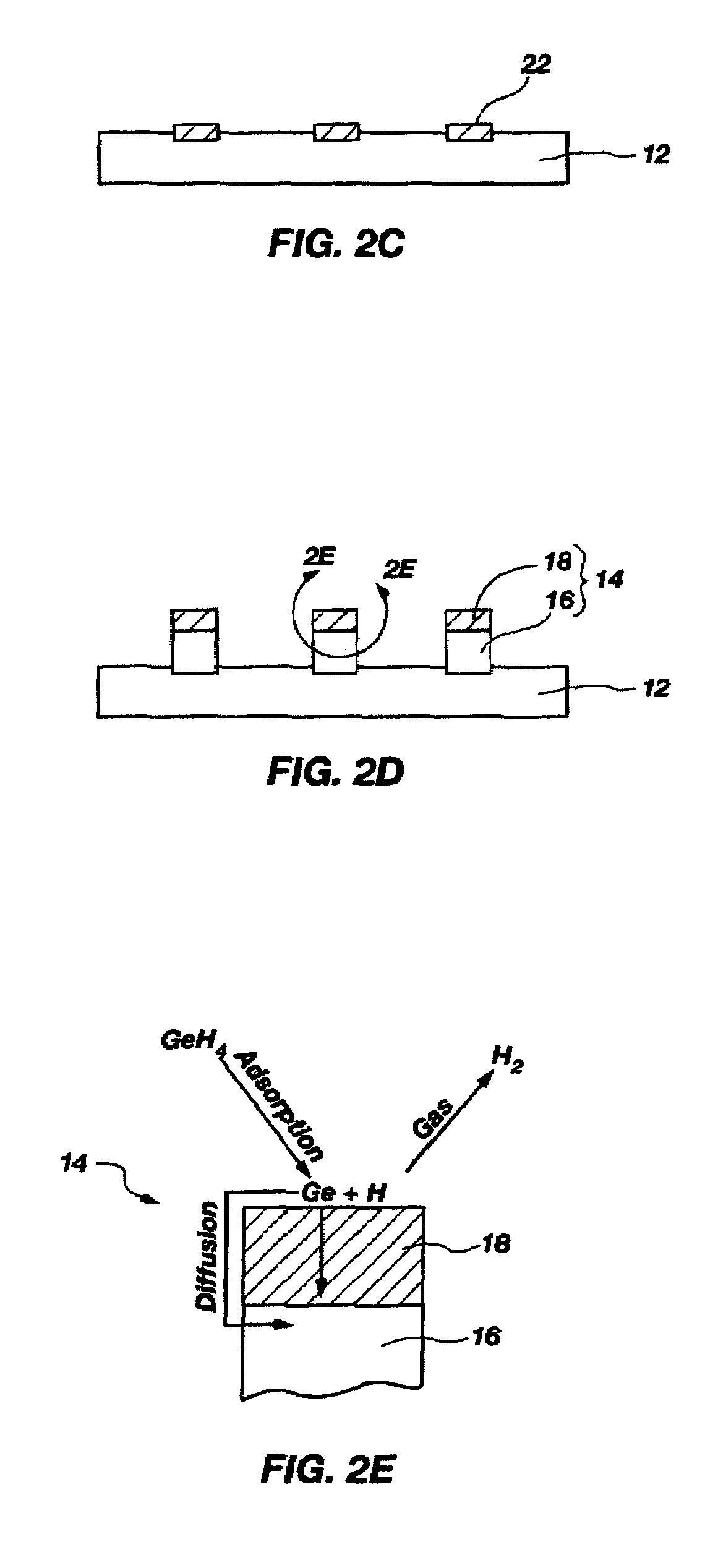
High-Resolution Molecular Sensor
ActiveUS20100327847A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanosensorsSolid-stateMolecular sensor
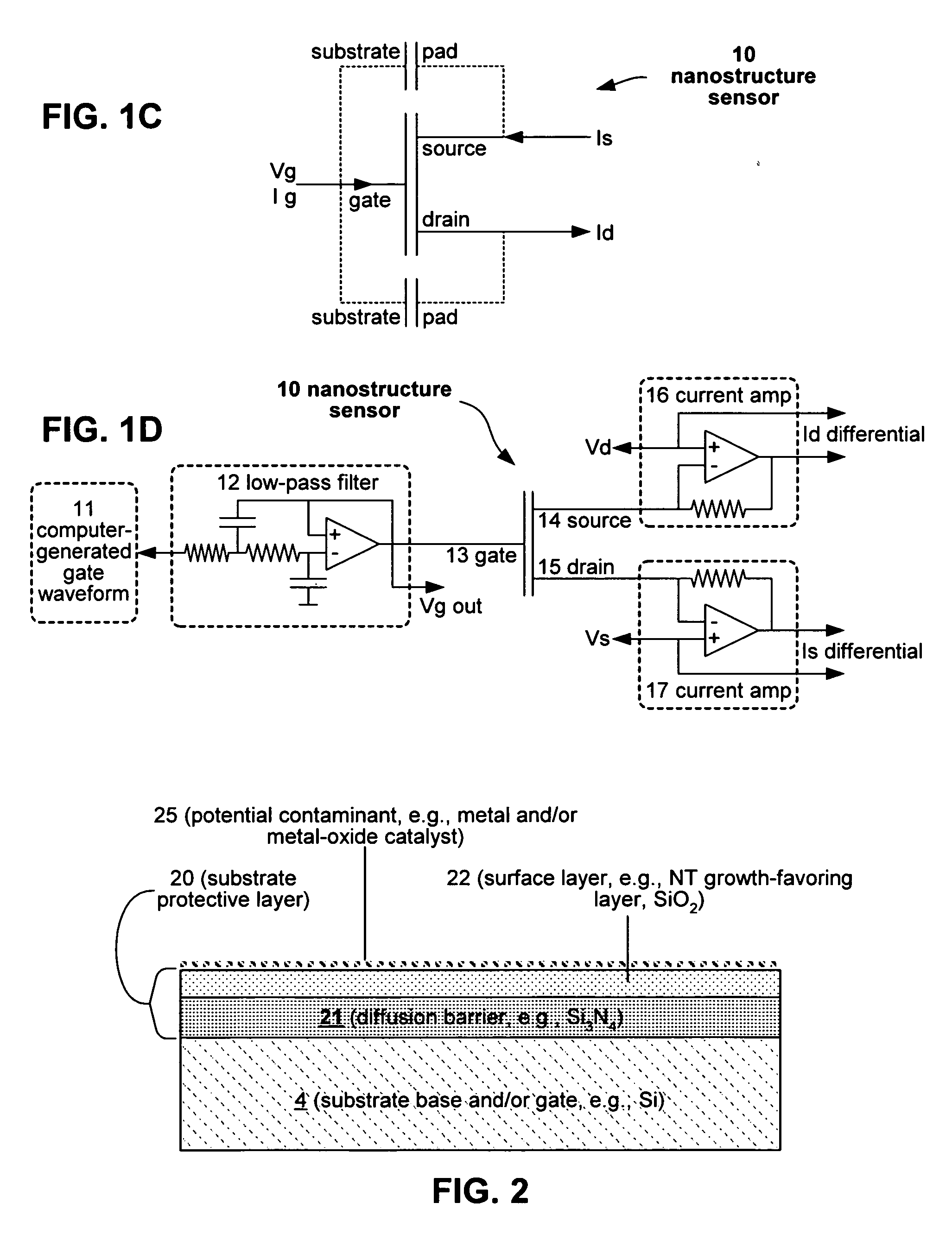
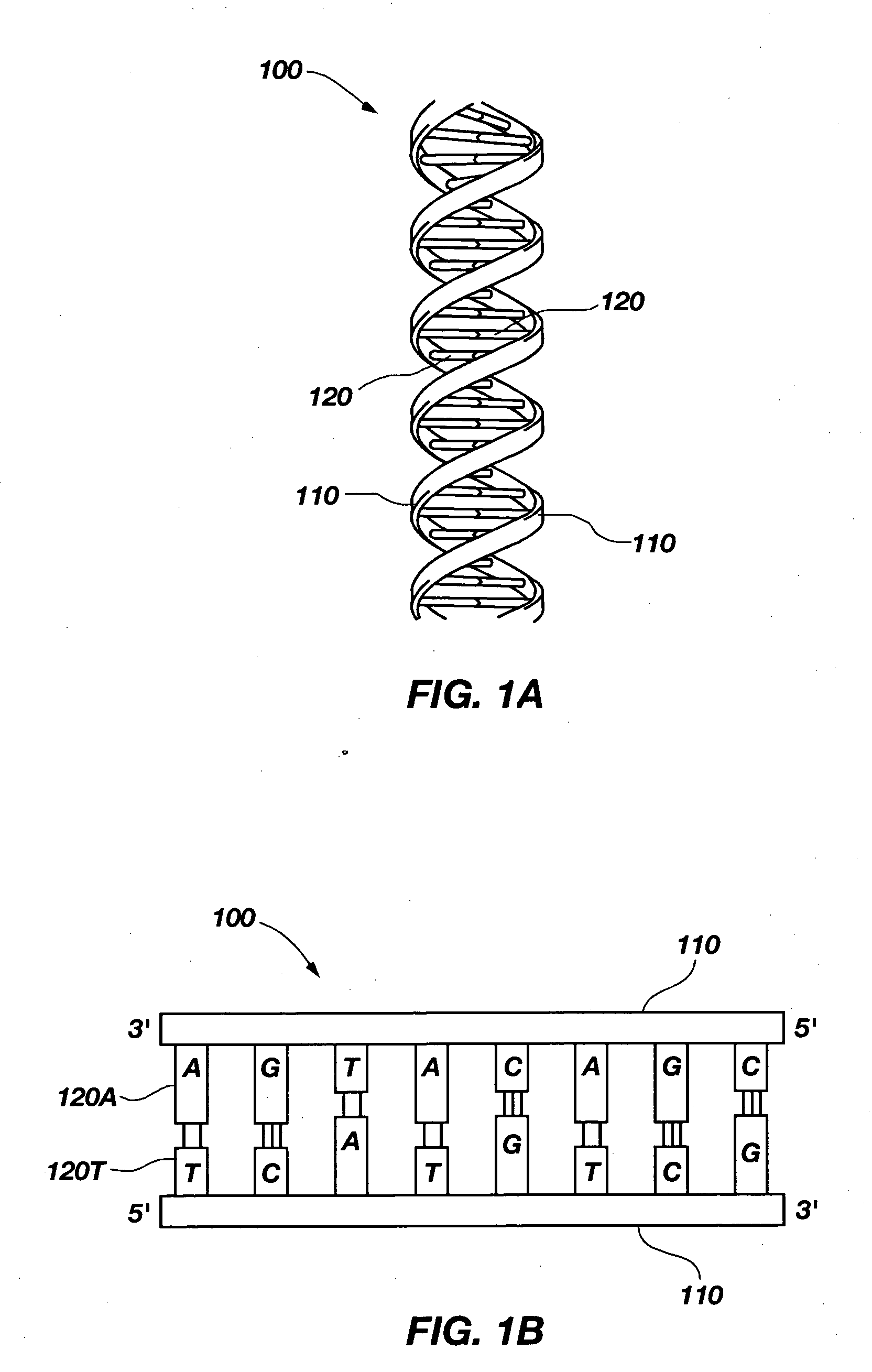
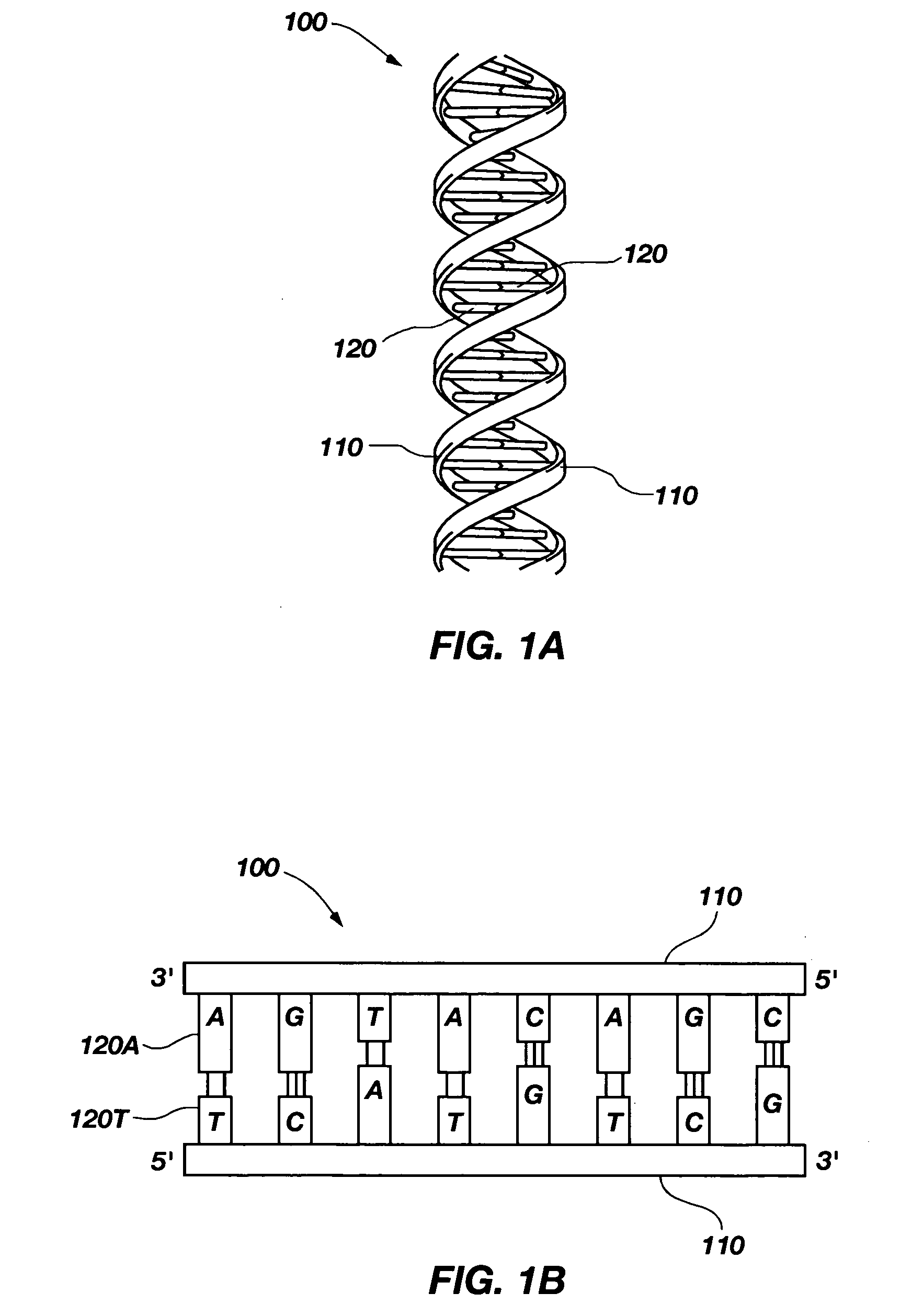
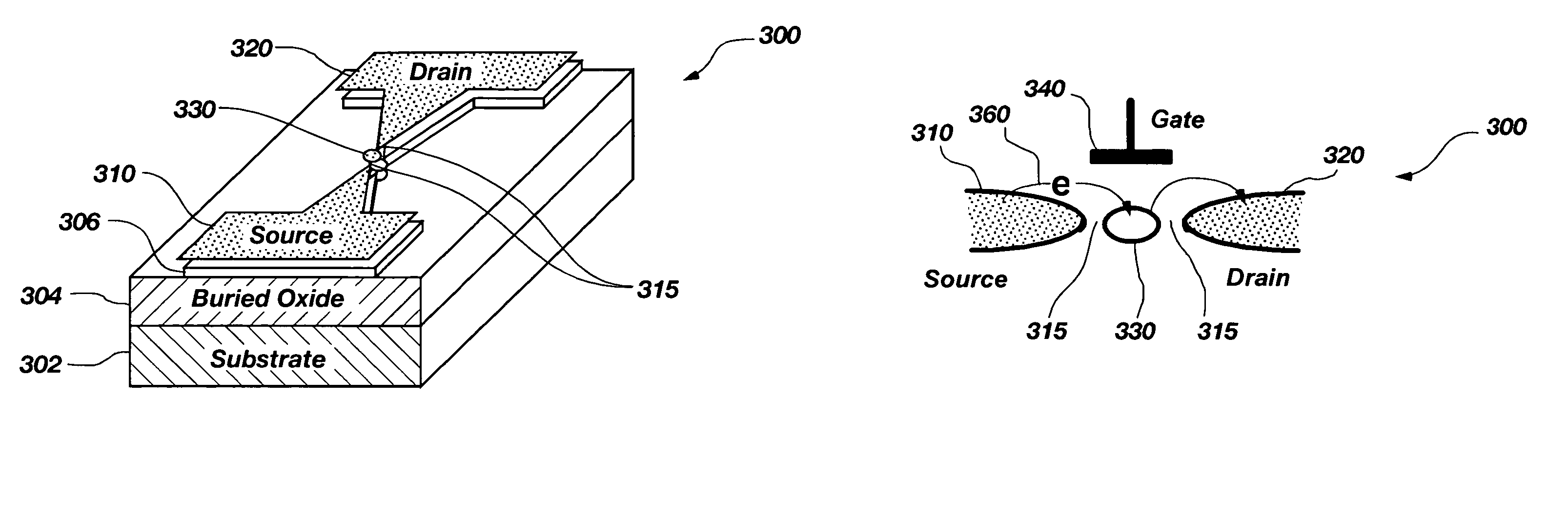
A solid state molecular sensor having an aperture extending through a thickness of a sensing region is configured with a sensing region thickness that corresponds to the characteristic extent of at least a component of a molecular species to be translocated through the aperture. A change in an electrical characteristic of the sensing region is measured during the molecular species translocation. The sensor can be configured as a field effect transistor molecular sensor. The sensing region can be a region of graphene including an aperture extending through a thickness of the graphene.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
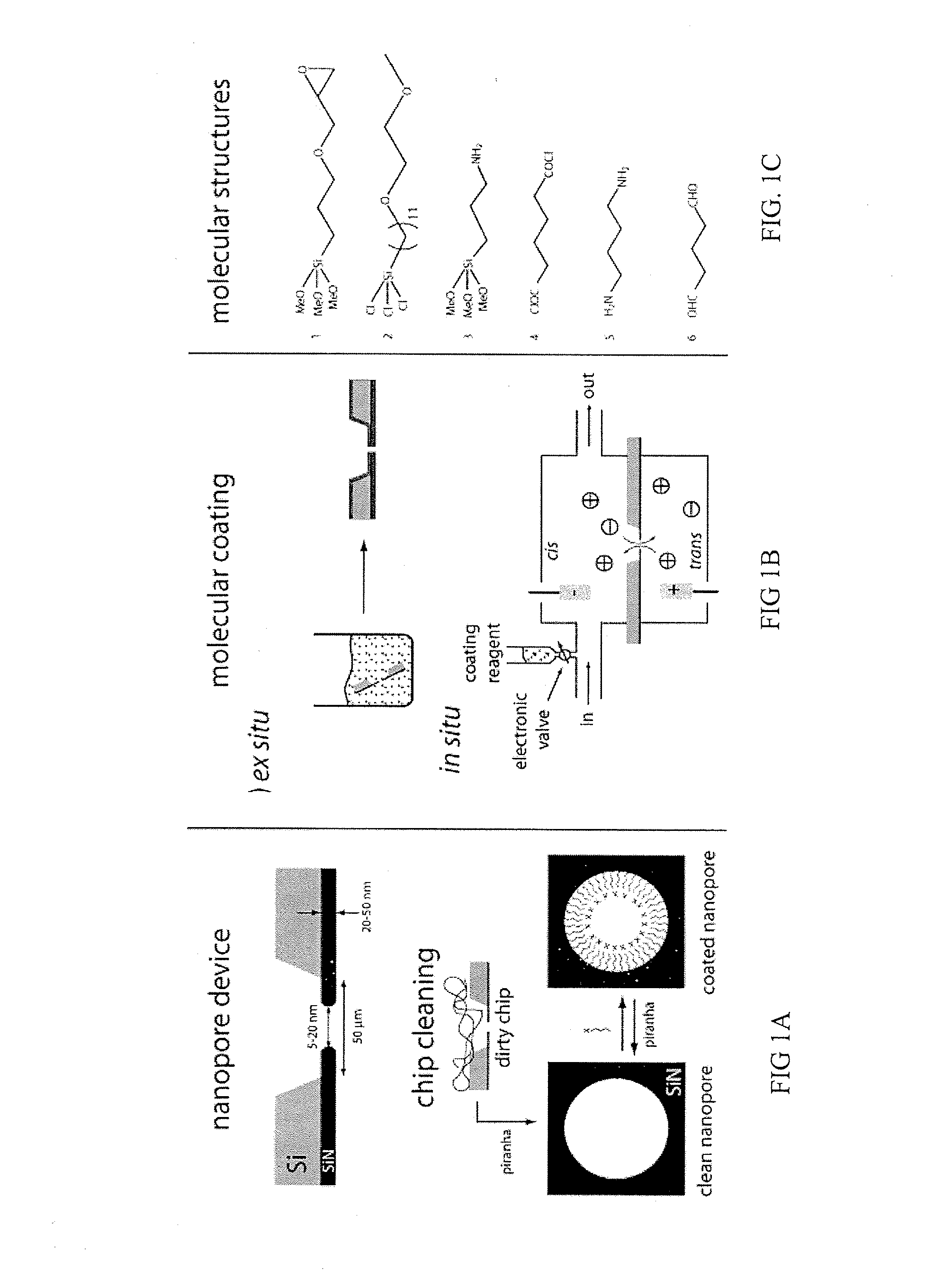
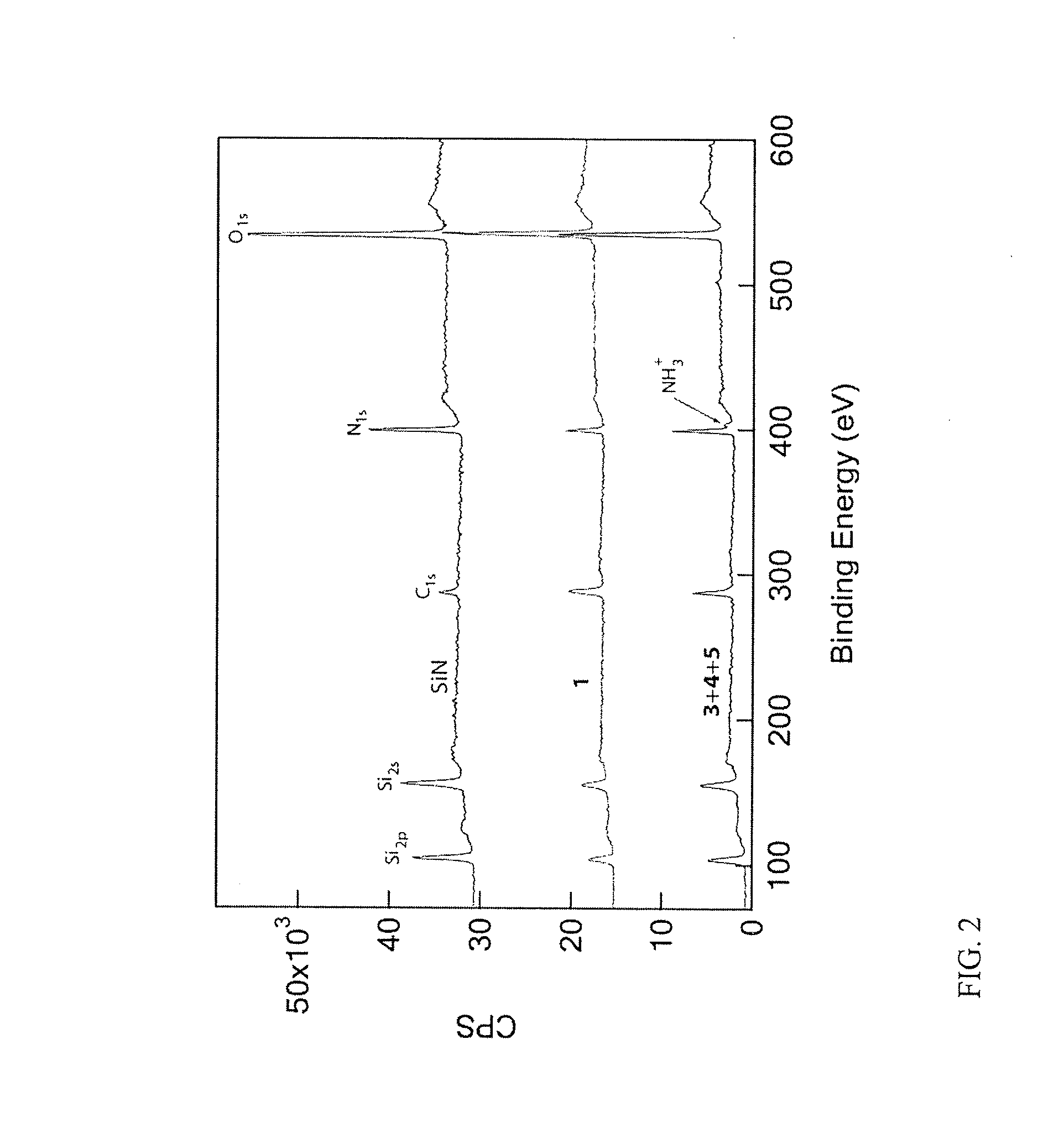
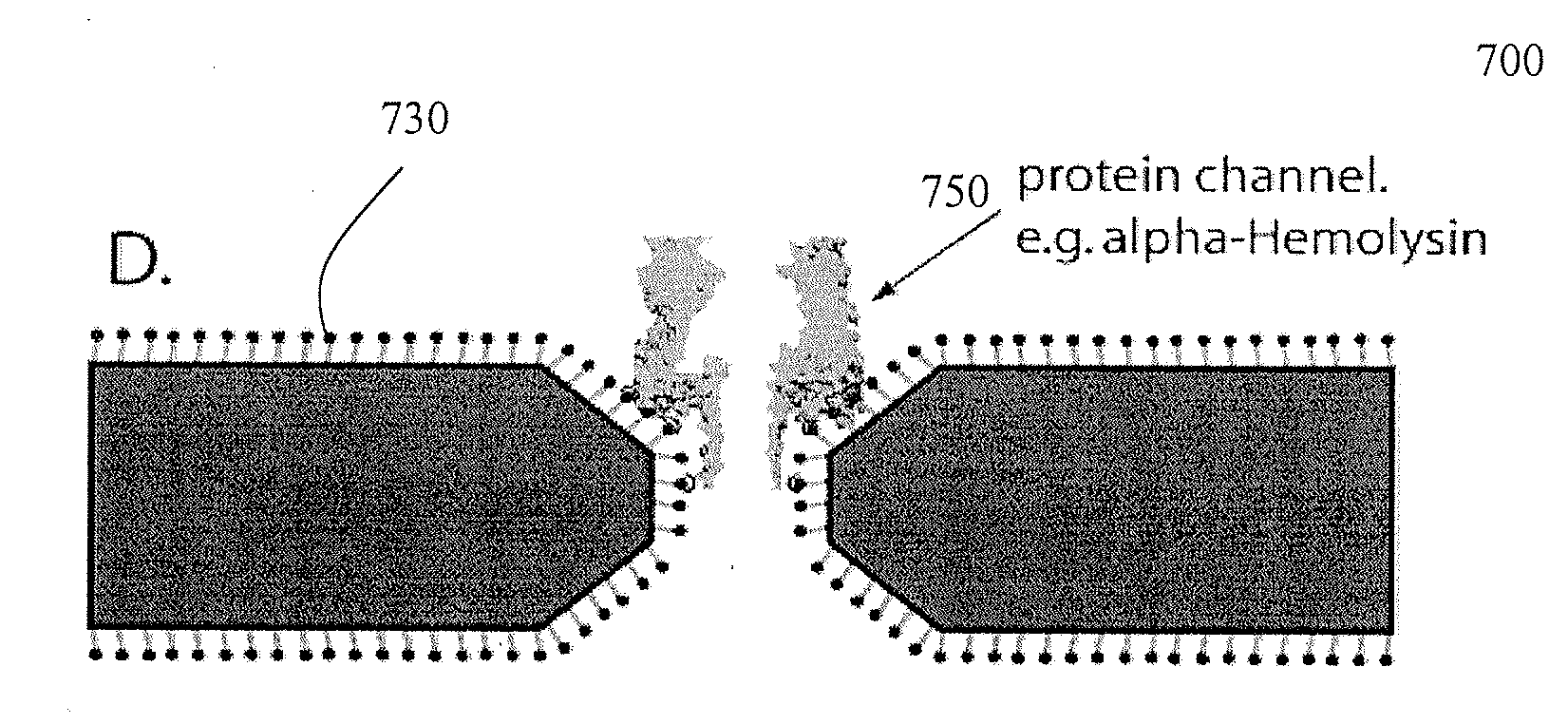
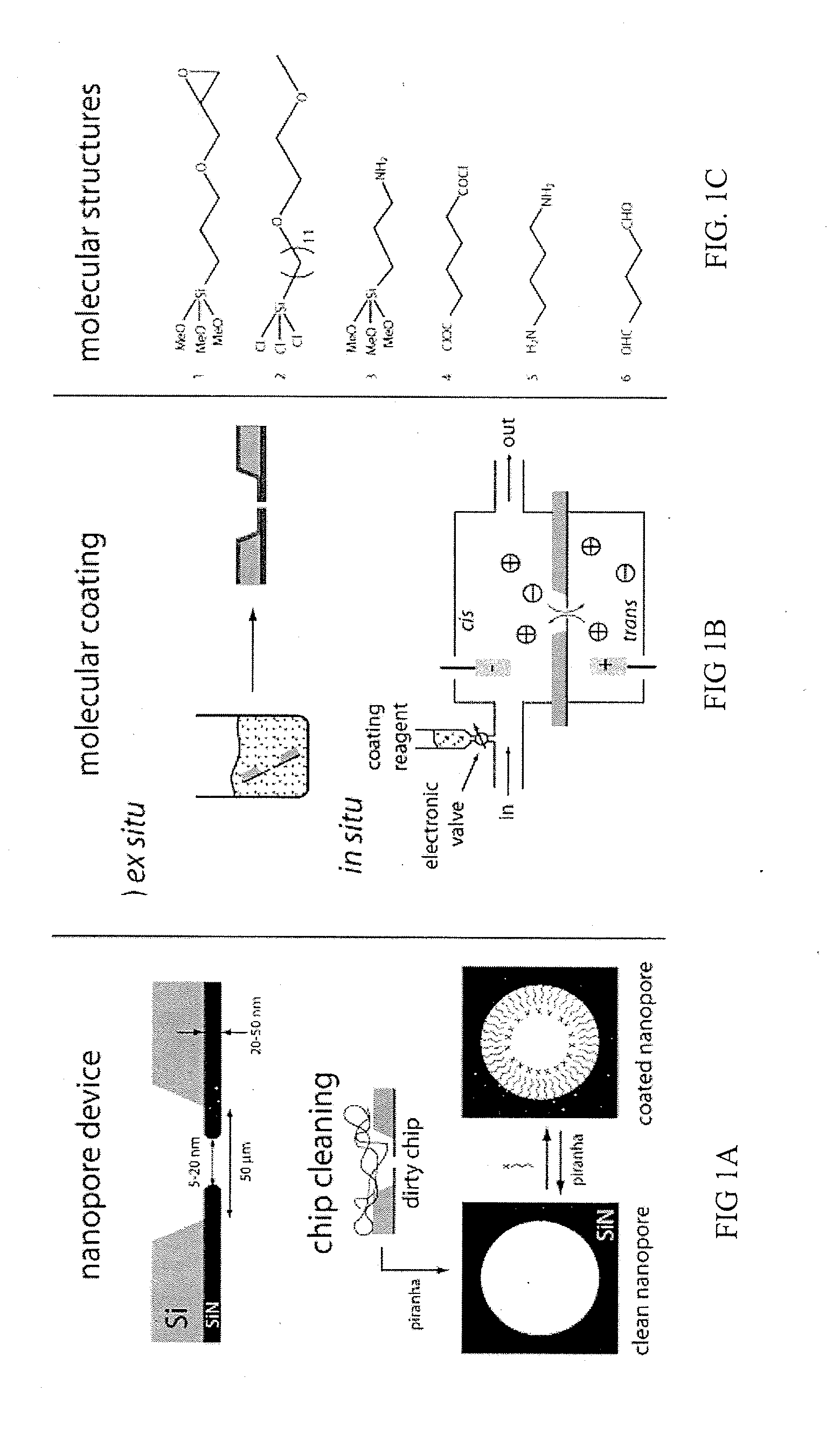
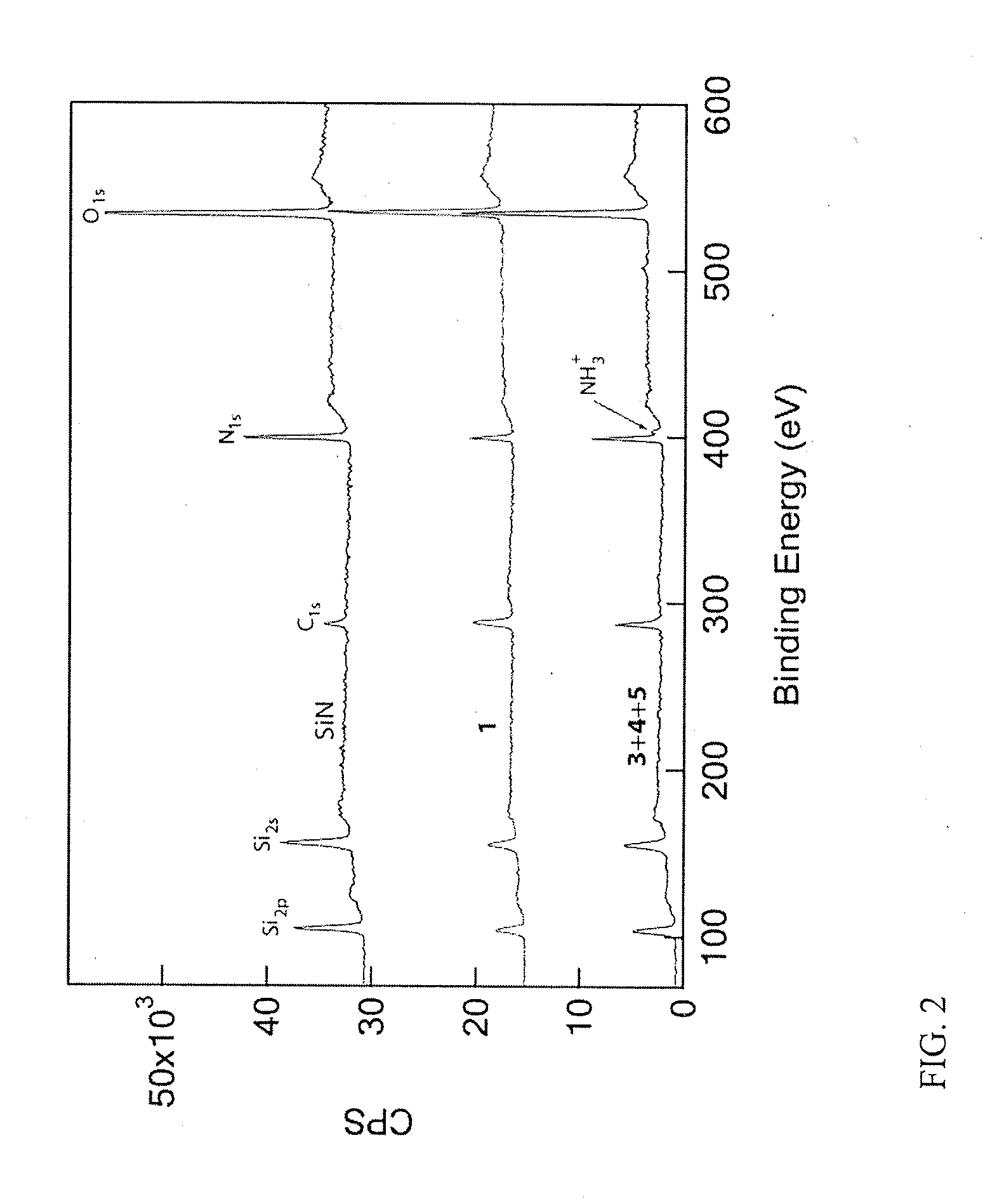
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof
ActiveUS20110053284A1Avoid stickingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiopolymerElectron
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof. Nanopores are extremely sensitive single-molecule sensors. Recently, electron beams have been used to fabricate synthetic nanopores in thin solid-state membranes with sub-nanometer resolution. A new class of chemically modified nanopore sensors are provided with two approaches for monolayer coating of nanopores by: (1) self-assembly from solution, in which nanopores −10 nm diameter can be reproducibly coated, and (2) self-assembly under voltage-driven electrolyte flow, in which 5 nm nanopores may be coated. Applications of chemically modified nanopore are provided including: the detection of biopolymers such as DNA and RNA; immobilizing enzymes or other proteins for detection or for generating chemical gradients; and localized pH sensing.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
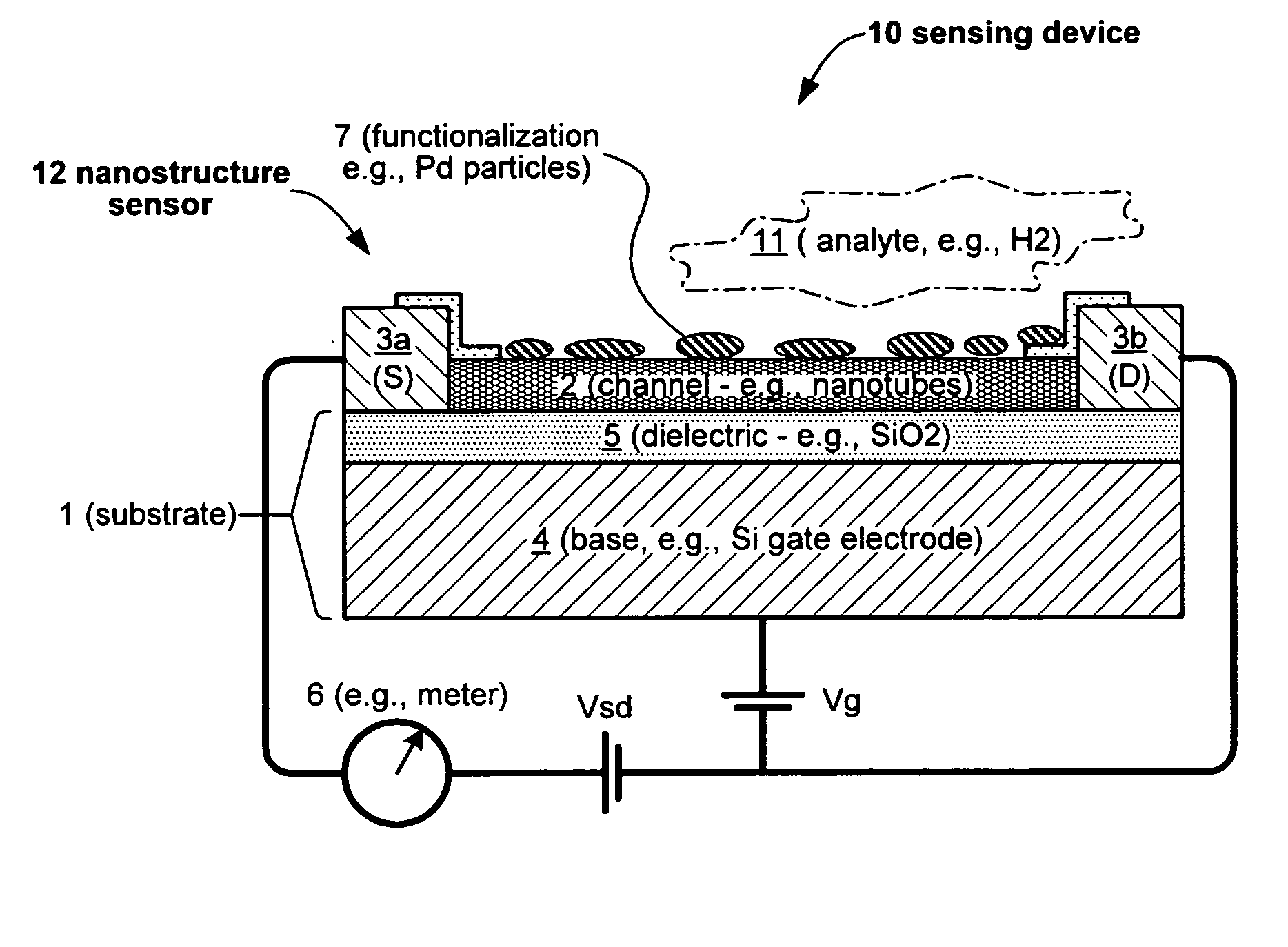
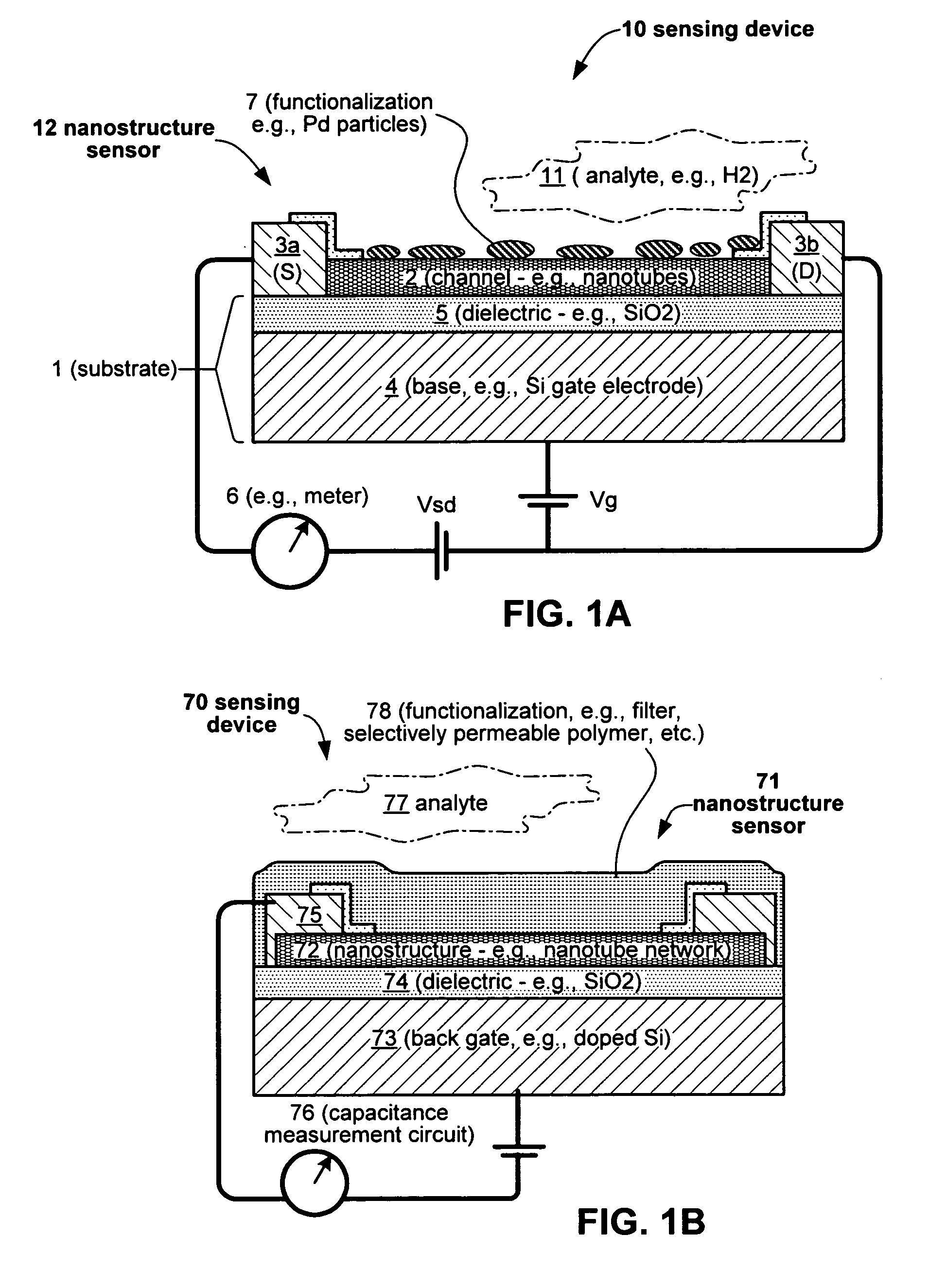
Nanoelectronic sensor system and hydrogen-sensitive functionalization
InactiveUS20060263255A1Reduce distortion problemsSmall sizeMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsHydrogenControl system
A new sensing technology for chemical / biomolecular sensors is provided. One such sensor detects molecular hydrogen (H2) using nanoelectronic components. A tiny, low-cost nanosensor chip can offer: (i) performance that matches or exceeds that of existing technology, (ii) plug-and-play simplicity with both digital and analog control systems, and (ii) the small size and low power consumption needed for wireless integration.
Owner:NANOMIX
Electrochemical method and resulting structures for attaching molecular and biomolecular structures to semiconductor micro and nanostructures
InactiveUS20050032100A1Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanometreElectrochemical cell
A method by which silicon nanostructures may be selectively coated with molecules or biomolecules using an electrochemical process. This chemical process may be employed as a method for coating many different nanostructures within a circuit, each with a different molecular or biomolecular material. The density of devices within a circuit of devices that can be coated with different molecules is limited only by the ability to electronically address each device separately. This invention has applications toward the fabrication of molecular electronic circuitry and toward the fabrication of nanoelectronic molecular sensor arrays.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for moleclular analysis using nanostructure-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20060275911A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansMolecular analysisBiopolymer
Devices and methods for detecting the constituent parts of biological polymers are disclosed. A molecular analysis device includes a molecule sensor and a molecule guide. The molecule sensor comprises a nanostructure, which is configured for producing a nanostructure-enhanced Raman scattered radiation when an excitation radiation irradiates at least a portion of a molecule disposed near the NERS structure.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method and apparatus for molecular analysis using nanoelectronic circuits
InactiveUS20060275778A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle electronNanoelectronic circuits
Devices and methods for detecting the constituent parts of biological polymers are disclosed. A molecular analysis device comprises a molecule sensor and a molecule guide. The molecule sensor comprises a single electron transistor including a first terminal, a second terminal, and a nanogap or at least one quantum dot positioned between the first terminal and the second terminal. A nitrogenous material disposed on the at least one quantum dot is configured for an interaction with an identifiable configuration of a molecule. The molecule sensor develops an electronic effect responsive to the interaction. The molecule guide is configured for guiding at least a portion of the molecule substantially near the molecule sensor to enable the interaction.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and apparatus for detection of molecules using nanopores
InactiveUS20070178507A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle electronMolecular analysis
A molecular analysis device comprises a molecule sensor and a nanopore that passes through, partially through, or substantially near the molecule sensor. The molecule sensor may comprise a single electron transistor including a first terminal, a second terminal, and a nanogap or at least one quantum dot positioned between the first terminal and the second terminal. The molecular sensor may also comprise a nanowire that operably couples a first and a second terminal. A nitrogenous material that may be disposed on at least part of the molecule sensor is configured for a chemical interaction with an identifiable configuration of a molecule. The molecule sensor develops an electronic effect responsive to a molecule or responsive to a chemical interaction.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
High-resolution molecular sensor
ActiveUS8698481B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGrapheneField-effect transistor
A solid state molecular sensor having an aperture extending through a thickness of a sensing region is configured with a sensing region thickness that corresponds to the characteristic extent of at least a component of a molecular species to be translocated through the aperture. A change in an electrical characteristic of the sensing region is measured during the molecular species translocation. The sensor can be configured as a field effect transistor molecular sensor. The sensing region can be a region of graphene including an aperture extending through a thickness of the graphene.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Friction-nanogenerator-based molecular sensor
ActiveCN103364460AReduce volumeSelf-drivingMaterial electrochemical variablesNanogeneratorEngineering
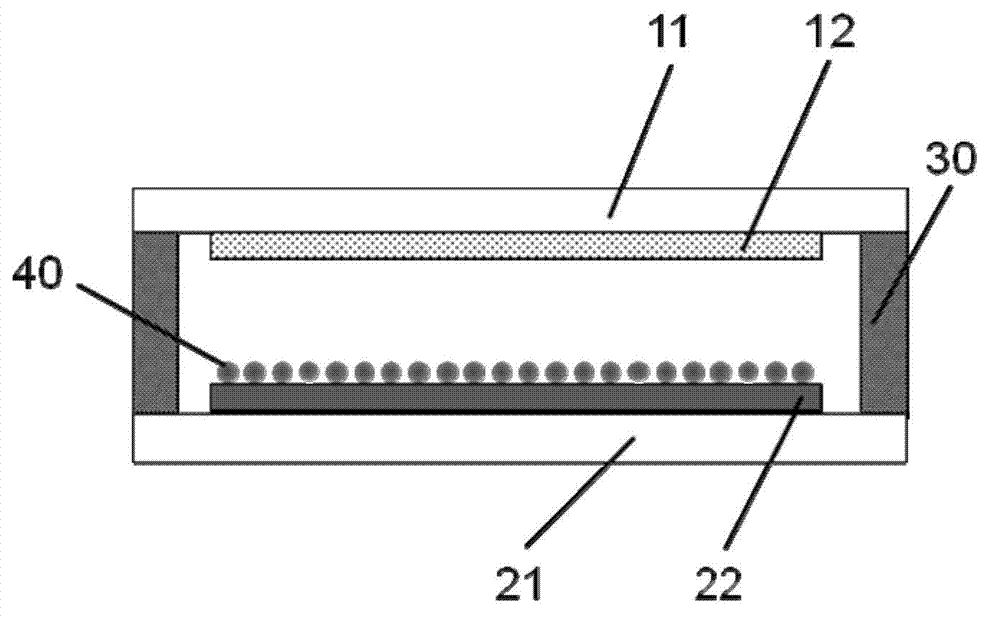
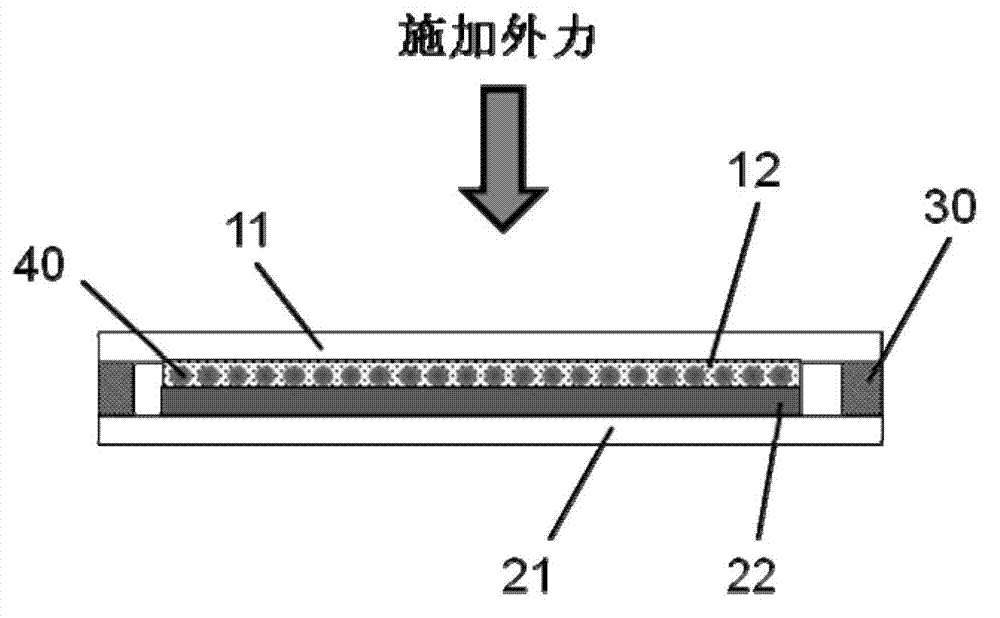
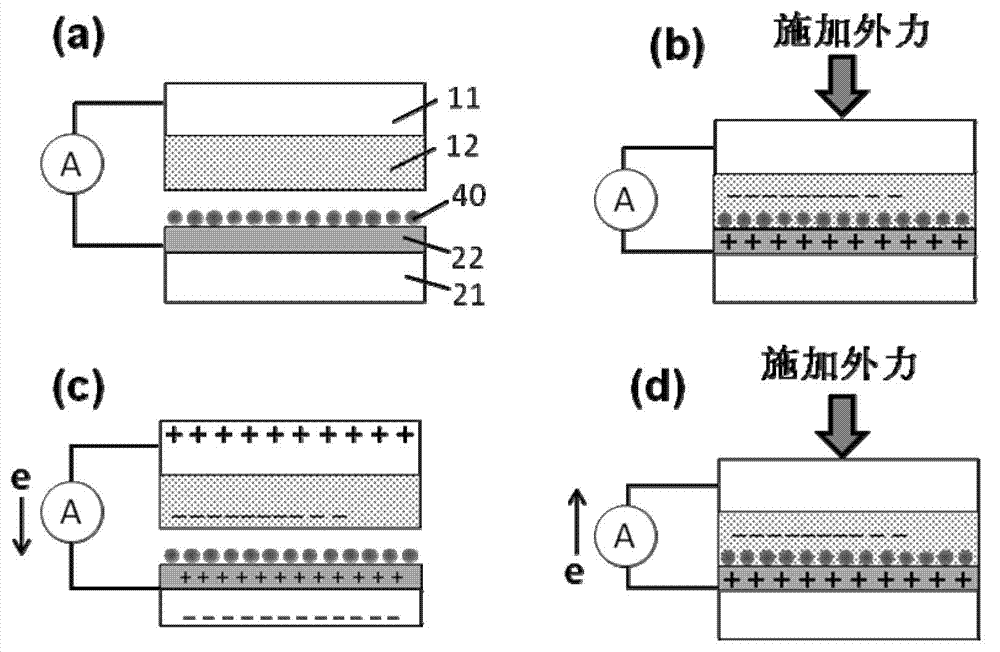
The invention provides a friction-nanogenerator-based molecular sensor. The sensor comprises a first conducting element, a first friction layer, a second conducting element, a second friction layer, a modified layer and an elastic connecting component, wherein the first friction layer is placed on the lower surface of the first conducting element in a contact mode, the second friction layer is placed on the upper surface of the second conducting element in the contact mode, and the modified layer is combined with the upper surface of the second friction layer; by the elastic connecting component, the lower surface of the first friction layer is opposite to the upper surface of the second friction layer, and a certain distance is respectively kept between the lower surface of the first friction layer and the upper surface of the second friction layer; the lower surface of the first friction layer is at least partially in contact with the upper surfaces of the second friction layer under the action of external force, and the distance respectively between the lower surface of the first friction layer and the upper surfaces of the second friction layer can be restored under the action of the elastic connecting component when external force is removed, and simultaneously, electrical signals are outputted outwards through the first conducting element and the second conducting element; the electrical signals can be changed after the modified layer is combined with a target material to be detected.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
Method and apparatus for molecular analysis using nanowires
InactiveUS20060275779A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanowireMolecular analysis
Devices and methods for detecting the constituent parts of biological polymers are disclosed. A molecular analysis device comprises a molecule sensor and a molecule guide. The molecule sensor comprises a nanowire operably coupling a first terminal and a second terminal and a nitrogenous material disposed on the nanowire. The nitrogenous material is configured to interact with an identifiable configuration of a molecule such that the molecule sensor develops a conductance change responsive to the interaction. The molecule guide is configured for guiding at least a portion of the molecule near the molecule sensor to enable the interaction.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Nanowire-based sensor configurations
ActiveUS20090124025A1Increase hydrodynamic dragIncrease rangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityNanowire
This invention provides nanowire based molecular sensors and methods for detecting analytes in a microfluidic system. Methods for sensing analytes include detecting changed electrical parameters associated with contact of a nanowire with the analyte in a microfluidic system. Sensors of the invention include nanowires mounted in microchambers of a microfluidic system in electrical contact with the detector, whereby electrical parameter changes induced in the nanowire by the analyte can be monitored by the detector.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Electrochemical method for attaching molecular and biomolecular structures to semiconductor microstructures and nanostructures
InactiveUS7416911B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyElectrochemistryNanometre
A method by which silicon nanostructures may be selectively coated with molecules or biomolecules using an electrochemical process. This chemical process may be employed as a method for coating many different nanostructures within a circuit, each with a different molecular or biomolecular material. The density of devices within a circuit of devices that can be coated with different molecules is limited only by the ability to electronically address each device separately. This invention has applications toward the fabrication of molecular electronic circuitry and toward the fabrication of nanoelectronic molecular sensor arrays.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Photochromic and electrochromic compounds and methods of synthesizing and using same
ActiveUS7777055B2Efficiently neutralizedMinimize diffusionLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryFiberCyclopentene
This invention relates to novel photochromic and electrochromic monomers and polymers based on 1,2-dithienylcyclopentene derivatives and method of using and synthesizing same. The compounds are reversibly interconvertible between different isomeric forms under suitable photochromic or electrochromic conditions. The electrochromic conversion may be catalytic. The application also relates to ultra-high density homopolymers prepared using ring-opening methathesis polymerization (ROMP) where the central ring of the 1,2-bis(3-thienyl)-cyclopentene is incorporated directly into the polymer backbone. The monomer units may be readily functionalized to enable the synthesis of polymers with diverse structural and electronic properties. The compounds have many potential applications including high-density optical information storage systems, photoregulated molecular switches, reversible holographic systems, ophthalmic lenses, actinometry and molecular sensors, photochromic inks, paints and fibers and optoelectronic systems such as optical waveguides, Bragg reflectors and dielectric mirrors.
Owner:SOLUTIA CANADA INC
Nanowires for surface-enhanced Raman scattering molecular sensors
A SERS-active structure is disclosed that includes a substrate and at least two nanowires disposed on the substrate. Each of the at least two nanowires has a first end and a second end, the first end being attached to the substrate and the second end having a SERS-active tip. A SERS system is also disclosed that includes a SERS-active structure. Also disclosed are methods for forming a SERS-active structure and methods for performing SERS with SERS-active structures.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
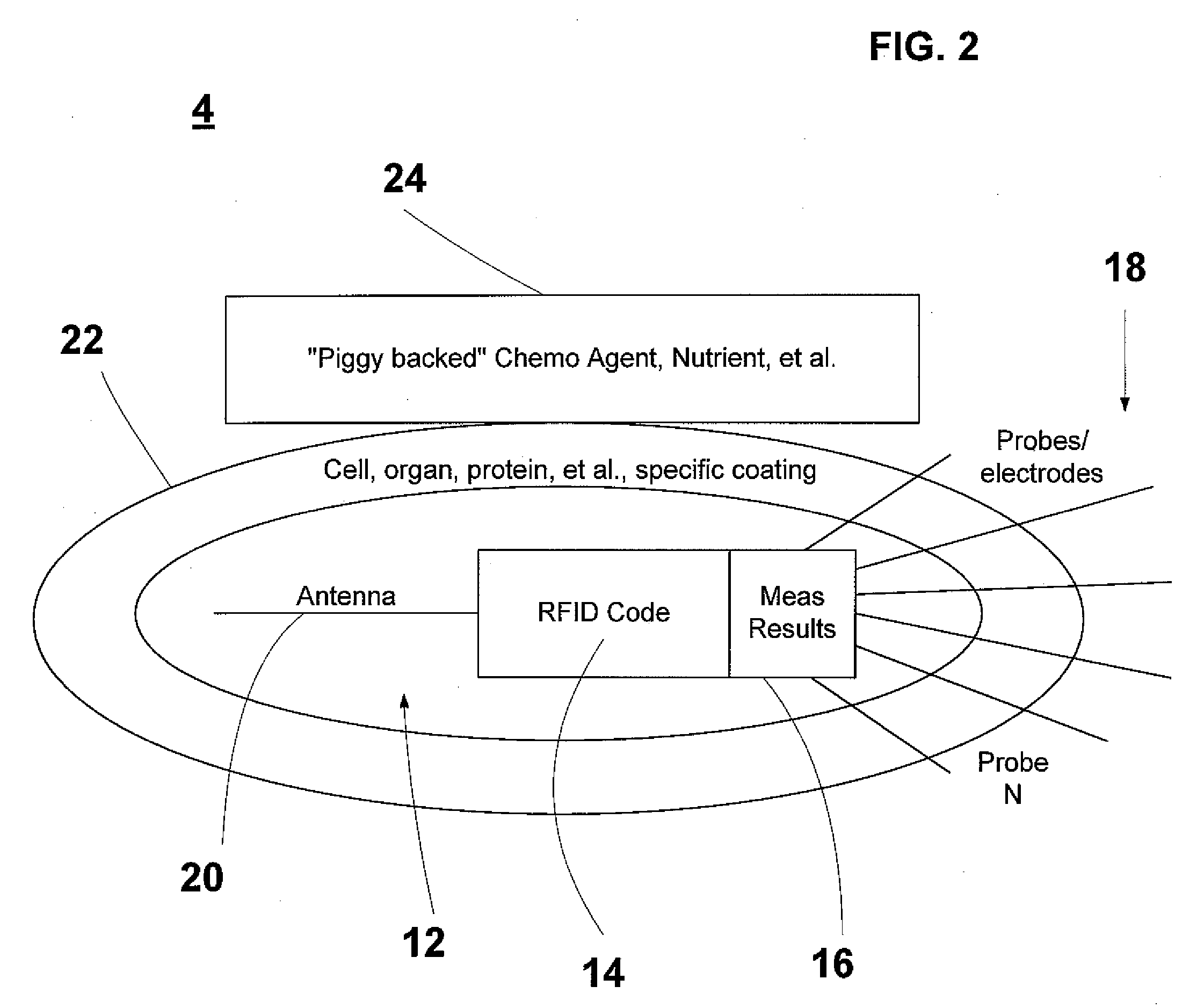
Molecular Sensors for Bio-Metric Measurements and Bio-Assays
A sensor system, for performing measurement and diagnostic testing within a body comprises a sensor, for sensing a characteristic of the interior of a body under study, the sensor including a passive identification tag. The system further comprises a communication apparatus, to be disposed in proximity to the body, for communicating with the sensor to obtain information on the characteristic.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Molecular Switches And Methods For Their Use
ActiveUS20100136536A1Increasing and decreasing effectGuaranteed detection effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular switchSelf-assembly
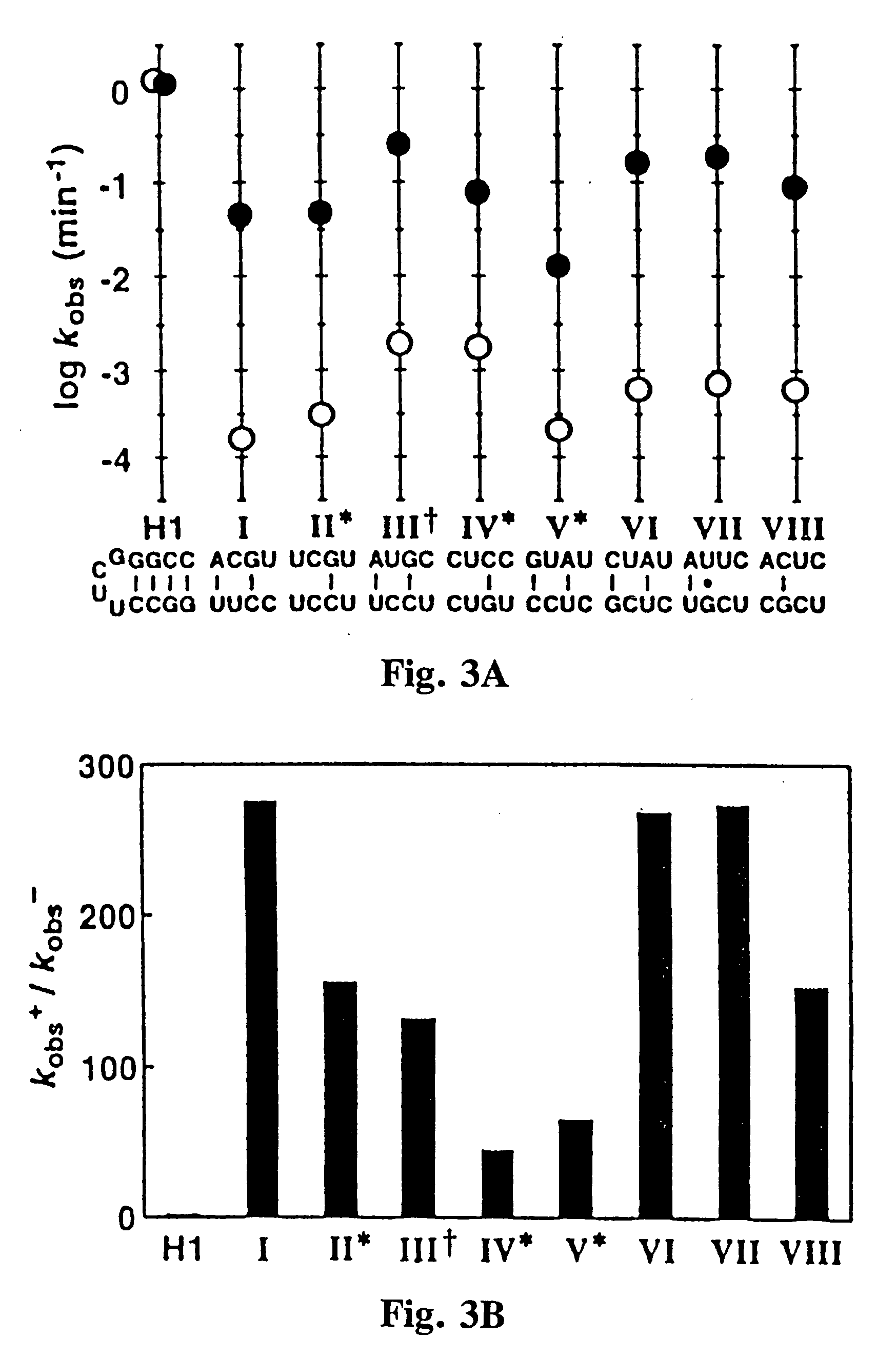
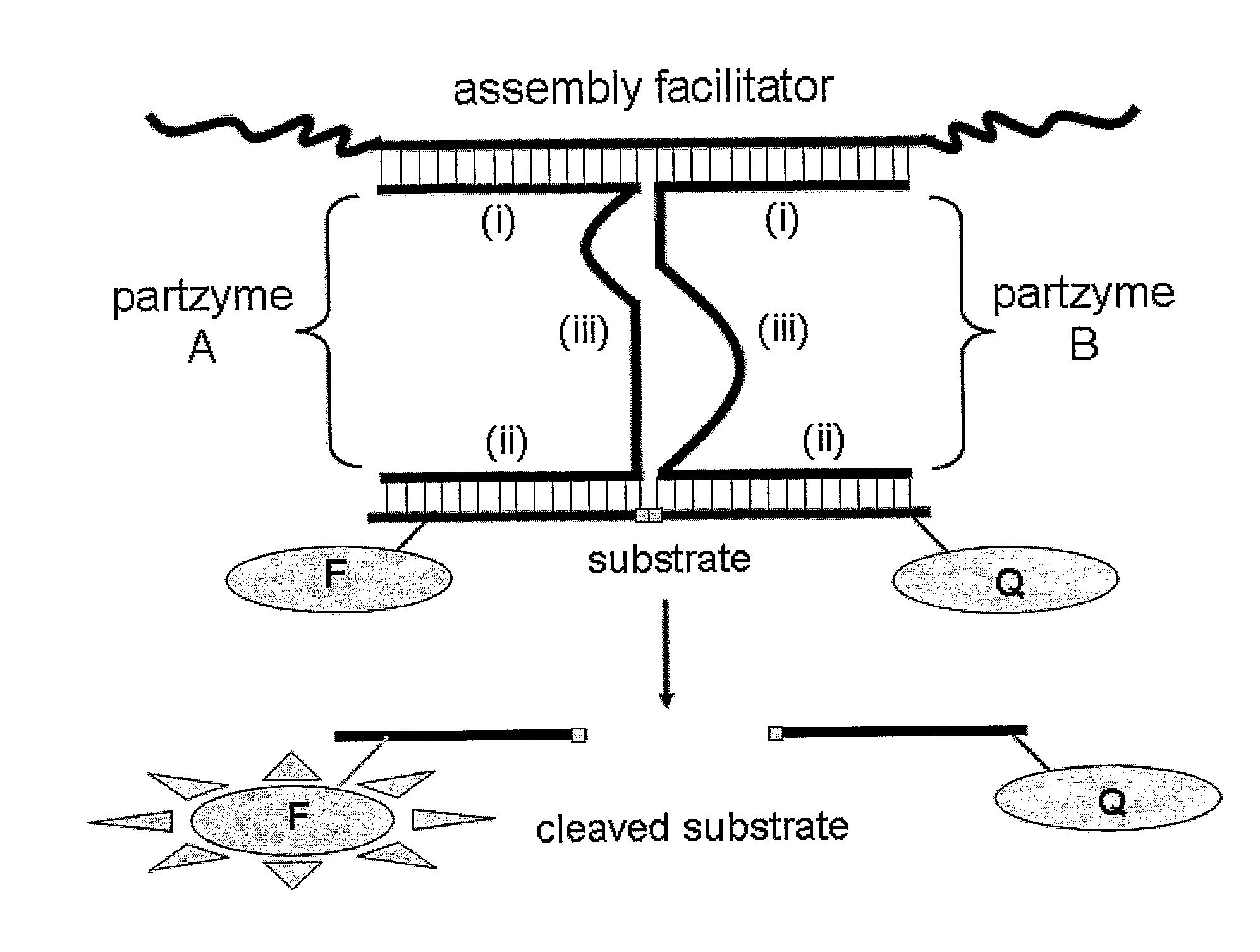
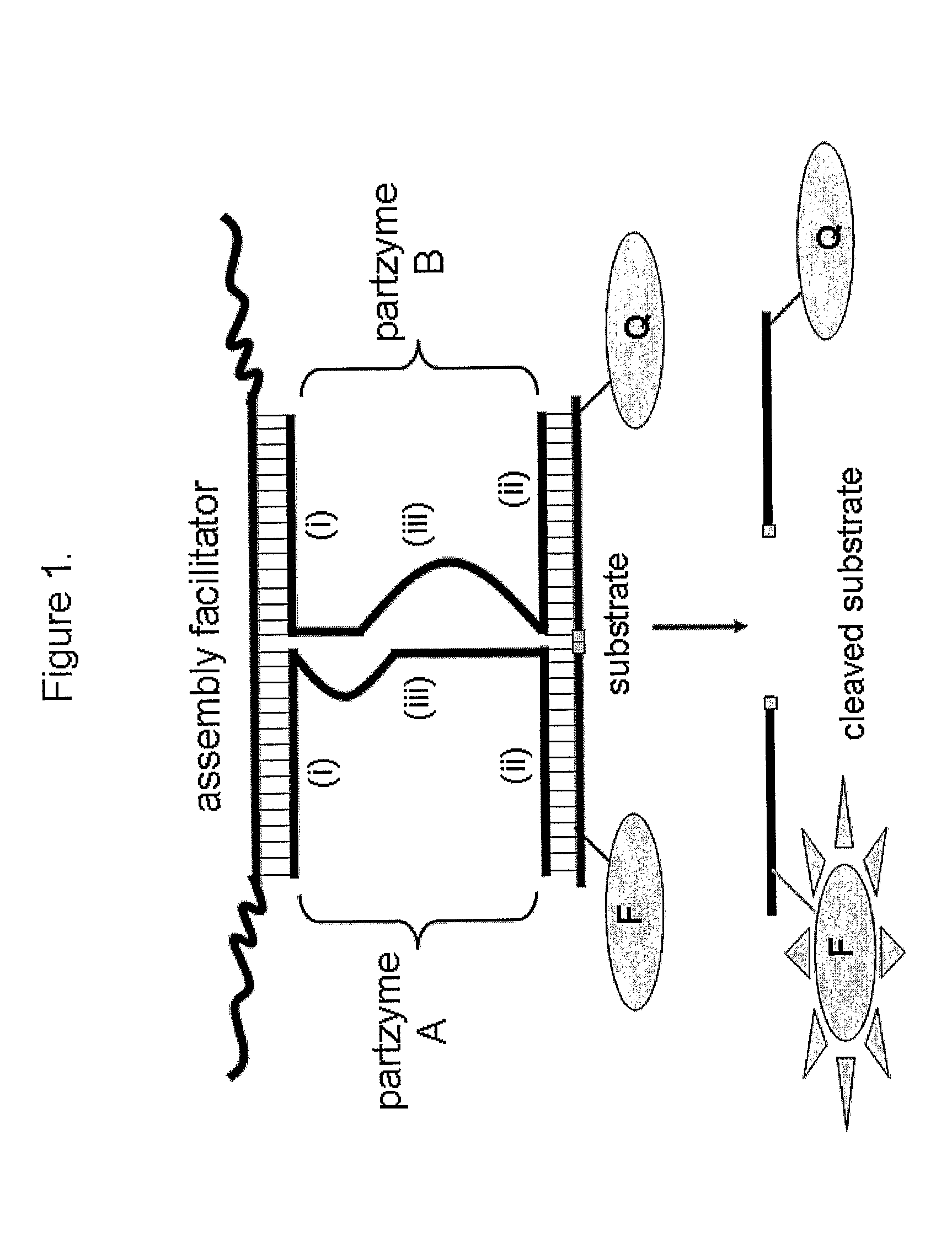
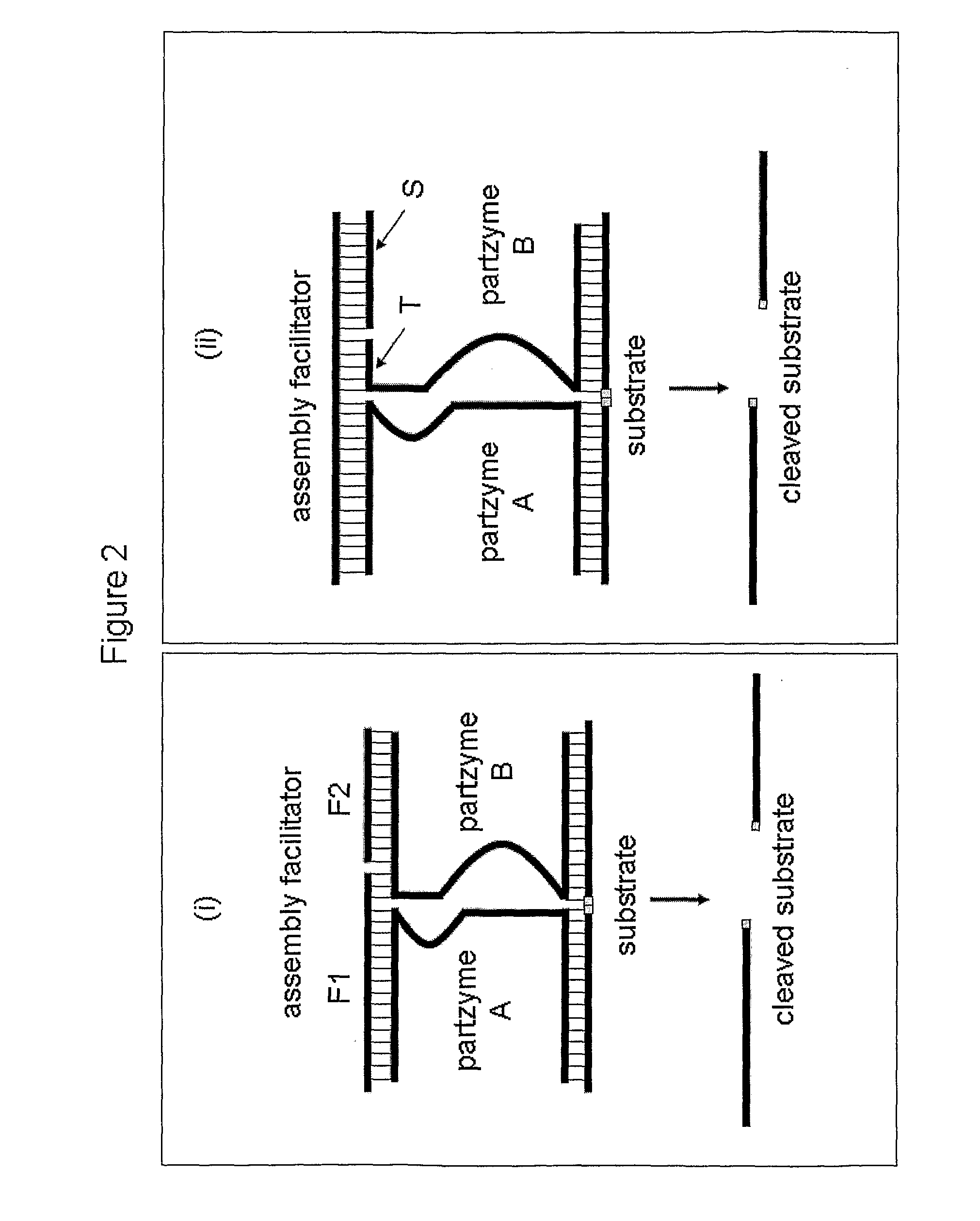
The present invention relates to compositions and methods that allow the manipulation of the catalytic activity of multi-component nucleic acid complexes. Further, the invention provides methods which use these compositions and methods to create molecular sensors, molecular switches, and / or modulators or propagators of autocatalytic self-replicating cascades and other iterative processes. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions allowing self-assembly of active and inactive multicomponent nucleic acid complexes, methods of making such compositions, and methods for use.
Owner:SPEEDX
Method and apparatus for molecular analysis using nanoelectronic circuits
InactiveUS7947485B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle electronNanoelectronic circuits
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Preparation and application of supermolecular sensor based on pillar [5] arene and pyridine functionalized naphthalene diformyl derivative
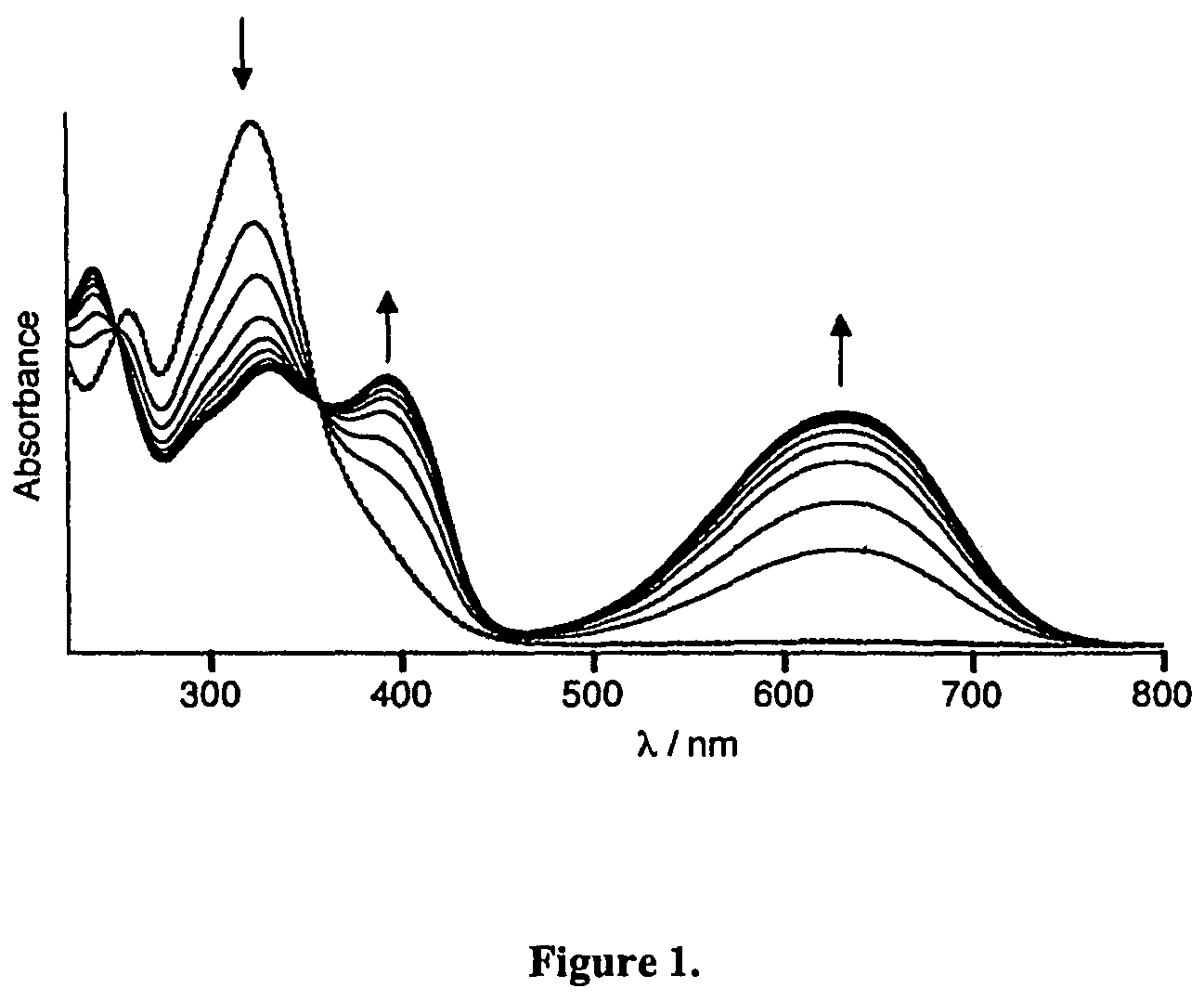
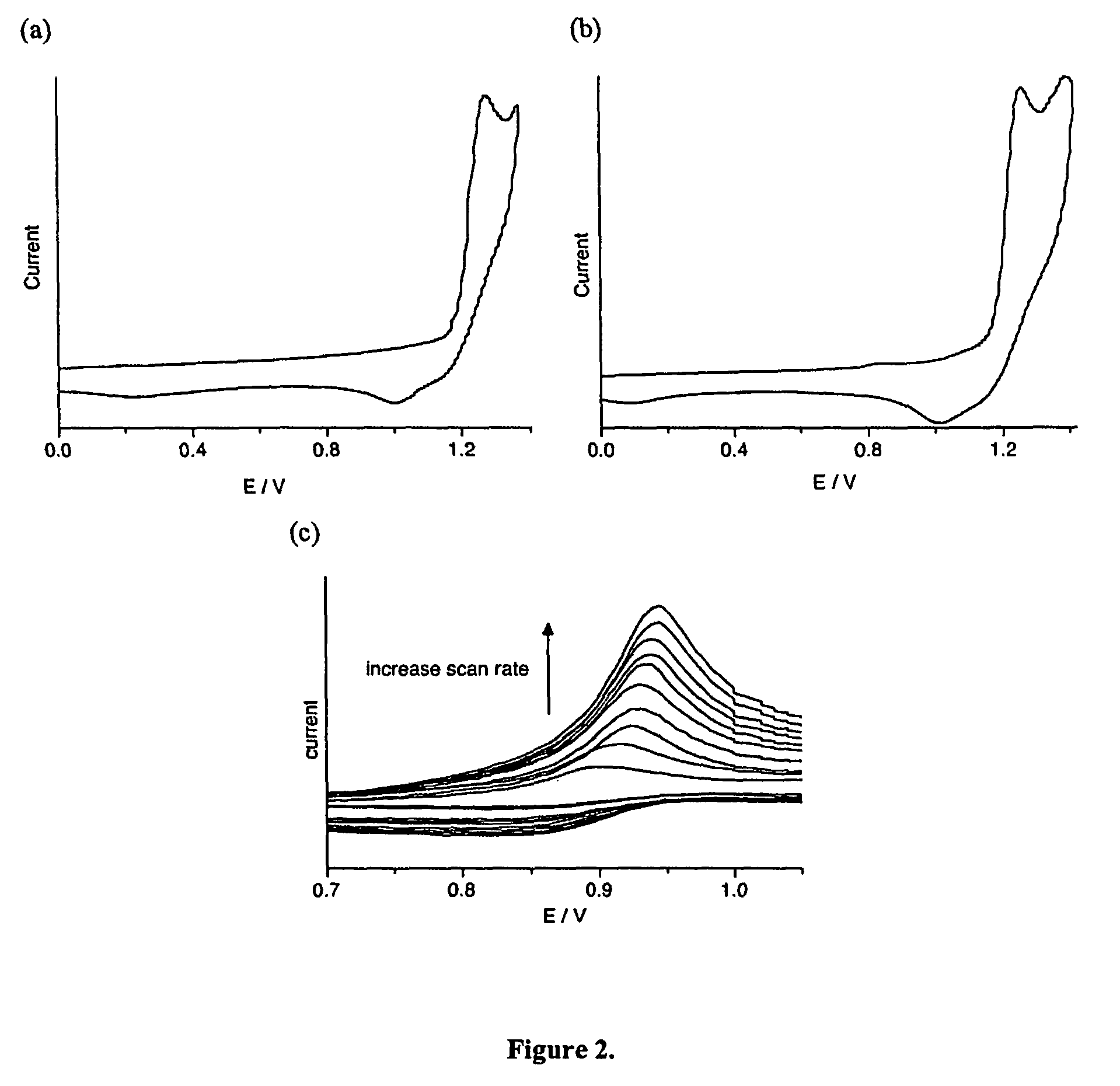
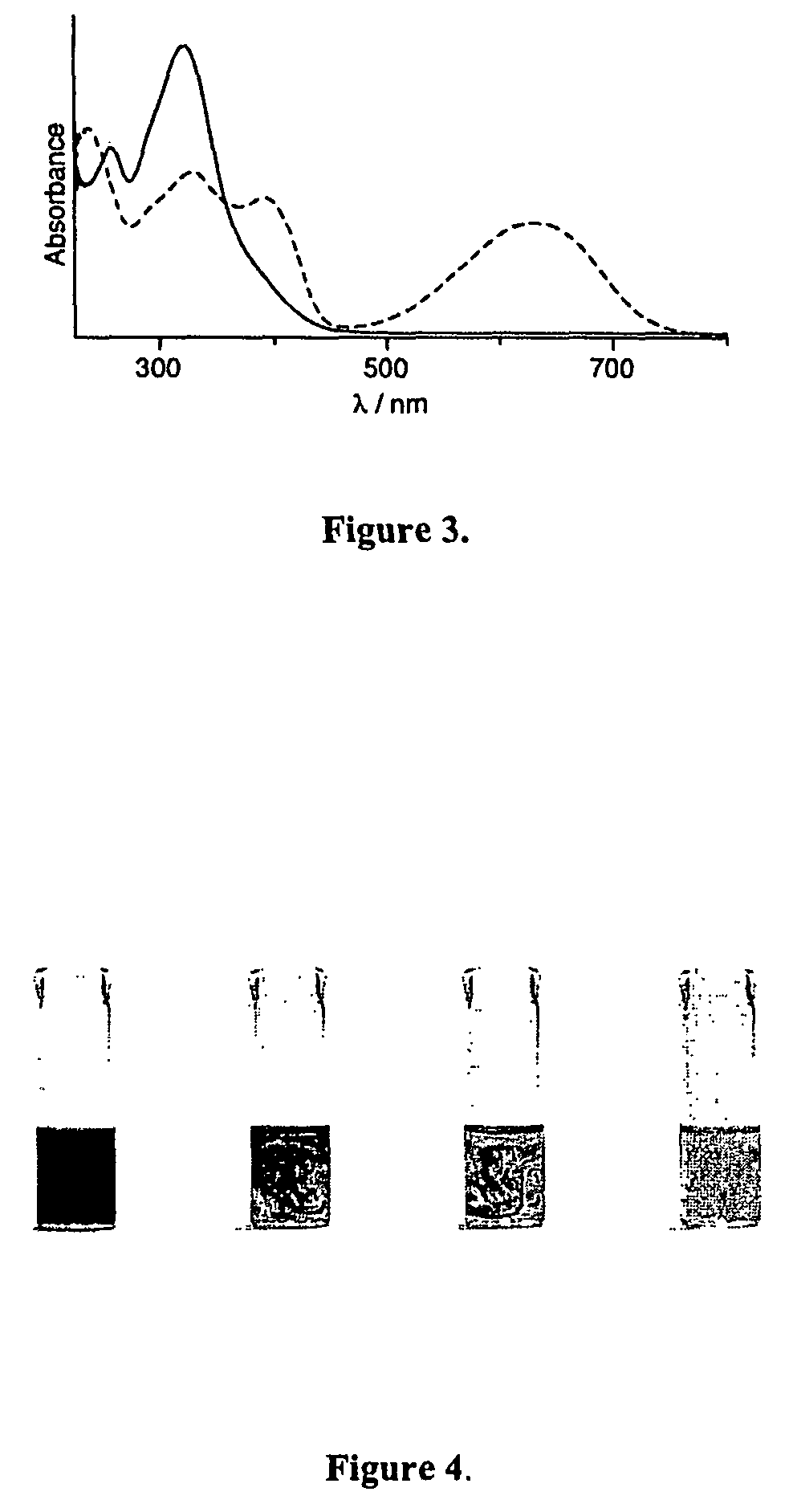
The invention designs and synthesizes a novel supermolecular sensor P5-B1. Pillar [5] arene P5 is adopted as a subject, a pyridine functionalized naphthalene diformyl derivative B1 is adopted as an object, the subject and the object are complexed in a H2O-DMSO system, the object B1 penetrates into a molecular cavity of the object P5 so as to form the supermolecule P5-B1, the supermolecular sensor can be coordinated with Fe3+ to form a supermolecular sensor complex P5-B1Fe, and fluorescence quenching is carried out at the same time, so that supermolecular sensor can be applied in single selective fluorescent recognition of the Fe3+, and the lowest limit of detection is 5.01*10<-7>. F- is added in the sensor complex P5-B1Fe, and green fluorescence of the sensor complex is recovered, so that the F- can be efficiently selected and recognized, and the lowest limit of detection is 4.07*10<-6>. In addition, competitiveness distinguishing complex can be also used as an 'ON-OFF-ON' type fluorescence switch, and the recognition performance has important application value in the ion recognition field.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
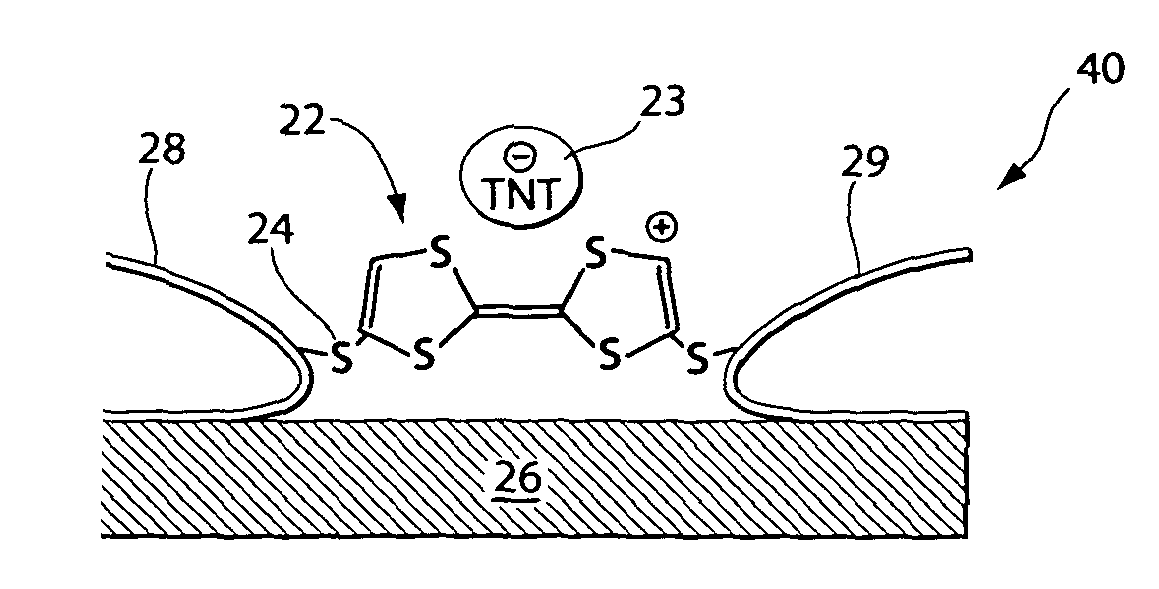
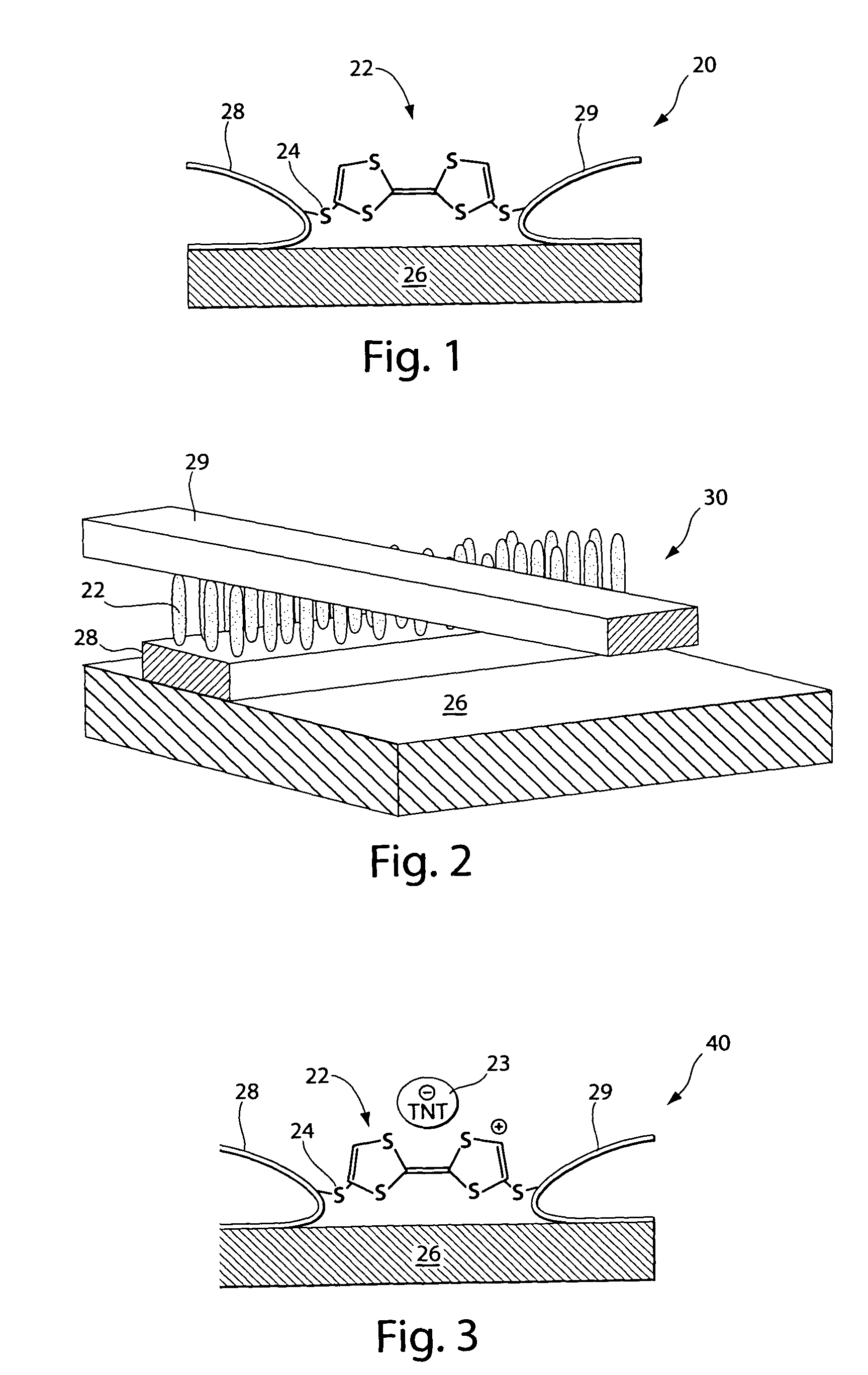
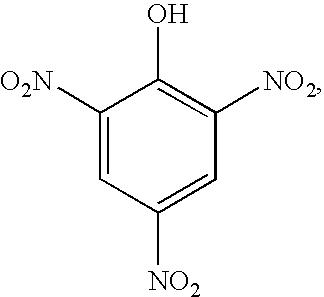
Molecular sensors for explosives
InactiveUS7824619B1Easy to operateFast communicationComponent separationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceAnalyte
The present invention relates to a molecular sensor for detecting the presence of a target analyte comprising a nitro-containing explosive molecule, the sensor comprising: a support substrate; a pair of electrodes comprising (i) a first electrode and (ii) a second electrode, wherein at least one of (i) and (ii) is at the substrate; an electron donor (ED) molecule capable of forming an electron donor-acceptor (EDA) complex with the nitro-containing explosive molecule; and wherein the ED molecule is disposed between the electrodes and is attached to each electrode by an alligator clip comprising a pendant group, thereby forming a nanojunction between the electrodes; a detection means operably connected to the pair of electrodes, the detection means capable of detecting a change in the electrical resistance or in the capacitance of the sensor when the ED molecule forms an EDA complex with the explosive molecule, the sensor thereby detecting the presence of the explosive molecule. Also disclosed are methods of making and methods of using the sensor.
Owner:AVIRAM ARI
Binary arrays of nanoparticles for nano-enhanced raman scattering molecular sensors
ActiveUS20070252979A1Enhancing Raman scattered radiationRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringNanoparticleMaterials science
A nano-enhanced Raman scattering (NERS)-active structure includes a substrate, a monolayer of nanoparticles disposed on a surface of the substrate, and a spacer material surrounding each nanoparticle in the monolayer of nanoparticles. The monolayer of nanoparticles includes a first plurality of nanoparticles and a second plurality of nanoparticles. The nanoparticles of the second plurality are interspersed among the first plurality and exhibit a plasmon frequency that differs from any plasmon frequency exhibited by the first plurality. Also described are a method for forming such a NERS-active structure and a NERS system that includes a NERS-active structure, an excitation radiation source, and a detector for detecting Raman scattered radiation.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
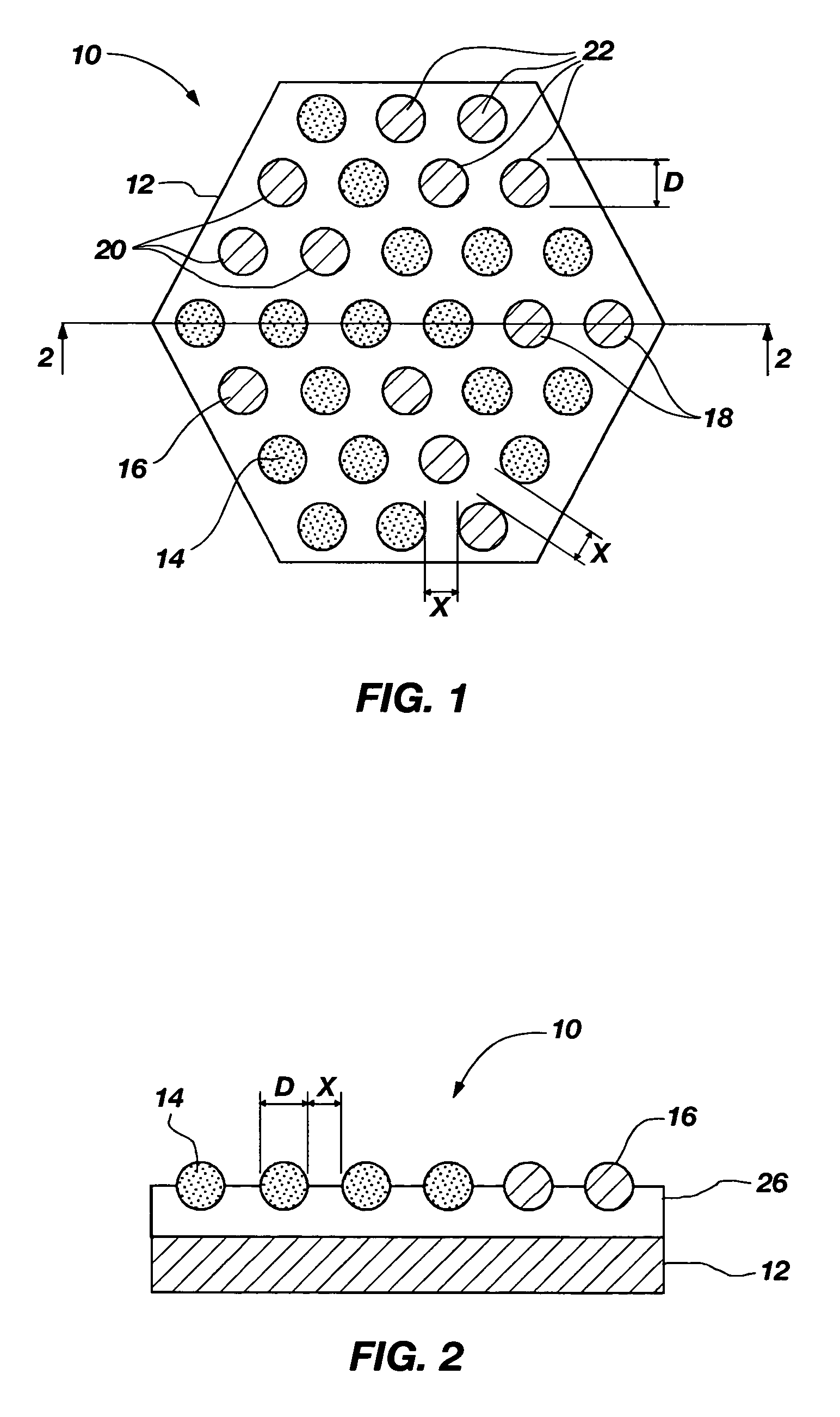
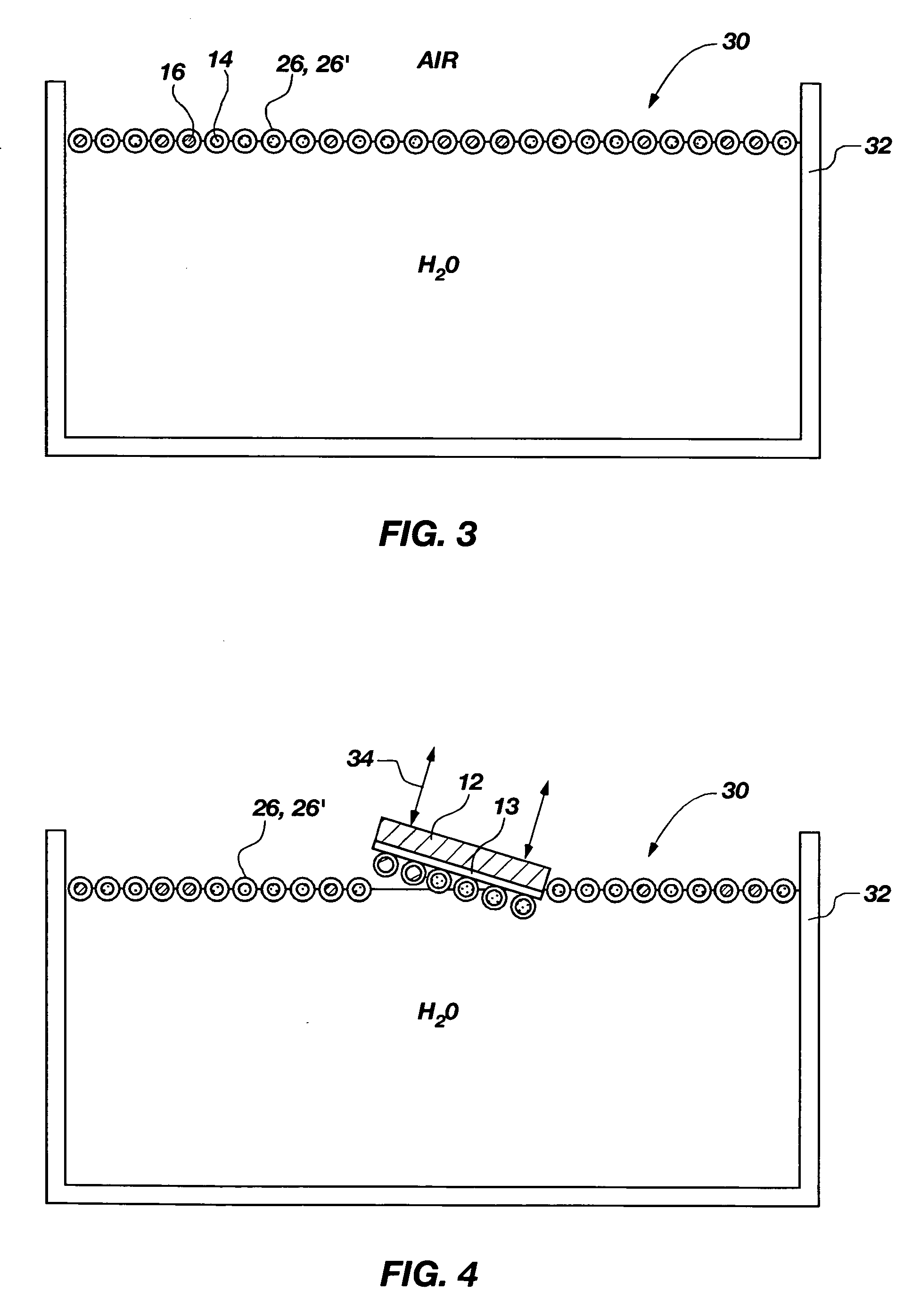
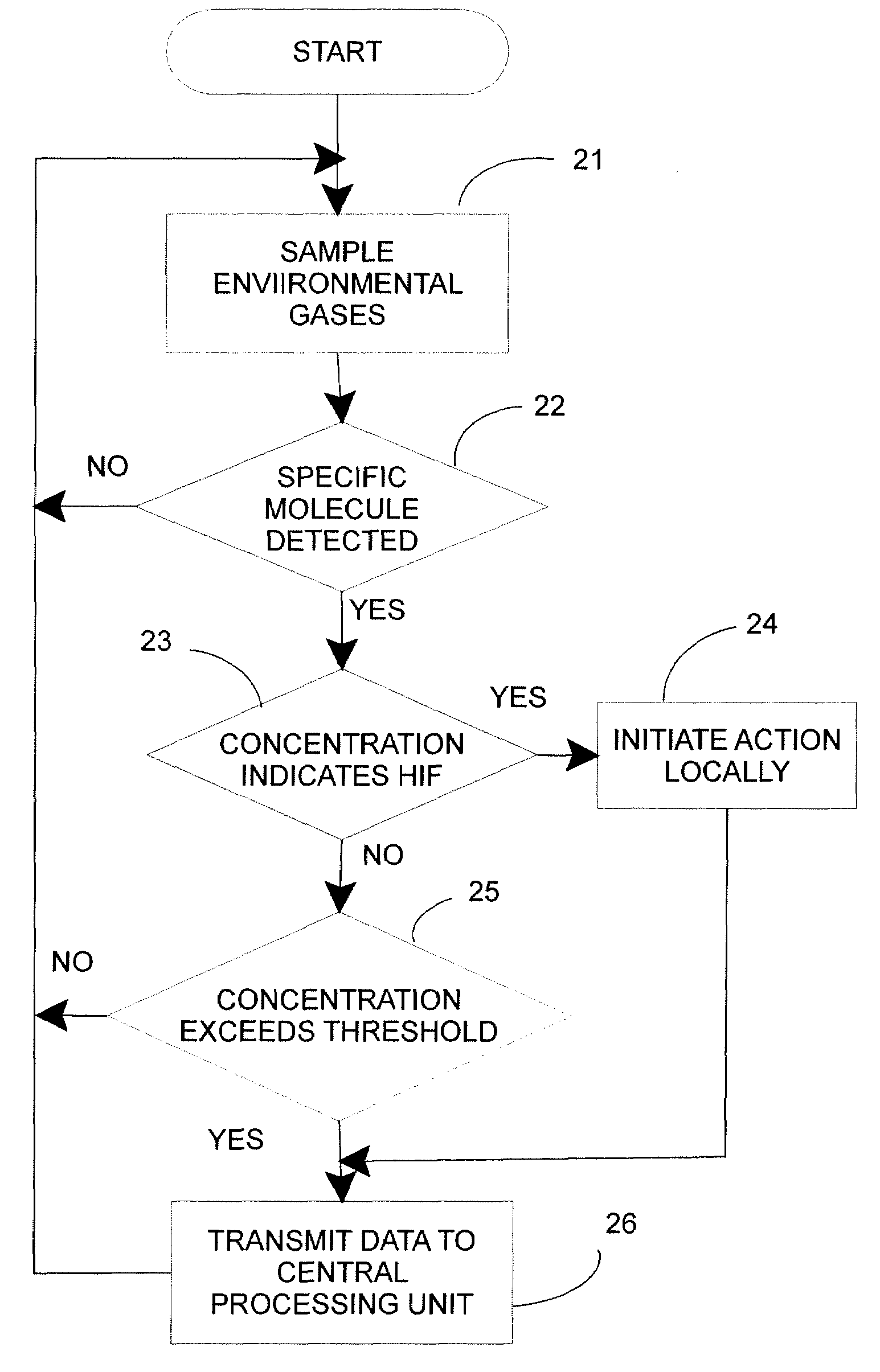
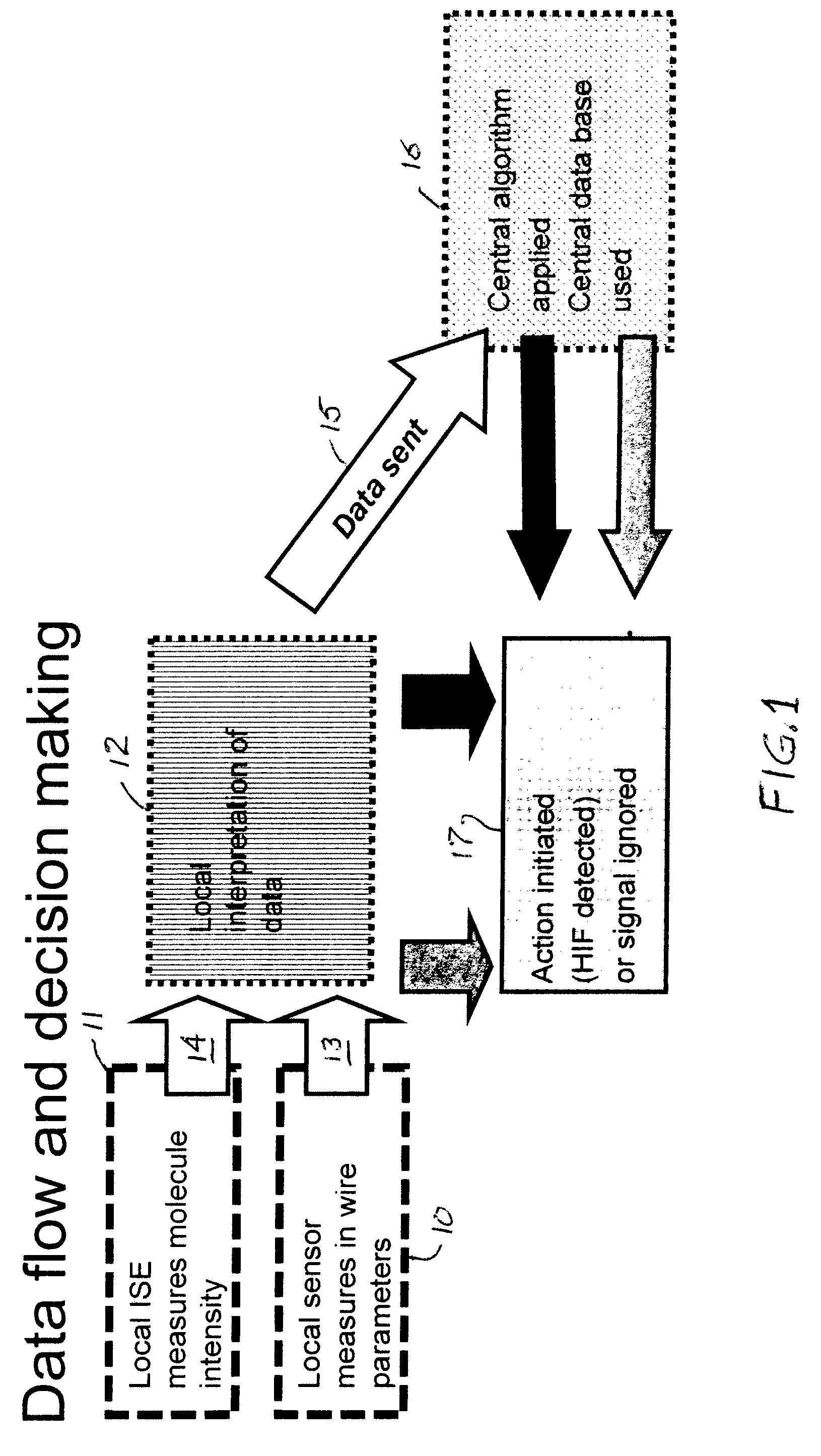
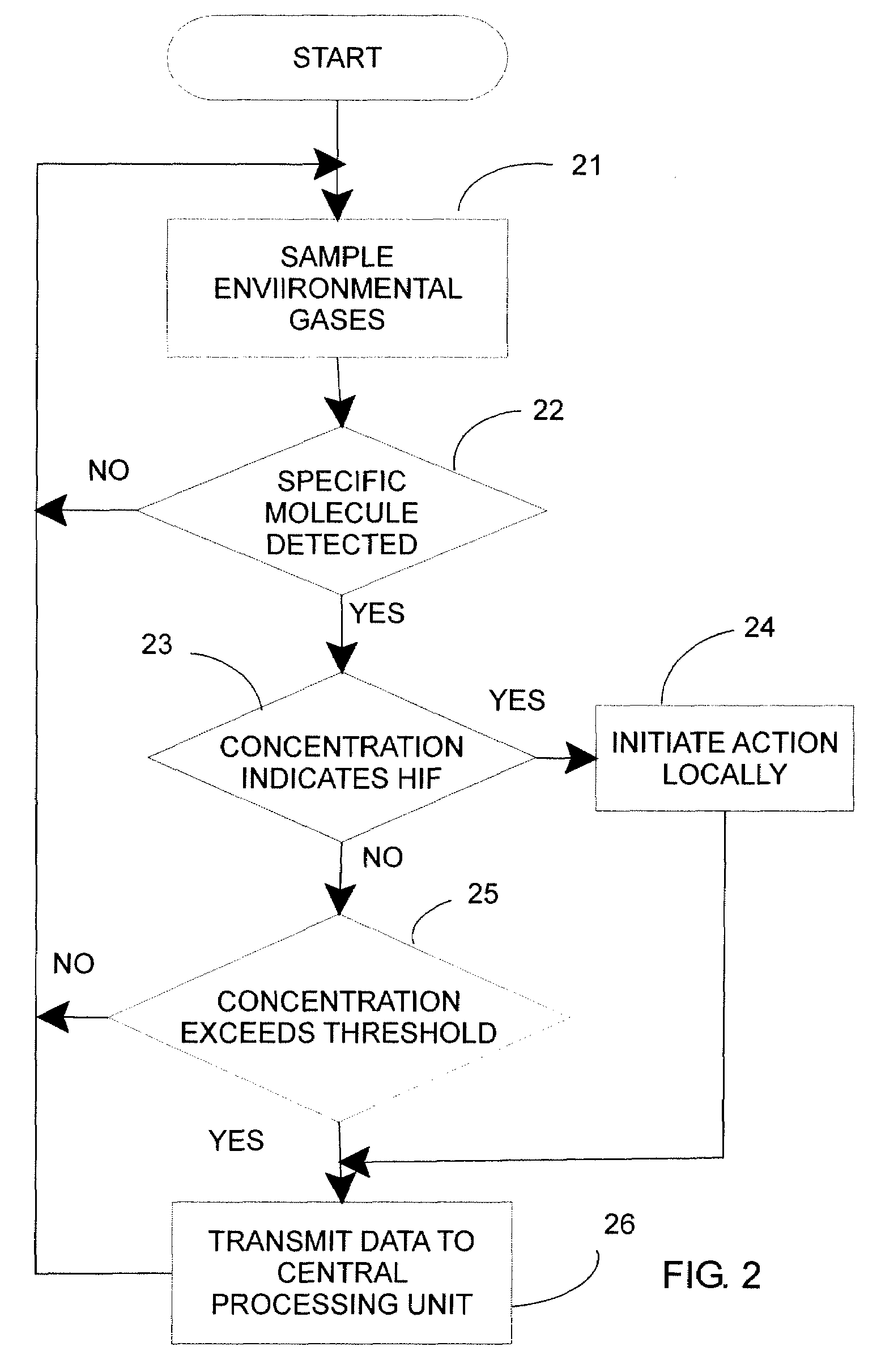
Ozone and other molecules sensors for electric fault detection
InactiveUS20080167754A1High impedanceMechanical power/torque controlDc network circuit arrangementsElectrical gridSulfur dioxide
High impedance fault detection uses, in addition to sensors that measure purely electrical (i.e., current and voltage), molecule sensors are provided in an electrical grid. These molecule sensors are sensitive to the surrounding environment and may detect one or more of a variety of molecules, such as ozone (O3), combustion gases (carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and oxygen levels), and odor molecules (ammonia, sulfur dioxide, burned hair / feather, burned proteins, and the like), depending on the type of environmental phenomena that may be expected in a particular location of the sensor(s). These sensors, in combination with conventional electrical sensors, provide a more complete set of data for evaluation and localization of a potential high impedance electrical fault. The use of such sensors is especially useful in confined areas like underground parking lots, substations, and the like.
Owner:IBM CORP
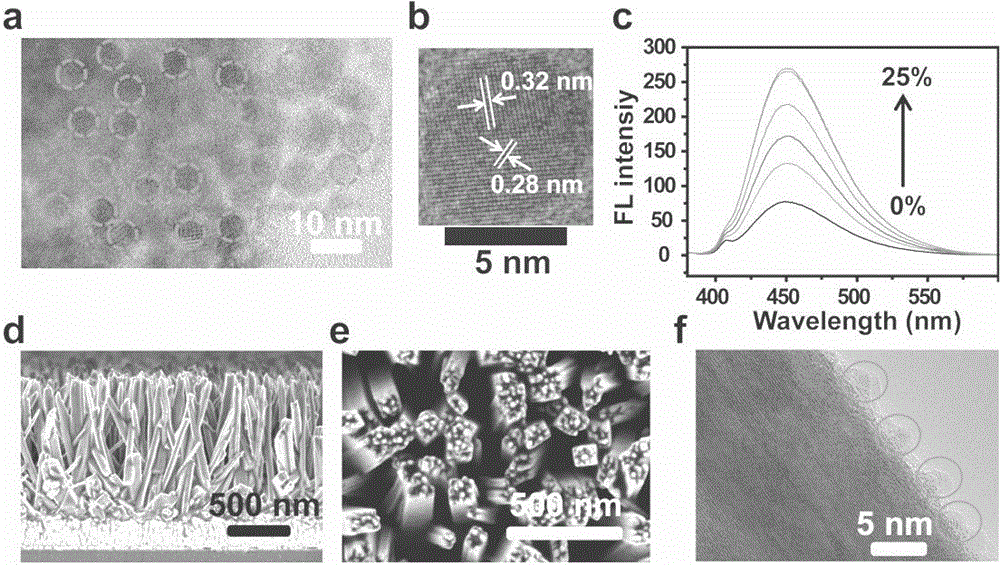
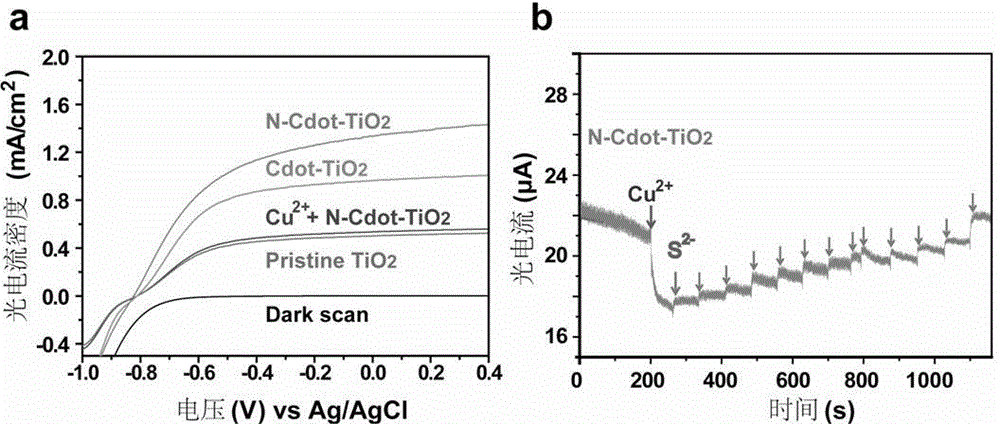
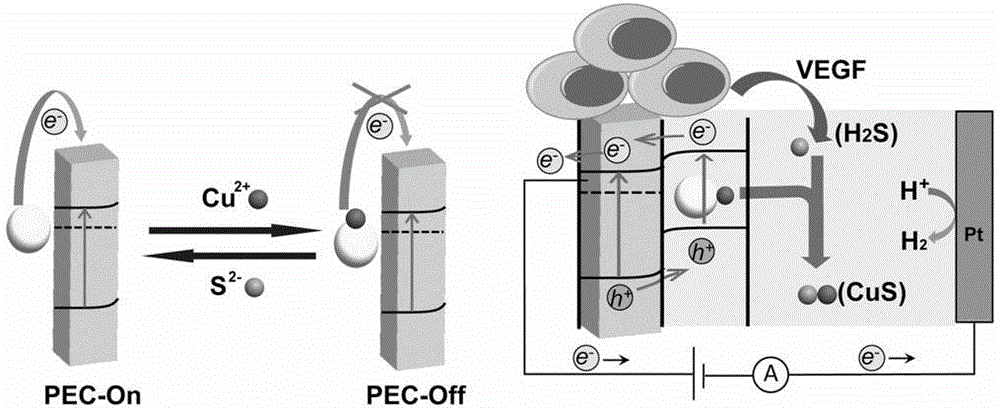
Carbon quantum dot-nanowire array-based cardiomyocyte signal molecule sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104089999AHigh sensitivityGood choiceMaterial electrochemical variablesMicrowave methodSignalling molecules
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectrochemical sensors, and particularly relates to a carbon quantum dot-nanowire array-based cardiomyocyte signal molecule sensor based on sunlight drive and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: under a hydrothermal system, growing a titanium dioxide nanowire array on a conductive glass substrate; obtaining silane-functionalized nitrogen-doped carbon dots (N-CDots) at one step in situ through using a microwave method; then placing titanium dioxide nanowires processed by concentrated sulfuric acid into an N-CDot ethanol solution, adding stronger ammonia water, standing and reacting, and defining as N-CDot-TiO2. The photoelectric current of the N-CDot-TiO2 is improved by almost two times compared with that of pure TiO2, and the prepared photoelectric current on-off sensor can be used for dynamically detecting the content of H2S star molecules of cardiomyocytes in real time in situ. The carbon quantum dot-nanowire array-based cardiomyocyte signal molecule sensor is smart in design and wide in the source of raw materials, the preparation method is simple, environment-friendly, low in price, fast to response, wide in linear range, high in selectivity, and beneficial to popularization and application.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
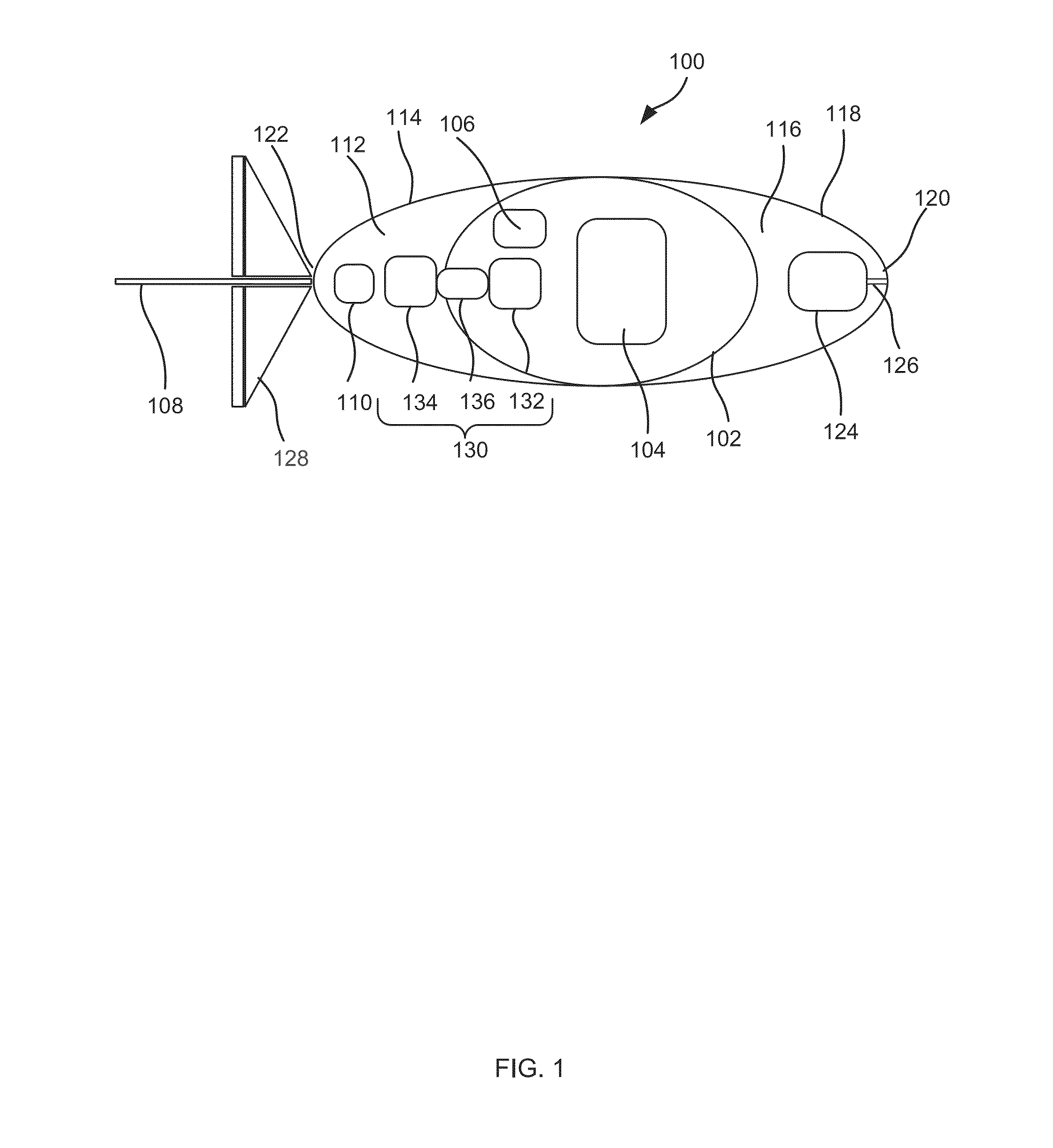
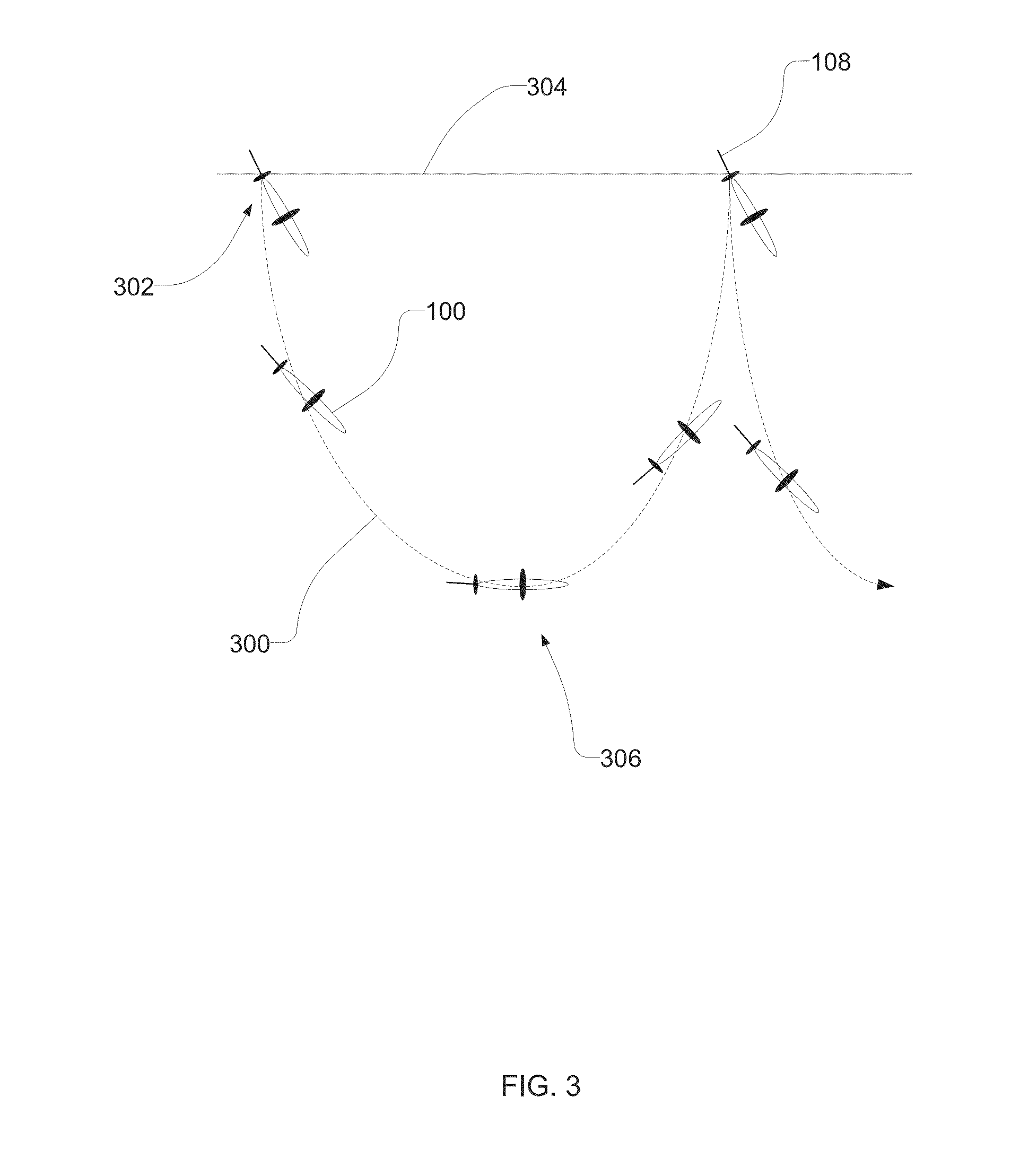
Underwater vehicle and sensor
Described herein is an underwater vehicle having a vehicle body with a buoyancy controller adapted to vary the buoyancy of the vehicle in order to control motion of the vehicle through an underwater environment. The vehicle further includes a sampling system and a sensor arrangement. The sampling system is adapted to sequentially sample fluid from the underwater environment at specified sampling times resulting in a sample sequence, each sample associated with a sample time and a fluid flow rate. The sensor arrangement includes a plurality of molecule sensors adapted to sense organic molecules in each respective sample of the sample sequence.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
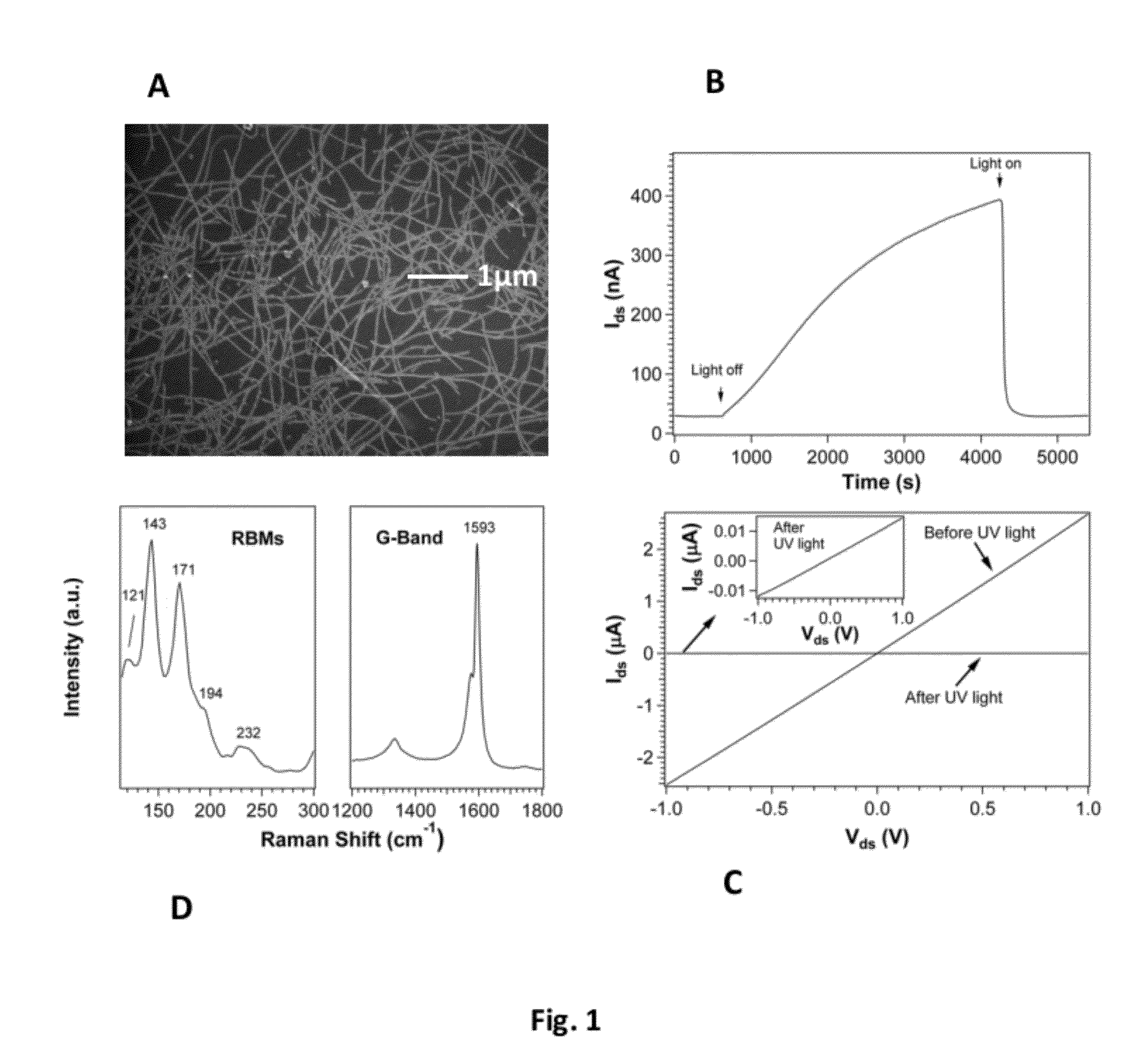
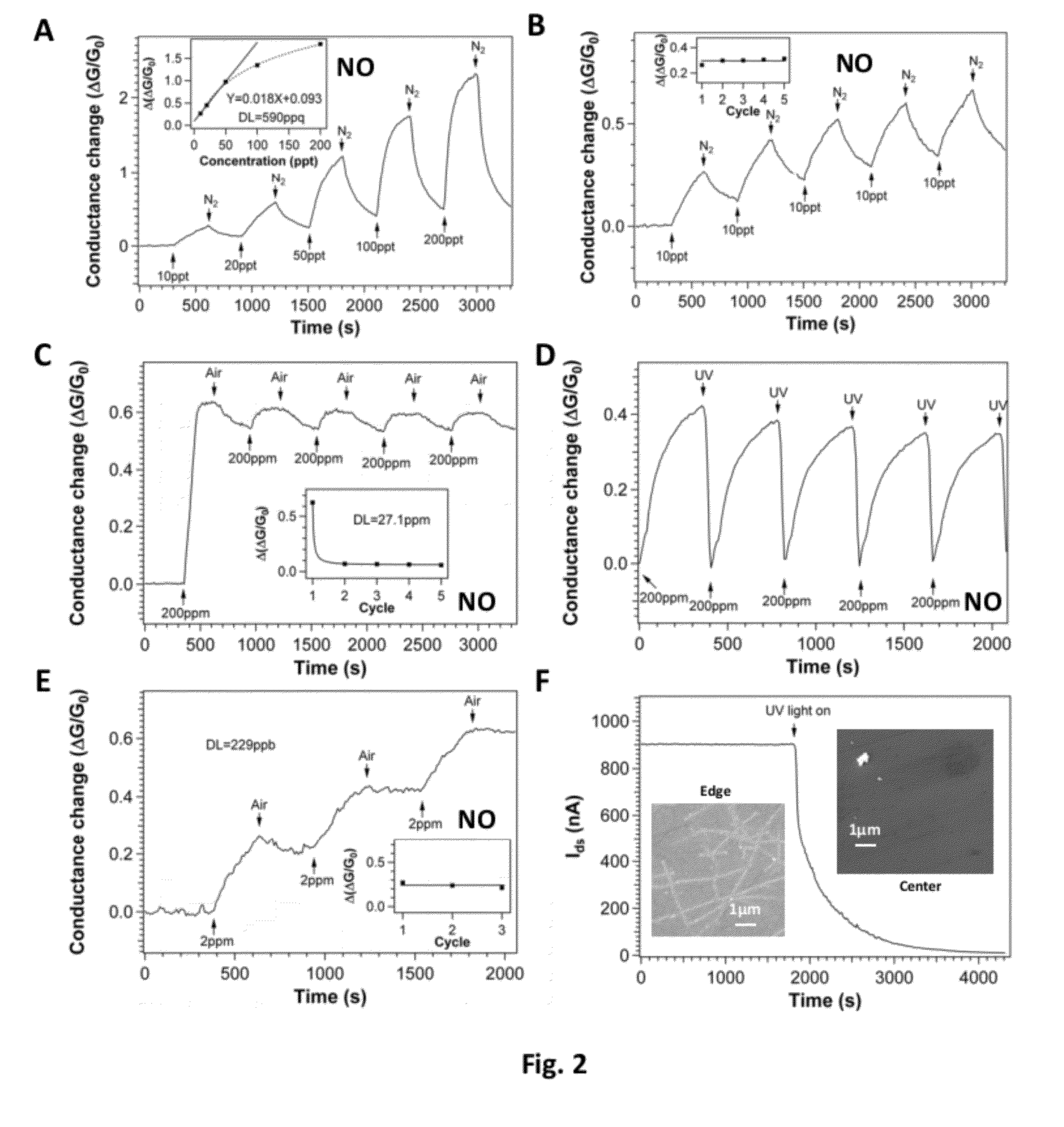
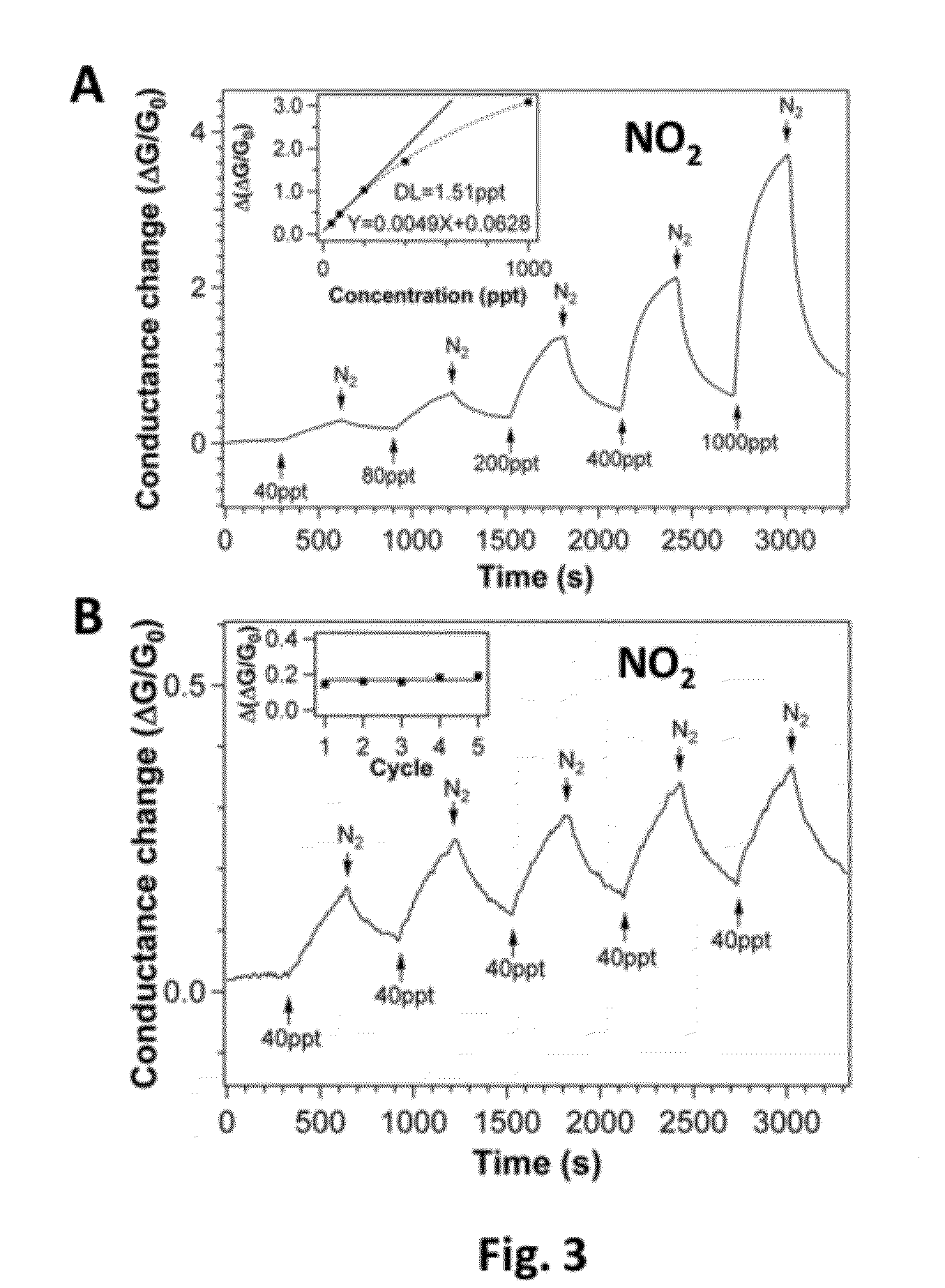
Method of enhanced detection for nanomaterial-based molecular sensors
InactiveUS20120282594A1Confirmed ultrasensitivityDetection is limitedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteCarbon nanotube
Sensors based on single-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene which demonstrate extreme sensitivity as reflected in their electrical conductivity to gaseous molecules, such as NO, NO2 and NH3, when exposed to in situ ultraviolet (UV) illumination during measurement of the analytes are disclosed. The sensors are capable of detection limits of NO down to almost 150 parts-per-quadrillion (“ppq”), detection limits of NO2 to 2 parts-per-trillion (“ppt”), and detection limits of NH3 of 33 ppt.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Nanopatterned surfaces and related methods for selective adhesion, sensing and separation
ActiveUS8117902B2Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteUltimate tensile strength
The invention is comprised, in part, of a surface that contains more than one component or construct. Such heterogenous surface compositions and configurations, related systems and methods for sensing particle or analyte interaction therewith can selectively and / or differentially interact with a range of particles / analytes, in lieu of specific molecular sensor-analyte interactions for each particle. These interactions of various analytes or particles can differ sufficiently in strength and range between multiple analyte types or particles to effect a separation of analytes or particles mixtures, in a way that requires no sensing or detection. With incorporation of a sensing mechanism, discrimination / detection of different compounds within an analyte mixture can be accomplished.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
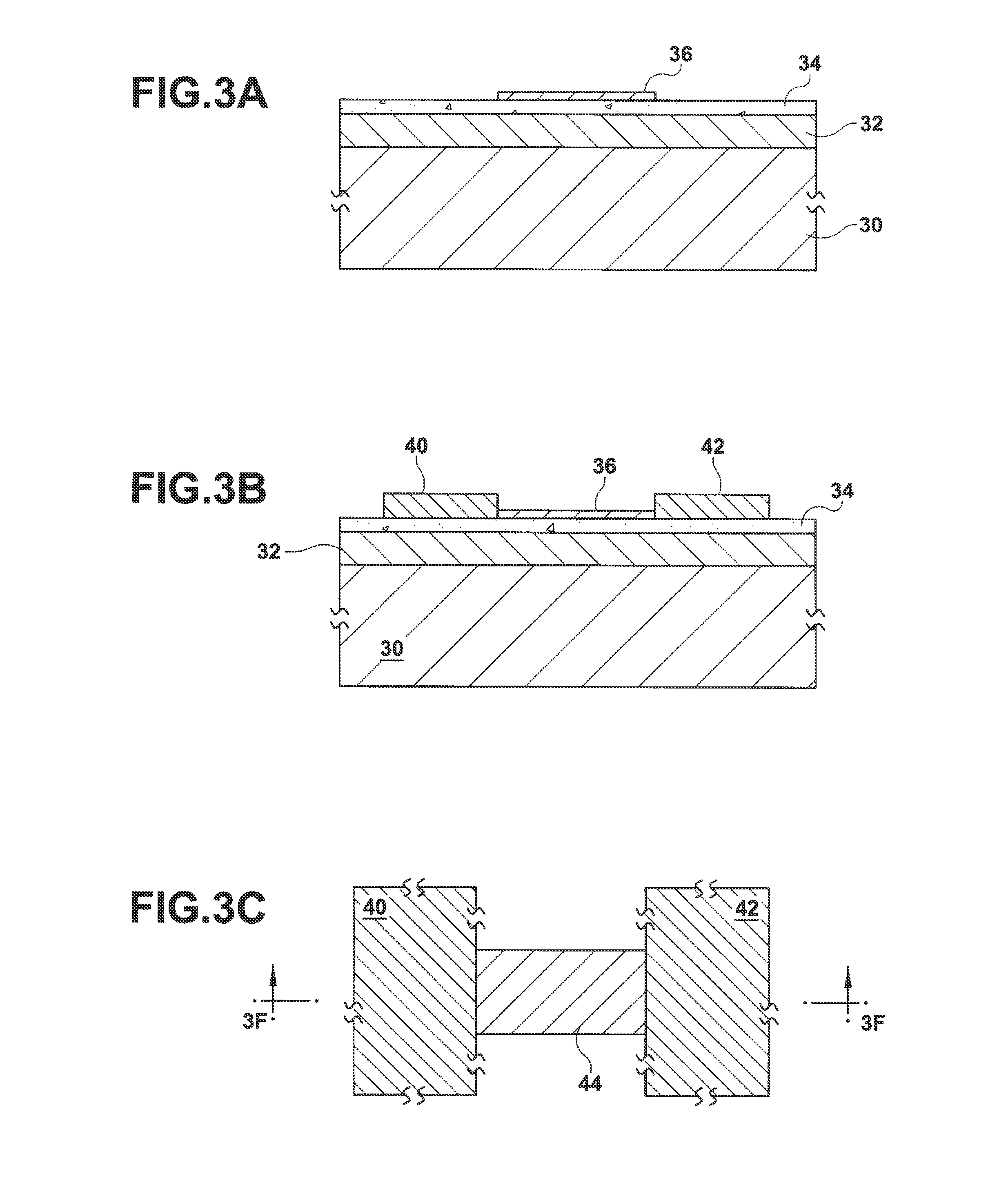
Chip for raman scattering enhancement and molecular sensing device including the chip
InactiveUS20090027668A1High sensitivitySuppress chemical reactionRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringSemiconductor materialsPhotovoltaic detectors
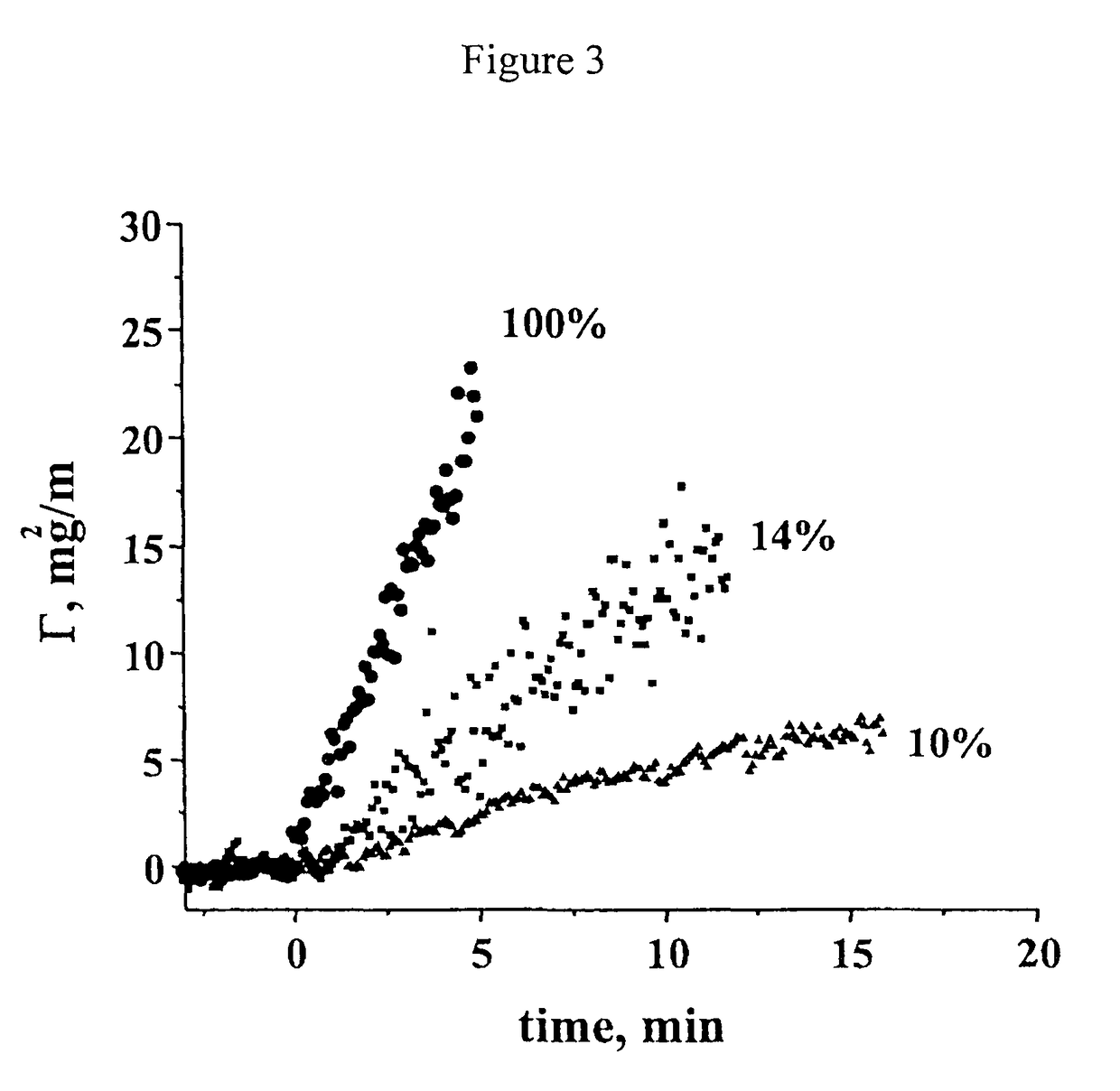
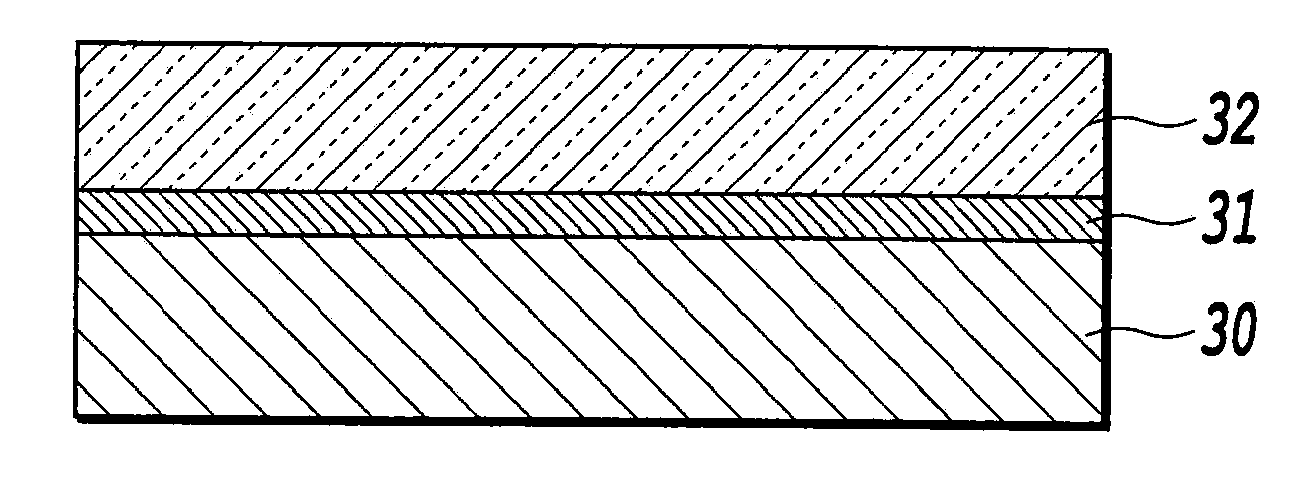
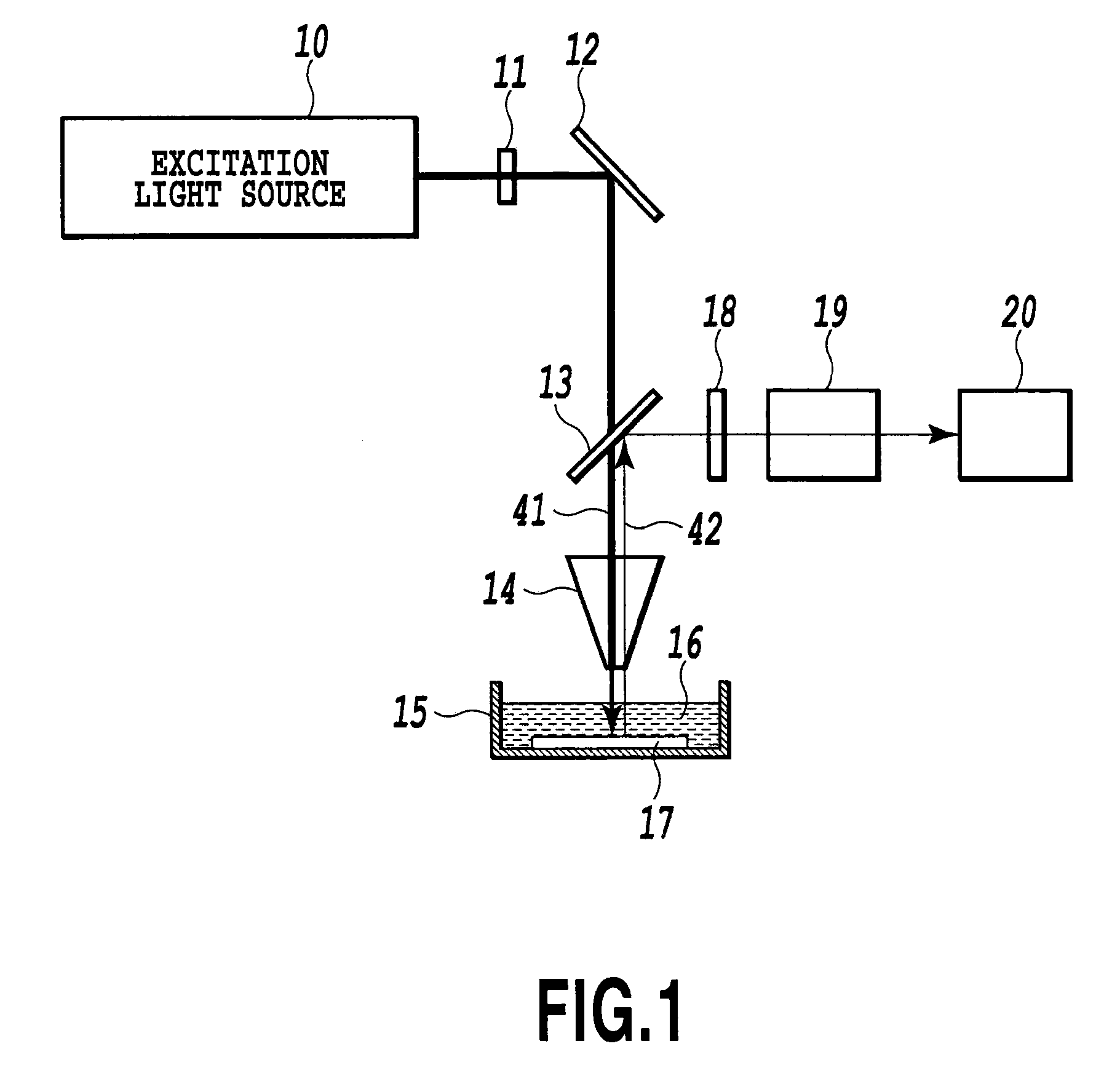
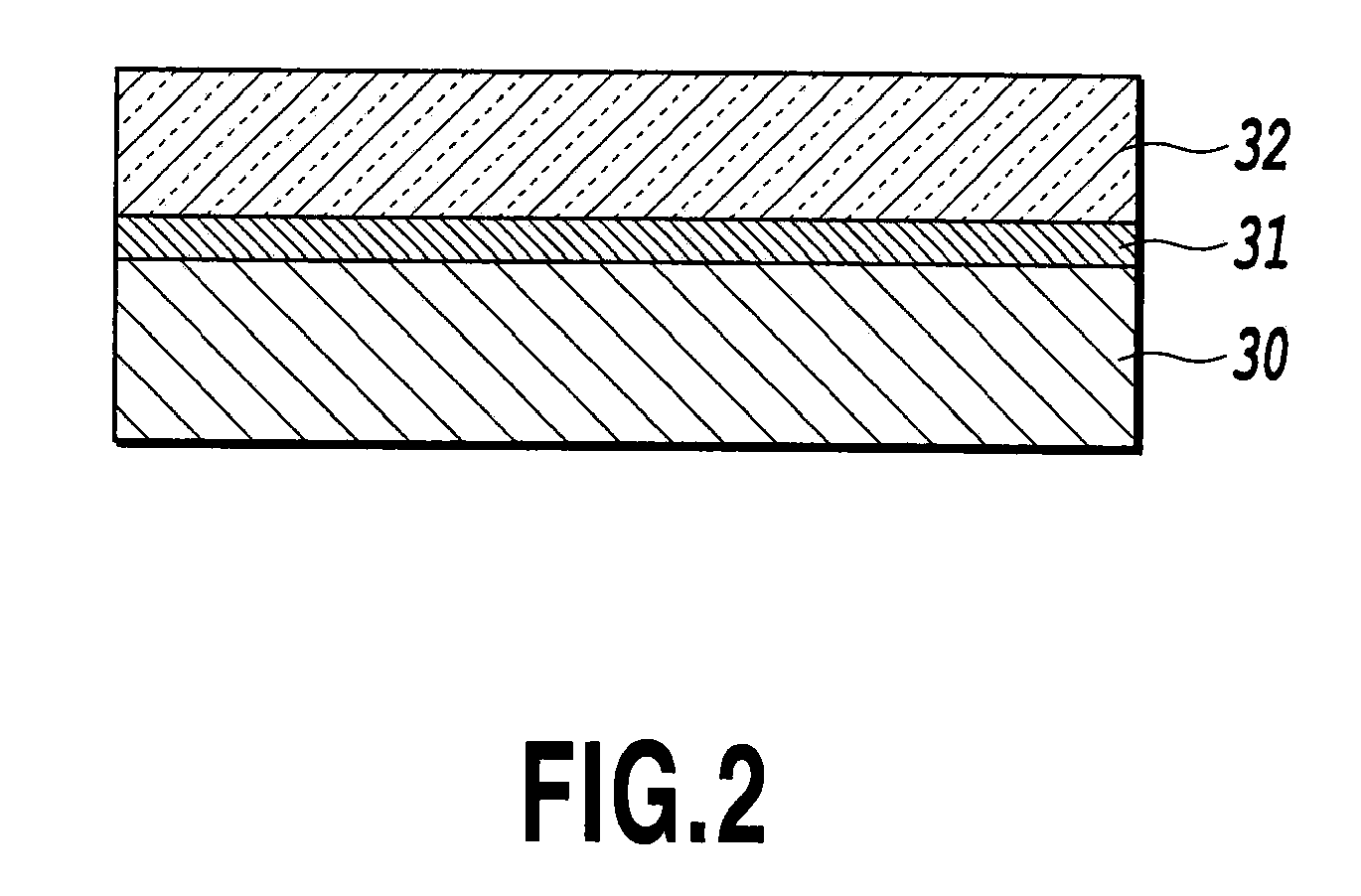
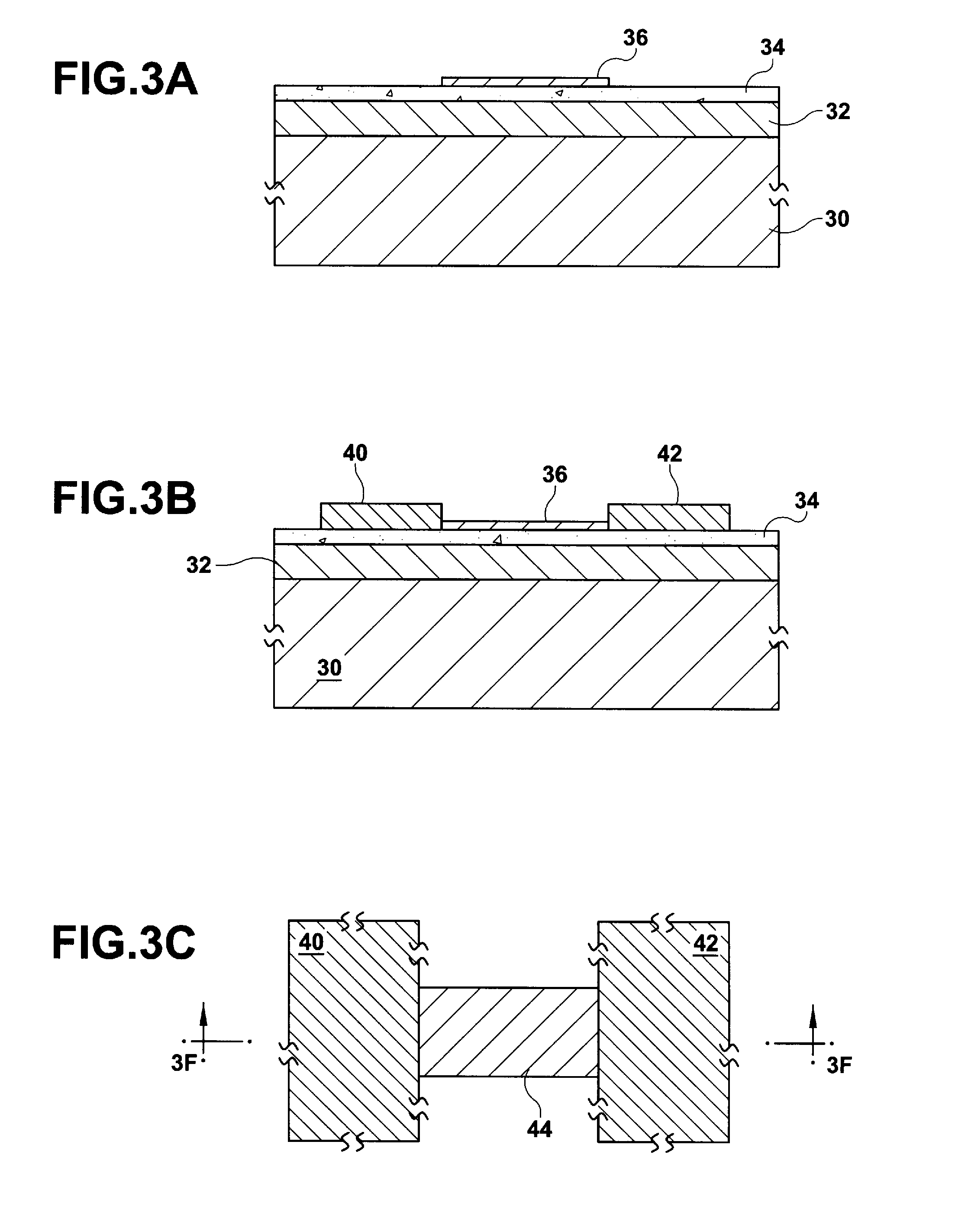
The present invention aims to provide a chip applied to a molecular sensing device which carries out Raman spectroscopic analysis utilizing Raman scattering enhancement due to plasmons, and that achieves higher sensitivity and stability of its sensing sensitivity and miniaturization, and to provide a molecular sensing device including the chip. As the chip for Raman scattering enhancement applied to the molecular sensing device using the Raman spectroscopic analysis, which has an excitation light source for Raman scattering, a chip for Raman scattering enhancement and a photodetector for observing the Raman scattering, the present invention employs a chip having a molecular detecting element in which a transparent protection material thin film 32 composed of a dielectric material thin film or semiconducting material thin film is formed on a thin film 31 containing the noble metal oxide, and utilizes the Raman scattering enhancement by the thin film containing the noble metal oxide.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Nano-scaled dendrimer-based colorimetric biosensors
InactiveUS7045367B2High densityRapid and convenient and economical detectionPeptide librariesAnalysis using chemical indicatorsDendrimerHigh density
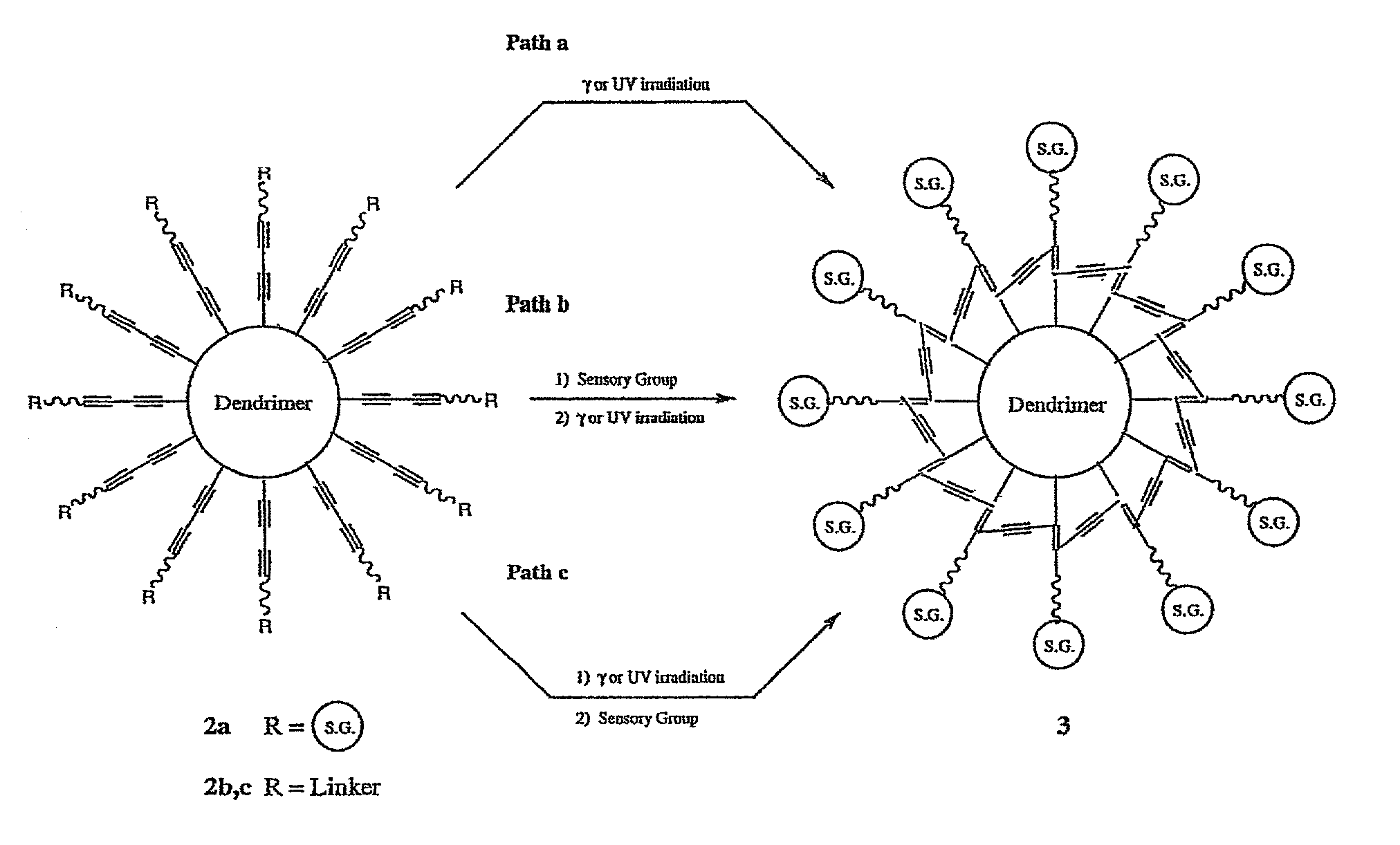
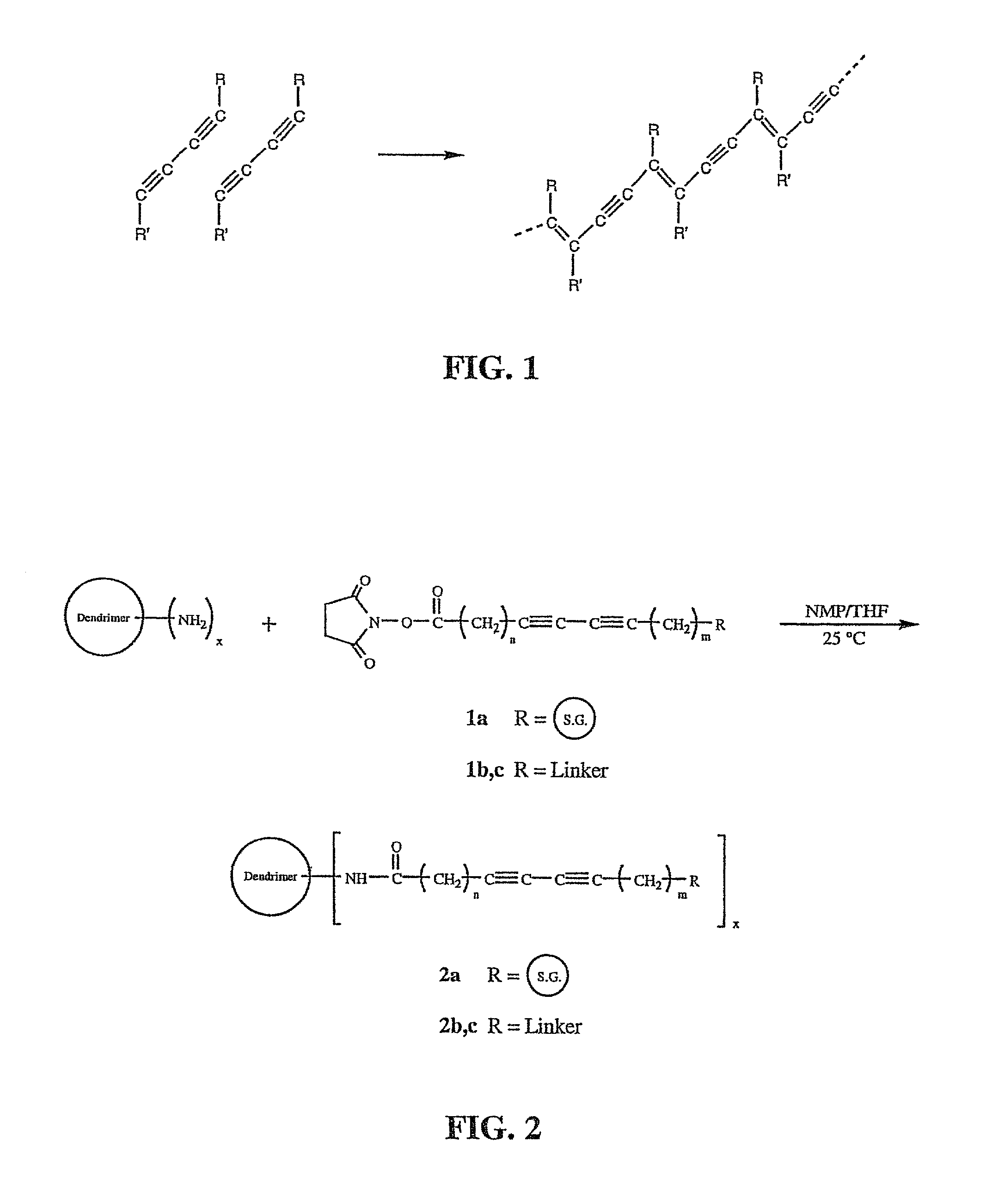
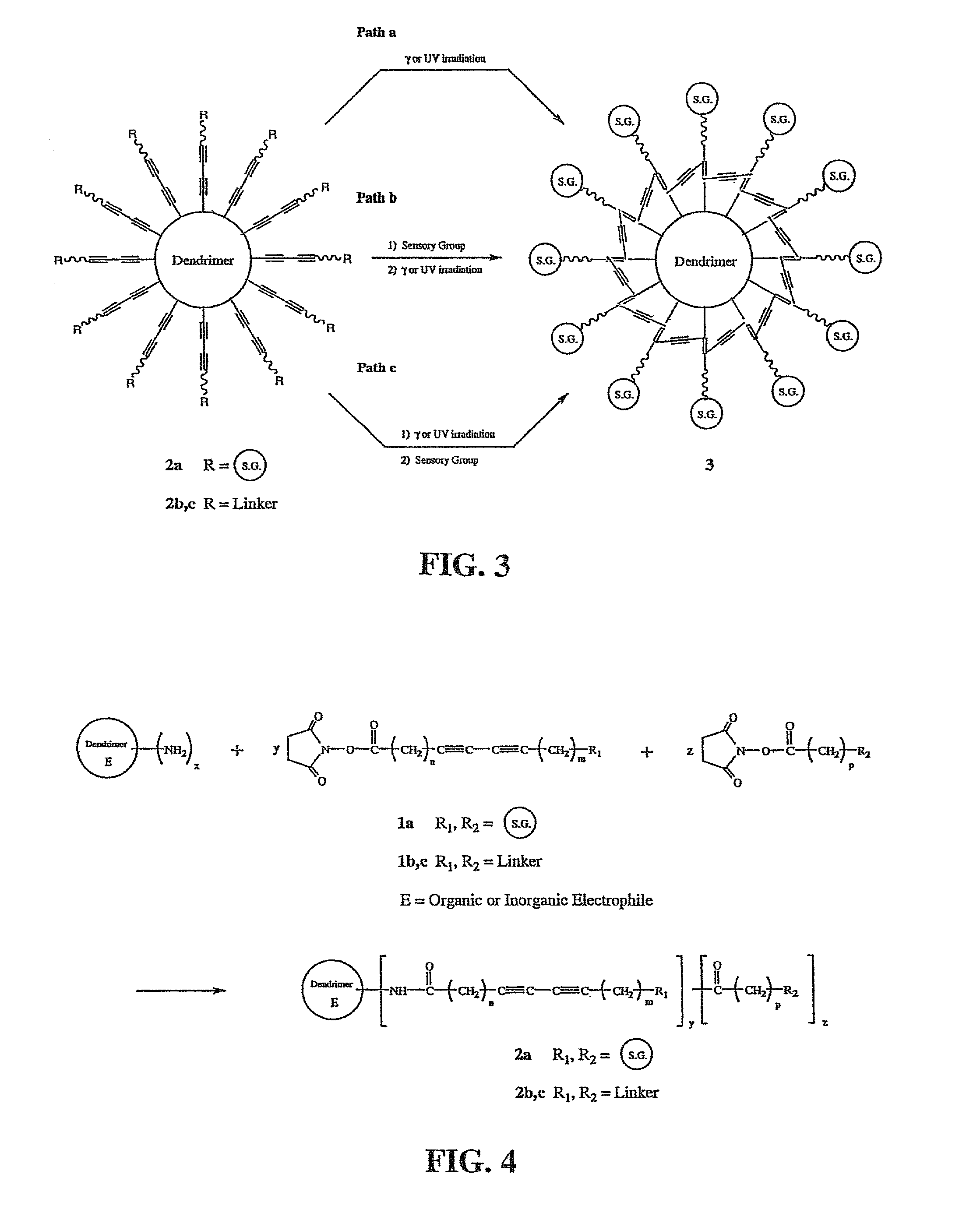
Molecular chemical and / or biological sensors that exhibit a very high density of sensing functionality and which are applicable to a wide variety of different analytes, and enable rapid, convenient and economical detection of analytes are prepared by reacting a dendritic polymer with a diacetylene reagent wherein the diacetylene functional groups are subsequently intramolecularly polymerized to form segments having alternating conjugated double and triple bonds. Sensory groups that can bind with an analyte are bonded to the acetylene monomer units to form molecular sensors that produce observable and measurable color changes when an analyte binds with the sensory groups.
Owner:MICHIGAN MOLECULAR INST
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof
ActiveUS9121843B2Avoid stickingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiopolymerElectron
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof. Nanopores are extremely sensitive single-molecule sensors. Recently, electron beams have been used to fabricate synthetic nanopores in thin solid-state membranes with sub-nanometer resolution. A new class of chemically modified nanopore sensors are provided with two approaches for monolayer coating of nanopores by: (1) self-assembly from solution, in which nanopores −10 nm diameter can be reproducibly coated, and (2) self-assembly under voltage-driven electrolyte flow, in which 5 nm nanopores may be coated. Applications of chemically modified nanopore are provided including: the detection of biopolymers such as DNA and RNA; immobilizing enzymes or other proteins for detection or for generating chemical gradients; and localized pH sensing.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
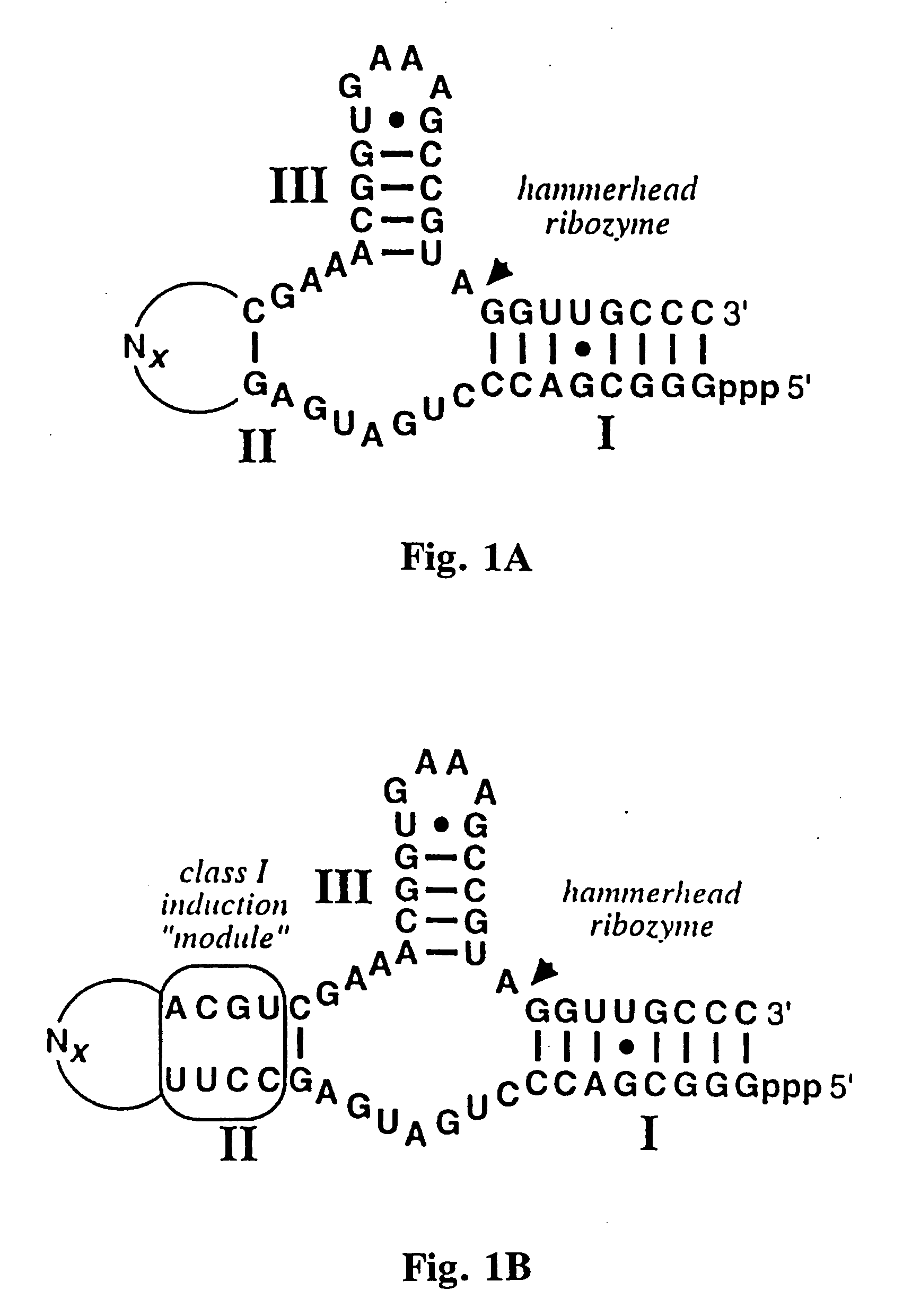
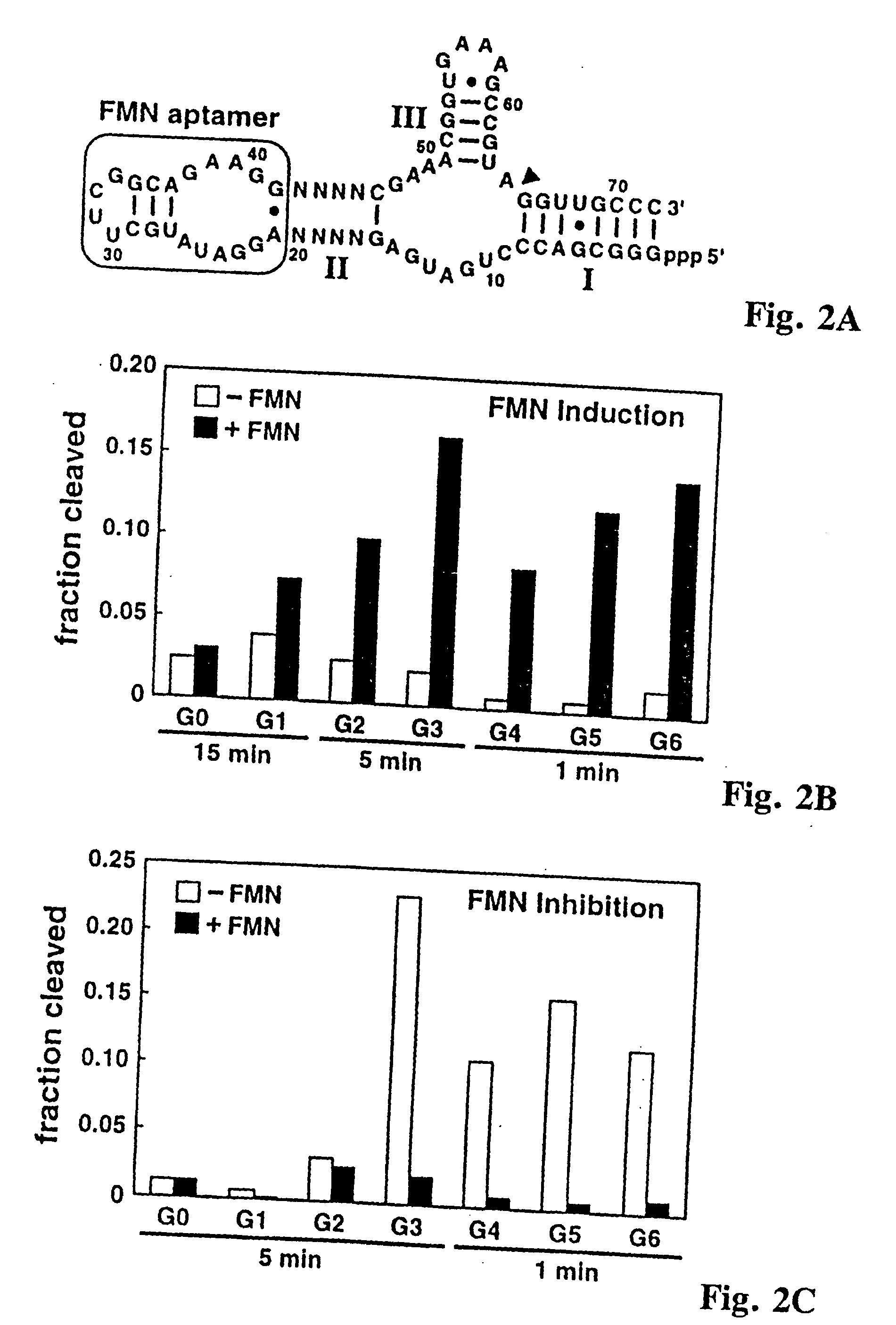
Multidomain polynucleotide molecular sensors
InactiveUS20060121510A1Wide applicationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSignal responseNucleotide
Multidomain polynucleotides responsive to signalling agents are designed and constructed to have at least three domains which can be partially or completely overlapping or nonoverlapping: an actuator (catalytic or reporter) domain, a bridging domain, and a receptor domain. In a typical embodiment, a signalling agent such as a chemical ligand interacts with the receptor domain, which changes conformation or otherwise influences the bridging domain so that the activity, catalytic, or reporter function of the actuator domain is stimulated or inhibited. In some ribozyme embodiments, for example, ligand-specific molecular sensors composed of RNA are created by coupling pre-existing catalytic and receptor domains via novel structural bridges which function such that binding of a ligand to the receptor domain triggers a conformational change within the bridge, and this structural reorganization dictates the activity of the adjoining ribozyme. Processes for allosterically selecting other multidomain polynucleotides typically involve mixing and matching domains to optimize binding or other signal response and / or reporter activity.
Owner:BREAKER RONALD +1
High-Resolution Molecular Sensor
ActiveUS20140166487A1CellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesElectricityElectrical connection
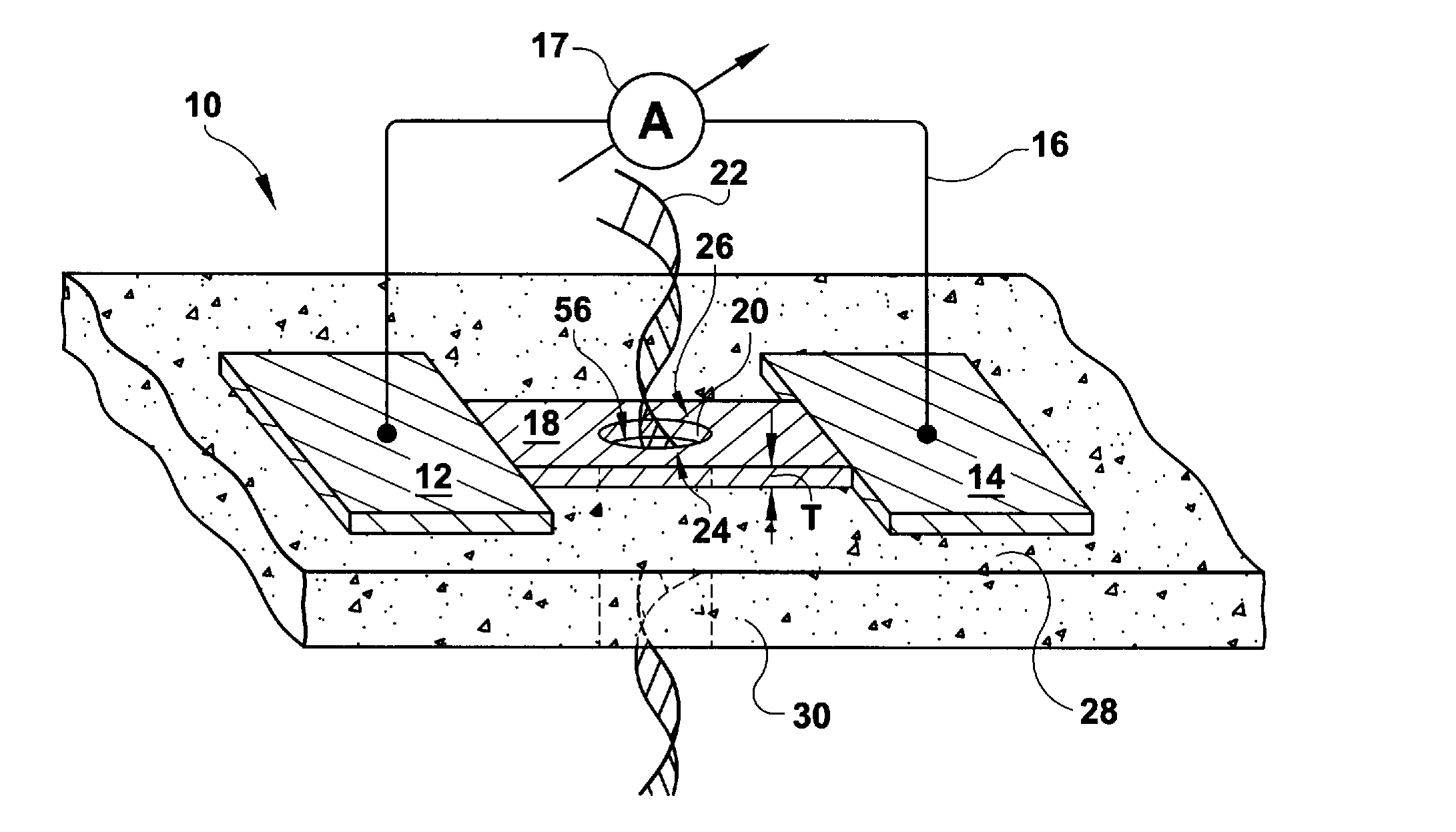
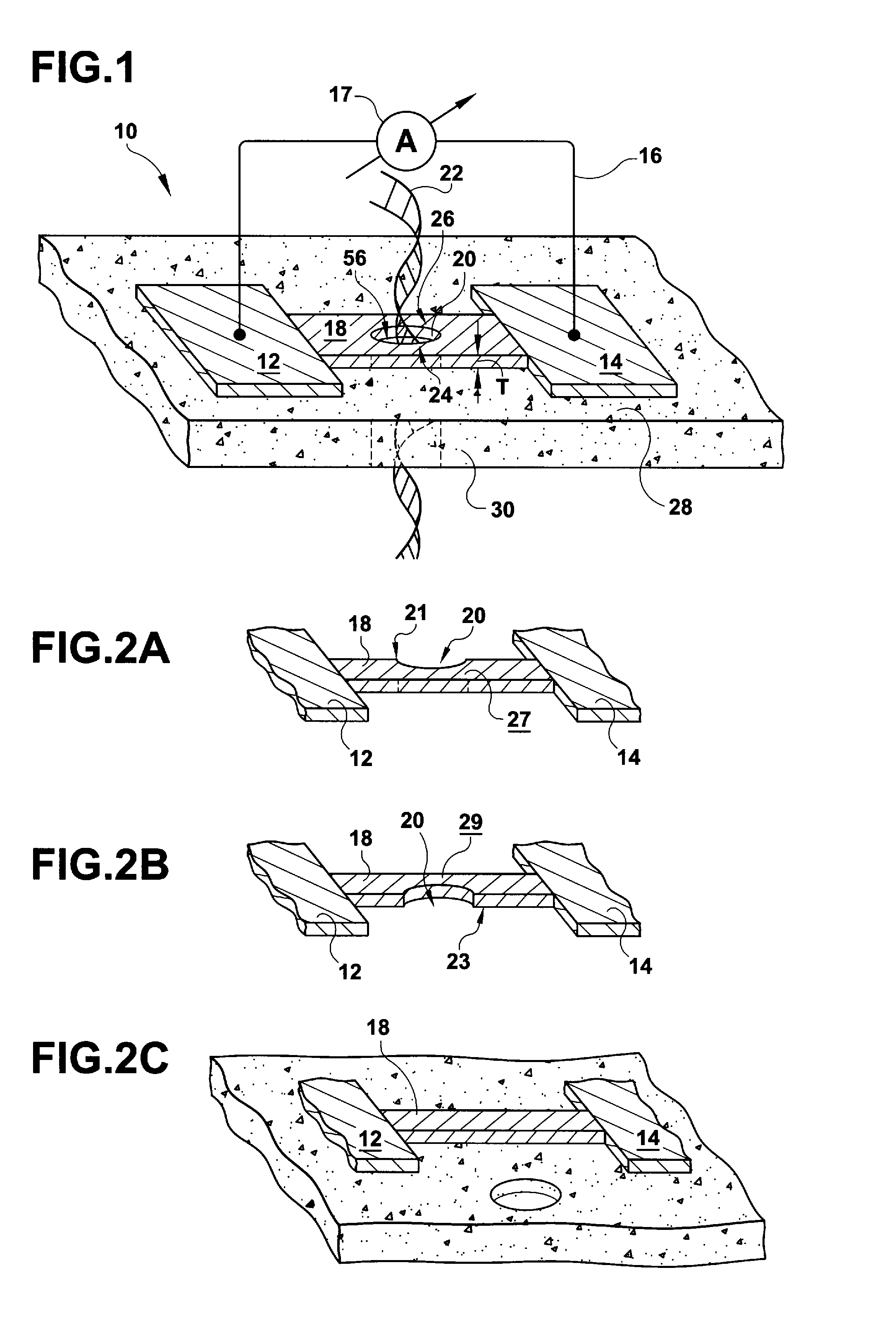
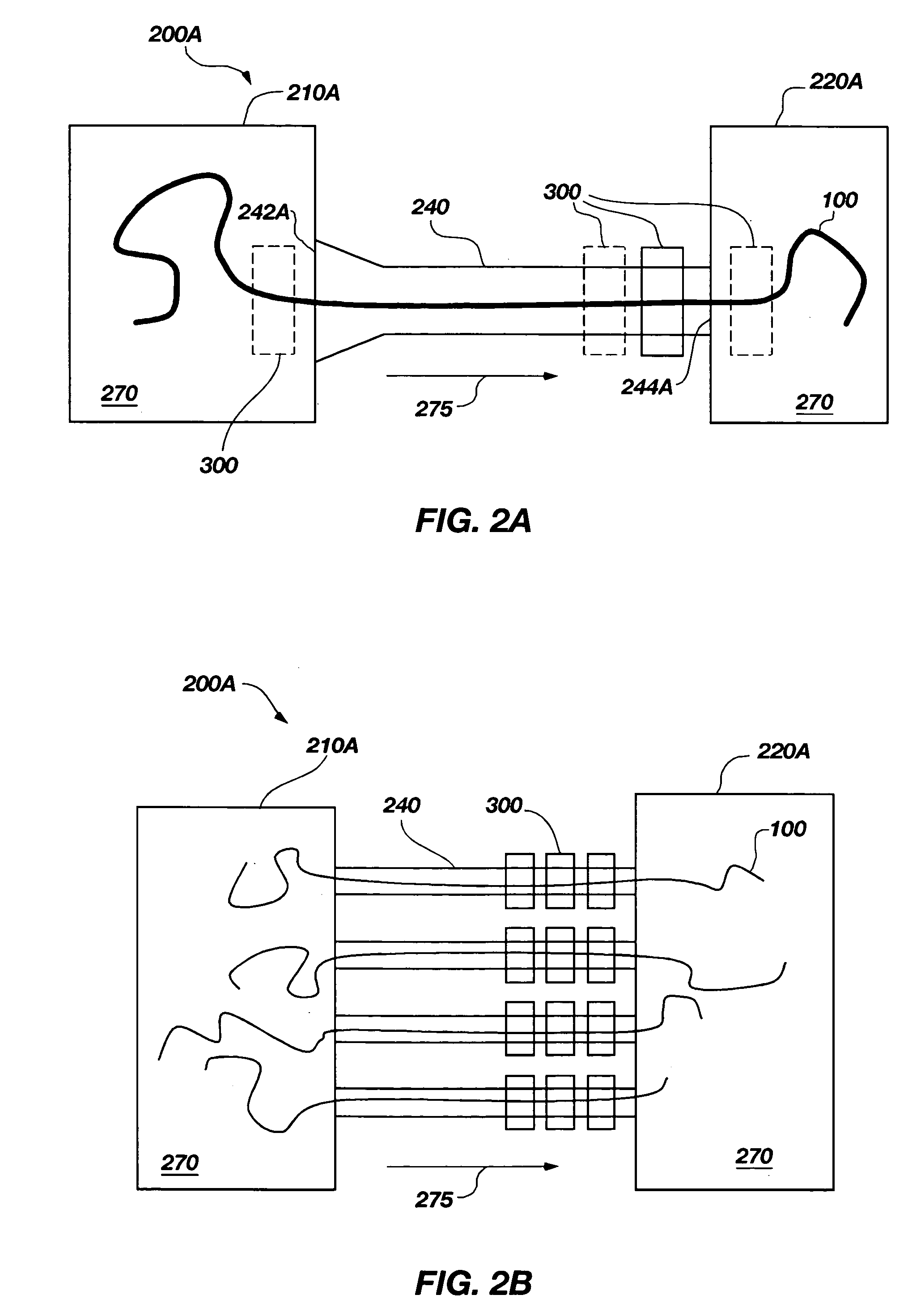
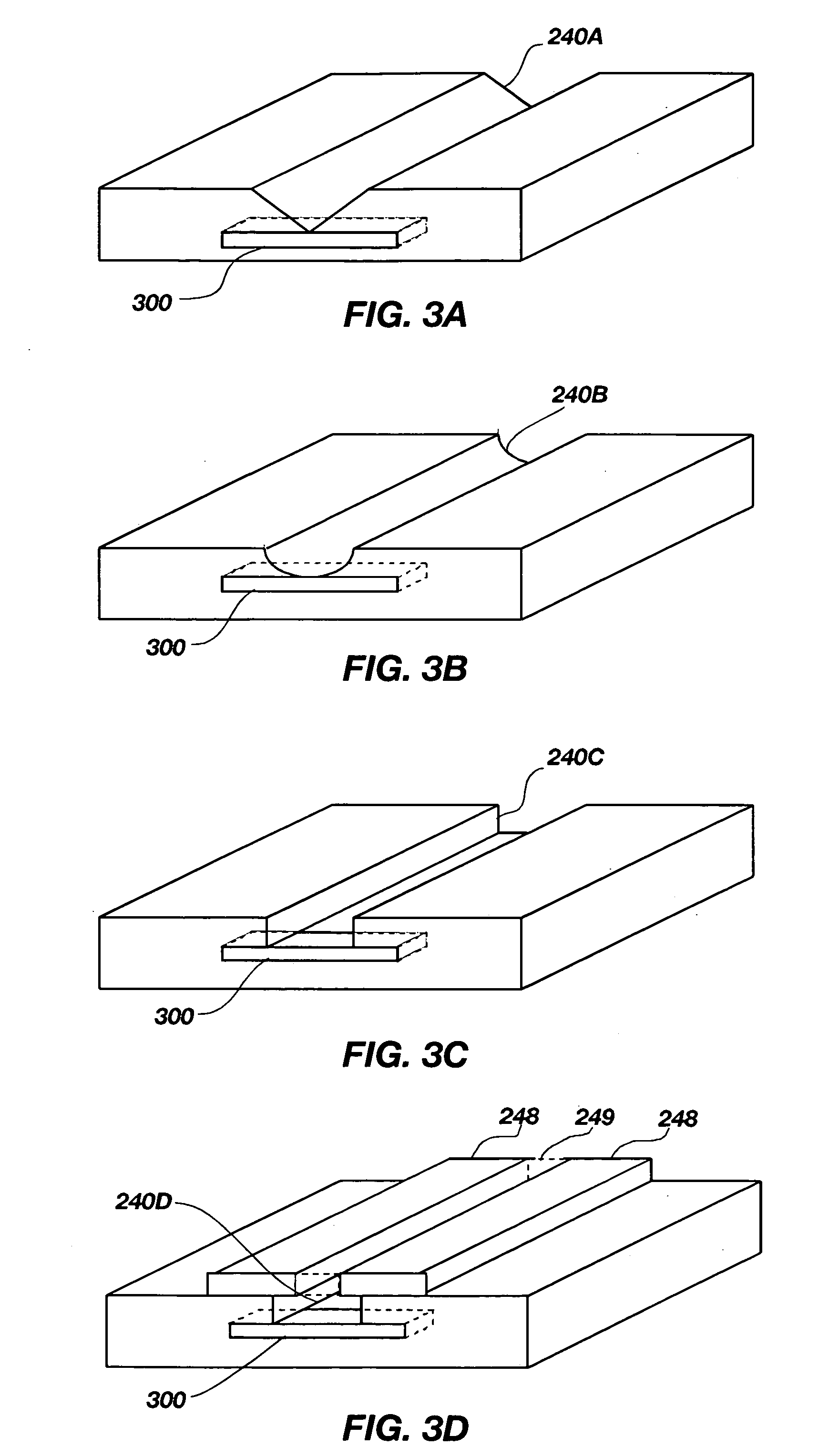
A solid state molecular sensor having an aperture extending through a thickness of a sensing material is configured with a continuous electrically-conducting path extending in the sensing material around the aperture. A supply reservoir is connected to provide a molecular species, having a molecular length, from the supply reservoir to an input port of the aperture. A collection reservoir is connected to collect the molecular species from an output port of the aperture after translocation of the molecular species from the supply reservoir through the sensing aperture. The sensing aperture has a length between the input and output ports, in the sensing material, that is substantially no greater than the molecular length of the molecular species from the supply reservoir. An electrical connection to the sensing material measures a change in an electrical characteristic of the sensing material during the molecular species translocation through the aperture.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Preparation and application of supermolecular sensor based on pillar [5] arene and pyridine functionalized naphthalene diformyl derivative Preparation and application of supermolecular sensor based on pillar [5] arene and pyridine functionalized naphthalene diformyl derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/eec34e8d-5d25-48a5-8241-42f8ecbbba52/170513180742.png)
![Preparation and application of supermolecular sensor based on pillar [5] arene and pyridine functionalized naphthalene diformyl derivative Preparation and application of supermolecular sensor based on pillar [5] arene and pyridine functionalized naphthalene diformyl derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/eec34e8d-5d25-48a5-8241-42f8ecbbba52/170513180749.png)
![Preparation and application of supermolecular sensor based on pillar [5] arene and pyridine functionalized naphthalene diformyl derivative Preparation and application of supermolecular sensor based on pillar [5] arene and pyridine functionalized naphthalene diformyl derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/eec34e8d-5d25-48a5-8241-42f8ecbbba52/170513180756.png)