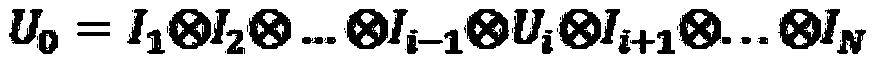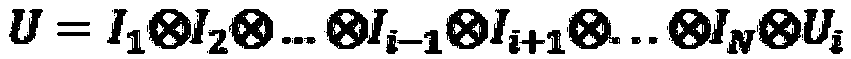Patents
Literature
771 results about "Quantum state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
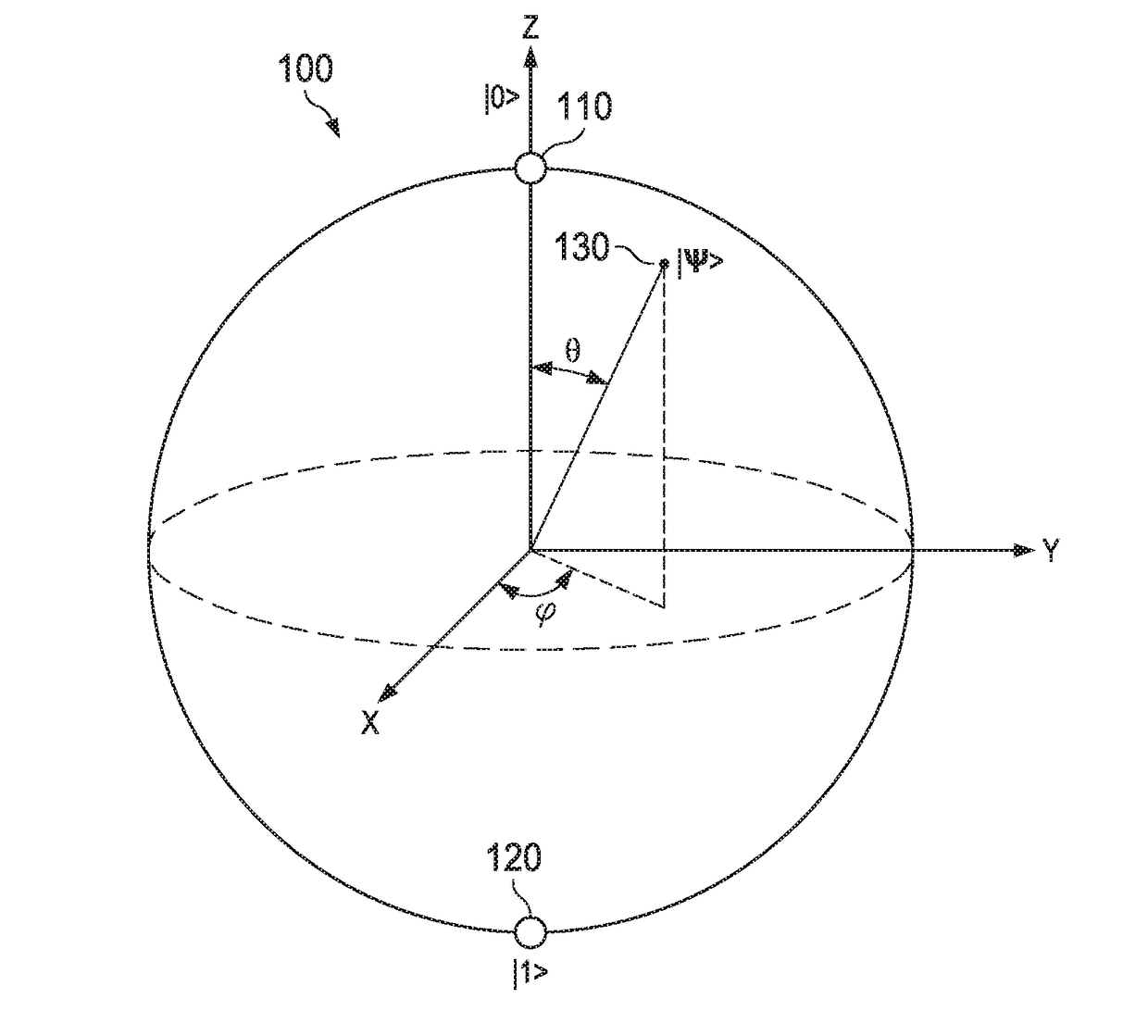
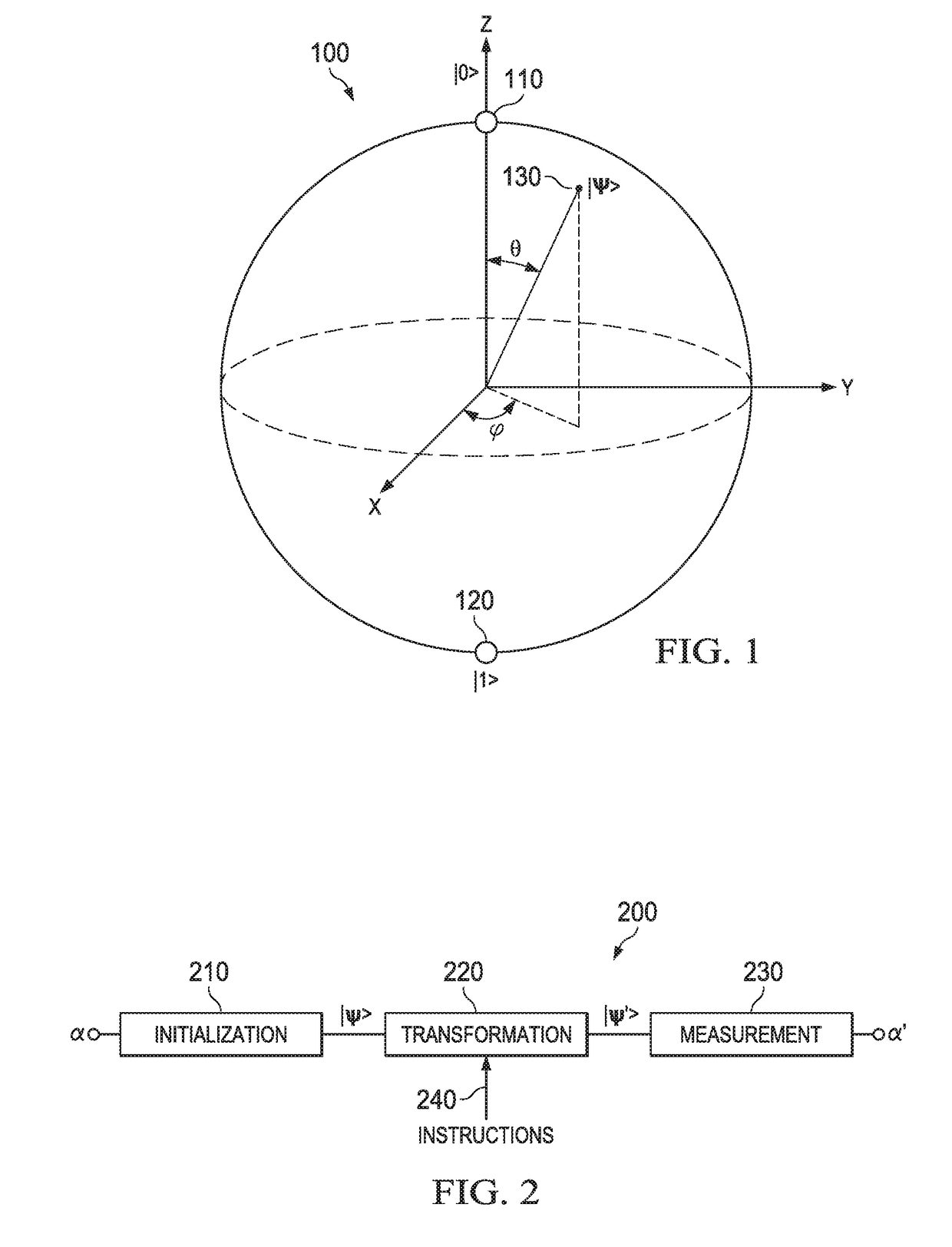
In quantum physics, a quantum state is the state of an isolated quantum system. A quantum state provides a probability distribution for the value of each observable, i.e. for the outcome of each possible measurement on the system. Knowledge of the quantum state together with the rules for the system's evolution in time exhausts all that can be predicted about the system's behavior. A mixture of quantum states is again a quantum state.
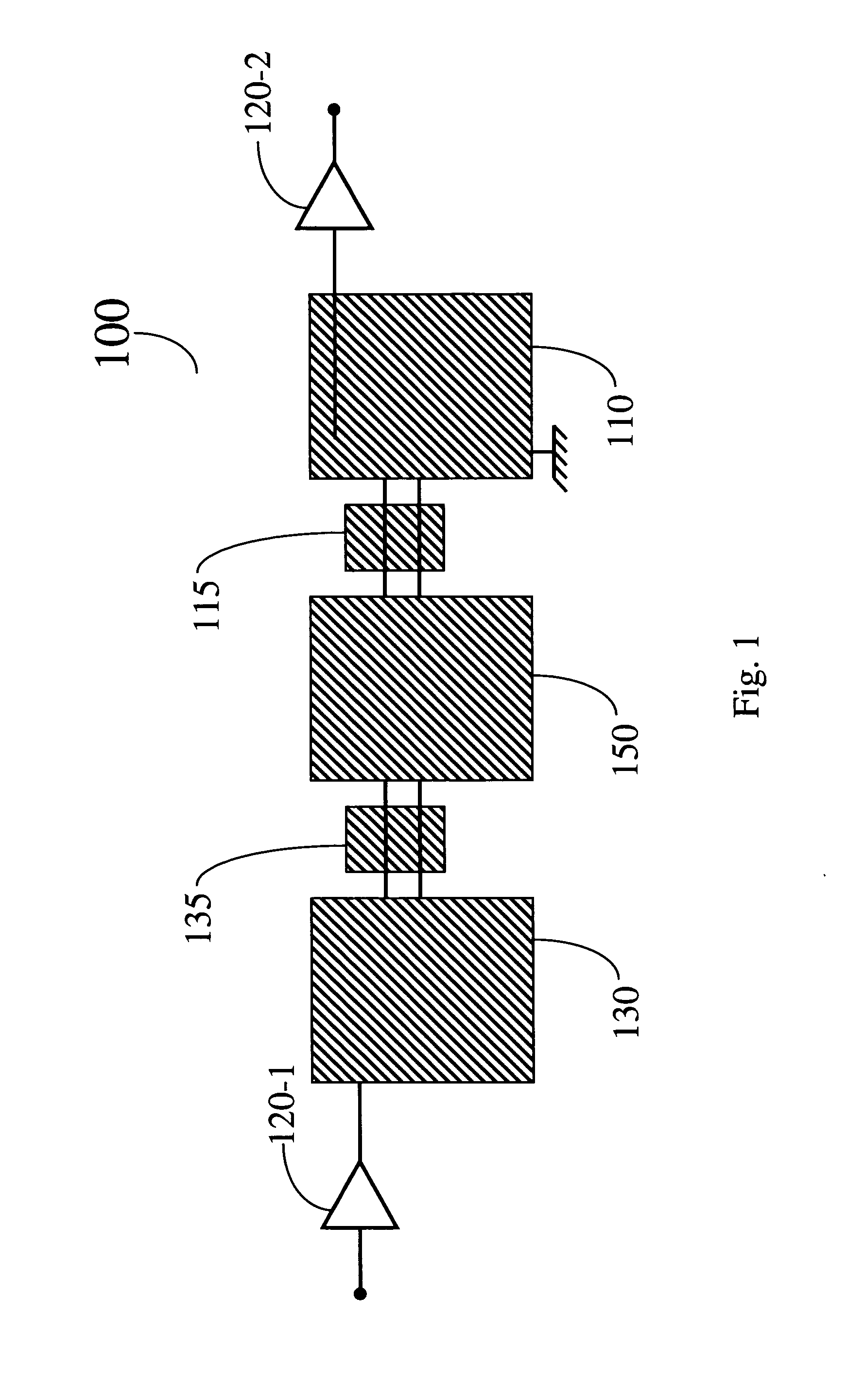
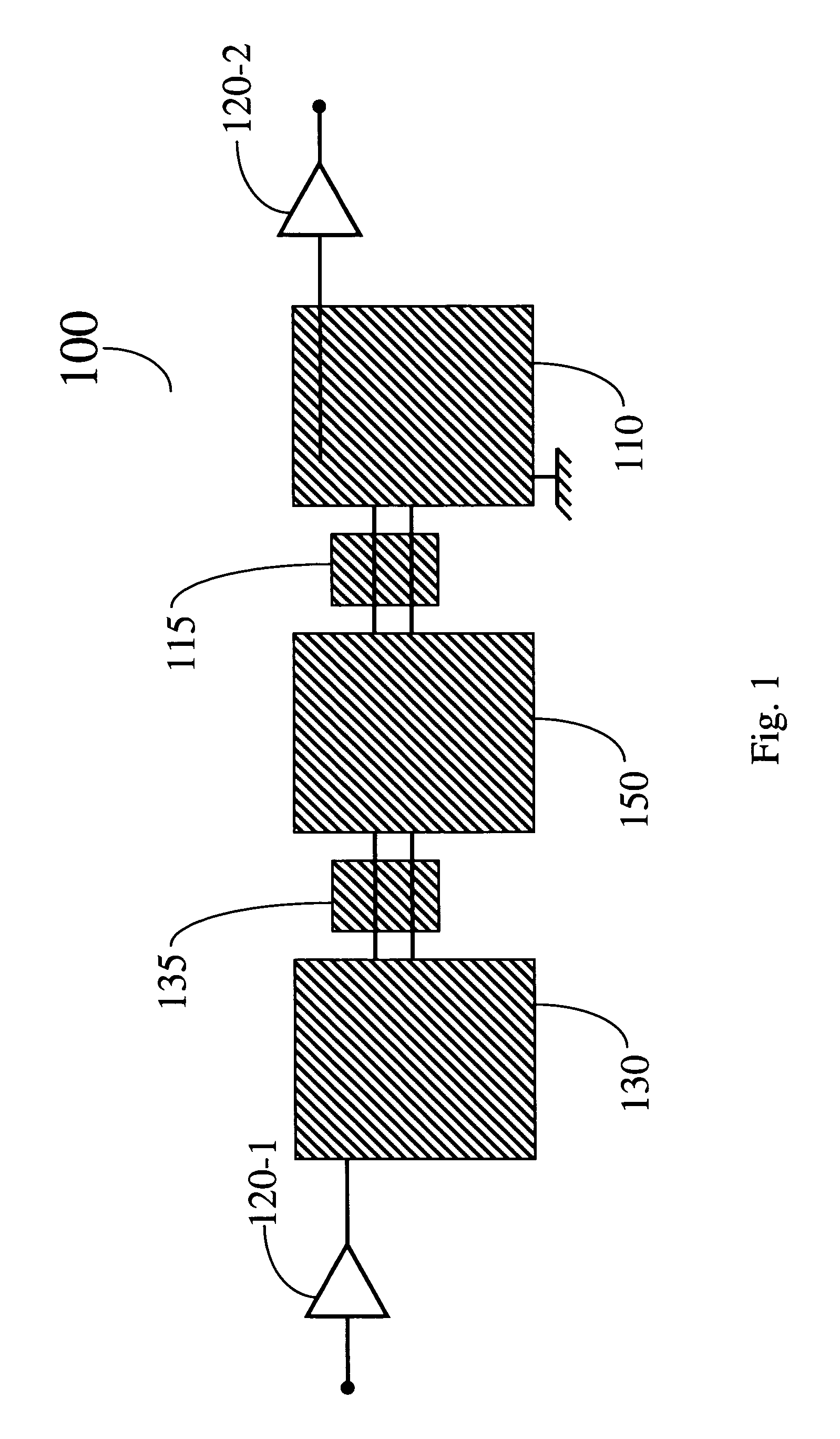
Adiabatic quantum computation with superconducting qubits
ActiveUS20050224784A1Increasing effective charging energyQuantum computersNanoinformaticsAdiabatic quantum computationComputational problem
A method for computing using a quantum system comprising a plurality of superconducting qubits is provided. Quantum system can be in any one of at least two configurations including (i) an initialization Hamiltonian H0 and (ii) a problem Hamiltonian HP. The plurality of superconducting qubits are arranged with respect to one another, with a predetermined number of couplings between respective pairs of superconducting qubits in the plurality of qubits, such that the plurality of superconducting qubits, coupled by the predetermined number of couplings, collectively define a computational problem to be solved. In the method, quantum system is initialized to the initialization Hamiltonian HO. Quantum system is then adiabatically changed until it is described by the ground state of the problem Hamiltonian HP. The quantum state of quantum system is then readout thereby solving the computational problem to be solved.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
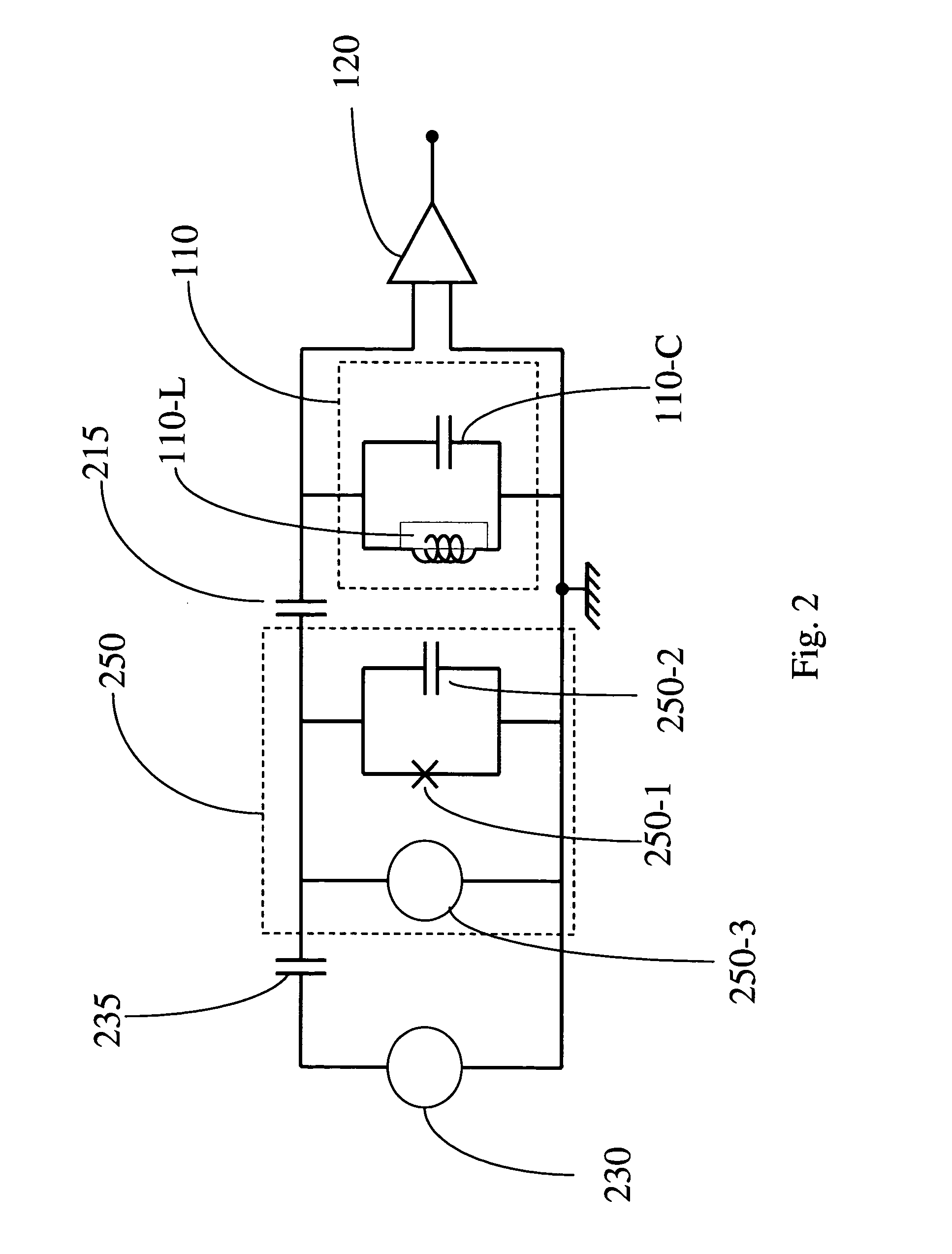
Conditional Rabi oscillation readout for quantum computing
A method for determining whether a first state of a quantum system is occupied is provided. A driving signal is applied to the system at a frequency corresponding to an energy level separation between a first and second state of the system. The system produces a readout frequency only when the first state is occupied. A property of a measurement resonator that is coupled to the quantum system is measured when the quantum system produces the readout frequency, thereby determining whether the first state of the quantum system is occupied. A structure for detecting a qubit state of a qubit is provided. The structure comprises a quantum system that includes the qubit. The qubit has first and second basis states and an ancillary quantum state. The ancillary quantum state can be coupled to the first or second basis states. The structure has a measurement resonator configured to couple to Rabi oscillations between (i) one of the first and second basis states and (ii) the ancillary state in the quantum system.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
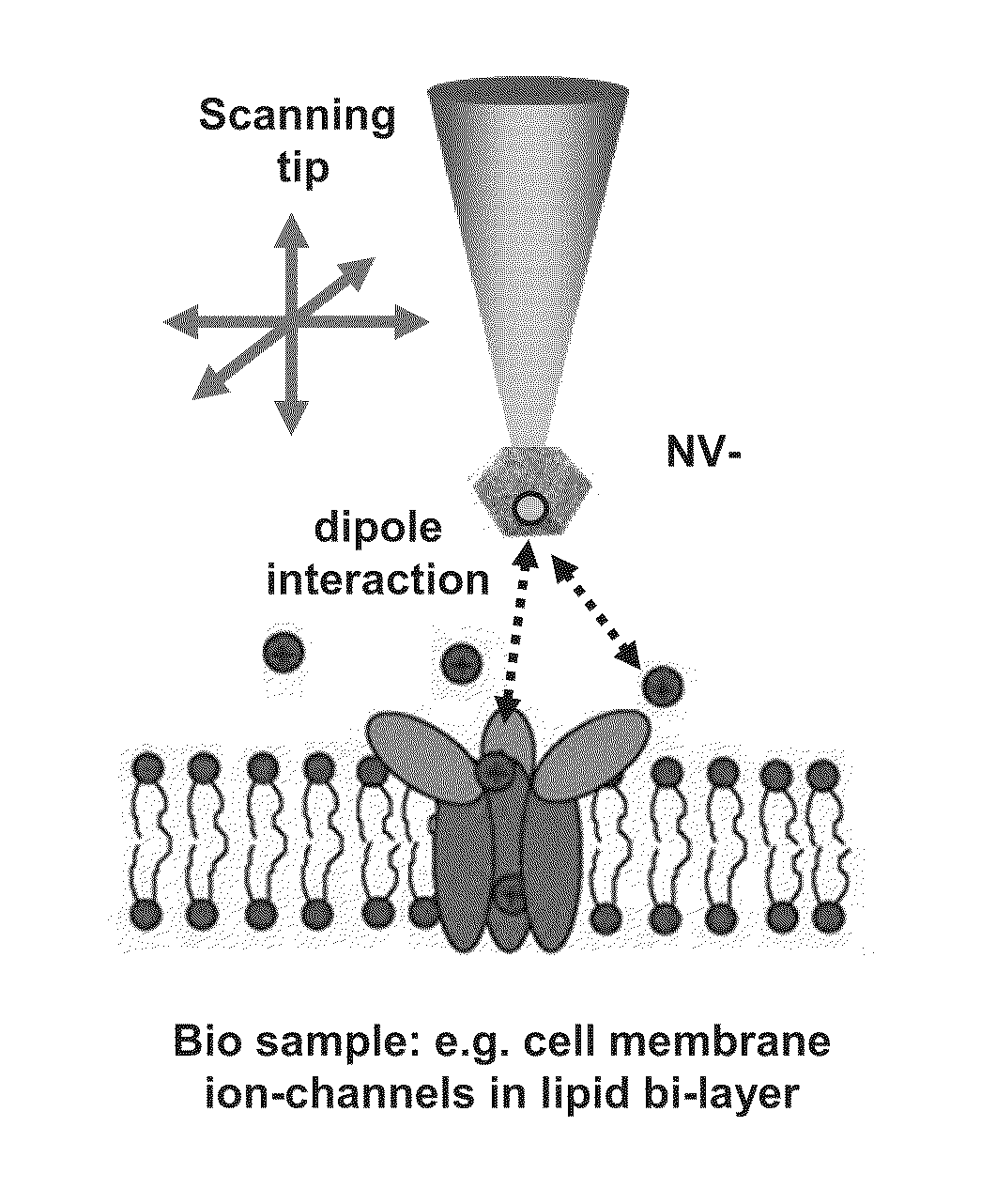
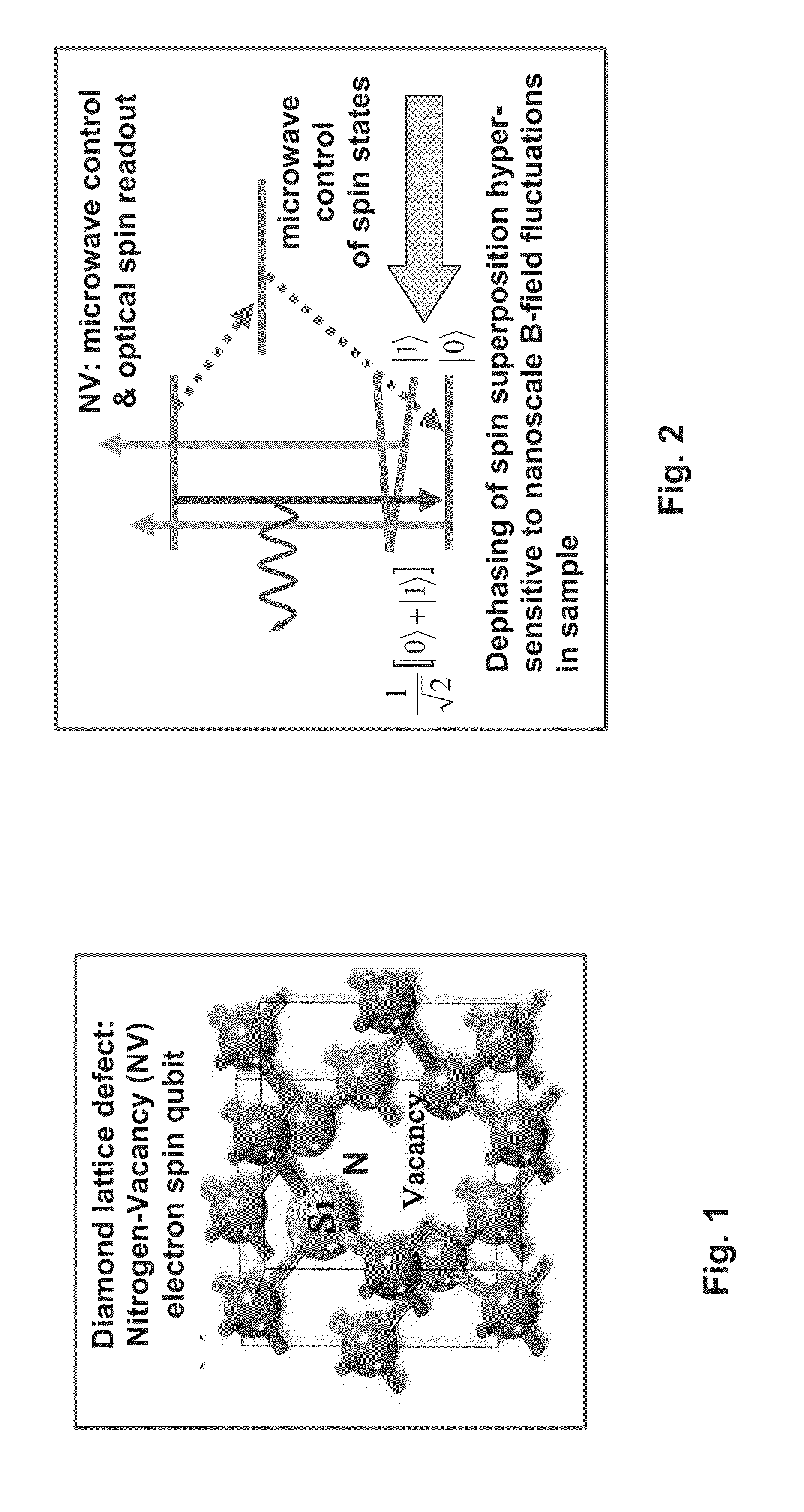
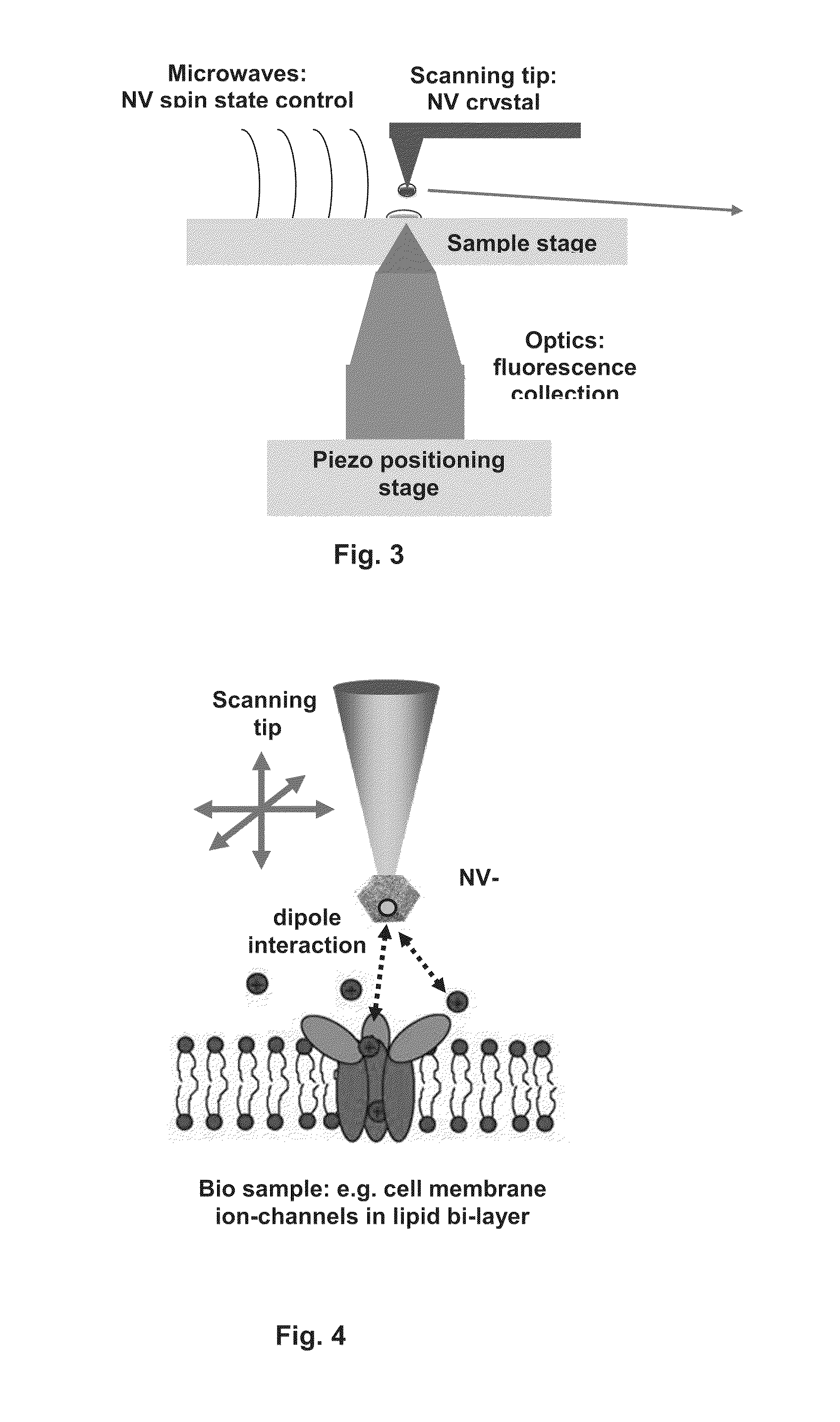
Method and apparatus for monitoring a property of a sample
ActiveUS20120019242A1Improve featuresMagnetic property measurementsNanosensorsCondensed matter physicsQuantum state
The present disclosure provides a method of monitoring a property of a sample, such as a nanoscopic property of the sample. The method comprises the steps of providing a quantum probe having a quantum state and exposing the quantum probe to the sample in a manner such that the property of the sample, in the proximity of the quantum probe, affects quantum coherence of the quantum probe. The method also comprises detecting a rate of quantum decoherence of the quantum probe to monitor the property of the sample. Further the present disclosure provides an apparatus for monitoring a property of a sample.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
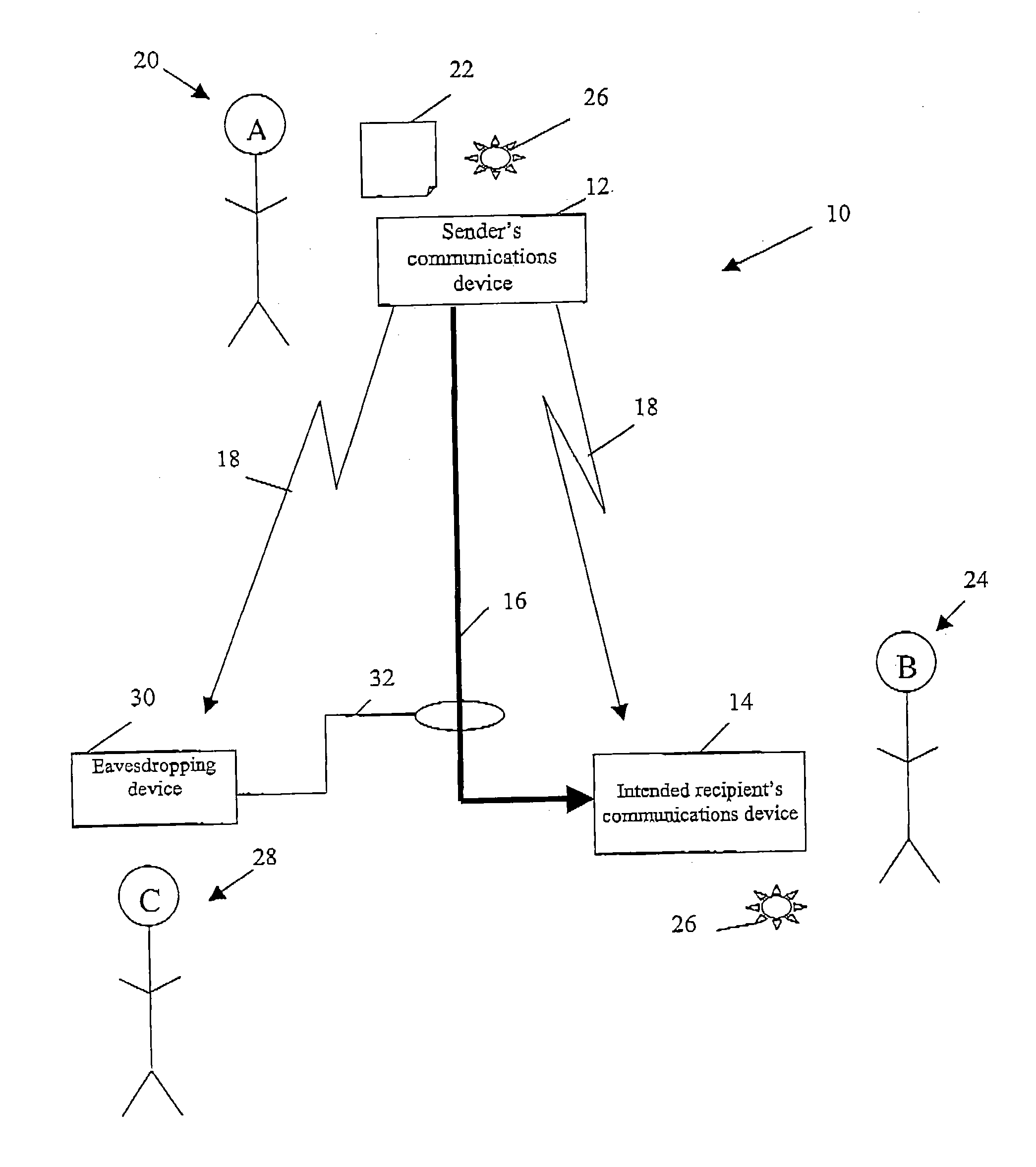
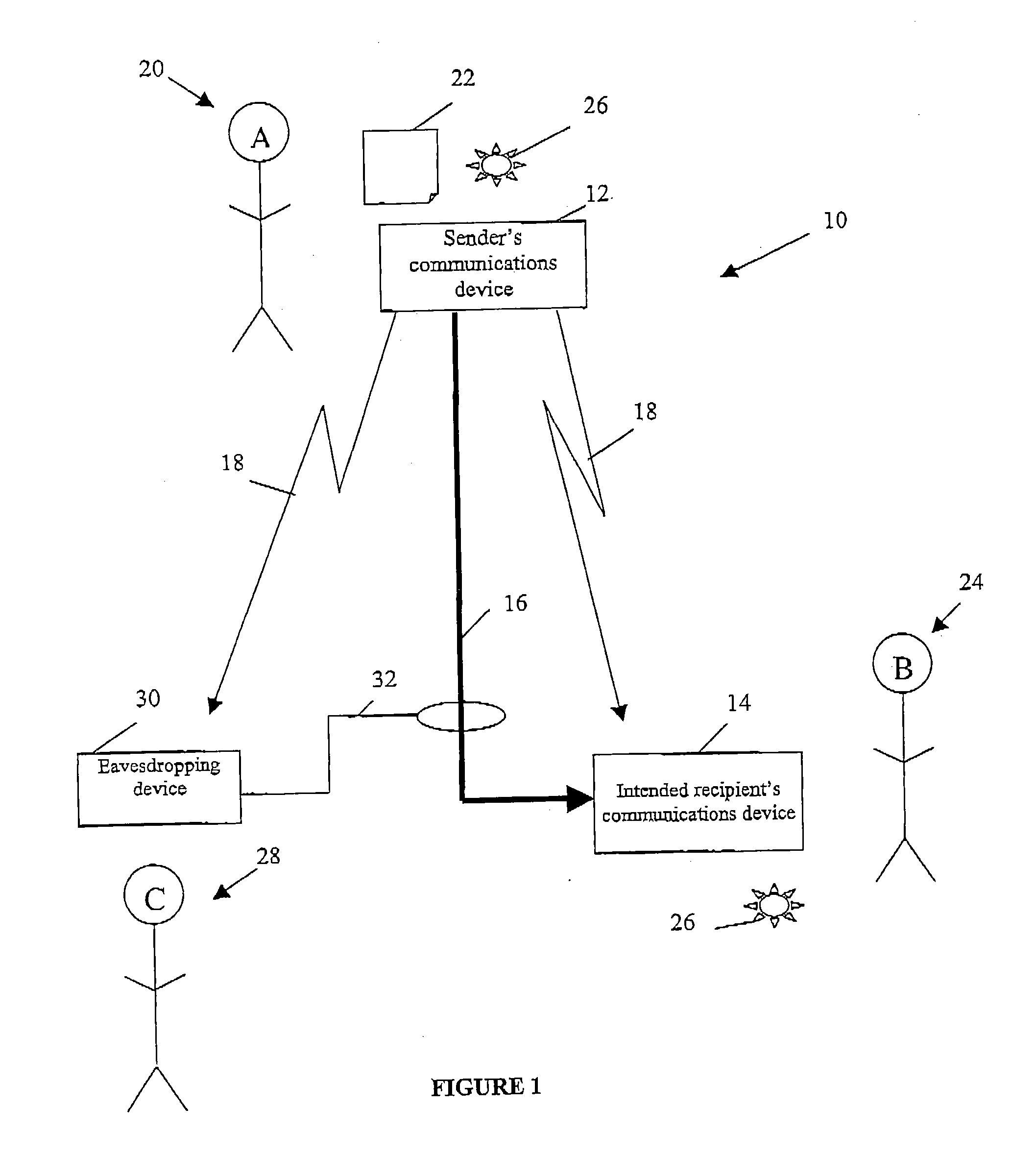
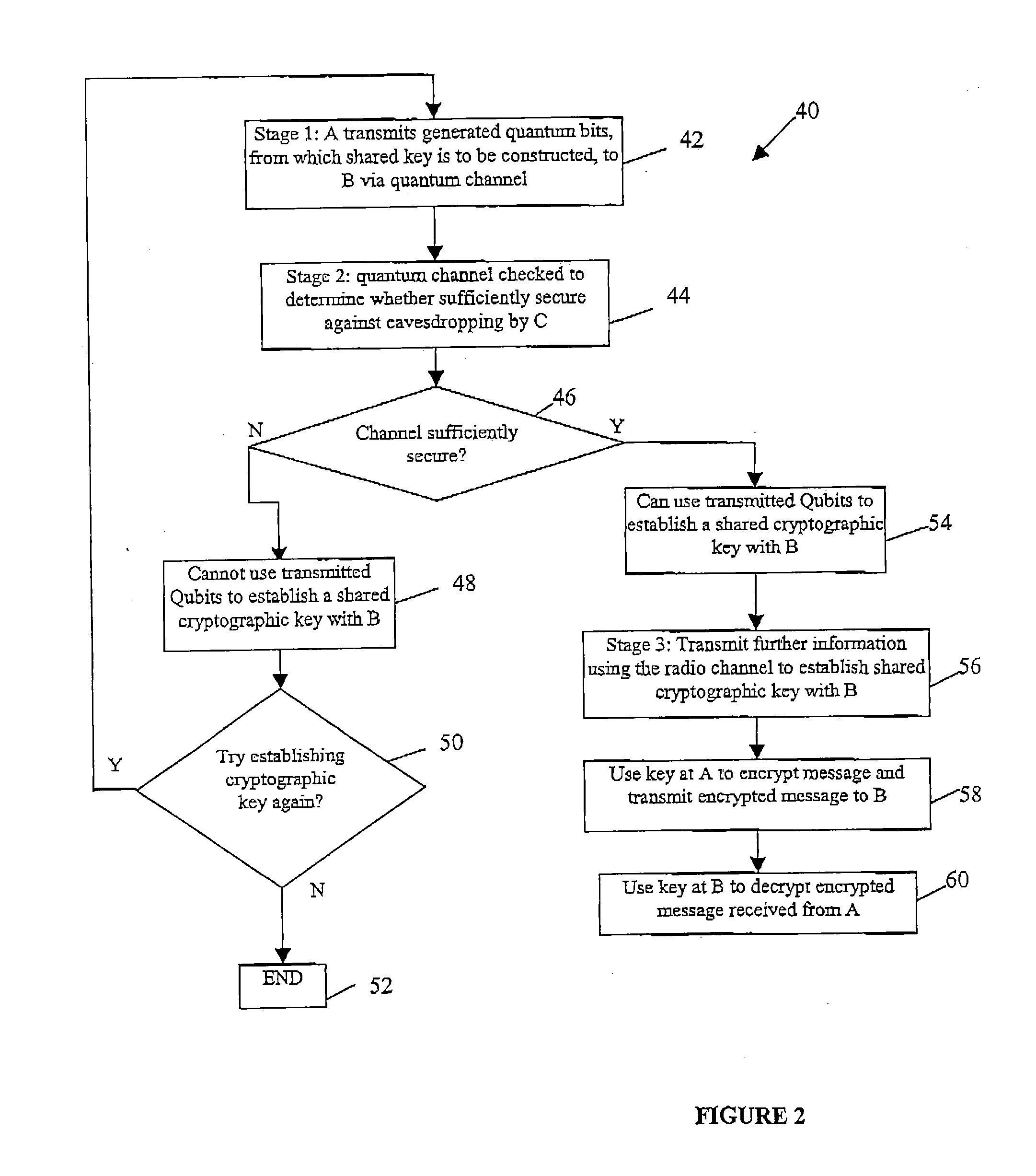
Quantum cryptography
ActiveUS20050036624A1Reduce bitrateIncrease bitrateKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum channelHilbert space
A method of establishing a shared secret random cryptographic key between a sender and a recipient using a quantum communications channel is described. The method comprises: generating a plurality of random quantum states of a quantum entity, each random state being defined by a randomly selected one of a first plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting the plurality of random quantum states of the quantum entity via the quantum channel to a recipient, measuring the quantum state of each of the received quantum states of the quantum entity with respect to a randomly selected one of a second plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting to the recipient composition information describing a subset of the plurality of random quantum states, analysing the received composition information and the measured quantum states corresponding to the subset to derive a first statistical distribution describing the subset of transmitted quantum states and a second statistical distribution describing the corresponding measured quantum states, establishing the level of confidence in the validity of the plurality of transmitted random quantum states by verifying that the first and second statistical distributions are sufficiently similar, deriving a first binary sting and a second binary string, correlated to the first binary string, respectively from the transmitted and received plurality of quantum states not in the subset, and carrying out a reconciliation of the second binary string to the first binary string by using error correction techniques to establish the shared secret random cryptographic key from the first and second binary strings.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
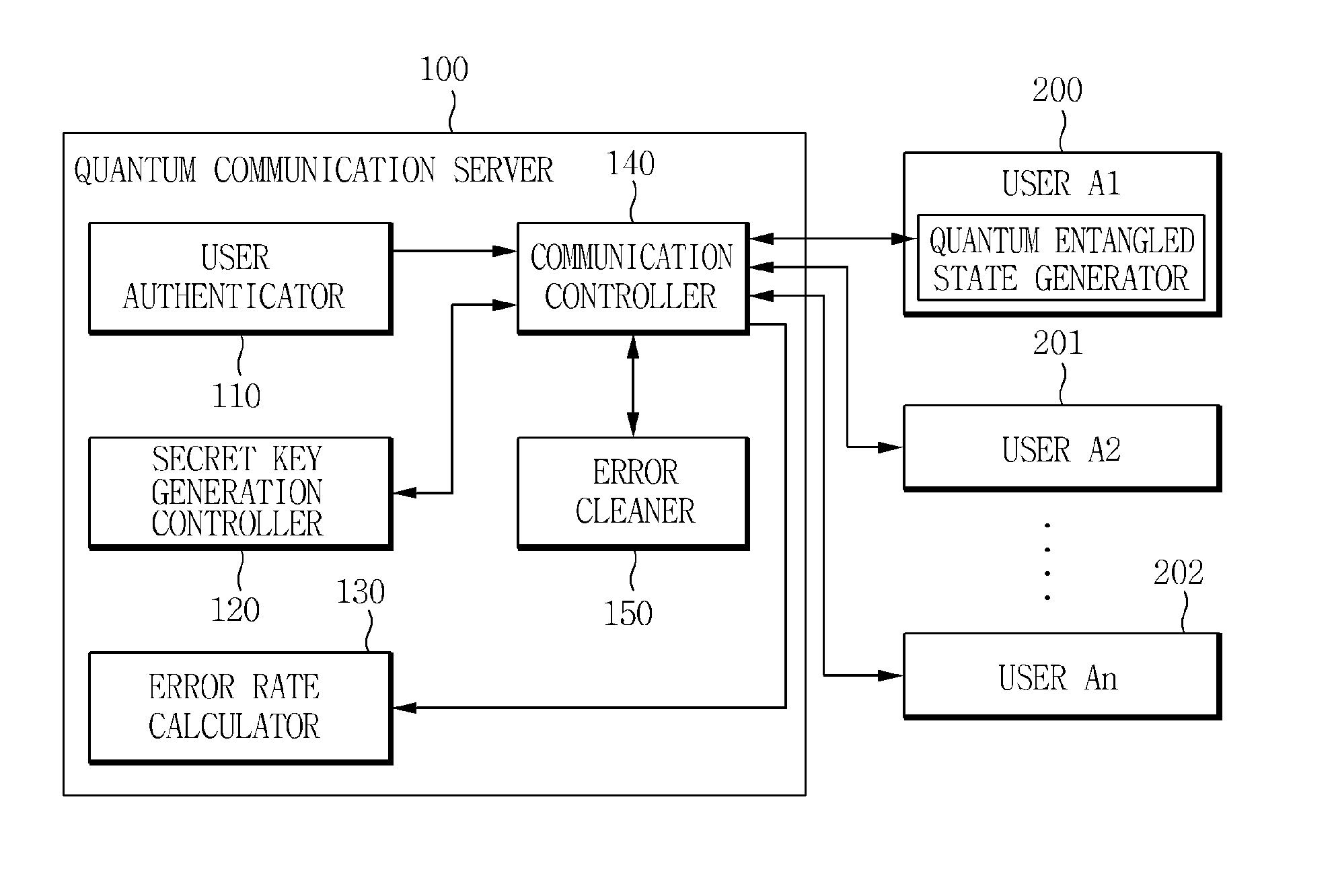
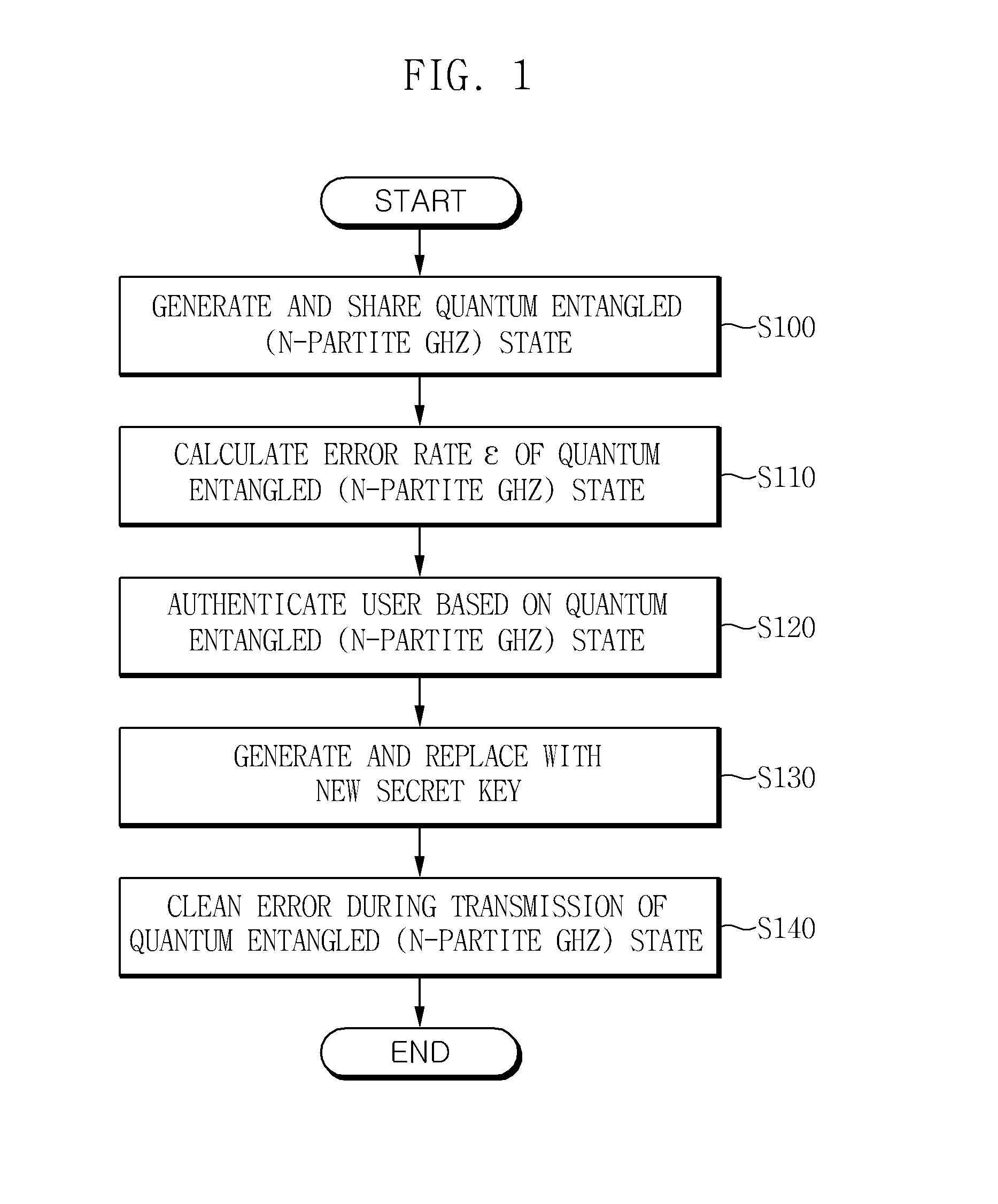
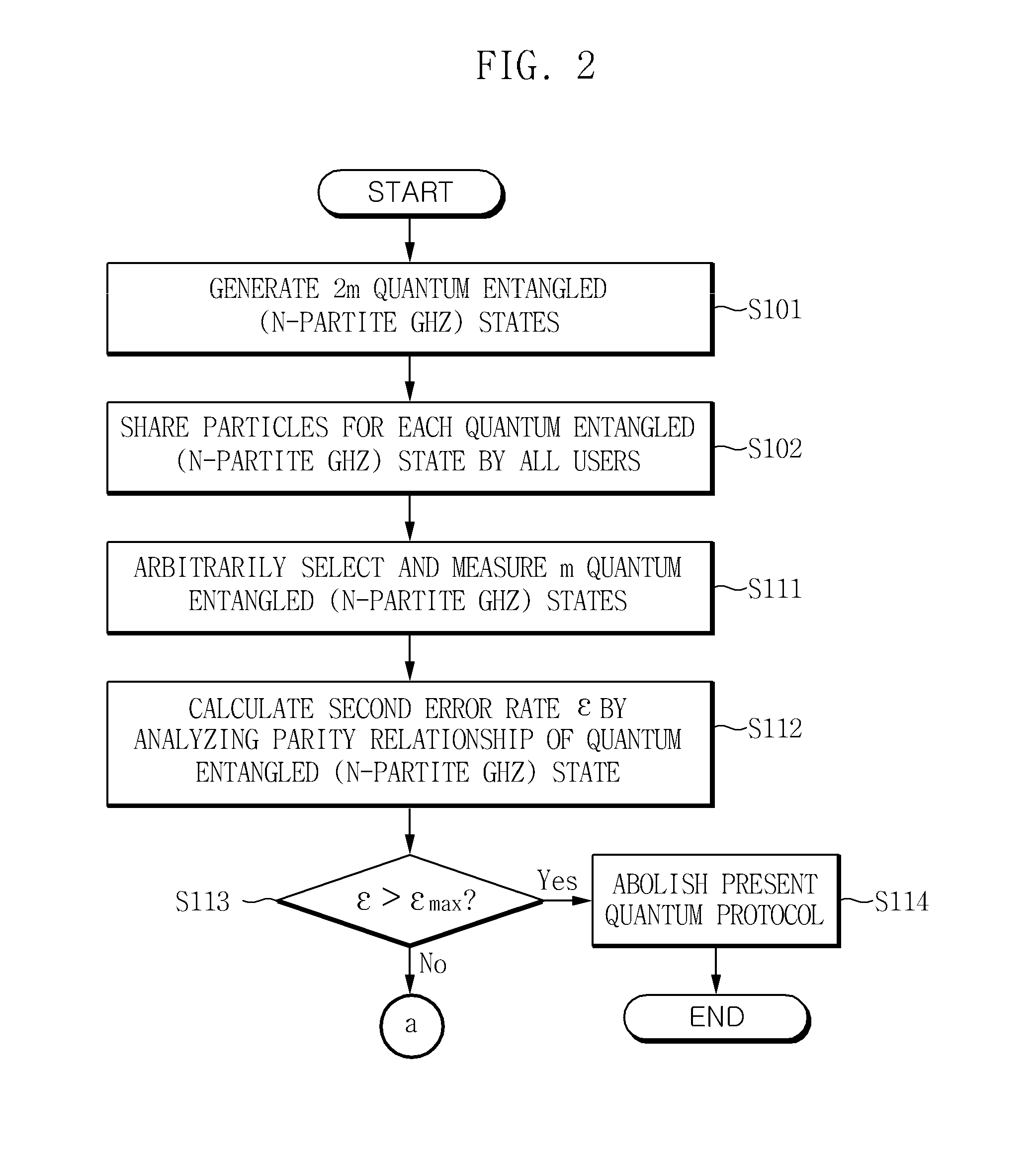
Method and apparatus for authenticating user in multiparty quantum communications
InactiveUS20140068765A1Ensure safetyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionQuantum entanglementRandom choice
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
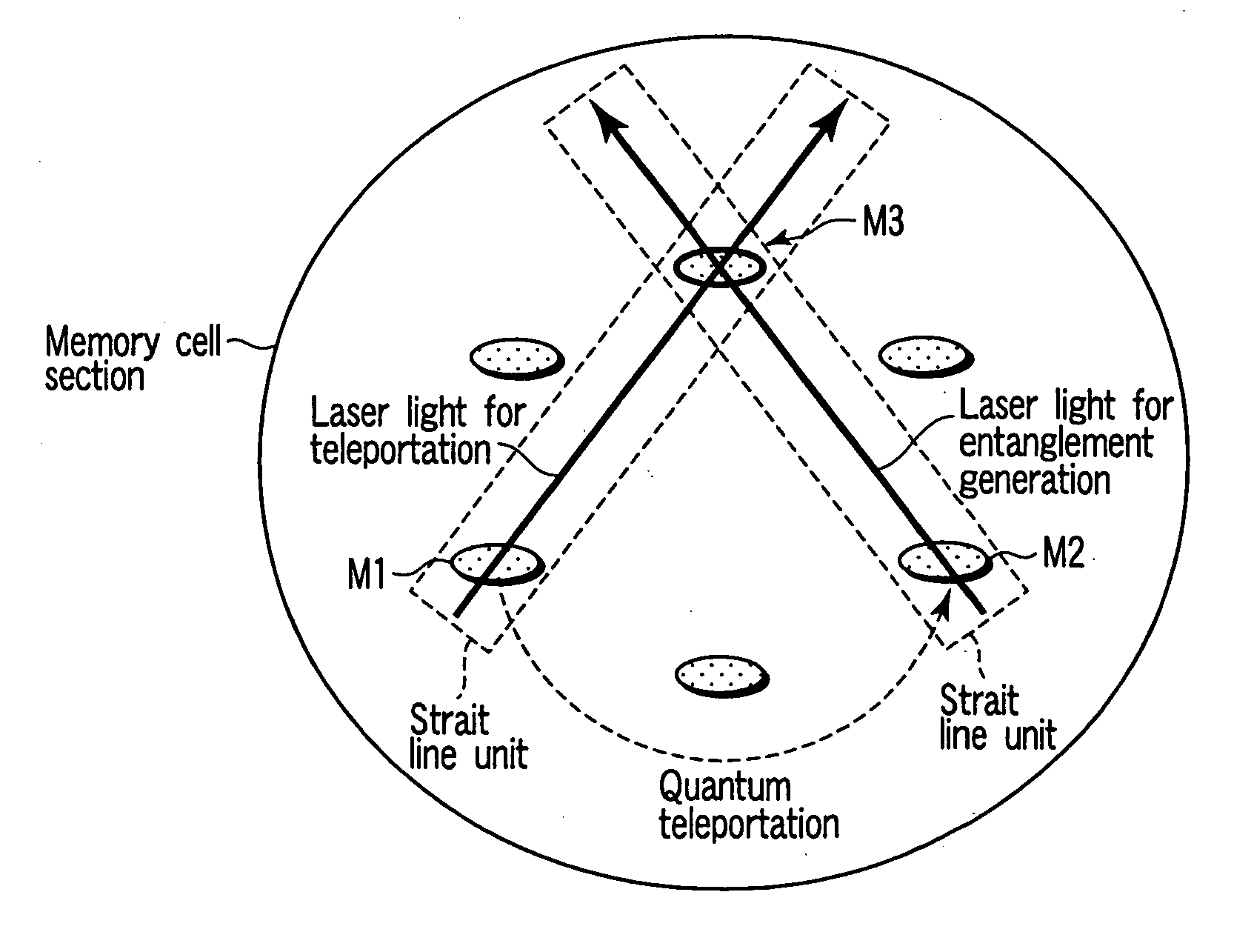
Quantum memory and information processing method using the same
InactiveUS20050190637A1Avoid interferenceQuantum computersNanoinformaticsInformation processingPhysical system
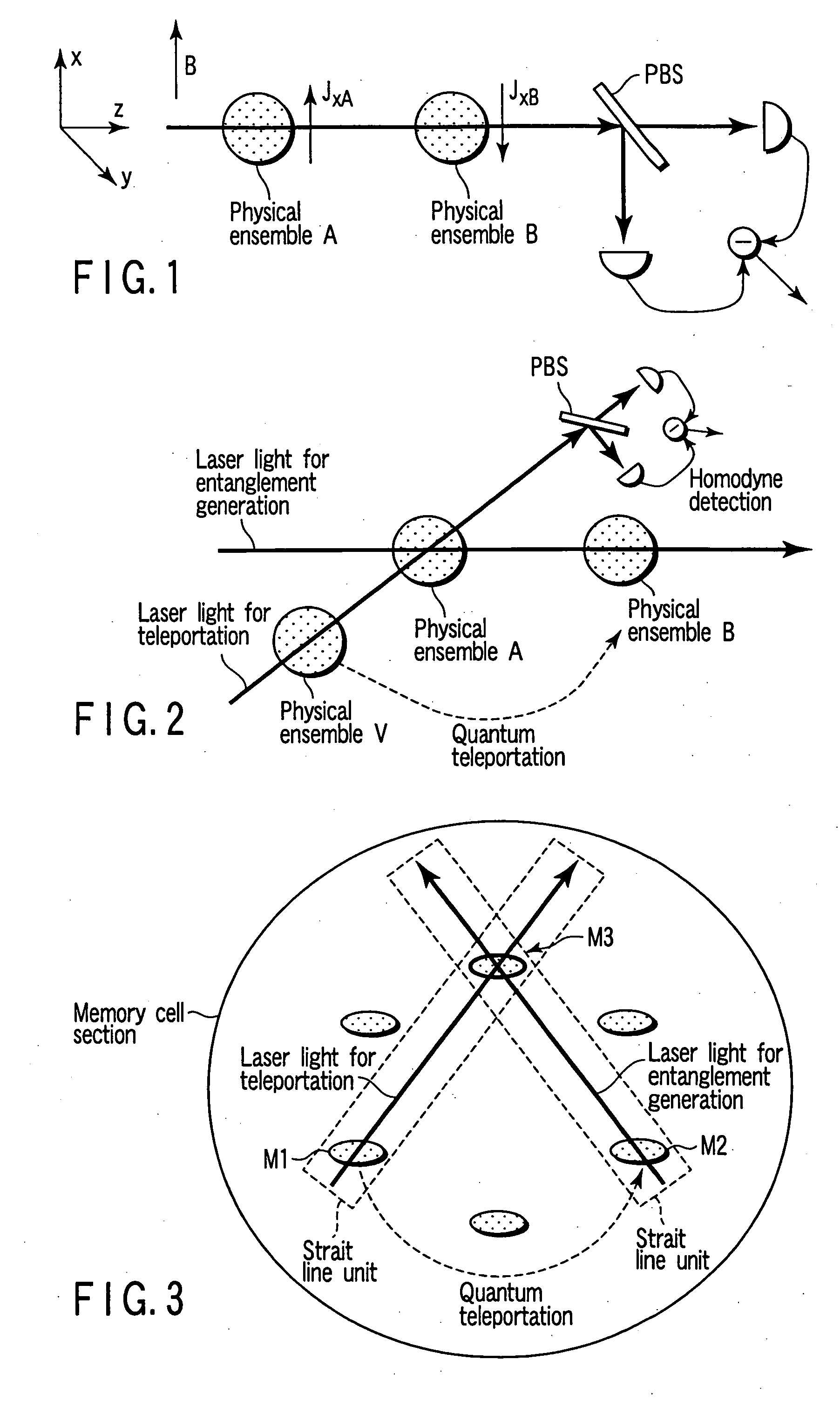
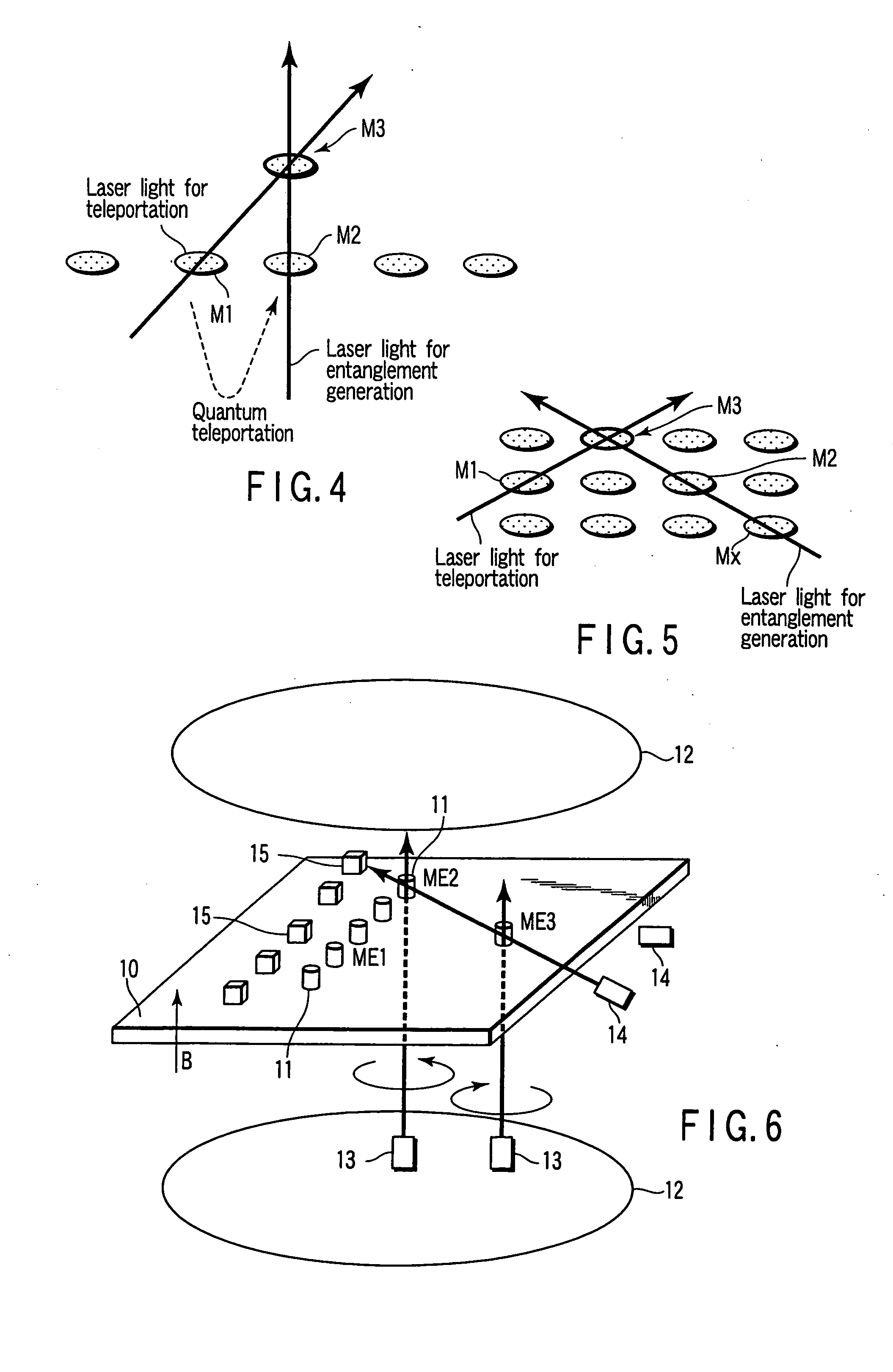
A quantum memory includes memory cells each comprising a physical system ensemble, quantum information of the physical system ensemble being expressed by a quantum state of whole amount of the total angular momentum of the physical systems, and the memory cells including two storage memory cells storing the quantum state and a transfer memory cell transferring the quantum state, only two of the memory cells being present on a straight line. The quantum memory also includes a magnet applying a magnetic field to the two storage memory cells and the transfer memory cell, a first light source irradiating the two storage memory cells and the transfer memory cell with right-handed or left-handed polarized light, a second light source simultaneously irradiating one of the two storage memory cells and the transfer memory cell with a laser beam, and a detector detecting a polarization state of the laser beam.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Public key encryption apparatus
InactiveUS20060088157A1Ensure safetyPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareEncryption
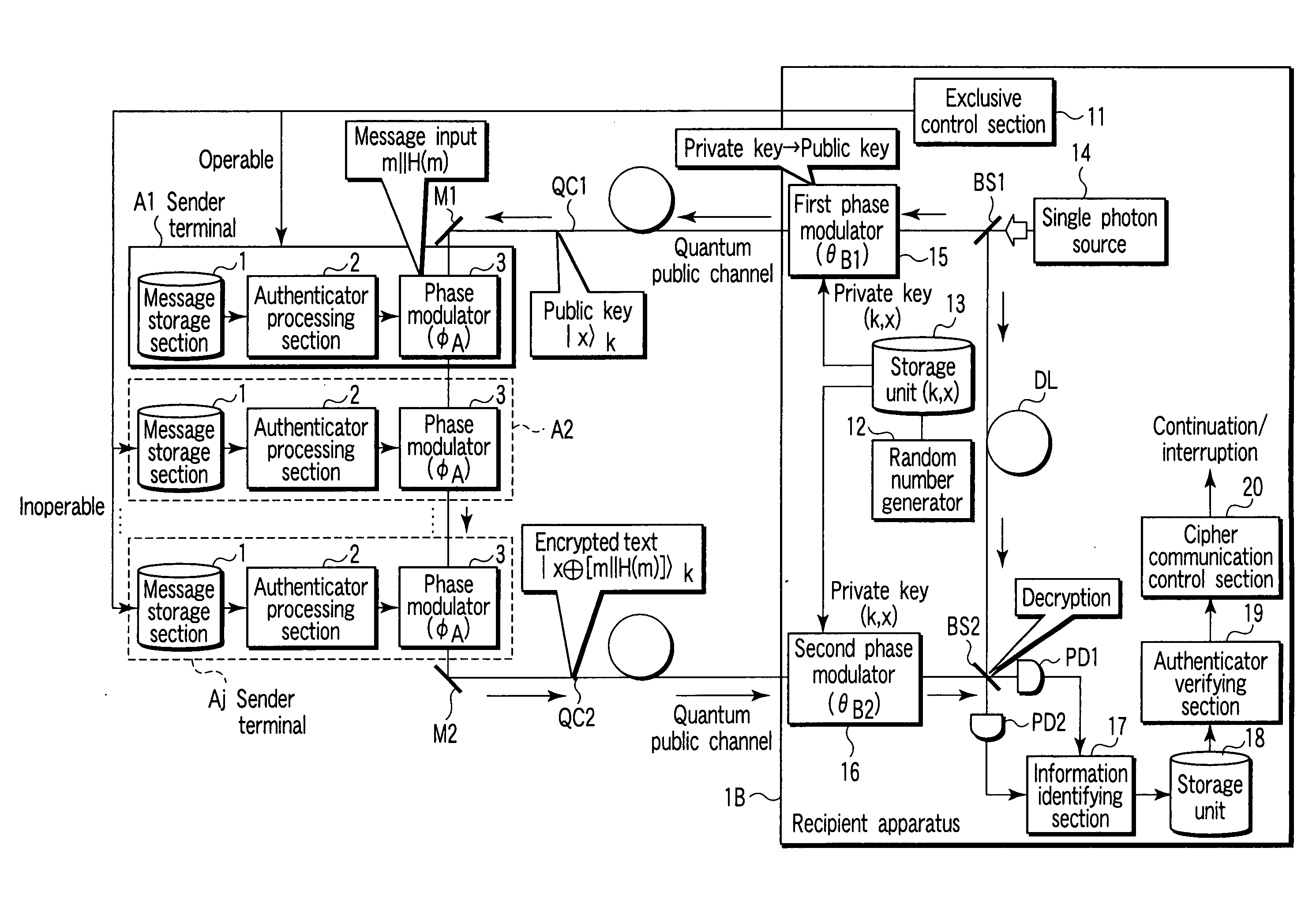
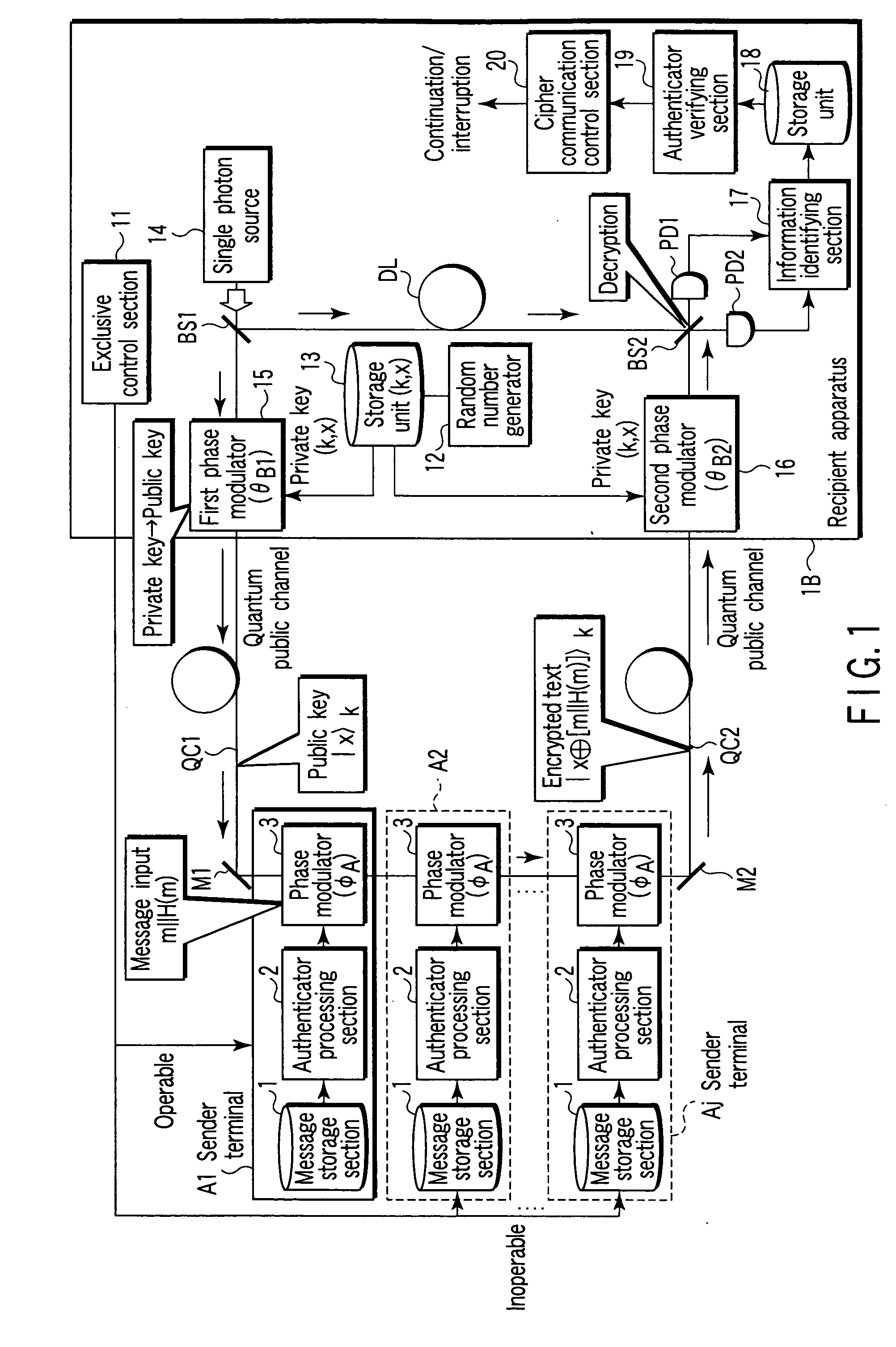
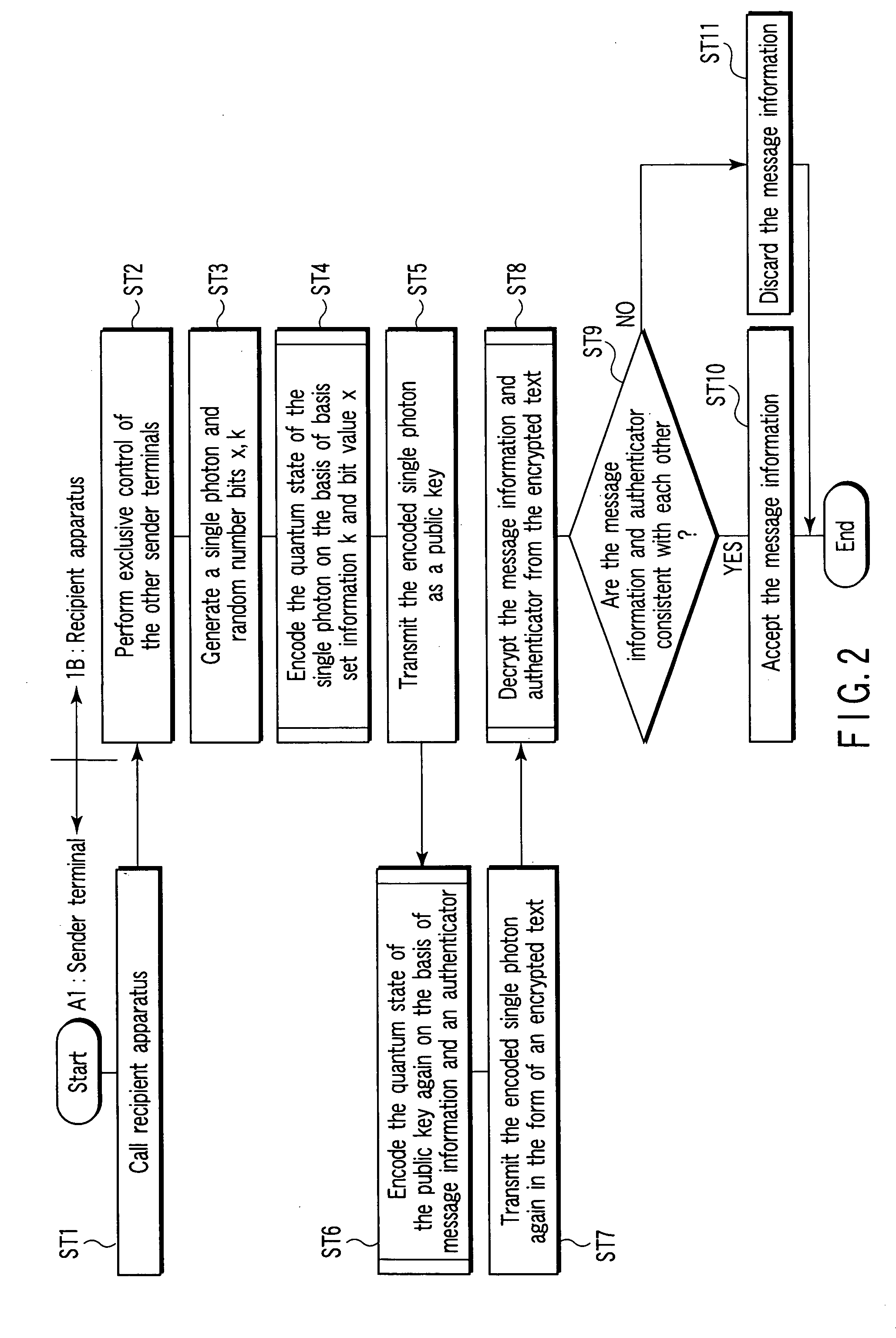
According to an aspect of this invention, there is provided a public key encryption apparatus comprising a device generating a single photon, a device generating a random number, a storage device storing the random number as a private key, a device which transmits a single photon encoded by the private key composed of a basis set identifying value section and a bit value section, a device receiving the single photon, a device creating message information and an authenticator, a device encrypting the quantum state of the received single photon on the basis of the message information and authenticator and transmitting the single photon, a device decrypting the message information and authenticator from the received single photon according to the private key, and a device which invalidates the message information if the authenticator calculated from the decrypted message information is inconsistent with the decrypted authenticator.
Owner:TOSHIBA SOLUTIONS
Systems and methods for framing quantum cryptographic links
InactiveUS20050190921A1Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareKey distribution
An optical transmitter includes a transmitting unit and a processing unit. The transmitting unit transmits multiple optical synchronization pulses at a first intensity, and transmits multiple optical quantum cryptographic key distribution (QKD) pulses at a second intensity. The processing unit encodes a cryptographic key symbol in a quantum state of each QKD pulse of the QKD pulses, and delays transmission of each of the multiple optical synchronization pulses a derived interval after transmission of a corresponding one of the multiple QKD pulses.
Owner:BBN TECHNOLOGIES CORP
Crytographic communication apparatus
InactiveUS20050157875A1Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesPseudo random number generationQuantum electrodynamics
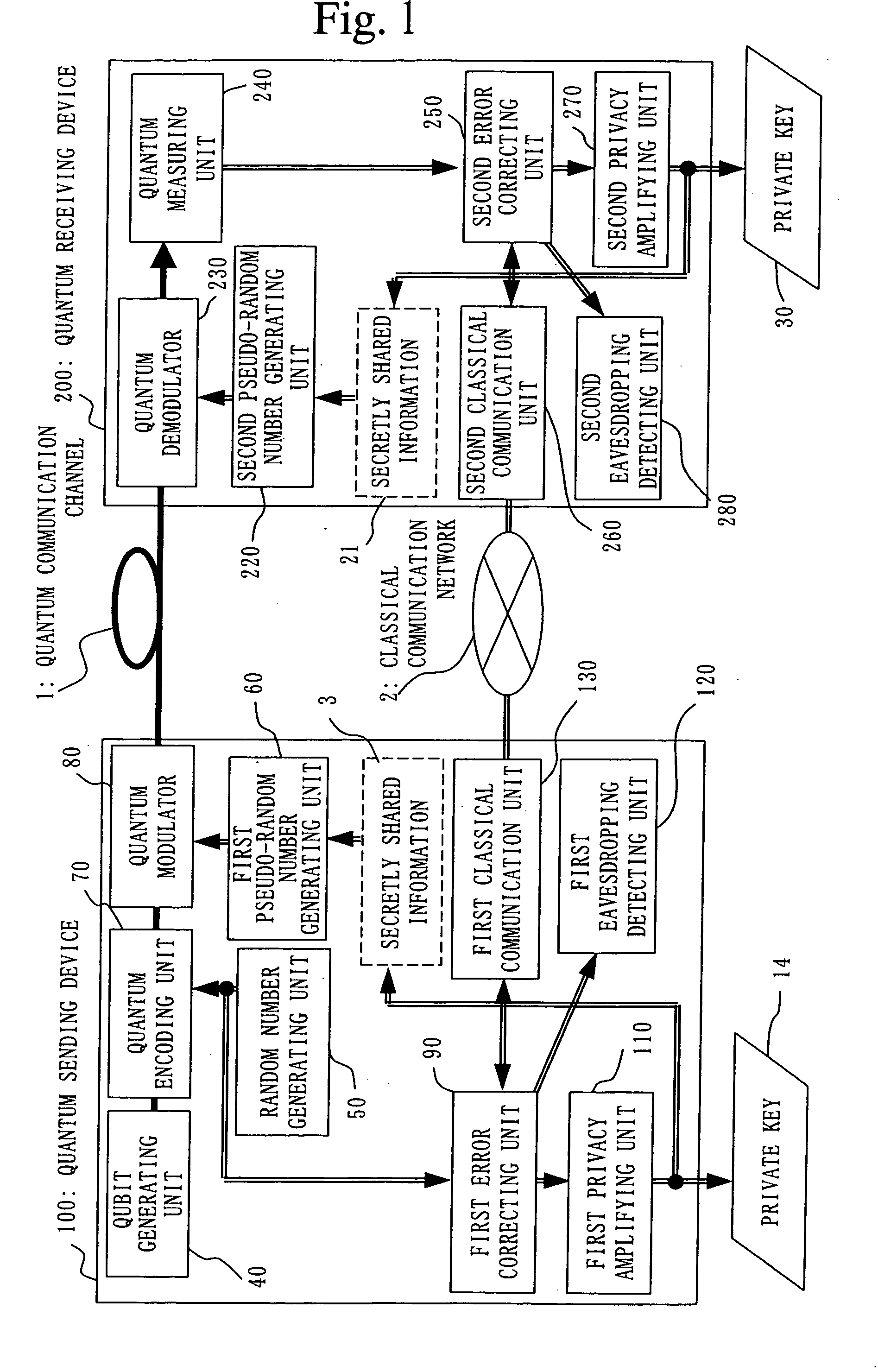
A qubit generating unit 40 generates a qubit having a predetermined quantum state. A qubit encoding unit 70 performs quantum encoding of the generated qubit. A first pseudo-random number generating unit 60 generates a first pseudo-random number from secretly shared information 3 which has been secretly shared with the quantum receiving device 200 in advance. A quantum modulator 80 performs quantum modulation of the qubit on which quantum encoding has been performed based on the first pseudo-random number and sends the modulated qubit to the quantum receiving device 200. A second pseudo-random number generating unit 220 generates a second pseudo-random number from secretly shared information 21 which has been secretly shared with the above quantum sending device 100 in advance synchronously with generation of the above first pseudo-random number. A qubit demodulator 230 performs quantum demodulation of the qubit which has been received from the quantum demodulator 80 based on the second pseudo-random number.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Quantum-key distribution method between a plurality of users or groups
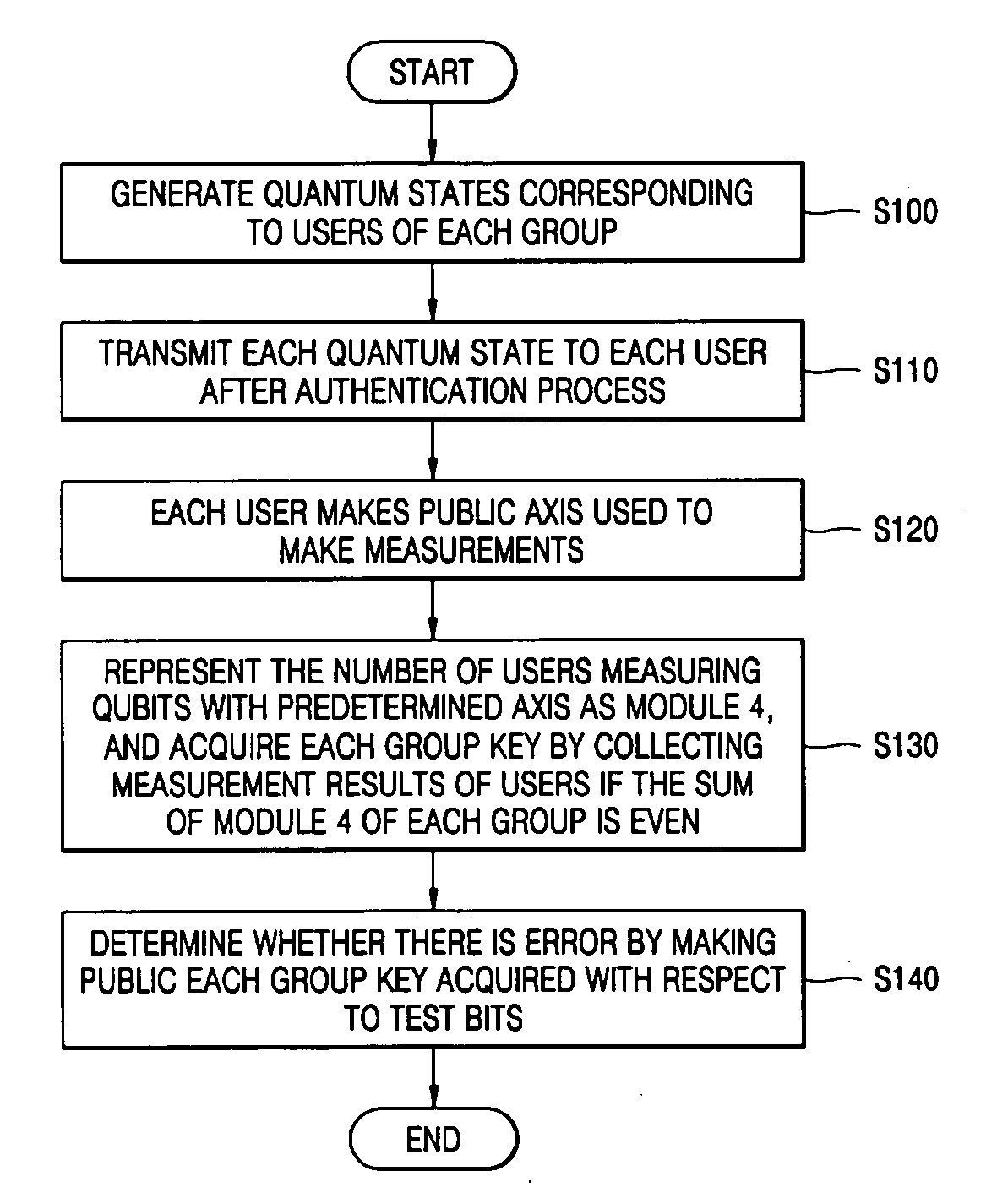
InactiveUS20050249352A1Improve securitySecure distributionKey distribution for secure communicationPump componentsComputer scienceQuantum state
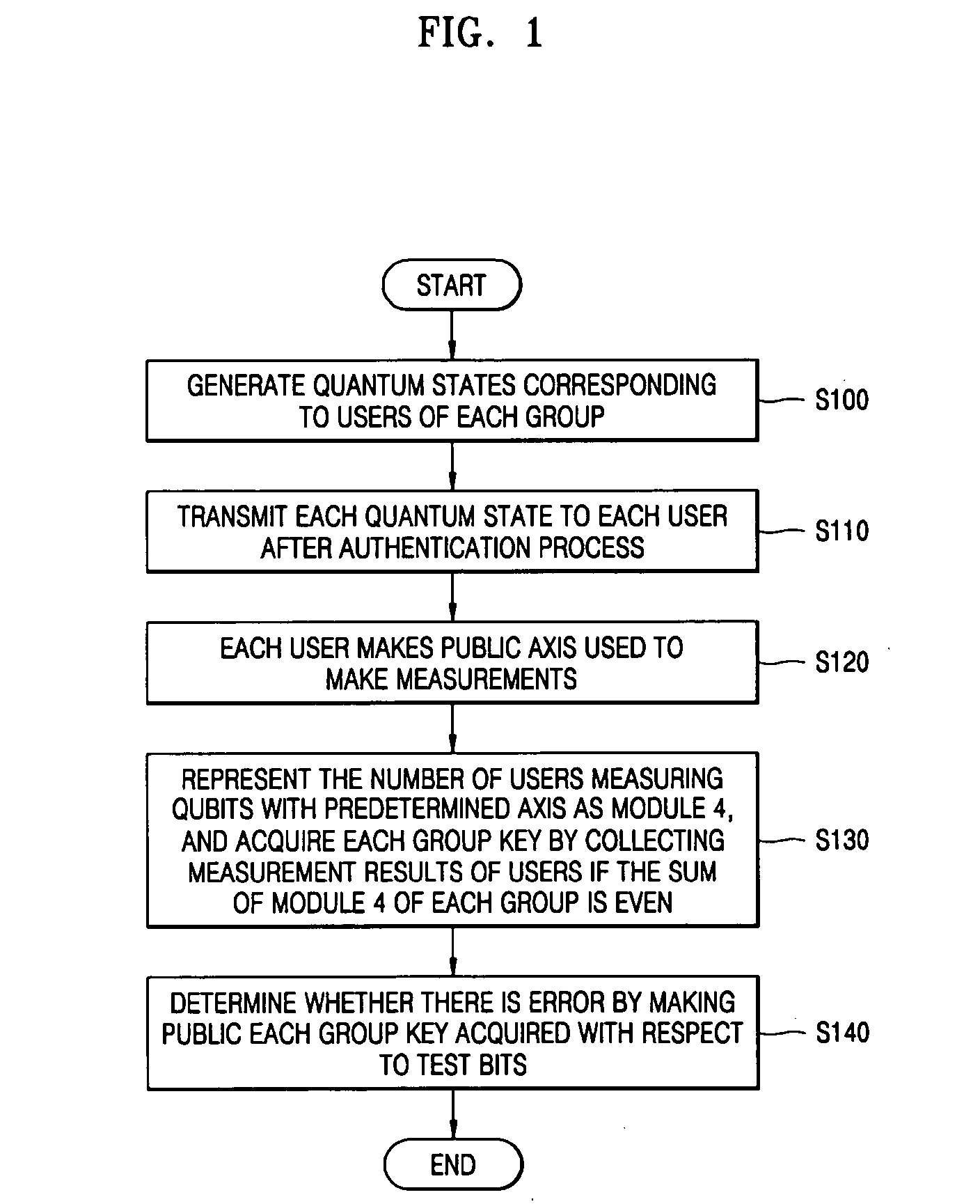
There is provided a quantum-key distribution method between a plurality of users or groups. A center prepares a predetermined number of entangled states consisting of qubits equal to the number of the users, and generates quantum states consisting of the qubits belonging to each of the entangled states and corresponding to each of the users. The center transmits each of the quantum states to each of the users after an authentication process. Each of the users receiving the quantum state makes public an axis used to measure each of the qubits constituting the quantum states. The number of users in each group measuring the qubits with a predetermined axis is represented by module 4. If the sum of the module 4 of each group is even, each group collects the qubit measurement results of the users and acquires each group key. Therefore, it is possible to provide a high-security quantum-key distribution method between an unspecified number of users or groups.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
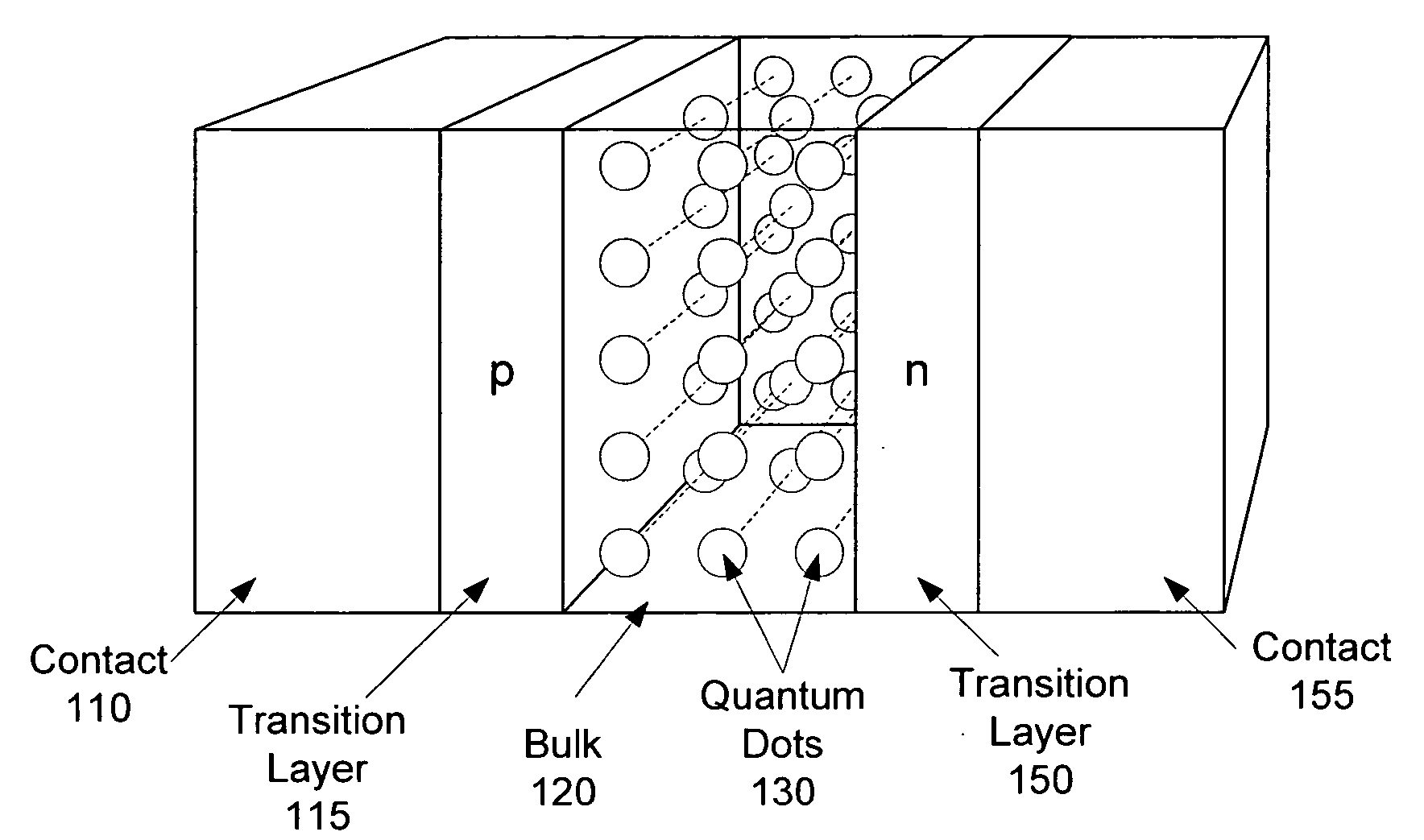
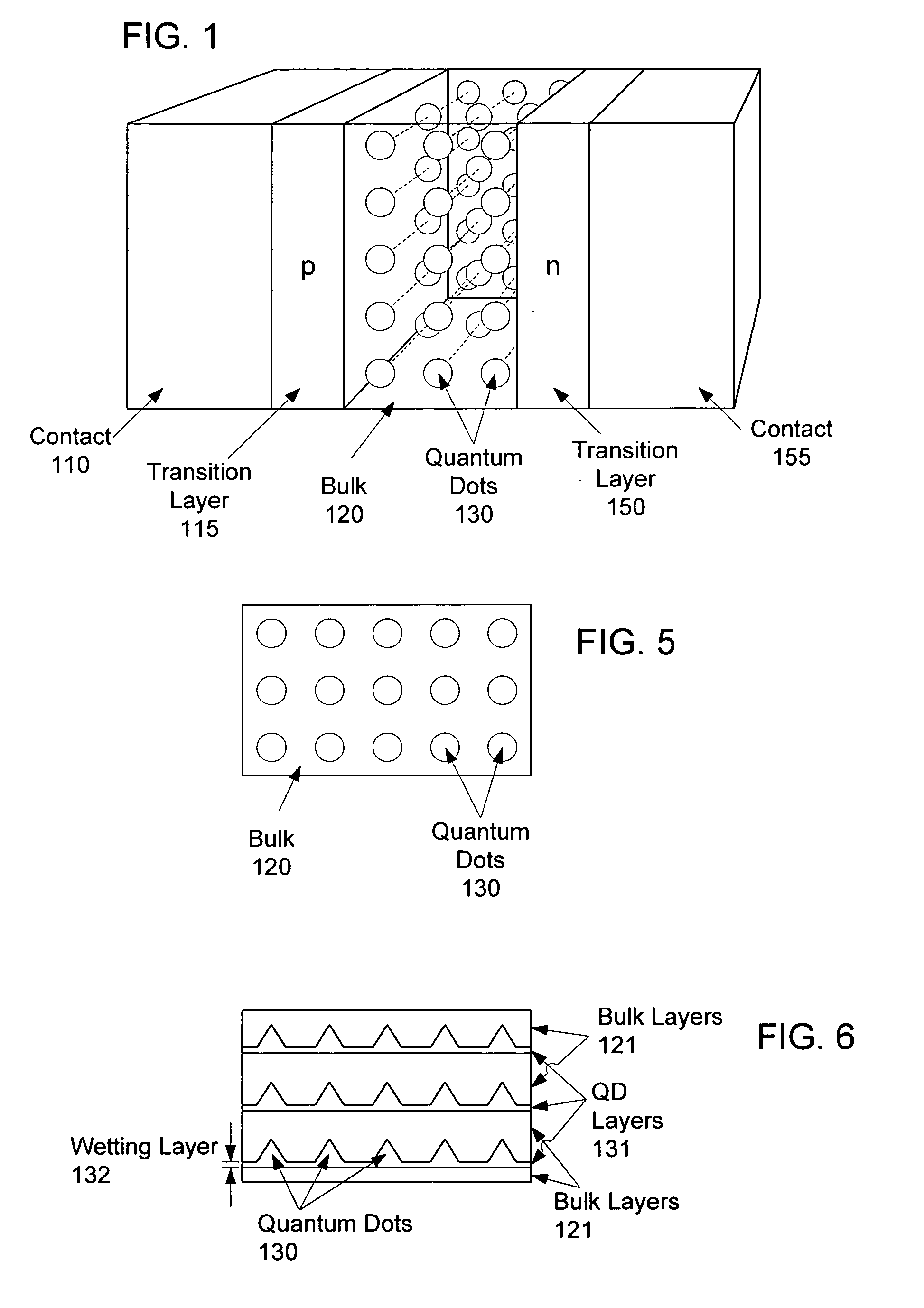
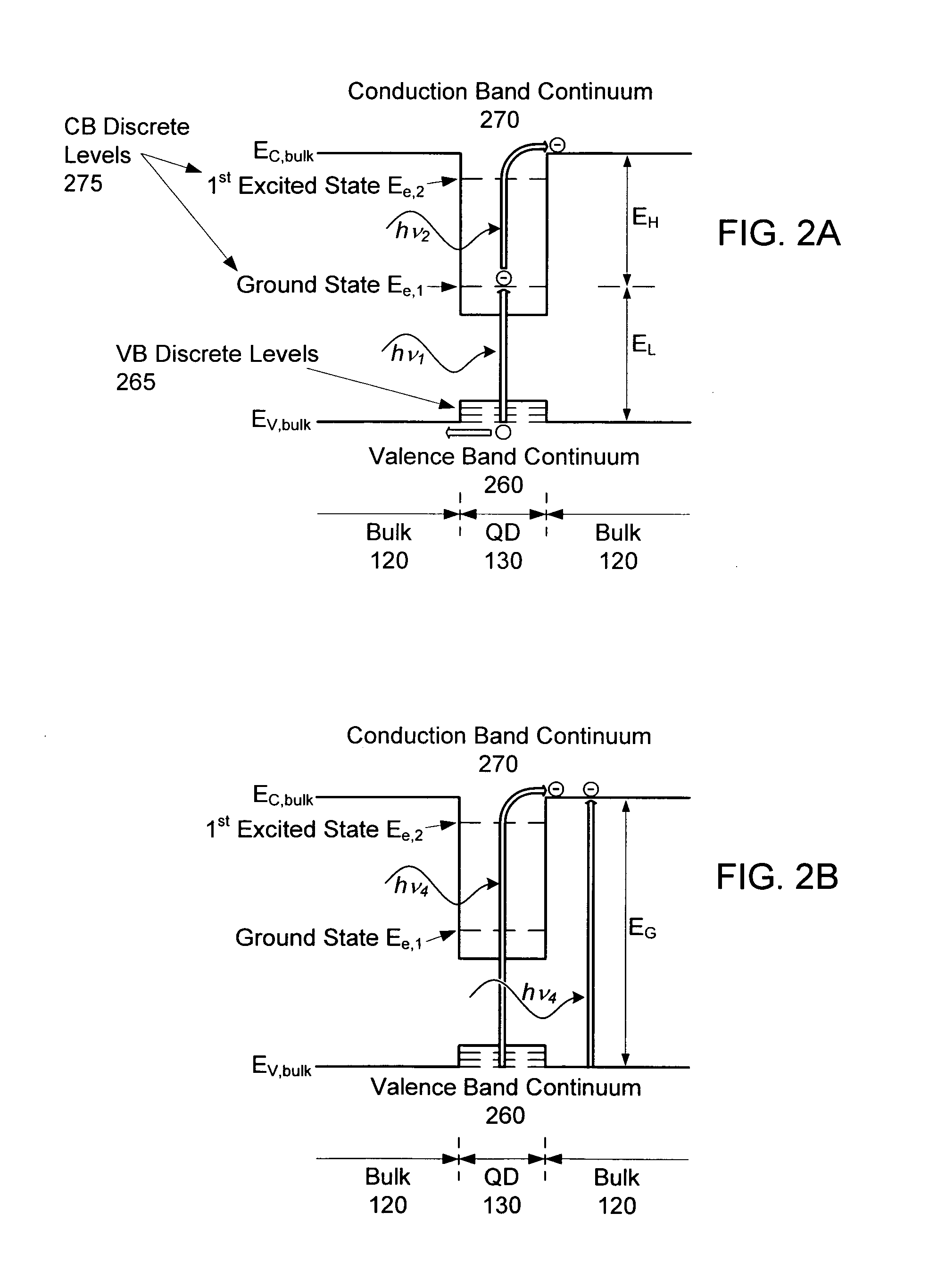
Intermediate-band photosensitive device with quantum dots having tunneling barrier embedded in organic matrix
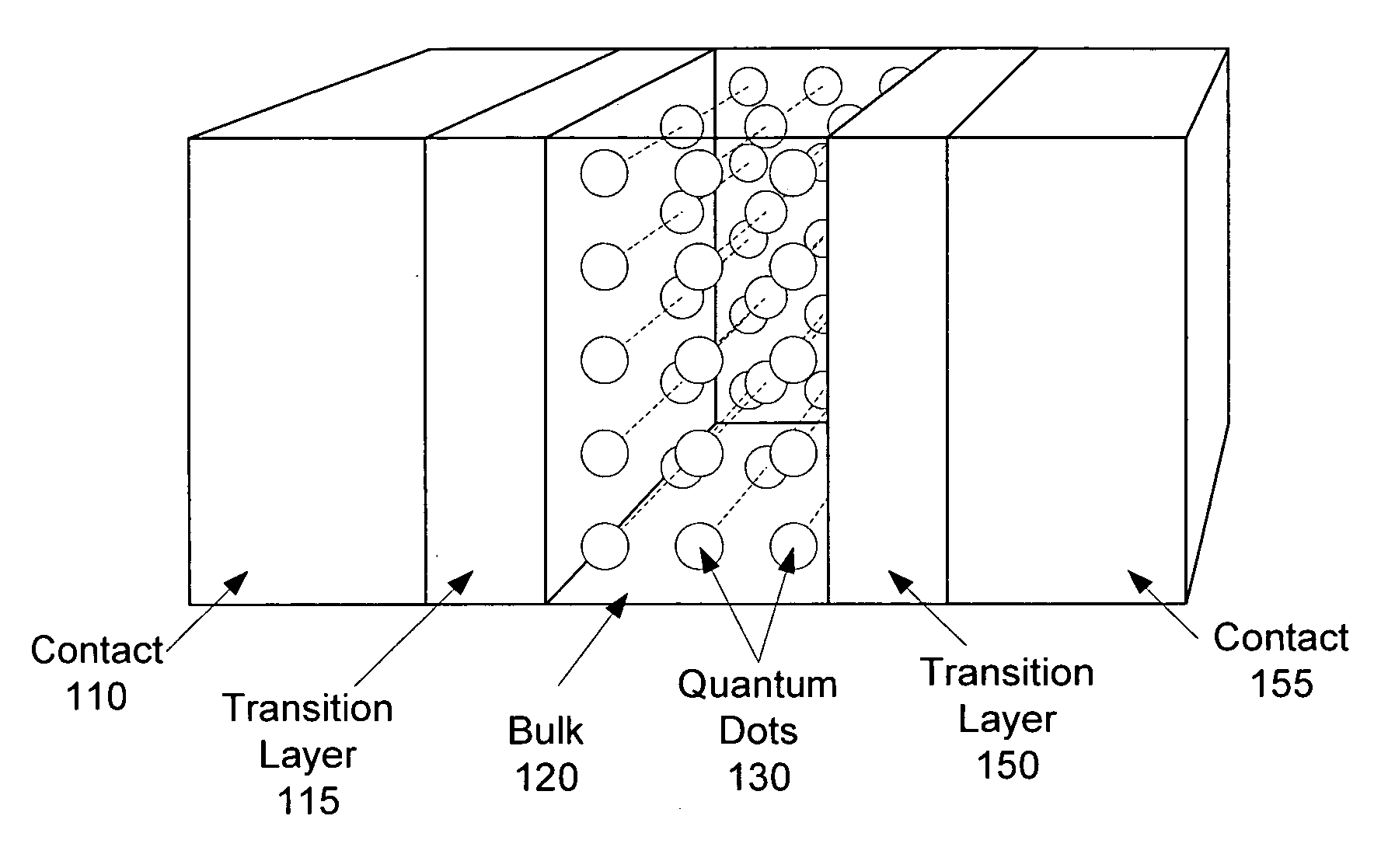
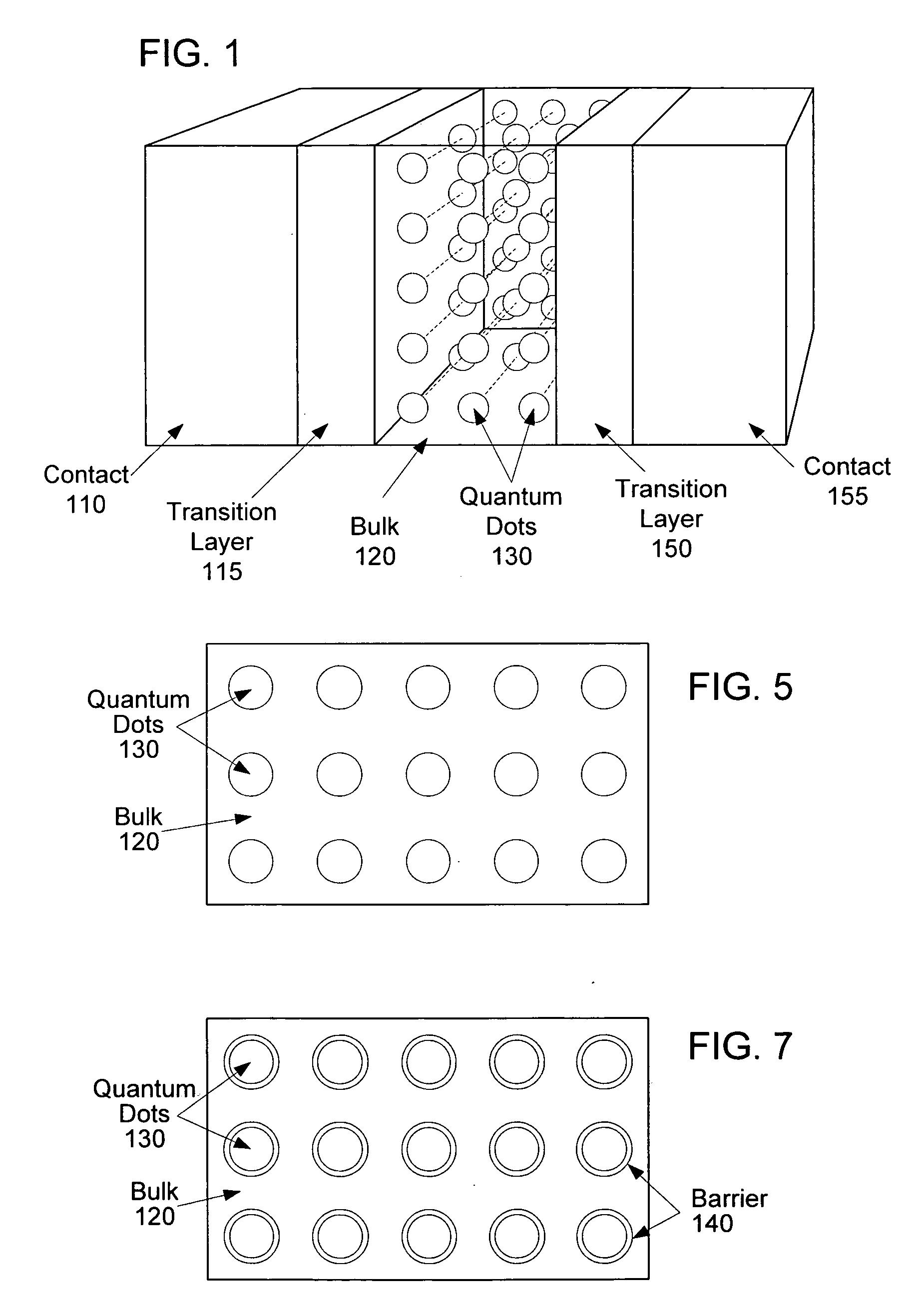
A plurality of quantum dots each have a shell. The quantum dots are embedded in an organic matrix. At least the quantum dots and the organic matrix are photoconductive semiconductors. The shell of each quantum dot is arranged as a tunneling barrier to require a charge carrier (an electron or a hole) at a base of the tunneling barrier in the organic matrix to perform quantum mechanical tunneling to reach the respective quantum dot. A first quantum state in each quantum dot is between a lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) and a highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) of the organic matrix. Wave functions of the first quantum state of the plurality of quantum dots may overlap to form an intermediate band.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
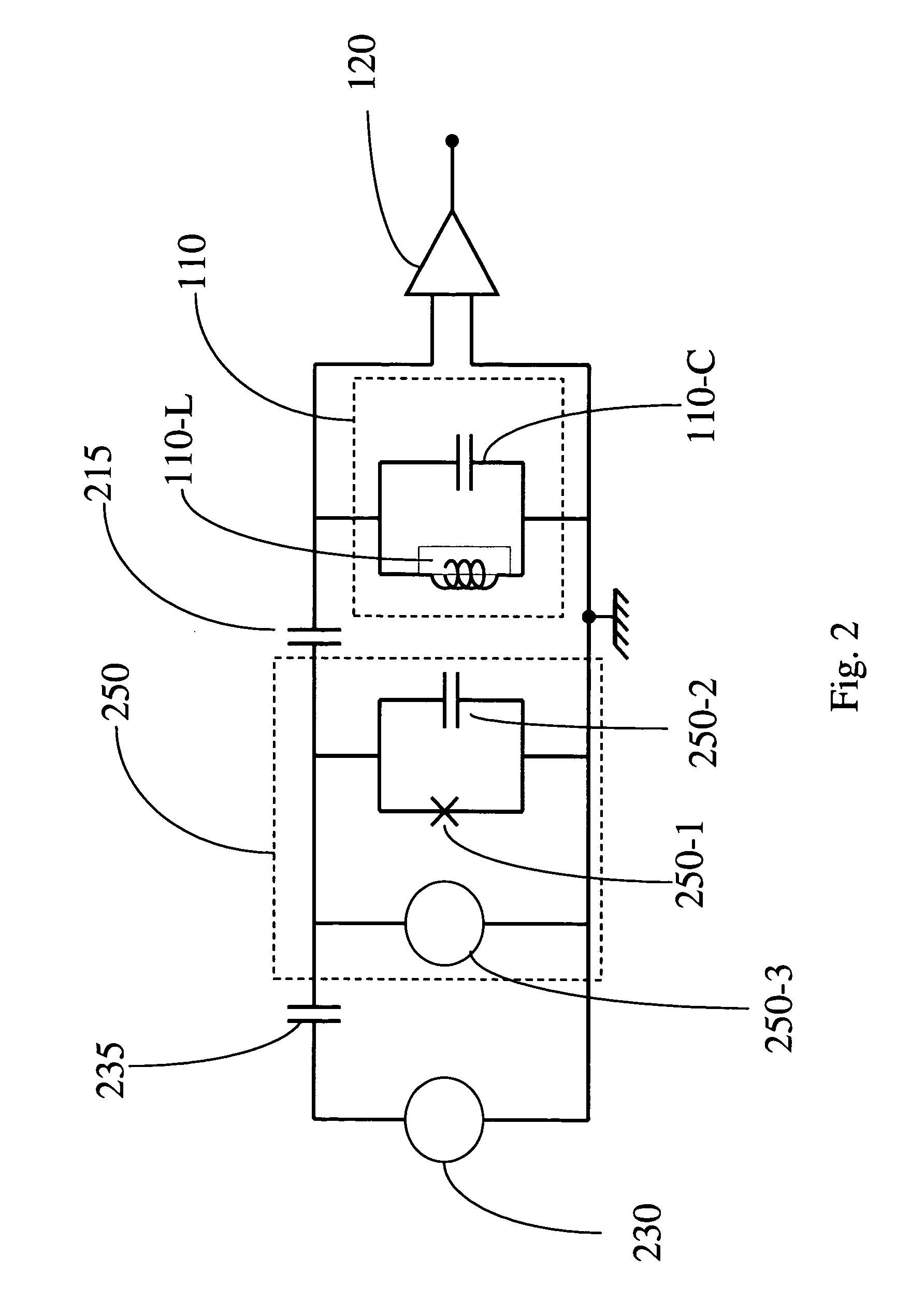
Permanent readout superconducting qubit
InactiveUS7015499B1Quantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSingle electronCrystal orientation
A solid-state quantum computing structure includes a d-wave superconductor in sets of islands that clean Josephson junctions separate from a first superconducting bank. The d-wave superconductor causes the ground state for the supercurrent at each junction to be doubly degenerate, with two supercurrent ground states having distinct magnetic moments. These quantum states of the supercurrents at the junctions create qubits for quantum computing. The quantum states can be uniformly initialized from the bank, and the crystal orientations of the islands relative to the bank influence the initial quantum state and tunneling probabilities between the ground states. A second bank, which a Josephson junction separates from the first bank, can be coupled to the islands through single electron transistors for selectably initializing one or more of the supercurrents in a different quantum state. Single electron transistors can also be used between the islands to control entanglements while the quantum states evolve. After the quantum states have evolved to complete a calculation, grounding the islands, for example, through yet another set of single electron transistors, fixes the junctions in states having definite magnetic moments and facilitates measurement of the supercurrent when determining a result of the quantum computing.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Intermediate-band photosensitive device with quantum dots having tunneling barrier embedded in inorganic matrix
A plurality of quantum dots comprise a first inorganic material, and each quantum dot is coated with a second inorganic material. The coated quantum dots being are in a matrix of a third inorganic material. At least the first and third materials are photoconductive semiconductors. The second material is arranged as a tunneling barrier to require a charge carrier (an electron or a hole) at a base of the tunneling barrier in the third material to perform quantum mechanical tunneling to reach the first material within a respective quantum dot. A first quantum state in each quantum dot is between a conduction band edge and a valence band edge of the third material in which the coated quantum dots are embedded. Wave functions of the first quantum state of the plurality of quantum dots may overlap to form an intermediate band.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
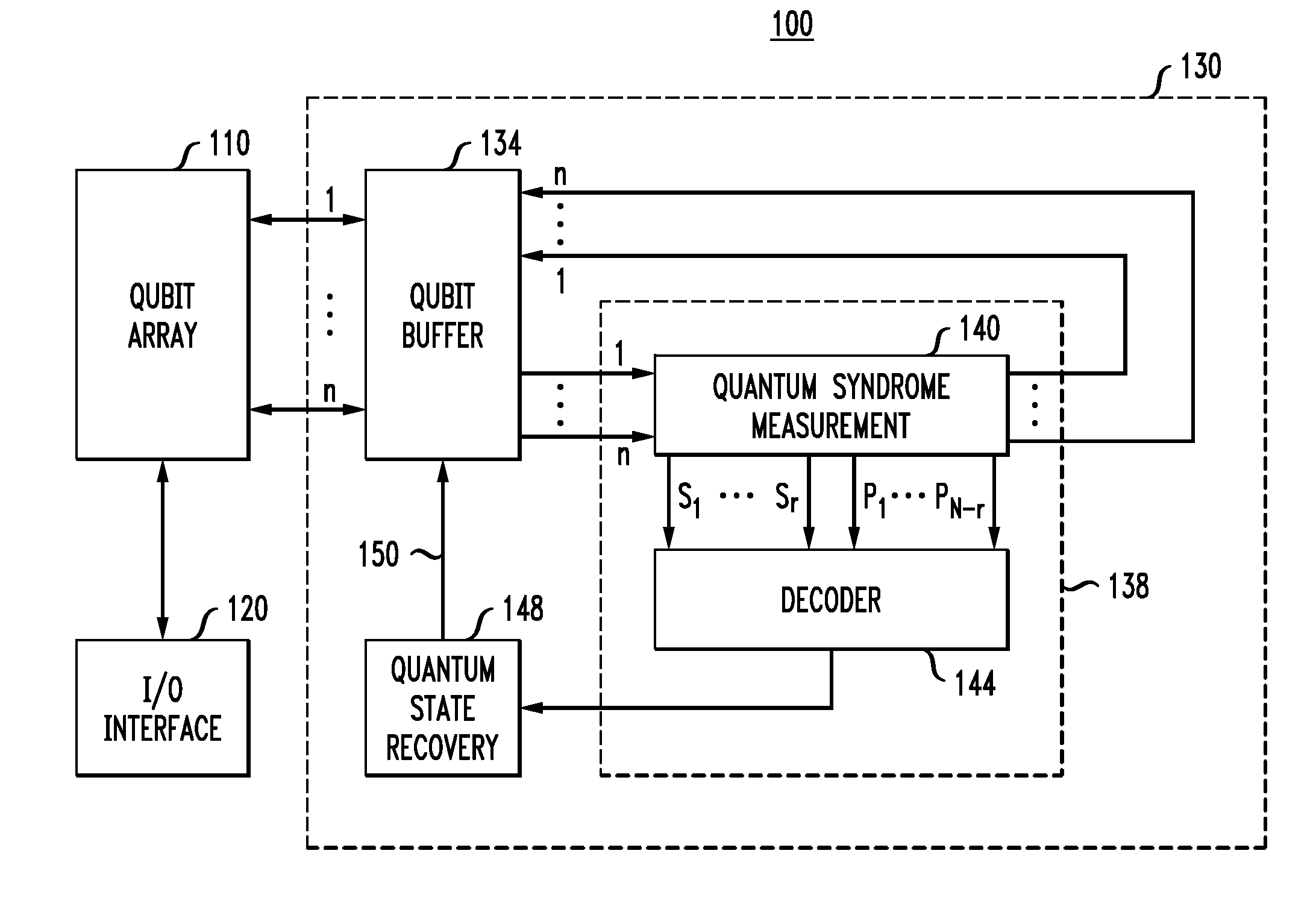
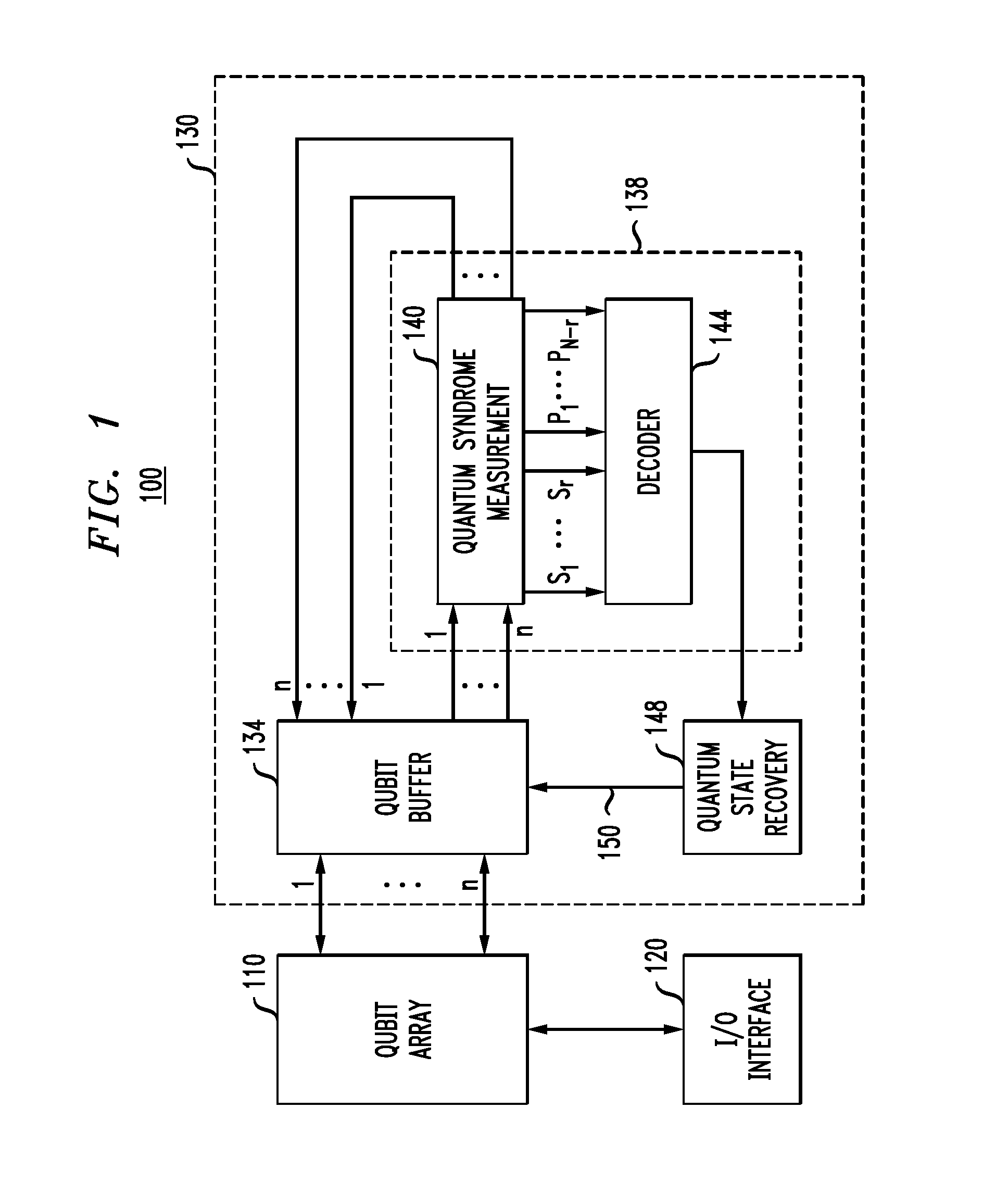
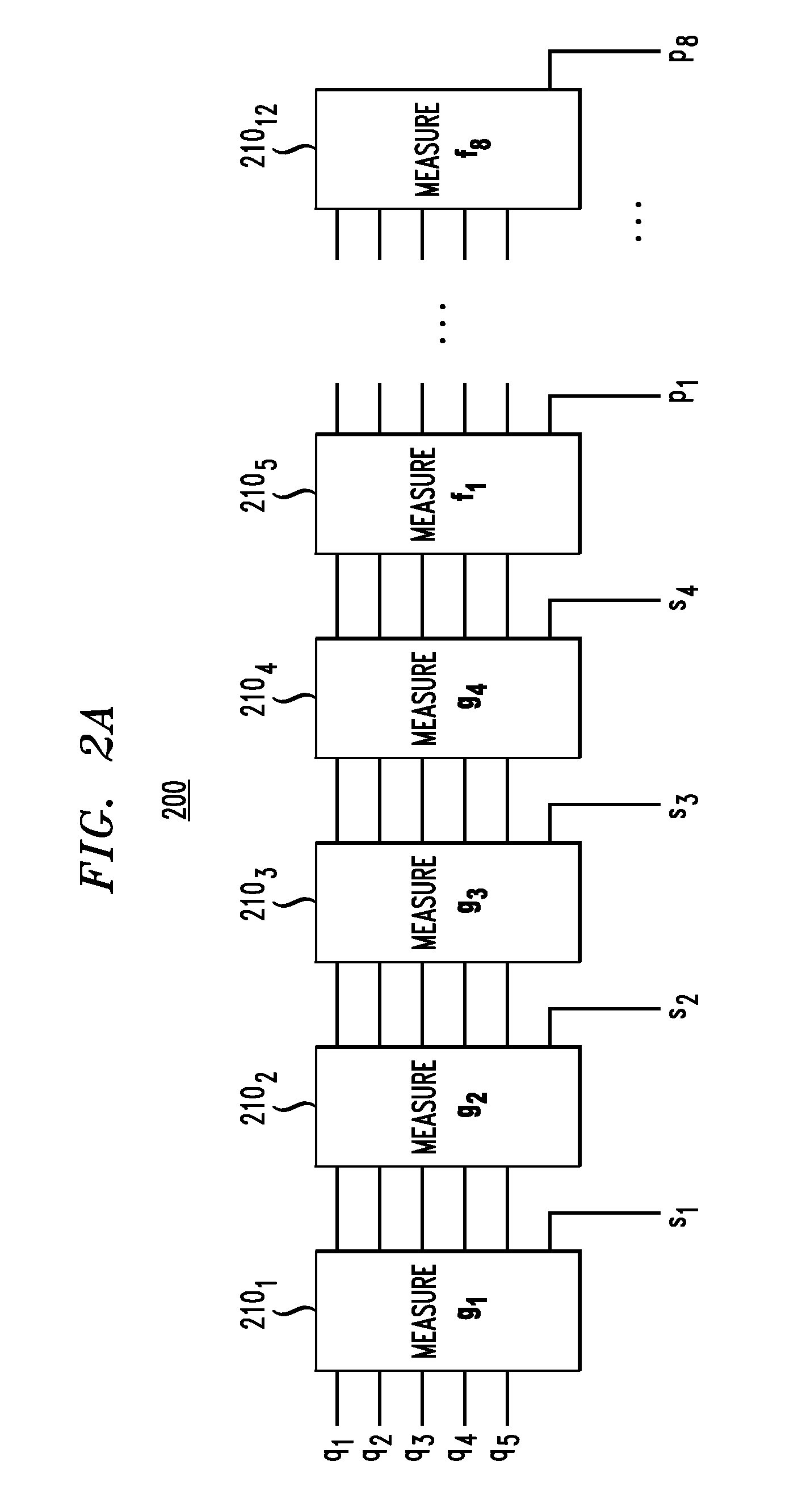
Error correction for entangled quantum states
ActiveUS20140365843A1Quantum computersCode conversionFunction optimizationLow-density parity-check code
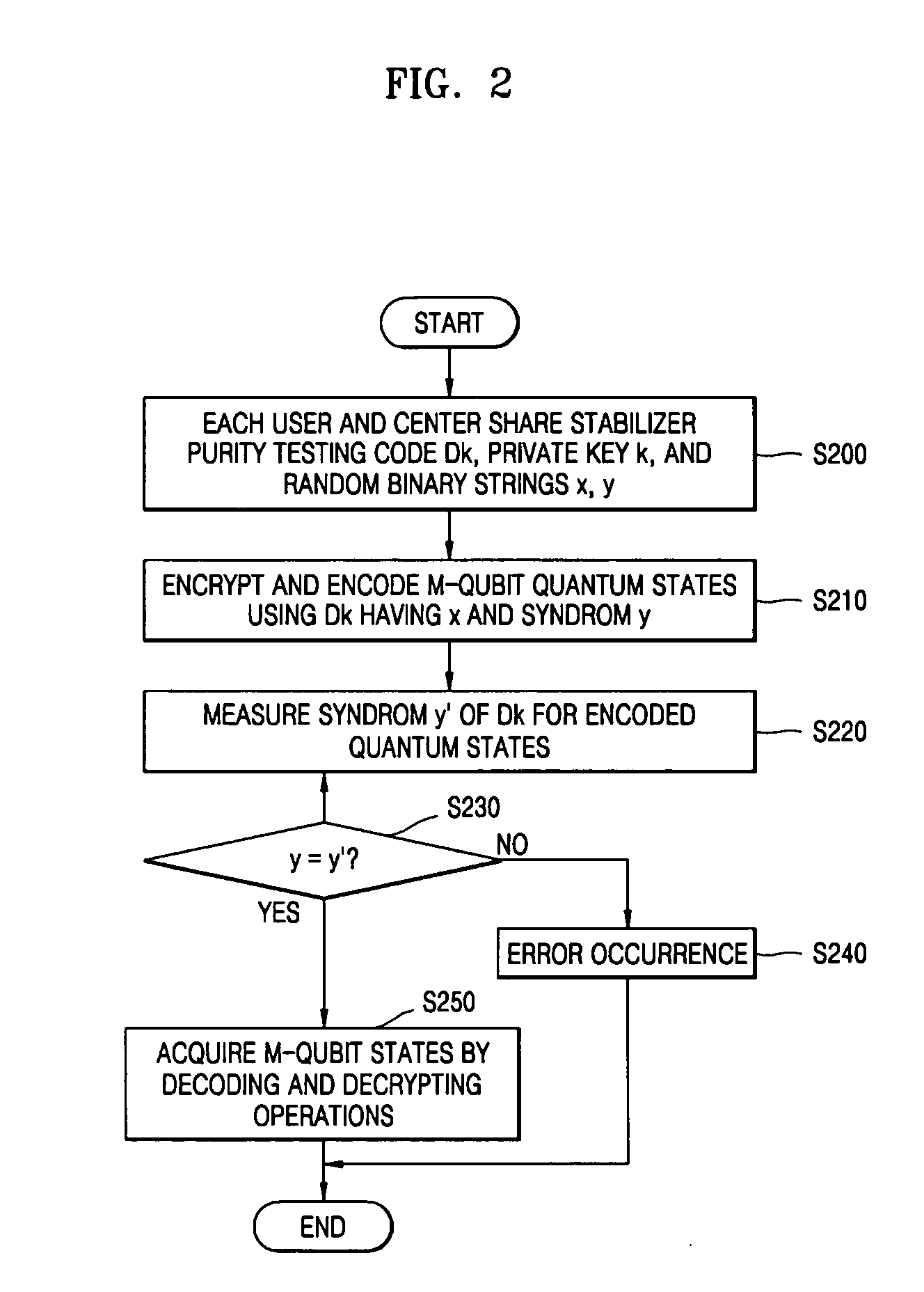
A memory system comprising a qubit array configured to store therein and read one or more entangled qubit states encoded using a quantum stabilizer code. The quantum-memory system further comprises a quantum-state-refresh module configured to change an entangled qubit state in the qubit array when an error is detected therein. The quantum-state-refresh module is configured to detect an error by performing a redundant measurement of a set of syndrome values corresponding to the quantum stabilizer code, with the redundant measurement being based on a block error-correction code. In one embodiment, the block error-correction code is a low-density generator-matrix code or a low-density parity-check code constructed using an EXIT-function optimization method.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
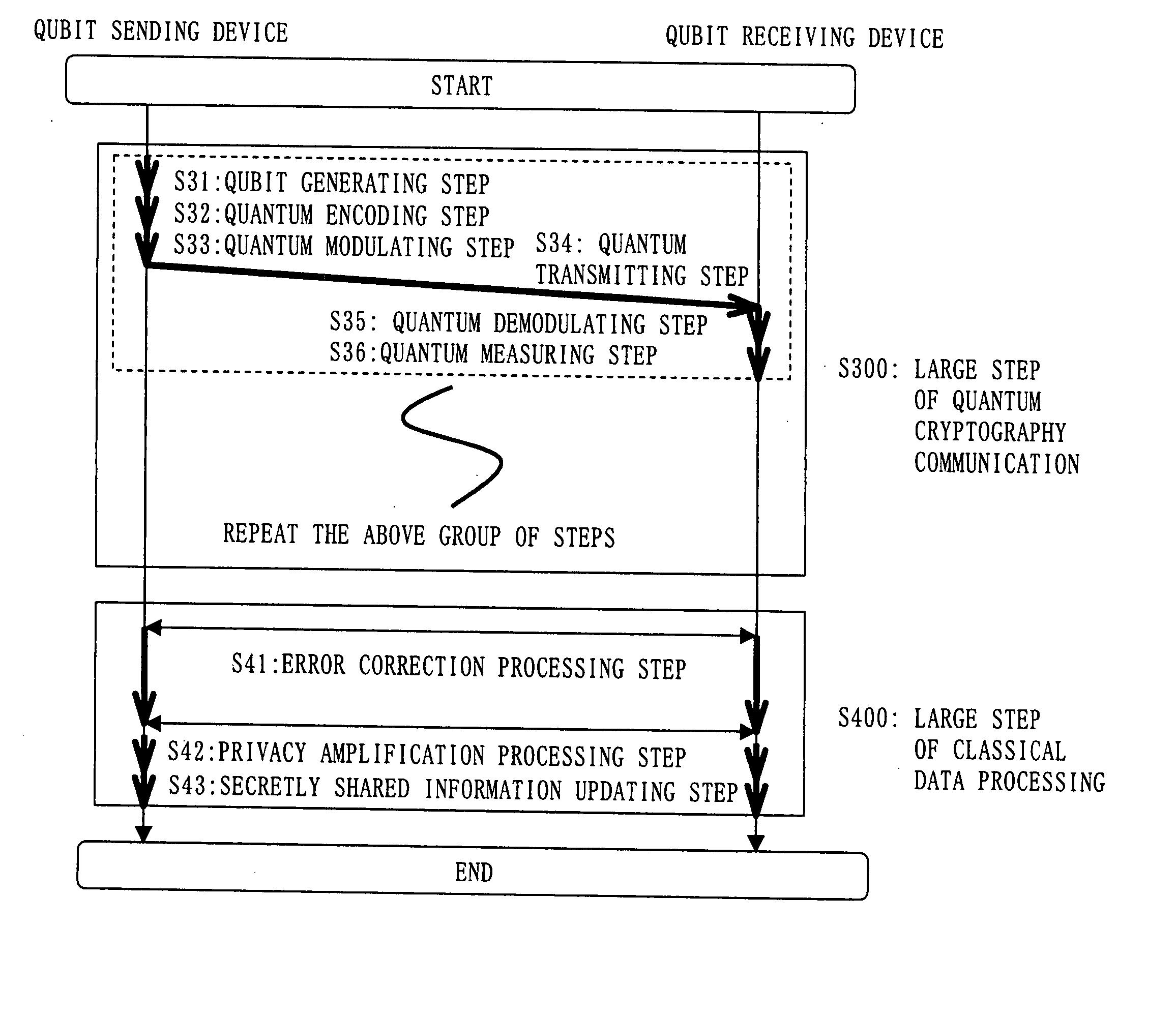
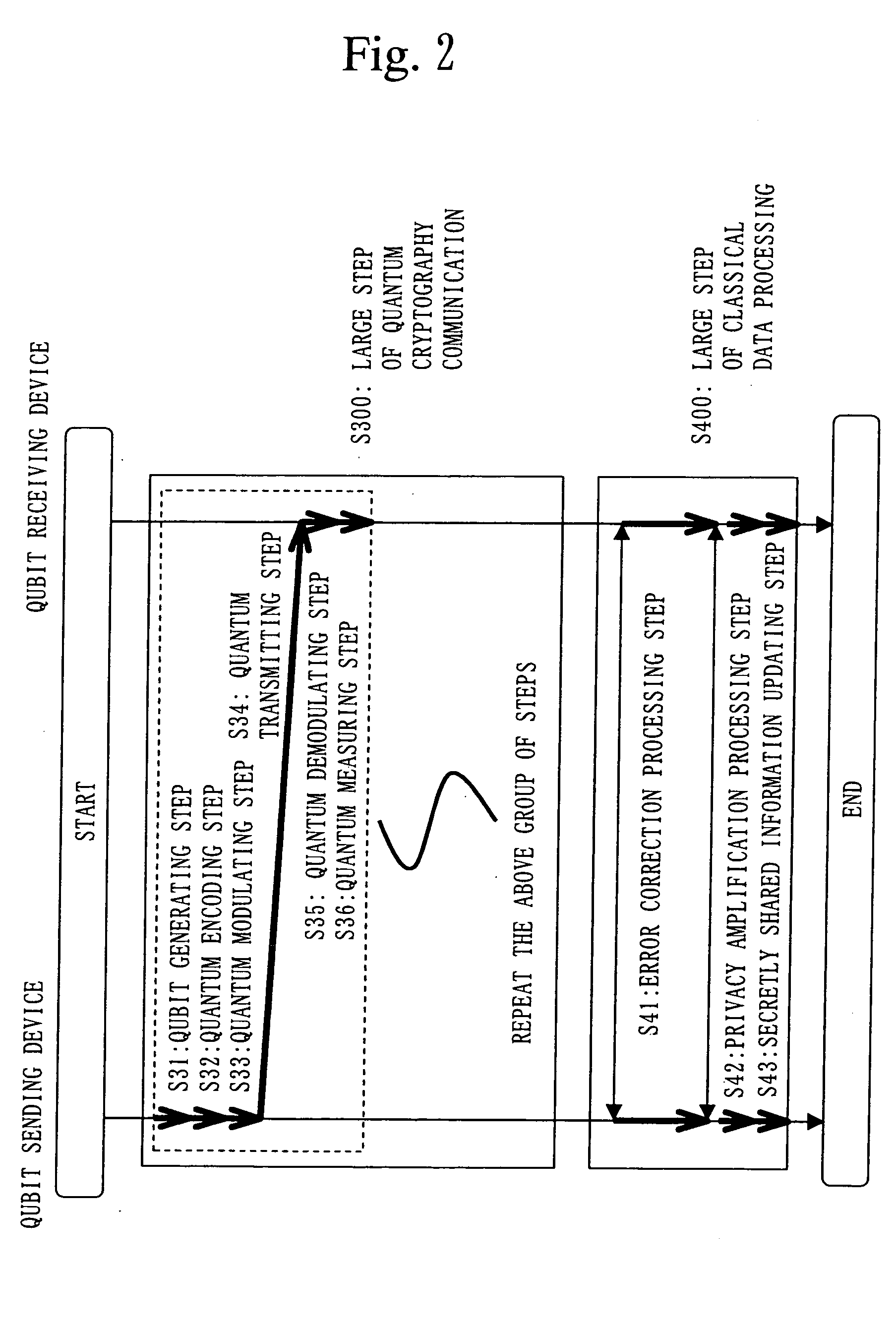
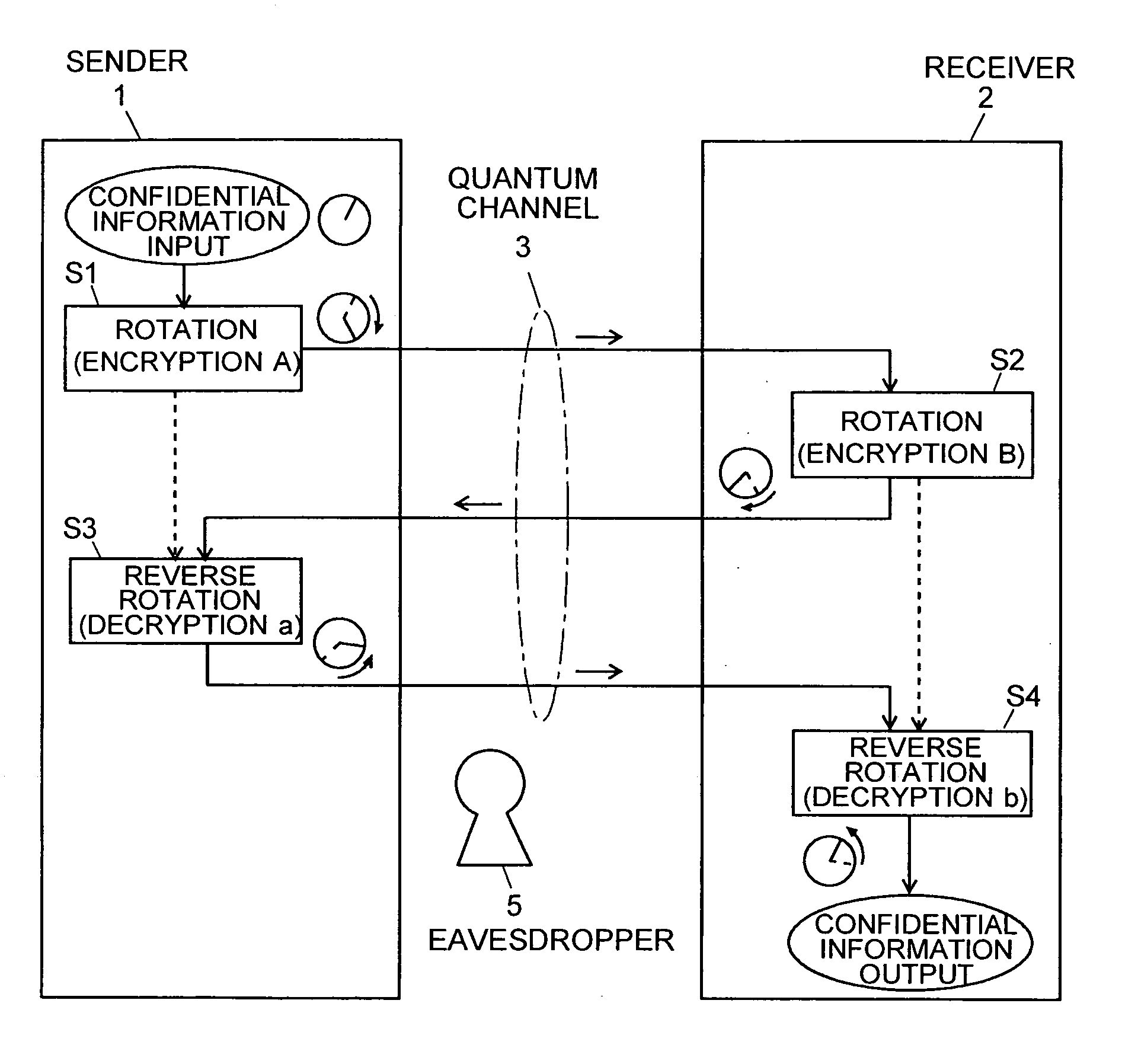
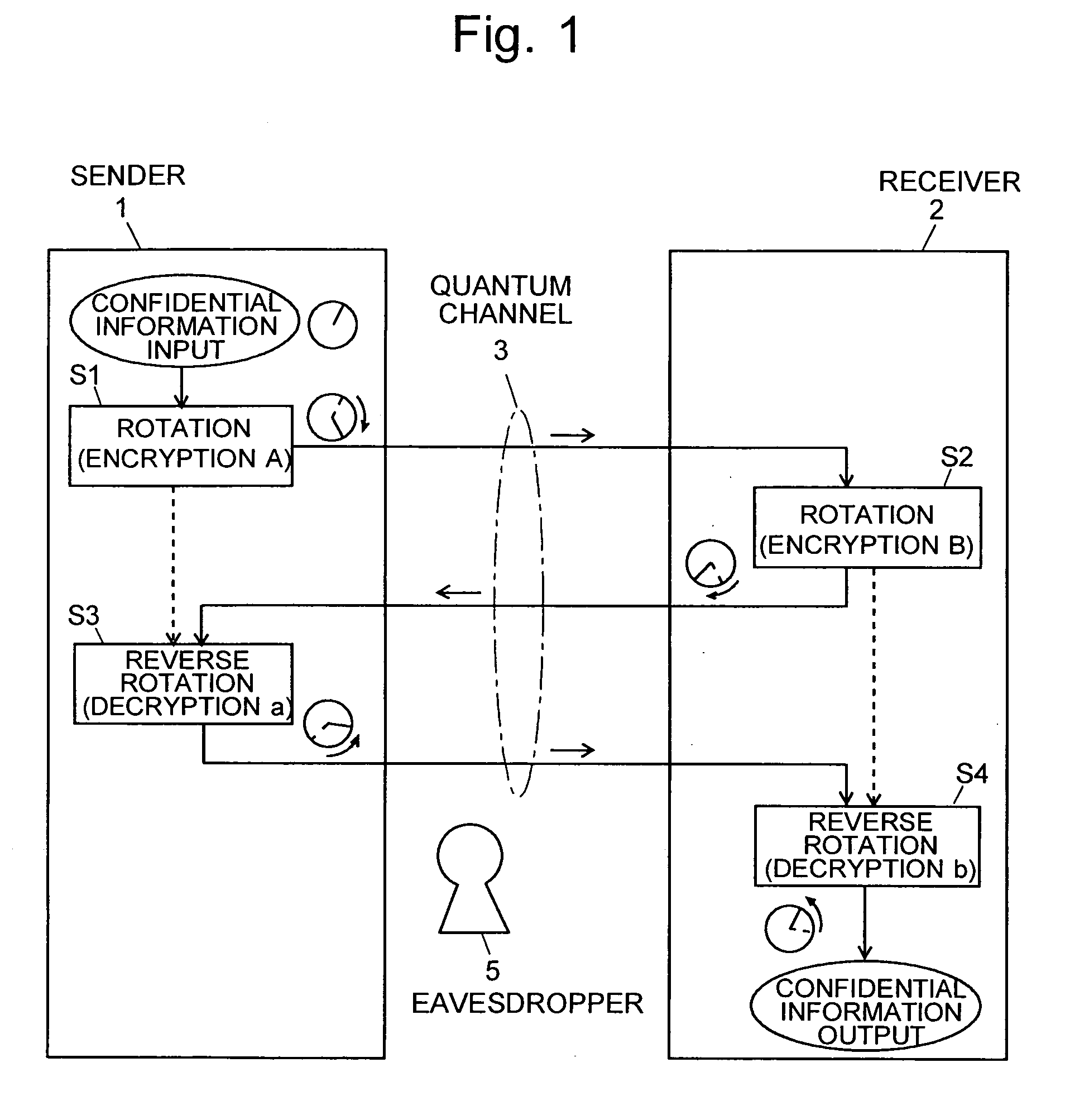
Quantum Cryptographic Communication Method
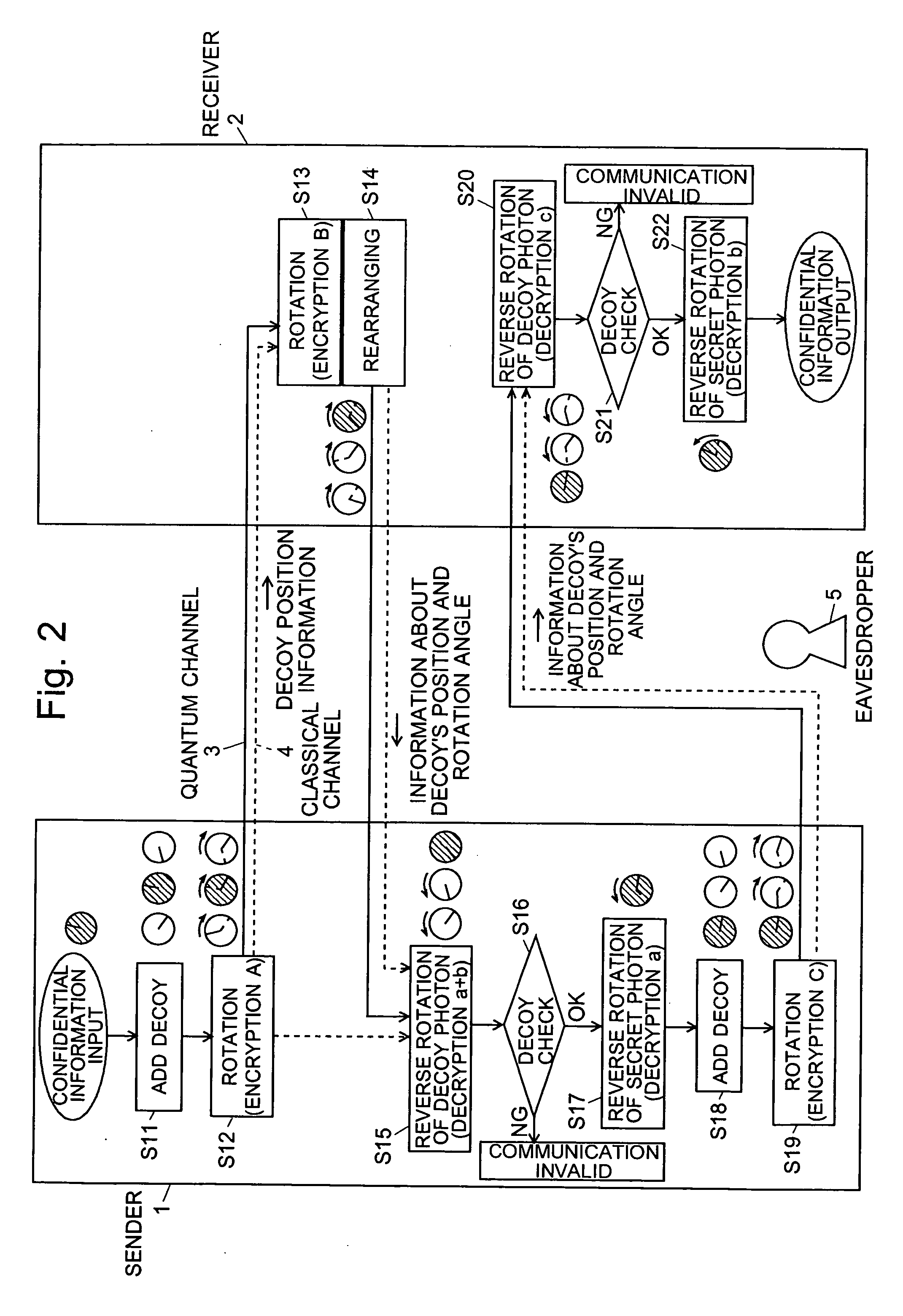
A sender (1) adds decoy photons to a secret photon having confidential information, then, subjects each photon to a different rotational manipulation, and passes the photons along a quantum channel (3) (S11 and S12). A receiver (2) receives those photons and then obtains information about the position of the decoy photons from the sender (1) through a classical channel (4). Using the information, the receiver (2) subjects each of the decoy and secret photons to a different rotational manipulation and transmits the photons in a rearranged order (S13 and S14). The receiver (1) obtains information about the position and manipulation quantities of the decoy photons from the receiver (2) and decodes the decoy photons. If the quantum state of the decoys is identical to their initial quantum state, the sender (1) determines that no eavesdropper (5) should be present (S15 and S16), cancels only the encryption of the secret photon performed by himself or herself in S12, and transmits the secret photon (S17). The receiver (2) cancels the encryption of the secret photon performed by himself or herself in S13 and thereby obtains the confidential information (S18). The present method can securely send quantum information as well as classical information such as key information, and also effectively detect eavesdropping.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method and system for detecting eavesdropping during data transmission
ActiveUS20170331623A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsKey distribution for secure communicationSecure communicationEavesdropping
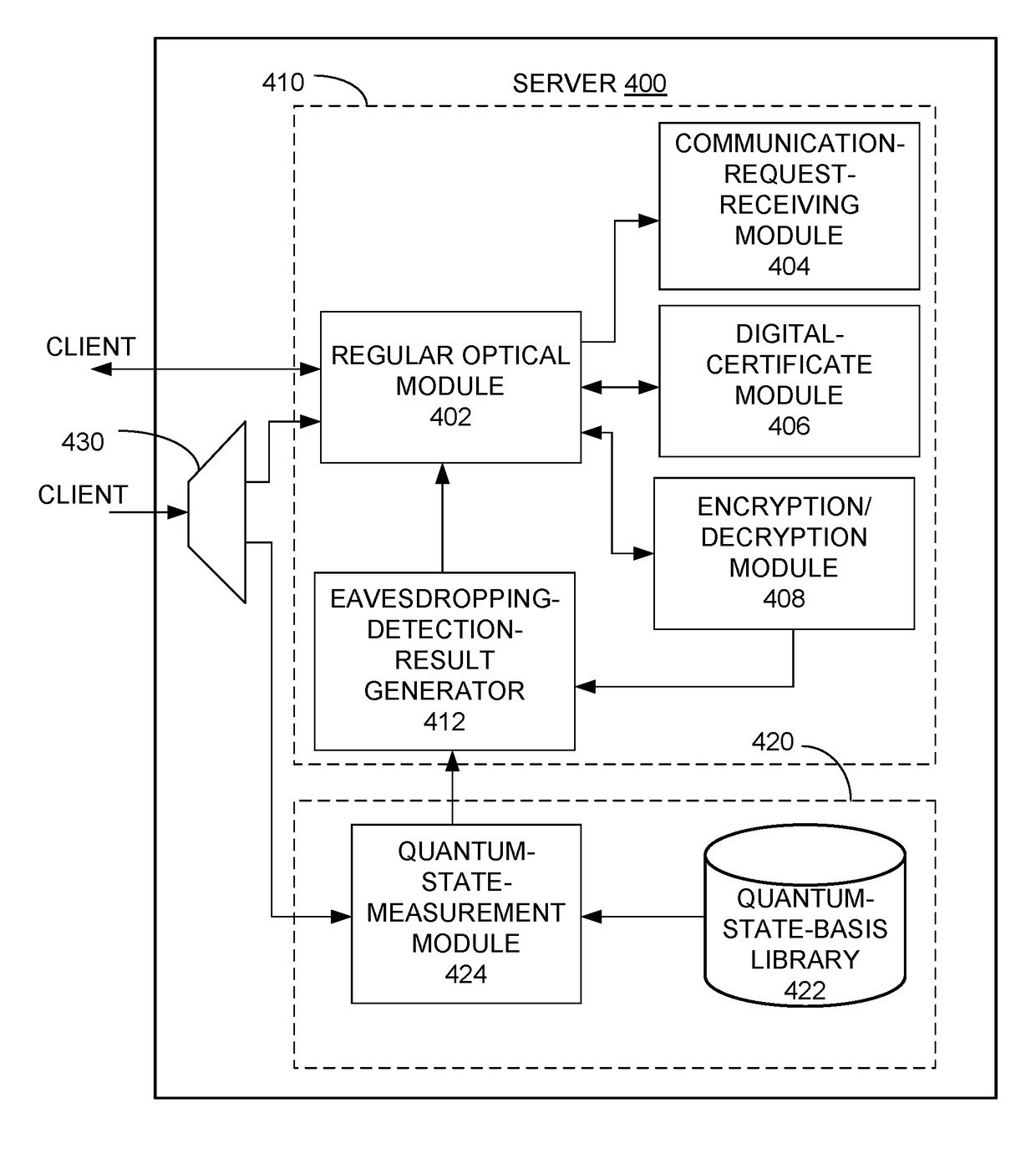
One embodiment provide a system and method for detecting eavesdropping while establishing secure communication between a local node and a remote node. During operation, the local node generates a random key and a regular optical signal based on the random key. The local node also generates a quantum optical signal based on a control sequence and a set of quantum state bases, and multiplexes the regular optical signal and the quantum optical signal to produce a hybrid optical signal. The local node transmits the hybrid optical signal to the remote node, sends information associated with the control sequence and information associated with the set of quantum state bases to the remote node, and receives an eavesdropping-detection result from the remote node based on measurement of the quantum optical signal, the information associated with the control sequence, and the information associated with the set of quantum state bases.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Quantum key distribution, privacy amplification and data transmission methods, apparatuses, and system
ActiveCN105553648AImprove securityEliminate potential safety hazardsKey distribution for secure communicationError preventionComputer hardwareComputer science
The application discloses a quantum key distribution method and an apparatus, a privacy amplification method and an apparatus for the process of quantum key distribution, a data transmission method based on quantum keys, and a data transmission system based on the quantum keys. The quantum key distribution method includes: obtaining bit streams with the same basis vector by sending or receiving coding quantum states of random bit streams and comparing and measuring basis vectors; extracting parameter information related to privacy amplification and initial keys from the bit streams with the same basis vector after error code correction according to a pre-appointed method; and regarding the initial key as input, implementing the privacy amplification algorithm according to the parameter information, and obtaining a shared quantum key. By employing the method, hidden risks for negotiation of privacy amplification parameters in classical channels can be eliminated, and the security of the quantum key distribution process is effectively improved.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Decompose method for arbitrarily quantum bit gate
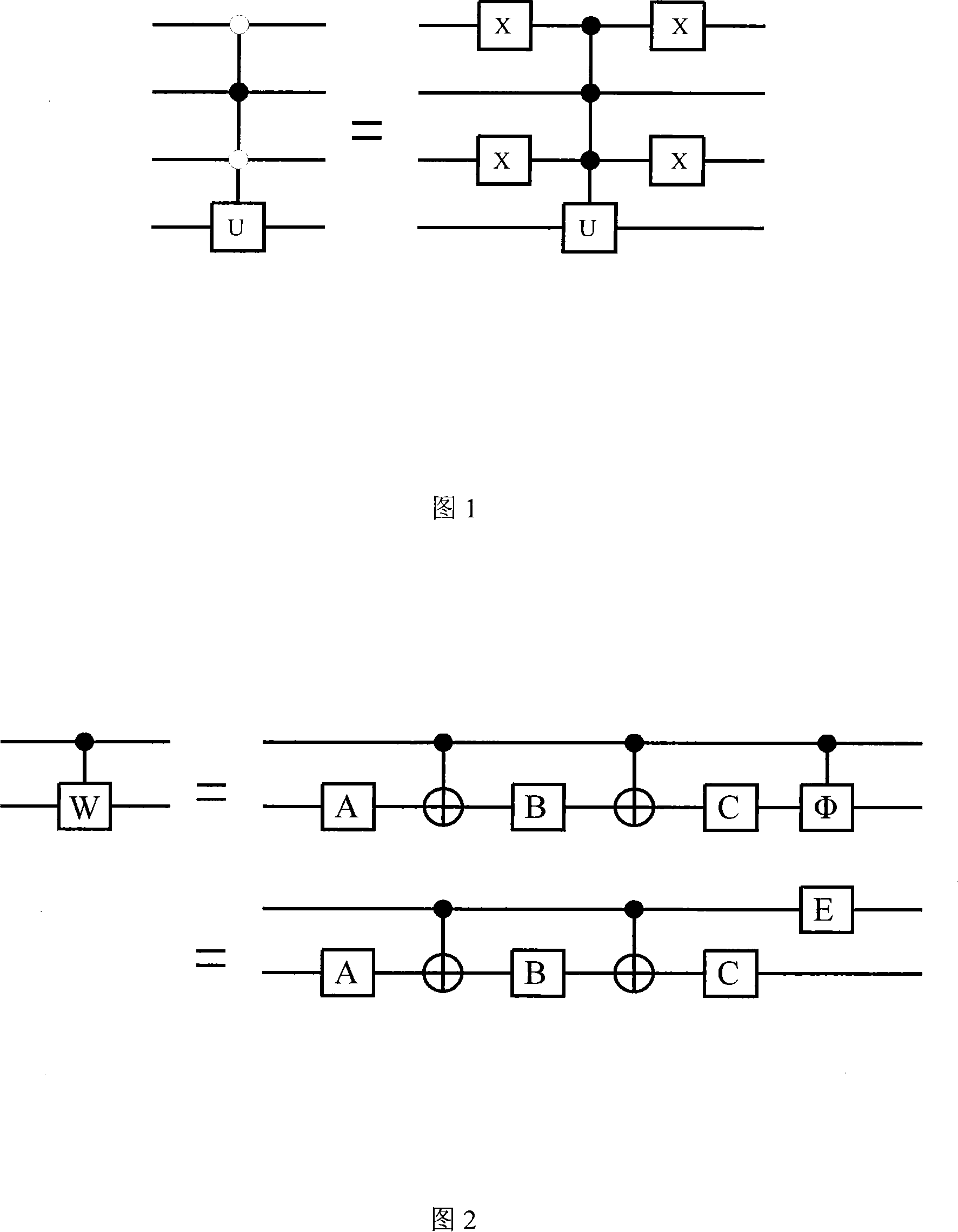
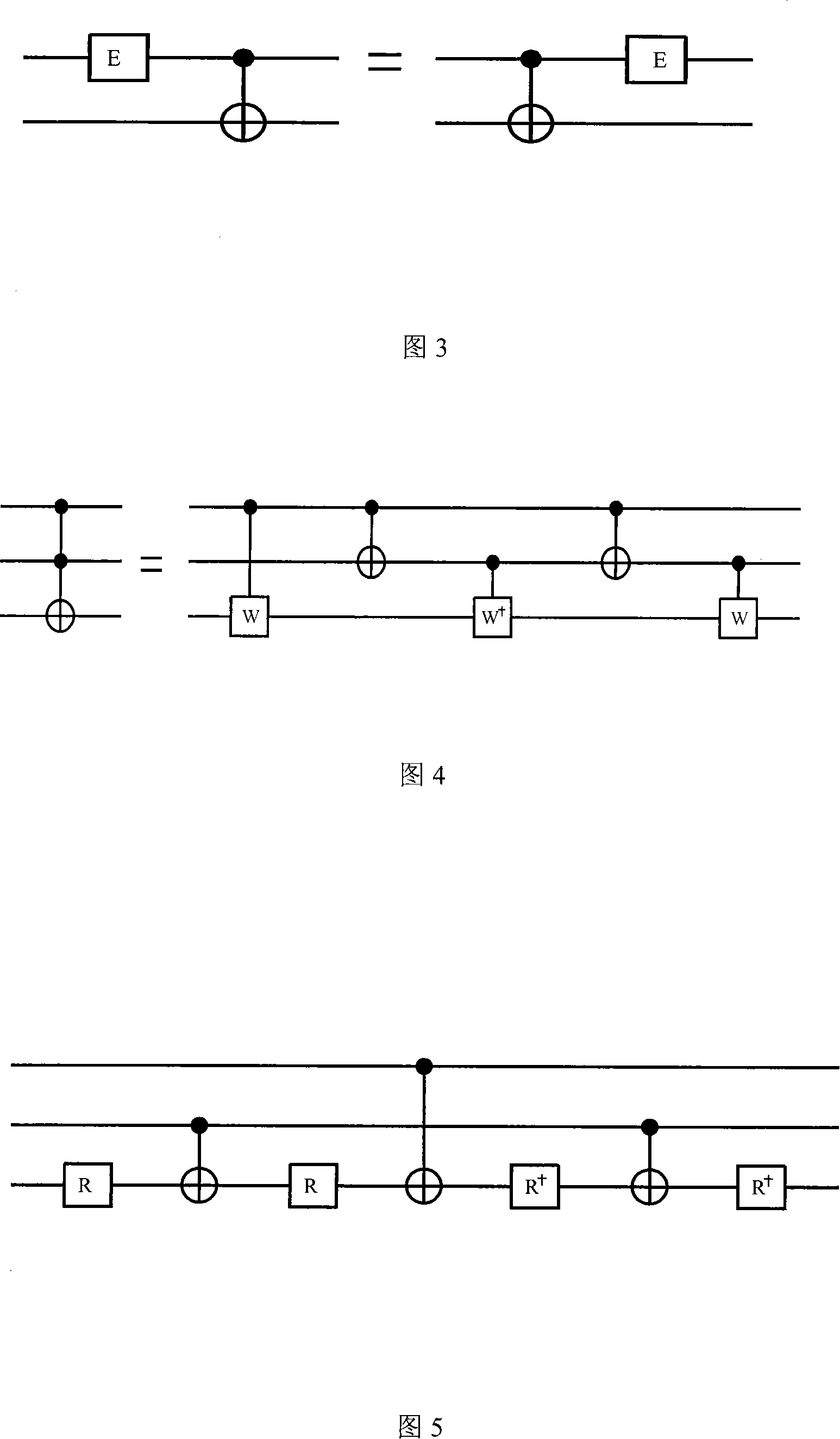
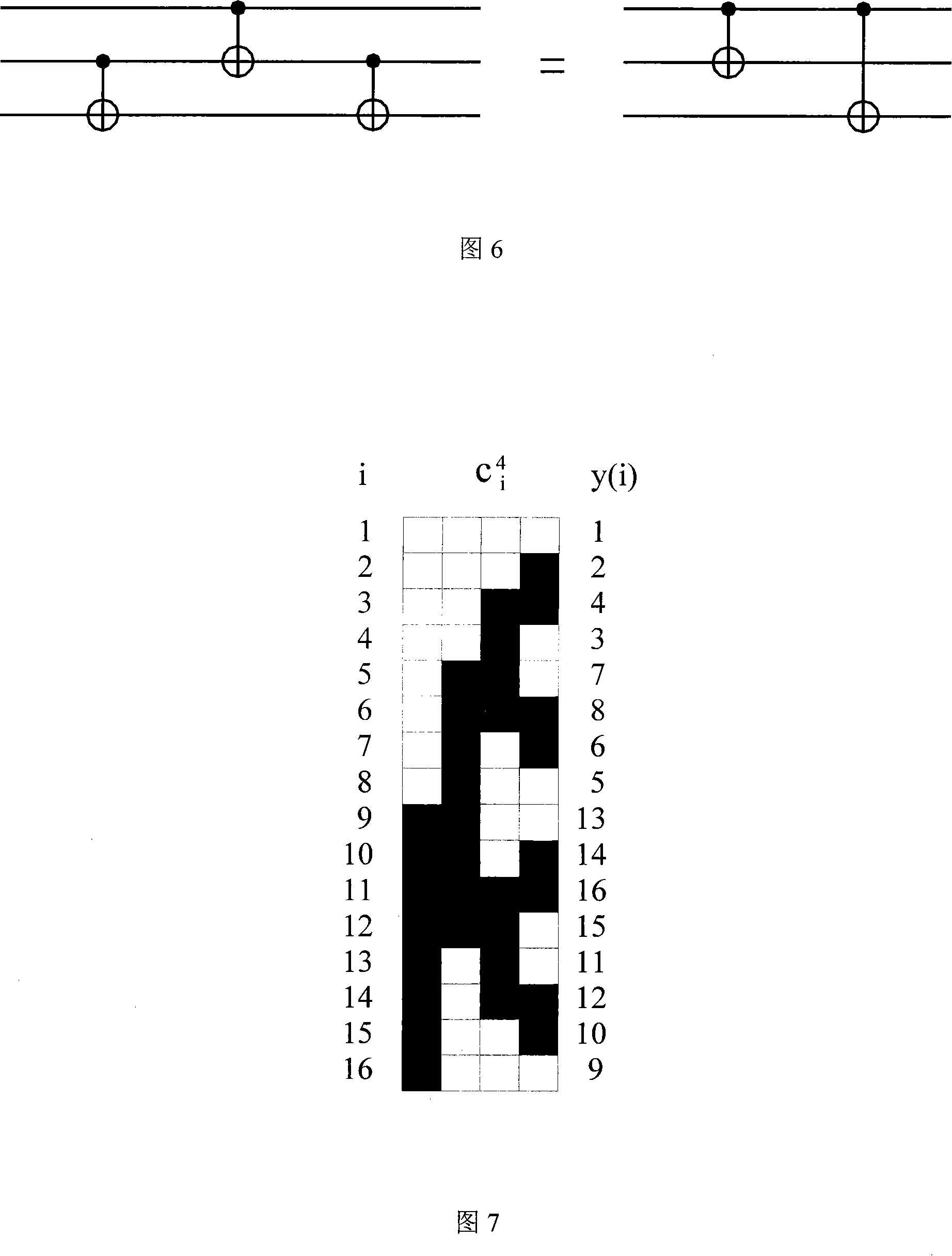
ActiveCN101118608AReduce complexityReduce the numberComputing modelsCircuit complexityQuantum circuit
The present invention discloses a decomposition method for a random quantum bit gate, and belongs to the field of the quantum state manipulating technology. The method includes: the bit gate U of a random quantum n is decomposed into a plurality of uninterrupted Cn (U) and the decomposition of a random quantum bit gate is achieved by adopting an index decomposition mode and a polynomial decomposition mode with circuit complexities of O (2n) and O (n2) respectively through the fundamental segment and the correcting segment of the structure and utilizing the mode of nested recursion. The present invention achieves that a random quantum bit gate is decomposed into a qubit index form and a polynomial form of complexities, gives the quantum circuit and the relevant analytical expression containing only two quantum bit CNOTs and a single quantum bit accurately, thereby achieving an arbitrary operation to a quantum state in the transmission process of the quantum state, figures out the number of a basic logic gate that the two decomposed forms need, uses a phaseshift approximate gate to replace the Toffolin gate and reduces the complexity of the circuit greatly.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Low-complexity quantum circuit simulation system
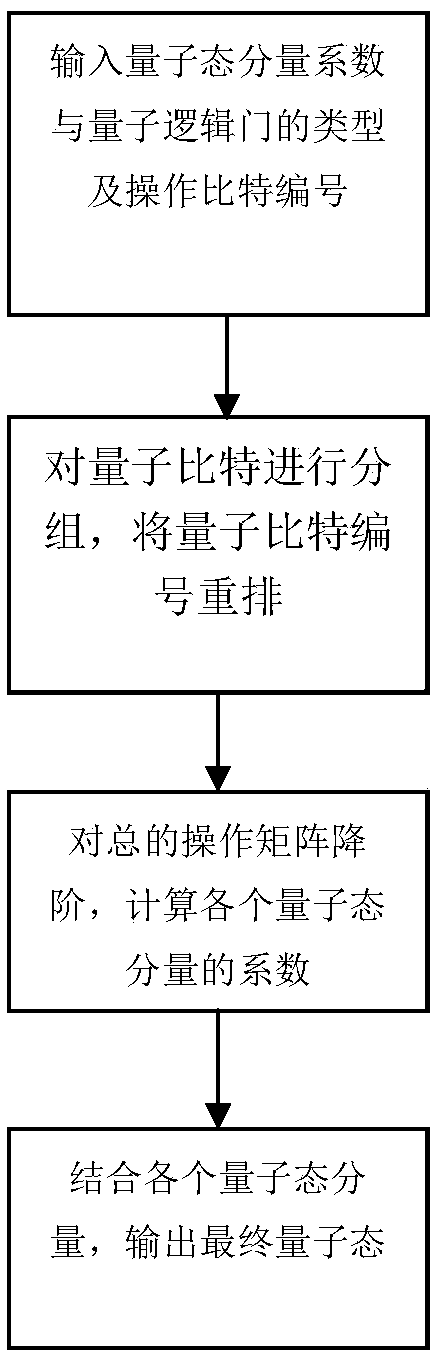
ActiveCN108154240AScalableAvoid the disadvantage of too manyQuantum computersSupercomputerQuantum logic
The invention discloses a low-complexity quantum circuit simulation system, and belongs to the field of quantum computing. The low-complexity quantum circuit simulation system overcomes the technicalproblems in the prior art that the quantum circuit simulation storage space is too large and the calculation time is too long. The system comprises an input module, a storage module and an output module, the storage process of the storage module for data is as follows: (1) a mathematical model is established to represent the operation of a quantum state and quantum logic gate; (2) quantum bits aregrouped and the serial numbers of the quantum bits are rearranged; (3) degree reduction is conducted on a total operation matrix U0, and an output state is calculated. According to the system, a matrix element of a quantum state vector is directly operated by using an connotative inherent law of a quantum logic gate, at the same time, the method has expandability, in the future, a supercomputer can be used to simulate a quantum computer with more bits.
Owner:ORIGIN QUANTUM COMPUTING TECH (HEFEI) CO LTD
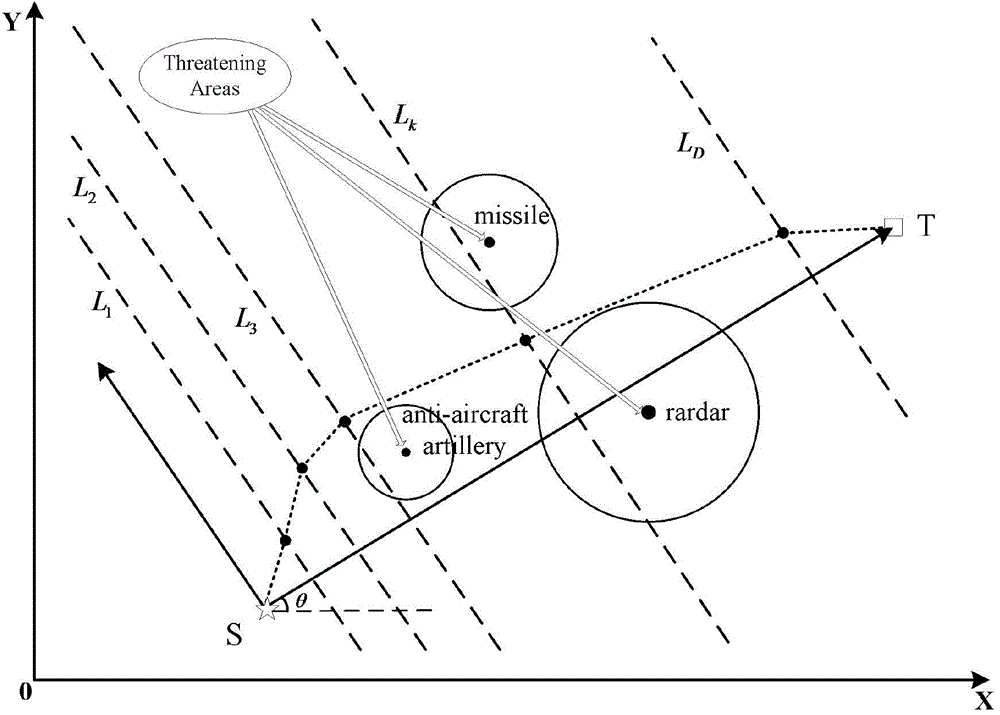
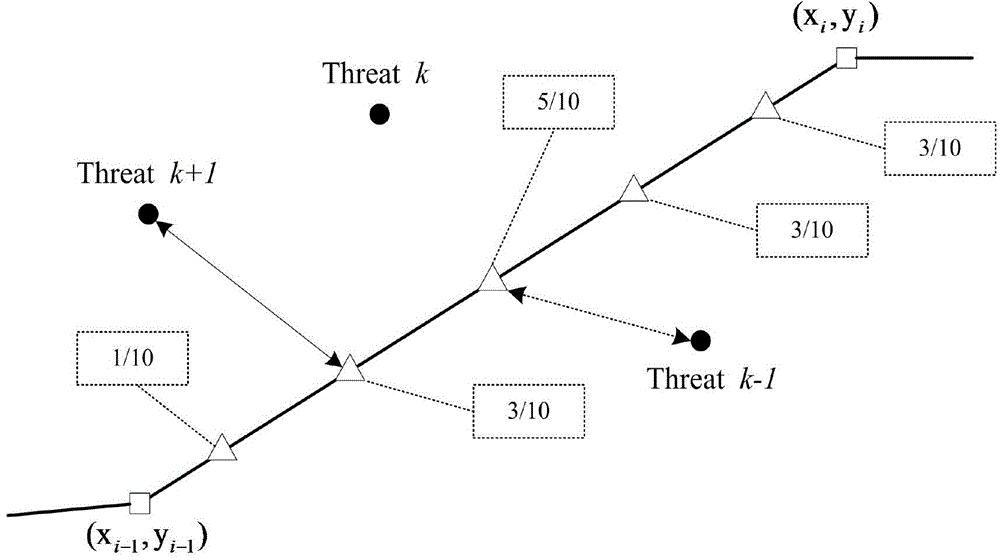
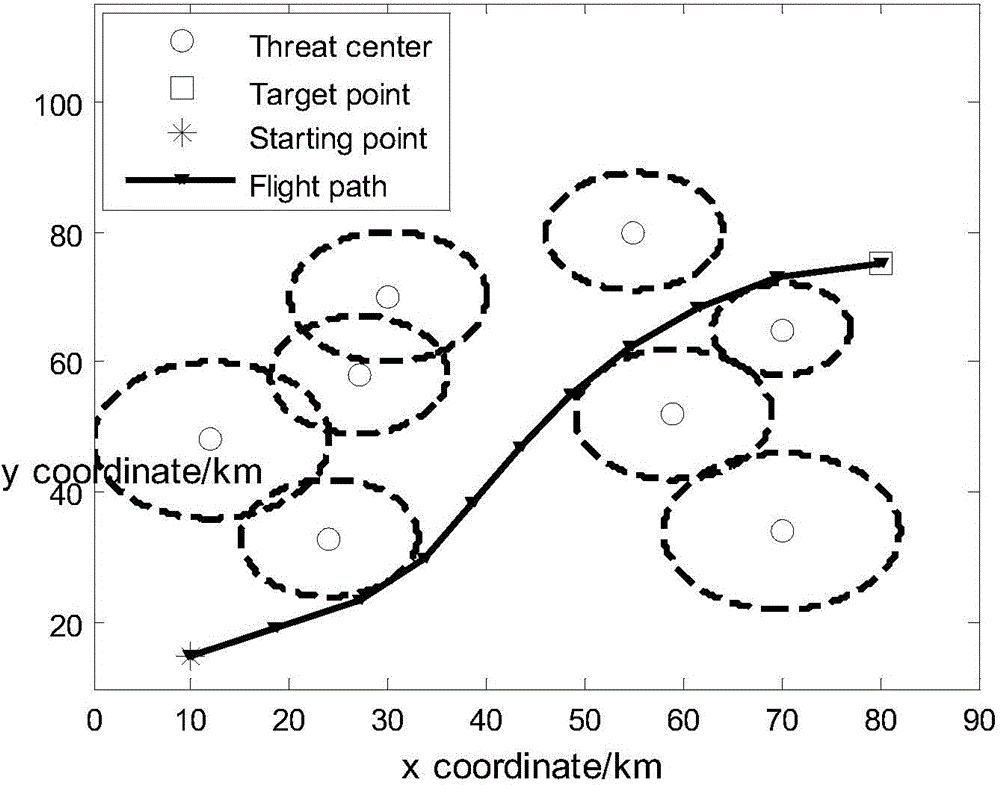
Method for determining optimal route of airway of unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN104406593AImprove global search performanceAvoid premature convergenceNavigational calculation instrumentsMicrochiropteraBat algorithm
The invention provides a method for determining an optimal route of the airway of an unmanned aerial vehicle. According to the method, the threat of an operation area is more sufficiently considered, more efficient global searching ability is achieved and a more accurate flying route is provided for the unmanned aerial vehicle. The method comprises the following steps: by adopting a quantum encoding mode, changing the state of a basic quantum bit by using a quantum rotating gate and a quantum not-gate, and further updating the position of a bat individual. Because of the diversity of the quantum state, a quantum bat algorithm (QBA) is relatively high in global searching ability and an available or even optimal route avoiding the threat and limiting conditions can be found for the unmanned aerial vehicle. The experiment result shows that the quantum bat algorithm is an effective and stable method for solving the airway route planning problem of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and the search performance of the quantum bat algorithm is superior to that of other swarm intelligence algorithms.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES
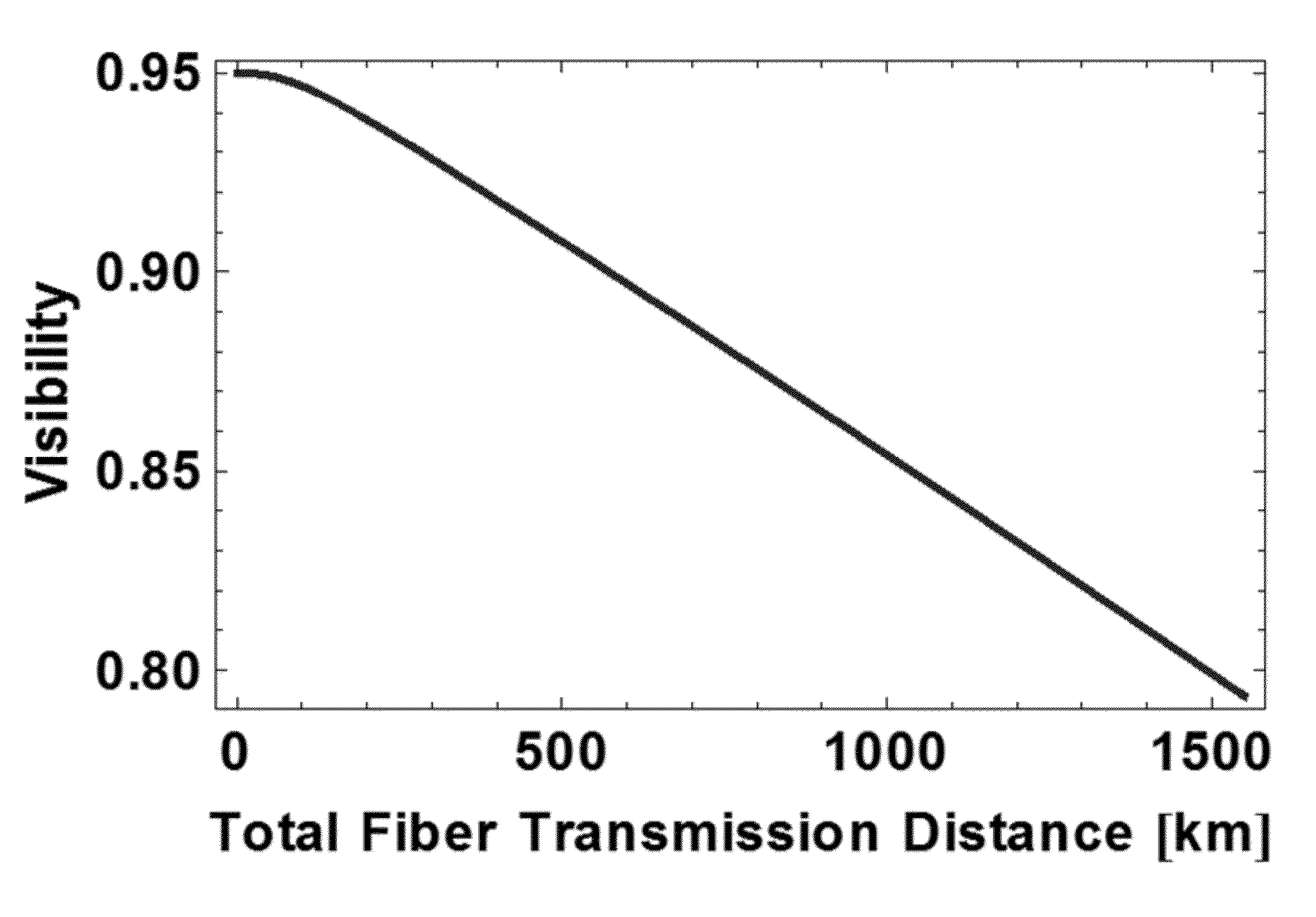
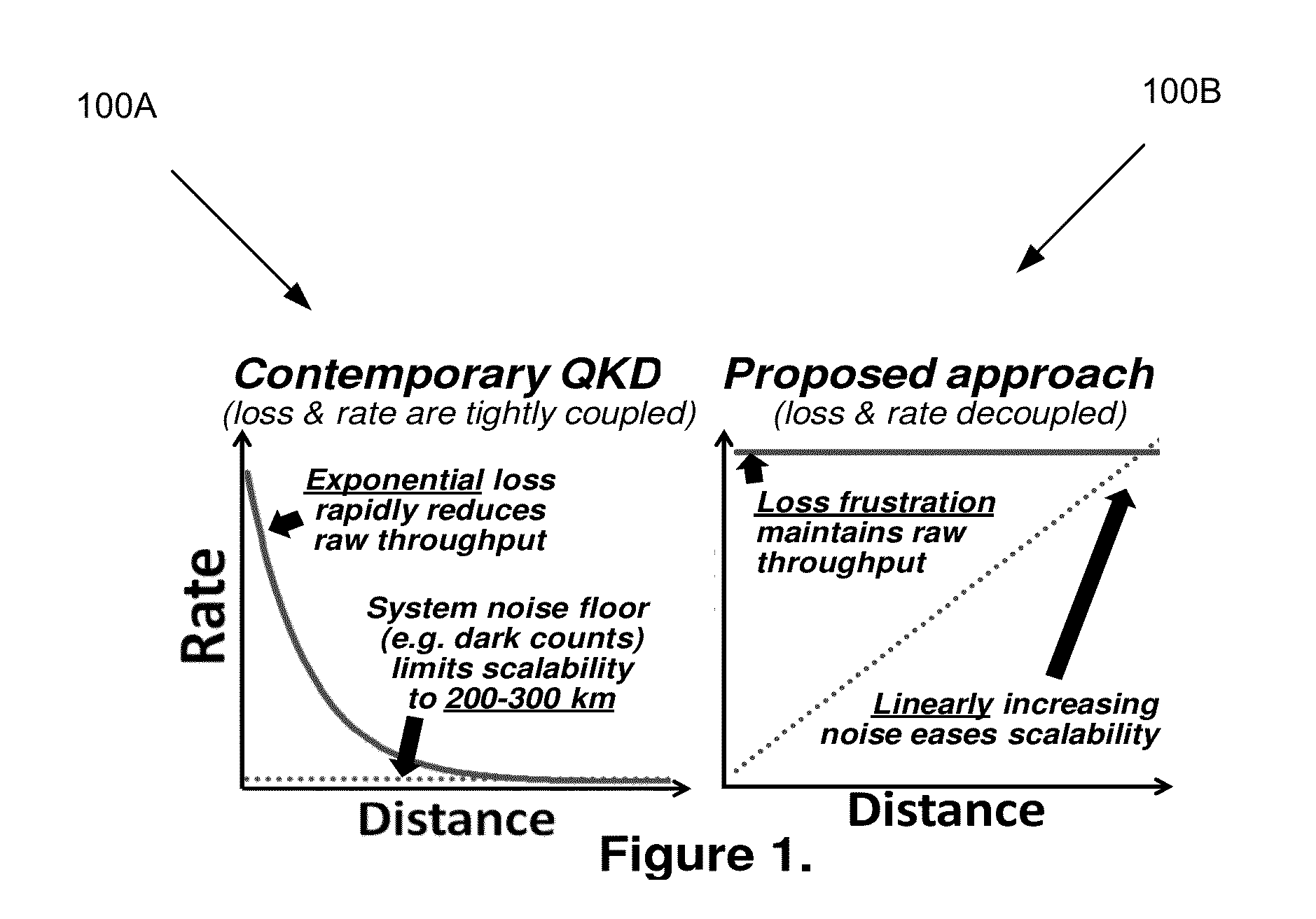
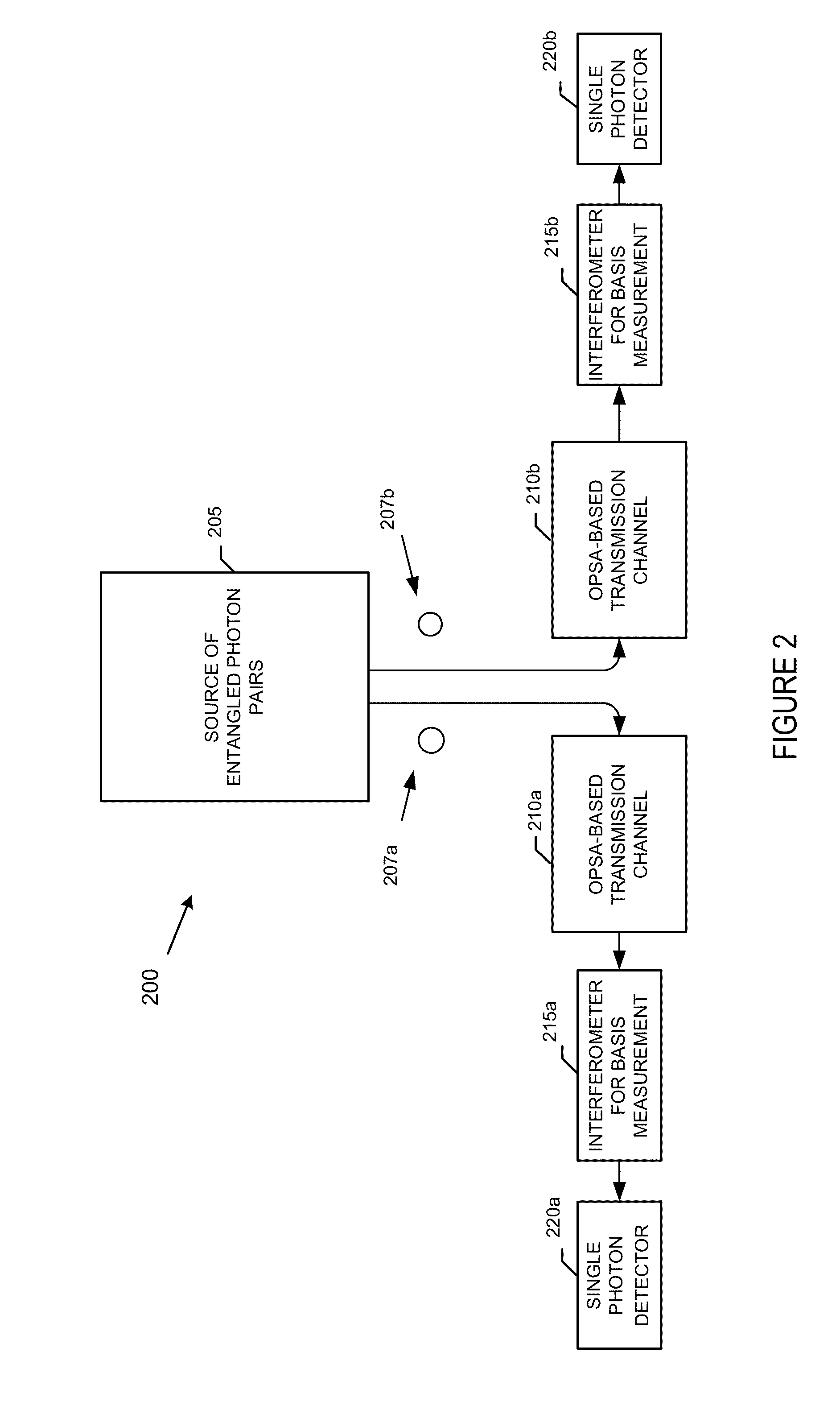
Method to mitigate propagation loss in waveguide transmission of quantum states
ActiveUS20140099104A1Facilitating quantum communicationFacilitate communicationPhotonic quantum communicationDistortion/dispersion eliminationTransmission channelTransmission loss
A system comprises a source of entangled photon pairs. The source is to place a signal photon and an idler photon in individual unknown quantum states but in a known entangled quantum state. One or more transmission channels are connected to the source. Each of the one or more transmission channels transmits one of the signal photon or the idler photon. Each of the one or more transmission channels is to substantially balance an instantaneous transmission loss with an instantaneous transmission gain distributed over a transmission distance. Analysis interferometers are configured to receive a corresponding one of the signal photon or the idler photon. Each of the one or more analysis interferometers is to perform a basis measurement on one of the signal photon or the idler photon. Single-photon detectors detect one of the signal photon or the idler photon.
Owner:PERSPECTA LABS INC
Method and system for anti-interference quantum secure direct communication
ActiveCN101697512ASolve decoding problemsOvercoming the high bit error rate problemKey distribution for secure communicationError preventionInterference resistanceQuantum secure direct communication
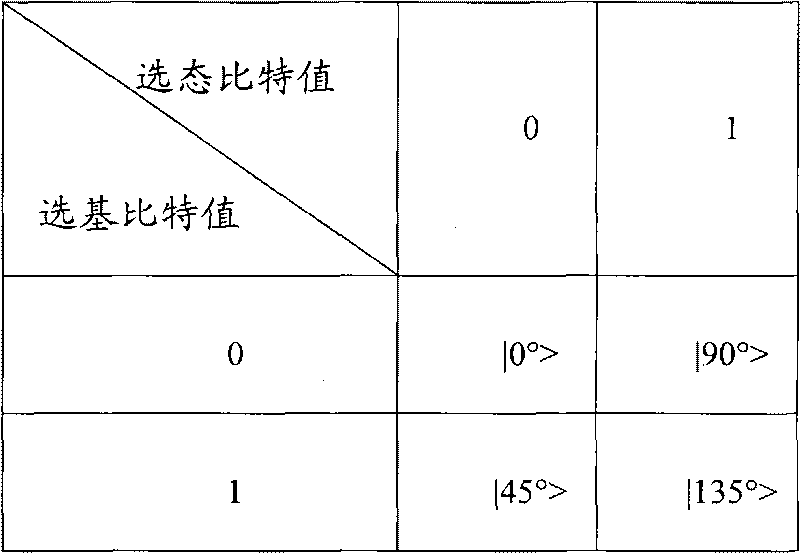
The invention provides a method and a system for anti-interference quantum secure direct communication. The method comprises the following steps that: a sending end performs non-orthogonal state combination coding, randomly expands a bit to two bits, randomly selects two different base combinations, converts the two bits into corresponding quantum states in the base combinations and then sends the two bits through a quantum channel; and a receiving end randomly selects two same base combinations for quantum state measurement so as to realize definite measurement on one bit. The method and the system can effectively solve the problem of quantum secure direct communication under the condition of not accurate measurement on the quantum, and realize point-to-multipoint quantum information distribution.
Owner:NO 30 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP
Remote communication method directly safely communicating with quantum by using quantum state injection reinforcement
A long-distance communication method for enhancing direct and secure communication with a quantum by injecting a quantum state belongs to the technical field of quantum communication and is characterized in that a long distance between a sender and a receiver is divided into N sections of equal short distances, so that N minus one valid user nodes are formed; the information sender and the N minus one valid user nodes are equipped with the same devices for producing entangled photon pairs; after the N minus one valid user nodes and the receiver are equipped with the same bell's joint measurement device, a relay method is adopted; direct and secure quantum communication in accordance with the preset fault tolerant rate between the sender and a first valid user node is conducted; when the transmission is confirmed to be secure, the first valid user node prepares an entangled photon pair and conducts direct and secure communication with a second valid user node according to the acquired information; and the relay continues until the communication reaches the receiver. The method aims to increase the transmission efficiency, and greatly saves the required resources for transmitting the same information.
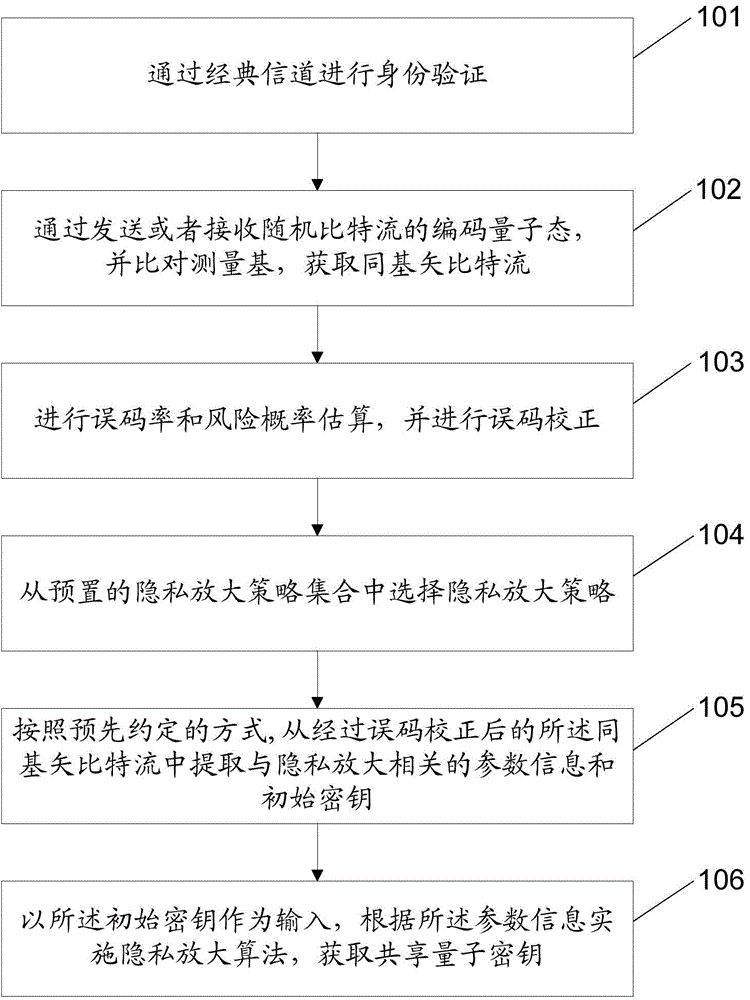
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods for single qubit gate teleportation
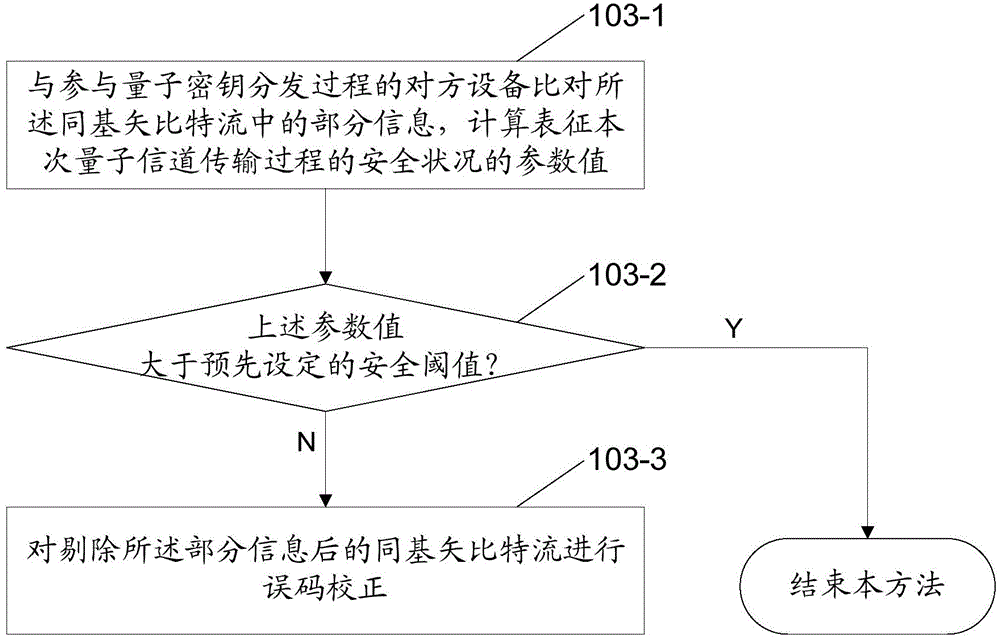
ActiveUS7018852B2Addressing Insufficient ControlReducing overall available computational timeQuantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsQuantum electrodynamicsSecond ancillary
A method for performing a single-qubit gate on an arbitrary quantum state. An ancillary qubit is set to an initial state |I>. The data qubit is coupled to an ancillary qubit. The state of the ancillary qubit is measured, and the data qubit and the ancillary qubit are coupled for a first period of time. A method for applying a single-qubit gate to an arbitrary quantum state. A state of a first and second ancillary qubit are set to an entangled initial state |I>. A state of a data qubit and the first ancillary qubit are measured thereby potentially performing a single qubit operation on the arbitrary quantum state. A first result is determined. The first result indicates whether the single qubit operation applied the single qubit gate to the arbitrary quantum state.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC +1
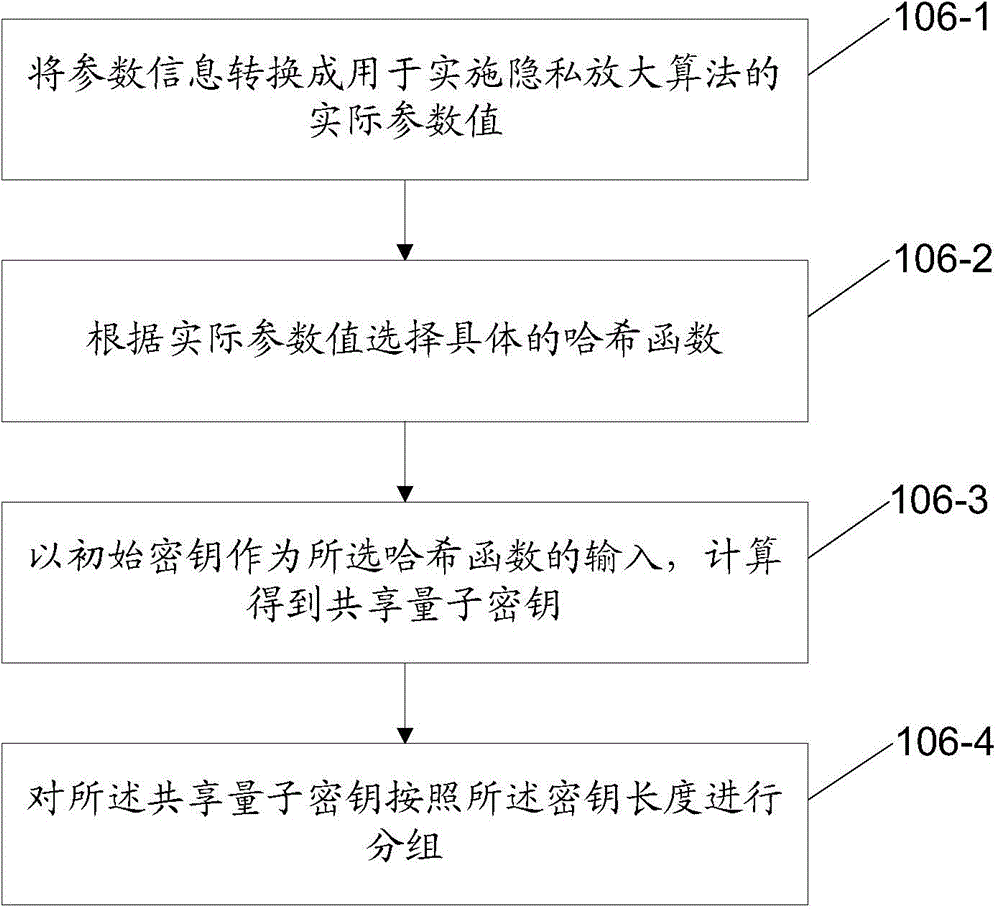
Conditional Rabi oscillation readout for quantum computing
A method for determining whether a first state of a quantum system is occupied is provided. A driving signal is applied to the system at a frequency corresponding to an energy level separation between a first and second state of the system. The system produces a readout frequency only when the first state is occupied. A property of a measurement resonator that is coupled to the quantum system is measured when the quantum system produces the readout frequency, thereby determining whether the first state of the quantum system is occupied. A structure for detecting a qubit state of a qubit is provided. The structure comprises a quantum system that includes the qubit. The qubit has first and second basis states and an ancillary quantum state. The ancillary quantum state can be coupled to the first or second basis states. The structure has a measurement resonator configured to couple to Rabi oscillations between (i) one of the first and second basis states and (ii) the ancillary state in the quantum system.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
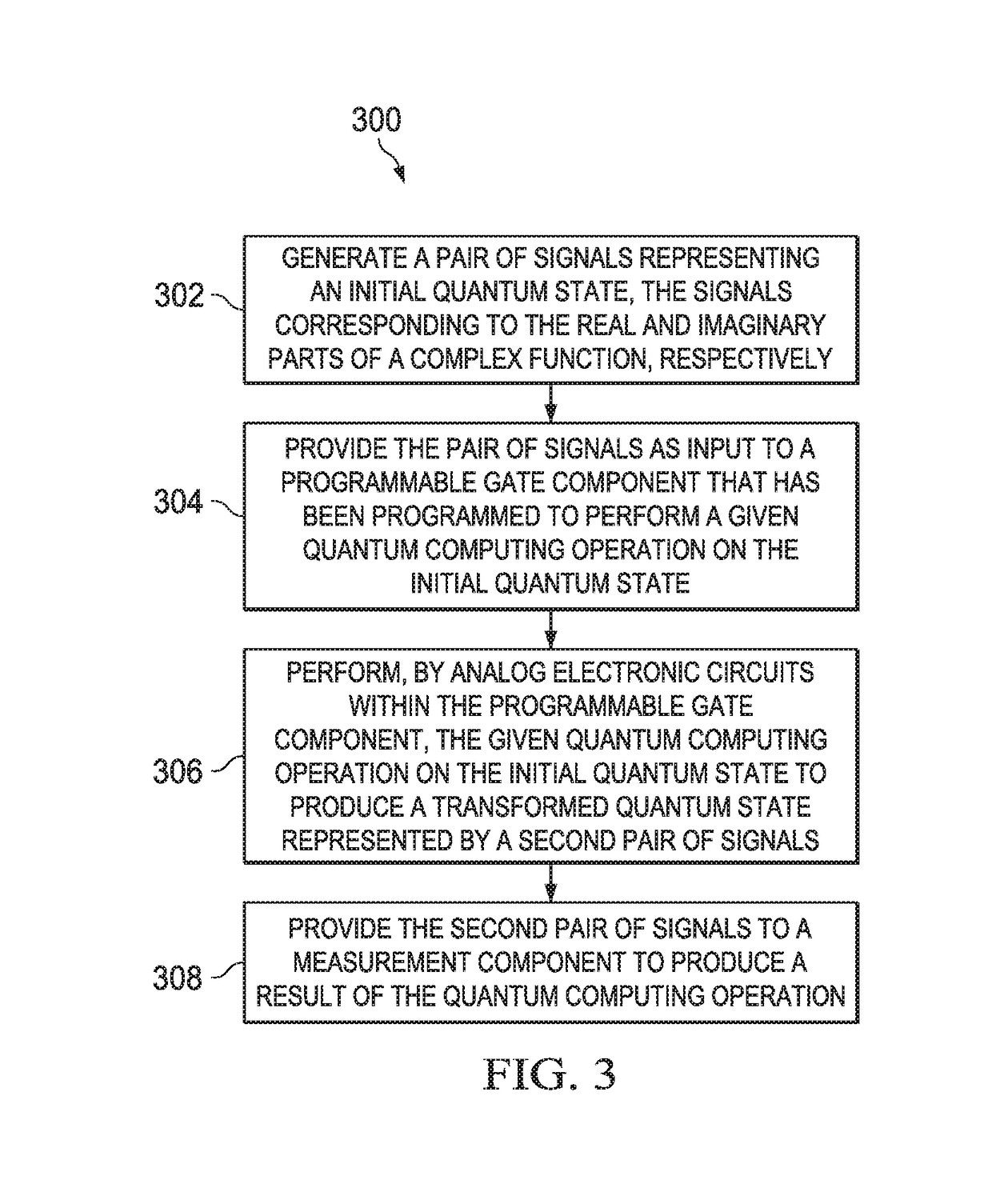
System and method for controlling a quantum computing emulation device
InactiveUS20180046933A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationQuantum computersMaster controllerControl switch
A quantum computing emulation platform may be used to control operation of a quantum computing emulation device in performing, by analog electronic circuits within the device, a quantum computing exercise. The platform may include a master controller to determine an initial quantum state for the exercise, a number and sequence of gate operations to be applied in sets of execution runs, and a transformation type for each run, to define and allocate storage for data collection variables, to initiate performance of the exercise by the device, and to store results. The platform may include a set controller to prepare control values for the gate operations and to prepare the platform to collect results, and a run controller to provide the control values for each run to the device and record results. The control values may control switches on the device and program analog electronic circuits to perform particular gate operations.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Quantum bit with a multi-terminal junction and loop with a phase shift
A solid-state quantum computing qubit includes a multi-terminal junction coupled to a superconducting loop where the superconducting loop introduces a phase shift to the superconducting order parameter. The ground state of the supercurrent in the superconducting loop and multi-terminal junction is doubly degenerate, with two supercurrent ground states having distinct magnetic moments. These quantum states of the supercurrents in the superconducting loop create qubits for quantum computing. The quantum states can be initialized by applying transport currents to the external leads. Arbitrary single qubit operations may be performed by varying the transport current and / or an externally applied magnetic field. Read-out may be performed using direct measurement of the magnetic moment of the qubit state, or alternatively, radio-frequency single electron transistor electrometers can be used as read-out devices when determining a result of the quantum computing. Further, qubits as described above can form arrays of qubits for performing controlled quantum computing calculations. In one example, an array of qubits can be utilized as a random number generator.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Method and device for quantum random number generation
ActiveUS20190243611A1Less complexEasy to implementQuantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationMeasurement devicePhysical system
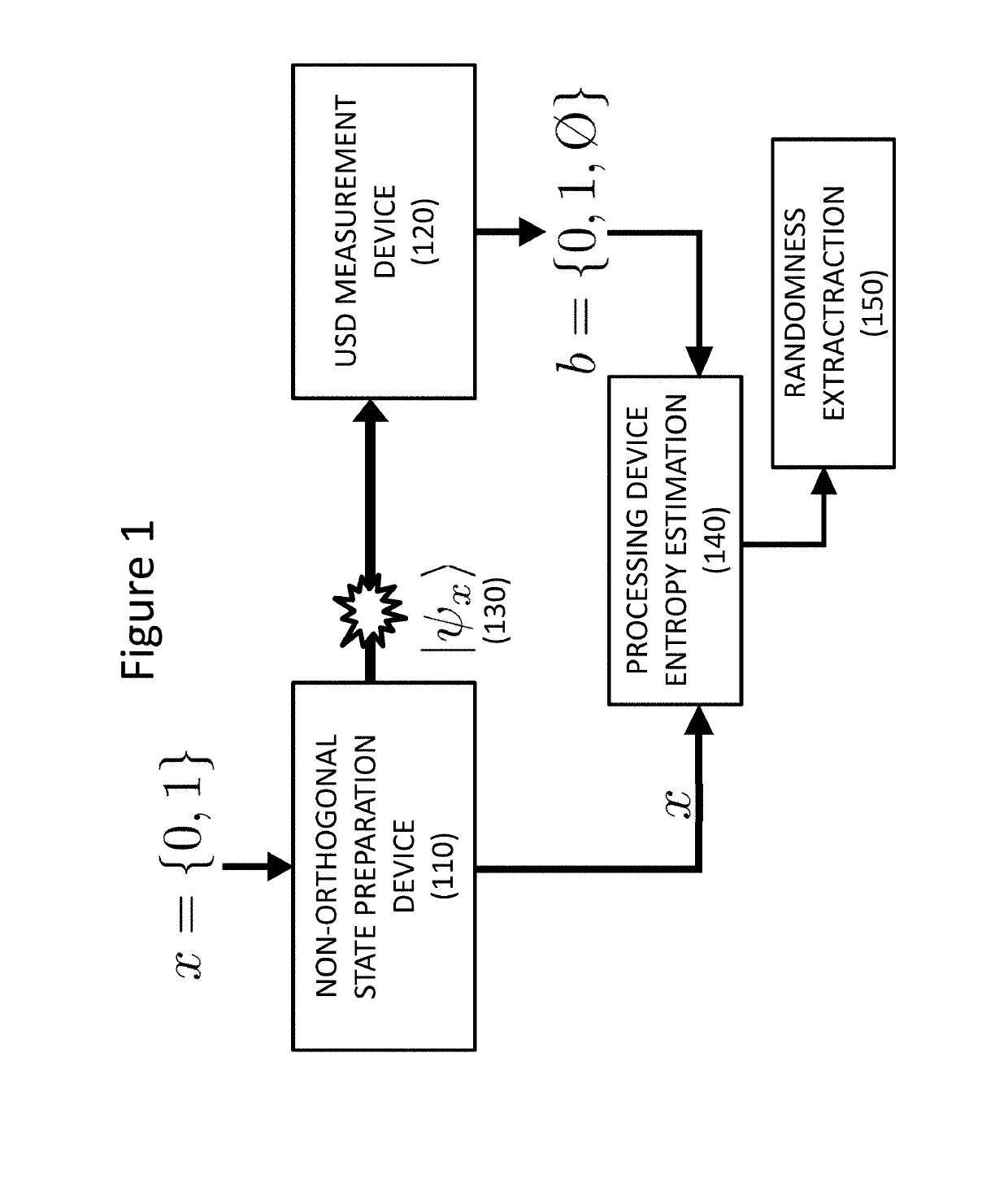
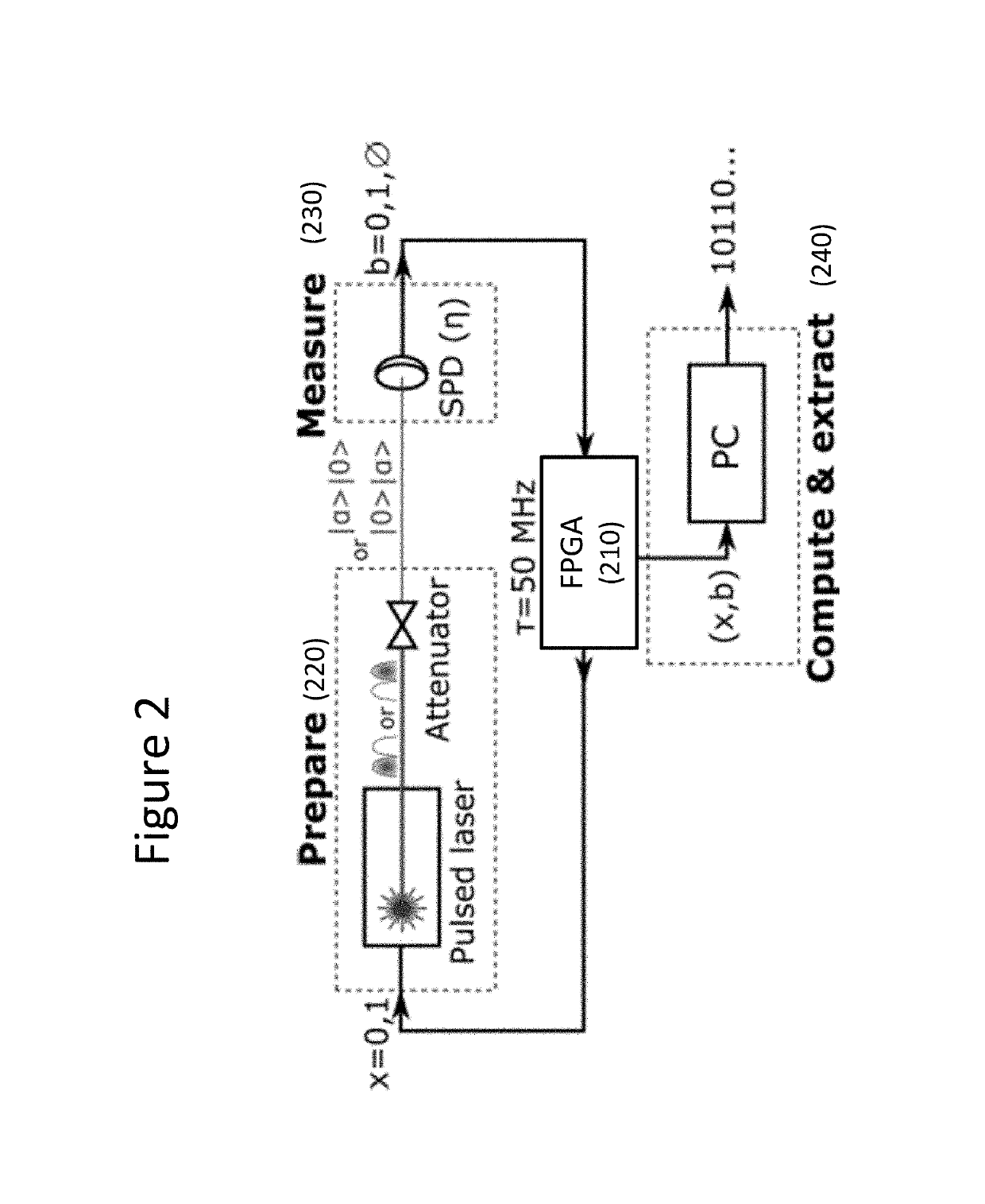
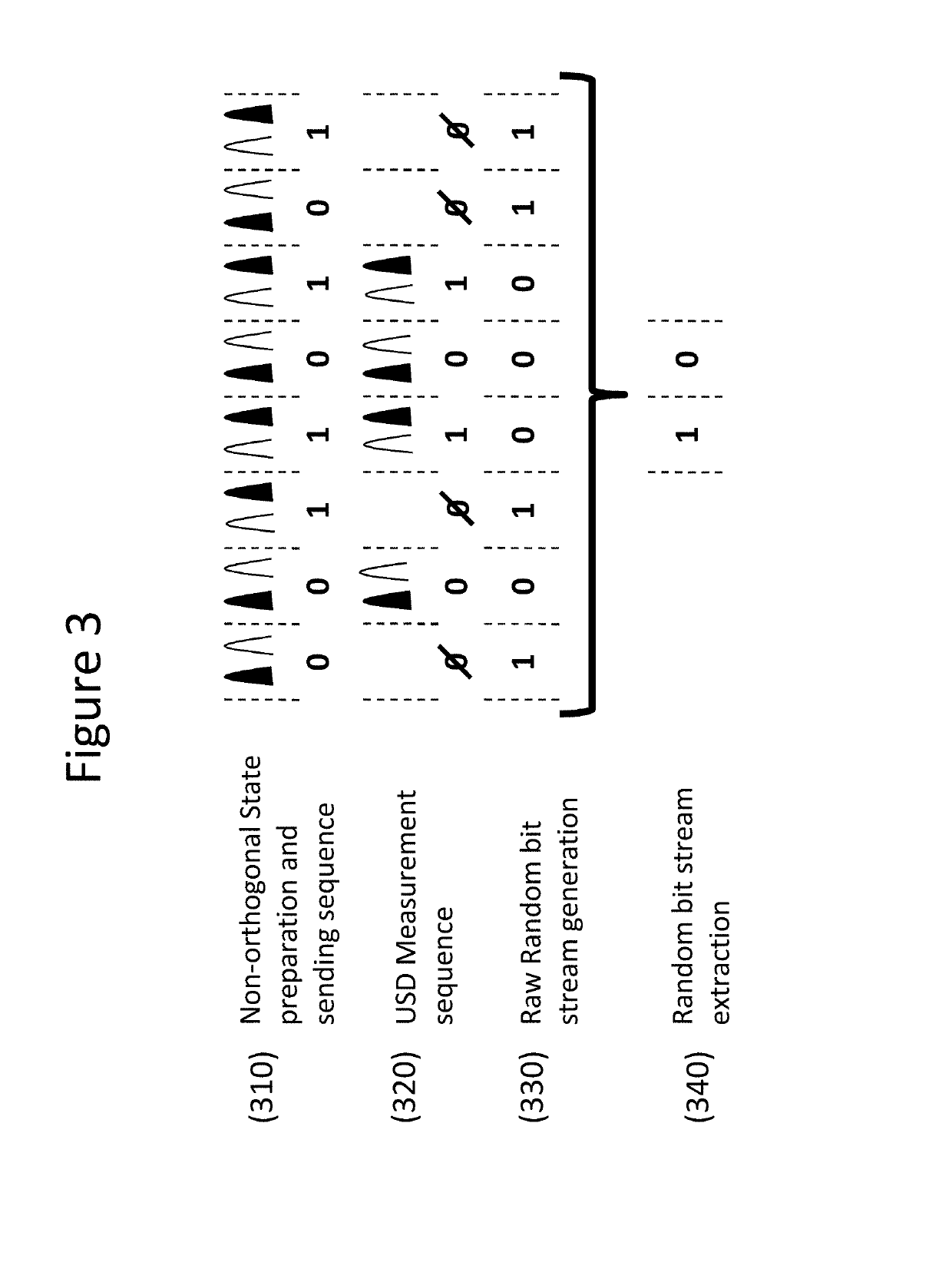
The invention is directed to a Quantum Random Number Generator comprising an emitting device (110) triggered by a signal representing an input bit x and adapted to generate and send a physical system (130) characterized by one of two possible quantum states determined by said input bit x, a measurement device (120) adapted to detect said physical system, to identify the quantum state of said physical system through an unambiguous state discrimination measurement and to generate an output b first representing whether the quantum state has been identified or not and, if it has been identified, which quantum state among the two possible quantum states was detected by the unambiguous state discrimination measurement to a processing device (140), the processing device (140) being adapted to estimate the entropy of the output b given the probabilities p(b|x) representing the probability of observing output b for a state preparation x, and a randomness extraction device (150) adapted to extract final random bit stream given the entropy estimate provided by the processing device (140).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Method and system for dynamic password authentication based on quantum states
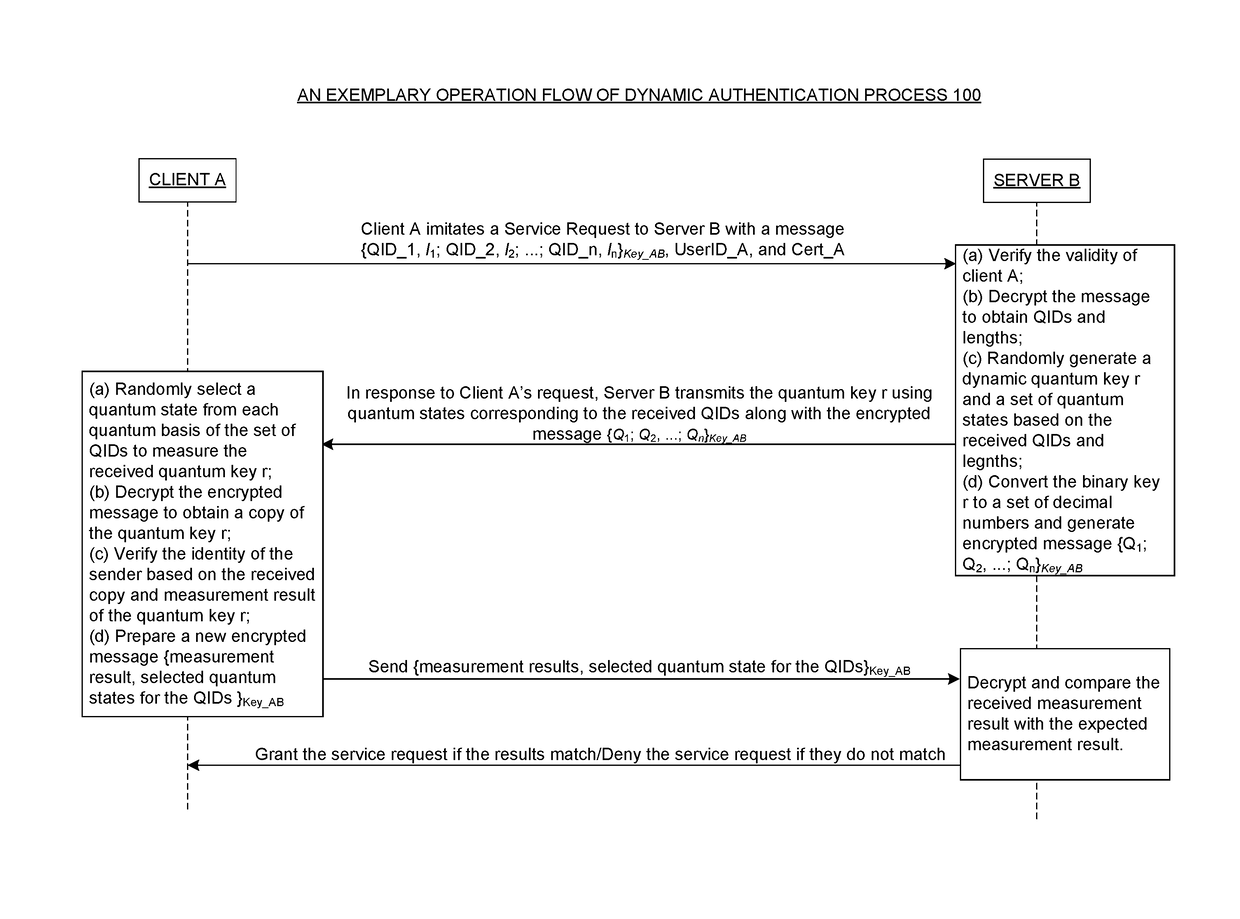
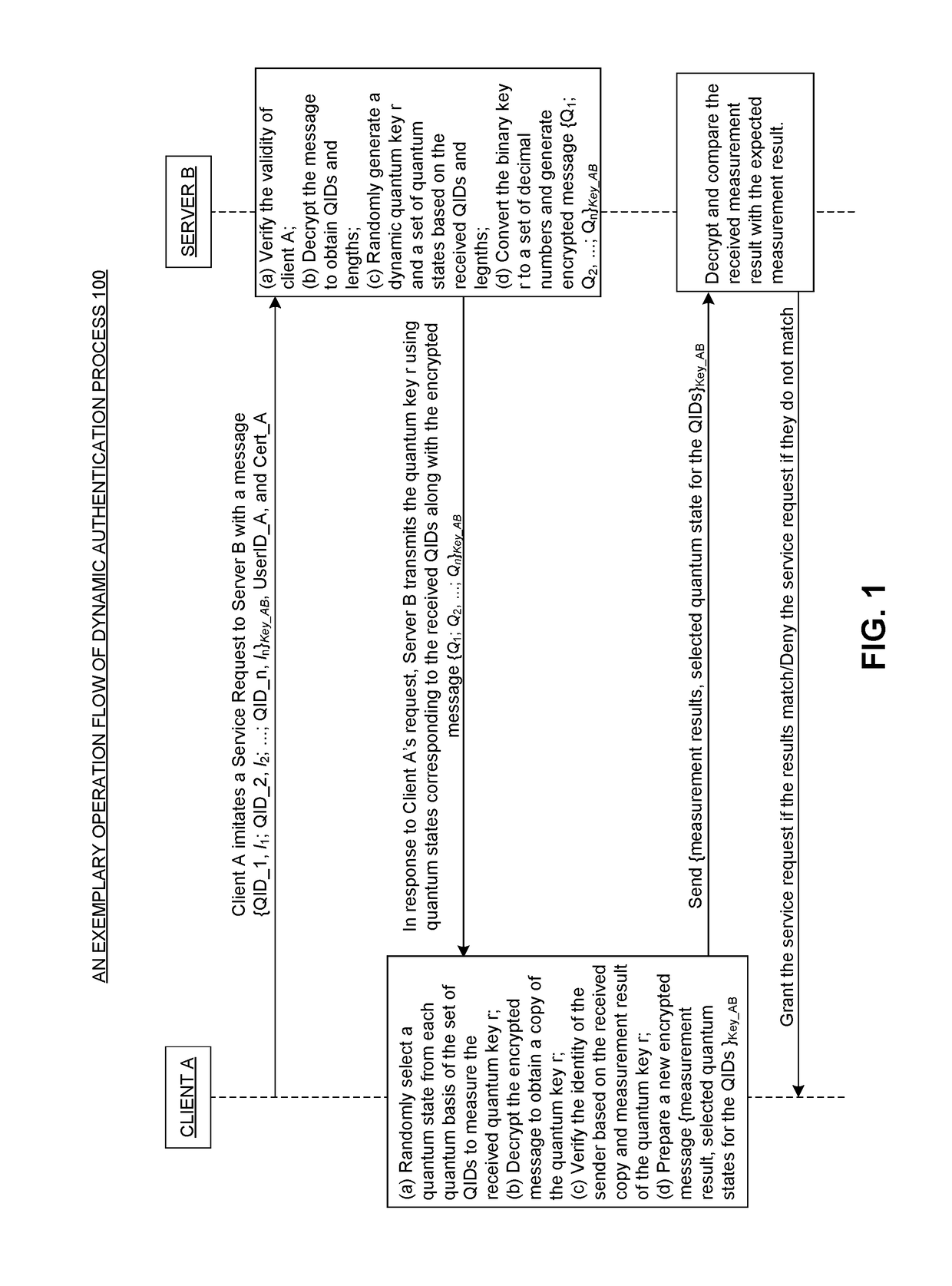
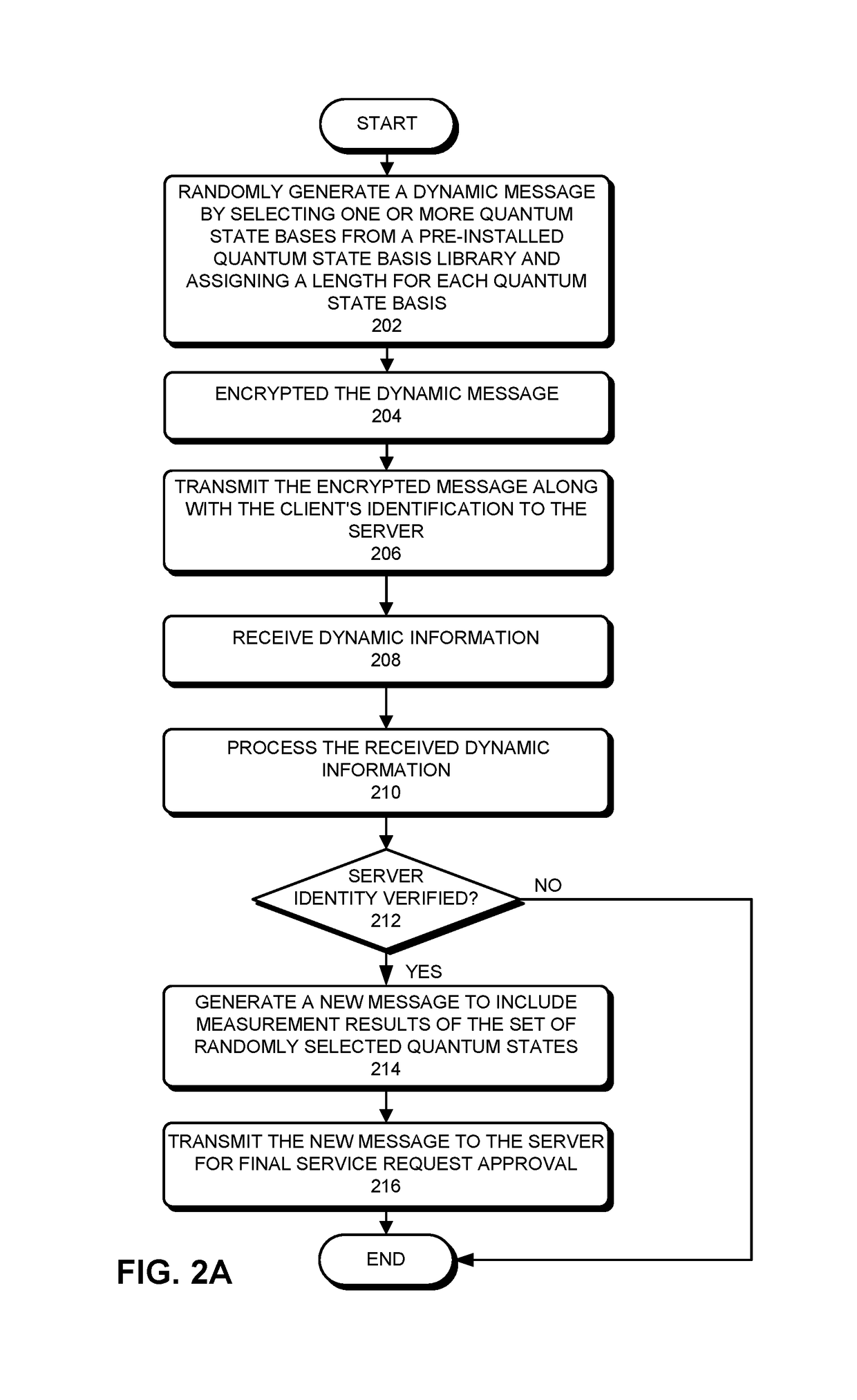
InactiveUS20170126654A1Cure deficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPasswordClient-side
One embodiment described herein provides a client-side process for performing dynamic-password authentication between a client and a server. This client-side process includes the steps of: generating, by the client, a service request comprising a first dynamic message; transmitting the first service request to the server; receiving a second dynamic message from the server in response to the first dynamic message for cross-validating the server; authenticating the second dynamic message to verify the validity of the server. If the validity of the server is verified, the client-side process further includes: generating a third dynamic message based on the second dynamic message; and transmitting the third dynamic message to the server for a final approval of the service request.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
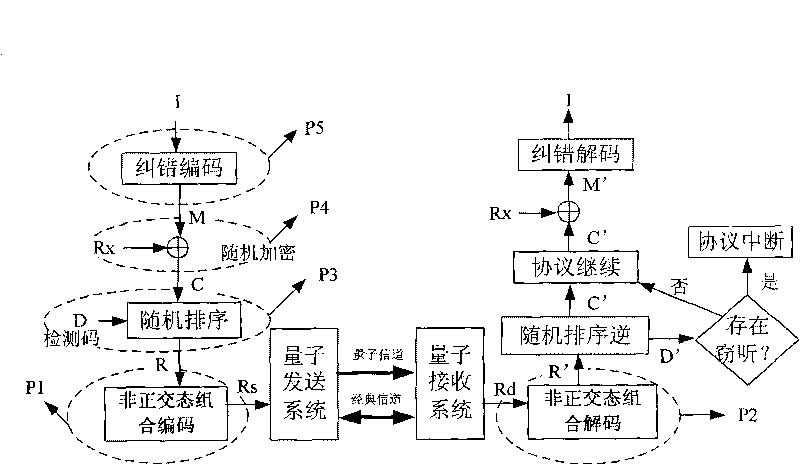
Quantum state classical sequence rearrangement encrypition method in quantum key distribution
InactiveCN1477809ASecret communicationSecuring communicationGeneration processData processing system
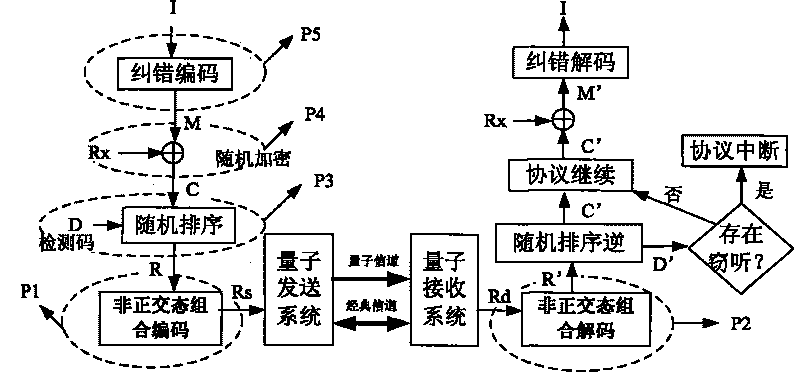
The quantum state classical sequence rearrangement encryption method in quantum key distribution belongs to the field of quantum secret communication. It mainly utilizes the characteristics of quantum to encipher the production process of quantum key, under the condition of ensuring safety, at the same time, and transfer all the particles of tangled system so as to raise transmission distance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com